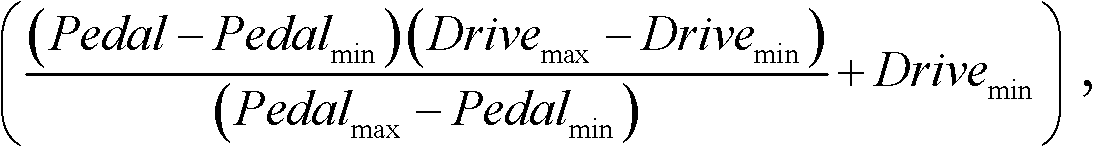Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4771 results about "Steering control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
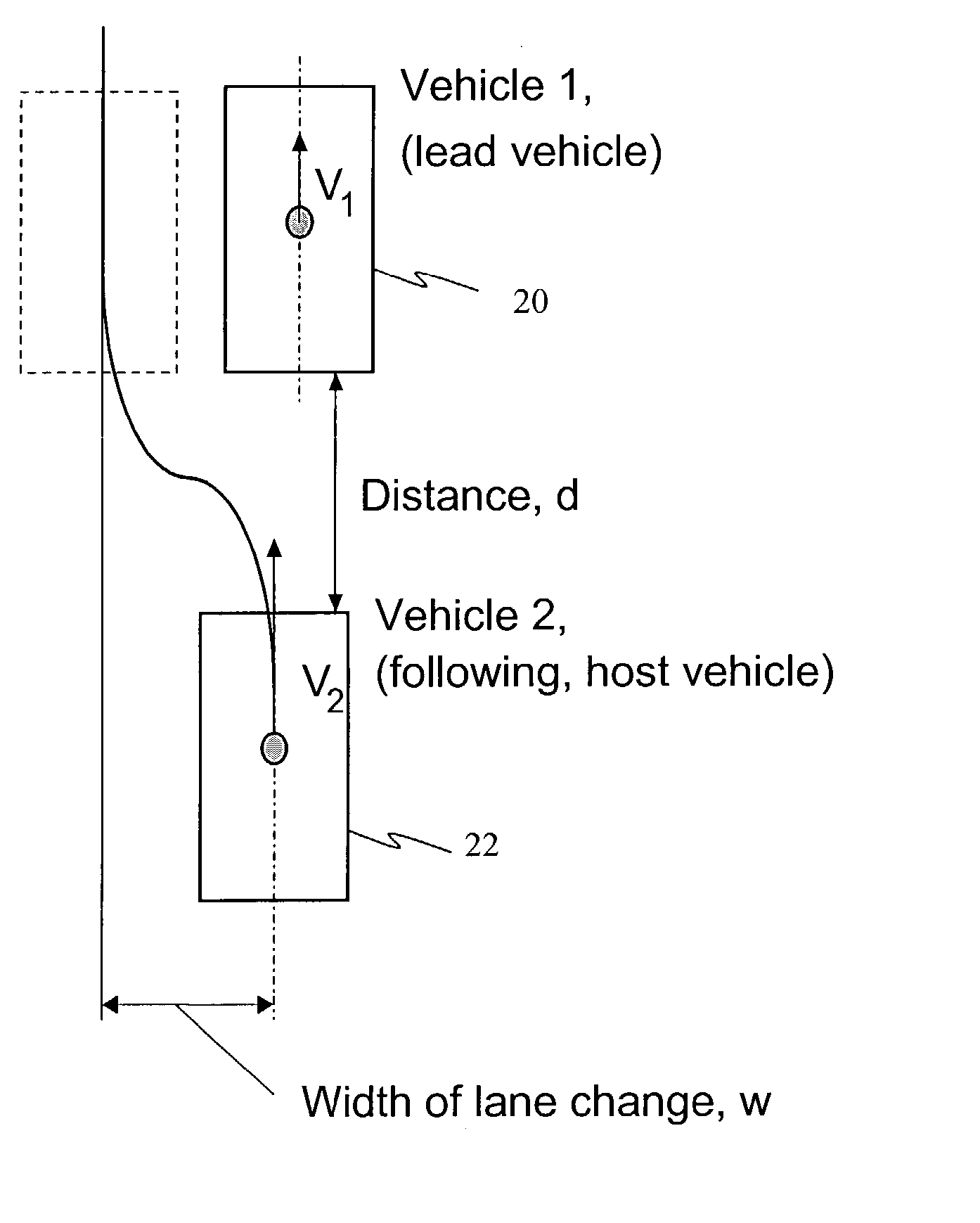
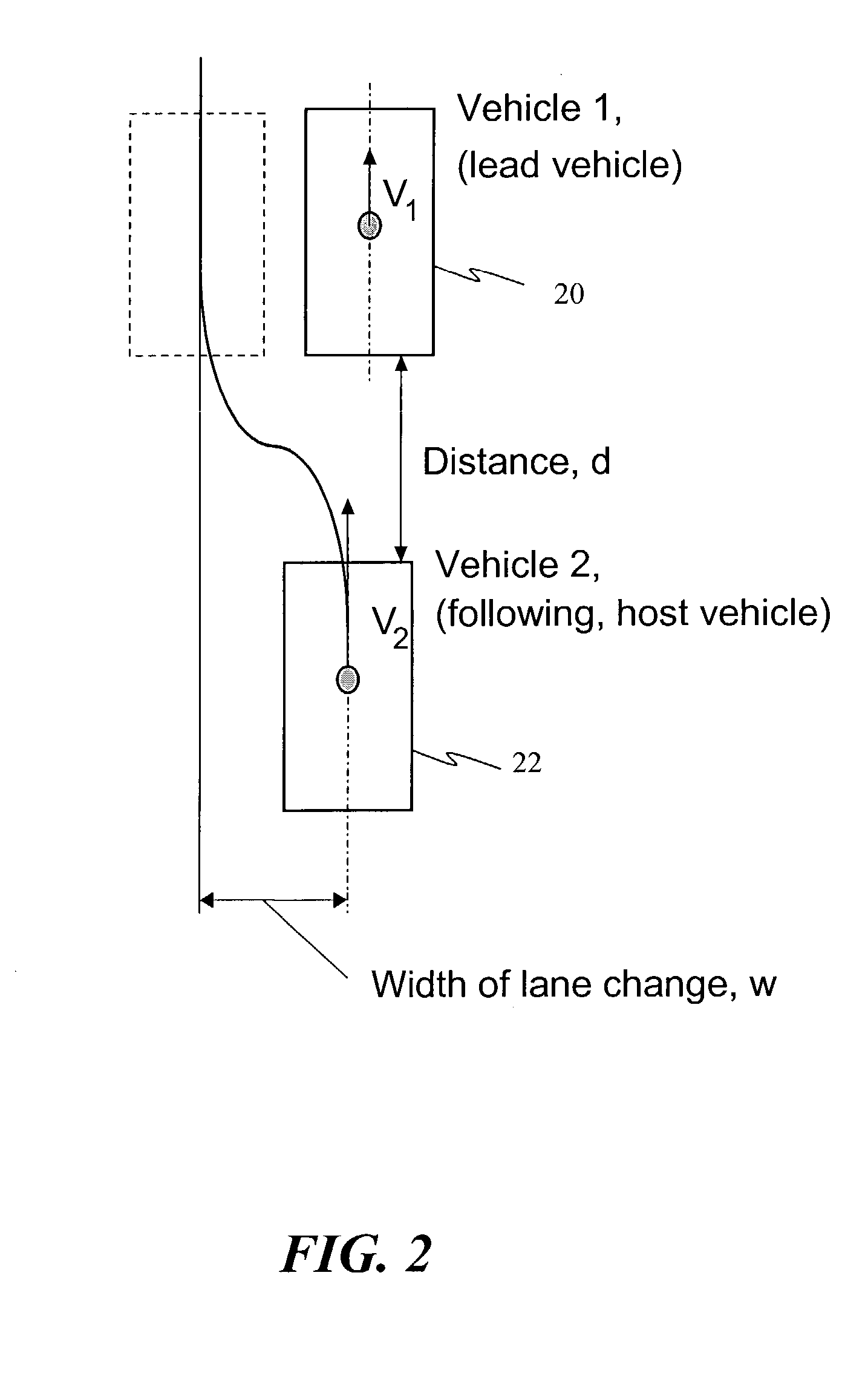
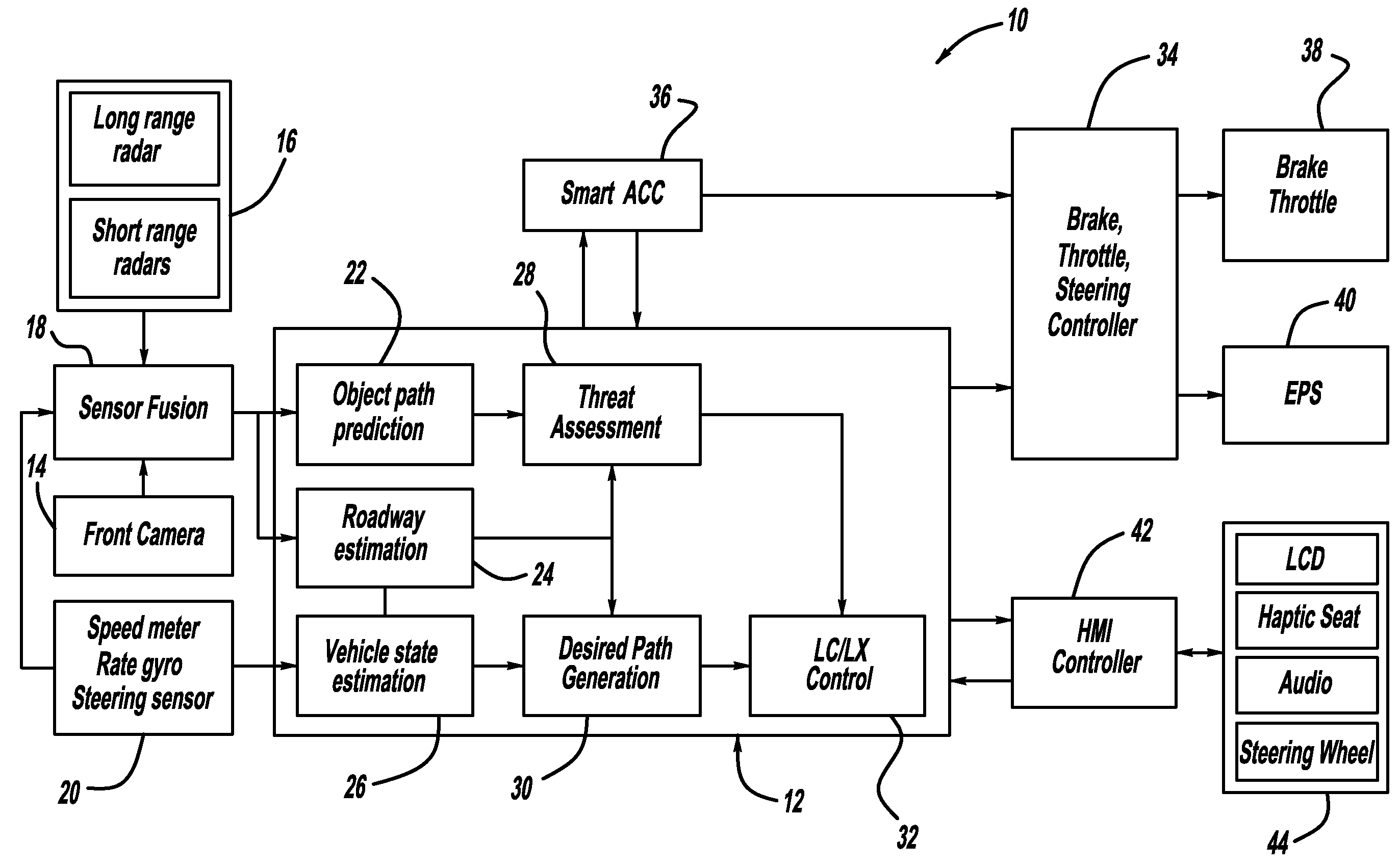
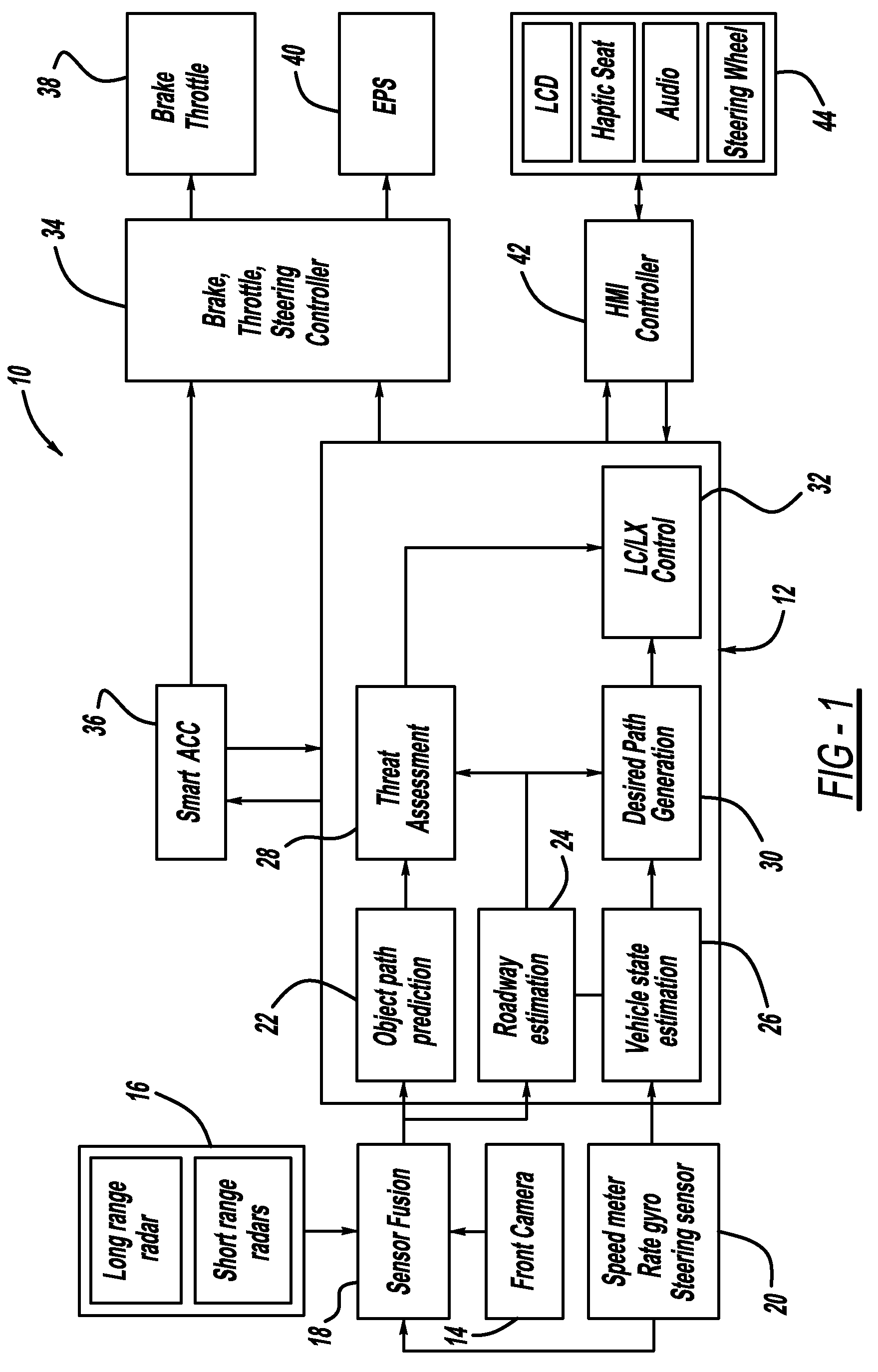
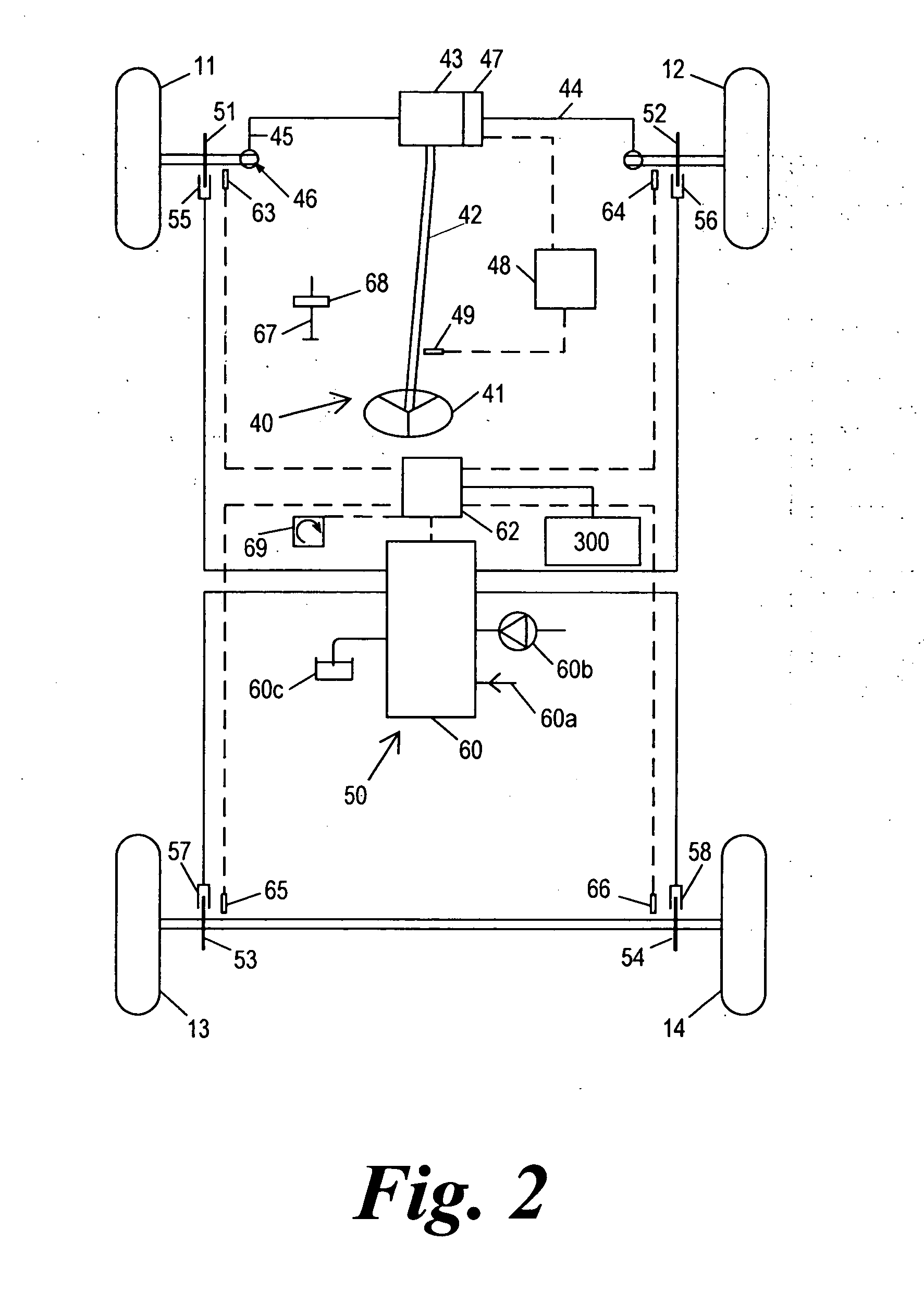
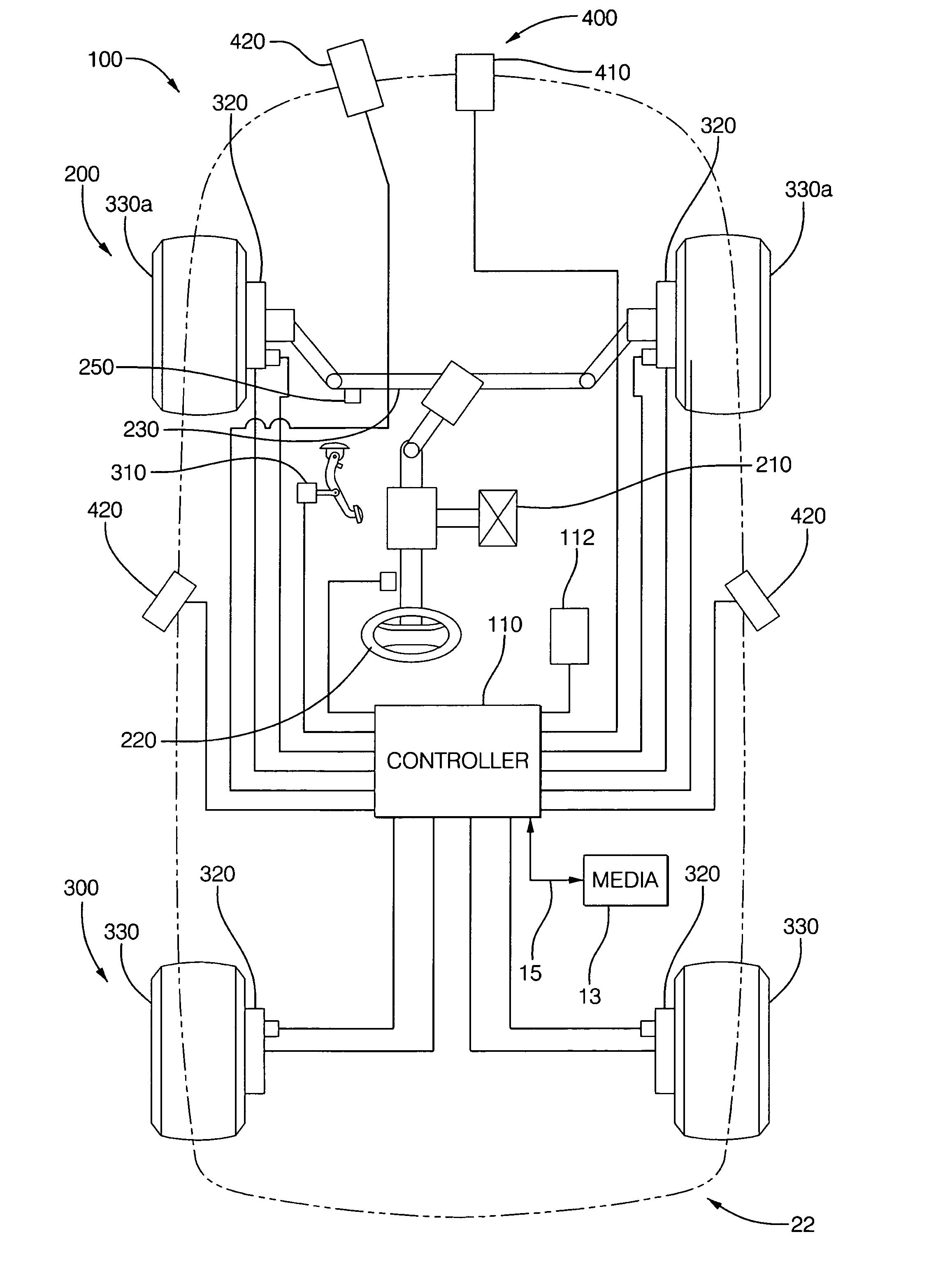
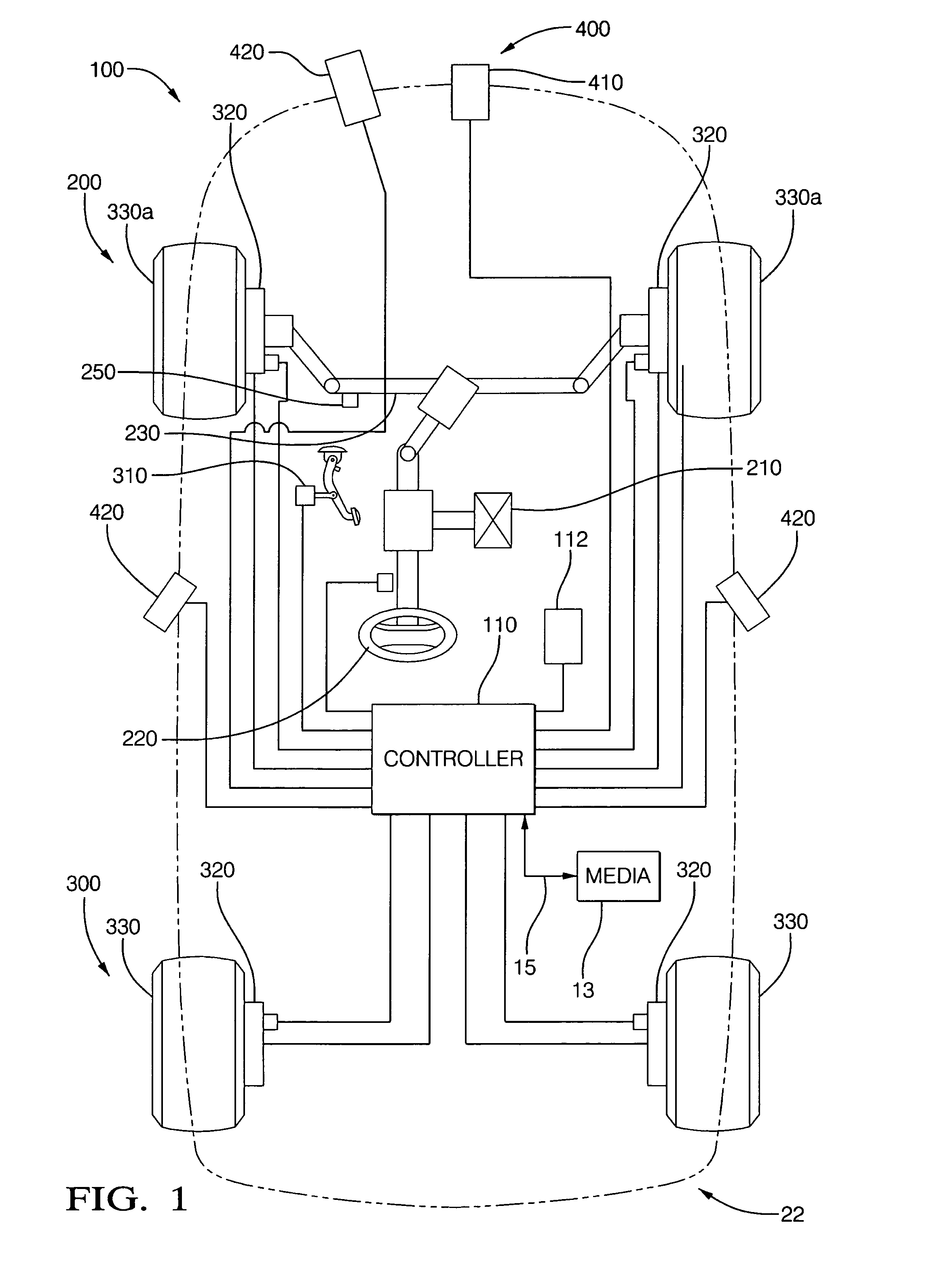
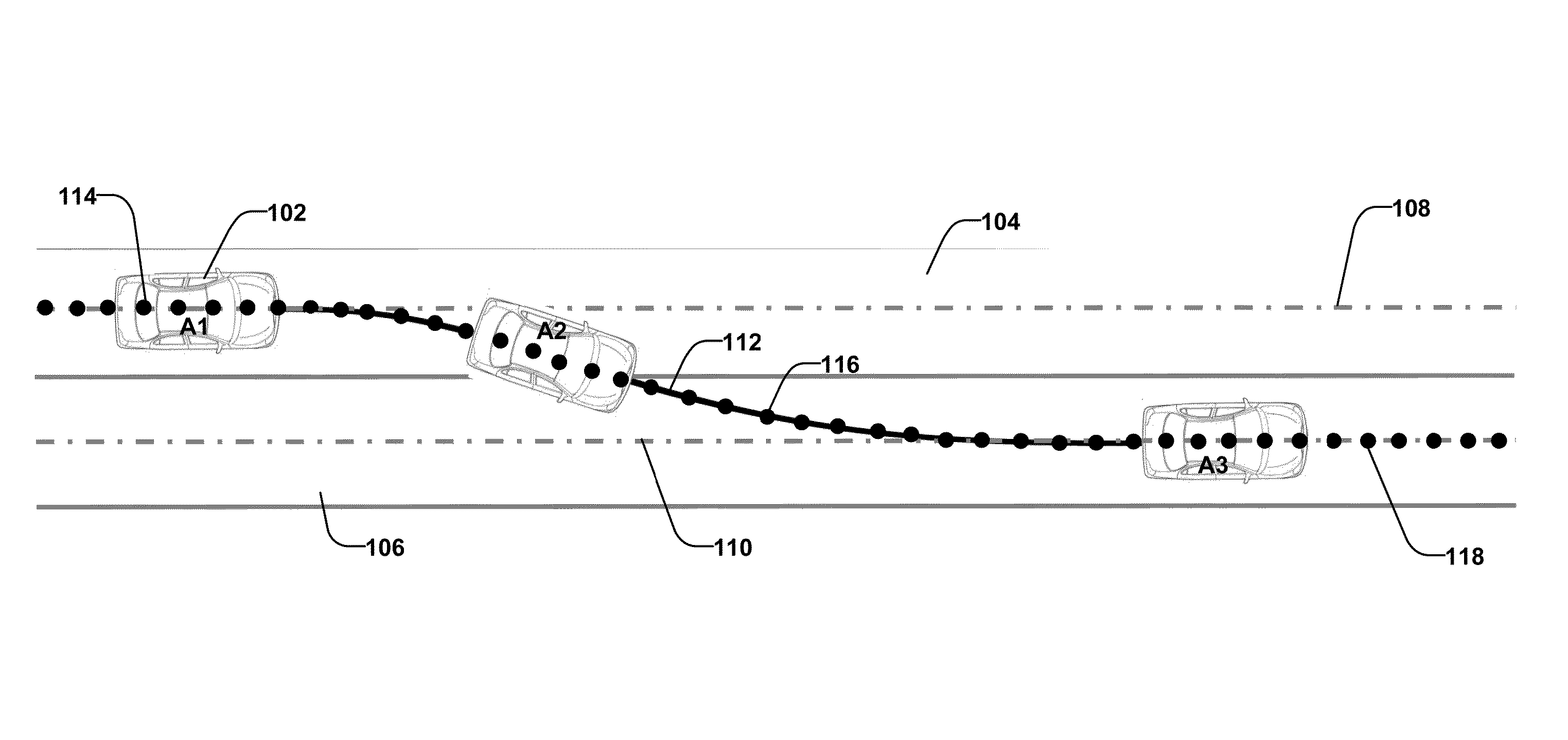
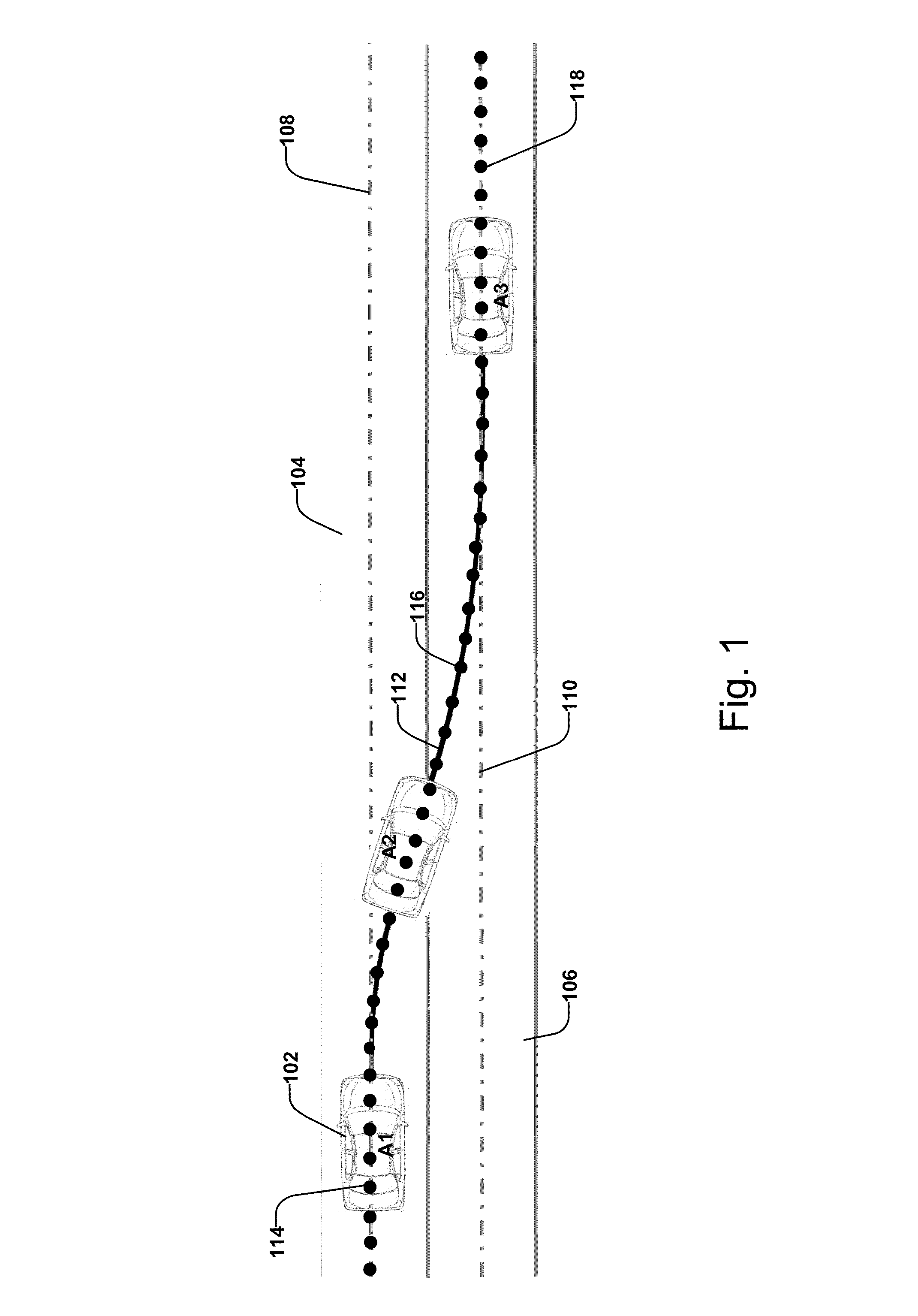
Collision avoidance with active steering and braking
A method for collision avoidance using automated braking and steering comprising: determining an actual distance to an obstacle in a path of a vehicle; determining a relative velocity between the obstacle and the vehicle; determining a first distance sufficient to avoid collision by braking only; determining a second distance sufficient to avoid collision by combined braking and steering around the obstacle. The method also includes: applying braking if at least one of, the first distance exceeds the actual distance and the first distance is within a selected threshold of the actual distance. If the actual distance exceeds the second distance and a lane change is permitted, steering control to affect a lane change is applied.
