Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
670 results about "Protein translocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Translocation (botany), transport of nutrients through phloem or xylem. Protein translocation, also called protein targeting, a process in protein biosynthesis. Species translocation, movement of a species, by people, from one area to another.
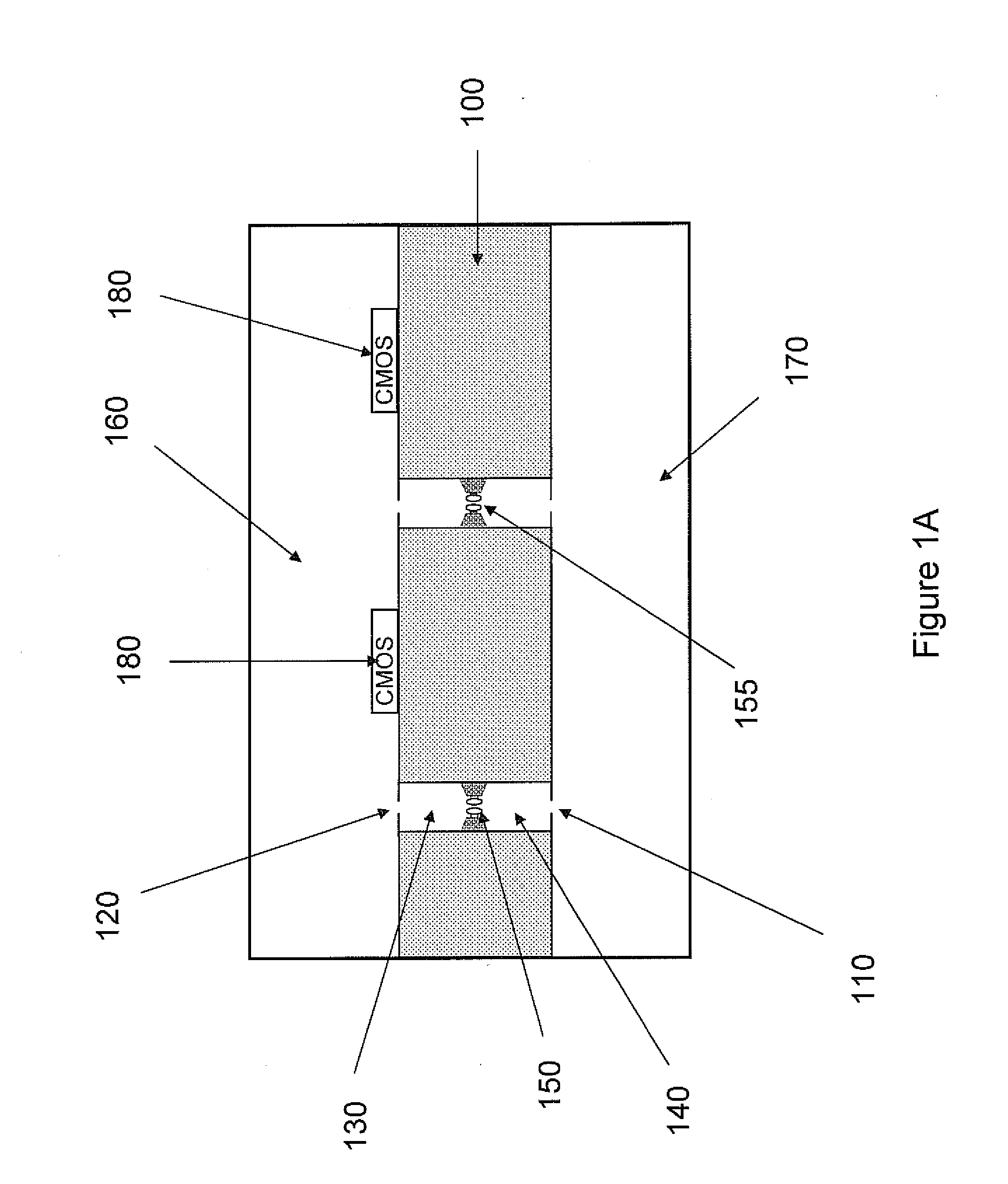
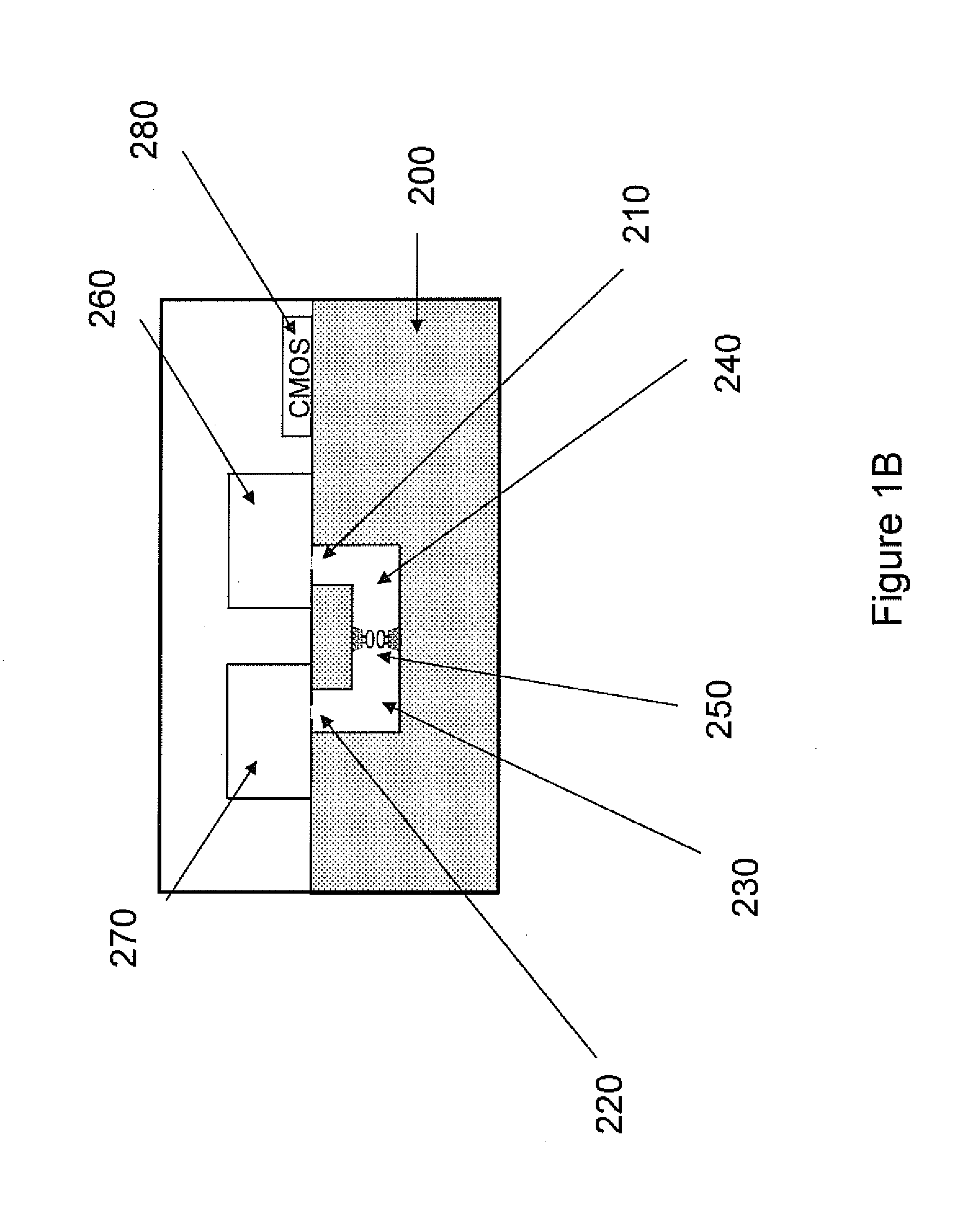
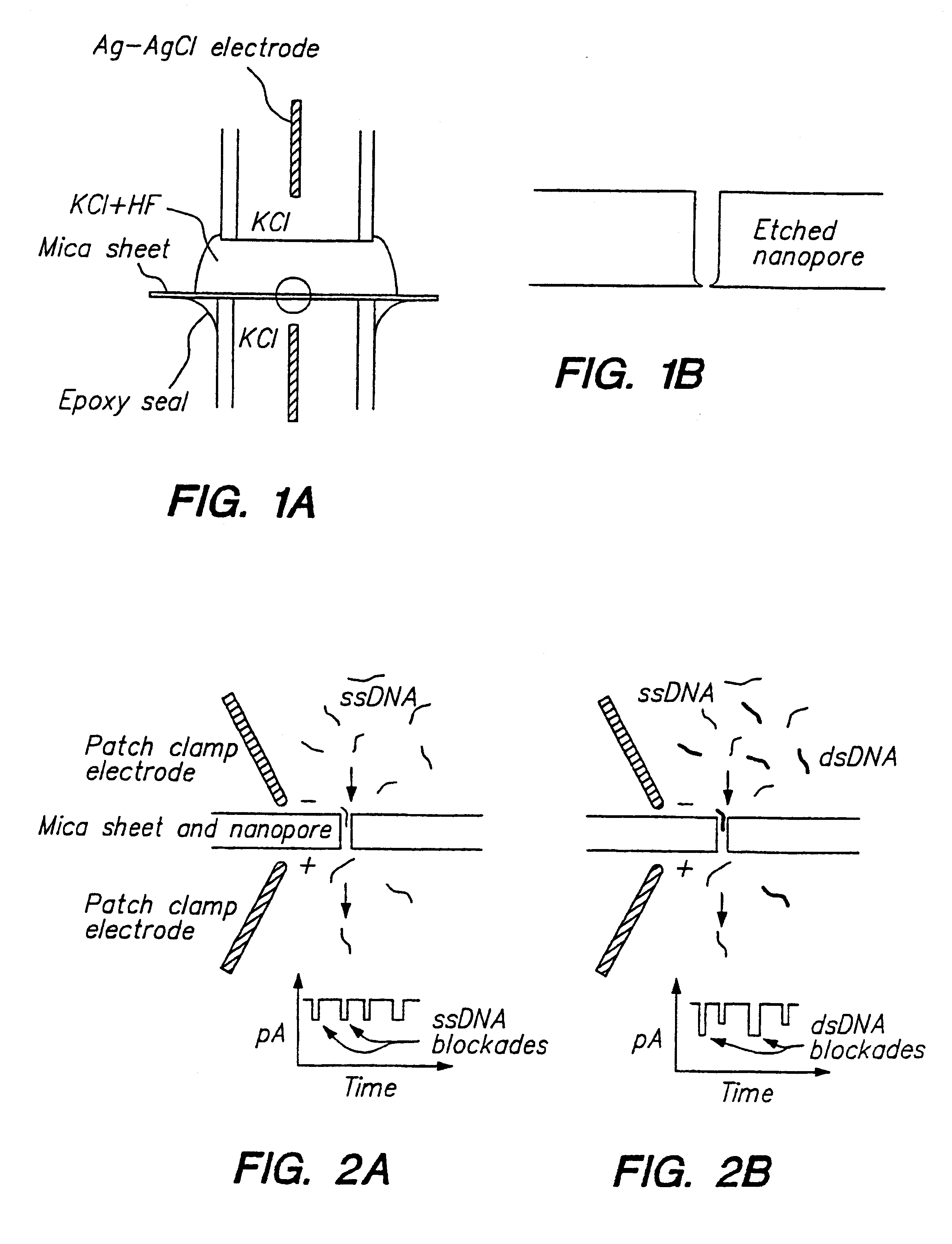
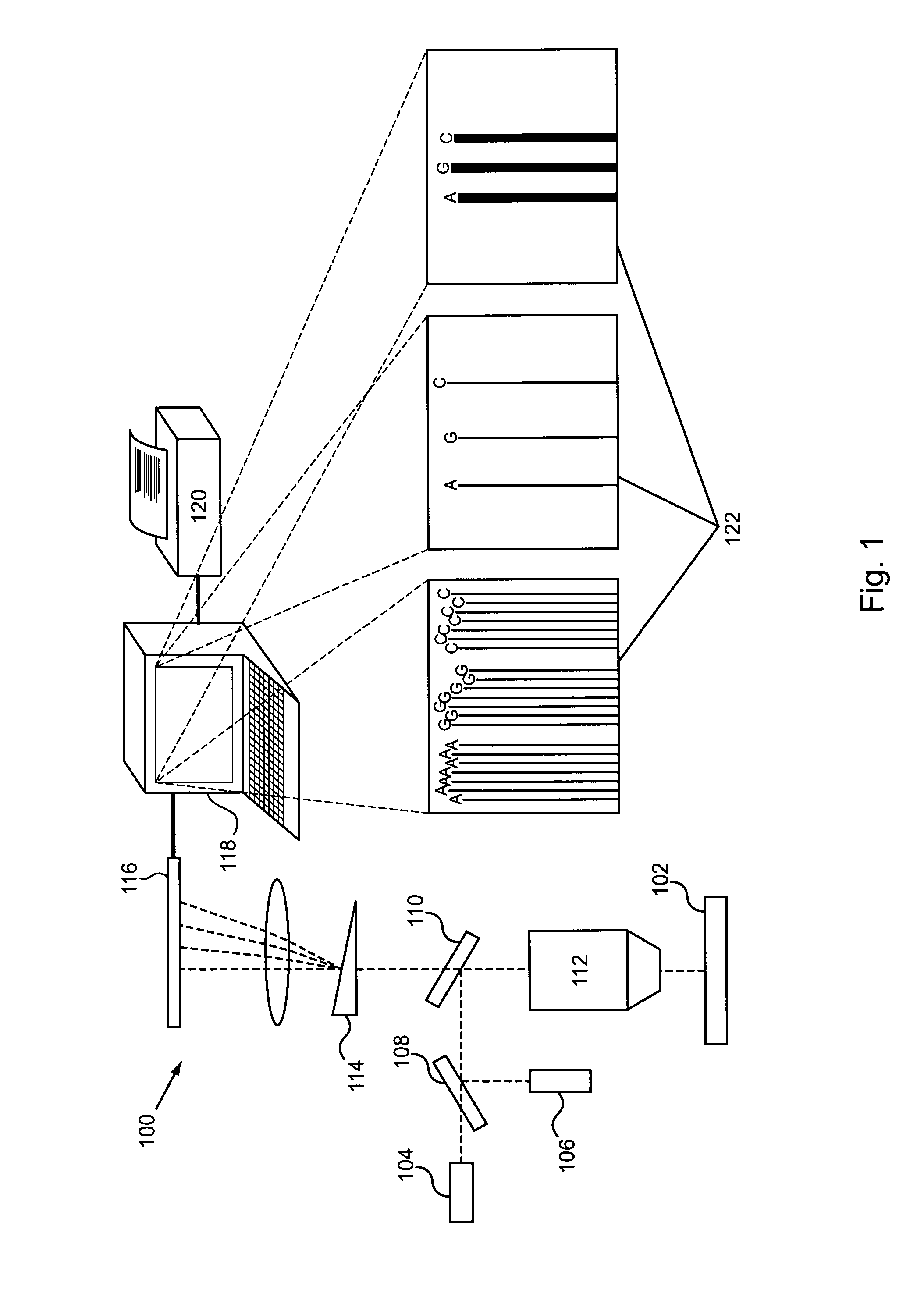
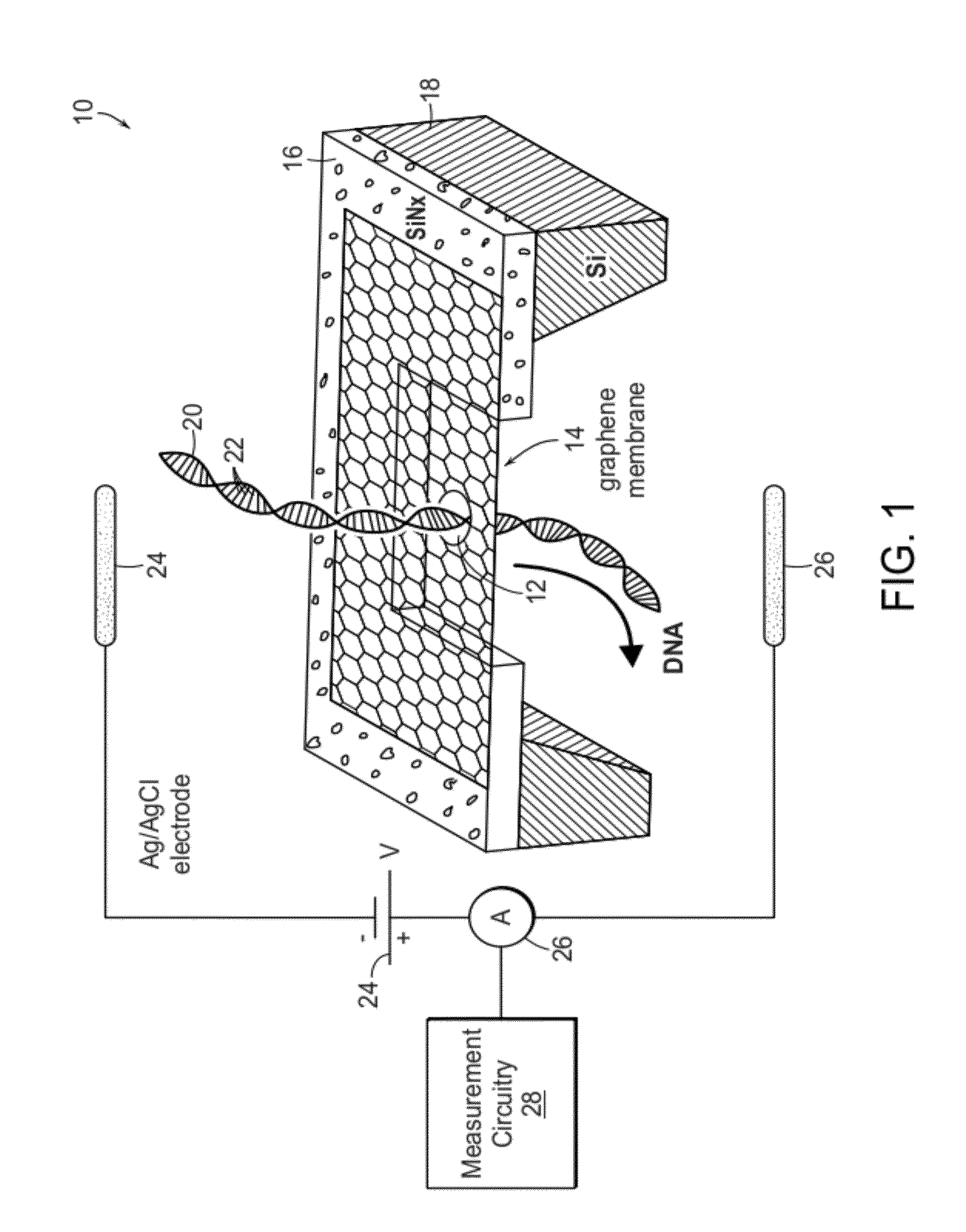
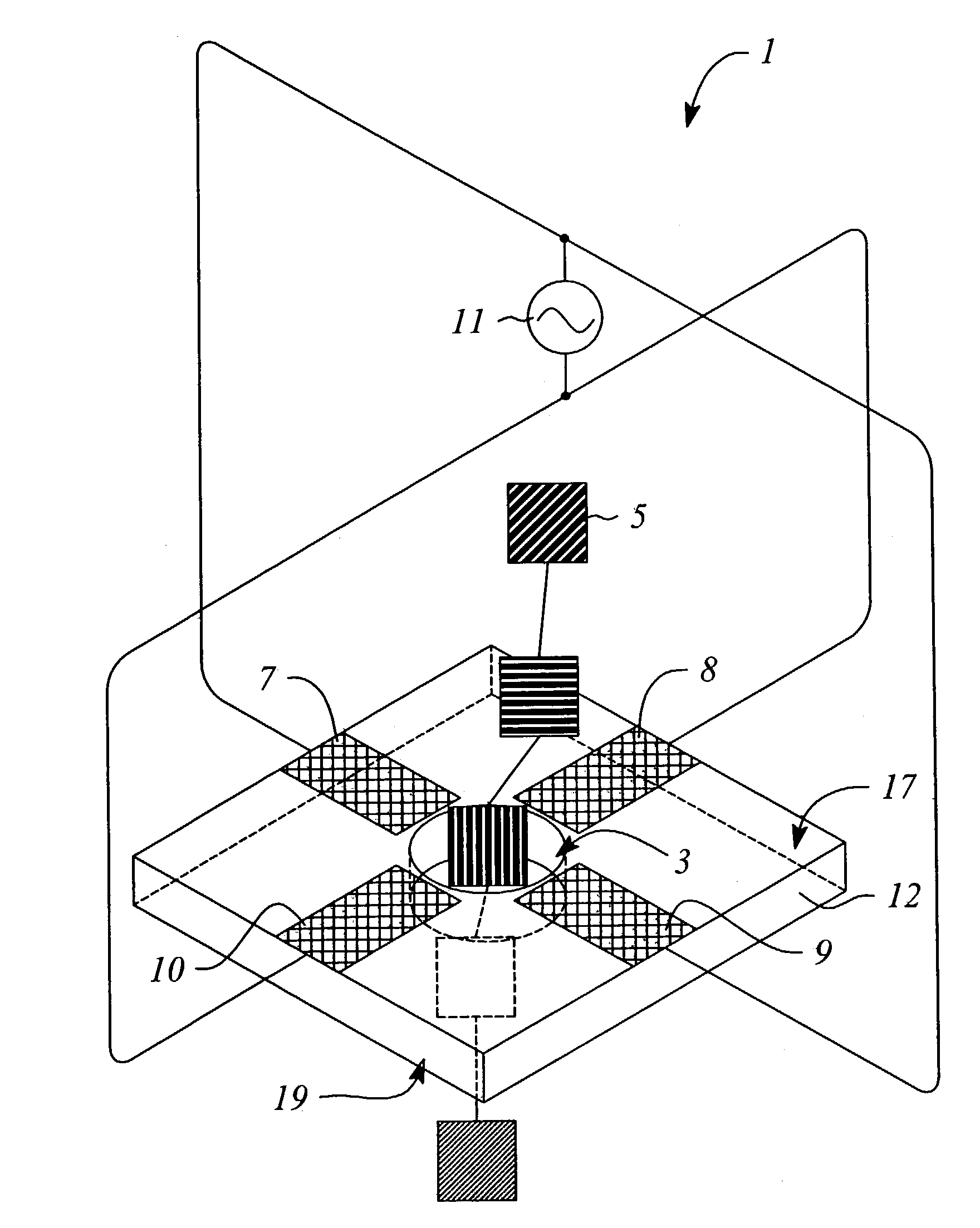
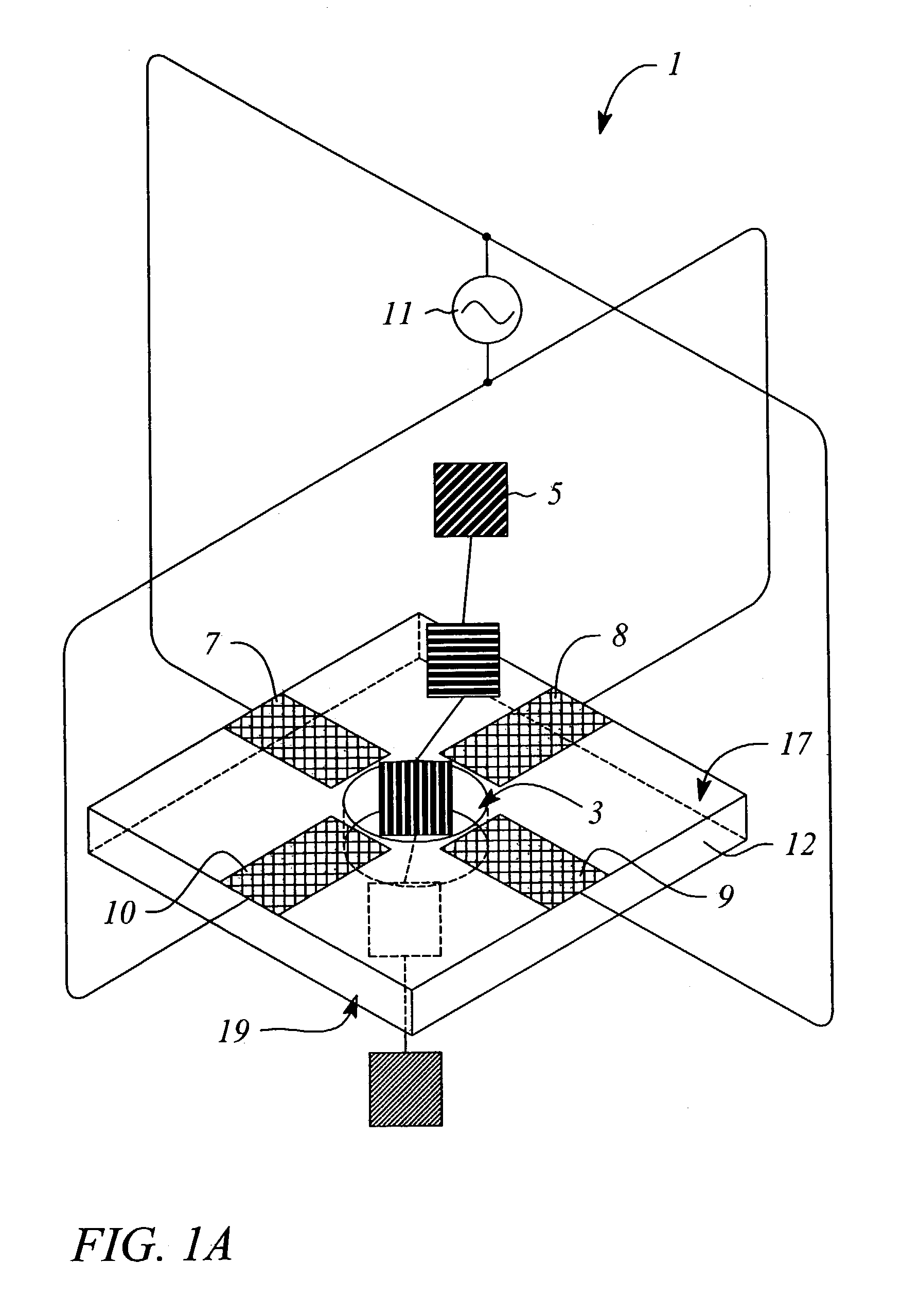
Nanopore sequencing devices and methods
ActiveUS20100331194A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
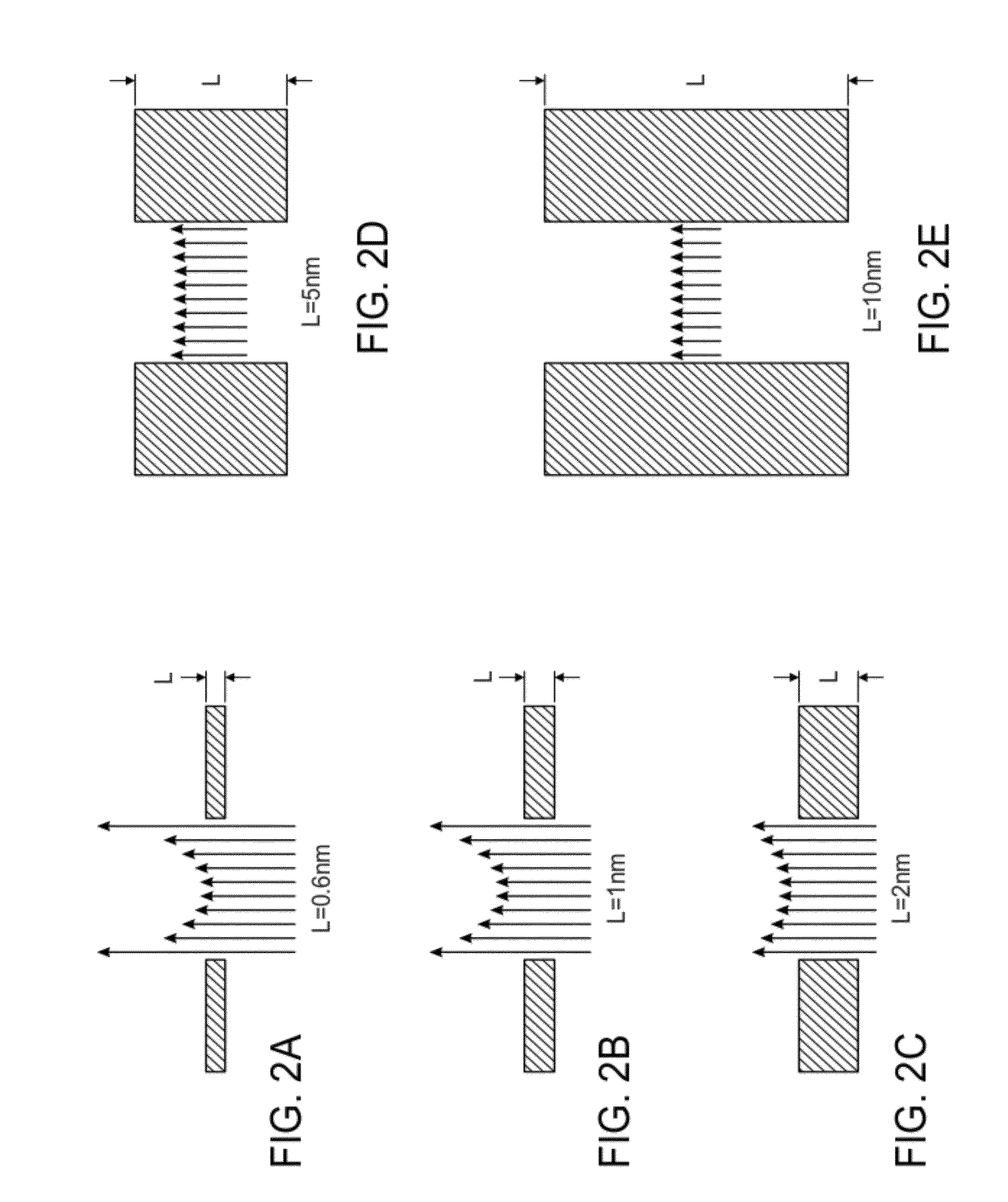
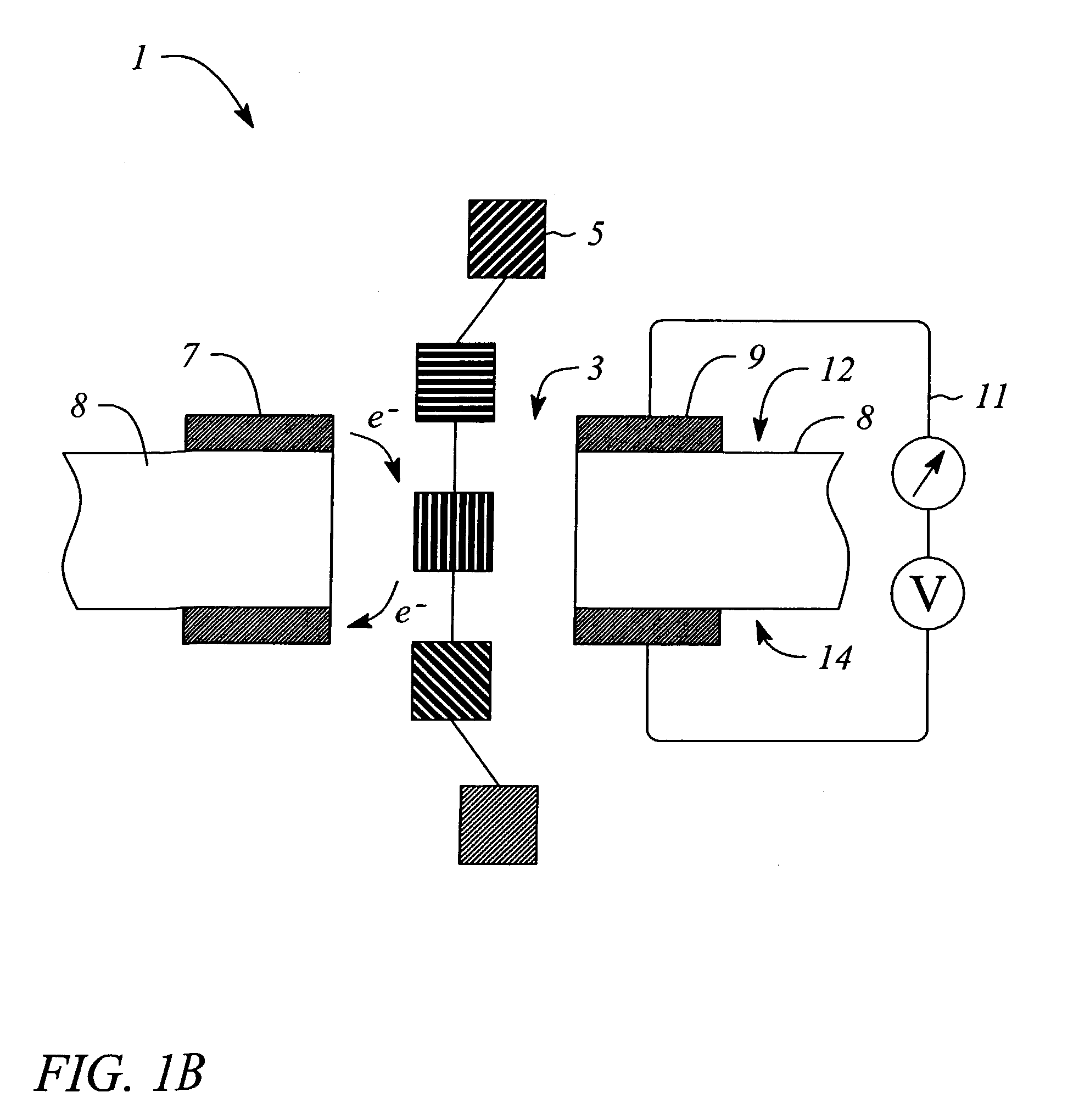
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes arrays of nanopores having incorporated electronic circuits, for example, in CMOS. In some cases, the arrays of nanopores comprise resistive openings for isolating the electronic signals for improved sequencing. Methods for controlling translocation of through the nanopore are disclosed.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
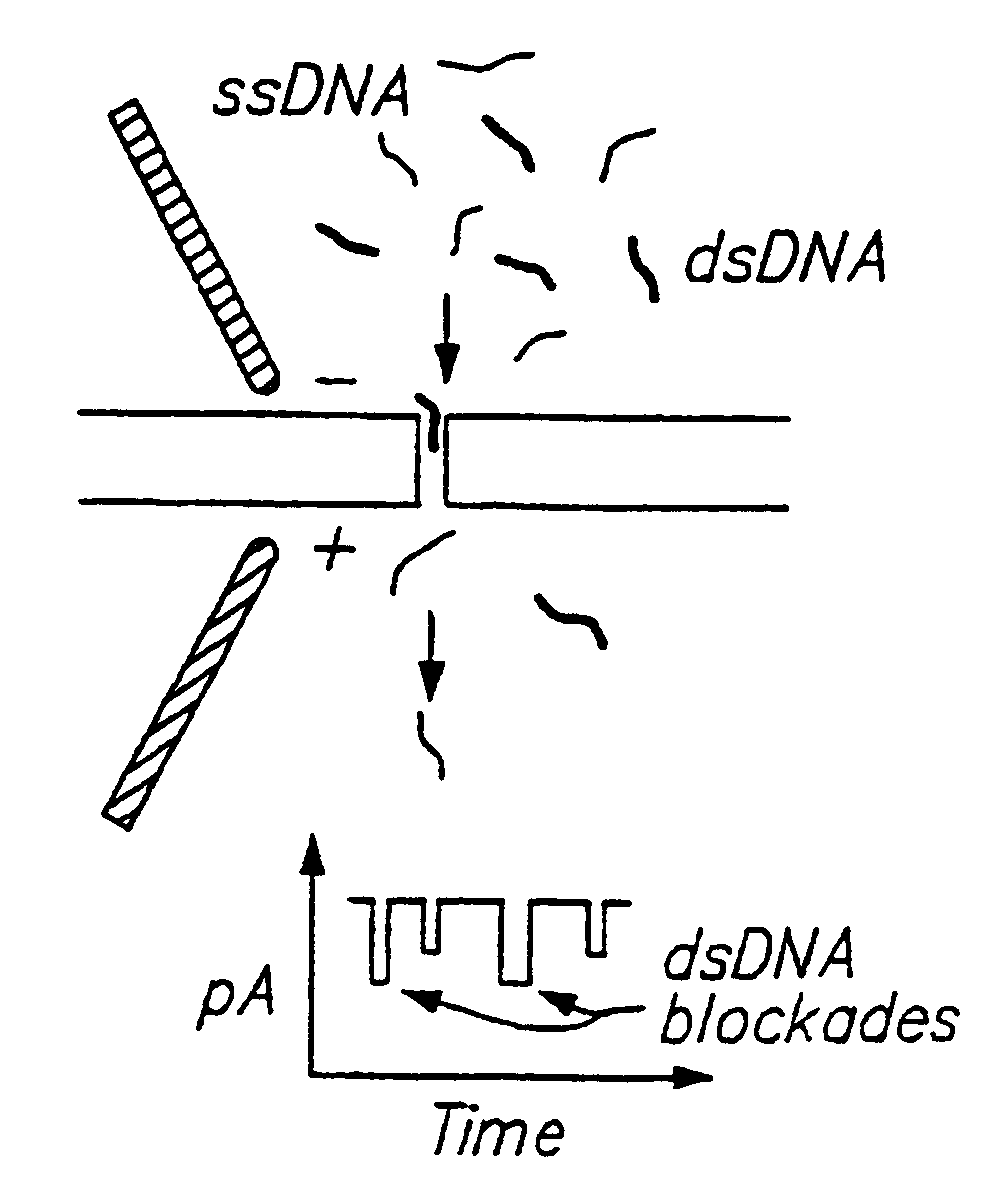
Methods of determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample
InactiveUS6428959B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRNA blottingAssay
Methods for determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample are provided. In the subject methods, nucleic acids present in a fluid sample are translocated through a nanopore, e.g. by application of an electric field to the fluid sample. The current amplitude through the nanopore is monitored during the translocation process and changes in the amplitude are related to the passage of single- or double-stranded molecules through the nanopore. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the detection of the presence of double-stranded nucleic acids in a sample is desired, e.g. in hybridization assays, such as Northern blot assays, Southern blot assays, array based hybridization assays, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
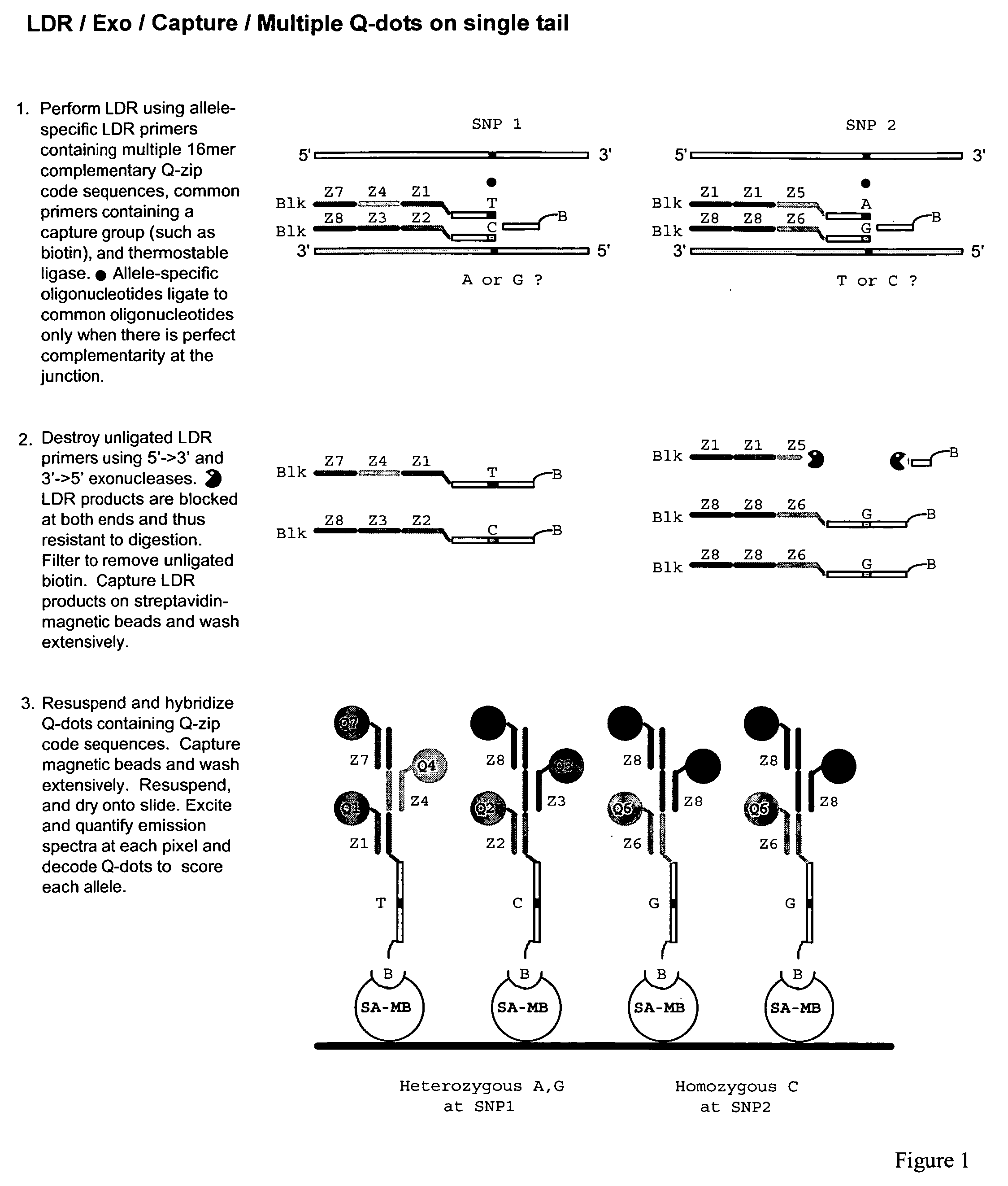
