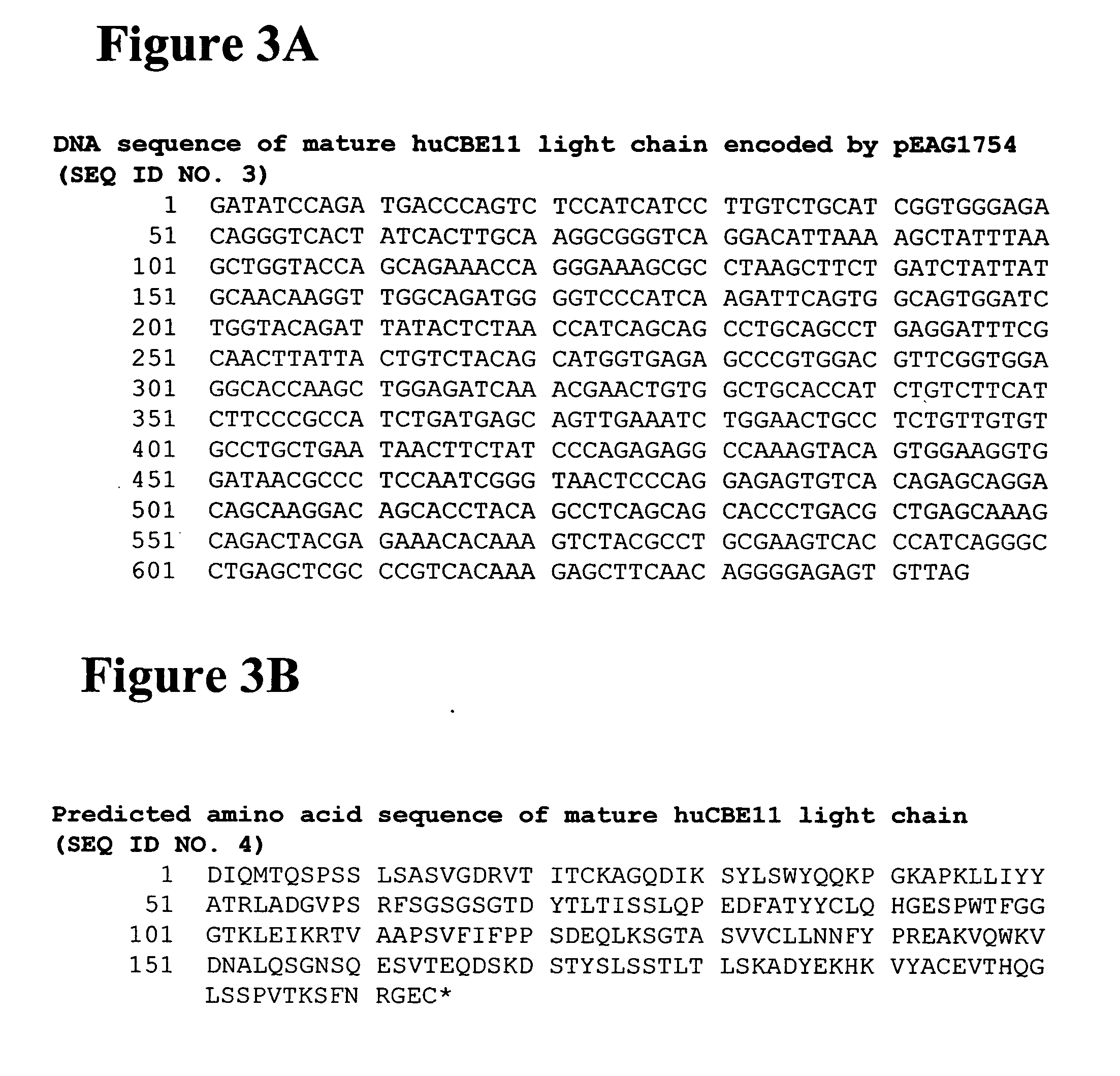
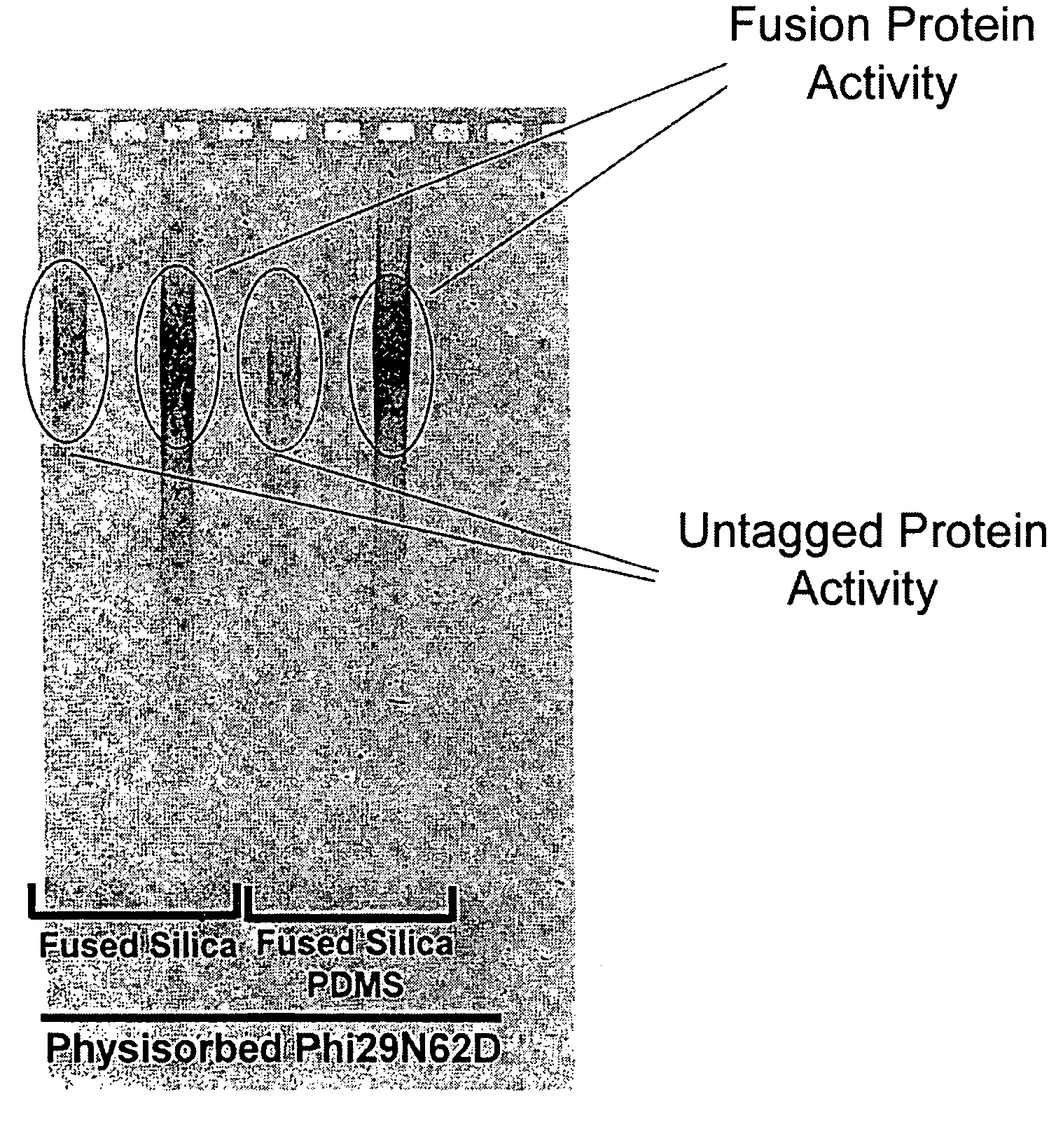
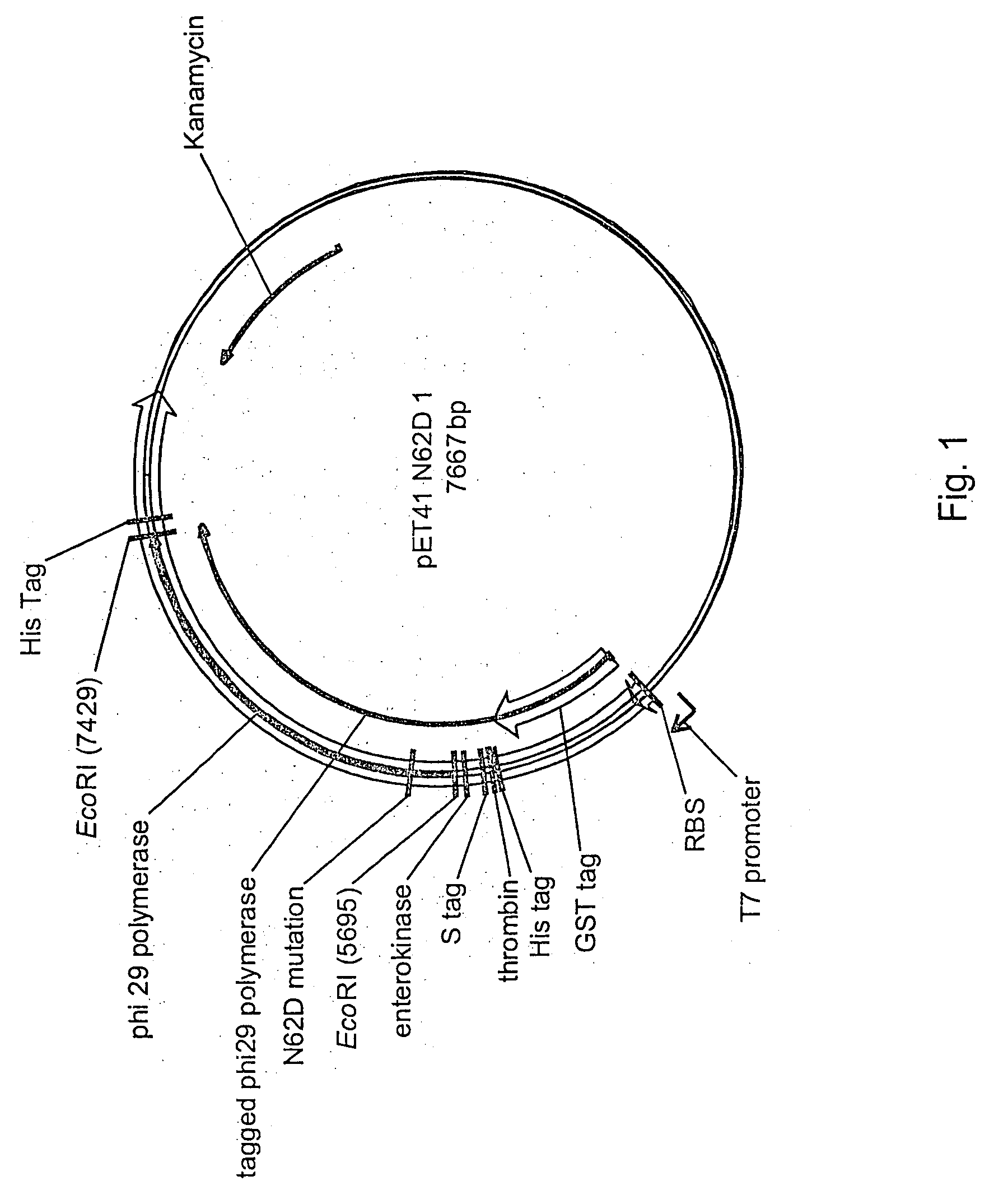
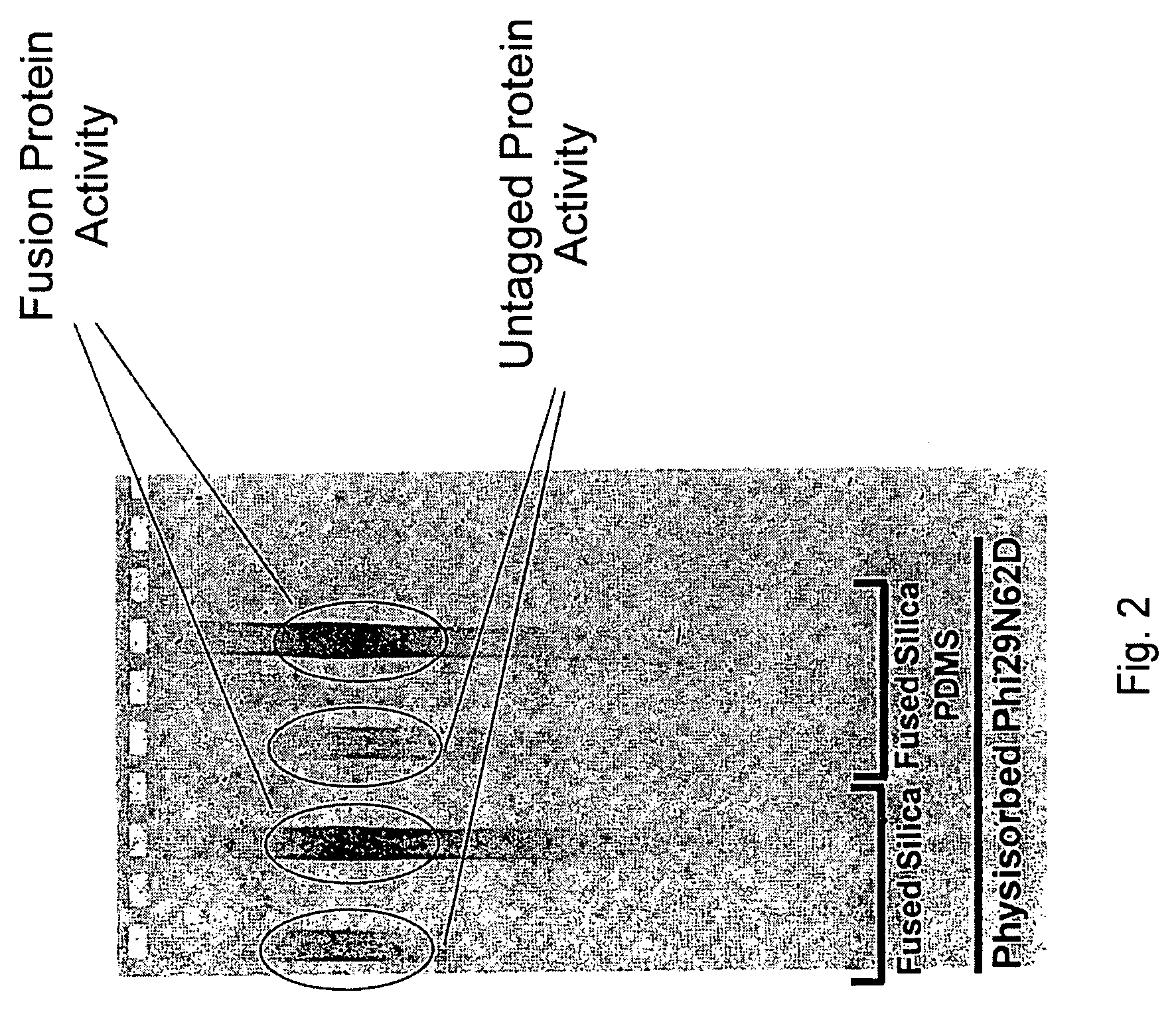
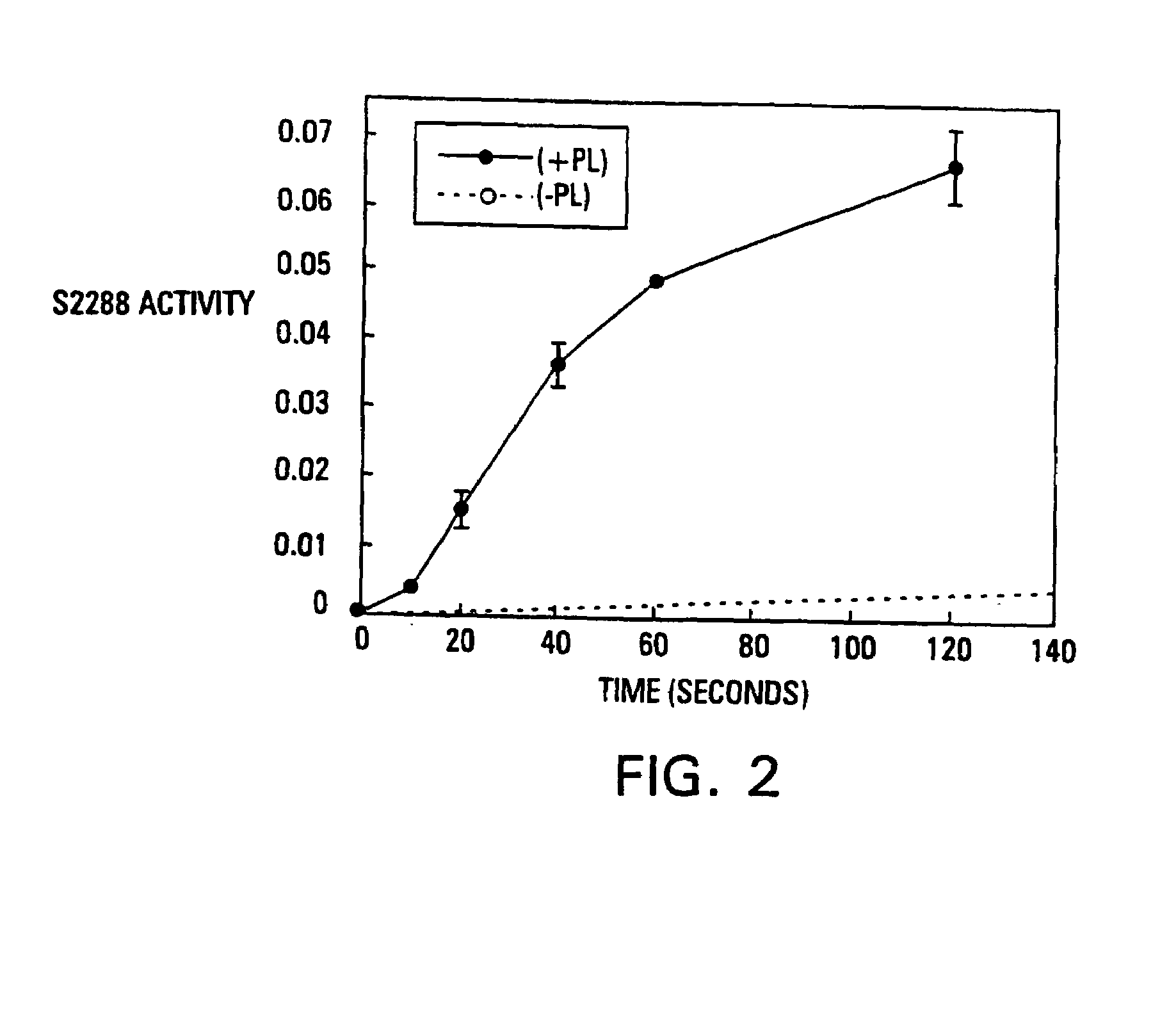
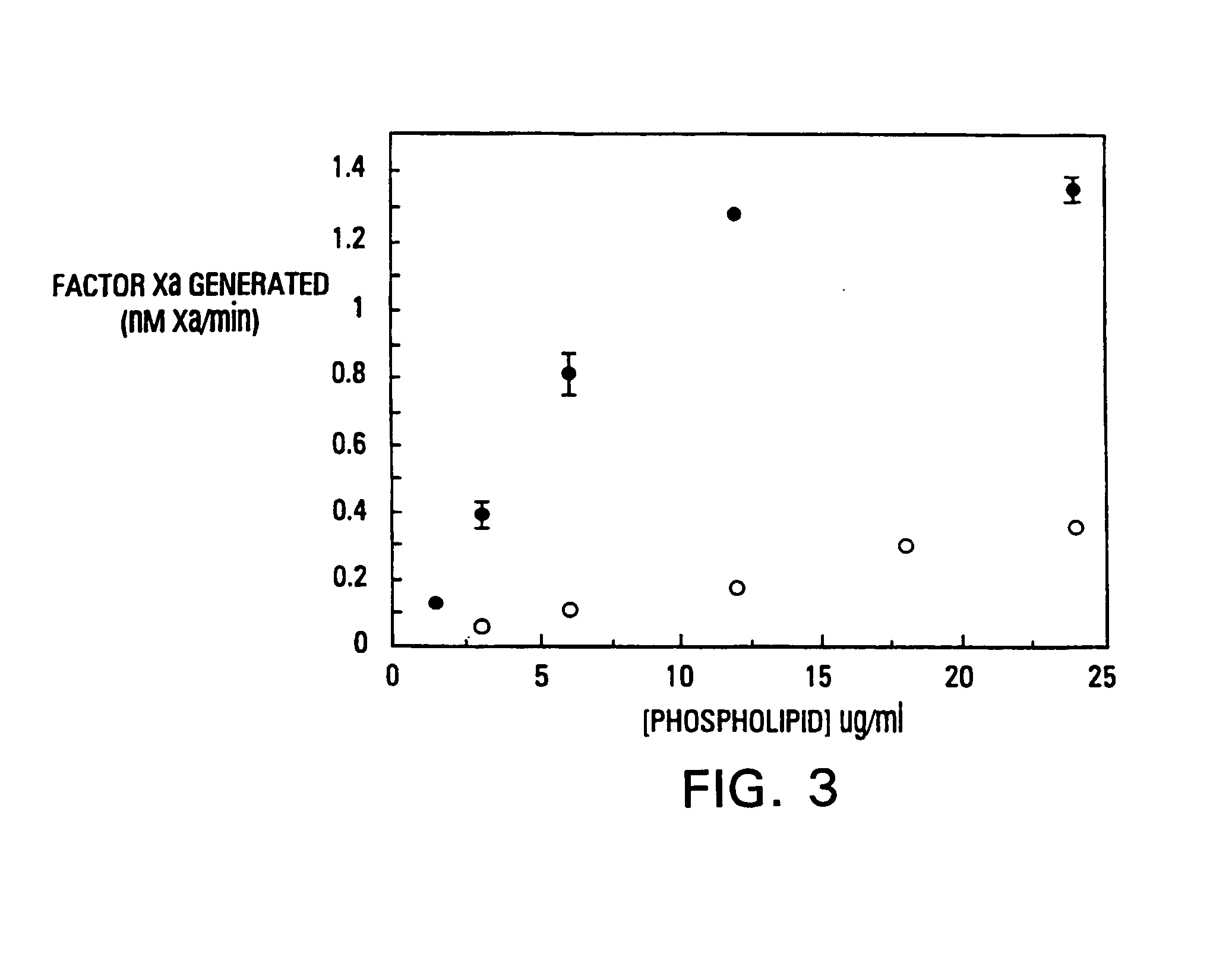
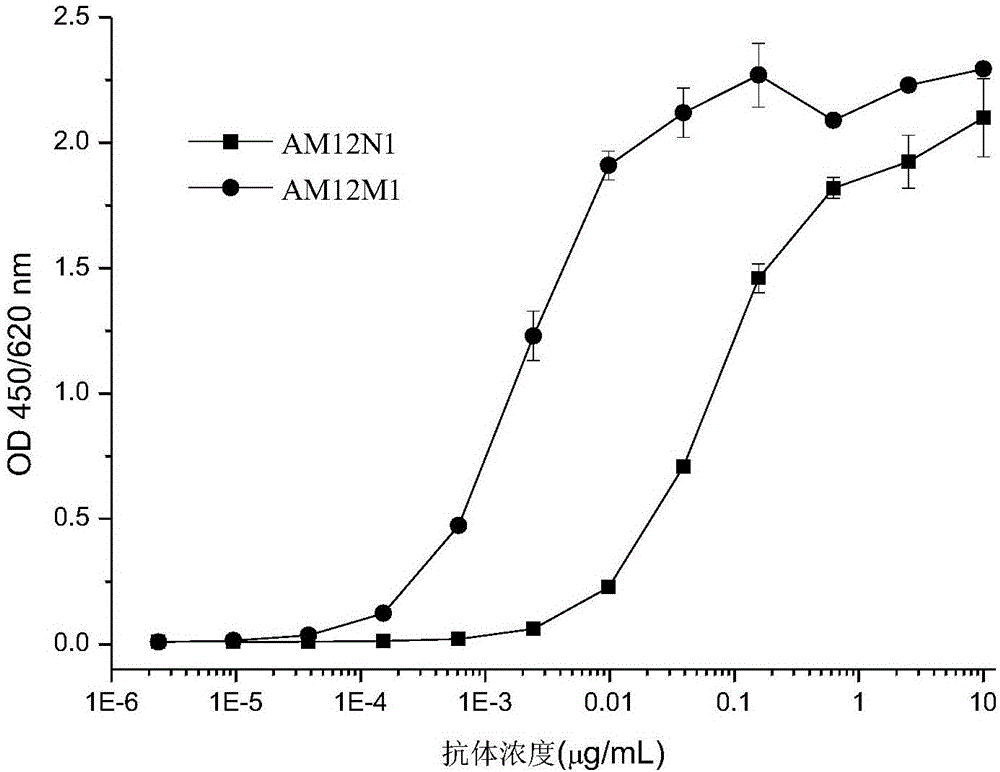
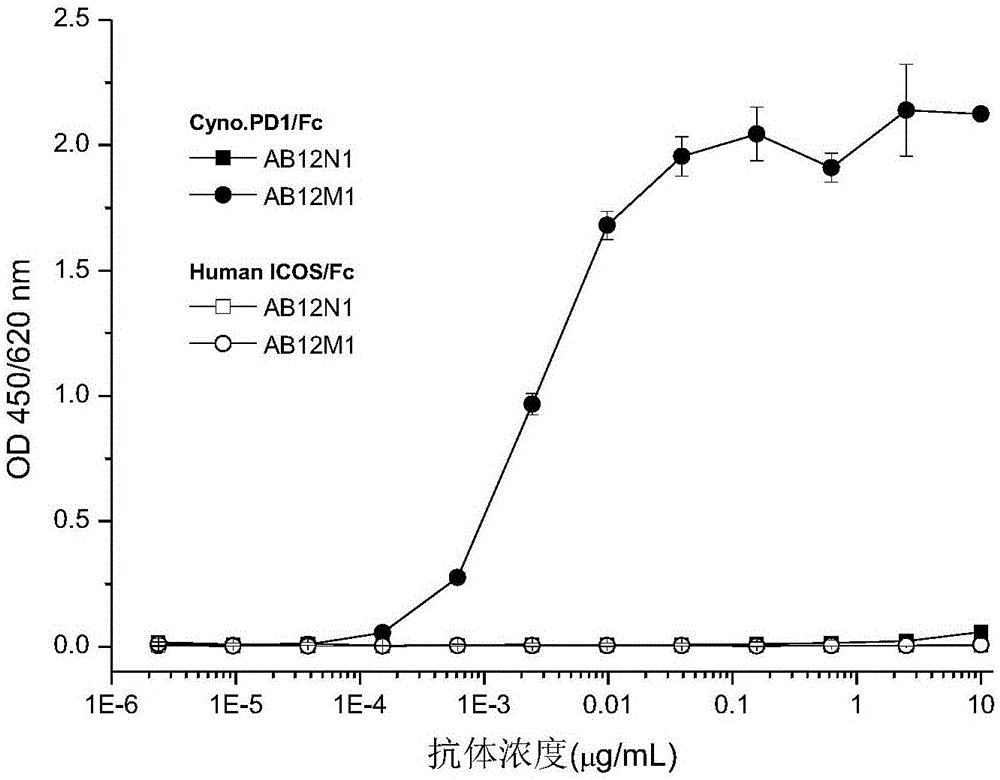
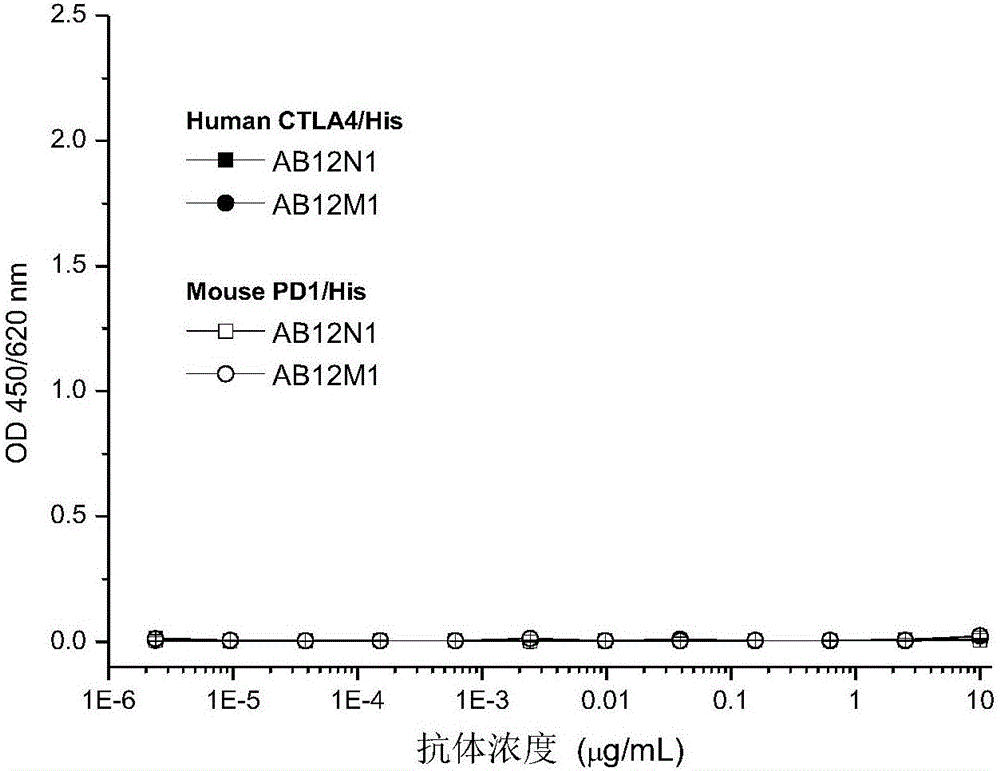
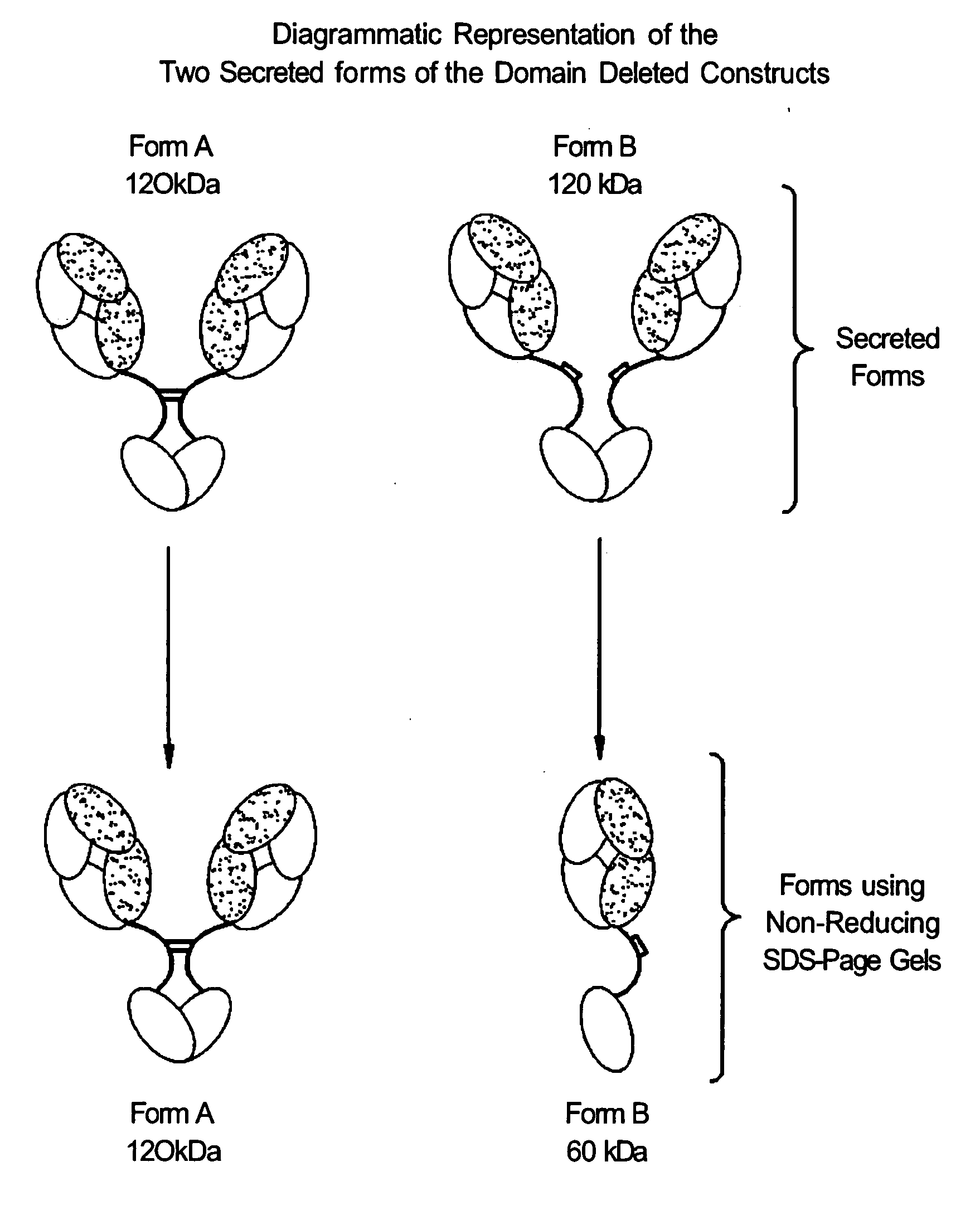
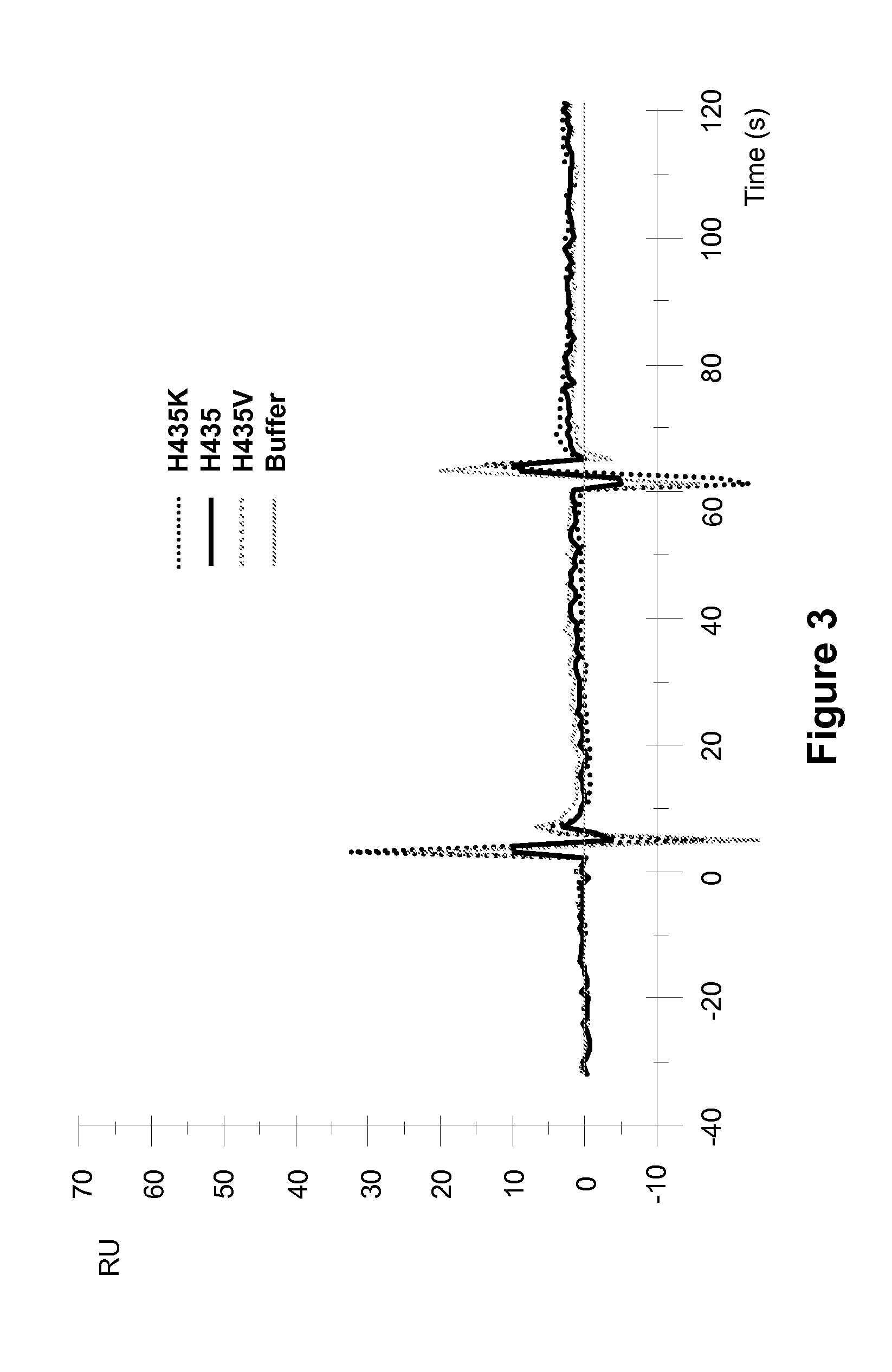
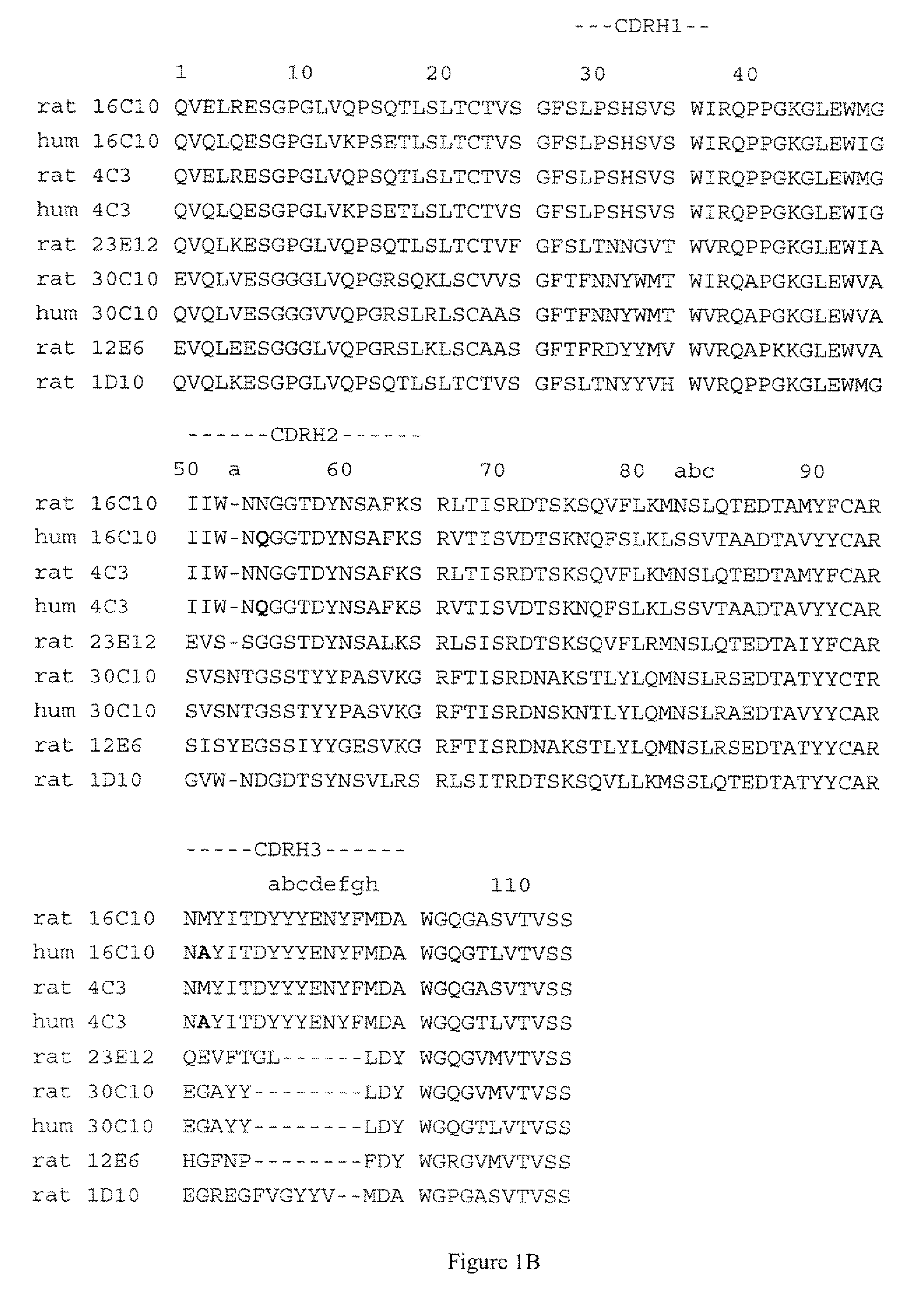
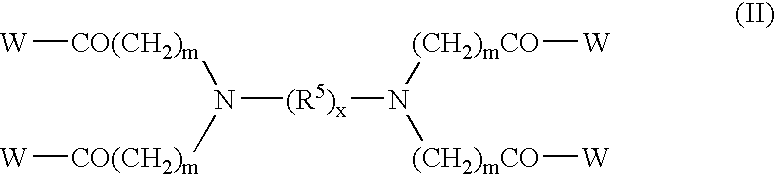Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
277results about How to "High binding affinity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
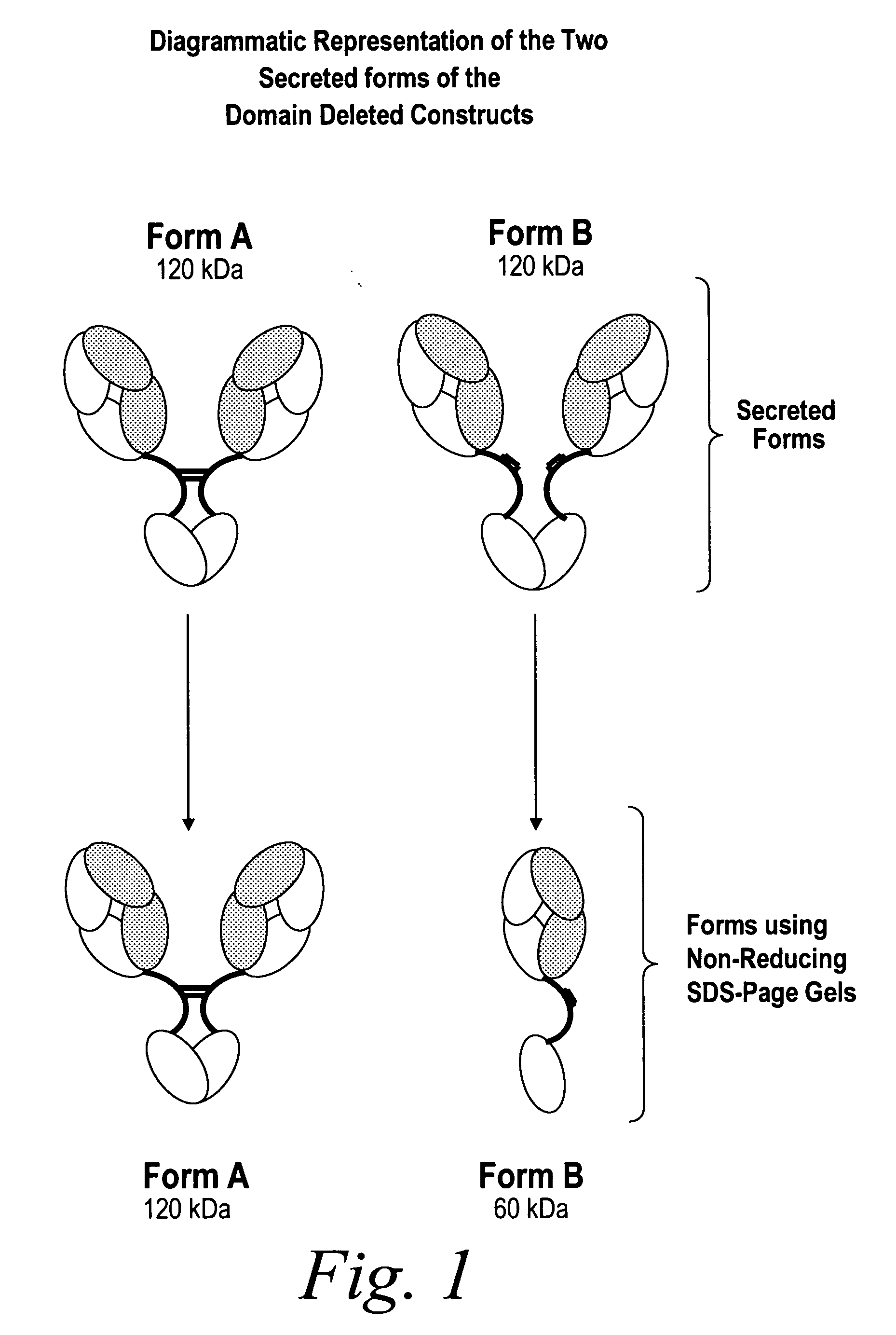
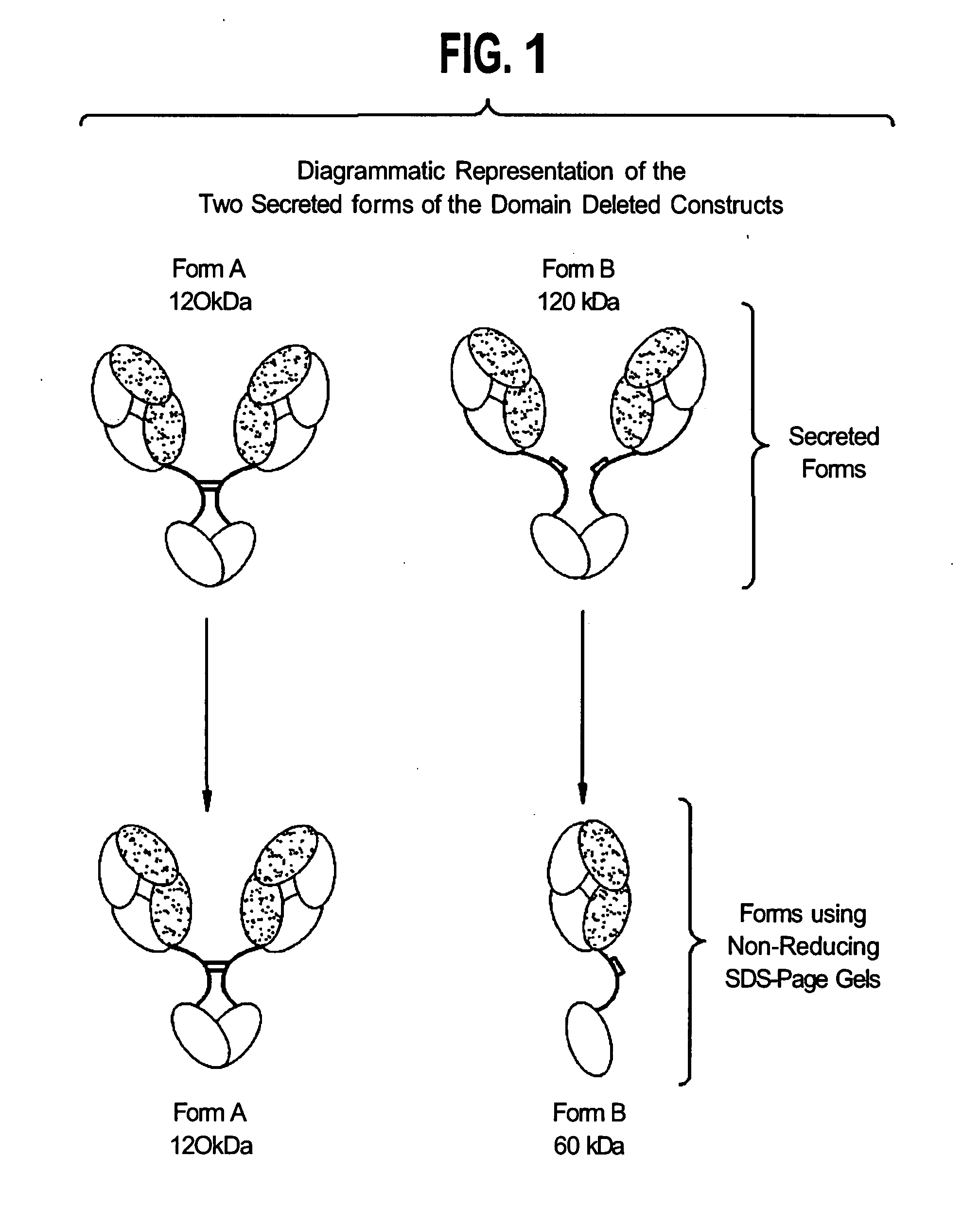
Modified binding molecules comprising connecting peptides
InactiveUS20050163782A1Well formedIncreased formationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDisulfide LinkagePeptide
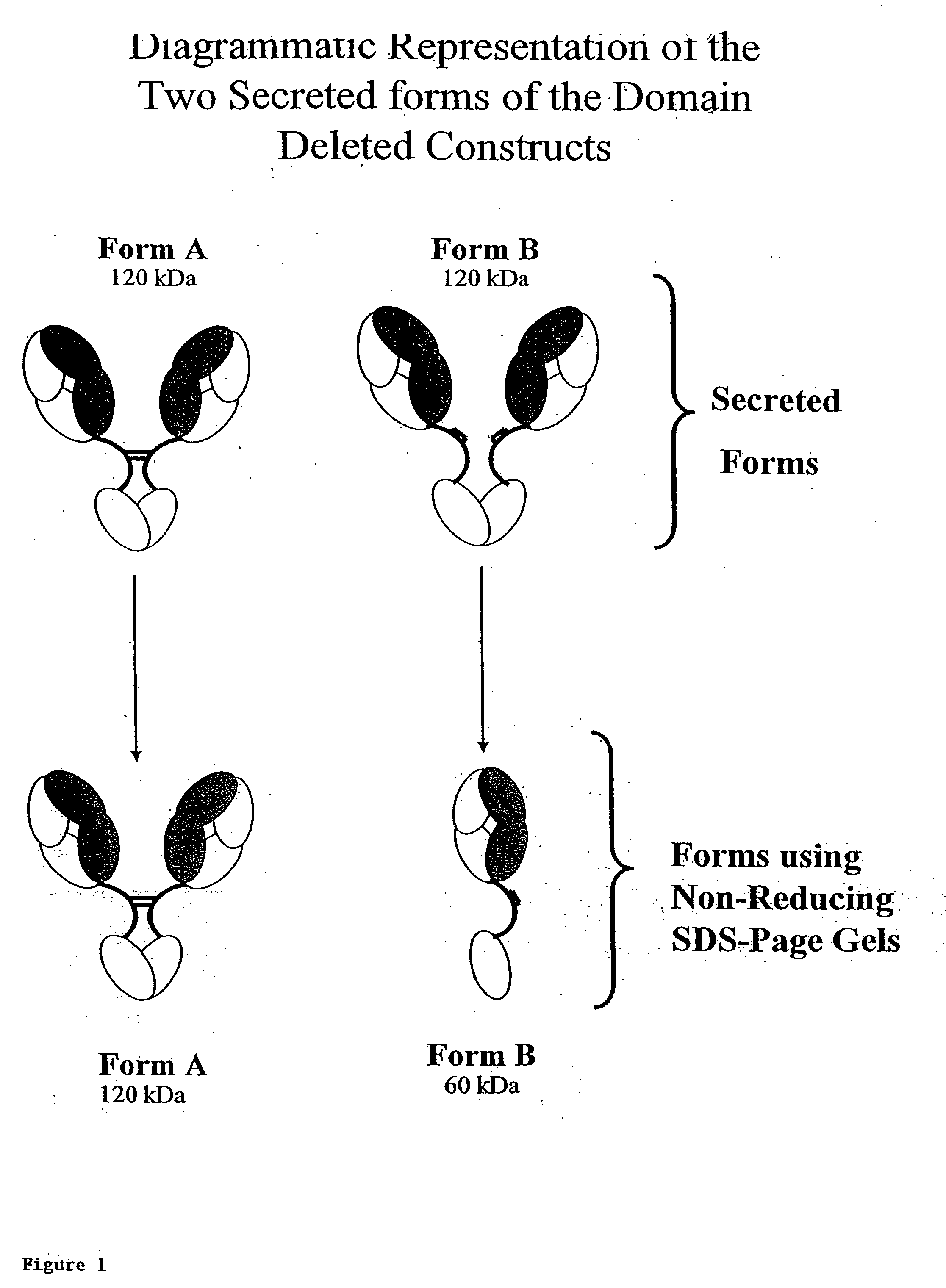
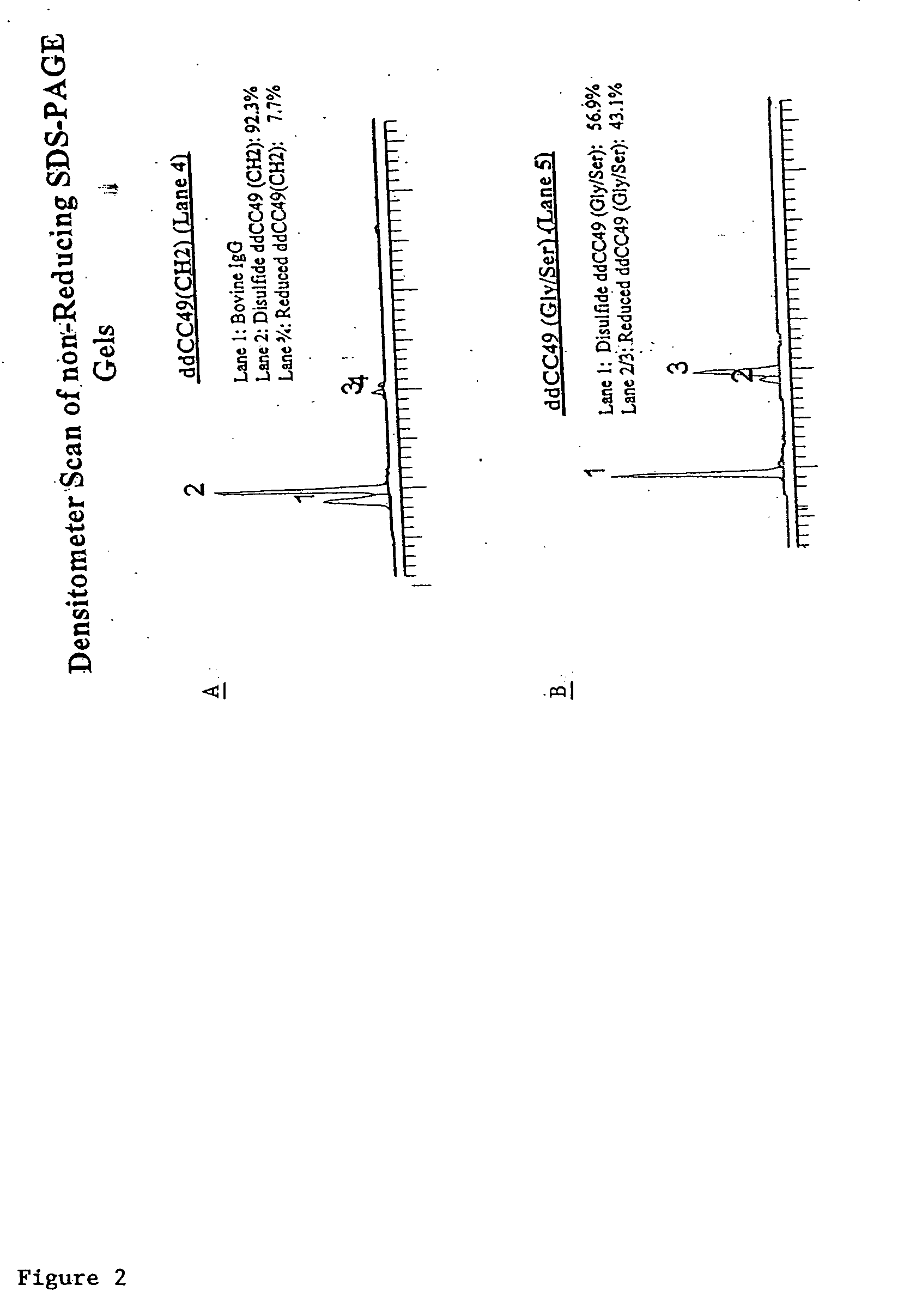
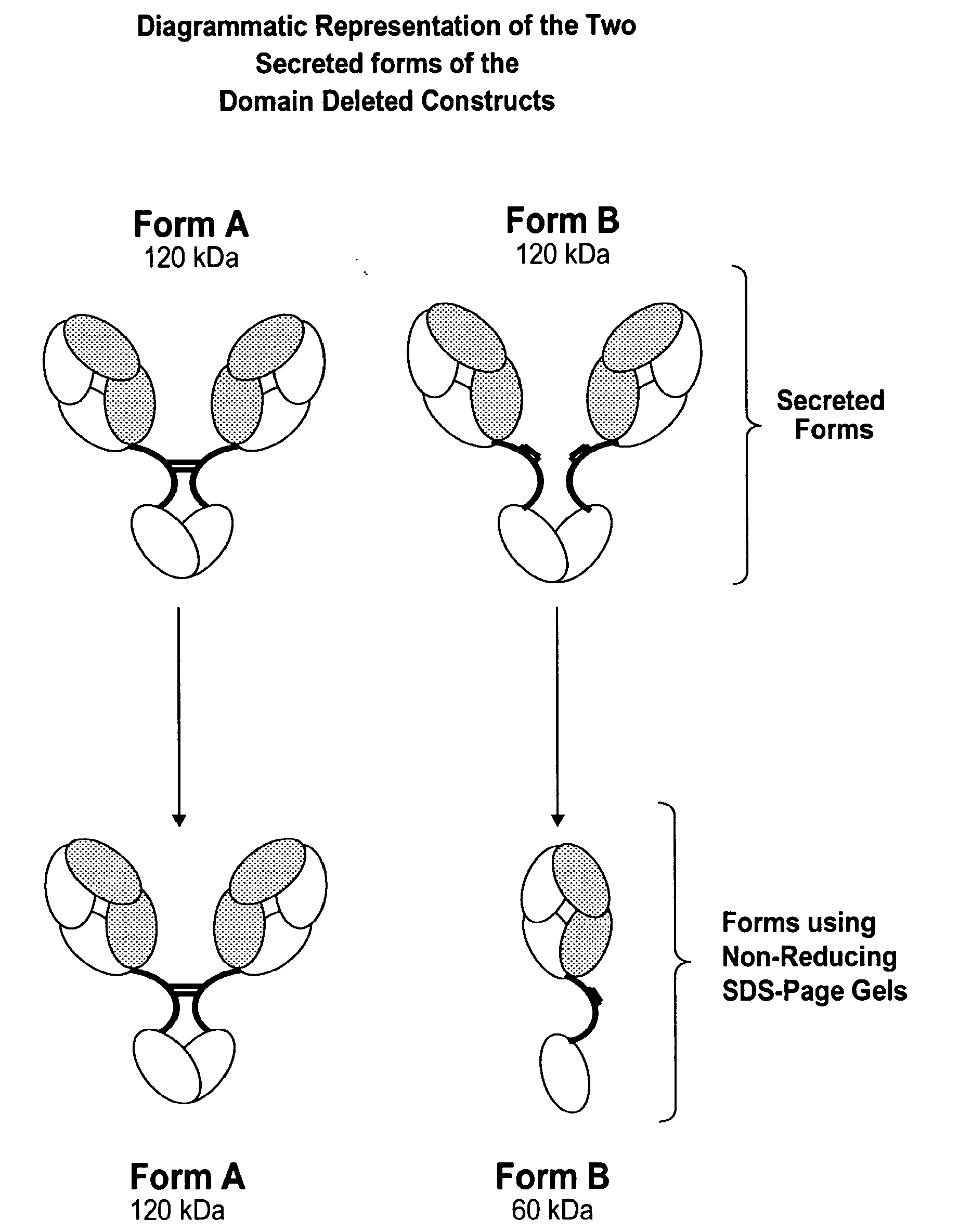
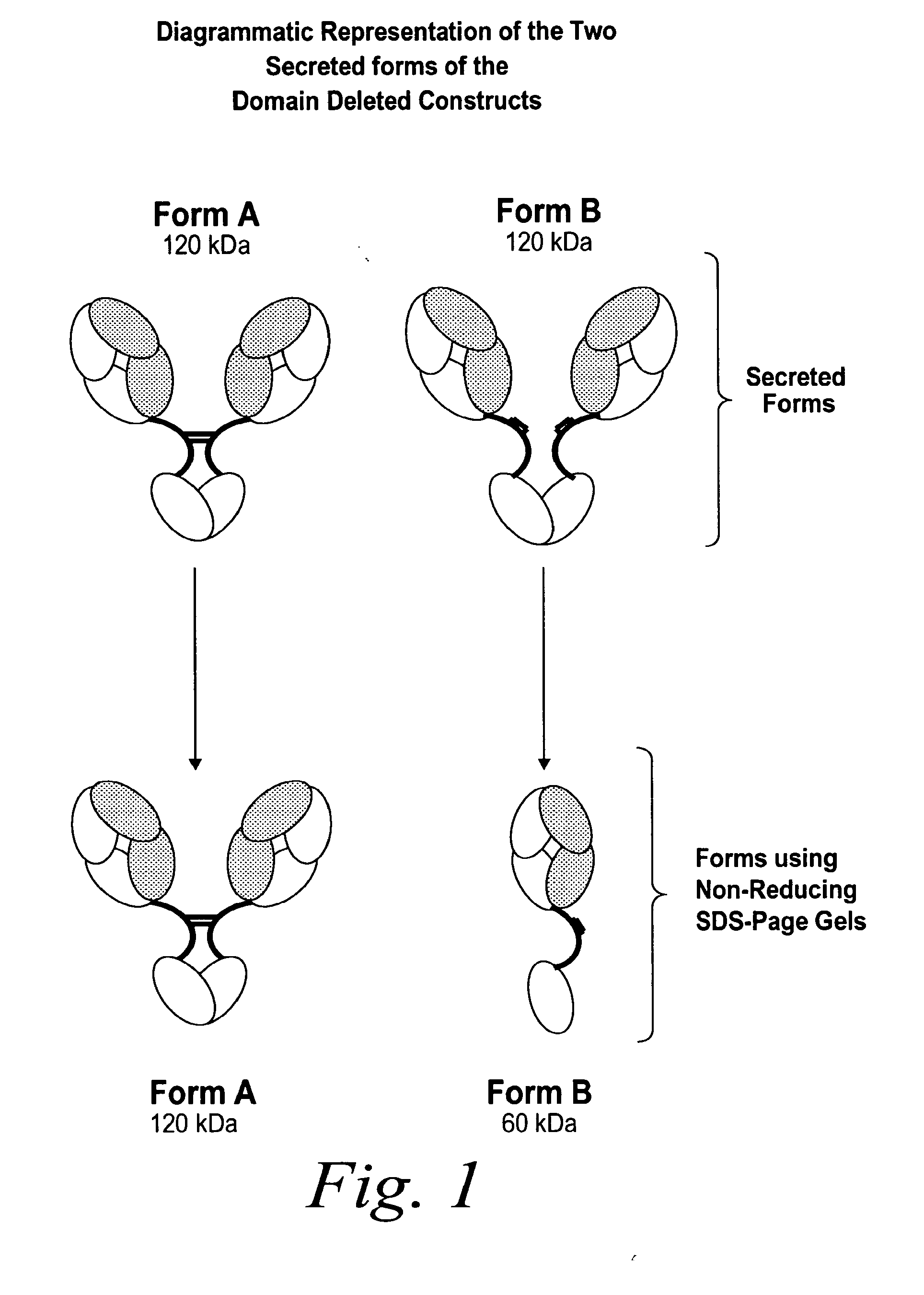
The instant invention describes methods of separating or preferentially synthesizing dimers which are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from dimers which are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from a mixture comprising the two types of polypeptide dimers. These forms can be separated from each other using hydrophobic interaction chromatography. In addition, the invention pertains to connecting peptides that result in the preferential biosynthesis of dimers that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or that are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention also pertains to compositions in which a majority of the dimers are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention still further pertains to novel binding molecules, e.g., comprising connecting peptides of the invention.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)-binding polypeptide variants, dimeric Fc binding proteins and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20070148164A1Increase free energyReduced binding affinityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesFc bindingNeonatal Fc receptor
