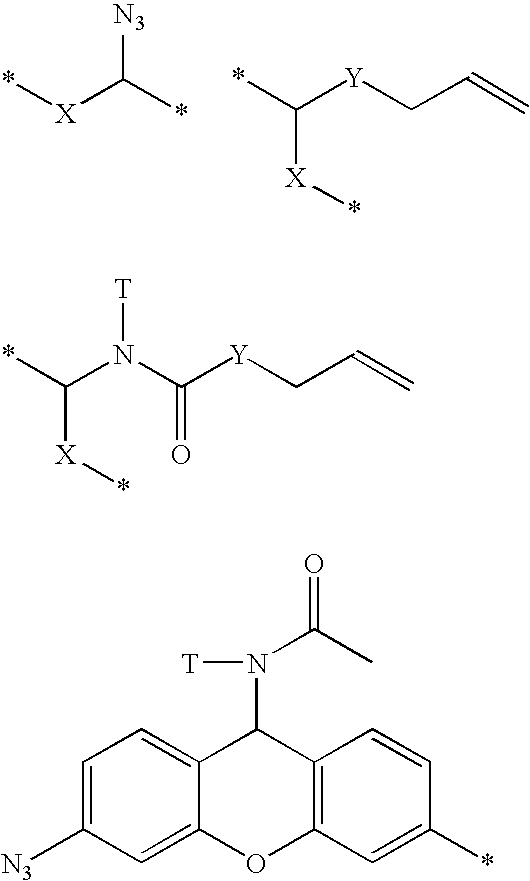
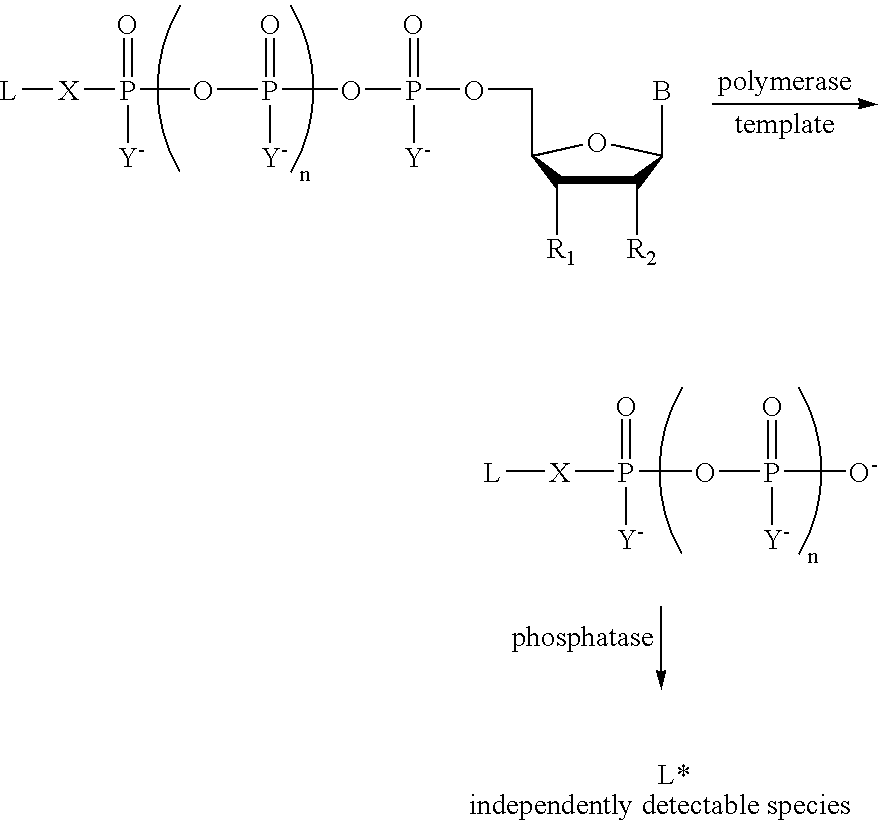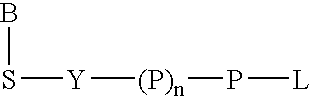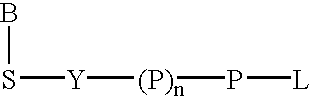Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2085 results about "Polymerase L" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
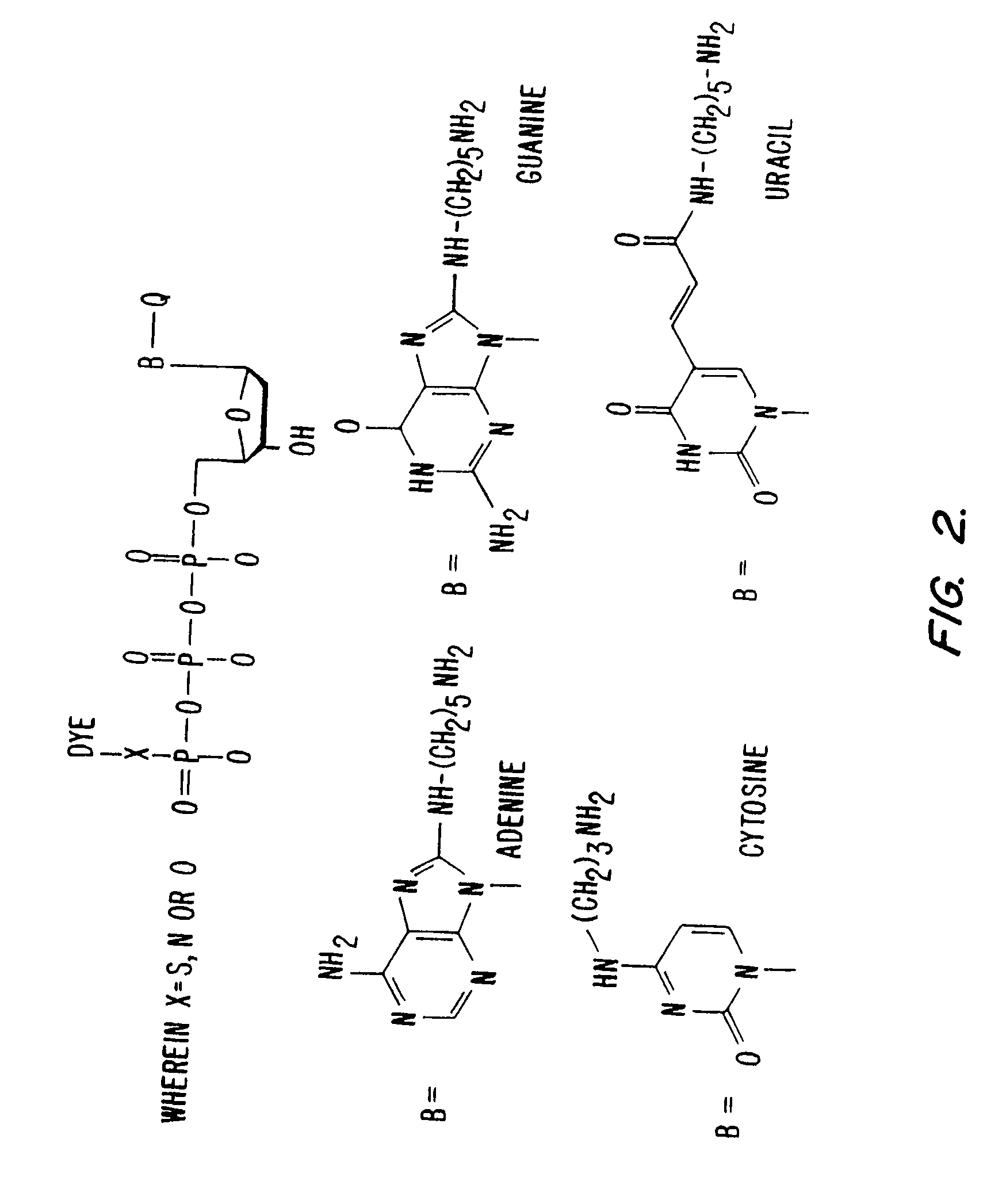
A polymerase is an enzyme (EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids.
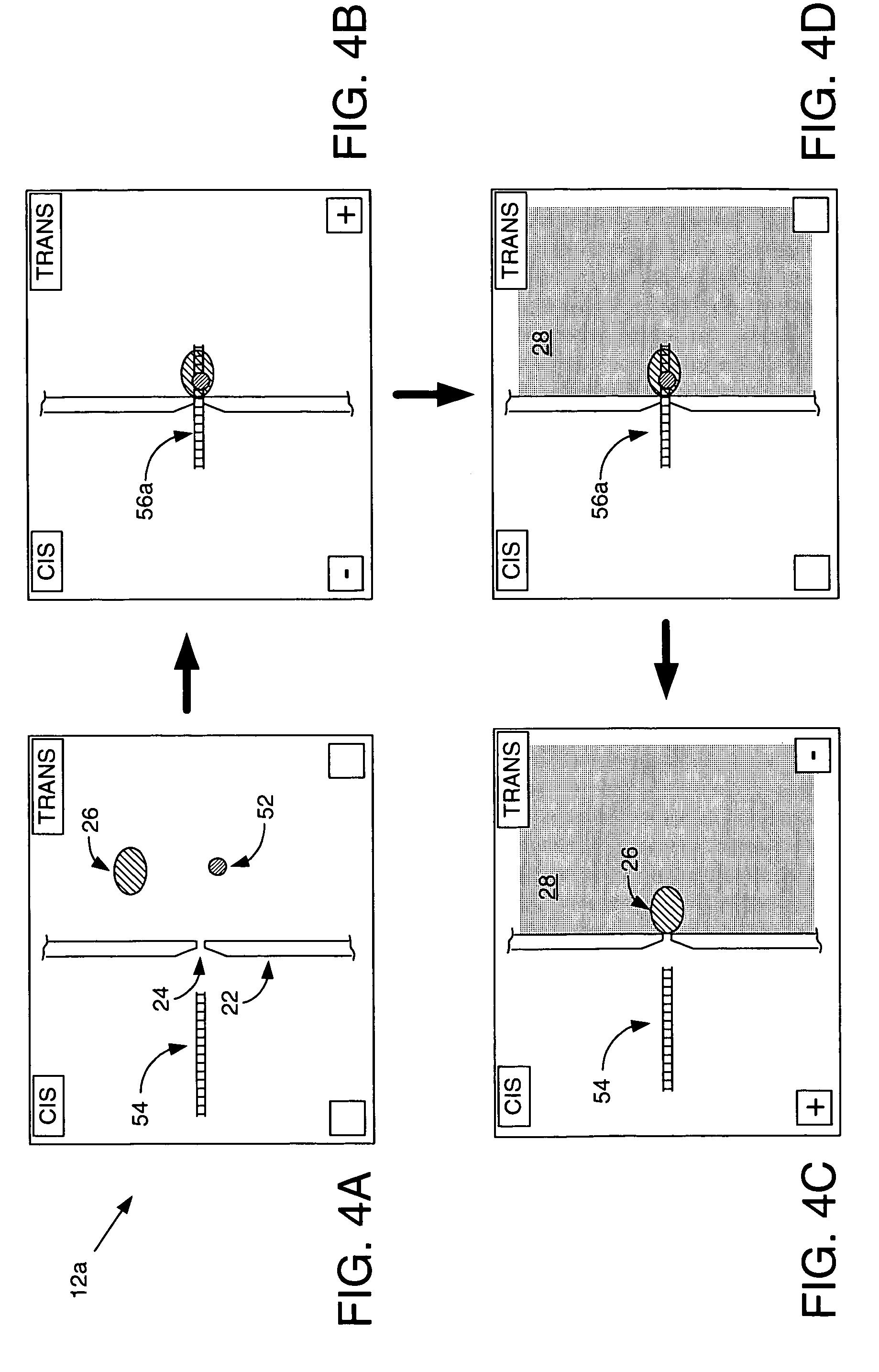
Polynucleotide sequencing
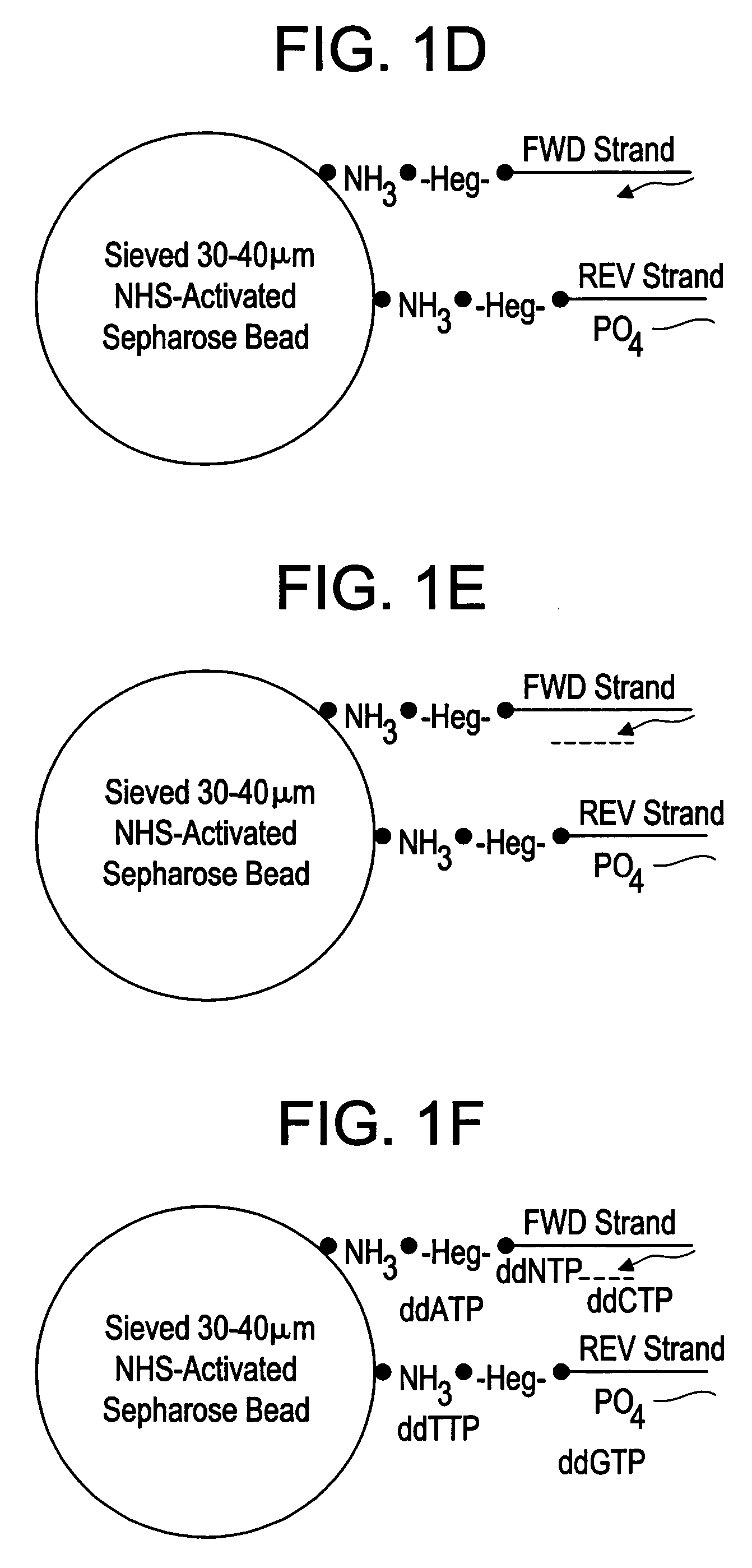
InactiveUS6833246B2Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
The invention relates to the sequencing of a target polynucleotide sequence, immobilized on a solid support, using the polymerase reaction to extend a suitable primer and characterizing the sequential addition of labelled bases. The present invention further relates to the presence of a polymerase enzyme that retains a 3' to 5' exonuclease function, which is induced to remove an incorporated labelled base after detection of incorporation. A corresponding non-labelled base may then be incorporated into the complementary strand to allow further sequence determinations to be made. Repeating the procedure allows the sequence of the complement to be identified, and thereby the target sequence.
