Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
647results about "Noise/vibration control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
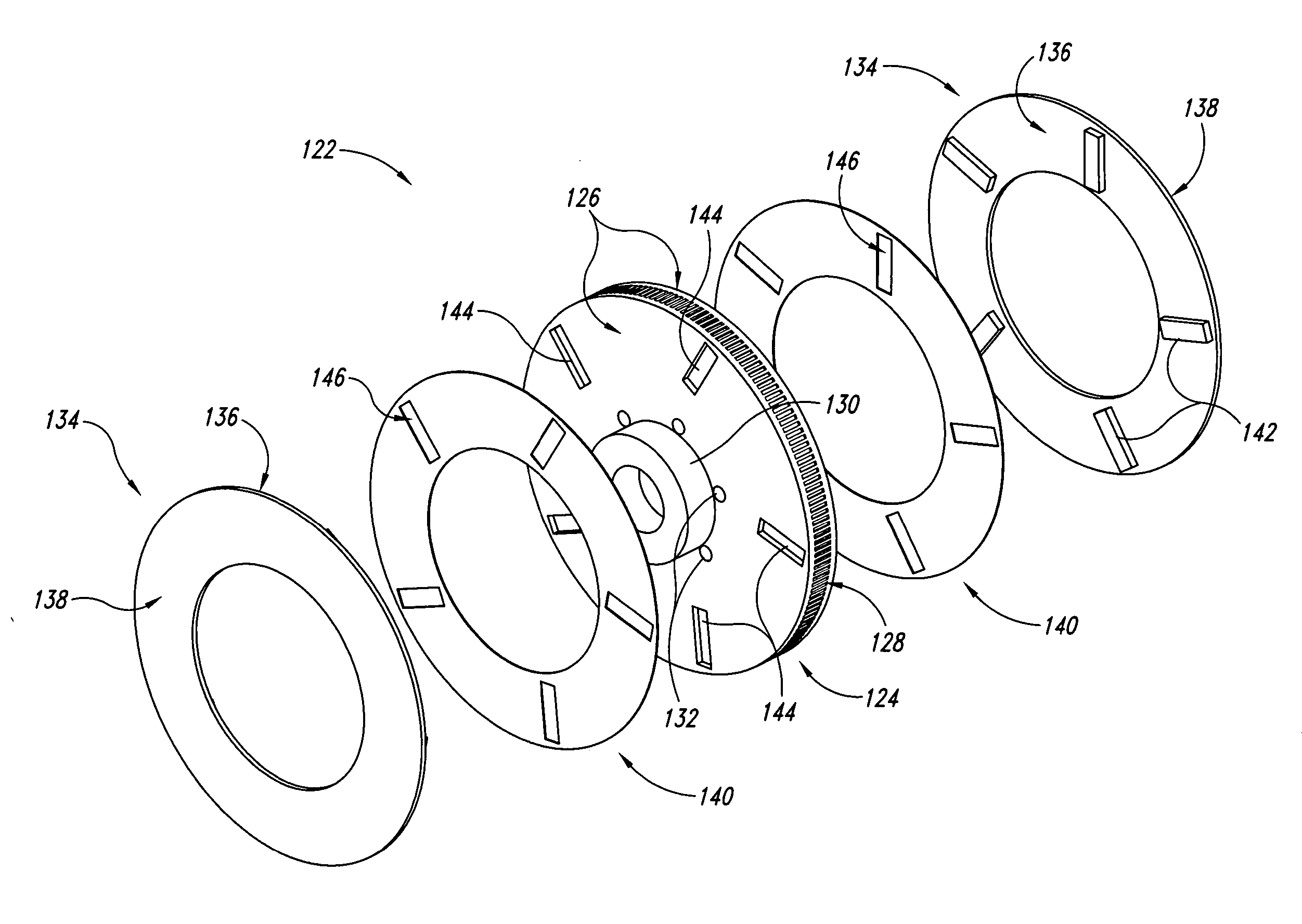
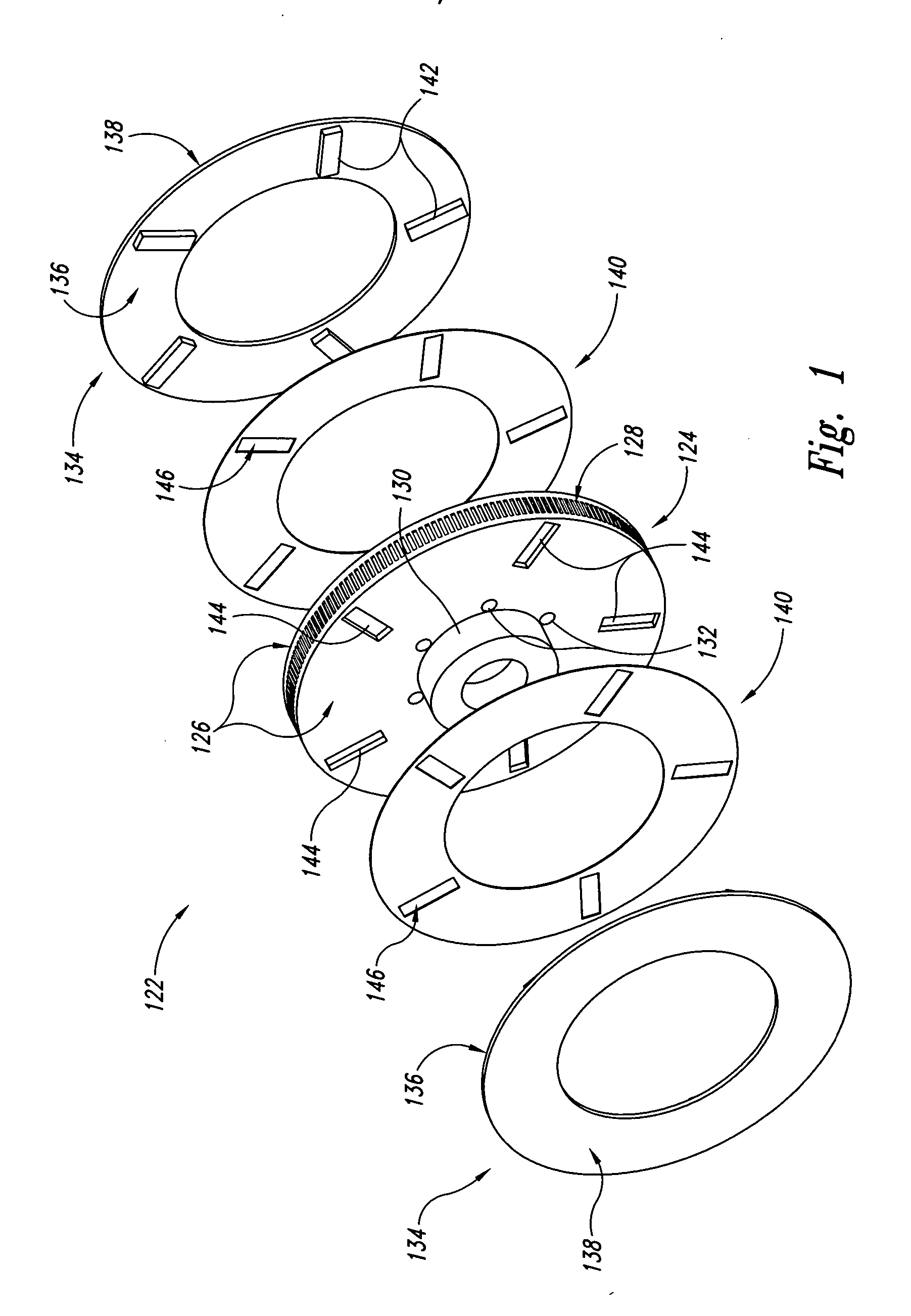
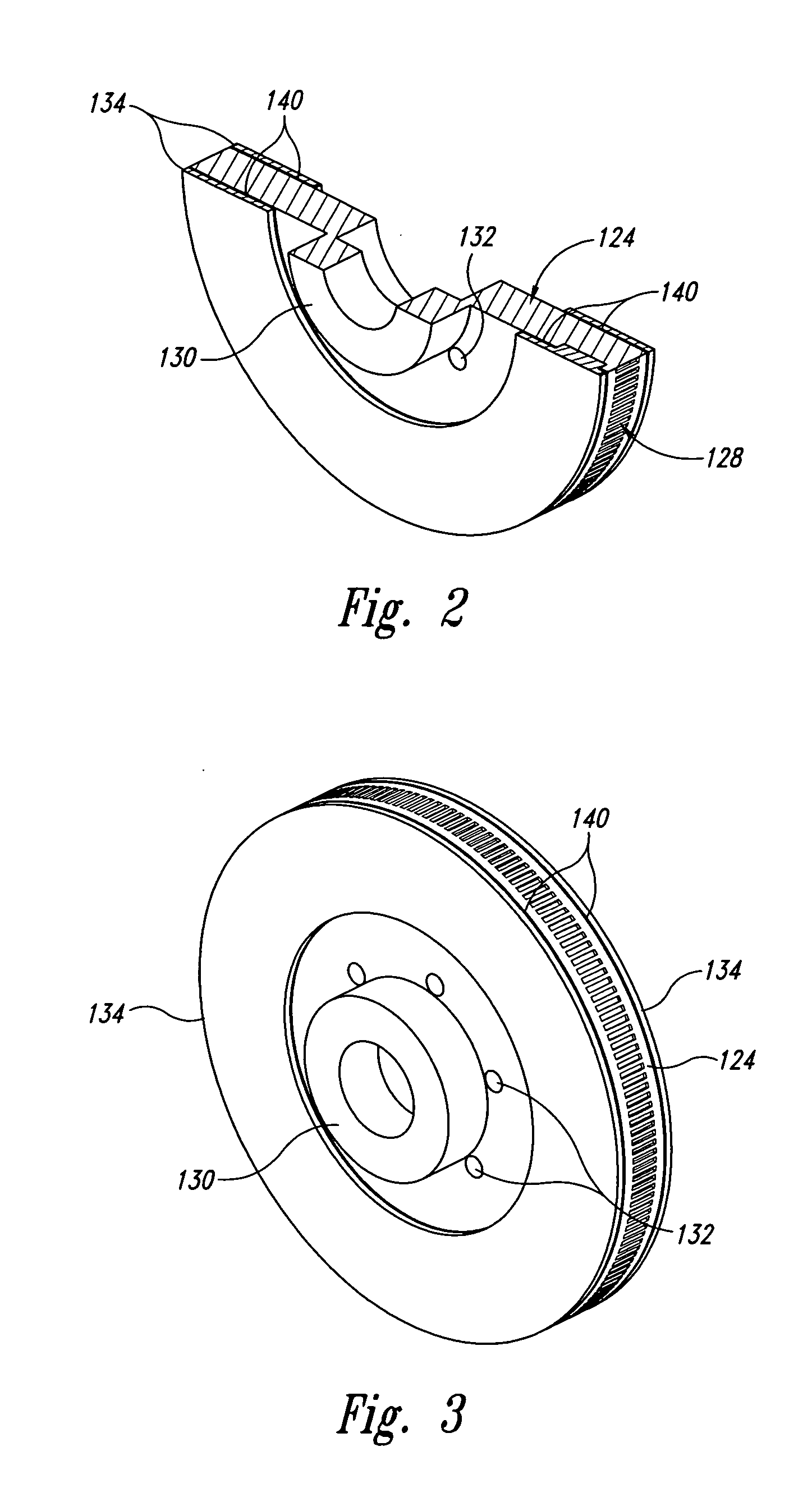
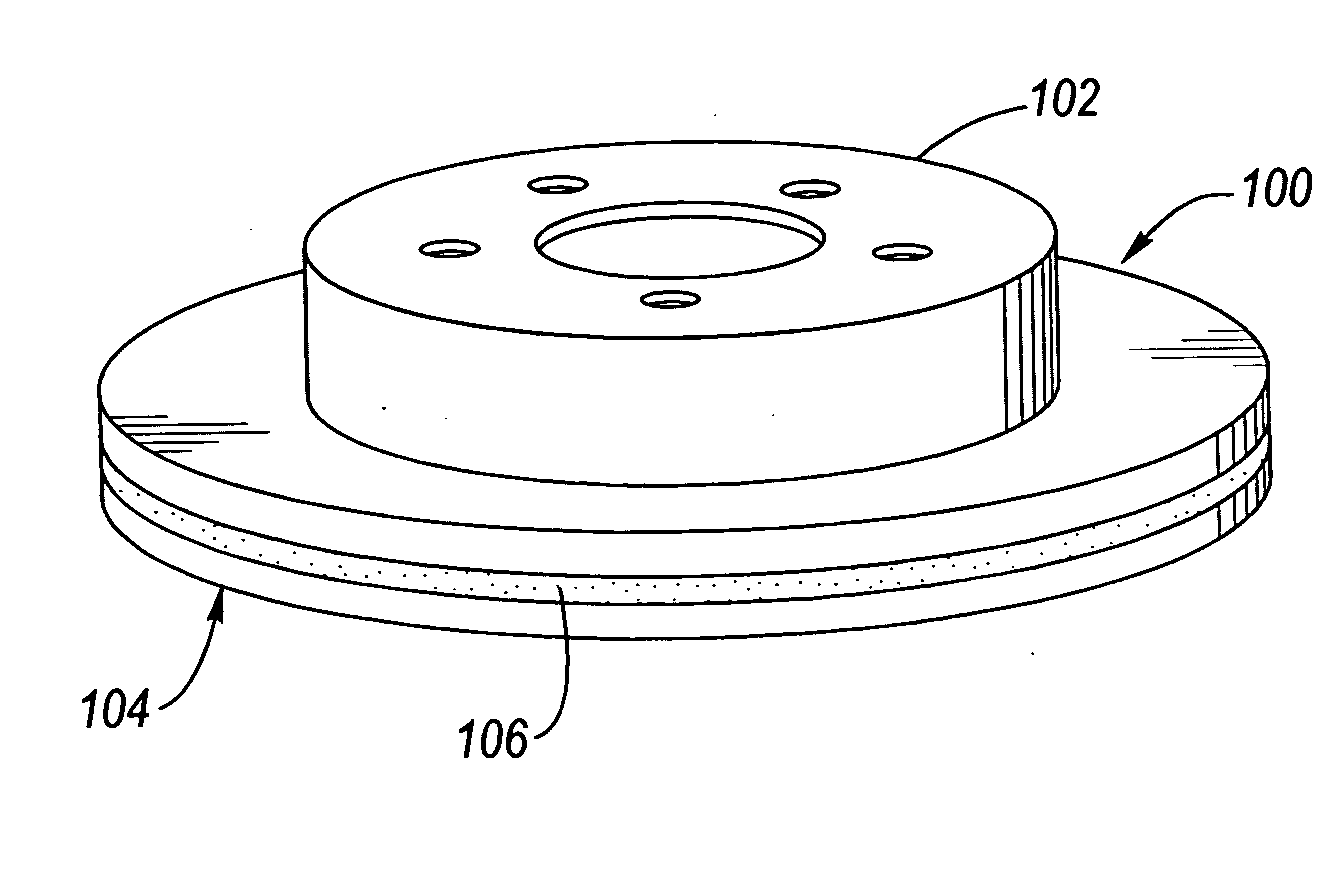
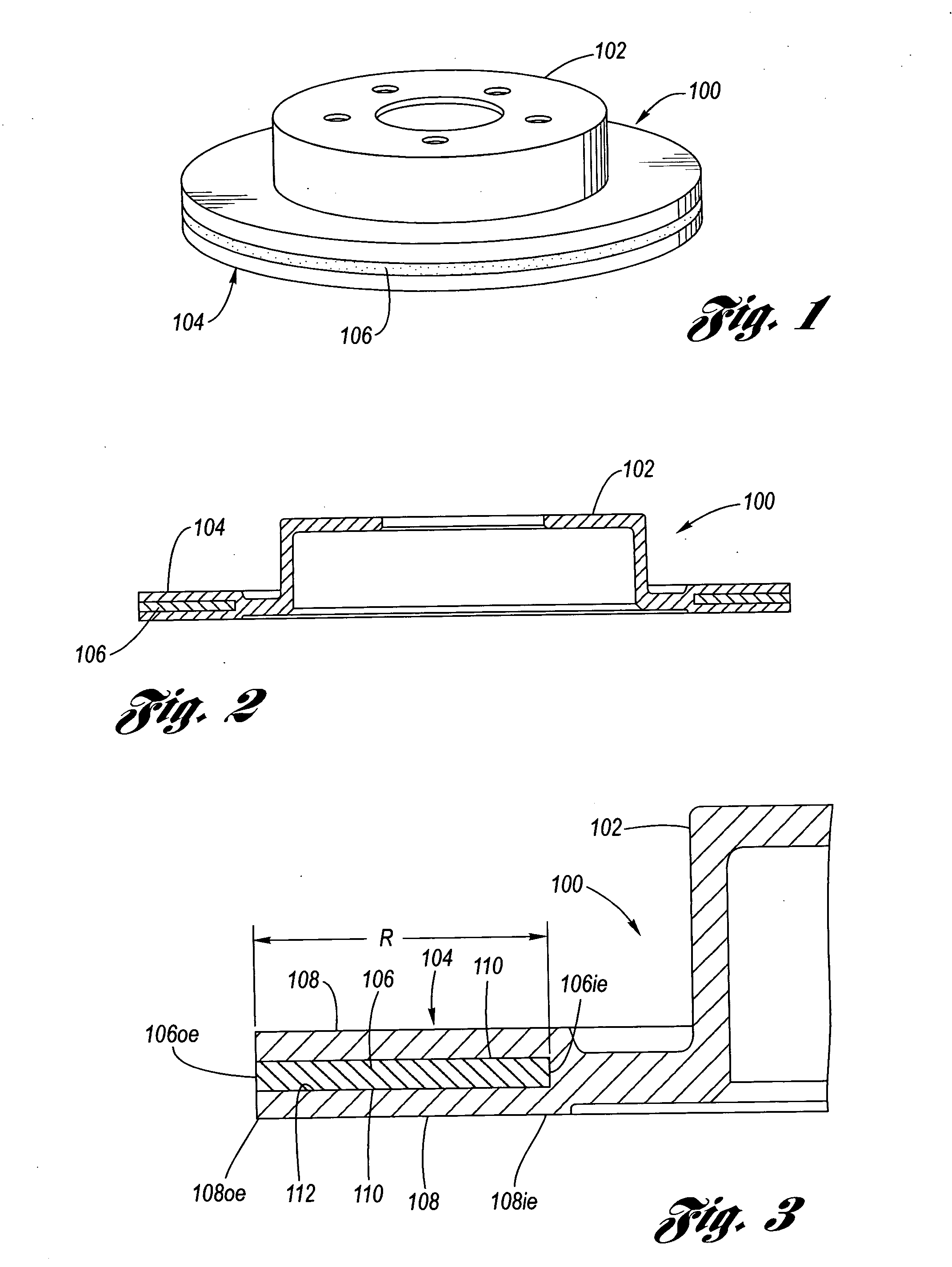
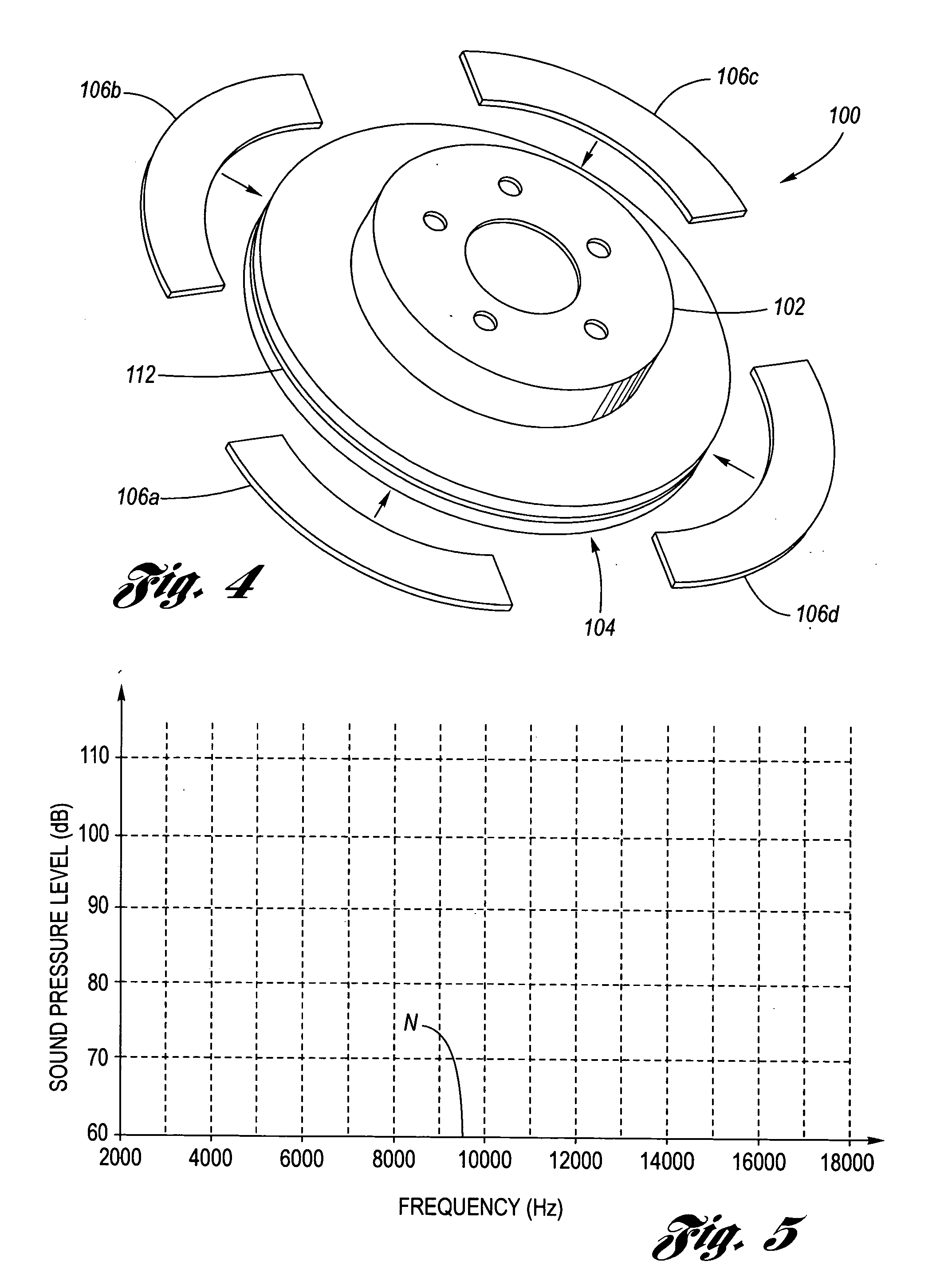
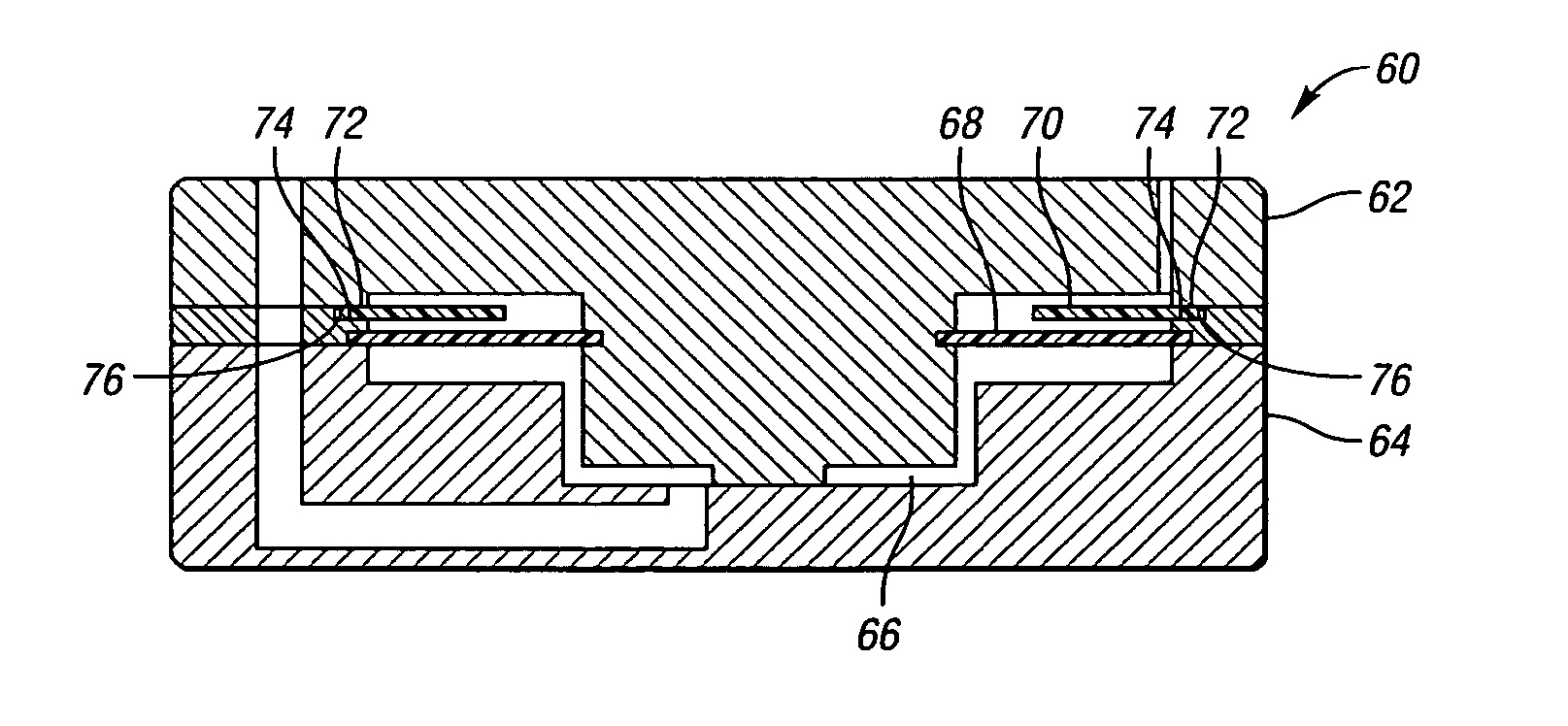
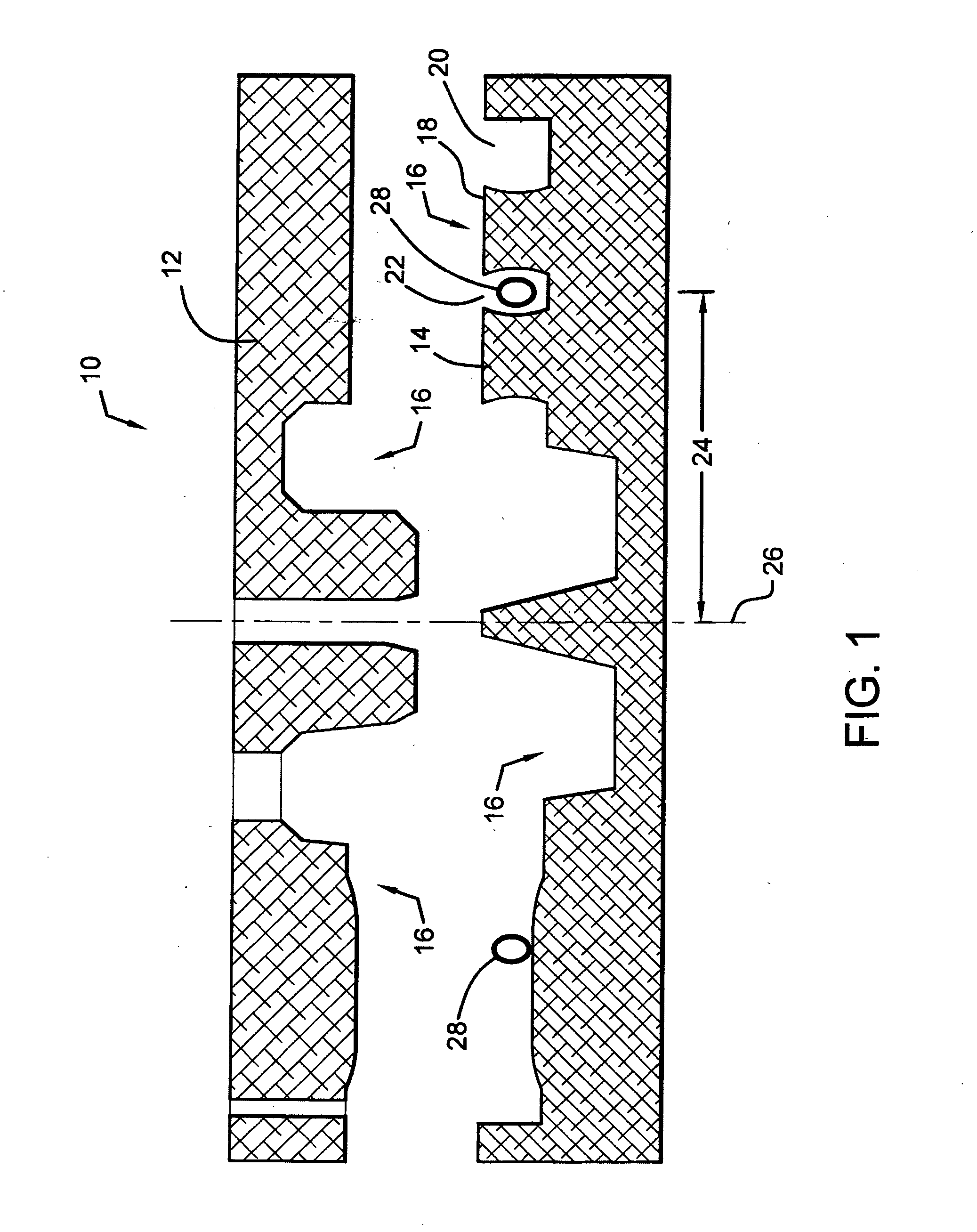
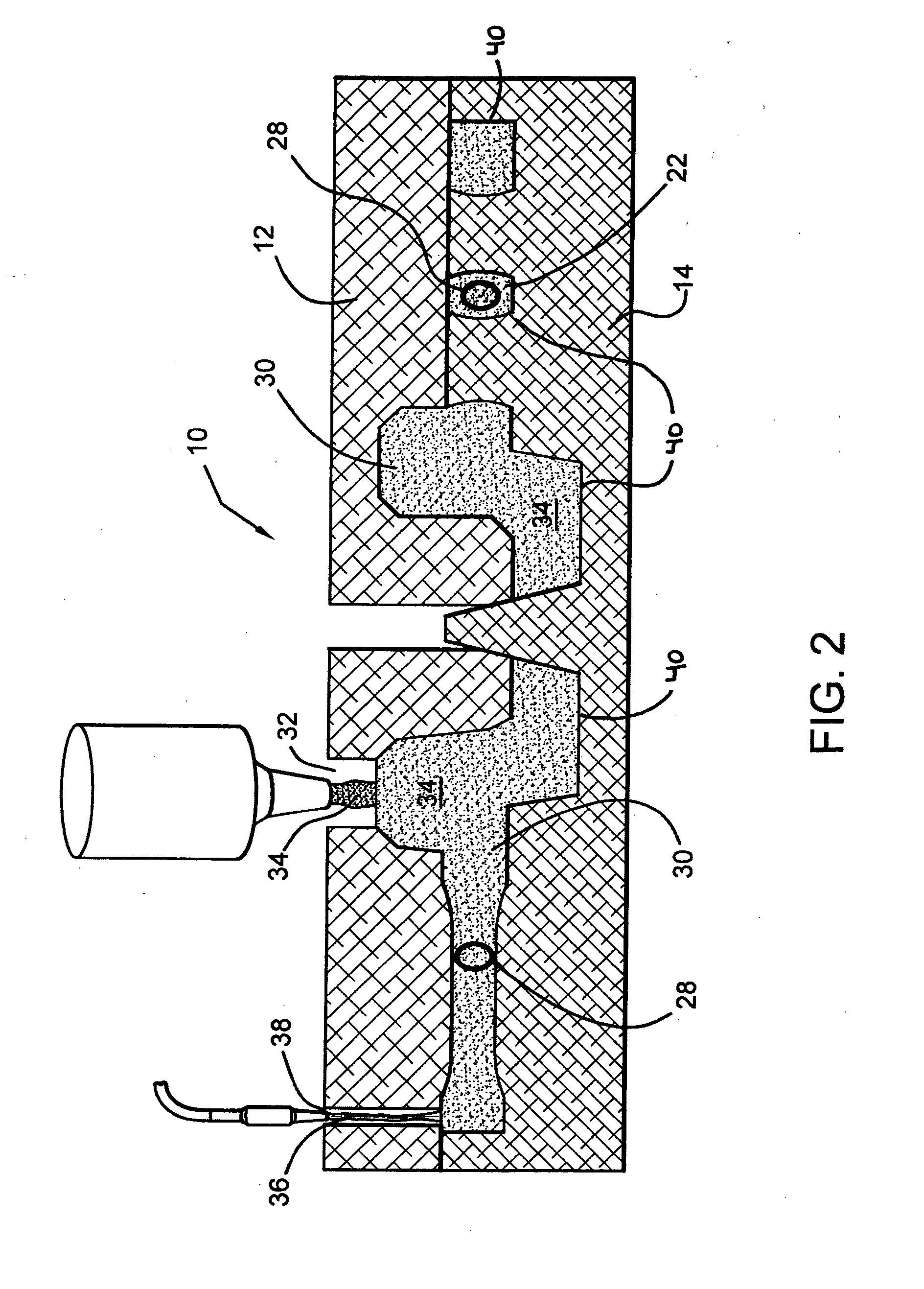
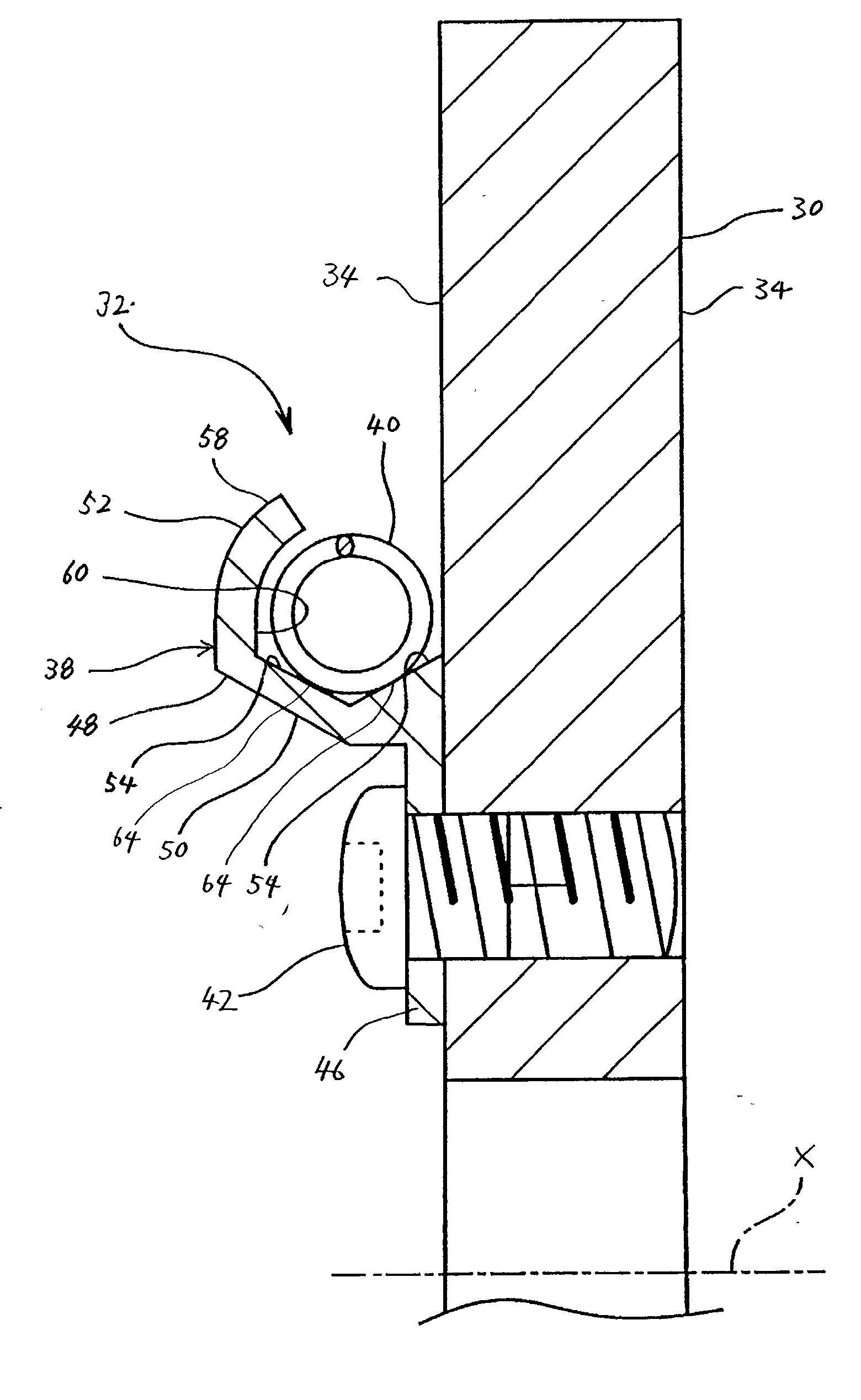
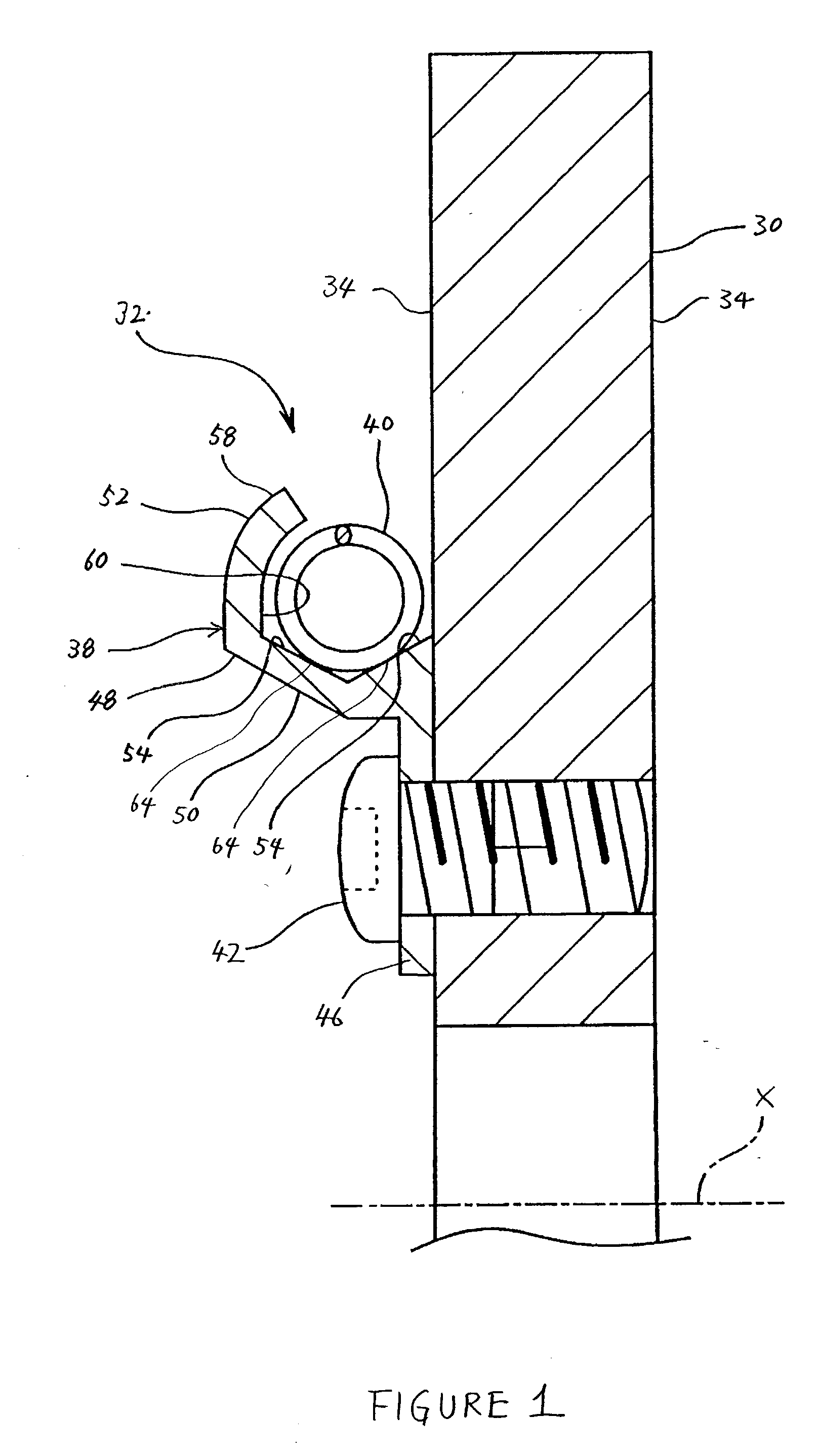
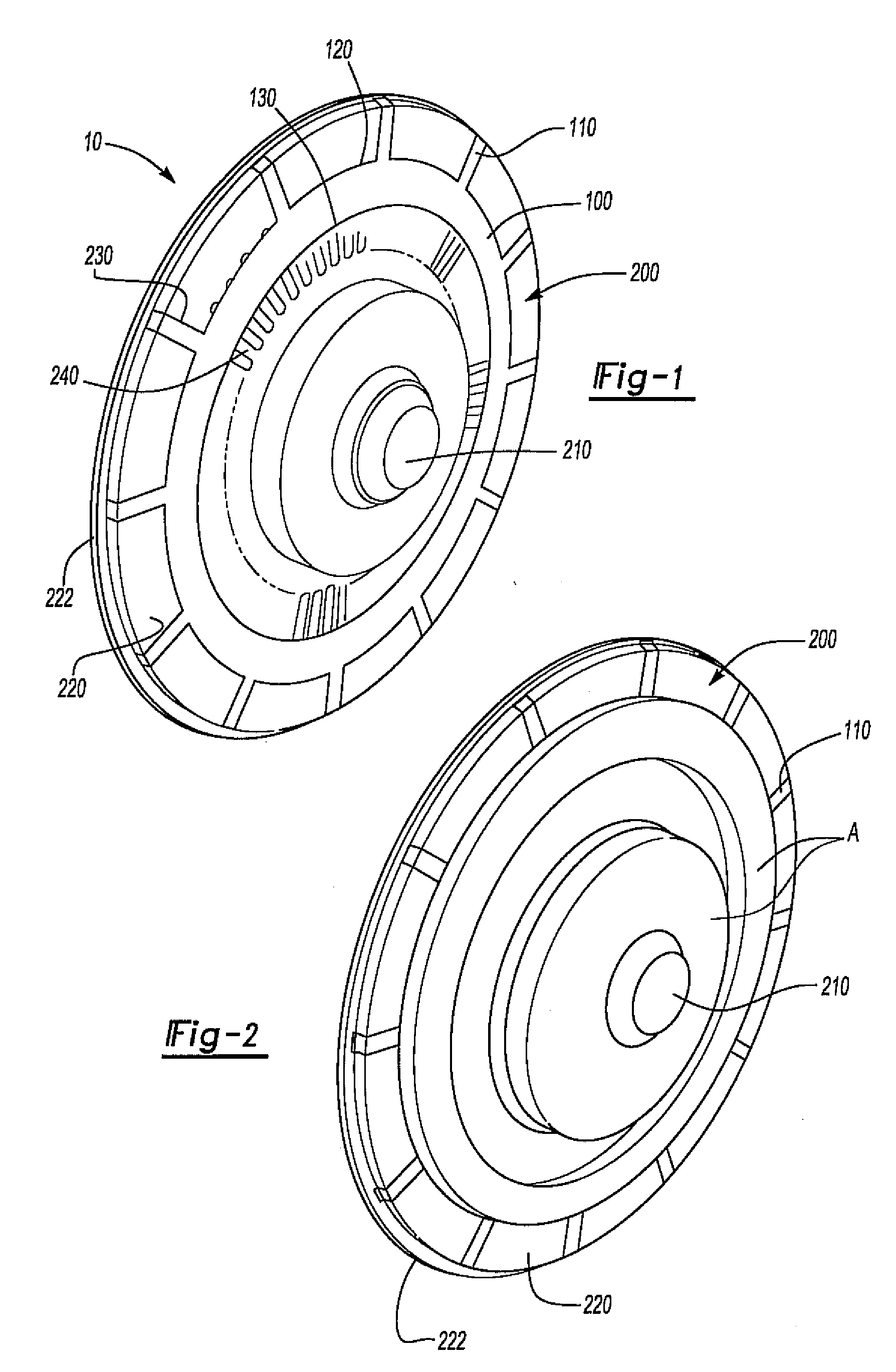
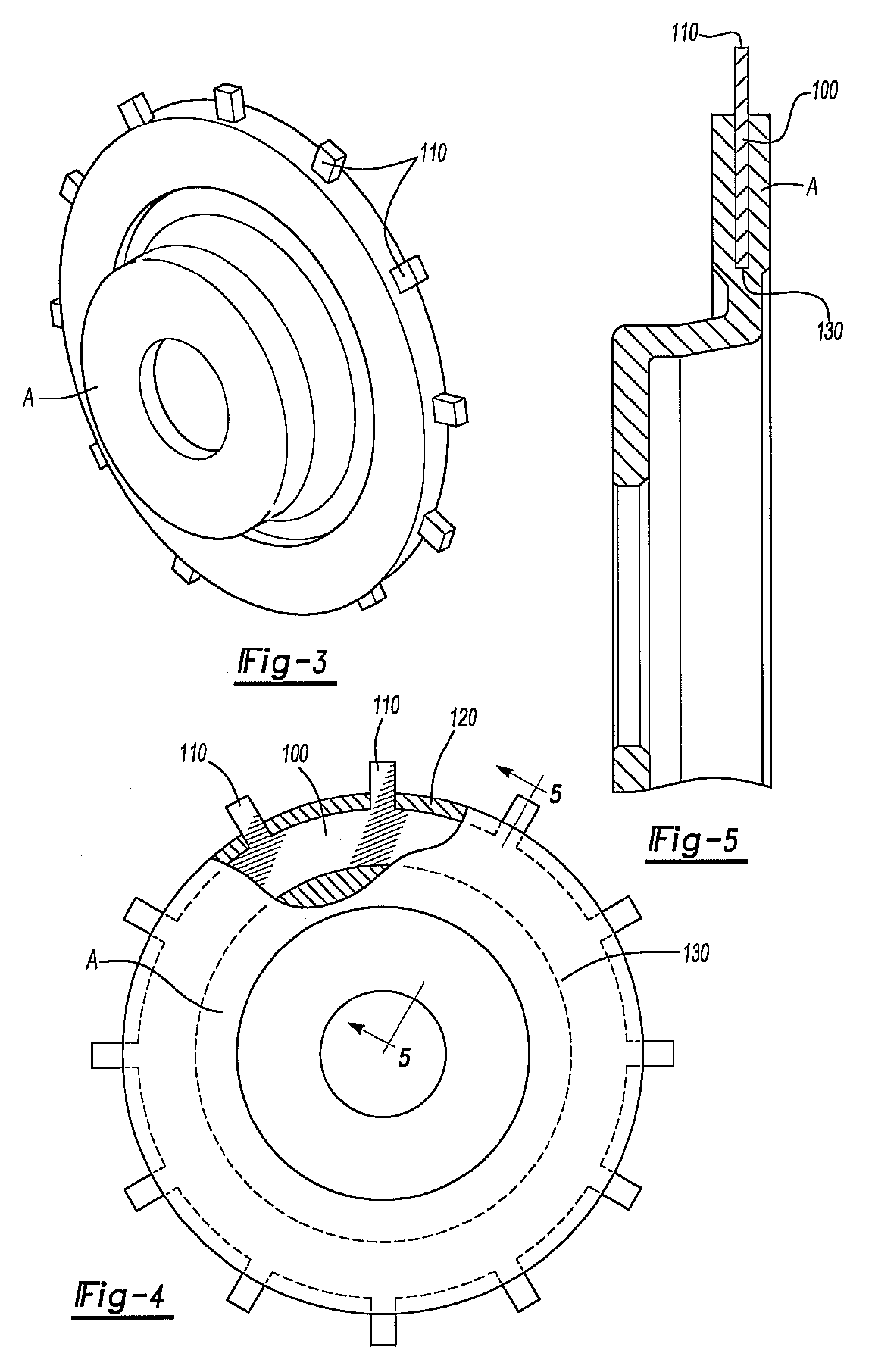
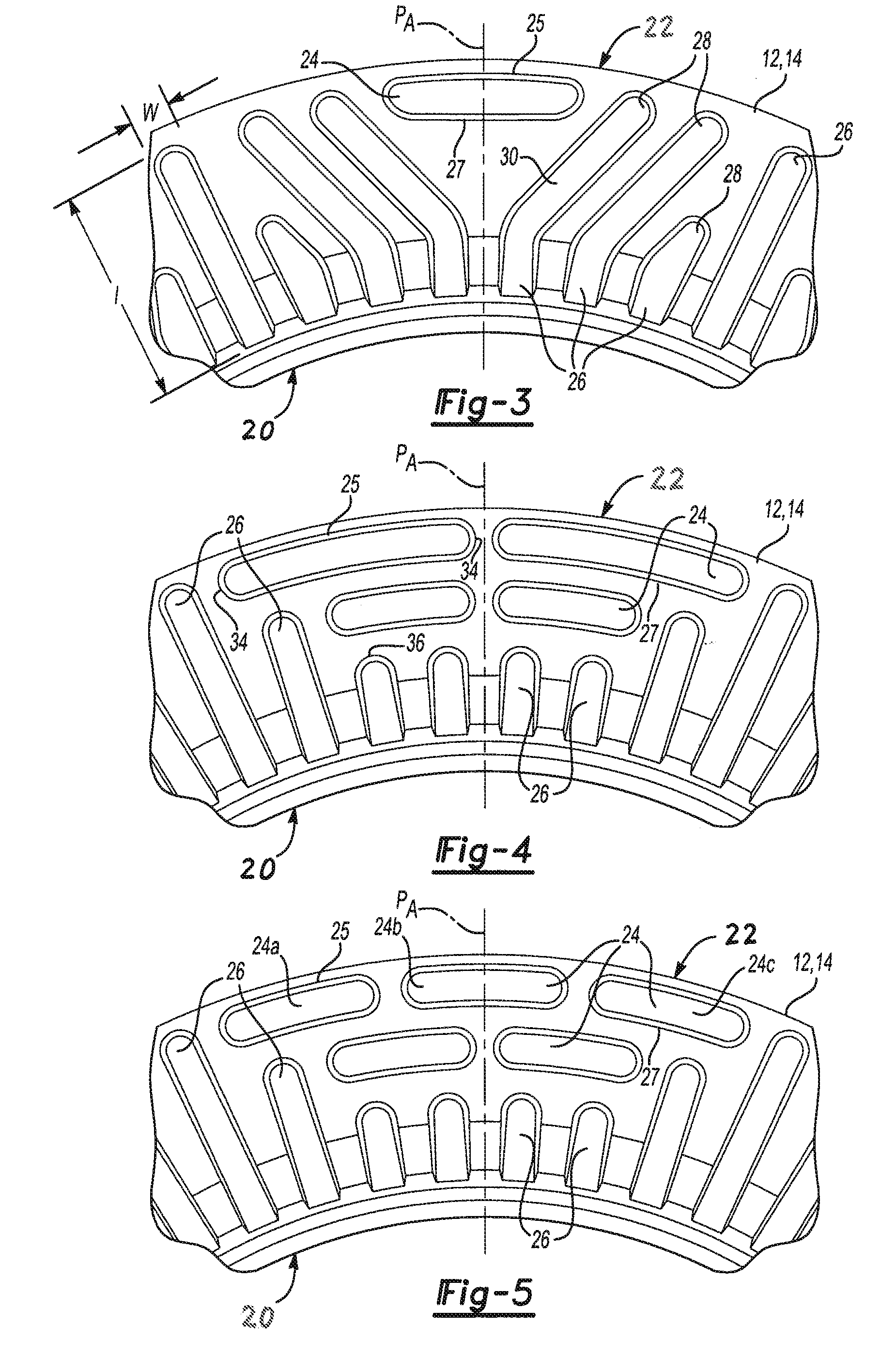
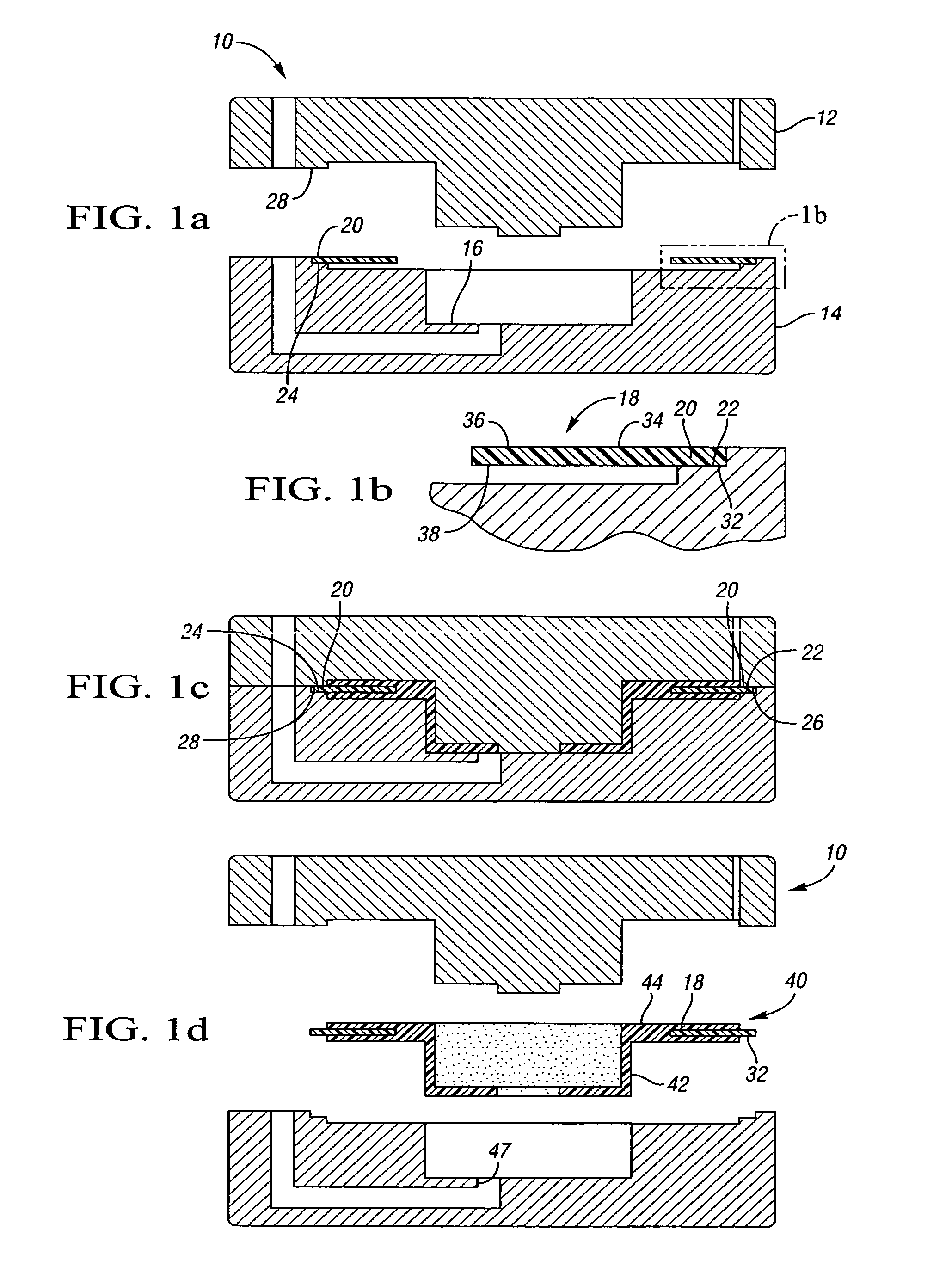
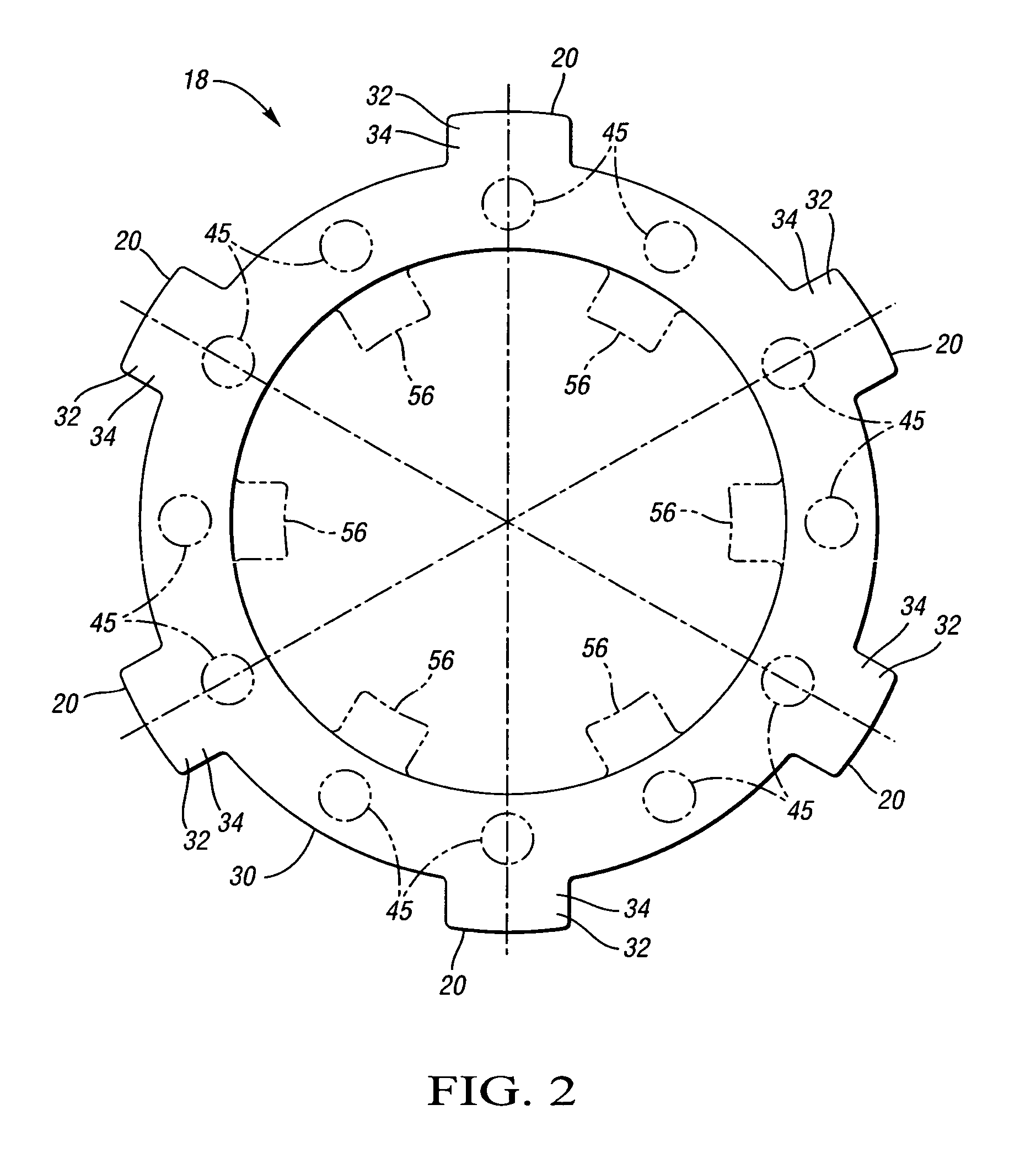
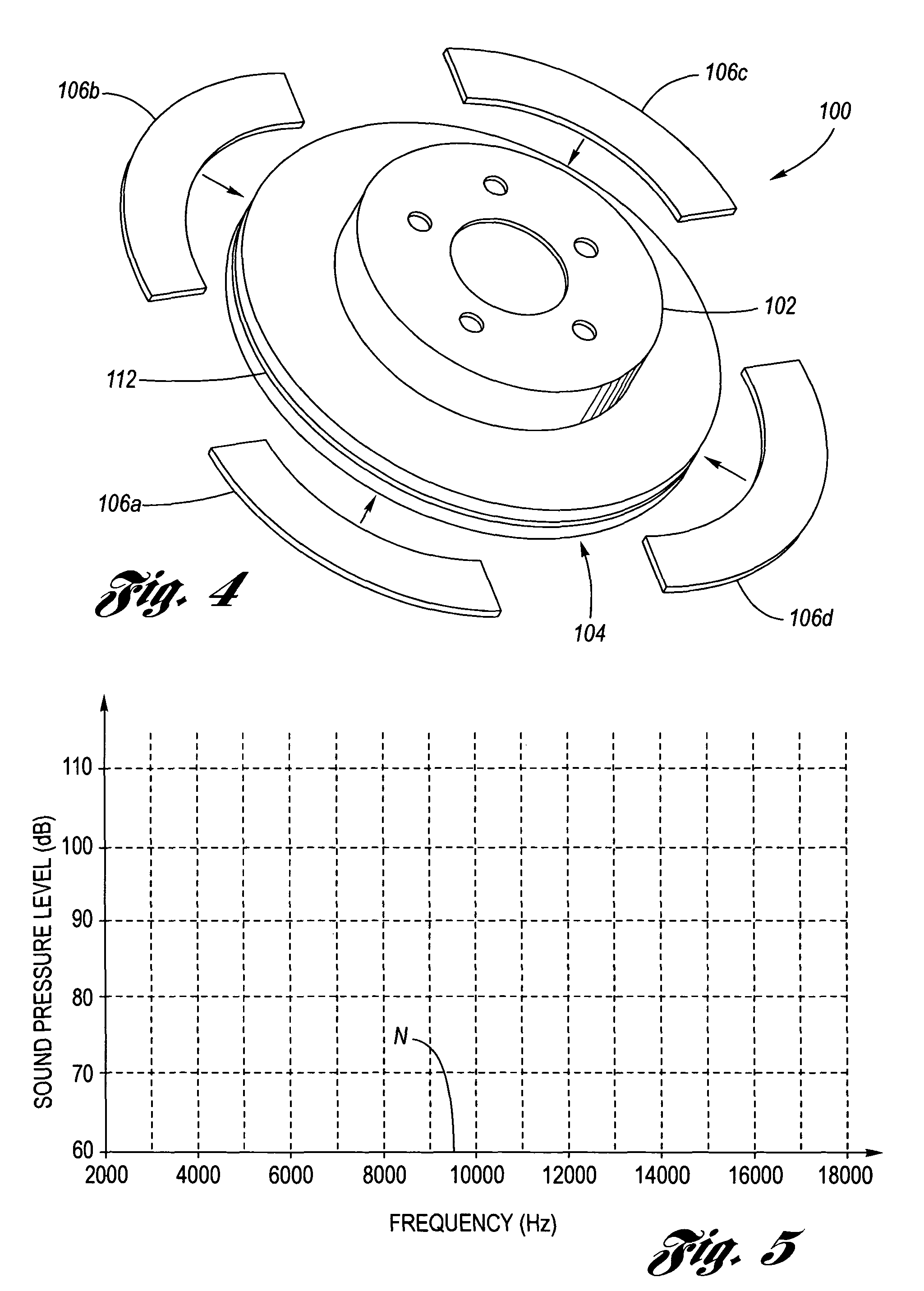
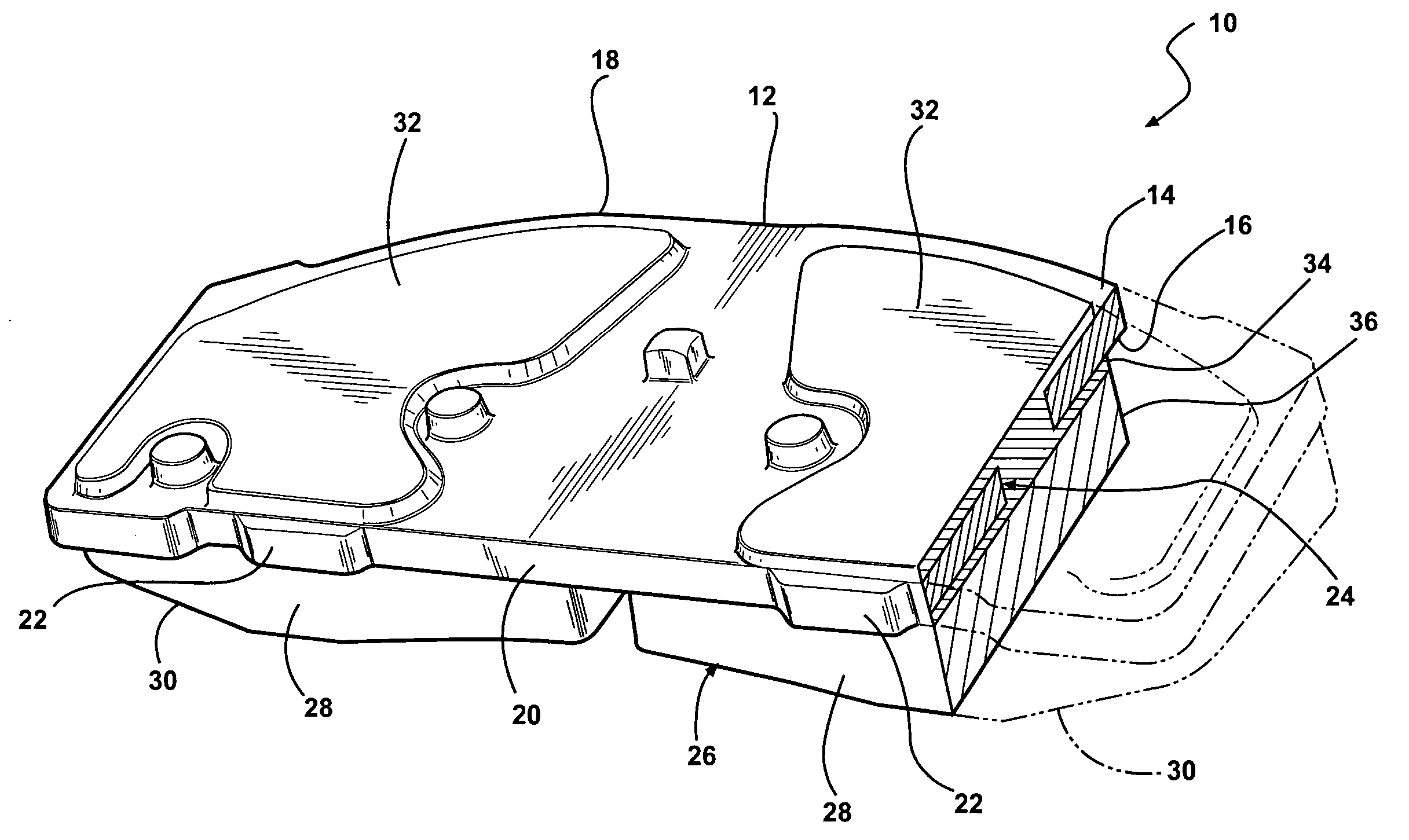
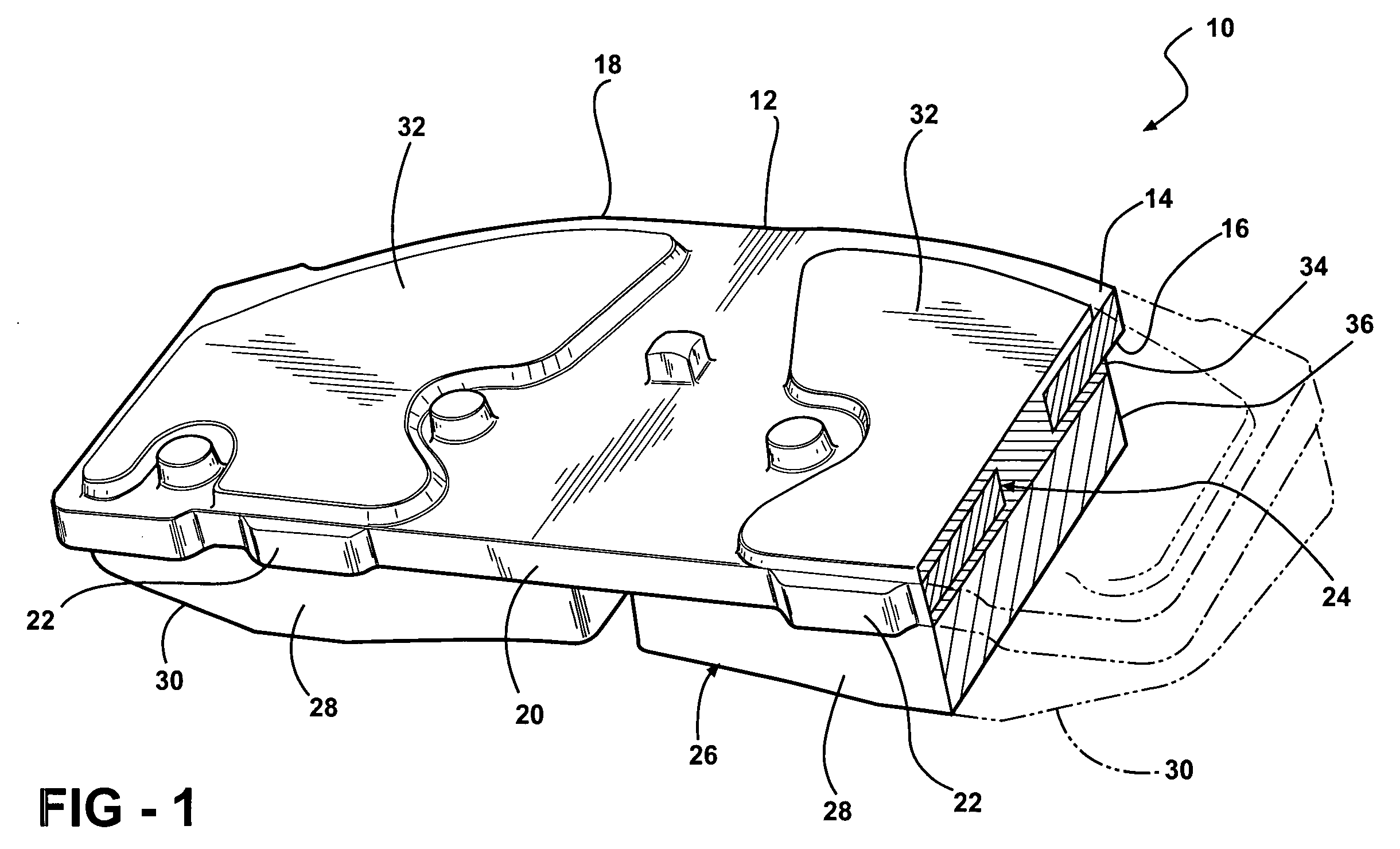
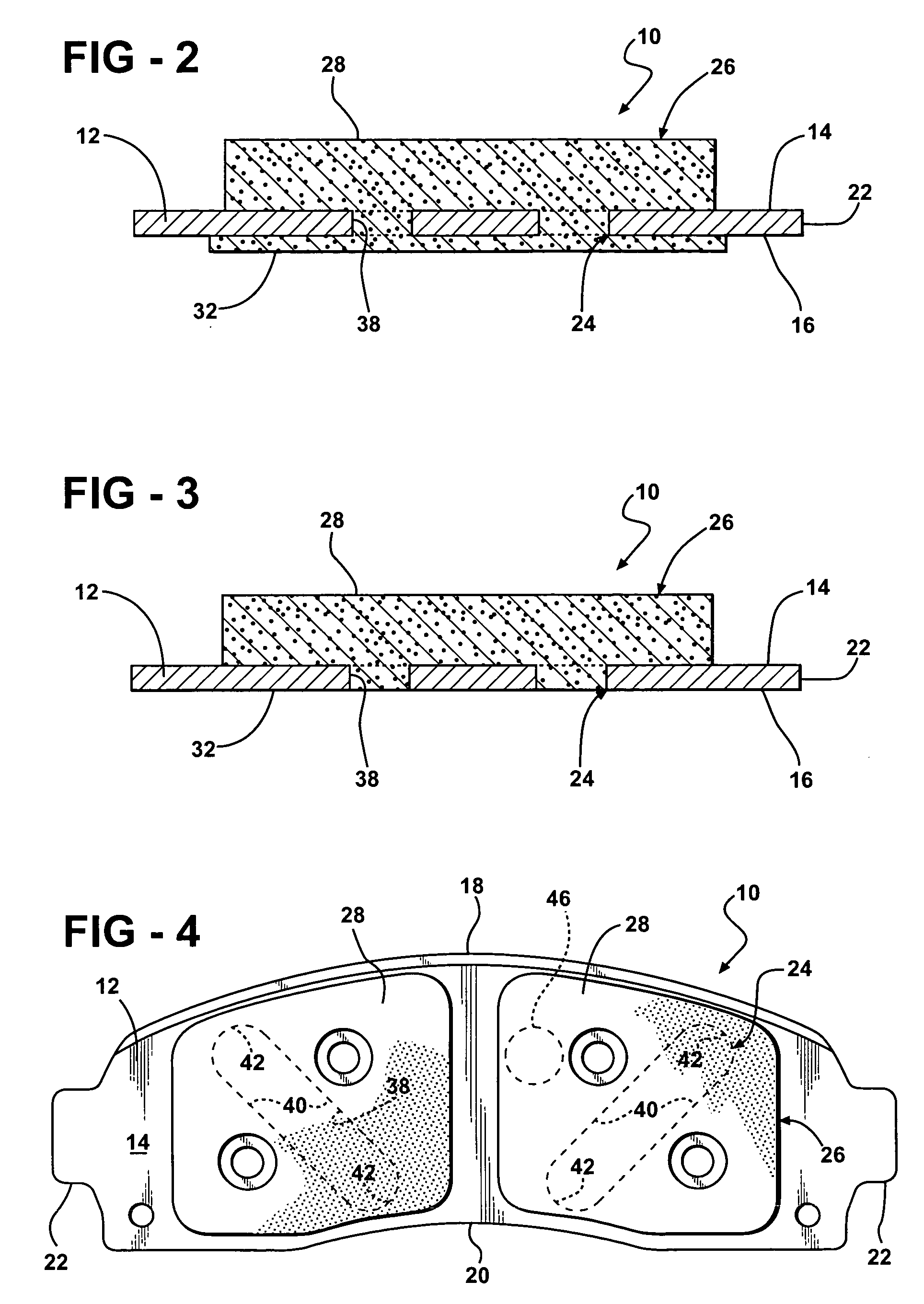
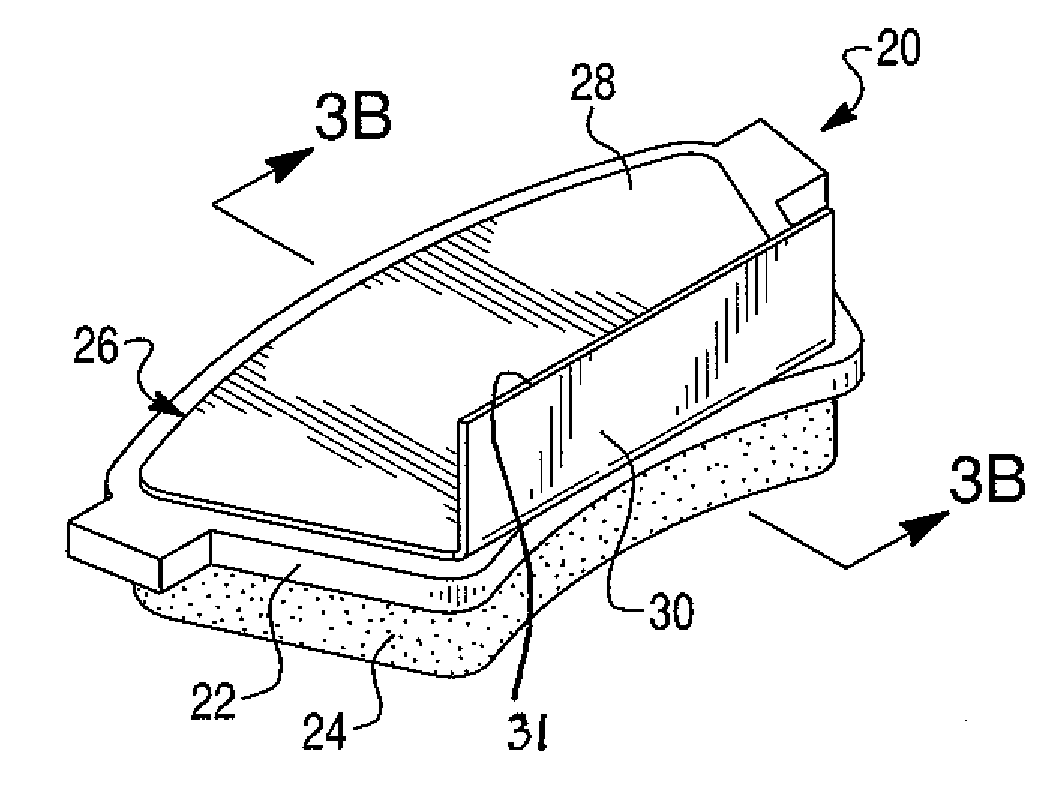
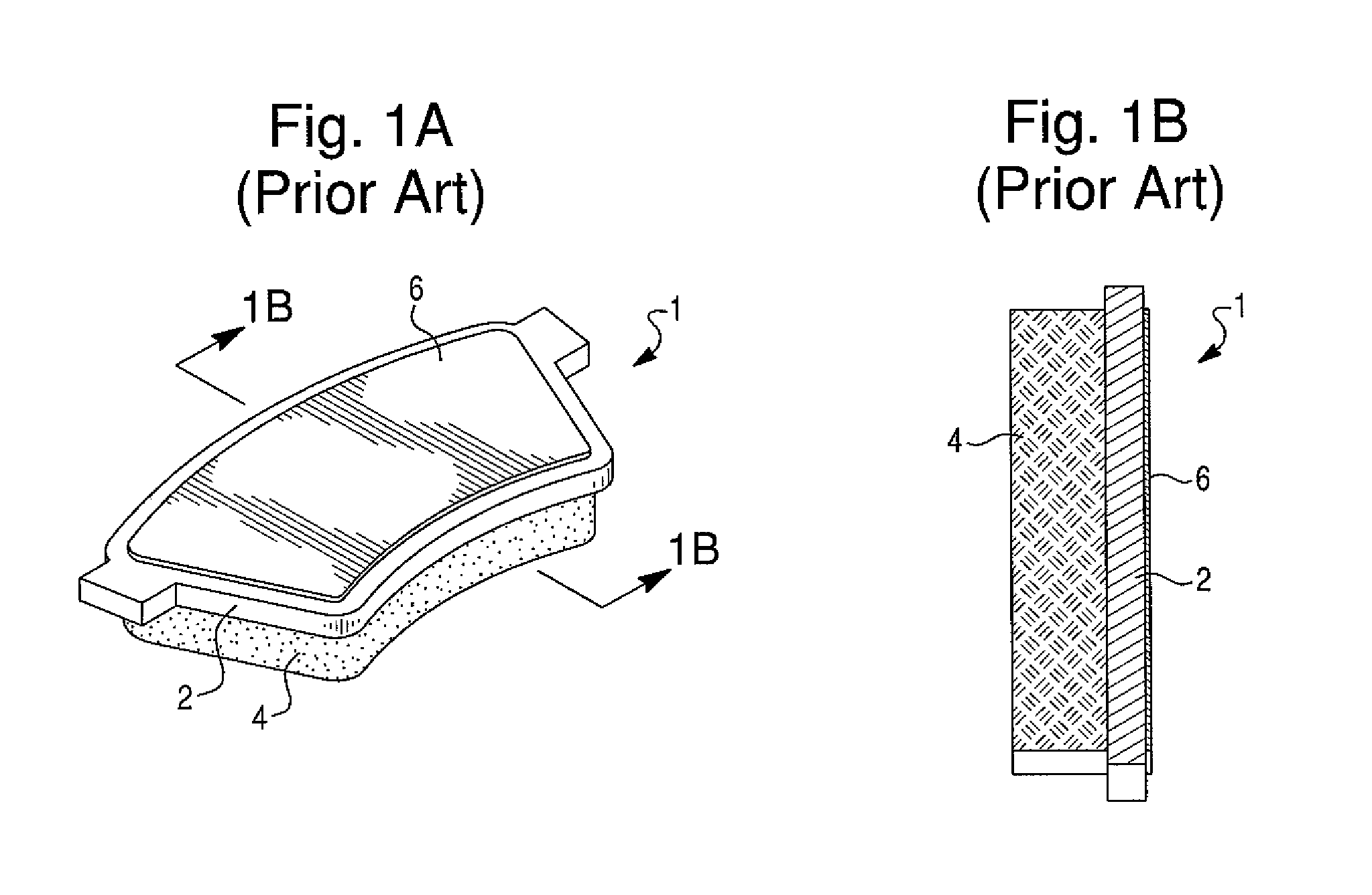
Disc brake rotor assembly and method for producing same
InactiveUS20050183909A1Improve thermal conductivityOptimize acoustic frequency transferBraking element arrangementsNoise/vibration controlAdhesiveMetal alloy
Novel composite disc brake rotor assemblies are provided, along with novel and efficient methods for manufacturing them. Preferably, the rotor assemblies comprise annular wear plates formed of particle reinforced aluminum-based metal matrix composite (MMC), ceramic matrix composite (CMC), or of ‘carbon graphite foam.’ The wear plates, made of a first material, are attached to annular surfaces of a central rotor, made of a second material, by fusing bonding layers between the wear plates and the rotor surfaces. The bonding layers are comprised of at least one of a metal alloy having a melting temperature lower than that of either the first or second materials, and a high-temperature adhesive. Preferably, the wear plates comprise projections that are positioned within adjacent receiving recesses in the center rotor. The bonding layers and projections enhance thermal and acoustical transference between the wear plates and the center rotor section. Carbon graphite foam provides for substantially enhanced heat transference. Use of the fusable binding layer, or adhesive provides for an efficient, low cost method of manufacturing for composite disc brake rotor assemblies.
Owner:BENMAXX
Brake unit
