Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2063 results about "Brake pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
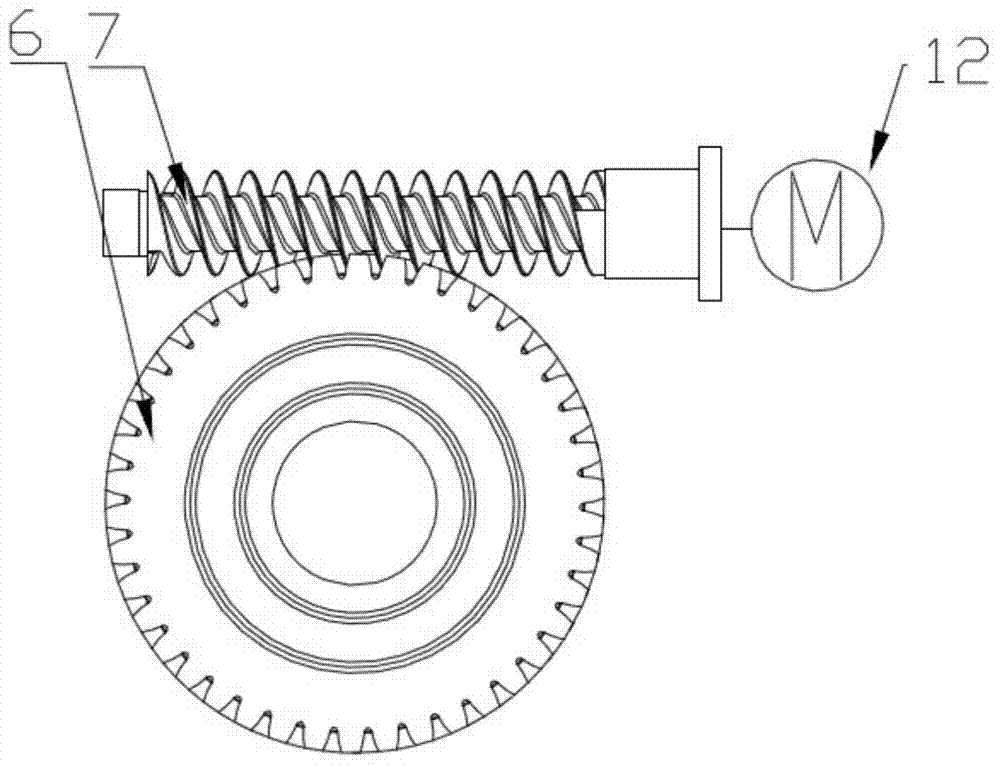
Electronic braking system and method for drawbar trailers
ActiveUS8267485B2Overcome disadvantagesReduce probabilityBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsAxle loadBraking system
A system and method for braking a drawbar trailer having a front axle and one or more further axles, each axle having at least two wheels, includes first sensors which sense the axle load of at least one axle, and second sensors which sense the rotational wheel speeds. Brakes actuatable with a pneumatic brake pressure brake the trailer. Brake signals generated in the towing vehicle are transmitted between the towing vehicle and the trailer. A control unit receives these brake signals and the sensor signals, and determines the axle load. The operating pressure is adapted to the brake pressure which is fed to the brakes. The control unit detects the brake pressure value as a function of (i) the specific axle loads of the front axle and the other axles and (ii) the received brake signals, and actuates the brakes such that the detected brake pressure is made available.
Owner:WABCO EURO BVBA SPRL
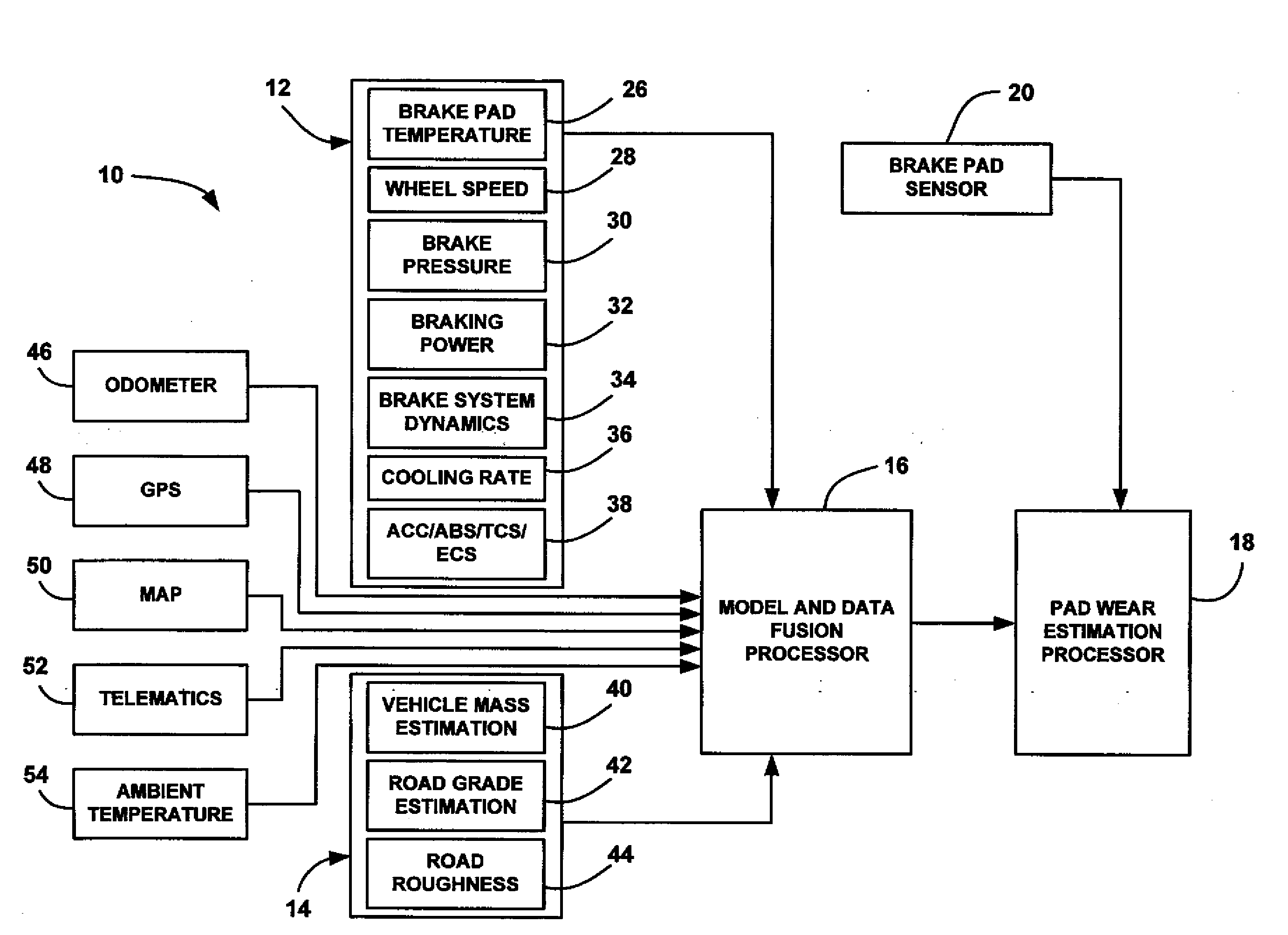
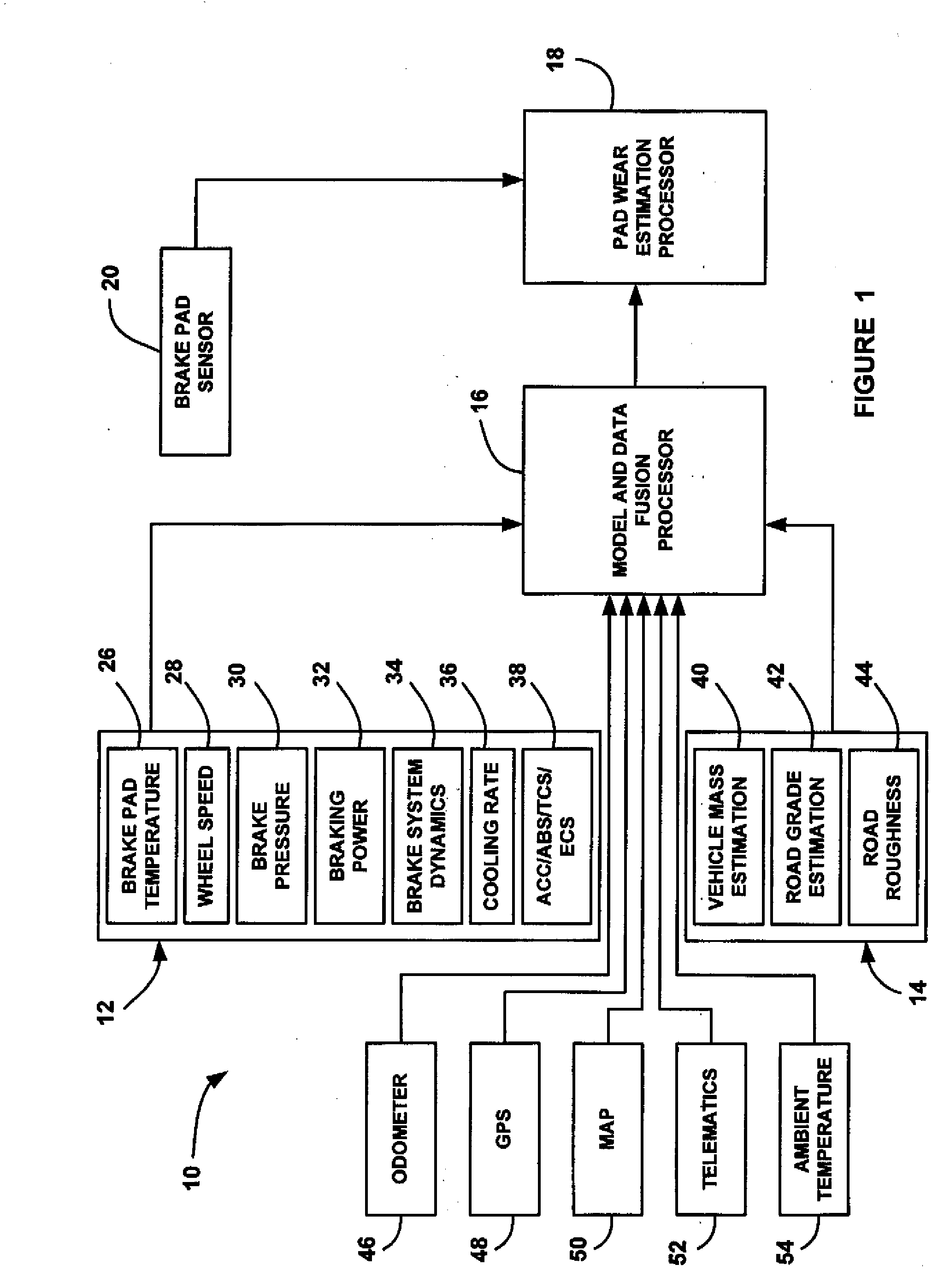
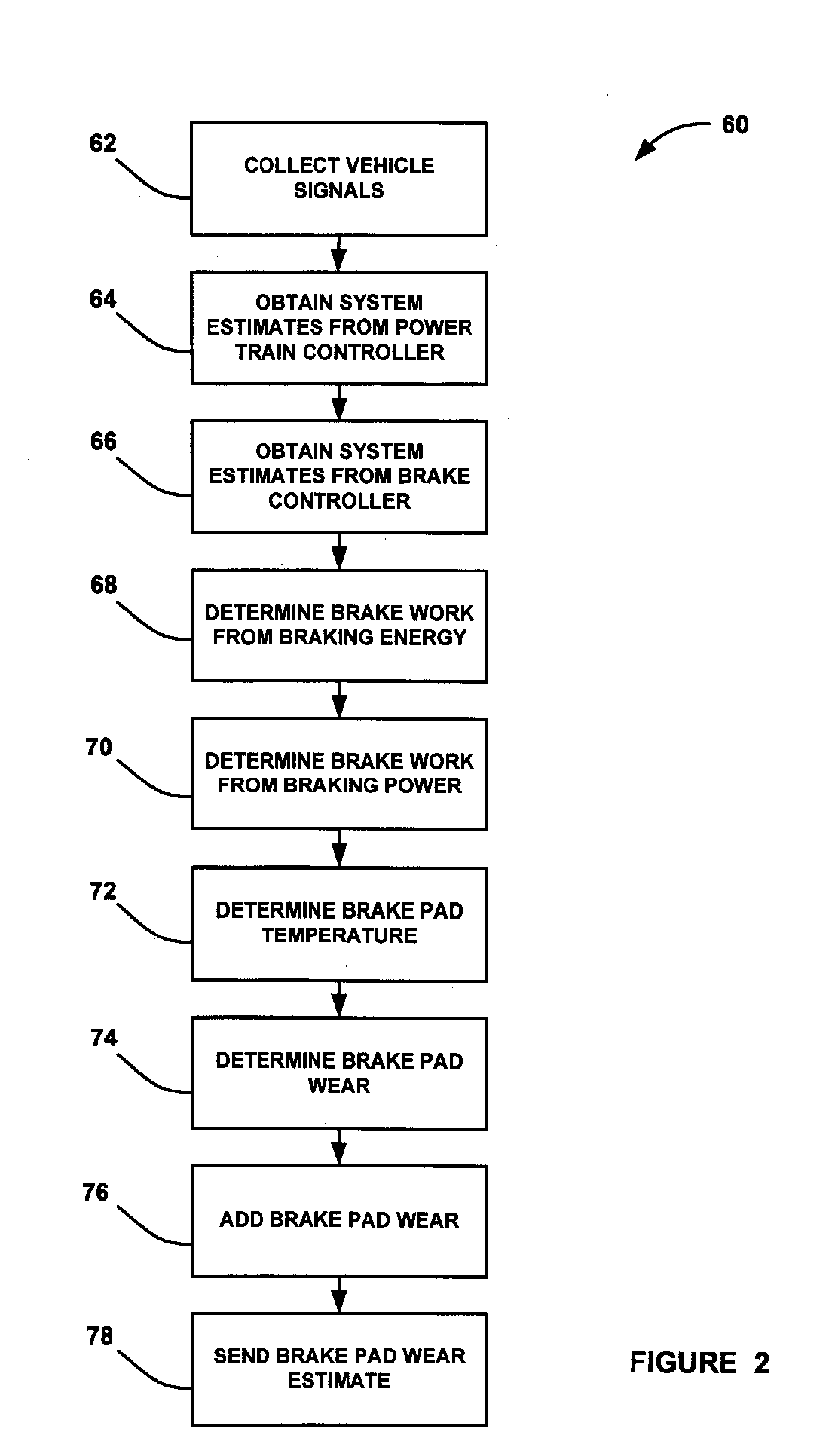
Brake pad prognosis system
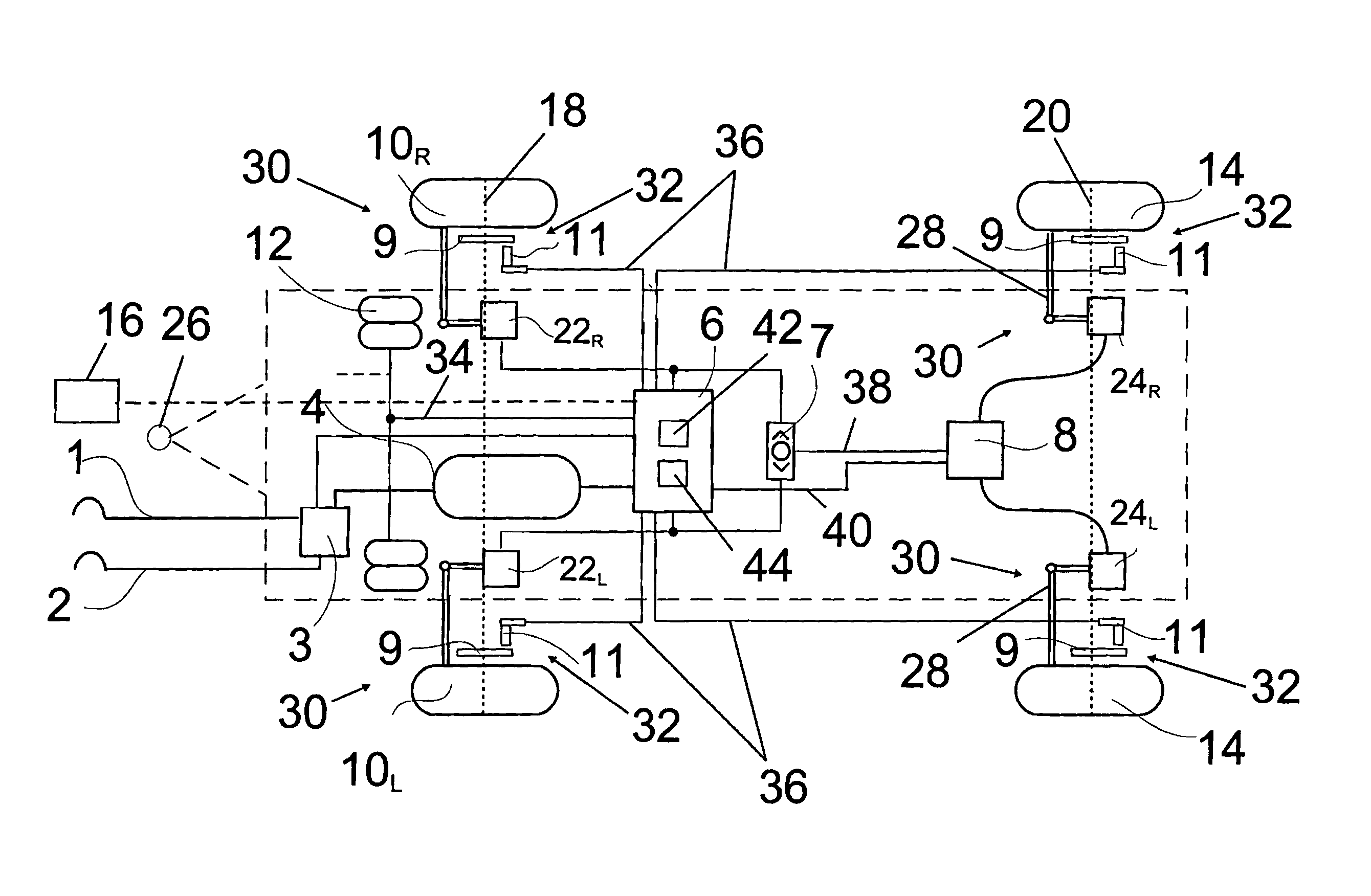
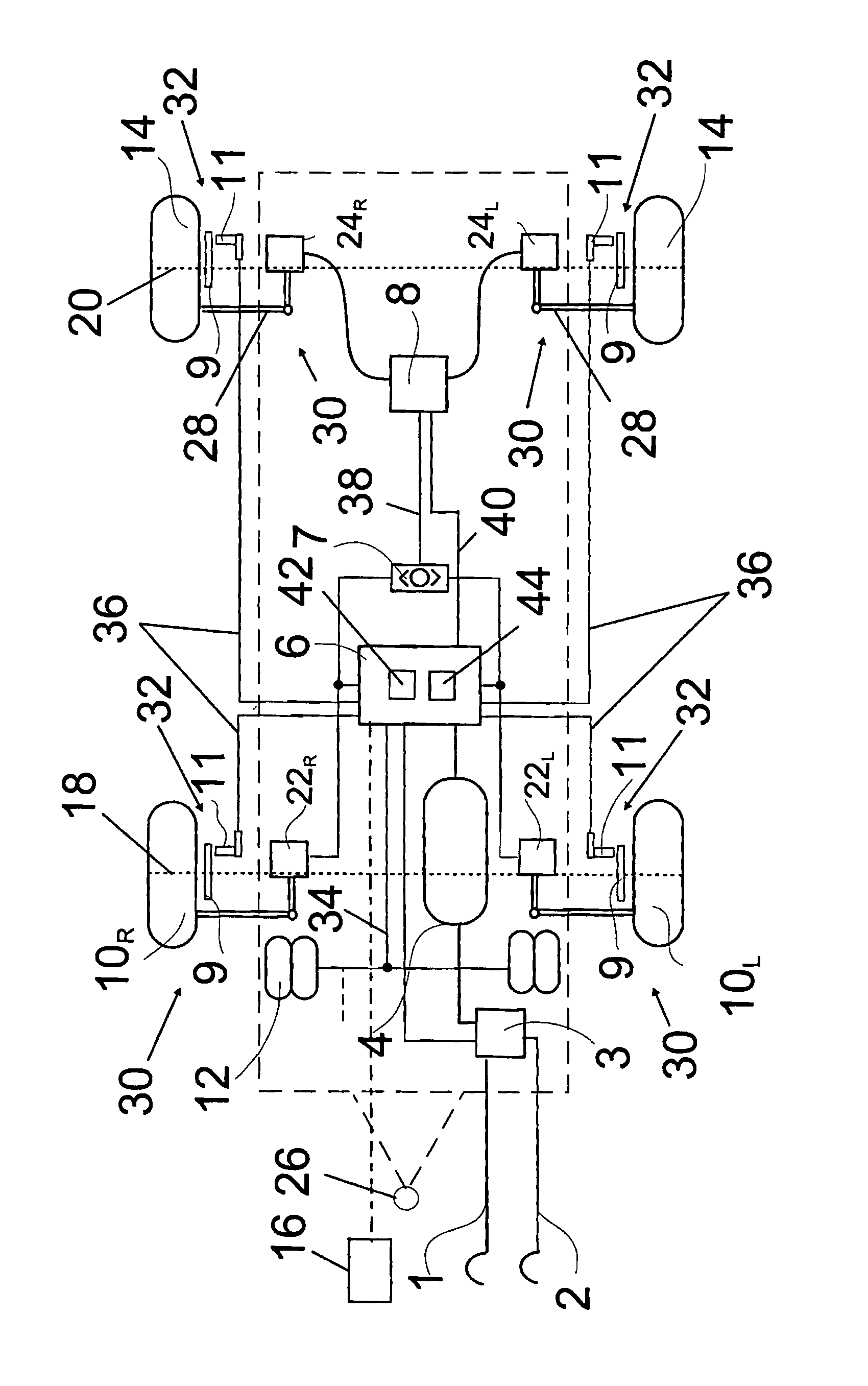
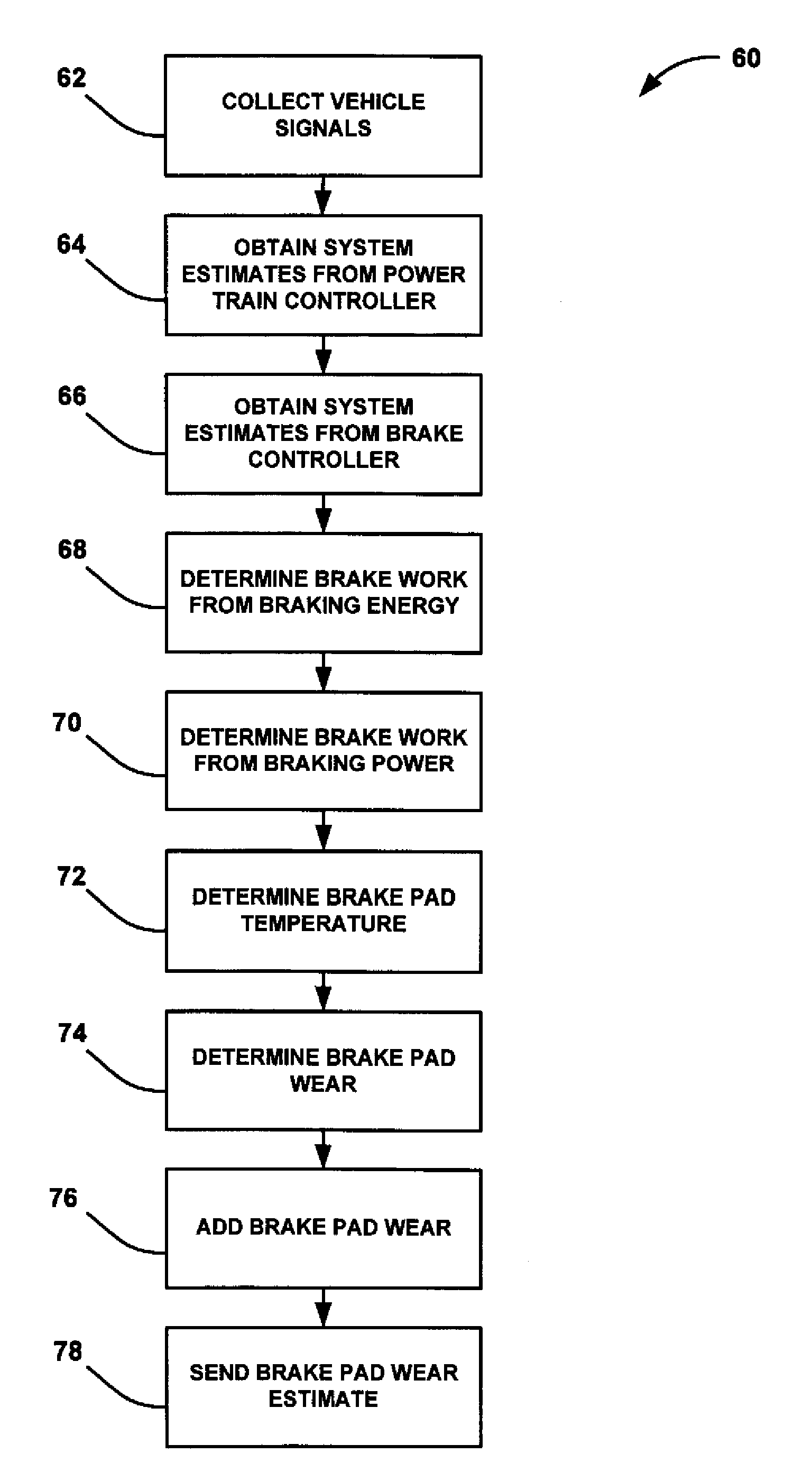
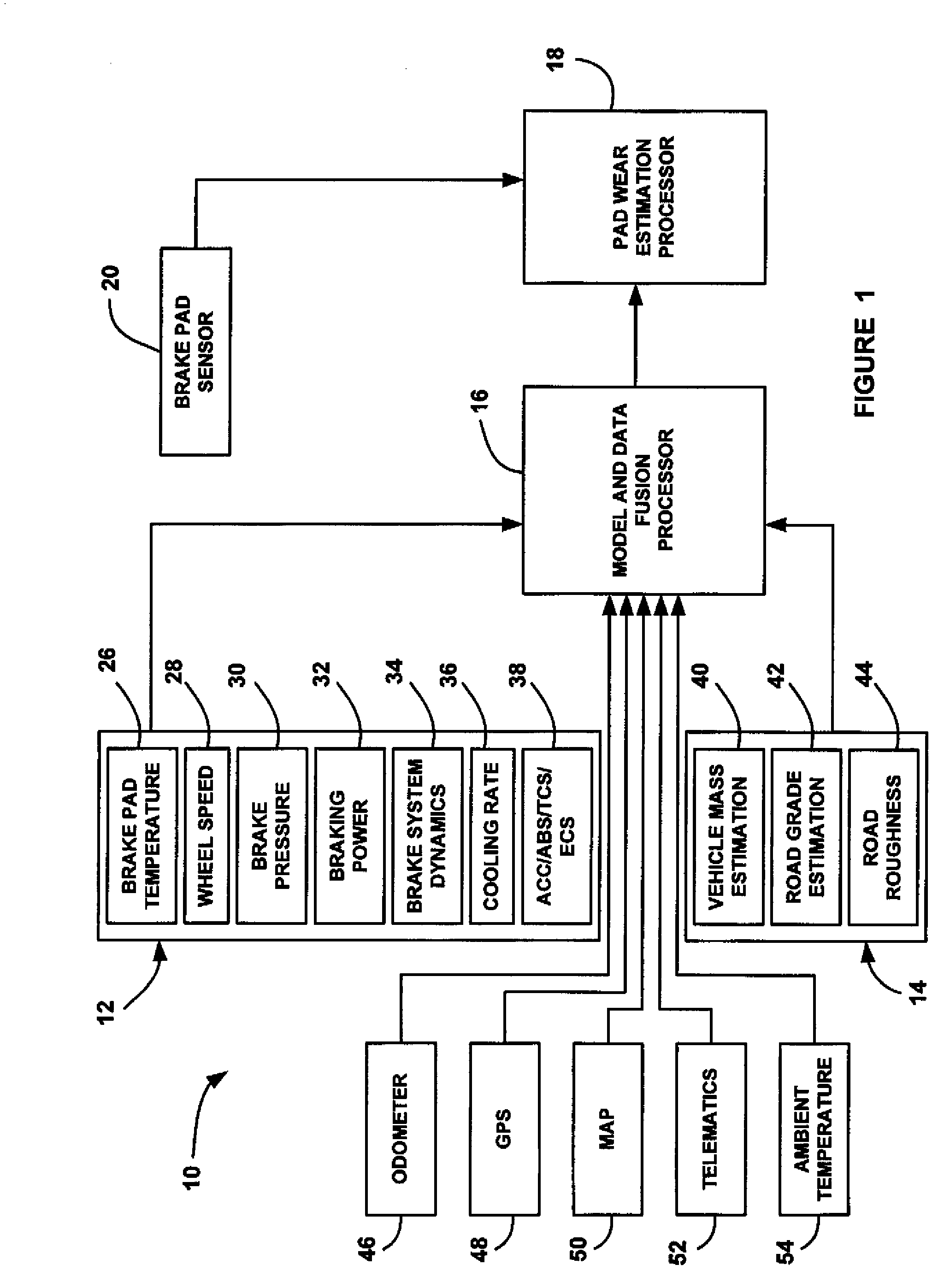
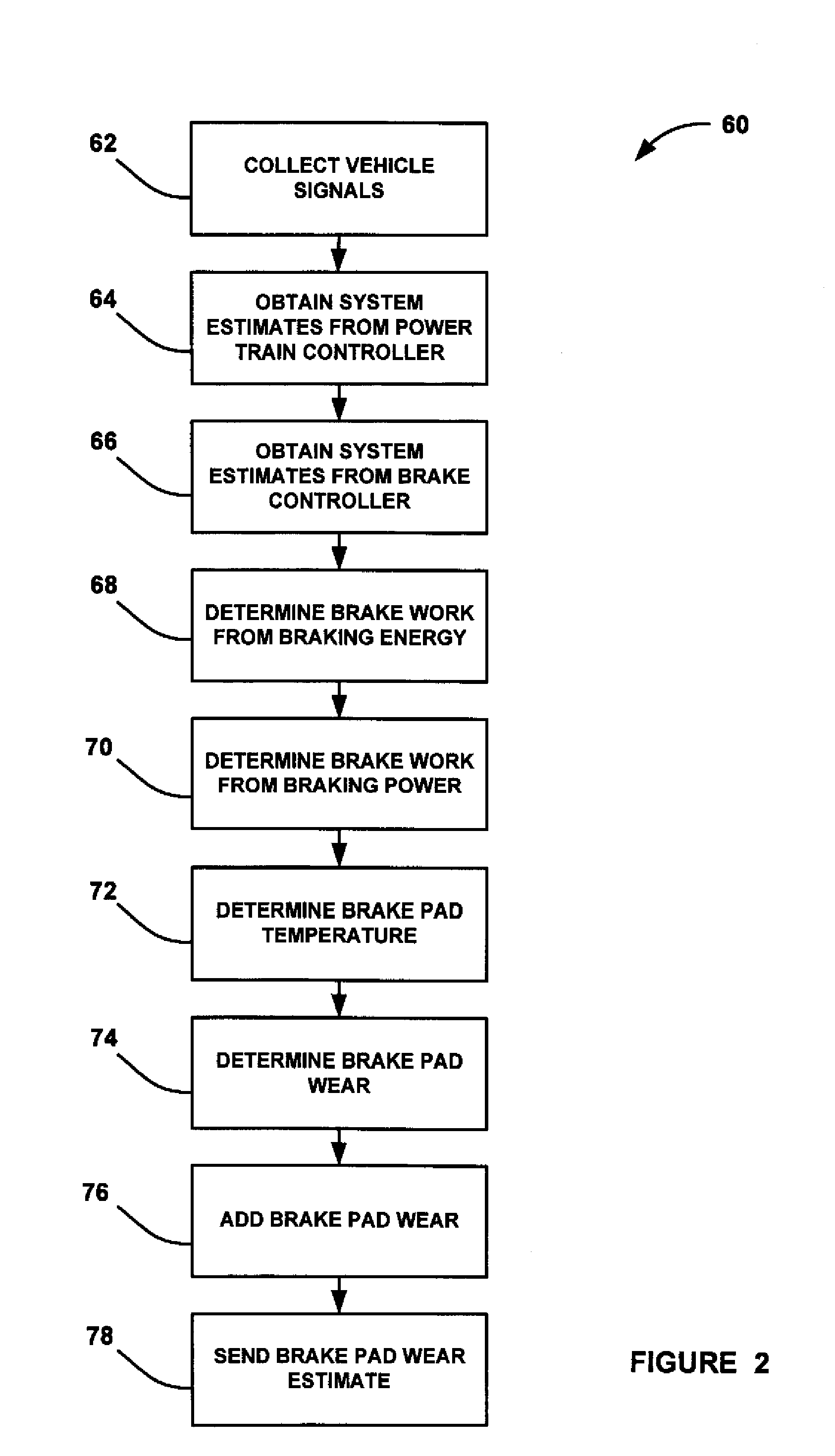
A method for providing an estimate of brake pad thickness. The method employs fusion of sensors, if used, and driver brake modeling to predict the vehicle brake pad life. An algorithm is employed that uses various inputs, such as brake pad friction material properties, brake pad cooling rate, brake temperature, vehicle mass, road grade, weight distribution, brake pressure, brake energy, braking power, etc. to provide the estimation. The method calculates brake work using total work minus losses, such as aerodynamic drag resistance, engine braking and / or braking power as braking torque times velocity divided by rolling resistance to determine the brake rotor and lining temperature. The method then uses the brake temperature to determine the brake pad wear, where the wear is accumulated for each braking event. A brake pad sensor can be included to provide one or more indications of brake pad thickness from which the estimation can be revised.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for controlling vehicular traffic flow
InactiveUS20070135989A1Minimizes distributionImprove securityAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficModem deviceControl communications
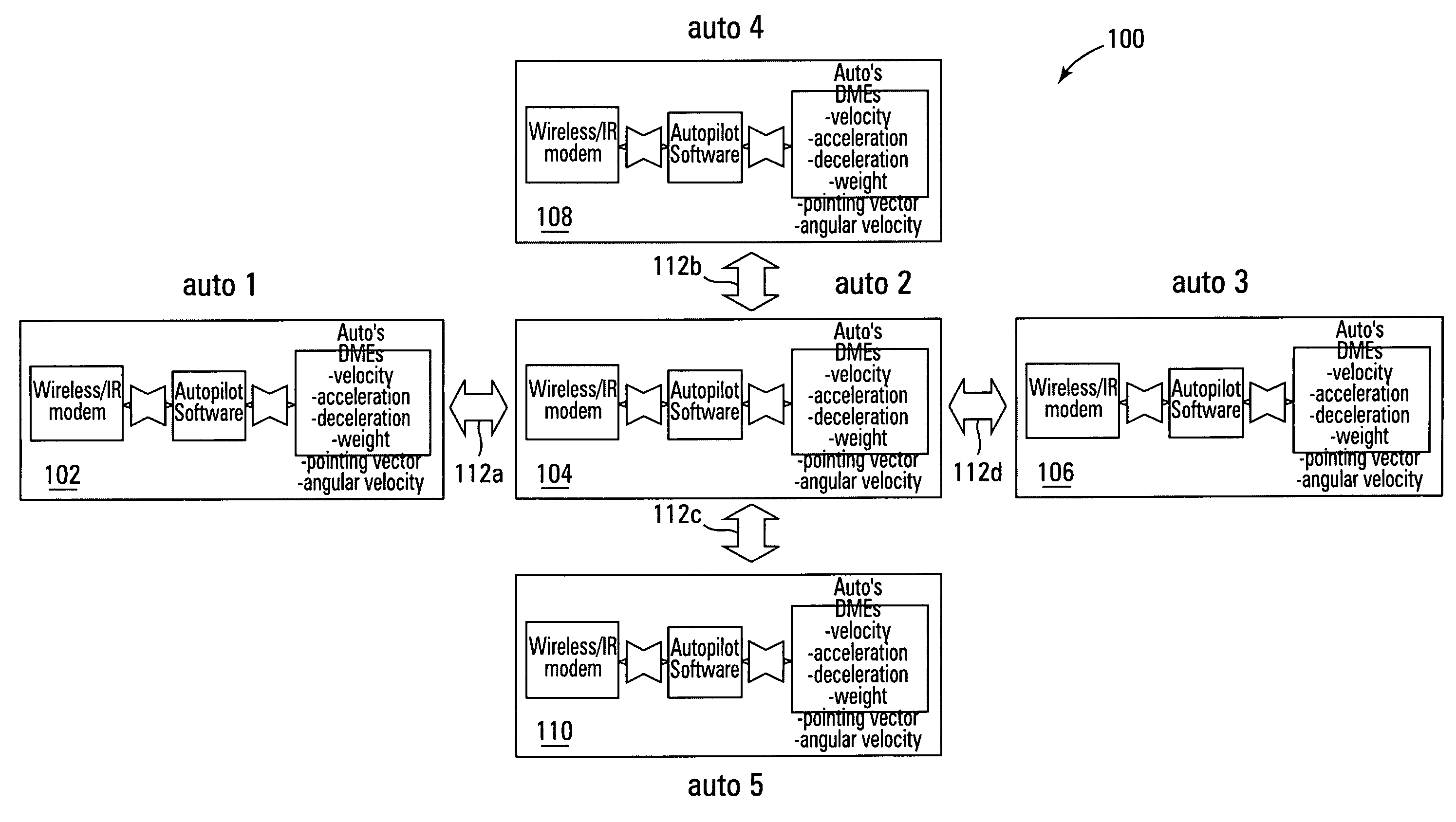
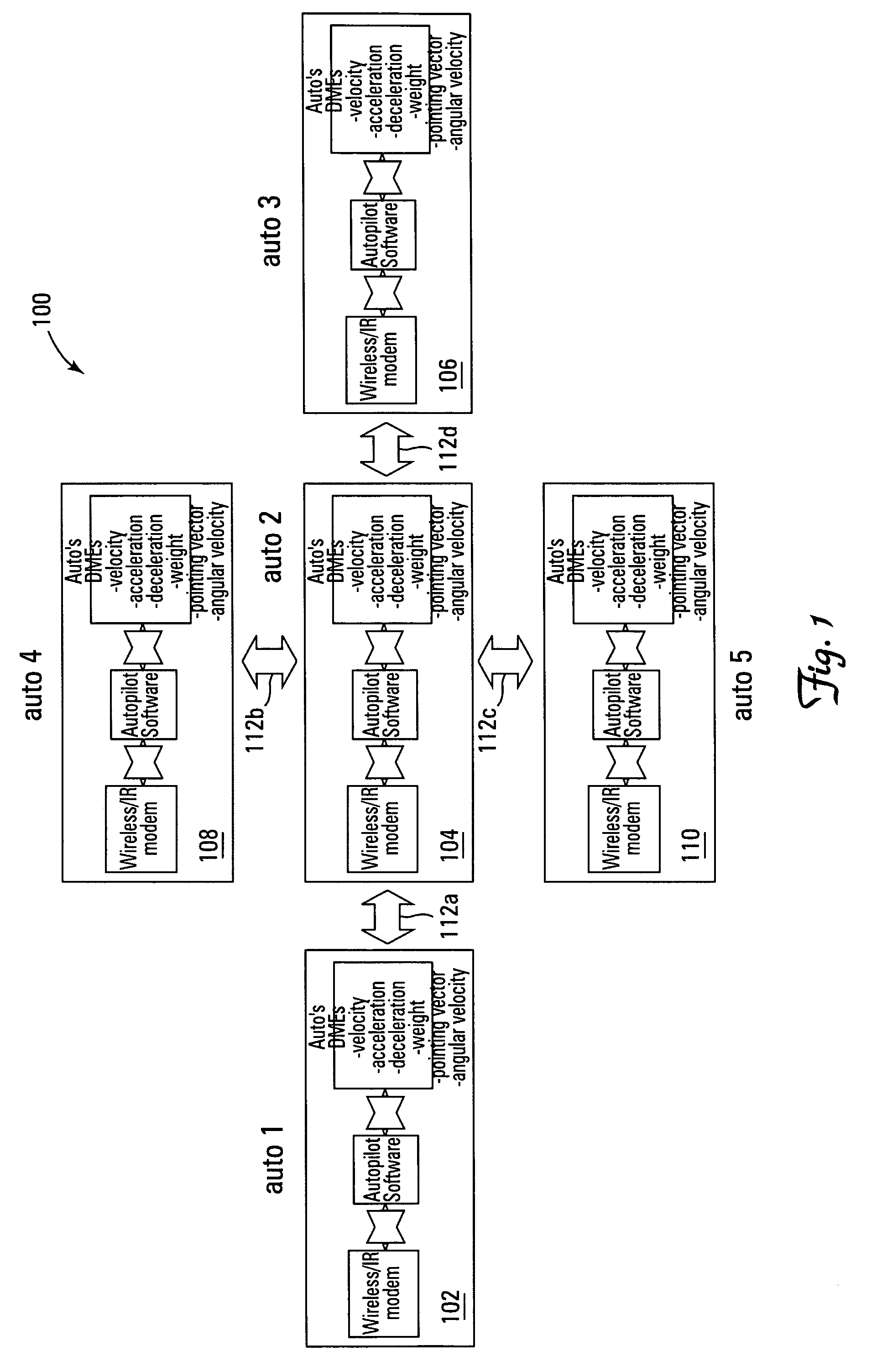
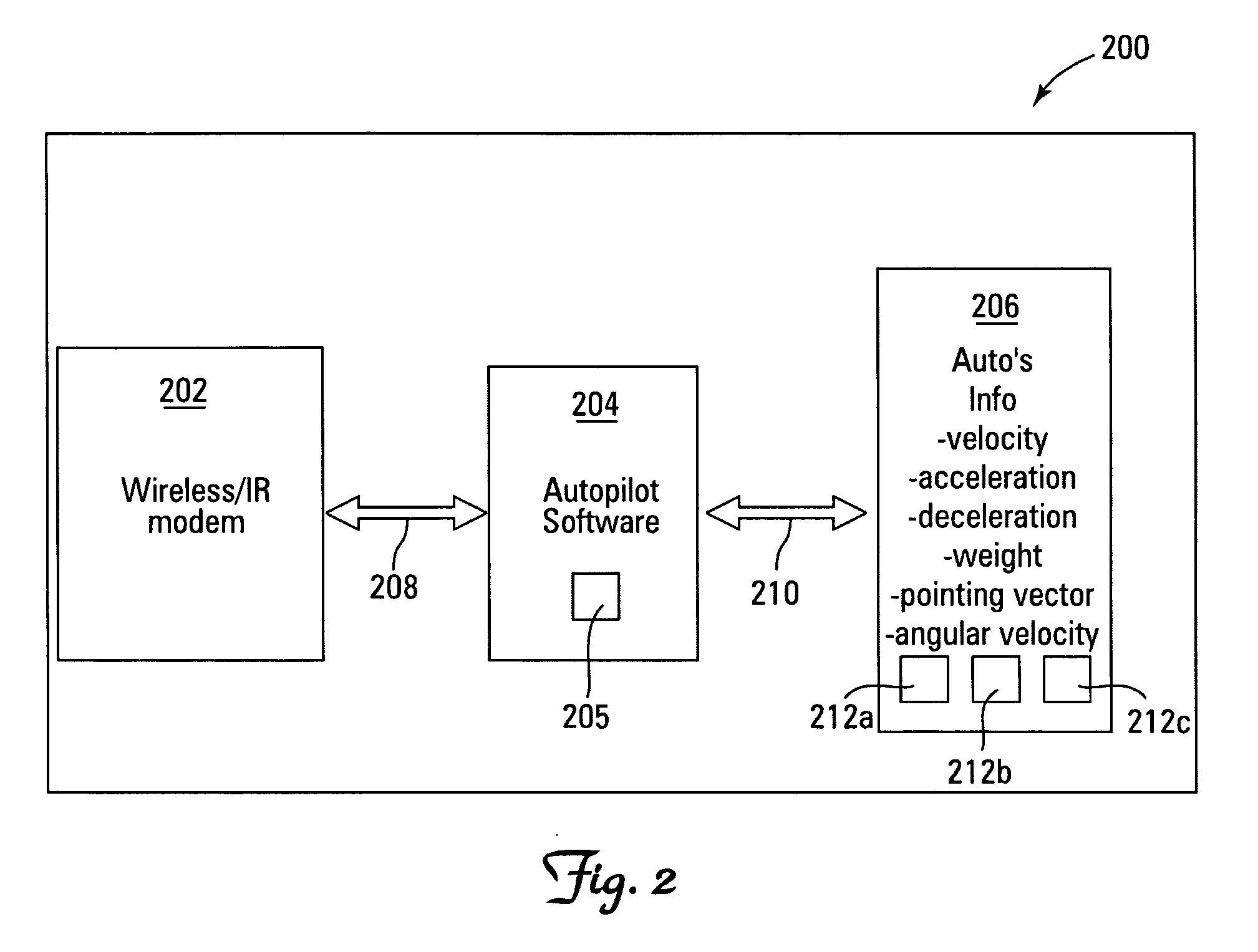
A system and method for controlling vehicular traffic flow is disclosed, which creates a communication system between vehicles that allows the vehicles to share their respective velocities and acceleration or deceleration rates. Thus, each vehicle within the system can respond immediately to any acceleration or deceleration rate changes of the surrounding vehicles (e.g., the vehicle directly in front, directly in back, and in the adjacent lane). Essentially, the system functions similar to a wireless vehicular train, with a queue of cars linked together by a stiff, wireless communications “chain”. Notably, the term “vehicle” is not limited only to land-based vehicles (e.g., motor vehicles), and the system can include airborne vehicles (e.g., multiple aircraft flying in close formation, military aircraft flying in drone formation, etc.). For example, a system for controlling vehicular traffic flow is disclosed, which includes in each vehicle of a plurality of vehicles, a wireless or infrared (IR) modem for inter-vehicular communications, a range finder for determining the distance and closing rate between vehicles, a processing unit for retrieving vehicular operational data (e.g., velocity, angular velocity, acceleration rate, deceleration rate, braking pressure, weight, pointing vector, etc.) and executing flow control system software instructions, and a vehicular flow control communications protocol that enables the communication of various flow control parameters between vehicles via the wireless or IR modem. Thus, each vehicle in the system “knows” what the surrounding vehicles are doing and can respond immediately to changes in the traffic flow. As such, the system minimizes the distribution of vehicles' velocities in the queue, and increases traffic throughput and safety as a result.