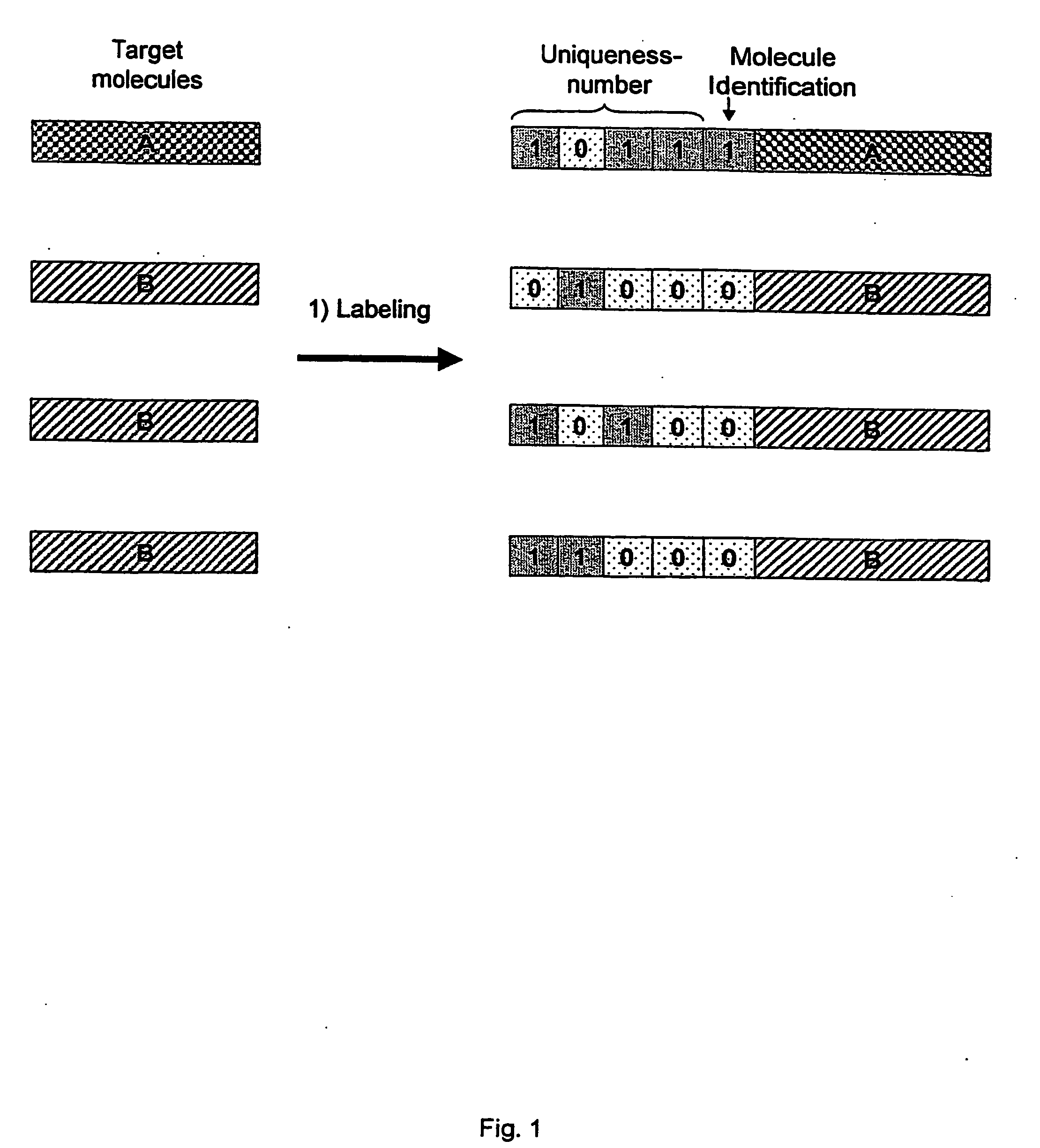
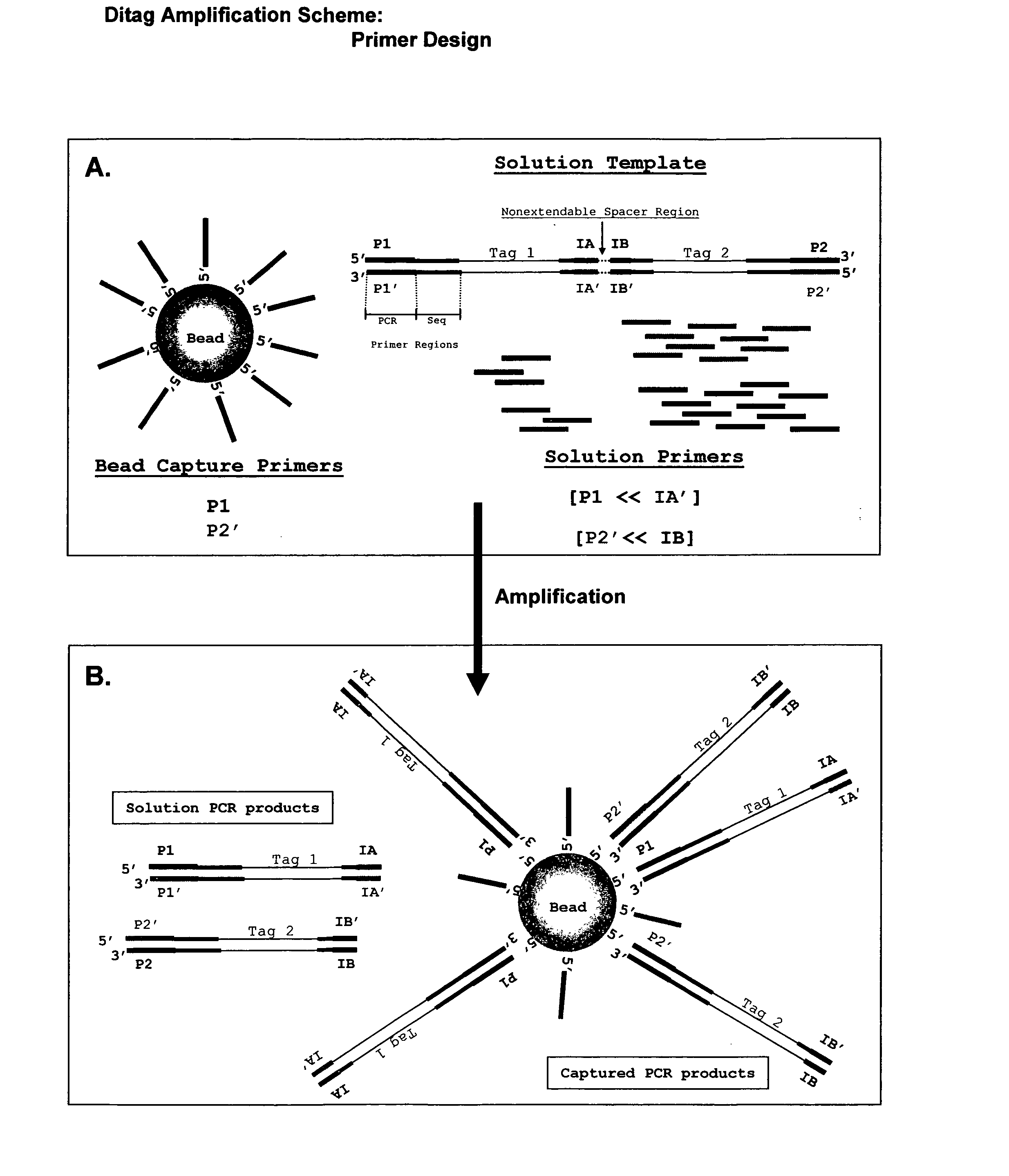
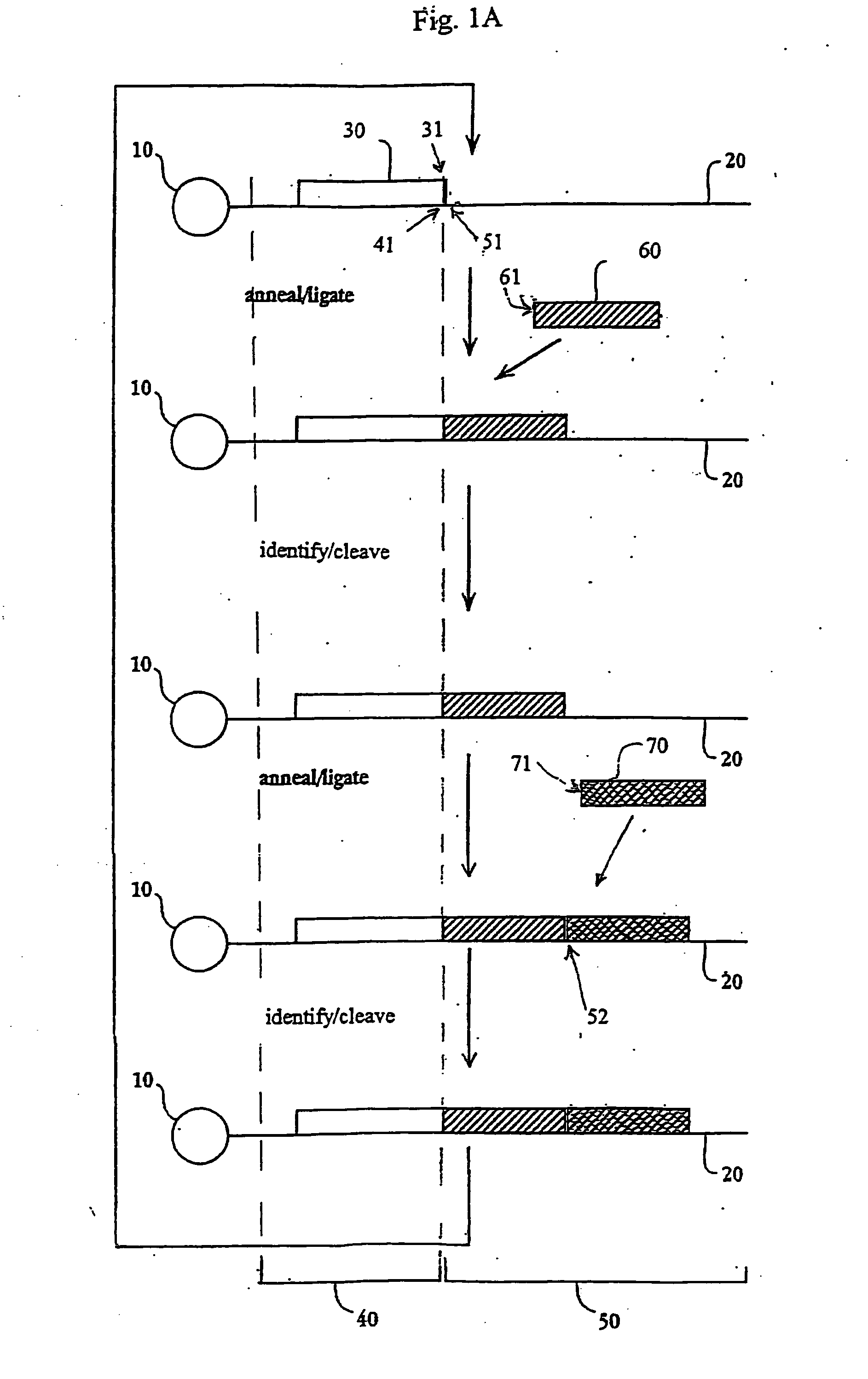
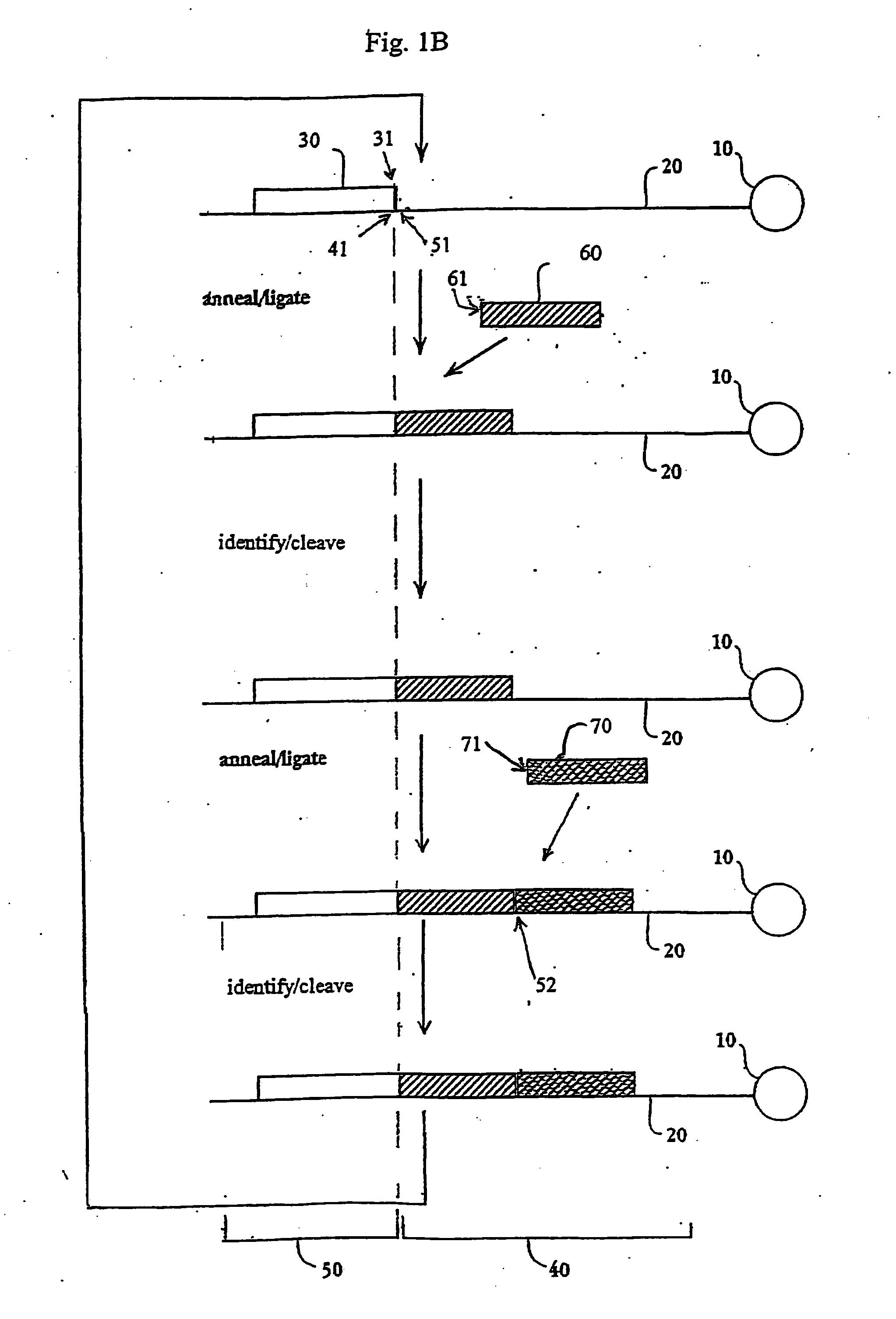
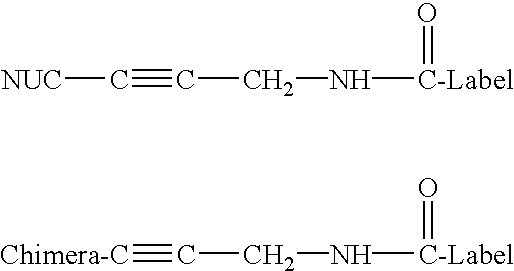Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
450 results about "Ligation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
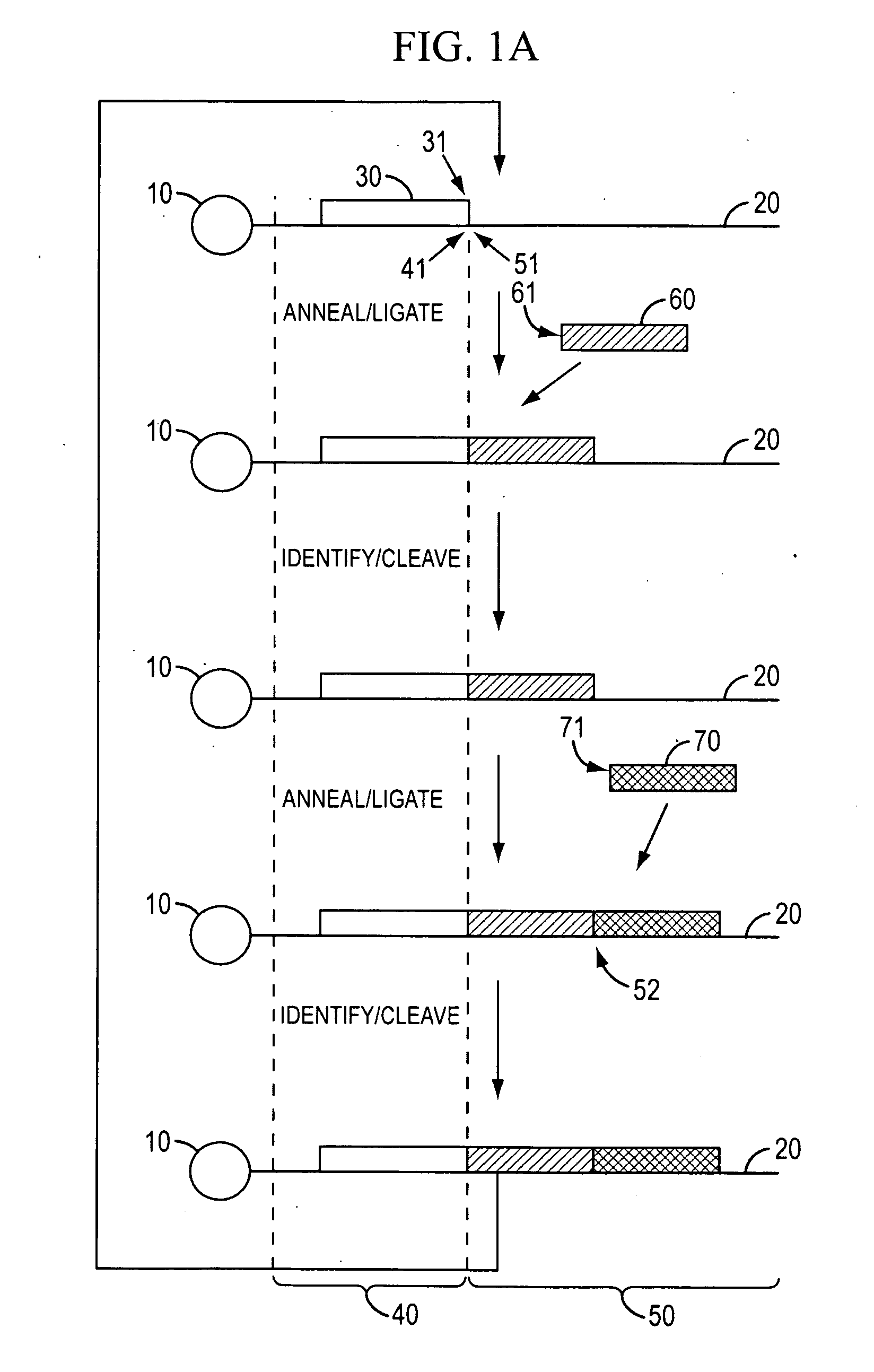
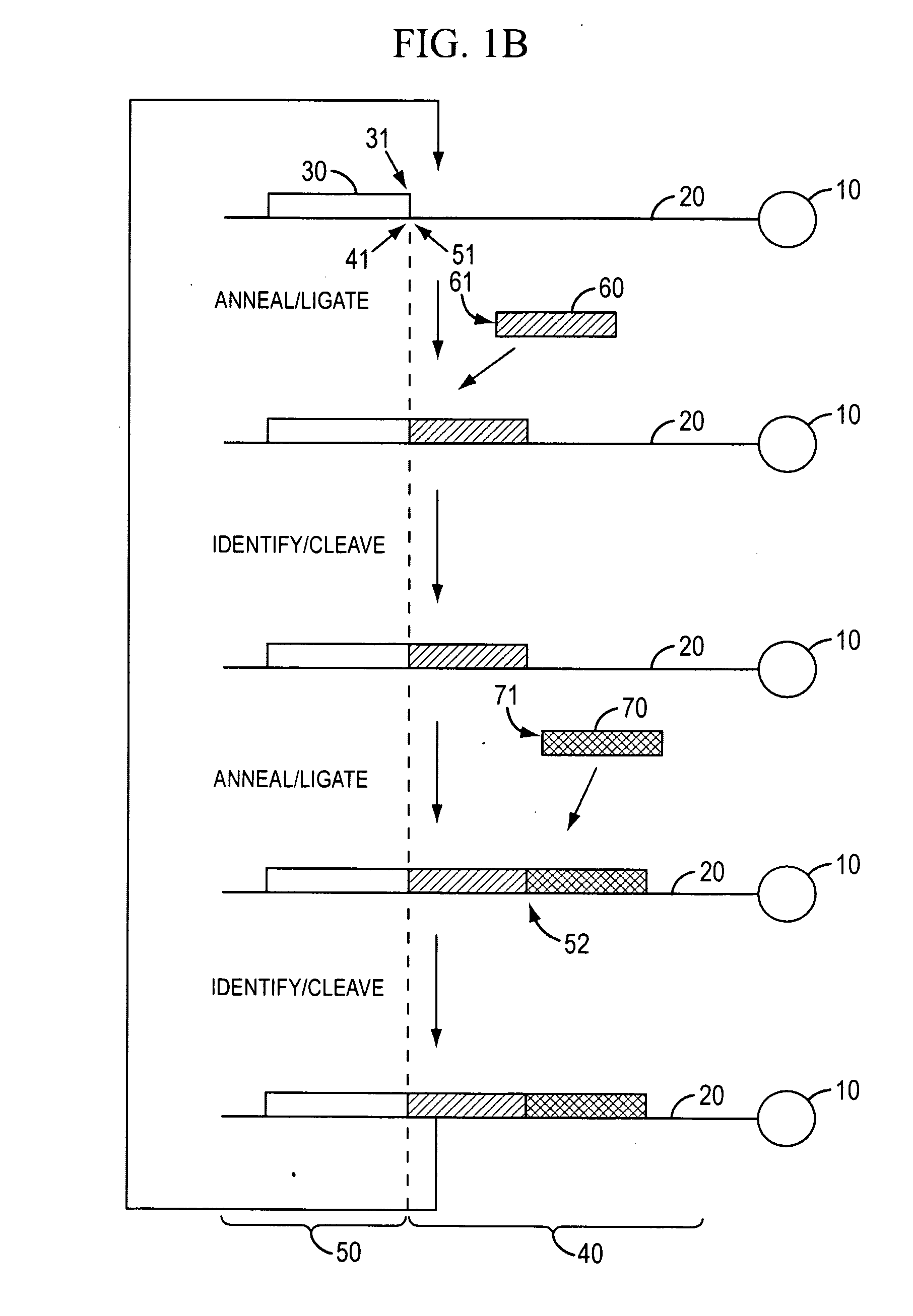
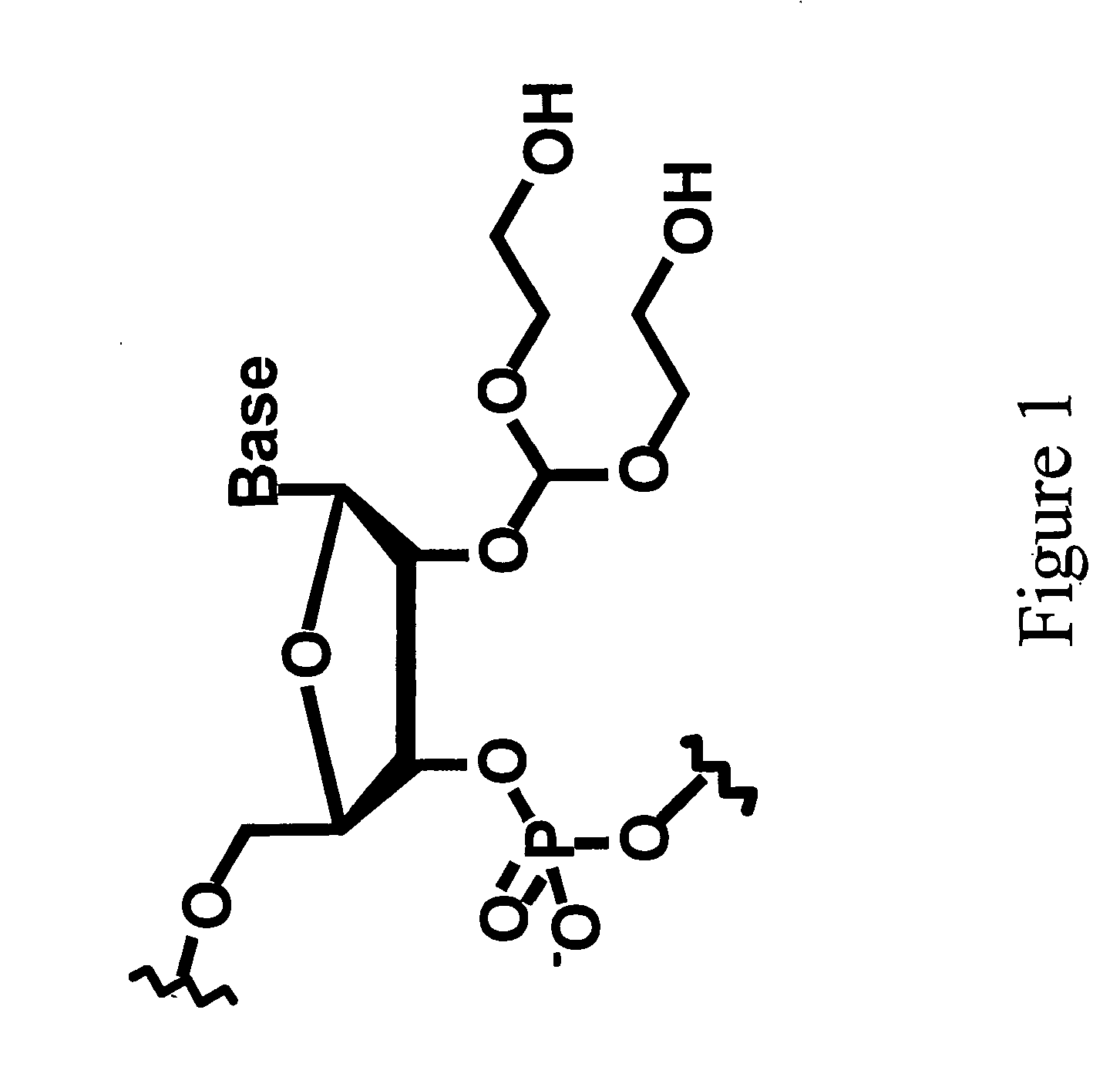
In molecular biology, ligation is the joining of two nucleic acid fragments through the action of an enzyme. It is an essential laboratory procedure in the molecular cloning of DNA whereby DNA fragments are joined together to create recombinant DNA molecules, such as when a foreign DNA fragment is inserted into a plasmid. The ends of DNA fragments are joined together by the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the 3'-hydroxyl of one DNA terminus with the 5'-phosphoryl of another. RNA may also be ligated similarly. A co-factor is generally involved in the reaction, and this is usually ATP or NAD⁺.
