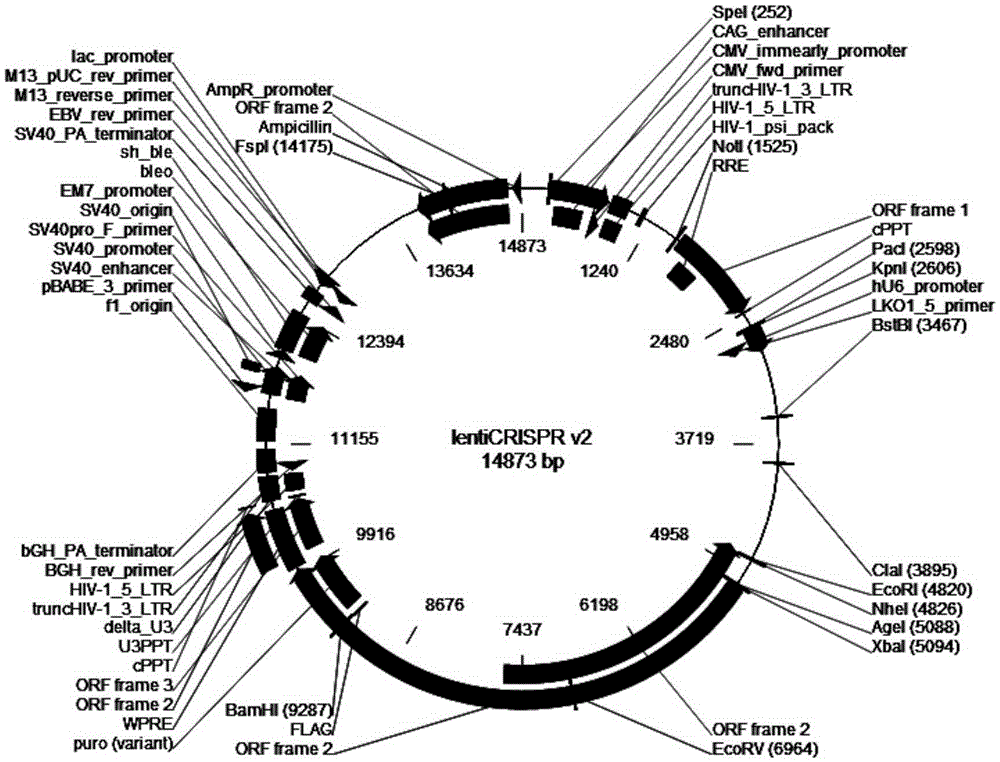
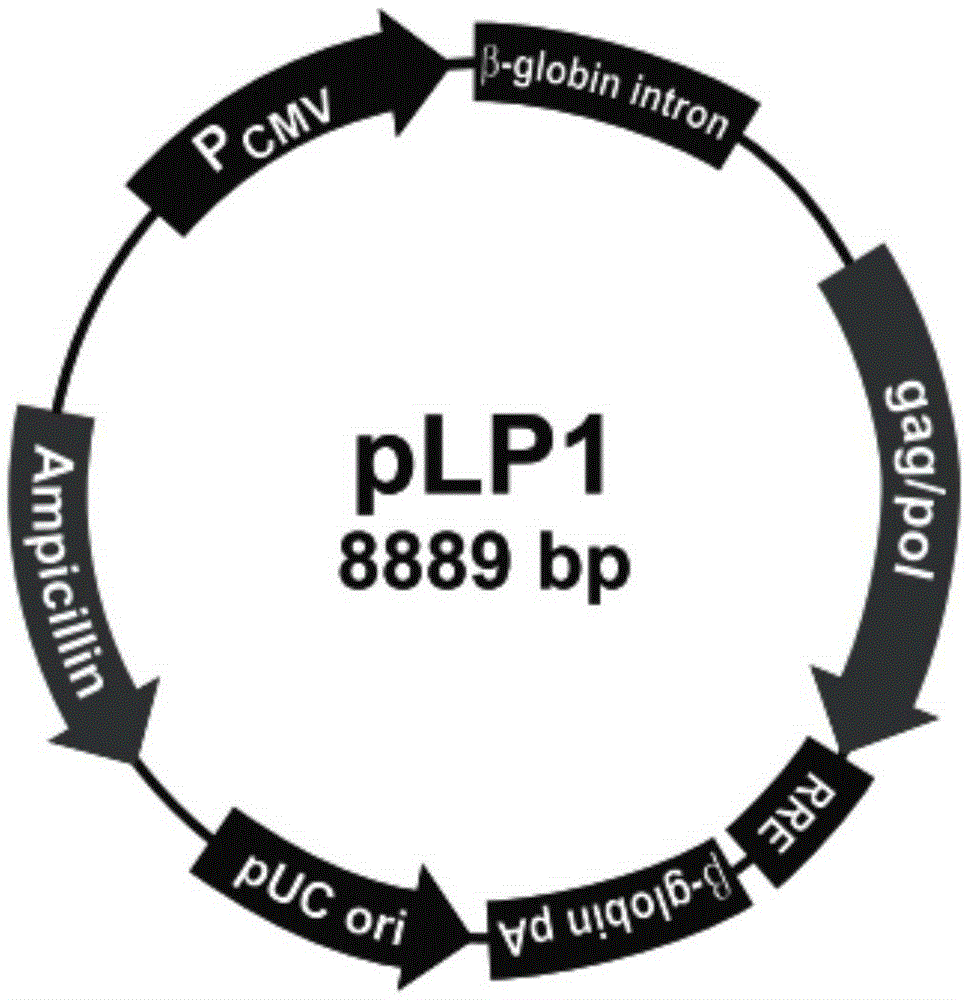
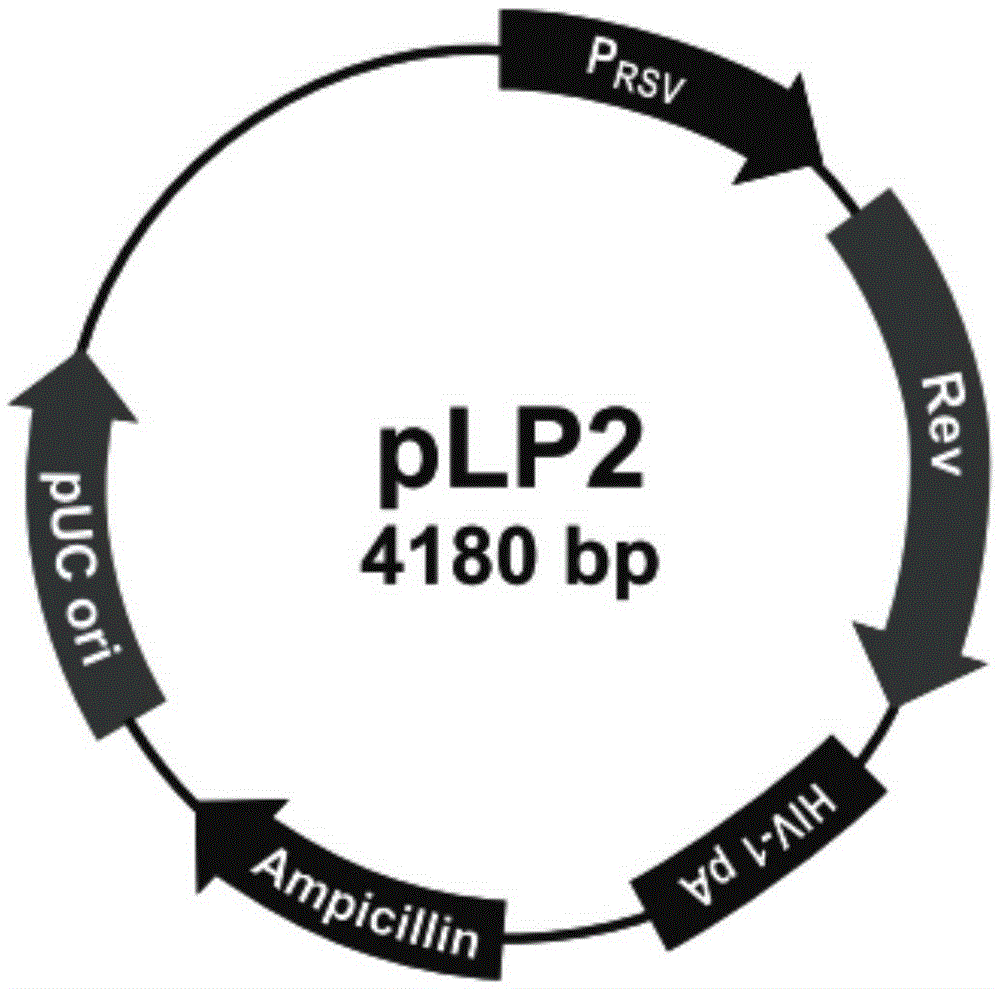
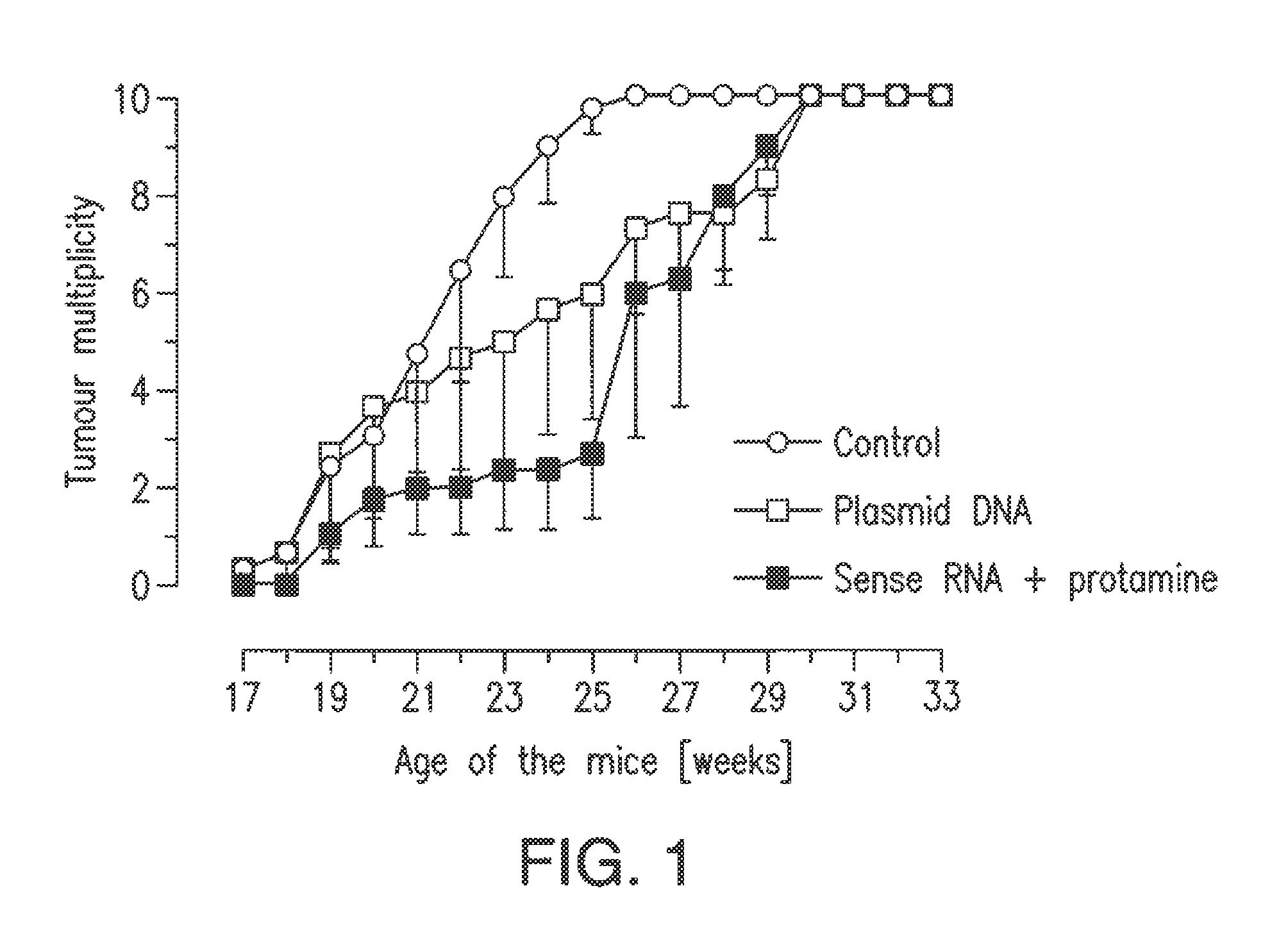
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1534 results about "Coding region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The coding region of a gene, also known as the CDS (from coding sequence), is that portion of a gene's DNA or RNA that codes for protein. The region usually begins at the 5' end by a start codon and ends at the 3' end with a stop codon.