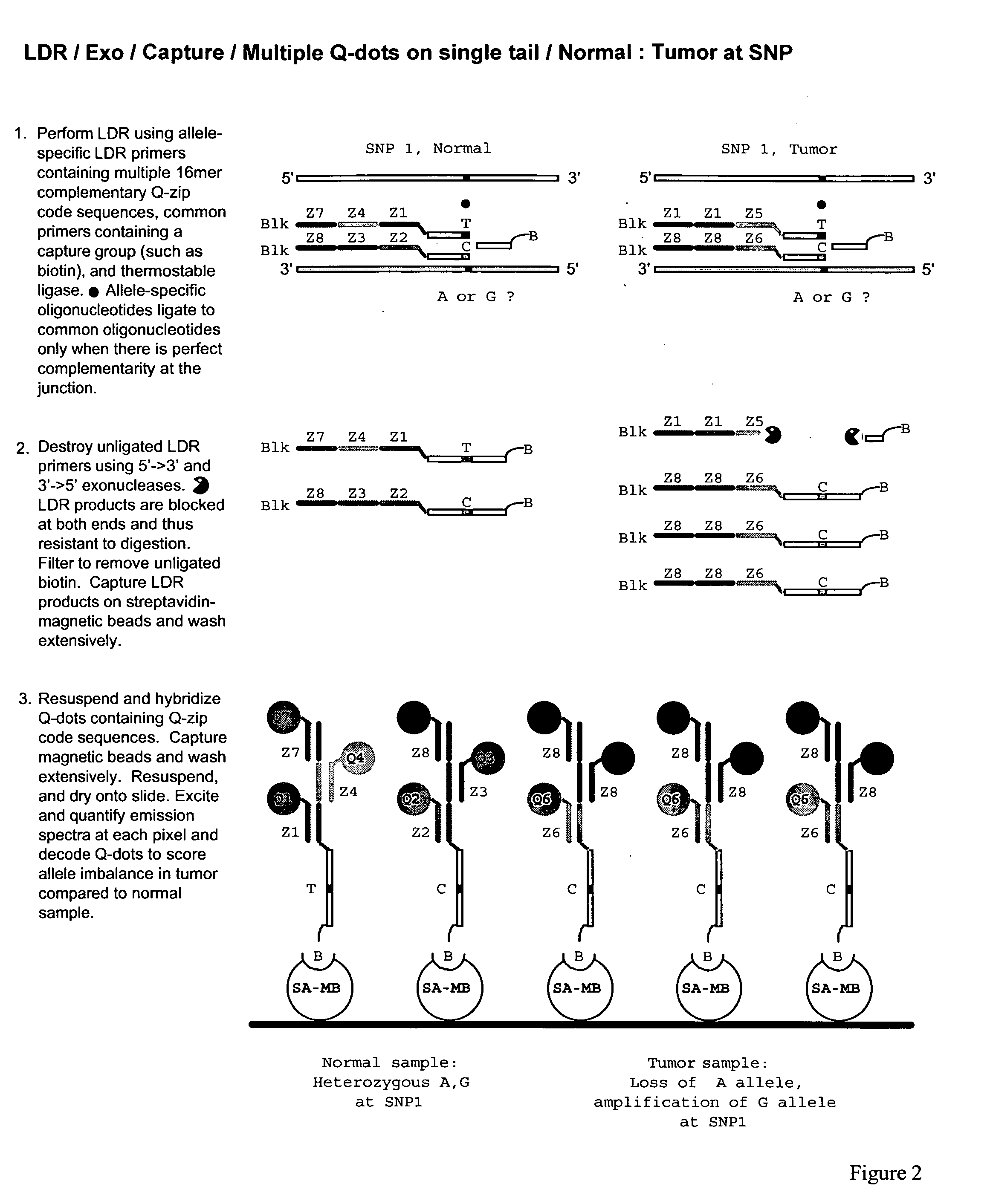
Detection of nucleic acid sequence differences using the ligase detection reaction with addressable arrays
InactiveUS7083917B2Avoid signalingFalse signalMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNucleic acid sequencingNucleotide sequencing
The present invention describes a method for identifying one or more of a plurality of sequences differing by one or more single base changes, insertions, deletions, or translocations in a plurality of target nucleotide sequences. The method includes a ligation phase, a capture phase, and a detection phase. The ligation phase utilizes a ligation detection reaction between one oligonucleotide probe, which has a target sequence-specific portion and an addressable array-specific portion, and a second oligonucleotide probe, having a target sequence-specific portion and a detectable label. After the ligation phase, the capture phase is carried out by hybridizing the ligated oligonucleotide probes to a solid support with an array of immobilized capture oligonucleotides at least some of which are complementary to the addressable array-specific portion. Following completion of the capture phase, a detection phase is carried out to detect the labels of ligated oligonucleotide probes hybridized to the solid support. The ligation phase can be preceded by an amplification process. The present invention also relates to a kit for practicing this method, a method of forming arrays on solid supports, and the supports themselves.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods and compositions for the treatment of pancreatitis
InactiveUS6843998B1Prevents and reduces extent of fusionInhibition formationBacterial antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein translocationDigestive enzyme
Methods and compositions for the treatment of acute pancreatitis in a mammal. Particular compositions comprise a binding element, a translocation element, and a therapeutic element able to prevent accumulation of digestive enzymes within the pancreas.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
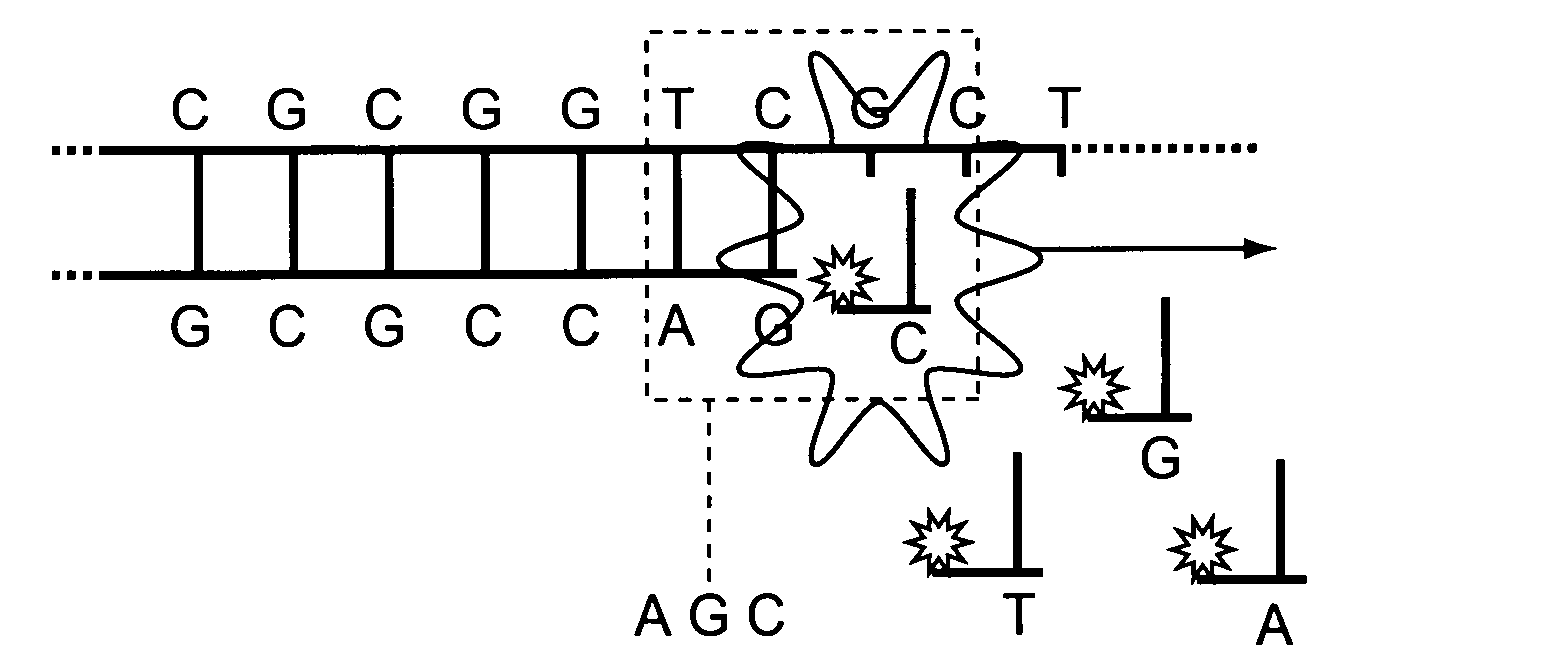
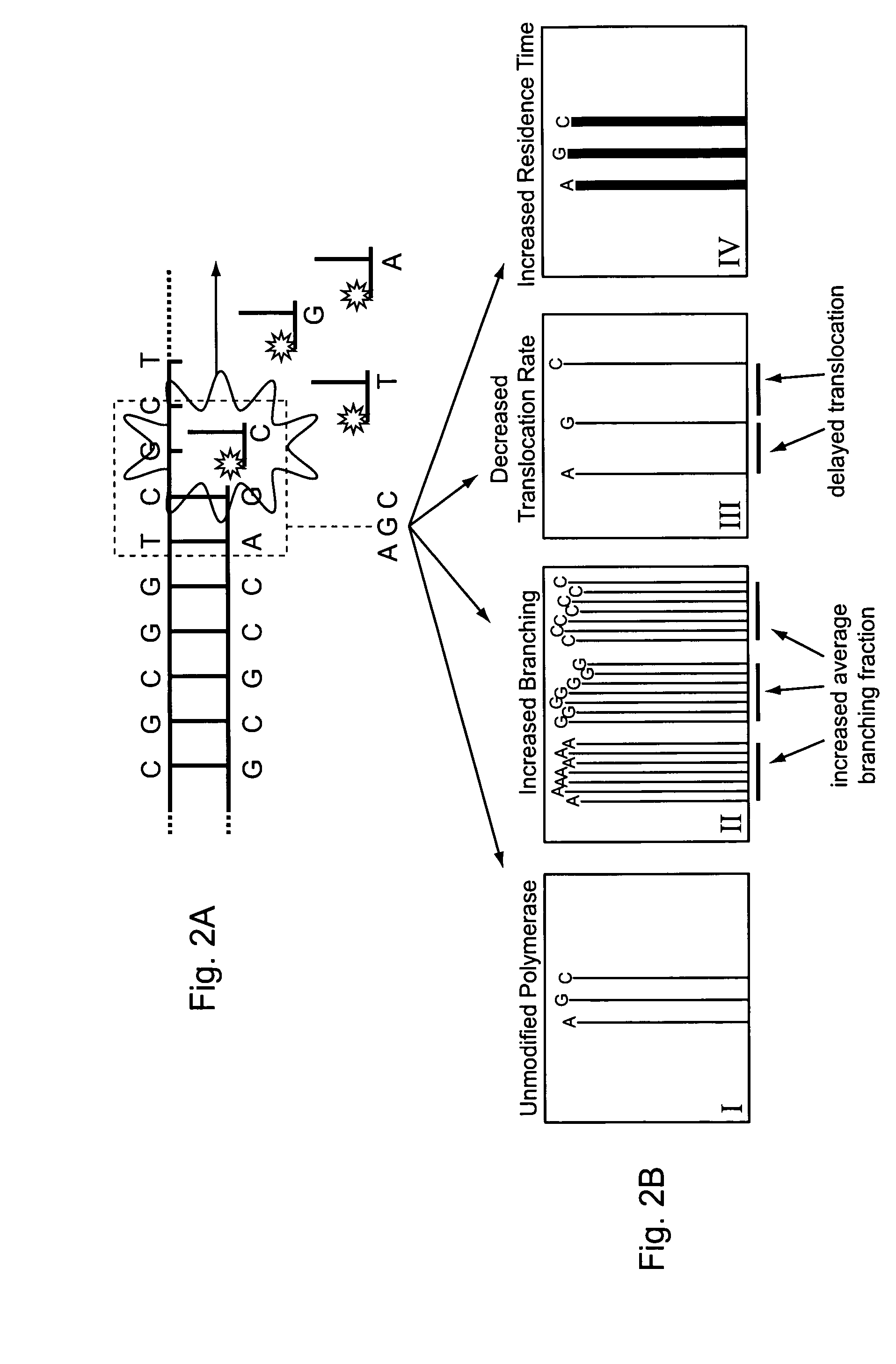
Engineering polymerases and reaction conditions for modified incorporation properties
