Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)-binding polypeptide variants, dimeric Fc binding proteins and methods related thereto
a technology of fc receptor and binding protein, which is applied in the field of fcrn-binding polypeptide variants and dimeric fc binding proteins, can solve the problem of a relative low percentage of patients that exhibit a complete response, and achieve the effect of increasing decreasing the binding affinity of altered fc-containing polypeptides, and decreasing the free energy of binding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production of Altered Antibodies with Chimeric Fc Regions
[0683] To evaluate the binding of human rabbit IgG chimera constructs, the amino acids likely to impact binding were first defined as being within 10 Å of the interface of interaction between the two interacting proteins. Based on the crystal structure of the ratIgG2a and rat FcRn, the amino acids on the ratIgG2a Fc within 10 Å of the interface for these two molecules was defined. A homology alignment of rabbit IgG1 Fc and the rat IgG1 Fc regions then allows determination of which amino acids on the rabbit Fc region are likely to be within 10 Å of the interaction face. Correspondence of the rat and human Fc regions is then determined. A chimeric molecule is then constructed including all of the mutants within the 10 Å interface. The individual amino acids are then substituted into the hFc and assayed to determine the contribution of the individual component amino acids to binding. Combinations of the amino acid mutants are th...
example 2
Identification of Candidate Residues by Electrostatic Optimization
