Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
227 results about "Straight ahead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
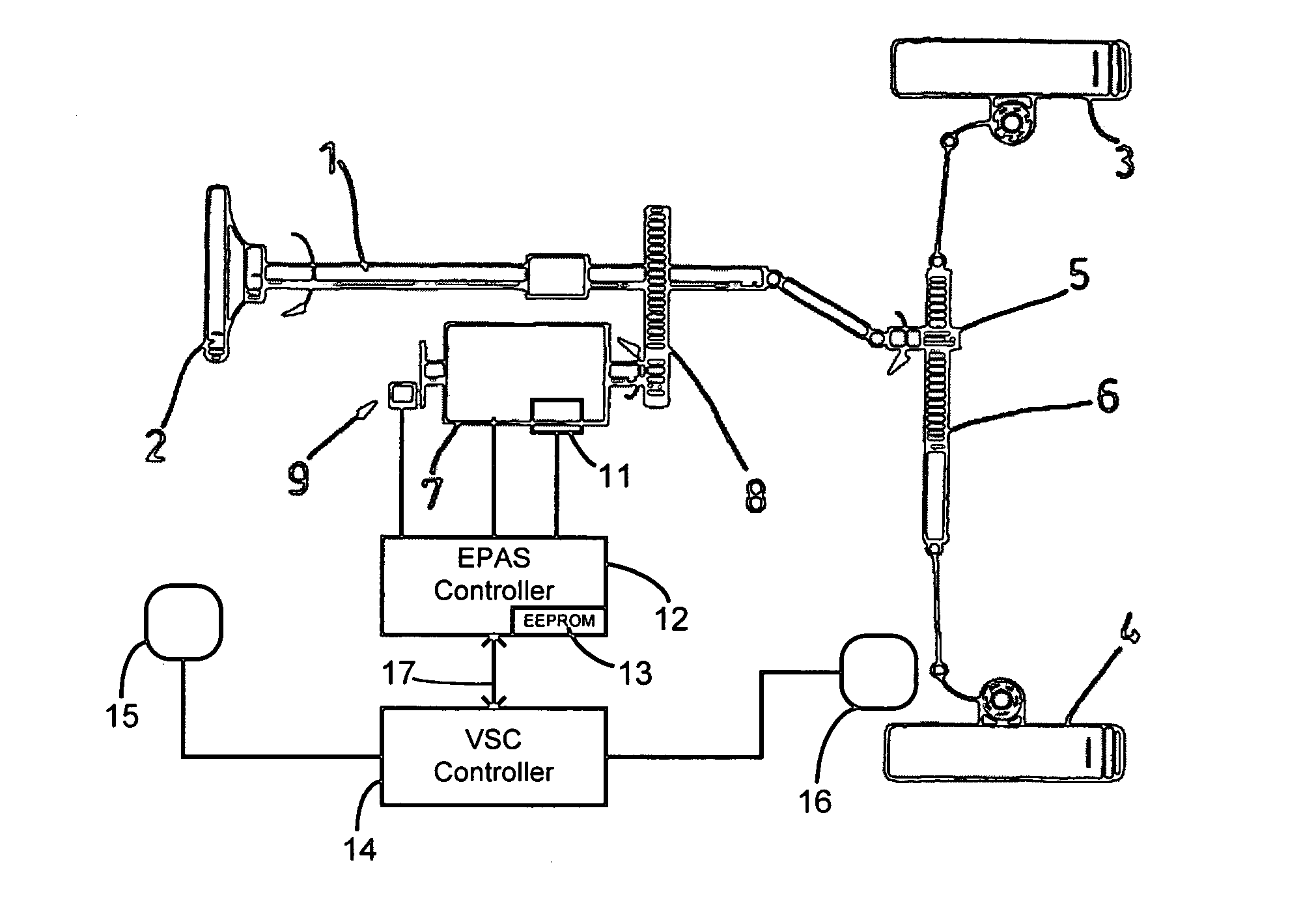
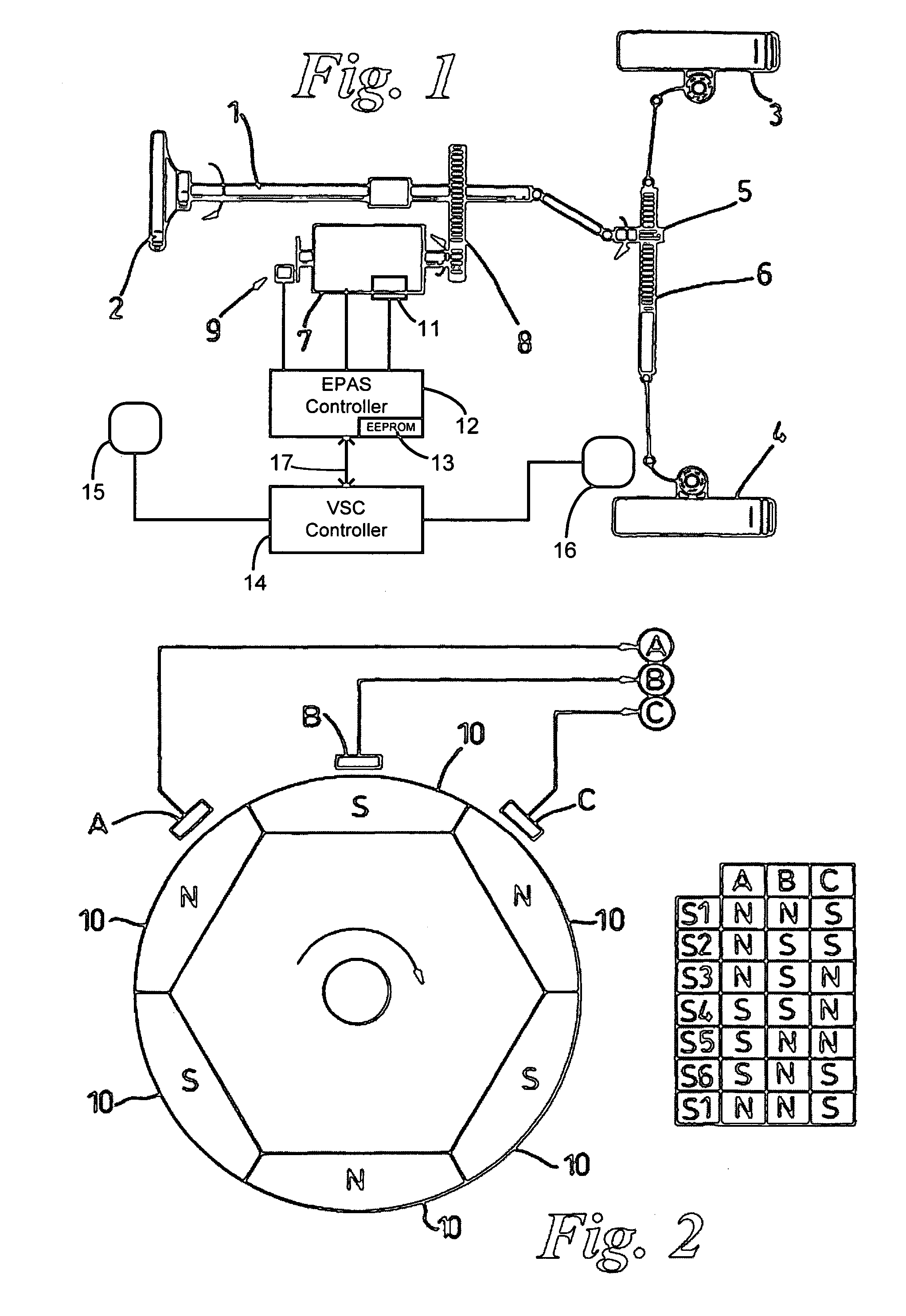
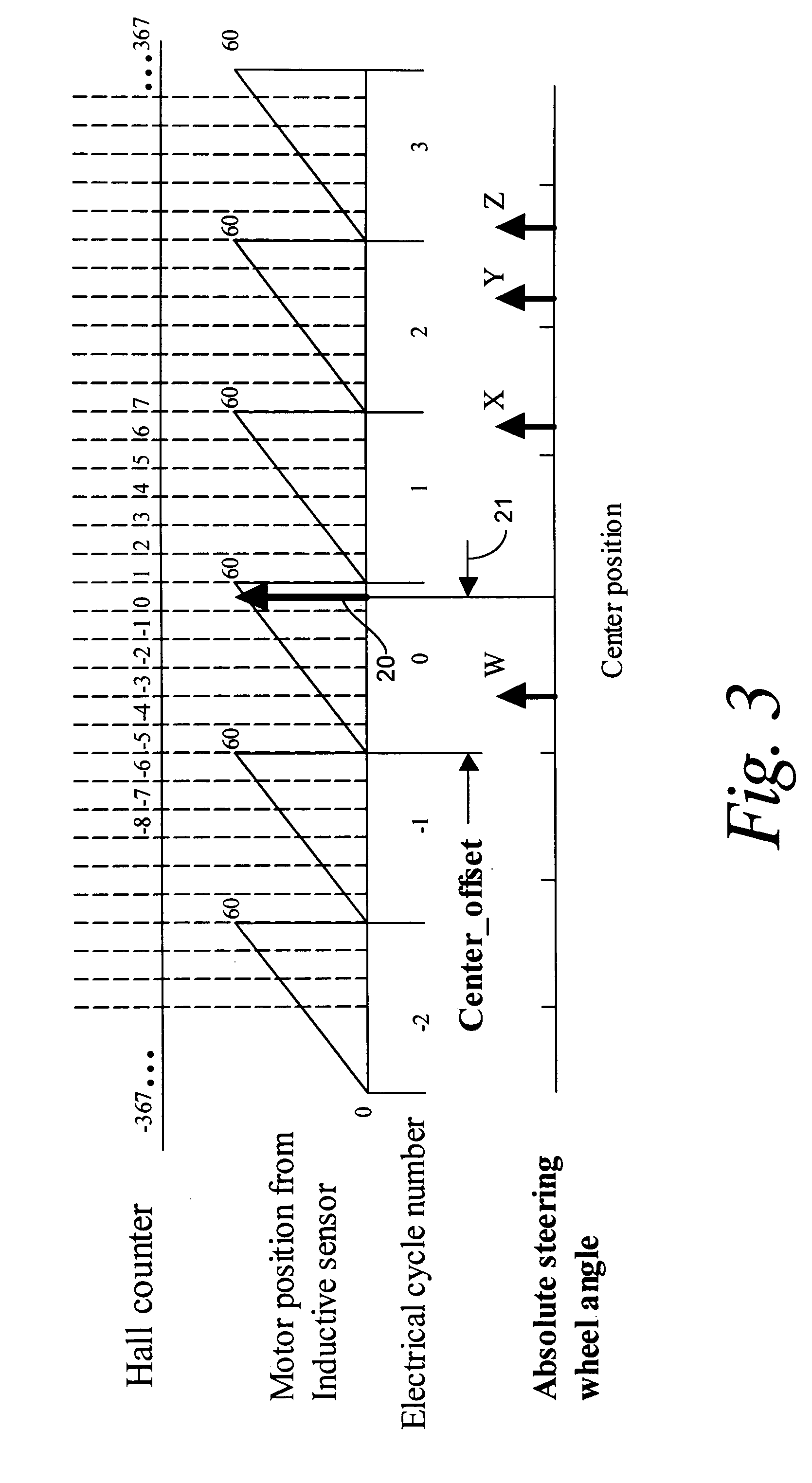
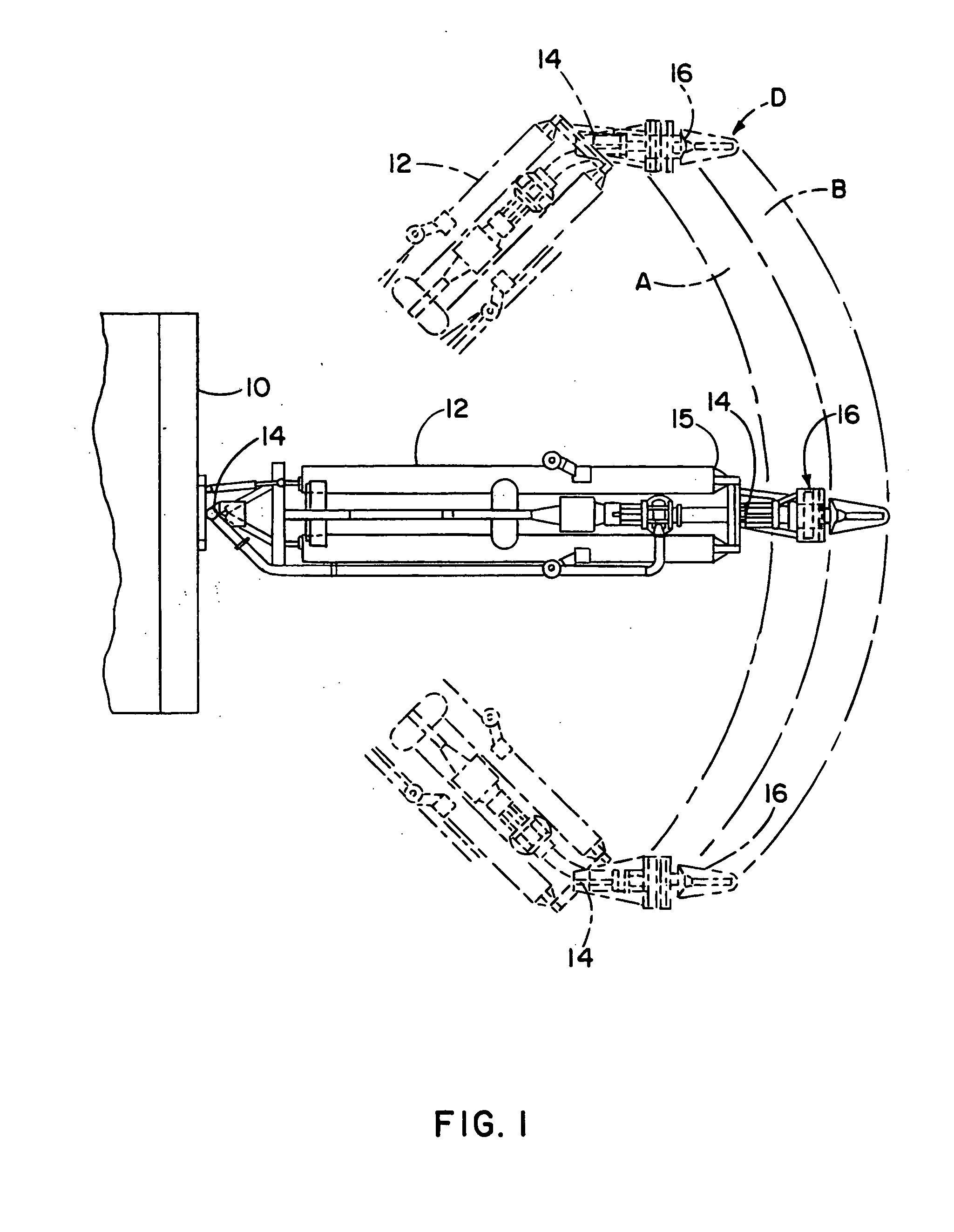
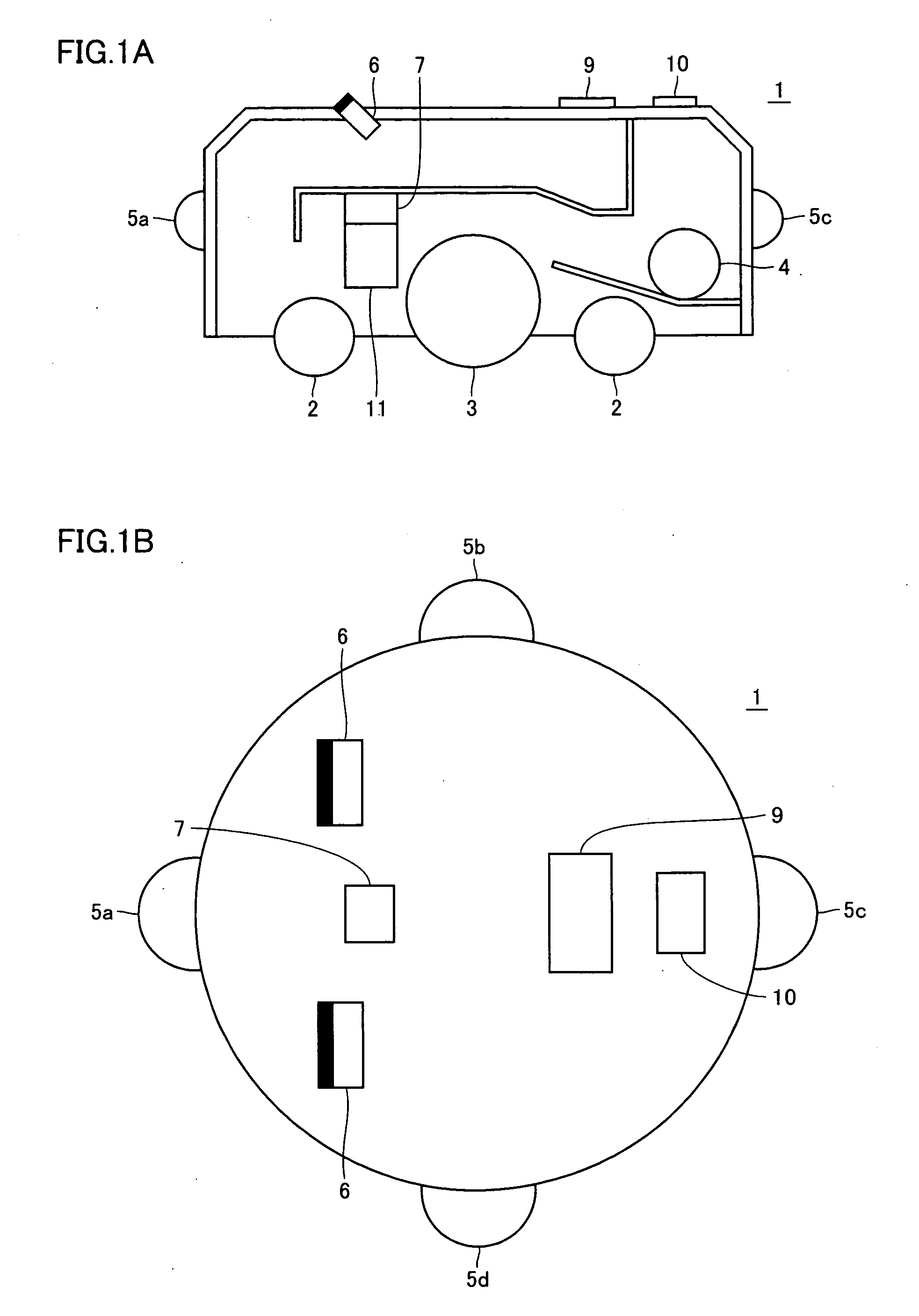
Recovery of calibrated center steering position after loss of battery power
ActiveUS7295907B2Accurate absolute steering angleAvoid the needDigital data processing detailsOptical signallingElectric power steeringSteering angle
The steering angle of a vehicle is monitored using position sensors of an electric motor of an electric power assisted steering (EPAS) system. A position of the electric motor corresponding to the straight-ahead, center position of the steering system is stored in non-volatile memory during a steering calibration procedure, such as an end-of-line calibration in a vehicle assembly plant. Following power loss due to a dead battery, a steering angle zeroing procedure performed in a vehicle stability control (VSC) system generates a center position with enough accuracy to be within one electrical cycle of the motor. The pre-stored electric motor position is then used to determine the electrical cycle where the center position was located, and accurate monitoring of steering angle is resumed.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
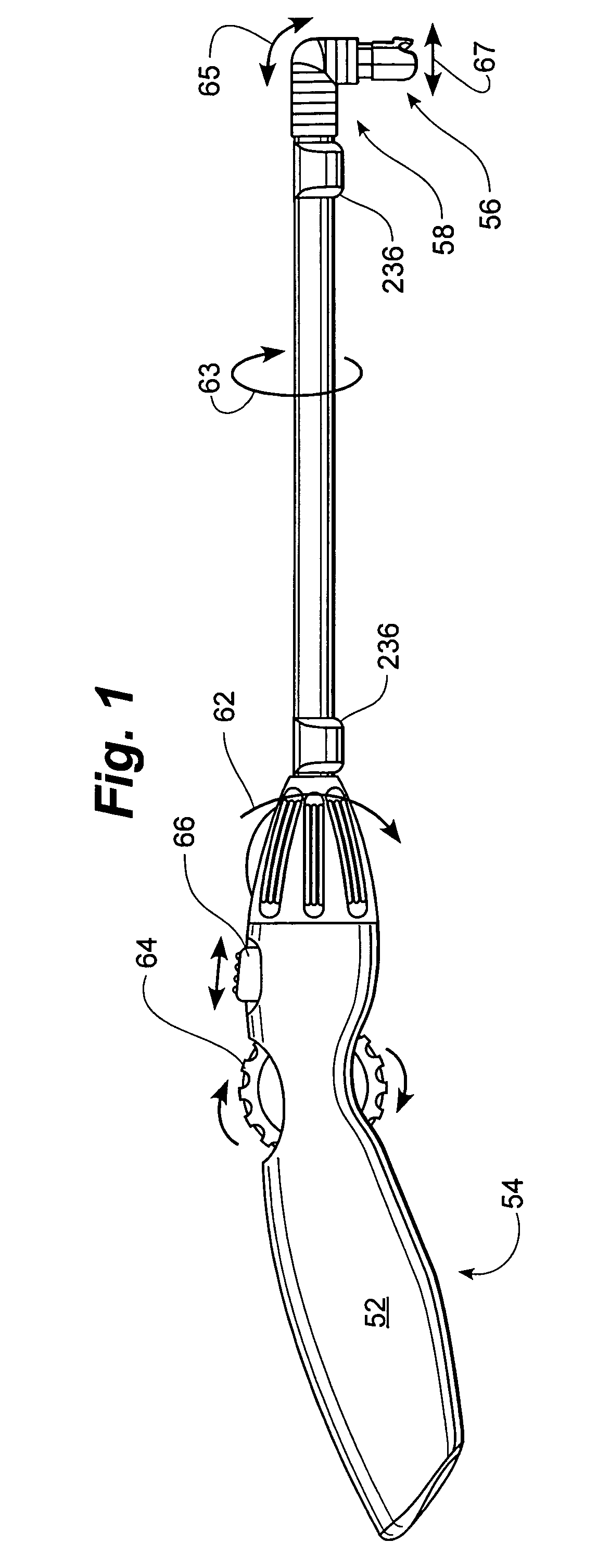
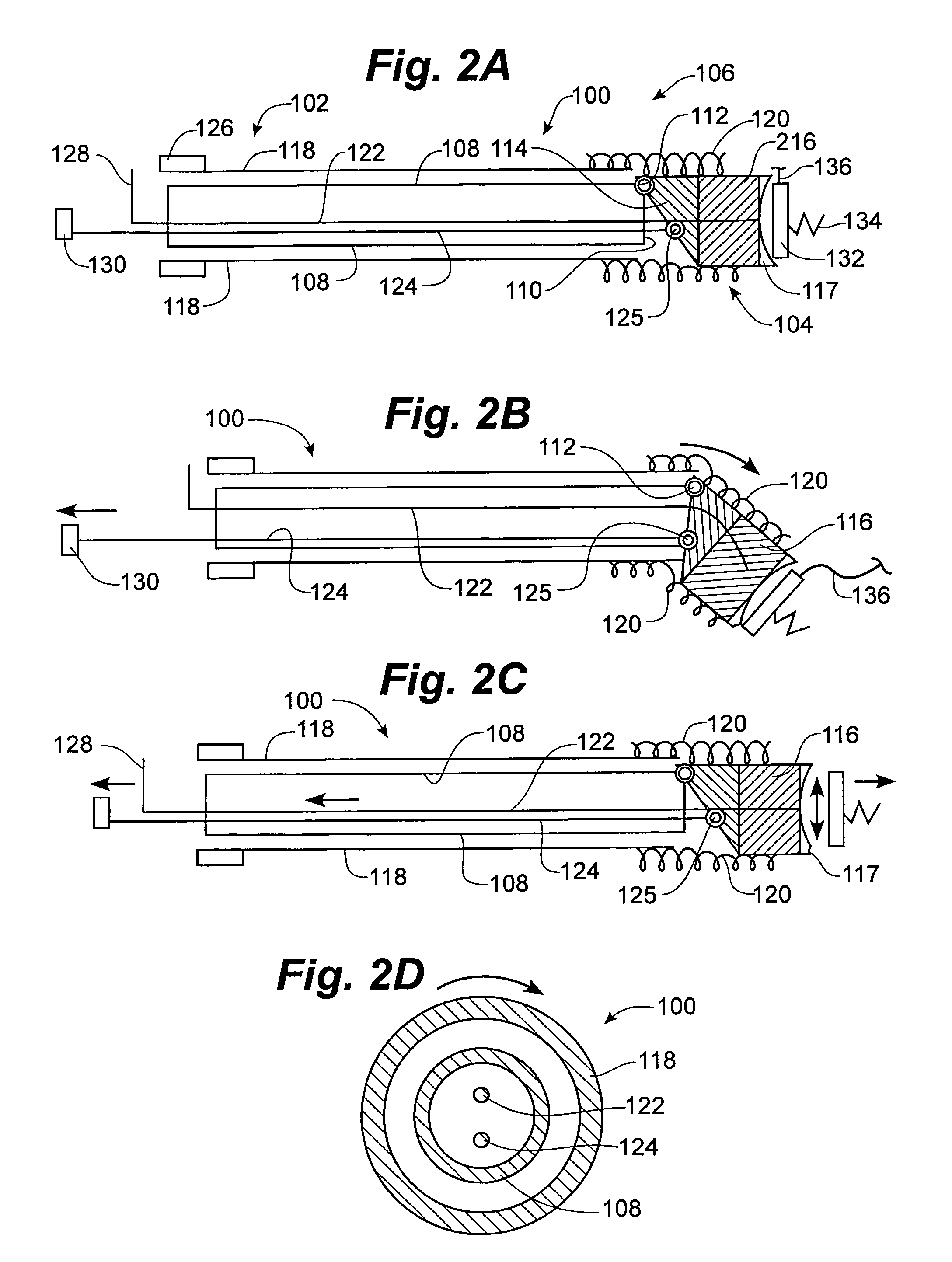
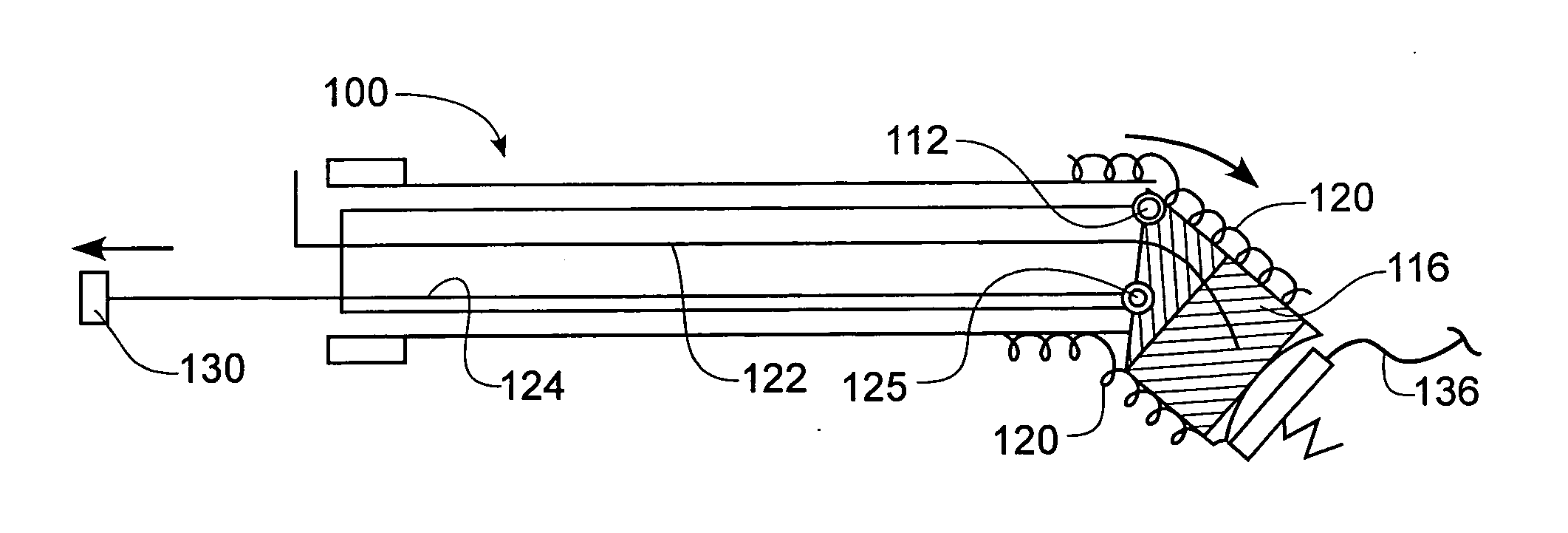
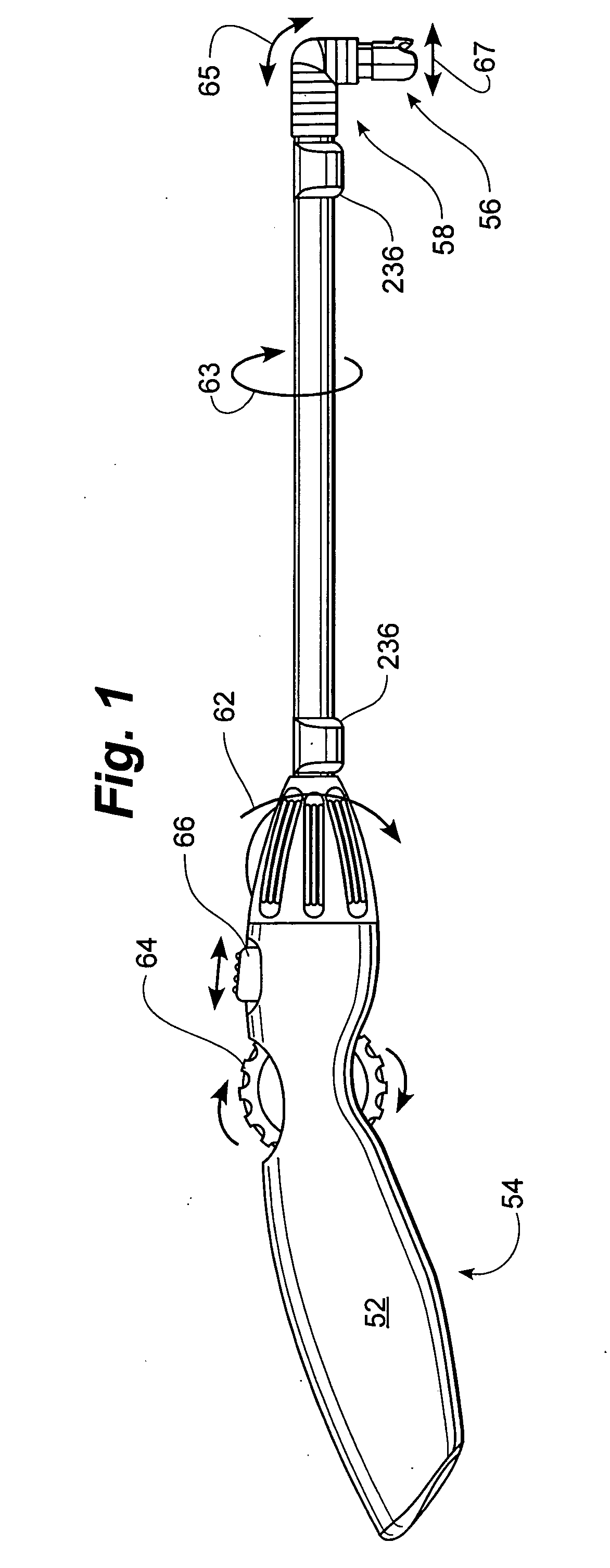
Rotatable lead introducer
Minimally invasive introducers and methods that can be used for rotationally securing devices within the human body. Introducers can include a distal element for releasably engaging a lead head controllable from a proximal control located outside of the body. An inner stem can extend between a proximal portion and a distal portion, and be pivotally and rotatably coupled to the distal lead engagement mechanism. An outer tube can be rotatably disposed over the inner stem and be flexibly coupled over the pivot to rotationally drive the distal element. A helical epicardial-myocardial lead electrode can be secured and oriented straight ahead and introduced through a port or small incision with the introducer in a straight configuration. The introducer can then be bent and rotated to screw the helical electrode into the heart.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Rotatable lead introducer
Minimally invasive introducers and methods that can be used for rotationally securing devices within the human body. Introducers can include a distal element for releasably engaging a lead head controllable from a proximal control located outside of the body. An inner stem can extend between a proximal portion and a distal portion, and be pivotally and rotatably coupled to the distal lead engagement mechanism. An outer tube can be rotatably disposed over the inner stem and be flexibly coupled over the pivot to rotationally drive the distal element. A helical epicardial-myocardial lead electrode can be secured and oriented straight ahead and introduced through a port or small incision with the introducer in a straight configuration. The introducer can then be bent and rotated to screw the helical electrode into the heart.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
