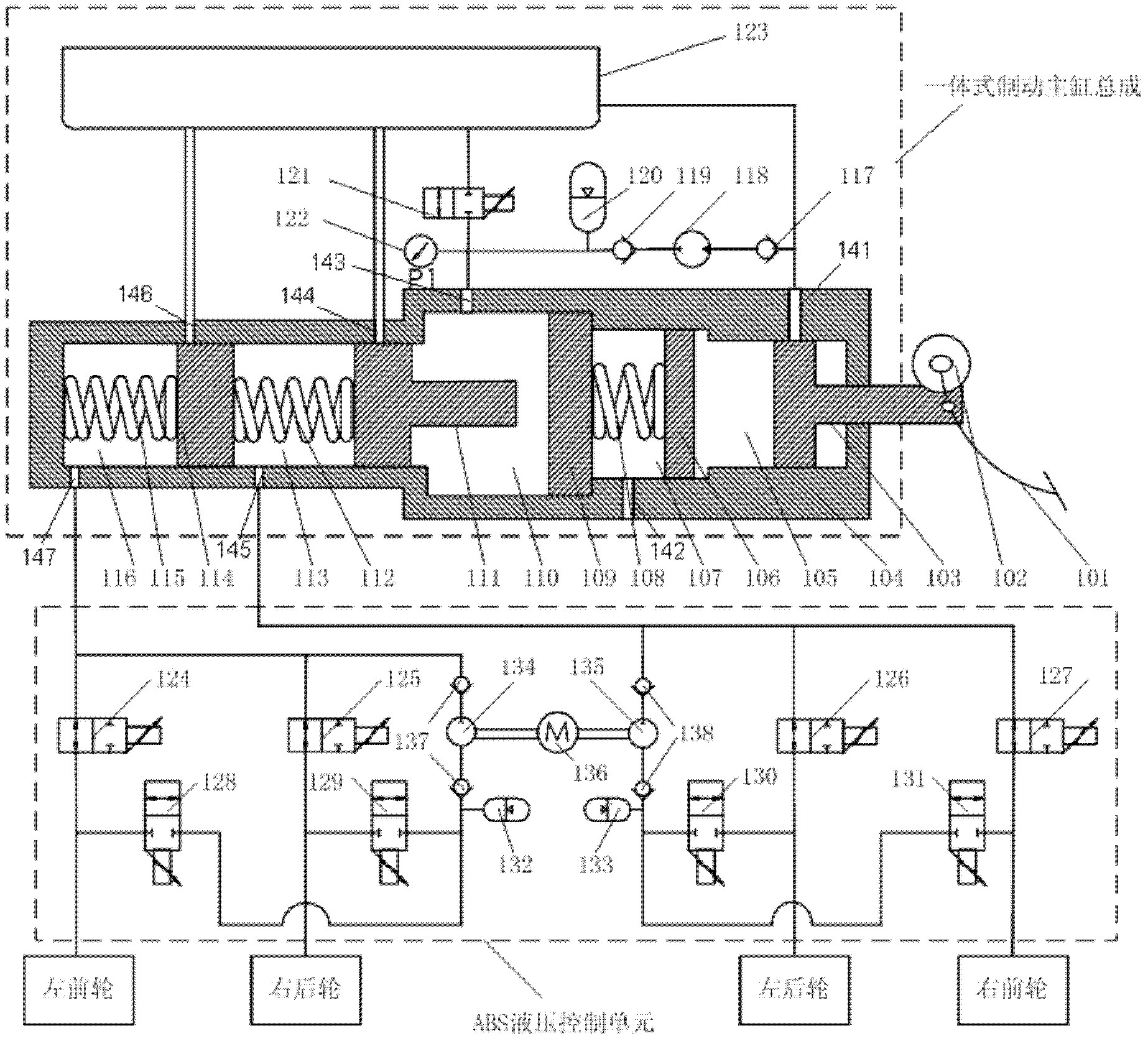
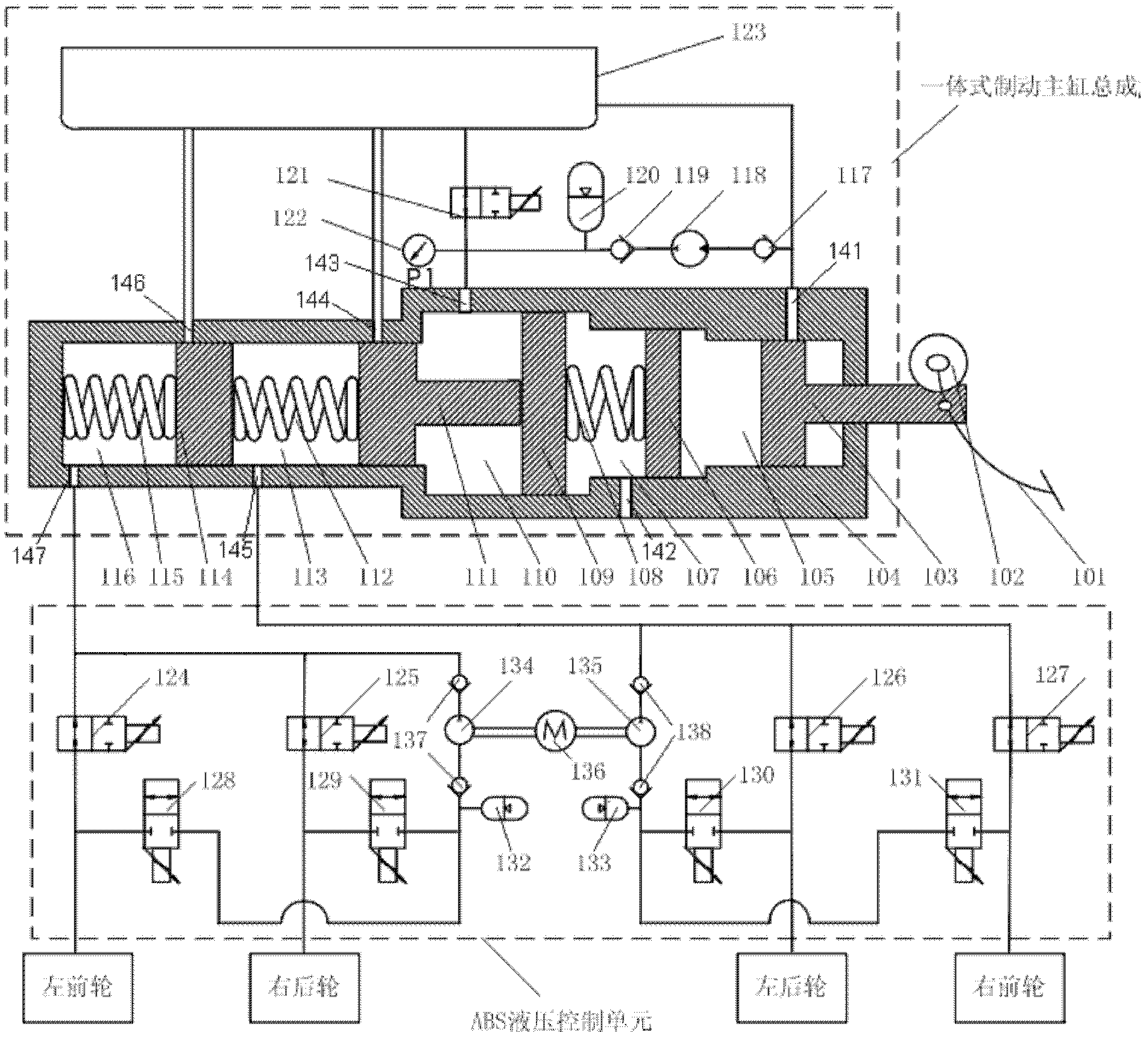
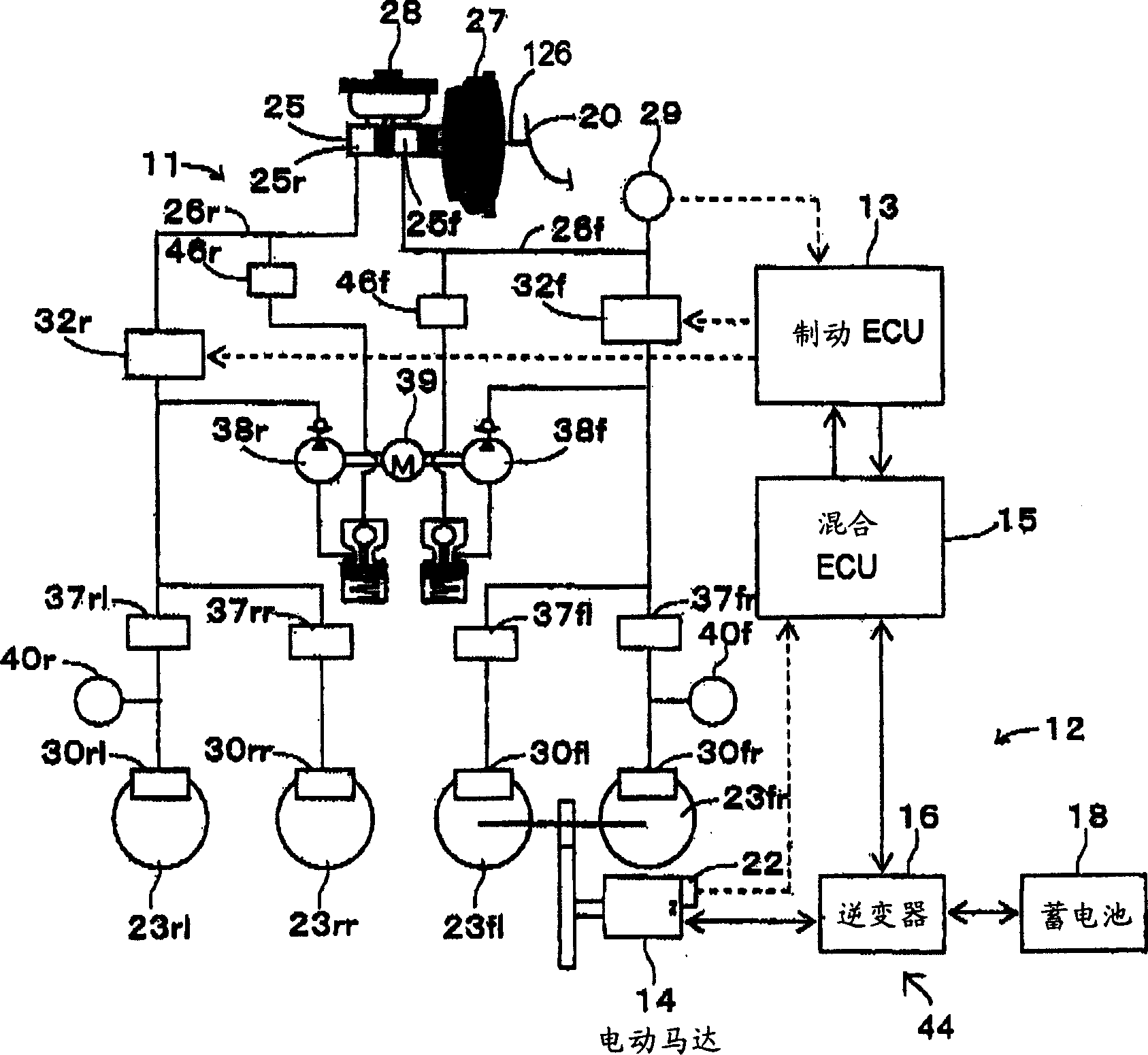
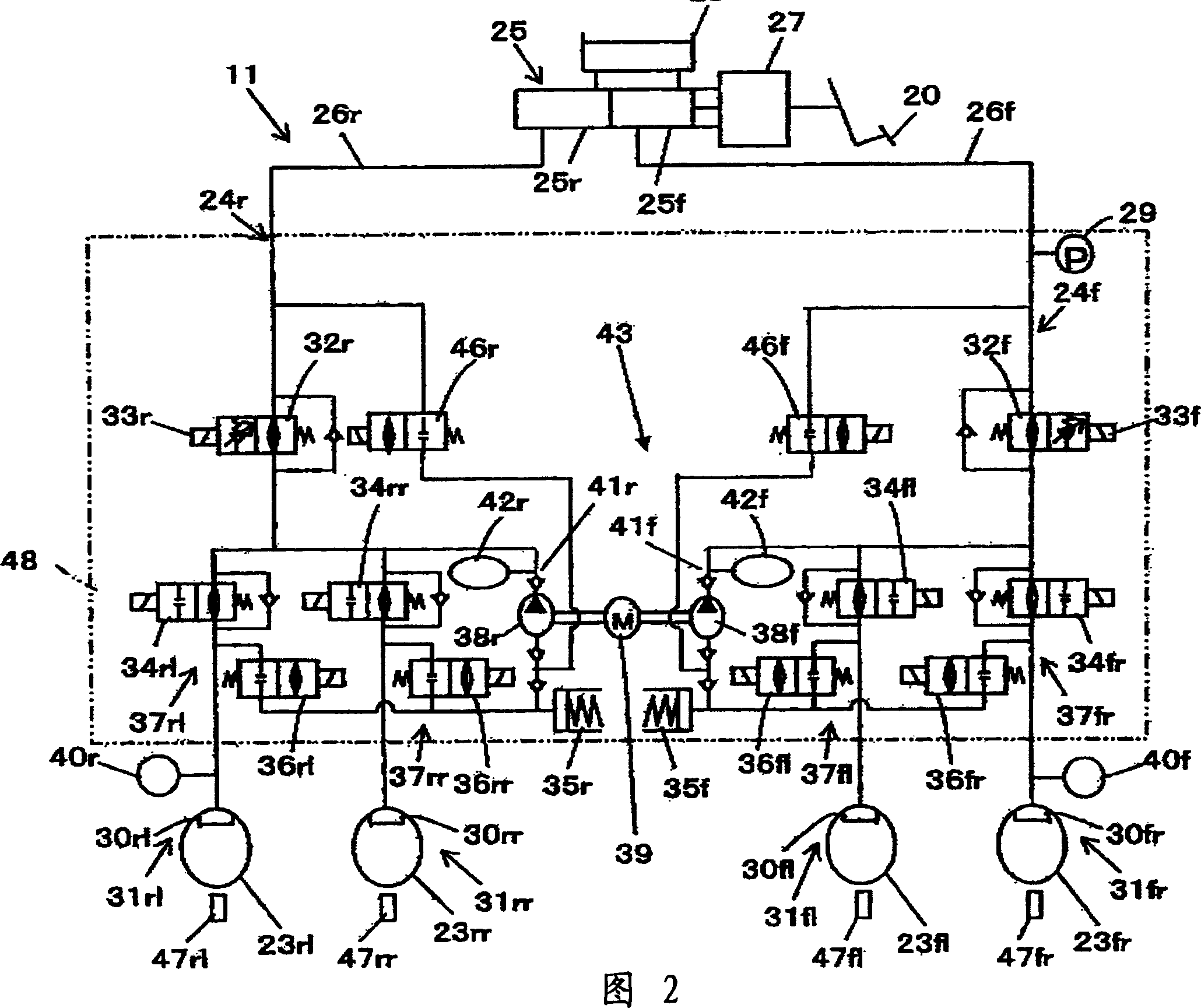
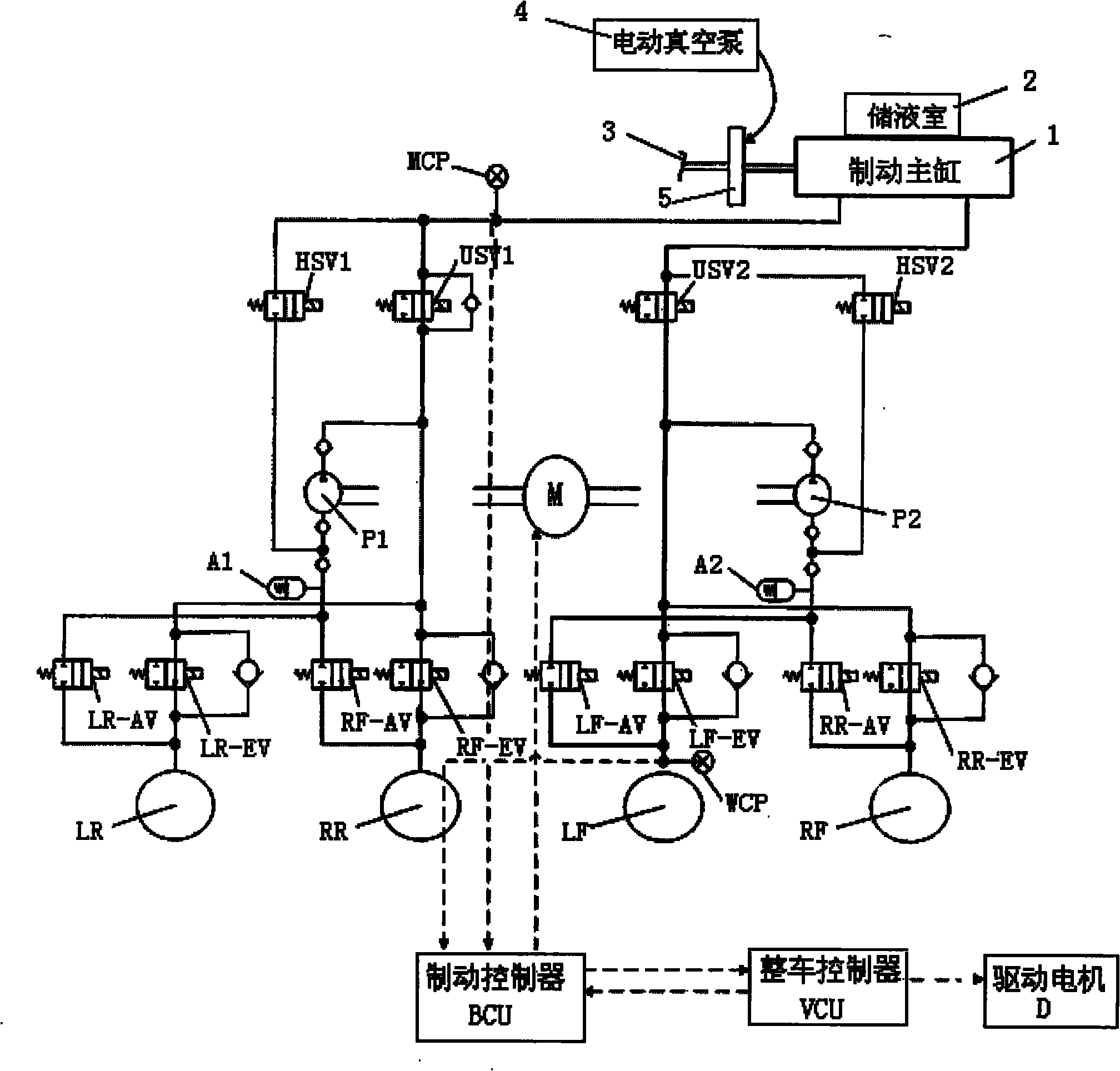
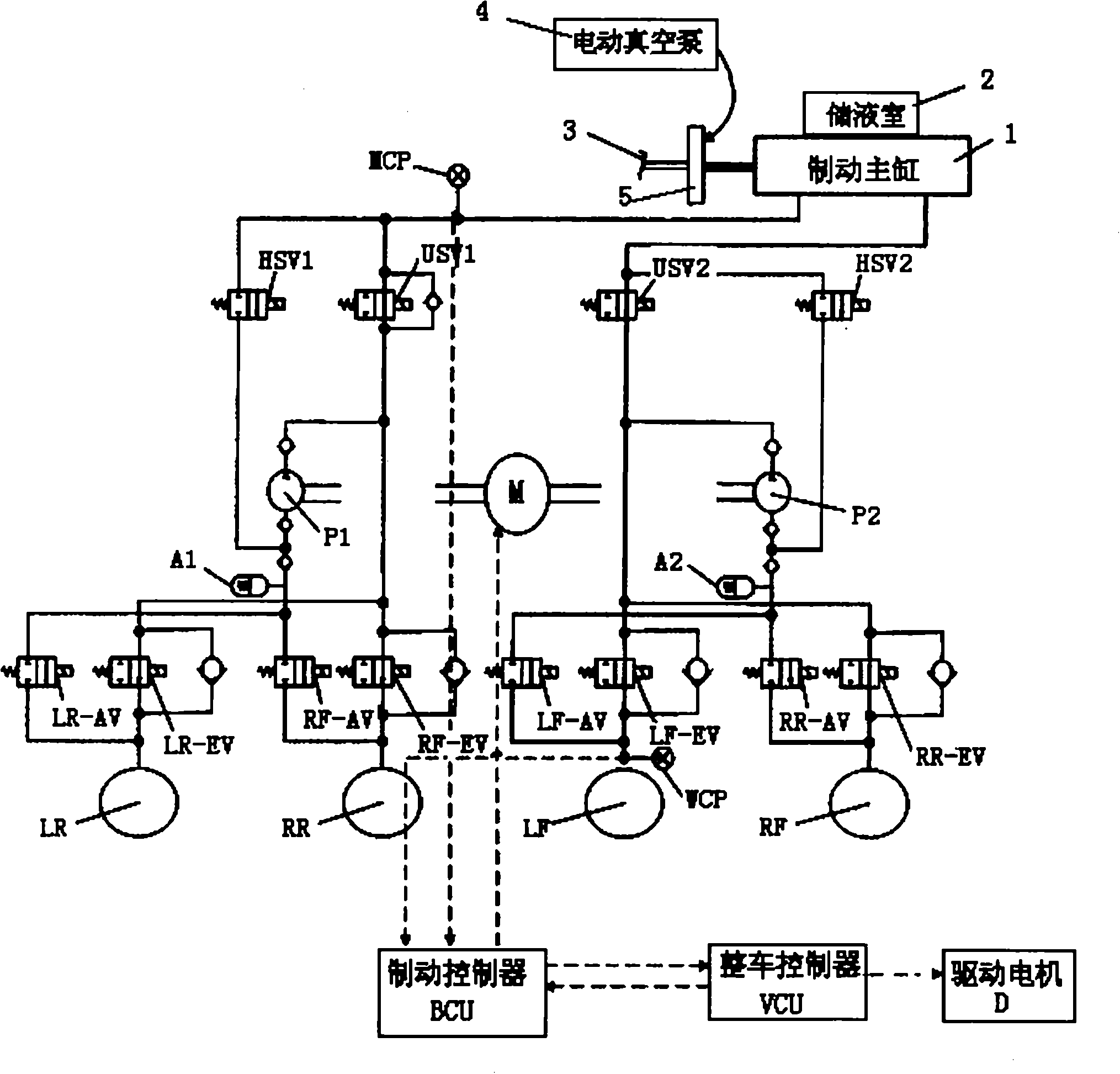
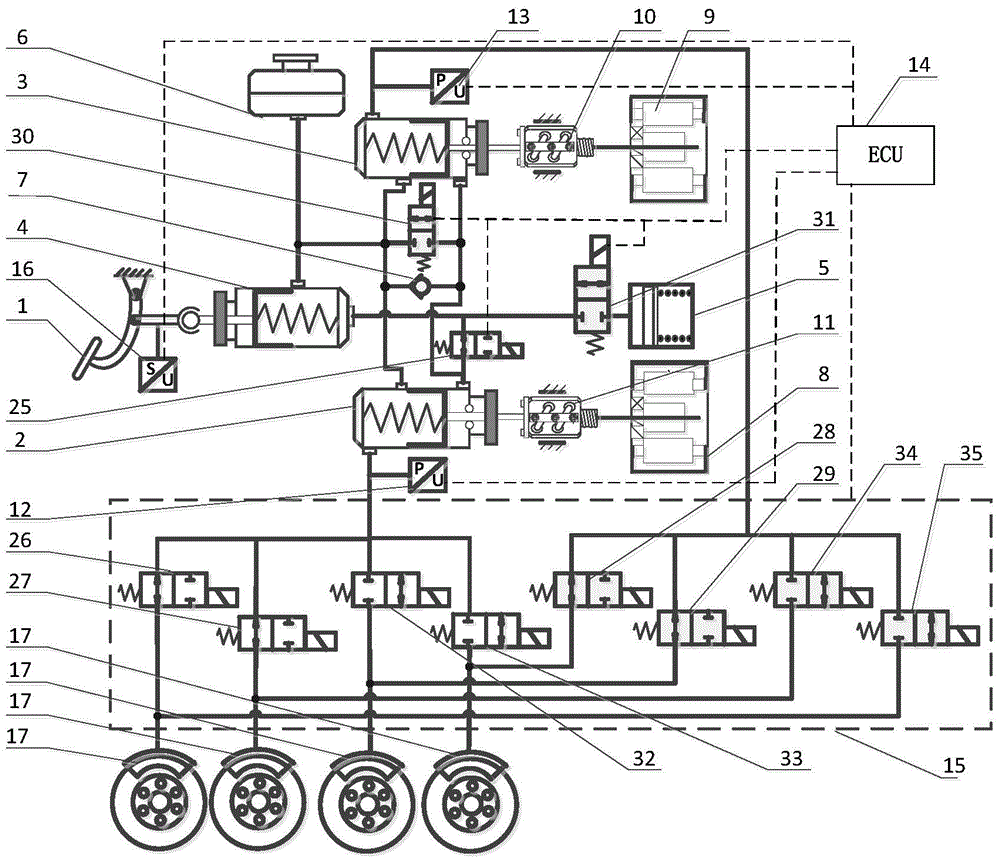
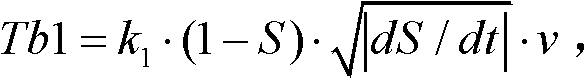Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1405 results about "Wheel cylinder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
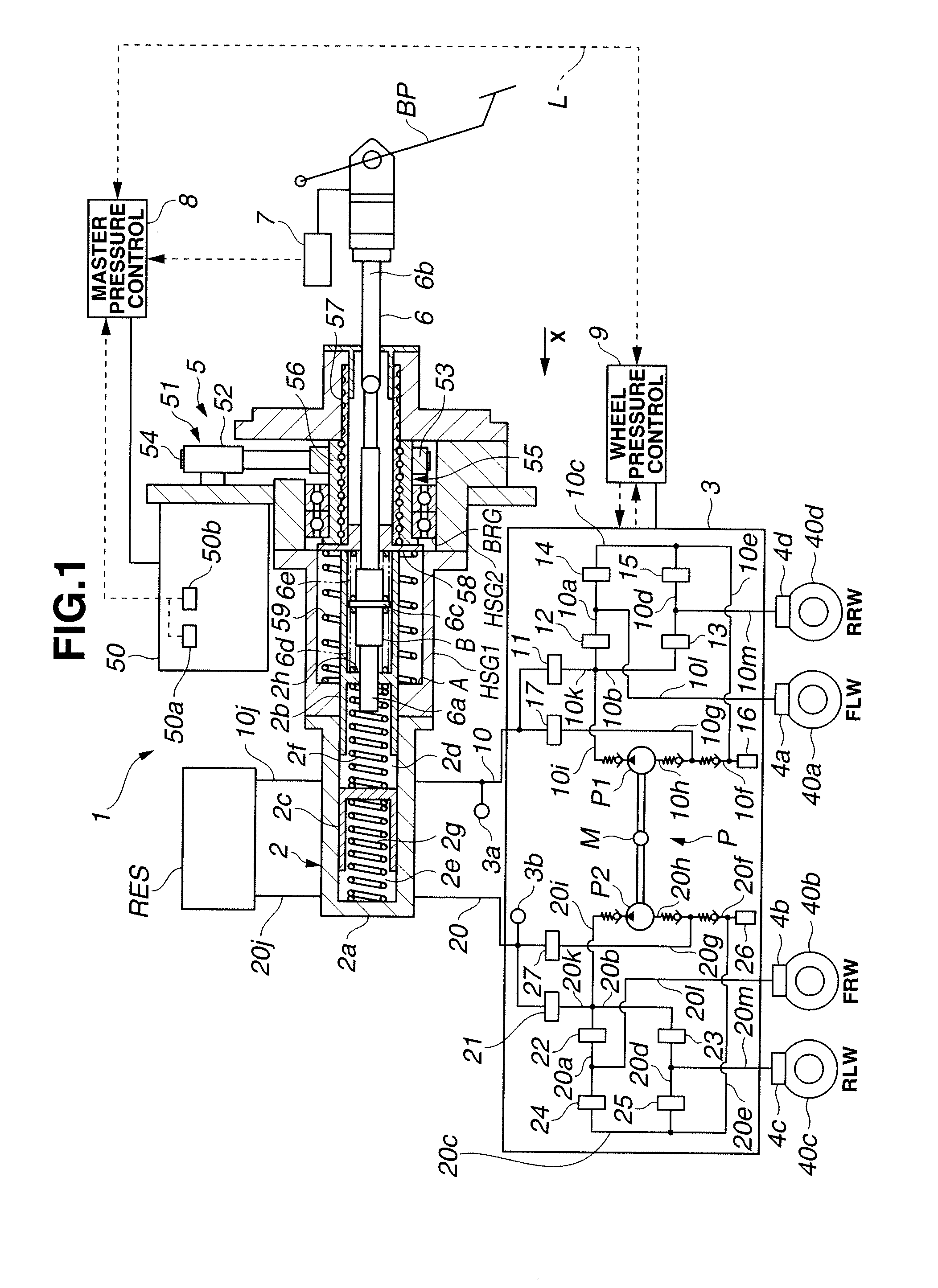
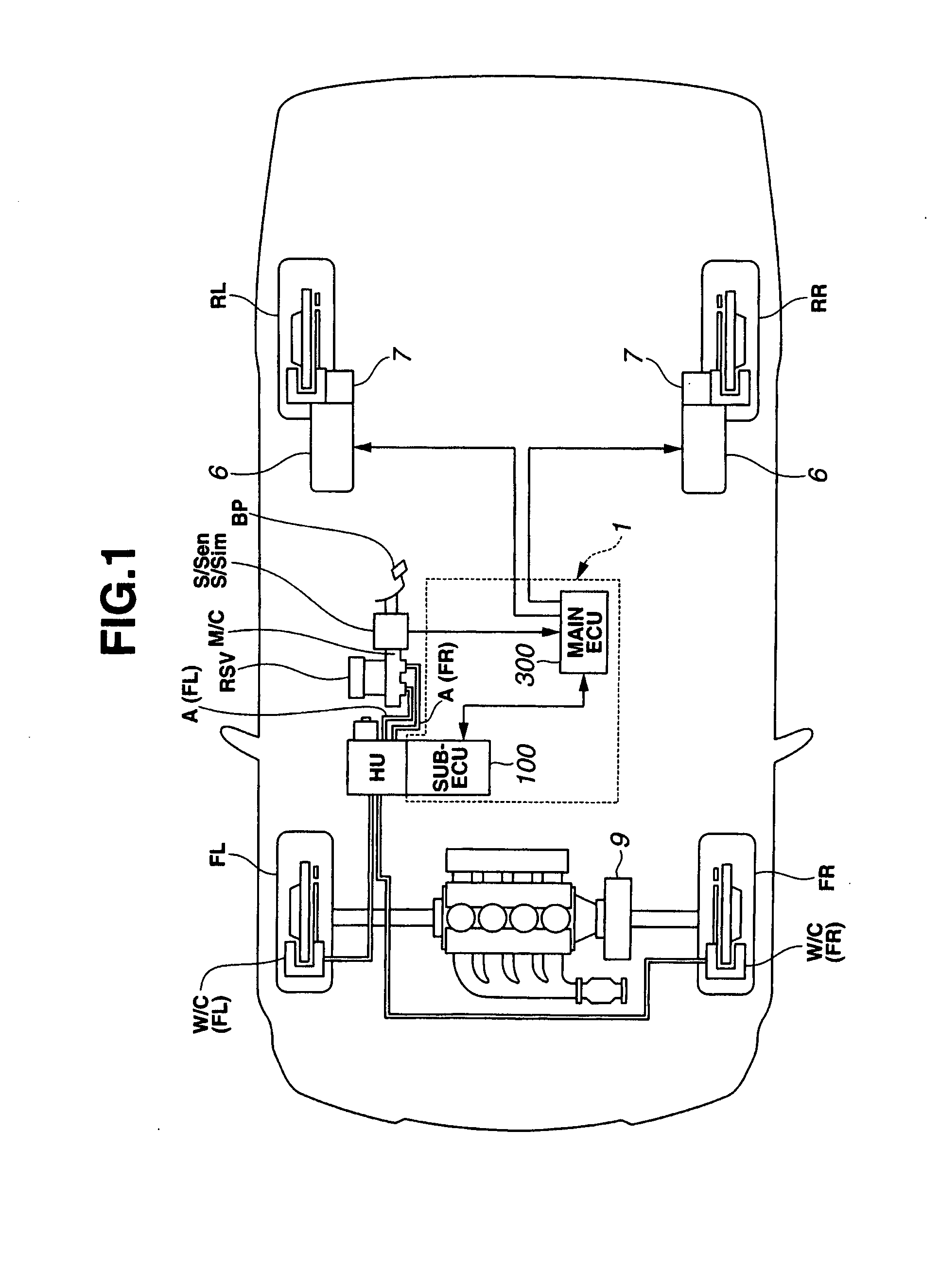
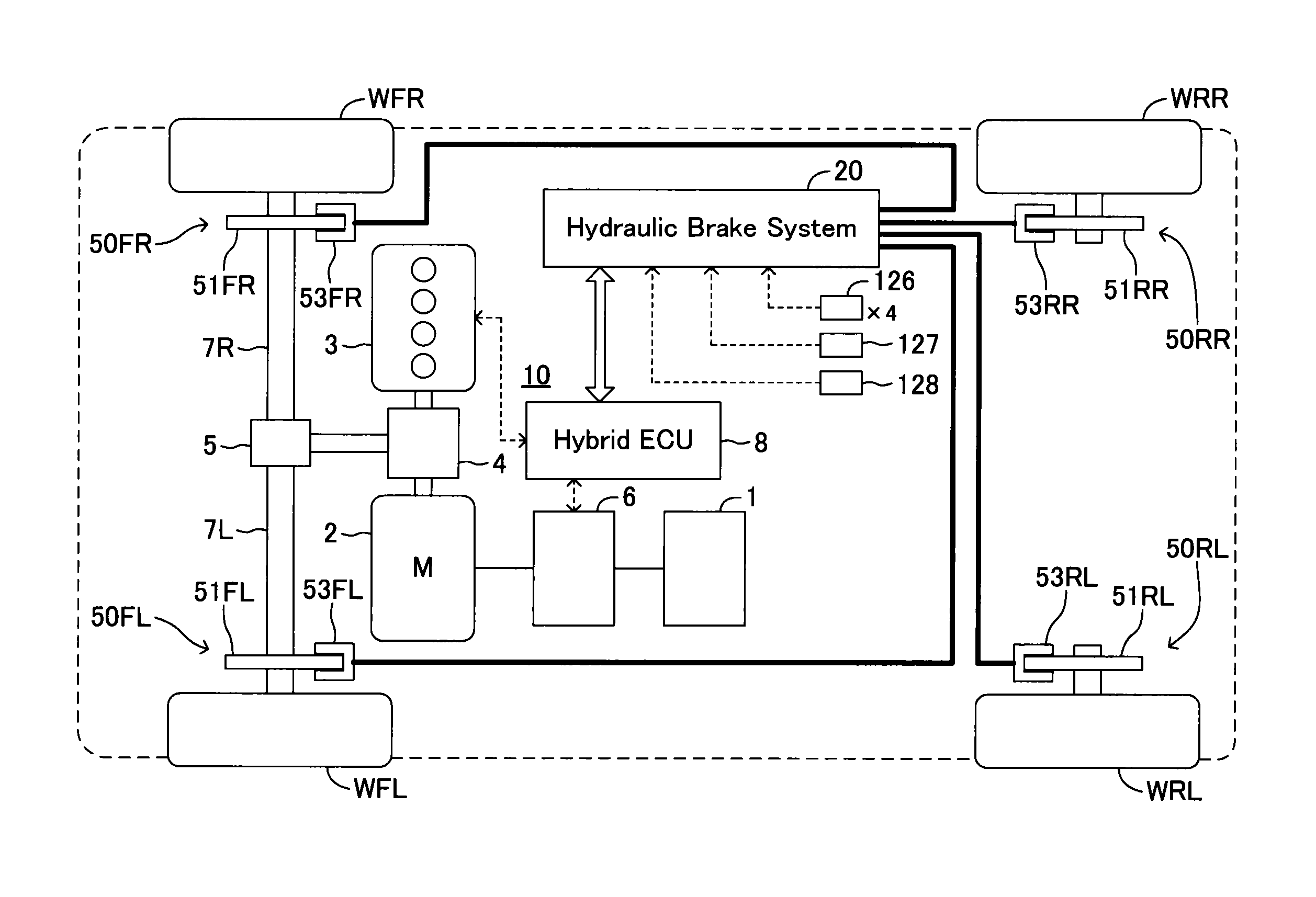
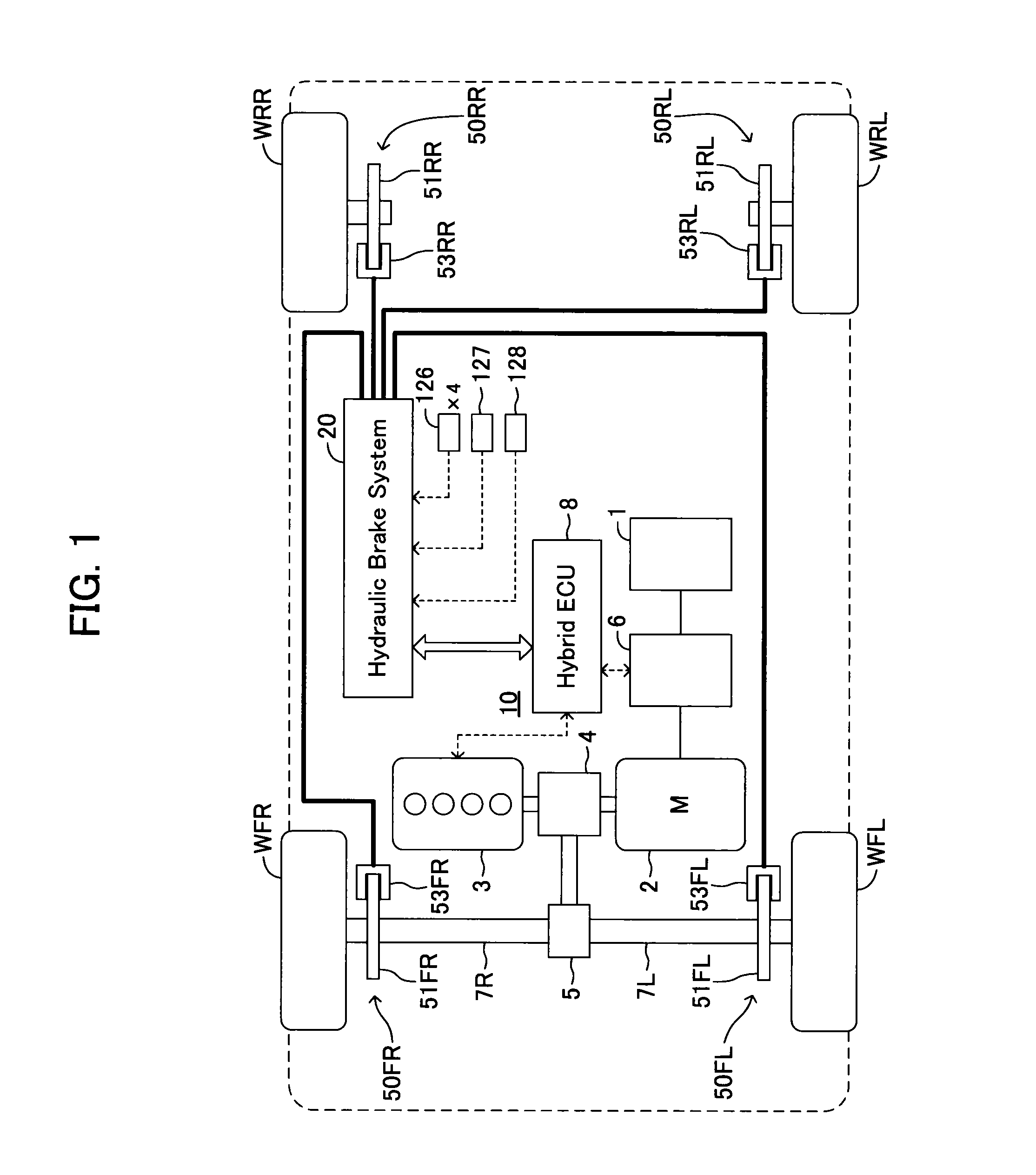
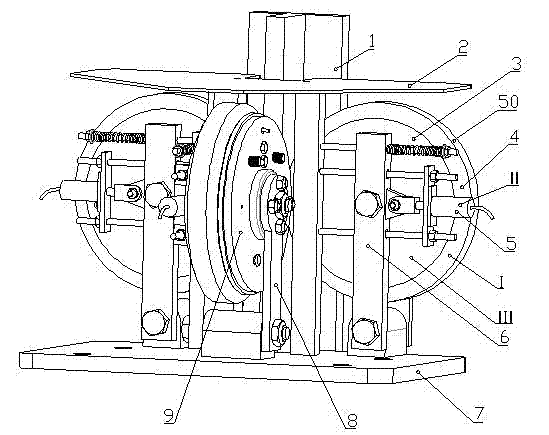
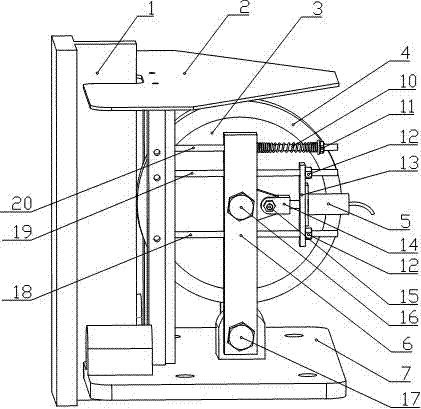
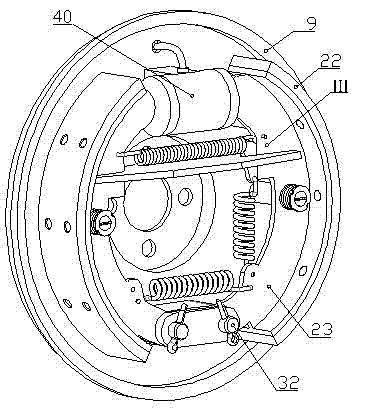
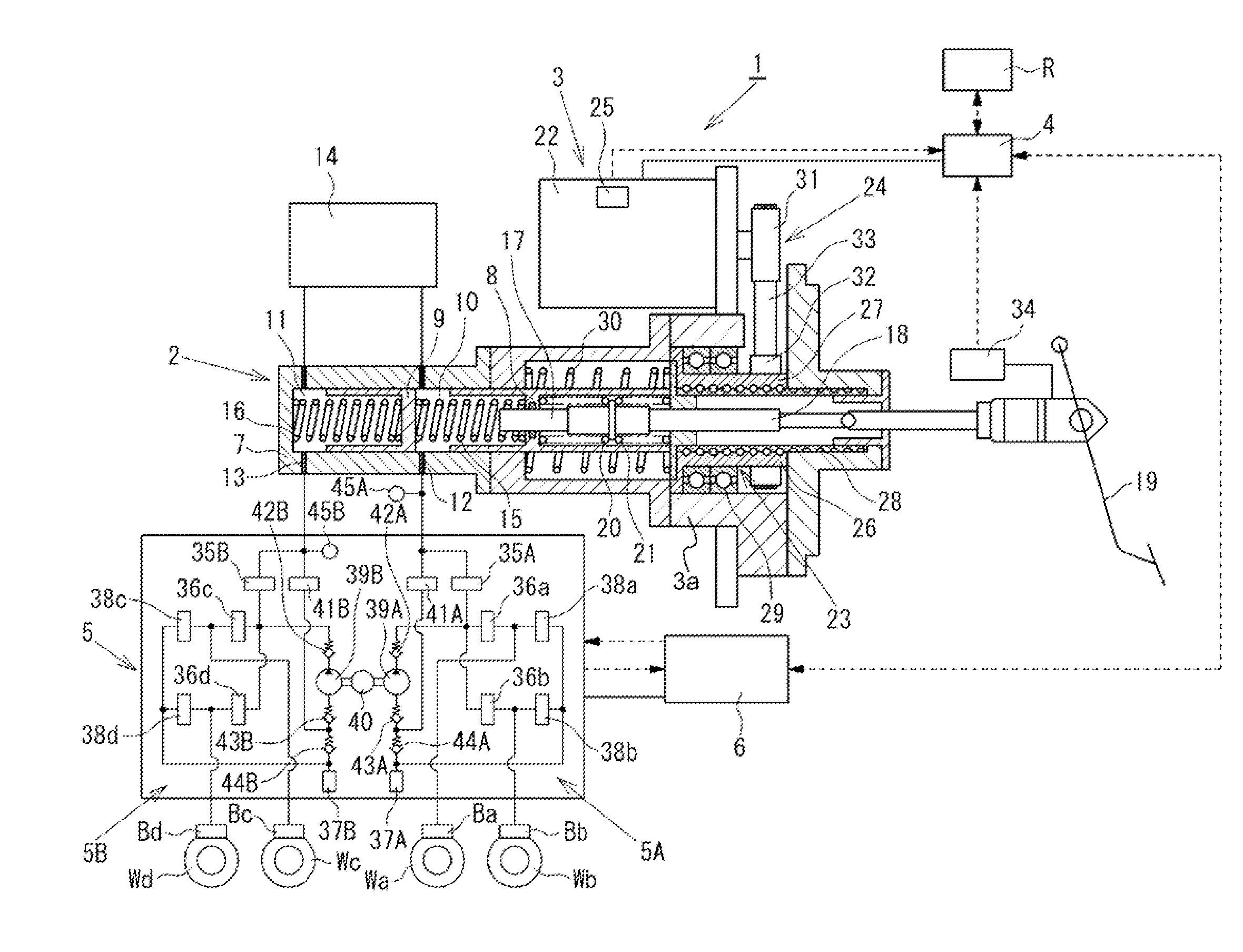
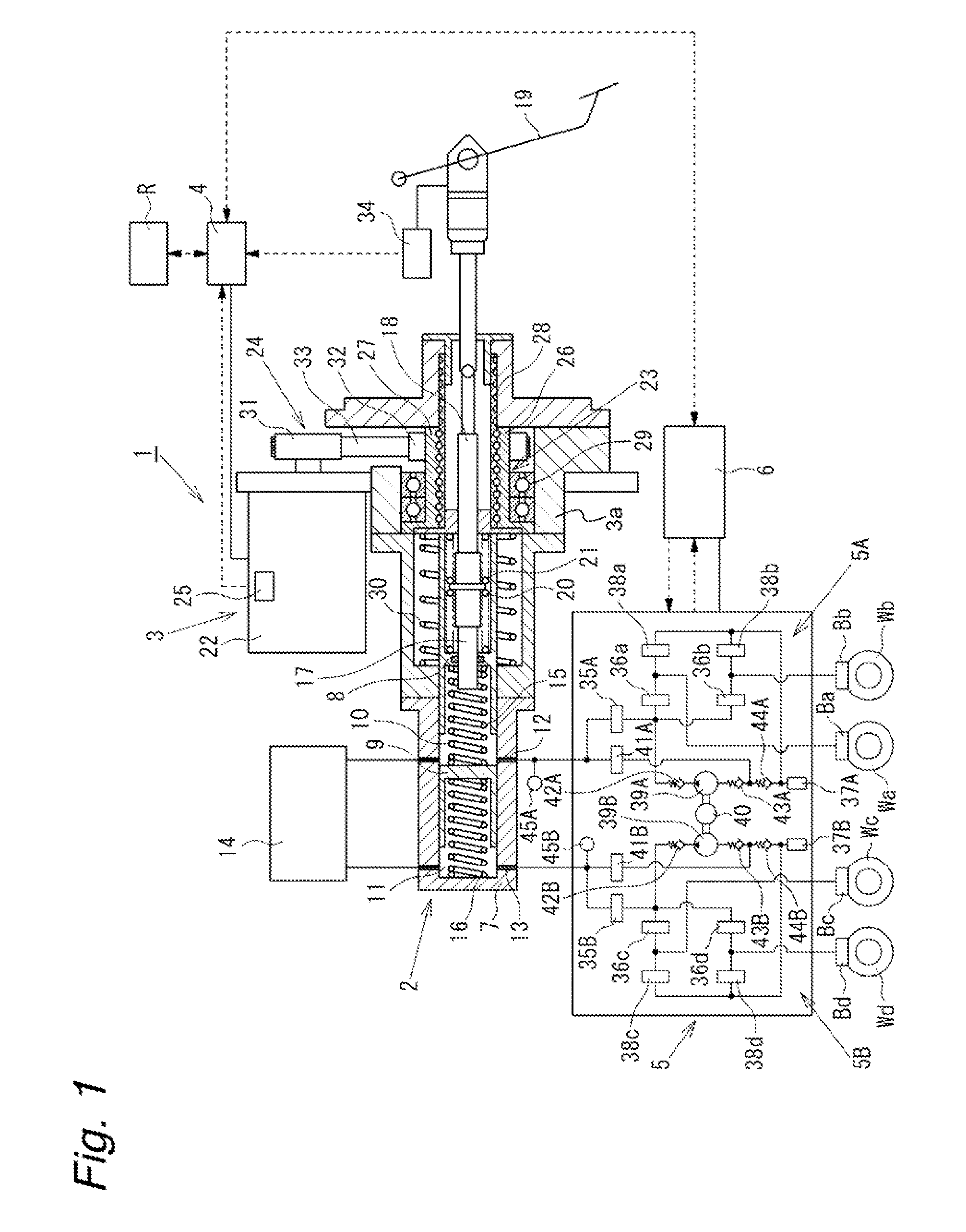
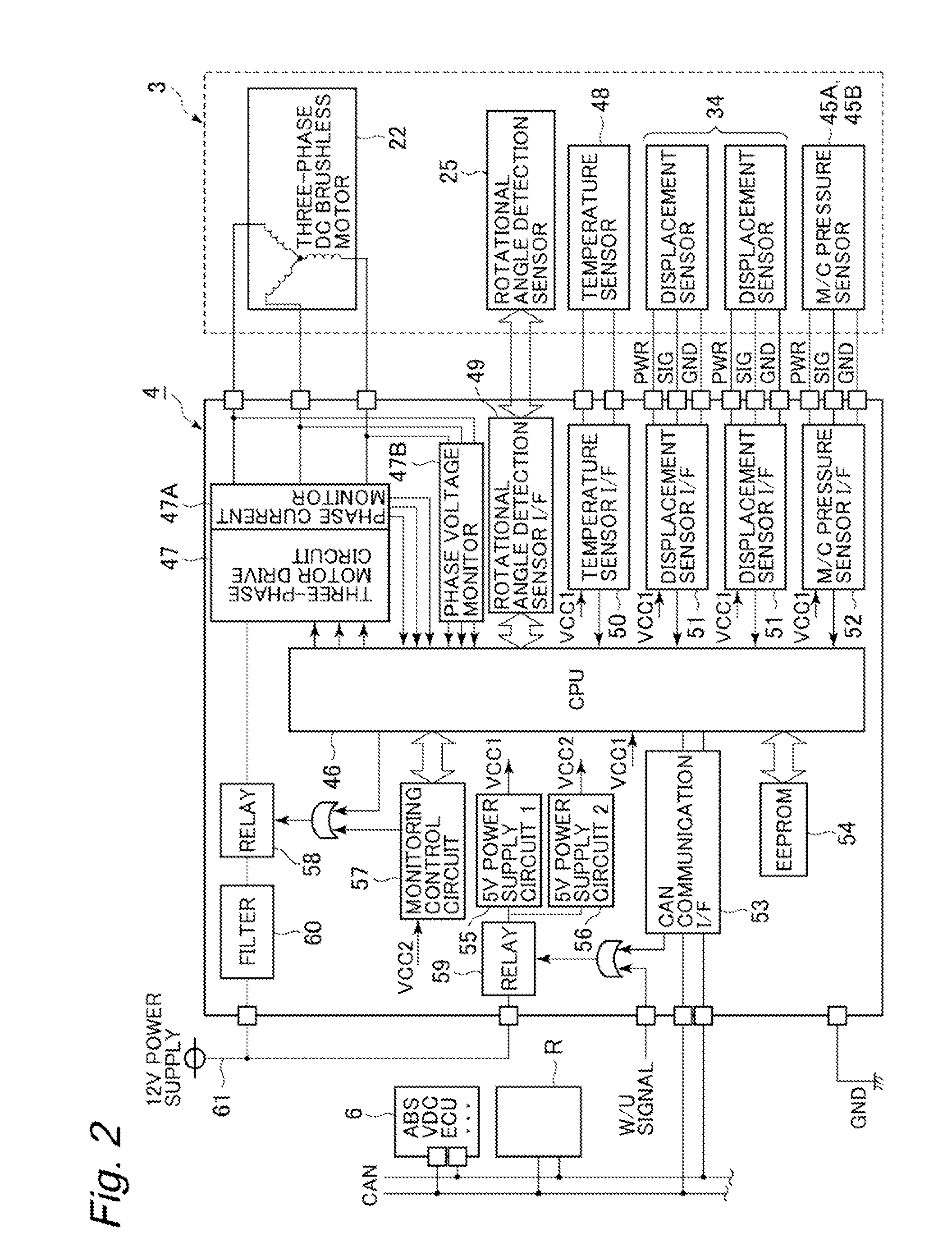
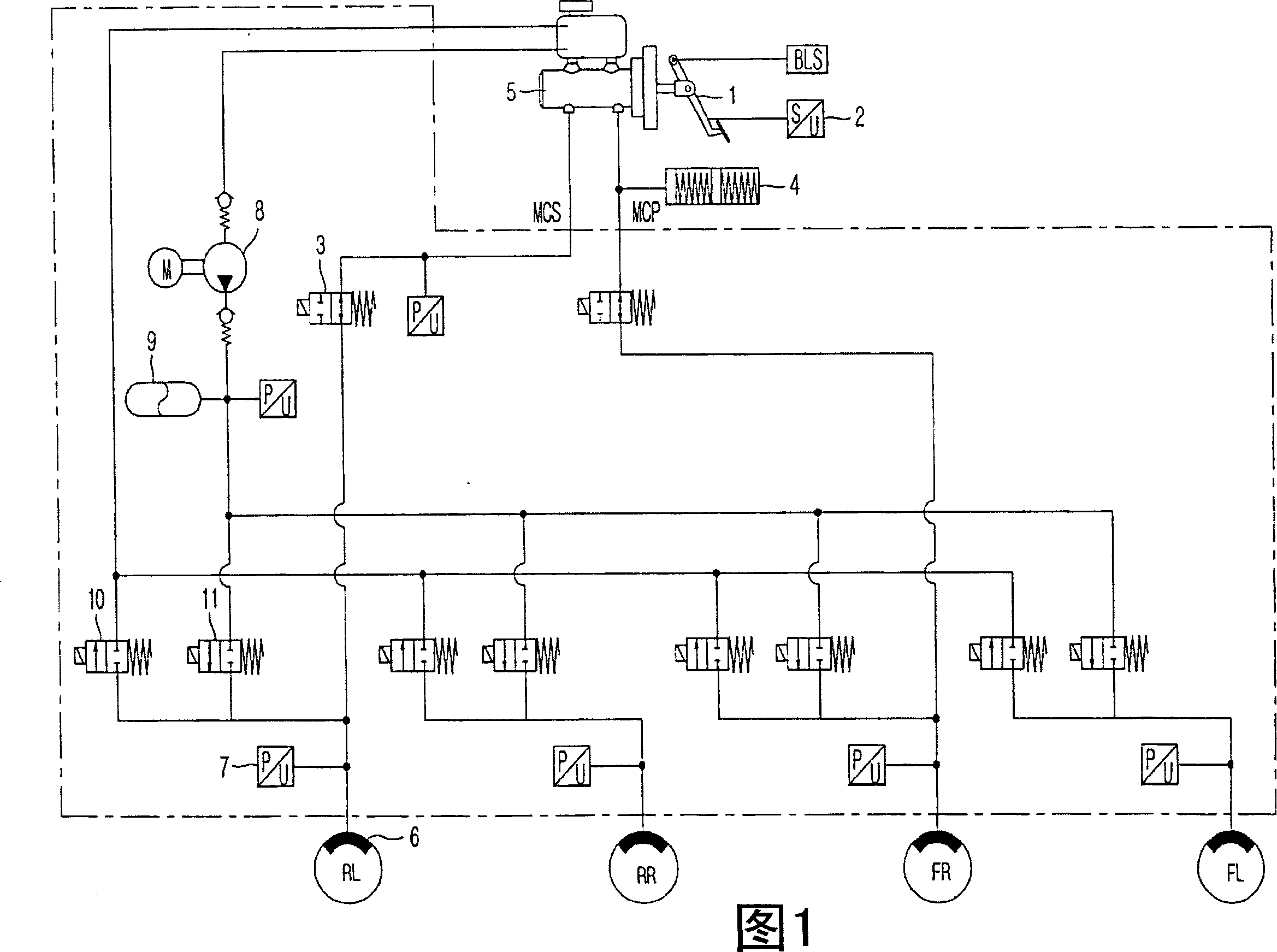
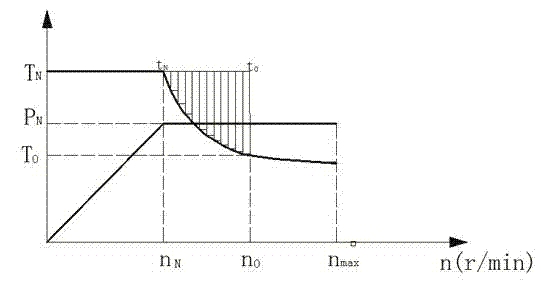
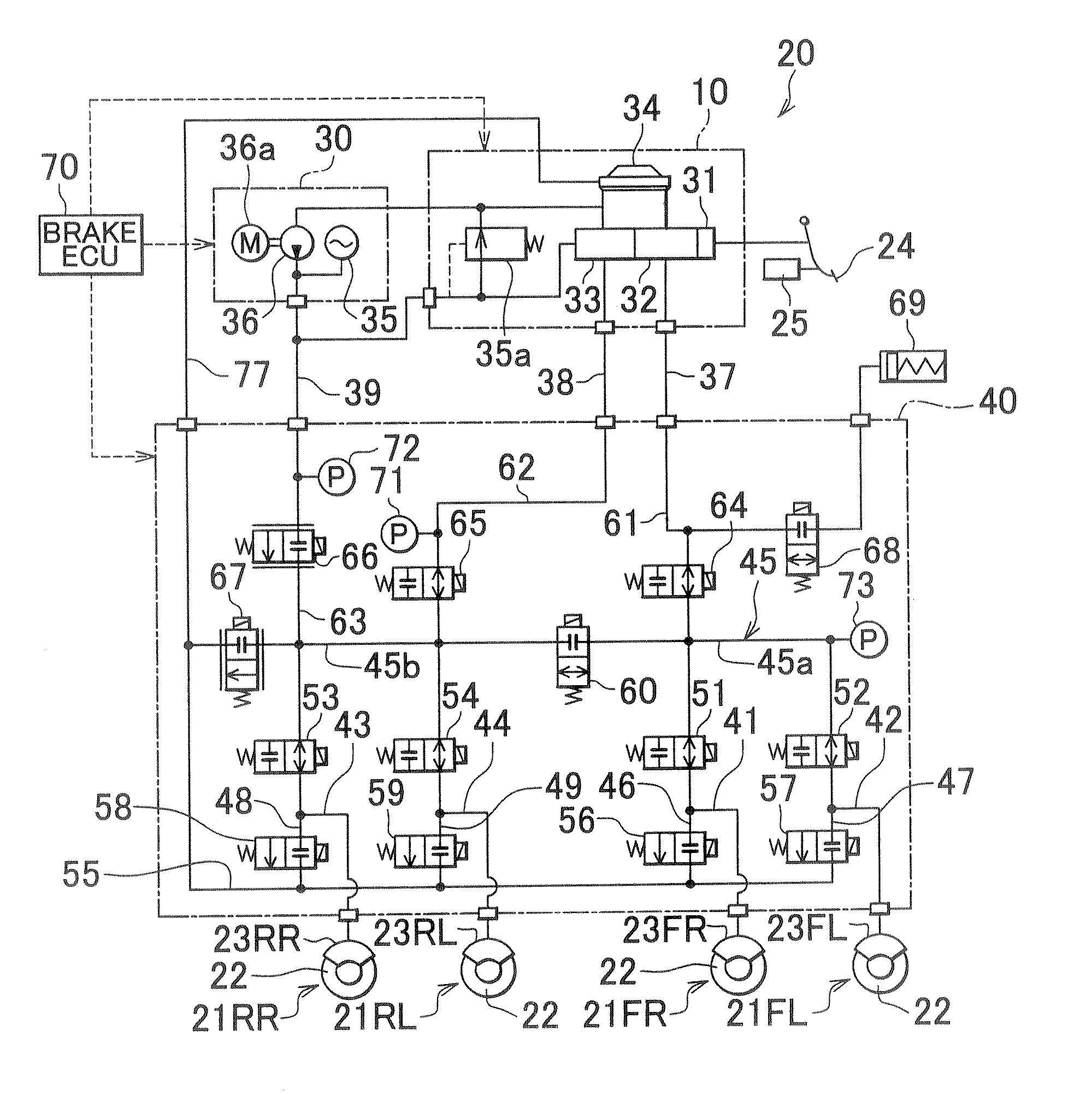
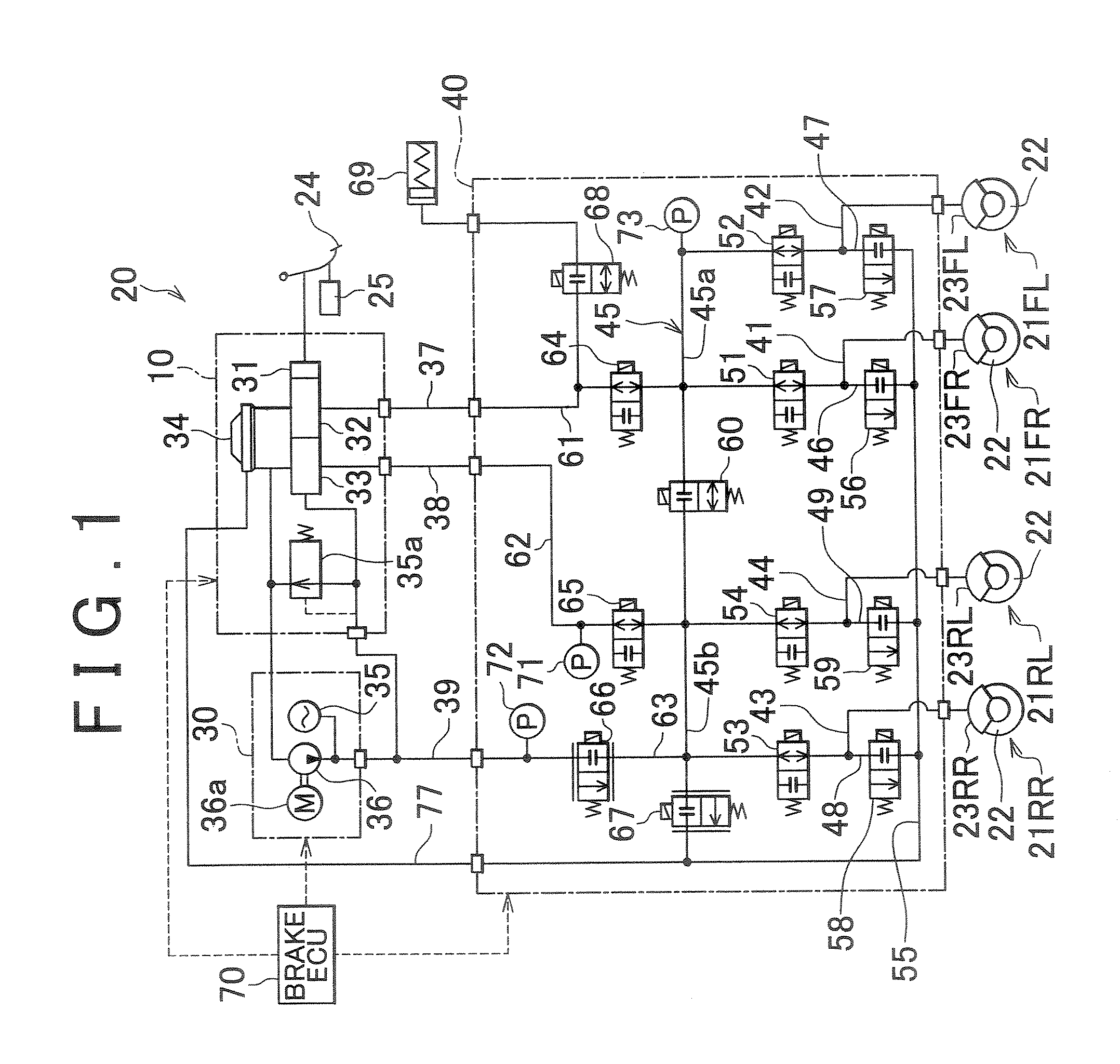
A wheel cylinder is a component of a hydraulic drum brake system. It is located in each wheel and is usually positioned at the top of the wheel, above the shoes. Its function is to exert force onto the shoes so as to bring them into contact with the drum and stop the vehicle with friction. The wheel cylinders are usually connected to the shoes with small bird-beak shaped rods. Wheel cylinders were first invented by Bendix in 1958, 21 21 21.
Vehicle brake device
InactiveUS20050269875A1Small dimensionLight weightPropulsion by batteries/cellsVehicular energy storageRegenerative brakeEngineering
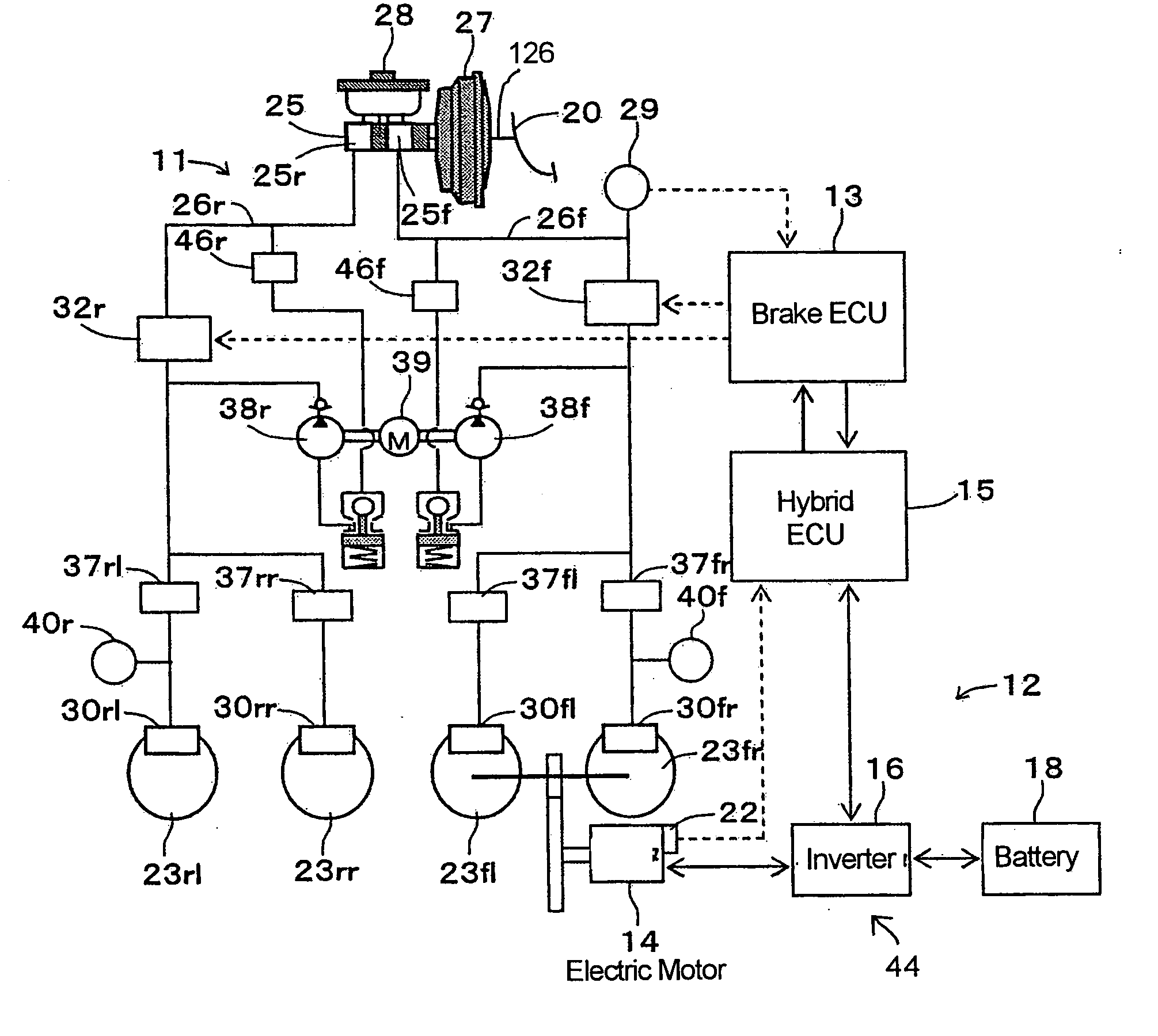
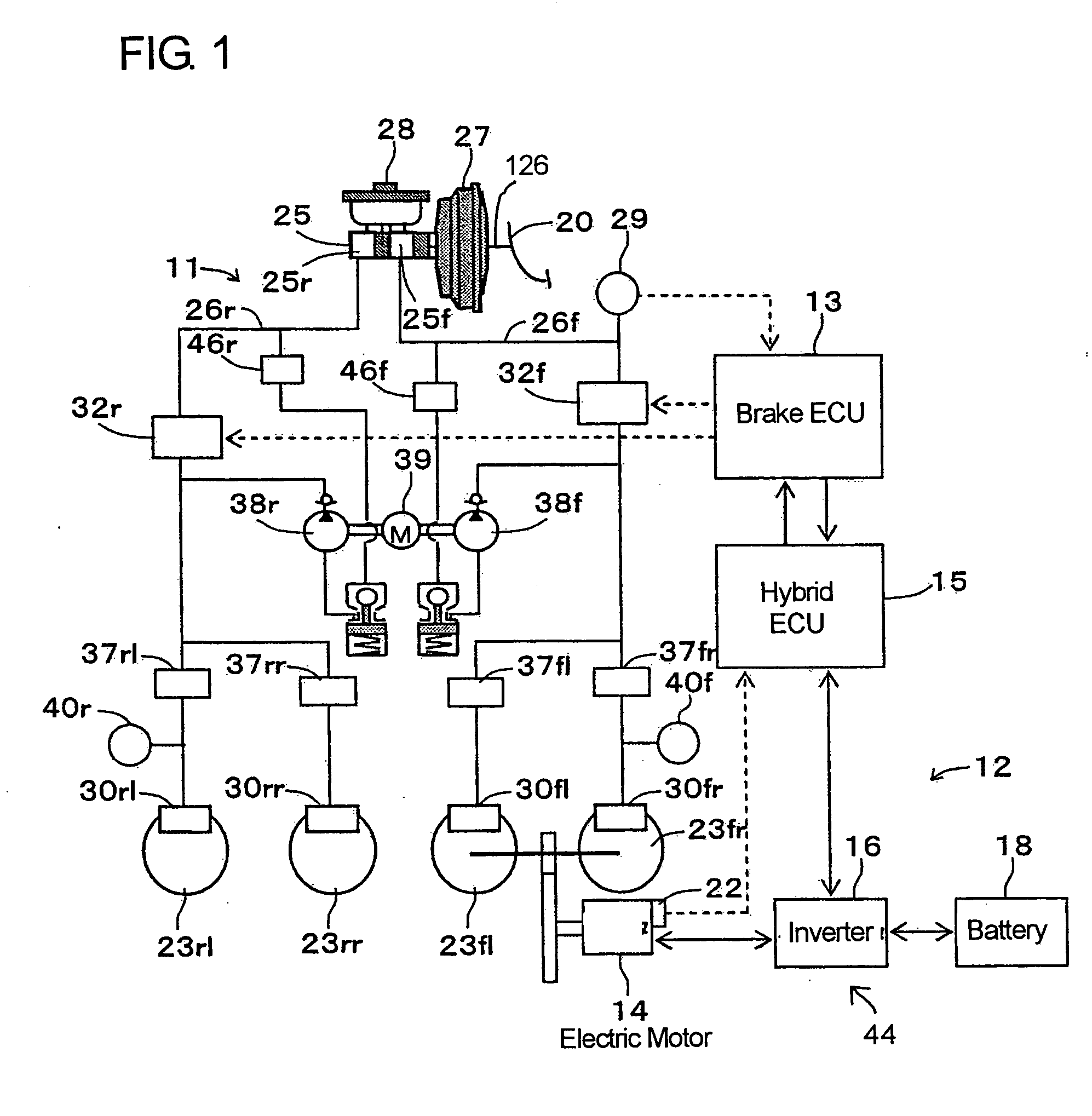
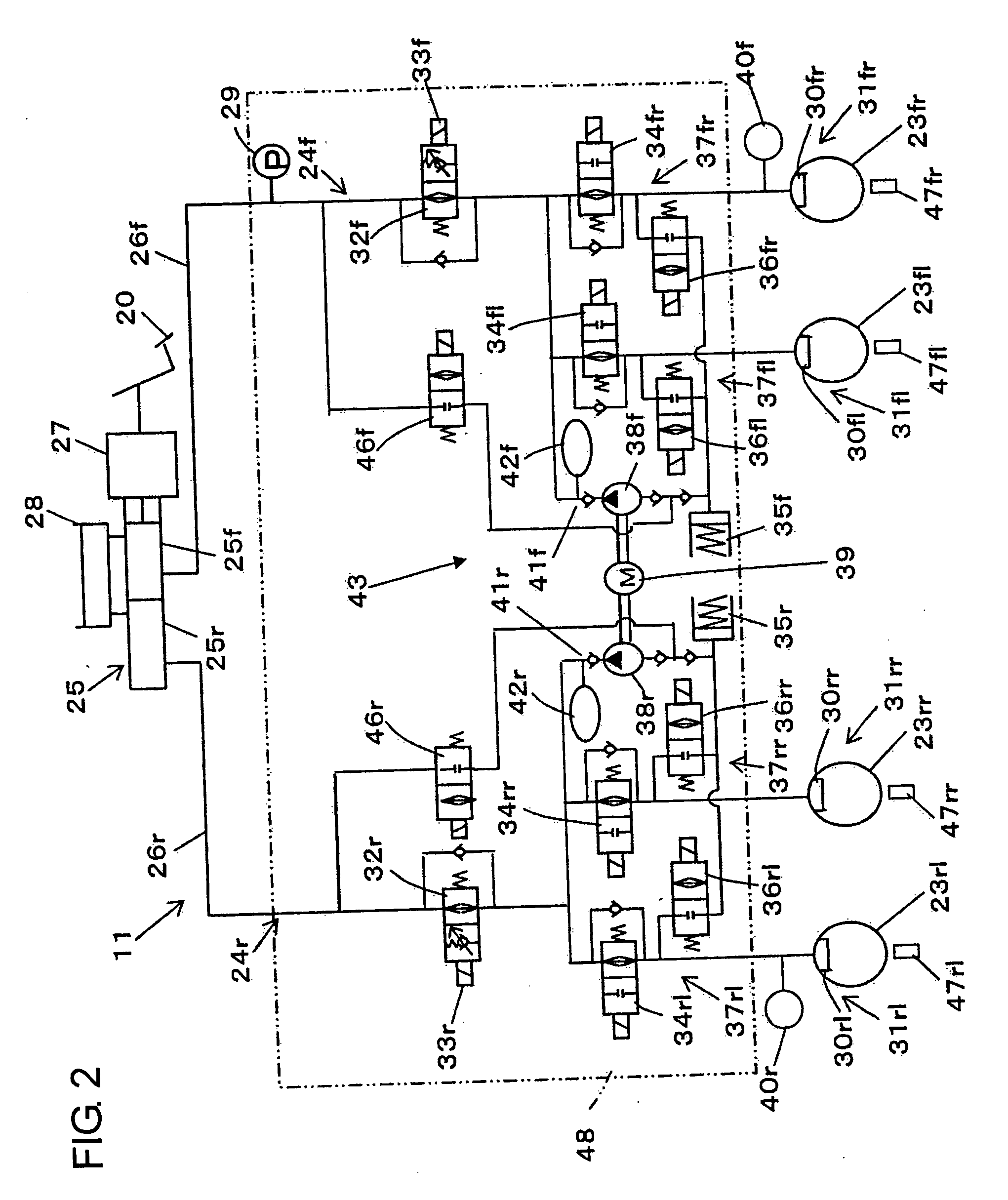
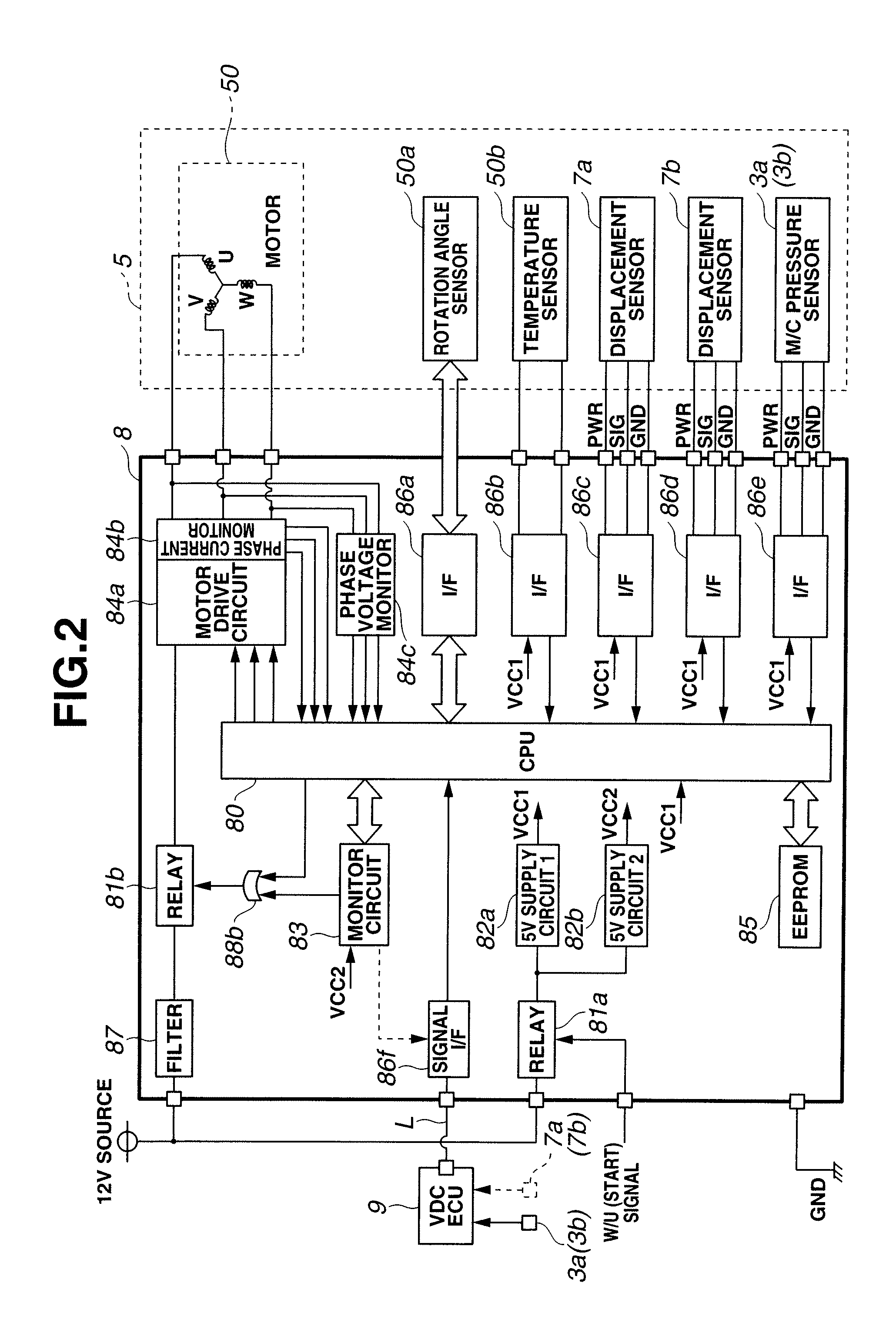
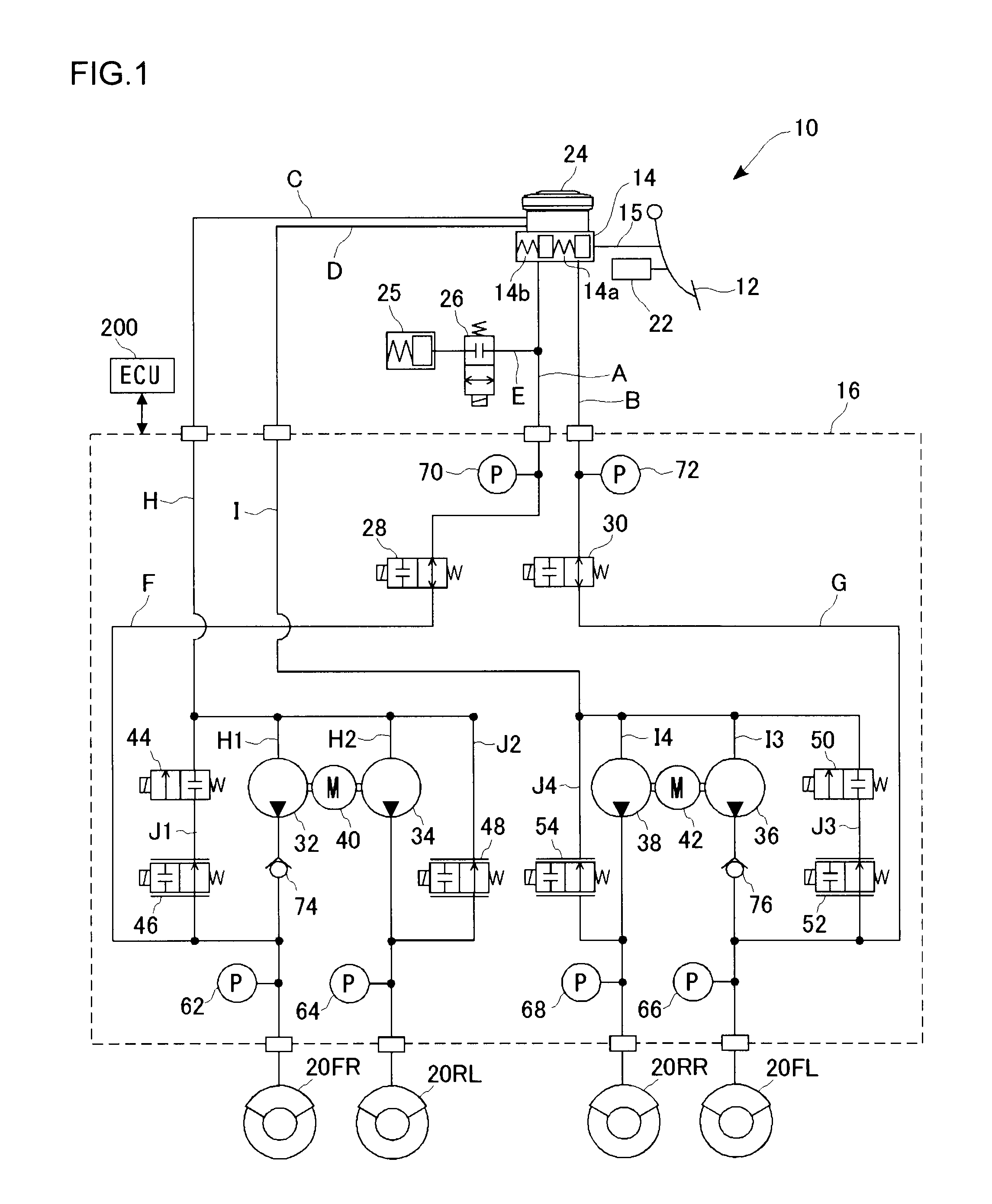
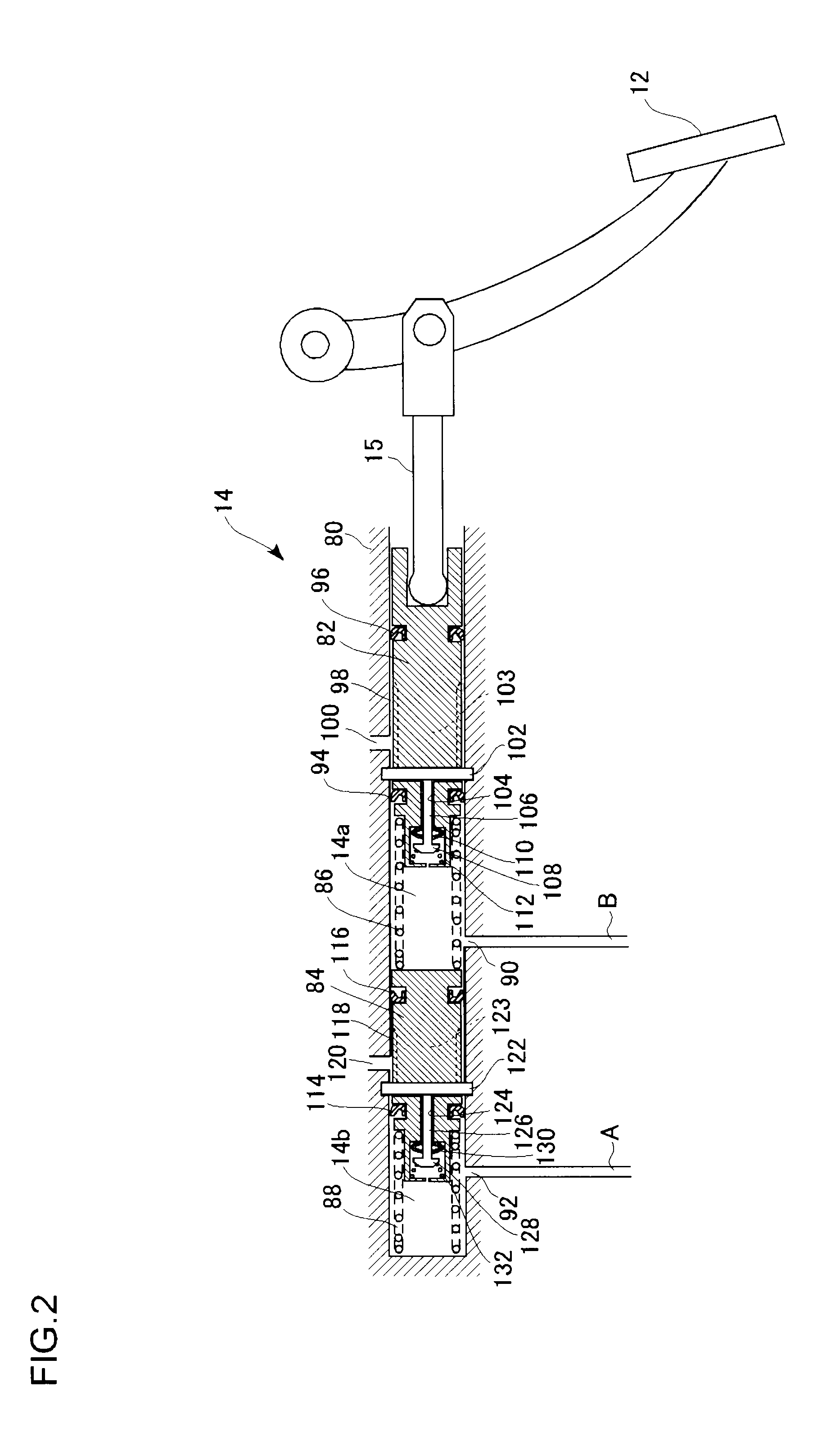
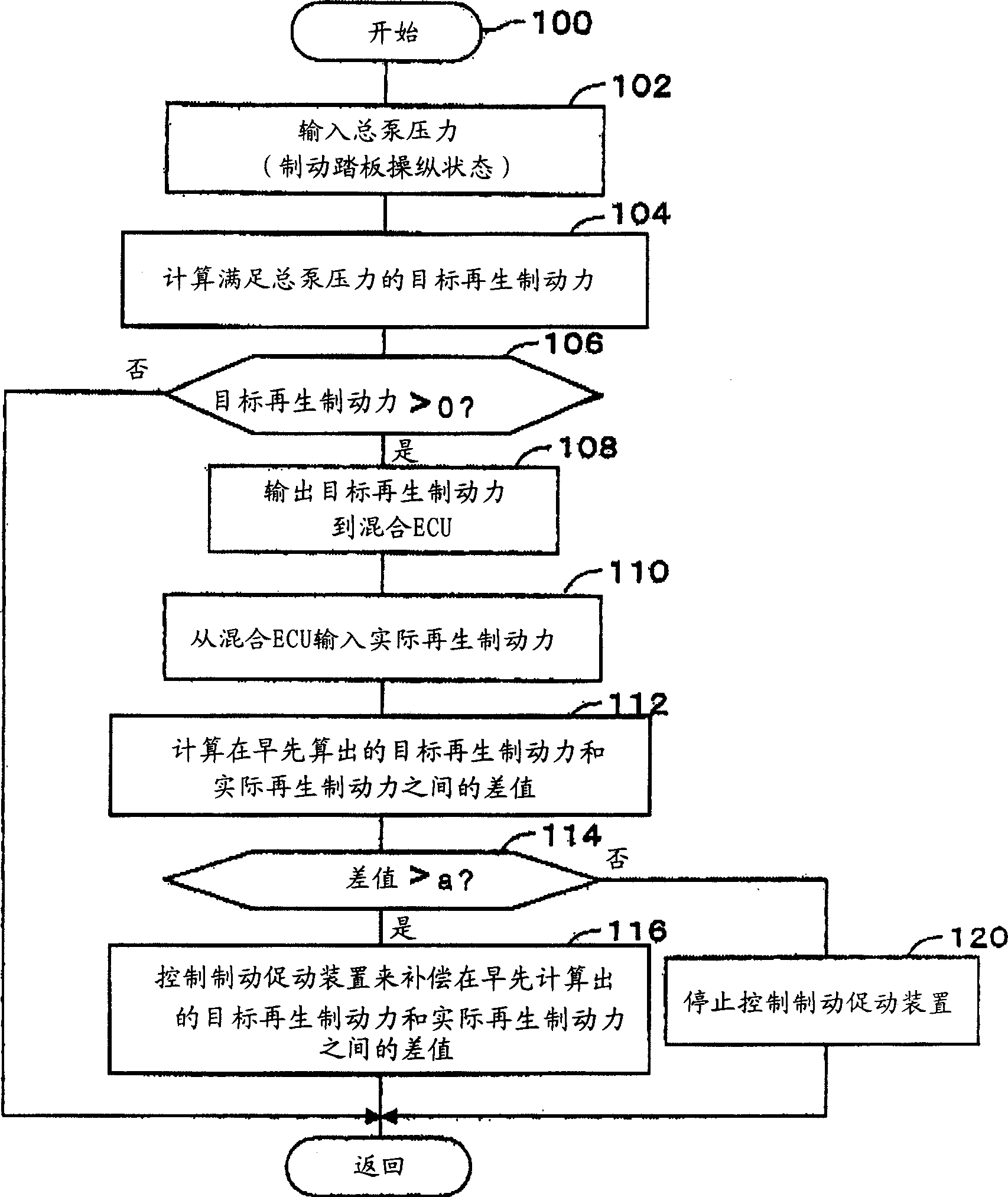
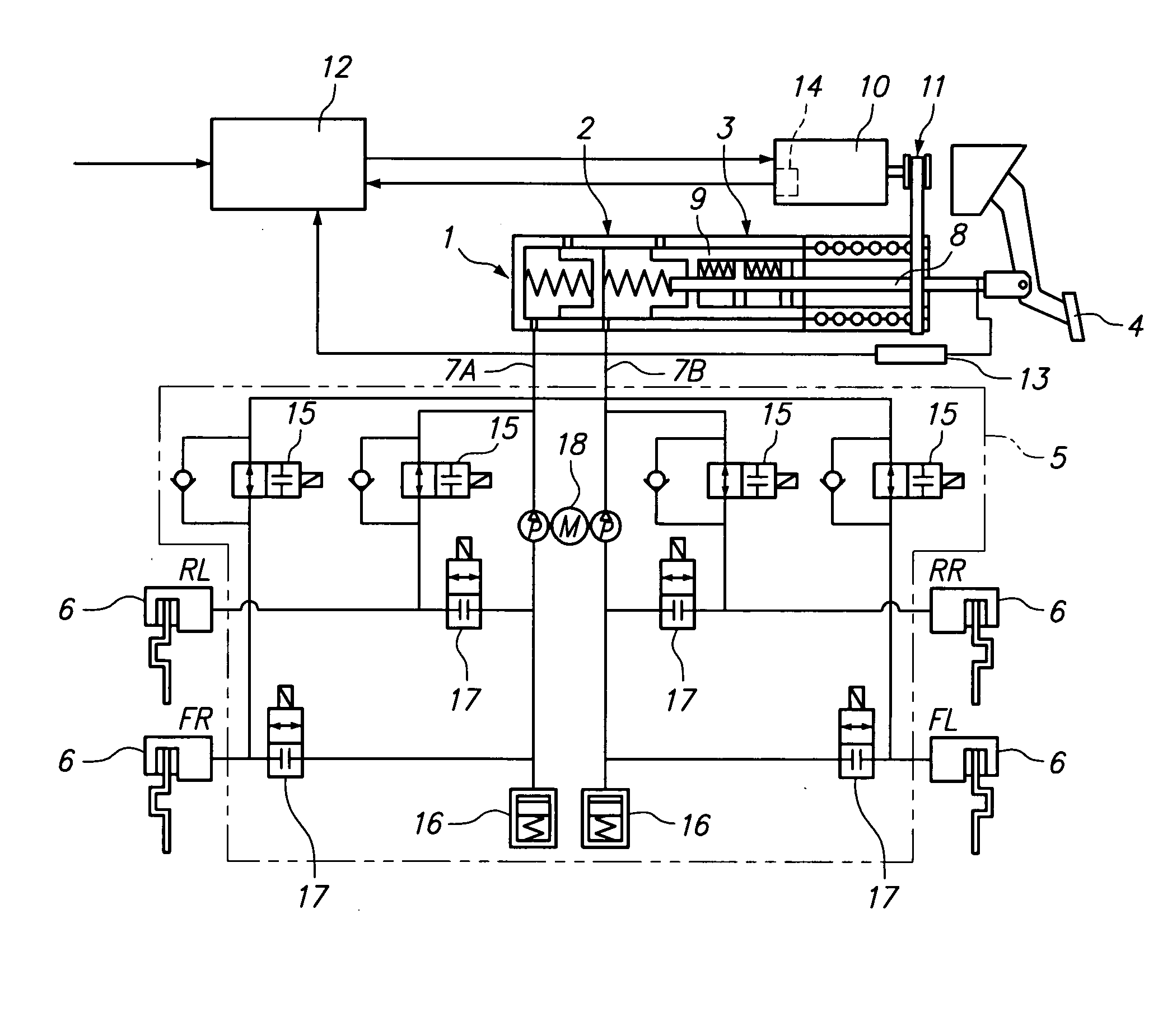
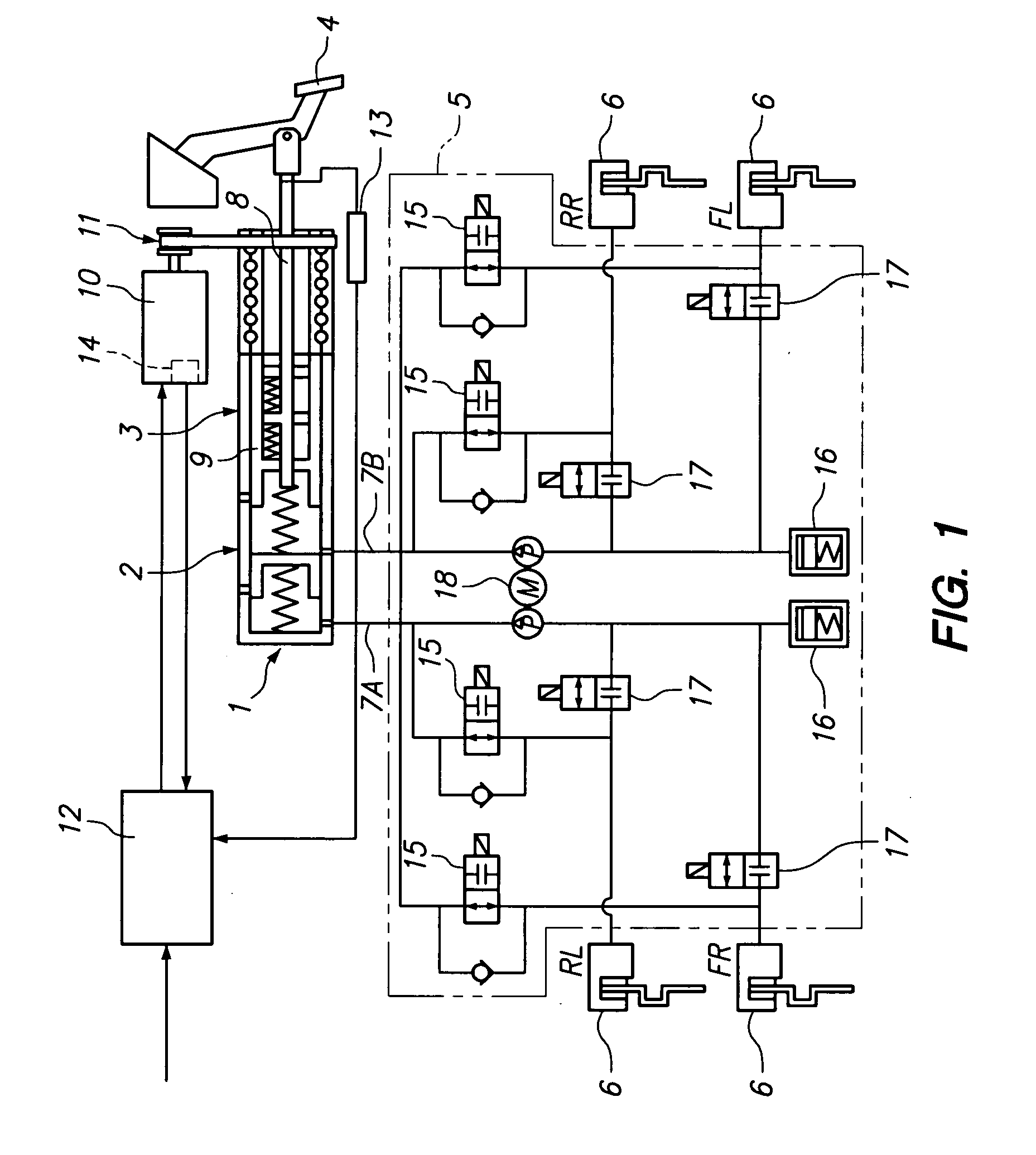
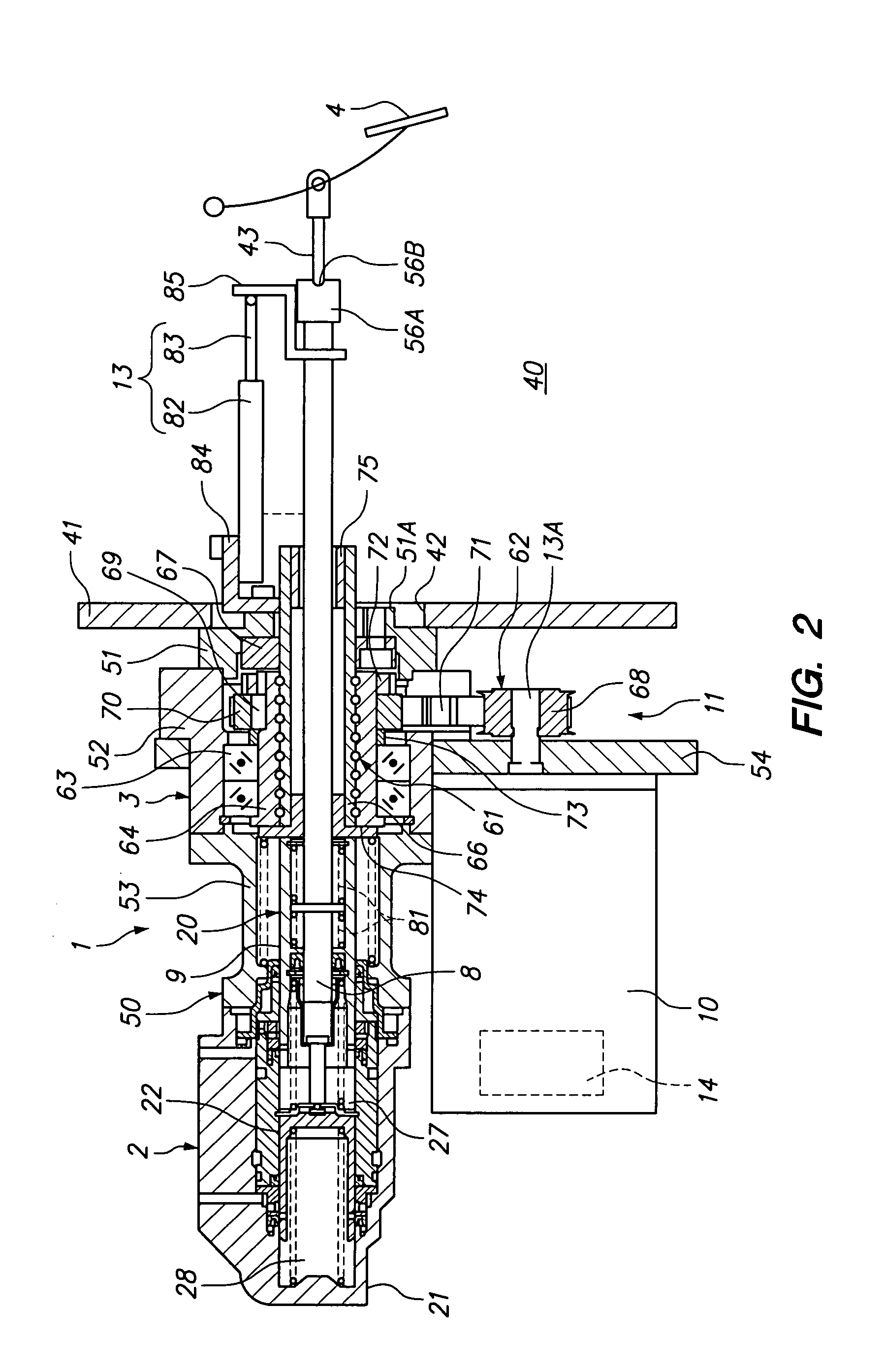
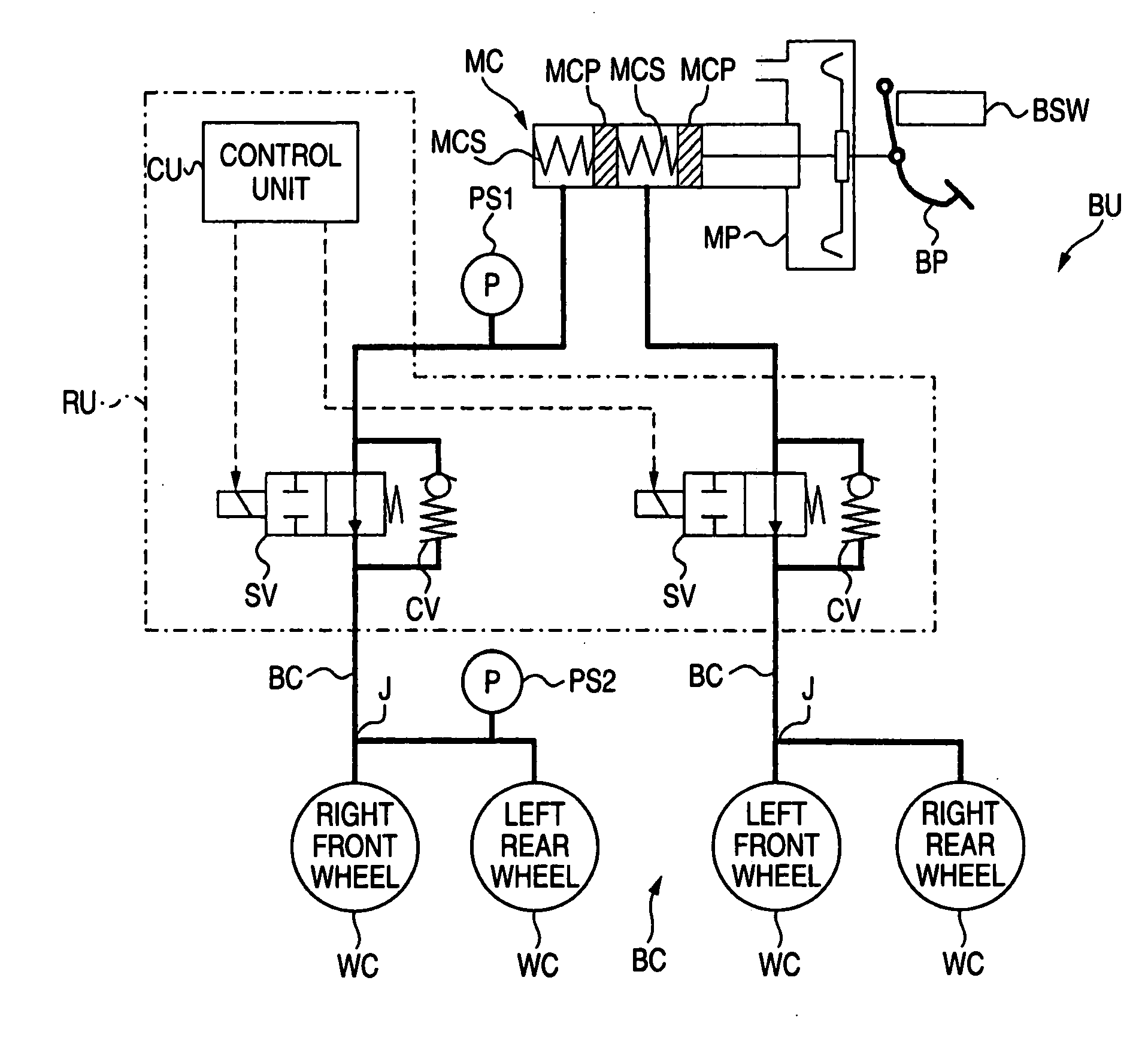
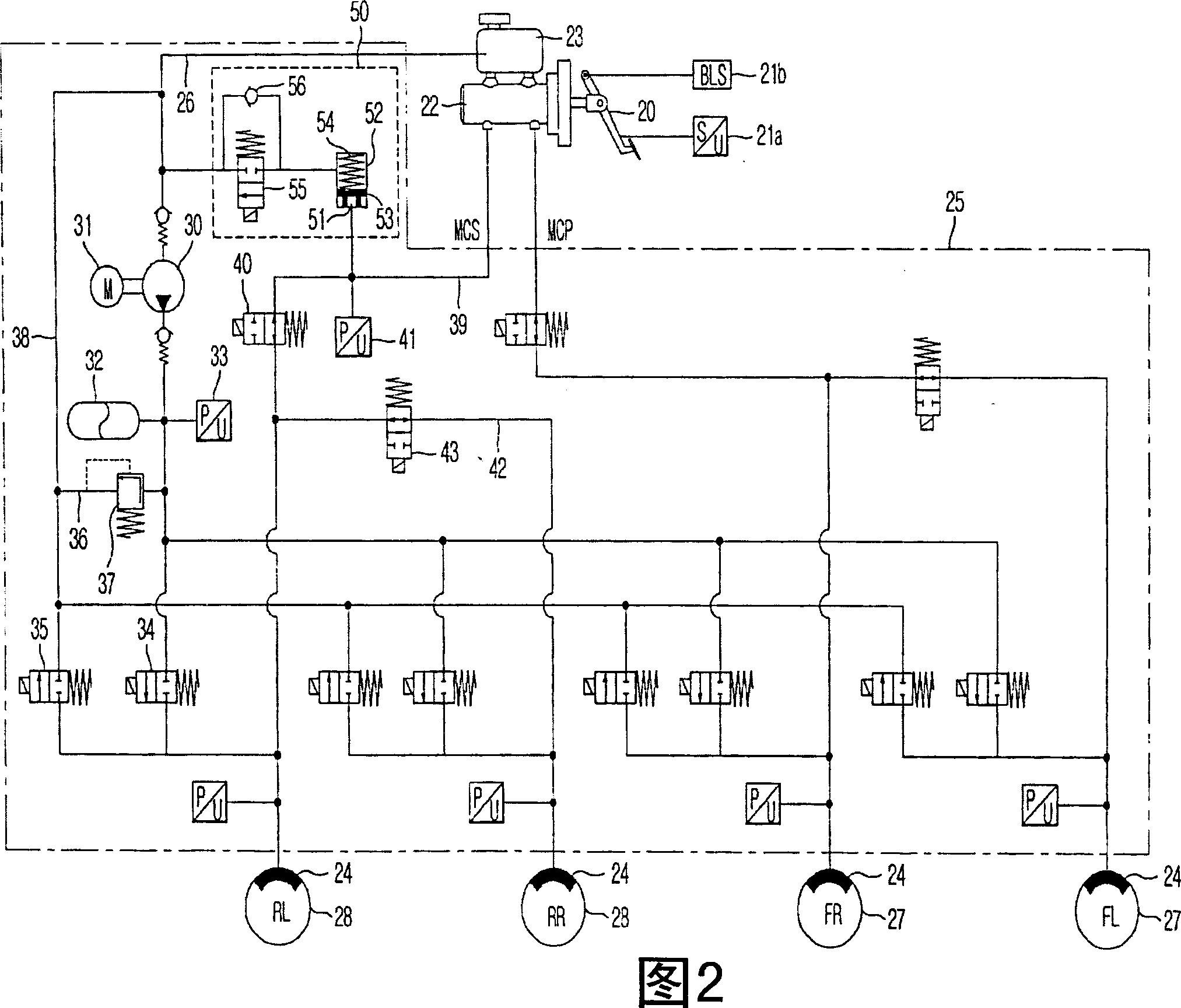
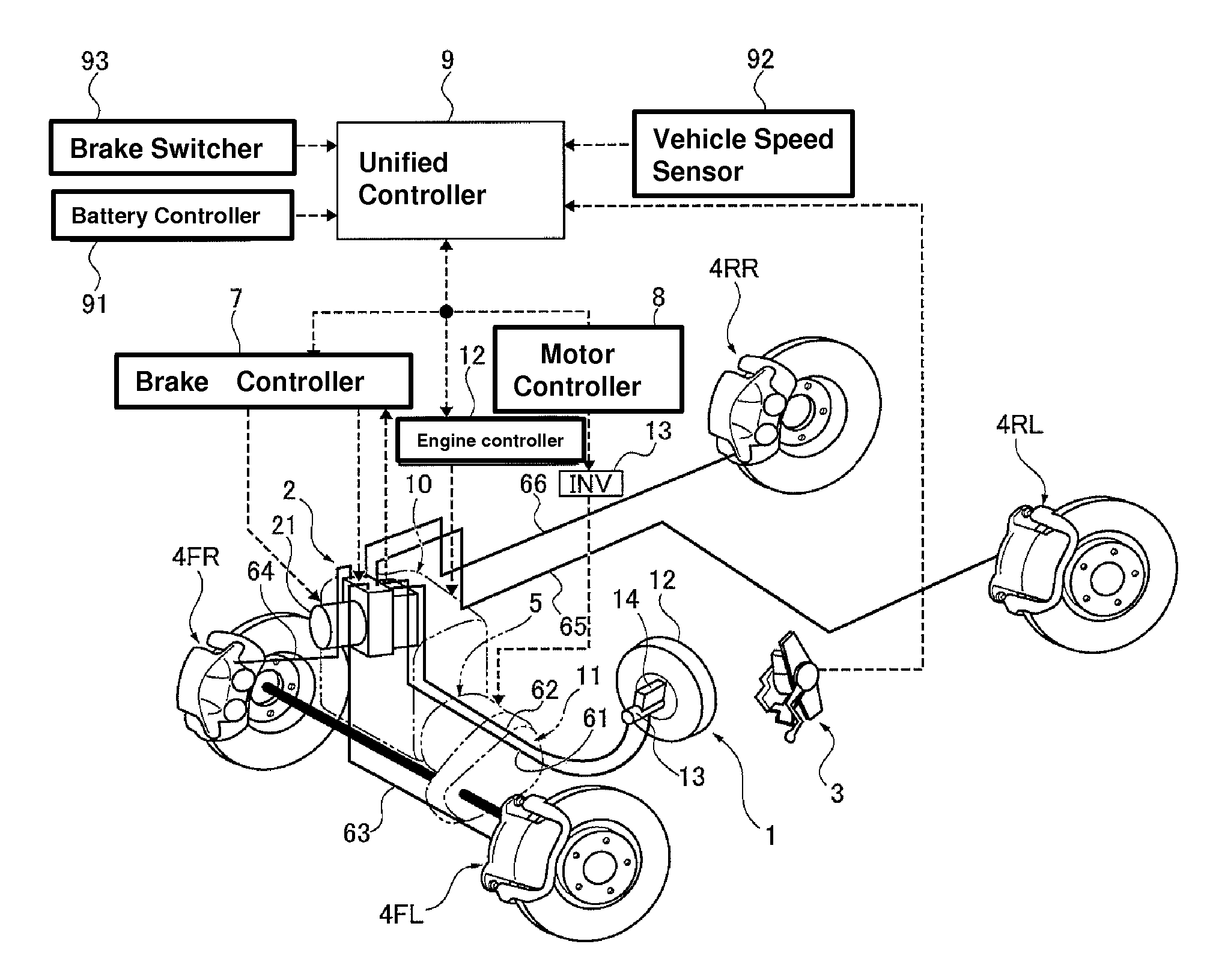
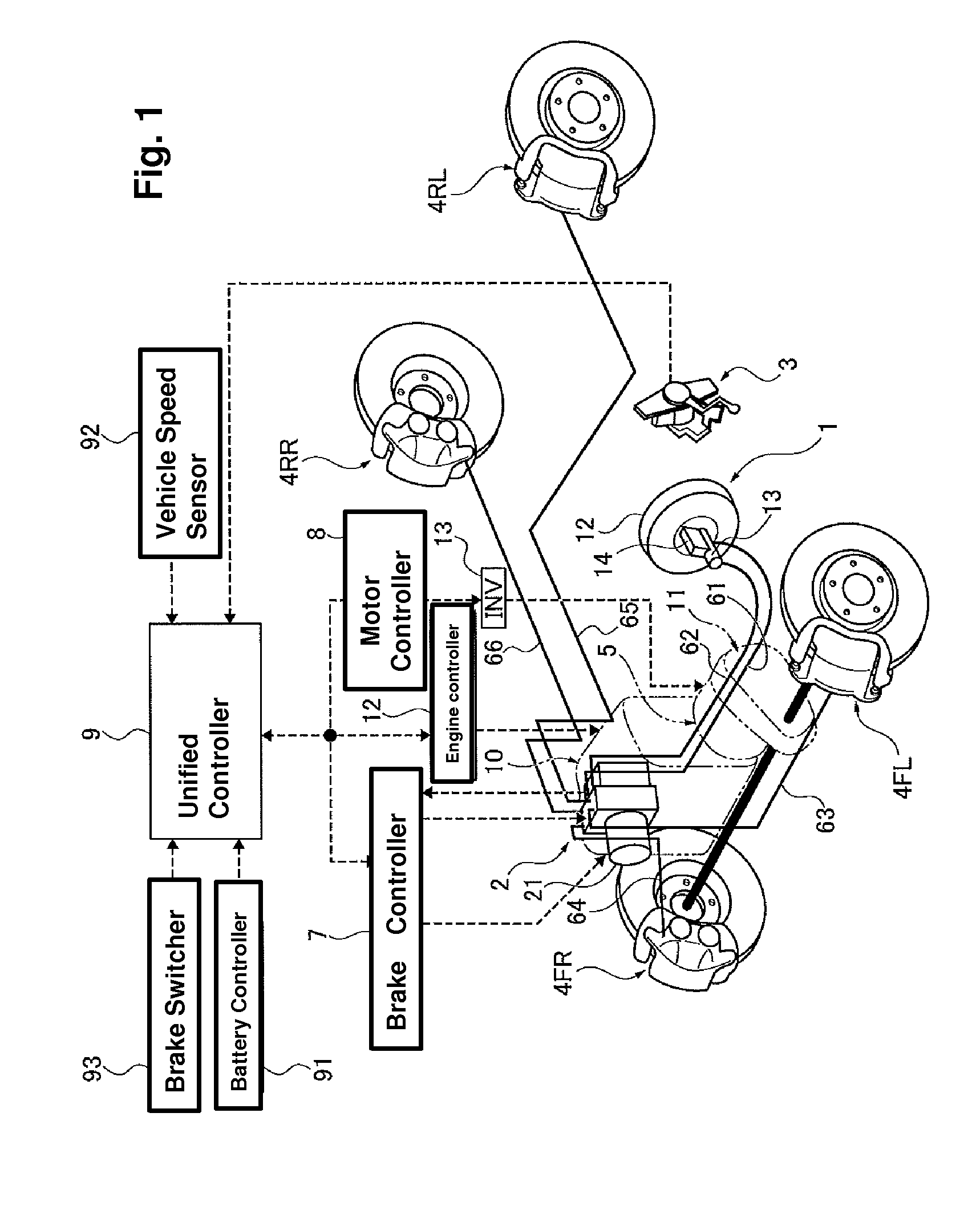
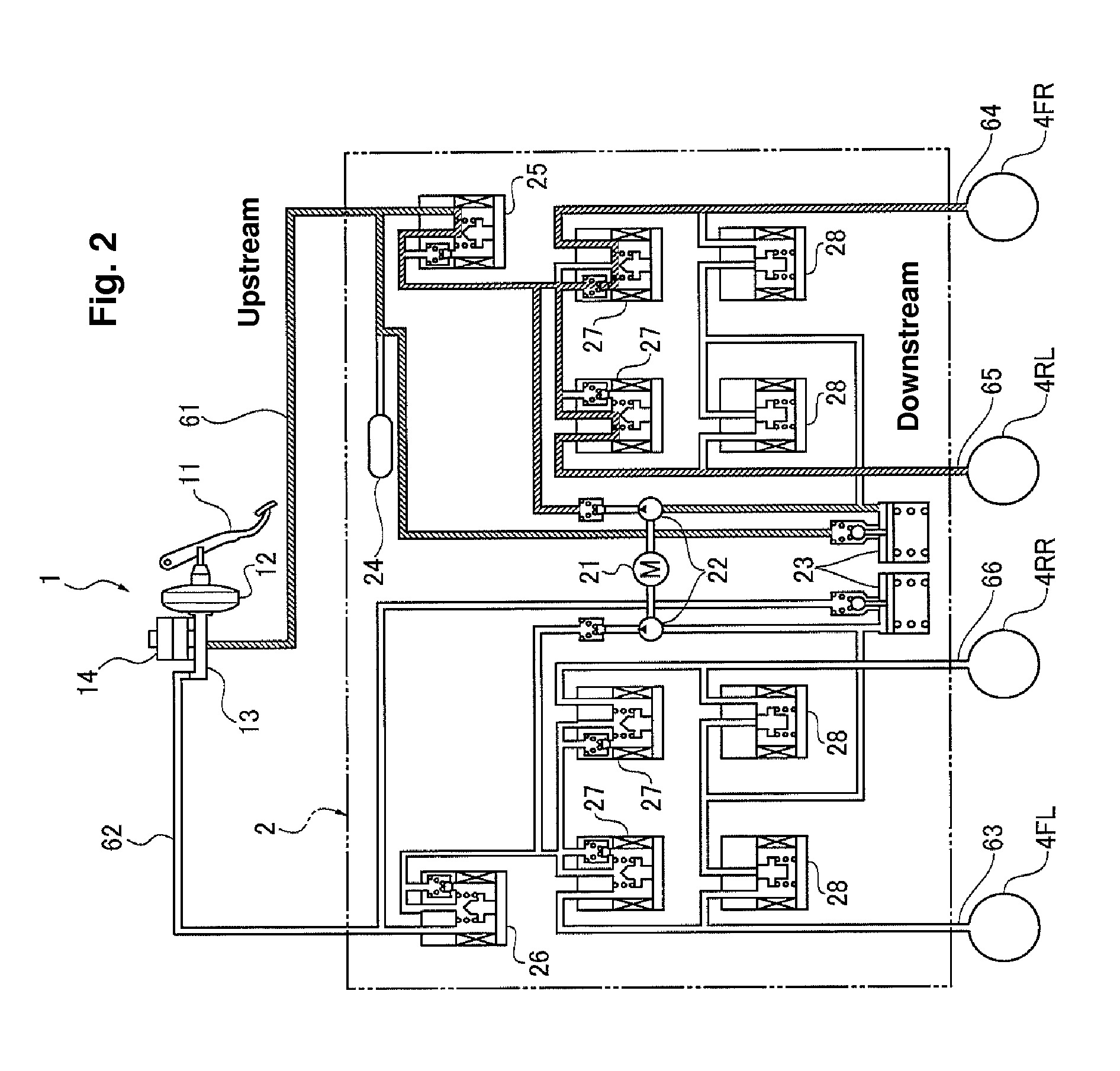
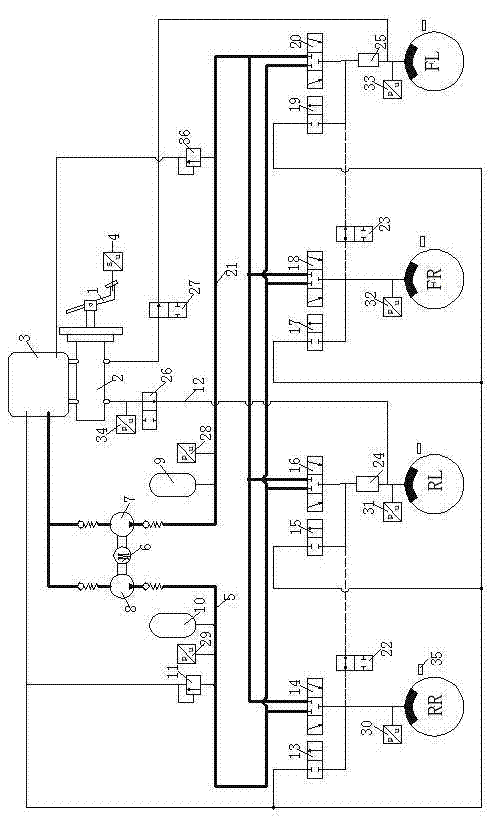
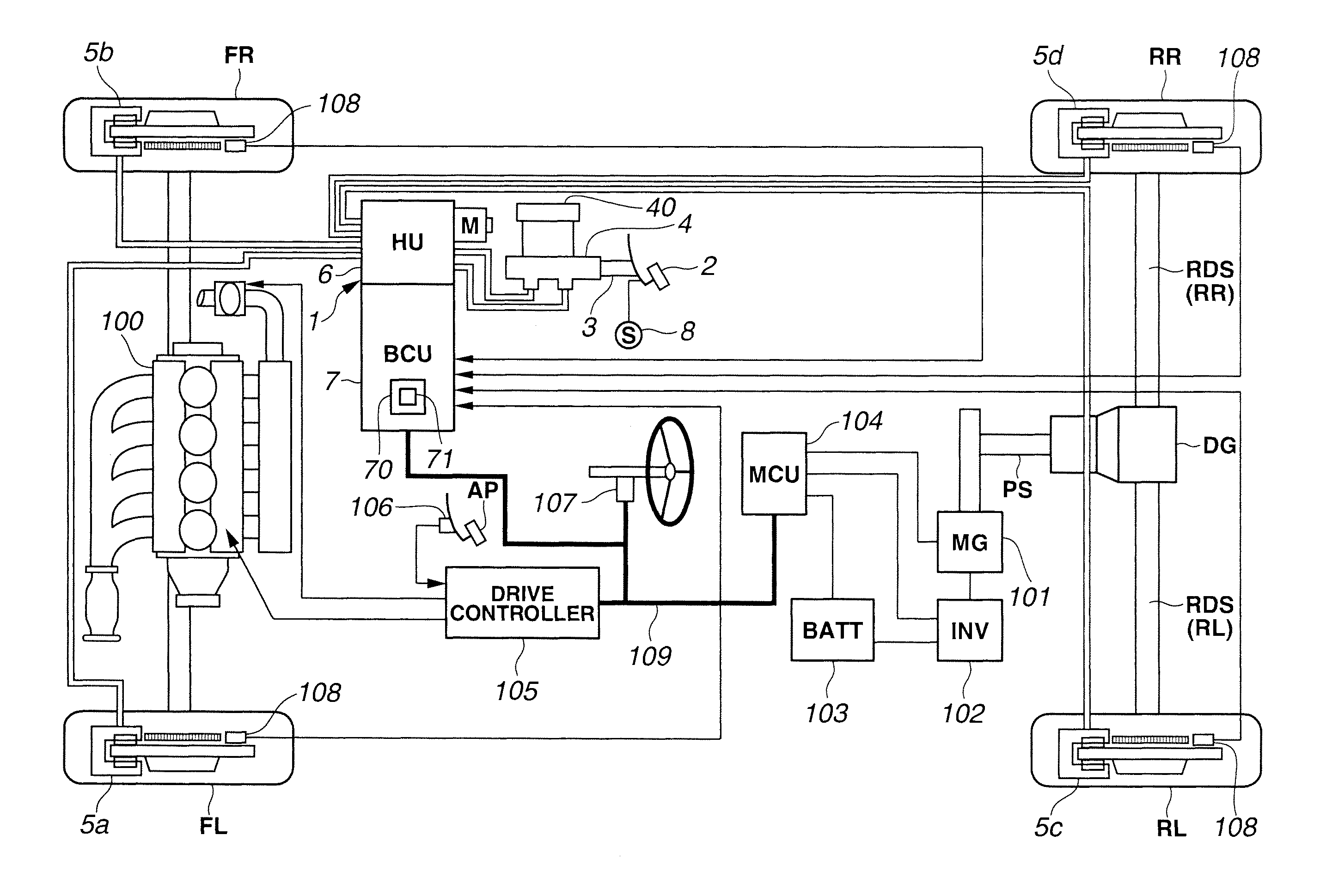
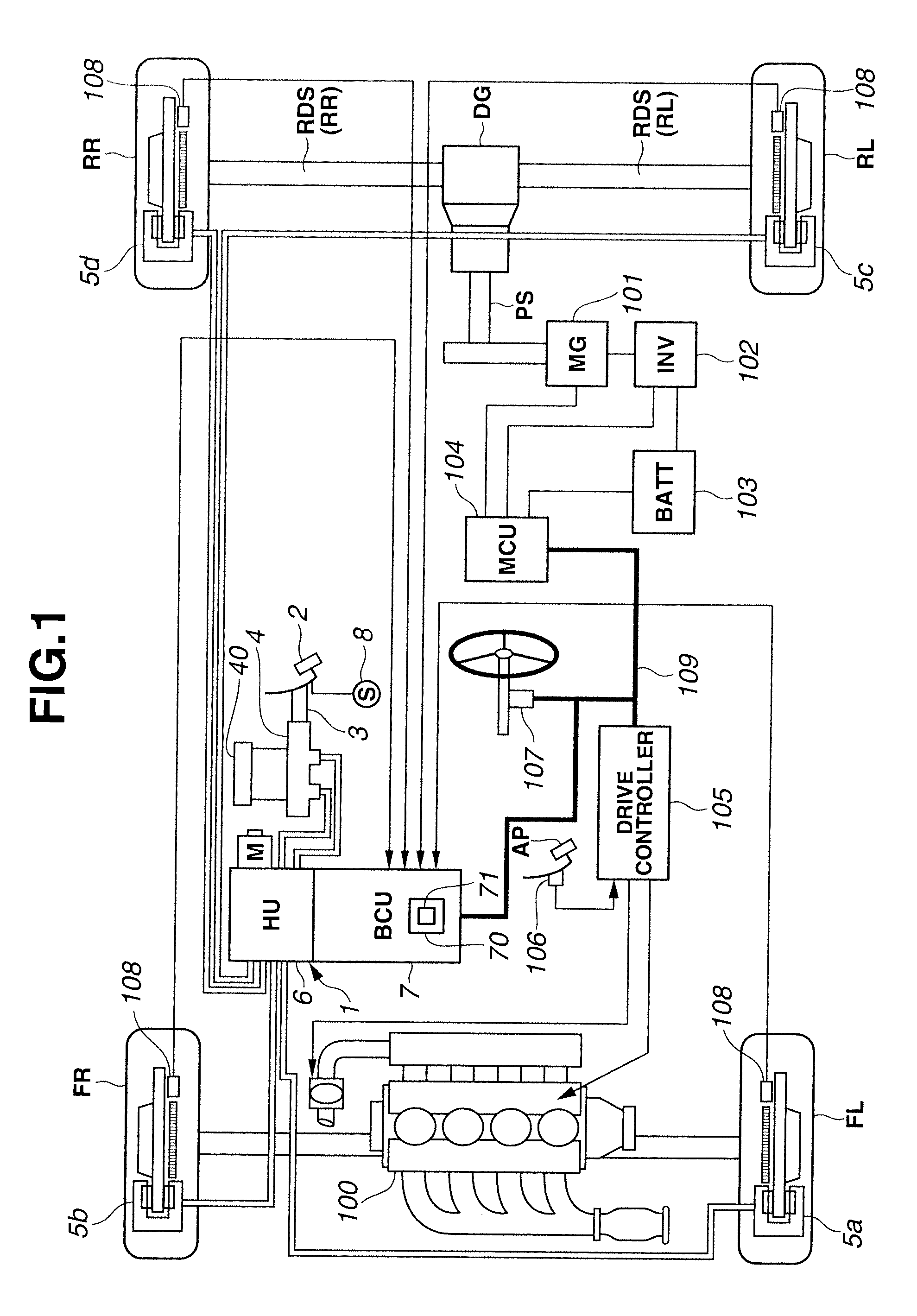
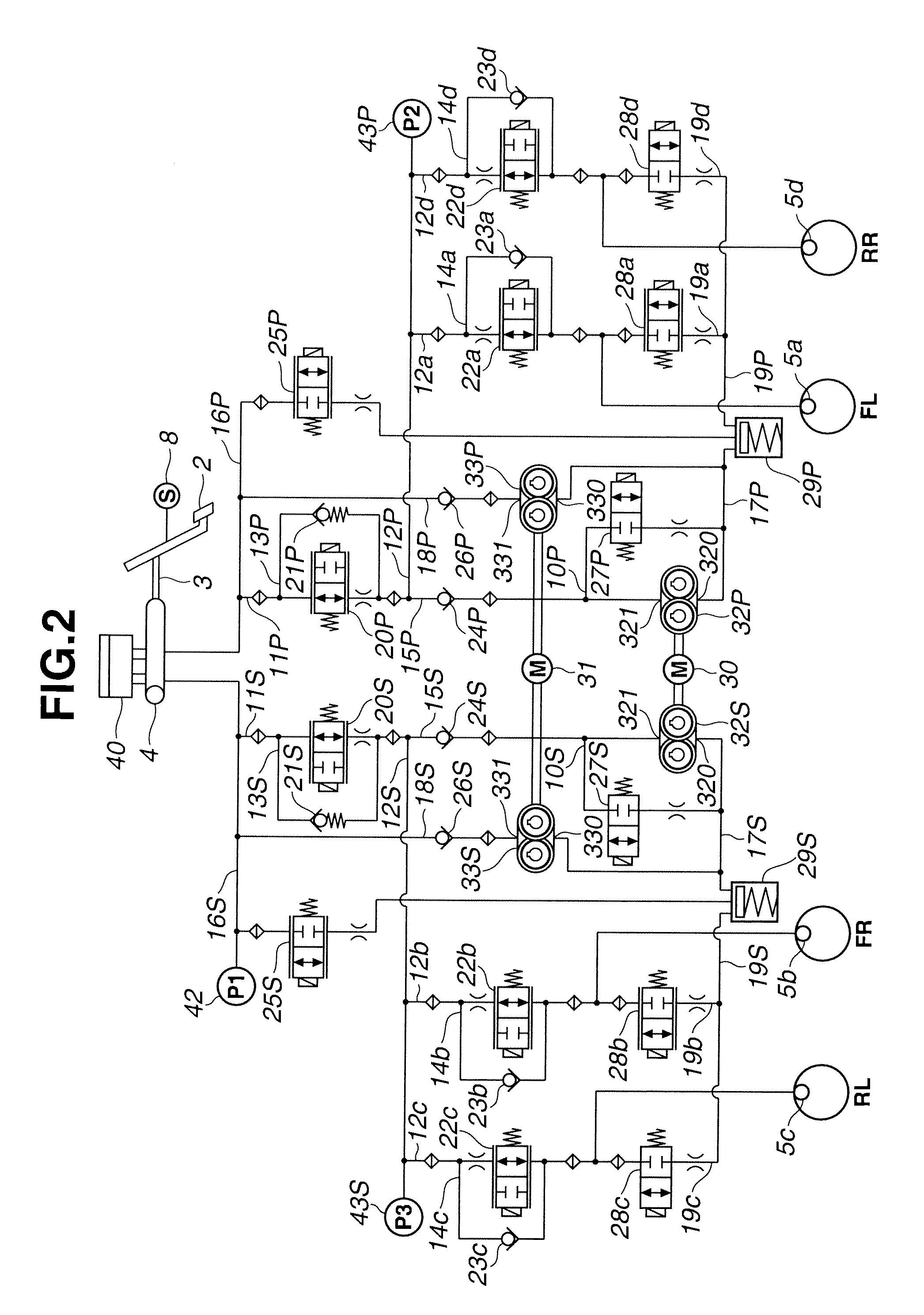