[0691] In this example, method for modifying the antibody constant domain affinity towards human FcRn is described. To obtain mutants with altered binding affinity of an Fc region to FcRn at acidic pH and neutral pH, we applied electrostatic charge optimization techniques to a homology model of human Fc bound to human FcRn. The models of human Fc / FcRn complex at acidic (6.0) pH and neutral (7.4) pH were derived from a crystal structure of rat Fc / FcRn complex (PDB code: 1I1A) using MODELLER program, (Accelrys, Inc., San Diego, Calif.) and were energy-minimized in CHARMM (Accelrys, Inc., San Diego, Calif.). In a computational optimization procedure, we used electrostatic charge optimization to determine the position(s) of the Fc residue(s) that can modulate Fc binding (Lee and Tidor, J. Chem. Phys. 106:8681-8690, 1997; Kangas and Tidor, J. Chem. Phys. 109:7522-7545, 1998) to FcRn at acidic pH and neutral pH. These calc...
example 4
Construction of Altered Fc Polypeptides
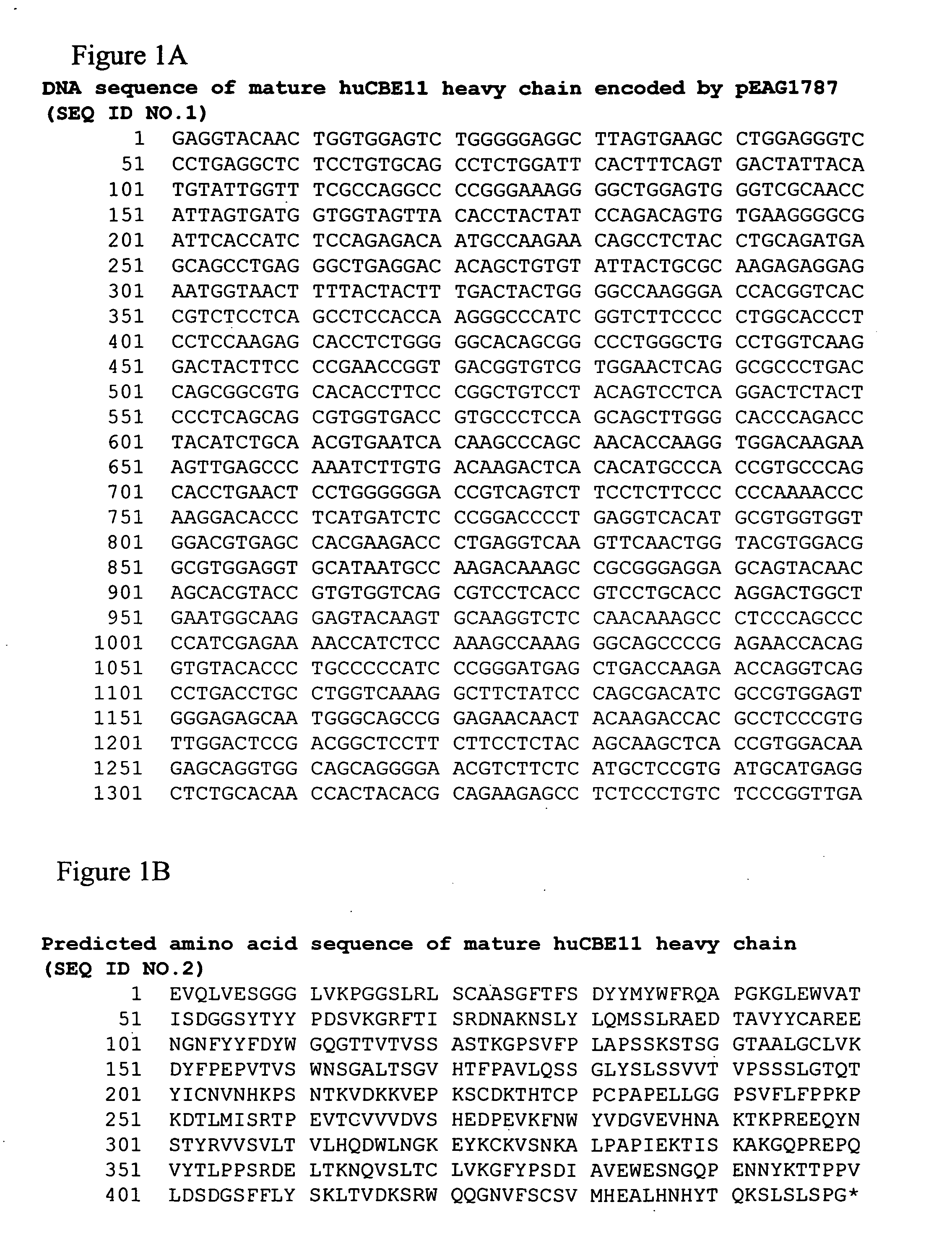
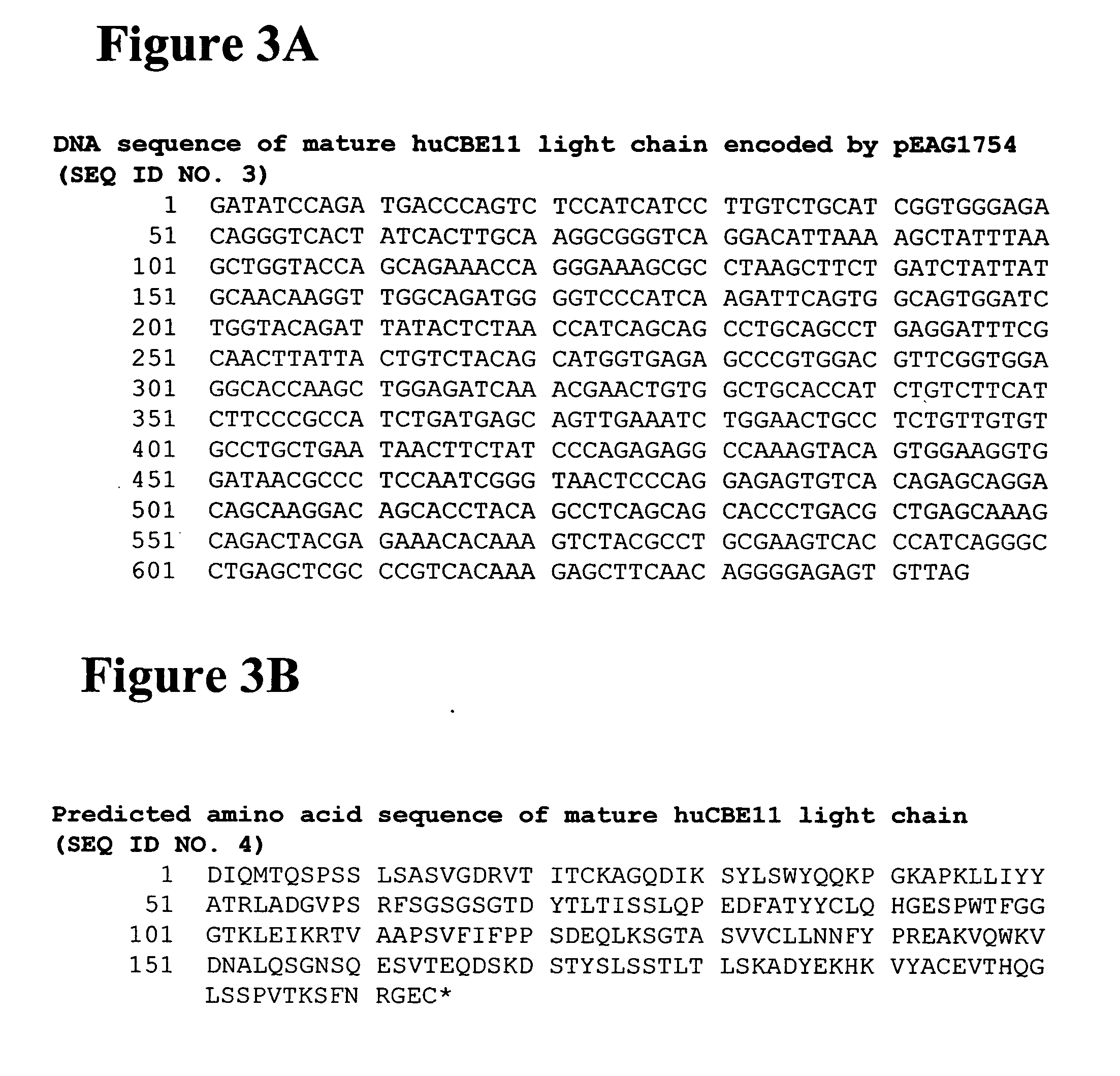
[0699] Alterations predicted by the methods of the invention were introduced into a starting polypeptide encoding the heavy chain of humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody huCBE11. FIGS. 1A and 1B display the nucleotide (SEQ ID NO. 3) and predicted amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO. 4) of this heavy chain respectively. Mutations were introduced in the huCBE11 heavy chain carried on an expression vector called pEAG1787 using site-directed mutagenesis by standard recombinant DNA techniques. The variable domain of the antibody is residues 1-120, the human IgG1 constant domain is residues 121-449. The huIgG1's C-terminal lysine residue was genetically removed. For reference: the N-linked glycosylation site (EU residue number N297) is residue 300 in the sequence above. FIG. 2 displays the amino acids sequence of the Fc region of huCBE11 in EU numbering index.
[0700] The huCBE11 monoclonal antibody is a humanized IgG1, kappa recombinant antibody that recog...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com