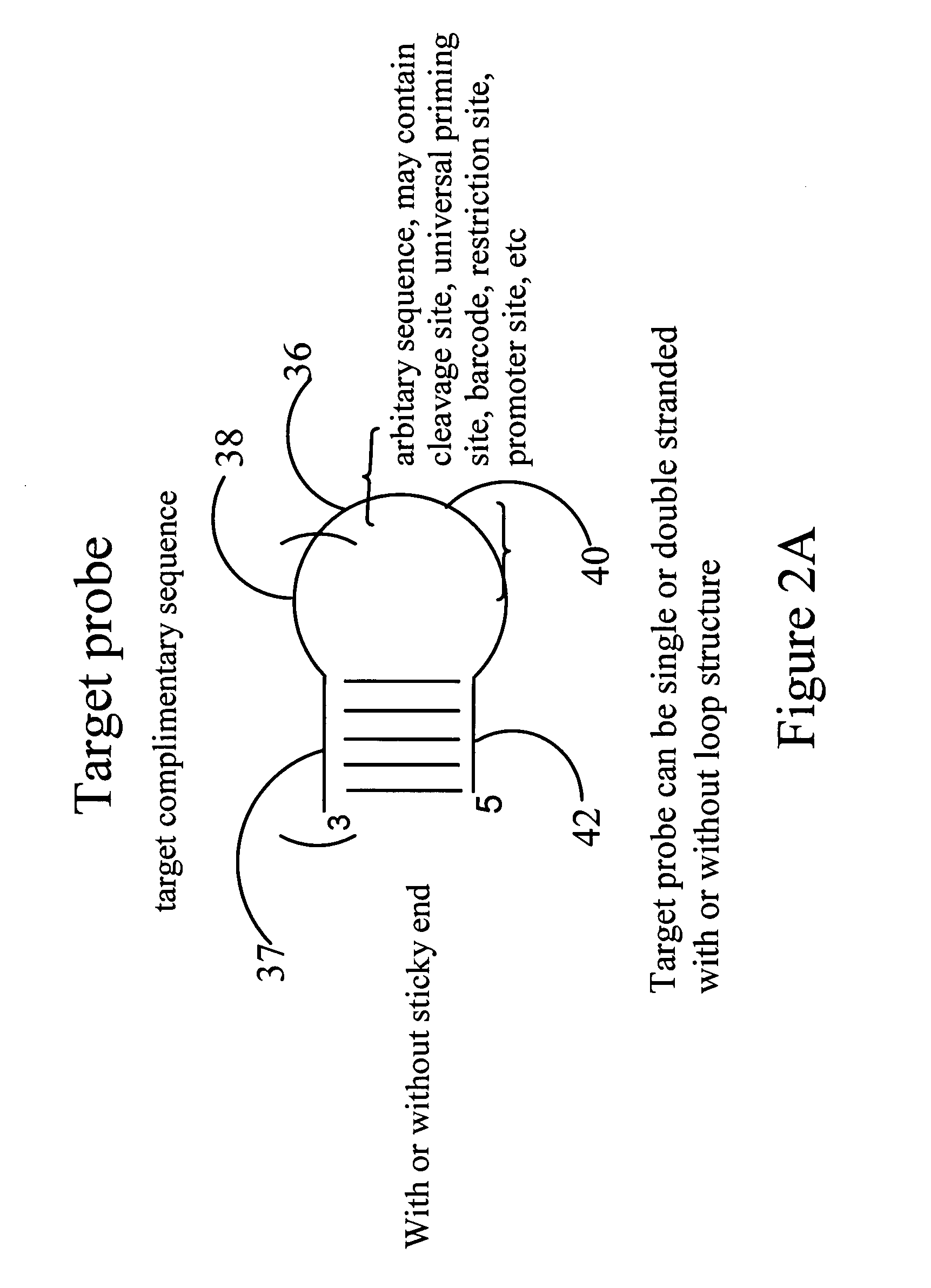
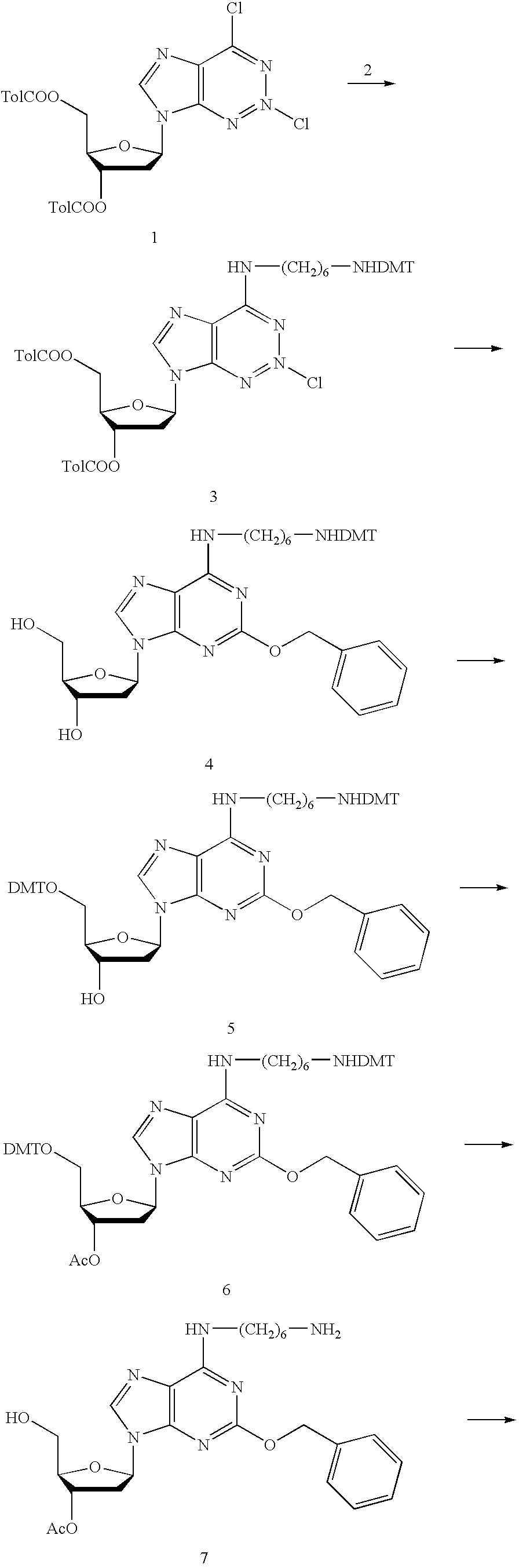
Oligonucleotide arrays and their use for sorting, isolating, sequencing, and manipulating nucleic acids
InactiveUS6322971B1Increase in hybridization specificityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyHybridization ArrayBioinformatics
Ligation methods for manipulating nucleic acid stands and oligonucleotides utilizing hybridization arrays of immobilized oligonucleotides. The oligonucleotide arrays may be plain or sectioned, comprehensive or non-comprehensive. The immobilized oligonucleotides may in some cases be binary oligonucleotides having constant as well as variable segments. Some embodiments include amplification of ligated products.
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY
Polynucleotide Ligation Reactions
InactiveUS20080261204A1Simplify the rebuild processMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPolynucleotideBiology
Owner:LINGVITAE AS
Reagents, methods, and libraries for bead-based sequencing
InactiveUS20080003571A1Efficient methodEfficient implementationMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
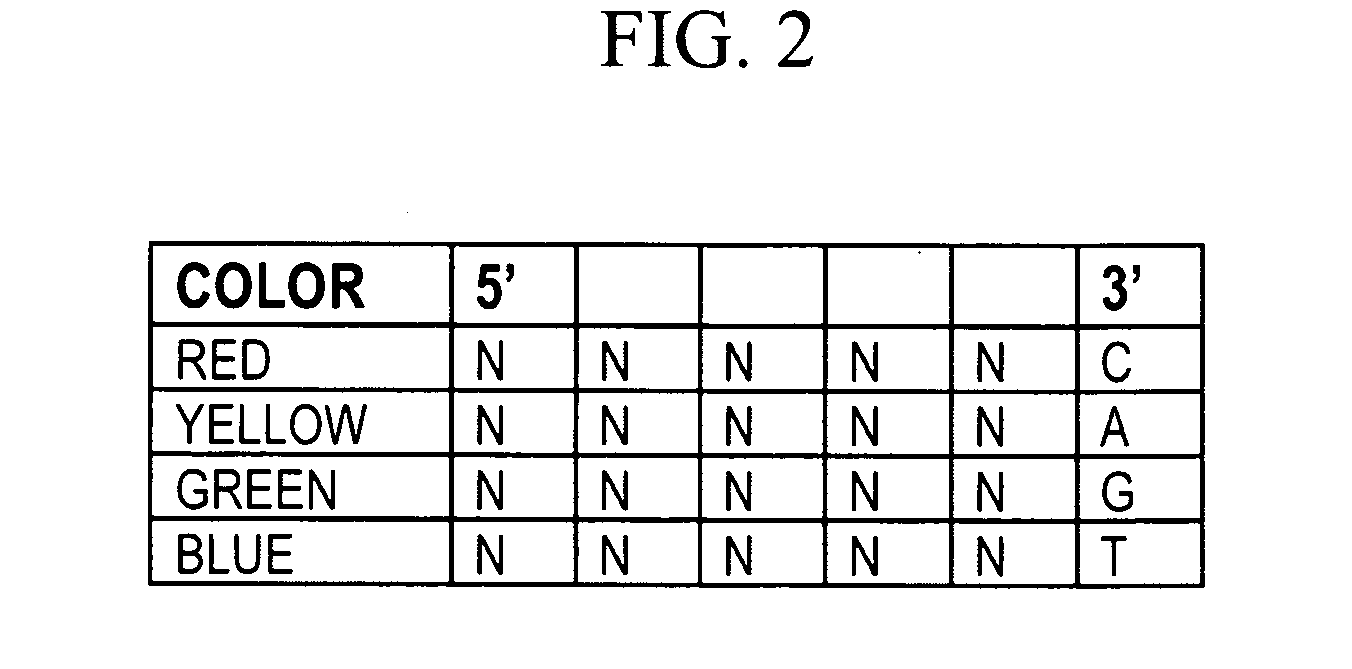
The present invention provides methods for determining a nucleic acid sequence by performing successive cycles of duplex extension along a single stranded template. The cycles comprise steps of extension, ligation, and, preferably, cleavage. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages and employ agents appropriate to cleave such linkages. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing an abasic residue or a damaged base and employ agents appropriate to cleave linkages between a nucleoside and an abasic residue and / or agents appropriate to remove a damaged base from a nucleic acid. The invention provides methods of determining information about a sequence using at least two distinguishably labeled probe families. In certain embodiments the methods acquire less than 2 bits of information from each of a plurality of nucleotides in the template in each cycle. In certain embodiments the sequencing reactions are performed on templates attached to beads, which are immobilized in or on a semi-solid support. The invention further provides sets of labeled extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages or trigger residues that are suitable for use in the method. In addition, the invention includes performing multiple sequencing reactions on a single template by removing initializing oligonucleotides and extended strands and performing subsequent reactions using different initializing oligonucleotides. The invention further provides efficient methods for preparing templates, particularly for performing sequencing multiple different templates in parallel. The invention also provides methods for performing ligation and cleavage. The invention also provides new libraries of nucleic acid fragments containing paired tags, and methods of preparing microparticles having multiple different templates (e.g., containing paired tags) attached thereto and of sequencing the templates individually. The invention also provides automated sequencing systems, flow cells, image processing methods, and computer-readable media that store computer-executable instructions (e.g., to perform the image-processing methods) and / or sequence information. In certain embodiments the sequence information is stored in a database.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
High throughput genome sequencing on DNA arrays
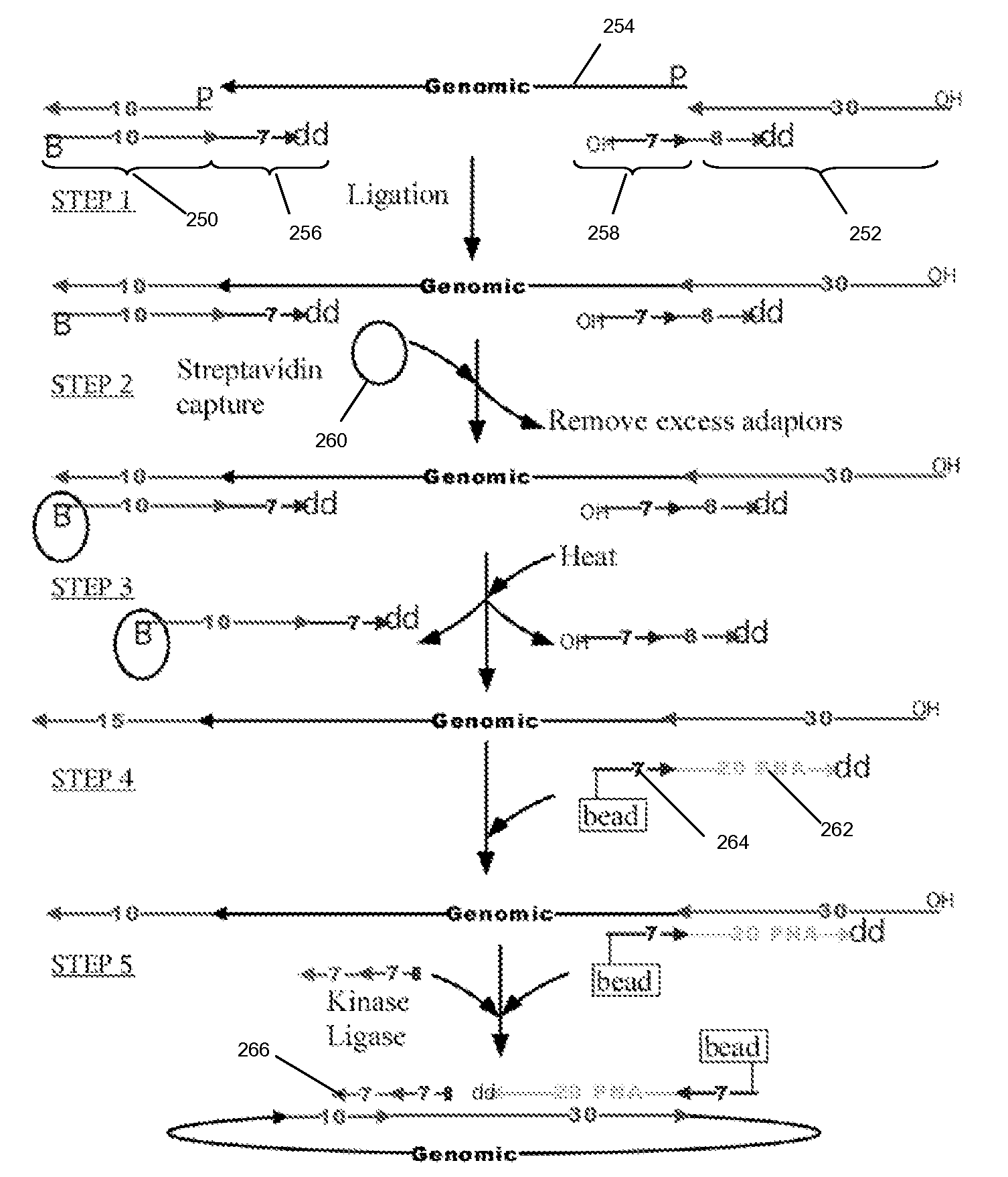
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for acquiring nucleotide sequence information of target sequences using adaptors interspersed in target polynucleotides. The sequence information can be new, e.g. sequencing unknown nucleic acids, re-sequencing, or genotyping. The invention preferably includes methods for inserting a plurality of adaptors at spaced locations within a target polynucleotide or a fragment of a polynucleotide. Such adaptors may serve as platforms for interrogating adjacent sequences using various sequencing chemistries, such as those that identify nucleotides by primer extension, probe ligation, and the like. Encompassed in the invention are methods and compositions for the insertion of known adaptor sequences into target sequences, such that there is an interruption of contiguous target sequence with the adaptors. By sequencing both “upstream” and “downstream” of the adaptors, identification of entire target sequences may be accomplished.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