A vehicle brake device is provided with a hydraulic brake device for boosting by a booster device a braking manipulation force generated upon a braking manipulation, for applying a base fluid pressure generated in dependence on the boosted brake manipulation force, to wheel cylinders of wheels so that a base hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels, and for driving a pump to generate and apply a controlled fluid pressure to the wheel cylinders so that a controlled hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels; braking manipulation state detecting means for detecting the braking manipulation state; a regenerative brake device for causing an electric motor to generate a regenerative brake force corresponding to the braking manipulation state on the wheels driven by the electric motor; variation detecting means for detecting the variation of an actual regenerative brake force actually generated by the regeneration braking device; and brake force compensating means for generating the controlled fluid pressure by driving the pump of the hydraulic brake device so that a controlled hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels to compensate for the lack of the regenerative brake force due to the variation which is detected by the variation detecting means.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
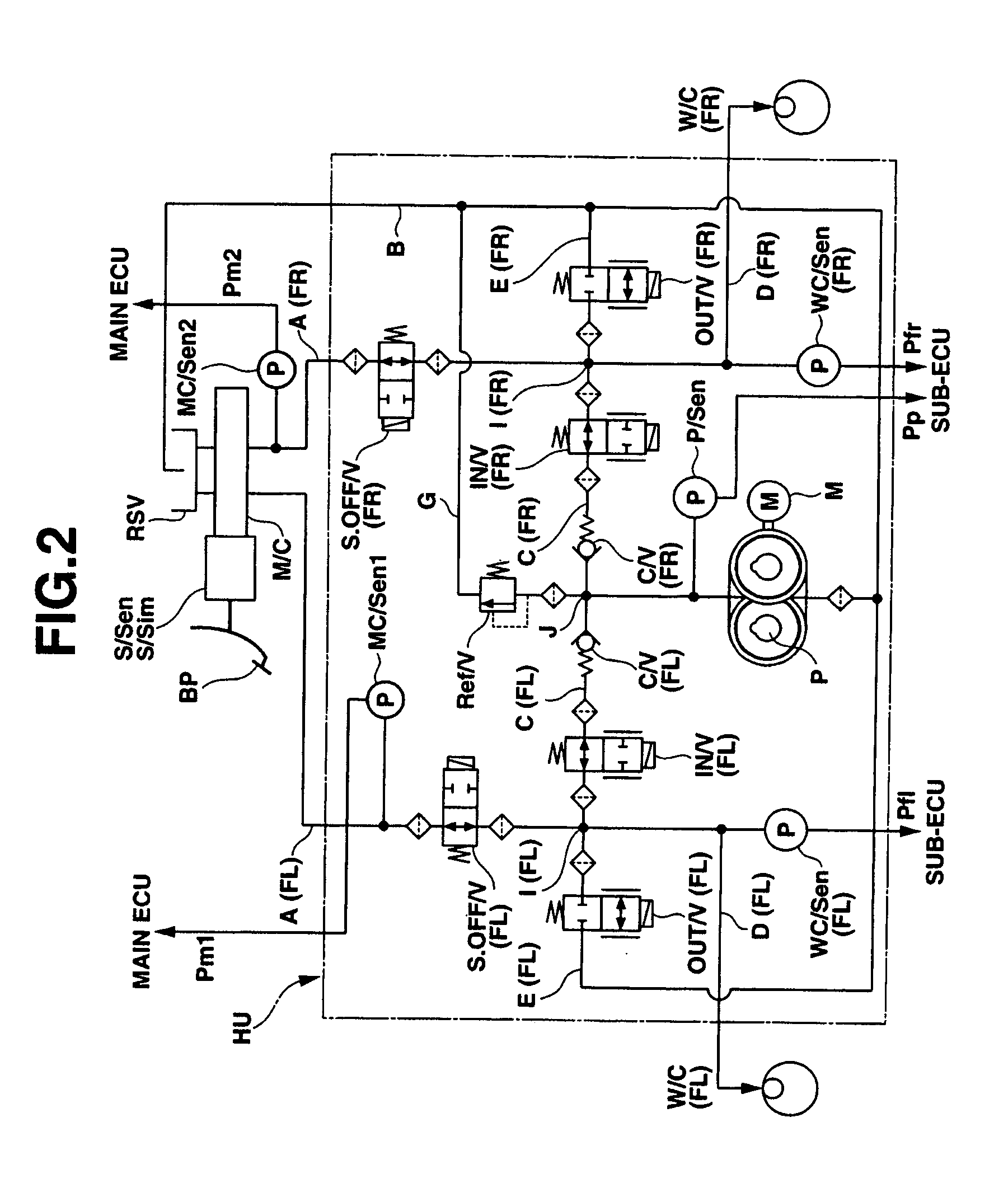
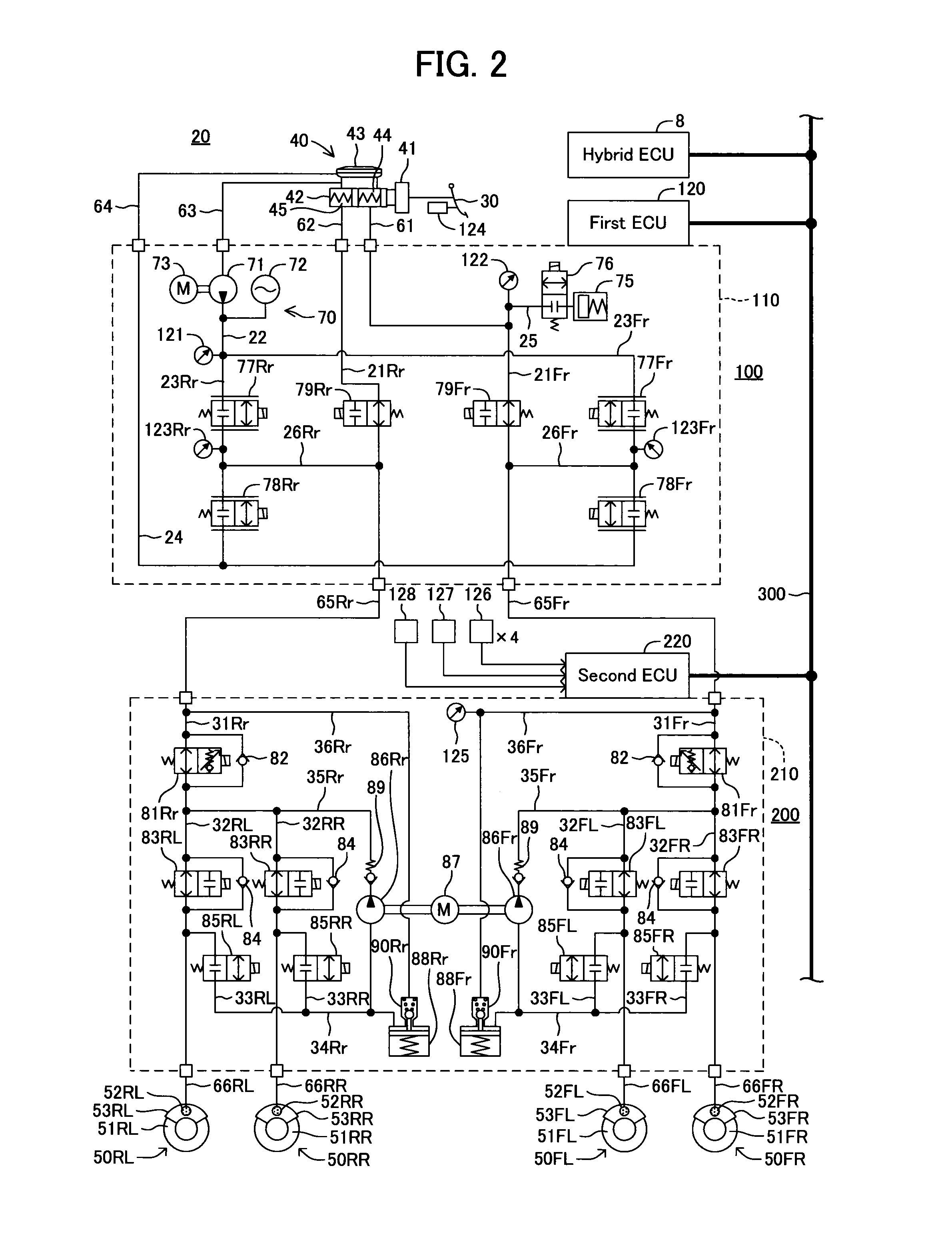
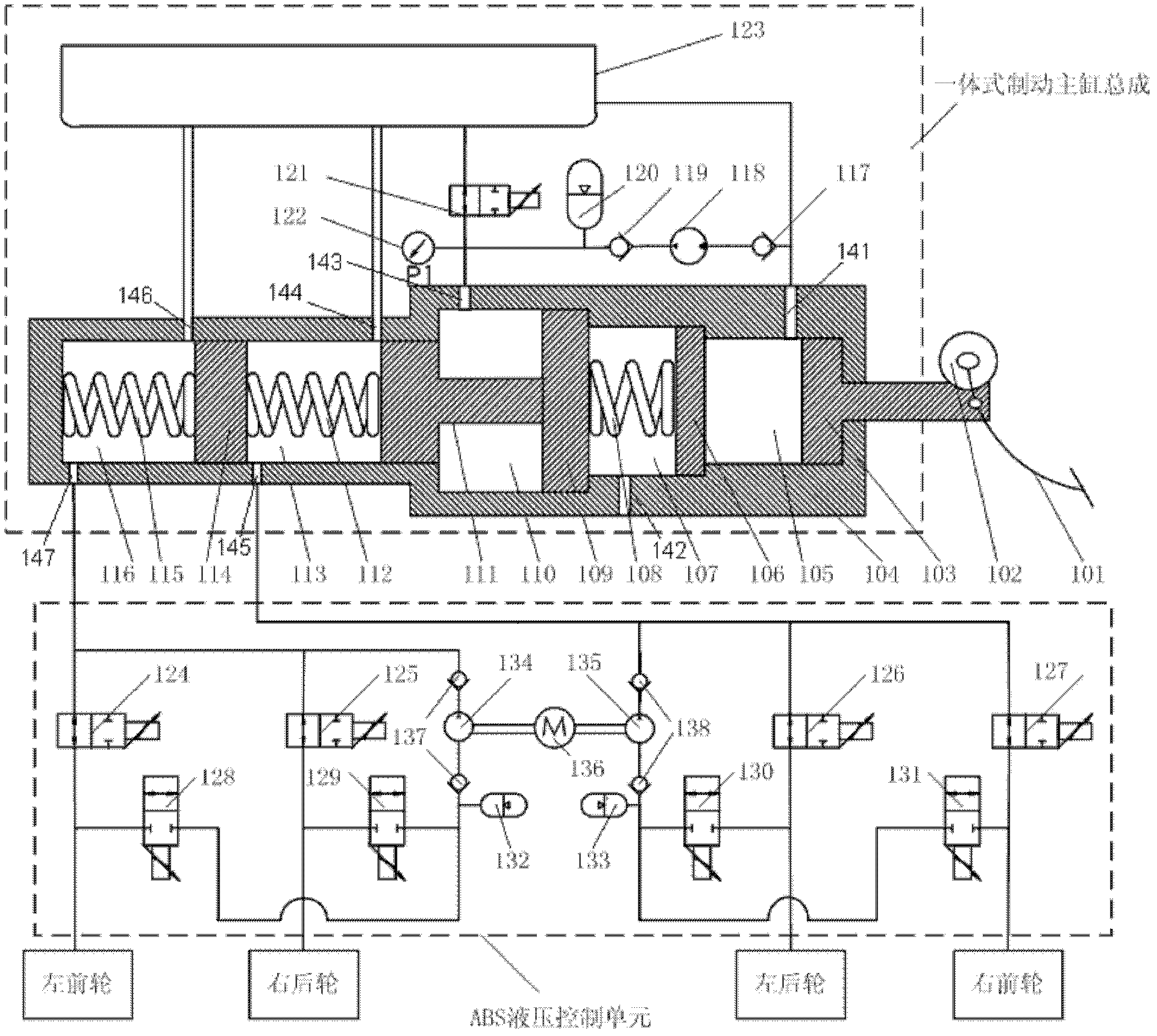
Brake control apparatus and method
ActiveUS20090045672A1Improve securityApplication and release valvesBrake action initiationsControl systemWheel cylinder
A brake control system includes a master cylinder to produce a master cylinder pressure, a brake booster to assist the master cylinder, a first control unit to control the booster, a hydraulic modulator to supply a wheel cylinder pressure to a wheel cylinder, and a second control unit to control the hydraulic modulator. The hydraulic modulator includes a pressure source, such as a pump, to increase the wheel cylinder pressure. The first and second control units are connected together by a communication line. The brake control system may further include a boost condition transmitting section to transmit, through the communicating line, a condition of a boost system formed by the brake booster and the first control unit.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Manual backup system for controlling fluid flow to cylinders within an agricultural implement
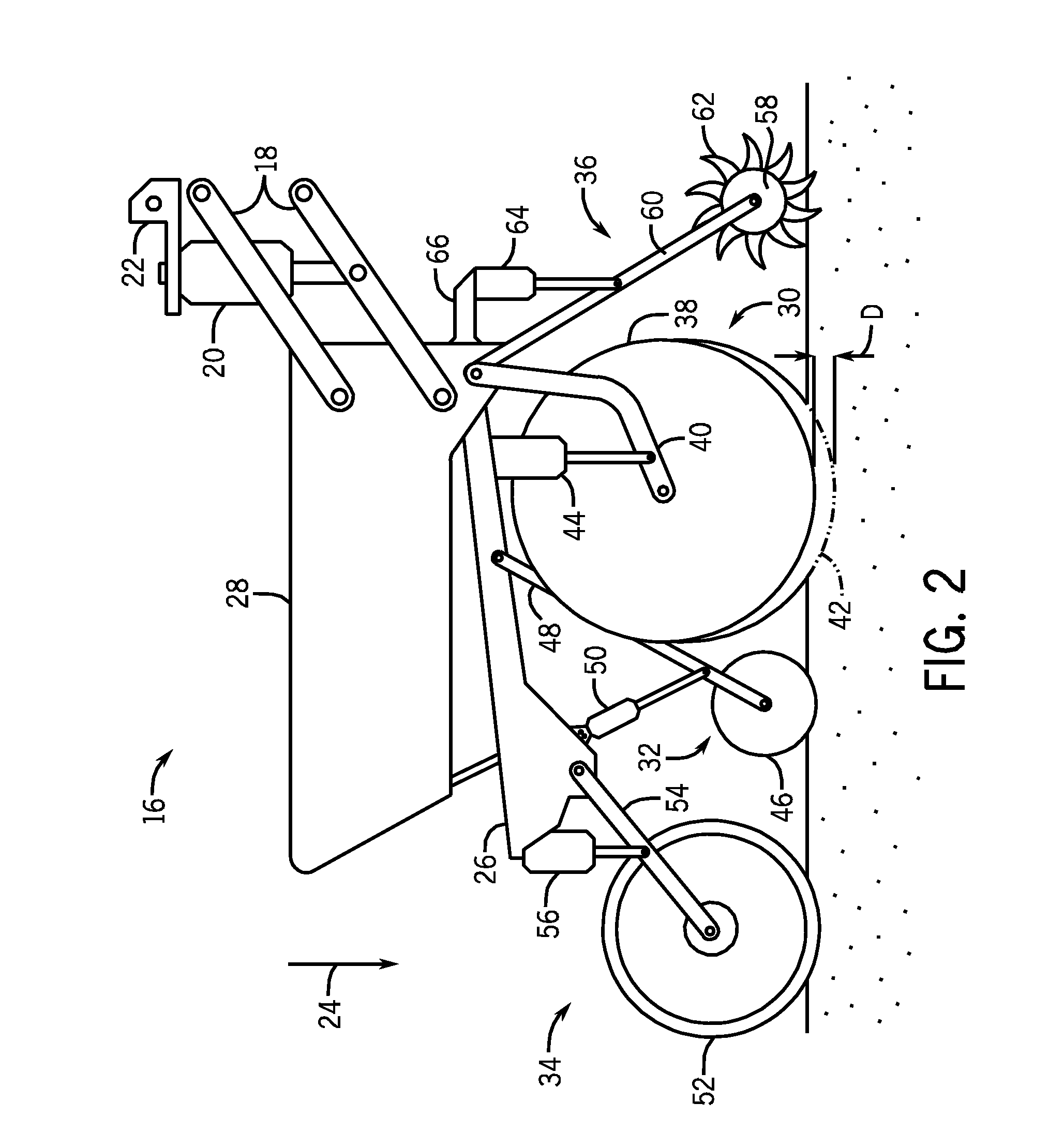
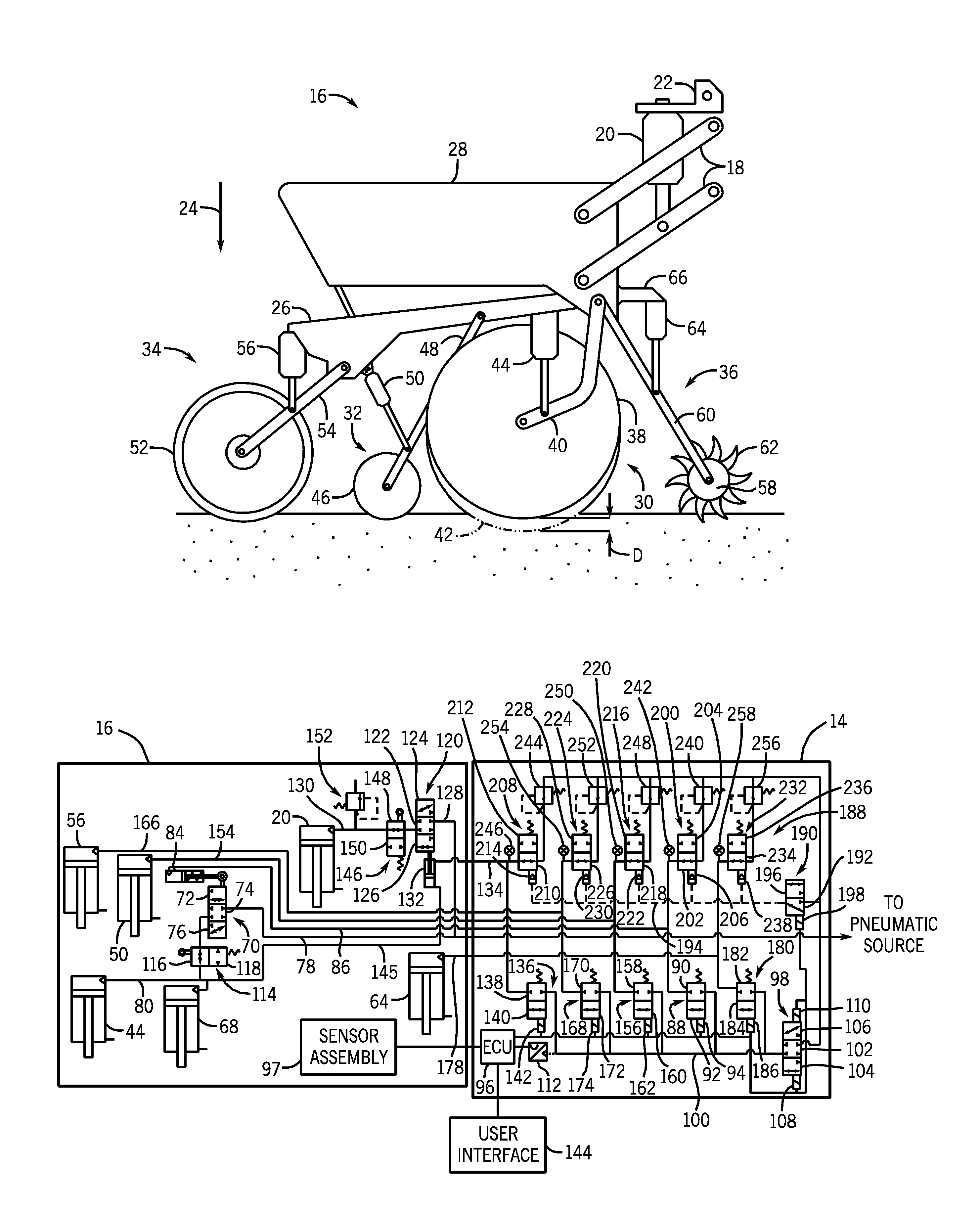
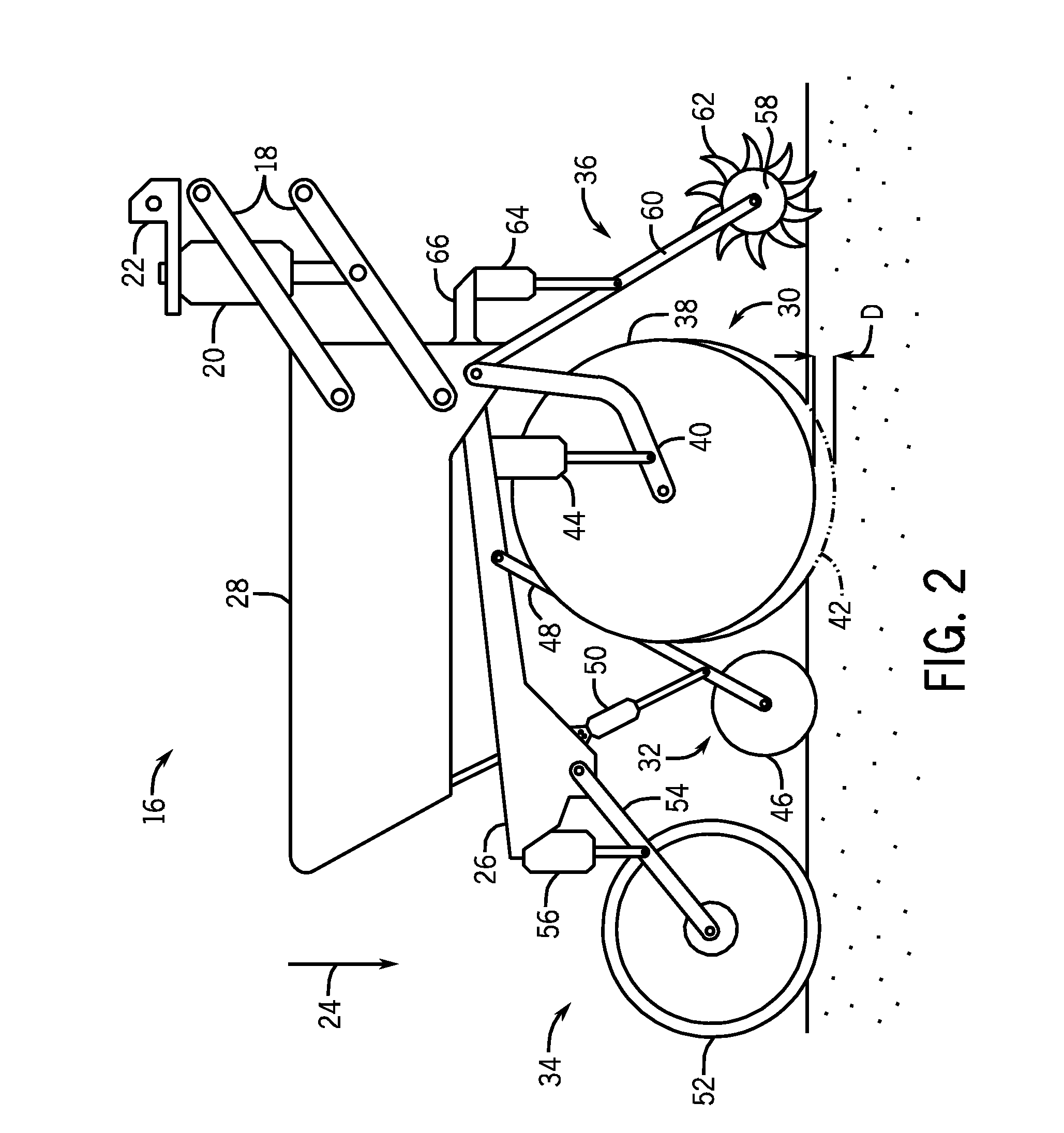