ActiveUS20100075332A1Easy to identifyDelayed translocationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolymerase LA-DNA
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Conjugates of galactose-binding lectins and clostridial neurotoxins as analgesics
InactiveUS7052702B1Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderBacteriaGalactose binding lectinProtein translocation
A class of novel agents that are able to modify nociceptive afferent function is provided. The agents may inhibit the release of neurotransmitters from discrete populations of neurones and thereby reduce or preferably prevent the transmission of afferent pain signals from peripheral to central pain fibers. They comprise a galactose-binding lectin linked to a derivative of a clostridial neurotoxin. The derivative of the clostridial neurotoxin comprises the L-chain, or a fragment thereof, which includes the active proteolytic enzyme domain of the light (L) chain, linked to a molecule or domain with membrane translocating activity. The agents may be used in or as pharmaceuticals for the treatment of pain, particularly chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
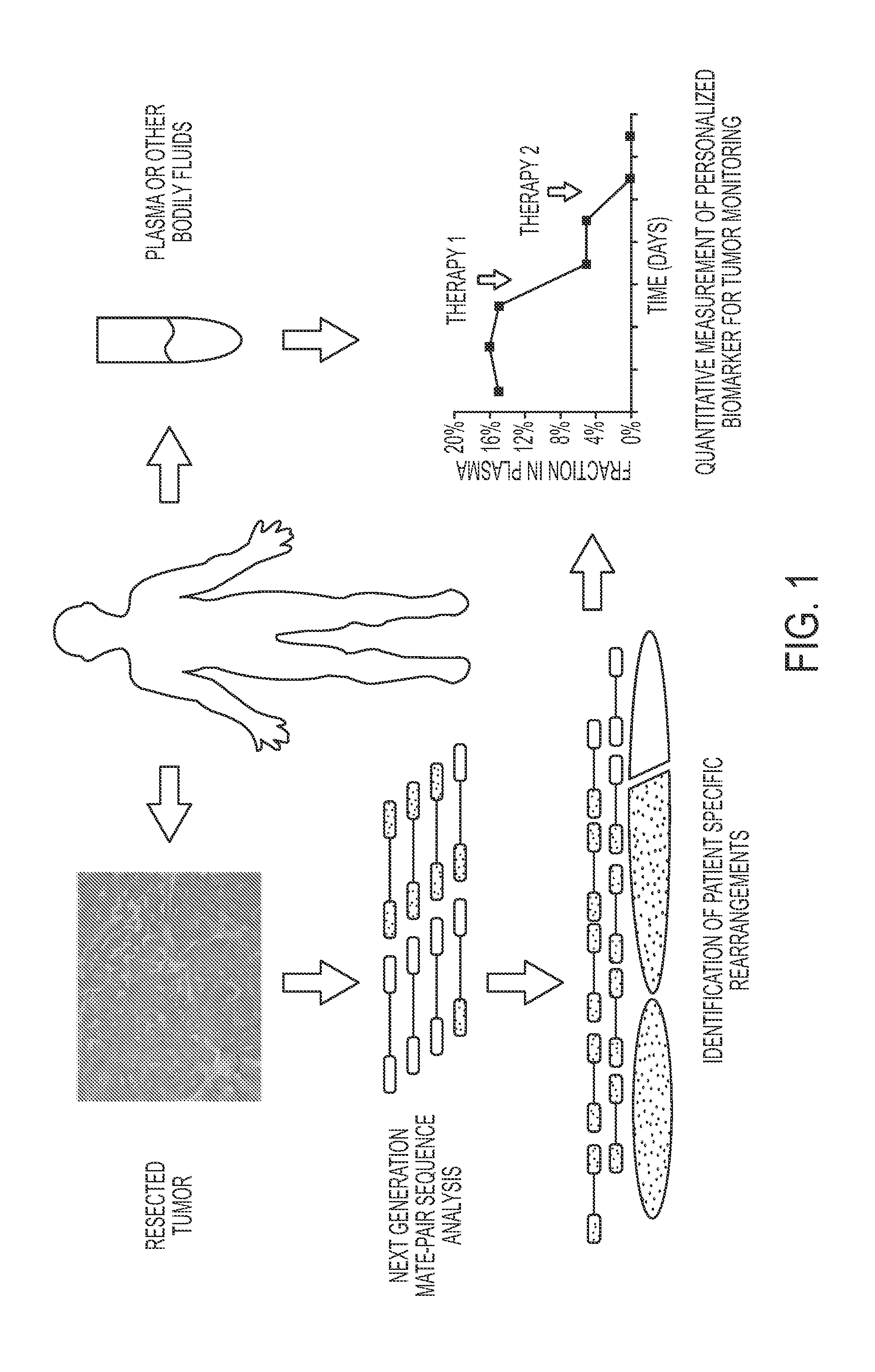
Personalized Tumor Biomarkers
ActiveUS20150344970A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBlood plasmaWilms' tumor
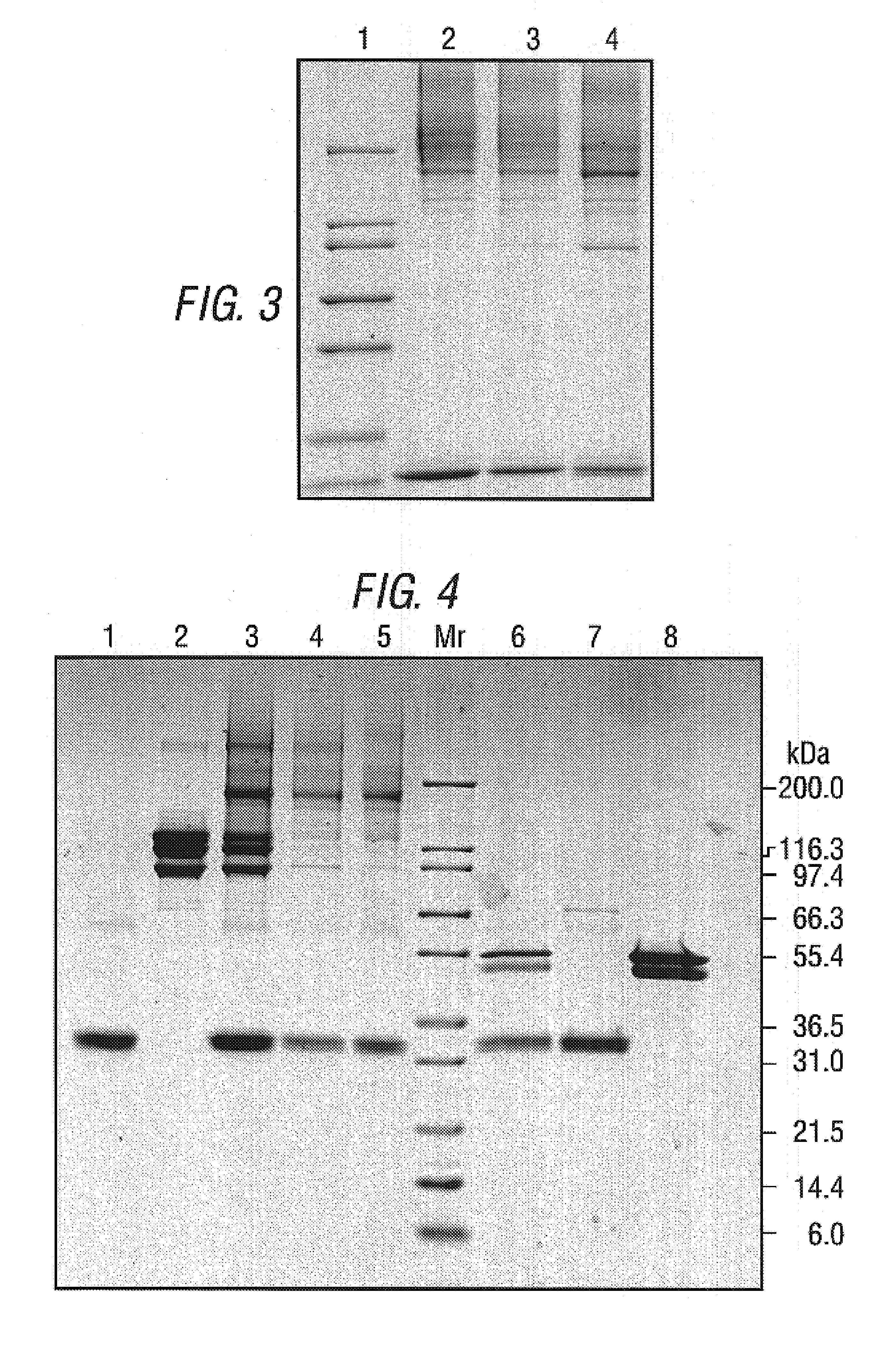
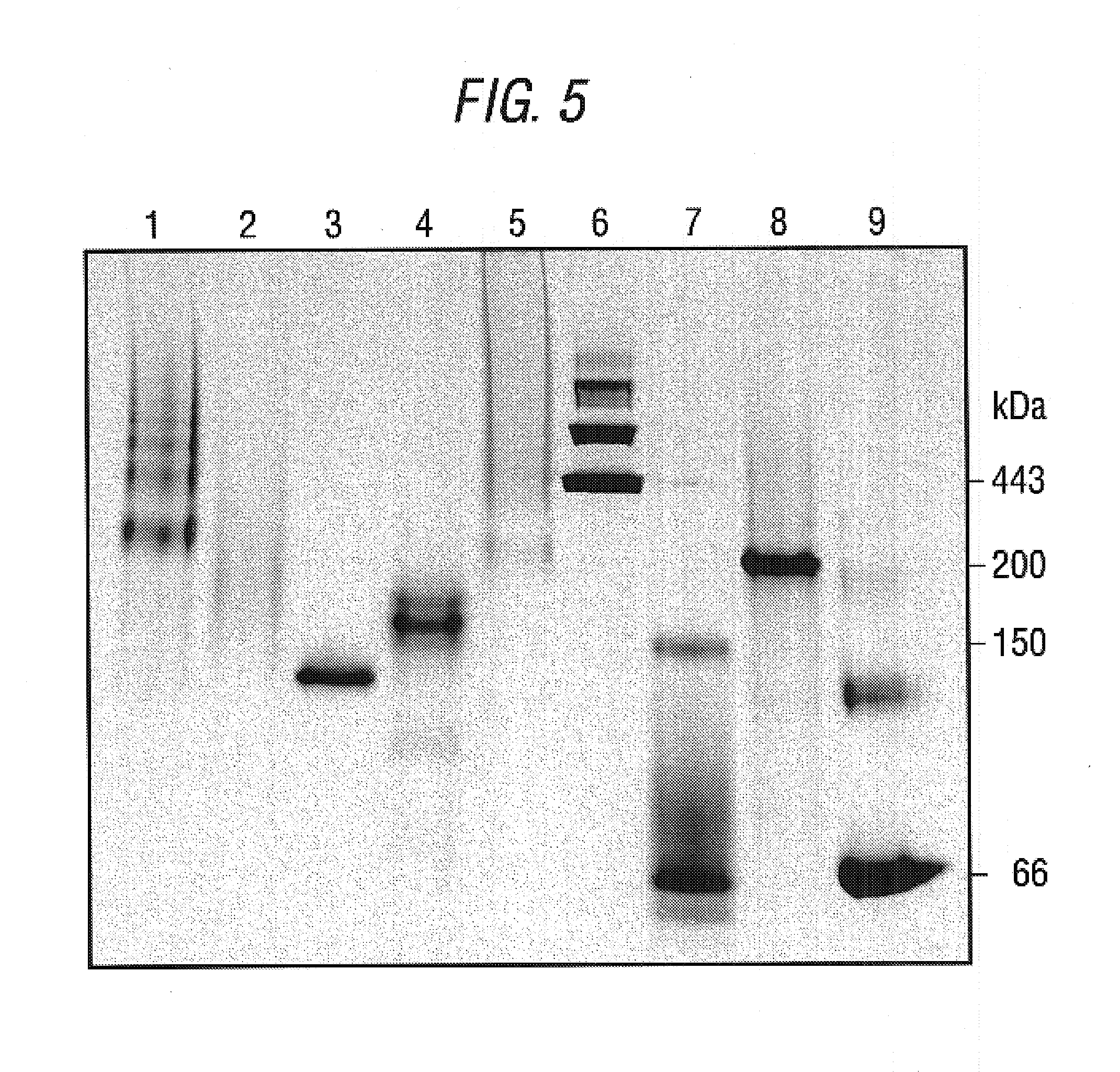
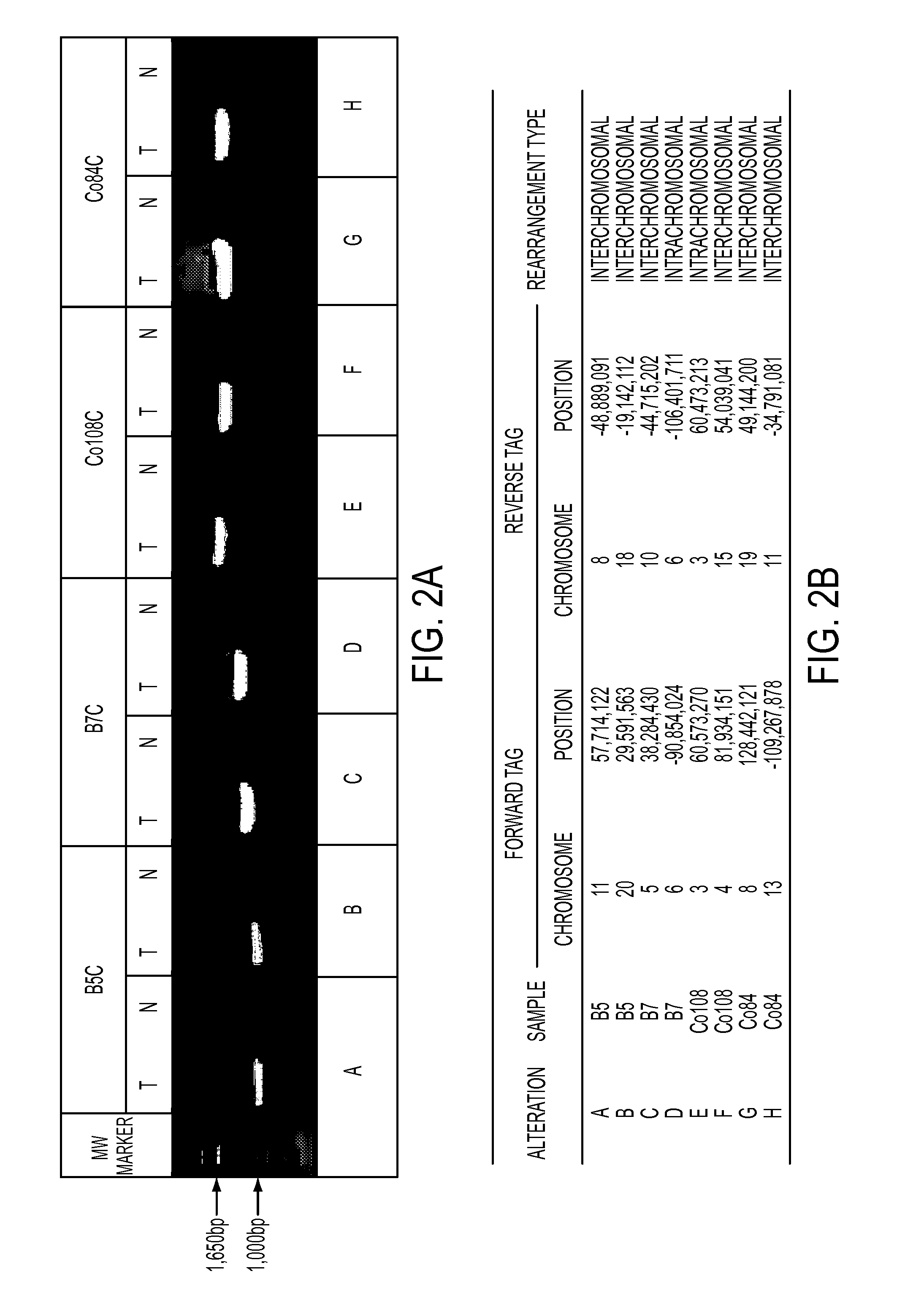
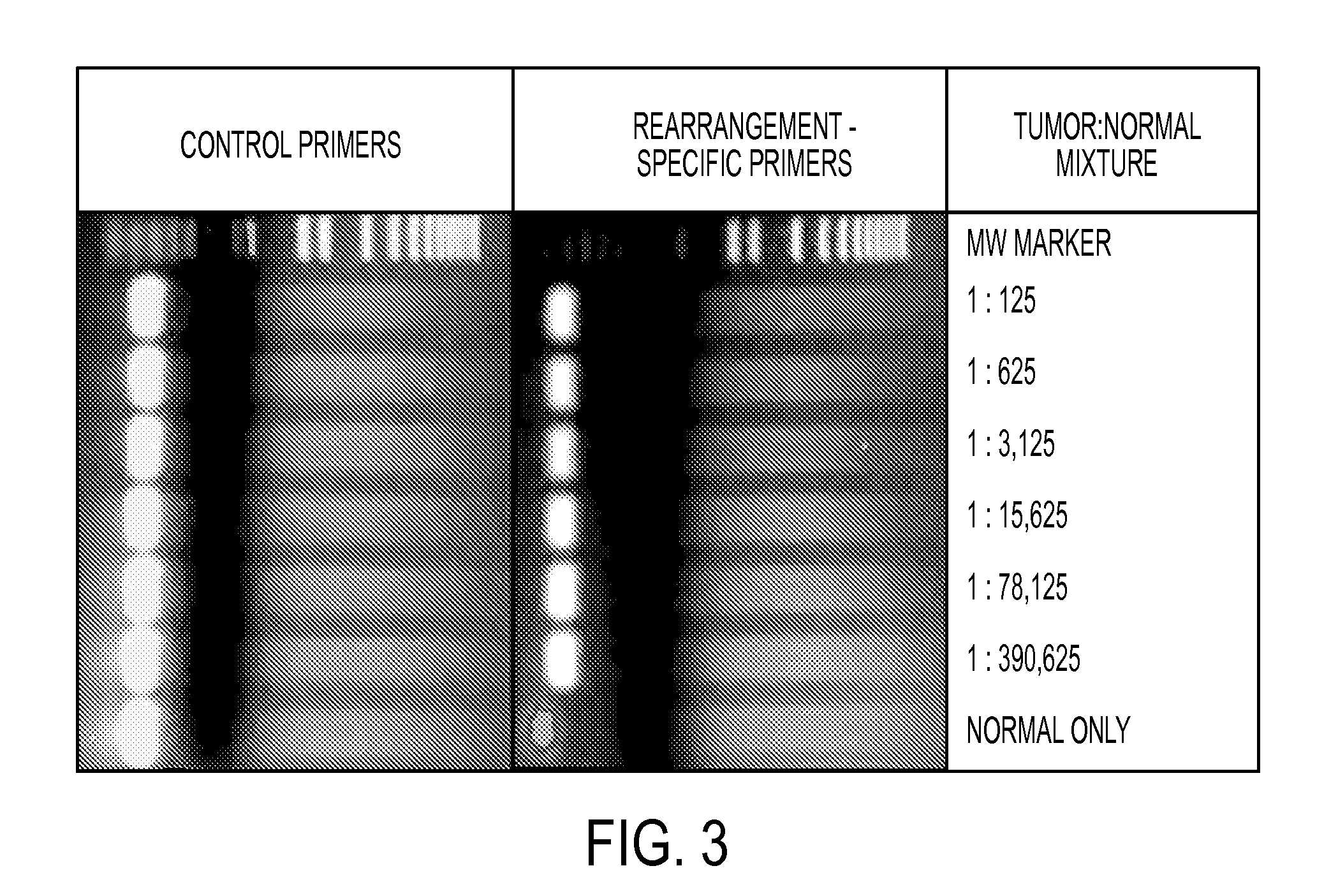
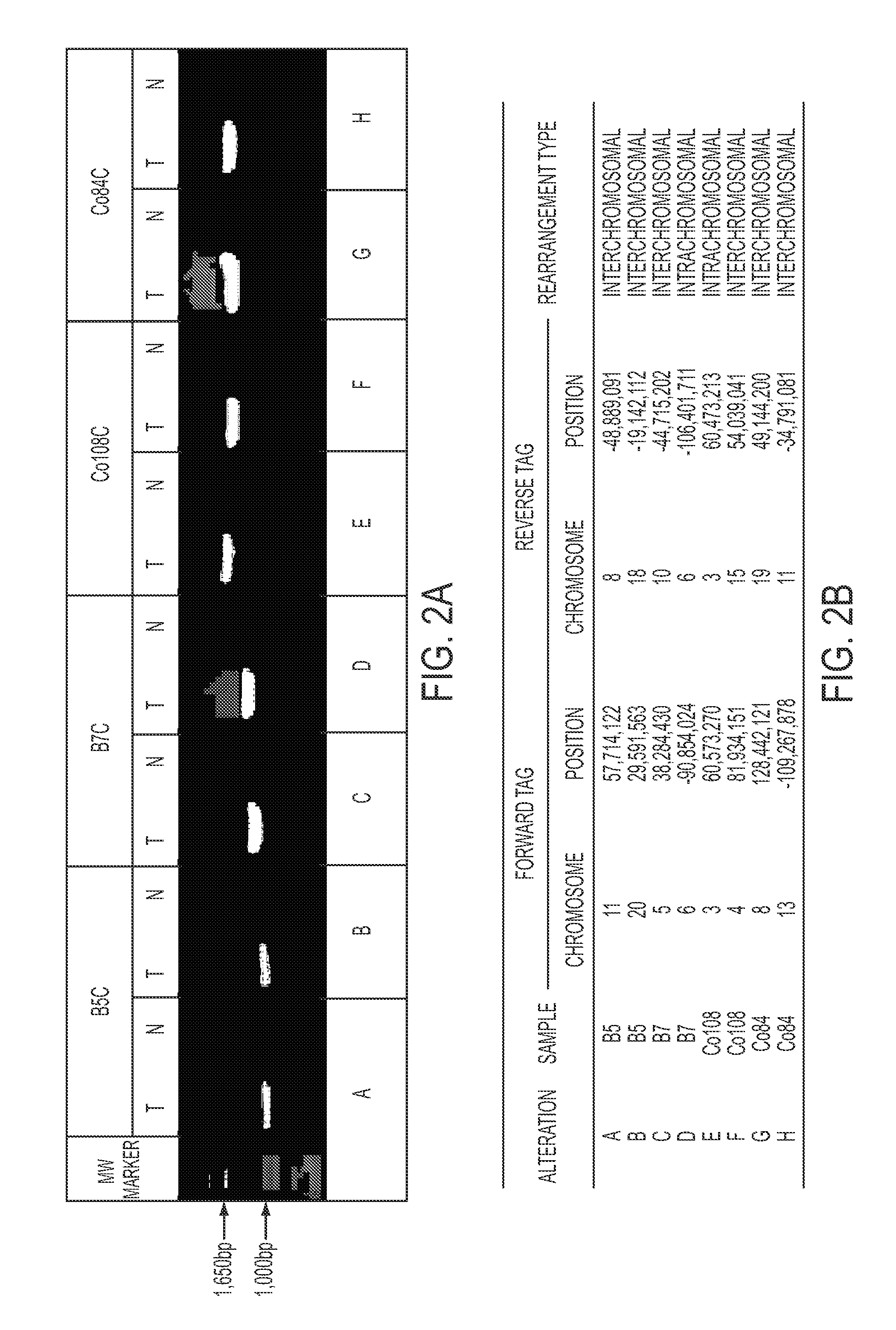
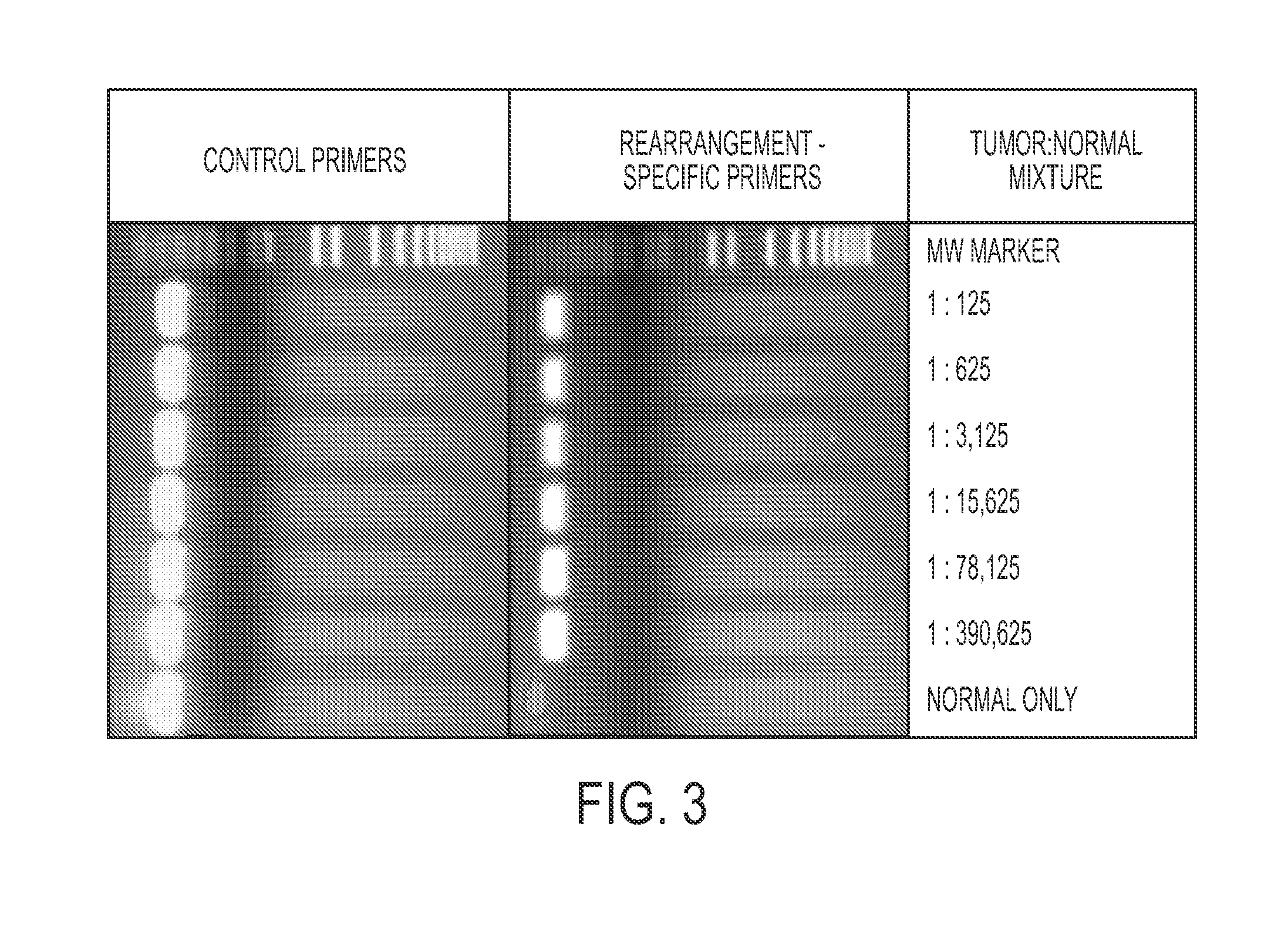
Clinical management of human cancer is dependent on the accurate monitoring of residual and recurrent tumors. We have developed a method, called personalized analysis of rearranged ends (PARE), which can identify translocations in solid tumors. Analysis of four colorectal and two breast cancers revealed an average of nine rearranged sequences (range 4 to 15) per tumor. Polymerase chain reaction with primers spanning the breakpoints were able to detect mutant DNA molecules present at levels lower than 0.001% and readily identified mutated circulating DNA in patient plasma samples. This approach provides an exquisitely sensitive and broadly applicable approach for the development of personalized biomarkers to enhance the clinical management of cancer patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Fusion antigen used as vaccine