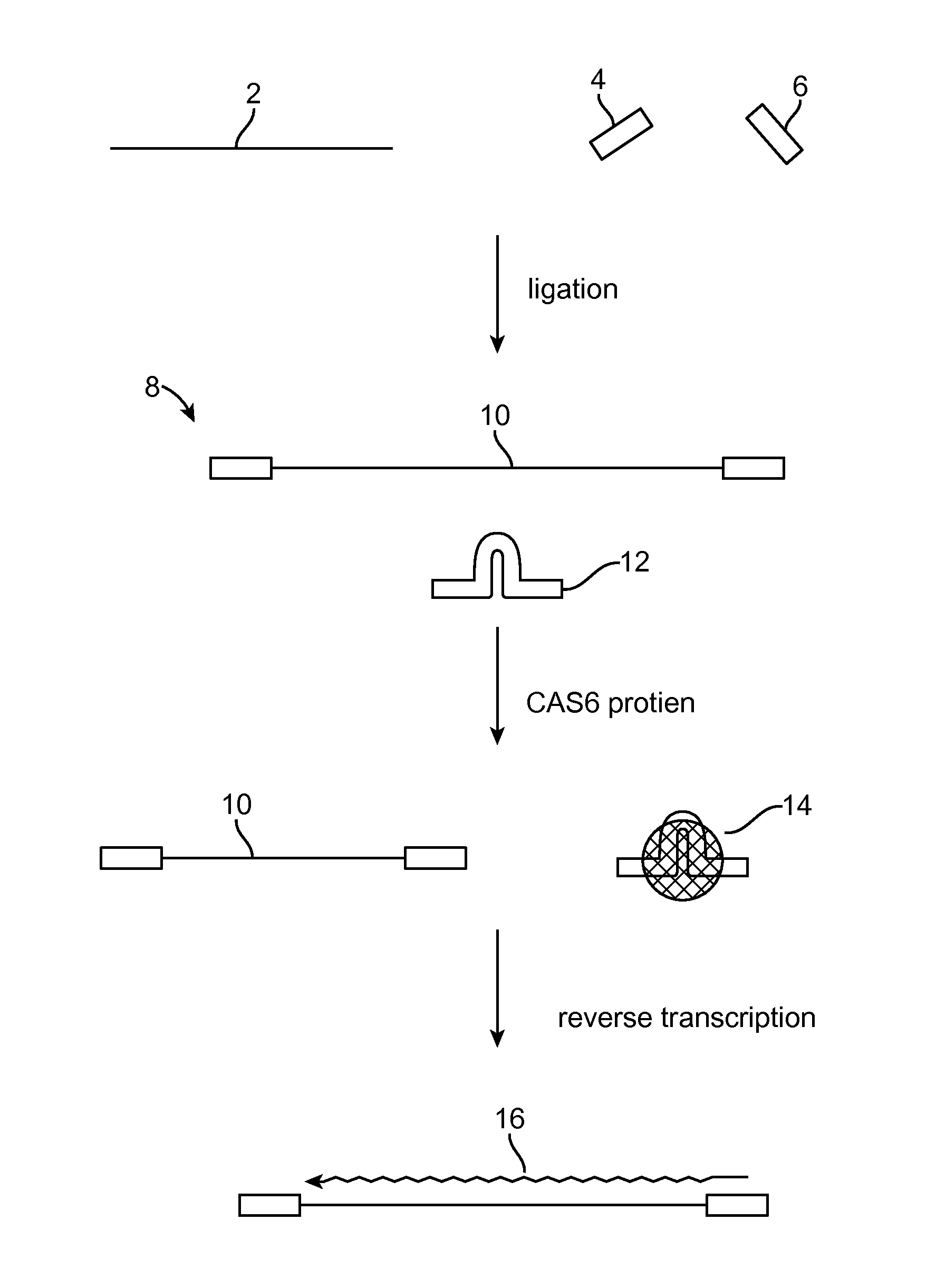
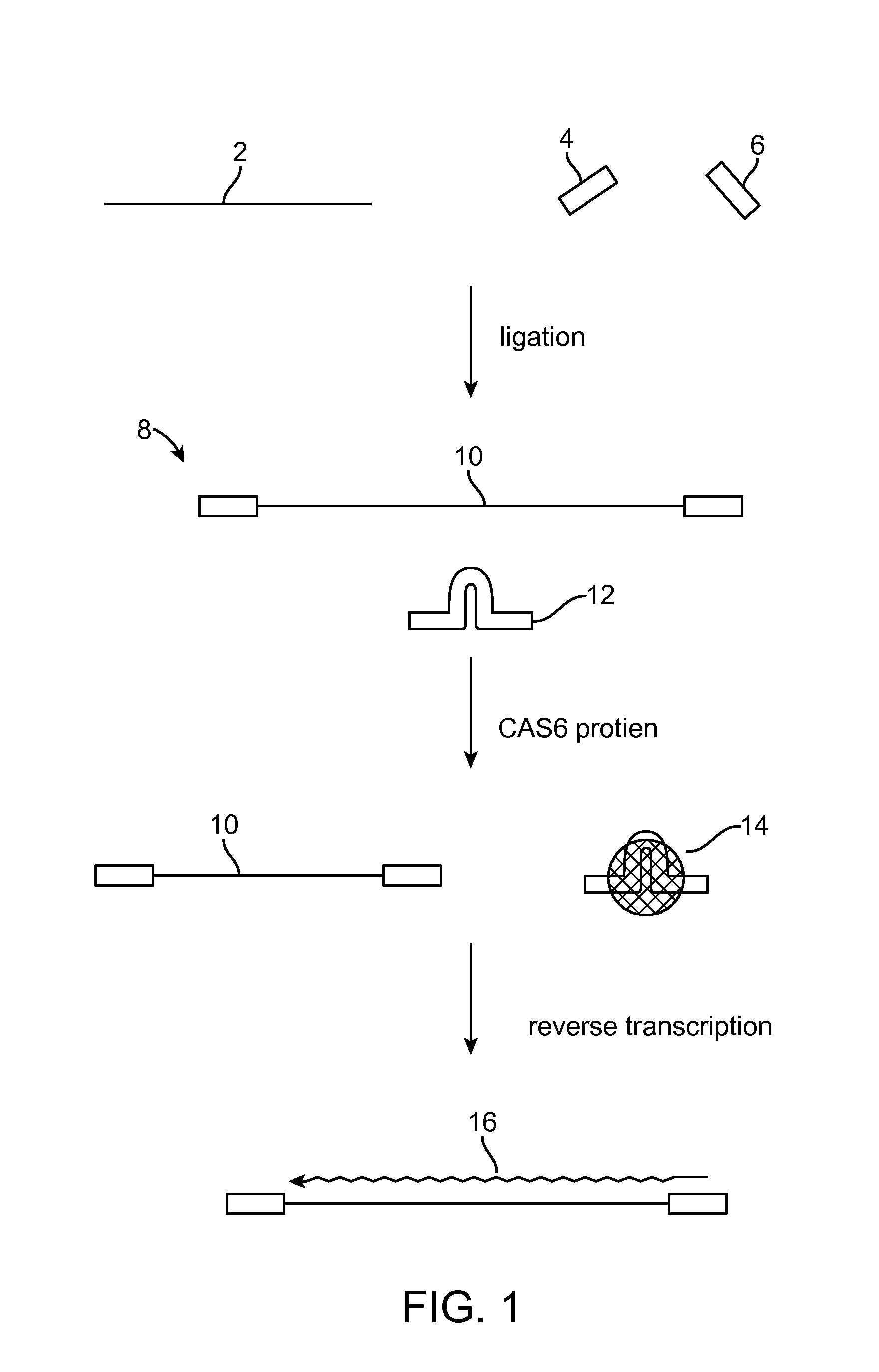
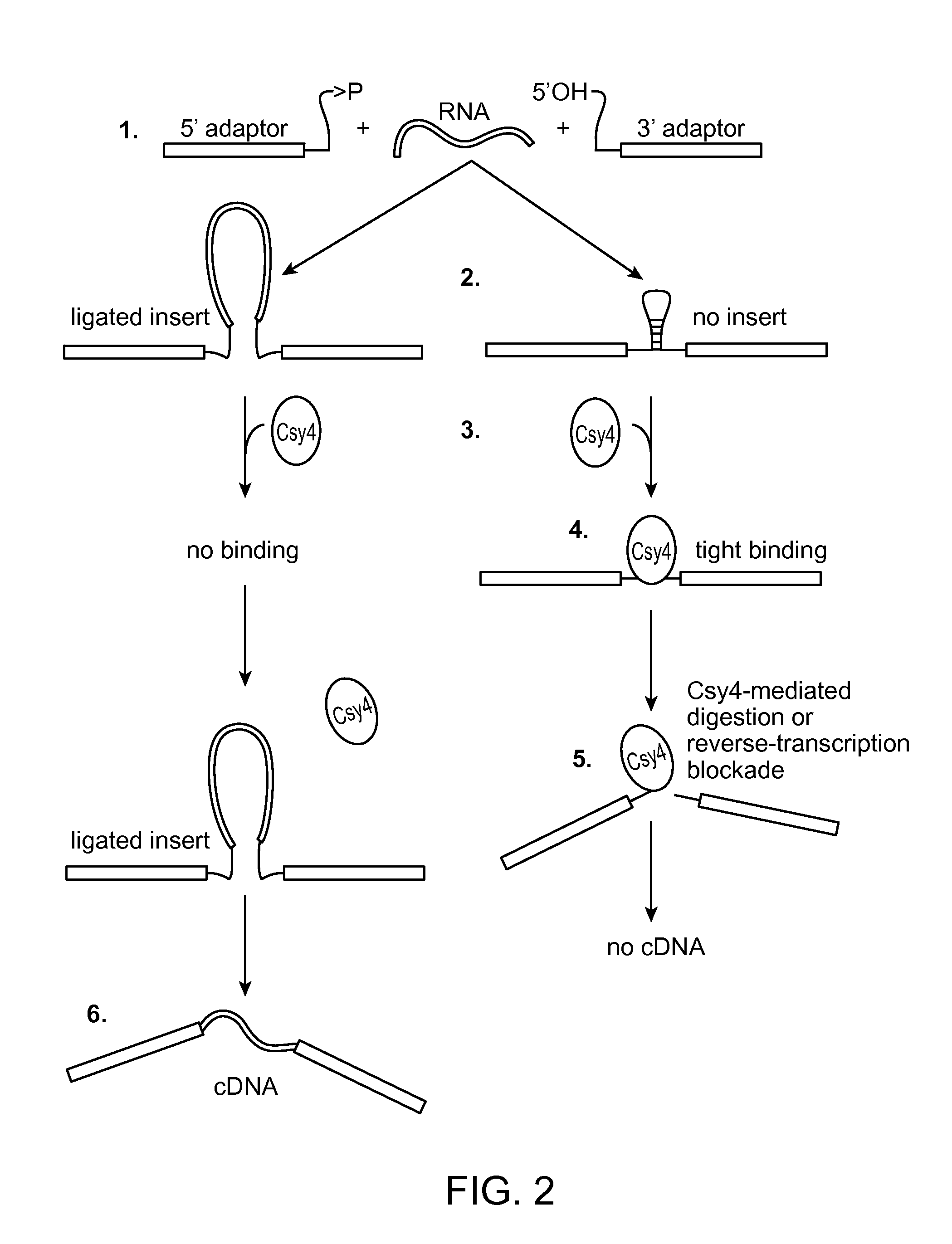
Method of adaptor-dimer subtraction using a crispr cas6 protein
A method of processing a target RNA is provided. In certain embodiments, this method comprises: contacting the products of an RNA ligase-mediated ligation reaction with an CAS6 protein, wherein: (i) the RNA ligase-mediated ligation reaction comprises: a target RNA, an RNA ligase, and first and second adaptors that can ligate together to produce an adaptor dimer that contains a CRISPR stem loop; and (ii) the CAS6 protein recognizes the CRISPR stem loop; thereby preventing the adaptor dimer from being reverse transcribed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods and compositions for assay readouts on multiple analytical platforms
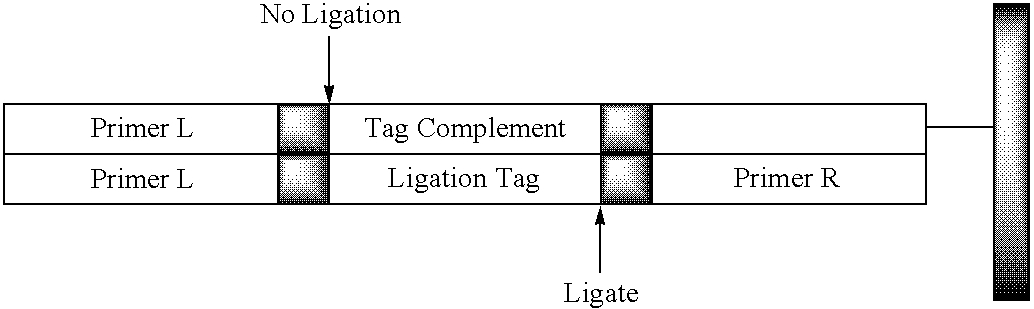
The invention provides methods and compositions for reading out the results of multiplex assays on various analytical platforms, such as microarrays, bead arrays, electrophoresis devices, and the like. An important feature of the invention includes methods for converting different sets of oligonucleotide tags used for labeling into oligonucleotide tags specific for a particular analytical platform. The invention further includes compositions comprising oligonucleotide tags having convenient properties for labeling and conversion, particularly ligation tags that employ ligation reaction specificity as well as sequence specificity in order to discriminate between tags.
Owner:POPULATION GENETICS TECH
Method for making linear, covalently closed DNA constructs
InactiveUS6451563B1Bulking digestionHigh processivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructGenomic DNA
A process to obtain linear double-stranded covalently closed DNA "dumbbell" constructs from plasmids by restriction digest, subsequent ligation with hairpin oligodesoxyribonucleotides, optionally in the presence of restriction enzyme, and a final digestion with endo- and exonucleolytic enzymes that degrade all contaminating polymeric DNA molecules but the desired construct. The invention also provides a process to obtain said dumbbell constructs employing endonuclease class II enzymes. Furthermore, the invention provides a process to obtain linear, covalently closed DNA molecules, such as plasmids, free from contamination by genomic DNA, by submitting the DNA preparation to a facultative endonucleolytic degradation step and an obligatory exonucleolytic degradation step.
Owner:MOLOGEN AG +1
Methods and compositions for universal detection of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20110212846A1Increase distanceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPolymerase chain reactionClinical settings
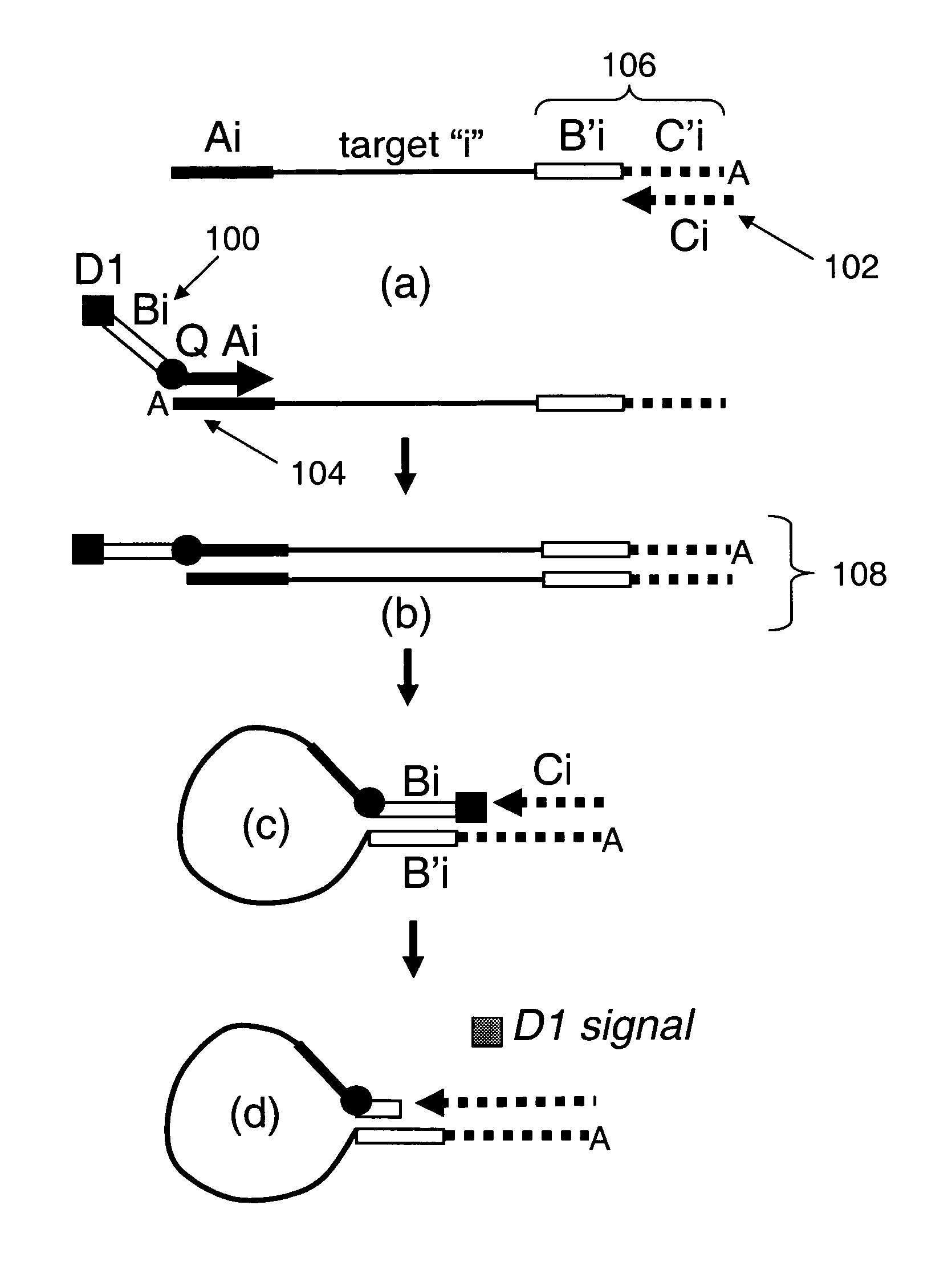
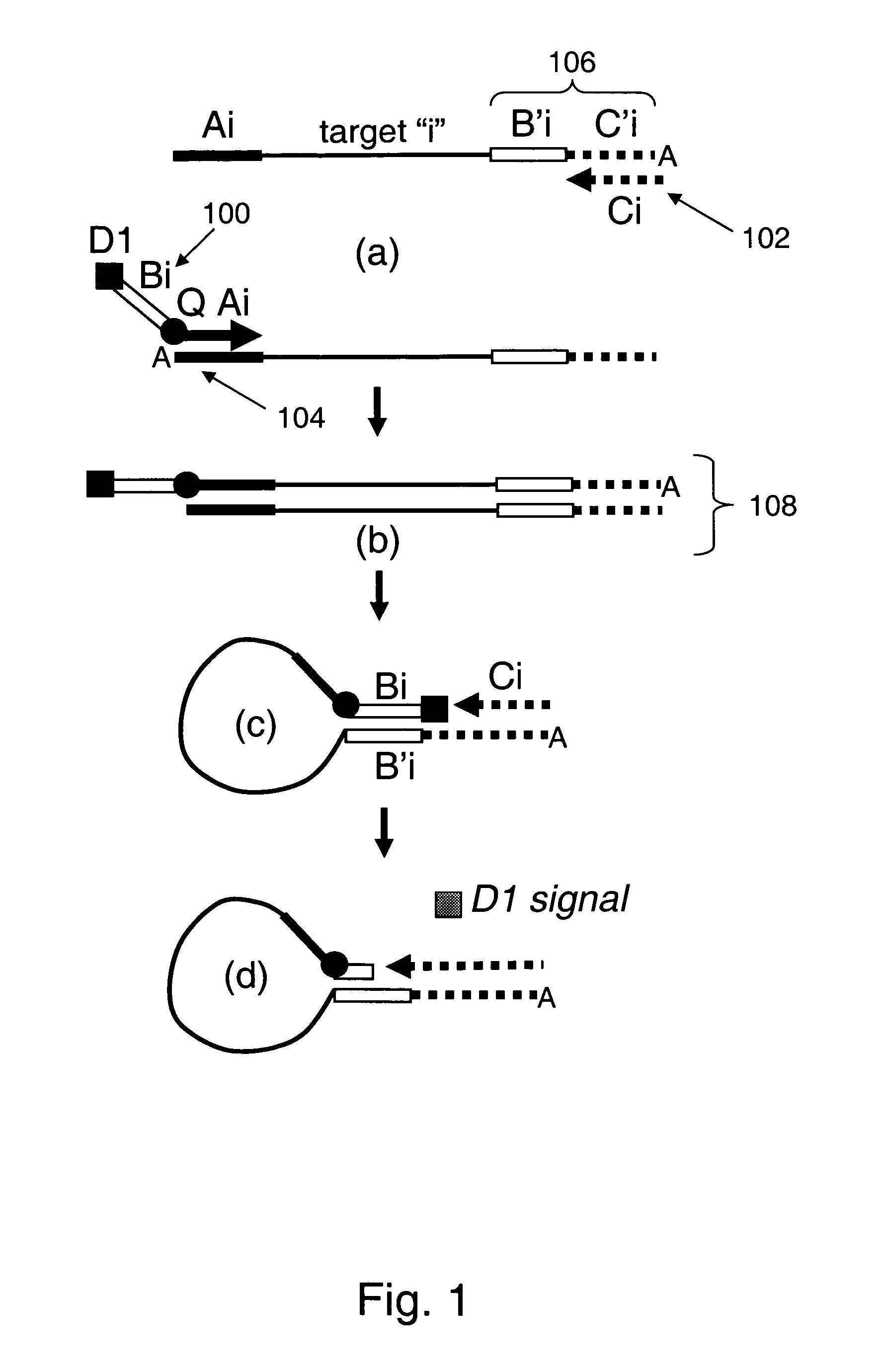
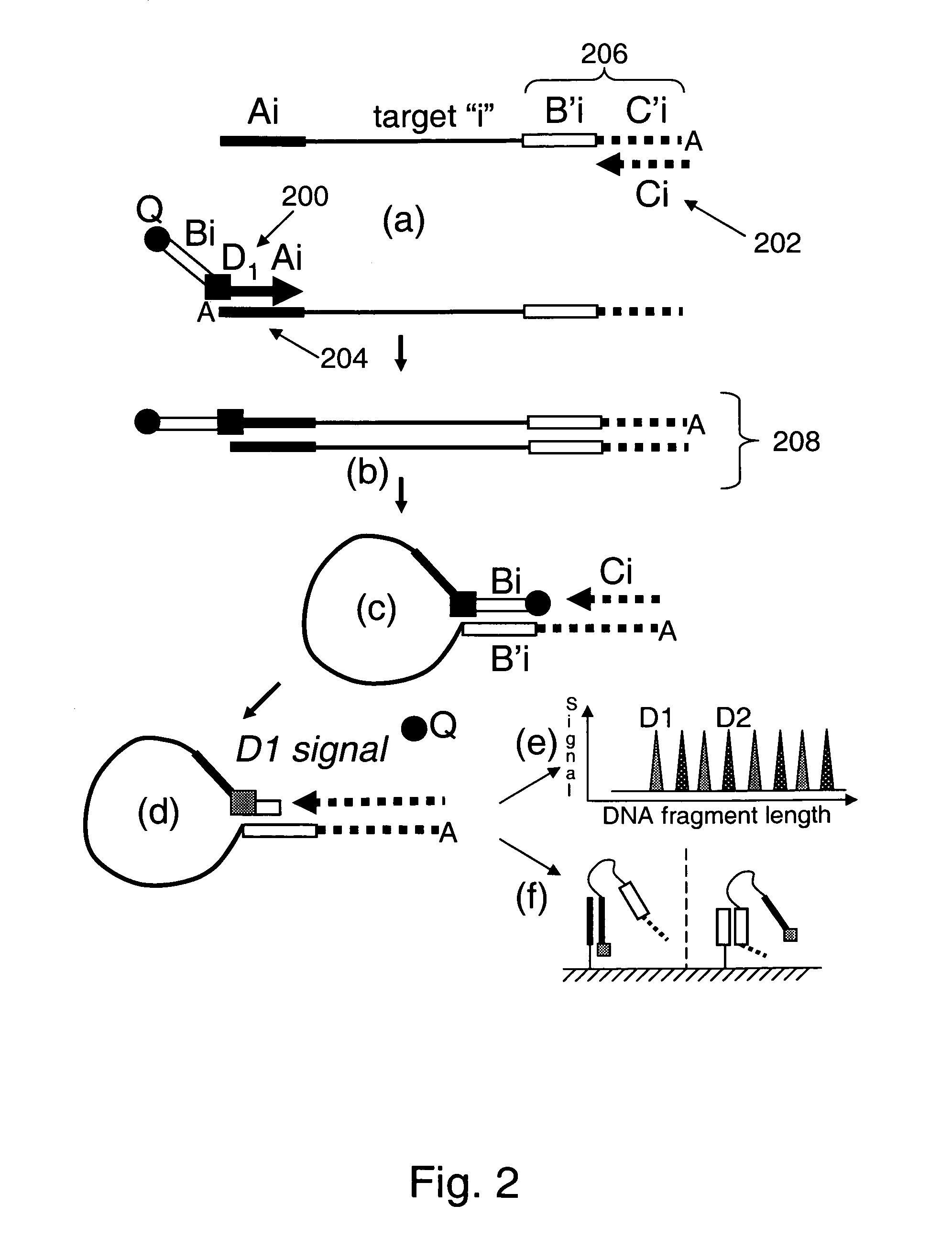
Provided are methods and compositions for detecting the presence or amount of one or more target nucleic acids in a sample. Methods of the present invention include linking universal nucleic acid segments into a single molecule in a linking reaction dependent on a target nucleic acid of interest. A variety of universal segment linking strategies are provided, including preamplification by polymerase chain reaction, ligation-based strategies, reverse transcription and linear polymerase extension. Linking the universal segments into a single molecule generates a tagged target nucleic acid which is detected in a manner dependent on an intramolecular interaction between one universal segment and a second portion of the tagged target nucleic acid. In certain embodiments, the intramolecular interaction includes the formation of a hairpin having a stem between a universal segment at one end of the tagged target nucleic acid and a second universal segment at the opposite end of the tagged target nucleic acid. A variety of detection formats are provided, including solution-phase and surface-based formats. The methods and compositions are well-suited for highly multiplexed nucleic acid detection, and are applicable for the detection of any target nucleic acid of interest in both research and clinical settings.
