Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4842 results about "Vehicle braking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In an automobile vehicle, a braking system is an arrangement of various linkages and components (brake lines or mechanical linkages, brake drum or brake disc , master cylinder or fulcrums etc) that are arranged in such a fashion that it converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into the heat energy which in turn stops or de accelerate...
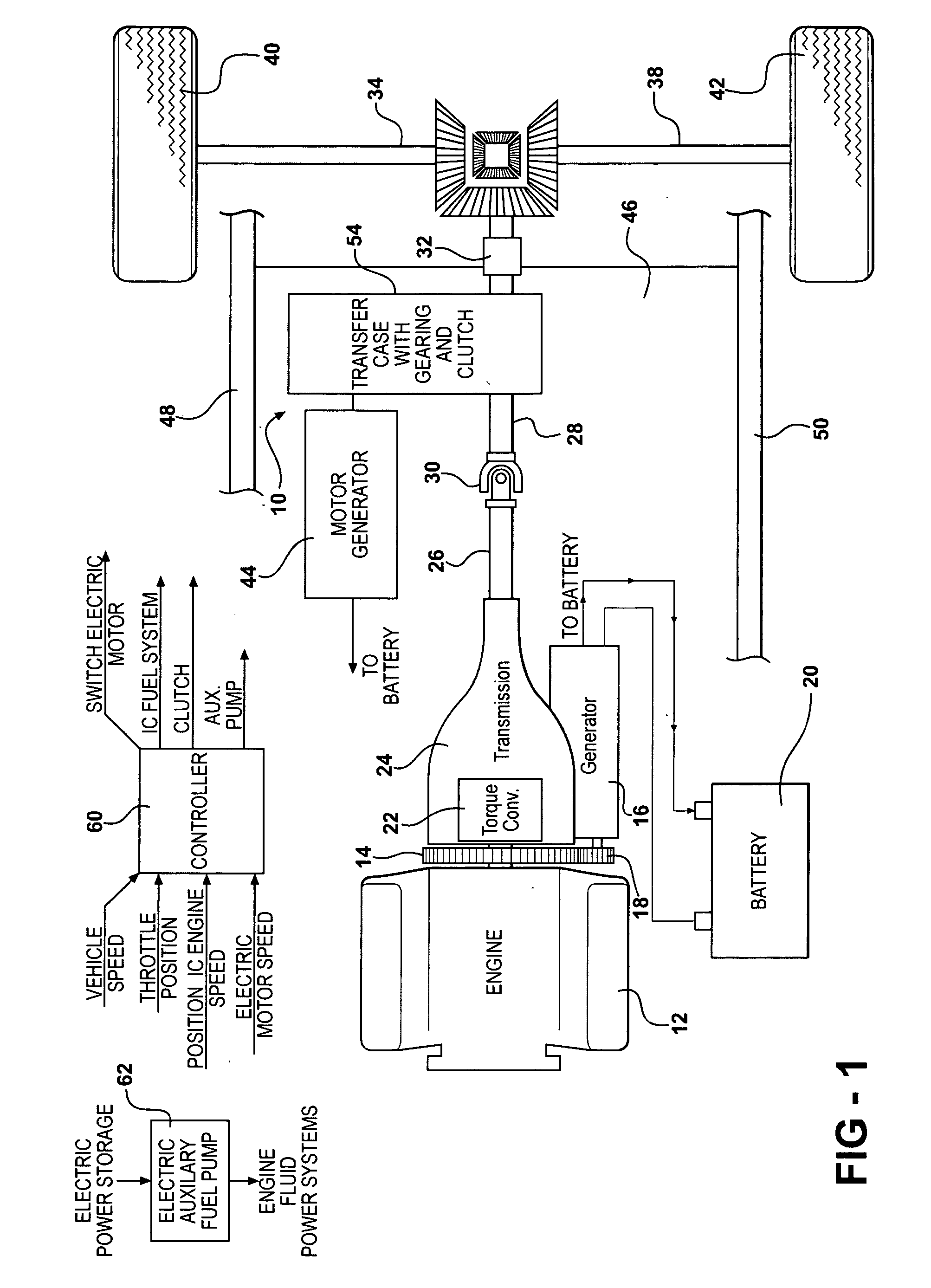
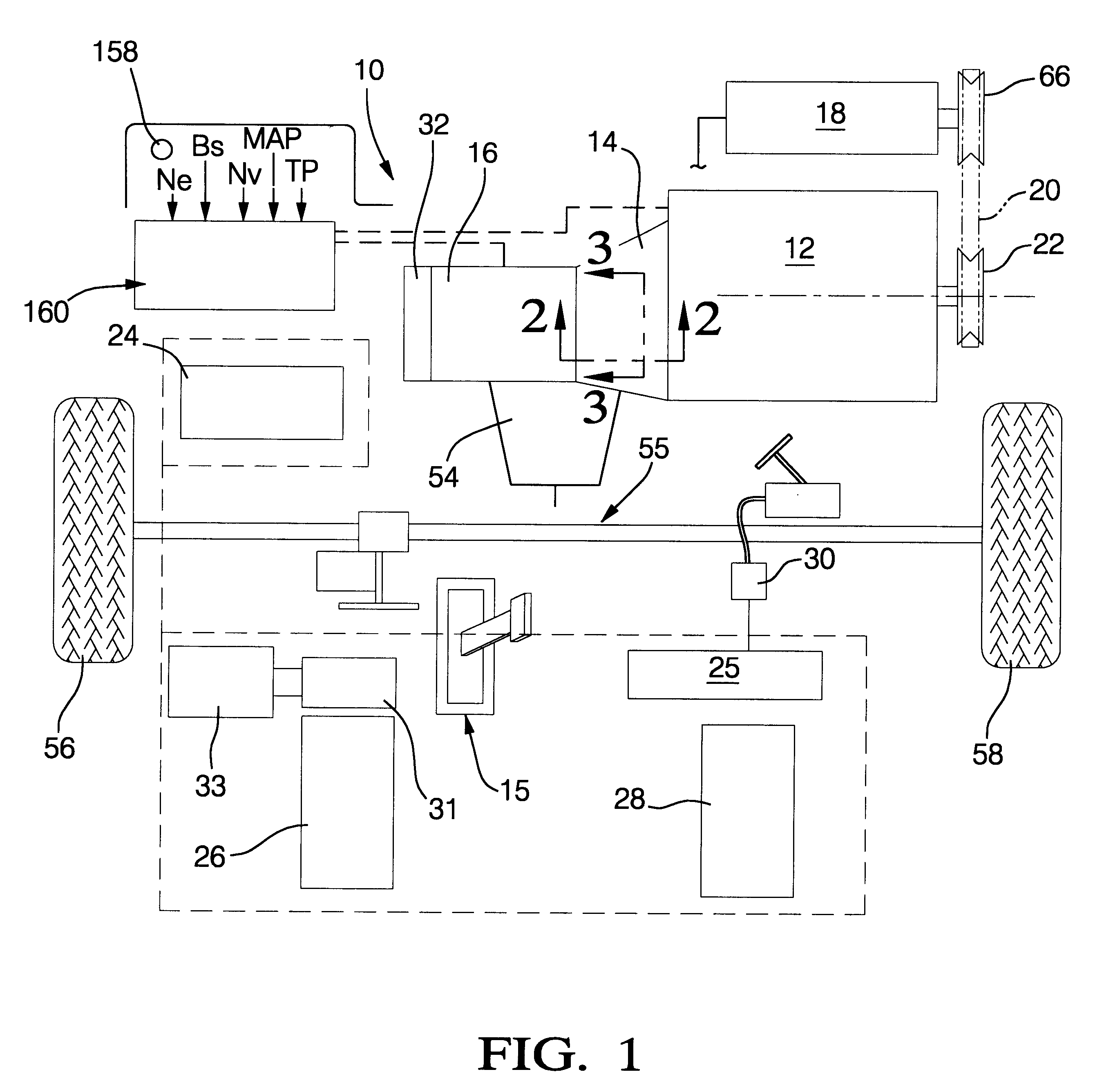
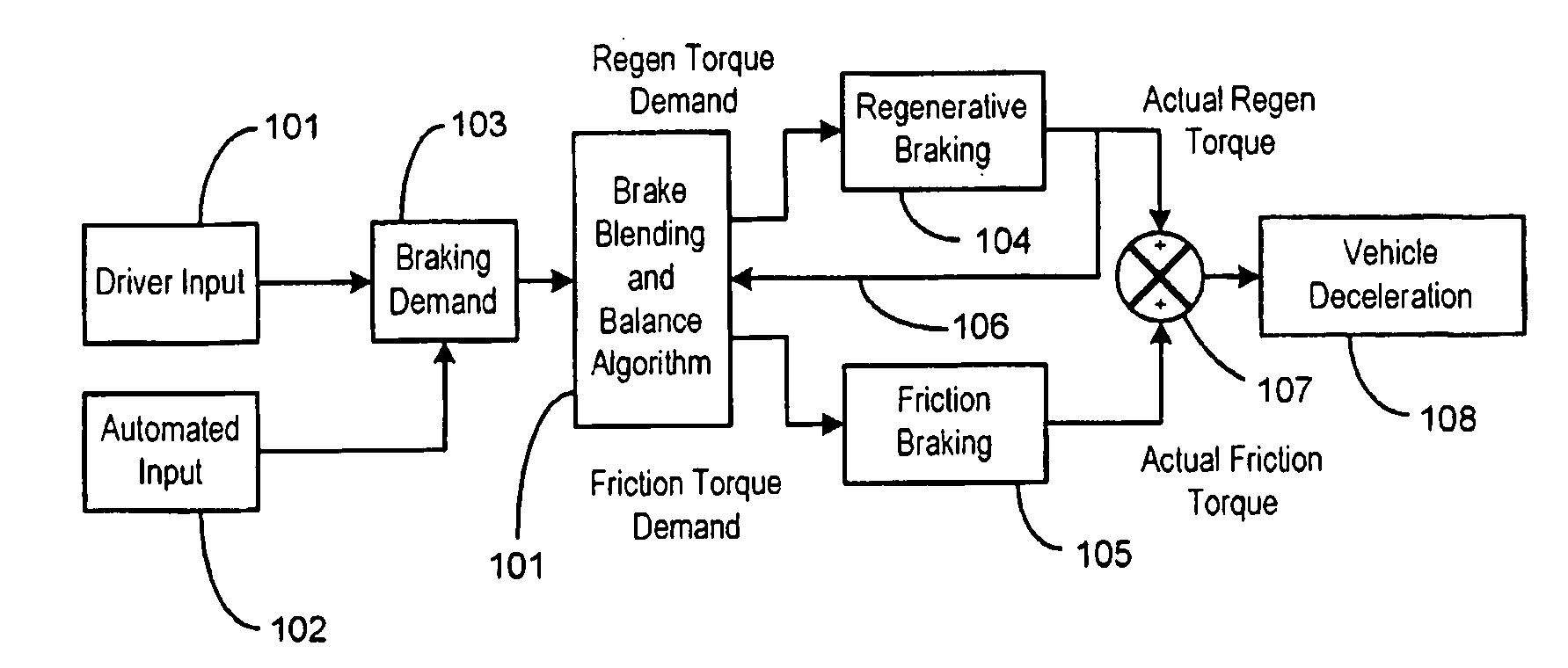
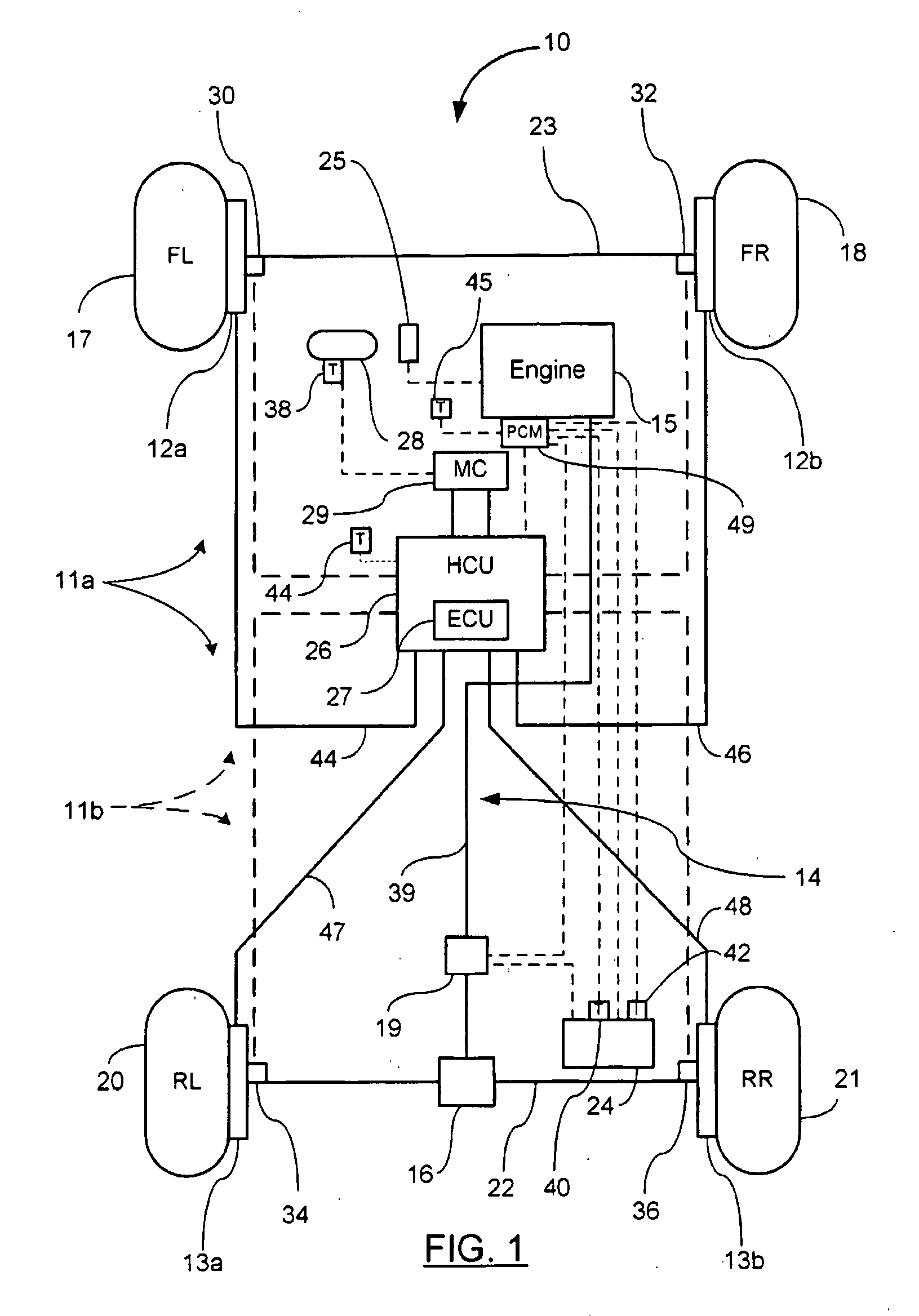
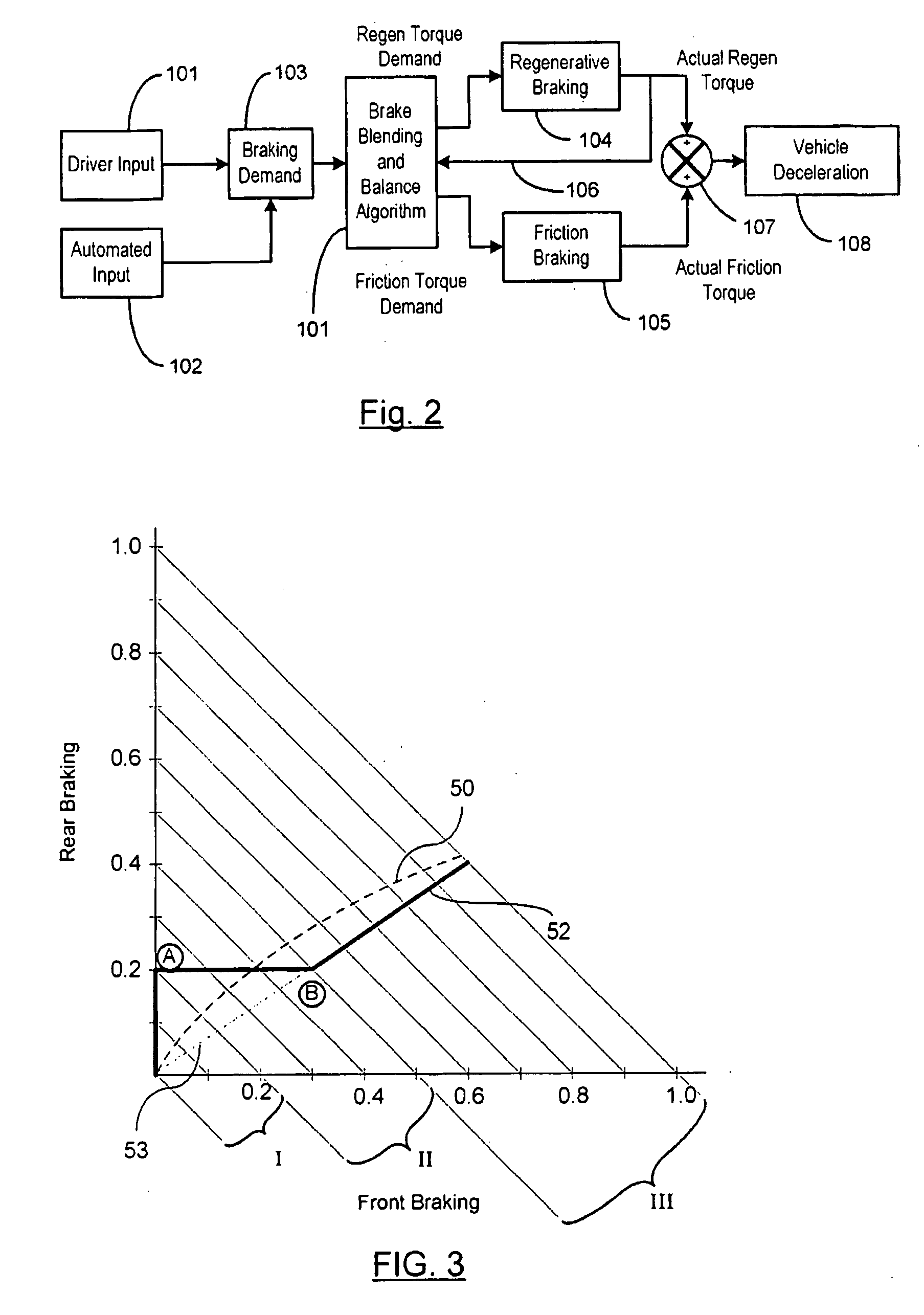
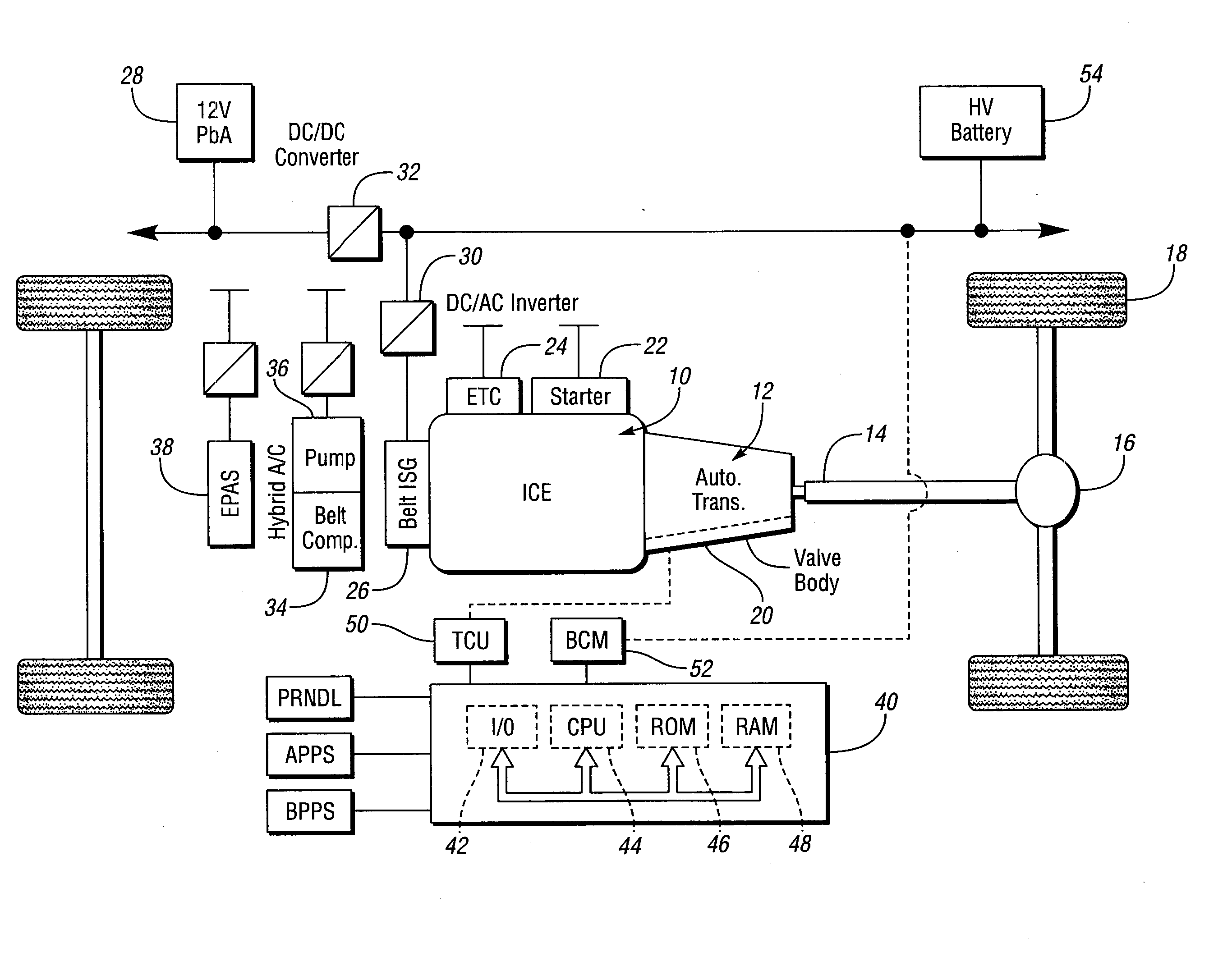
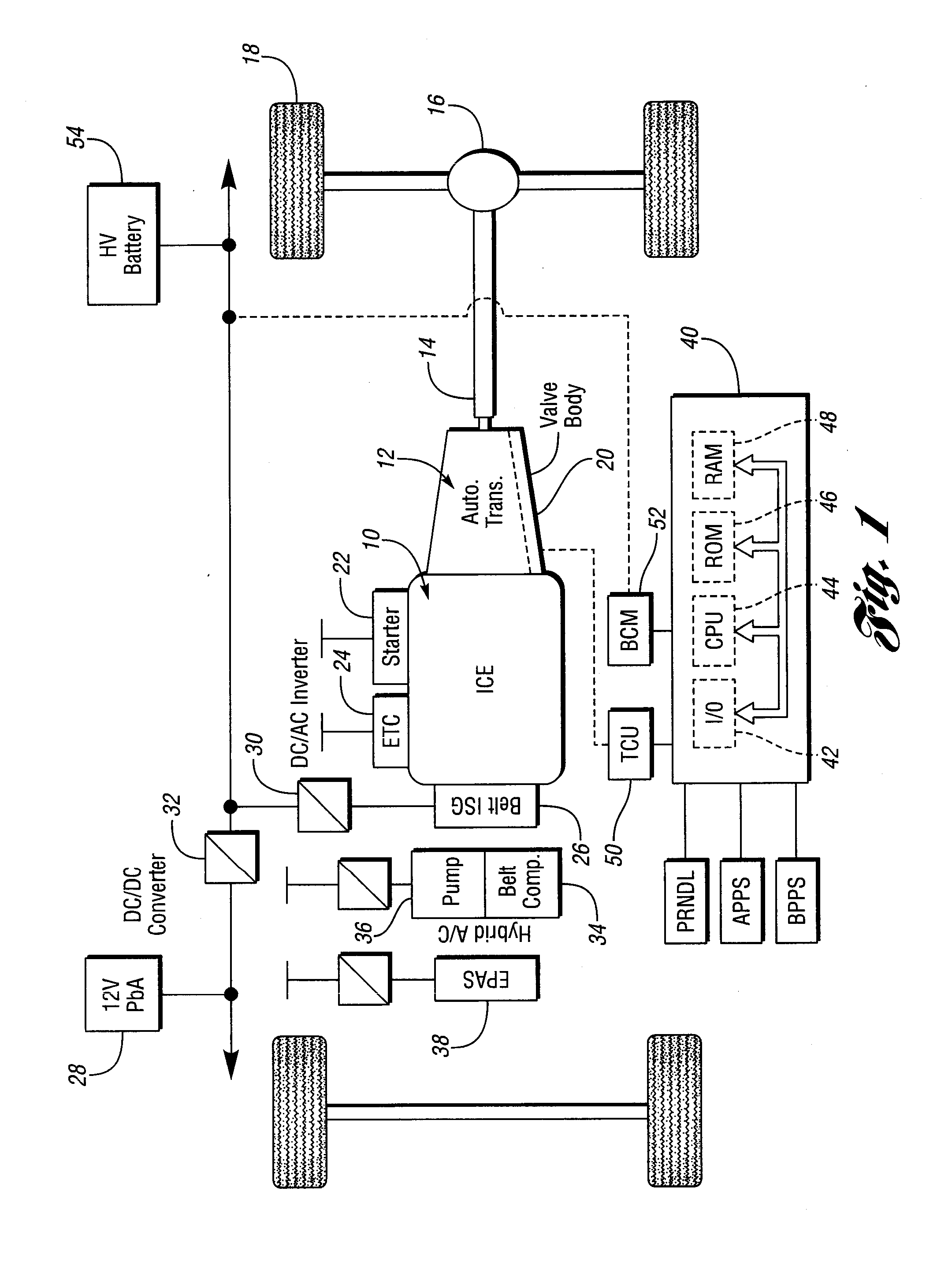
Vehicle braking control
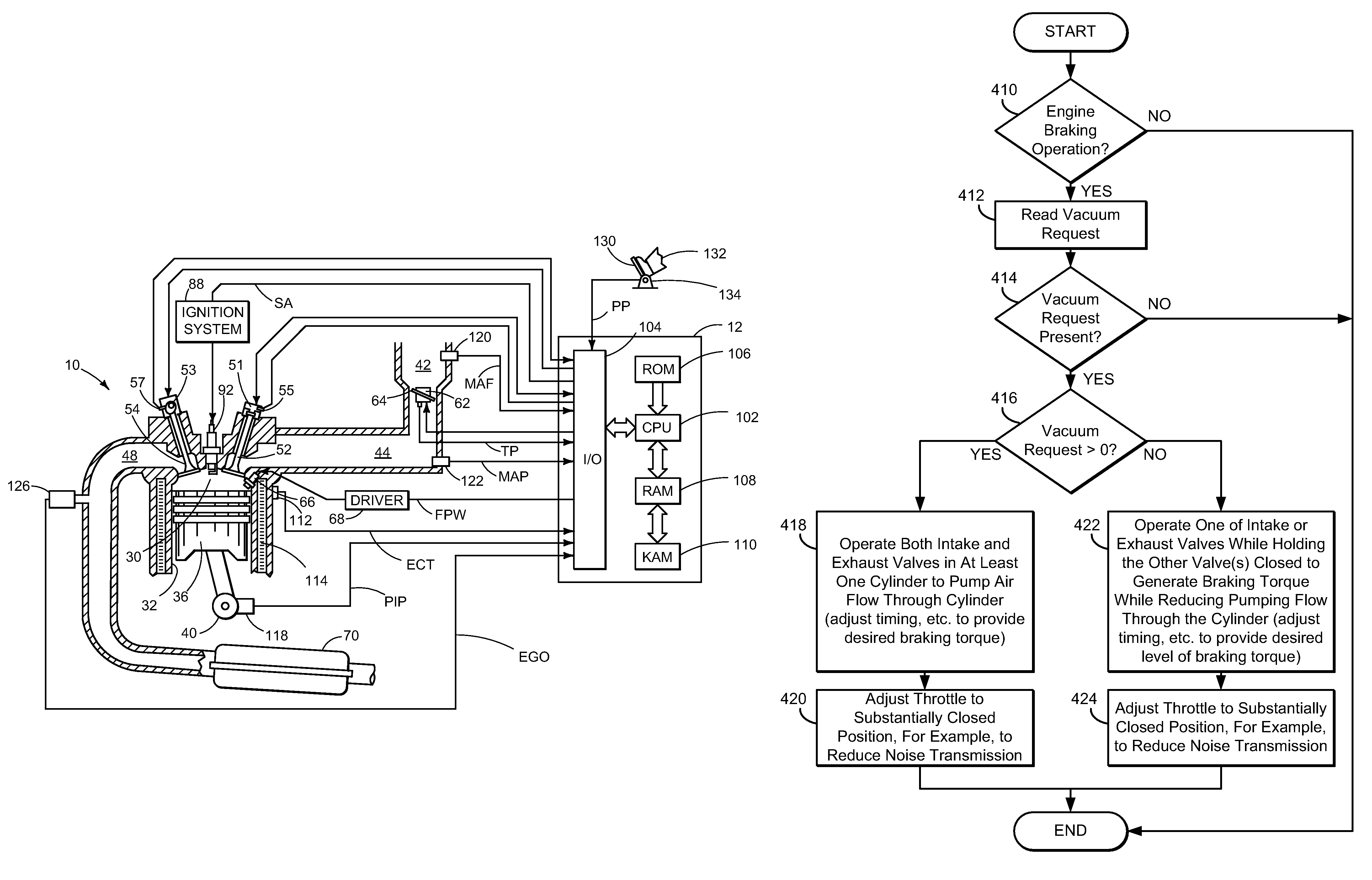
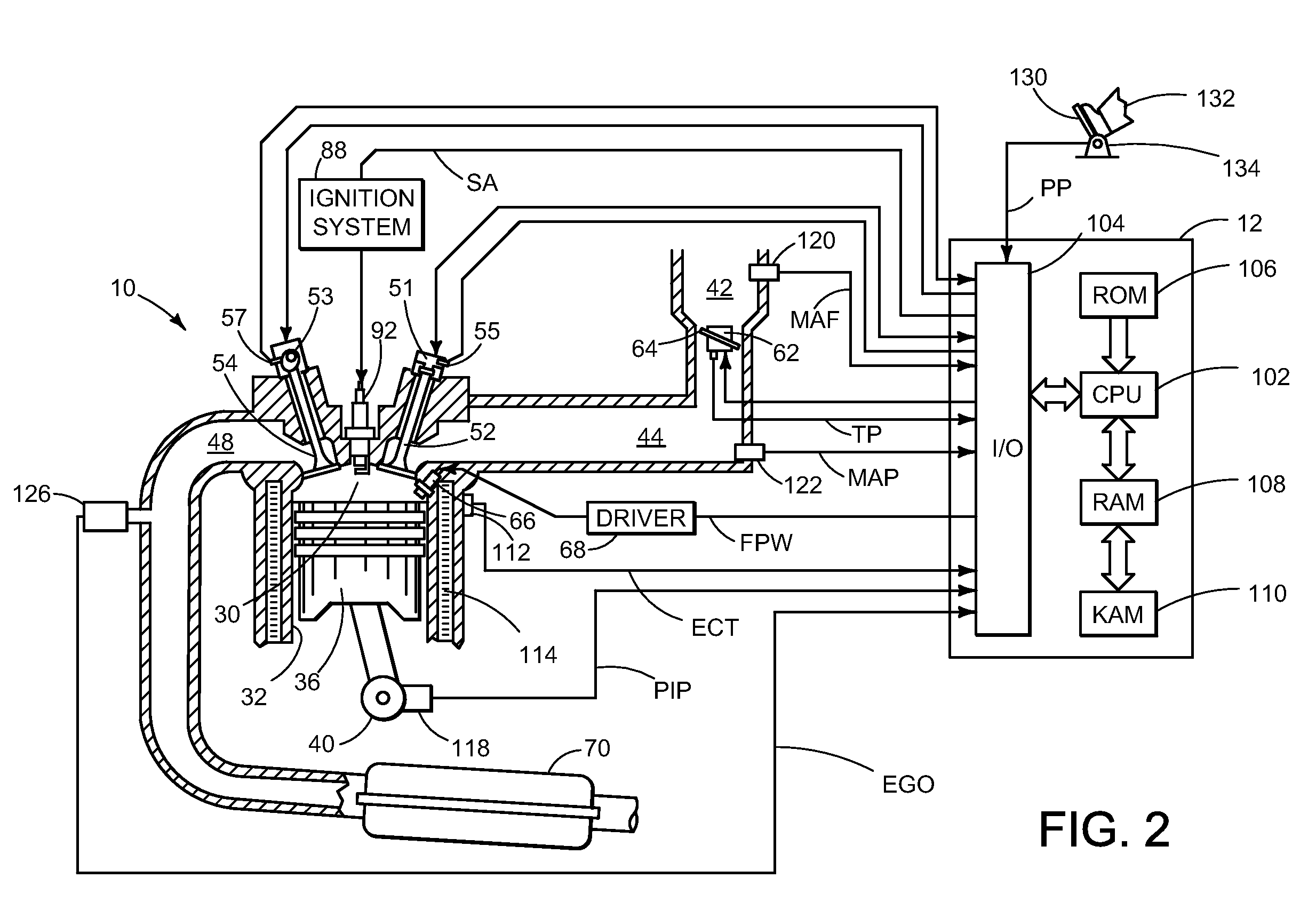
ActiveUS7930087B2Reduced effectivenessImprove fuel economyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveInlet valve
A method of operating an engine for a vehicle having at least a first cylinder, the method comprising of operating the first cylinder to provide at least one of compression braking and expansion braking by holding one of an intake valve and an exhaust valve of the first cylinder closed while opening, closing, and opening the other of the intake valve and the exhaust valve during a cycle of the first cylinder and during a first vacuum level of an intake manifold upstream of the first cylinder; and operating the first cylinder to provide at least one of compression braking and expansion braking by operating both the intake valve and the exhaust valve of the first cylinder during a cycle of the first cylinder to allow at least some air to flow through the first cylinder during a second vacuum level of the intake manifold.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
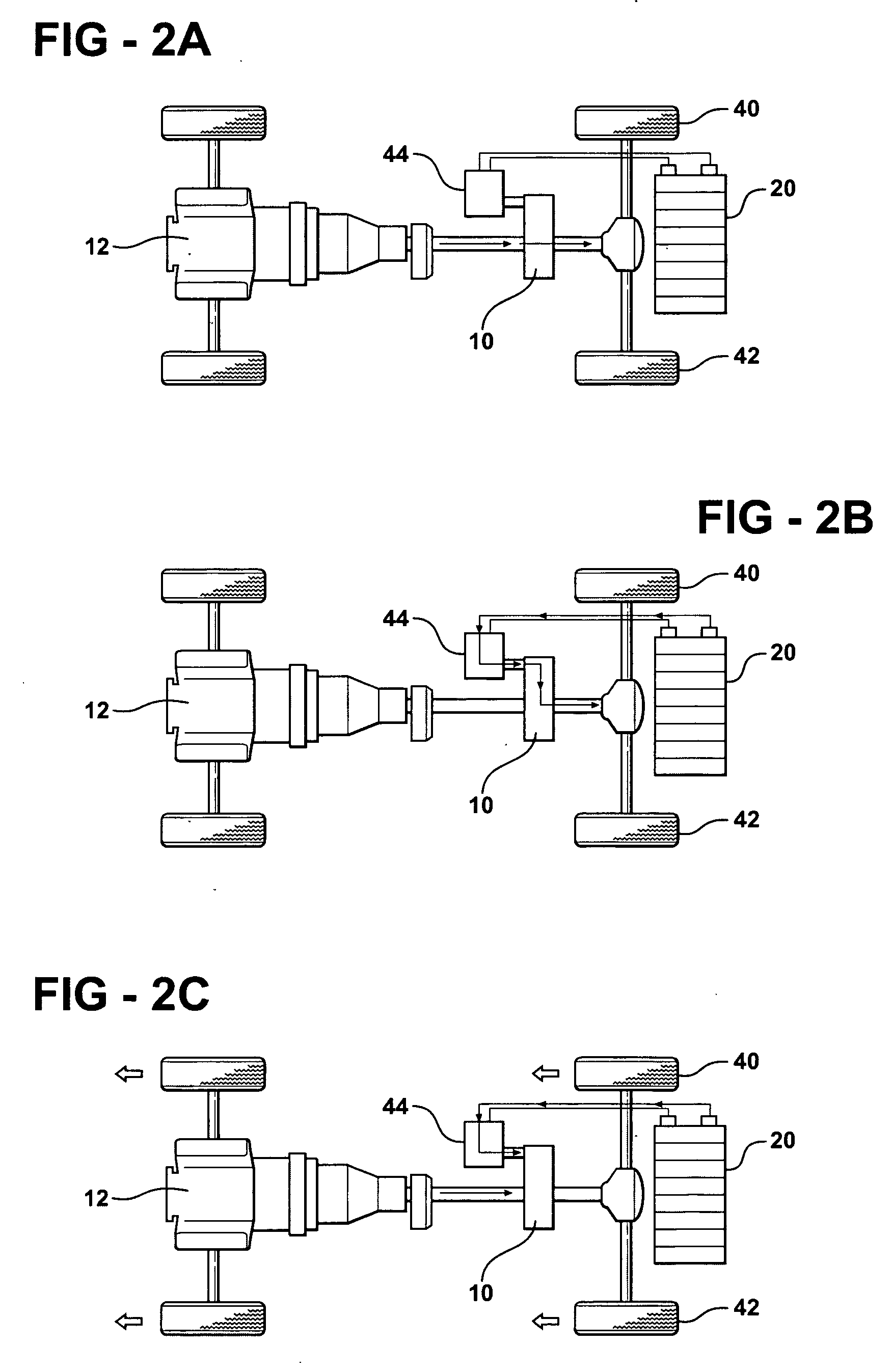
Hybrid vehicle formed by converting a conventional IC engine powered vehicle and method of such conversion
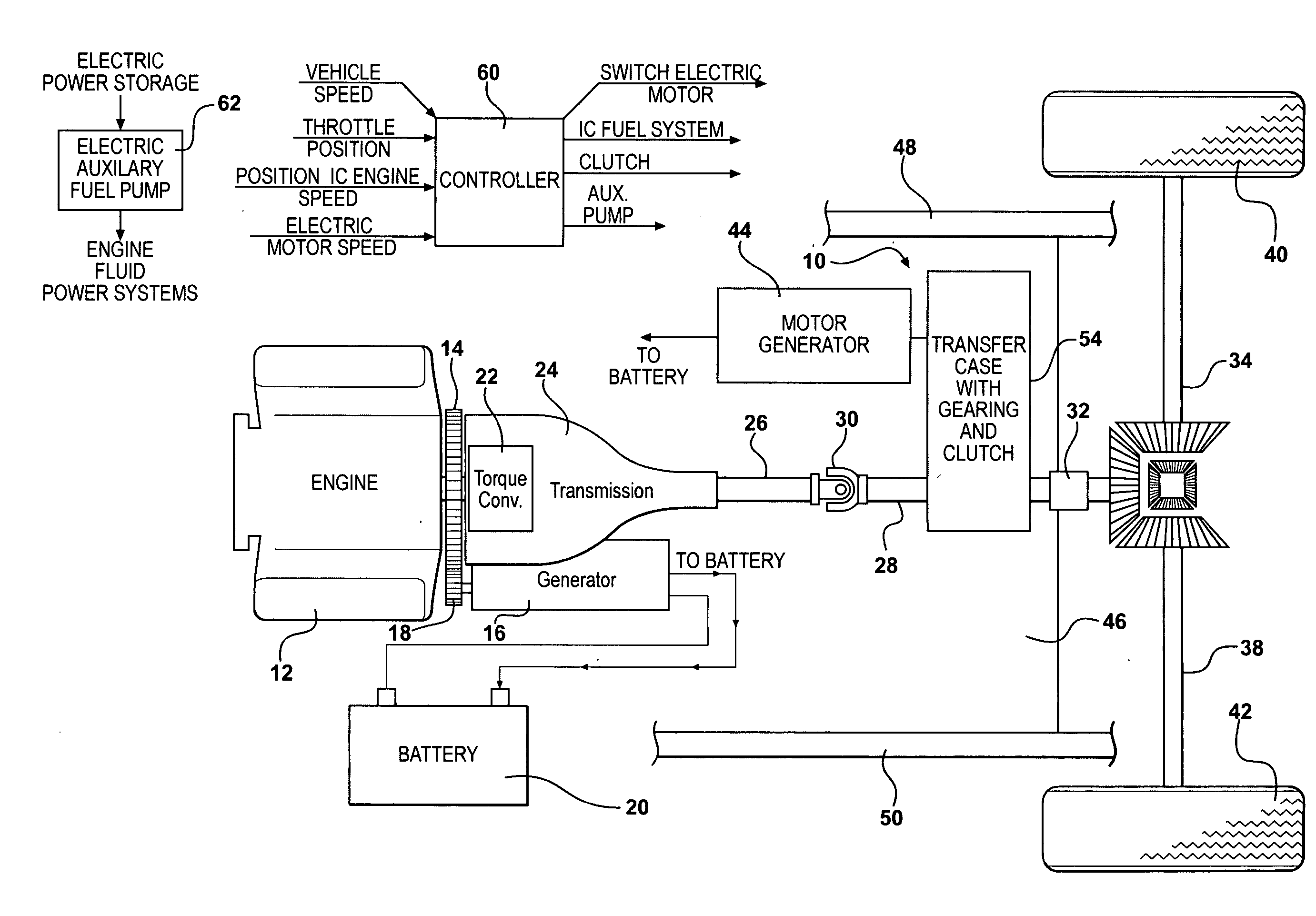
InactiveUS20060030450A1Reduce operating costsMaximize recoveryElectric propulsion mountingPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectricityCombustion
A method of converting a conventional internal combustion powered vehicle into a hybrid vehicle and apparatus for achieving that and modifying one of the serial elements of the drive train interconnecting the internal combustion to the driving wheels of the vehicle by providing an auxiliary power connection which allows the motor / generator to provide or remove mechanical power from the drive train during driving operation or regenerative braking. Generators switchingly connected to a vehicle battery and an electronic controller intercede the system relative to the operation of the vehicle and control the motor / generator switching the vehicle engine to apply an electric drive power to the vehicle at appropriate points in the vehicle operation and to drive the generator during braking of the vehicle to recharge the power source. The electric drive power elements are supported on a cross-member added to the vehicle.
Owner:HYBRID ELECTRIC CONVERSION
Hybrid electric drive and control method therefor
InactiveUS6376927B1Increase fuel consumptionImprove drivabilityInternal combustion piston enginesGearing controlHysteresisEngineering
A fuel management control method for a hybrid electric vehicle drive having an internal combustion engine and an electric motor arranged in parallel such that both can propel the vehicle; the system including an electric motor driven fuel pump and a programmable microprocessor; and wherein the method further includes monitoring vehicle speed and sensing braking pressure and directing signals of both vehicle speed and braking to the microprocessor and processing such inputs in accordance with an aggressive fuel management program including shut-off of fuel flow to the gas engine in response to vehicle braking at vehicle speeds above a predetermined maximum hysteresis speed and maintaining the fuel shut off during vehicle coasting above a predetermined speed while controlling the electric motor to provide regenerative braking or vehicle start during such fuel shut off modes of operation.