ActiveUS7335361B2SsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPseudomonas tolaasiiReticulum cell
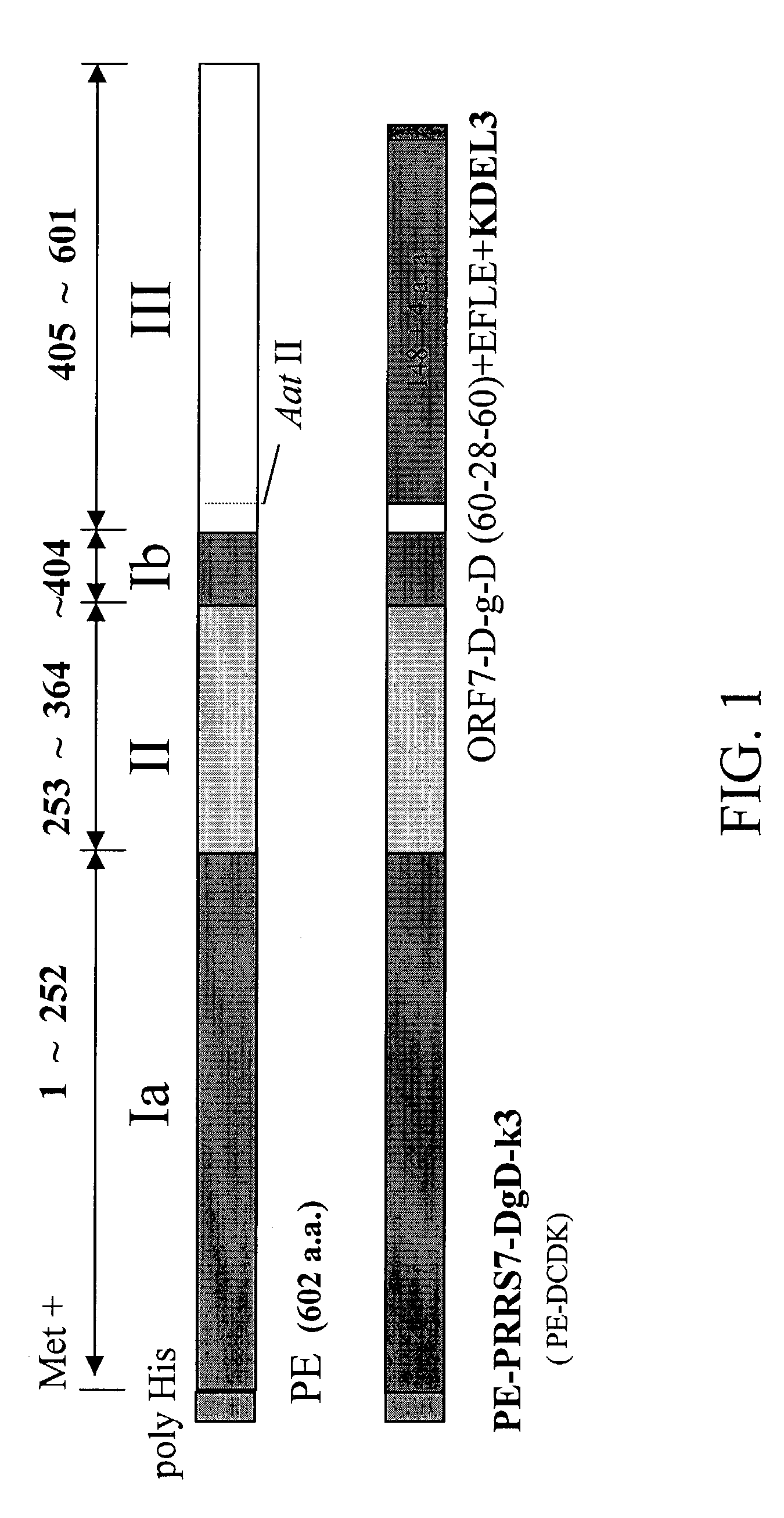
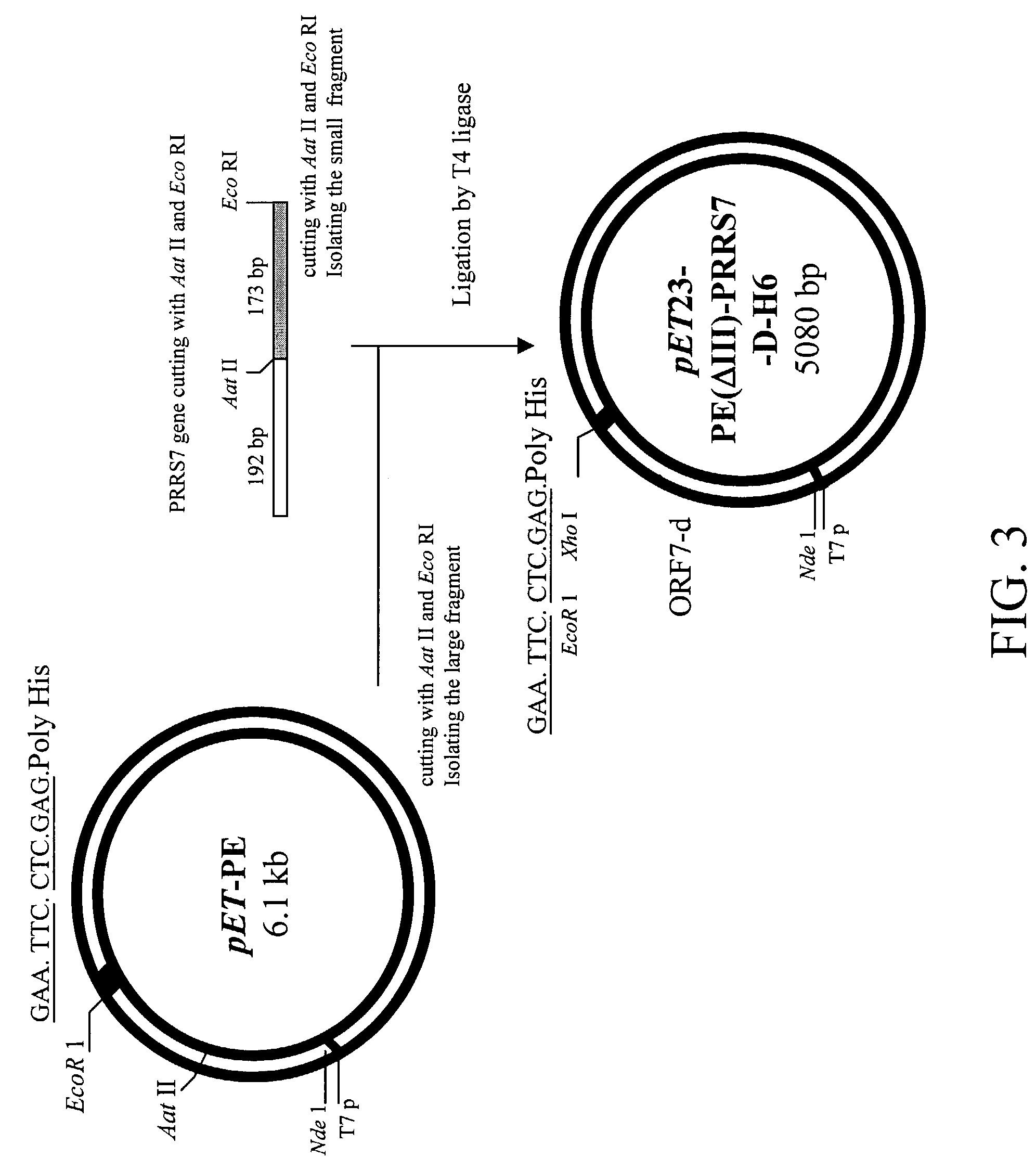
The present invention mainly provides a fusion antigen specific for a target cell comprising a ligand moiety which is capable of reacting, recognizing or binding to the receptors on the target cell, a Pseudomonas exotoxin A translocation domain II, an antigenic moiety, and a carboxyl terminal moiety which permits combination of the fusion antigen to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane of the target cell. A method of immunizing an animal using the fusion antigen is also provided.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Method for controlling cancer metastasis or cancer cell migration by modulating the cellular level of lysyl trna synthetase
ActiveUS20110189195A1Promote migrationCancer metastasisOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBreast cancer metastasisDisease
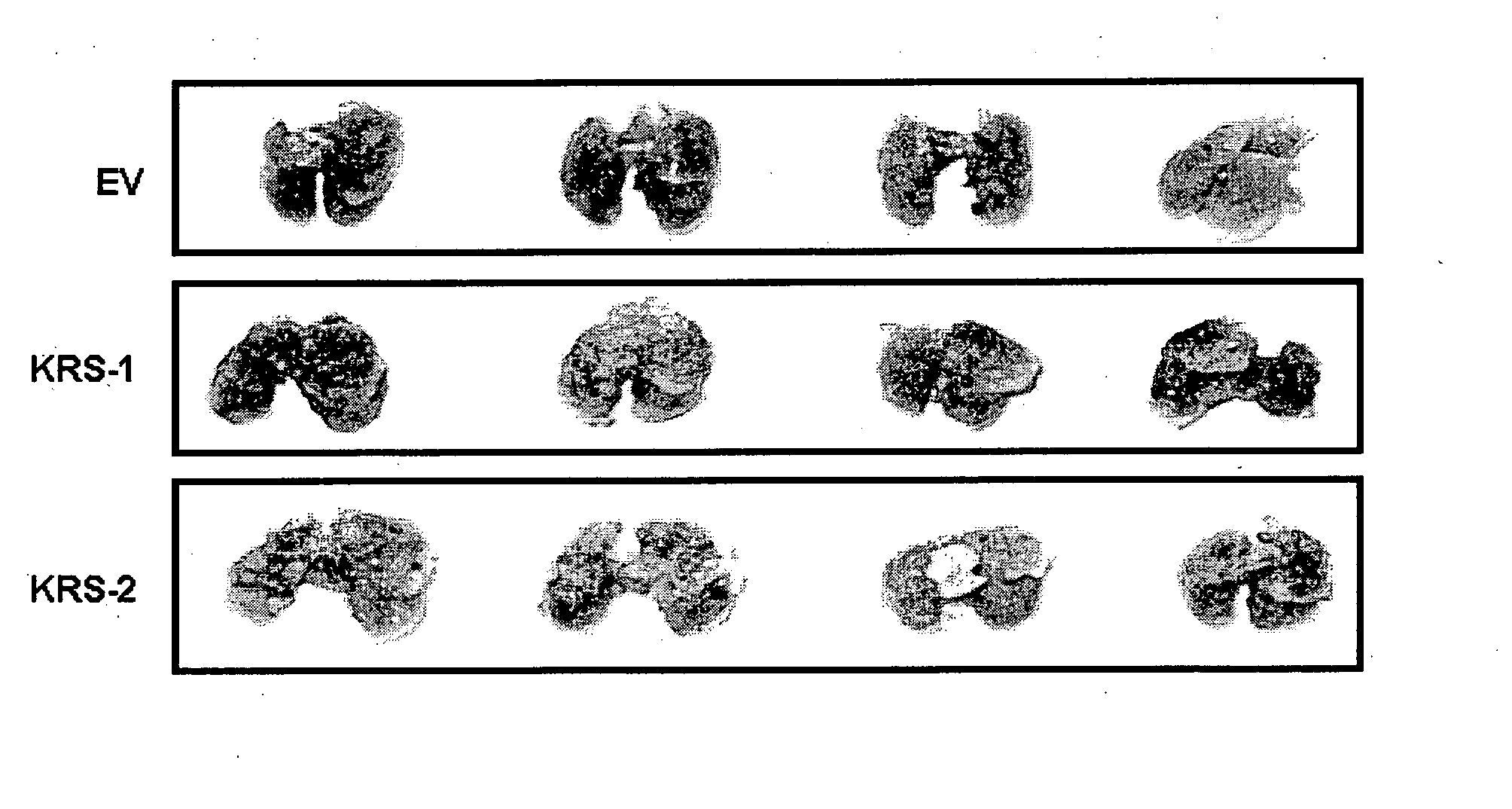
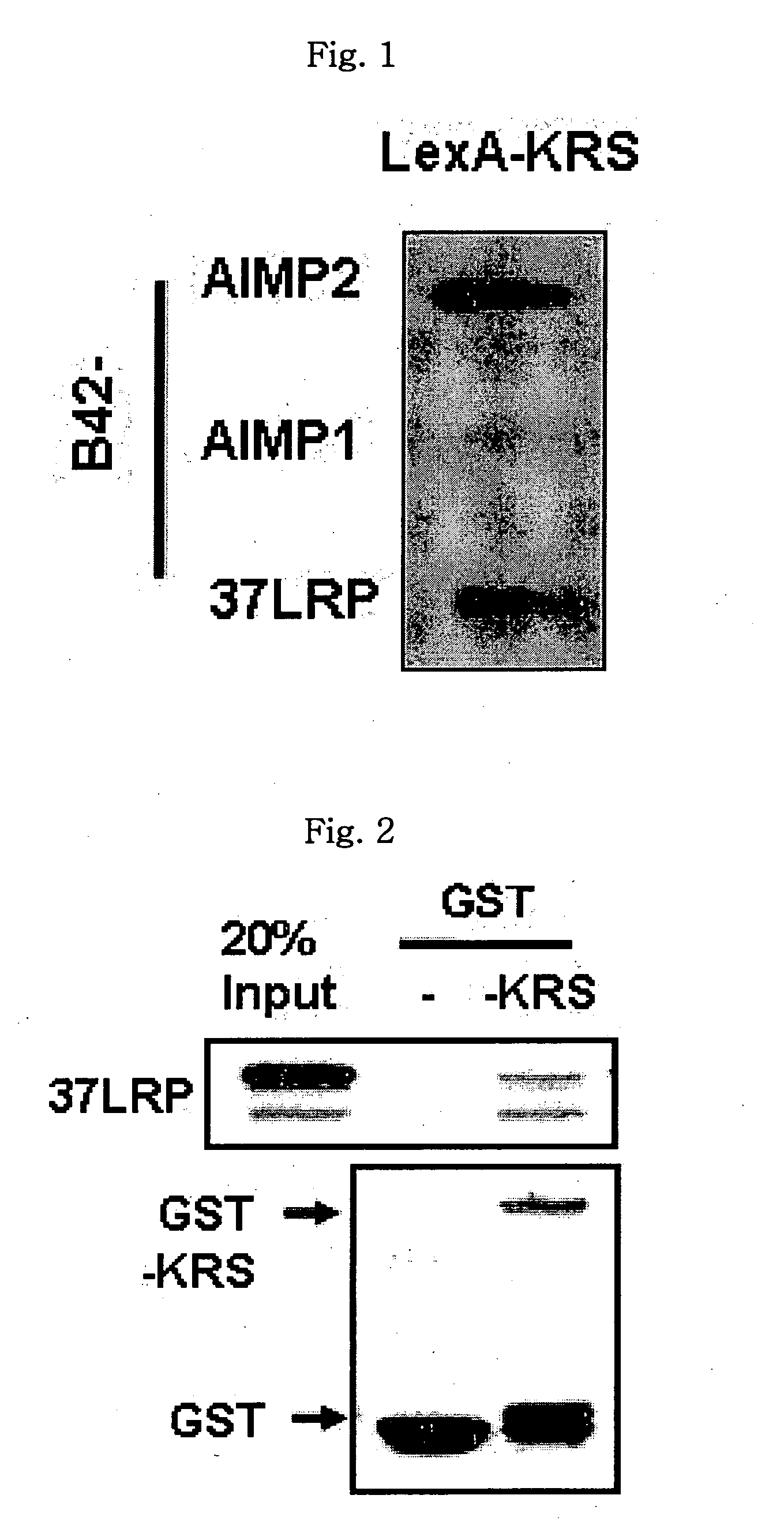
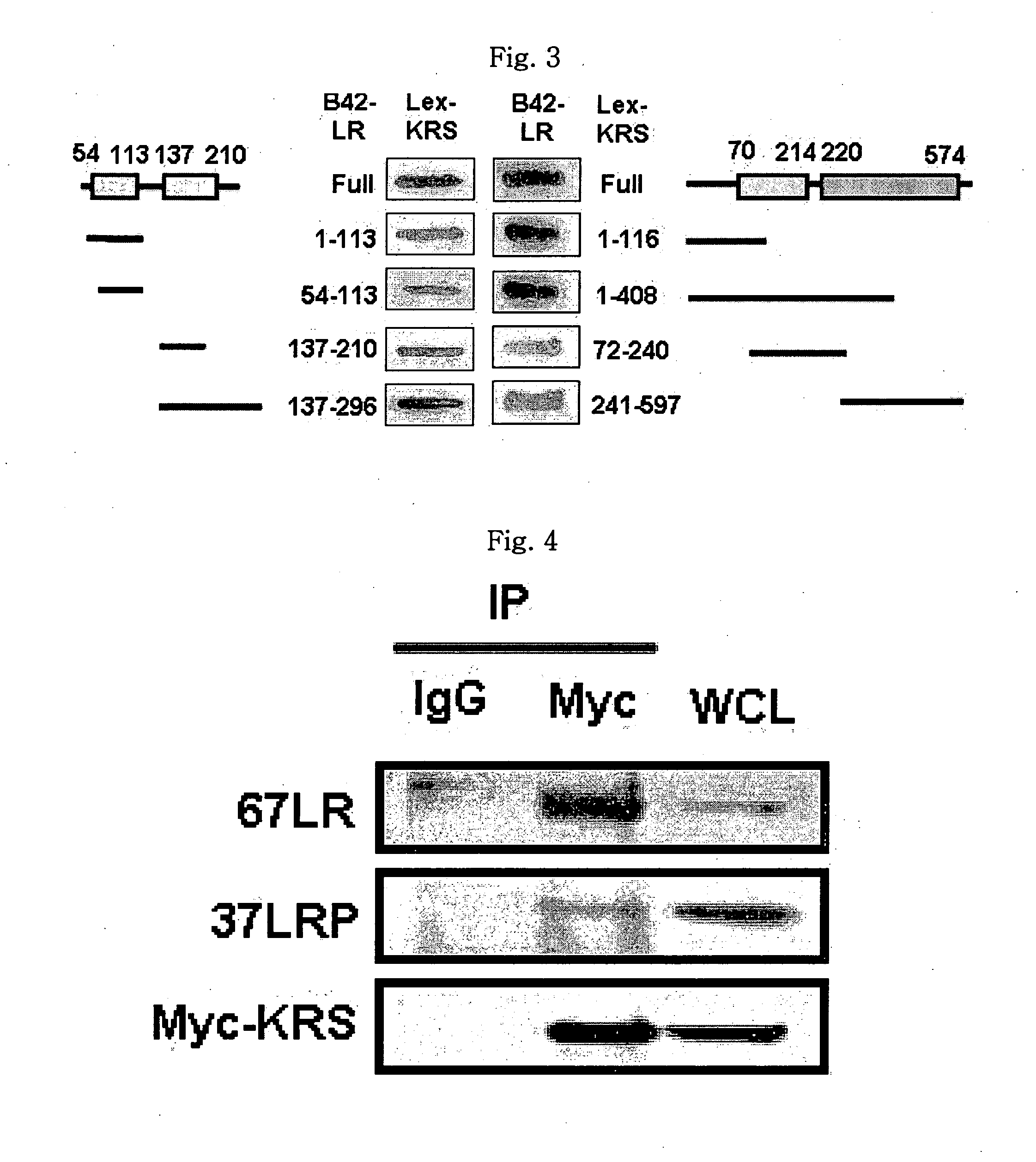
The present invention relates to a novel function of lysyl tRNA synthetase (KRS) which enhances tumor cell migration and affects cancer metastasis via KRS's interaction with laminin receptor (67LR) by its translocation to membrane. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for modulating cancer metastasis or migration, which comprises regulating intracellular levels of KRS; a composition for preventing or treating cancer; use of expression vector for inhibiting the expression of KRS; a method for preventing or treating cancer; use of an agent for inhibiting an activity of KRS; a method for screening an agent which modulates cancer metastasis or migration; and a method for screening an agent which inhibits the interaction of KRS with 67LR, by said novel function. Thus, KRS can modulate cancer metastasis or migration and furthermore, can modulate intra-cellular metabolism related to 67LR. The interaction between KRS and 67LR can be used effectively in treating, preventing and / or diagnosing of various diseases or disorders related to the interaction.