An agricultural implement system is provided that includes a down force cylinder configured to apply a downward force to a row unit, a depth control cylinder configured to vary a penetration depth of a ground engaging tool of the row unit, a press wheel cylinder configured to vary contact force between a press wheel and a soil surface, a closing disk cylinder configured to vary contact force between a closing disk and the soil surface, a residue manager cylinder configured to vary contact force between a residue manager and the soil surface, or a combination thereof. The agricultural implement system also includes an electronic control unit configured to automatically regulate a pressure within the cylinders, and a manual backup system configured to facilitate manual pressure adjustment of the cylinders.
Owner:CNH IND AMERICA LLC
Manual backup system for controlling fluid flow to cylinders within an agricultural implement
An agricultural implement system is provided that includes a down force cylinder configured to apply a downward force to a row unit, a depth control cylinder configured to vary a penetration depth of a ground engaging tool of the row unit, a press wheel cylinder configured to vary contact force between a press wheel and a soil surface, a closing disk cylinder configured to vary contact force between a closing disk and the soil surface, a residue manager cylinder configured to vary contact force between a residue manager and the soil surface, or a combination thereof. The agricultural implement system also includes an electronic control unit configured to automatically regulate a pressure within the cylinders, and a manual backup system configured to facilitate manual pressure adjustment of the cylinders.
Owner:CNH IND AMERICA LLC
Brake system
InactiveUS20080079309A1Prevents hydraulic pressure changePrevent leakageApplication and release valvesEngineeringWheel cylinder
When an electrical fluid pressure generator fails and a wheel cylinder is operated by brake fluid pressure generated by a master cylinder, if a first fluid pressure system leading to a rear fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator fails and is opened to the atmosphere, braking is performed by brake fluid pressure of a second fluid pressure system transmitted from the master cylinder through a front fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator to a wheel cylinder. At this time, a front supply port, which communicates through a front second cup seal facing rearward with the rear fluid chamber opened to the atmosphere due to the failure, does not communicate with the master cylinder but with a reservoir. Therefore, it is possible to prevent leakage of the brake fluid pressure generated by the master cylinder through the front supply port, the front second cup seal and the rear fluid chamber, thereby ensuring braking by the second fluid pressure system leading to the front fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Brake control apparatus and pump-up system