The compositions and methods of the present invention are based, in part, on our discovery that an effector function mediated by an Fc-containing polypeptide can be altered by modifying one or more amino acid residues within the polypeptide (by, for example, electrostatic optimization). The polypeptides that can be generated according to the methods of the invention are highly variable, and they can include antibodies and fusion proteins that contain an Fc region or a biologically active portion thereof.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
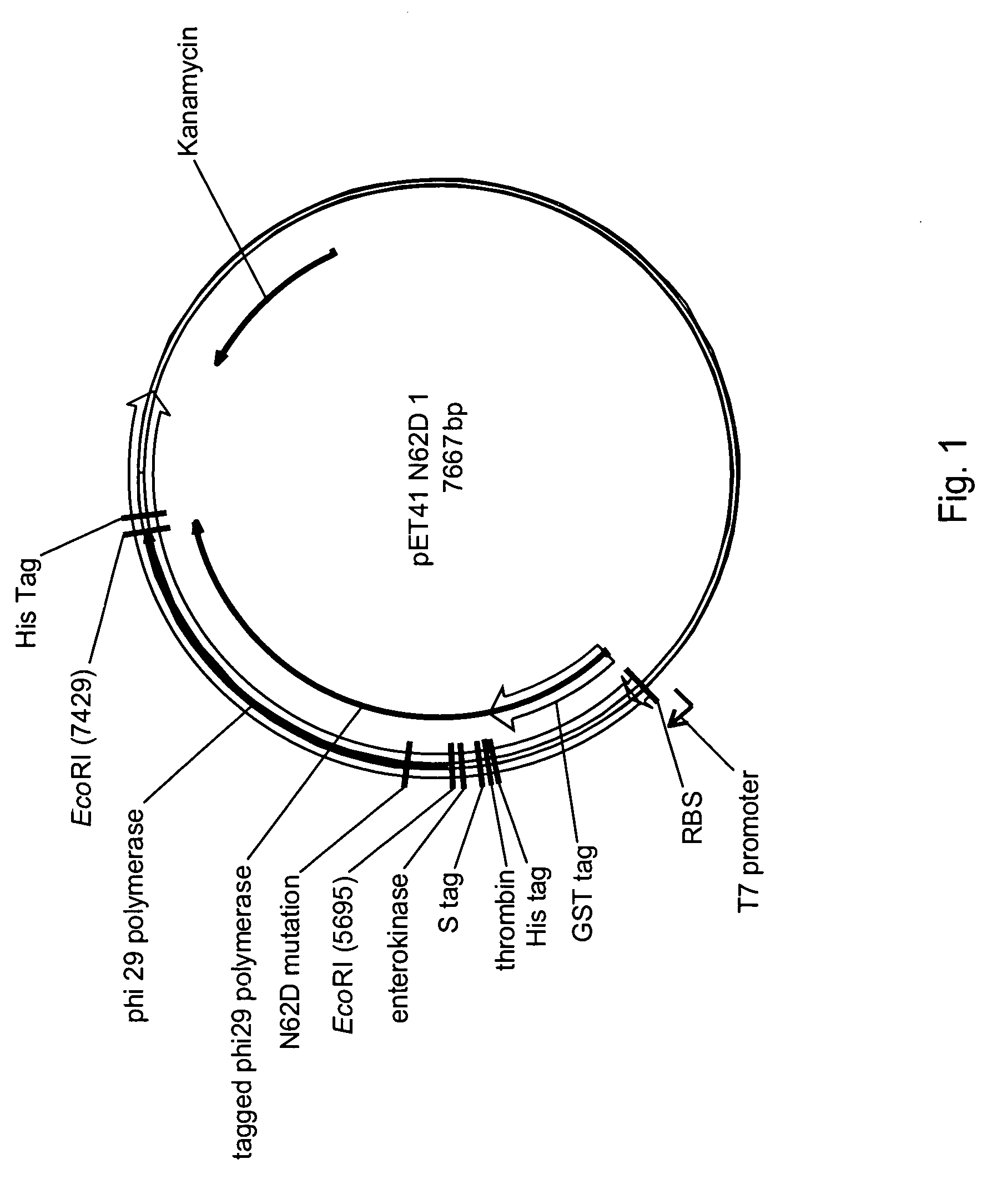
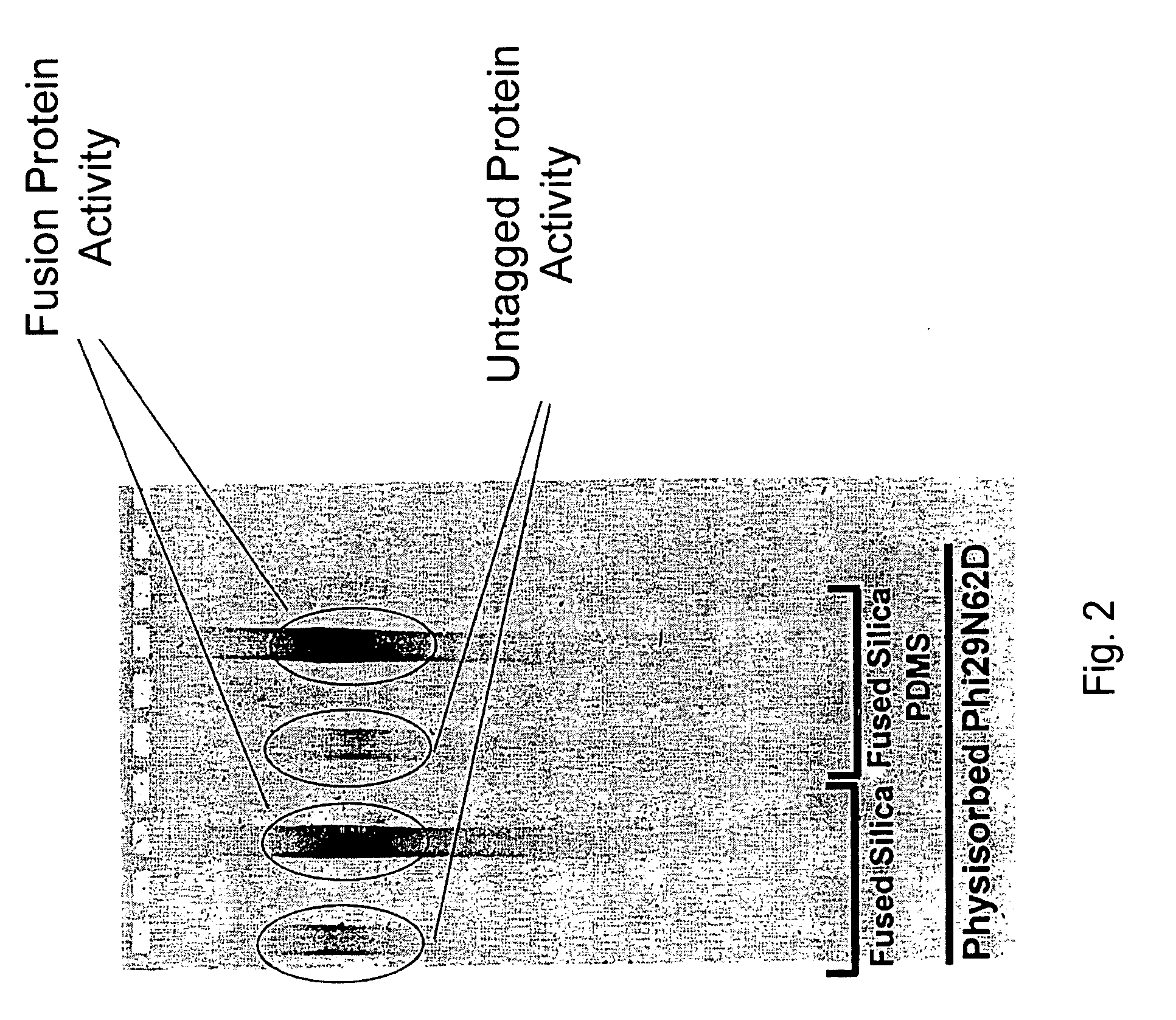
Active surface coupled polymerases
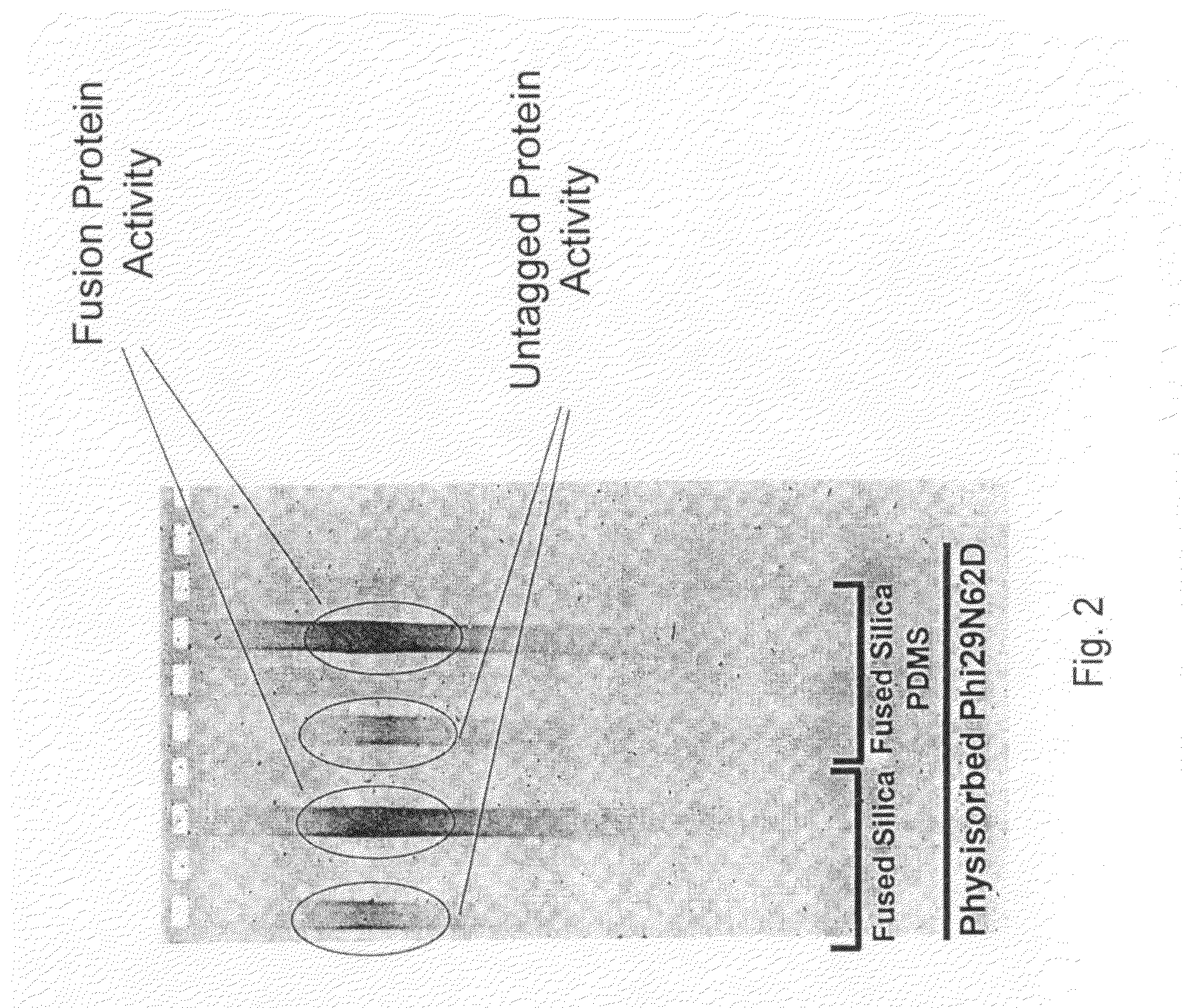
ActiveUS20080199932A1Without substantial loss of activityHigh binding affinityMicrobiological testing/measurementOn/in organic carrierPolymerase LBiomedical engineering
Active surface coupled polymerases, surfaces that include such polymerases, and methods of making and using surface-attached polymerases are provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Microrna as ligands and target molecules
InactiveUS20050142581A1Improve bindingIncreased binding affinityMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processMicroRNAMass spectrometry
The present invention provides methods for the identification of target molecules that bind to ligands, particularly microRNA ligands and mimics thereof and / or microRNA target molecules and mimics thereof, with as little as millimolar (mM) affinity using mass spectrometry. The methods may be used to determine the mode of binding interaction between two or more of these target molecules to the ligand as well as their relative affinities. Also provided are methods for designing compounds having greater affinity to a ligand by identifying two or more target molecules using mass spectrometry methods of the invention and linking the target molecules together to form a novel compound.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
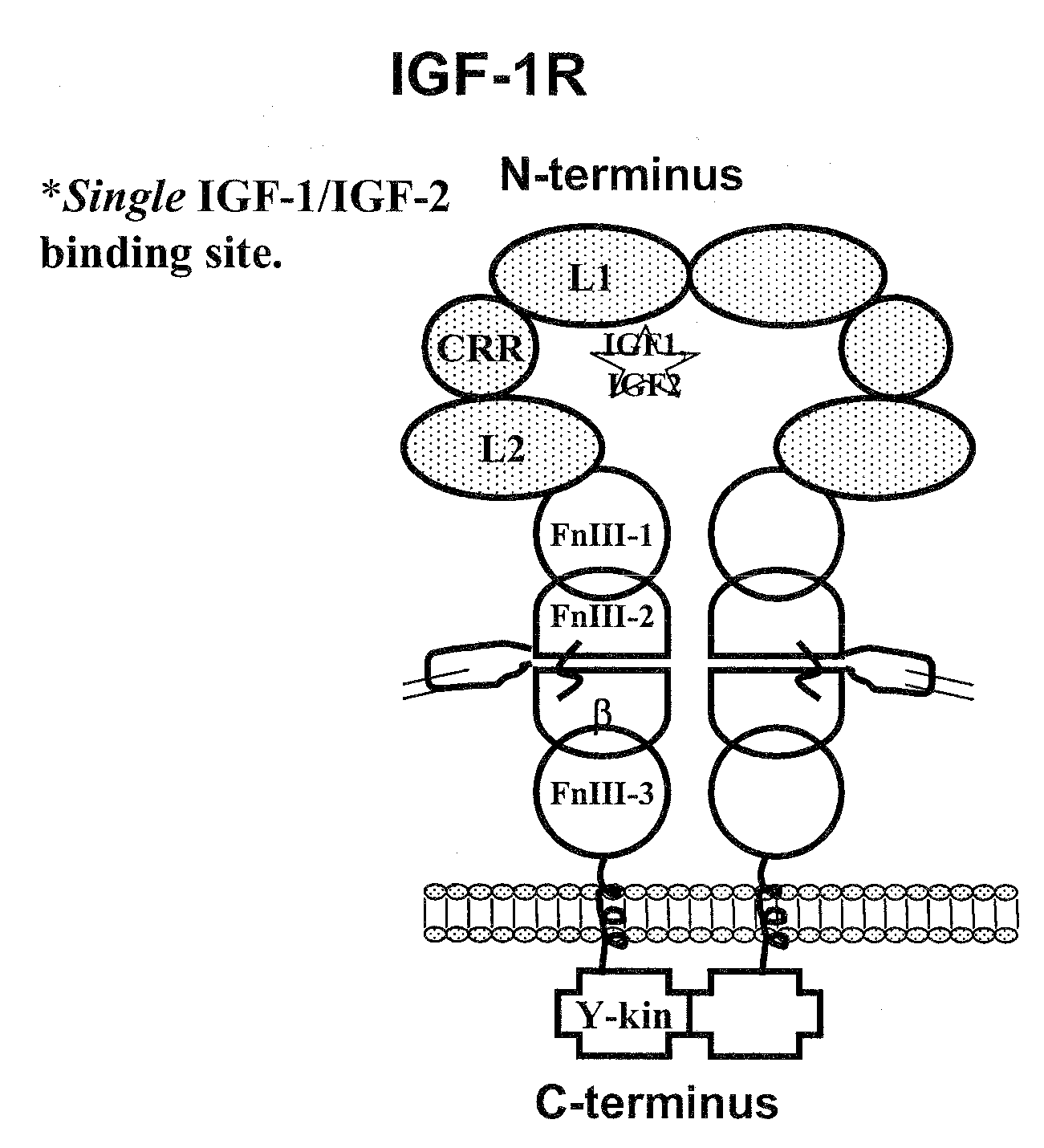
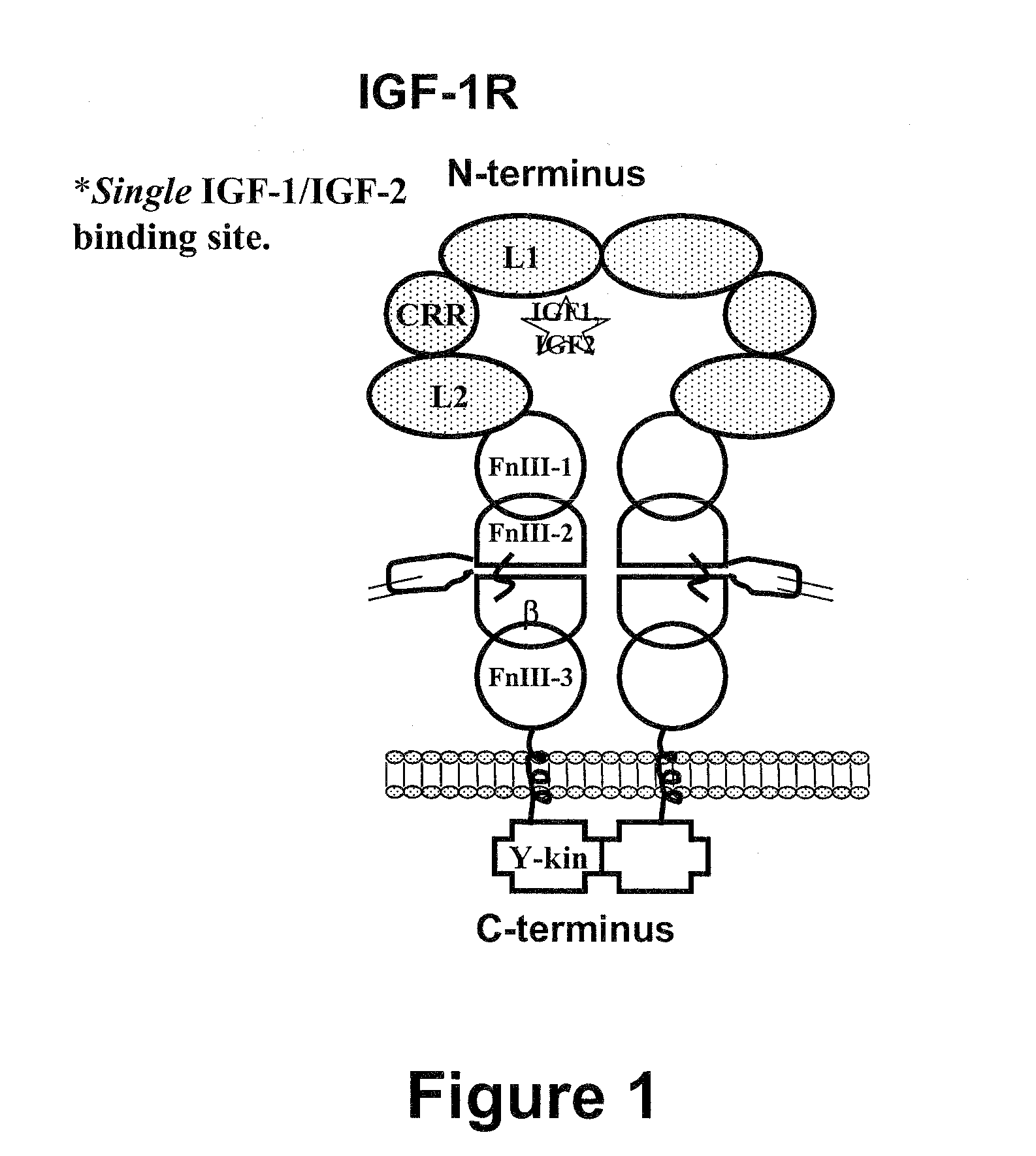
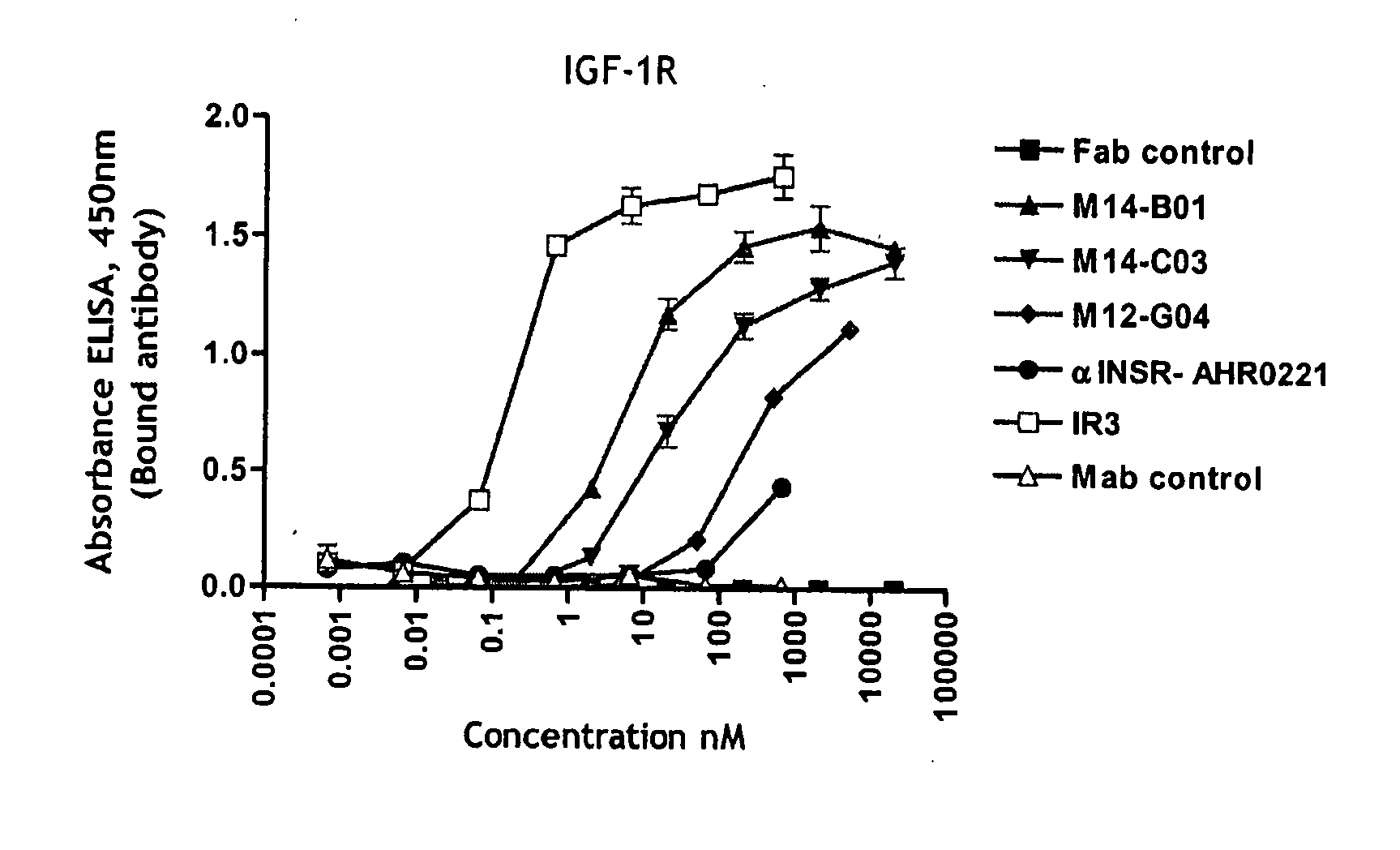
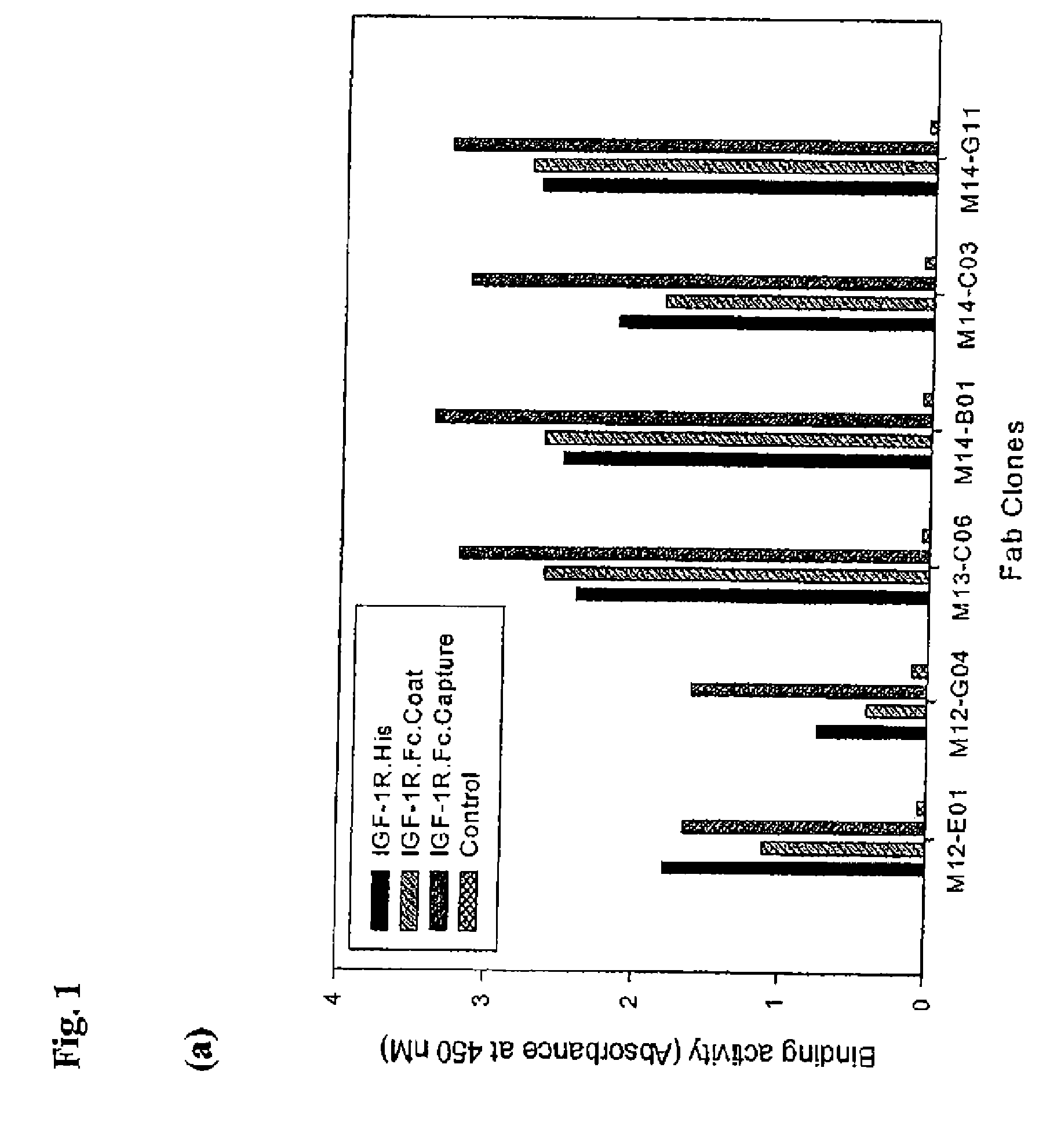
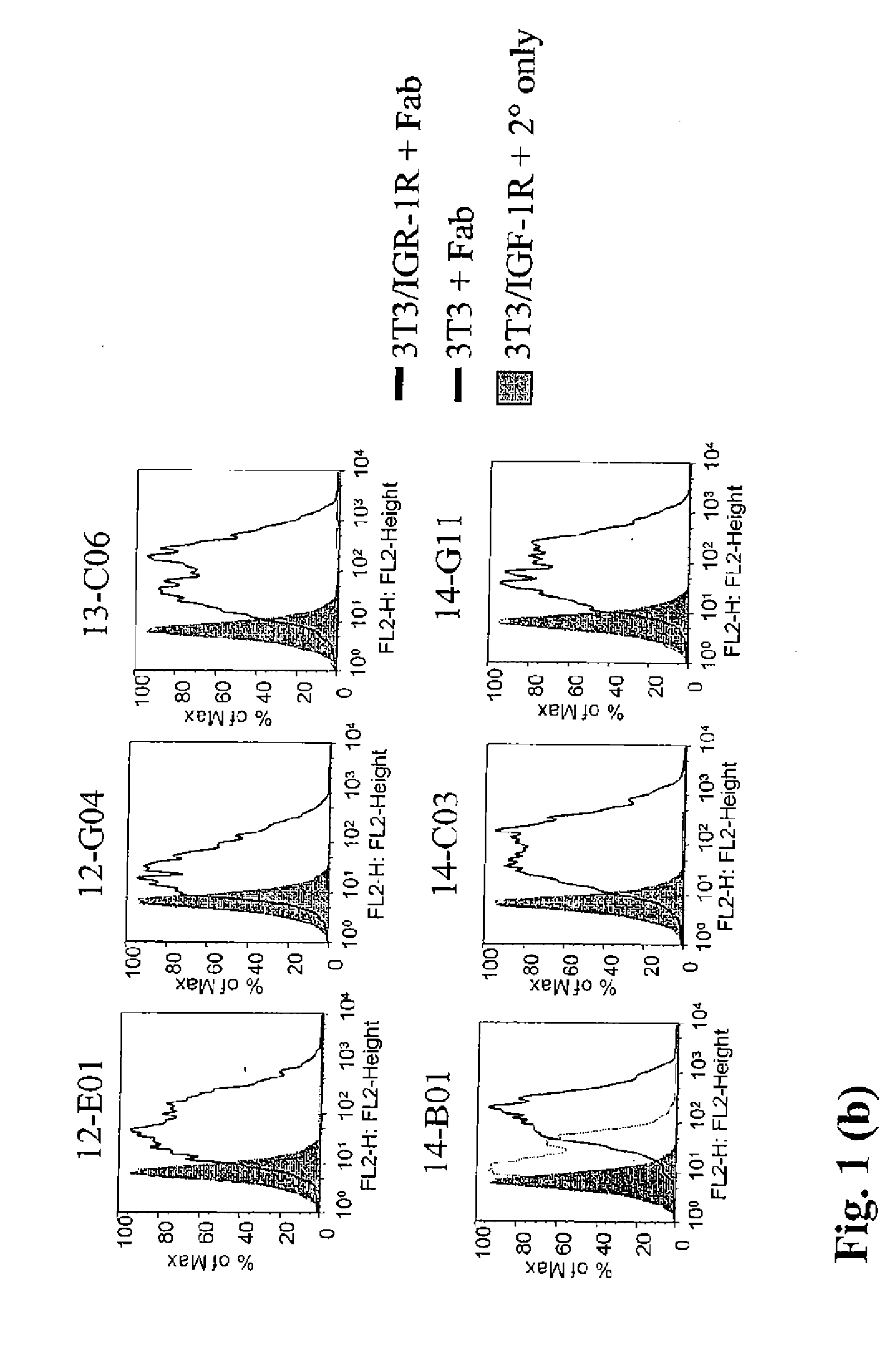
Compositions that bind multiple epitopes of igf-1r
InactiveUS20090130105A1Reduce dwell timeHigh binding affinitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeBiochemistry
