Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5446 results about "Steering angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
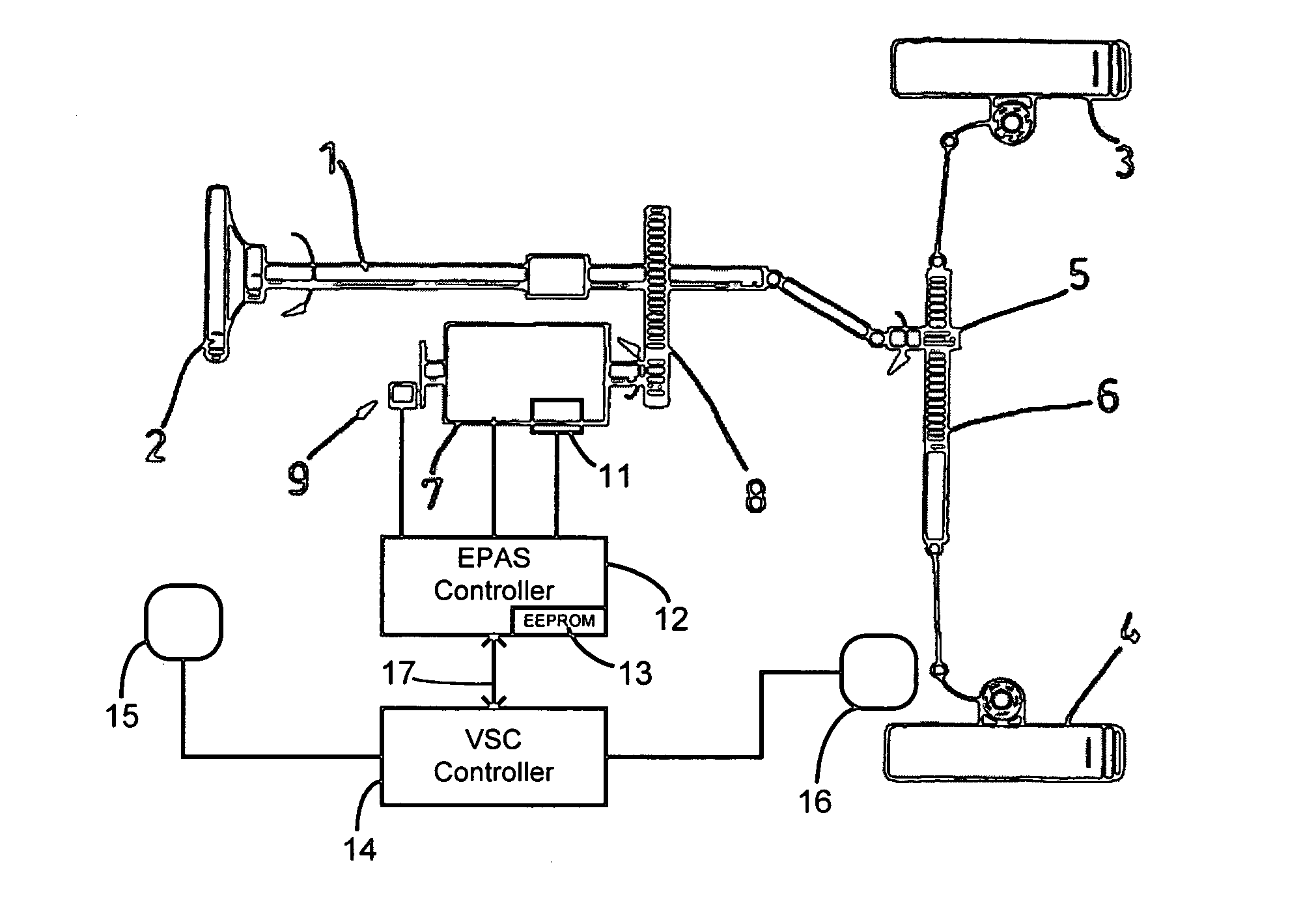
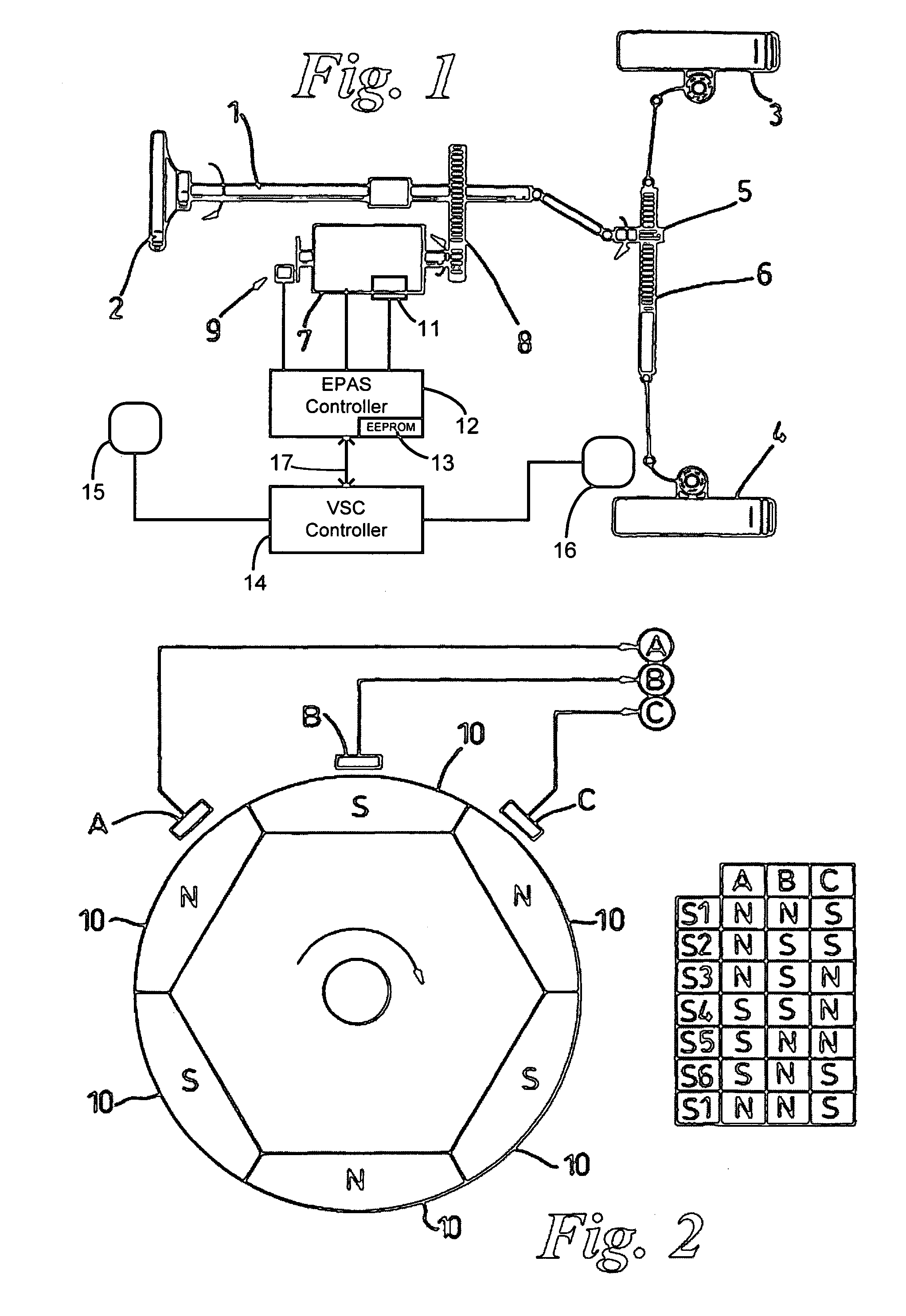
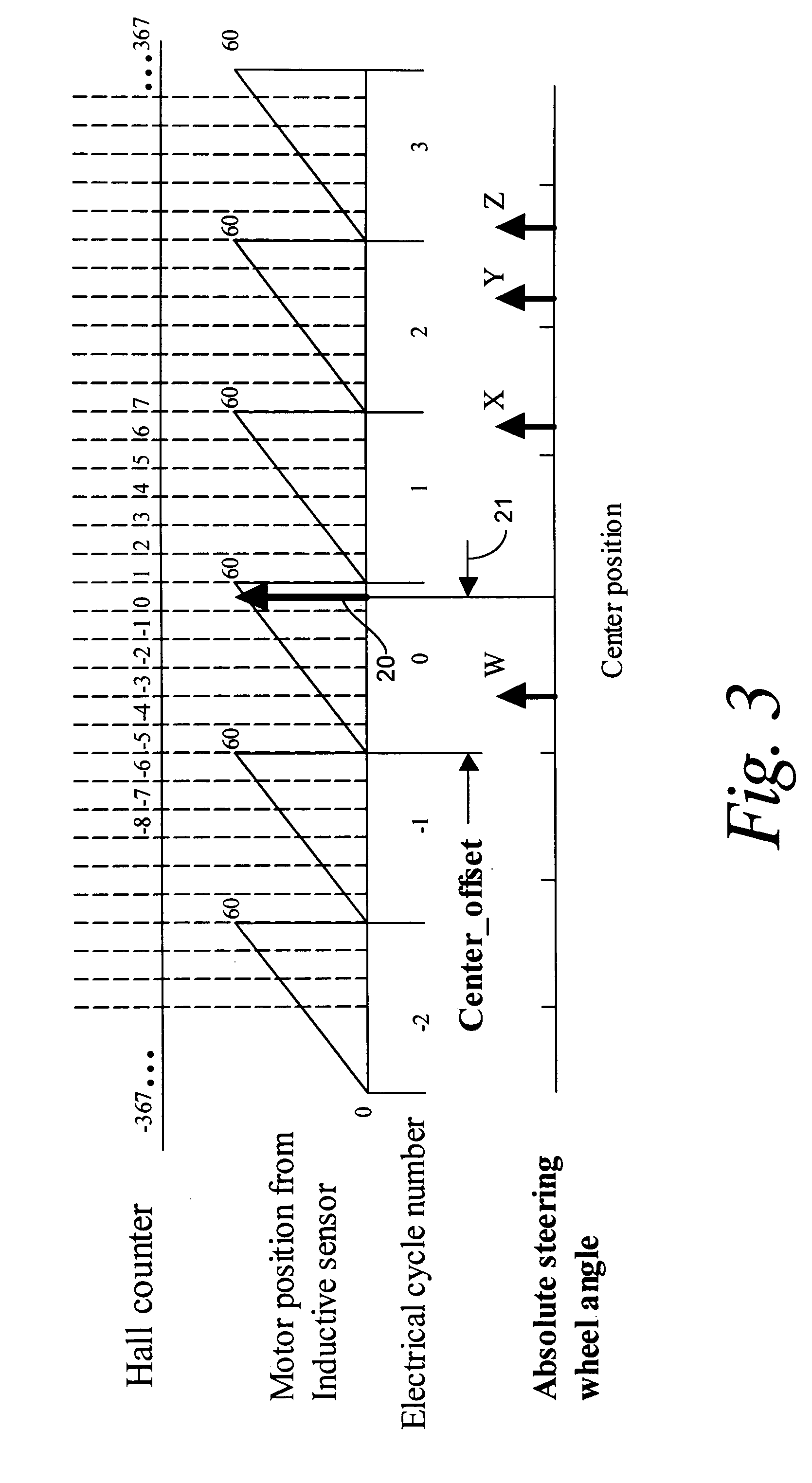
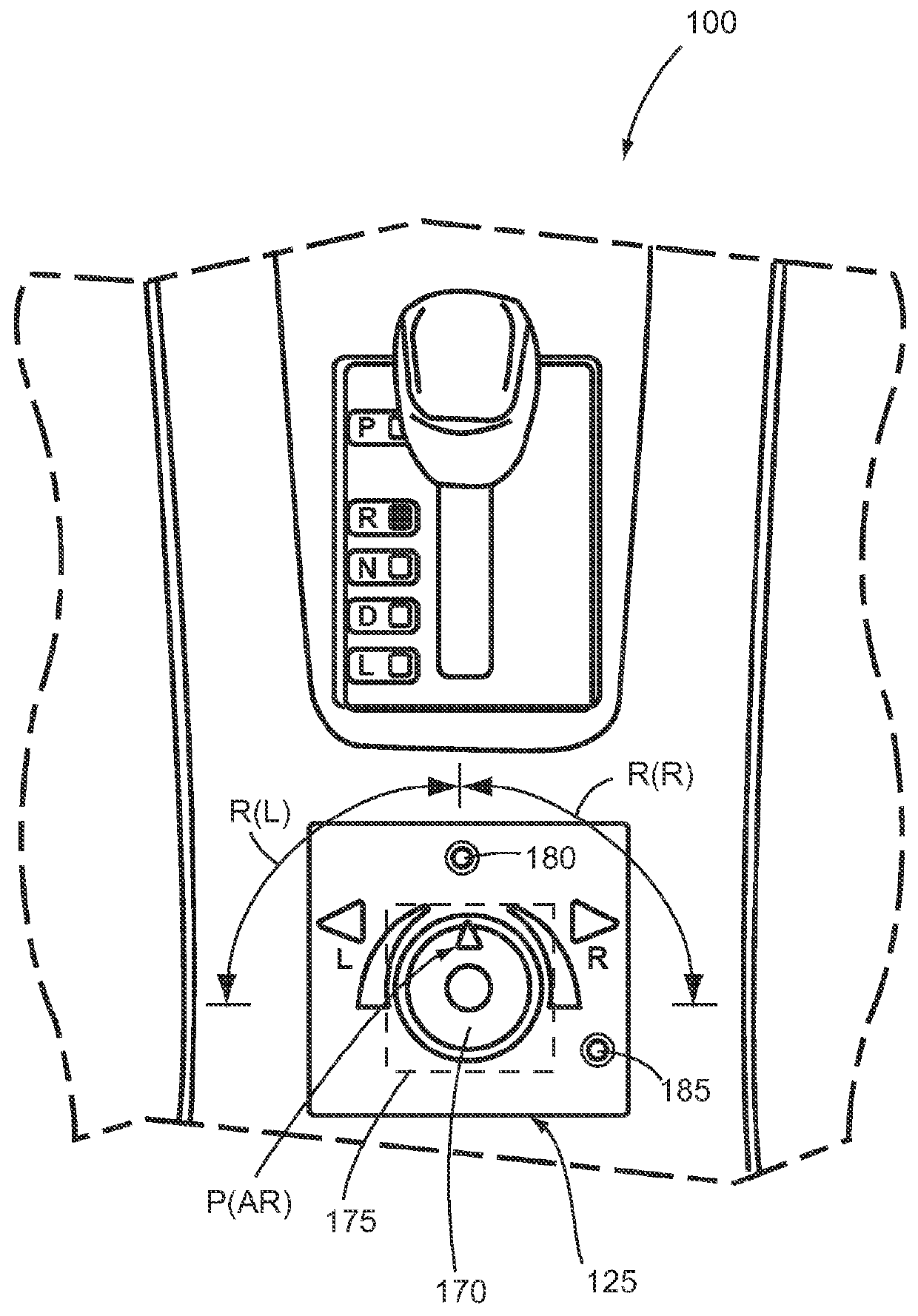
Recovery of calibrated center steering position after loss of battery power
ActiveUS7295907B2Accurate absolute steering angleAvoid the needDigital data processing detailsOptical signallingElectric power steeringSteering angle
The steering angle of a vehicle is monitored using position sensors of an electric motor of an electric power assisted steering (EPAS) system. A position of the electric motor corresponding to the straight-ahead, center position of the steering system is stored in non-volatile memory during a steering calibration procedure, such as an end-of-line calibration in a vehicle assembly plant. Following power loss due to a dead battery, a steering angle zeroing procedure performed in a vehicle stability control (VSC) system generates a center position with enough accuracy to be within one electrical cycle of the motor. The pre-stored electric motor position is then used to determine the electrical cycle where the center position was located, and accurate monitoring of steering angle is resumed.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
Object detection system for vehicle
ActiveUS7720580B2Reduce processing requirementsReduce the possibilityTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsData setSteering angle
An imaging system for a vehicle includes an imaging array sensor and a control. The image array sensor comprises a plurality of photo-sensing pixels and is positioned at the vehicle with a field of view exteriorly of the vehicle. The imaging array sensor is operable to capture an image of a scene occurring exteriorly of the vehicle. The captured image comprises an image data set representative of the exterior scene. The control algorithmically processes the image data set to a reduced image data set of the image data set. The control processes the reduced image data set to extract information from the reduced image data set. The control selects the reduced image data set based on a steering angle of the vehicle.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
Object detection system for vehicle
ActiveUS20060184297A1Reduce processing requirementsReduce the possibilityTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsData setSteering angle
An imaging system for a vehicle includes an imaging array sensor and a control. The image array sensor comprises a plurality of photo-sensing pixels and is positioned at the vehicle with a field of view exteriorly of the vehicle. The imaging array sensor is operable to capture an image of a scene occurring exteriorly of the vehicle. The captured image comprises an image data set representative of the exterior scene. The control algorithmically processes the image data set to a reduced image data set of the image data set. The control processes the reduced image data set to extract information from the reduced image data set. The control selects the reduced image data set based on a steering angle of the vehicle.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
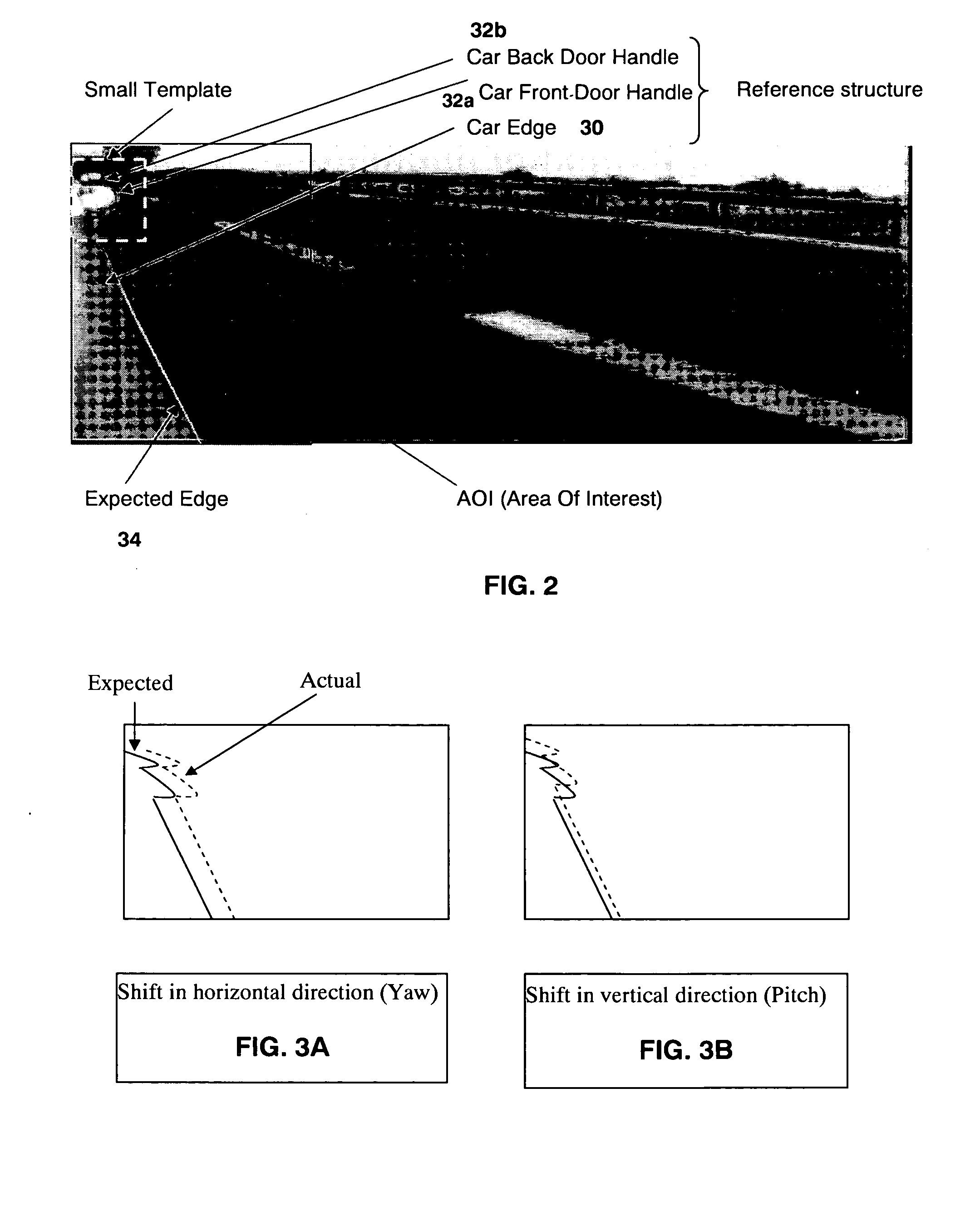
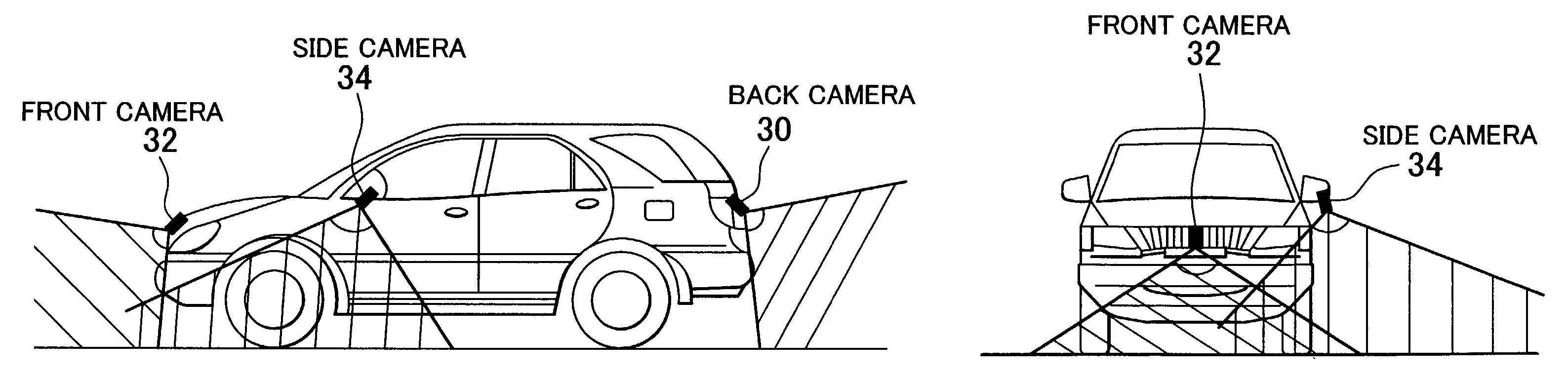
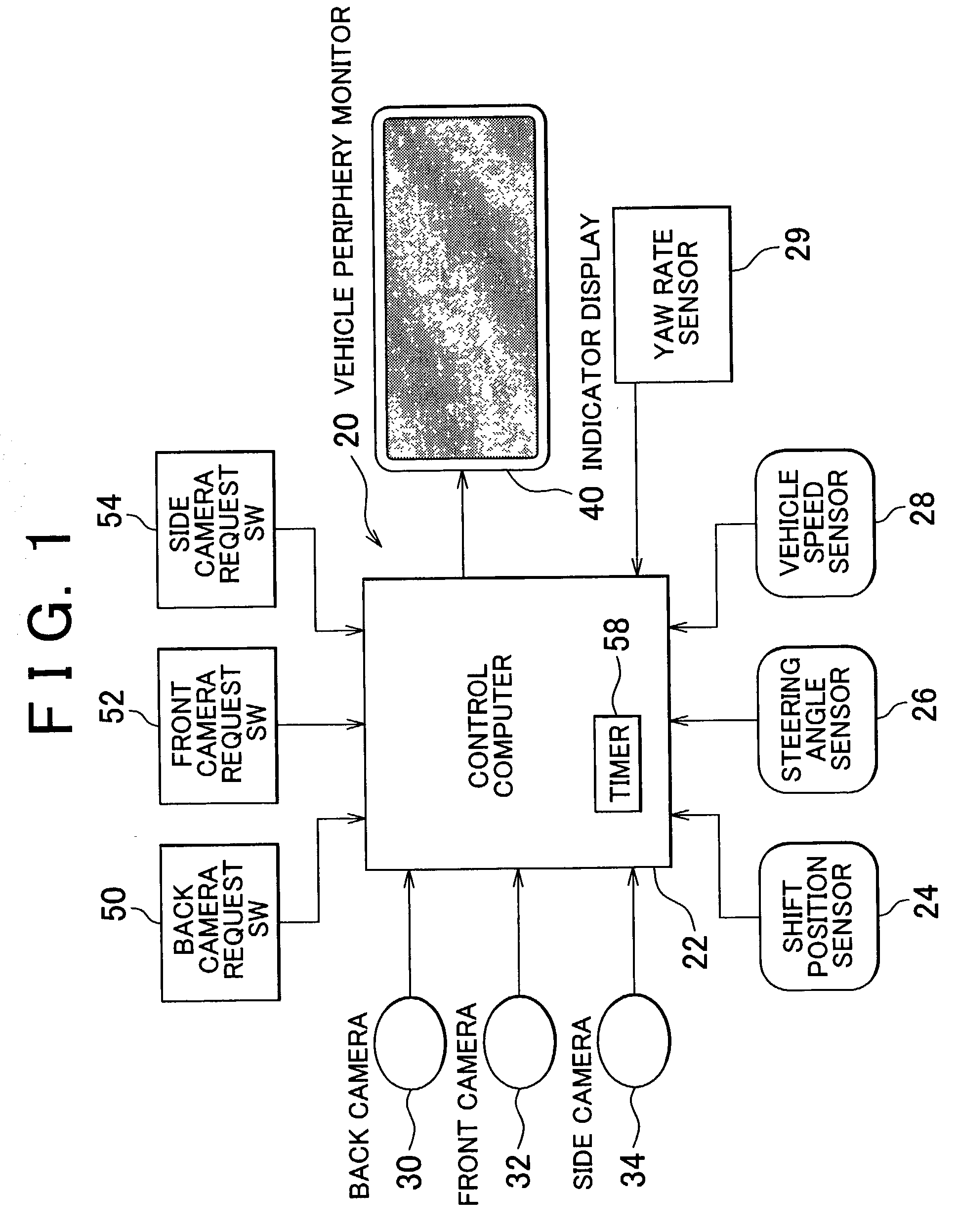
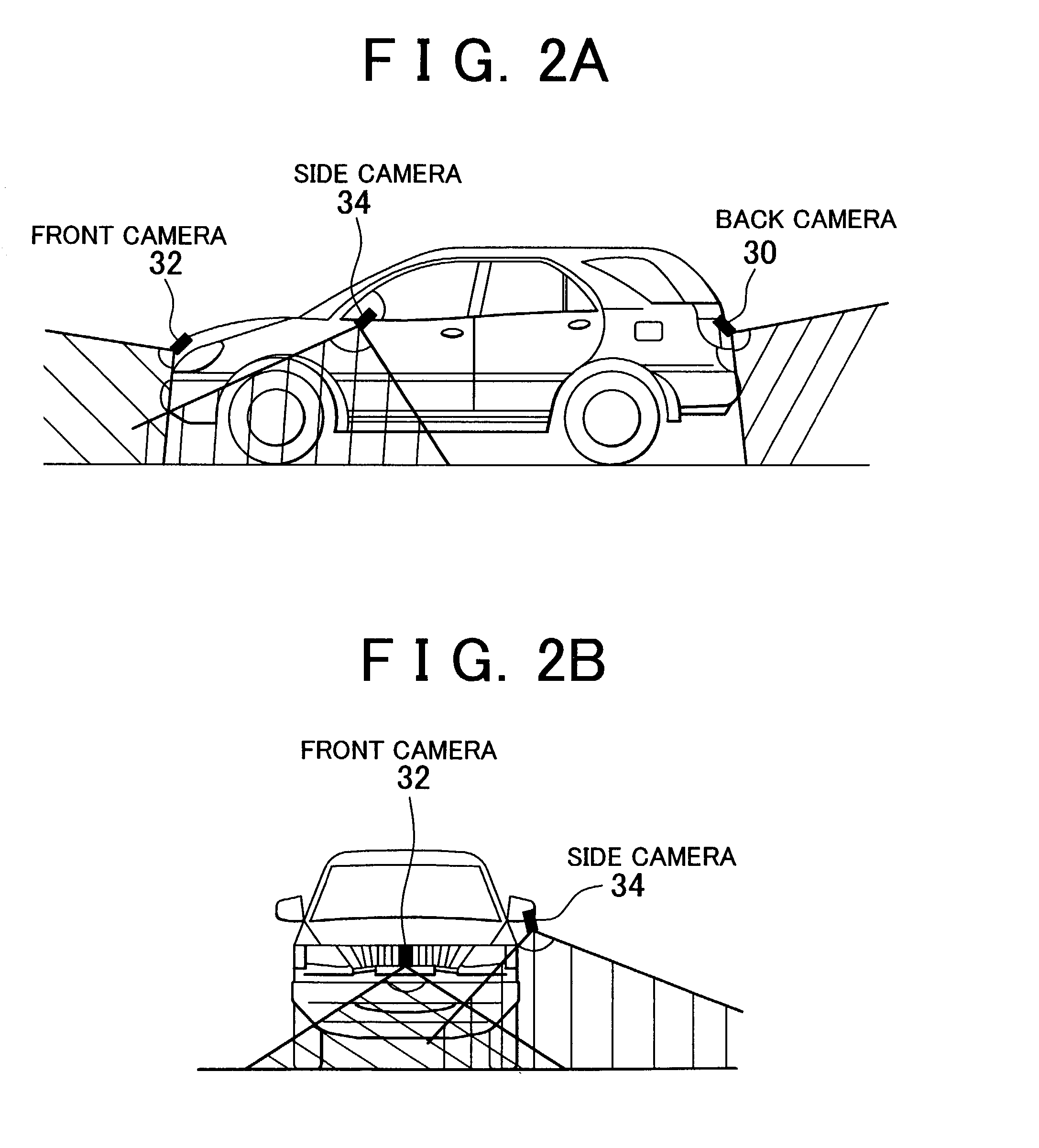
Vehicle periphery monitor
ActiveUS7248283B2Increased operational burdenImprove visibilityTelevision system detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlSteering wheelSteering angle