InactiveUS20080234909A1Solve insufficient braking forceSufficient forceBraking element arrangementsAnalogue computers for trafficDriver/operatorWorking fluid
A brake control apparatus of an automotive vehicle employs a pump incorporated in a hydraulic actuator, a separate pressure control valve disposed between the pump and each individual wheel-brake cylinder and having an orifice having a predetermined orifice-constriction flow passage area, and vehicle sensors including at least wheel cylinder pressure sensors. Also provided is a controller configured to be connected to the vehicle sensors and the hydraulic actuator, for calculating, based on a driver's manipulated variable, target wheel cylinder pressures, and for controlling the hydraulic actuator responsively to the target wheel cylinder pressures. The controller is further configured for calculating a fluid-pressure deviation between the target wheel cylinder pressure and the actual wheel cylinder pressure, and for stopping working-fluid supply from the pump to the abnormal wheel-brake cylinder having an abnormality in the fluid-pressure deviation exceeding a predetermined threshold value.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus for and method of controlling brakes
InactiveUS20090072615A1Improve controllabilityDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsEngineeringWheel cylinder
An apparatus for controlling brakes, includes a first brake circuit for supplying brake fluid, pressure-increased by a booster, to a wheel-brake cylinder, a first control valve disposed in the first brake circuit for establishing and blocking fluid communication between a master cylinder and the wheel-brake cylinder, a second brake circuit arranged in parallel with the first brake circuit for supplying brake fluid, pressure-increased by a fluid-pressure source, to the wheel-brake cylinder, and a second control valve disposed in the second brake circuit for establishing and blocking fluid communication between the fluid-pressure source and the wheel-brake cylinder. Also provided is a control unit, which is configured to selectively control the first and second control valves when building-up wheel-cylinder pressure, and further configured to build-up the wheel-cylinder pressure by operating the fluid-pressure source when at least the second control valve is controlled to a valve-open position.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Brake control apparatus
ActiveUS20070018498A1Increase flexibilityEfficiency and flexibilityFluid braking transmissionApplication and release valvesLine tubingEngineering
