Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11416results about "Braking action transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
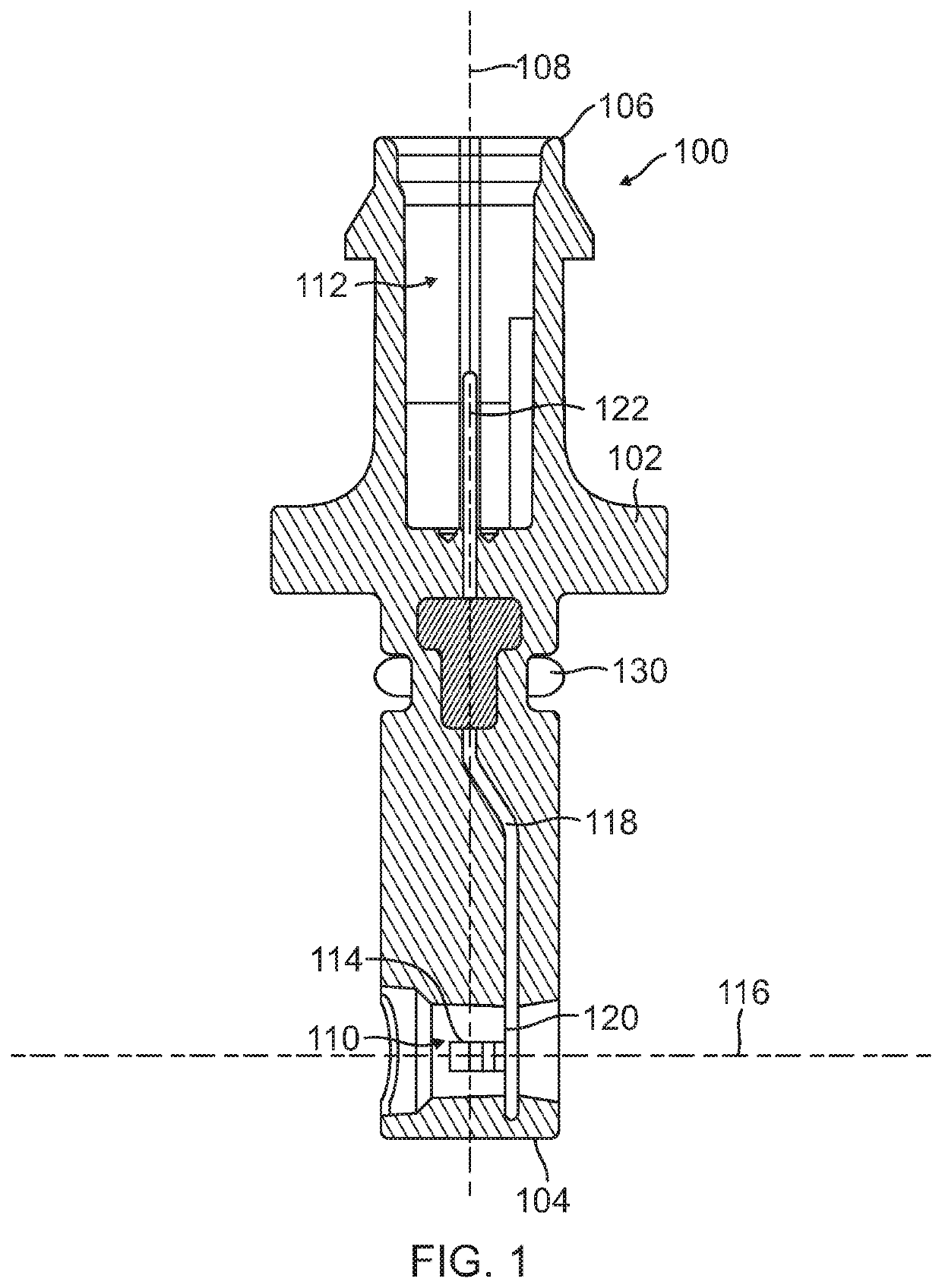
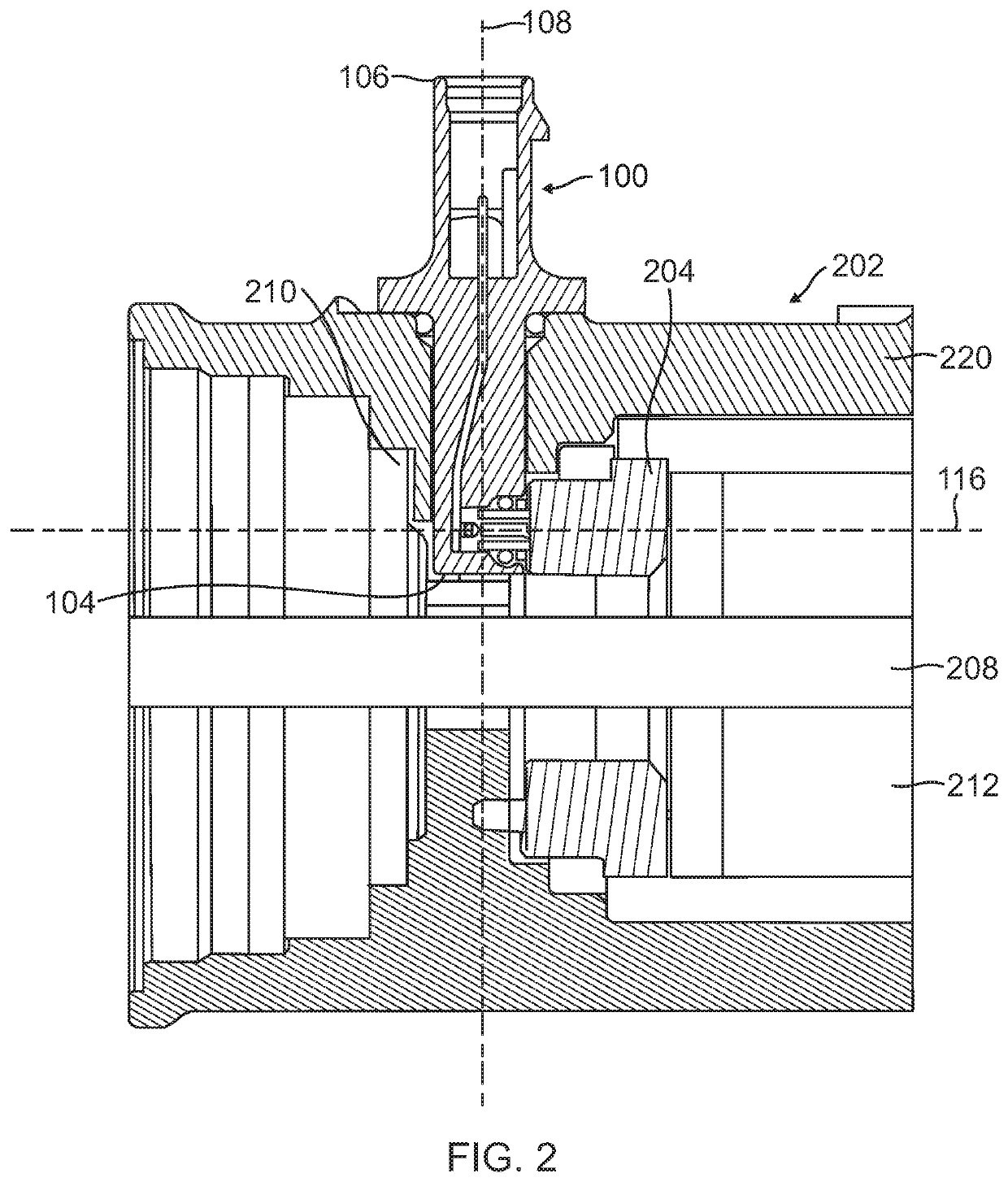
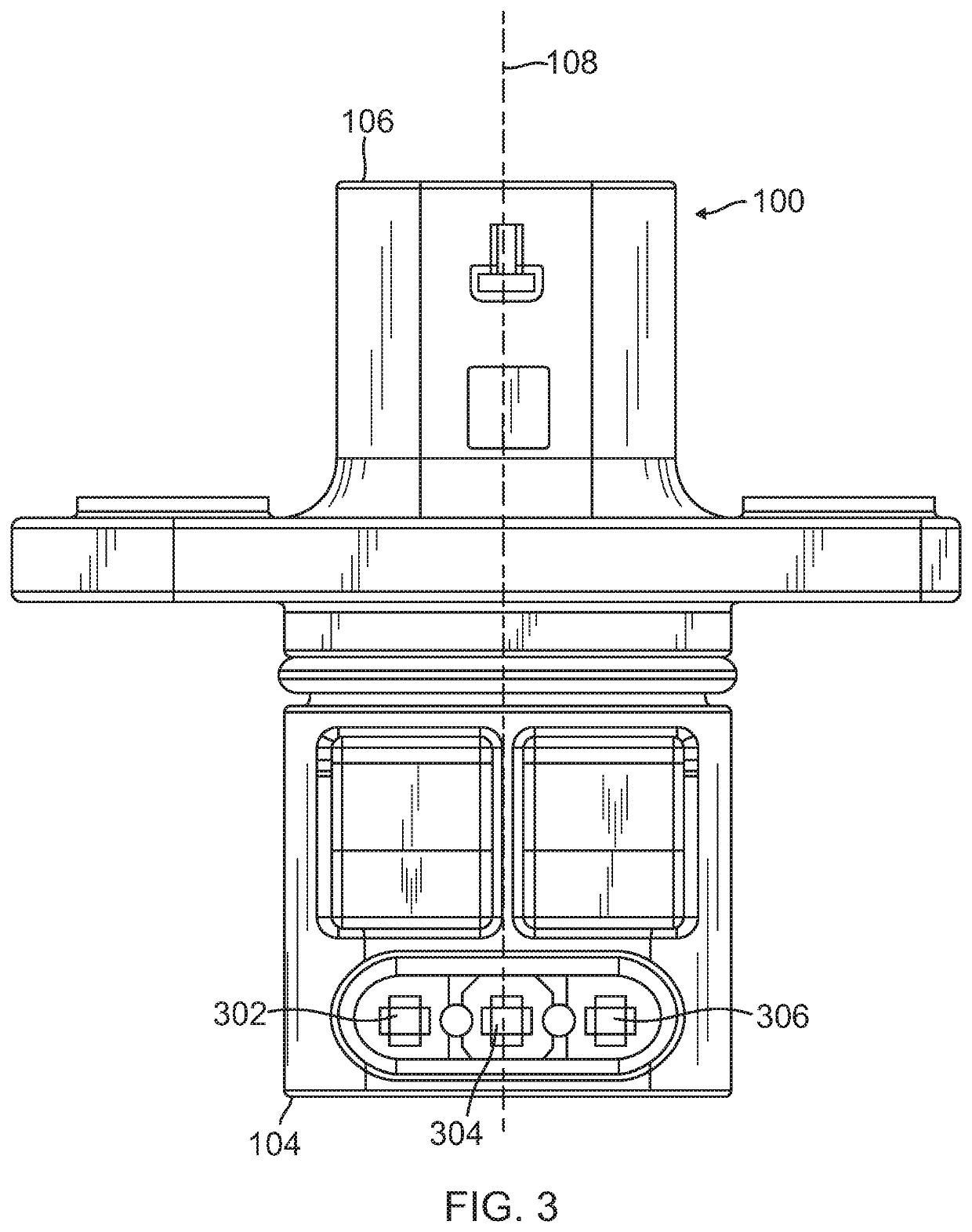
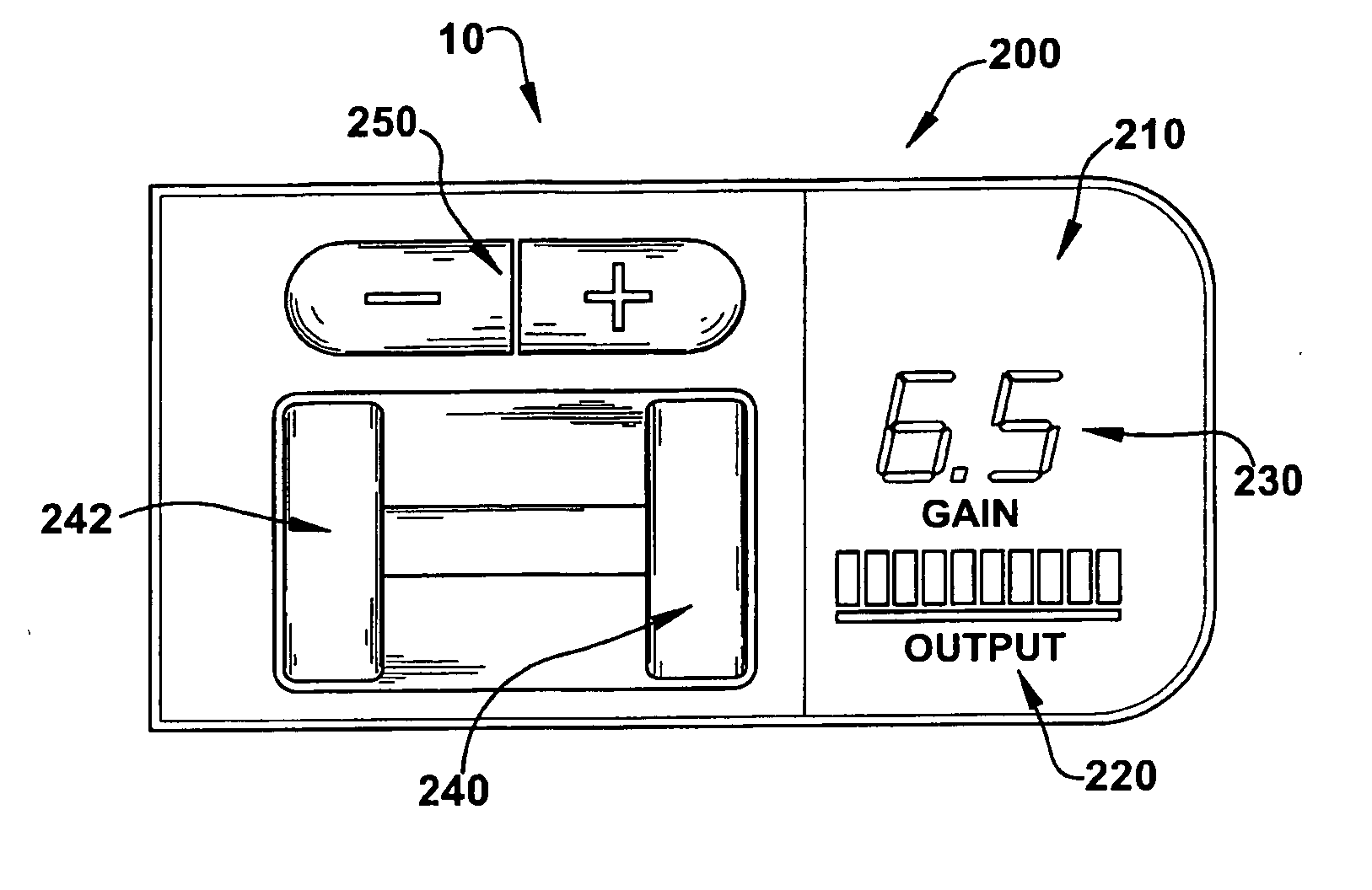
Electromechanical braking connector
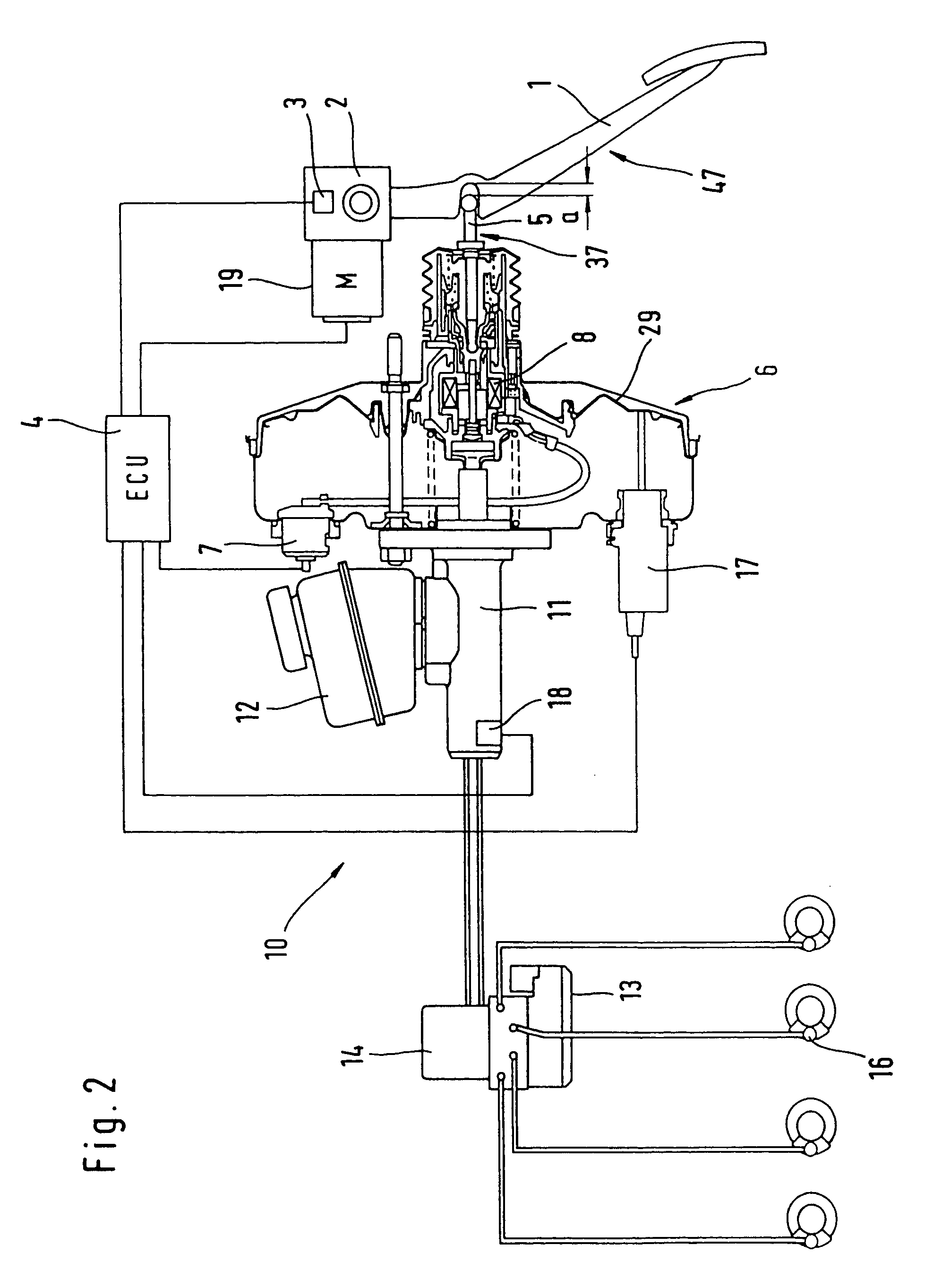
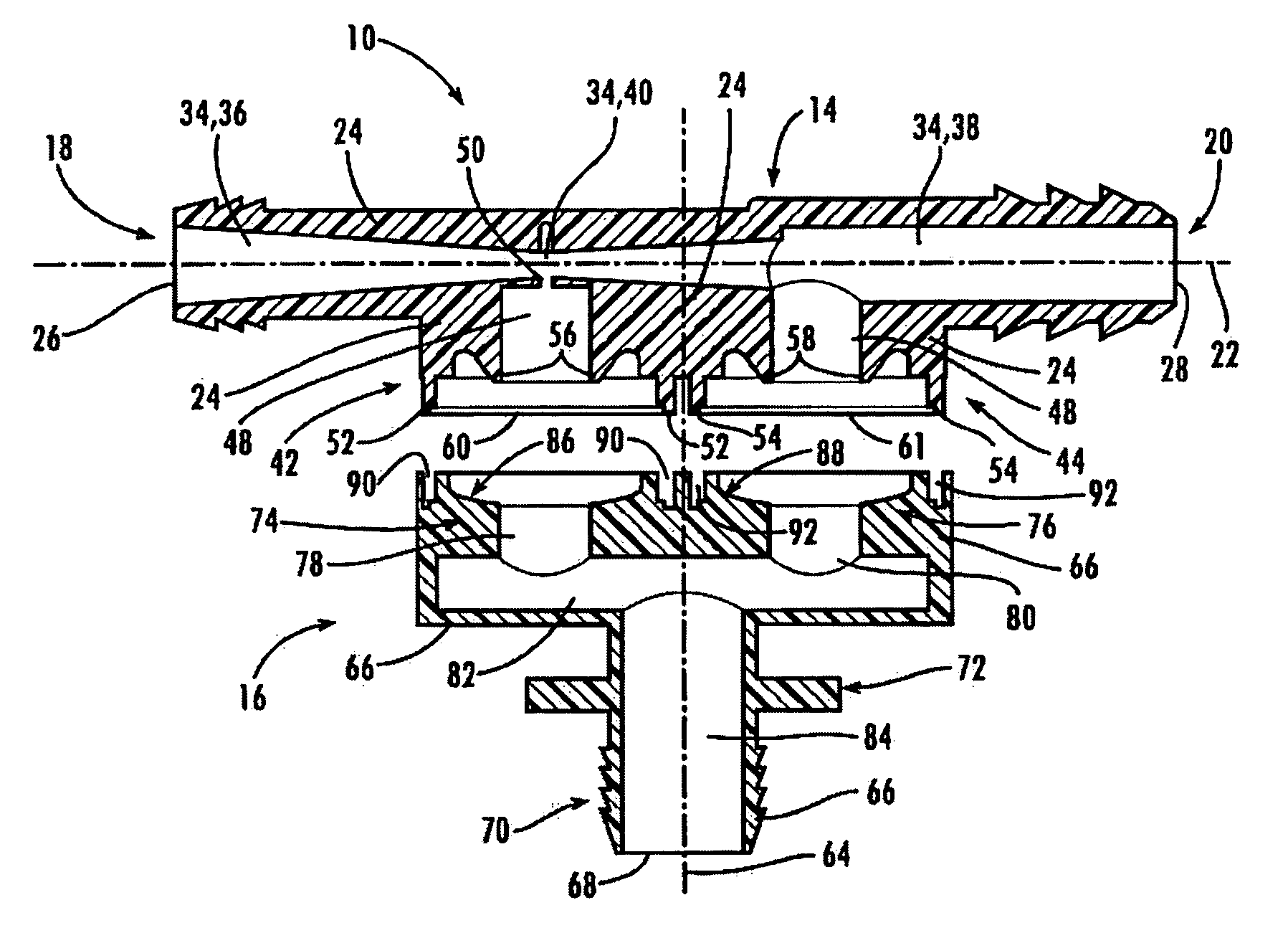
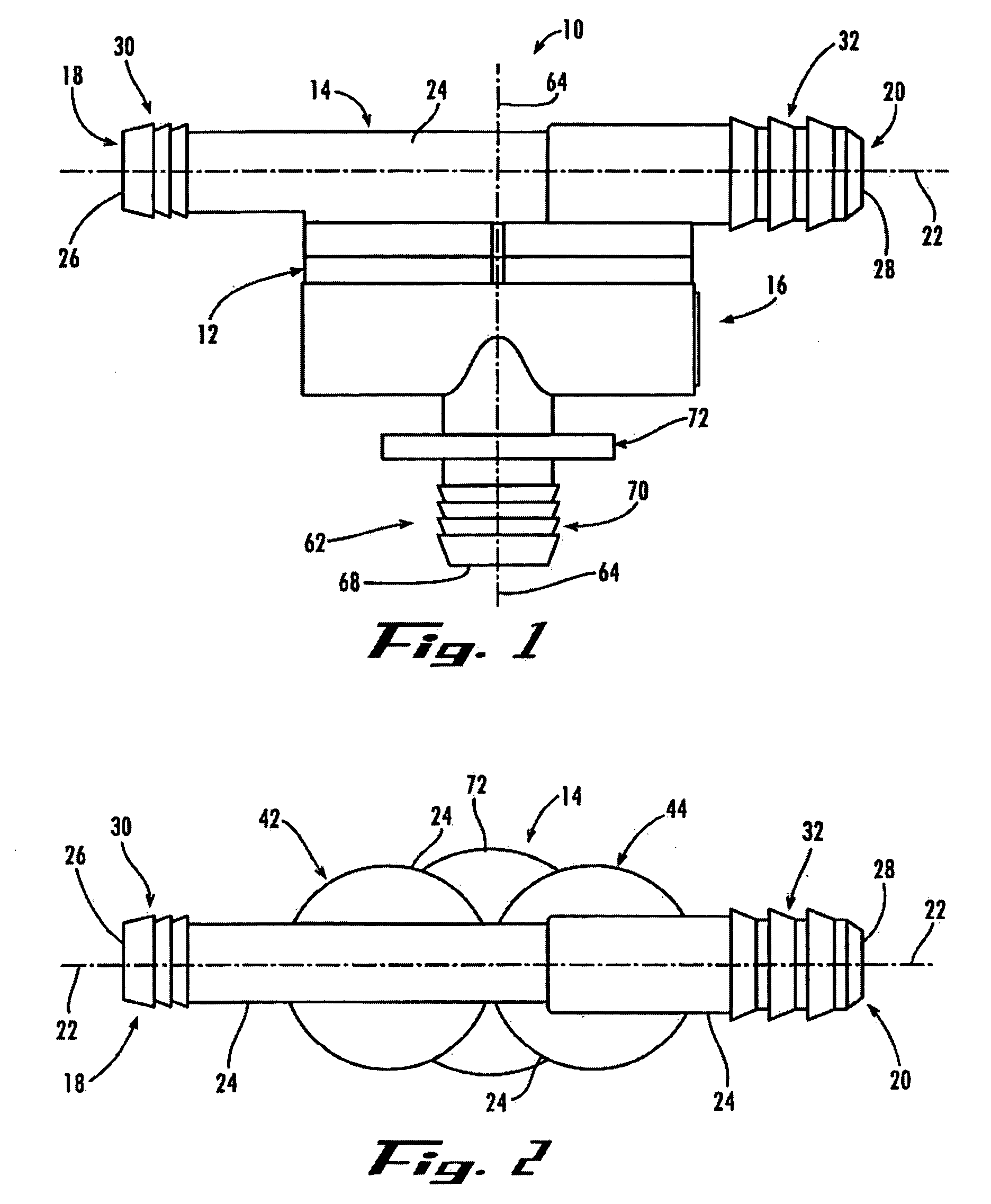
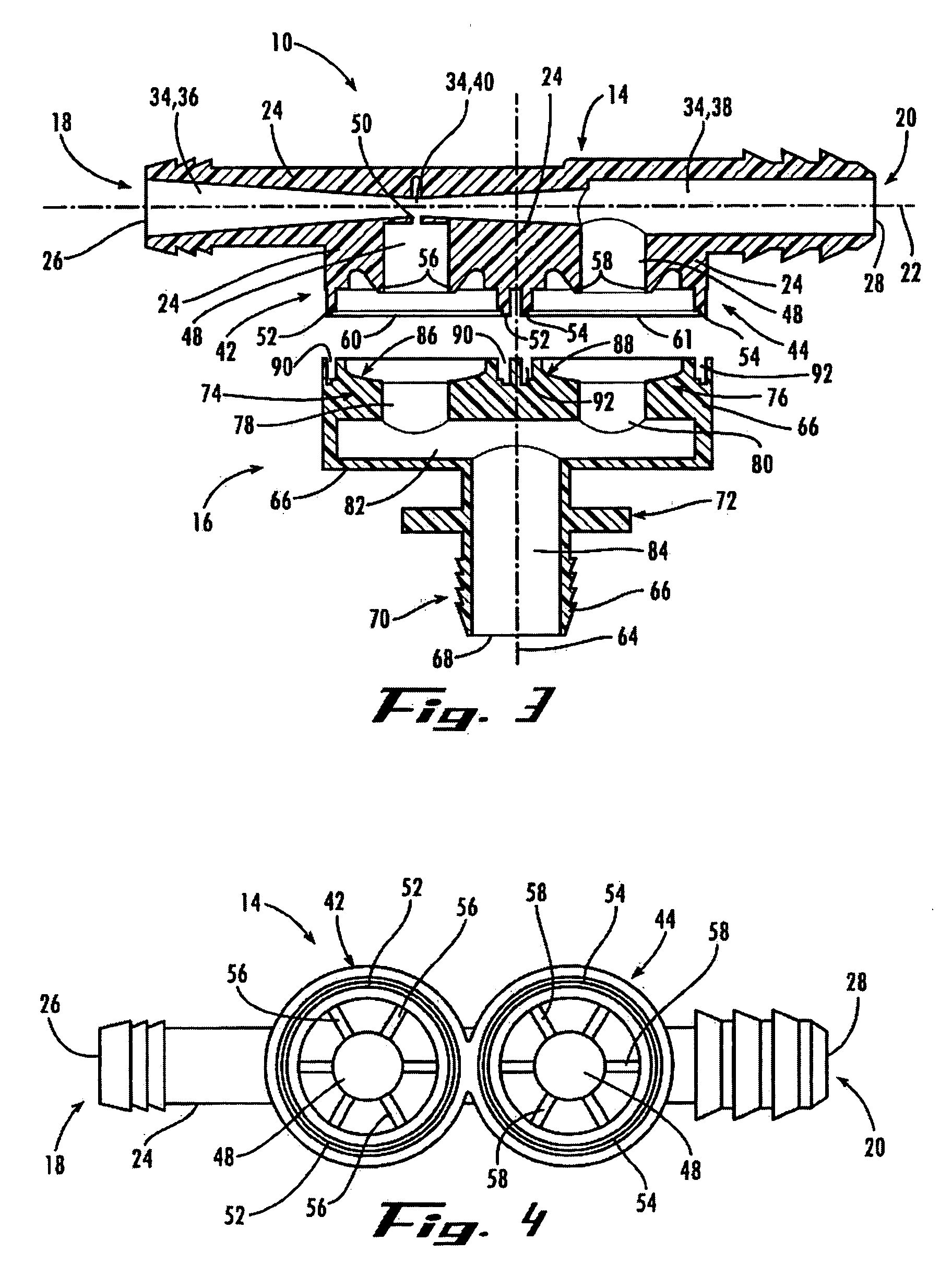
ActiveUS20190375383A1Reduce excess spaceImprove the environmentBraking action transmissionCoupling device detailsBody axisElectrical connection
An electromechanical braking (EMB) connector for electrical communication between an interior of a brake caliper assembly and an exterior of the brake caliper assembly is disclosed. The EMB connector includes a body having a distal end for insertion into the interior of the brake caliper assembly and a proximal end for exposure on the exterior of the brake caliper assembly, with the distal end and the proximal end defining a body axis. The EMB connector also includes a load sensor connector for coupling with a load sensor disposed on the interior of the brake caliper assembly. The load sensor connector is compressible along a load sensor axis that is substantially perpendicular to the body axis. The EMB connector further includes a conductive component coupled to the load sensor connector. The conductive component enables electrical connection of the load sensor to the exterior of the brake caliper assembly.