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Anti-lock braking system based on an estimated gradient of friction torque, method of determining a starting point for anti-lock brake control, and wheel-behavior-quantity servo control means equipped with limit determination means
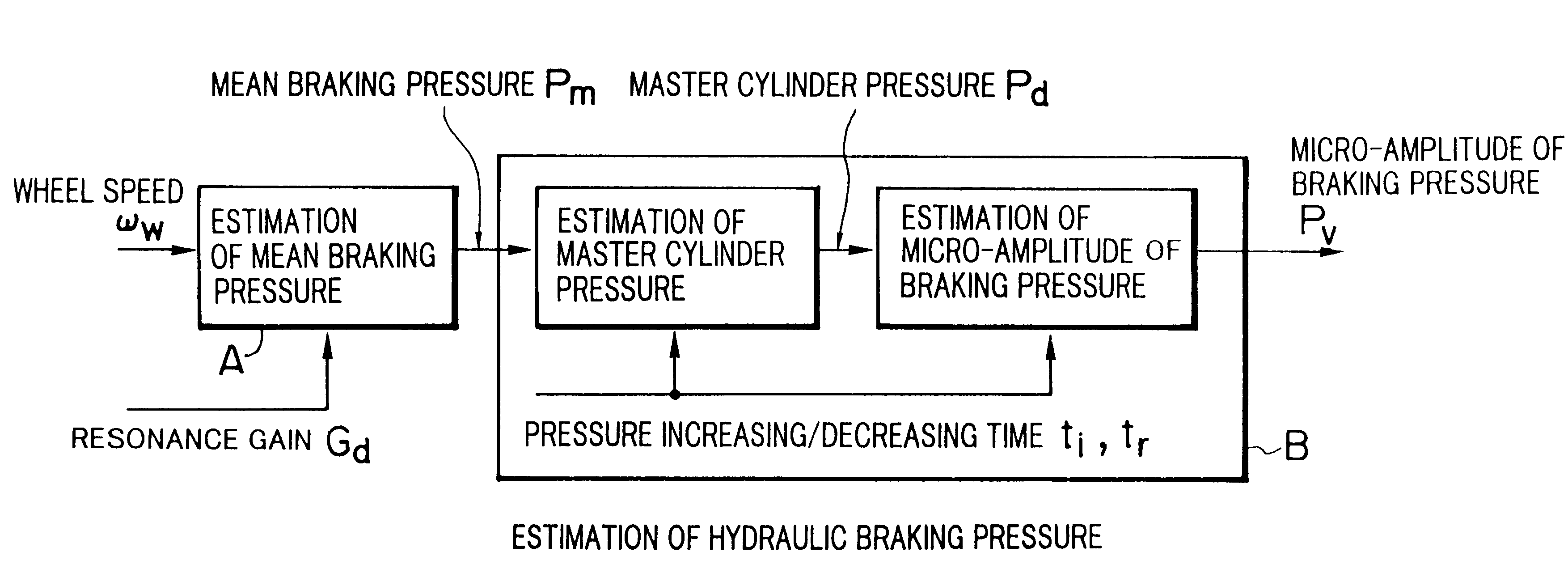
An anti-lock braking system includes a friction torque gradient estimating unit for estimating, from a small number of parameters, the gradient of friction torque with respect to a slip speed, and controls a braking force acting on wheels on the basis of the friction torque gradient estimated by the friction torque gradient estimating unit. The friction torque gradient estimating unit may employ several types of estimating methods; e.g., a method of estimating the gradient of friction torque from only time-series data concerning a wheel speed; a method of estimating the friction torque gradient from time-series data concerning wheel deceleration as well as from braking torque or time-series data concerning physical quantities associated with the braking torque; or a method of estimating the friction torque gradient from micro-gains which are obtained when brake pressure is excited in a very small amount at the resonance frequency of a vibration system comprising a vehicle, wheels, and a road surface and which represent the characteristics of the vibration system. Further, there is also disclosed a method of determining, from the thus-estimated friction torque gradient, the limit of the characteristics of friction torque developed between the wheels and the road surface.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Vehicle adaptive cruise control system
ActiveCN103754221AEnsure lane change safetyImprove functional limitationsExternal condition input parametersVehicle dynamicsControl system
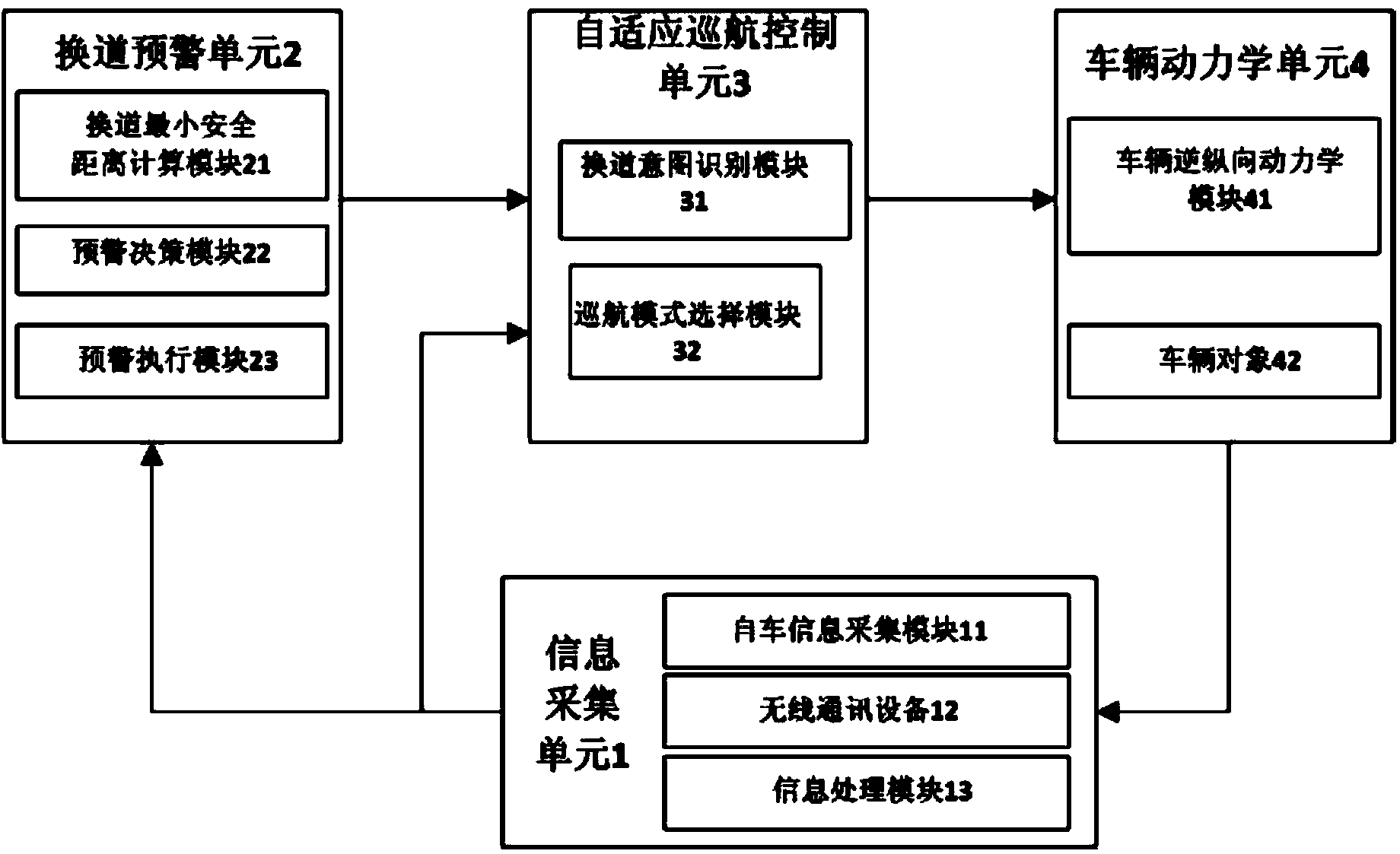
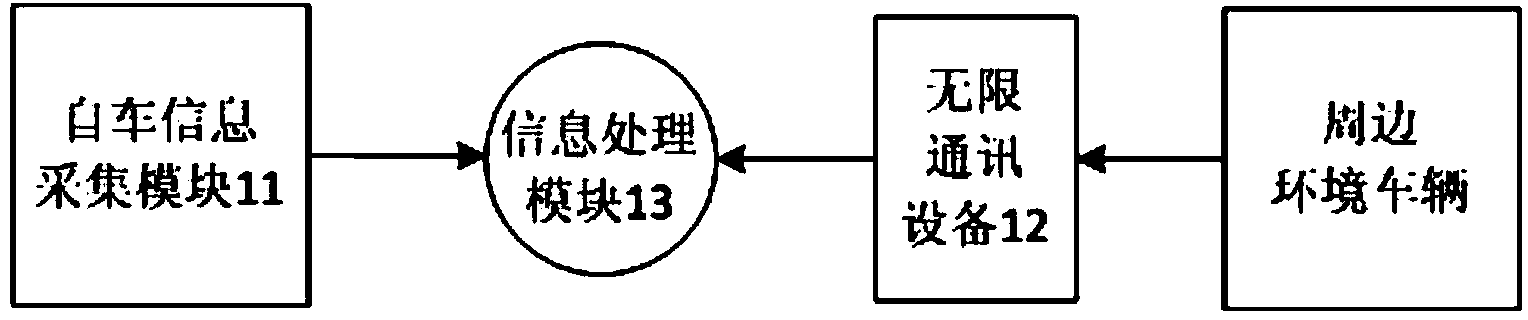
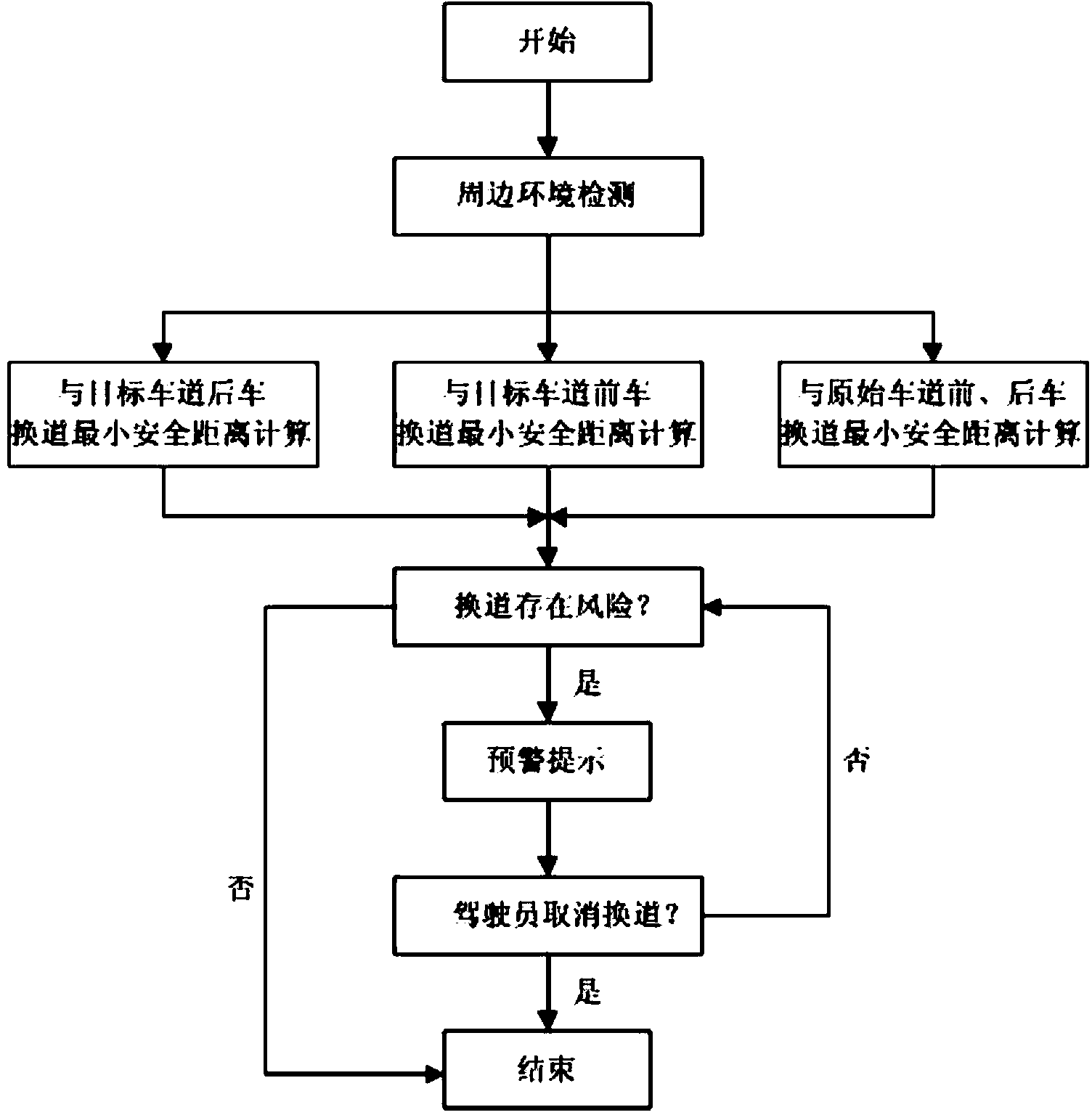
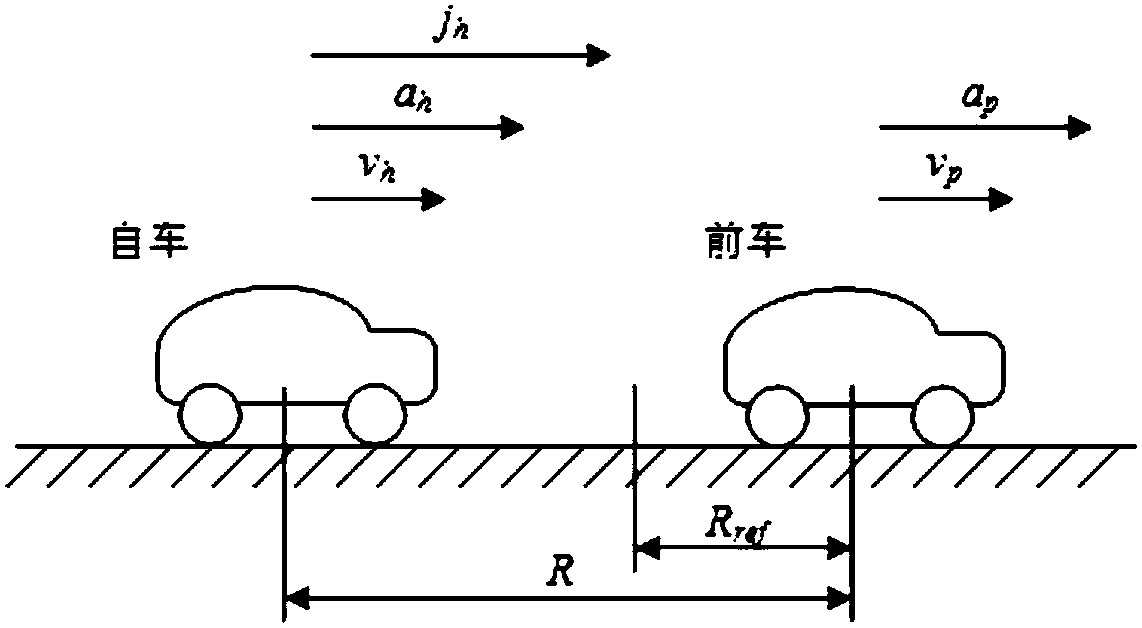
The invention relates to a vehicle adaptive cruise control system. The vehicle adaptive cruise control system is characterized in that an information collecting unit, a lane changing early warning unit, an adaptive cruise control unit and a vehicle dynamics unit are included; the information collecting unit collects and processes the driving state information of a vehicle, and sends the driving state information to the lane changing early warning unit and the adaptive cruise control unit; the lane changing early warning unit calculates the lane changing minimum safety distance between the own vehicle and surrounding vehicles according to the received effective vehicle movement information, and judges lane changing risks according to a calculation result, an early warning is carried out on the vehicle according to a judgment result, and the judgment result is sent to the vehicle adaptive cruise control unit; the vehicle adaptive cruise control unit selects a control mode according to the vehicle movement information and the lane changing risk judgment result, calculates expected longitudinal acceleration needed by vehicle longitudinal driving, and sends the calculated expected longitudinal acceleration to the vehicle dynamics unit; the vehicle dynamics unit converts the expected longitudinal acceleration into an expected air valve opening degree or braking pressure and sends the expected air valve opening degree or the braking pressure to a vehicle object, and the longitudinal control over the vehicle object is completed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Motor-driven electronic hydraulic braking system
ActiveCN103754210AQuick responsePrecise control of hydraulic braking forceBraking action transmissionSystems designLinear control