The instant invention is based, at least in part on the finding that binding molecules which bind to different epitopes within IGF-1R result in improved IGF-1 and / or IGF-2 blocking capabilities when compared to binding molecules that bind to a single IGF-1R epitope. The instant invention provides compositions that bind to multiple epitopes of IGF-1R, for example, combinations of monospecific binding molecules or multispecific binding molecules (e.g., bispecific molecules). Methods of making the subject binding molecules and methods of using the binding molecules of the invention to antagonize IGF-1R signaling are also provided.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
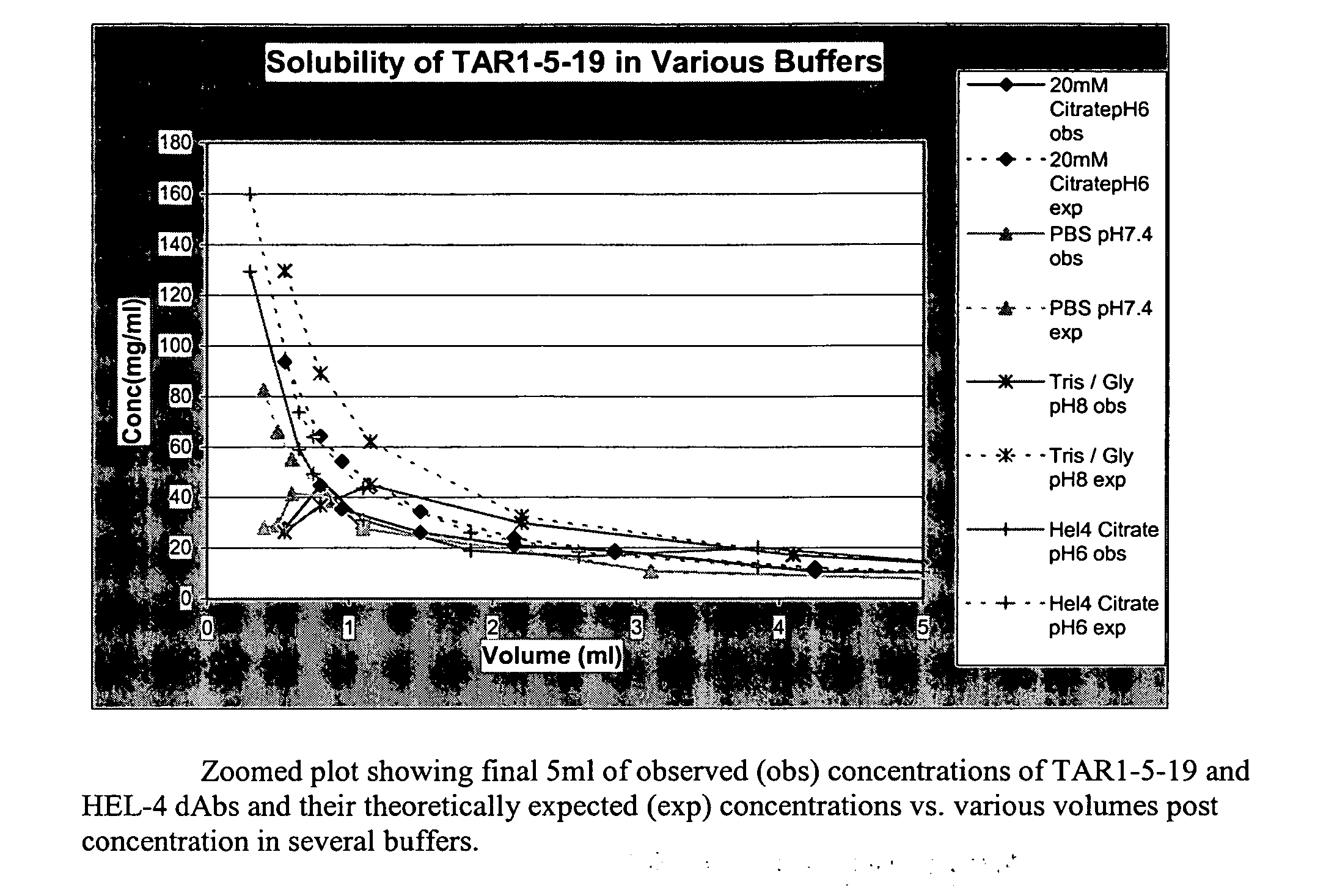
Antibody compositions and methods
InactiveUS20070065440A1High affinitySmall sizeAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHigh concentrationVariable domain
Provided are concentrated preparations comprising single immunoglobulin variable domain polypeptides that bind target antigen with high affinity and are soluble at high concentration, without aggregation or precipitation, providing, for example, for increased storage stability and the ability to administer higher therapeutic doses.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Active surface coupled polymerases
ActiveUS20100261247A1High affinityReduce surface denaturation effectMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme stabilisationPolymerase LActive surface
Active surface coupled polymerases, surfaces that include such polymerases, and methods of making and using surface-attached polymerases are provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Nanoparticulate lipase inhibitor formulations
InactiveUS20060246141A1Equal efficacyHigh binding affinityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChemistryIntestinal Lipase Inhibitor
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD
Lipoxin compounds and their use in treating cell proliferative disorders
InactiveUS6887901B1Increased in vive potencyHigh binding affinitySalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideHalf-lifeMedicine
Compounds having the active site of natural lipoxins, but a longer tissue half-life are disclosed. In particular, 15-epi-lipoxins and their use in ameliorating undesired cell proliferation, which characterizes diseases such as cancer, are also disclosed.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