A front camera for filming an area stretching forwards is disposed in a front portion of a vehicle. A side camera for filming an area stretching laterally and diagonally forwards is disposed in a lateral-left portion of the vehicle. An indicator display that can be visually recognized by a driver is disposed in a compartment of the vehicle. An amount of change in the direction of the vehicle, that is, a deflection angle of the vehicle is detected on the basis of a vehicle speed and a steering angle of a steering wheel, which have been detected by means of various sensors. After the indicator display has started displaying a lateral photo image filmed by the side camera, the photo image displayed by the indicator display is shifted from the lateral photo image filmed by the side camera to a front photo image filmed by the front camera if the deflection angle has reached a predetermined angle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Vehicle drive assist system
InactiveUS20060287826A1Simple image displayIntuitive displayInstruments for road network navigationInstrument arrangements/adaptationsSteering angleEngineering
A vehicle drive assist system comprises a camera for picking up an image of an area existing in an advancing direction of a vehicle; display means for displaying the image picked up by the camera; steering angle detecting means for detecting a steering angle for steering the vehicle; traveling path predicting means for predicting a traveling path of the vehicle on the basis of the steering angle detected by the steering angle detecting means; and drive assist means for overlaying on the display means drive assist information containing the vehicle predictive traveling path predicted by the traveling path predicting means and guide lines prolonged from the lines defining the width of the vehicle body on the image of the area existing in the vehicle advancing direction.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Autonomous Driving Vehicle and Autonomous Driving System
ActiveUS20160282874A1Improve securityAvoid stopAutonomous decision making processElectromagnetic wave reradiationSteering angleMotion barrier
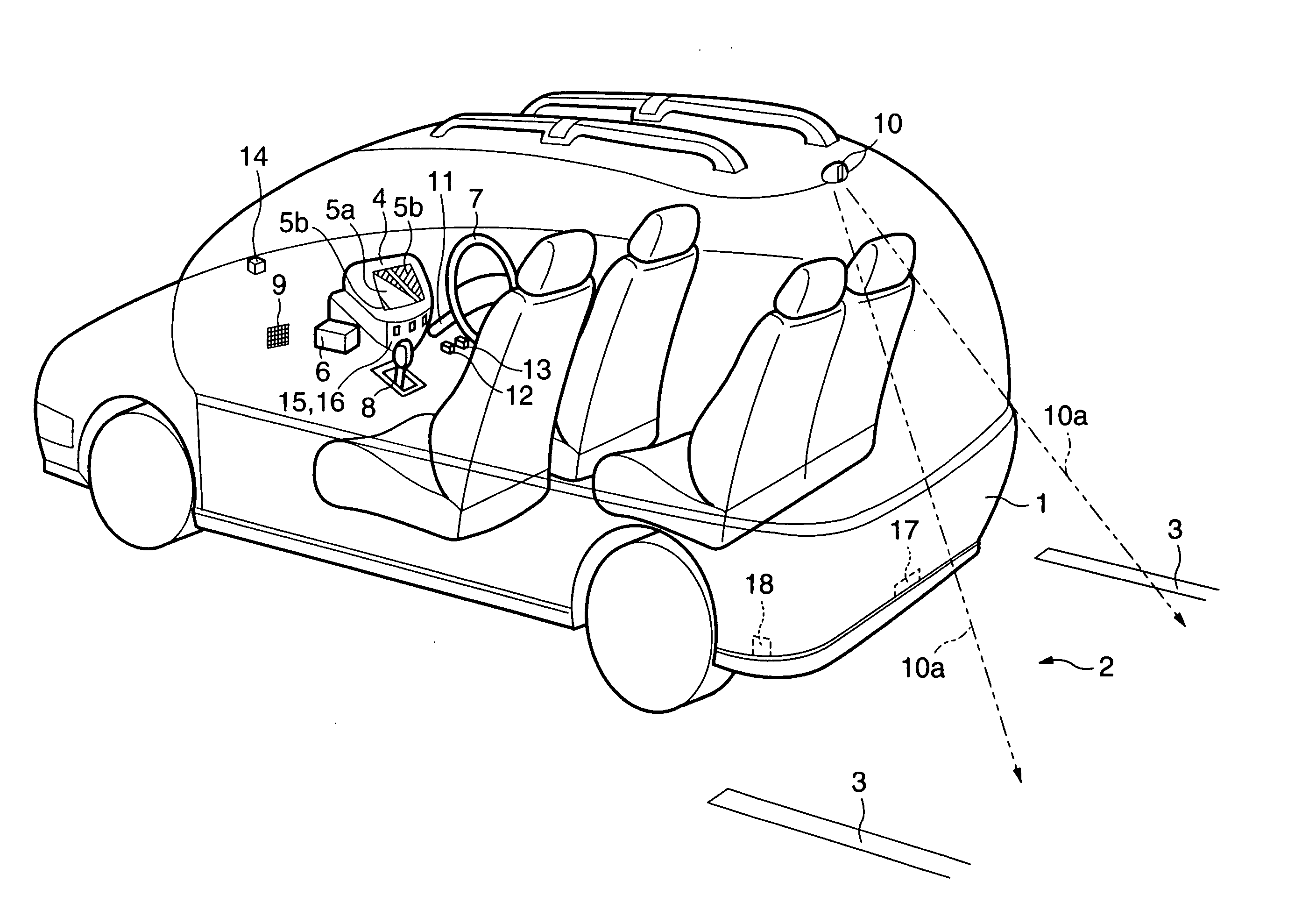
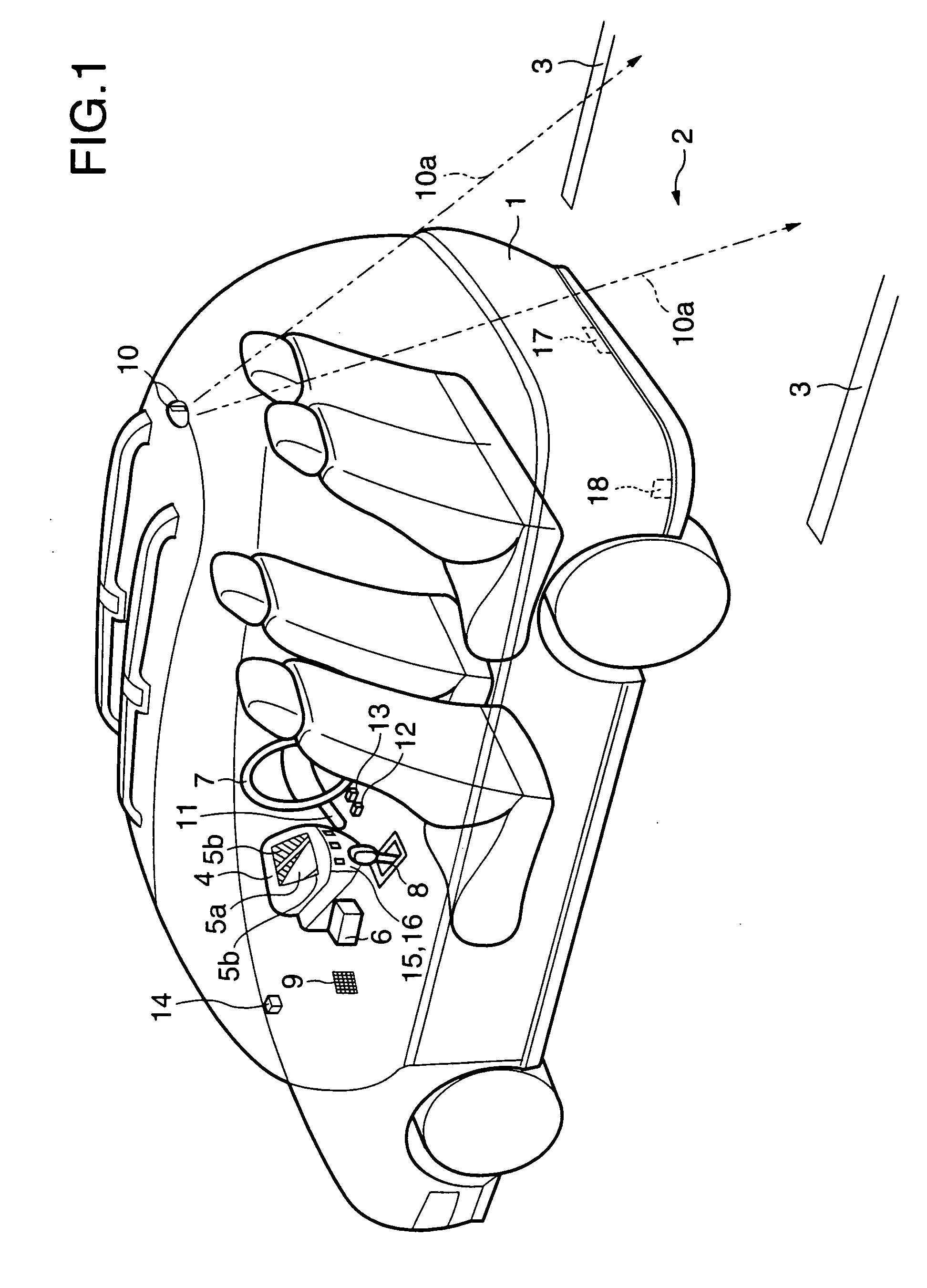
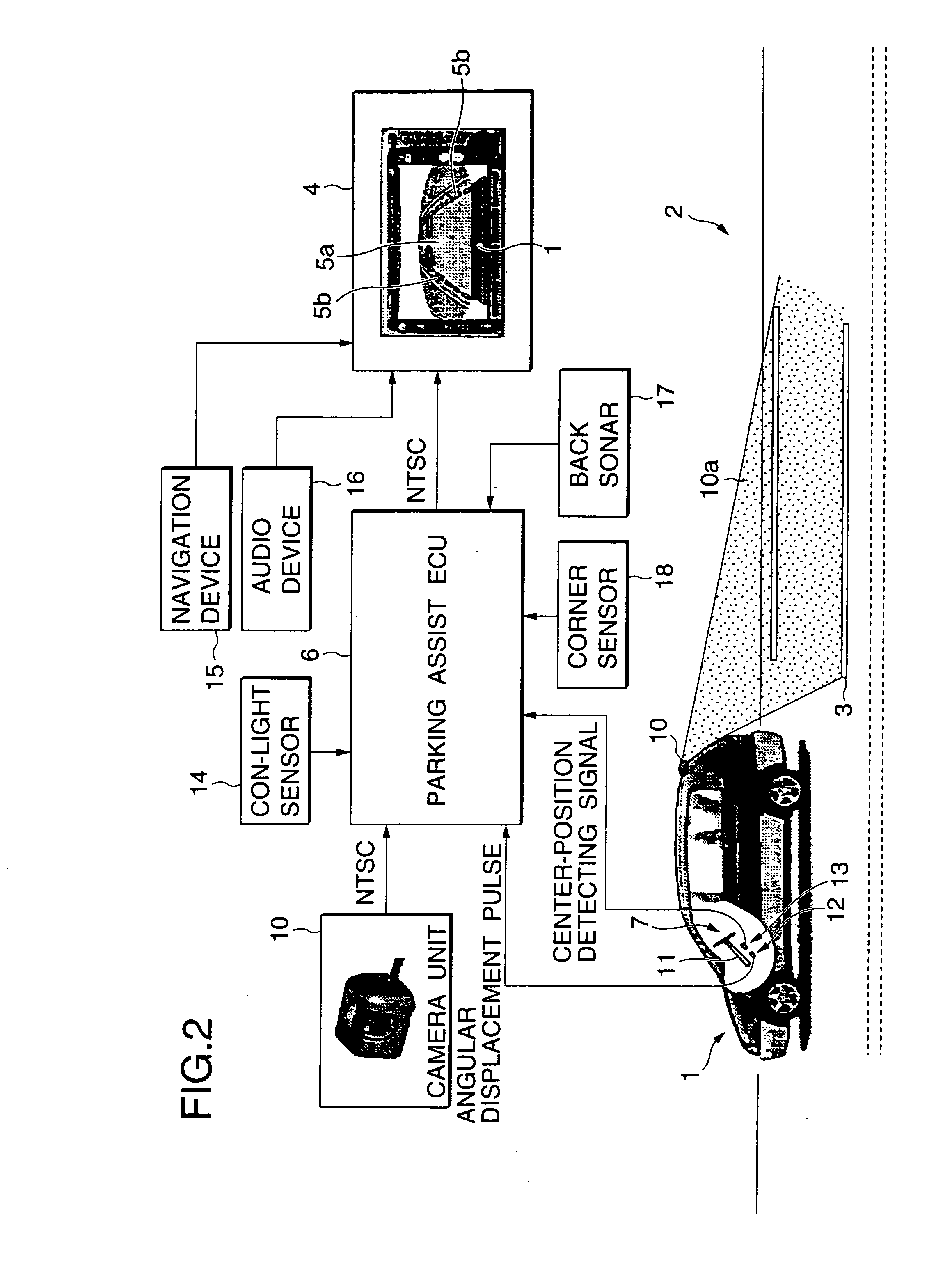
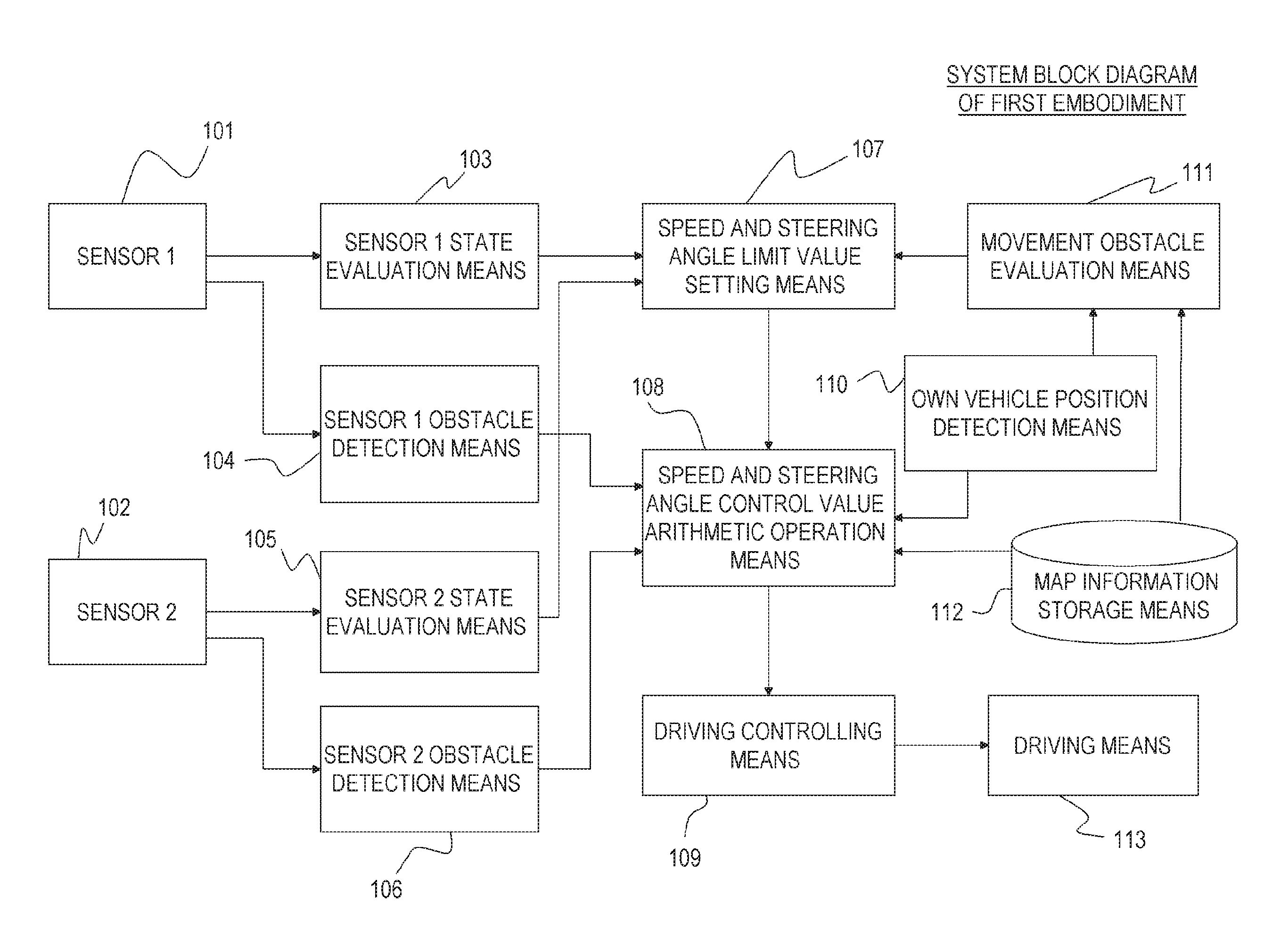
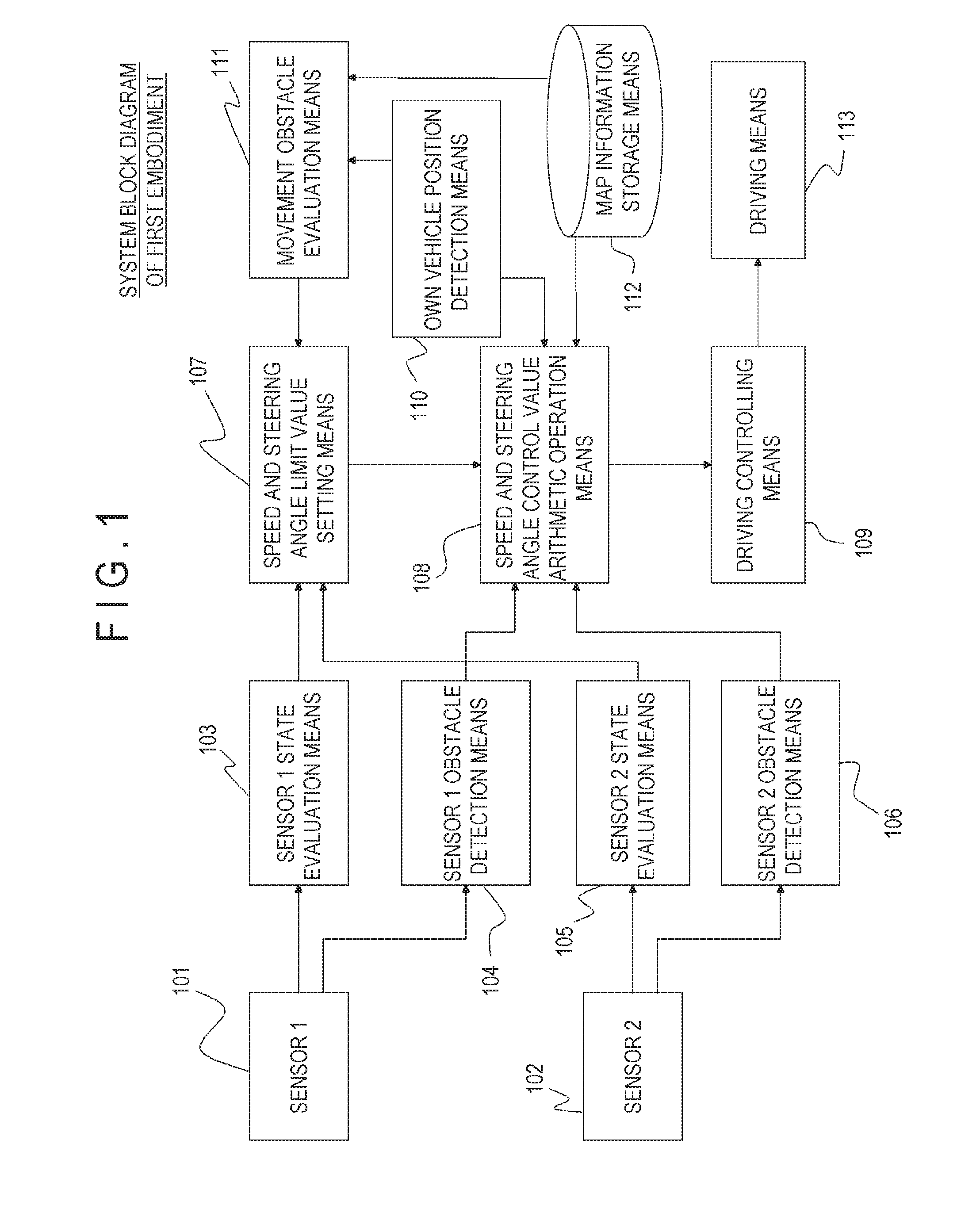
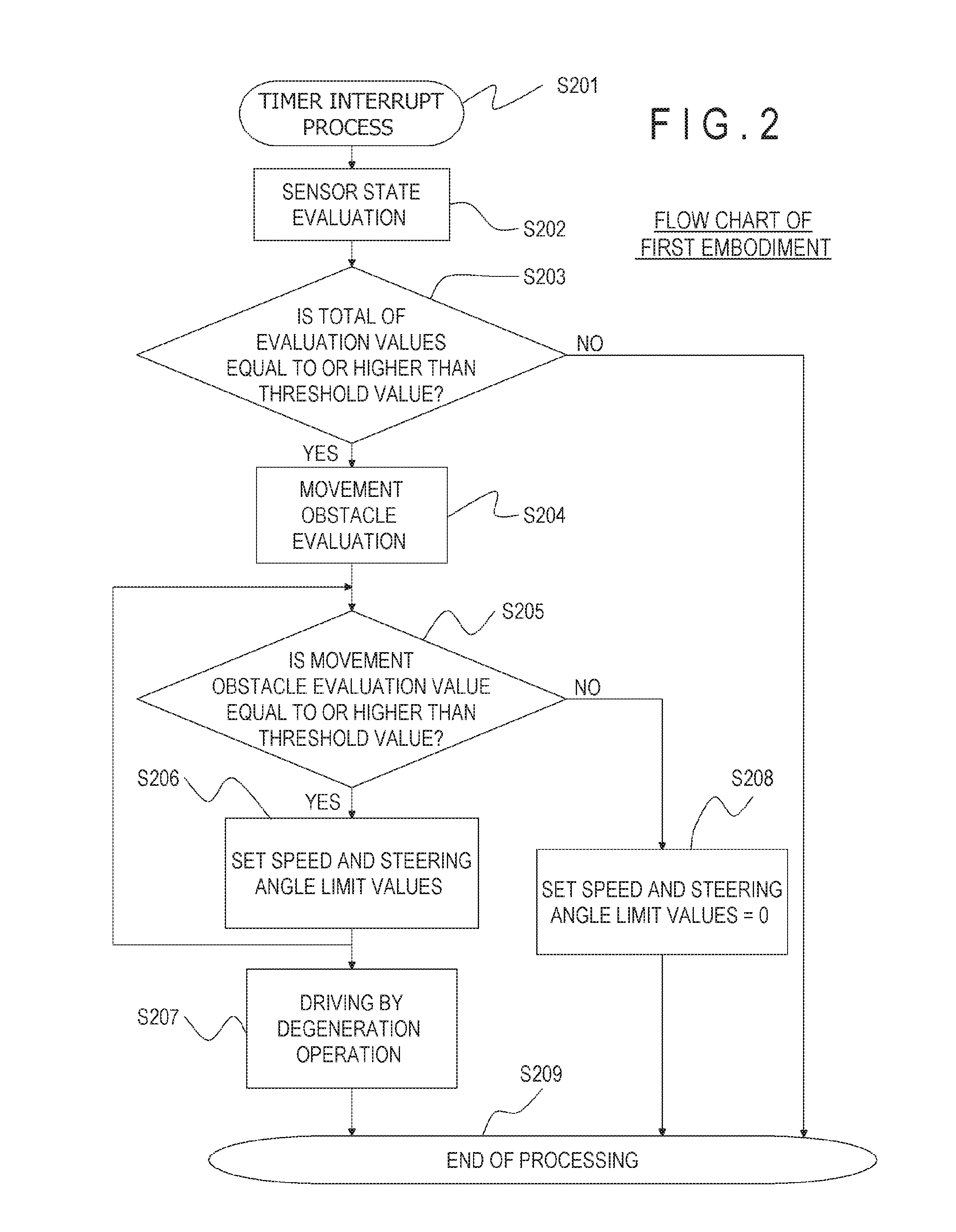
In an autonomous driving system in which a plurality of autonomous driving vehicles drive under the control by occlusion control, such a situation is prevented that a vehicle is disabled to drive by a failure of an external world sensor for recognizing an obstacle and stops in an occlusion region thereby to obstruct advancement of overall succeeding vehicles to remarkably degrade the efficiency of the overall transportation work. In the autonomous driving system of the present invention, an autonomous driving vehicle which detects an obstacle or a driving road by a sensor and performs autonomous driving includes sensor state evaluation means configured to evaluate a state of performance degradation of the sensor, speed and steering angle control value setting means configured to provide limit values to the driving speed and the steering angle based on a state of performance degradation of the sensor, and movement obstacle evaluation means configured to evaluate an influence on movement of other vehicles when the vehicle stops at a position at present. When the sensor suffers from performance degradation, the vehicle stops after it drives within the set limit values to the speed and the steering angle to a point at which the vehicle does not obstruct movement of other vehicles.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
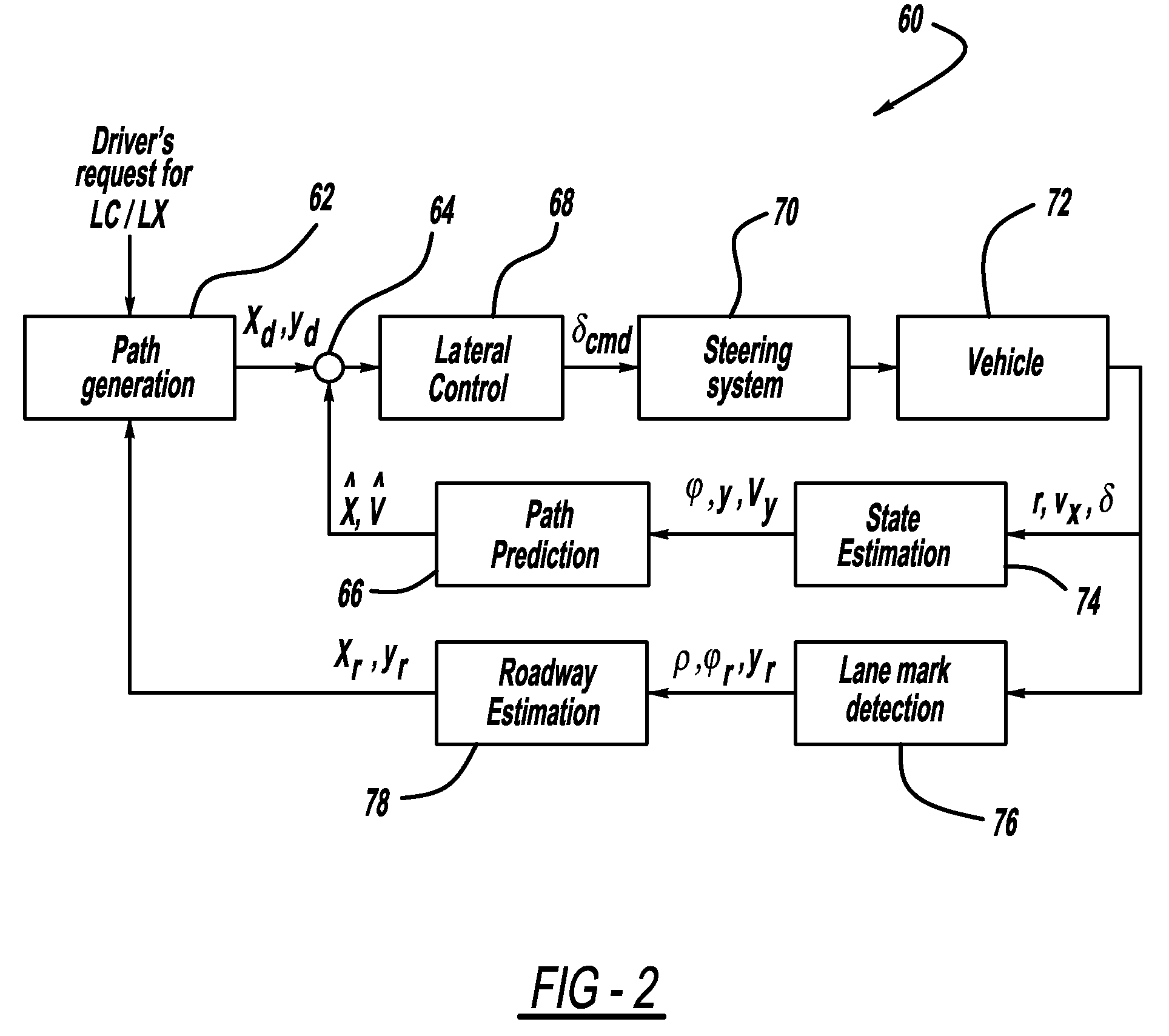
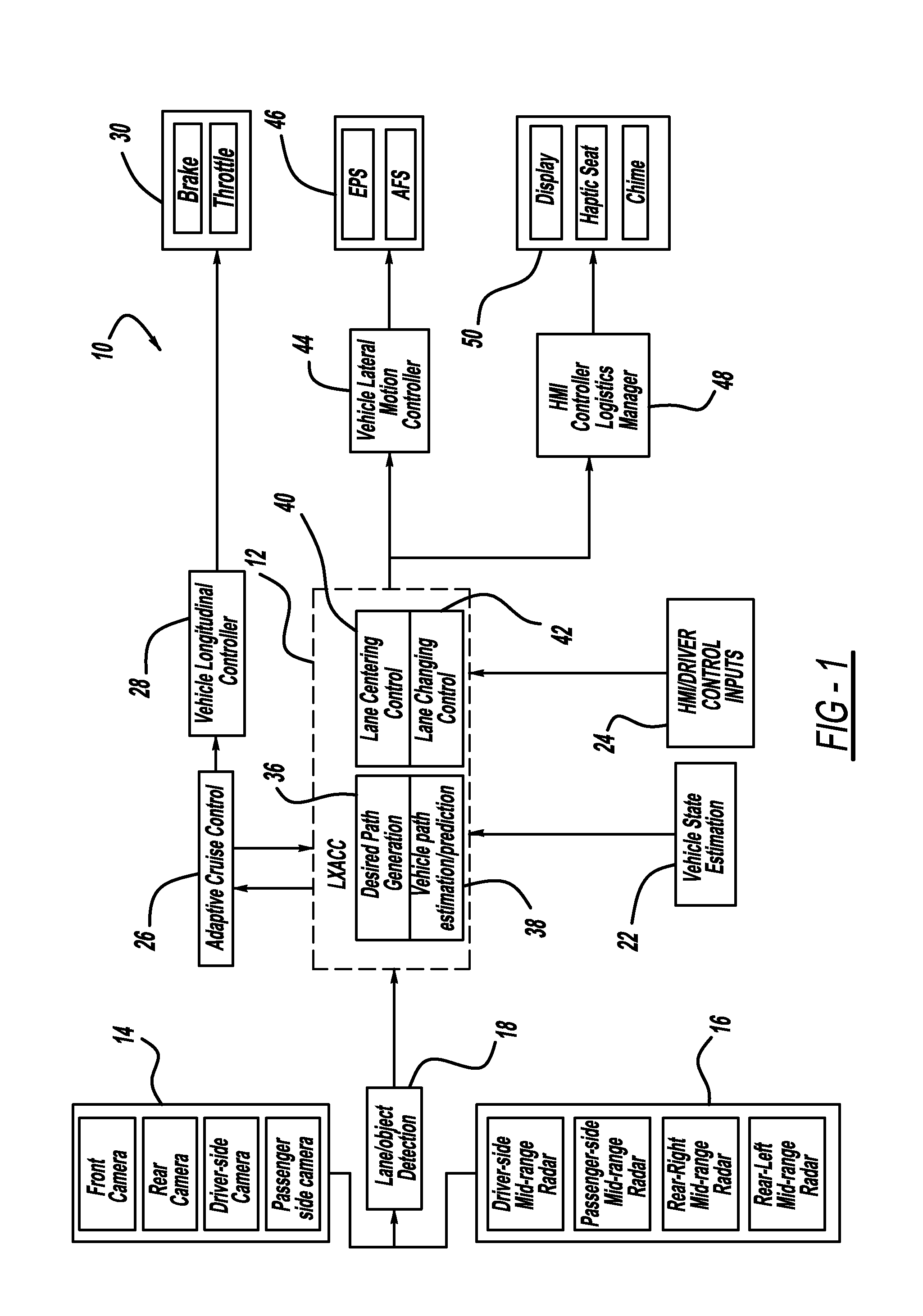
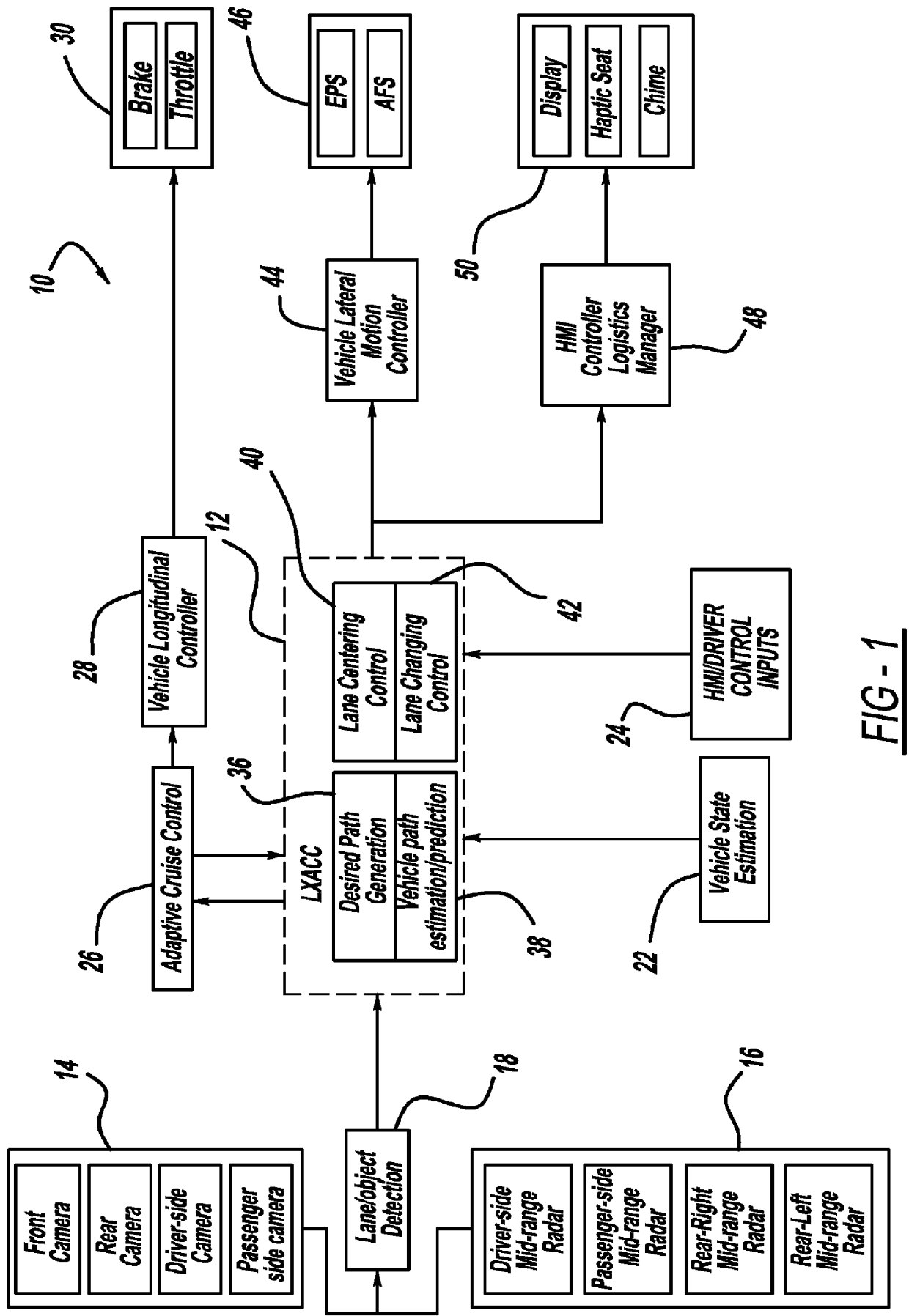
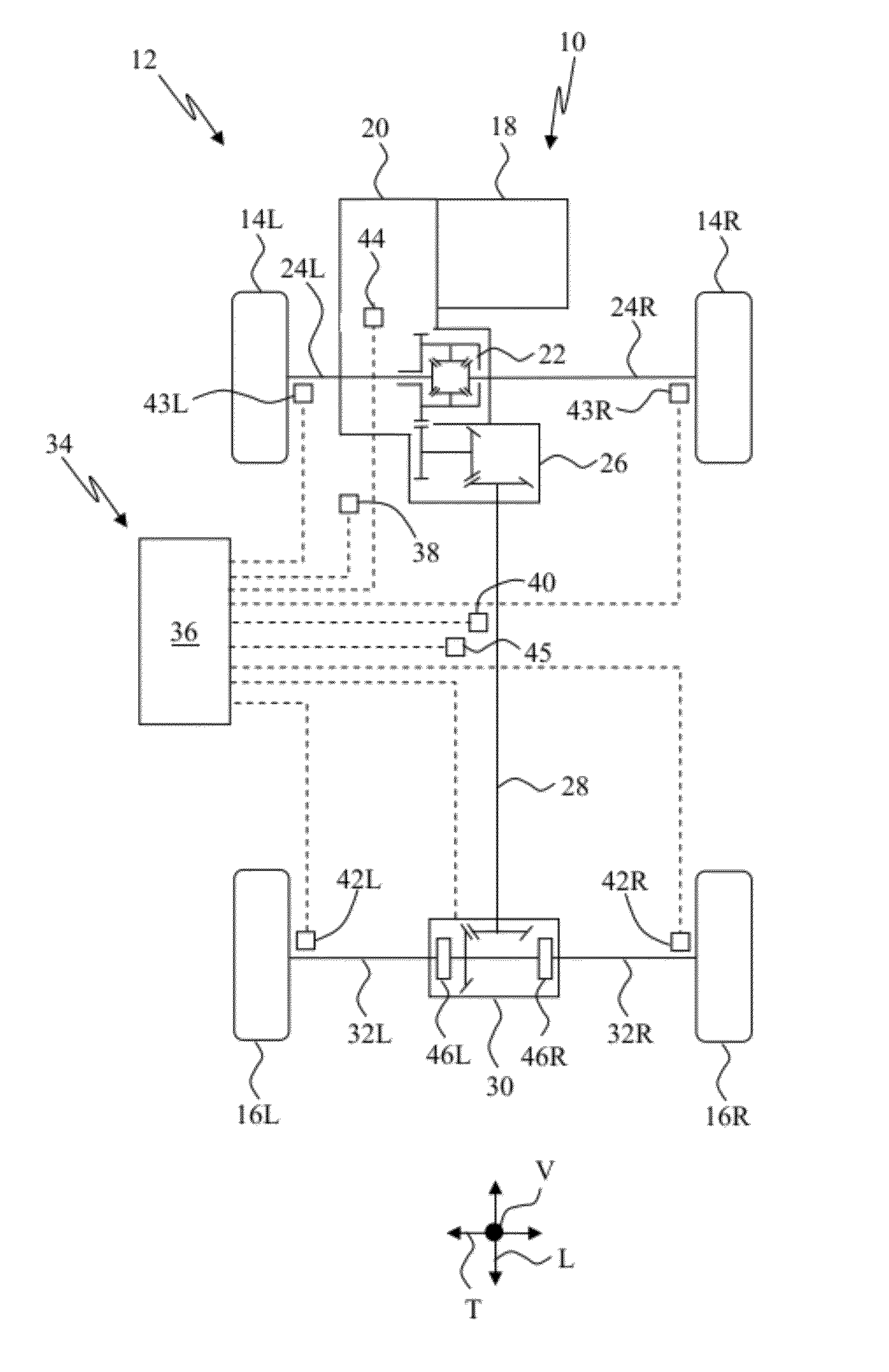
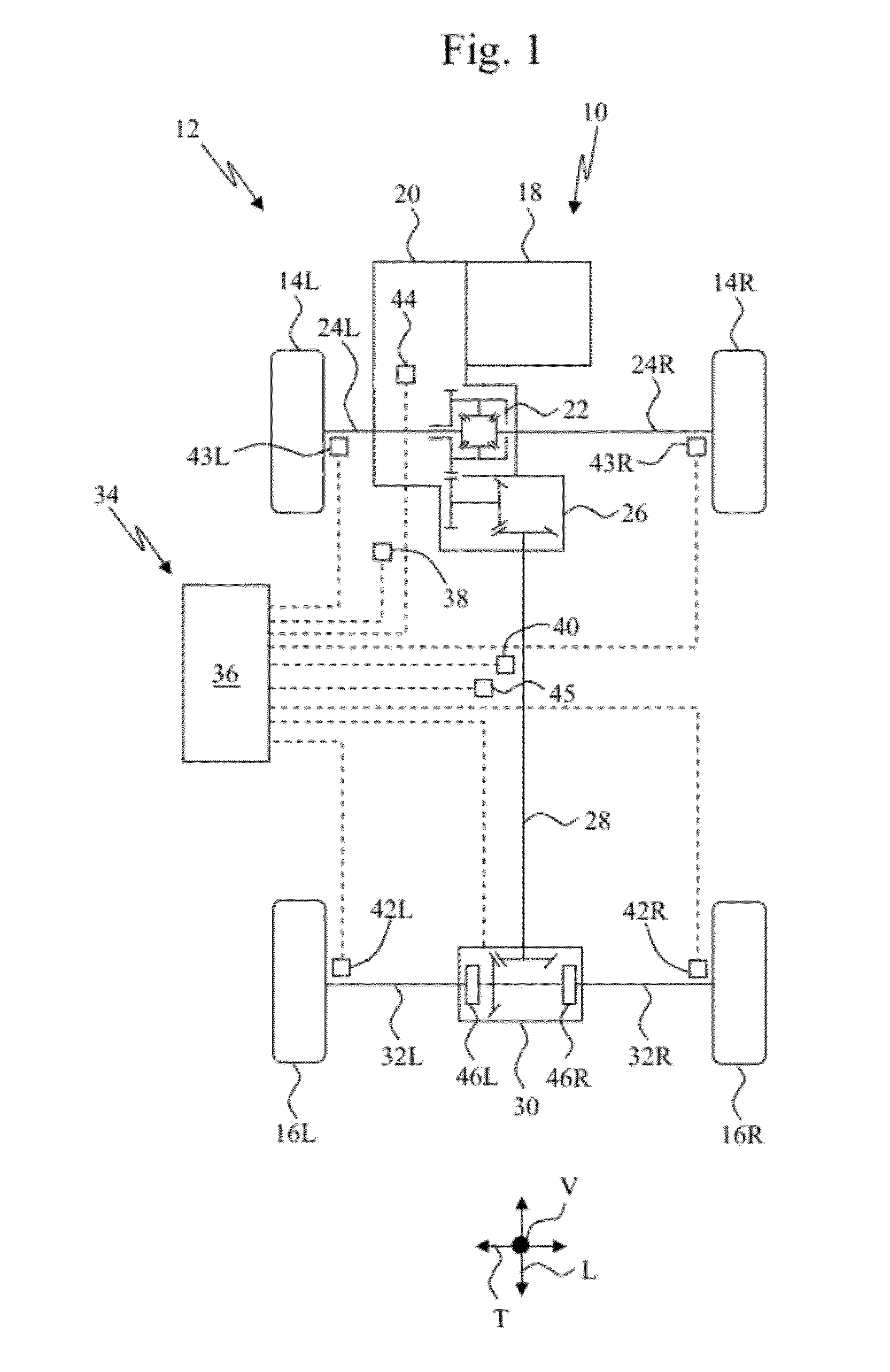
Model based predictive control for automated lane centering/changing control systems
ActiveUS20100228420A1Minimize error valueDigital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsVehicle dynamicsCompletion time