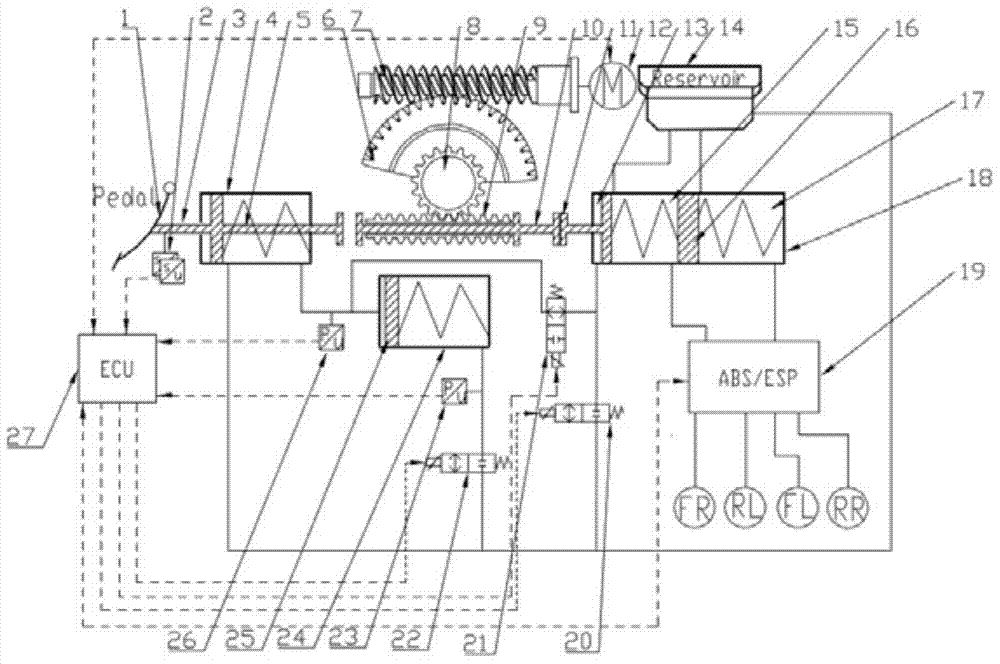
A motor-driven electronic hydraulic braking system comprises a brake pedal, a pedal displacement sensor, a secondary master cylinder, a pedal simulator pressure sensor, a pedal simulator, pedal simulator solenoid valves, a push rod, an electrically-controlled linear movement module, a brake master cylinder and an ABS / ESP (anti-skid brake system / electronic stability program) module. The electrically-controlled linear movement module drives the push rod to move by means of driving a movement regulating mechanism through a motor, the motor is controlled through a displacement signal, and linear control on braking pressure is realized. The brake master cylinder passes the ABS / ESP module to be hydraulically coupled with vehicle wheel brakes. The ABS / ESP module can passively regulate pressure transmitted from the master cylinder to the wheel brakes, and can actively regulate the pressure of the brake of each wheel. The motor-driven electronic hydraulic braking system has the advantages of rapid response, accurate control on brake fluid pressure, capabilities of well simulating brake pedal feeling of a driver and maximally recovering braking energy, and the like; meanwhile, the system is designed with a dual failure protection mode, thereby having high safety and reliability.
Owner:上海同驭汽车科技有限公司
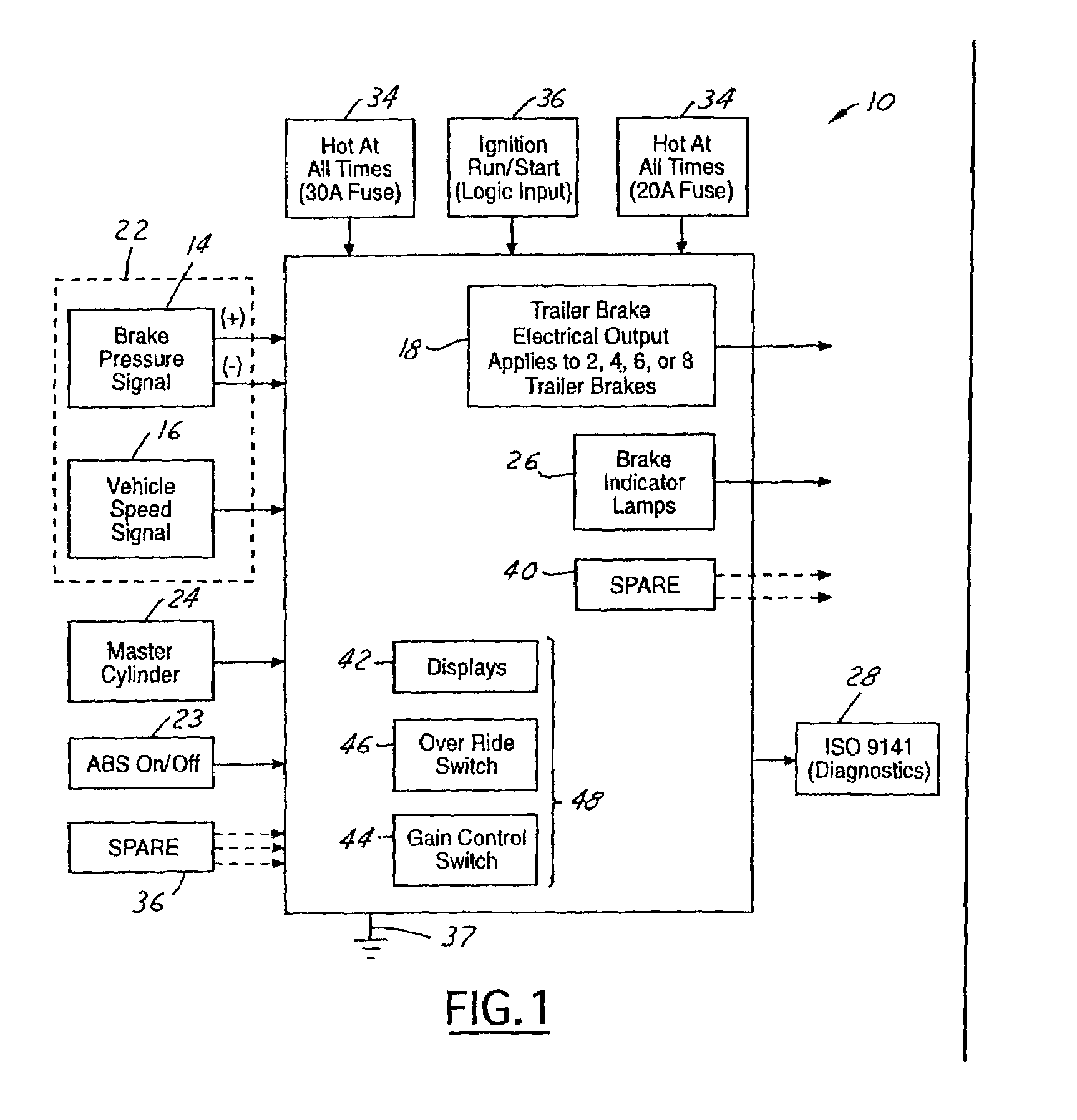
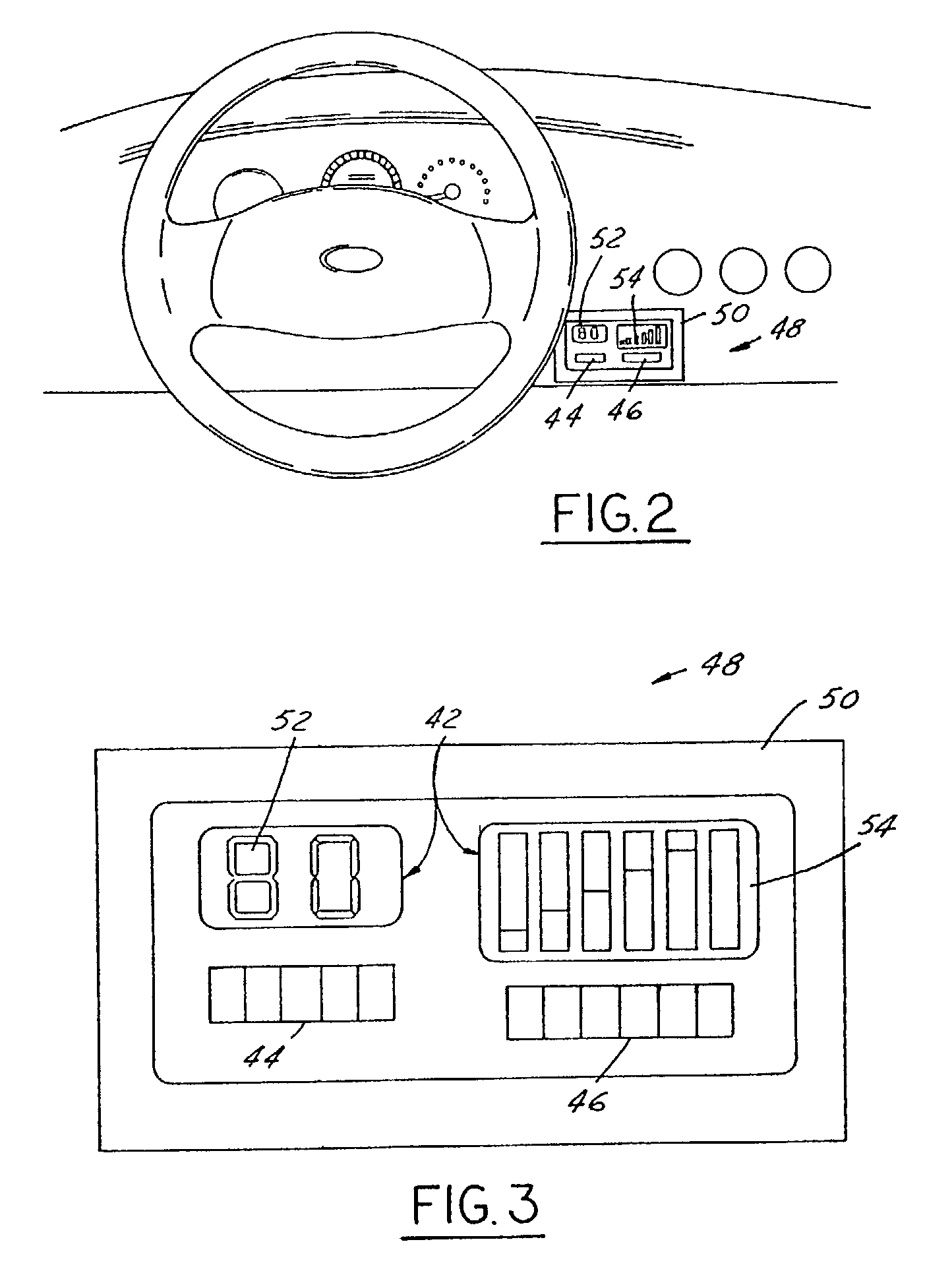
Integrated passenger vehicle trailer brake controller
InactiveUS6966613B2Improve cooperationBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsTrailer brake controllerVehicle brake
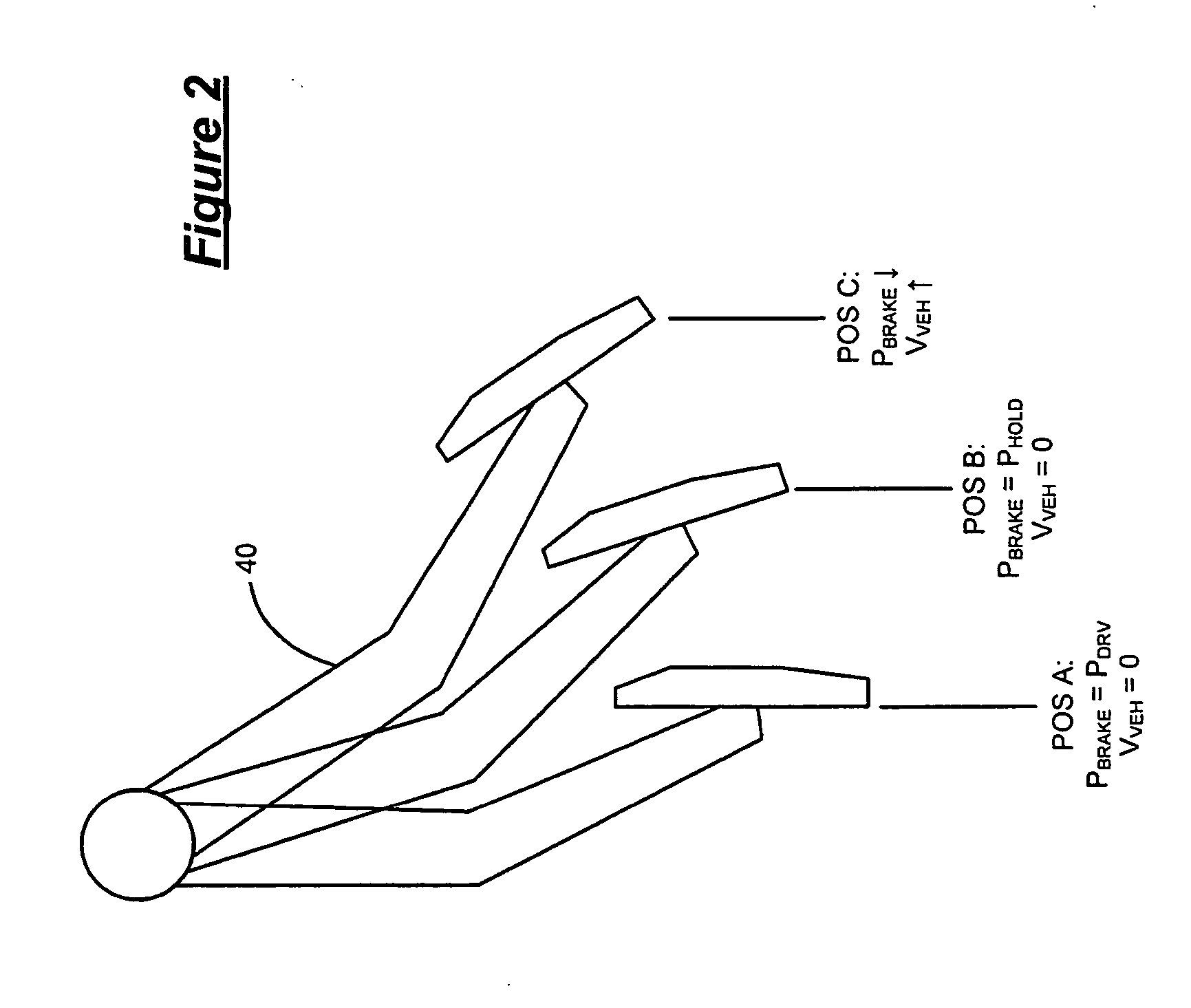
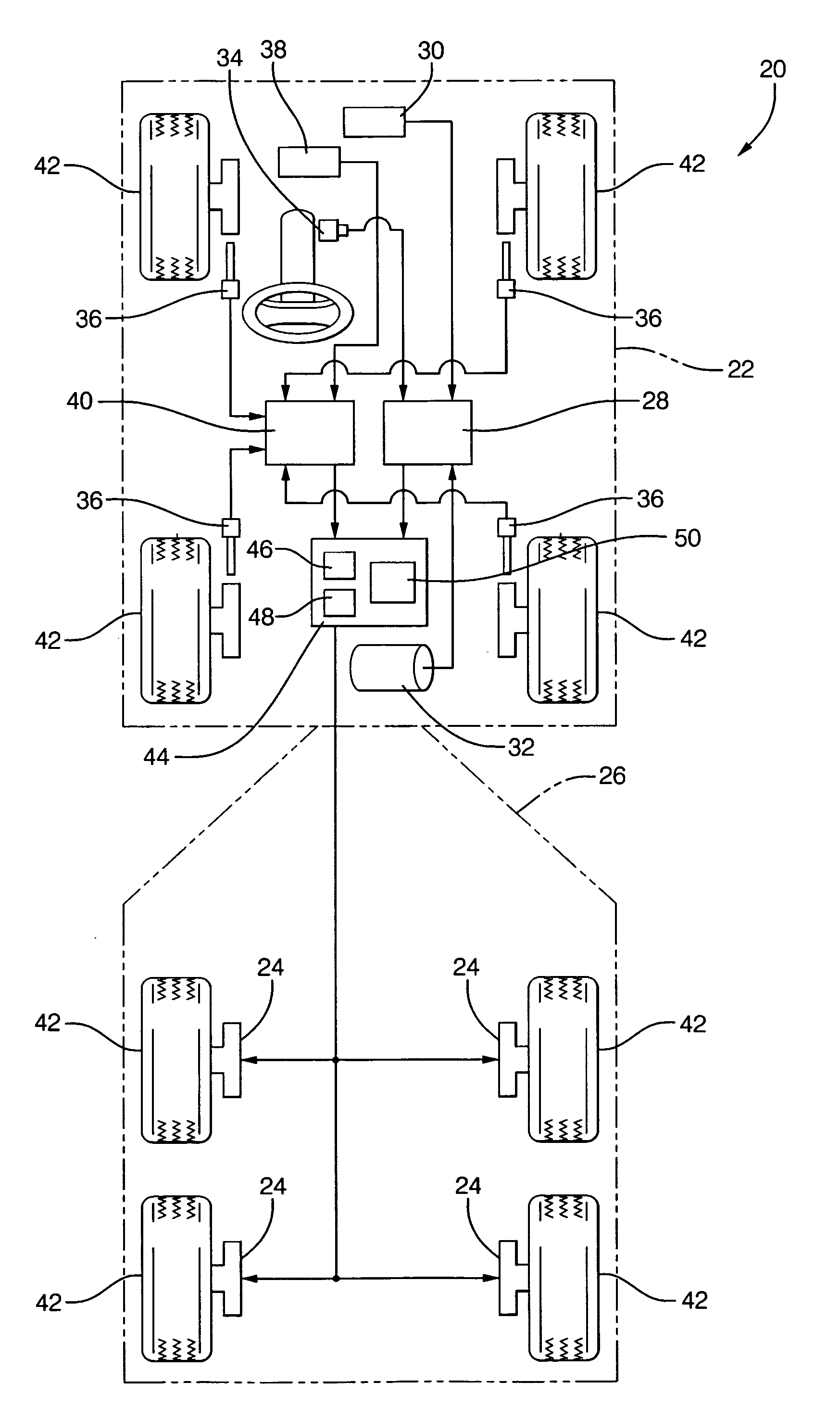
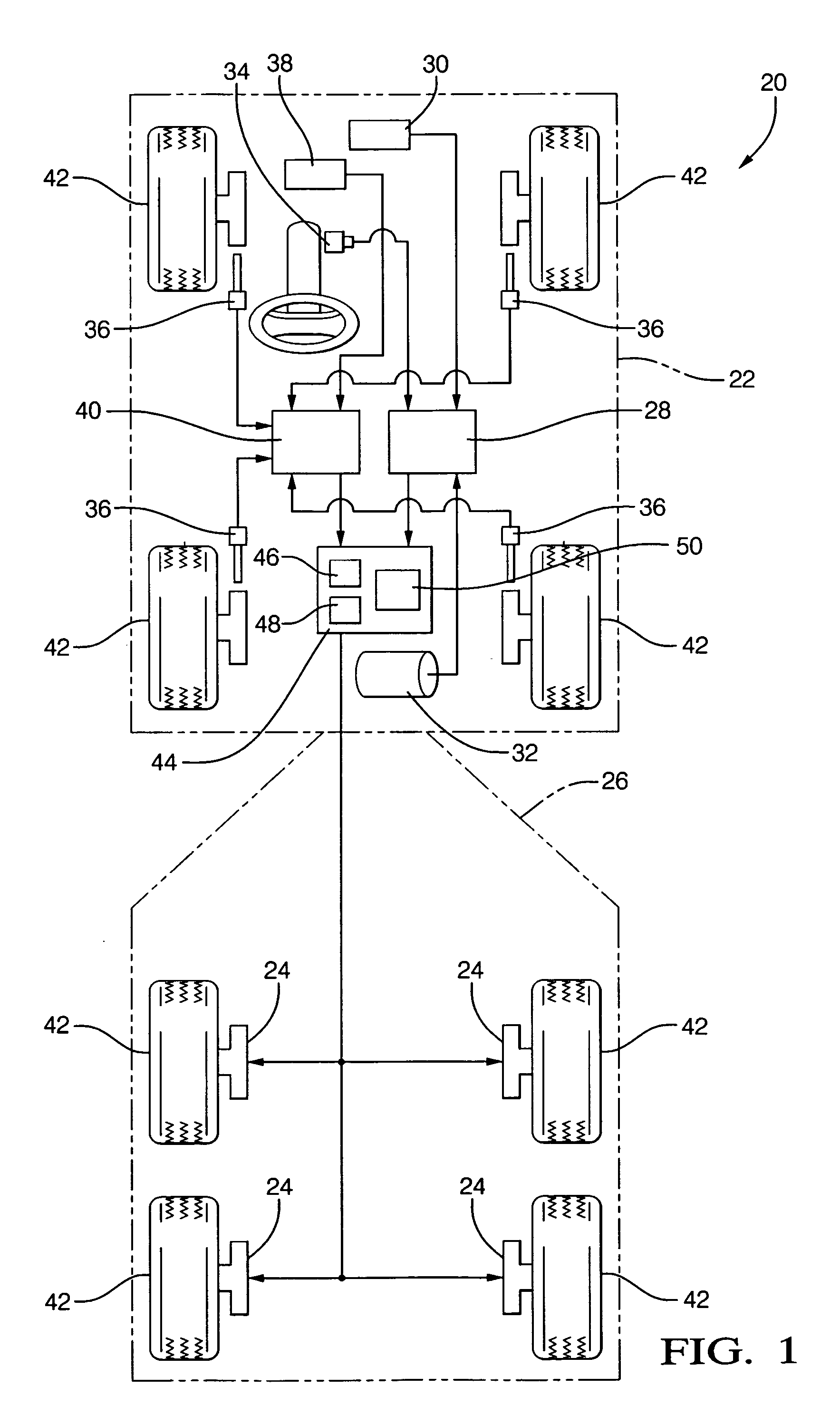
A trailer brake controller 10 for use in a passenger vehicle 12 is provided, including a control element 11 positioned within the passenger vehicle 12, a vehicle speed input 16 and a vehicle brake pressure input 14 providing speed and brake pressure data to the control element 11, and a trailer brake output 18 sending a signal to the trailer in response to the vehicle speed input 16 and the vehicle brake pressure input 14.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Braking estimation device, anti-lock brake controller, and braking pressure controller
InactiveUS6182001B1Inflated body pressure measurementDigital data processing detailsVibratory signalAtmospheric pressure
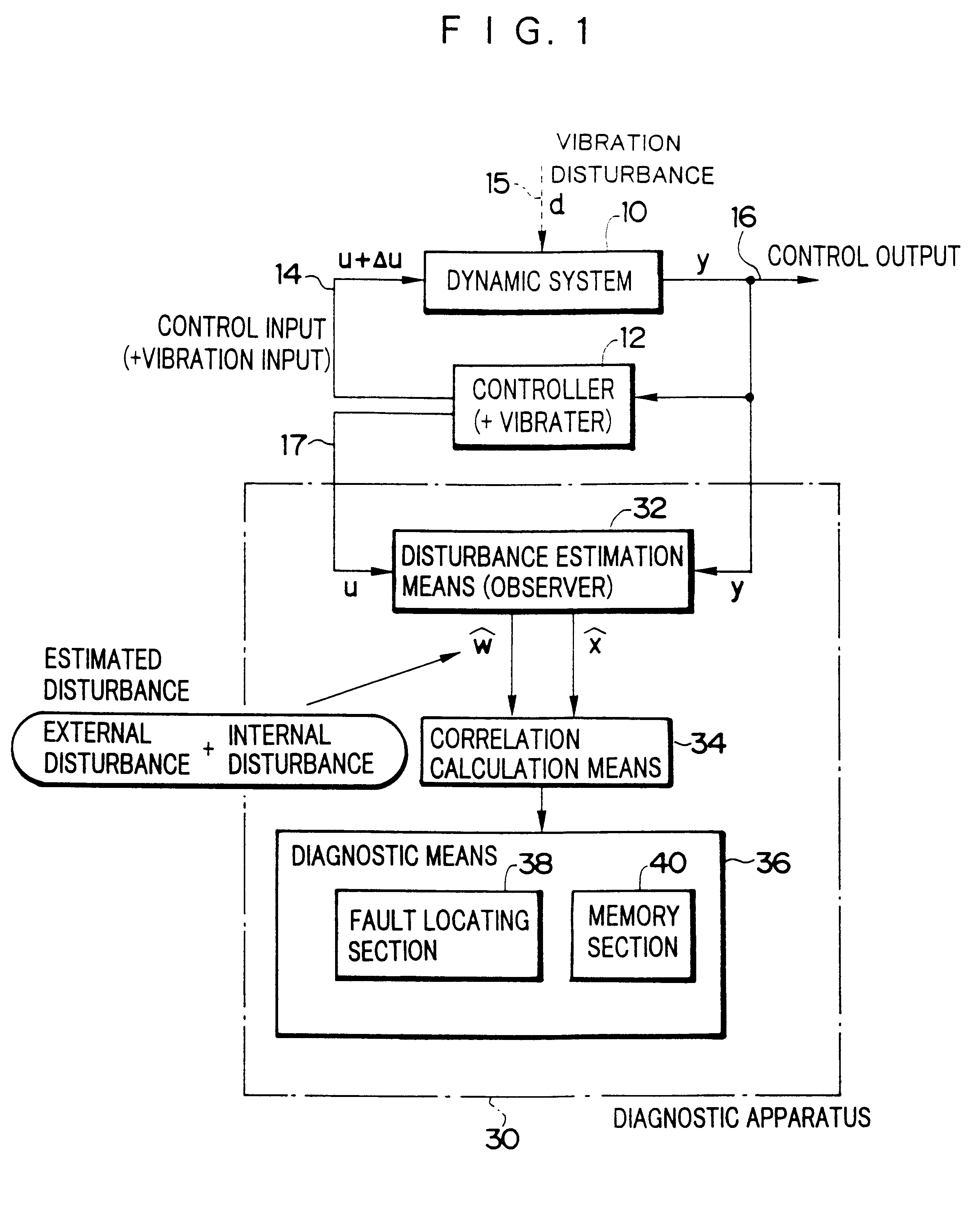
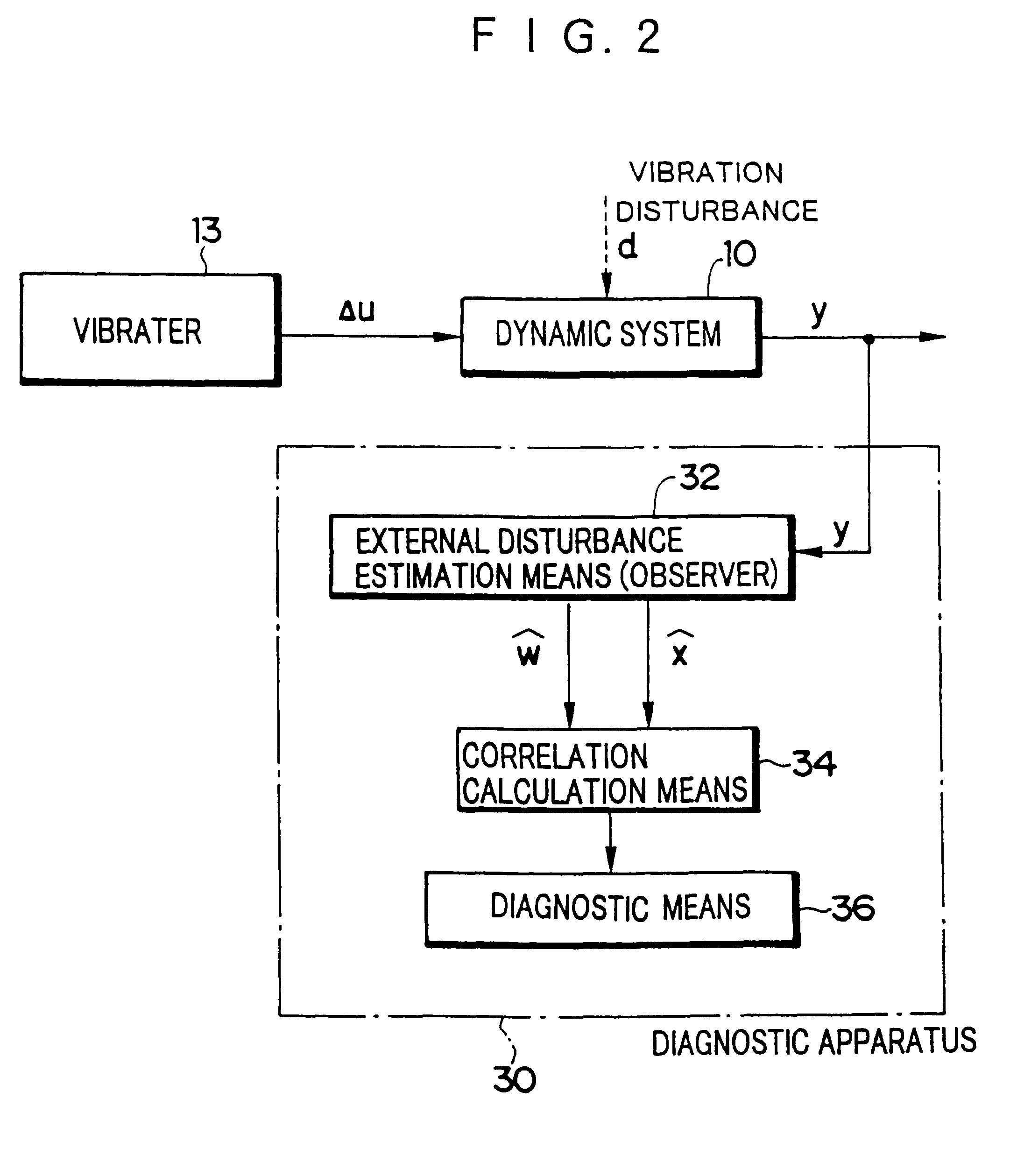
An apparatus for diagnosing a fault in a dynamic system includes a controller which controls the dynamic system through use of a control input signal and vibrates the dynamic system through use of an vibration signal irrelevant to the internal state quantity of the dynamic system; an observer for estimating, on the basis of a response output from the vibration dynamic system, total disturbance which is a sum of an internal disturbance vector stemming from a fault in the dynamic system and a vibration disturbance vector occurring in the dynamic system through vibration; a correlation calculation unit which calculates cross-correlation between the thus-estimated total disturbance and the internal state quantity of the dynamic system and separates a component related to the internal disturbance from the total disturbance; and a diagnostic unit for diagnosing a fault in the dynamic system on the basis of the thus-separated component related to the internal disturbance. Since the dynamic system is vibrated, the response output can be increased even when there exists small external disturbance. As a result, a fault or a variation in air pressure in a tire can be highly accurately diagnosed.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
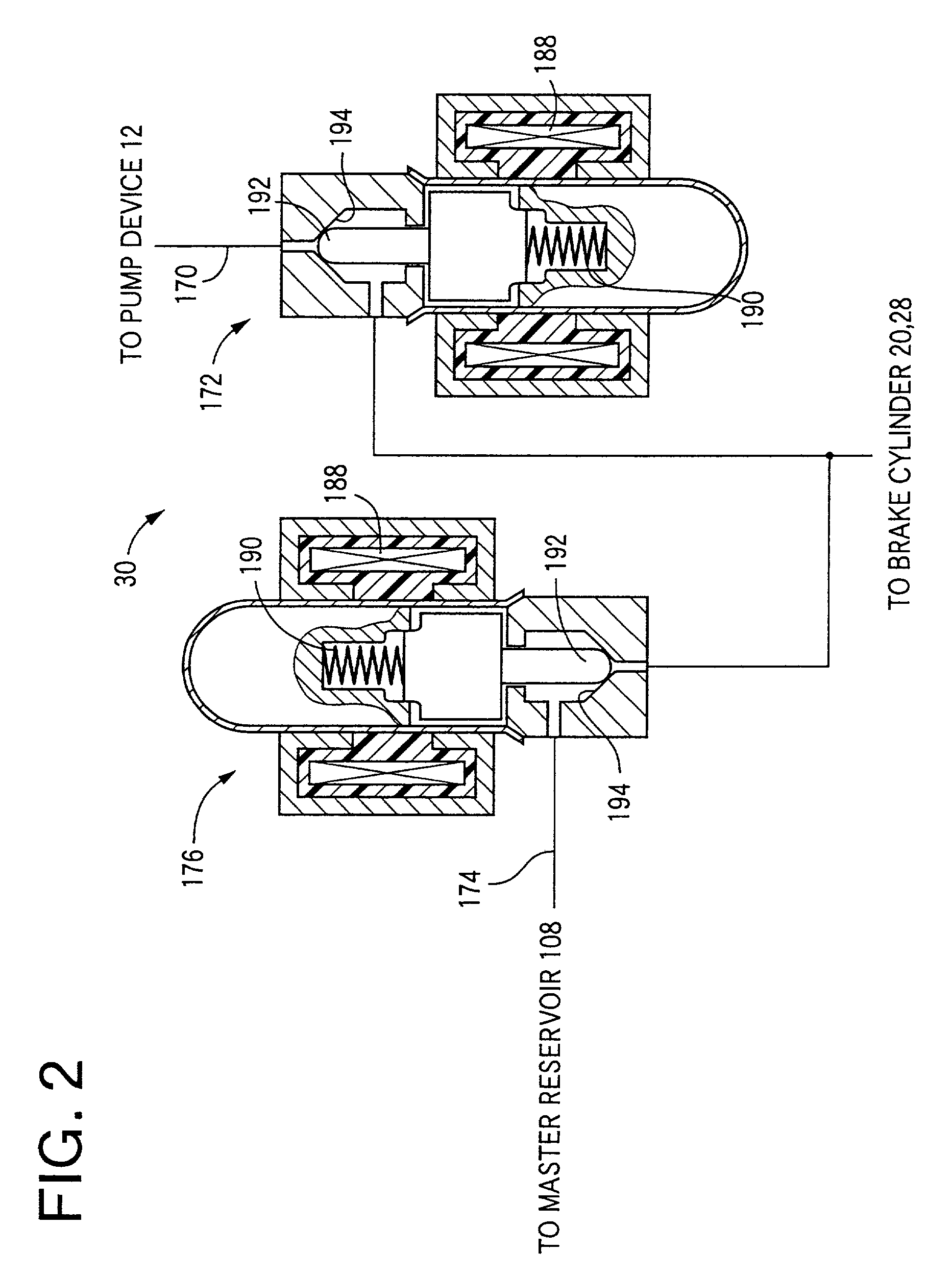
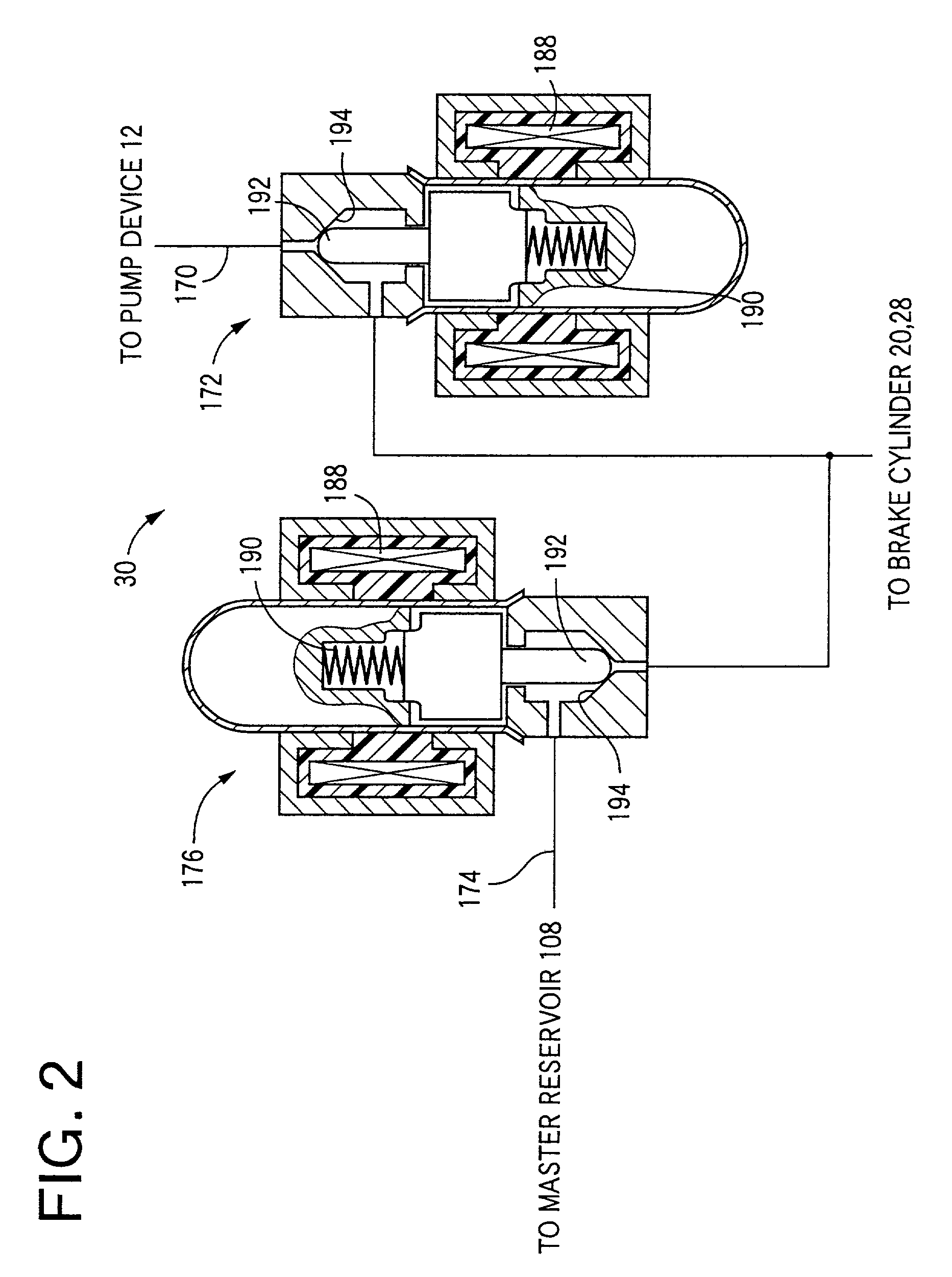
Braking pressure control apparatus capable of switching between two brake operating states using power-operated and manually operated pressure sources, respectively
InactiveUS20010006306A1Efficient workBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsPressure controlled ventilationBraking system