Owner:SATURN CORPORATION
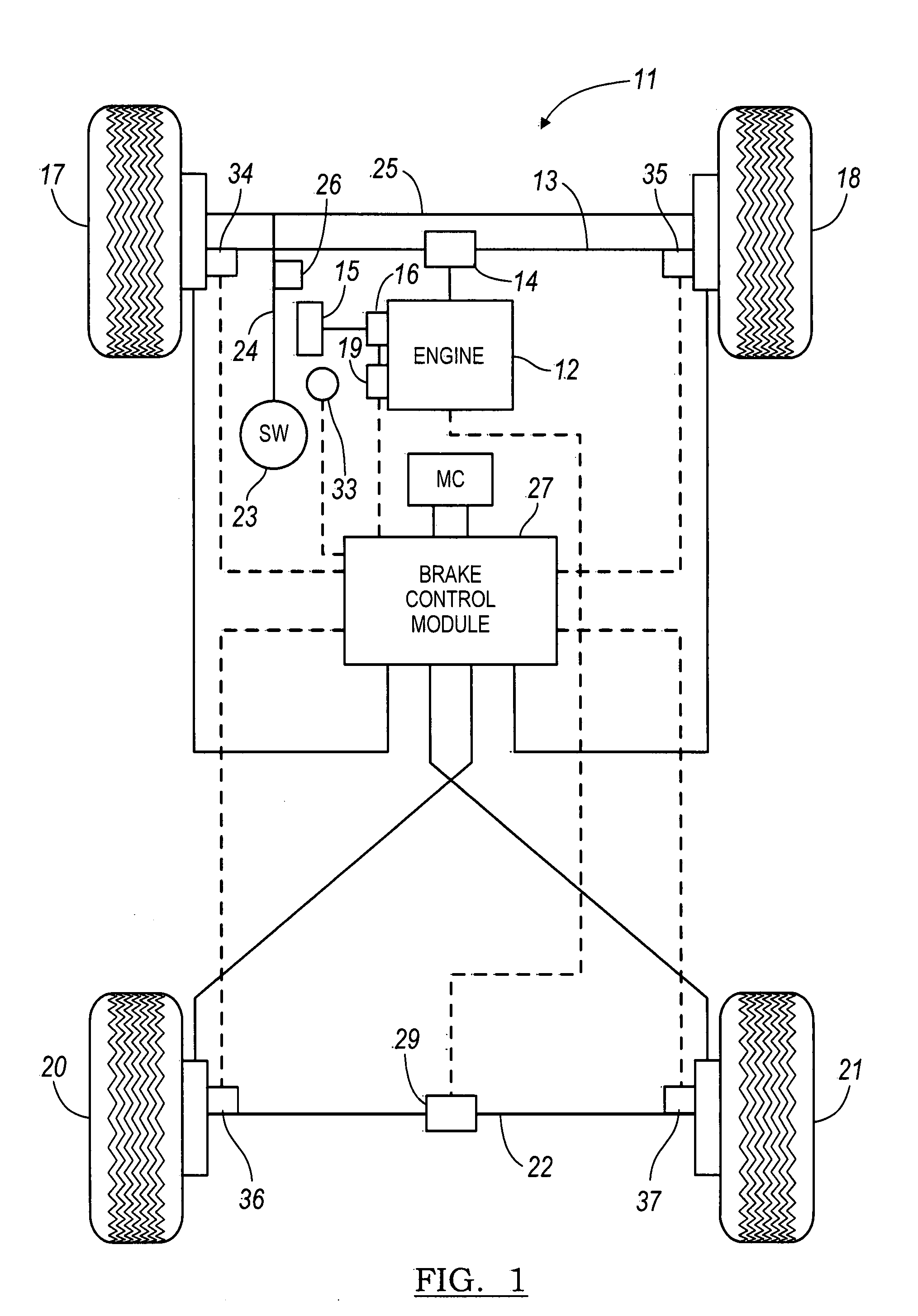
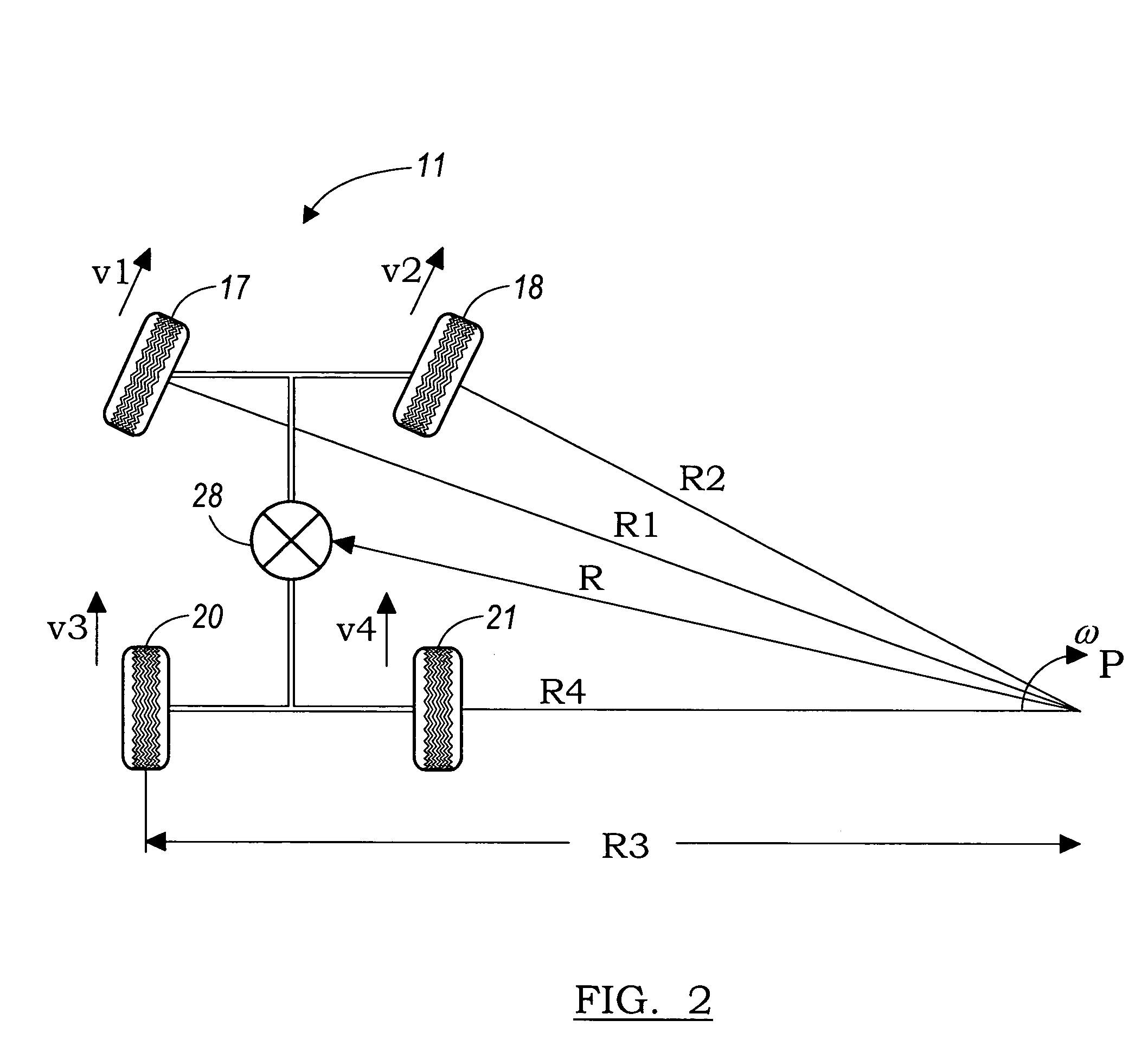
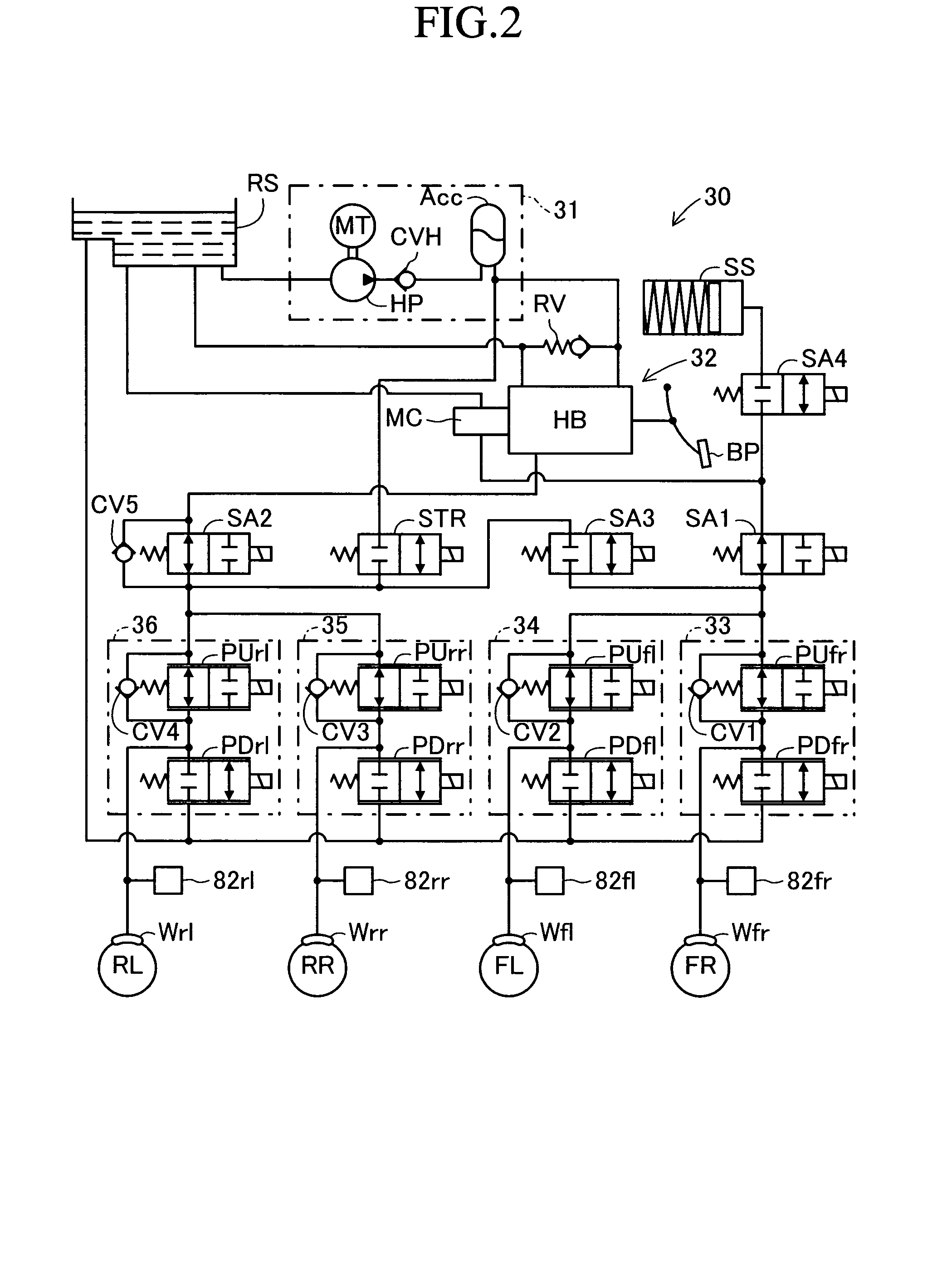
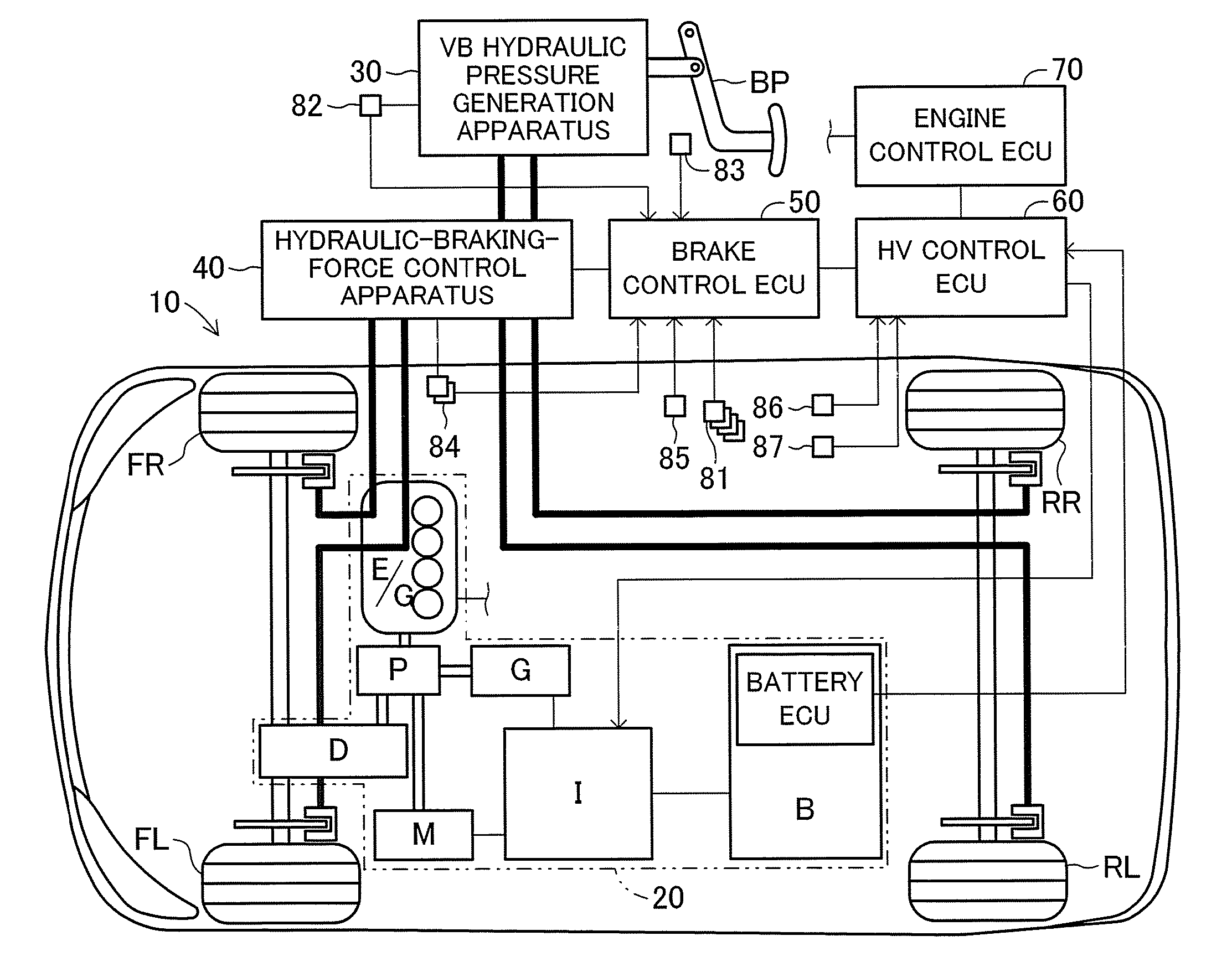
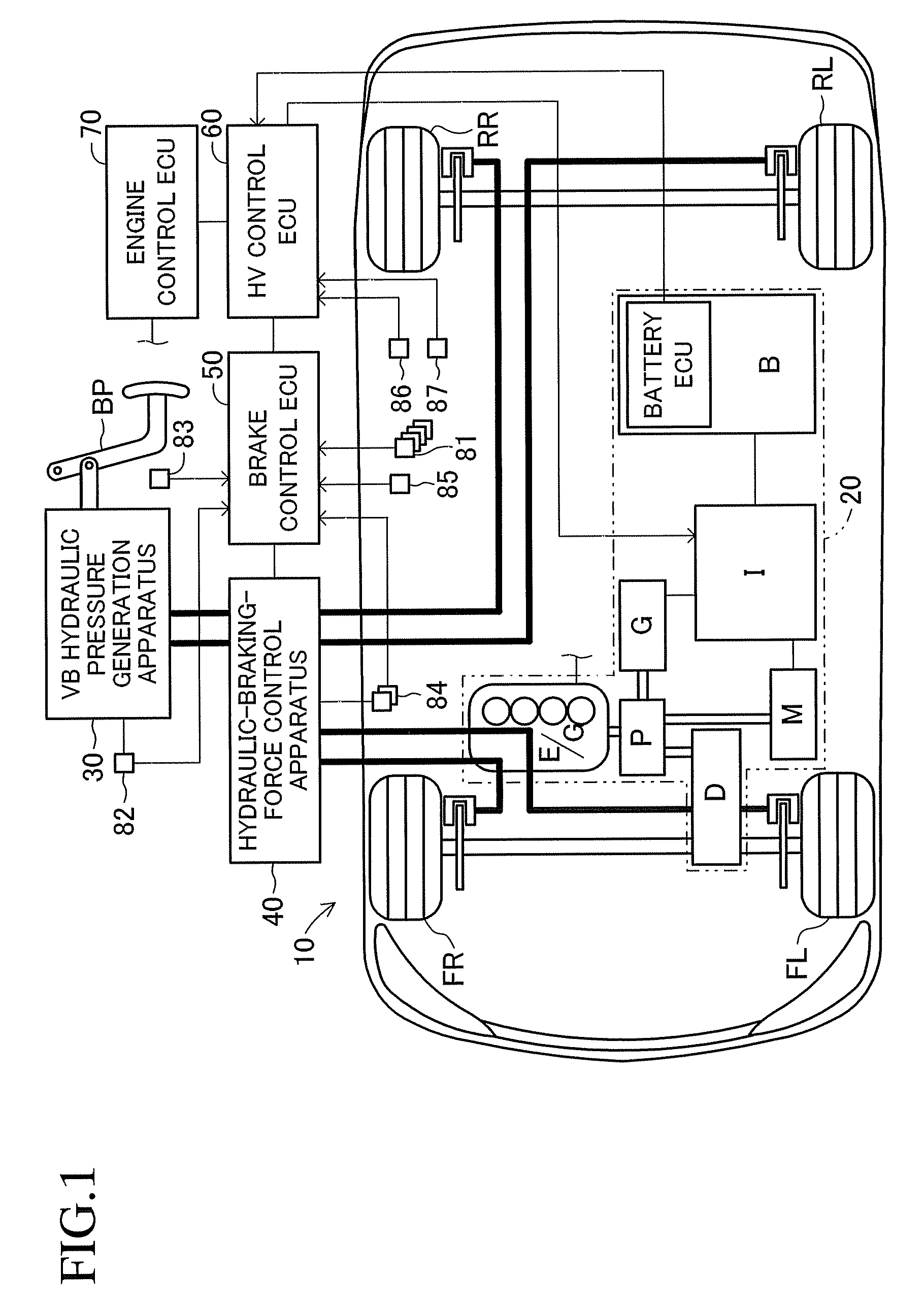
Vehicle brake device
InactiveUS20050269875A1Small dimensionLight weightPropulsion by batteries/cellsVehicular energy storageRegenerative brakeEngineering
A vehicle brake device is provided with a hydraulic brake device for boosting by a booster device a braking manipulation force generated upon a braking manipulation, for applying a base fluid pressure generated in dependence on the boosted brake manipulation force, to wheel cylinders of wheels so that a base hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels, and for driving a pump to generate and apply a controlled fluid pressure to the wheel cylinders so that a controlled hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels; braking manipulation state detecting means for detecting the braking manipulation state; a regenerative brake device for causing an electric motor to generate a regenerative brake force corresponding to the braking manipulation state on the wheels driven by the electric motor; variation detecting means for detecting the variation of an actual regenerative brake force actually generated by the regeneration braking device; and brake force compensating means for generating the controlled fluid pressure by driving the pump of the hydraulic brake device so that a controlled hydraulic brake force is generated on the wheels to compensate for the lack of the regenerative brake force due to the variation which is detected by the variation detecting means.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Vehicle System Having Regenerative Brake Control
ActiveUS20080100129A1Analogue computers for trafficBraking action transmissionRegenerative brakeKinetic energy
A method is provided for controlling the braking of a vehicle that has a first set of friction brakes for applying a first apply brake force to a first set of wheels and a second set of friction brakes for applying a second brake apply force to a second set of wheels. A powertrain assembly is coupled to the second set of wheels. The powertrain assembly includes a regenerative braking unit capable of recapturing kinetic energy from the second set of wheels. The vehicle is braked in a first phase of control using regenerative braking to brake the second set of wheels to achieve up to a first value of braking. The vehicle is braked in a second phase of control using the regenerative braking to maintain braking of the second set of wheels at the first value of braking force while selectively applying the first friction brakes to the first set of wheels up to a second value of braking.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Method for a changing safety signaling system
The present invention provides a method for a changing safety signaling system. The safety signaling system can change as a result of changing driving conditions that stem from changes in the weather or changes in vehicle velocity. As a vehicle brakes, coasts, turns, or accelerates, front-facing, side-facing, top-facing, and / or rear facing indicators can communicate vehicular acceleration, coasting, and braking to a pedestrian or other vehicles. A distance sensor can be used to trigger a signal to alert a second vehicle that the first vehicle is braking hard and slowing fast or can be used to warn the operator of the first car that a collision may be imminent and can be used to warn the operator of a second car that measures can be taken to avoid a collision or minimize damage from a collision. The instant invention can be utilized by either a first car or a second car.