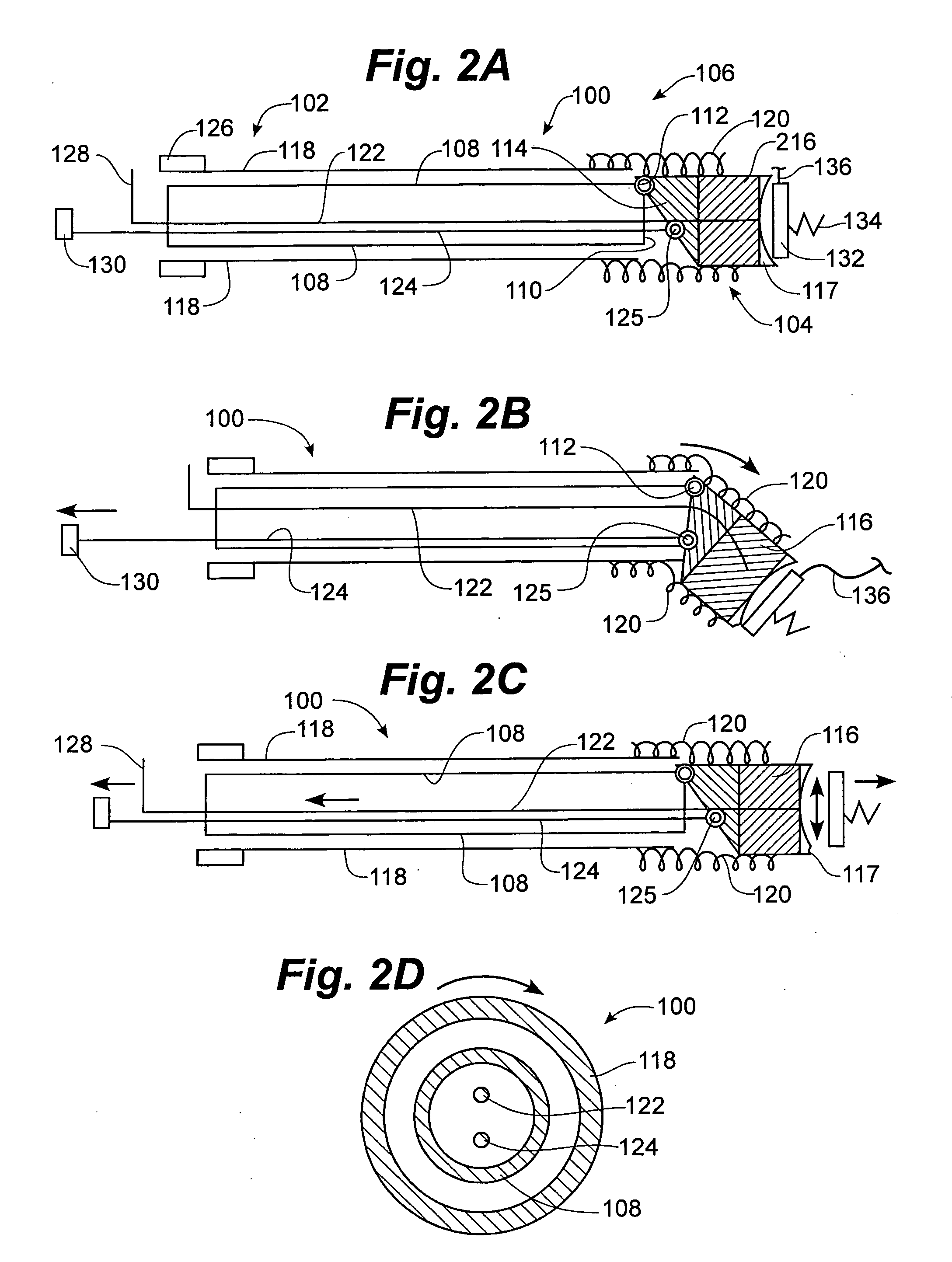
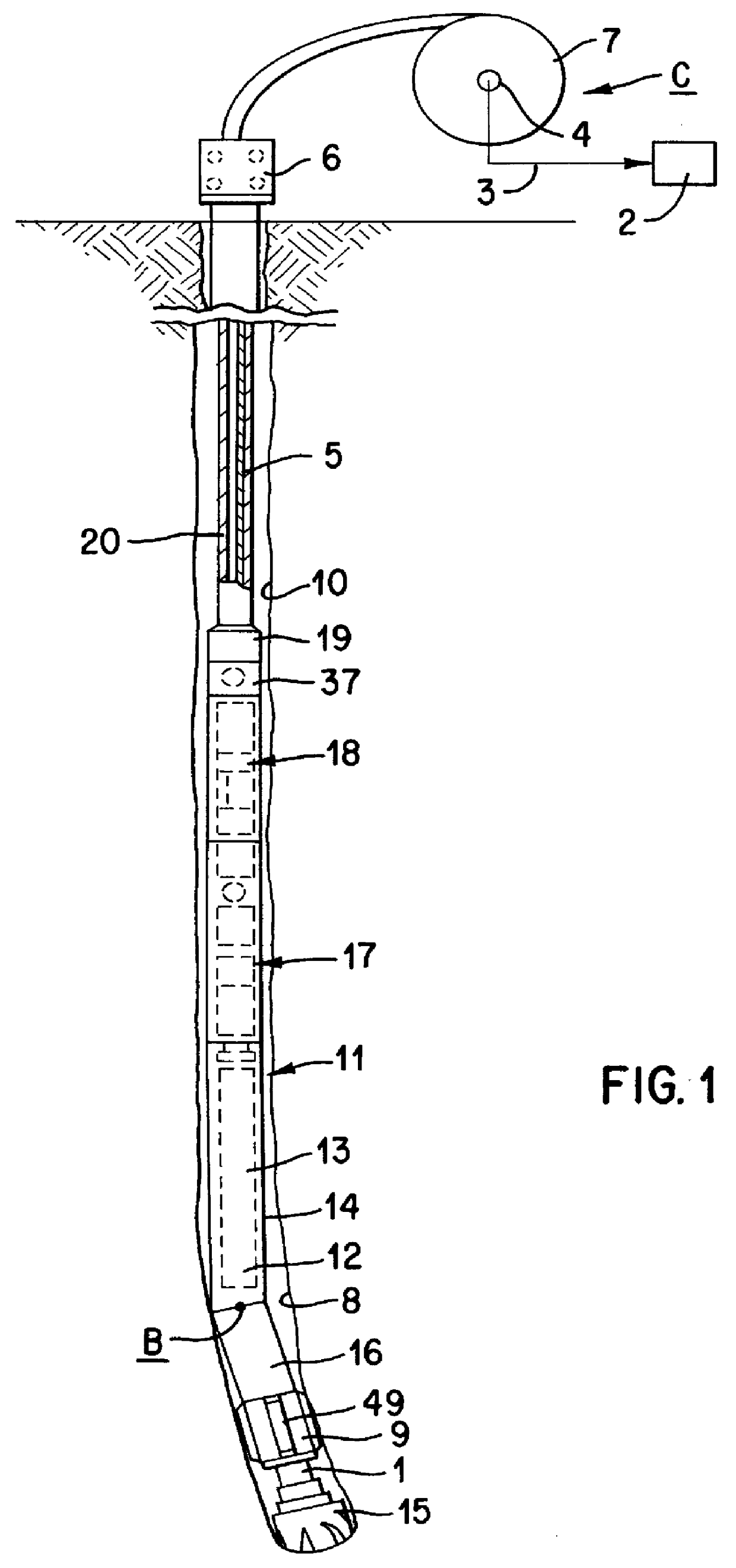
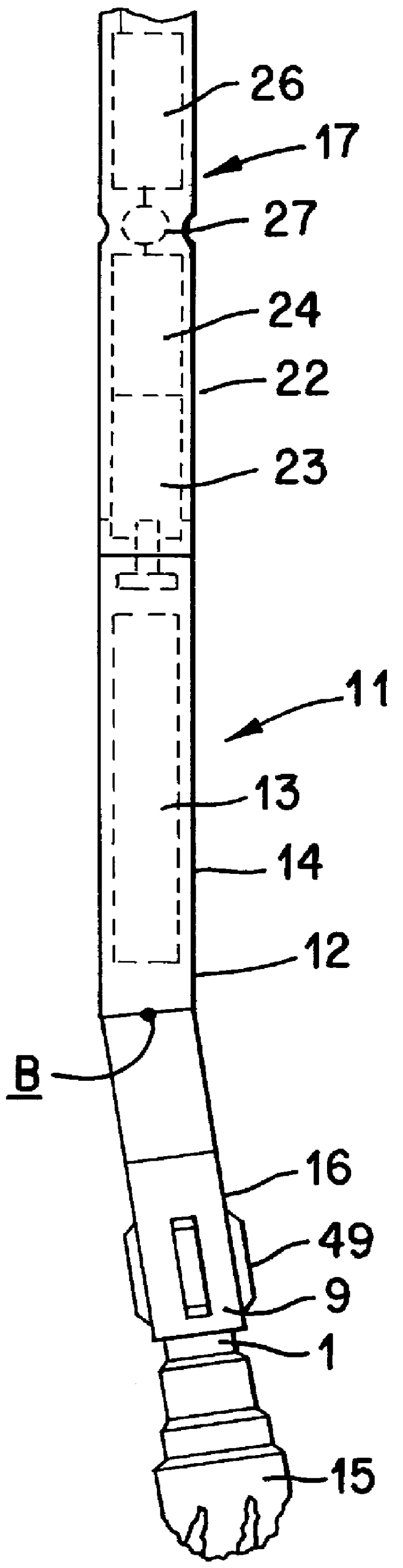
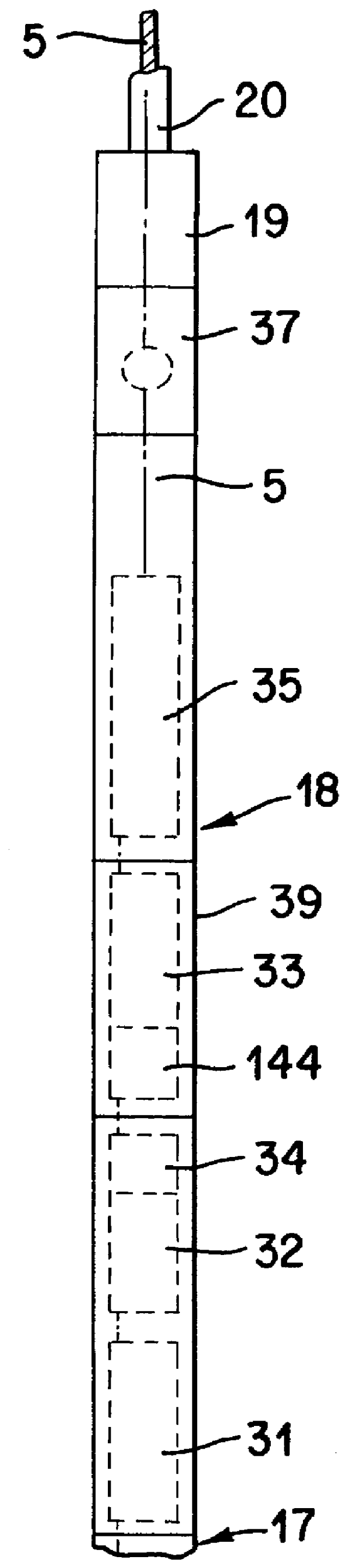
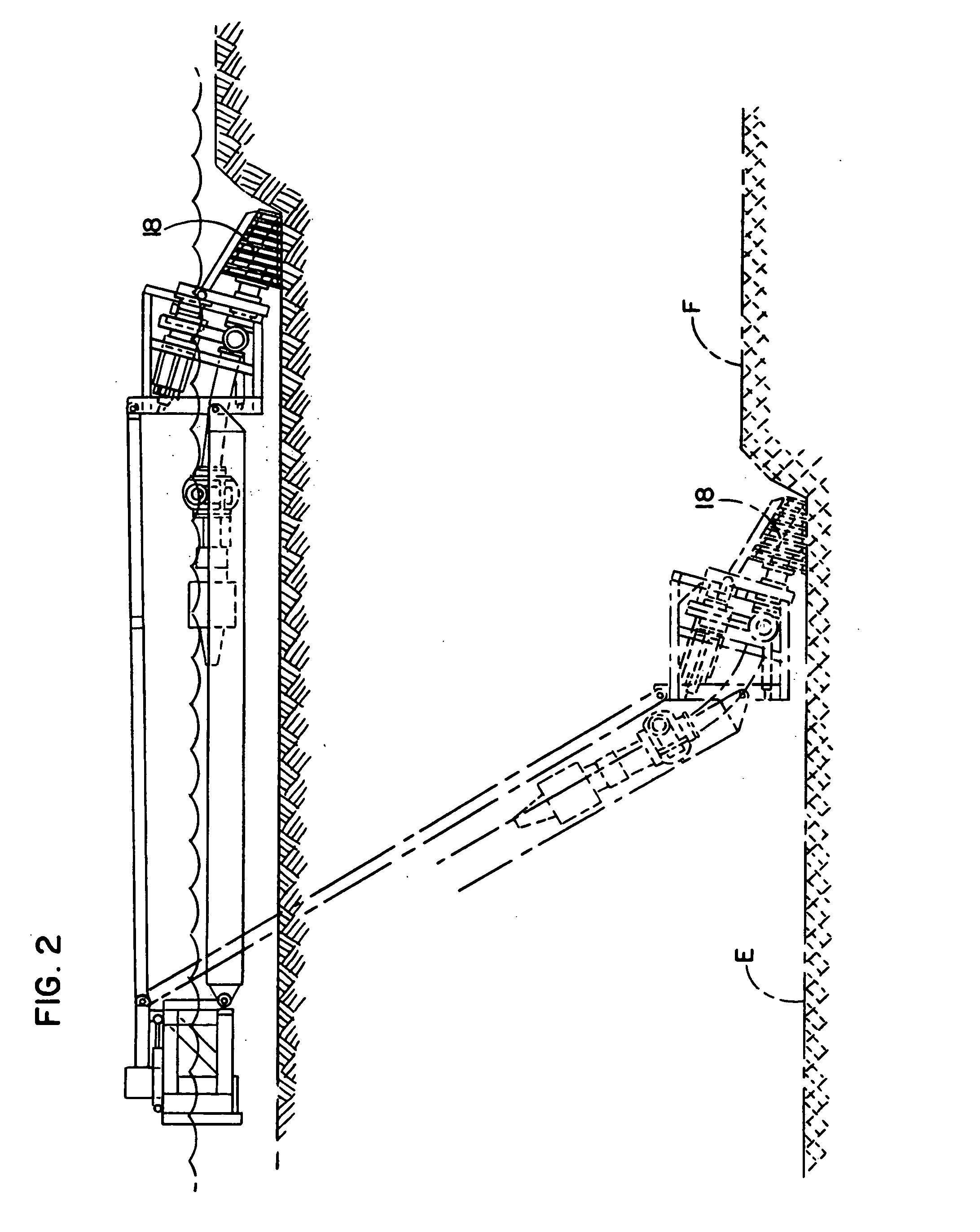
Apparatus and method for directional drilling using coiled tubing
A steerable directional drilling tool assembly includes a bent housing defining a bend angle and having a mud motor in its upper section and a drill bit below its lower section, an orienting tool rotatably coupled to such upper section and suspended on coiled tubing that extends upward to the surface, an electric motor in the orienting tool operable to rotate the bent housing in either hand direction to change or adjust the tool face angle of the bit, or continuously rotate the bent housing so that the bit drills straight-ahead, and an electric cable extending throughout the coiled tubing to furnish power from the surface to the electric motor and transmit electric signals to and from the surface. A logging tool can be included in the assembly for measuring characteristics of the formation, the borehole, and the tool assembly.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
Method of protecting the health and well-being of coal mine machine operators
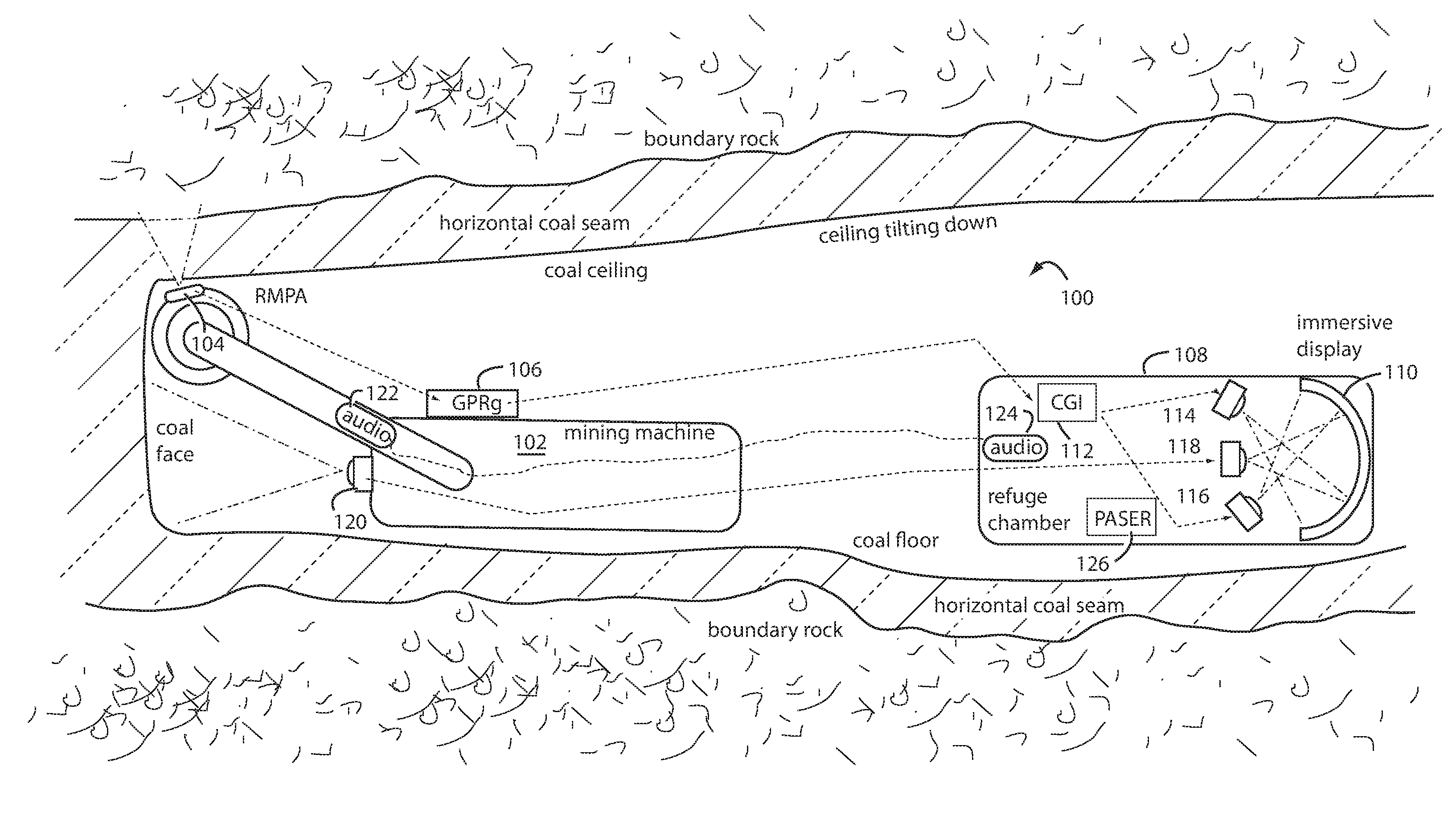
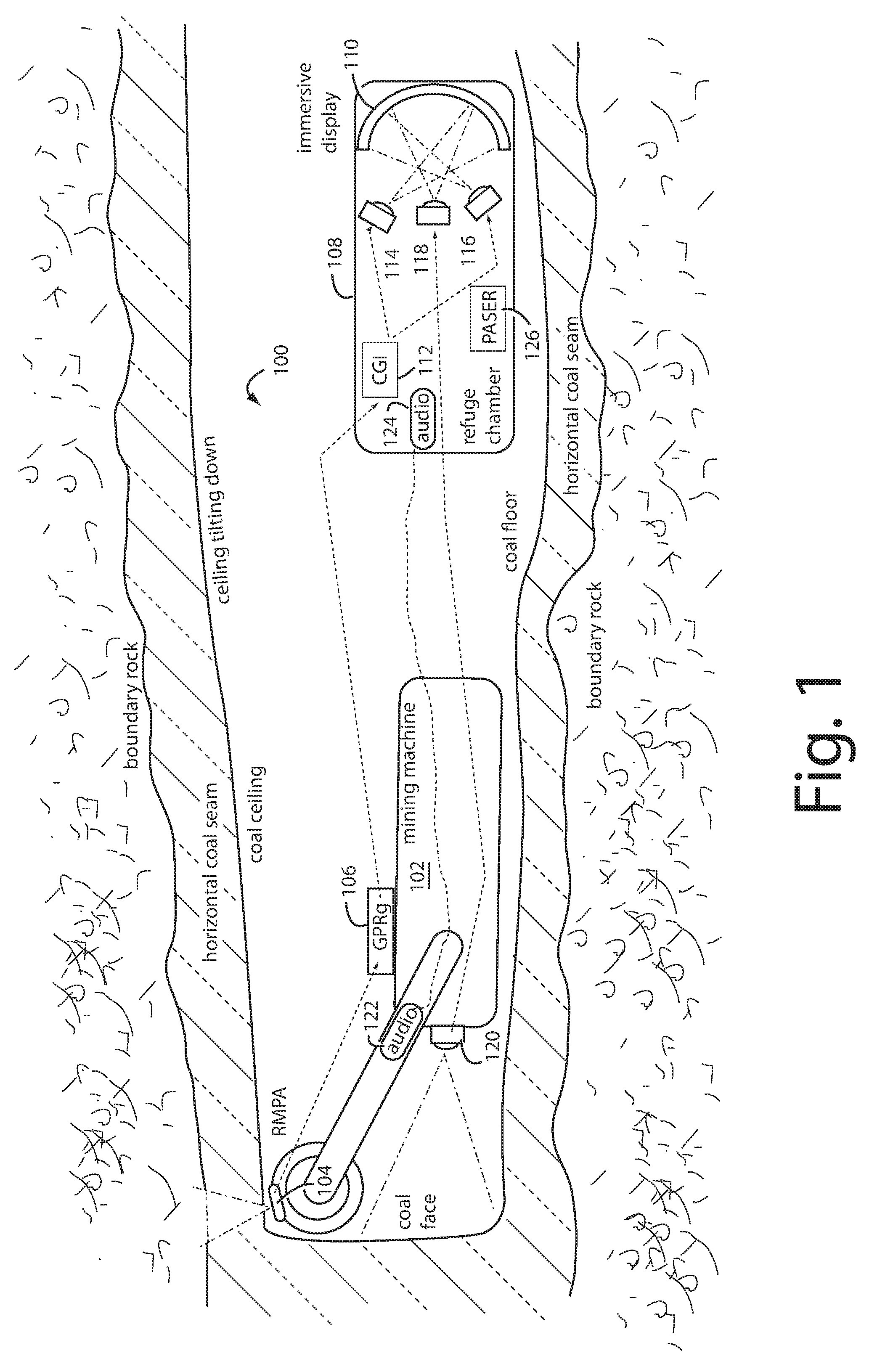
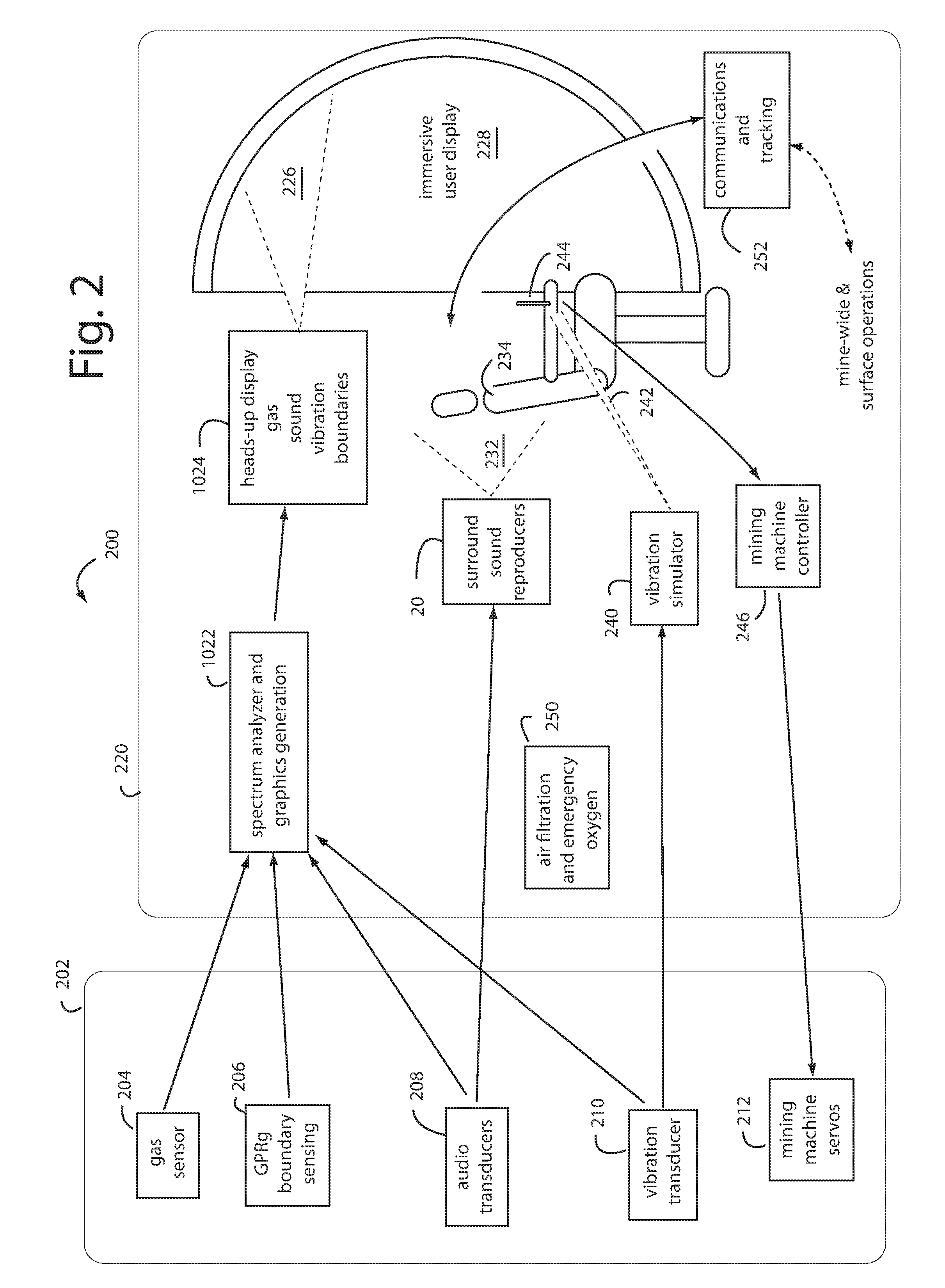
A method of operating coal mine machinery that protects and maintains machine operators' health and well-being removes the machine operators to a clean, low-noise environment inside a refuge chamber. Inside, are controls, cameras, audio, and informational displays needed to run continuous mining machines nearby and communicate mine-wide with other personnel. Cameras fitted to the mining machines provide straight-ahead views, ground penetrating radars fitted to the cutting drums measure the coal depths in the ceilings above, the floors below, and the coal face ahead. Guidance data is presented on informational displays, and the data from the ceilings and floors is used to drive computer graphics special effects to graphically represent the coal ceilings and coal floors overlaying boundary rock. Audio pickups on the mining machine allow the operator to hear and feel how the machine is functioning, just as operators have always employed their other senses.
Owner:STOLARCZYK LARRY G
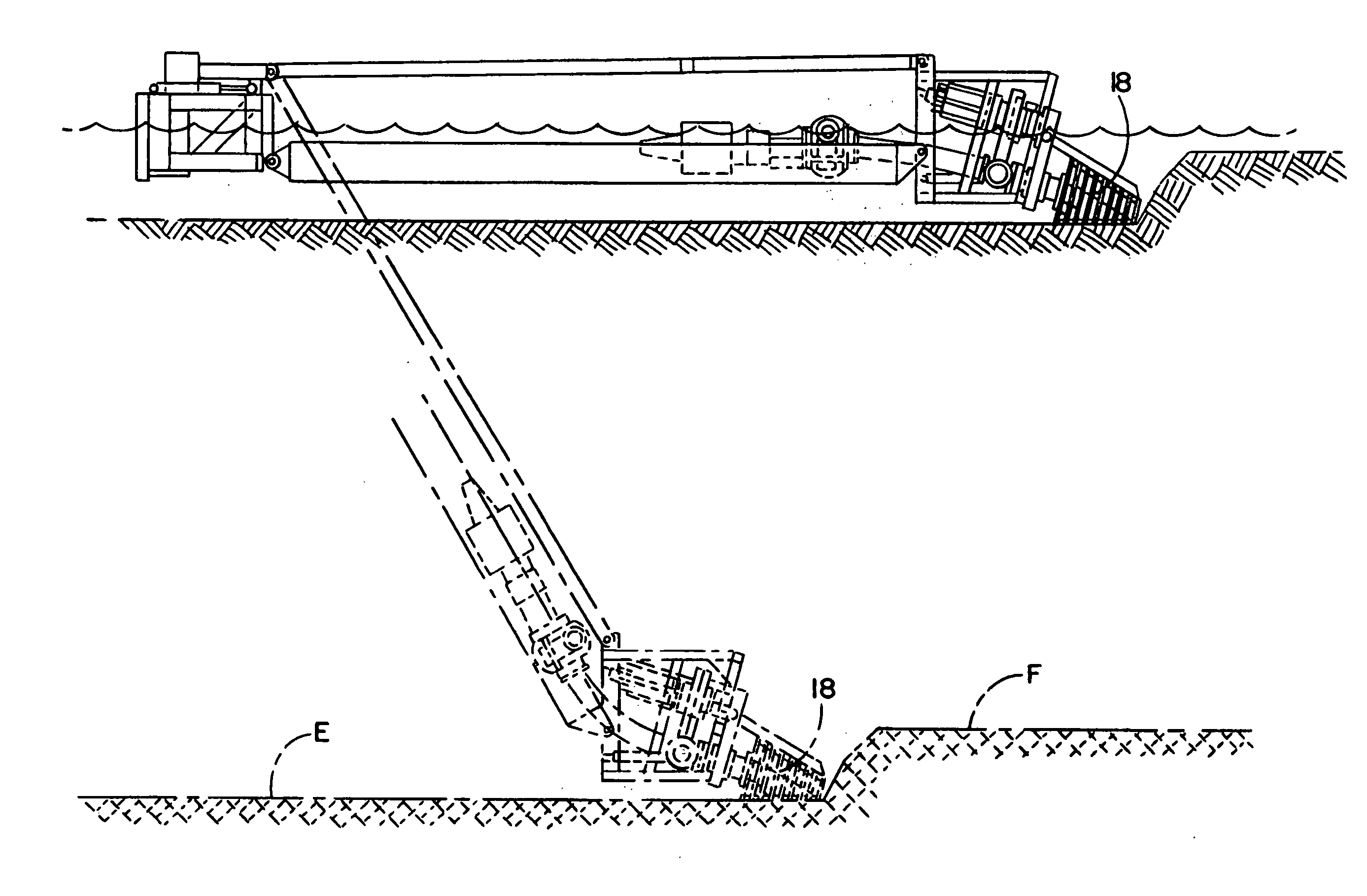
Method and apparatus for pumping with a dredge
InactiveUS20050268499A1Reduce turbidityGreat tractionSpecific fluid pumpsAgricultural machinesFlow transducerTurbidity