A braking pressure control apparatus including a first pressure source including a power-operated pressurizing device, a second pressure source operable by a manually operable brake operating member to pressurize a fluid to a pressure higher than a level corresponding to the operating force of the brake operating member, a switching device for selectively placing the braking system in a first state in which a brake cylinder is operated with the fluid pressurized by the first pressure source and a second state in which the brake cylinder is operated with the fluid pressurized by the second pressure source, and a change restricting device operable upon a switching between the first and second states, to restrict a change of the operating state of the brake operating member and a change of the brake cylinder pressure, which change take place due to the switching, or a switching control device for controlling the switching device on the basis of the running condition of a vehicle whose wheel is braked by the braking pressure.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
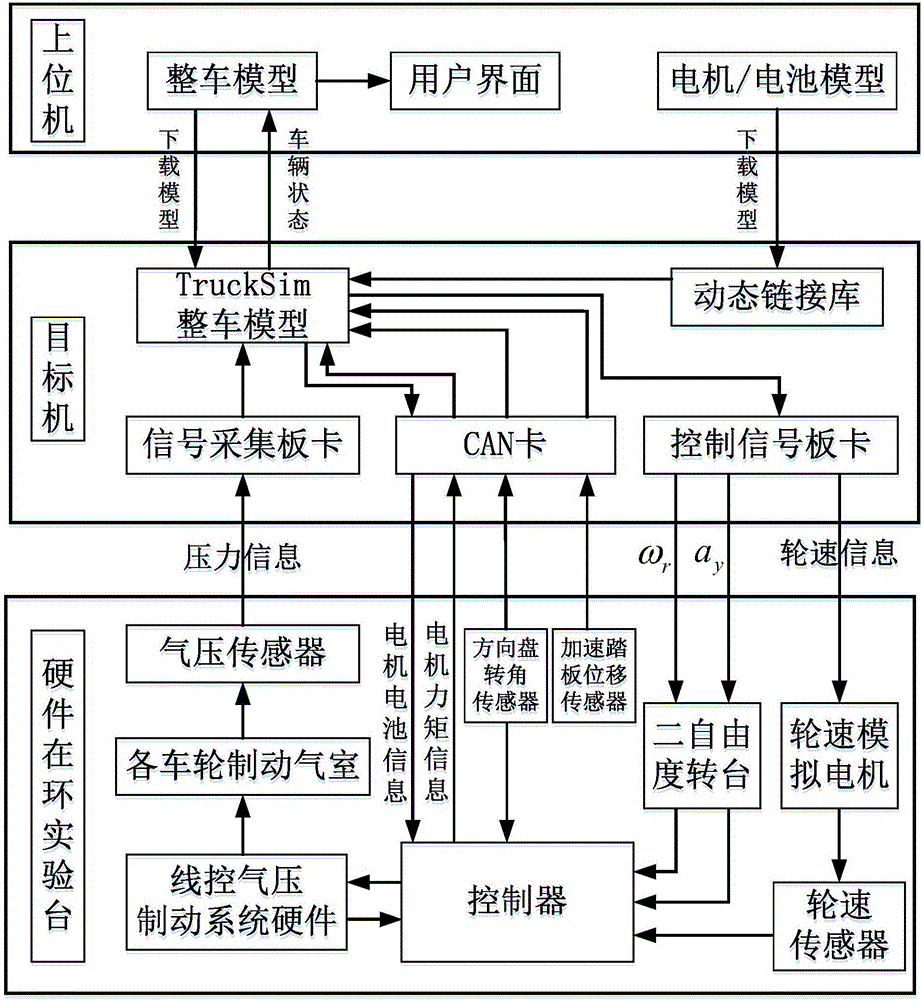
Electric bus integrated control hardware in-loop test platform and test method
InactiveCN106802650AAchieve integrated controlReduce the number of trialsElectric testing/monitoringRelay valveSolenoid valve
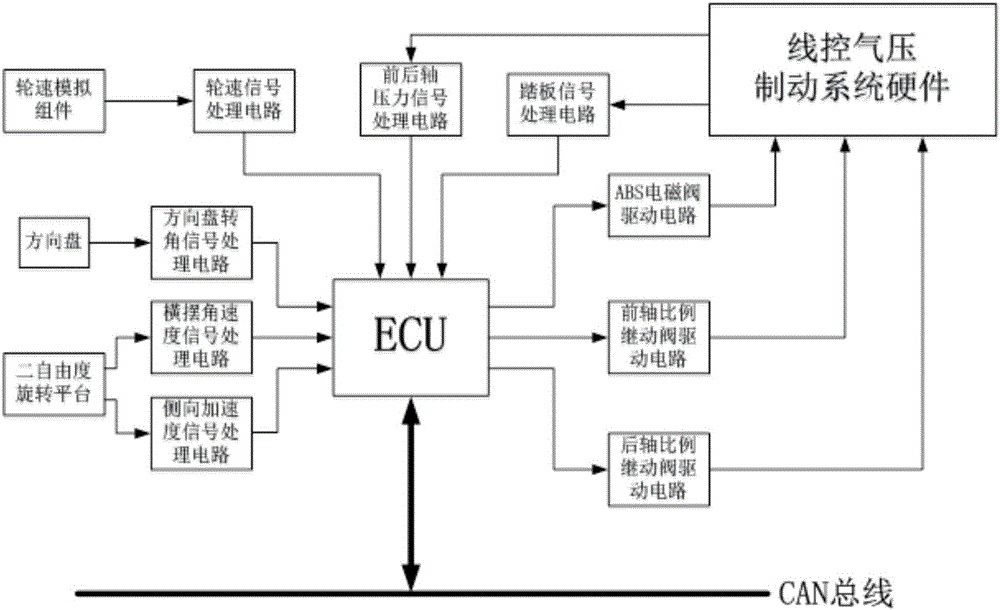
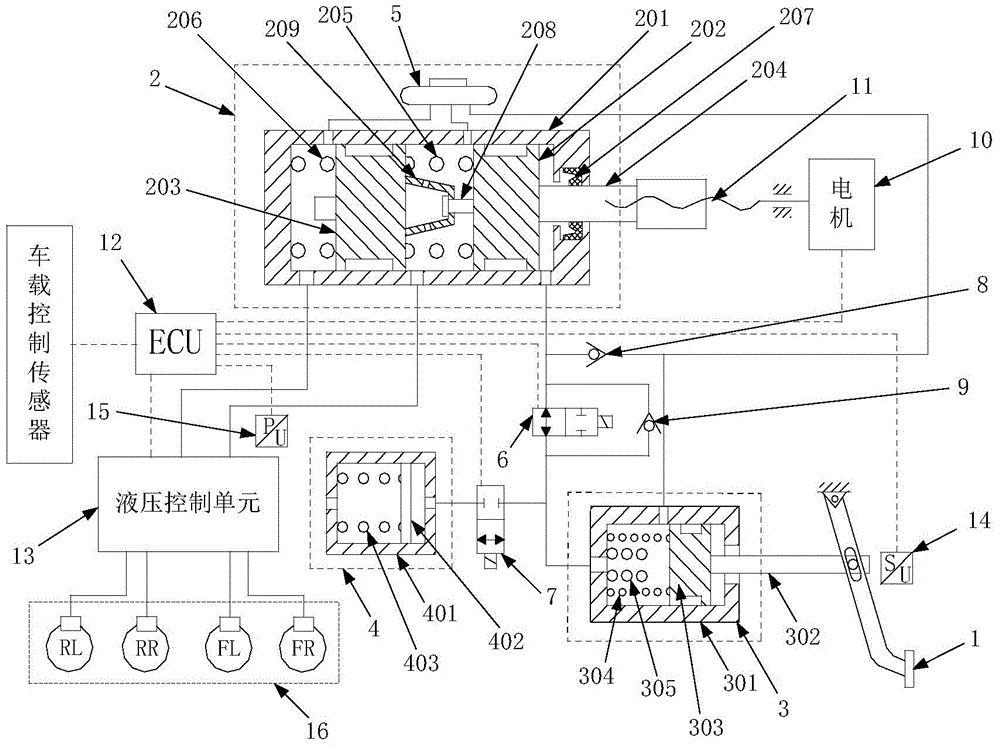
The invention provides an electric bus integrated control hardware in-loop test platform and a test method. The electric bus integrated control hardware in-loop test platform is formed by an air source component, a line control air brake system, a conventional brake component, a driving control component, a signal simulation component, a target machine, and a host computer based on line control air brake, and the electric bus integrated control hardware in-loop test method comprises an acceleration test, a brake test and a steering test. According to the test platform and the test method, accurate adjustment of the brake pressure of four wheels is realized through front and rear axle proportion relay valves and four ABS solenoid valves in a line control air brake system, and integrated control of electric buses is realized with the combination of signal simulation components including a two-degree-of-freedom rotation platform and a wheel speed simulation motor and the corresponding test method.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
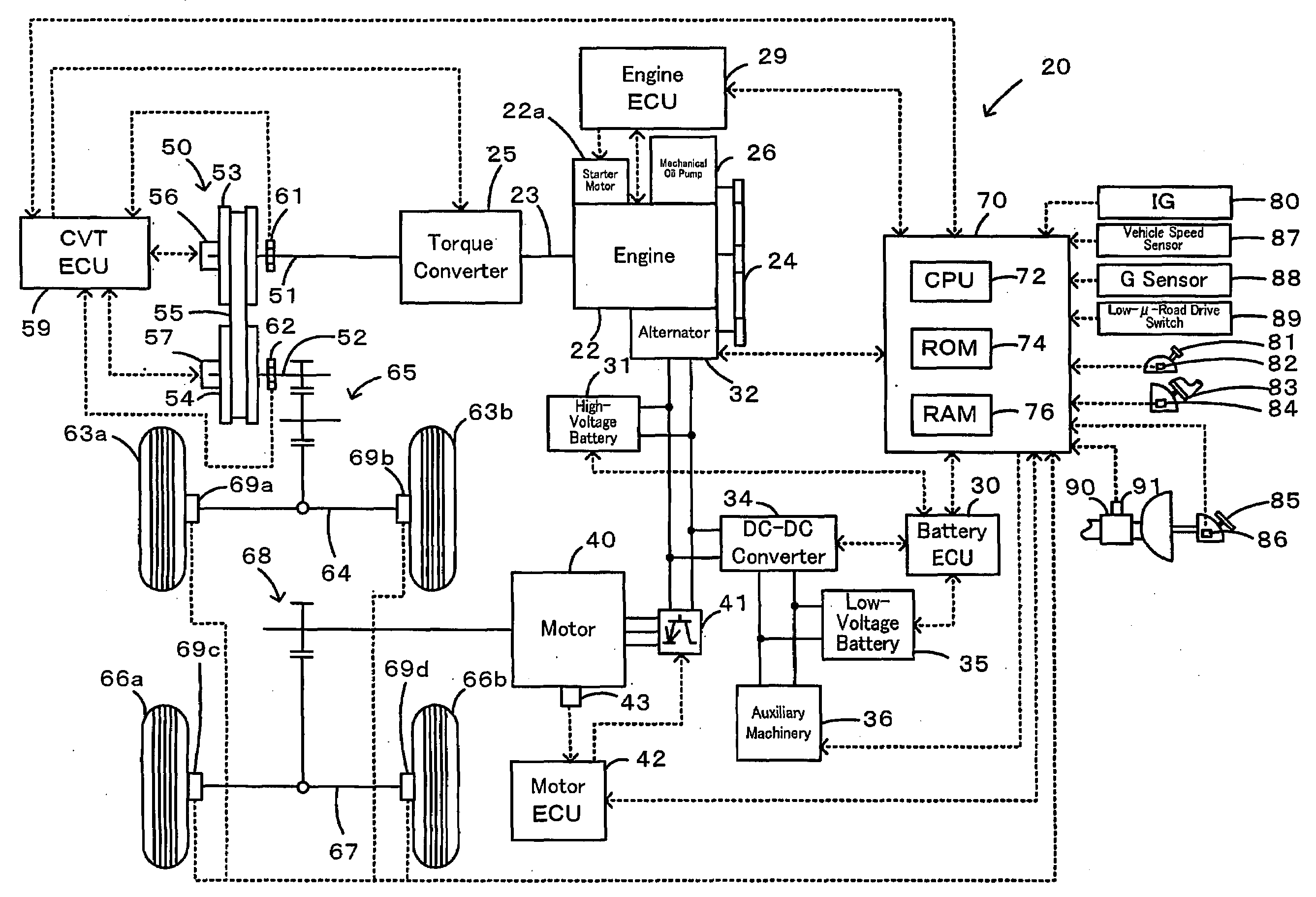
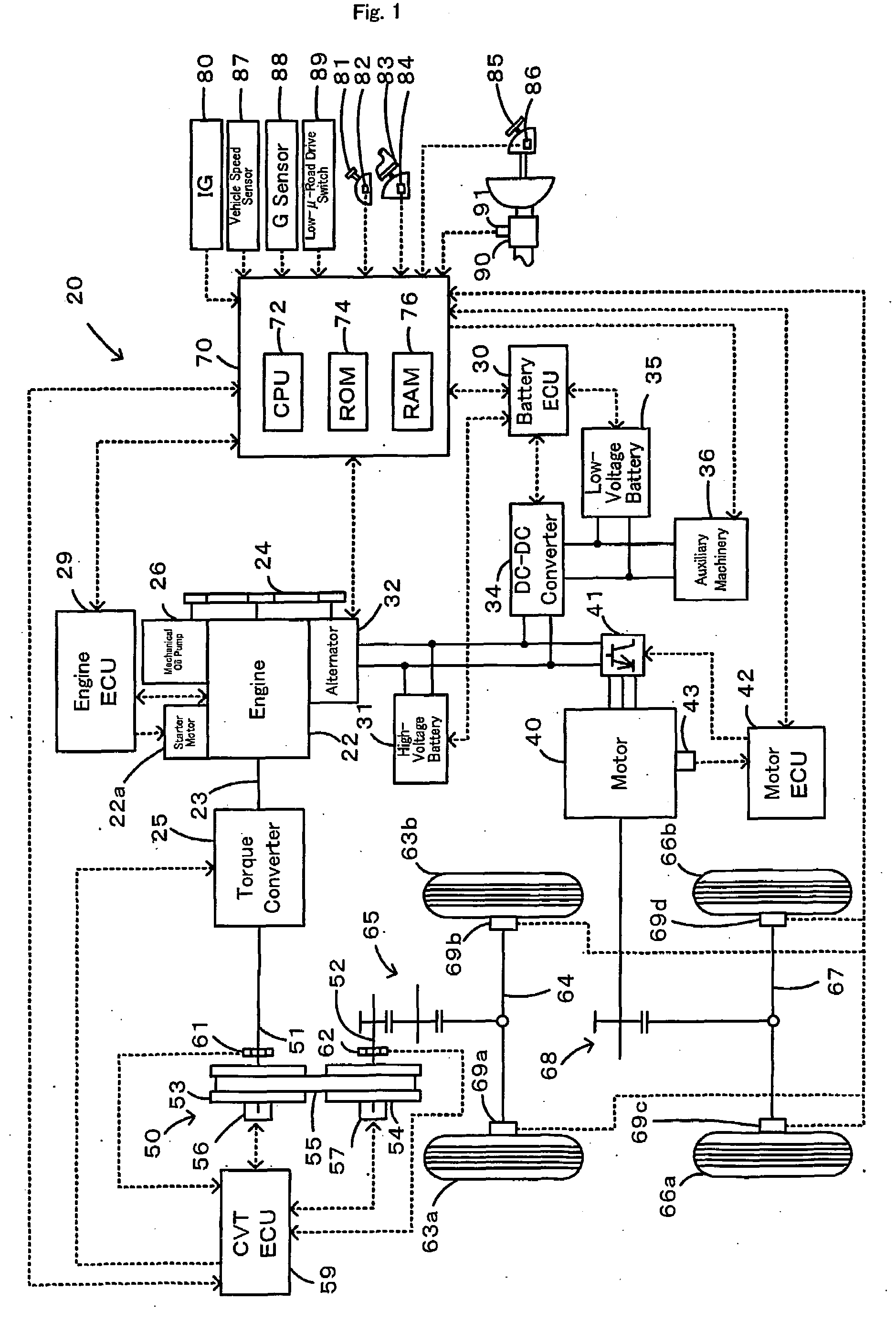
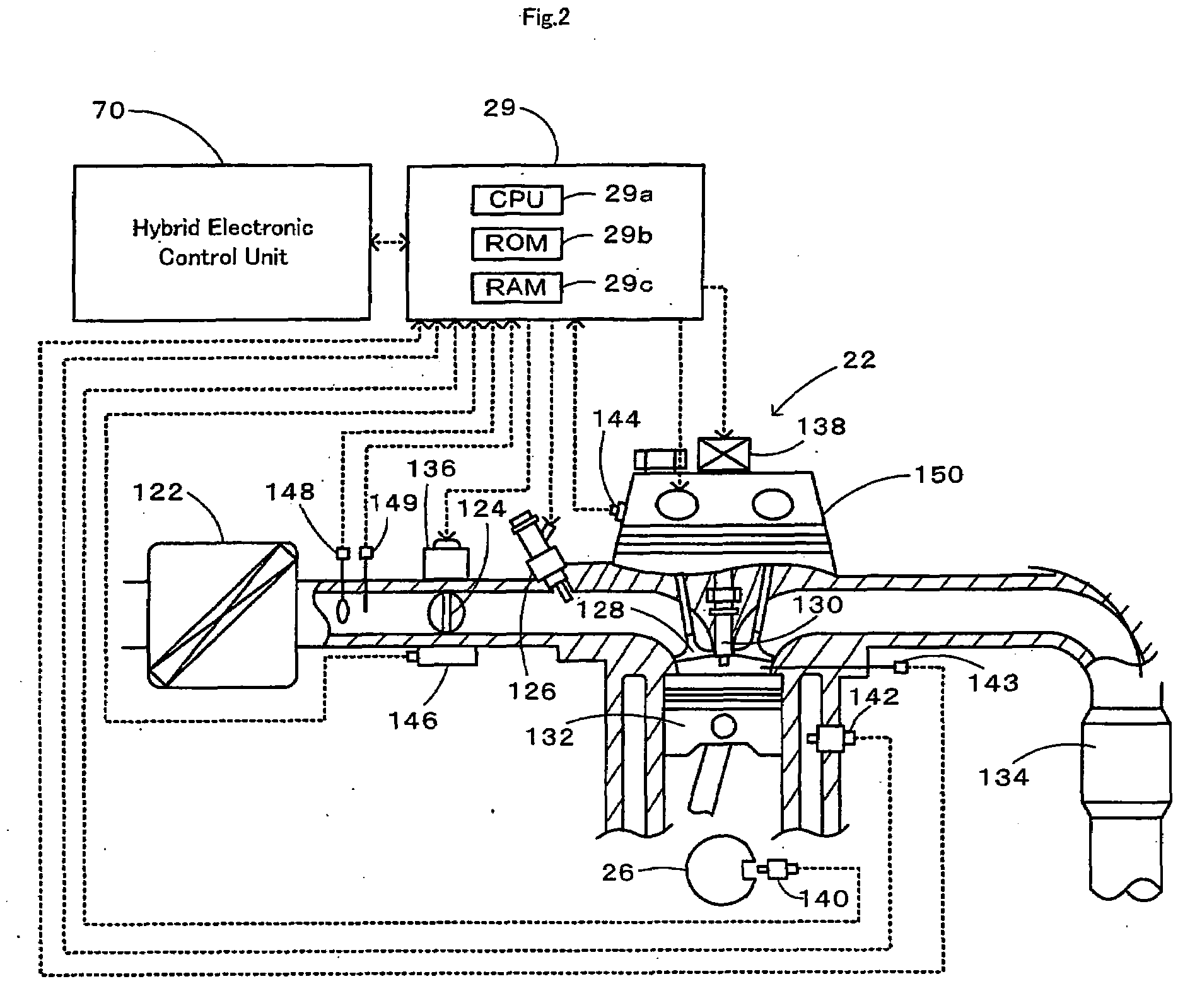
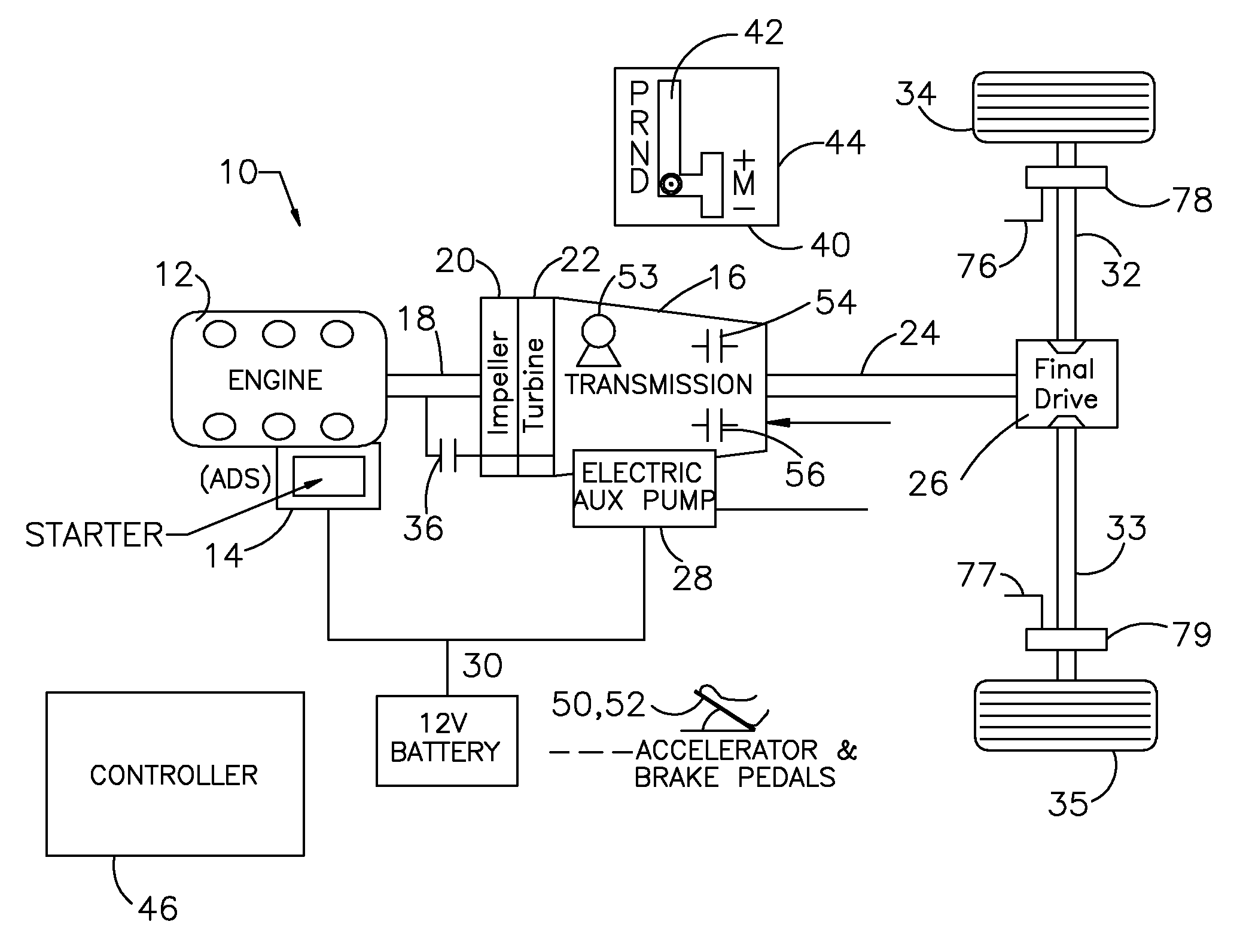
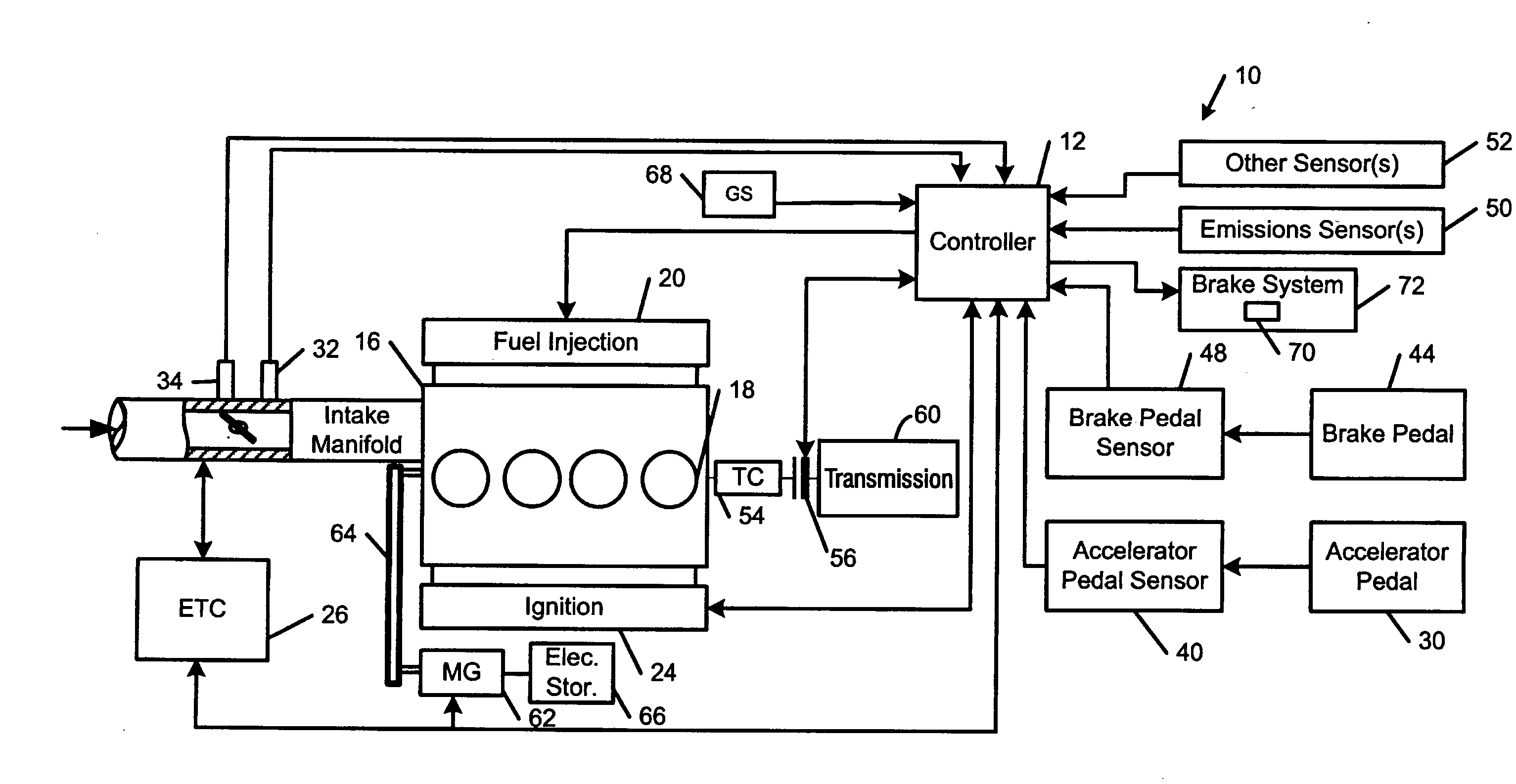
Motor Vehicle and Control Method of Motor Vehicle
InactiveUS20080154472A1Smooth hill startSmooth hill driveVehicle fittingsGearing controlBrake pressureEngineering
During a starting operation or a low-speed drive of a vehicle on a slope, the drive control of the invention sets a gradient-corresponding rotation speed N? as a rotation speed of an engine to output a required driving force against a longitudinal vehicle gradient ?fr (step S110), and sequentially sets a low-?-road correction rotation speed Nlow upon identification of a low-?-road drive condition, a vehicle speed difference-compensating rotation speed Nv based on a vehicle speed V, and a brake-based correction rotation speed Nb based on a brake pressure Pb (steps S120 through S250). The drive control sets a target engine rotation speed Ne* based on these settings (step S260) and subsequently sets a target throttle opening THtag (step S270). The operation of the engine is controlled with the greater between the target throttle opening THtag and a required throttle opening THreq corresponding to an accelerator opening Acc (step S290). This arrangement effectively prevents an unexpected slide-down of the vehicle along the slope.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Brake Pad Prognosis System