Owner:BWI +1
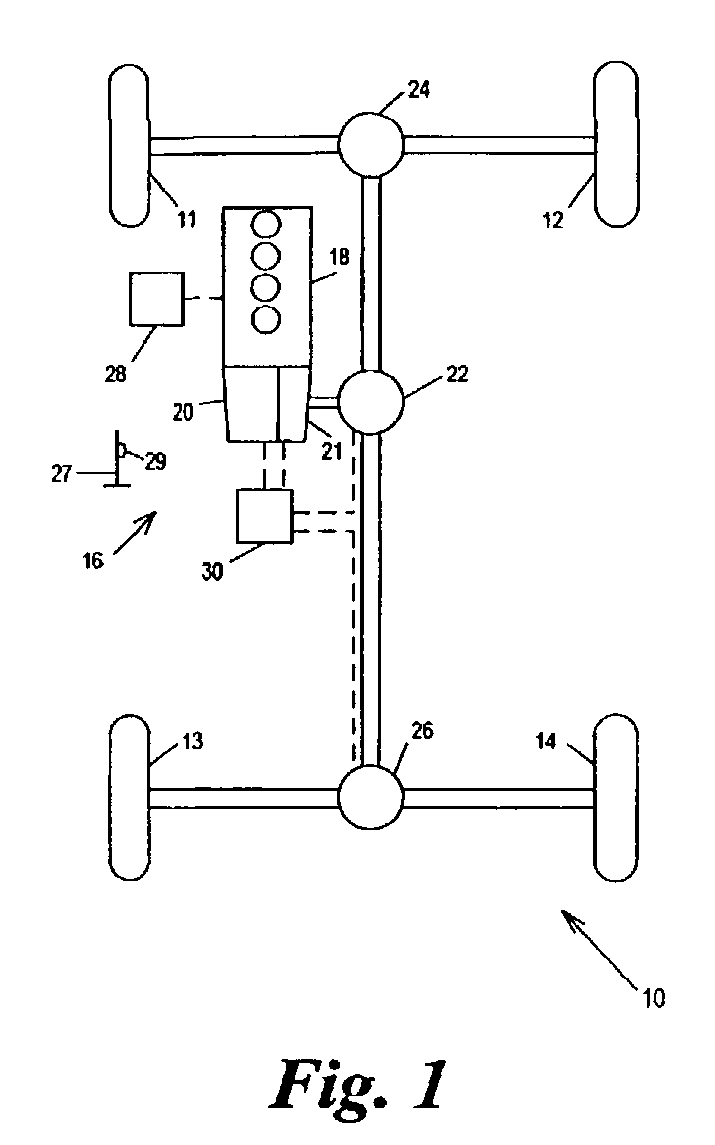
Vehicle control
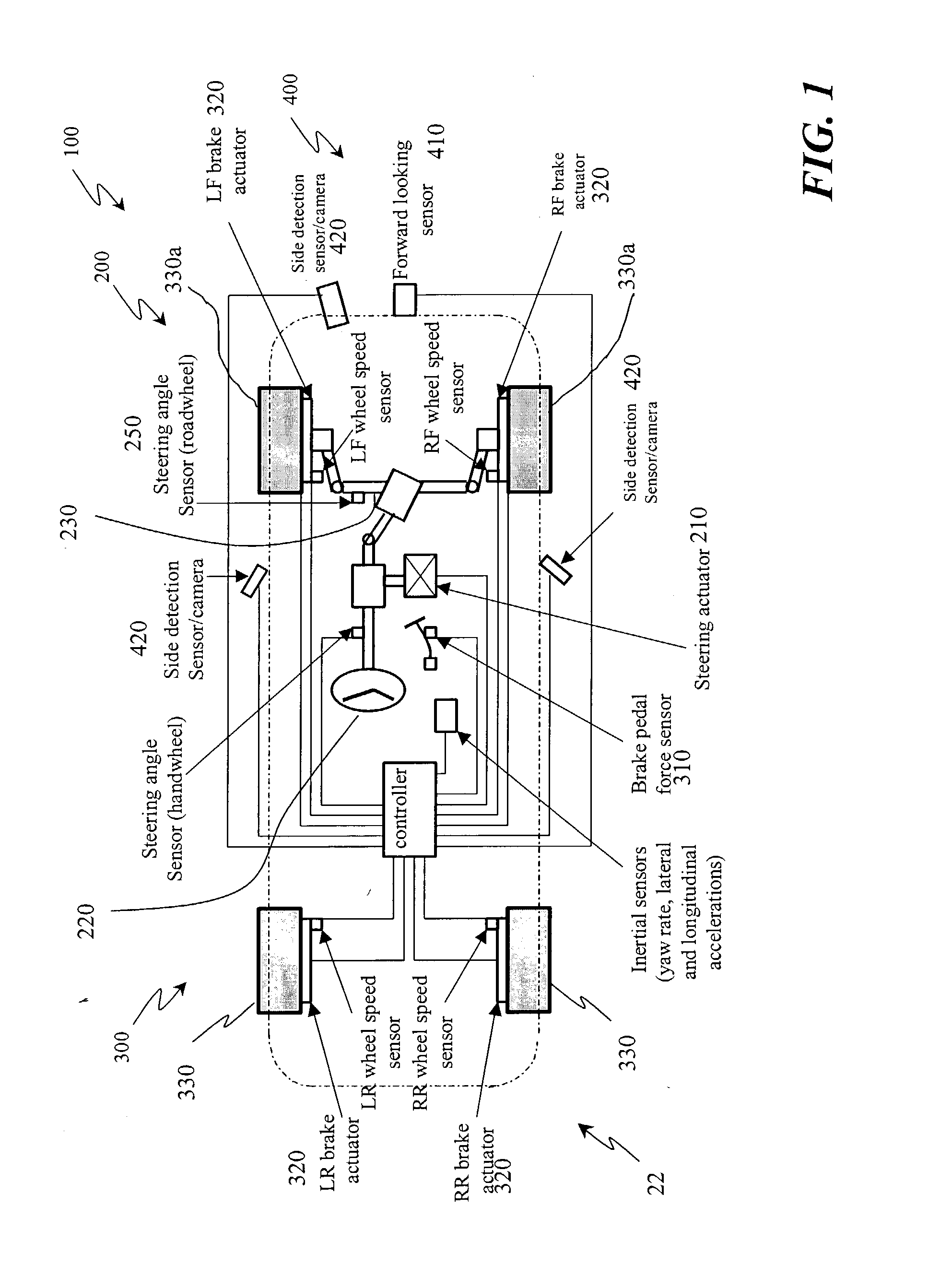
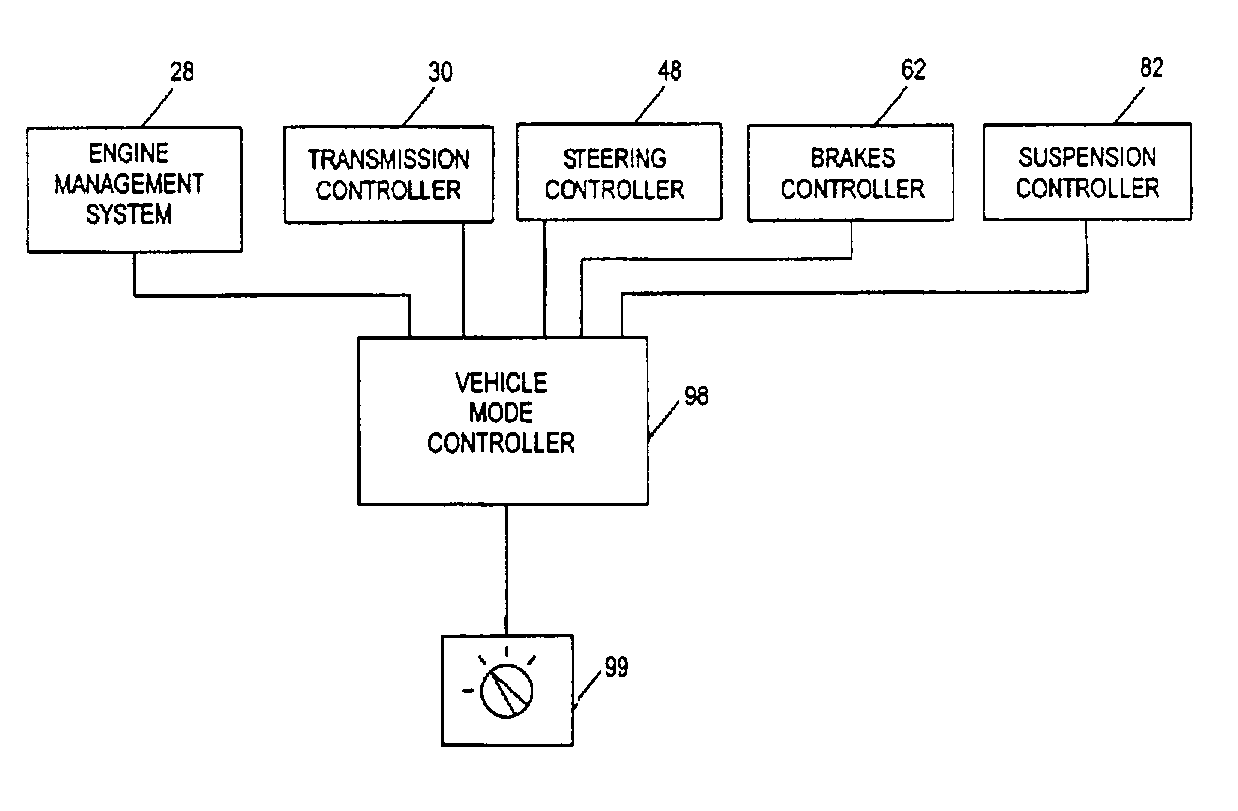
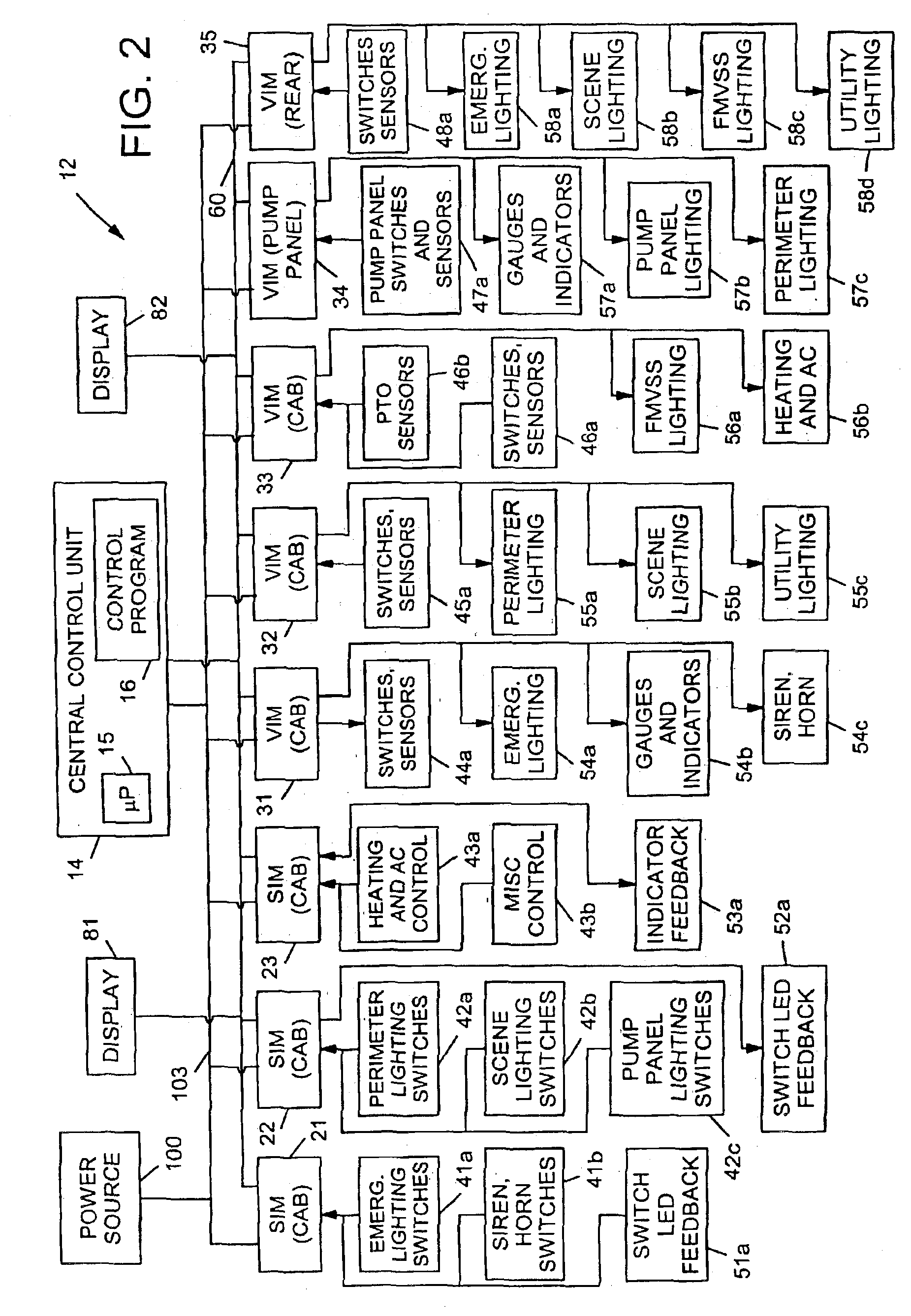
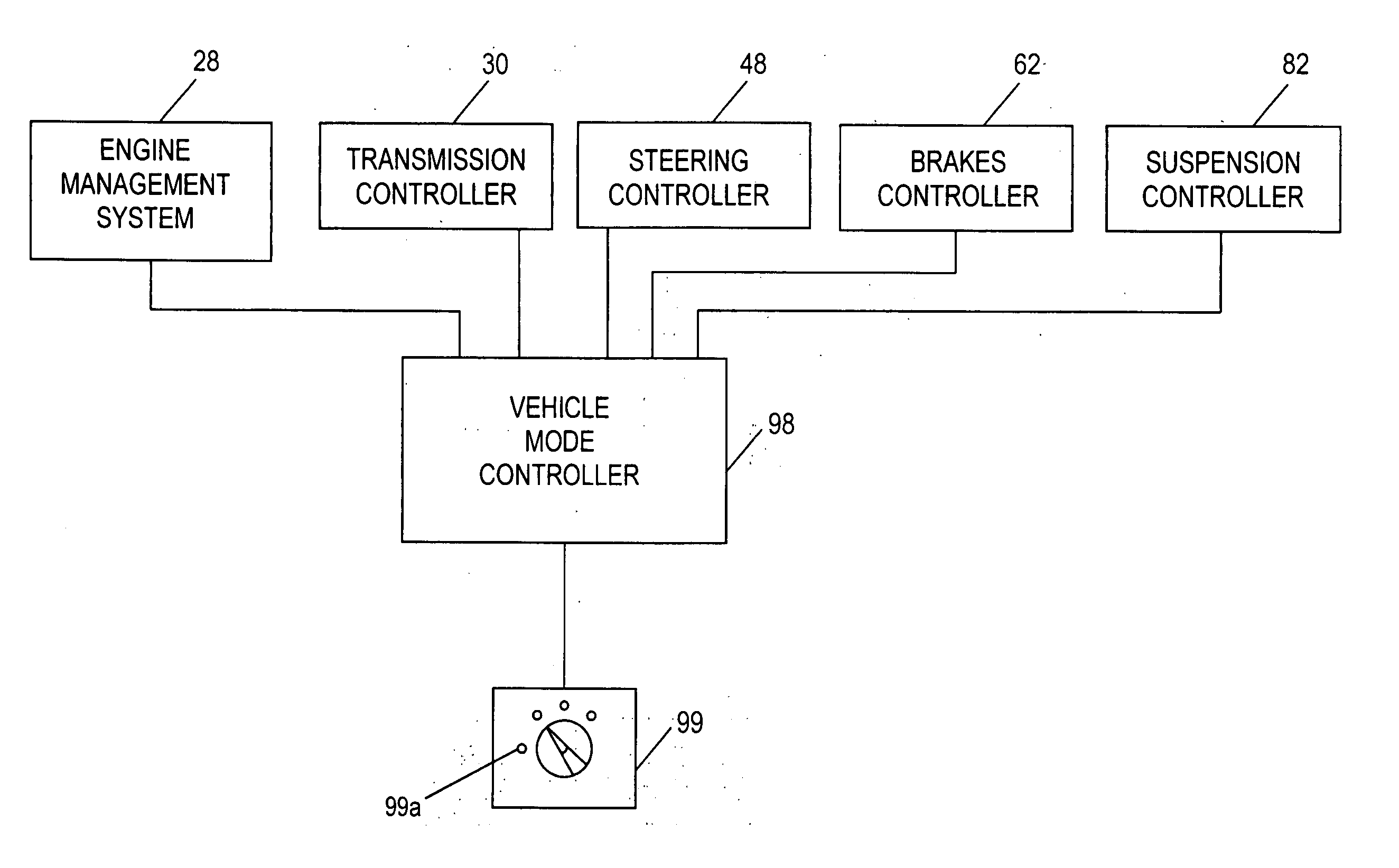
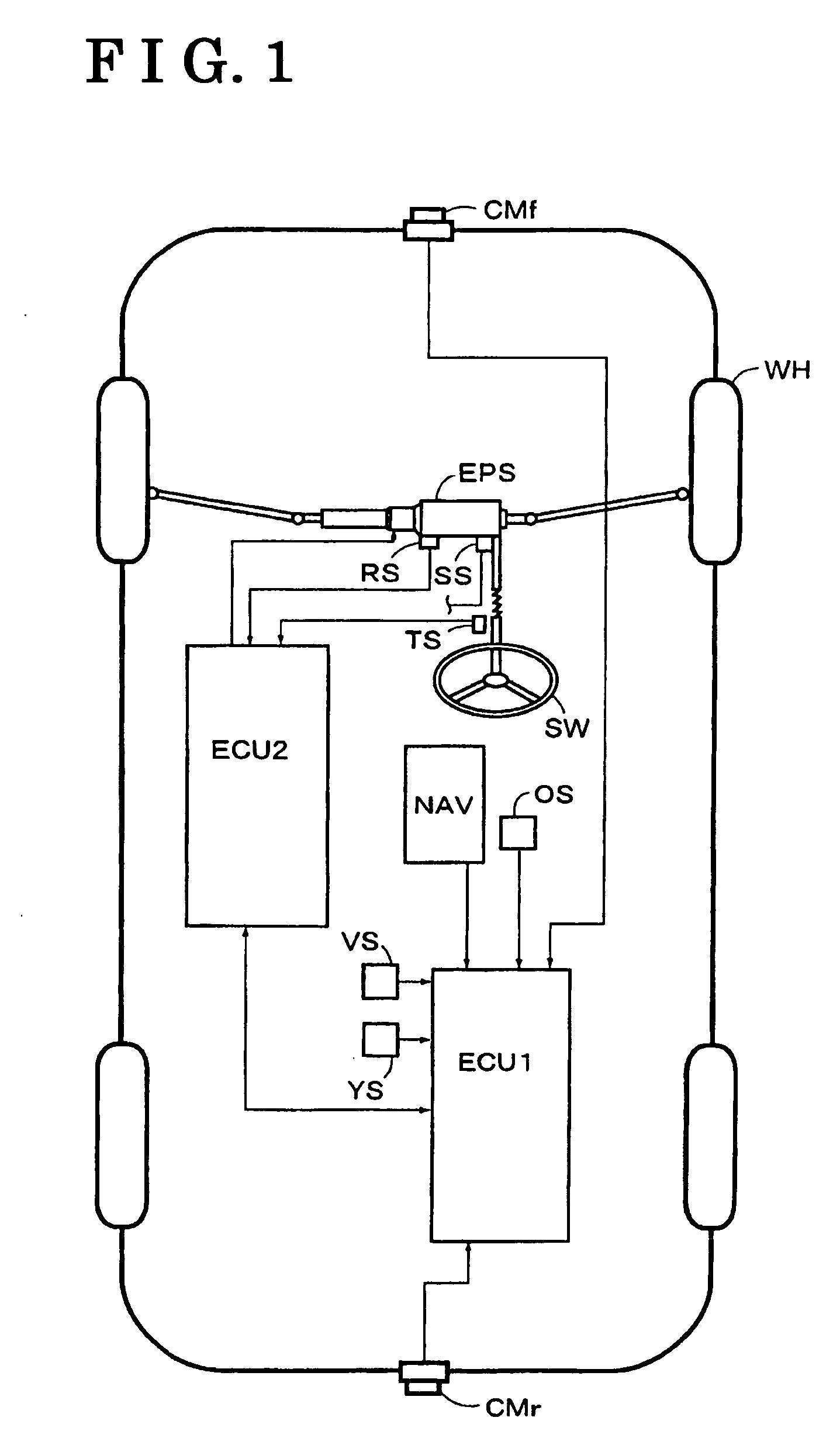
ActiveUS7349776B2Improved vehicle controlEasy to controlBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsControl systemMode control
A vehicle control system has a plurality of subsystem controllers including an engine management system 28, a transmission controller 30, a steering controller 48, a brakes controller 62 and a suspension controller 82. These subsystem controllers are each operable in a plurality of subsystem modes, and are all connected to a vehicle mode controller 98 which controls the modes of operation of each of the subsystem controllers so as to provide a number of driving modes for the vehicle. Each of the modes corresponds to a particular driving condition or set of driving conditions, and in each mode each of the functions is set to the function in mode most appropriate to those conditions.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
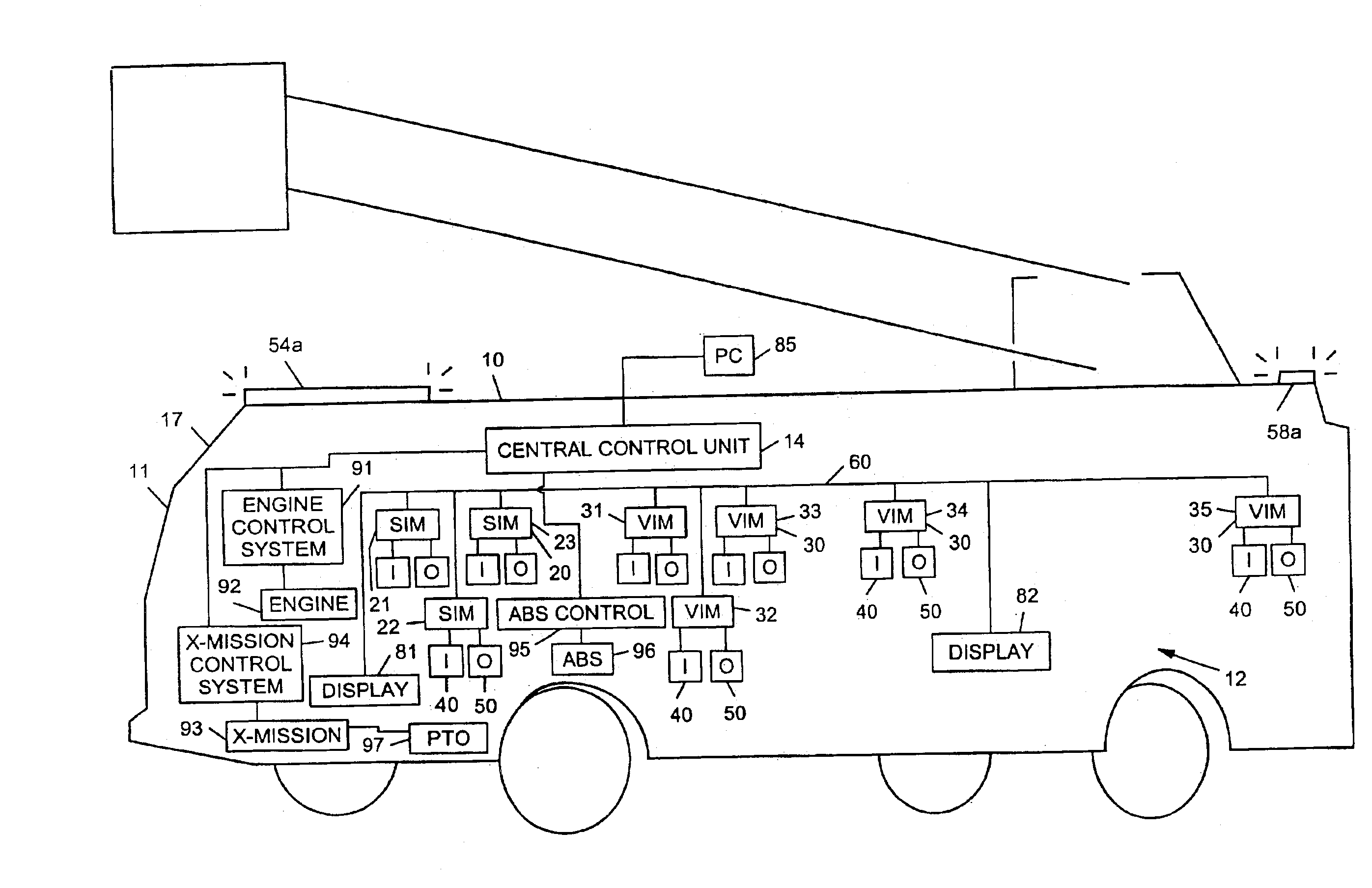
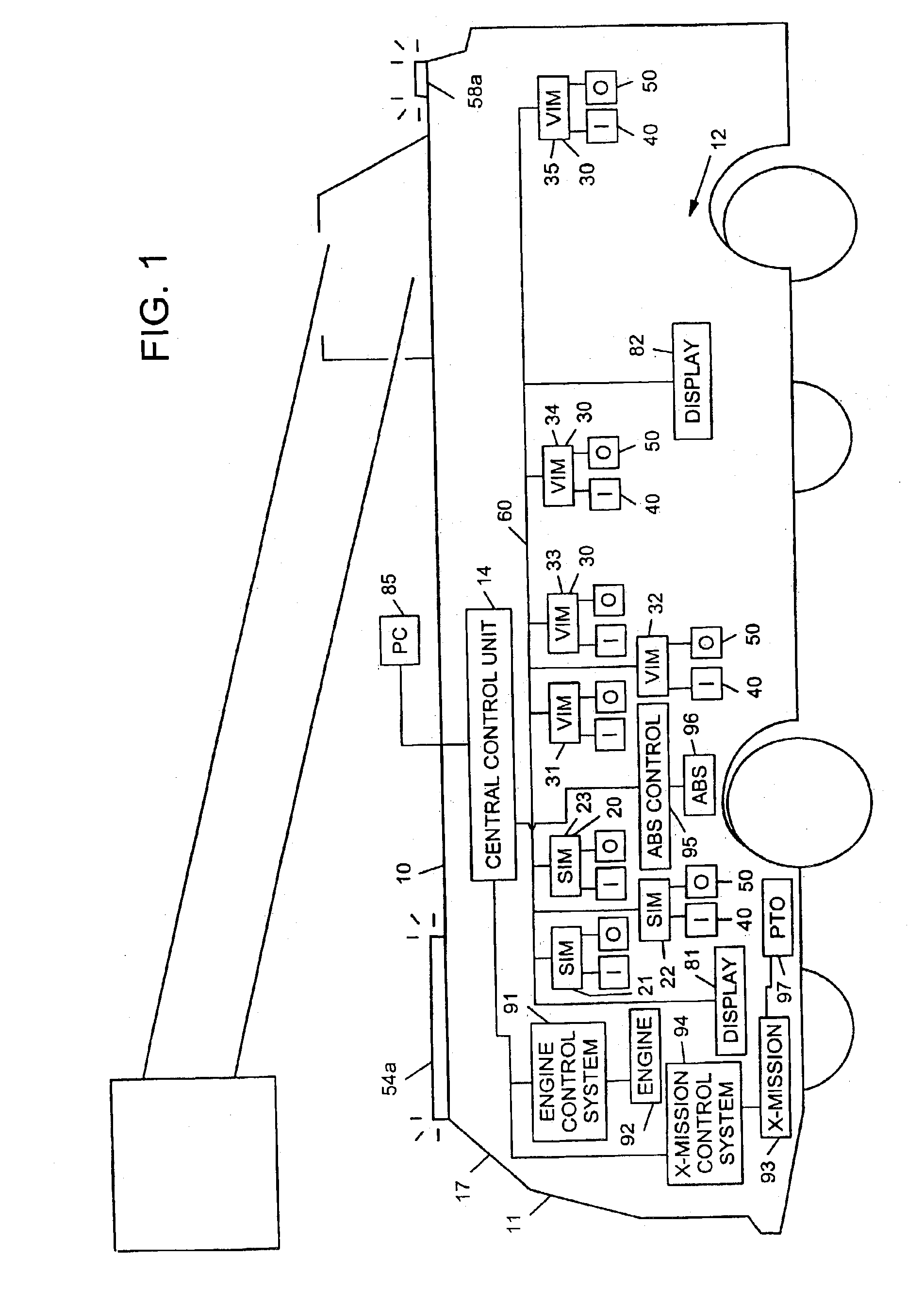
Steering control system and method
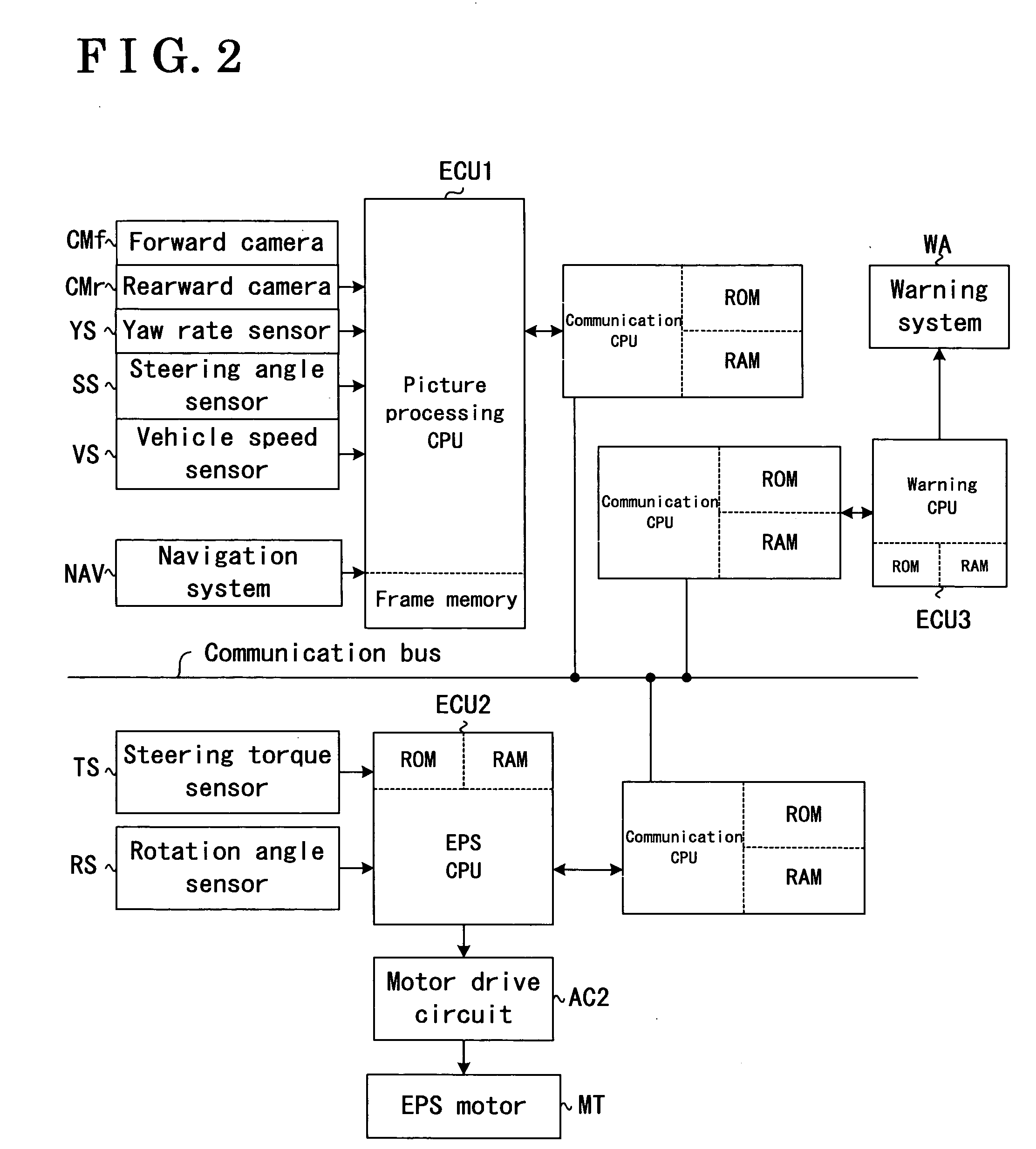
InactiveUS6882917B2Auxillary drivesRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesInformation controlElectronic control system
An electronic control system for a vehicle includes a plurality of input devices, a plurality of output devices, a communication network, and a plurality of interface modules. The plurality of input devices may include a first input device that provides information pertaining to an angular position of a first vehicle wheel. The plurality of output devices may include an actuator capable of adjusting one or both of the angular position of the first vehicle wheel or an angular position of a second vehicle wheel. The plurality of interface modules can be microprocessor based and can be interconnected to each other by way of the communication network. The plurality of interface modules may also be coupled to the plurality of input devices and to the plurality of output devices. The plurality of interface modules may include one or more interface modules that is coupled to the first input device and to the actuator. The electronic control system can be configured to control the angular position of one or both of the first and second vehicle wheels as a function of the information from the first input device.