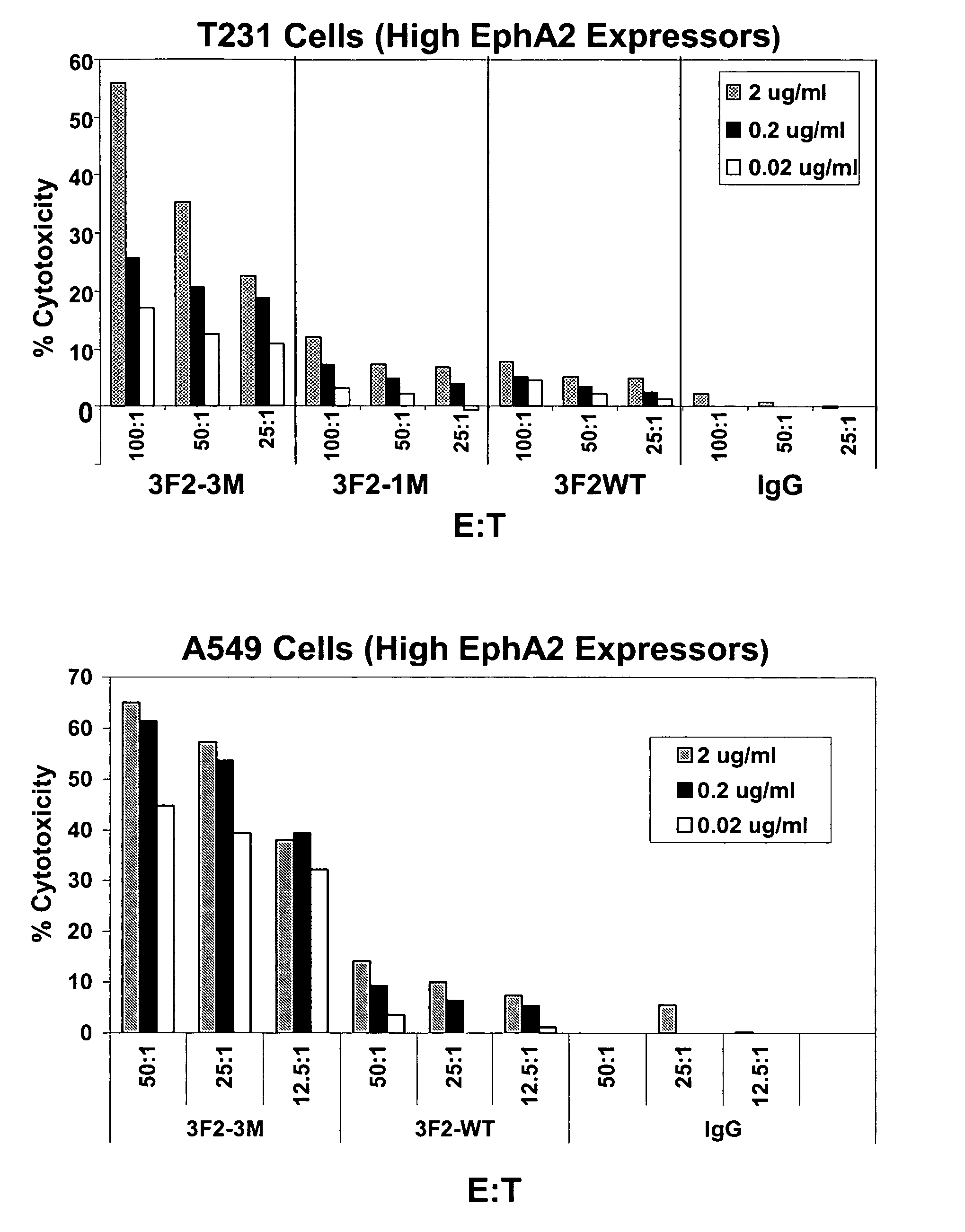
EPH receptor Fc variants with enhanced antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity
InactiveUS20060039904A1Altered binding affinityHigh binding affinityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionComplement-dependent cytotoxicityReceptor
The present invention relates to novel Fc variants that immuno-specifically bind to an Eph receptor. The Fc variants comprise a binding region that immunospecifically binds to an Eph receptor and an Fc region that further comprises at least one novel amino acid residue which may provide for enhanced effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more Fc ligand (e.g., FcγR, C1q). Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants that immunospecifically bind to an Eph receptor, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
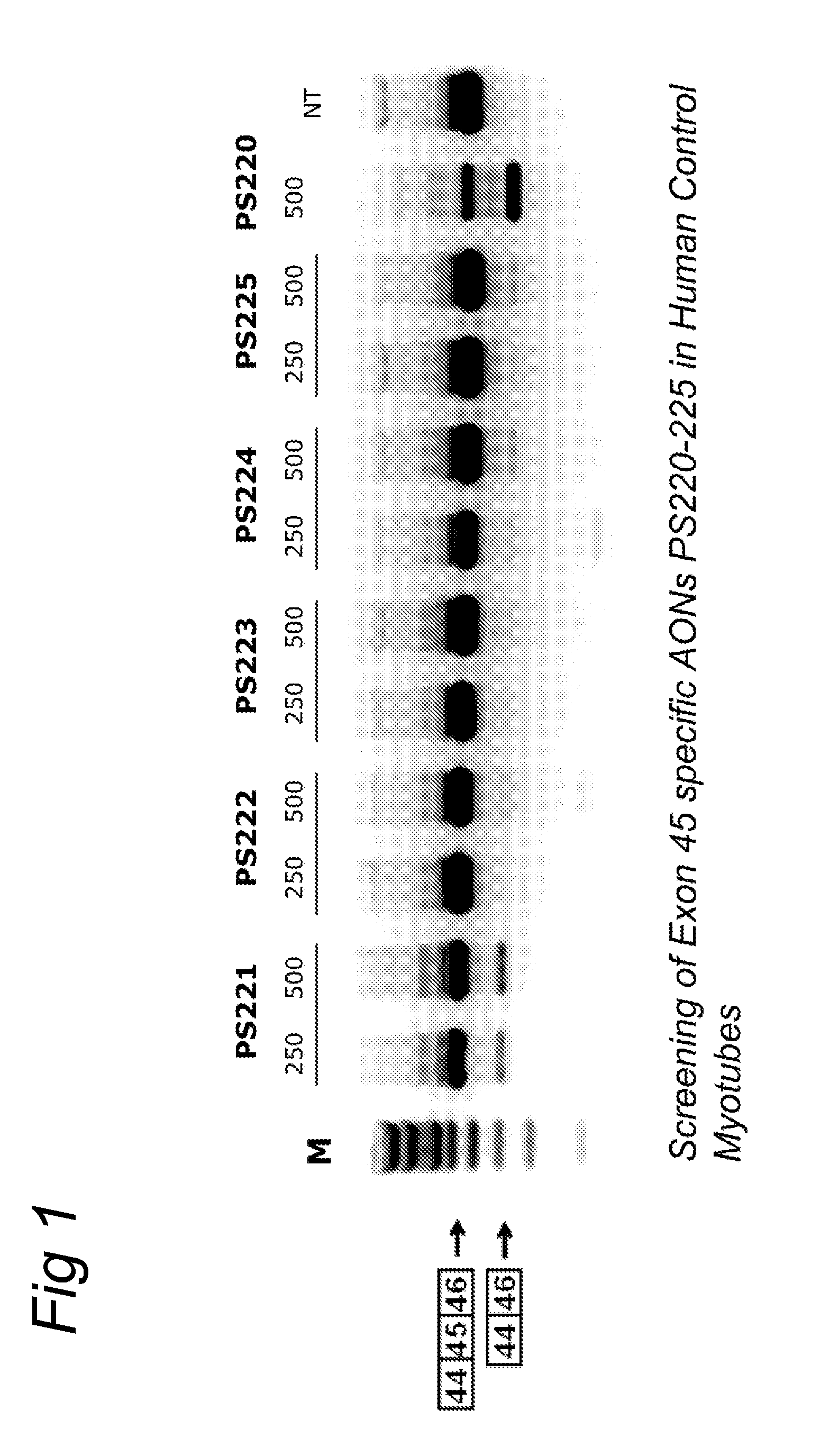
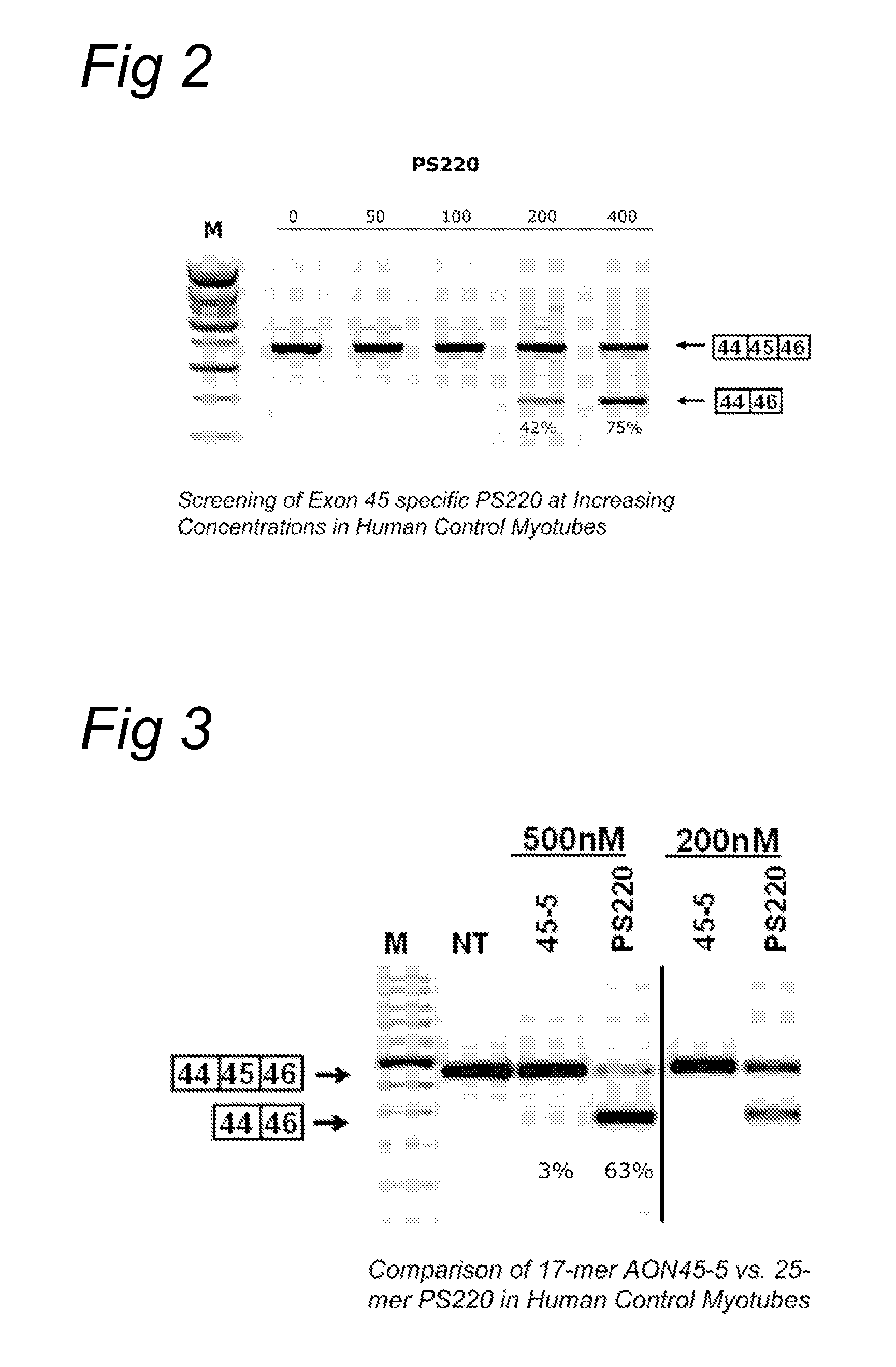
METHODS AND MEANS FOR EFFICIENT SKIPPING OF EXON 45 IN DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY PRE-mRNA
ActiveUS20120022134A1Reduced calcium uptake by muscle cellsReduce synthesisOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationNucleotidePrecursor mRNA
The invention relates to a method for inducing or promoting skipping of exon 45 of DMD pre-mRNA in a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patient, preferably in an isolated (muscle) cell, the method comprising providing said cell with a molecule that binds to a continuous stretch of at least 21 nucleotides within said exon. The invention further relates to such molecule used in said method.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV +2
Purification and preferential synthesis of binding molecules
ActiveUS20050163783A1Well formedImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDisulfide LinkageMedicinal chemistry
The instant invention describes methods of separating or preferentially synthesizing dimers which are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from dimers which are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from a mixture comprising the two types of polypeptide dimers. These forms can be separated from each other using hydrophobic interaction chromatography. In addition, the invention pertains to connecting peptides that result in the preferential biosynthesis of dimers that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or that are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention also pertains to compositions in which a majority of the dimers are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention still further pertains to novel binding molecules, e.g., comprising connecting peptides of the invention.