A method for providing an estimate of brake pad thickness. The method employs fusion of sensors, if used, and driver brake modeling to predict the vehicle brake pad life. An algorithm is employed that uses various inputs, such as brake pad friction material properties, brake pad cooling rate, brake temperature, vehicle mass, road grade, weight distribution, brake pressure, brake energy, braking power, etc. to provide the estimation. The method calculates brake work using total work minus losses, such as aerodynamic drag resistance, engine braking and / or braking power as braking torque times velocity divided by rolling resistance to determine the brake rotor and lining temperature. The method then uses the brake temperature to determine the brake pad wear, where the wear is accumulated for each braking event. A brake pad sensor can be included to provide one or more indications of brake pad thickness from which the estimation can be revised.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Brake Assisted Vehicle Engine Restart on a Road Grade
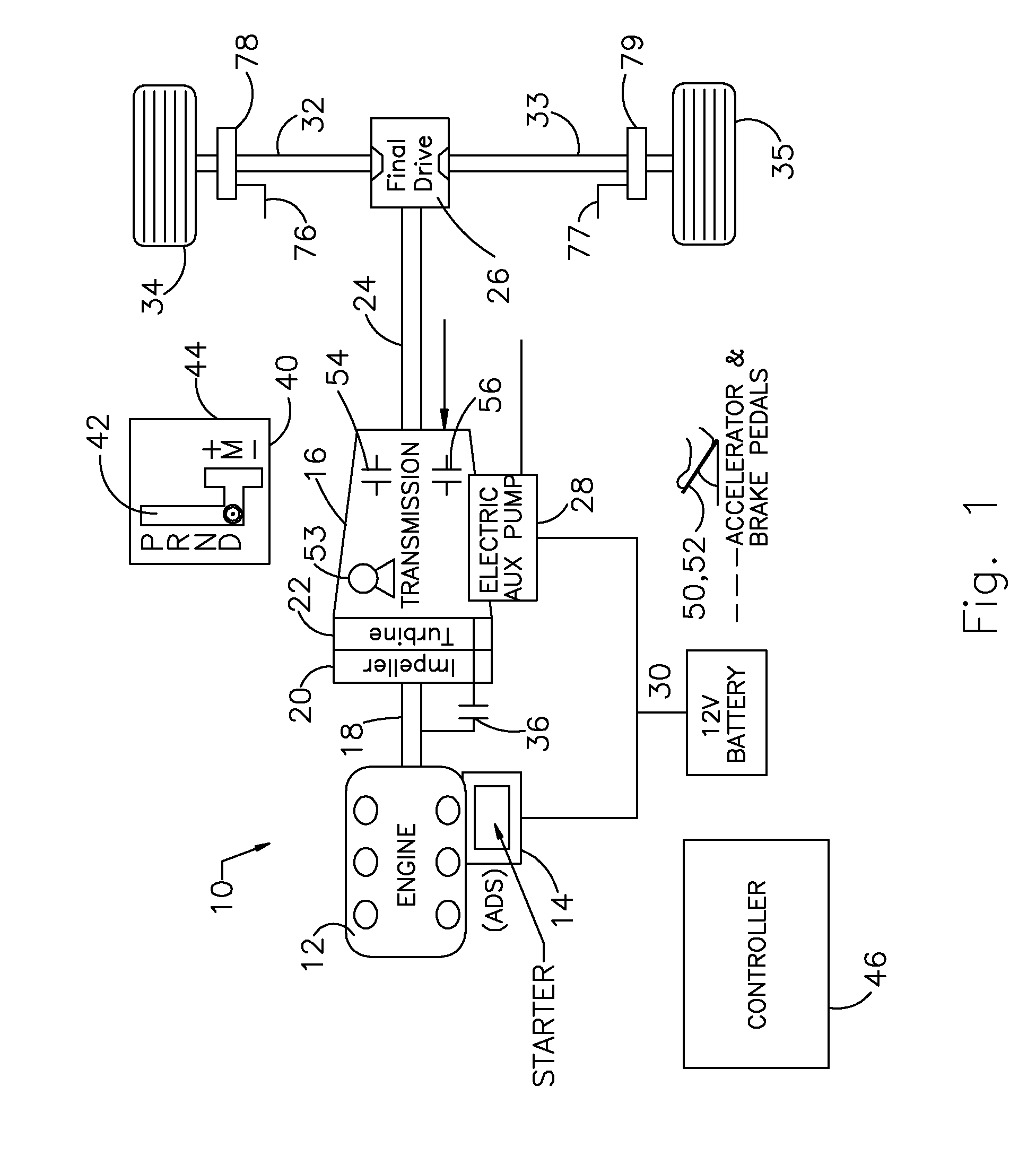
ActiveUS20110065548A1Suppress powertrain torque disturbanceReduce brake pressureEngine controllersMachines/enginesBrake pressureAutomotive engineering
A method for restarting an engine of a vehicle stopped on a grade, comprising the steps of engaging a gear of a transmission through which the engine and wheels of the vehicle are driveably connected mutually, using brake pressure to engage wheel brakes and produce a road gradient wheel torque that holds the vehicle stationary on the grade, initiating an engine restart, operating the engine to produce wheel torque equal to or greater than the road gradient wheel torque, and releasing the brake pressure.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for predicting braking system friction
InactiveUS20090187320A1Hybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficConstant coefficientsOperant conditioning
A brake system control method determines vehicle operating conditions, compares the conditions to an allowable range, and uses a neural network to predict an expected coefficient of friction when the conditions are within the range. When the conditions fall outside of the range, the method determines an amount of required braking force using a constant coefficient of friction, and calculates the required braking force using the expected coefficient of friction when the conditions are within the range. The vehicle operating conditions include a vehicle speed, brake pressure, modeled brake rotor temperature, and apply state. The expected coefficient is multiplied by a constant or a calculated correction factor. A vehicle has an engine, transmission, and braking system, with a controller and an algorithm for predicting a coefficient of friction for two brake rotors, calculating a hydraulic brake pressure, and for applying the braking system using the hydraulic brake pressure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
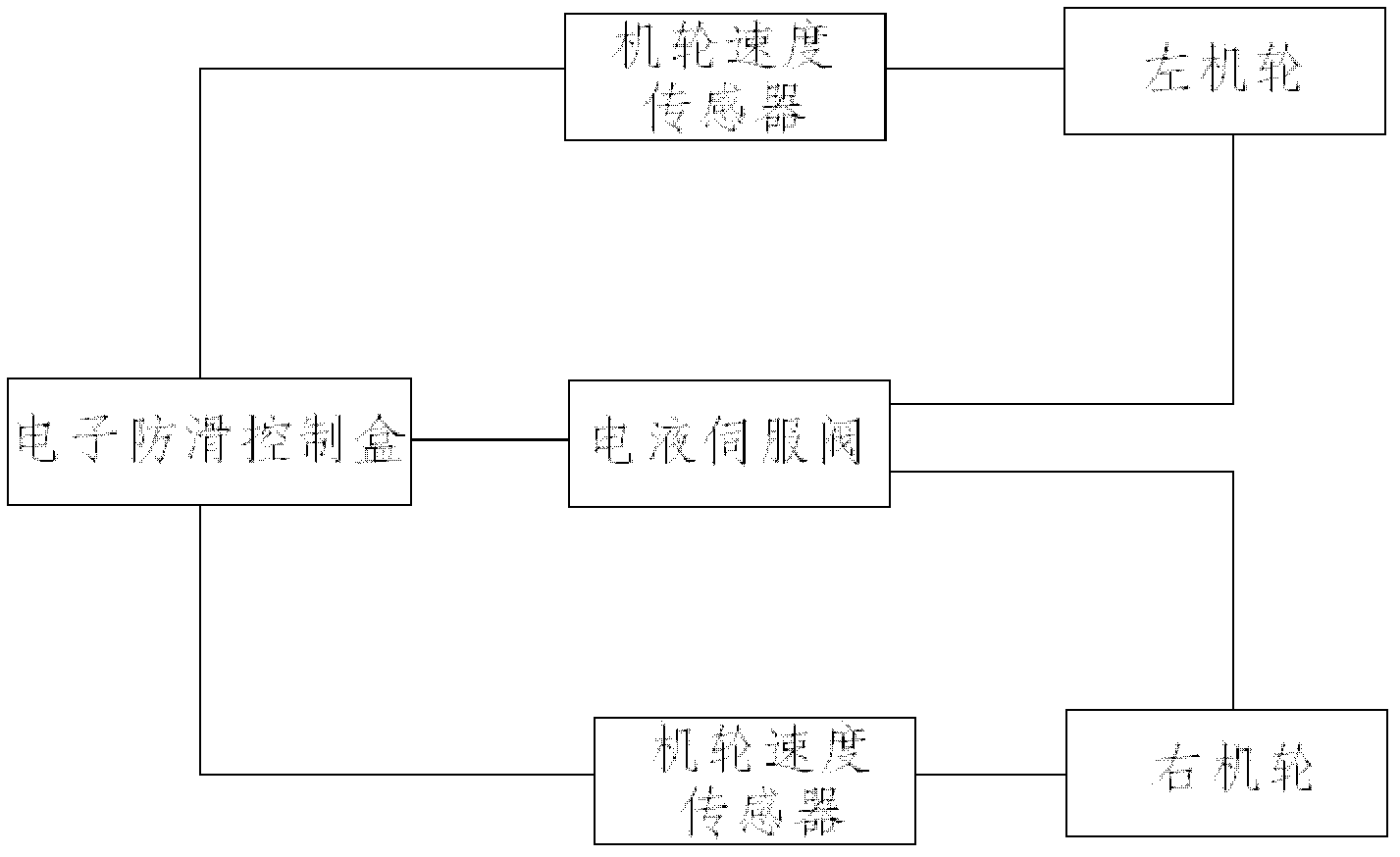
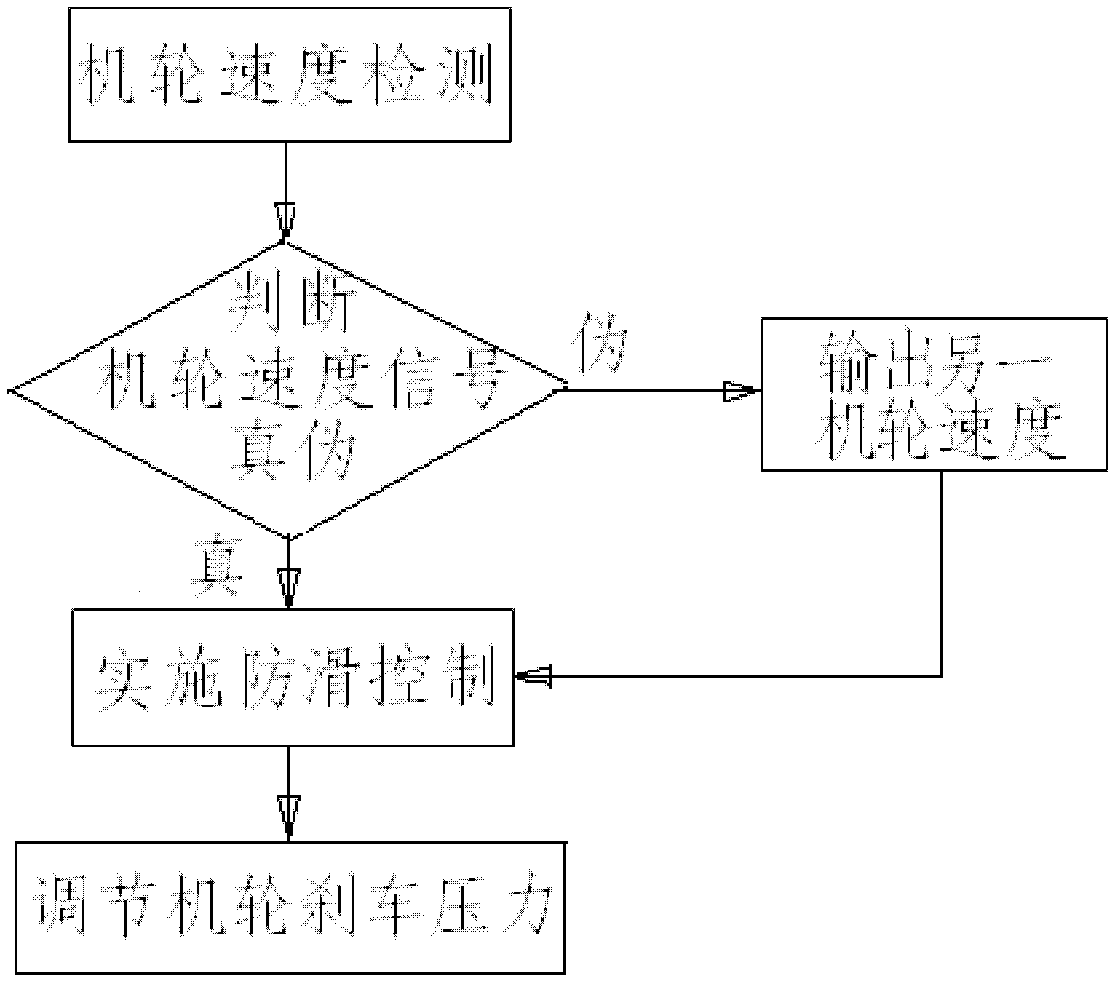
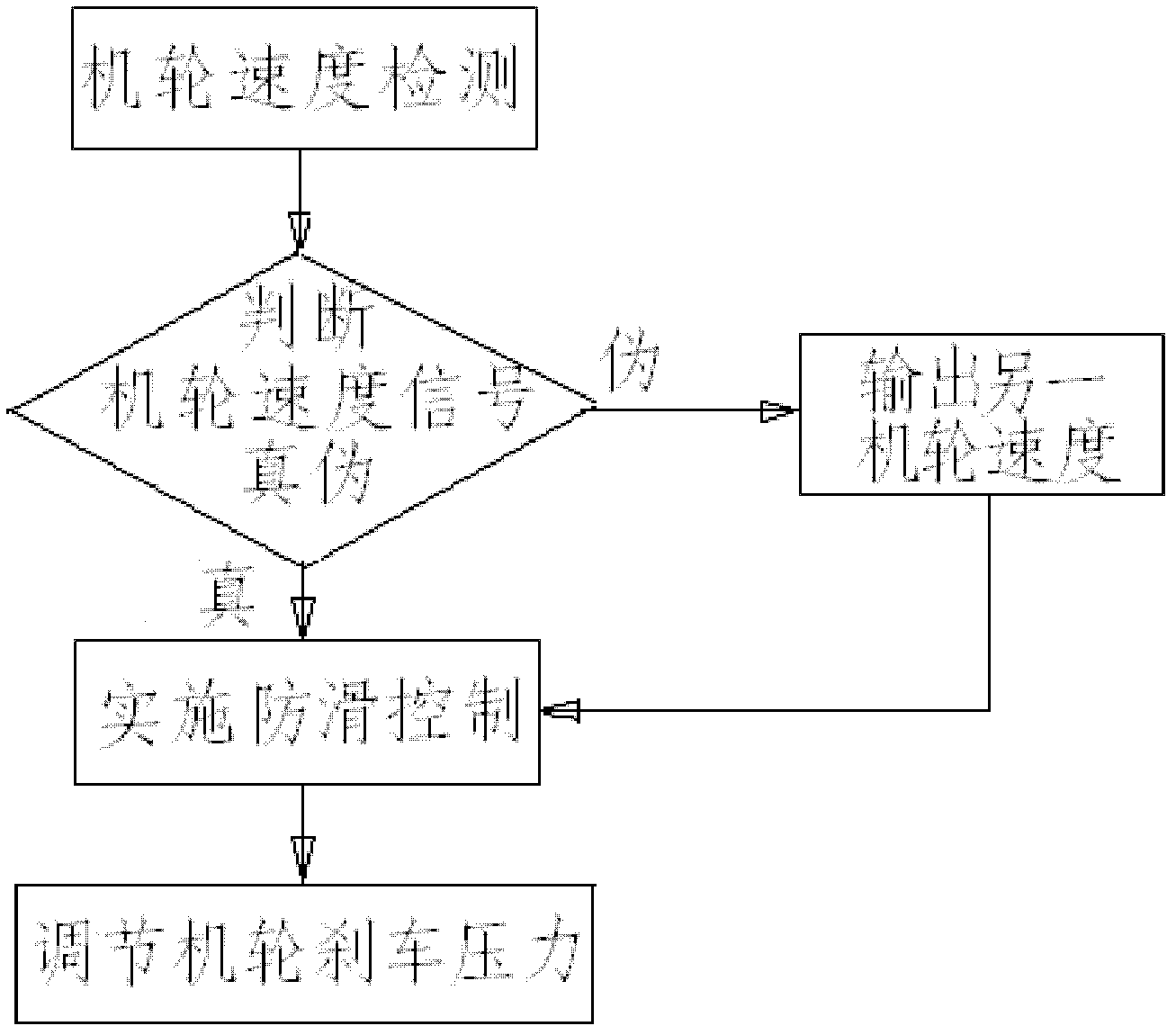
Airplane anti-skid brake control system and method
InactiveCN102556340AAnti-skid brake control method is simple and easyEasy to controlBrake regulatorsApplication and release valvesWheel speed sensorControl system
The invention relates to an airplane anti-skid brake control system and an airplane anti-skid brake control method. In the airplane anti-skid brake control system, two airplane wheel speed sensors are respectively applied to a left airplane wheel and a right airplane wheel of the airplane and connected with the input end of an electronic anti-skid control box; an electro-hydraulic servo valve is connected with a brake valve, a brake device, the electro-hydraulic servo valve and the electronic anti-skid control box respectively; the input port of the electronic anti-skid control box is connected with the airplane wheel speed sensors; and the output port of the electronic anti-skid control box is connected with the electro-hydraulic servo valve. In the invention, the electronic anti-skid control box judges true and false of the received airplane speed signal by comparing the airplane speed signal to be judged with the speed of the airplane wheels at different time or comparing the speed signals of the two airplane wheels so as to perform anti-skid control according to the speed signals of the airplane wheels which are judged to be true; and the airplane wheel brake pressure is adjusted according to the received instruction through the electro-hydraulic servo valve, so safe and reliable brake of the airplane wheels is realized.
