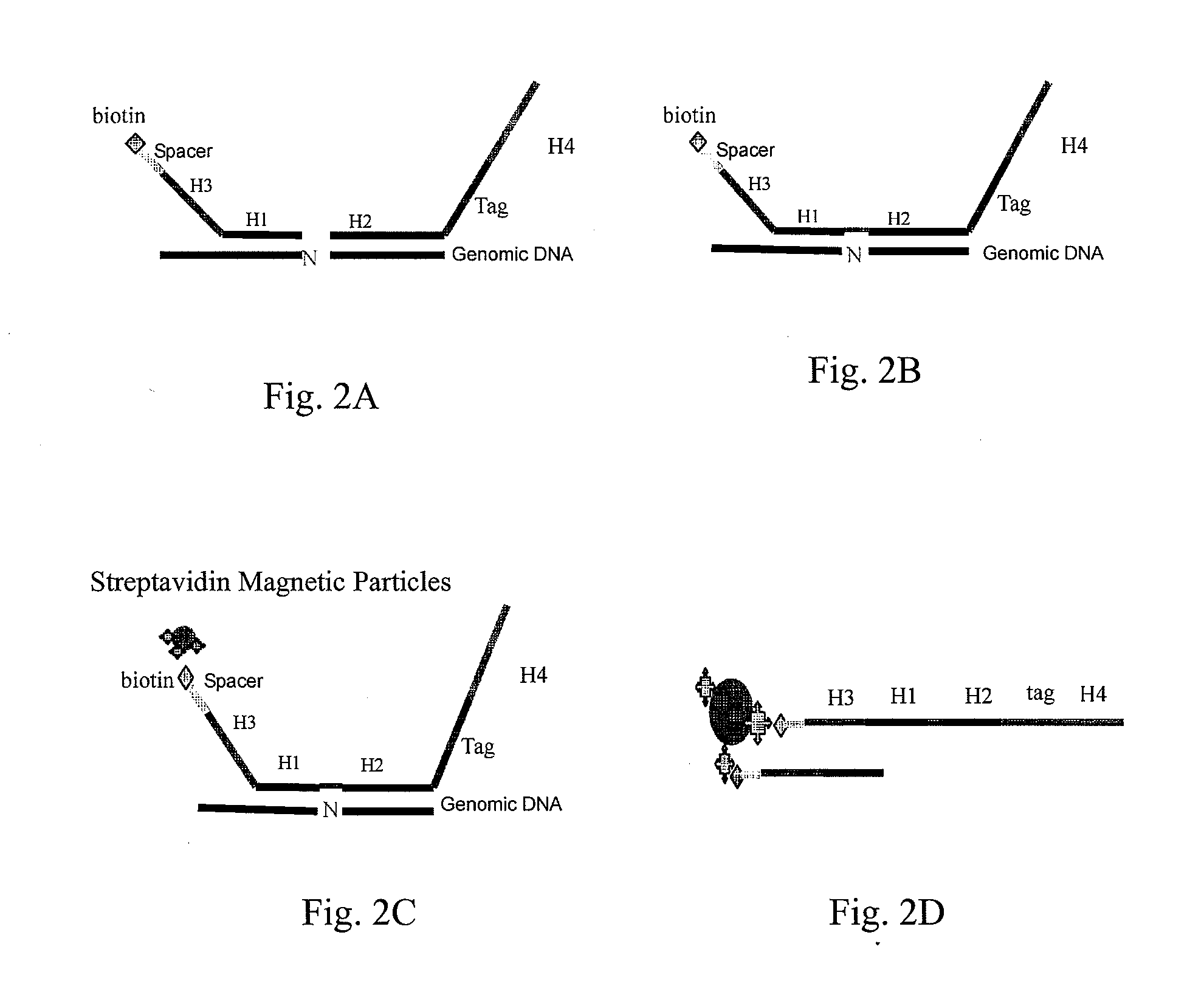
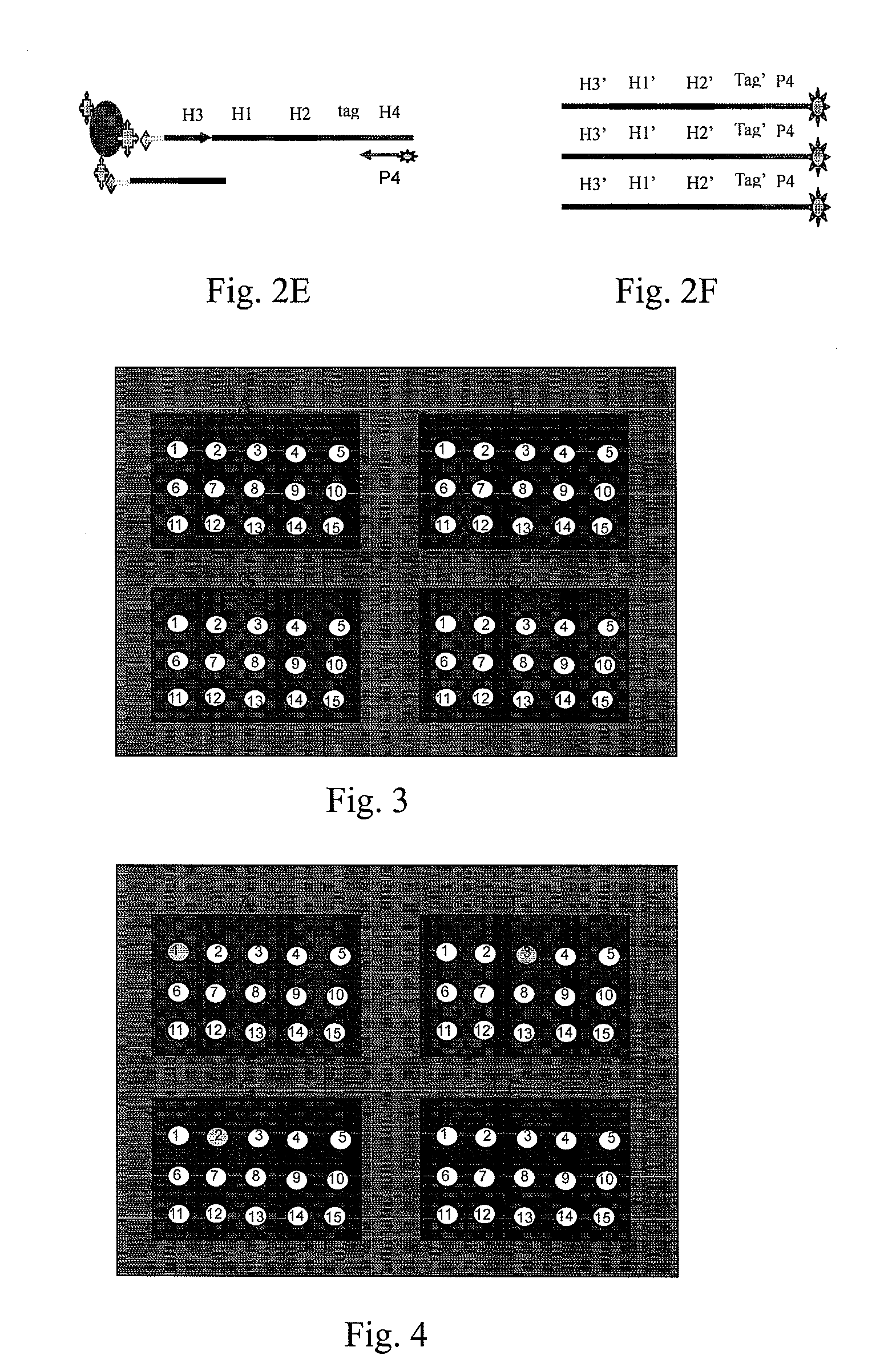
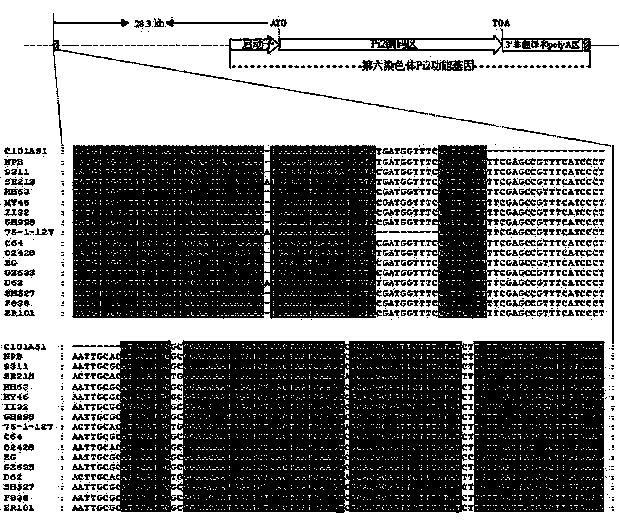
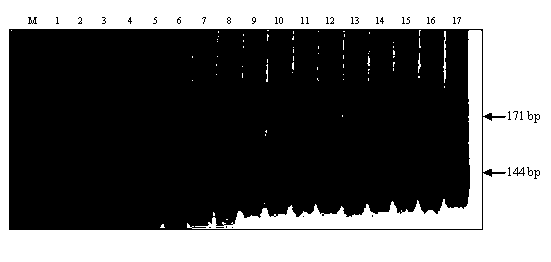
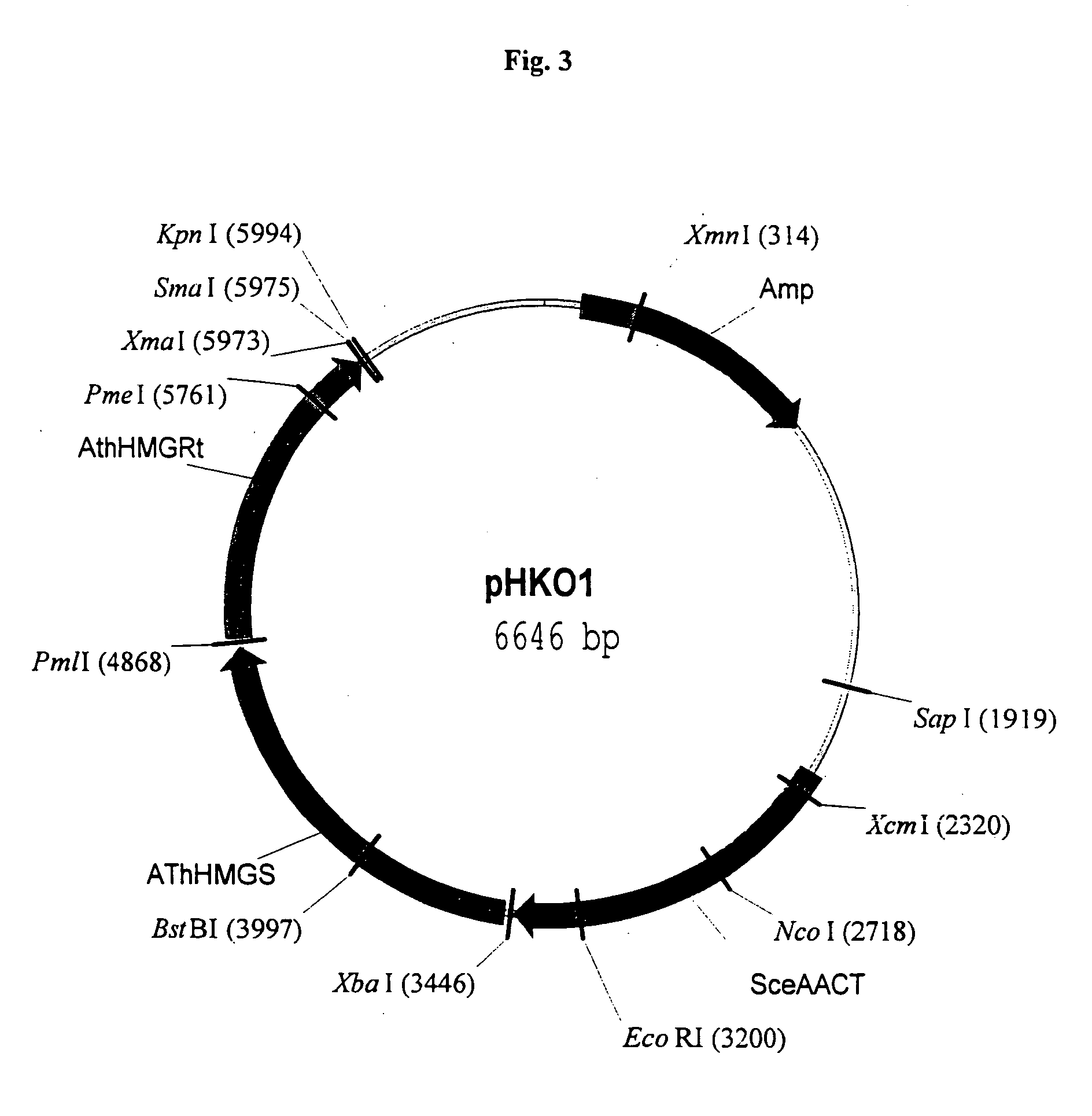
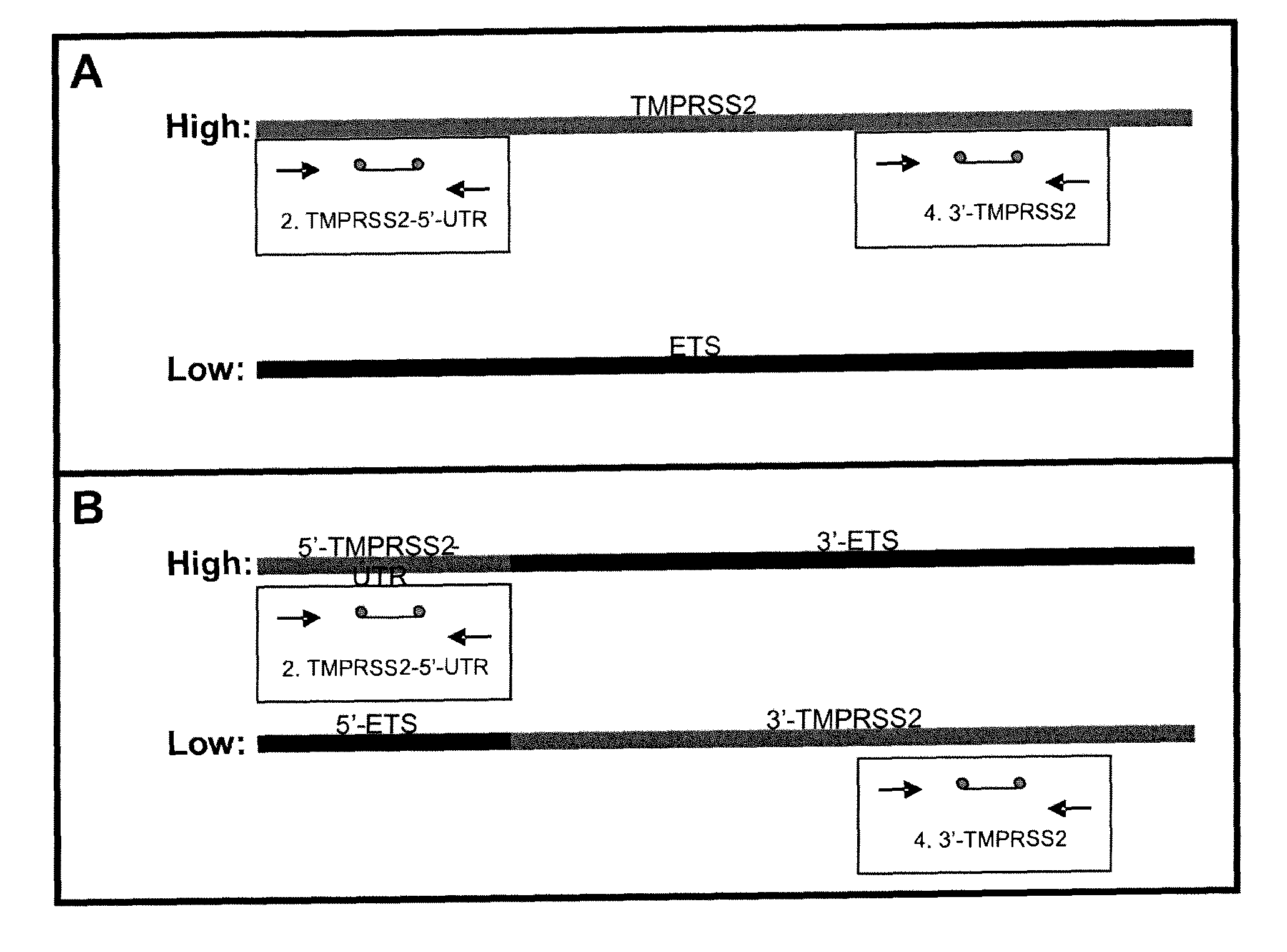
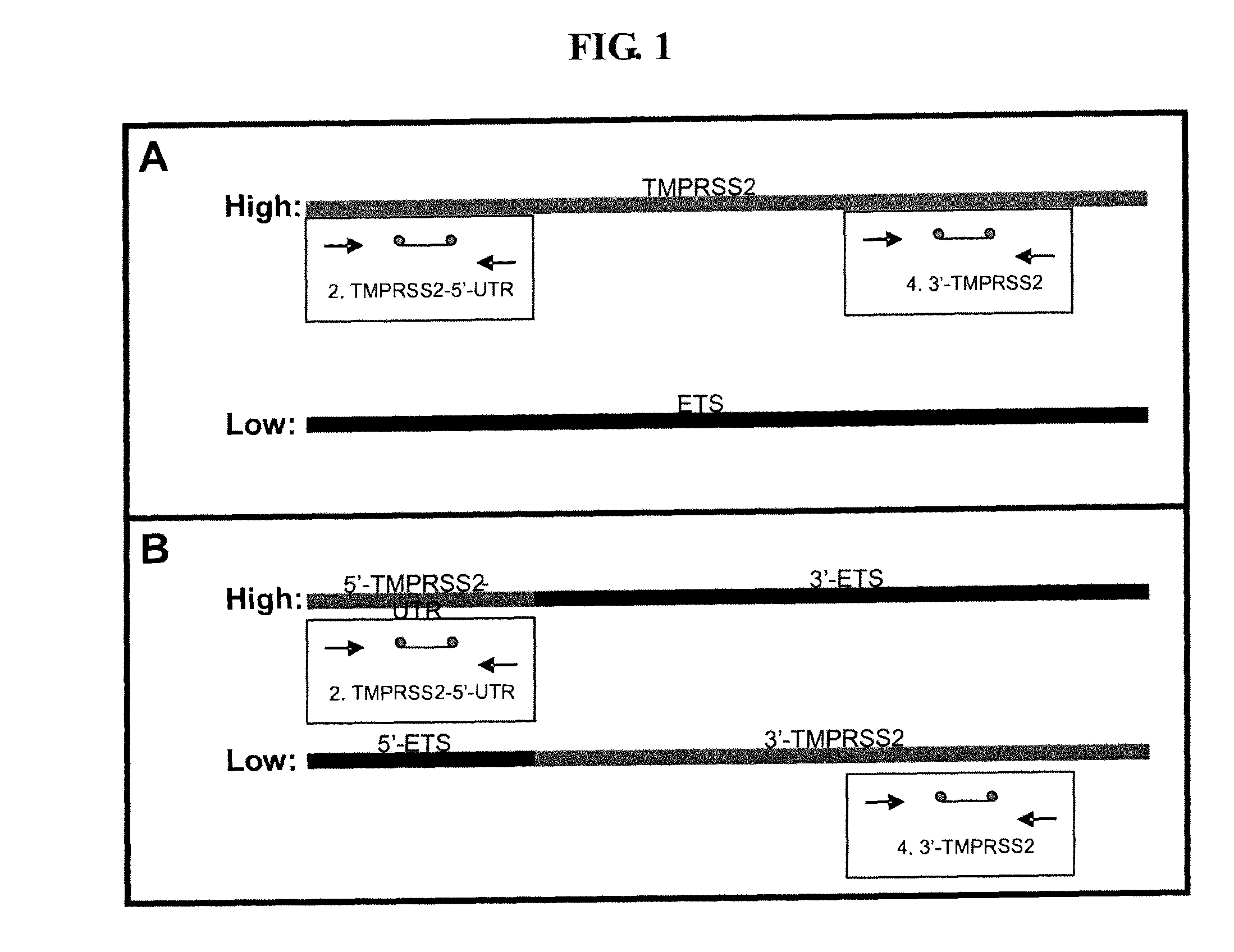
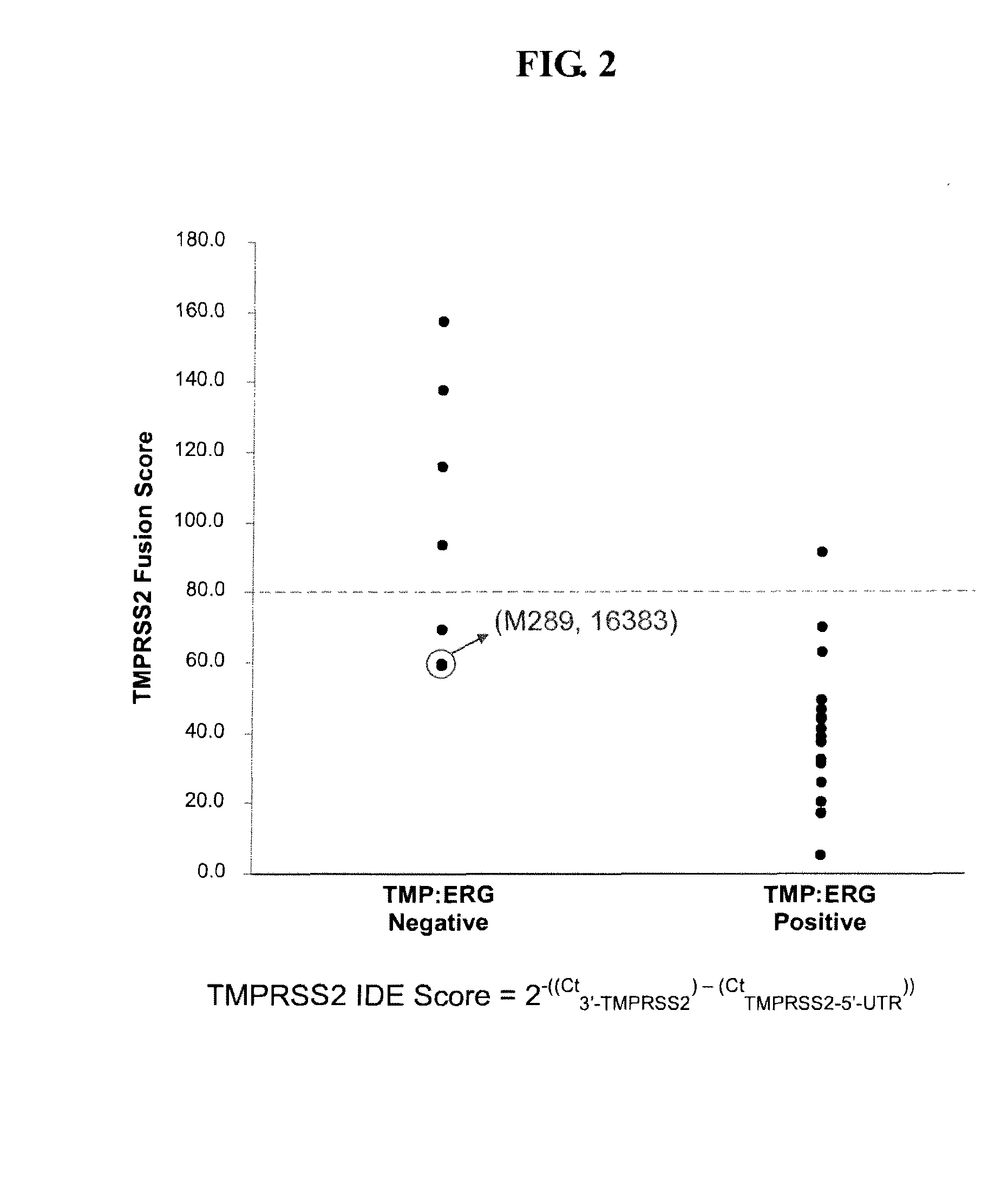
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
790 results about "Insertion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, an insertion (also called an insertion mutation) is the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence. This can often happen in microsatellite regions due to the DNA polymerase slipping. Insertions can be anywhere in size from one base pair incorrectly inserted into a DNA sequence to a section of one chromosome inserted into another. The mechanism of the smallest single base insertion mutations is believed to be through base-pair separation between the template and primer strands followed by non-neighbor base stacking, which can occur locally within the DNA polymerase active site. On a chromosome level, an insertion refers to the insertion of a larger sequence into a chromosome. This can happen due to unequal crossover during meiosis.
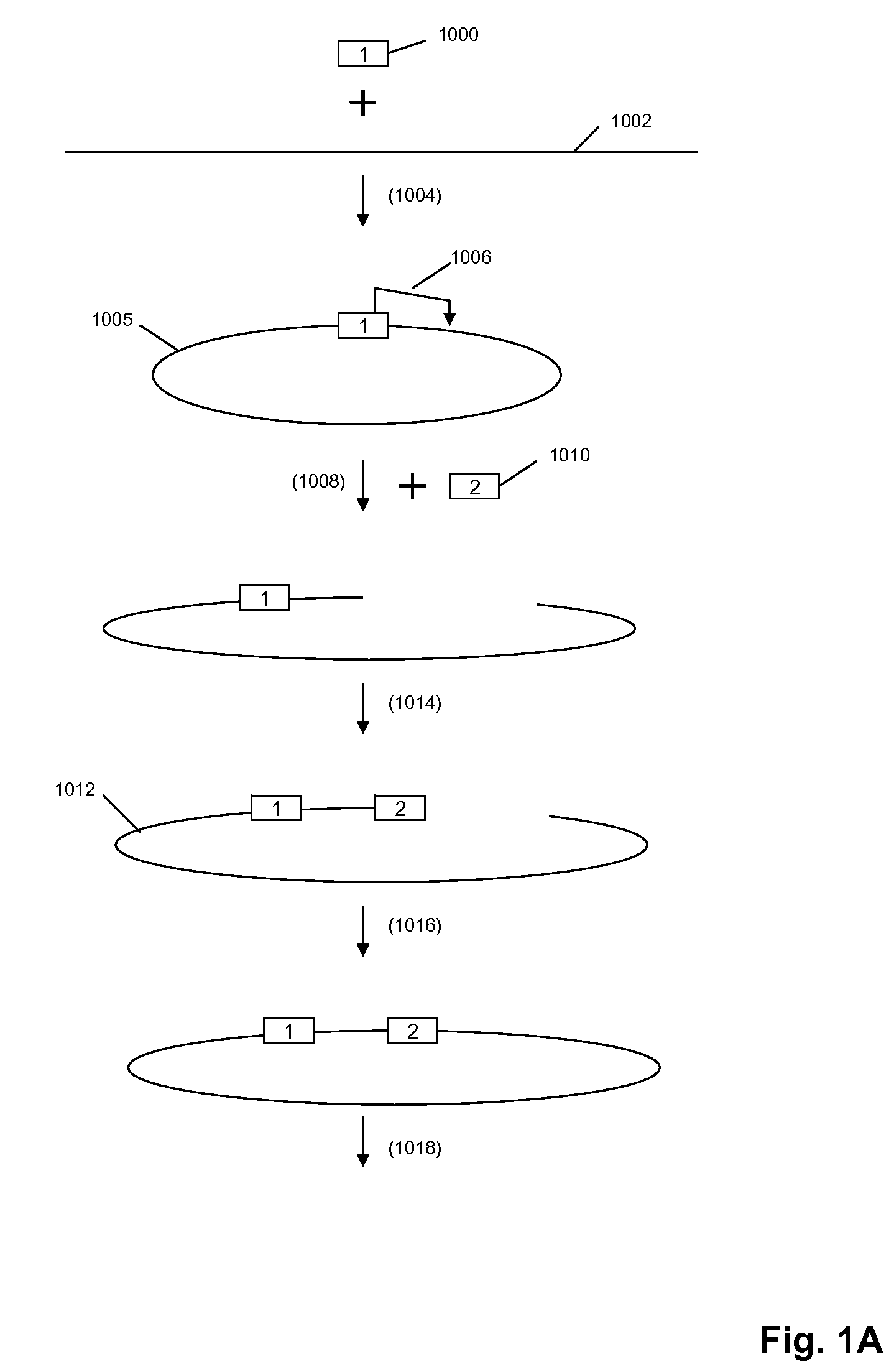
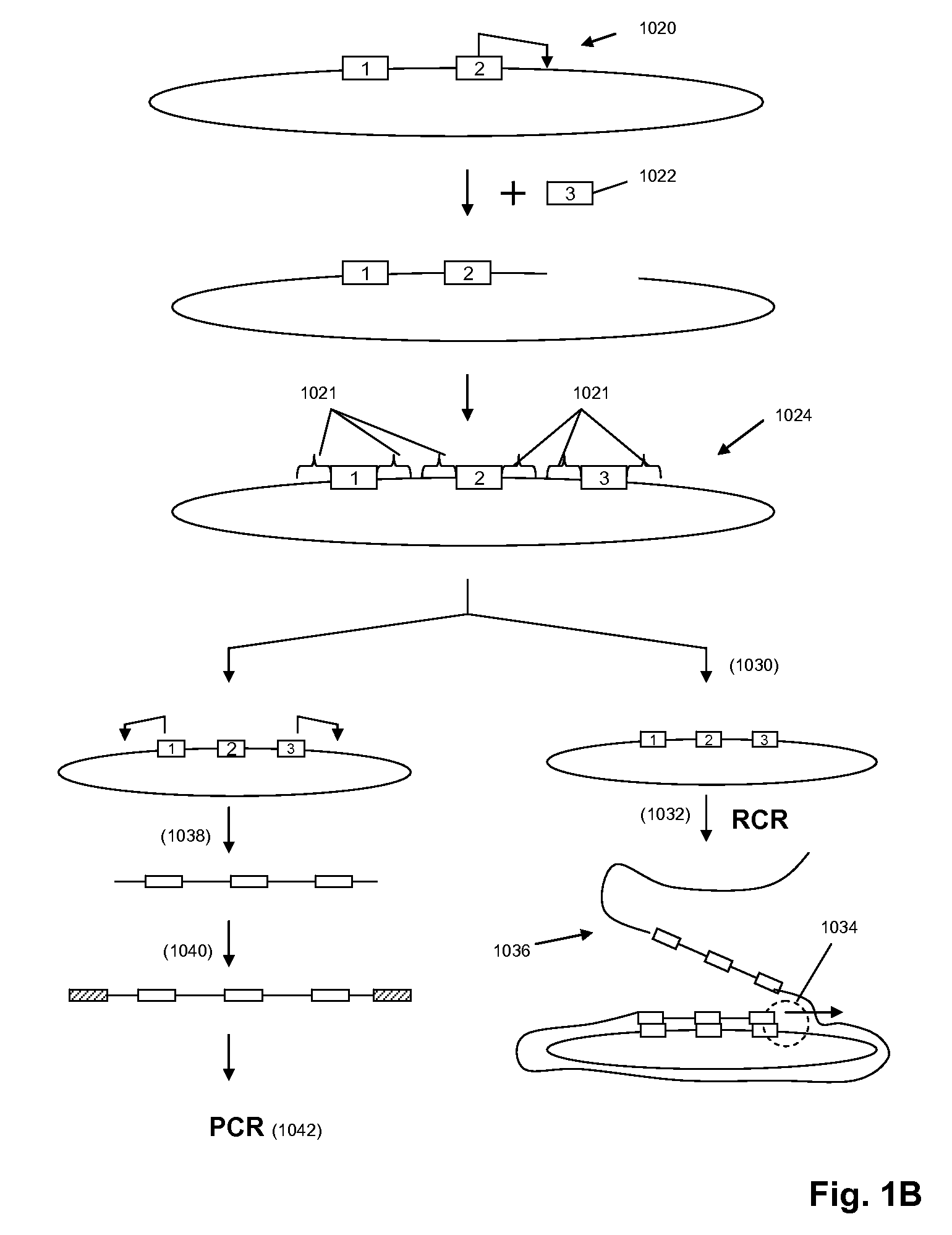
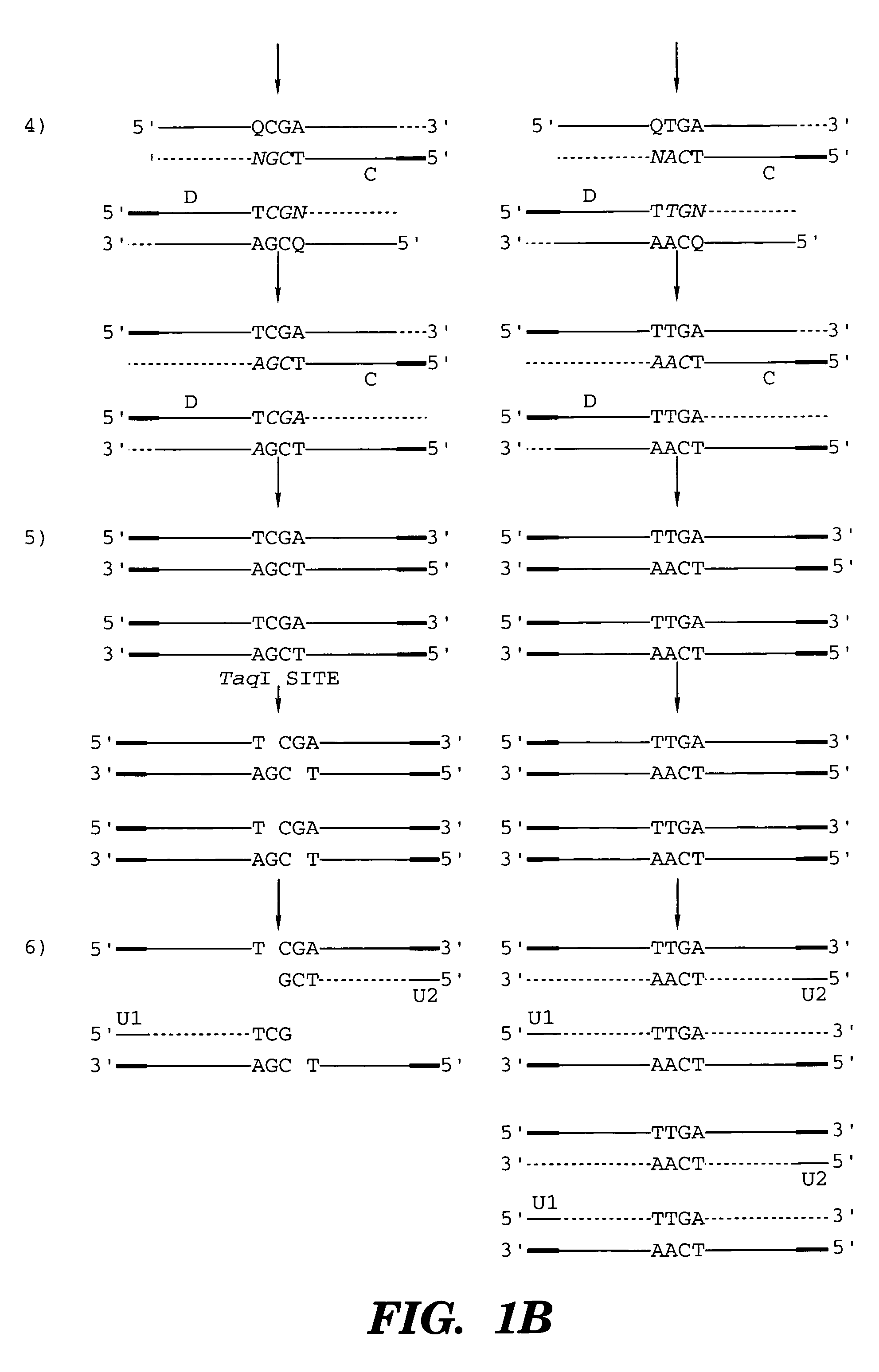
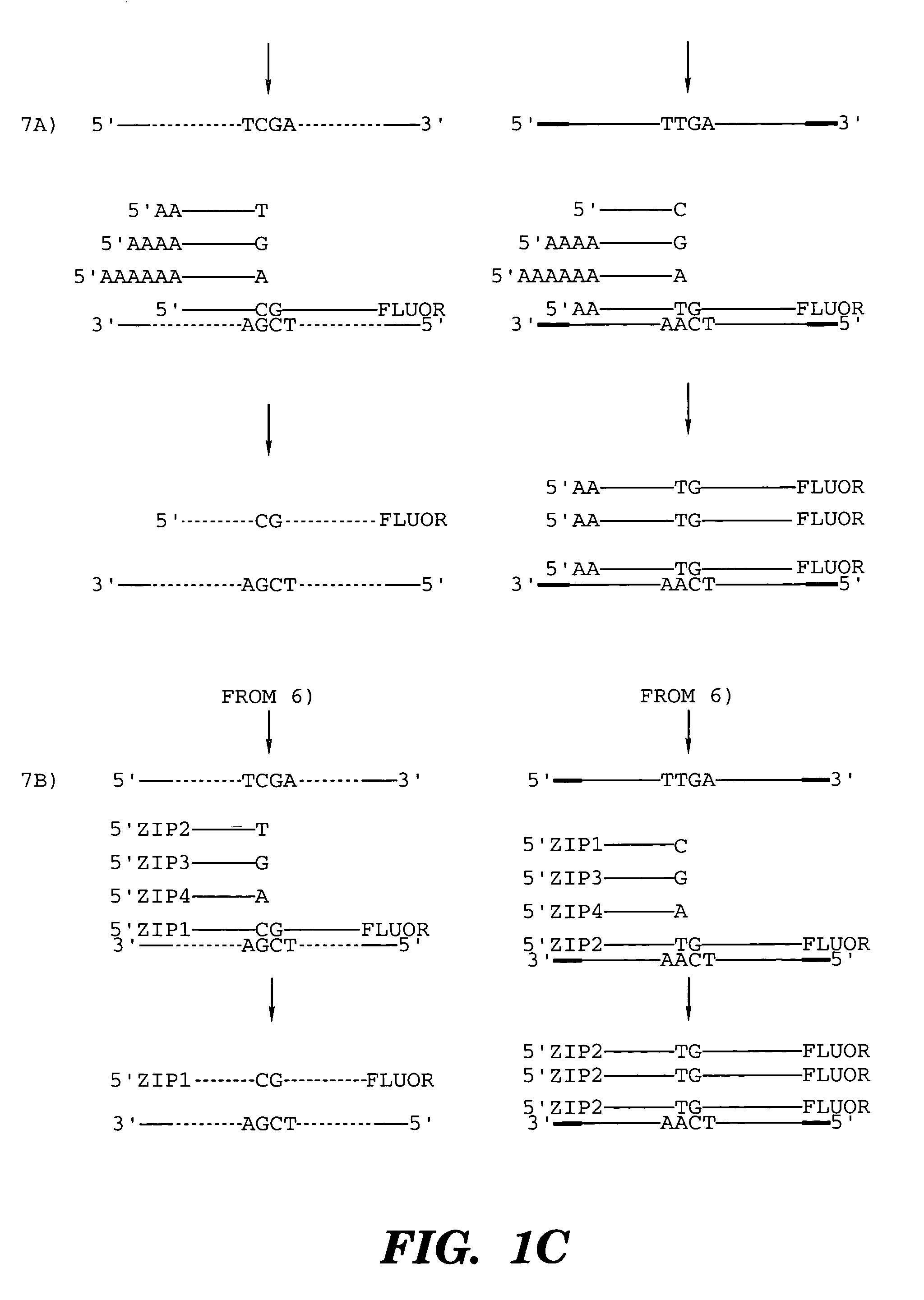
High throughput genome sequencing on DNA arrays
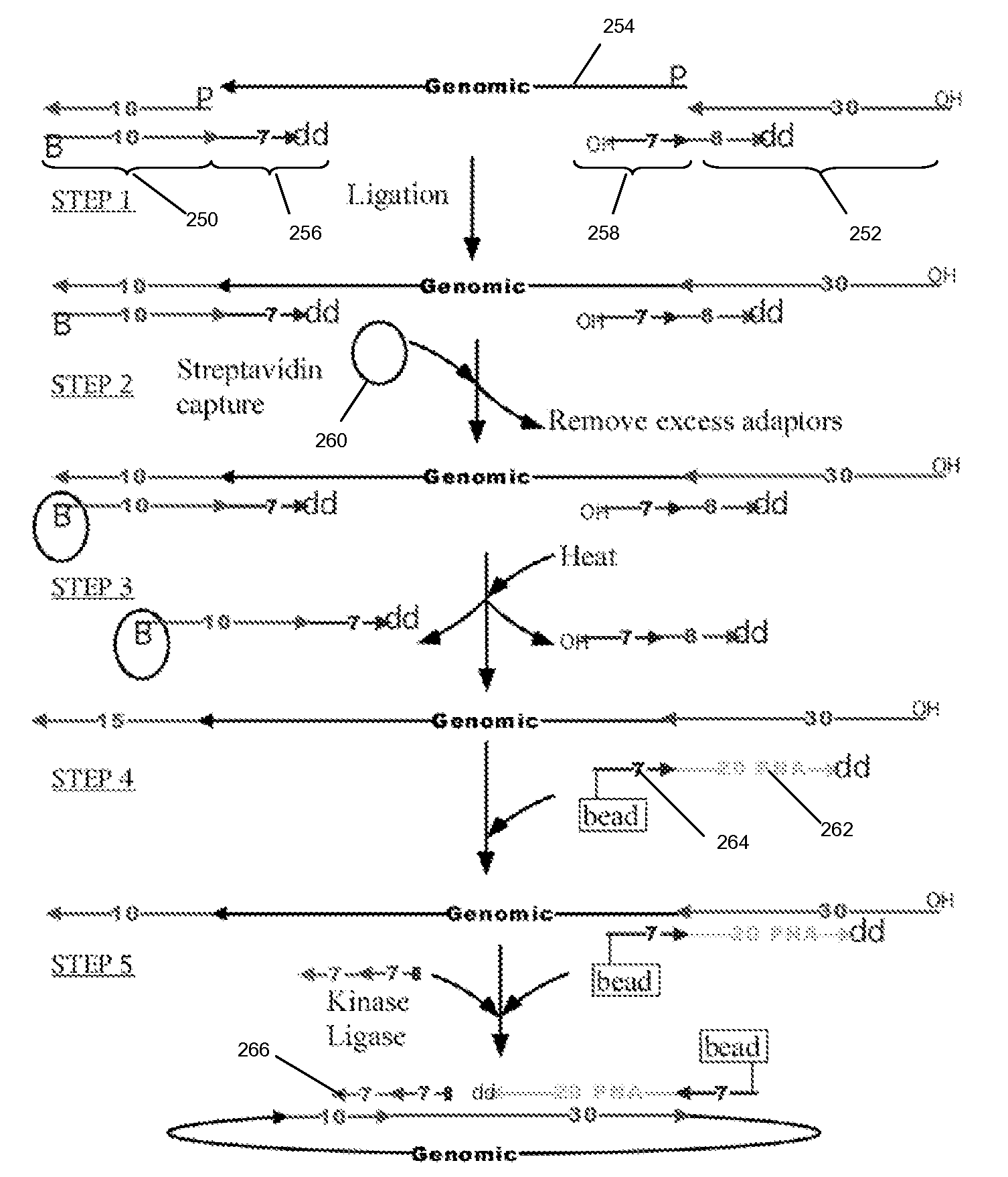