InactiveUS6302246B1Prolong lifeImprove flatnessBraking element arrangementsNoise/vibration controlEngineeringCeramic metal
A brake unit comprising at least one brake and at least one brake pad having at least one friction lining is described. The brake has a disk brake with a brake rotor made of a ceramic-metal composite (CMC) whose outer surface or surfaces at least partially form a friction surface for the at least one friction lining, and a disk brake cup that is mounted on the disk brake by way of one or more mounting elements. The friction surface of the disk brake has a hardness of approximately 1600 to 2500 HV, and the at least one friction lining has a coefficient of friction of approximately 0.3 to 0.5. The disk brake cup and / or the mounting elements form a corrosion-inhibiting attachment to the disk brake. The brake unit can be operated in corrosion-free fashion over a service life of at least approximately eight to 10 years or approximately 200,000 to 300,000 km.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotors
InactiveUS20060076200A1Average thicknessSmall thicknessNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
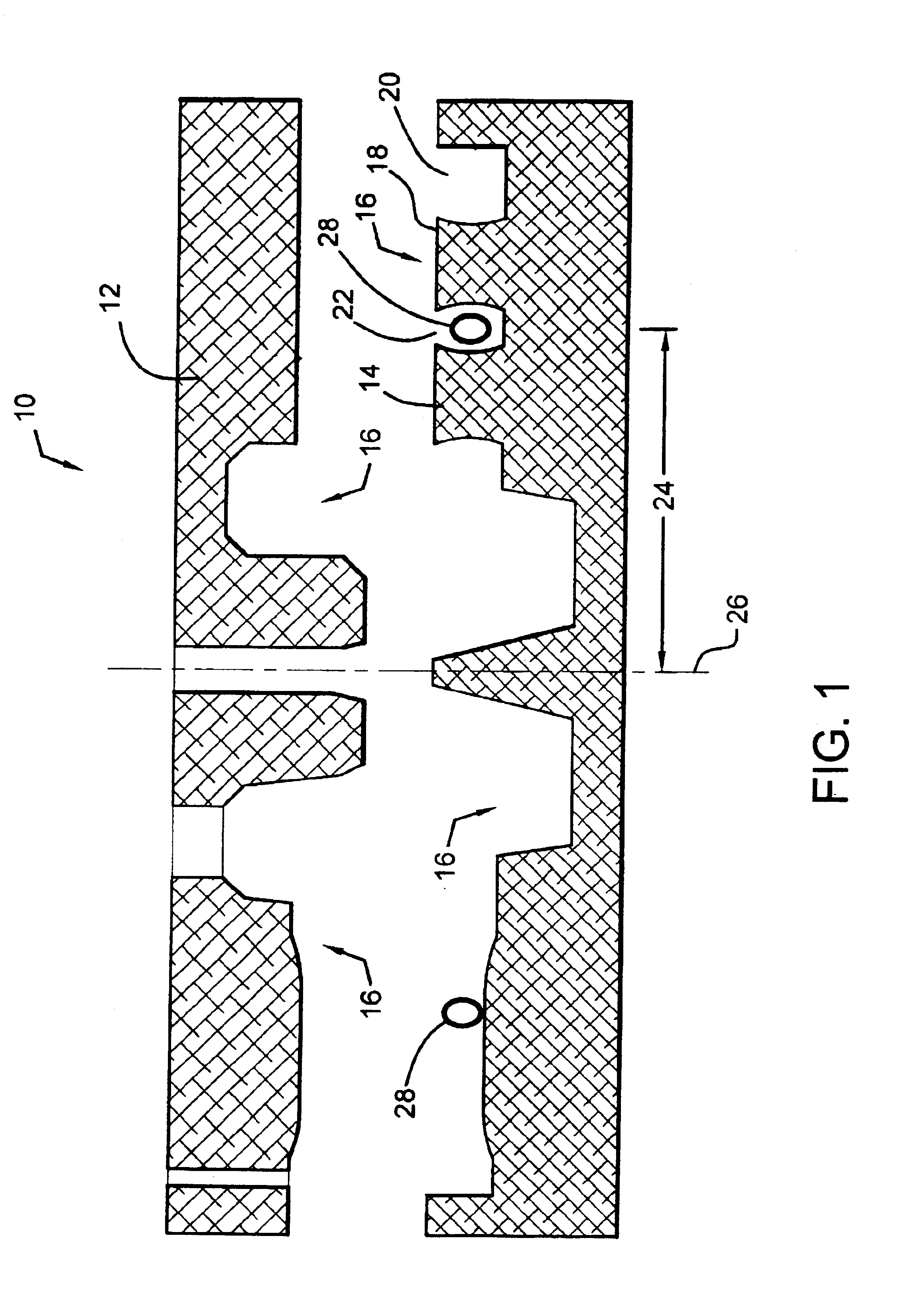
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor, wherein damping is provided Coulomb friction in generally coextensive relation with the braking surfaces of the one or more rotor cheeks. The Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor has at least one interfacial boundary formed in at least one rotor cheek disposed in generally coextensive relation to the braking surface thereof. The interfacial boundary provides a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Bi-metal disc brake rotor and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS20070062768A1Avoid problemsImprove bindingNoise/vibration controlMetal rolling stand detailsCeramic coatingMaterials science
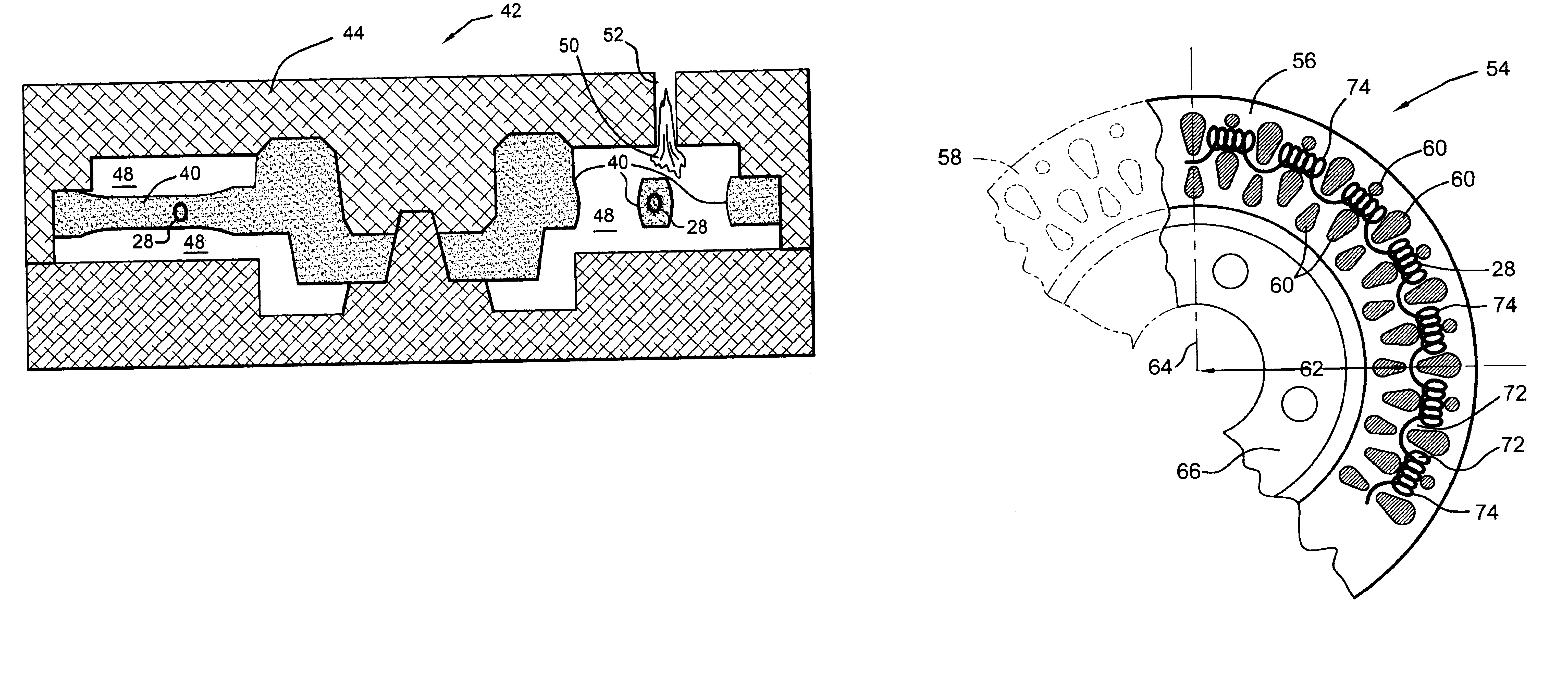
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a friction damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) providing a ceramic coating on an insert, wherein the insert has a body with tabs extending therefrom to hold the insert in a desired position within a mold; (B) washing the ceramic coating off of the tabs; (C) positioning the insert into the mold; and (D) casting a rotor cheek of the disc brake rotor in the mold around the insert such that a portion of each tab is bonded with the rotor cheek, and such that the coating is substantially non-bonded with the rotor cheek so that the coating provides a proper interfacial boundary between the body and the cheek for damping, and the at least partial bonding of each tab with the rotor cheek prevents corrosion-causing exterior elements from reaching the interfacial boundary when the friction damped disc brake rotor is in use.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for forming a part with dampener