A system usable for dredging may include a suction bypass system for automatically maintaining a sufficiently high, liquid flow velocity. Preferably, a flow sensor monitors flow velocity and when the monitor flow decreases to an extent that plugging may occur, a liquid bypass valve is opened and an intake line valve is closed until the flow velocity increases whereupon the valves are returned to their original positions. An automatic level cut removes a relatively constant layer of material from a contoured bottom. The illustrated automatic level cut process comprises adjusting the force with which the suction head engages the bottom, moving the suction head in a direction opposite to the direction of the swing of the boom to keep the suction head pointing straight ahead, and maintaining the suction head to stay substantially level with the bottom even though the angle of the boom increases to the surface of the water body. A leveling device comprising a parallelogram linkage may be used to maintain the suction head substantially level with the bottom. A predetermined amount of load force may be applied by the head against the bottom. Herein, a winch and cable and the controller are operated to lift some of the head weight until the desired predetermined head force is applied to the bottom. A walking system moves the pipe intake for taking a sideways cut without the use of a spud pole, anchors and anchor lines. Large blade members or feet travels in an endless path with the feet entering the bottom while vertically disposed and remained disposed vertically while entering and leaving the bottom so as not to dig or stir the bottom that will cause large liquid turbidity. A low turbidity head cleaning system prevents the head from being plugged and debris or sticky material. Preferably, a rotatable cone-shaped head is provided with spaced rings and bars that define sized openings that limit the size of debris entering into the intake. A fixed comb removes material stuck on the rotating head. A shroud has an open bottom side thereby preventing bottom material from escaping and increasing with turbidity. A suction head articulation system keeps the head pointed in the forward direction of dredge advancement to create a smooth finish grade.
Owner:EDDY PUMP CORP
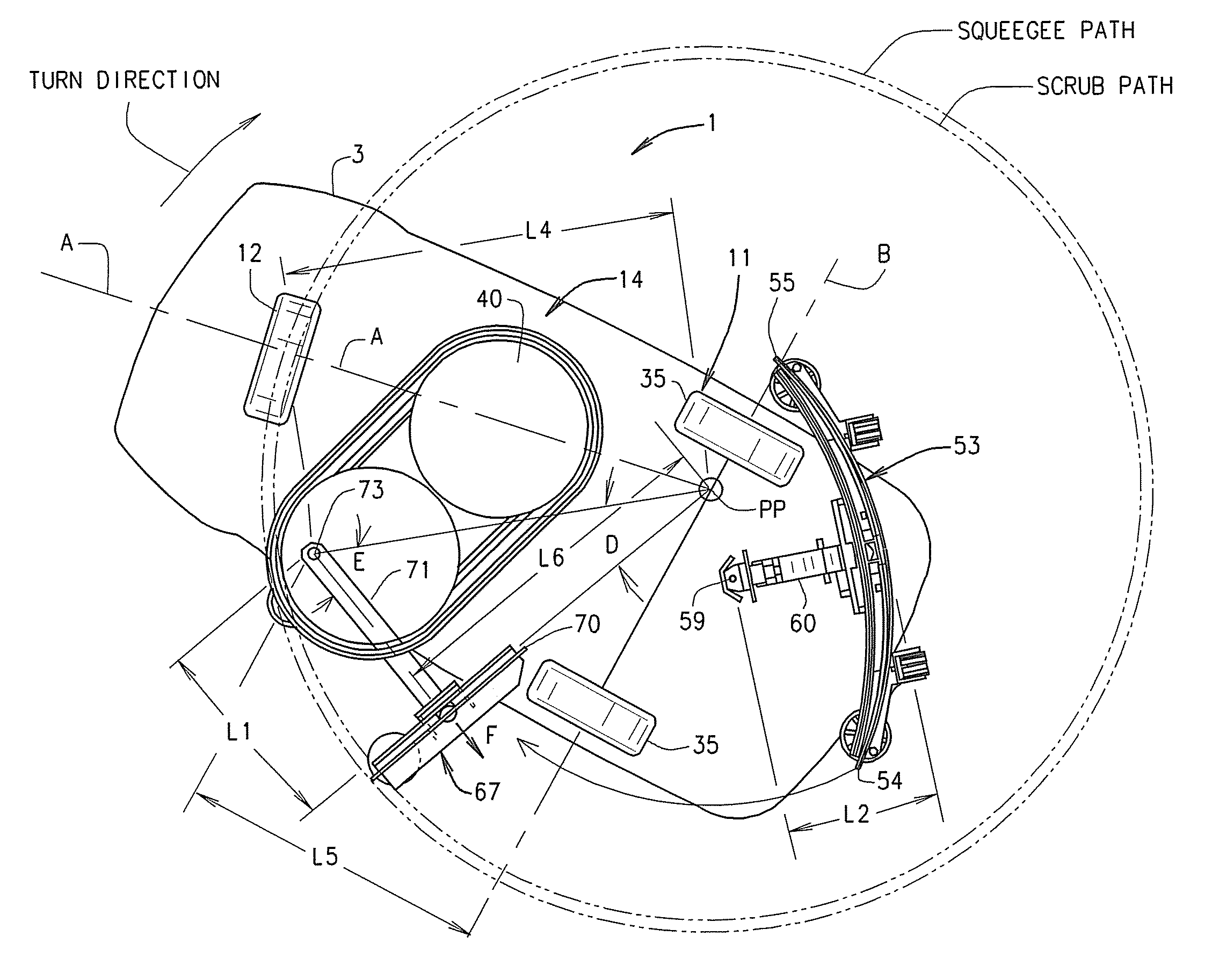
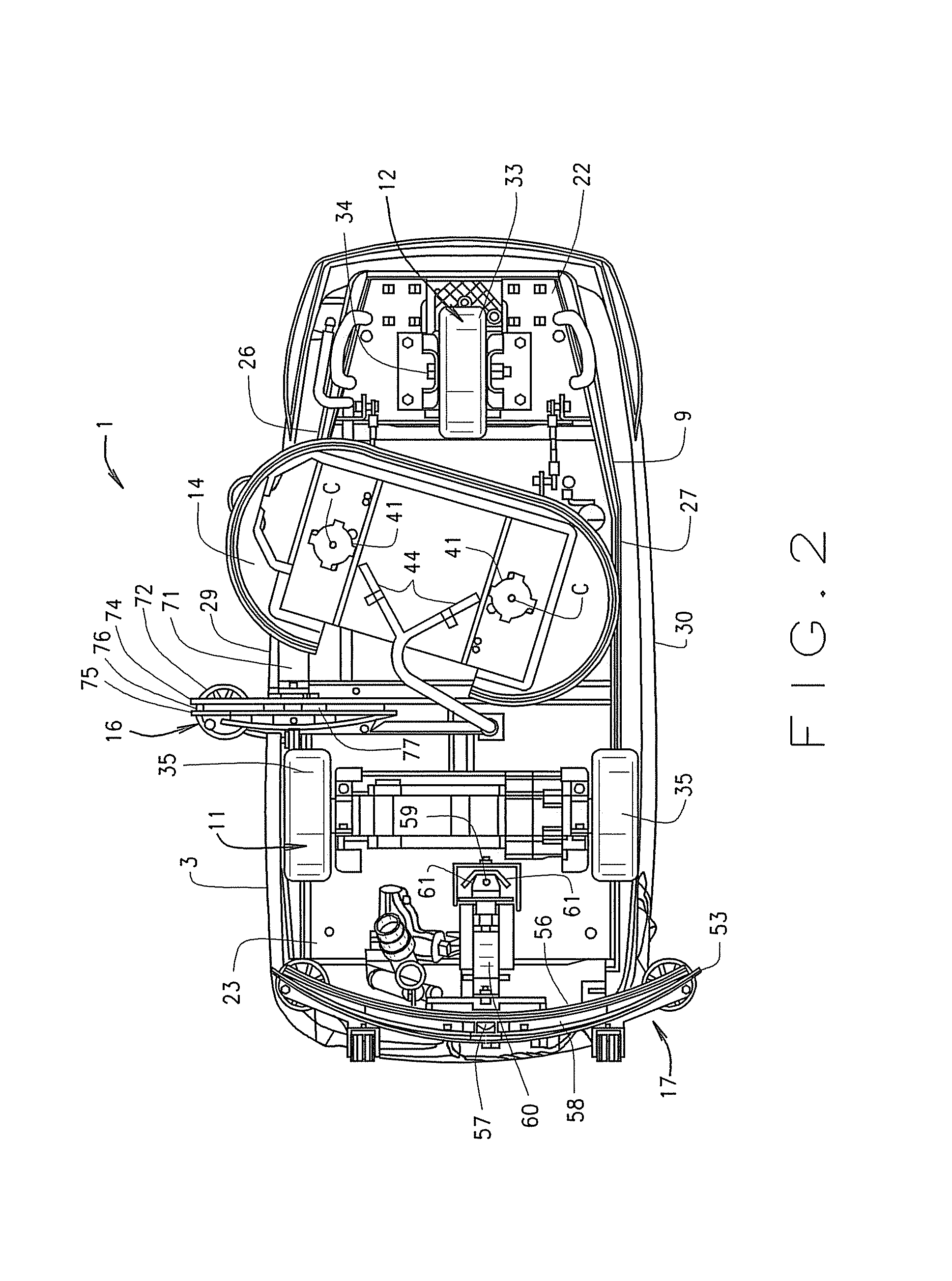
Floor cleaning machine
A floor cleaning machine is provided with at least two movable squeegees to provide coverage of the liquid applied to the floor in a path with the squeegees extending beyond the outer perimeter sides of the liquid path both during straight ahead movement and during turning maneuvers. The squeegee assemblies are carried by a chassis. A floor scrubbing device is provided to apply liquid to the floor and to mix dirt on the floor with the applied liquid. A liquid pickup device is also provided to remove the applied liquid from the floor at a position adjacent to each of the squeegee assemblies.