A brake control apparatus includes a brake unit. The brake unit includes: a first port set hydraulically connected to a master cylinder via a first fluid line set; a second port set hydraulically connected to a wheel cylinder set via a second fluid line set; a first fluid passage hydraulically connecting the first port set to the second port set; a first switching valve arranged to vary a state of fluid communication through the first fluid passage; a fluid pressure source arranged to produce a fluid pressure supplied to the second port set; a fluid accommodating section adapted to accommodate a variable amount of brake fluid; a branch fluid passage hydraulically connecting the first port set to the fluid accommodating section; and a second switching valve arranged to vary a state of fluid communication through the branch fluid passage.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Braking apparatus
InactiveUS20110241417A1Low costBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsWorking fluidWheel cylinder
A braking apparatus according to an embodiment includes: a fluid pressure circuit that is provided between a master cylinder and a wheel cylinder, and that includes both a first system flow channel connecting a reservoir and at least one of the plurality of wheel cylinders, and a second system flow channel connecting at least one of the plurality of wheel cylinders and the master cylinder, and that forms a flow channel for supplying operating fluid to each of the wheel cylinders; and a pump provided in the first system flow channel and driven by the motor to increase the fluid pressure of the operating fluid to be supplied from the reservoir to the wheel cylinders. A control unit controls the driving state of the pump in order to drive, when a predetermined fail standard for braking control has been satisfied, the motor in accordance with the information detected by an operating state detection means, and executes fail-safe control for providing braking force by supplying the operating fluid discharged from the pump to the fluid pressure chamber in the master cylinder.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
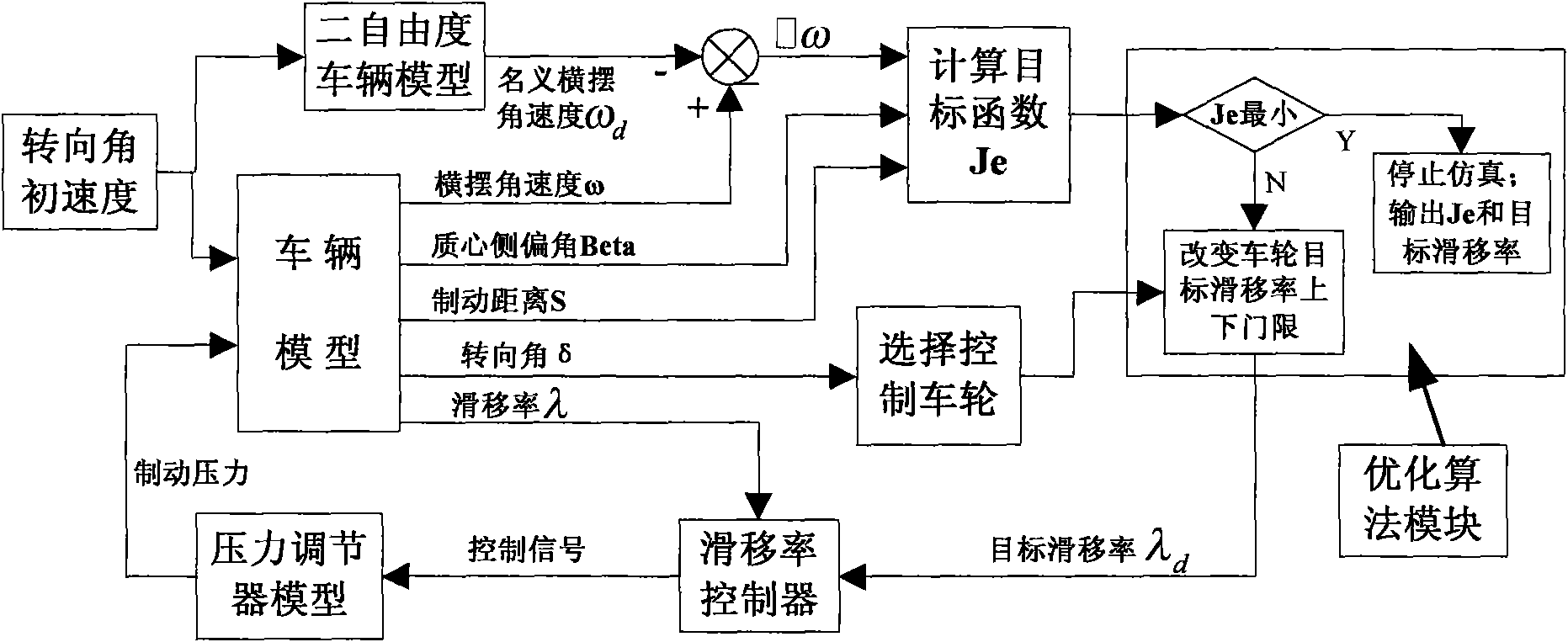
Stability integrated control method of vehicle
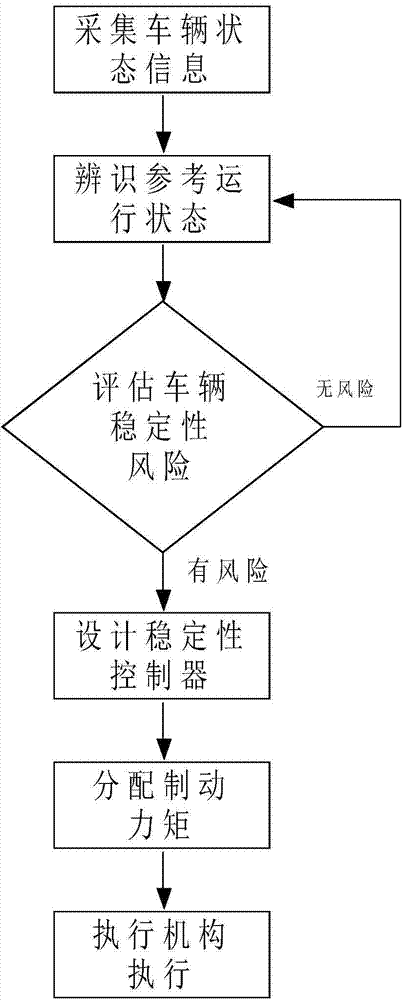
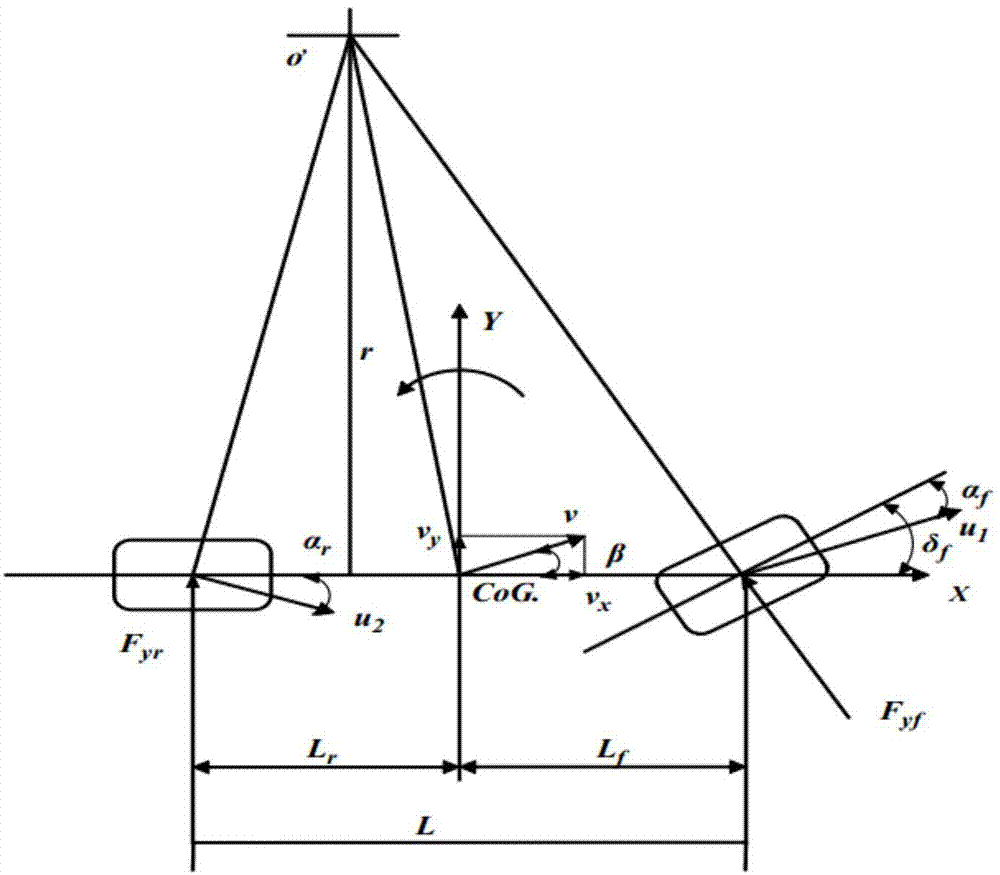
The invention discloses a stability integrated control method of a vehicle. The stability and the ride comfort of the vehicle are guaranteed by regulating the front-wheel steering angles and the braking force of corresponding tires. The control method comprises the following steps of collecting the running state information of the vehicle, and carrying out wave filtering and estimation treatment; planning a reference state value through