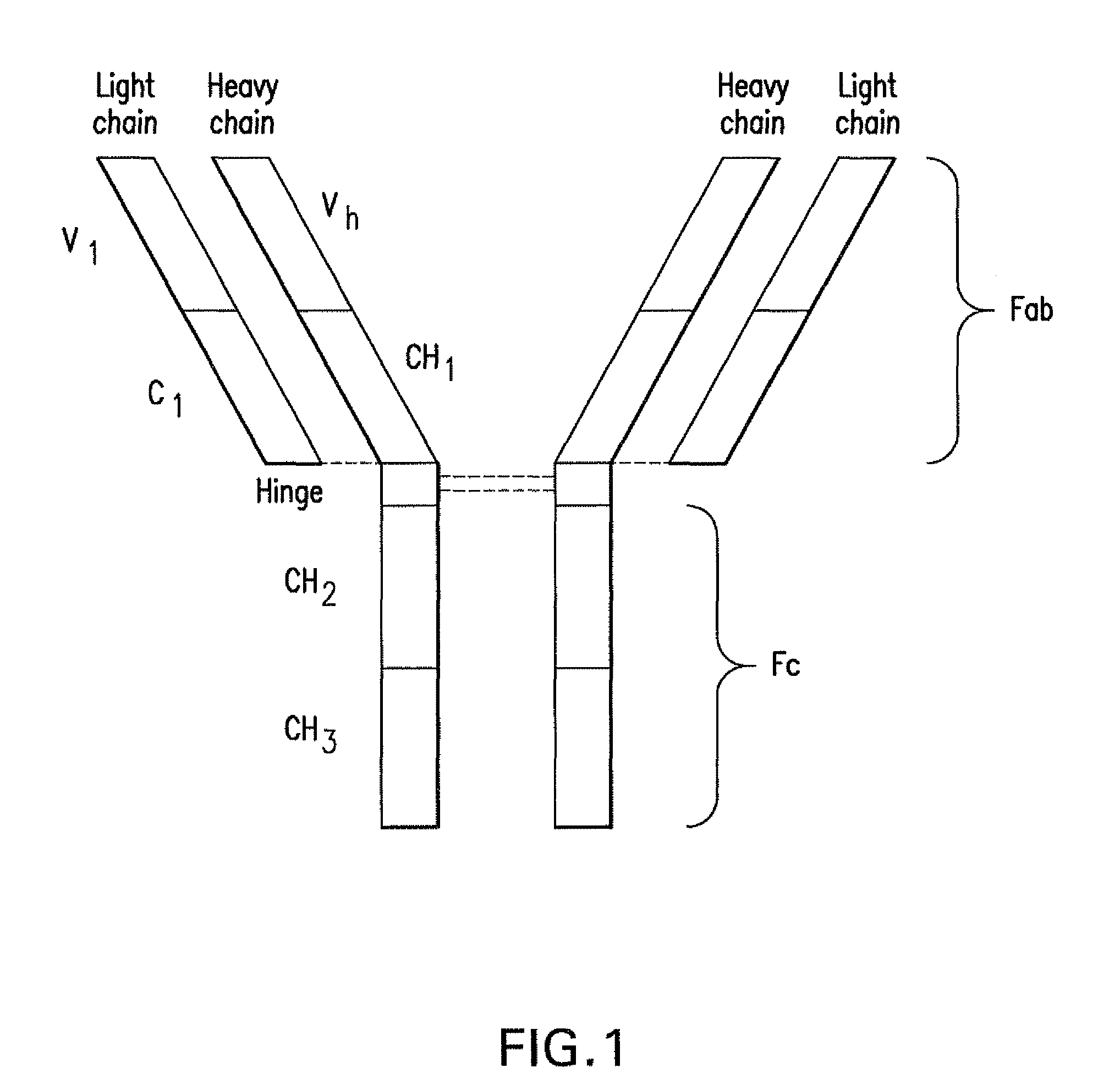
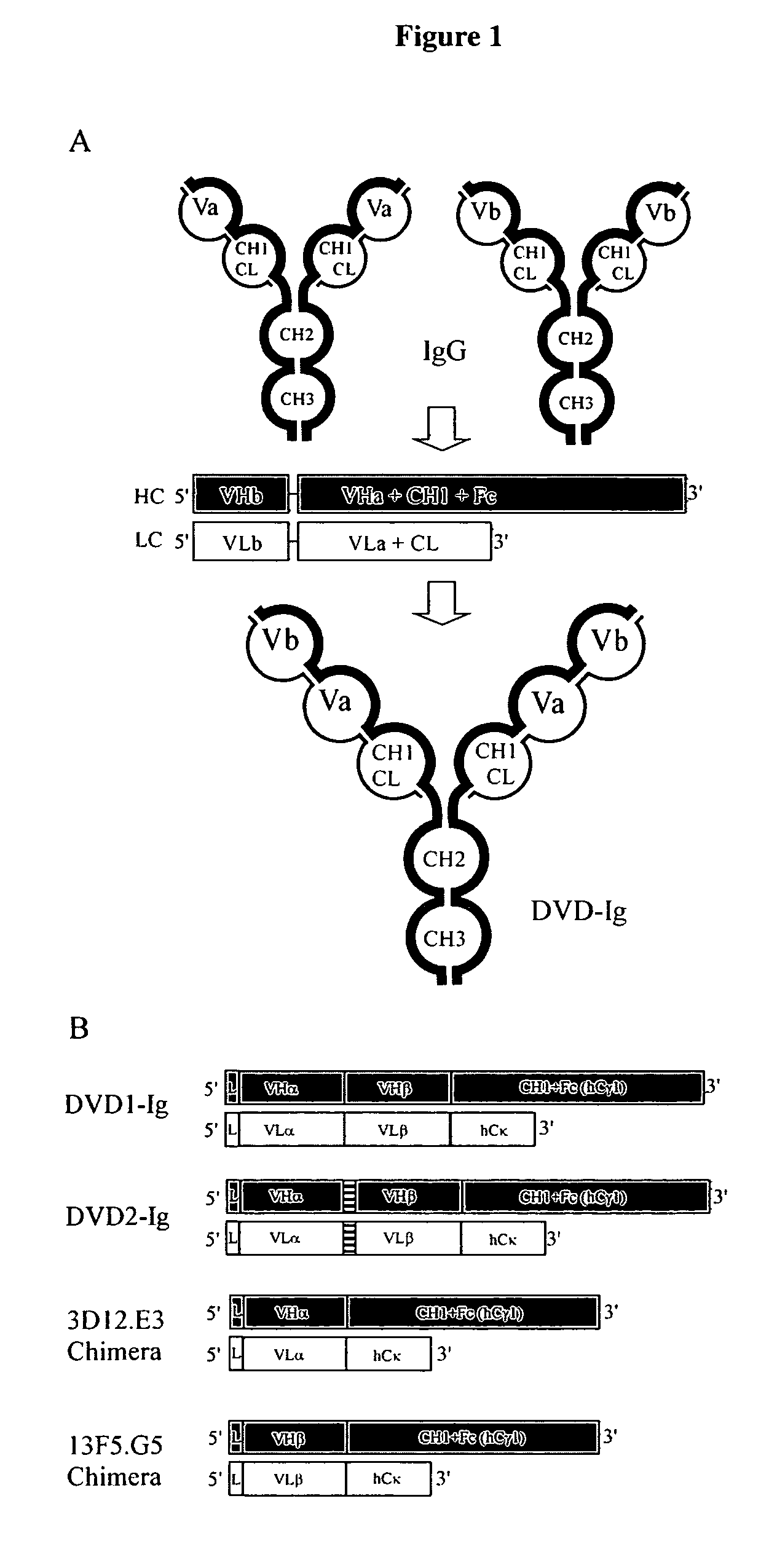
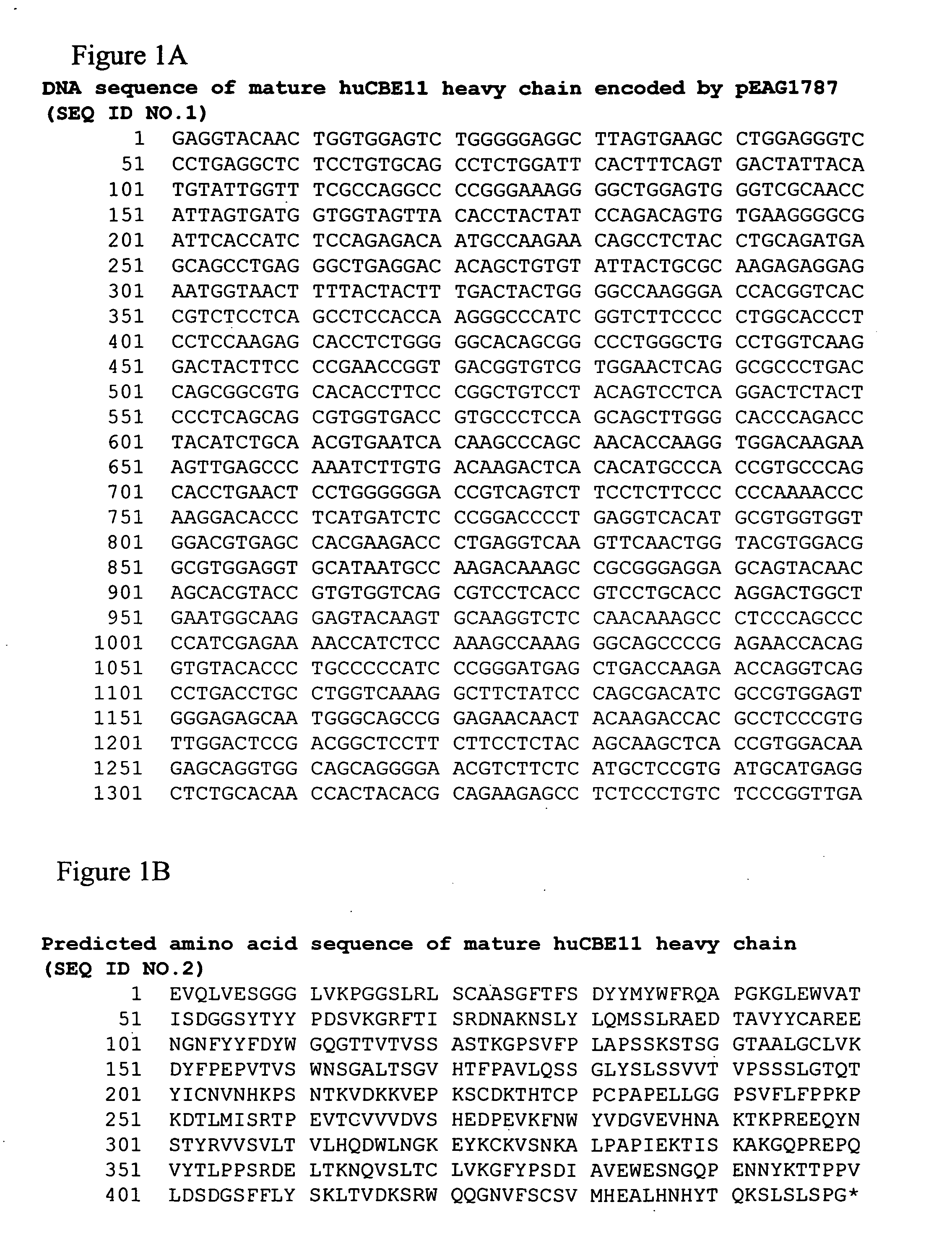
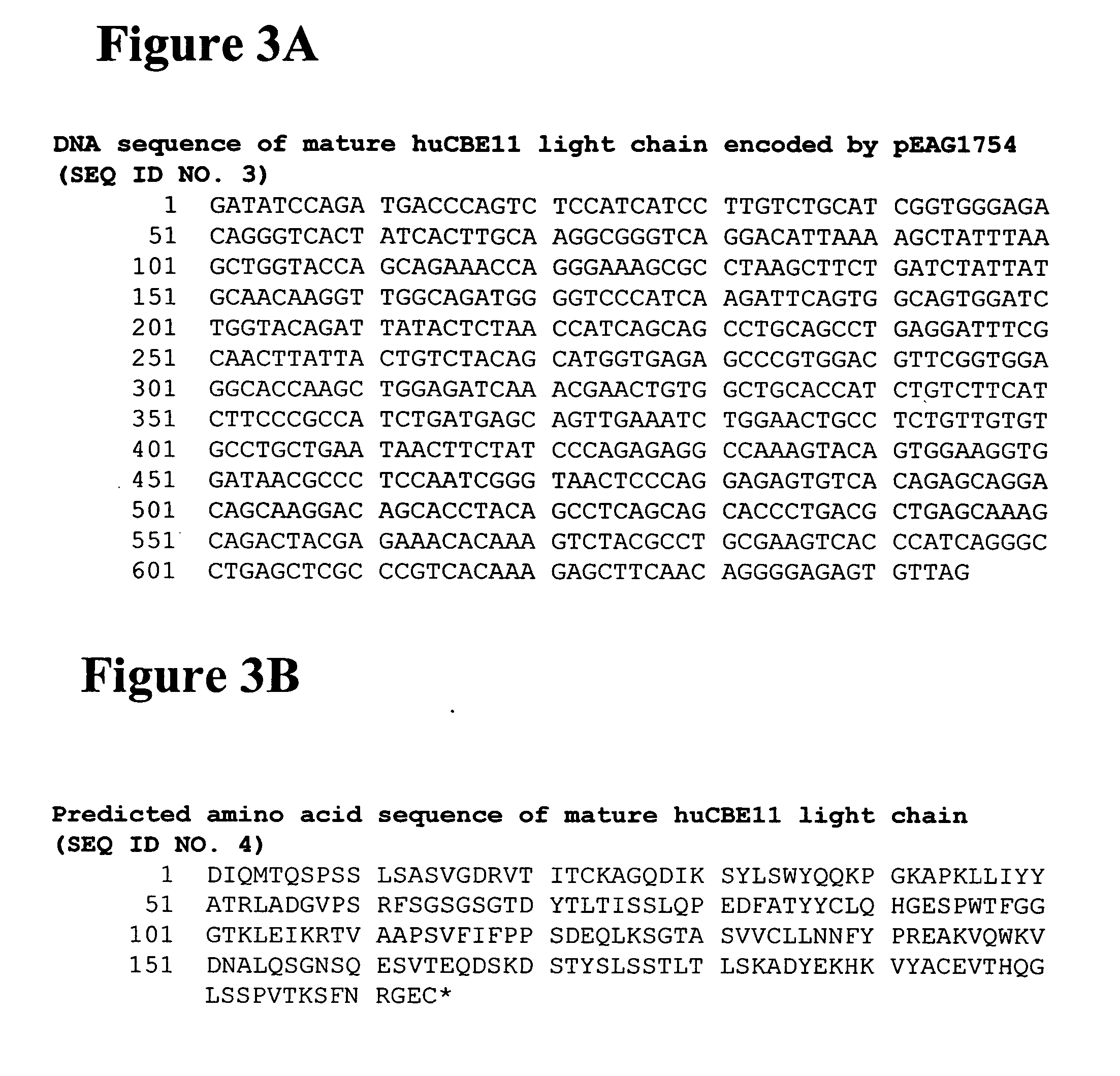
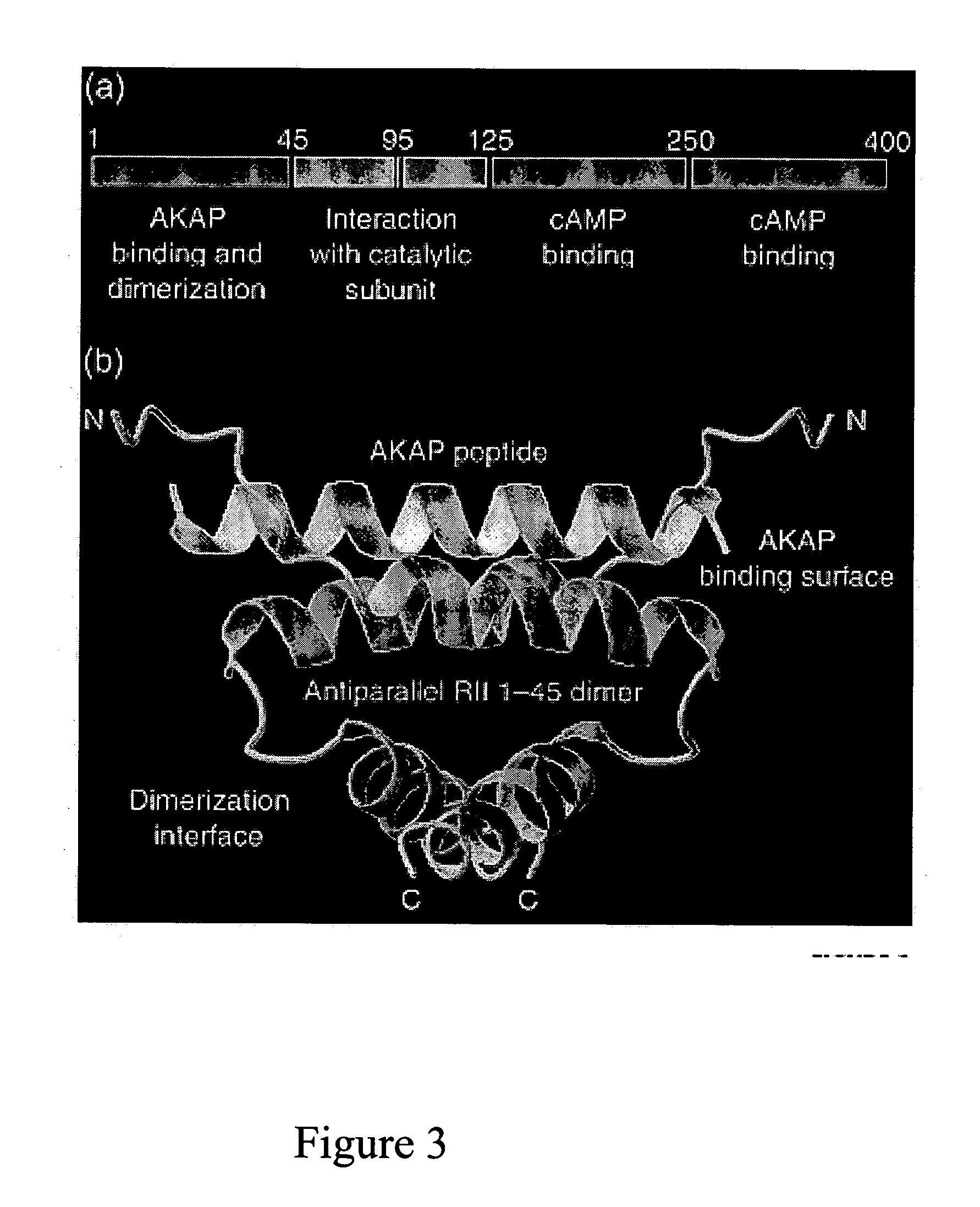
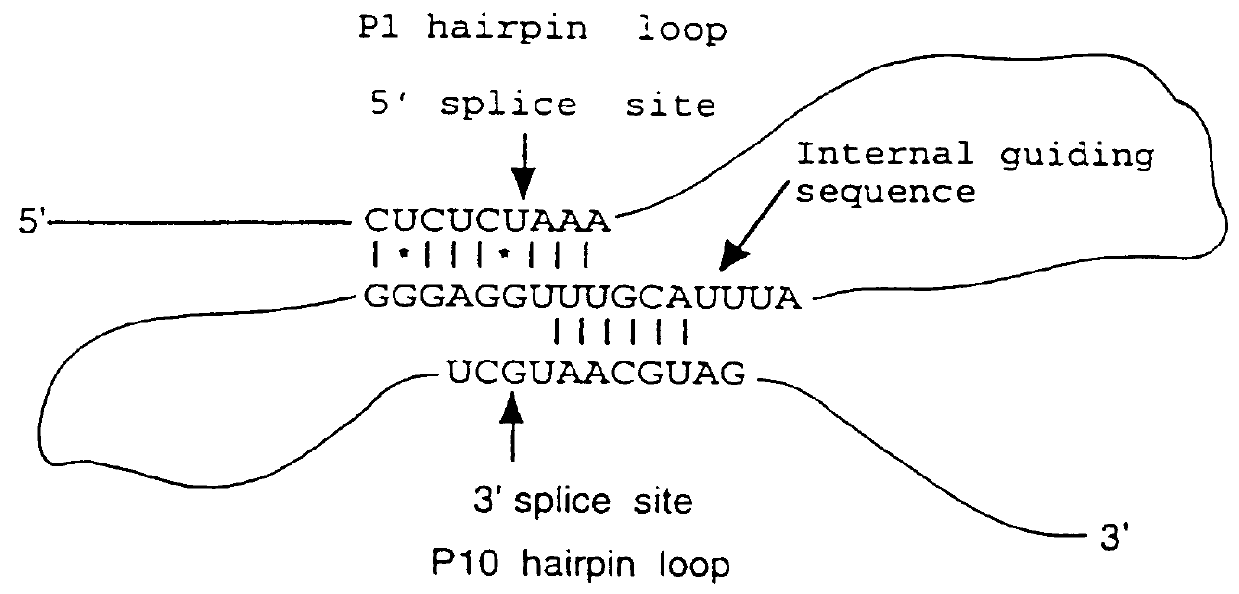
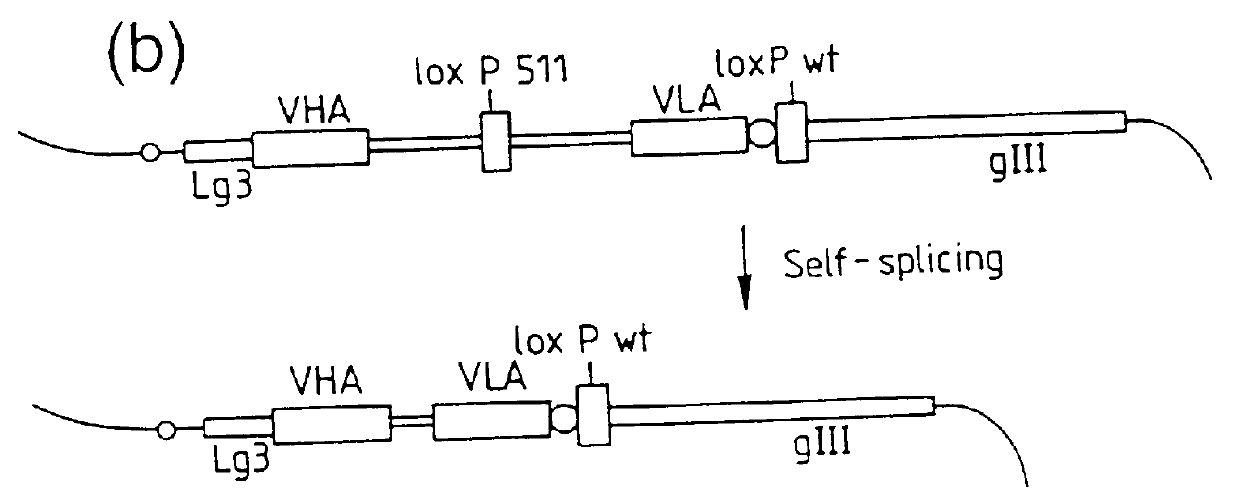
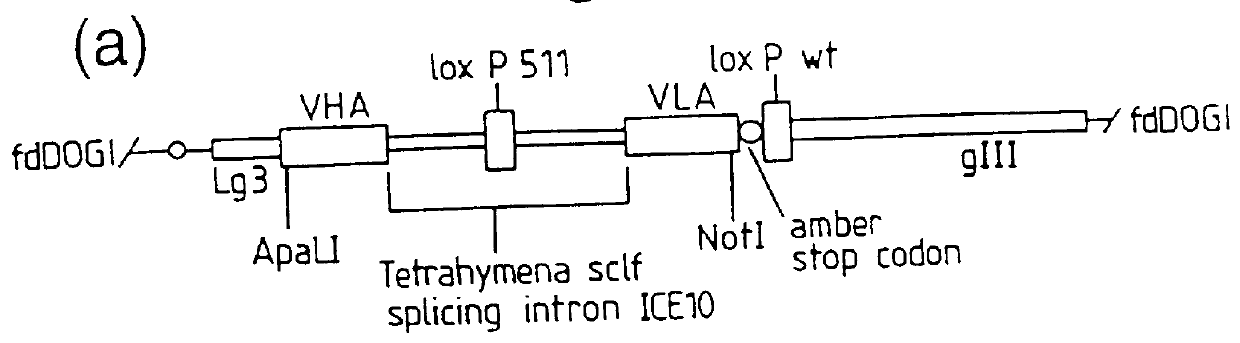
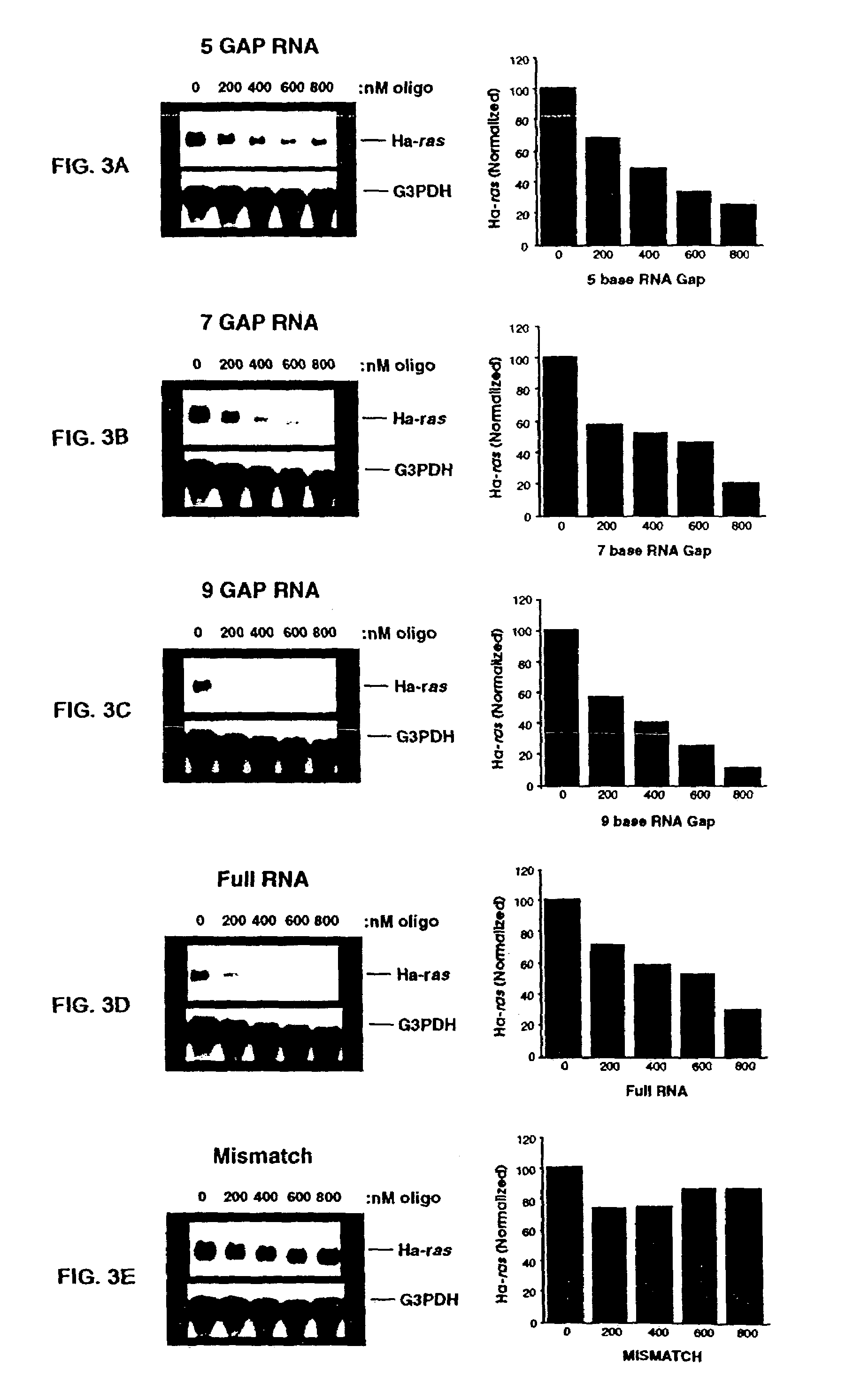
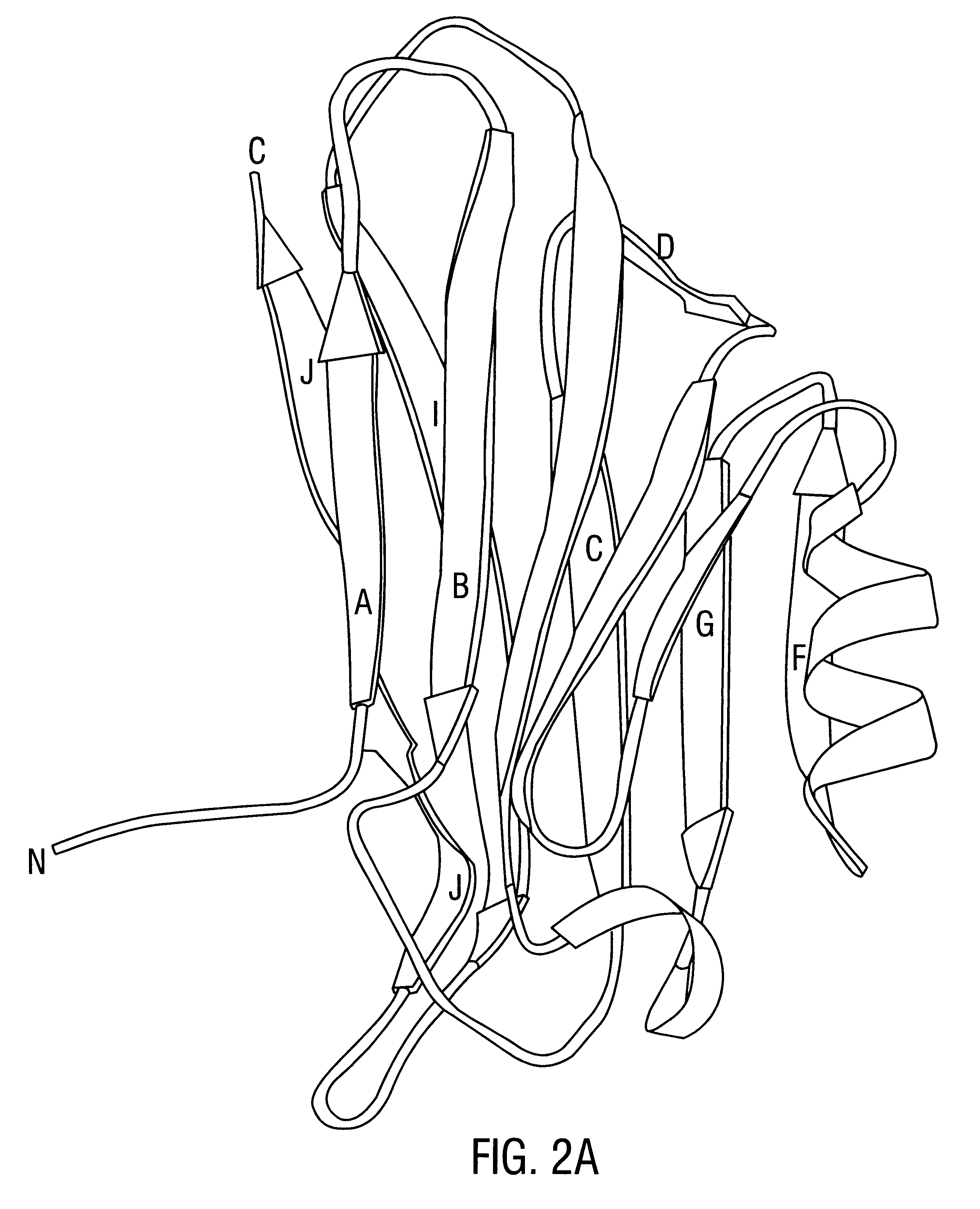
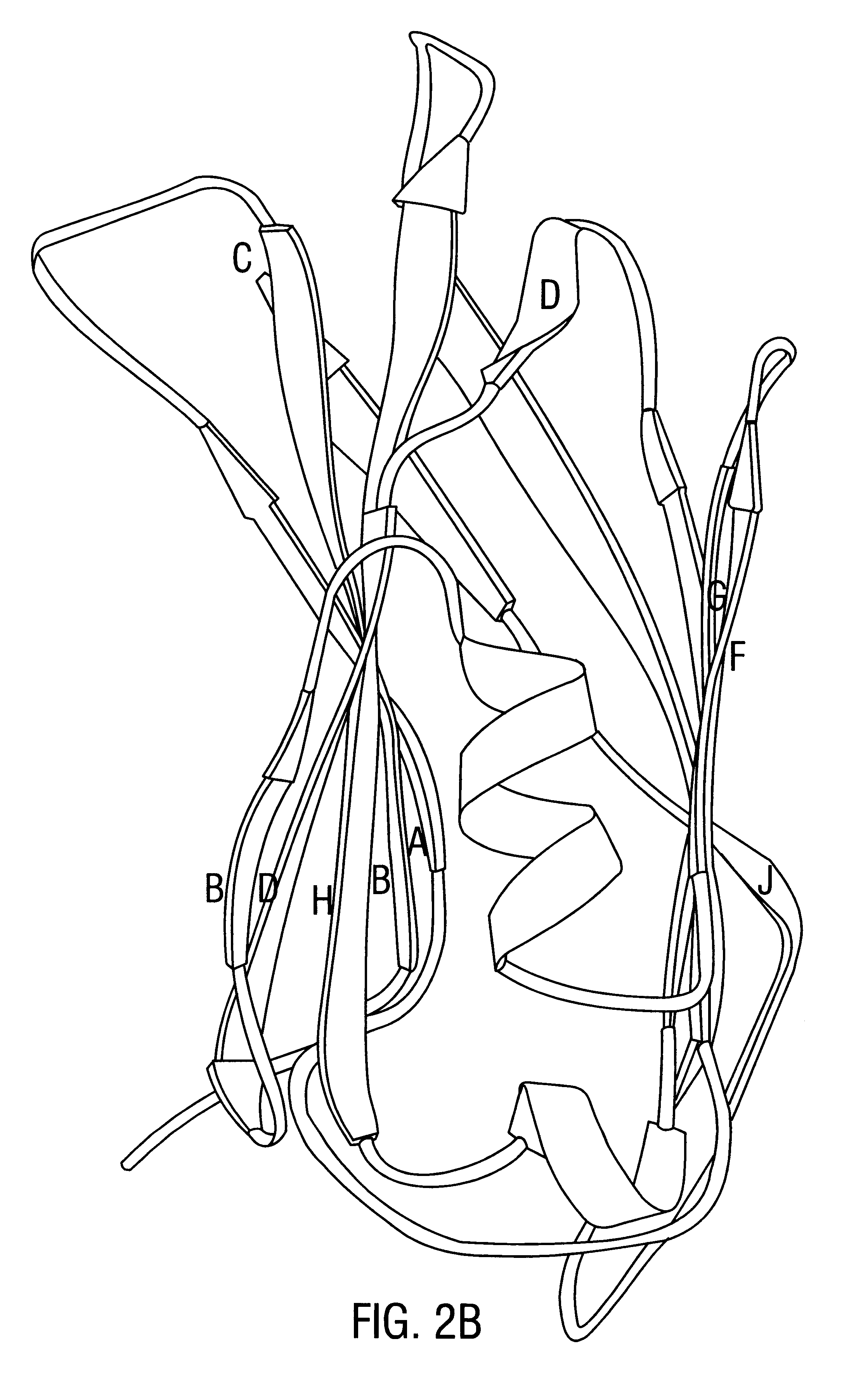
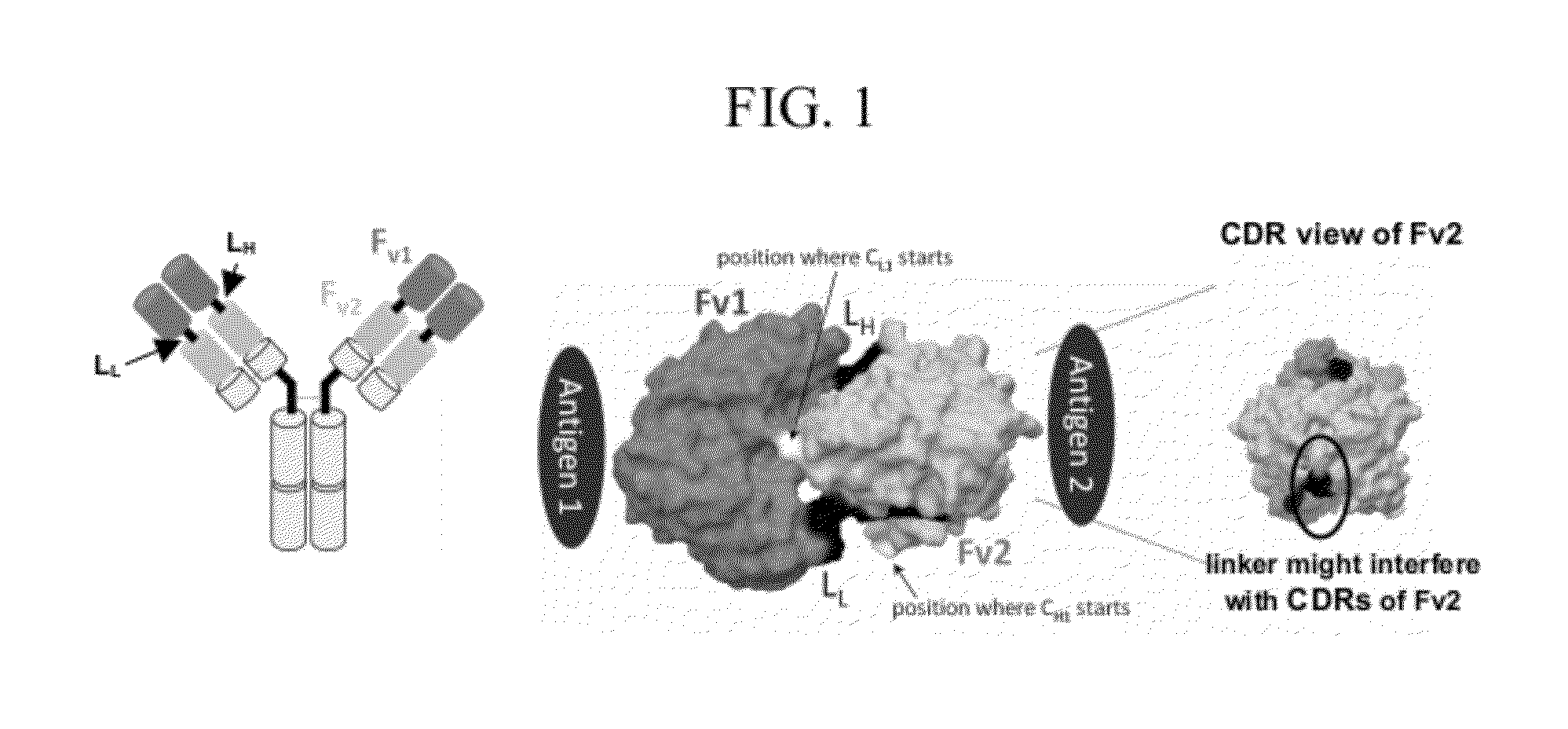
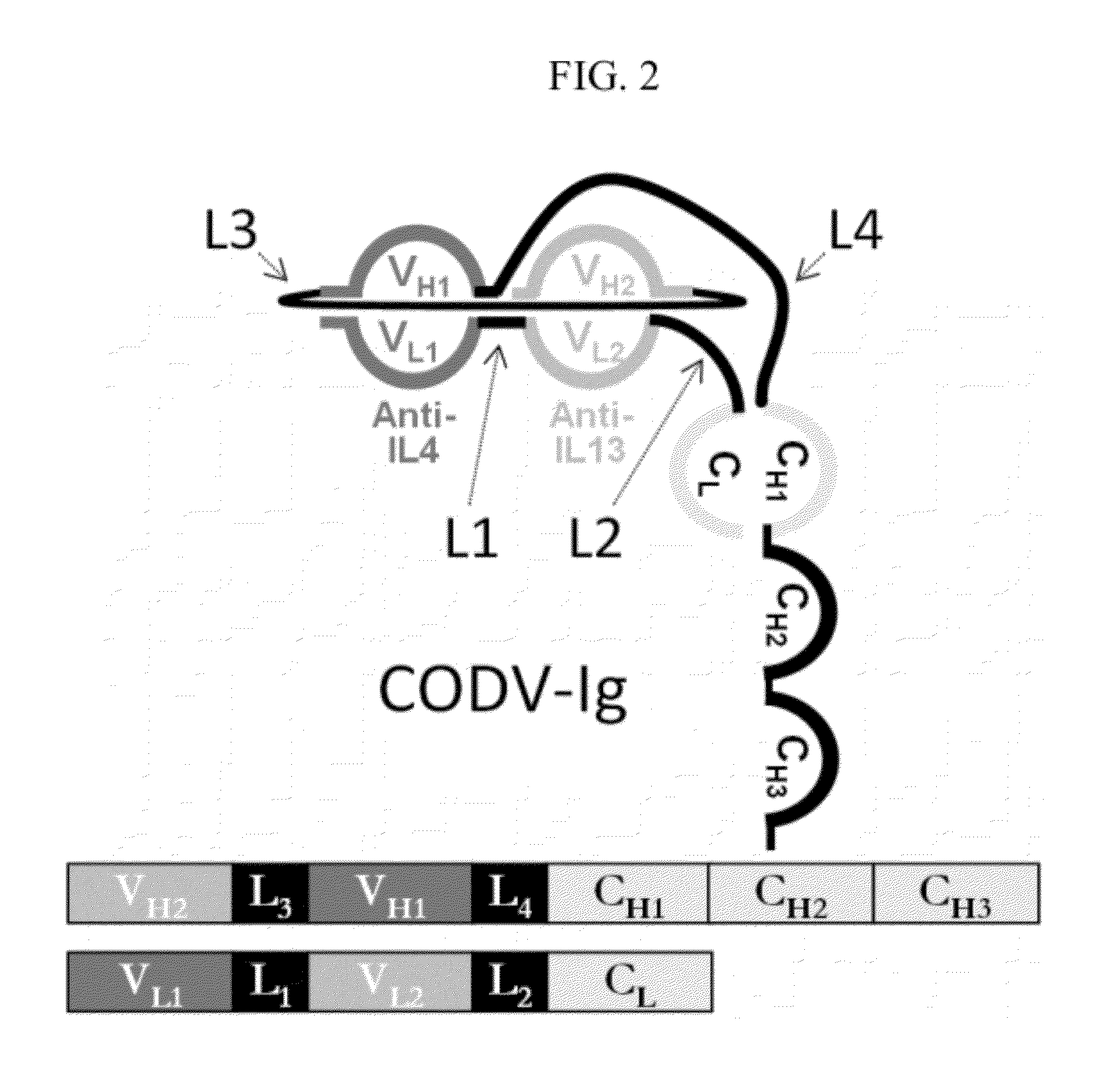
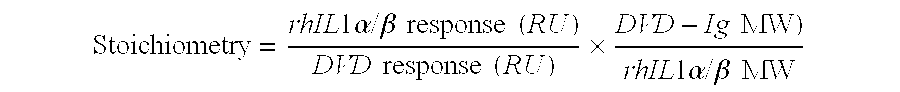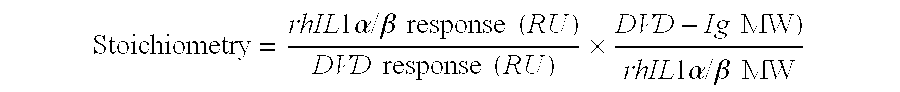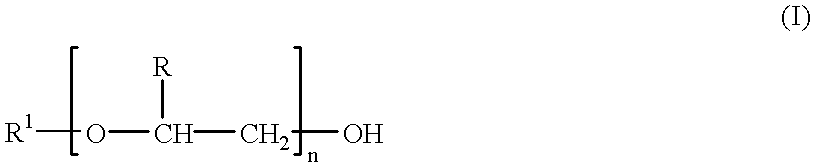Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3399 results about "Binding protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
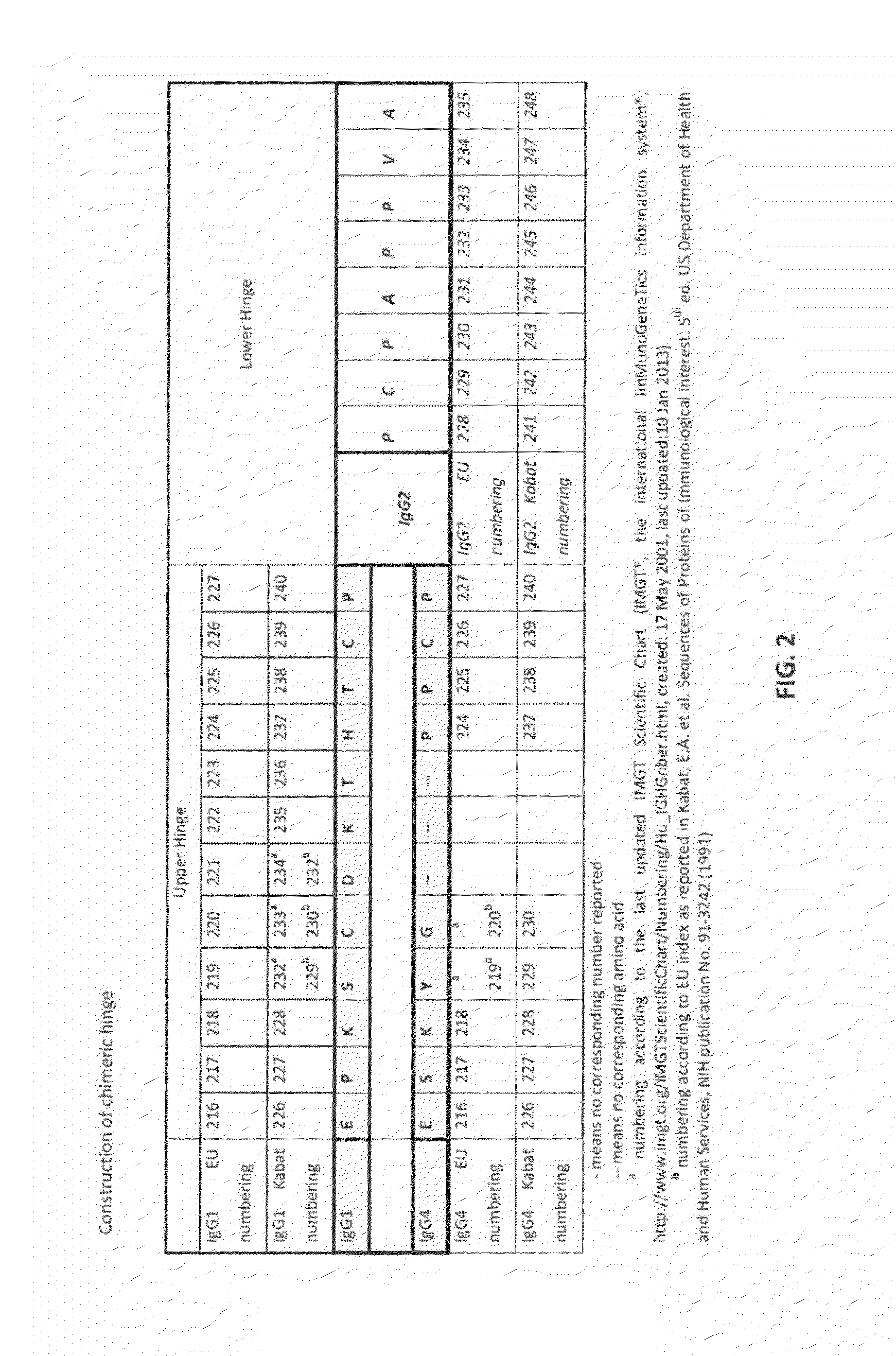
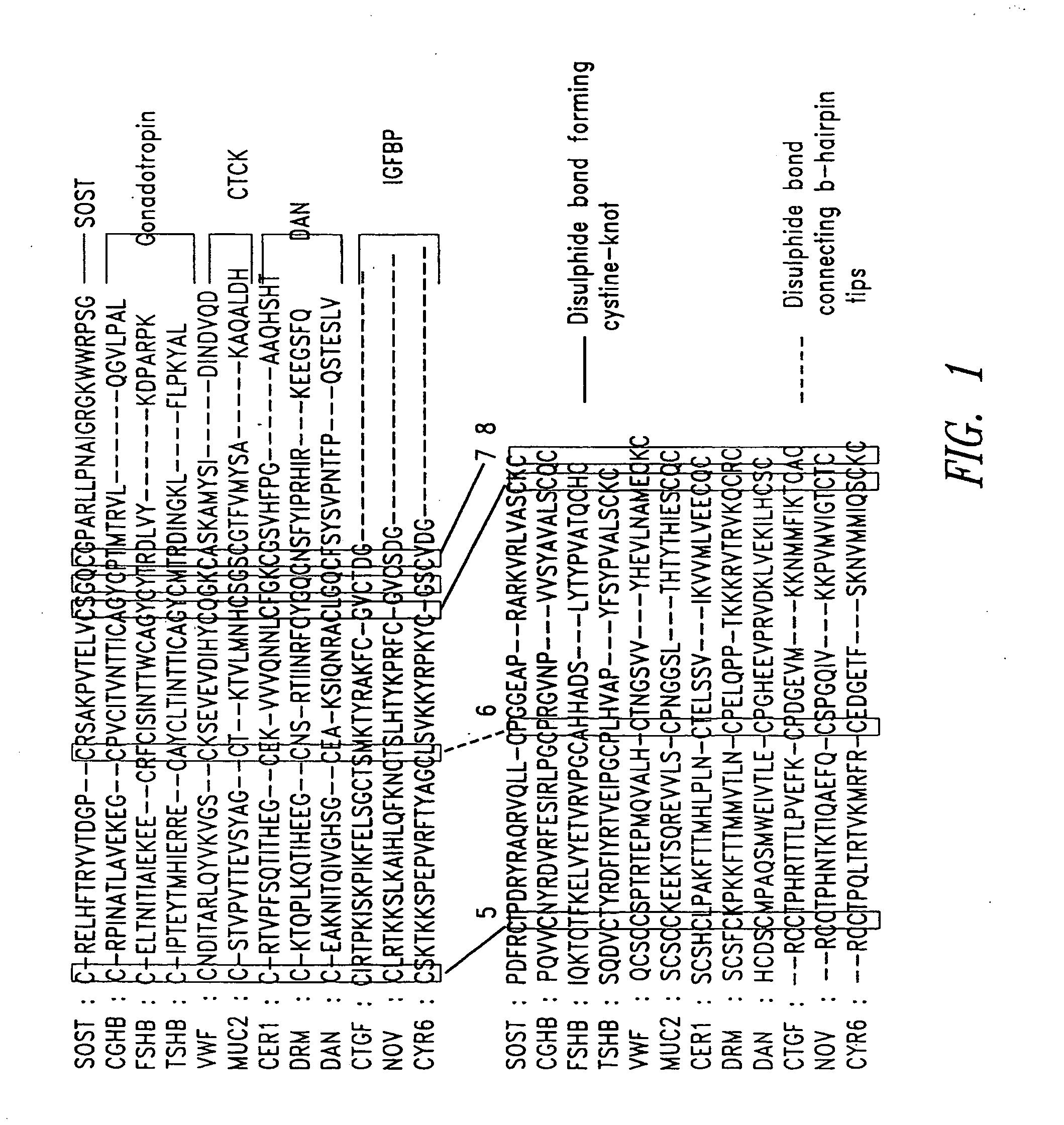
A binding protein is any protein that acts as an agent to bind two or more molecules together. Examples include: DNA-binding protein Single-strand binding protein Telomere-binding protein RNA-binding protein Poly-binding protein Nuclear cap-binding protein complex CREB-binding protein Calcium-binding protein Calcium-binding protein 1 S100 calcium-binding protein A1 TATA-binding protein Actin-binding protein Penicillin binding proteins Retinol binding protein Retinol binding protein 4 EP300 Binding immunoglobulin protein Odorant