Owner:XIAN AVIATION BRAKE TECH
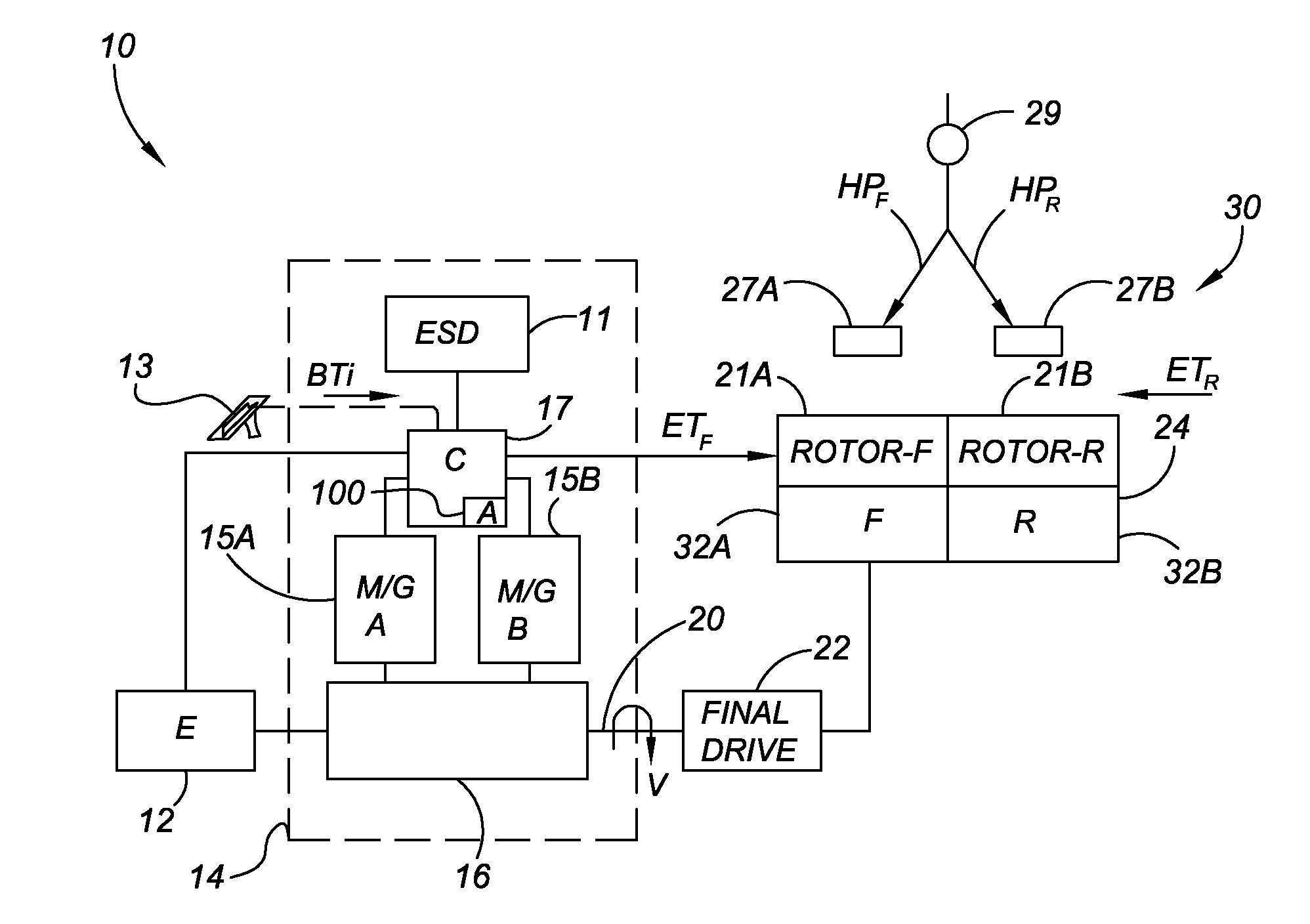
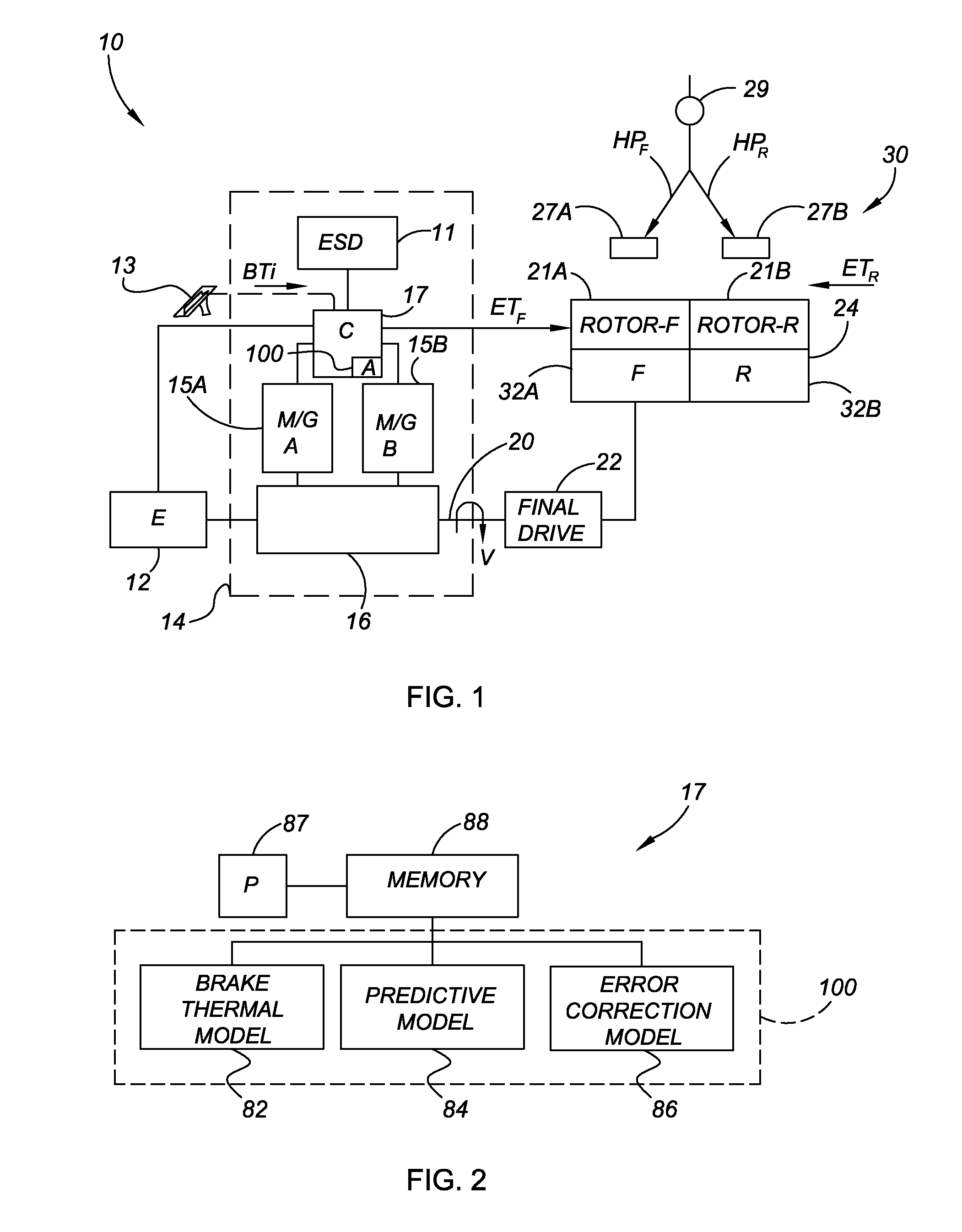
Anti-rollback control via grade information for hybrid and conventional vehicles
InactiveUS20060111823A1Reduce rollbackDigital data processing detailsElectric propulsion mountingControl systemElectric generator
A vehicle control system reduces vehicle rollback upon brake release. The control system includes a brake system, a vehicle grade measurement device and a controller that modulates applied brake pressure of the brake system based on a grade measurement of the grade measurement device. The controller actuates brake-hold device communicating with the brake system based on the grade measurement through pulse width modulation. The control system communicates with a motor generator and an engine to provide a start power to the engine upon brake release based on the grade measurement. Fuel injectors of the engine are enabled upon brake release based on the grade measurement. The control system further communicates with a transmission forward clutch to provide selective rotational communication between the transmission and the engine based on the grade measurement.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Brake monitoring system and method
ActiveUS20100188203A1Vehicle speed is limitedVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMonitoring systemActuator
A brake monitoring system and method for a vehicle having multiple axles and a plurality of brake actuators and an engine control module, each brake actuator being associated with one of the axle. The system include sensors for measuring, in real-time, brake pressure and brake lining wear, and generating first and second signals. The first and second signals are received and stored in a chassis communications module. The chassis communications module detects fault condition of the brakes as a function of the first and / or second signals and for recording the fault condition, the fault condition being one of a brake monitor warning and a brake lining warning and provides an indication of status via warning lights.
Owner:INDIAN HEAD INDUSTRIES INC
Rollback reduction in hybrid or conventional powertrain vehicle via vehicle stability enhancement system (VSES)
InactiveUS20070096557A1Reduce brake pressurePrevent rollbackSpeed controllerOperating modesDriver/operatorControl system
An anti-rollback control system for a vehicle having a brake system includes a brake pedal that is operable to induce a brake pressure in the brake system and a control module that holds the brake pressure equal to a hold pressure that is based on an incline angle to inhibit rollback of the vehicle when pressure is relieved from the brake pedal. The control module initiates forward propulsion of the vehicle based on a driver input and reduces the brake pressure from the hold pressure concurrent to initiating the forward propulsion.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Integrated trailer brake control system
InactiveUS20080177454A1Improve stabilityAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsSteering angleTrailer brake controller
A control system for actuating a trailer braking system on a trailer is disclosed. The control system includes a trailer brake controller in communication with an antilock braking controller and an electronic stability controller of a towing vehicle to receive a wheel speed, a brake pressure, a yaw rate, a lateral acceleration, and a steering angle. The trailer brake controller utilizes the wheel speed, the brake pressure, the yaw rate, the lateral acceleration, and the steering angle to determine the attitude of the towing vehicle, and to calculate a desired braking force for the trailer. The trailer brake controller sends an appropriate output to actuate the trailer braking system on the trailer to stabilize the towing vehicle during extreme braking conditions.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA +1