Owner:SOLEXA
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100120098A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingPolymerase L
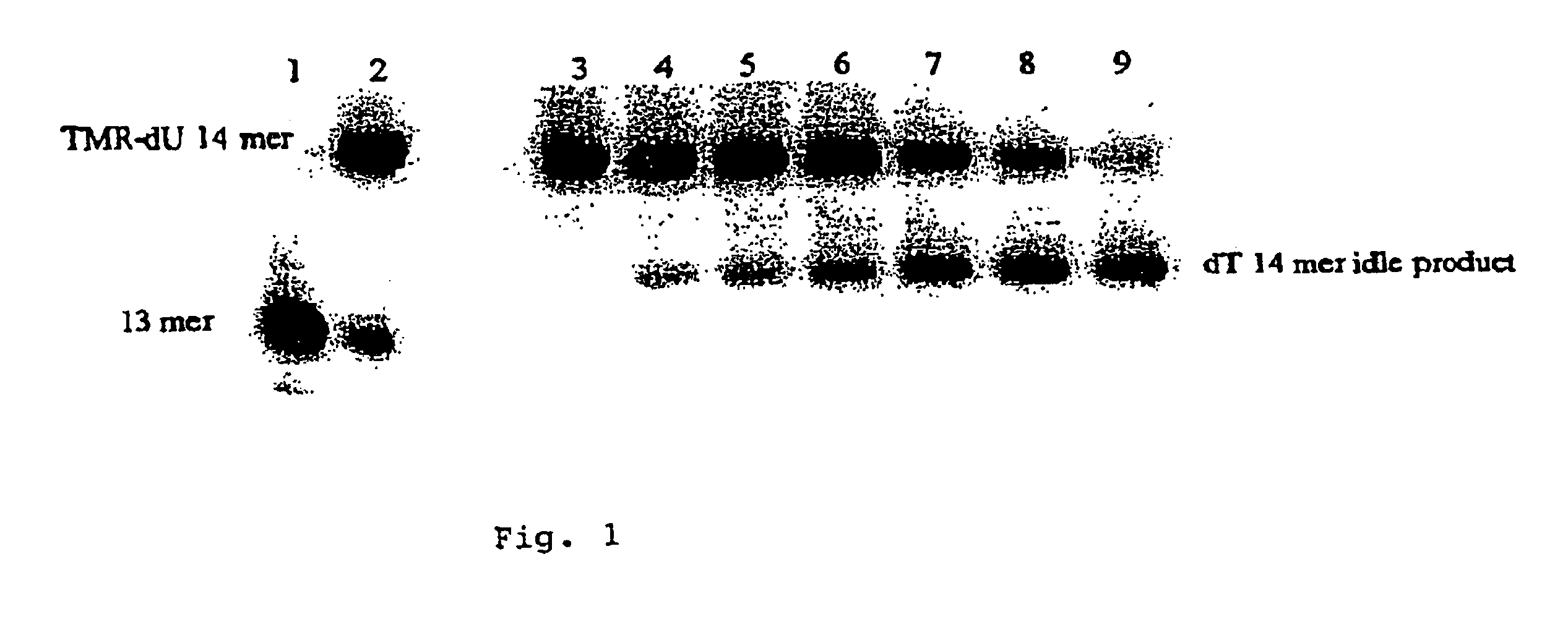
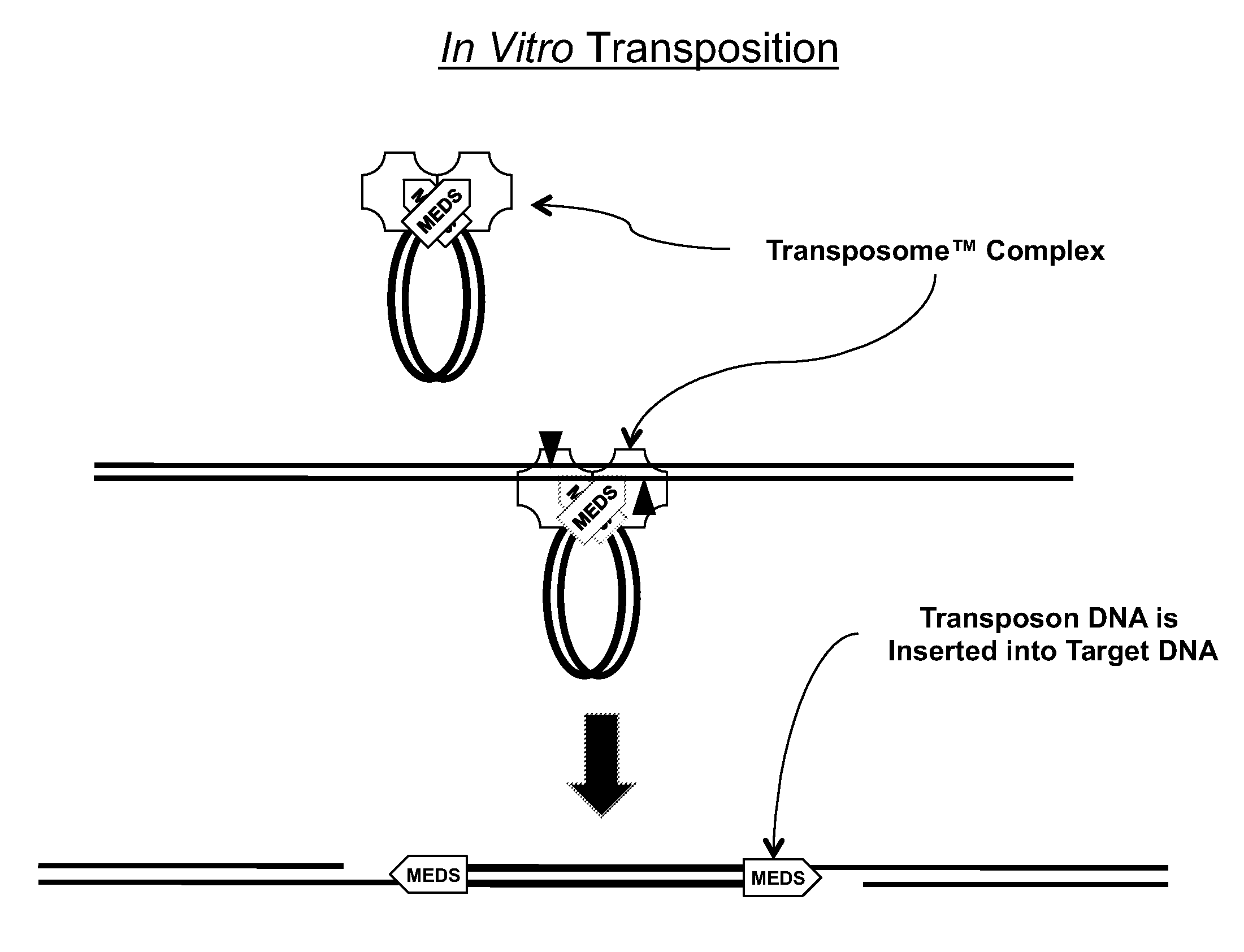
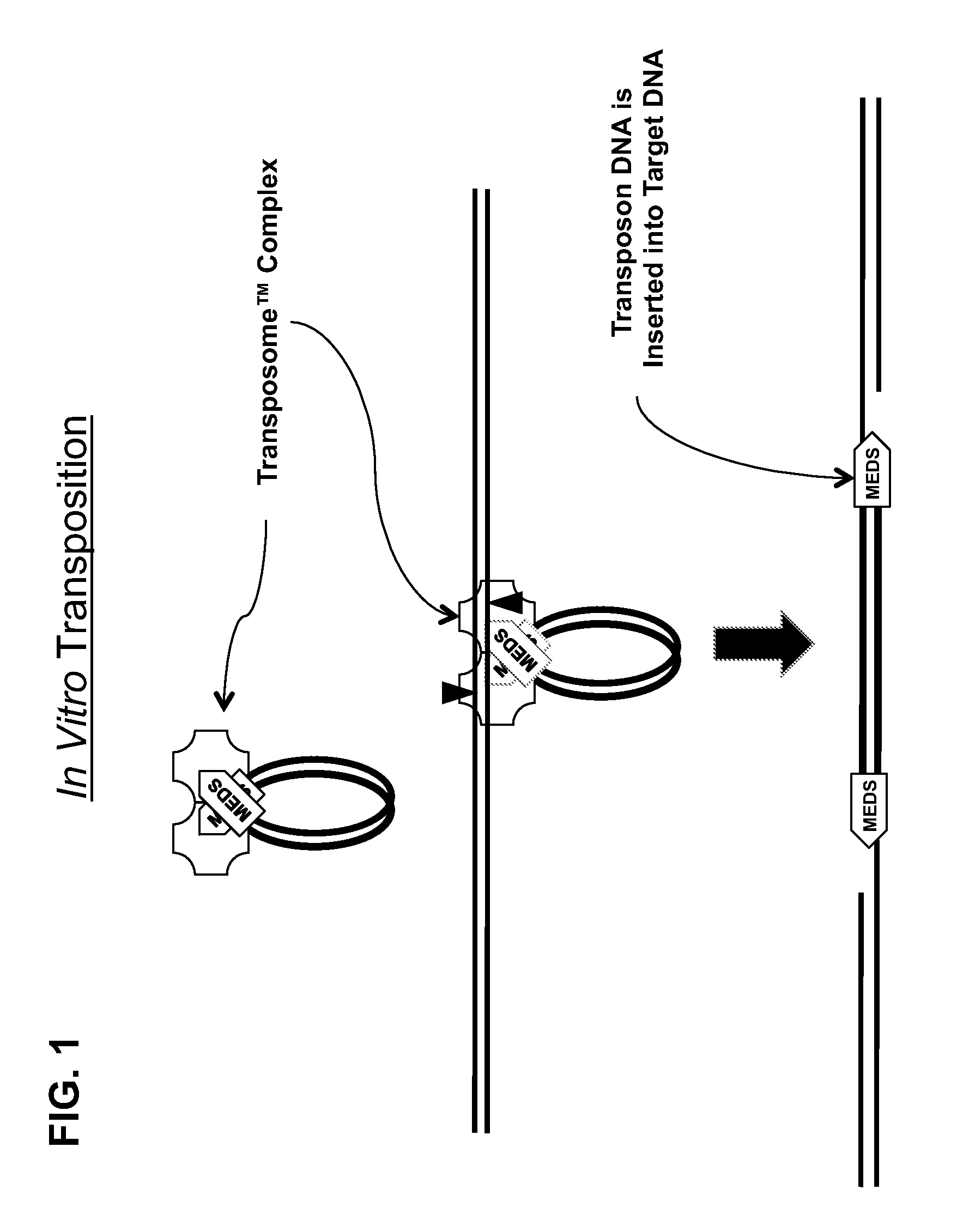
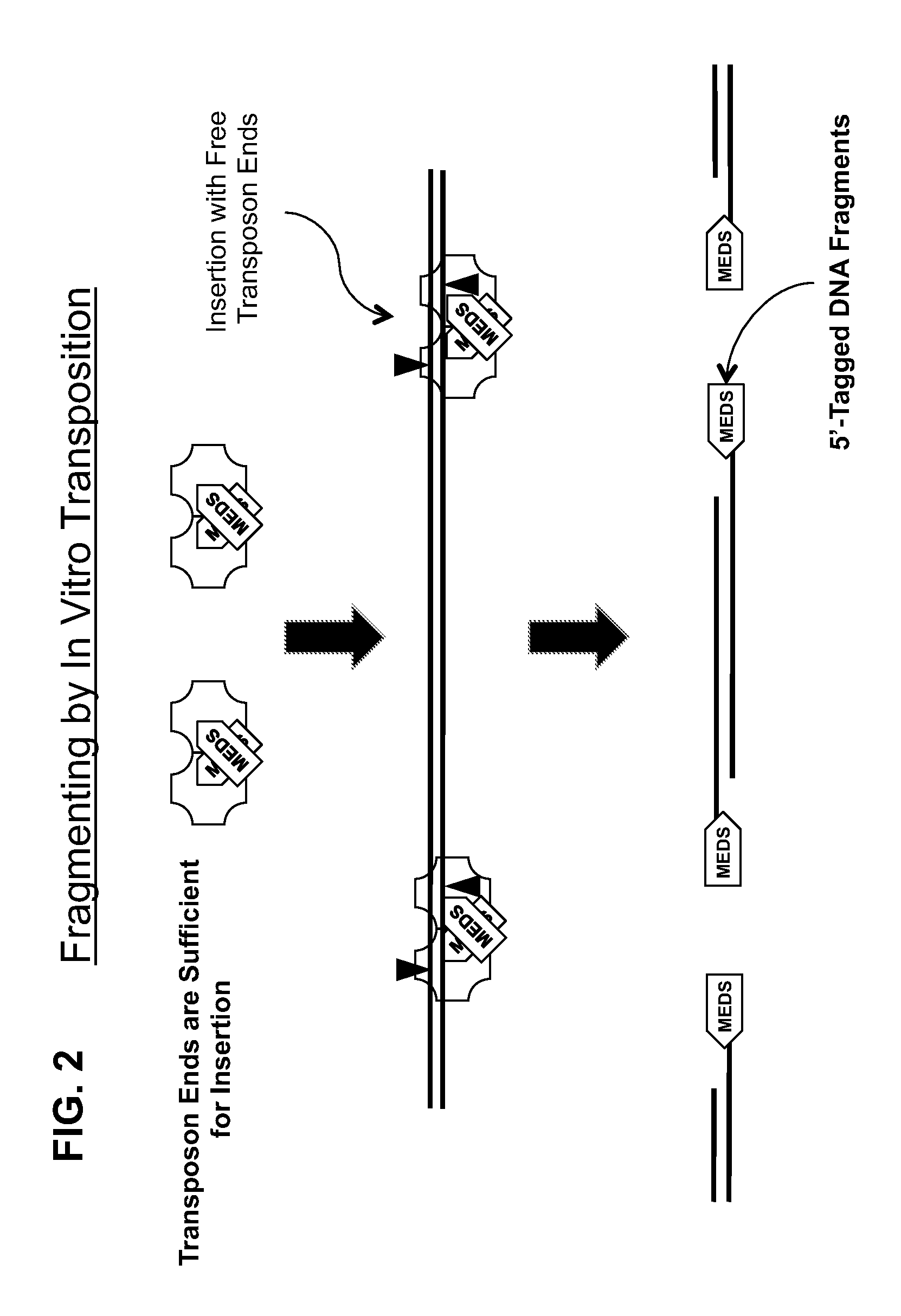
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for using a transposase and a transposon end for generating extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, then using a DNA polymerase for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged single-stranded DNA fragments without performing a PCR amplification reaction, wherein the first tag on the 5′-ends exhibits the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally, an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second tag on the 3′-ends exhibits a different sequence from the sequence exhibited by the first tag. The method is useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including processes for metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and comparative genomic sequencing (CGS), including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called “next-generation sequencing.)