Owner:UNITAQ BIO
Reagents, methods, and libraries for bead-based sequencing
InactiveUS20090181385A1Efficient implementationQuick sortingMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand
The present invention provides methods for determining a nucleic acid sequence by performing successive cycles of duplex extension along a single stranded template. The cycles comprise steps of extension, ligation, and, preferably, cleavage. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages and employ agents appropriate to cleave such linkages. The invention provides methods of determining information about a sequence using at least two distinguishably labeled probe families. In certain embodiments the methods acquire less than 2 bits of information from each of a plurality of nucleotides in the template in each cycle. In certain embodiments the sequencing reactions are performed on templates attached to immobilized beads. The invention further provides sets of labeled probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages. In addition, the invention includes performing multiple sequencing reactions on a single template by removing initializing oligonucleotides and extended strands and performing subsequent reactions using different initializing oligonucleotides.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
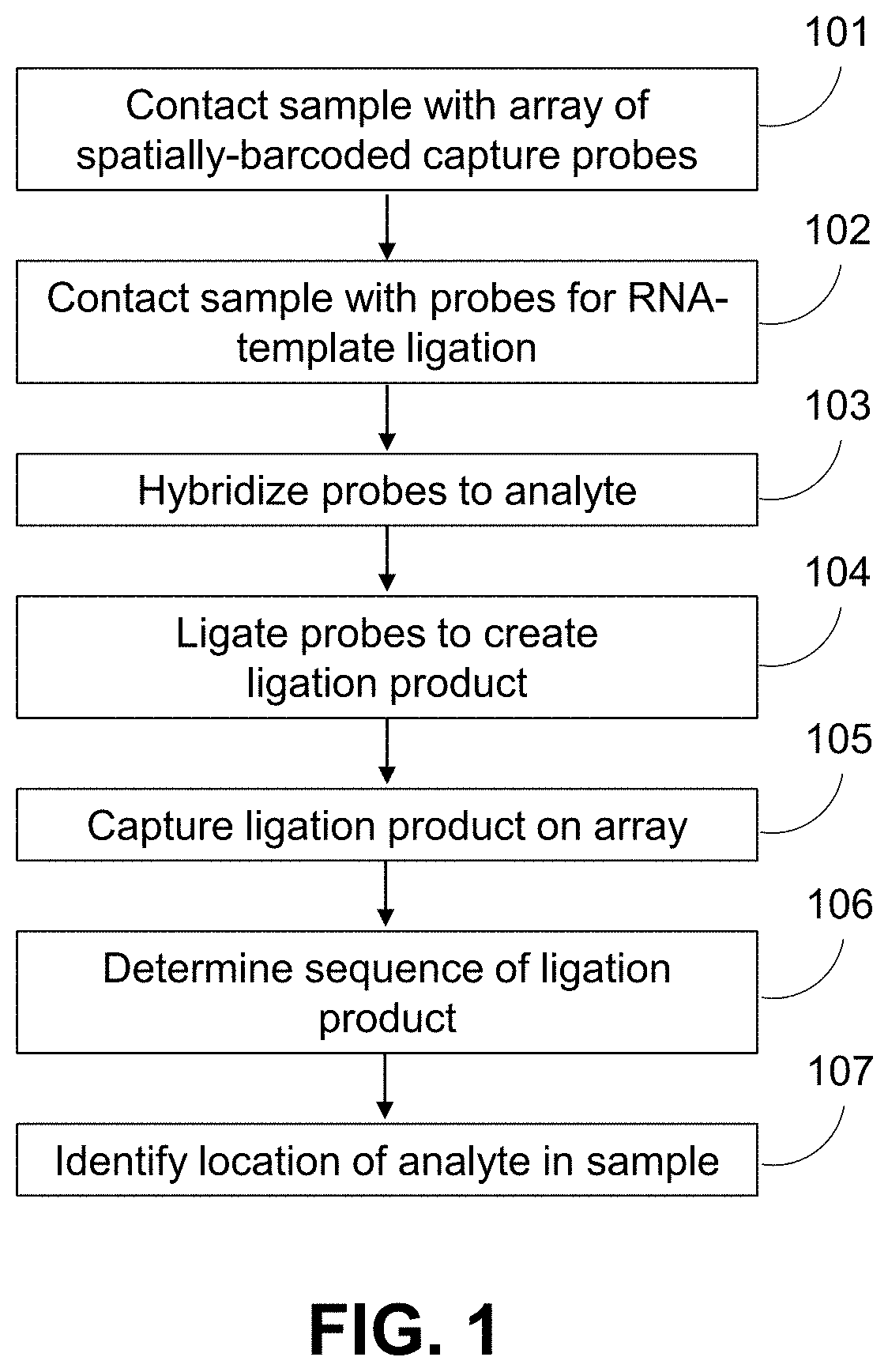
Methods for spatial analysis using RNA-templated ligation
ActiveUS11332790B2Avoid excessive degradationSensitive measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteLigation
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Multipotent adult stem cells, sources thereof, methods of obtaining and maintaining same, methods of differentiation thereof, methods of use thereof and cells derived thereof
InactiveUS20050283844A1Improve angiogenesisAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderOligonucleotideBioinformatics
Methods and compositions are provided for circularizing target sequences in a sample. In particular, ligation oligonucleotides are employed to selectively hybridize with the target such that the target can be ligated into a closed circular target. Rolling circle amplification can then be performed directly on the target sequence for subsequent detection and analysis.
Owner:FURCHT LEO +2
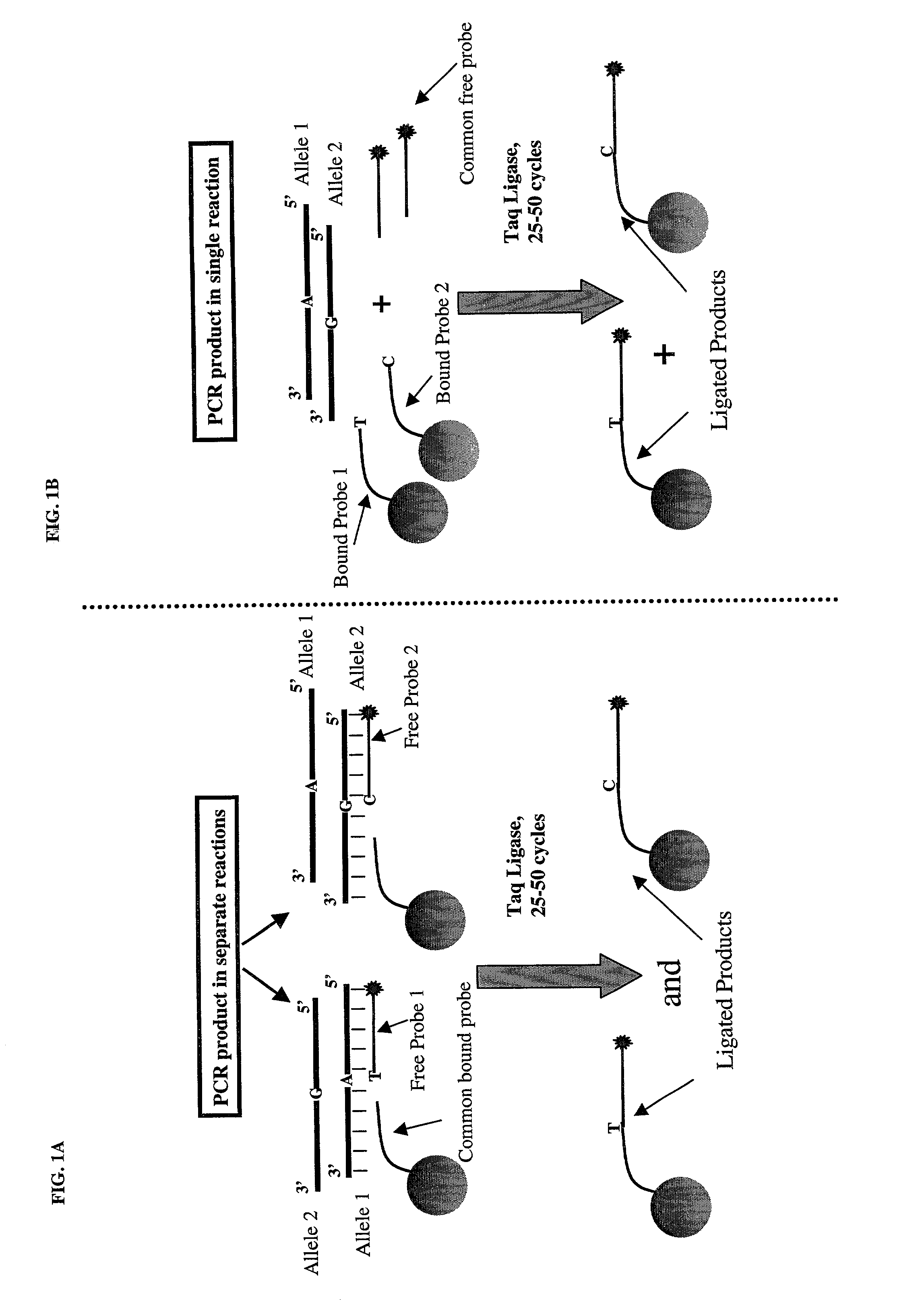
Microsphere based oligonucleotide ligation assays, kits, and methods of use, including high-throughput genotyping
InactiveUS20020182609A1Rapid and economical and high throughputSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention teaches a novel approach to detecting and / or analyzing nucleic acid sequences. Generally, the invention relates to detecting and / or analyzing nucleic acid sequences using microsphere-based assays. More specifically, the invention relates to detecting and / or analyzing nucleic acid sequences using microsphere-based oligonucleotide ligation multiplexed assays. The present invention also provides methods and kits for performing microsphere-based oligonucleotide ligation assays, which include bound probes attached to addressable microspheres and free probes bearing a detectable label.
Owner:LUMINEX
Method and kit for nucleic acid sequence detection
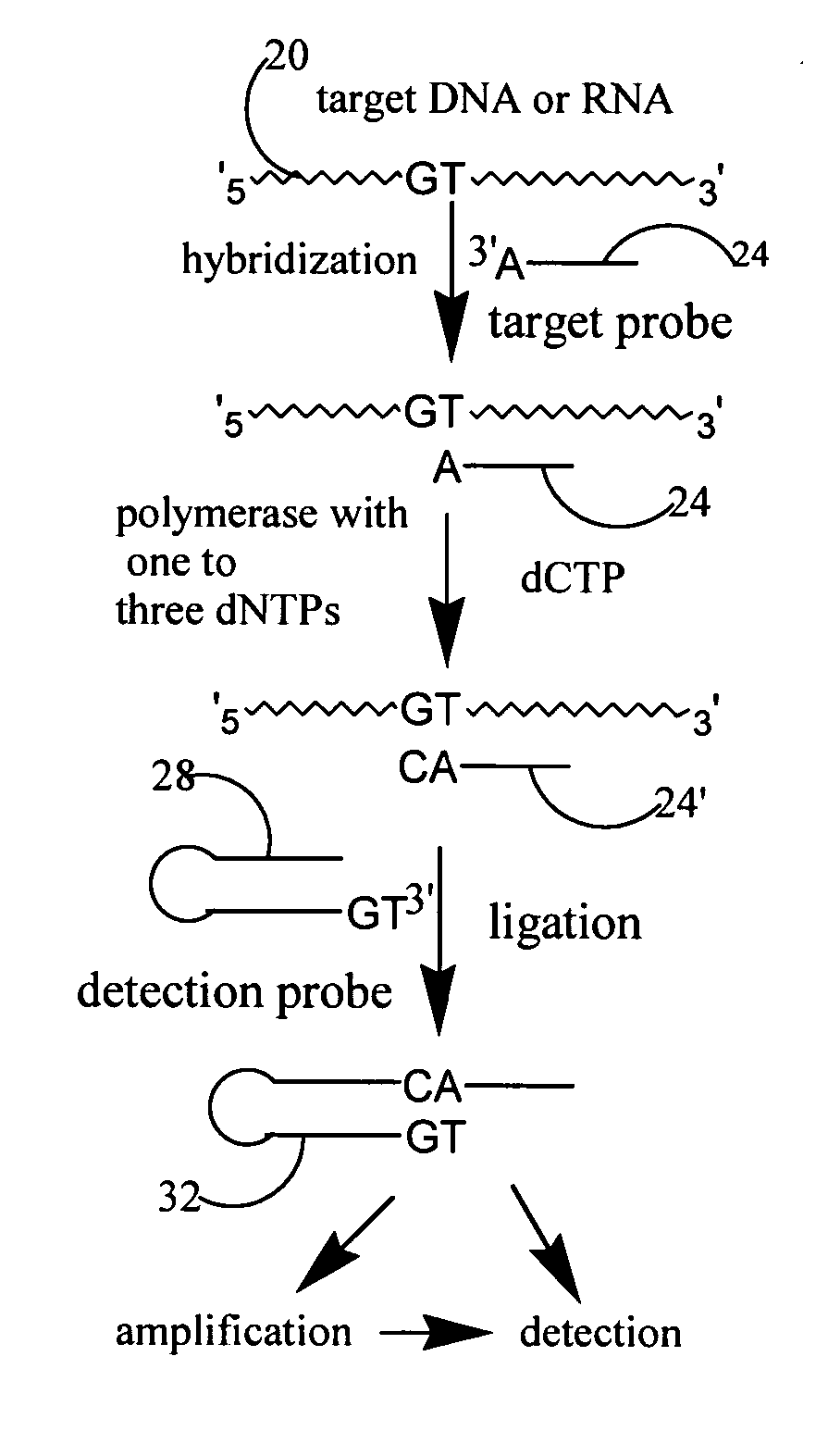
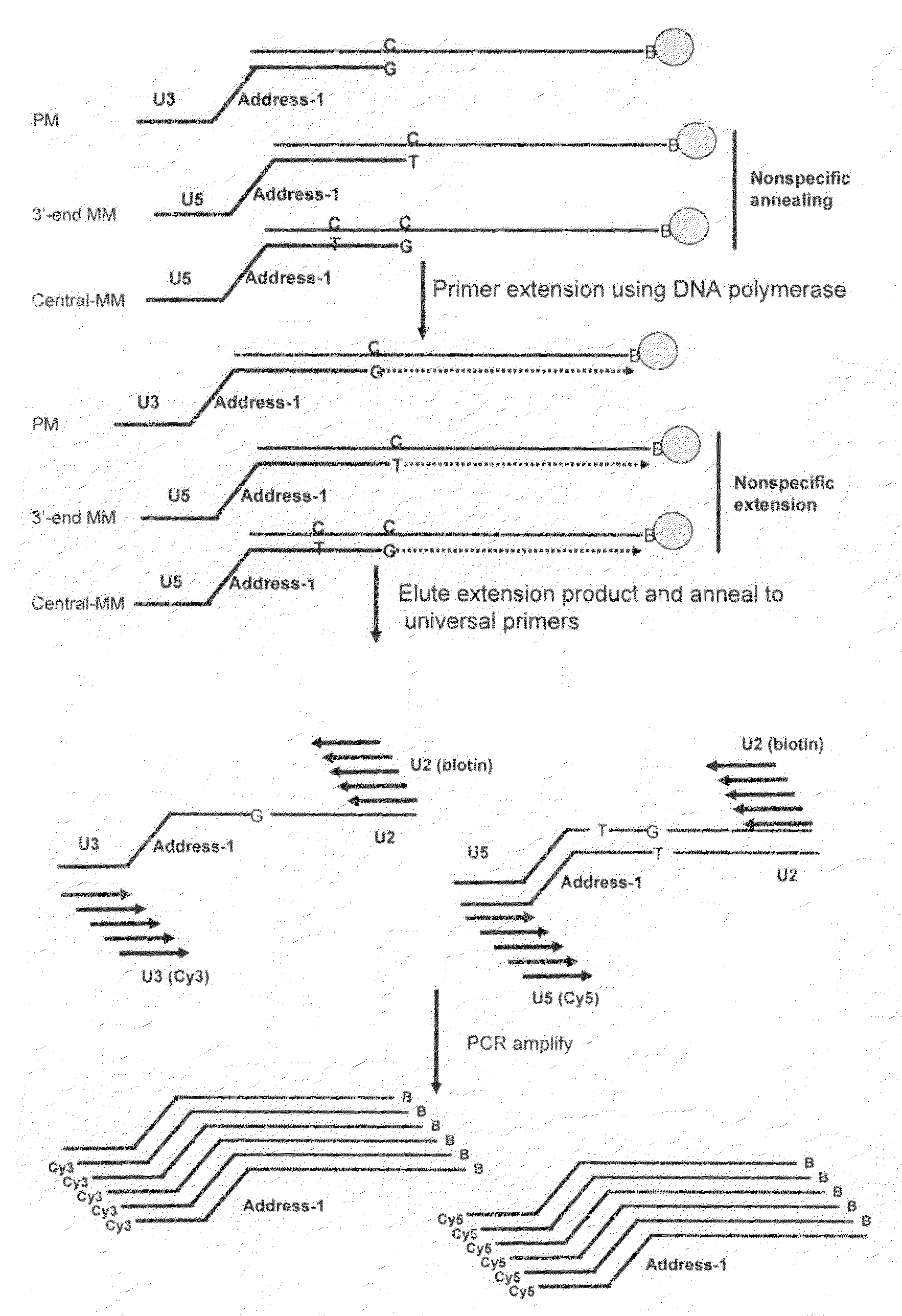
A method and kit for detecting the presence of a target sequence in a polynucleotide analyte contained in a sample are disclosed. In practicing the method, the sample is mixed with a target probe having a sequence capable of hybridizing with said target sequence, under conditions effective to form a double-stranded complex of the analyte and the probe, and the probe in the complex is reacted in the presence of a polymerase and a selected one to three of four possible nucleotide triphosphates, to add a selected one or more target-directed nucleotide bases to the probe's 3′ end to produce a modified probe. The modified probe is hybridized with a detection probe, the two probes are ligated to form a two-probe ligation product, and the presence of the ligation product is detected.
Owner:ATILA BIOSYST
Splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis of polyribounucleotides
InactiveUS20050130201A1Ligate RNA moleculesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnzymatic synthesisPolyribonucleotides
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis of polyribonucleotides using an RNA polymerizing enzyme. The invention provides ligating ribonucleotides comprising ligating a donor RNA molecule to an acceptor RNA molecule in the presence of RNA ligase and a splint, wherein the donor RNA molecule is comprised of at least one nucleotide and a ligation linker moiety, the acceptor RNA molecule is comprised of at least one nucleotide and a ligation linker moiety and the splint is comprised of a polyribonucleotide. The invention also provides splints for use in splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis using an RNA polymerizing enzyme.
Owner:DHARMACON INC
Methods for spatial analysis using rna-templated ligation
ActiveUS20210285046A1Avoid excessive degradationSensitive measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteLigation
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Methods for spatial analysis using rna-templated ligation
ActiveUS20210348221A1Avoid excessive degradationSensitive measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteLigation
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Methods for detecting small RNA species
InactiveUS20080241831A1Microbiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleotide sequencing
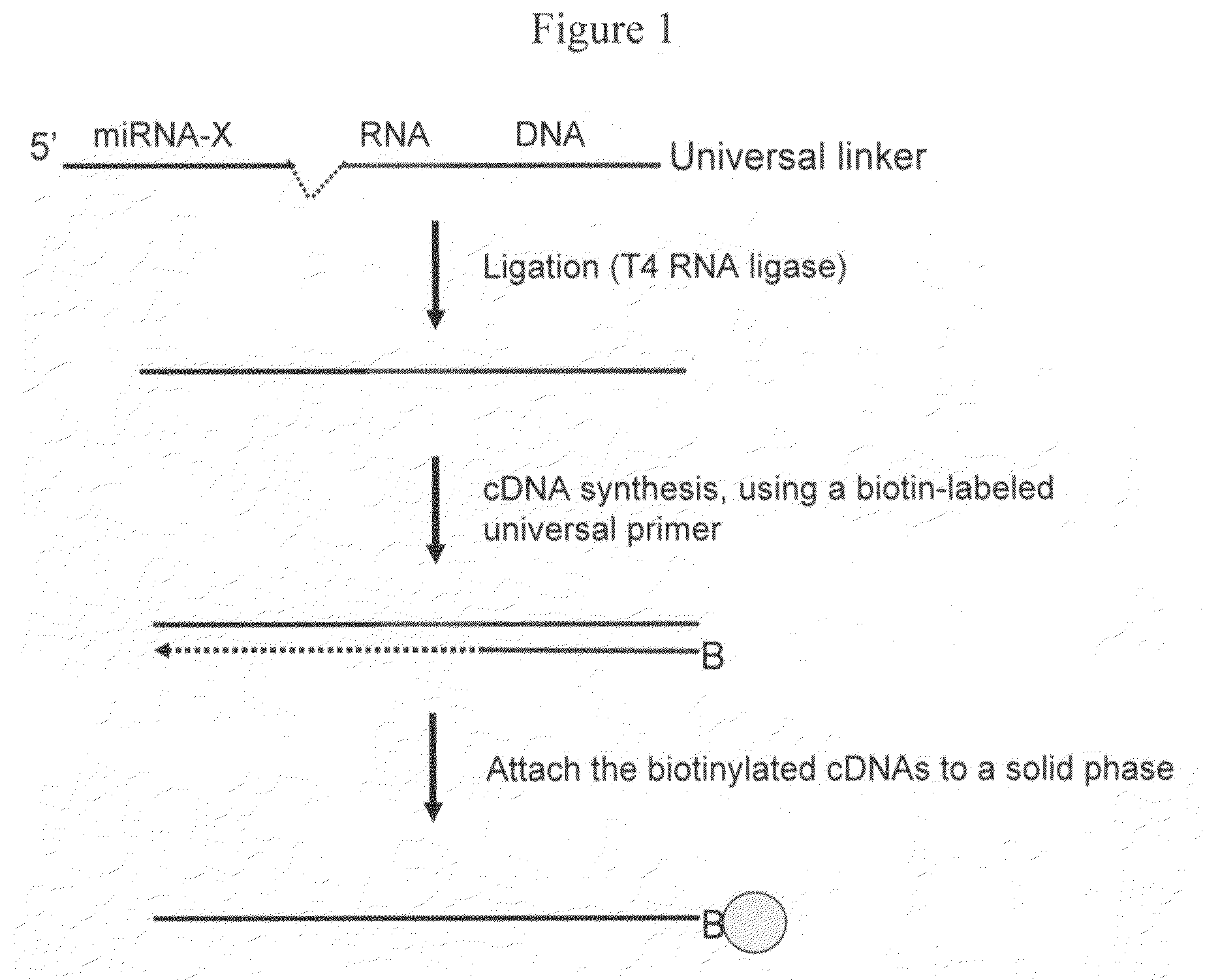
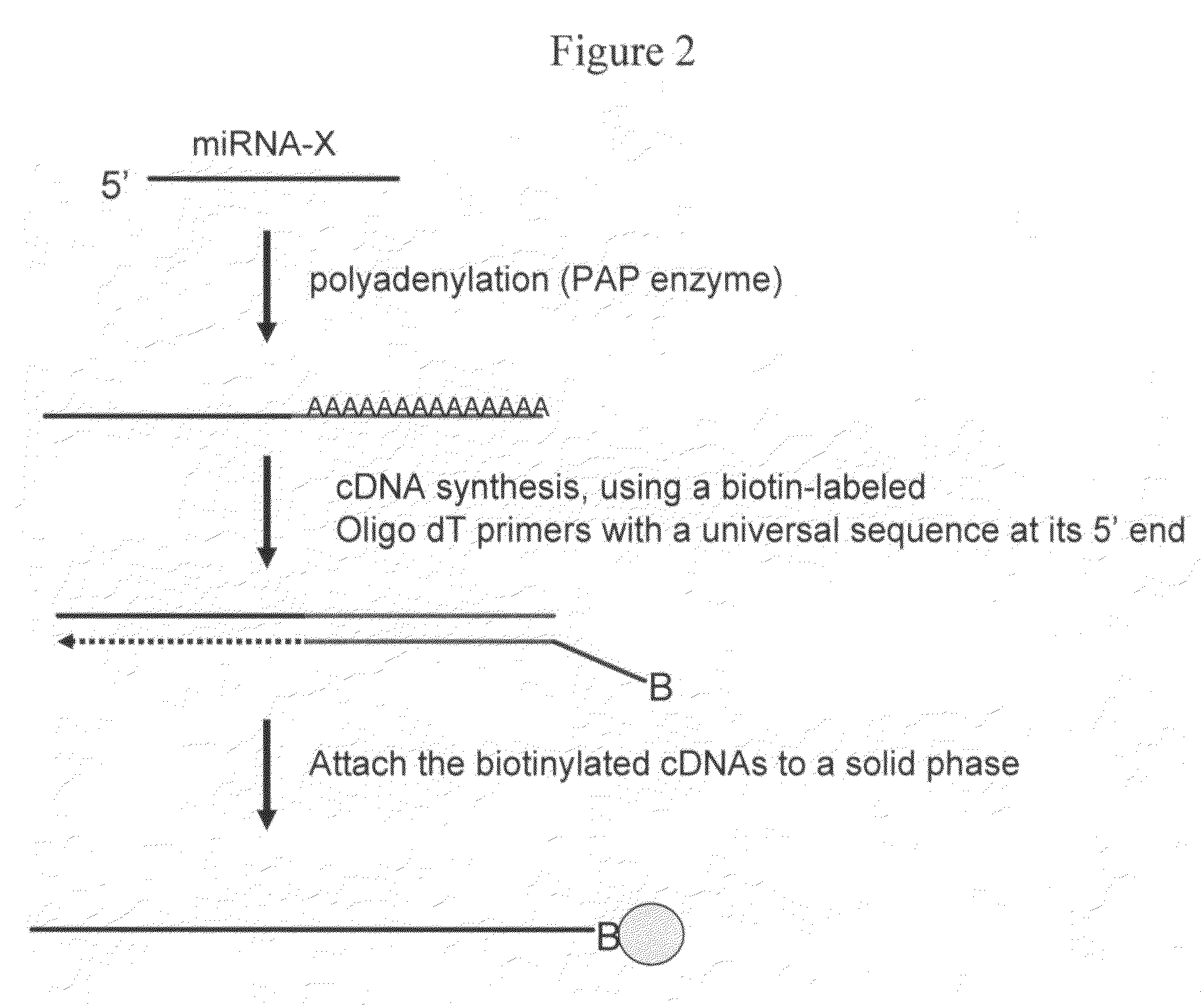
The invention provides a method of detecting small target nucleotide sequences, in particular, small RNA species that are present in a sample. The method generally comprises a poly-A polymerization step or a ligation step to add a universal sequence to the 3′-end of all RNA molecules, followed by a universal primer-mediated cDNA synthesis, solid-phase selection, assay oligo annealing, extension and PCR amplification / labeling. The method of the invention can be practiced to amplify and label a small amount of miRNA or other ncRNA. The resulting amplification product can be read out on a universal array or an array with miRNA-specific or ncRNA-specific probes. The invention has multiple embodiments, including methods, compositions, and kits. In general, the nucleic acids, compositions, and kits comprise materials that are useful in carrying out the methods of the invention or are produced by the methods, and that can be used to detect small target nucleic acid sequences present in samples, in particular, small RNA species.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
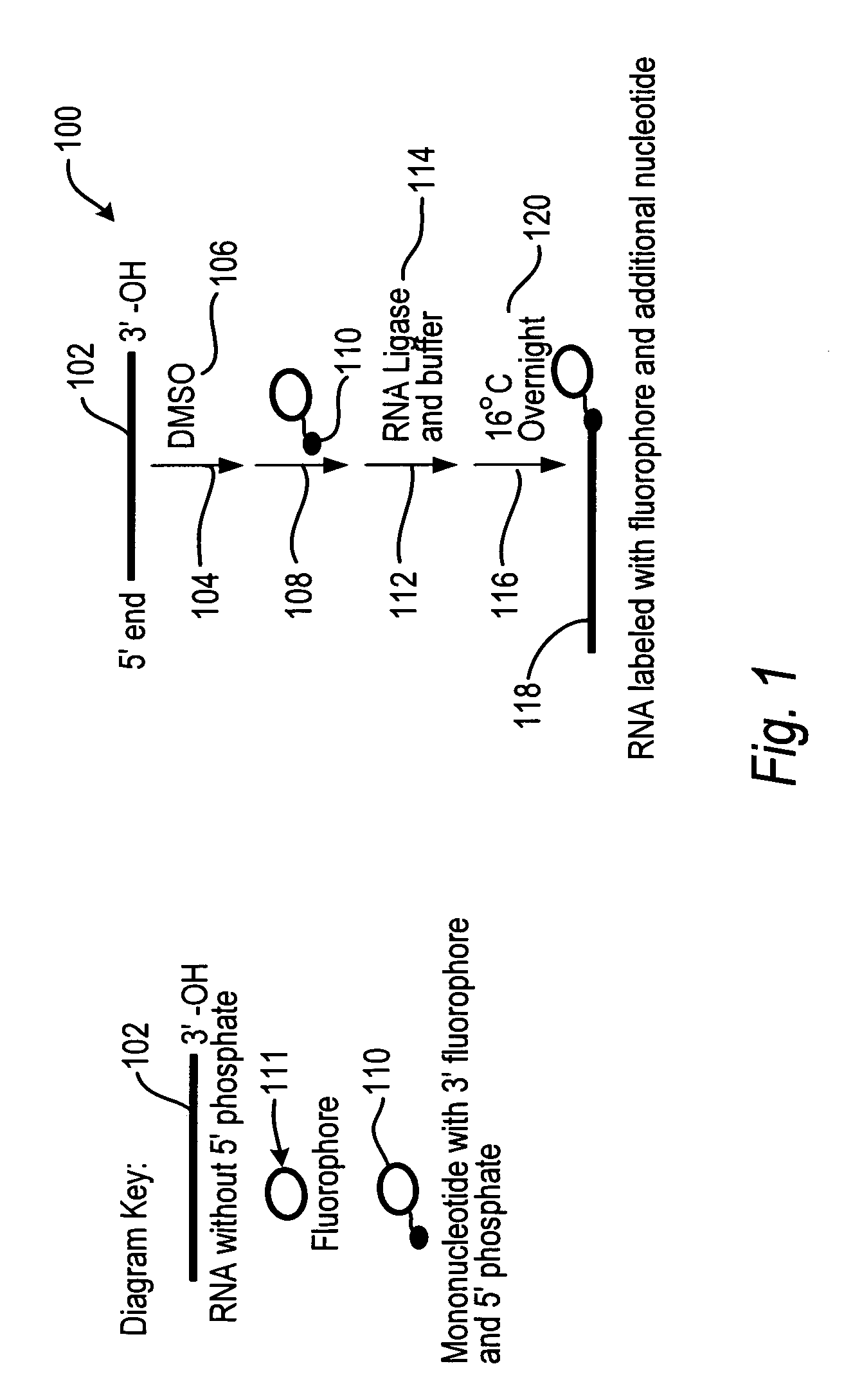
Labeled nucleotide composition
Embodiments of labeled nucleotide compositions are described. Methods are described in which a sample containing RNA is contacted with an enzyme having an RNA ligation activity in the presence of a labeled nucleotide composition to provide labeled RNA. Methods of performing an array analysis of a labeled RNA sample are also described.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method for amplifying specific nucleic acids in parallel
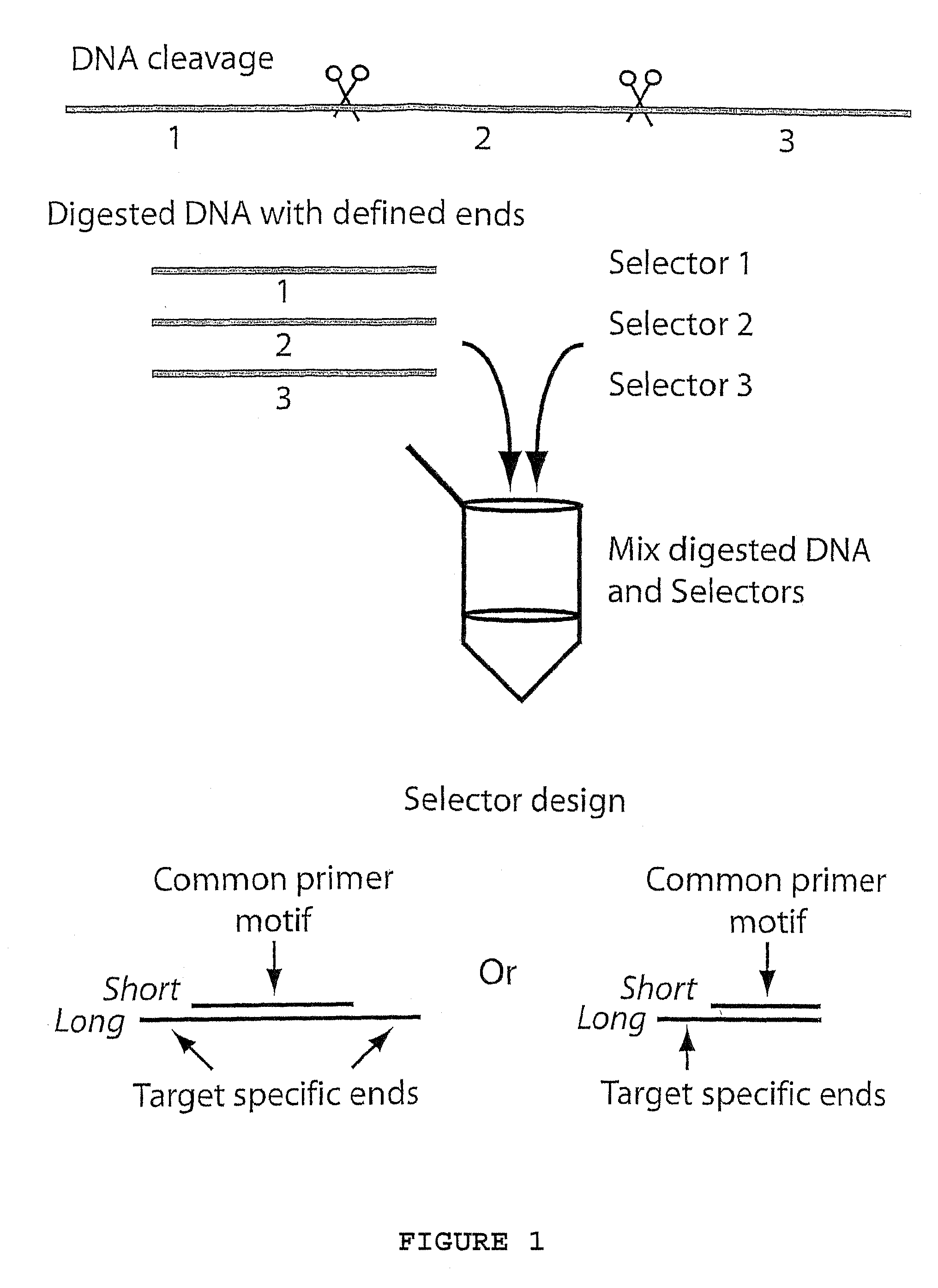
ActiveUS7883849B1Few amplification reactionReduce total usageMicrobiological testing/measurementComputational biologyNucleic acid
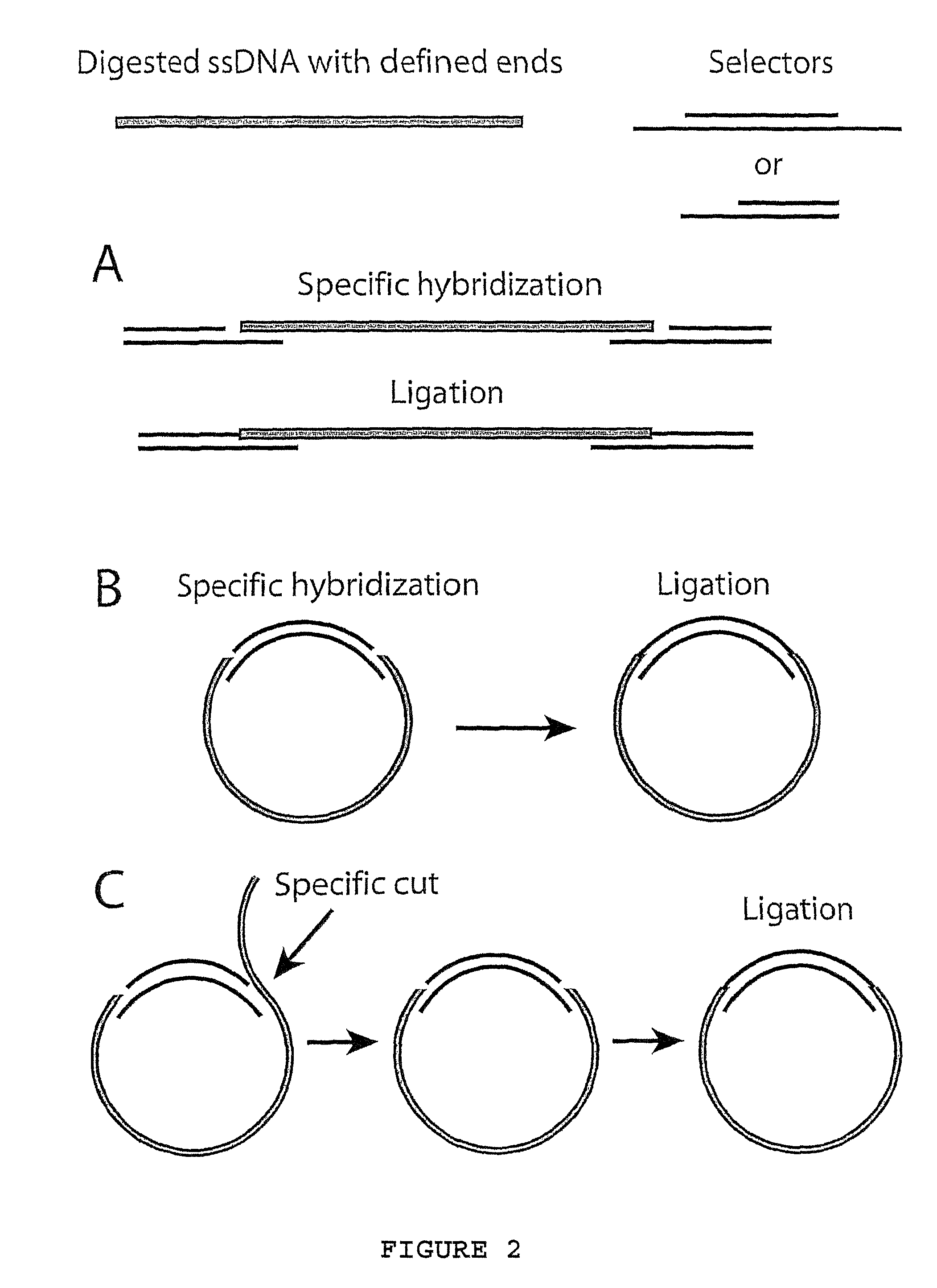
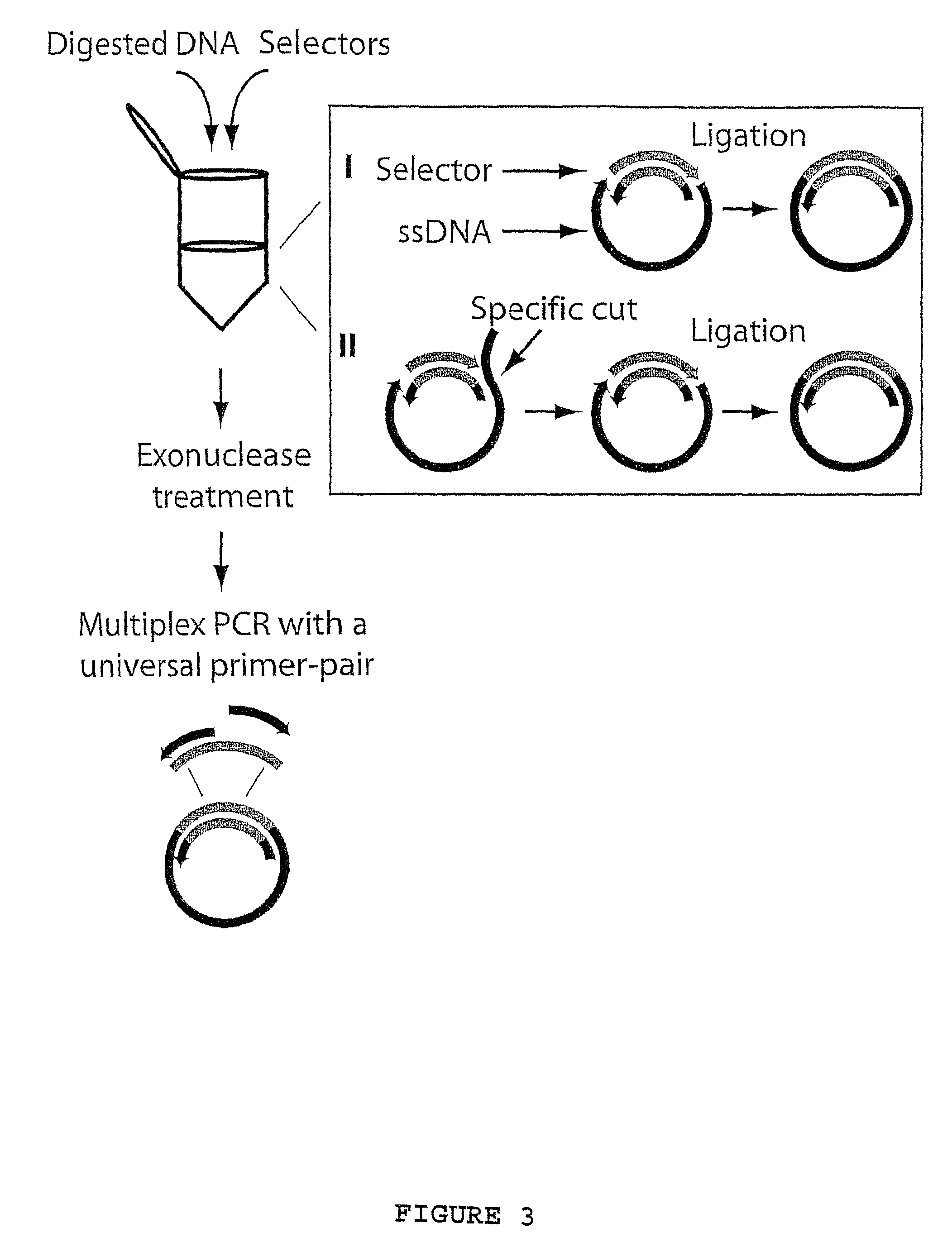
A method for amplifying a plurality of target sequences that minimizes amplification artefacts is provided. A sample of interest is fragmented into fragments, where each fragment that includes a target sequence has at least one defined end sequence. Selector constructs, all comprising a primer pair motif and each individual selector comprising one or two protruding ends complementary to the defined end sequences of the fragments containing the target sequences, are brought in contact with the fragments. After ligation, the selected target sequences are amplified in parallel using a primer-pair specific for the primer-pair motif common to the selectors.