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for acquiring nucleotide sequence information of target sequences using adaptors interspersed in target polynucleotides. The sequence information can be new, e.g. sequencing unknown nucleic acids, re-sequencing, or genotyping. The invention preferably includes methods for inserting a plurality of adaptors at spaced locations within a target polynucleotide or a fragment of a polynucleotide. Such adaptors may serve as platforms for interrogating adjacent sequences using various sequencing chemistries, such as those that identify nucleotides by primer extension, probe ligation, and the like. Encompassed in the invention are methods and compositions for the insertion of known adaptor sequences into target sequences, such that there is an interruption of contiguous target sequence with the adaptors. By sequencing both “upstream” and “downstream” of the adaptors, identification of entire target sequences may be accomplished.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
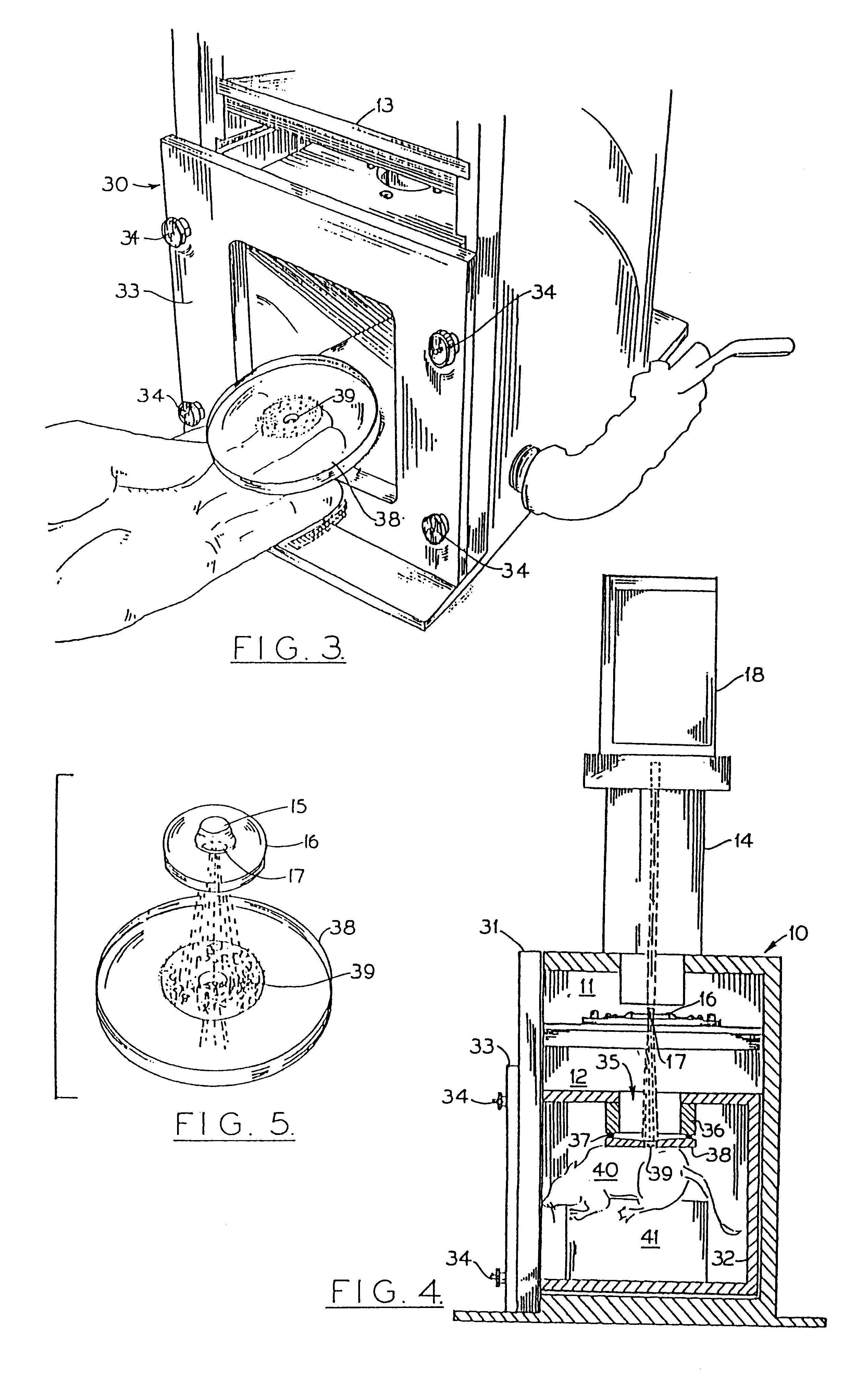
Particle-mediated bombardment of DNA sequences into tissue to induce an immune response
InactiveUS6194389B1Genetic material ingredientsMicroinjection basedNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
A method of transferring a gene to vertebrate cells is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: (a) providing microprojectiles, the microprojectiles carrying polynucleic acid sequences, the sequences comprising, in the 5' to 3' direction, a regulatory sequence operable in the tissue cells and a gene positioned downstream of the regulatory sequence and under the transcriptional