InactiveUS20050011628A1Effectively and efficiently constructedDampening structureNoise/vibration controlFoundry mouldsMaterials scienceShock absorber
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
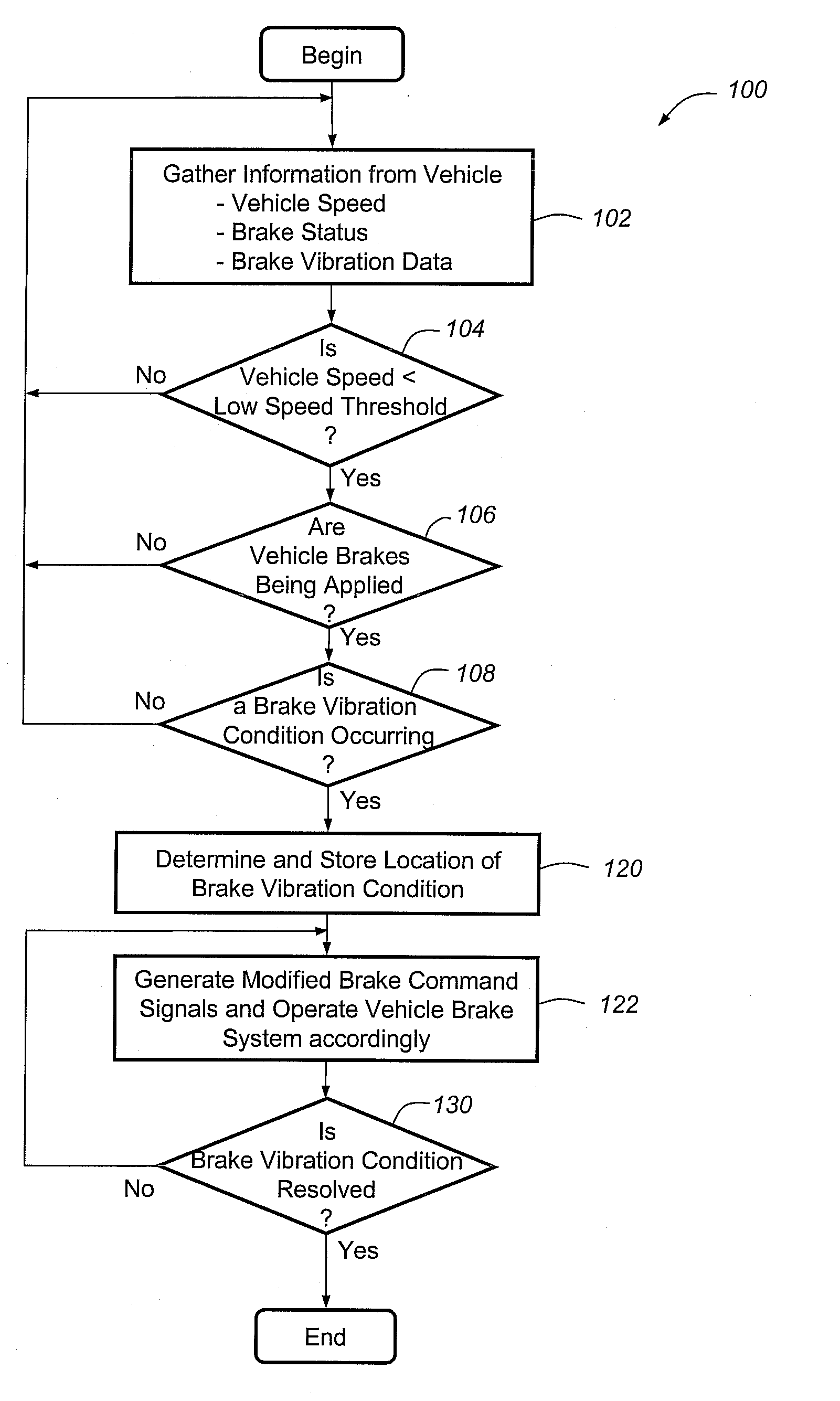
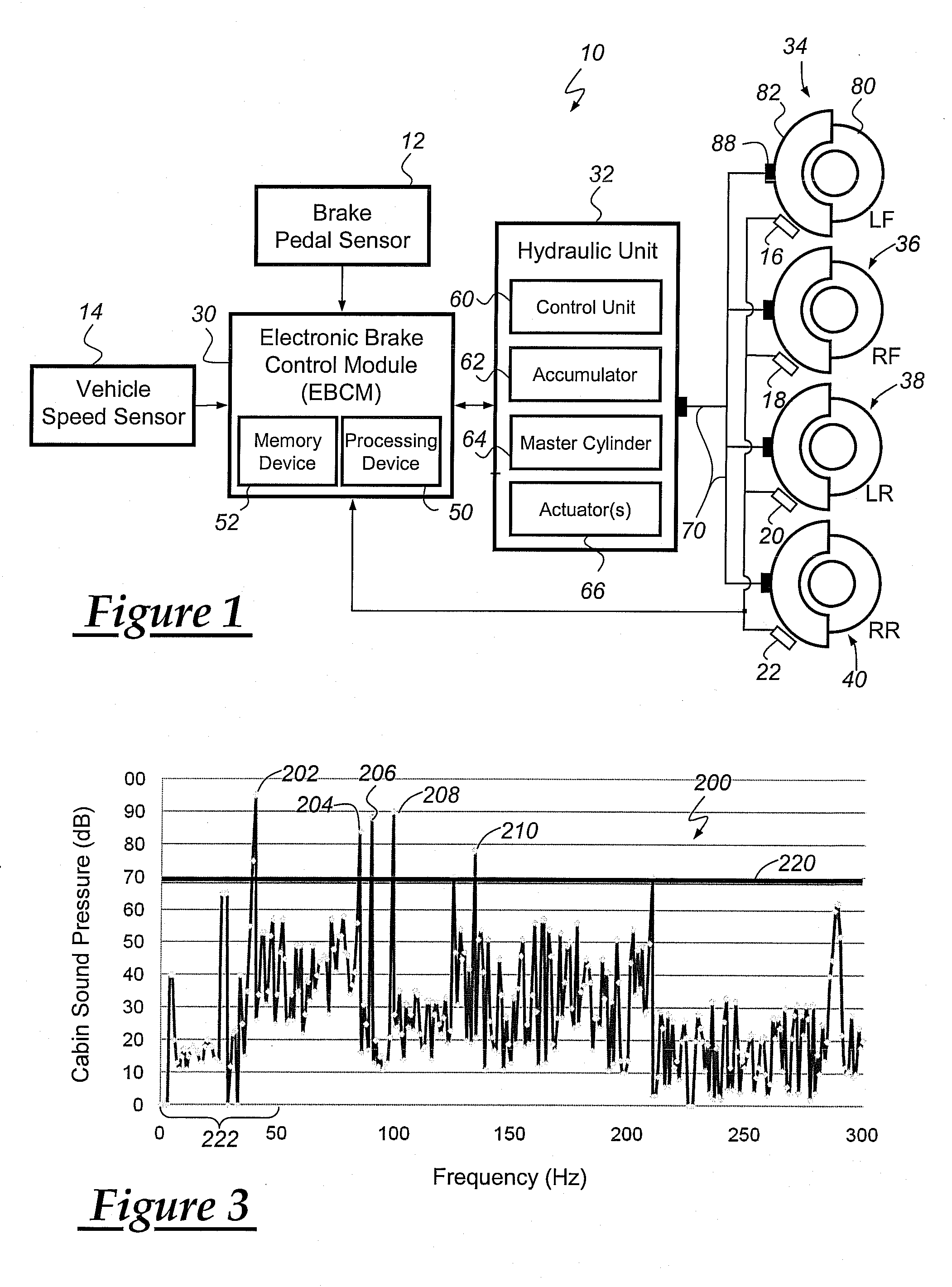
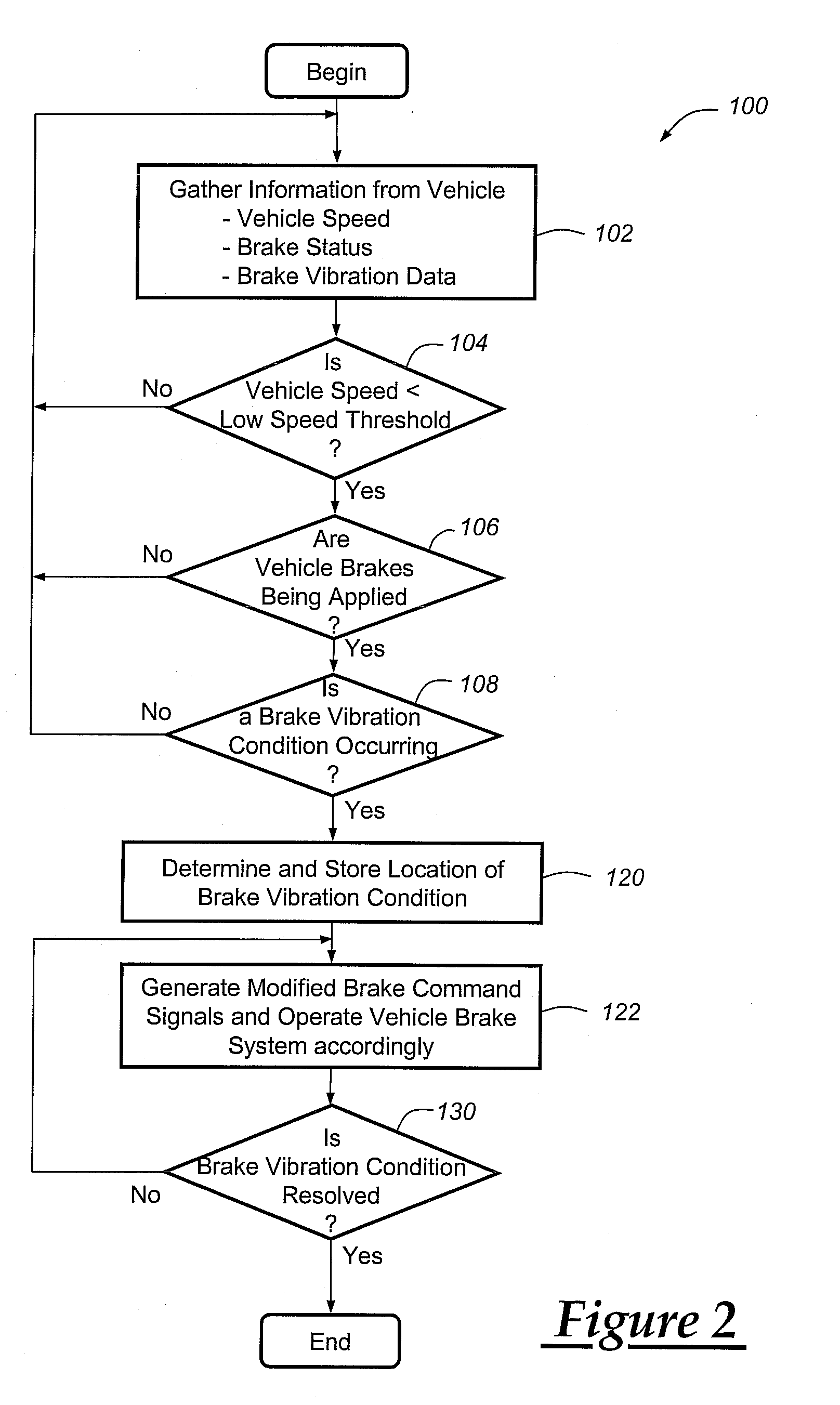
Method for operating a vehicle brake system
InactiveUS20100250081A1Reducing brake groan noiseReduce noiseVehicle testingNoise/vibration controlBrake torqueVehicle brake
A method for reducing or mitigating the effects of vibration in a vehicle brake system, particularly those that can lead to brake groan or other unwanted noise. According to an exemplary embodiment, when the vehicle brake system detects certain vibratory conditions, it makes slight braking adjustments (e.g., adjustments to fluid pressure, brake force, brake torque, etc.) that are aimed to address the brake groan. The vehicle brake system can then determine the effectiveness of the braking adjustments and, if need be, make additional braking adjustments. The method is particularly well suited for use with brake-by-wire systems, but can be used with a number of different vehicle braking systems.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Coulomb damped disc brake rotor and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS20080099289A1Avoid bondingExternal exposure is reducedNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a coulomb damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) providing a mold having the general shape of the coulomb damped disc brake rotor; (B) placing a coulomb damper insert having a generally annular body and at least one tab extending generally radially from the generally annular body, wherein the at least one tab operates to locate the coulomb damper insert within the mold, and wherein the at least one tab at least partially defines an orifice with its major axis generally coincident with the periphery of the coulomb damped disc brake rotor; and (C) causing casting material to enter the mold to substantially encapsulate the coulomb damper insert with the casting material to form a rotor cheek of the coulomb damped disc brake rotor. A coulomb damper insert and coulomb damped disc brake rotor are also disclosed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