binding protein Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein C4b-binding protein Rap GTP-binding protein Calmodulin-binding proteins Iron-binding proteins Thyroxine-binding proteins Folate-binding protein Sterol regulatory element-binding protein GTP-binding protein Retinaldehyde-binding protein 1 Ccaat-enhancer-binding proteins Androgen-binding protein Maltose-binding protein Phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein 1 Syntaxin binding protein 3 Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein Methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2 Growth hormone-binding protein Vitamin D-binding protein Syntaxin binding protein 2 Oxysterol-binding protein E3 binding protein
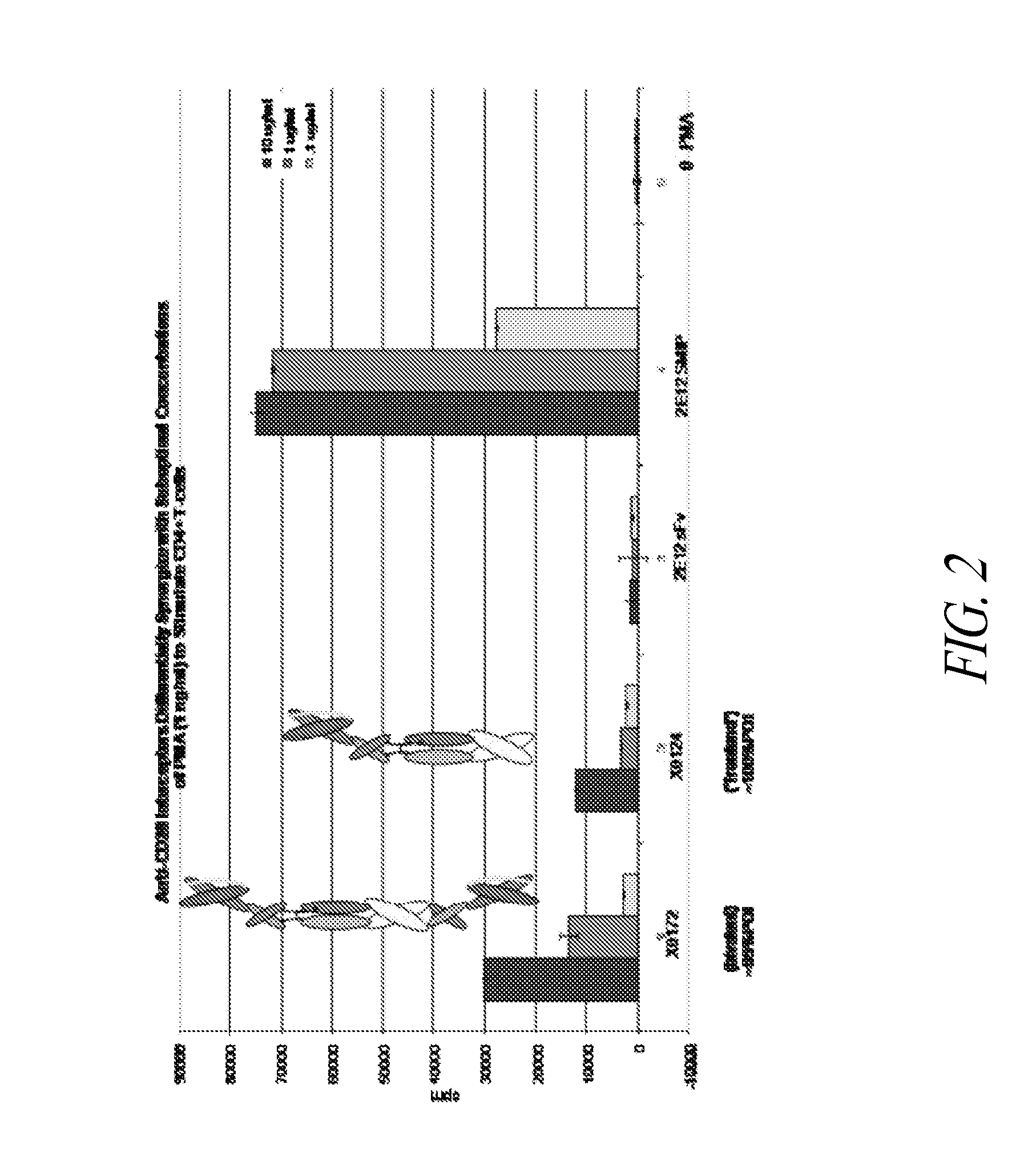
PD-1 binding proteins
ActiveUS8168757B2Regulating T cell responsesImprove immunityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody ingredientsHost immunitySignalling pathways
The present invention features PD-1 binding proteins, a subset of which inhibits binding of PD-L1 to the PD-1 receptor. These binding proteins can be employed to modulate the immune system through the manipulation of the PD-1 signaling pathway, enhancing host immunity to treat infections and cancer.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
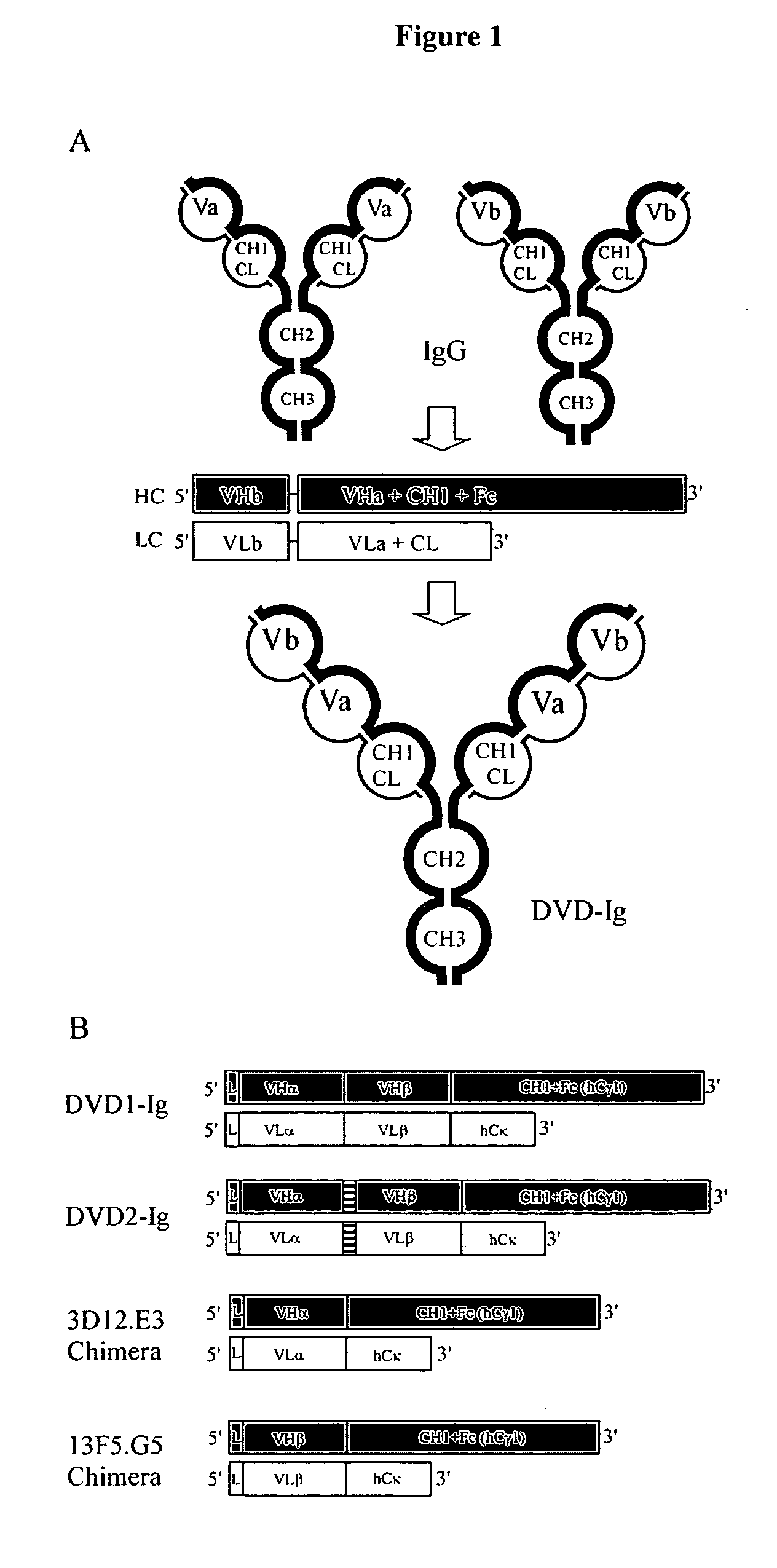
Dual variable domain immunoglobulin and uses thereof