Owner:SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES INC
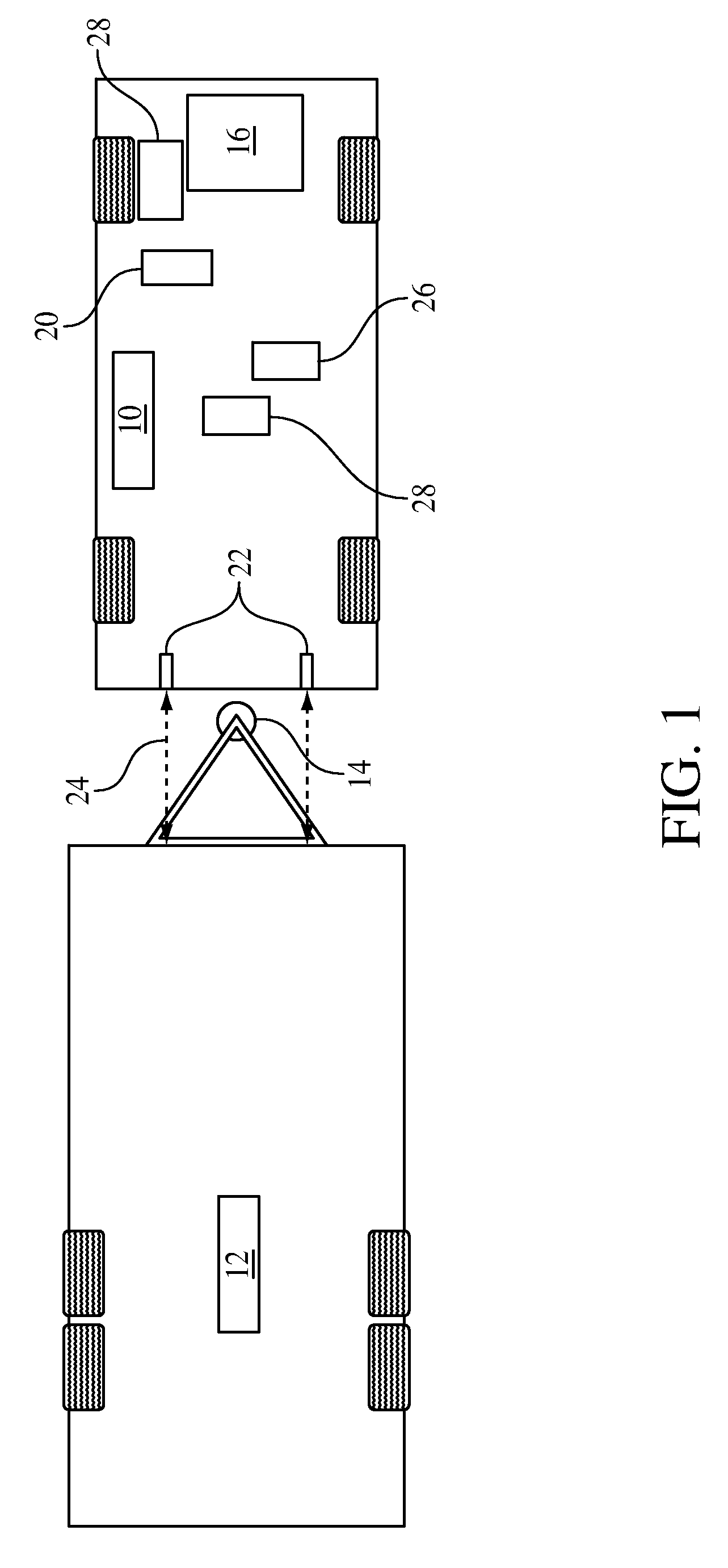
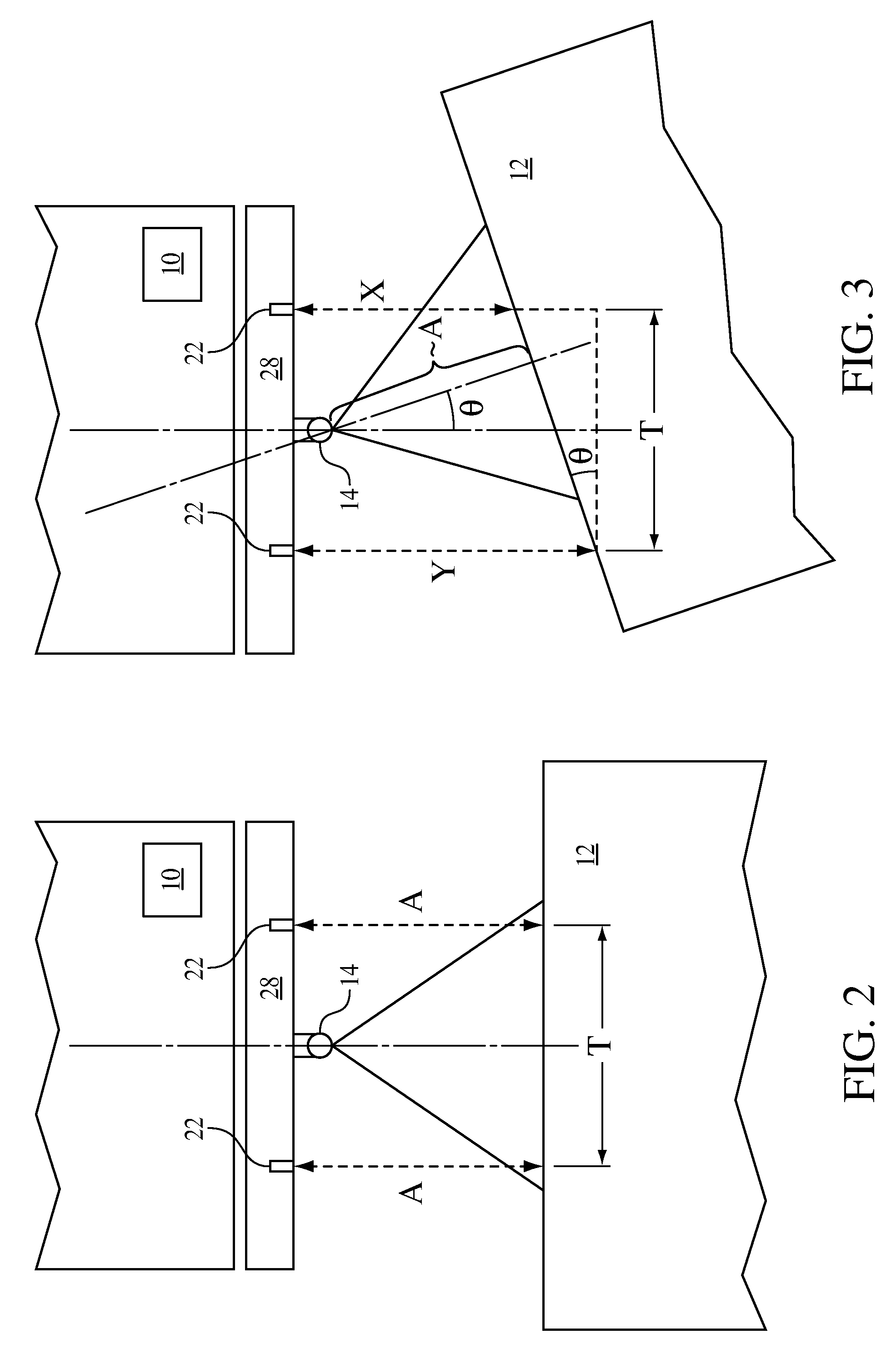
Trailer sway control with reverse sensors
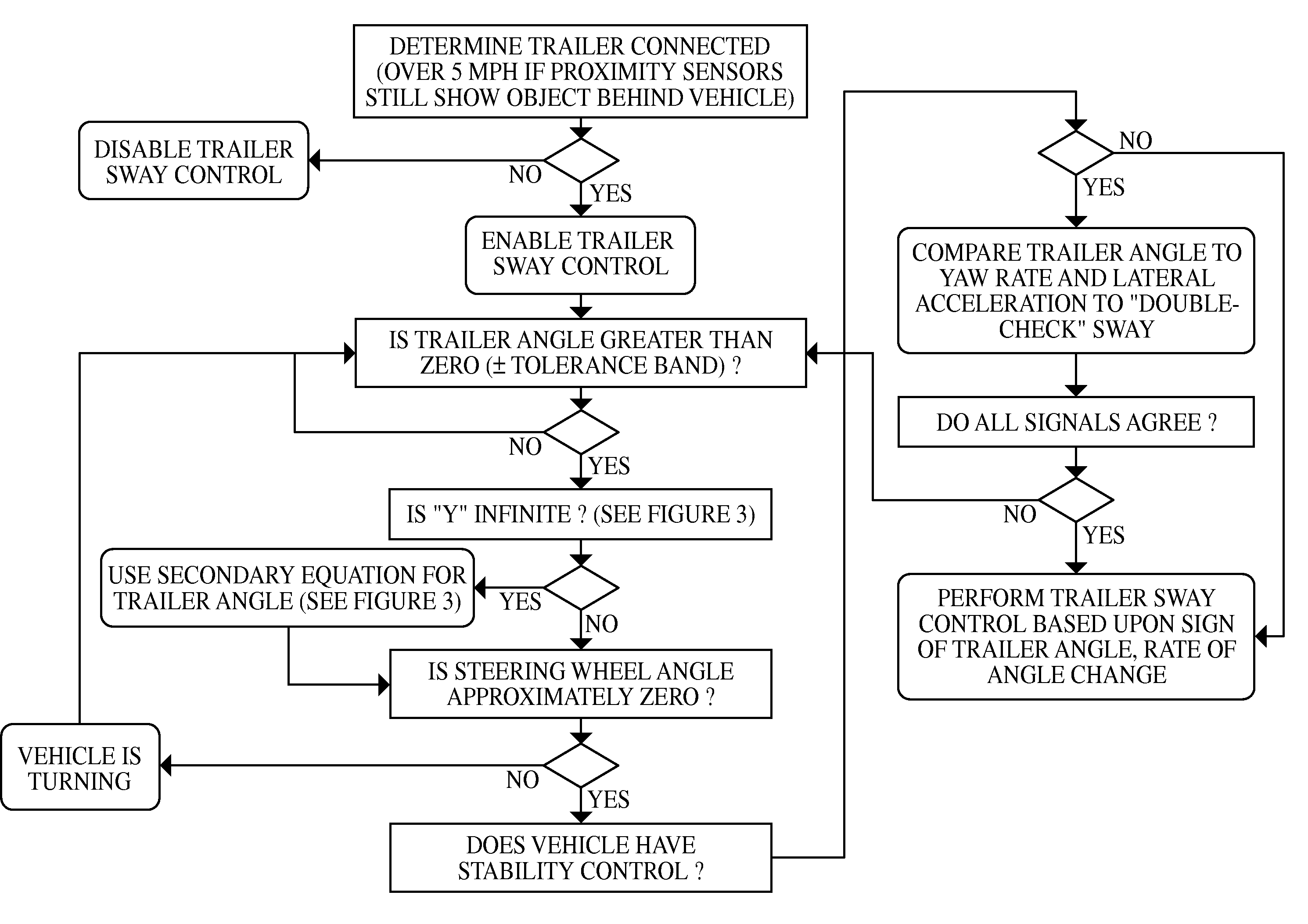
InactiveUS20090198425A1Furthers stabilizationHand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficProximity sensorSteering wheel
Reverse proximity sensors are used to determine an angle between a towed trailer and the towing vehicle. The trailer sway control determines a trailer angle of sway based upon proximity sensor readings from the reverse proximity sensors and from a sensor reading of an angle of turn of a steering wheel of the towing vehicle. Provided the determined trailer angle of sway exceeds a range that can be tolerated, a controller sends instructions to apply necessary braking to the vehicle or trailer to mitigate the trailer sway.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Vehicle brake device
InactiveUS20050269875A1Small dimensionLight weightPropulsion by batteries/cellsVehicular energy storageRegenerative brakeEngineering
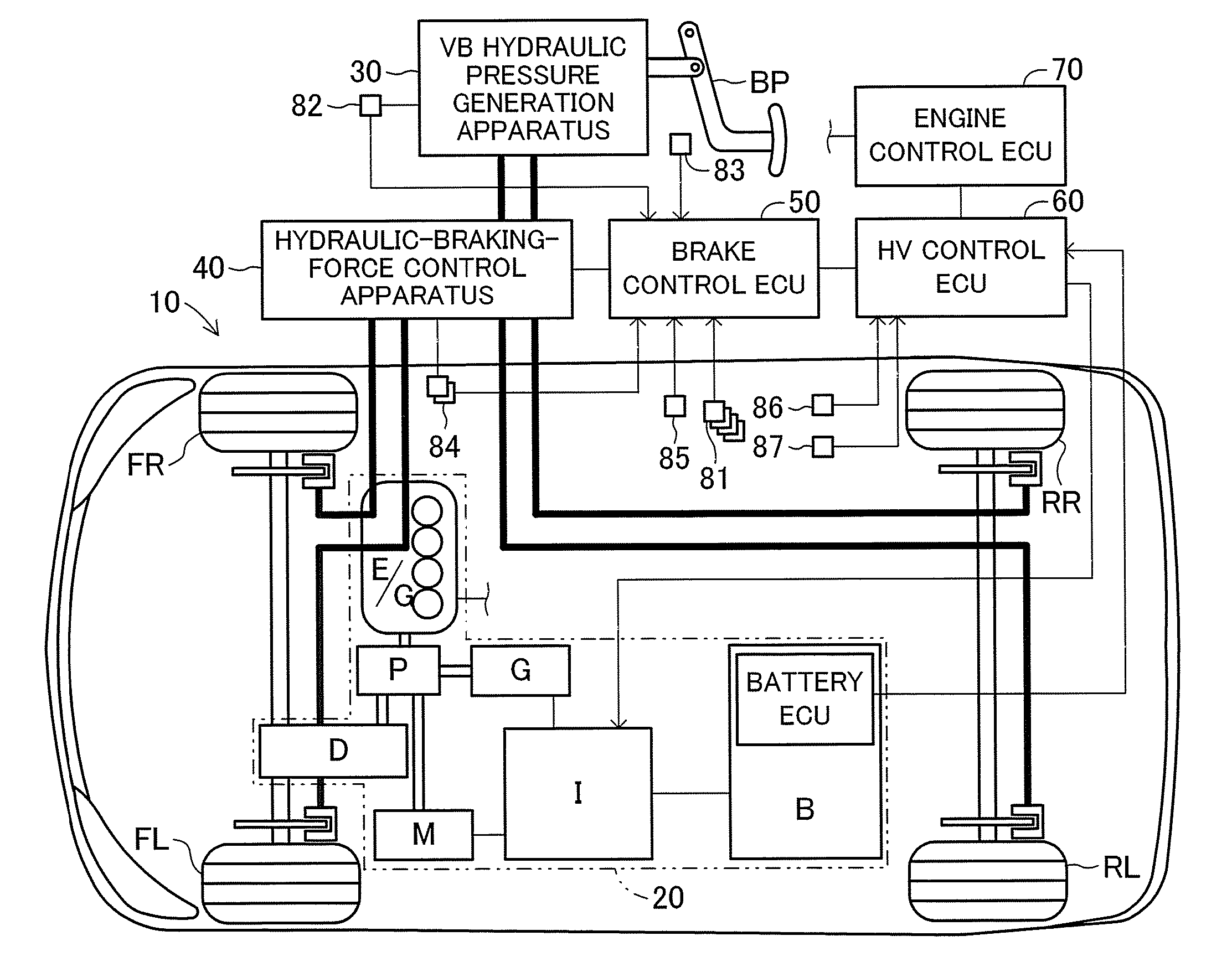
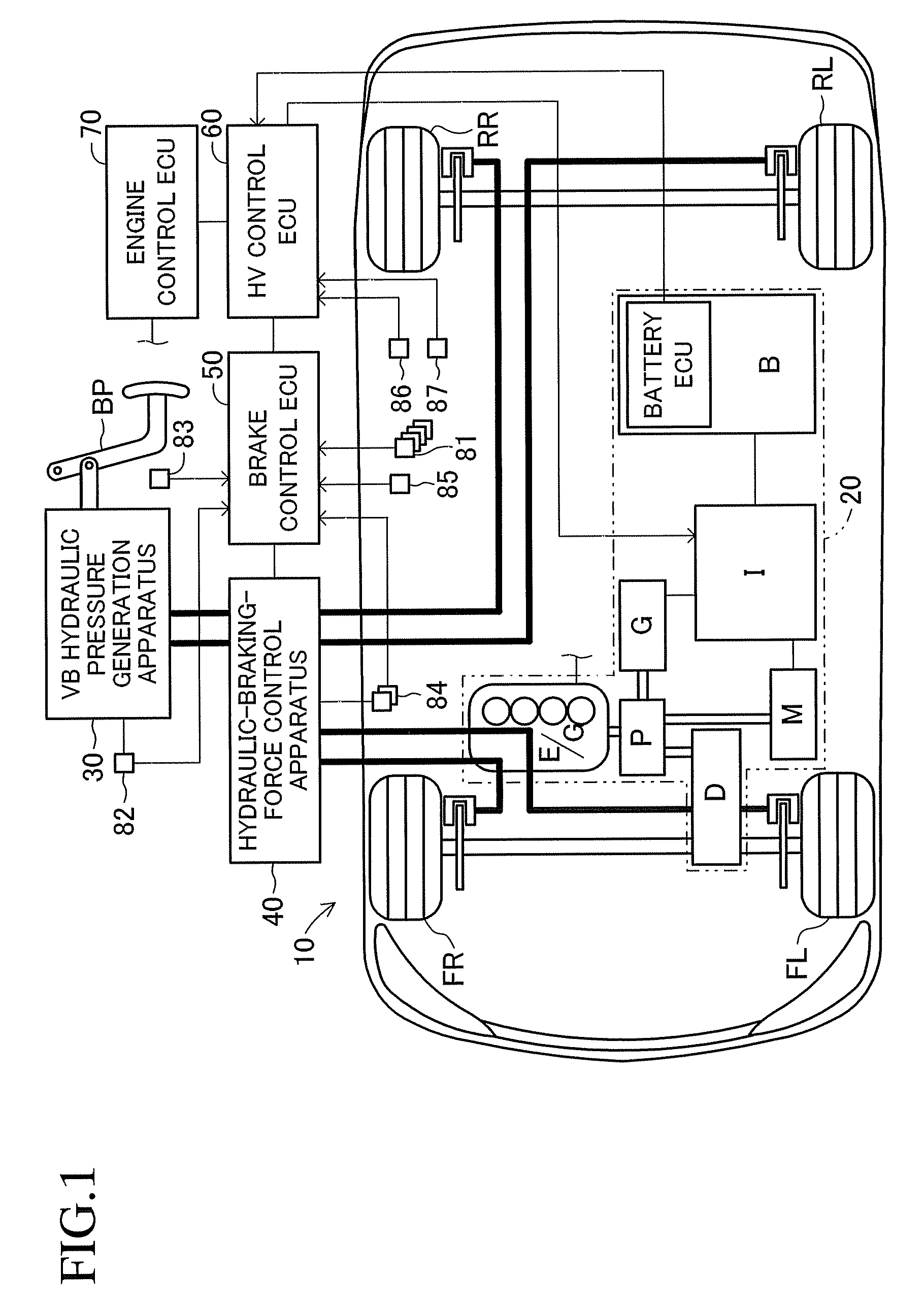
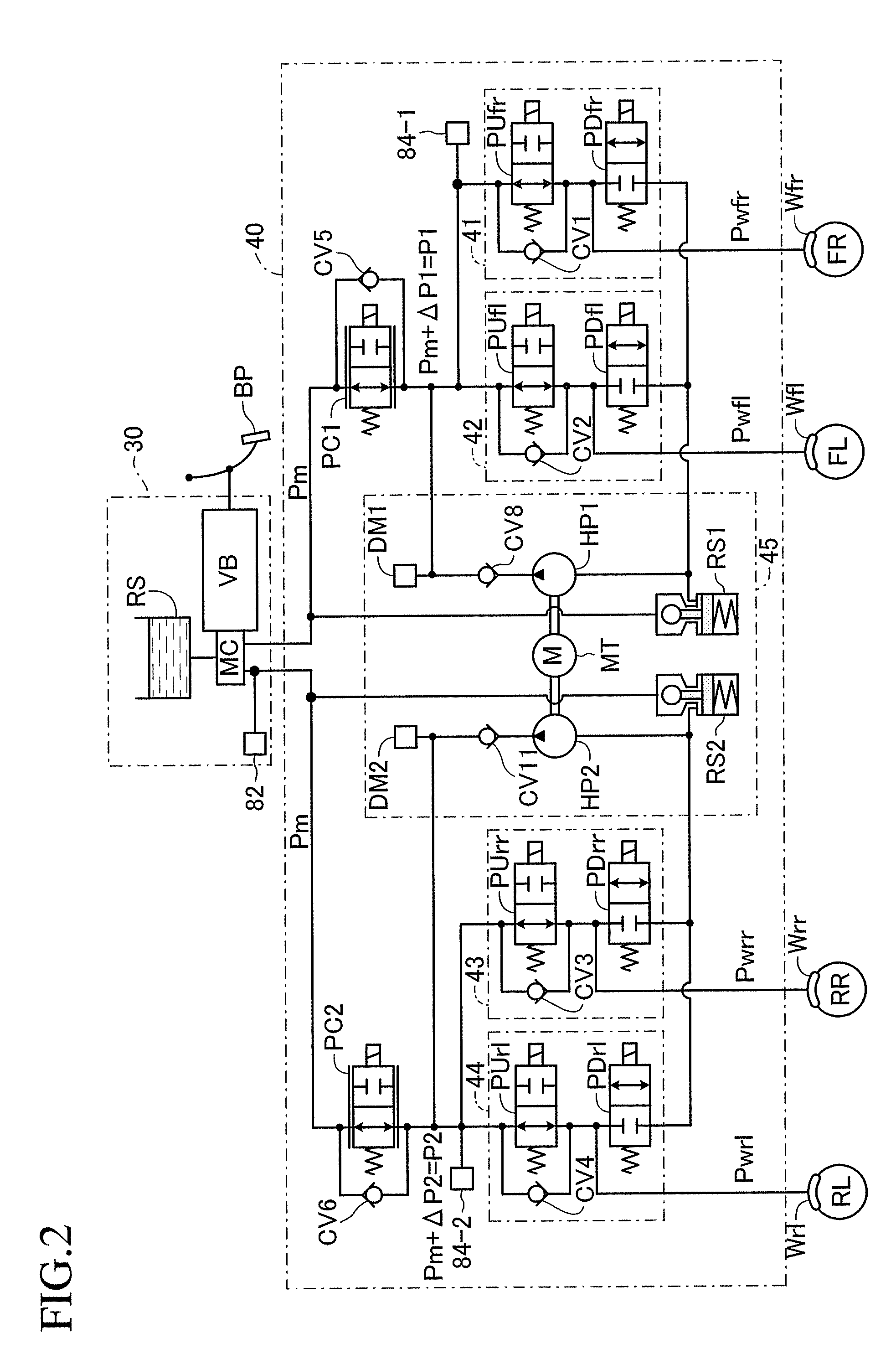
A vehicle brake device is provided with a hydraulic brake device for boosting by a booster device a braking manipulation force generated upon a braking manipulation, for applying a base fluid pressure generated in dependence on the boosted brake manipulation force, to wheel cylinders of wheels so that a base hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels, and for driving a pump to generate and apply a controlled fluid pressure to the wheel cylinders so that a controlled hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels; braking manipulation state detecting means for detecting the braking manipulation state; a regenerative brake device for causing an electric motor to generate a regenerative brake force corresponding to the braking manipulation state on the wheels driven by the electric motor; variation detecting means for detecting the variation of an actual regenerative brake force actually generated by the regeneration braking device; and brake force compensating means for generating the controlled fluid pressure by driving the pump of the hydraulic brake device so that a controlled hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels to compensate for the lack of the regenerative brake force due to the variation which is detected by the variation detecting means.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
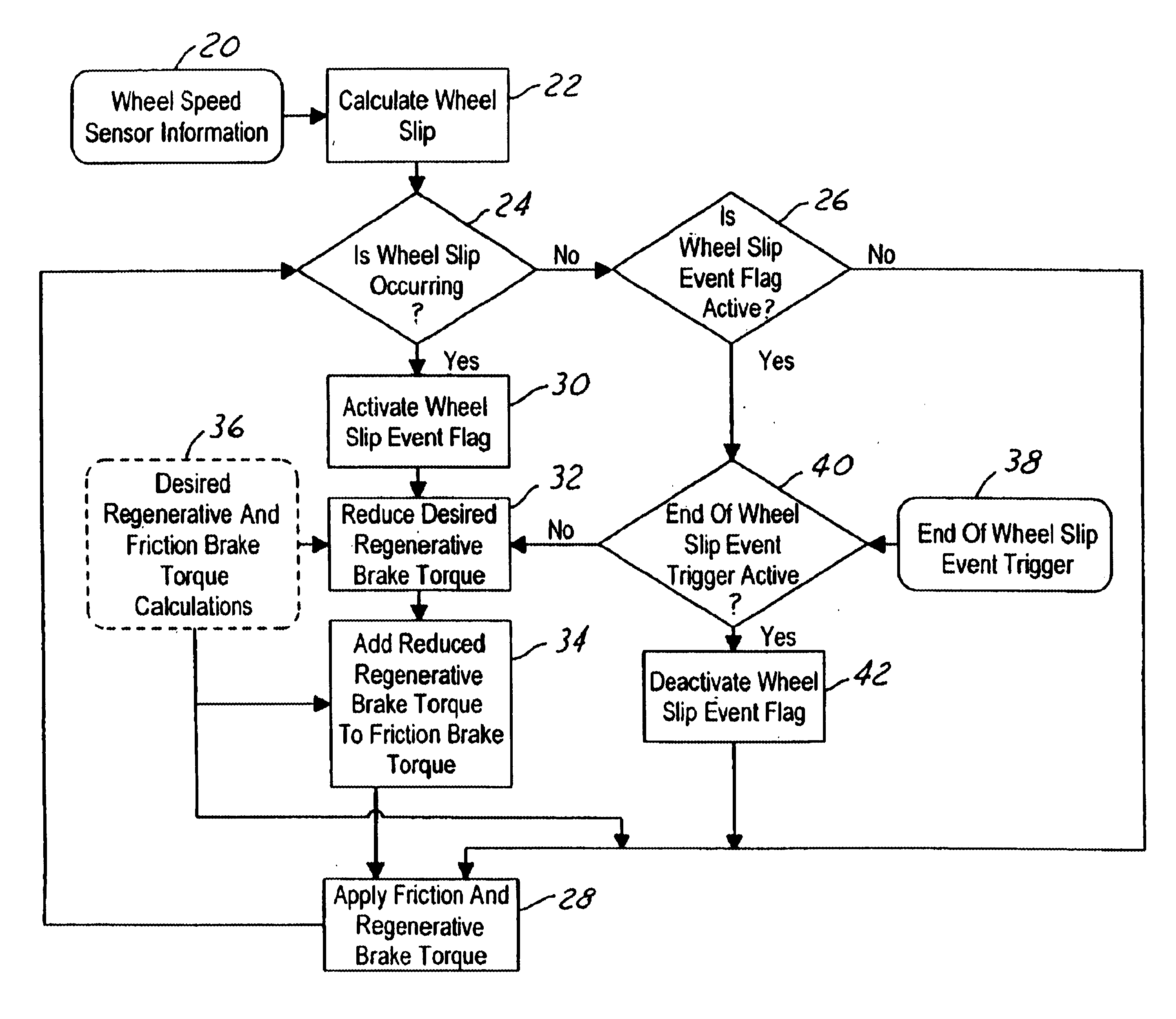
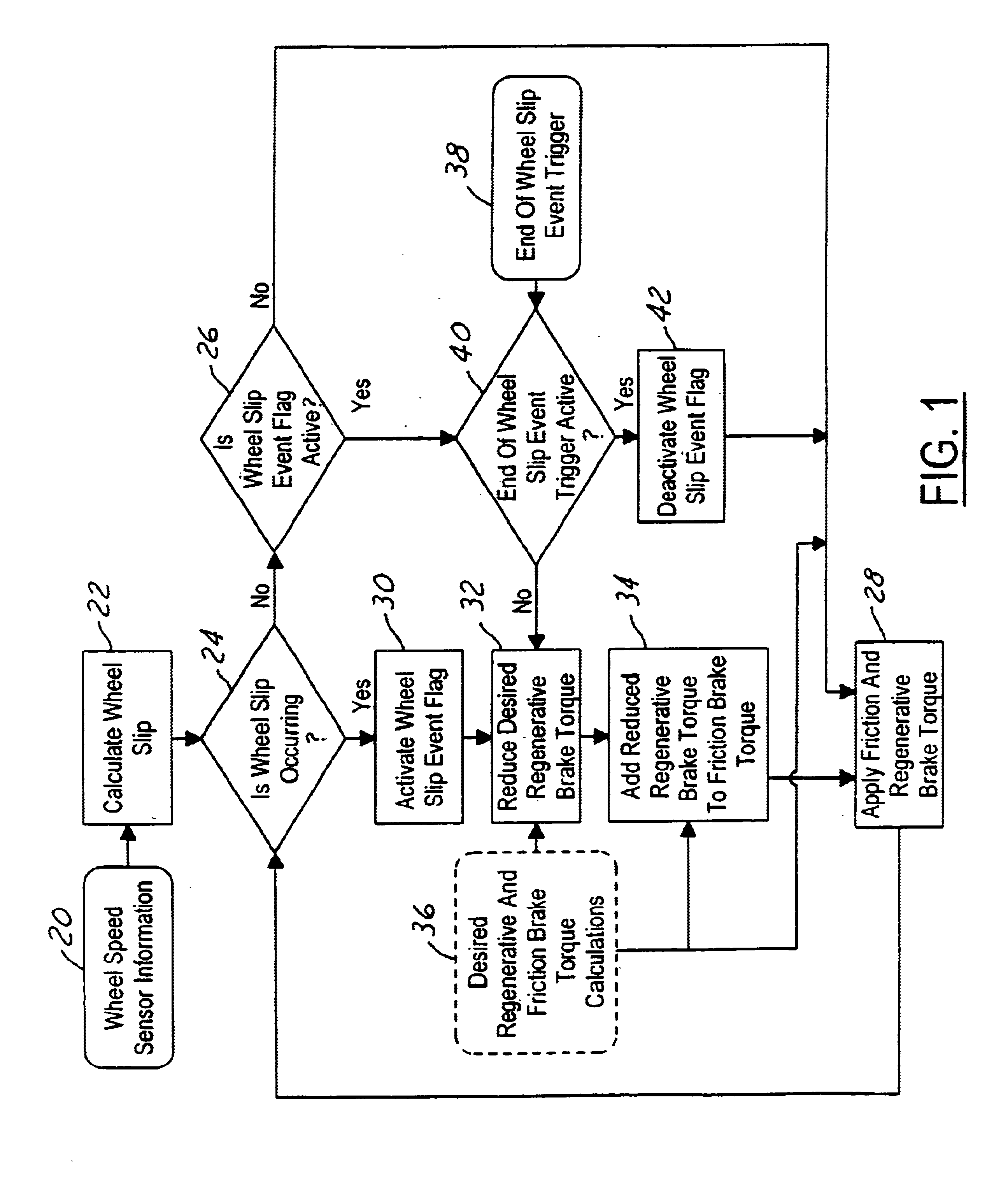
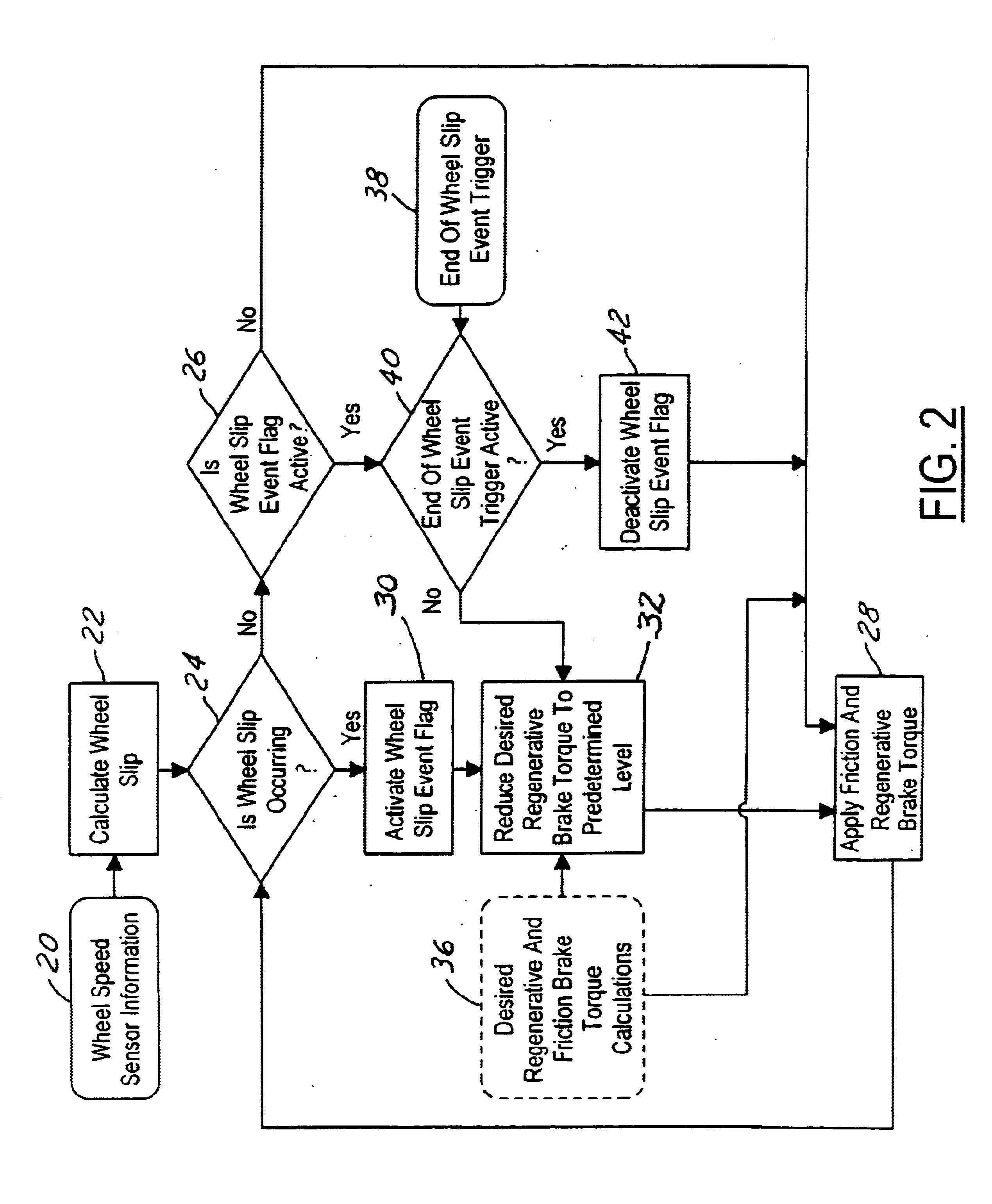
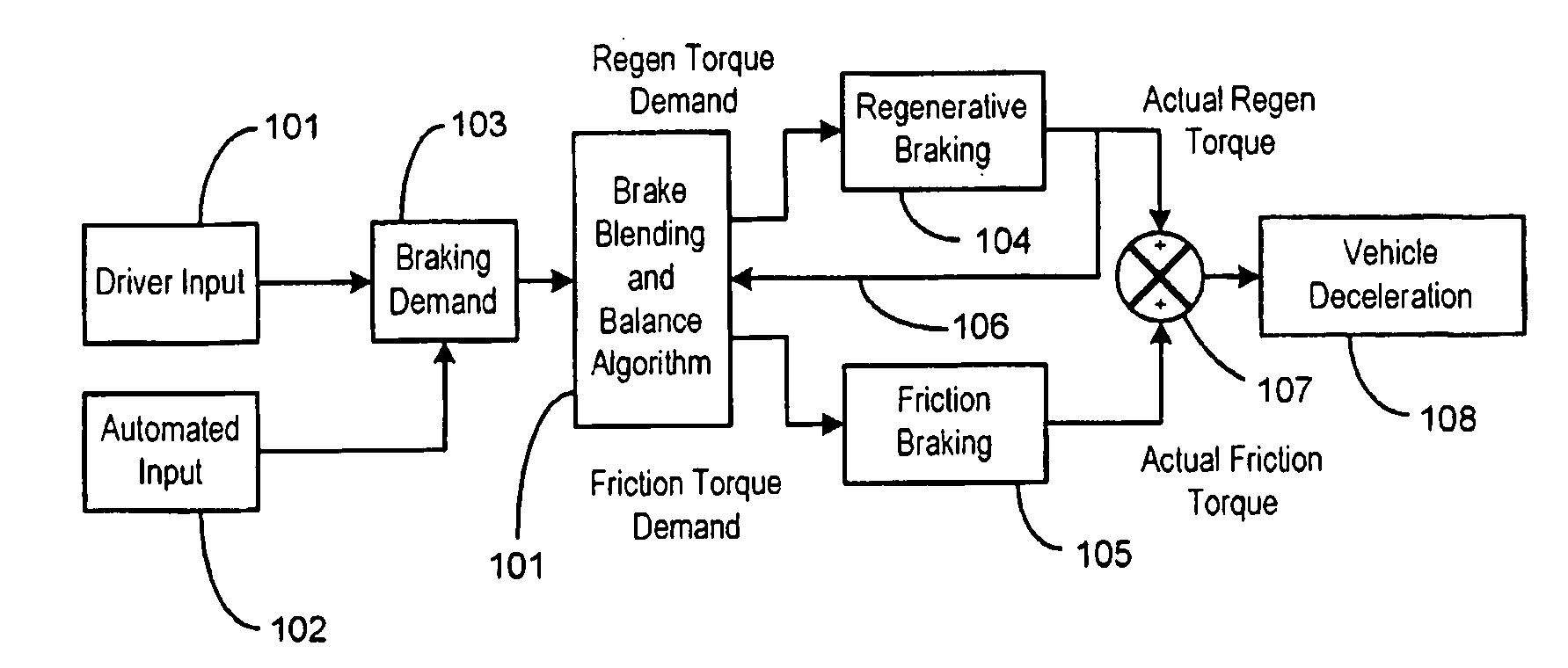
System and method for braking an electric drive vehicle on a low Mu surface
Strategies other than immediate elimination of regenerative braking (FIG. 2) are invoked when an incipient wheel lock-up is detected, the ABS becomes active, and / or incipient wheel slip is detected. The strategies include: reducing the regenerative braking torque as a function of the coefficient of friction of a surface on which the vehicle is traveling (FIG. 3); and adjusting regenerative braking in relation to the rate at which wheel slip is changing (FIG. 4). Some of the strategies may be applied on an individual wheel basis (FIG. 5), and some of the strategies may be applied in conjunction with operating friction brakes of the vehicle to apply at least some of the reduction in regenerative braking torque as friction brake torque (FIG. 1).
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Piston ring