Owner:NILFISK
Driving assist device
InactiveUS20120277957A1Accurate measurementDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsEngineeringStraight ahead
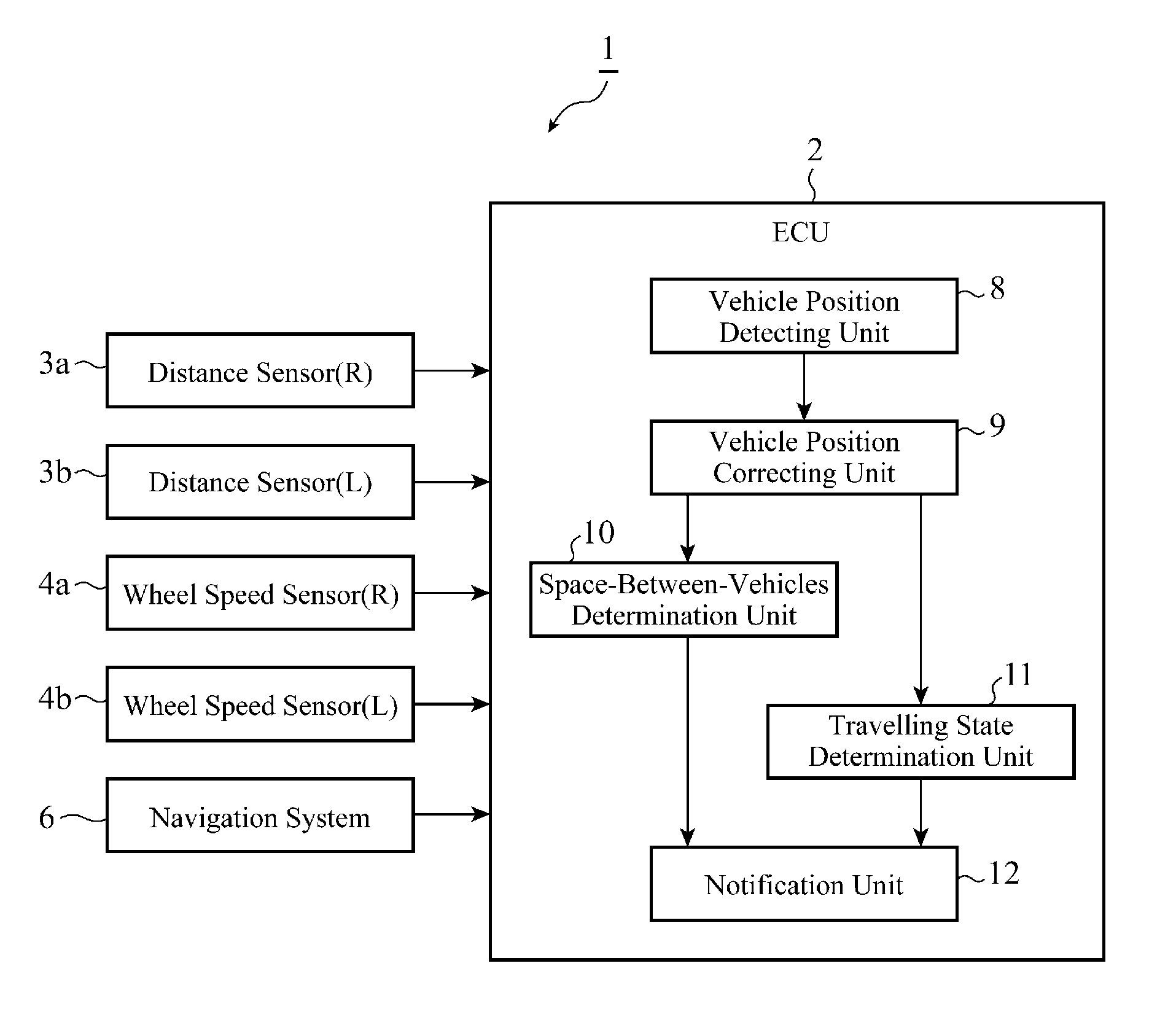
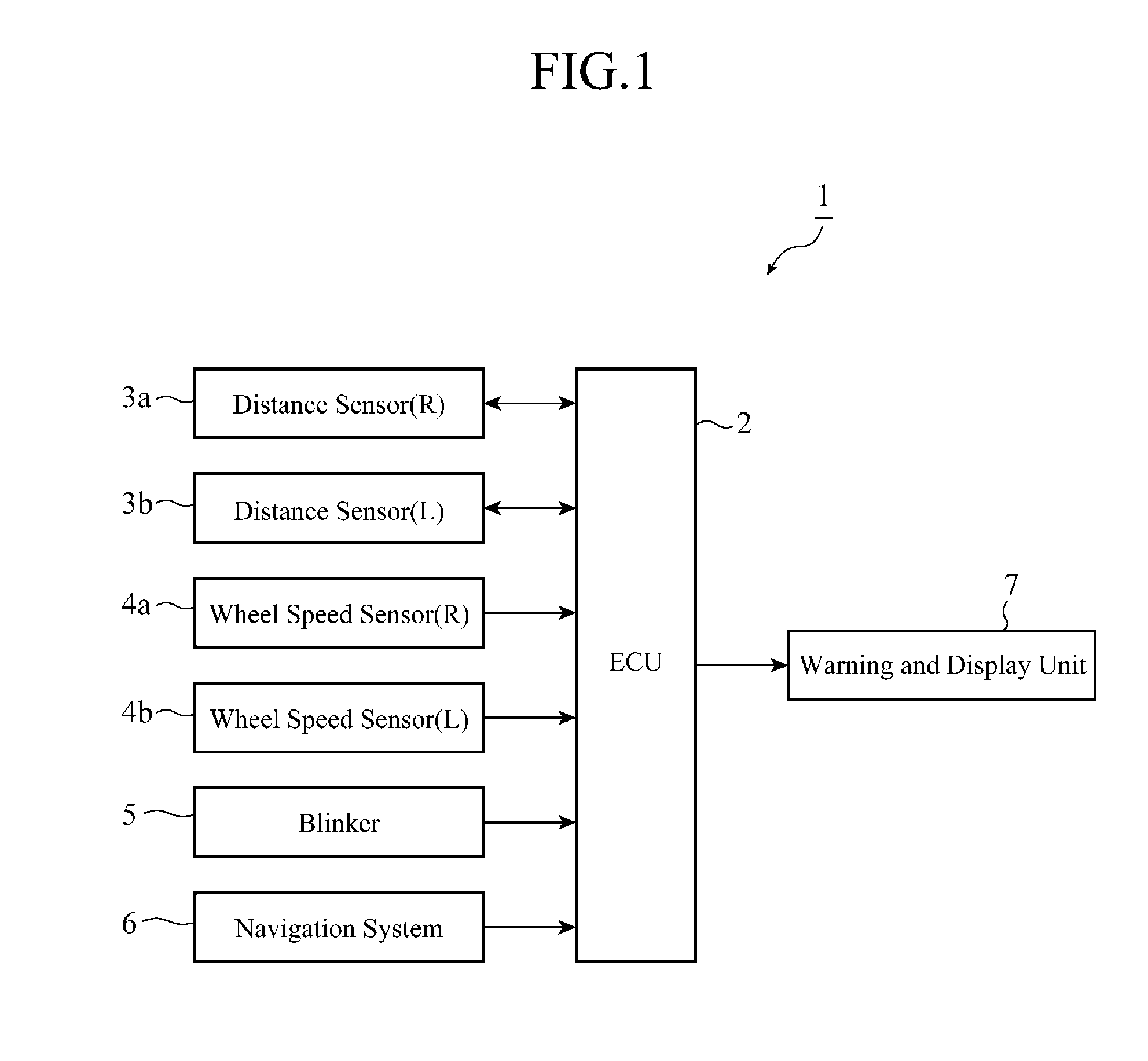
A driving assist device detects the position of a vehicle 13 in a direction of the width of a road by using both distance data on both right and left sides of the vehicle and road width data on the width of the road, specifies distance data having a time-varying change equal to or larger than a predetermined threshold from among the distance data showing the vehicle position detected to correct the vehicle position in such a way that the vehicle position is shown by the distance data from which the distance data specified are removed when the travelling path of the vehicle 13 shows a straight ahead movement, determines the travelling state of the vehicle 13 from a time-varying change of the vehicle position corrected, and notifies a content according to the travelling state determined.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Driving support apparatus
ActiveUS8482431B2Troublesome feelingArrangements for variable traffic instructionsDetection of traffic movementDriver/operatorBody size
When an own vehicle waits to turn left or right, a vehicle data processing unit processes information of an oncoming vehicle based on data analyzed by data analyzing units. A support processing unit sets a blind angle rank according to a difficulty degree of recognizing a following vehicle due to the blind angle of a lead vehicle from the relationship in the vehicle body size between the lead and following vehicles based on the oncoming vehicle information, and sets the highest blind angle rank value as an oncoming straight-ahead vehicle rank flag. It also sets an evaluation rank according to a risk degree when the own vehicle turns left or right, based on the oncoming straight-ahead vehicle rank flag and an oncoming vehicle rank flag set according to the size of an oncoming vehicle waiting to turn left or right, and informs the driver of driving support information according to the evaluation rank.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Vehicle transmission apparatus having a valve for controlling cornering behavior
InactiveUS6354392B1Improve behaviorEasy to set upGearing controlMotor depositionHydraulic motorMotor drive
Owner:POCLAIN HYDRAULICS IND
Floor cleaning machine
A floor cleaning machine is provided with at least two movable squeegees to provide coverage of the liquid applied to the floor in a path with the squeegees extending beyond the outer perimeter sides of the liquid path both during straight ahead movement and during turning maneuvers. The squeegee assemblies are carried by a chassis. A floor scrubbing device is provided to apply liquid to the floor and to mix dirt on the floor with the applied liquid. A liquid pickup device is also provided to remove the applied liquid from the floor at a position adjacent to each of the squeegee assemblies.
Owner:NILFISK
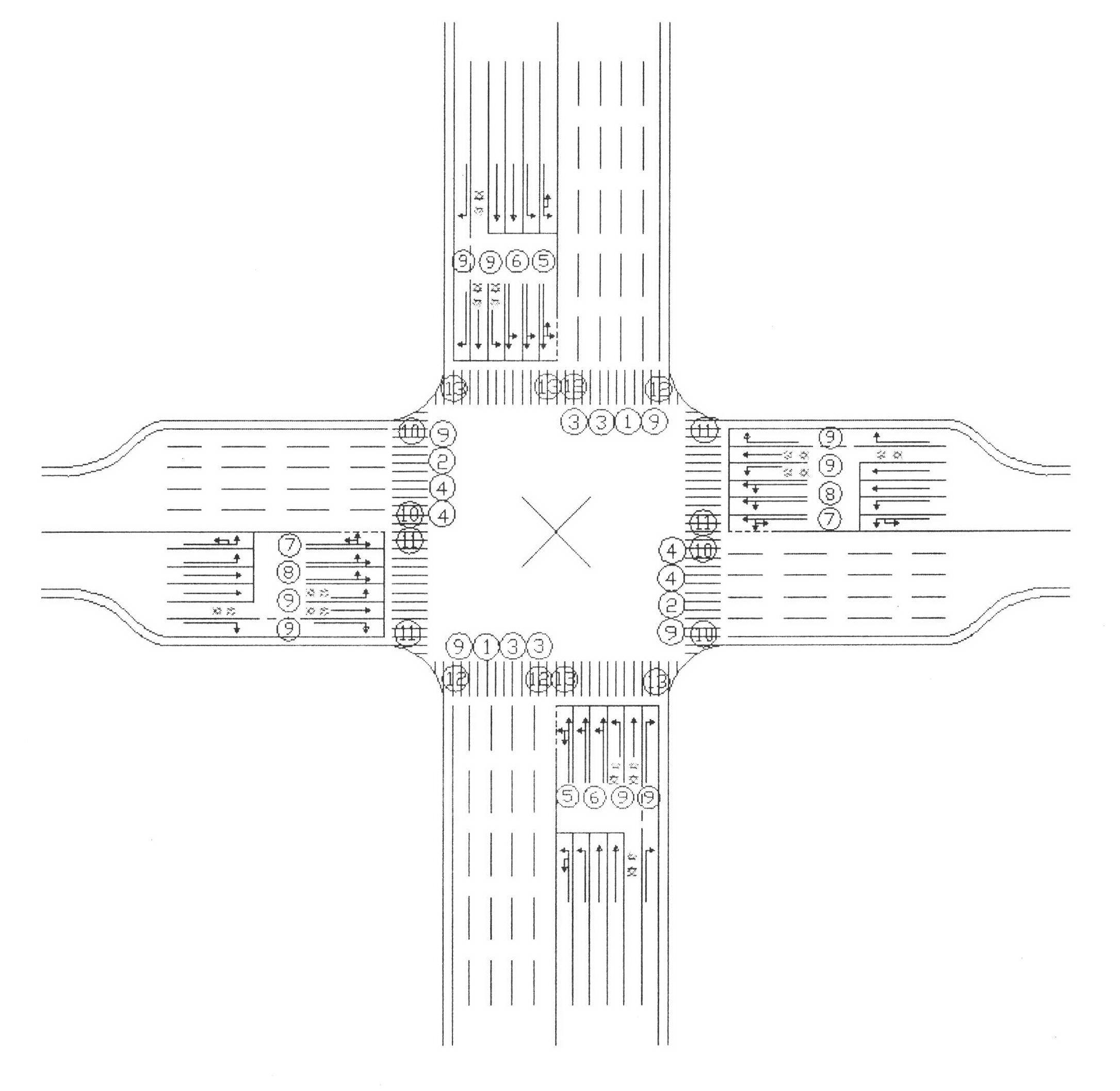
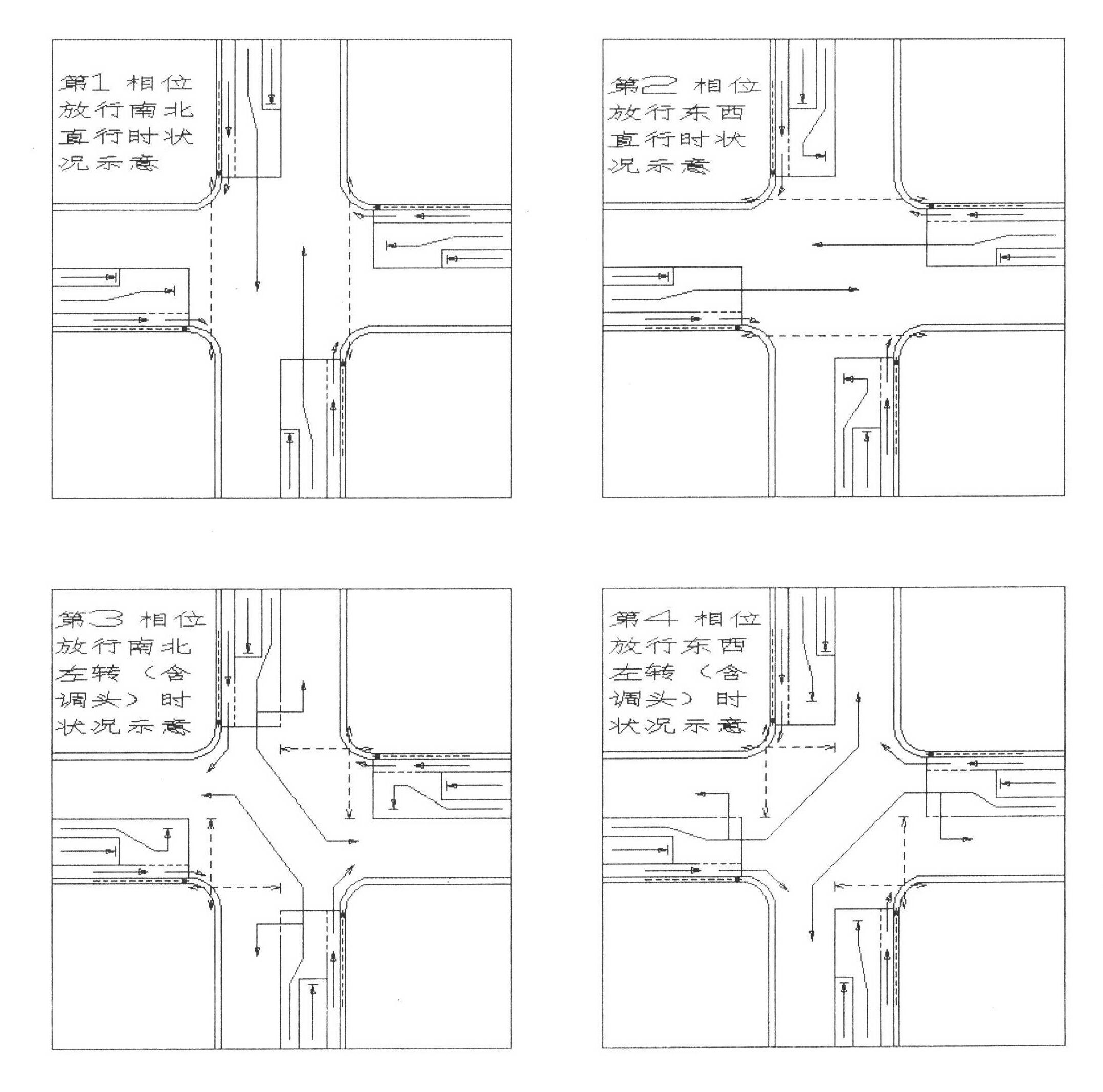
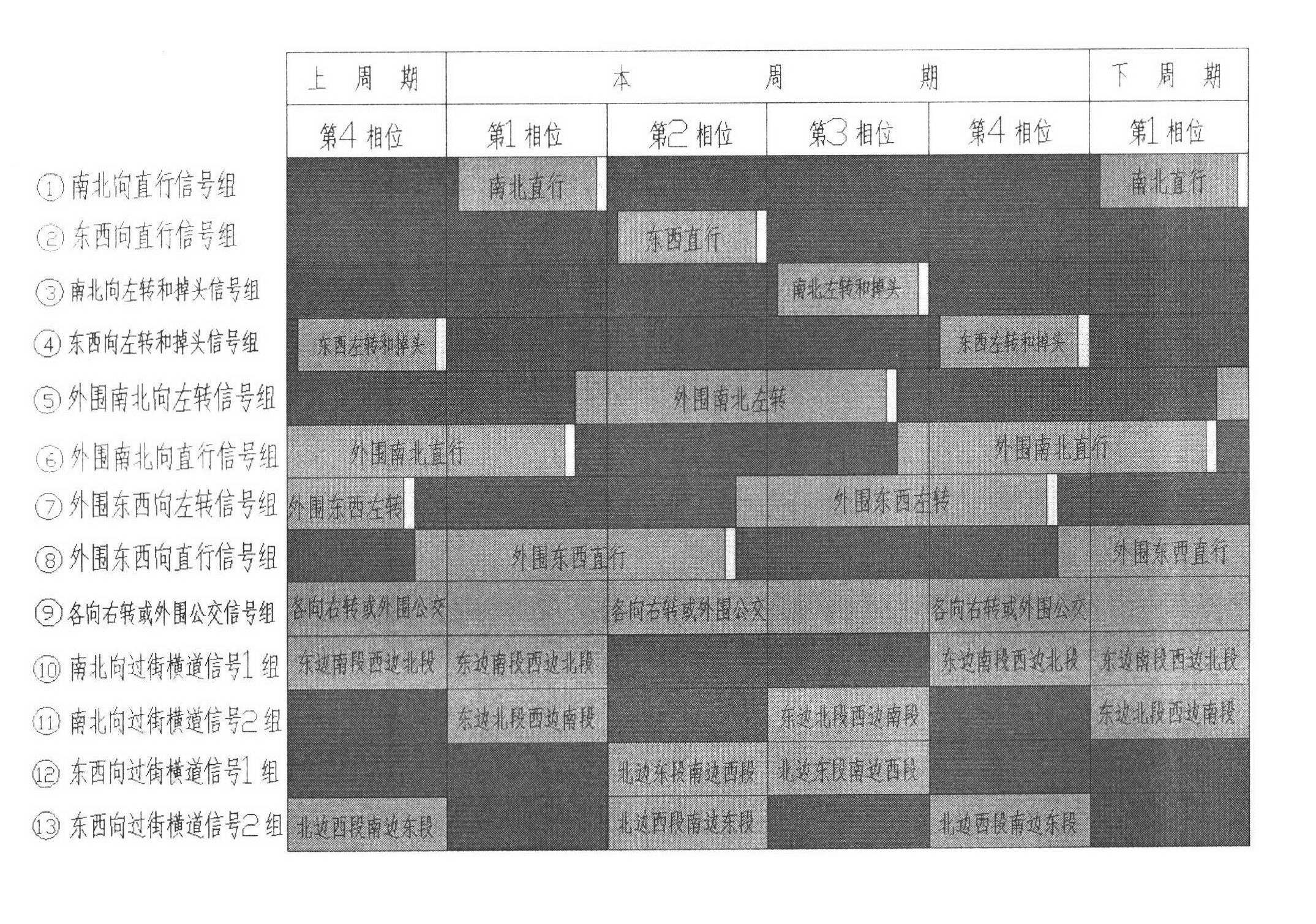
Lane setting at road intersection and corresponding traffic light control method
ActiveCN102277804AImprove traffic capacityFlexible useControlling traffic signalsRoadwaysHorizontal axisEngineering
A lane setting at a road intersection and a corresponding traffic light control method. It does not distinguish between primary and secondary roads, so that the number of entrance and exit lanes of each main phase is kept equal; the entrance lanes are divided into three parts: "entrance guide lane", "peripheral guide lane" and "bus and right-turn lane"; according to the direction of travel Arrange the lanes, light groups, signal groups and phases symmetrically on the horizontal axis of the horizontal axis; at the intersection, run the main phase of A going straight——B going straight——A turning left (including U-turn)——B turning left (including U-turn); The "peripheral traffic lights" alternately operate the two phases of straight-going vehicles moving forward and left-turning (including U-turn) vehicles moving forward, and an evergreen phase and "electronic police" for directing right-turning vehicles and buses to pass; according to the number of left-turning vehicles Decide whether to control the clearance of pedestrian crossings in units of full or half-way. This method can make the number of lanes passing by each phase of the intersection reach the maximum on the basis of equilibrium, and is conducive to the priority of public transportation and the convenience of pedestrians.
Owner:胡又宏 +2
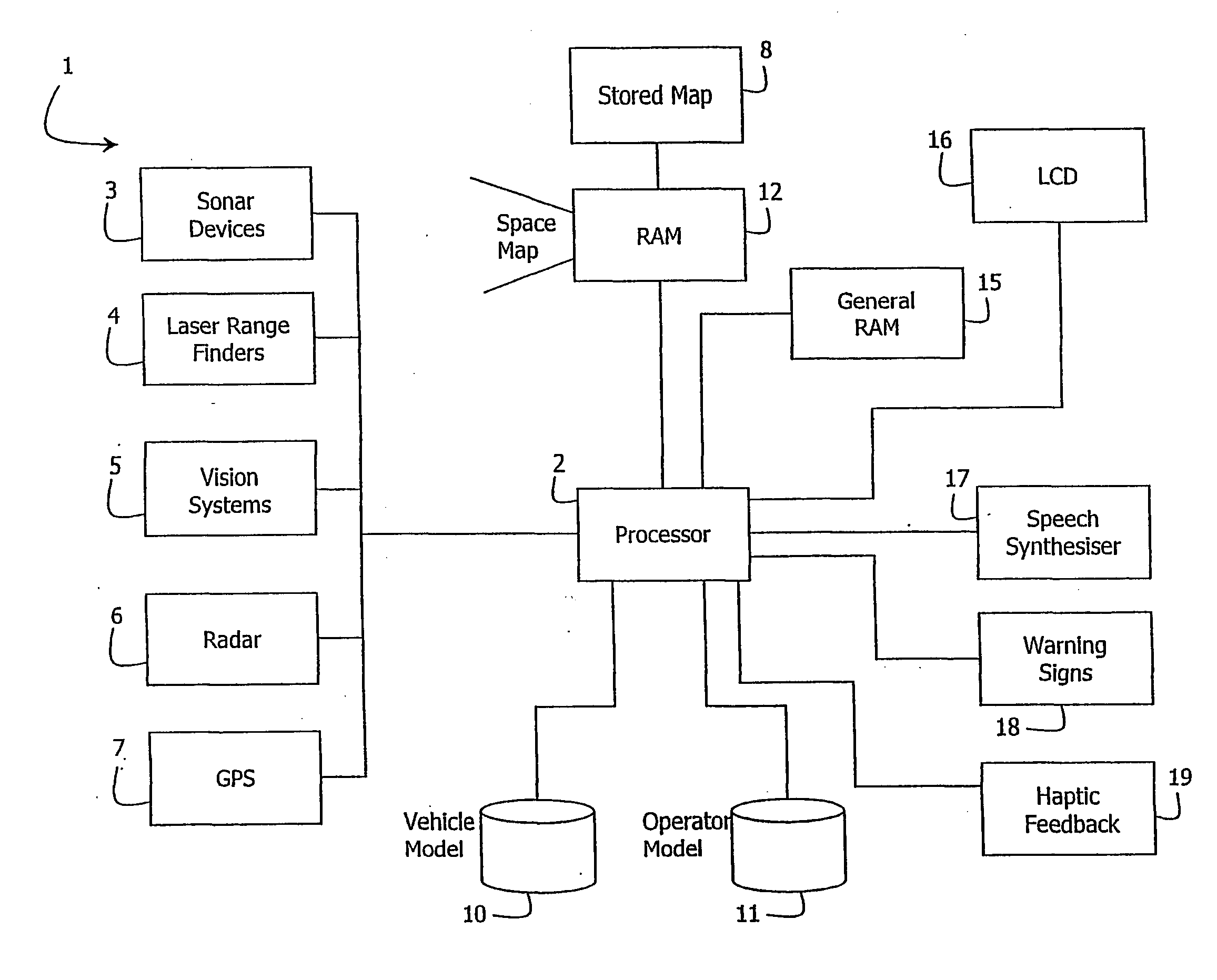
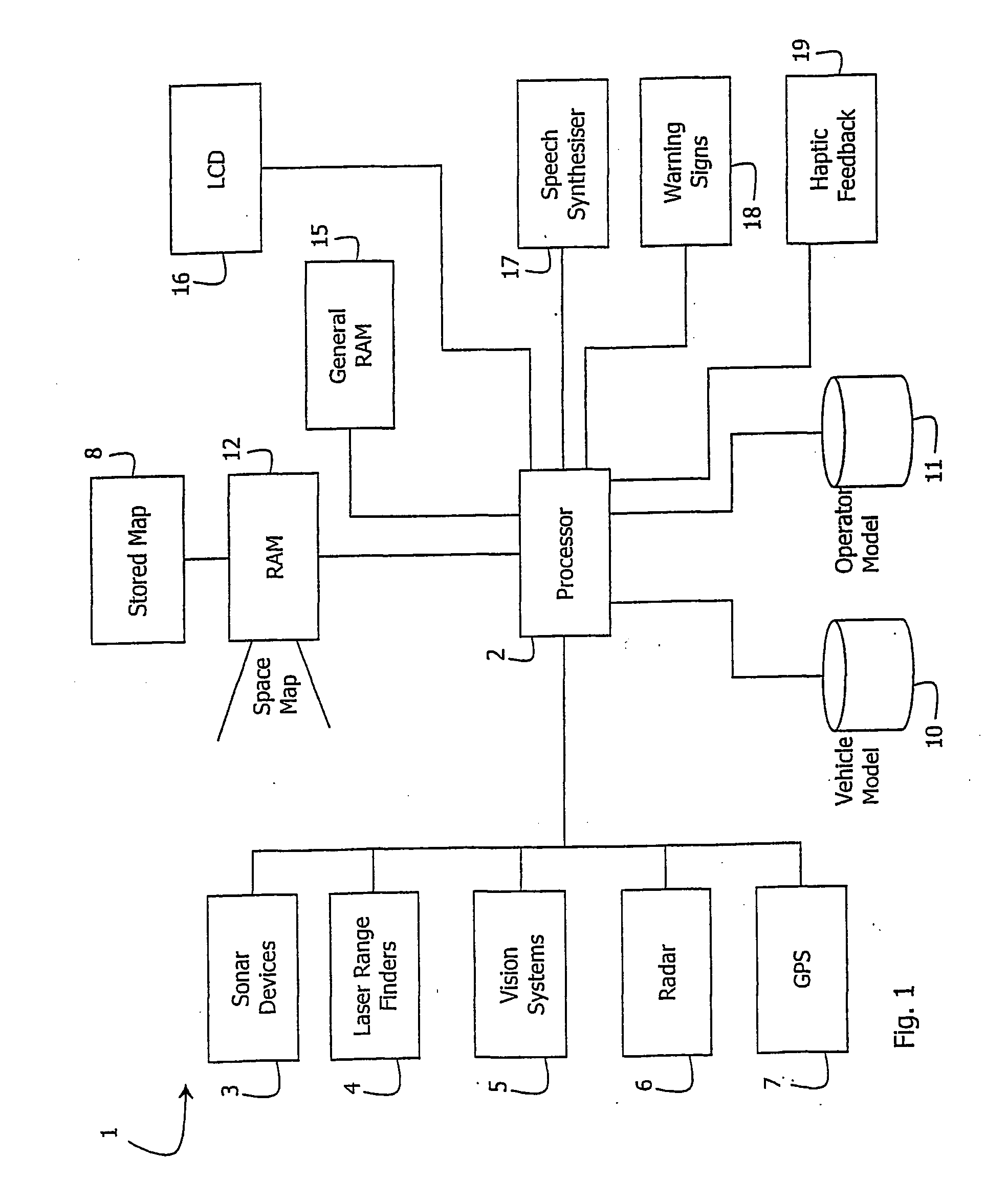
Method and system for guiding a vehicle
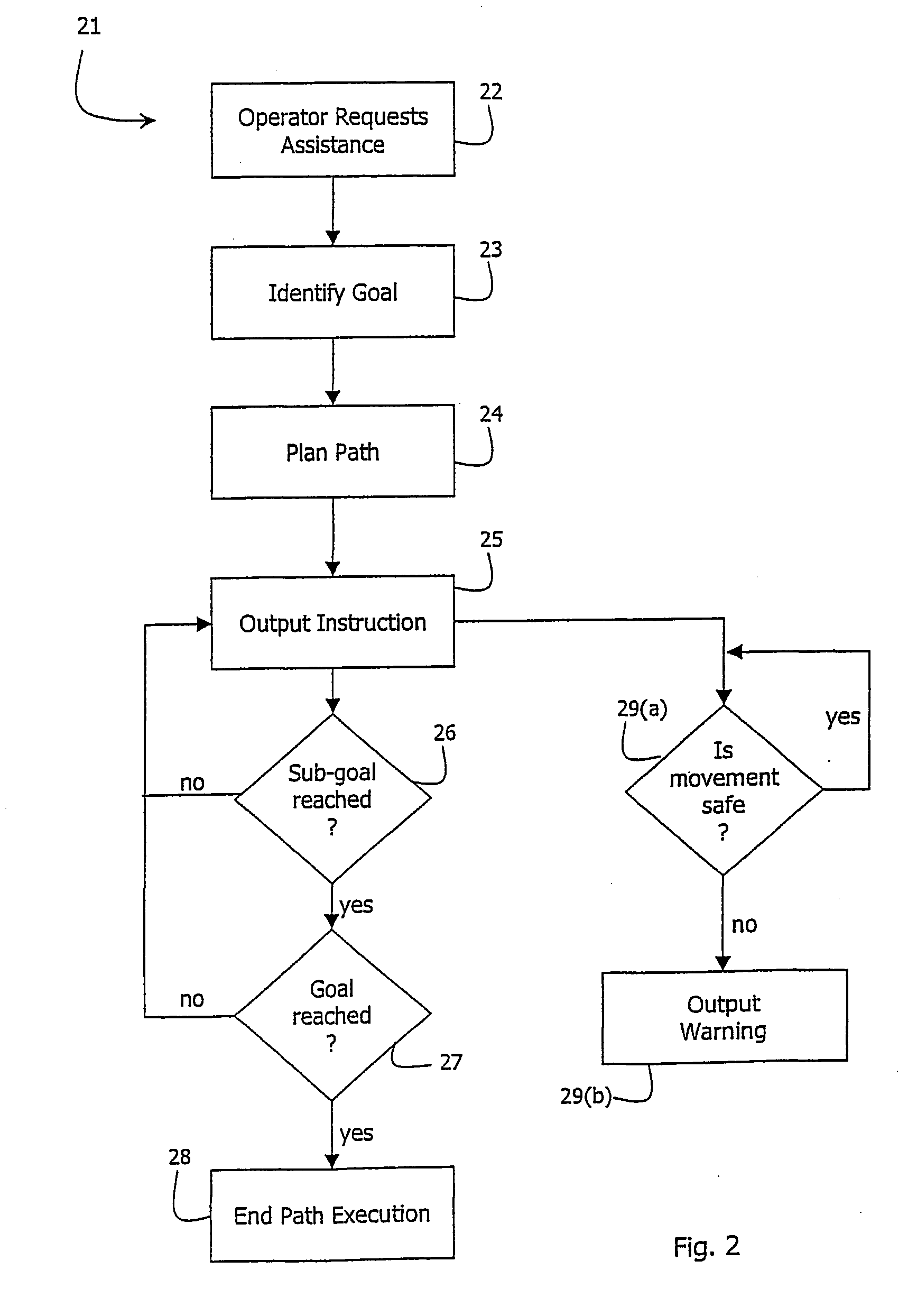
InactiveUS20040064249A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsEngineeringSingle vehicle
Movement of a vehicle such as a boat (30) is guided by dynamically monitoring parameters and generating instructions for the operator. The instructions are at a level to attain a number of sub-goals to reach a goal position (33) from a current position (32). Each sub-goal is attained in a single vehicle manoeuvre such as straight-ahead or rotation, each manoeuvre being instructable to the operator. The instructions are generated using a space model (12) of the space around the vehicle, an operator model (11) of operator vehicle control characteristics, and a vehicle model (12) of vehicle movement characteristics.