Owner:OSHKOSH CORPORATION
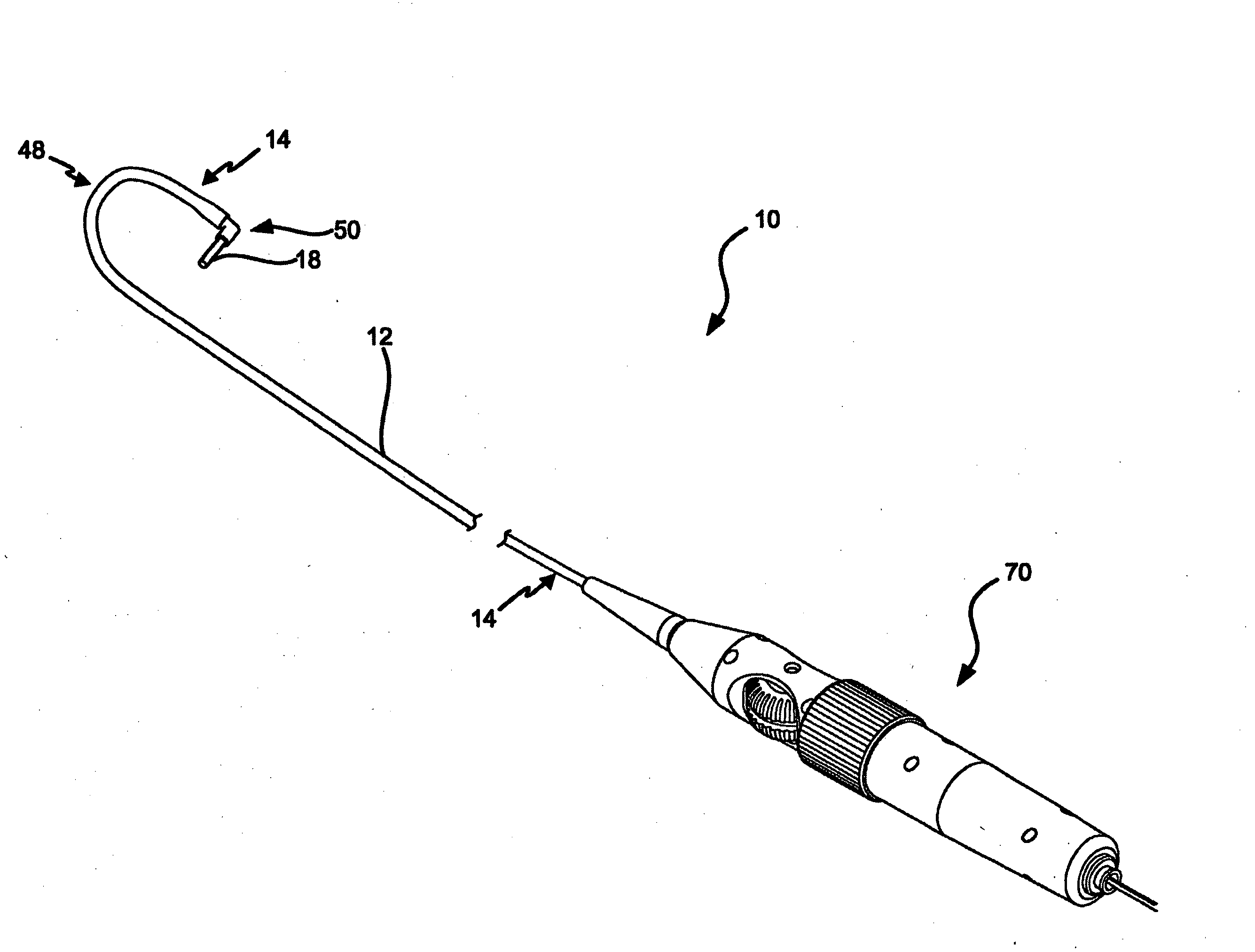
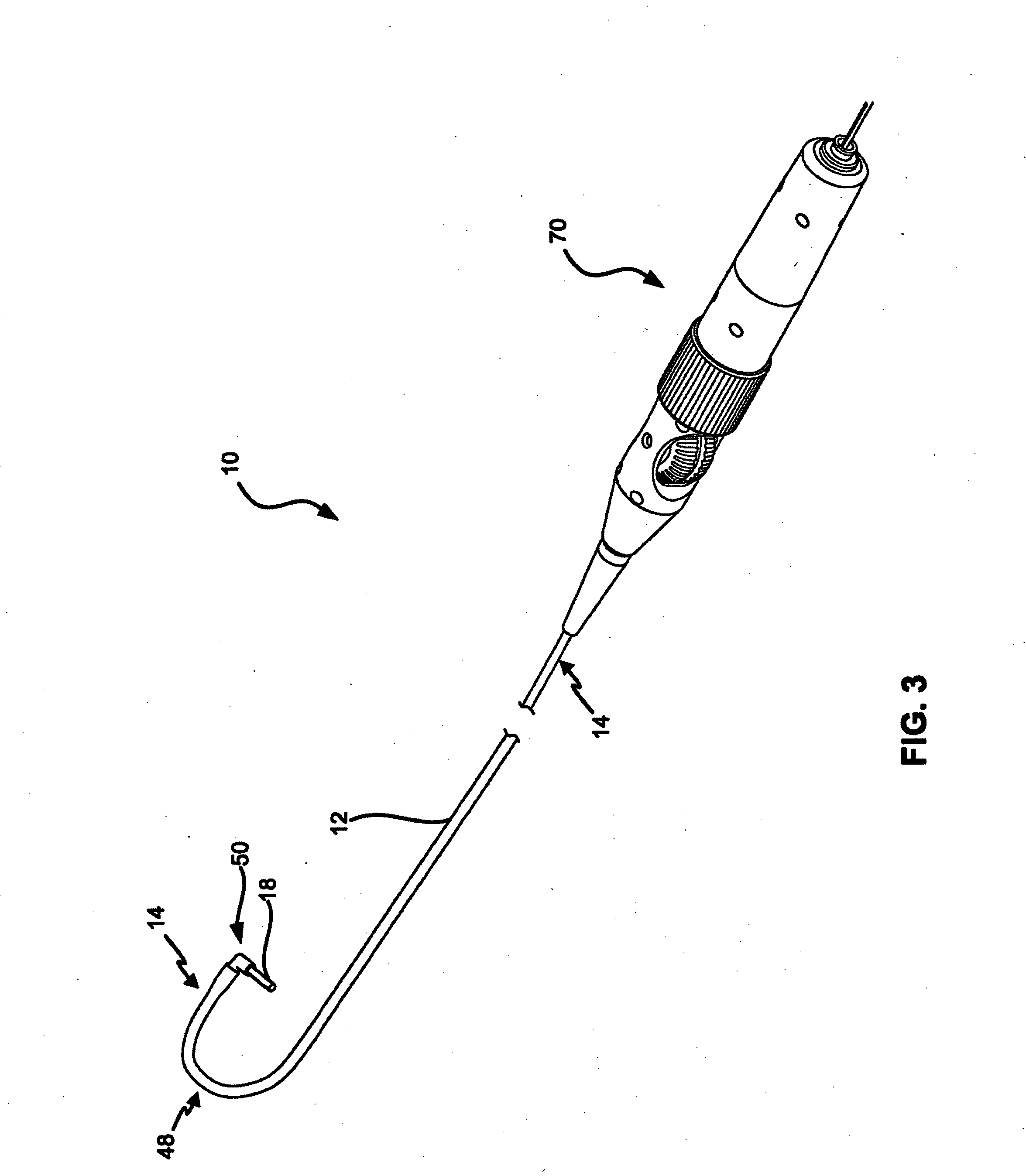
Ultrasound Imaging Catheter With Pivoting Head
ActiveUS20090264759A1Easy to viewUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryAnatomical structuresUltrasound imaging
An ultrasound imaging catheter system includes a pivot head assembly coupled between a ultrasound transducer array and the distal end of the catheter. The pivot head assembly includes a pivot joint enabling the transducer array to pivot through a large angle about the catheter centerline in response pivot cables controlled by a wheel within a handle assembly. Pivoting the ultrasound transducer array approximately 90° once the catheter is positioned by rotating the catheter shaft and bending the distal section of the catheter, clinicians may obtain orthogonal 2-D ultrasound images of anatomical structures of interest in 3-D space. Combining bending of the catheter by steering controls with pivoting of the transducer head enables a greater range of viewing perspectives. The pivot head assembly enables the transducer array to pan through a large angle to image of a larger volume than possible with conventional ultrasound imaging catheter systems.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
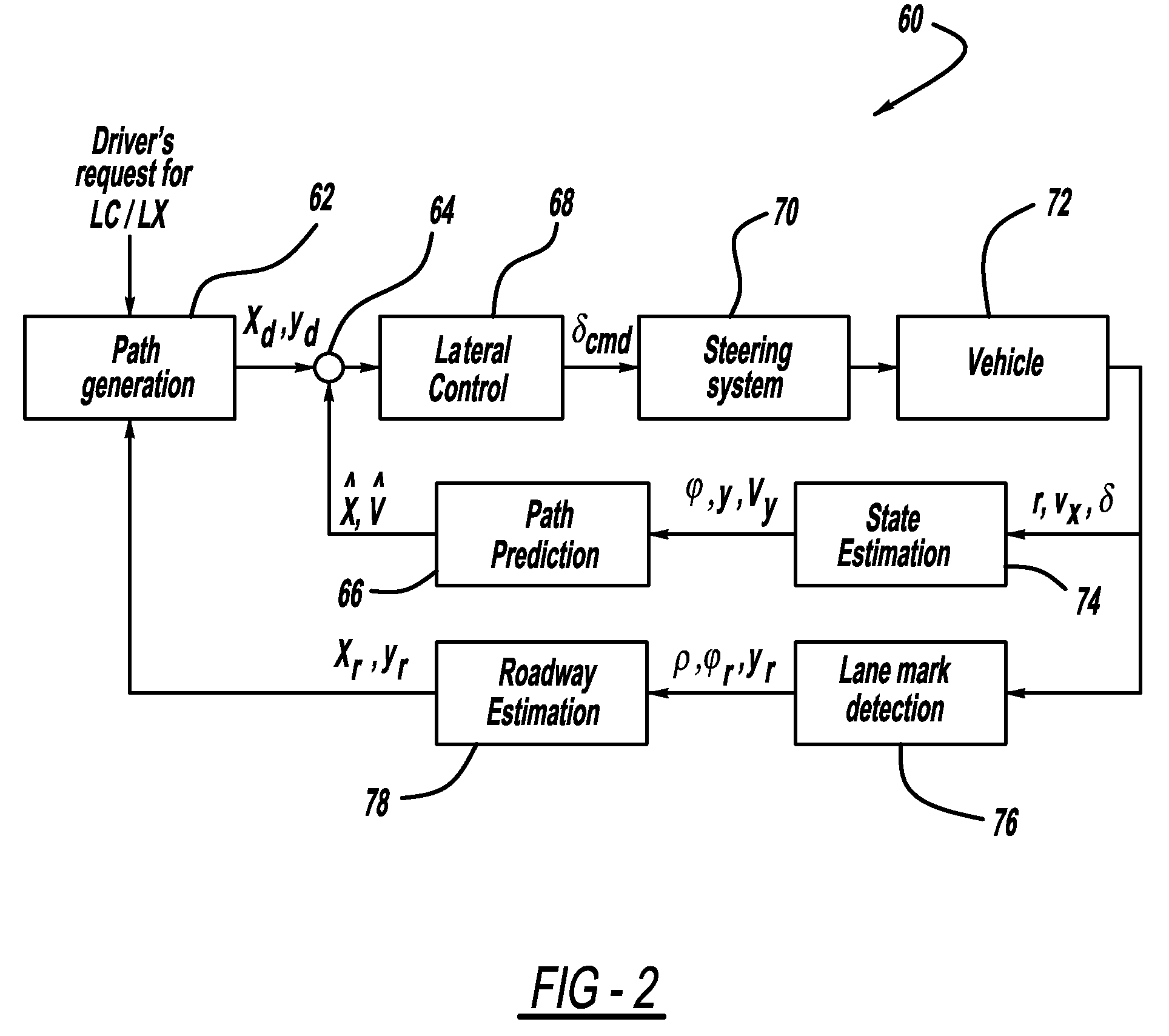
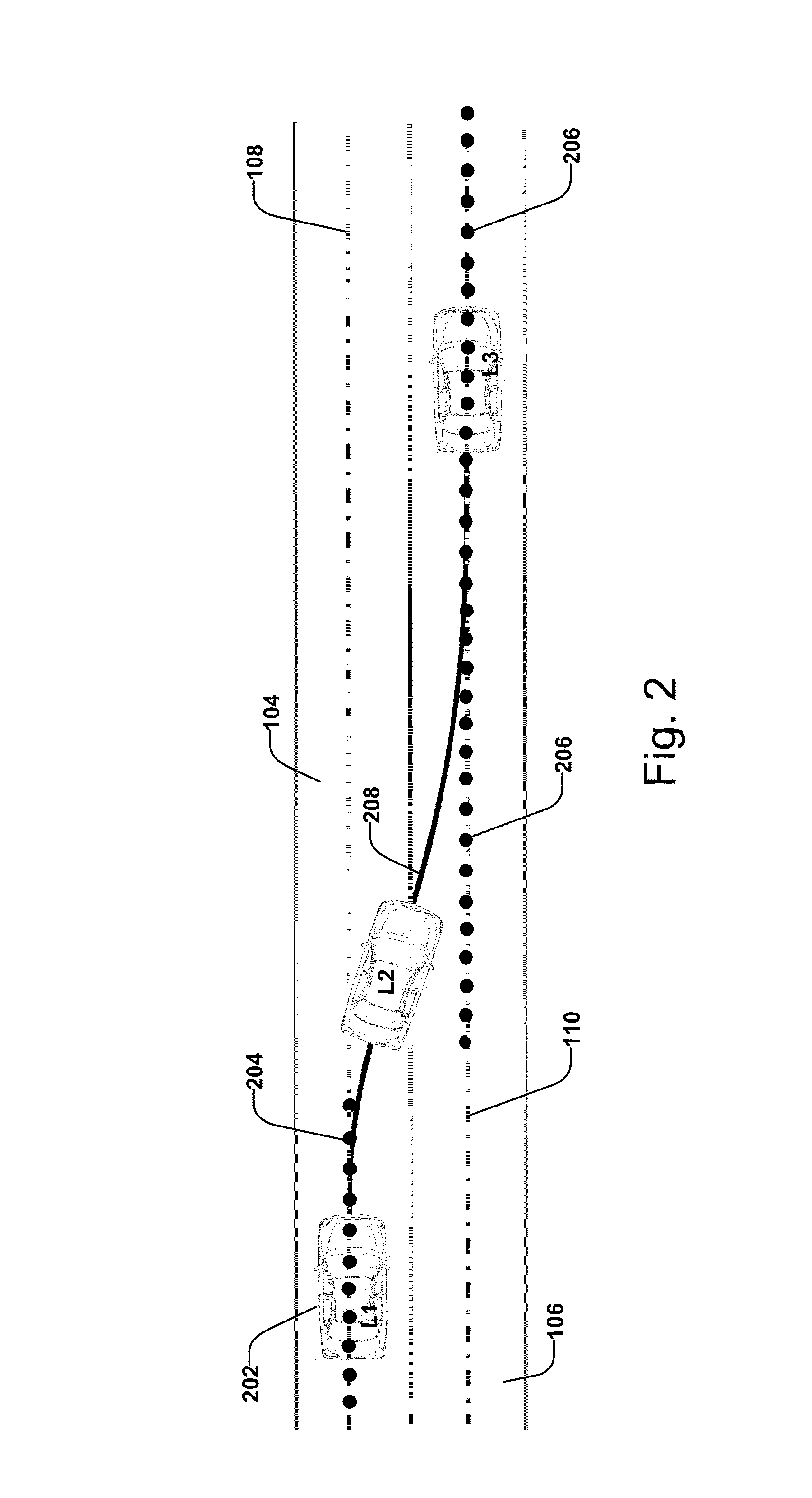
Model based predictive control for automated lane centering/changing control systems
ActiveUS20100228420A1Minimize error valueDigital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsVehicle dynamicsCompletion time
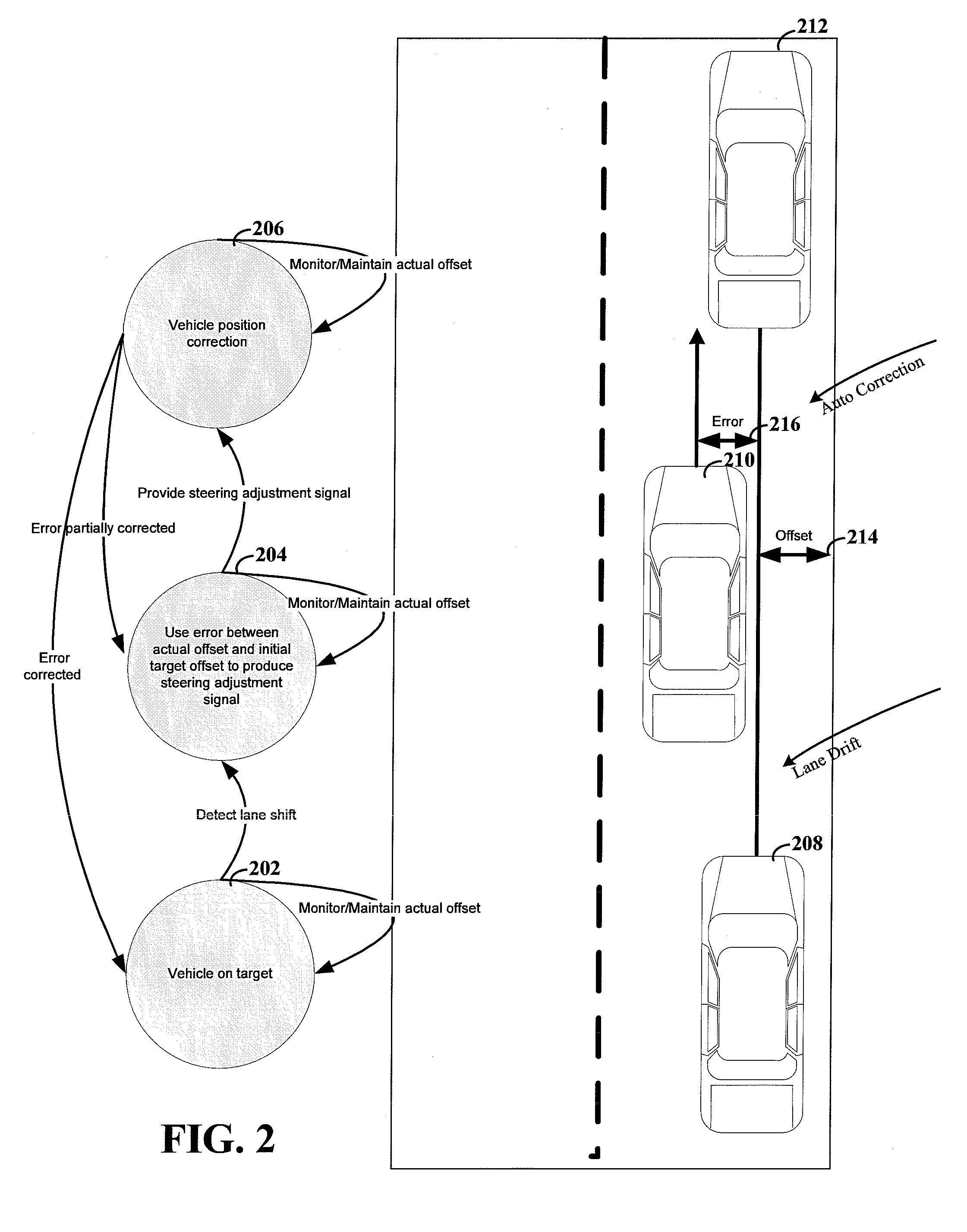
A system and method for providing steering control for lane changing and lane centering purposes in an autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle system. A vehicle vision system calculates roadway lane marking information, such as lateral offset, yaw angle and roadway curvature with respect to the vehicle's centered coordinate system. The roadway is then modeled as a second order polynomial equation. The method then predicts roadway lateral position and yaw angle over a pre-defined lane change completion time using a vehicle dynamic model. The method then compares a predicted vehicle path with a desired vehicle path to generate an error value, and calculates a steering angle command to minimize the error value, where the steering angle command is calculated as a function of vehicle lateral position, vehicle lateral speed, vehicle yaw rate and vehicle yaw angle. The steering angle command is then sent to the vehicle steering system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
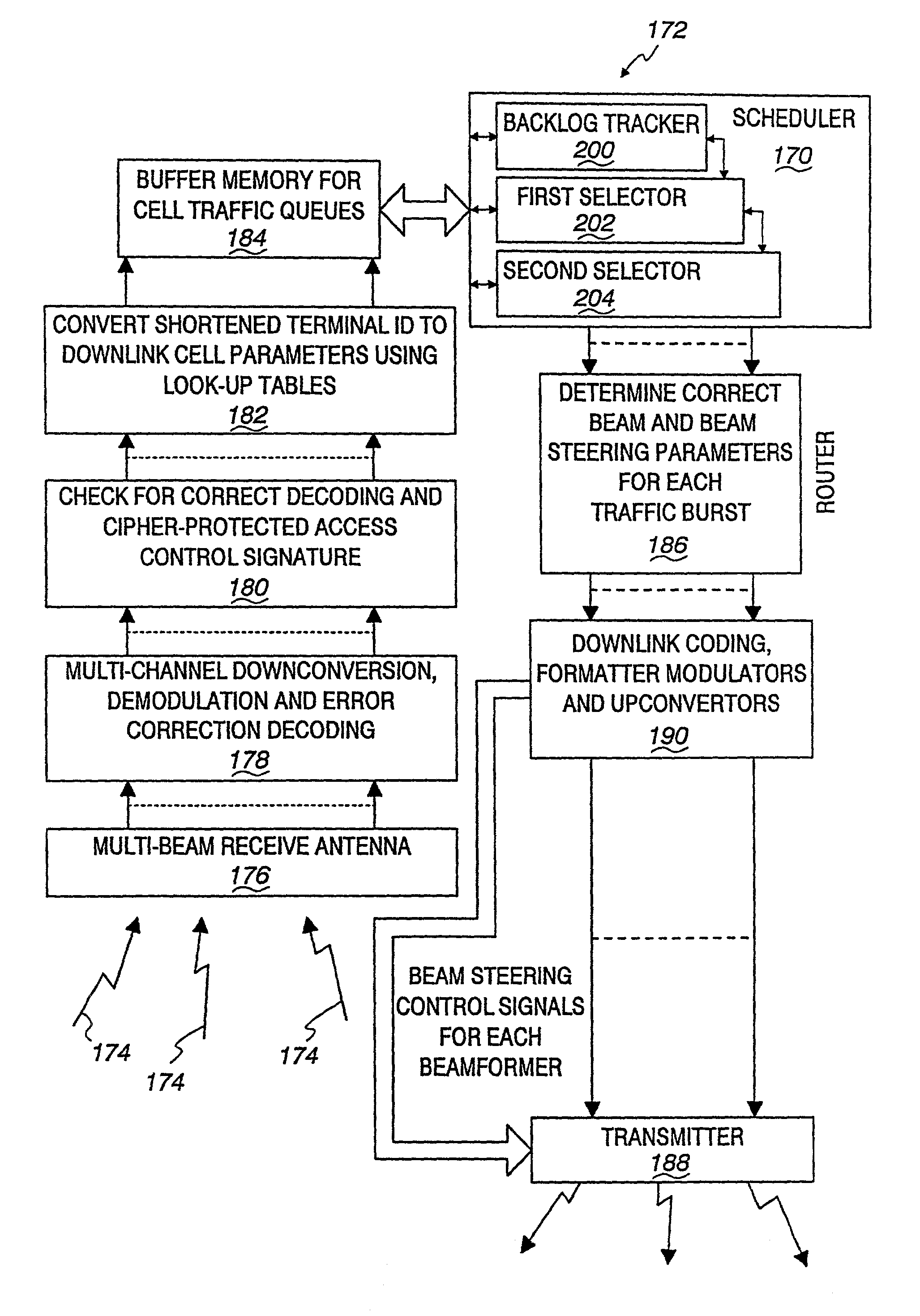
Multi-signal transmit array with low intermodulation
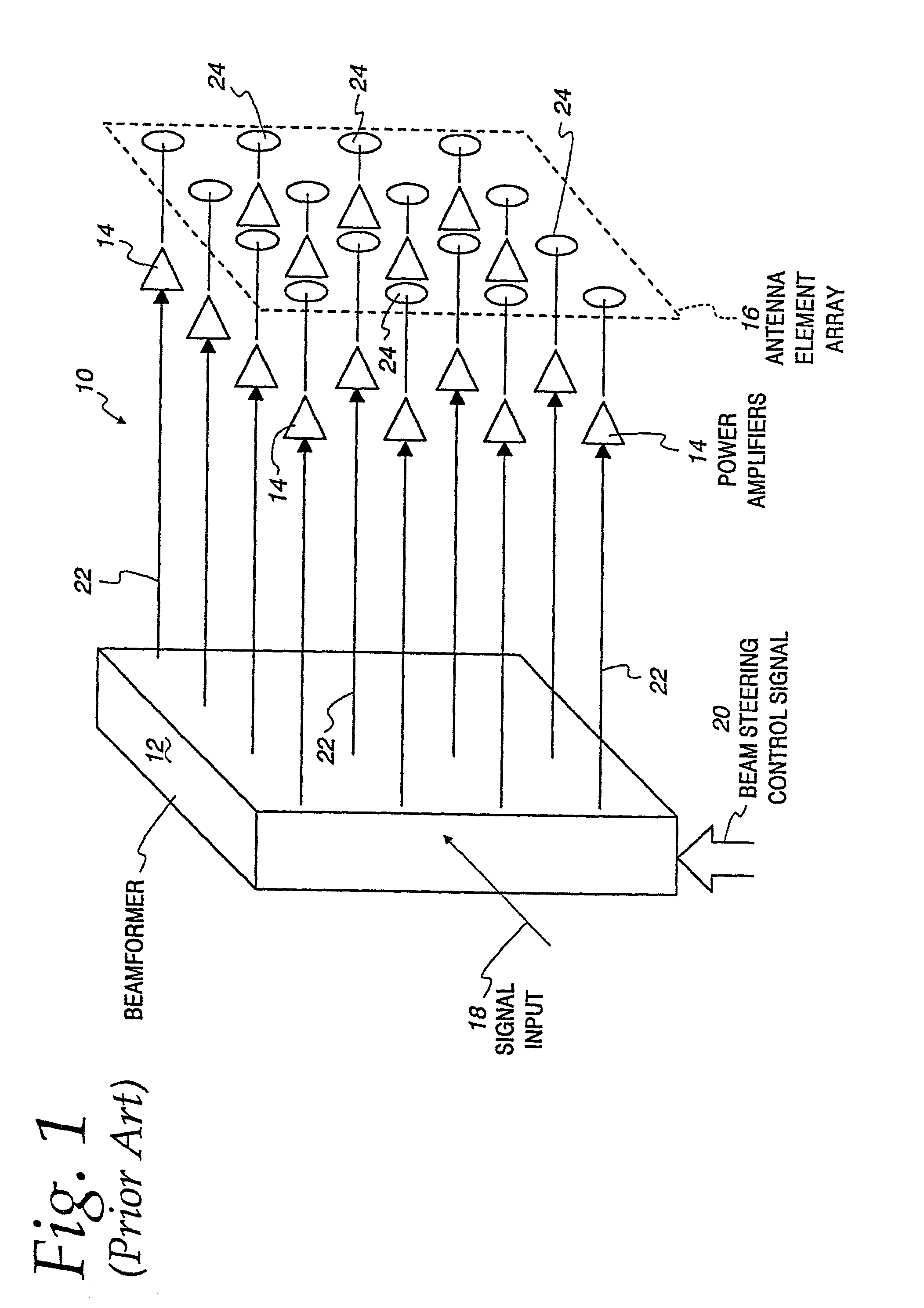
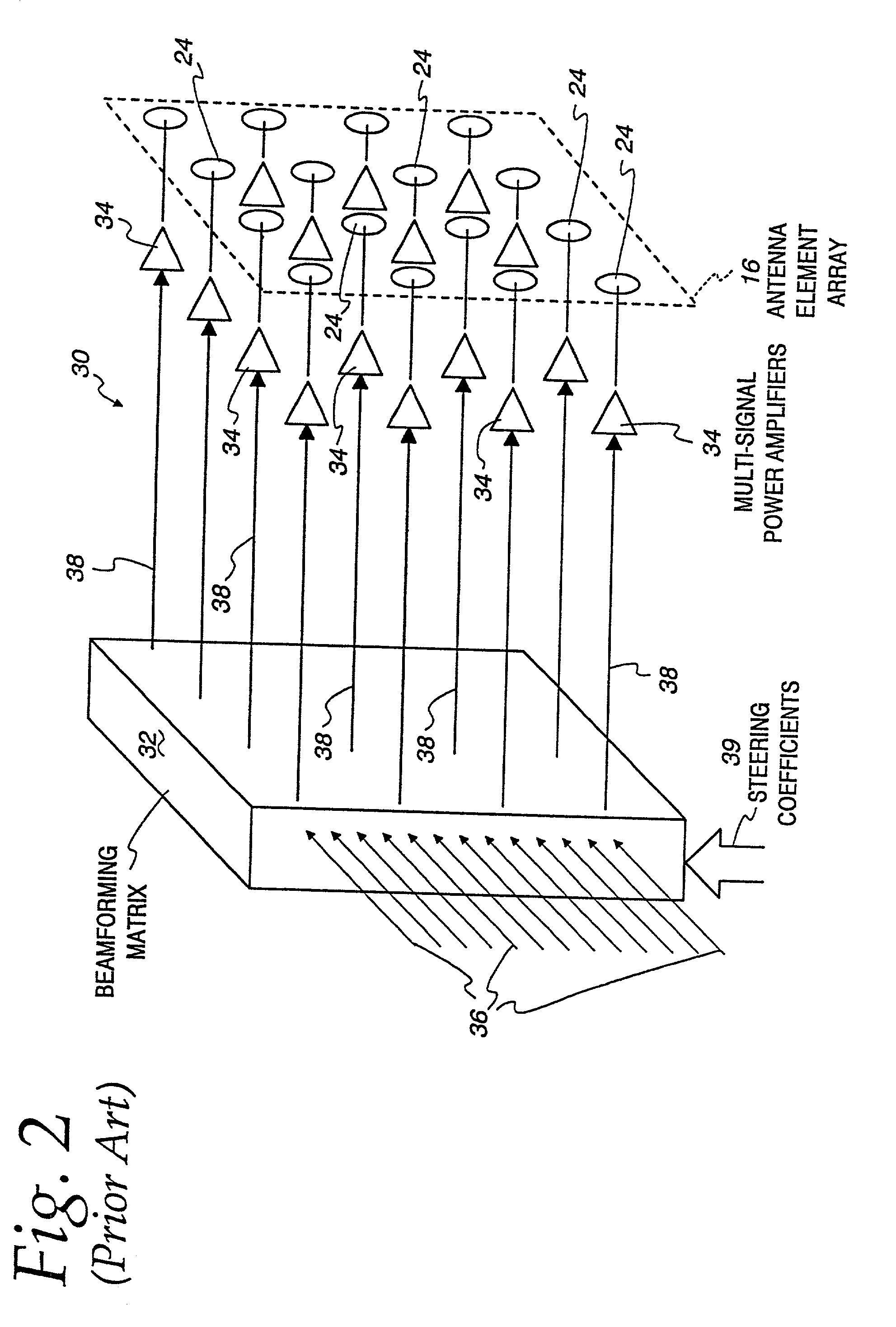
InactiveUS7027454B2Reduce unwanted out-of-band radiationImprove transmission efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsSteering controlAntenna element
A transmitter is provided for simultaneously transmitting a plurality of signals in a plurality of directive beams to corresponding destination stations, each destination station located in a separate fan within a service area. The transmitter includes a plurality of beamformers, each beamformer receiving one of the signals to be transmitted to an associated fan, each of the beamformers having a plurality of outputs for each different signal to be transmitted. A plurality of Butler matrices each receive one of the plurality of outputs from the plurality of beamformers for each different signal to be transmitted, each Butler matrix having a plurality of outputs in phased relationship to one another, wherein each of the signals to be transmitted is simultaneously provided across the outputs of each Butler matrix in a phased relationship. An antenna is provided with an aperture within which a two-dimensional array of antenna elements are disposed, wherein equal fractions of adjacent antenna elements are connected to the outputs of each Butler matrix, and wherein each of the plurality of signals are simultaneously transmitted by the entire two-dimensional array of antenna elements. Each of the plurality of beamformers receives steering control signals for steering the direction of each beam within its respective fan.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