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Fully human antibodies to BTLA
ActiveUS8563694B2High binding affinityImprove pharmacokineticsSenses disorderNervous disorderAntibodyLuetic disease
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
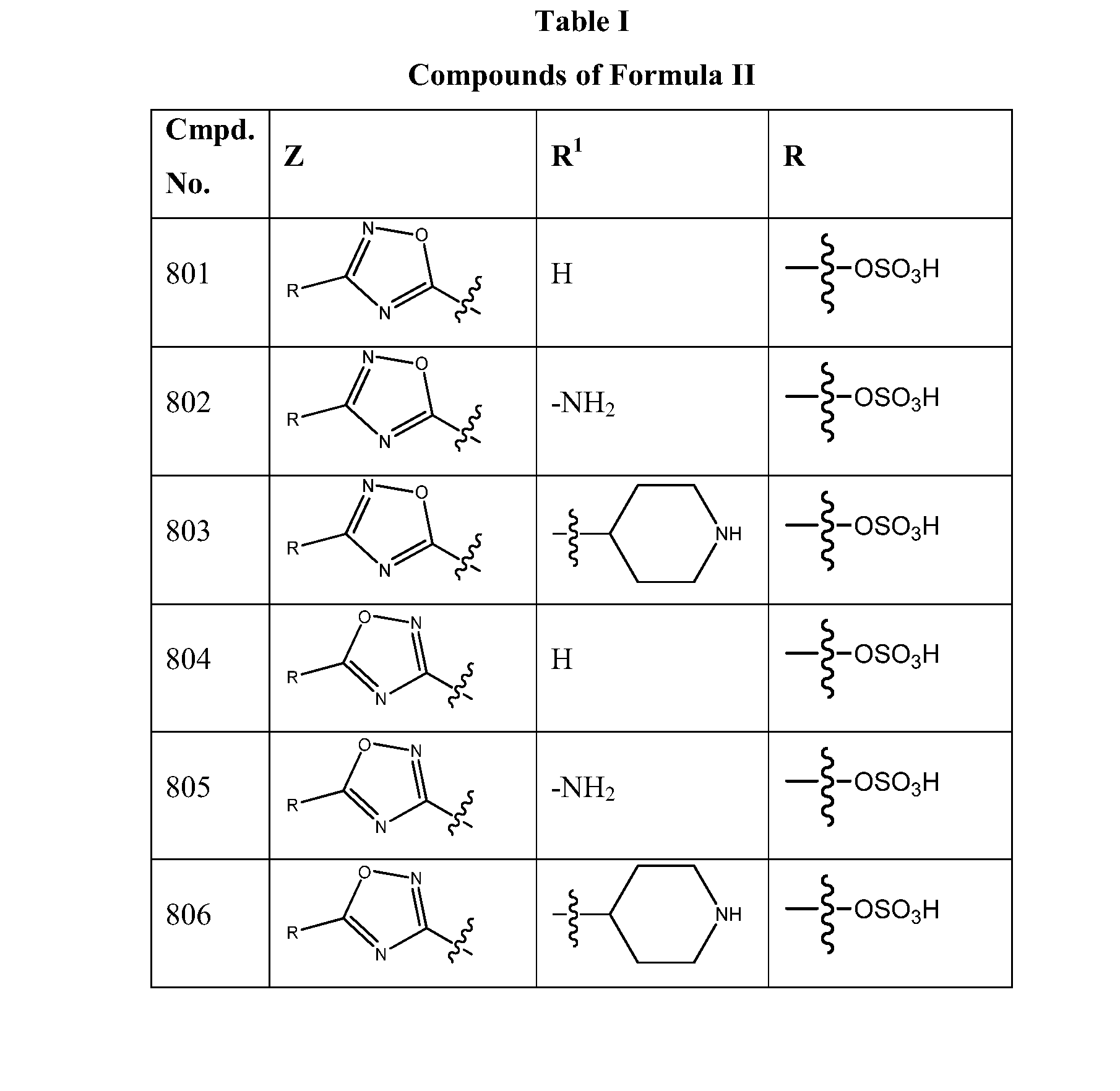
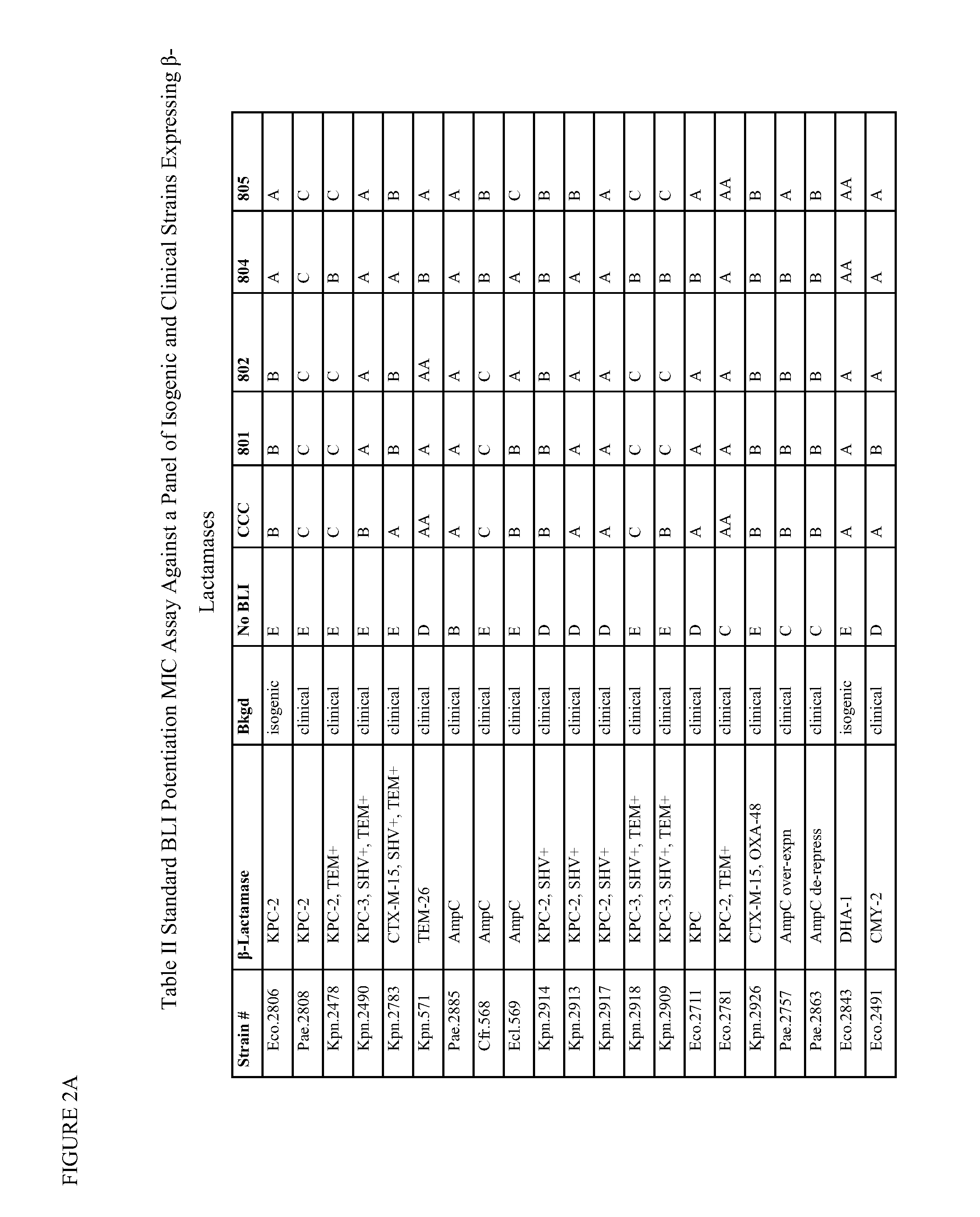
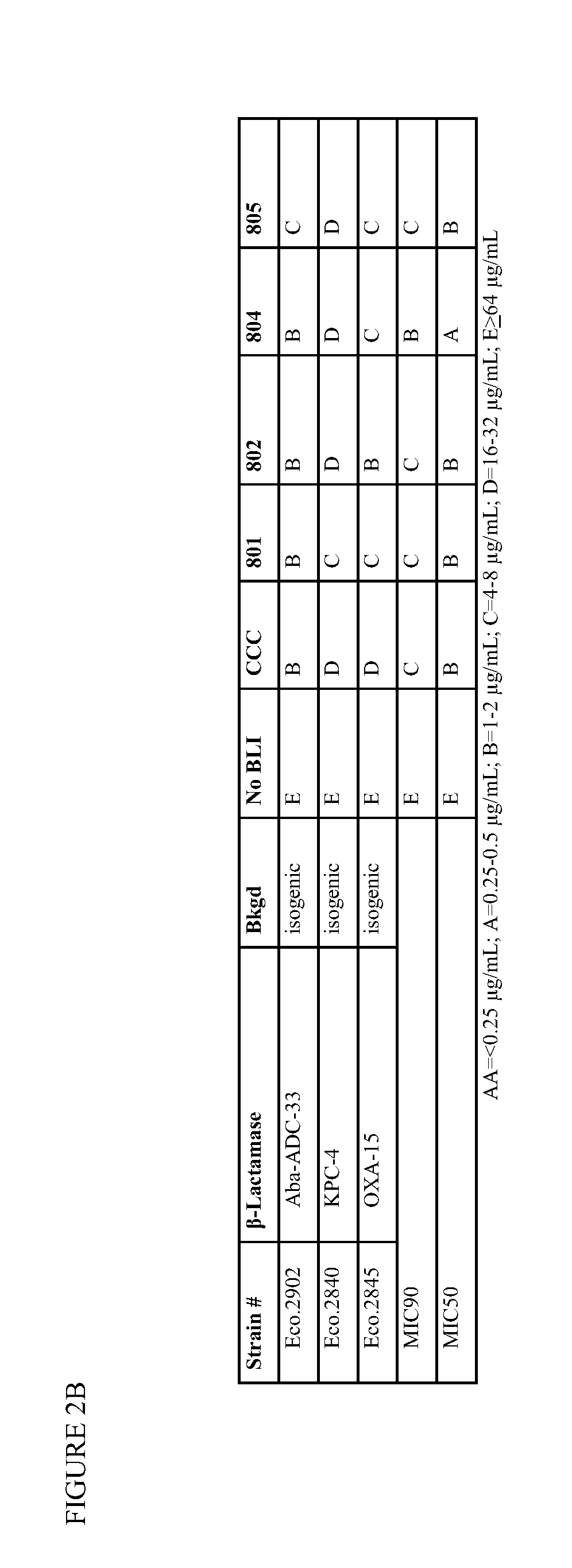
1,2,4-oxadiazole and 1,2,4-thiadiazole beta-lactamase inhibitors
β-Lactamase inhibitor compounds (BLIs) are disclosed, including compounds that have activity against class A, class C or class D β-lactamases. Methods of manufacturing the BLIs, and uses of the compounds in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions and antibacterial applications are also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
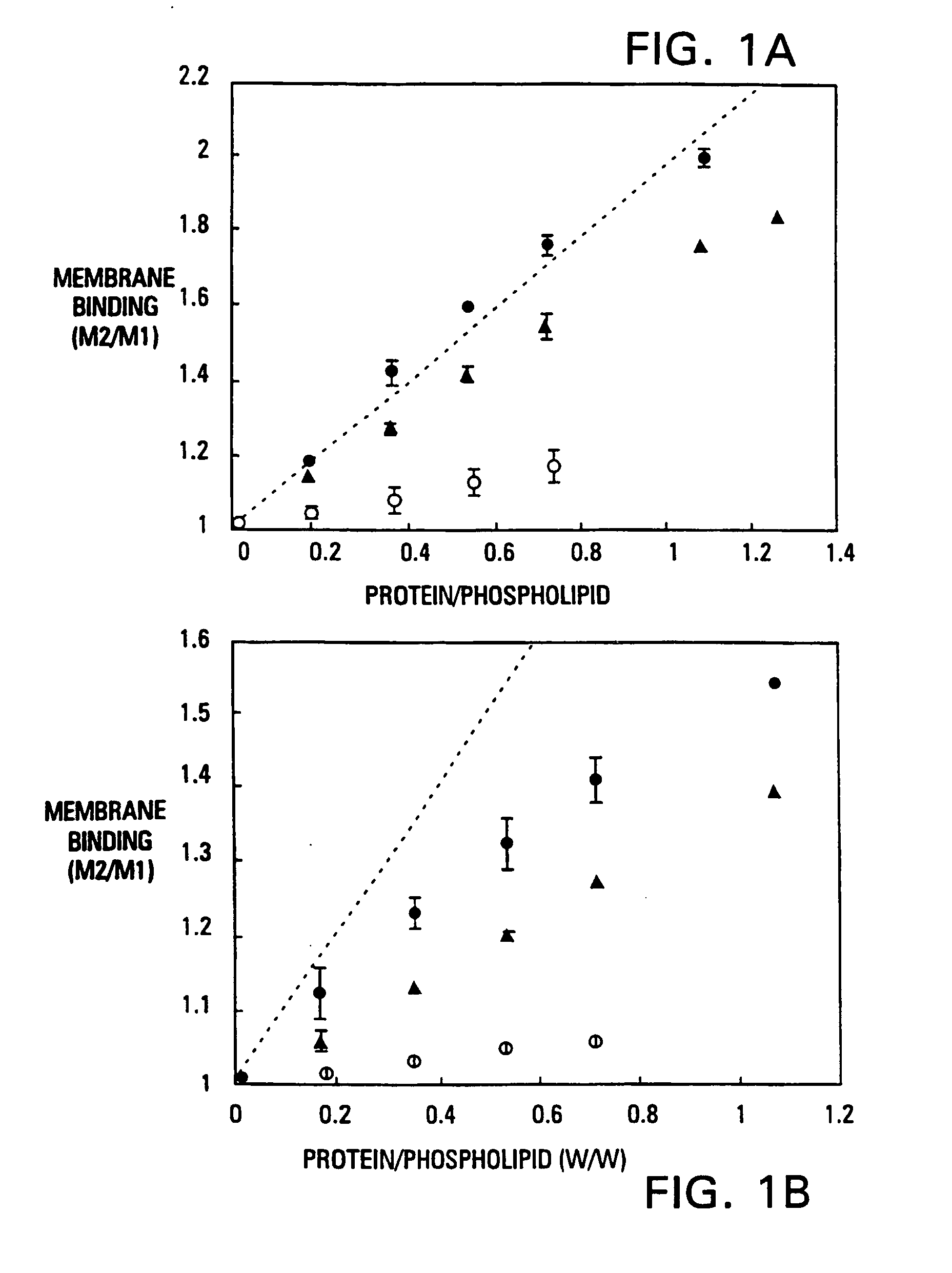
Modified vitamin K-dependent polypeptides
InactiveUS7220837B1High binding affinityHigh activityMammal material medical ingredientsSaccharide peptide ingredientsMembrane bindingMammal
The invention provides vitamin K-dependent polypeptides with enhanced membrane binding affinity. These polypeptides can be used to modulate clot formation in mammals. Methods of modulating clot formation in mammals are also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Modulation of antibody effector function by hinge domain engineering
ActiveUS20090221803A1Enhance prophylacticGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntigen binding
The present invention relates to novel molecules (Fc variants) comprising at least one antigen binding region and an Fc region that further comprises a modified hinge which alters the binding of Fc to one or more Fc ligand (e.g., FcγRs) and / or modulates effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more FcγR and / or CIq. Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Anti-IGF-1R antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070243194A1Inhibit functioningReduce dwell timeAnimal cellsSugar derivativesWilms' tumorMurine monoclonal antibody