Owner:CAE HEALTHCARE CANADA
Steering system for articulated vehicles
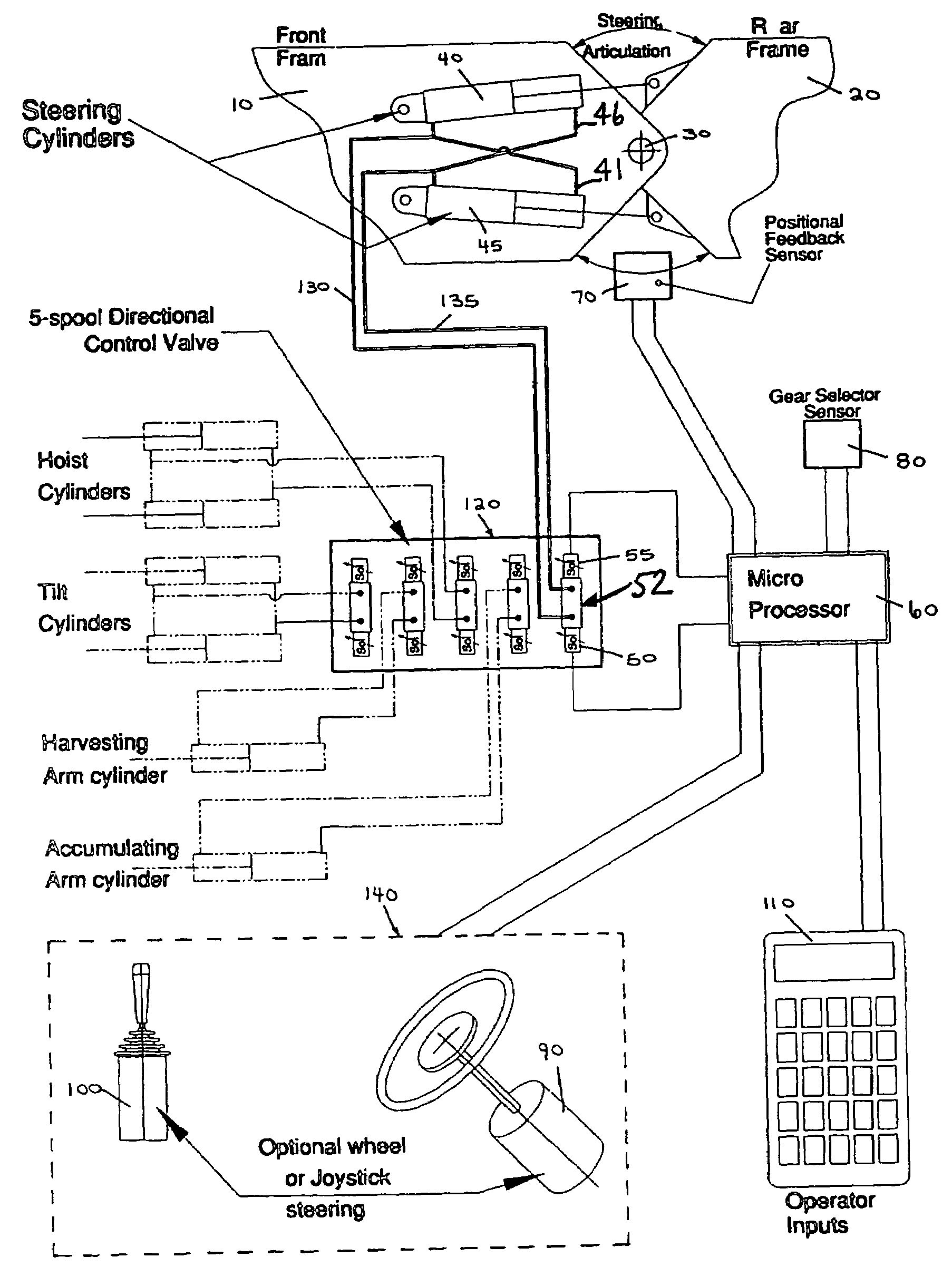
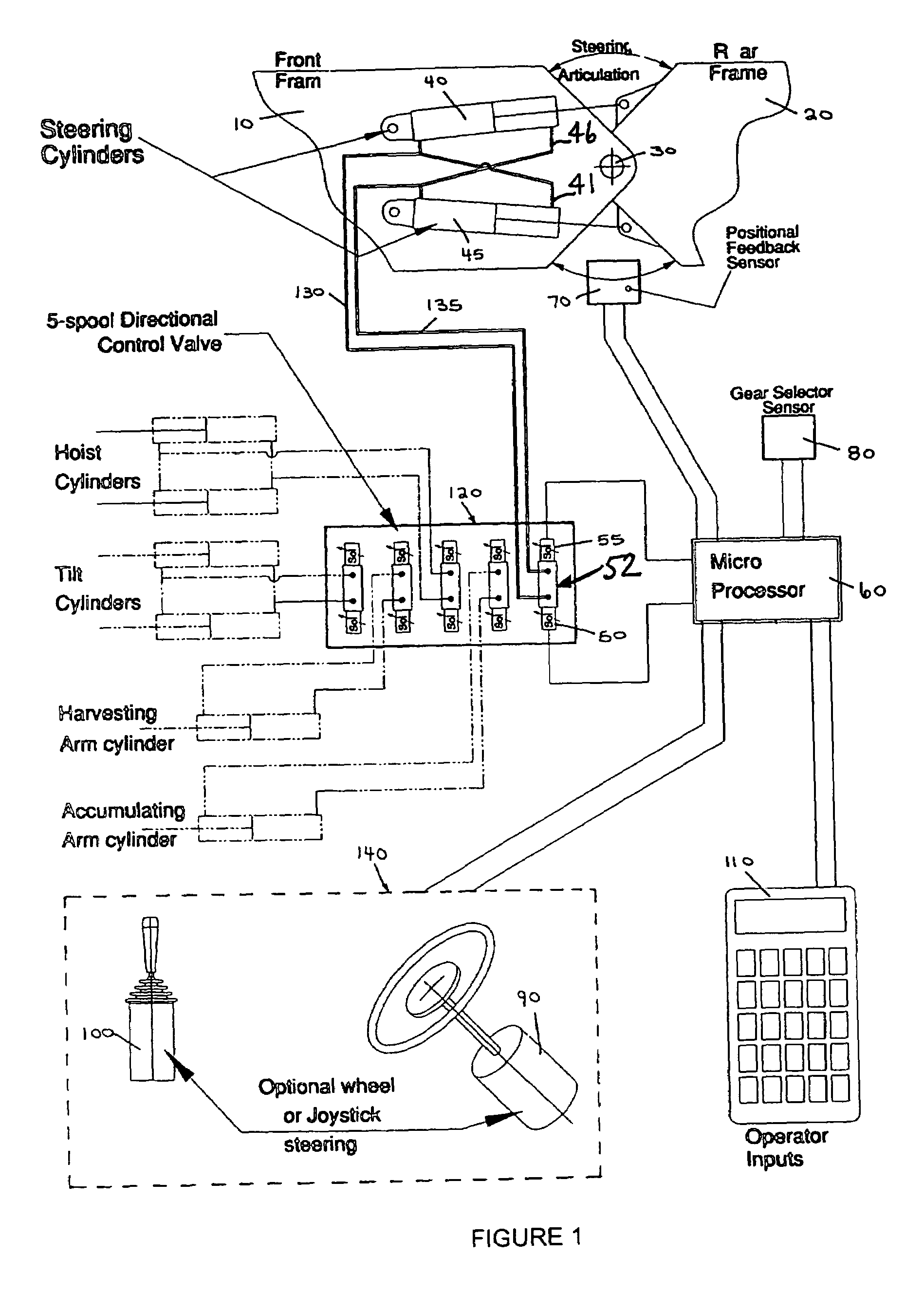
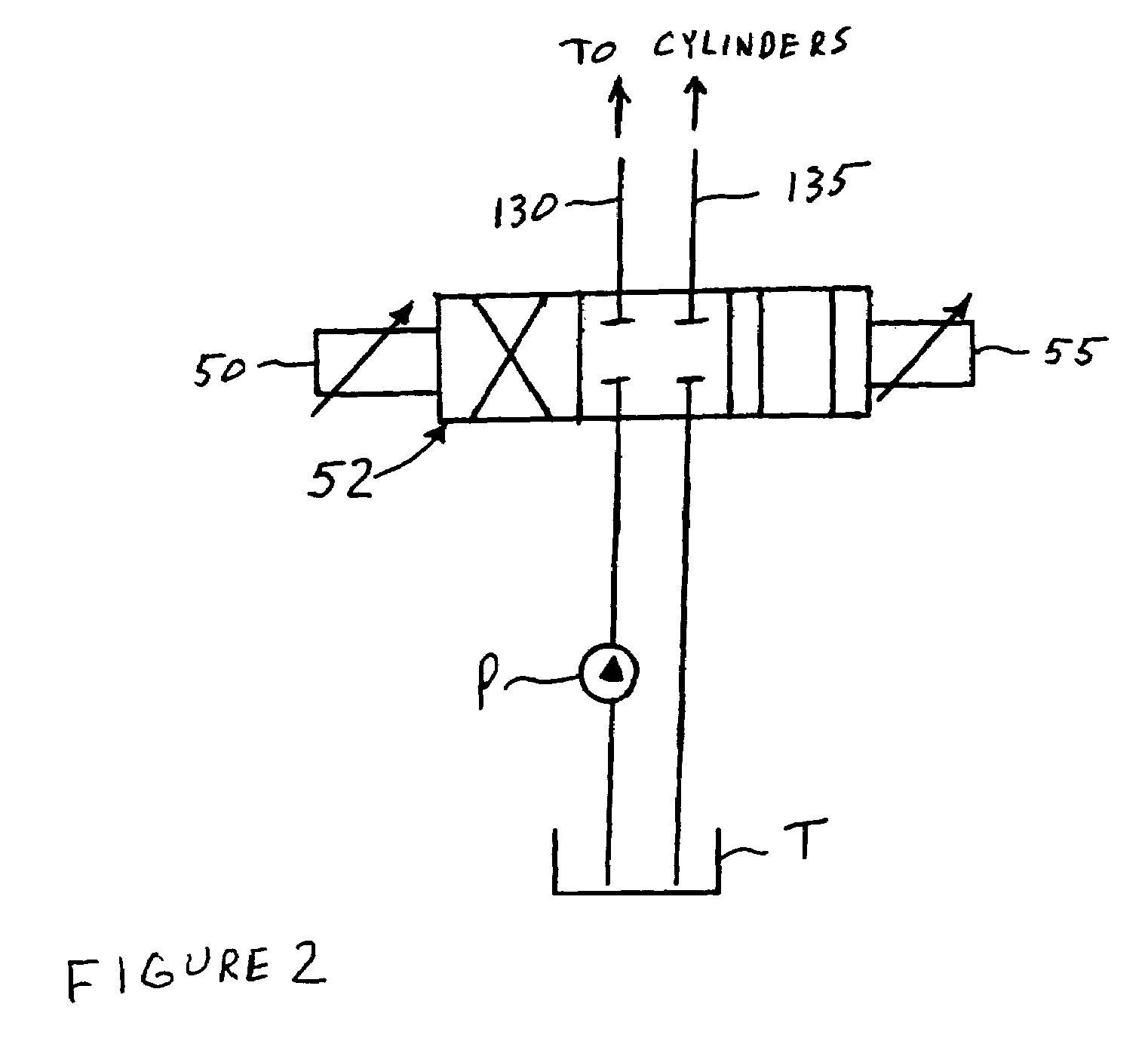
InactiveUS7412315B2Avoid contactSmoother steering controlDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlSteering wheelJoystick
A steering system for an articulated vehicle has a microprocessor connected to a proportional solenoid valve which controls the direction, amount and rate of flow of hydraulic fluid to and from hydraulic articulation cylinders, which provide articulation between the frames of the articulated vehicle. A positional feedback sensor measures the angle of articulation between the frames and communicates the angle of articulation to the processor. A gear sensor monitors the gear that the vehicle is in and communicates it to the processor. A user input device allows a user to select the desired level of steering sensitivity and also allows the user to input the size of the tires installed on the vehicle. A steering device allows the operator to provide steering input and communicates electrical steering signals to the processor based on the steering input from the operator. The processor controls the valve to provide the steering response selected by the operator, to emulate castoring so that the vehicle is returned to a straight ahead position in the center position of the steering device, to vary the stop angle based on the tire size and to gradually stop articulation at the stop angle, to gradually start and stop articulation so as to avoid hydraulic hammering. If the steering valve has a source of supply which is common to other valves of the hydraulic system, the processor can also control all of the valves to give priority to the steering valve. In addition, the interface between the steering device and the processor is the same for different types of steering devices, i.e., a steering wheel or a joystick, so that different types of steering devices may be easily provided, depending on a customer's request.
Owner:TIMBERJACK
Rotary steerable drilling tool and associated method of use
The device contemplated provides a method for positioning the drill bit in a drilling operation to achieve small changes in hole angle or azimuth as drilling proceeds. Two different positions are available to the operator. The first is a straight ahead position where the tool essentially becomes a packed hole stabilizer assembly. The second position tilts the bit across a rotating fulcrum to give a calculated offset at the bit-formation interface. The direction that the bit offset is applied in relation to current hole direction is controlled by positioning the orienting pistons prior to each drilling cycle, through the use of current measurement-while-drilling (MWD) technology. Components of the tool comprise a MWD housing, upper steering and drive mandrel, non-rotating position housing, lower drive mandrel splined with the upper mandrel, rotating fulcrum stabilizer and drill bit.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
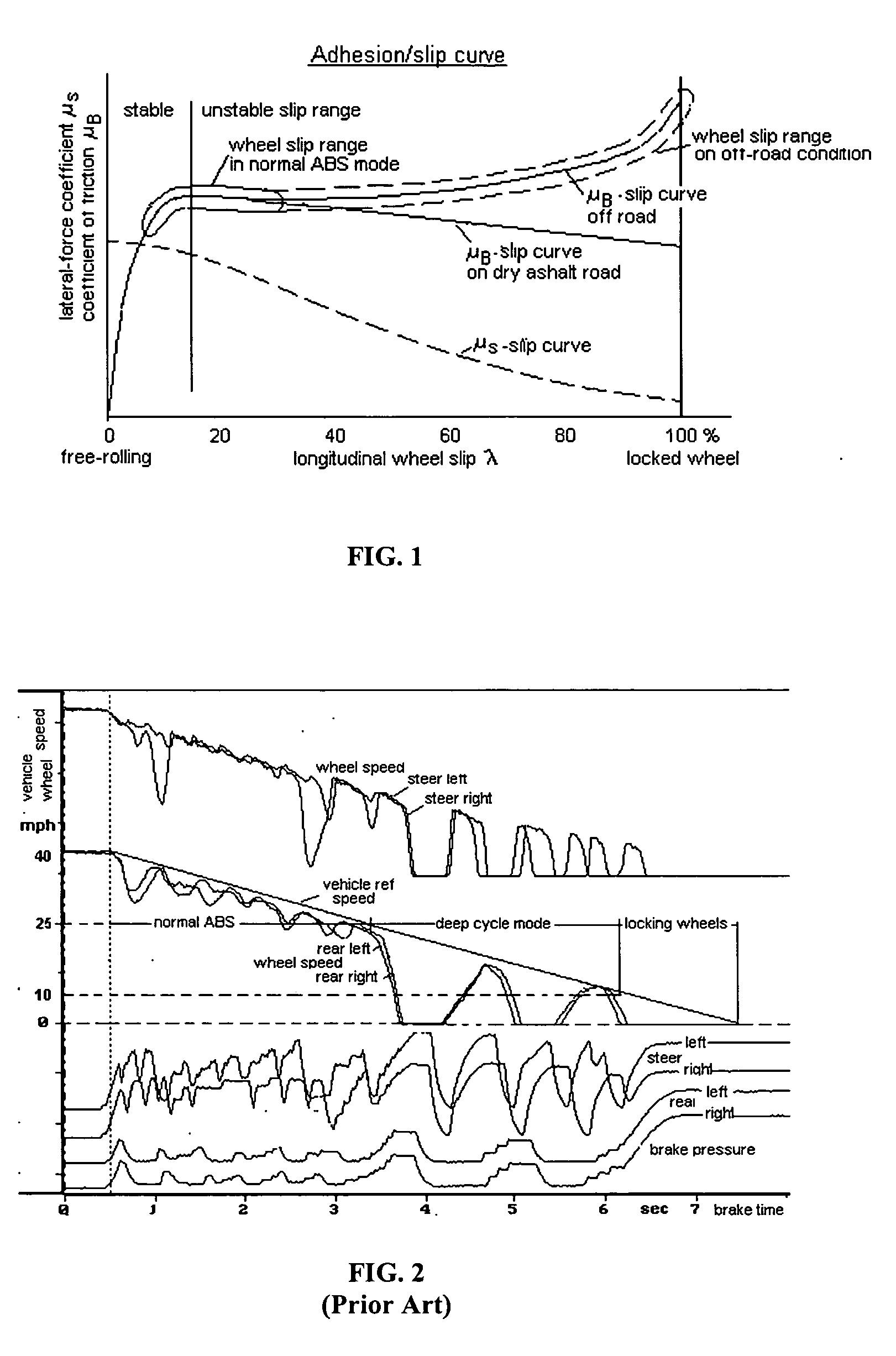
ABS control system for off-road driving conditions
InactiveUS20050140207A1Lower slip thresholdShort timeBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesSteering angleControl system
A system for controlling at least one of the slip threshold and the time period for an extended wheel slippage for a vehicle that is operating in the off-road ABS mode. When driving in a curve pattern and / or at high speeds, the individual wheel speeds are controlled with a lower slip threshold and / or shorter time period for the extended wheel slippage than when driving straight ahead and / or at a lower vehicle speed. Control of the brakes is accomplished by (i) controlling at least one of the individual wheel slip threshold and the time period for an extended wheel slippage based on the actual vehicle speed; (ii) controlling at least one of the individual wheel slip threshold and the time period for an extended wheel slippage depending on actual lateral acceleration; (iii) using a lateral acceleration sensor to measure actual lateral acceleration; (iv) measuring the actual steering angle with a sensor and controlling the wheel speed cycles in conjunction with the actual vehicle speed; (v) using a yaw rate sensor to determine at least one of the deepness and the time period of the wheel slippage; (vi) controlling the speed of the wheels on either side of the vehicle with different slip thresholds and / or different time periods for the slippage extension; (vii) controlling at least one of the individual wheel slip threshold and the time period for an extended wheel slippage depending on the wheel speed difference of a non-driven axle; and / or (viii) deactivating the off-road mode automatically when the vehicle reaches a predetermined speed.