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Dual variable domain immunoglobulin and uses thereof
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Stably tethered structures of defined compositions with multiple functions or binding specificities
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Protein scaffolds for antibody mimics and other binding proteins
InactiveUS7115396B2Easy to foldImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsWAS PROTEINAntibody
Disclosed herein are proteins that include an immunoglobulin fold and that can be used as scaffolds. Also disclosed herein are nucleic acids encoding such proteins and the use of such proteins in diagnostic methods and in methods for evolving novel compound-binding species and their ligands.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Multispecific epitope binding proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090155275A1Stimulate immune responseEnhanced interactionAntipyreticAnalgesicsEpitopeDisease
The present invention relates to multispecific epitope binding proteins, methods of making, and uses thereof in the prevention, management, treatment or diagnosis of acute or chronic diseases.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)-binding polypeptide variants, dimeric Fc binding proteins and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20070148164A1Increase free energyReduced binding affinityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesFc bindingNeonatal Fc receptor
The compositions and methods of the present invention are based, in part, on our discovery that an effector function mediated by an Fc-containing polypeptide can be altered by modifying one or more amino acid residues within the polypeptide (by, for example, electrostatic optimization). The polypeptides that can be generated according to the methods of the invention are highly variable, and they can include antibodies and fusion proteins that contain an Fc region or a biologically active portion thereof.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Use of single-stranded nucleic acid binding proteins in sequencing
InactiveUS20060024678A1Stabilizing sequencingIncrease speedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingSingle strand
The invention provides methods for stabilizing a nucleic acid sequencing reaction. Generally, methods of the invention include exposing a target nucleic acid to a single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein and performing a sequencing reaction.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
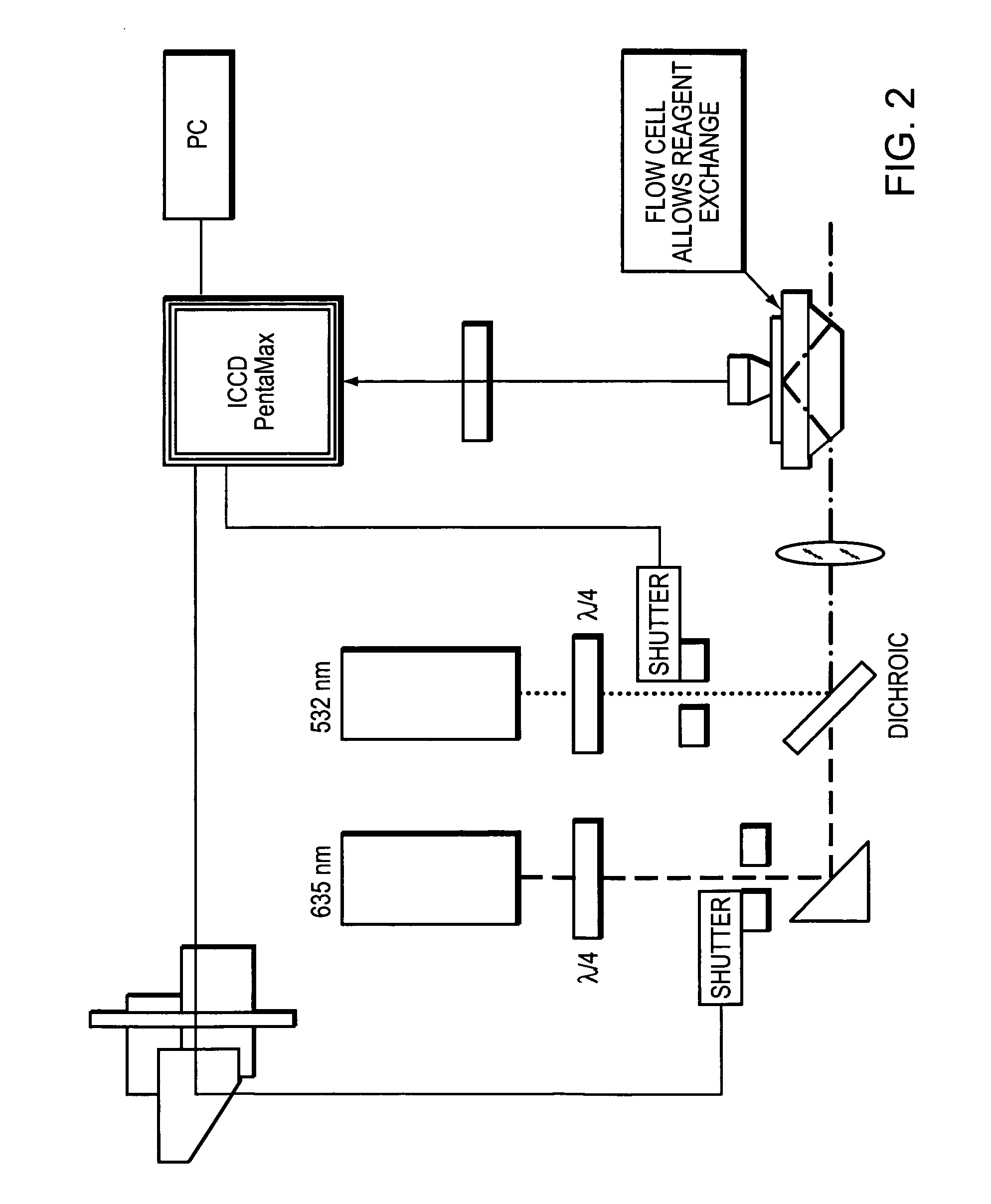
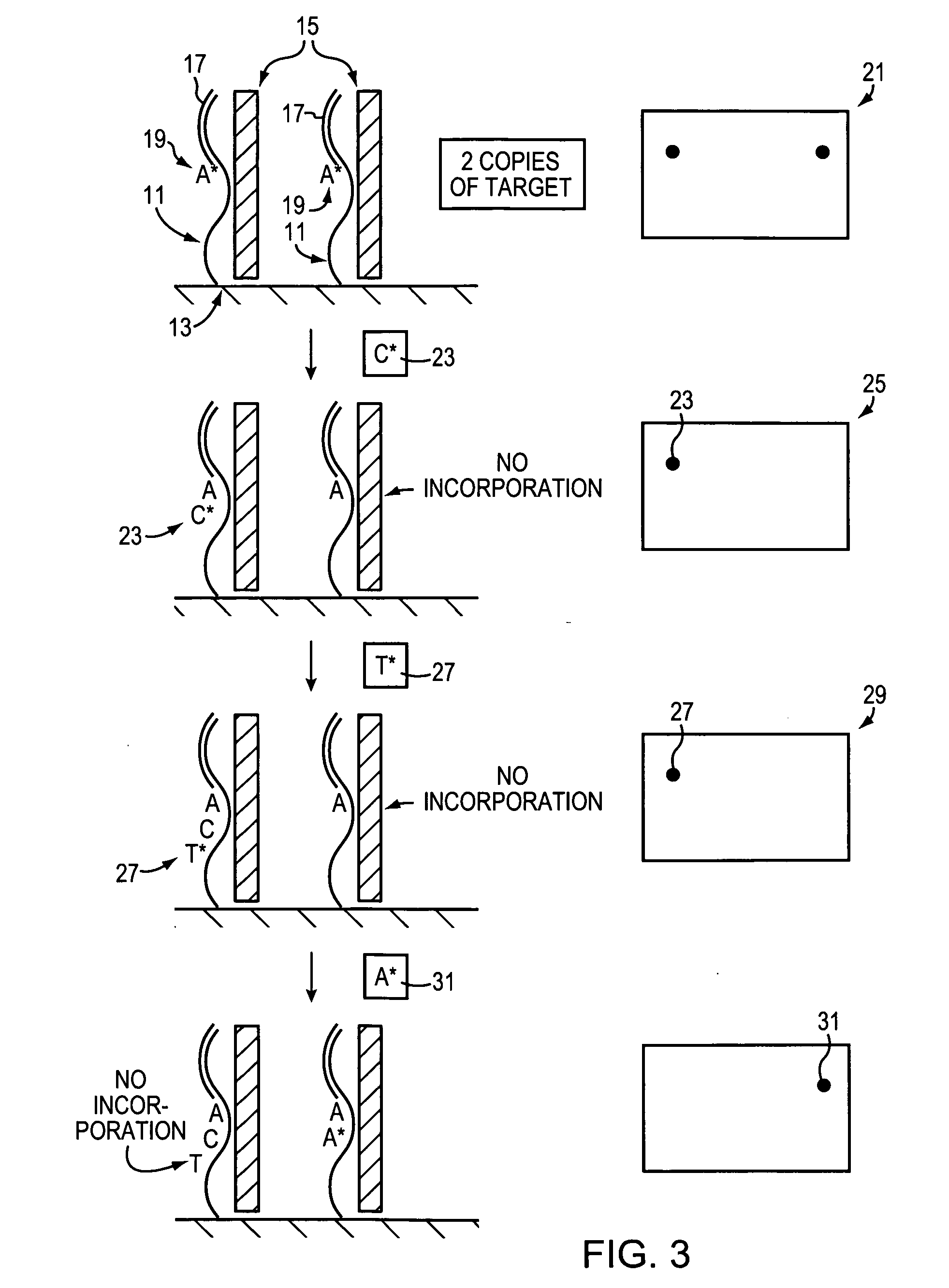
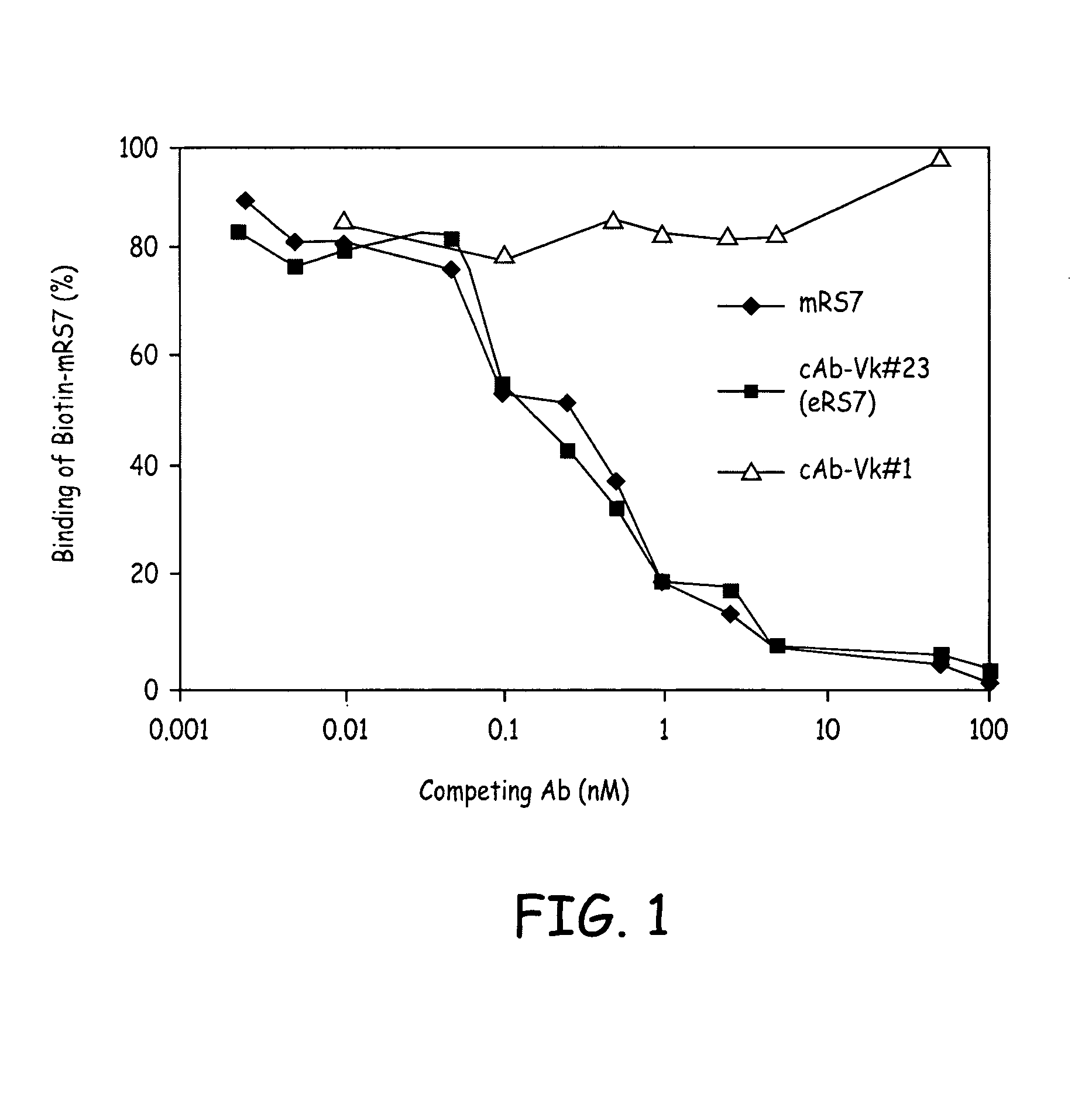
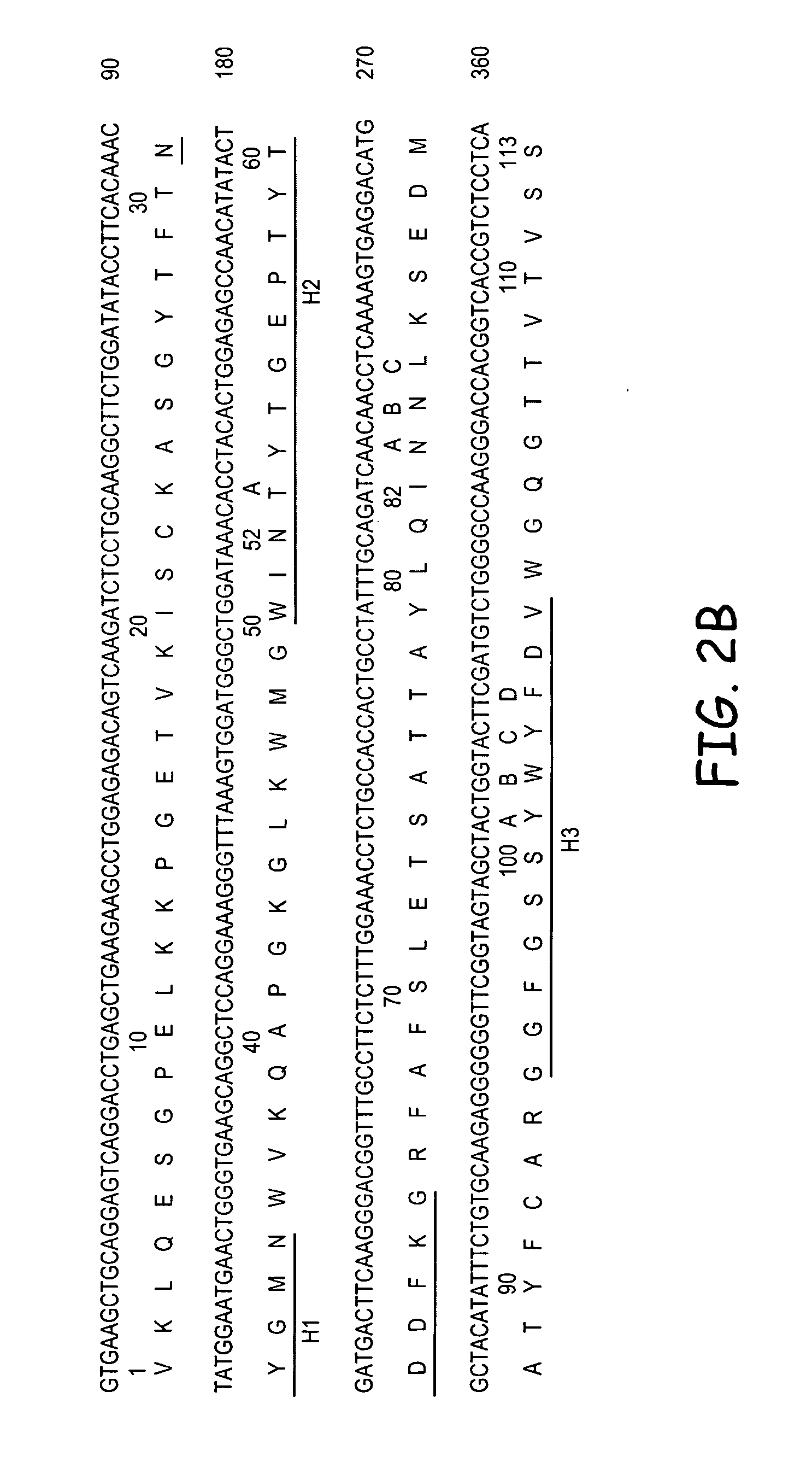
RS7 antibodies