Owner:OLINK AB
Means and Method for the Detection of Target Nucleotide Sequences Using Ligation Assays With Improved Oligonucleotide Probe Pairs
InactiveUS20070275375A1Advantageous hybridisation characteristicQuality improvementSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingOligonucleotide
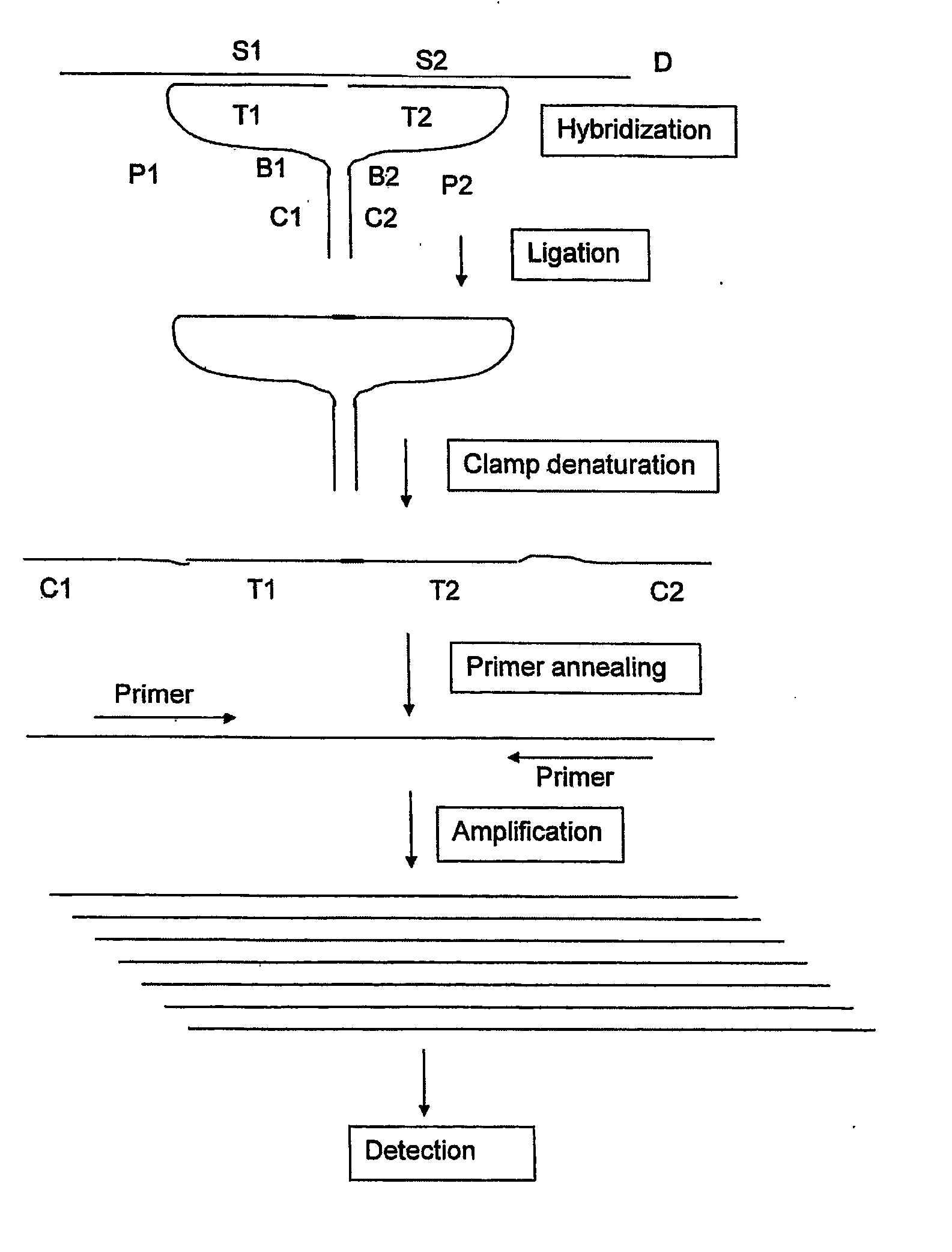
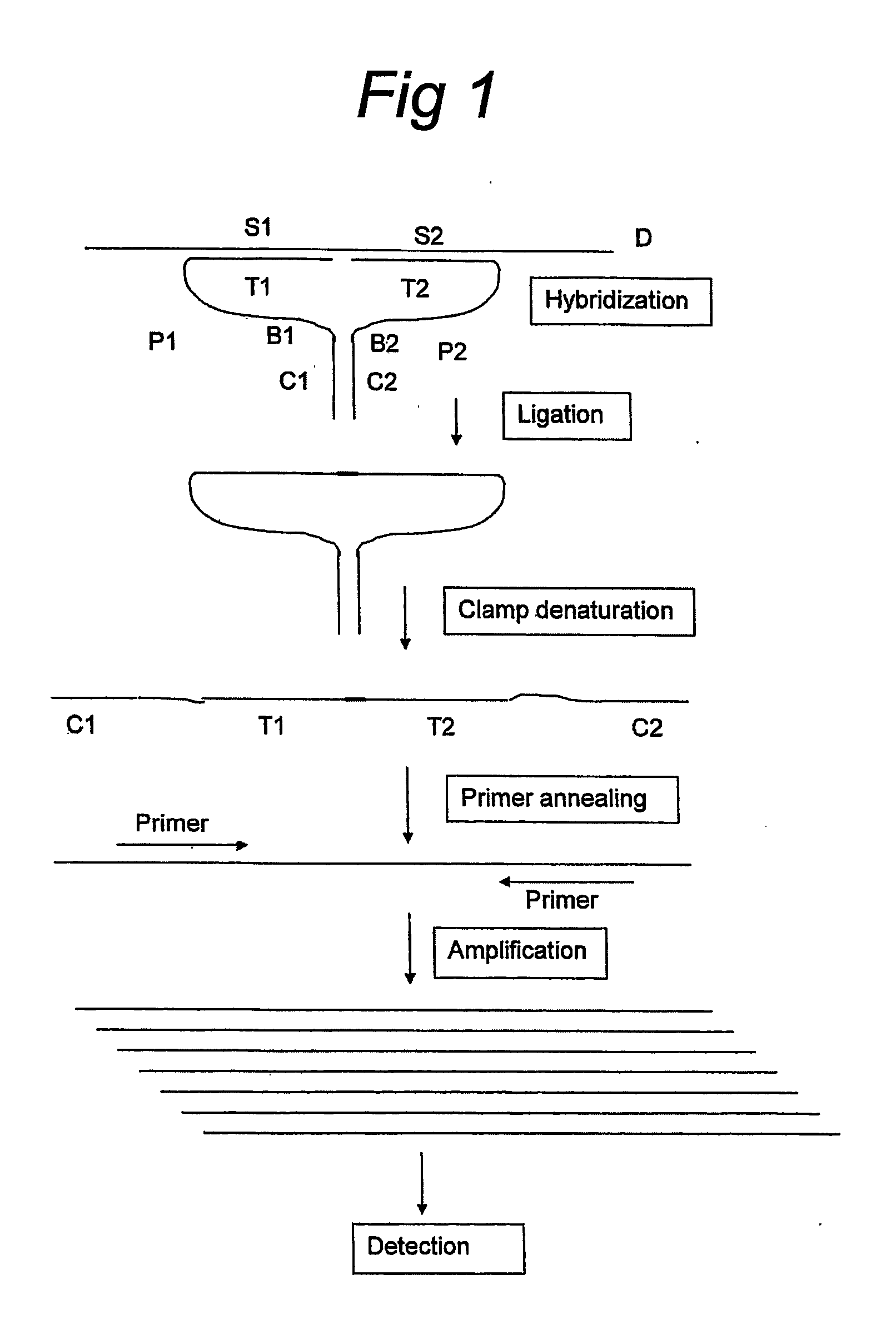
A pair of oligonucleotide probes comprising a first oligonucleotide probe that comprises a first clamp section that is capable of hybridising to a second clamp section of a second oligonucleotide probe and a first target section that is capable of hybridising to a first section of a target DNA sequence to be detected, a second oligonucleotide probe that comprises a second clamp section that is capable of hybridising to the first clamp section of the first oligonucleotide probe and a second target section that is capable of hybridising to a second section of the target DNA sequence to be detected.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
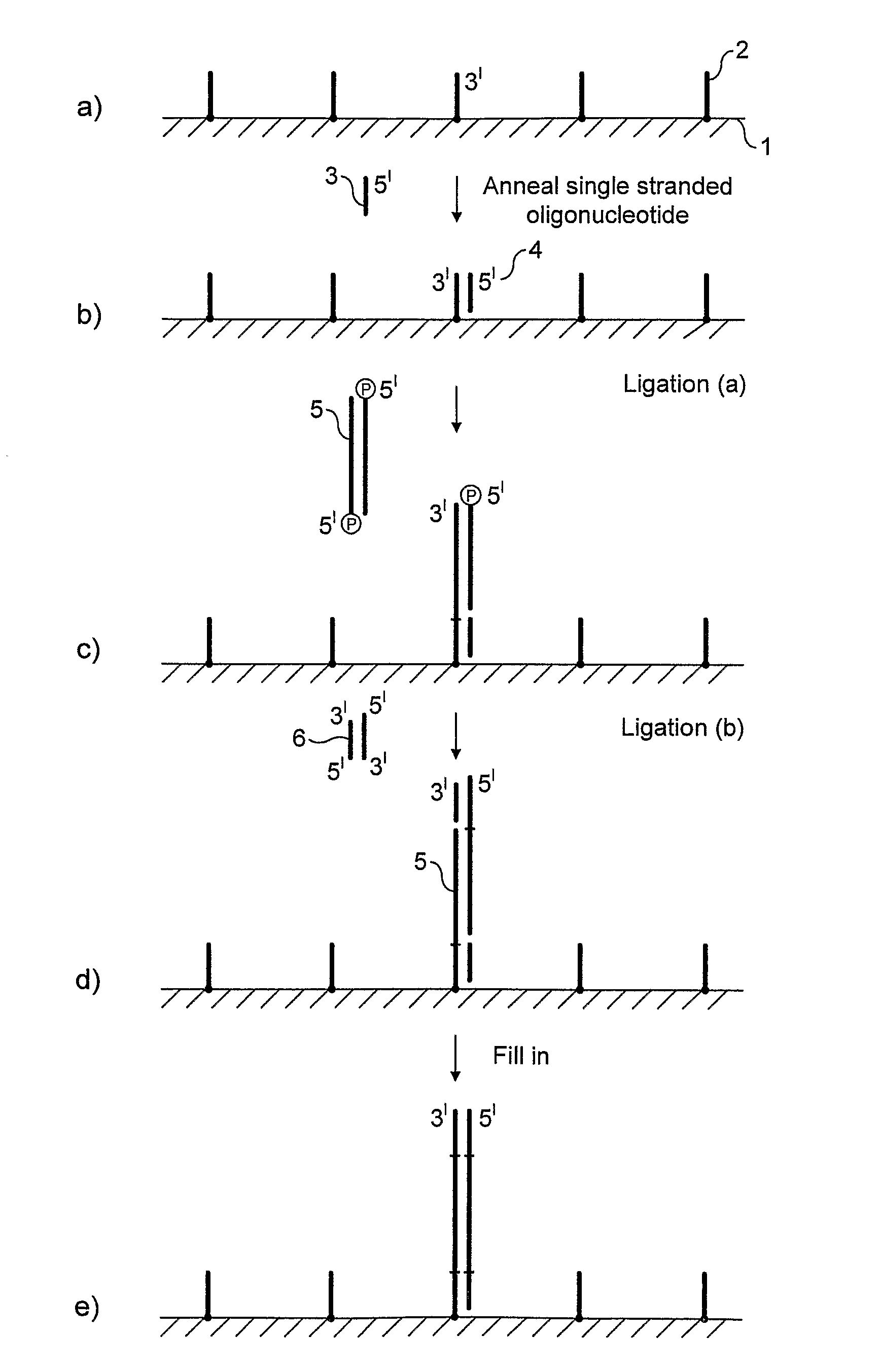
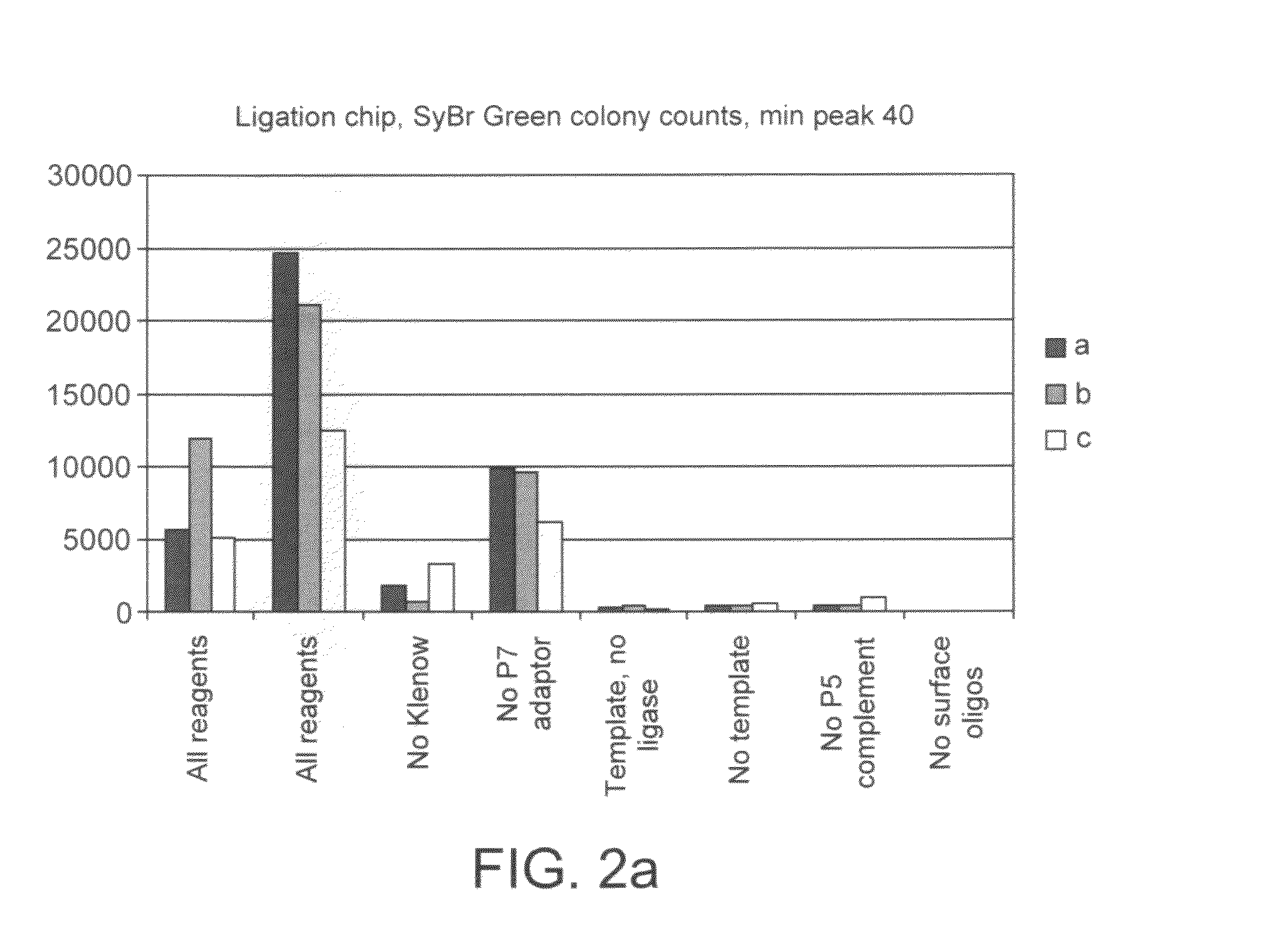
Preparation of nucleic acid templates for solid phase amplification
The invention relates to a method of preparing template constructs for solid-phase nucleic acid amplification and to use of the templates in methods of solid-phase nucleic acid amplification. The method involves carrying out two ligation reactions: (a) a ligation reaction in which the first end of one or more target polynucleotide molecules are ligated to surface-bound adaptor polynucleotide molecules, and (b) a ligation reaction in which solution-phase adaptor polynucleotide molecules are ligated to the second end of said target polynucleotide molecules, in order to produce one or more template constructs attached to a solid support.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
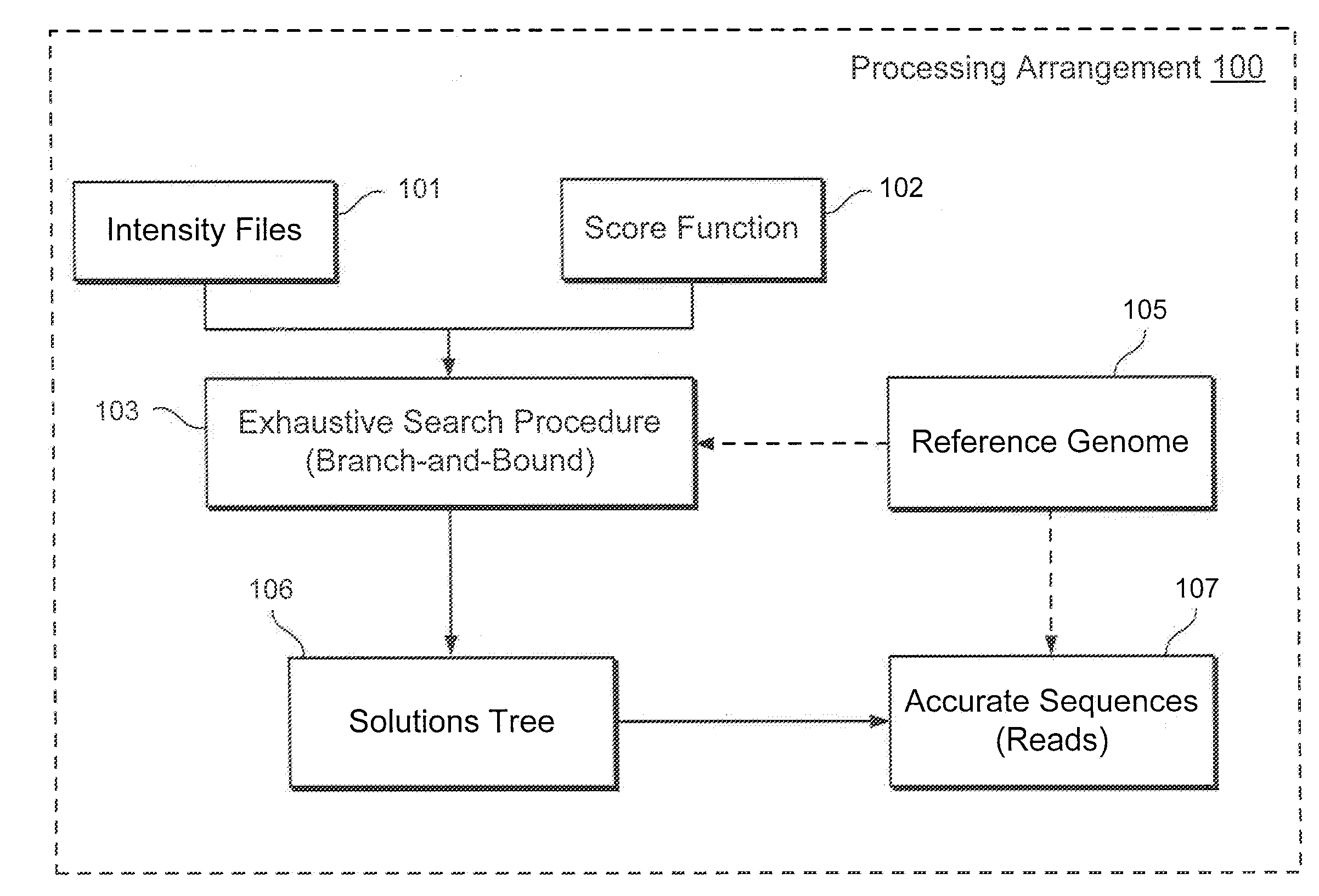
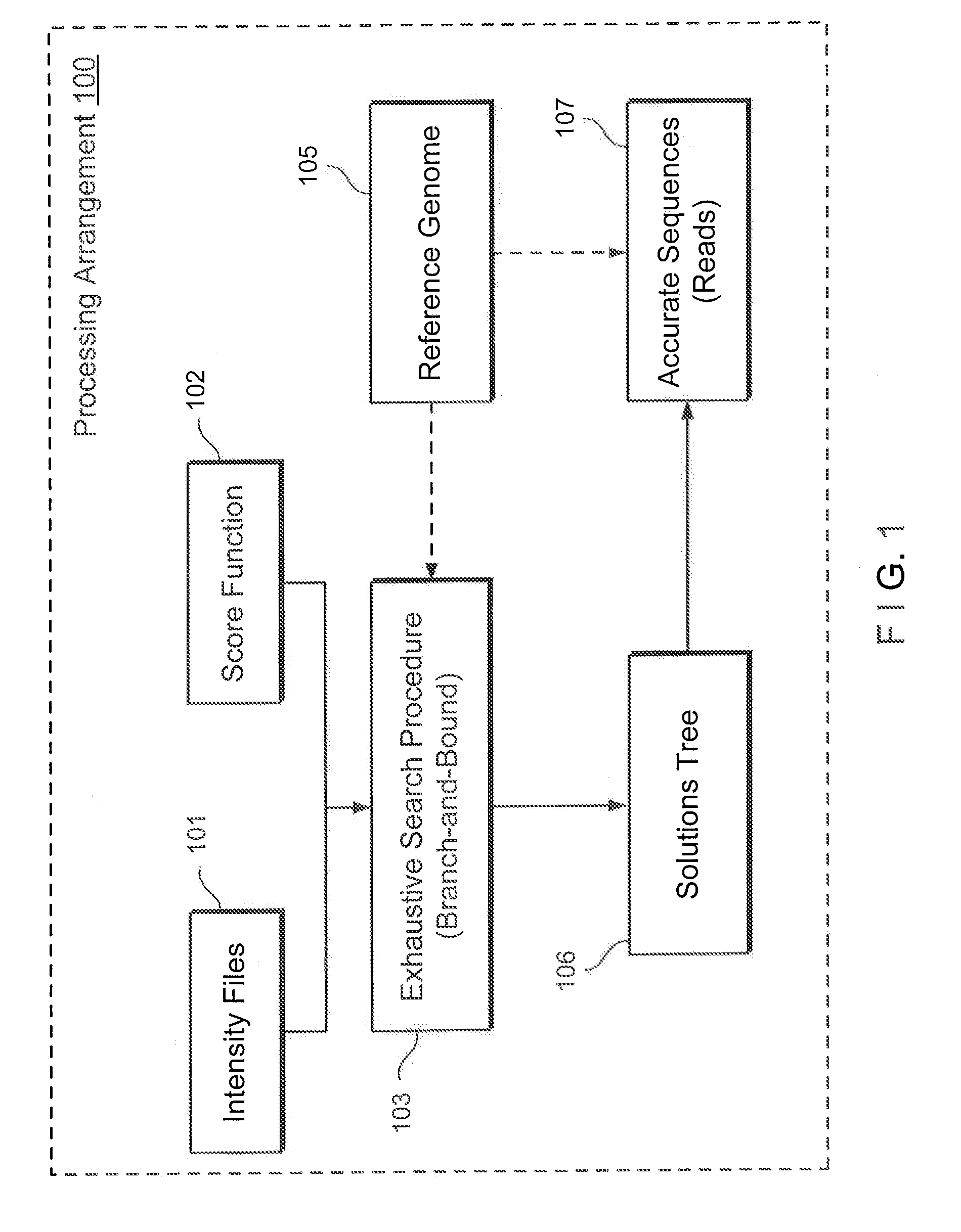
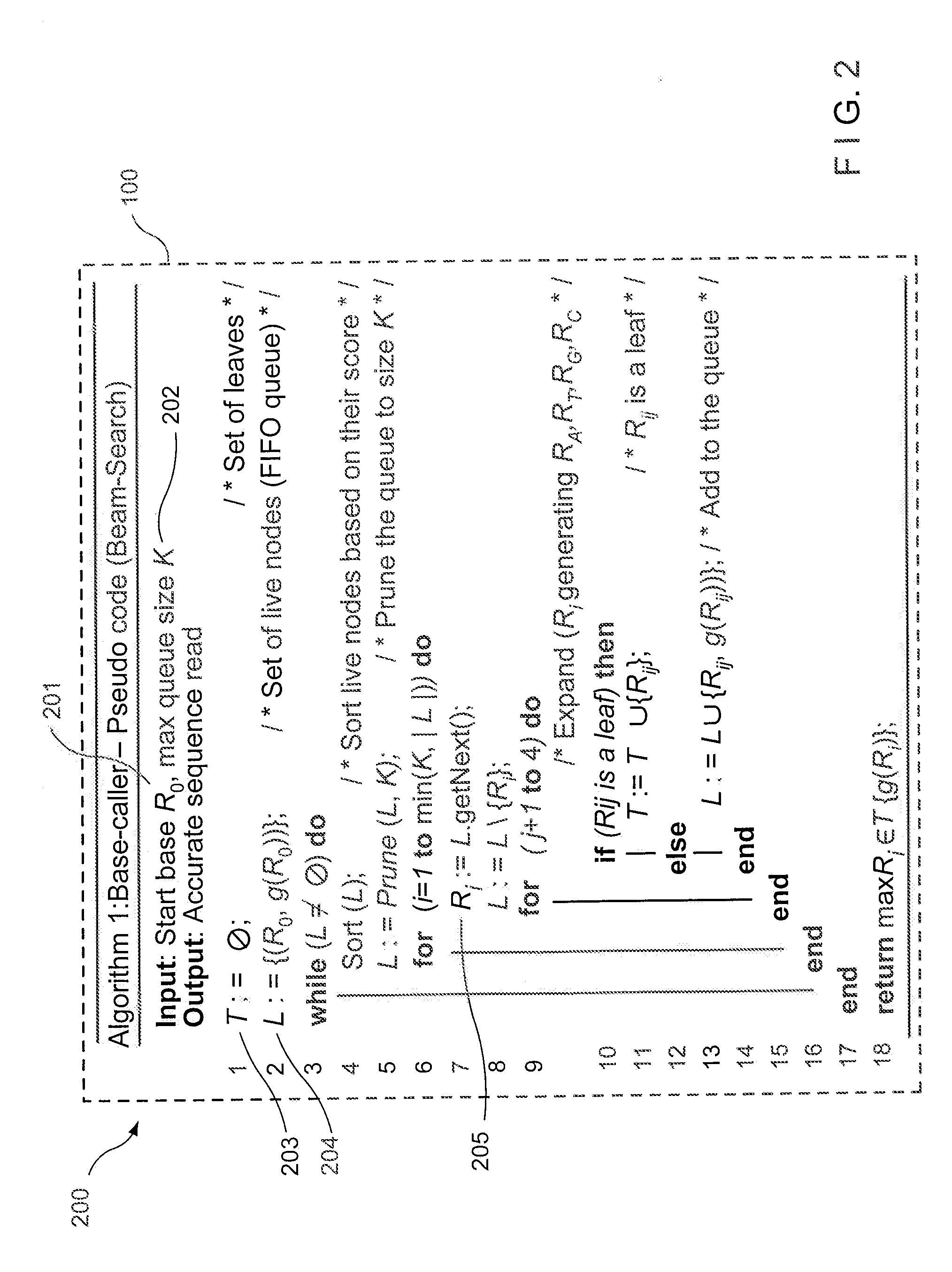
Method, computer-accessible medium and system for base-calling and alignment
Exemplary methods, procedures, computer-accessible medium, and systems for base-calling, aligning and polymorphism detection and analysis using raw output from a sequencing platform can be provided. A set of raw outputs can be used to detect polymorphisms in an individual by obtaining a plurality of sequence read data from one or more technologies (e.g., using sequencing-by-synthesis, sequencing-by-ligation, sequencing-by-hybridization, Sanger sequencing, etc.). For example, provided herein are exemplary methods, procedures, computer-accessible medium and systems, which can include and / or be configured for obtaining raw output from a sequencing platform configured to be used for reading fragment(s) of genomes, obtaining reference sequences for the genomes obtained independently from the raw output, and generating a base-call interpretation and / or alignment using the raw output and the reference sequences. For example, a score function can be determined based on information associated with the sequencing platform that can be used to analyze polymorphisms based on the base-call interpretation and / or alignment.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
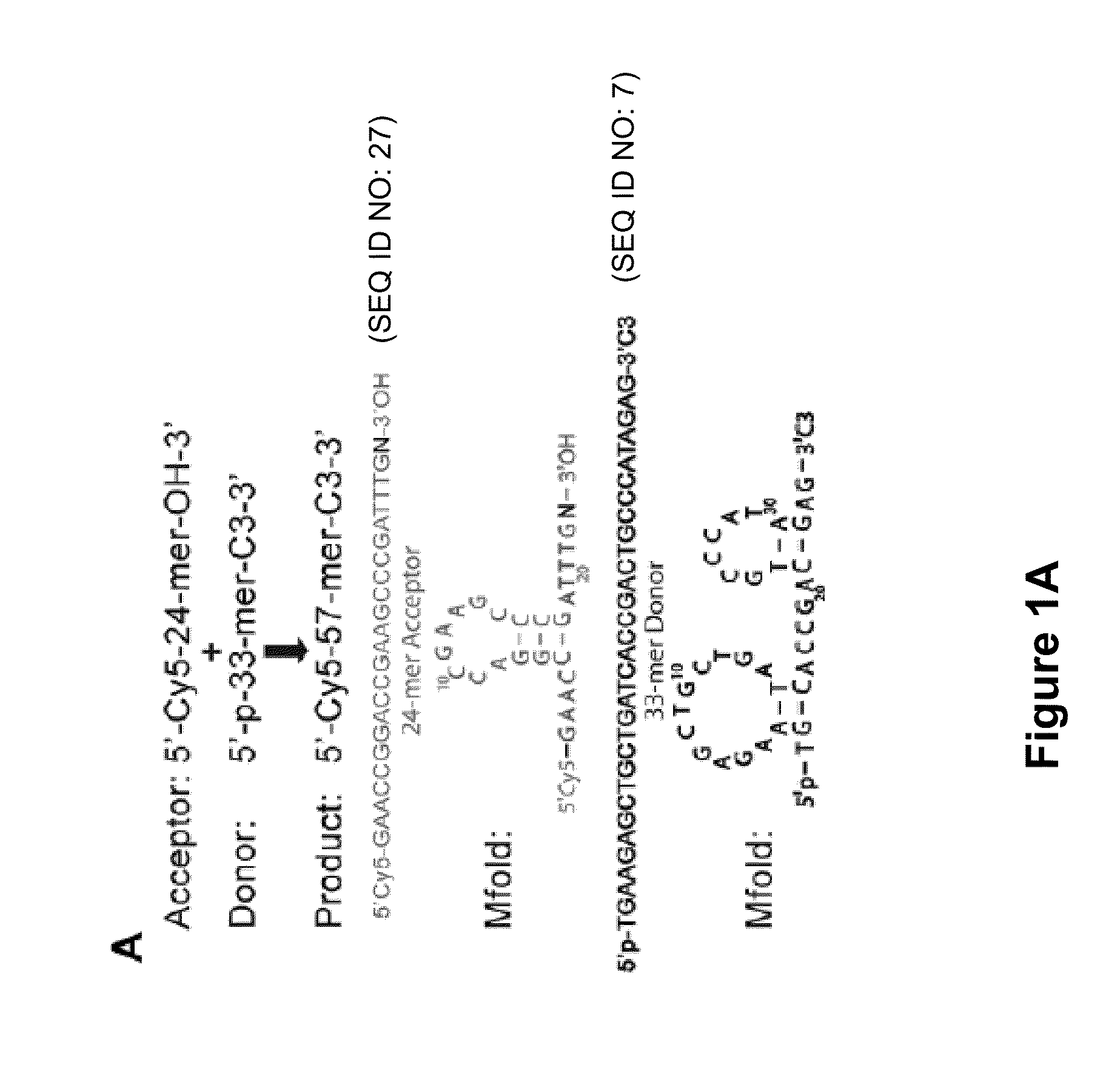
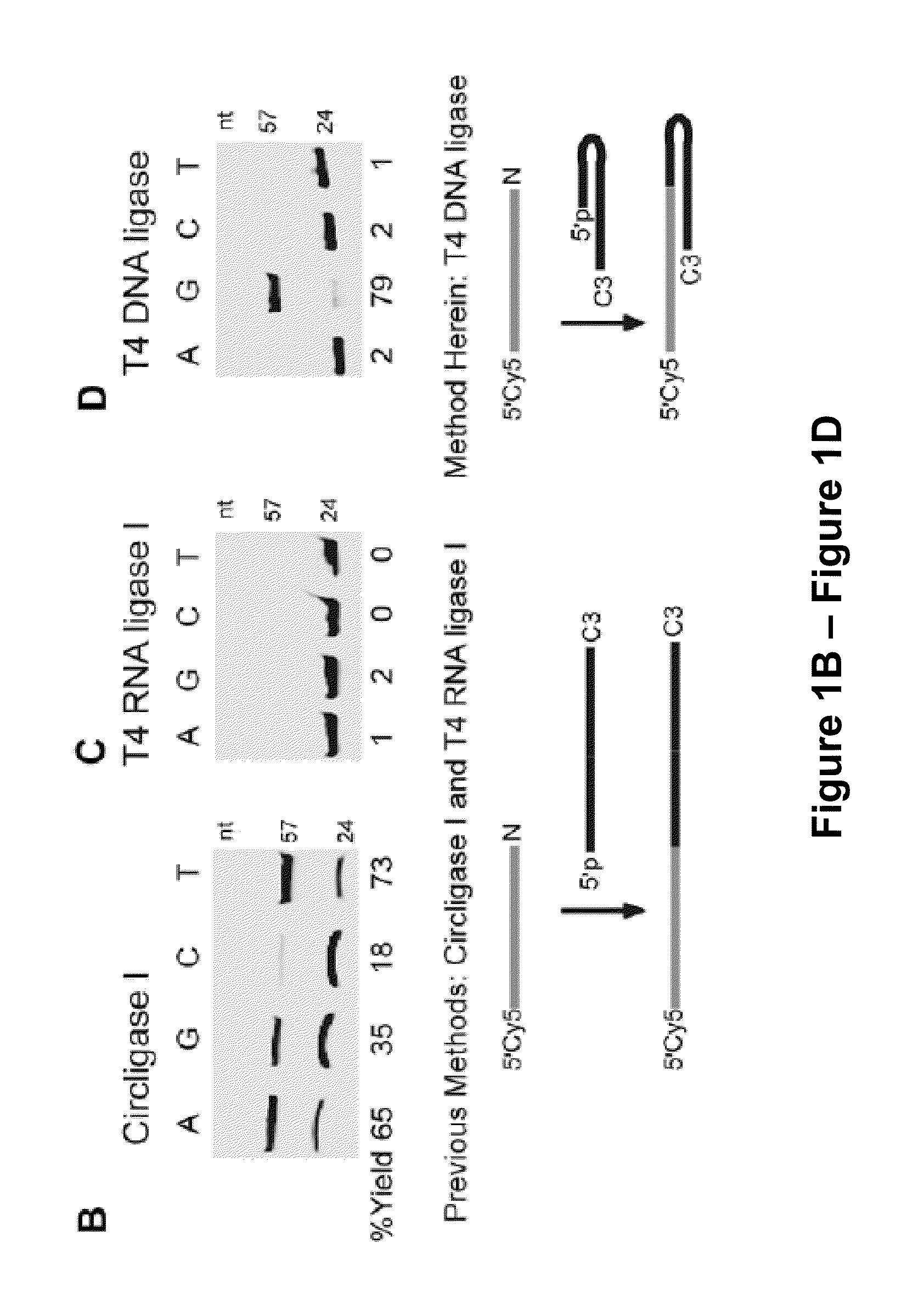
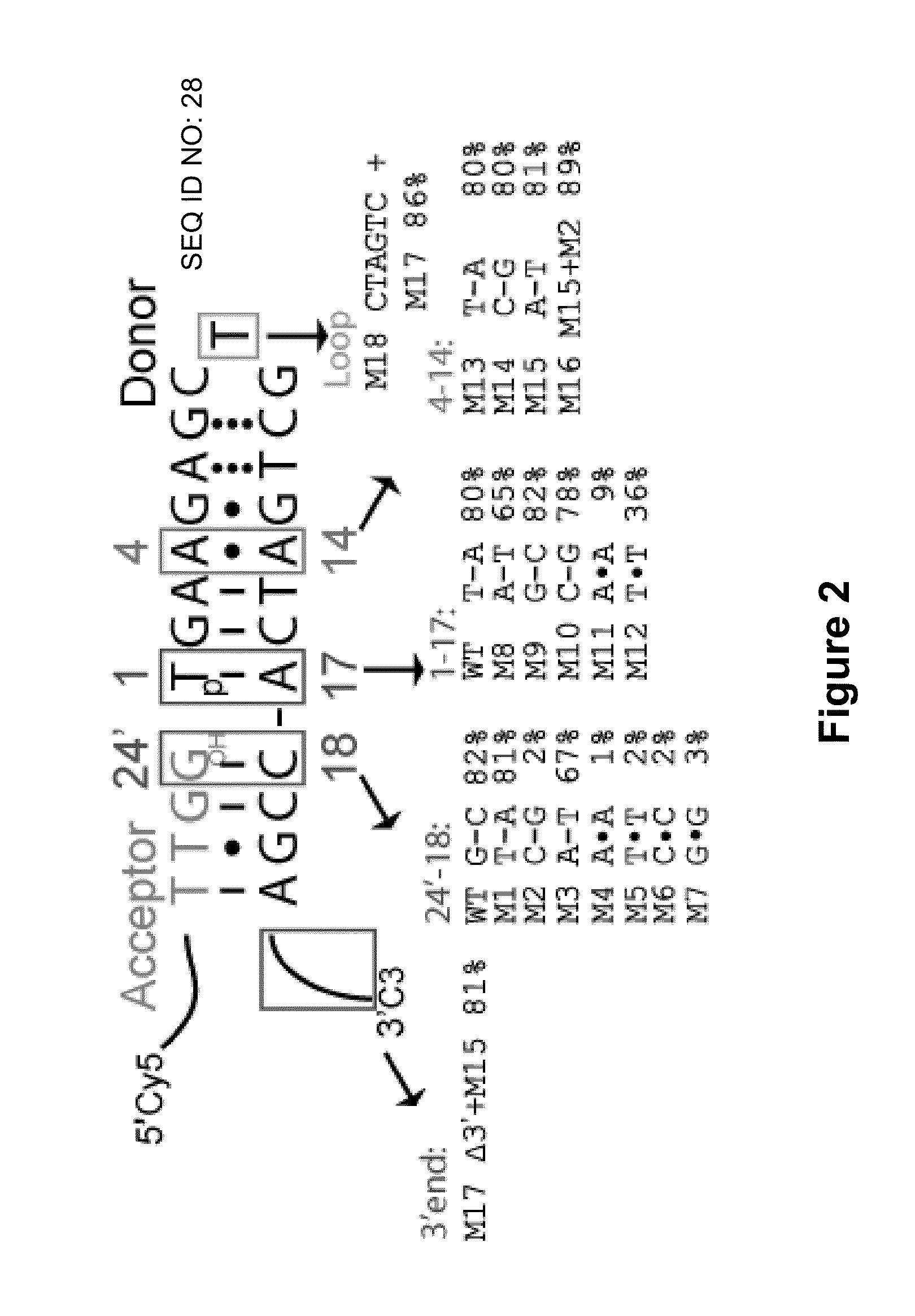
Low Sequence Bias Single-Stranded DNA Ligation