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Polymerases
ActiveUS20060281109A1Improve the level ofProceed efficientlySugar derivativesHydrolasesModified dnaPolymerase L
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
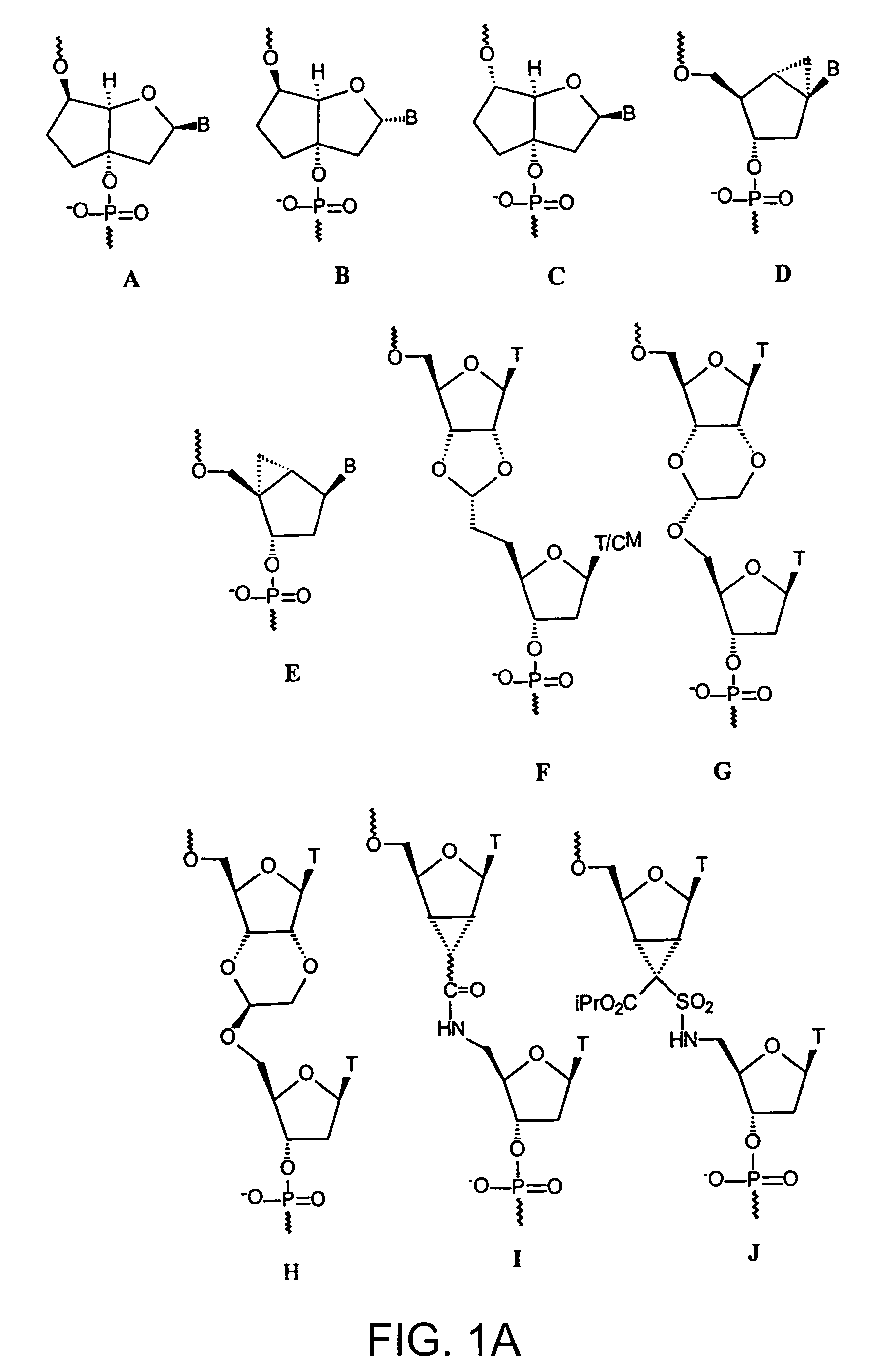
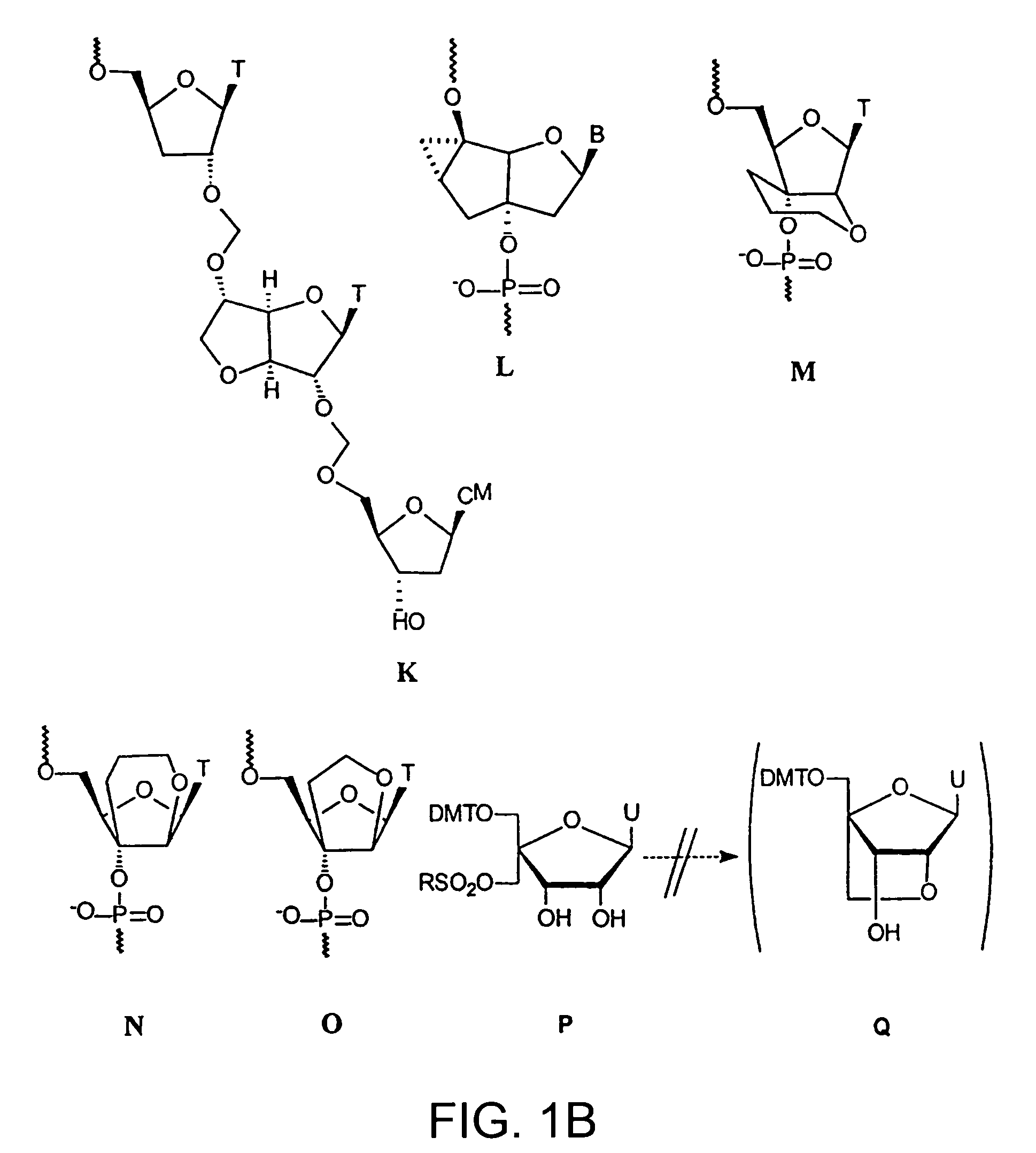
Oligonucleotide analogues
The present invention relates to novel bicyclic and tricyclic nucleoside and nucleotide analogues as well as to oligonucleotides comprising such elements. The nucleotide analogues, LNAs (Locked Nucleoside Analogues), are able to provide valuable improvements to oligonucleotides with respect to affinity and specificity towards complementary RNA and DNA oligomers. The novel type of LNA modified oligonucleotides, as well as the LNAs as such, are useful in a wide range of diagnostic applications as well as therapeutic applications. Among these can be mentioned antisense applications, PCR applications, strand displacement oligomers, as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases, as nucleotide based drugs, etc. The present invention also relates to such applications.