InactiveUS6325385B1Good sliding propertiesRelieve pressurePiston ringsBraking action transmissionCarbon filmDiamond-like carbon
Owner:TEIKOKU PISTON RING CO LTD
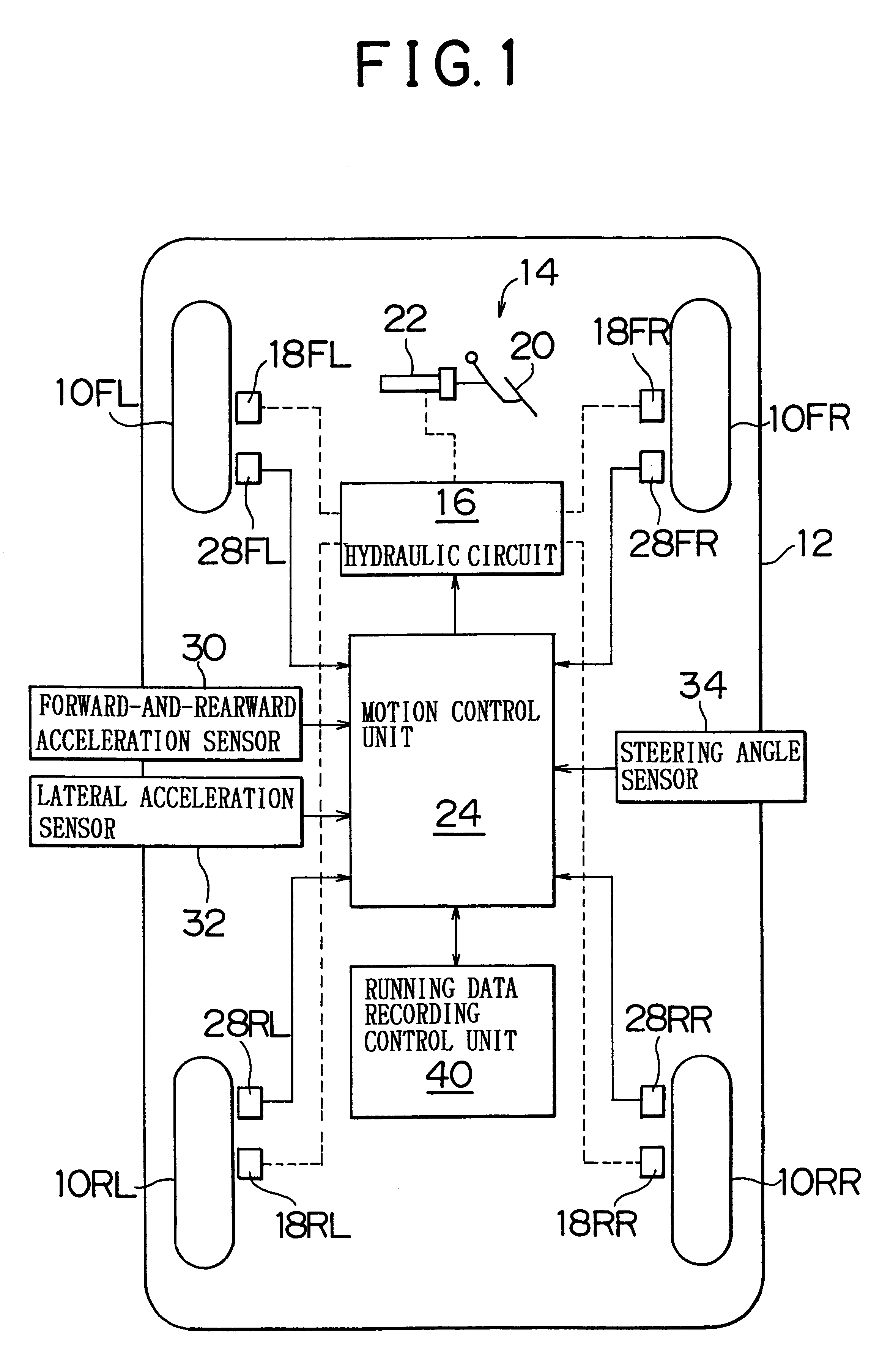
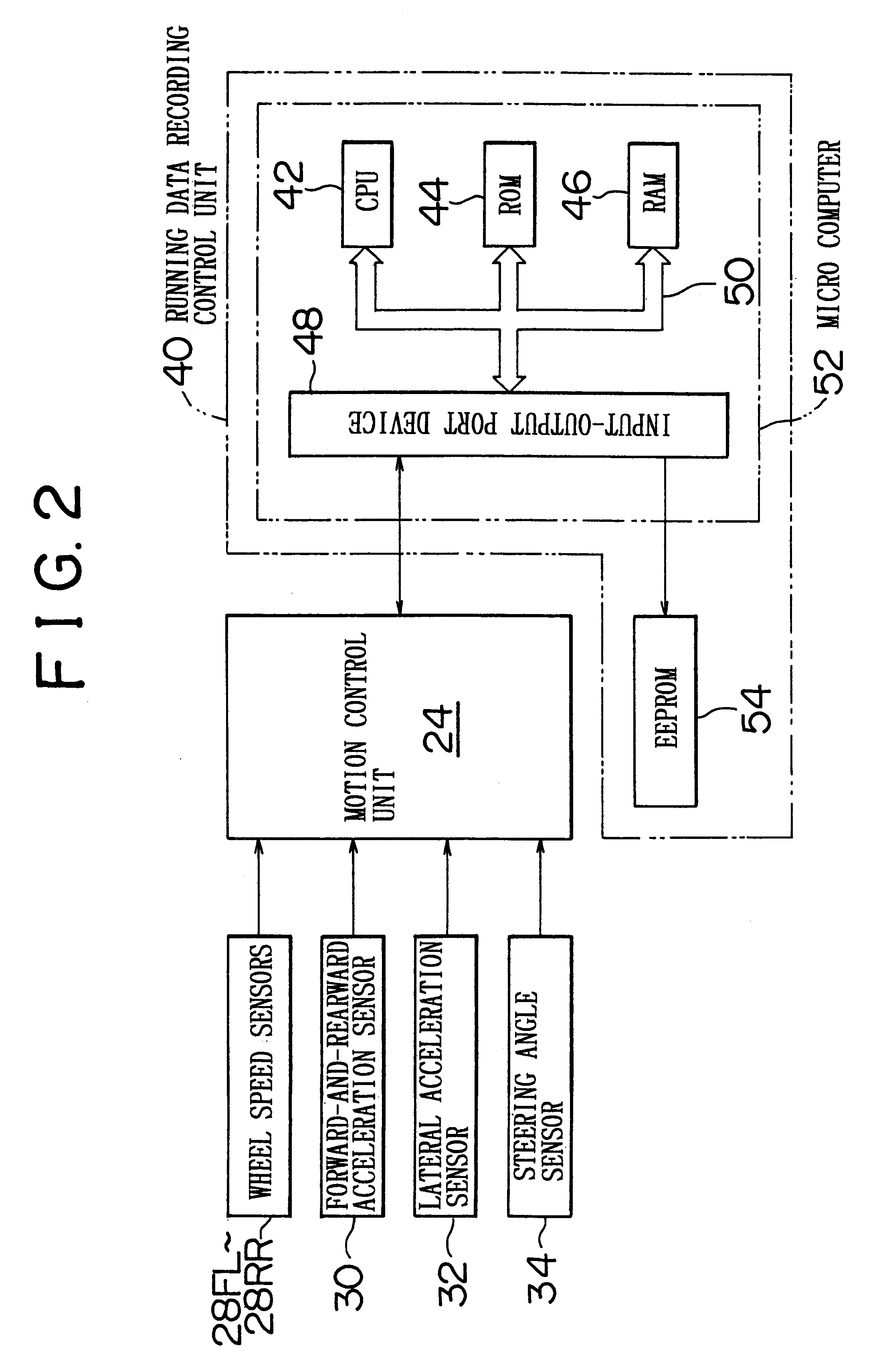
Vehicular data recording apparatus and method
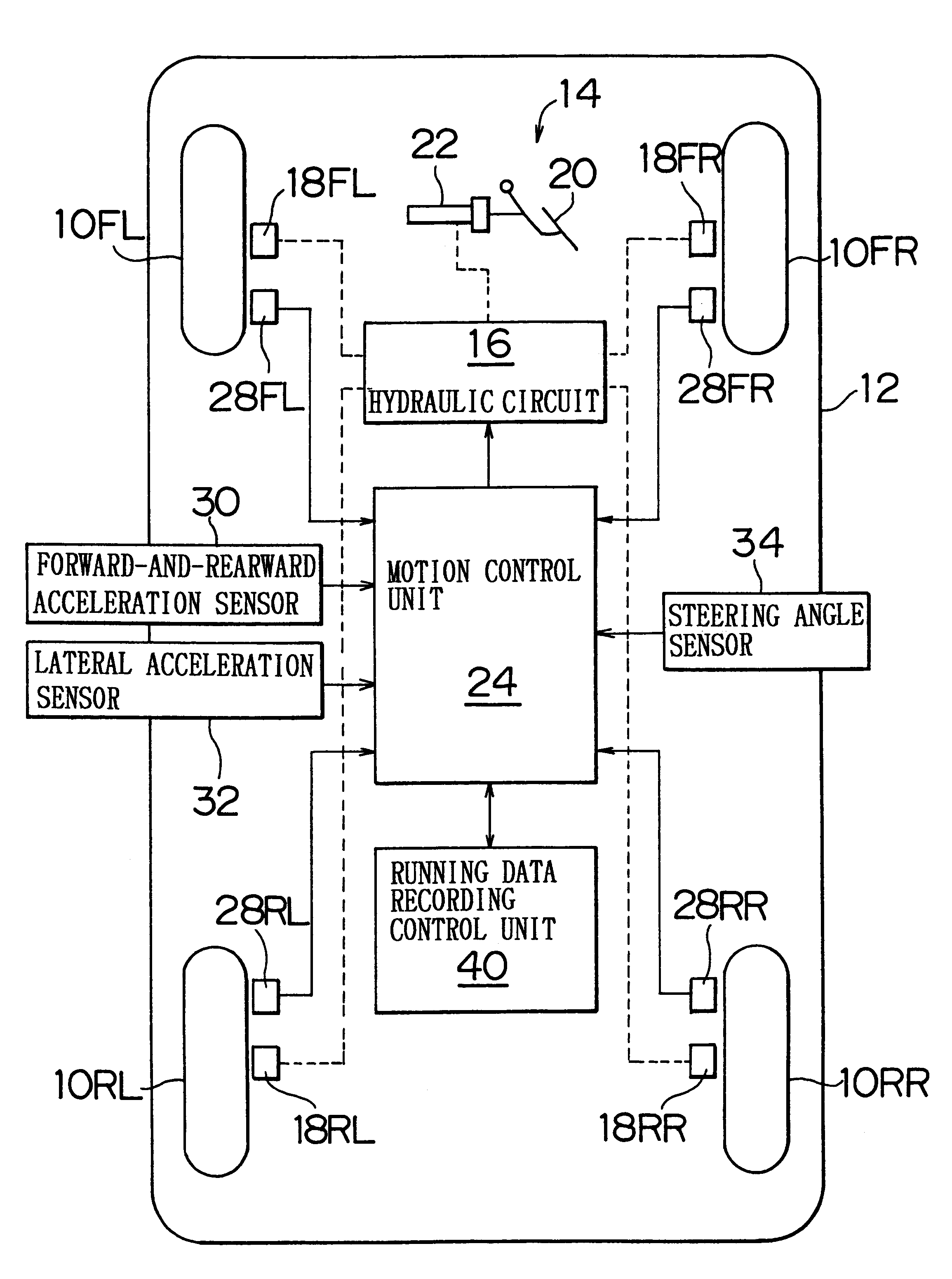
A vehicular data recording apparatus records running data regarding a vehicle into a memory in an overwrite manner when the running data needs to be recorded. If the vehicle enters an abnormal state, such as a crash or the like, the apparatus prevents the recording, and retains the running data recorded up to that moment in the memory. The apparatus determines whether the vehicle is in the abnormal state, for example, on the basis of a determination as to whether the vehicle has entered a stopped state within a predetermined time Tc following a time point at which the absolute value of a longitudinal acceleration Gx of the vehicle becomes equal to or greater than a reference value Gx1 and / or a time point at which the absolute value of a lateral acceleration Gy becomes equal to or greater than a reference value Gy1. Alternatively, or in addition, the vehicle is determined to be in an abnormal state based on a determination as to whether the vehicle is in the stopped state and the absolute value of the longitudinal acceleration Gx is equal to or greater than a reference value Gx2, and / or the absolute value of the lateral acceleration Gy is equal to or greater than a reference value Gy2.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
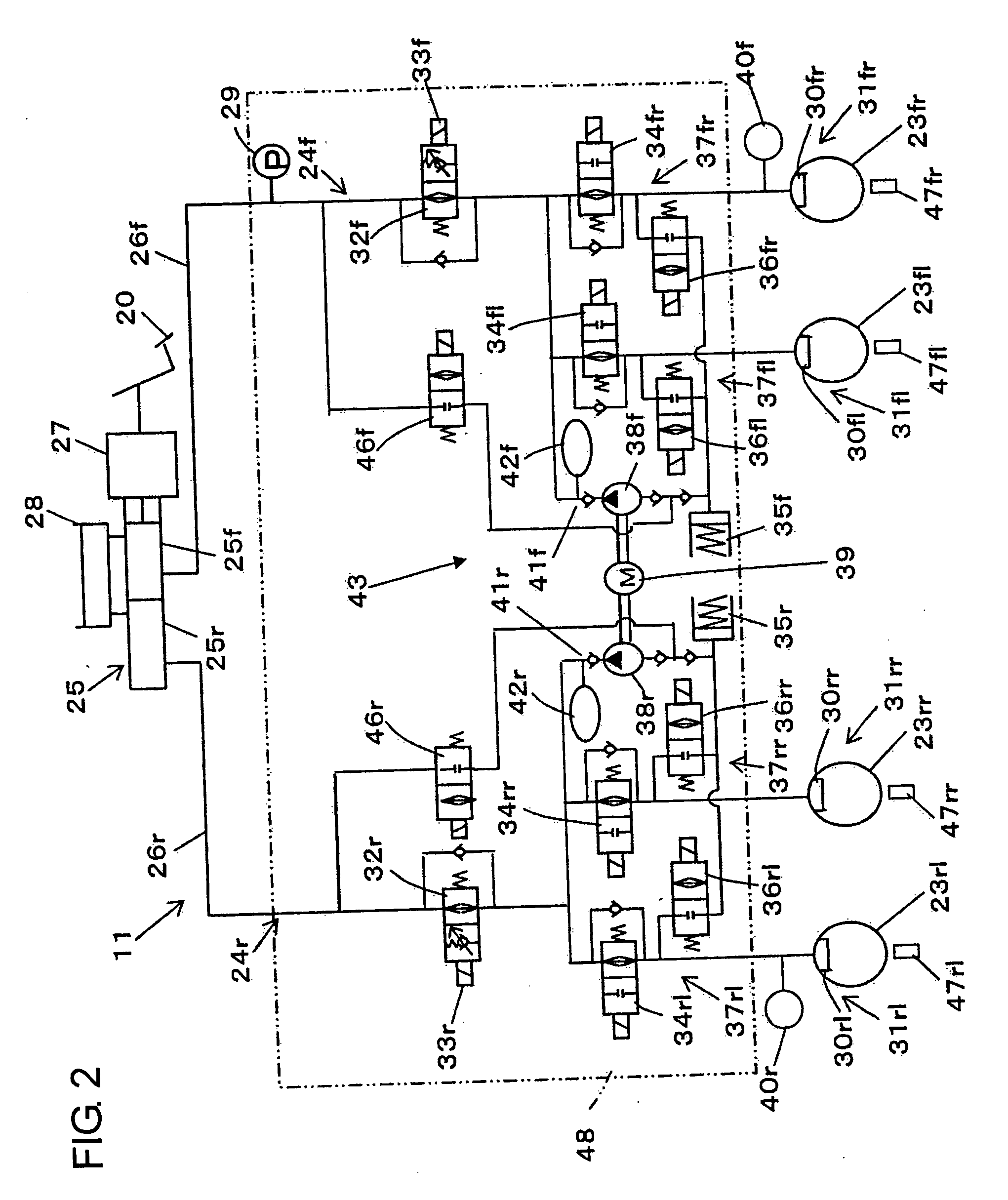
Vehicle System Having Regenerative Brake Control
ActiveUS20080100129A1Analogue computers for trafficBraking action transmissionRegenerative brakeKinetic energy
A method is provided for controlling the braking of a vehicle that has a first set of friction brakes for applying a first apply brake force to a first set of wheels and a second set of friction brakes for applying a second brake apply force to a second set of wheels. A powertrain assembly is coupled to the second set of wheels. The powertrain assembly includes a regenerative braking unit capable of recapturing kinetic energy from the second set of wheels. The vehicle is braked in a first phase of control using regenerative braking to brake the second set of wheels to achieve up to a first value of braking. The vehicle is braked in a second phase of control using the regenerative braking to maintain braking of the second set of wheels at the first value of braking force while selectively applying the first friction brakes to the first set of wheels up to a second value of braking.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Fluid-pressure brake system for a vehicle
InactiveUS20050029859A1Guaranteed functionObvious advantagesBraking action transmissionAnti-theft devicesElectricityActuator
A fluid-pressure brake system for a vehicle having a parking brake function in which, in response to actuation of an electrical parking brake signal transmitter, and without actuation of a brake pedal, at least one wheel brake of the brake system is actuated via an actuator to which the fluid is admitted. A parking brake module is provided in which there is integrated an electronic control unit as well as valve devices that are electrically actuatable by the electronic control unit. The electronic control unit actuates the parking brake function upon receiving from the parking brake signal transmitter an electrical actuating signal demanding actuation of the parking brake function and, as part of the parking brake function, the electronic control unit controls the admission of fluid to the actuator by means of the electrically actuatable valve devices.