Owner:SONG WON MOO
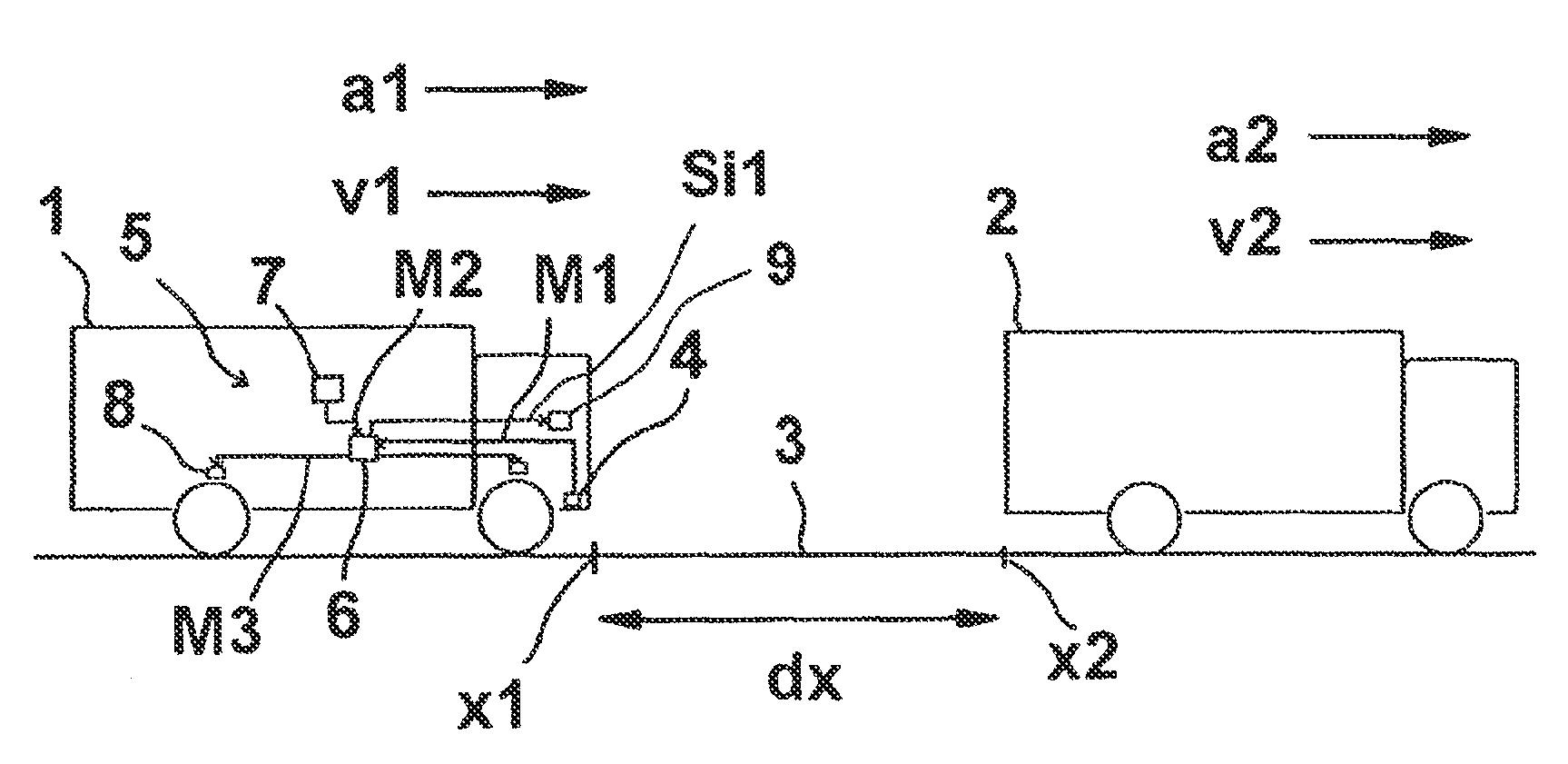
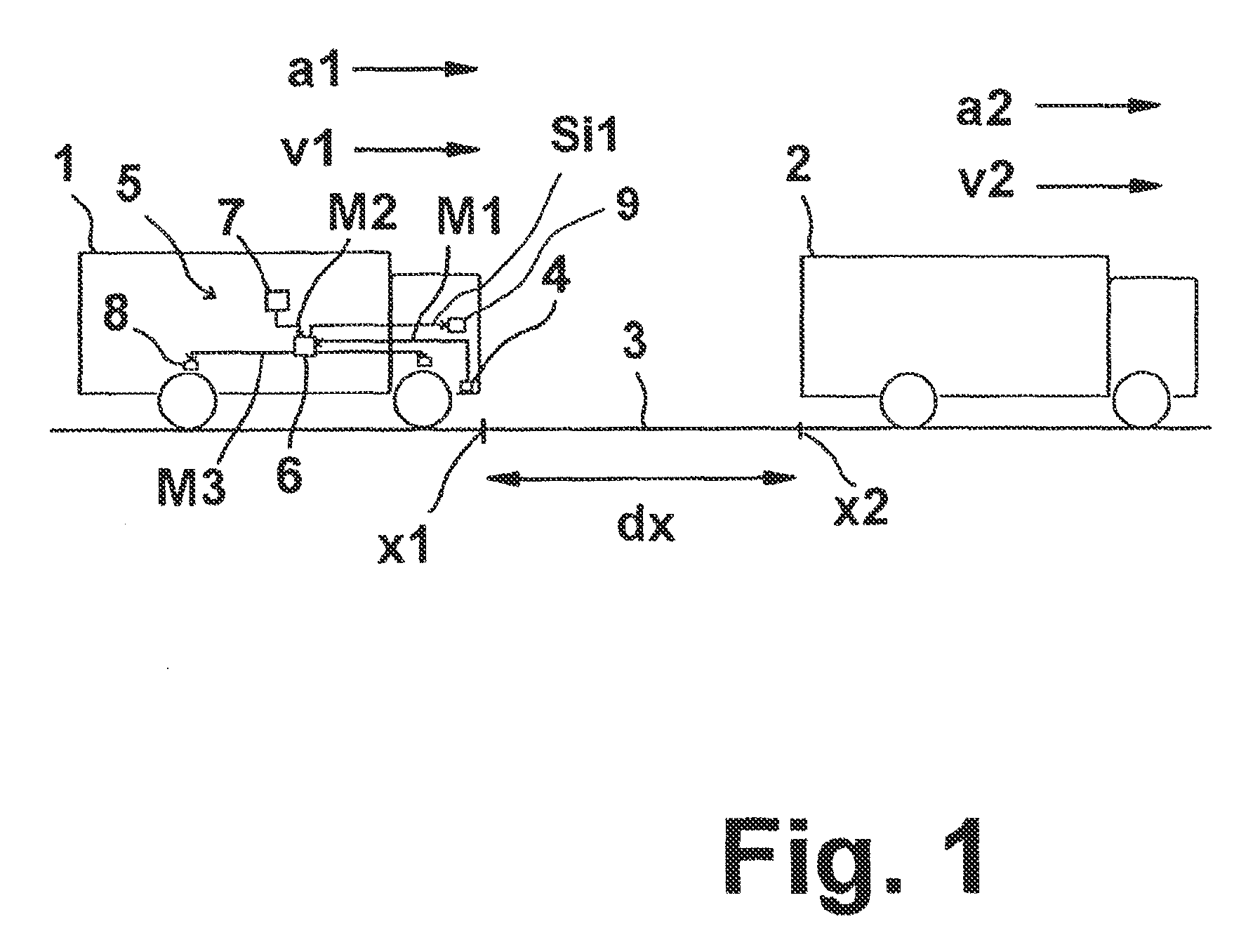
Method for determining an emergency braking situation of a vehicle
ActiveUS9566959B2Reliable recognitionReduce the possibilityVehicle fittingsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementControl theoryComputer science
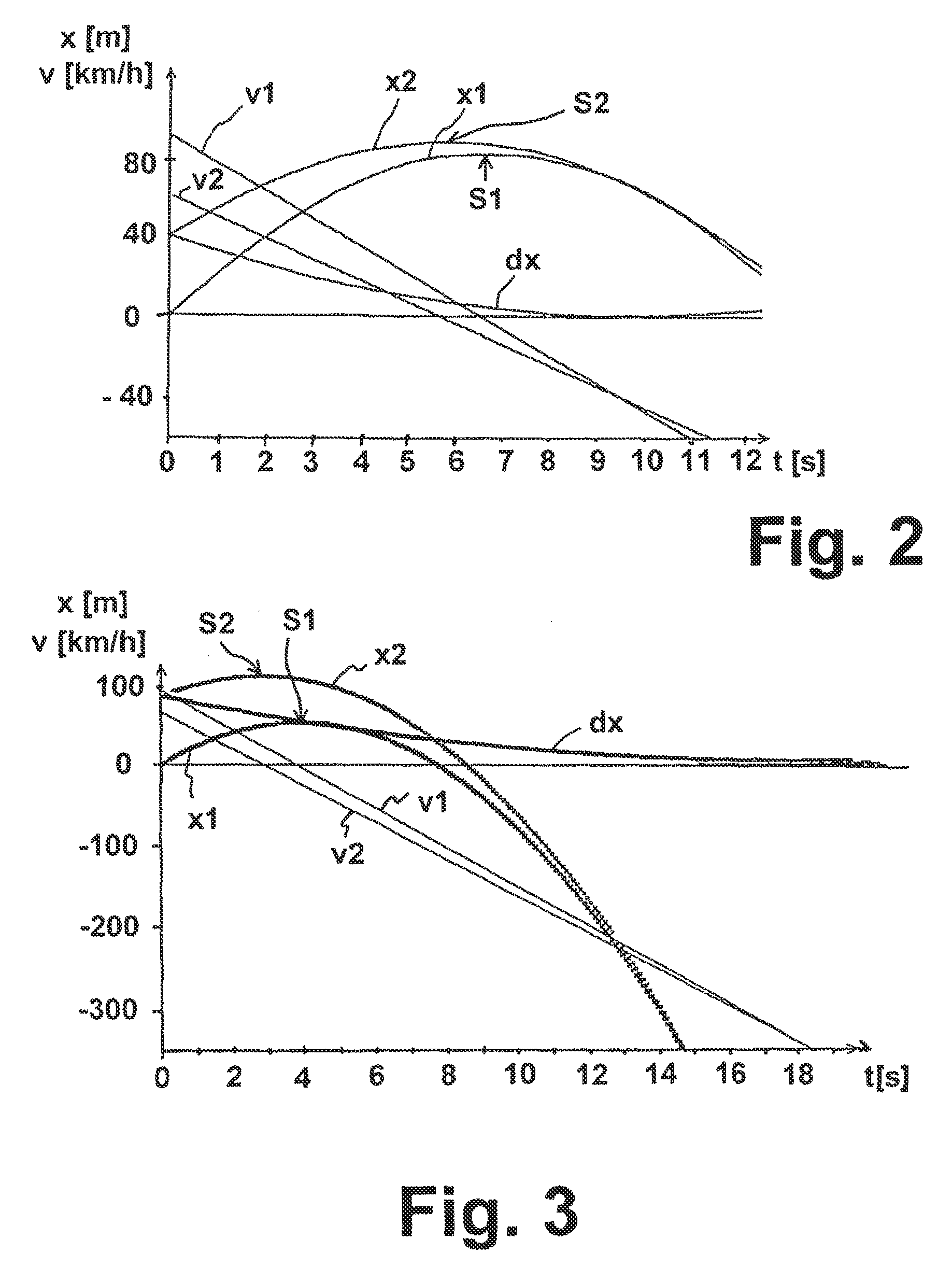
To determine whether an emergency braking situation exists for a vehicle, the vehicle determines at least the following state variables: its own velocity, its own longitudinal acceleration, its relative distance from an object in front, and the speed and acceleration of the object in front. A suitable evaluation method to assess whether an emergency braking situation is present is determined as a function of these state variables from a plurality of evaluation method options, including at least a movement equation evaluation method in which a movement equation system of the vehicle and of the object in front is determined, and an evaluation method in which a braking distance of the vehicle is determined.
Owner:ZF CV SYST EURO BV
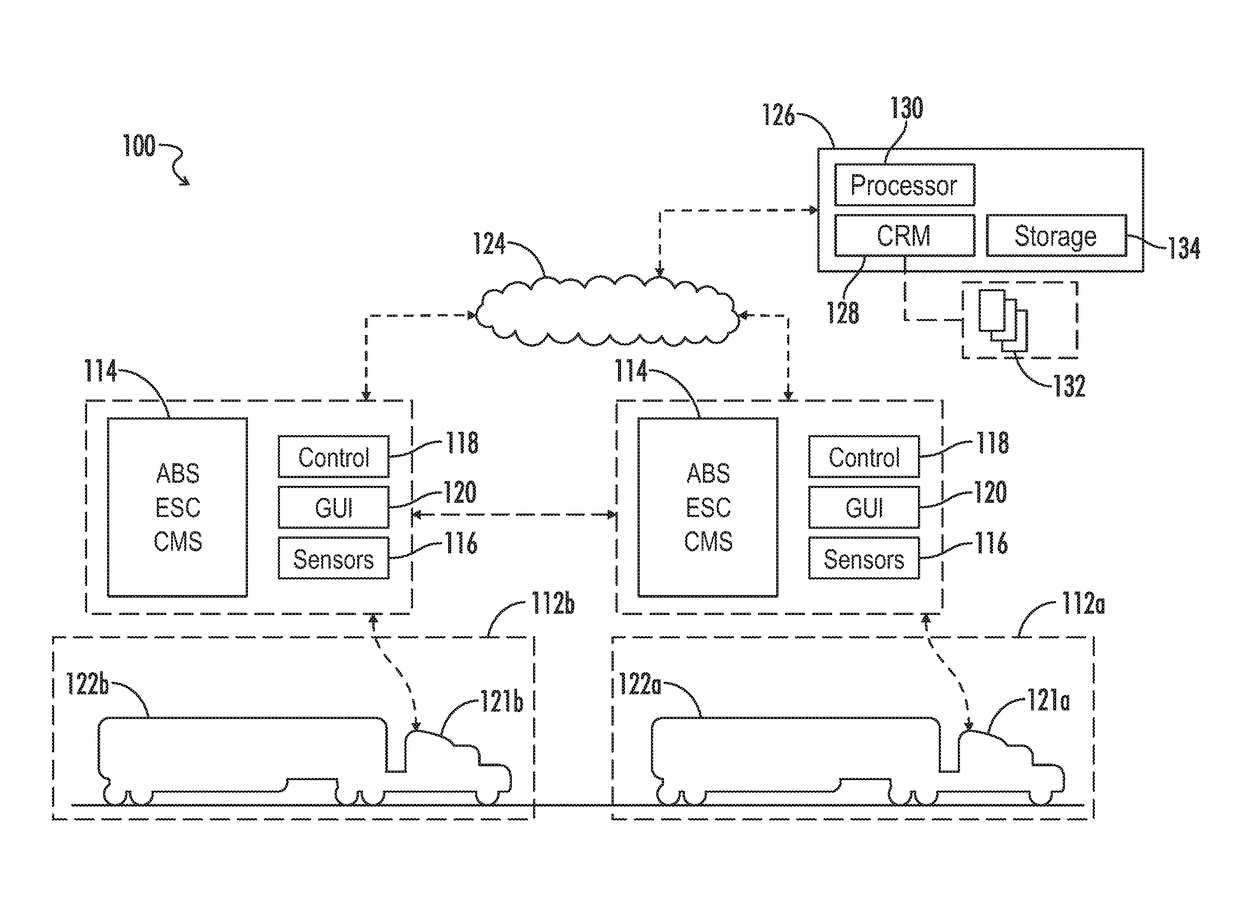
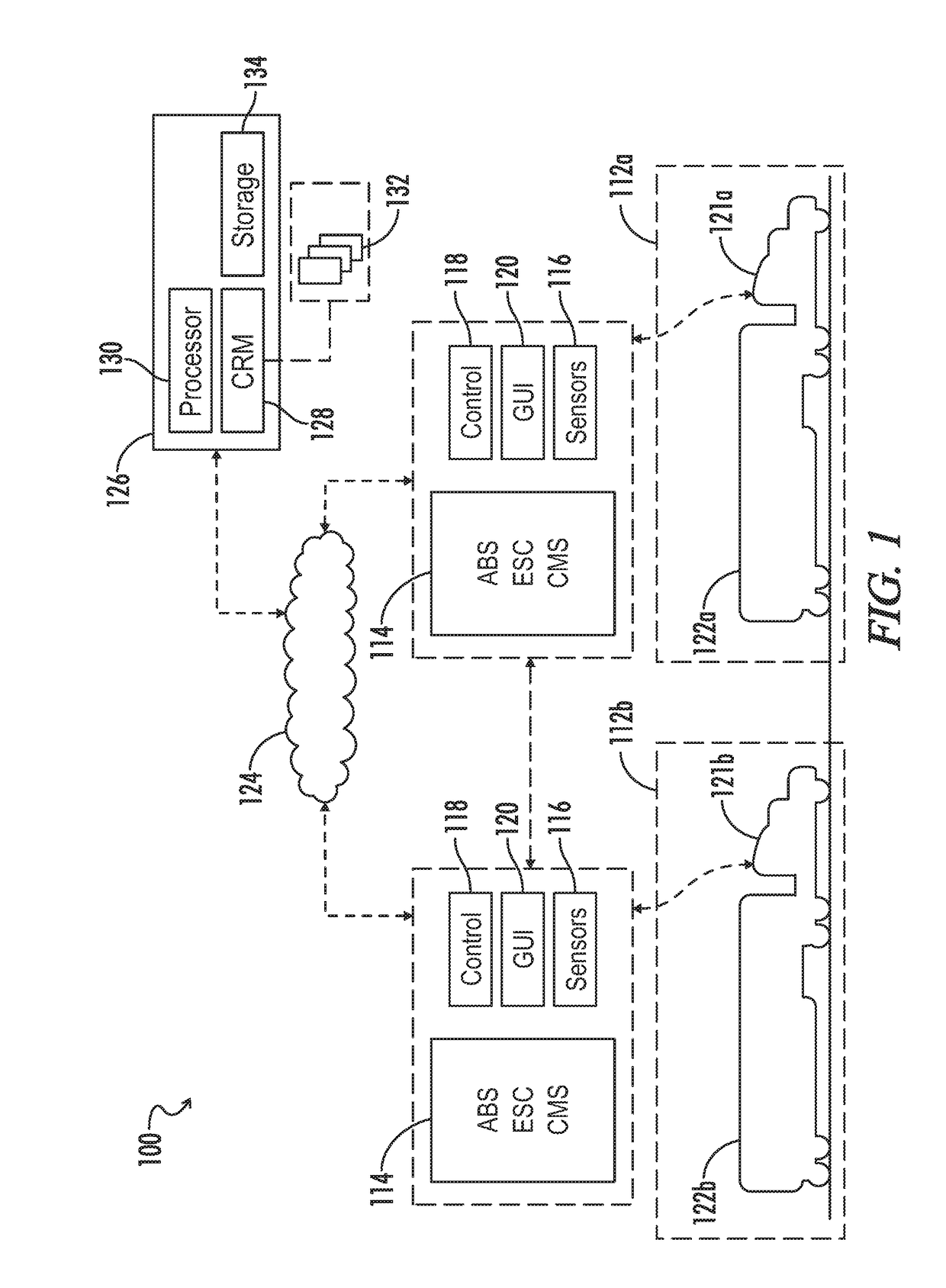
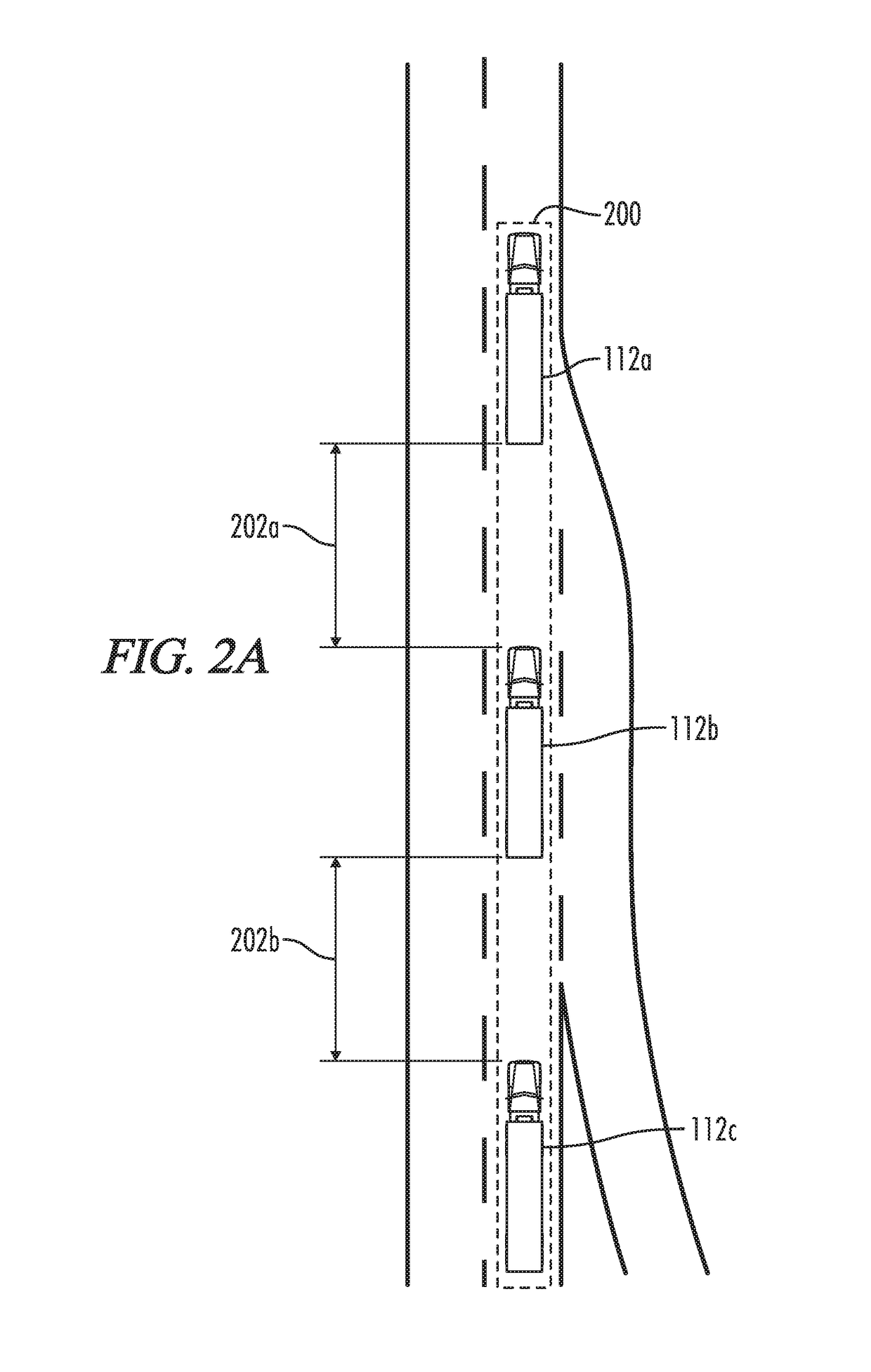
System and method for adjusting vehicle platoon distances based on predicted external perturbations
A control system is provided for platooning a plurality of vehicles, each of which equipped with vehicle braking control systems and V2V communication system components. The system determines nominal following distances for each of said following vehicles relative to an immediately preceding vehicle, based in part on brake performance capabilities. Vehicle sensors throughout the platoon are implemented to monitor target vehicles positioned relative to the platoon, and some or all of the nominal following distances are dynamically adjusted to account for braking event risks associated with the target vehicles. Adjustment to following distances for trailing vehicles may be proactively applied even before braking reaction is determined or applied for a lead vehicle, and control signals are simultaneously generated implementing vehicle movement adjustments based on the following distance adjustments. Adjustments may be based on threshold violations associated with target vehicles in front, laterally merging into, or tailgating behind the platoon.