Owner:MEDICINAL BIOCONVERGENCE RES CENT
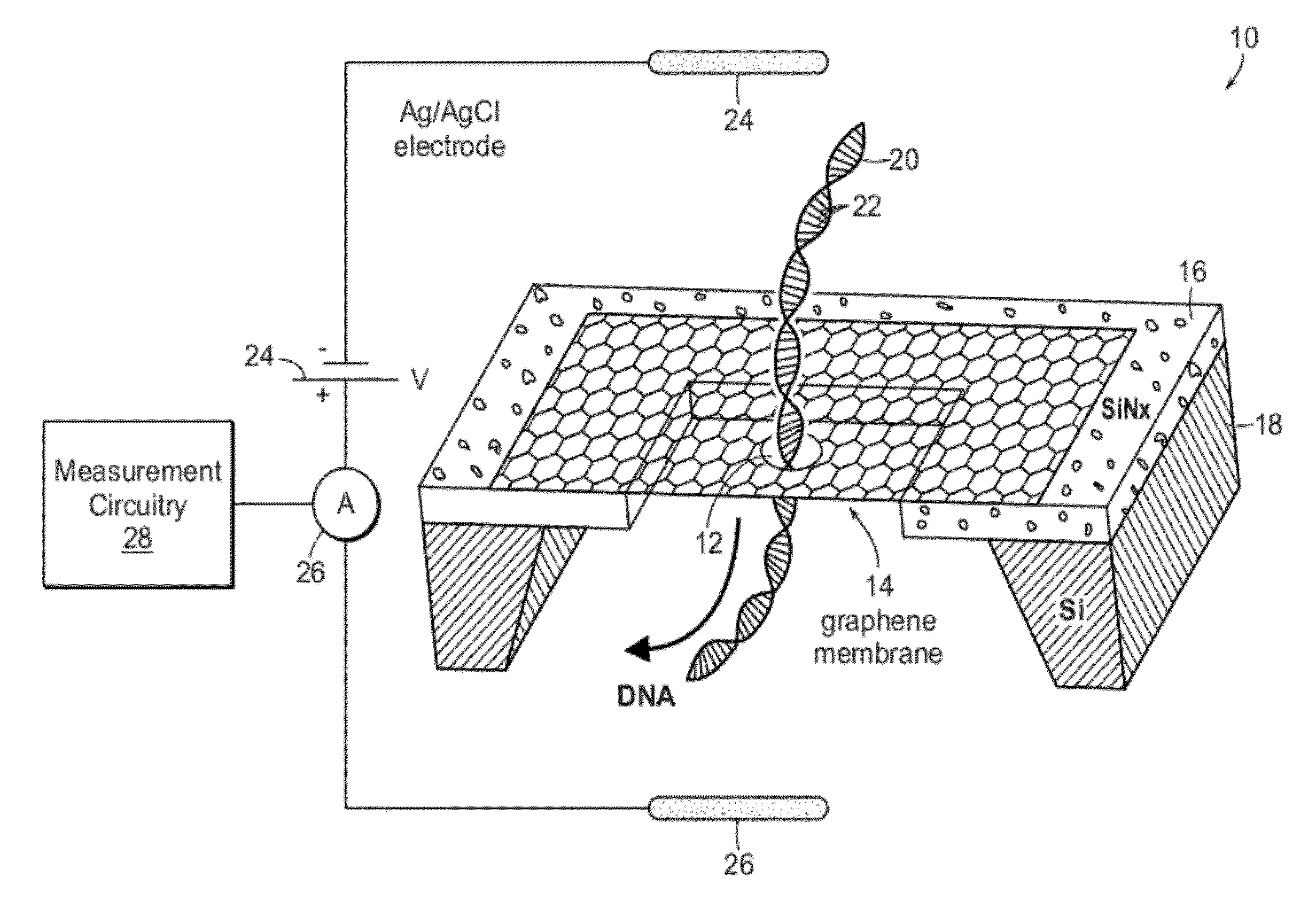
Nanometric Material Having a Nanopore Enabling High-Sensitivity Molecular Detection and Analysis
ActiveUS20120234679A1Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementSingle layer grapheneProtein translocation
There is provided a substantially bare, self-supported single-layer graphene membrane including a nanopore extending through a thickness of the graphene membrane from a first to a second membrane surface opposite the first graphene membrane surface. A connection from the first graphene membrane surface to a first reservoir provides, at the first graphene membrane surface, a species in an ionic solution to the nanopore, and a connection from the second graphene membrane surface to a second reservoir is provided to collect the species and ionic solution after translocation of the species and ionic solution through the nanopore from the first graphene membrane surface to the second graphene membrane surface. An electrical circuit is connected on opposite sides of the nanopore to measure flow of ionic current through the nanopore in the graphene membrane.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
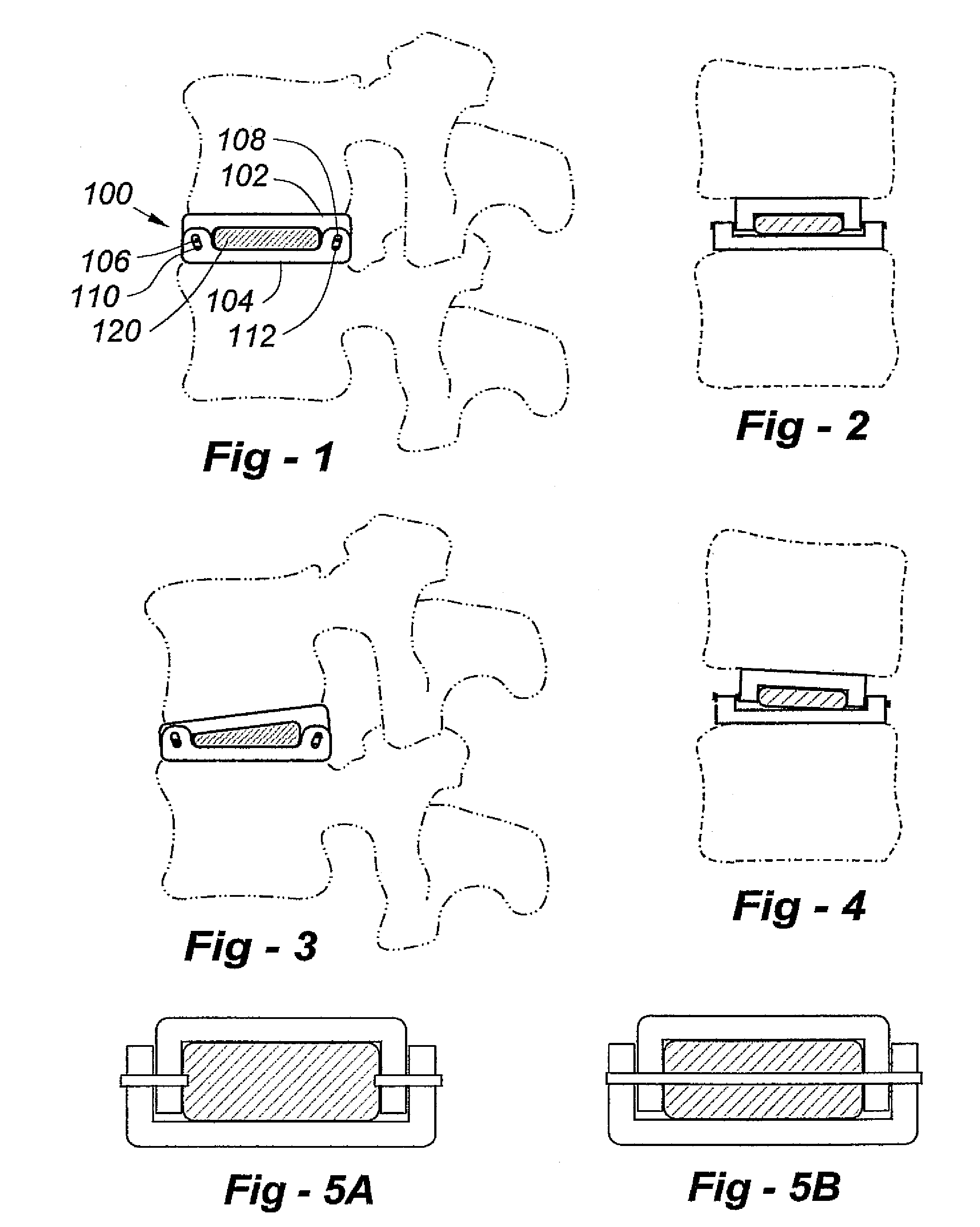
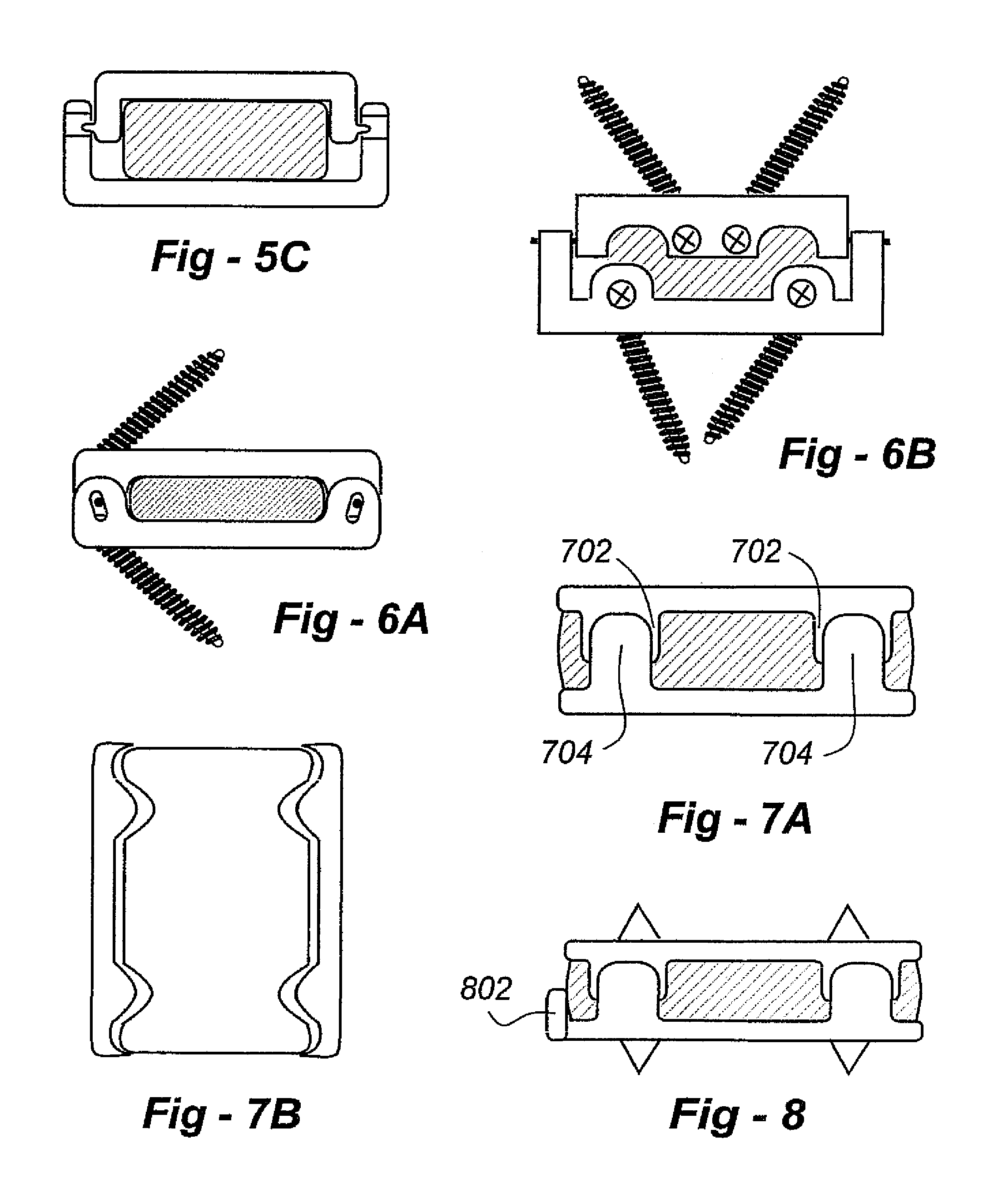
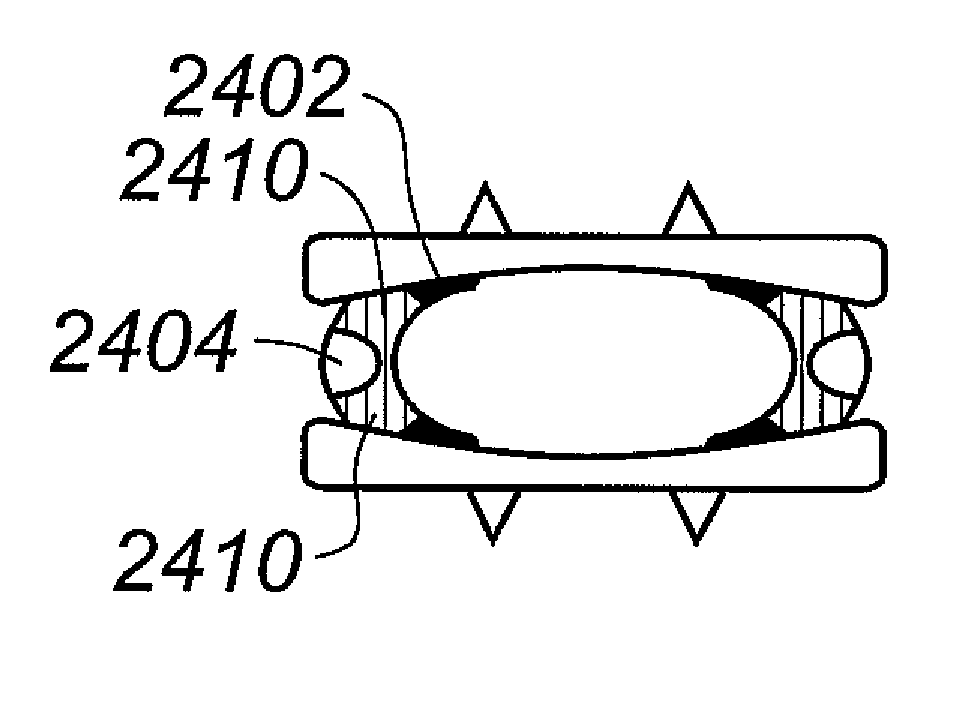
Biaxial artificial disc replacement
An artificial disc replacement (ADR) is designed to protect a cushioning component from excessive force. Physical features on the front and back of the ADR enable the device to replicate the normal movements of the spine through predetermined, limited, movements of the endplate components relative to one another. For example, though not limited to these characteristics, the components of the ADR could be dimensioned to allow 15 degrees of flexion, 5 degrees of extension, 5 degrees of lateral bending, and 1-2 mm of translocation. In the preferred embodiment the physical features are axles that extend through overlapping lateral portions associated with the endplate components. A desirable configuration includes a pair of axles, one in the anterior portion and another in the posterior portion, wherein some or all of the axles extend through an oversized aperture that allows the limited relative movement of the endplate components. Alternatively, the anterior and posterior physical features may include mating projections and depressions to permit a desired degree of relative movement.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