Owner:WABCO GMBH
Vibration control apparatus for automotive vehicle
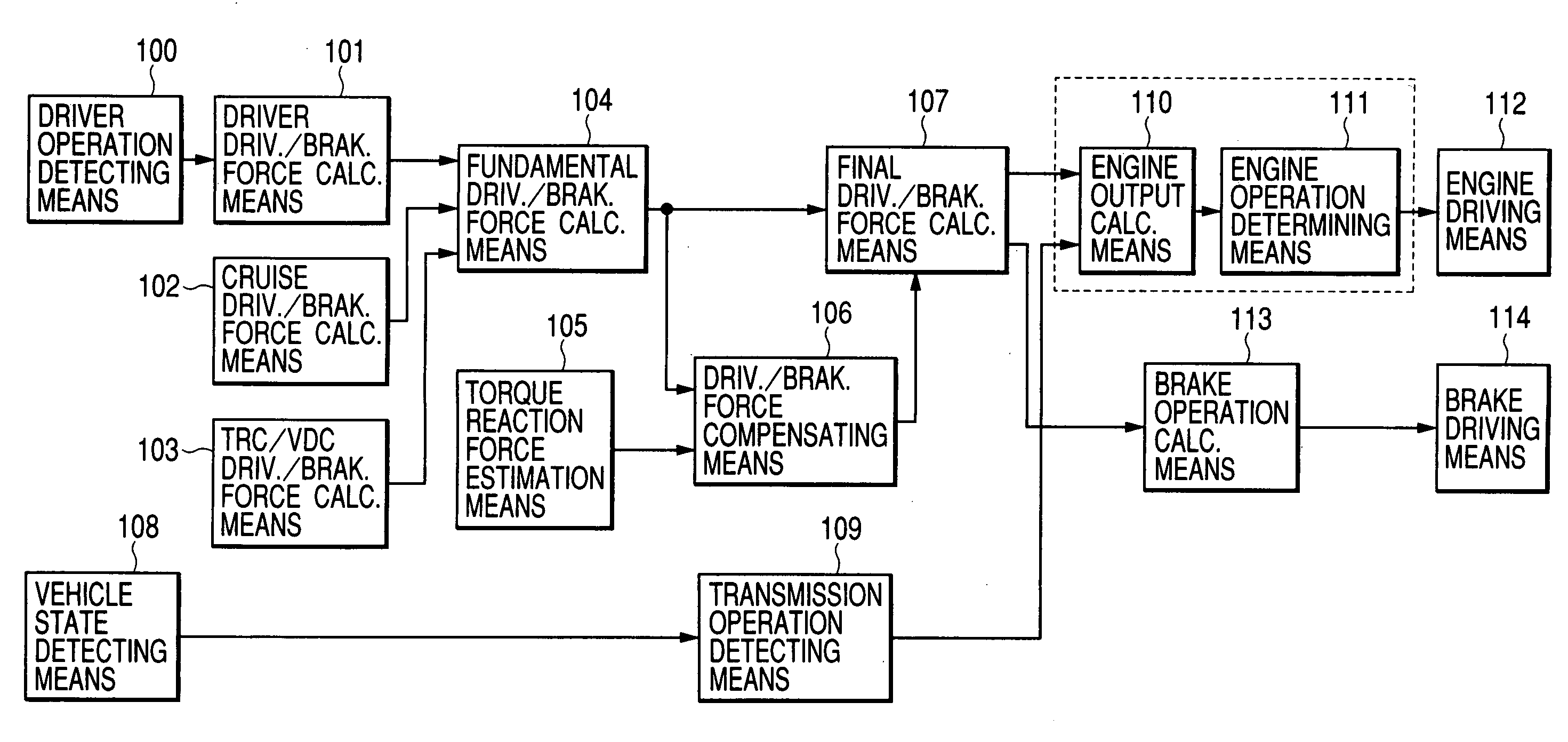
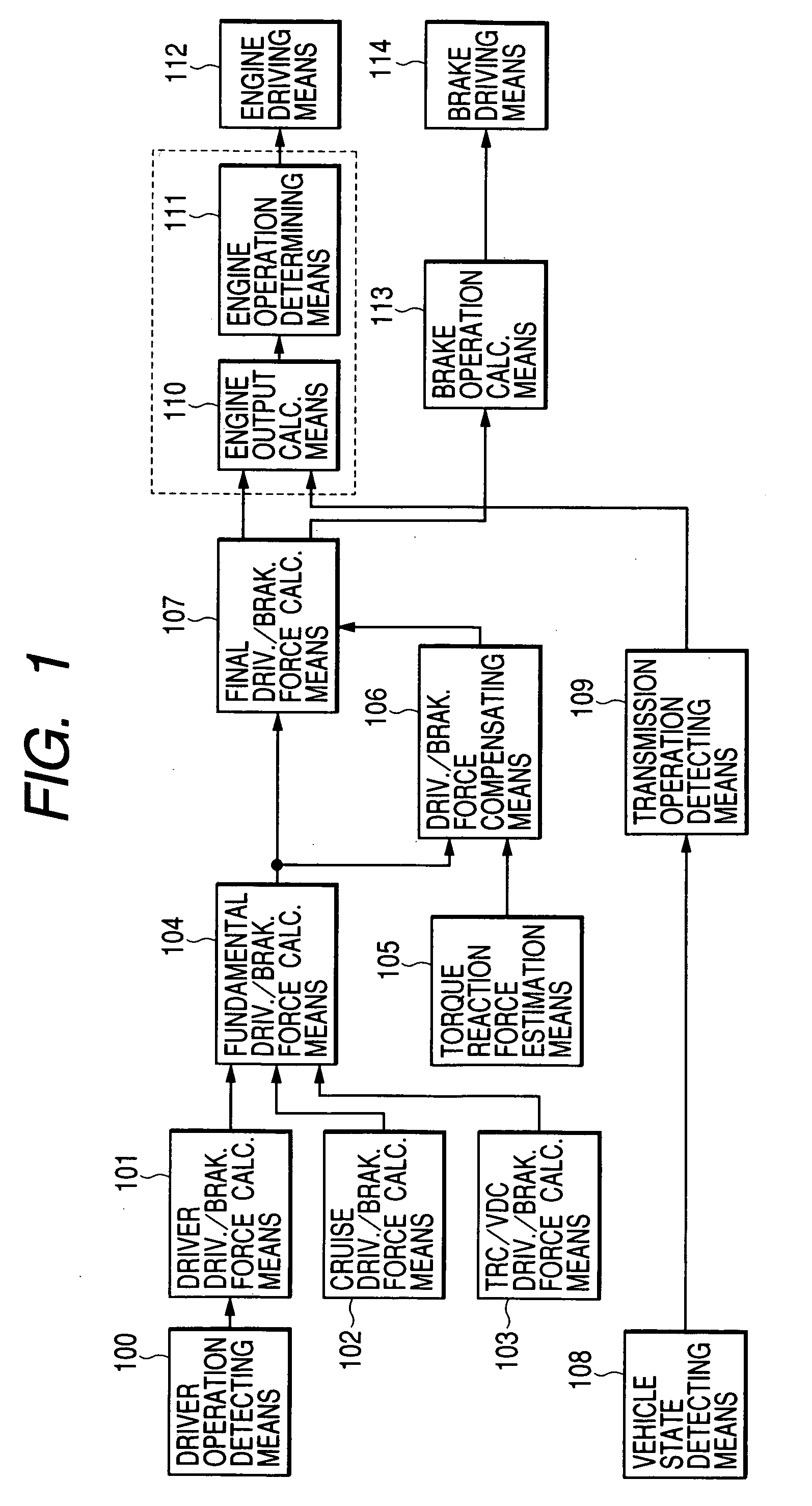
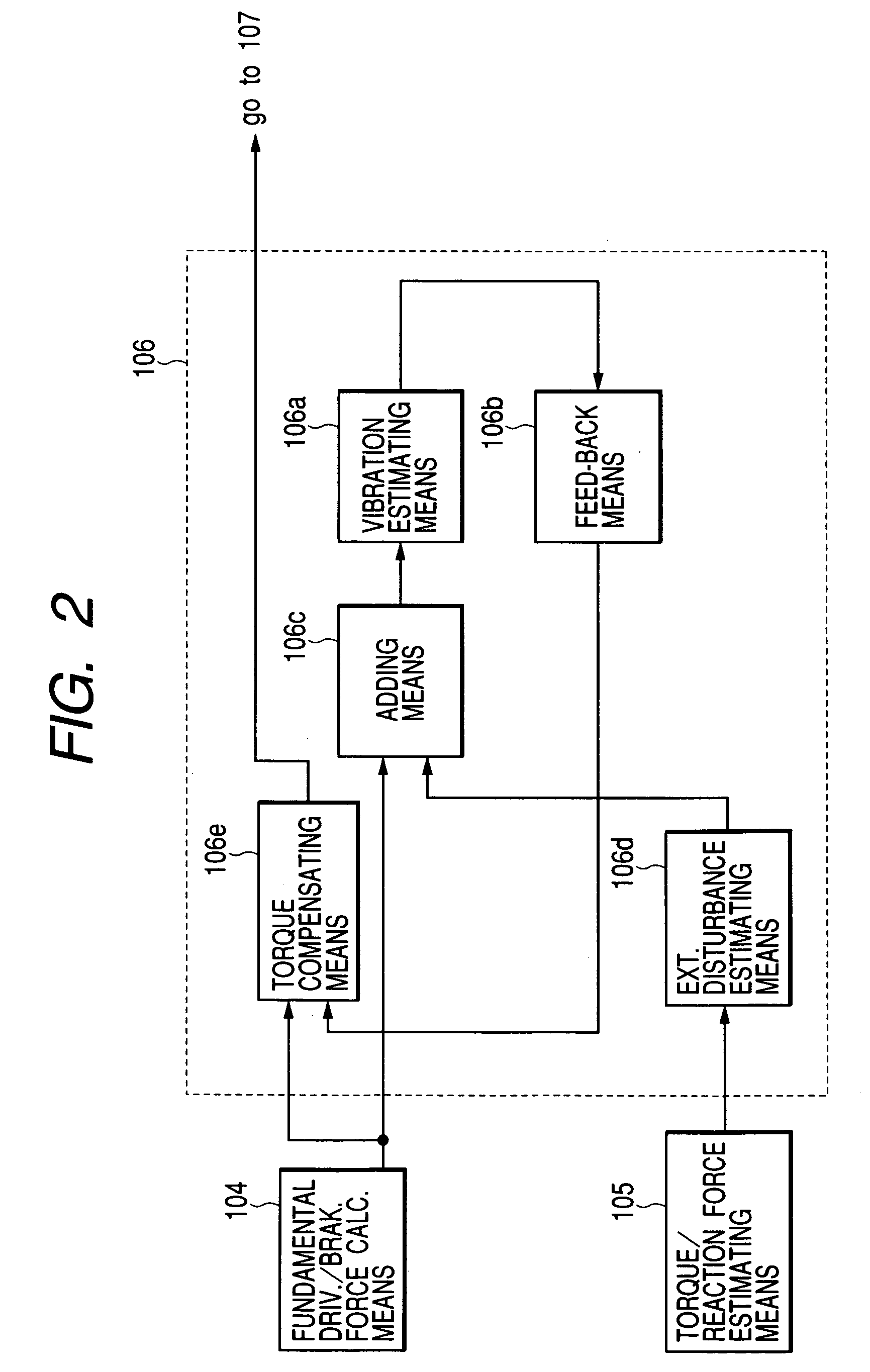
InactiveUS20050049761A1Accurate compensationRapid responseInternal combustion piston enginesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMobile vehicleResidual vibration
An object of the present invention is to execute an optimum control of vibrations due to a driver's operation of an accelerator pedal, steering wheel and brake pedal. The operation instructions are inputted into a vibration calculating means (kinetic model) comprising a vehicle body model, suspension model and tire model. Conventional kinetic model controlled the suspension in order to suppress the vehicle body vibration. However, in the kinetic model of the present invention, the tire vibration due to a change in the engine output is first absorbed by the suspension, whereby a residual vibration which was not be absorbed yet by the suspension is transferred to the vehicle body. The operation inputs are compensated by the three feed-back loops between the outputs of the above-mentioned three portions and input of the tire portion, giving the highest priority on the vehicle body model.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Trailer sway control with reverse sensors
InactiveUS8260518B2Furthers stabilizationHand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficProximity sensorSteering wheel
Reverse proximity sensors are used to determine an angle between a towed trailer and the towing vehicle. The trailer sway control determines a trailer angle of sway based upon proximity sensor readings from the reverse proximity sensors and from a sensor reading of an angle of turn of a steering wheel of the towing vehicle. Provided the determined trailer angle of sway exceeds a range that can be tolerated, a controller sends instructions to apply necessary braking to the vehicle or trailer to mitigate the trailer sway.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Brake by-wire actuator
InactiveUS20060163941A1High brake pressureReduce tractionBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsMobile vehicleDistributor
The present invention relates to a brake-by-wire actuator for actuating the brake system of a motor vehicle, comprising a simulator which can be acted upon by a brake pedal, with a signal of an actuation sensor being sent to an electronic control unit which controls a pressure source in response to the signal of the actuation sensor, and wherein an output of the pressure source is connected to a distributor device for the brake force and actuates individual wheel brakes of the vehicle, also comprising means for enabling actuation of the brakes by muscular power within a fallback mode. In order to provide an improved fallback mode in a brake-by-wire actuator, according to the invention, a lost travel is provided between a first actuation component such as a brake pedal in particular or a component articulated at the brake pedal and an actuation component that is connected downstream in the flux of force, in particular an input member, in order to uncouple the first actuation component mechanically from the reactions of force of the motor vehicle brake system in the by-wire mode.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Vacuum enhancing check valve
InactiveUS20060016477A1Reducing vehicle 's costReduce complexityBraking action transmissionRatio controlEngineeringCheck valve
A vacuum enhancing check valve for direct connection to a vehicle brake booster which increases the partial vacuum provided thereto and restricts possible air back flow into the brake booster. The valve comprises a venturi for reducing the pressure of air induced to flow between a first air inlet and an air outlet by a partial vacuum at a vehicle engine's intake manifold. By significantly reducing the air pressure, the valve enhances the partial vacuum available for provision to the brake booster. The venturi is also in air communication with a second air inlet directly attachable to the brake booster such that the air pressure at the second air inlet tends toward the enhanced partial vacuum within the venturi. A valve seat and seal member within the valve are cooperative to allow air flow from the second air inlet toward the venturi, but not in the reverse direction.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Electronic braking system and method for drawbar trailers
ActiveUS8267485B2Overcome disadvantagesReduce probabilityBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsAxle loadBraking system
A system and method for braking a drawbar trailer having a front axle and one or more further axles, each axle having at least two wheels, includes first sensors which sense the axle load of at least one axle, and second sensors which sense the rotational wheel speeds. Brakes actuatable with a pneumatic brake pressure brake the trailer. Brake signals generated in the towing vehicle are transmitted between the towing vehicle and the trailer. A control unit receives these brake signals and the sensor signals, and determines the axle load. The operating pressure is adapted to the brake pressure which is fed to the brakes. The control unit detects the brake pressure value as a function of (i) the specific axle loads of the front axle and the other axles and (ii) the received brake signals, and actuates the brakes such that the detected brake pressure is made available.