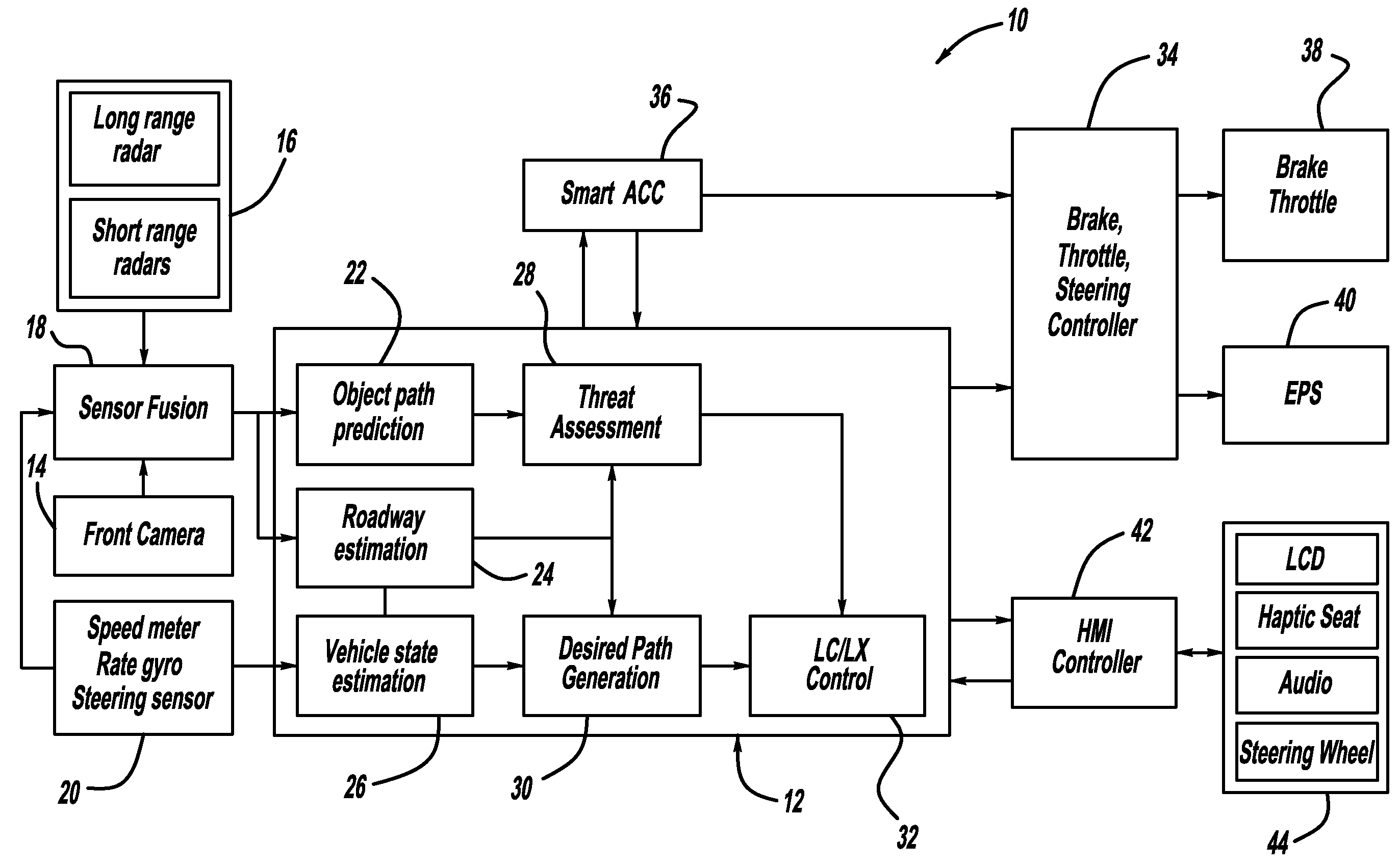
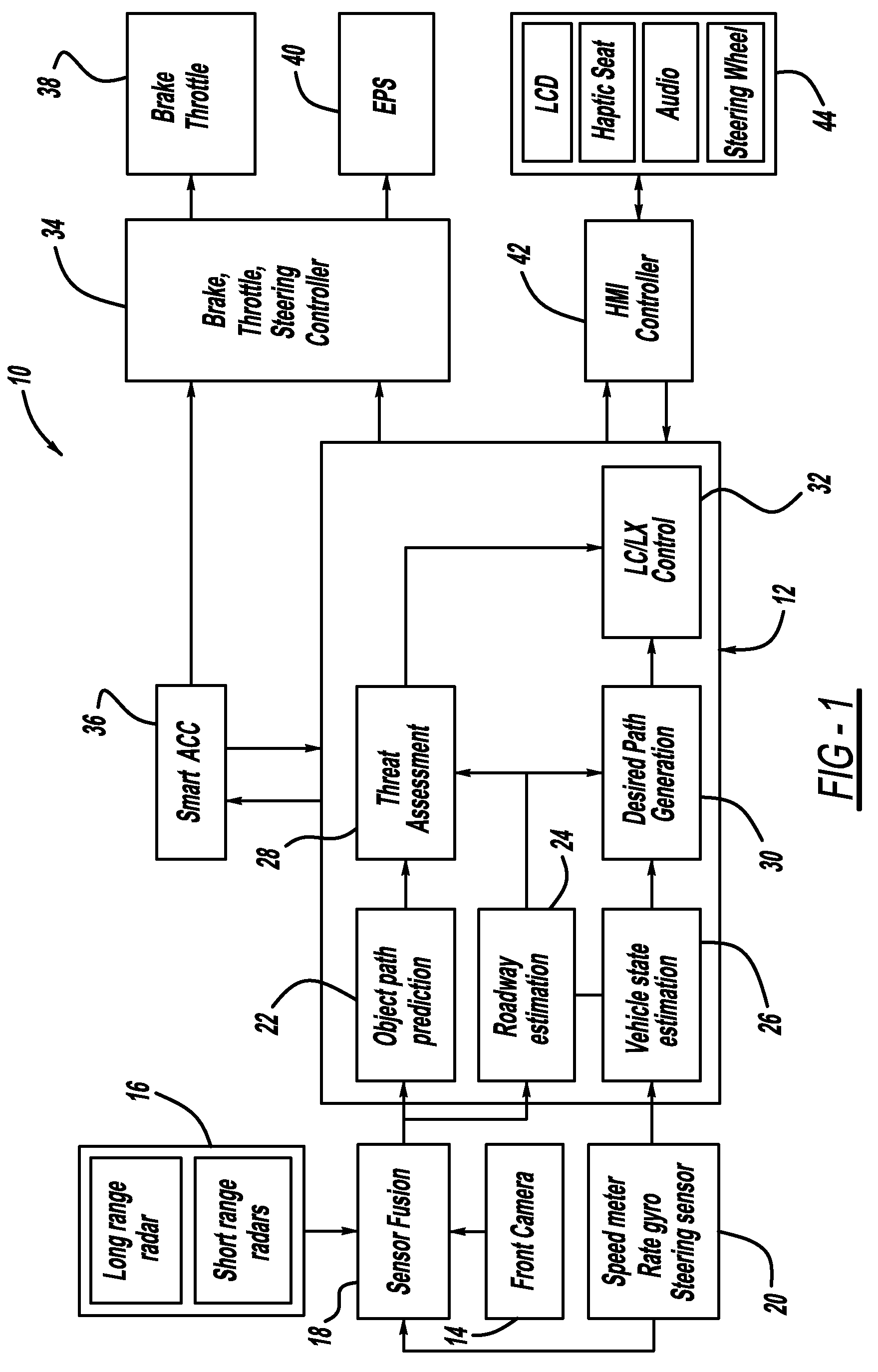
A system and method for providing steering control for lane changing and lane centering purposes in an autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle system. A vehicle vision system calculates roadway lane marking information, such as lateral offset, yaw angle and roadway curvature with respect to the vehicle's centered coordinate system. The roadway is then modeled as a second order polynomial equation. The method then predicts roadway lateral position and yaw angle over a pre-defined lane change completion time using a vehicle dynamic model. The method then compares a predicted vehicle path with a desired vehicle path to generate an error value, and calculates a steering angle command to minimize the error value, where the steering angle command is calculated as a function of vehicle lateral position, vehicle lateral speed, vehicle yaw rate and vehicle yaw angle. The steering angle command is then sent to the vehicle steering system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
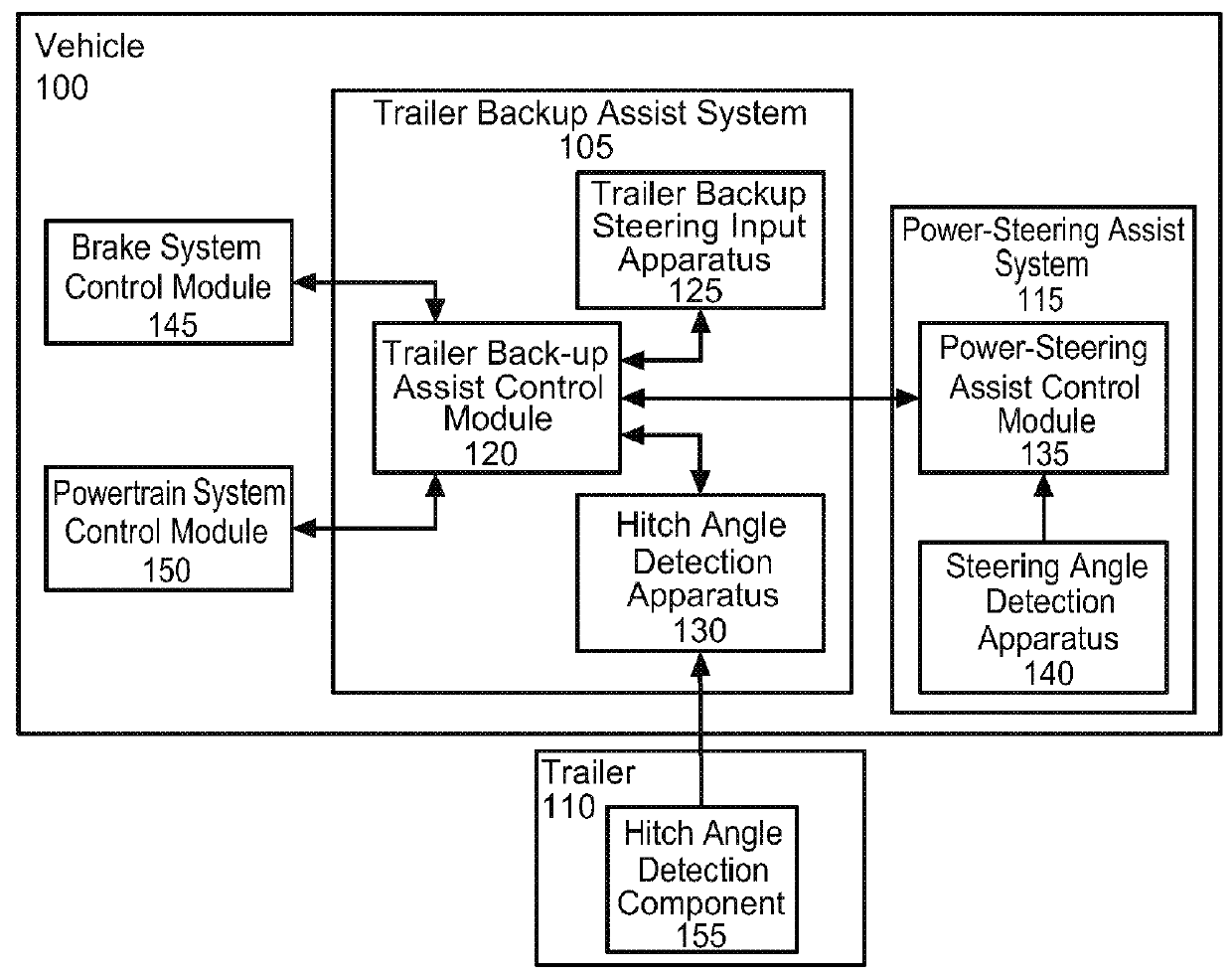
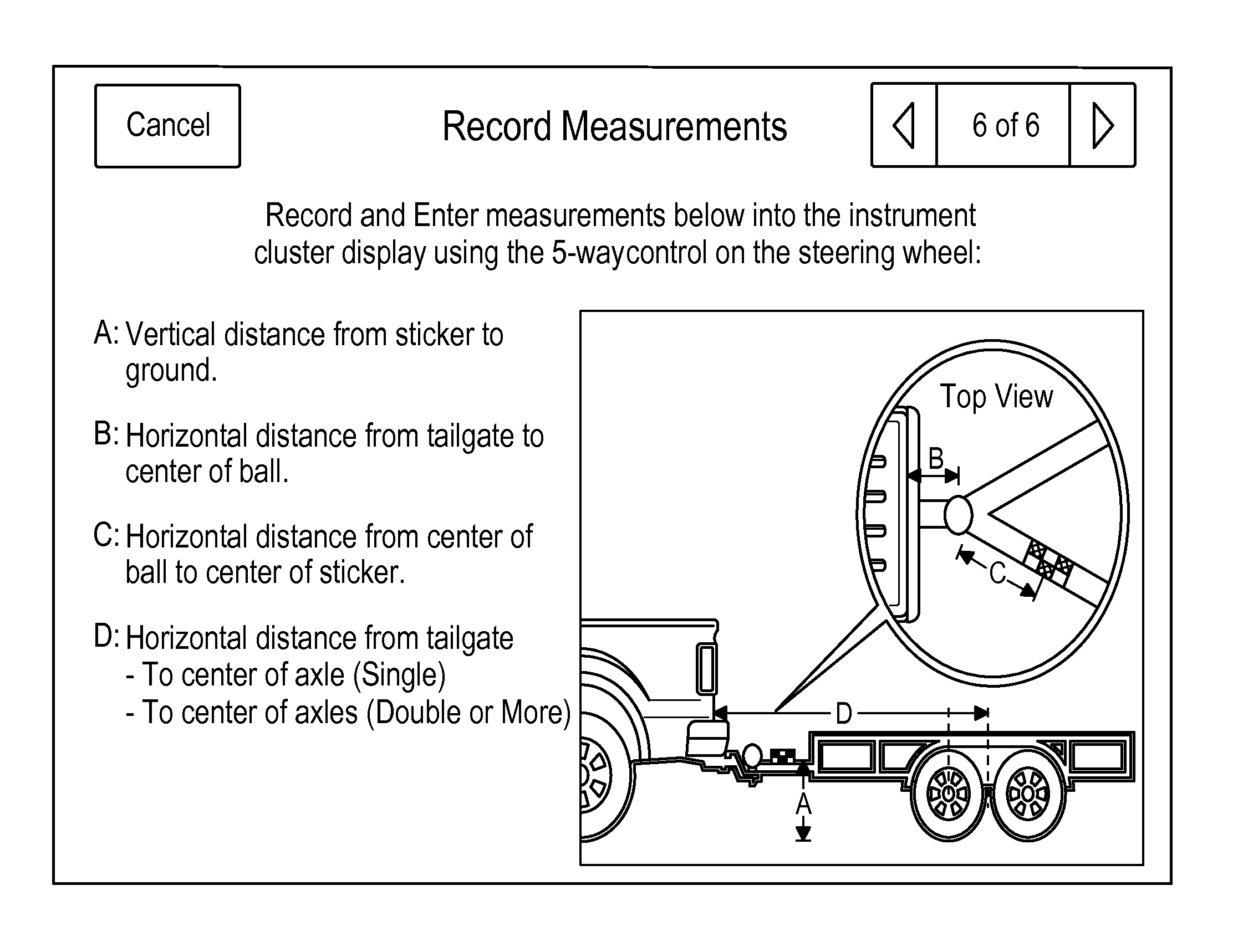
Trailer length estimation in hitch angle applications
ActiveUS20140277942A1Digital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlSteering angleEngineering
A vehicle system for estimating a trailer length is disclosed. The system incorporates at least one sensor configured to measure a wheel steer angle and a trailer angle in communication with a processor. The processor is operable to determine a first length by a first computation method and determine a second length by a second computation method. The processor is further operable to validate an estimated trailer length based on the first length and the second length and perform a back-up function for the trailer based on the estimated trailer length.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
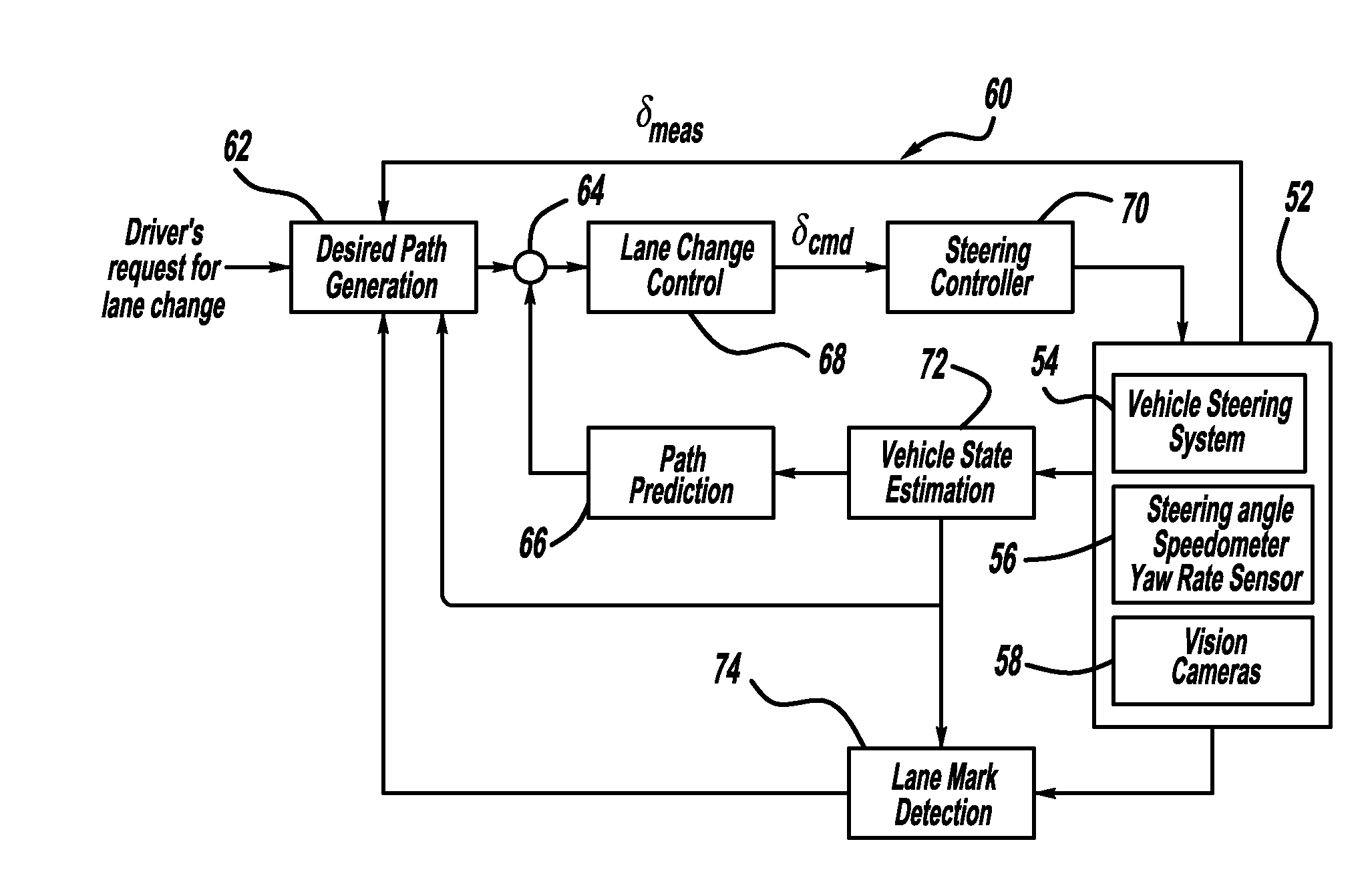
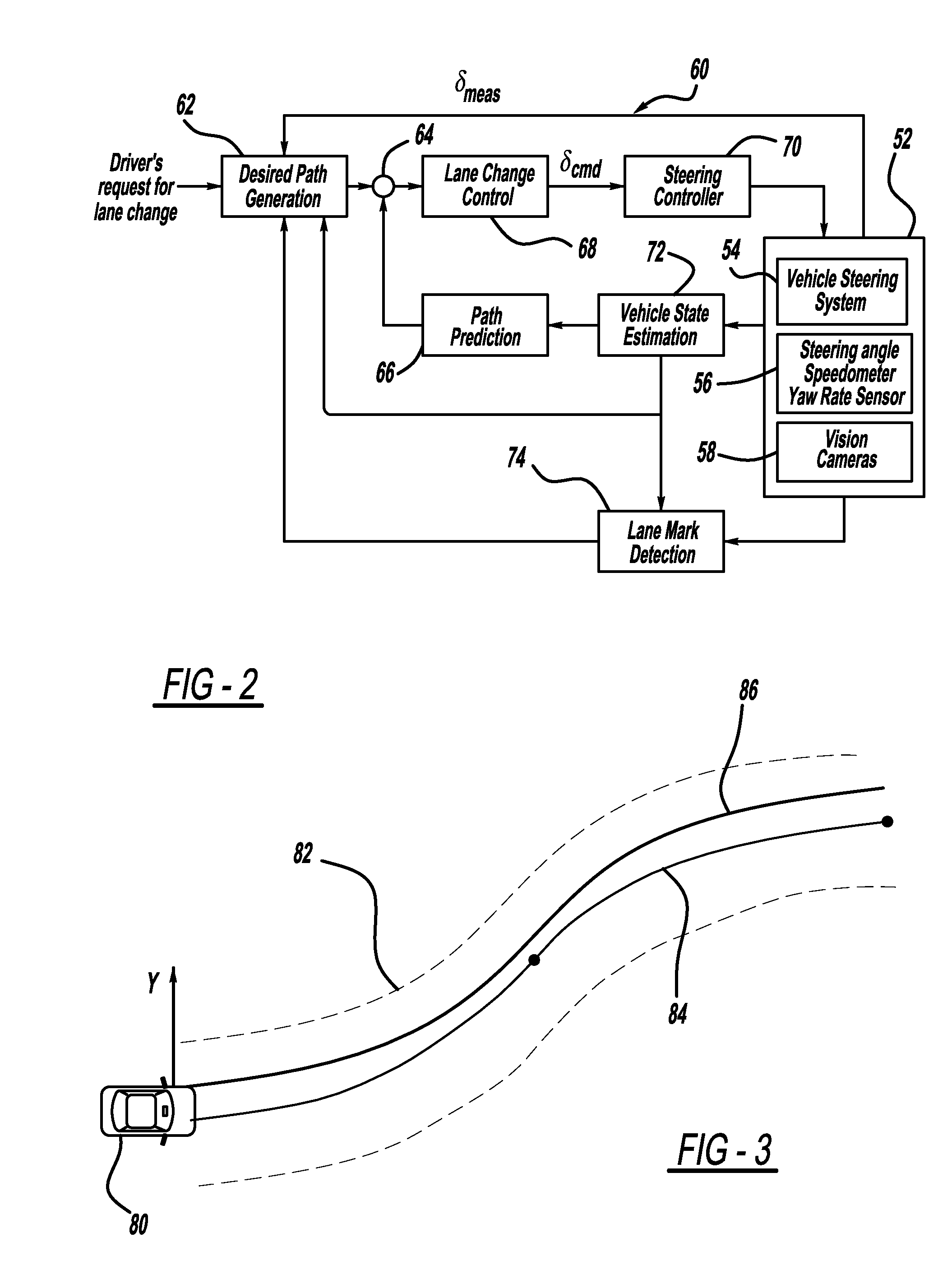
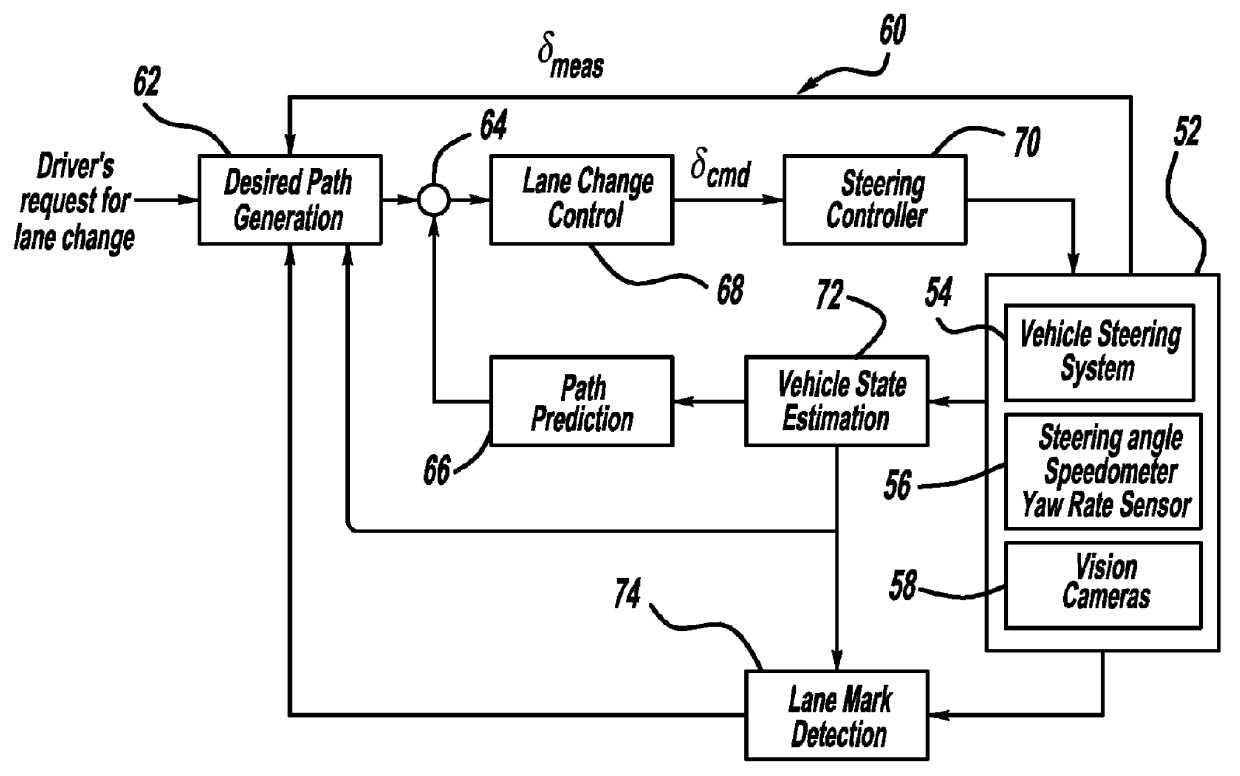
Path generation algorithm for automated lane centering and lane changing control system
ActiveUS20090319113A1Reduce error signalDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsSteering angleControl system
A system for providing path generation for automated lane centering and / or lane changing purposes. The system includes a desired path generation processor that receives signals detecting the roadway on which the vehicle is traveling, a request for a lane change, vehicle state information and a steering angle of the vehicle. The system also includes a path prediction processor that predicts the vehicle path based on vehicle state information including vehicle longitudinal speed, vehicle lateral speed, vehicle yaw-rate and vehicle steering angle. The desired path information and the predicted path information are compared to generate an error signal that is sent to a lane change controller that provides a steering angle signal to turn the vehicle and reduce the error signal. The desired path generation processor can use a fifth order polynomial equation to determine the desired path of the vehicle based on the input signals.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
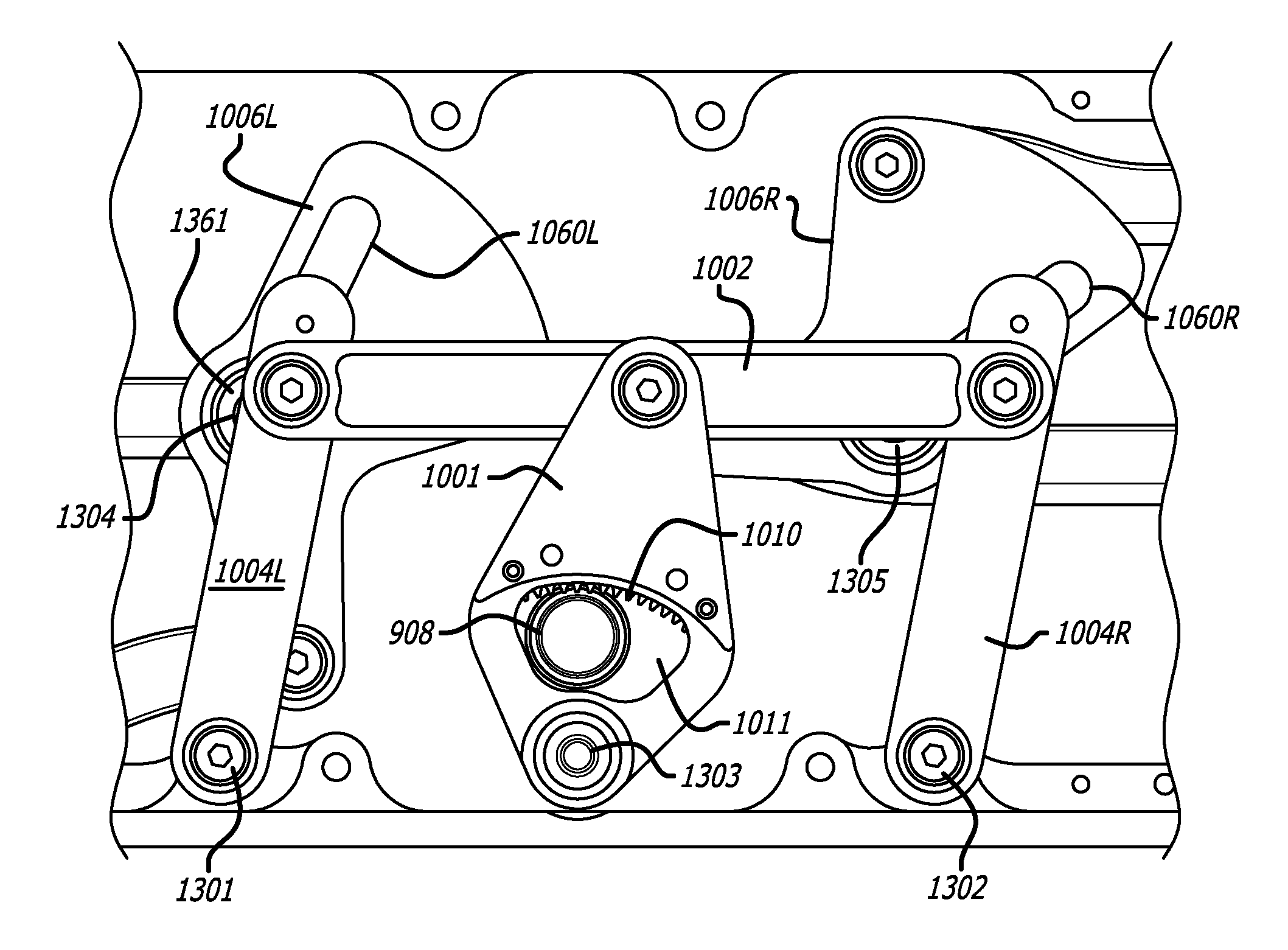
Steering system for heavy mobile medical equipment
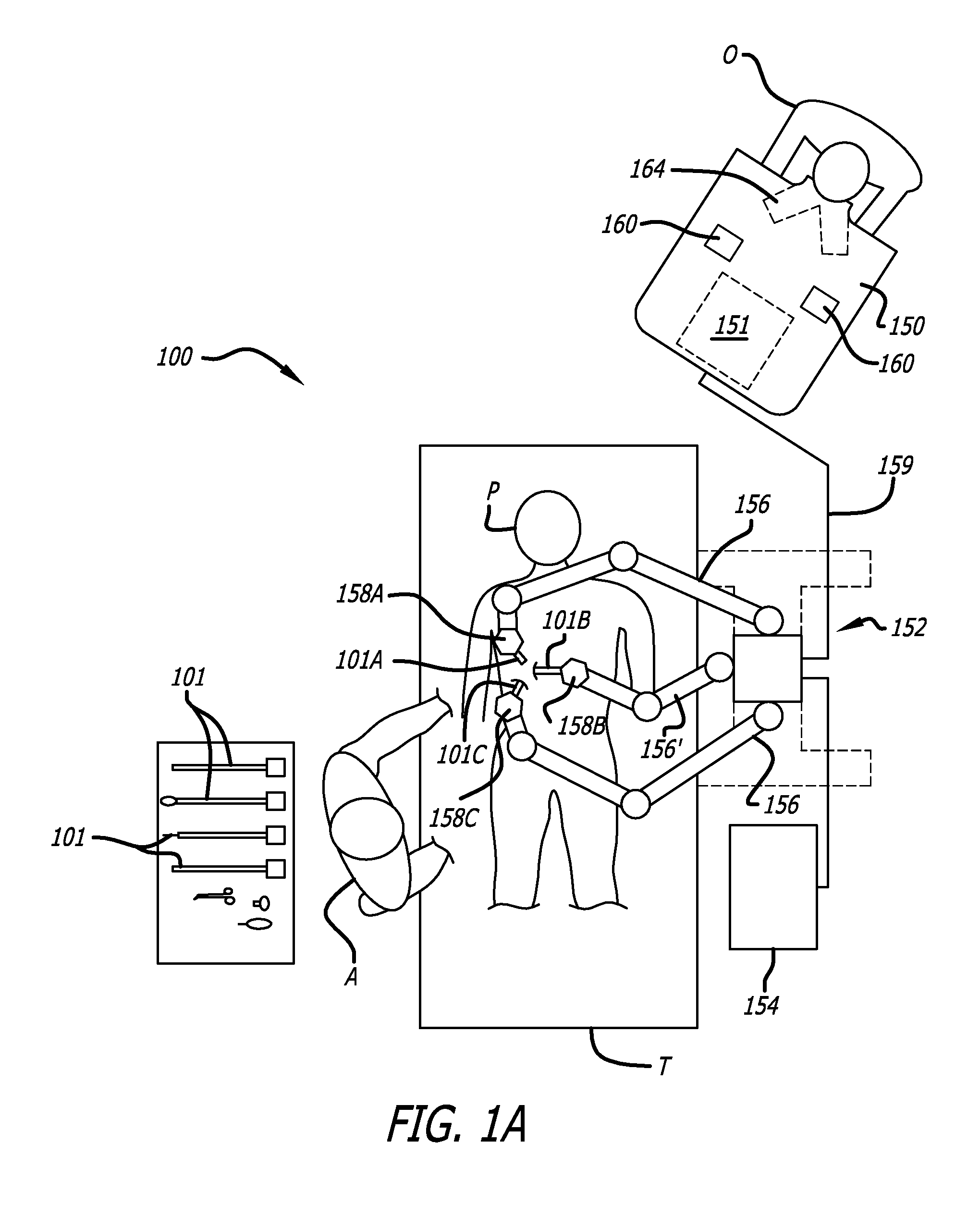
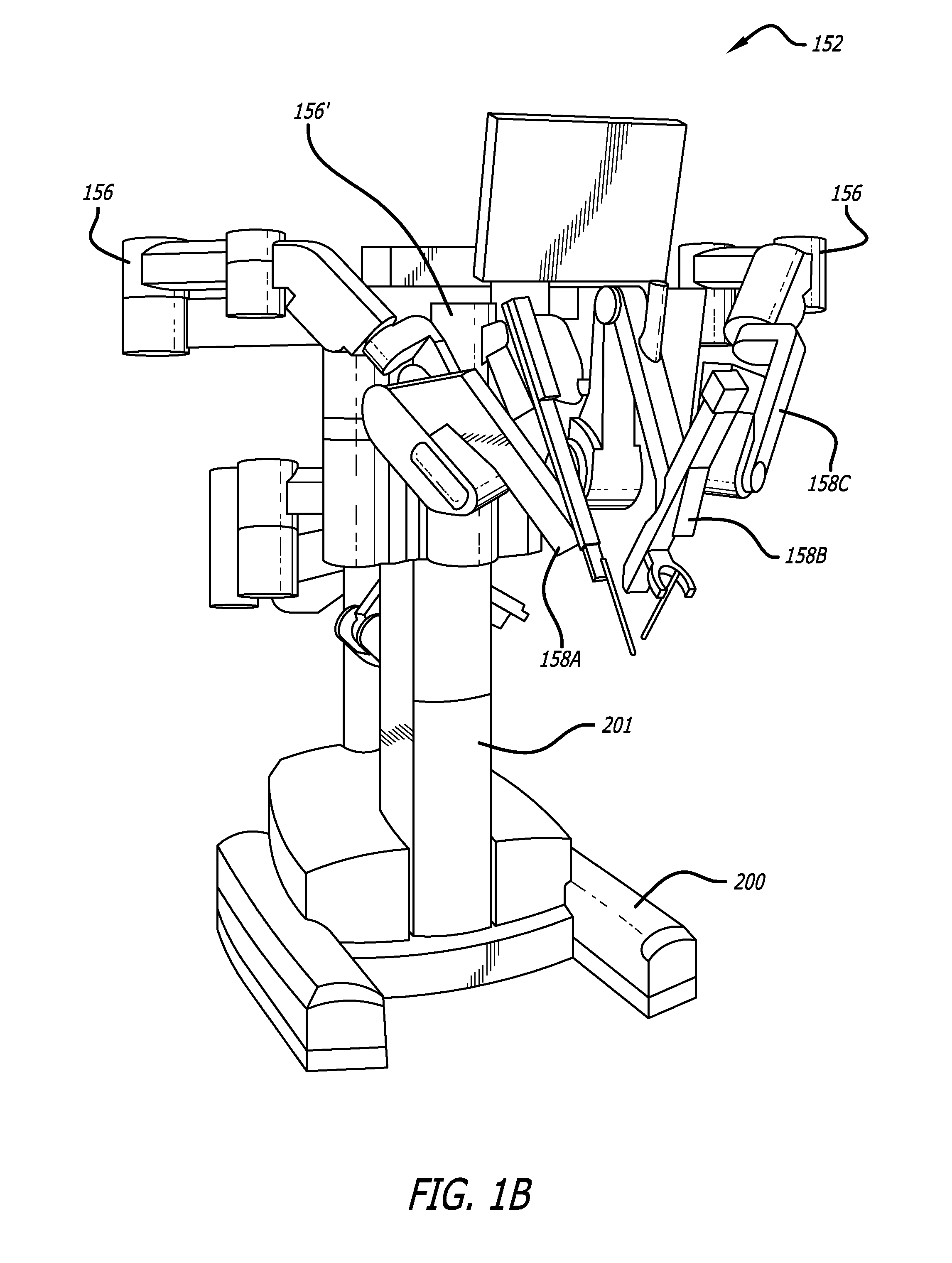
ActiveUS7533892B2Surgical furnitureCarriage/perambulator with multiple axesSteering angleEngineering