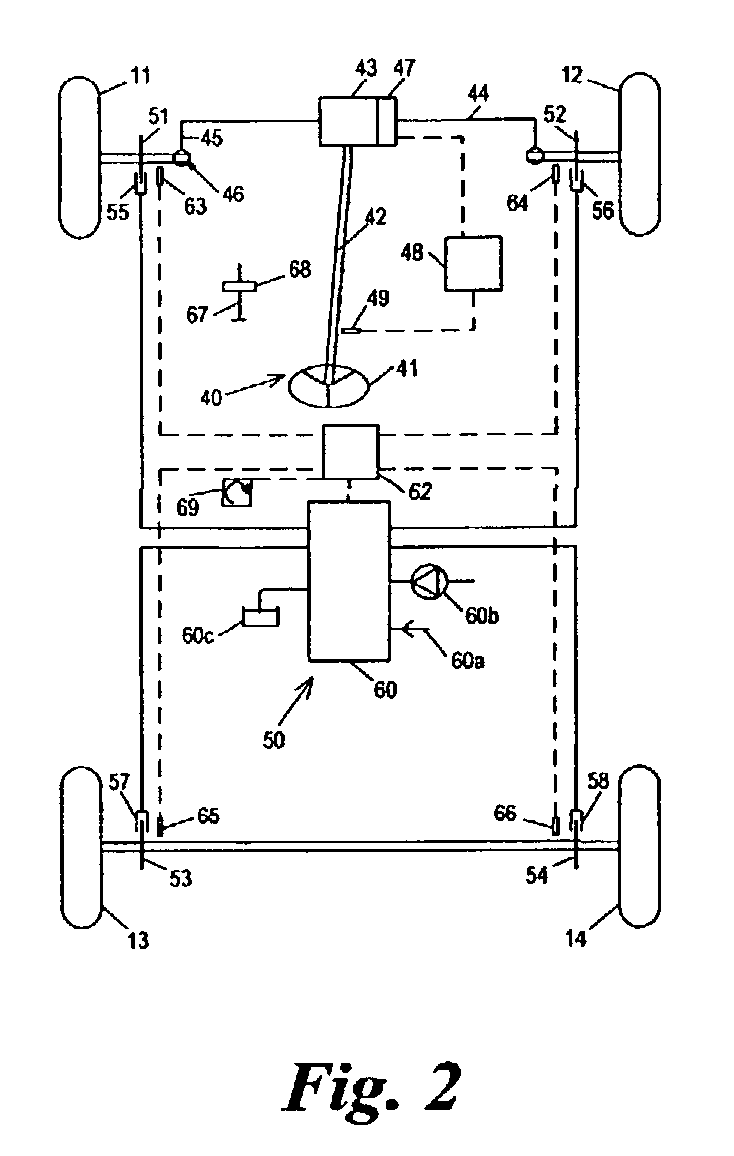
Vehicle control method and apparatus
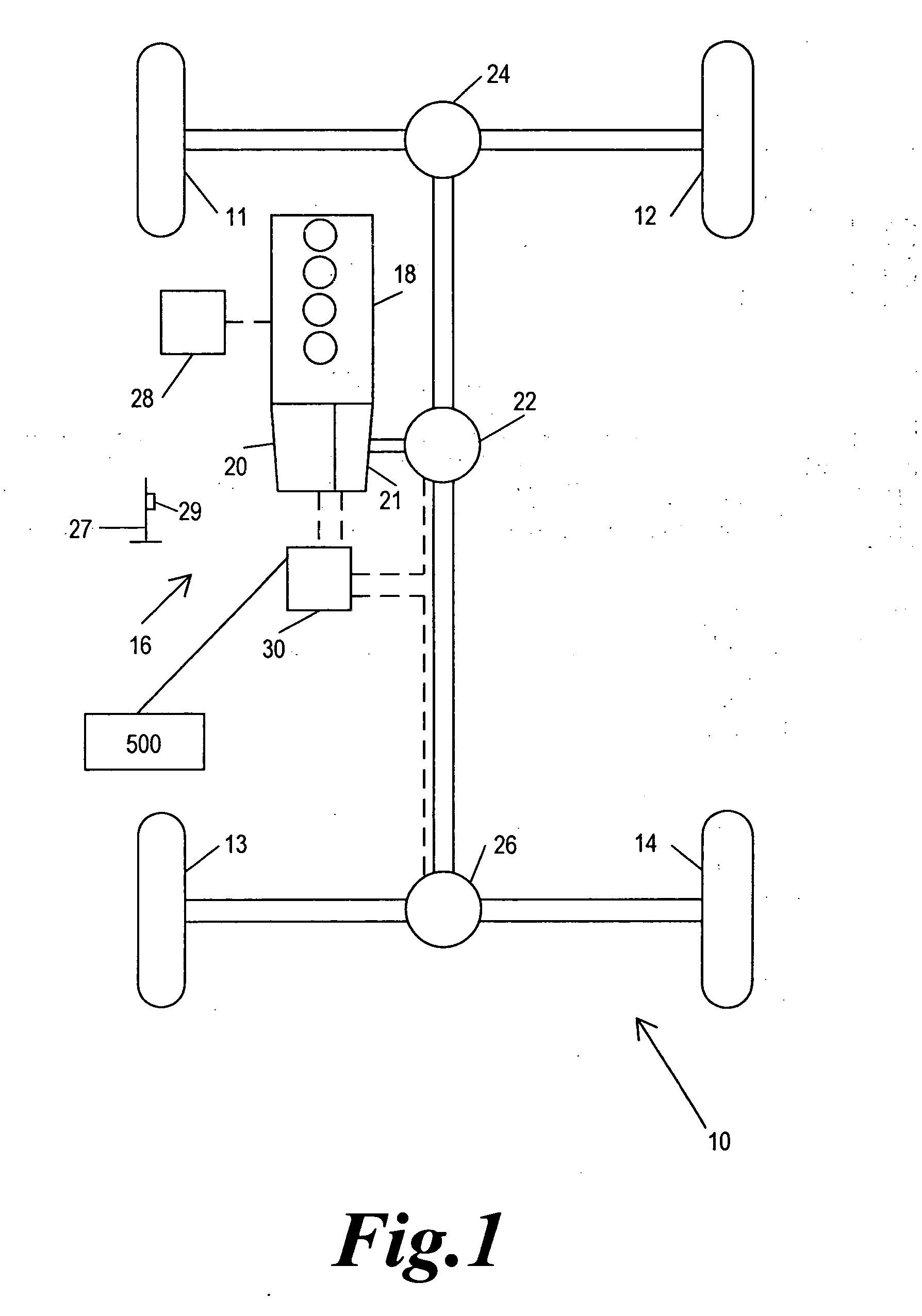
ActiveUS20050004732A1Minimizes combinationMaximize controlVehicle body stabilisationDigital data processing detailsTerrainMode control
A vehicle mode controller, a driving mode collecting means, and a plurality of subsystem controllers including an engine management system, a transmission controller, a steering controller, a brakes controller and a suspension controller, provide an improved system and method of operating a vehicle control system in a host vehicle in a manner suitable for a respective driving surface in a plurality of different off-road surfaces and terrains such as might be encountered when driving off-road. An improved method is provided for controlling a vehicle control system by avoiding unplanned combinations of subsystem configuration modes and minimizing the transition time when changing between subsystem configuration modes.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
Steering control sensor for an automatic vacuum cleaner
InactiveUS20070017061A1Automatic obstacle detectionTravelling automatic controlEngineeringSteering control
Owner:YAN JASON
Systems, methods and devices for adaptive steering control of automotive vehicles
ActiveUS20090299573A1Steering driverSteering evenDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsMobile vehicleDriver/operator
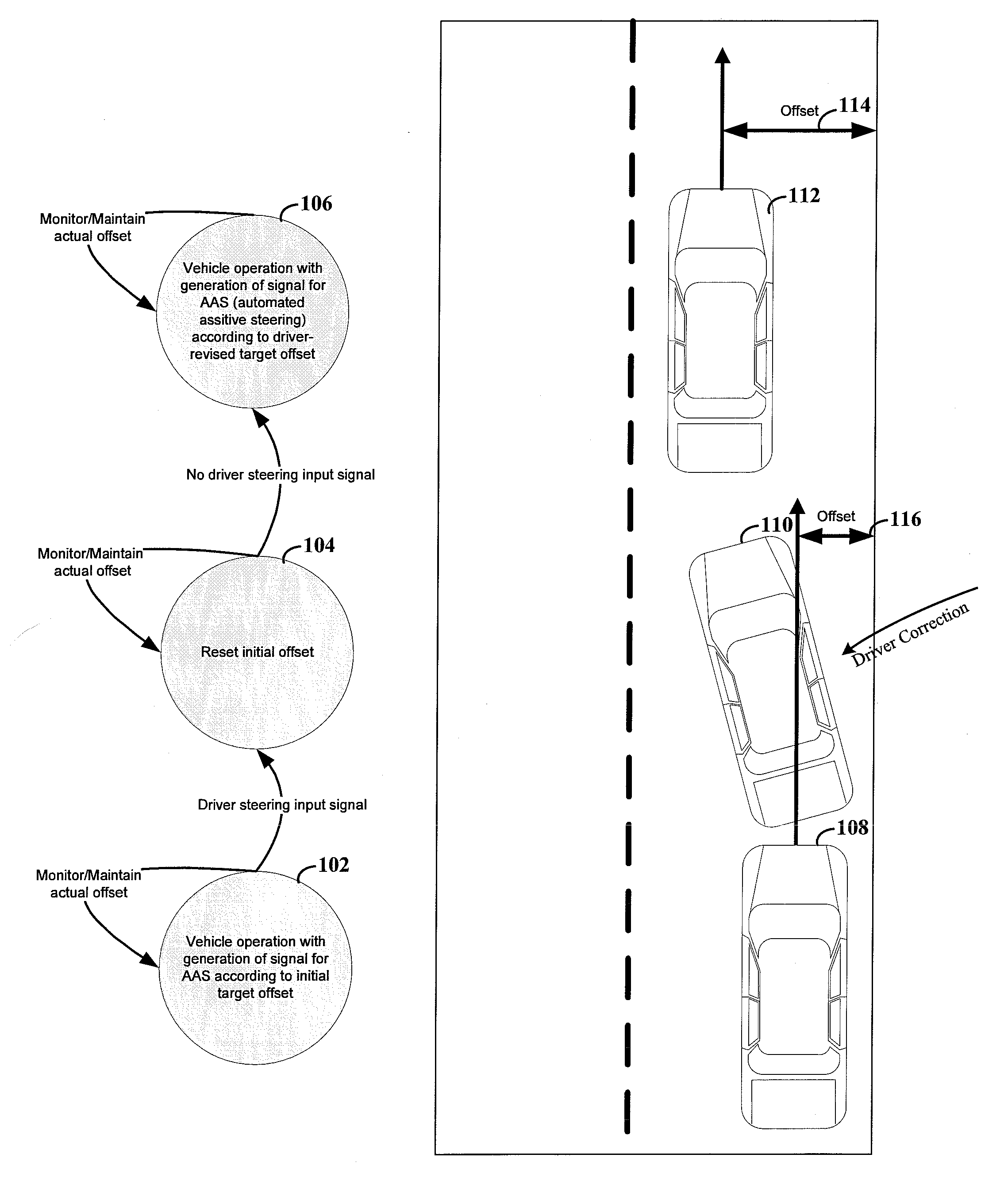
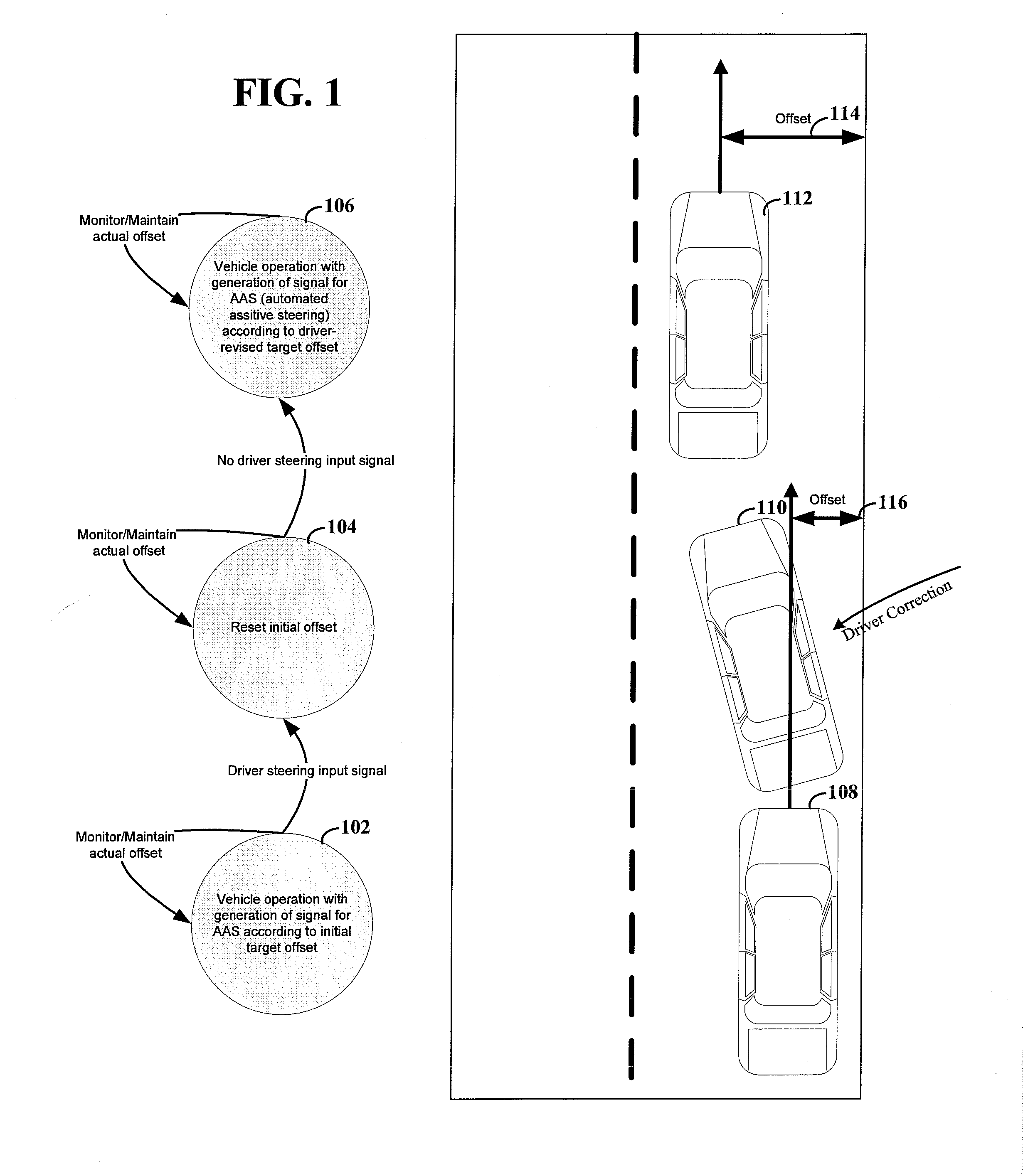
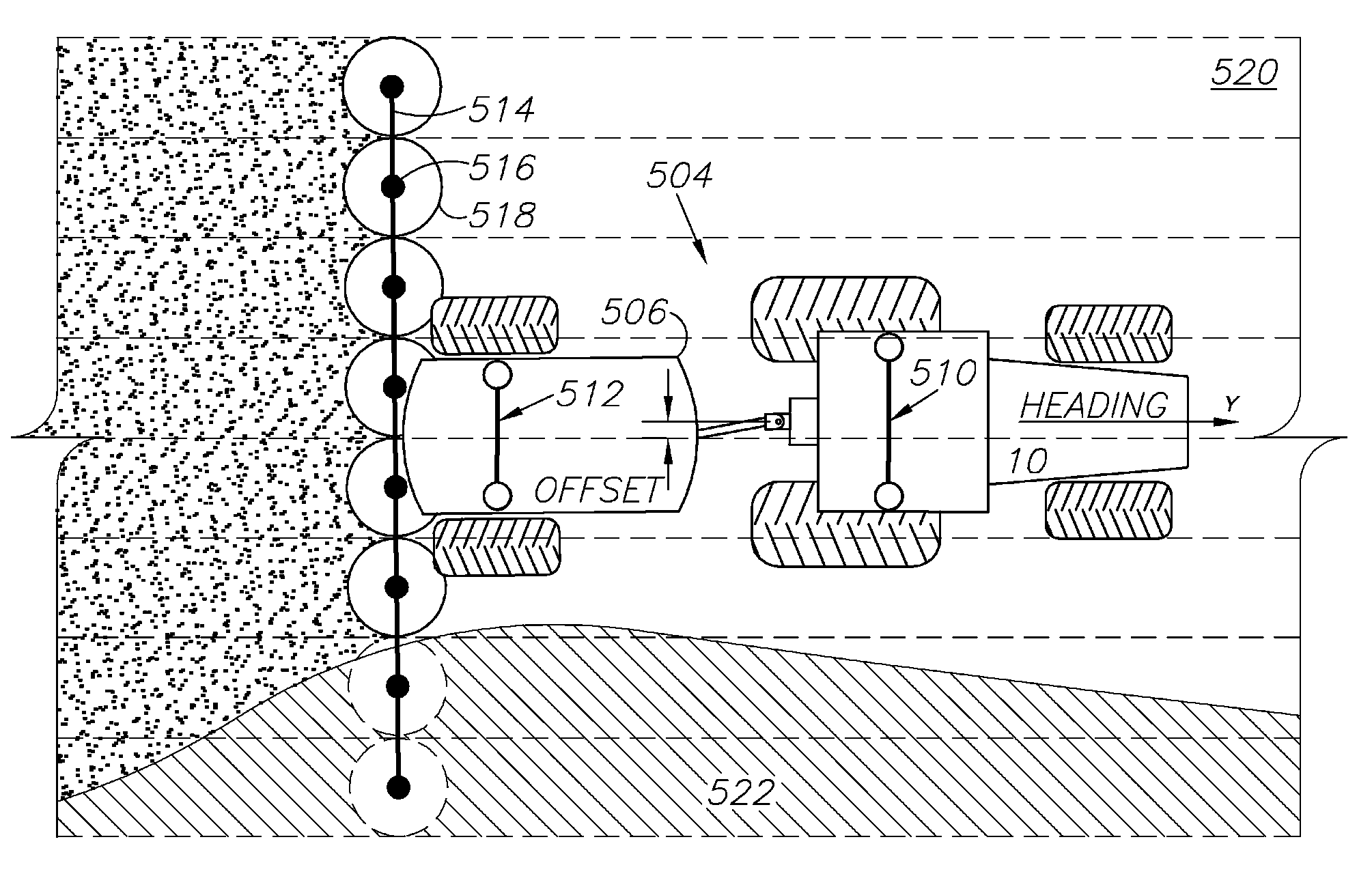
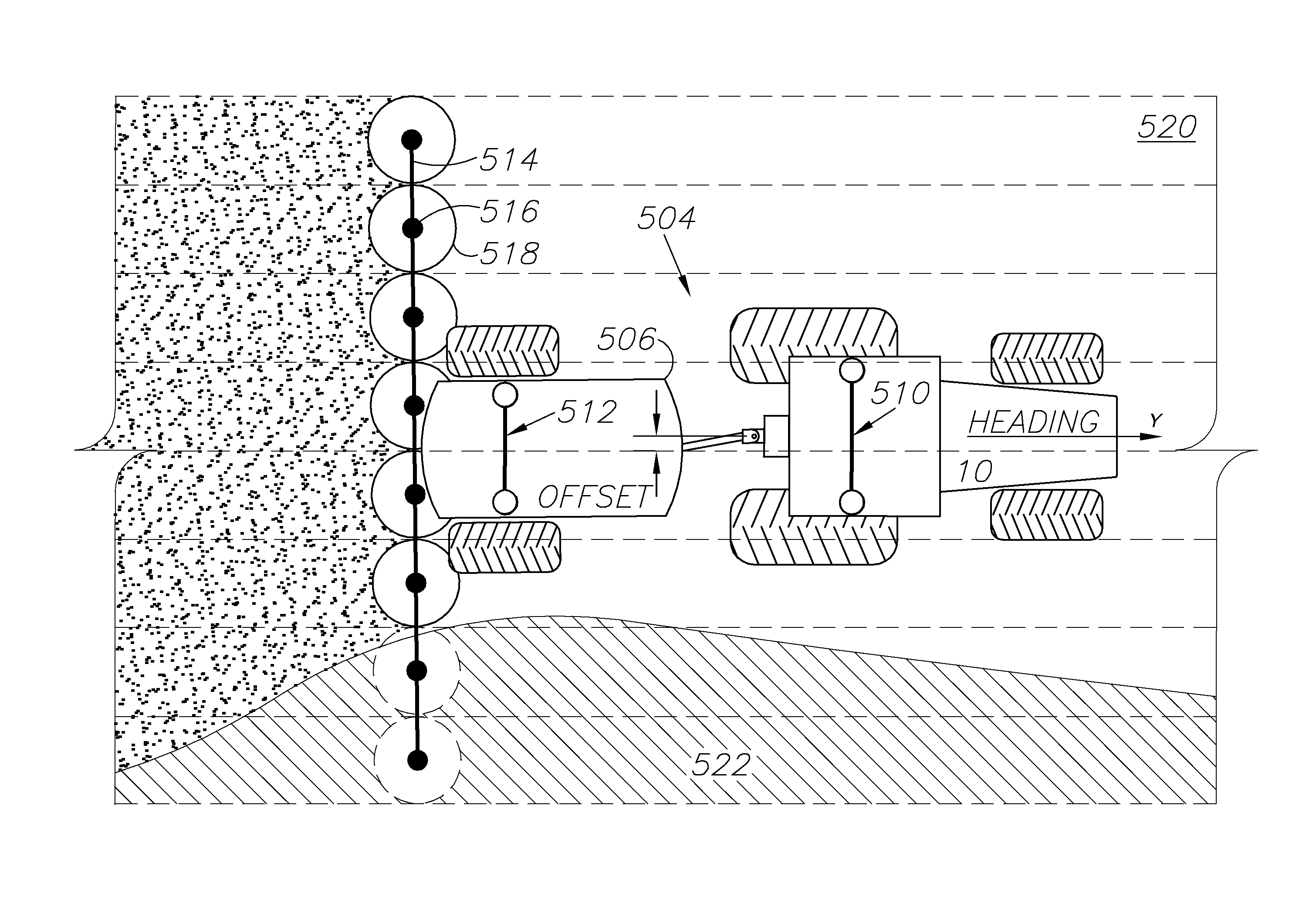
A variety of methods, systems, devices and arrangements are implemented for automated assistance for a driver. One such method relates to a synergistic combination of automation and human control for a motor vehicle traveling on a lane, thereby allowing human-based decisions to be supplement (or be supplemented by) automated decisions. Specific aspects facilitate maintenance of the vehicle on the lane. The vehicle is automatically steered towards a lateral offset within the vehicle lane. Steering input from the driver results in changes to this lateral offset. This modification of the lateral offset can be used to allow the driver to follow any trajectory parallel to the road, including trajectories where the vehicle is not centered within the lane.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Systems and methods for navigating a vehicle
An autonomous system includes a processing device programmed to receive, from an image capture device, an image of an environment of the host vehicle; detect an obstacle in the environment, based on an analysis of the image; monitor a driver input to at least one of a throttle control, a brake control, or a steering control associated with the host vehicle; determine whether the driver input results in the host vehicle navigating within a proximity buffer relative to the obstacle; allow the driver input to cause a corresponding change in one or more host vehicle motion control systems, if the processing device determines that the driver input would not result in the host vehicle navigating within the proximity buffer relative to the obstacle; and prevent the driver input to cause the change if the driver input results in the host vehicle navigating within the proximity buffer relative to the obstacle.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
Collision avoidance with active steering and braking