control thereof; and (b) accelerating the microprojectiles at the cells, with the microprojectiles contacting the cells at a speed sufficient to penetrate the cells and deposit the polynucleic acid sequences therein. Preferably, the target cells reside in situ in the animal subject when they are transformed. Preferred target cells are dermis or hypodermis cells, and preferred genes for insertion into the target cells are genes which code for proteins or peptides which produce a physiological response in the animal subject.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +2
DNA detection methods for site specific nuclease activity
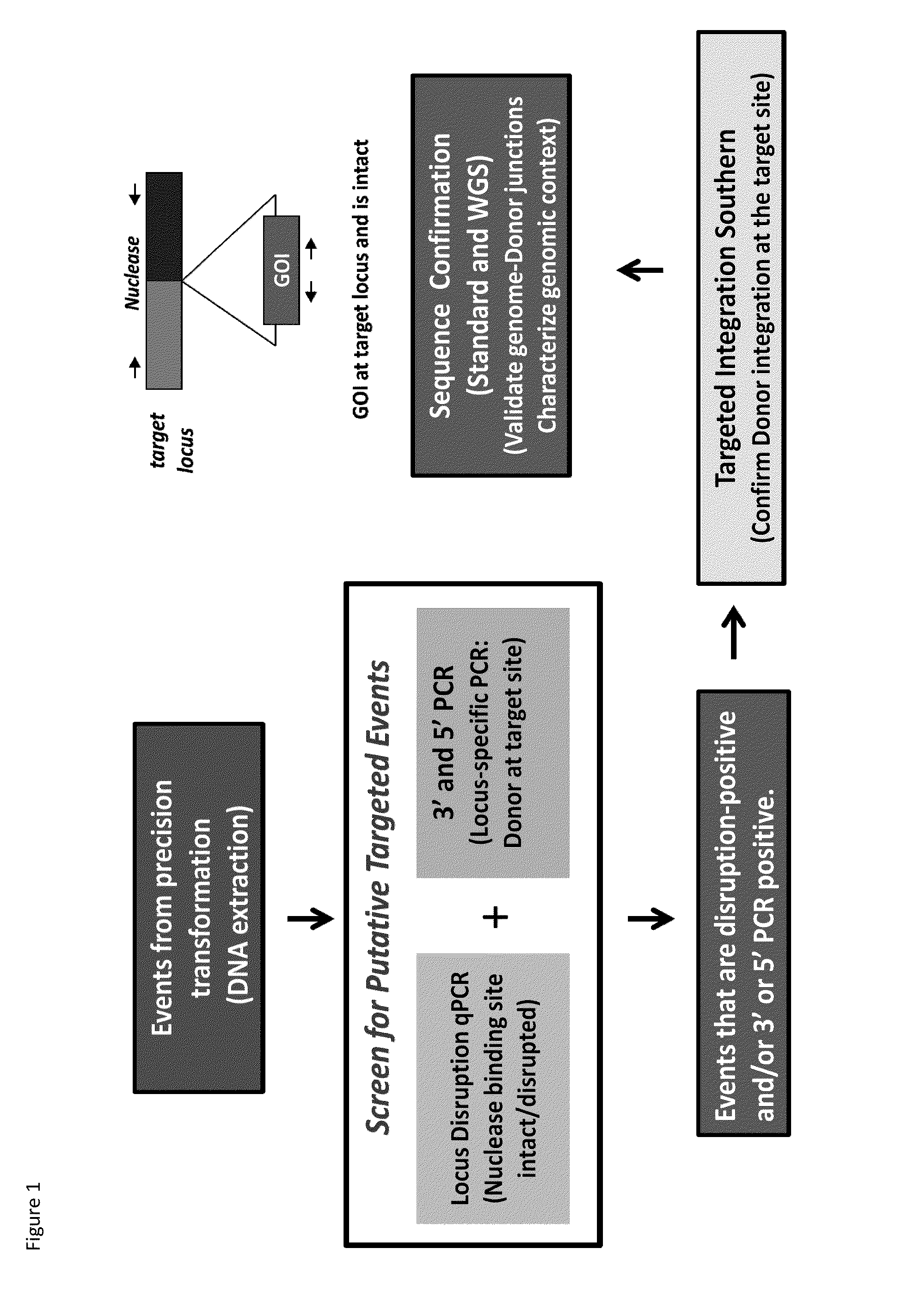
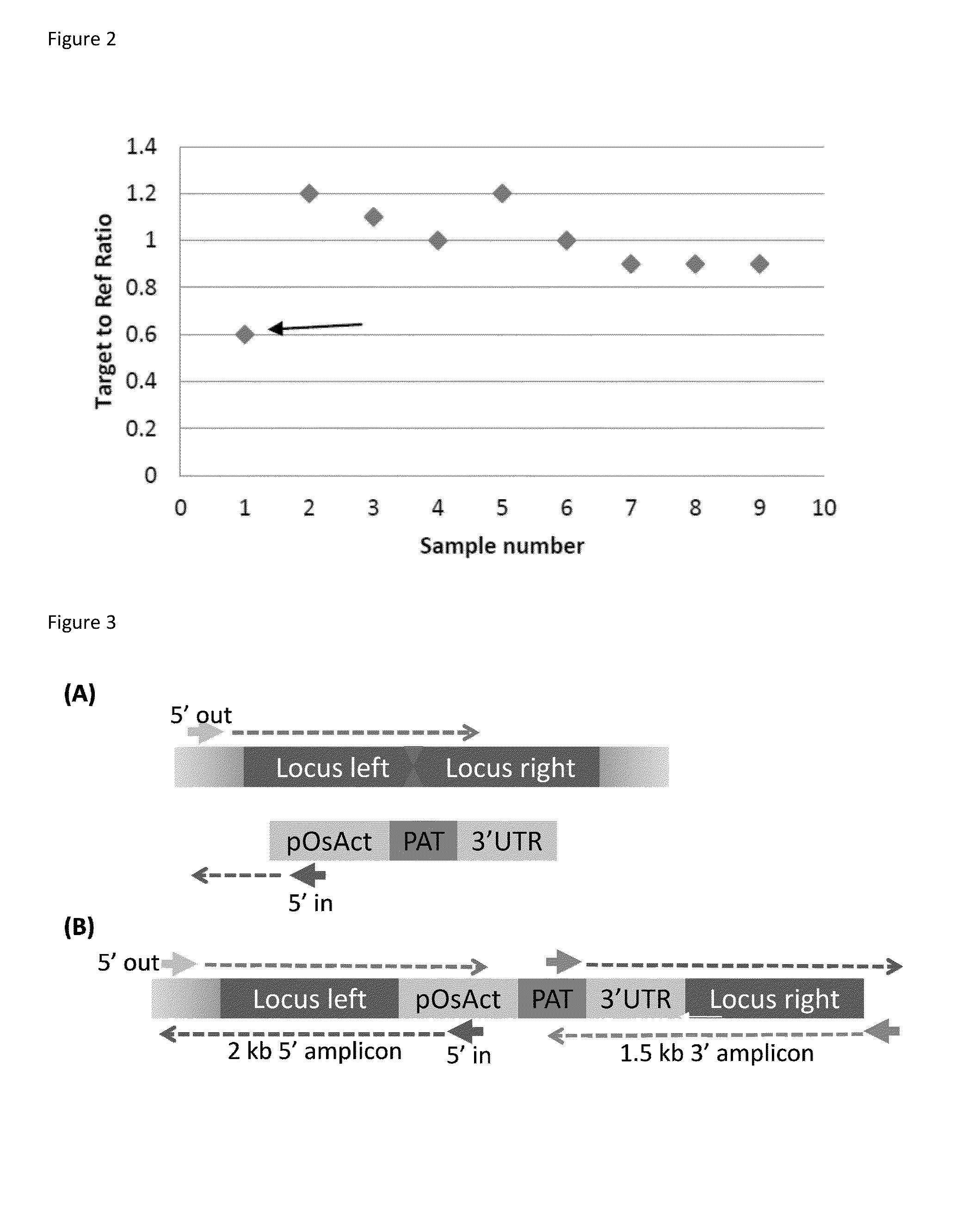
The present disclosure provides methods for detecting and identifying plant events that contain precision targeted genomic loci, and plants and plant cells comprising such targeted genomic loci. The method can be deployed as a high throughput process utilized for screening the intactness or disruption of a targeted genomic loci and optionally for detecting a donor DNA polynucleotide insertion at the targeted genomic loci. The methods are readily applicable for the identification of plant events produced via a targeting method which results from the use of a site specific nuclease.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
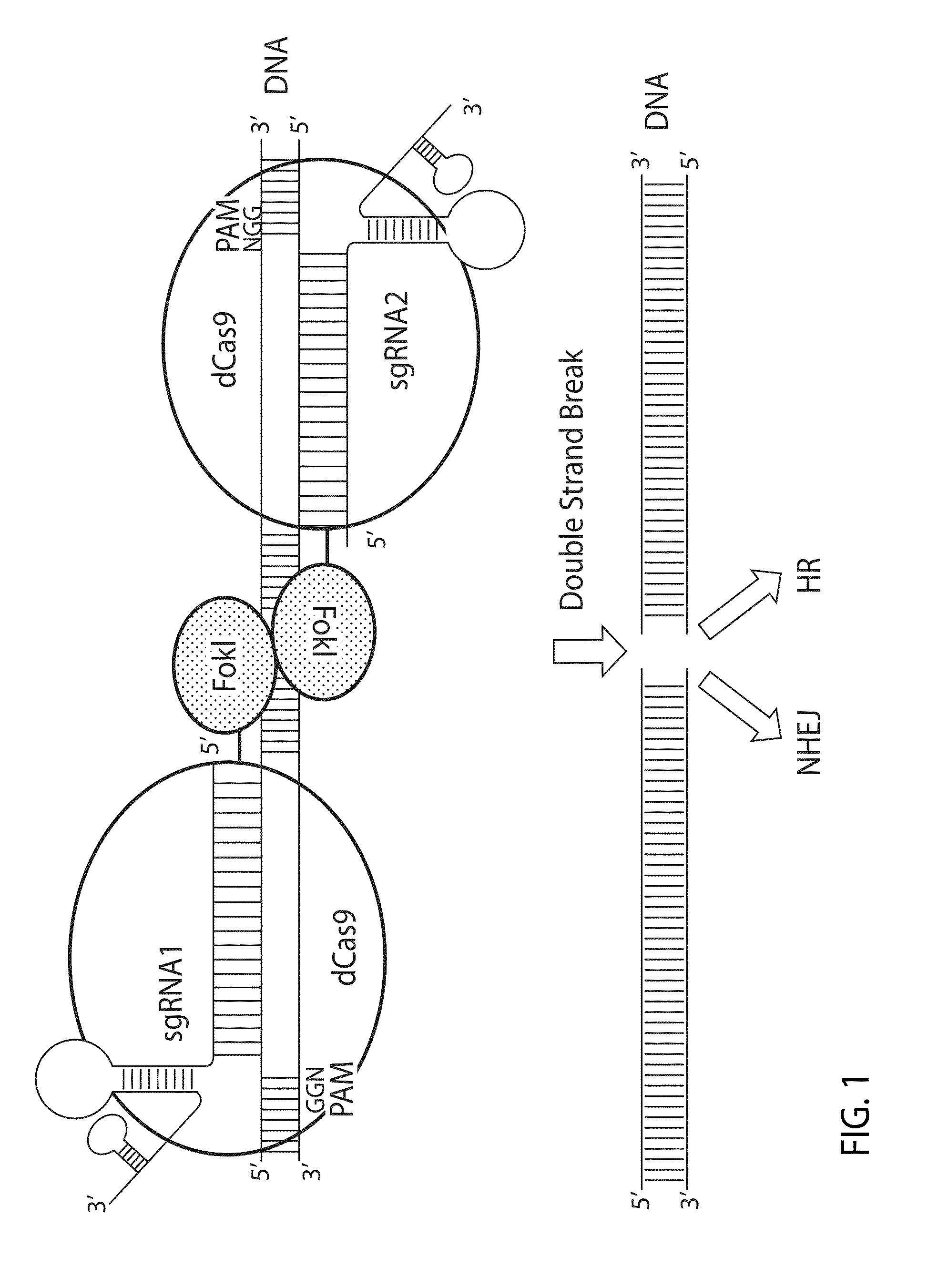
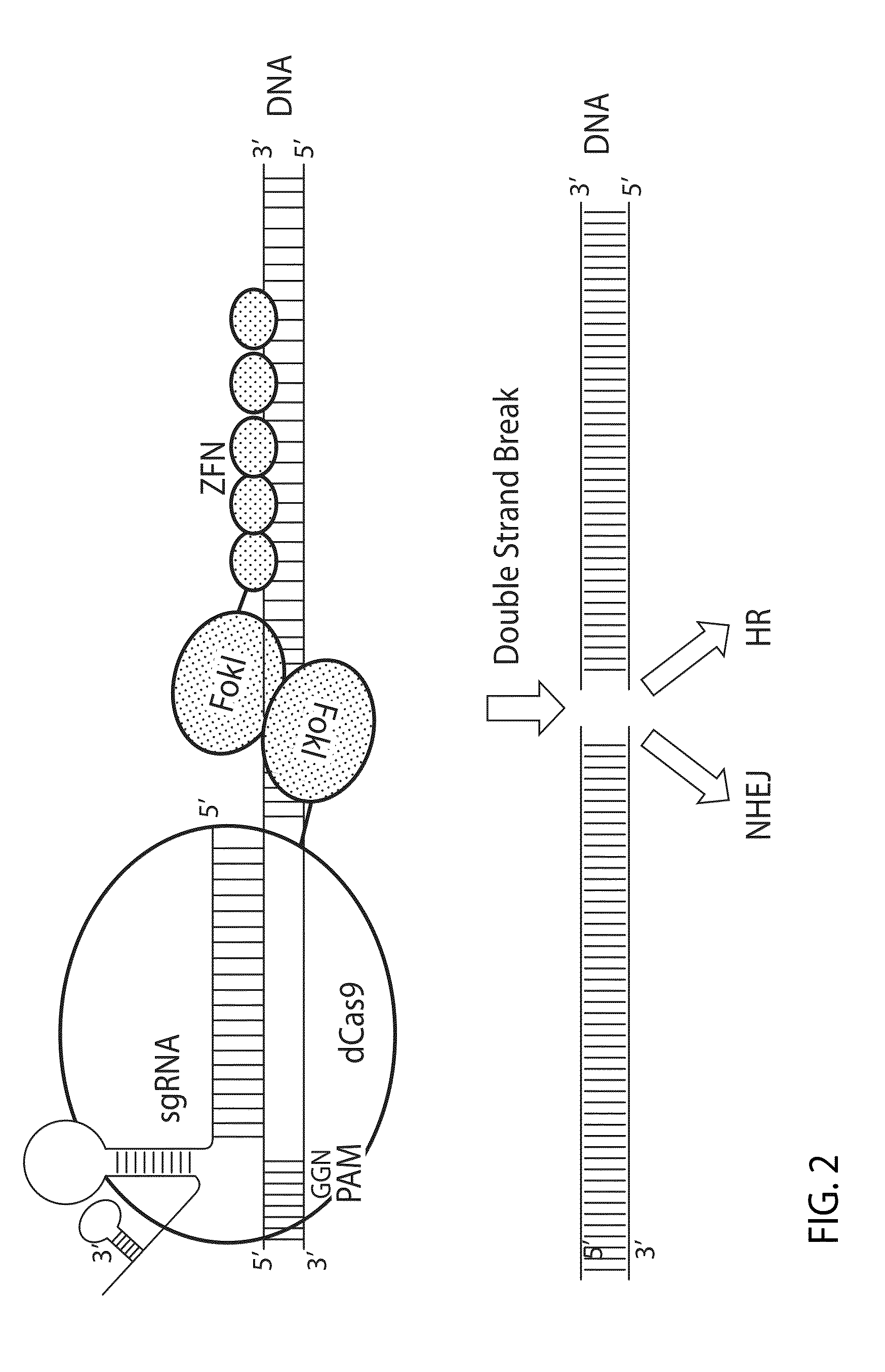
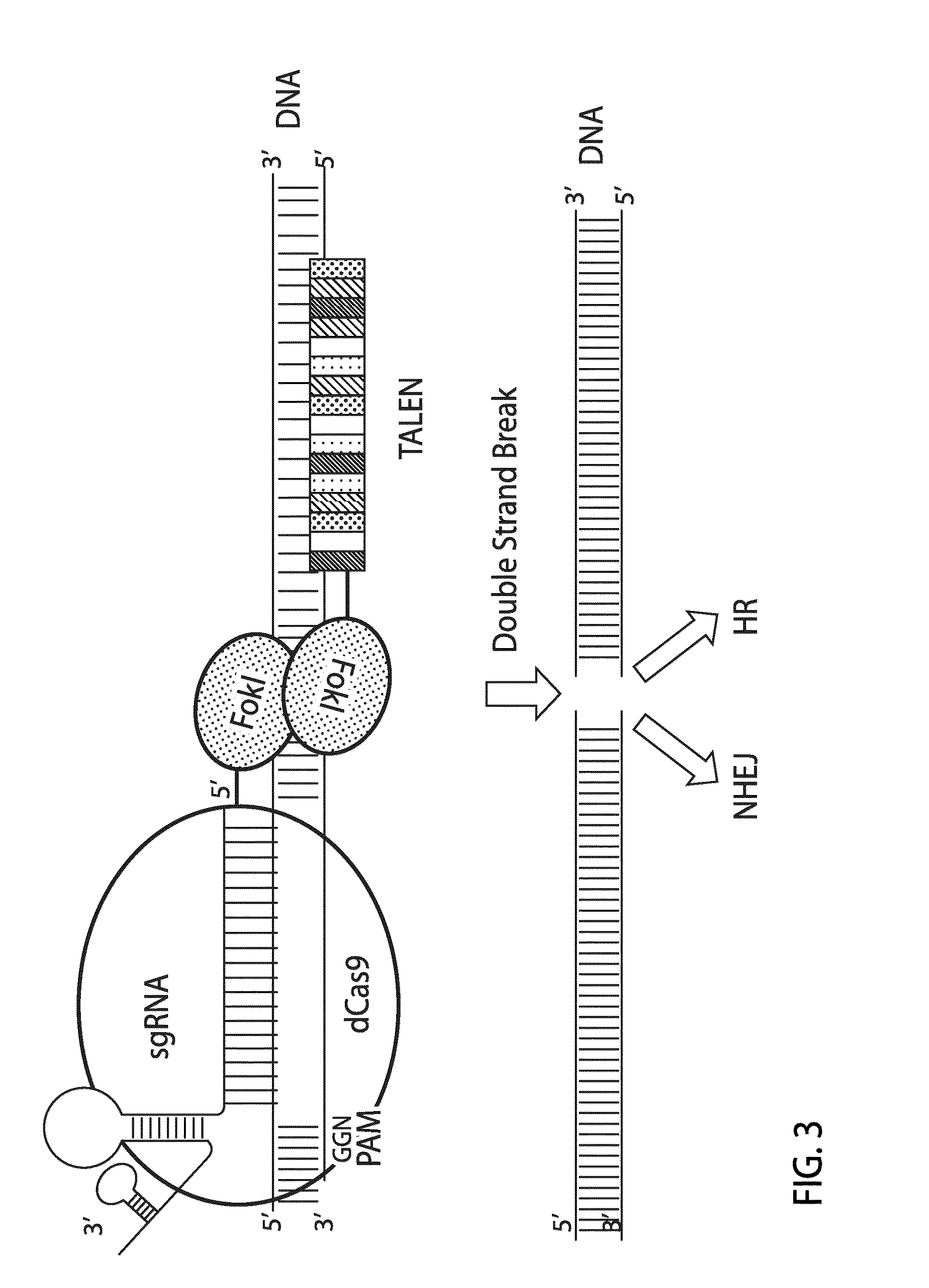
Crispr/cas system-based novel fusion protein and its applications in genome editing