Full-length plant cDNA and uses thereof
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
Pharmaceutical composition containing a stabilised mRNA optimised for translation in its coding regions
ActiveUS20050032730A1Overcome disadvantagesImprove efficiencyAntibacterial agentsVirusesTranslational efficiencyCoding region
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a modified mRNA that is stabilised by sequence modifications and optimised for translation. The pharmaceutical composition according to the invention is particularly well suited for use as an inoculating agent, as well as a therapeutic agent for tissue regeneration. In addition, a process is described for determining sequence modifications that promote stabilisation and translational efficiency of modified mRNA of the invention.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Method of eliminating inhibitory/instability regions from mRNA
InactiveUS6174666B1Microbiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesImmunodeficiency virusInstability
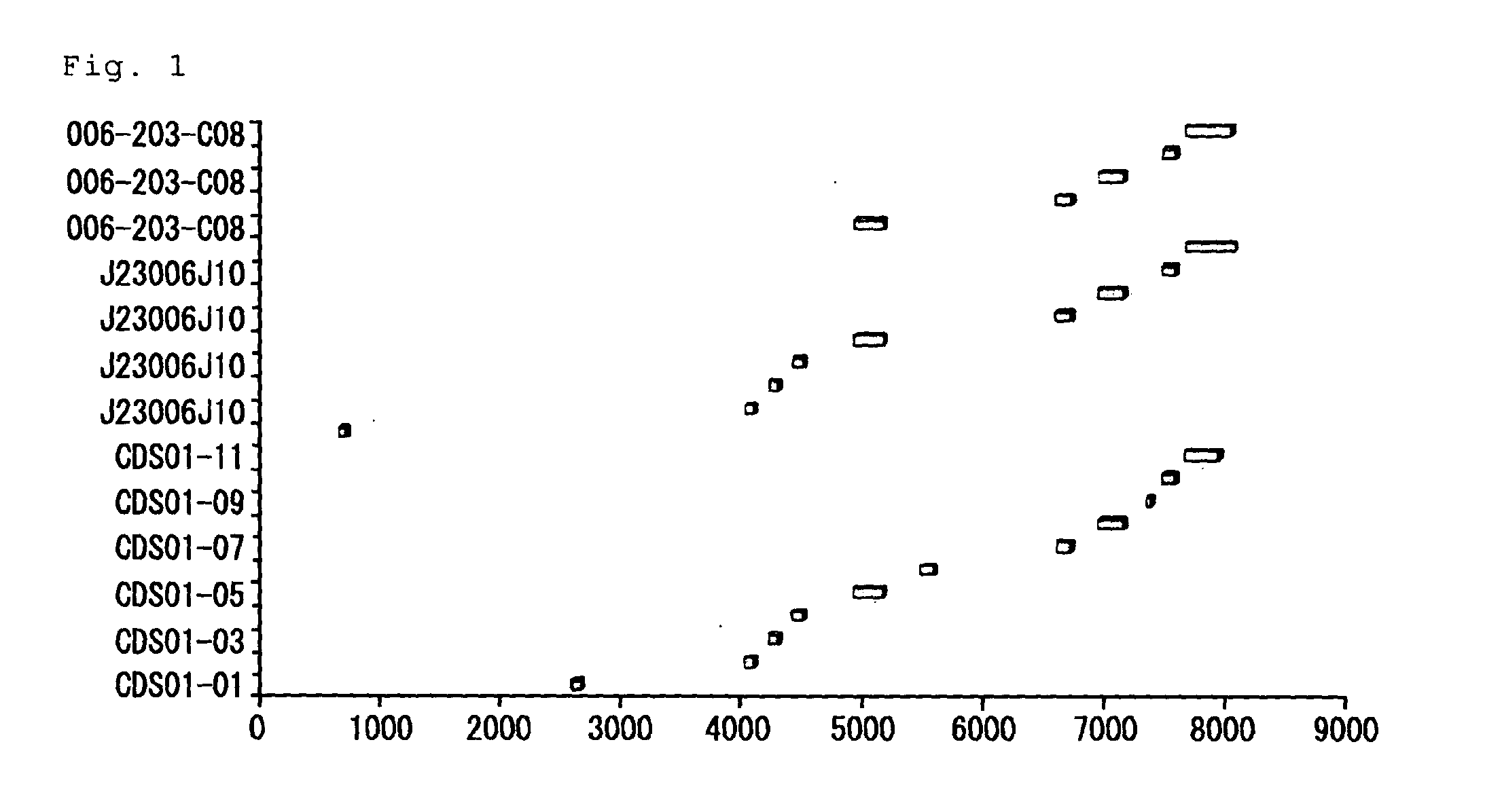
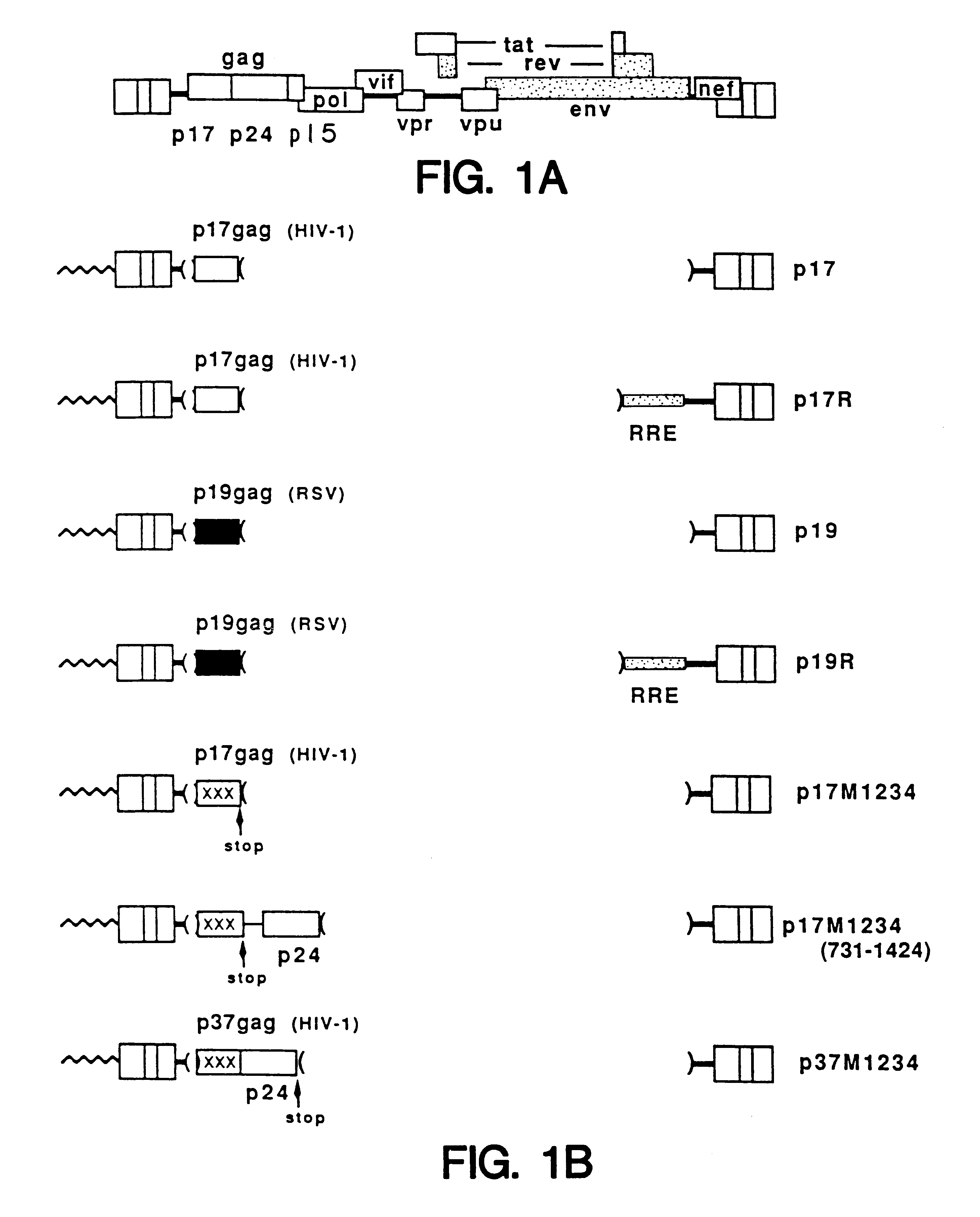
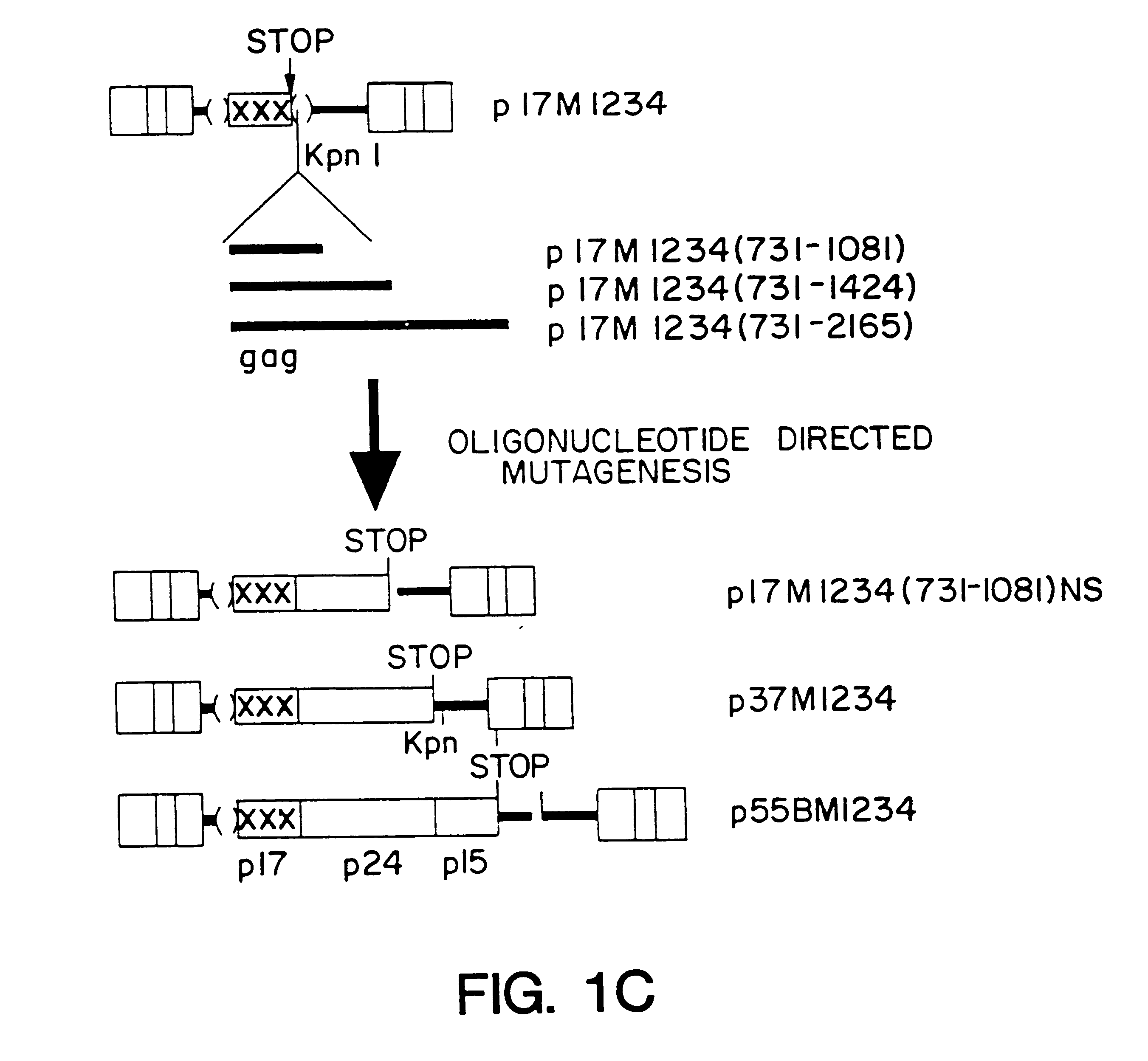
A method of locating an inhibitory / instability sequence or sequences within the coding region of an mRNA and modifying the gene encoding that mRNA to remove these inhibitory / instability sequences by making clustered nucleotide substitutions without altering the coding capacity of the gene is disclosed. Constructs containing these mutated genes and host cells containing these constructs are also disclosed. The method and constructs are exemplified by the mutation of a Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Rev-dependent gag gene to a Rev-independent gag gene. Constructs useful in locating inhibitory / instability sequences within either the coding region or the 3' untranslated region of an mRNA are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION CONTAINING A STABILISED mRNA OPTIMISED FOR TRANSLATION IN ITS CODING REGIONS
InactiveUS20100239608A1Improve efficiencyOvercome disadvantagesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCoding regionBiology
Owner:CUREVAC AG
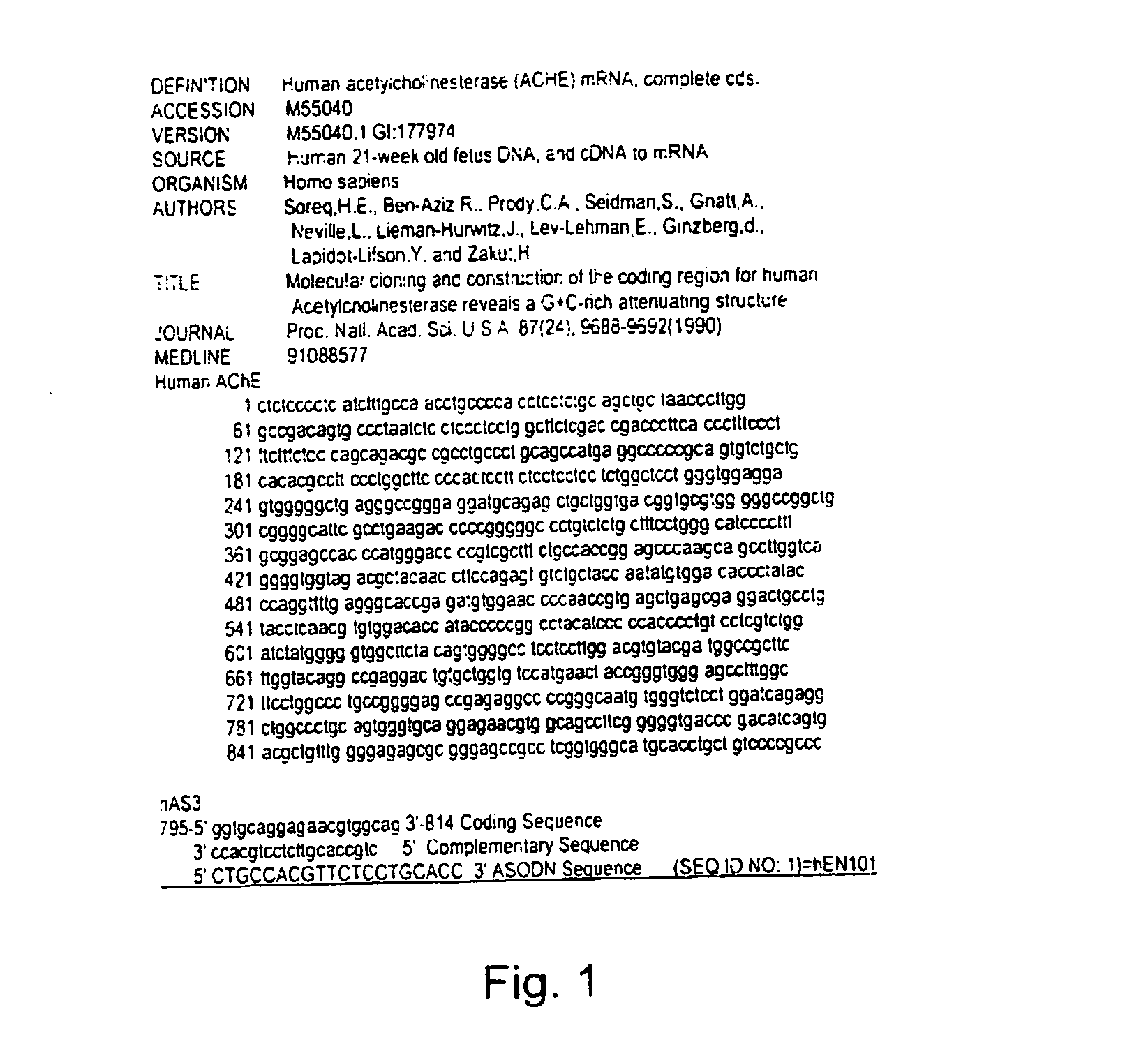
Antisense oligonucleotide against human acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060178333A1Improving stamina in physical exerciseReduce muscle fatigueOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The invention relates to an antisense oligonucleotide targeted to the coding region of the human acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which selectively suppresses the AChE-R isoform of the enzyme. The antisense oligonucleotide is intended for use in the treatment and / or prevention of neuromuscular disorders, preferably myasthenia gravis. In addition, it can penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and destroy AChE-R within central nervous system neurons, while also serving as a carrier to transport molecules across the BBB.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against human cytomegalovirus infection
InactiveUS20080085870A1Reduce in quantityDecreased immunological responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based cytomegalovirus vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding HCMV antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the HCMV antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. HCMV antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to pp65, glycoprotein B (gB), IE1, and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. In certain embodiments, sequences have been deleted, e.g., the Arg435-Lys438 putative kinase in pp65 and the membrane anchor and endocellular domains in gB. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to HCMV in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
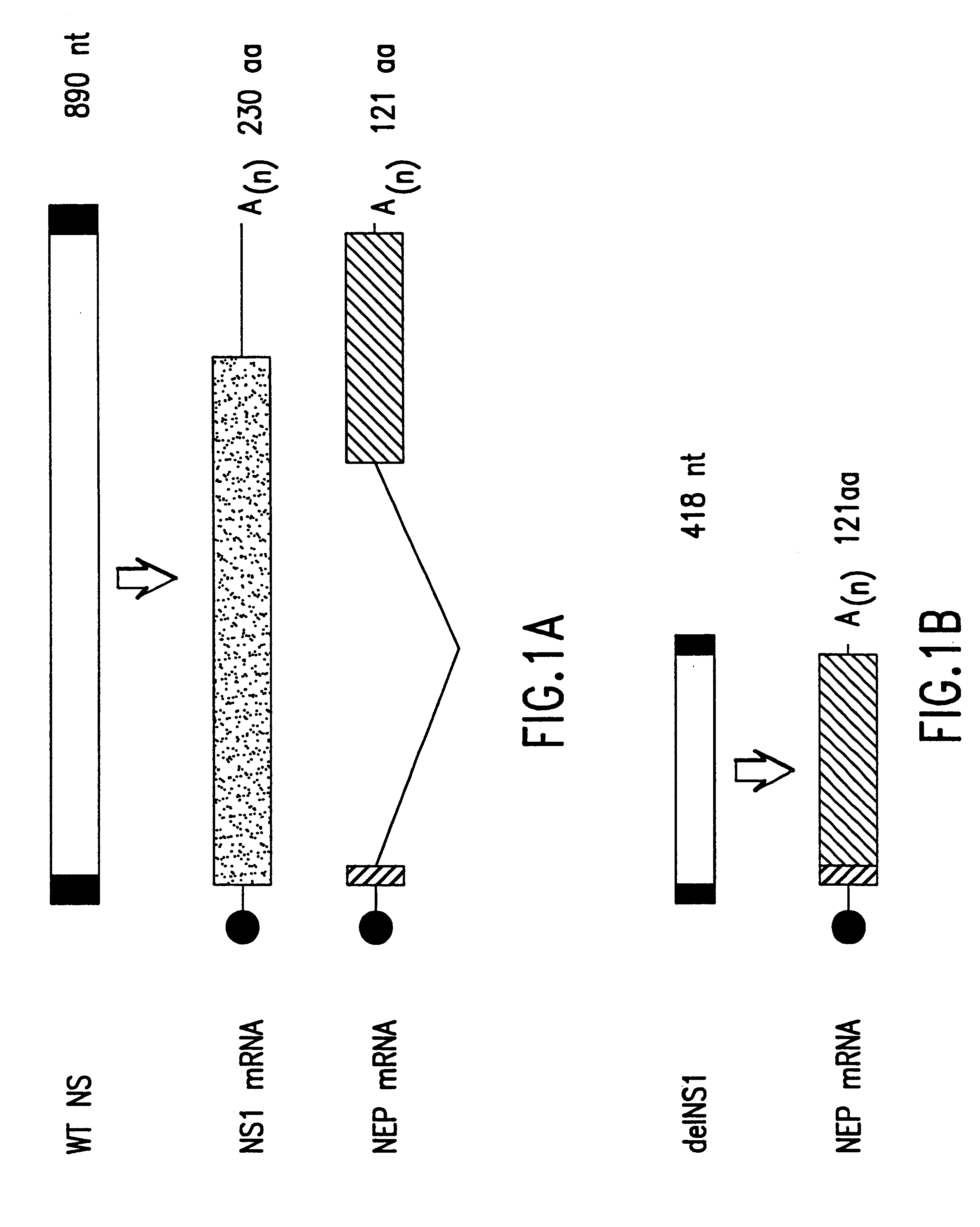
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS6468544B1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetic engineeringRecombinant DNA
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Direct expression of peptides into culture media
InactiveUS6103495AReduced viabilityImprove breathabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth phaseBiotechnology
Expression systems are disclosed for the direct expression of peptide products into the culture media where genetically engineered host cells are grown. High yield was achieved with novel vectors, a special selection of hosts, and / or fermentation processes which include careful control of cell growth rate, and use of an inducer during growth phase. Special vectors are provided which include control regions having multiple promoters linked operably with coding regions encoding a signal peptide upstream from a coding region encoding the peptide of interest. Multiple transcription cassettes are also used to increase yield. The production of amidated peptides using the expression systems is also disclosed.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
Peptides from the E2, E6, and E7 proteins of human papilloma viruses 16 and 18 for detecting and/or diagnosing cervical and other human papillomavirus associated cancers
InactiveUS6933123B2Simple and rapid and and more testMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesCysteine thiolateTryptophan
Owner:HU YAO XIONG
Rabies vaccine
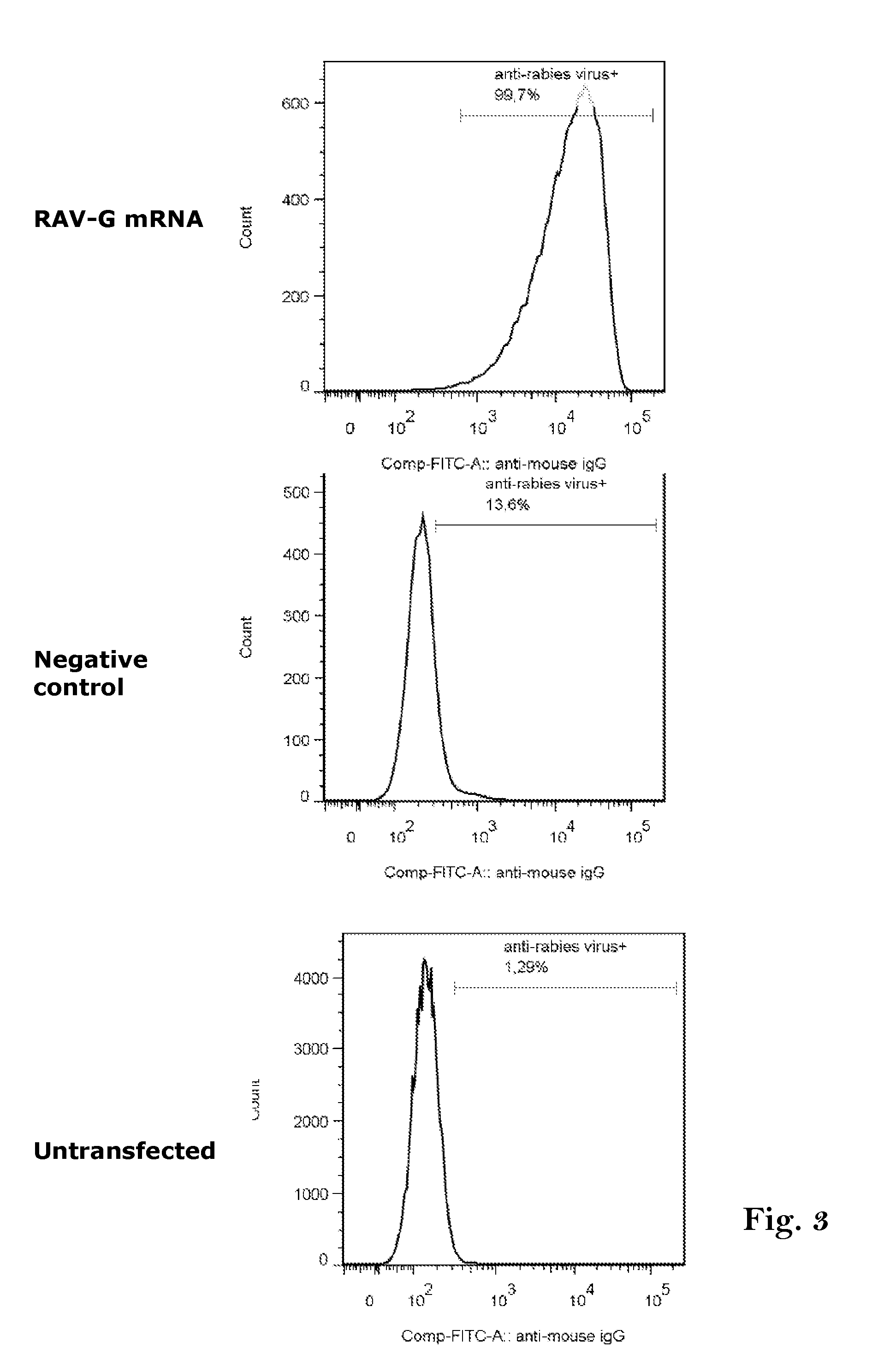
ActiveUS20160166711A1Easy to identifyFaster and strong attackSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesCoding regionRabies vaccine
The present invention relates to an mRNA sequence, comprising a coding region, encoding at least one antigenic peptide or protein of Rabies virus or a fragment, variant or derivative thereof. Additionally the present invention relates to a composition comprising a plurality of mRNA sequences comprising a coding region, encoding at least one antigenic peptide or protein of Rabies virus or a fragment, variant or derivative thereof.Furthermore it also discloses the use of the mRNA sequence or the composition comprising a plurality of mRNA sequences for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition, especially a vaccine, e.g. for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of Rabies virus infections. The present invention further describes a method of treatment or prophylaxis of rabies using the mRNA sequence.