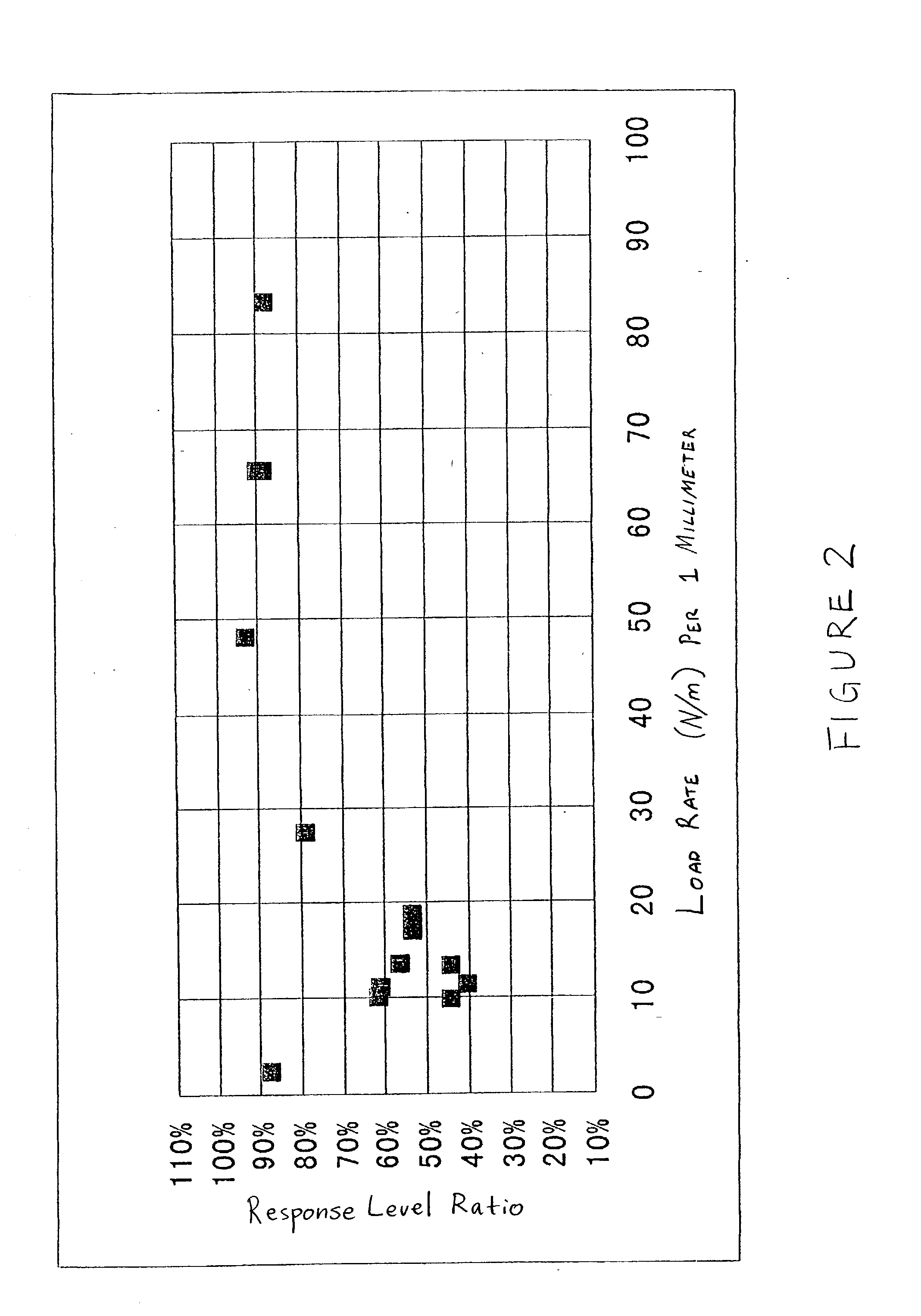
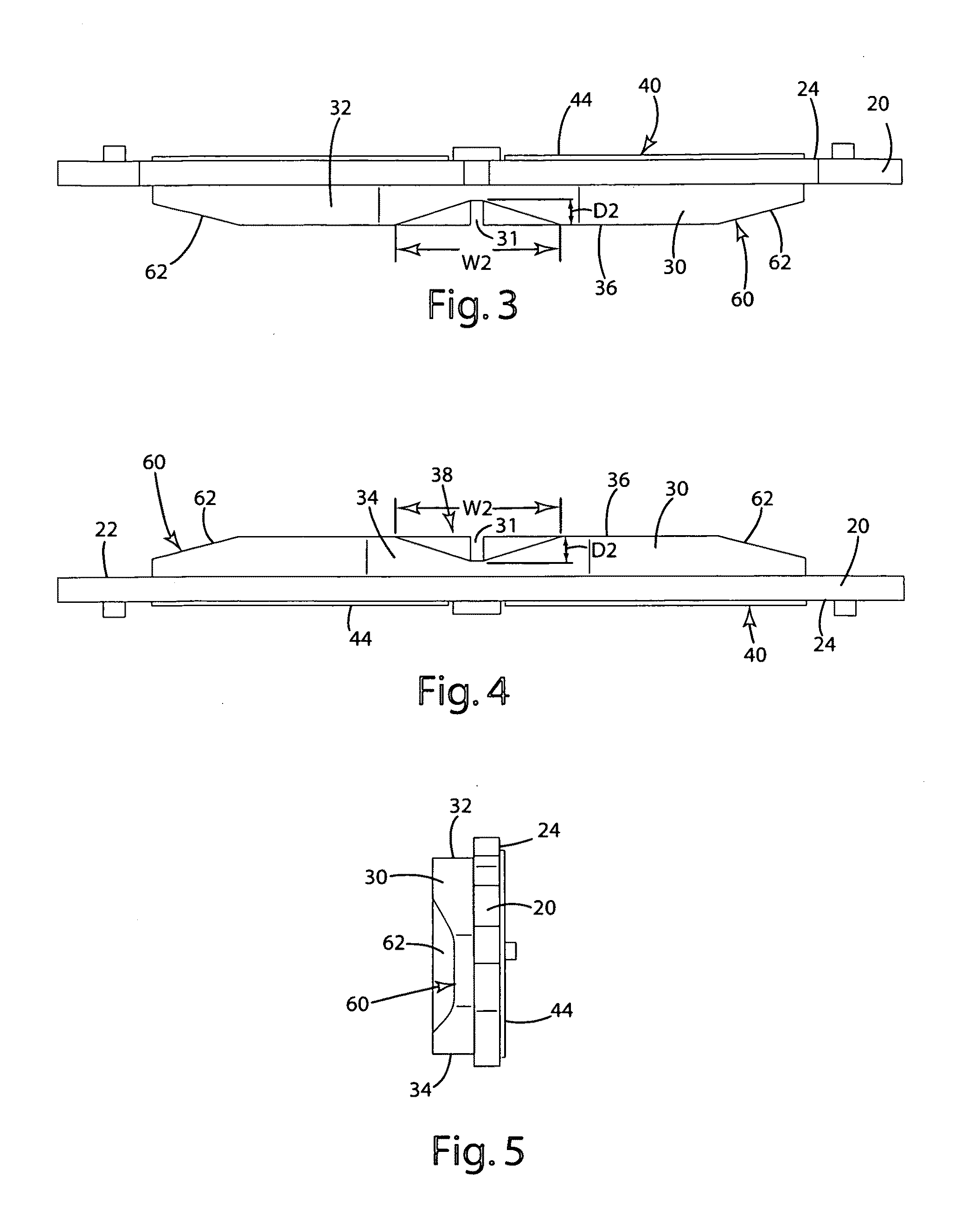
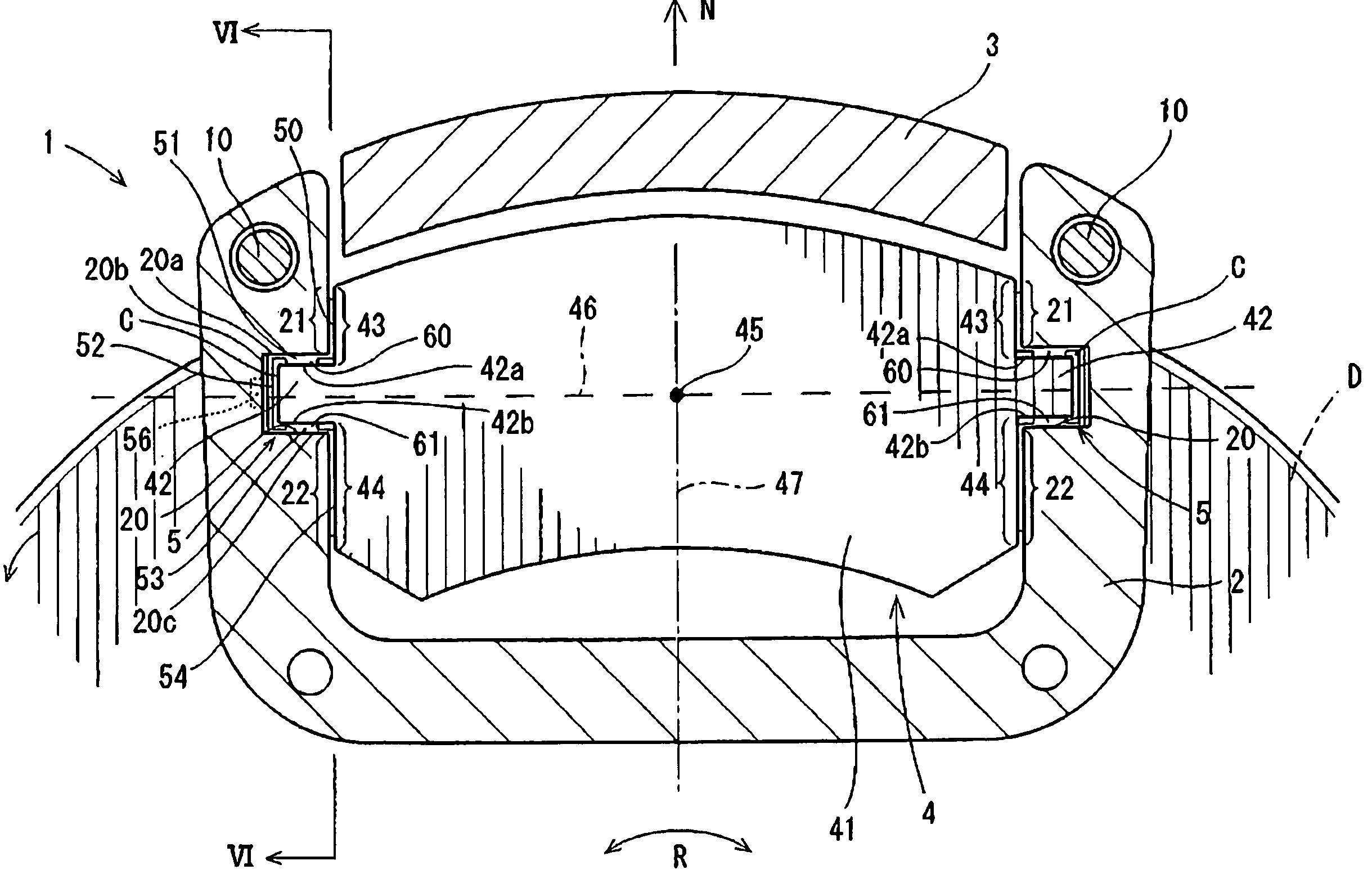
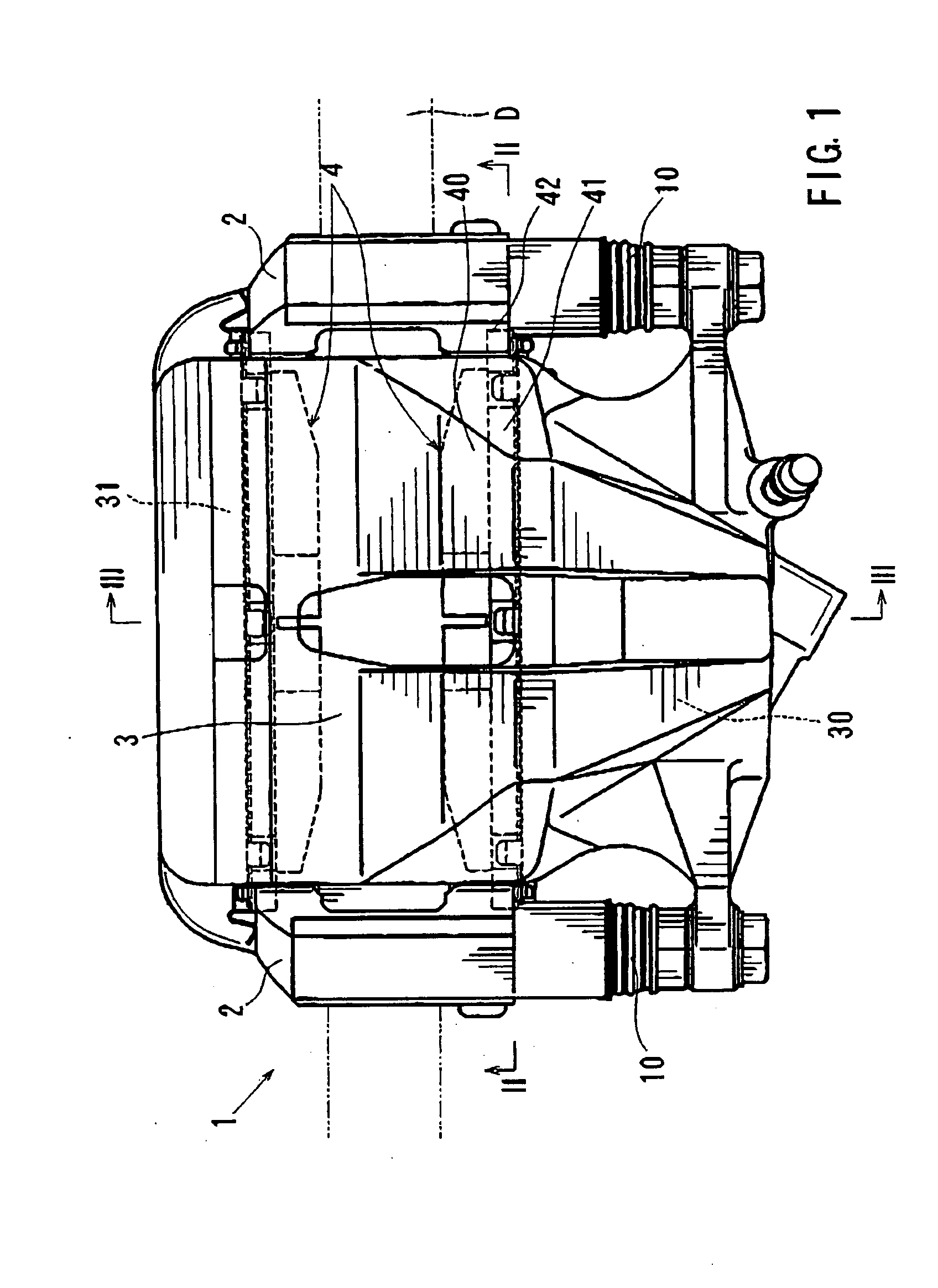
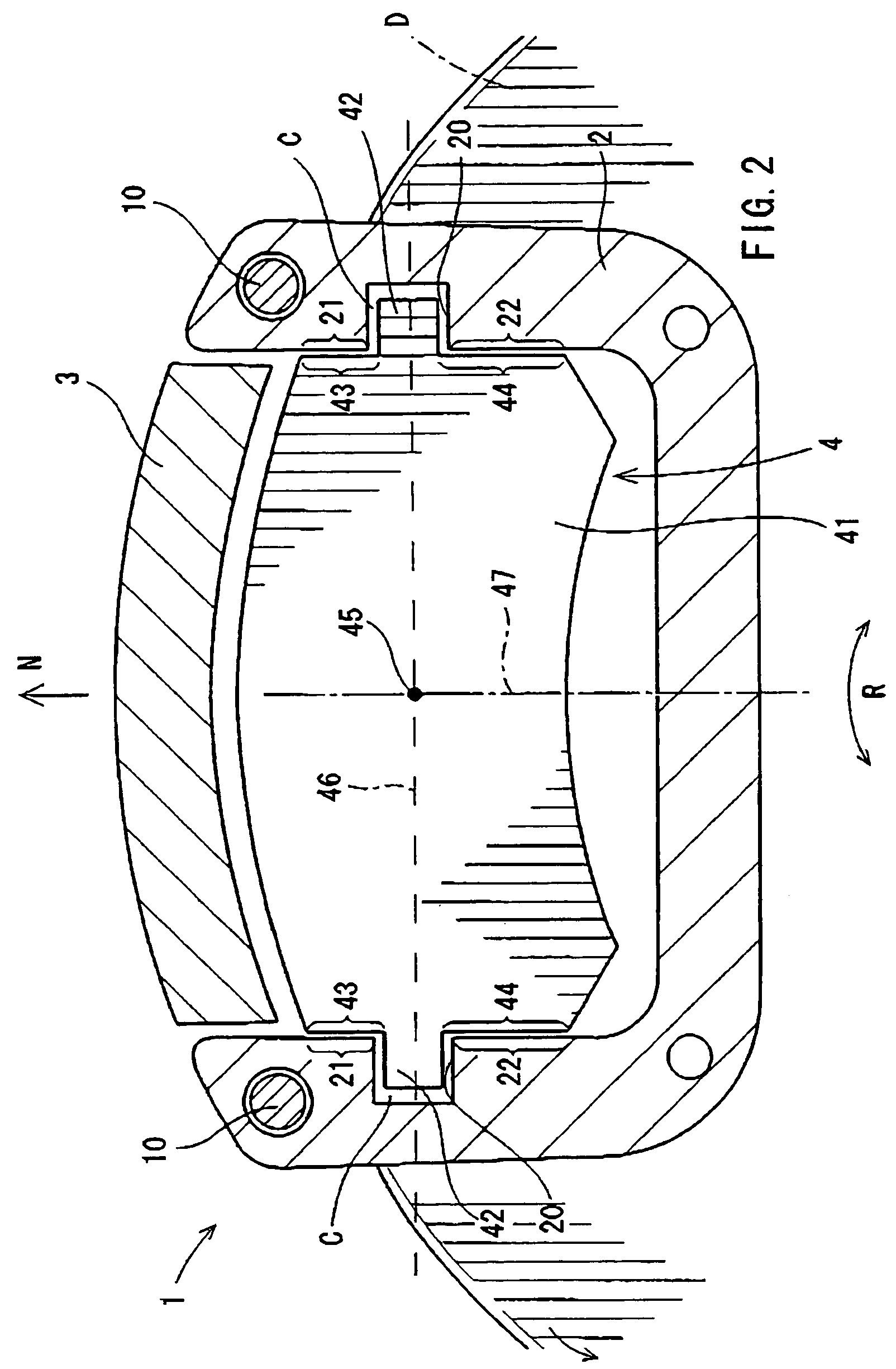
Vibration inhibiting structure for rotor
InactiveUS20030037999A1Improved vibration inhibiting structureSimple structureNoise/vibration controlBraking discsCoil springEngineering
A rotor such as a brake disk for a vehicle has a spring holder that circumferentially extends around an axis of the disk. A coil spring extends around the axis along the spring holder. The spring is loaded onto the spring holder by its own resilience. The spring has a load rate that generates a tension that allows the spring to move circumferentially relative to the spring holder.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Brake Pad
The subject invention generally relates to a disc brake pad which has reduced brake squeal in response to a braking event by the incorporation of a relieved portion to the center section of a friction pad along an outer edge or inner edge thereof, or along both edges. The invention is a disc brake pad which includes a backing plate and friction pad attached to the backing plate.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL PROD US LLC
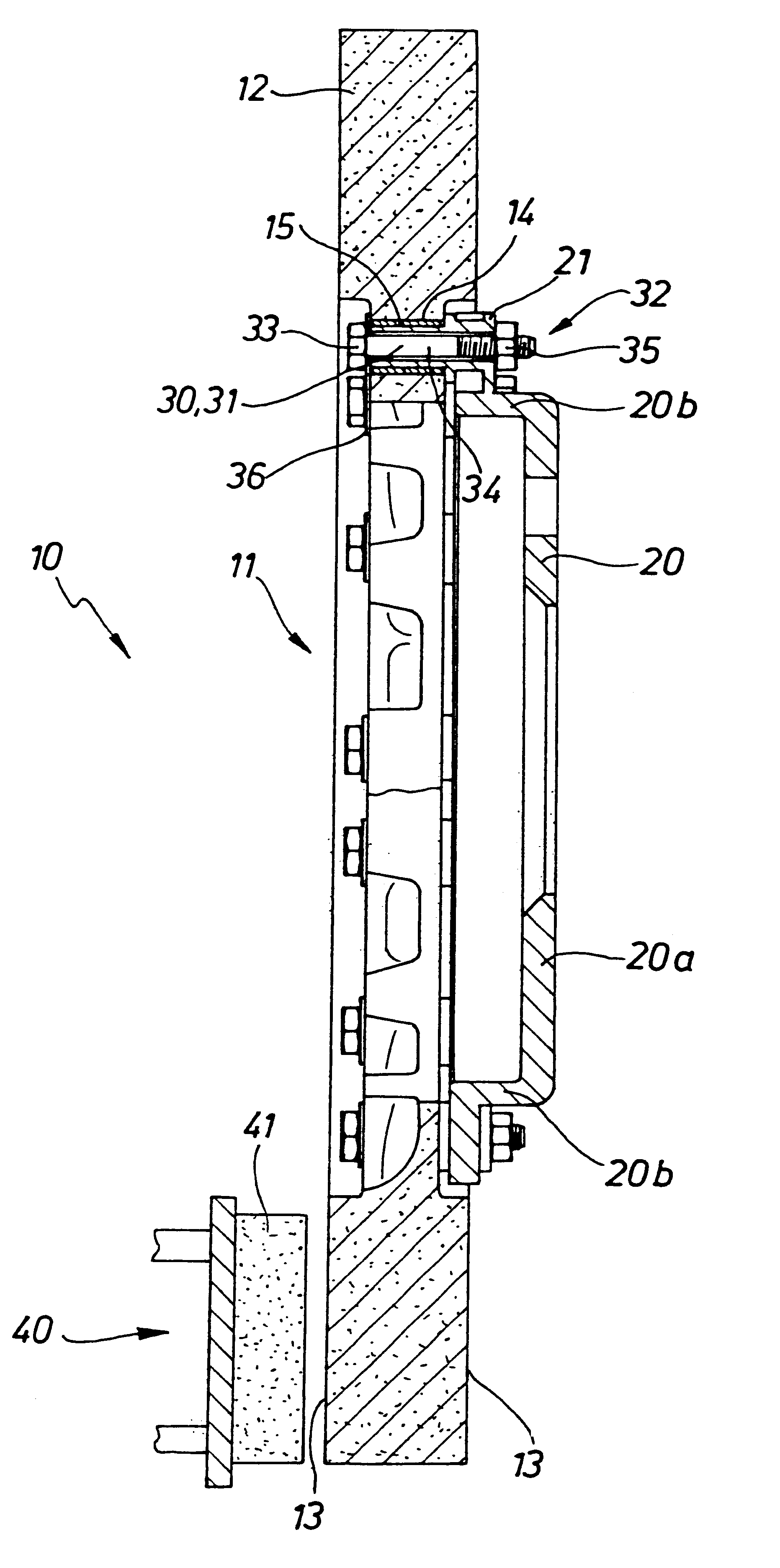
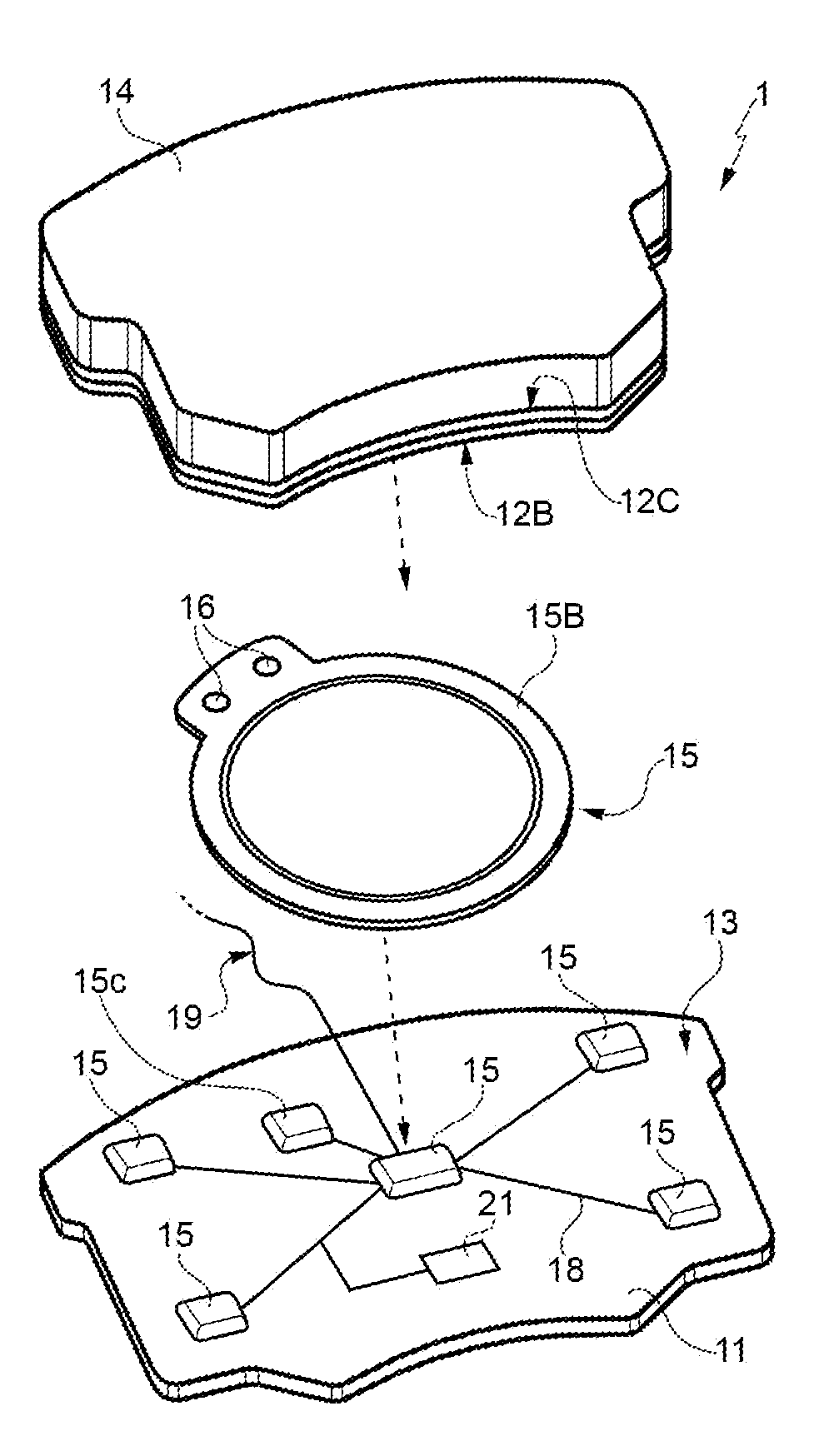
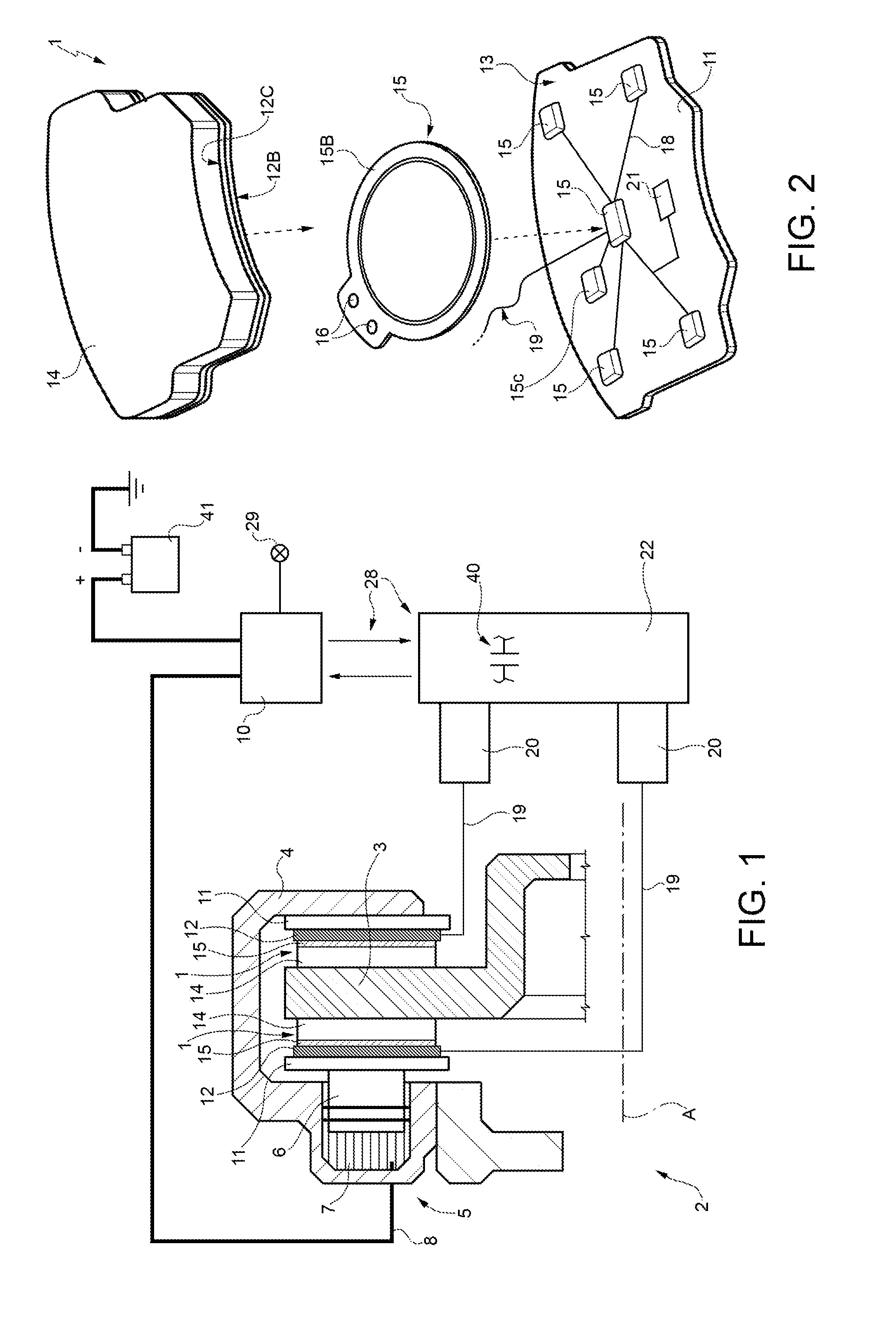
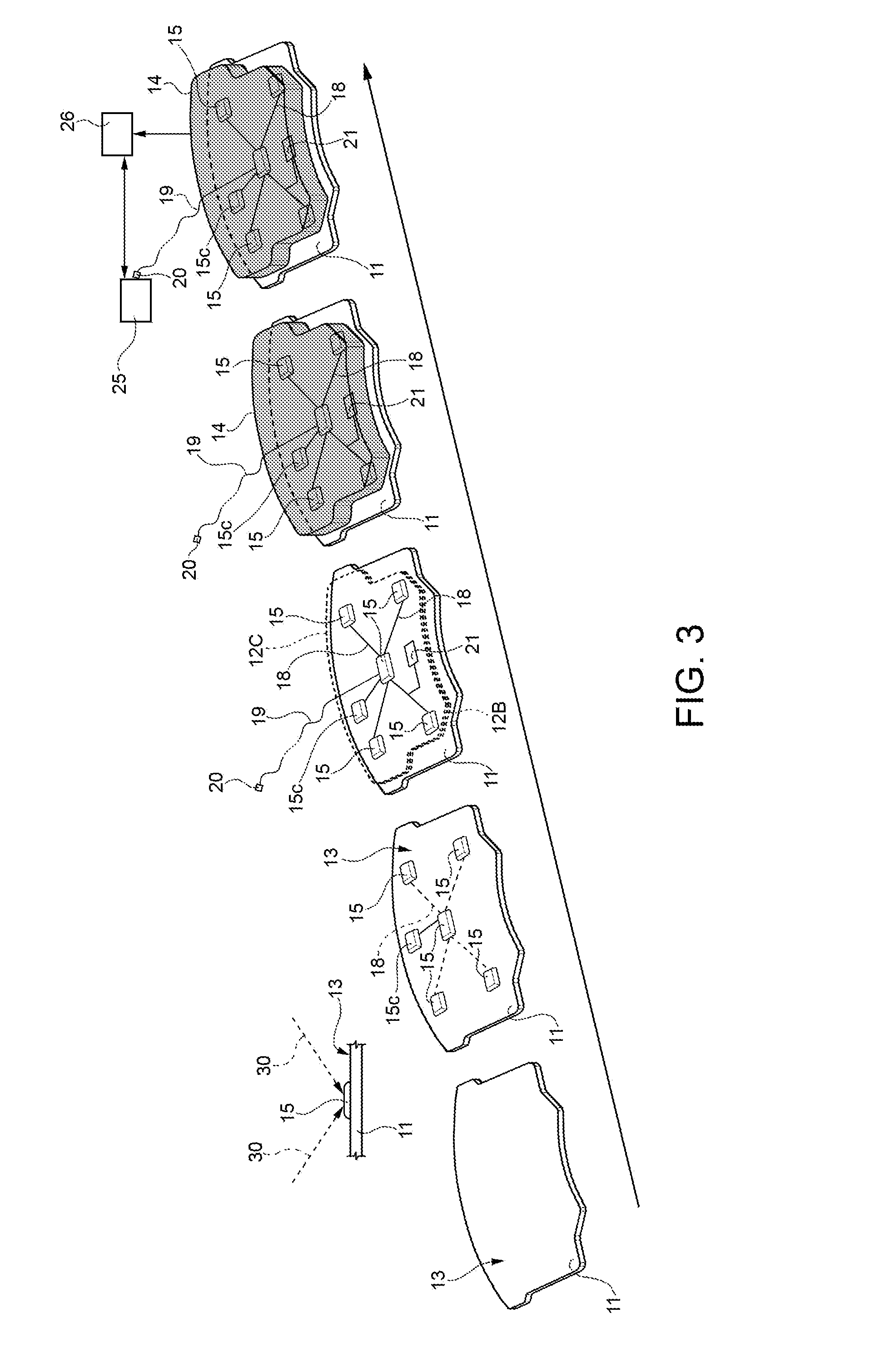
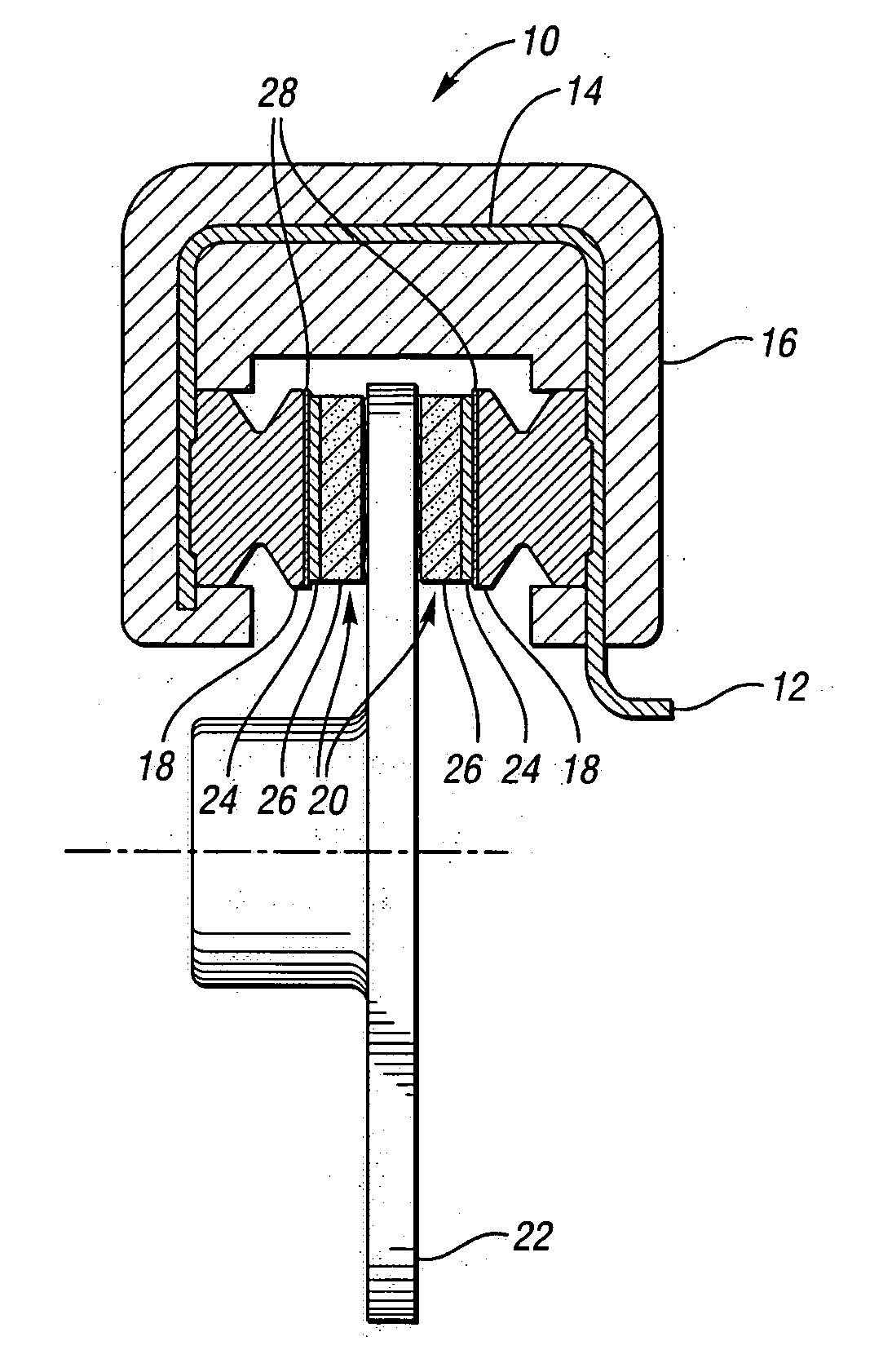
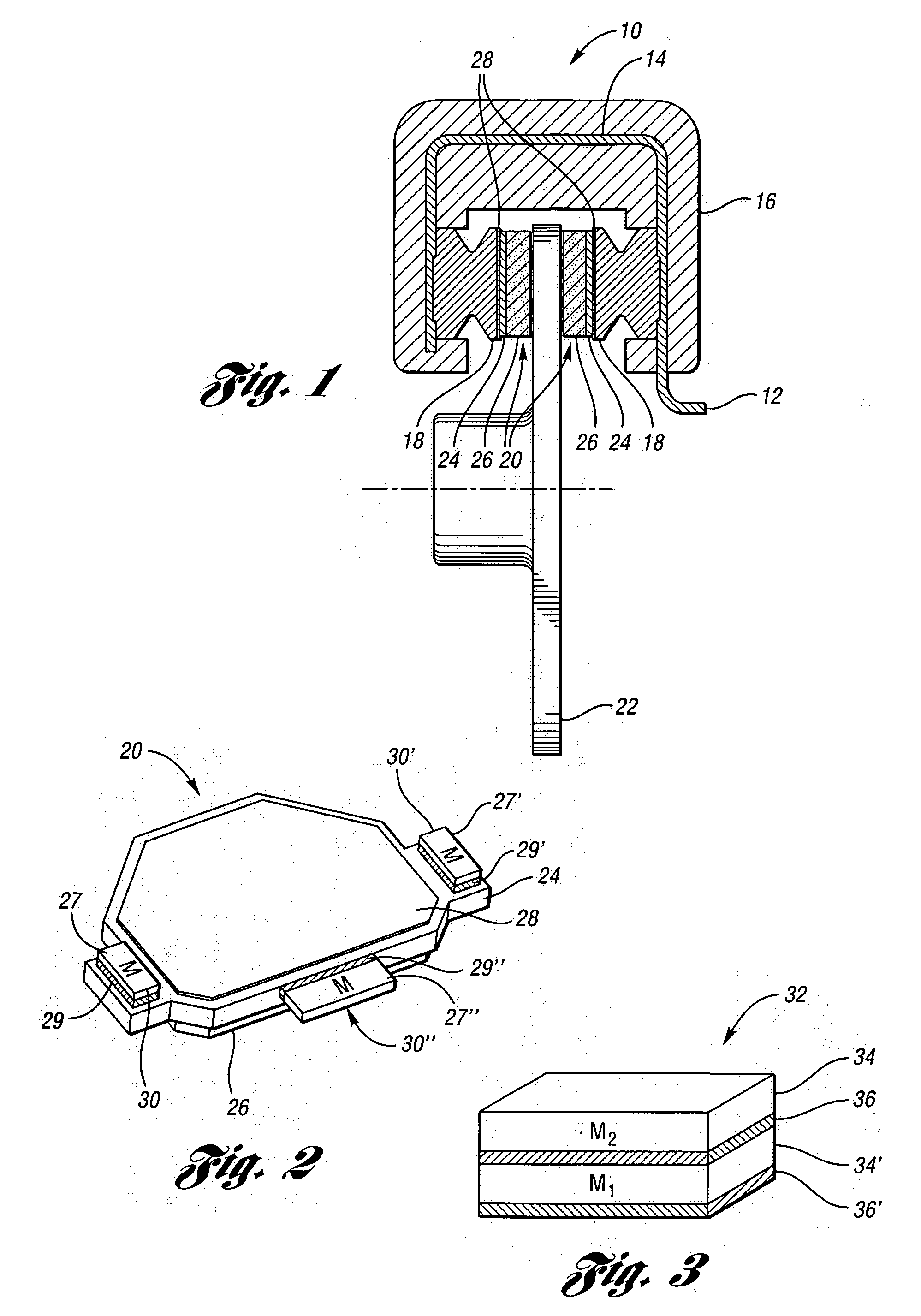
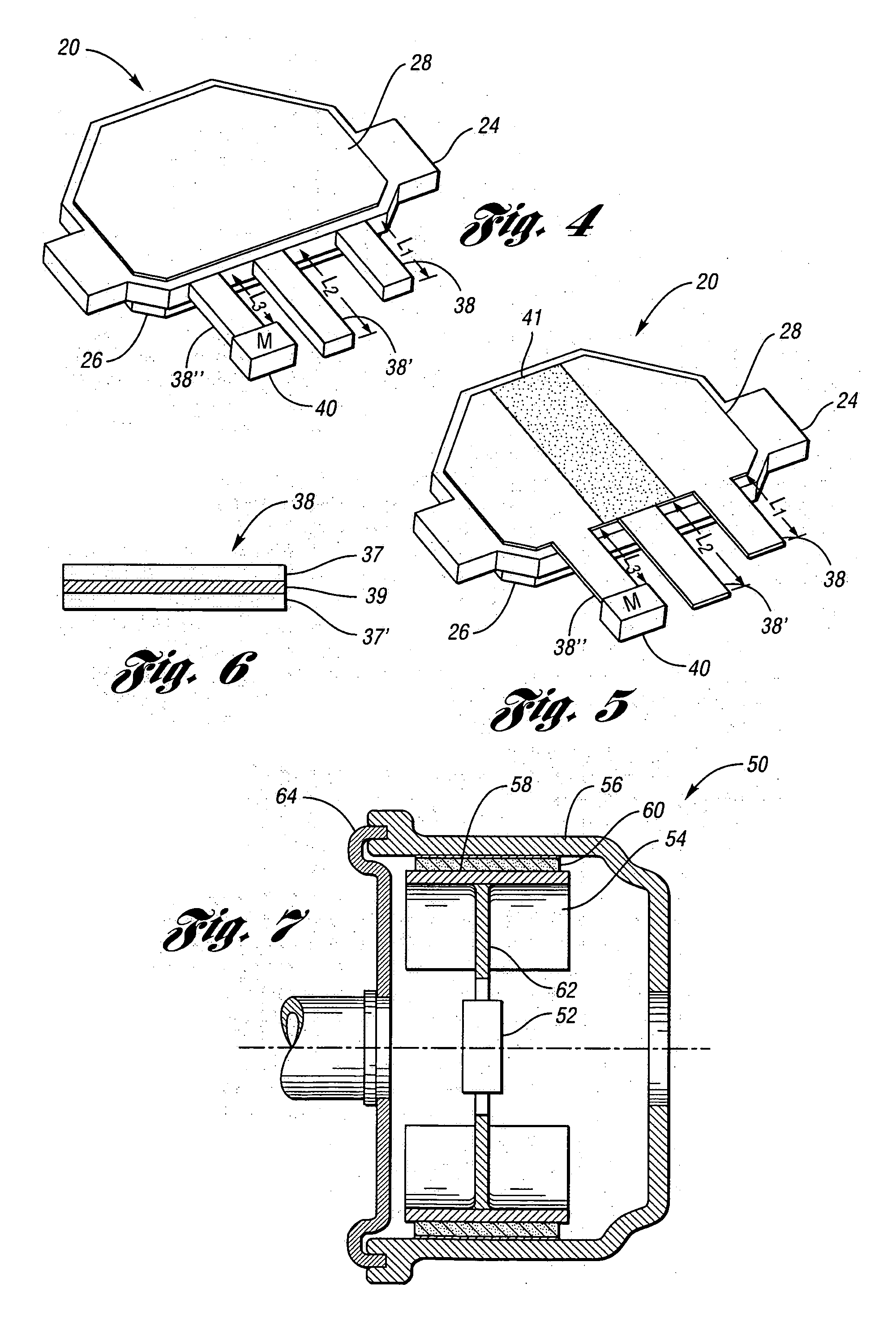
Method for manufacturing a braking element with integrated sensor, in particular a brake pad, brake pad with integrated sensor, vehicle braking system and associated method
ActiveUS20140311833A1Significant energy savingAvoid spendingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyNoise/vibration controlElectricityPotential difference
A method in which at least one piezoceramic sensor, which converts every mechanical force to which it is subjected into an electrical signal and having a Curie temperature higher than 200° C., is solidarized directly onto the surface of a metal support element of a vehicle braking element, which during use faces a vehicle element to be braked. While in contact with such a surface, an electrical circuit is implemented that picks up and eventually