Owner:WABCO USA LLC
Implantable medical device telemetry control systems and methods of use
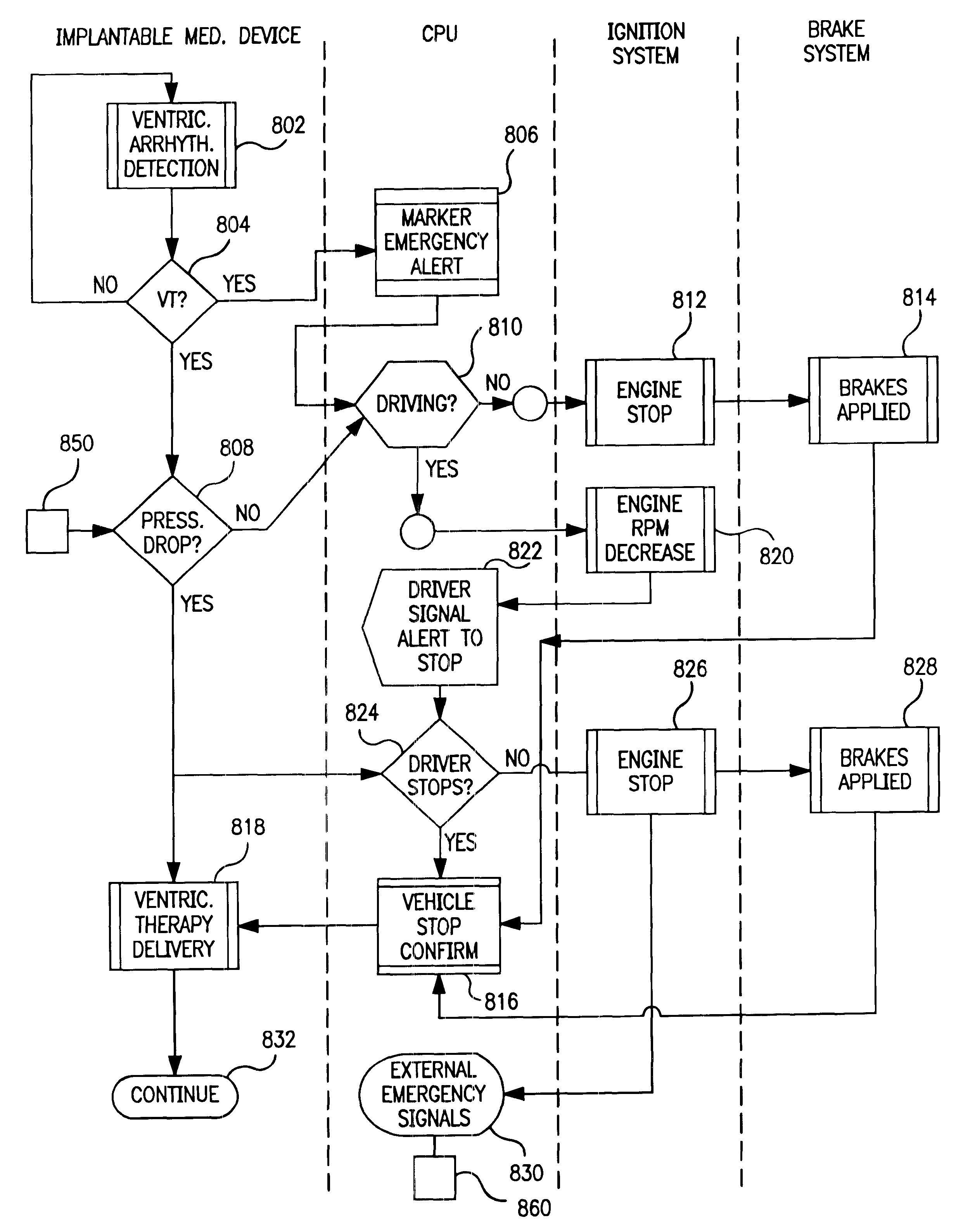
Implantable medical device telemetry control systems and methods are used to coordinate medical therapy delivery from an implantable medical device (IMD) to a patient-driver of a vehicle, e.g., automobile. In one embodiment, the control system alerts the patient-driver to stop the vehicle after a medical event is detected by the IMD. Once the vehicle is stopped, the therapy is delivered. In another embodiment, a vehicle control module is provided which actively controls various subsystems of the car in response to a detected medical event. For example, the vehicle control module may control vehicle engine speed or vehicle braking to slow or stop the vehicle or, alternatively, assist the patient-driver in stopping the vehicle, prior to or simultaneously with therapy delivery. In still other embodiments, an emergency communication is automatically transmitted to emergency personnel informing the same of the medical event.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
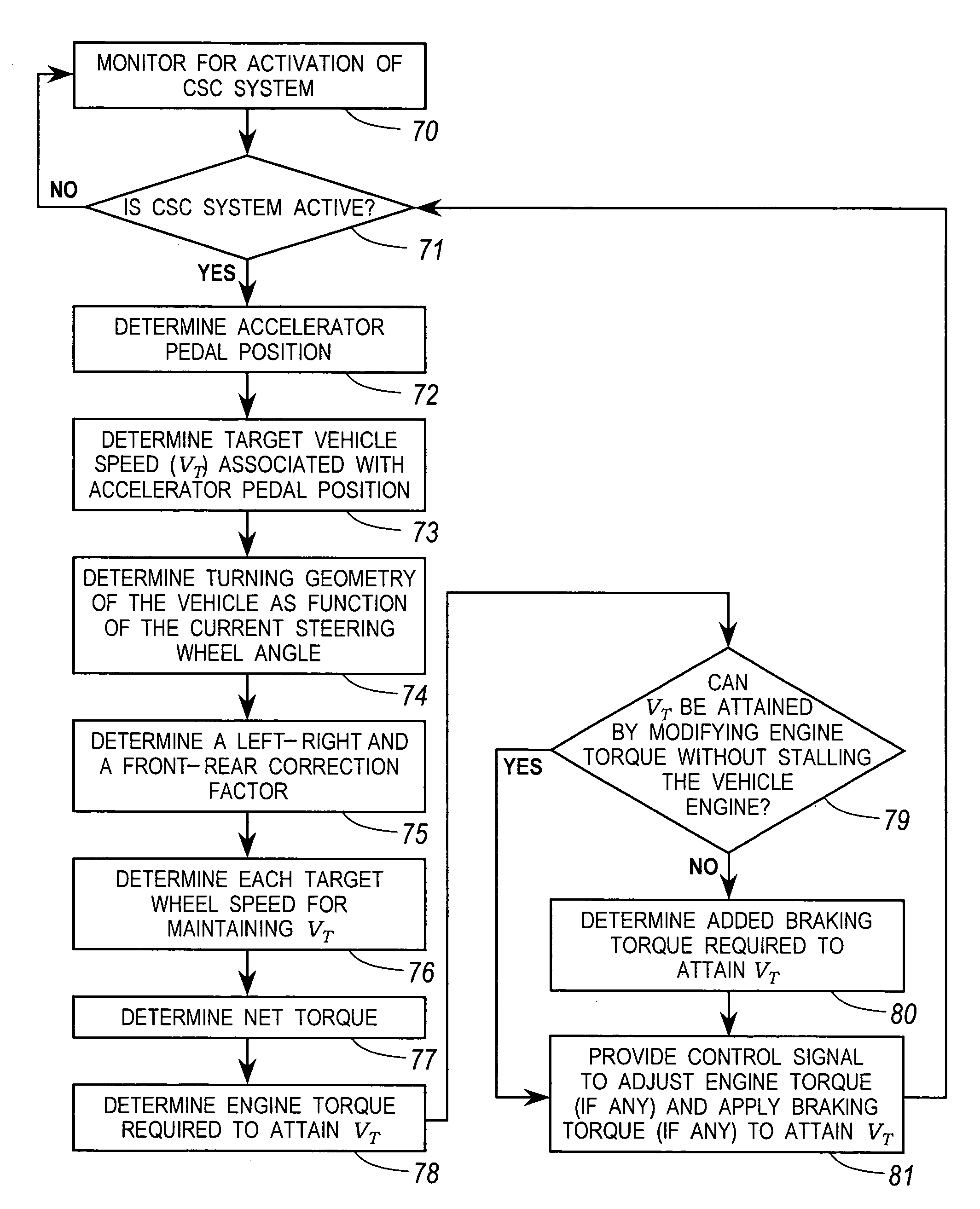
Constant speed control system
A method is provided for controlling a low speed operation of a vehicle. A speed activation switch is activated. A target vehicle speed is calculated in response to an accelerator pedal demand as determined by an accelerator pedal position where each respective accelerator pedal position is associated with a respective predetermined target vehicle speed. A vehicle turning geometry is determined in response to a steering wheel angle input. A target wheel speed of each of a plurality of vehicle wheels is calculated as a function of the target vehicle speed and turning geometry. An actual wheel speed of each wheel is measured. A net torque is determined in response to the target wheel speeds and actual wheel speeds. An engine output torque and a braking torque are determined in response to the net torque. The engine output torque and the total vehicle braking torque are controlled for cooperatively maintaining the target vehicle speed.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
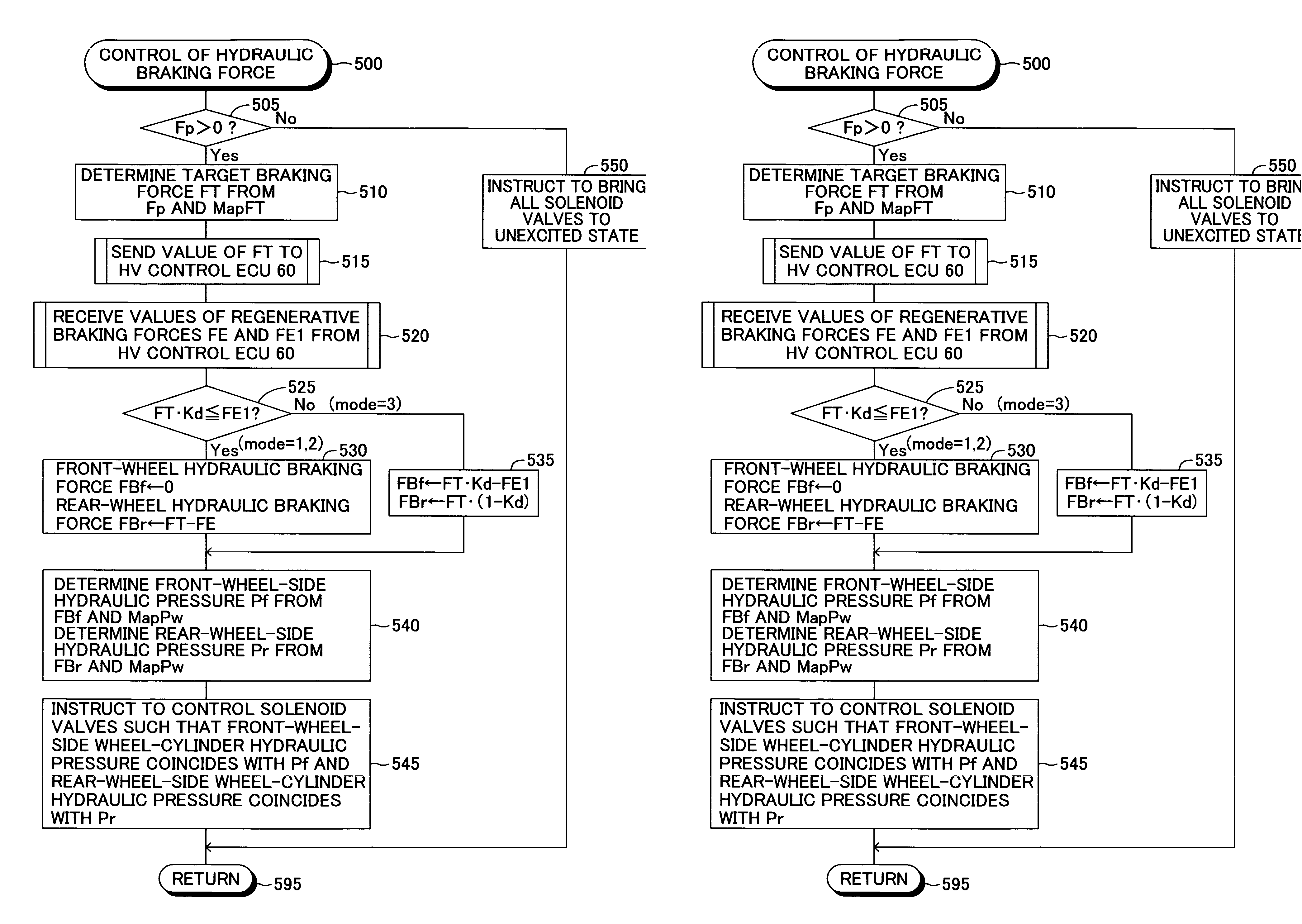
Brake control apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20070018499A1Suppress spinoutHighly efficient collection of electrical energyPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingPropulsion by batteries/cellsDrive wheelRegenerative brake
A brake apparatus for a vehicle generally sets an upper limit value of regenerative braking force to the maximum value of the regenerative braking force which can be generated at the present. In the case of a front-wheel-drive vehicle, the total braking force, the sum of front-wheel braking force (front-wheel hydraulic braking force+regenerative braking force) and rear-wheel braking force (rear-wheel hydraulic braking force), is rendered coincident with a target braking force corresponding to a brake pedal depressing force, and the regenerative braking force is set to a largest possible value equal to or less than the upper limit value. As a result, the regenerative braking force can be larger than front-wheel-side target distribution braking force. The upper limit value is decreased from the maximum value by an amount corresponding to the degree of easiness of occurrence of a locking tendency at the driven wheels (front wheels).
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Brake monitoring system
InactiveUS20080257656A1Variably controlEasy to assembleAutomatic initiationsBrake typesDisplay deviceMonitoring system
A brake monitoring system is disclosed. The monitoring system includes a primary braking system located in a towing vehicle. A towed vehicle is releasably attached to the towing vehicle. A towed vehicle braking system is mounted in the towed vehicle. An auxiliary braking device is configured to activate the towed vehicle braking system and to sense at least one parameter of the auxiliary braking device or of the towed vehicle braking system. A transmitter is in communication with the auxiliary braking device. The transmitter is configured to send a signal about the parameter. A receiver is located in the towing vehicle. The receiver is configured to receive the signal from the transmitter. A display is located in the towing vehicle and is in communication with the receiver. The display is configured to display a message to a towing vehicle occupant about the parameter.
Owner:EDWARDS JERRY A
Brake control apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20060220453A1Improve energy efficiencyBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionRegenerative brakeDifferential pressure