The invention relates to antibodies which bind to insulin like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R) and uses thereof, in particular in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Specific human and murine monoclonal antibodies which inhibit IGF-1R-mediated pro-survival and tumor proliferation pathways, and variants, fragments, and derivatives thereof are provided. Also provided are specific human and murine monoclonal antibodies which block the ability of the ligands, insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and insulin like growth factor 2 (IGF-2) to bind to IGF-1R, as well as fragments, variants and derivatives of such antibodies. The invention also includes polynucleotides encoding the above antibodies or fragments, variants or derivatives thereof, as well as vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotides. The invention further includes methods of diagnosing and treating cancer using antibodies of the invention.
Owner:BIOGEN IDEC MA INC
Surface comprising DNA polymerase having mutations bound through an affinity tag
ActiveUS8323939B2High affinityReduce surface denaturation effectMicrobiological testing/measurementOn/in organic carrierPolymerase LActive surface
Active surface coupled polymerases, surfaces that include such polymerases, and methods of making and using surface-attached polymerases are provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Products and drug delivery vehicles
InactiveUS20040208844A1Ameliorate and prevent disease stateGood water solubilityAntipyreticAnalgesicsMedicineDrug delivery
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Anti-PD-1 (Programmed Death-1) antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN106519034AHigh binding affinityIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticInfective disorderAntibody
The invention provides an antibody specifically combined with PD-1 (Programmed Death-1) with high affinity, and also provides a nucleic acid molecule for coding the antibody, an expression vector and a host cell for expressing the antibody, and a production method of the antibody. In addition, the invention also provides an immune conjugate and a medicinal composition containing the antibody, and application of the antibody to the preparation of a medicine for treating multiple diseases (including a cancer, an infectious disease and an inflammatory disease).