Airplane electrical signal transmission brake antiskid control system
InactiveCN103158867AAutomatic recording of failure status modesGuaranteed uptimeBrake regulatorsTransmission brakeControl system
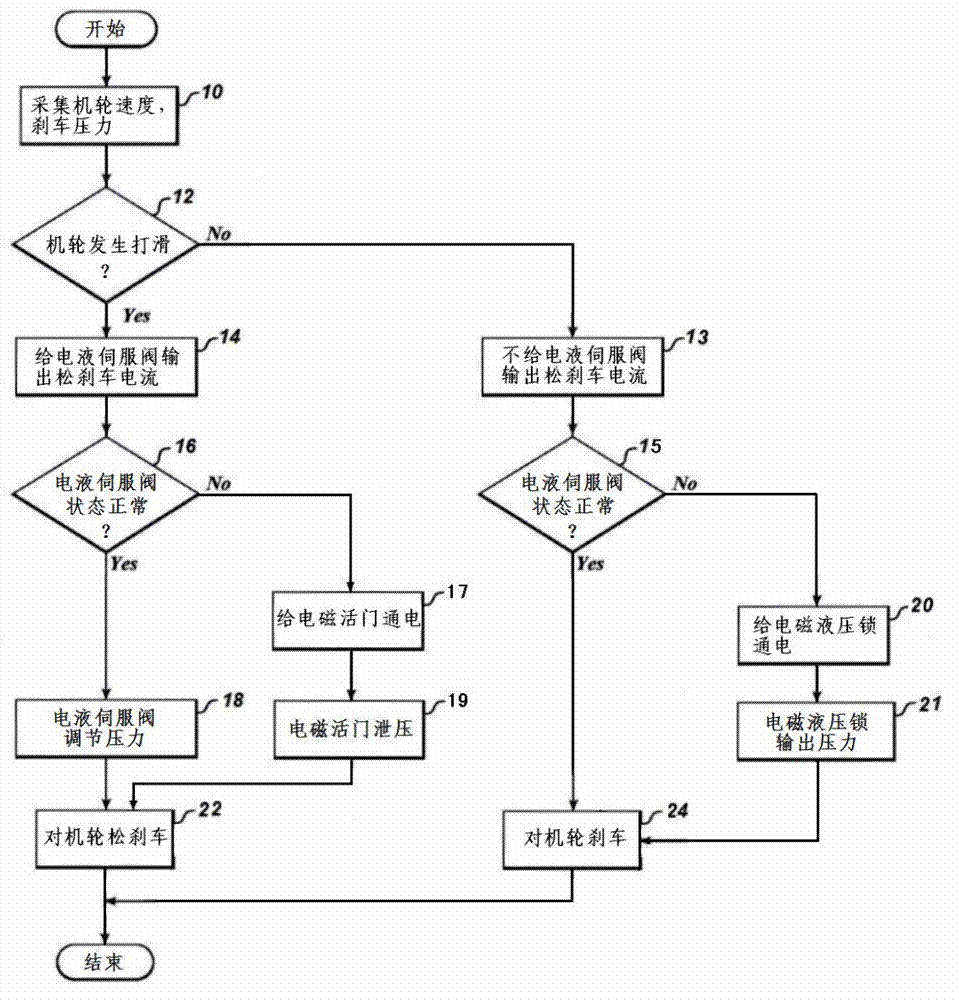
The invention relates to an airplane electrical signal transmission brake antiskid control system. When brake is carried out, an electro hydraulic servo valve can not output brake pressure, a control box emits a control signal to an electromagnetic hydraulic lock, the electromagnetic hydraulic lock unlocks by energization, the hydraulic power source is switched on, and the brake is carried out on a brake machine wheel with maximum brake pressure. During a brake process, if the machine wheel slips, the control box controls the electromagnetic valve for energization to release pressure. The system is simple and easy to be carried out, the reliability and security of the brake system operation can be greatly increased during taking off, landing rollout processes, the work load of a driver is reduced, even the electro hydraulic servo valve generates fault, the tire burst can be effectively avoided, and the airplane usage safety is ensured.
Owner:XIAN AVIATION BRAKE TECH
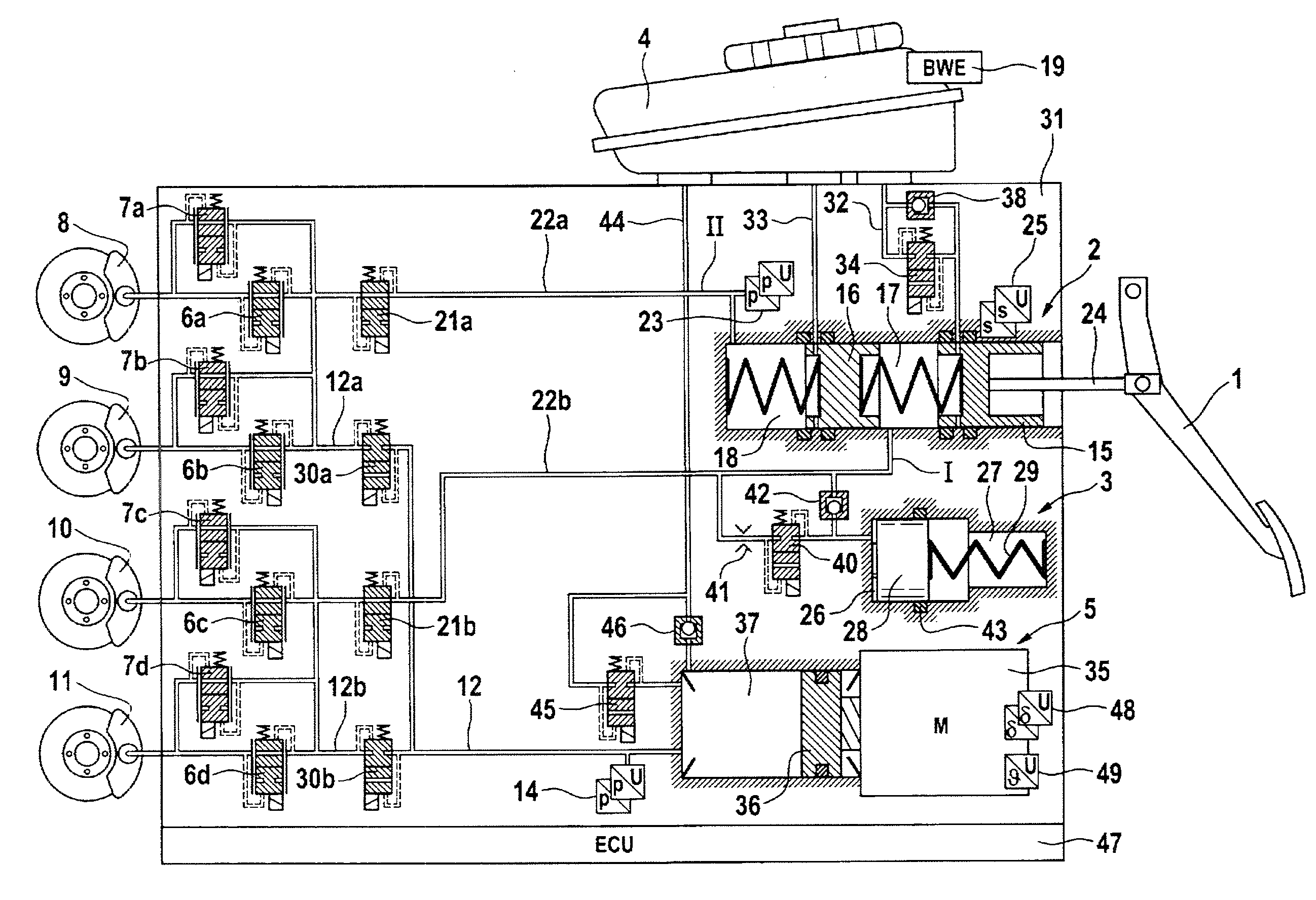
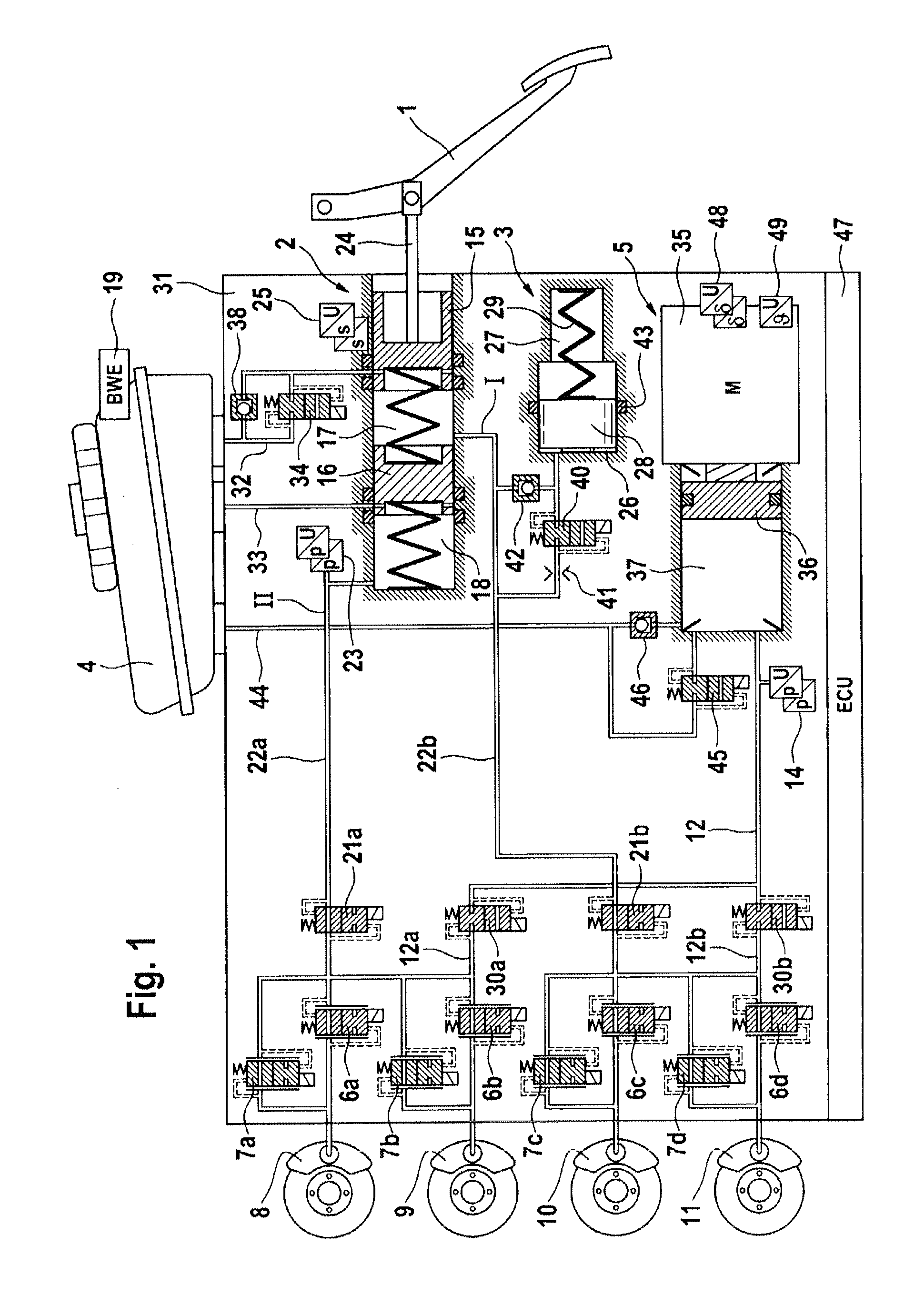
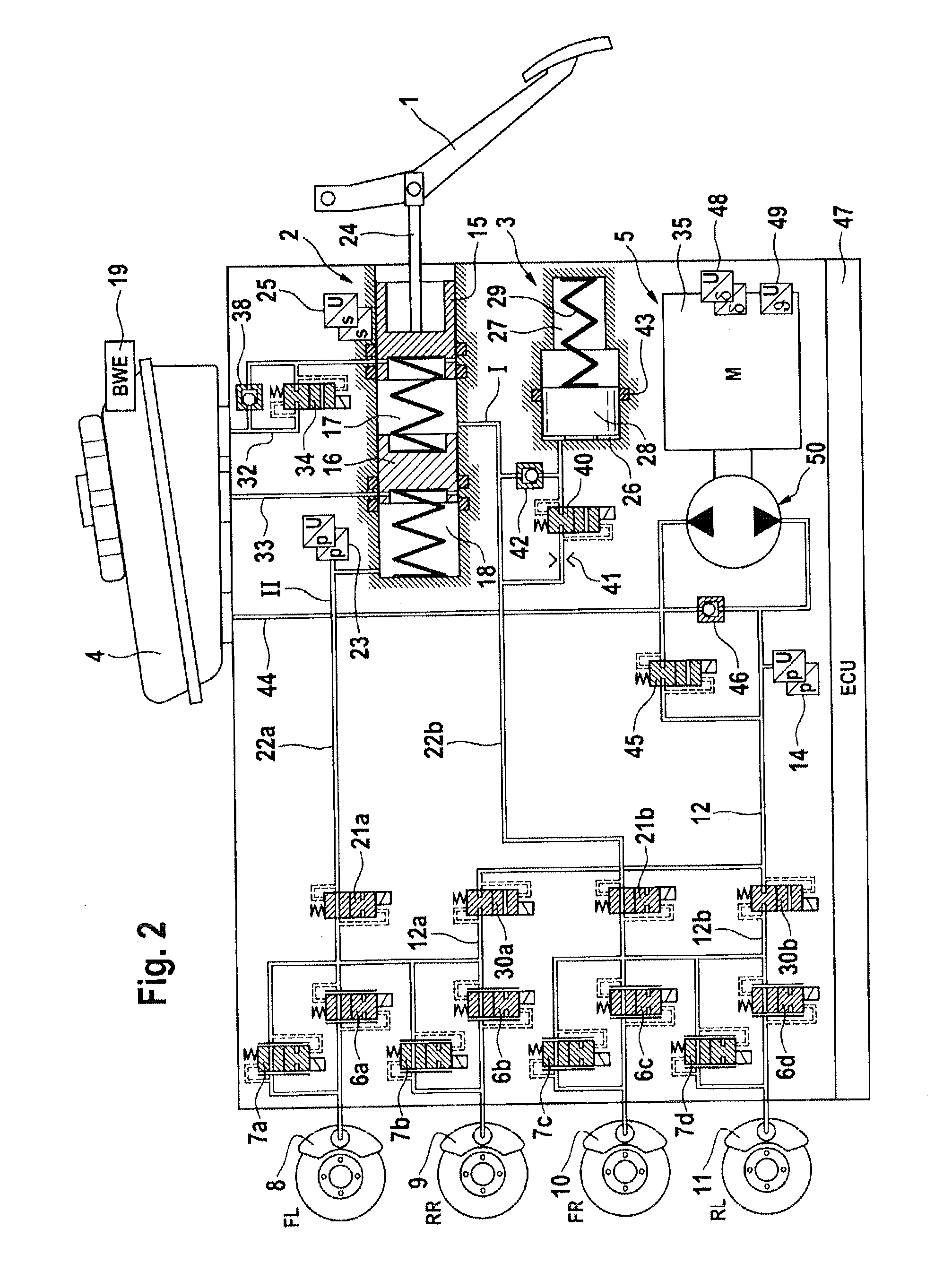
Brake System for Motor Vehicles
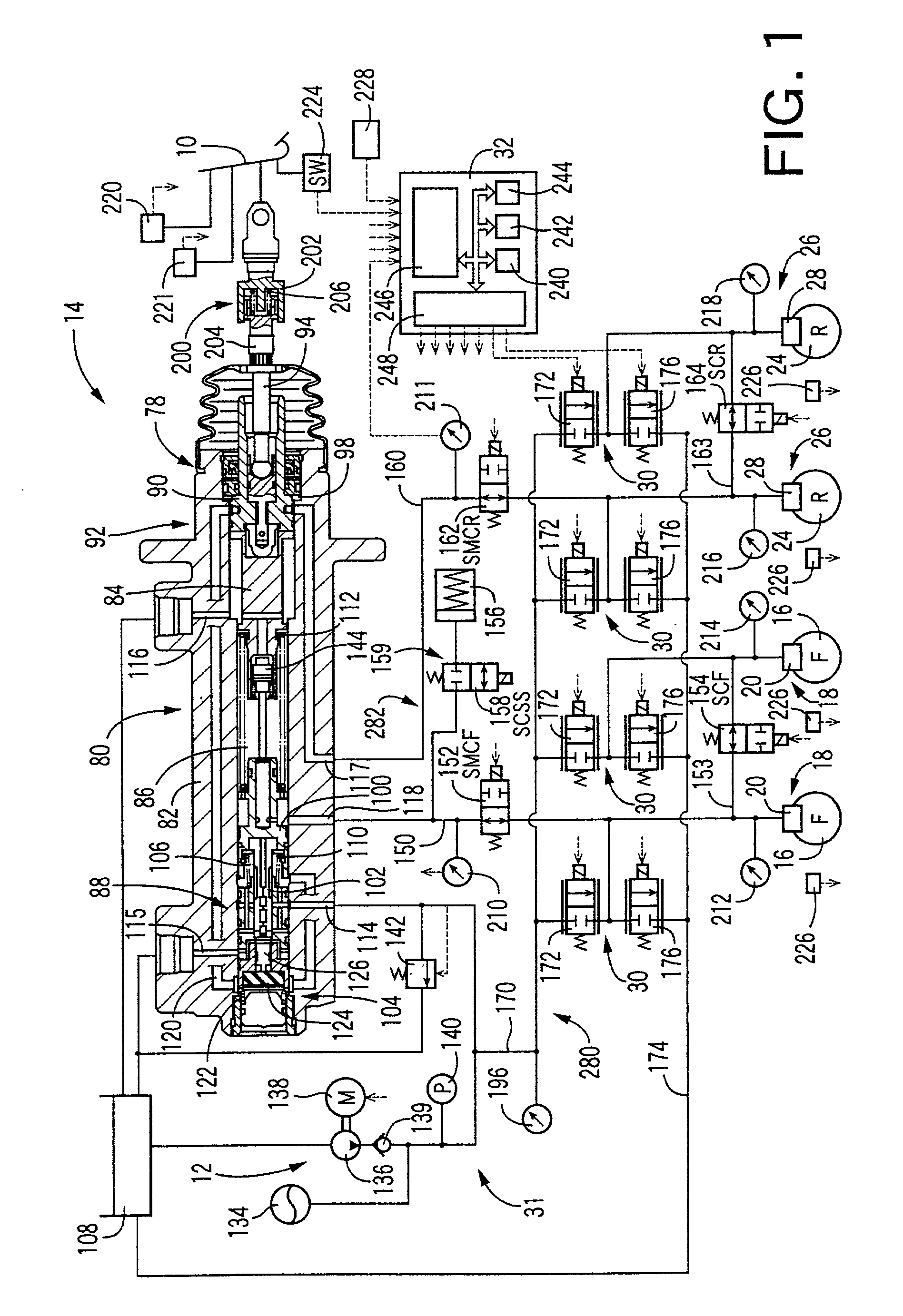
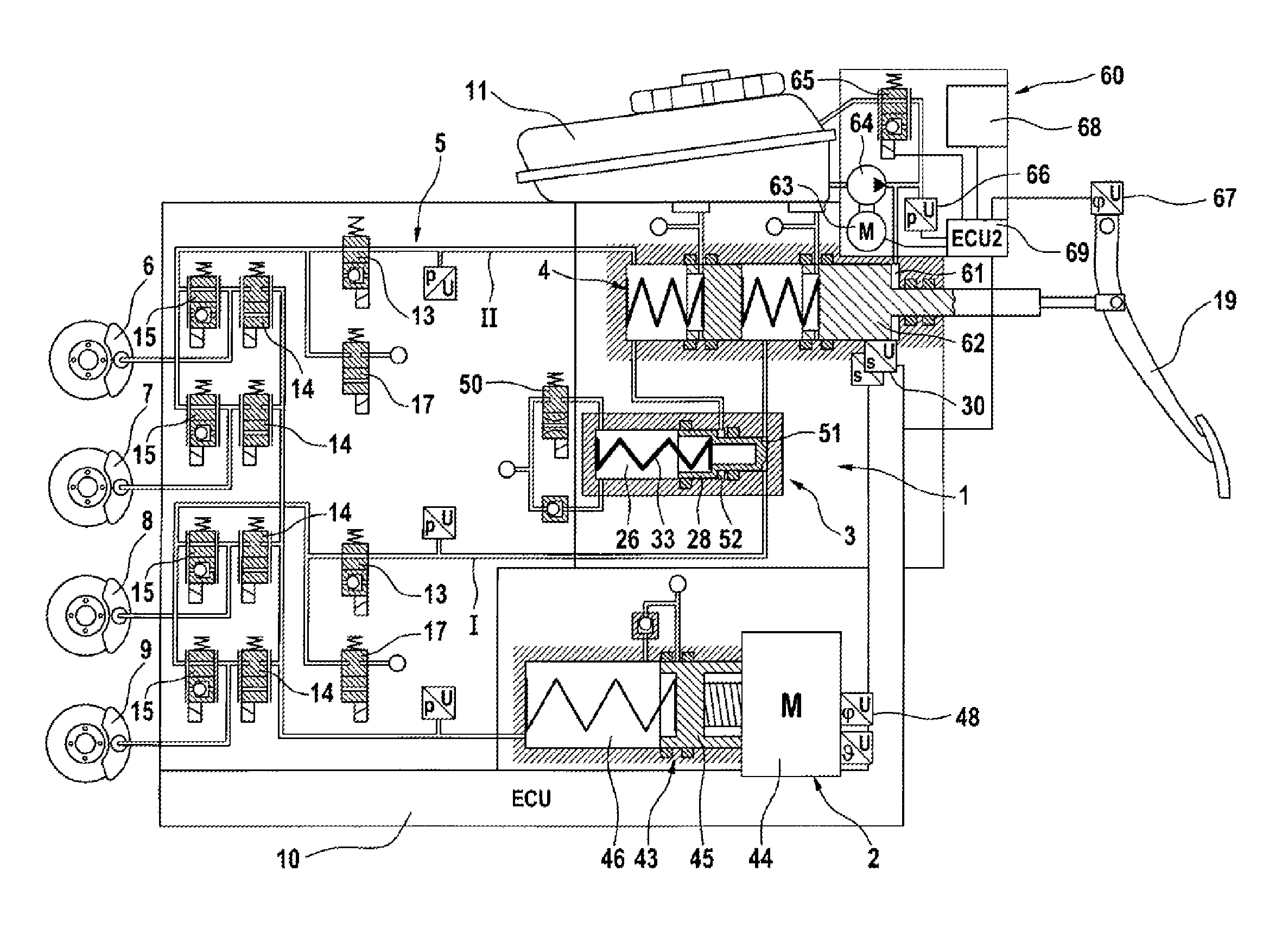
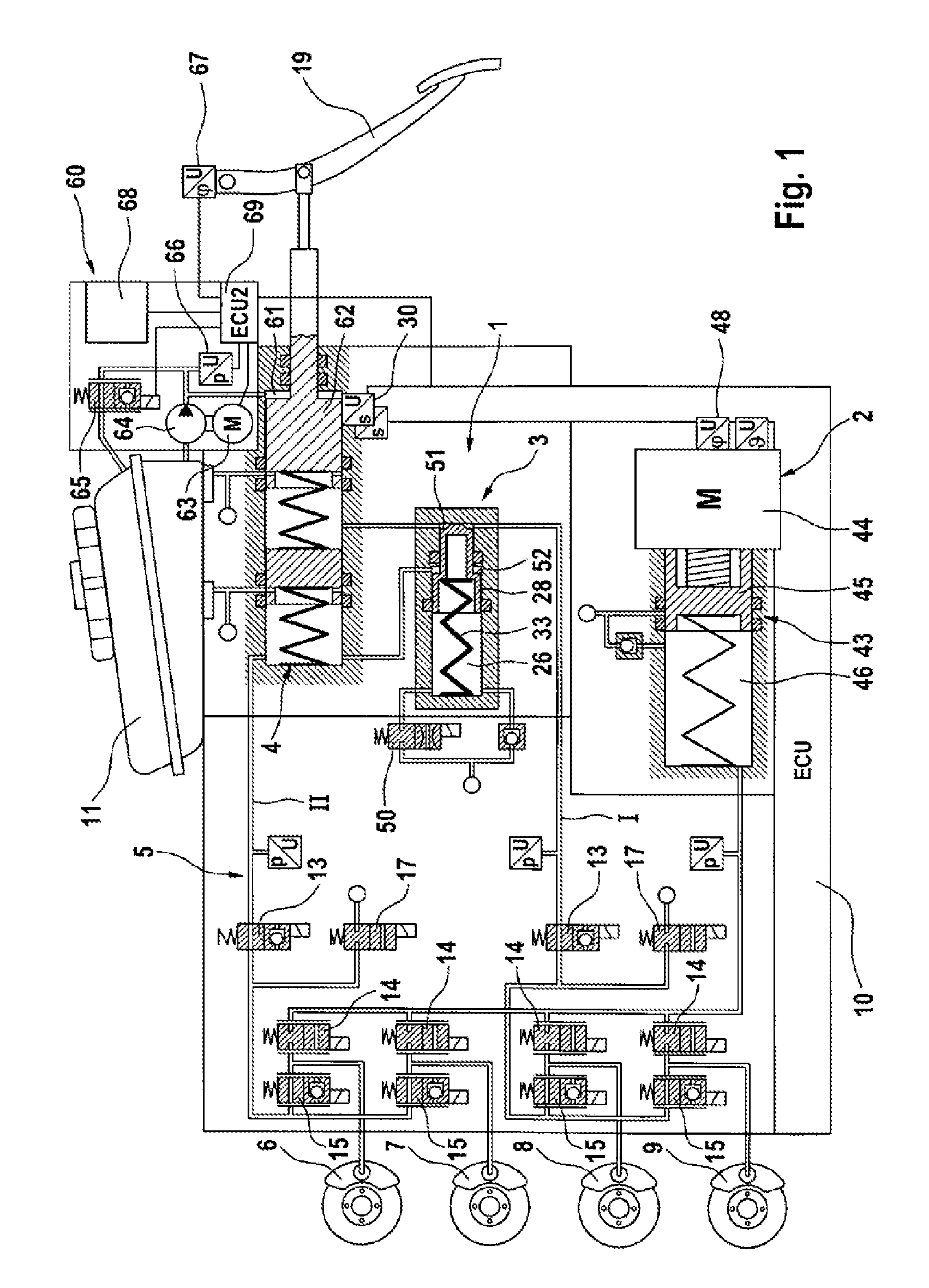
ActiveUS20130147259A1Sufficient forceEasy to manufactureFoot actuated initiationsFluid braking transmissionMobile vehicleMaster cylinder
A brake system for motor vehicles comprising a brake master cylinder which can be activated by means of a brake pedal and to which wheel brakes are connected. The brake system also comprises an electrically controllable pressure-generating device, a pressure-regulating valve arrangement to regulate a wheel brake pressure set at a wheel brake, a first electronic control and regulating unit which controls at least one of the pressure-generating device, the pressure-regulating valve arrangement, and an electrically controllable auxiliary pressure-generating device by means of which the brake master cylinder can be activated by means of which a pressure in an intermediate chamber of the brake master cylinder can be controlled or regulated.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
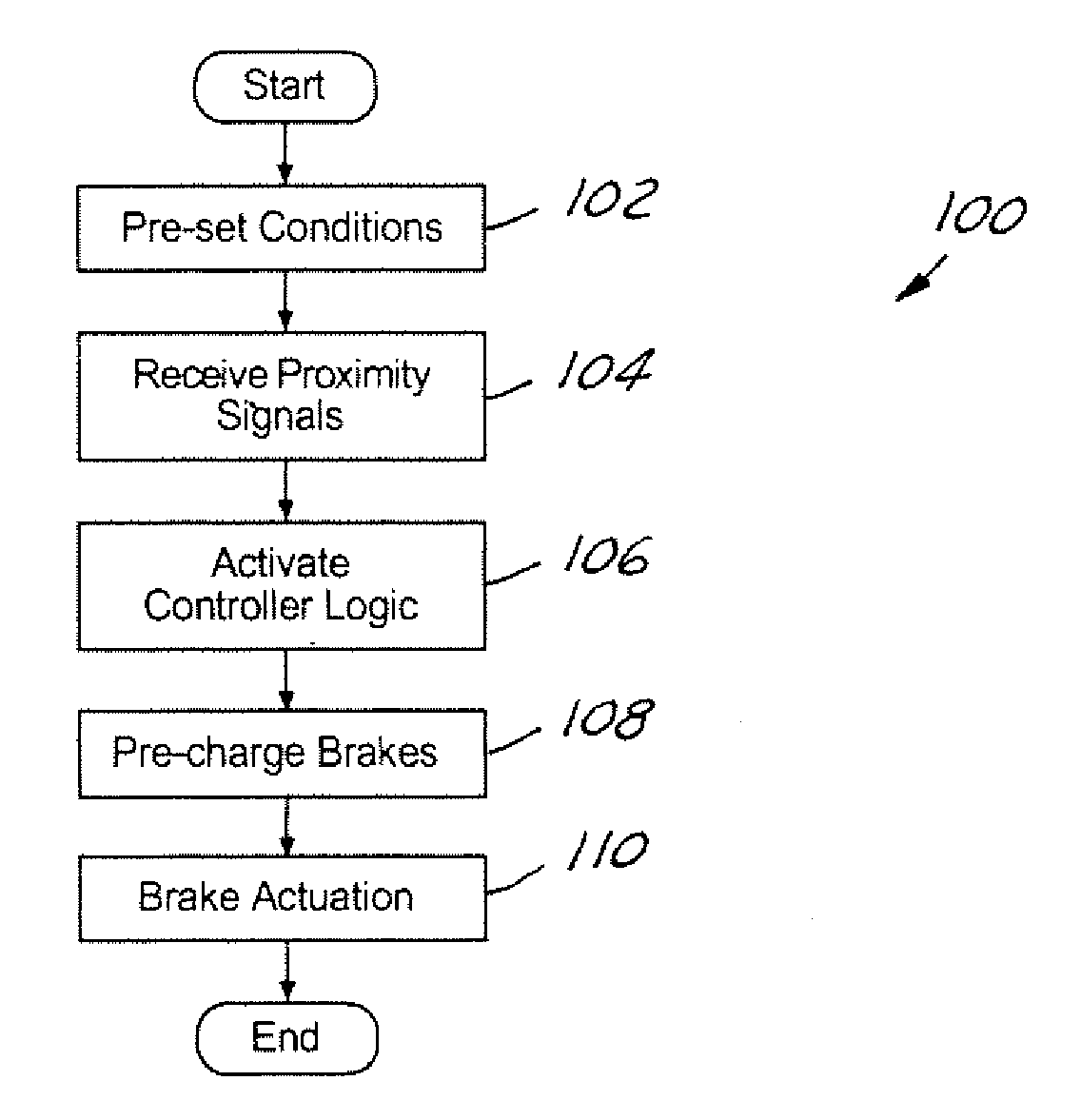
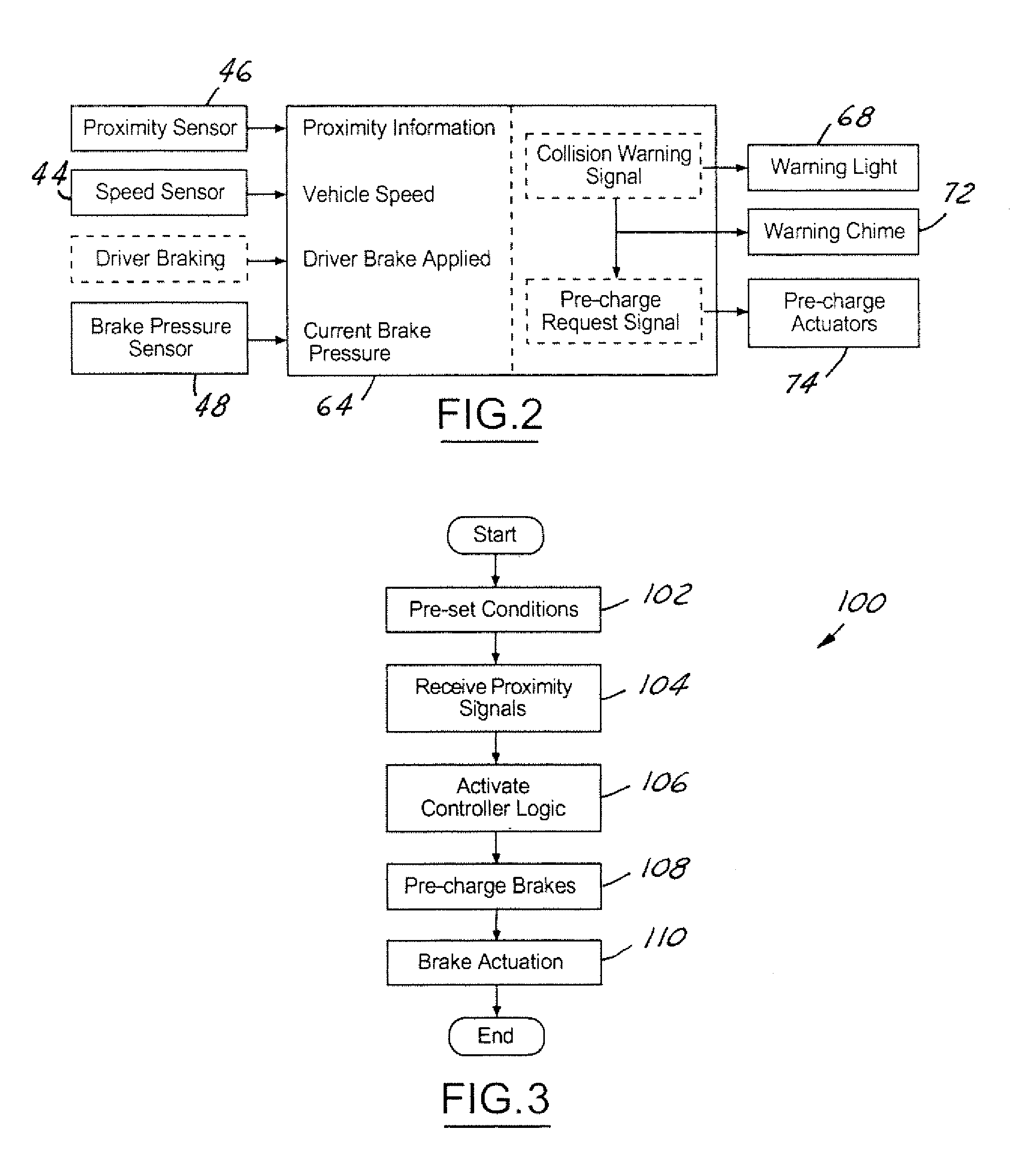
System and method for brake pre-charging
A system and method for brake pre-charging includes pre-filling brakes, based on proximity information from a forward-looking sensor, to reduce the initial delays associated with braking. By reducing the initial delay in converting driver brake pressure requests into actual brake torque to the wheels, the stopping distance required for braking is reduced.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
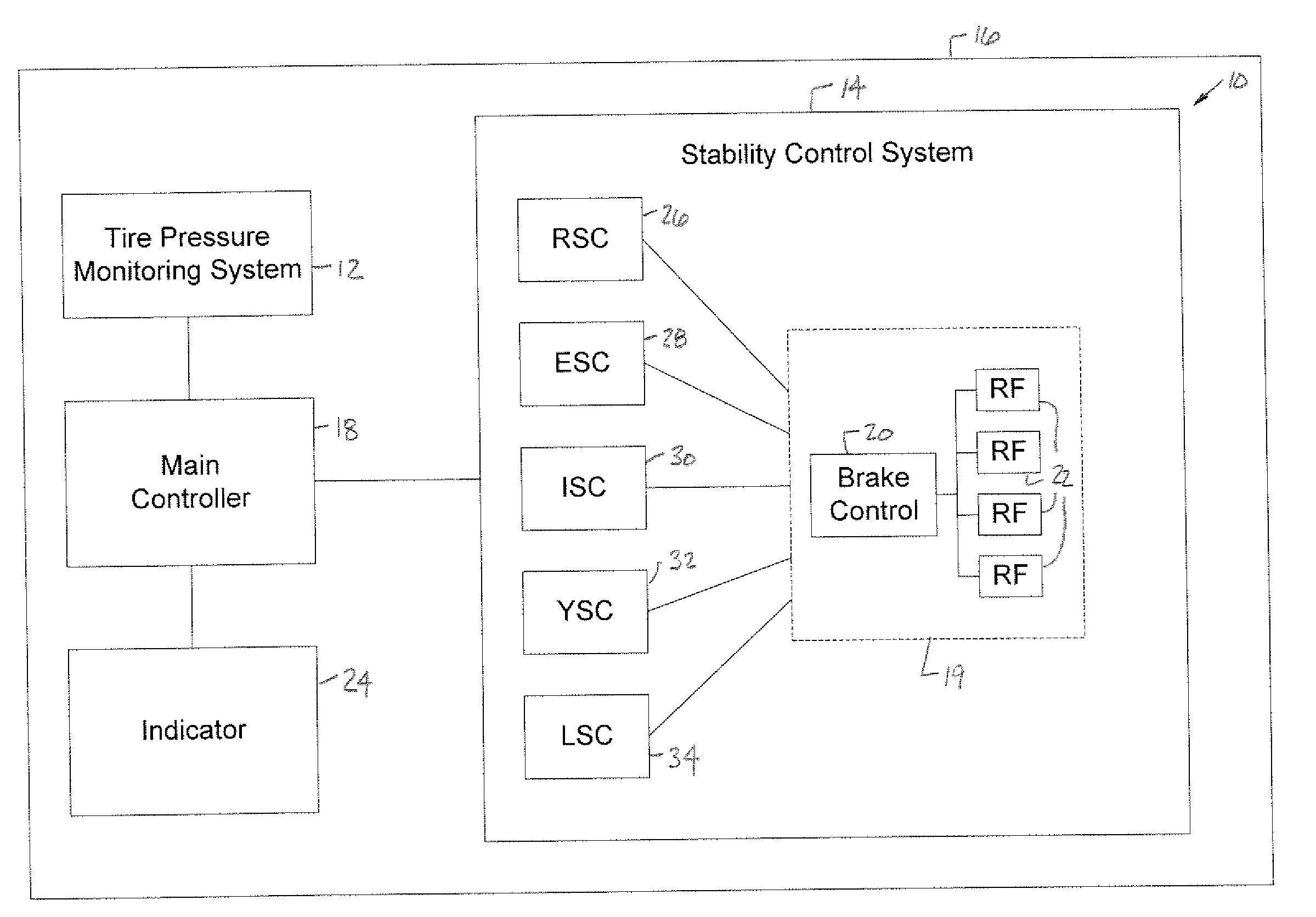
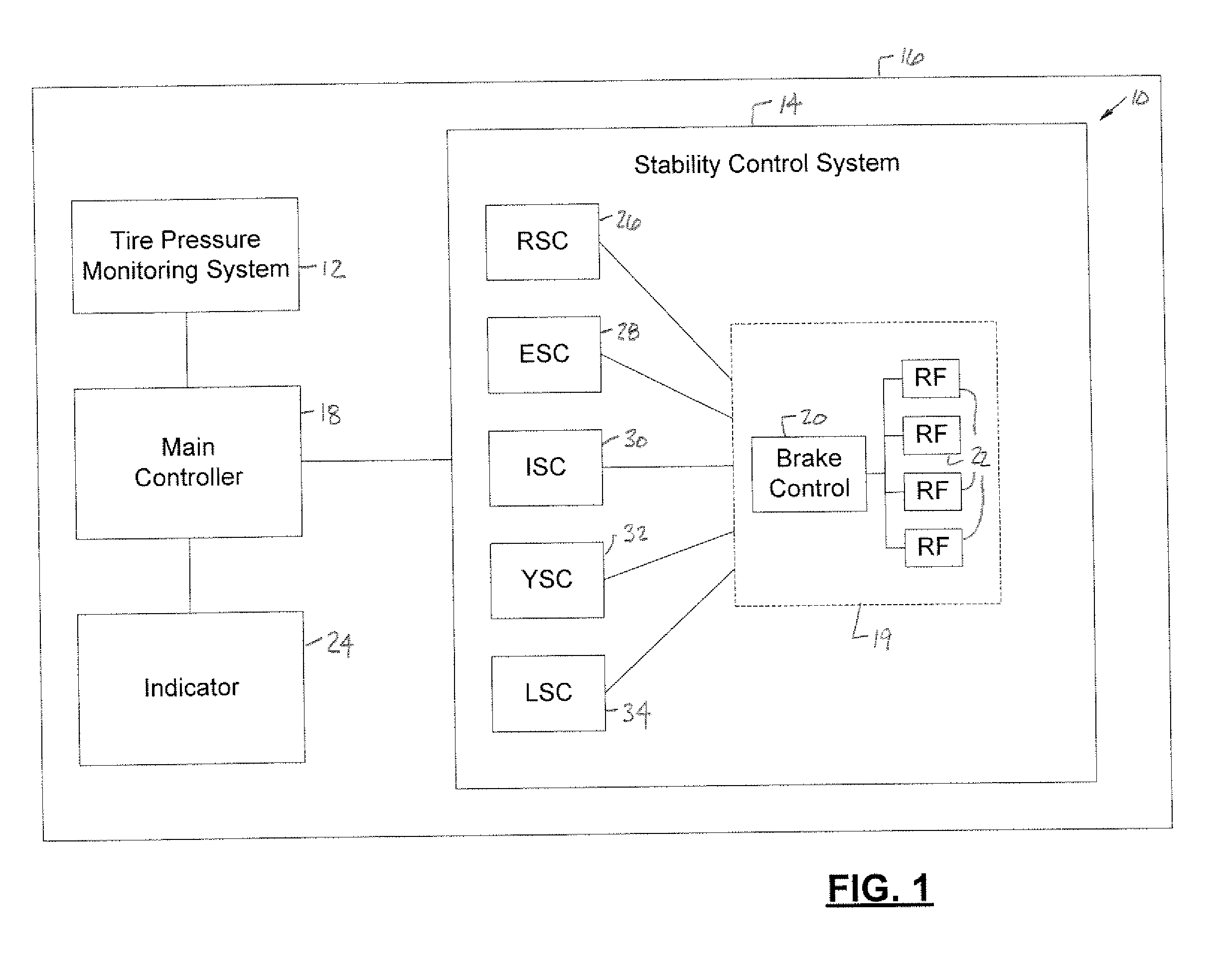
Vehicle stability control system for low tire pressure situations
InactiveUS20080061625A1Reduce amountPrevent tire-debeadingTyre measurementsBraking systemsControl systemTire-pressure monitoring system
A control system (10) for a vehicle (16) includes a sensor (228-240) that generates a sensor signal and a stability control system (14). A tire pressure monitoring system (12) generates a tire pressure signal. A brake (262) is coupled to the stability control system (14) and is associated with a rotational object (212) of the vehicle (16). A controller (18, 226) is coupled to the sensor (228-240), has multiple tire pressure associated brake control ranges R1-R3, and detects an unstable event in response to the sensor signal. The controller (18, 226) also applies a brake pressure in response to the tire pressure signal and the tire pressure associated brake control ranges R1-R3 via the stability control system (14).