InactiveUS7238785B2Diagnosing and treating malignancyRadioactive preparation carriersImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeBinding site
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Tumour necrosis factor antibodies
InactiveUS6451983B2Enhance or inhibit TNF alpha activityInduction of endothelial procoagulant activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman tumorSingle-Chain Antibodies
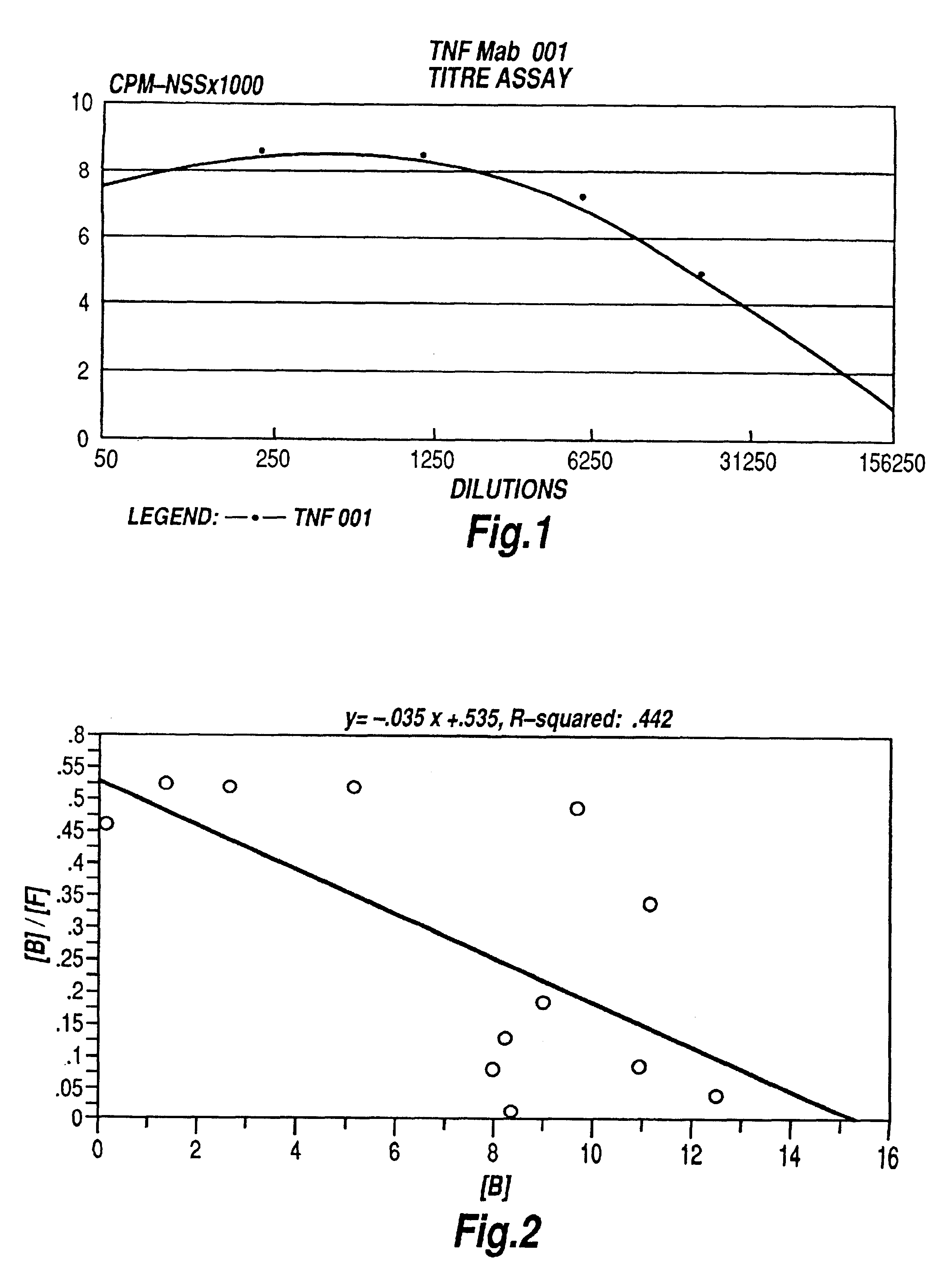
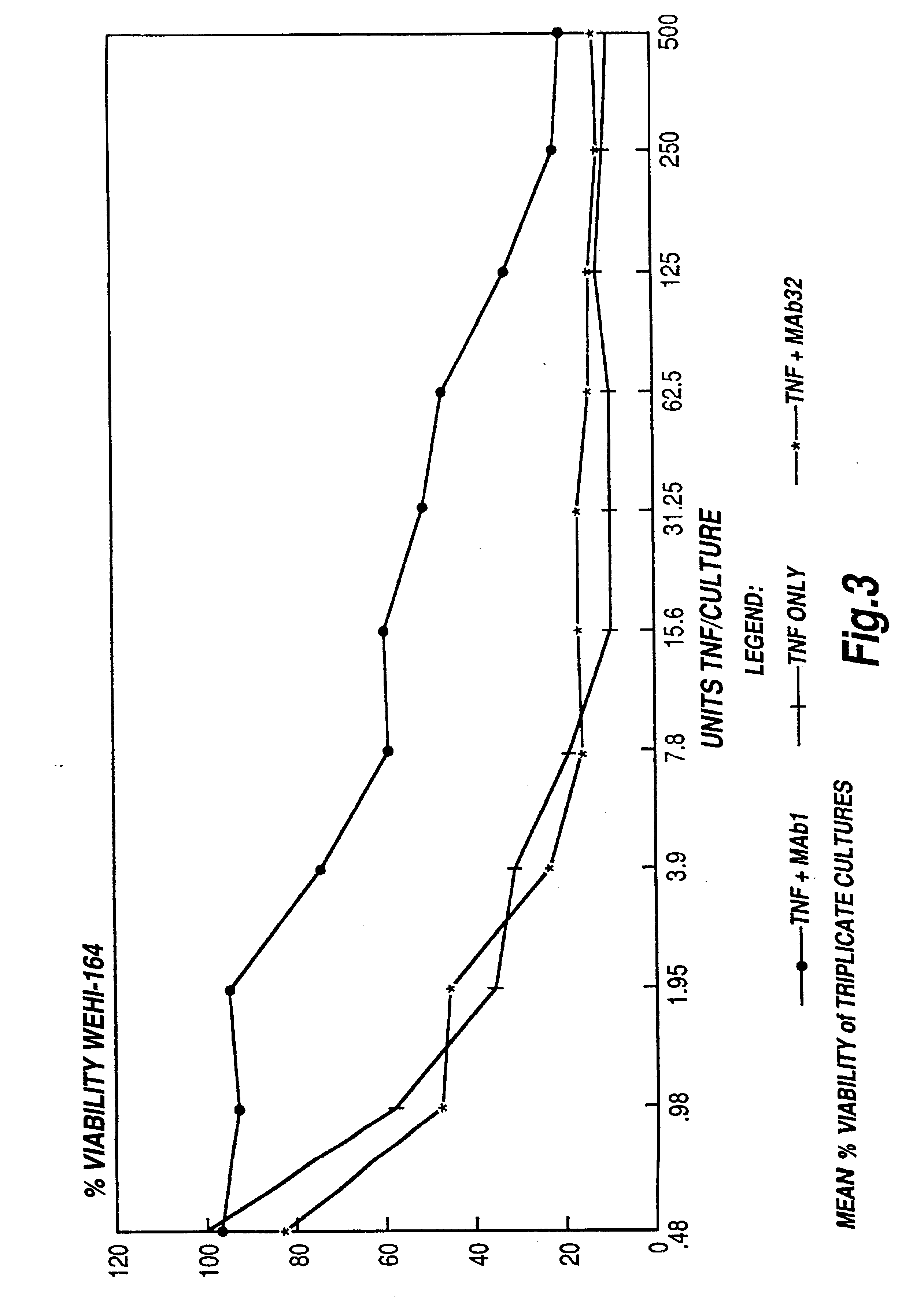
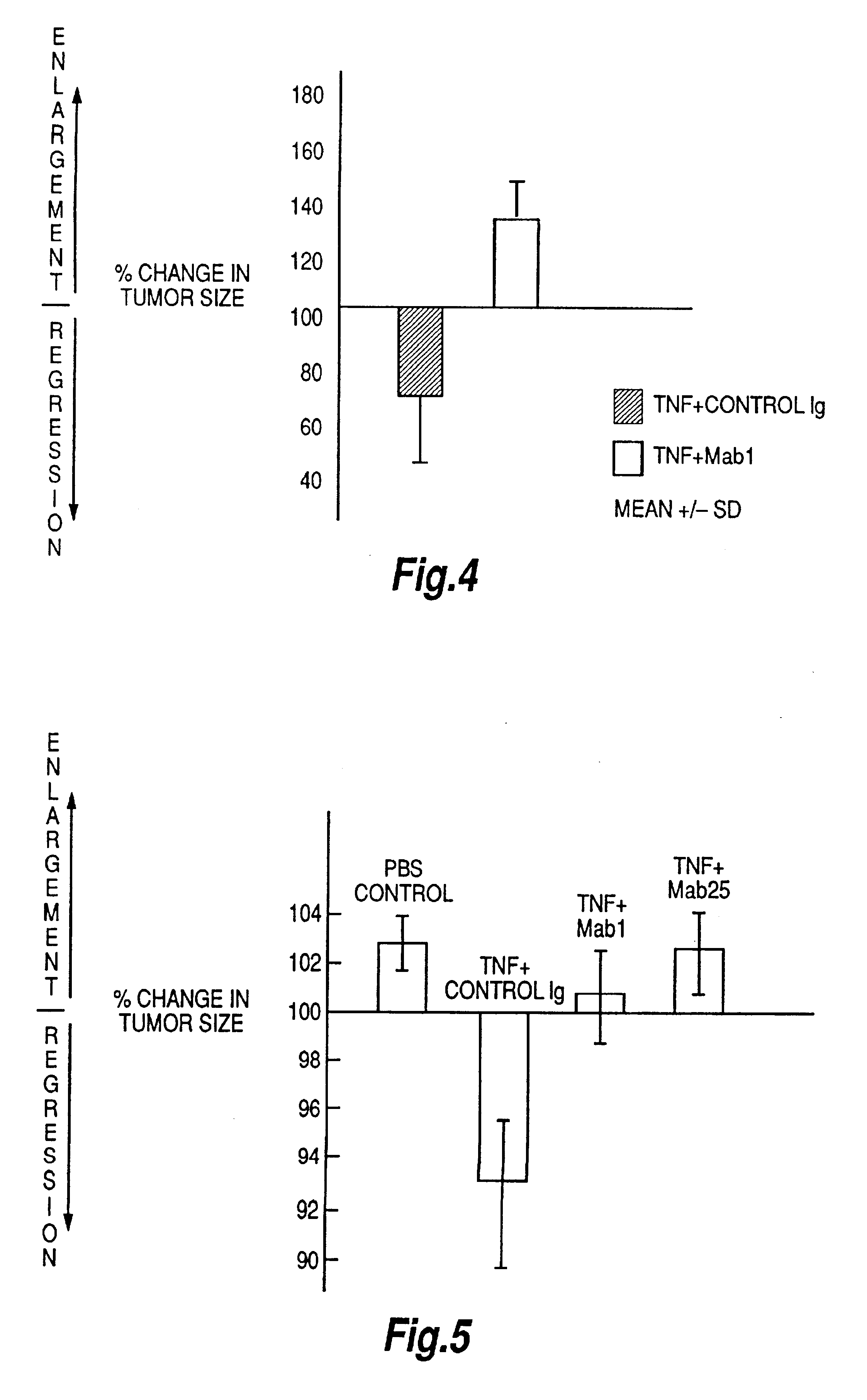
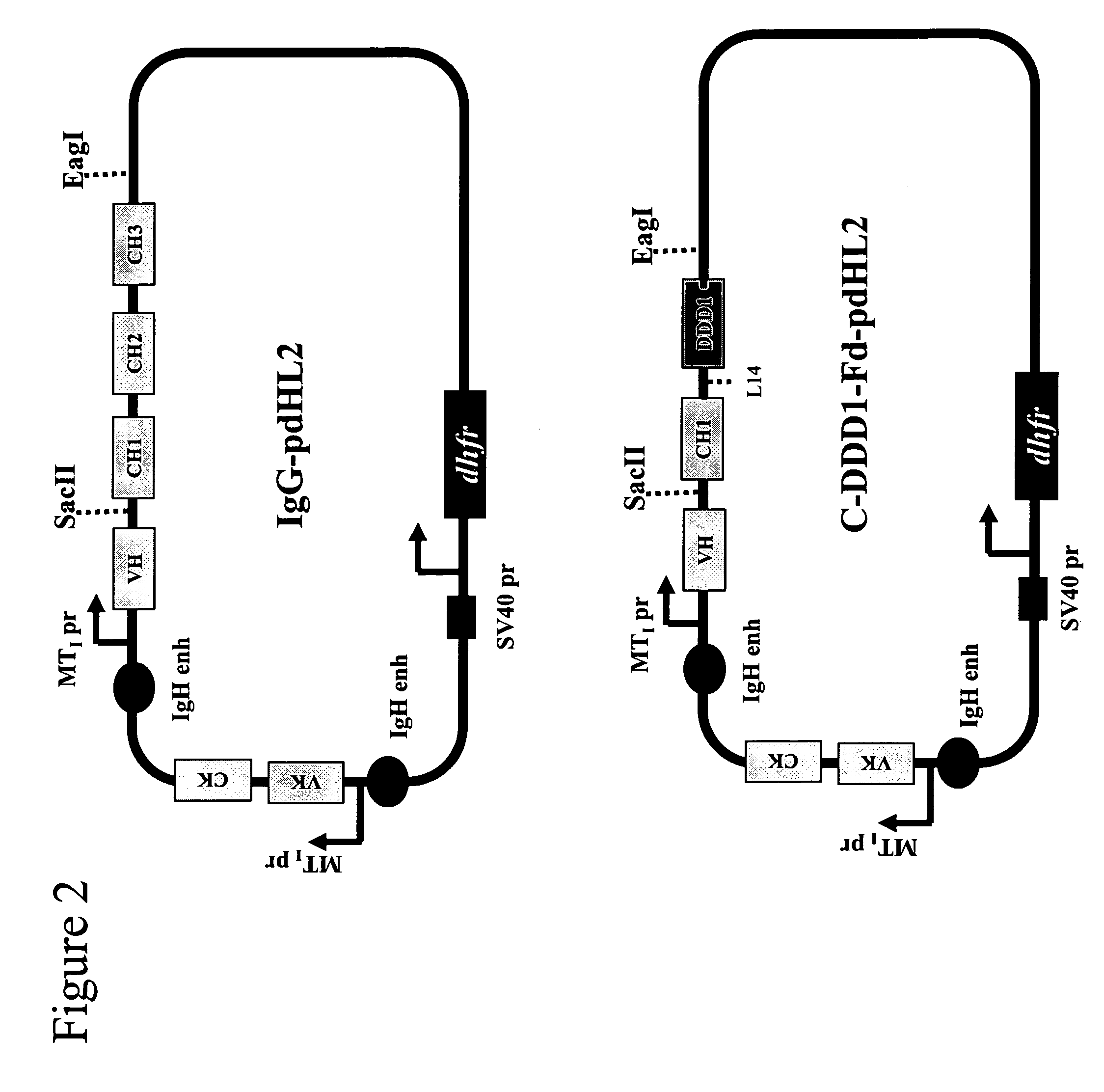
The present invention relates to ligands which bind to human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) in a manner such that upon binding of these ligands to TNF the biological activity of TNF is modified. In preferred forms the ligand binds to TNF in a manner such that the induction of endothelial procoagulant activity of the TNF is inhibited; the binding of TNF to receptors on endothelial cells is inhibited; the induction of fibrin deposition in the tumor and tumor regression activities of the TNF are enhanced; and the cytotoxicity and receptor binding activities of the TNF are unaffected or enhanced on tumor cells. The ligand is preferably an antibody, F(ab) fragment, single domain antibody (dABs) single chain antibody or a serum binding protein. It is preferred, however, that the ligand is a monoclonal antibody or F(ab) fragment thereof.