A brake apparatus for a vehicle controls braking force acting on front wheels by hydraulic braking force (front-wheel-side vacuum-booster hydraulic pressure fraction+linear-valve differential pressure fraction), which is frictional braking force, and regenerative braking force, and controls braking force acting on rear wheels by hydraulic braking force (rear-wheel-side vacuum-booster hydraulic pressure fraction) only, to thereby perform regeneration-coordinative brake control. During performance of ABS control, the apparatus sets the limit regenerative braking force to a force under which locking of the front wheels does not occur in a case in which the force acts on the front wheels, which are wheels undergoing regenerative braking, and adjusts the regenerative braking force such that the regenerative braking force does not exceed the limit regenerative braking force.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
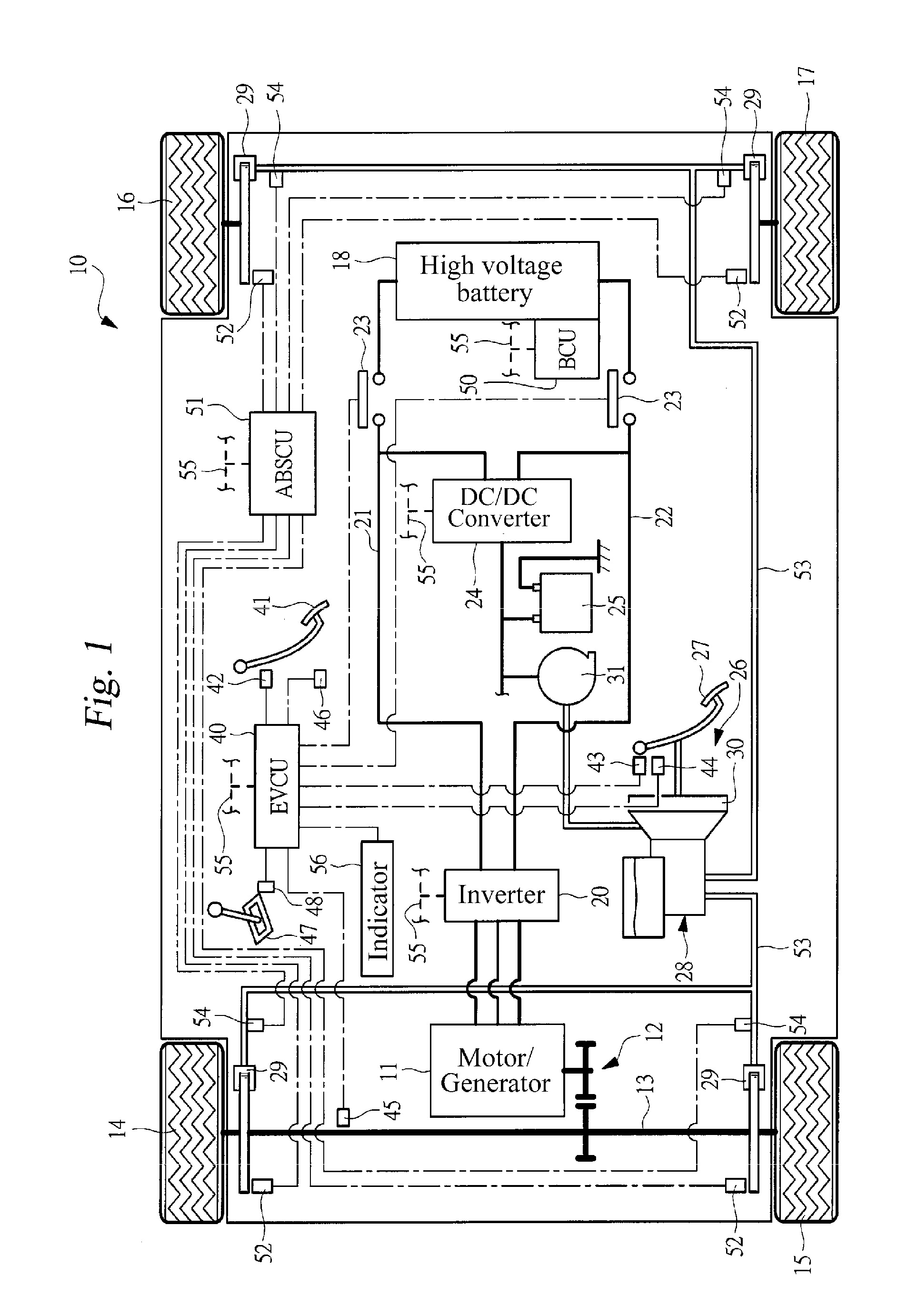
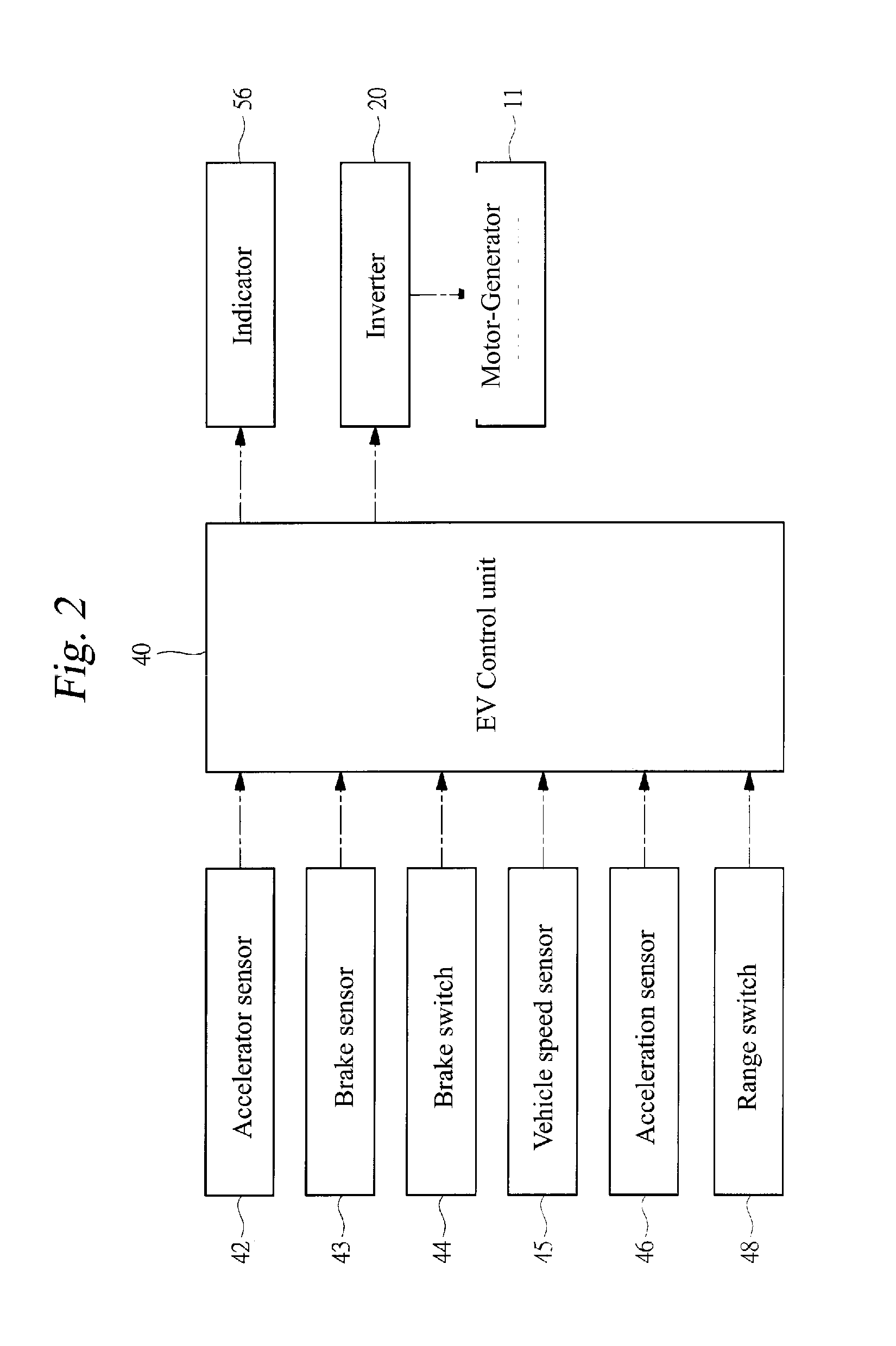
Control apparatus for electric vehicle
ActiveUS20100235043A1Creep travel capabilitySufficient creep torqueVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesElectric vehicleControl theory
A creep travel capability of an electric vehicle is secured when an abnormality occurs in a brake sensor. When an accelerator operation amount reaches 0% in a low vehicle speed region, a target creep torque is set, whereupon a motor-generator is controlled toward the target creep torque. The target creep torque is reduced as a brake pedal is depressed in order to suppress heat generation and the like in the motor-generator during vehicle braking. Hence, in an electric vehicle in which the target creep torque is varied in accordance with the brake operation amount, when an abnormality occurs (step S11) in a brake sensor for detecting a brake operation amount, a preset prescribed creep torque is employed as the target creep torque regardless of the brake operation amount (step S15). The prescribed creep torque is set at a required magnitude for securing the creep travel capability.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
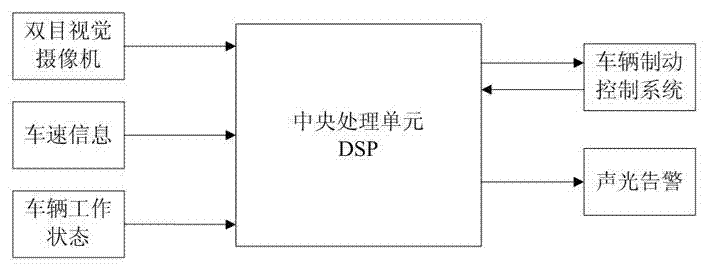
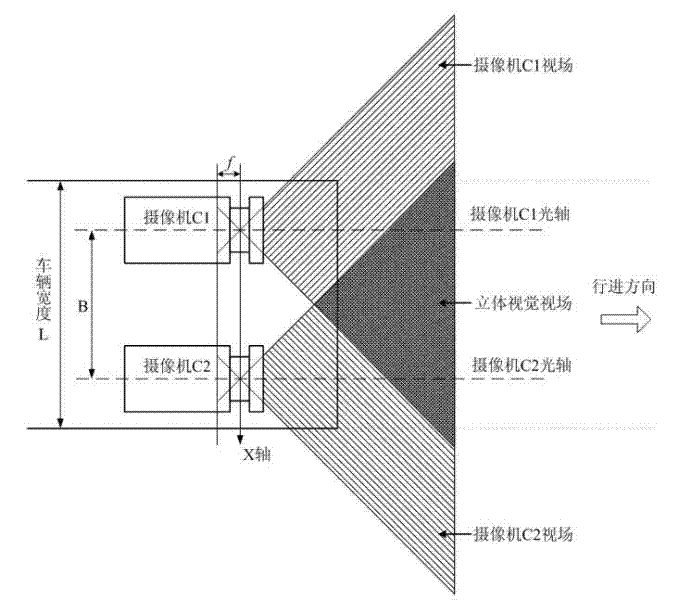
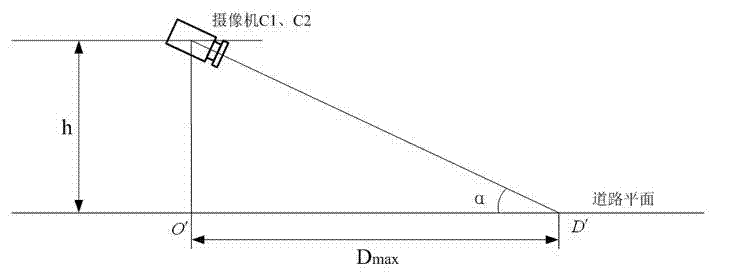
Stereoscopic vision based emergency treatment device and method for running vehicles
ActiveCN102390370AReduce speedAcoustic signal devicesAutomatic initiationsDriver/operatorVision based
The invention relates to a stereoscopic vision based emergency treatment device and method for running vehicles, wherein the device comprises a binocular-vision image pick-up unit, an on-board bus interface, a central processing unit, a vehicle braking control system and an acousto-optic alarm circuit. The binocular-vision image pick-up unit is used for capturing an image of a road in front of a vehicle; the DSP (digital signal processor) based central processing unit is adopted for carrying out real-time quick calculation on a visual image so as to obtain a three-dimensional road scene, and compares the obtained three-dimensional road scene with a safe driving road model set up by a system so as to judge whether obstacles or dangers exist in the traveling direction of the vehicle; when adanger is found, the vehicle braking control system is started so as to reduce the speed of the vehicle and send an acousto-optic alarm to a driver; meanwhile, the central processing unit is connected with a vehicle sensor by an inter-vehicle bus so as to detect the state of the vehicle, and when the vehicle has mechanical or circuit faults, a braking system is started so as to reduce the speed of the vehicle and send an acousto-optic alarm. The device disclosed by the invention can be arranged on ordinary motor vehicles so as to avoid the occurrence of accidents or reduce the accident loss, thereby improving the driving safety performance.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
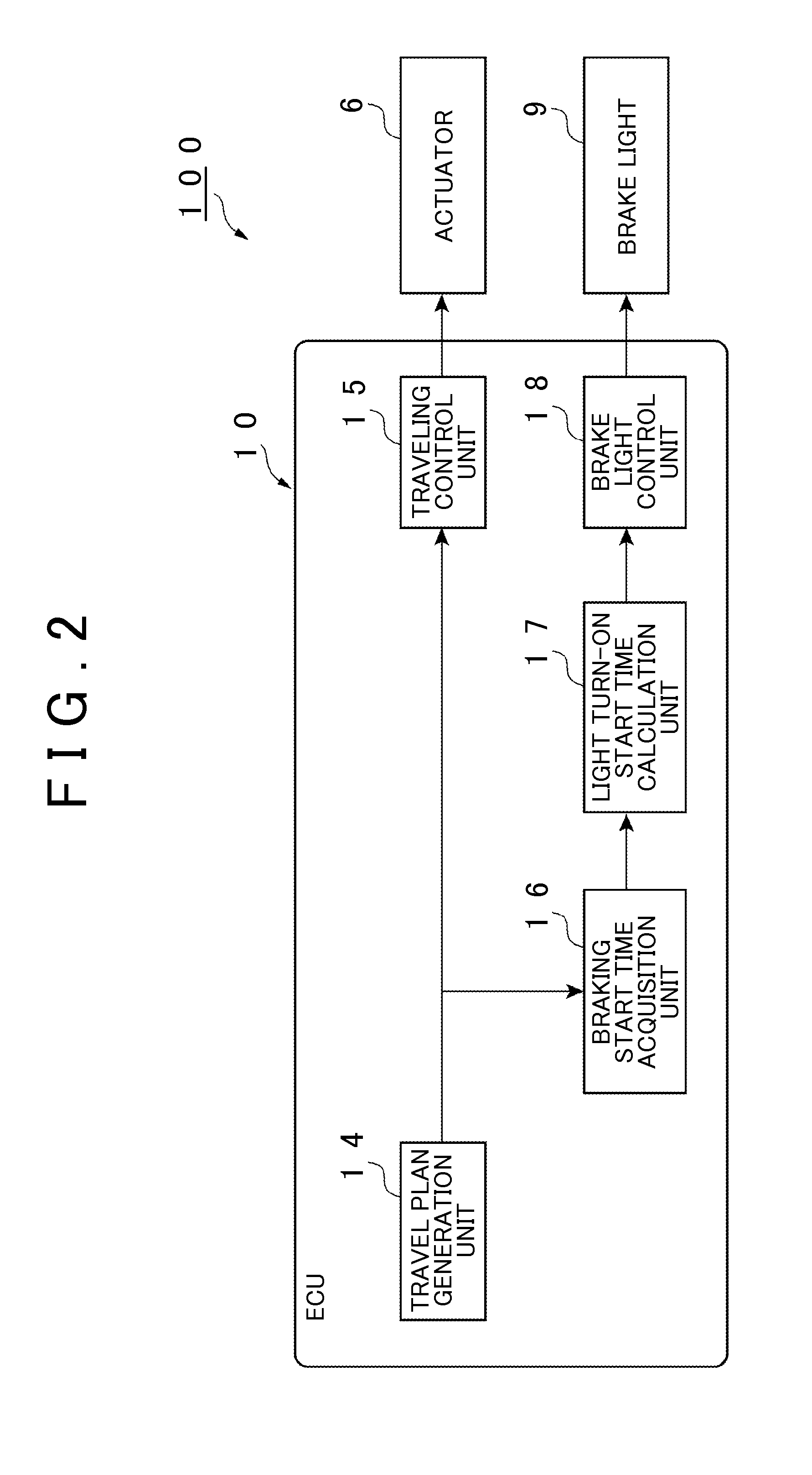
Autonomous driving vehicle system
ActiveUS20160139598A1Reduce the possibilityInstruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processStart timeEngineering
An autonomous driving vehicle system includes: a surrounding information detection unit that is configured to detect surrounding information on a vehicle; and at least one electronic control unit including: a travel plan generation unit configured to generate a travel plan along a pre-set target route based on the surrounding information and map information; a traveling control unit configured to autonomously control a traveling of the vehicle based on the travel plan; and a warning light control unit configured to turn on a warning light earlier than a start time of a braking of the vehicle in the travel plan, the warning light informing a following vehicle about the braking.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
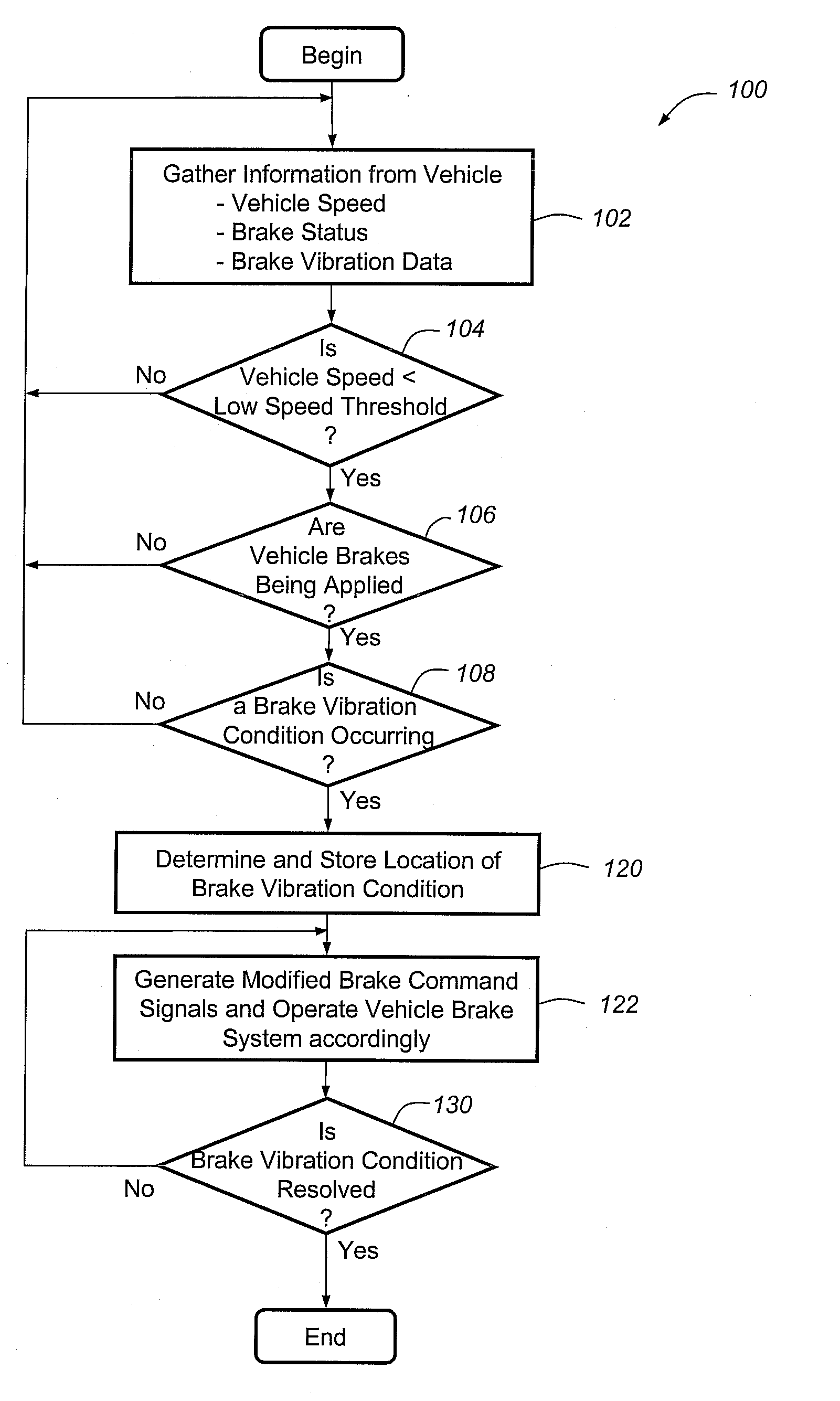
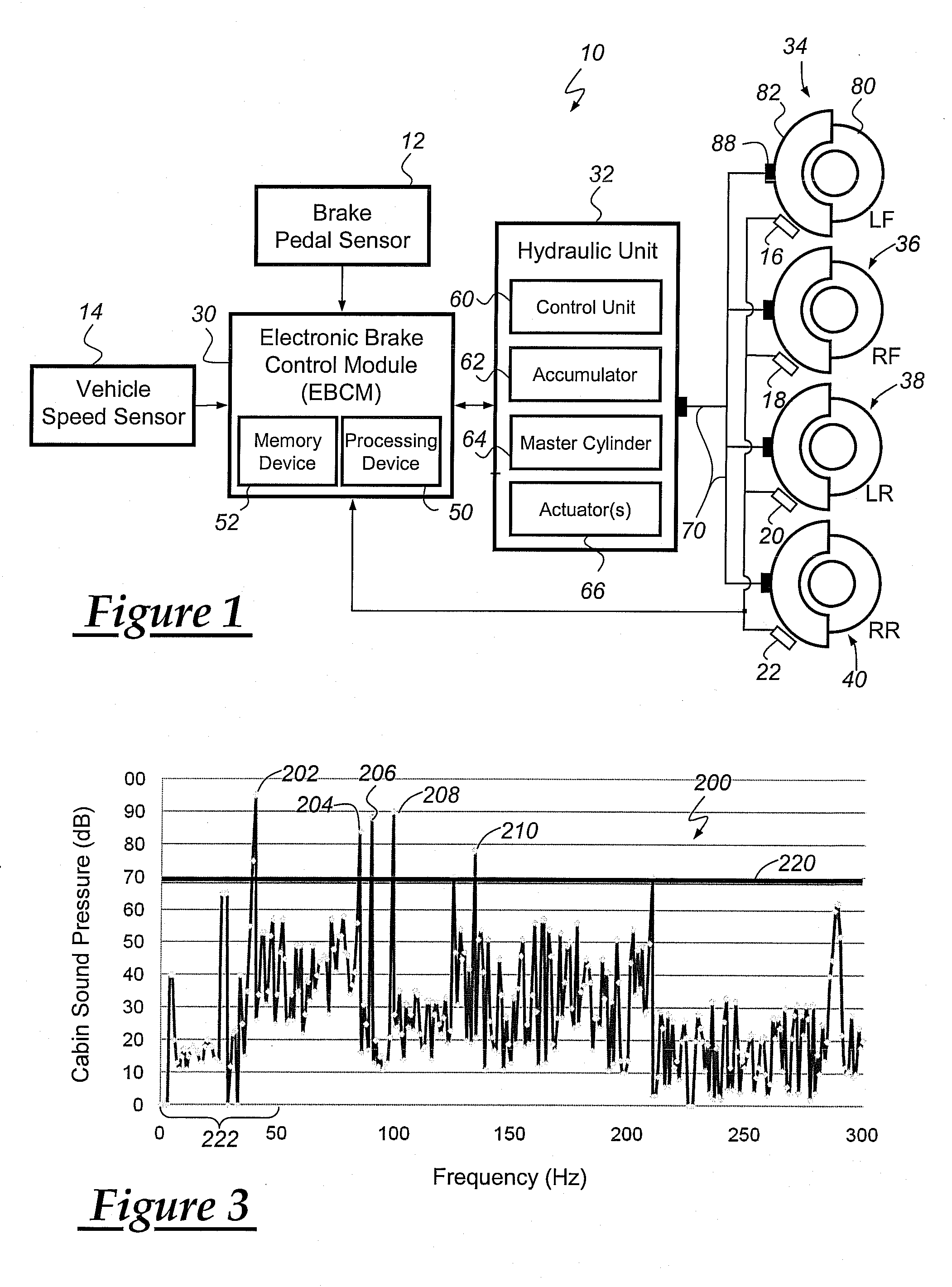
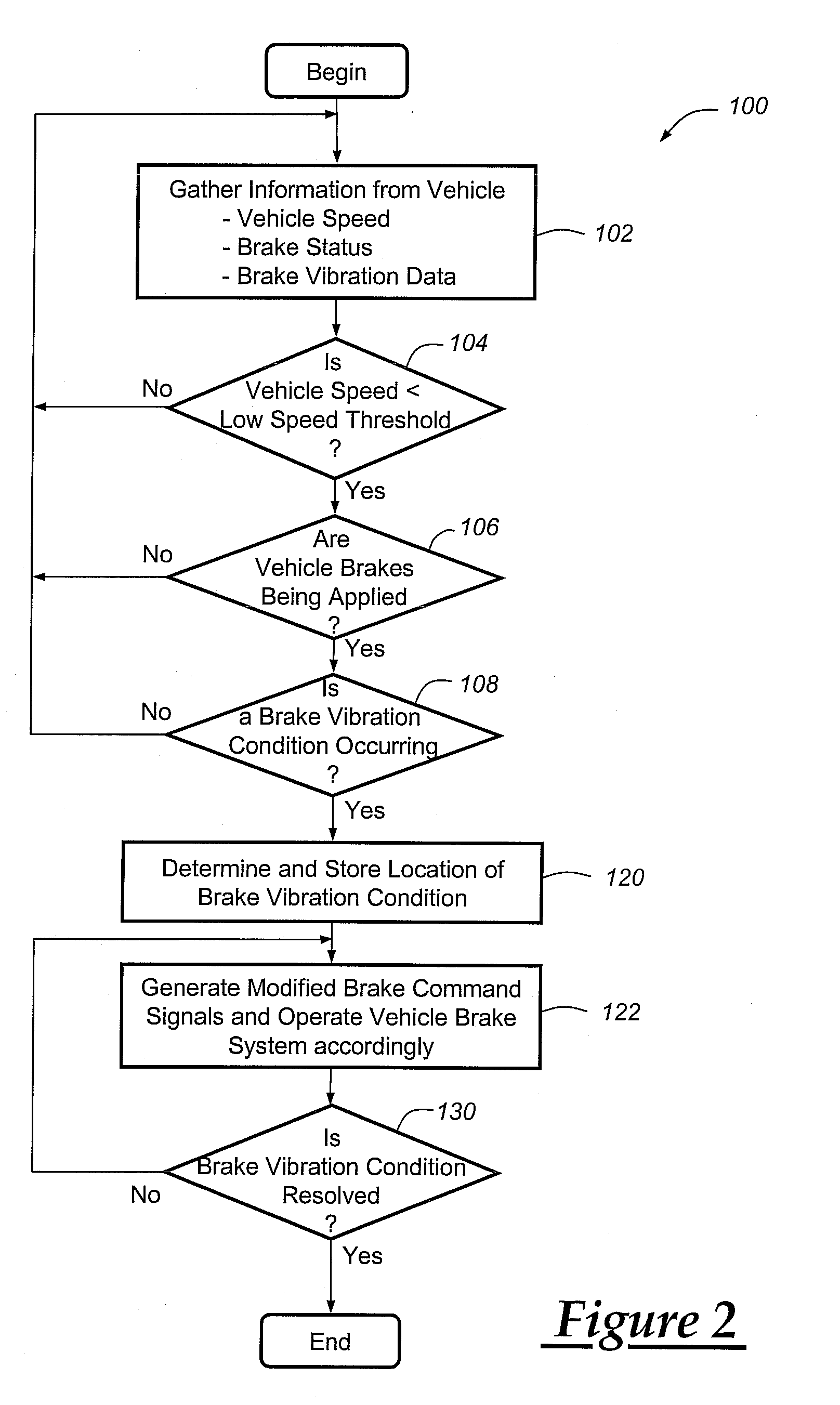
Method for operating a vehicle brake system
InactiveUS20100250081A1Reducing brake groan noiseReduce noiseVehicle testingNoise/vibration controlBrake torqueVehicle brake