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
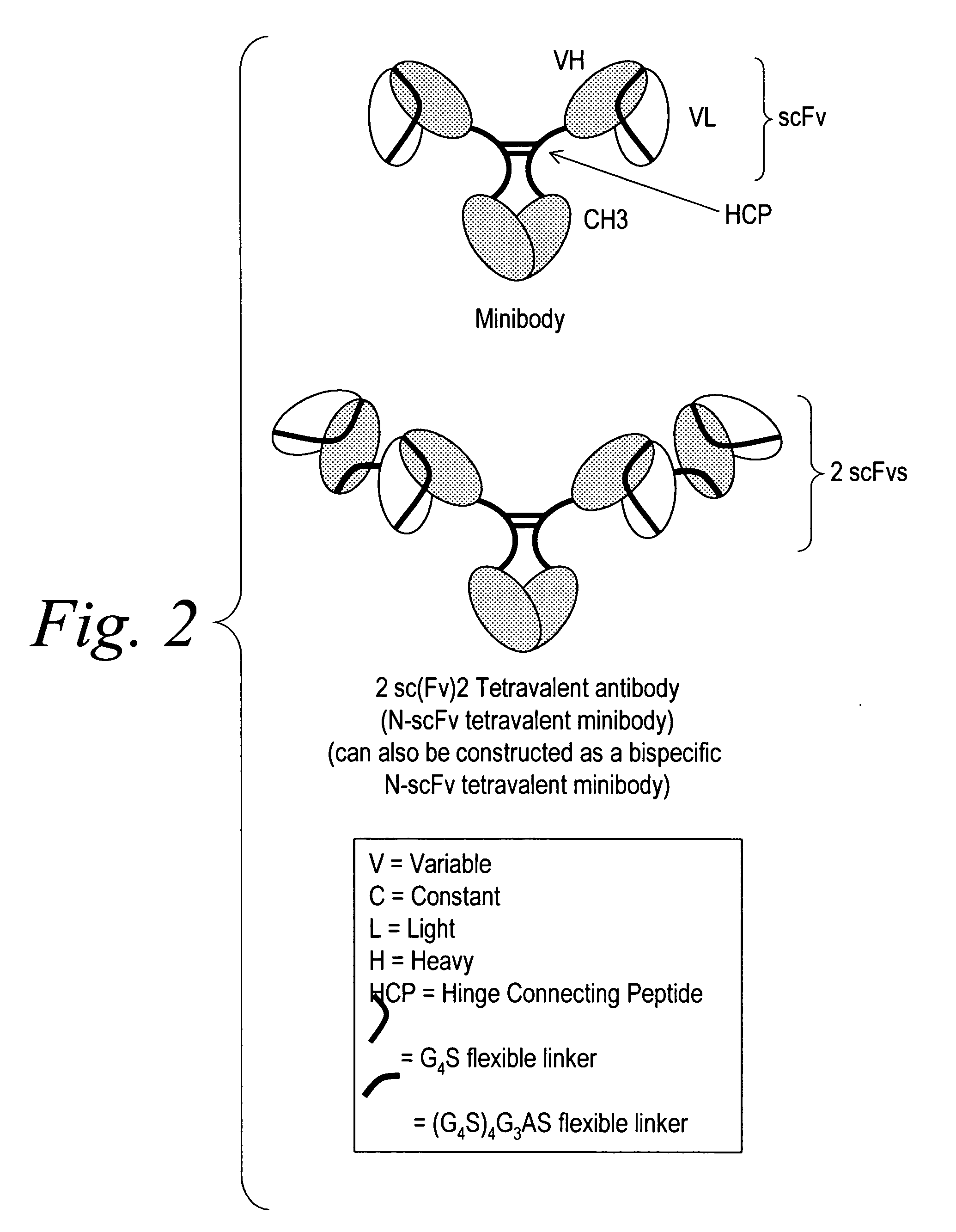
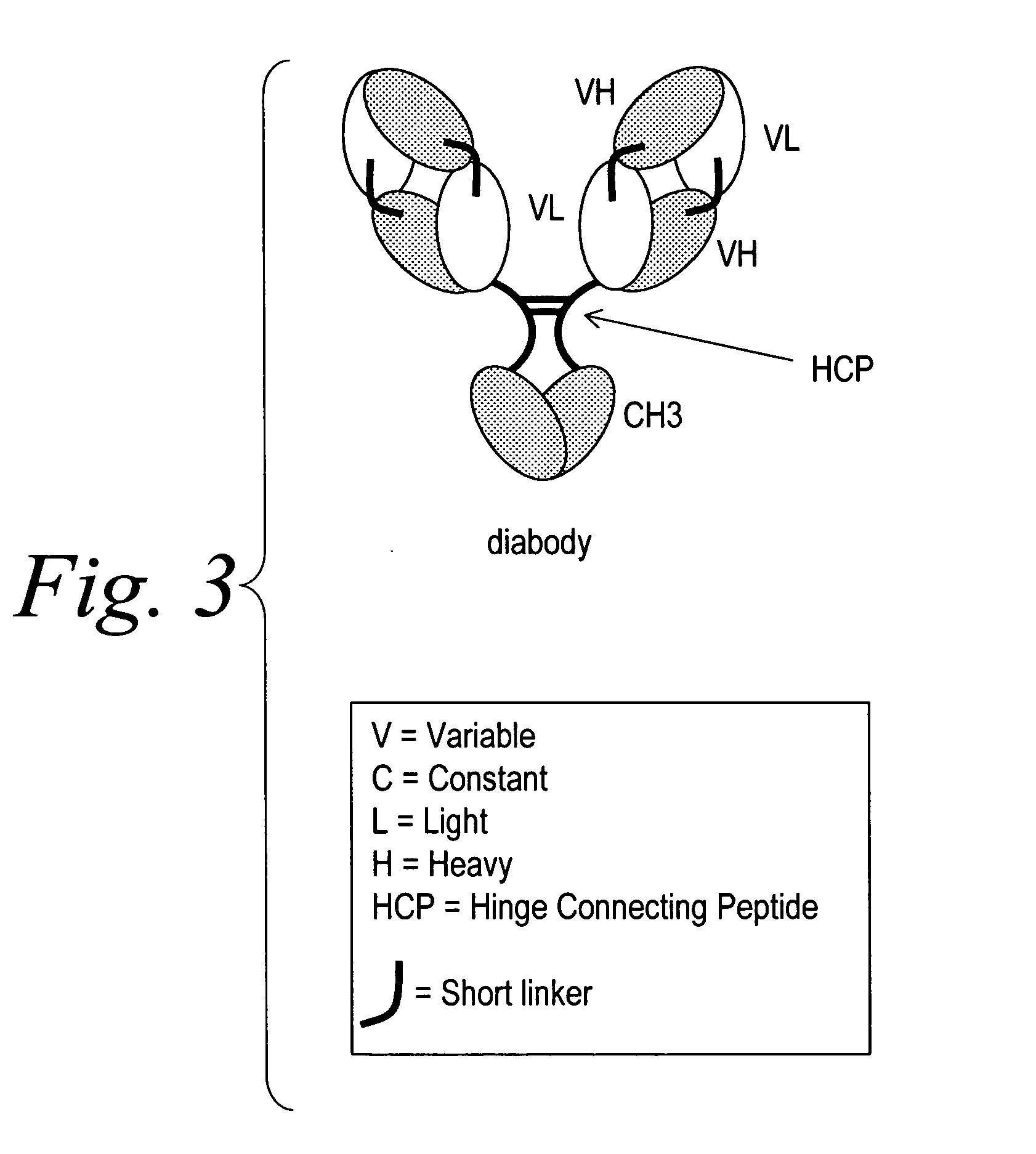
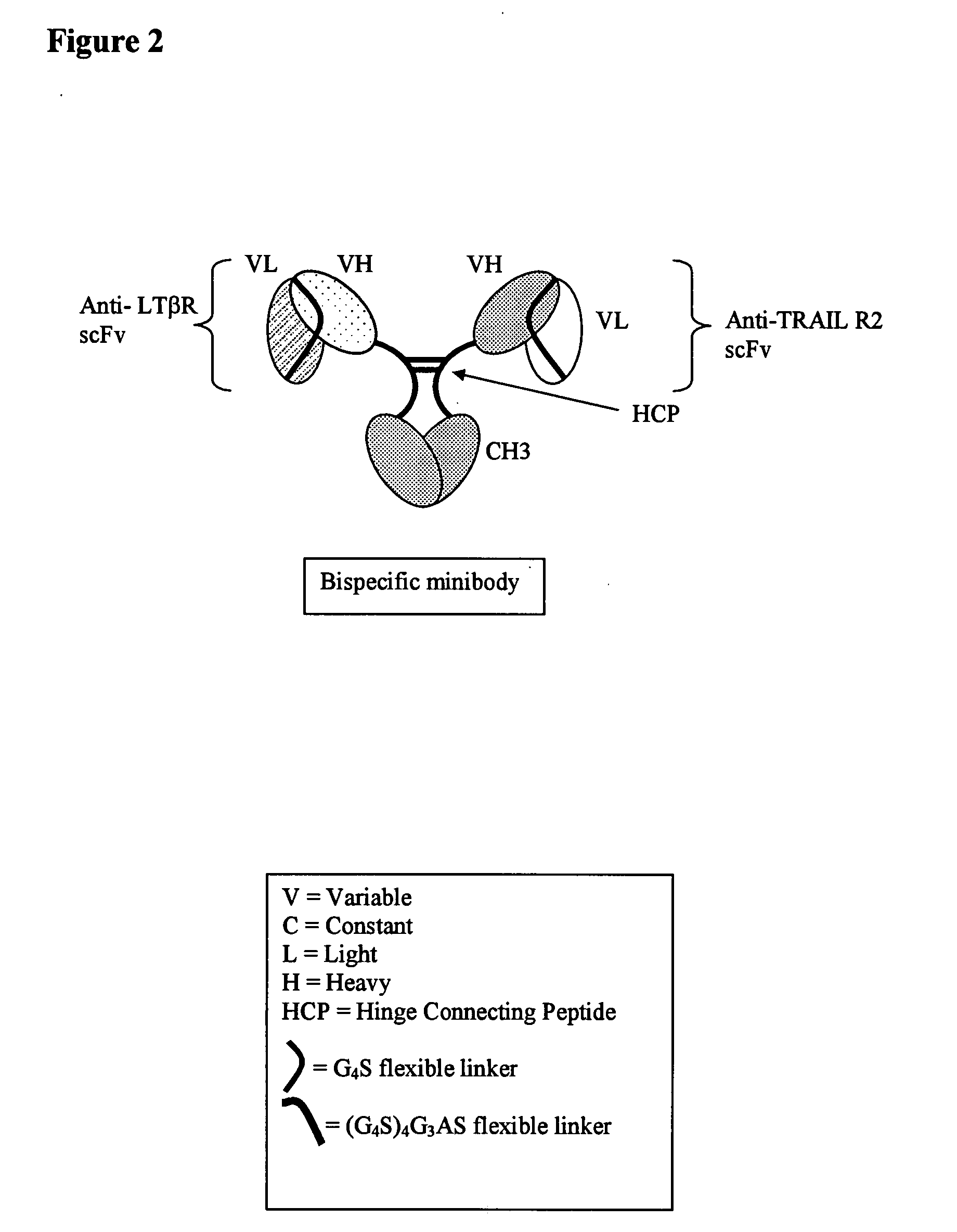
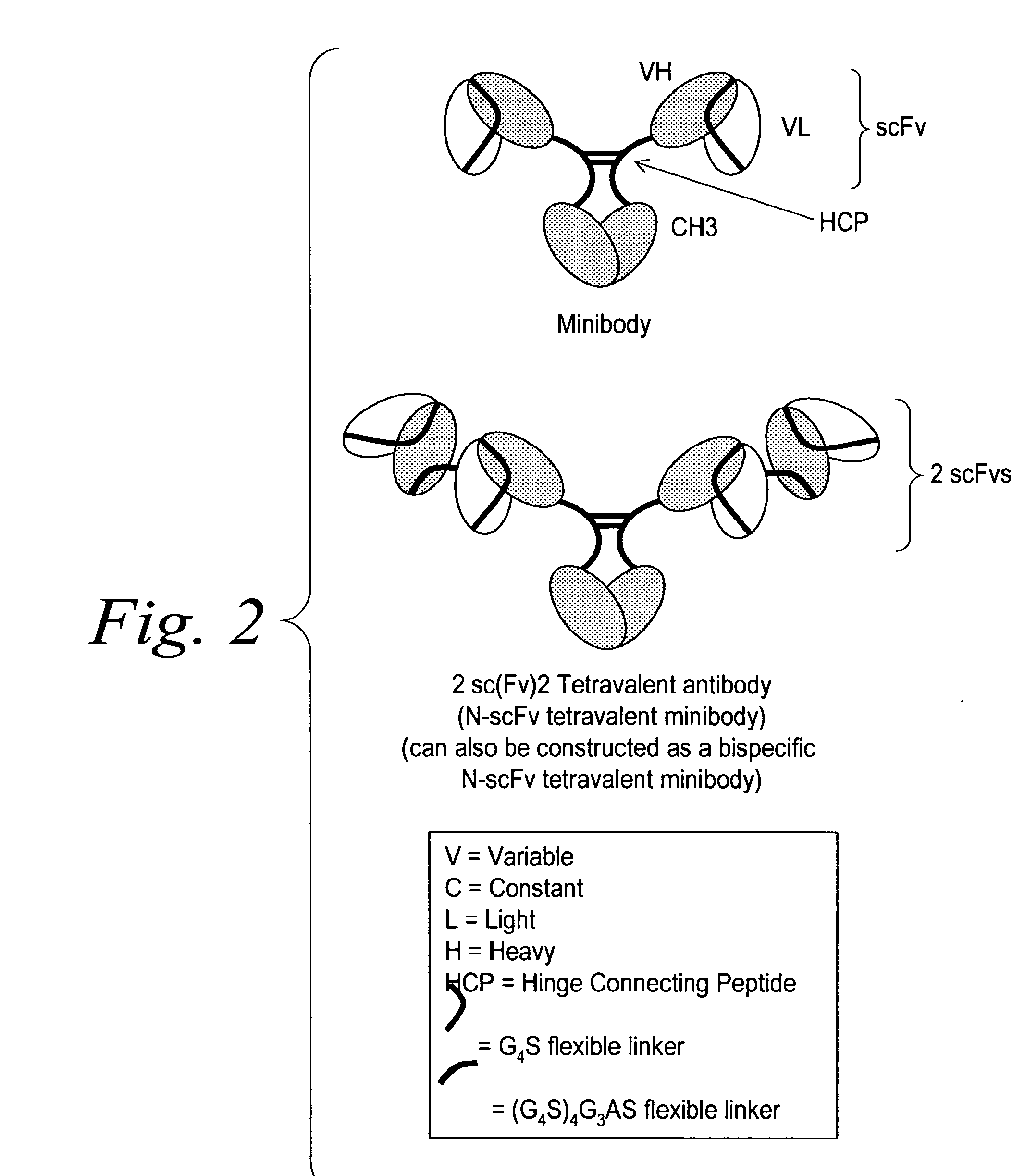
Multispecific binding molecules comprising connecting peptides
ActiveUS20090162380A1Enhance receptor signalingEnhanced signalSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsHeavy chainBinding site
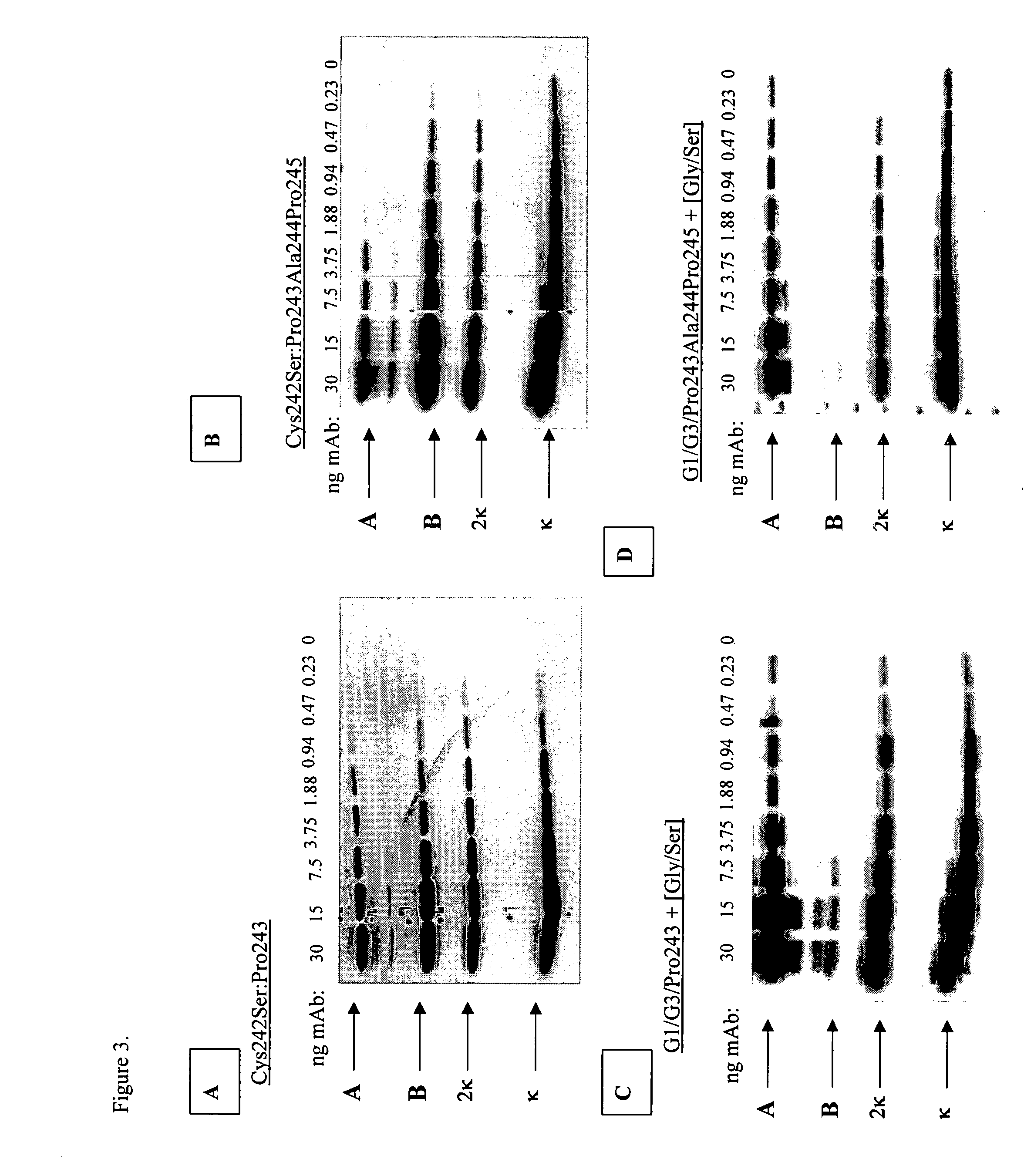
The instant invention describes novel multispecific binding molecules comprising synthetic connecting peptides. The synthetic connecting peptides result in the preferential synthesis of multispecific binding molecules comprising polypeptide chains that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. In addition, the invention pertains to compositions in which a majority of the multispecific binding molecules comprising polypeptide chain that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one intrachain disulfide linkage. In a specific embodiment, the invention pertains to compositions comprising multispecific dimeric binding molecules said molecules comprising at least a first binding site specific for a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor or a ligand of a TNF receptor family member and at least a second binding site; and at least two polypeptide chains comprising at least one heavy chain portion and a synthetic connecting peptide; wherein greater than about 50% of the dimers comprise polypeptide chains that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage.
Owner:BIOGEN IDEC MA INC
Antibodies with Altered Binding to FcRn and Methods of Using Same
InactiveUS20110081347A1Increased serum half-lifeHigh binding affinitySugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAutoimmune diseaseAntibody
This invention relates to antibodies with altered binding to FcRn, and particularly antibodies having enhanced binding to FcRn and / or enhanced serum half-lives. The invention also relates to methods of using the antibodies and compositions comprising them in the diagnosis, prognosis and therapy of diseases such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disorders, and infectious disease.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
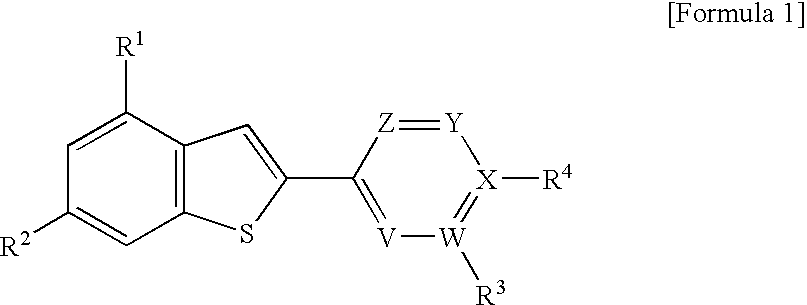
2-arylbenzothiophene derivatives or pharceutically acceptable salts thereof, preparation method thereof, and pharceutical composition for the diagnosis or treatment of degenerative brain disease containing the same as active ingredient
InactiveUS20100261727A1Suppress generationHigh binding affinityBiocideNervous disorderThiophene derivativesBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
2-arylbenzothiophene derivatives or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, a preparation method thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition for the diagnosis or treatment of degenerative brain disease containing the same as an active ingredient. Since the 2-arylbenzothiophene derivatives of Formula 1 have a relatively high binding affinity for β-amyloid, they can be used as diagnostic reagents for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease at an early stage by non-invasive techniques when they are labeled with radioisotopes:wherein R1-R4, V, W, X, Y and Z are as defined in the Detailed Descript of the specification. Further, when the pharmaceutical composition containing the 2-arylbenzothiophene derivative binds with a low-molecular weight β-amyloid peptide binding compound, generation of malignant high-molecular weight β-amyloid deposits is minimized. Accordingly, the pharmaceutical composition can be used as a therapeutic agent of degenerative brain disease such as Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:IND UNIV COOP FOUND SOGANG UNIV
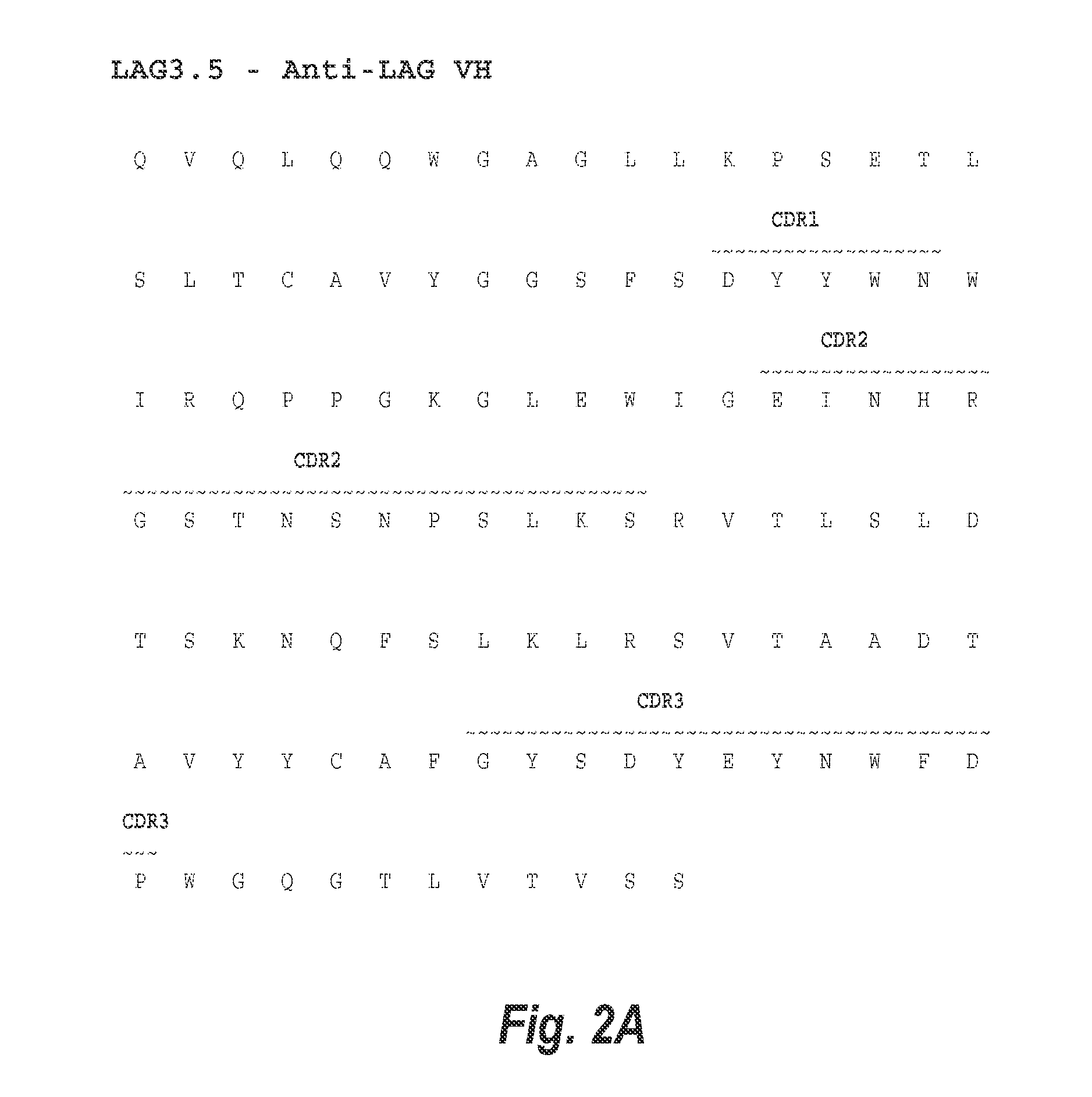
Optimization of antibodies that bind lymphocyte activation gene-3 (lag-3), and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150307609A1Improve stabilityHigh binding affinitySugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLymphocyteLymphocyte activation
The present invention provides isolated monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind LAG-3, and have optimized functional properties compared to previously described anti-LAG-3 antibodies, such as antibody 25F7 (US 2011 / 0150892 A1). These properties include reduced deamidation sites, while still retaining high affinity binding to human LAG-3, and physical (i.e., thermal and chemical) stability. Nucleic acid molecules encoding the antibodies of the invention, expression vectors, host cells and methods for expressing the antibodies of the invention are also provided, as well as immunoconjugates, bispecific molecules and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies. The present invention also provides methods for detecting LAG-3, as well as methods for treating stimulating immune responses using an anti-LAG-3 antibody of the invention. Combination therapy, in which the antibodies are co-administered with at least one additional immunostimulatory antibody, is also provided.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
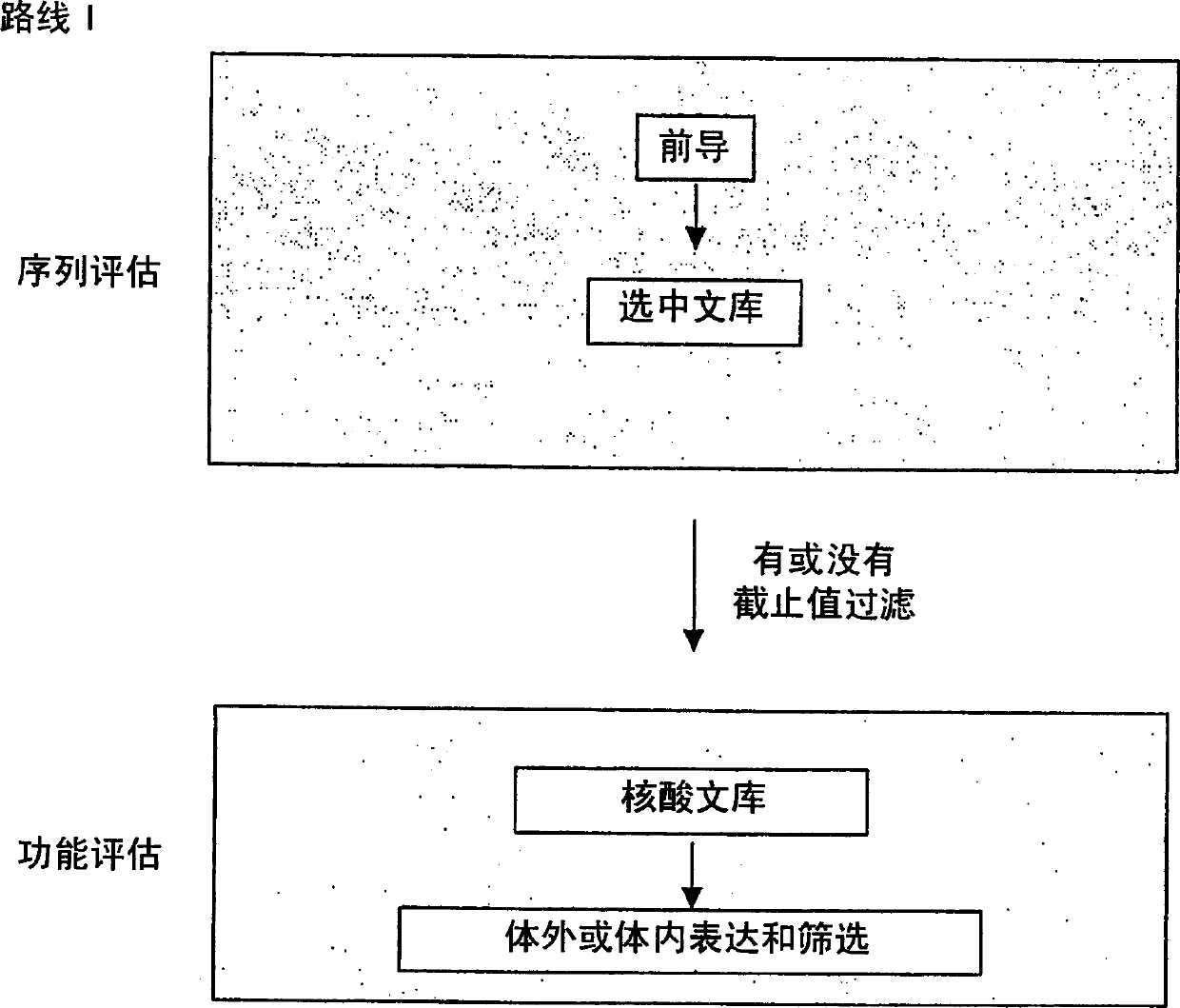
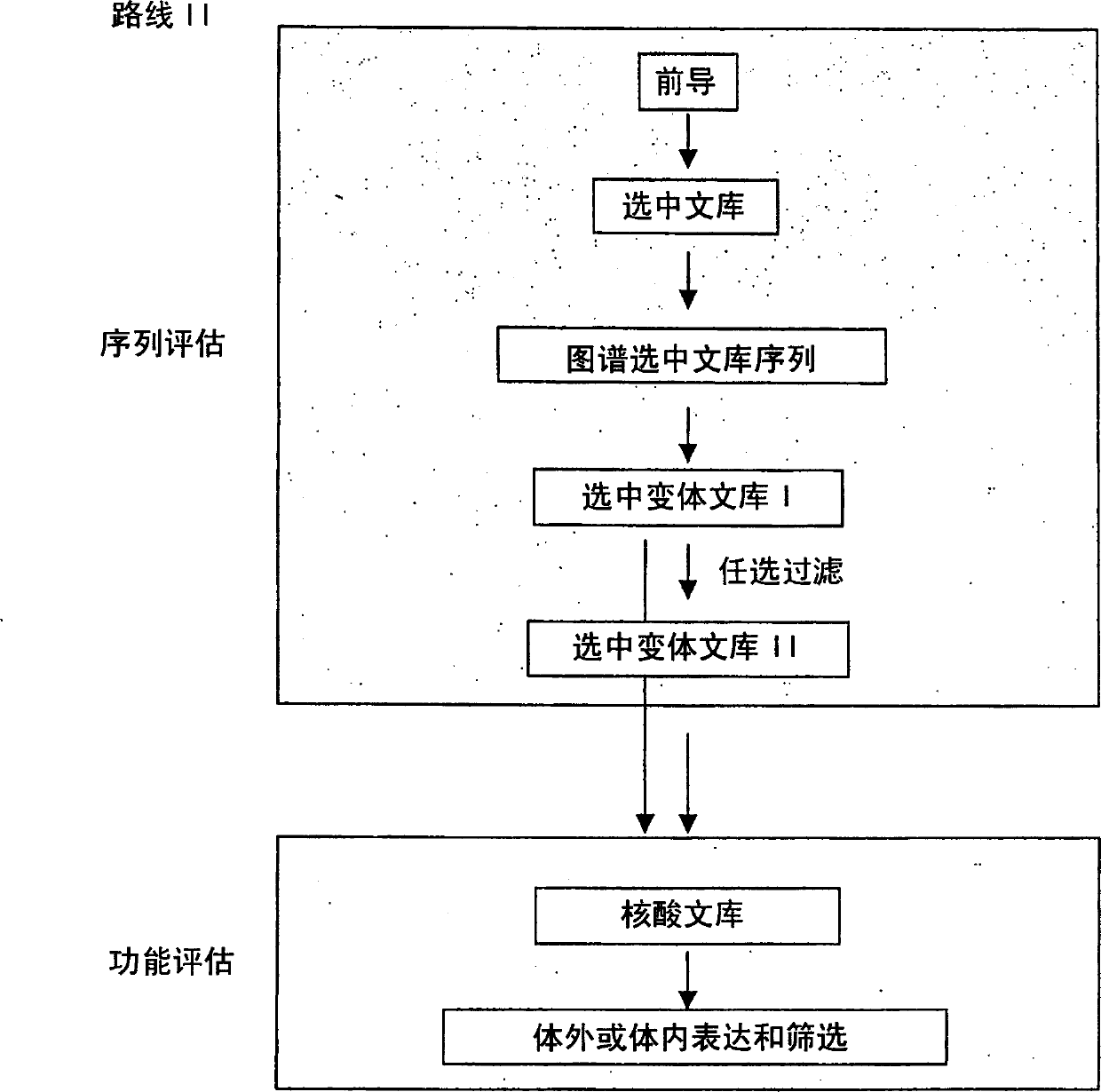
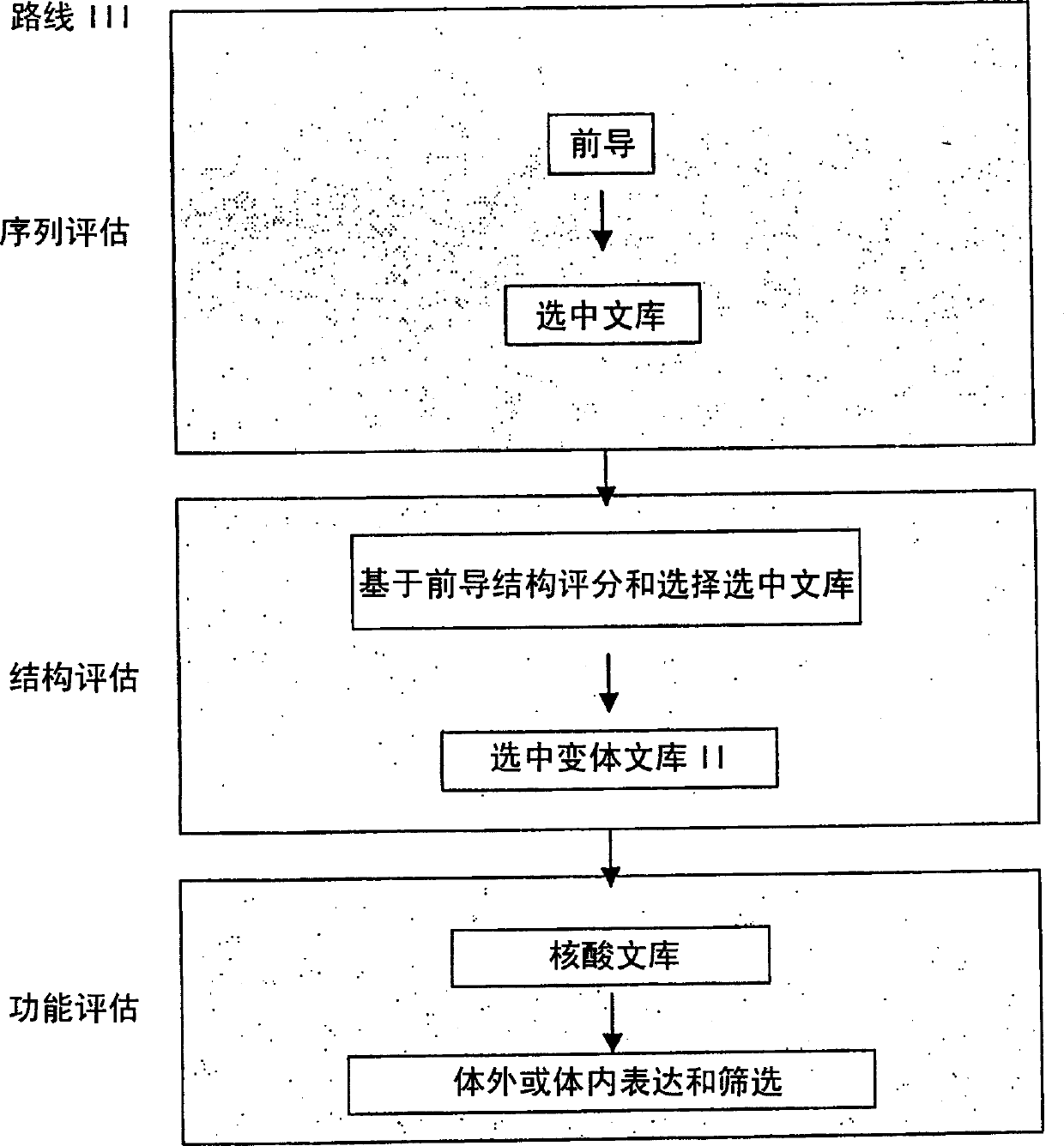
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