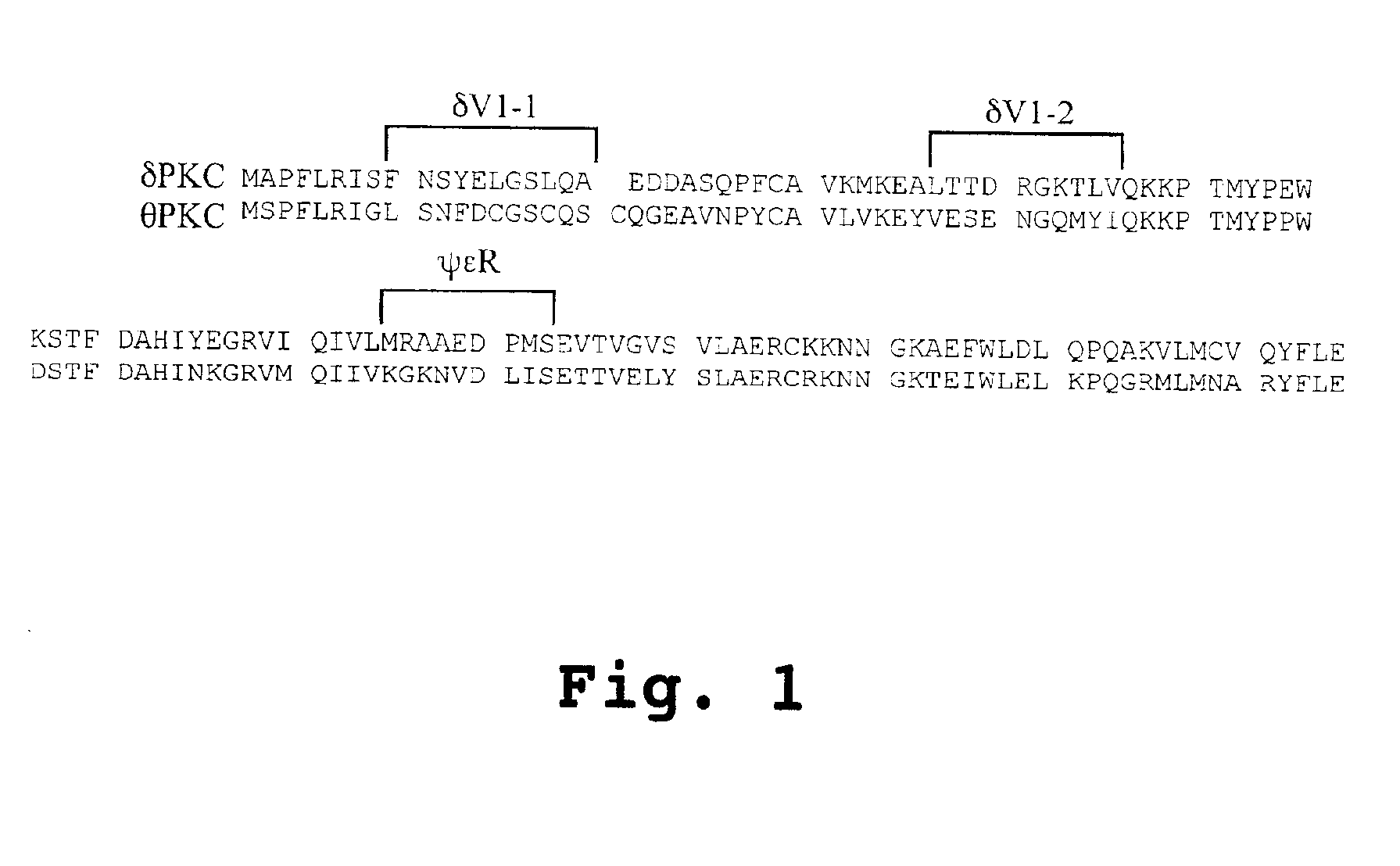
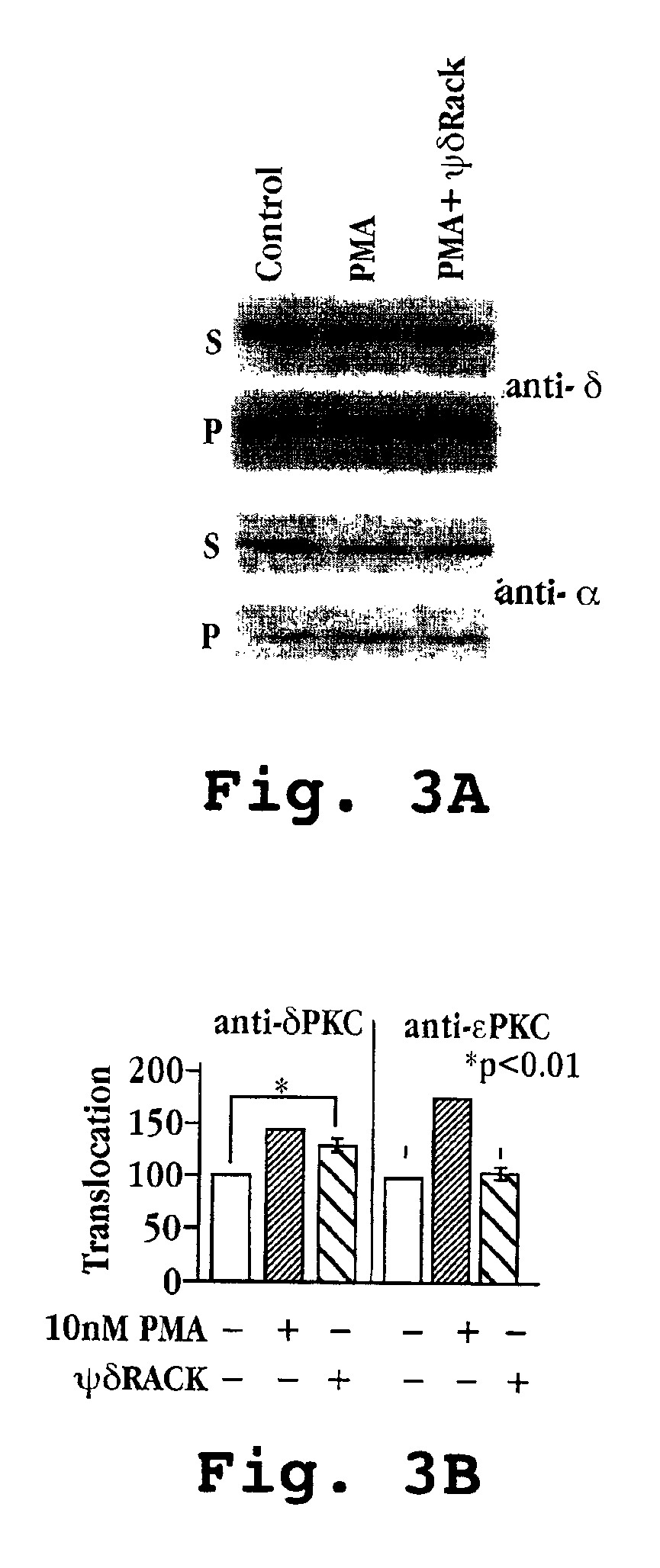
Peptides for activation and inhibition of δPKC
InactiveUS6855693B2Protection from damageEasily damagedSenses disorderNervous disorderMedicineCell damage
Peptides able to inhibit or activate the translocation or function of δPKC are identified. Administration of the peptides for protection or enhancement of cell damage due to ischemia is described. Therapeutic methods to reduce damage to cells or to enhance damage to cells due to ischemia are also described, as well as methods for screening test compounds for δPKC-selective agonists and antagonists.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Cell membrane translocation of regulated snare inhibitors, compositions therefor, and methods for treatment of disease
Compositions and methods of modulating cellular function and treatment of disease in mammals comprising locally administering a regulated SNARE inhibitor and a translocating agent to the mammal. Regulated SNARE inhibitors include clostridial neurotoxins, tetanus neurotoxin and their free light chain portions and IgA protease. Translocating agents include acids, encapsulating vectors, and transduction domains.
Owner:SANDERS
Artificial disc replacement (ADR) using elastic tether member
InactiveUS7291171B2Prevent dislocationAvoid excessive compressionJoint implantsSpinal implantsDislocationProtein translocation
Artificial disc (ADR) and joint replacement components, particularly those associated with the knee and hip, use compressible, resilient materials to approximate natural kinematics, often in conjunction with elastic or spring components to tether articulating components to avoid dislocation, excessive compression, flexion or other out-of-range movements. The preferred embodiments require only two or a few articulating components. The designs allow for normal flexion, extension, lateral bending, rotation, and translocation, depending upon the application.