A method for reducing or mitigating the effects of vibration in a vehicle brake system, particularly those that can lead to brake groan or other unwanted noise. According to an exemplary embodiment, when the vehicle brake system detects certain vibratory conditions, it makes slight braking adjustments (e.g., adjustments to fluid pressure, brake force, brake torque, etc.) that are aimed to address the brake groan. The vehicle brake system can then determine the effectiveness of the braking adjustments and, if need be, make additional braking adjustments. The method is particularly well suited for use with brake-by-wire systems, but can be used with a number of different vehicle braking systems.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Formula of ceramic radical friction material for automobile braking friction facing
InactiveCN101113204AImprove braking effectImprove yieldFriction liningFilling materialsMaterials processing
The invention discloses a prescription of a ceramic-based friction material used in a vehicle braking friction pad, comprising the components (by weight): adhesives 5 percent-15 percent, intensifier 23.5 percent-33.5 percent, grinding aid 0 percent-7 percent anti-wearing lubricant 11.3 percent-21.3 percent, elastic toughening agent 5.7 percent-15.7 percent and filling material 27.5 percent-37.5 percent. The total amount of the components is 100 percent. The materials of the invention can be processed and molded into the vehicle braking pad that is applicable to friction braking on a vehicle braking device. The anti-wearing performance of the pad can be greatly enhanced, thereby reducing noise pollution and promoting the performance of the braking system of the vehicle.
Owner:SHAANXI LIZHIQUAN IND TRADE
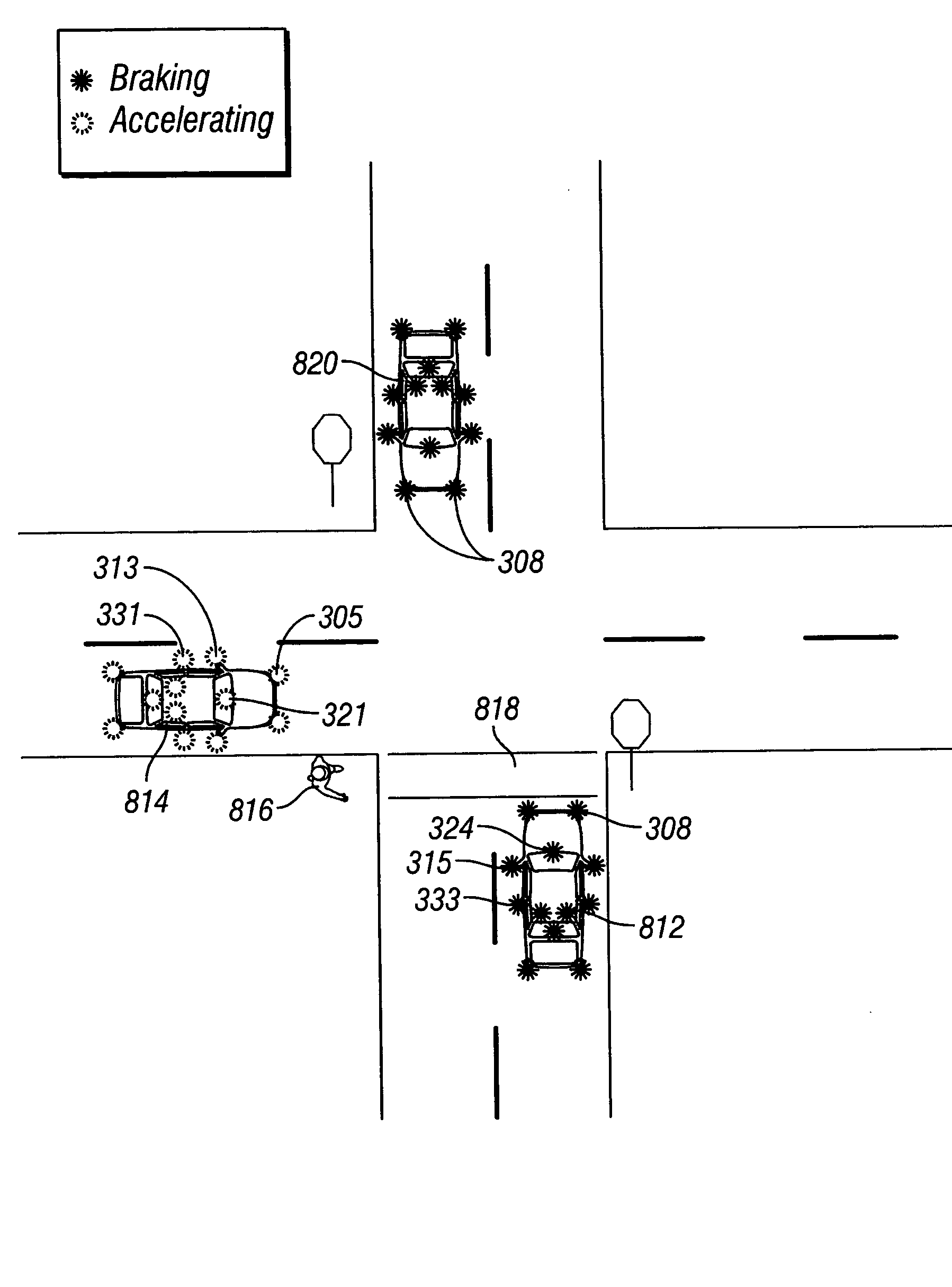
Optimal acceleration profile for enhanced collision avoidance
ActiveUS20120101713A1Avoid collisionConvenient distanceAnti-collision systemsExternal condition input parametersEllipseAcceleration Unit
A system and method for providing an optimal collision avoidance path for a host vehicle that may potentially collide with a target vehicle. The method includes providing off-line an optimization look-up table for storing on the host vehicle that includes an optimal vehicle braking or longitudinal deceleration and an optimal distance along the optimal path based on a range of speeds of the host vehicle and coefficients of friction of the roadway surface. The method determines the current speed of the host vehicle and the coefficient of friction of the roadway surface during the potential collision, and uses the look-up table to determine the optimal longitudinal deceleration or braking of the host vehicle for the optimal vehicle path. The method also determines an optimal lateral acceleration or steering of the host vehicle for the optimal vehicle path based on a friction ellipse and the optimal braking.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Double-motor driving type electronic hydraulic brake system capable of actively simulating pedal feeling
InactiveCN104760586AMeet braking requirementsImprove securityBraking action transmissionEnergy recoveryElectric control
A double-motor driving type electronic hydraulic brake system capable of actively simulating pedal feeling comprises a brake pedal, a fluid storage tank used for storing brake fluid, a pedal displacement sensor, a pedal force sensor, a hydraulic force sensor, an electronic control unit, an electromagnetic valve, an electronic stability control module, a brake master cylinder and a secondary master cylinder. An electric control linear movement module comprises a rotating motor and a speed reduction and moment increasing mechanism which converts the rotating movement of the motor into linear movement to achieve the active control over system hydraulic brake force and pedal force. The pedal force of a driver can be fully used for reducing pressure. While the active control over the pedal force is achieved, a pedal force simulator of a complex structure is omitted, the feeling of a brake pedal is guaranteed, and the accurate automobile brake condition is fed back to the driver. The active control over the hydraulic force is achieved, and the brake requirement for automatic driving vehicles is met; maximum braking energy recovery is achieved, control is precise, and the response speed is high; double-loop braking is achieved, failure protection is considered thoroughly, and the safety is good.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
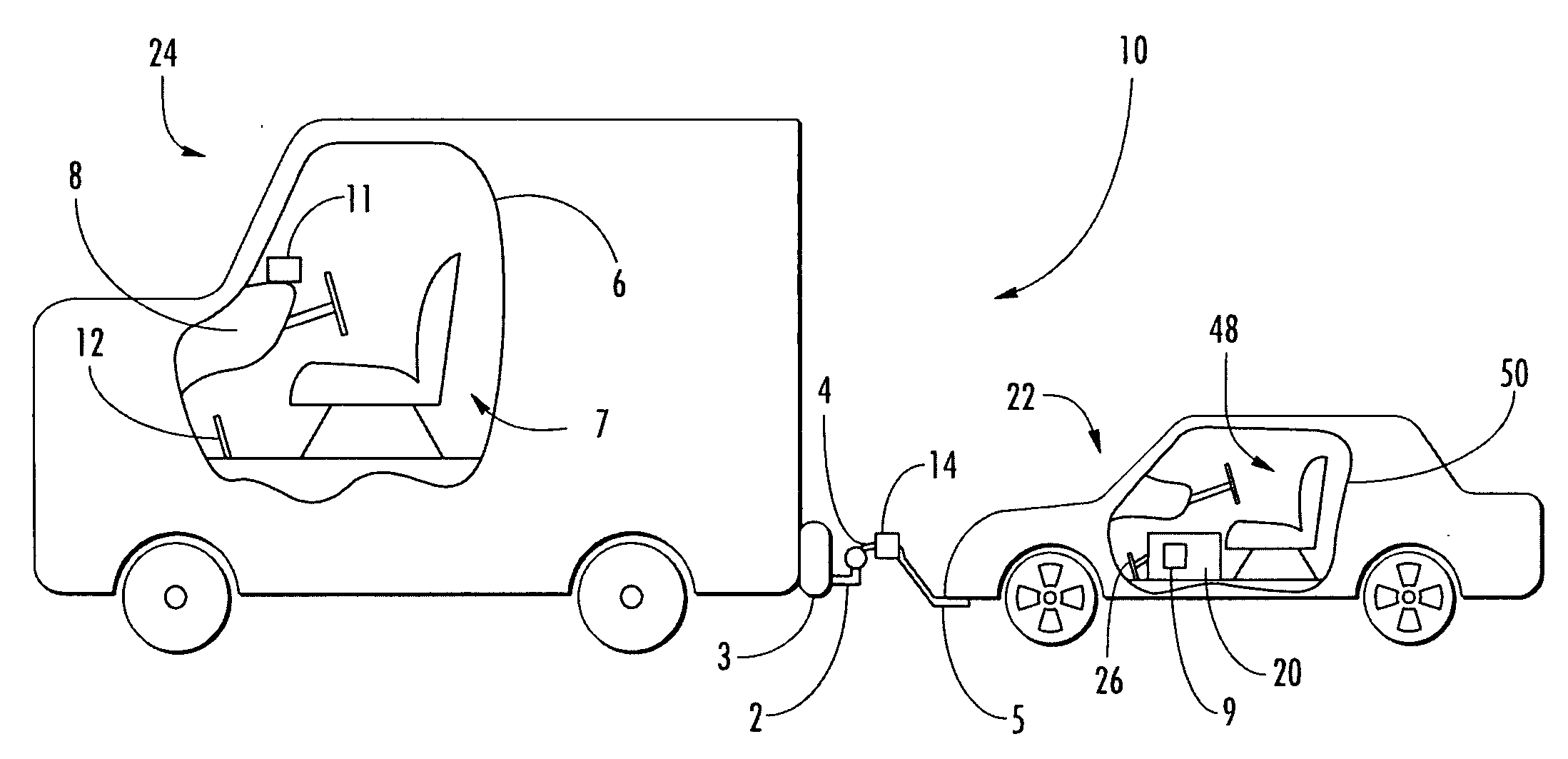
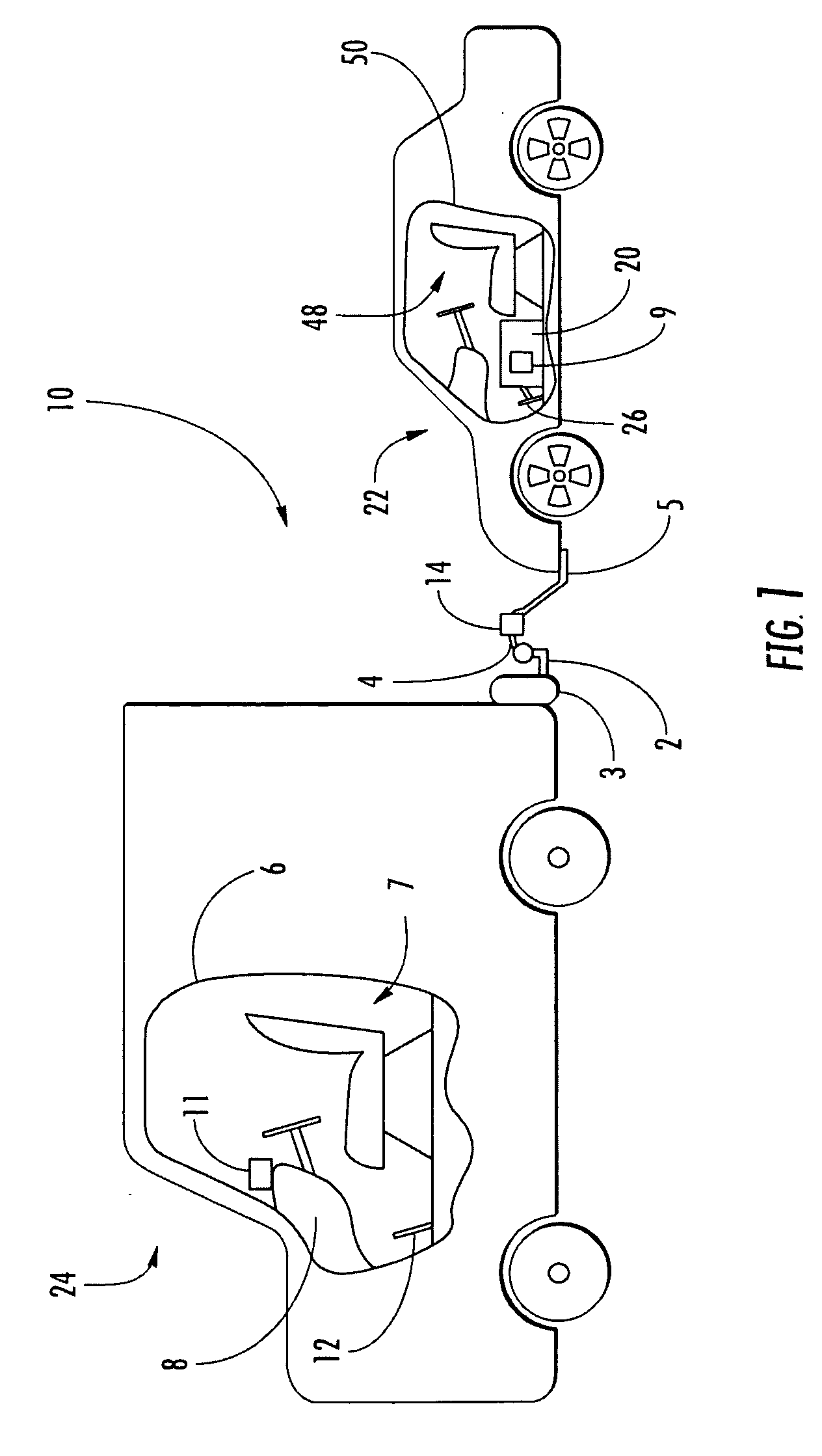
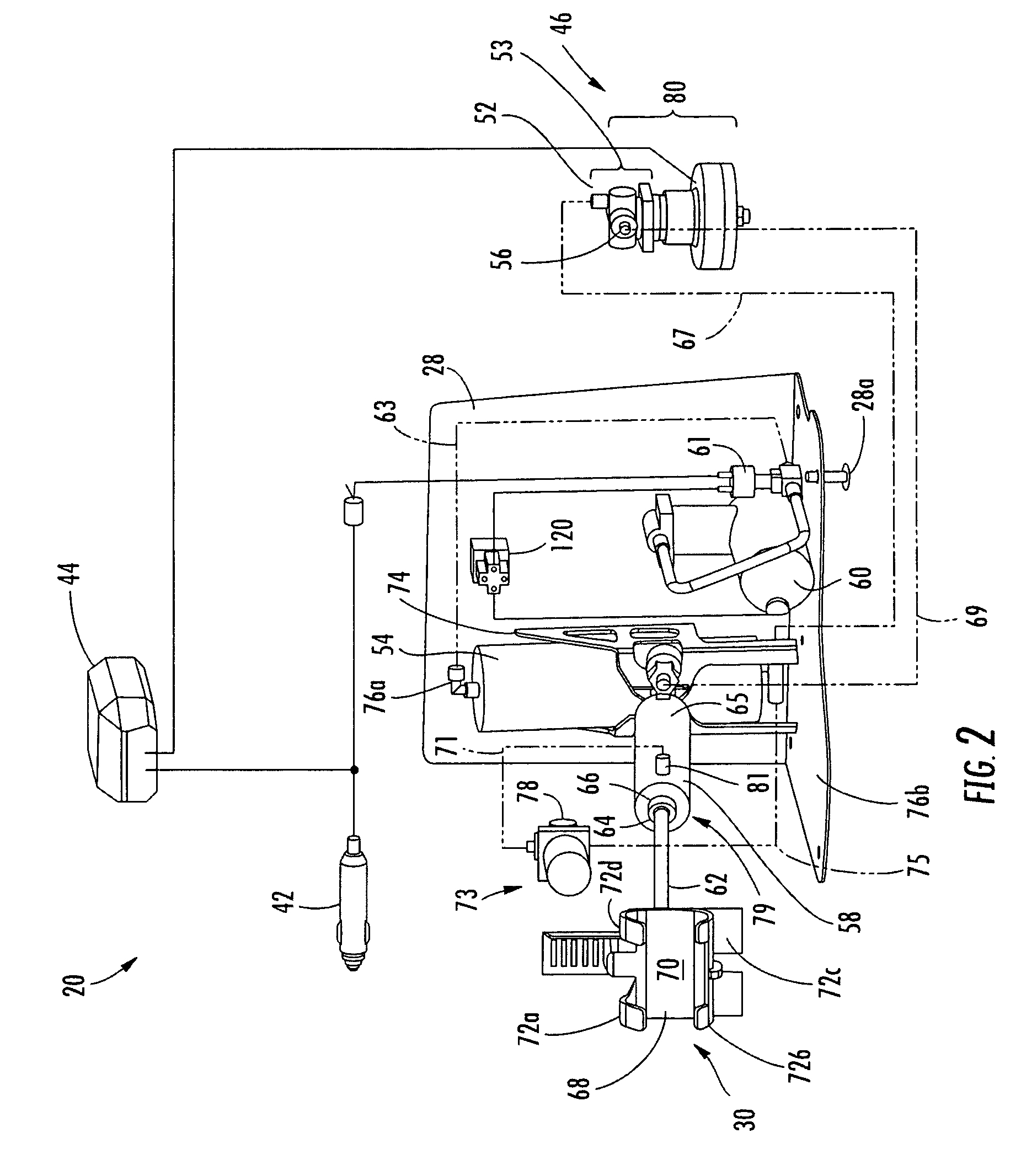
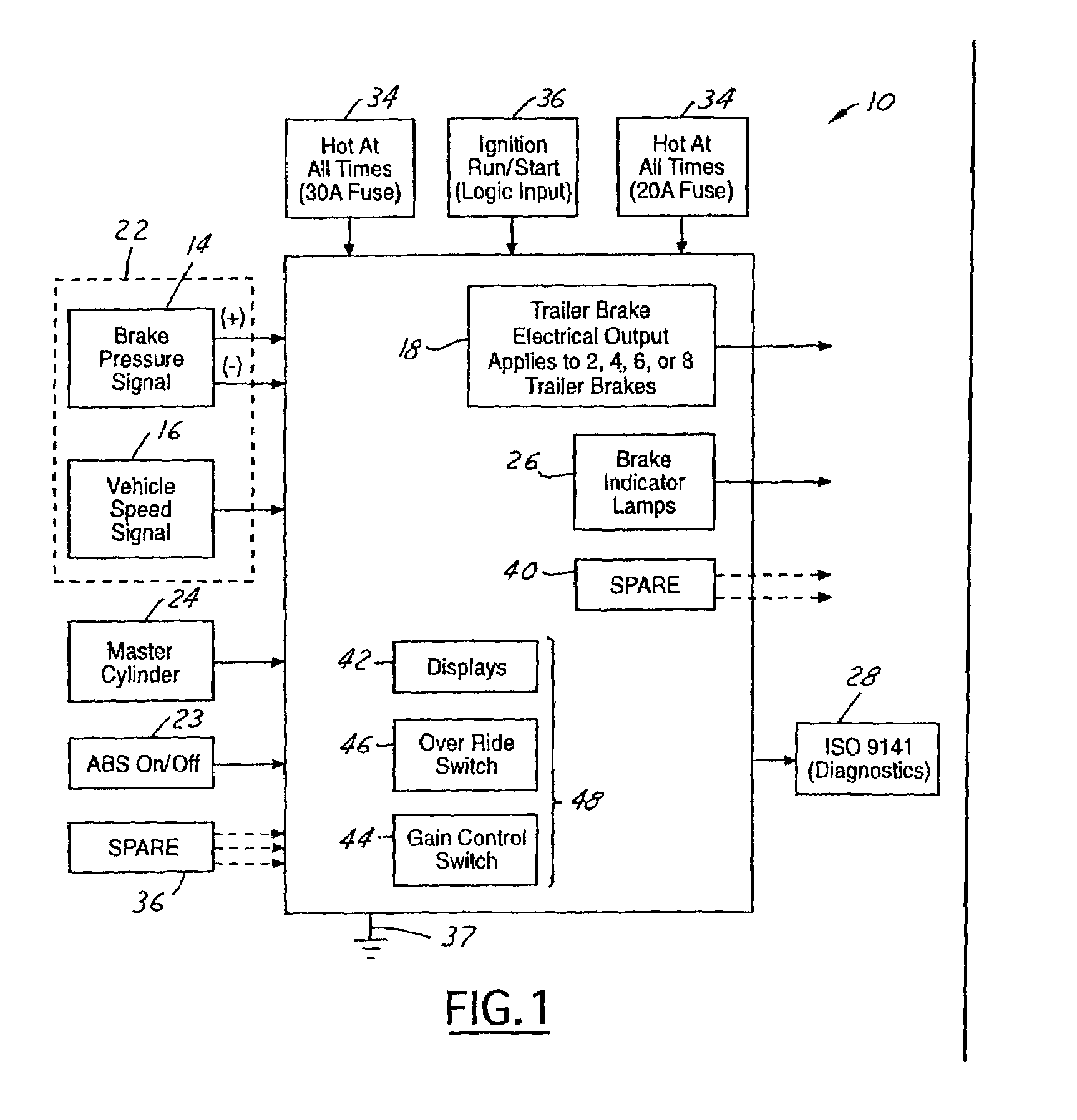
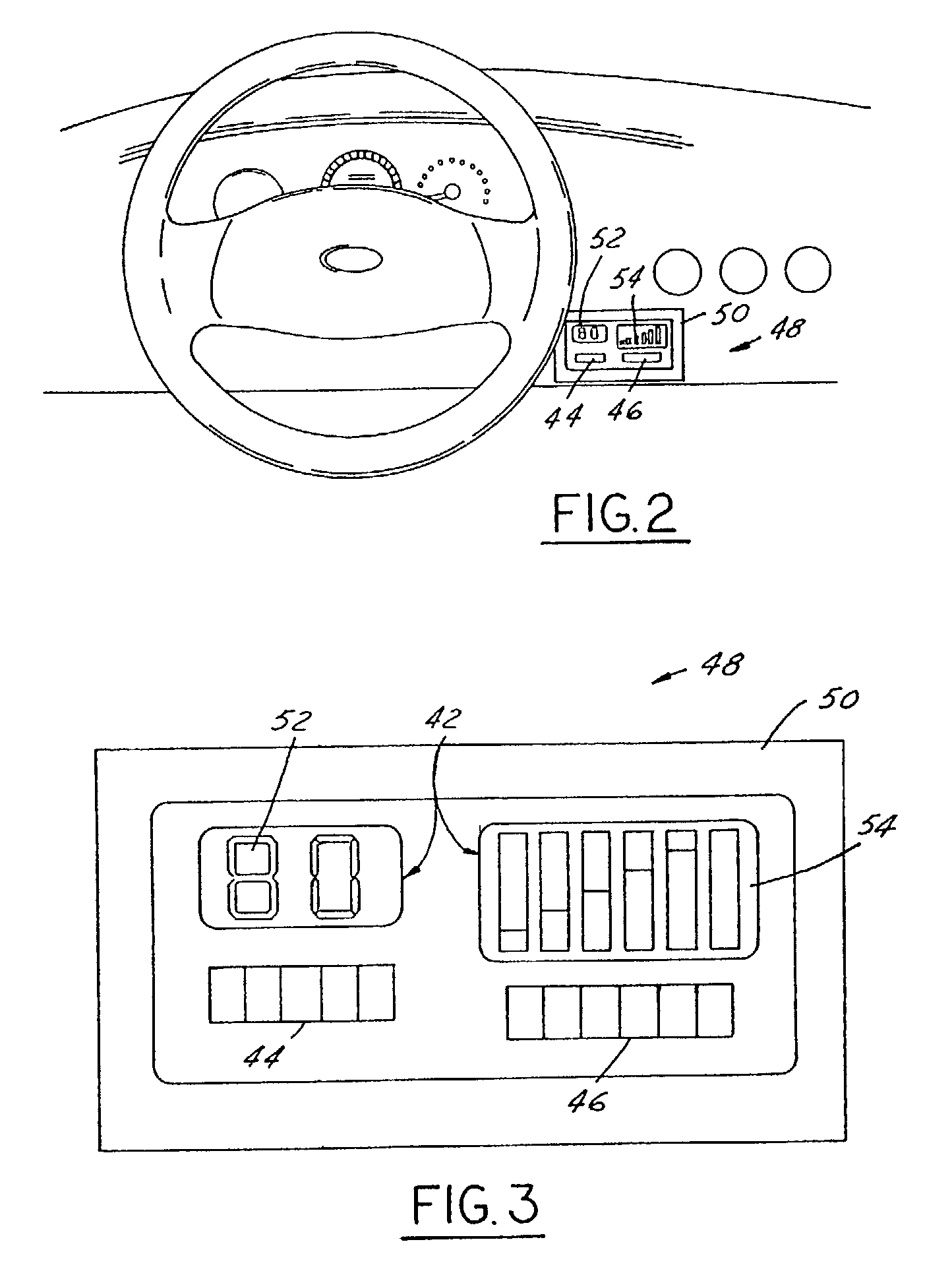
Integrated passenger vehicle trailer brake controller
InactiveUS6966613B2Improve cooperationBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsTrailer brake controllerVehicle brake