The present invention provides methods for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimal proteins with desired biological functions, such as improved binding affinity for biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The method is performed in silico in a high-throughput fashion by mining the ever-expanding database of protein sequences in all living things, especially humans. In one embodiment, a method of constructing a designer protein library comprises the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, referred to as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of test protein sequences; Select at least two peptide fragments having at least 15% sequence identity with the leader sequence from each test protein sequence, and the selected peptide fragments form a selection library; a library of designed proteins is formed by replacing the leader sequence with the selection library. Libraries of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to generate libraries of recombinant proteins that can be screened for new or improved functions relative to lead proteins, such as antibodies against a therapeutically important target.
Owner:埃博马可西斯公司
Modified binding molecules comprising connecting peptides
ActiveUS20090041758A1High binding affinityImprove localizationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDisulfide bondPeptide
The instant invention describes methods of separating or preferentially synthesizing dimers which are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from dimers which are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from a mixture comprising the two types of polypeptide dimers. These forms can be separated from each other using hydrophobic interaction chromatography. In addition, the invention pertains to connecting peptides that result in the preferential biosynthesis of dimers that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or that are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention also pertains to compositions in which a majority of the dimers are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention still further pertains to novel binding molecules, e.g., comprising connecting peptides of the invention.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Antibodies to IL-17A
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
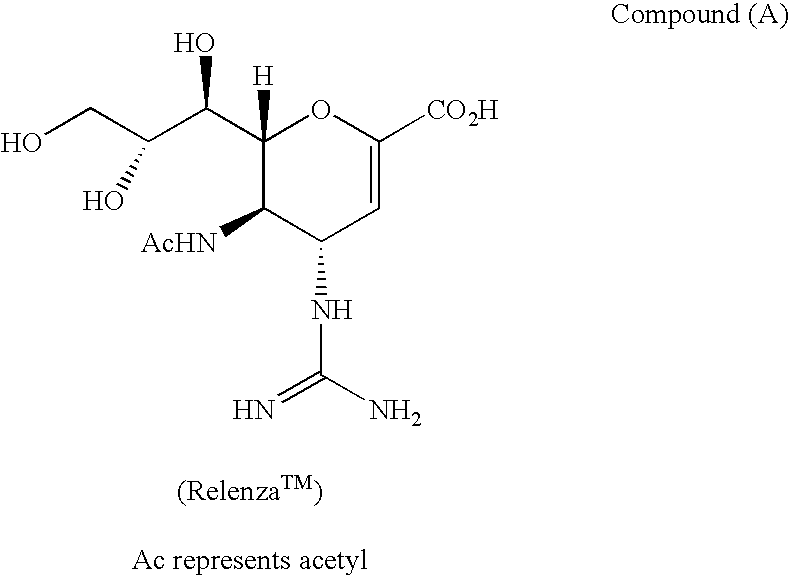
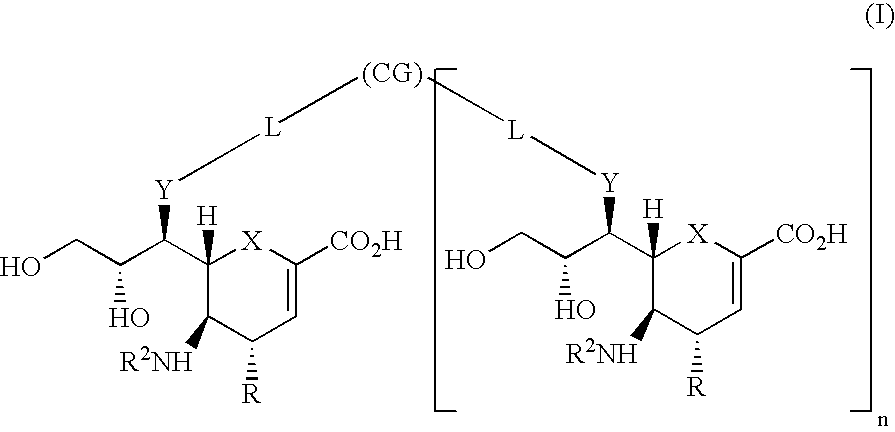
Multivalent neuraminidase inhibitor conjugates
InactiveUS7205333B2High binding affinityReduce capacityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementReactive siteActive site
The invention relates to a multimeric compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or derivative thereof which comprises three or more neuraminidase-binding groups attached to a spacer or linking group, in which the neuraminidase-binding group is a compound which binds to the active site of influenza virus neuraminidase, but is not cleaved by the neuraminidase. The invention also relates to processes for the preparation of the multimeric compound defined above, pharmaceutical compositions containing them or methods for the treatment and / or prophylaxis of a viral infection involving them.
Owner:BIOTA SCI MANAGEMENT PTI LTD
Eph receptor Fc variants with enhanced antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity
InactiveUS7659374B2Altered binding affinityHigh binding affinityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionComplement-dependent cytotoxicityImmunologic specificity
The present invention relates to novel Fc variants that immuno-specifically bind to an Eph receptor. The Fc variants comprise a binding region that immunospecifically binds to an Eph receptor and an Fc region that further comprises at least one novel amino acid residue which may provide for enhanced effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more Fc ligand (e.g., FcγR, C1q). Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants that immunospecifically bind to an Eph receptor, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
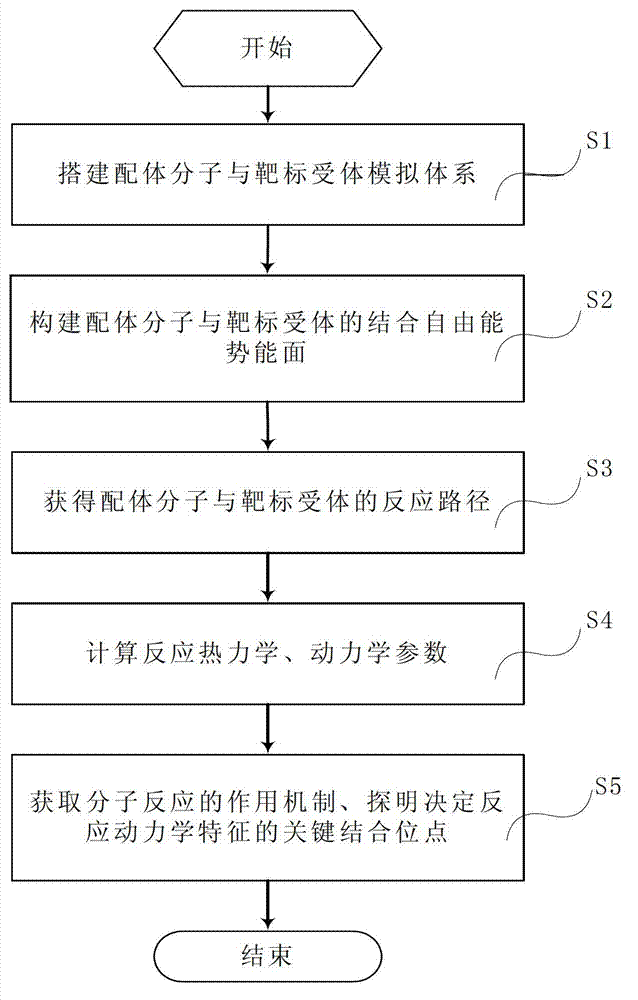
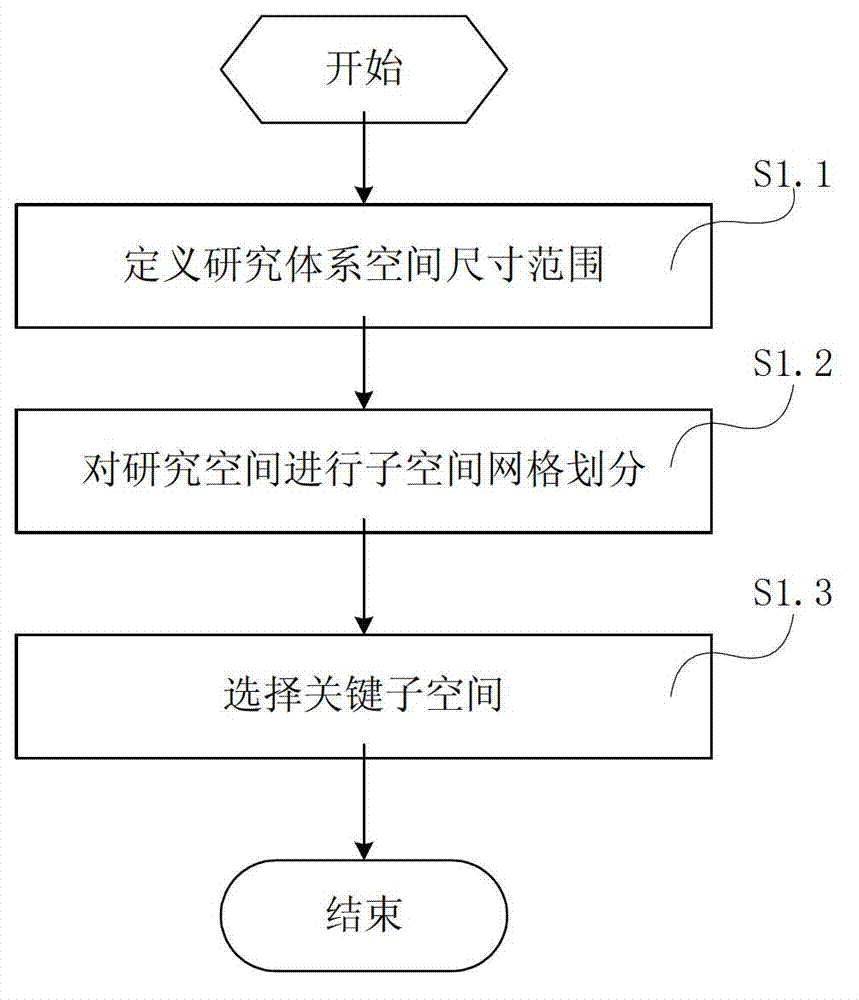
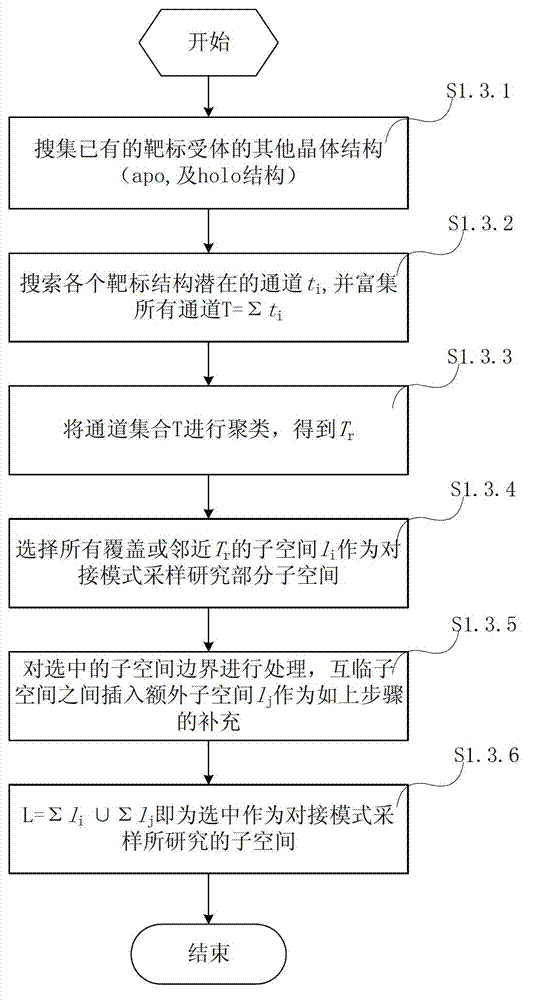
Method and system for simulating ligand molecule and target receptor reaction and calculating and forecasting thermodynamics and kinetics parameters of reaction
InactiveCN102930152AAvoid Computational BiasImprove biological activitySpecial data processing applicationsComputer basedChemistry
The invention relates to a method and application system for simulating ligand molecule and target receptor reaction based on a computer and calculating and forecasting thermodynamics and kinetics parameters of the reaction. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: designing a method for calculating combined free energy of a ligand molecule and a target receptor, and designing a multi-target molecule docking method and developing an application system of the docking method based on the calculating method; simulating and sampling the interaction mode of the ligand molecule and the target receptor by the system, grading the free energy combination of the ligand molecule and the target receptor, and building a method and system for the potential energy surface of the combined free energy of the ligand molecule and the target receptor according to the simulating and sampling result; building a method and system for identifying a reaction path of the ligand molecule and the target receptor according to the potential energy surface; and determining a active site and a transition site of the reaction to calculate the thermodynamics and kinetics parameters. The method and the system provide important basis and a forecast evaluation method for drug development, and are expected to improve the drug development efficiency and save experimental expenses greatly, thus serving as an effective auxiliary means for the drug development.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com