An inactive CRISPR / Cas system-based fusion protein and its applications in gene editing are disclosed. More particularly, chimeric fusion proteins including an inCas fused to a DNA modifying enzyme and methods of using the chimeric fusion proteins in gene editing are disclosed. The methods can be used to induce double-strand breaks and single-strand nicks in target DNAs, to generate gene disruptions, deletions, point mutations, gene replacements, insertions, inversions and other modifications of a genomic DNA within cells and organisms.
Owner:SAGE LABS
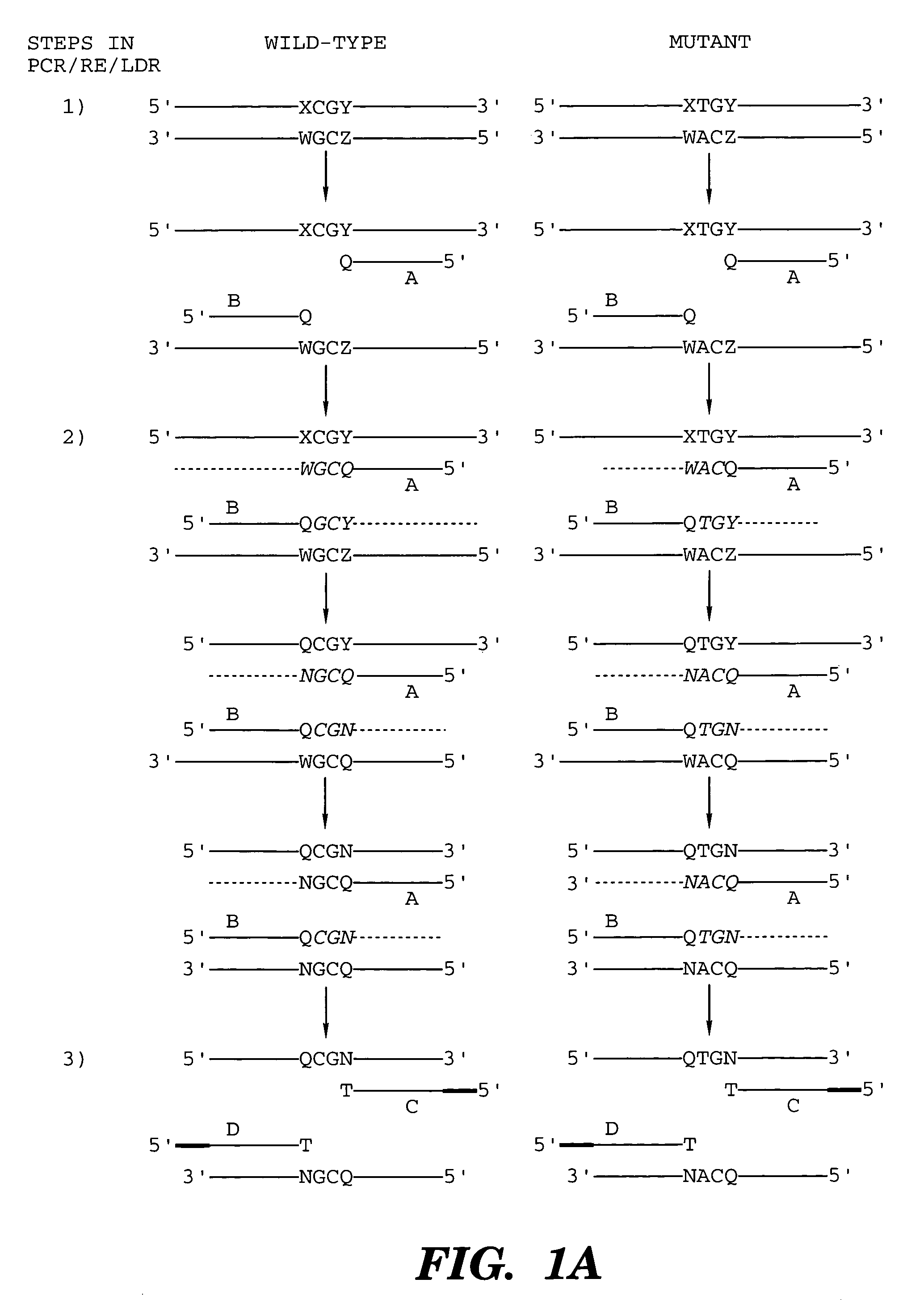
Coupled polymerase chain reaction-restriction-endonuclease digestion-ligase detection reaction process
InactiveUS7014994B1Sensitive highOptimizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideWild type
The present invention provides a method for identifying one or more low abundance sequences differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, or deletions, from a high abundance sequence in a plurality of target nucleotide sequences. The high abundance wild-type sequence is selectively removed using high fidelity polymerase chain reaction analog conversion, facilitated by optimal buffer conditions, to create a restriction endonuclease site in the high abundance wild-type gene, but not in the low abundance mutant gene. This allows for digestion of the high abundance DNA. Subsequently the low abundant mutant DNA is amplified and detected by the ligase detection reaction assay. The present invention also relates to a kit for carrying out this procedure.