Owner:ANOVA
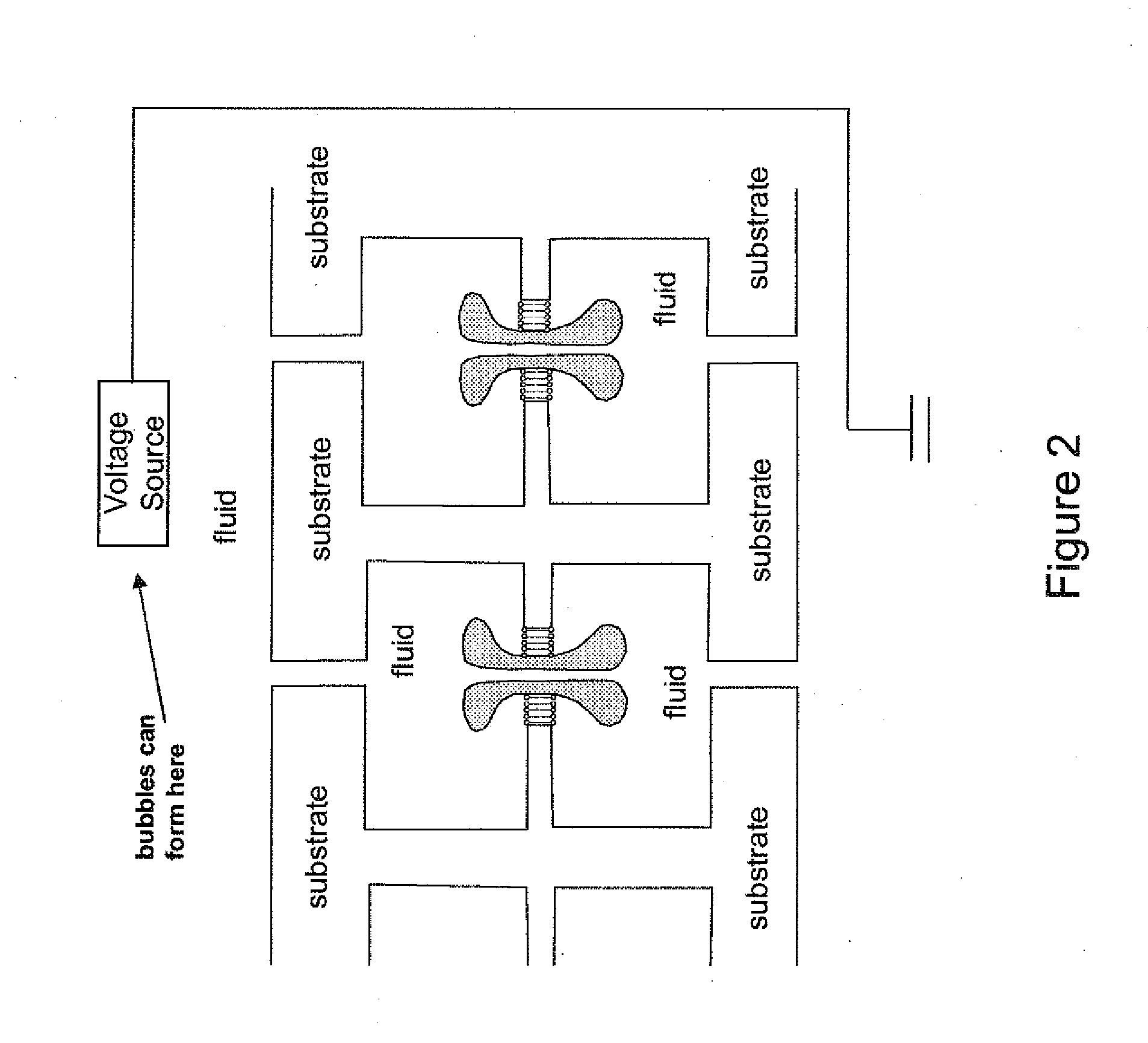
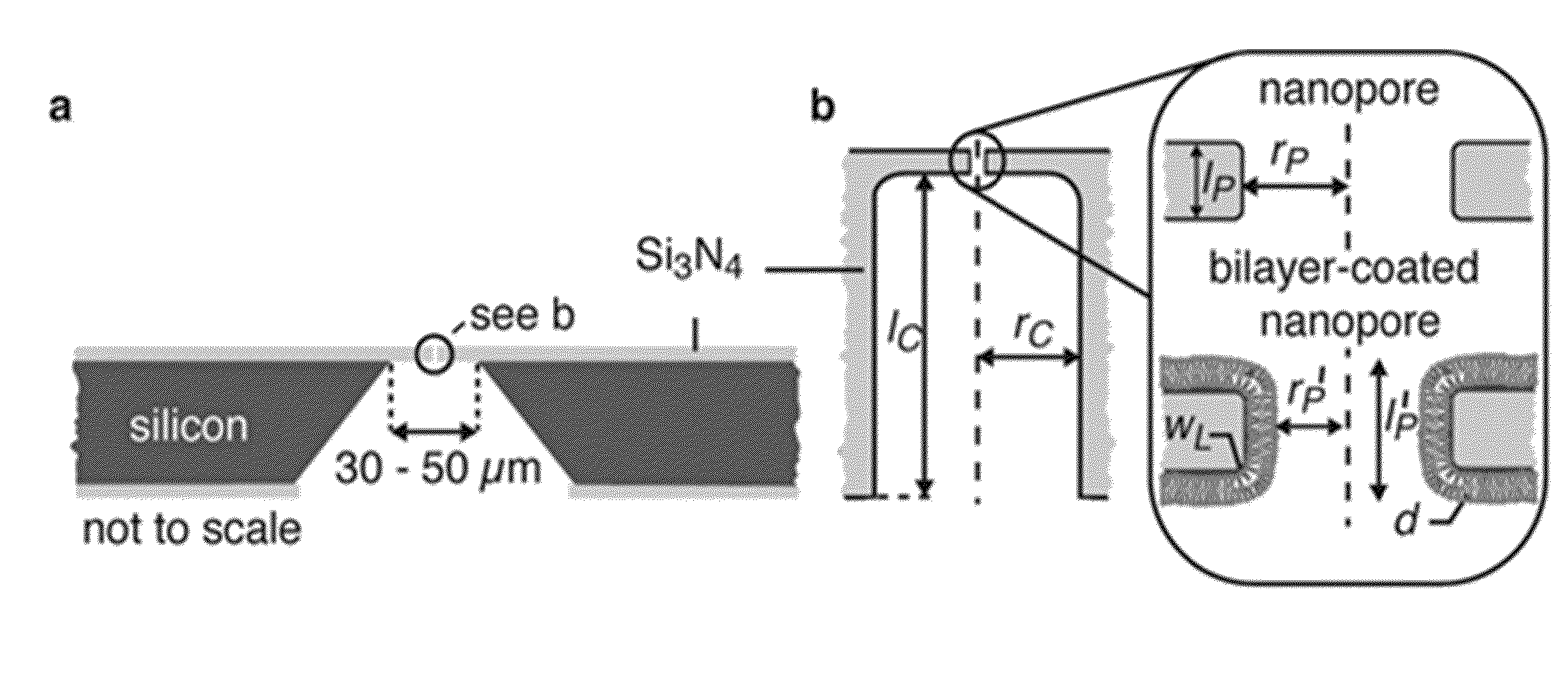
Controlling translocation through nanopores with fluid wall
ActiveUS20130048499A1Improved resolution and detectionPrevents clogged poresMaterial nanotechnologySludge treatmentLipid formationNanoparticle
Improved resolution and detection of nanoparticles are achieved when a nanopore connecting liquid compartments in a device running on the Coulter principle is provided with fluid lipid walls. The fluid lipid walls are made of a lipid bilayer, and preferably include lipid anchored mobile ligands as part of the lipid bilayer. By varying the nature and concentration of the mobile ligand in the lipid bilayer, multifunctional coatings of lipids are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods for identifying target nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20050266417A1Rapid and accurate hybridizationReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSplice Site SNPTarget mrna
The present invention relates to methods for identifying target nucleic acid molecules differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, deletions, or translocations; and identifying one or more target mRNA molecules differing by one or more splice site variations in a plurality of mRNA molecules. Also disclosed is a method of generating a linearly amplified representation of a whole genome. Other aspects of the present invention relate to labeled detection oligonucleotide probes and translational oligonucleotide probes as well as to methods of designing such probes.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Personalized tumor biomarkers
InactiveUS20130210645A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood plasmaRecurrent Tumor
Clinical management of human cancer is dependent on the accurate monitoring of residual and recurrent tumors. We have developed a method, called personalized analysis of rearranged ends (PARE), which can identify translocations in solid tumors. Analysis of four colorectal and two breast cancers revealed an average of nine rearranged sequences (range 4 to 15) per tumor. Polymerase chain reaction with primers spanning the breakpoints were able to detect mutant DNA molecules present at levels lower than 0.001% and readily identified mutated circulating DNA in patient plasma samples. This approach provides an exquisitely sensitive and broadly applicable approach for the development of personalized biomarkers to enhance the clinical management of cancer patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Controlled translocation of a polymer in an electrolytic sensing system
ActiveUS20080041733A1Reduce thermally induced motionImprove spatial resolutionImmobilised enzymesElectrostatic separatorsTemperature controlElectricity
Owner:ELECTRONICS BIOSCI
Apparatus and method for biopolymer identification during translocation through a nanopore
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for identifying and sequencing a biopolymer translocating a nanopore. The apparatus of the present invention provides a first electrode, a second electrode and a potential means for applying a bias ramping potential across the electrodes to produce resonant tunneling of current carriers between the two electrodes. As the bias potential is ramped across the electrodes the increase in tunneling current occurs as the carrier energy sequentially matches the conduction band energies of the translocating biopolymer. This technique allows for real-time identification and sequencing of a biopolymer as the band energy spectra of the individual portions of the bipolymer are recorded, differentiated and identified. A method for identifying the biopolymer is also disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
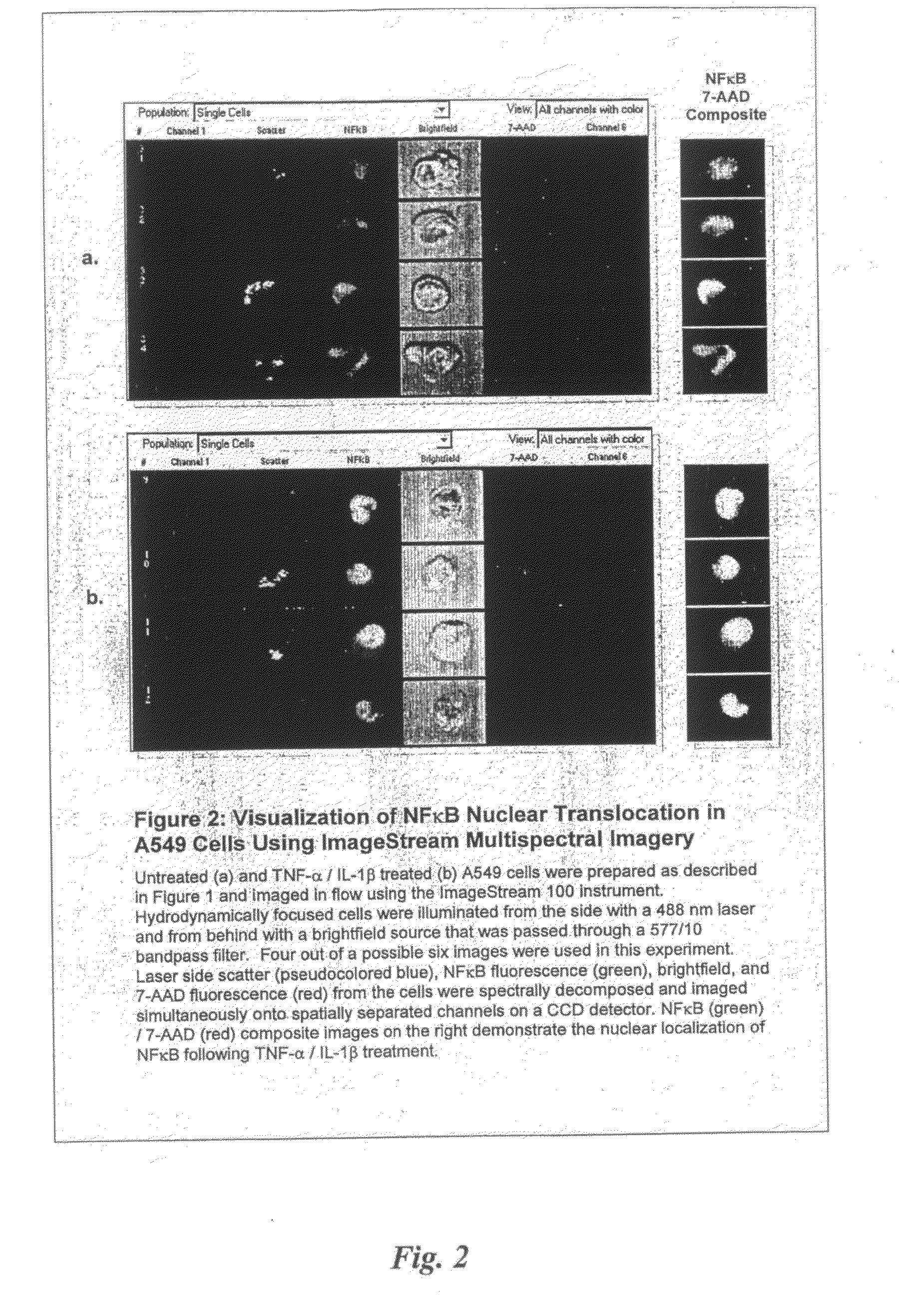
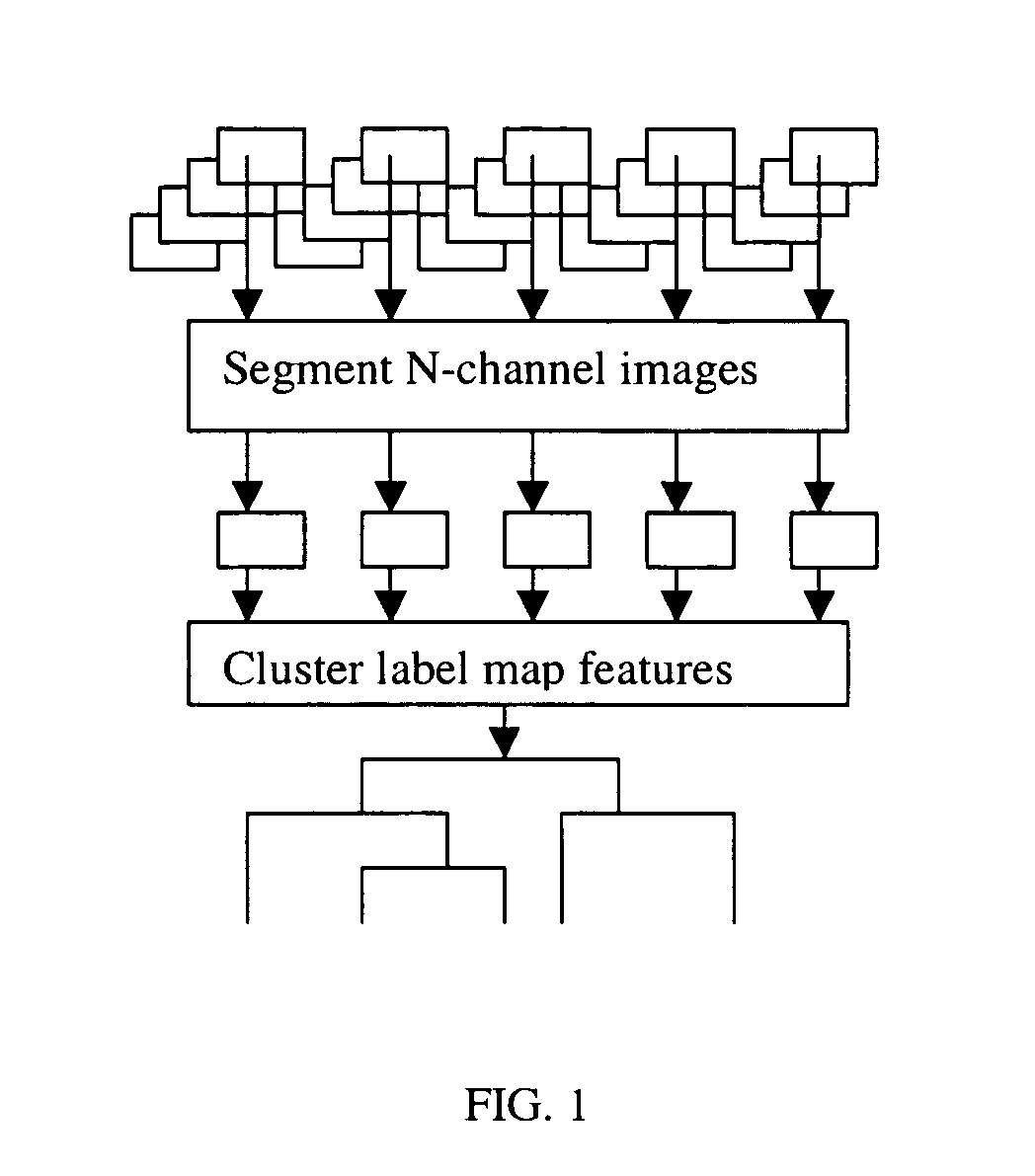
System and method for automatic color segmentation and minimum significant response for measurement of fractional localized intensity of cellular compartments
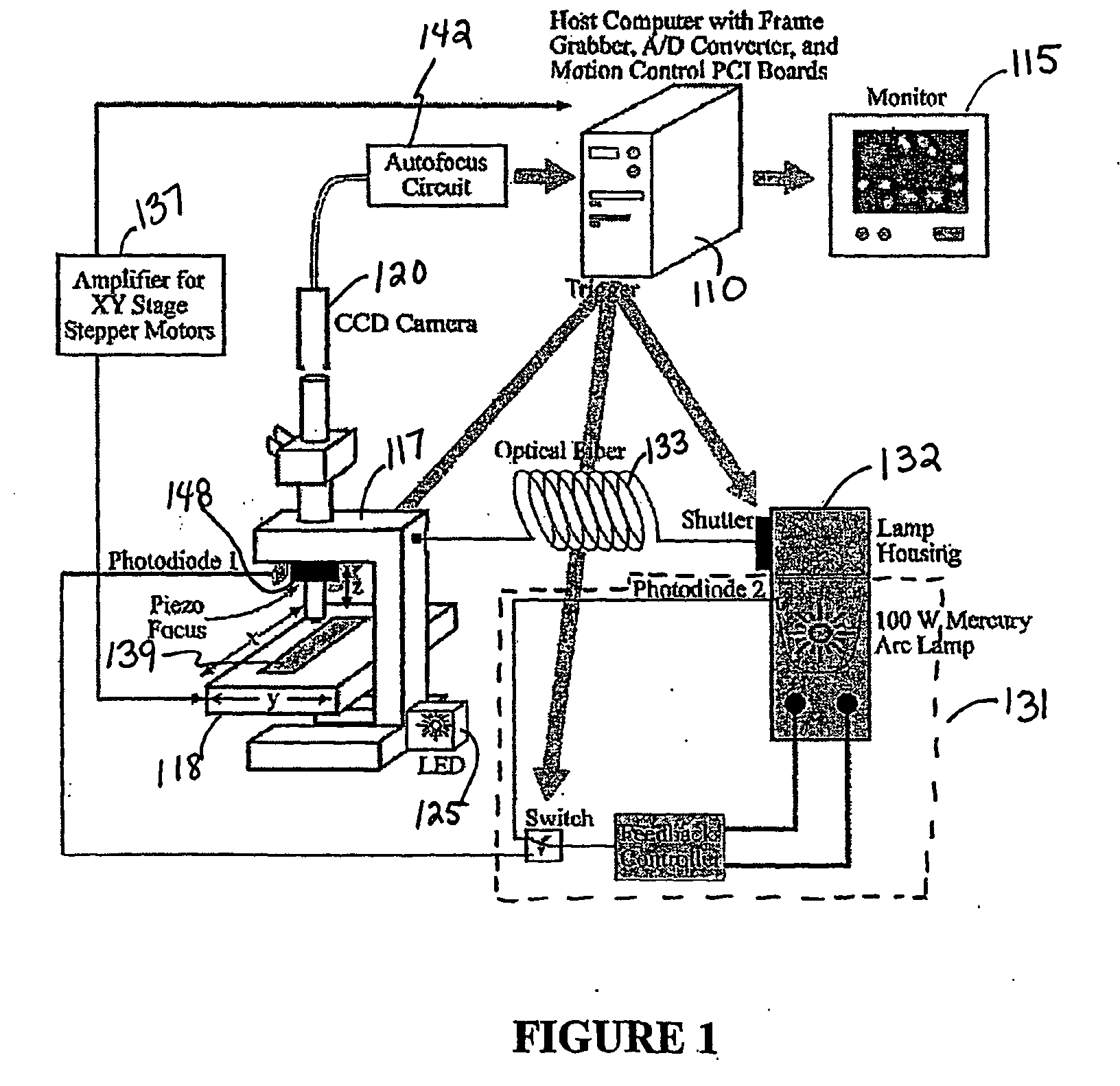
ActiveUS20070016373A1Improve throughputInteraction is complexBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementSystems approachesComputer science
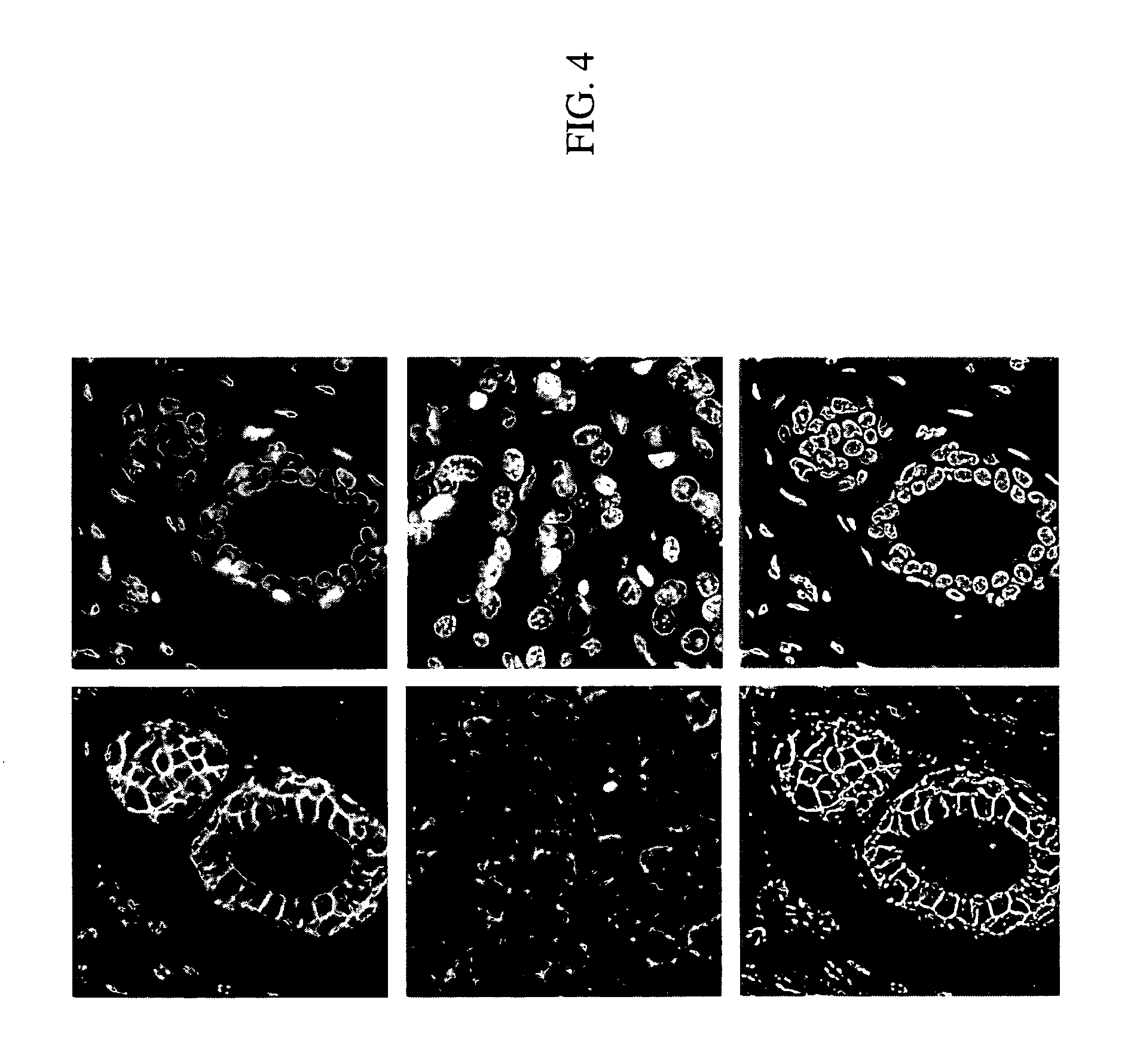
A system, a method, and a programmed device for measurement of translocational activity among cellular compartments process magnified images of cellular material exposed to an agent by segmenting and compartmentalizing the images and then measuring fractional localized intensity of two or more components in the segmented, compartmentalized image. The measured fractional localized intensities are compared to determine translocation of cellular material among the measured components caused by the agent.
Owner:VALA SCI
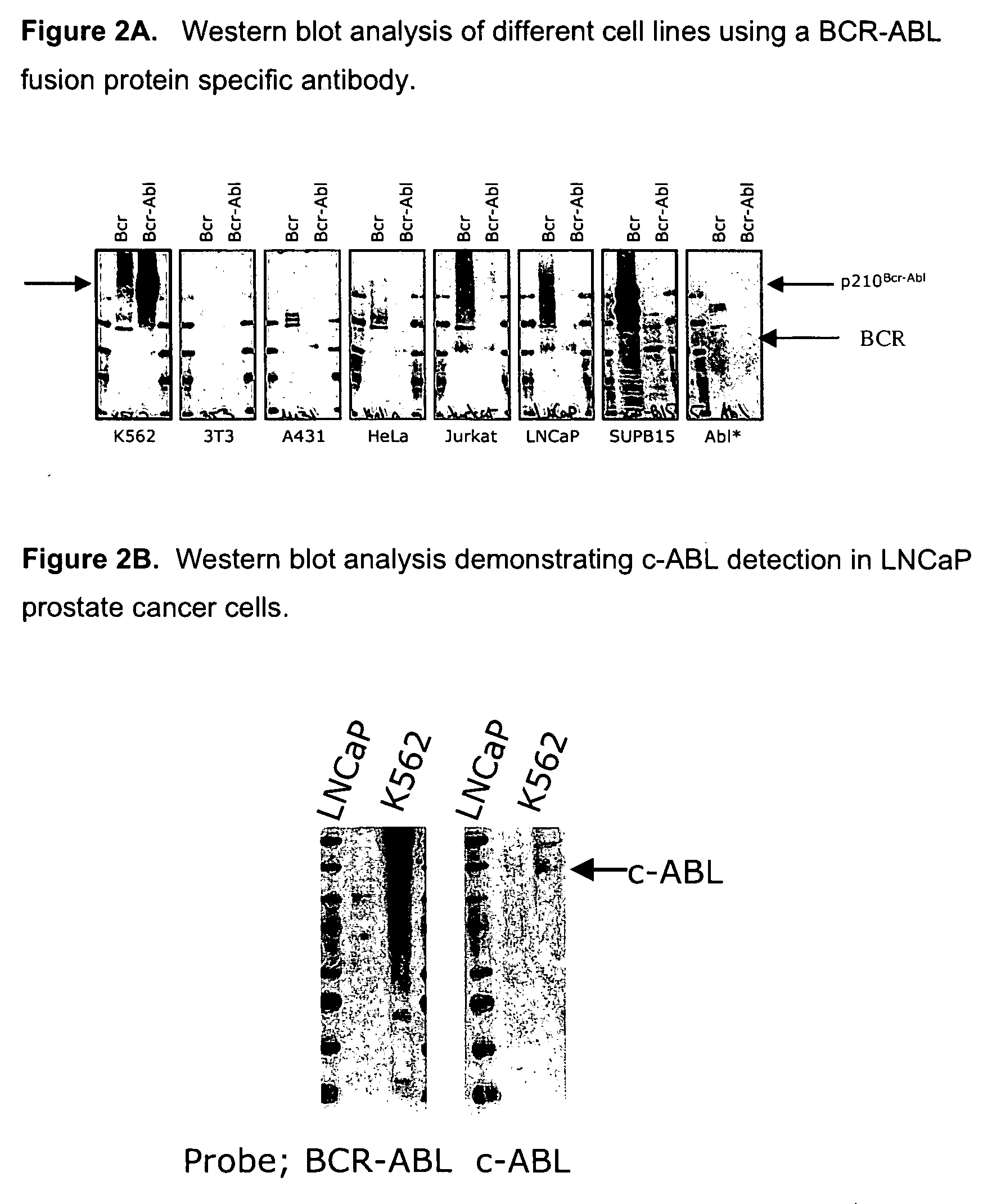
Antibodies specific for BCR-ABL fusion protein and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050214301A1Animal cellsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWild typeP210(bcr-abl) Fusion Proteins
The invention provides isolated antibodies that specifically bind human P210 BCR-ABL fusion protein, but do not bind the respective wild type BCR and c-ABL proteins. The detection of this fusion protein is relevant to CML and other diseases characterized by the P210 BCR-ABL translocation. Also provided are methods for determining the level or expression of P210 BCR-ABL in a biological sample, or identifying a compound that modulates such expression, by using the disclosed BCR-ABL specific antibodies.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Image based quantitation of molecular translocation
ActiveUS20090202130A1Character and pattern recognitionBiological testingProtein translocationMolecular marker
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Method and system for elasto-modulation of ocular tissue
InactiveUS20070203478A1Eliminate side effectsOptimize rateLaser surgeryUltrasound therapyAqueous outflowIntraocular pressure
Excitation and radiation techniques and apparatus for performing customized elasto-modulation of ocular tissue in an annular region around the cornea, such as for the purpose of ciliary translocation (ACT) or promotion of aqueous outflow to relieve ocular pressure are provided utilizing a transconjunctival incisionless scleral treatment. Laser radiation is for example applied to scleral tissue to decrease zonular slack, or alter equatorial offsets between lens and ciliary muscles as a treatment for presbyopia by way of example.