Owner:CUREVAC AG
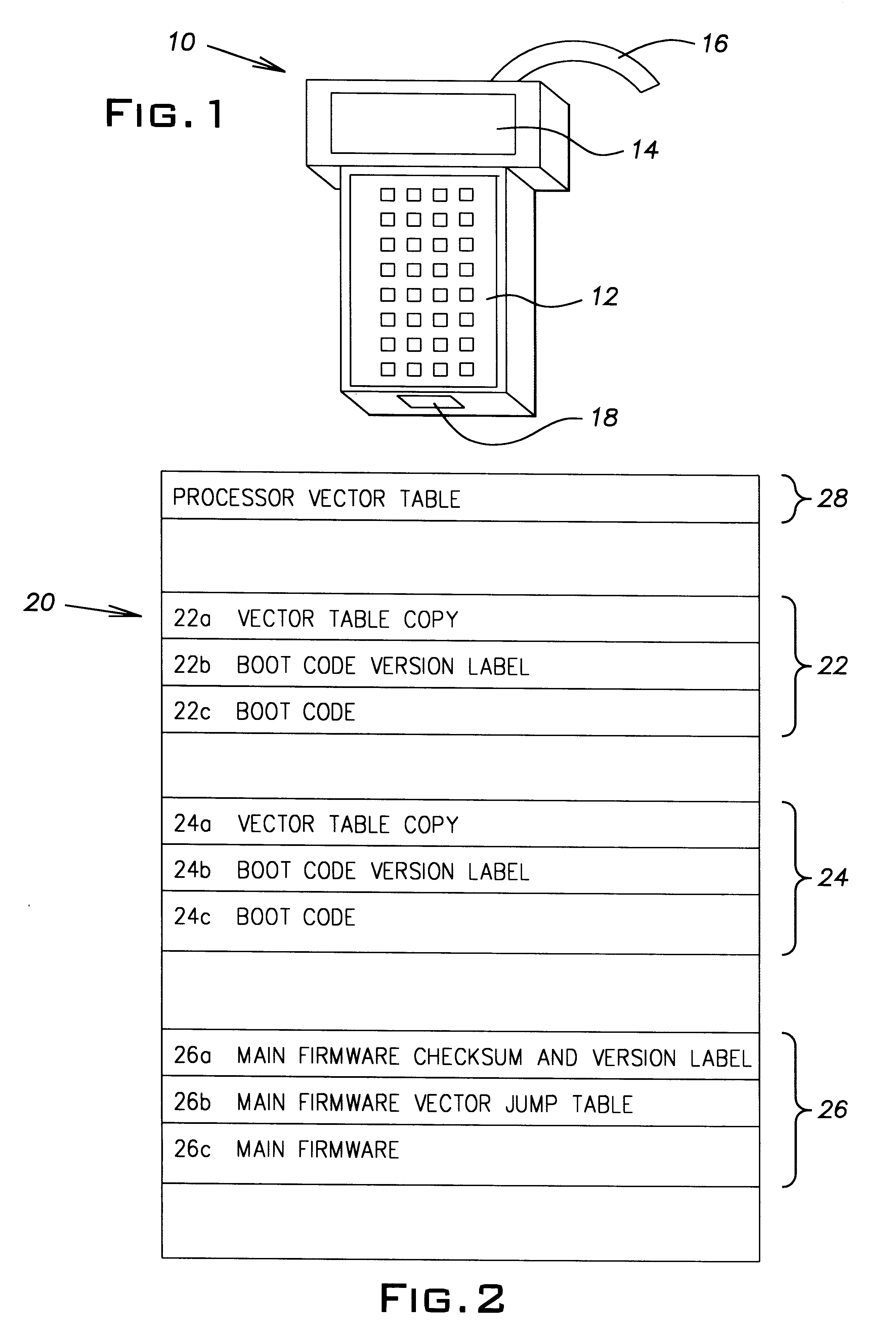
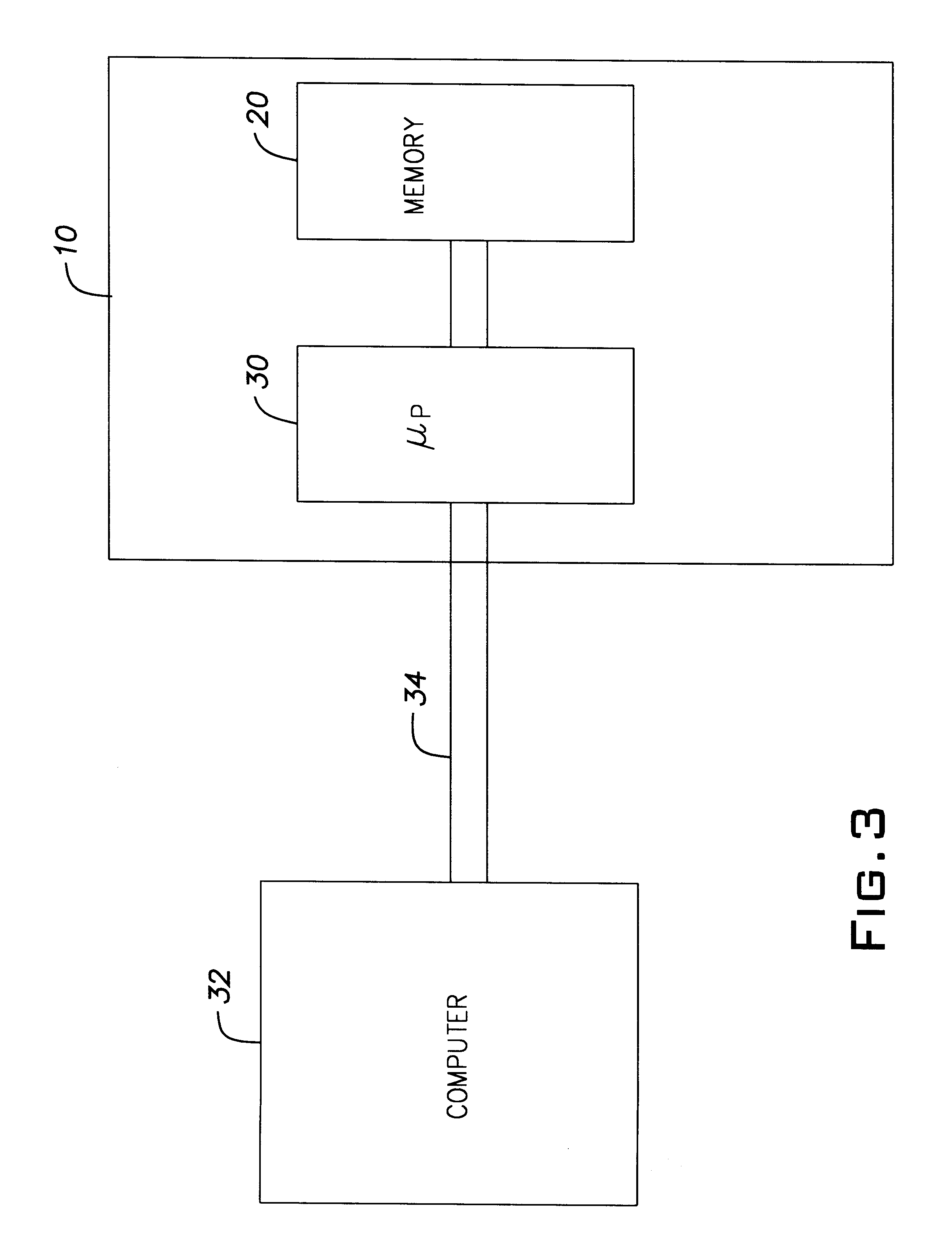
Method and apparatus for upgrading firmware boot and main codes in a programmable memory
A system for loading upgraded, that is, new boot code and / or main firm ware has a programmable memory that has two boot code regions. One of the regions holds the active boot code while the other region holds the inactive boot code. During a boot code upgrade, the boot code in the inactive region, is under control of the boot code in the active region, replaced with the new boot code. Once the replacement process is verified as having been successful and the vector table in the new boot code is copied to the processor vector table in the memory, the processor can be reset so that the new boot code becomes the active boot code and the previously active boot code becomes the inactive boot code.
Owner:ABB AUTOMATION INC
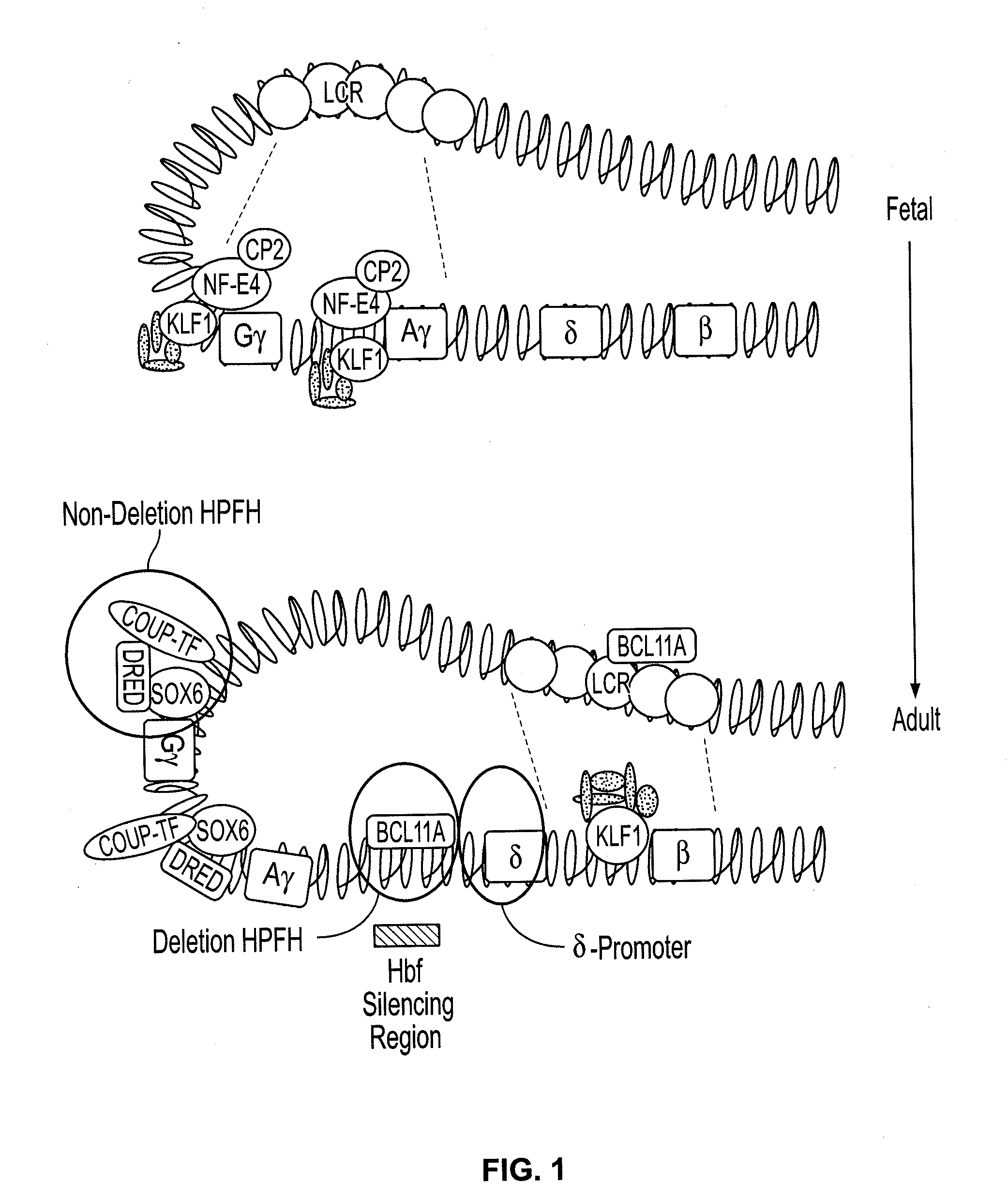
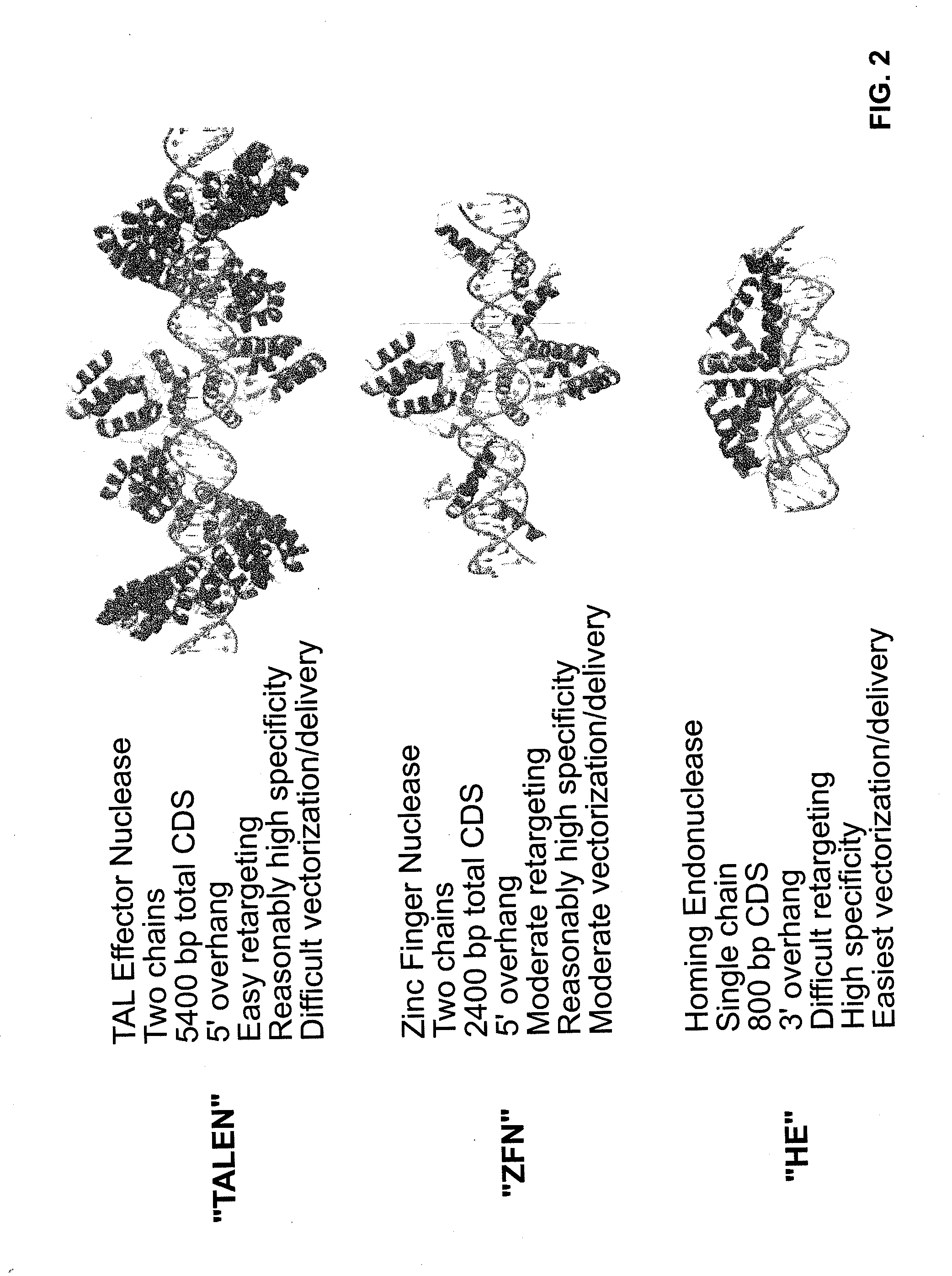
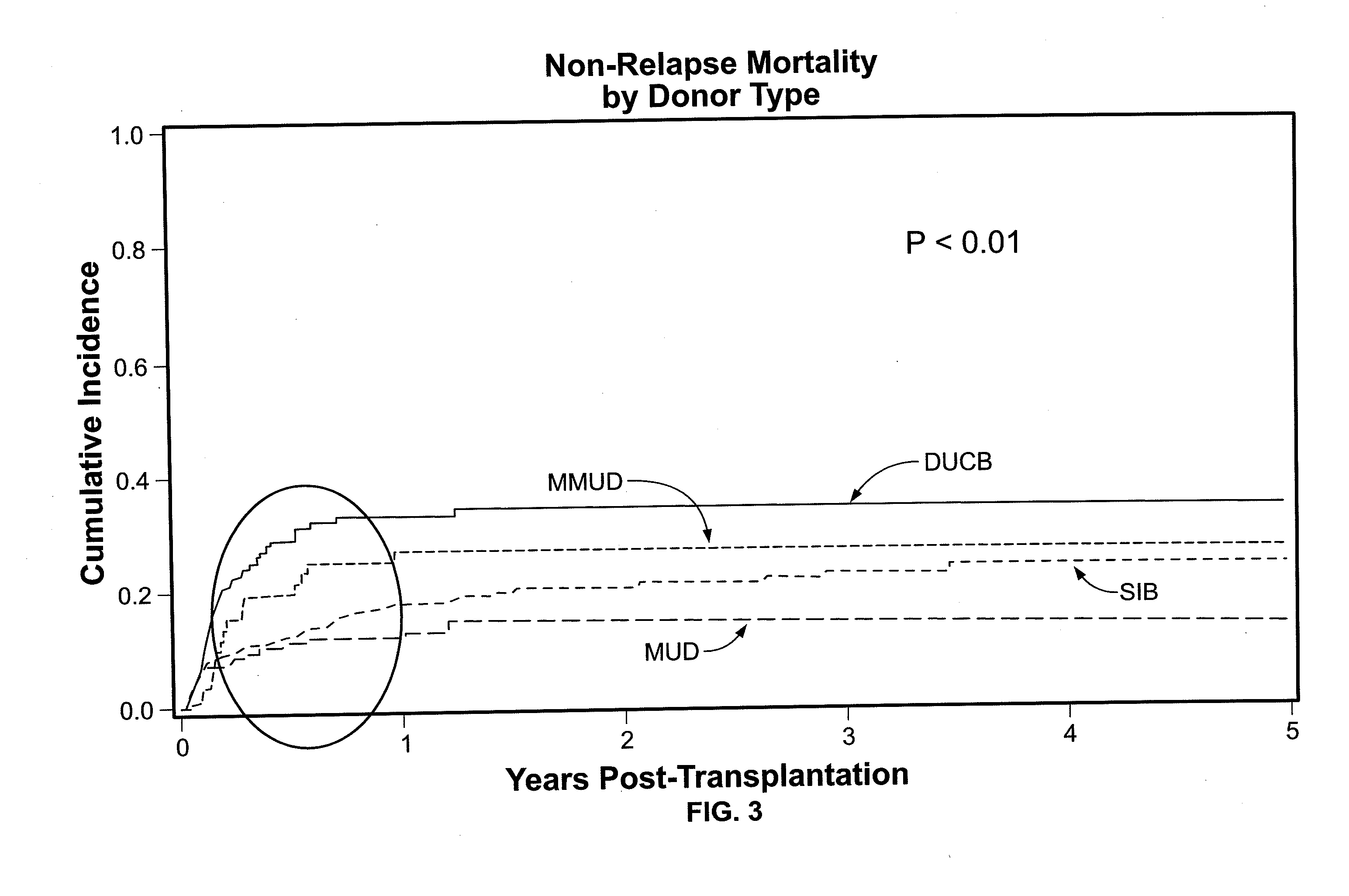
Compositions and methods for the treatment of hemoglobinopathies
InactiveUS20150166969A1Improve the level ofAvoid the insertion of vector sequencesFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesThalassemiaGlobin genes
Provided are compositions and methods for the treatment of hemoglobinopathies such as thalassemias and sickle cell disease. Compositions and methods include one or more endonuclease(s) or endonuclease fusion protein(s), including one or more homing endonuclease(s) and / or homing endonuclease fusion protein(s) and / or CRISPR