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
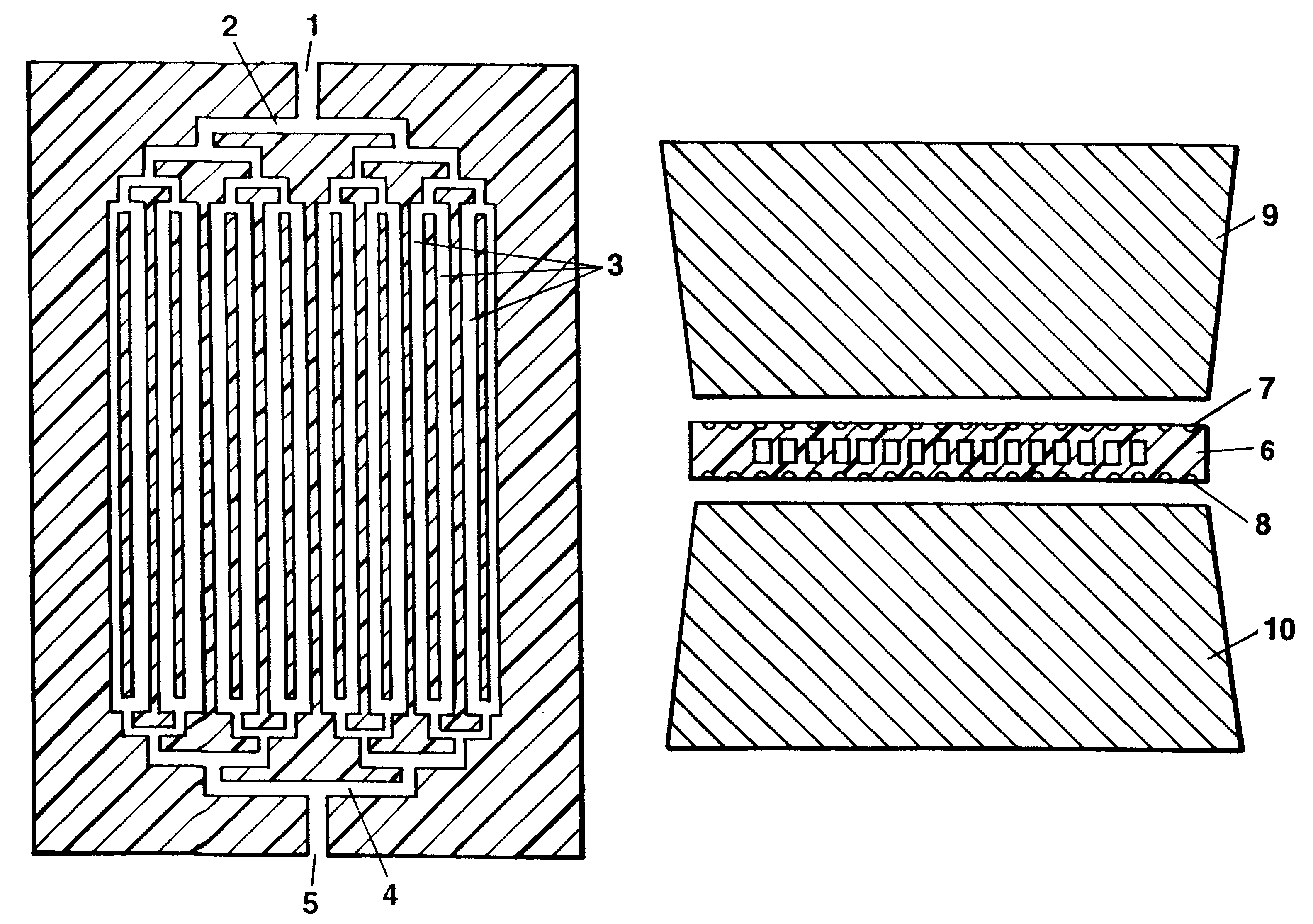
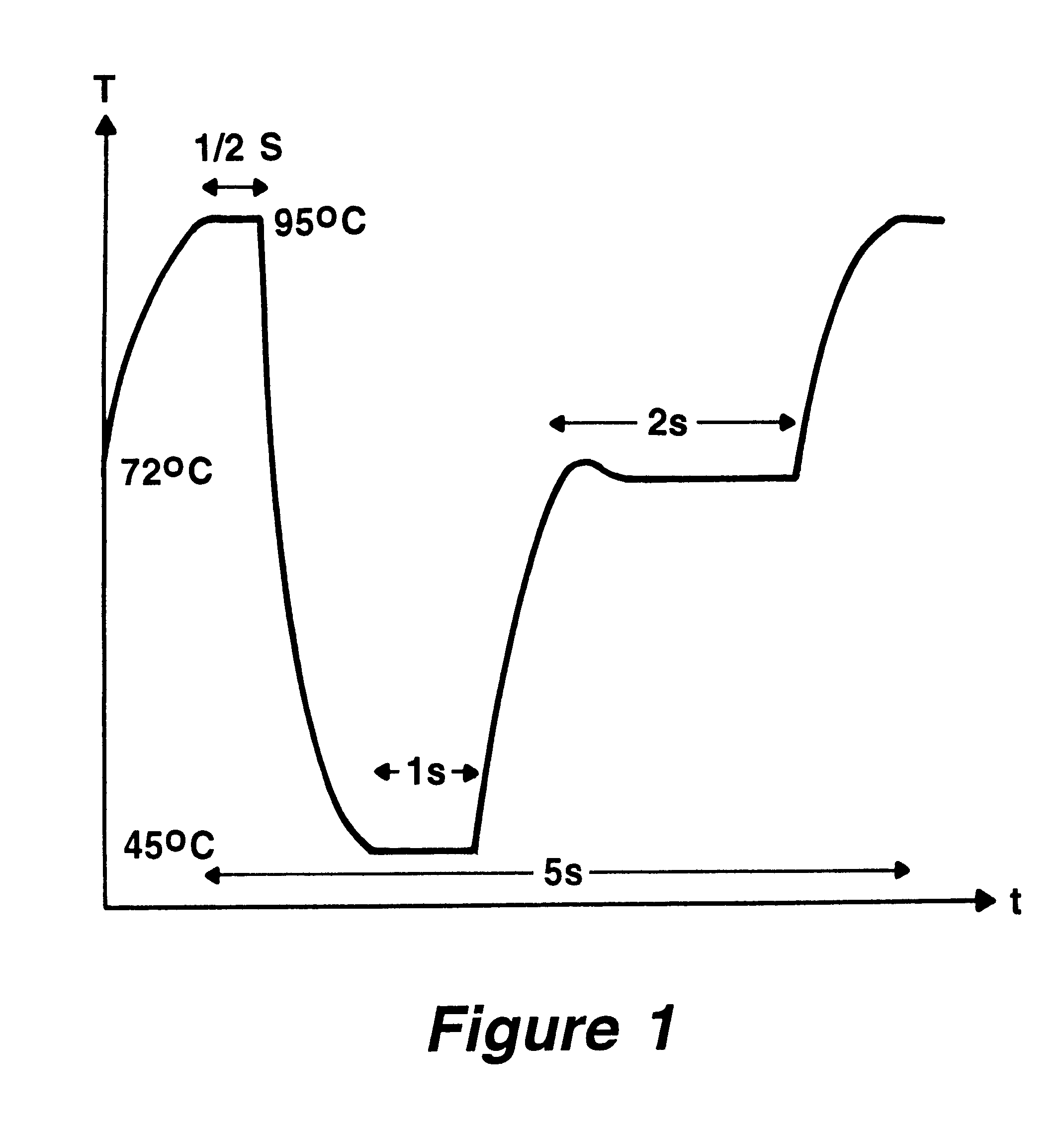
Method and devices for extremely fast DNA replication by polymerase chain reactions (PCR)
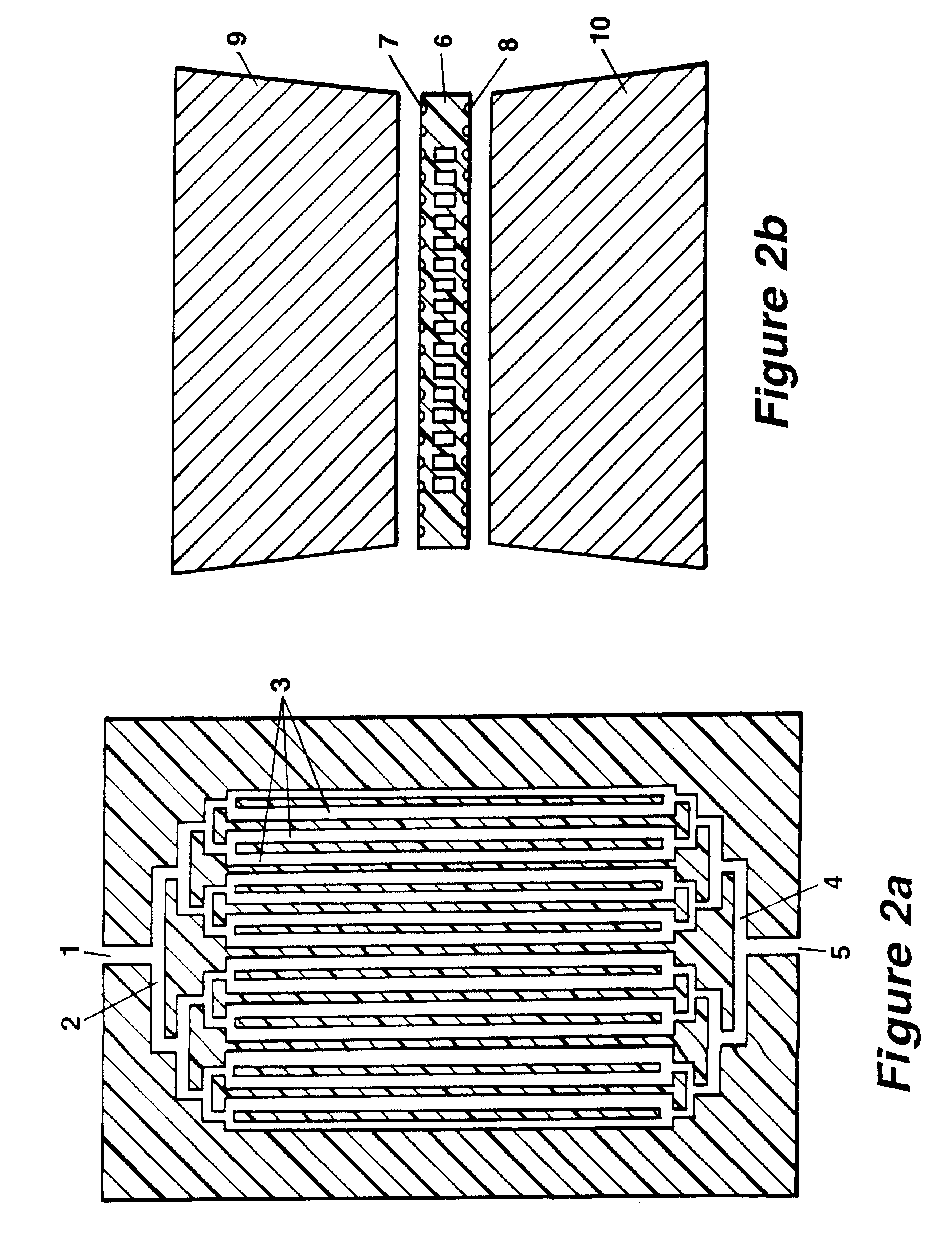
InactiveUS6180372B1Shorten cycle timeHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechPolymerase LBiological materials
The invention concerns methods and instruments for fast, selective replication of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from biomaterial through the known polymerase chain reaction (PCR), working in individual duplication thermocycles. The invention consists of extremely brief cycle times of only a few seconds for the PCR reactions, generated, on the one hand, by reaction chambers for the reception of the reaction solution constructed of a pattern of fine capillaries in close proximity to