processes the electrical signal, the electrical circuit being connected with a connector integrated with the metal support element. An electrically insulating layer sandwiches the at least one piezoceramic sensor and the electrical circuit, and a block of friction material with an underlying damping layer is formed upon the electrically insulating layer. After forming the block of friction material, the piezoceramic sensor is polarized by applying a predetermined potential difference thereto by means of the connector.
Owner:ITT ITAL SRL
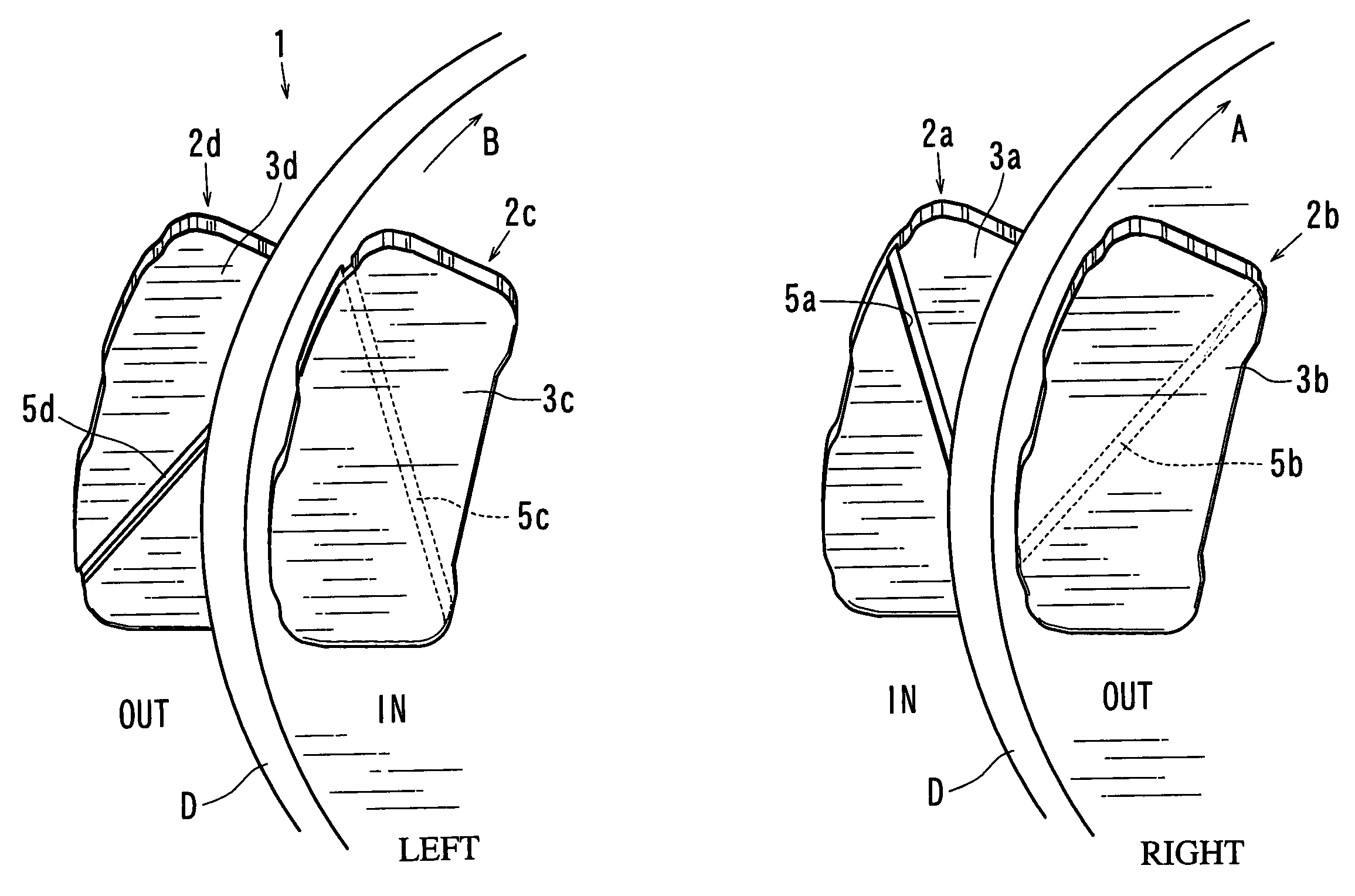
Disk brake devices
ActiveUS7111709B2Effectively reduce the squealing soundsImprove distortionNoise/vibration controlBraking membersEngineeringMechanical engineering
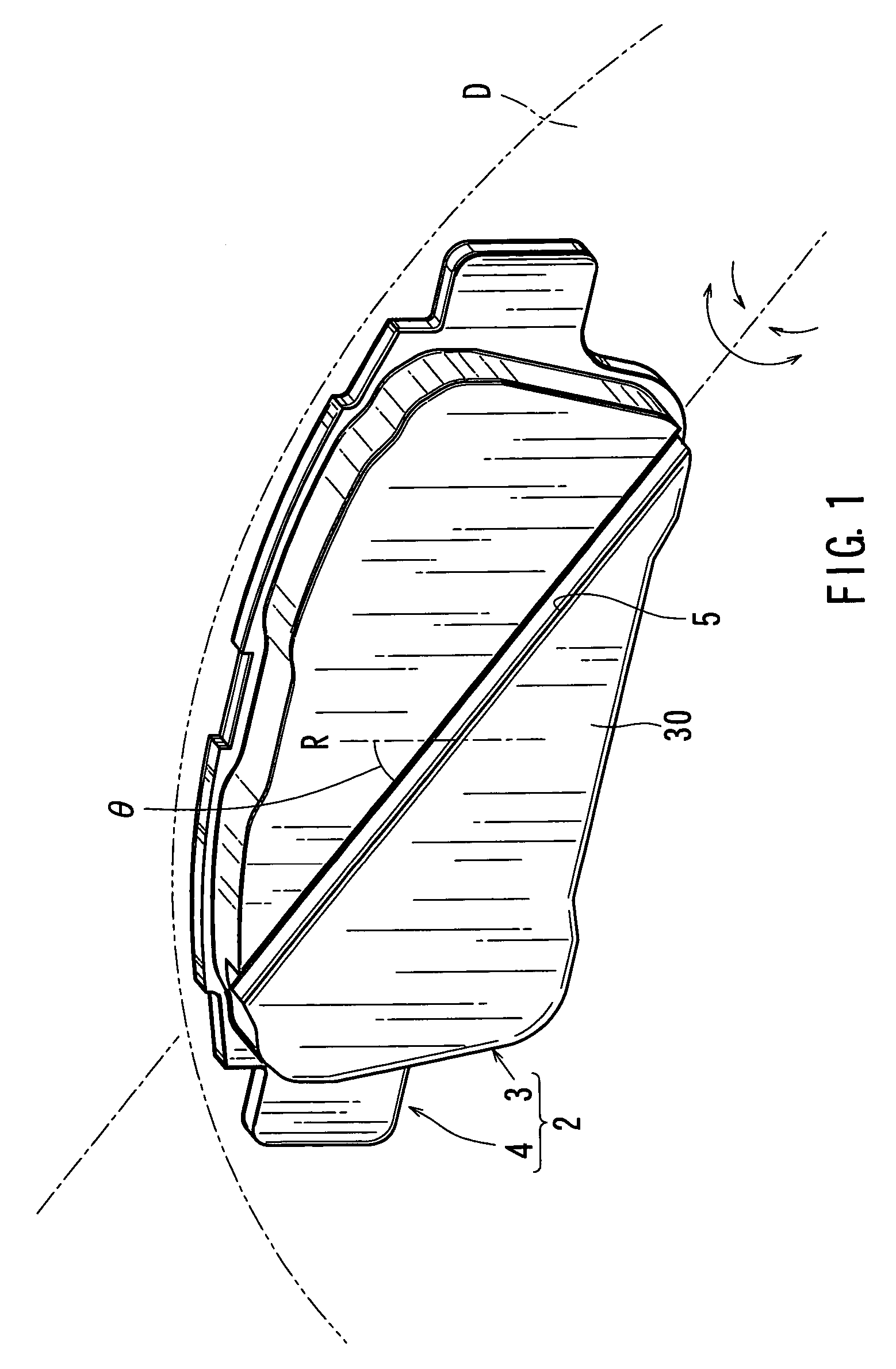
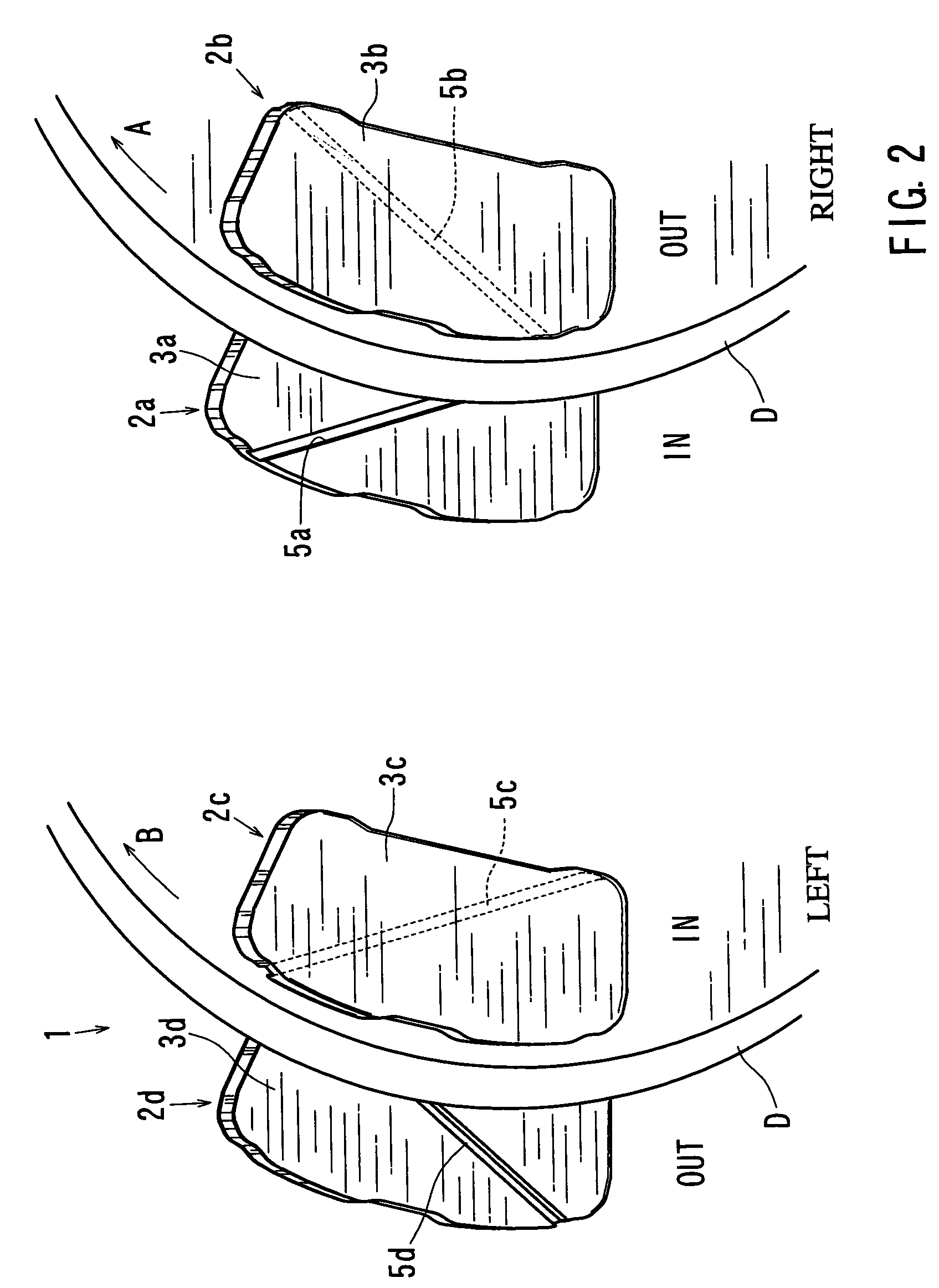
A disk brake device includes a pair of brake disks and right and left pairs of pads. Each pad includes a twisting compliant section that extends along a line inclined by an angle relative to a radial direction of the corresponding brake disk. The twisting compliant section facilitates the twisting of the pad about the compliant section. The twisting compliant sections of the right inner pad and the left inner pad are inclined in opposite directions relative to the twisting compliant sections of the right outer pad and the right inner pad. The twisting compliant sections of the right inner pad and the left inner pad are inclined in substantially the same direction with one another.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for forming a part with dampener
InactiveUS6945309B2Dampening structureEffectively and efficiently constructedNoise/vibration controlBraking discsMaterials scienceShock absorber
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket, wherein damping is provided by Coulomb friction, most preferably at the outboard tie-bar thereof. In one form, at least one clamping member applies compressive force externally to the caliper bracket, and in a second form, at least one interfacial boundary is internally disposed in the caliper bracket. Provided thereby is a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
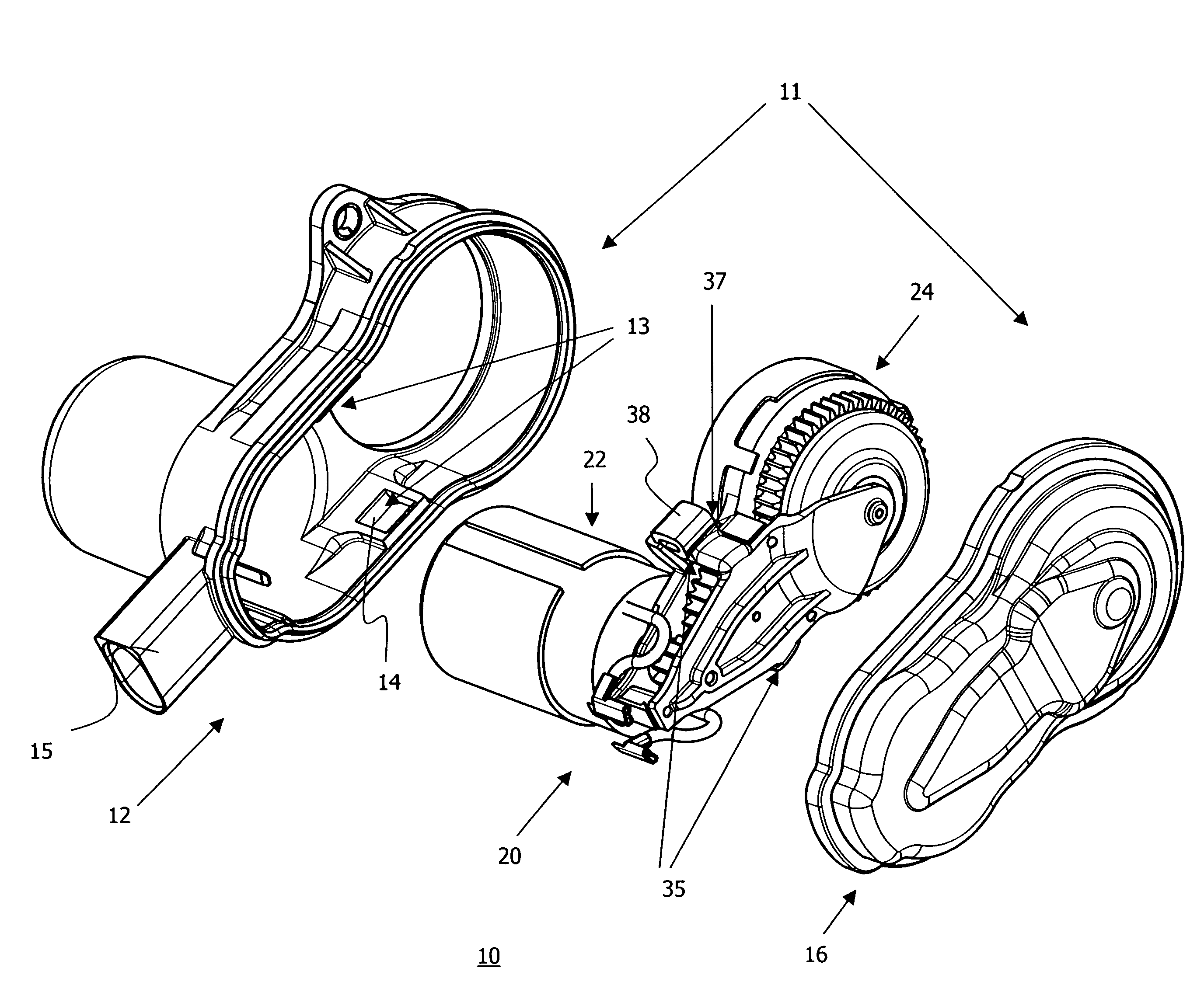
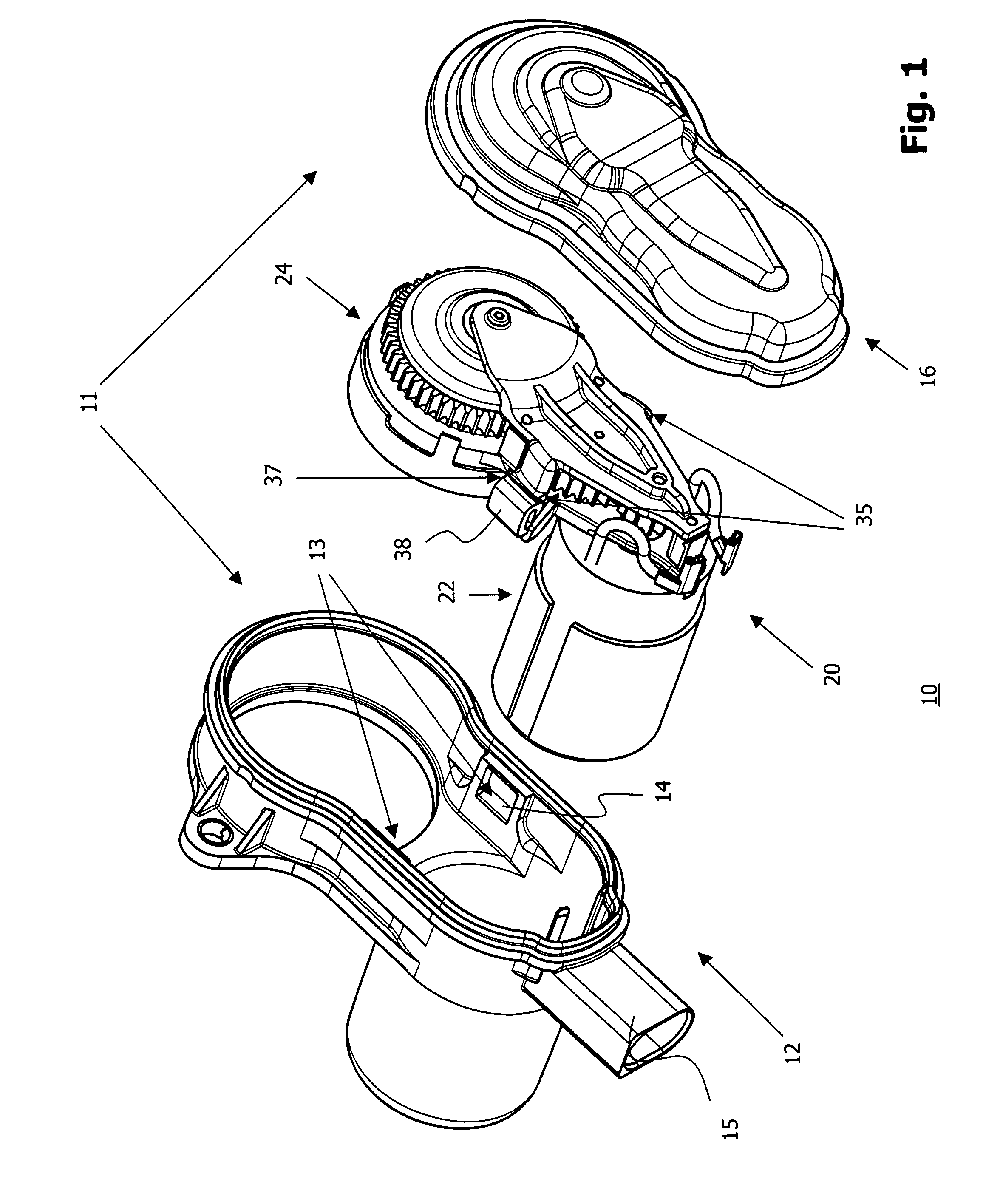
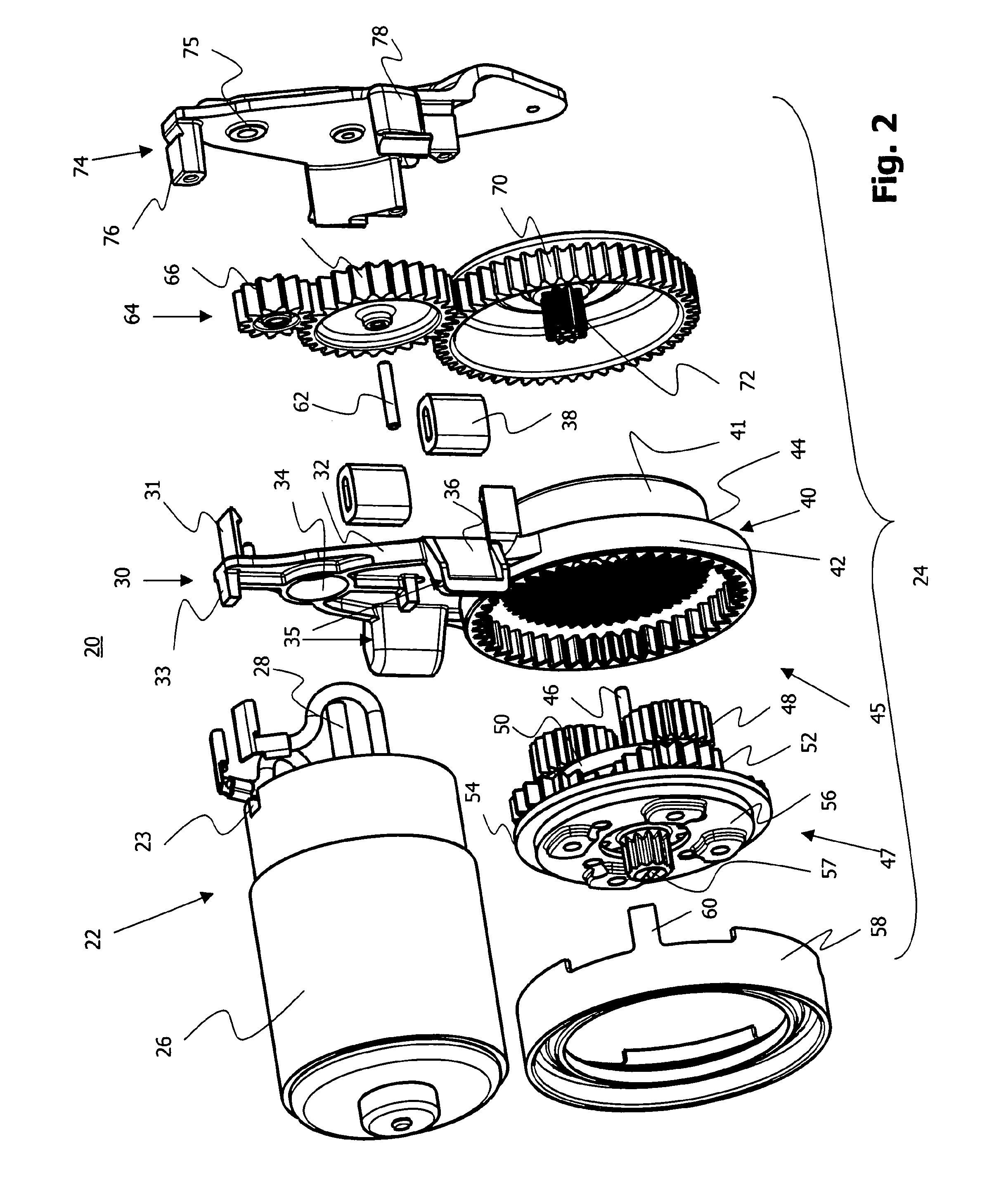
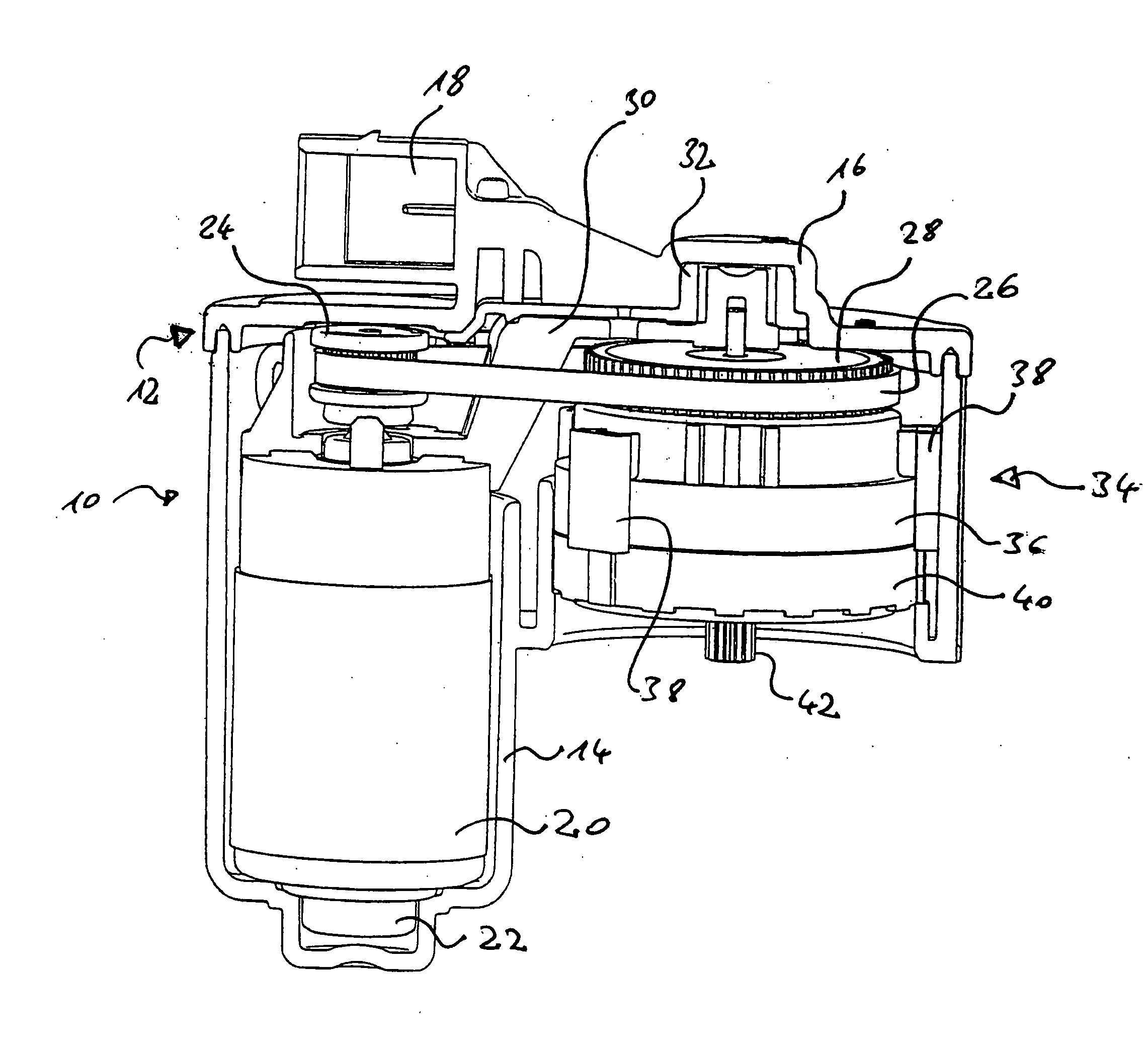
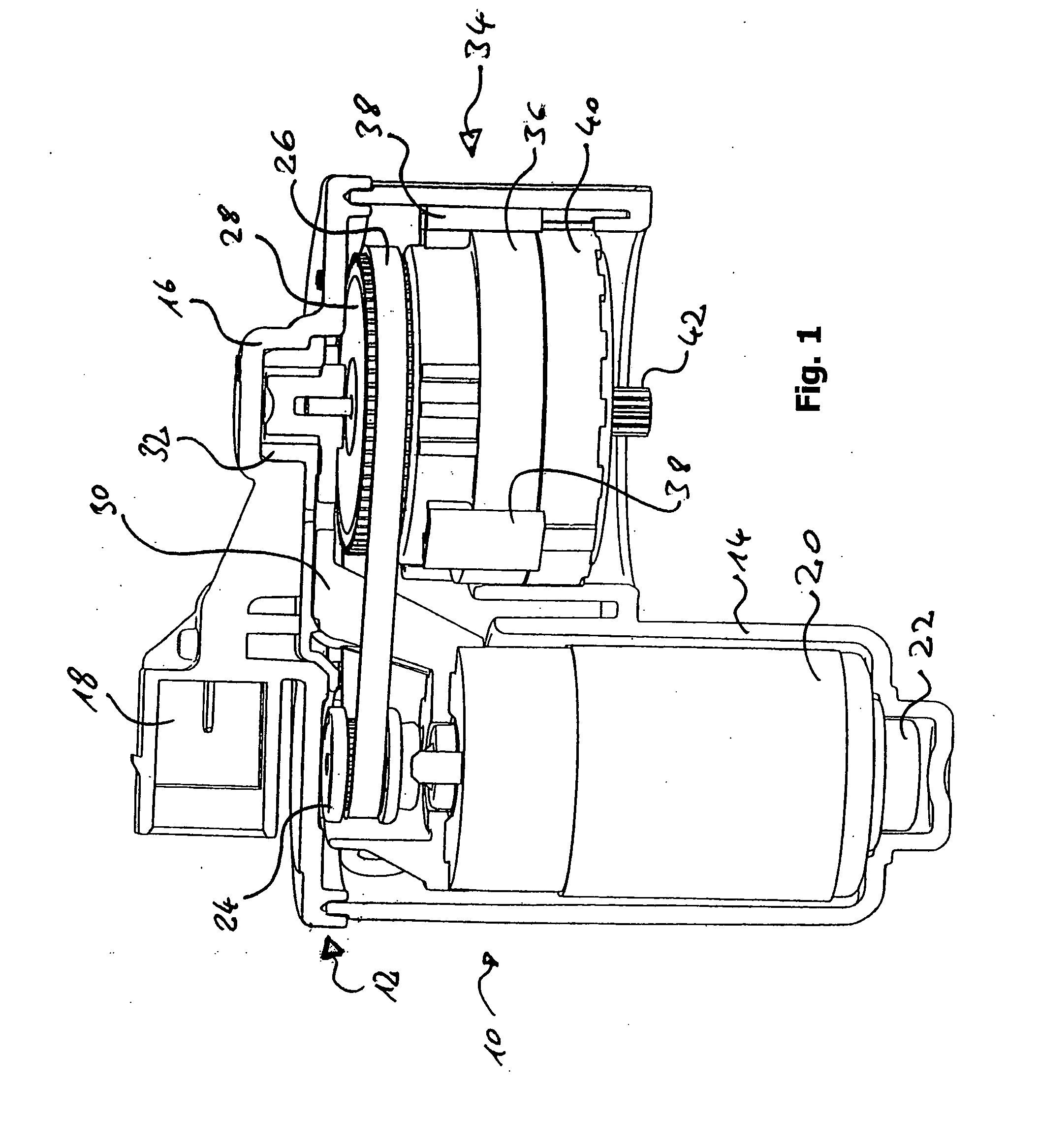
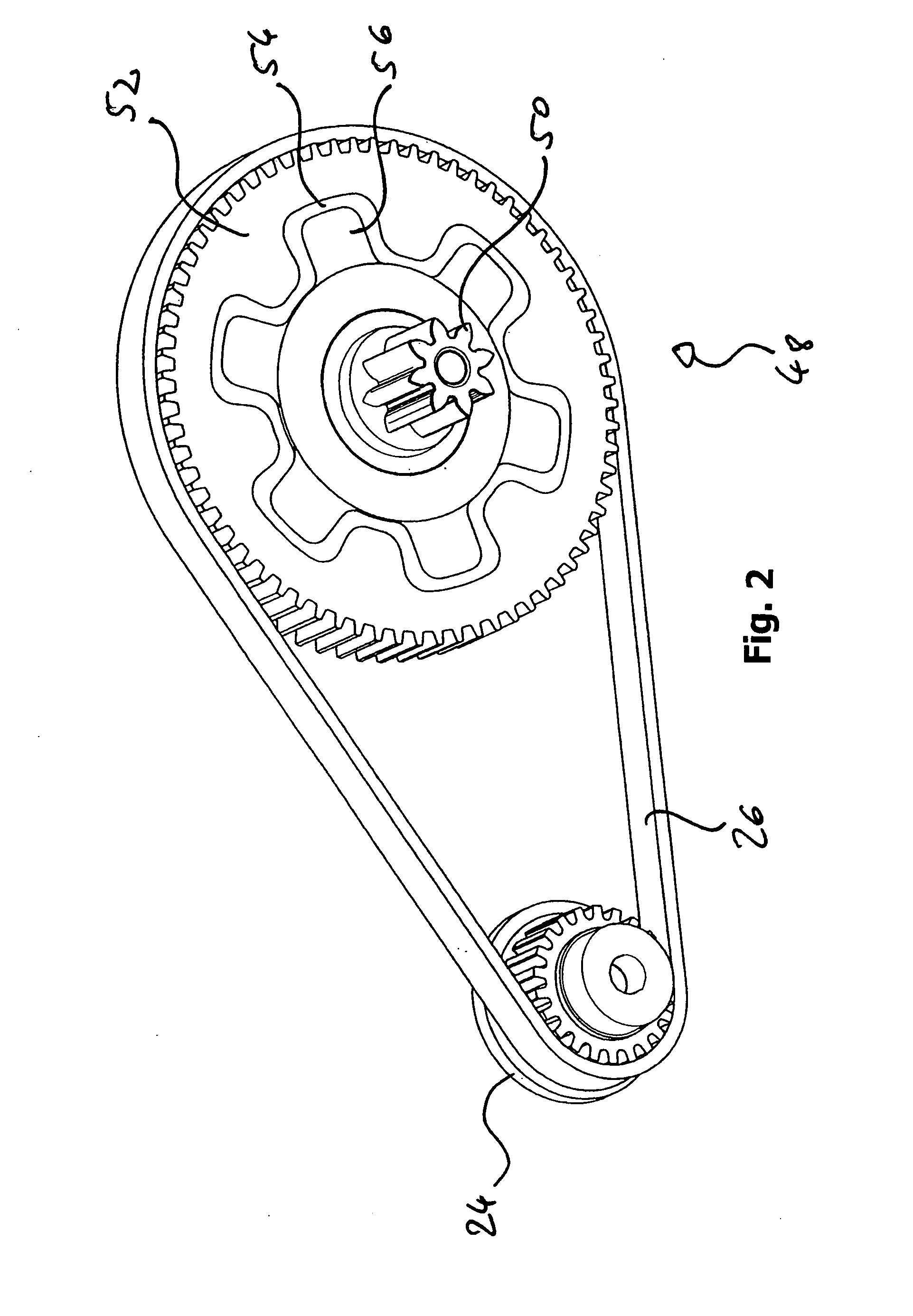
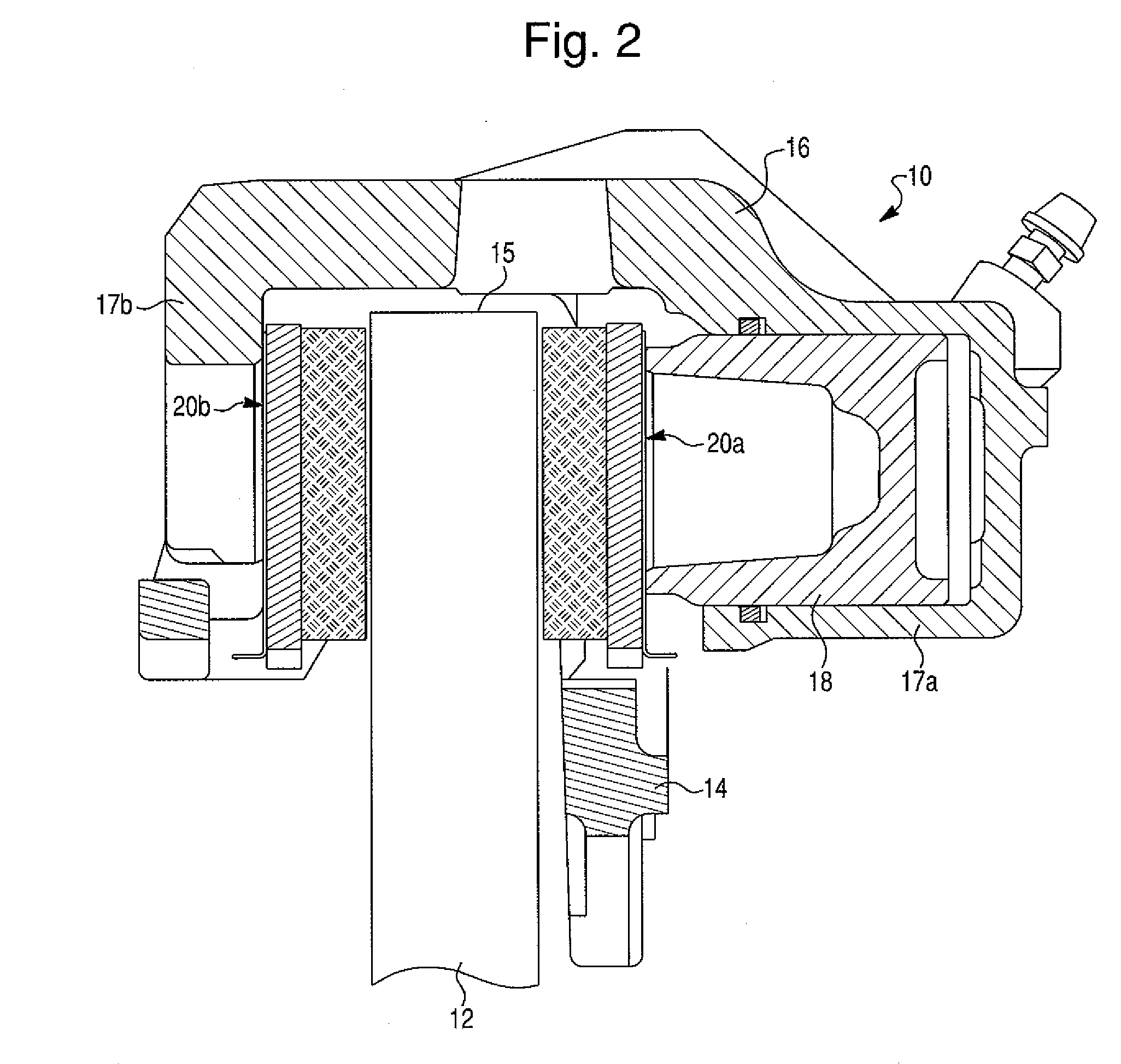
Sub-Assembly for an Electromechanical Brake Actuator