In one embodiment of the invention, a steering system for mobile medical equipment is disclosed including left and right steerable wheel assemblies including left and right steerable wheels, left and right parallelogram linkages coupled to the left and right steerable wheel assemblies, a steering function generator coupled to the left and right parallelogram linkages, and a steering tiller coupled to the steering function generator. The left and right parallelogram linkages transfer differing left and right wheel angles to the left and right steerable wheel assemblies respectively. The steering function generator generates the left wheel angle (LWA) of the left steerable wheel and the right wheel angle (RWA) of the right steerable wheel. The steering tiller receives an input steering angle to generate the left wheel angle and the right wheel angle to control the direction of the mobile medical equipment around flooring.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Vehicle drive assist system
InactiveUS7366595B1Intuitive displaySimple voice systemInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsSteering angleEngineering
A vehicle drive assist system comprises a camera for picking up an image of an area existing in an advancing direction of a vehicle; display means for displaying the image picked up by the camera; steering angle detecting means for detecting a steering angle for steering the vehicle; traveling path predicting means for predicting a traveling path of the vehicle on the basis of the steering angle detected by the steering angle detecting means; and drive assist means for overlaying on the display means drive assist information containing the vehicle predictive traveling path predicted by the traveling path predicting means and guide lines prolonged from the lines defining the width of the vehicle body on the image of the area existing in the vehicle advancing direction.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
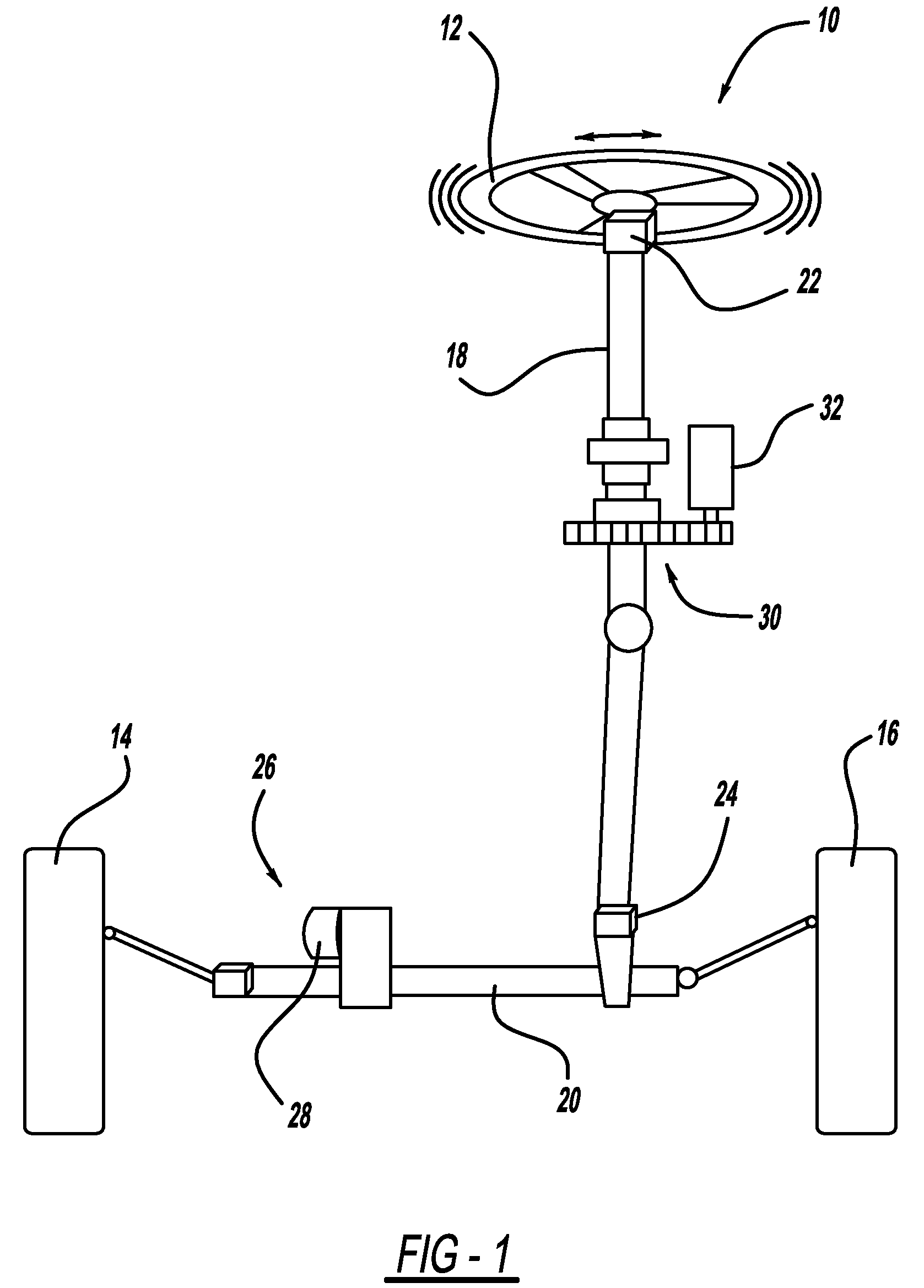
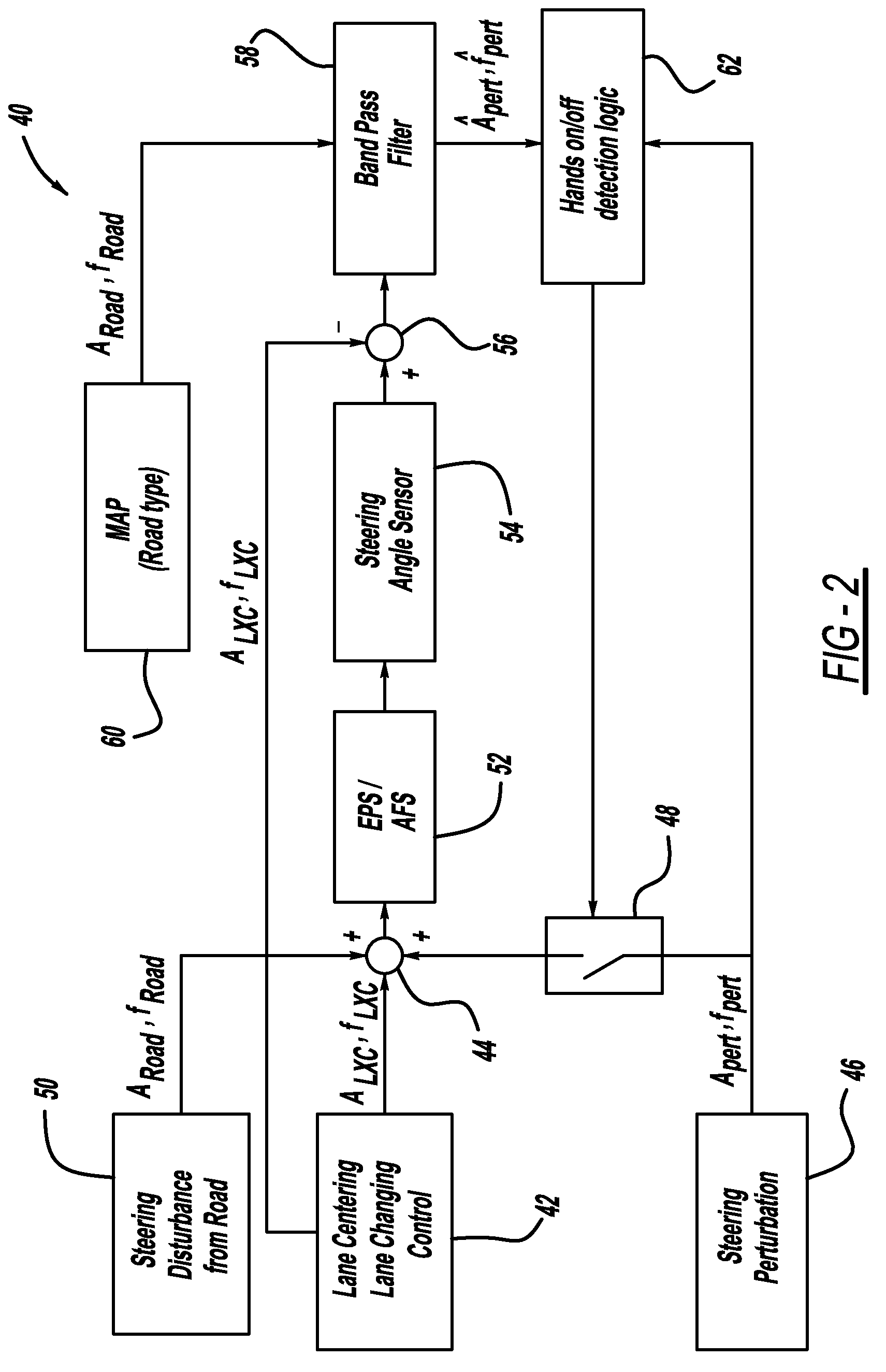
Driver hands on/off detection during automated lane centering/changing maneuver
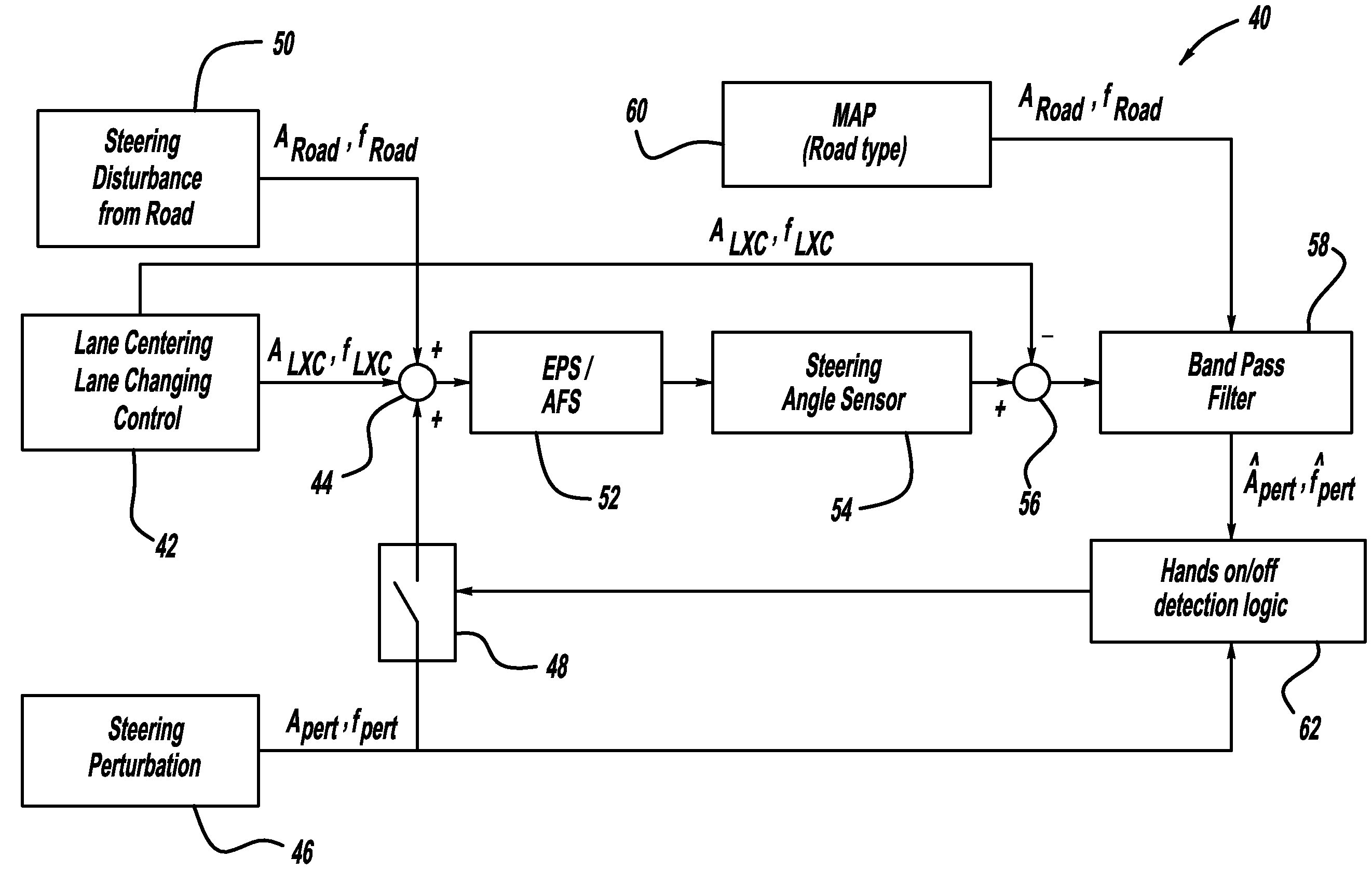
InactiveUS20100228417A1Digital data processing detailsSteering partsElectric power steeringSteering wheel
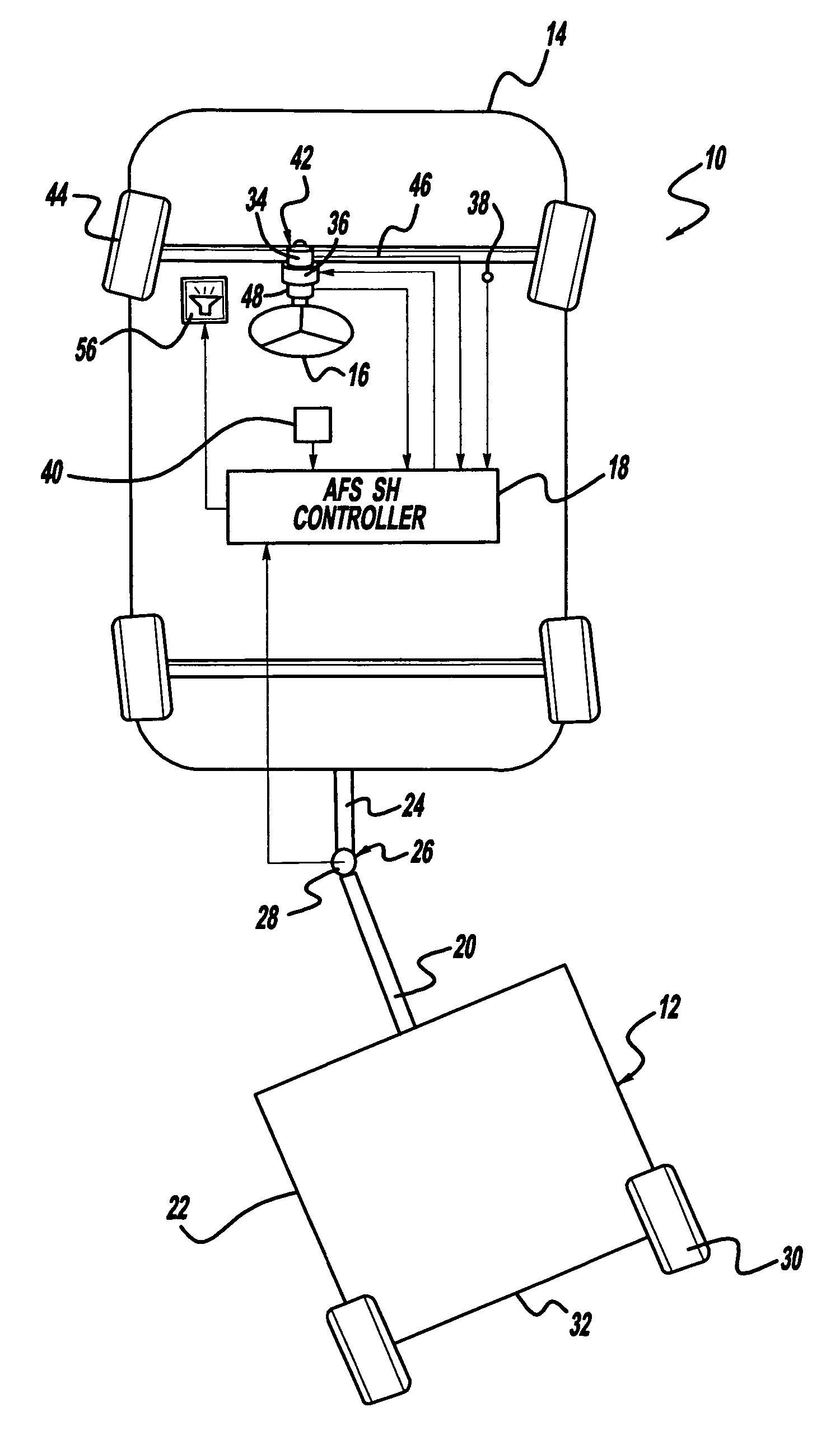
A system and method for determining whether a vehicle driver is holding a steering wheel of the vehicle while the vehicle is in an autonomous driving mode. The vehicle will include an electric power steering (EPS) system and may include an active front steering (AFS) system, both of which include a motor that can apply a high frequency and low amplitude perturbation signal to the steering wheel of the vehicle that is not felt by the vehicle driver and does not cause the vehicle to turn, but is able to be detected by a steering angle sensor. The method subtracts a steering angle command signal from the steering angle signal and removes road disturbances, and then determines whether the induced perturbation signal is present in the steering angle sensor signal. If the perturbation signal is present, then the system knows that the vehicle driver is not holding the steering wheel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
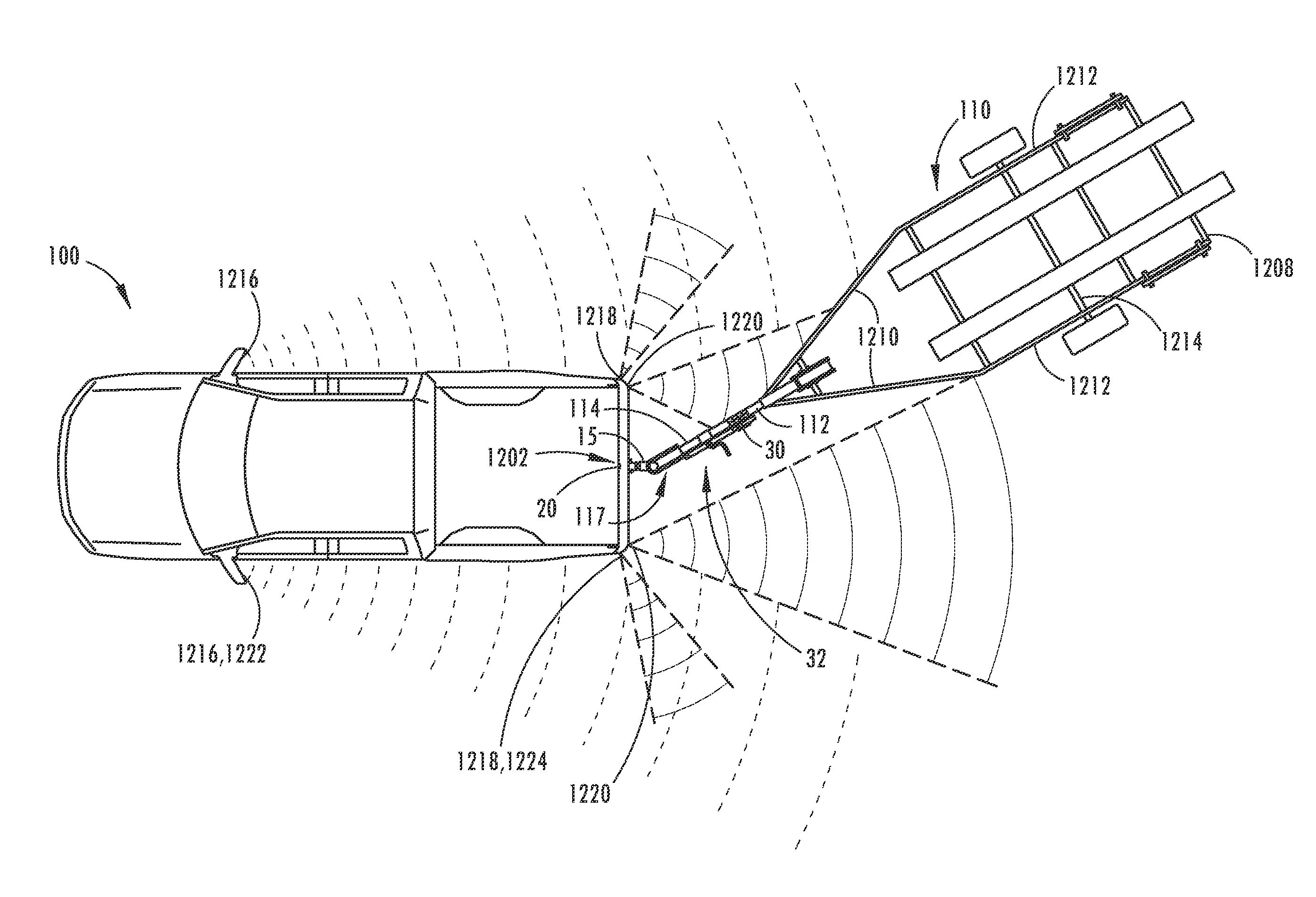
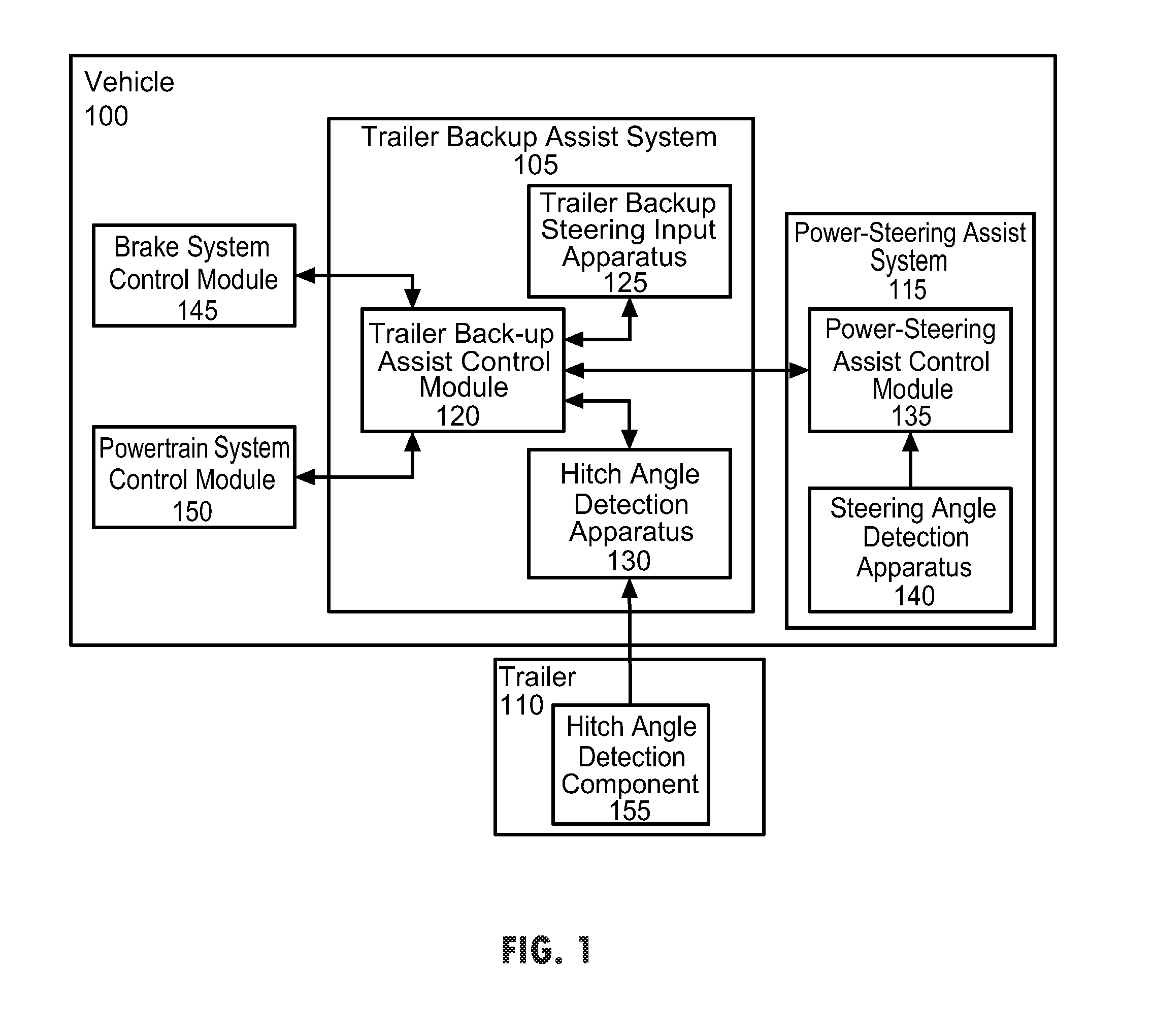
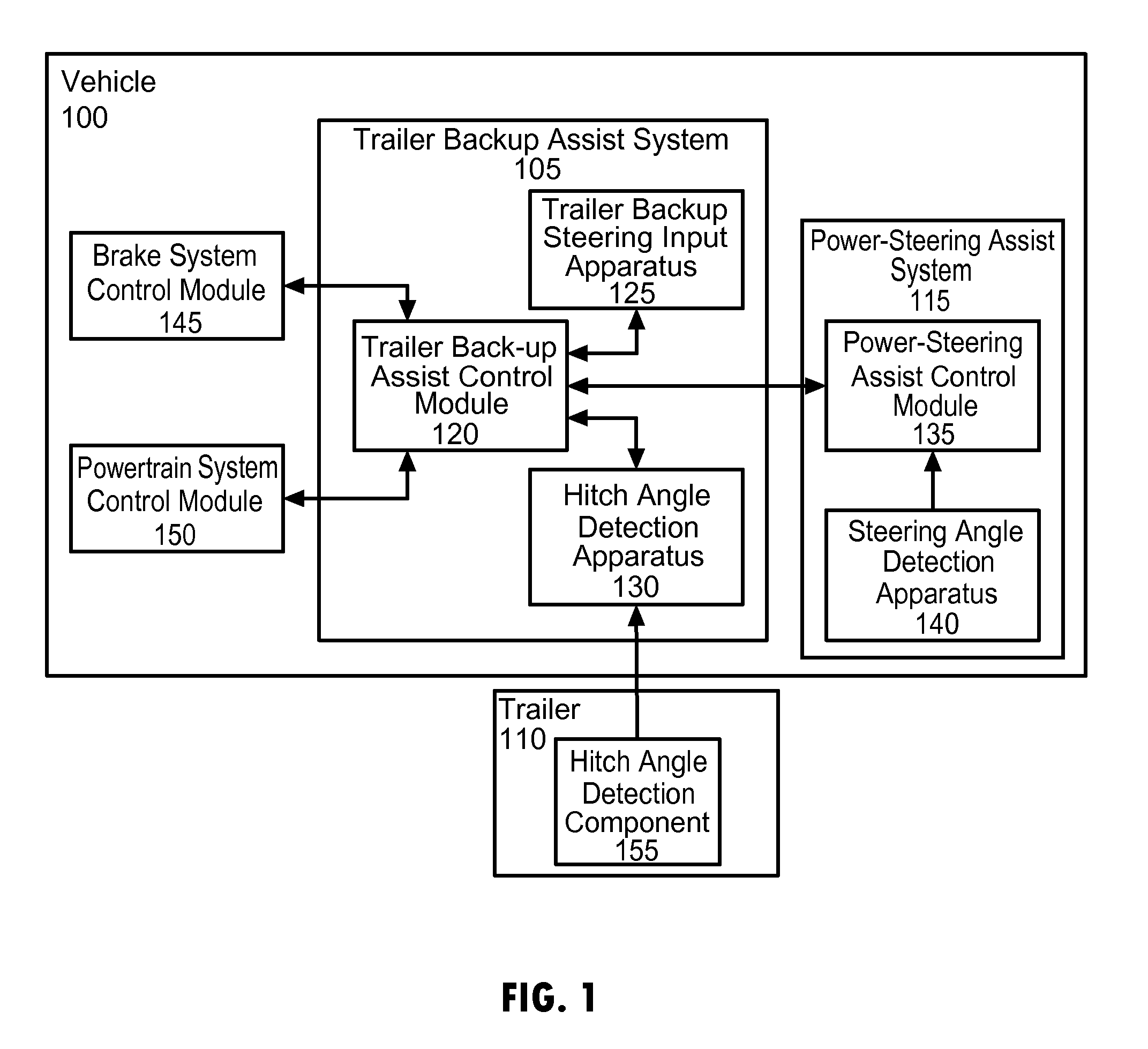
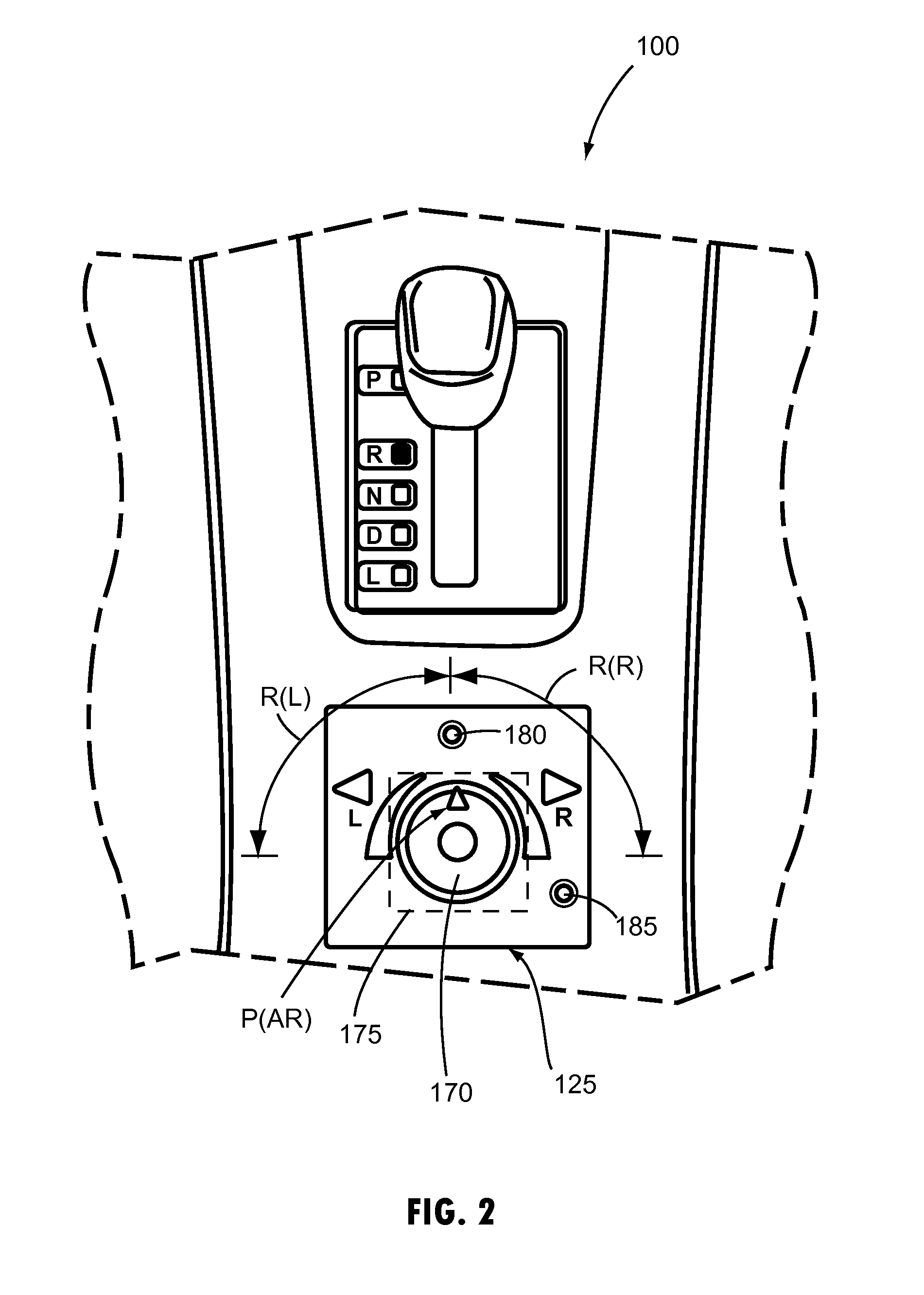
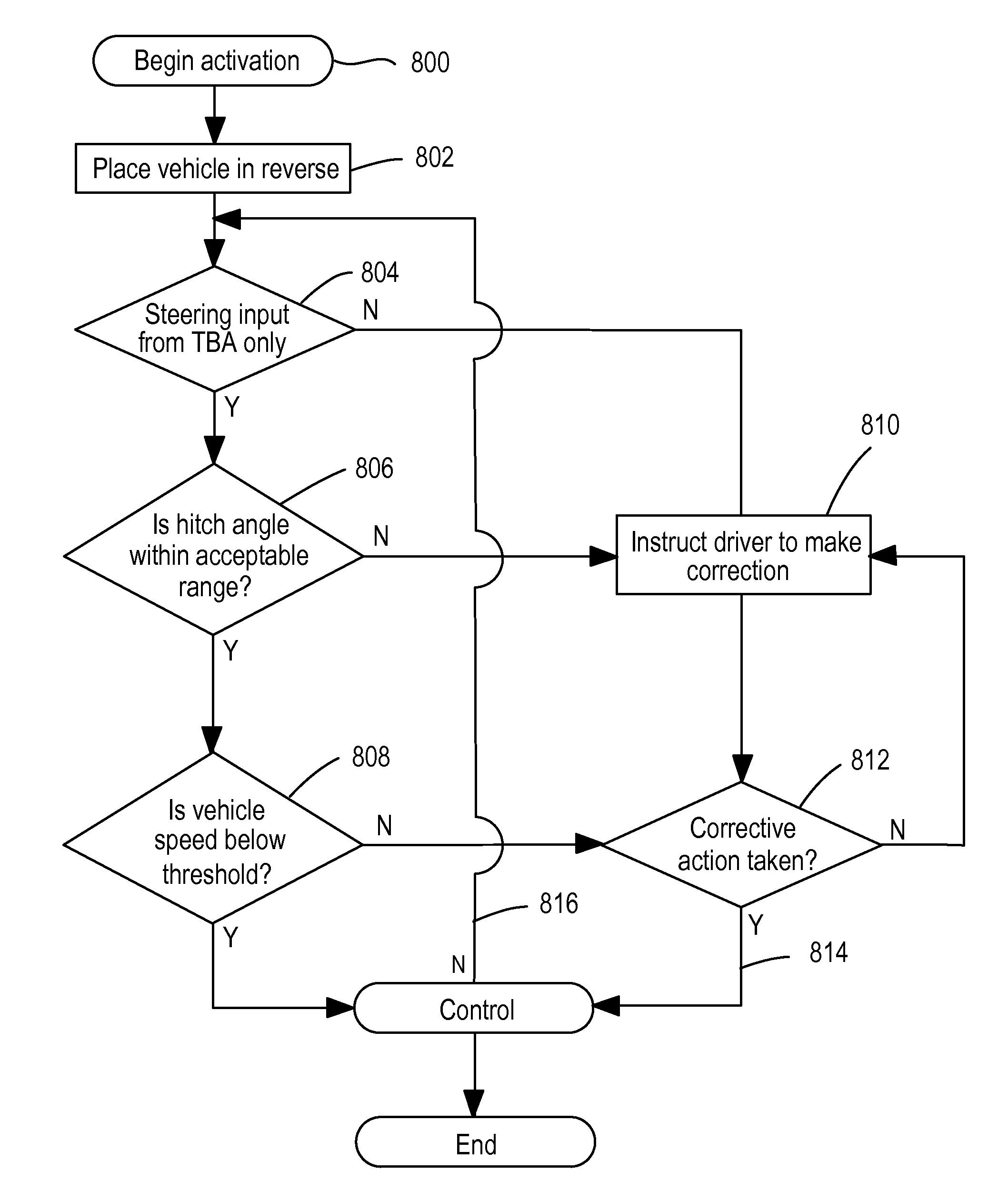
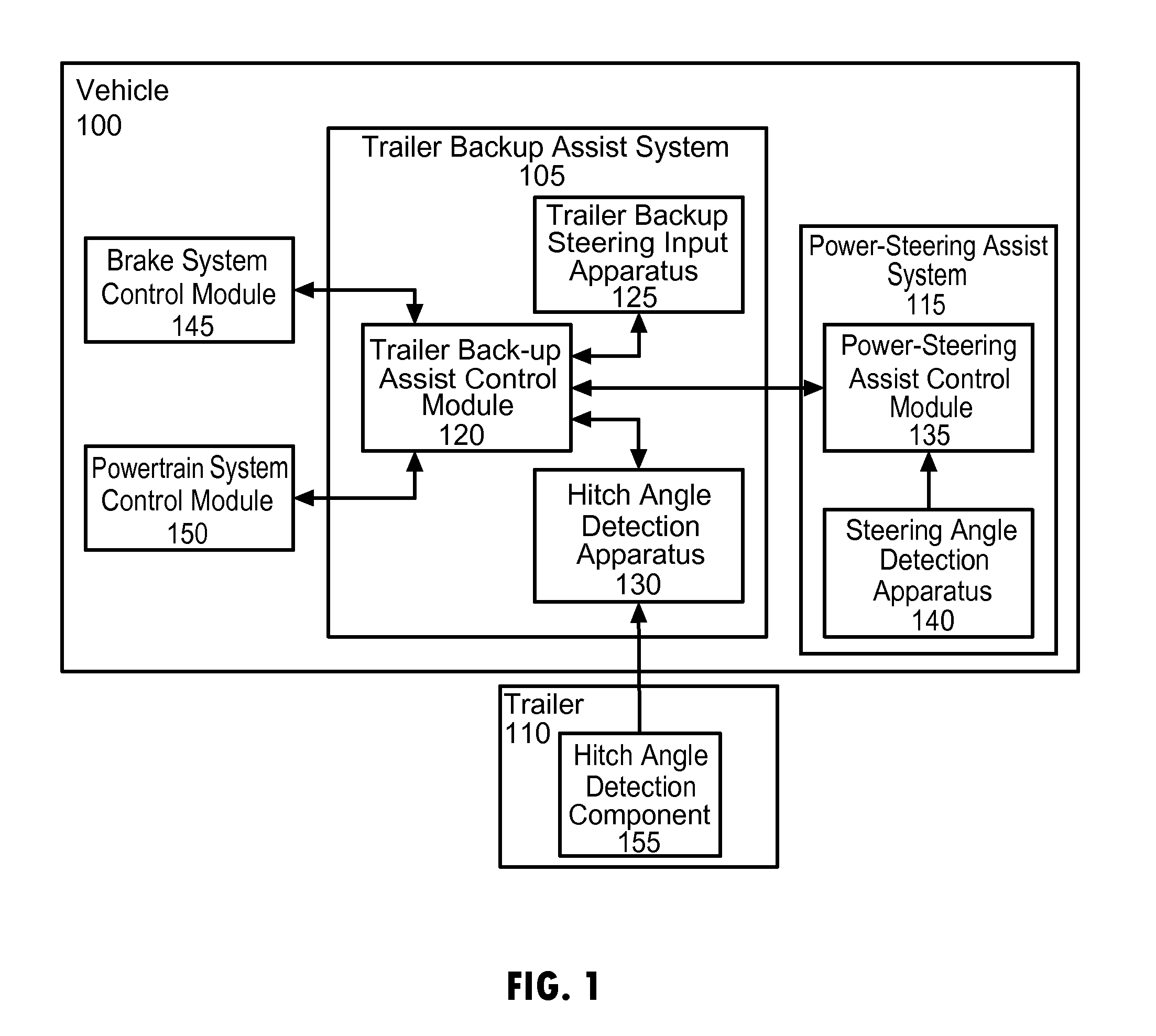
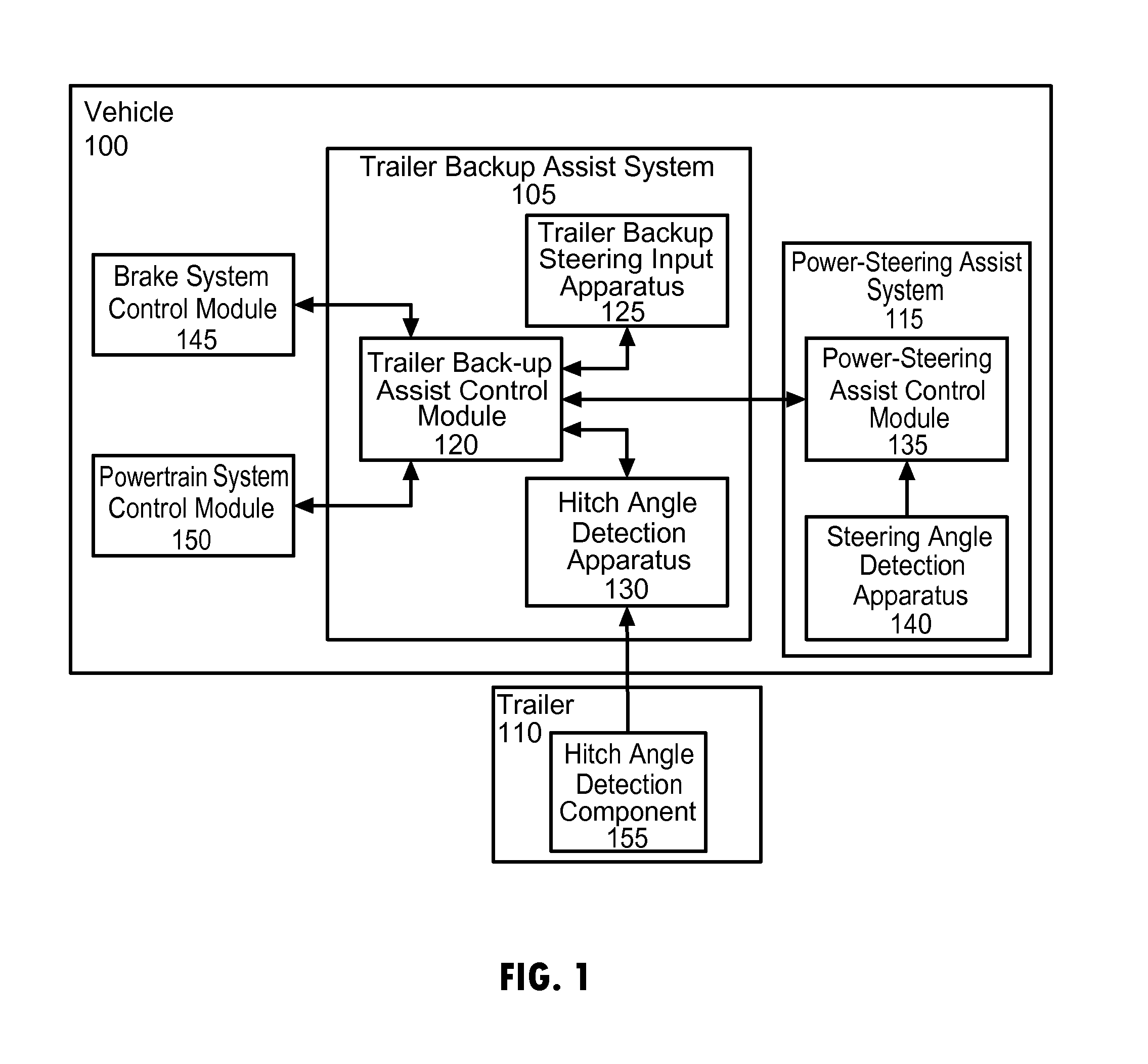
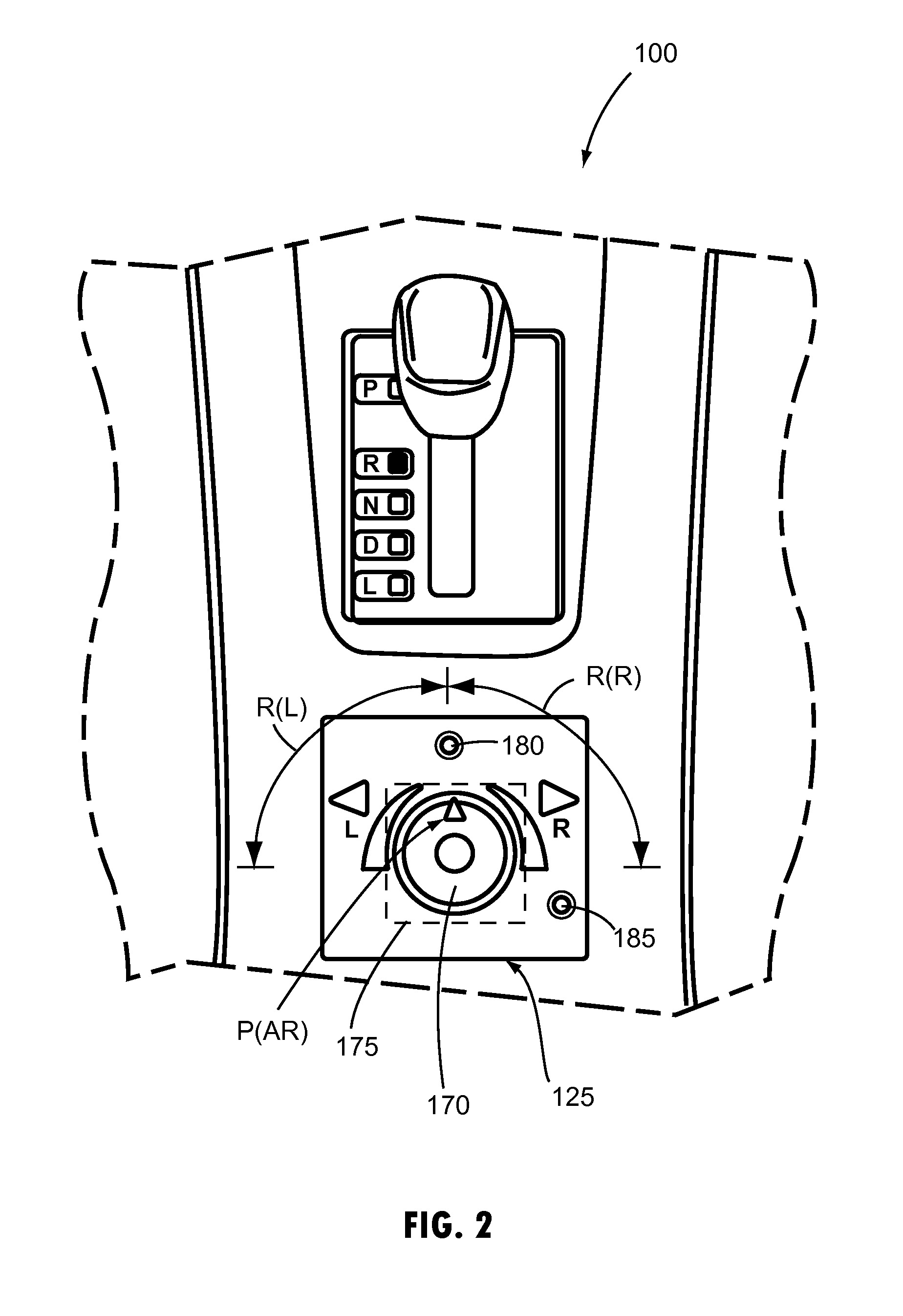
Vehicle-trailer backing up system using active front steer
InactiveUS20060103511A1Digital data processing detailsSteering initiationsSteering wheelSteering angle