Owner:WABCO EURO BVBA SPRL
Valve assembly having improved conductance control
InactiveUS20050067603A1High conductanceEasy to controlPiston ringsBraking action transmissionSlide plateVALVE PORT
A valve assembly including a housing having a flow channel and an annular surface surrounding the flow channel, a slide plate movable to a closed position, and a seal ring positioned between the annular surface and the slide plate. The seal ring includes a first and second sides, a first surface extending between the first and the second sides and facing towards the annular surface of the housing, and a second surface axially spaced from the first surface and extending between the first and the second sides and facing towards the slide plate. The second surface includes a continuous annular sealing portion for contacting the slide plate when the seal ring is biased against the slide plate so that a fluid-tight seal can be formed between the continuous annular sealing portion and the slide plate, and at least one passageway positioned between the annular sealing portion and the second side.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Device for controlling spin/driftout of vehicle compatibly with roll control
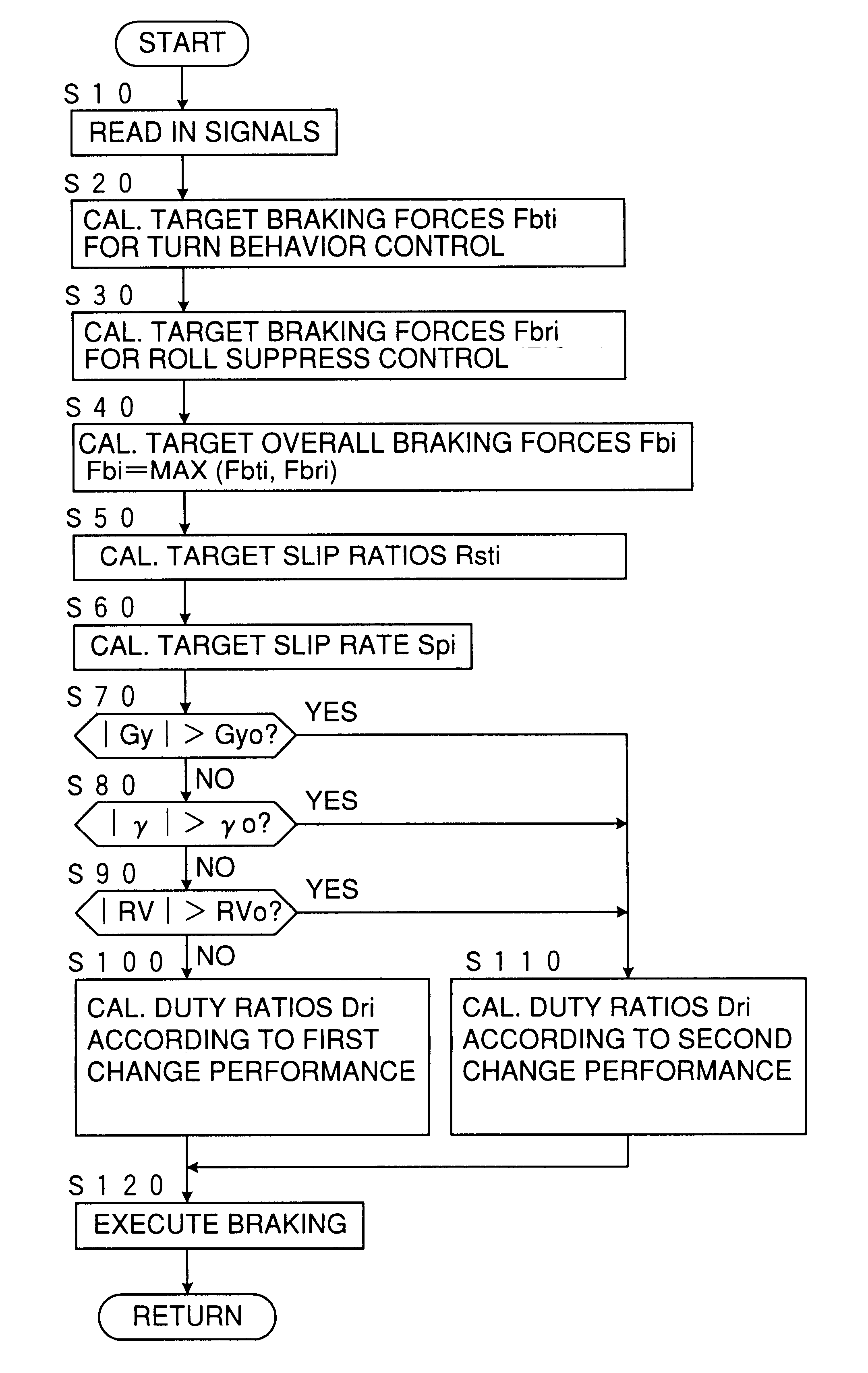
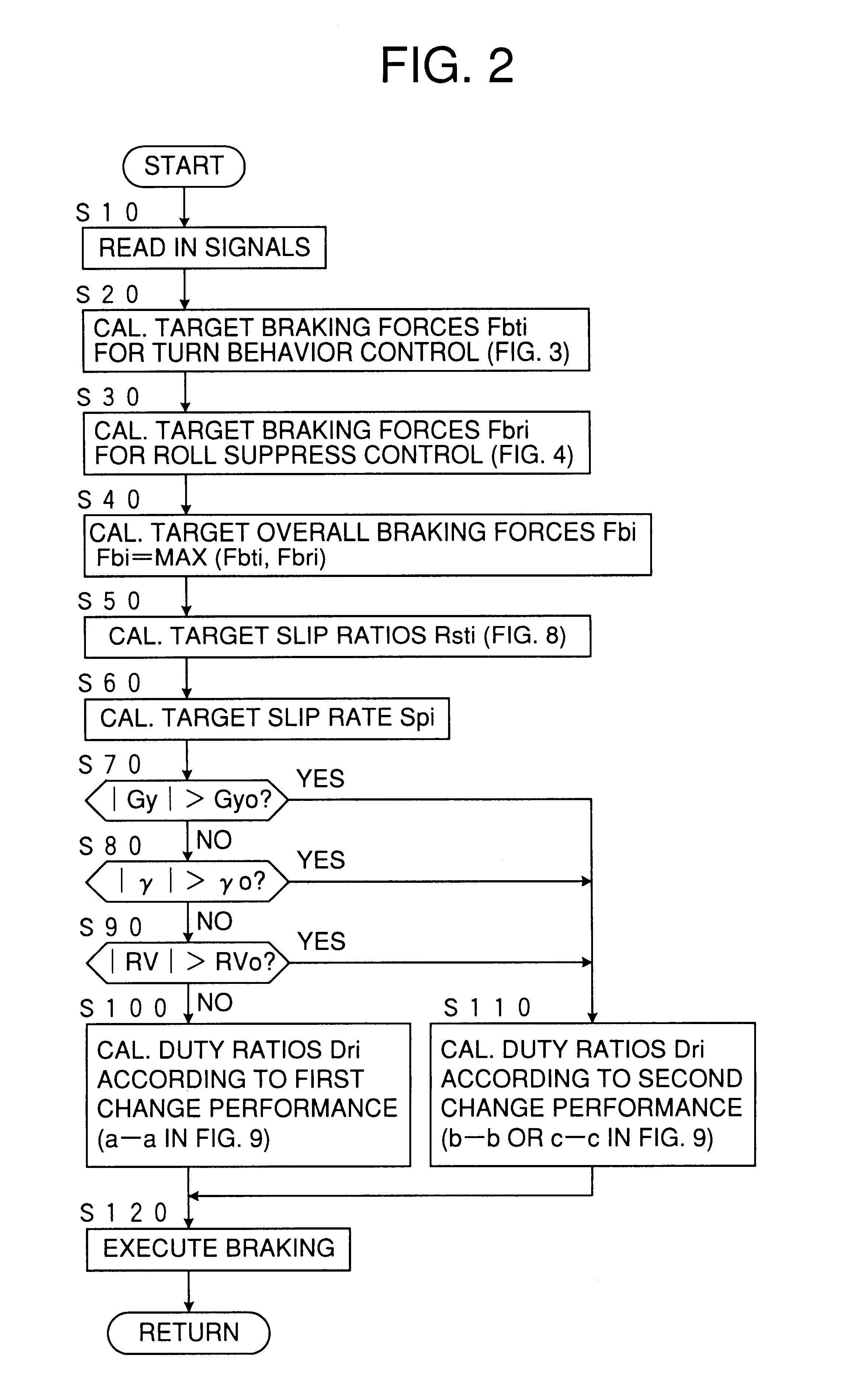
InactiveUS6278930B1Suppress a vehicle from excessively rollingHand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficInstabilityEngineering
A moving behavior control device for a vehicle calculates first target braking forces to be applied to the respective wheels for stabilizing the vehicle against a turn instability, second target braking forces to be applied to the respective wheels for stabilizing the vehicle against a roll instability, and target overall braking forces to be applied to the respective wheels by integrating the first and second target braking forces, and applies braking forces to the respective wheels according to the target overall braking forces, wherein the applied braking forces are decreased according to a first rate schedule by which the applied braking forces are decreased at a first rate according to an excess of the applied braking forces relative to the target overall braking forces when the vehicle is running at no probability of rolling beyond a predetermined threshold roll, and according to a second rate schedule by which the braking forces are lowered at a second rate smaller than the first rate according to the excess when the vehicle is running at such a probability.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
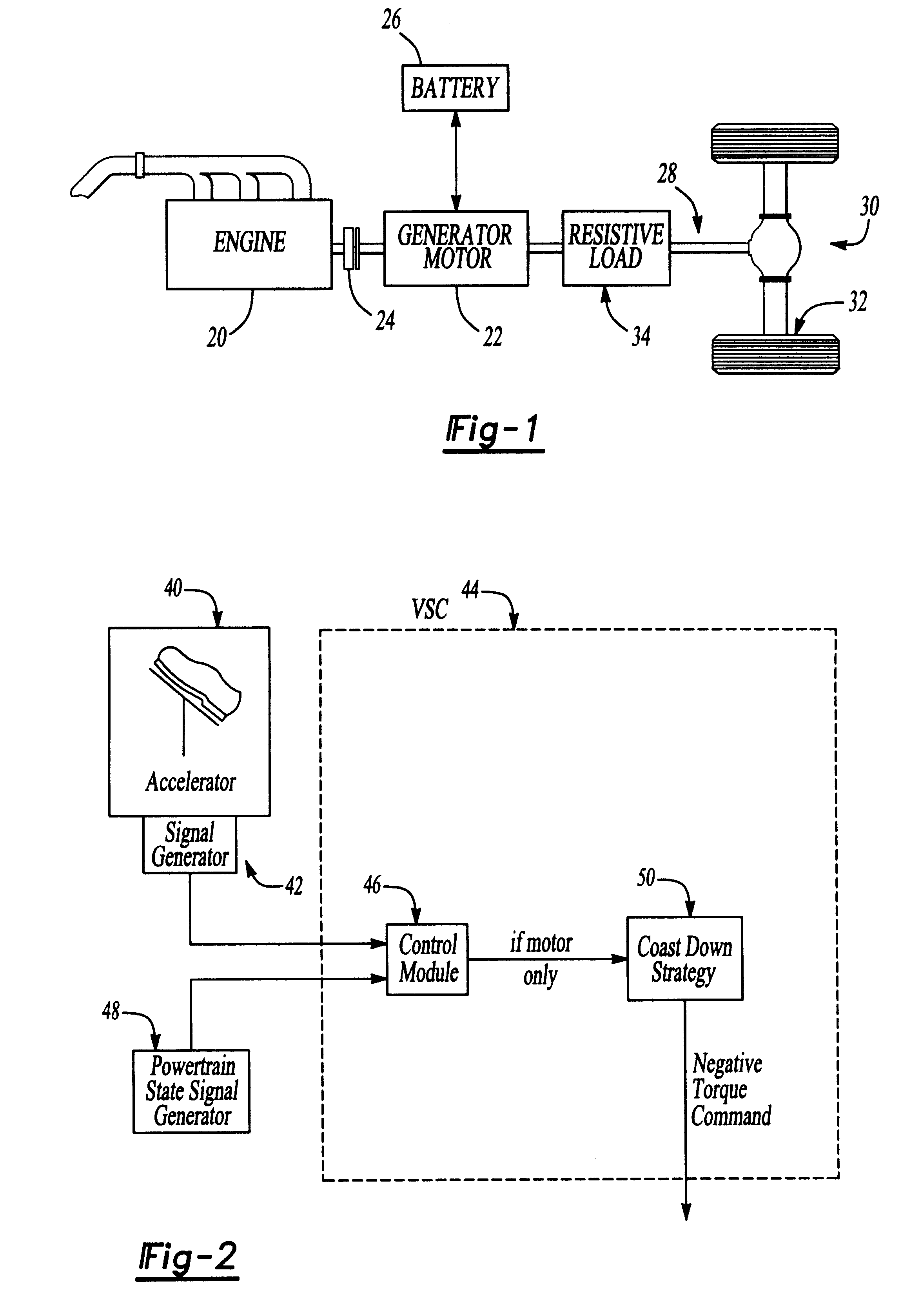
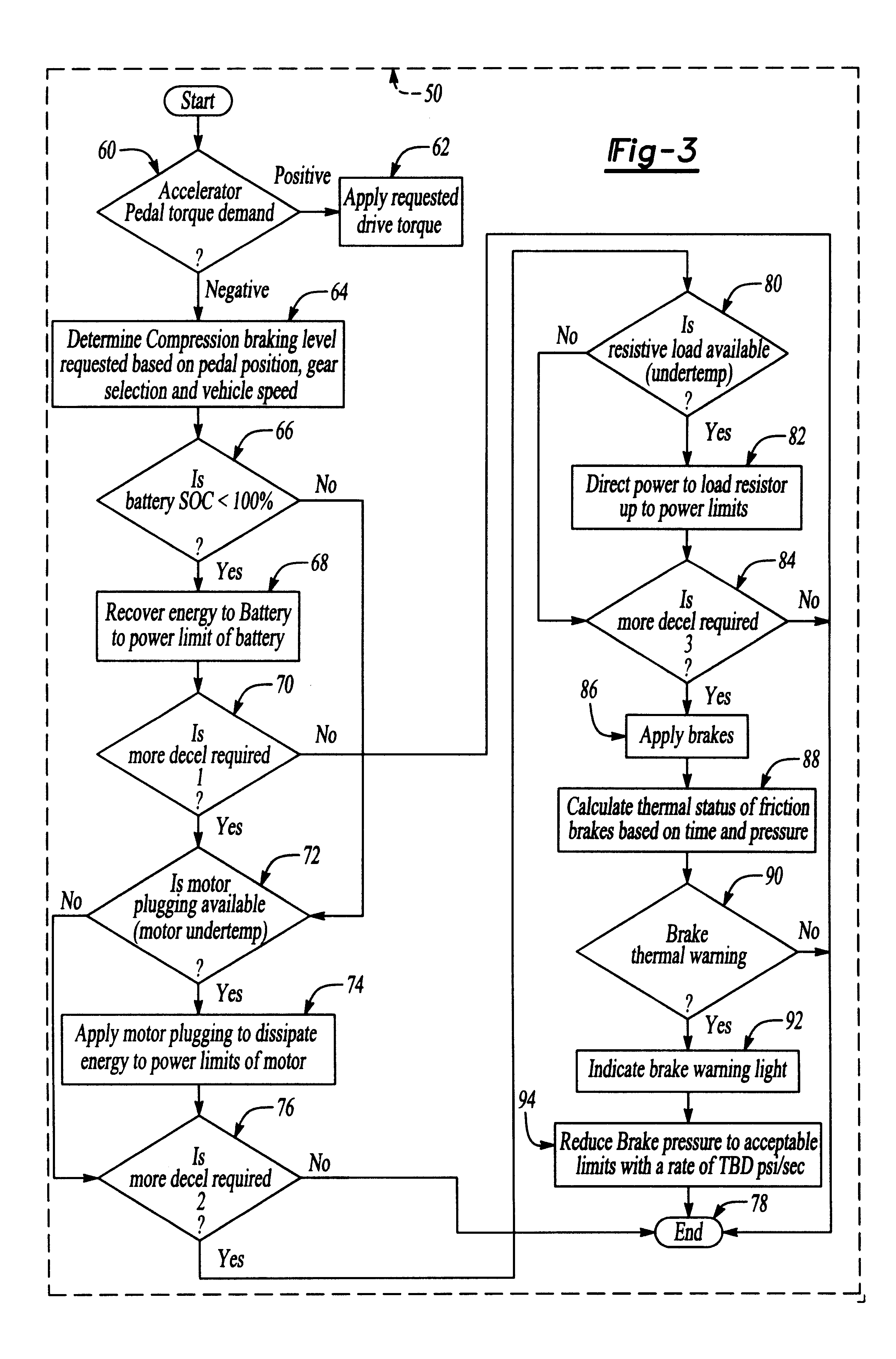
Method and system for providing for vehicle drivability feel after accelerator release in an electric or hybrid electric vehicle
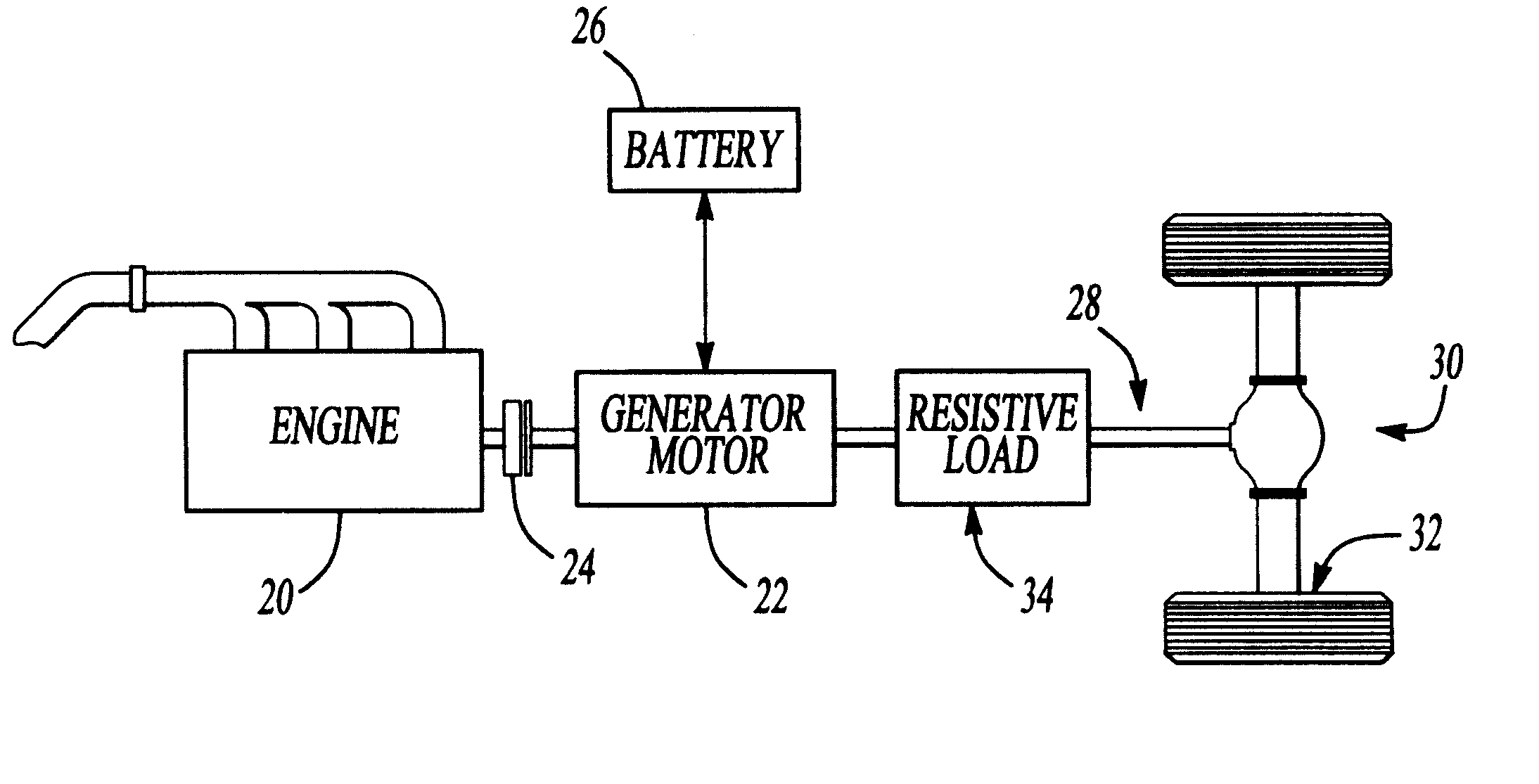
InactiveUS6378636B1Digital data processing detailsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingDriver/operatorEnergy recovery
The invention is a method and system to provide negative torque to an electric vehicle (EV, FCEV, hybrid electric powertrain (HEV)) powertrain when only the electric motor is engaged and the accelerator pedal is released with the ultimate objective to provide consistent vehicle performance under varying operating conditions. This deceleration is at a calibratable amount for a calibratable time period using a hierarchical strategy employing a variety of means including dissipating the vehicle's kinetic energy as heat in the motor; regenerative braking; and activating a mechanical braking system. This negative torque on the powertrain is provided only briefly thereby reducing the total kinetic energy dissipation. The invention provides the driver a vehicle deceleration response similar in "feel" to releasing the accelerator of a conventional ICE vehicle under all operating modes, while maintaining optimal energy recovery.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
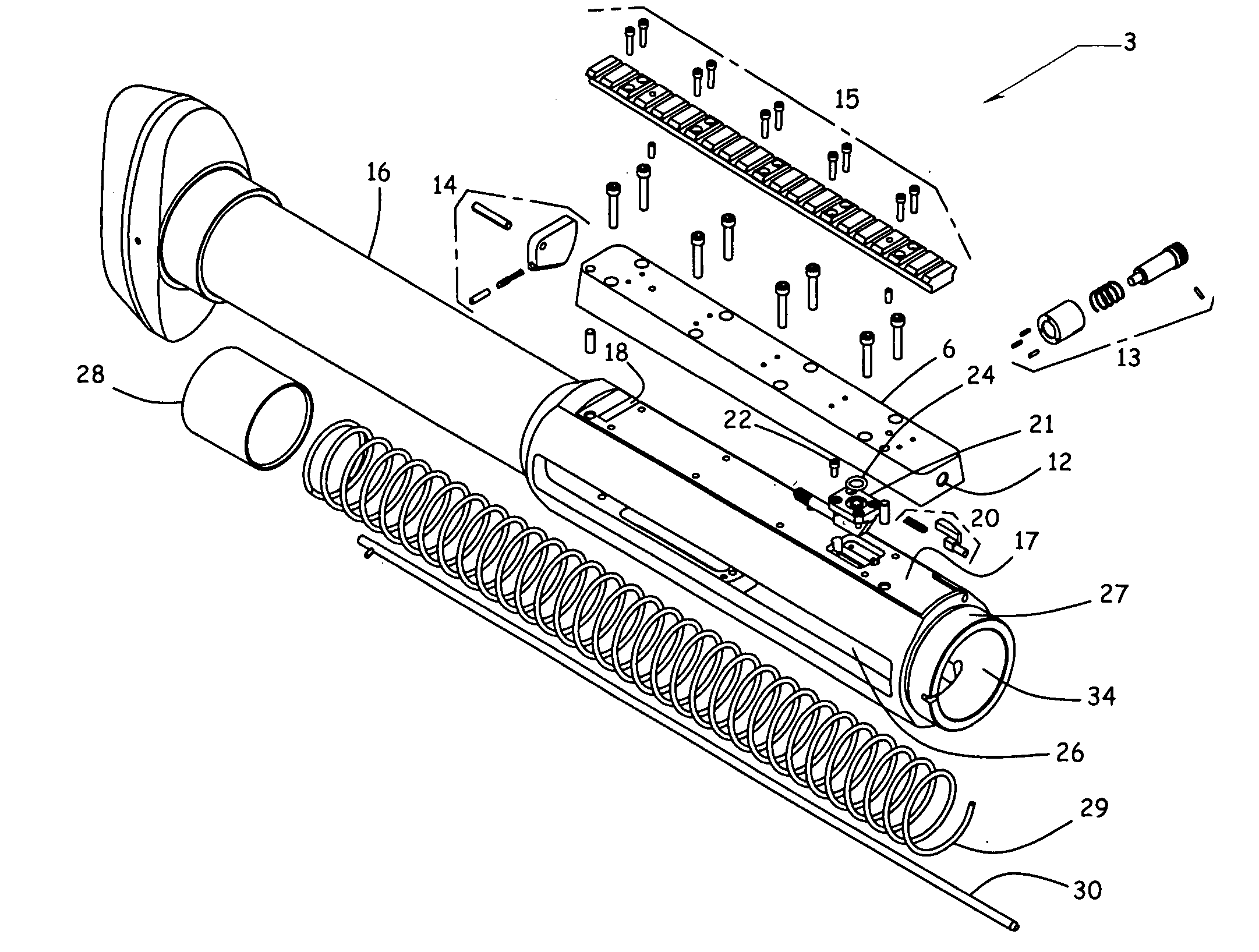
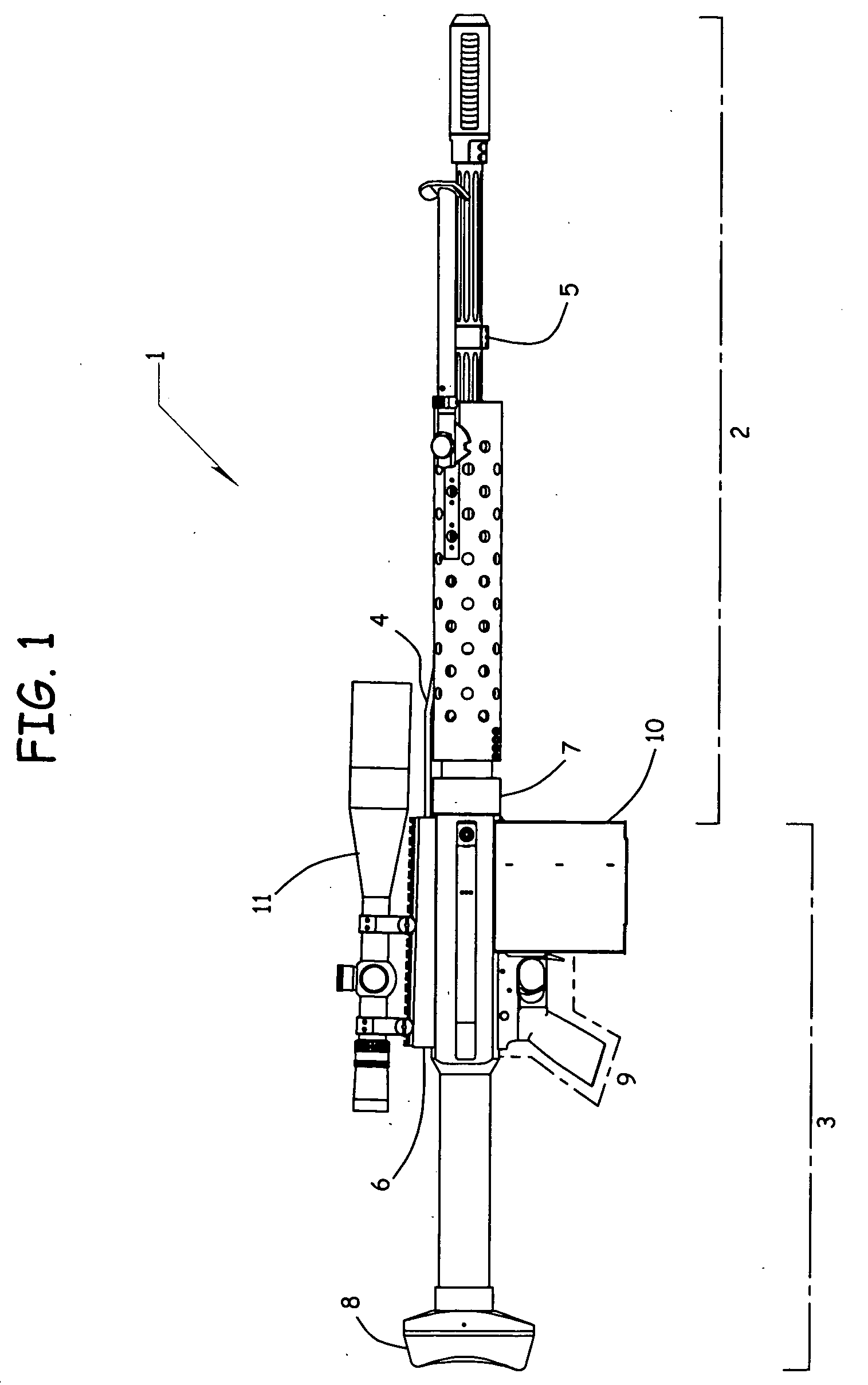
Gas operated action for auto-loading firearms
ActiveUS20050223613A1Reduce wearLarge outside diameterBraking action transmissionBreech mechanismsReciprocating motionEngineering
A gas operated action for auto-loading guns may comprise a receiver, a biasing spring, a bolt-carrier reciprocable within the receiver, a bolt having a cam pin, and an action rod fixedly attached to the receiver. The cam pin may engage the action rod during recoil travel of the bolt and bolt-carrier, thereby preventing rotation of the bolt when the cam pin is engaged with the action rod.
Owner:BENDER TERRENCE
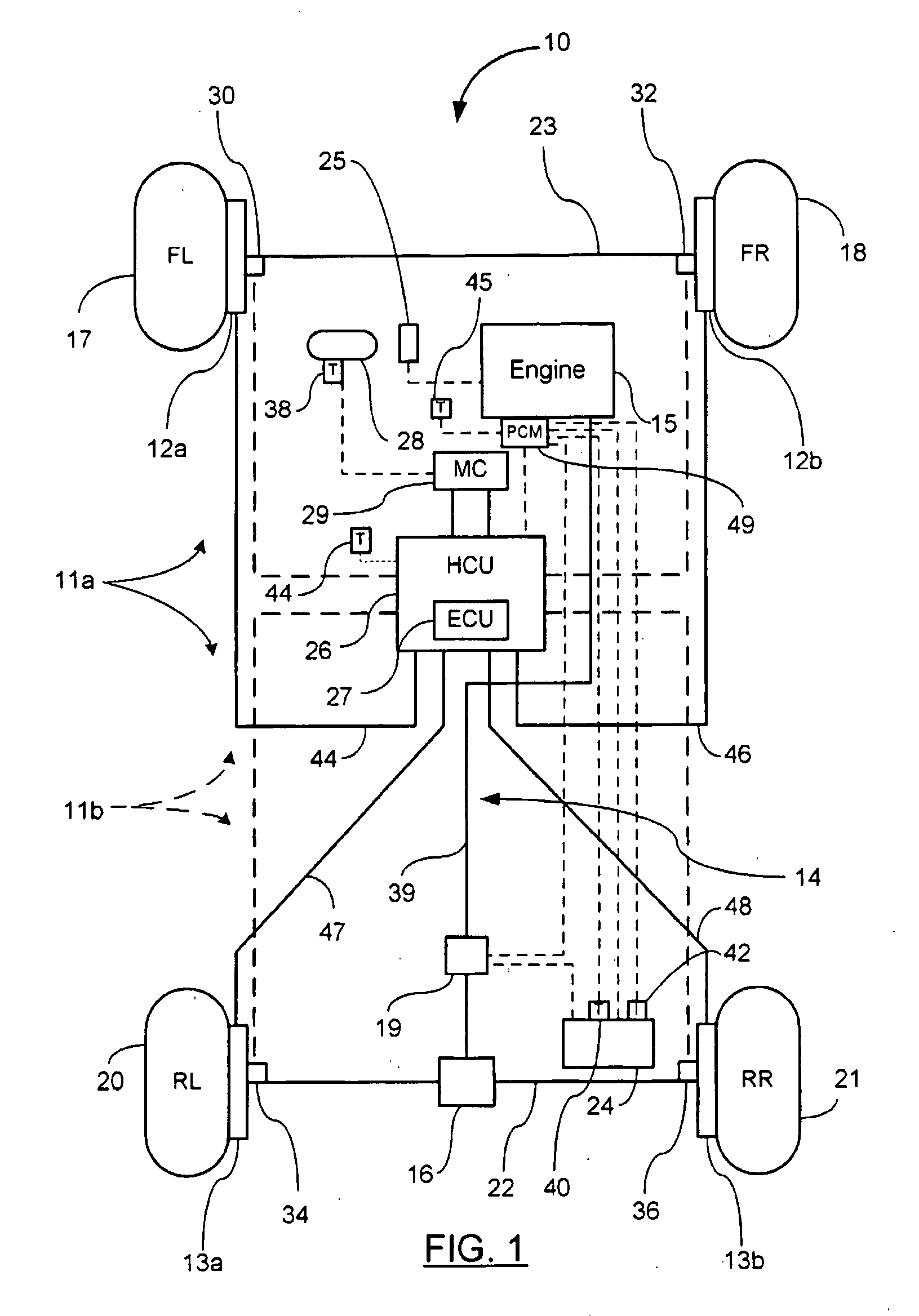
Brake control apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20070018499A1Suppress spinoutHighly efficient collection of electrical energyPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingPropulsion by batteries/cellsDrive wheelRegenerative brake
A brake apparatus for a vehicle generally sets an upper limit value of regenerative braking force to the maximum value of the regenerative braking force which can be generated at the present. In the case of a front-wheel-drive vehicle, the total braking force, the sum of front-wheel braking force (front-wheel hydraulic braking force+regenerative braking force) and rear-wheel braking force (rear-wheel hydraulic braking force), is rendered coincident with a target braking force corresponding to a brake pedal depressing force, and the regenerative braking force is set to a largest possible value equal to or less than the upper limit value. As a result, the regenerative braking force can be larger than front-wheel-side target distribution braking force. The upper limit value is decreased from the maximum value by an amount corresponding to the degree of easiness of occurrence of a locking tendency at the driven wheels (front wheels).
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Brake control unit
Towed vehicles can be extremely heavy. Accordingly, it is too much of a burden to the braking system of a towing vehicle to not have brakes on the towed vehicle. Controlling the brakes of the towed vehicle must be accurately applied otherwise undesirable conditions can be created. There is a need for a method for controlling braking of a towed vehicle. This method comprises receiving a first signal via a communication bus of a towing vehicle, the first signal relating to at least one operating condition of at least one the towing vehicle and a towed vehicle, sending a second signal to brakes of the towed vehicle, the second signal based on said first signal.
Owner:HORIZON GLOBAL AMERICAS INC
Self-centering rotor bearing assembly for submersible pump motors
The invention provides a submersible pumping system which includes a motor containing self-centering rotor bearing assemblies. Each rotor bearing assembly in accordance with the present invention includes a sleeve, a journal, and at least two seals. The journal is preferably disposed about the sleeve which is keyed to the power transmission shaft of the motor. The journal has a peripheral surface which is configured to have at least two circumferential support regions which are spaced apart from one another. Each of these circumferential support regions supports a corresponding seal. Each seal includes an interface member and an activating member. When in place in a rotor section of a submersible pump motor, the seals frictionally engage the inner surface of the stator and exert a centering force against the journal and thus against the bearing sleeve and the power transmission shaft. The seals also exert a force against the inner surface of the stator which prevents rotation of the journal when the power transmission shaft is rotating.