Owner:LOUISIANA STATE UNIV +1
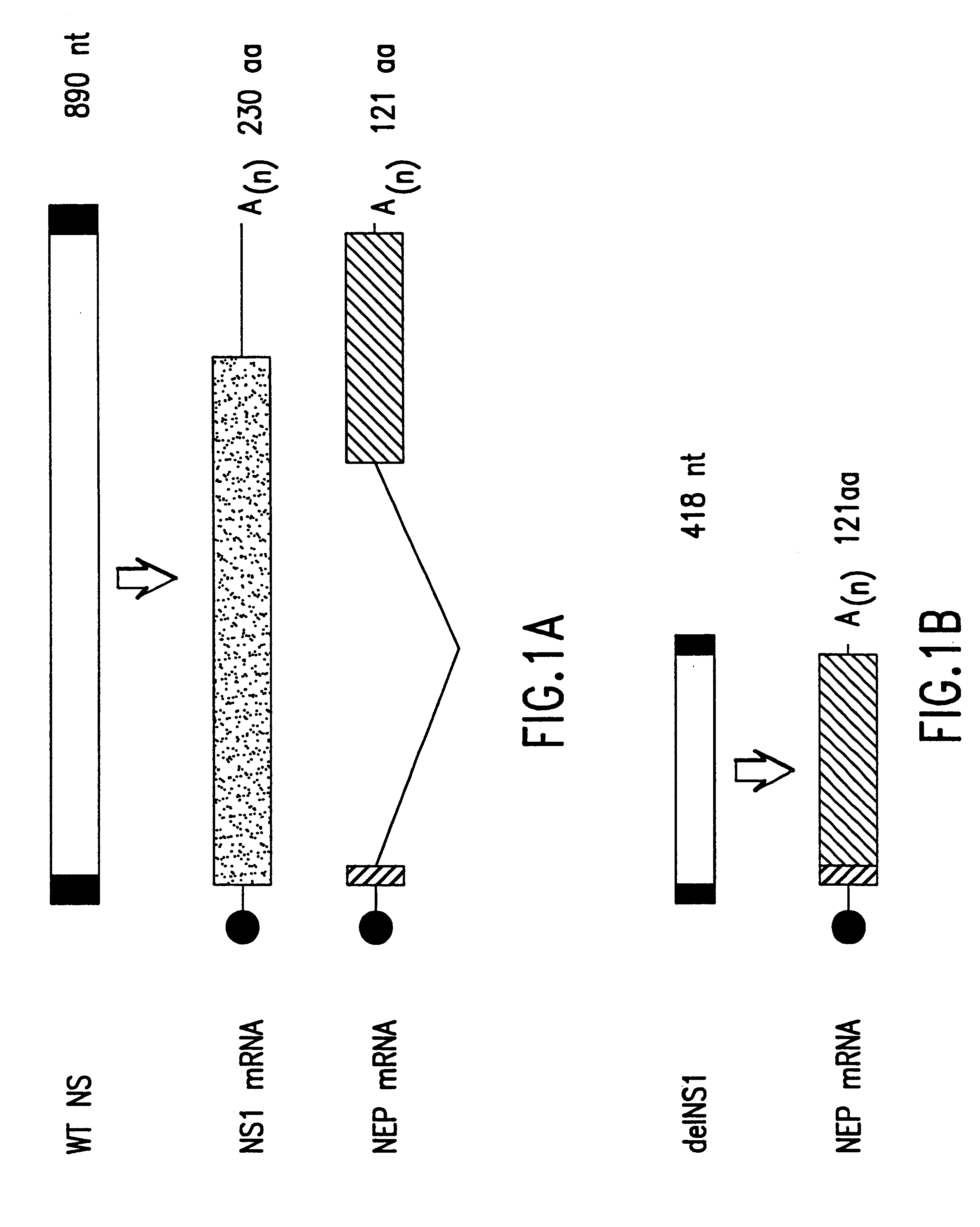
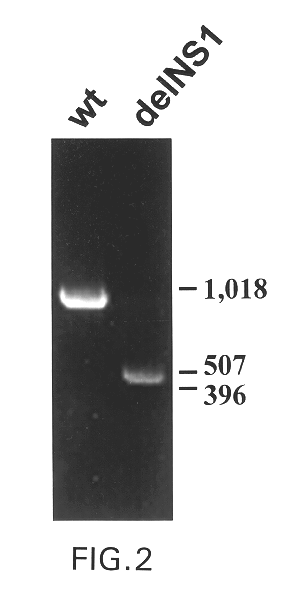
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS6468544B1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetic engineeringRecombinant DNA
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Methods for identifying target nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20050266417A1Rapid and accurate hybridizationReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSplice Site SNPTarget mrna
The present invention relates to methods for identifying target nucleic acid molecules differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, deletions, or translocations; and identifying one or more target mRNA molecules differing by one or more splice site variations in a plurality of mRNA molecules. Also disclosed is a method of generating a linearly amplified representation of a whole genome. Other aspects of the present invention relate to labeled detection oligonucleotide probes and translational oligonucleotide probes as well as to methods of designing such probes.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods for Identifying Genetic Linkage
InactiveUS20110015084A1Suppress expression of endogenousMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHomopolynucleotideNucleotide
The present invention provides a high-throughput system for determining linkage of distinct polynucleotides and determining the sequence of polynucleotides that are linked to the distinct polynucleotides. The methods are particularly useful for analyzing transgenes in a transformed host organism. The disclosed methods provide for the detection of linkage between distinct transgenic polynucleotides in transformed hosts and sequencing of DNA regions linked to the distinct transgenic polynucleotides. Methods for identifying a transgenic plant containing a transgene insertion in an undesirable genomic location are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Amplification based polymorphism detection
InactiveUS7250252B2Improve automationEasy to mergeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementImproved methodPolymorphism Detection
An improved method of amplifying nucleic acids comprising the use of four discrete temperature steps in a thermocyclic amplification reaction, as well as, a method of detecting large nucleic acid insertions or deletions such as those that occur from gene duplication or deletion.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
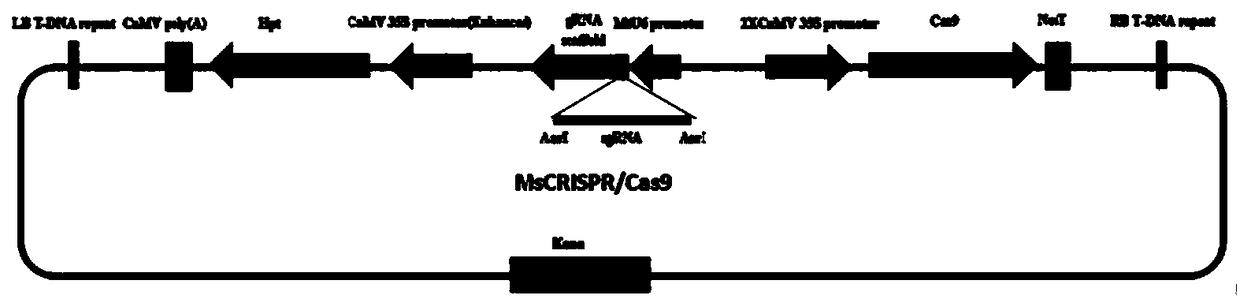
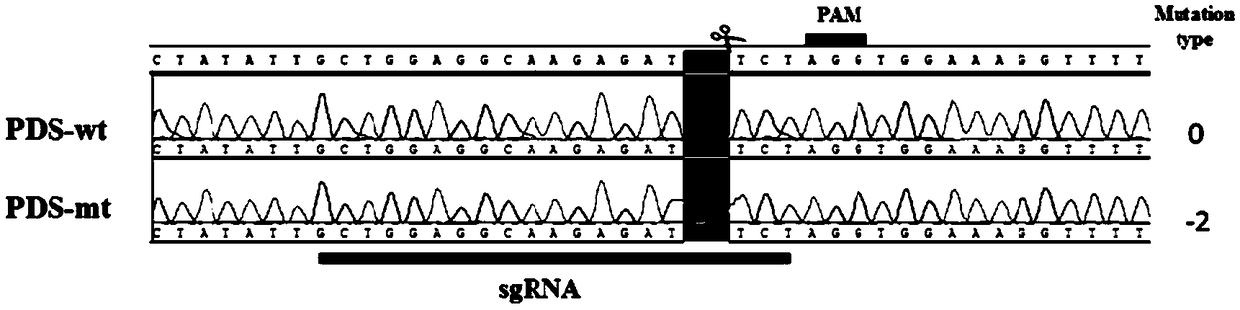
Method for site-specific mutagenesis of medicago sativa gene by employing CRISPR/Cas9 system
ActiveCN108866093AHigh Species EfficiencyEasy to breedHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorMutagenic ProcessSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention discloses a method for site-specific mutagenesis of medicago sativa genes by employing a CRISPR / Cas9 system. First of all, a binary expression vector MsCRISPR / Cas9 is constructed; the vector is designed and constructed for a target gene; then, agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation is used to achieve site-specific mutagenesis of a specific gene, and a mutant transformed plant with the target gene knocked out is obtained by screening; the method uses the CRISPR / Cas9 technology for cross-pollination autotetraploid plant medicago sativa for the first time, and obtains a mutant plant; a MtU6 promoter is used for the first time to initiate sgRNA transcription in the medicago sativa, thereby improving the transcription efficiency; the mutation rate can reach 52%; the method realizes direct mutation on the coding sequence of the gene, and opens up a new field for gene editing in the medicago sativa, laying a technical foundation for simultaneous silencing of a plurality of genes, deletion of large chromosome fragments, precise insertion of foreign genes into targets, gene regulation and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG SANJIE HERBAGE BIOTECH CO LTD
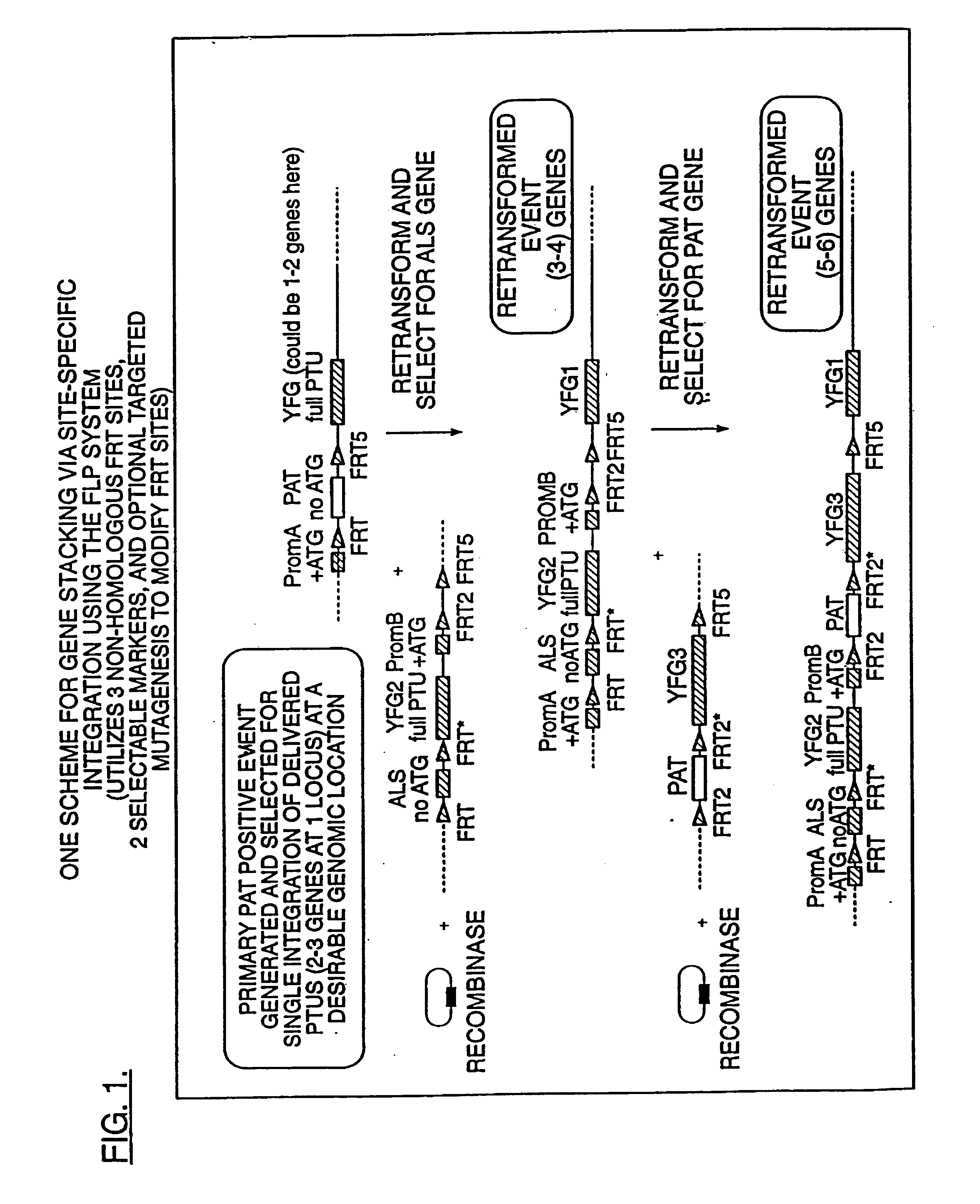
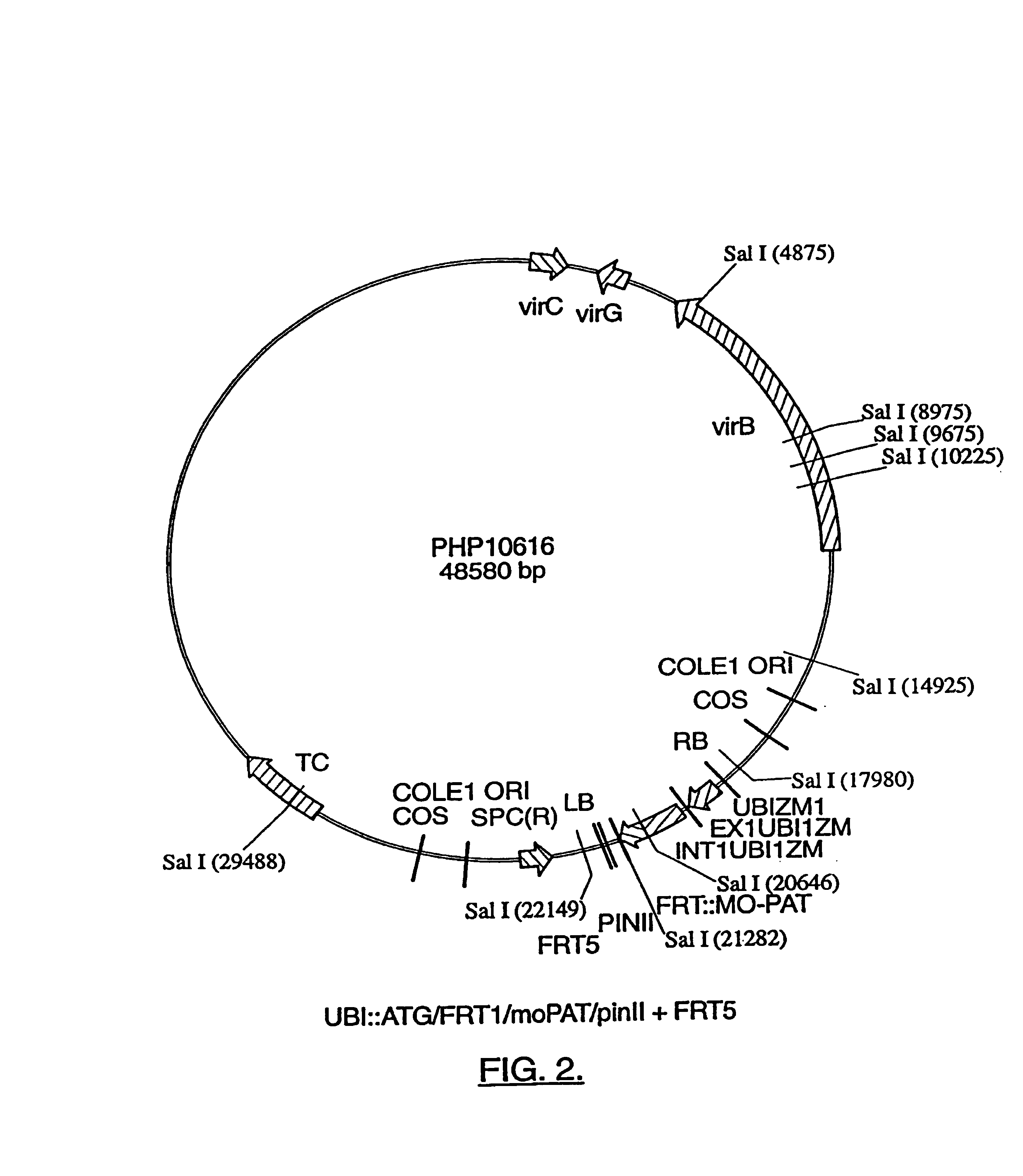
Compositions and methods for the targeted insertion of a nucleotide sequence of interest into the genome of a plant
InactiveUS7102055B1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsStable introduction of DNANucleotide sequencingRecombinase
Methods for the targeted integration of nucleotide sequences into a plant are provided. Transfer cassettes comprising nucleotide sequences of interest flanked by non-identical recombination sites are used to transform a plant comprising a target site. The target site contains at least a set of non-identical recombination sites corresponding to those on the transfer cassette. Exchange of the nucleotide sequences flanked by the recombination sites is effected by a recombinase.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
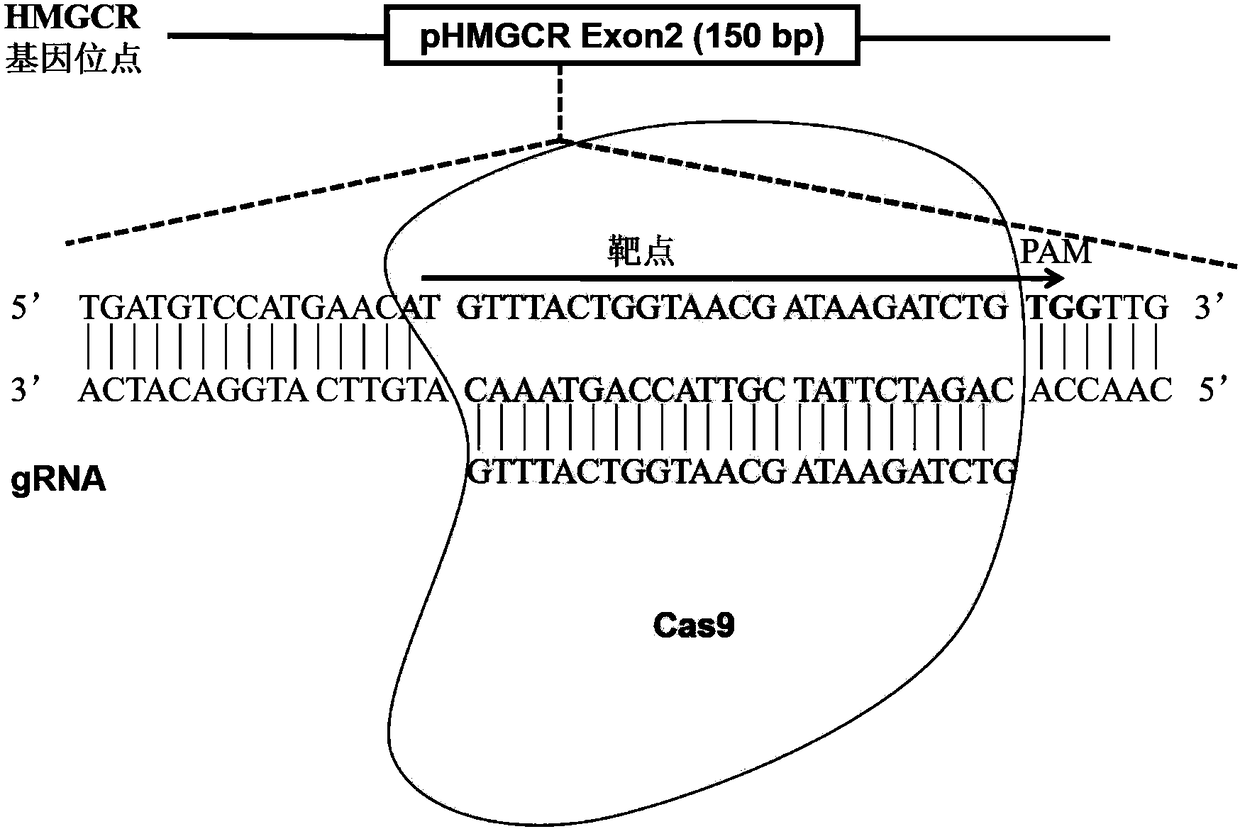
Method for achieving HMGCR gene knockout based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology
The invention relates to a method for achieving HMGCR gene knockout based on the CRISPR / Cas9 technology. The method is characterized in that two CRISPR / Cas9 target sequence aiming at the HMGCR gene isdesigned, a gRNA single chain is synthesized in vitro, annealing is performed to obtain two gRNA double-chain DNA target insertion fragments, the insertion fragments are inserted into PX459 (pSpCas9(BB)-2A-Puro)V2.0 vectors to obtain the two different-locus plasmids of the target HMGCR gene; the two plasmids are transfected into PK15 cells, puromycin is used to process the cells, the processed cell genome DNA is extracted to perform PCR amplification, the PCR product is denatured, annealing is performed, and then T7E1 is used to perform HMGCR gene knockout identification. The method has the advantages that method can be used for analyzing the expression conditions of sequence and mRNA after the HMGCR gene knockout, whether an off-target phenomenon exists or not can be verified by using amethod combining PCR and T7E1 enzyme treatment, and accordingly the specificity based on target sequence HMGCR-gRNA can be determined; the method is applicable to cell and animal models to achieve fixed-point HMGCR gene knockout, has a reference value to the knockout of other genes, and is good in effect, simple, economical, short in time and the like.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Methods, systems, and reagents for direct RNA sequencing
ActiveUS20170159033A1Improve polymerase performanceDesirable propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAmino acid substitutionPolymerase L
Provided are compositions comprising recombinant polymerases that include amino acid substitutions, insertions, deletions, and / or exogenous features that confer modified properties upon the polymerase for sequencing RNA or RNA / DNA templates. Polymerases that topologically encircle the template nucleic acid are provided. Also provided are methods of using such polymerases to make a DNA or to sequence a template comprising RNA.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
High efficiency gene targeting in plants
The present invention provides a method for the targeted insertion of a nucleotide of interest into a specific chromosomal site within a plant cell. The method comprises the steps of: (a) providing a plant cell, the plant cell optionally but preferably having a heterologous target site on a chromosome thereof, wherein said target site is flanked by at least one recombination site; and then (b) transforming said plant cell with a transformation vector (e.g., with an Agrobacterium transformation vector) carrying a nucleotide sequence of interest, wherein said nucleotide sequence of interest is flanked by at least one recombination site that corresponds to the recombination sites of said target site, so that said nucleotide of interest is inserted into said chromosome at said target site (when a target site is employed).
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
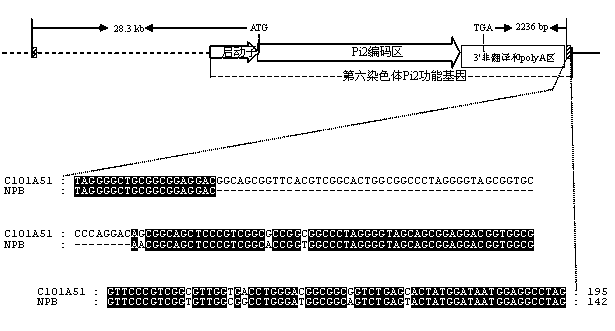
Functional molecular marker for rice anti-blast gene Pi9 and application thereof
ActiveCN103146695AImprove breeding efficiencyImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a functional molecular marker for rice anti-blast gene Pi9 and application thereof, belonging to the field of crop molecular genetic breeding science. The invention finds out that the rice anti-blast gene Pi9 has a 10bp insertion / deletion site positioned between the gene promoter -516 and -517, wherein the nucleotide sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1; and on such basis, the invention develops a method of the functional molecular marker for gene Pi9. By detecting the functional molecular marker, the invention can accurately detect whether genomes of different rice species contain the Pi9 functional gene and detect the homozygotic state, and can be used for screening rice hybrid transformed descendant plants to enhance the breeding efficiency of the rice anti-blast material, thereby effectively controlling the size of the breeding population, obviously saving the breeding and screening cost and obtaining the anti-blast rice species containing the Pi9 functional gene.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
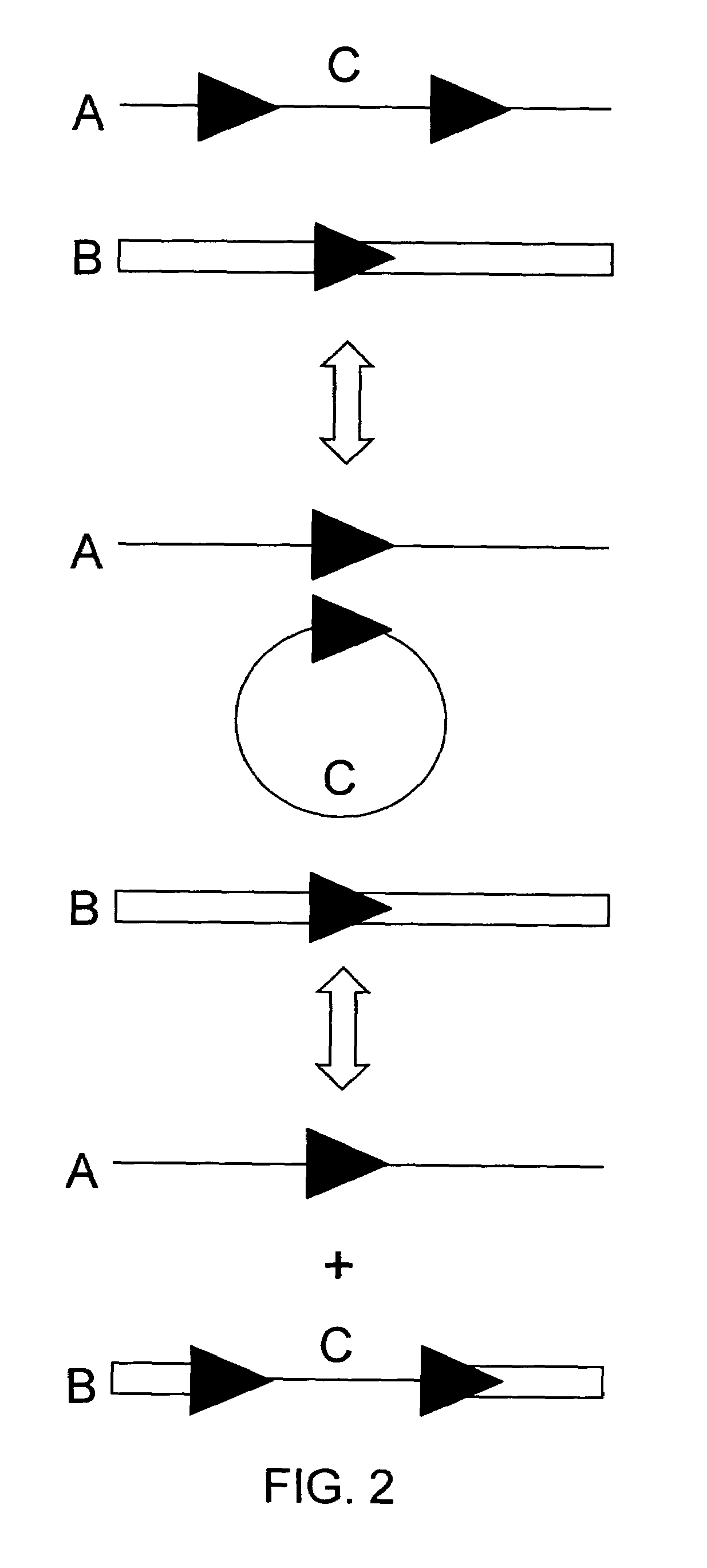
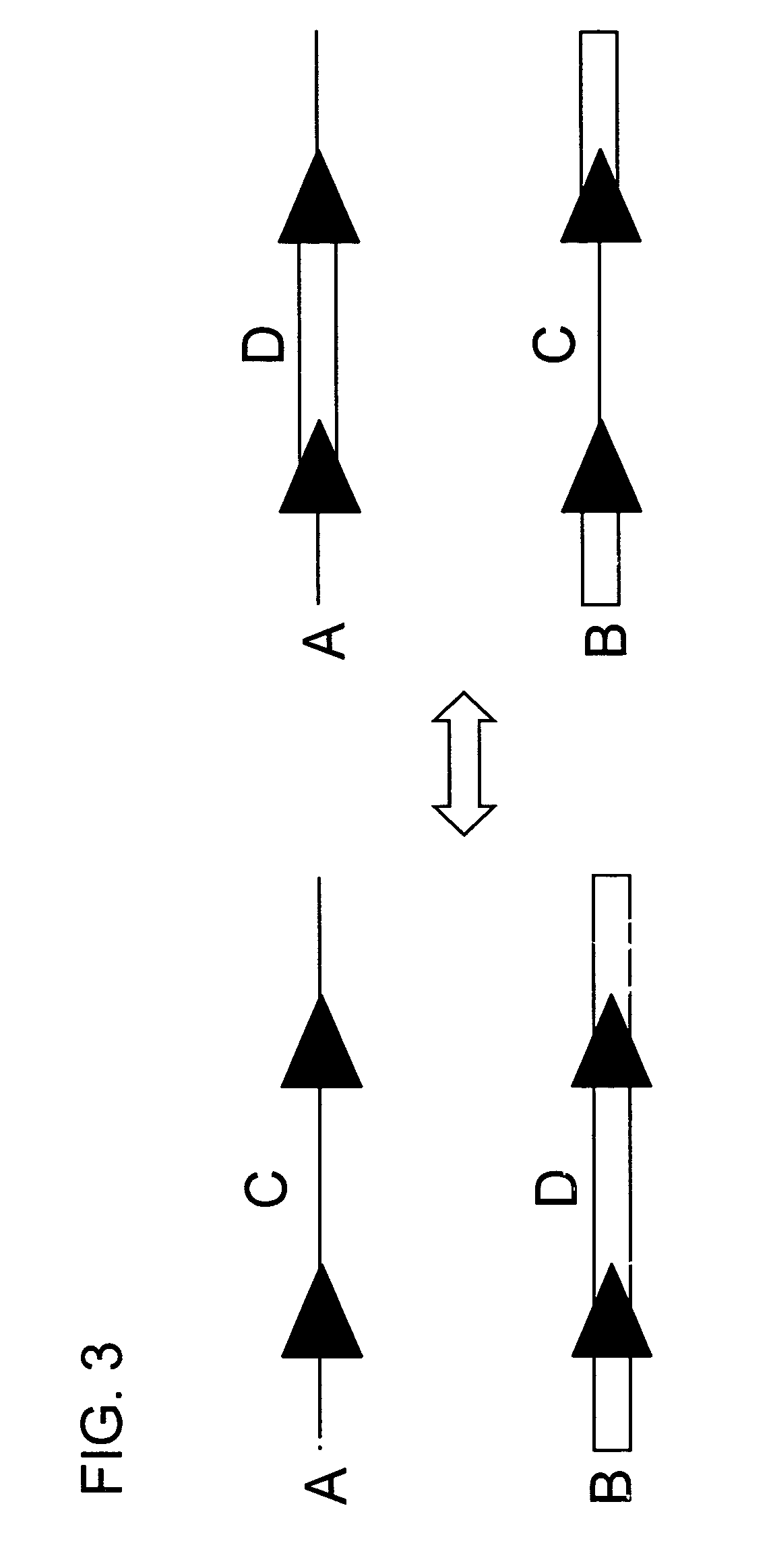
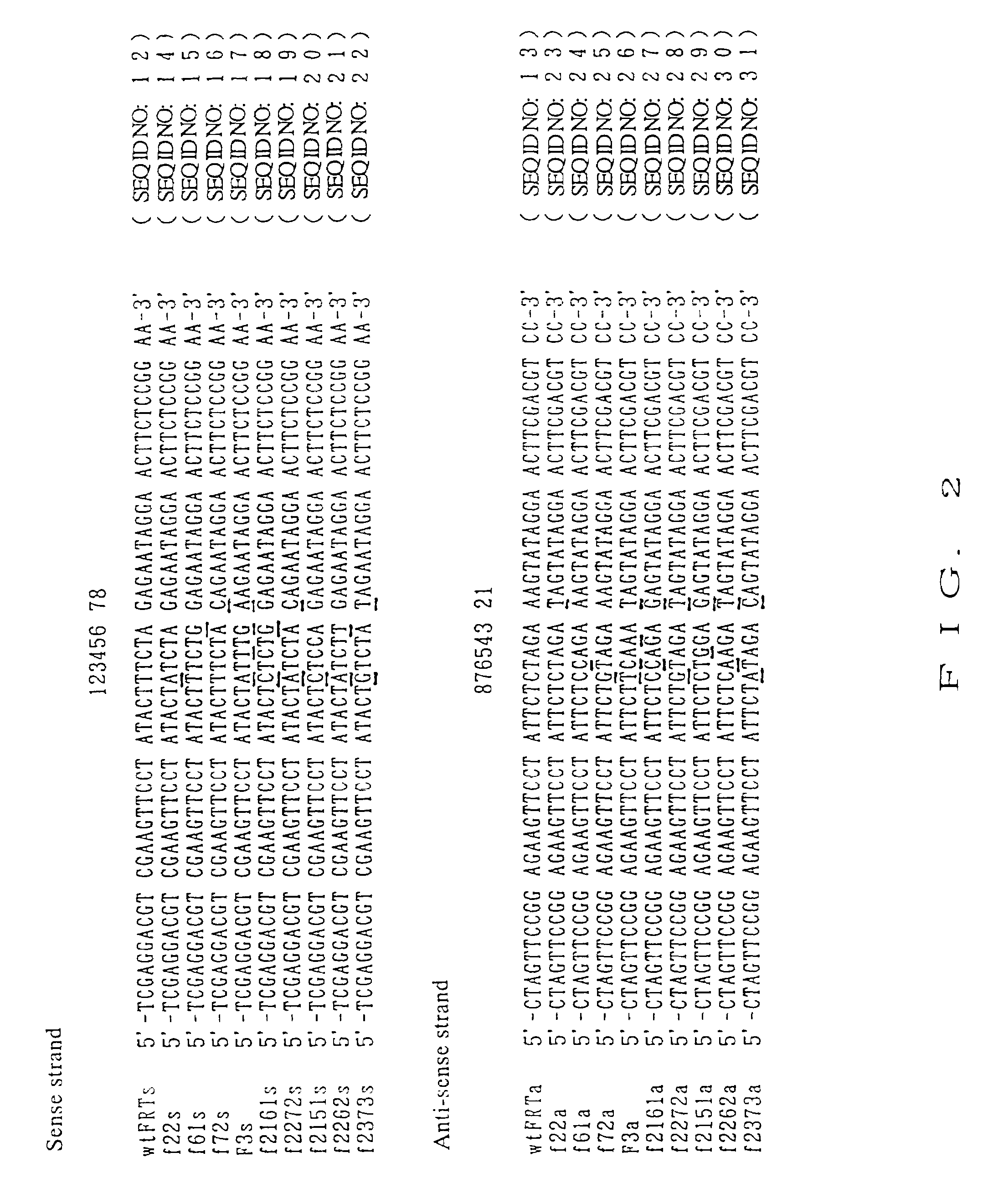
DNA containing variant FRT sequences
To provide DNA comprising mutant FRT sequence which causes recombination reaction between two mutant FRT sequences having an identical sequence to each other but does not cause recombination reaction with a wild-type FRT sequence, in the presence of FLP recombinase; and a method for performing high-efficiency, gene insertion or gene replacement. A DNA comprising a mutant FRT sequence. A DNA comprising a mutant FRT sequence possessing (A) causing no specific DNA recombination reaction with wild type FRT, even if FLP recombinase is present, and (B) causing specific DNA recombination reaction with another mutant FRT sequence having an identical sequence thereto in the presence of recombinase FLP; gene replacement method using the DNA in the presence of recombinase FLP; and a specific DNA recombination method, characterized in that a specific DNA recombination reaction is carried out by using two mutant FRT sequences in the presence of recombinase FLP.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD +1
Methods and combinations for gene targeting by homologous recombination
InactiveUS20050118648A1Microbiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAA-DNAInsertion sequence
The invention provides methods and compositions for inserting a DNA sequence in the genome of a cell by homologous recombination. In particular, the method utilizes a selection scheme in which a selection marker gene that encodes a fluorescence protein, such as a green fluorescence protein, is used for selection against random, non homologous insertions.