ActiveUS20120325601A1Easy constructionReduce in quantityNoise/vibration controlBraking action transmissionActuatorControl theory
The invention relates to a subassembly for a brake actuator which is provided for an electromechanically operated parking brake. The subassembly comprises a drive device and gear device for generating and transmitting a torque to a brake device and a fixing element which secures the arrangement of the gear device relative to the drive device, an internal-toothed wheel of the gear device being integrated in the fixing element.
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
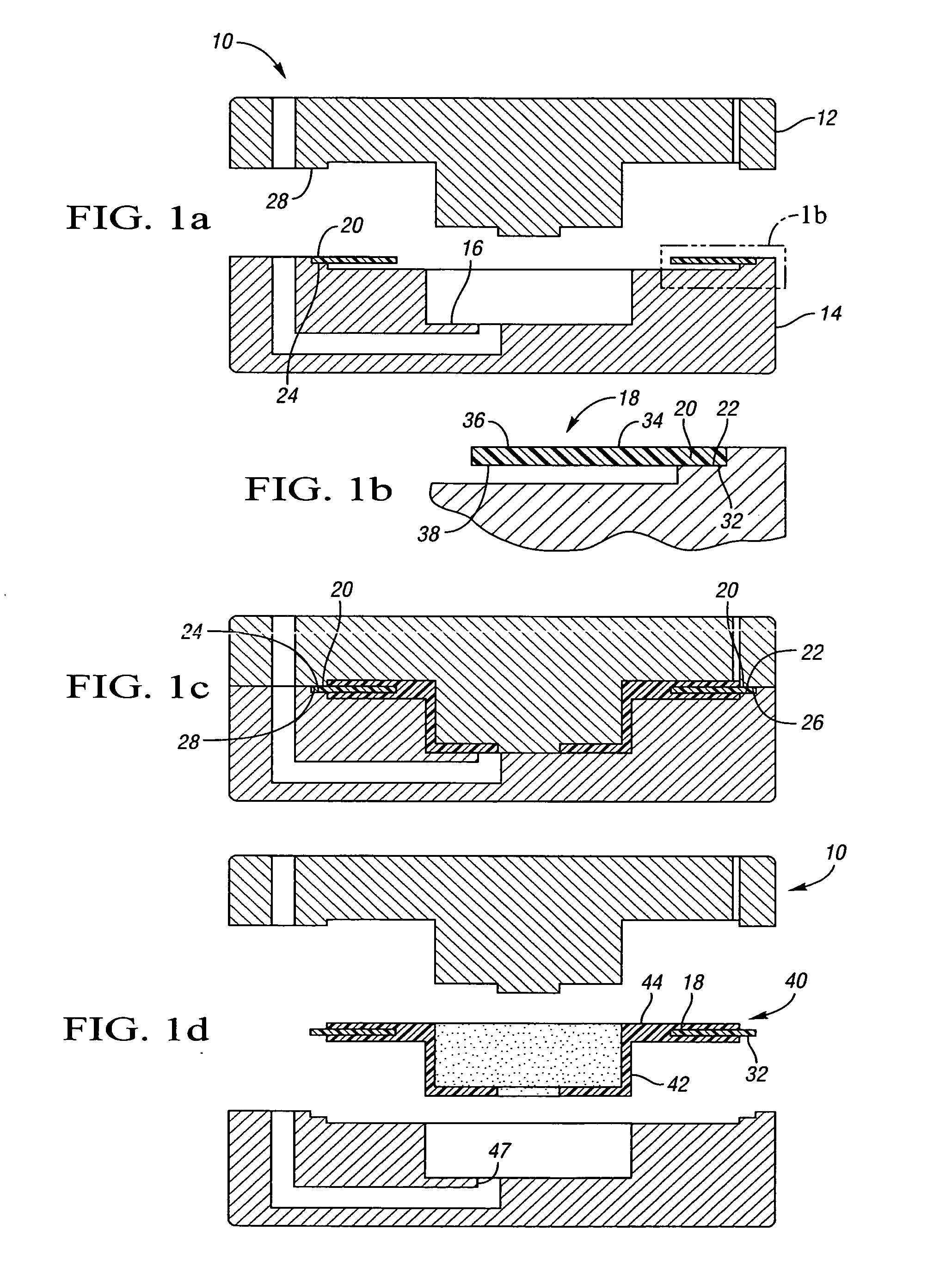
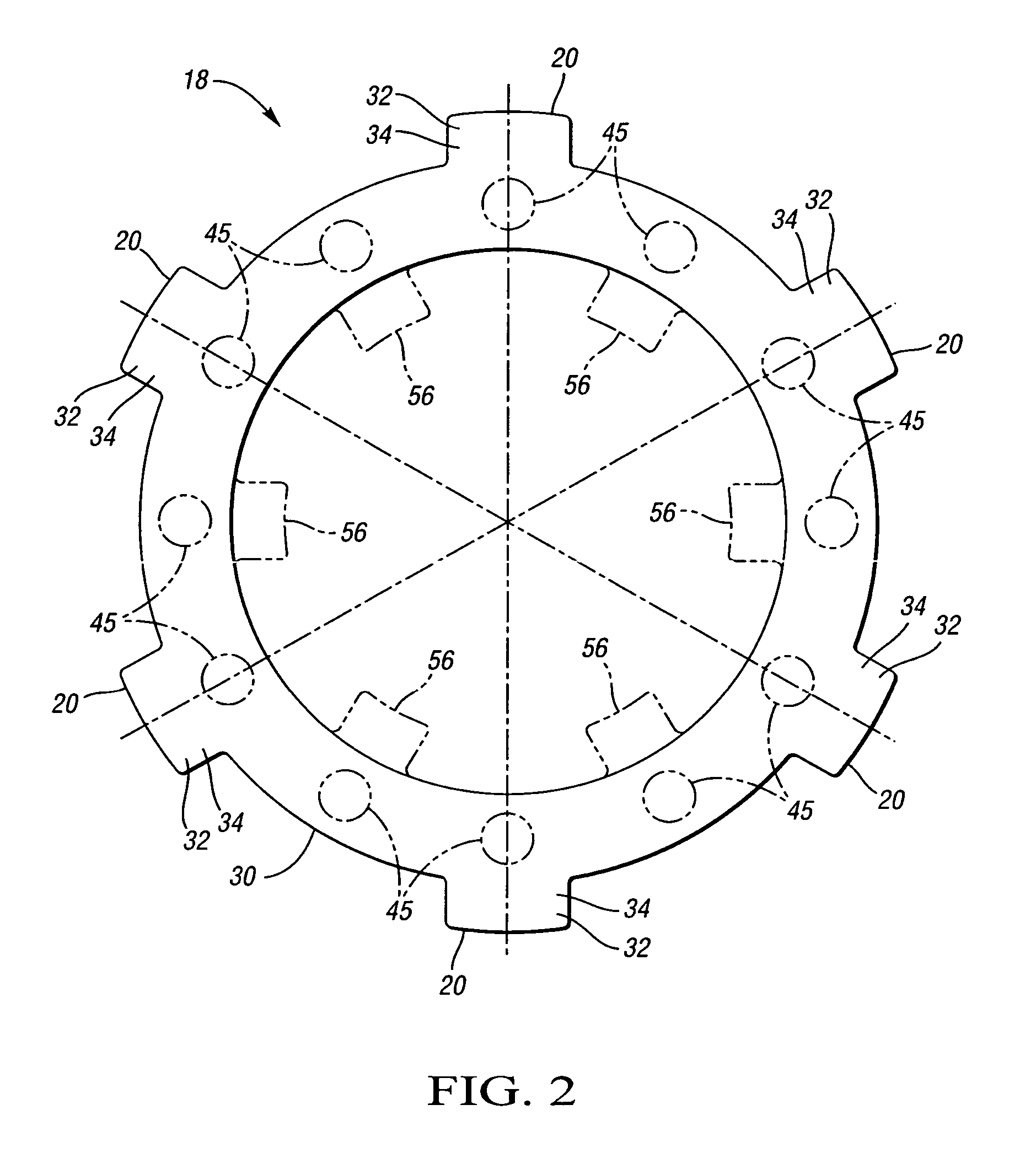
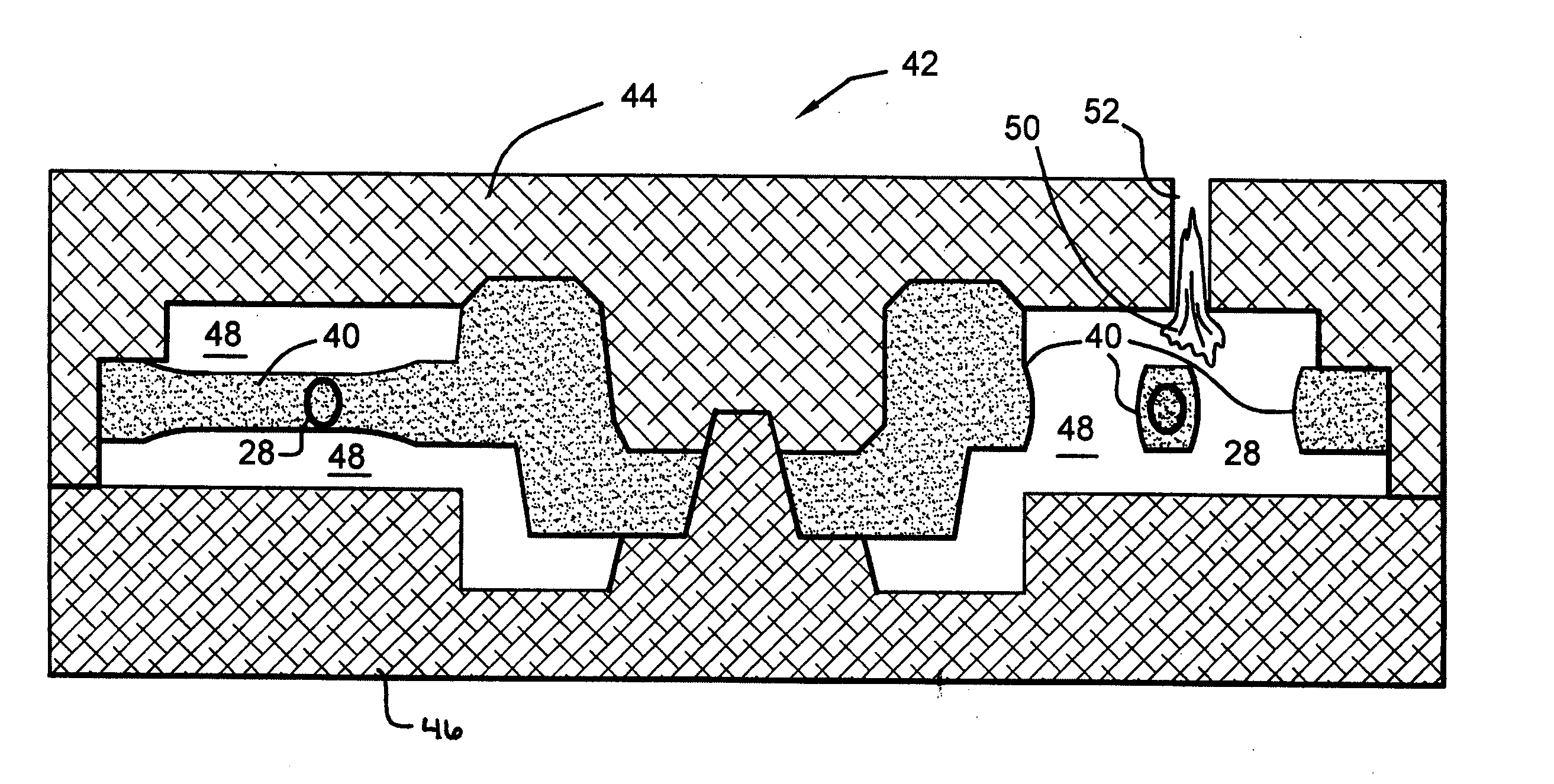
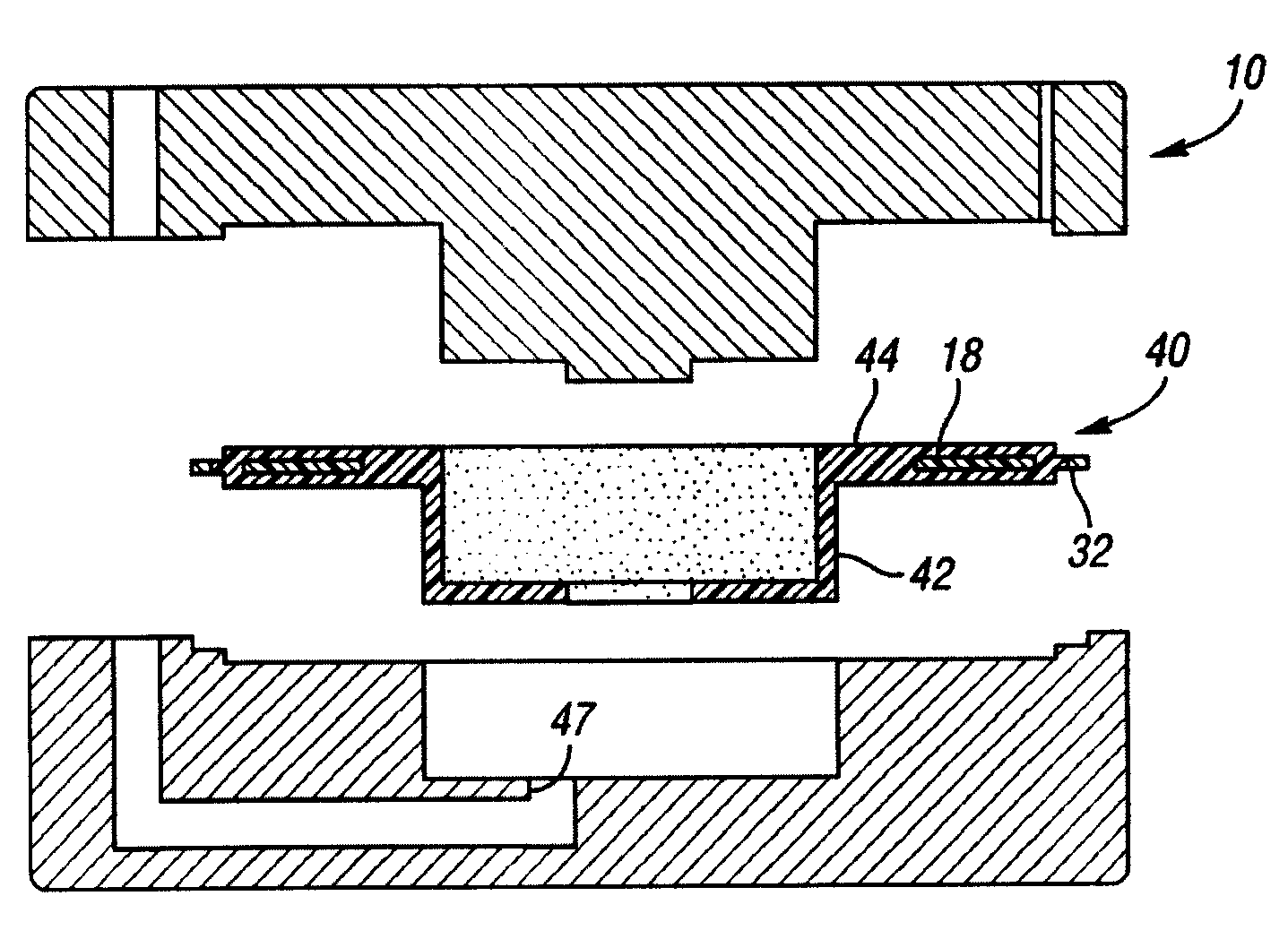
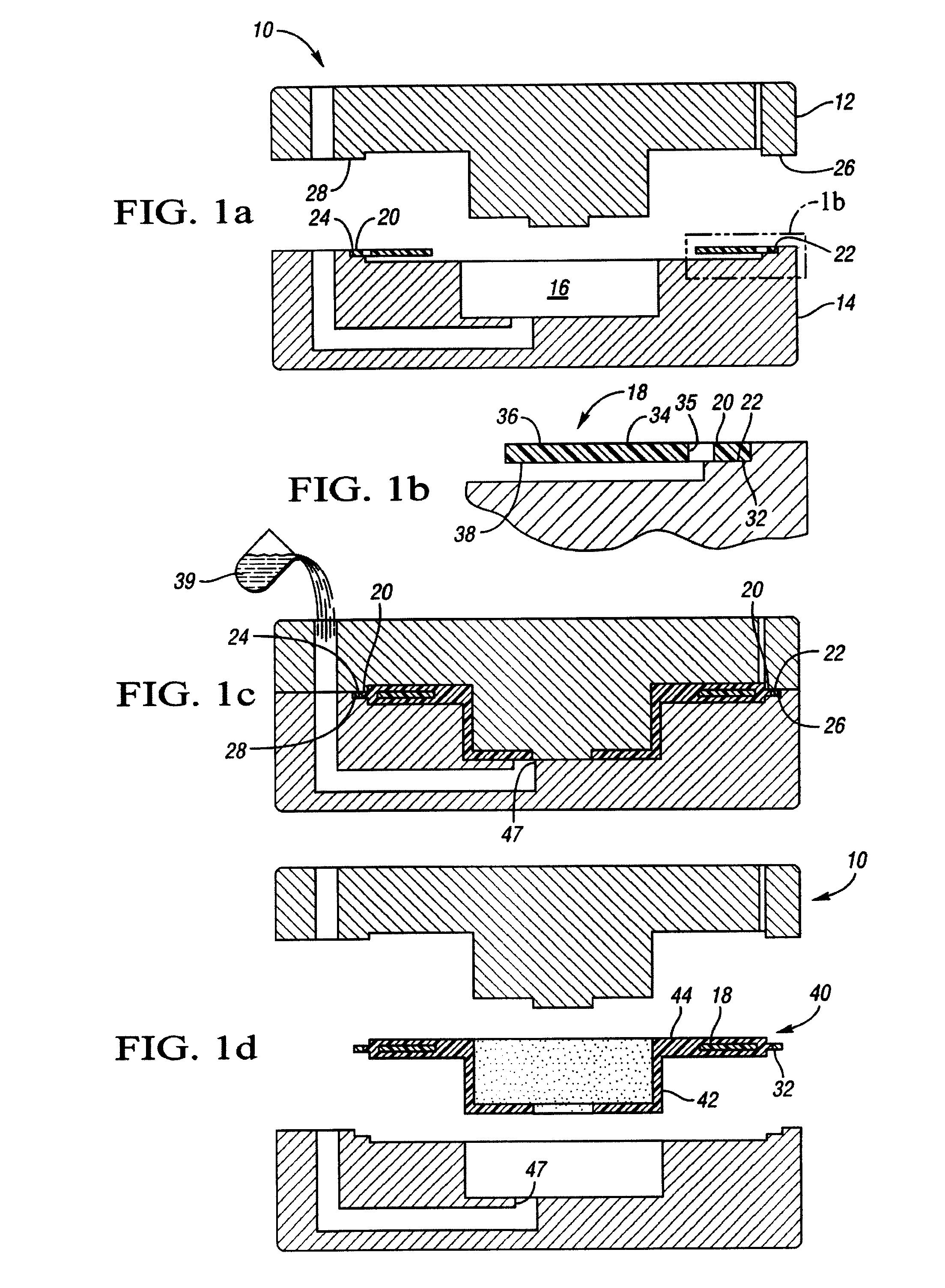
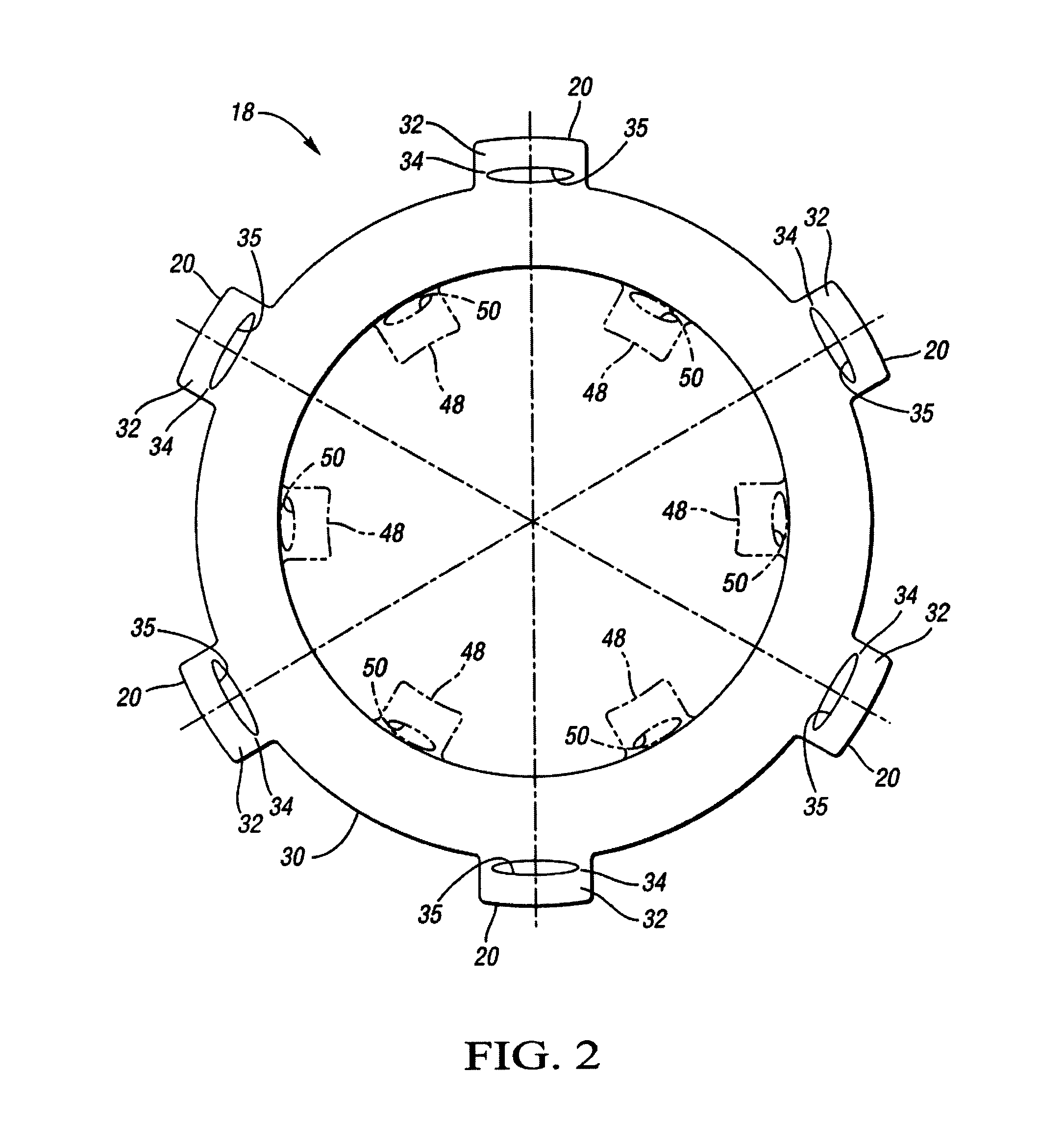
Insert for manufacture of an enhanced sound dampening composite rotor casting and method thereof
InactiveUS20070235270A1High melting pointIncrease expansionNoise/vibration controlBraking discsCasting moldCalipers
An insert for a casting mold used to produce a sound dampening rotor of a caliper disc brake is provided. The insert includes a ring having an inner diameter, an outer diameter and at least one tab. The insert also includes an inner core made from a refractory material, the inner core being adjacent to the ring. The tab of the ring is operable to position the ring relative to the inner core. Furthermore, the ring and the inner core together can be placed within the casting mold and afford for the desirable and accurate placement of the sound dampening ring within a cast sound dampening composite rotor of a caliper disc brake.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP WAUPACA DIV
Brake rotor
InactiveUS20090000884A1Improve noiseIncrease vibrationNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineering
Owner:AKEBONO CORP (NORTH AMERICA)
Control of brake noise by tuned mass dampers
InactiveUS20060266599A1Noise is producedImprove efficiencyNoise/vibration controlSlack adjustersTuned mass damperBrake pad
This invention relates to the braking system of a vehicle and a method to attenuate noise-producing vibrations of components of the braking system by the use of tuned mass dampers of various designs mounted with respect to the brake pads and / or damper plate of a disc brake system. In another embodiment, the tuned mass dampers are attached to the brake shoes and / or drum brake backplate of a drum brake system.