which the vehicle is enabled to run stably; evaluating the stability risk of the vehicle according to the actual running state of the vehicle and the reference state value; when the vehicle does not have the stability risk, unnecessarily carrying out control, otherwise, necessarily planning and deciding front-wheel steering angles and additional yawing moments, through which the vehicle is enabled to recover the stability; converting the additional yawing moments into the expected braking force of the corresponding tires, meanwhile, comparing the expected braking force with the actual pressure of a wheel cylinder, and determining a solenoid valve action instruction; actuating the solenoid valve action instruction and a front-wheel steering angle instruction by a braking actuator and a steering actuator, so that the vehicle is enabled to recover to run stably.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Electro-hydraulic composite braking system with electric braking assistant force and brake-by-wire function
ActiveCN103552557AWith electric brake assistFunctionalBraking action transmissionElectric machineElectro hydraulic
The invention discloses an electro-hydraulic composite braking system with an electric braking assistant force and a brake-by-wire function. The electro-hydraulic composite braking system provided by the invention has various working modes In the case of an electric braking assistant force mode, a brake fluid is input into a master cylinder from a man-power cylinder by a brake pedal, and meanwhile, an electronic control unit controls the output torque of a motor to apply an assistant force, so as to output brake pressure to a wheel cylinder. In the case of a regenerative braking mode, the electronic control unit controls the on / off of an electromagnetic valve, the brake fluid is input into the simulation cavity of a pedal travel simulator from the man-power cylinder by the brake pedal so as to generate pressure and provide a brake pedal feeling; if automobile deceleration requirement can not be met by the regenerative braking, the electronic control unit controls the output torque of the motor so as to allow the master cylinder to output brake pressure into the wheel cylinder to assist friction brake. In case of an active braking mode, the electronic control unit controls the output torque of the motor so as to allow the master cylinder to output brake pressure to the wheel cylinder. The electro-hydraulic composite braking system provided by the invention has the advantages of integration of advantages of wire control and non-wire control working modes, small pressure fluctuation, and high pressure regulation precision.