Owner:BENDIX COMML VEHICLE SYST LLC
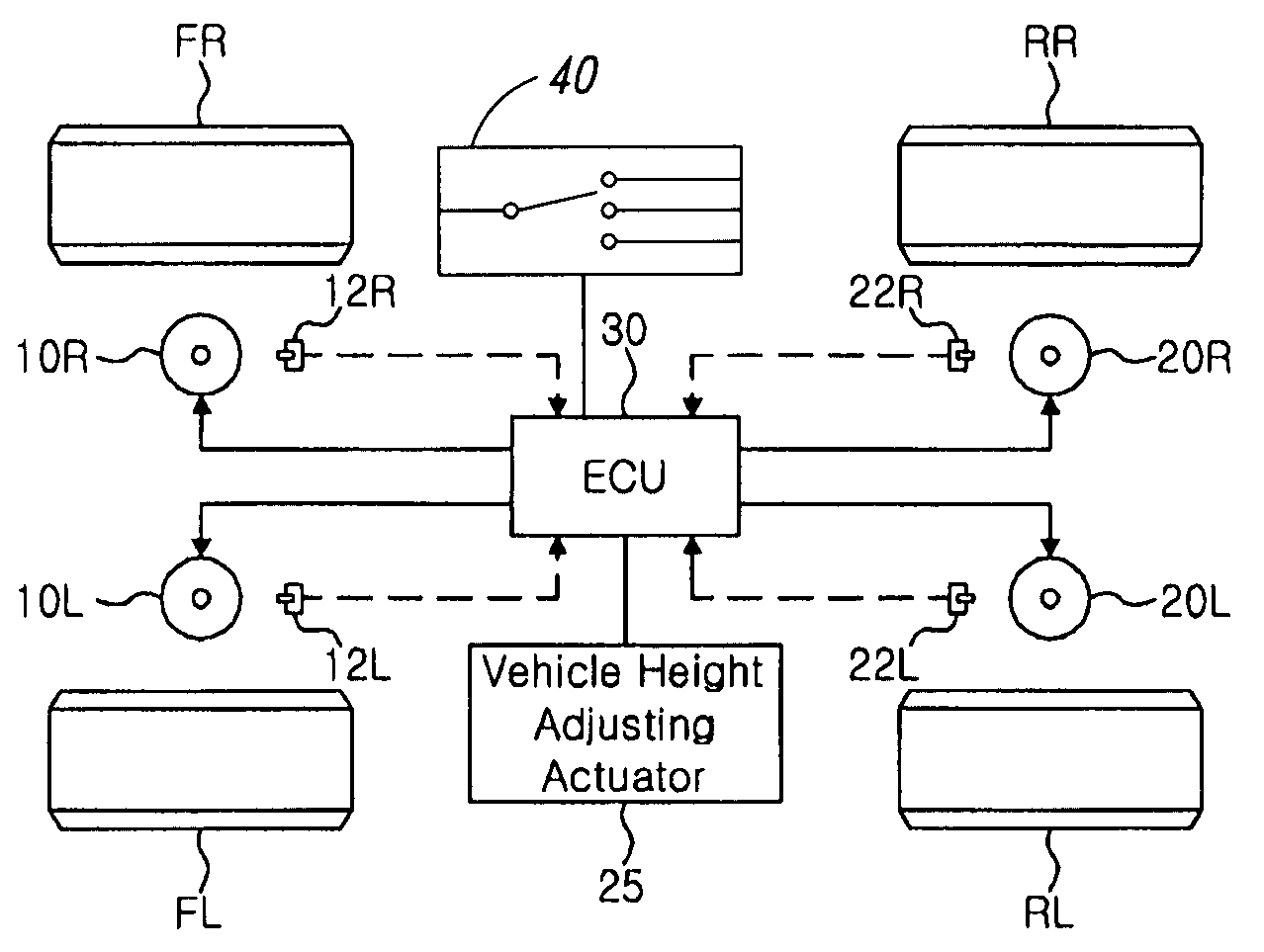
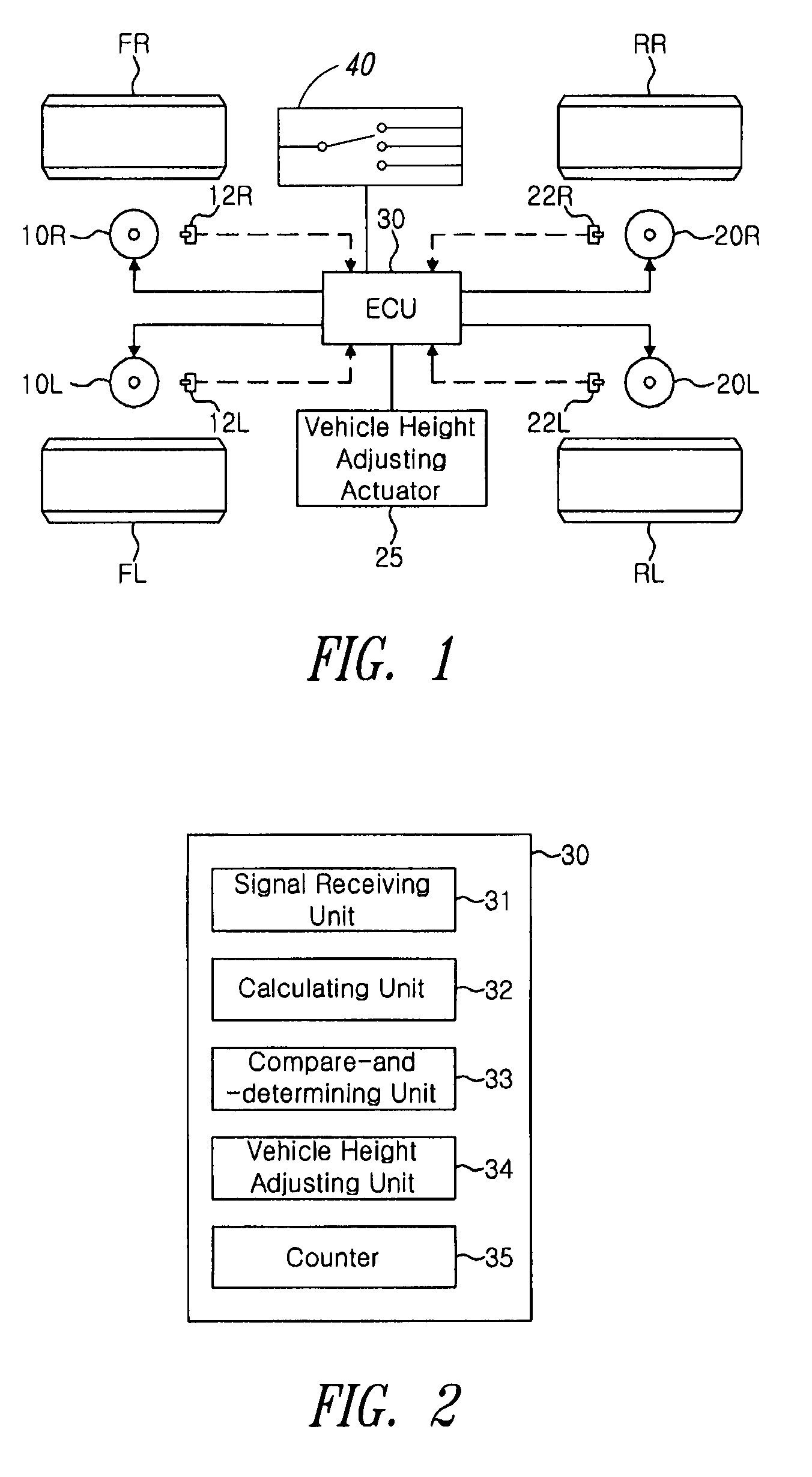
Electronic controlled suspension apparatus and vehicle height control method thereof
The present invention relates to an electronic controlled suspension apparatus capable of stopping vehicle height control when a vehicle turns and performing the vehicle height control when the vehicle goes straight ahead by using vehicle height sensors instead of a steering angle sensor, and a vehicle height control method of the electronic controlled suspension apparatus. To this end, there is provided an electronic controlled suspension apparatus, including a plurality of vehicle height sensors for measuring a height of a vehicle; a vehicle height adjusting actuator operable to adjust the height of the vehicle; air springs controlled by the vehicle height adjusting actuator; and an electronic controlled unit (ECU) for calculating a height difference value between the left and right sides of the vehicle based on vehicle height signals received from the vehicle height sensors and determining whether to operate or stop the vehicle height adjusting actuator through the comparison of the calculated height difference value between the left and right sides of the vehicle with a predetermined reference value.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Sealing nozzle
The present invention relates to a nozzle intended for the application of fluid materials, which at a front end thereof has an aperture opening into a slot. A central portion of the slot is functioning to release most of the material straight ahead. Furthermore, the slot has side portions functioning to release material in sideway directions. In a preferred embodiment, the front end is shaped like a truncated cone with a flat top, in which the slot is formed. The slot is thus divided into three straight portions with the central portion in the flat top and the angle of the side portions defined by the top angle of said cone. Under certain conditions, the jets of material released from the various portions are held together by a surface tension. As most of the material is released from the central portion, the jets from the angled side portions will be deflected towards the center jet, resulting in a jet with a relatively even width, and a resultant coating being thickest in the middle.
Owner:EFTEC EURO HLDG
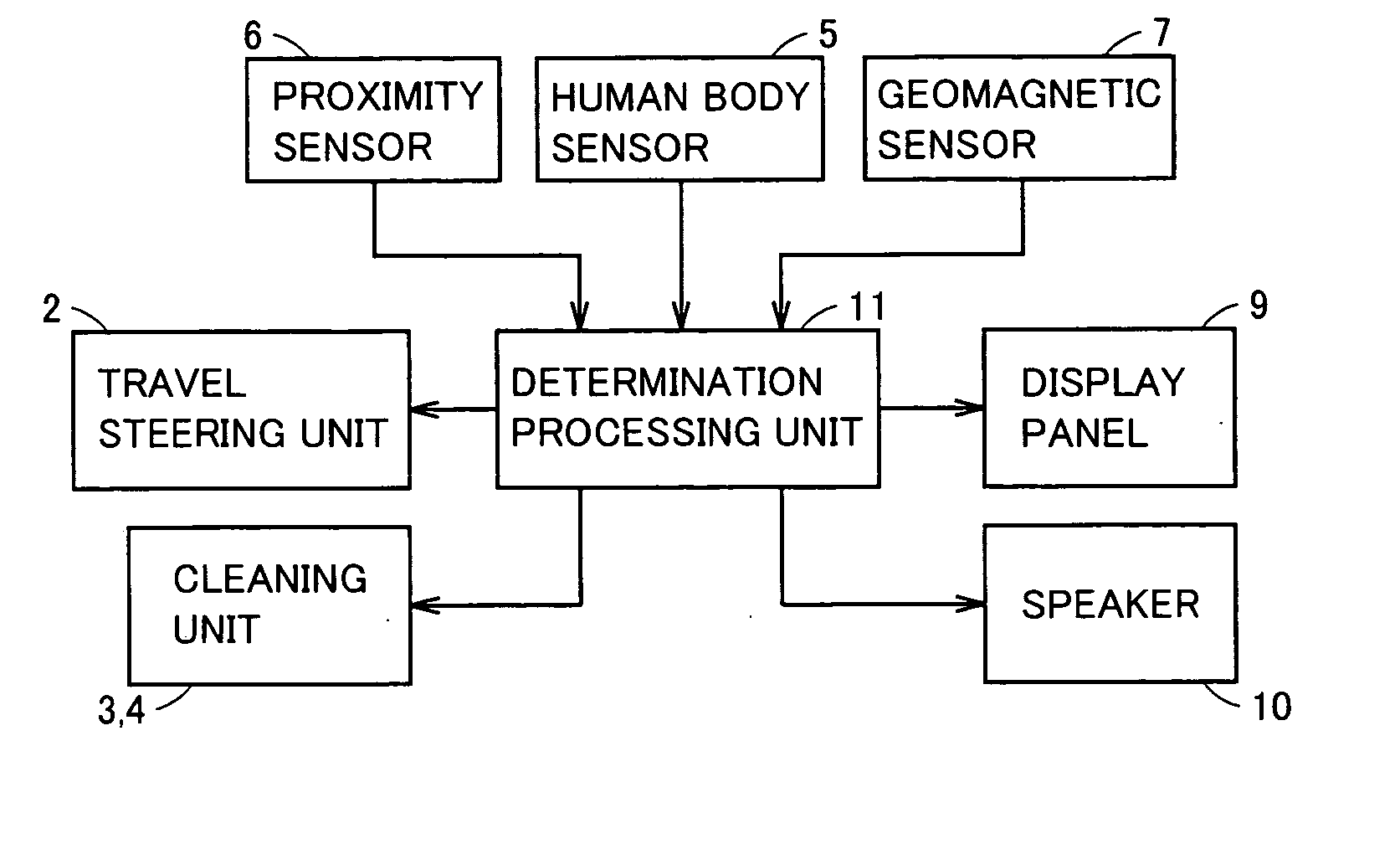
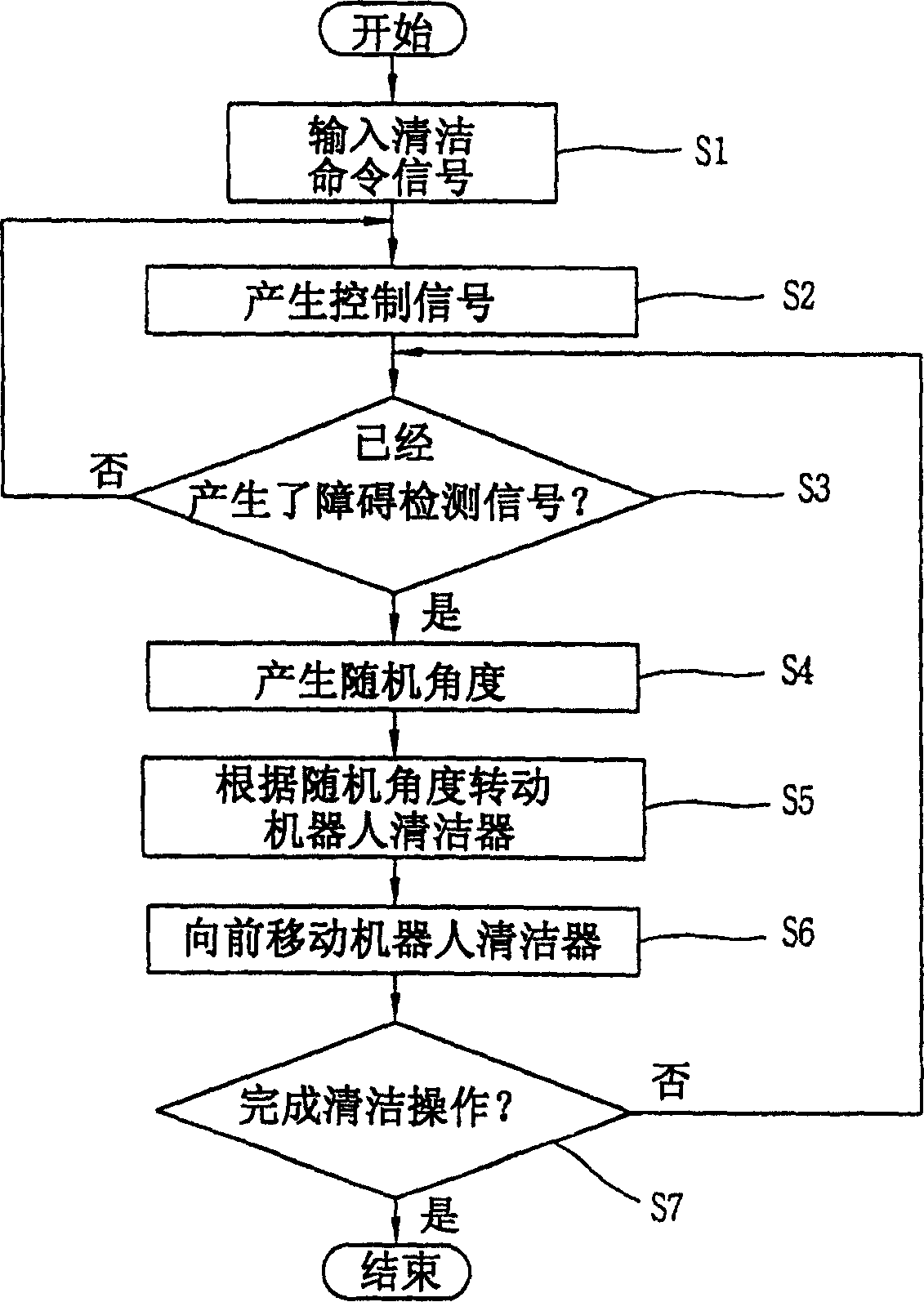
Self-running cleaner with collision obviation capability
InactiveUS20050171637A1Efficient executionImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsElectric equipment installationEngineeringVelocity vector
A main body of a self-running cleaner conducts a cleaning job while self-propelling at a velocity vector in the direction of the arrow. A person approaches with a movement vector in the direction of the arrow in front of the main body. A determination processing unit of the main body rotates the main body such that the velocity vector of the main body is orthogonal to the movement vector of the person when determination is made of the possibility of collision between the obstacle and the main body from a calculated result (rotation A). Then, the main body is moved straight ahead a predetermined distance in the direction of travel after the rotation. When the person continues to move during the withdrawal operation of the main body, and determination is made that there is no possibility of collision therebetween, the determination processing unit rotates the main body 180° (rotation B), and moves the main body straight ahead the predetermined distance, such that the main body returns to the former position immediately previous to the obviation operation. The main body is rotated such that the velocity vector of the main body corresponds to the direction of travel immediately previous to the sensing of a person (rotation C), and the cleaning job is resumed.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Steering angle sensor
ActiveUS20140208890A1Reduce reboundReduce false detectionControlling membersAngles/taper measurementsSteering wheelSteering angle
A steering angle sensor for a vehicle including a steering angle sensor housing, a first gear, a rotation transmitting portion, a second gear meshing with the first gear, a third gear meshing with the first gear or the second gear, first and second magnetoresistance effect elements to detect first and second rotation angles as rotation angles of the second and third gears, respectively, and a biasing member disposed in the steering angle sensor housing to bias the first gear toward the second gear, wherein the first and rotation angles are combined to determine an absolute steering angle indicative of an amount of rotation of a steering wheel when the steering wheel is rotated from a neutral position in which a steerable road wheel is oriented to a straight ahead direction of the vehicle.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
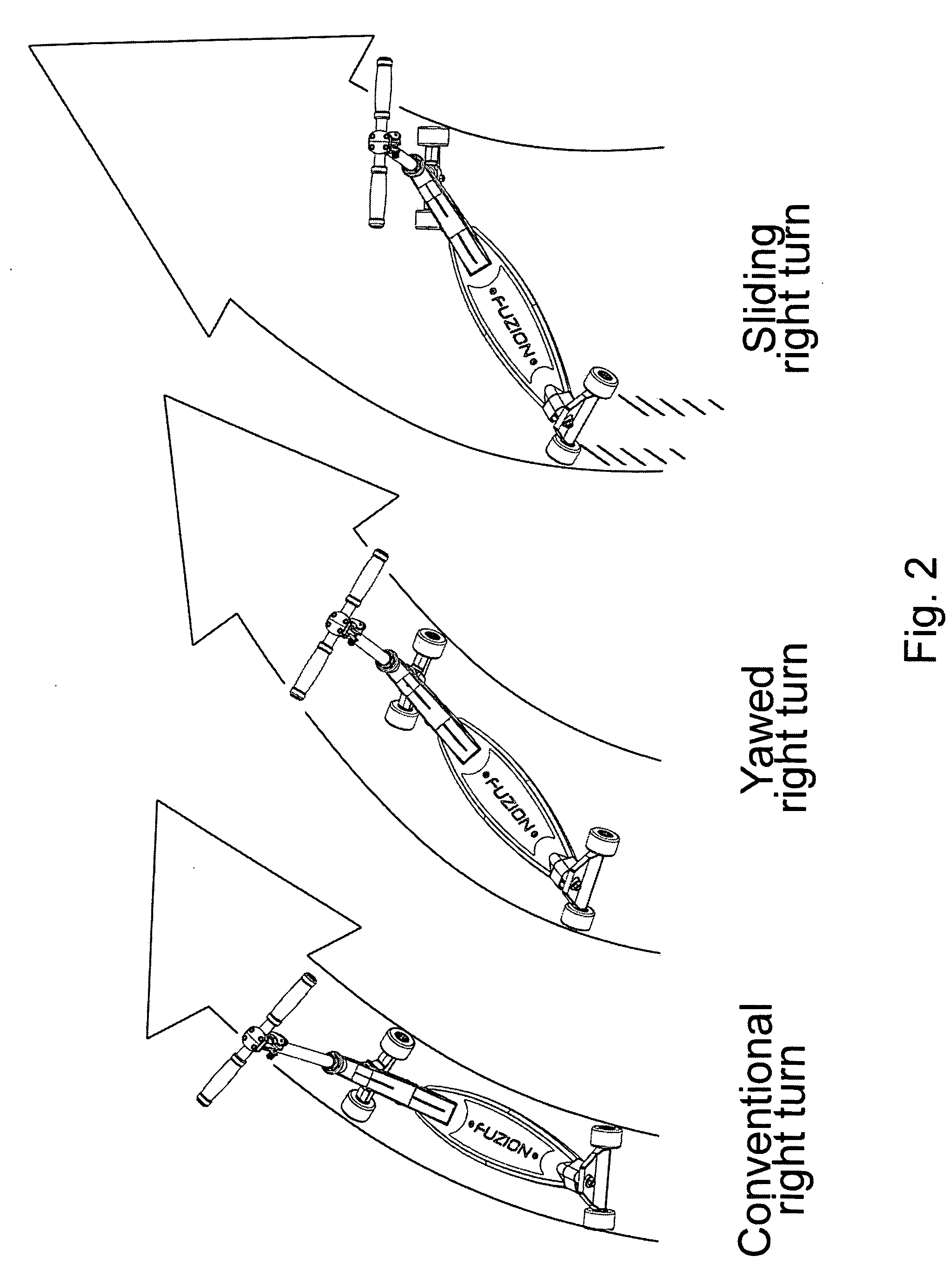
Rear truck and method
ActiveUS20090273152A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease ground clearanceFoldable cyclesRider propulsionCouplingEngineering
A compact lean steering truck assembly that provides deep deck lean capability. The lean steering truck assembly may be integrated into a four wheeled scooter. A pivotal coupling in the front hanger allows independent steering of the front and rear wheel assemblies. Front steering is controlled by the rider's hands twisting the handle bars to the right or left or straight ahead. Rear steering is controlled by the rider's feet and hands leaning the deck and handle bars relative to the plane of the ground. The ratio of deck lean to rear steering is a function of the hanger pivot axis angle but in general terms the deeper the deck lean the greater the rear wheel steering.