The invention provides compositions and methods for ligating single stranded nucleic acids wherein the ligation is based on fast, efficient, and low-sequence bias hybridization of an acceptor molecule with a donor molecule. In one embodiment, the structure of the donor molecule comprises a stem-loop intramolecular nucleotide base pairing (i.e., hairpin) and a 3′-overhang region such that the overhang is able to hybridize to nucleotides present in the 3′ end of the acceptor molecule.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Multi-gene expression constructs containing modified inteins
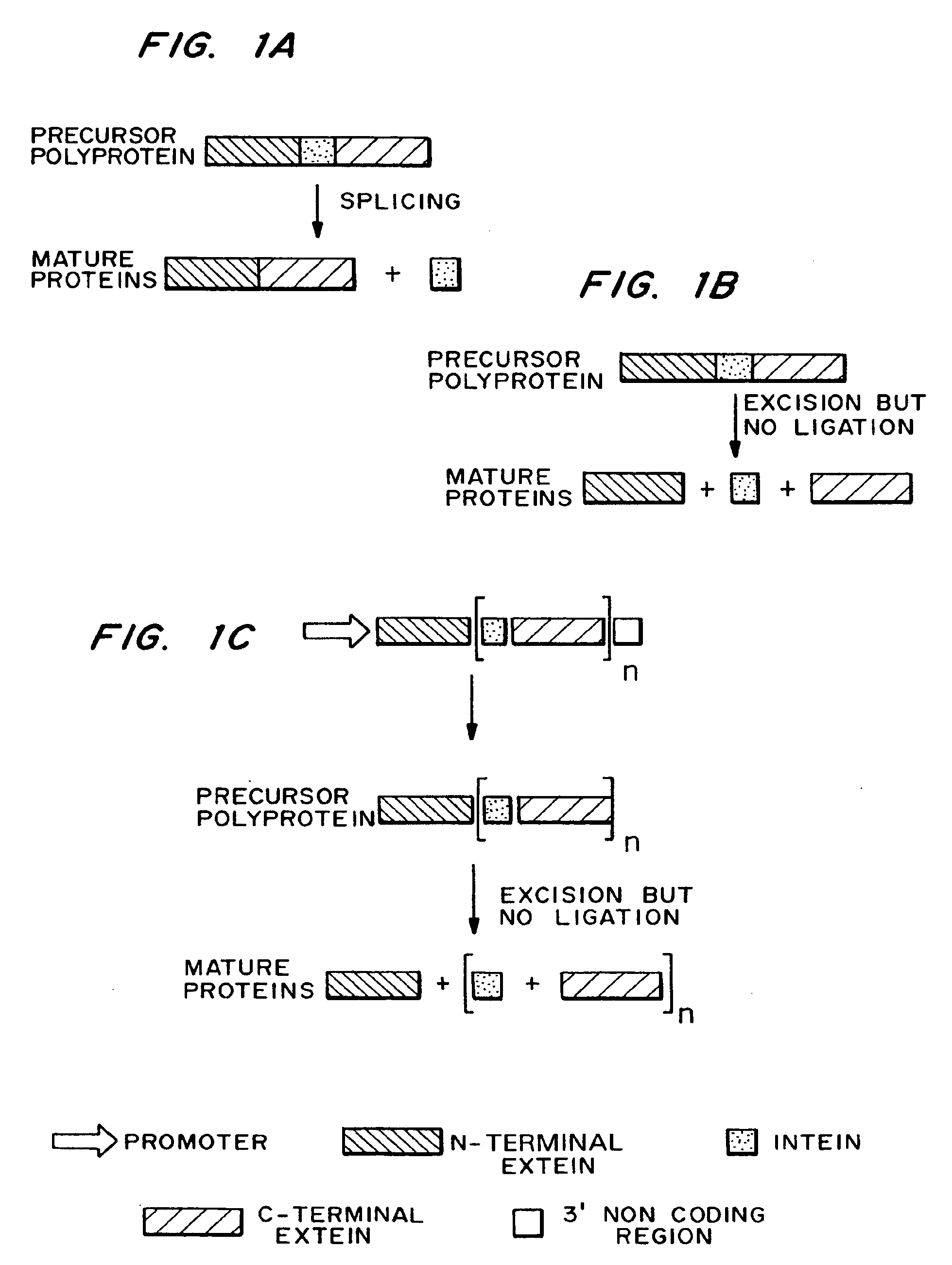
InactiveUS7026526B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPoly-A RNA
Methods and constructs for the introduction of multiple genes into plants using a single transformation event are described. Constructs contain a single 5′ promoter operably linked to DNA encoding a modified intein splicing unit. The splicing unit is expressed as a polyprotein and consists of a first protein fused to an intein fused to a second protein. The splicing unit has been engineered to promote excision of all non-essential components in the polyprotein but prevent the ligation reactions normally associated with protein splicing. Additional genetic elements encoding inteins and additional proteins can be fused in frame to the 5′-terminus of the coding region for the second protein to form a construct for expression of more than two proteins. A single 3′ termination sequence, such as a polyadenylation sequence when the construct is to be expressed in eucaryotic cells, follows the last coding sequence. These methods and constructs are particularly useful for creating plants with stacked input traits, illustrated by glyphosate tolerant plants producing BT toxin, and / or value added products, illustrated by the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in plants.
Owner:METABOLIX
Methods and compositions for detection of small rnas
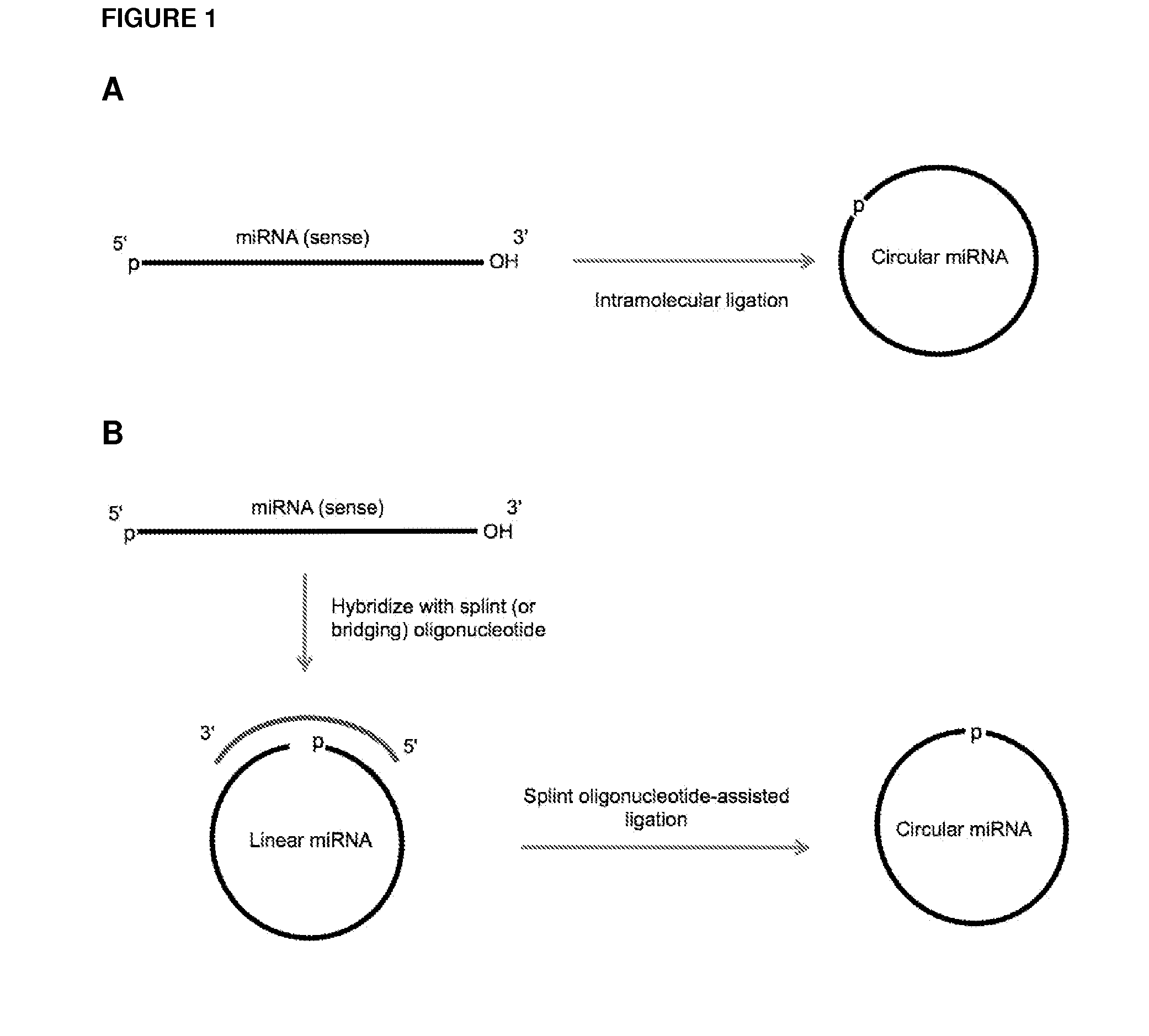
ActiveUS20120164651A1Improve efficiencySimilar efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTrue positive rateCircular RNA
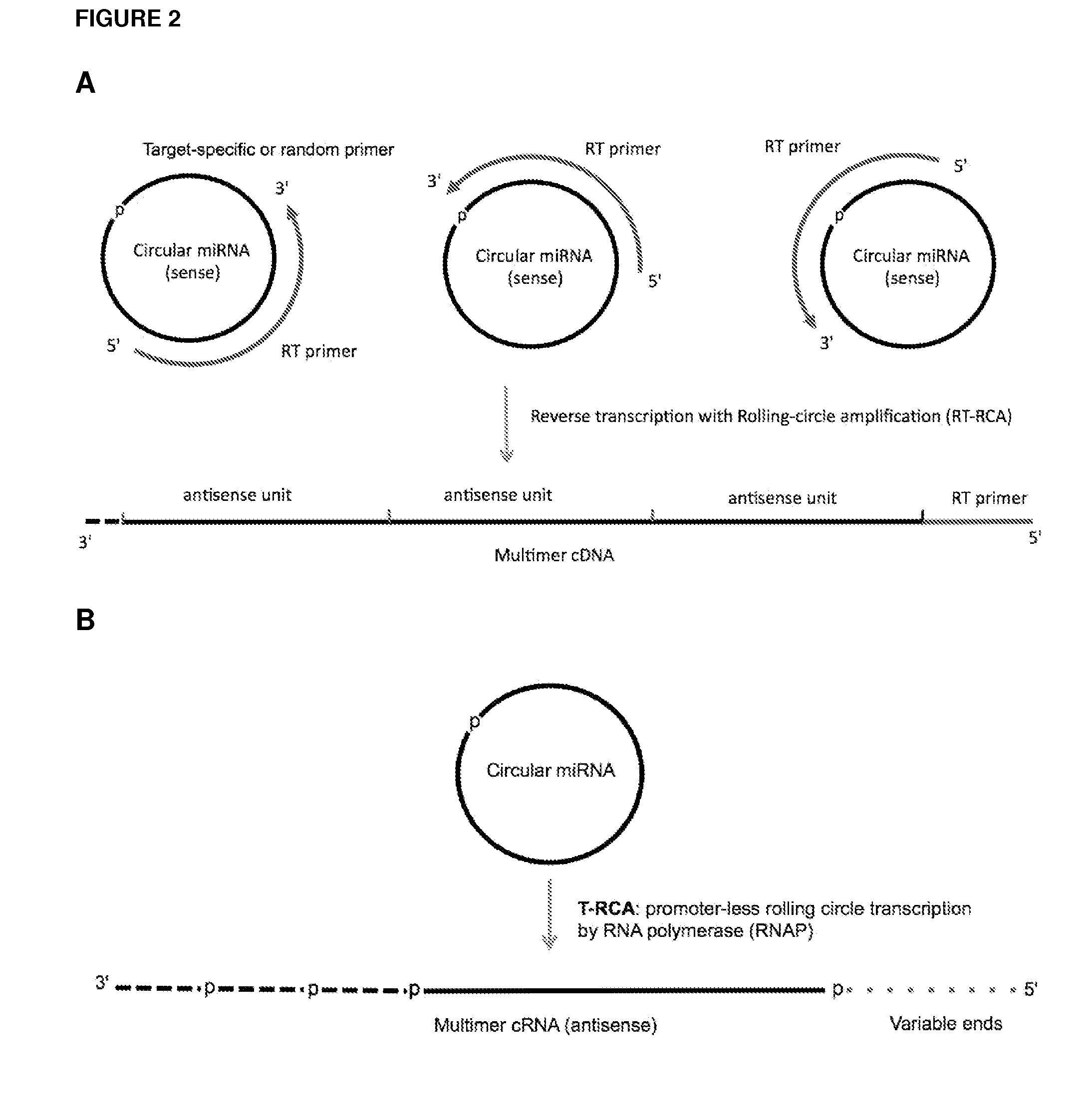
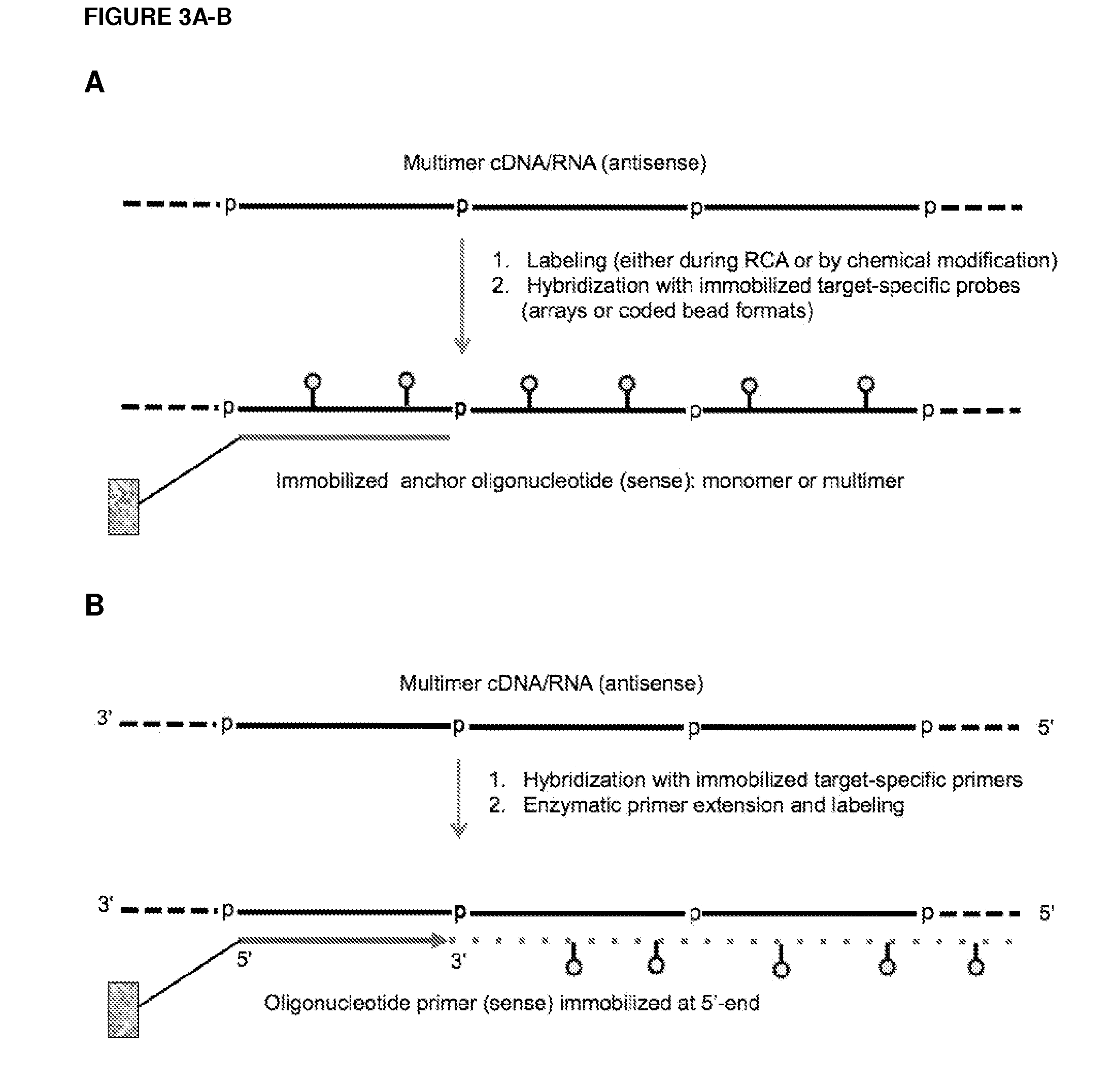
Currently, the circularization of small RNAs is broadly regarded as an obstacle in ligation-related assays and explicitly avoided while short lengths of linear RNA targets is broadly recognized as a factor limiting use of conventional primers in PCR-related assays. In contrast, the disclosed invention capitalizes on circularization of small RNA targets or their conjugates with oligonucleotide adapters. The circular RNA templates provide amplification of the target sequences via synthesis of multimer nucleic acids that can be either labeled for direct detection or subjected to PCR amplification and detection. Structure of small circular RNAs and corresponding multimeric nucleic acids provide certain advantages over current methods including flexibility in design of conventional RT and PCR primers as well as use of 5′-overlapping dimer-primers for efficient and sequence-specific amplification of short target sequences. Our invention also reduces number of steps and reagents while increasing sensitivity and accuracy of detection of small RNAs with both 2′OH and 2′-OMe at their 3′ ends. Our invention increase sensitivity and specificity of detection of microRNAs and other small RNAs with both 2′OH and 2′-OMe at their 3′ ends while allowing us to distinguish these two forms from each other.