Owner:CAMCO INT
Electric brake position and force sensing and control
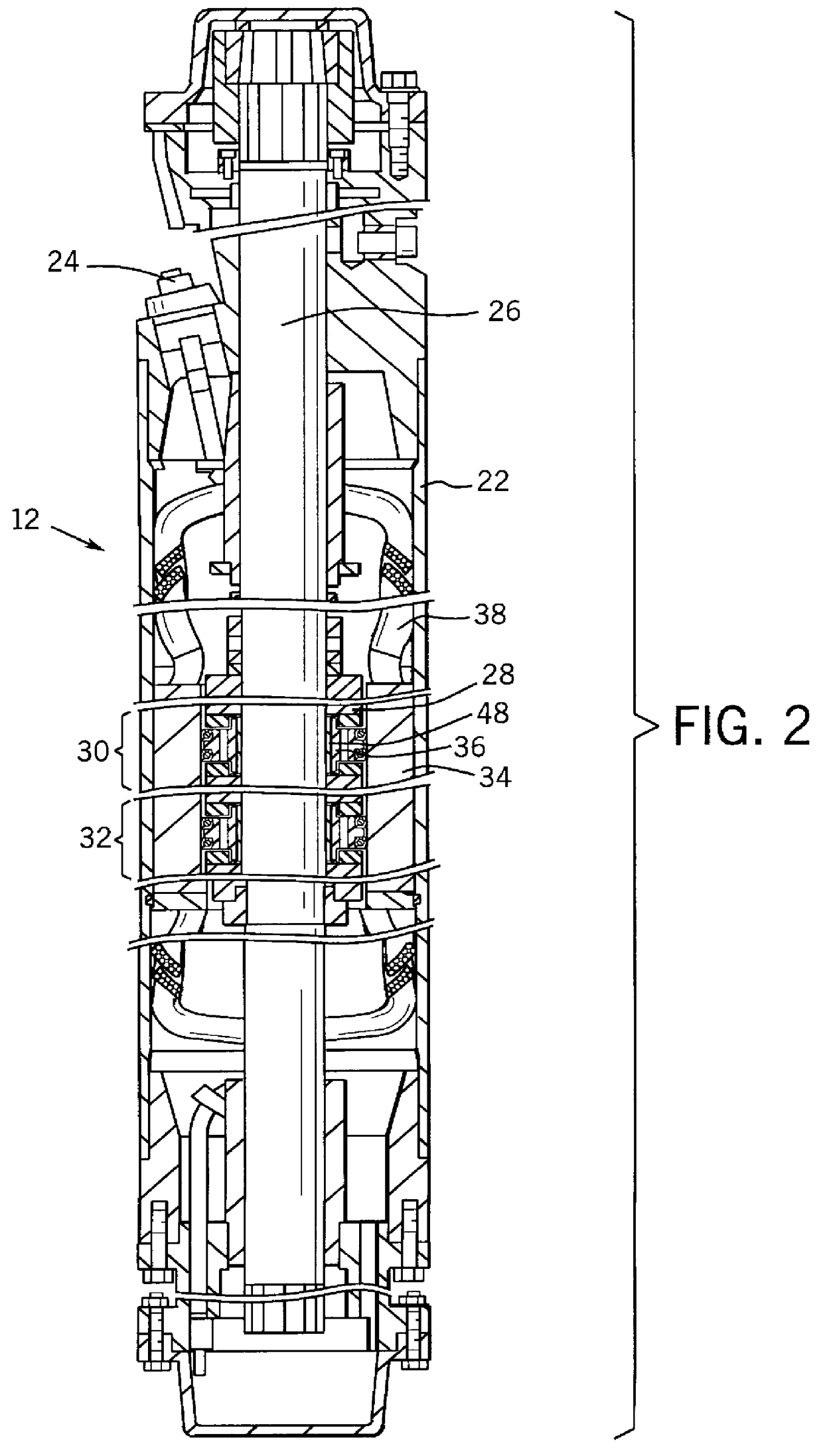
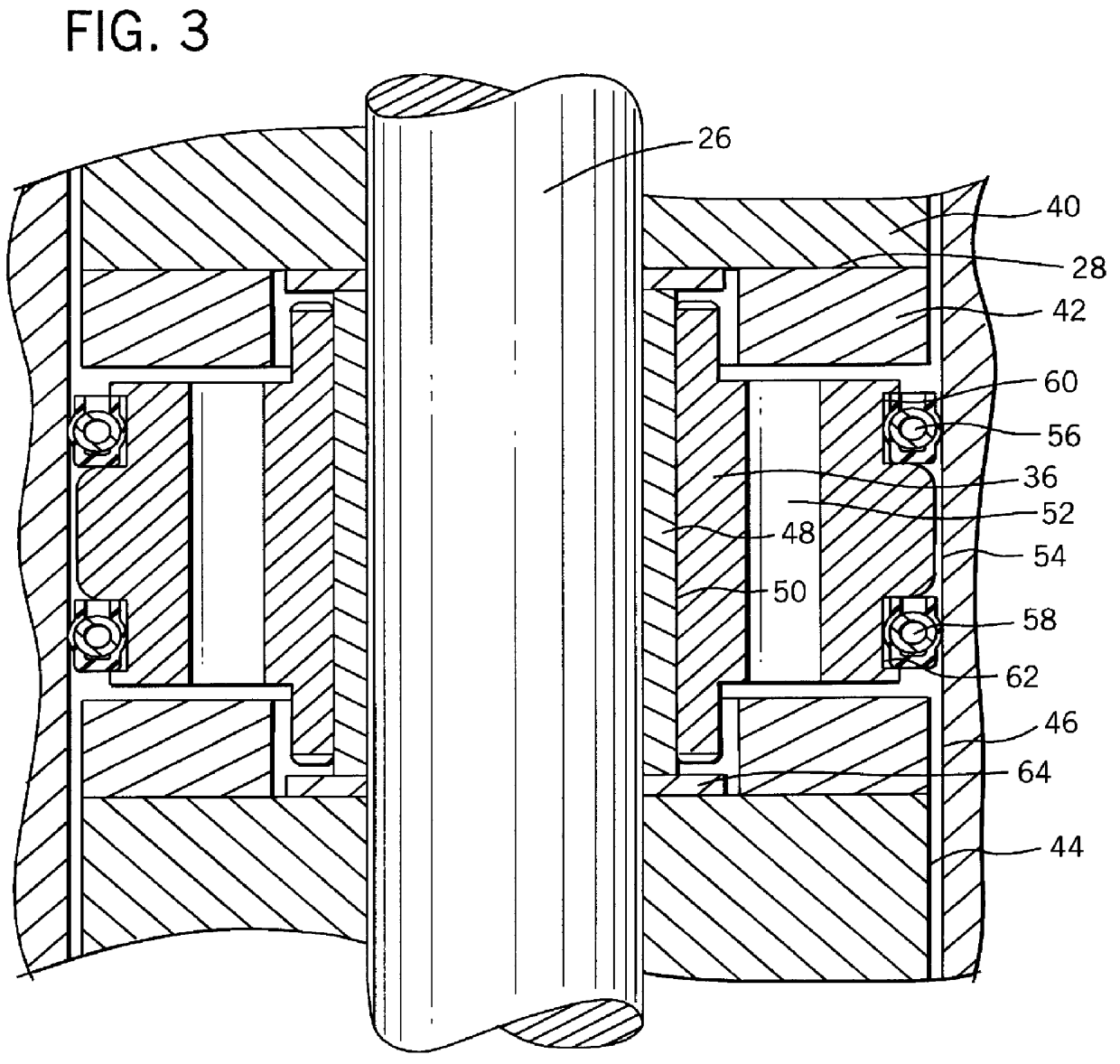
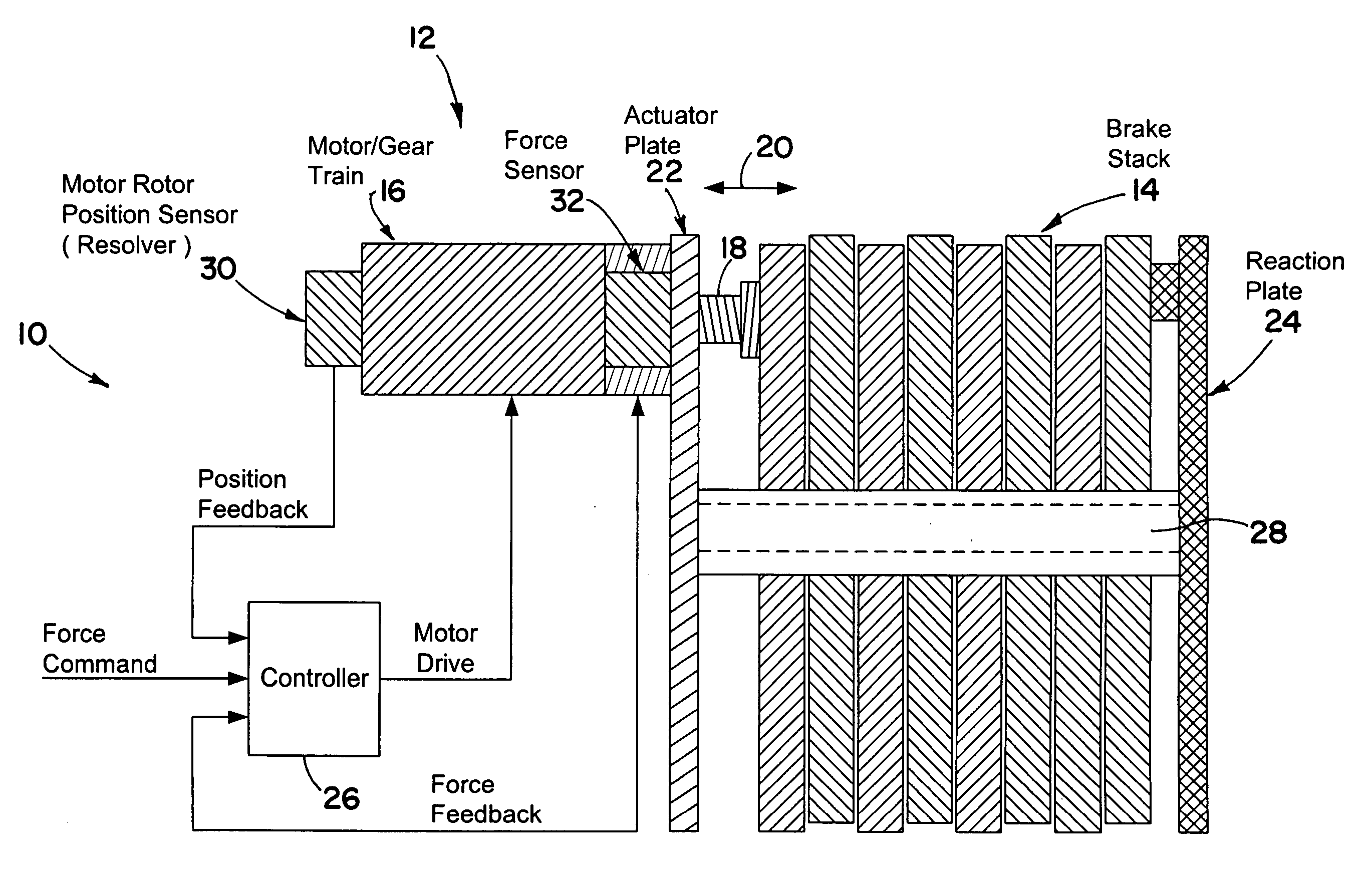
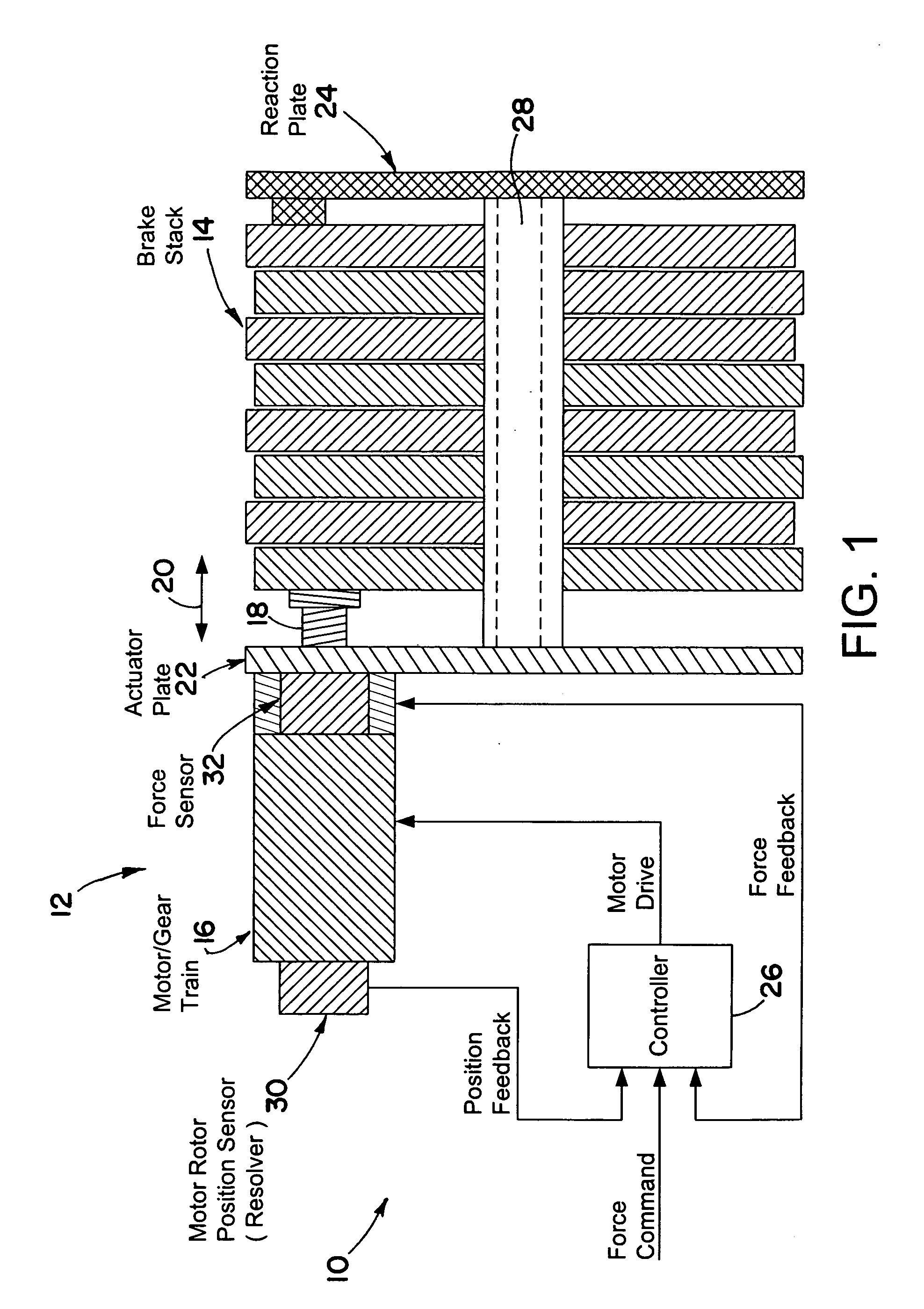
InactiveUS20050269872A1Braking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsControl signalEngineering
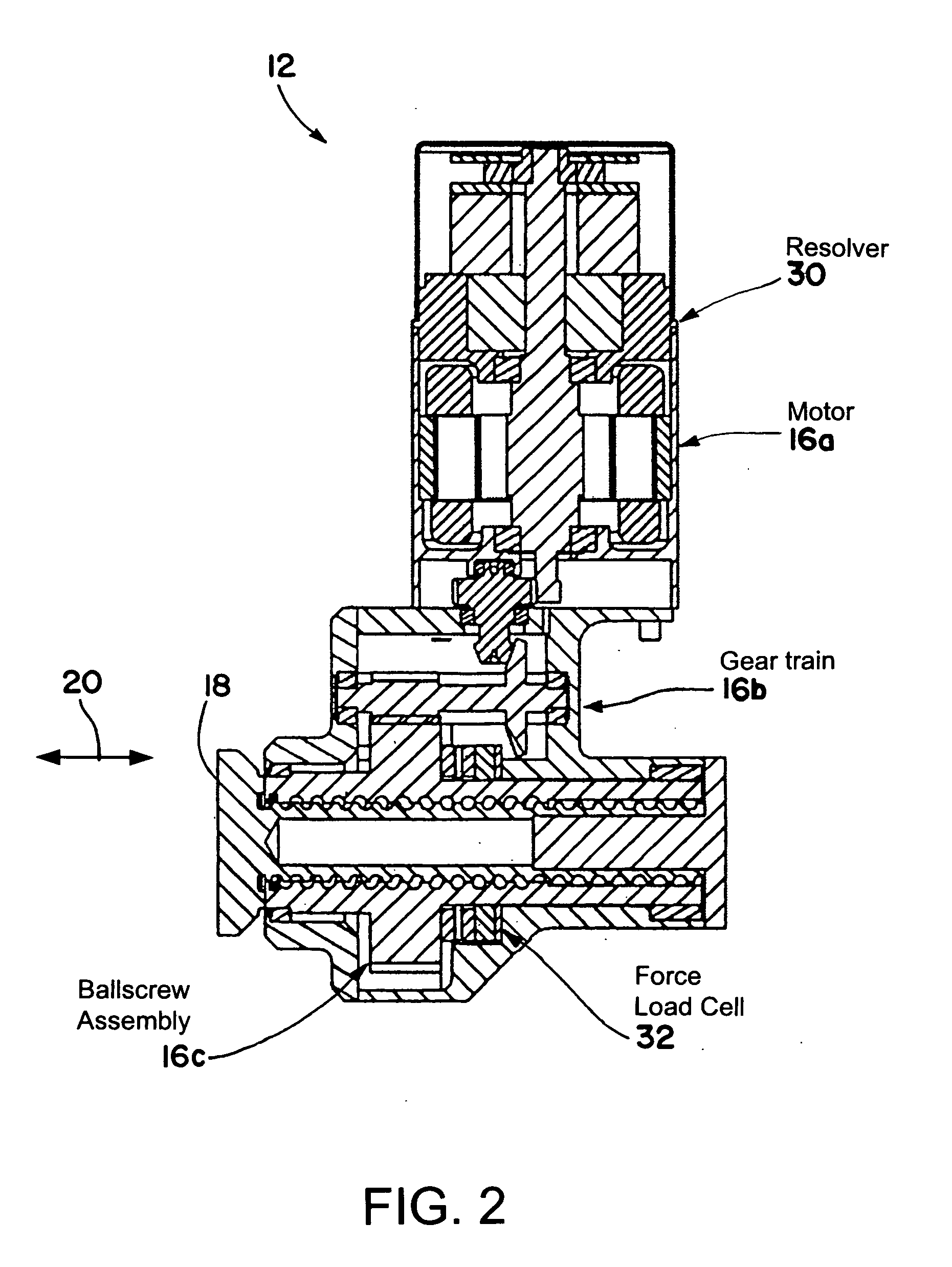
A brake system including an electromechanical brake actuator having an actuator ram for exerting a brake force on a brake stack of a wheel to be braked in response to a control signal. In addition, the brake system includes a force sensor for sensing the brake force exerted on the brake stack by the actuator ram and outputting a force feedback signal based thereon; and a position sensor for sensing a position of the actuator ram and outputting a position feedback signal based thereon. Moreover, the brake system includes a controller for providing the control signal to the electromechanical brake actuator based on the force feedback signal and the position feedback signal.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Brake control apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20060220453A1Improve energy efficiencyBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionRegenerative brakeDifferential pressure
A brake apparatus for a vehicle controls braking force acting on front wheels by hydraulic braking force (front-wheel-side vacuum-booster hydraulic pressure fraction+linear-valve differential pressure fraction), which is frictional braking force, and regenerative braking force, and controls braking force acting on rear wheels by hydraulic braking force (rear-wheel-side vacuum-booster hydraulic pressure fraction) only, to thereby perform regeneration-coordinative brake control. During performance of ABS control, the apparatus sets the limit regenerative braking force to a force under which locking of the front wheels does not occur in a case in which the force acts on the front wheels, which are wheels undergoing regenerative braking, and adjusts the regenerative braking force such that the regenerative braking force does not exceed the limit regenerative braking force.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
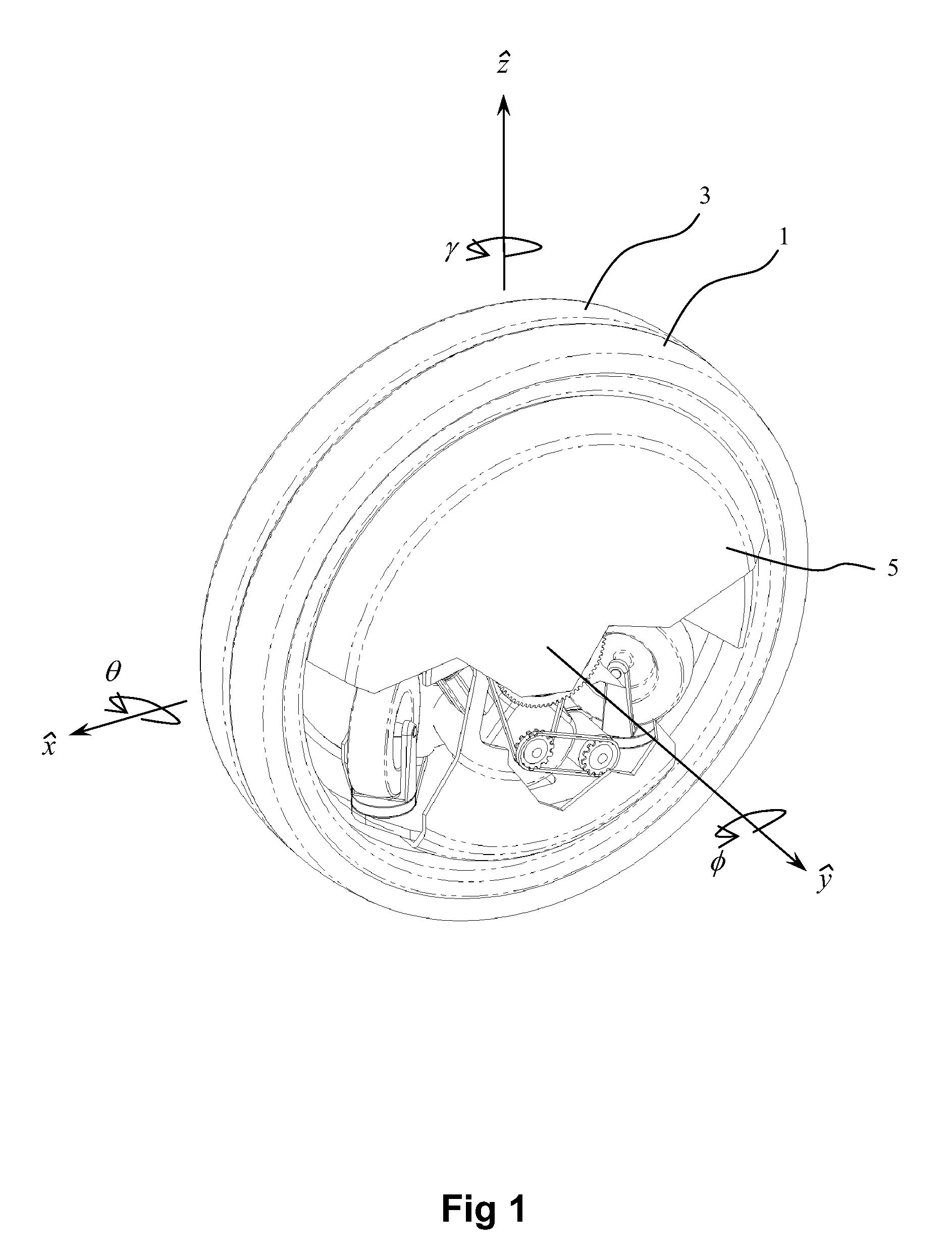
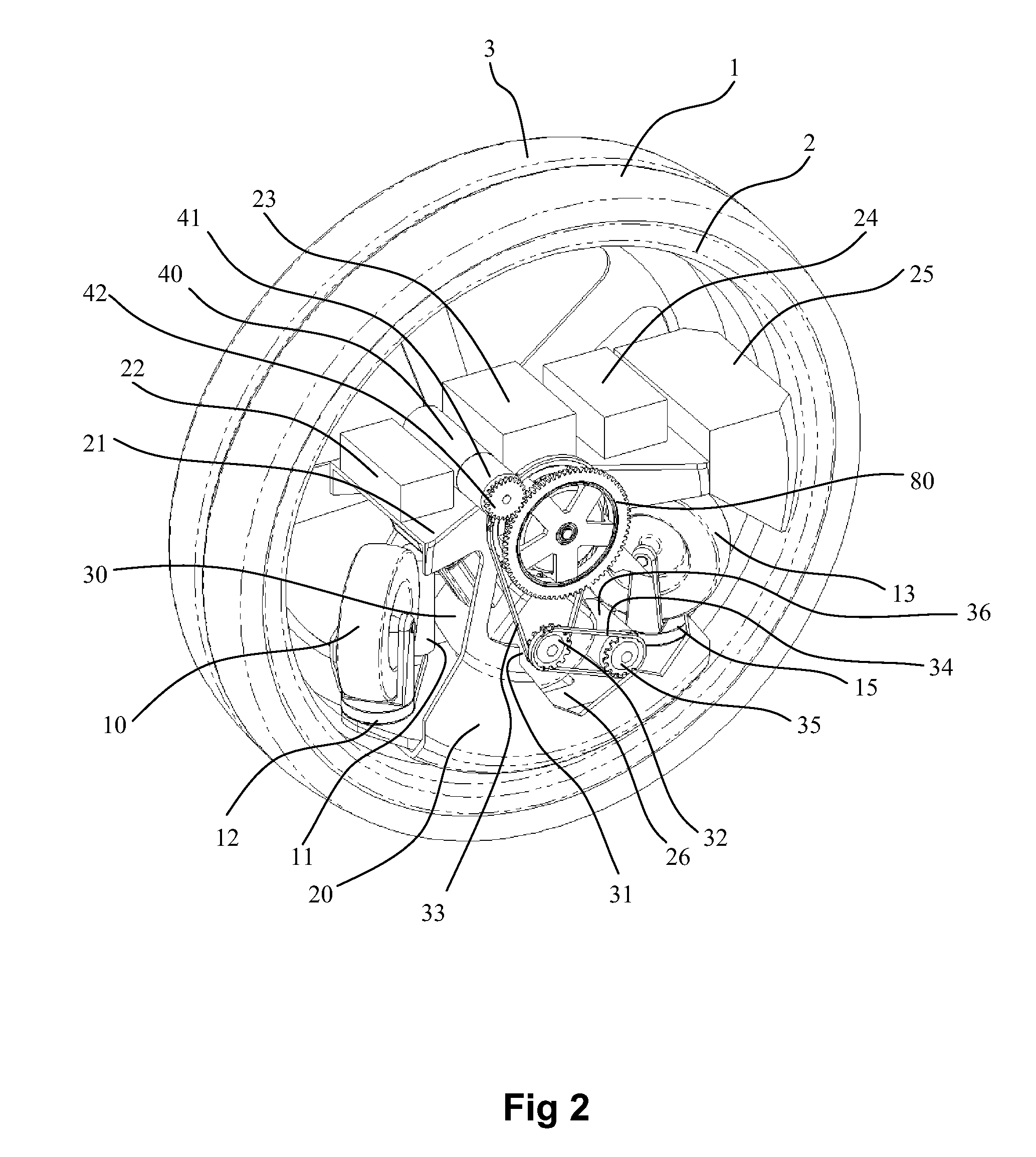
Monowheel Type Vehicle
An engine-propelled monowheel vehicle comprises two wheels, close together, that circumscribe the remainder of the vehicle. When the vehicle is moving forward, the closely spaced wheels act as a single wheel, and the vehicle turns by leaning the wheels. A single propulsion system provides a drive torque that is shared by the two wheels. A separate steering torque, provided by a steering motor, is added to one wheel while being subtracted from the other wheel, enabling the wheels to rotate in opposite directions for turning the vehicle at zero forward velocity. The vehicle employs attitude sensors, for sensing roll, pitch, and yaw, and an automatic balancing system. A flywheel in the vehicle spins at a high rate around a spin axis, wherein the spin axis is rotatable with respect to the vehicle's frame. The axis angle and flywheel spin speed are continually adjustable to generate torques for automatic balancing.