Owner:南京经纬达汽车科技有限公司
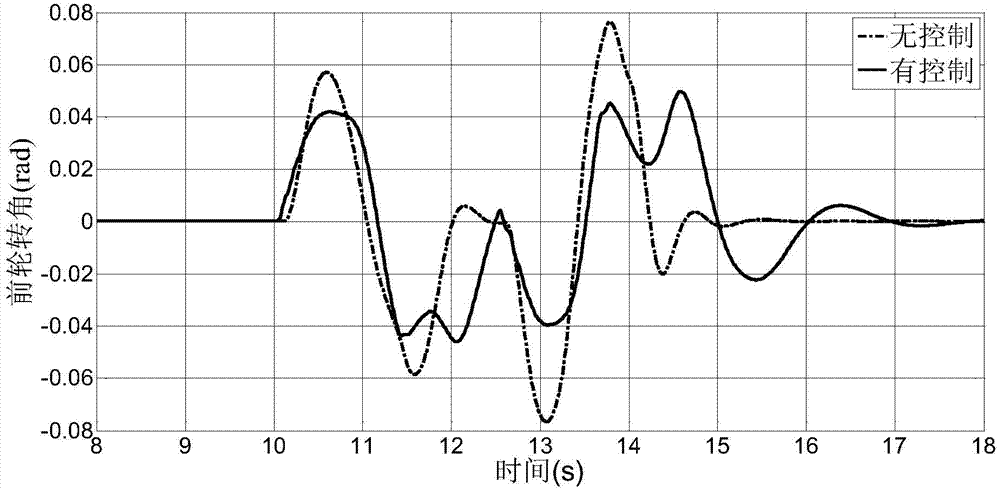
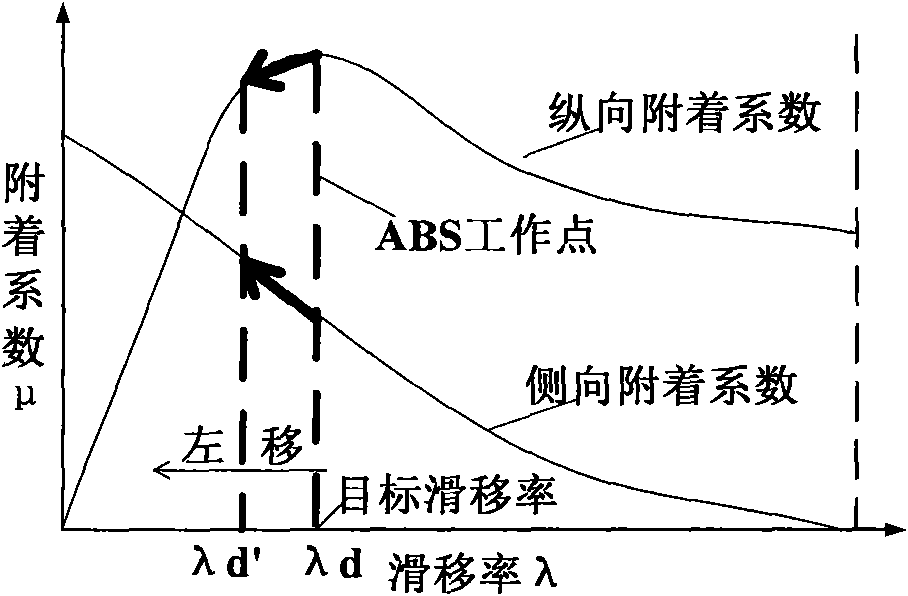
Automobile brake control method for improving lateral stability of turning/braking vehicles
The invention relates to a method for improving lateral stability under the condition of turning / braking vehicles, in particular to an automobile brake control method for improving lateral stability of turning / braking vehicles. By an off-line simulation method, from the angle of whole-vehicle dynamics, based on optimization technology, the invention calibrates an optimal target slip-rate working interval of an automobile ABS system comprehensively considering both longitudinal braking performance and lateral braking performance under the turning / braking condition, forms a curved surface from target slip rate to steering angle to initial braking speed, and then supplies the target slip rate for dynamically adjusting wheels inside and outside a bend to an online ABS system. The online ABS system adjusts the pressure of a braking wheel cylinder to reasonably allocate longitudinal force and lateral force that every wheel bears when a vehicle turns / brakes so as to improve the lateral stability of the vehicle. On the basis of the prior ABS system, the method has the advantage of allowing the ABS system to have part of the functions of an ESP system without increasing any cost.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Brake apparatus
InactiveUS20160082937A1Assist brakingReduction of braking function can be suppressedBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsWheel cylinderActuator
A hydraulic brake system includes a first actuator for a regeneration coordination brake control and a second actuator for maintaining the stability of a vehicle in a hydraulic pressure passage between a master cylinder and a wheel cylinder. The first actuator is controlled by a first ECU, and the second actuator is controlled by a second ECU. When a failure occurs in the first actuator or the first ECU, the second ECU operates the second actuator according to the amount of a brake operation, and assists braking of a wheel.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Electric-hydro complex brake system employing integral brake master cylinder assembly
InactiveCN102582601ASmall footprintEasy to installBraking action transmissionHydraulic control unitWheel cylinder
The invention relates to an electric-hydro complex brake system employing an integral brake master cylinder assembly for vehicle, including: a brake pedal, a pedal displacement sensor, an integral brake master cylinder assembly and an ABS hydraulic control unit, which are in turn connected. The ABS hydraulic control unit is connected with brake wheel cylinders of four wheels of the vehicle. Compared with the prior art, in a state that the electric system of the vehicle does not work, the hydraulic pressure inside the integral brake master cylinder assembly assists a first chamber to amplify the input force of the push rod of the master cylinder, and a pedal simulation spring drives and assists a second piston, a first piston for the master cylinder and a second piston for the master cylinder, in order to form the pressure required by braking.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Vehicle brake device
A vehicle braking device provided with a hydraulic braking device for increasing the braking operating force generated during braking operation through a booster device and for applying braking force dependent on the increase. The basic fluid pressure of the dynamic control force is applied to the wheel cylinder to generate basic hydraulic braking force on the wheel, and is used to drive the pump to generate and apply controlled fluid pressure to the wheel cylinder to generate controlled hydraulic braking force on the wheel; brake The dynamic control state detection device is used to detect the braking control state; the regenerative braking device is used to cause the electric motor to generate a regenerative braking force corresponding to the braking control state at the wheel driven by the electric motor; the change detection device is used to detect the braking control state caused by the electric motor. a change in the actual regenerative braking force actually generated by the regenerative braking device; and a braking force compensation device for generating a controlled fluid pressure by driving a pump of the hydraulic braking device so that a controlled hydraulic braking force is generated on the wheels to compensate for the attribution The lack of regenerative braking force due to changes detected by the change detection device.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Brake apparatus
InactiveUS20080231109A1Improving pedal feelingPreventing hydraulic pressureBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesWheel cylinderActuator
An object of the present invention is to provide a brake apparatus in which a hydraulic pressure in a master cylinder is prevented from being increasingly varied while an anti-lock brake system is in operation, and therefore a pedal feeling can be improved. The brake apparatus comprises an electric booster including an input member which moves forward or backward in response to an operation of a brake pedal, an assist member which moves forward or backward by being driven by an electric actuator using an electric motor as its driving source. The electric booster generates a boosted brake hydraulic pressure in the master cylinder under an input thrust provided to the input member through the brake pedal and an assist thrust provided to the assist member by the electric actuator. In the brake apparatus, the brake hydraulic pressure generated in the master cylinder is supplied to a wheel cylinder through a hydraulic pressure circuit of an anti-lock brake system, and, while the anti-lock brake system in operation, an operation of the assist member is restricted by a booster control, whereby a change in a hydraulic pressure in the master cylinder due to the operation of the assist member can be restrained.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Elevator rolling guide shoe with brake function
InactiveCN102897633AFunction increaseThere will be no mutual interferenceElevatorsHydraulic cylinderWear resistant
The invention provides an elevator rolling guide shoe with a brake function. The elevator rolling guide shoe is provided with a rolling guide wheel mechanism, hydraulic execution mechanisms and stop mechanisms, wherein three guide wheels of the rolling guide wheel mechanism cling to three working surfaces of a T-shaped guide rail and are used for limiting the horizontal movement of an elevator car; the hydraulic execution mechanisms are connected with the guide wheels of the guide shoe and used for determining whether pressures are applied to the guide wheels according to a detected elevator running state; and the stop mechanisms are integrated in the guide wheels and used for stopping the guide wheels when an elevator is in a post stall state and enabling the guide wheels to tightly hold the guide rail in combination with pressing forces provided by the hydraulic execution mechanisms, so that the emergency braking is achieved; and each stop mechanism is composed of the following parts: a guide shoe base, a long connecting rod, a main swing rod, a secondary swing rod, a brake bottom plate, a hydraulic wheel cylinder, a brake shoe, a brake pad and a brake drum covered by wear-resistant rubber.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
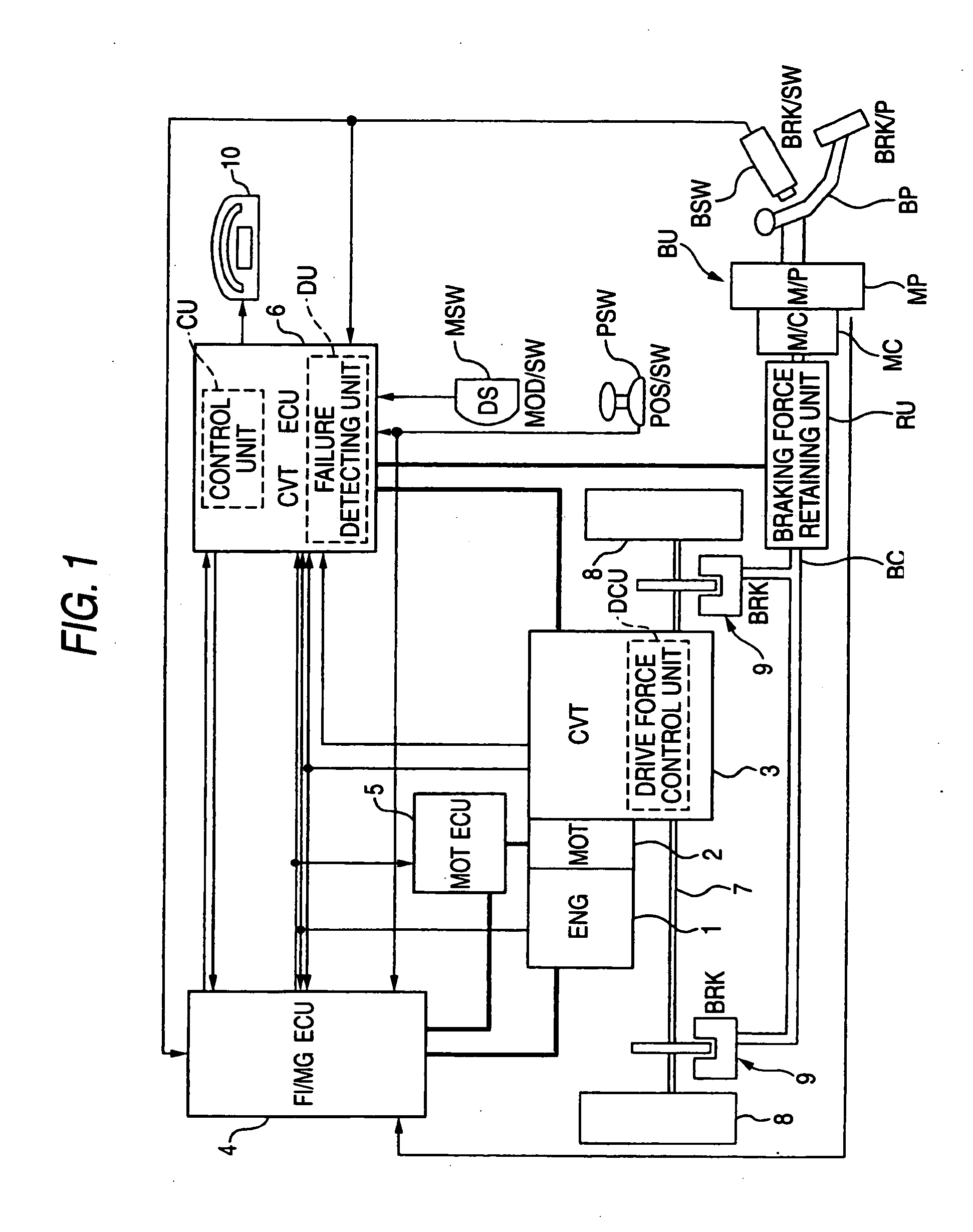
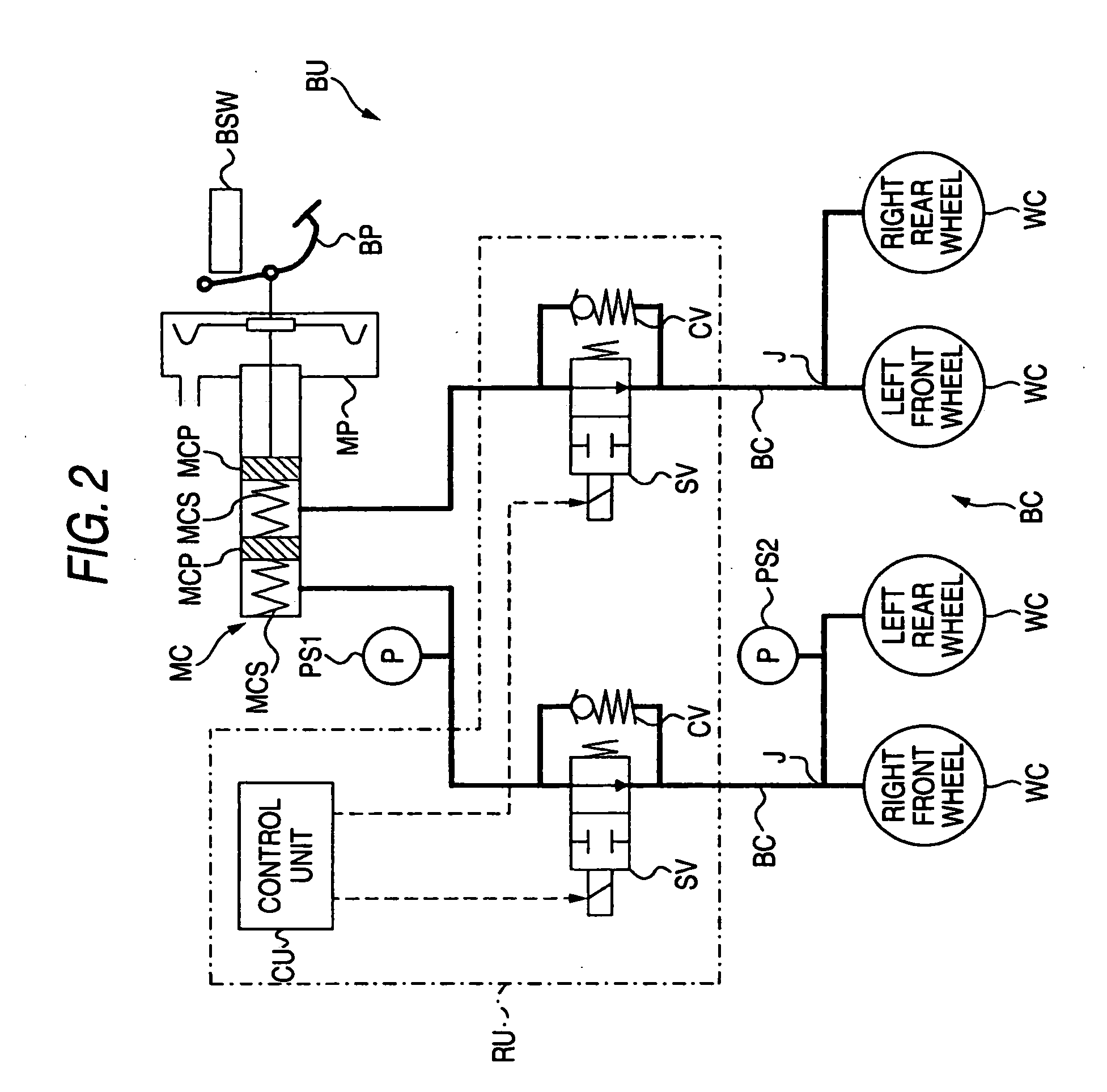
Braking force retaining unit
ActiveUS20060108868A1Smooth startReducing feeling of abruptnessBraking action transmissionBrake action initiationsEngineeringWheel cylinder
A braking force retaining unit has a cut-off valve and a control unit. The cut-off valve retains predetermined brake hydraulic pressure at the wheel cylinders until a predetermined releasing condition is established even after the depression of a brake pedal is released when a vehicle is stopped, whereas when the predetermined releasing condition is established, the brake hydraulic pressure so retained is released, when the depression of the brake pedal is released, the control unit controls the cut-off valve so as to retain the brake hydraulic pressure while reducing the retained brake hydraulic pressure at a first reduction speed. When the predetermined releasing condition is established, the control unit controls the cut-off valve so as to allow the brake hydraulic pressure retained at the wheel cylinders to be reduced at a second reduction speed which is faster than the first reduction speed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Floating synchronous curl-up film roller type seedling plastic film collector
InactiveCN101911865AAvoid secondary pollutionHigh yieldGatherer machinesWebs handlingAgricultural engineeringWheel cylinder
The invention provides a floating synchronous curl-up film roller type seedling plastic film collector which is characterized by comprising a stand. The middle part of the stand is rotatably connected with a land axle, two land wheels are respectively fixed at both ends of the land axle, a soil shaking mechanism is rotatably connected to the stand arranged above the land axle, a gripper-shaped film loosening mechanism is fixed on the stand arranged behind the soil shaking mechanism, two adjustable break shovels are respectively arranged at both sides of the front end of the stand, two U-shaped brackets are respectively fixed at both sides of the back end of the stand, a curl-up film roller is supported in the two U-shaped bracket through a curl-up film roller axle, a tension spring is respectively connected between each end of the curl-up film roller axle at the outer side of the two U-shaped brackets and the stand, a wheel cylinder which is driven by the curl-up film roller through friction is arranged below the curl-up film roller, extension ends at both ends of the wheel cylinder are rotatably connected to the stand, the extension end at one end is connected with a side land axle through a wheel cylinder transmission mechanism, and the extension end at the other end is connected with the soil shaking mechanism through a soil shaking transmission mechanism. The film curling speed of the invention is consistent with the advancing speed of a machine, thereby efficiently avoiding the phenomena of film tearing and breaking and ensuring normal continuous work of the machine.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
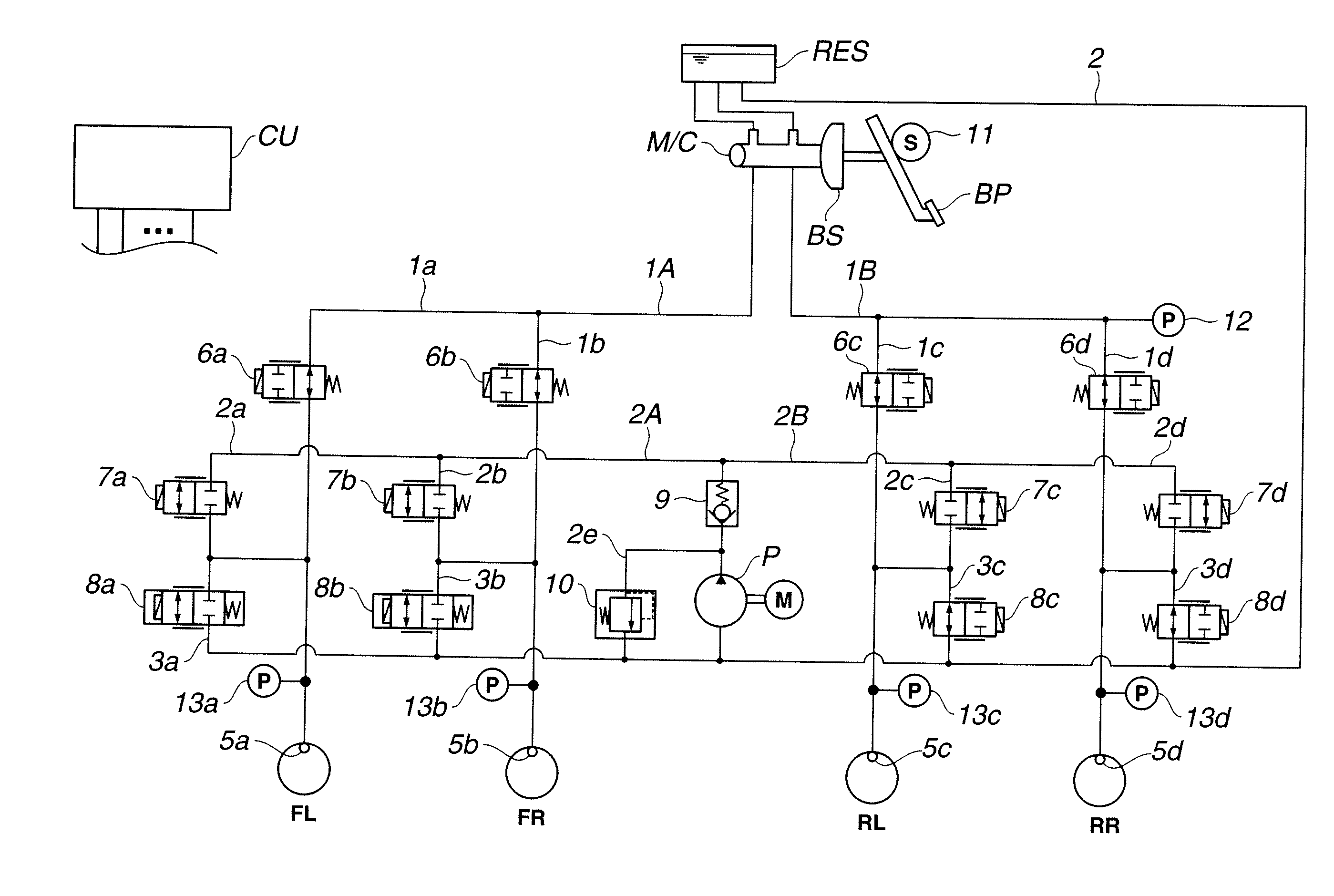
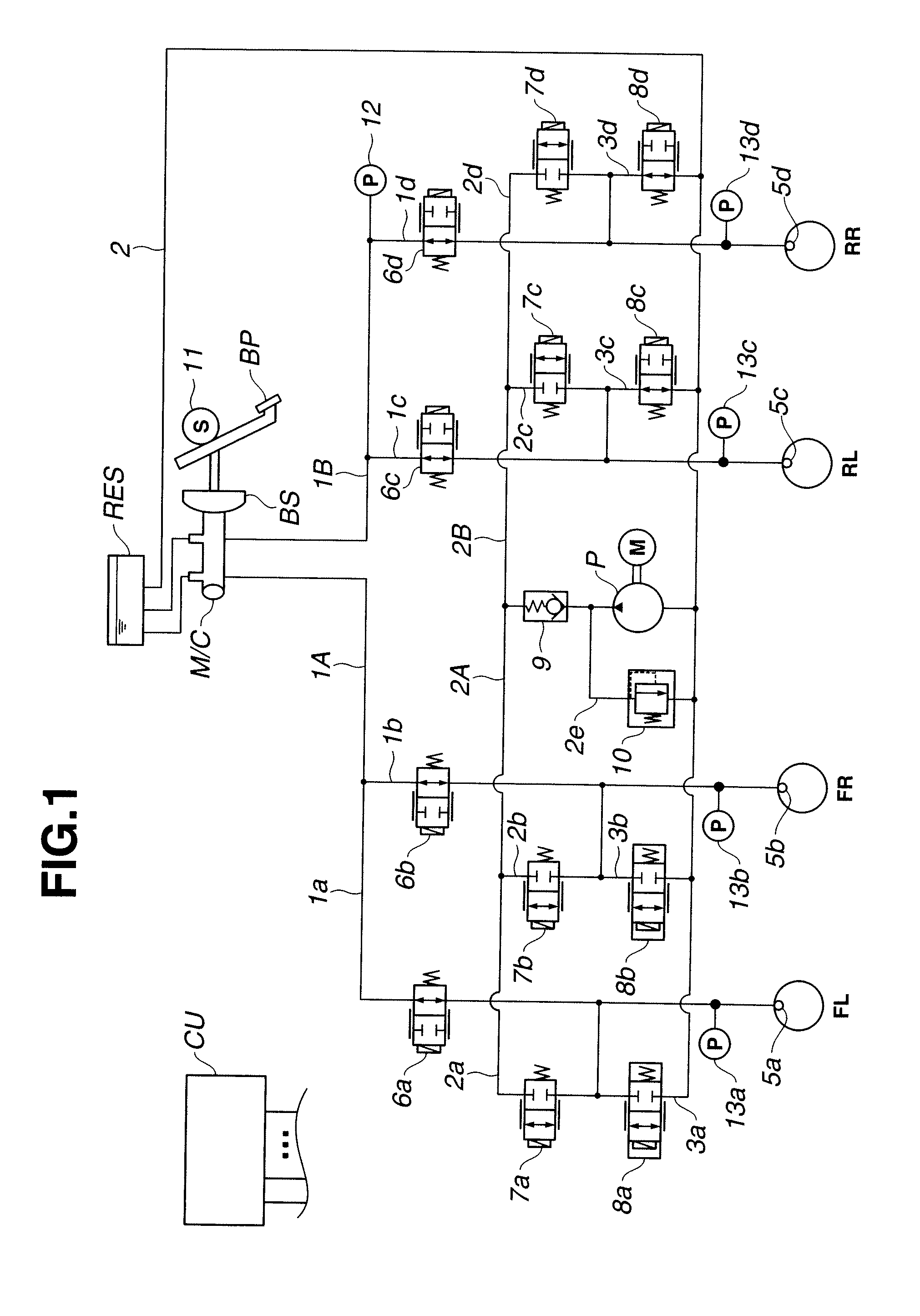
Brake control apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveUS20070108837A1Accuracy in determiningImprove accuracyBrake control systemsBrake typesWorking fluidDifferential pressure
A brake control apparatus has first and second wheel cylinders; a master cylinder unit; first and second systems; a separation valve; a pressure control mechanism that controls the working fluid pressure transferred to at least one of the first and second wheel cylinders independently of the brake operation, and a brake ECU. The brake ECU generates a differential pressure across the separation valve by operating the pressure control mechanism when there is no brake operation while a running drive source of a vehicle is stopped to determine whether the separation valve has a leakage abnormality.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Brake control system
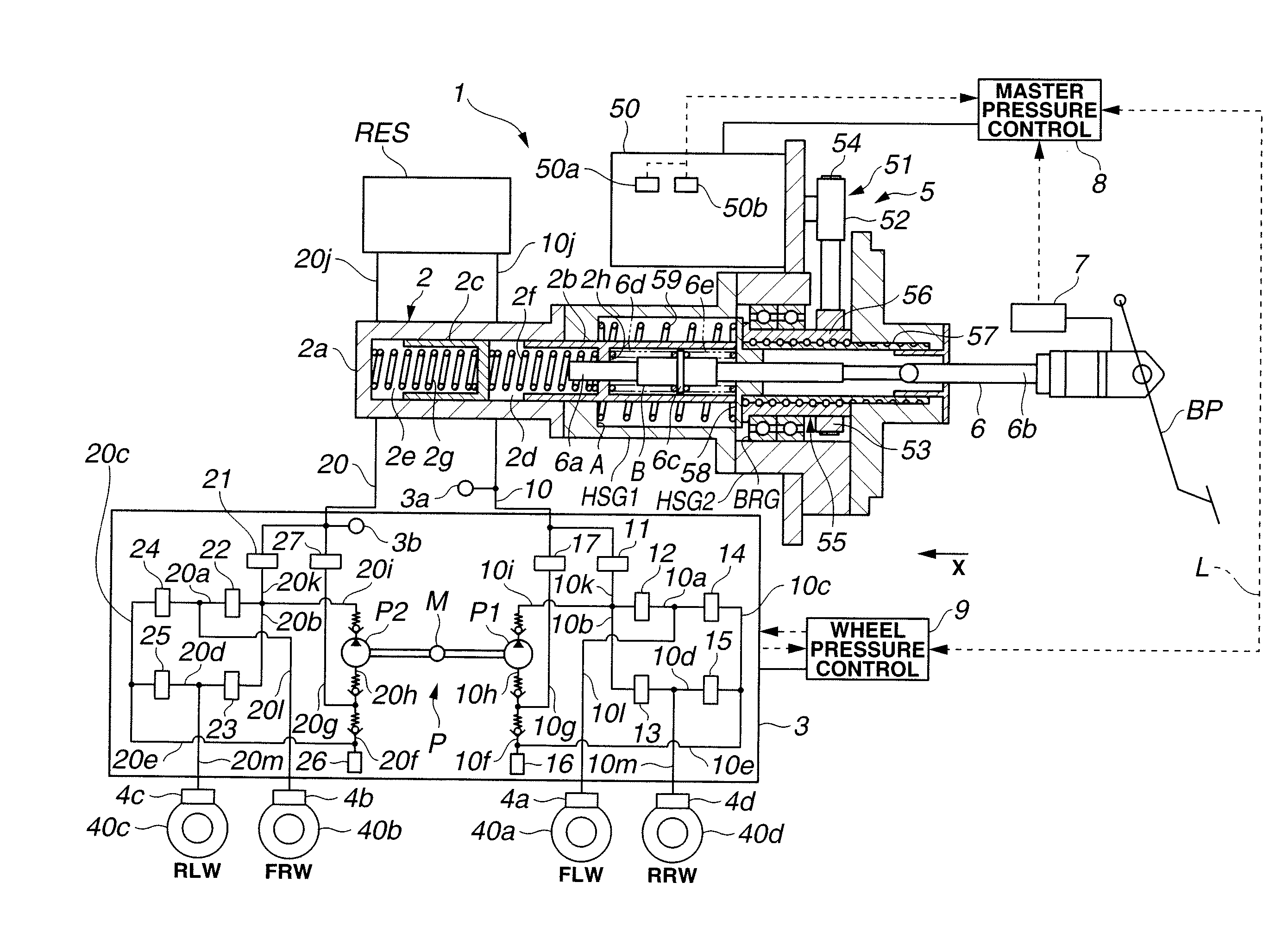
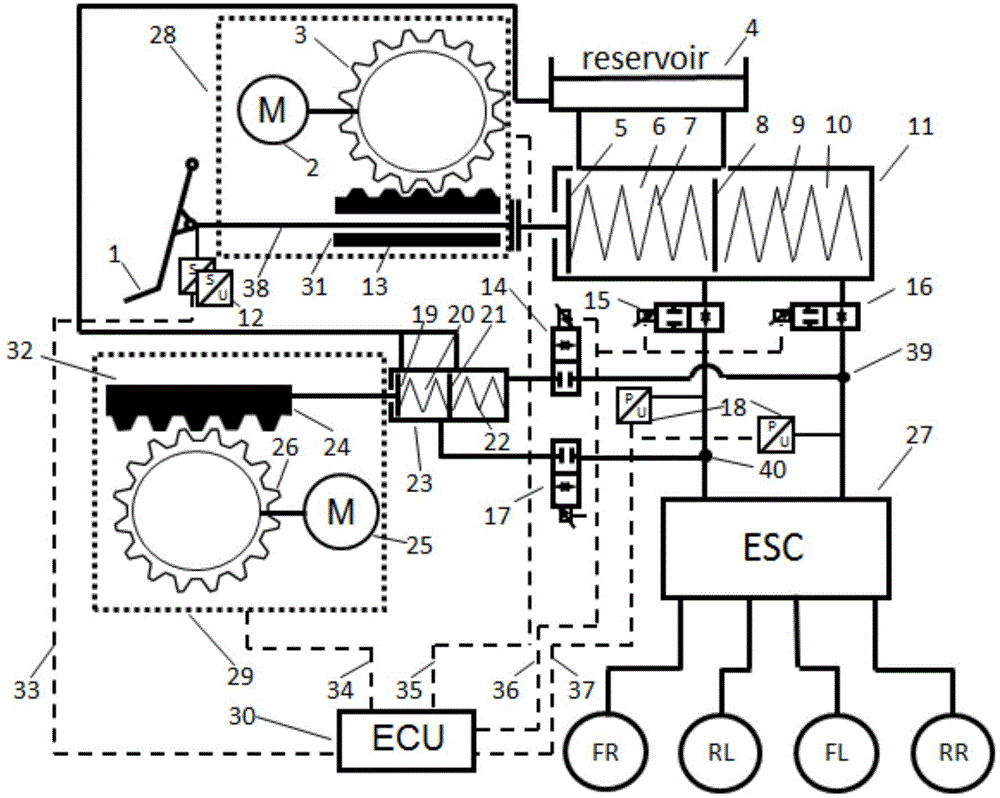
ActiveUS20110241418A1Appropriate performanceBraking element arrangementsAnalogue computers for trafficRelative displacementControl system
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Electro-hydraulic brake system