heating and cooling elements in order to optimally accelerate the temperature setting in the reaction solution for the three temperature phases of the PCR duplication cycles and, on the other hand, by keeping the flow rates in the capillaries to a minimum during the amplification phase so that the polymerase reaction is not disturbed. The capillary pattern can be simply produced by means of microsystern technology.
Owner:BRUKER FRANZEN ANALYTIK
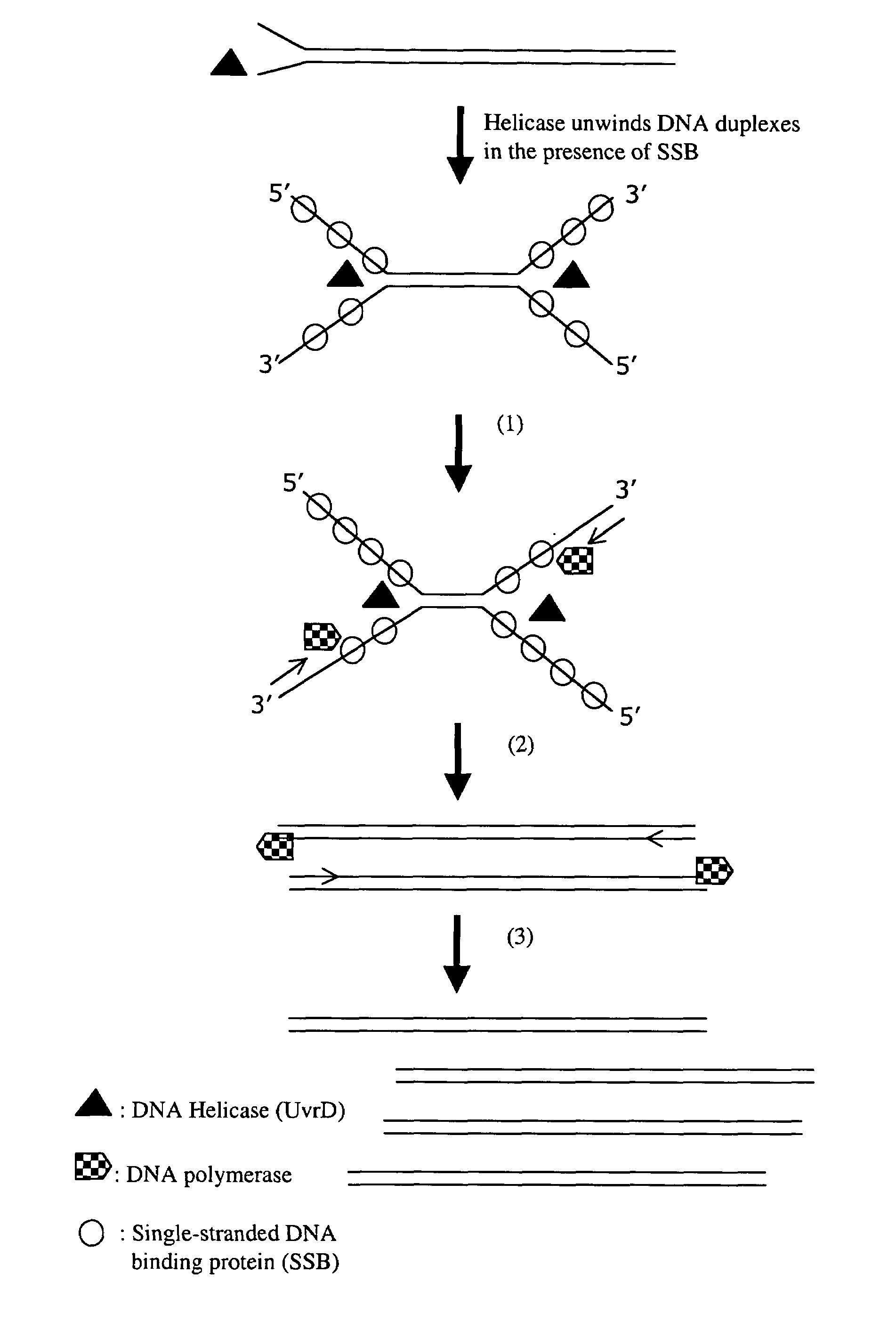
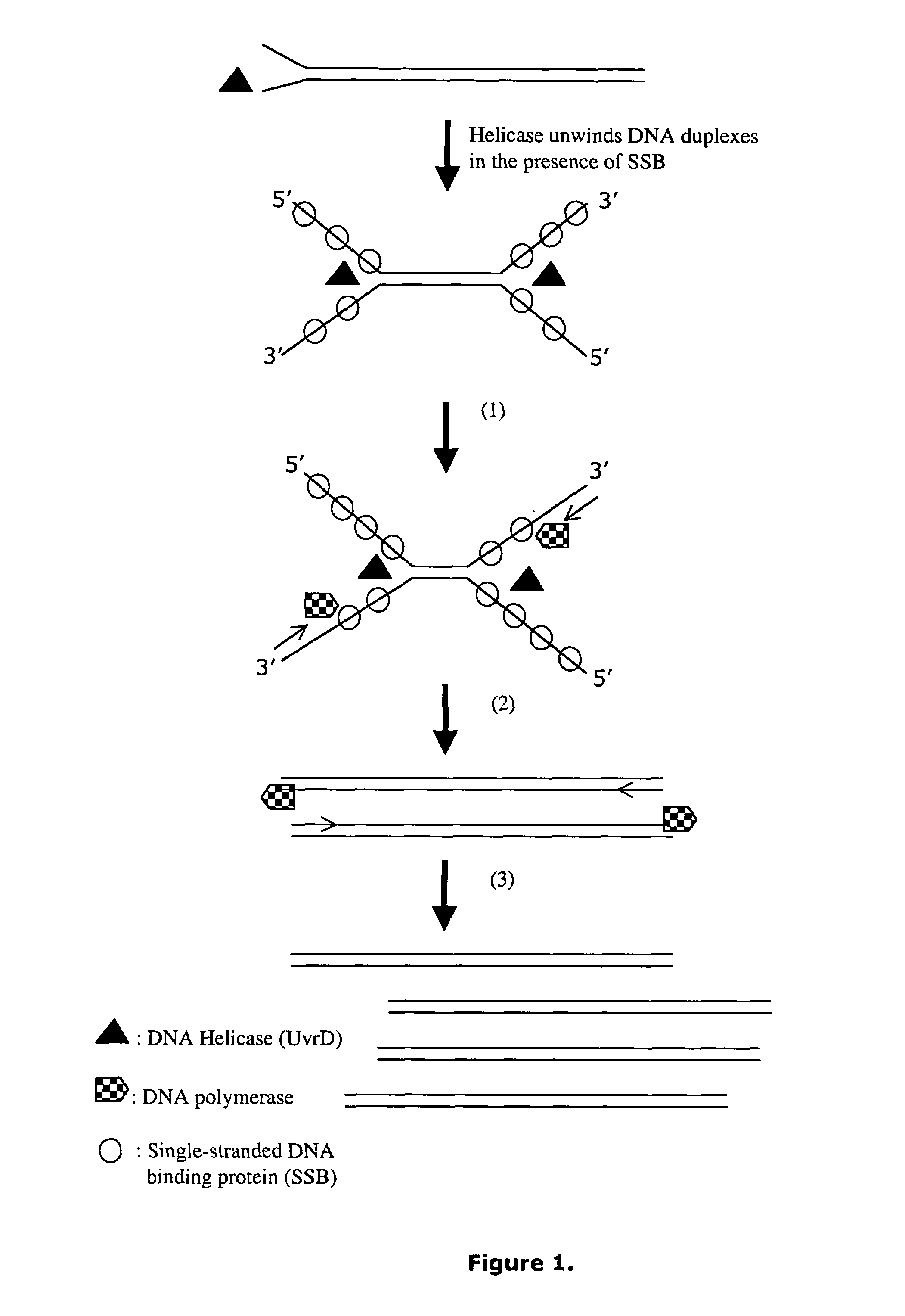
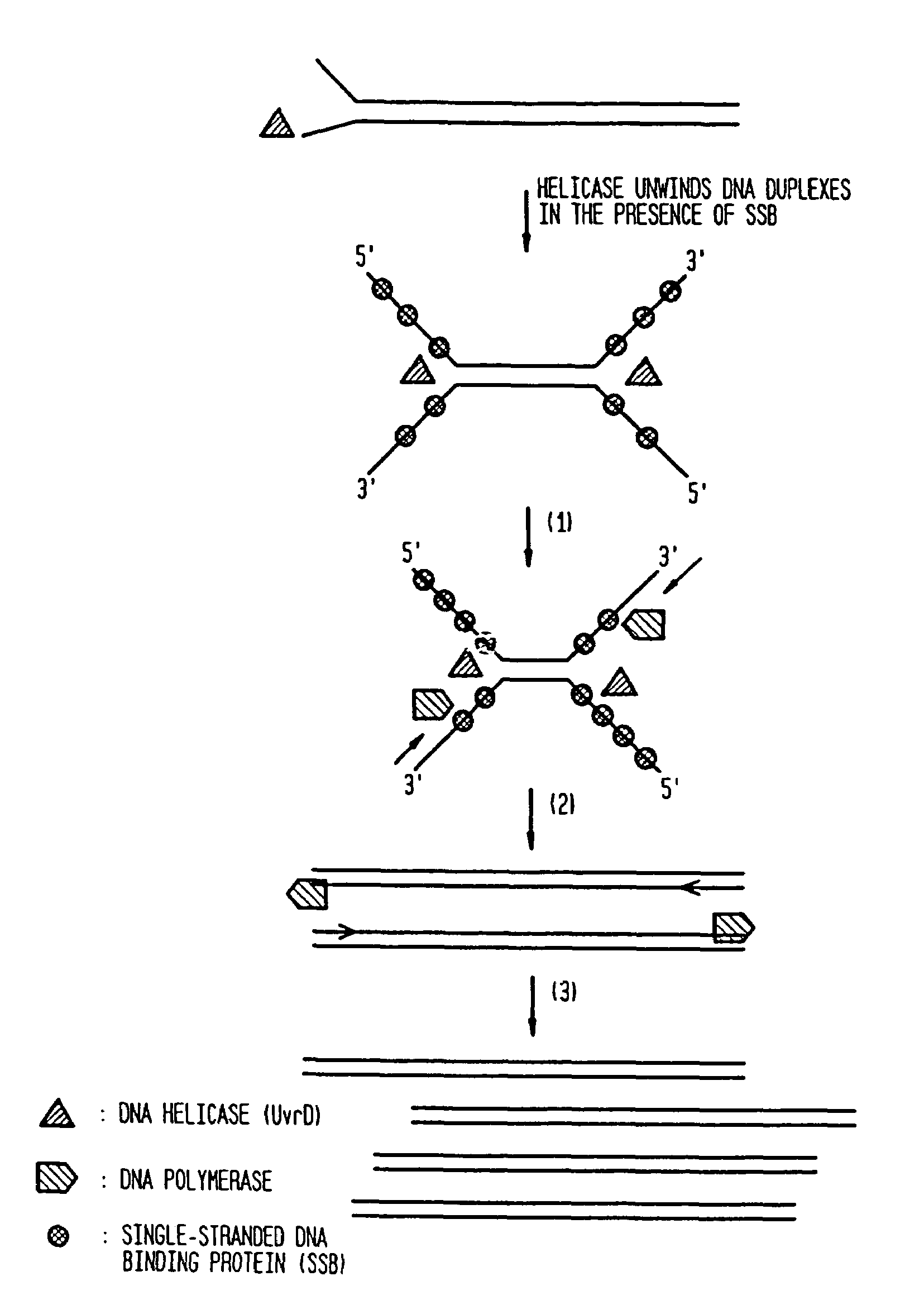
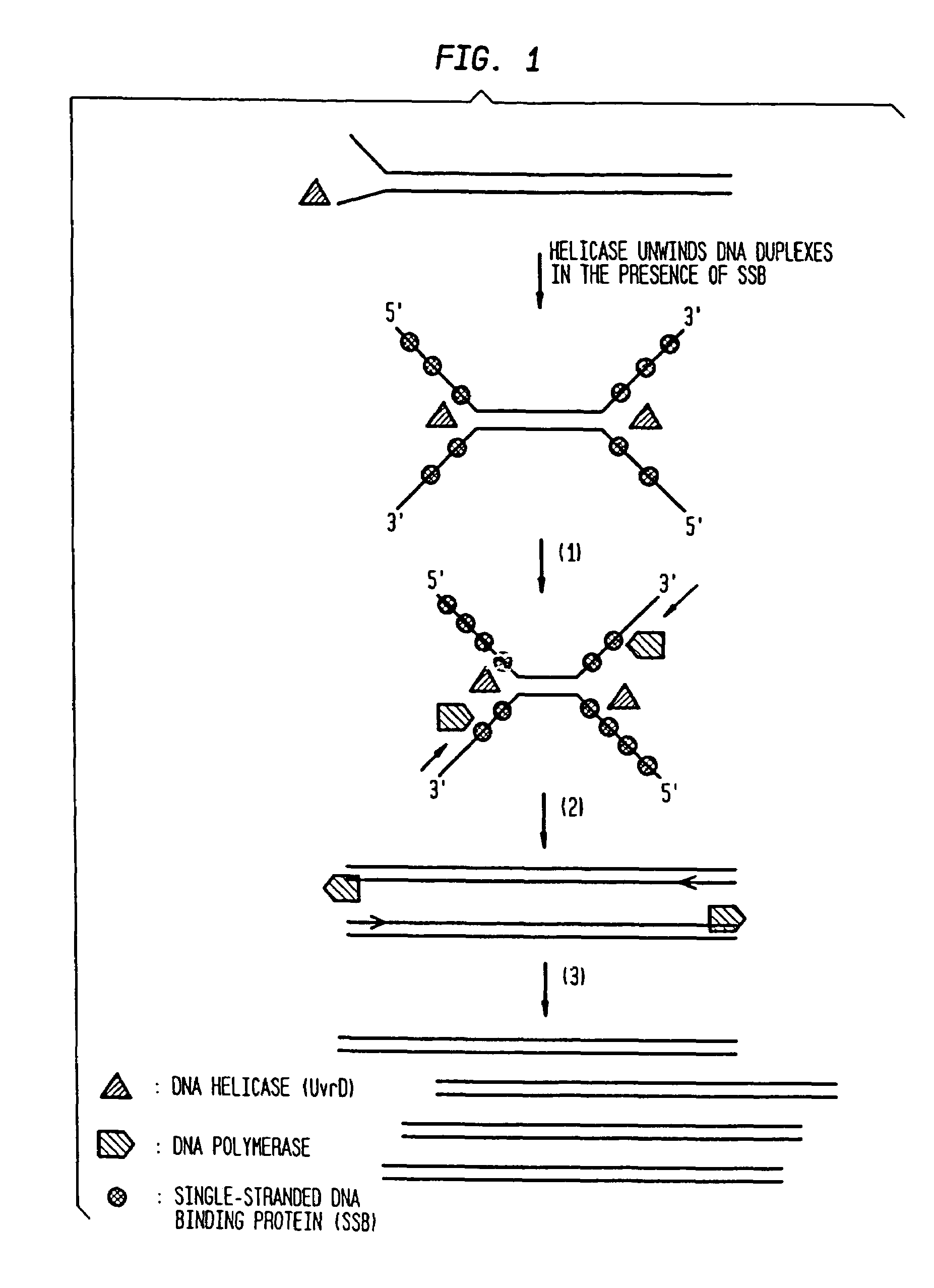
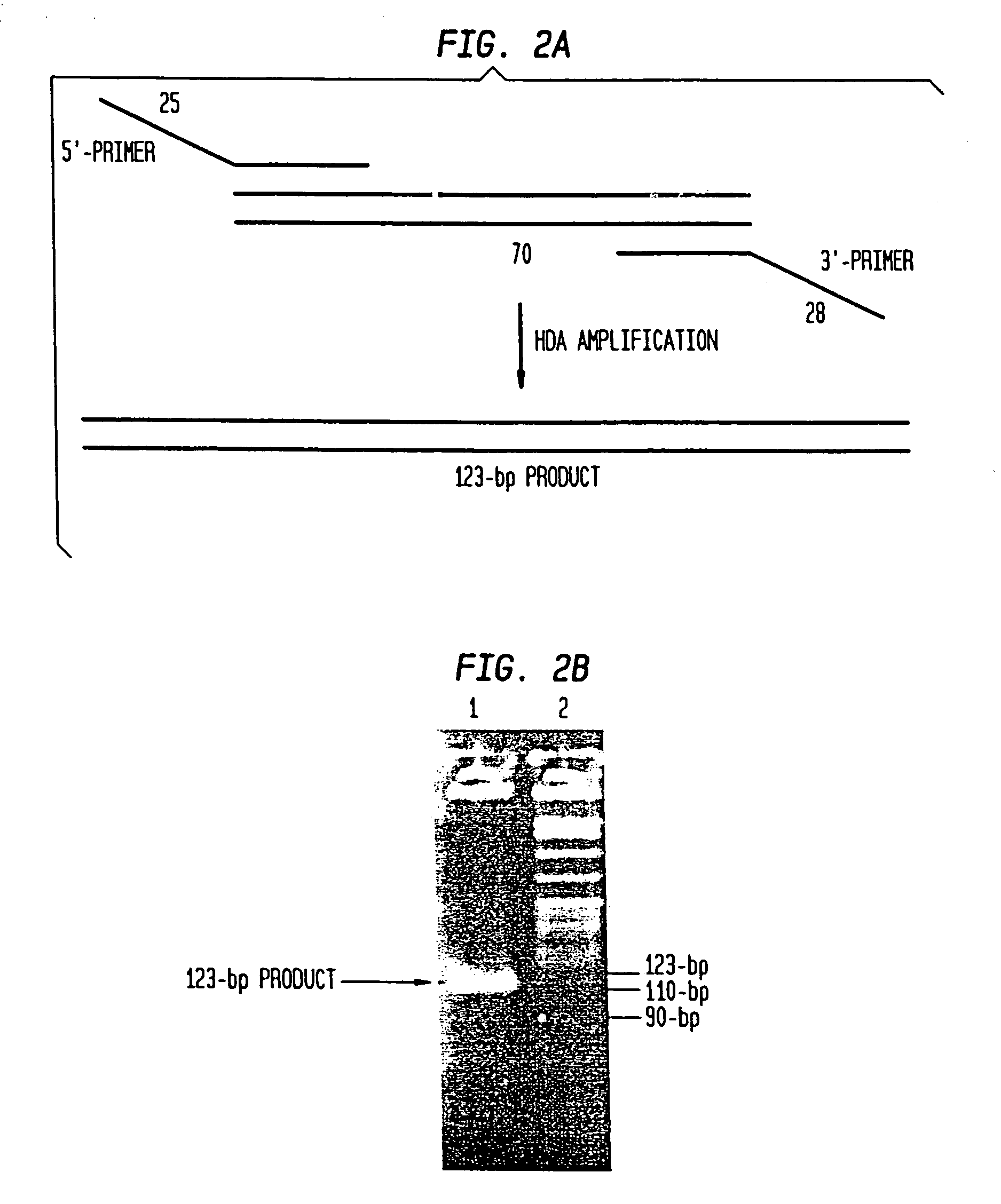
Helicase dependent amplification of nucleic acids
ActiveUS7282328B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionDNA unwinding enzyme
Methods and a kit are provided for selectively and exponentially amplifying nucleic acids and include the use of a helicase preparation and a DNA polymerase such that the amplification can be performed isothermally.