A trailer brake controller 10 for use in a passenger vehicle 12 is provided, including a control element 11 positioned within the passenger vehicle 12, a vehicle speed input 16 and a vehicle brake pressure input 14 providing speed and brake pressure data to the control element 11, and a trailer brake output 18 sending a signal to the trailer in response to the vehicle speed input 16 and the vehicle brake pressure input 14.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
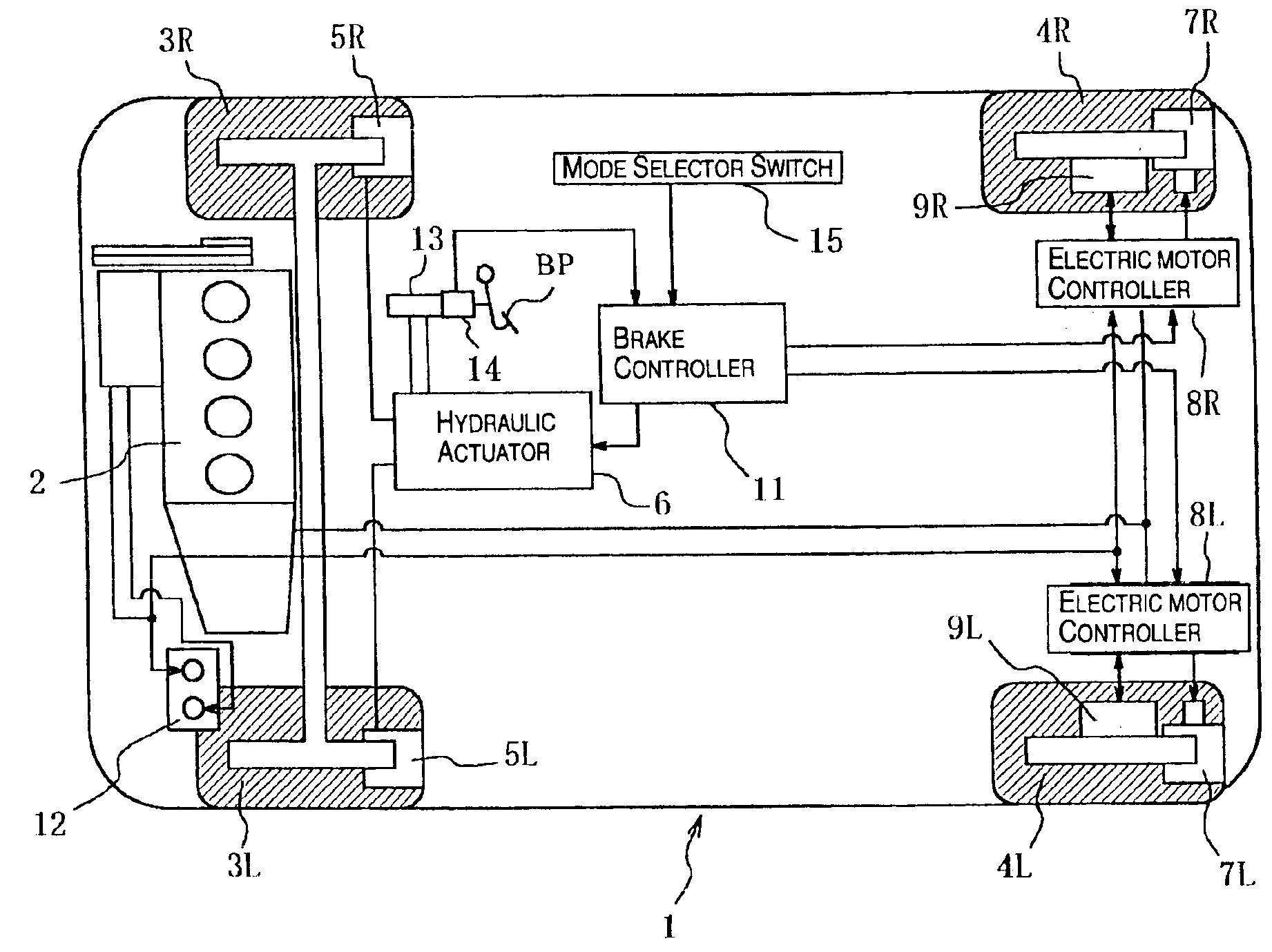
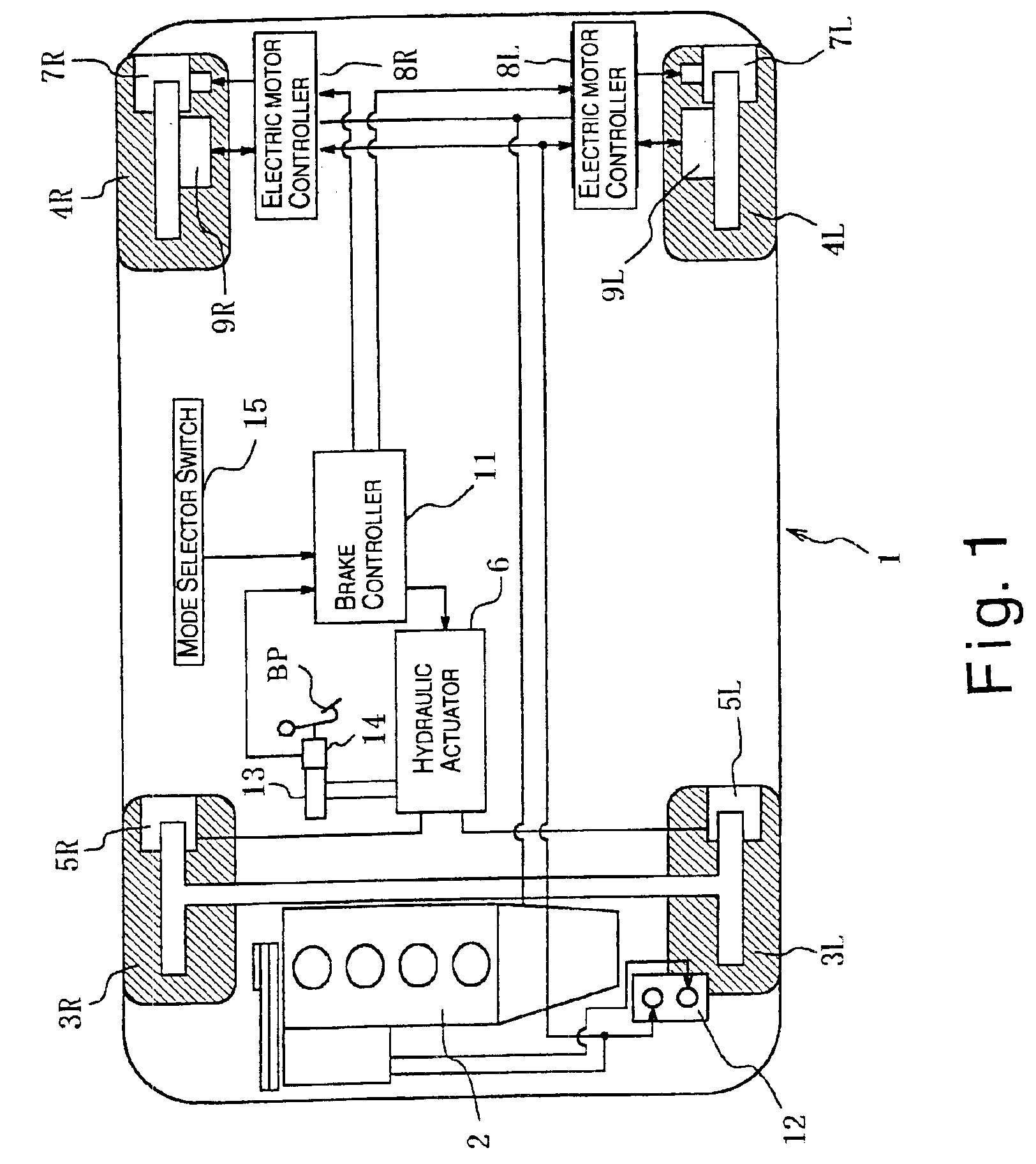
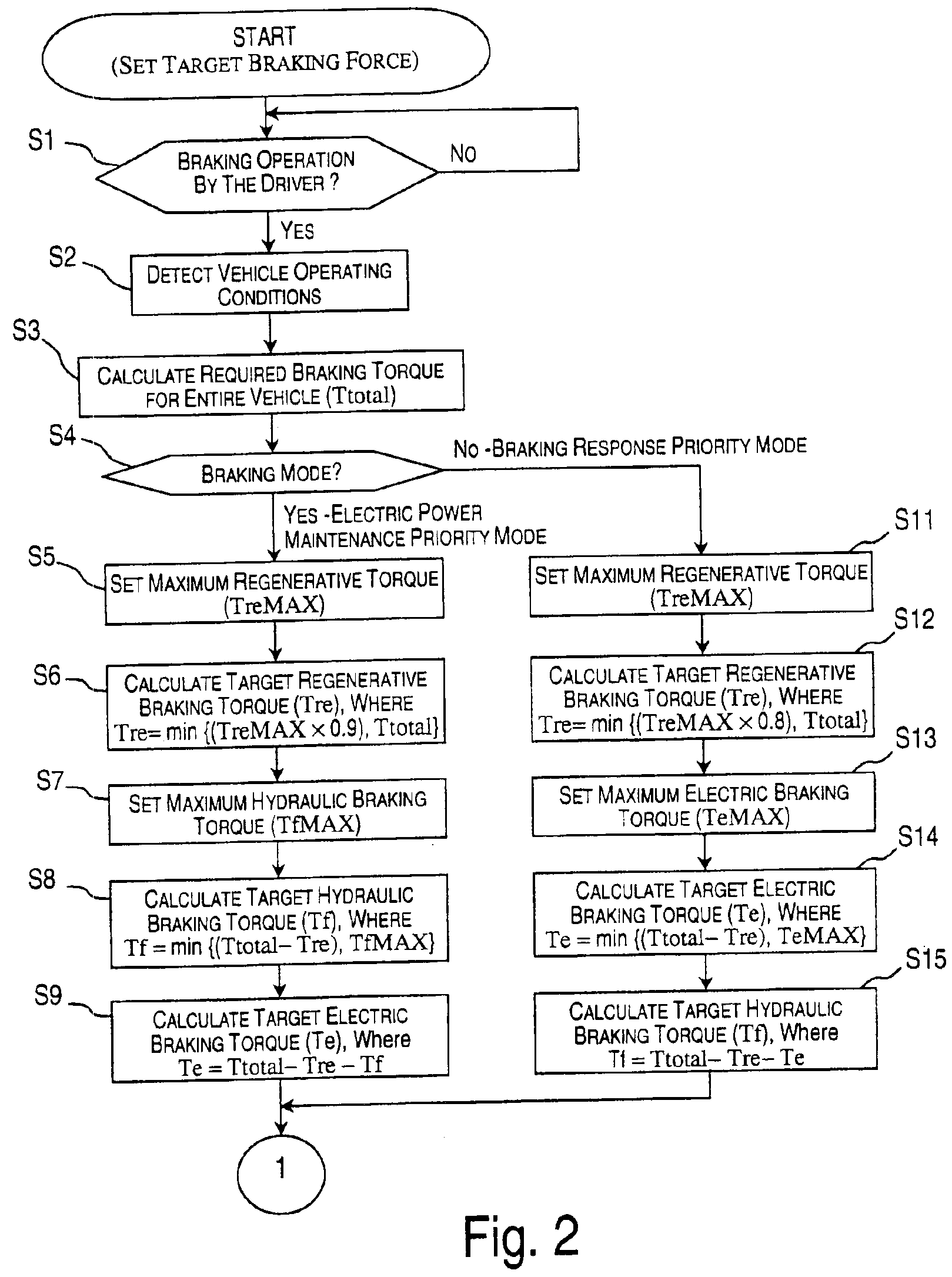
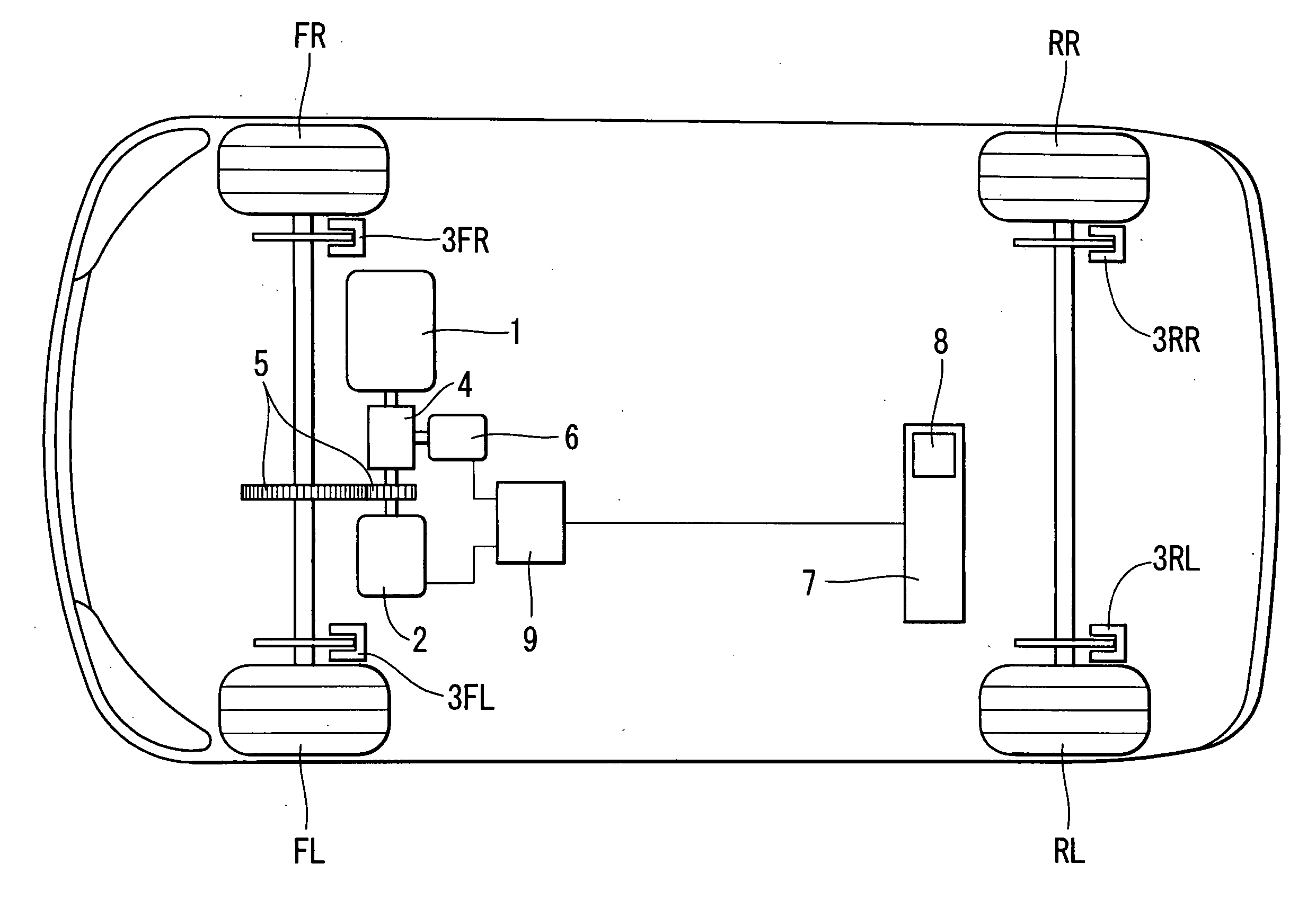
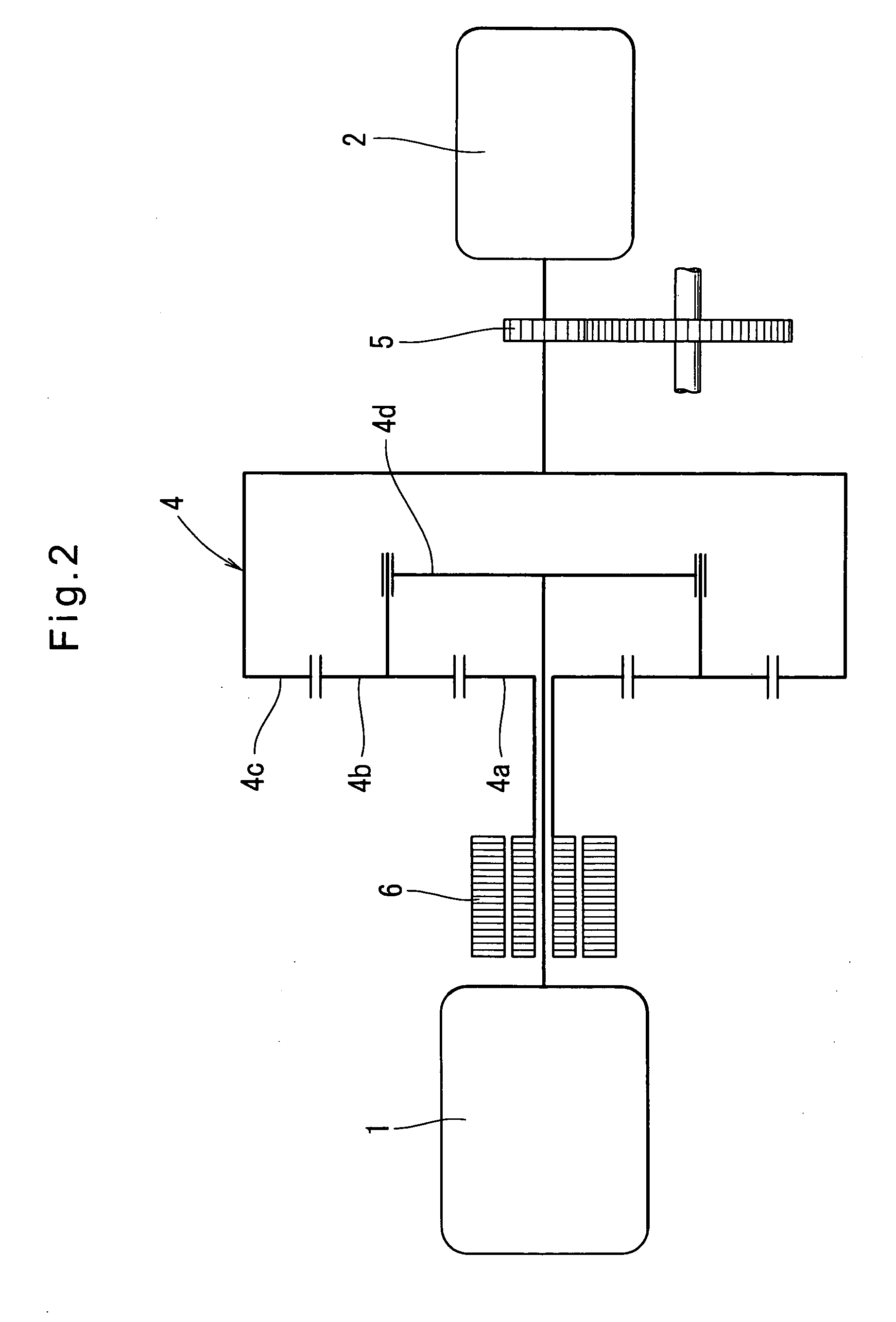
Vehicle braking control system
InactiveUS6910747B2Improve energy efficiencyExcellent control response characteristicBraking element arrangementsElectric devicesElectricityRegenerative brake
A vehicle braking control system is provided that controls at least three braking devices including a regenerative braking device, a hydraulic braking device and an electric braking device. The vehicle braking control system basically comprises a braking mode selecting section, a required braking force determining section and a target braking force setting section. The braking mode selecting section sets one of a plurality of braking modes having a different braking control priority for each of the target braking forces. The required braking force determining section determines a required braking force for an entire vehicle. The target braking force setting section sets each of the target braking forces based on the braking control priority of the selected braking mode to produce the required braking force for the entire vehicle. Preferably, the braking mode selecting section set at least an electric power maintenance priority mode and a braking response priority mode.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
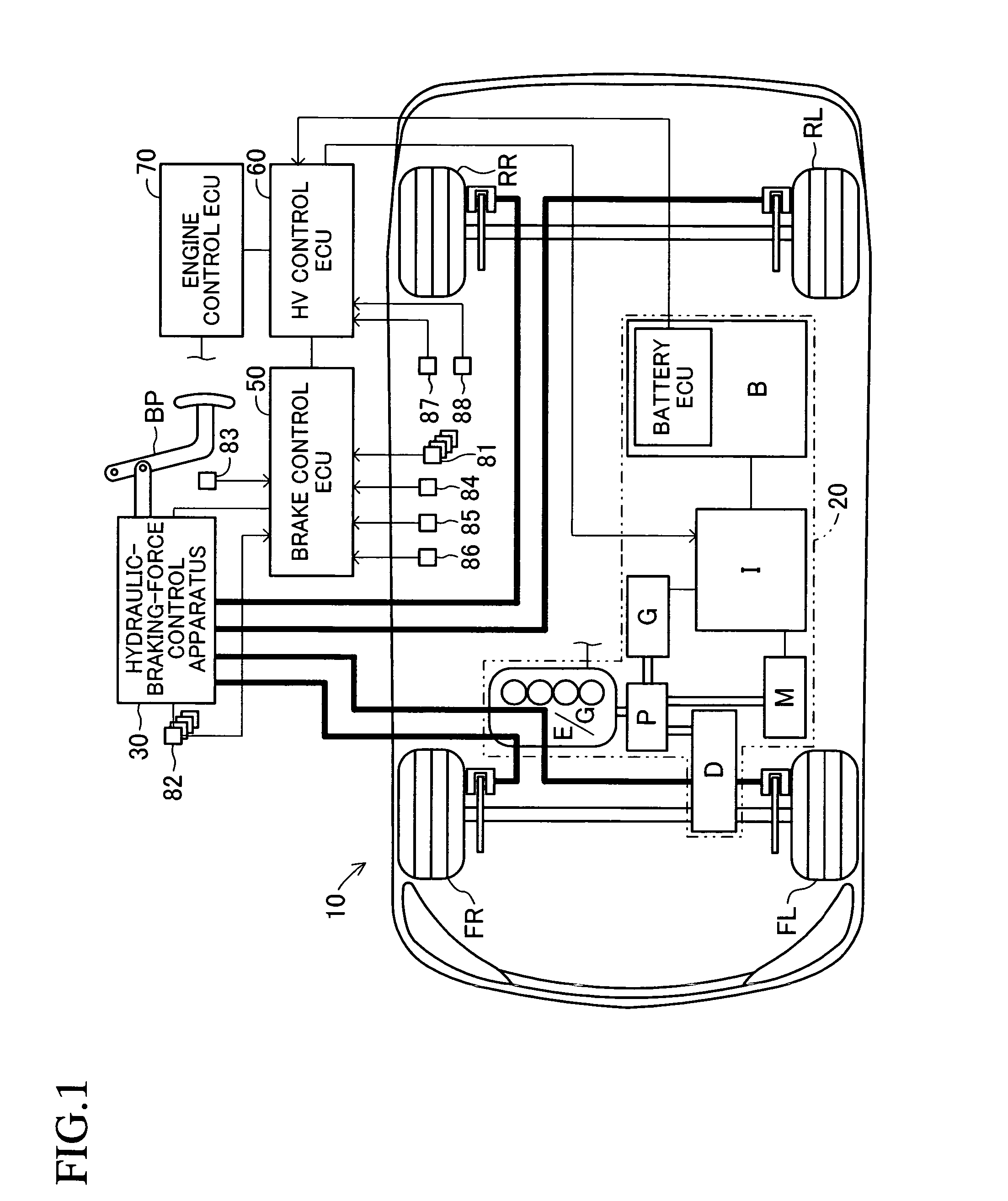
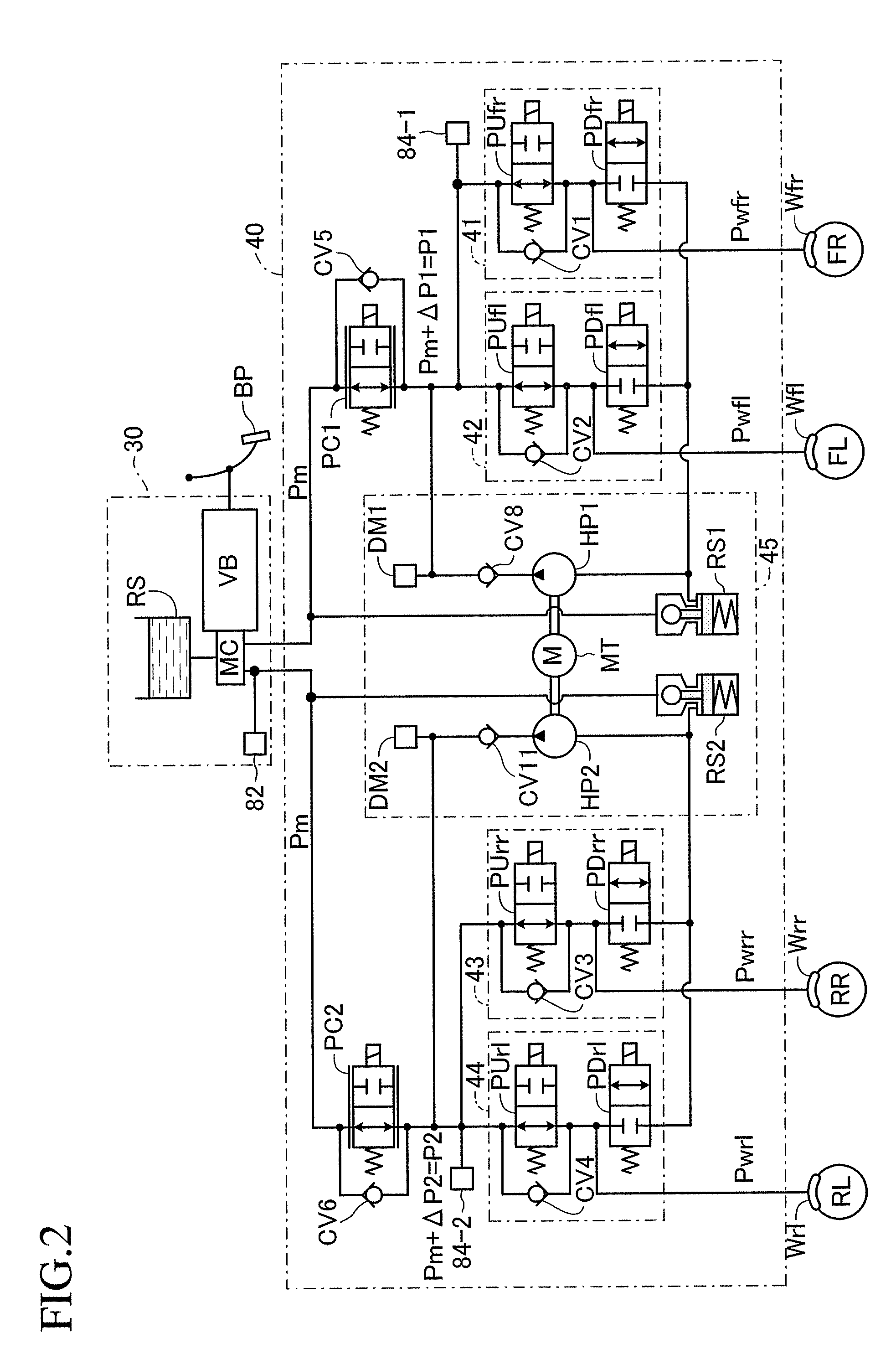
Braking apparatus for vehicle
A braking apparatus for a vehicle includes a hydraulic brake apparatus generating a basic hydraulic pressure so that a basic hydraulic braking force is generated at wheels, the hydraulic brake apparatus generating a controlled hydraulic pressure so that a controlled hydraulic braking force is generated at the wheels, a regenerative brake apparatus causing a regenerative braking force to be generated at any of the wheels, and braking force replacement controlling means for gradually replacing the regenerative braking force with the controlled hydraulic braking force while braking during which at least the regenerative braking force is applied for a purpose of achieving a braking force replacement control to ensure a total braking force required for the wheels by decreasing the regenerative braking force at a gradient within a predetermined range and by increasing the controlled hydraulic braking force in response to the decrease of the regenerative braking force.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Vehicle Braking Control
ActiveUS20080041336A1Increased intake manifold vacuumEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveVacuum level
A method of operating an engine for a vehicle having at least a first cylinder, the method comprising of operating the first cylinder to provide at least one of compression braking and expansion braking by holding one of an intake valve and an exhaust valve of the first cylinder closed while opening, closing, and opening the other of the intake valve and the exhaust valve during a cycle of the first cylinder and during a first vacuum level of an intake manifold upstream of the first cylinder; and operating the first cylinder to provide at least one of compression braking and expansion braking by operating both the intake valve and the exhaust valve of the first cylinder during a cycle of the first cylinder to allow at least some air to flow through the first cylinder during a second vacuum level of the intake manifold.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
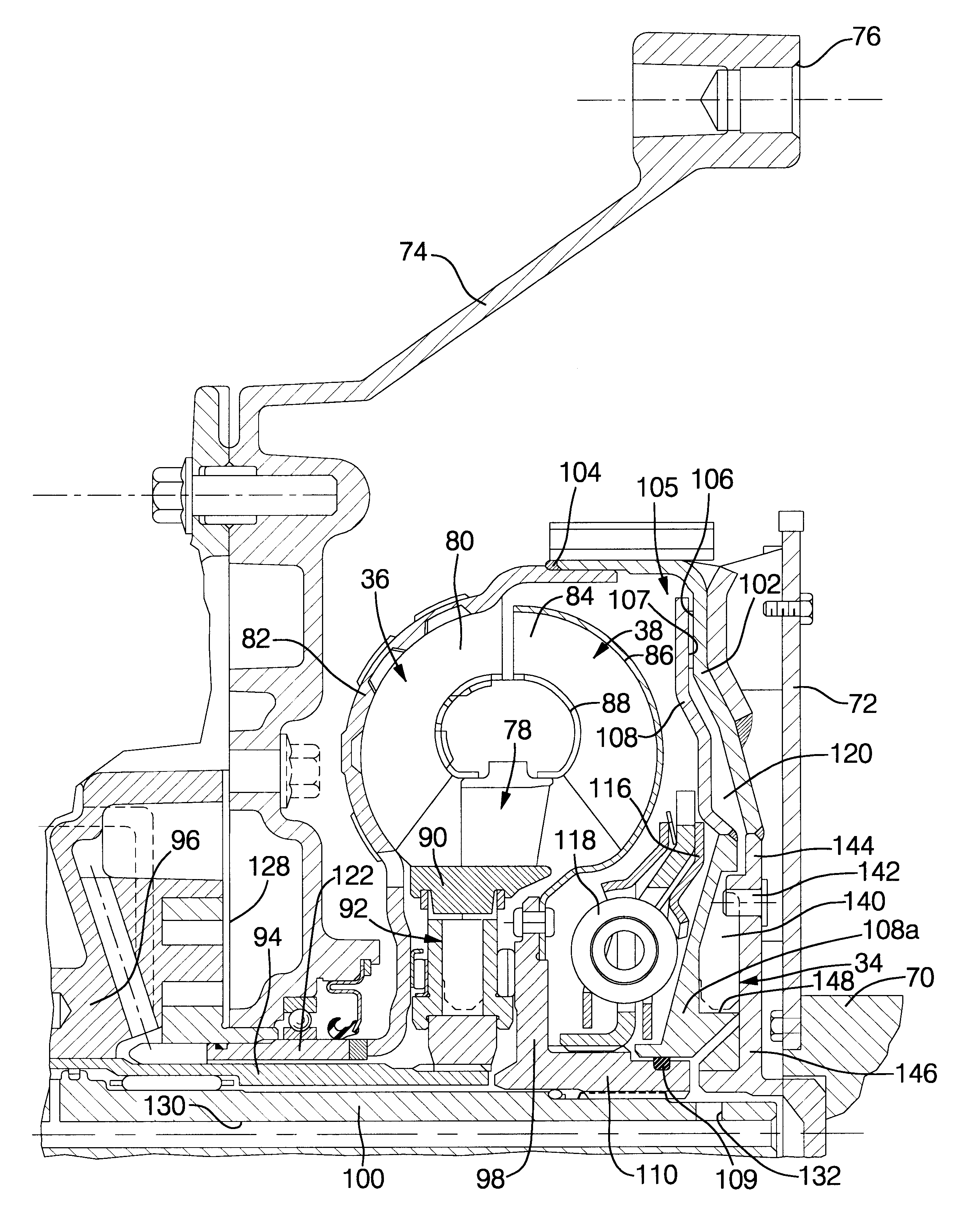
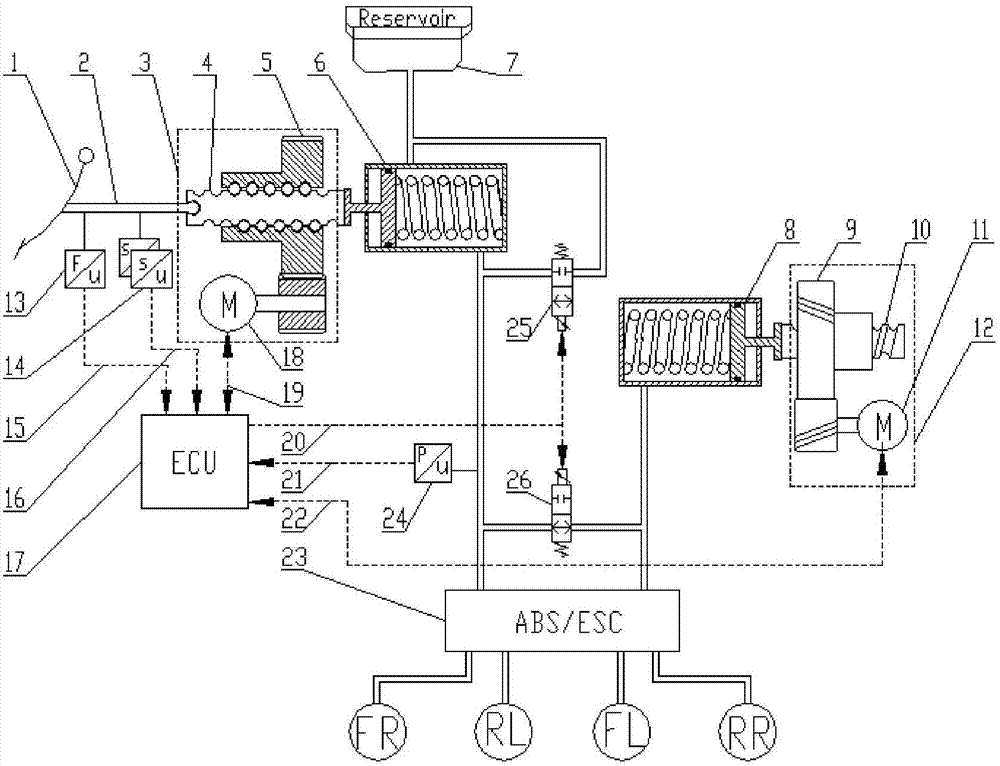
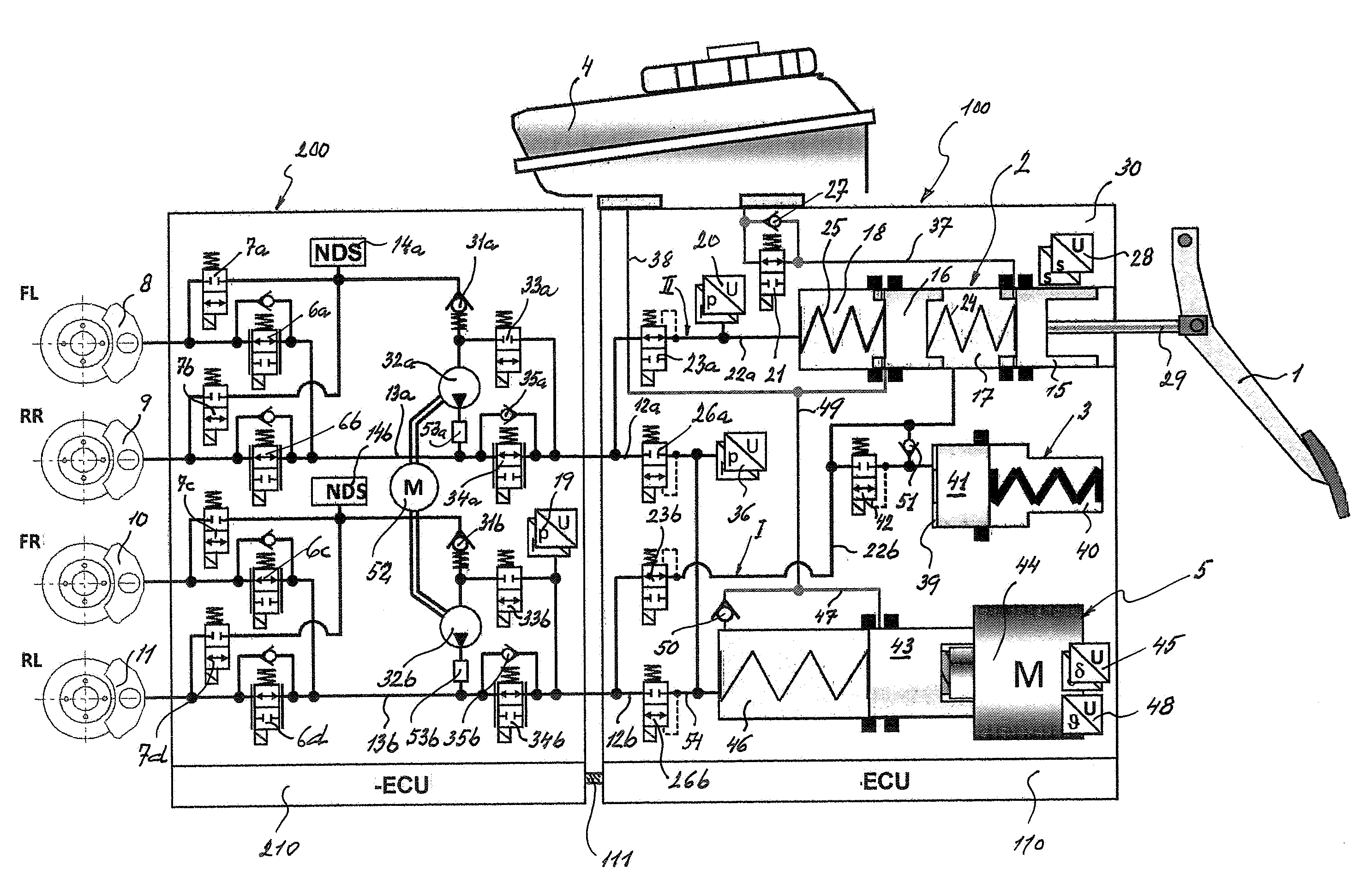
Brake System for Motor Vehicles
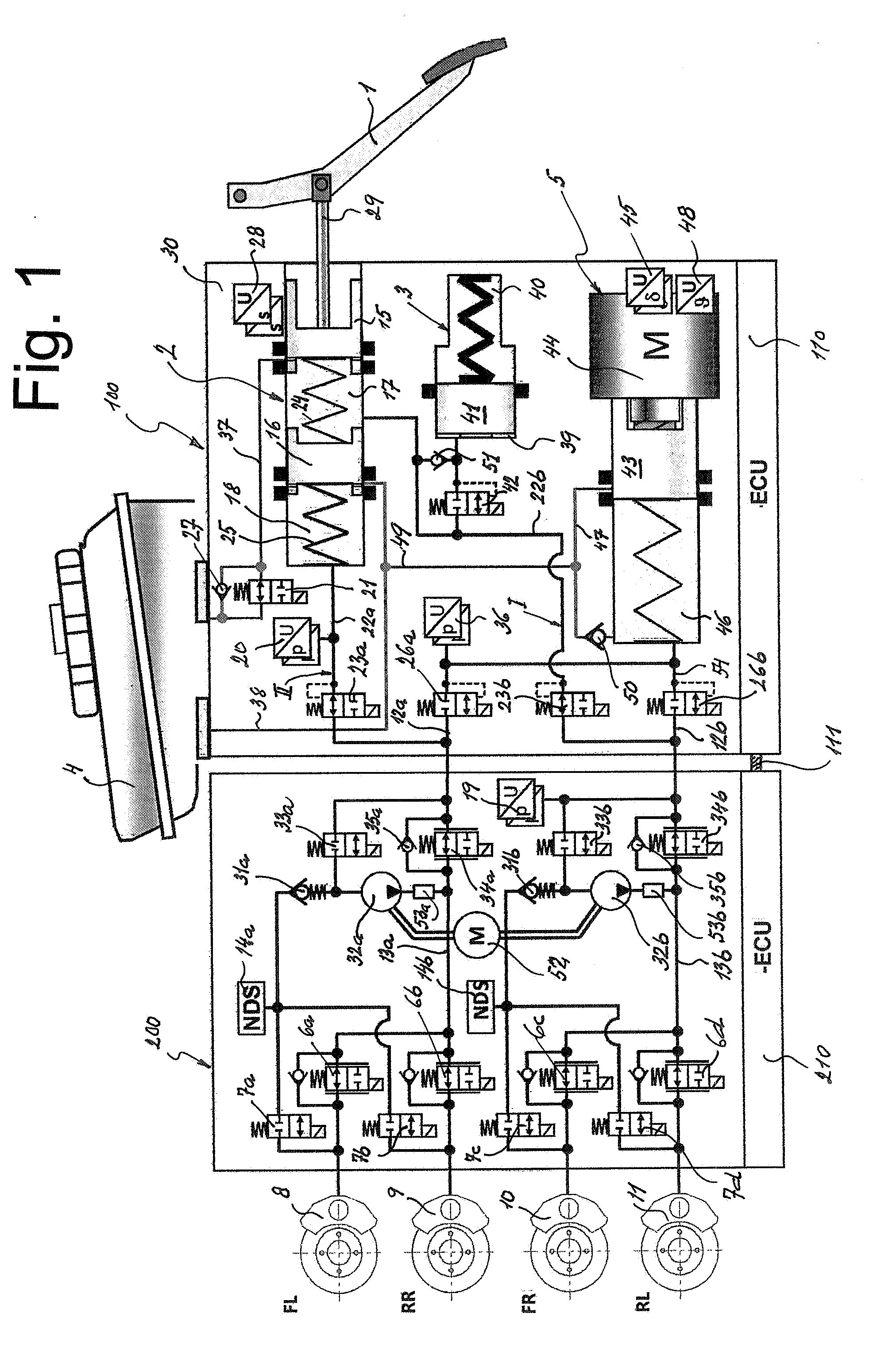
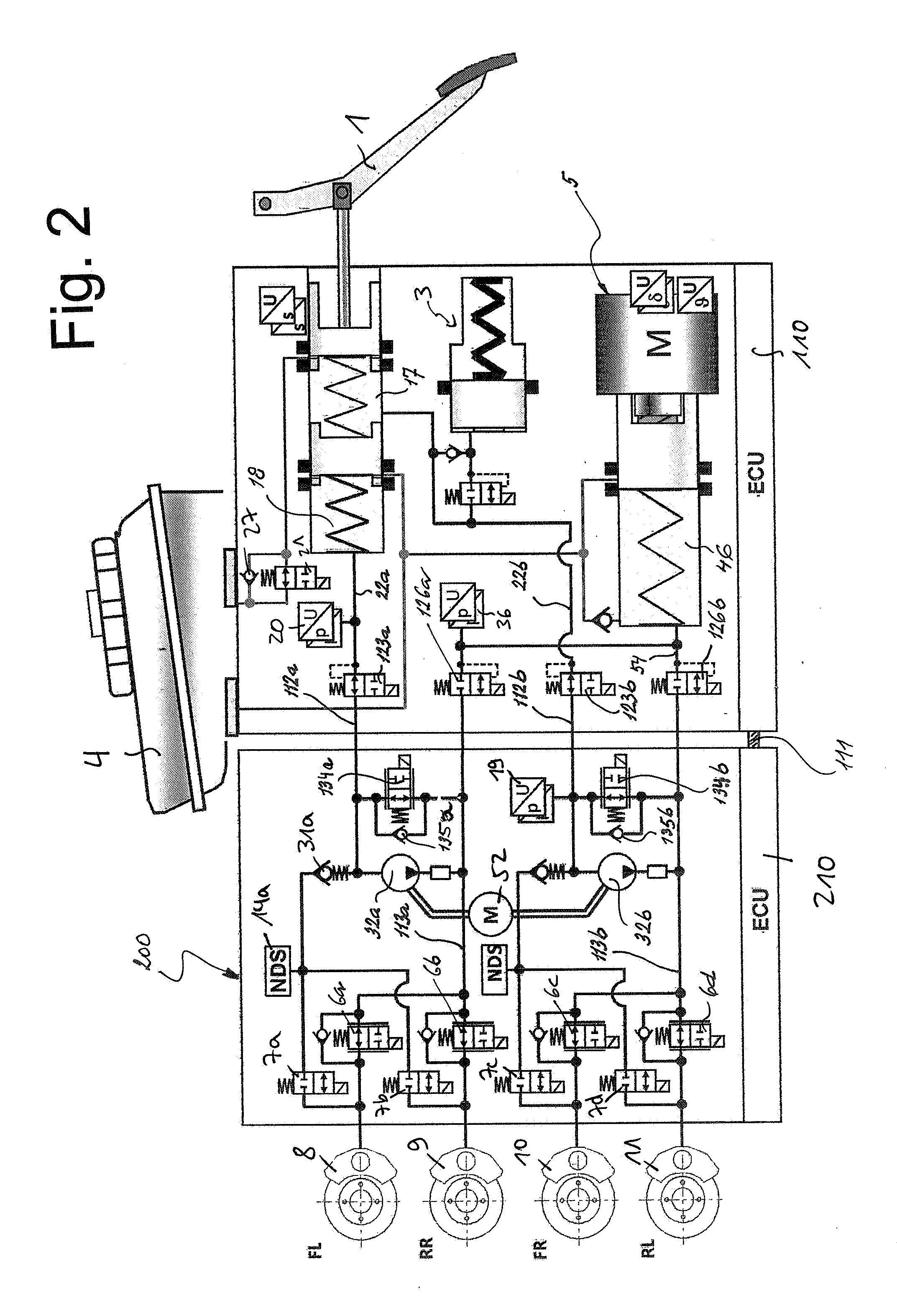
A motor vehicle brake system operable in a brake-by-wire and fallback modes. The system includes a brake pedal (1), a master cylinder (2), a reservoir (4), a travel simulator (3), an electrically controllable pressure source (5), isolation valves (23a, 23b) pumps (32a, 32b) and a low-pressure accumulator (14a, 14b), an inlet valve (6a-6d) and an outlet valve (7a-7d) for each wheel brake (8, 9, 10, 11), valves (34a, 34b; 134a, 134b) connected to the pumps (32a, 32b), and a control and regulation unit (110, 210). A valve arrangement (23a, 23b) establishes for each brake circuit (I, II) a connection from the pressure chamber (17, 18) of the master cylinder (2) to the modulator admission pressure line (13a, 13b; 113a, 113b) and disconnects the connection when unenergized, the valve arrangement (23a, 23b) preventing the pressure source (5) from being subjected to pressure from the pressure chambers (17, 18).