A vehicle-trailer back-up control system that employs an active front steer sub-system. The system includes a smart hitch controller that receives a vehicle speed signal and a hand-wheel angle signal, and calculates a hitch angle command signal. The system further includes a hitch angle sensor that measures the hitch angle between the vehicle and the trailer that is compared to the hitch angle command signal to generate a hitch angle error signal. A PID control unit receives the hitch angle error signal, and generates a corrected road wheel angle signal based on proportional and derivative gains. The corrected road wheel angle signal is used to generate a motor angle signal that is applied to a steering actuator to be combined with the steering angle signal to generate the front wheel steering signal during a back-up maneuver.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Multiple zone sensing for materials handling vehicles
ActiveUS20100114405A1Transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsSteering angleControl system
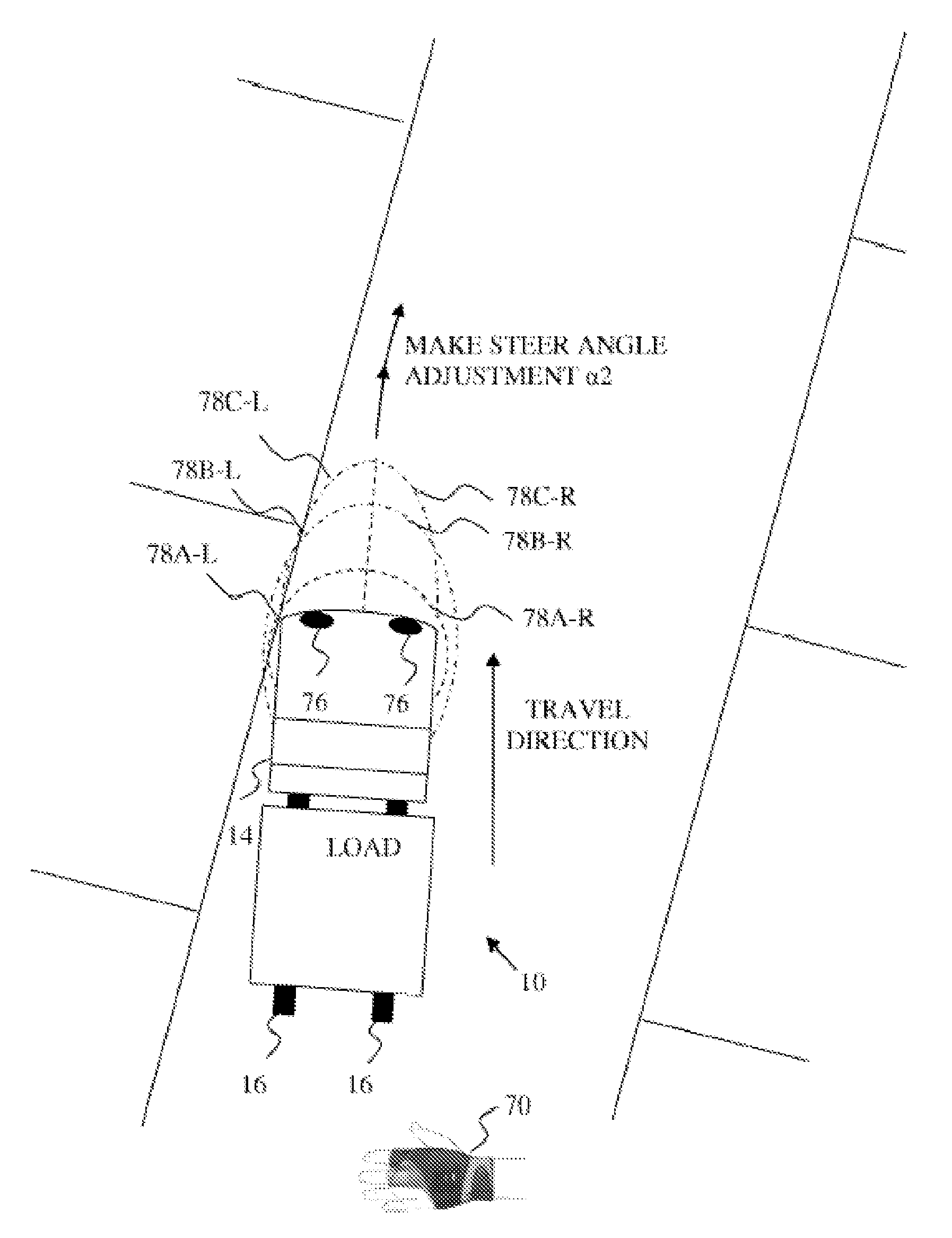
A supplemental control system for a materials handling vehicle comprises one or more sensors capable of defining multiple contactless detection zones at least towards the front of the forward travel direction of a remotely controlled vehicle. The vehicle responds to the detection of objects within the designated zones based upon predetermined actions, such as to slow down or stop the vehicle, and / or to take other action, such as to perform a steer angle correction.
Owner:CROWN EQUIP CORP
Trailer length estimation in hitch angle applications
A vehicle system for estimating a trailer length is disclosed and includes a first sensor for measuring a wheel steer angle and a second sensor for measuring a hitch angle. A processor is in communication with the at least one sensor and is operable to determine a ratio between the wheel steer angle and the hitch angle, generate a running average of the ratio, and calculate the trailer length based on an average ratio between the wheel steer angle and the hitch angle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
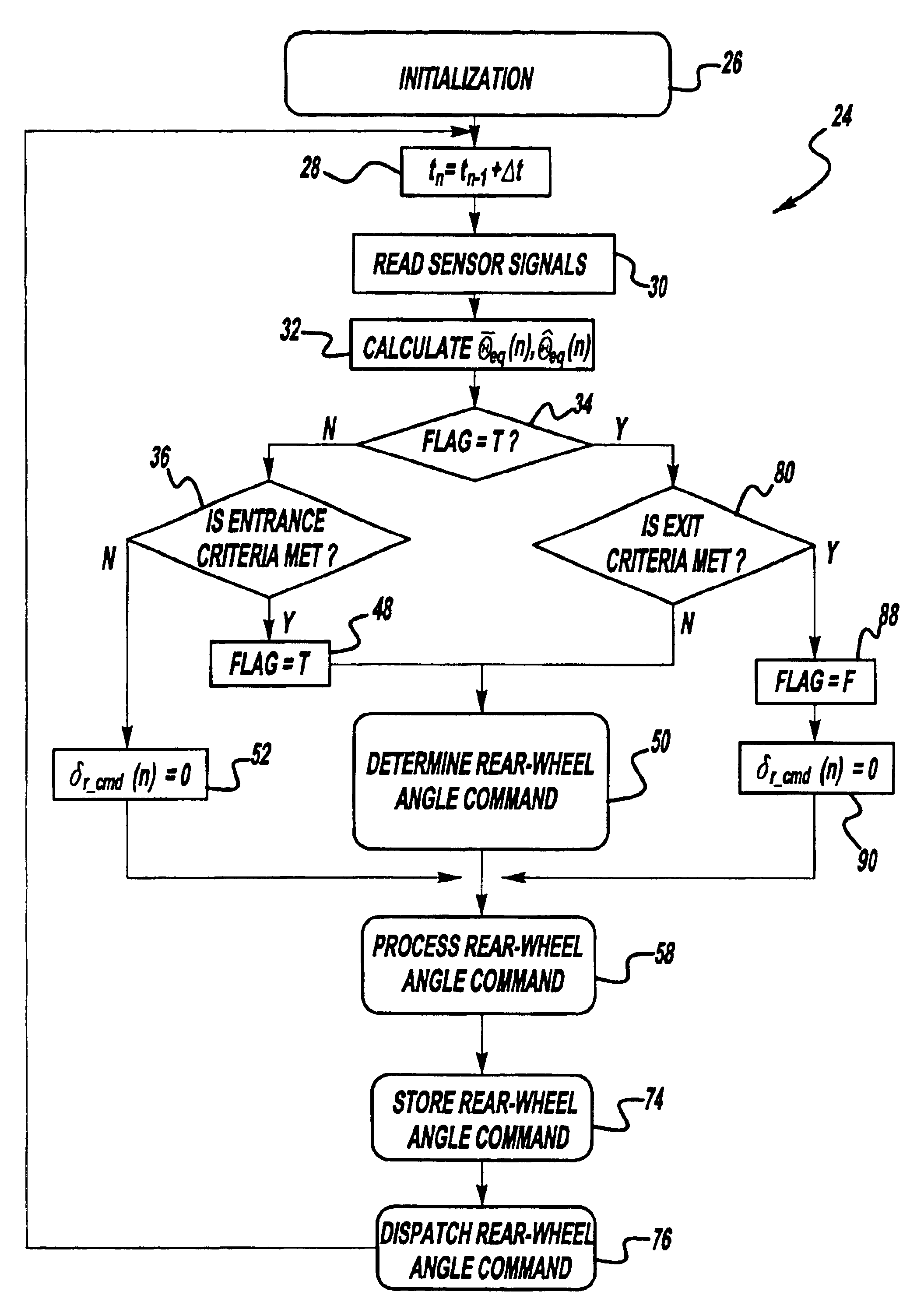
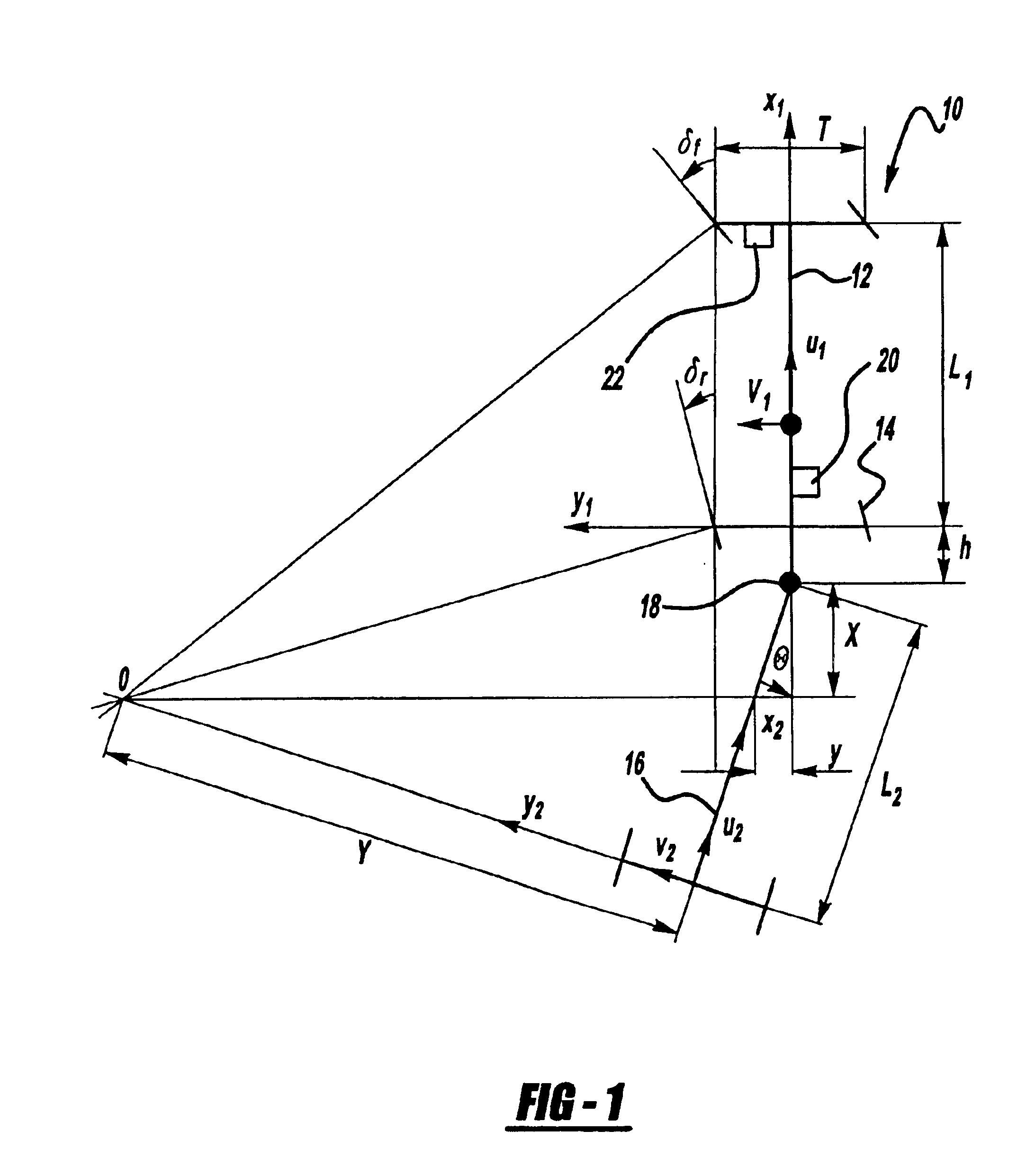
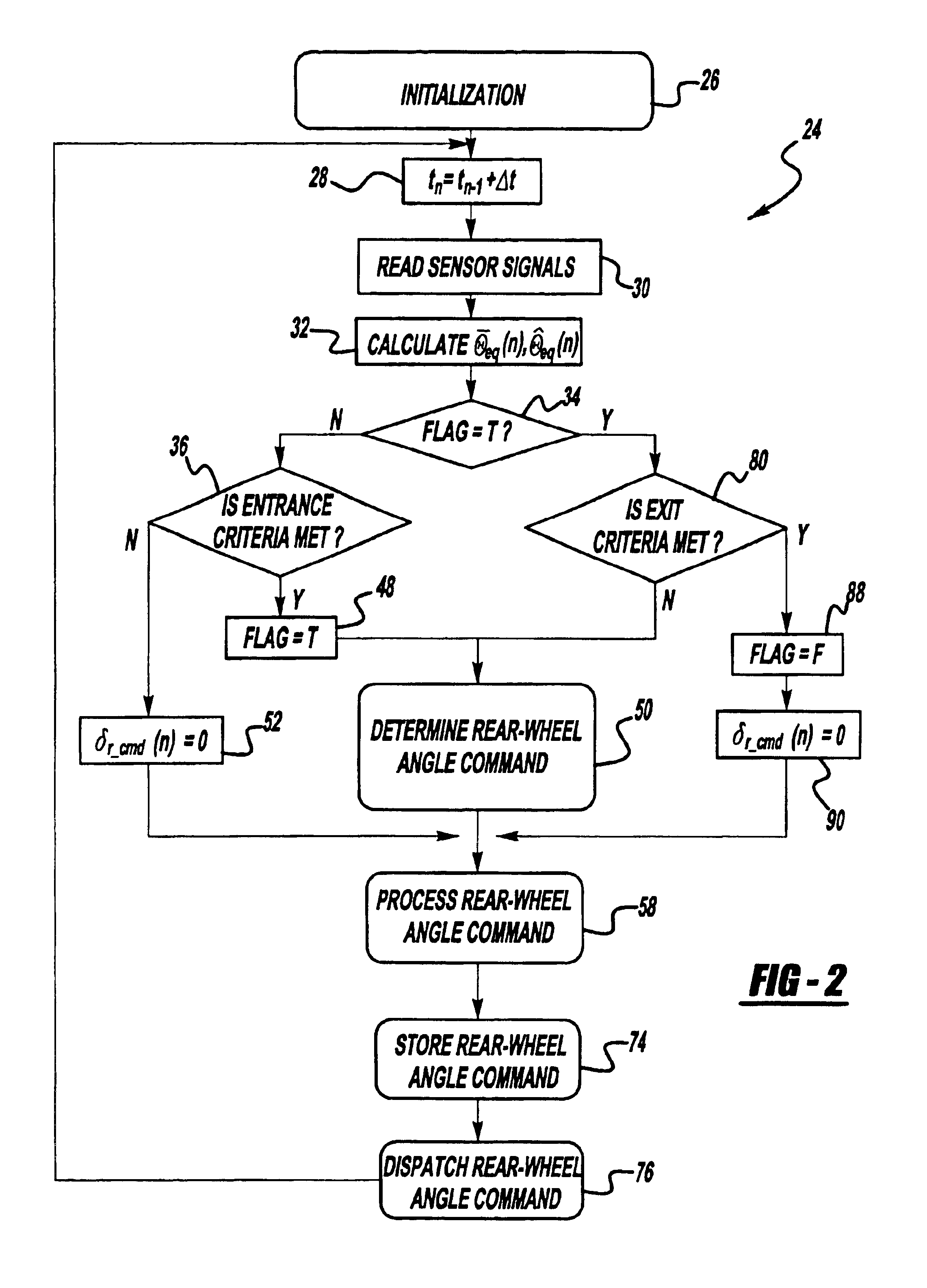
Anti-jackknife control for vehicle-trailer backing up using rear-wheel steer control
A vehicle control system that selectively provides rear-wheel steering to prevent a vehicle-trailer from jackknifing during a back-up maneuver. The system senses a steering angle of the vehicle, a speed of the vehicle and a hitch angle between the vehicle and the trailer. The system calculates an equilibrium hitch angle that is a steady-state hitch angle position based on the steering angle and the vehicle speed, and a pseudo-equilibrium hitch angle that is a steady-state hitch angle at a maximum rear-wheel steering input based on the steering angle and the vehicle speed. The system then determines whether the rear-wheel steering should be provided based on a predetermined relationship between the sensed hitch angle, the equilibrium hitch angle and the pseudo-equilibrium hitch angle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Trailer length estimation in hitch angle applications
A vehicle system for estimating a trailer length is disclosed and includes a first sensor for measuring a wheel steer angle and a second sensor for measuring a hitch angle. A processor is in communication with the first and second sensors and is operable to determine a wheel steer angle change and a hitch angle change. The processor performs a first computation if the wheel steer angle change and the hitch angle change satisfy a threshold requirement and performs a second computation if at least one of the wheel steer angle change and the hitch angle change does not satisfy the threshold requirement.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Vehicle-trailer backing up system using active front steer
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
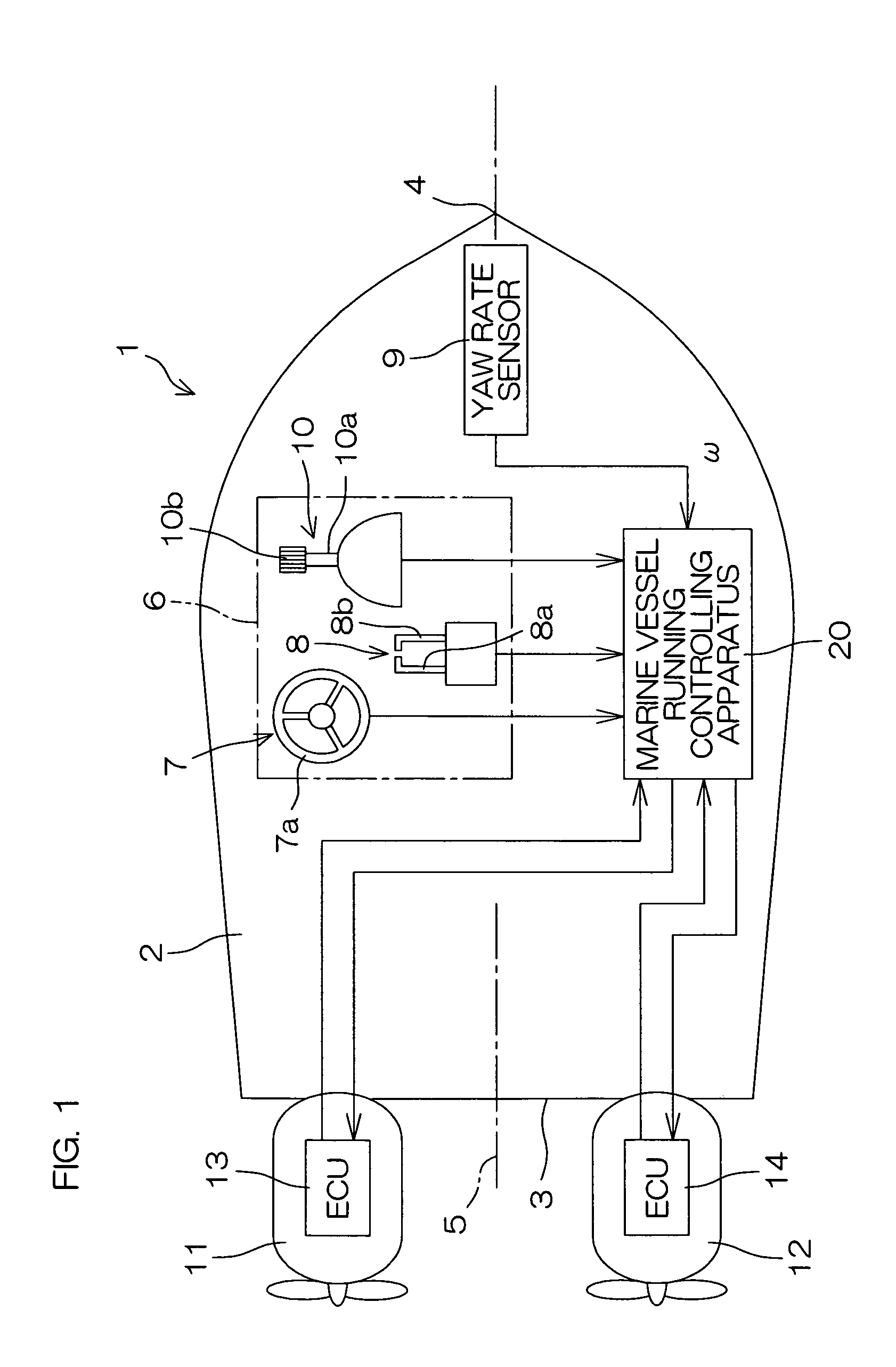
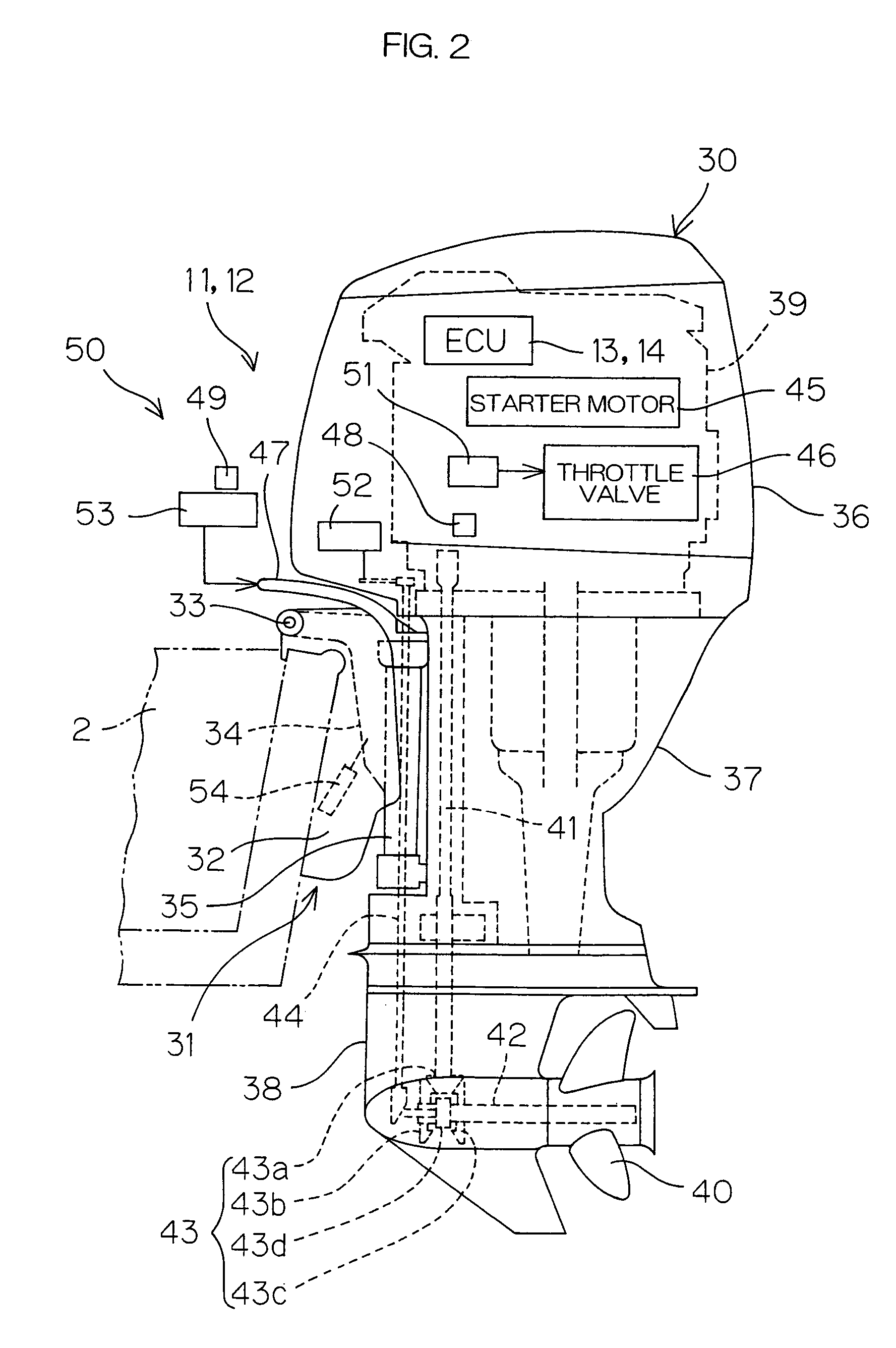
Marine vessel running controlling apparatus, marine vessel maneuvering supporting system and marine vessel each including the marine vessel running controlling apparatus, and marine vessel running controlling method
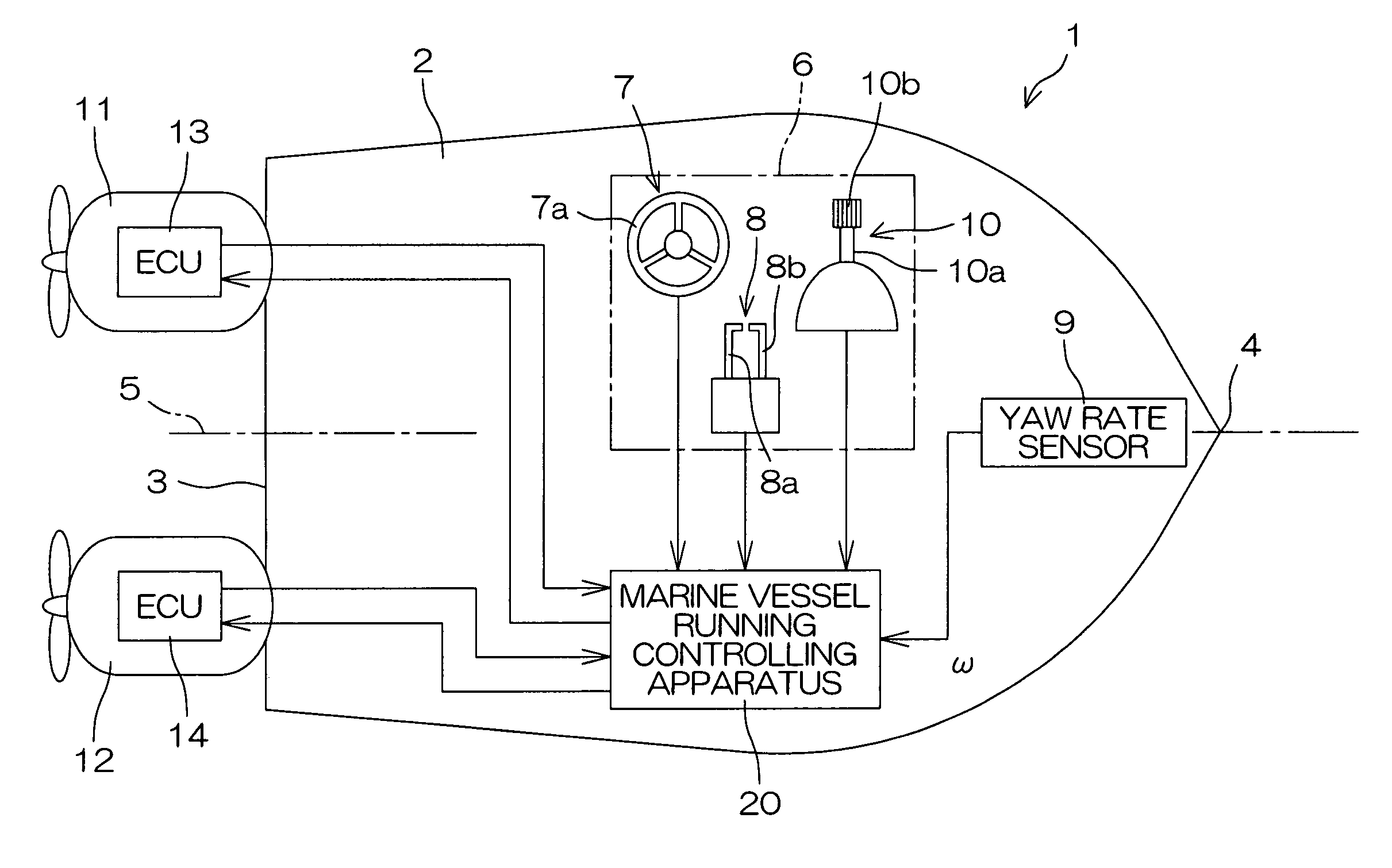