Owner:FUNCTIONAL GENETICS
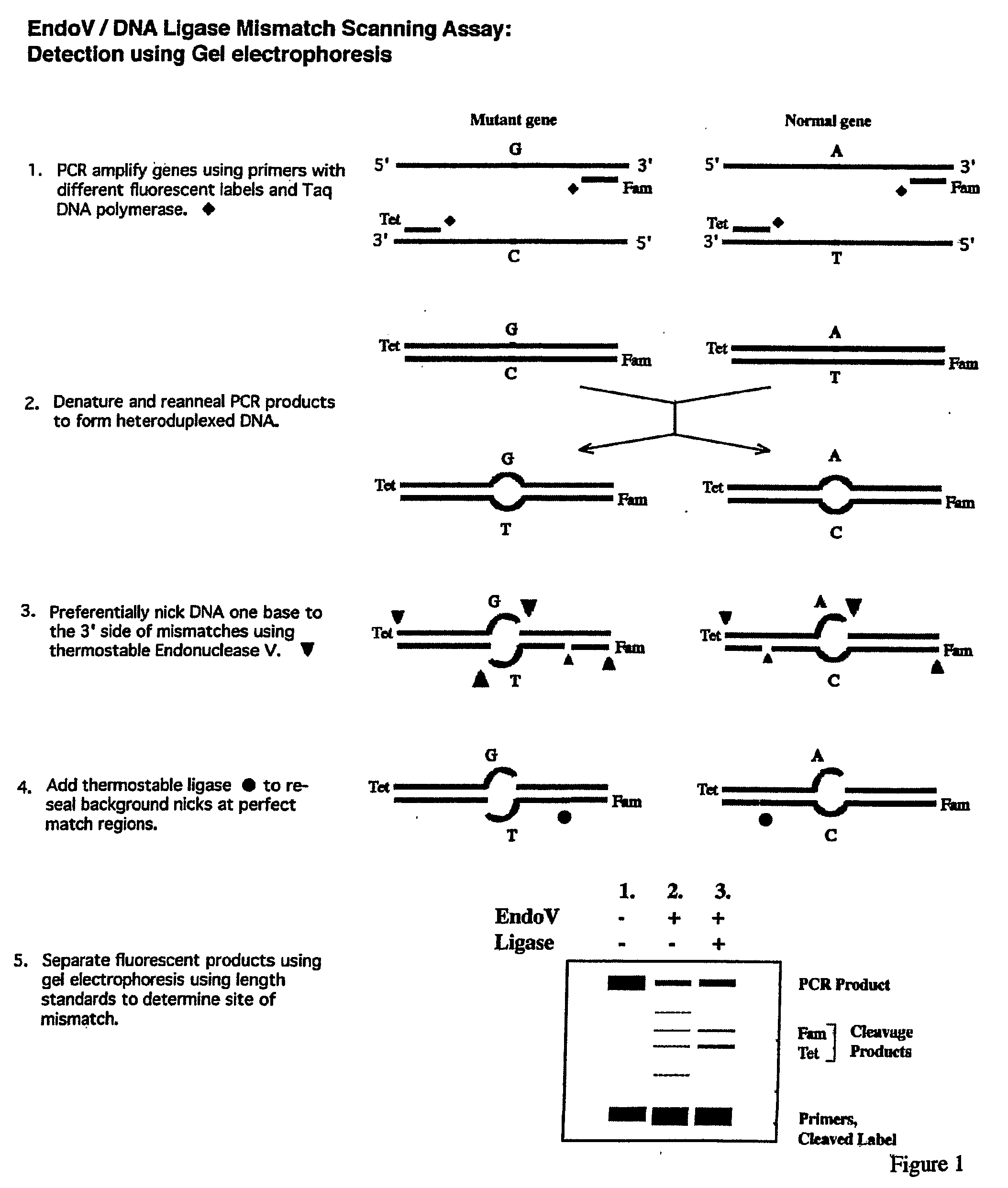
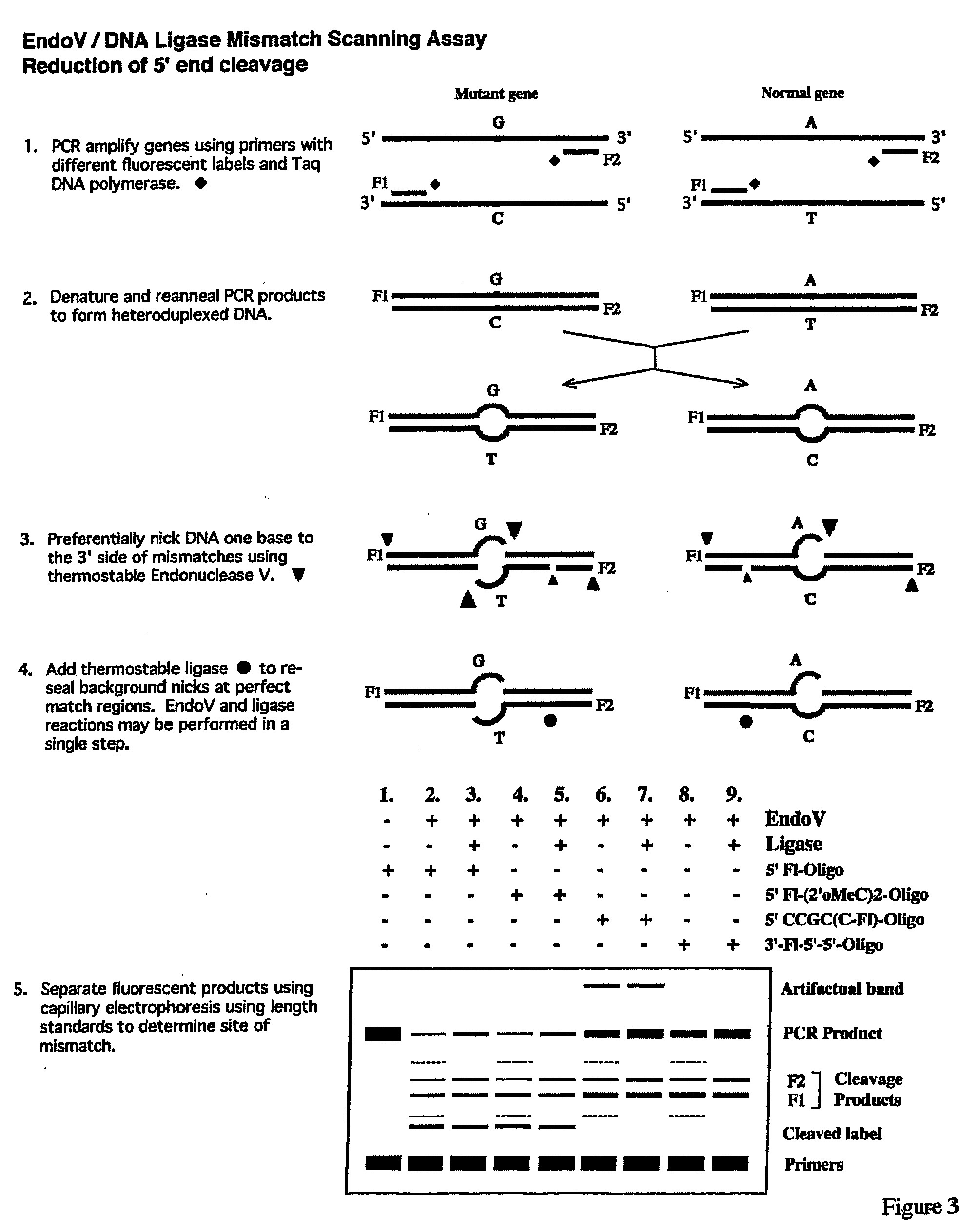
Detection of nucleic acid differences using endonuclease cleavage/ligase resealing reactions and capillary electrophoresis or microarrays
InactiveUS20090123913A1Reduce noiseObstruction is producedMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeteroduplexA-DNA
The present invention is directed to various methods for detecting DNA sequence differences, including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and, to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Test probes, common oligonucleotide chips, nucleic acid detection method, and their uses
ActiveUS8501459B2Strong specificityHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRe sequencingPathogenic microorganism
High-throughput detection for the interesting base or the mutation site in the nucleic acid sample can be achieved by means of the linear test probe pairs P1 and P2. The test probe pairs P1 and P2 respectively comprise either of the flanking complementary sequences which are adjacent to the interesting base or the mutation site in the nucleic acid sample. The invention can be applied to the re-sequencing the target nucleic acid sequence, the detection and analysis for the mutation, insertion, or deletion sites of a known nucleic acid sequence, and the genotyping of the pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:SHANXI LIFEGEN
Molecular marker of rice-blast-resistant gene Pi2 and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN104073487AChoose a clear goalImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of crop biotechnology and in particular relates to a molecular marker of a rice-blast-resistant gene Pi2 and application of the molecular marker. The upstream and downstream molecular markers are based on specific insertion / deletion loci polymorphism of nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The two molecular markers are co-dominant molecular markers developed for close linkage regions on two sides of the functional gene Pi2, and have the advantages of being high in accuracy and capable of being widely applied to different breeding parents. By detecting the two molecular markers, whether a detected rice material has the rice-blast-resistant gene Pi2 or not can be accurately judged. By virtue of a molecular marker combination, whether a hybrid transferred progeny plant genome of a parent of the functional gene Pi2 and other parents has the functional gene Pi2 or not and the homozygous state of the functional gene Pi2 can be accurately detected, and the breeding efficiency of a rice-blast-resistant rice variety with the functional gene Pi2 is improved.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Intergenic regions as novel sites for insertion of HIV DNA sequences in the genome of modified vaccinia virus ankara
ActiveUS20060188961A1Stably express multiple HIV proteinsRaise the possibilitySsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesInsertion siteIntergenic region
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Manipulation of genes of the mevalonate and isoprenoid pathways to create novel traits in transgenic organisms
InactiveUS20050241017A1Other foreign material introduction processesIsomerasesOpen reading frameNucleotide
Disclosed are the uses of specific genes of the mevalonate and isoprenoid biosynthetic pathways, and of inactive gene sites (the pseudogene) to (1) enhance biosynthesis of isopentenyl diphosphate, dimethylallyl diphosphate and isoprenoid pathway derived products in the plastids of transgenic plants and microalgae, (2) create novel antibiotic resistant transgenic plants and microalgae, and (3) create a novel selection system and / or targeting sites for mediating the insertion of genetic material into plant and microalgae plastids. The specific polynucleotides to be used, solely or in any combination thereof, are publicly available from GeneBank and contain open reading frames having sequences that upon expression will produce active proteins with the following enzyme activities: (a) acetoacetyl CoA thiolase (EC 2.3.1.9), (b) 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) synthase (EC 4.1.3.5), (c) HMG-CoA reductase (EC 1.1.1.34), (d) mevalonate kinase (EC 2.7.1.36), (e) phosphomevalonate kinase (EC 2.7.4.2), (f) mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.33), (g) isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) isomerase (EC 5.3.3.2), and (h) phytoene synthase (EC 2.5.1.32).