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Vehicle brake system
InactiveUS20070046099A1Eliminate locking tendencyReduce braking forceHybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsRegenerative brakeBraking system
An improved vehicle brake system for controlling the frictional braking force and the regenerative braking force to be applied to a wheel of a vehicle. The brake system reduces the regenerative braking force to a predetermined force and keeps the regenerative braking force at the predetermined force before the start of anti-lock control. When the anti-lock control starts, the brake system decreases the regenerative braking force from the predetermined force. With this arrangement, it is possible to quickly eliminate a locking tendency of any wheel of the vehicle, thereby stabilizing the vehicle.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Method for Controlling a Micro-Hybrid Electric Vehicle with an Automatic Transmission
InactiveUS20100076634A1Reduce cost-benefit ratioDigital data processing detailsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingStarter generatorAutomatic transmission
The micro-hybrid vehicle powertrain of the invention includes a geared transmission, an engine and a starter-generator mechanically coupled to the engine to start the engine as the transmission is shifted into gear. The engine is stopped when a vehicle brake is applied.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
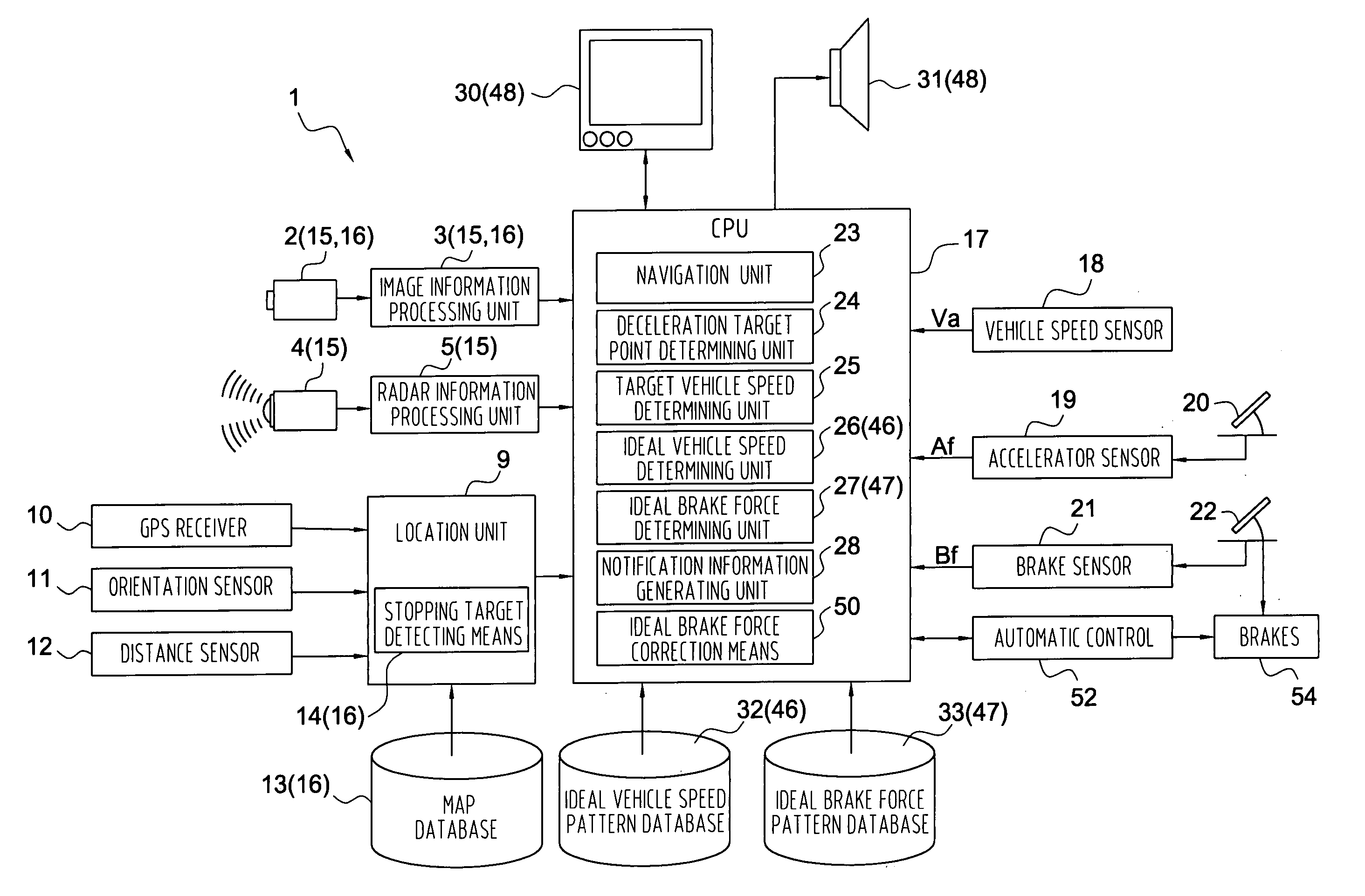
Vehicle braking control assistance system and method
InactiveUS20060290202A1Instruments for road network navigationVehicle fittingsDriver/operatorAuxiliary system
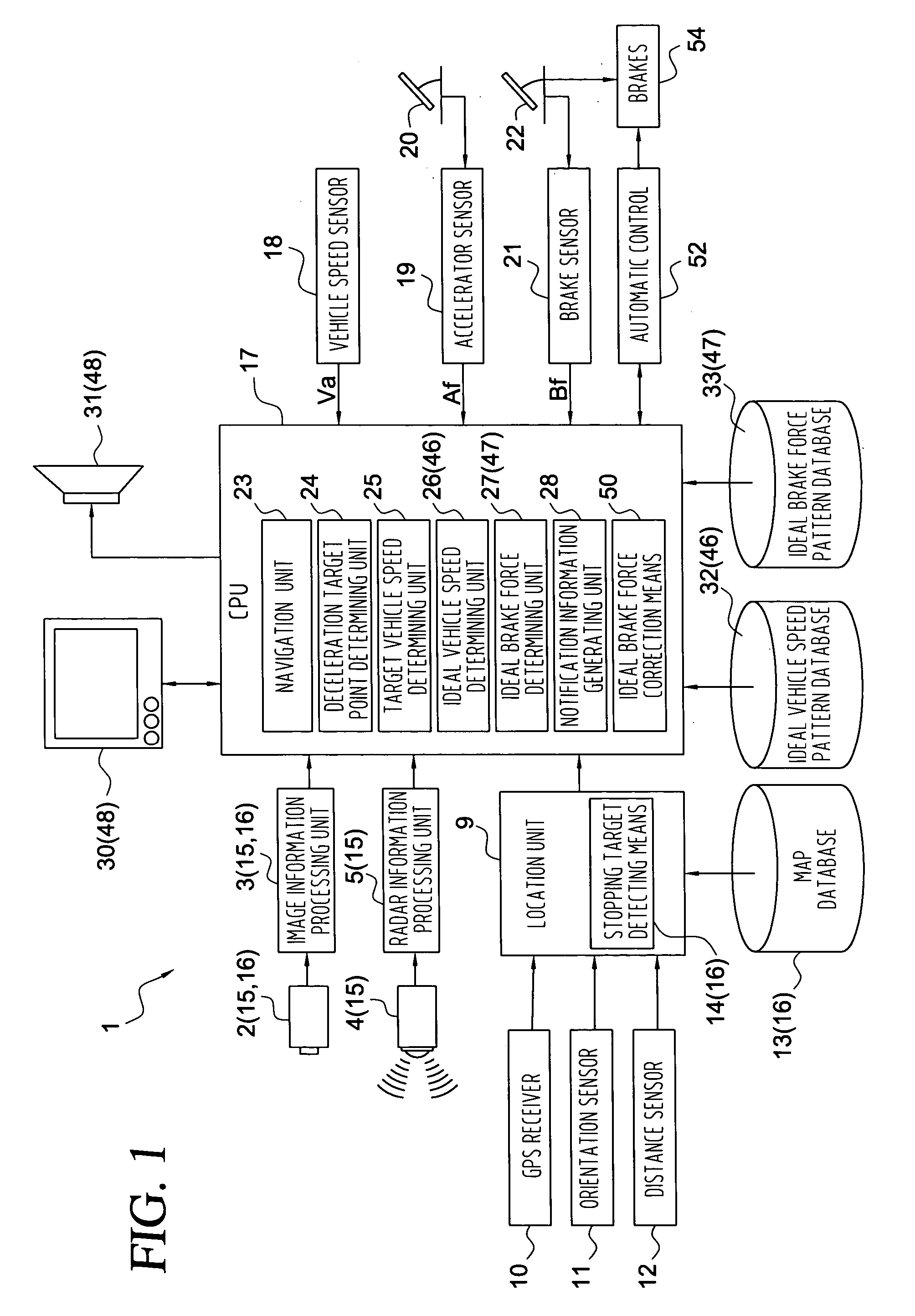
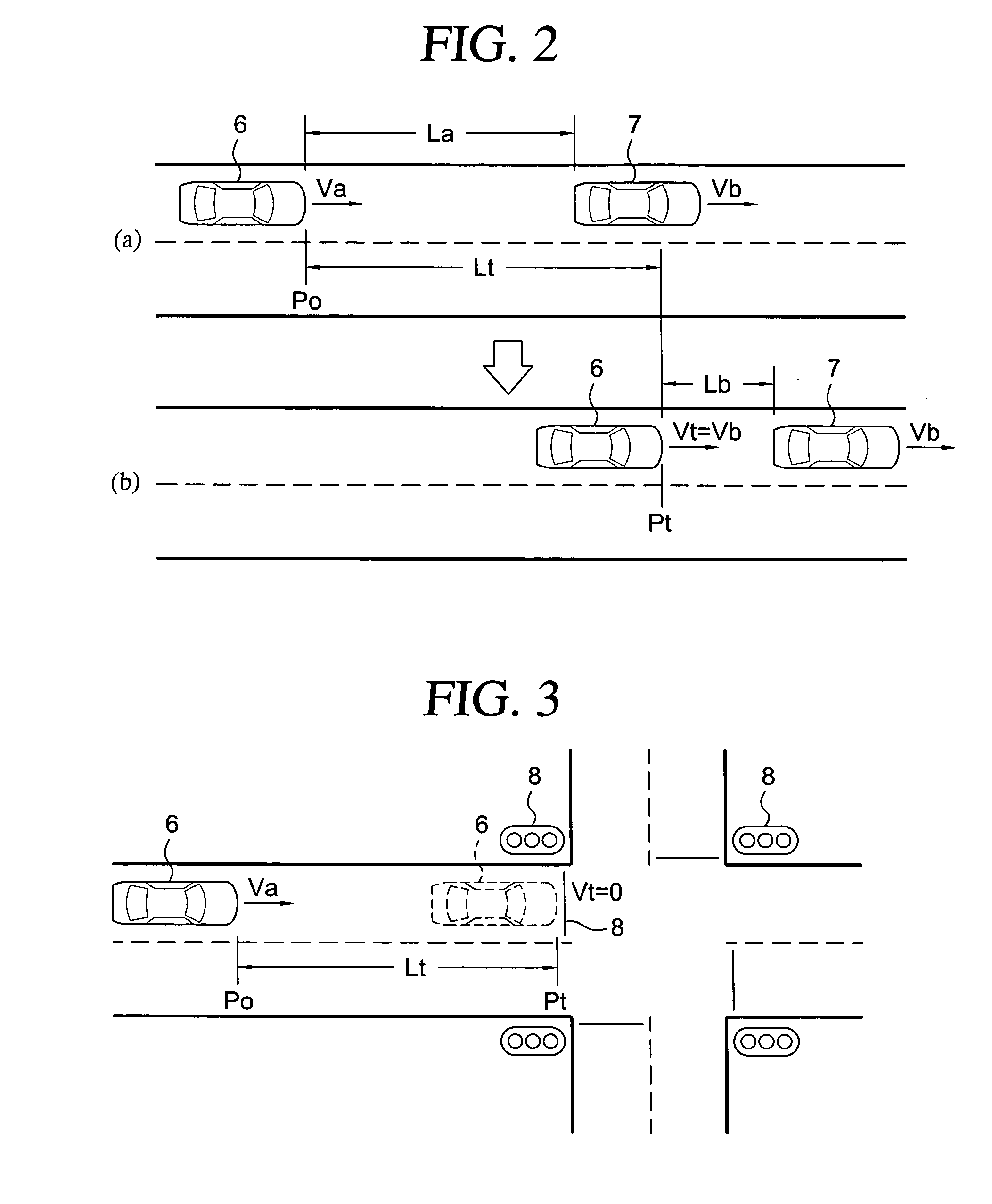
A vehicle braking control assistance device includes: a speed detecting unit for detecting current vehicle speed; a brake force detecting unit for detecting the current braking force; a deceleration target point determining unit for determining a target point for deceleration control; a target vehicle speed determining unit for determining a target vehicle speed at the deceleration target point; an ideal brake force determining unit for determining an ideal brake force to be applied in continued movement to the deceleration target point with the target vehicle speed realized at the deceleration target point, based on the current vehicle speed, the deceleration target point and the target vehicle speed; a notification information generating unit for generating notification information indicating the relationship between the ideal brake force and the current brake force; and a notification unit for bringing the generated notification information to the attention of the driver.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
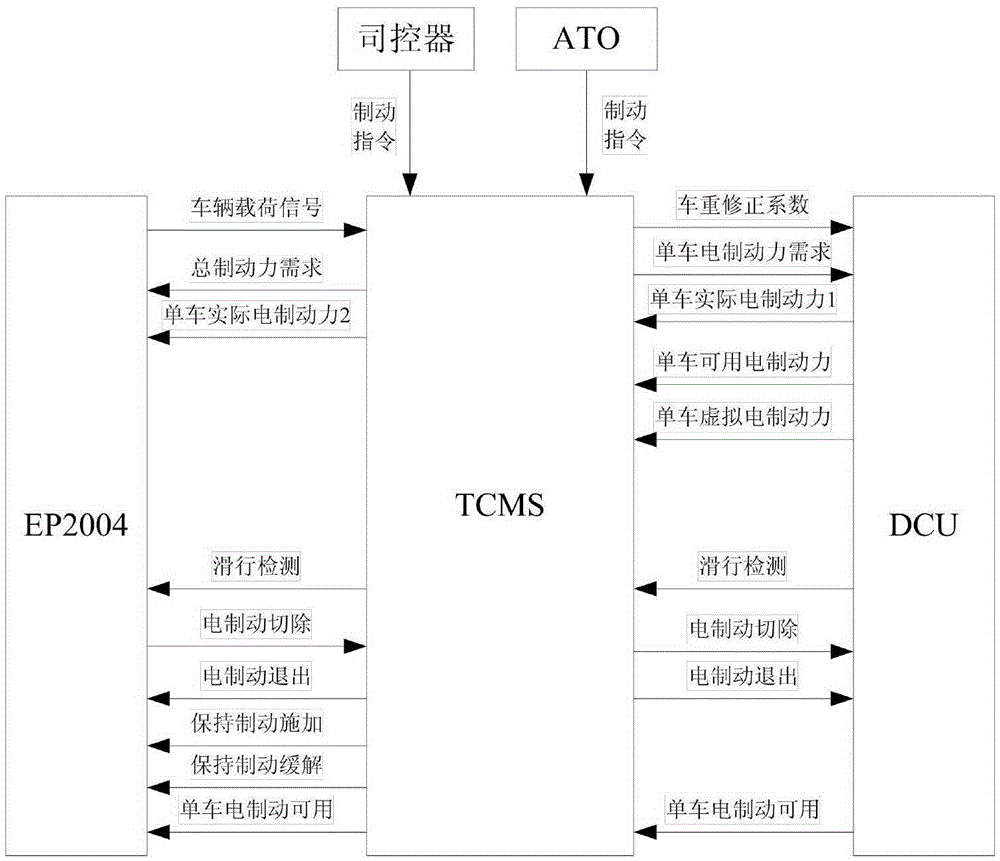
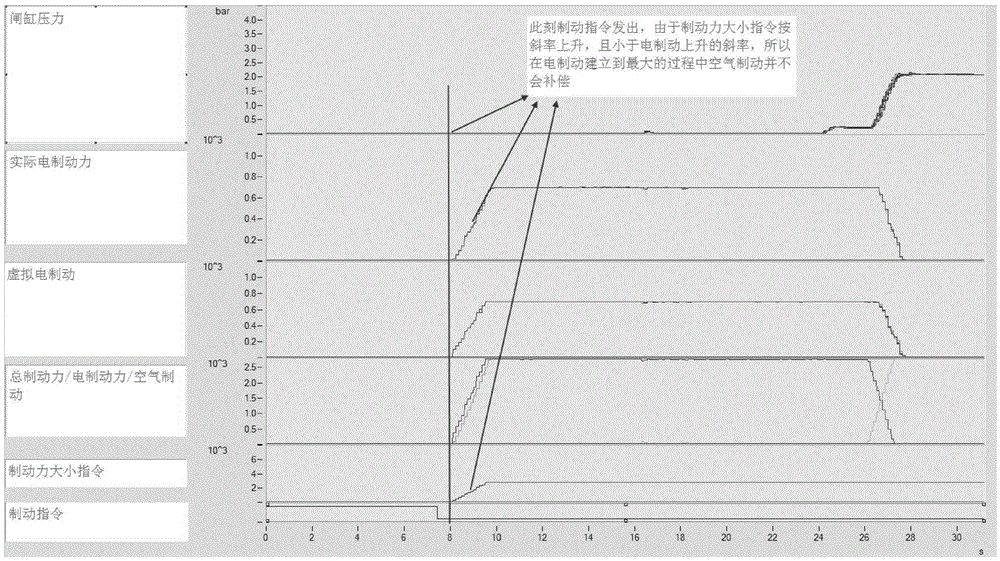
Urban railway vehicle braking force management method distributing braking force based on TCMS
ActiveCN105346556AGood energy saving effectExtend your lifeRailway hydrostatic brakesRailway hydrodynamic brakesElectricityPower grid
The invention belongs to the technical field of urban railway vehicle control, and relates to an urban railway vehicle braking force management method distributing braking force based on TCMS. According to the management method, electric braking force is used preferably, air braking serves as the supplementary for insufficient braking force, electric braking is in real-time coordinated matching with air braking, air braking is not used under the situation that the electric braking capability is enough, and the purposes that energy is fed back to a power grid to the maximum degree, and abrasion of a shoe is greatly reduced are achieved. When the electric braking capability is not enough, the air braking is preferably supplemented to a trailer and a motor vehicle with the electric braking fault, and after the maximum adhesion is reached, the purposes that the air braking is averagely supplemented on the motor vehicle with the normal electric braking, the average distribution of braking force for all vehicles is achieved, the interaction force among the vehicles is reduced, and the service life of the vehicles is prolonged are achieved. In the braking process and the starting process, the applying of the braking force is linearly controlled according to the whole vehicle impulsion limiting requirement, the vehicle impulsion is reduced, and conversion among traction force, electric braking and air braking is smooth.
Owner:CRRC CHANGCHUN RAILWAY VEHICLES CO LTD
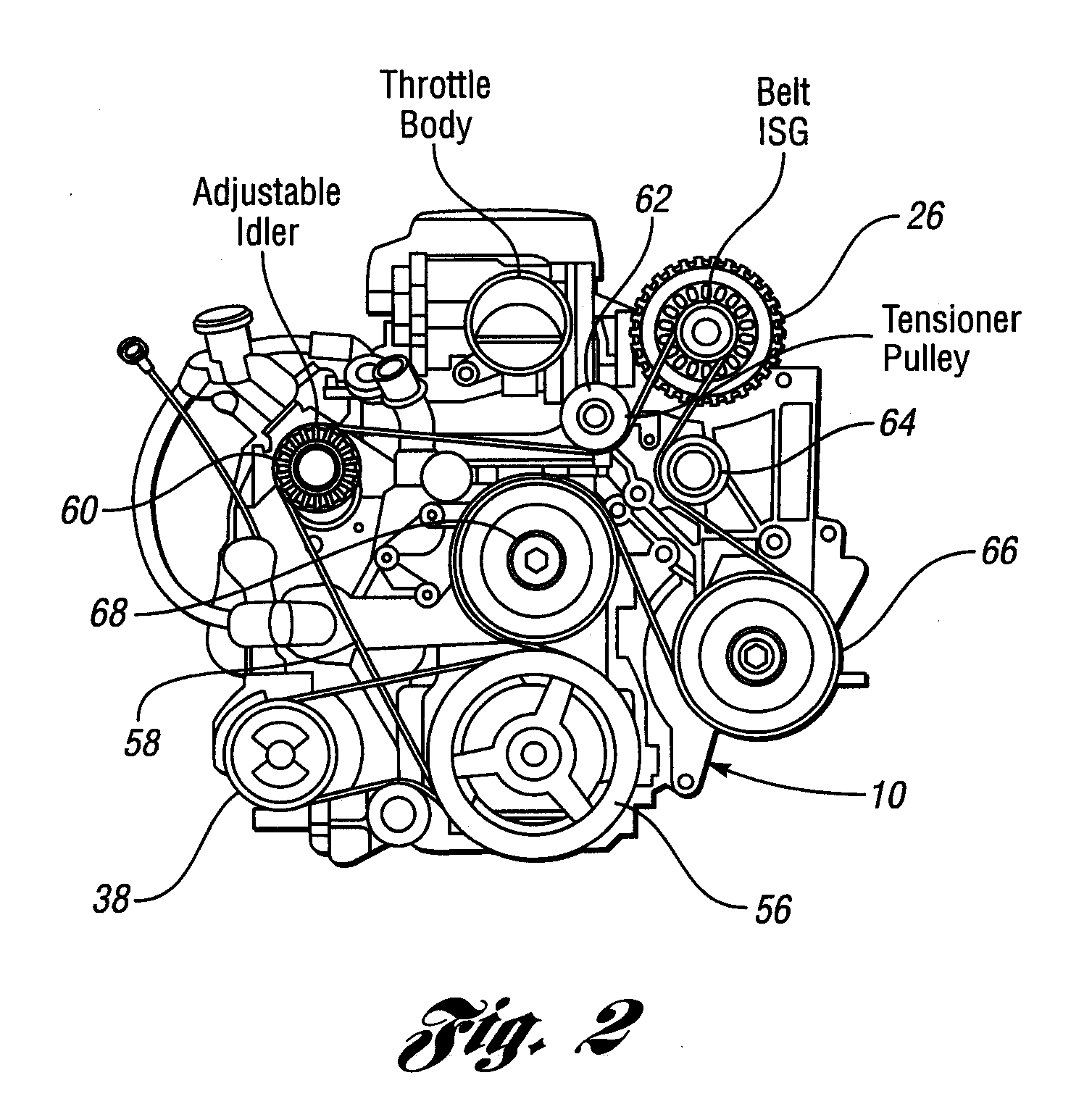
Compressed air engine electrically driven whole-variable valve actuating system
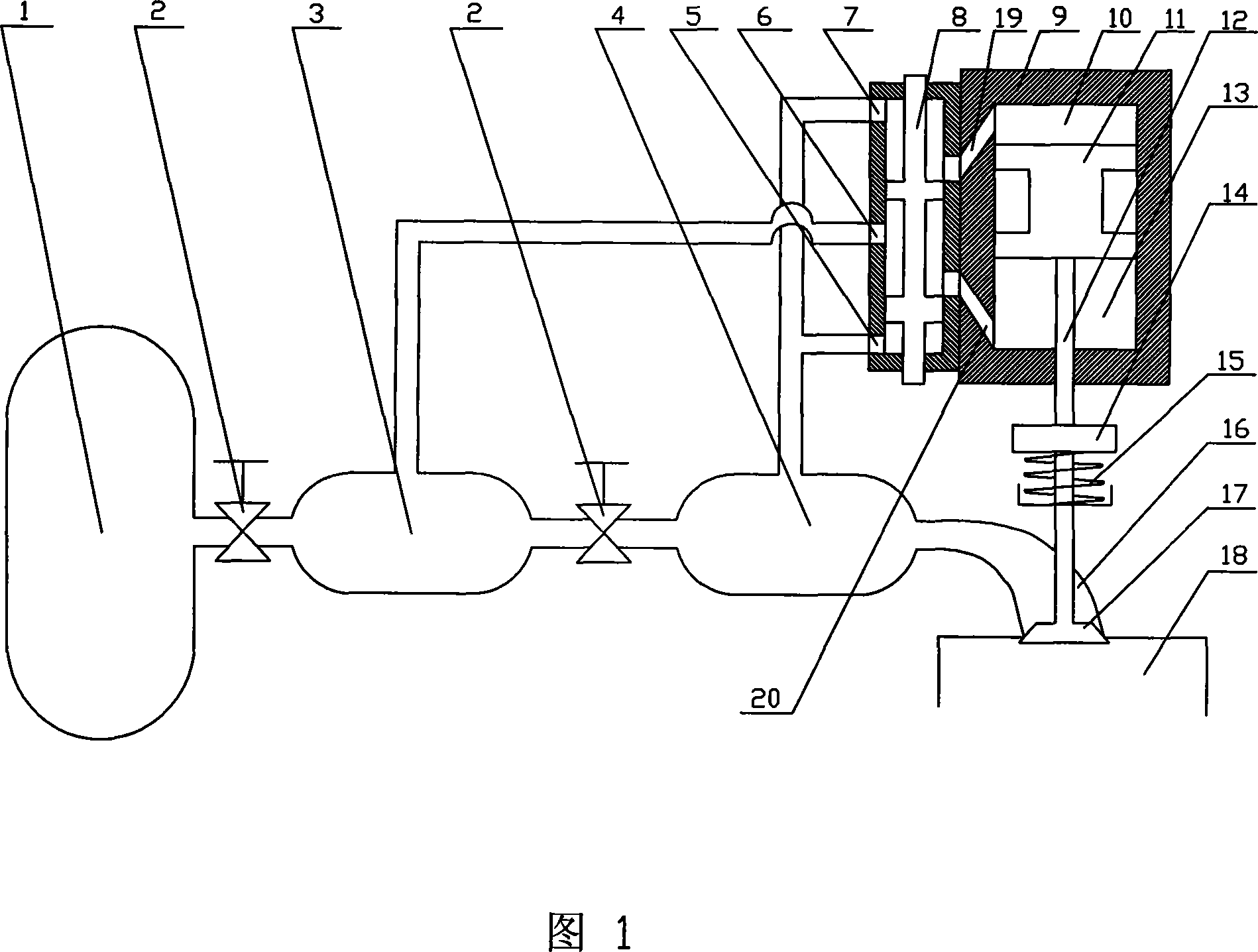
InactiveCN101149002AReduce throttling lossRealize time adjustmentReciprocating piston enginesNon-mechanical valveEngineeringEngine valve
The present invention relates to compressed air engine, and is especially one kind of variable air valve driving system for compressed air engine. The system includes one air valve spring, one shaft coupler, one piston rod and one piston inside a cylinder, connected successively to the air valve. There are two communication states between the air passage and the air exhaust electromagnetic directional valve based on the final position of the valve. The valve opening time may be controlled by means of controlling the power-on pulse duration. The present invention has the advantages of capacity of decoupling air valve motion and the crankshaft rotation speed of the pneumatic engine to optimize the air distributing phase, capacity of recovering the vehicle braking energy, convenient braking strength regulation, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com