Owner:CEPHALON AUSTRALIA
Methods for generating stably linked complexes composed of homodimers, homotetramers or dimers of dimers and uses
ActiveUS7550143B2Improve functionalityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHomotetramerAptamer
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for stably tethered structures of defined compositions, which may have multiple functionalities and / or binding specificities. Particular embodiments concern homodimers comprising monomers that contain a dimerization and docking domain attached to a precursor. The precursors may be virtually any molecule or structure, such as antibodies, antibody fragments, antibody analogs or mimetics, aptamers, binding peptides, fragments of binding proteins, known ligands for proteins or other molecules, enzymes, detectable labels or tags, therapeutic agents, toxins, pharmaceuticals, cytokines, interleukins, interferons, radioisotopes, proteins, peptides, peptide mimetics, polynucleotides, RNAi, oligosaccharides, natural or synthetic polymeric substances, nanoparticles, quantum dots, organic or inorganic compounds, etc. Other embodiments concern tetramers comprising a first and second homodimer, which may be identical or different. The disclosed methods and compositions provide a facile and general way to obtain homodimers, homotetramers and heterotetramers of virtually any functionality and / or binding specificity.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432250B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
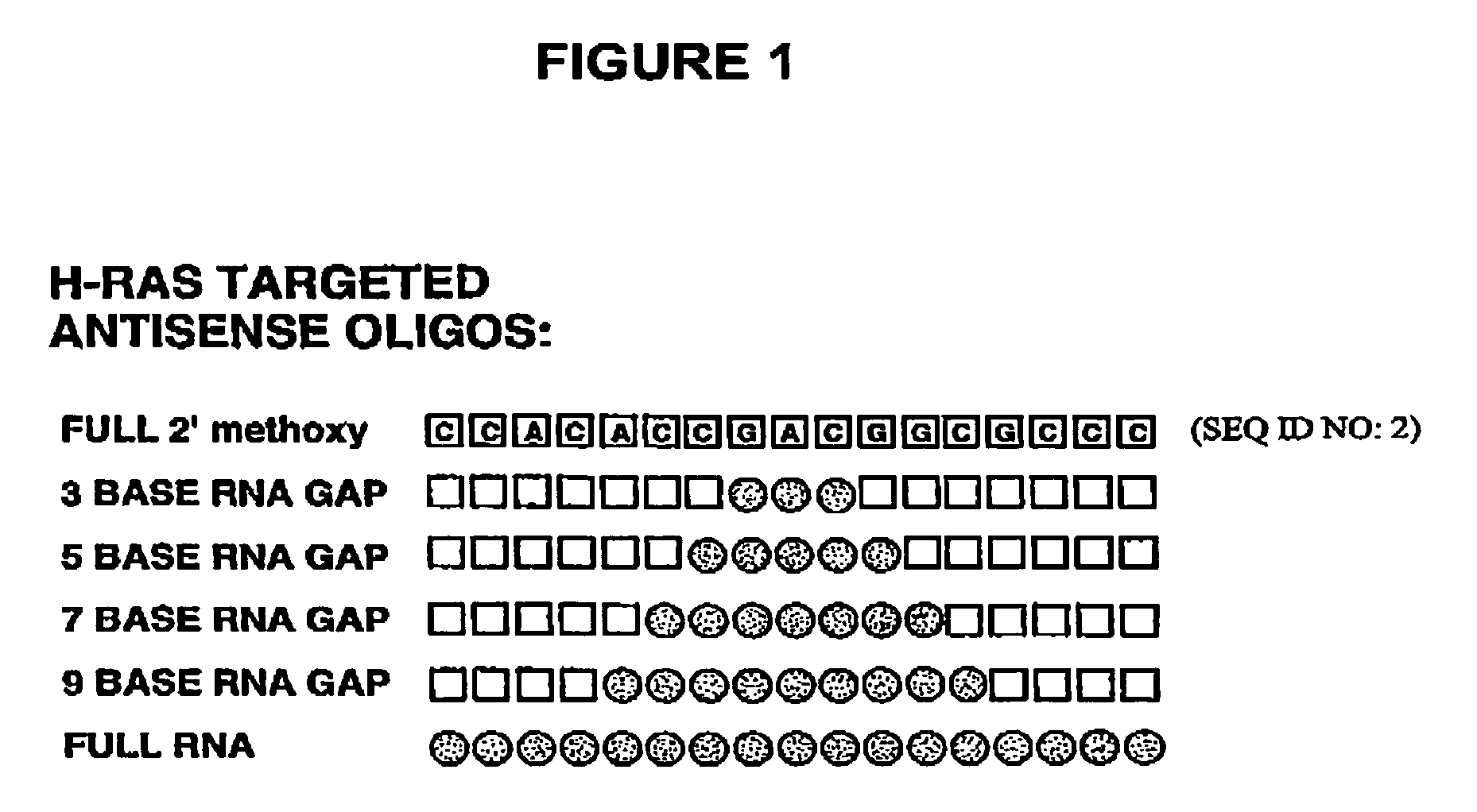
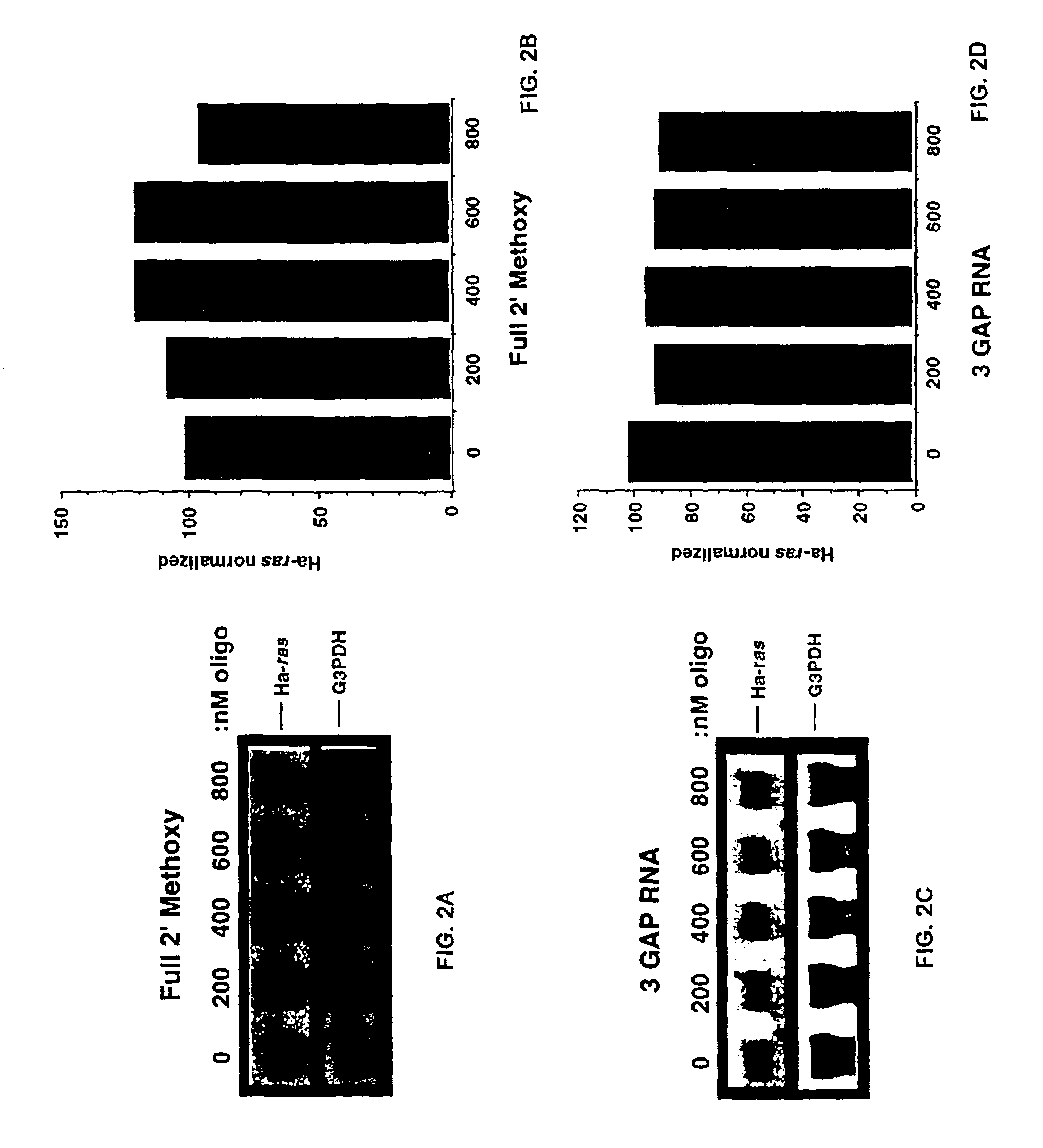
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS7868149B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsPlant biochemistry
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Anti-activin a antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090234106A1Loss of body weightMassive lossAntipyreticAnalgesicsNucleotideAntibody fragments
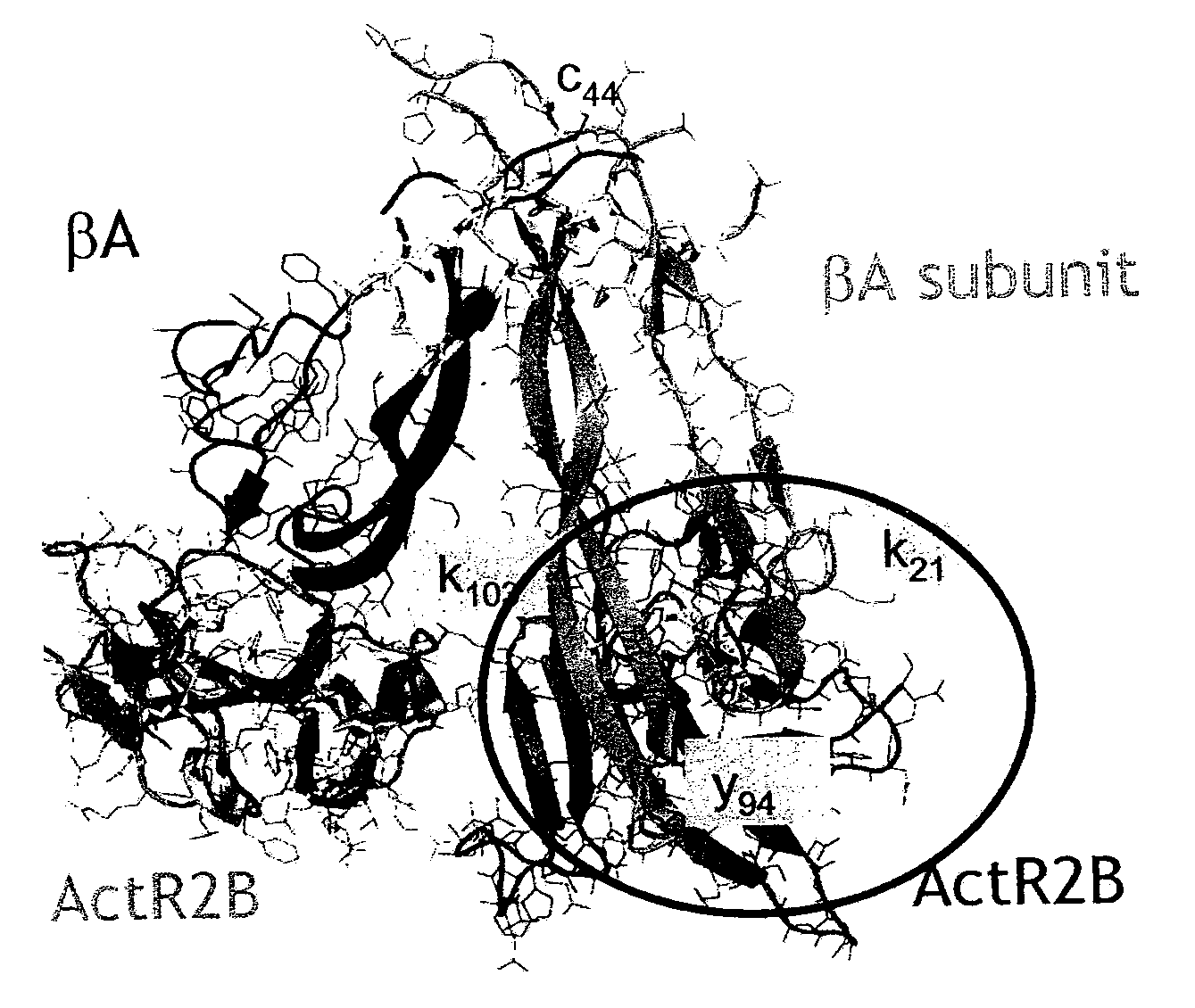
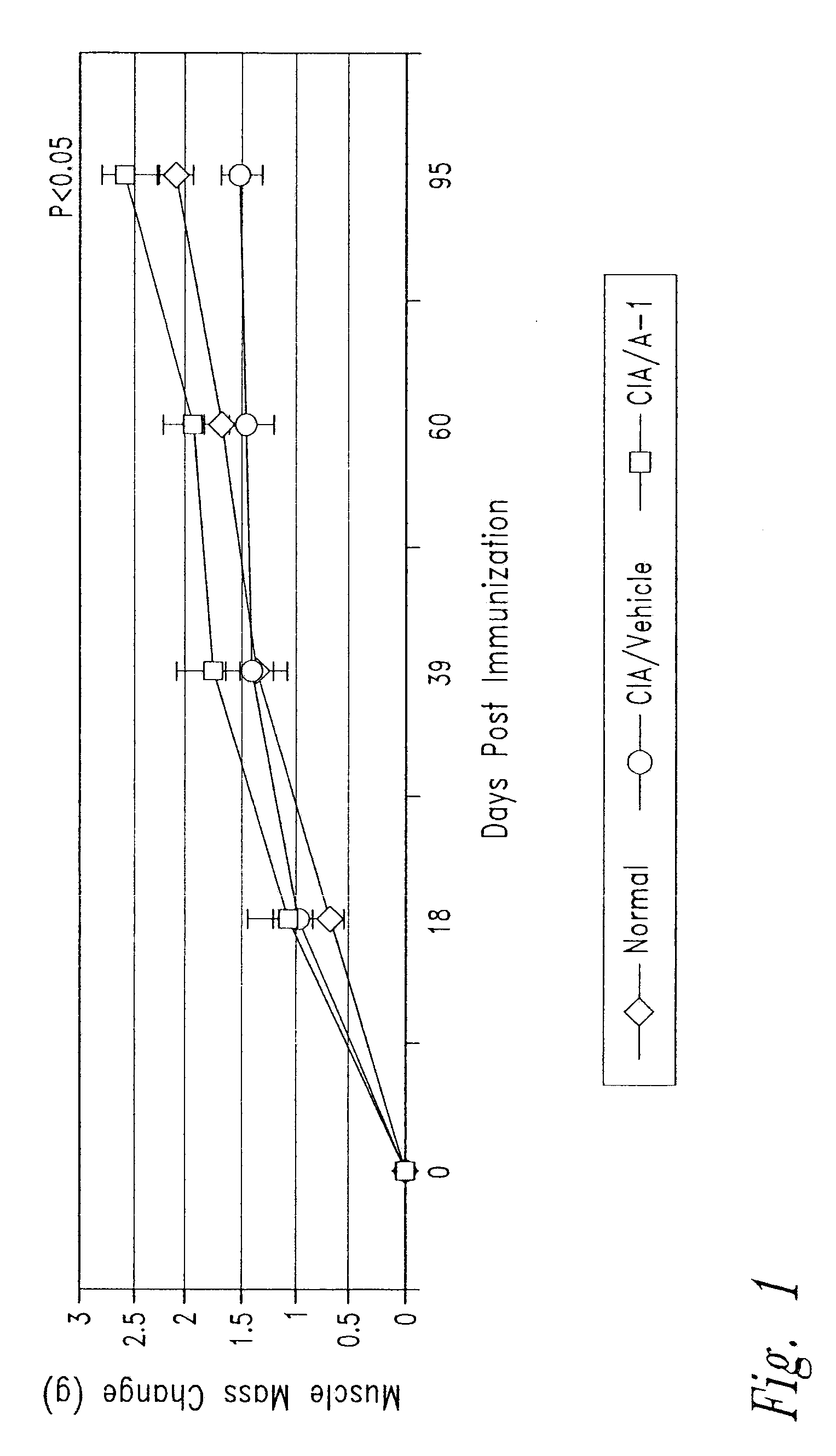
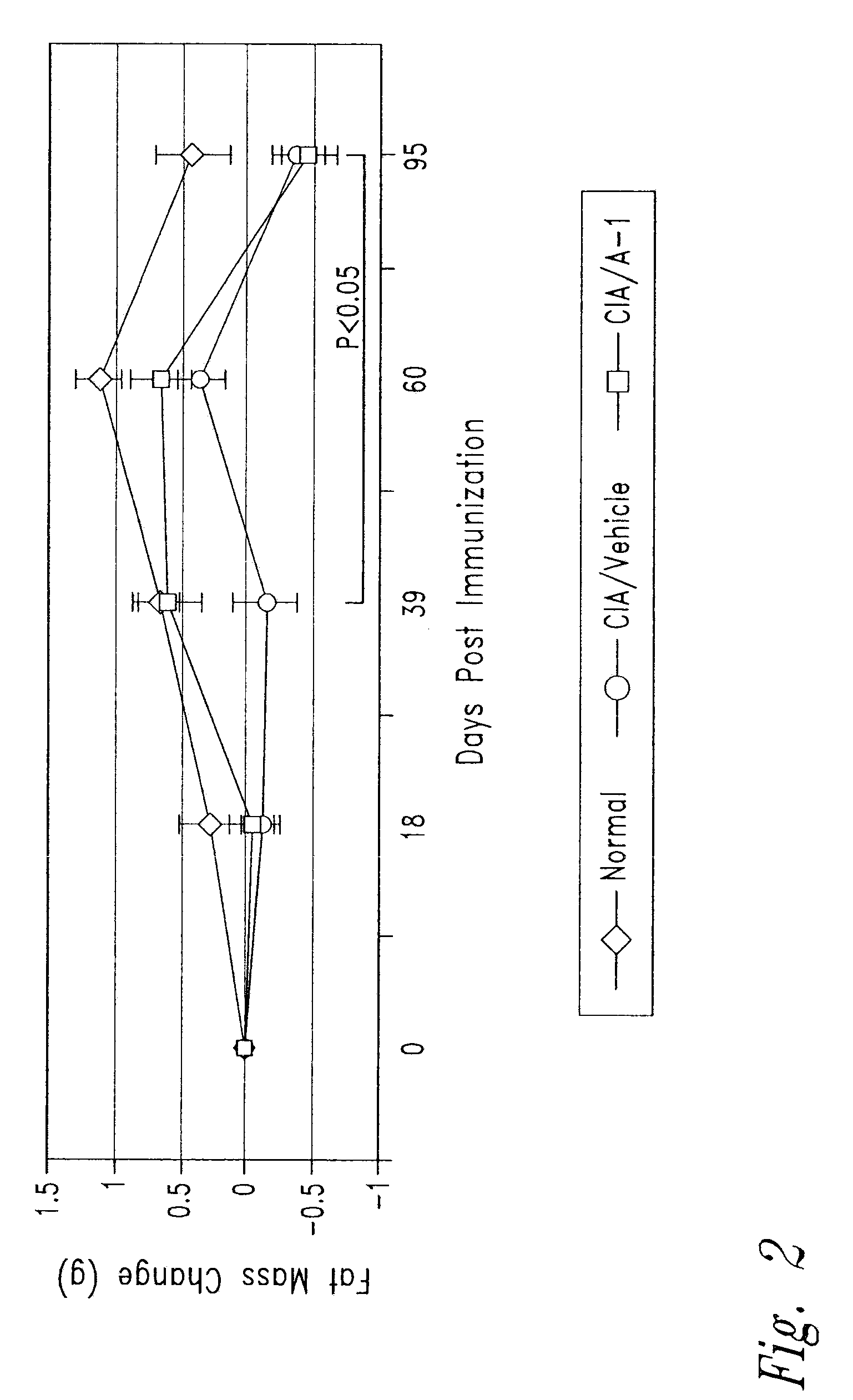
The disclosure provides compositions and methods relating to or derived from anti-activin A binding proteins, including antibodies. In particular embodiments, the disclosure provides fully human, humanized, and chimeric anti-activin A antibodies that bind human activin A, activin A-binding fragments and derivatives of such antibodies, and activin A-binding polypeptides comprising such fragments. Other embodiments provide nucleic acids encoding such antibodies, antibody fragments and derivatives and polypeptides, cells comprising such polynucleotides, methods of making such antibodies, antibody fragments and derivatives and polypeptides, and methods of using such antibodies, antibody fragments and derivatives and polypeptides, including methods of treating or diagnosing subjects having activin A-related disorders or conditions including cachexia related to gonadal cancer, other cancers, rheumatoid arthritis, and other diseases.