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Braking pressure control apparatus capable of switching between two brake operating states using power-operated and manually operated pressure sources, respectively
InactiveUS6957870B2Reduce disadvantagesEfficient workBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsEngineeringBraking system
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for operating a brake system and a brake system
ActiveUS20150035353A1Quality is easy to controlFoot actuated initiationsFluid braking transmissionMobile vehicleDriver/operator
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Hydraulic-mechanical transmission engineering machinery automatic shifting speed variator and control method
ActiveCN101216101AImprove economyTaking into account the powerGearing controlControl signalInput control
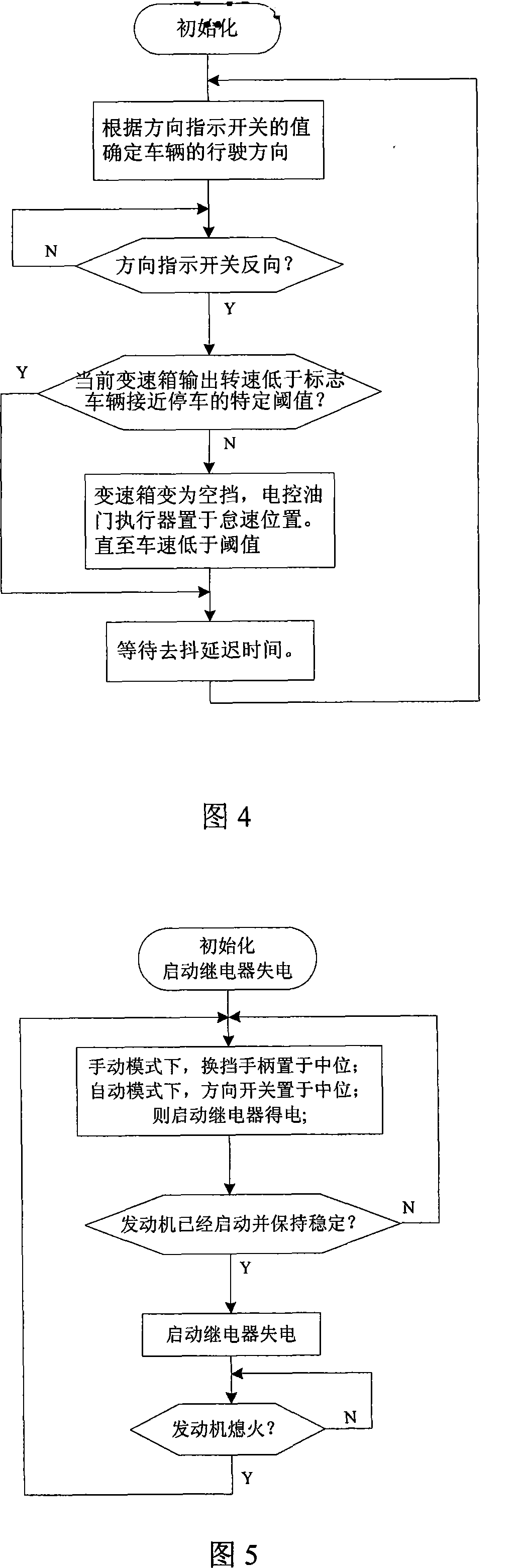
The invention relates to a mechanical automatic shift speed-changing device in hydraulic mechanical transmission engineering and a control method thereof. The device comprises an electro-hydraulic shift speed-changing unit, an electro-hydraulic engine, a microcomputer controller, an electro-hydraulic motor controller, a transmission case output rotational speed sensor, a shifting handle switch, a shifting mode selection switch, a brake pressure switch and an automatic direction switch. The electro-hydraulic motor controller is communicated with the microcomputer controller. The transmission case output rotational speed sensor, a torque converter turbine speed sensor, a shifting handle, the shifting mode selection switch, the brake pressure switch and the automatic direction switch serve to input signals to the input port of the microcomputer controller. The microcomputer controller serves to input control signals to a transmission case control module by the output port thereof. Based on the combination of two shift methods, the inventive device has the advantages of good economical efficiency, power efficiency and practicability, low energy consumption, automatic shift with high work efficiency, less working time, reduced labor intensity of the driver, and suitability for various working conditions.
Owner:TIANJIN ENG MACHINERY INST
Electro-hydraulic composite braking system with electric braking assistant force and brake-by-wire function
ActiveCN103552557AWith electric brake assistFunctionalBraking action transmissionElectric machineElectro hydraulic
The invention discloses an electro-hydraulic composite braking system with an electric braking assistant force and a brake-by-wire function. The electro-hydraulic composite braking system provided by the invention has various working modes In the case of an electric braking assistant force mode, a brake fluid is input into a master cylinder from a man-power cylinder by a brake pedal, and meanwhile, an electronic control unit controls the output torque of a motor to apply an assistant force, so as to output brake pressure to a wheel cylinder. In the case of a regenerative braking mode, the electronic control unit controls the on / off of an electromagnetic valve, the brake fluid is input into the simulation cavity of a pedal travel simulator from the man-power cylinder by the brake pedal so as to generate pressure and provide a brake pedal feeling; if automobile deceleration requirement can not be met by the regenerative braking, the electronic control unit controls the output torque of the motor so as to allow the master cylinder to output brake pressure into the wheel cylinder to assist friction brake. In case of an active braking mode, the electronic control unit controls the output torque of the motor so as to allow the master cylinder to output brake pressure to the wheel cylinder. The electro-hydraulic composite braking system provided by the invention has the advantages of integration of advantages of wire control and non-wire control working modes, small pressure fluctuation, and high pressure regulation precision.
Owner:南京经纬达汽车科技有限公司
Apparatus for controlling automatic stop and restart of engine
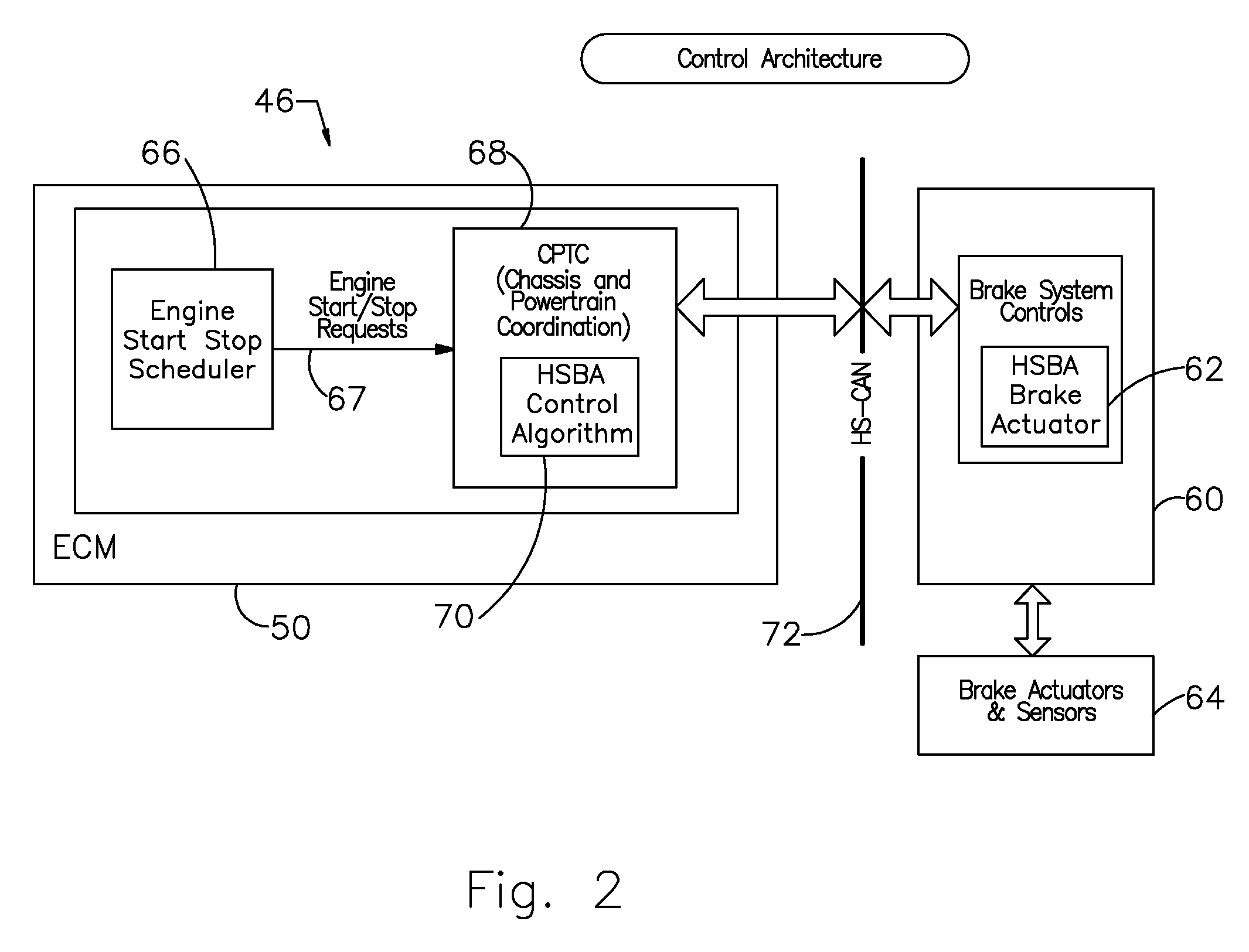
ActiveUS20110256981A1Ensure controllabilityControllability deterioratesInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersBraking systemControl unit
An apparatus for controlling automatic stop / restart of an engine, includes: an automatic-stop / restart-control-unit which stops / restarts the engine; a brake-pressure-detection-unit which detects brake pressure in a brake system and controls the brake pressure to perform anti-skid control; a first-determination-unit which determines whether the brake pressure is not less than a first-threshold; a second-determination-unit which determines whether the brake pressure is not less than a second-threshold larger than the-first threshold; a stop-allowing-unit which allows the automatic-stop / restart-control-unit to stop the engine while the engine operates, when the first-determination-unit determines that the brake pressure is not less than the first-threshold and the second-determination-unit determines that the brake pressure is less than the second-threshold; and a stop-inhibiting-unit which inhibits the automatic-stop / restart-control-unit from stopping the engine while the engine operates, when the-first-determination-unit determines that the brake pressure is less than the first-threshold and the second-determination-unit determines that the brake pressure is not less than the second-threshold.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Adaptive vehicle following algorithm based on improved model prediction control
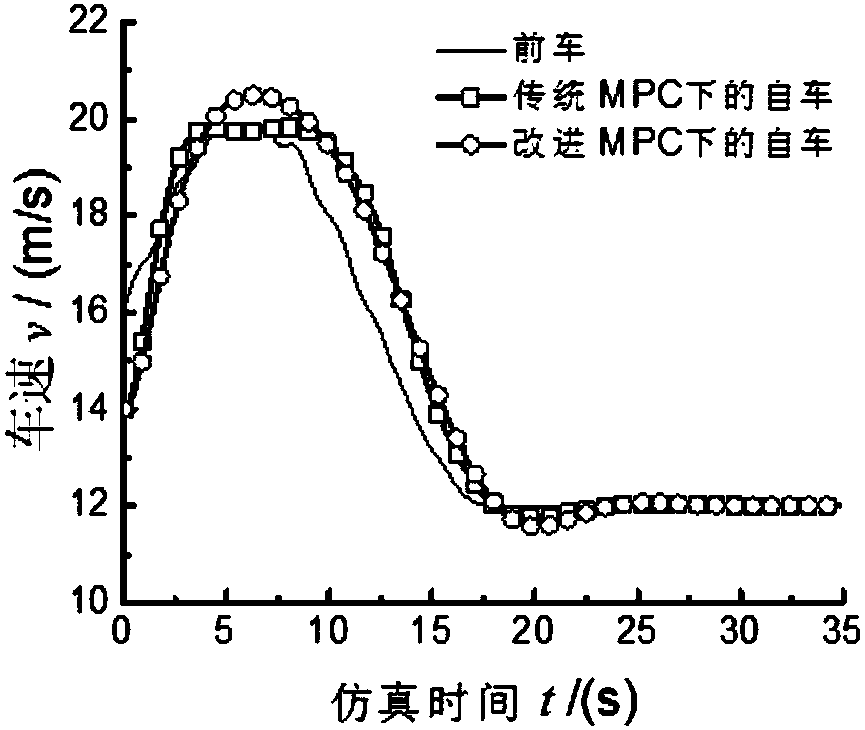
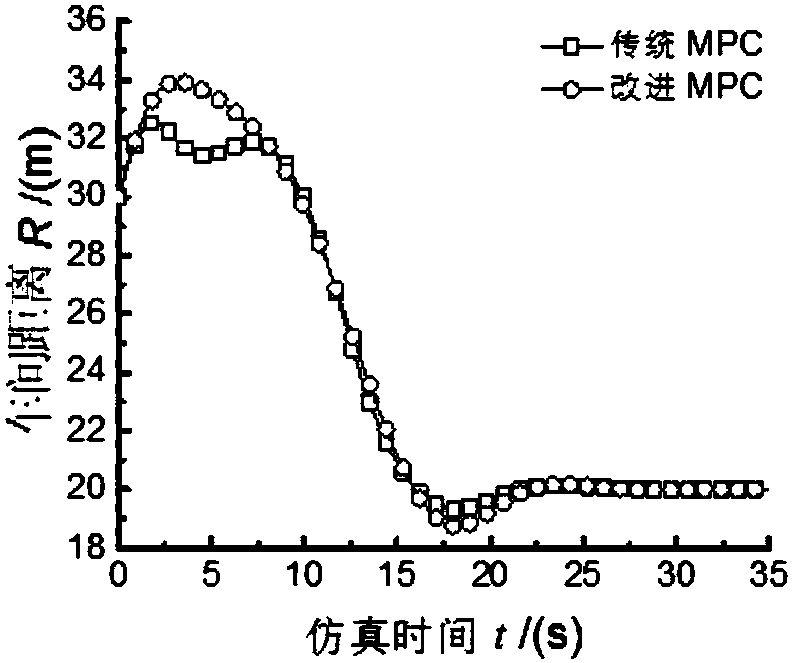
ActiveCN107808027AImprove the optimal solutionImproved Predictive ControlGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationBrake pressureLeast squares
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Engine of working truck, hydraulic pump controller and method for controlling hydraulic pump
InactiveCN101287876AReduce heatReduce loadSoil-shifting machines/dredgersEngine controllersHydraulic pumpCam
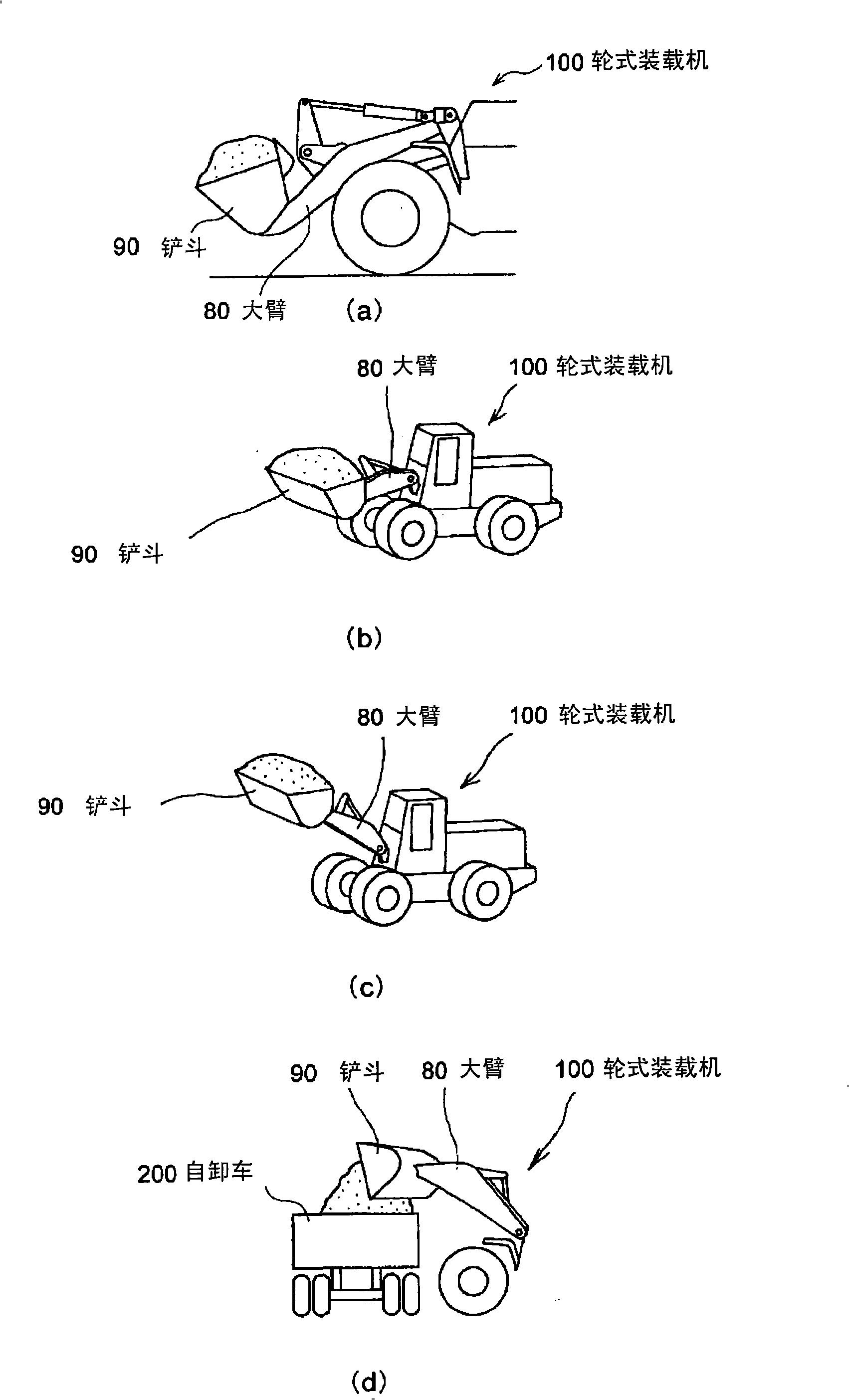
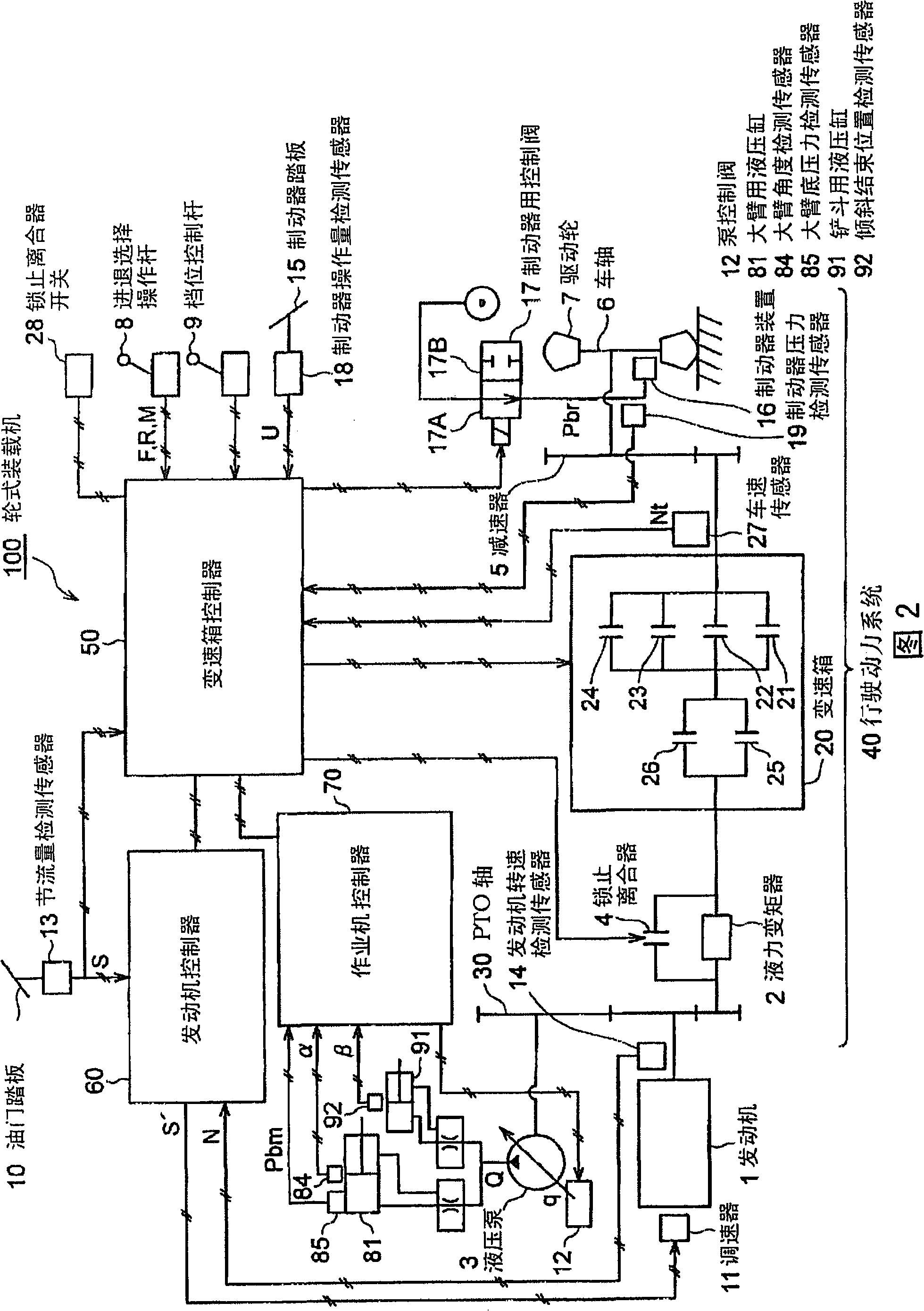
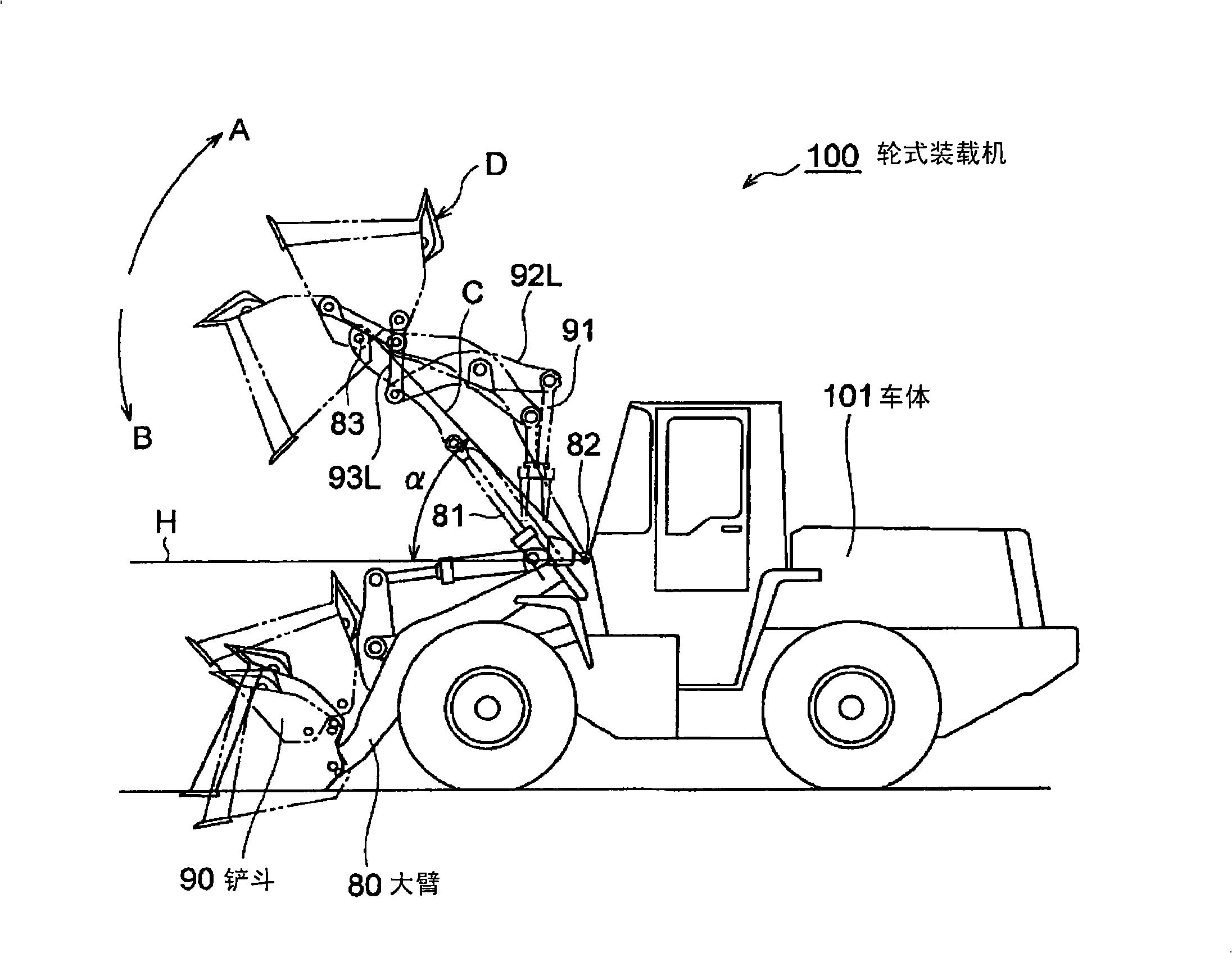
An engine of a working truck in which adverse effect of oil temperature rise is avoided, by lessening the load applied to an accelerator when the working truck is traveling while elevating the boom and approaching a place for discharging the load in the bucket during dump approach and, reducing heat generated through operation of a brake, and deterioration in work efficiency of the working truck is avoided by preventing the elevating speed of a boom from decreasing. A hydraulic pump controller and a method for controlling the hydraulic pump are also provided. On condition that a throttle amount sensor detects the operating amount of an acceleration pedal reaching a prescribed threshold value (operation amount 70%), a brake pressure sensor detects operation (brake on) of a brake, and a vehicle speed sensor detects the body speed reaching a prescribed threshold value, a transmission controller delivers a throttle correction command signal for reducing the target engine speed to a governor through an engine controller, and delivers a boom elevating time cam plate inclination angle alteration command for sustaining delivery flow rate of the hydraulic pump by supplementing reduction in delivery flow rate of the hydraulic pump by a throttle correction command to a pump control valve through a working machine controller.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com