Owner:SEROS MEDICAL
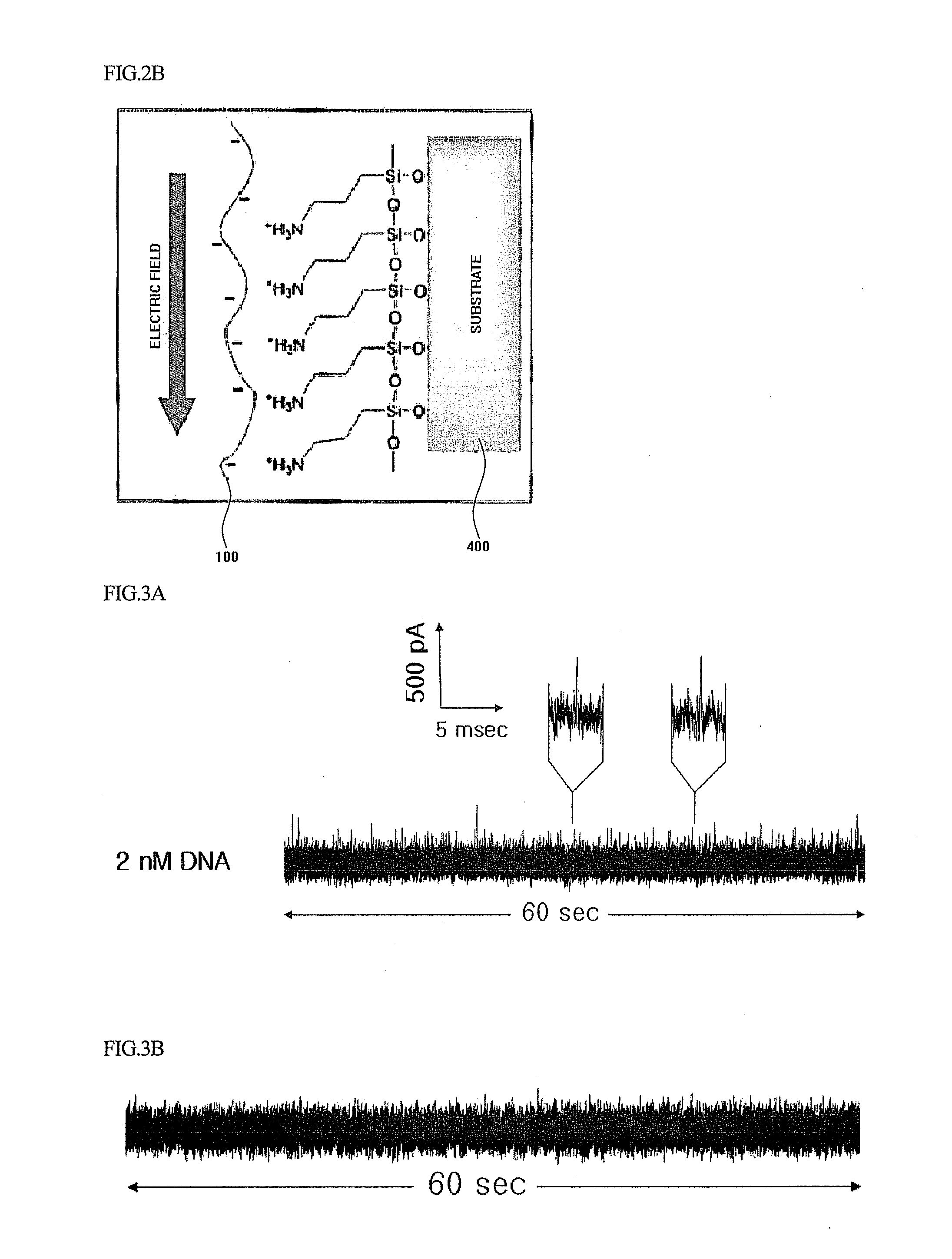
Method and device for detecting DNA using surface-treated nanopore
InactiveUS20070218471A1Enhanced interactionExtended durationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsA-DNASolid substrate
Disclosed herein is a method for detecting DNA using a nanopore including treating the surface of a nanopore formed in a solid substrate with a substance carrying positive charges; introducing a DNA-containing sample into the surface-treated nanopore; and detecting electrical signals generated during translocation of the sample through the nanopore. Also disclosed herein is device for detecting DNA using a nanopore including a solid substrate including a nanopore, treated with a substance which carries positive charges to change a surface property of the nanopore so that the nanopore surface carries positive charges; an electrode applying voltage to the nanopore of the solid substrate; and a measurement unit measuring an electrical signal generated during translocation of a DNA-containing sample through the nanopore.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
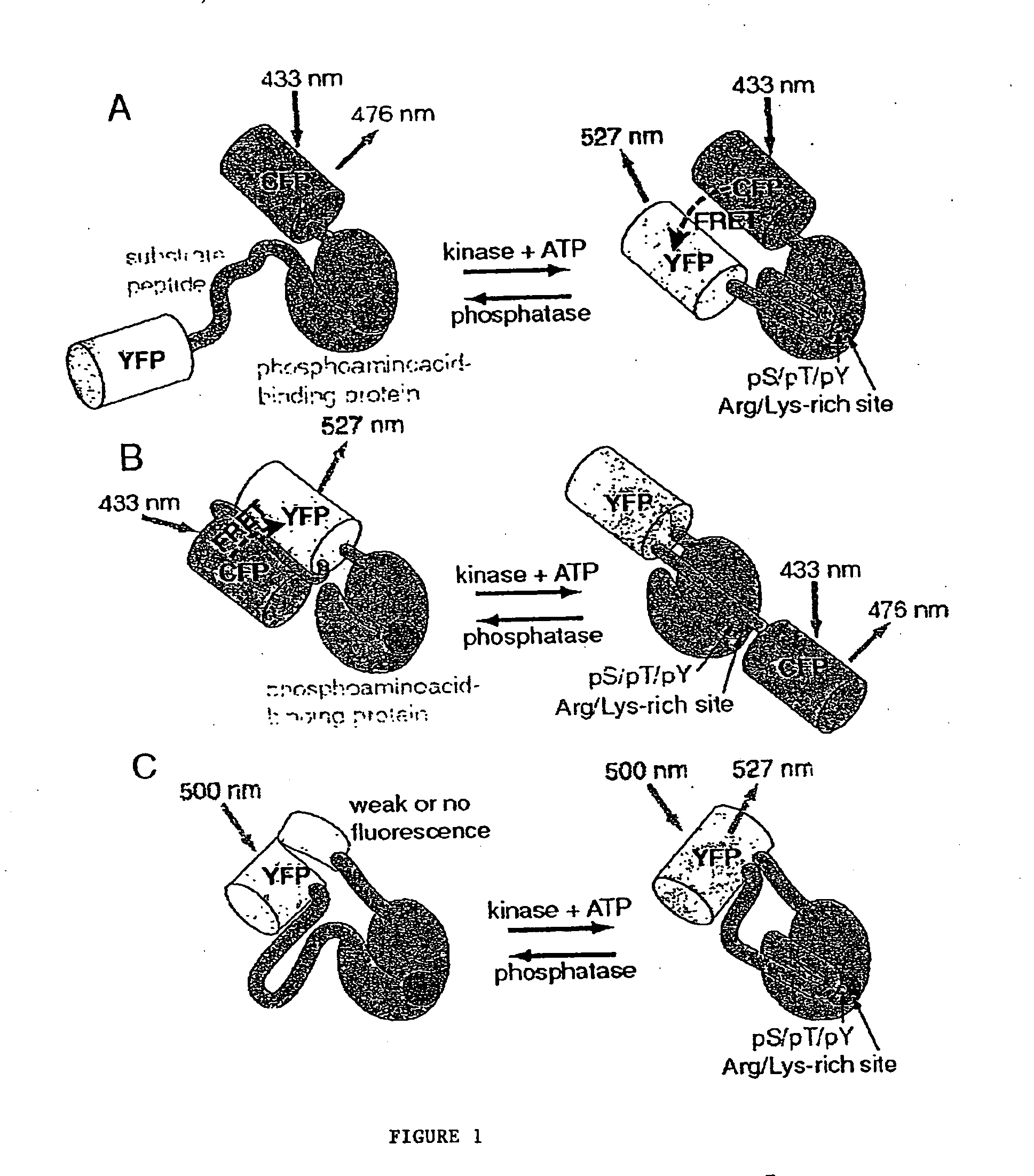
Emission ratiometric indicators of phosphorylation by C-kinase
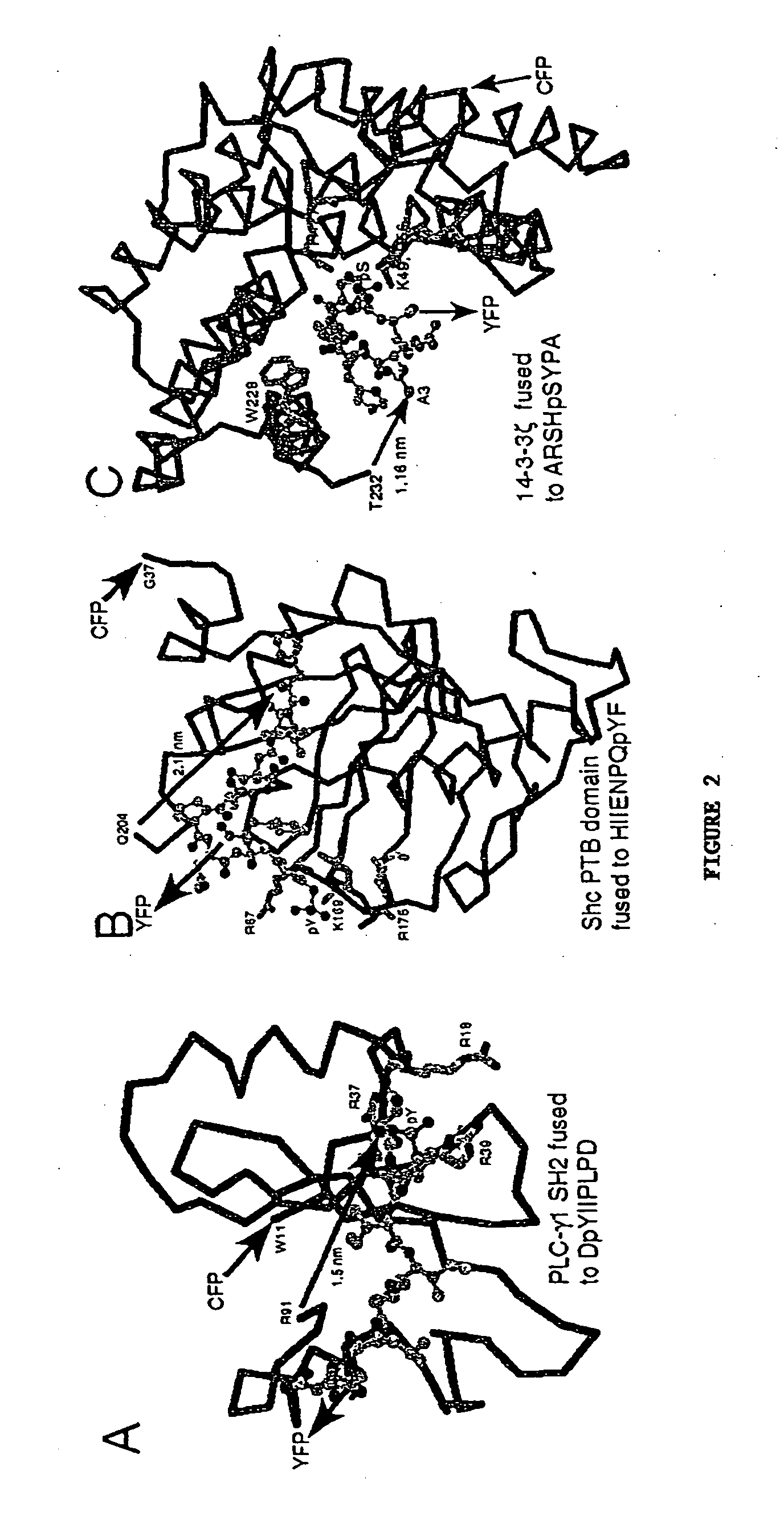
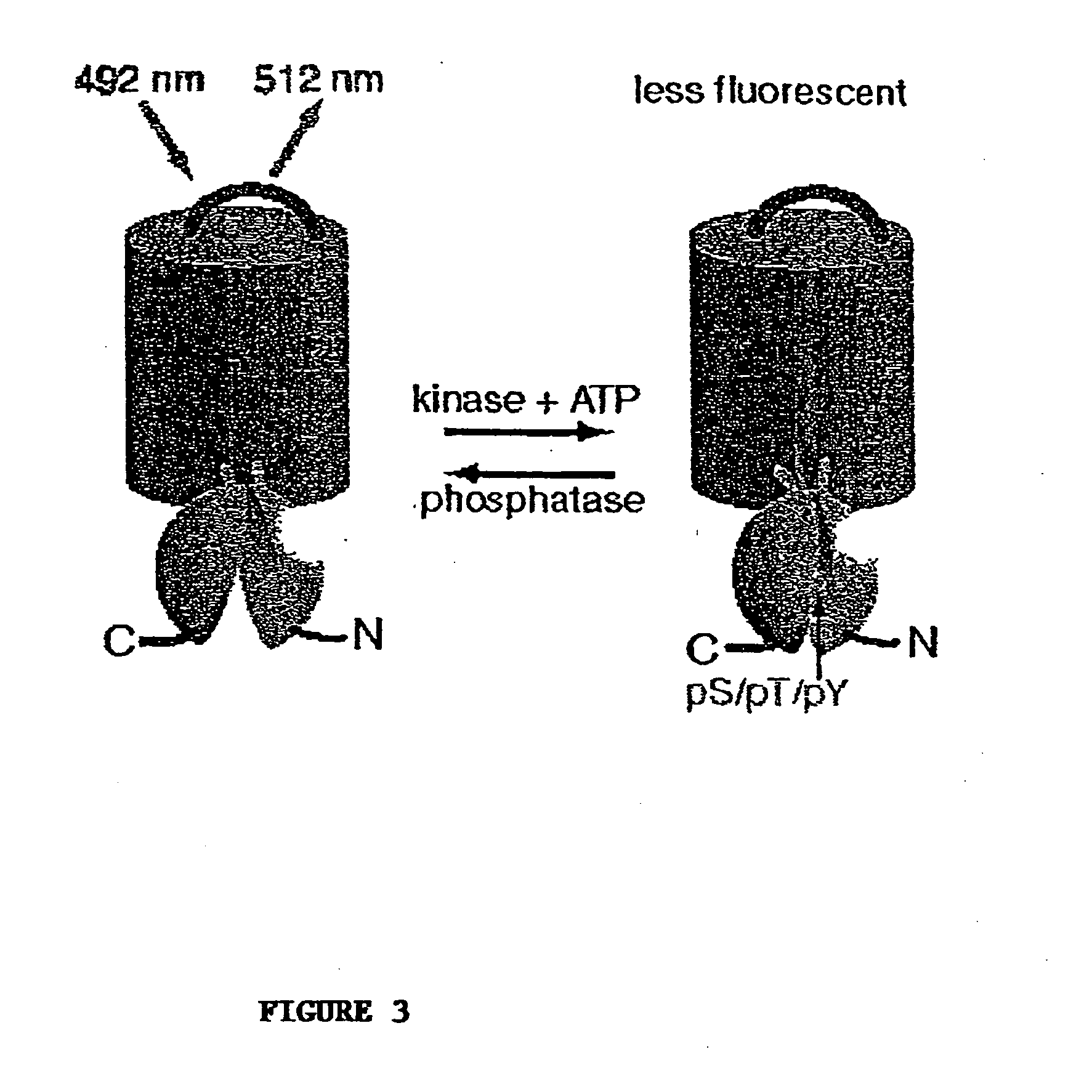
InactiveUS20050026234A1Facilitate its translocationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideFluorophore
A chimeric phosphorylation indicator (CPI) as provided herein can contain a donor molecule, a phosphorylatable domain, a phosphoaminoacid binding domain (PAABD), and an acceptor molecule. Where the phosphorylatable domain is phosphorylatable by protein kinase C (PKC), the CPI is a c-kinase activity reporter (CKAR). Donor and acceptor molecules may be, independently, fluorescent proteins such as non-oligomerizing fluorescent proteins. A CPI can contain a phosphorylatable polypeptide and a fluorescent protein; the phosphorylatable polypeptide may be contained within the sequence of the fluorescent protein, or the fluorescent protein may be contained within the sequence of the phosphorylatable polypeptide. The spatiotemporal properties of the PKC signal pathway may be tested with CKAR, calcium-sensing fluorophores and FRET-based translocation assays. Polynucleotides encoding such CPIs, and kits containing the indicators and / or the polynucleotides, are provided. A method of using the chimeric phosphorylation indicators to detect a kinase or phosphatase in a sample is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
System and Method to Improve Accuracy of a Polymer
InactiveUS20090222216A1Reduce relative motionGain is not constantMicrobiological testing/measurementMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDiffusionMeasurement device
The sequencing of individual monomers (e.g., a single nucleotide) of a polymer (e.g., DNA, RNA) is improved by reducing the motion of the polymer due to thermally-driven diffusion to reduce the spatial error in the position of the polymer within a measurement device. A major system parameter, such as average translocation velocity or measurement time, is selected based on the characteristics of the sensing system utilized, and an algorithm jointly optimizes the sequencing order error rate and the monomer identification error rate of the system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS BIOSCI
Methods for identifying agents that inhibit cell migration, promote cell adhesion and prevent metastasis
Disclosed are methods for identification of agents that modulate cell attachment, cell migration and cell viability. Cancer and primary cells adhered to a matrix are treated with agent(s) that modulate ActRII signaling and cell adhesion. Agents are tested that modulate cell adhesion, detachment, invasion and viability. Agents that modulate the expression, phosphorylation, function and translocation of ActRII signaling pathway members also can predict agents that modulate cell adhesion, detachment, invasion and viability. The methods have utility in identifying agents that prevent cancer cell metastasis, wound dehiscence, aortic dissection and aid retina attachment and skin replacement and fertility.
Owner:GENREMEDY
Apparatus and method for control of biopolymer translocation through a nanopore
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for controlling the movement of a biopolymer translocating a nanopore. The invention provides a first electrode, a second electrode adjacent to the first electrode, a third electrode adjacent to the second electrode and a fourth electrode adjacent to the third electrode. The first electrode is in electrical connection with the third electrode to define a first set of electrodes and the second electrode is in electrical connection with the fourth electrode to define a second set of electrodes. A DC voltage and radio frequency voltage is applied to the first set of electrodes while an opposite DC voltage and phase shifted radio frequency voltage is applied to the second set of electrodes to produce an electric field between the first set of electrodes and the second set of electrodes. The electric field is used to control the movement of a biopolymer translocating a nanopore. A method for controlling the movement of a biopolymer is also disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and methods for scoring images of a tissue micro array
A system for analyzing tissue samples, that generally comprises, a storage device for at least temporarily storing one or more images of one or more cells, wherein the images comprise a plurality of channels; and a processor that is adapted to determine the extent to which a biomarker may have translocated from at least one subcellular region to another subcellular region; and then to generate a score corresponding to the extent of translocation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Conjugates of galactose-binding lectins and clostridial neurotoxins as analgesics
InactiveUS7452543B2Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderBacteriaGalactose binding lectinProtein translocation
A class of novel agents that are able to modify nociceptive afferent function is provided. The agents may inhibit the release of neurotransmitters from discrete populations of neurones and thereby reduce or preferably prevent the transmission of afferent pain signals from peripheral to central pain fibers. They comprise a galactose-binding lectin linked to a derivative of a clostridial neurotoxin. The derivative of the clostridial neurotoxin comprises the L-chain, or a fragment thereof, which includes the active proteolytic enzyme domain of the light (L) chain, linked to a molecule or domain with membrane translocating activity. The agents may be used in or as pharmaceuticals for the treatment of pain, particular chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com