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
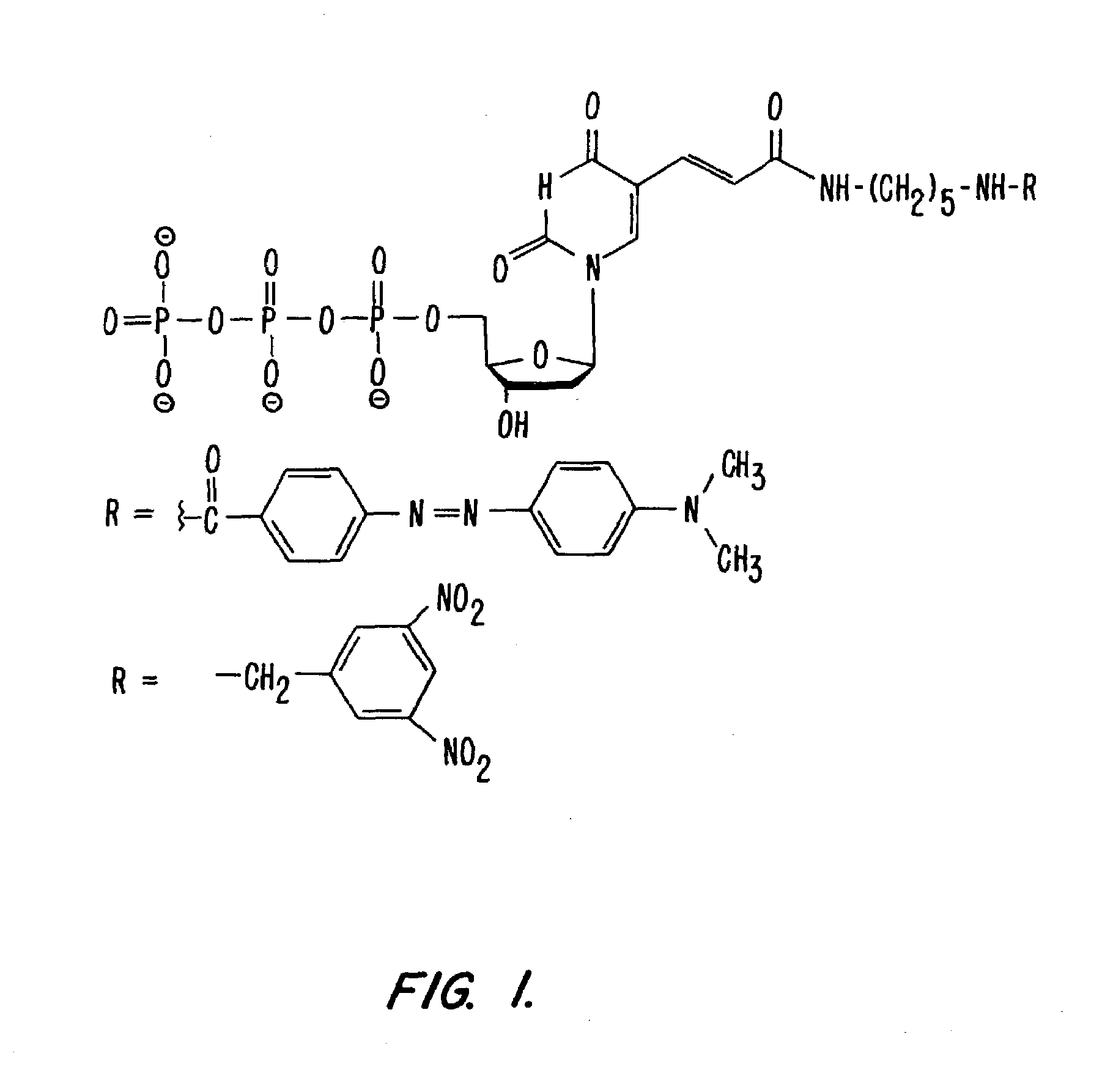
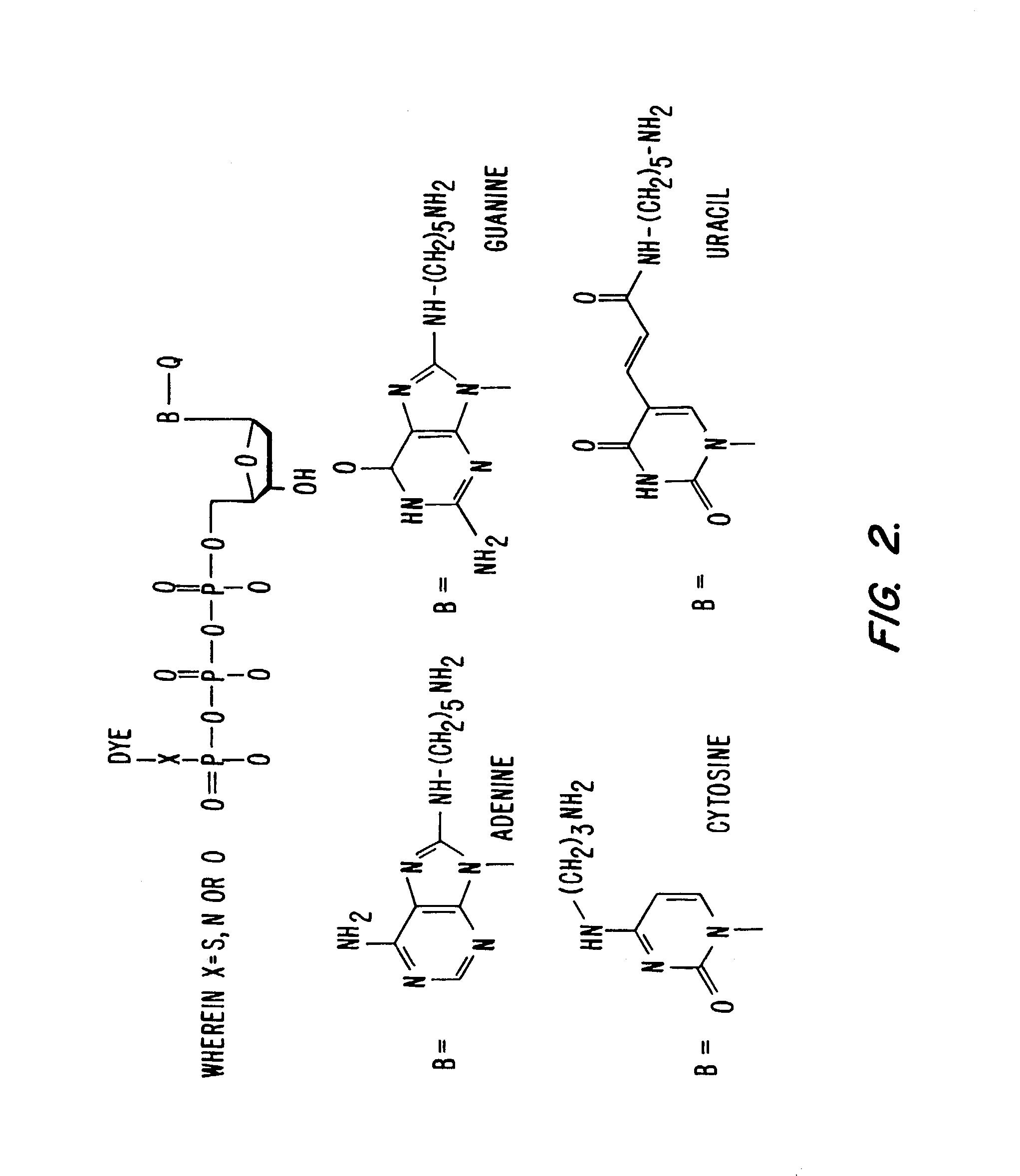
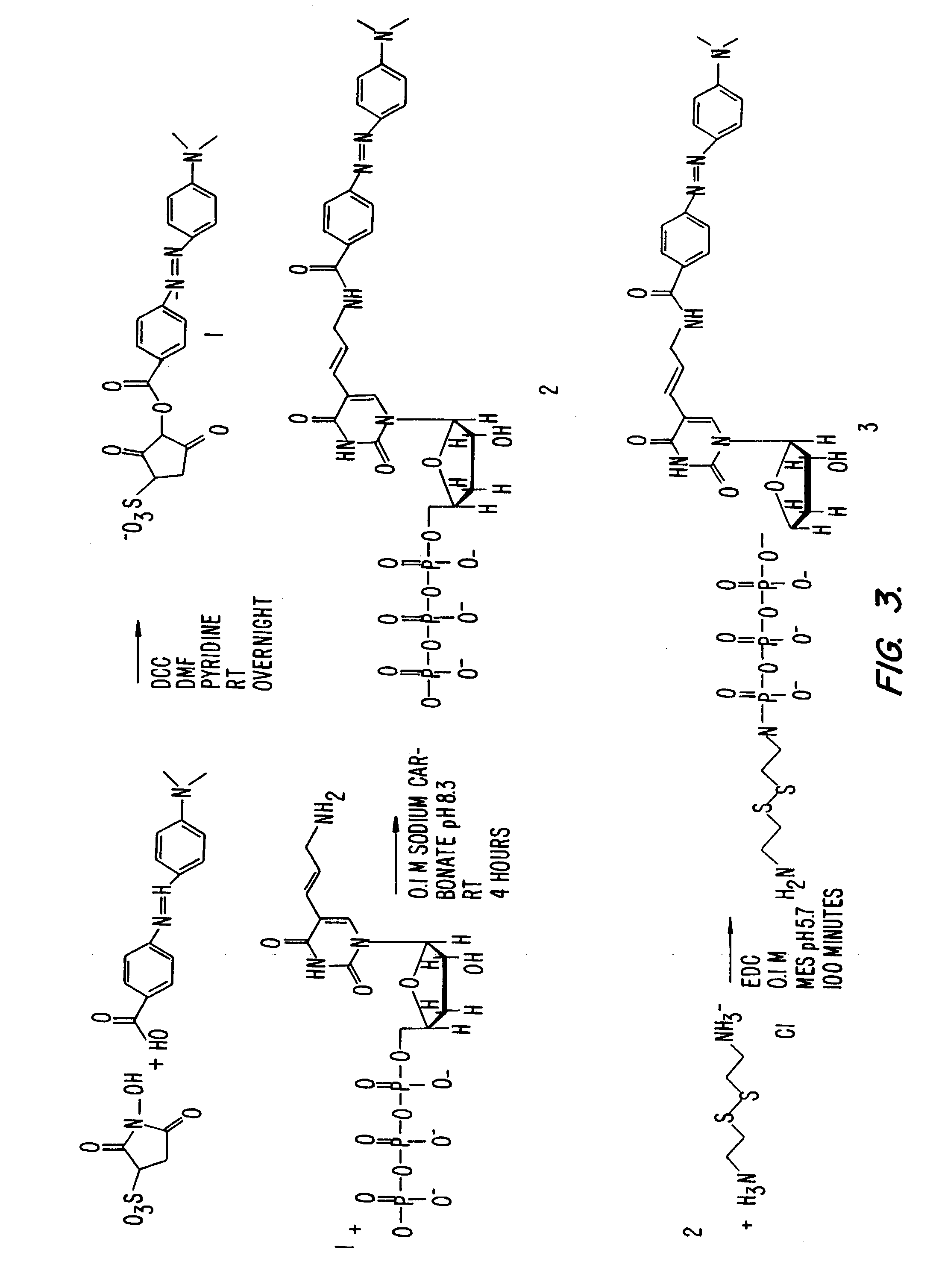
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS7041812B2Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
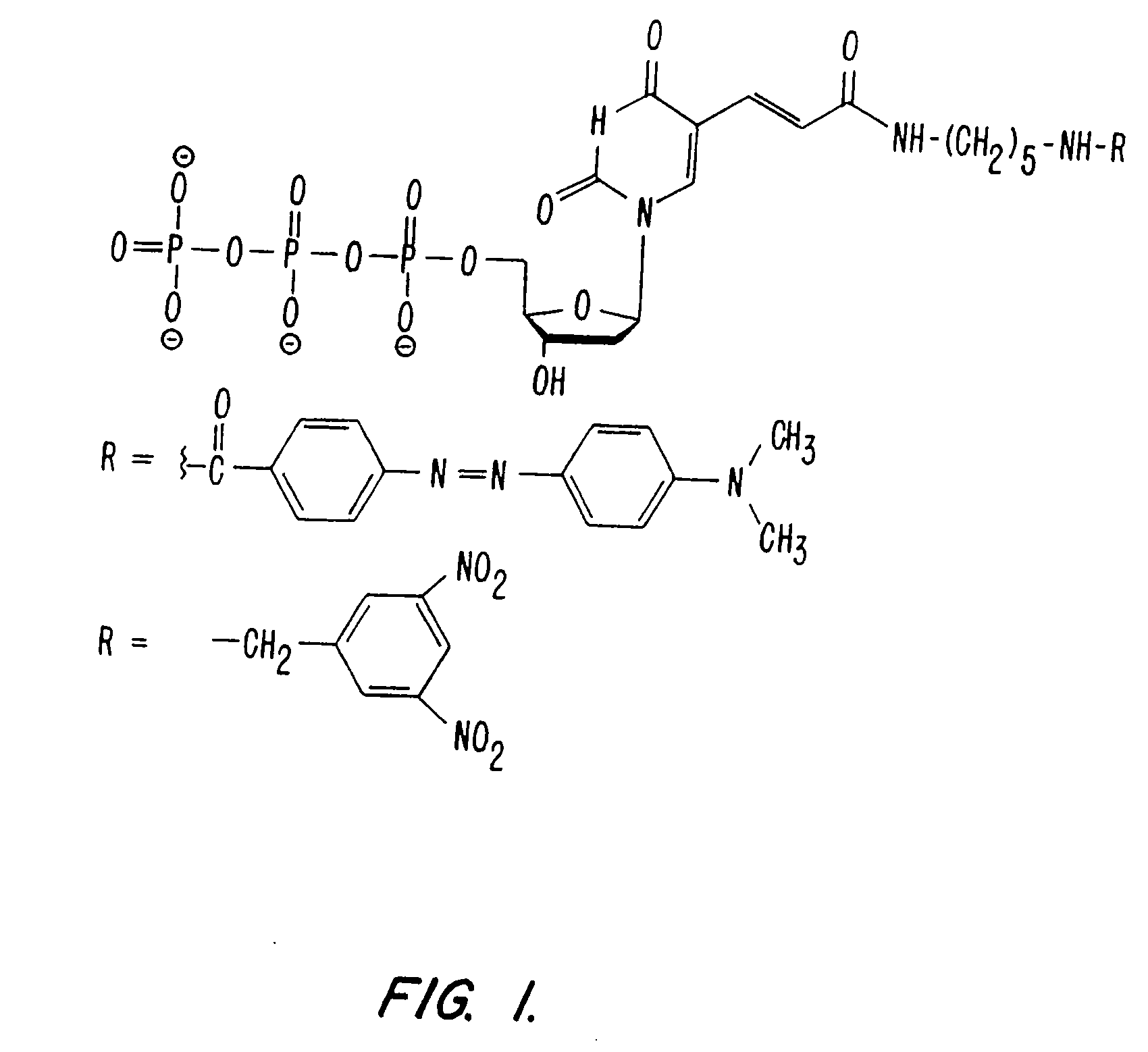
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, characterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have colorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Removal of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphate or polyphosphate transferring enzyme leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
High speed parallel molecular nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS6982146B1Minimize shearImprove automationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
A method and device is disclosed for high speed, automated sequencing of nucleic acid molecules. A nucleic acid molecule to be sequenced is exposed to a polymerase in the presence of nucleotides which are to be incorporated into a complementary nucleic acid strand. The polymerase carries a donor fluorophore, and each type of nucleotide (e.g. A, T / U, C and G) carries a distinguishable acceptor fluorophore characteristic of the particular type of nucleotide. As the polymerase incorporates individual nucleic acid molecules into a complementary strand, a laser continuously irradiates the donor fluorophore, at a wavelength that causes it to emit an emission signal (but the laser wavelength does not stimulate the acceptor fluorophore). In