A method for collision avoidance using automated braking and steering comprising: determining an actual distance to an obstacle in a path of a vehicle; determining a relative velocity between the obstacle and the vehicle; determining a first distance sufficient to avoid collision by braking only; determining a second distance sufficient to avoid collision by combined braking and steering around the obstacle. The method also includes: applying braking if at least one of, the first distance exceeds the actual distance and the first distance is within a selected threshold of the actual distance. If the actual distance exceeds the second distance and a lane change is permitted, steering control to affect a lane change is applied.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA +1
GNSS and optical guidance and machine control
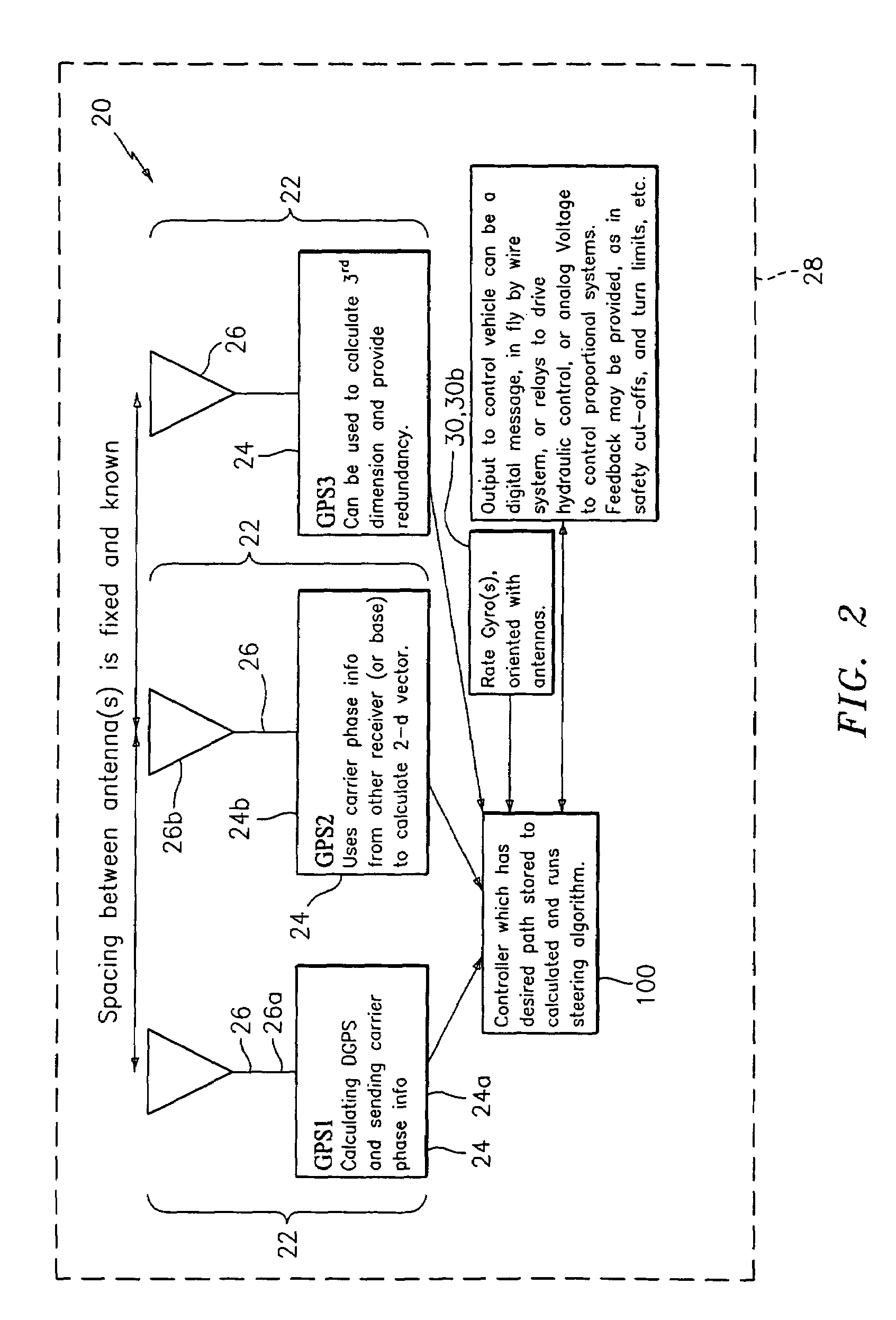
ActiveUS20140324291A1Accurate and economical preplannedEasy to correctDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCarrier signalSteering control
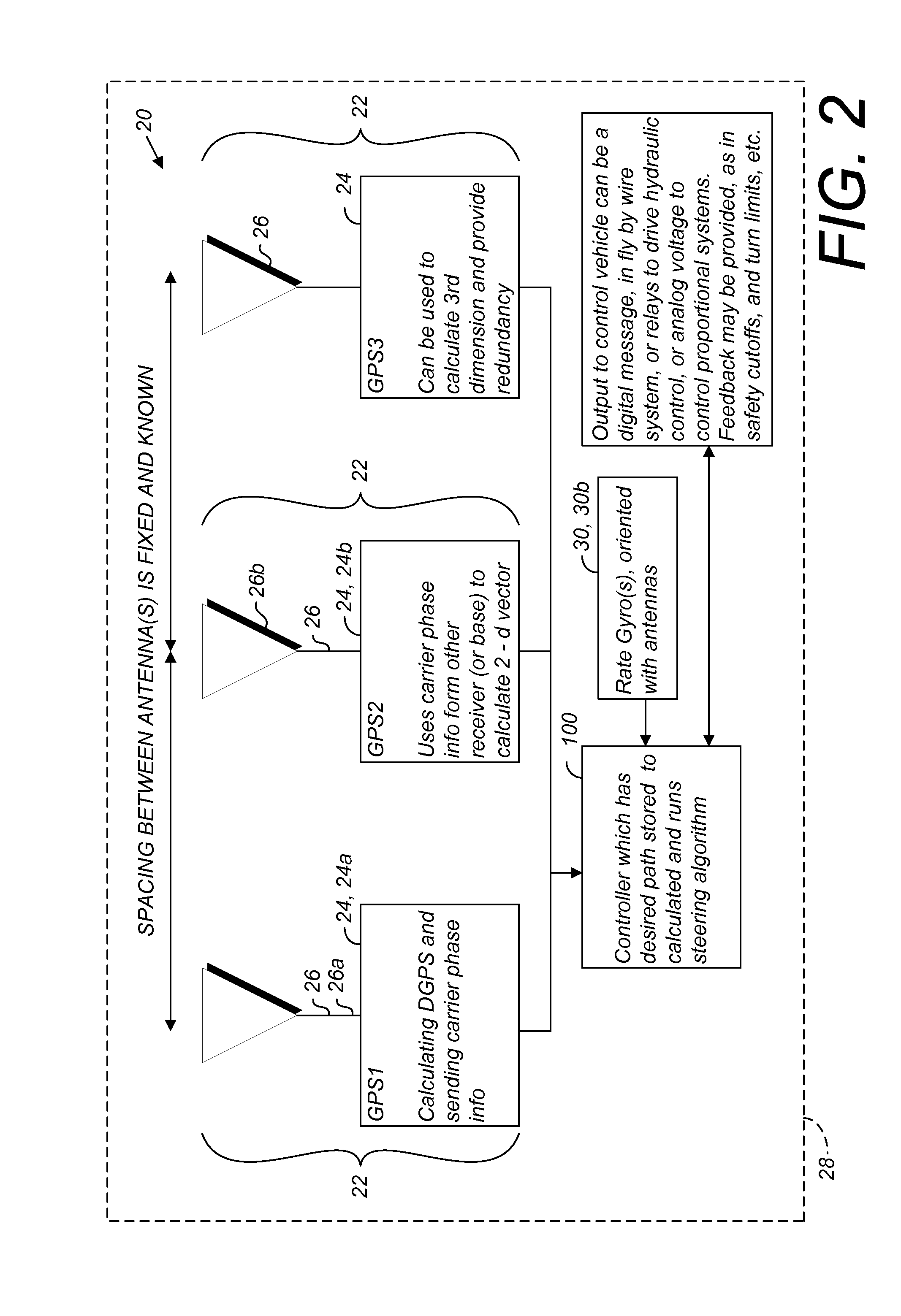
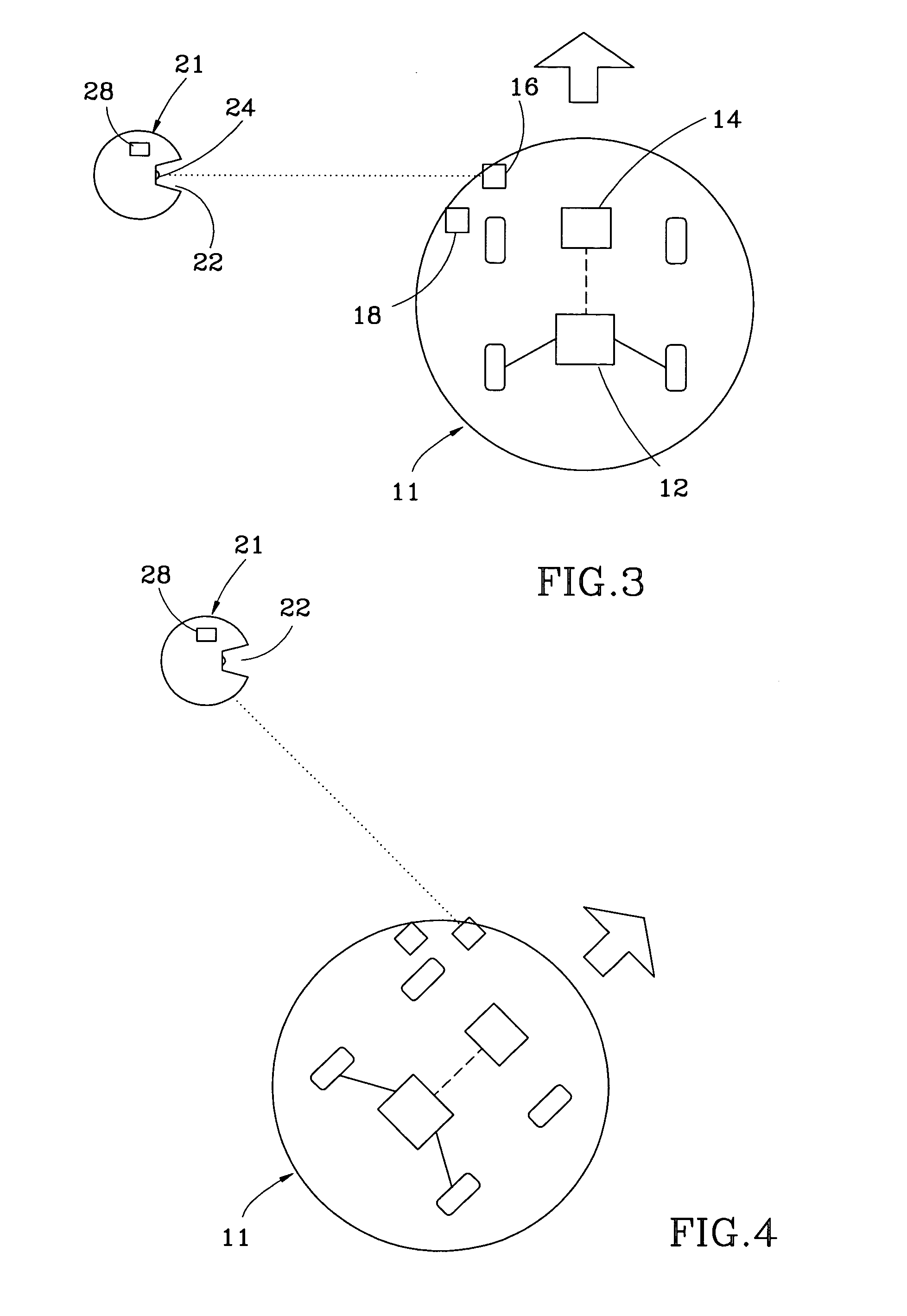
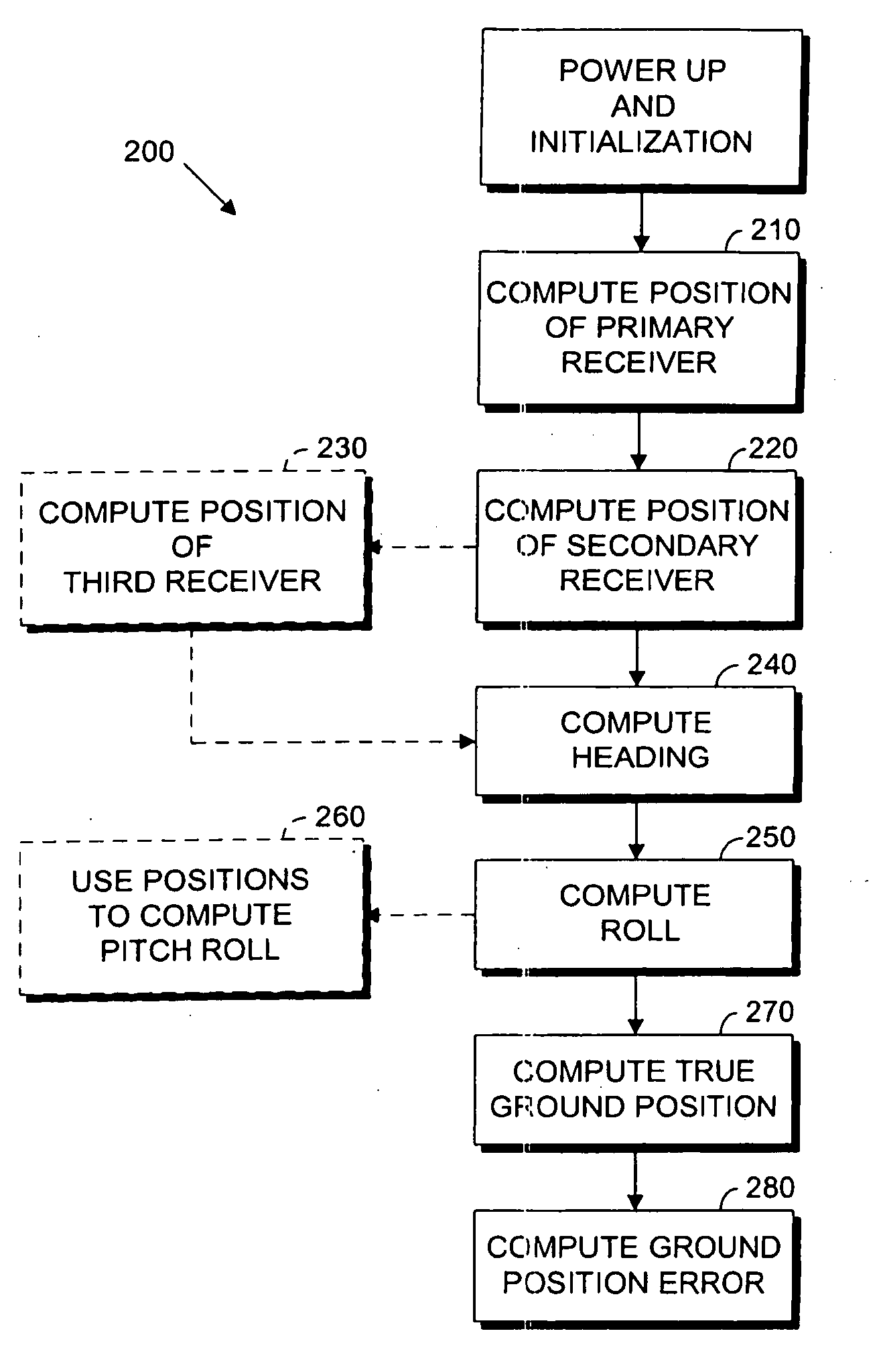
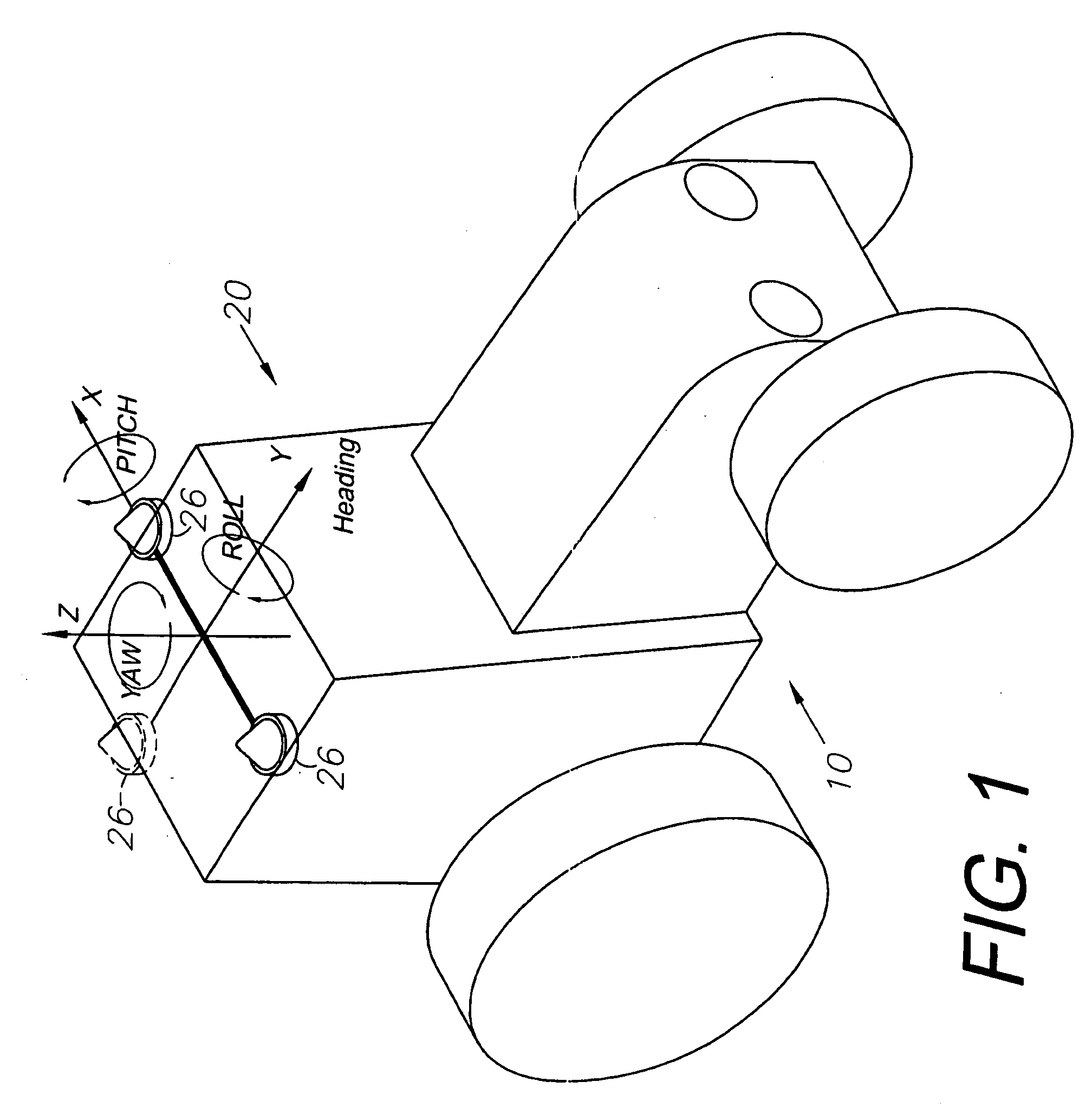
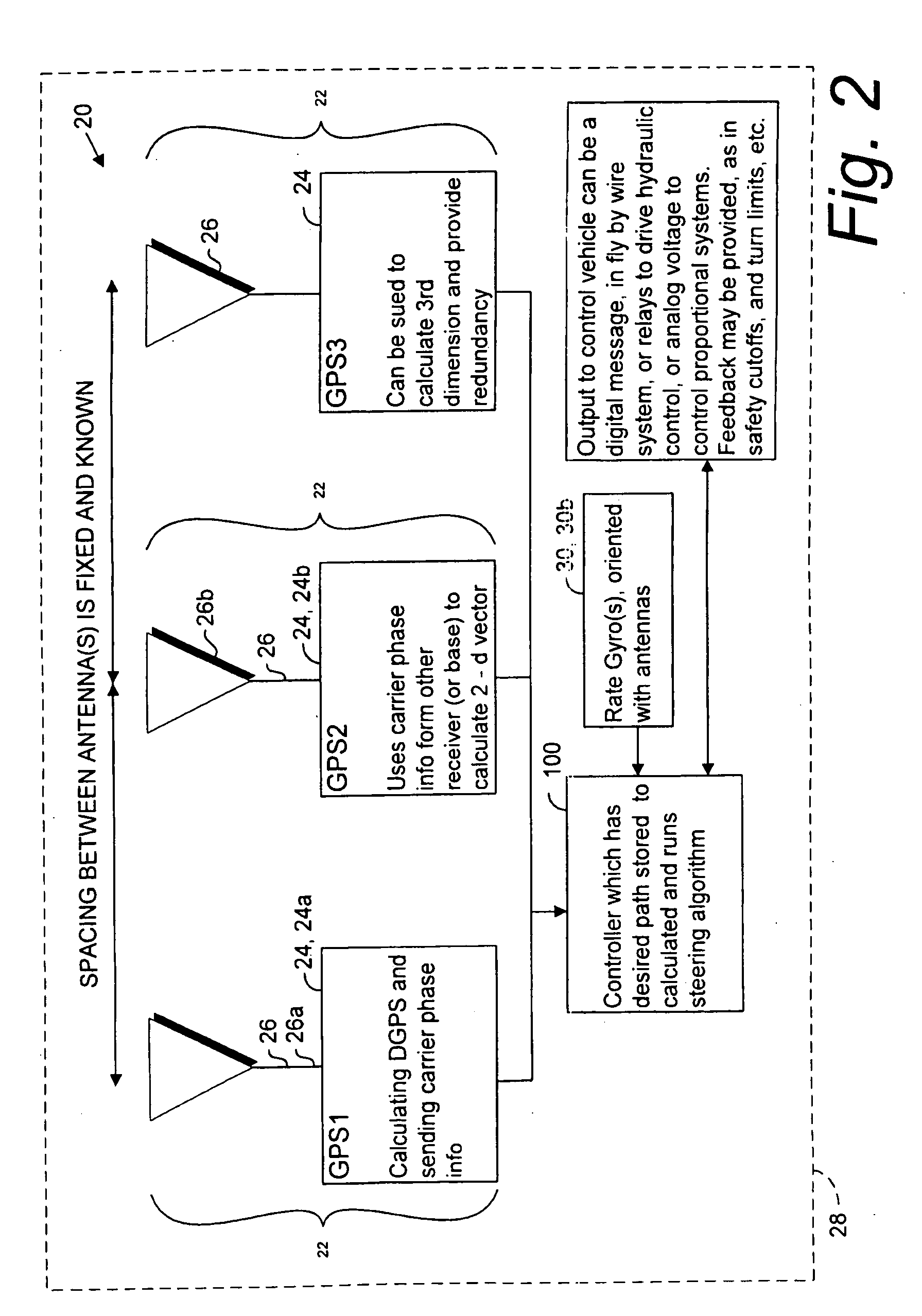
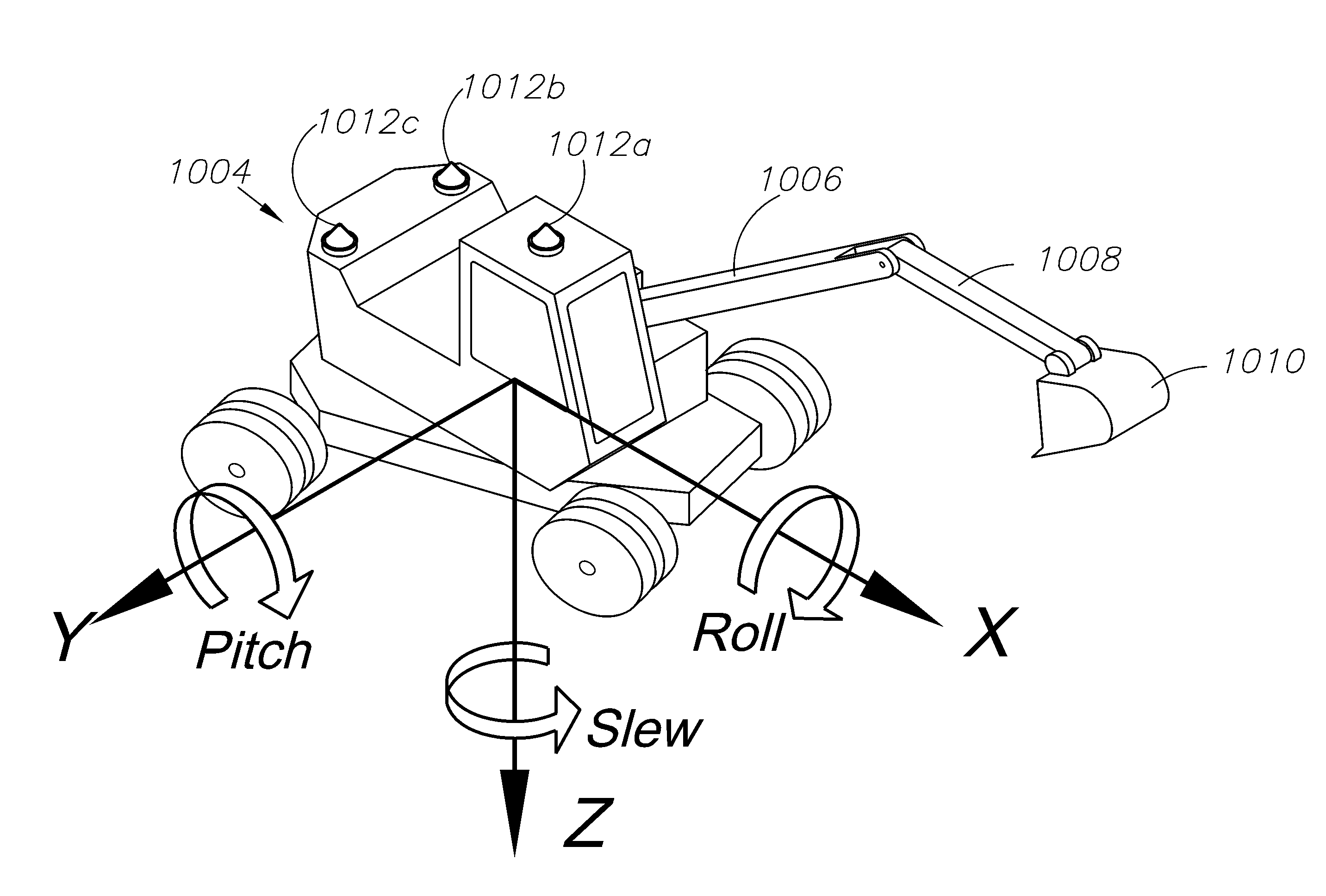
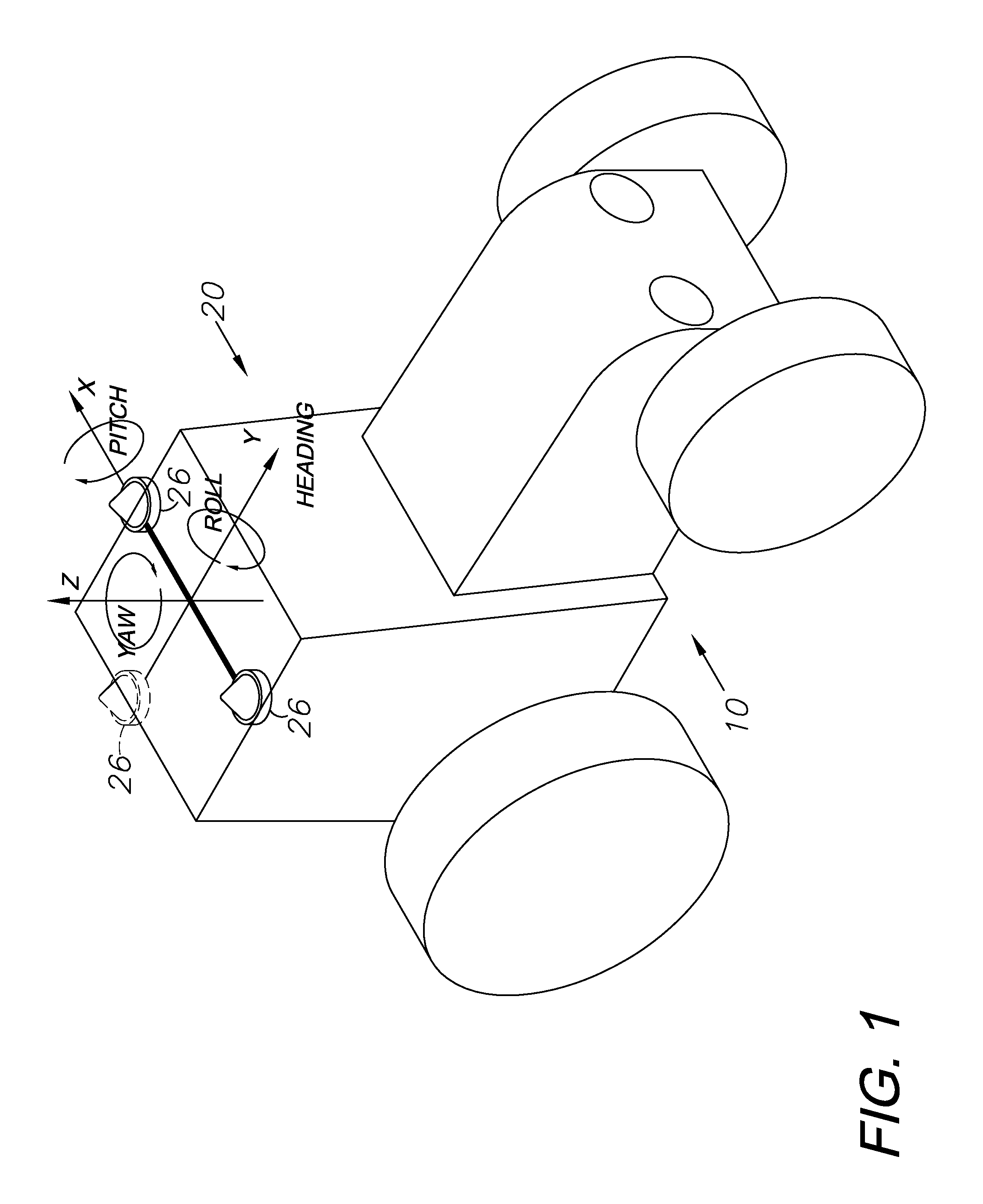
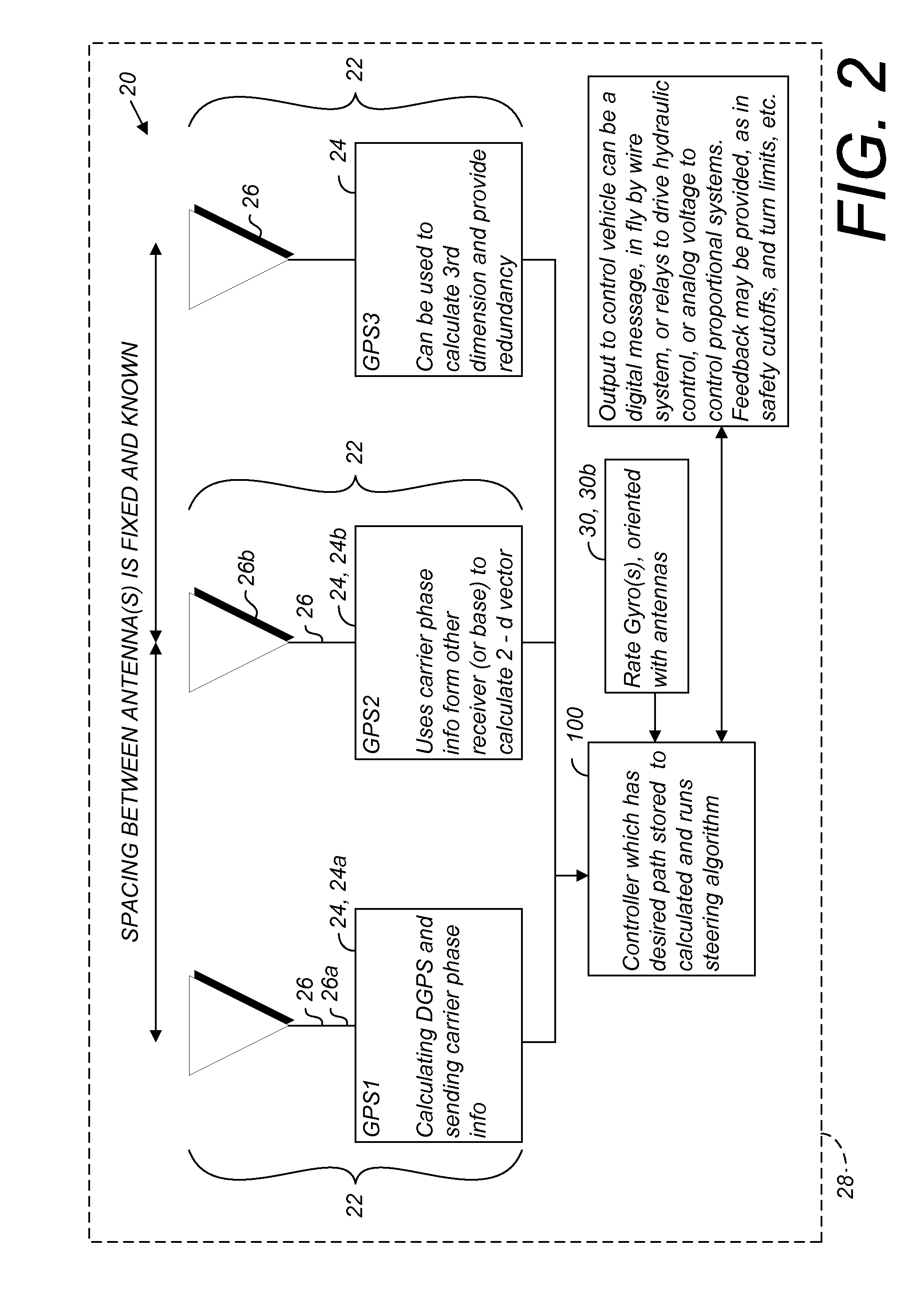
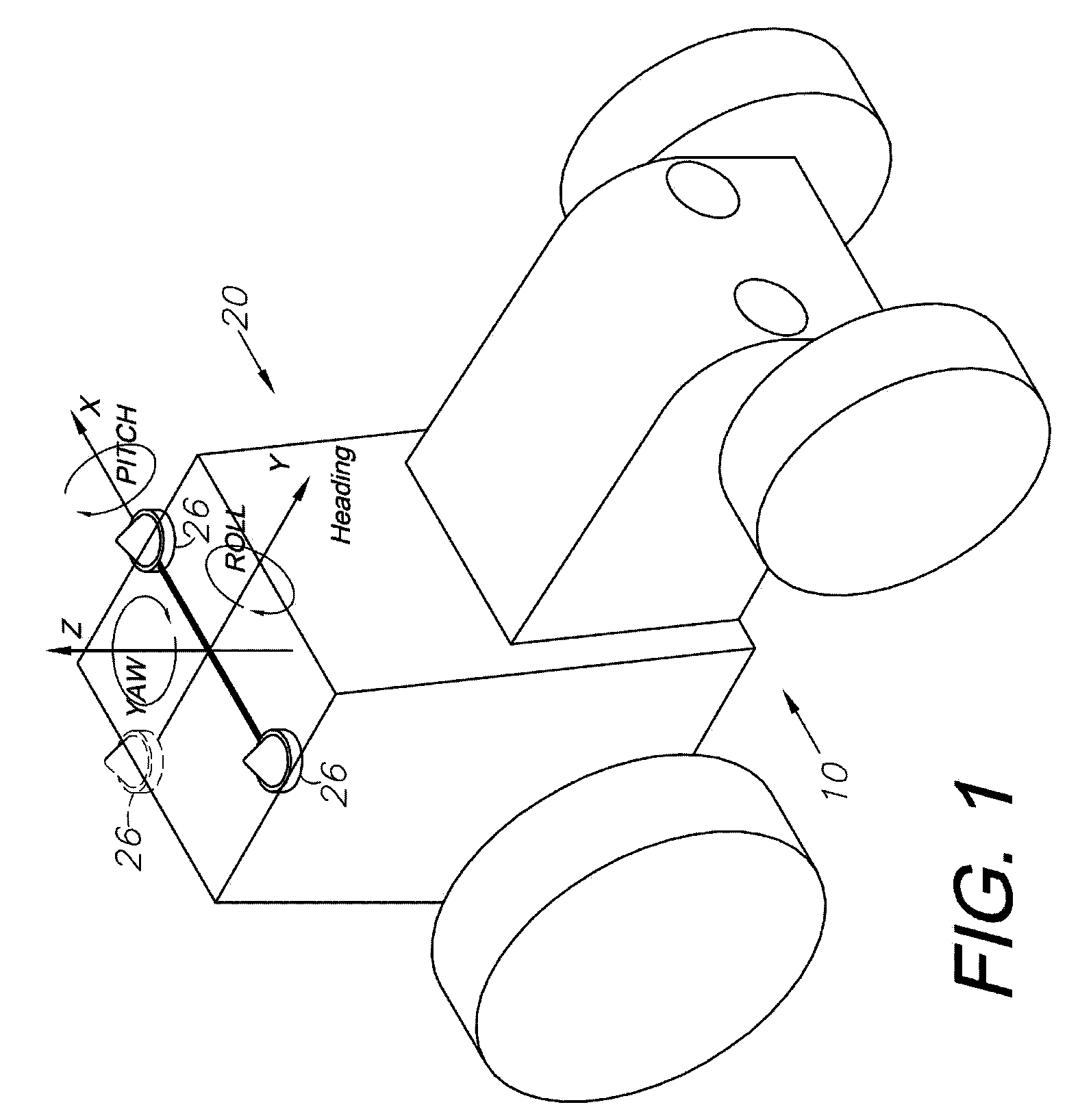
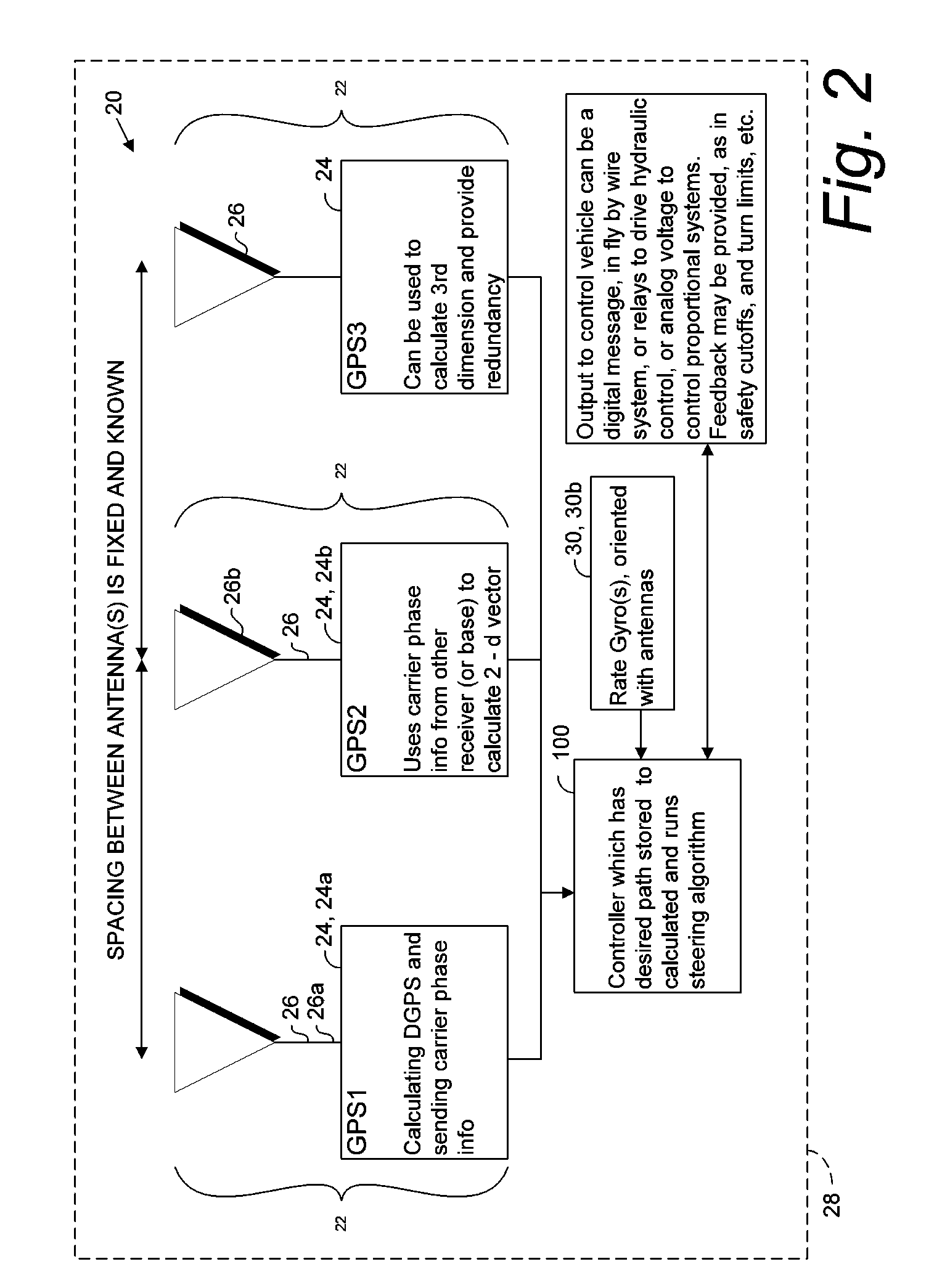
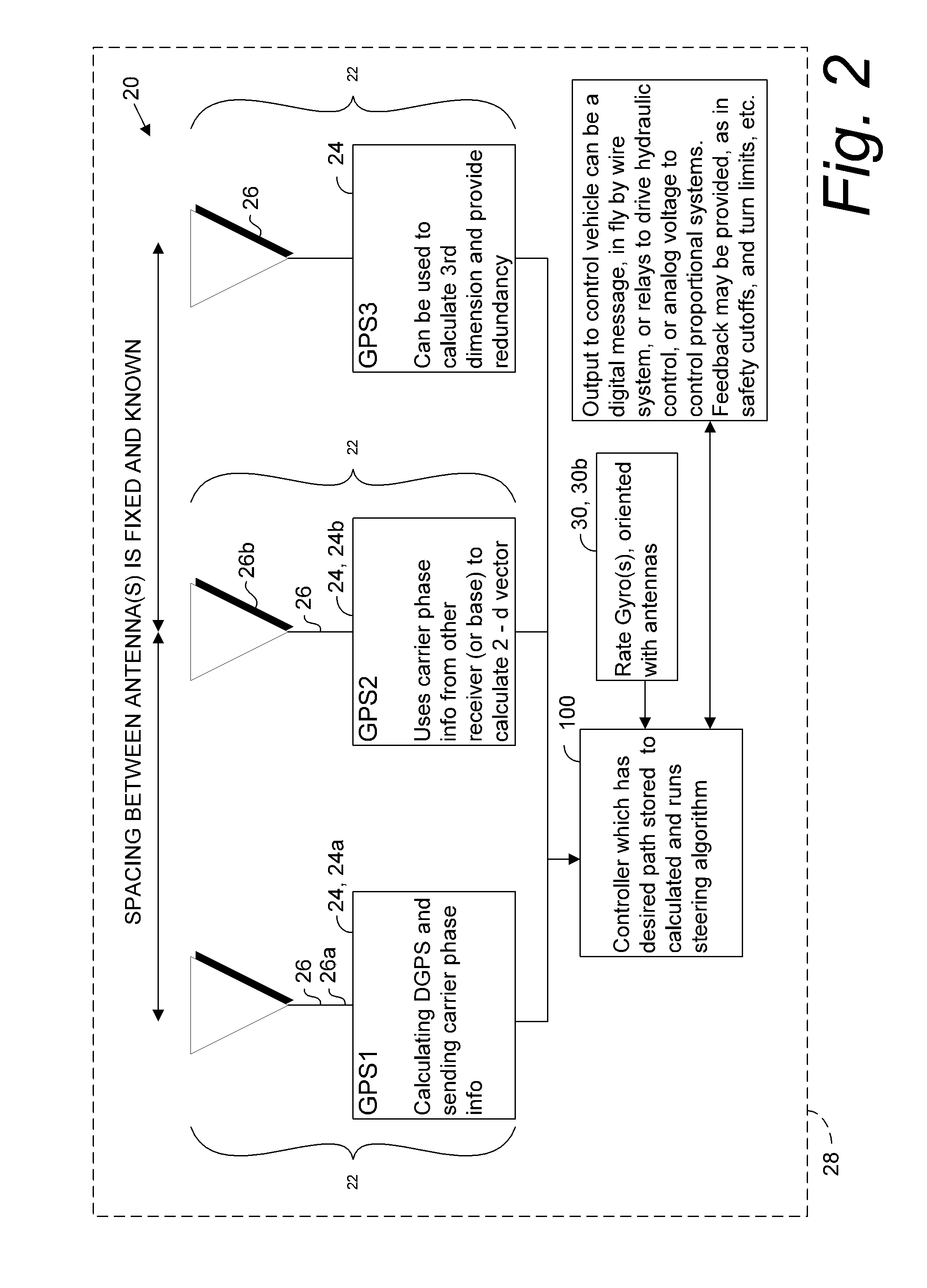
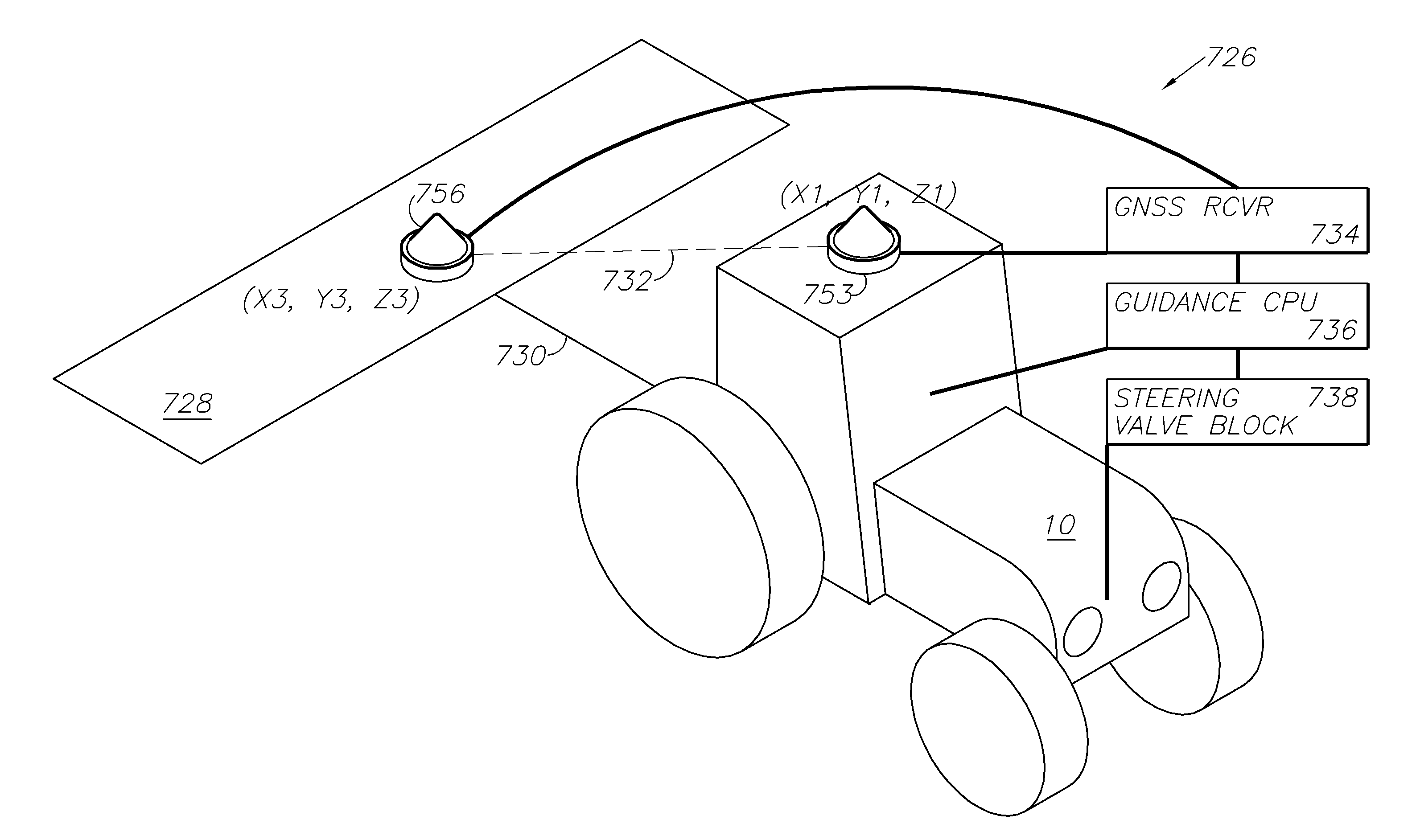
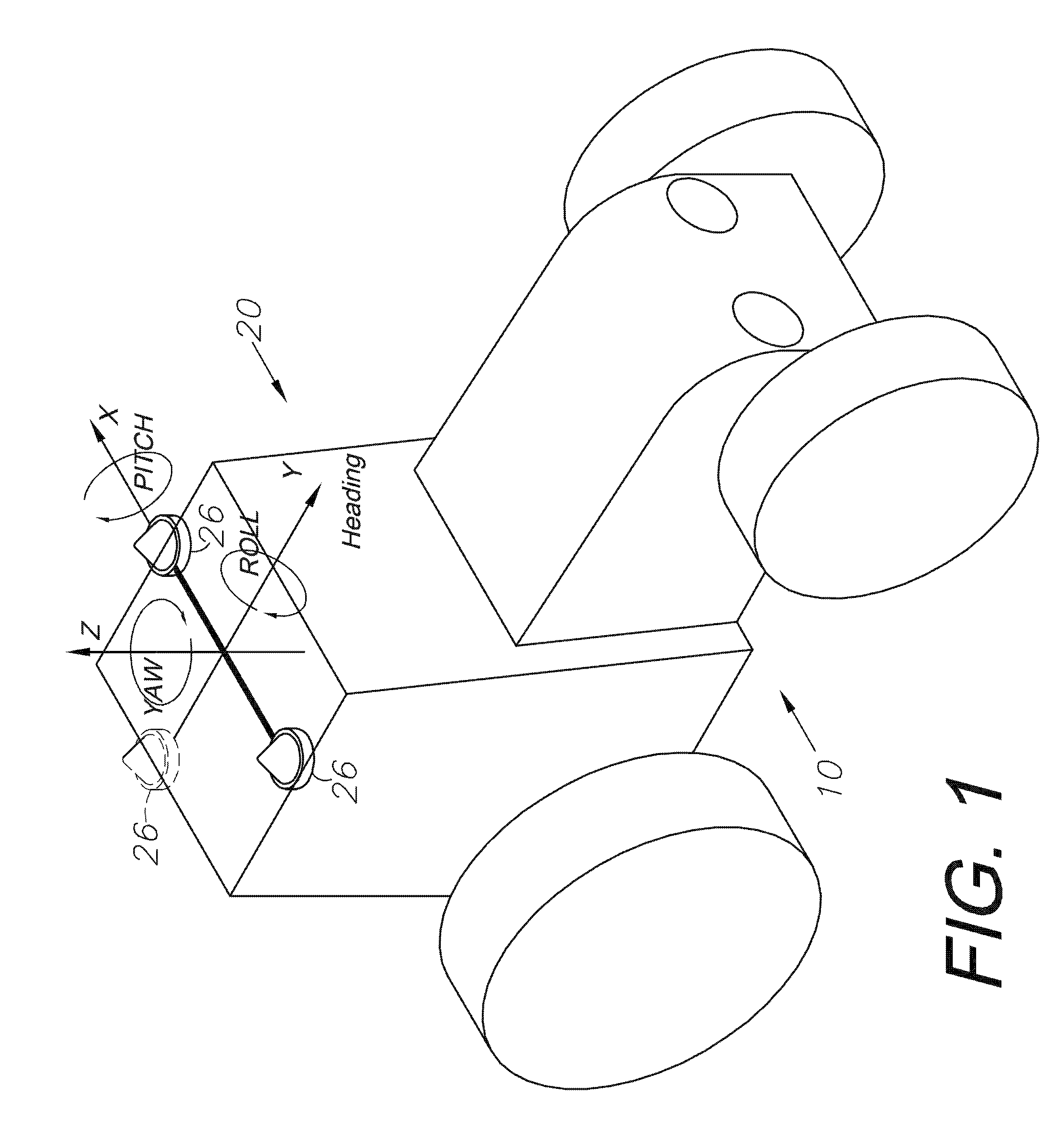
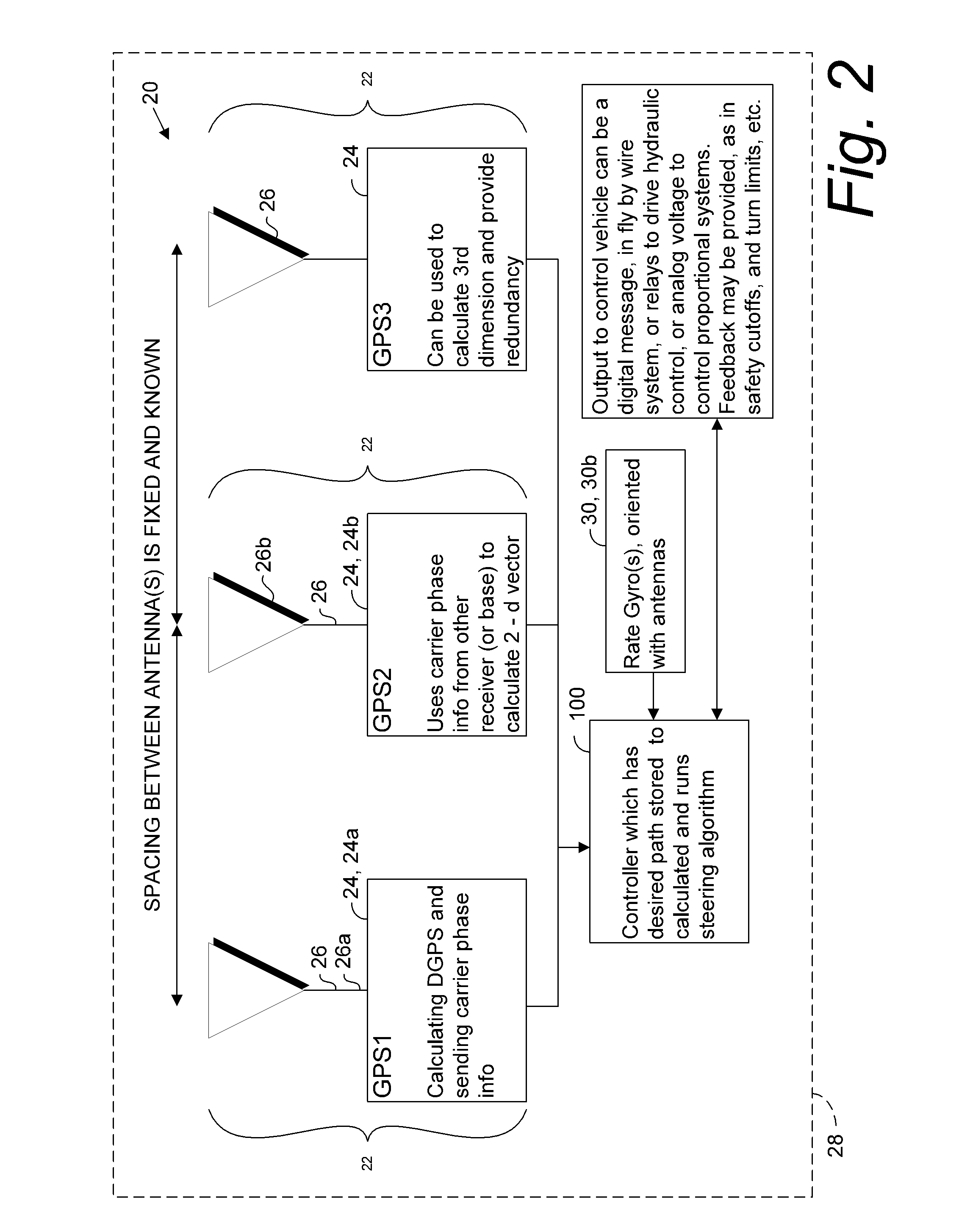
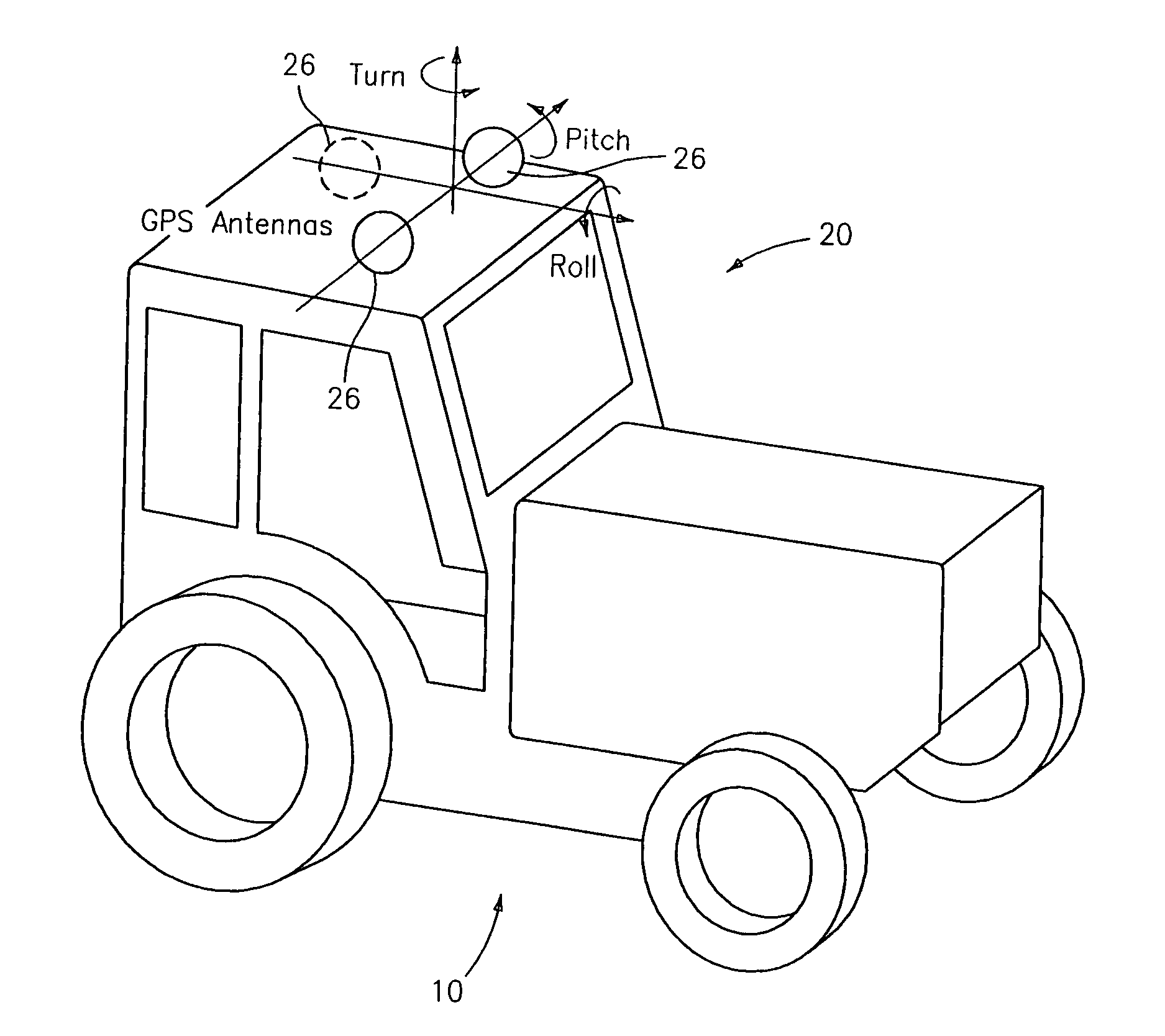
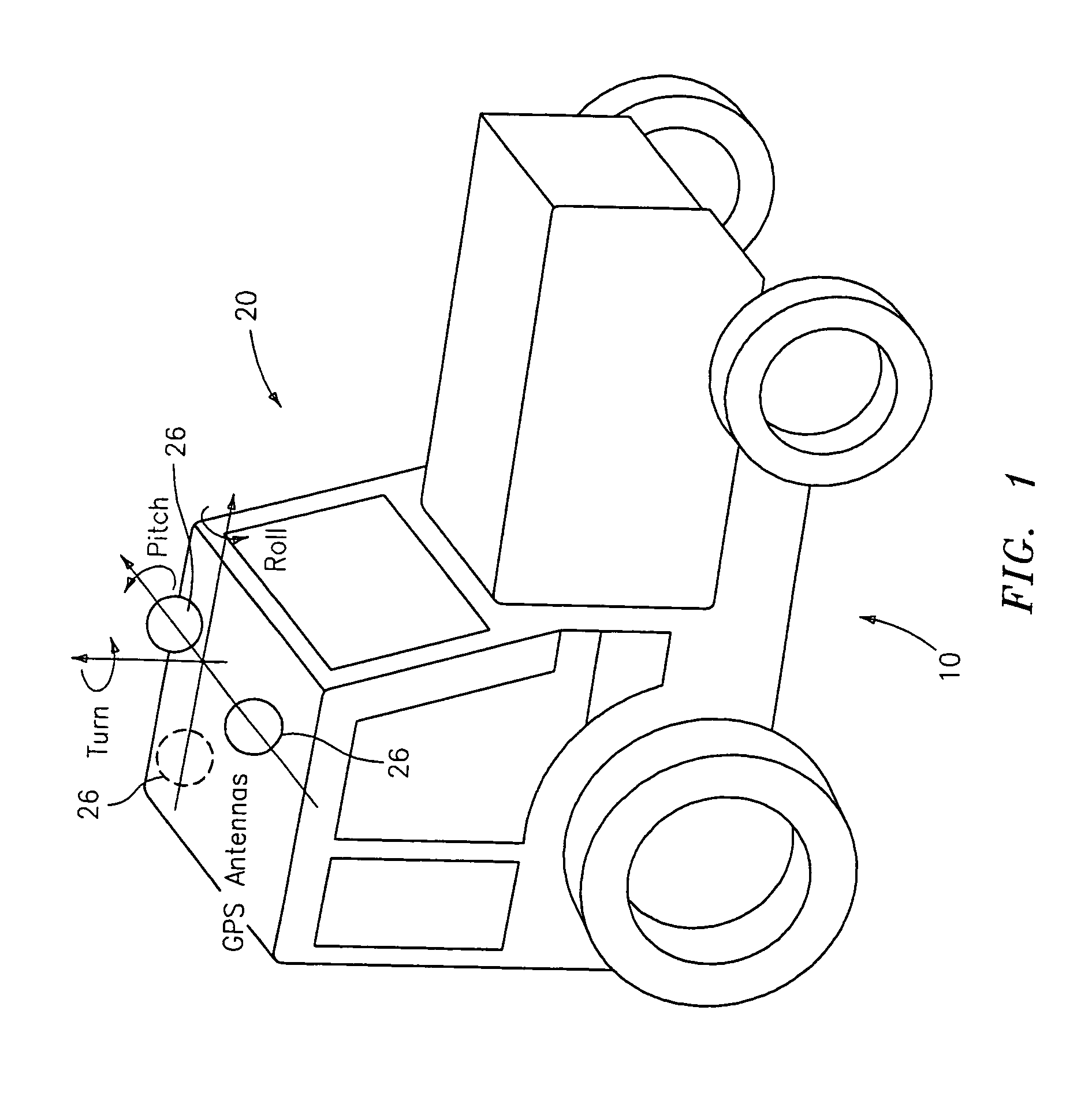
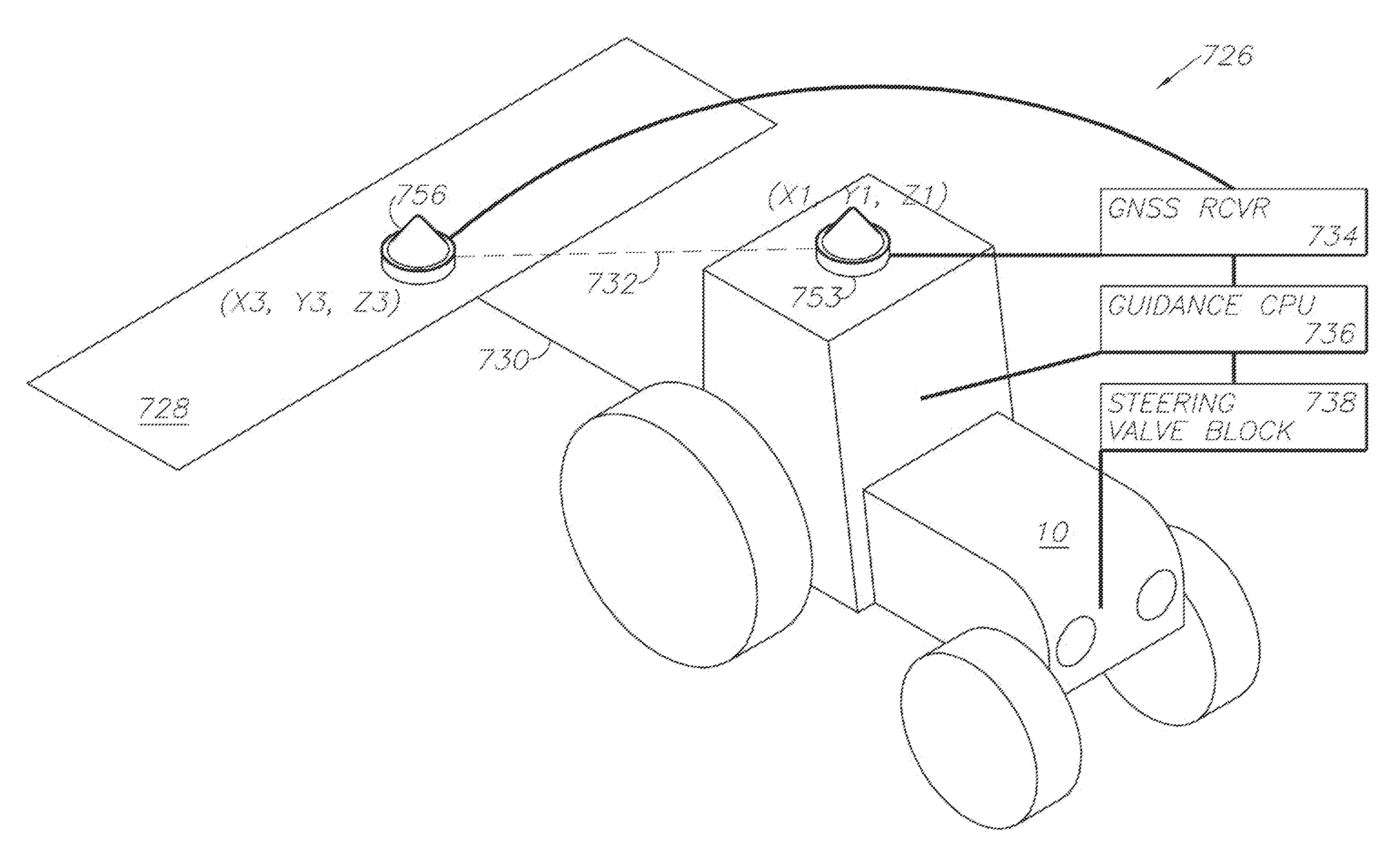
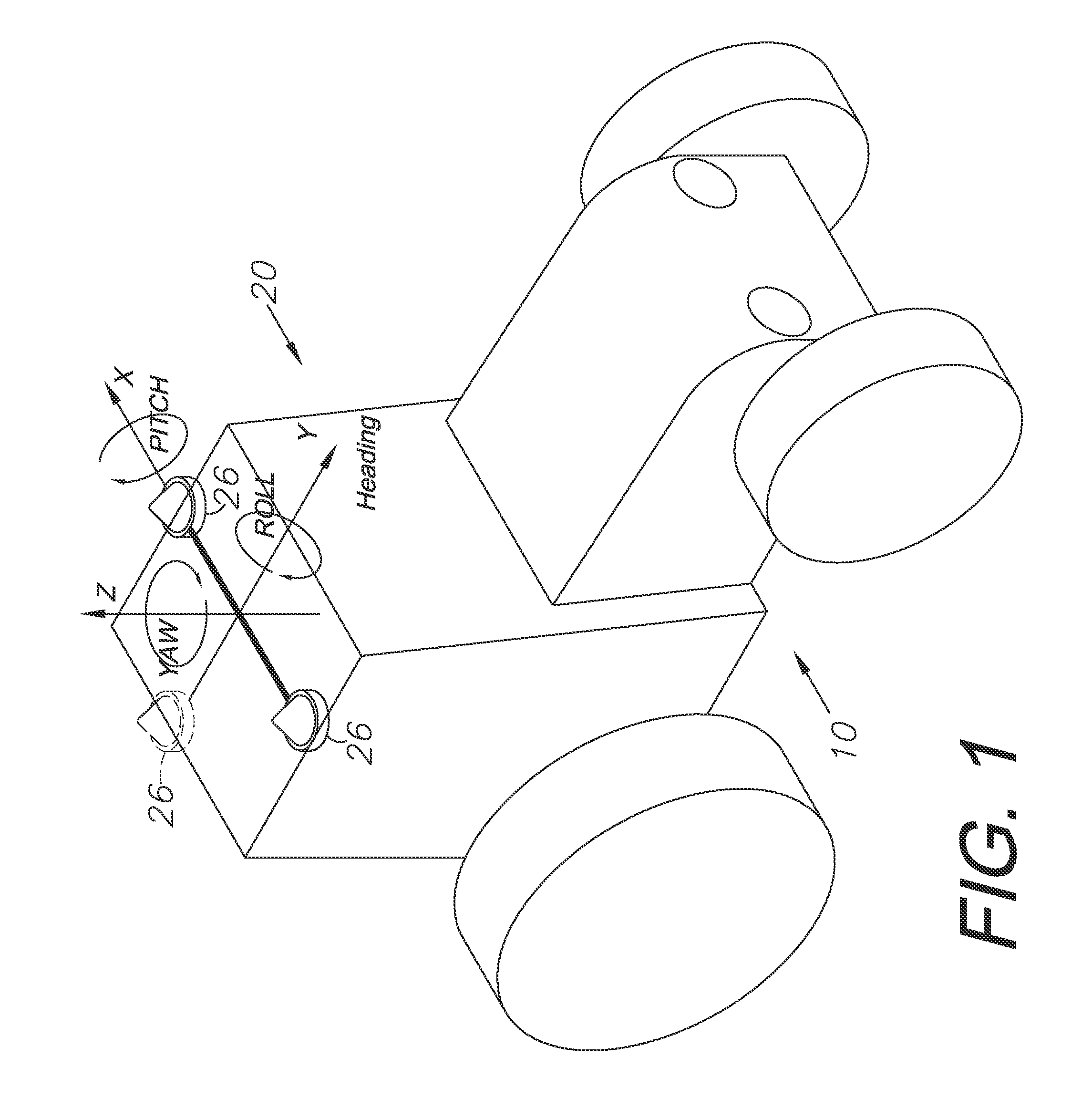
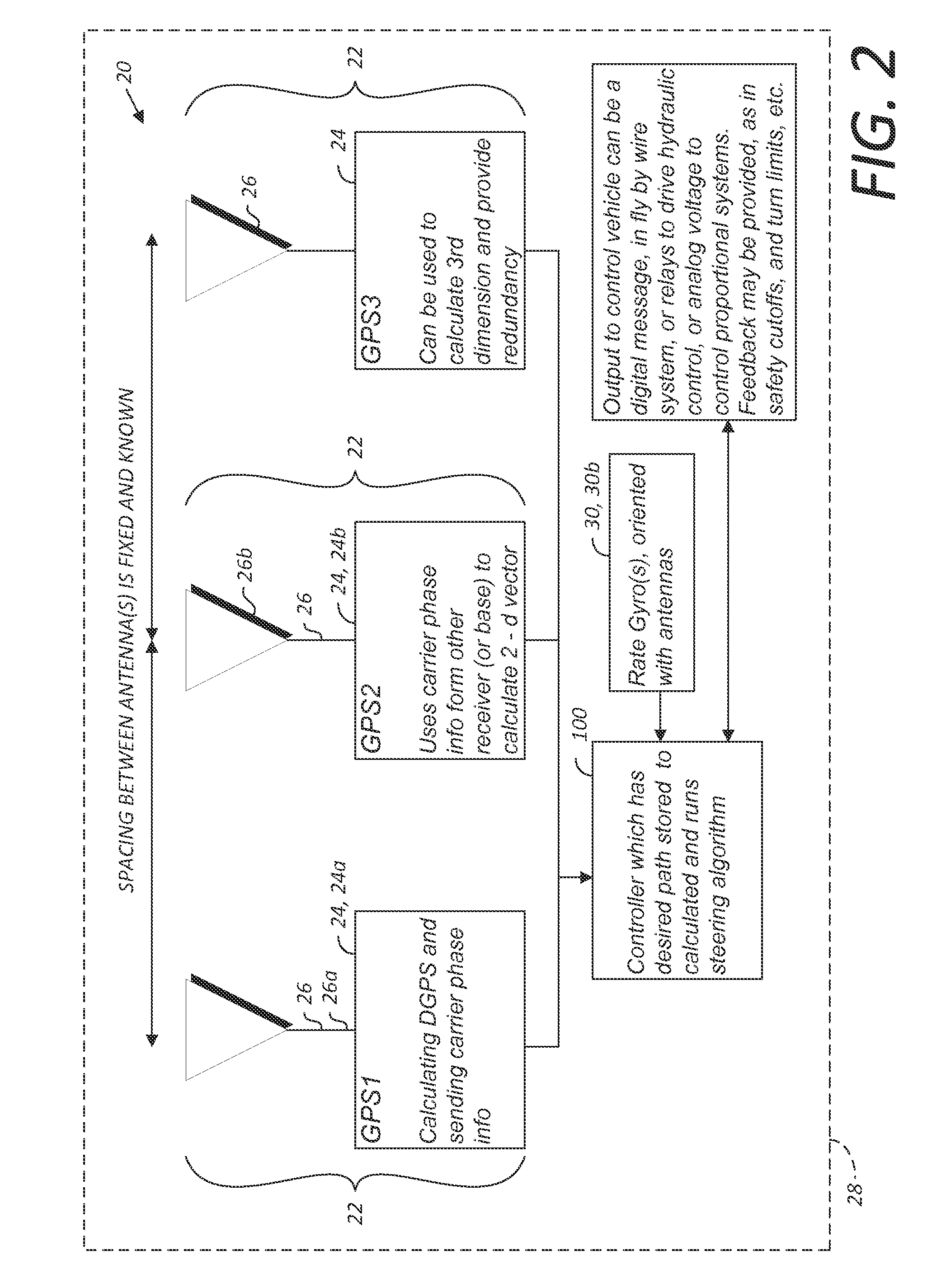
A global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Relative orientations and attitudes between tractors and implements can be determined using optical sensors and cameras. Laser detectors and rangefinders can also be used.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
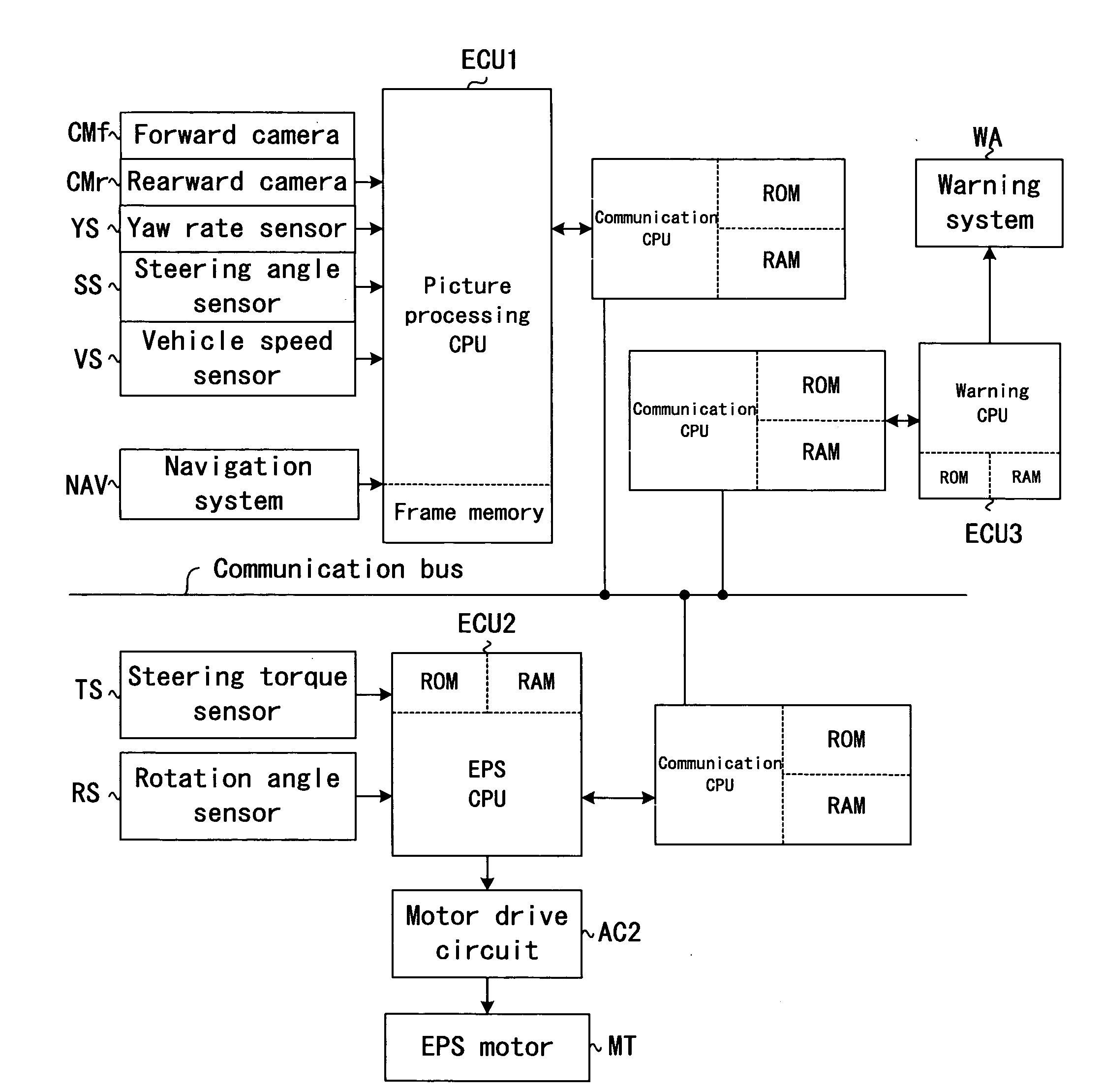
Vehicle and steering control device for vehicle
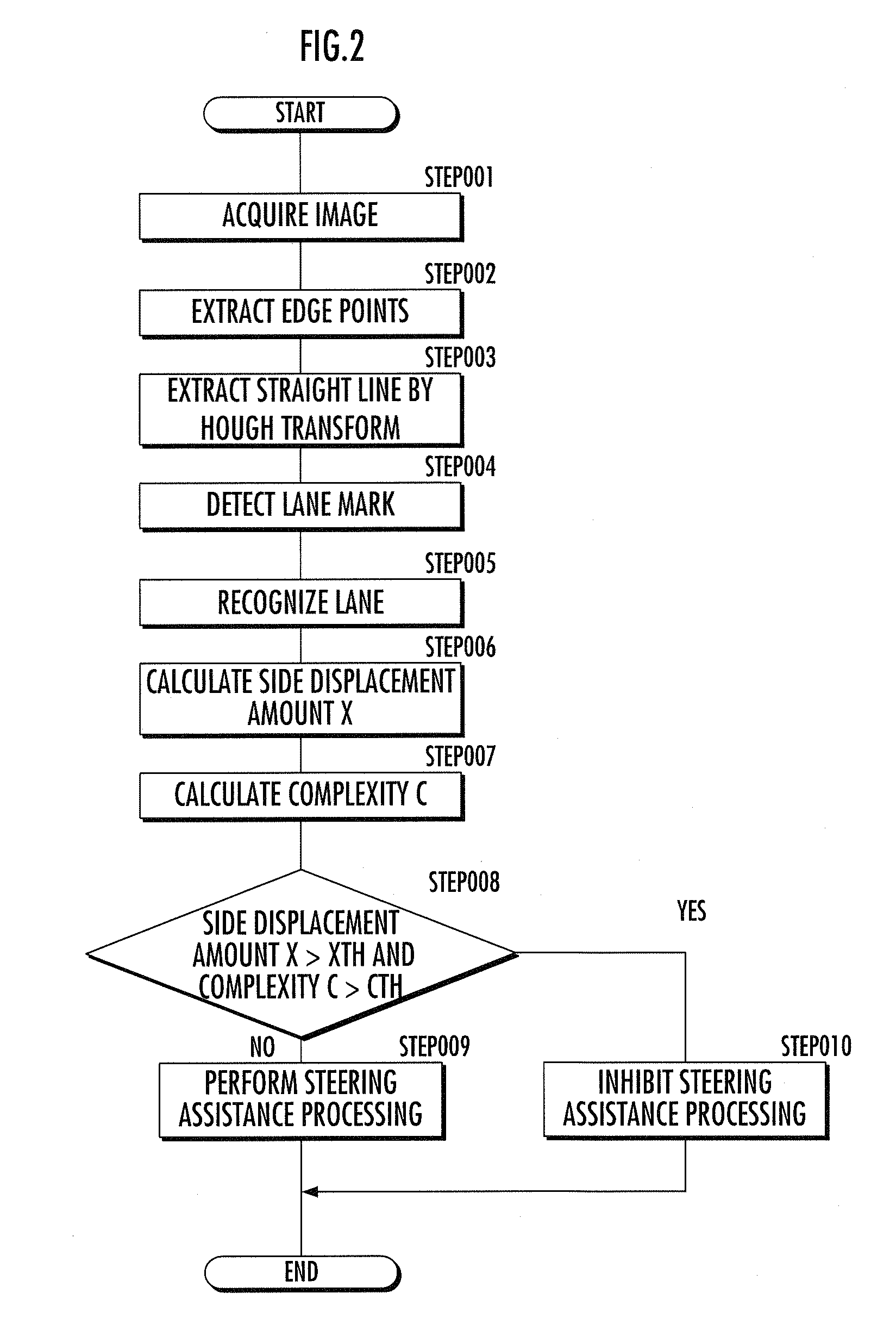
ActiveUS20100228437A1Preventing inappropriate steering controlIncreased complexitySteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering controlEngineering
A steering control device for a vehicle has a steering assistance means (7) which performs steering assistance processing for driving an actuator (6) so that a vehicle (1) travels along a lane recognized by a lane recognition means (5) from an image acquired by an image acquisition means (4); a side displacement amount calculation means (8) which calculates a displacement amount in the lane width direction between the position of the vehicle (1) and the center of the recognized lane; a complexity calculation means (10) which calculates the complexity of the acquired image; and a steering assistance inhibition means (11) which inhibits, according to the displacement amount in the lane width direction calculated based on the lane recognized from the acquired image at a given time point and the complexity of the acquired image, steering assistance processing based on the lane by the steering assistance means (7). This prevents inappropriate steering control based on an incorrectly recognized lane when performing the steering control of the vehicle so that the vehicle travels along the lane recognized from the road image.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
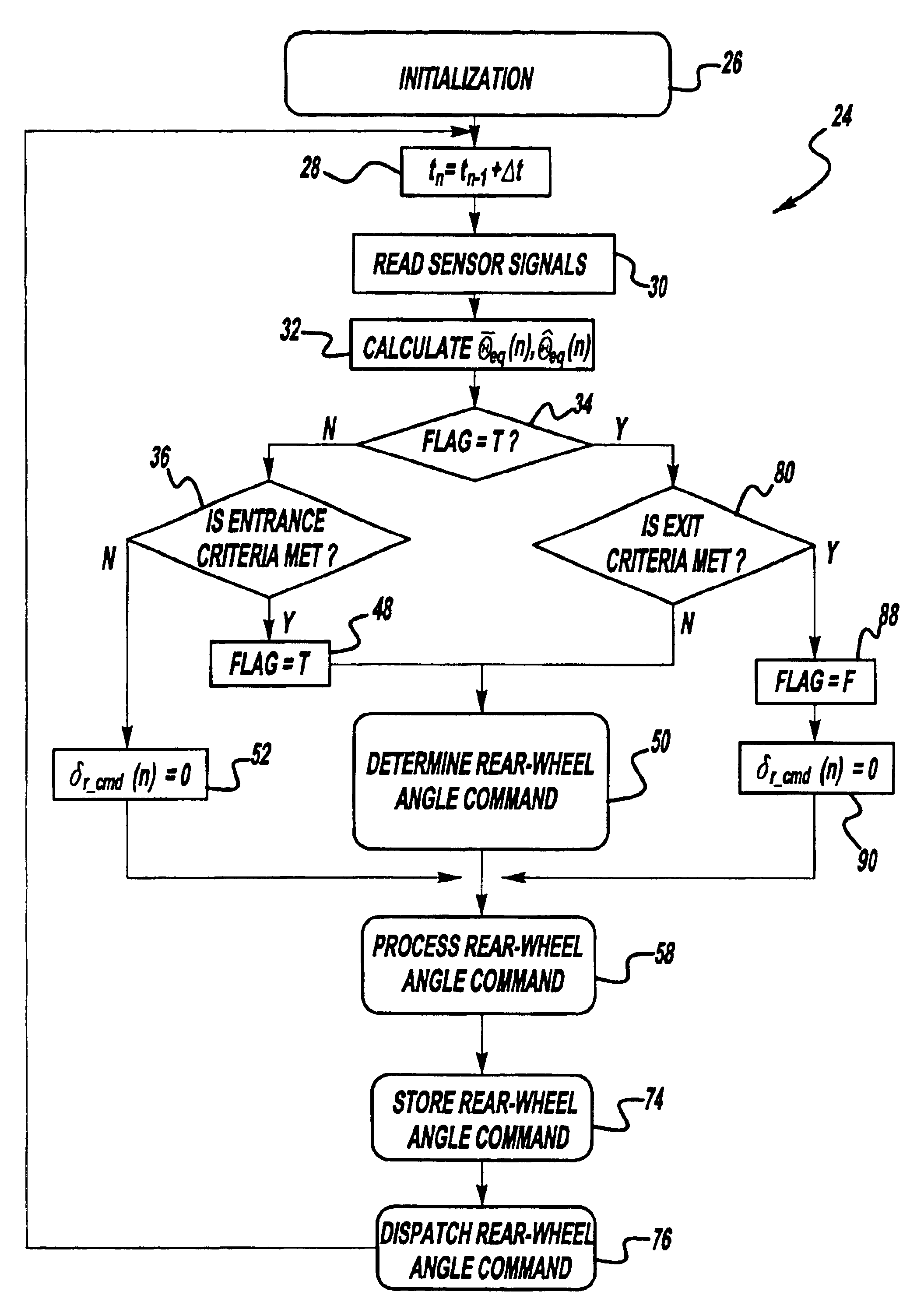
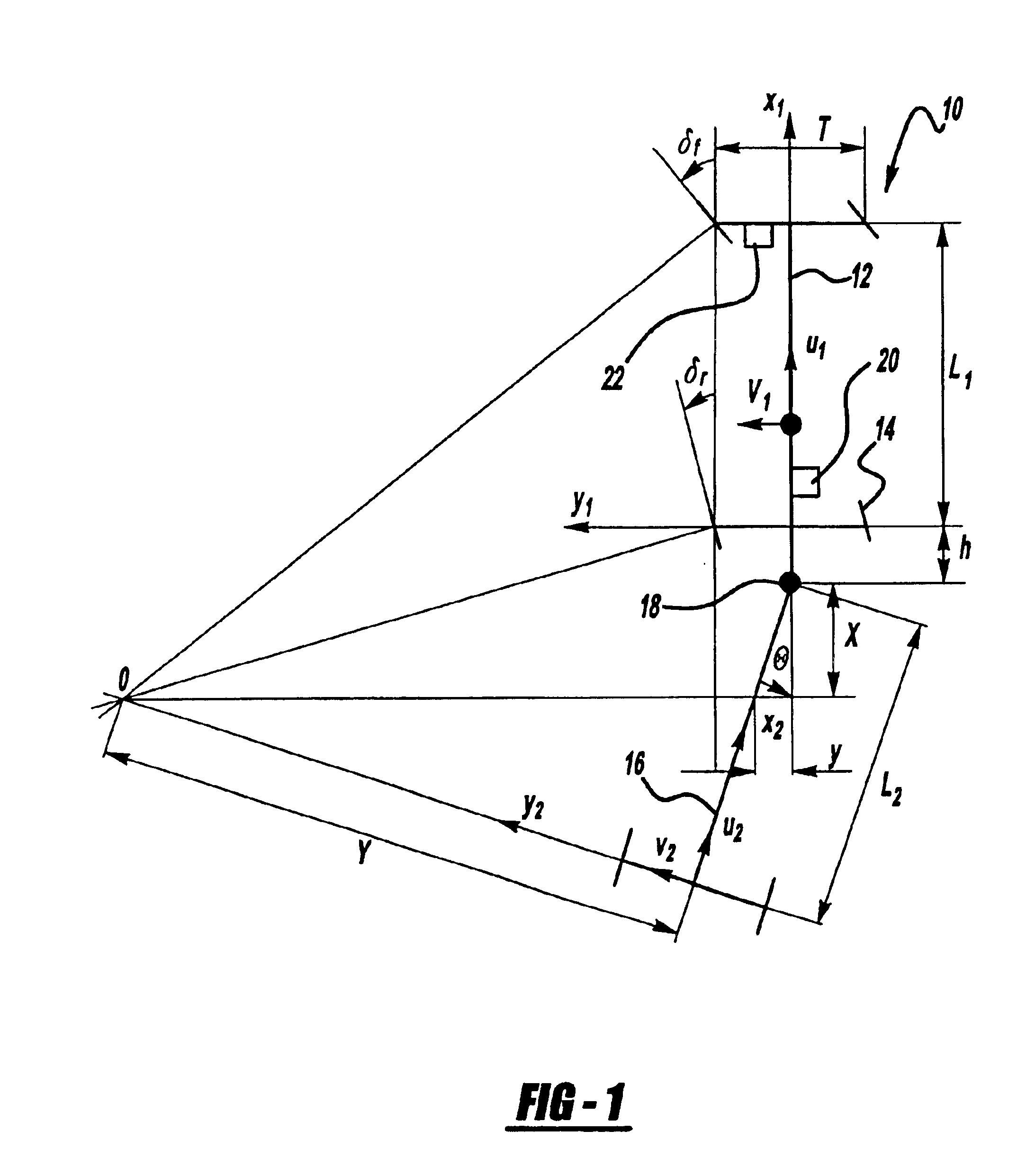
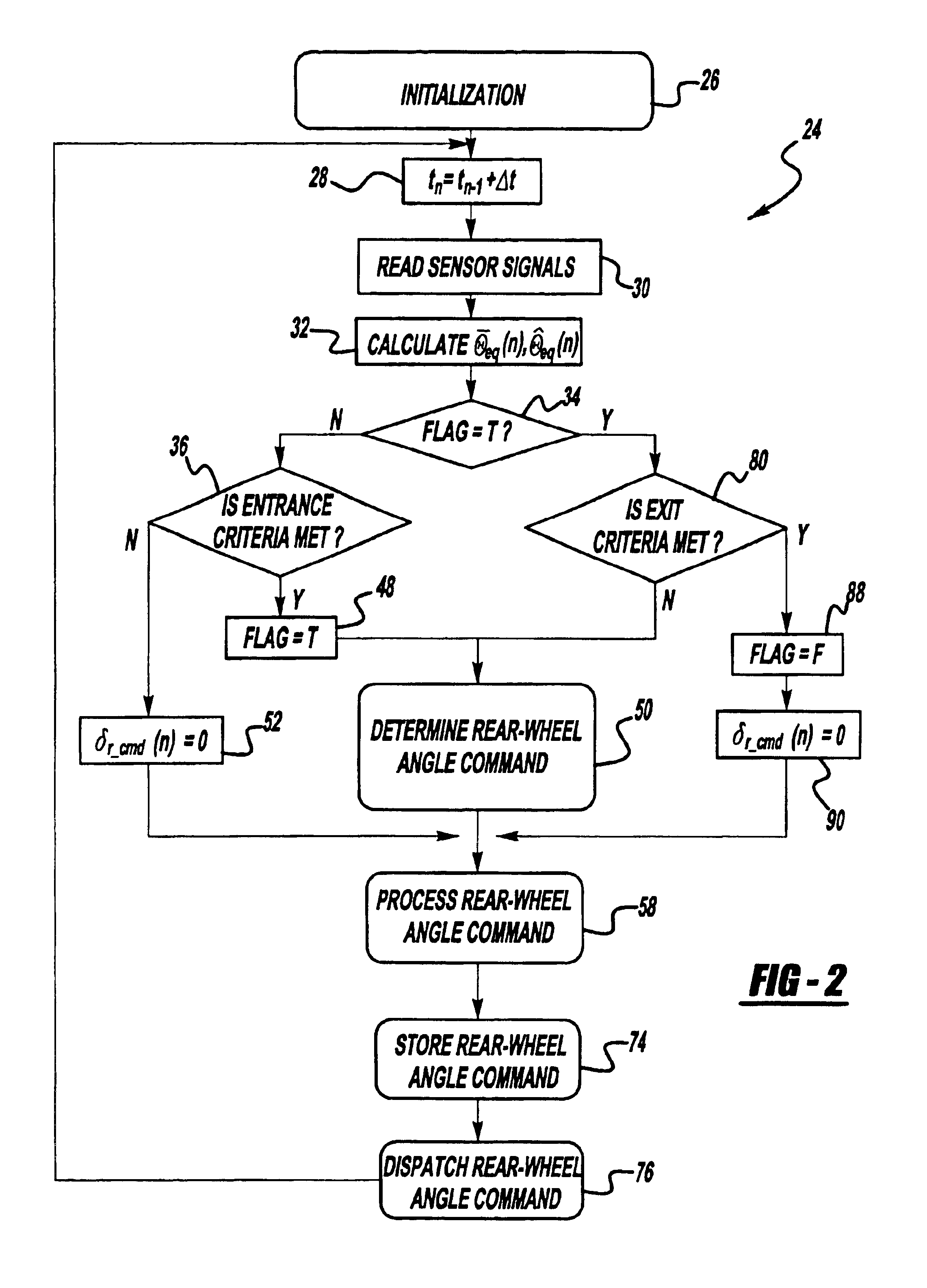
Anti-jackknife control for vehicle-trailer backing up using rear-wheel steer control