endonuclease(s) ad / or CRISPR endonuclease fusion protein(s): (a) to disrupt a Bcl11a coding region; (b) to disrupt a Bcl11a gene regulatory region; (c) to modify an adult human β-globin locus; (d) to disrupt a HbP silencing DNA regulatory element or pathway, such as a Bcl11a-regulated HbP silencing region; (e) to mutate one or more γ-globin gene promoter(s) to achieve increased expression of a γ-globin gene; (f) to mutate one or more δ-globin gene promoter(s) to achieve increased expression of a δ-globin gene; and / or (g) to correct one or more β-globin gene mutation(s).
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH DIRECTOR DEITR
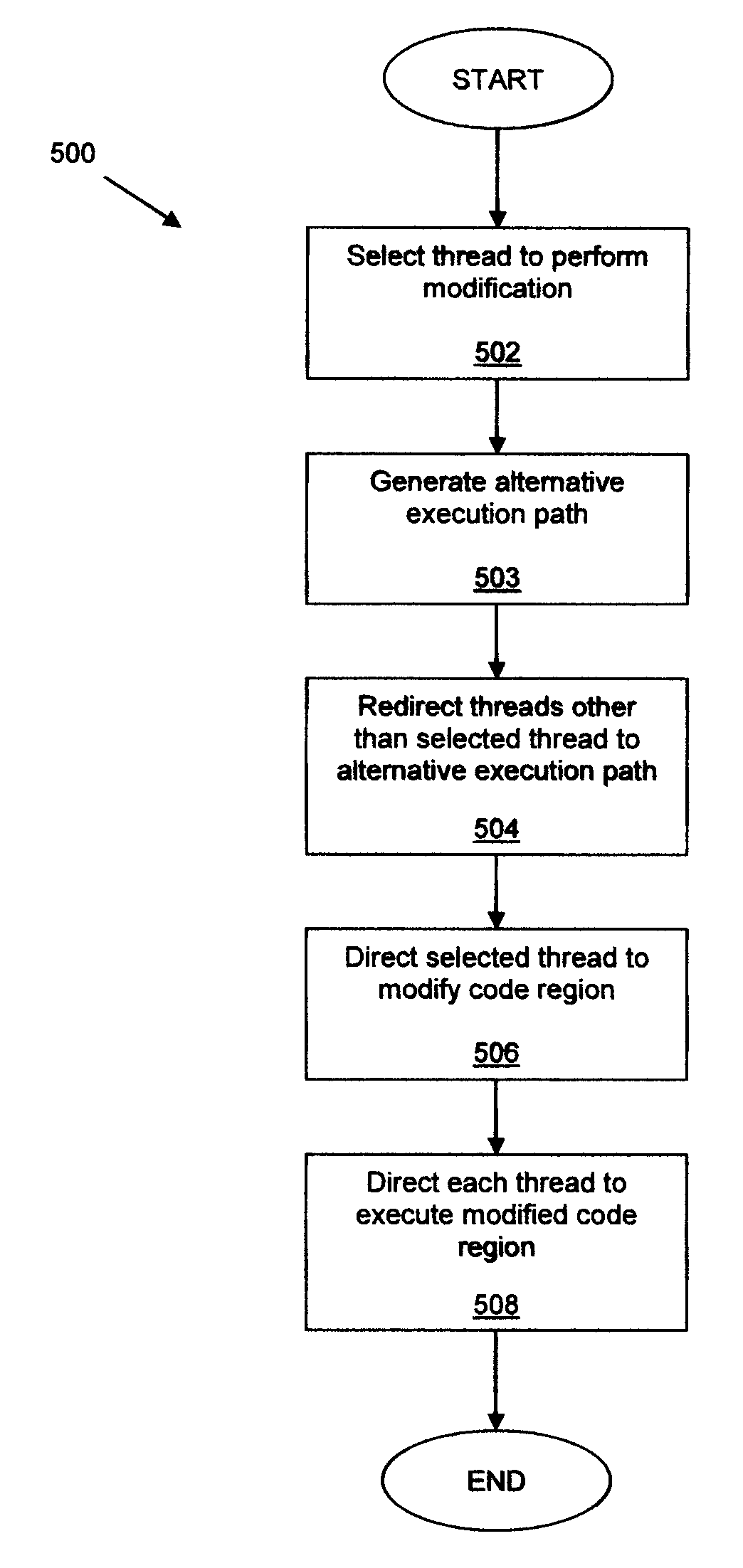
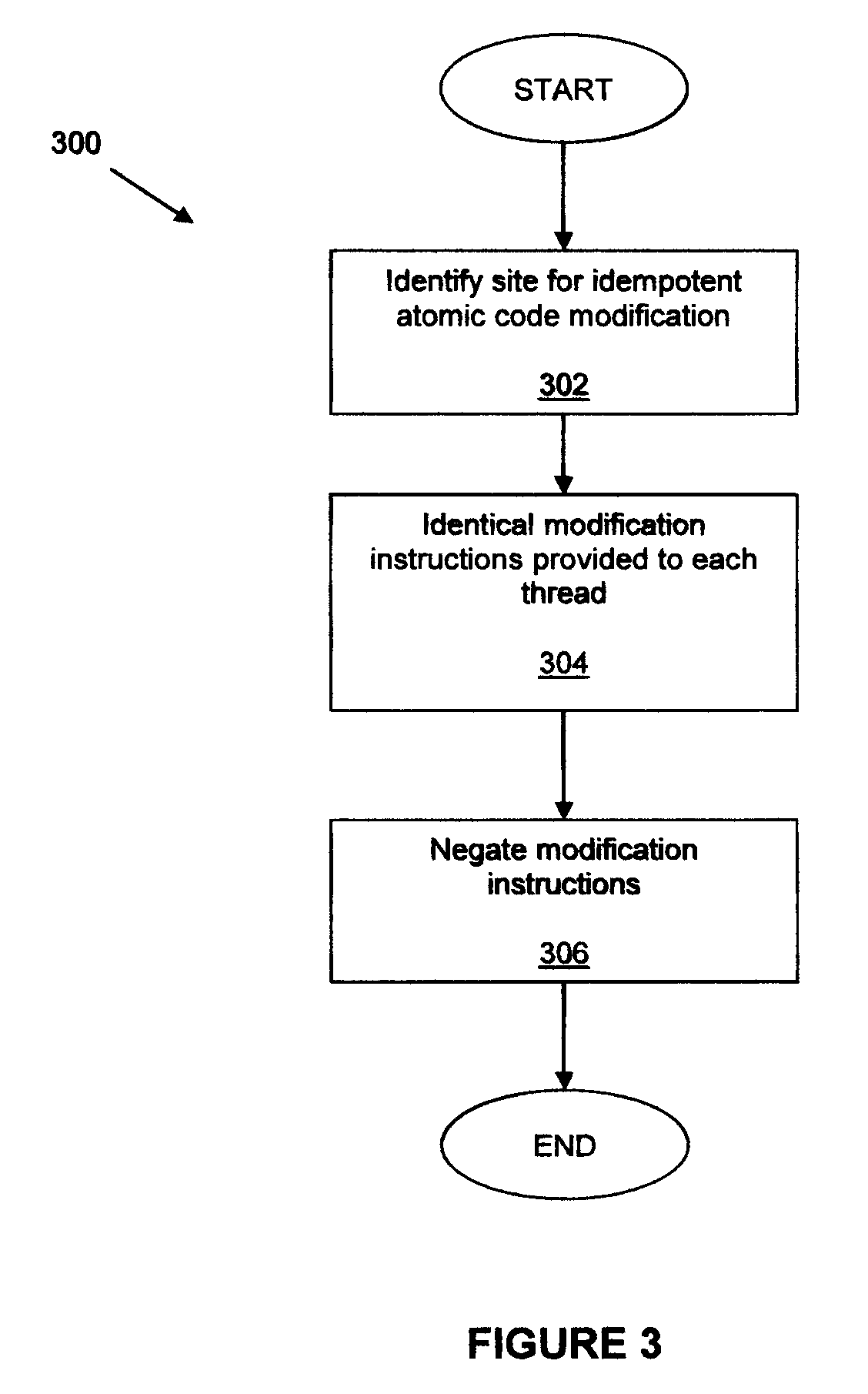
Runtime code modification in a multi-threaded environment
A code region forming part of a computer program is modified during execution of the computer program by a plurality of threads. In one aspect, identical modification instructions are provided to each thread for modifying a site in the code region having a desirable idempotent atomic modification, and the modification instructions direct each thread to make the desirable idempotent atomic modification. In another aspect, a thread is selected to modify the code region, each thread other than the selected thread is directed to execute an alternative execution path that generates output identical to the output of the code region after the code region has been modified, and, responsive to directing each thread other than the selected thread, the selected thread is directed to modify the code region.