Owner:RC INNOVATION LLC
Driving assist device
ActiveCN102822880AAnti-collision systemsExternal condition input parametersTemporal changeEngineering
A driving assist device detects the position of a vehicle 13 in a direction of the width of a road by using both distance data on both right and left sides of the vehicle and road width data on the width of the road, specifies distance data having a time-varying change equal to or larger than a predetermined threshold from among the distance data showing the vehicle position detected to correct the vehicle position in such a way that the vehicle position is shown by the distance data from which the distance data specified are removed when the travelling path of the vehicle 13 shows a straight ahead movement, determines the travelling state of the vehicle 13 from a time-varying change of the vehicle position corrected, and notifies a content according to the travelling state determined.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
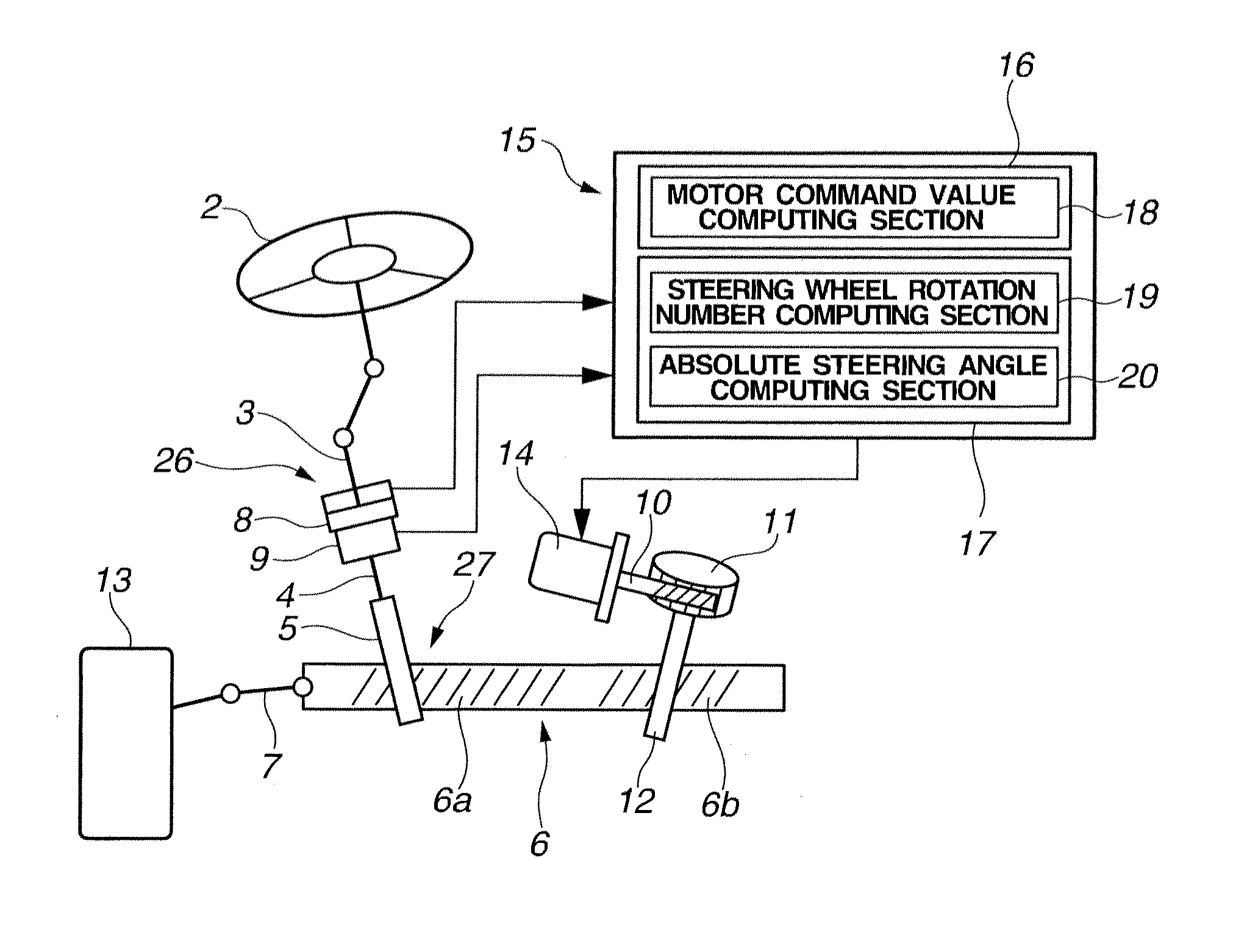
Steering control device
InactiveUS7325644B2Effectively and rationally addressDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsLower limitSteering wheel
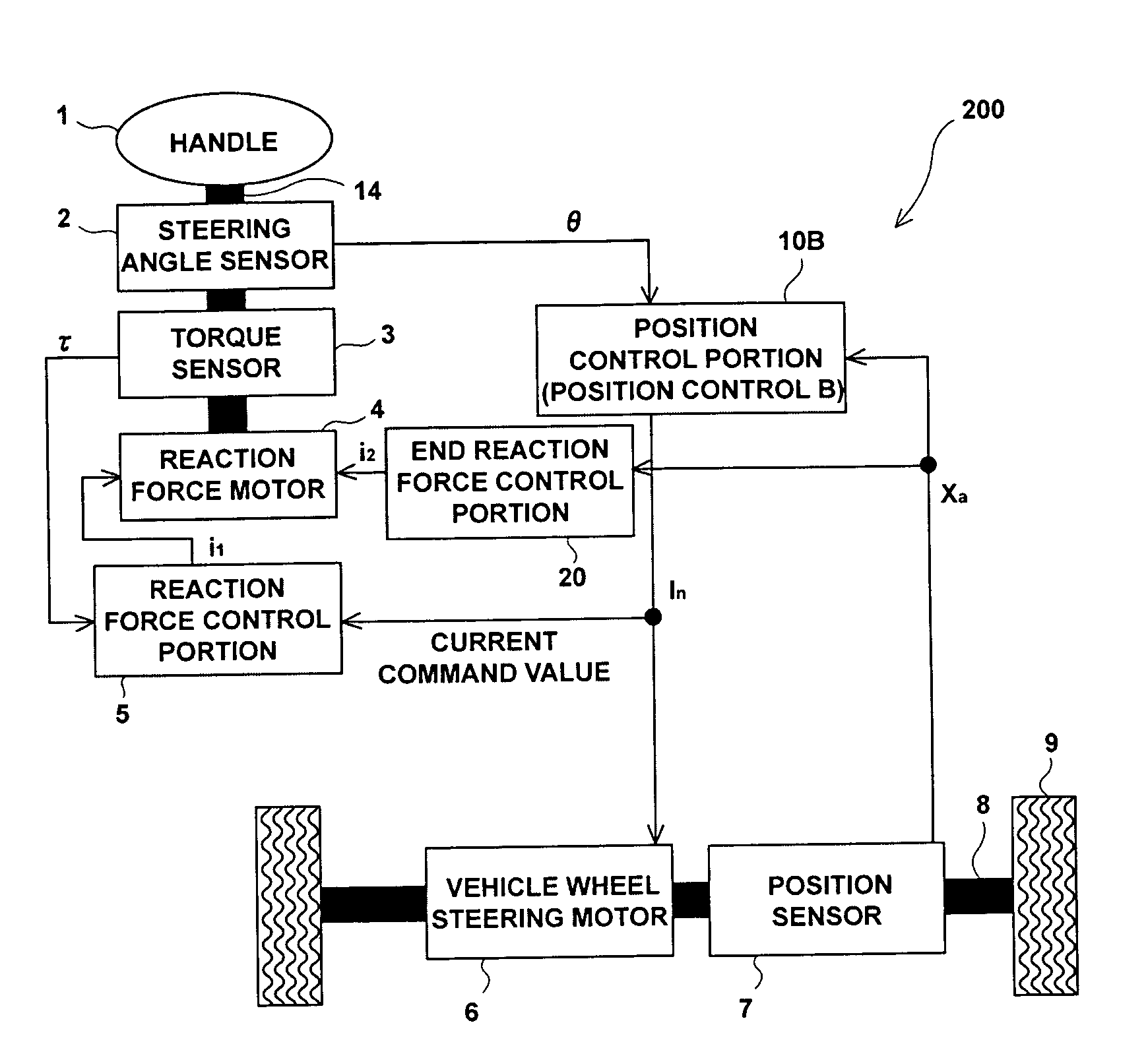
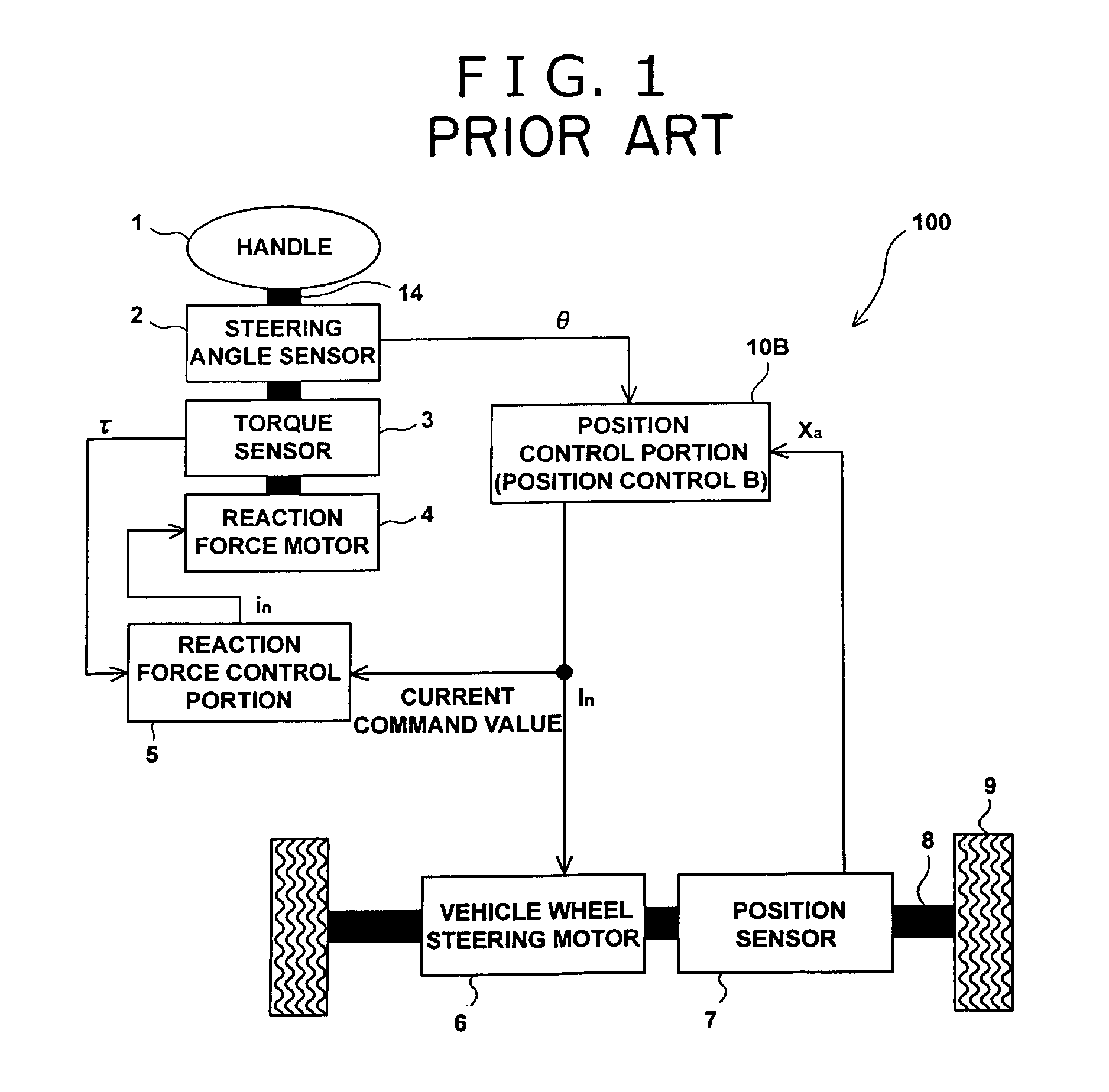
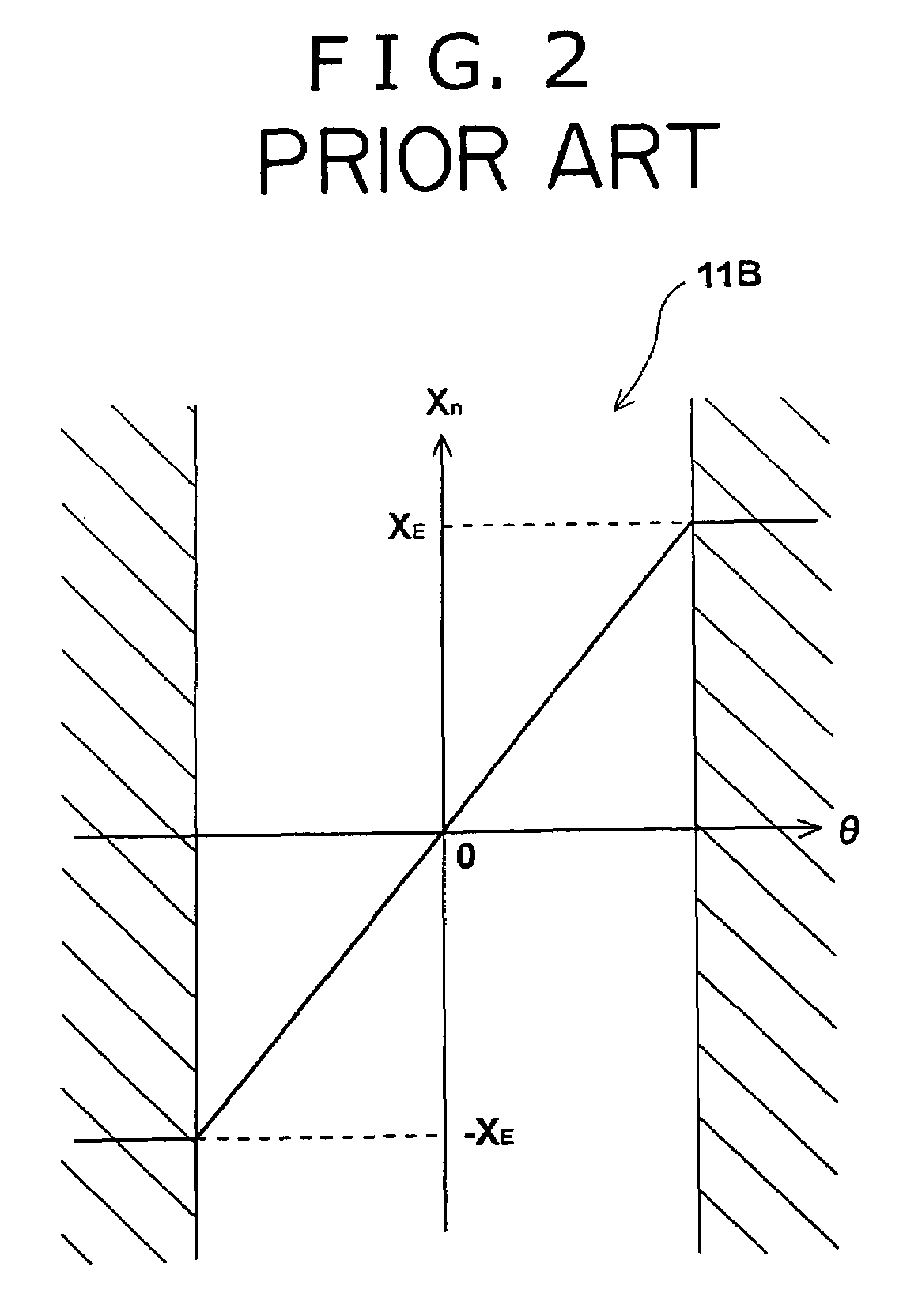
A steering control device (200) is provided with a end-of-movement reaction force generation unit (an end reaction force control portion (20)). An end reaction force generating current i2 which act as return a handle toward a straight-ahead position is rapidly generated in the vicinity of an upper and a lower limit of a vehicle wheel steering range. For example, a reaction force motor (4) may be additionally commanded using a newly generated command current i2. Accordingly, an output torque of the reaction force motor (4) becomes proportional to a new command value in of an Equation in=i1+i2, where i1 is a current command of a reaction force control portion (5). As a result of configuring the end-of-movement reaction force generation unit is this manner, for example, it is possible to generate a virtual contact resistance force (a steering reaction force) for a steering angle θ without causing heat build-up, or the like, of a motor, when no physical limit (an end-of-movement of contact point) is provided for a rotation range of a steering wheel (handle).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Apparatus and method for calling mobile robot
An apparatus for calling a mobile robot (200) includes a generator (101,102) installed at a remote controller (100), and generating an RF signal and infrared signal for calling a mobile robot (200) when a call signal is inputted by a user; and a controller (202) installed at the mobile robot (200), calculating a direction of the remote controller (100) based on a position of an infrared ray receiver that receives the infrared signal when an RF signal is received, rotating the mobile robot (200) in the calculated direction, and then making the mobile robot (200) to go straight ahead. When a user calls the mobile robot (200) from a specific place, the mobile robot (200) can move by itself to the specific space, thereby enhancing users' convenience.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
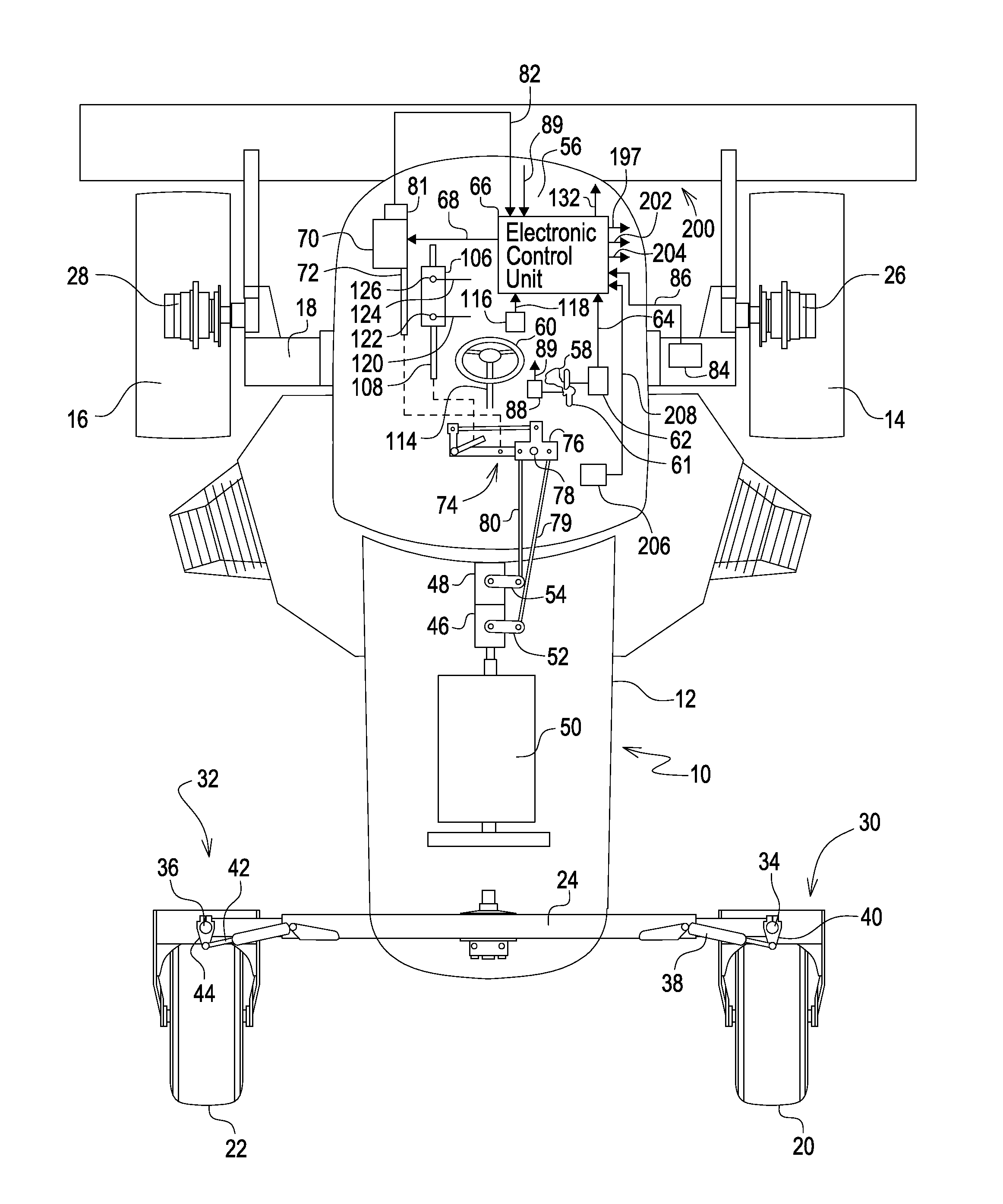
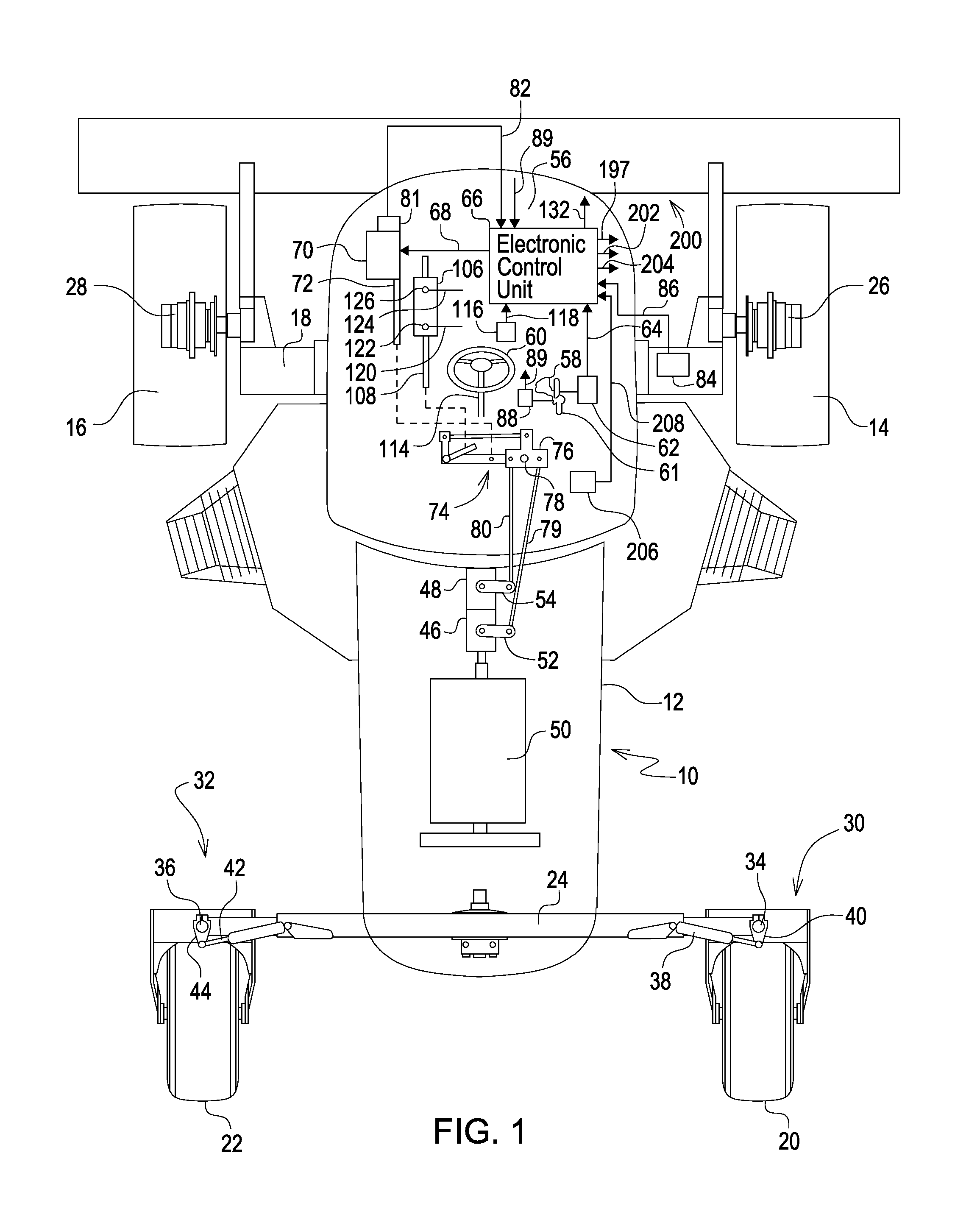
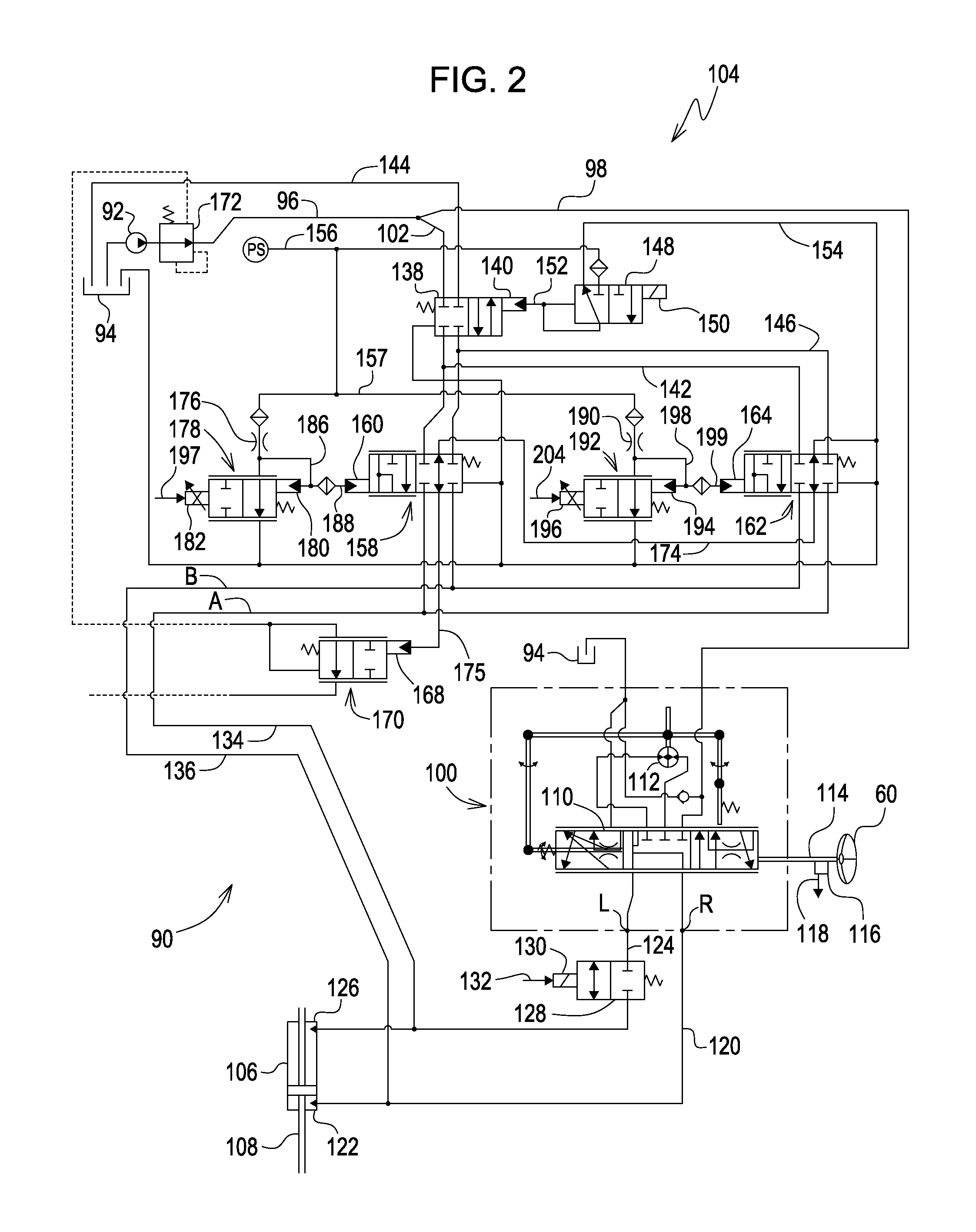
Steering control system for hydrostatically driven front vehicle ground wheels and steerable rear caster wheels
ActiveUS8925672B2Adding undue costLeak characteristicSteering linkagesFluid steeringAutomatic controlAutomatic steering
An integrated steering control system includes a primary, automatic and rear control valves. A steering wheel operates the primary steering control valve and is of a type which includes a leakage characteristic. Steering wheel movement is sensed and a signal is sent which results in the automatic steering control valve being operated for adding fluid that supplied to a steering cylinder by the primary steering control valve in order to compensate for leakage, the amount of added fluid being a function of vehicle ground speed. An electric actuator with position feedback is used for ground speed control. Whenever the actuator position shows that the ground speed is set to zero and a switch in the hydro-handle slot shows that the handle is in the Park position, the automatic steering control valve is activated to move the steering cylinder to a neutral, straight ahead position, as determined by a sensor in a mechanical linkage of the steering control.