Owner:AMGEN INC
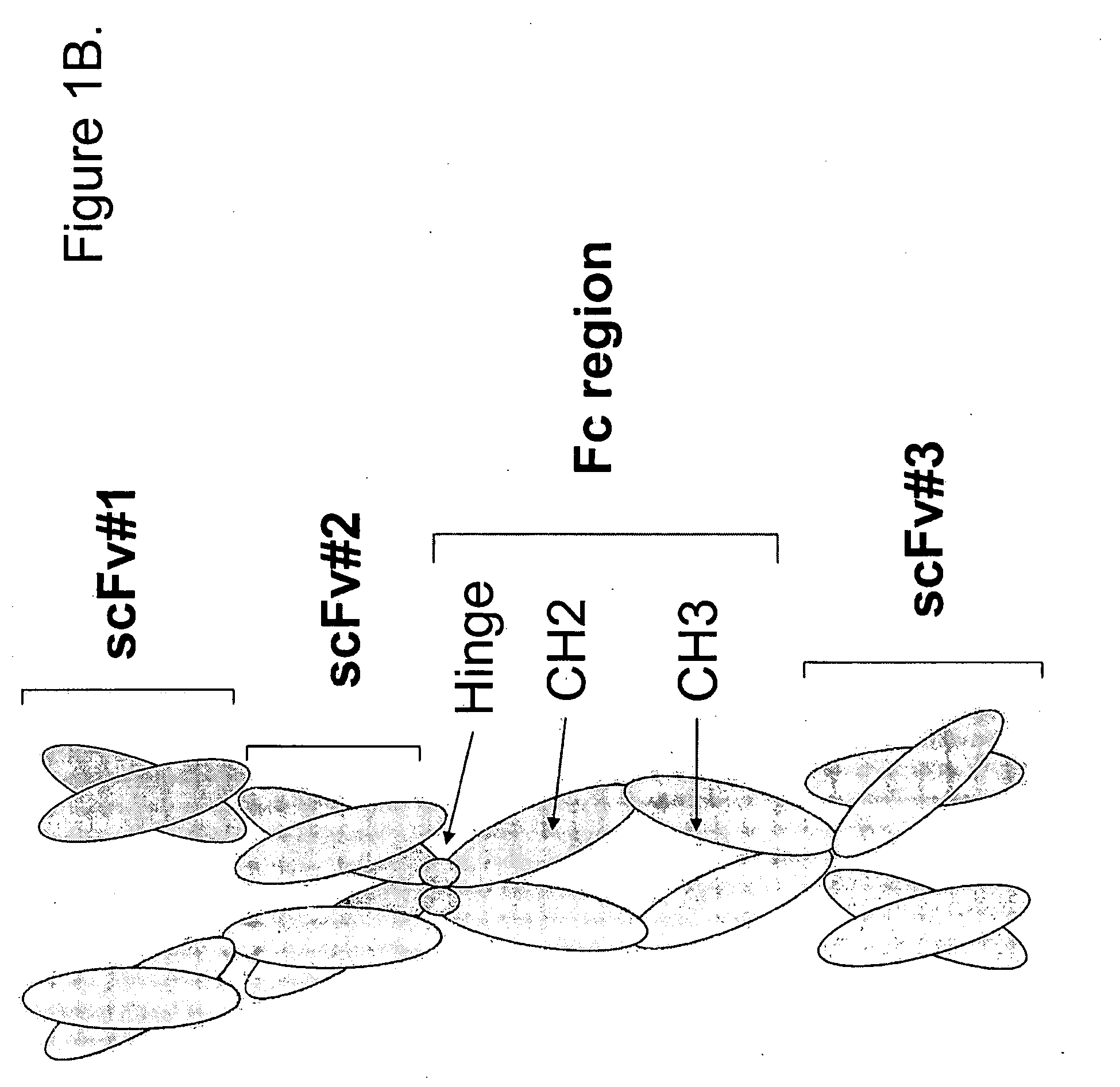
Single-chain antigen-binding proteins capable of glycosylation, production and uses thereof
The present invention relates to single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of glycosylation. Compositions of, genetic constructions coding for, and methods for producing monovalent and multivalent single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of glycosylation are described and claimed. Composition of, genetic constructions coding for, and methods for producing glycosylated monovalent and multivalent single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of polyalkylene oxide conjugation are described and claimed. The invention also relates to methods for producing a polypeptide having increased glycosylation and the polypeptide produced by the described method. Uses resulting from the multifunctionality of a glycosylated / polyalkylene oxide conjugated antigen-binding protein are also described and claimed.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC
Serum albumin binding proteins with long half-lives
InactiveUS20070269422A1Increased serum half-lifeReduce dosing frequencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igePrimate
The present invention relates to amino acid sequences that are capable of binding to serum albumin; to compounds, proteins and polypeptides comprising or essentially consisting of such amino acid sequences; to nucleic acids that encode such amino acid sequences, proteins or polypeptides; to compositions, and in particular pharmaceutical compositions, that comprise such amino acid sequences, proteins and polypeptides; and to uses of such amino acid sequences, proteins and polypeptides. Particularly, the amino acid sequences and compounds of the present invention bind to or otherwise associate with serum albumin in such a way that, when the amino acid sequence or compound is bound to or otherwise associated with a serum albumin molecule in a primate, it exhibits a serum half-life of at least 50% of the natural half-life of serum albumin in said primate.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
Stably tethered structures of defined compositions with multiple functions or binding specificities
ActiveUS20060228300A1Reduce exposureReduce deliveryAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderAntibody fragmentsBinding peptide
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for stably tethered structures of defined compositions with multiple functionalities and / or binding specificities. Particular embodiments concern stably tethered structures comprising a homodimer of a first monomer, comprising a dimerization and docking domain attached to a first precursor, and a second monomer comprising an anchoring domain attached to a second precursor. The first and second precursors may be virtually any molecule or structure, such as antibodies, antibody fragments, antibody analogs or mimetics, aptamers, binding peptides, fragments of binding proteins, known ligands for proteins or other molecules, enzymes, detectable labels or tags, therapeutic agents, toxins, pharmaceuticals, cytokines, interleukins, interferons, radioisotopes, proteins, peptides, peptide mimetics, polynucleotides, RNAi, oligosaccharides, natural or synthetic polymeric substances, nanoparticles, quantum dots, organic or inorganic compounds, etc. The disclosed methods and compositions provide a simple, easy to purify way to obtain any binary compound attached to any monomeric compound, or any trinary compound.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Recombinant binding proteins and peptides
DNA constructs comprise a first exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a first peptide or polypeptide, a second exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a second peptide or polypeptide and a third sequence of nucleotides between the first and second sequences encoding a heterologous intron, for example that of Tetrahymena thermophila nuclear pre-rRNA, between RNA splice sites and a site-specific recombination sequence, such as loxP, within the intron, the exons together encoding a product peptide or polypeptide. Such constructs are of use in methods of production of peptides or polypeptides, transcription leading to splicing out of the intron enabling translation of a single chain product peptide or polypeptide. Isolated nucleic acid constructs consisting essentially of a sequence of nucleotides encoding a self-splicing intron with a site-specific recombination sequence within the intron, for use in creation of constructs for expression of peptides or polypeptides, are also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Protein scaffolds for antibody mimics and other binding proteins
InactiveUS20050255548A1Easy to foldImprove stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsWAS PROTEINAntibody
Disclosed herein are proteins that include a fibronectin type III domain having at least one randomized loop. Also disclosed herein are nucleic acids encoding such proteins and the use of such proteins in diagnostic methods and in methods for evolving novel compound-binding species and their ligands.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
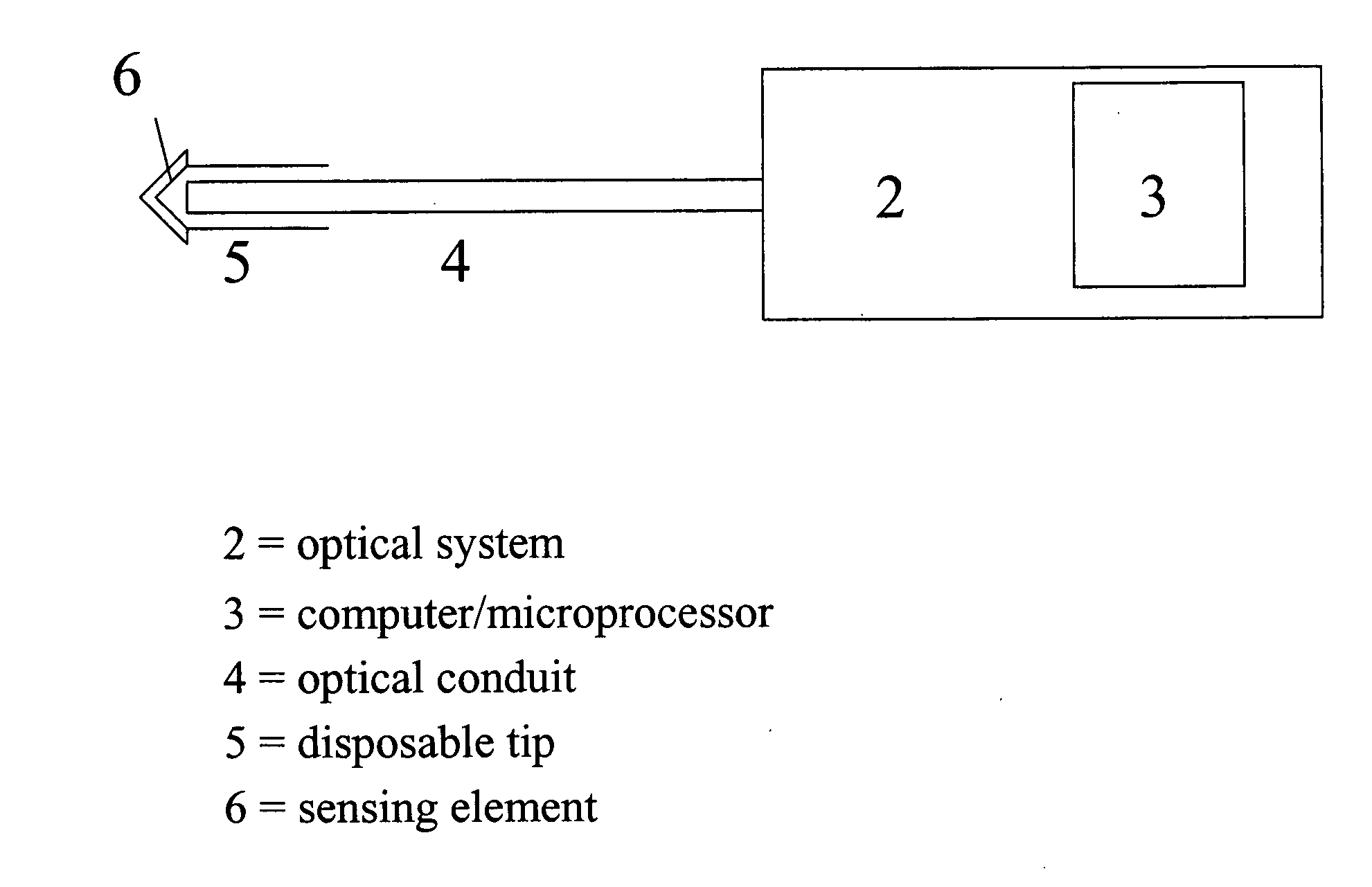
Fiber optic device for sensing analytes
InactiveUS20050113657A1Reduce power consumptionExtended service lifeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberAnalyte
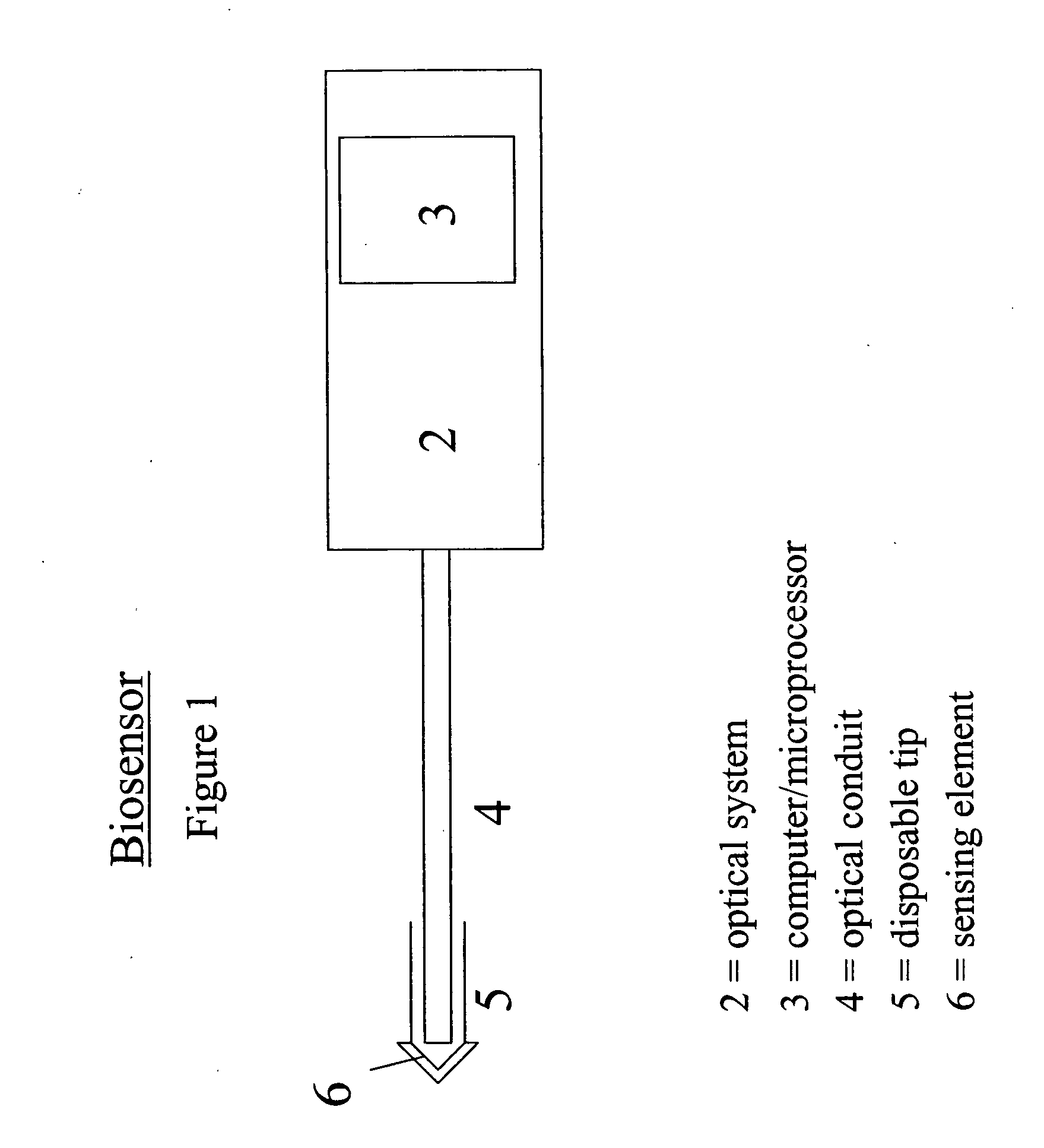
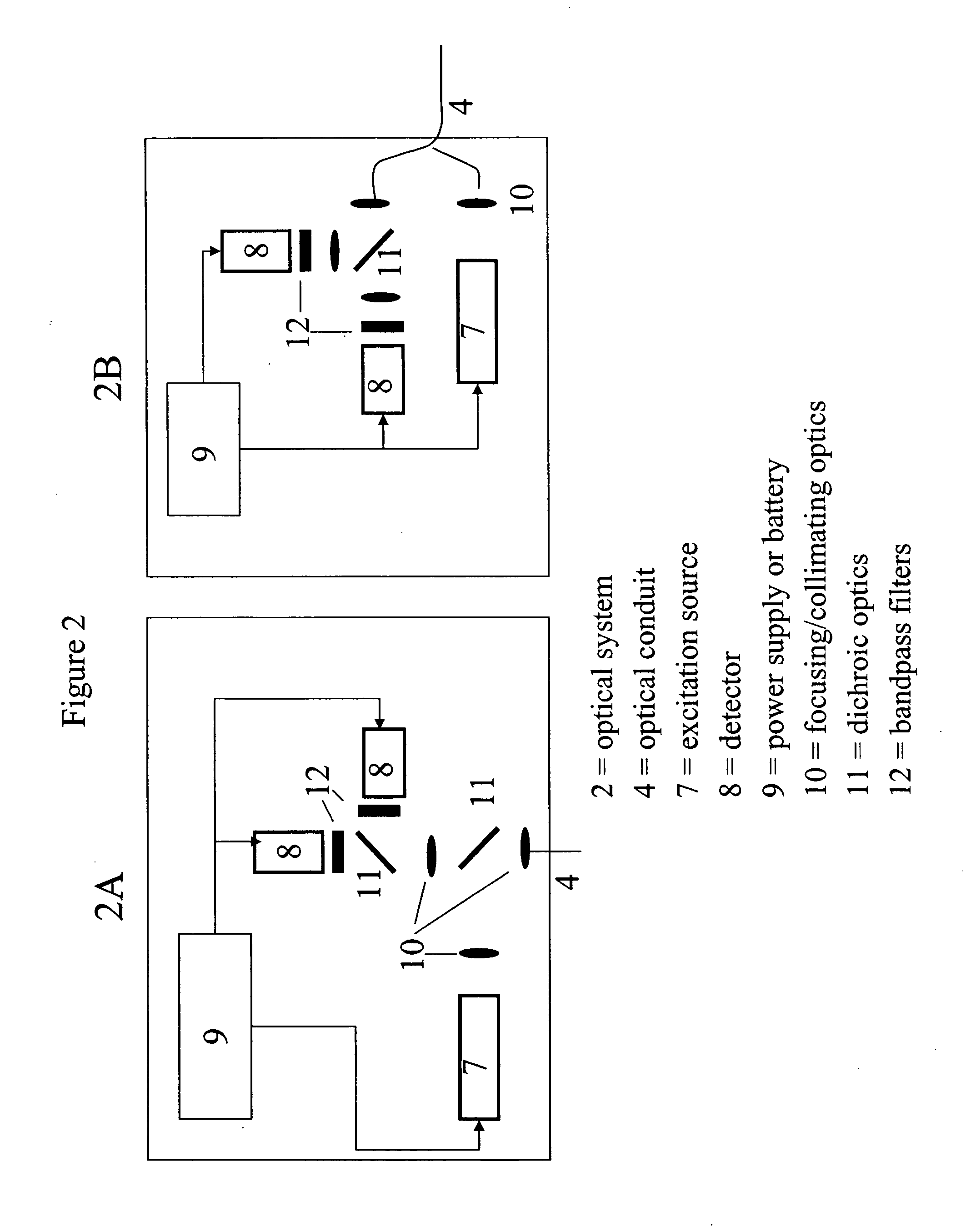
A device for sensing analyte concentration, and in particular glucose concentration, in vivo or in vitro is disclosed. An optical conduit, preferably an optical fiber has an optical system at the proximal end of the optical conduit. A sensing element is attached to the distal end of the optical conduit, and comprises at least one binding protein adapted to bind with at least one target analyte. The sensing element further comprises at least one reporter group that undergoes a luminescence change with changing analyte concentrations. Optionally, the sensing element includes reference groups with luminescence properties that are substantially unchanged by variations in the analyte concentrations.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432249B2High affinityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesADAMTS ProteinsOrganism
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Methods For Making Fully Human Bispecific Antibodies Using A Common Light Chain
InactiveUS20130045492A1Reduce in quantitySimple methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeProtein insertion
A genetically modified mouse is provided, wherein the mouse expresses an immunoglobulin light chain repertoire characterized by a limited number of light chain variable domains. Mice are provided that express just one or a few immunoglobulin light chain variable domains from a limited repertoire in their germline. Methods for making bispecific antibodies having universal light chains using mice as described herein, including human light chain variable regions, are provided. Methods for making human variable regions suitable for use in multispecific binding proteins, e.g., bispecific antibodies, and host cells are provided. Bispecific antibodies capable of binding first and second antigens are provided, wherein the first and second antigens are separate epitopes of a single protein or separate epitopes on two different proteins are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Antibodies comprising chimeric constant domains
ActiveUS20140243504A1Reduced effector functionAnimal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
Antibodies, antigen-binding proteins and Fc-fusion proteins that comprise recombinant polypeptides containing a chimeric heavy chain constant region sequence are provided that bind to certain Fc receptors however have reduced effector functions. Methods of making constructs for expression of such chimeric Fc-containing antibodies, antigen-binding proteins and Fc-fusion proteins in cell systems, and methods of producing and isolating the chimeric Fc-containing proteins are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Antigen binding proteins capable of binding thymic stromal lymphopoietin
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods relating to antigen binding proteins which bind to human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), including antibodies. In particular embodiments, the disclosure provides fully human, humanized and chimeric anti-TSLP antibodies and derivatives of such antibodies. The disclosure further provides nucleic acids encoding such antibodies and antibody fragments and derivatives, and methods of making and using such antibodies including methods of treating and preventing TSLP-related inflammatory and fibrotic disorders.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Antibodies specific for sclerostin and methods for increasing bone mineralization
ActiveUS20050106683A1Skeletal disorderImmunoglobulins against growth factorsGreek letter betaIncreased bone mineral density
Compositions and methods relating to antibodies that specifically bind to TGF-beta binding proteins are provided. These methods and compositions relate to altering bone mineral density by interfering with the interaction between a TGF-beta binding protein sclerostin and a TGF-beta superfamily member, particularly a bone morphogenic protein. Increasing bone mineral density has uses in diseases and conditions in which low bone mineral density typifies the condition, such as osteopenia, osteoporosis, and bone fractures.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Collagen binding protein compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6288214B1Prevent and lessen adhesionReduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsCarrier protein
Disclosed are the cna gene and cna-derived nucleic acid segments from Staphylococcus aureus, and DNA segments encoding cna from related bacteria. Also disclosed are Col binding protein (CBP) compositions and methods of use. The CBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to Col. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(Col binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of bacterial colonization in an animal such as a human. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of S. aureus infection.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Dual Variable Region Antibody-Like Binding Proteins Having Cross-Over Binding Region Orientation
The invention provides antibody-like binding proteins comprising four polypeptide chains that form four antigen binding sites, wherein each pair of polypeptides forming an antibody-like binding protein possesses dual variable domains having a cross-over orientation. The invention also provides methods for making such antigen-like binding proteins.