Owner:IBM CORP
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine
ActiveUS20160168207A1Easy to identifyFaster and strong attackSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesRespiratory syncytial virus BRSV Infections
The present invention relates to an mRNA sequence, comprising a coding region, encoding at least one antigenic peptide or protein of RSV infections Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or a fragment, variant or derivative thereof. Additionally the present invention relates to a composition comprising a plurality of mRNA sequences comprising a coding region, encoding at least one antigenic peptide or protein of RSV infections Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or a fragment, variant or derivative thereof. Furthermore it also discloses the use of the mRNA sequence or the composition comprising a plurality of mRNA sequences for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition, especially a vaccine, e.g. for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of RSV infections Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections. The present invention further describes a method of treatment or prophylaxis of RSV infections using the mRNA sequence.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
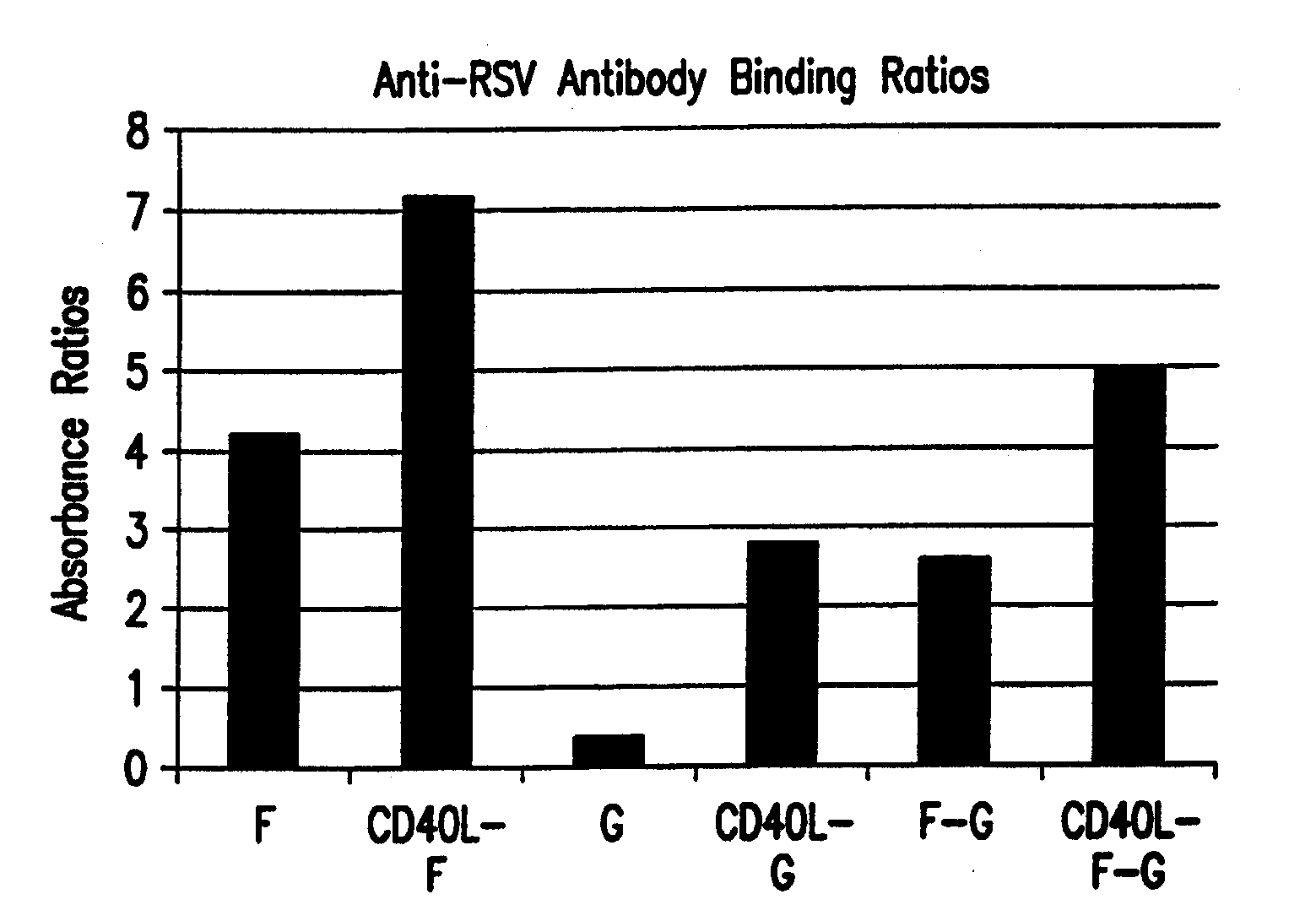
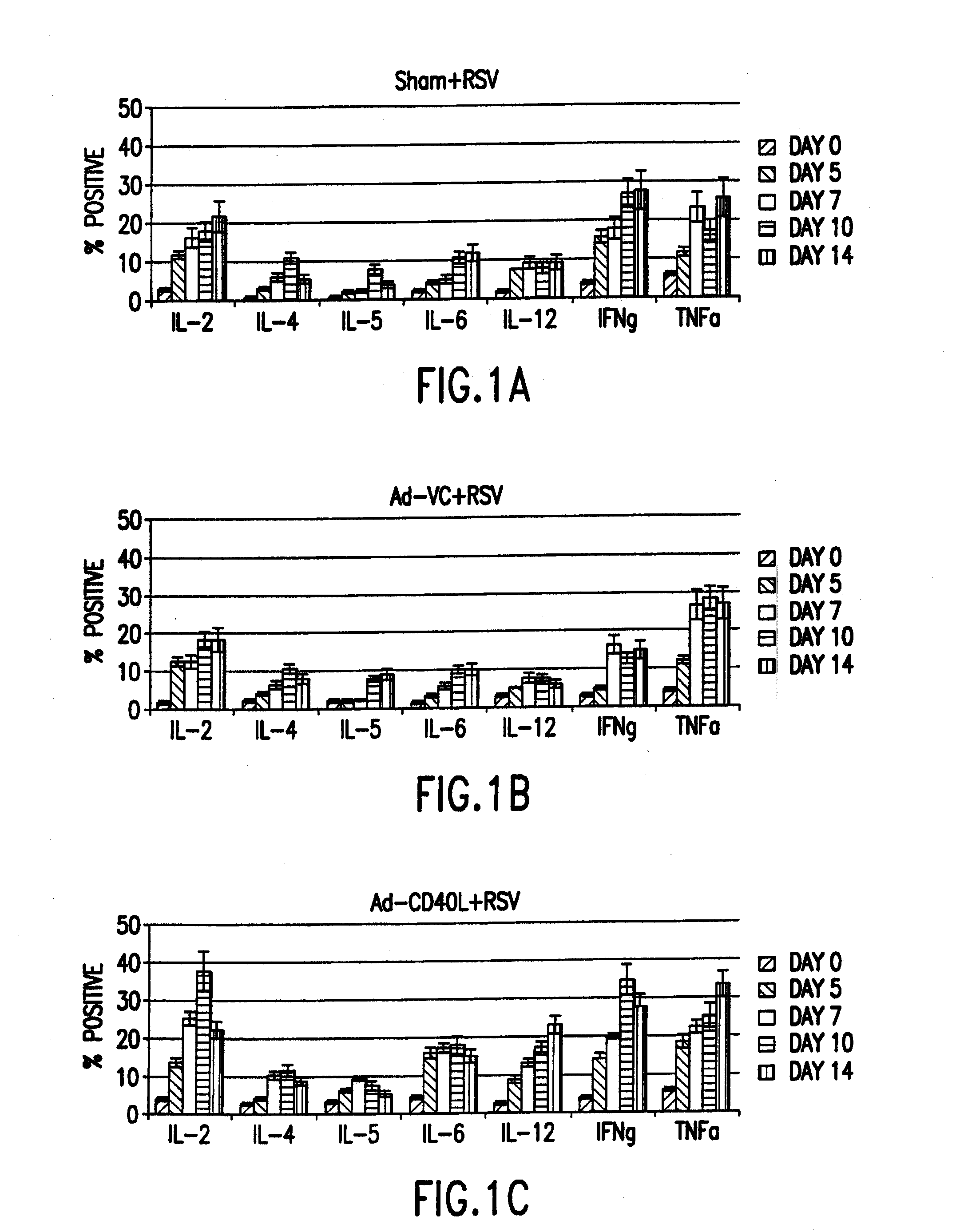
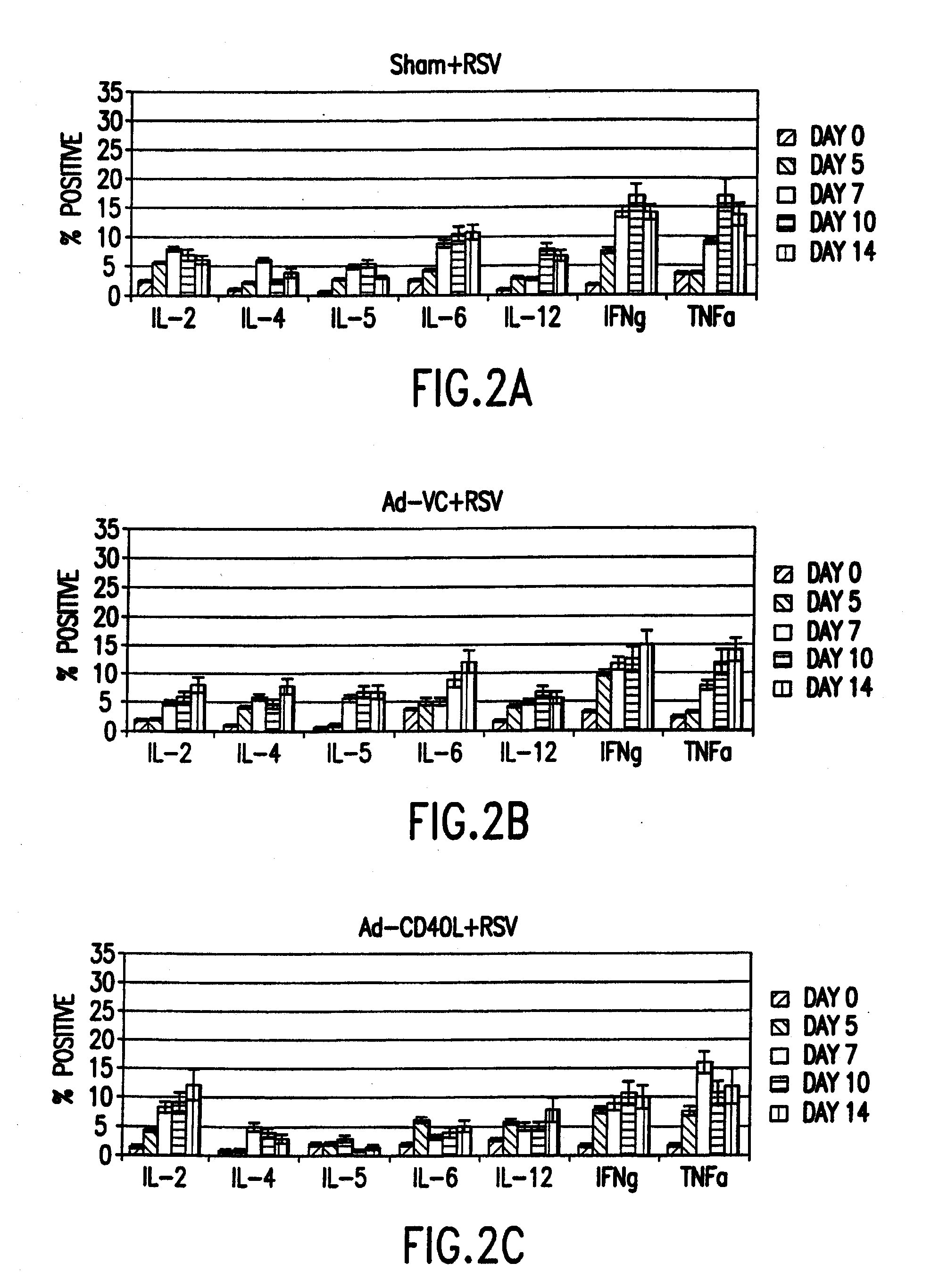
Cd40 ligand adjuvant for respiratory syncytial virus
The present invention provides methods and adjuvants for enhancing an immune response to RSV in a host, wherein the methods and adjuvants comprise a source of a CD40 binding protein. Preferably, the CD40 binding protein is CD40L and the source is a vector comprising a promoter operatively linked to a CD40L coding region. The enhanced immune response produced by the adjuvants and methods of the current invention includes both increased expression of Th1 cytokines and increased production of antibody.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
mRNA and vaccine for coding a SARS-CoV-2 viral antigen and preparation method of vaccine
ActiveCN111218458AImproving immunogenicityRapid R&DSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsTGE VACCINECoding region
The invention provides mRNA and a vaccine for coding a SARS-CoV-2 viral antigen and a preparation method of the vaccine, and relates to the technical field of vaccines. The mRNA for coding the SARS-CoV-2 viral antigen at least contains at least one of S protein and N protein for coding SARS-CoV-2 virus and / or a coding region of a fragment of the at least one protein, and the mRNA is delivered intoa body to enable the body to generate an immune reaction.
Owner:LIVERNA THERAPEUTICS INC
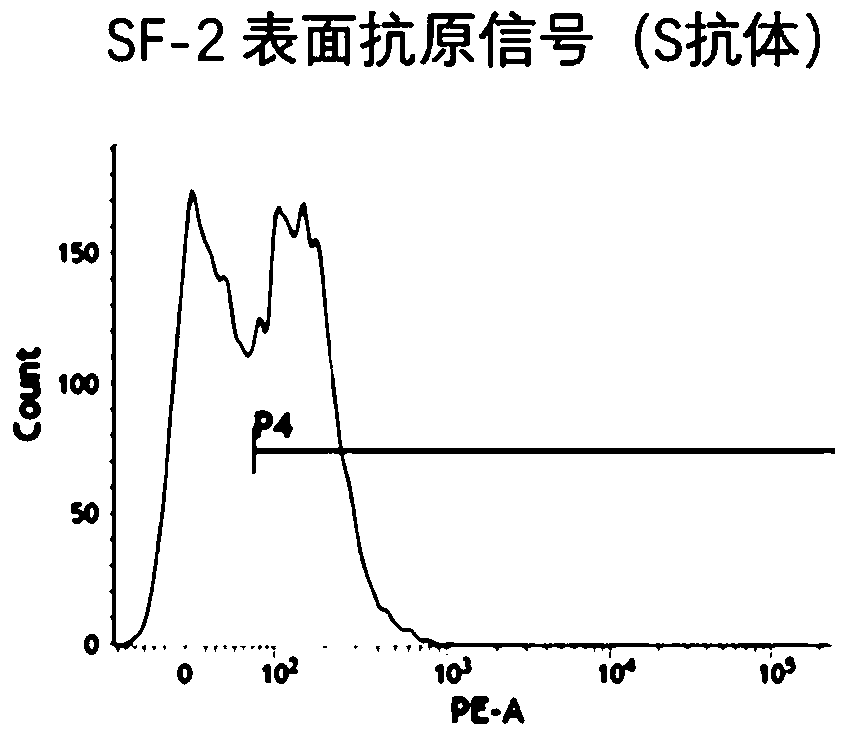
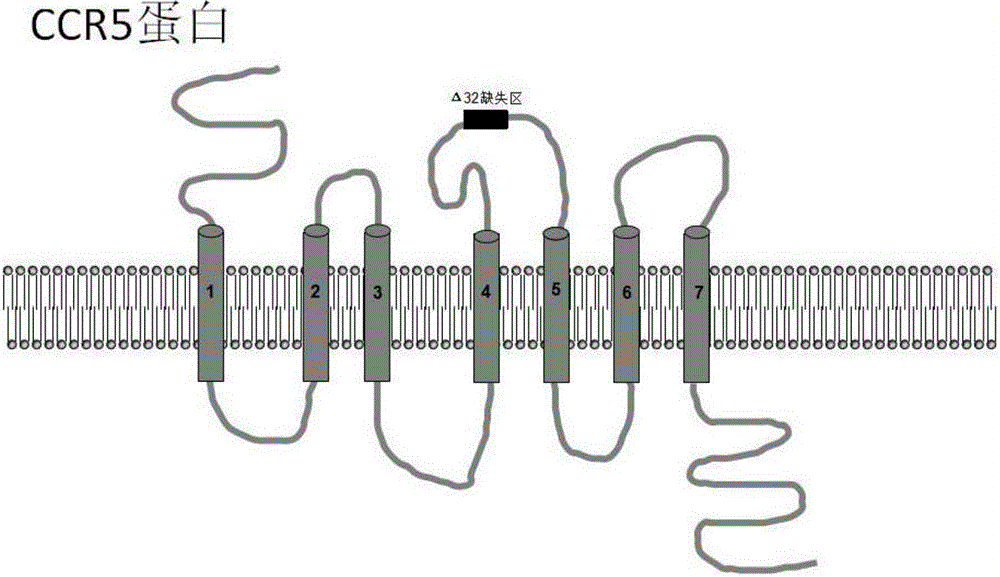
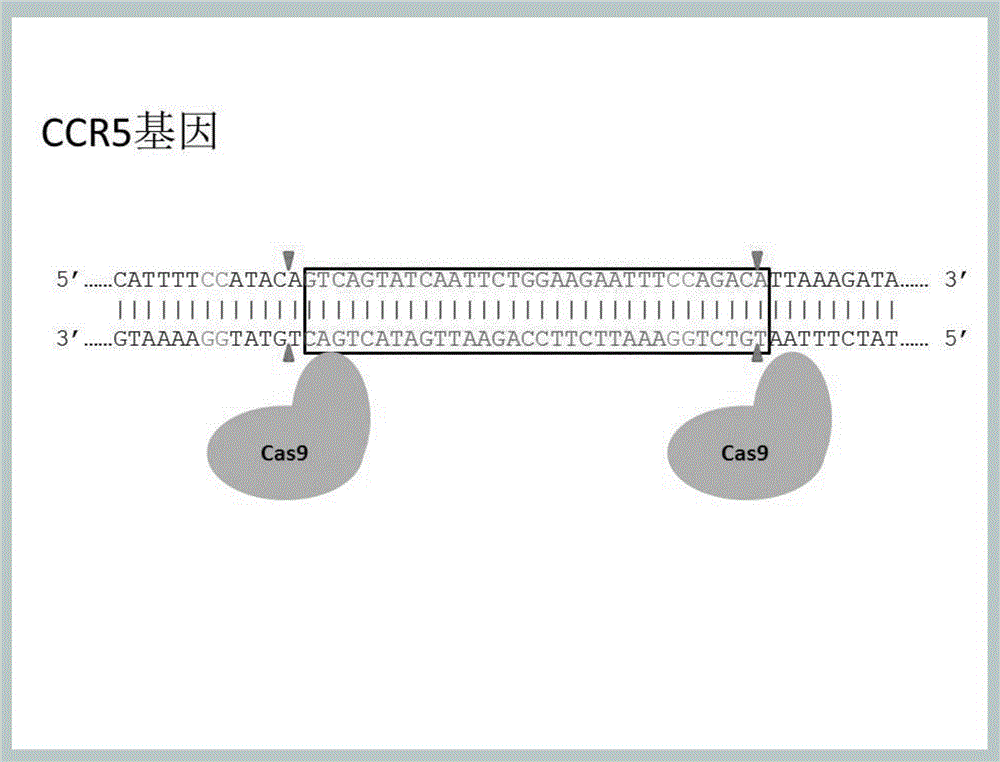
Method for inducing CCR5-delta32 deletion with genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9