Owner:LEESER KARL F
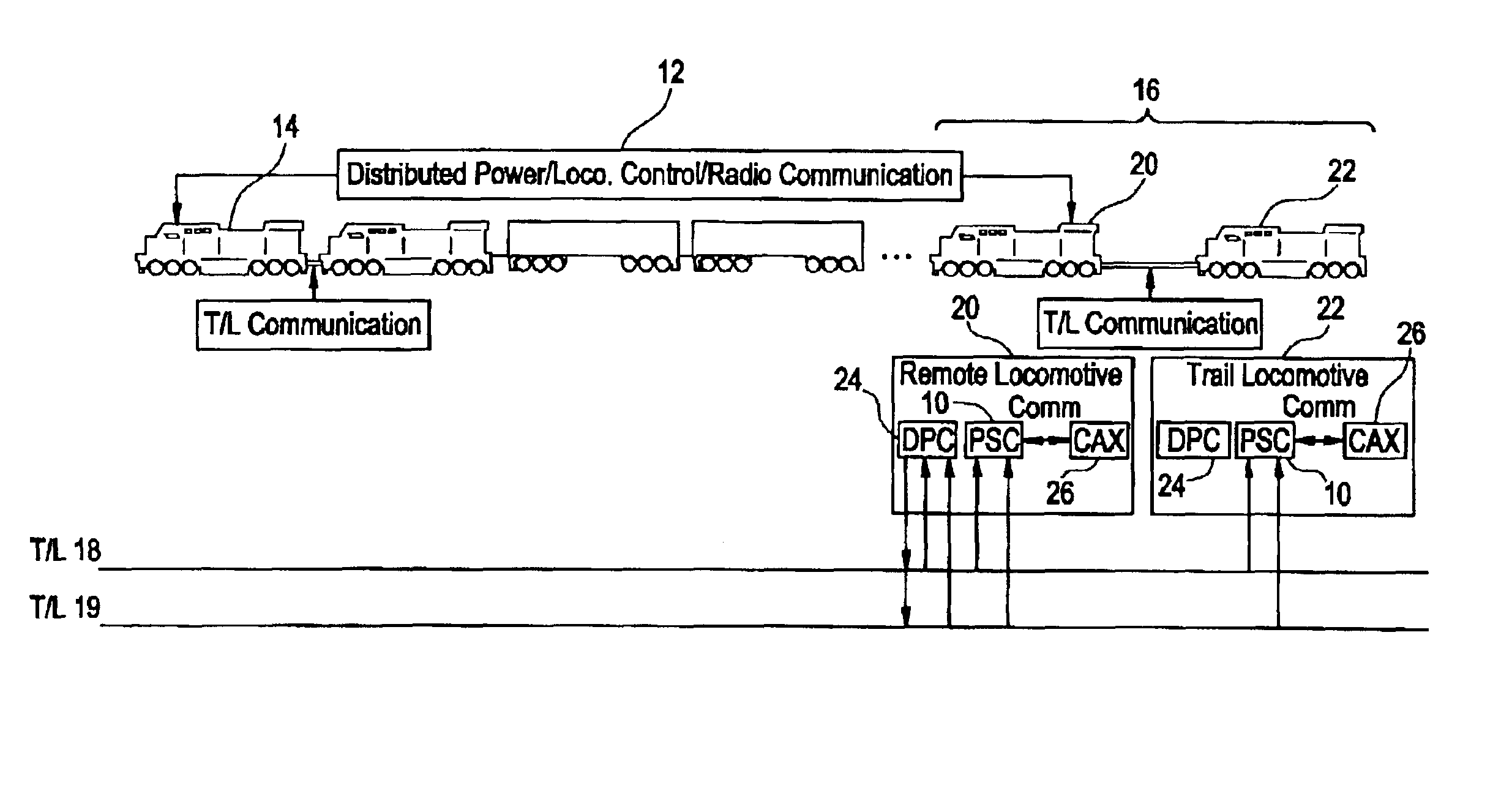
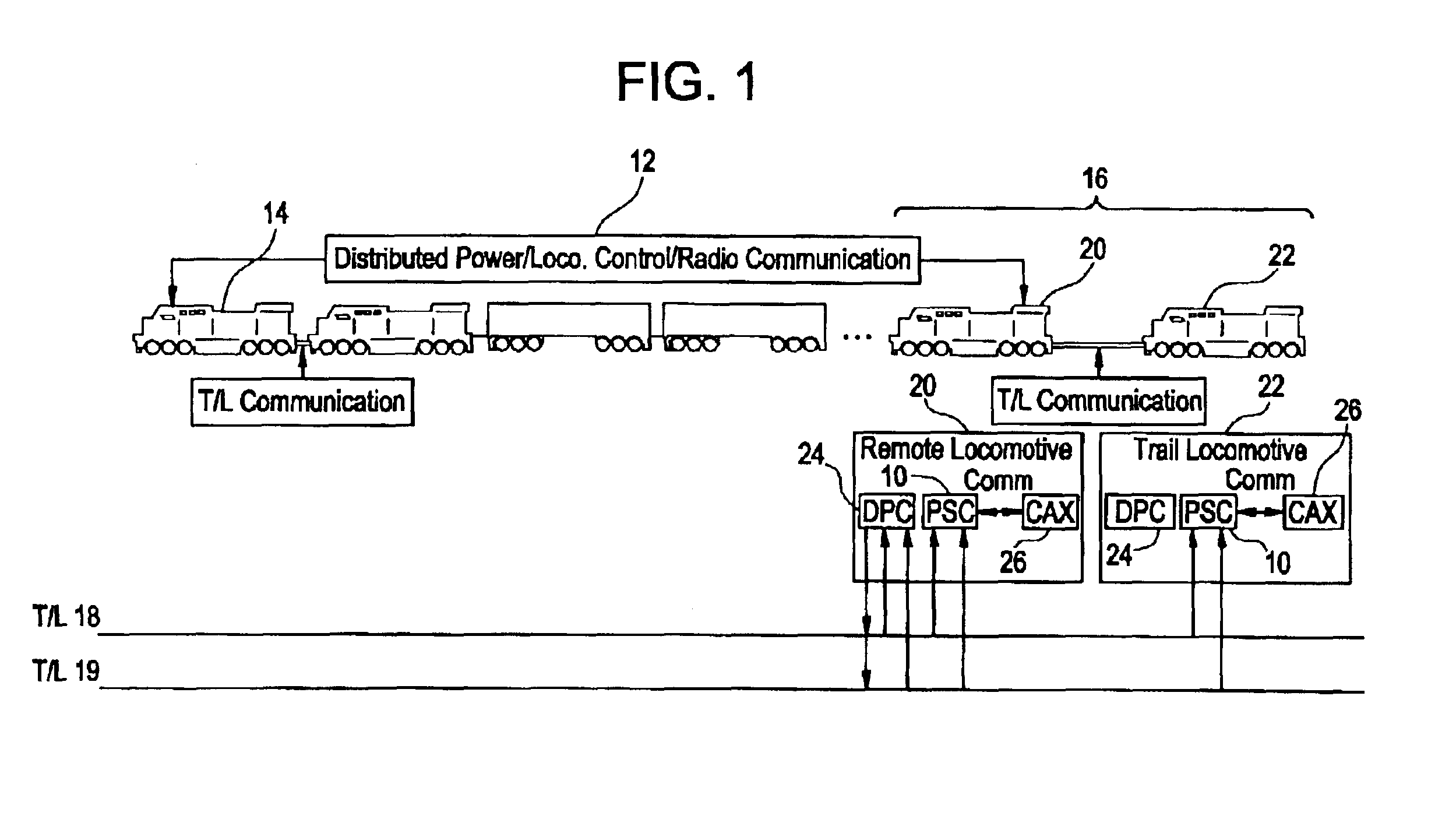
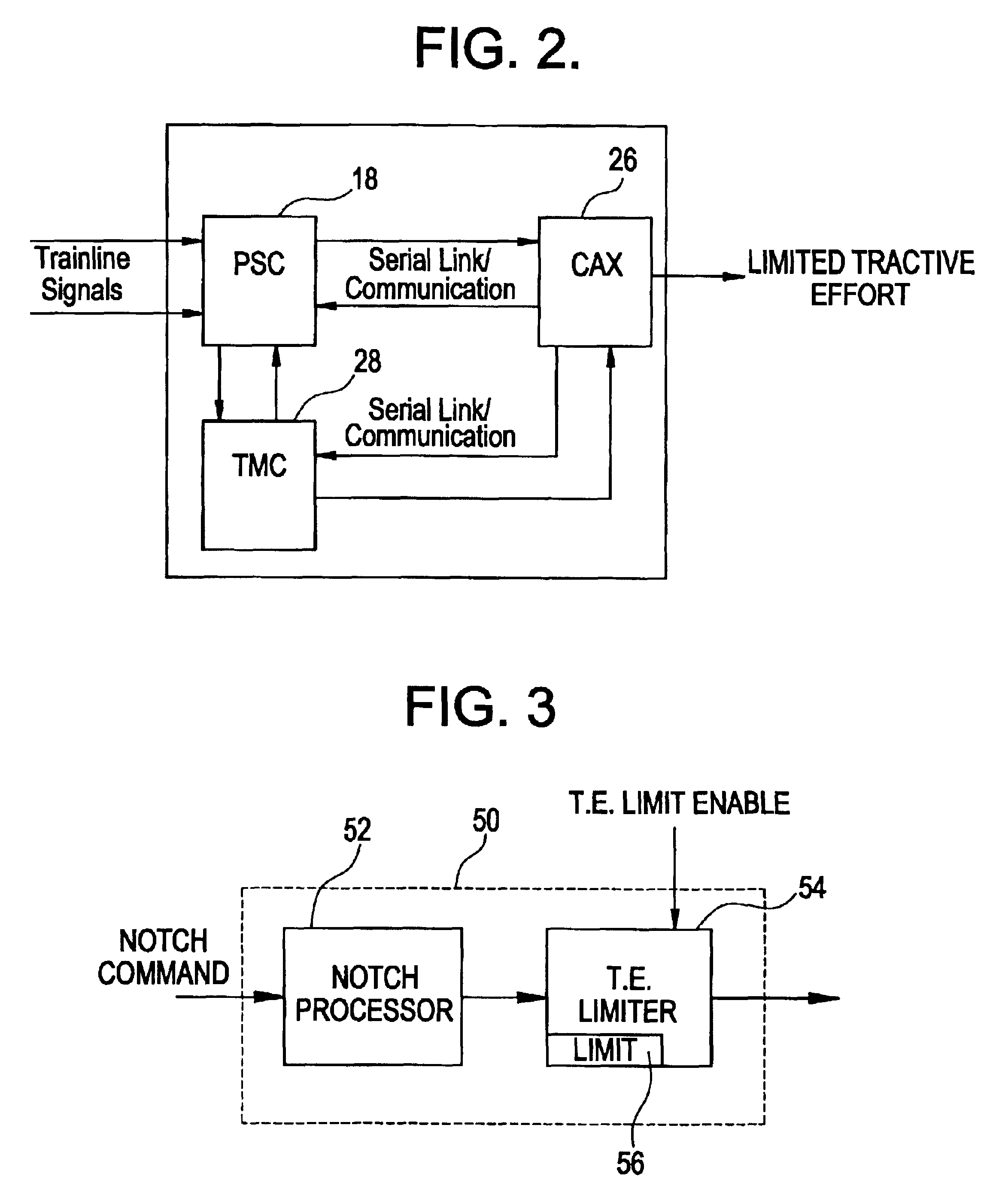
System and method for selectively limiting tractive effort to facilitate train control
Method for controlling the level of tractive efforts in a train having a first locomotive at a head end of the train, constituting a lead locomotive, and a second locomotive positioned in the train behind the lead locomotive, constituting a remote locomotive, with the remote locomotive being configured to selectively operate in either of two modes of operation, such as a first mode in which the locomotive operates at a full tractive effort level of operation and a second mode in which the locomotive operates in a partial tractive effort level of operation producing a tractive effort which is less than the full tractive effort of the locomotive. The method allows selecting (e.g., at the lead locomotive) one of the two modes of operation for producing a level of tractive effort appropriate for conditions as the train moves along a length of track. The method further allows transmitting a signal indicative of the selected mode of operation from the lead locomotive to the remote locomotive. The signal is received at the remote locomotive. The tractive effort generated at the remote locomotive is controlled so as not to exceed the selected level.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and Driving Dynamics Control System for Stabilizing a Car-Trailer Combination
ActiveUS20090228182A1Reliably carry-outHand manipulated computer devicesBrake system interactionsControl systemSemi-trailer
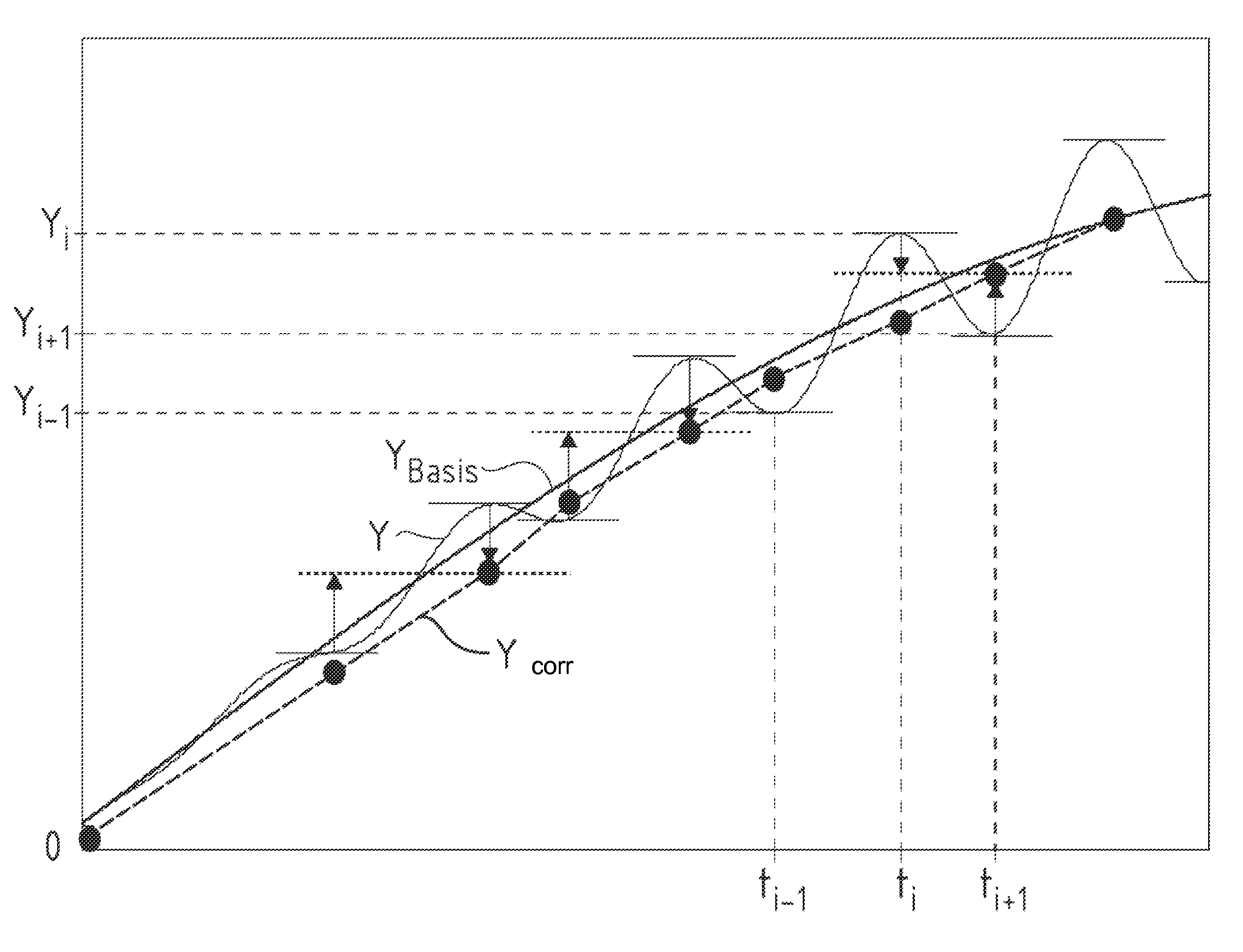
When swaying motions of a trailer or semi-trailer of a car-trailer combination are encountered, input signals which are taken into consideration to calculate a reference signal frequently include also oscillation components, due to which driving dynamics control for stabilization of the car-trailer combination can become very unreliable. To enhance the reliability of driving dynamics control of this type, a method is disclosed in which an input signal (Y) is sensed that includes signal oscillations which are due to a swaying motion of the trailer or semi-trailer and are superimposed on a base component (YBasis) of the input signal (Y). A reference signal is calculated from the input signal (Y), in which case the calculation is executed in such a way that the reference signal by approximation corresponds to a reference signal which is determined from the base component (YBasis) of the input signal (Y). A correcting variable for influencing the driving behavior of the towing vehicle of the car-trailer combination is then determined depending on a deviation between the reference signal and a detected actual signal. Furthermore, the invention discloses a driving dynamics control system which is appropriate to implement the method.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
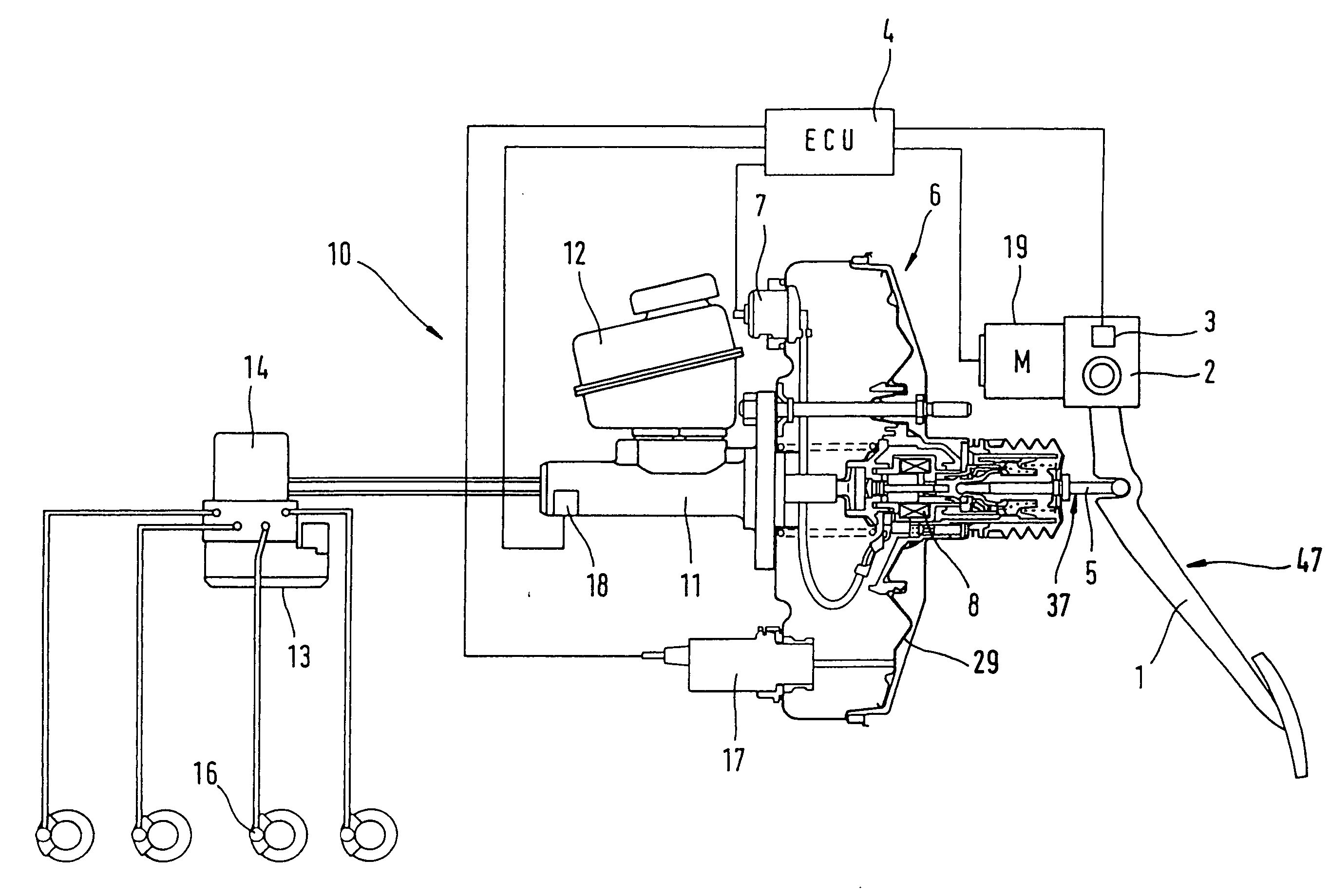
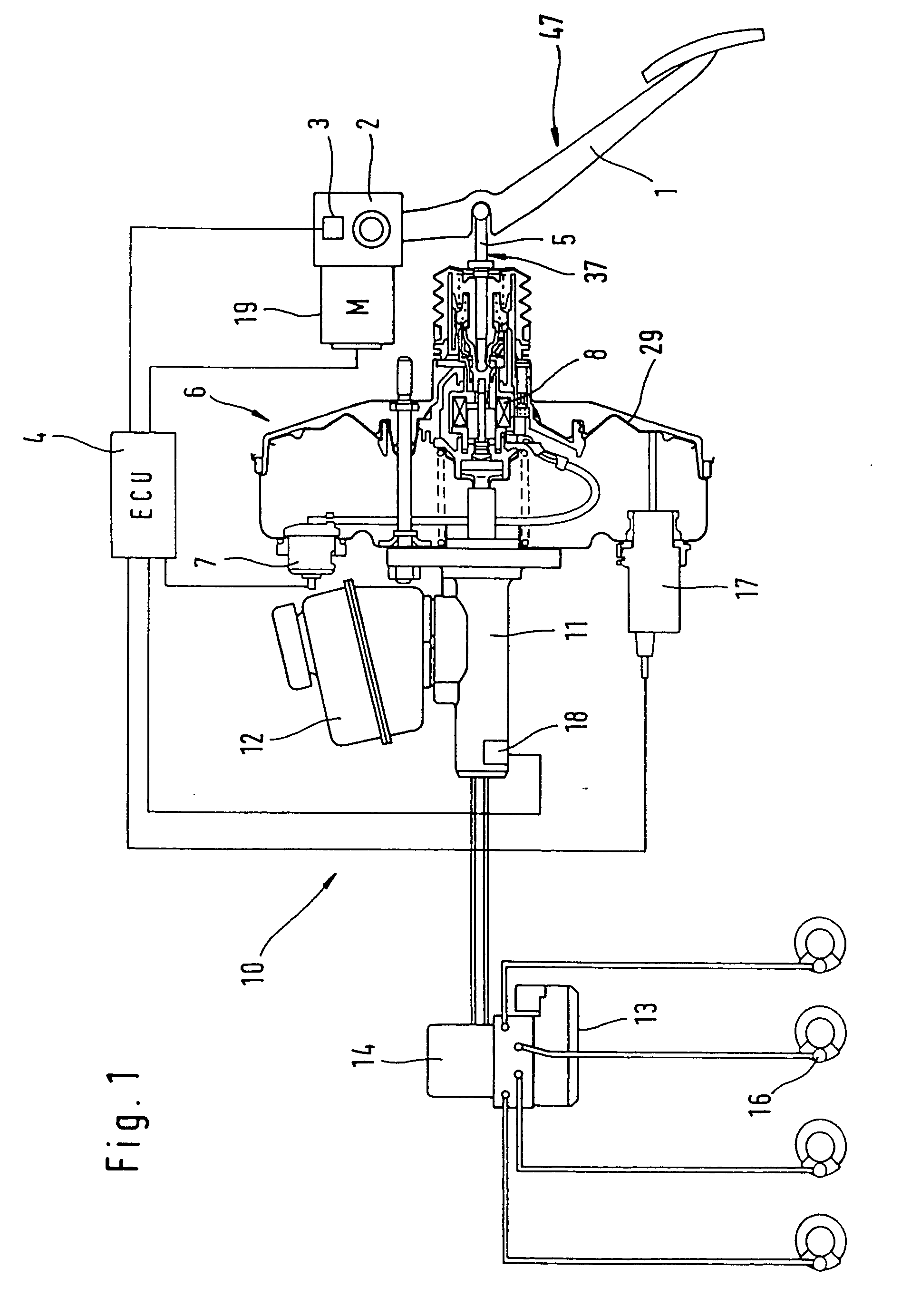
Brake system for motor vehicles
ActiveUS20110115282A1Braking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsMechanical engineeringBraking system
A brake system includes a main brake cylinder and a pedal decoupling unit provided with a holding piston, the first ring surface thereof together with a first primary brake cylinder piston defining a first hydraulic chamber that is hydraulically pressurized with an electrically controllable pressure supply device. In order to improve the pedal characteristics of the brake system, in particular in a brake-by-wire brake system, the holding piston is embodied as a differential piston, the second ring surface thereof defining a second, blockable hydraulic chamber, and a piston effect in the second chamber corresponds to a force that acts counter to the direction of actuation on the holding piston.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Hydraulic circuit having a rotary type pump and brake apparatus for a vehicle provided with the same
InactiveUS6142581APrevent leakagePrevent liquid leakageBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsRotary pumpDrive shaft
A hydraulic circuit has a rotary type pump comprising a rotor rotating with a driving shaft and a casing which holds the rotor and the driving shaft. The casing further comprises an inlet port through which fluid is introduced to spaces formed by the rotor, an outlet port through which fluid is discharged from the spaces, and a hydraulic path for leading fluid from clearance around said driving shaft to the outside of the casing. A reservoir is provided to store fluid coming through the hydraulic path. A return conduit is disposed between the reservoir and an upstream side conduit connected to the inlet port in order that fluid stored in the reservoir is returned to the upstream side conduit. In the return conduit, a check valve is disposed to prevent the reverse flow of fluid from the upstream side conduit to the reservoir.