Owner:SANOFI SA
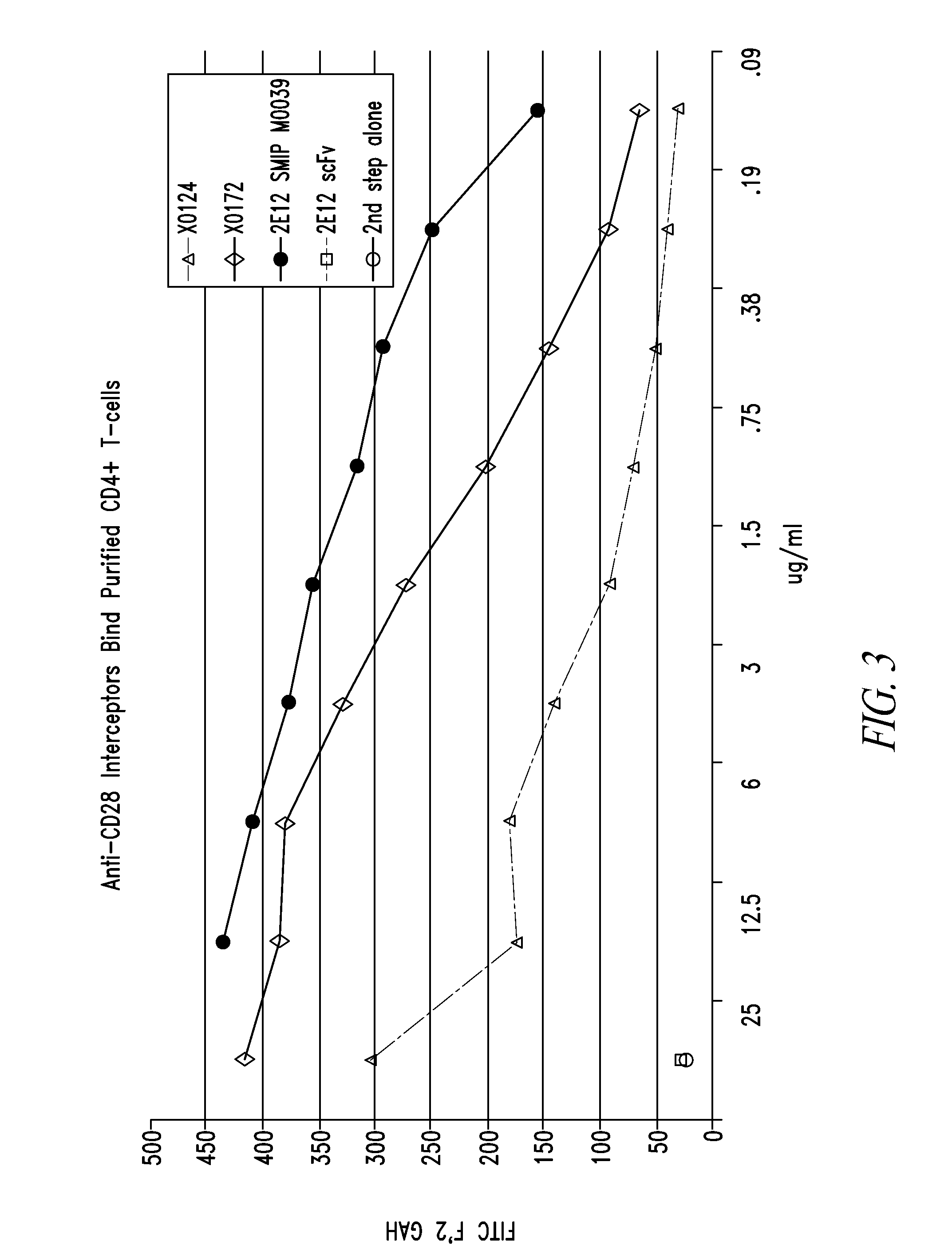
Heterodimer Binding Proteins and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20130129723A1Animal cellsFused cellsImmunoglobulin Joining RegionImmunoglobulin light chain
The present disclosure provides polypeptide heterodimers formed between two different single chain fusion polypeptides via natural heterodimerization of an immunoglobulin CH1 region and an immunoglobulin light chain constant region (CL). The polypeptide heterodimer comprises two or more binding domains that specifically bind one or more targets (e.g., a receptor). In addition, both chains of the heterodimer further comprise an Fc region portion. The present disclosure also provides nucleic acids, vectors, host cells and methods for making polypeptide heterodimers as well as methods for using such polypeptide heterodimers, such as in directing T cell activation, inhibiting solid malignancy growth, and treating autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
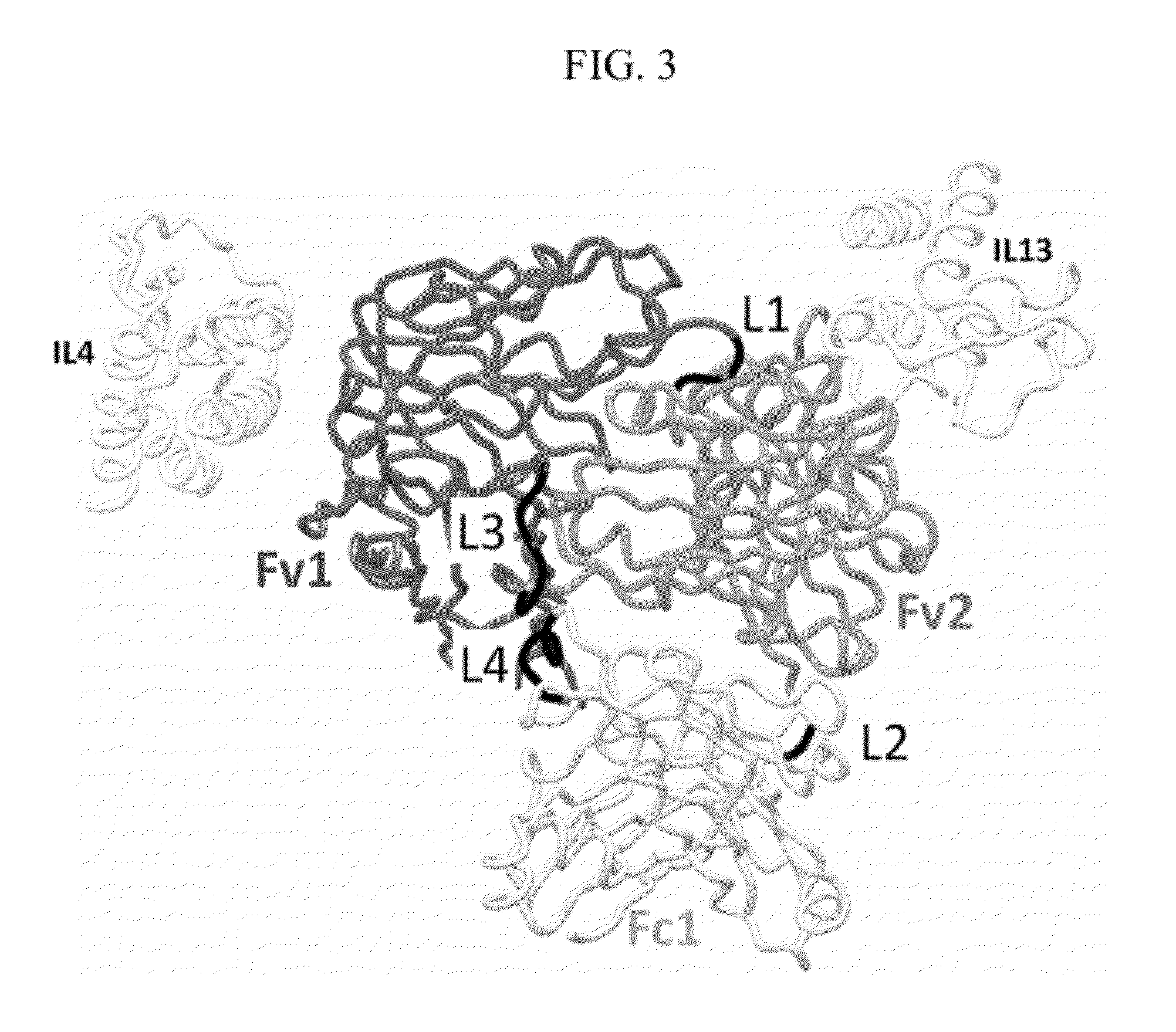
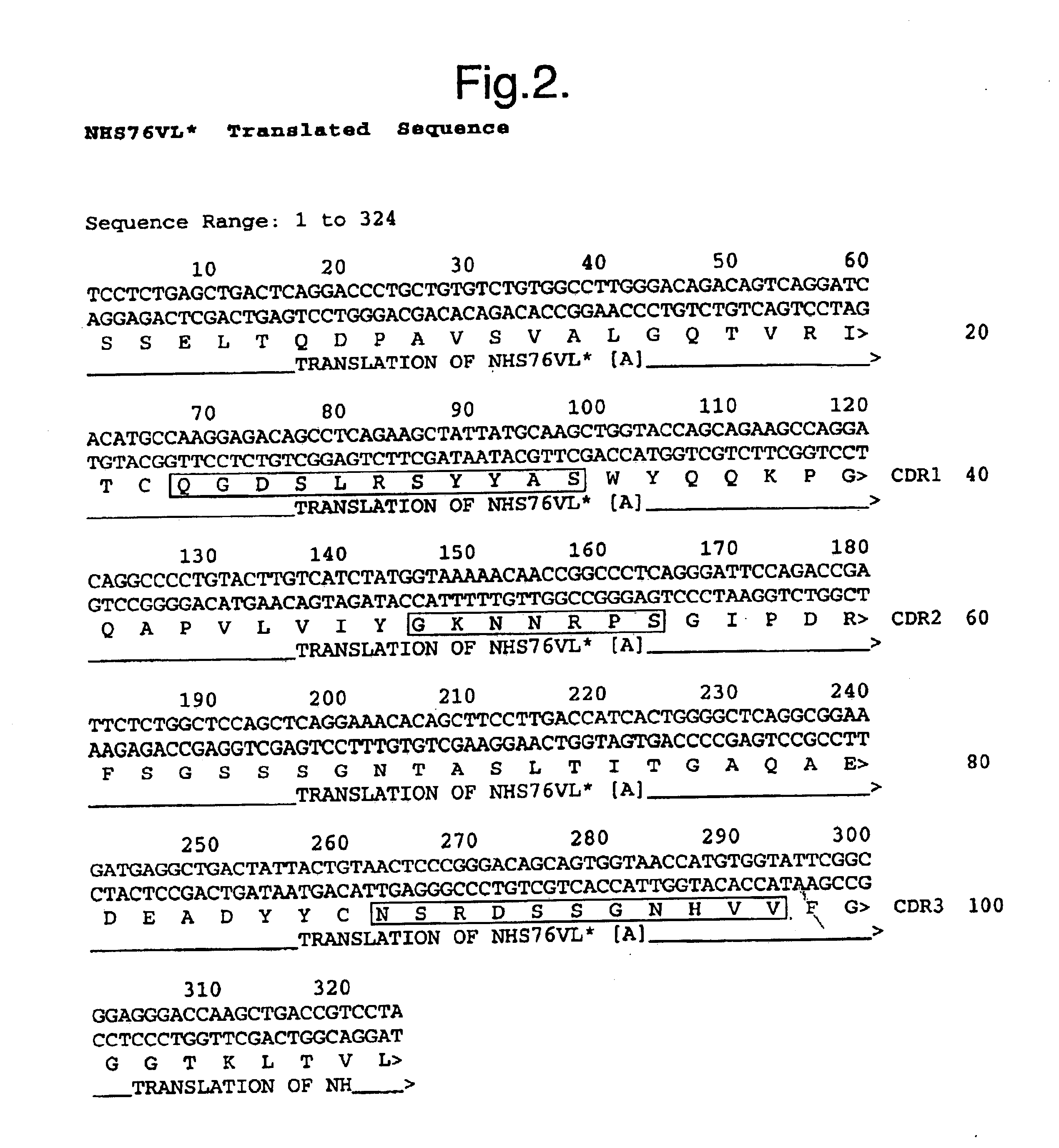
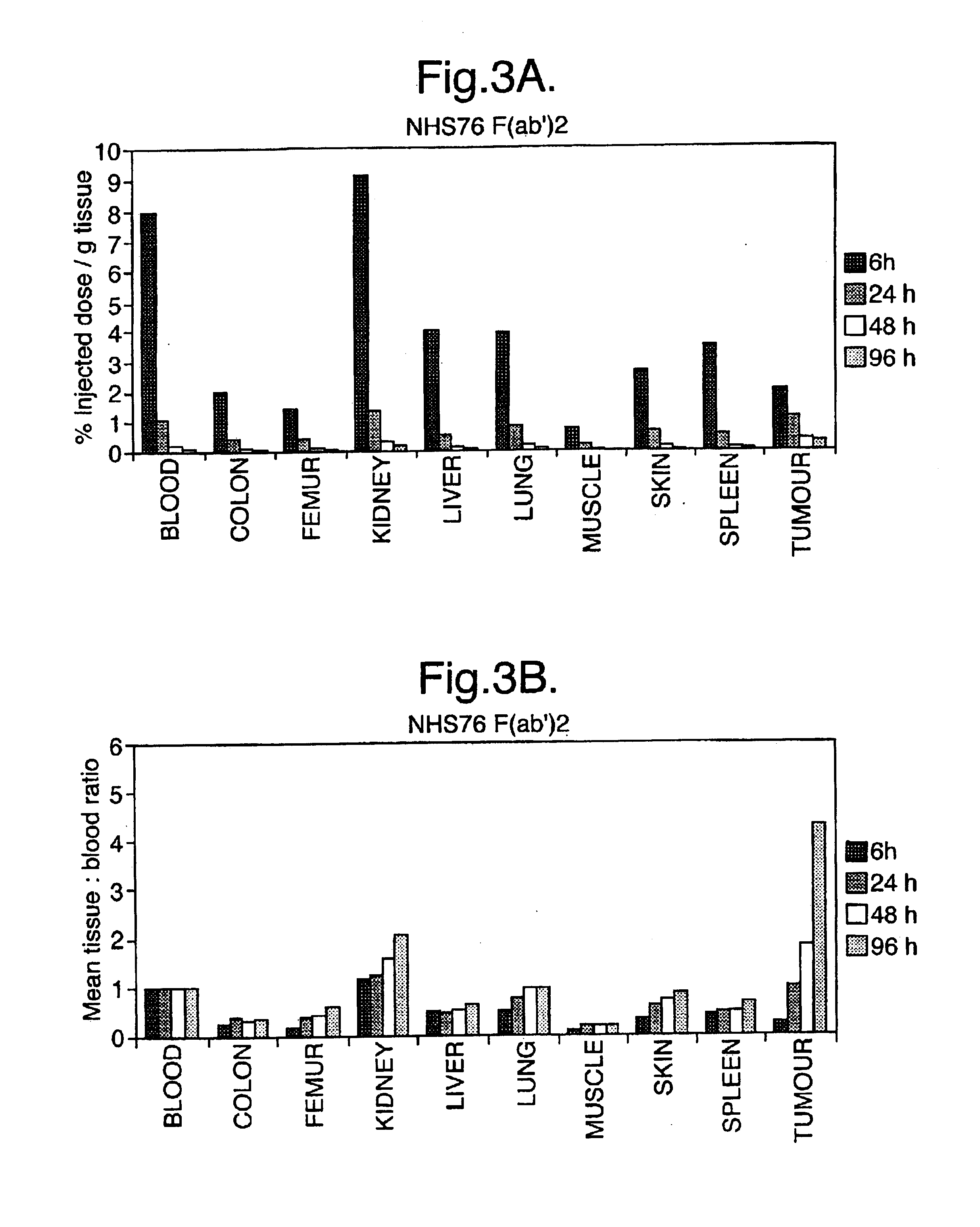
Specific binding proteins including antibodies which bind to the necrotic center of tumors, and uses thereof
Specific binding members, based on the third CDR of the antibody NHS76 (SEQ ID NO: 2) are provided, together with their use in methods of treatment and diagnosis.
Owner:PEREGRINE PHARMA INC +1
Peptidoglycan recognition proteins
InactiveUS7041802B2Regulate growth activityPrevent septic shockAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsFhit geneBiology
The present invention relates to three novel peptidoglycan recognition binding proteins expressed by keratinocytes, wound-healing tissues and chondrosarcoma tissue. More specifically, isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding human peptidoglycan recognition protein-related proteins, referred to herein as PGRP-K (Keratinocytes), PGRP-W (Wound-healing), and PGRP-C (Chondrosarcoma) of FIGS. 1A–B, FIGS. 2A–C, and FIG. 3, respectively, each having homology to both human peptidoglycan recognition protein (PGRP) as well as murine Tag-7. PGRP-K, PGRP-W, and PGRP-C polypeptides are also provided. Further provided are vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same. The invention also relates to both the inhibition and enhancement of activities of PGRP-K, PGRP-W, and PGRP-c polypeptides and diagnostic methods for detecting PGRP-K, PGRP-W, and PGRP-C gene expression.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com