The invention relates to a method for successfully inducing cell chemokine receptor CCR5 genes to be mutated into CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes with a new genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9. CCR5 is an important receptor for human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) to invade personal host cells. CCR5-delta32 deletion means deletion of 32 basic groups occurs in a CCR5 coding region, so that the sequence after the 185th amino acid is changed, and early termination occurs. CCR5-delta32 biallelic-gene homozygous deletion has natural resistance to HIV infection, and can not be infected by HIV. By means of the method, a slow virus packaging system and the CRISPR technology are used at the same time; as the slow virus infecting host range is wide, the method can be applied to cells such as bone marrow stem cells and CD4T cells, and the CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes hopefully become medicine for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome or other diseases.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
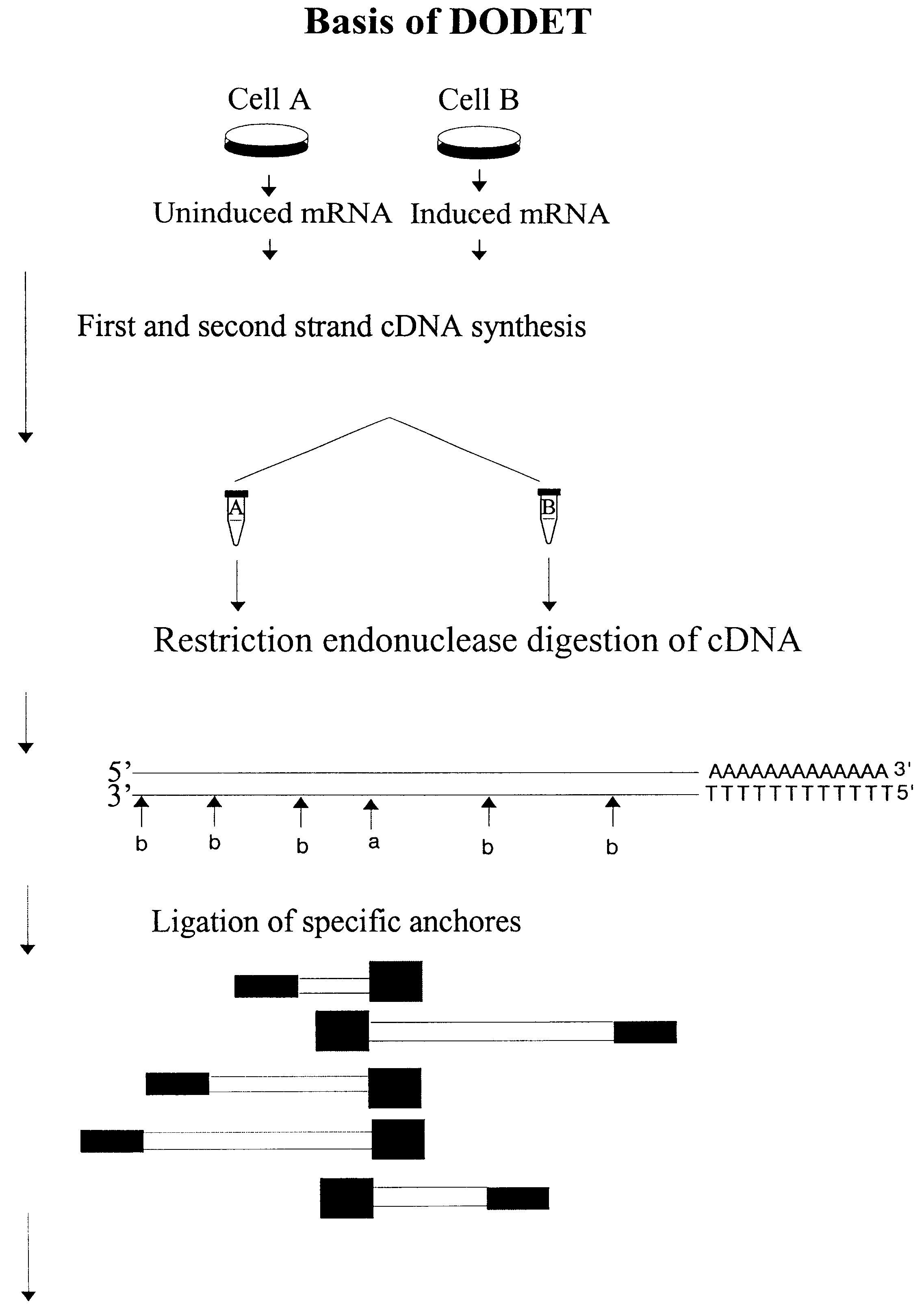
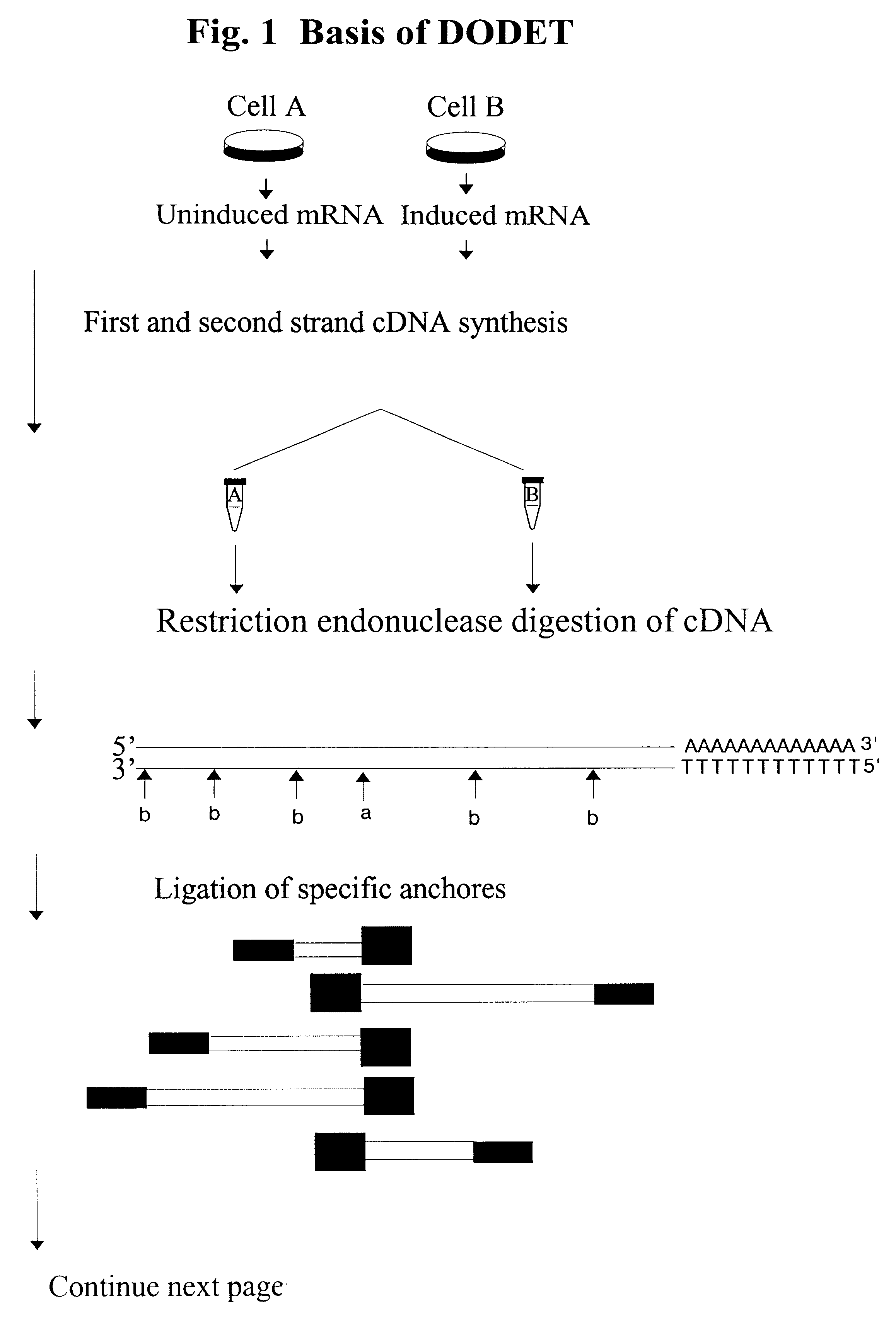
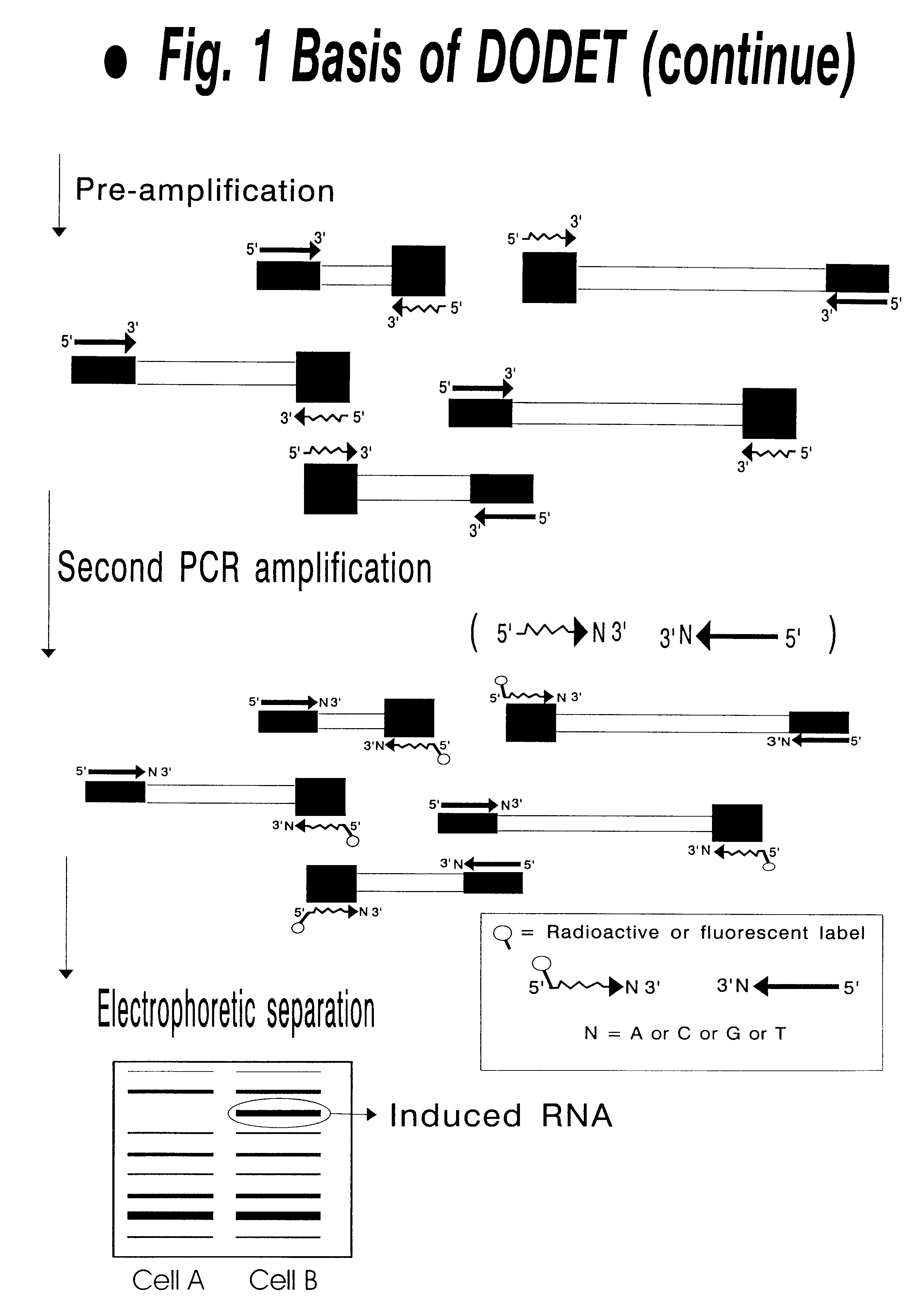
Method to clone mRNAs
InactiveUS6261770B1Convenient verificationHigh homologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Disclosed and claimed is a method for preparing a normalized sub-divided library of amplified cDNA fragments from the coding region of mRNAs contained in a sample. The method includes the steps of: a) subjecting the mRNA population to reverse transcription using at least one cDNA primer, thereby obtaining first strand cDNA fragments, b) synthesizing second strand cDNA complementary to the first strand cDNA fragments by use of the first strand DNA fragments as templates, thereby obtaining double stranded cDNA fragments, c) digesting the double stranded cDNA fragments with at least one restriction endonuclease, the endonuclease leaving protruding sticky ends of similar size at the termini of the DNA after digestion, thereby obtaining cleaved cDNA fragments, d) adding at least two adapter fragments containing known sequences to the cleaved cDNA fragments obtained in step c), the at least two adapter fragments being able to bind specifically to the sticky ends of the double stranded cDNA produced in step c), the one adapter fragment being able to anneal to the primer having formula I in step f), the second adapter fragment being a termination fragment introducing a block against DNA polymerization in the 5'->3' direction setting out from said termination fragment and the termination fragment being unable to anneal to any primer of the at least two primer sets in step f) during the molecular amplification procedure, the at least two adapter fragments being ligated to the cleaved cDNA fragments obtained in step c) so as to obtain ligated cDNA fragments, e) sub-dividing the ligated cDNA fragments obtained in step d) into 4n1 pools where 1<=n1<=4, and f) subjecting each pool of ligated cDNA fragments obtained in step e) to a molecular amplification procedure so as to obtain amplified cDNA fragments, wherein is used, for an adapter fragment used in step d), a set of amplification primers having the general formula Iwherein Com is a sequence complementary to at least the 5'-end of an adapter fragment which is ligated to the 3'-end of a cleaved cDNA fragment, N is A, G, T, or C, the one primer having the general formula I where n1=0, and the second primer having the general formula I where 1<=n1<=4, the second primer being capable of priming amplification of any nucleotide sequence ligated in its 3'-end to the adapter fragment complementary in its 5'-end to Com.
Owner:AZIGN BIOSCI
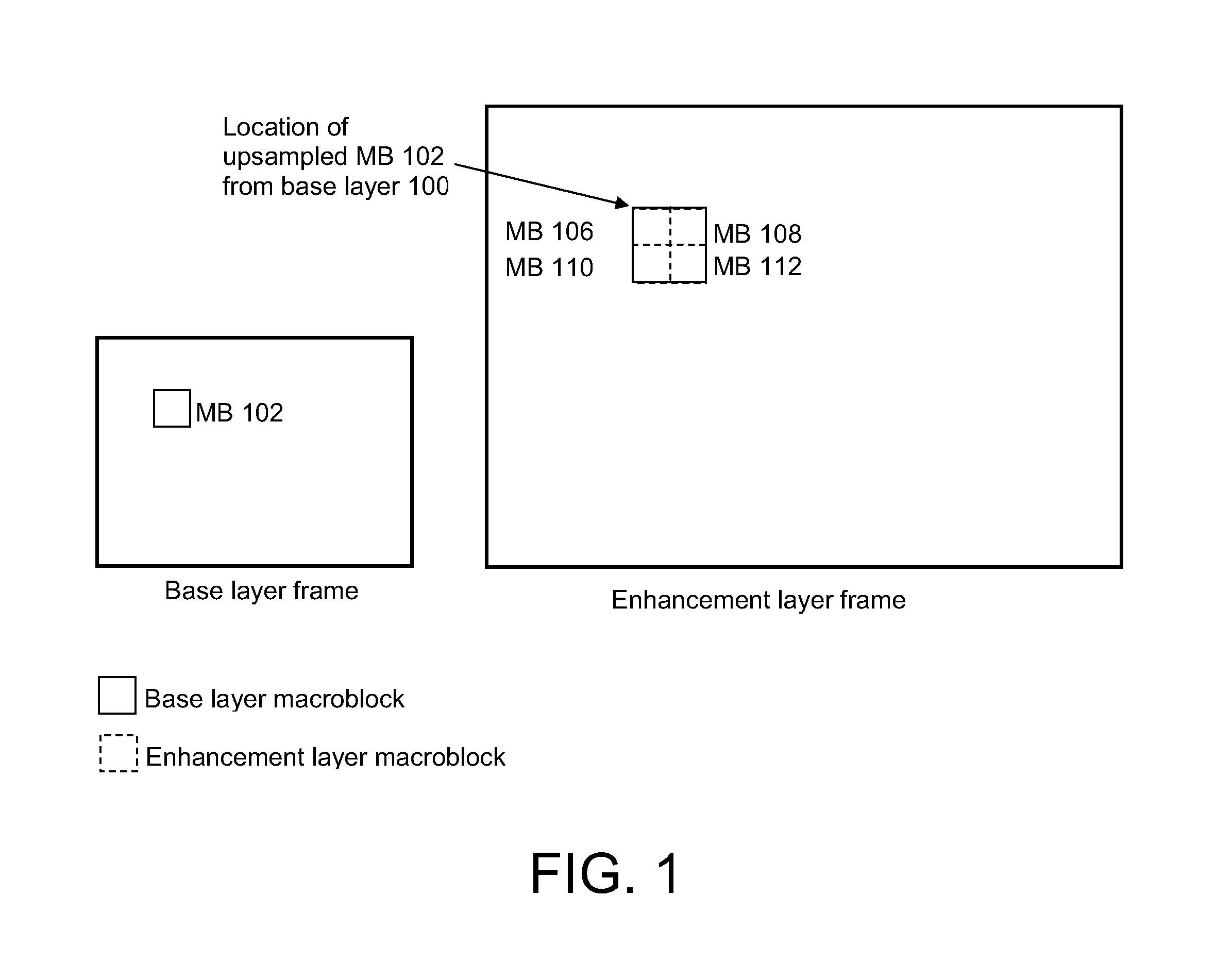