Owner:DEERE & CO
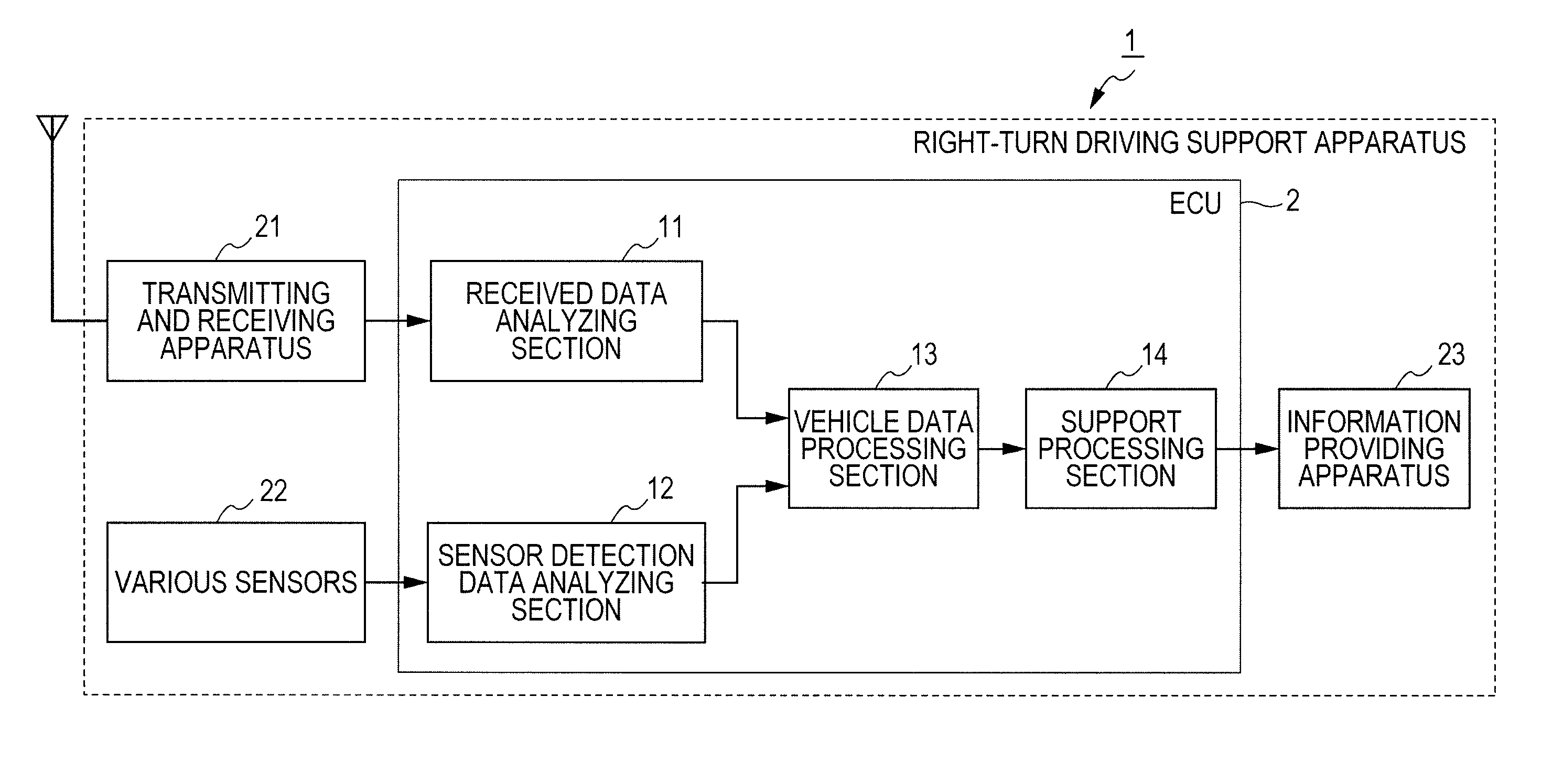
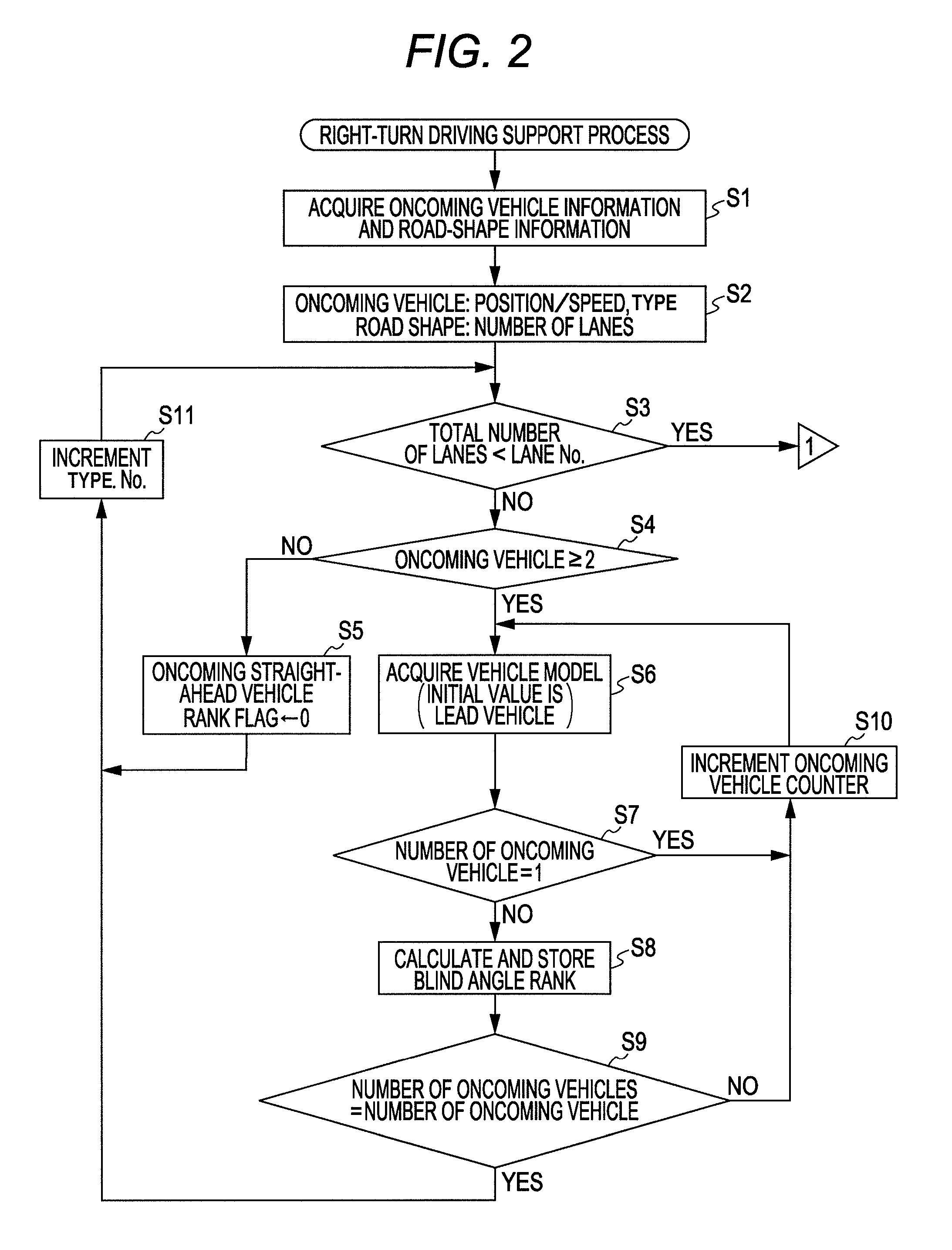
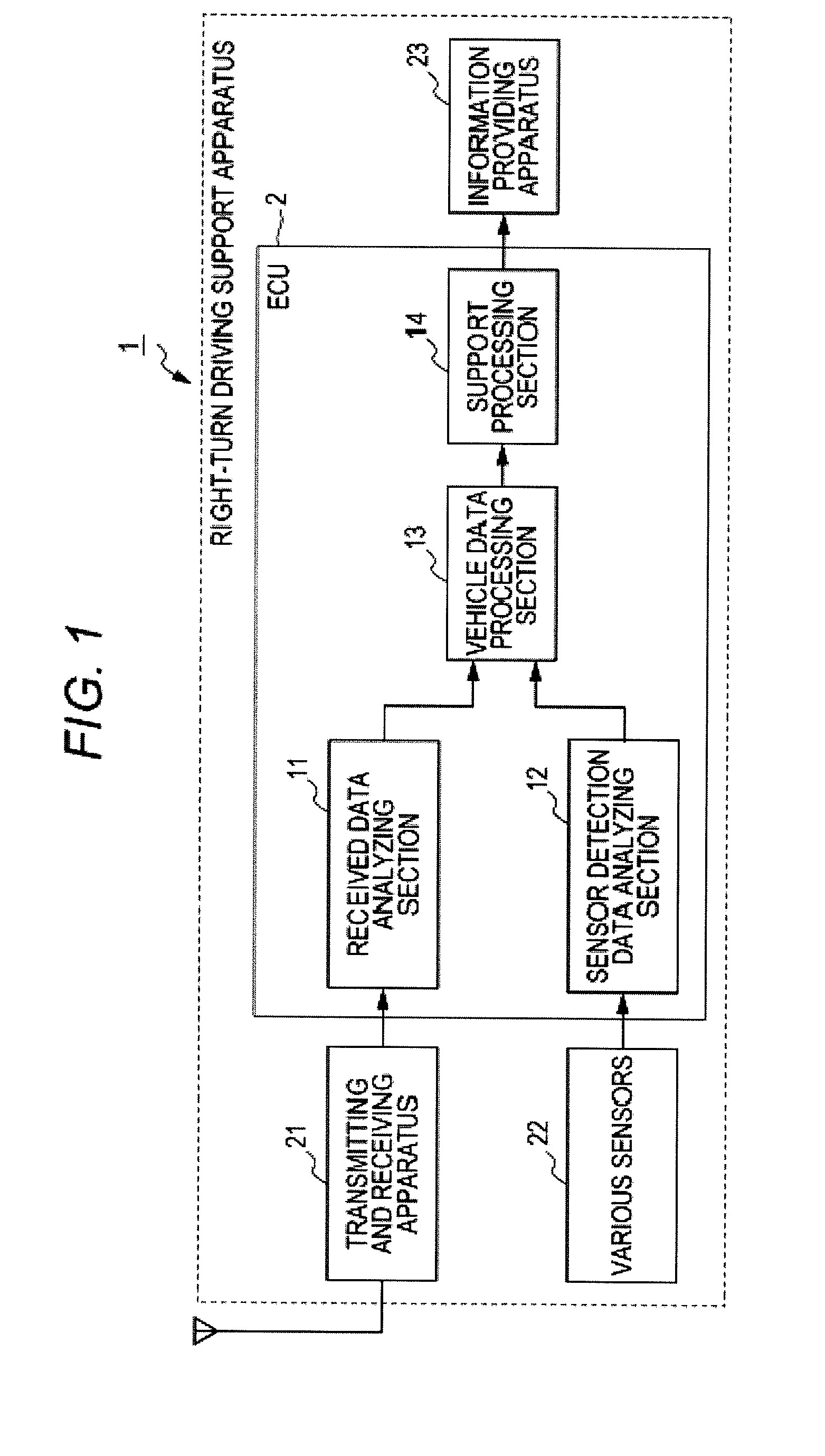
Right-turn driving support apparatus
InactiveUS20110095907A1Troublesome feelingTroublesome feeling given to the driverArrangements for variable traffic instructionsAnti-collision systemsBody sizeComputer science
When an own vehicle waits to turn right, a vehicle data processing unit processes information of an oncoming vehicle based on data analyzed by data analyzing units. A support processing unit sets a blind angle rank according to a difficulty degree of recognizing a following vehicle due to the blind angle of a lead vehicle from the relationship in the vehicle body size between the lead and following vehicles based on the oncoming vehicle information, and sets the highest blind angle rank value as an oncoming straight-ahead vehicle rank flag. It also sets an evaluation rank according to a risk degree when the own vehicle turns right, based on the oncoming straight-ahead vehicle rank flag and an oncoming right-turning vehicle rank flag set according to the size of an oncoming vehicle waiting to turn right, and informs the driver of right-turn driving support information according to the evaluation rank.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Apparatus and method for measuring and compensating steering-angle sensitive alignment measurements
ActiveUS20060080015A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesSteering angleEngineering
A method for measuring and compensating steered-angle sensitive wheel alignment angle and distance measurements for the effects of steering a wheel from a straight ahead position, thereby enabling an operator to carry out a vehicle wheel alignment angle adjustment without having to maintain a wheel in a straight-ahead steered condition during an alignment angle or distance adjustment, or to require the operator to continually return the wheel to the straight-ahead steered condition to acquire updated measurements of an alignment angle or distance currently being adjusted.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
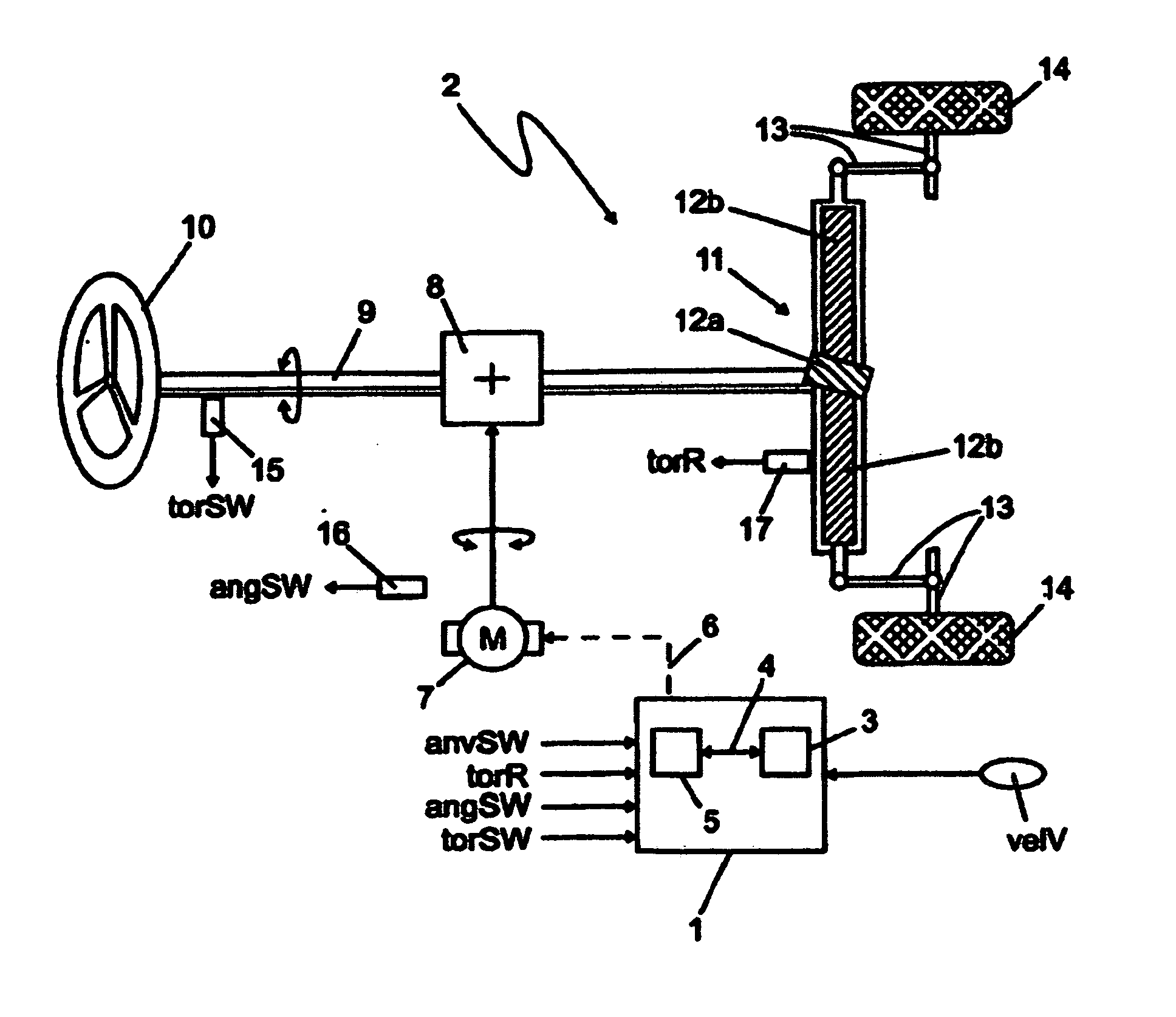
Determining a target steering torque in a steering device
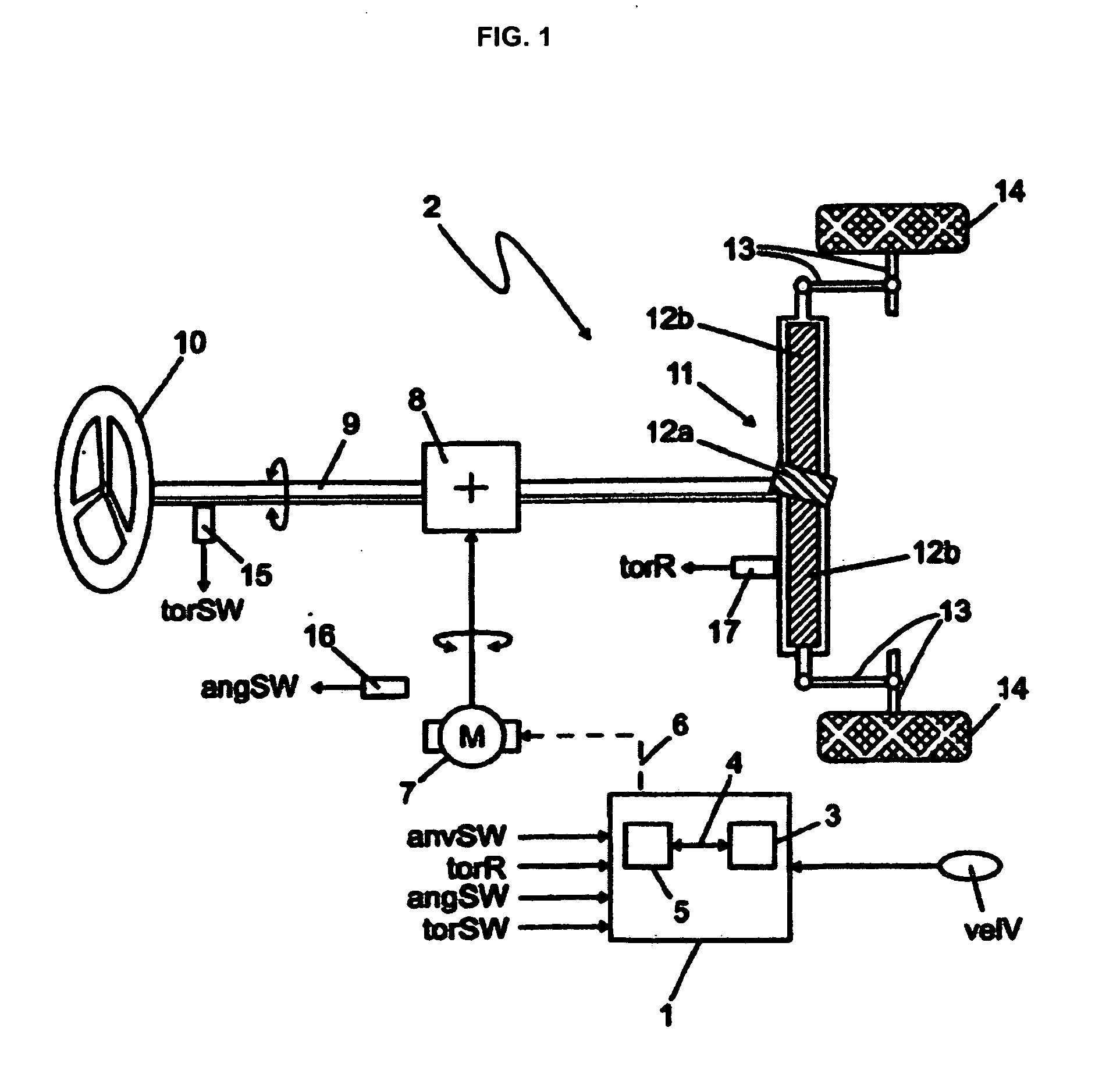
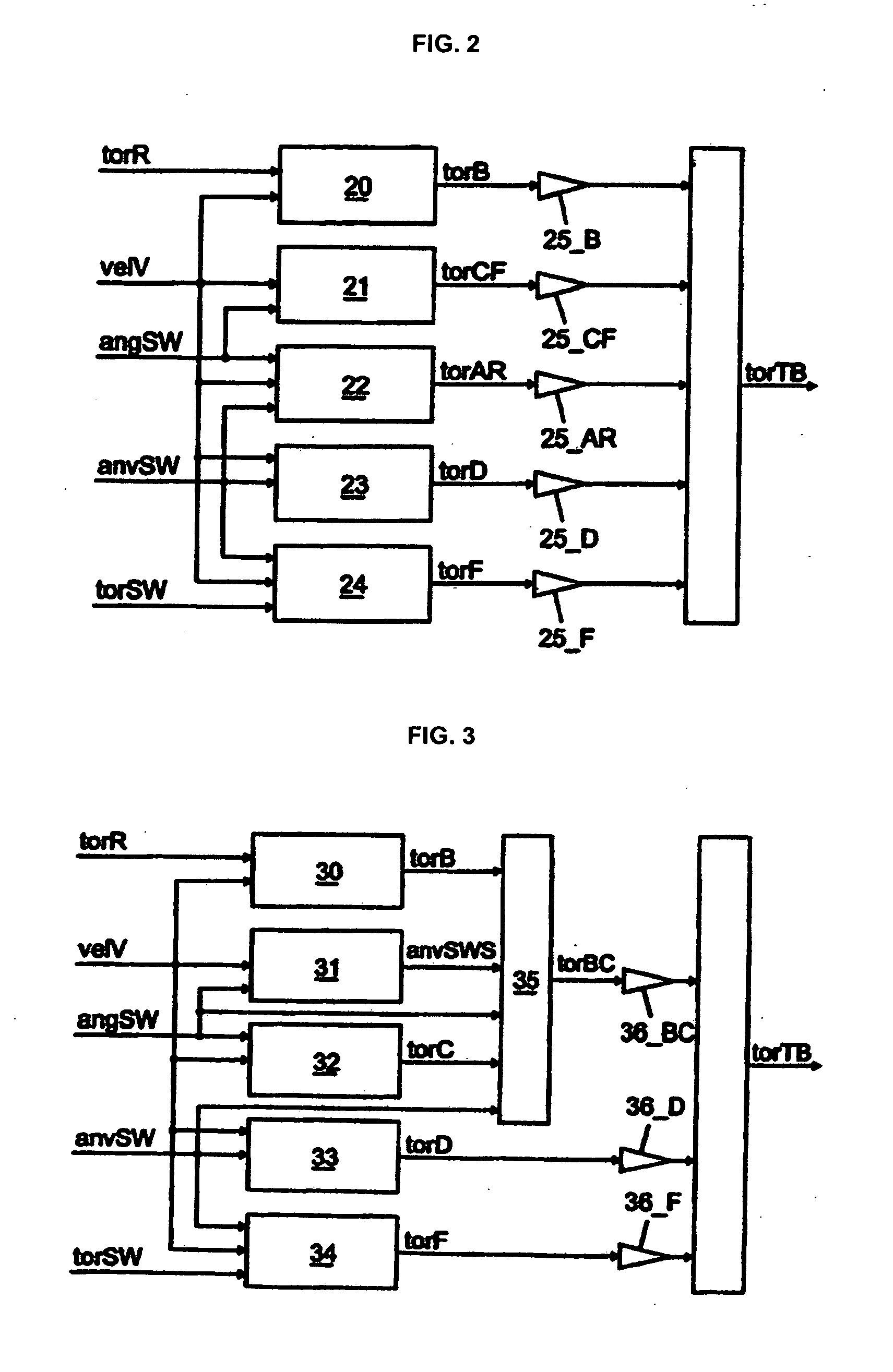
In order to achieve a steering feel for SbW systems and EPS systems having a control design for controlling the steering torque by generating a target steering torque (torTB) that can be adapted to various steering systems, vehicle types, or requirements, in which the resulting steering feel is a steering feel, in all driving conditions and driving situations, which is equivalent to, or better than, hydraulic and electromechanical steering systems available on the market today, according to the invention: a base steering torque (torB) is determined as a function of an externally acting force (torR) and a vehicle speed (velV); a damping torque (torD) is determined as a function of a steering speed (anvSW) and the vehicle speed (velV); a hysteresis torque (torF) is determined as a function of the steering speed (anvSW) and the vehicle speed (velV); a centering torque (torCF; torC) in the direction of the straight-ahead position is determined as a function of a steering wheel angle (angSW) and the vehicle speed (velV); and the base steering torque (torB), the damping torque (torD), the hysteresis torque (torF) and the centering torque (torCF; torC) form individual components, as a function of which the target steering torque (torTB) is determined.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE STEERING
Vehicle with a variable rear toe angle
ActiveUS20090177348A1Minimal inconvenienceVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesStraight aheadAutomotive engineering
In a vehicle provided with a rear wheel toe angle varying device for individually varying toe angles of rear wheels, upon detection of a failure to steer one of the rear wheels, the rear wheel of a healthy side is steered in a direction to enable the vehicle to travel straight ahead. Preferably, a control unit of the rear wheel toe angle varying device steers the rear wheel of a healthy side in parallel to the rear wheel of the faulty side, and the vehicle is enabled to travel straight ahead even though the traveling direction of the vehicle is at a certain angle with respect to the longitudinal line of the vehicle body. At this time, front wheels are typically steered at the same angle as the rear wheels. The device may further comprise a toe angle estimating unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Wing structure of air swirling device for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6932049B2Increase speedHigh densityContinuous combustion chamberInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineStraight ahead
Disclosed is a wing structure of air swirling device for internal combustion engine, which has a swirling device body mounted in an air cleaner, a plurality of wings mounted slantingly and radially on the swirling device body for accelerating or increasing an airflow revolution, and one or more slits formed on prescribed positions of the plurality of wings for suppressing the formation of eddy in a negative pressure zone on the rear surface of each of the plurality of wings, includes a plurality of auxiliary wings protrudedly provided to the outside with reference to the surface of each of the wings, so that the airflow collided against the surface of each of said wings go straight ahead.
Owner:KIM SEI YOUNG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com