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +1
Methods for detecting gene dysregulations
ActiveUS20100304390A1Microbiological testing/measurementHybridisationProtein translocationChromosomal Abnormality
Described herein are methods, compositions and kits directed to the detection of gene dysregulations such as those arising from gene fusions and / or chromosomal abnormalities, e.g. translocations, insertions, inversions and deletions. Samples containing dysregulated gene(s) of interest may show independent expression patterns for the 5′ and 3′ regions of the gene. The methods, compositions and kits are useful for detecting mutations that cause the differential expression of a 5′ portion of a target gene relative to the 3′ region of the target gene.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Novel nitrile hydratase
ActiveUS20070009985A1Impairing the enzyme's original activityImpairment of activityFungiBacteriaNovel mutationMutant
The amino acid sequence of a mutant which is obtained by introducing a novel mutation into a Pseudonocardia thermophila JCM3095-derived nitrile hydratase consisting of two types of heterogeneous subunits, and the base sequence of the gene are provided. The nitrile hydratase is modified by specifying the region to be modified in the stereostructure / amino acid sequence of the nitrile hydratase, and applying alteration such as substitution, insertion, deletion or the like, to the amino acids in the amino acid sequence which are corresponding to the amino acid residues forming the region. Also provided is a method for modifying an enzyme having a nitrile hydratase activity.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
3'-o-fluorescently modified nucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110076679A1Improve efficiencyHigh yieldAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesFluorescenceA-DNA
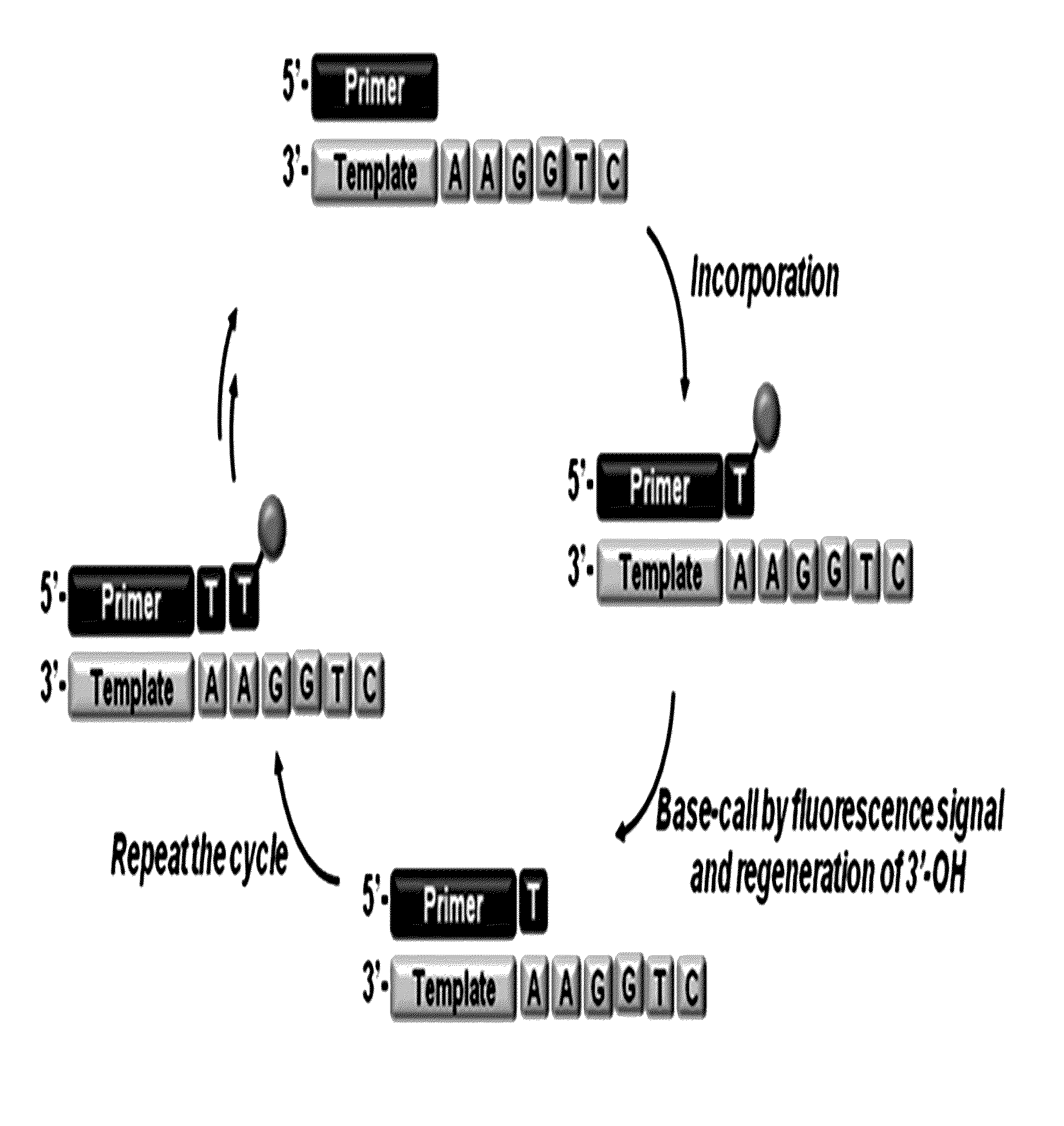
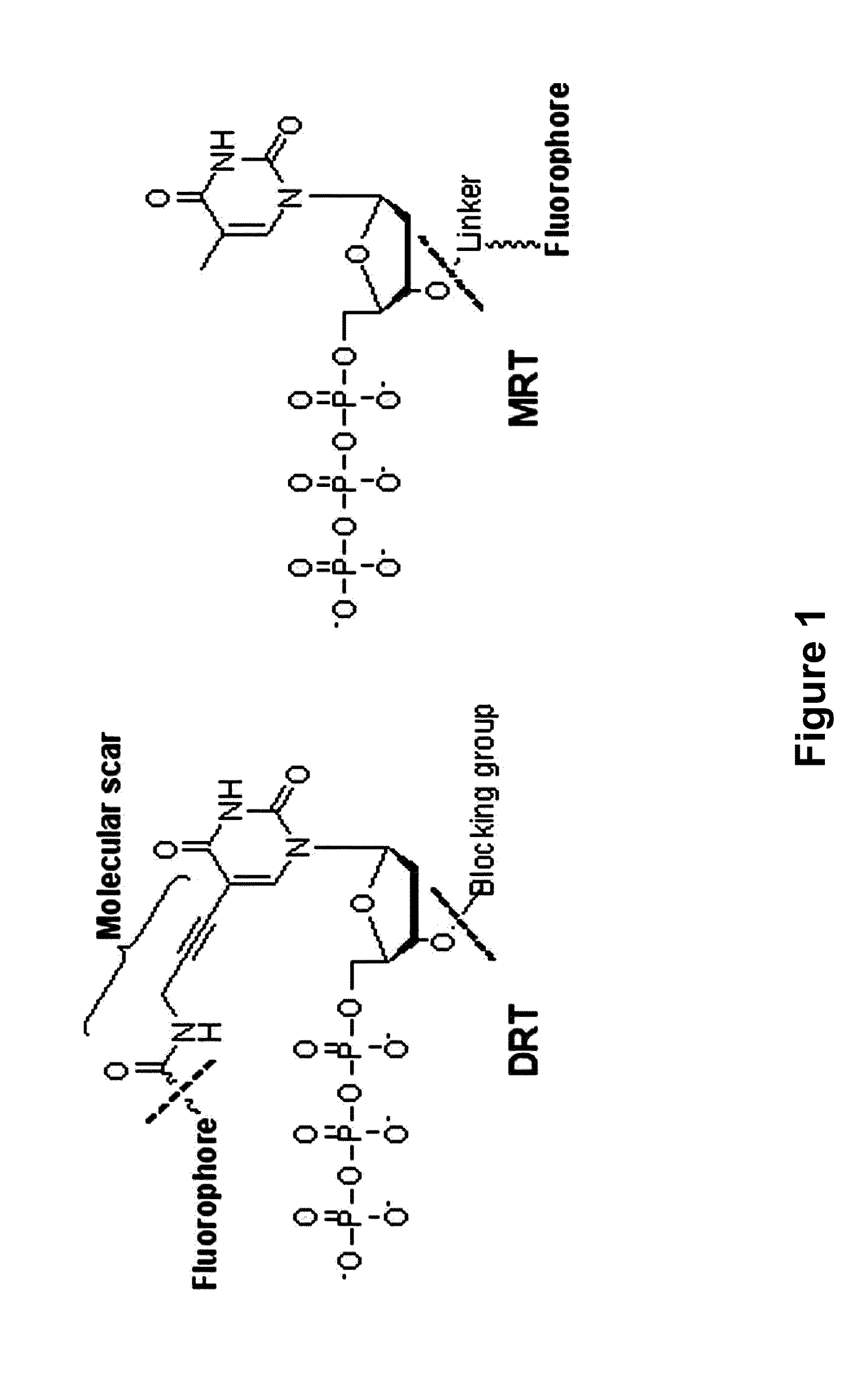
The present invention relates to a DNA sequencing method using a nucleoside triphosphate with a fluorescent blocking group on its 3′-OH end as a reversible terminator. Further, the present invention relates to sequencing-by-synthesis method using the mono-modified reversible terminator (MRT), the novel nucleotide monomer having a reversible fluorescent blocking group removable chemically or enzymatically at its 3′-OH end. The sequencing method of the present invention facilitates sequencing of bases inserted by terminating extension of a nucleotide chain by the nucleotide monomer and then detecting fluorescence signal from 3′-OH end. At this time, after analyzing the fluorescence signal, the blocking group conjugated to the 3′-OH end can be effectively removed, indicating that a free 3′-OH functional group can be successfully restored, so that the next monomer insertion is possible, making continuous sequencing possible.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Fluorescently-labeled insertion/deletion (InDel) genetic polymorphism locus composite amplification system and application thereof
ActiveCN101956005AHigh sensitivityHigh individual recognition rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseaseFluorescein
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and in particular relates to a fluorescently-labeled insertion / deletion (InDel) genetic polymorphism locus composite amplification system and application thereof. The application comprises the following steps of: selecting 35 InDel loci, designing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification primers of the 35 InDel loci, matching fluorescein labels of the PCR primers, compositely amplifying and detecting the 35 InDel loci, and the like. The system can analyze 35 InDel genetic polymorphism loci by the composite amplification. The 35 InDel loci are labeled by FAM, HEX, TAMRA and ROX fluorescein with four different colors respectively. The composite amplification system based on the invention can be made into a kit, serves as an InDel locus fluorescence composite amplification kit with Chinese characteristics, and is applied to the fields, such as triplet paternity test, doublet paternity test, grandparent and grandchild test, sibling test, individual recognition, disease diagnosis, anthropology and the like.
Owner:ACADEMY OF FORENSIC SCIENCE
Transgenic soybean event B4J8049 exogenous inserted fragment flanking sequence and applications thereof
InactiveCN105567682AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseSpecific detection
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant biology, and relates to a transgenic soybean event B4J8049 exogenous inserted fragment flanking sequence and applications thereof. The provided anti-disease transgenic soybean event B4J8049 is identified as unit point insertion through the Southern hybrid, and the right boundary flanking sequence of the exogenous fragment of the insertion site is represented by SEQ-1. The specific primers, which are designed according to the flanking sequence, are represented by the SEQ-5 and SEQ-6, and a specific PCR detection method of the anti-disease transgenic soybean event B4J8049 is established. The provided detection primer and detection method are suitable for carrying out specific detection on the anti-disease transgenic soybean event B4J8049, which comprises parent, derivation species, and products (plants, tissue, seed, and product).
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
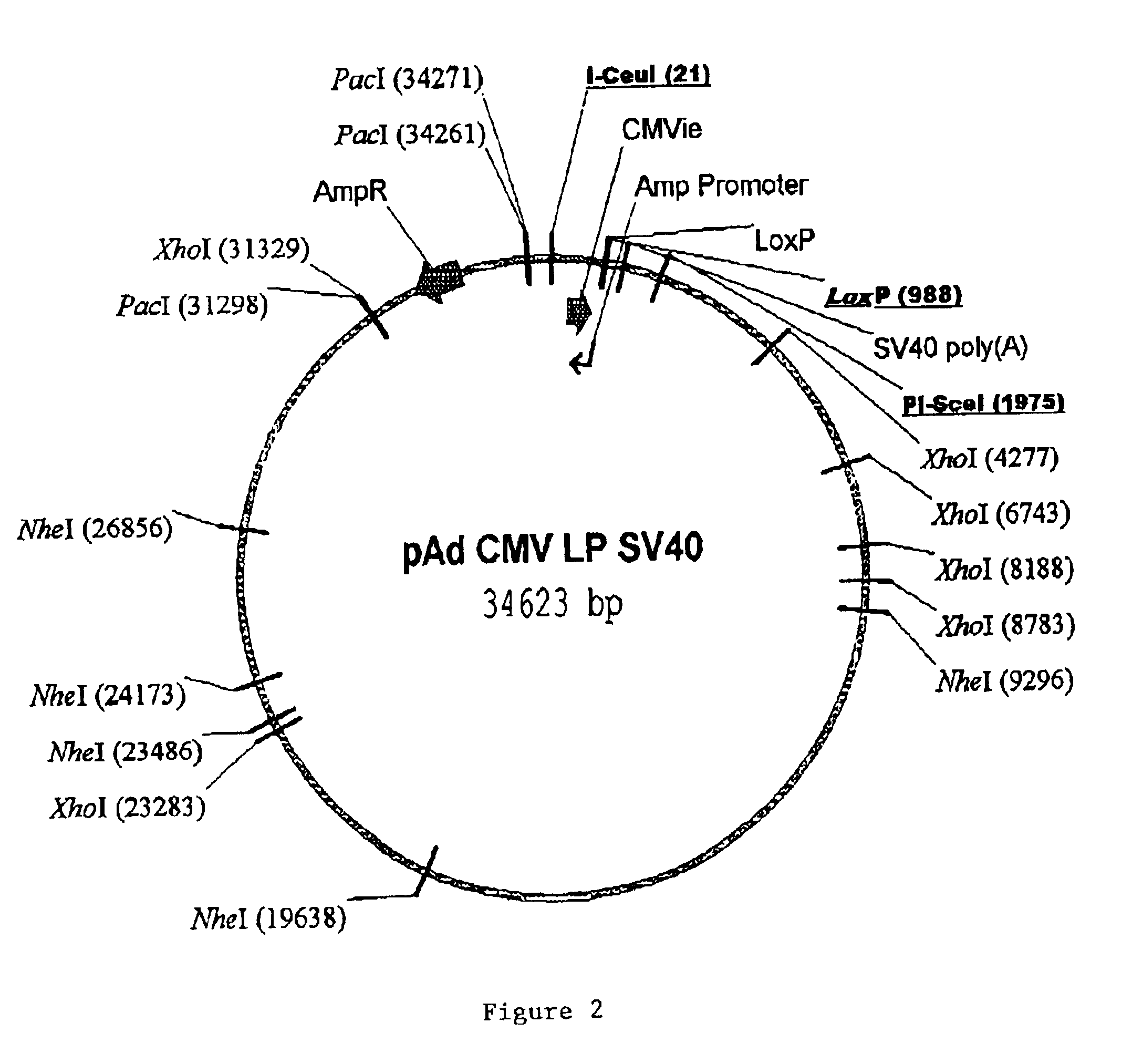
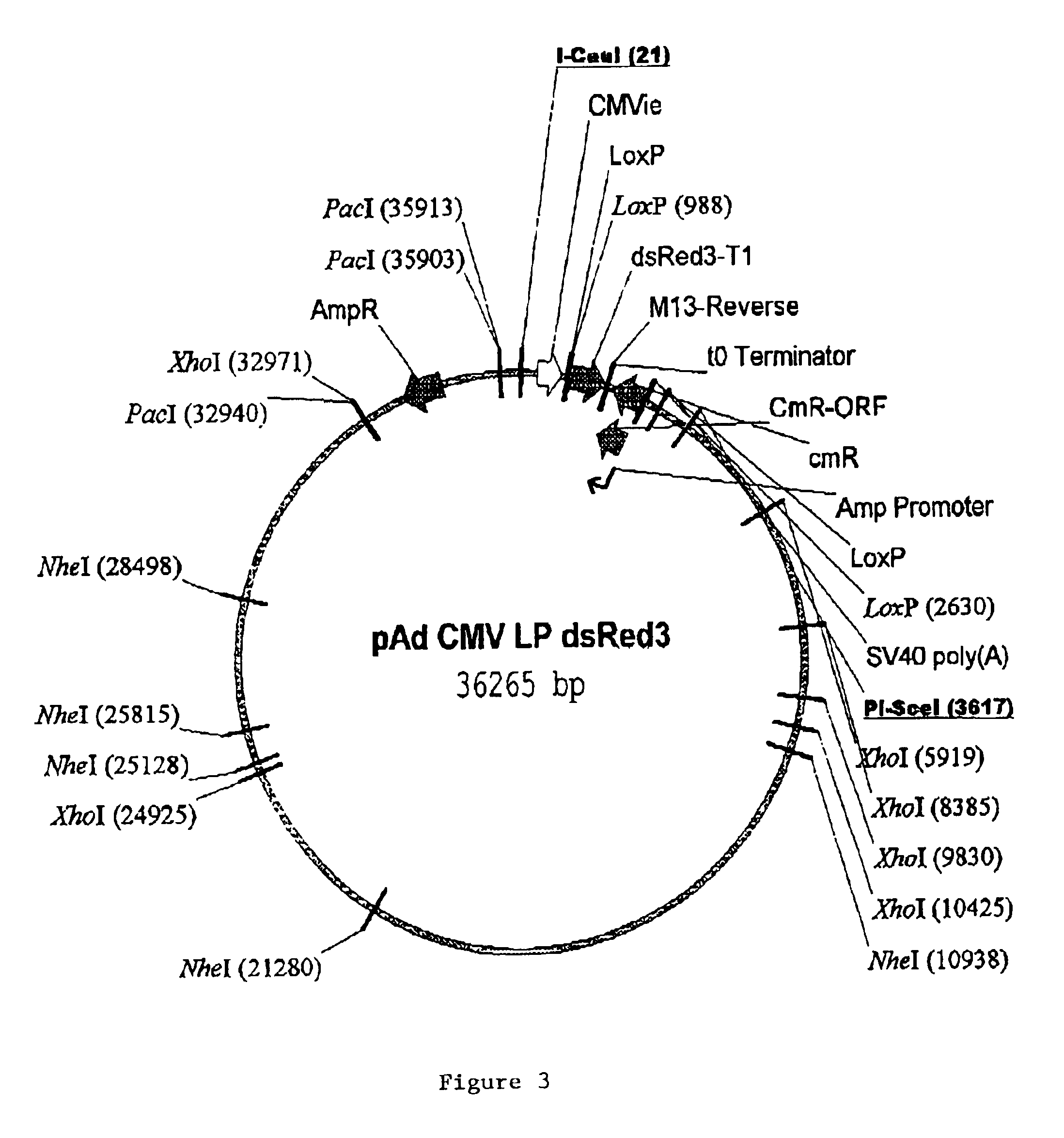
Site specific recombinase based method for producing adenoviral vectors
Site-specific recombinase based methods for making a recombinant adenoviral genome, as well as kits for practicing the same and the recombinant adenovirus vectors produced thereby, are provided. In the subject methods, the subject genomes are prepared from donor and acceptor vectors that each include at least one site recombinase recognition site, where in certain preferred embodiments, one of the donor and acceptor vectors includes a single recombinase recognition site while the other includes two recombinase recognition sites. The acceptor vector includes an adenoviral genome having an E region deletion. The donor vector includes an insertion nucleic acid. In the subject methods, the donor and acceptor vectors are combined in the presence of a recombinase to produce an adenoviral genome that includes the insertion nucleic acid. The subject adenoviral genomes find use in a variety of applications, including as vectors for use in a variety of applications.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
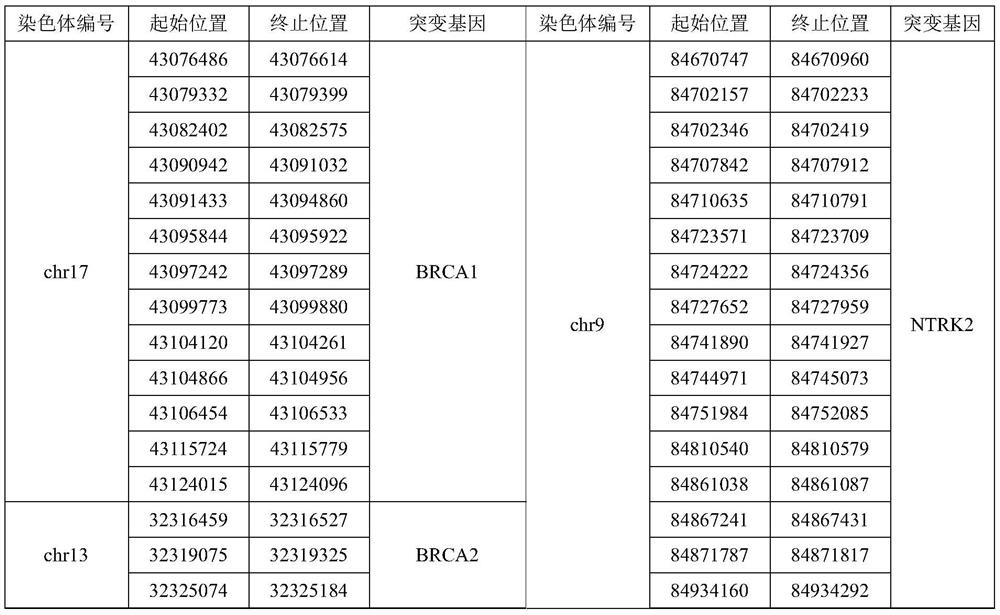
Gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, detection method used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation and application of gene panel
InactiveCN111647648AComprehensive immunotherapyComprehensive treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
The invention relates to a gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, and a detection method and application of the gene panel. The panel disclosed by the invention comprises 54419 pieces of targeted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) probes. The targeted DNA comprises the exon regions of 445 pieces of genes on the human genomes, 2573 pieces of MSI (microsatellite instability) sites and 566 position intervals used for detecting gene fusion. The detection method in the invention can be used for detecting SNV (single nucleotide variation), Indel (Insertion and Deletion), CNV (Copy Number Variation), Fusion, MSI, TMB (Tumor Mutational Burden), HLA (human leucocyte antigen) parting and the like of a tumor somatic cell multi-site DNA mutation. An optimal individual treatment medicine and scheme can be conveniently selected according to the genome features of patients in a breast cancer immunotherapy process.
Owner:北斗生命科学(广州)有限公司 +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com