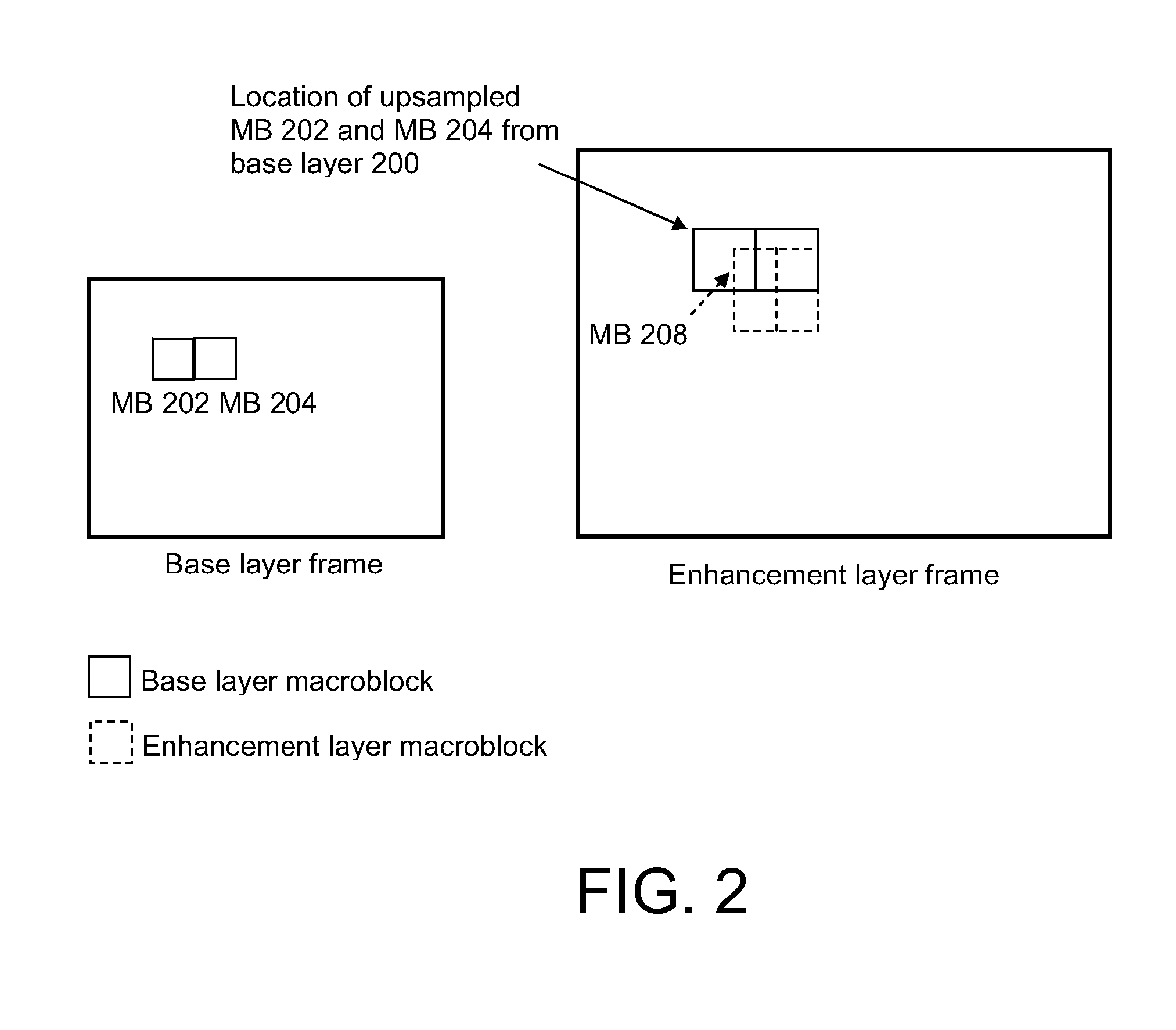
Scalable video coding
ActiveUS20080056356A1Smooth effectAccurate predictionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInter layerBoundary effects
A system and method for predicting an enhancement layer macroblock. A base layer frame is divided into intra-coded and inter-coded regions. If any portion of the enhancement layer macroblock is covered by both an intra-coded base layer macroblock and an inter-coded base layer macroblock, predictions utilizing the intra-coded and inter-coded macroblocks are established independently to generate at least two prediction values. The at least two prediction values are then combined to give a prediction from which the enhancement layer block is coded. Various embodiments serve to smooth the boundary effect between intra-coded regions and inter-coded regions inside the inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
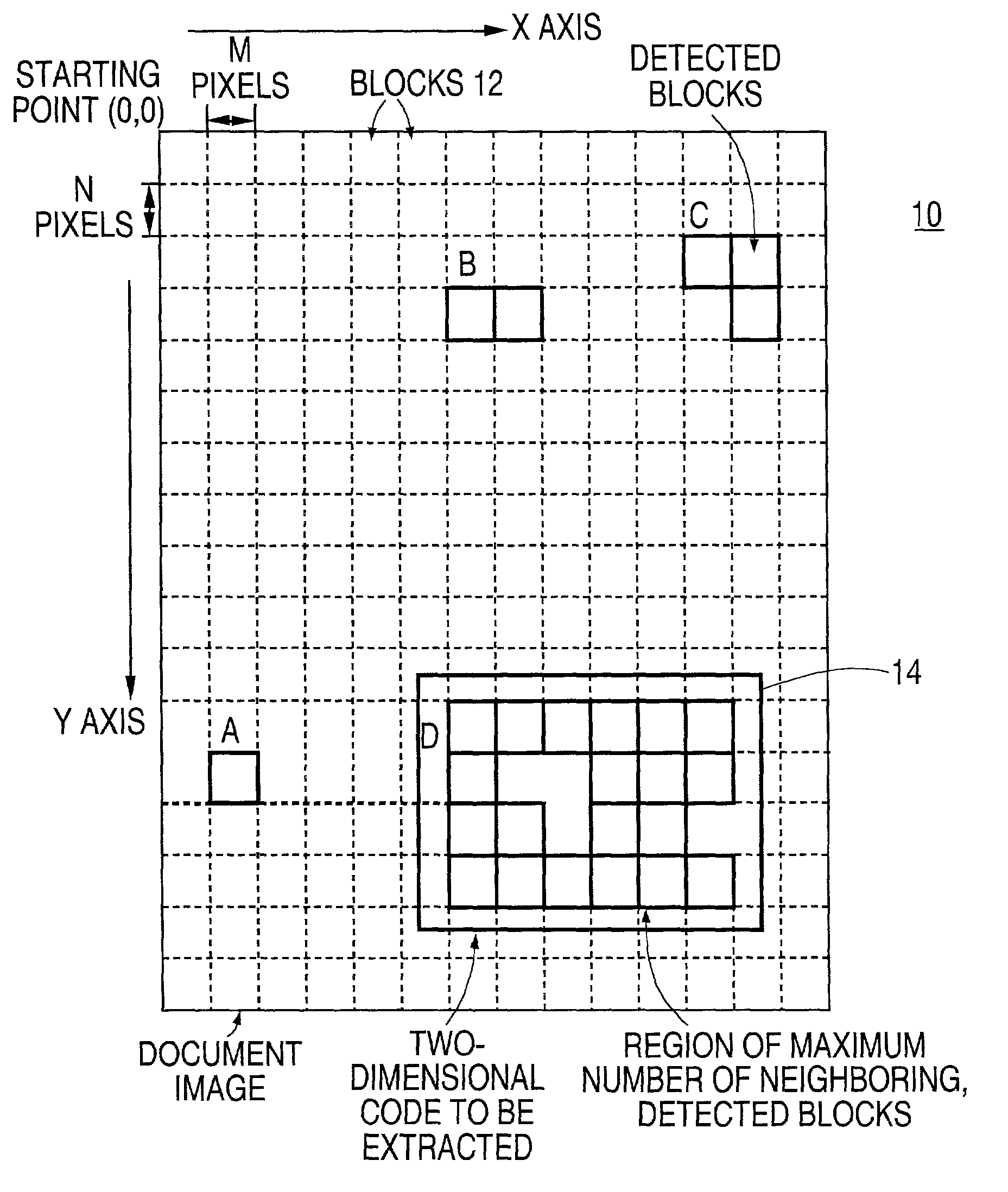
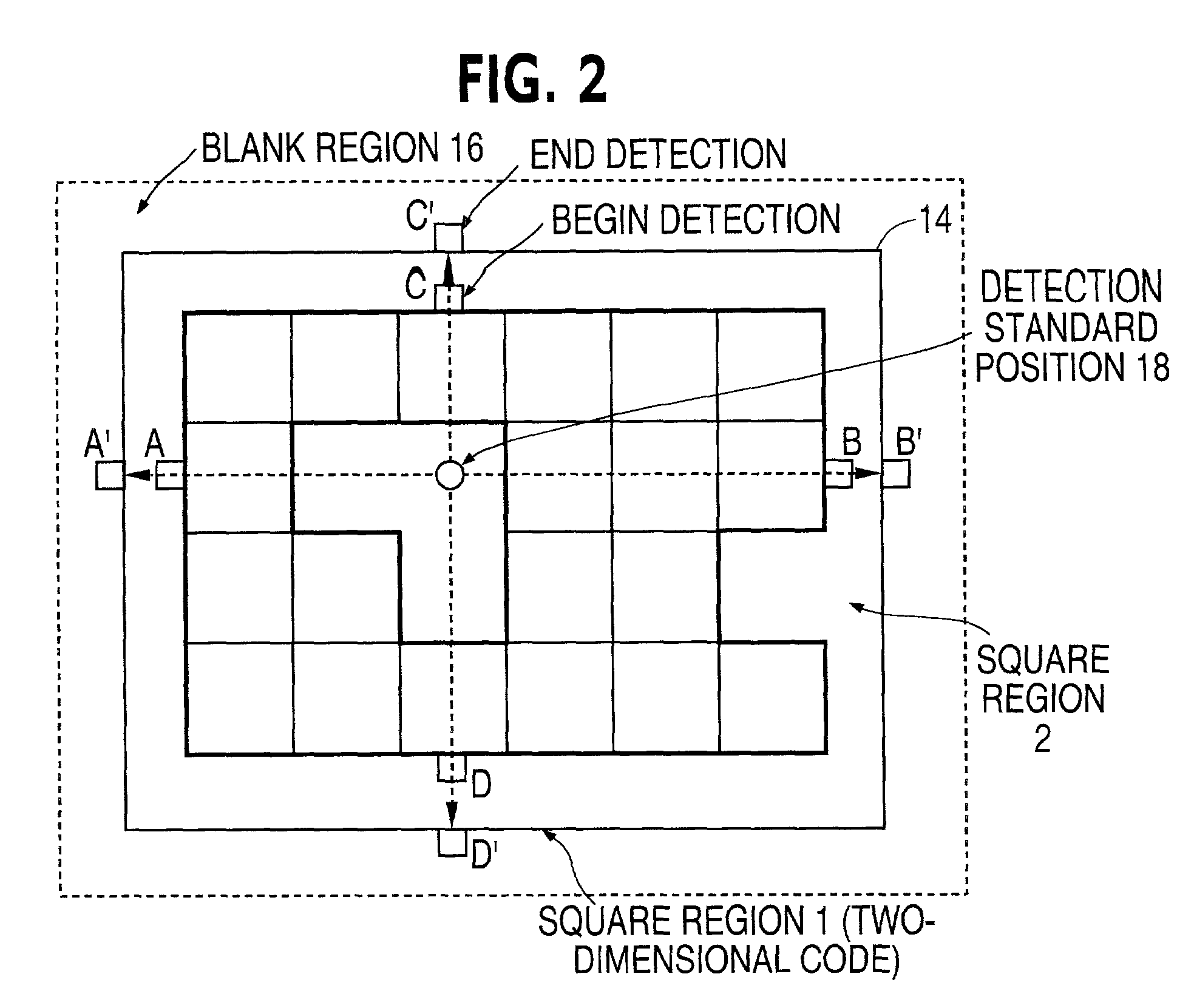
Two-dimensional code extracting method
InactiveUS20020051573A1Easy to distinguishDetection precision can be improvedImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCoding region
An image data is inputted by using a device such as a document scanner. The input image data is scanned in a square block unit of MxN pixels, and blocks that satisfy specific conditions is detected based on the scanning process. In one example, a ratio of white pixels and black pixels falls within scanned blocks is used as the specific condition to detect those blocks. Then a region that neighbored by the other blocks is detected, and is extracted as a two-dimensional code region.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
CRISPR-Cas9 specificity pig SLA-1 gene knockout method and sgRNA used for specific targeting SLA-1 gene
The present invention discloses a pig SLA-1 gene knockout method using CRISPR-Cas9 specificity and sgRNA used for specific targeting SLA-1 gene. The target sequence of the sgRNA used for specific targeting SLA-1 gene in the SLA-1 gene complies with a 5'-N (20) NGG-3' sequence arrangement rule, wherein N (20) represents 20 consecutive basic groups, wherein each N represents a A or T or C or G; the target sequence in the SLA-1 gene is located at the four exon coding regions of the N-terminal of the SLA-1 gene or the junction of adjacent introns; and the target sequence in the SLA-1 gene is unique. The sgRNA used in the pig SLA-1 gene knockout method using CRISPR-Cas9 specificity, may fast, accurately, efficiently, and specifically knockout pig SLA-1 gene, effectively solve long cycle and high cost in construction of SLA-1 gene knockout pig.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Application of mRNA for use as a therapeutic against tumour diseases
InactiveUS9155788B2Improve stabilityExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCancer prevention
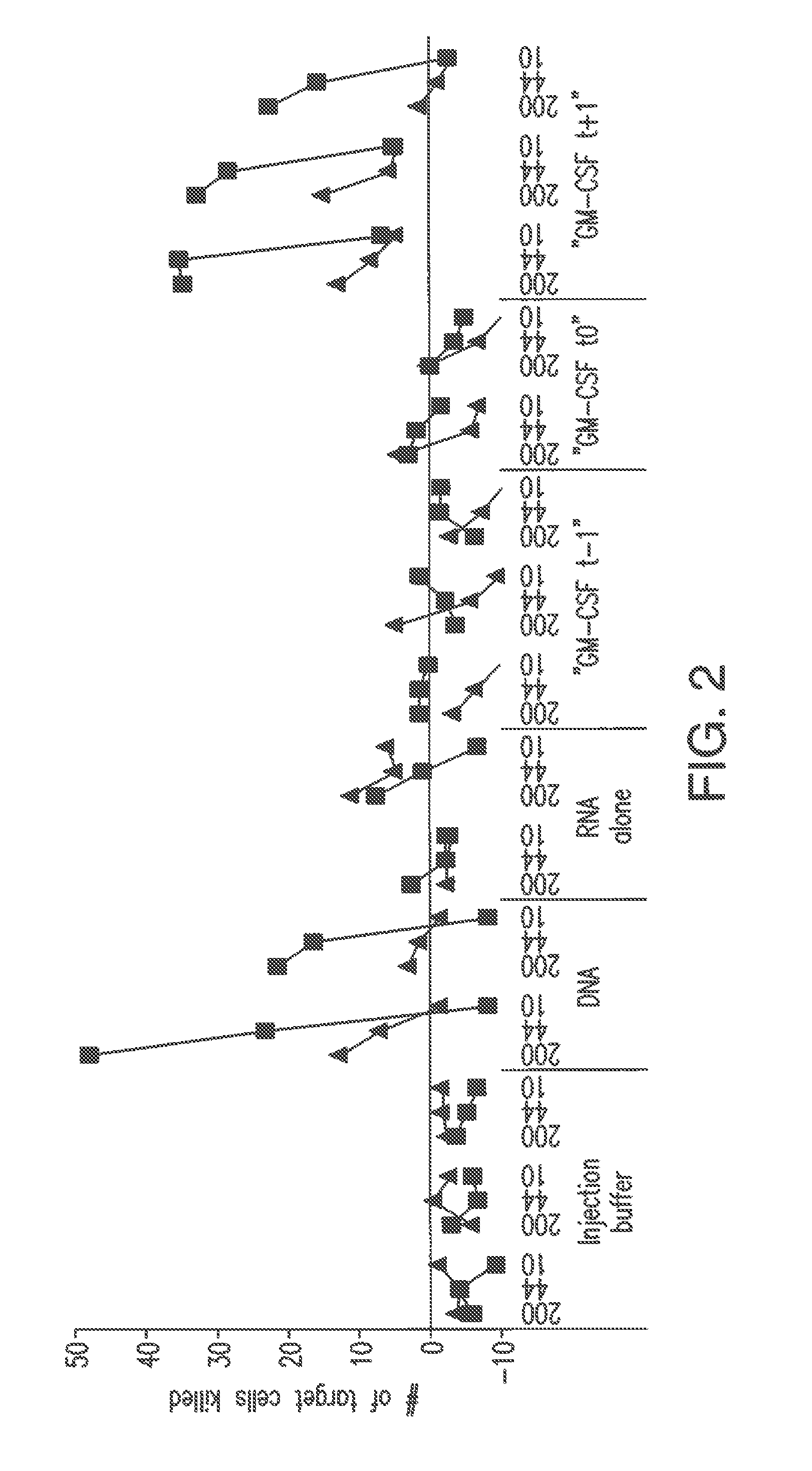
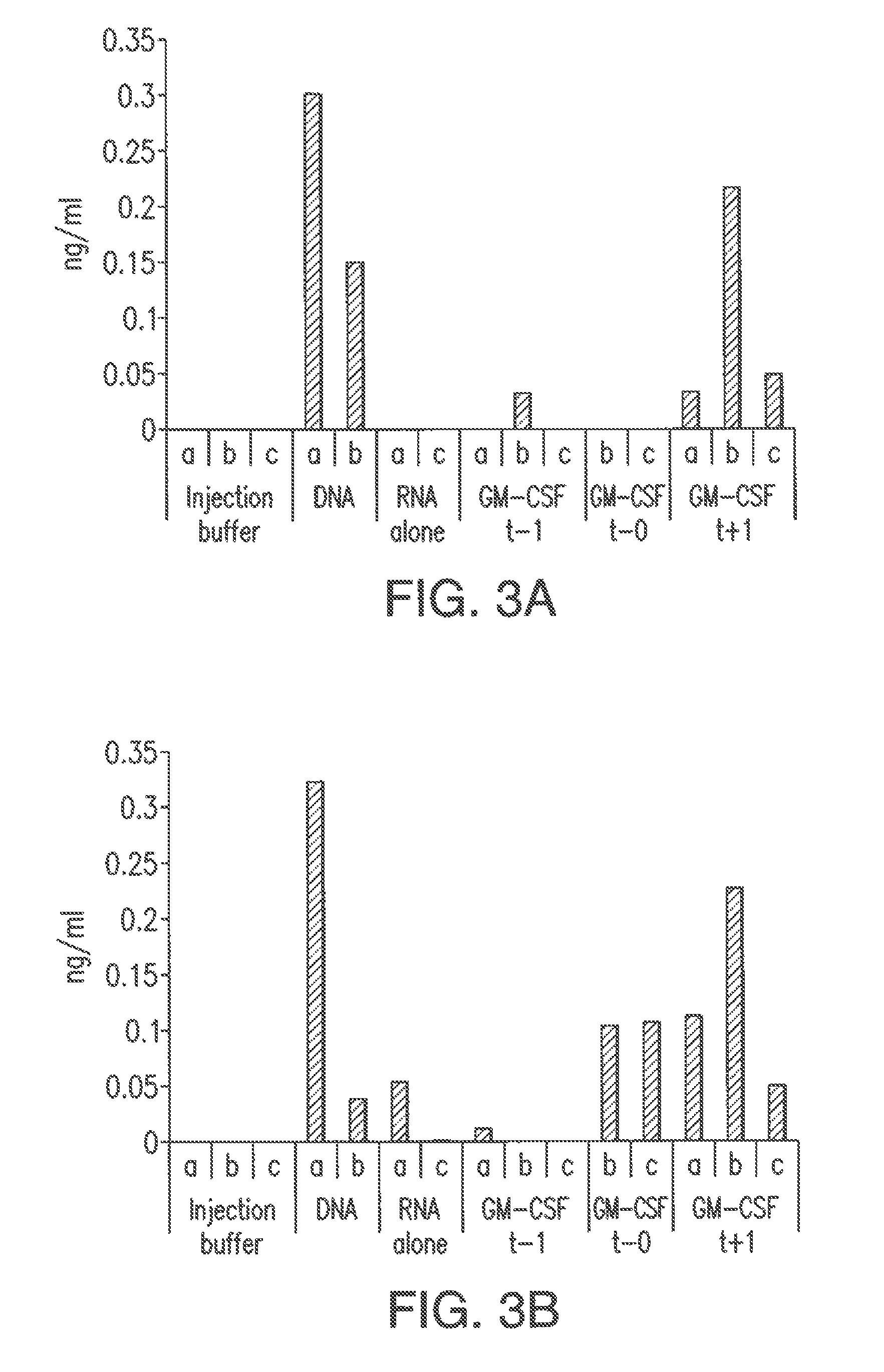
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one mRNA comprising at least one coding region for at least one antigen from a tumor, in combination with an aqueous solvent and preferably a cytokine, e.g. GM-CSF, and a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition. The pharmaceutical composition according to the invention is used in particular for therapy and / or prophylaxis against cancer.