InactiveUS6994046B2Facilitate maneuveringSteering ruddersSteering initiationsSupporting systemSteering angle
A marine vessel running controlling apparatus controls running of a marine vessel and includes a pair of propulsion systems which respectively generate propulsive forces on a rear port side and a rear starboard side of a hull, and a pair of steering mechanisms which respectively change steering angles defined by directions of the propulsive forces with respect to the hull. The apparatus includes a target combined propulsive force acquiring section, a target movement angle acquiring section, a steering controlling section which controls the steering angles of the respective steering mechanisms such that a turning angular speed of the hull is substantially equal to a predetermined target angular speed, a target propulsive force calculating section which calculates target propulsive forces to be generated from the respective propulsion systems based on the target combined propulsive force, the target movement angle and the steering angles of the respective steering mechanisms, and a propulsive force controlling section which controls the respective propulsion systems so as to attain the target propulsive forces.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Drive Assisting Method for Reversal Path with Drawn Vehicle
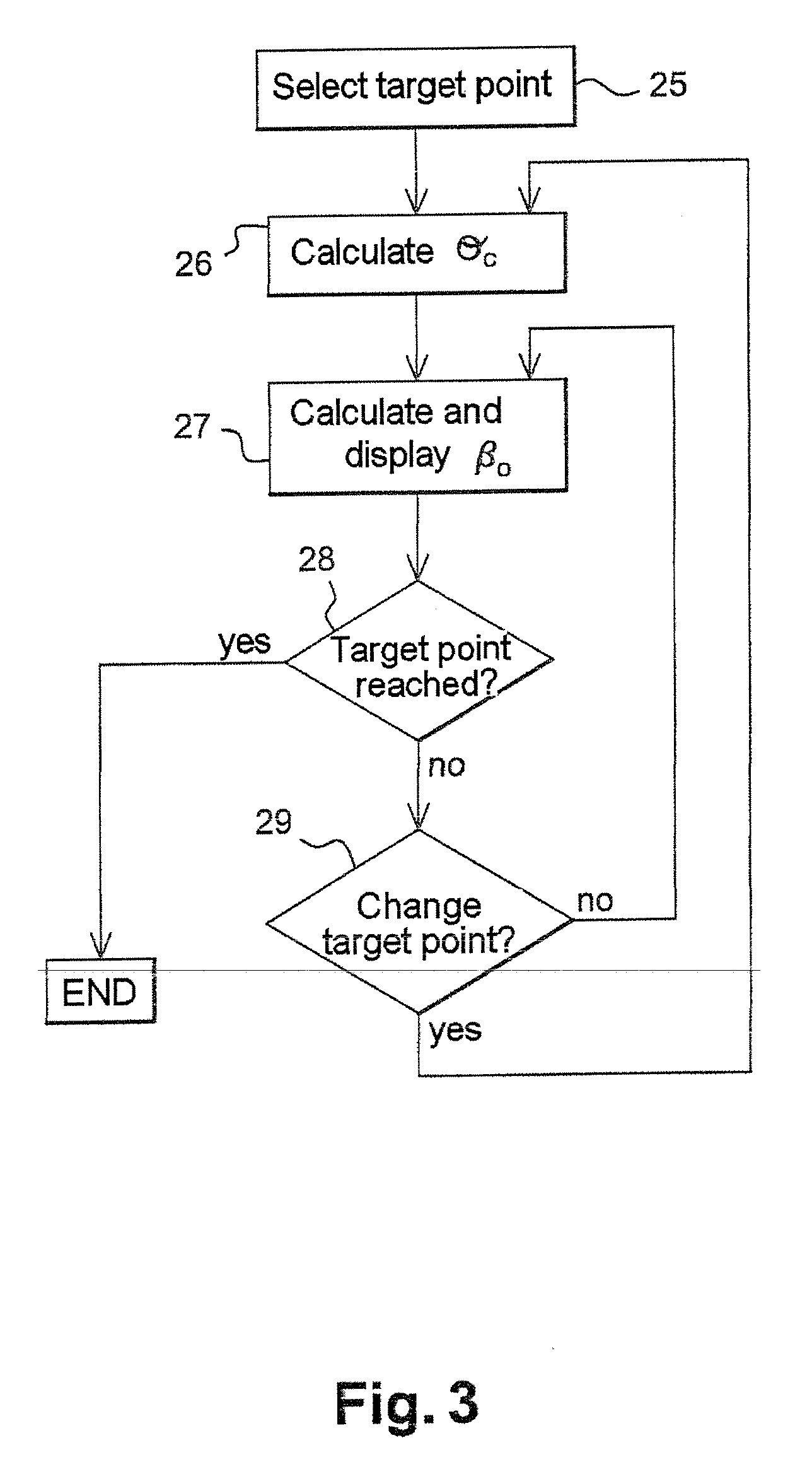
ActiveUS20080312792A1Simple processEasy to operateSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering angleDriver/operator
The invention relates to a drive assisting method for the reversal path of a vehicle which consists of a tow track and a trailer pivotable with respect thereto and is provided with a conventional mechanical steering device. The inventive method consists in selecting a target point (C), which the vehicle path should pass through, Determination in calculating the steering angle instruction β0 according to said target point (C) and the vehicle geometry and in displaying said steering angle instruction β0 in comparison with an actual steering angle β, which corresponds to the position of the member (21) of the steering device, on a display device accessible to a driver.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
Vehicle drive assist system
InactiveUS20060287825A1Simple image displayIntuitive displayInstruments for road network navigationInstrument arrangements/adaptationsSteering angleEngineering
A vehicle drive assist system comprises a camera for picking up an image of an area existing in an advancing direction of a vehicle; display means for displaying the image picked up by the camera; steering angle detecting means for detecting a steering angle for steering the vehicle; traveling path predicting means for predicting a traveling path of the vehicle on the basis of the steering angle detected by the steering angle detecting means; and drive assist means for overlaying on the display means drive assist information containing the vehicle predictive traveling path predicted by the traveling path predicting means and guide lines prolonged from the lines defining the width of the vehicle body on the image of the area existing in the vehicle advancing direction.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Path generation algorithm for automated lane centering and lane changing control system
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Trailer length estimation in hitch angle applications
A vehicle system for estimating a trailer length is disclosed. The system incorporates at least one sensor configured to measure a wheel steer angle and a trailer angle in communication with a processor. The processor is operable to determine a first length by a first computation method and determine a second length by a second computation method. The processor is further operable to validate an estimated trailer length based on the first length and the second length and perform a back-up function for the trailer based on the estimated trailer length.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