A vehicle control system that selectively provides rear-wheel steering to prevent a vehicle-trailer from jackknifing during a back-up maneuver. The system senses a steering angle of the vehicle, a speed of the vehicle and a hitch angle between the vehicle and the trailer. The system calculates an equilibrium hitch angle that is a steady-state hitch angle position based on the steering angle and the vehicle speed, and a pseudo-equilibrium hitch angle that is a steady-state hitch angle at a maximum rear-wheel steering input based on the steering angle and the vehicle speed. The system then determines whether the rear-wheel steering should be provided based on a predetermined relationship between the sensed hitch angle, the equilibrium hitch angle and the pseudo-equilibrium hitch angle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
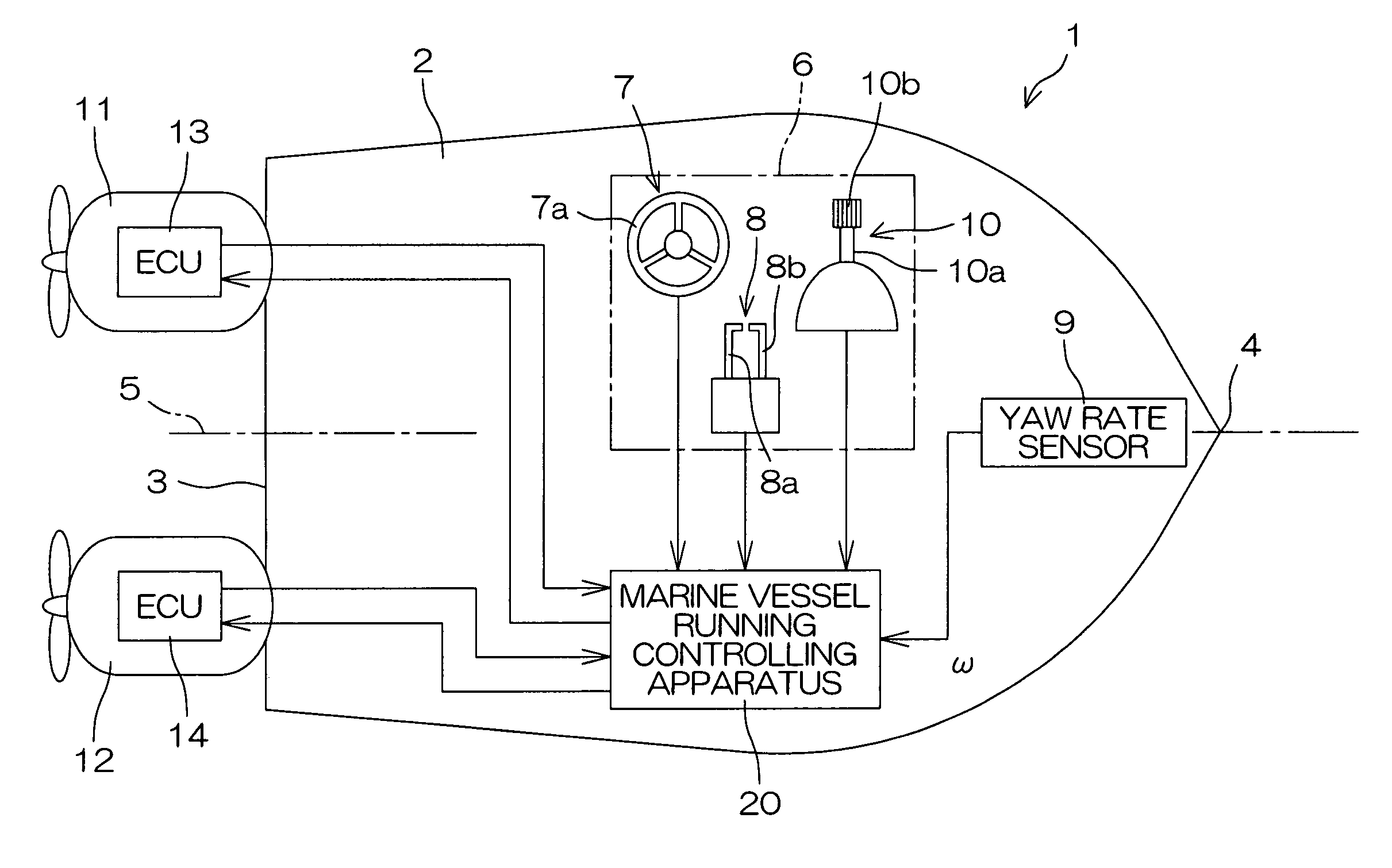
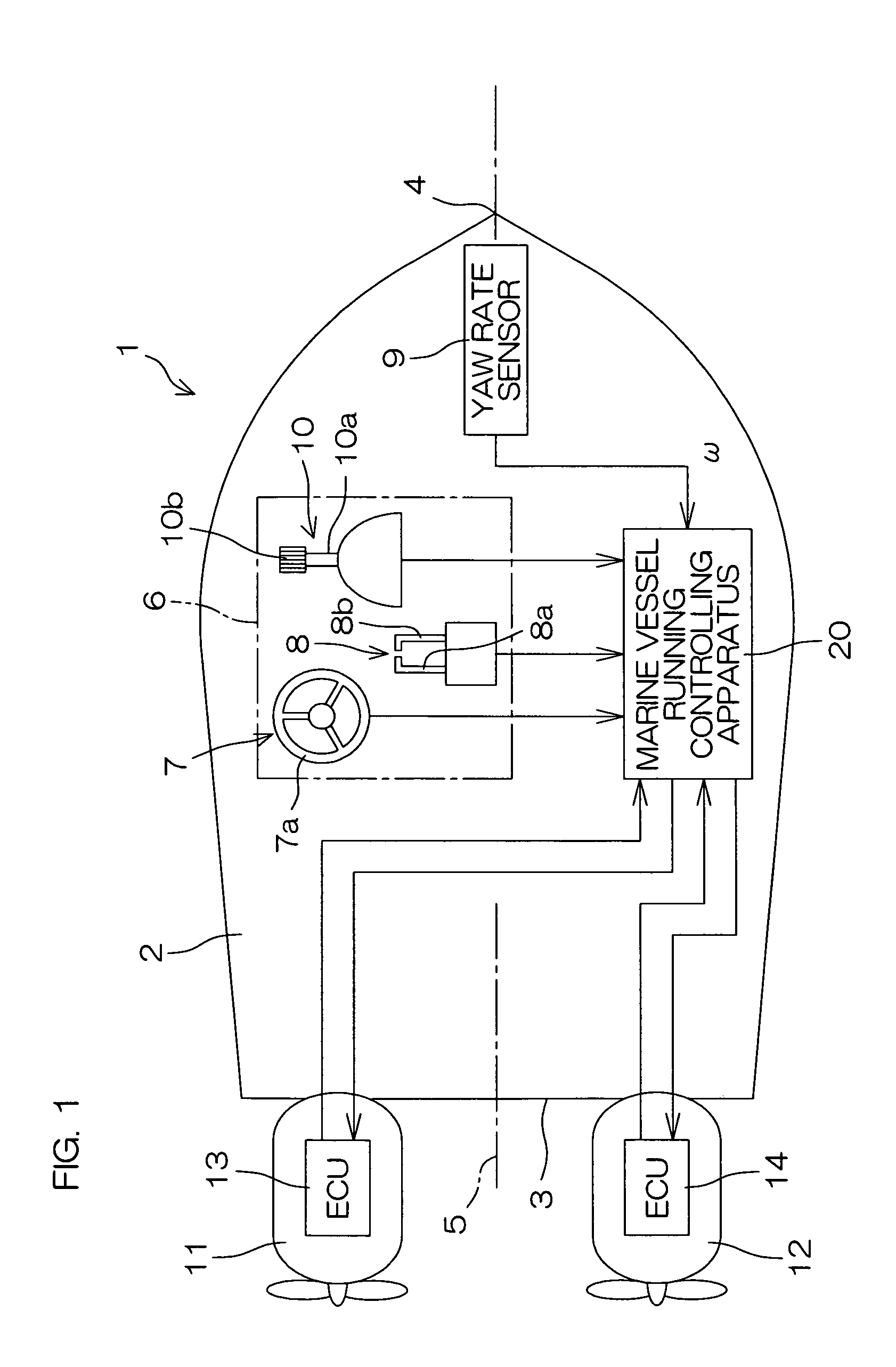
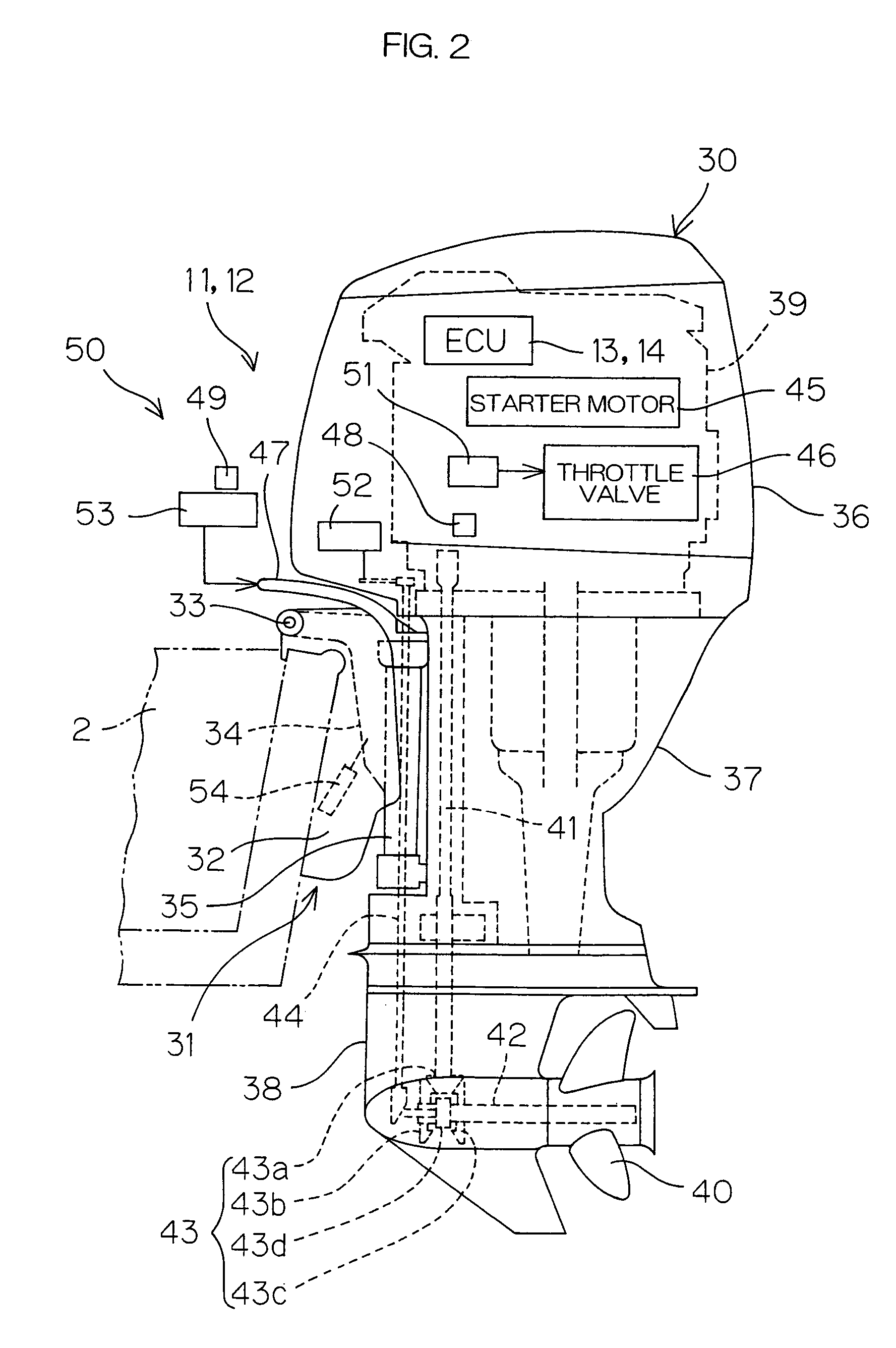
Marine vessel running controlling apparatus, marine vessel maneuvering supporting system and marine vessel each including the marine vessel running controlling apparatus, and marine vessel running controlling method
InactiveUS6994046B2Facilitate maneuveringSteering ruddersSteering initiationsSupporting systemSteering angle
A marine vessel running controlling apparatus controls running of a marine vessel and includes a pair of propulsion systems which respectively generate propulsive forces on a rear port side and a rear starboard side of a hull, and a pair of steering mechanisms which respectively change steering angles defined by directions of the propulsive forces with respect to the hull. The apparatus includes a target combined propulsive force acquiring section, a target movement angle acquiring section, a steering controlling section which controls the steering angles of the respective steering mechanisms such that a turning angular speed of the hull is substantially equal to a predetermined target angular speed, a target propulsive force calculating section which calculates target propulsive forces to be generated from the respective propulsion systems based on the target combined propulsive force, the target movement angle and the steering angles of the respective steering mechanisms, and a propulsive force controlling section which controls the respective propulsion systems so as to attain the target propulsive forces.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for vehicle steering control
ActiveUS20160107682A1Improve accuracyMaintain relatively stableSteering linkagesExternal condition input parametersControl engineeringSteering control
A method for steering control of a vehicle having an actuator which turns steered wheels of the vehicle. The steering control method comprises obtaining a location of a target point at a look-ahead distance away from the vehicle based on a maneuver the vehicle is performing, predicting a forward location of the vehicle at the look-ahead distance away from the vehicle, determining a distance between the location of the target point and the forward location, computing a normalized error by dividing the distance with the look-ahead distance, and determining a steering control command based on an integration of the normalized error. The actuator then turns the steered wheels of the vehicle according to the steering control command so as to steer the vehicle to perform various maneuvers.
Owner:HUA CHUANG AUTOMOBILE INFORMATION TECHN CENT +2
Lane keeping assist device for vehicle
InactiveUS20060030987A1Digital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsEngineeringSteering control