Owner:CUREVAC GMBH
Composition and method for producing an immune response against tumor-related antigens
Disclosed are a novel prostatic acid phosphatase and corresponding coding region derived from mouse. Also disclosed is a method of producing an immune response against an autologous polypeptide tumor antigen by immunizing a subject with a xenogeneic polypeptide antigen, either alone, as part of a viral antigen construct, or as part of a pulsed dendritic cell preparation.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA LLC
Multi-gene expression constructs containing modified inteins
InactiveUS7026526B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPoly-A RNA
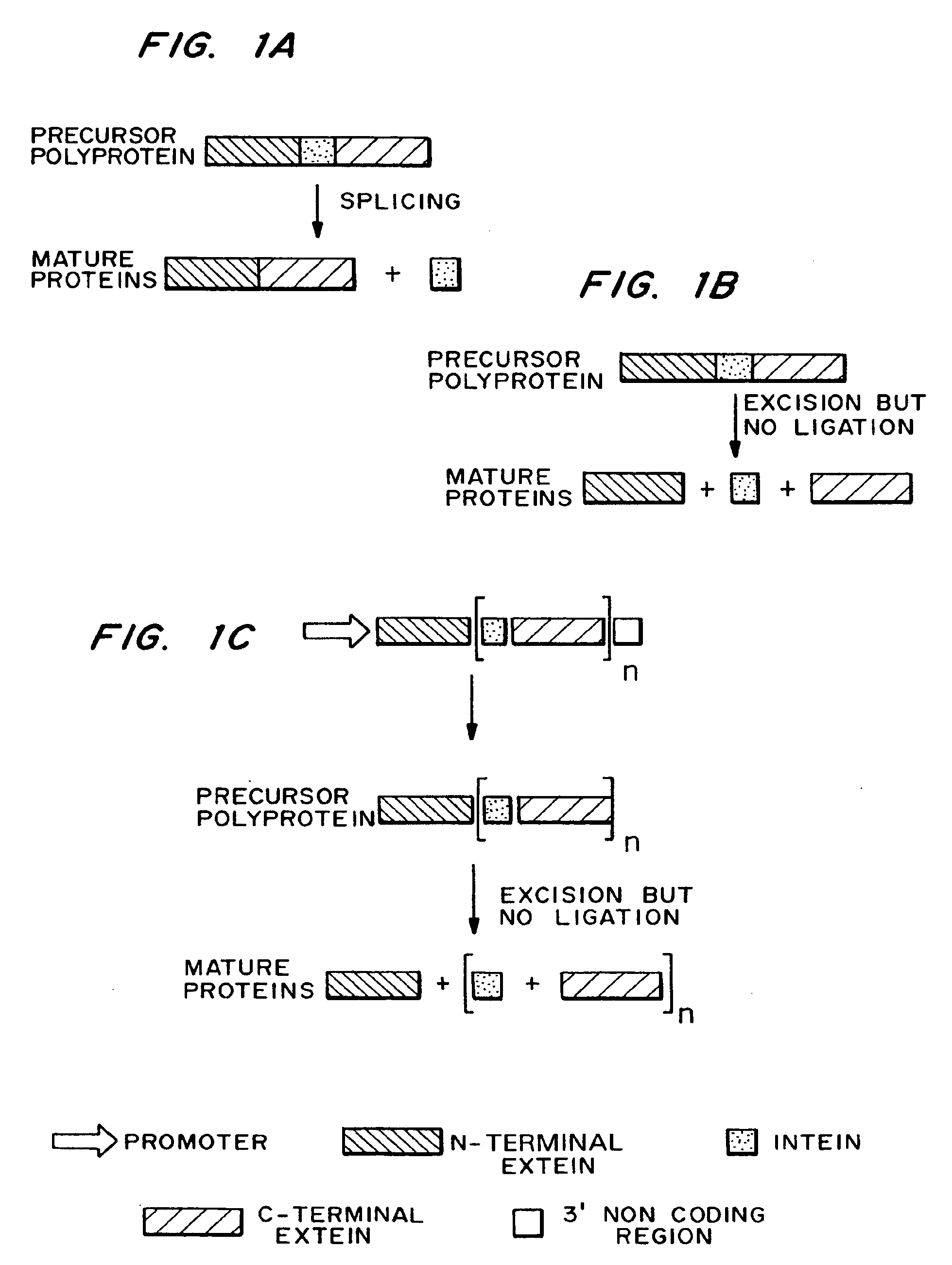
Methods and constructs for the introduction of multiple genes into plants using a single transformation event are described. Constructs contain a single 5′ promoter operably linked to DNA encoding a modified intein splicing unit. The splicing unit is expressed as a polyprotein and consists of a first protein fused to an intein fused to a second protein. The splicing unit has been engineered to promote excision of all non-essential components in the polyprotein but prevent the ligation reactions normally associated with protein splicing. Additional genetic elements encoding inteins and additional proteins can be fused in frame to the 5′-terminus of the coding region for the second protein to form a construct for expression of more than two proteins. A single 3′ termination sequence, such as a polyadenylation sequence when the construct is to be expressed in eucaryotic cells, follows the last coding sequence. These methods and constructs are particularly useful for creating plants with stacked input traits, illustrated by glyphosate tolerant plants producing BT toxin, and / or value added products, illustrated by the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in plants.
Owner:METABOLIX
Direct expression of peptides into culture media
InactiveUS6210925B1Reduced viabilityImprove breathabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth phaseBiotechnology
Expression systems are disclosed for the direct expression of peptide products into the culture media where genetically engineered host cells are grown. High yield was achieved with novel vectors, a special selection of hosts, and / or fermentation processes which include careful control of cell growth rate, and use of an inducer during growth phase. Special vectors are provided which include control regions having multiple promoters linked operably with coding regions encoding a signal peptide upstream from a coding region encoding the peptide of interest. Multiple transcription cassettes are also used to increase yield. The production of amidated peptides using the expression systems is also disclosed.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
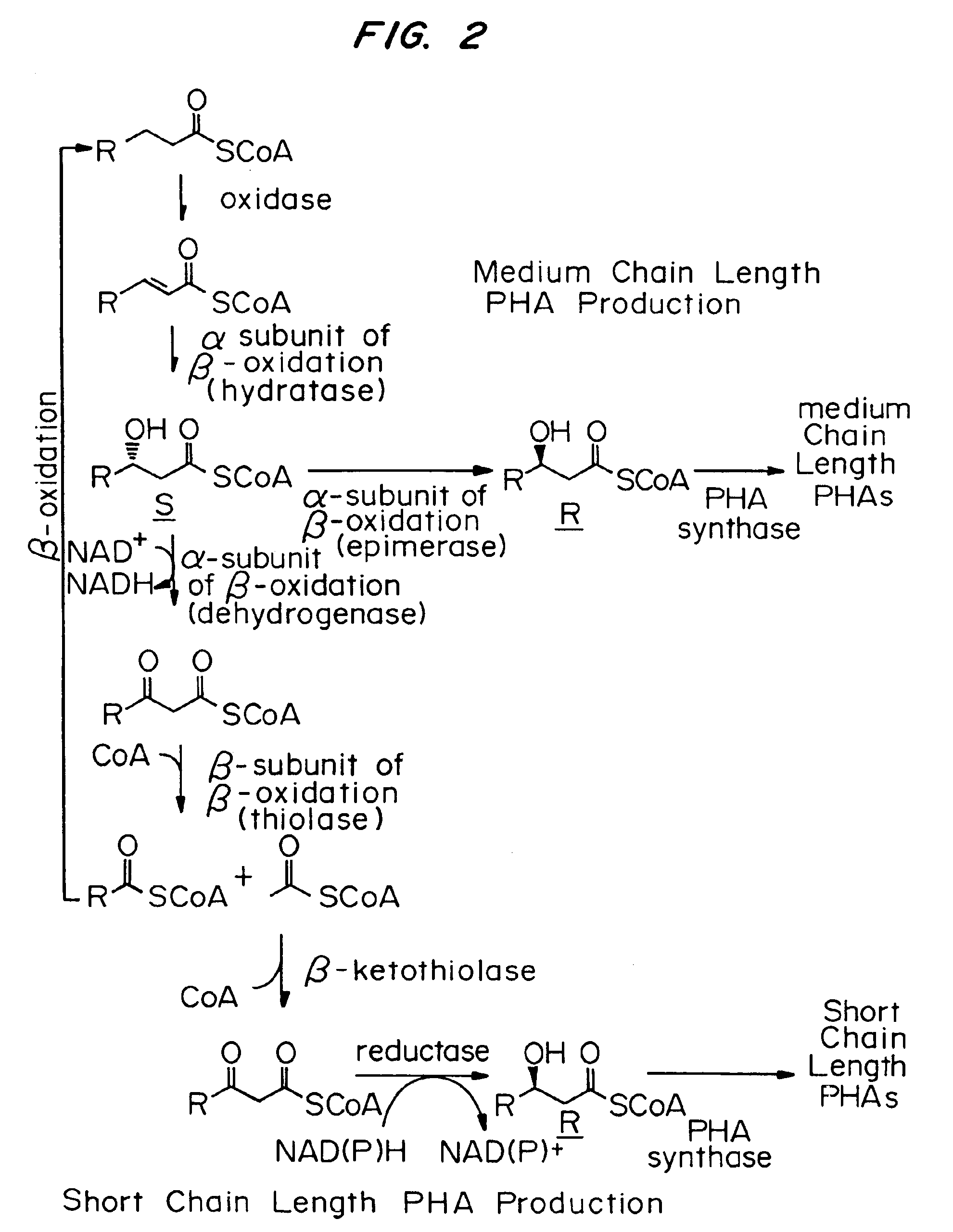
Strain comprising increased expression of a CFA coding region for butanol production
ActiveUS8518678B2High activityReduce accumulationBacteriaSugar derivativesCyclopropane fatty acid synthaseBacterial strain
Screening of fatty acid fed bacteria which are not natural butanol producers identified increased membrane cyclopropane fatty acid as providing improved butanol tolerance. Increasing expression of cyclopropane fatty acid synthase in the presence of the enzyme substrate that is either endogenous to the cell or fed to the cell, increased butanol tolerance. Bacterial strains with increased cyclopropane fatty acid synthase and having a butanol biosynthetic pathway are useful for production of butanol.
Owner:GEVO INC
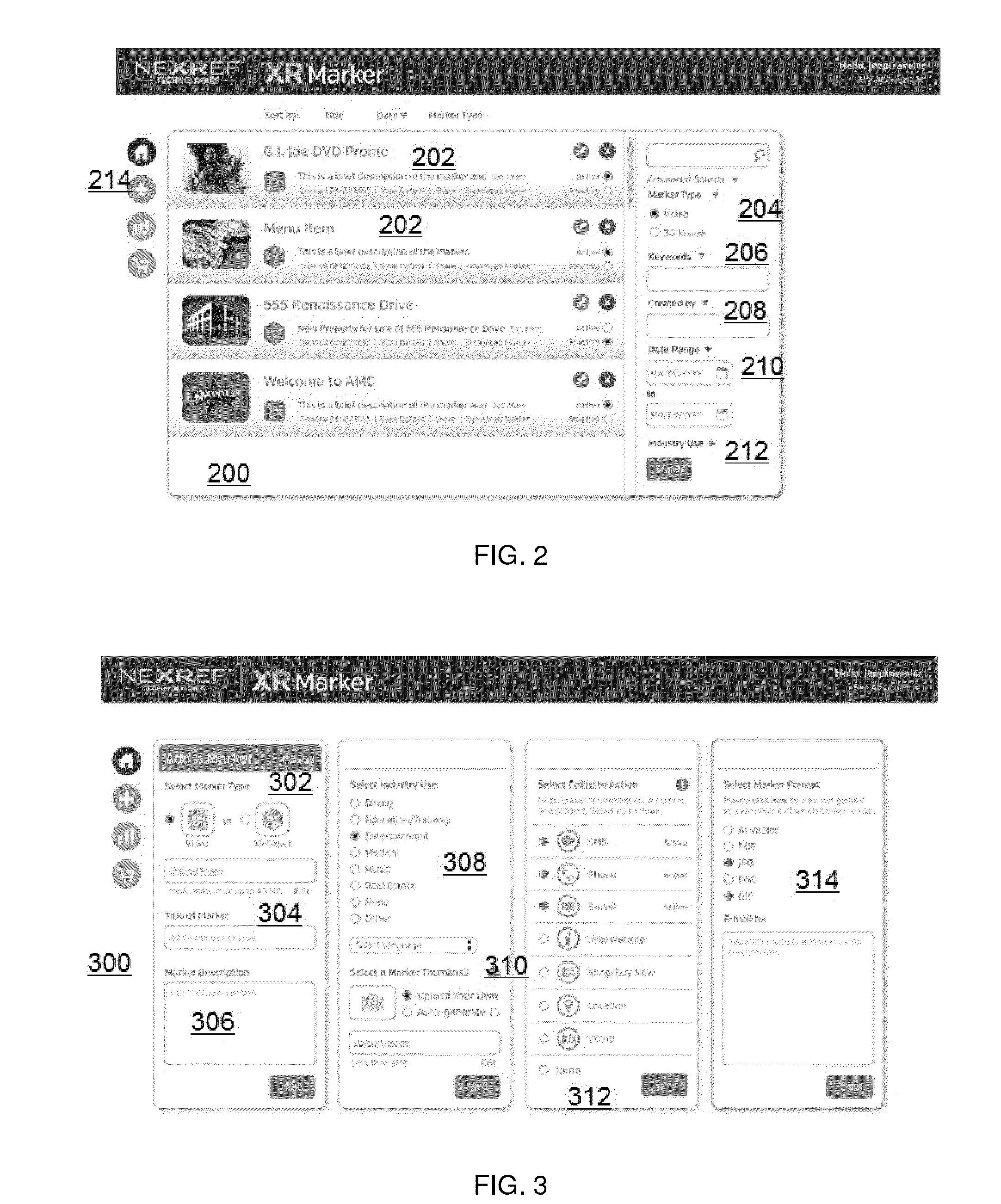
Marker-based augmented reality (AR) display with inventory management
InactiveUS20140340423A1Reduce sizeExtensive contentImage enhancementImage analysisPattern matchingInventory management
A platform to enable configuration, administration and management of augmented reality markers adapted to be scanned by an end user mobile device to enable AR experience. The platform enables control of marker provisioning by entities who decide what content should appear in mobile applications when their AR codes are scanned by end users. The platform generates unique AR markers. A marker has a first code region, and a second code region. The code regions are adapted to be scanned, preferably sequentially, and the first code region encodes a first identifier identifying an External marker ID in a pattern matching approach, and second code region that encodes a second identifier identifying an Internal marker ID in a encoding / decoding approach. In one embodiment, the first code region is generally circular and includes a central area, and the second code region is located within the central area of the first code region.
Owner:NEXREF TECH
Method using CRISPR-Cas9 to specifically knock off pig PDX1 gene and sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting
The invention discloses a method using CRISPR-Cas9 to specifically knock off pig PDX1 gene and sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting. The target sequence of sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting on PDX1 gene is accord with the sequence alignment rule of 5'-N(20)NGG-3', wherein N(20) represents 20 continuous bases, and each N represent A, T, C or G; the target sequence of PDX1 gene is arranged in the first exon coding region on the N terminal of PDX1 gene or a junction between the coding region and neighbored intron, and the target sequence of PDX1 gene is unique. The provided method can rapidly, precisely, efficiently and specifically knock off PDX1 gene of pigs, and solves the problems of long period and high cost of pig PDX1 gene knocking.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Plant Genome Sequence and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080113342A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsGenomic DNAPlant cell
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid sequences from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana plants. The invention encompasses nucleic acid molecules present in non-coding regions as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode proteins and fragments of proteins. In addition, the invention also encompasses proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding these proteins or fragments. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against human cytomegalovirus infection
InactiveUS7410795B2Enhance transfectionHigh expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesAntigenAdjuvant
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based cytomegalovirus vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding HCMV antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the HCMV antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. HCMV antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to pp65, glycoprotein B (gB), IE1, and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. In certain embodiments, sequences have been deleted, e.g., the Arg435-Lys438 putative kinase in pp65 and the membrane anchor and endocellular domains in gB. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to HCMV in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com