An electro-hydraulic brake (EHB) system including a pump to pump and discharge oil in a reservoir, an accumulator to temporarily store the oil discharged from the pump, inlet valves to deliver the oil stored in the accumulator into the respective wheel cylinders, a return flow path connecting the wheel cylinders to the reservoir, outlet valves provided on the return flow path and adapted to discharge the oil from the wheel cylinders to the reservoir, cut-off valves to open and close flow paths between the wheel cylinders and an exit of a master cylinder, and a simulator. The simulator includes a first chamber communicating with the exit of the master cylinder, a second chamber connected to an entrance of the pump, and a simulator valve. The simulator having the above described configuration is able to prevent deterioration in the reliability and durability of the EHB system and to reduce the installation space of the master cylinder.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Accelerator pedal and brake pedal-based electrically driven automobile feedback brake control method
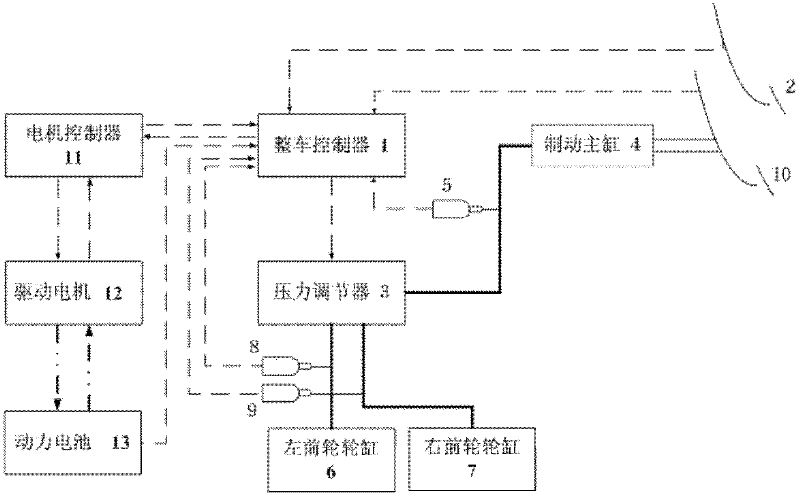
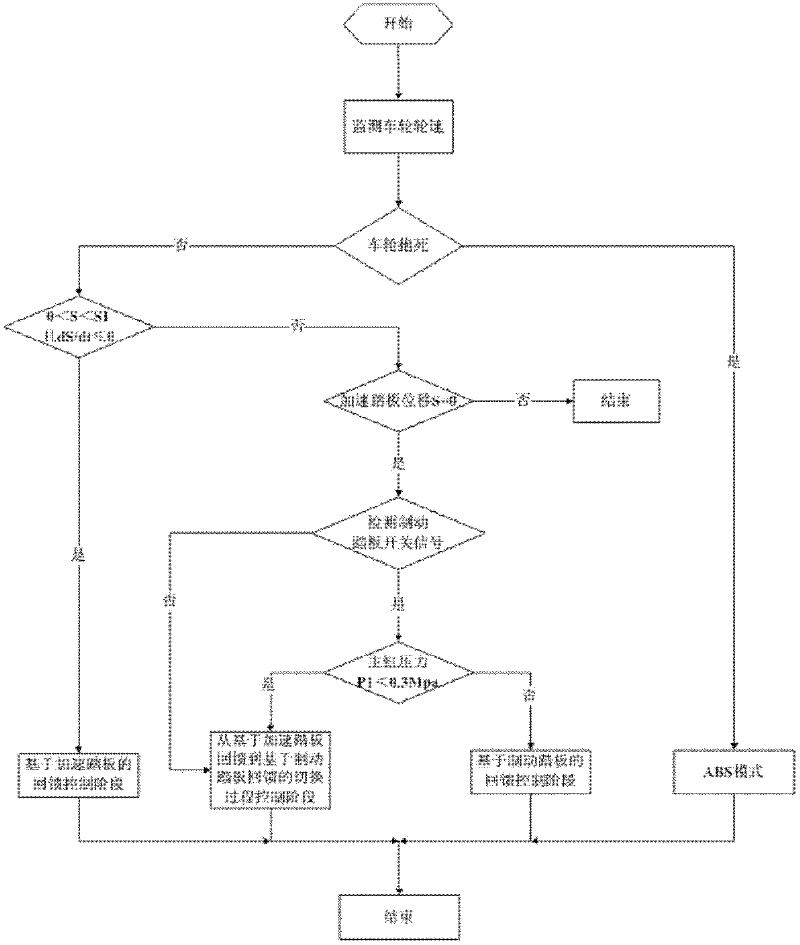
ActiveCN102642474AImprove energy economyEnsure smooth brakingElectrodynamic brake systemsWheel speed sensorWheel cylinder
The invention relates to an accelerator pedal and brake pedal-based electrically driven automobile feedback brake control method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) arranging an electrically driven automobile feedback brake control system comprising a vehicle controller, a wheel speed sensor, an accelerator pedal displacement sensor, a pressure regulator, a main cylinder pressure sensor, a front wheel cylinder pressure sensor and a brake pedal switch; (2) judging, by the vehicle controller, braking intention of a driver according to a current operation state of the automobile, dividing brake feedback control into three stages, i.e., an accelerator pedal-based feedback control stage, a brake pedal-based feedback control stage and a control stage of a switching process from accelerator pedal-based feedback to brake pedal-based feedback; and (3) calculating, by the electrically driven automobile feedback brake control system, motor feedback braking force of the three feedback control stages respectively, thereby keeping the vehicle total brake force consistent with the driver brake requirement. The accelerator pedal and brake pedal-based electrically driven automobile feedback brake control method can be widely applied to electrically driven automobile feedback brake control of a pure electric vehicle, a hybrid electric vehicle and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Brake control system for an electrically driven vehicle
ActiveUS20120139330A1Comfortable brake feelSafe recoveryBraking element arrangementsAnalogue computers for trafficRegenerative brakeControl system
During regenerative coordinate braking control, a target brake force is defined by eliminating influences of brake system component tolerances to achieve a comfortable brake feel and secure regenerative energy. A brake control system includes a master cylinder, wheel cylinders, a VDC brake fluid pressure unit and a motor controller. In response to a brake pedal operation by a driver, a brake pedal stroke position is detected at which a pressure in a master cylinder actually begins to be generated. A target deceleration characteristic is adjusted from a theoretical characteristic so that the target deceleration equals a maximum value of an add-on brake force (i.e., the regenerative brake gap) at the detected brake pedal stroke position.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Electro-hydraulic braking system and control method thereof
InactiveCN102785654AReduce consumptionIncrease mileageFluid braking transmissionLow voltageElectro hydraulic
The invention discloses an electro-hydraulic braking system and a control method thereof for an electric automobile. The electro-hydraulic braking system is provided with a high-voltage brake circuit, a low-voltage brake circuit and a standby brake circuit, wherein the high-voltage brake circuit comprises a first hydraulic pump, a high-voltage energy accumulator, a three-position and three-way valve and a corresponding brake wheel cylinder which are sequentially connected; a pressure sensor is arranged near a pipeline at an output rear end of the high-voltage energy accumulator; the low-voltage brake circuit comprises a second hydraulic pump, a low-voltage energy accumulator, a three-position and three-way valve and a corresponding brake wheel cylinder which are sequentially connected; when the pressure of the pressure sensor is lower than a preset value; the first hydraulic pump sucks hydraulic oil and pumps the hydraulic oil into the high-voltage energy accumulator for enabling the automobile to brake; the second hydraulic pump sucks hydraulic oil and pumps the hydraulic oil into the low-voltage energy accumulator for enabling the automobile to brake; when the brake strength is higher than the brake strength which can be provided by the low-voltage brake circuit, the high-voltage brake circuit is started; when the brake strength which can be provided by the low-voltage brake circuit meets the required brake strength, a low-voltage brake mode is started; and a favorable safety performance is obtained and brake energy can be recovered to the maximum extent.
Owner:郑州宇通集团有限公司
Brake control apparatus
InactiveUS20130062932A1Easy to operateBraking element arrangementsVehicular energy storageWheel cylinderBrake fluid
A brake control apparatus for a vehicle provided with a regenerative braking device, the brake control apparatus includes: a first brake circuit connecting a master cylinder configured to generate a brake hydraulic pressure by a brake operation of a driver, and a wheel cylinder to which the brake hydraulic pressure is applied; a booster configured to increase a pressure of a brake fluid within the master cylinder, and to transmit the pressurized brake fluid to the wheel cylinder through a second brake circuit connected with the first brake circuit; a third brake circuit bifurcated from the first brake circuit, and connected with the booster; a reservoir provided on the third brake circuit; and a recirculating device configured to recirculate the brake fluid stored in the reservoir, to the first brake circuit's side.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Brake control apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveUS20070114842A1Improve controllabilityMinimize fluctuationPiping arrangementsBrake cylindersWorking fluidWheel cylinder
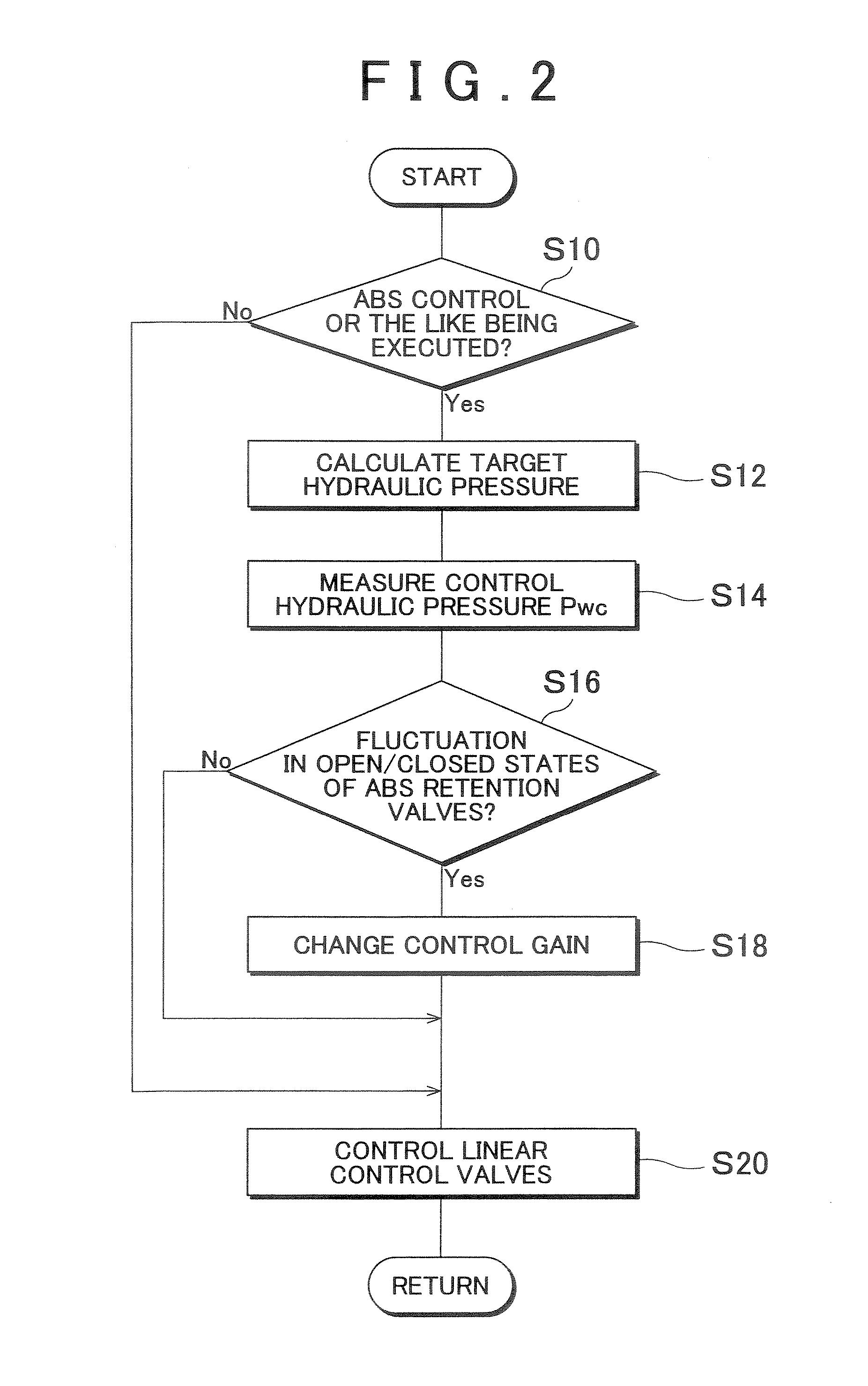
The invention provides a brake control apparatus that improves the controllability of a vehicle in the control for restraining slip of the wheels. The brake control apparatus includes: wheel cylinders that apply braking force individually to wheels by supplying a working fluid; retention valves that are provided respectively upstream of the wheel cylinders and that are opened and closed so as to restrain slip of the wheels; a common control valve provided upstream of the retention valves to supply the working fluid to the wheel cylinders; and a control portion that controls the common control valve by different control laws to restrain fluctuations in pressure on a primary side of the retention valves caused by fluctuations in a capacity to which the working fluid from the common control valve is supplied, by opening or closing of the retention valves.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Hydraulic double-motor driving electronic hydraulic braking system
InactiveCN103950445ALow powerExtend your lifeBraking action transmissionMotor driveLiquid storage tank
A hydraulic double-motor driving electronic hydraulic braking system comprises a braking pedal, a braking master cylinder, a secondary master cylinder, a liquid storage tank, a pedal displacement sensor, a hydraulic pressure sensor, an electronic control unit ECU, a first electronic control linear moving module and a second electronic control linear moving module for performing active control on hydraulic braking force and pedal force of the system, an electronic stability control module ESC for regulating the hydraulic braking force of each wheel cylinder, a tee joint for connecting hydraulic pipelines between the braking master cylinder and the inlet of the electronic stability control (ESC) module as well as between the secondary master cylinder and the inlet of the ESC module. According to the invention, the pedal force of a driver can be utilized for pressure establishing, the active control on the pedal force is realized while a pedal force simulator with a complex structure is omitted, braking pedal feel is ensured, the braking intention of the driver can be correctly reflected, the active control on hydraulic pressure is realized, the braking requirement of a vehicle is met, maximum braking energy recycling can be realized, the control is precise, and the response speed is high.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Brake energy recovery hydraulic braking system based on VDC (Vehicle Dynamics Control)/VSC (Vehicle Stability Control)/ESP (Electronic Stability Program) pressure regulator
InactiveCN101837773AReduce development costsDoes not affect driving habitsFluid braking transmissionVehicle dynamicsArea network
The invention discloses a brake energy recovery hydraulic braking system based on a VDC (Vehicle Dynamics Control) / VSC (Vehicle Stability Control) / ESP (Electronic Stability Program) pressure regulator, comprising a pressure regulator with the function of VDC / VSC / ESP, a braking main cylinder, a braking electric motor, a braking controller and a hybrid control unit. The brake energy recovery hydraulic braking system is characterized in that a main cylinder pressure sensor is arranged on an oil outlet pipeline of the braking main cylinder; a wheel cylinder pressure sensor is arranged on a front wheel cylinder of the pressure regulator; signals of the main cylinder pressure sensor and the wheel cylinder pressure sensor are all fed back to the braking controller; a drive electric motor is controlled by the hybrid control unit; and the braking controller performs CAN (Controller Area Network) communication with the hybrid control unit. The pressure regulator controls two paths of braking oil paths of front left wheel-right rear wheel and right front wheel-left rear wheel. The invention utilizes the drive electric motor to return braking torque to carry out brake energy feedback, utilizes the VDC / VSC / ESP pressure regulator to realize the increase, the maintenance and the decrease of the pressure of the wheel cylinder, ensures the drive safety, and can realize the regenerative braking and the integrated control of ABS (Anti-lock Brake System), ASR (Acceleration Slip Regulation) and ESP (Electronic Stability Program).
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Dual-motor BBW (brake-by-wire) system with multiple working modes and voltage regulation modes
ActiveCN103552556AFeel adjustableWith active braking functionBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsAxial thrustWheel cylinder
The invention discloses a dual-motor BBW system with multiple working modes and voltage regulation modes. A brake fluid in a manual cylinder flows into two main cylinders by means of a brake pedal, and brake pressure is generated; and meanwhile, output power torque of two motors is controlled, and axial thrust is overlaid to pistons of the two main cylinders through a transmission device, so that electric power brake is realized. Through control of output torque of the two motors, pressure of the two main cylinders is transmitted to wheel cylinders, brake by wire is realized, and a pedal travel simulator is used for providing force for the brake pedal. Under the condition that the brake pedal is not stepped, the output torque of the two motors is controlled, so that the two cylinders generate pressure which is transmitted to the wheel cylinders through a hydraulic control unit, and accordingly, the active brake is realized. The invention further discloses a structure of a hydraulic control system, and the structure has multiple voltage regulation modes. The dual-motor BBW system has the advantages as follows: the system has multiple braking modes and voltage regulation modes, the most appropriate braking mode and voltage regulation mode can be selected according to dynamic properties of the motors during implementation and application, the reliability is high, and the failure protection capacity is high.
Owner:南京经纬达汽车科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com