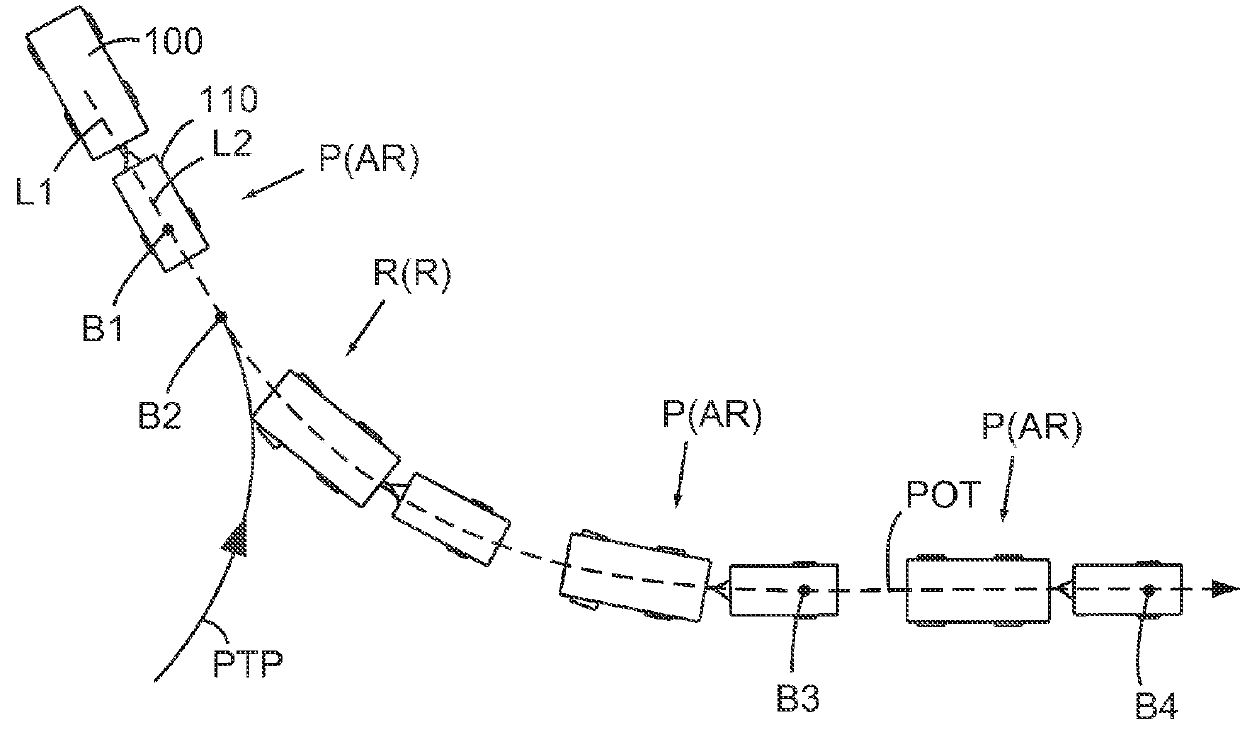
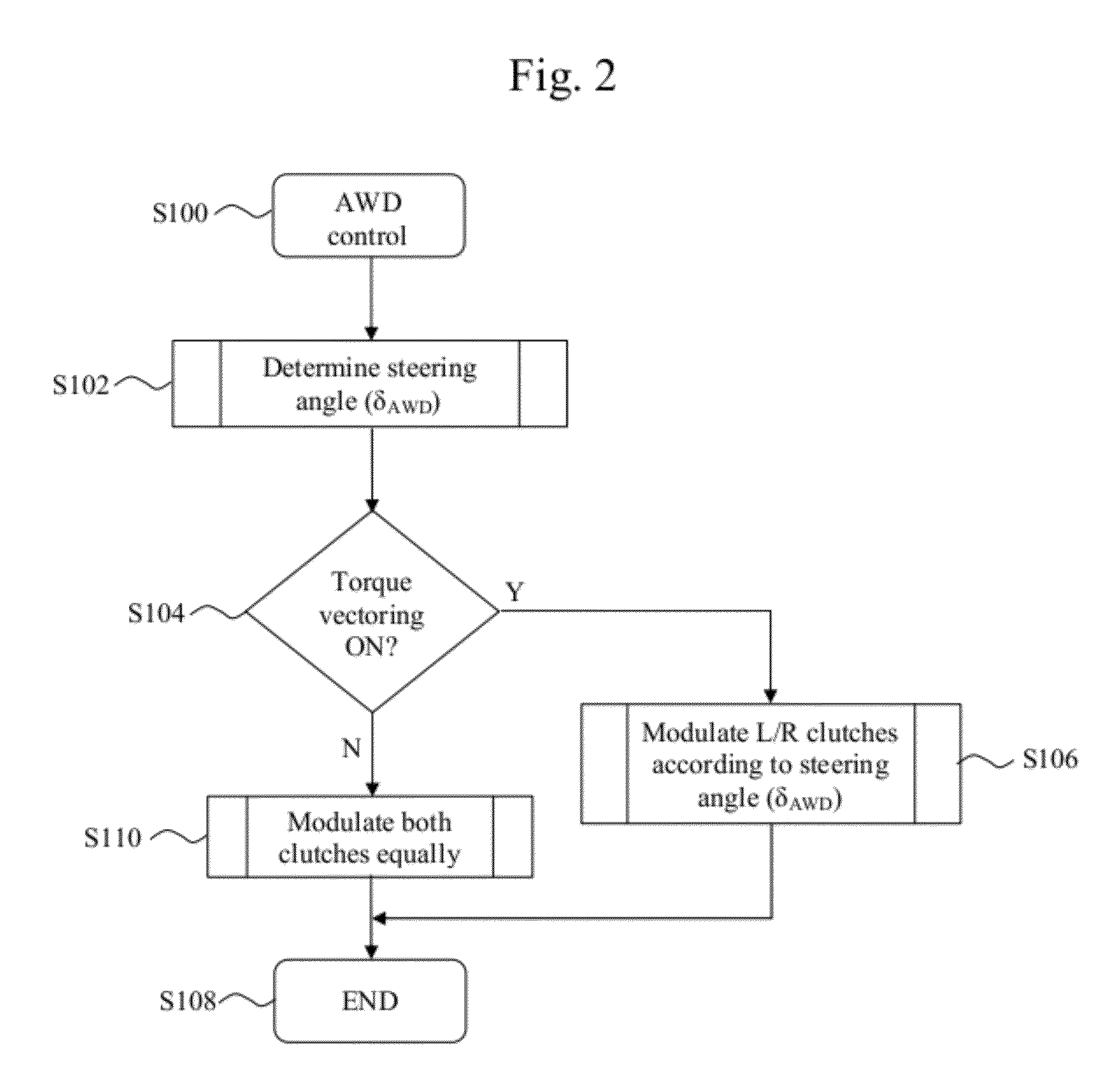
System and method for determining a steering angle for a vehicle and system and method for controlling a vehicle based on same
A system for determining an angular position of a steerable wheel of a vehicle can include a plurality of sensors and a controller in electrical communication with each of these sensors. The controller can be configured to compare a first data set and a second data set to respective straight path conditions, wherein the first data set includes data from a first set of the sensors and the second data includes data from a second set of the sensors. The controller can be configured to determine a substantially straight path of travel condition when the comparison of at least one of the first data set and the second data set satisfies the respective straight path conditions, and can then associate that data acquired from the steering angle sensor(s) with a neutral position.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for determining a hitch angle offset
ActiveUS20140188346A1Steering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering angleSteering linkage
A system and a method are provided for estimating an actual hitch angle between a vehicle and a trailer. A hitch sensor on the vehicle continuously senses a measured hitch angle and a steering sensor continuously senses a steering angle of steered wheels of the vehicle. A controller determines an offset between the measured hitch angle and the actual hitch angle when the measured hitch angle and the steering angle are substantially constant while the vehicle and trailer are reversing.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
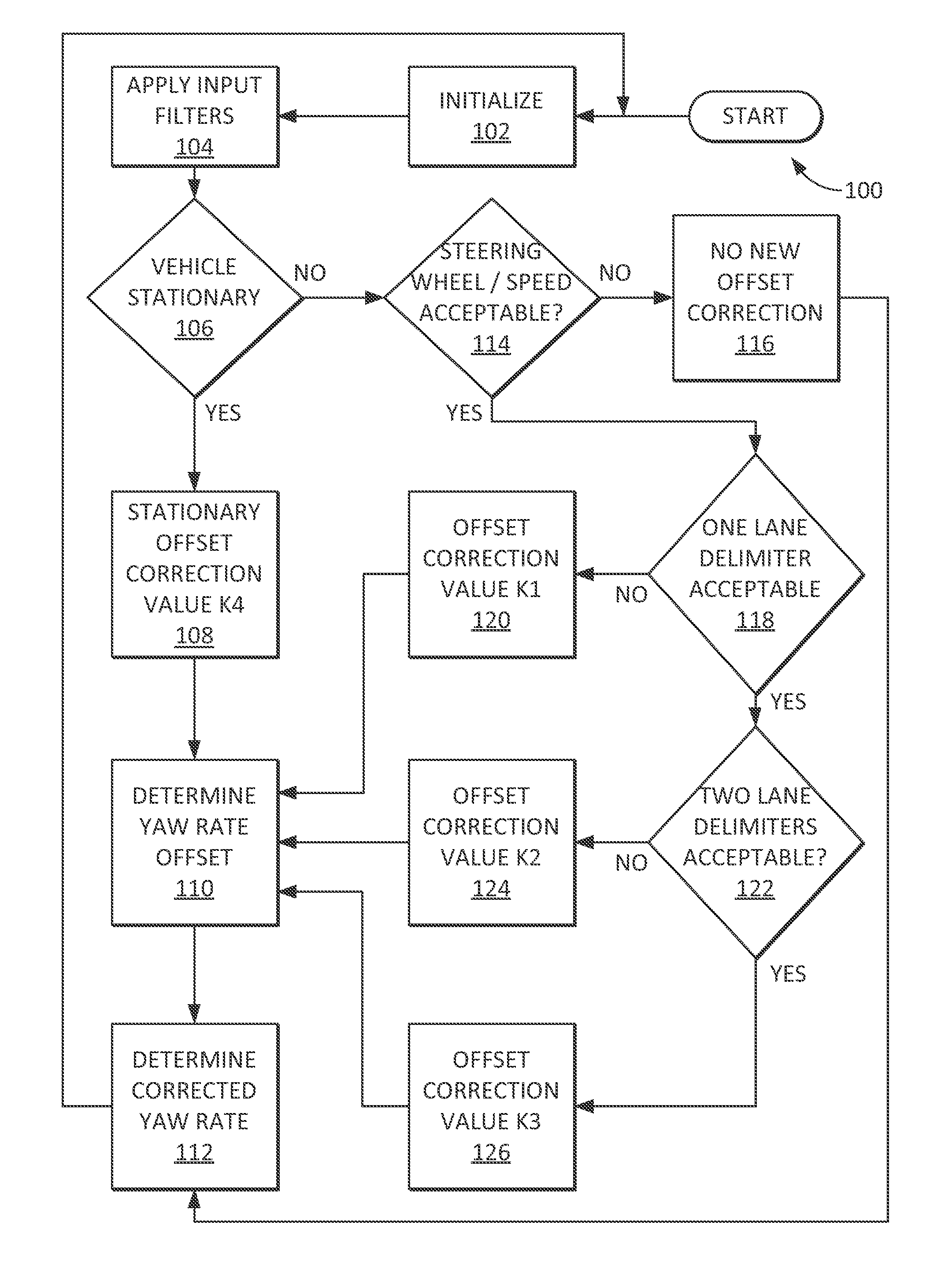
Vehicle yaw rate correction
A control system or method for a vehicle references a camera and sensors to determine when an offset of a yaw rate sensor may be updated. The sensors may include a longitudinal accelerometer, a transmission sensor, a vehicle speed sensor, and a steering angle sensor. The offset of the yaw rate sensor may be updated when the vehicle is determined to be stationary by referencing at least a derivative of an acceleration from the longitudinal accelerometer. The offset of the yaw rate sensor may be updated when the vehicle is determined to be moving straight by referencing at least image data captured by the camera. Lane delimiters may be detected in the captured image data and evaluated to determine a level of confidence in the straight movement. When the offset of the yaw rate sensor is to be updated, a ratio of new offset to old offset may be used.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
Vehicle steering apparatus
InactiveUS20060086560A1Reduce impactFeel goodDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsSteering columnSteering angle
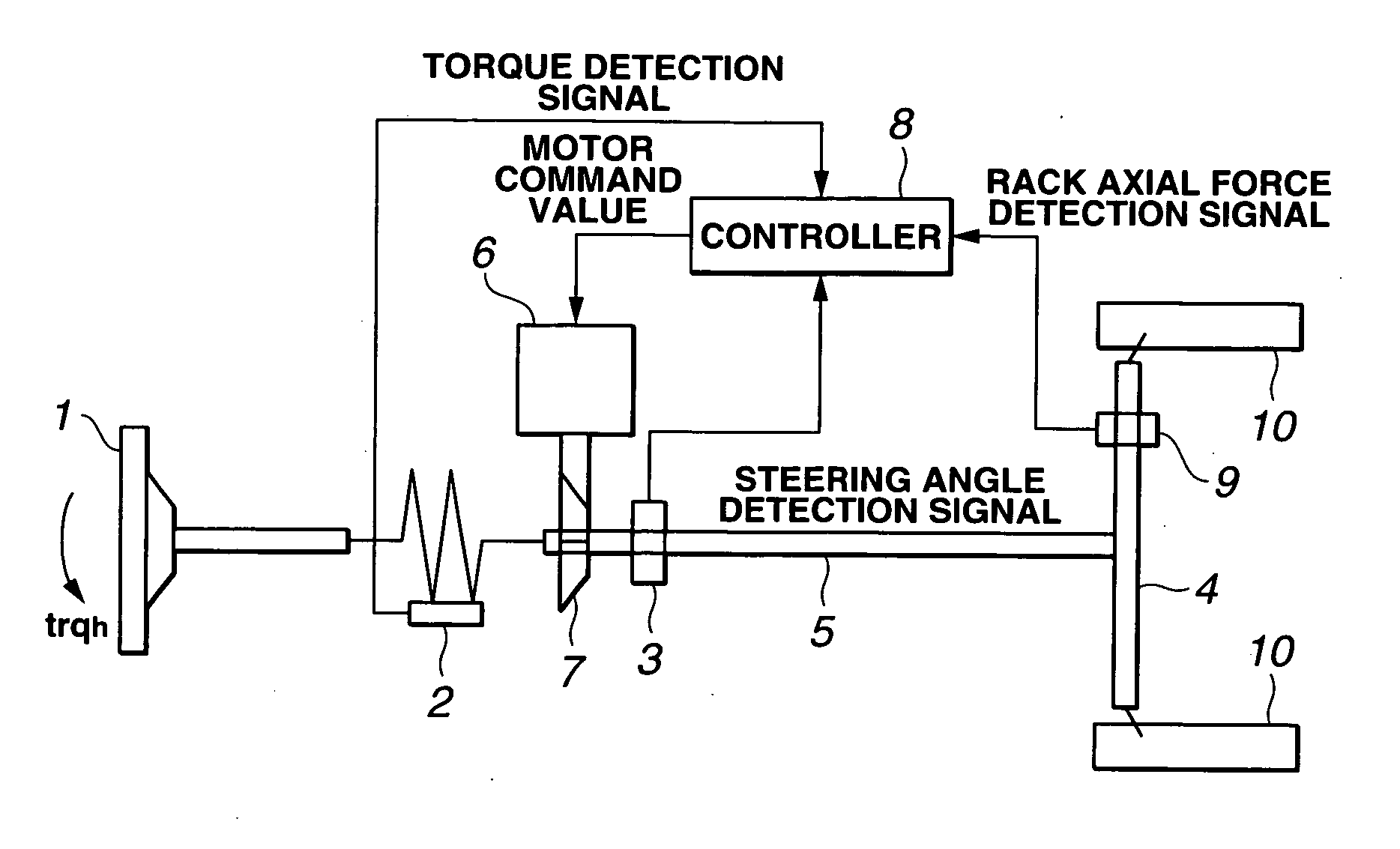
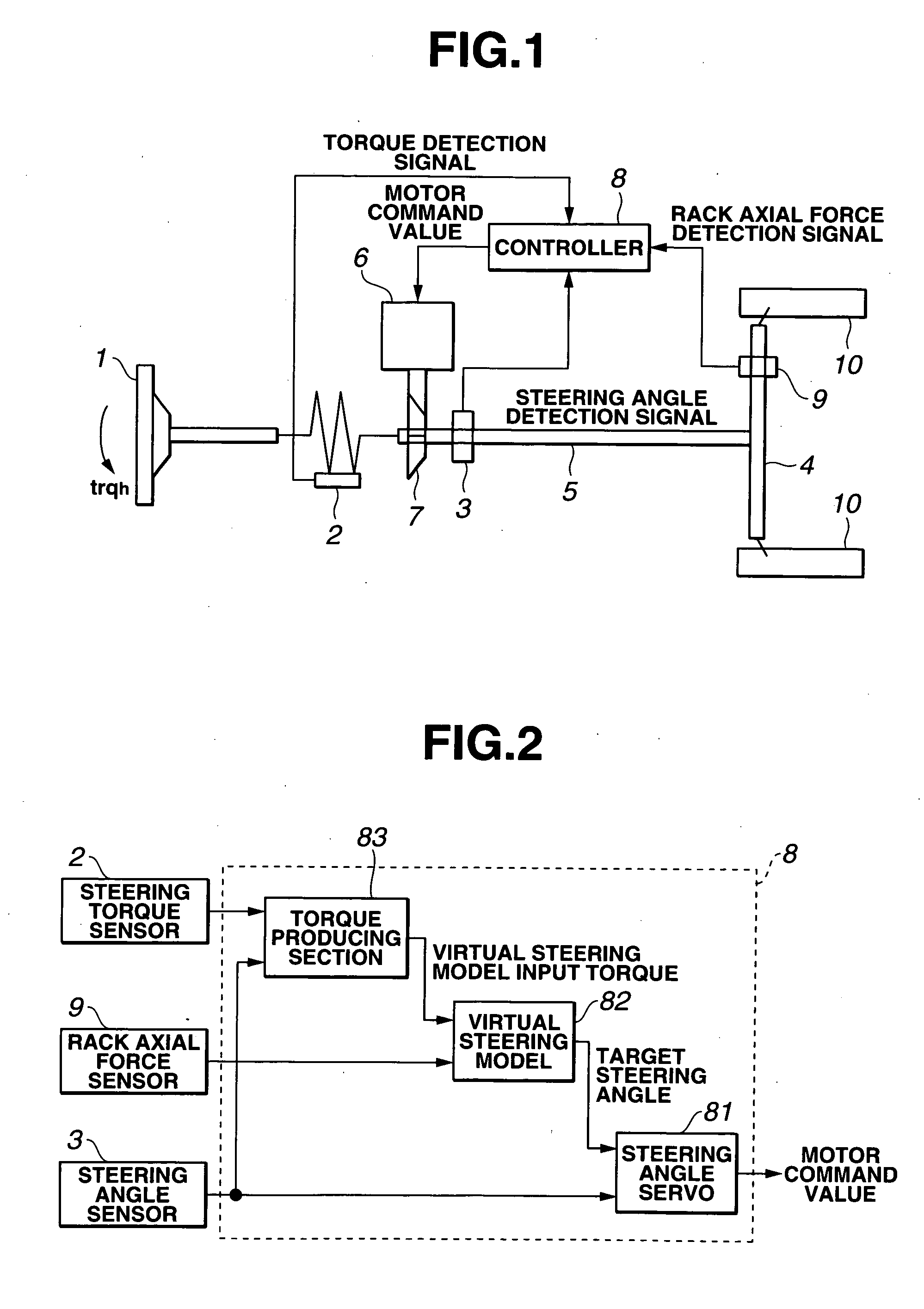
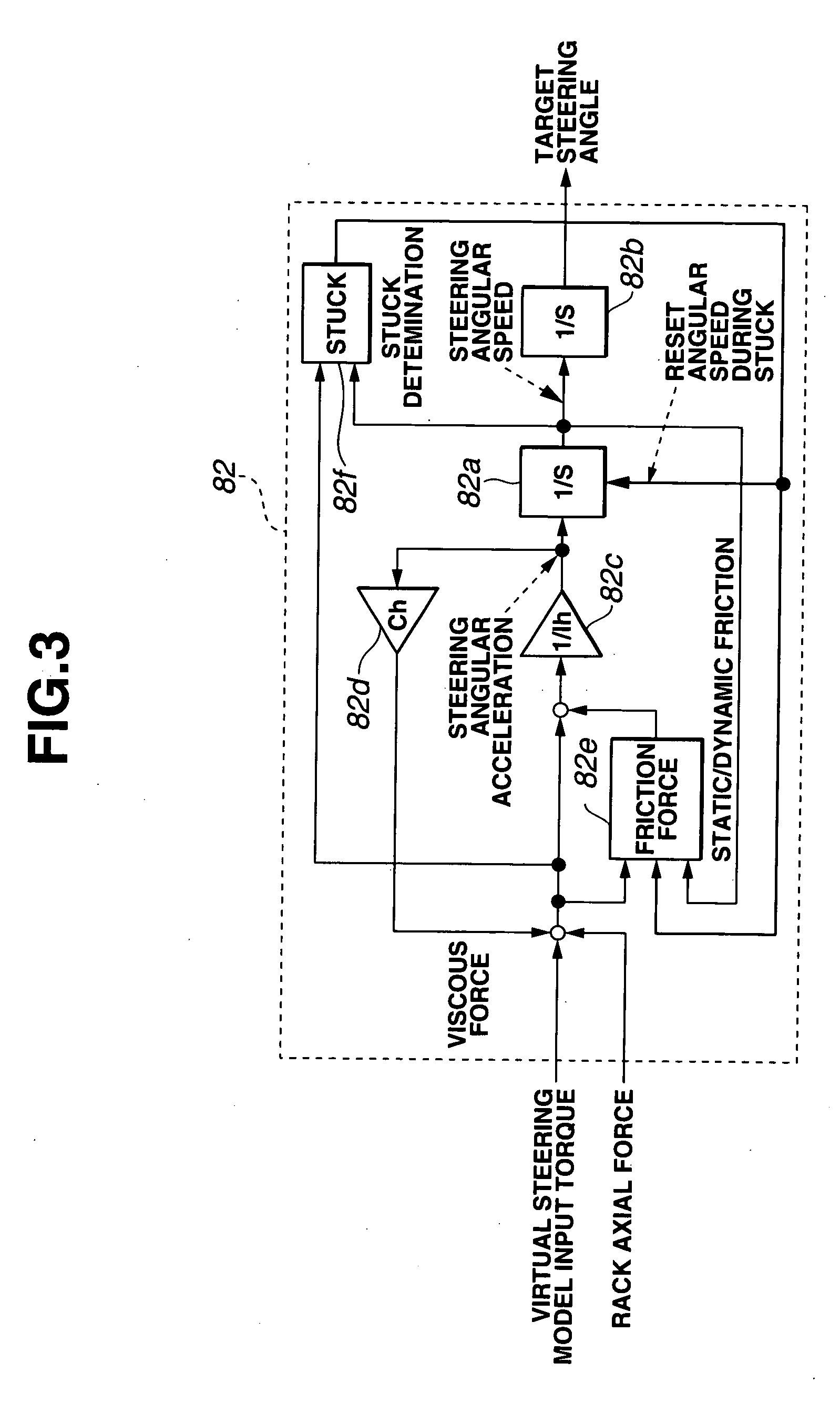
A vehicle steering apparatus is comprised of an assist motor, a steering torque sensor, a steering angle sensor, and a controller. The controller has a torque producing section for estimating a virtual steering model input torque from a torque sensor detection value and a steering angle detection value, a virtual steering model of representing a desired steering characteristic which receives the virtual steering model input torque and outputs a target steering angle of a steering column shaft, and a steering angle servo for controlling an output of the assist motor so that the steering angle detection angle follows the target steering angle.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Vehicle steering apparatus