A lane keeping assist device for a vehicle includes a steering control device, a detection device for lane of travel for assisting travel of the vehicle in a lane of travel in accordance with detection results and steering state and traveling state of the vehicle. Road curvature in a direction the vehicle traveling in is estimated on the basis of a first road curvature calculated on the basis of calculation result of a vehicle state amount calculation device and detection result of a state detection device, and a second road curvature calculated on the basis of positional coordinates by a predetermined distance in the direction the vehicle traveling in detected by a navigation system NAV. Target state amount is set on the basis of the road curvature and the steering state and traveling state of the vehicle.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Virtual wall system
InactiveUS20060259194A1Save powerBeacon systemsVehicle position/course/altitude controlAcoustic waveSteering control
A virtual wall system includes a mobile robotic device having a steering unit for steering itself, a steering control unit connected with the steering unit for controlling the steering of the steering unit, at least one signal transmitter mounted thereon for emitting a signal, and a sonic receiver for receiving a sonic signal; and a virtual wall generator having at least one signal receiver for receiving the signal, at least one sonic transmitter for emitting a sonic signal, and a signal controller for identifying the signal and controlling the emission of the sonic transmitter. While the mobile robotic device is moving, the signal controller controls the sonic transmitter to emit the sonic signal after the signal receiver receives the signal emitted by the signal transmitter and then the sonic receiver receives the sonic signal, enabling the steering control unit to control the steering unit to steer the mobile robotic device.
Owner:INFINITE ELECTRONICS
Combined GNSS gyroscope control system and method
ActiveUS20080269988A1Avoid crossingEasy to correctSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering controlLateral movement
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS8639416B2Easy to correctAnalogue computers for trafficSteering initiationsGyroscopeMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other, and snow grooming equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Multi-antenna GNSS control system and method
ActiveUS20110054729A1Accurate and economical preplannedEasy to correctVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficSteering controlEngineering
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, articulated implements with multiple antennas on each implement section, video input and guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Self-adaptive balance steering control method of double-hub motor driving system
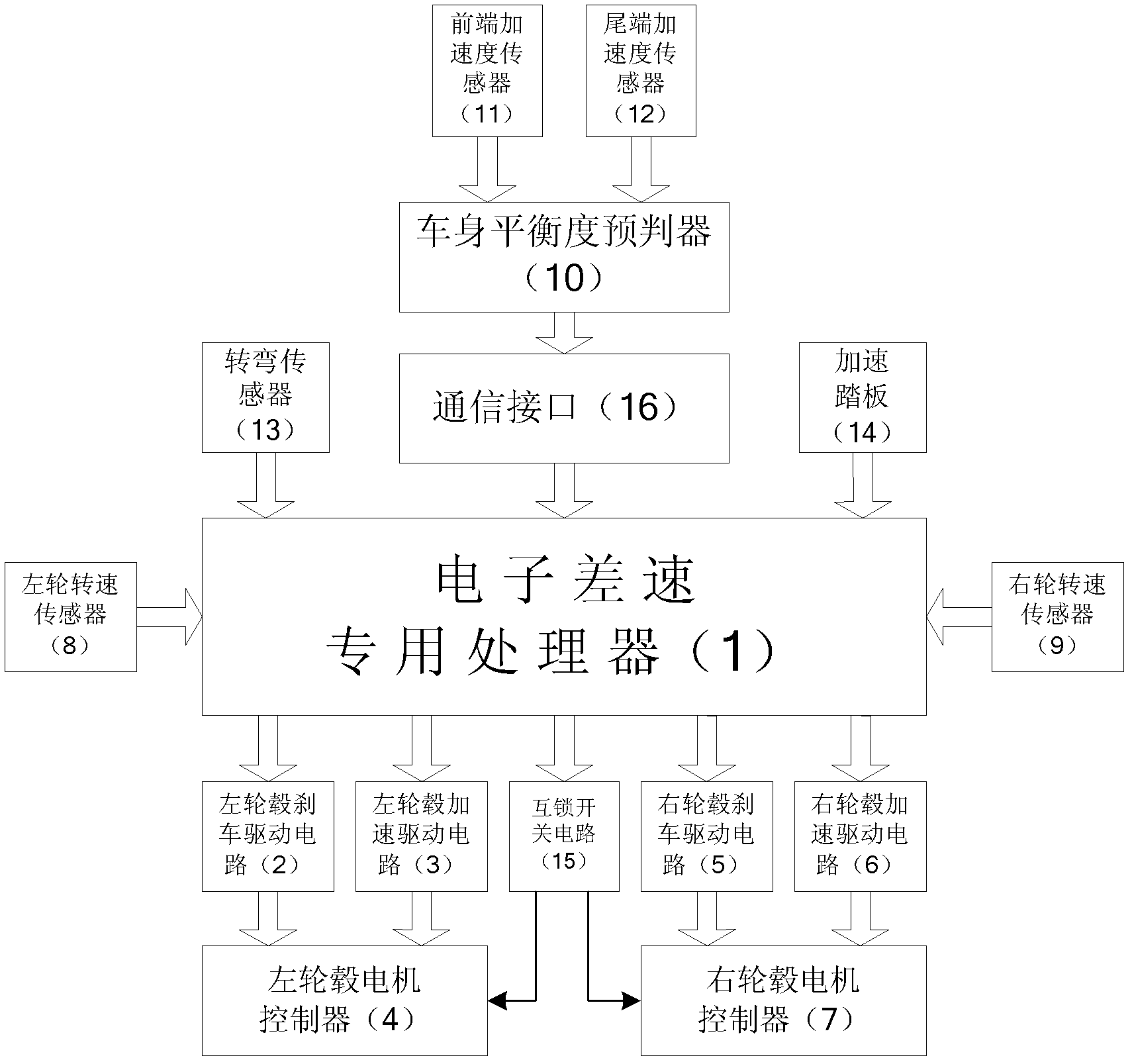
ActiveCN103204180APrecise and effective differential speed controlHazard containmentSpeed controllerElectric devicesCommunication interfaceBody balance
The invention provides a self-adaptive balance steering control method of a double-hub motor driving system. A basic control system comprises an electronic differential speed special processor, a left hub brake driving circuit, a left hub acceleration driving circuit, a left hub motor controller, a right hub brake driving circuit, a right hub acceleration driving circuit, a right hub motor controller, a left wheel rotation speed sensor, a right wheel rotation speed sensor, an inter-locking switch circuit, a vehicle body balance degree prejudging device, a front acceleration sensor, a tail acceleration sensor, a steering sensor, an acceleration pedal and a communication interface. The method has the advantage that a method for evaluating a vehicle steering safety degree is established by utilizing steering sensing information, vehicle body tilting degree information, vehicle speed and vehicle speed deviation rate, an electronic brake processing method is adopted in the field of steering control, and then the steering balance of the double-hub motor driving system can be controlled more efficiently and accurately, so the stability of the vehicle in the running process is improved.