Owner:REALSEQ BIOSCI INC
PNA-DNA chimeric probe arrays and methods of use
InactiveUS6469151B1Strong specificityHigh affinitySugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluorescenceOligonucleotide
The invention provides methods, kits, and compositions for ligation of PNA-DNA chimeric probes and oligonucleotides when they are hybridized adjacently to template nucleic acids using ligases and ligation reagents. Structural requirements of the chimeras for ligation include 5 to 15 contiguous PNA monomer units, 2 or more contiguous nucleotides, and a 3' hydroxyl or 5' hydroxyl terminus. The chimera and / or oligonucleotide may be labelled with fluorescent dyes or other labels. The methods include, for example, oligonucleotide-ligation assays (OLA) and single nucleotide polymorphism detection.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
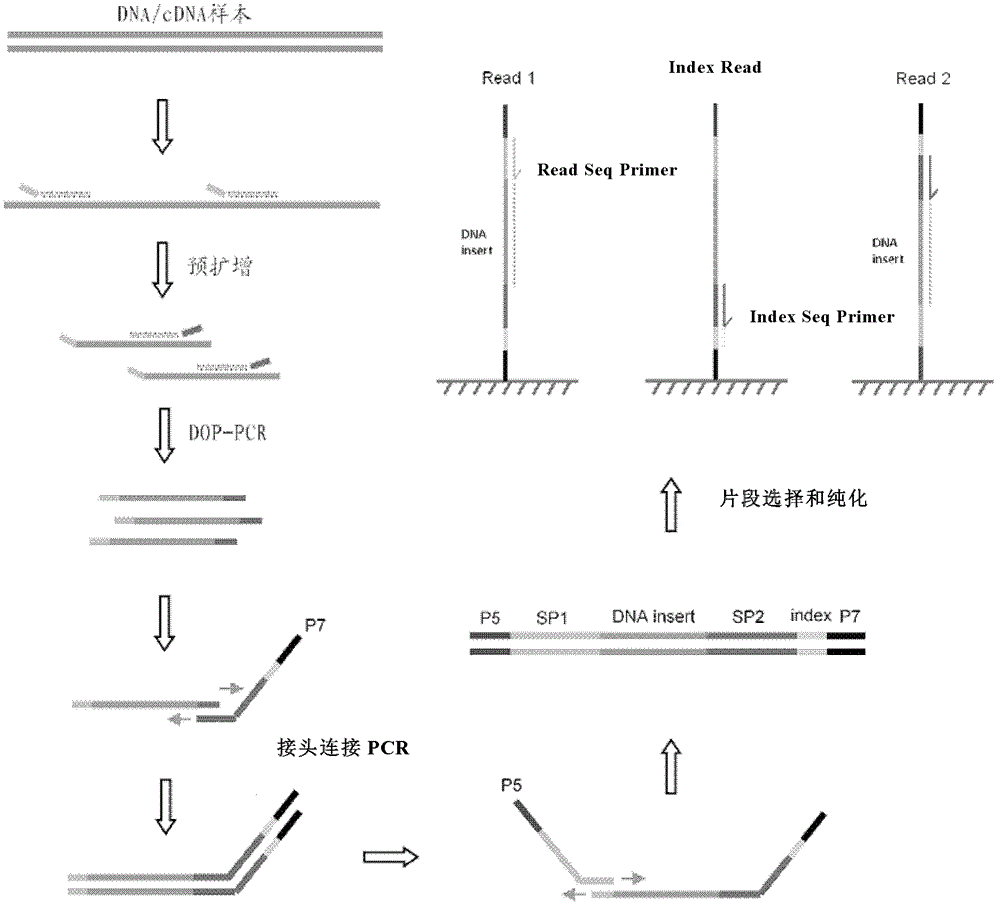
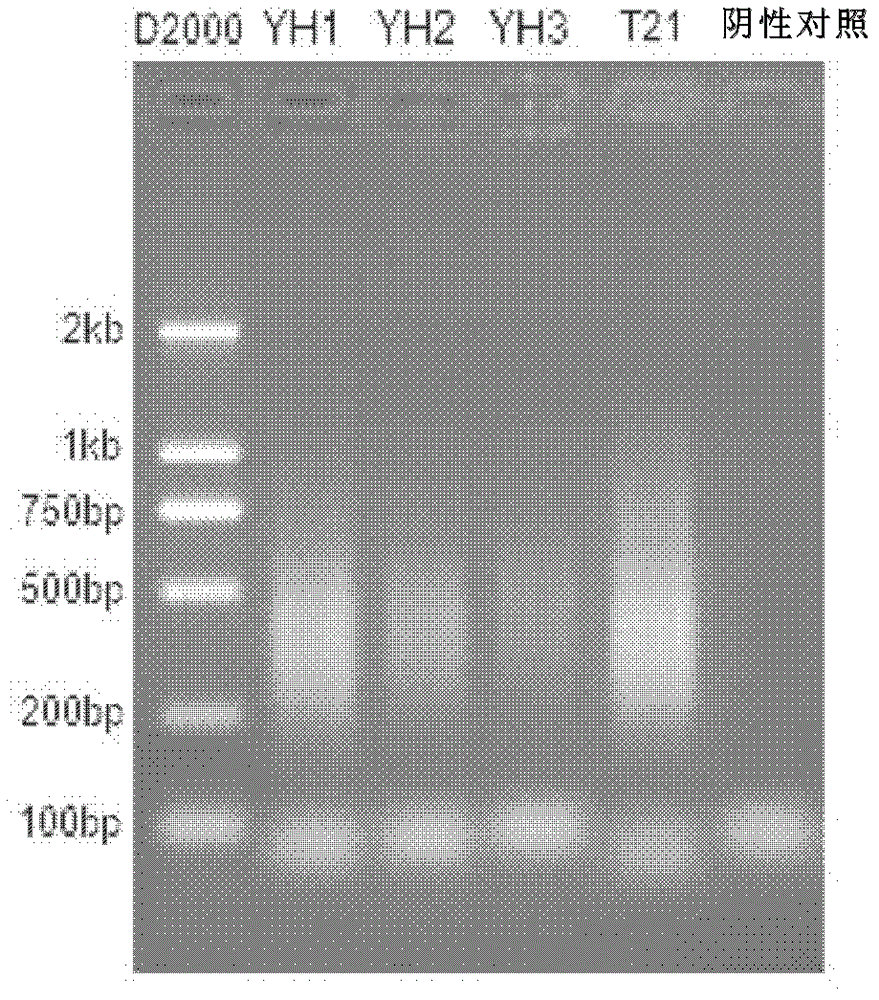
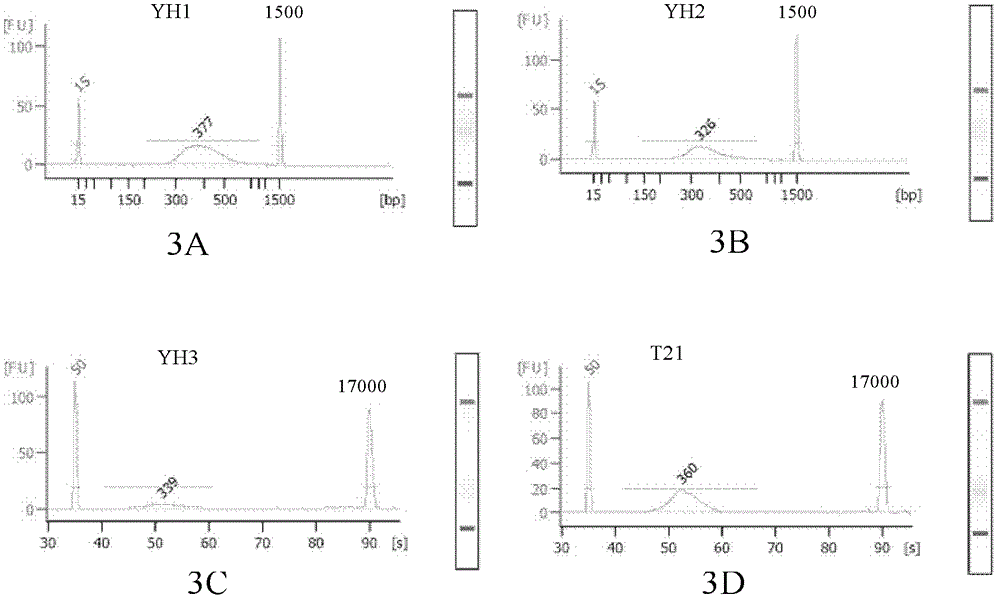
Library preparation method of trace nucleic acid sample and application thereof
ActiveCN103060924ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideLibrary preparation
The invention relates to a library preparation method of a trace nucleic acid sample and application thereof. The method comprises: using a DOP (Degenerate Oligonucleotide Primed) primer to perform first amplification on DNA in the sample, with a DOP primer sequence having at least a 5' terminal nondegenerate nucleotide zone and a 3' terminal degenerate nucleotide zone; employing a DOP-Amp primer to conduct second amplification on a first PCR product so as to obtain a second PCR amplification product; and carrying out adaptor-ligation PCR on the second PCR amplification product to obtain a third PCR product, and taking the third PCR product with sequencing adaptors on both ends as the nucleic acid library. The library can be used for fragment size selection and high-throughput sequencing to obtain gene information related to diseases in the sample. The invention also provides a kit and its application in preparation of the trace nucleic acid sample library.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
Solid support assay systems and methods utilizing non-standard bases
Solid support assays using non-standard bases are described. A capture oligonucleotide comprising a molecular recognition sequence is attached to a solid support and hybridized with a target oligonucleotide. In some instances, the molecular recognition sequence includes one or more non-standard bases and hybridizes to a complementary tagging sequence of the target oligonucleotide. In other instances, incorporation of a non-standard base (e.g., via PCR or ligation) is used in the assay.
Owner:LUMINEX
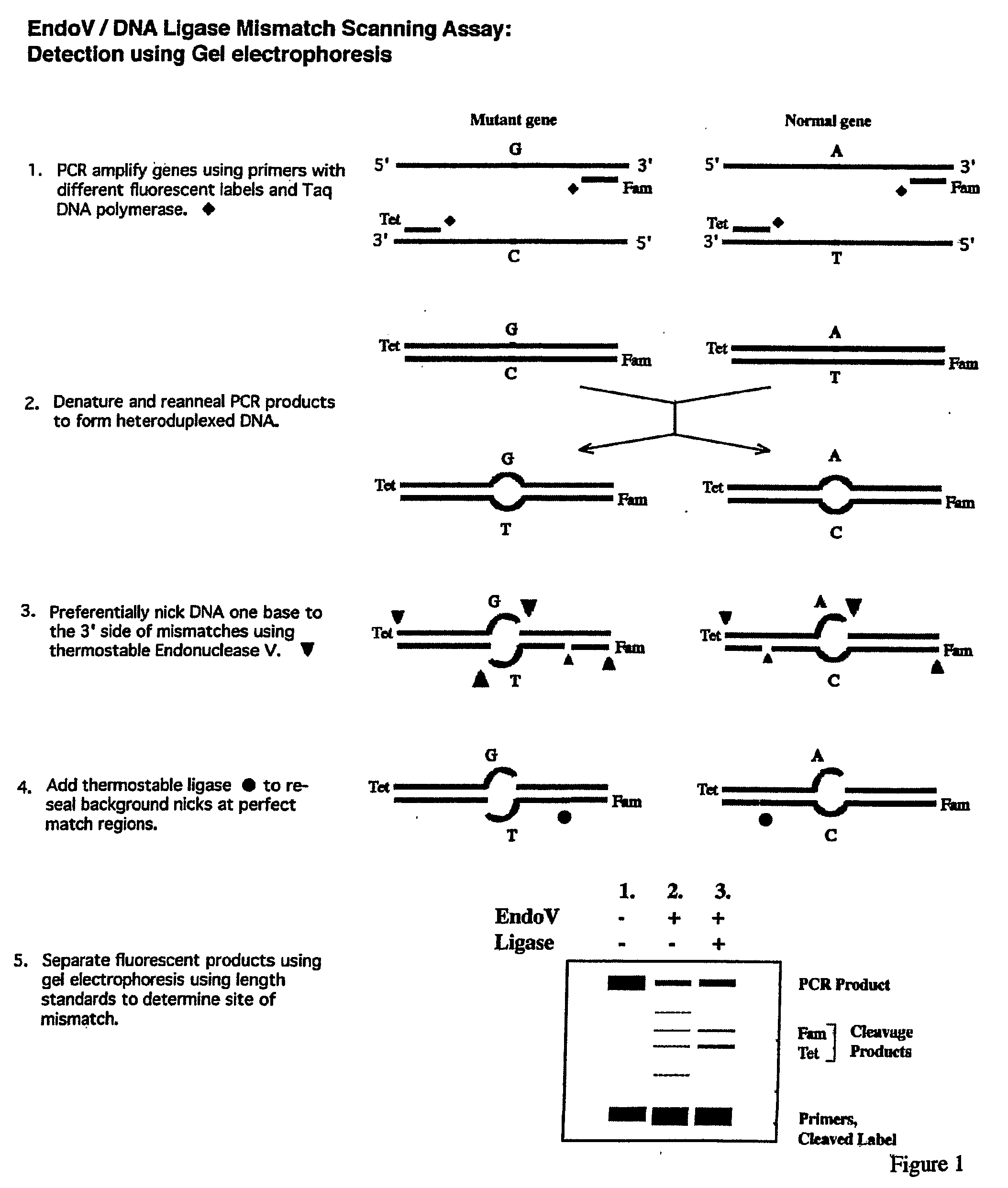
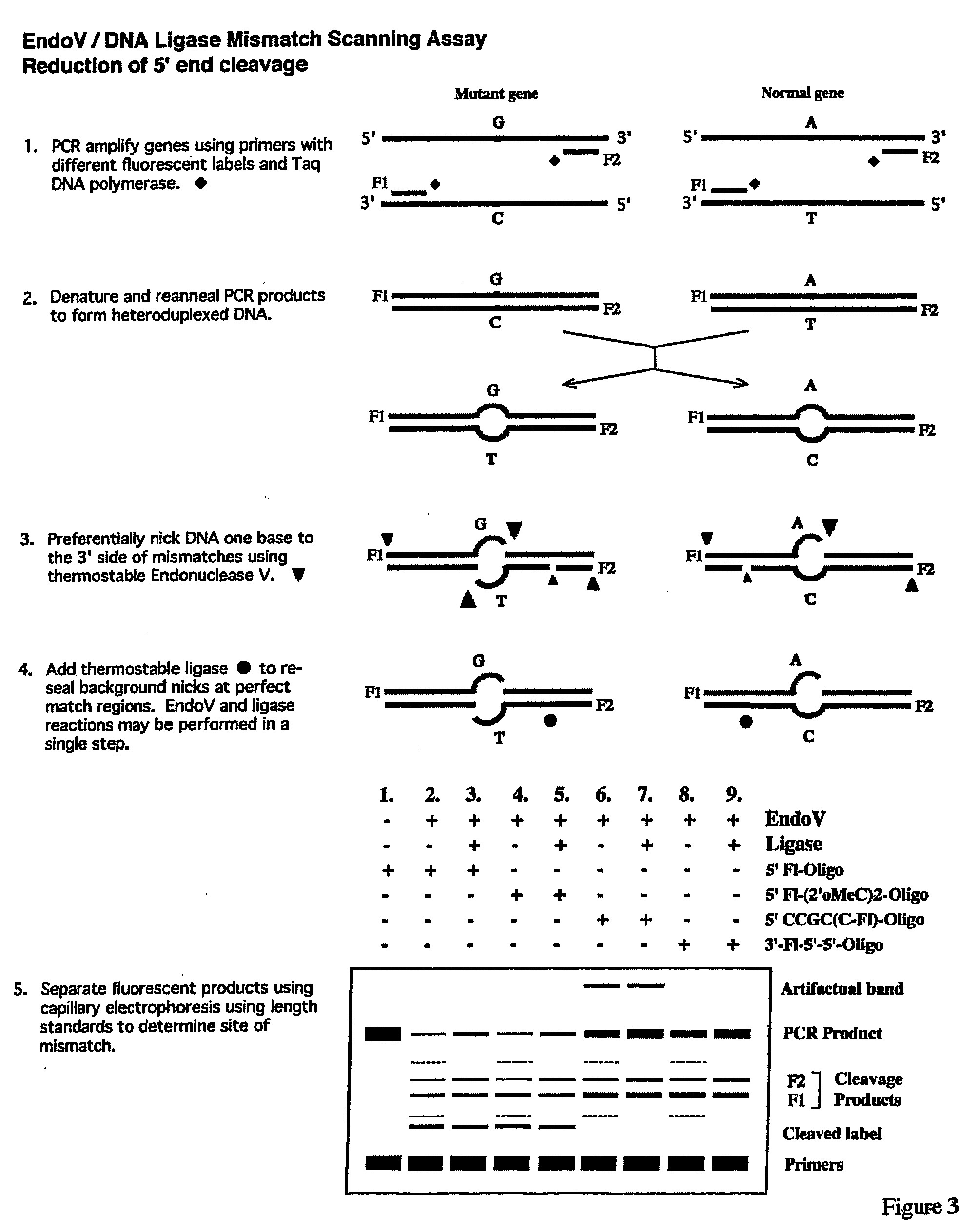
Detection of nucleic acid differences using endonuclease cleavage/ligase resealing reactions and capillary electrophoresis or microarrays
InactiveUS20090123913A1Reduce noiseObstruction is producedMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeteroduplexA-DNA
The present invention is directed to various methods for detecting DNA sequence differences, including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and, to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
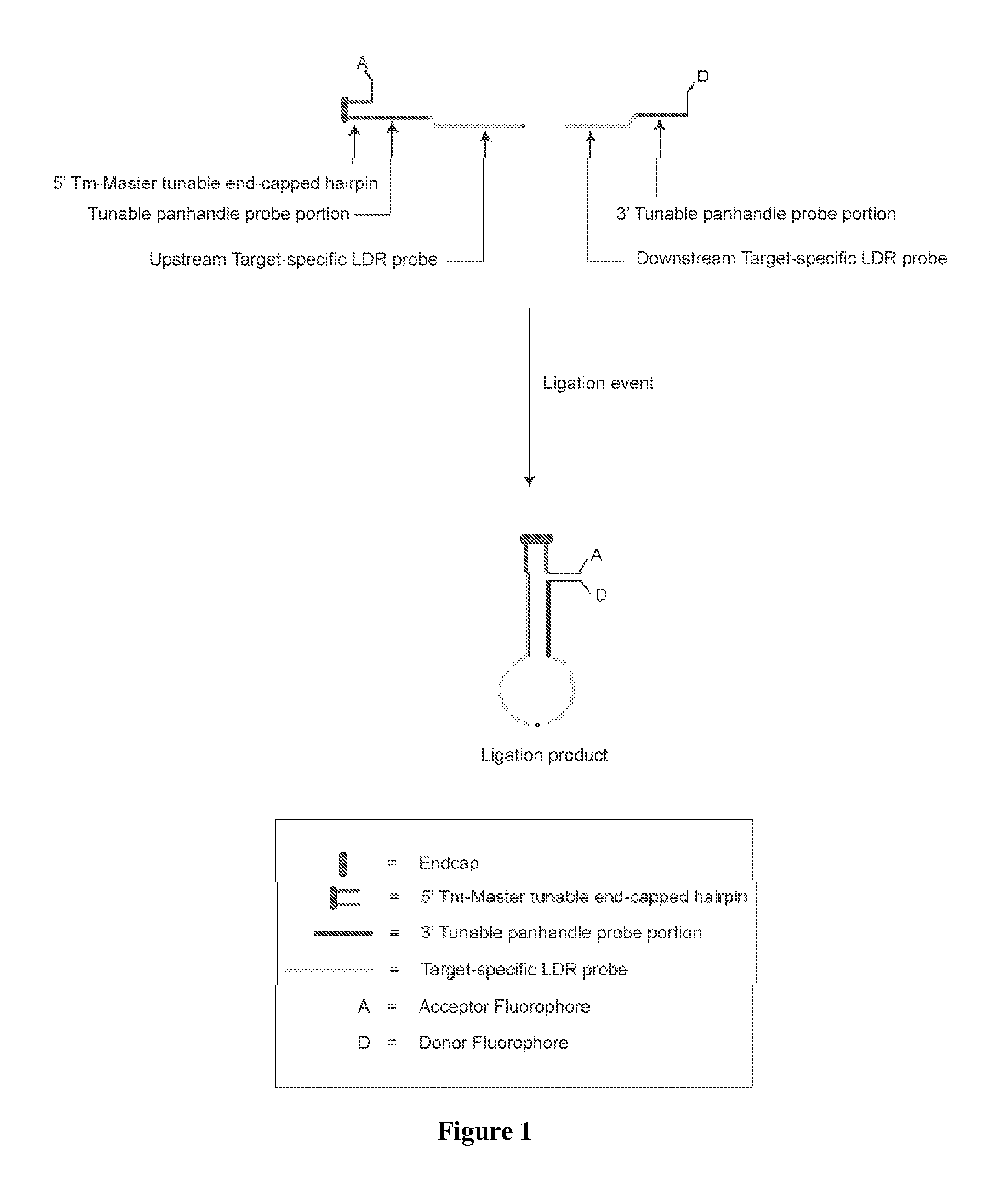
Detection of target nucleic acid sequences using fluorescence resonance energy transfer
InactiveUS20110136116A1Overcome deficienciesEasy to distinguishMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
A method for identifying a plurality of target nucleic acid molecules in a sample. The method provides a plurality of oligonucleotide probe sets. Each set comprises a first and a second probe, each having a target-specific portion and a tunable portion with an acceptor or a donor group. The first probe further comprises an endcapped hairpin. A reaction comprises a denaturation and hybridization cycle. Under the hybridization, the set of probes hybridize in a base-specific manner to their respective target nucleotide sequences, and ligate to one another to form a ligation product. Under conditions that permit hybridization of the tunable portions of the ligation product to one another, an internally hybridized ligation product formed, which allows the detection of the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). A method comprising PCR amplification is also disclosed.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com