Owner:MATERIAL SCIENCES CORPORATION
Brake assembly with tuned mass damper
InactiveUS7032723B2Effective dampingEasily damagedNoise/vibration controlBraking membersSnubberTuned mass damper
A tuned mass damper for sound-dampening brake squeal noise is located within a hole formed in a brake component such as a backplate supporting a brake pad. The location of the hole and the weight and geometry of the tuned mass damper are tailored to provide effective damping for the particular frequencies that are to be eliminated in the brake system. Locating the tuned mass damper inside of a hole in the component has packaging and manufacturing advantages, and results in a tuned mass damper that is less susceptible to damage when in use. The hole may be blind, the bottom of the hole being thin enough to serve as a spring member to which a vibration damping mass is attached. In one embodiment, the tuned mass damper is a module adapted for insertion into the hole in the brake backplate. Contact between the module and inner surfaces of the hole transfers mechanical vibration of the backplate to the tuned mass damper.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control apparatus and method for friction device of vehicle
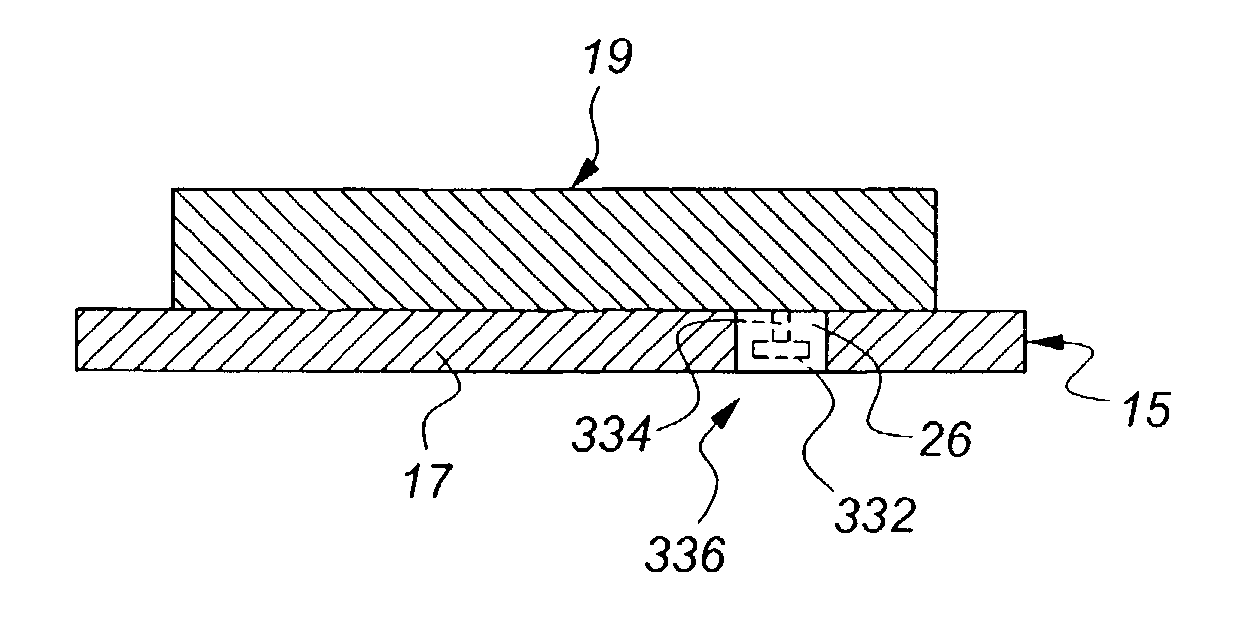
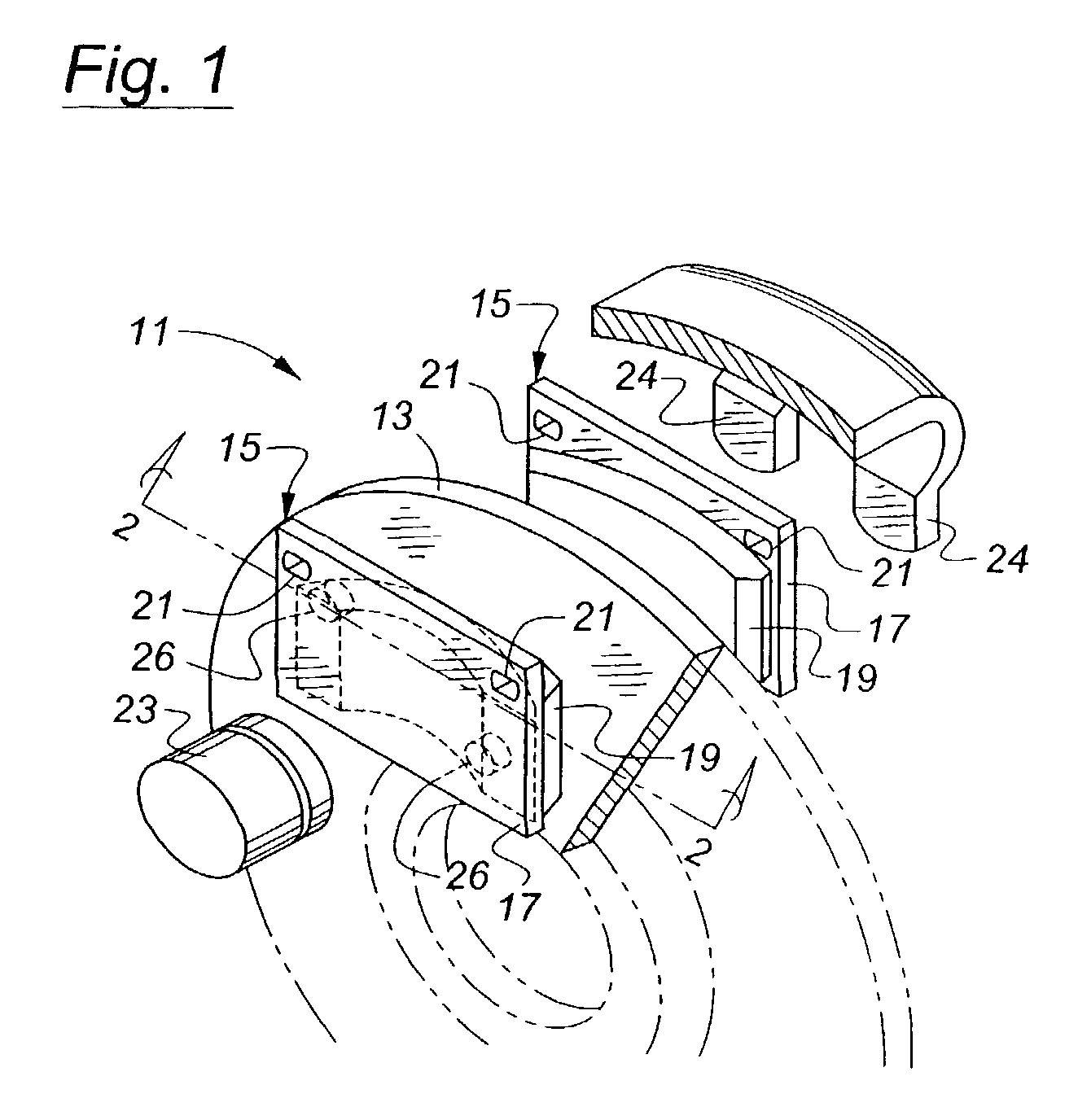
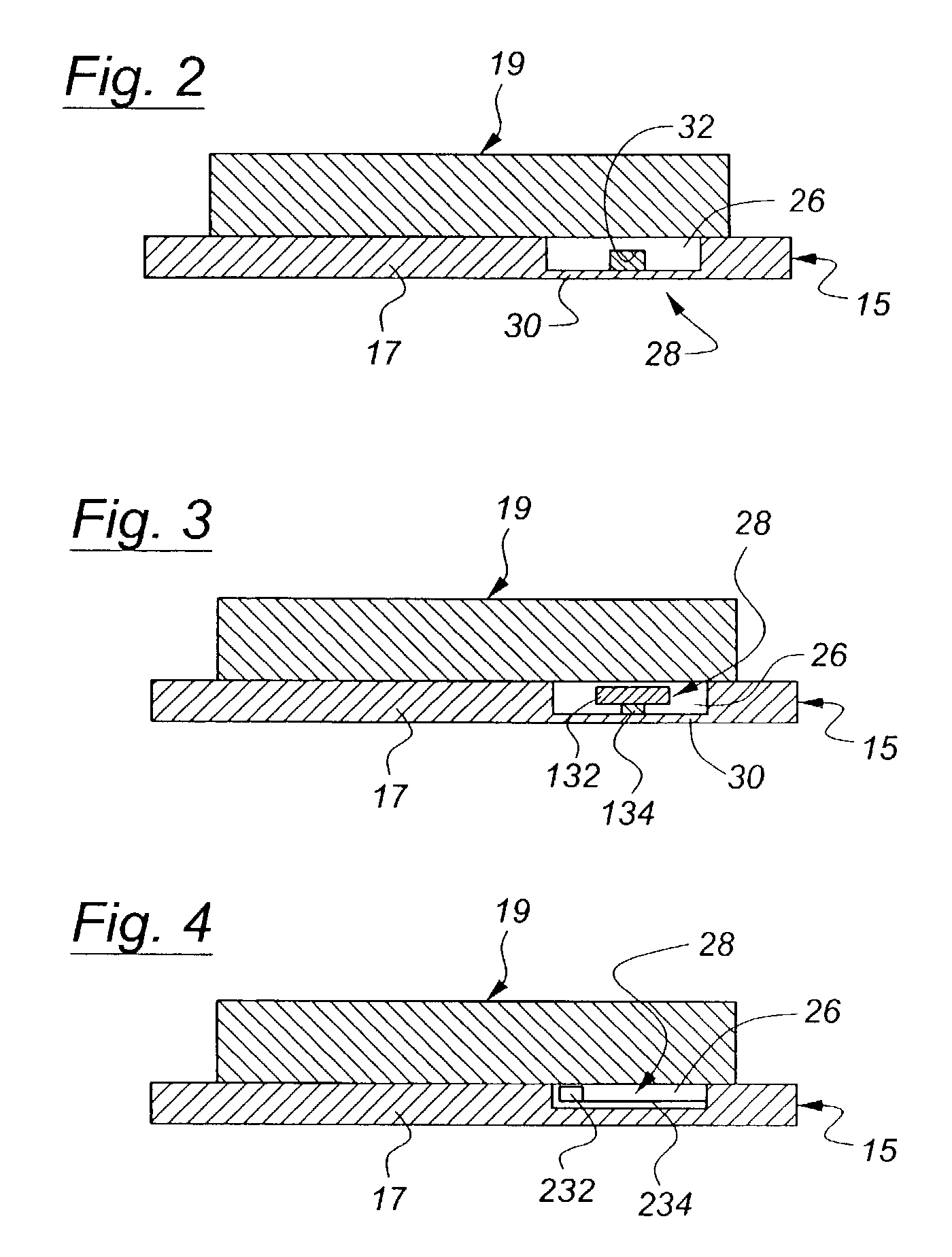
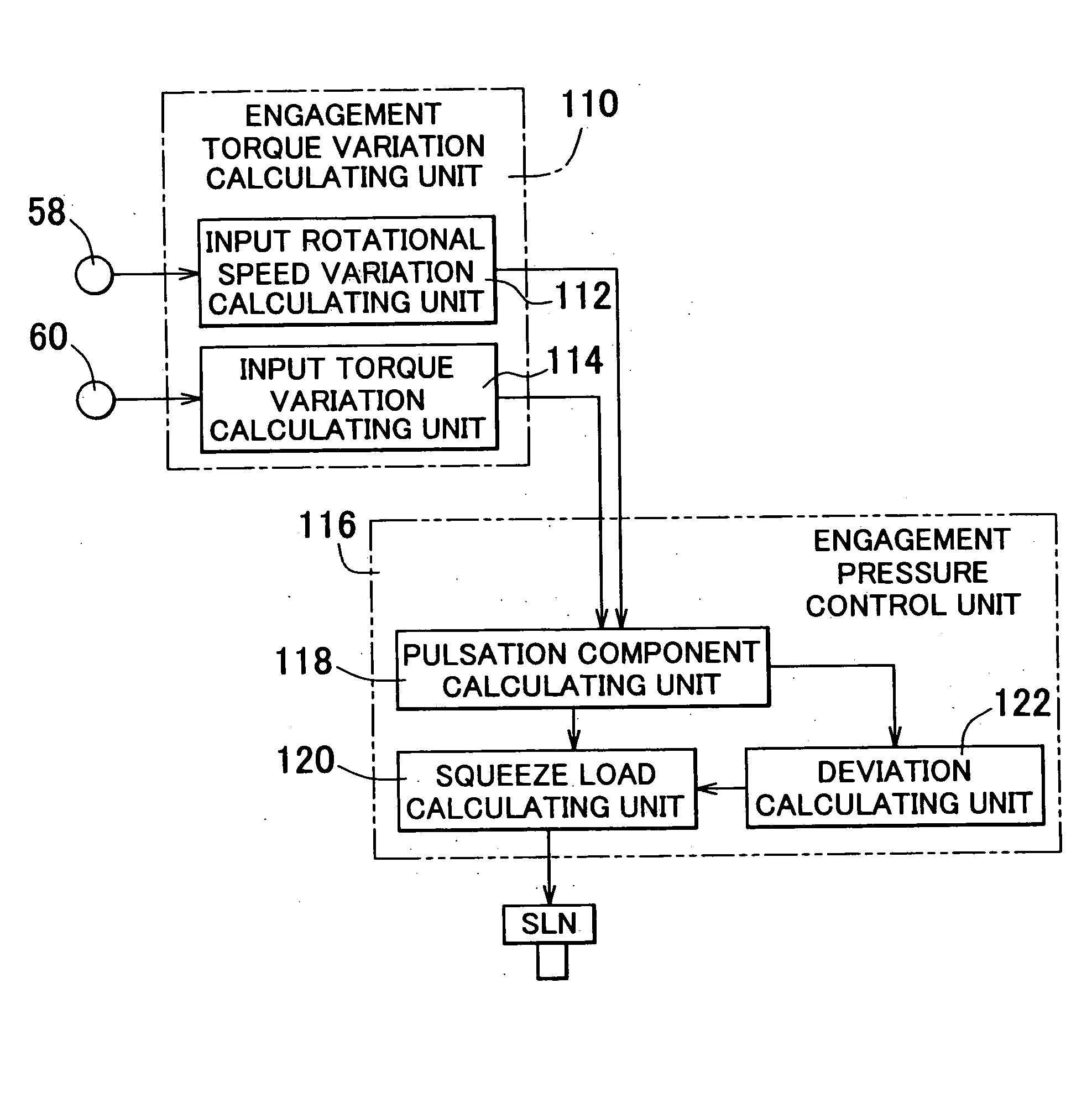
InactiveUS20040186645A1Avoid it happening againInhibitionClutchesBraking element arrangementsPower transmissionAutomotive engineering
A control apparatus for a friction device of a vehicle that is disposed in a power transmission path of the vehicle and is adapted to be engaged upon a start of the vehicle is provided. The control apparatus controls the engagement pressure of the friction device so as to eliminate a pulsation component contained in variations in an engagement torque of the friction device.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
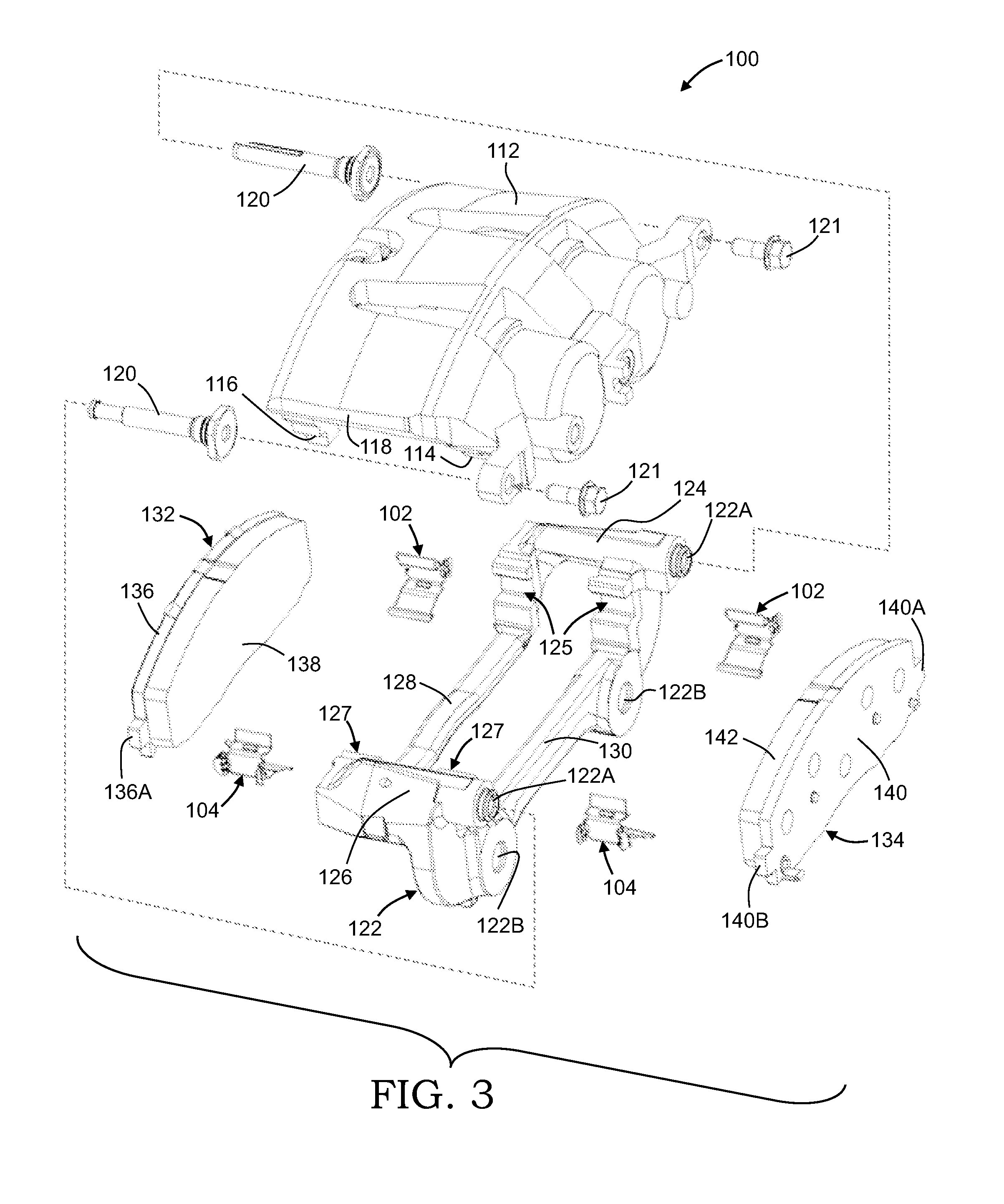
Clip for use in a disc brake assembly and disc brake assembly including such a clip
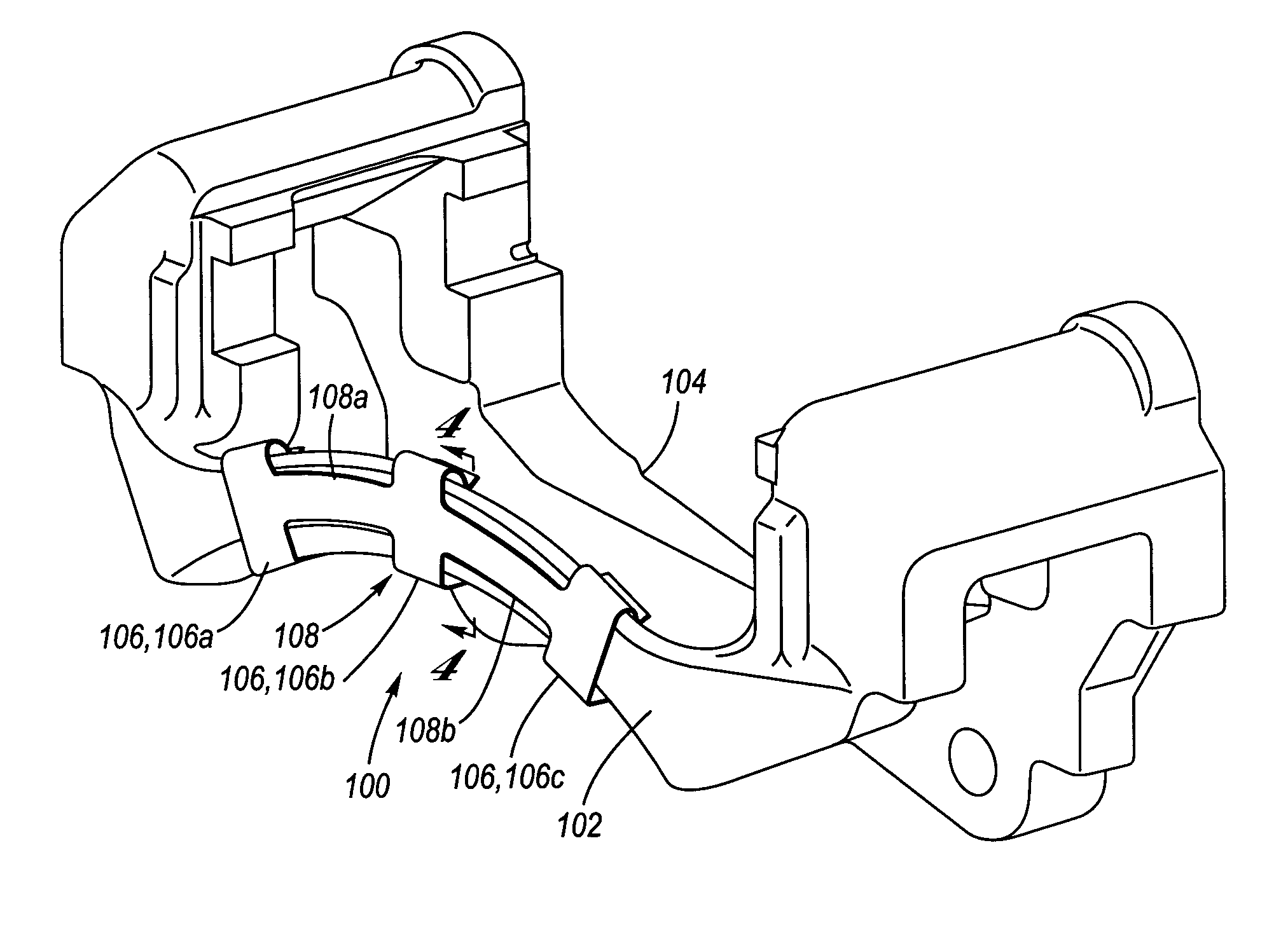
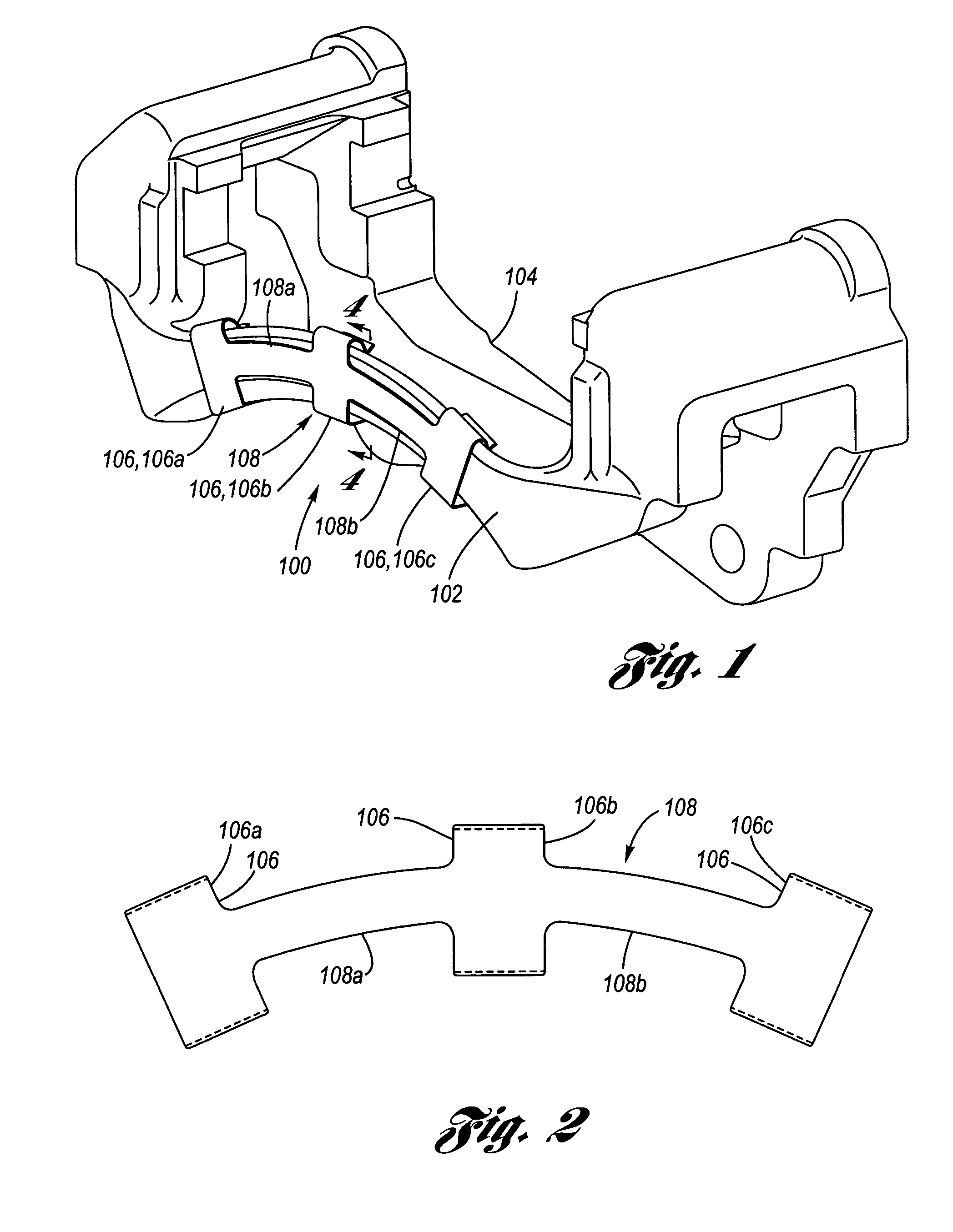
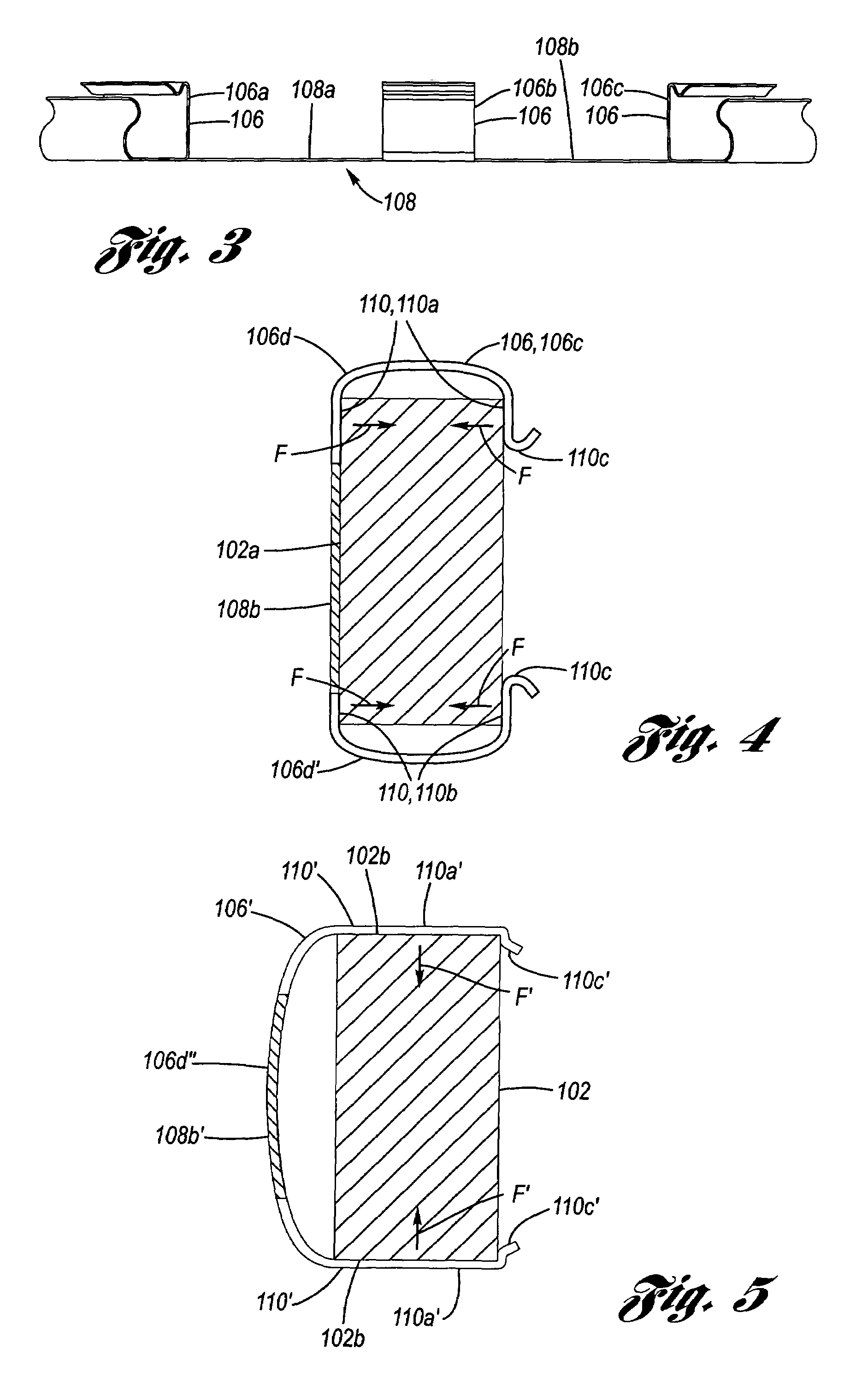
ActiveUS20130192938A1Reduce contact areaBraking element arrangementsNoise/vibration controlEngineeringMechanical engineering
This invention relates to a brake clip for use with a disc brake assembly. The brake clip includes a U-shaped section having a base leg with opposing first and second legs extending from the base leg. An abutment leg extends from at least one of the first and second legs of the U-shaped section. An extension leg extends from the abutment leg. The abutment leg is in contact with an anchor bracket of the disc brake assembly and the extension leg is in contact with a brake pad of the disc brake assembly when the brake clip is disposed therebetween.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
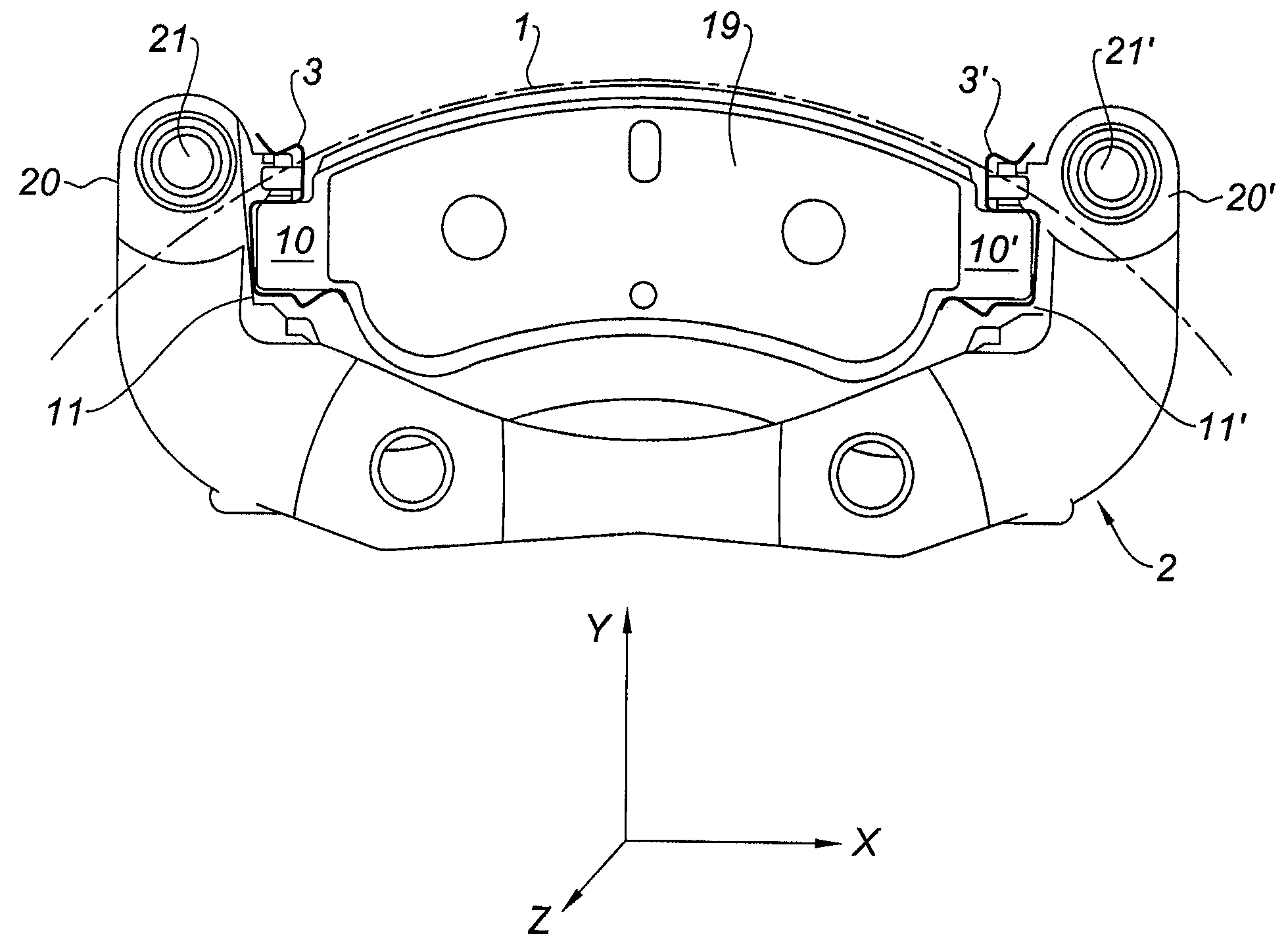
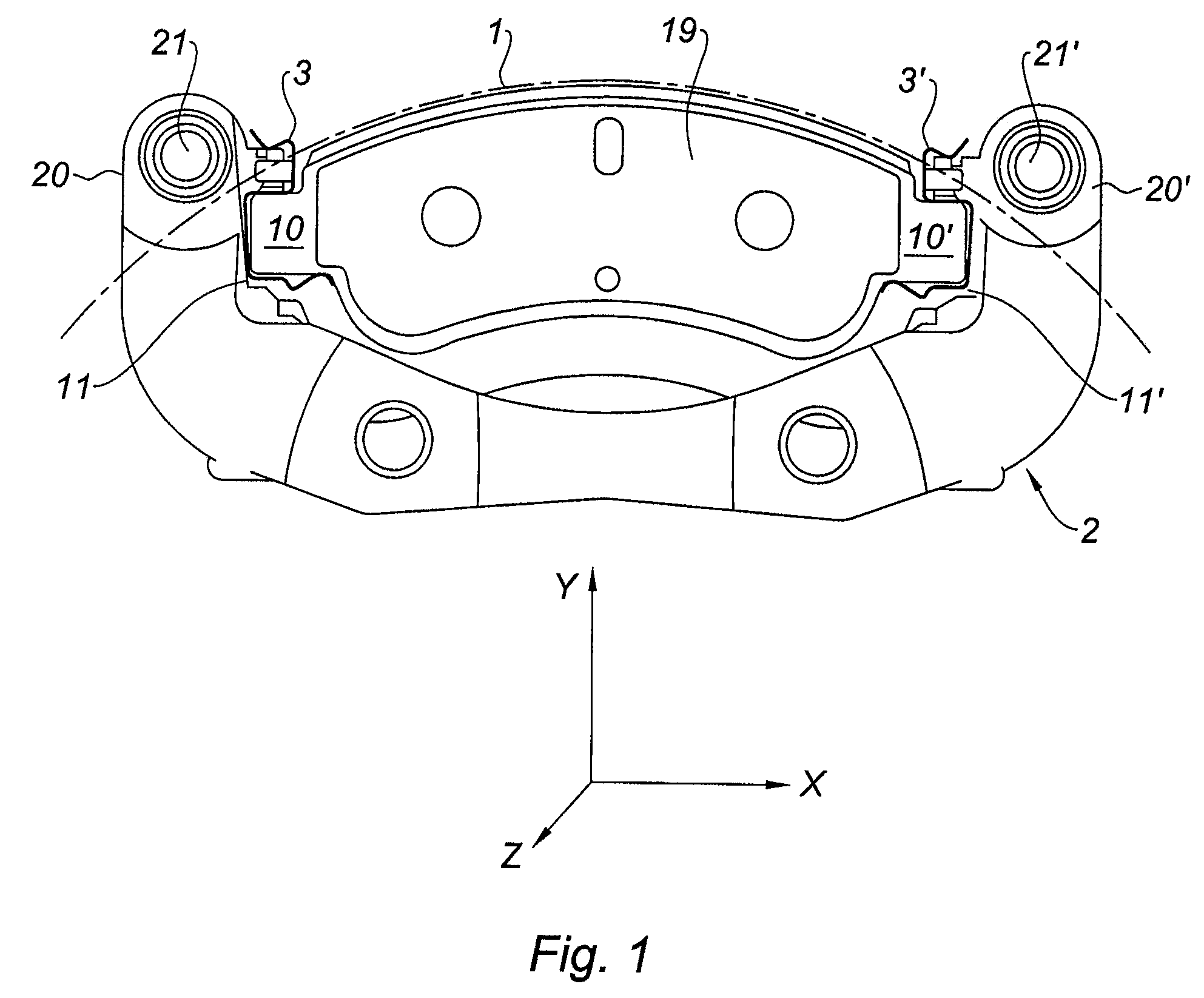
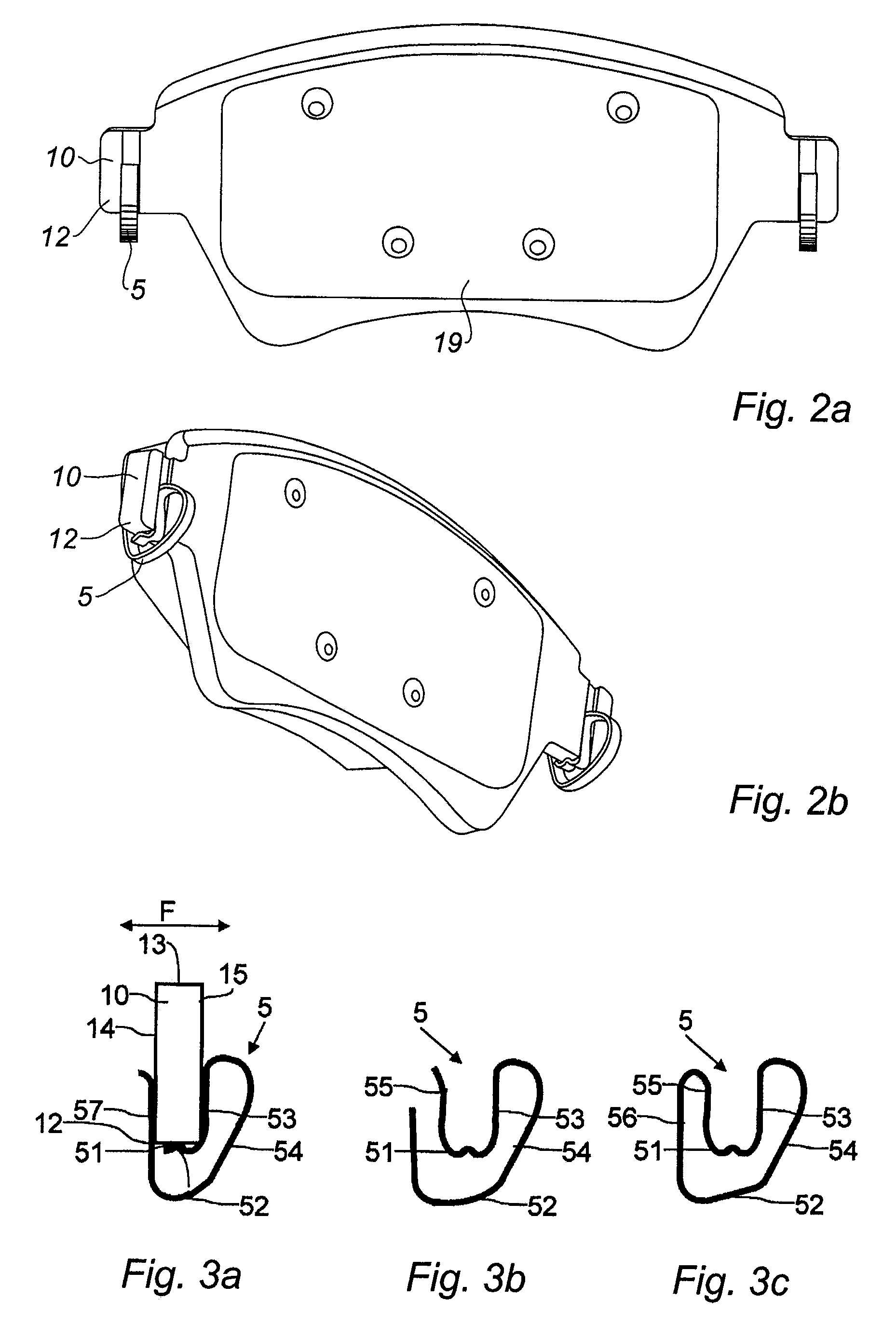
Mounting system for disk brake pad
ActiveUS20090159376A1Stimulate displacementAvoid noiseNoise/vibration controlAxially engaging brakesLower faceMechanical engineering
A mounting system for a brake pad in the housings of a disk brake yoke in which the brake pad comprises at its ends two mounting ears (10), each ear being mounted in a housing of a disk brake yoke. The mounting system comprises for each pad ear, a spring (5) of linear or lamella shape, intended to bear, on the one hand, below a lower face (12) of the ear and, on the other hand, on the lower face of the housing of the yoke so as to separate the lower face (12) of the ear from the lower face of the housing.
Owner:CHASSIS BRAKES INT BV
Lining, in particular friction lining for disc brakes
InactiveUS20040099493A1Improve strength propertiesMaintain propertiesNoise/vibration controlFriction liningSynthetic materialsMetal sheet
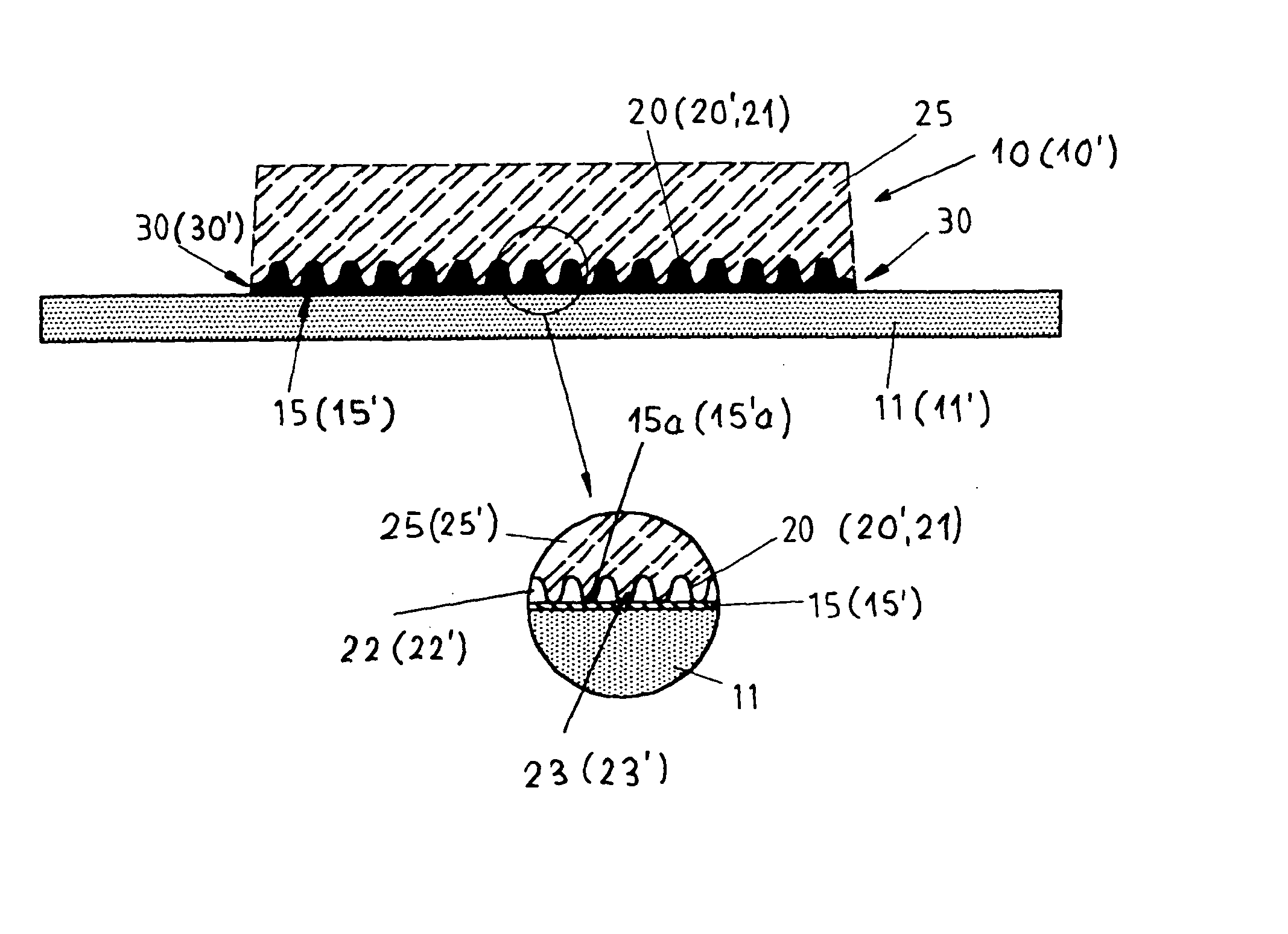
The lining or functional body (10) consists a carrier (11) in form of a ground plate, for example a carrier plate or a carrier sheet, of a thin-walled rough ground carrier (15; 15') made of a metal sheet or of another appropriate material placed on the carrier (11; 11'), of a rough ground (20') made of a support base (20; 20'; 21) sintered on the surface (15a; 15'a) of the rough ground carrier (15; 15') which is turned away from the lining carrier (11; 11'), this support base being made of single moulded bodies (22') with undercuts, recesses or the like which are positively and frictionally connected with the rough ground carrier (15; 15'), and of a functional block (25; 25') fixed on the rough ground carrier (15; 15') with the rough ground (20'), this functional block being made of a friction material, a synthetic material, in particular of such a synthetic material which is not appropriate to be glued together or to be applied in another manner, for example of a polymer or teflon, whereby the rough ground carrier (15; 15') is fixed on the lining carrier (11; 11') by means of a welded, riveted or glued joint (30; 30') or other connecting procedures, such as engraving.
Owner:HONEYWELL BREMSBELAG GMBH
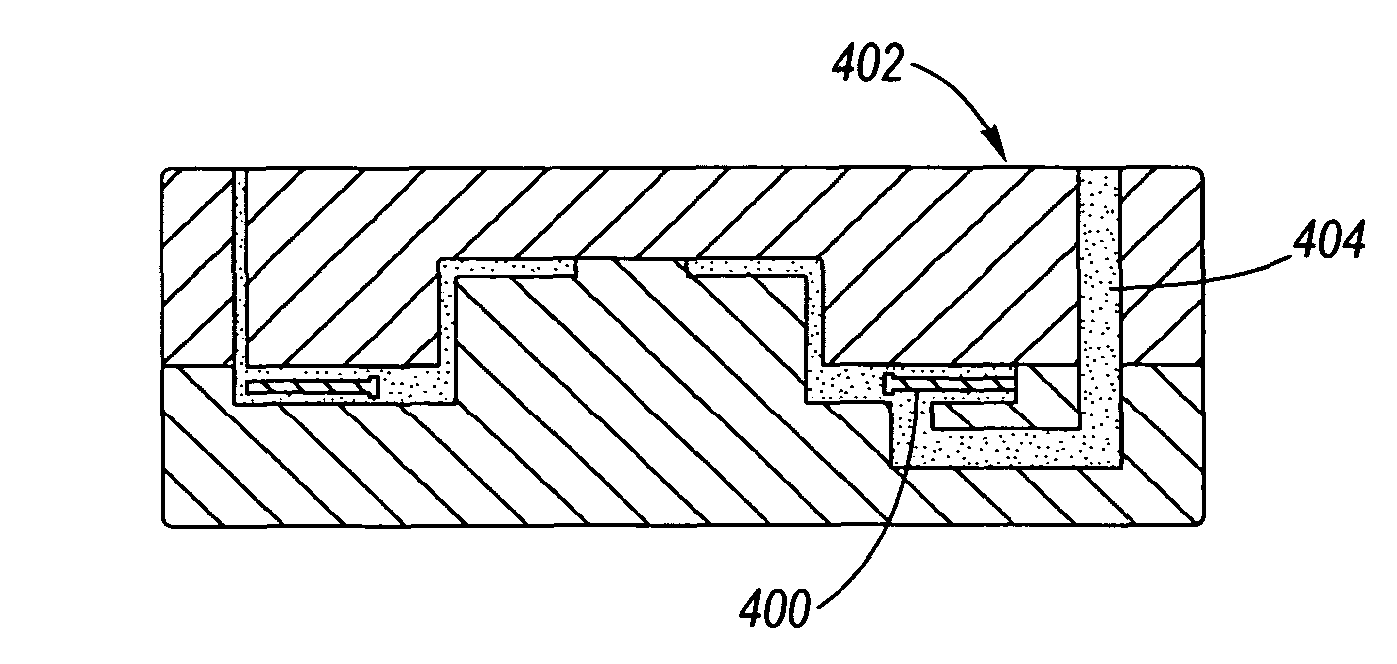
Method of manufacturing a friction damped disc brake rotor
InactiveUS7937819B2Avoid problemsImprove bindingNoise/vibration controlMetal rolling stand detailsCeramic coatingMaterials science
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a friction damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) providing a ceramic coating on an insert, wherein the insert has a body with tabs extending therefrom to hold the insert in a desired position within a mold; (B) washing the ceramic coating off of the tabs; (C) positioning the insert into the mold; and (D) casting a rotor cheek of the disc brake rotor in the mold around the insert such that a portion of each tab is bonded with the rotor cheek, and such that the coating is substantially non-bonded with the rotor cheek so that the coating provides a proper interfacial boundary between the body and the cheek for damping, and the at least partial bonding of each tab with the rotor cheek prevents corrosion-causing exterior elements from reaching the interfacial boundary when the friction damped disc brake rotor is in use.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotors
InactiveUS7975750B2Small thicknessReduce noiseNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineeringCoulomb friction
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor, wherein damping is provided Coulomb friction in generally coextensive relation with the braking surfaces of the one or more rotor cheeks. The Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor has at least one interfacial boundary formed in at least one rotor cheek disposed in generally coextensive relation to the braking surface thereof. The interfacial boundary provides a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Reduced-Noise Electric Brake Actuator
ActiveUS20090050420A1Strengthen the relative fixedGuaranteed isolationNoise/vibration controlElectrodynamic brake systemsActuatorControl theory
An electric brake actuator is described. The actuator comprises a housing, an electric motor, a device for torque transmission and an element for torque delivery. The device for torque transmission is a gear mechanism with a gear shaft which is parallel to the motor shaft, wherein the torque is transmitted from the electric motor to the gear mechanism by means of a belt drive. The distance between the motor shaft and the gear shaft is fixed by means of a rigid spacer, the opposite ends of which are located on different sides of the plane which is defined by a belt of the belt drive.
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Noise attenuating friction assembly
InactiveUS20050082124A1Reduce vibrationEnsure efficient flowNoise/vibration controlFriction liningEngineeringMechanical engineering
A brake pad assembly (10) comprising a molded material (26) affixed to a backing plate (12) having opposed faces (14, 16), one or more non-circular extrusion openings (24, 38) through its thickness, and tab-like extensions (22) or other integral attachment for incorporating the assembly (10) by location and support into a vehicle brake system. The molded material (26) extends over both opposed faces (14, 16) of the backing plate (12) by being extruded through the extrusion openings (24, 38) to provide a unitary structure wherein molded material (26) at one side of the backing plate (12) functions as a friction-generating pad material (28) and the portion of the molded material (26) at the opposite side of the backing plate (12) functions as the assembly shim-like noise attenuating element (32) due to vibration damping properties. The number, configuration, and placement of the extrusion openings (24, 36) through the thickness of the backing plate (12) is varied to alter the noise attenuating properties of the assembly (10), further reducing the tendency for modal locking of brake components.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE
Flanged shim for disc brake squeal attenuation
ActiveUS20090223753A1Large dampingArea maximizationFluid actuated brakesNoise/vibration controlUltrasound attenuationEngineering
A brake pad assembly provided for a disc brake apparatus. The brake pad assembly comprises a backing plate having a flat inner face and a flat outer face oriented opposite to the inner face, a friction member fixed to the inner face of the backing plate, and an anti-squeal shim attached to the outer face of the backing plate. The anti-squeal shim includes a flat support plate attached to the outer face of the backing plate and a straight flat flange plate. The support plate of the anti-squeal shim has a peripheral edge including opposite outer and inner edges and opposite side edges. The flange plate is in the form of a flexible cantilever formed integrally with the support plate of the anti-squeal shim and extends away from one of the outer, inner and opposite side edges of the support plate of the anti-squeal shim.
Owner:WOLVERINE ADVANCED MATERIALS
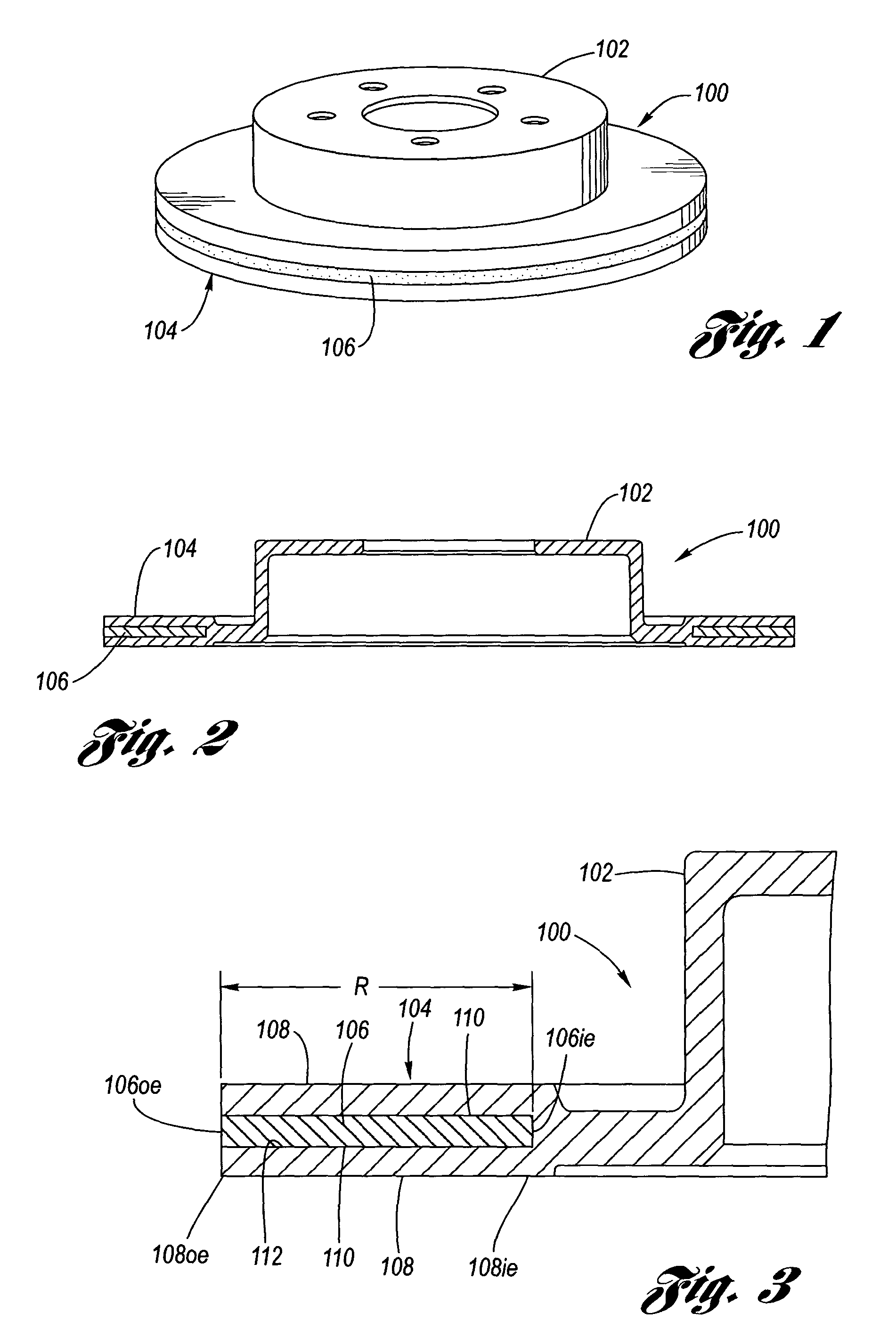
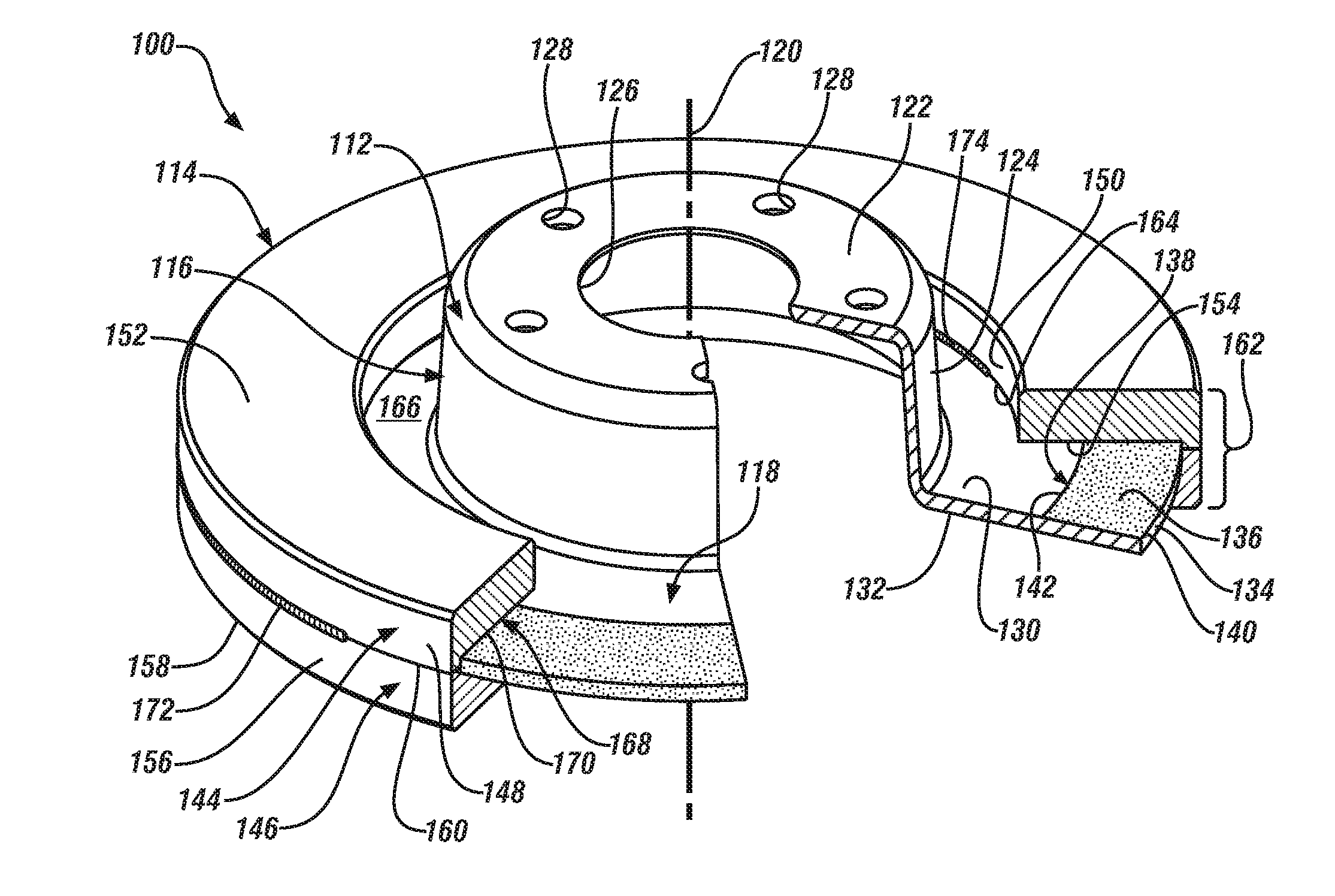
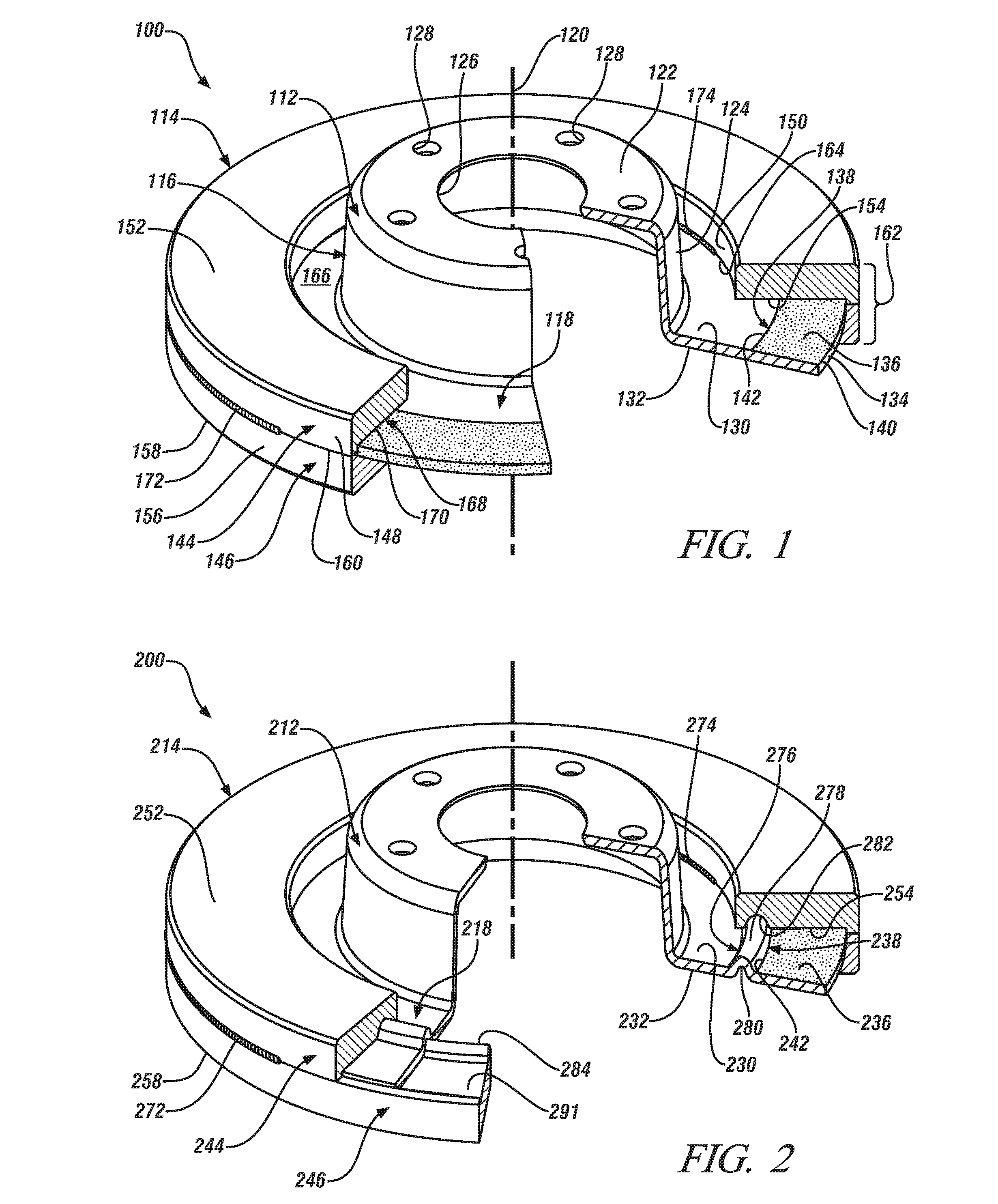
Light-weight and sound-damped brake rotor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130112514A1Reduce spreadEasy to manufactureNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineeringVehicle brake
A light-weight and sound-damped brake rotor for a vehicle braking system includes a rotor hat and a rotor cheek supported by the rotor hat. The rotor hat includes an axially-protruding central hub and a flange that extends radially from and circumferentially around the central hub. The rotor cheek, which provides at least one braking surface, is formed from two or more separate and distinct pieces which are fixedly secured to the flange of the rotor hat. Located within the rotor cheek underneath the at least one braking surface is a vibration damping element. The brake rotor derives its vibration-deadening and sound-damping effects from the vibration damping element through the occurrence of relative frictional contacting movement.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Laminated shim for disc brake and pad unit having the laminated shim
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Disk brake devices
ActiveUS7201257B2Noise/vibration controlAxially engaging brakesInternal pressureMechanical engineering
A disk brake device has a rotary brake disk, at least one pad, and a mount. The pad has a guide portion disposed on one end of the pad in the rotational direction of the brake disk. The mount has a support portion that slidably supports the guide portion, so that the pad can move in the axial direction of the brake. A radially outer pressure receiving surface and a radially inner pressure receiving surface are formed on an end of the pad in the rotational direction of the brake disk and serve to receive a reaction force from the mount in order to prevent the pad from moving in the rotational direction of the brake disk. A support member serves to bias the pad in an axial and rotational direction so as to reduce the production of audible sounds.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com