Owner:SNTO TECH GRP
Guidance, Navigation, and Control System for a Vehicle
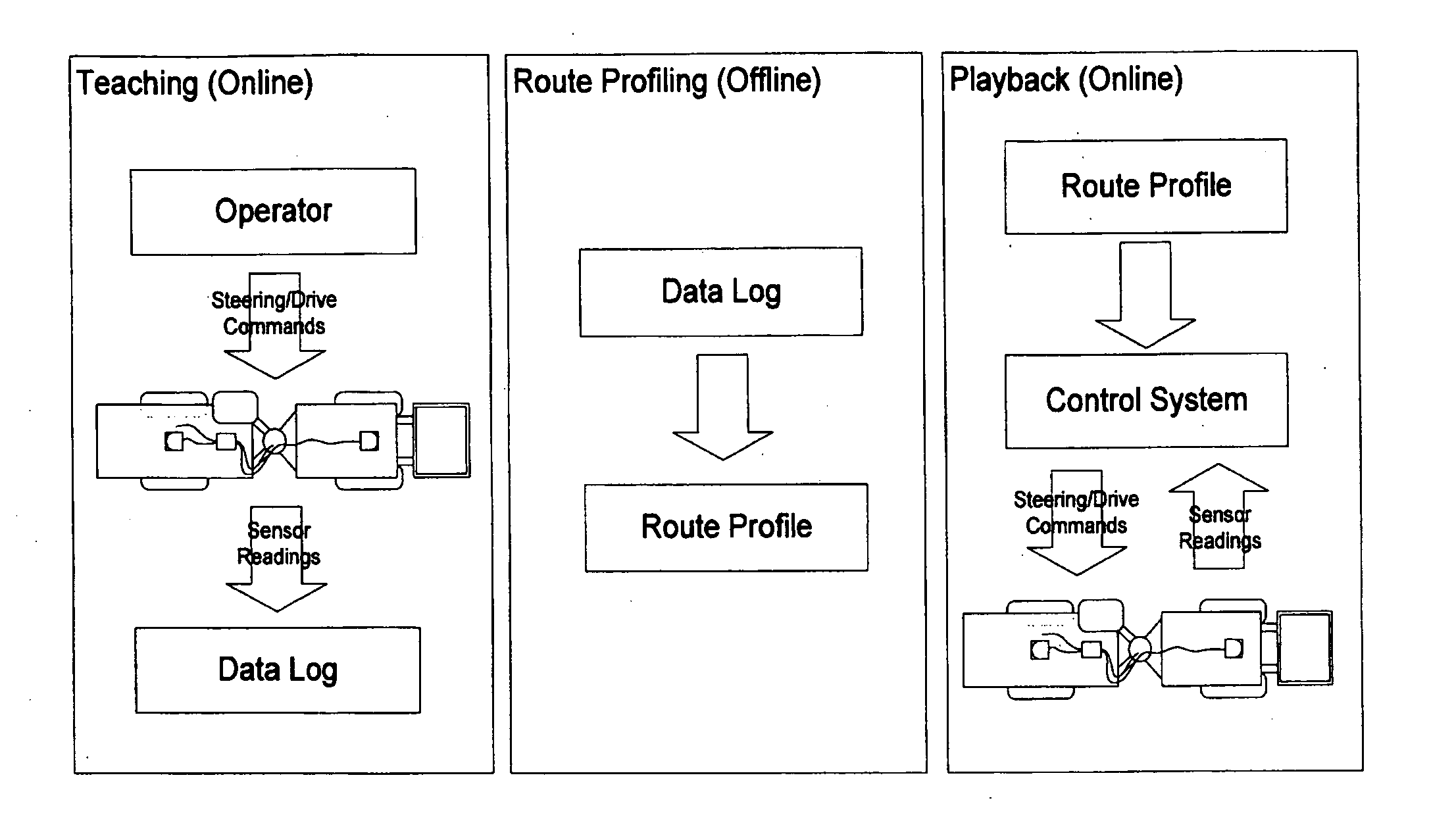
The present invention provides a guidance, navigation, and control method and system for an underground mining vehicle that allow said vehicle to be taught a route by a human operator and then have it automatically drive the route with no human intervention. The method works in three steps: teaching, route profiling, and playback. In the teaching step the vehicle is manually driven by a operator (or using tele-operation whereby the operator views a screen displaying live views from vehicle-mounted cameras and using remote controls) along a route which can consist of an arbitrary sequence of maneuvers including tramming forwards, switching directions, tramming backwards, turning, or pausing movement. During this phase raw data from vehicle-mounted sensors including odometric sensors and rangefinders are logged to a file throughout teaching for later processing. During the (offline) route profiling step, the raw data in the log file are processed into a route profile including a vehicle path, a sequence of local metric submaps located along the path, and a profile of desired speed as a function of distance along the path. During the playback step, the vehicle automatically repeats the route that was taught during the teaching phase, as represented by the route profile. This is accomplished by first determining where the vehicle is on the route using a localization method which uses the odometric and laser rangefinder sensors and the local metric maps to determine the vehicle location. A steering control method adjusts the vehicle's steering to ensure it tracks the intended path. A drive control method adjusts the vehicle's speed accordingly and safety method ensures the vehicle stops in the event that an obstruction is on the vehicle's intended path.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20120174445A1Accurate fillingEasy to correctNavigation instrumentsGuiding agricultural machinesGyroscopeMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other, and snow grooming equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Vehicle steering system having a rear steering control mechanism
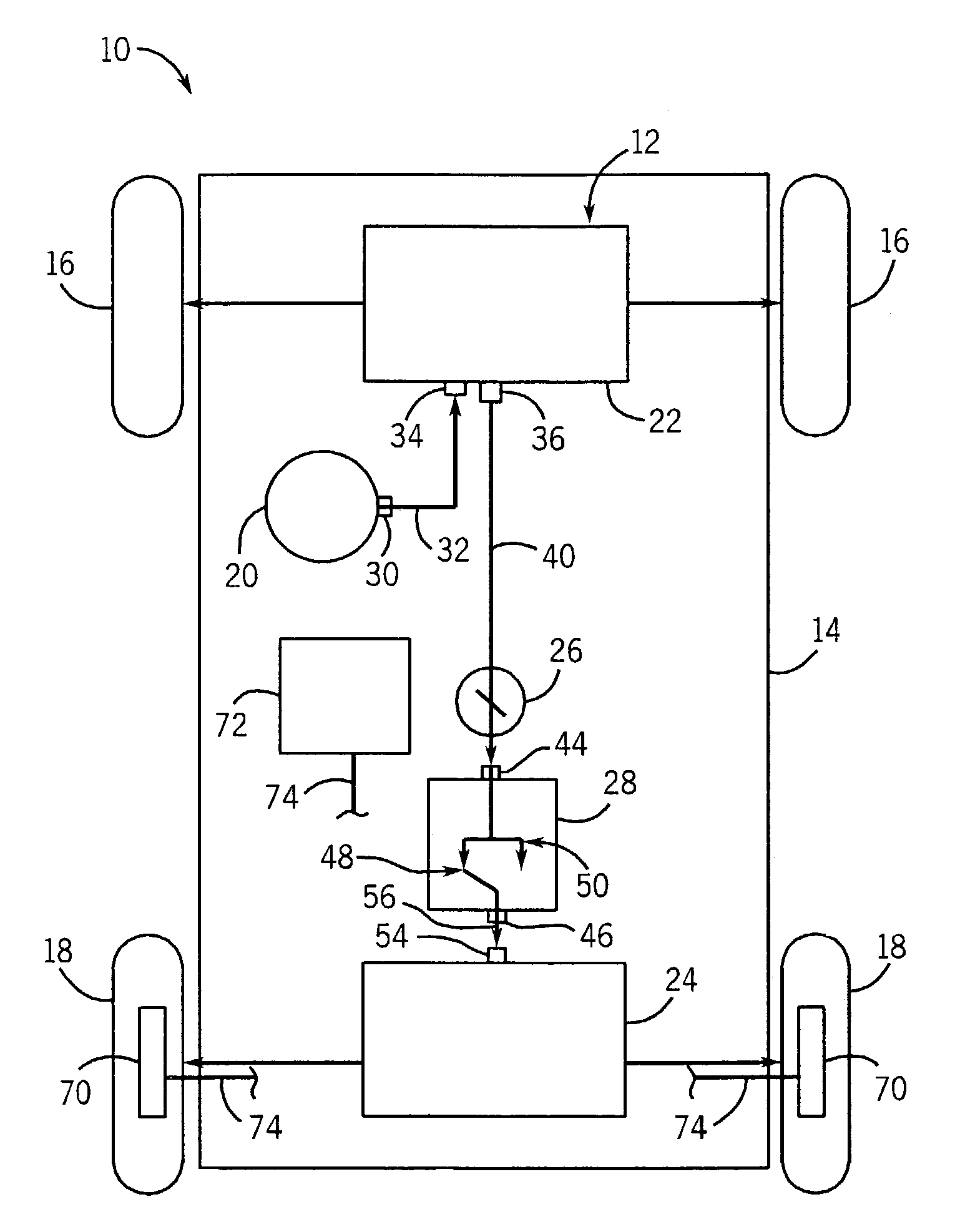
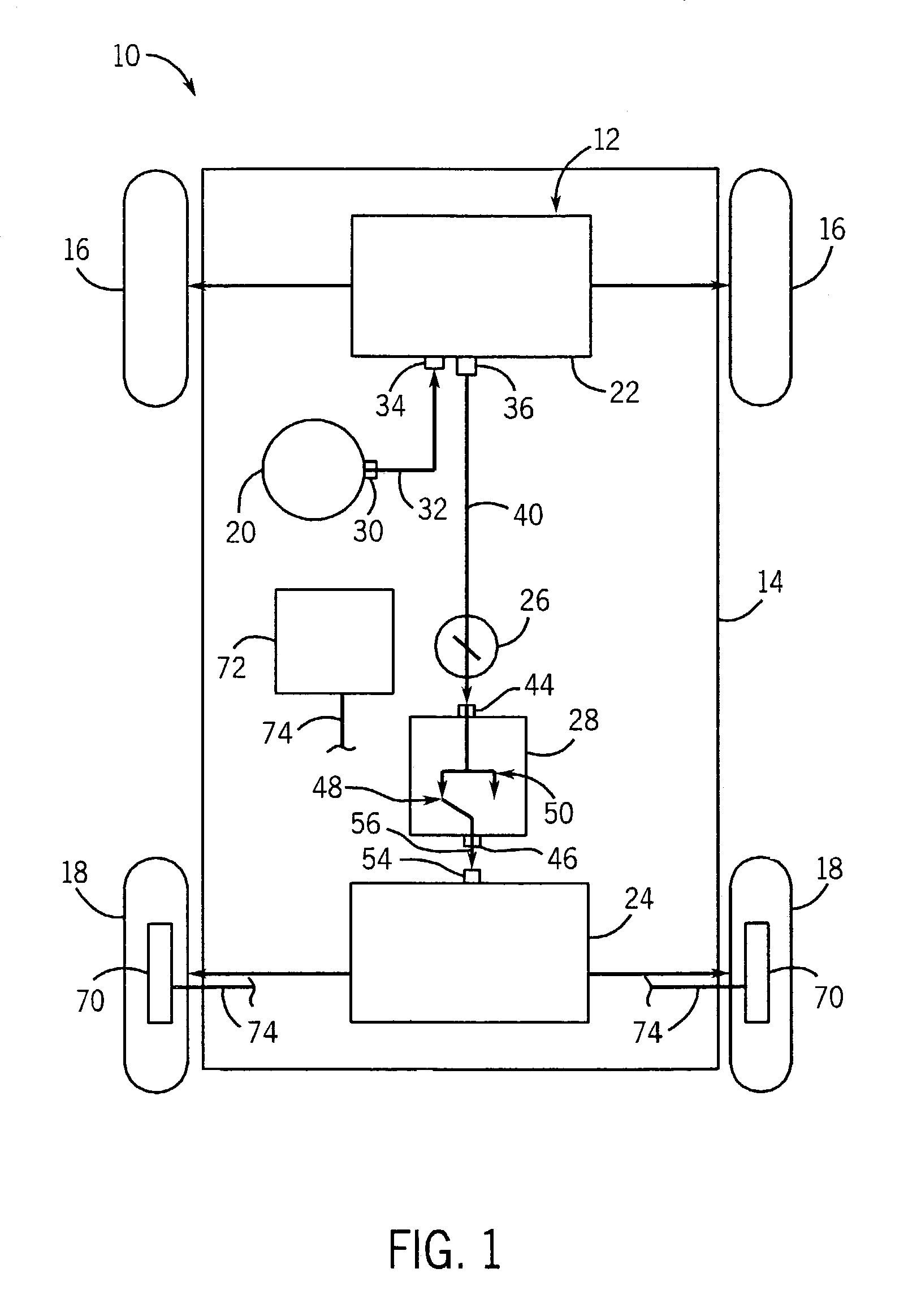
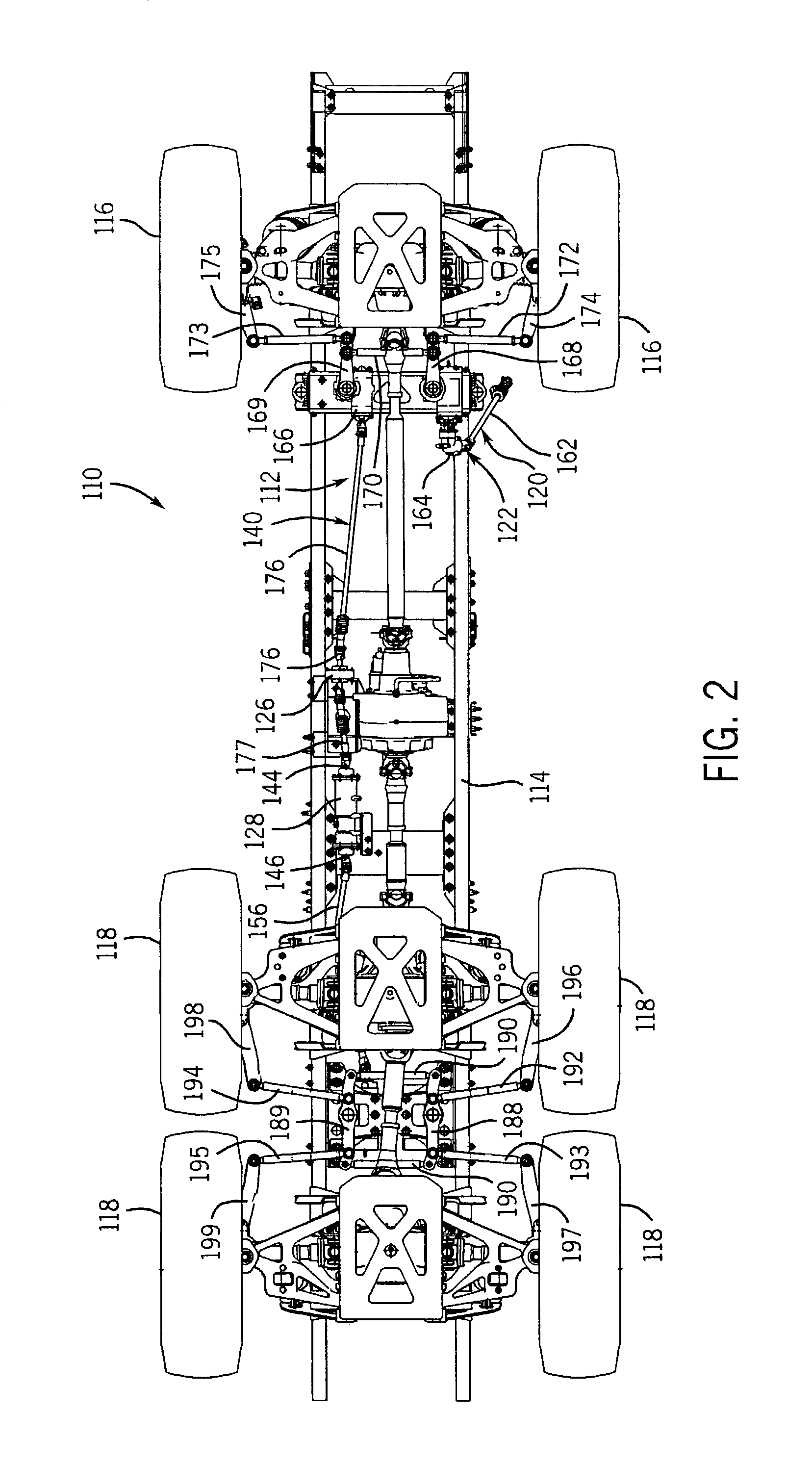
The vehicle steering system includes front vehicle motive members, rear vehicle motive members, a steering input device, a front steering subsystem, a rear steering subsystem and a rear steering control mechanism. The front steering subsystem is operably coupled to the steering input device and coupled to the front motive members to steer the front motive members. The rear steering subsystem is coupled to the rear motive members to steer the rear motive members. The rear steering control mechanism includes a movable input member coupled to the steering input device so as to move in response to input from the device and a movable output member coupled to the rear steering subsystem. The rear steering subsystem adjusts steering of the rear motive members in response to movement of the output member. The control mechanism operates in a rear steering state in which force is transmitted from the input member to the output member to move the output member and a dwell state in which the output member does not move in response to movement of the input member.
Owner:OSHKOSH CORPORATION
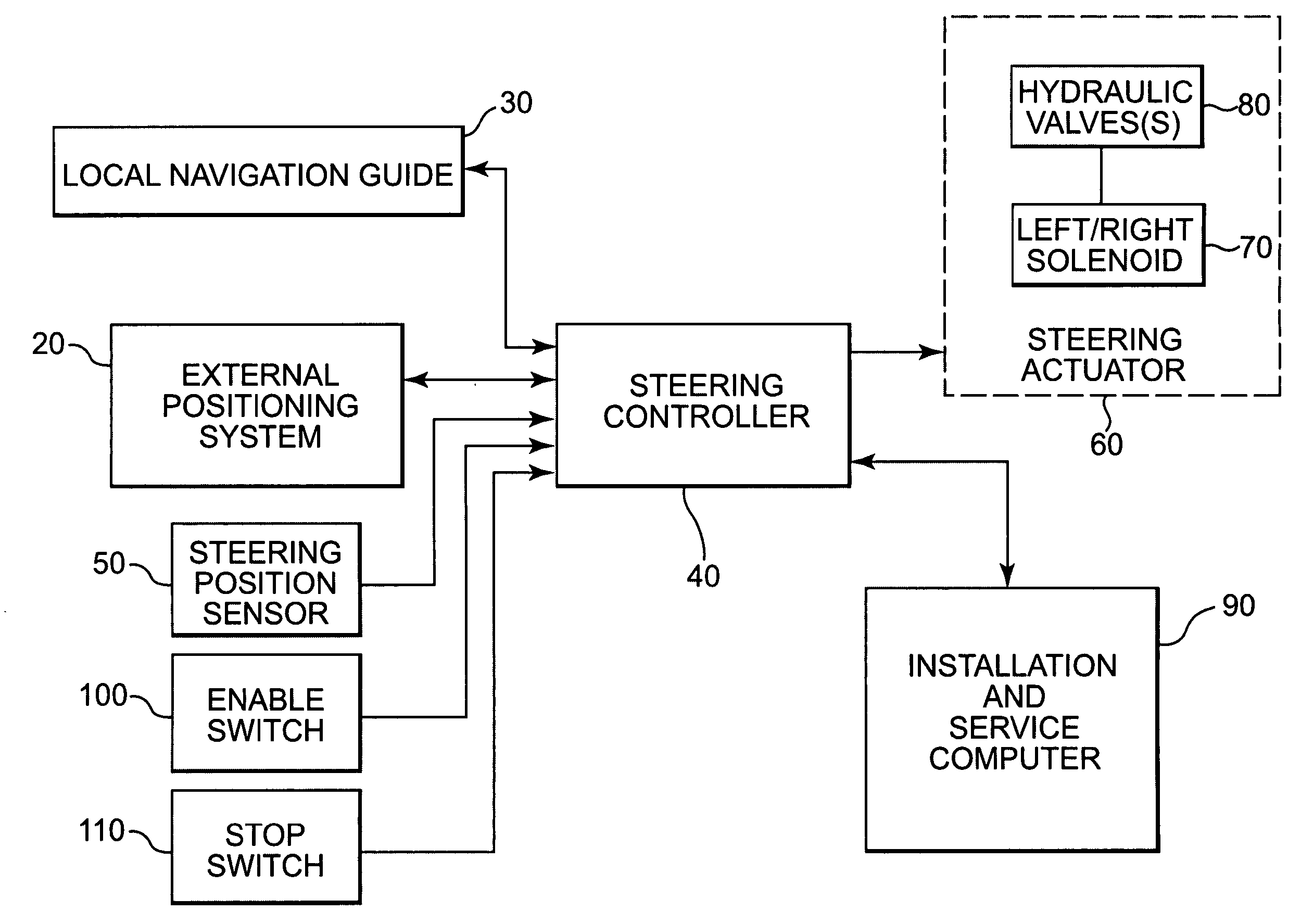
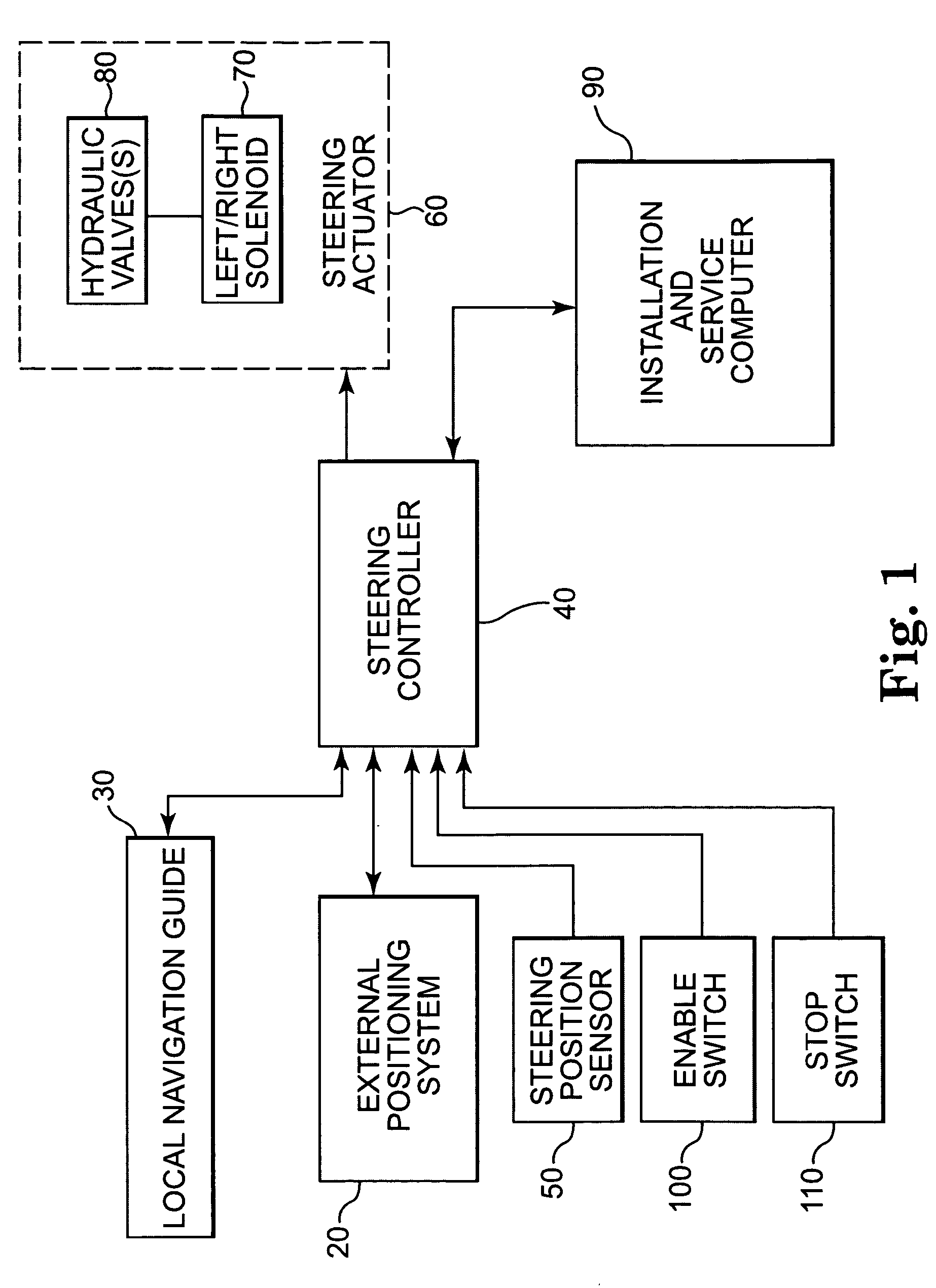
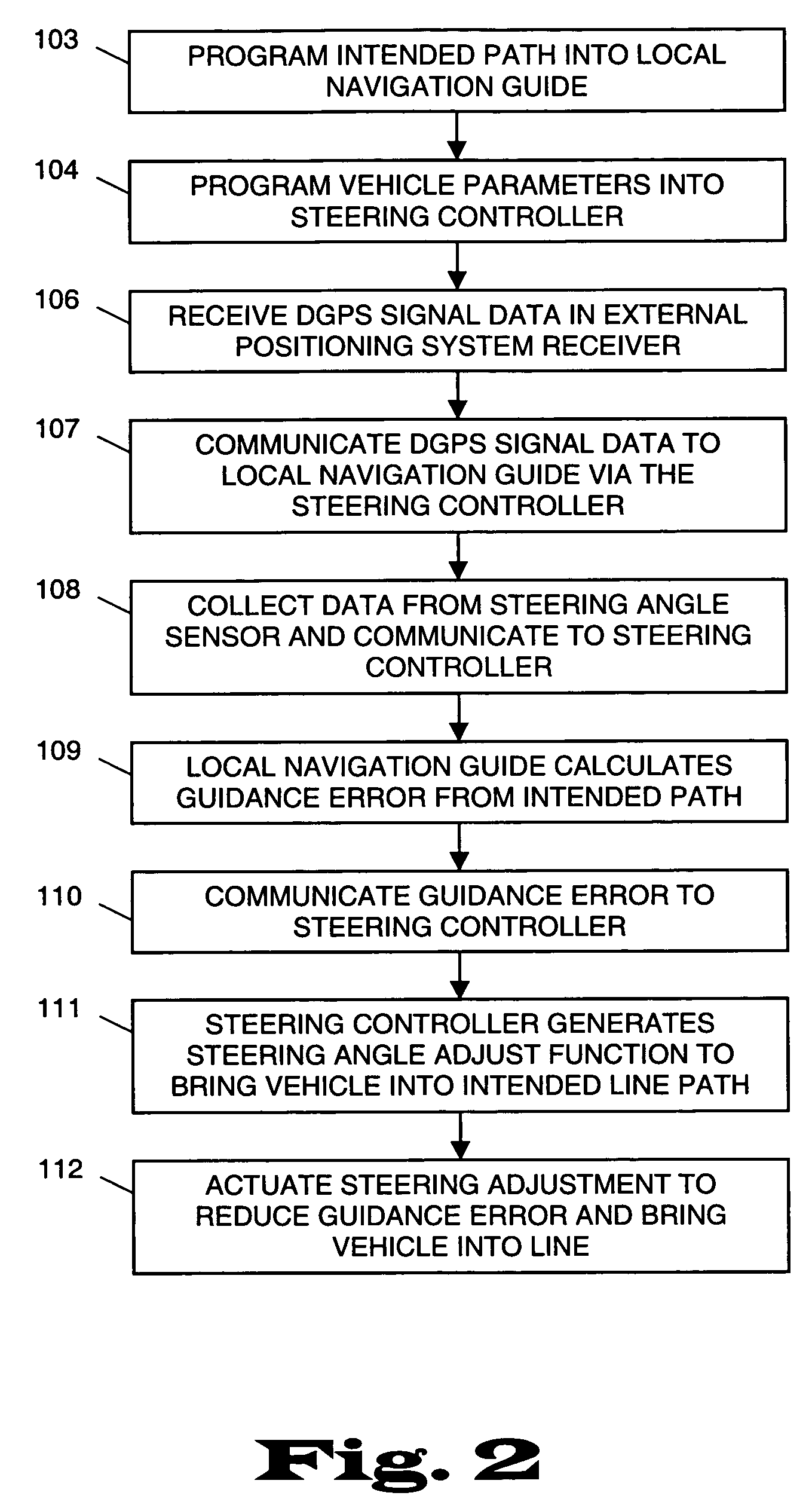
Architecturally partitioned automatic steering system and method
InactiveUS20060167600A1Delay variationMaximum performanceDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlAutomatic steeringSteering angle
A system and method for automatically steering a vehicle along an intended path is provided. The system is architecturally partitioned. The partitioned design allows each of the system elements to be designed and maintained independently while allowing variation and flexibility in system configuration. An embodiment of the system elements may comprise a local navigation guidance unit, an external positioning system, a steering controller, and an installation and service computer. Additional elements of an embodiment of the system may comprise a steering position sensor, and at least one steering actuator. The system allows the operator to enter an intended target path and certain vehicle parameters. The local navigation guidance unit receives positional data from an external positioning system, preferably DGPS, indicative of a navigational path traversed by the vehicle. The guidance unit compares the positional data with the intended target path to obtain guidance error and transmits the guidance error to the steering controller. The system allows for determination of the current steering angle and generation of a steering angle adjustment based upon the intended target, the navigational path traversed by the vehicle, the vehicle parameters, the steering angle and the guidance error. The steering angle adjustment is used to actuate a steering mechanism to smoothly guide the vehicle along the intended target path.
Owner:RAVEN INDUSTRIES INC
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20100312428A1Accurate fillingEasy to correctGuiding agricultural machinesSatellite radio beaconingSteering controlFixed interval
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other and earth-moving equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Satellite position and heading sensor for vehicle steering control
ActiveUS7400956B1Avoid crossingEasy to correctInstruments for road network navigationGuiding agricultural machinesControl systemCarrier signal
A sensor system for vehicle steering control comprising: a plurality of global navigation satellite sensor systems (GNSS) including receivers and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase corrected real time kinematic (RTK) position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system.
Owner:AGJUNCTION INC
Terrain conforming track assembly
An endless track assembly that mounts to a wheeled vehicle. The assembly provides 1) a track suspension having fixed or adjustable, independently biased sets of idler wheels to vary the track contour without affecting track tension, 2) an eccentric bearing housing at a drive sprocket controls track tension, 3) a contoured peripheral edge at the drive sprocket prevents ice and mud buildup, 4) rubber-coated, plastic idler wheels facilitate track movement, 5) a multi-vehicle compatible adapter mounting plate accommodates a variety of vehicles, 6) a rotation limited torsion coupler and / or rotation limiting coupler arms prevent track contact with the vehicle, 7) a locking steering arm coupler prevents loss of steering control, and 8) shaped track lugs and channels clear and direct debris away from the track suspension and drive assembly. The improved suspension particularly supports sets of idler wheels in pivotal relation to the track support frame and resiliently biases a pre-tensioned rocker arm that links adjacent suspension arms mounted to the adjoining idler wheels. Suspension arm movement induces expansion and contraction of tension springs coupled to the rocker arms to augments shape changes at the track contact surface to optimize traction and steering control.
Owner:BRAZIER GLEN
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS8594879B2Easy to correctGuiding agricultural machinesSatellite radio beaconingSteering controlMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other and earth-moving equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com