Owner:DENSO CORP
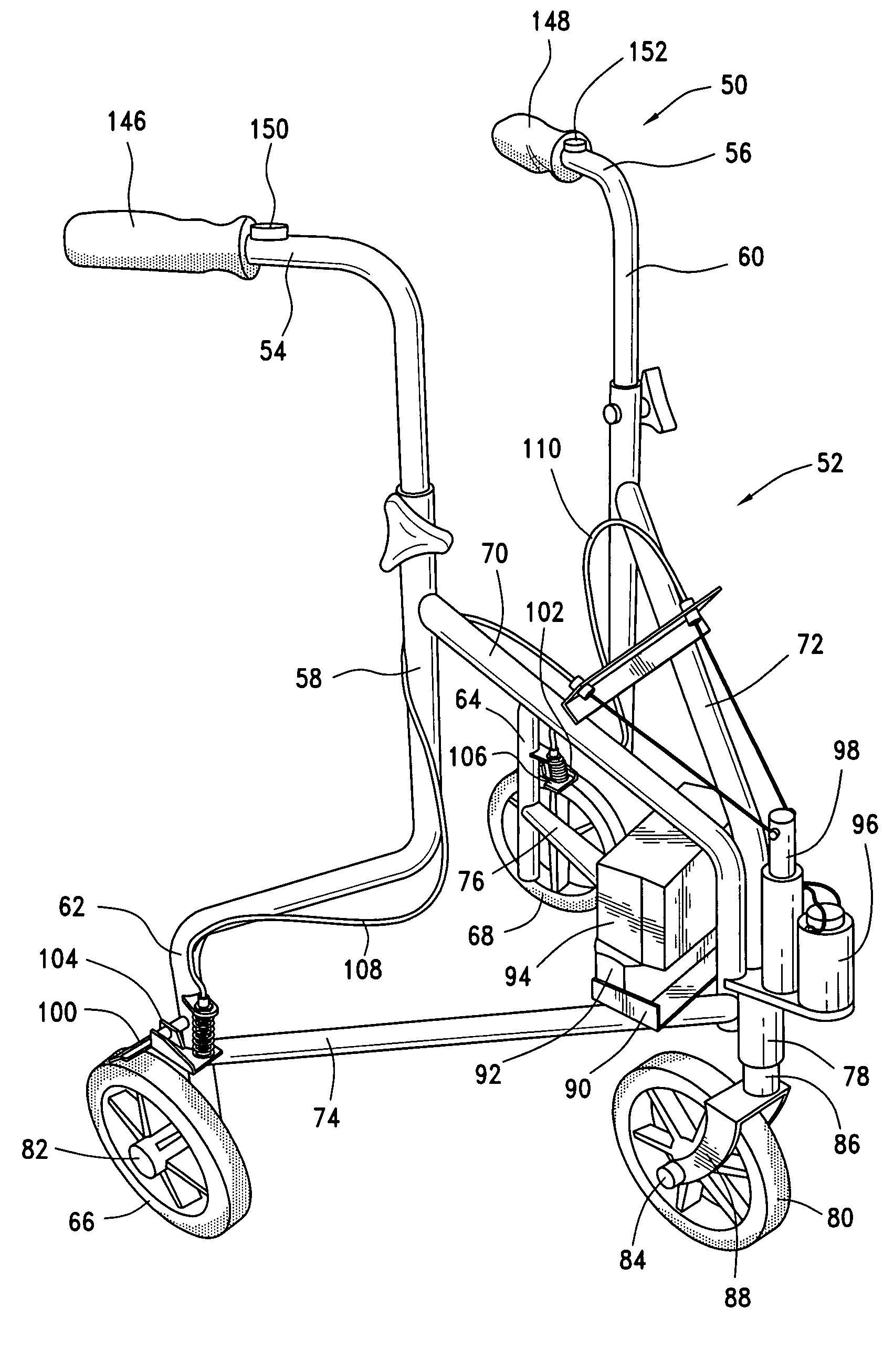
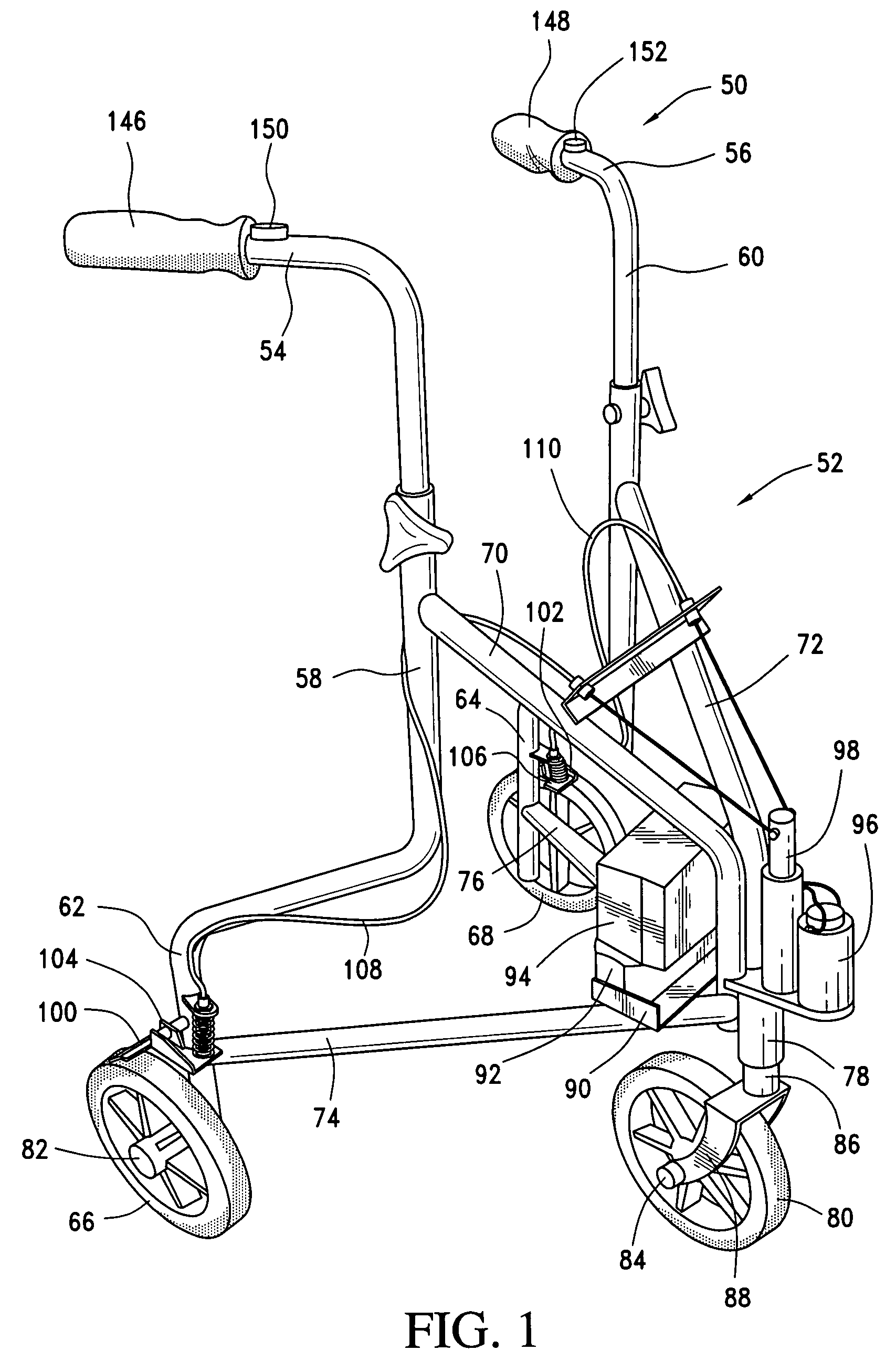
Electronically controlled brakes for walkers
InactiveUS7708120B2Easy to operateControl is lostBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionElectronic controllerControl theory
An improved electronic braking system for walkers that incorporates one or more electrically-operated brakes controlled by an electronic controller is disclosed. The controller is responsive to touch-sensitive switches for easy operation, and is adjustable and responsive to operator patterns of use to provide individualized control of the brake operation. The controller may also be responsive to environmental conditions such as the slope of the ground over which the walker is moving, to its rate of motion, or to the distance between the walker frame and the user, and may be adjusted to accommodate for the weight of the user or to set limits to the speed at which it can move.
Owner:EINBINDER ELI
Hydraulic braking system for automobiles
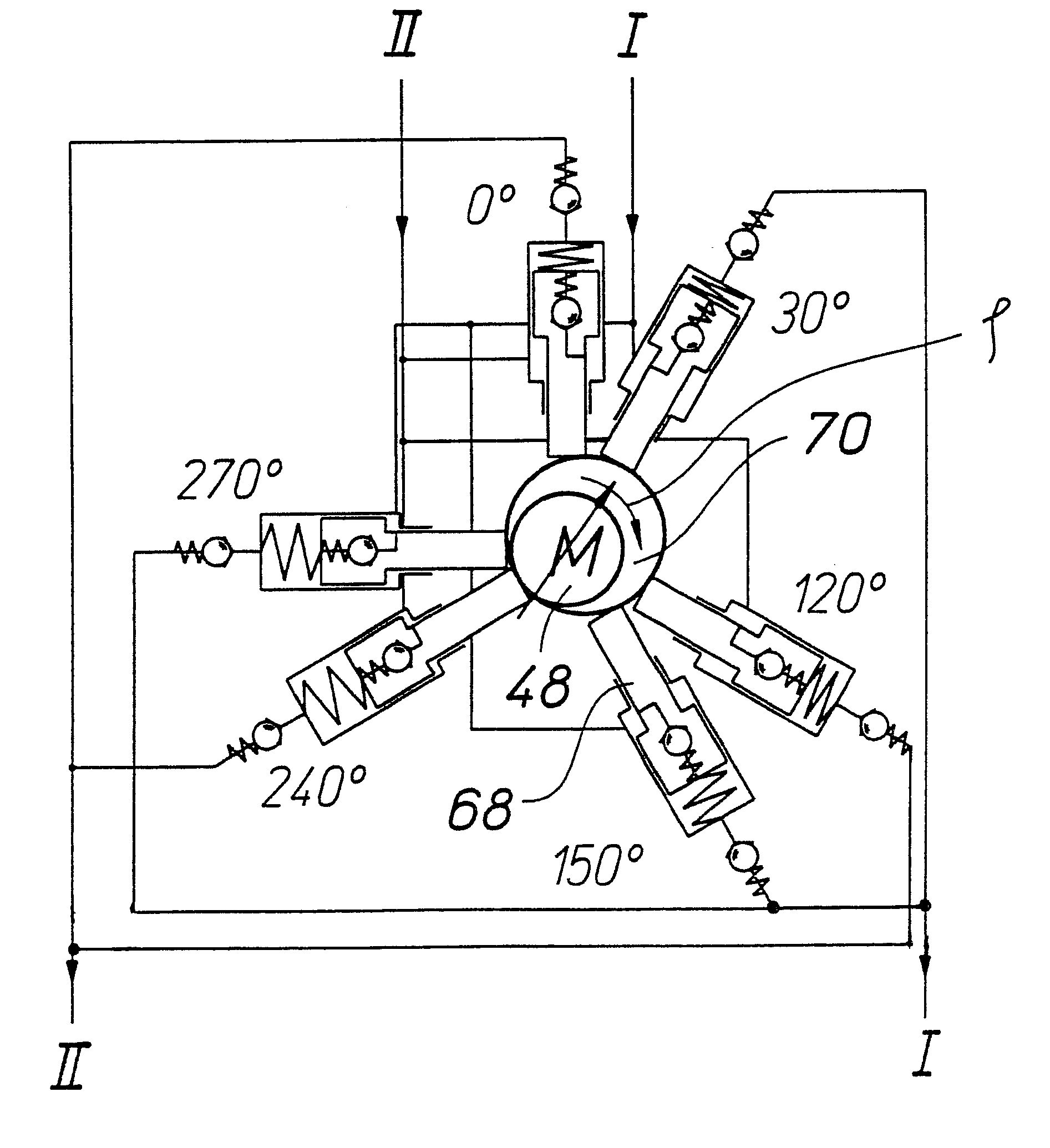
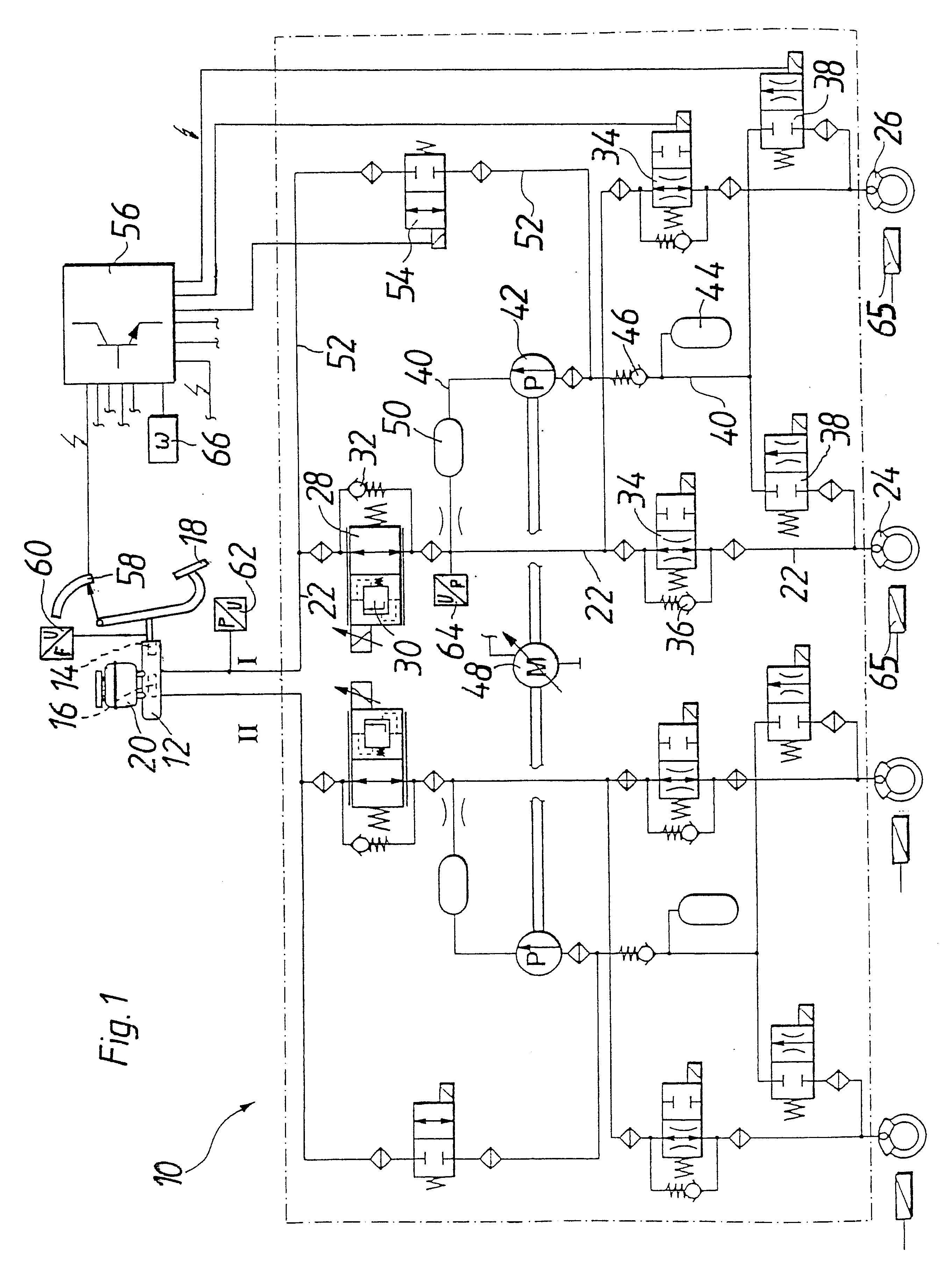
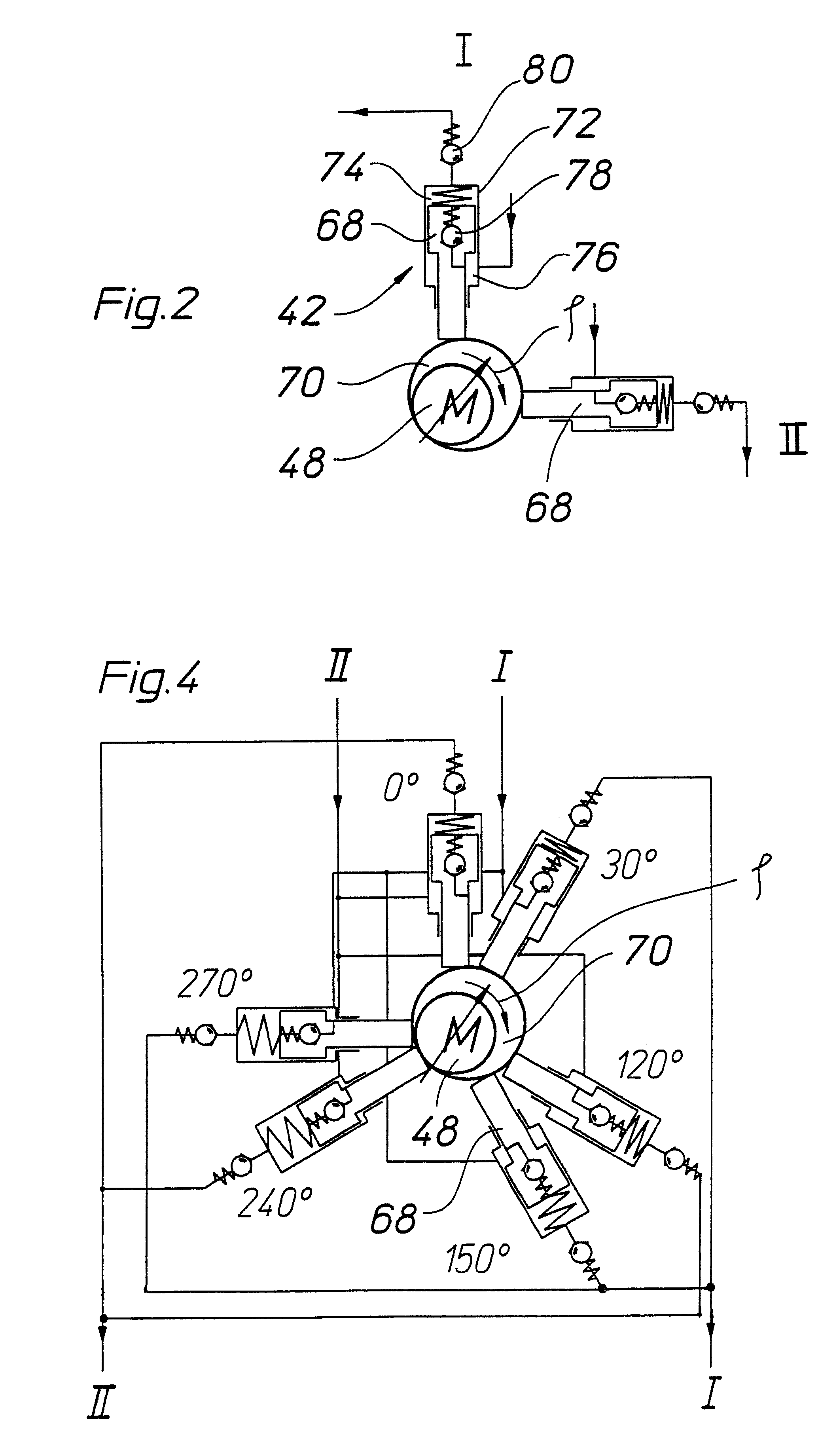
The invention relates to a vehicle hydraulic brake system with electrohydraulic brake boosting by a piston pump. In order to reduce pressure pulsations on an intake side of the multi-piston pump, the brake system embodies a multi-piston pump, for example, as a six-piston pump with stepped pistons that are driven with an alternating phase shift of 30° and 90° in relation to one another. The phase shift of the drive of the stepped pistons is selected so that the intake volume flows have a uniform phase shift, by which the total intake volume flow of the multi-piston pump has a reduced amplitude of the pressure pulsation, which reduces the repercussions on a master cylinder.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Braking system for motor vehicles and method for operating the same
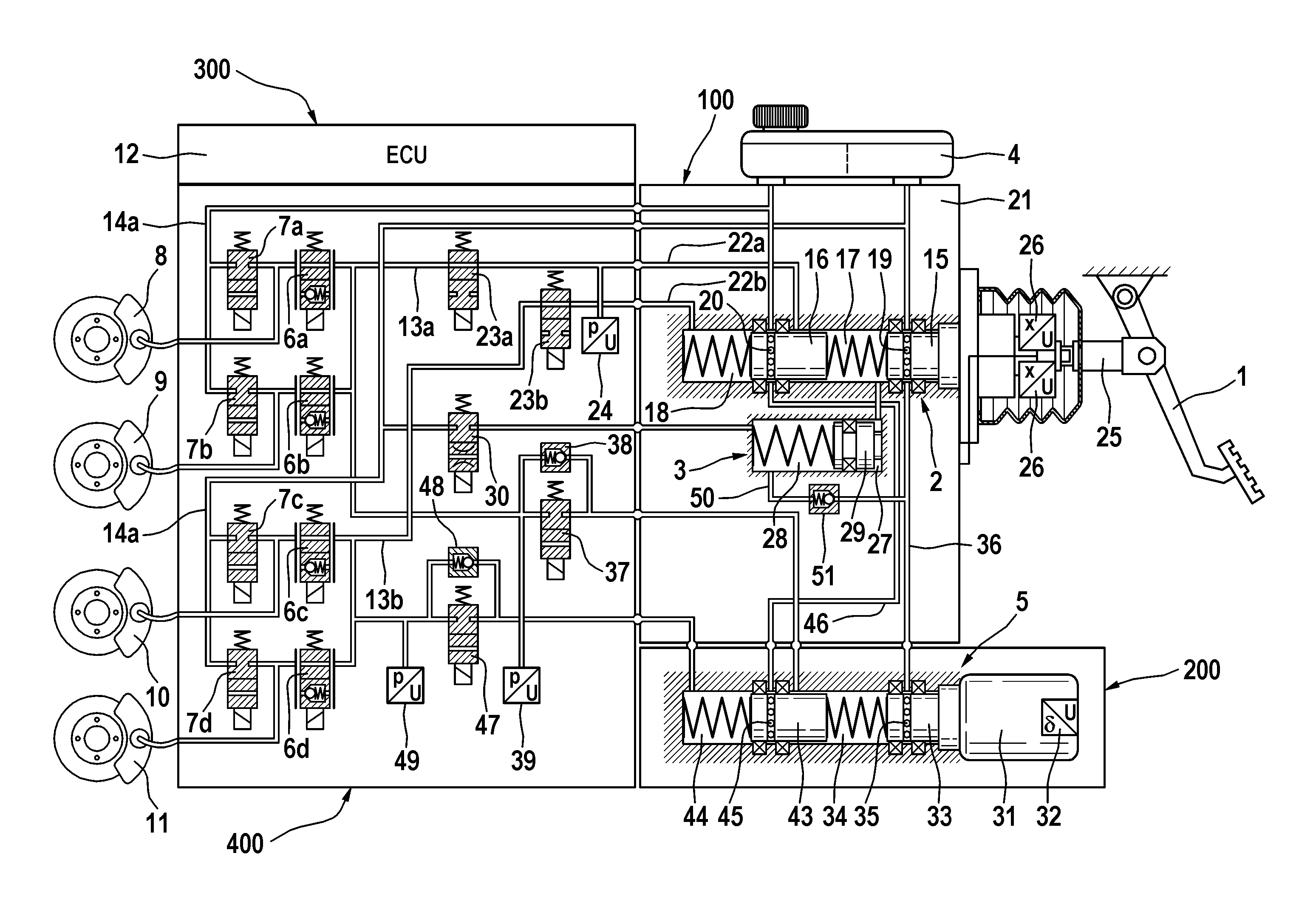
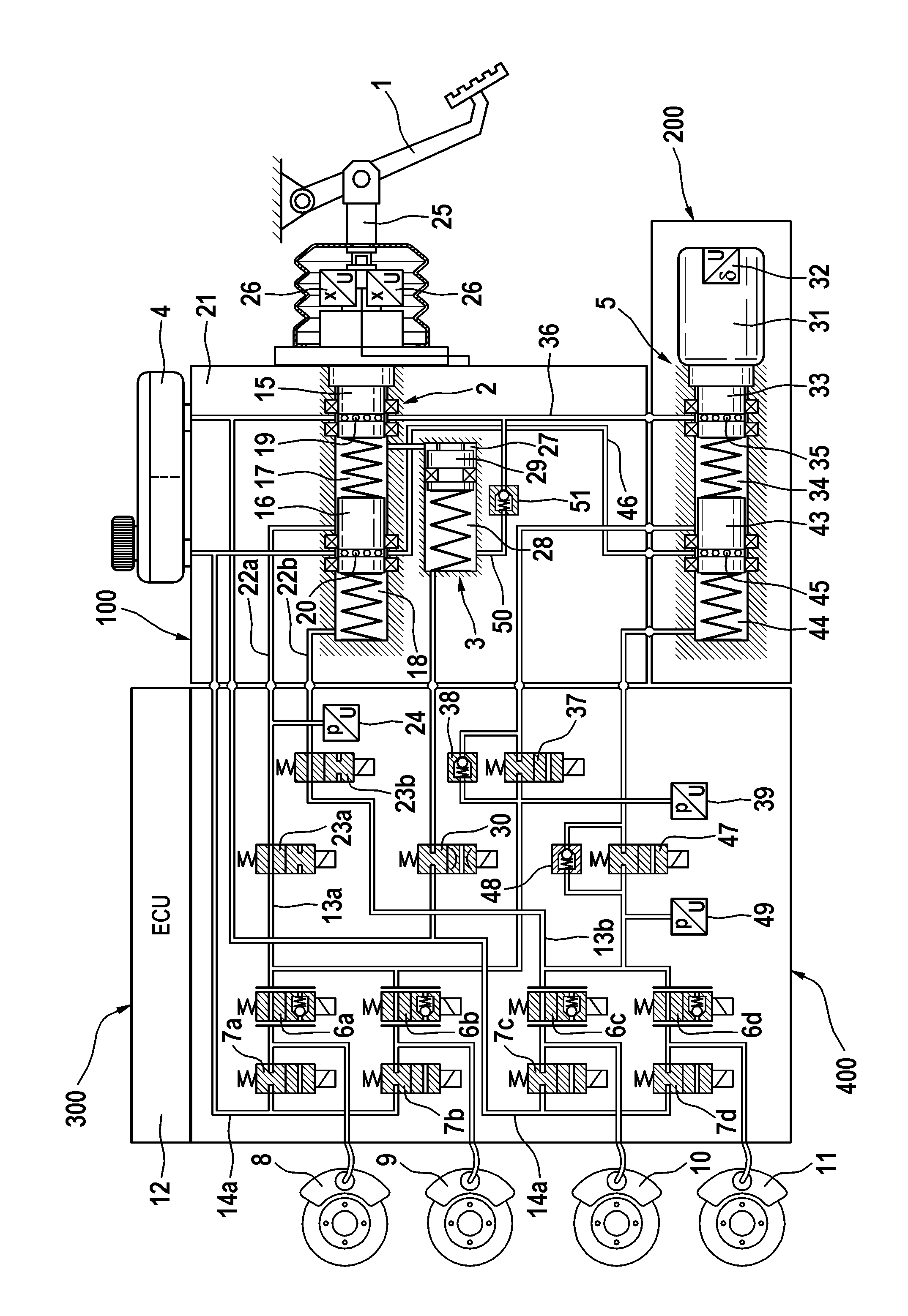
ActiveUS20120169112A1Braking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsVehicle drivingMotorized vehicle
A brake system for motor vehicles, which brake system can be actuated both by the vehicle driver and also independently of the vehicle driver in a “brake by wire” operating mode, is preferentially operated in the “brake by wire” operating mode, and can be operated in at least one fall-back operating mode in which only operation by the vehicle driver is possible. The brake system has inter alia an electrohydraulic pressure generating device (5) which outputs a brake system pressure, and a pressure modulation unit which has one inlet valve (6a-6d) and one outlet valve (7a-7d) per wheel brake (8, 9, 10, 11) for setting wheel-specific brake pressures derived from the brake system pressure, wherein the inlet and outlet valves (6a-6d, 7a-7d) output or transmit the brake system pressure when in the non-actuated state.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com