InactiveUS20050072621A1Enhanced steering link efficiencyCompensation deviationSteering linkagesMechanical steeringSteering wheelSteering angle
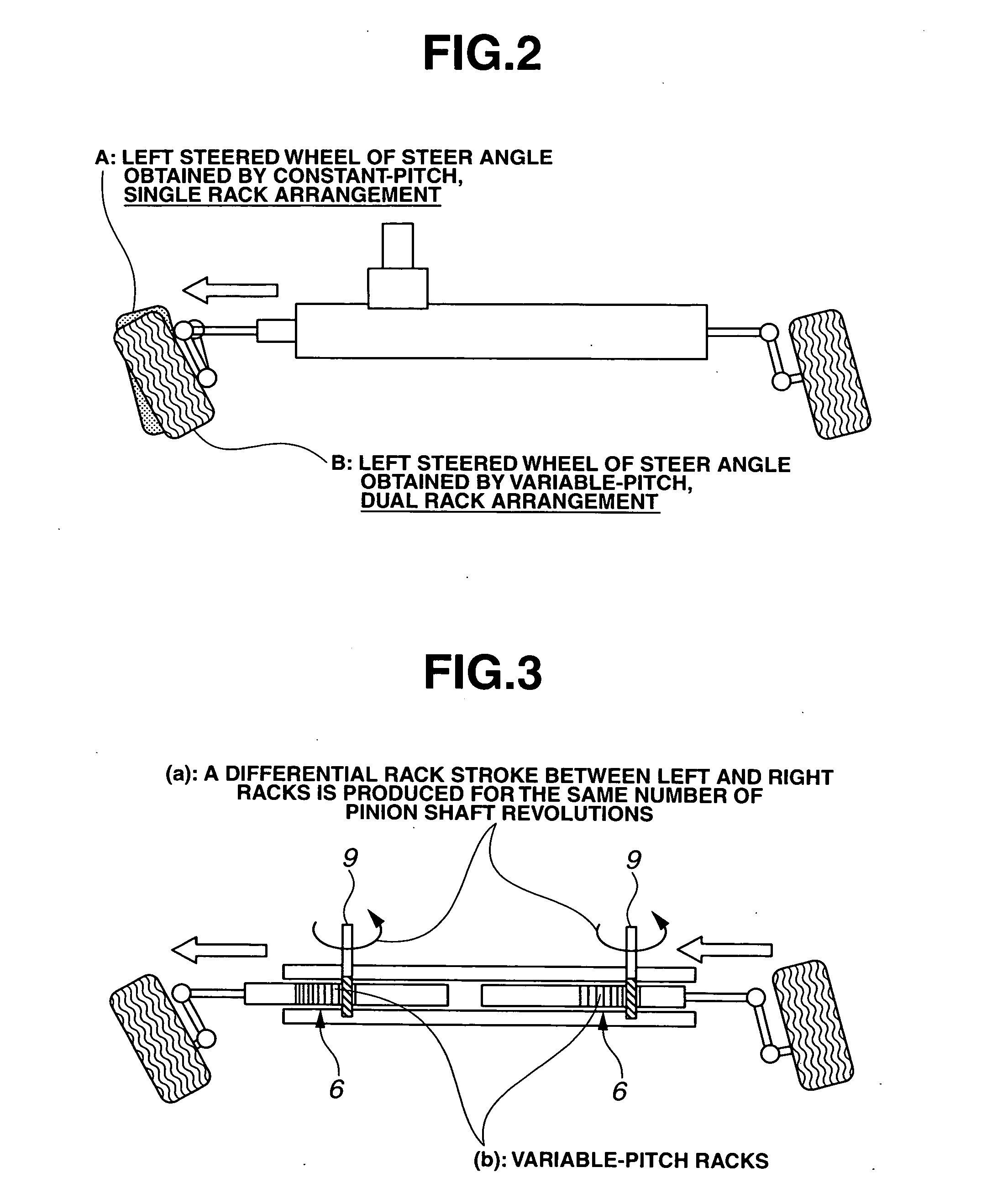
A vehicle steering apparatus includes a steering input section having at least a steering wheel to which steering input is applied, and a steering output section having at least a steering rack shaft and operatively associated with left and right steered wheels for steering the steered wheels by steering-rack-shaft movement produced by a steering force determined based on the steering input and transmitted directly or indirectly to the steering rack shaft. The steering rack shaft is split into left and right movable rack shaft portions. Also provided is a steer angle converter enabling a differential rack stroke between left and right rack strokes of the left and right movable rack shaft portions. The steer angle converter is constructed by at least one of a variable-pitch dual rack arrangement and a dual taper-pulley arrangement of a cable back-up mechanism.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
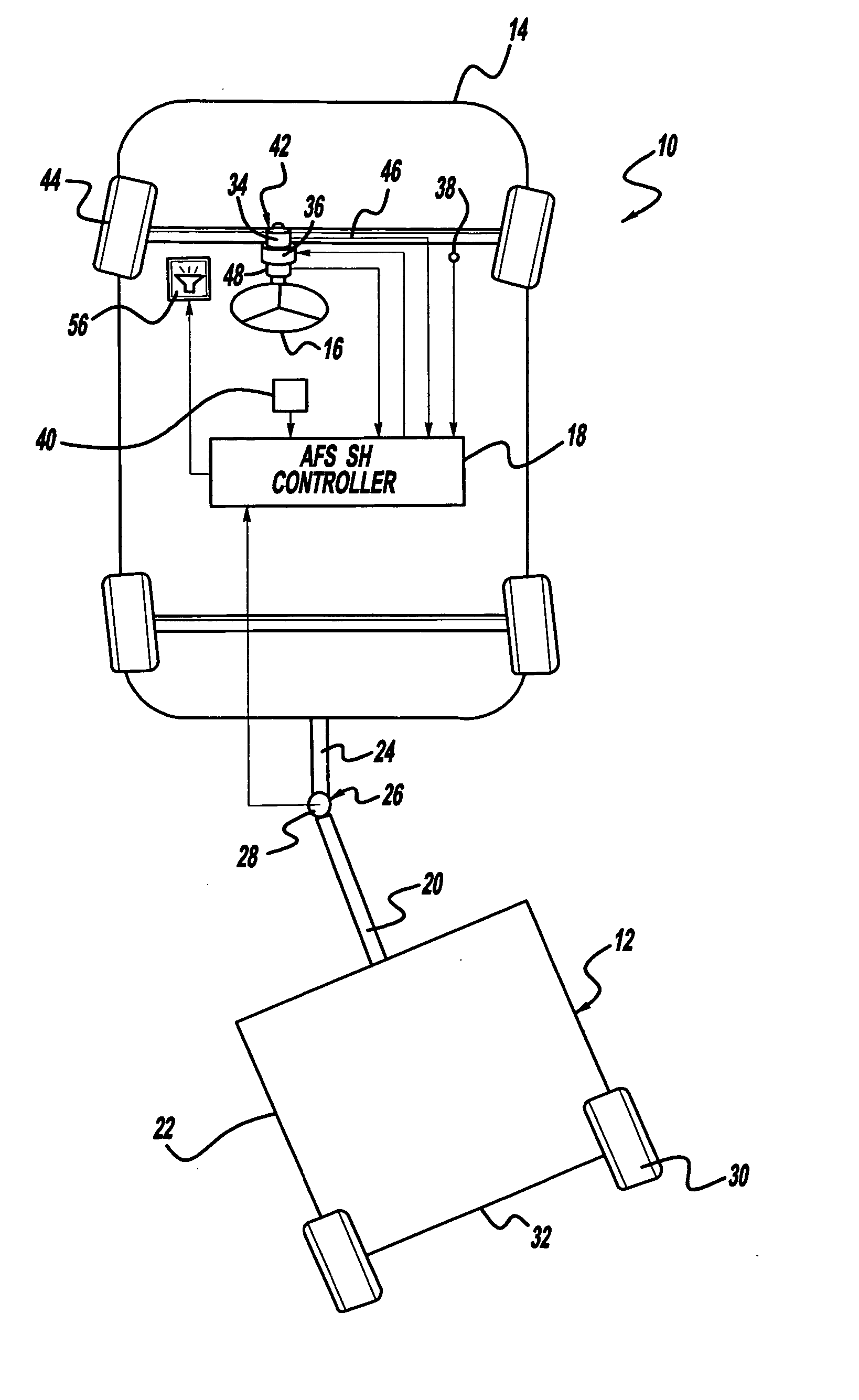
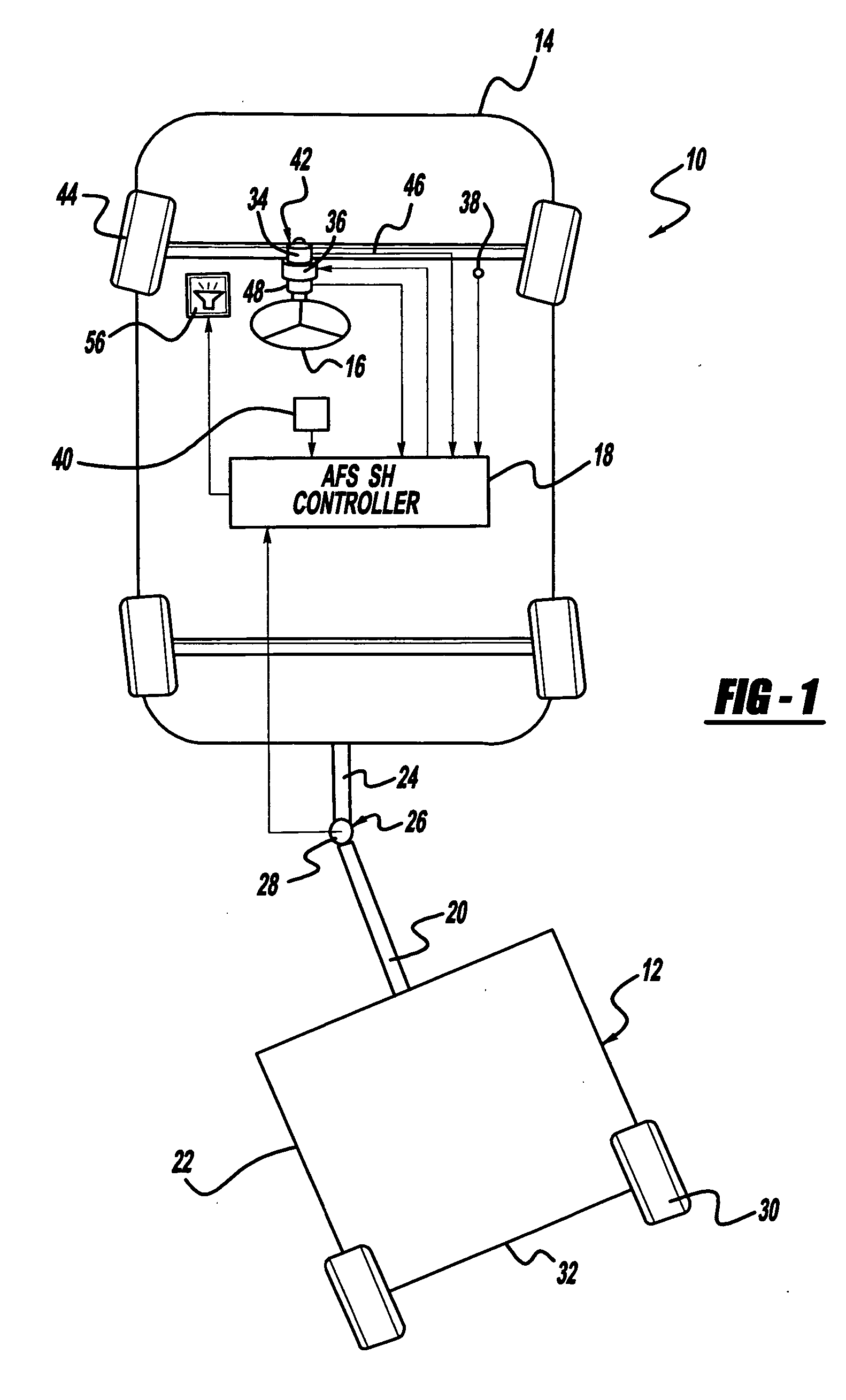
Architecturally partitioned automatic steering system and method
InactiveUS20060167600A1Delay variationMaximum performanceDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlAutomatic steeringSteering angle
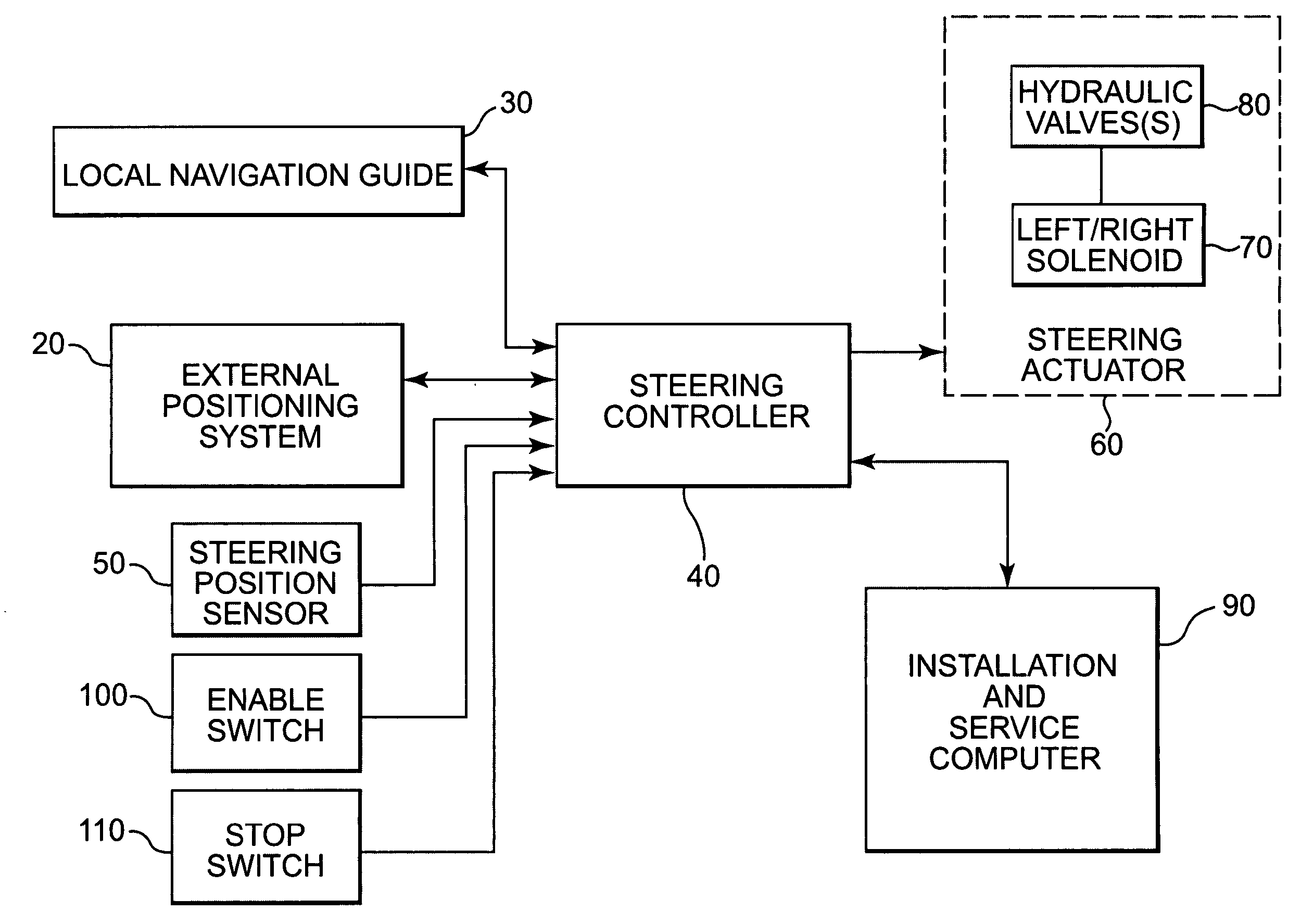
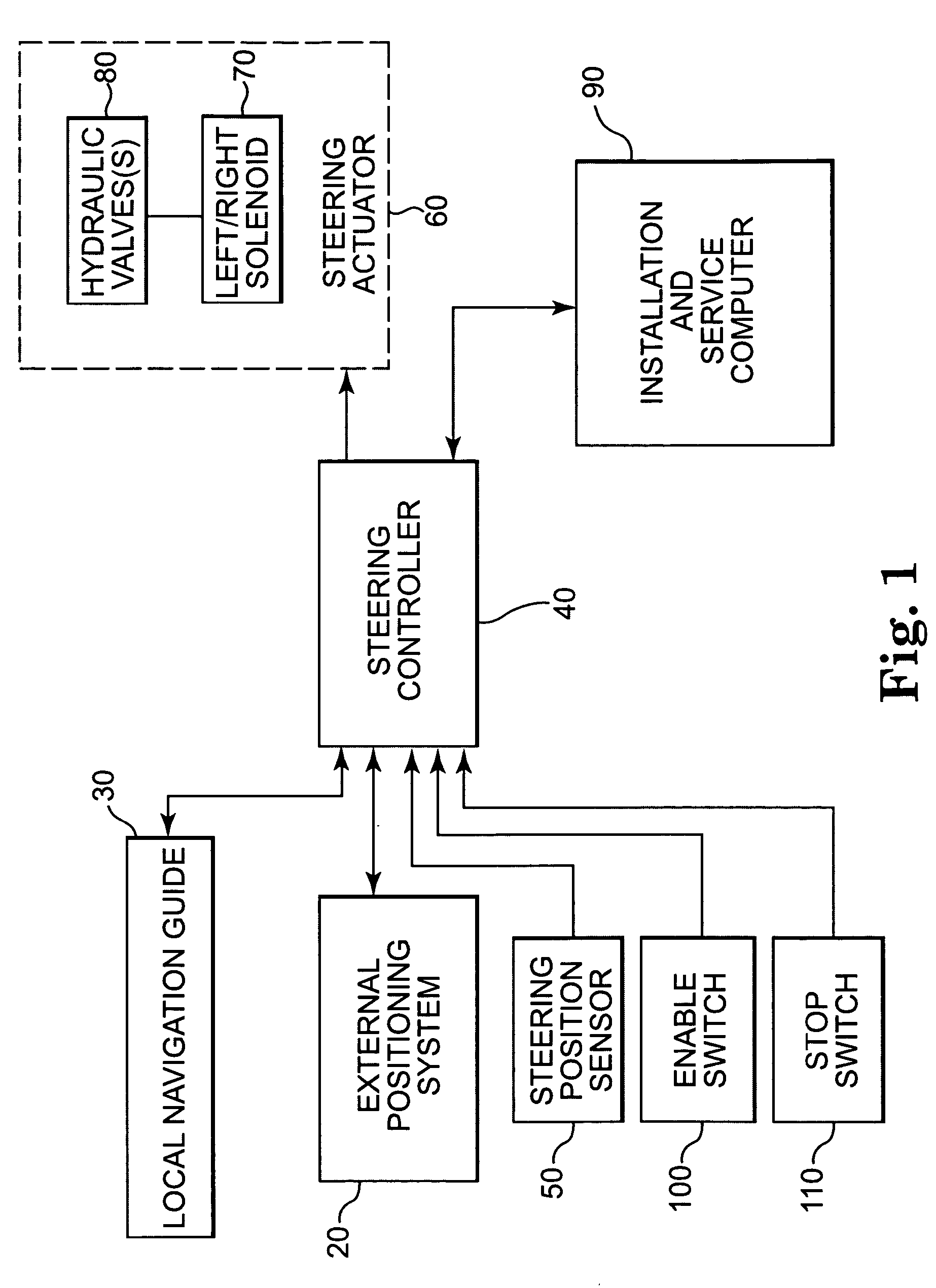
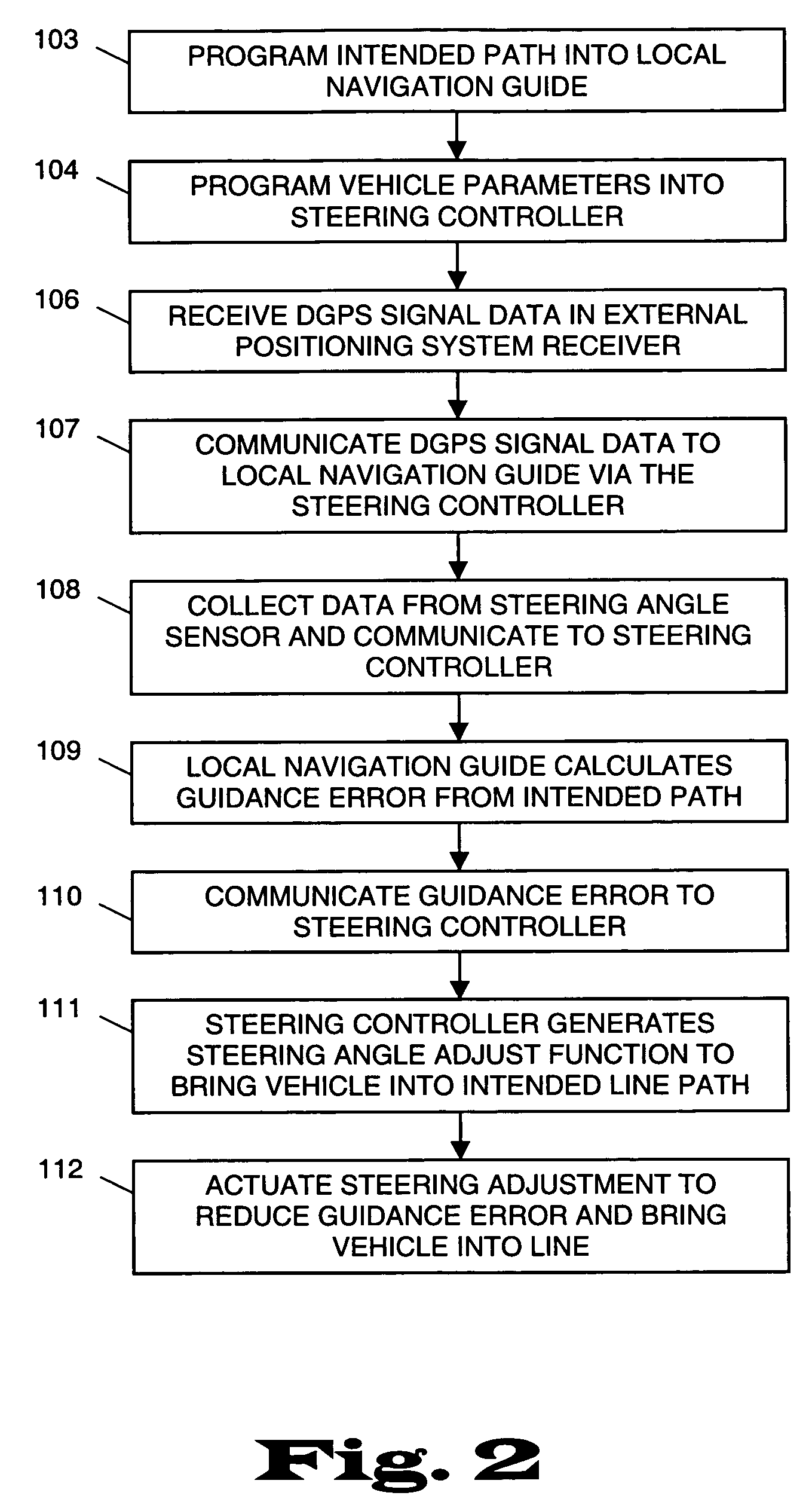
A system and method for automatically steering a vehicle along an intended path is provided. The system is architecturally partitioned. The partitioned design allows each of the system elements to be designed and maintained independently while allowing variation and flexibility in system configuration. An embodiment of the system elements may comprise a local navigation guidance unit, an external positioning system, a steering controller, and an installation and service computer. Additional elements of an embodiment of the system may comprise a steering position sensor, and at least one steering actuator. The system allows the operator to enter an intended target path and certain vehicle parameters. The local navigation guidance unit receives positional data from an external positioning system, preferably DGPS, indicative of a navigational path traversed by the vehicle. The guidance unit compares the positional data with the intended target path to obtain guidance error and transmits the guidance error to the steering controller. The system allows for determination of the current steering angle and generation of a steering angle adjustment based upon the intended target, the navigational path traversed by the vehicle, the vehicle parameters, the steering angle and the guidance error. The steering angle adjustment is used to actuate a steering mechanism to smoothly guide the vehicle along the intended target path.
Owner:RAVEN INDUSTRIES INC
Vehicle yaw rate correction
A control system or method for a vehicle references a camera and sensors to determine when an offset of a yaw rate sensor may be updated. The sensors may include a longitudinal accelerometer, a transmission sensor, a vehicle speed sensor, and a steering angle sensor. The offset of the yaw rate sensor may be updated when the vehicle is determined to be stationary by referencing at least a derivative of an acceleration from the longitudinal accelerometer. The offset of the yaw rate sensor may be updated when the vehicle is determined to be moving straight by referencing at least image data captured by the camera. Lane delimiters may be detected in the captured image data and evaluated to determine a level of confidence in the straight movement. When the offset of the yaw rate sensor is to be updated, a ratio of new offset to old offset may be used.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com