particular embodiments, no laser is needed if the donor fluorophore is a luminescent molecule or is stimulated by one. The emission signal from the polymerase is capable of stimulating any of the donor fluorophores (but not acceptor fluorophores), so that as a nucleotide is added by the polymerase, the acceptor fluorophore emits a signal associated with the type of nucleotide added to the complementary strand. The series of emission signals from the acceptor fluorophores is detected, and correlated with a sequence of nucleotides that correspond to the sequence of emission signals.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE
Methods and apparatus for characterizing polynucleotides
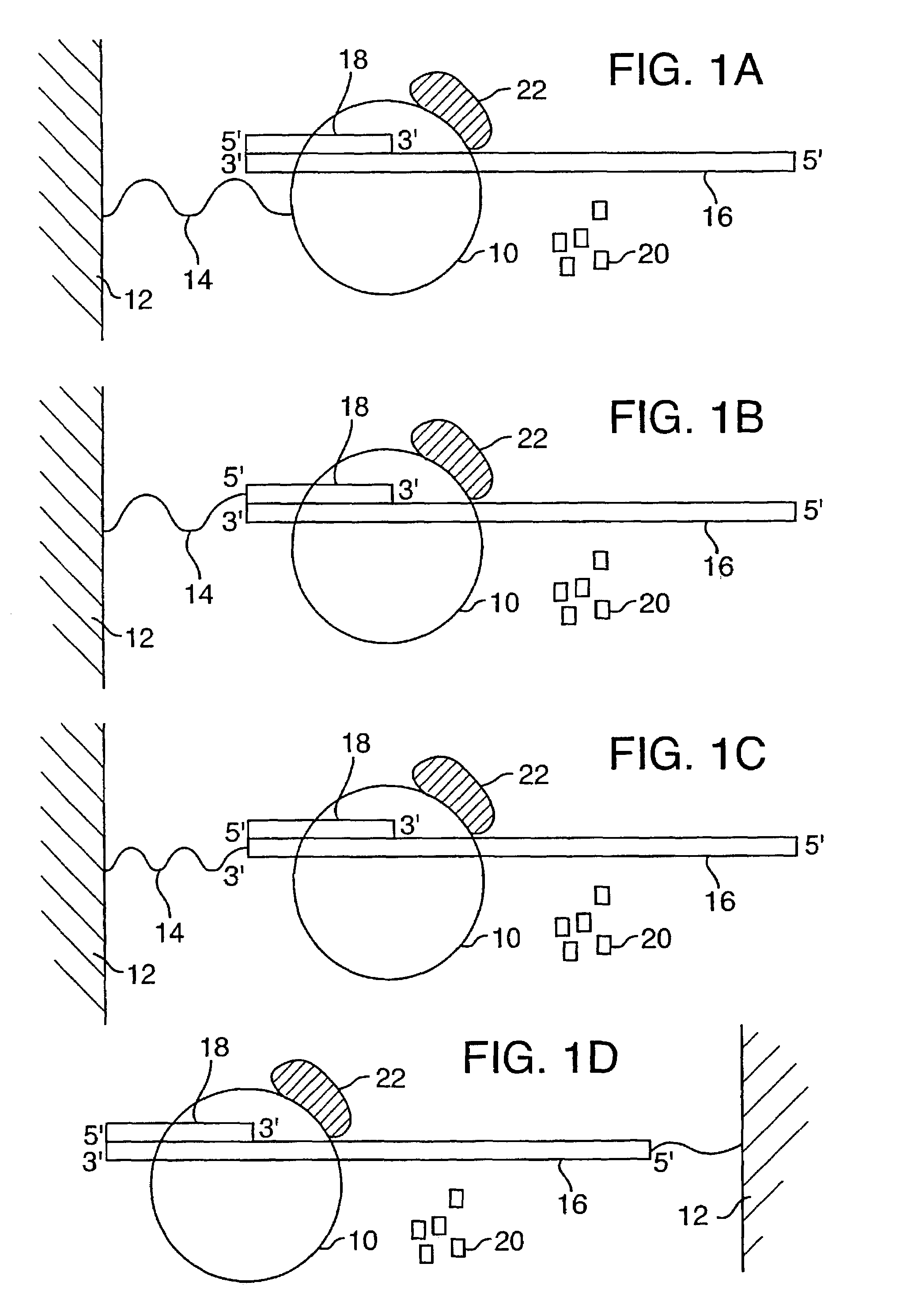
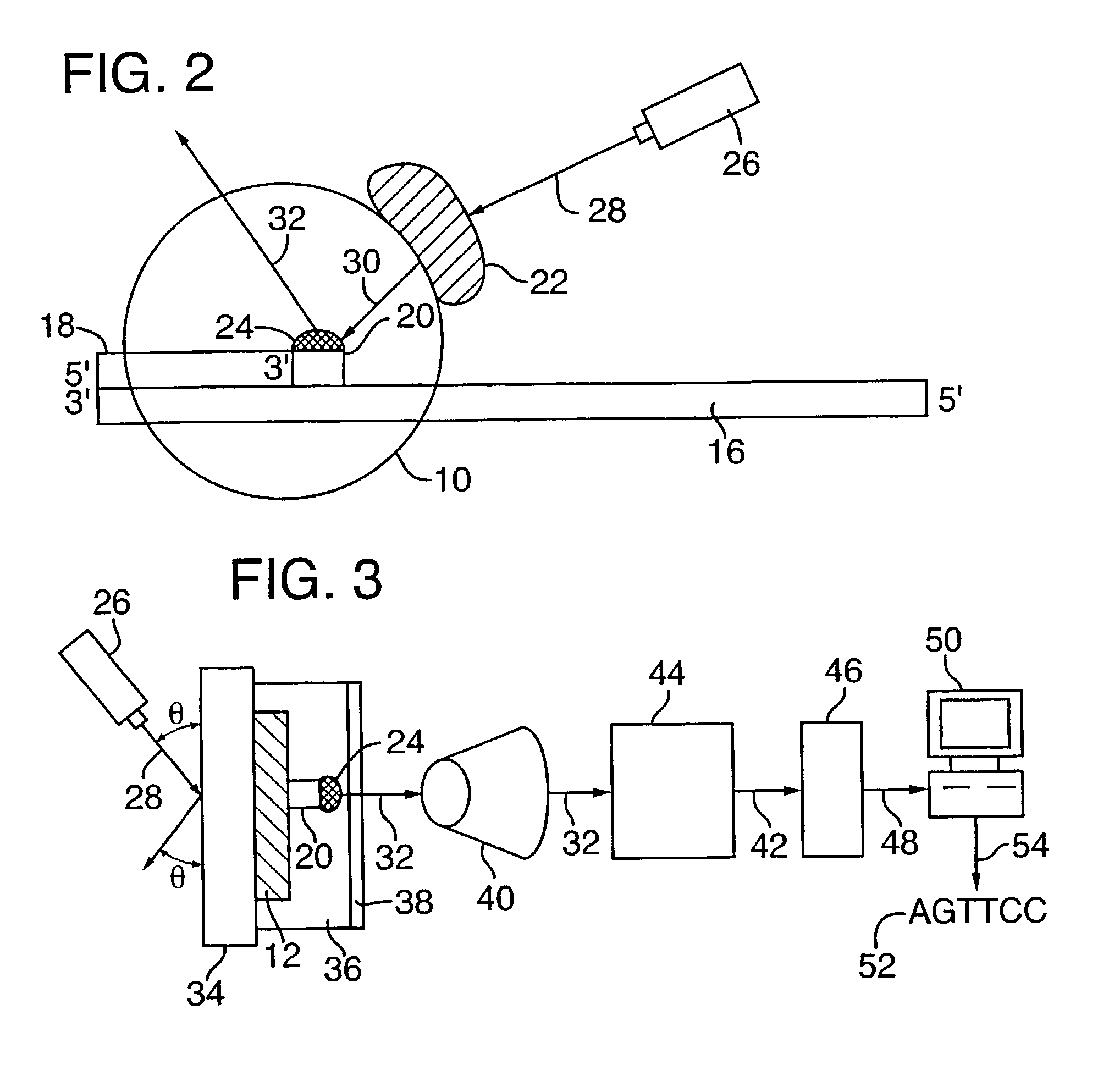
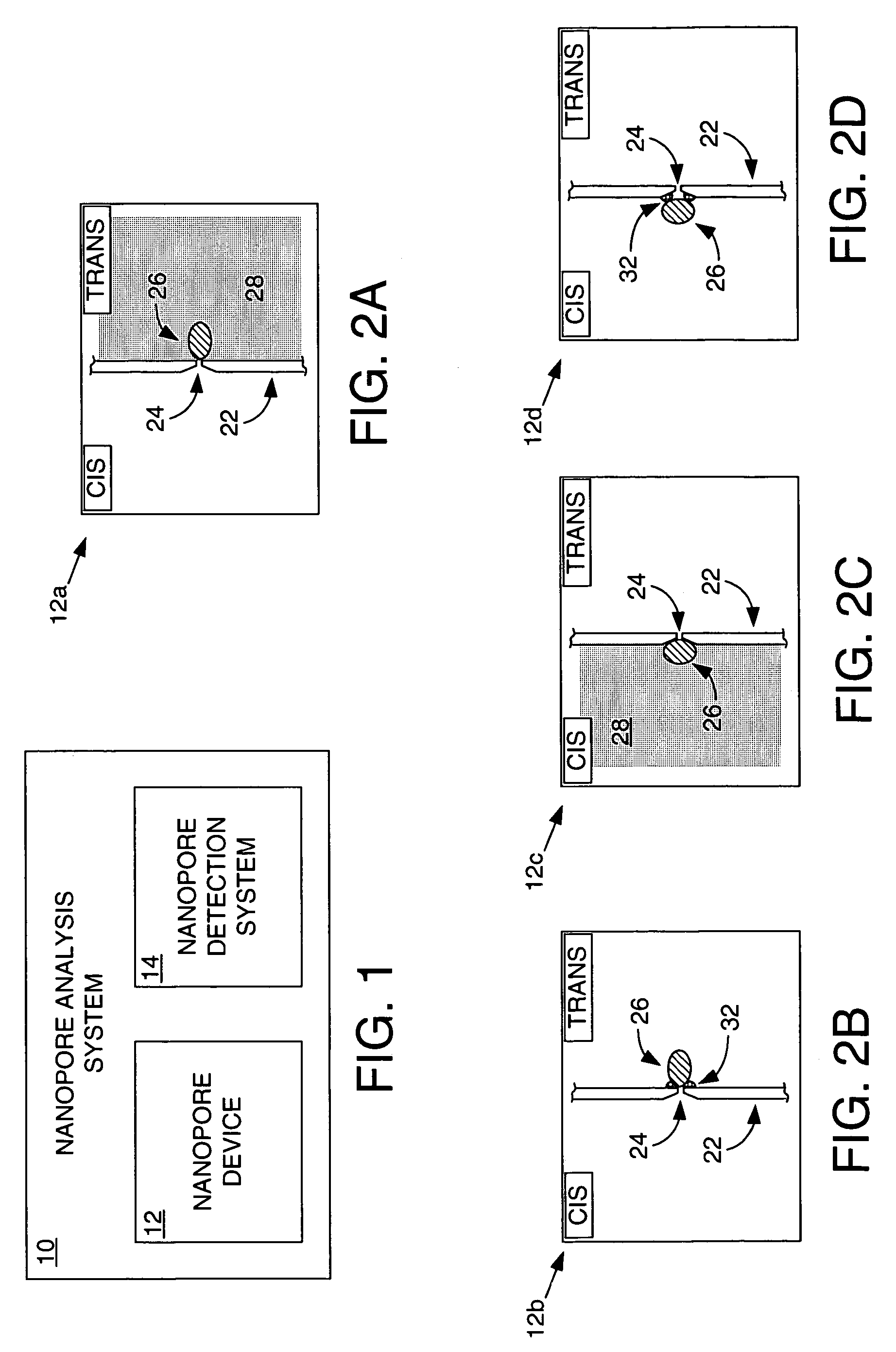
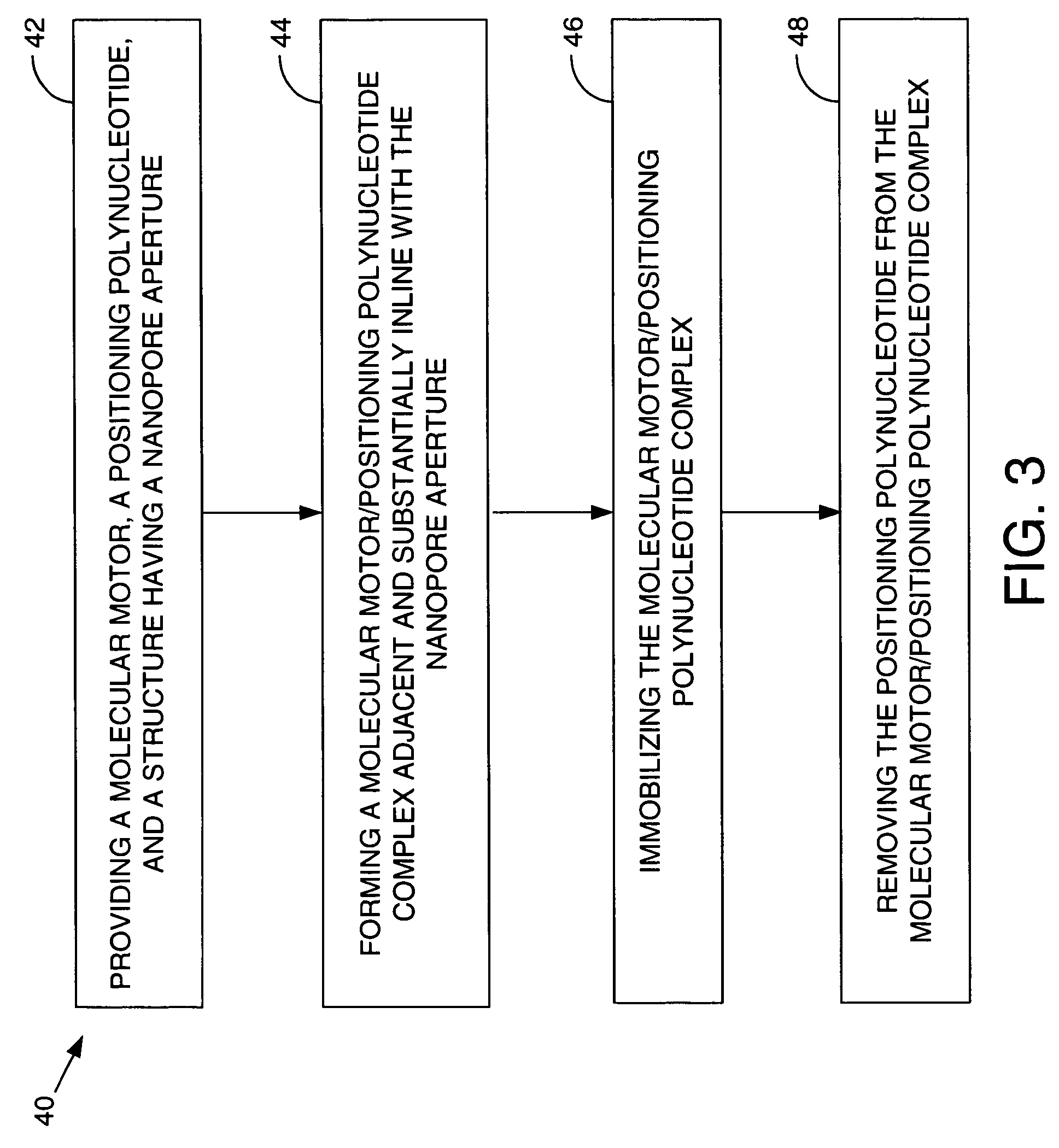
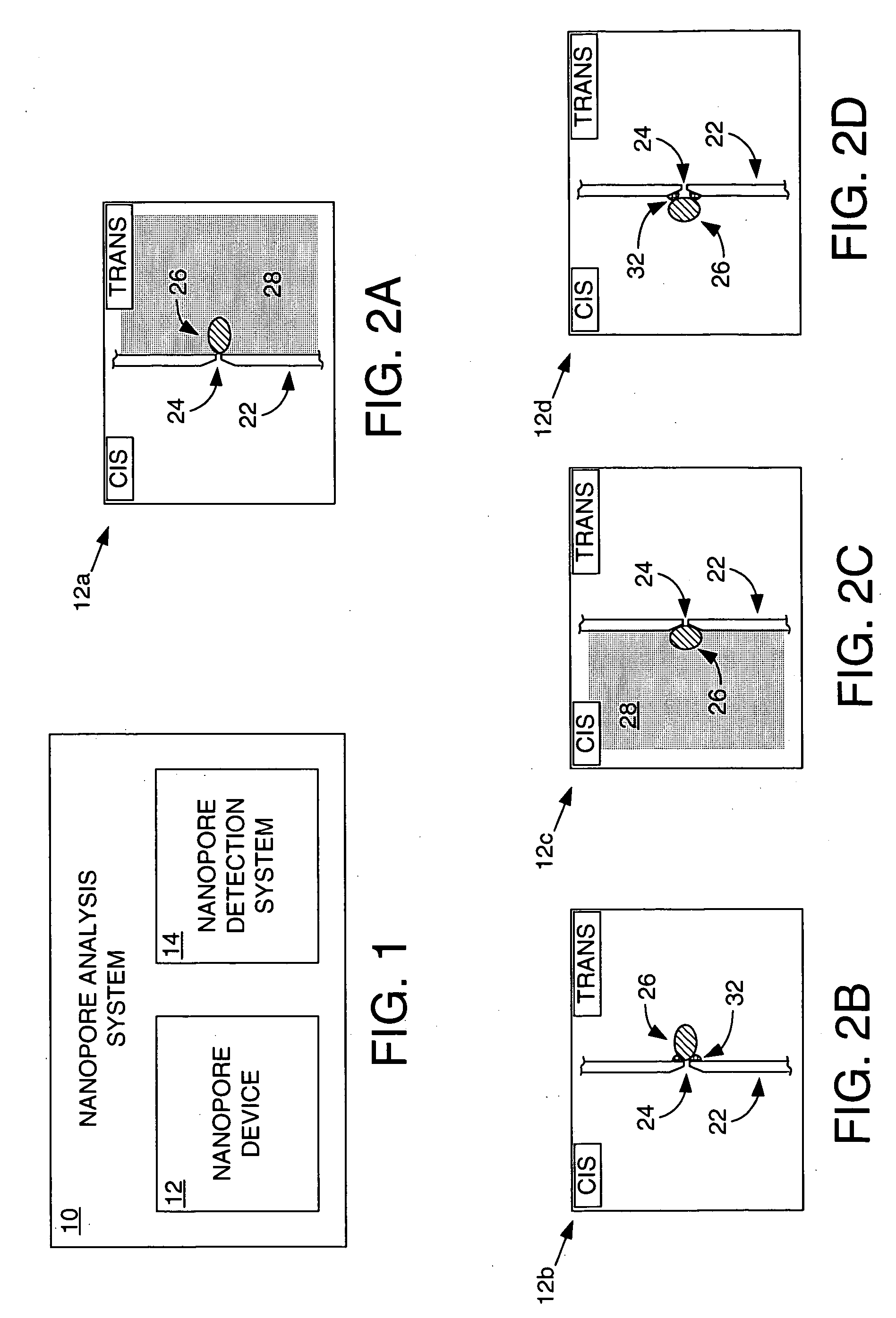
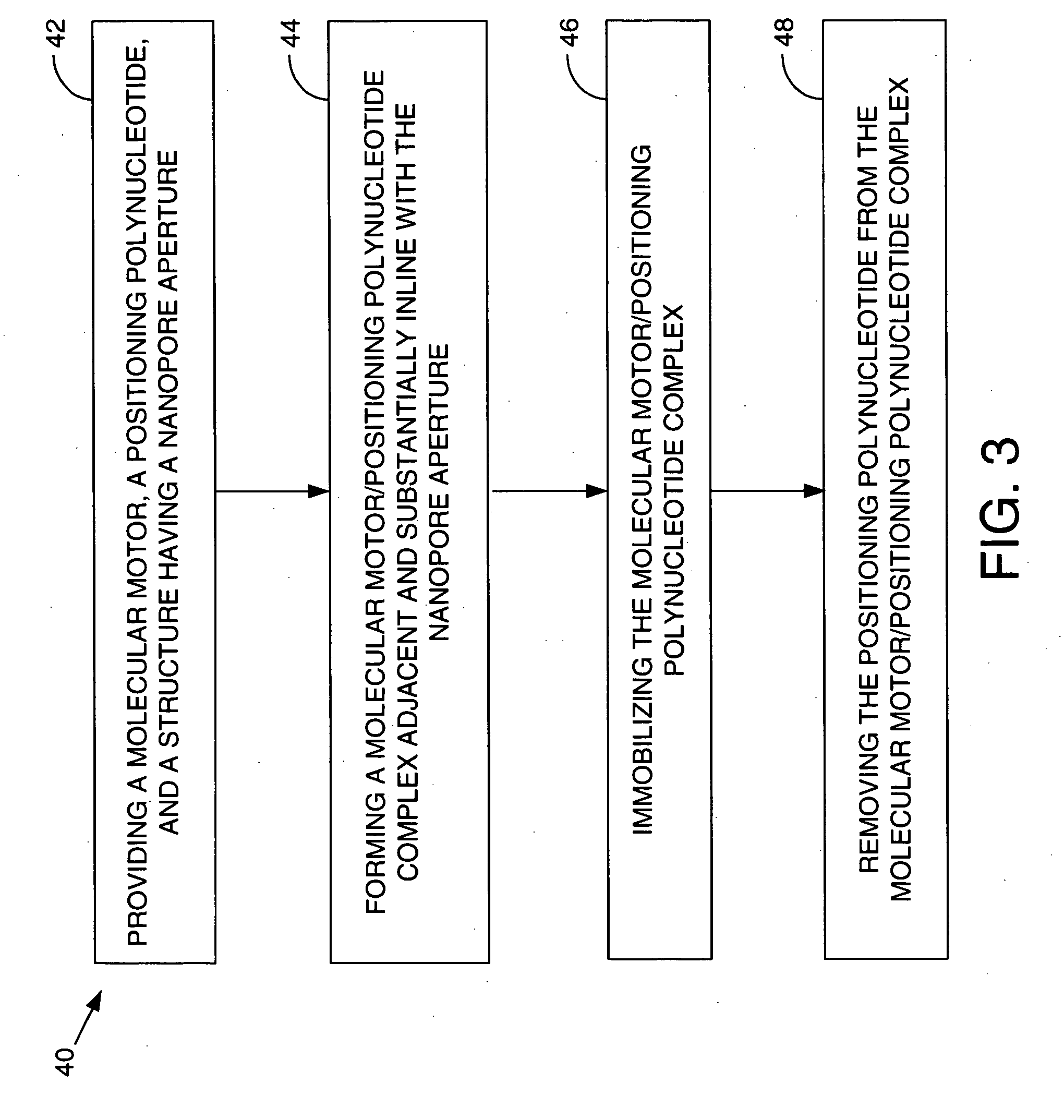
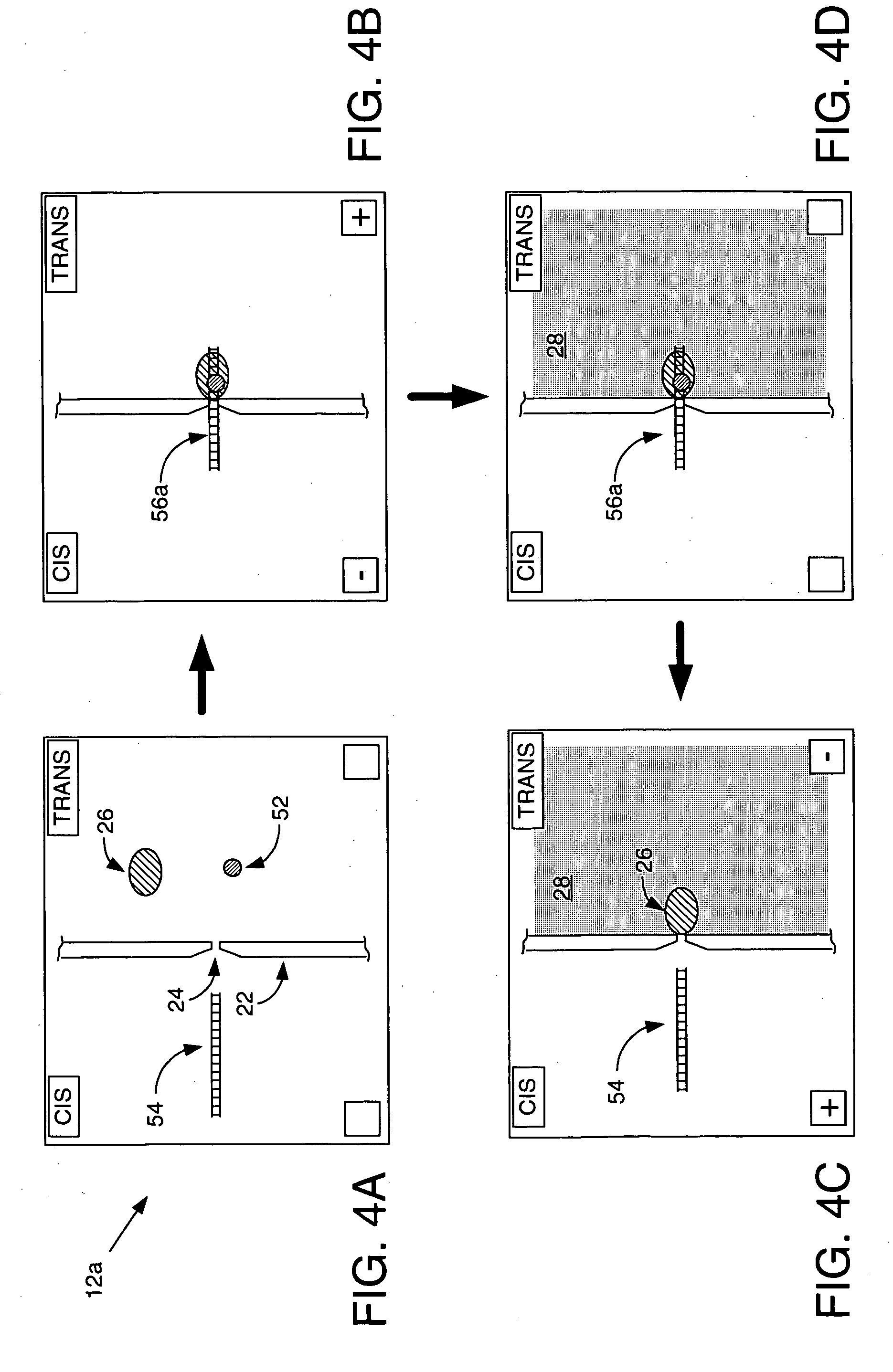
ActiveUS7238485B2Reduce probabilityMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCrystallographyMolecular motor
Systems and methods for analysis of polymers, e.g., polynucleotides, are provided. The systems are capable of analyzing a polymer at a specified rate. One such analysis system includes a structure having a nanopore aperture and a molecular motor, e.g., a polymerase, adjacent the nanopore aperture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Nucleoside derivatives as inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase
The present invention provides nucleoside derivatives which are inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase. These compounds are inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral replication and are useful for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection. They are particularly useful as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, as inhibitors of HCV replication, and / or for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. The invention also describes pharmaceutical compositions containing such nucleoside derivatives alone or in combination with other agents active against RNA-dependent RNA viral infection, in particular HCV infection. Also disclosed are methods of inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA viral replication, and / or treating RNA-dependent RNA viral infection with the nucleoside derivatives of the present invention.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +1
Methods and apparatus for characterizing polynucleotides
ActiveUS20060063171A1Reduce probabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyCrystallographyMolecular motor
Systems and methods for analysis of polymers, e.g., polynucleotides, are provided. The systems are capable of analyzing a polymer at a specified rate. One such analysis system includes a structure having a nanopore aperture and a molecular motor, e.g., a polymerase, adjacent the nanopore aperture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Rapid parallel nucleic acid analysis
ActiveUS7264934B2Efficiently determinedEliminates non-specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
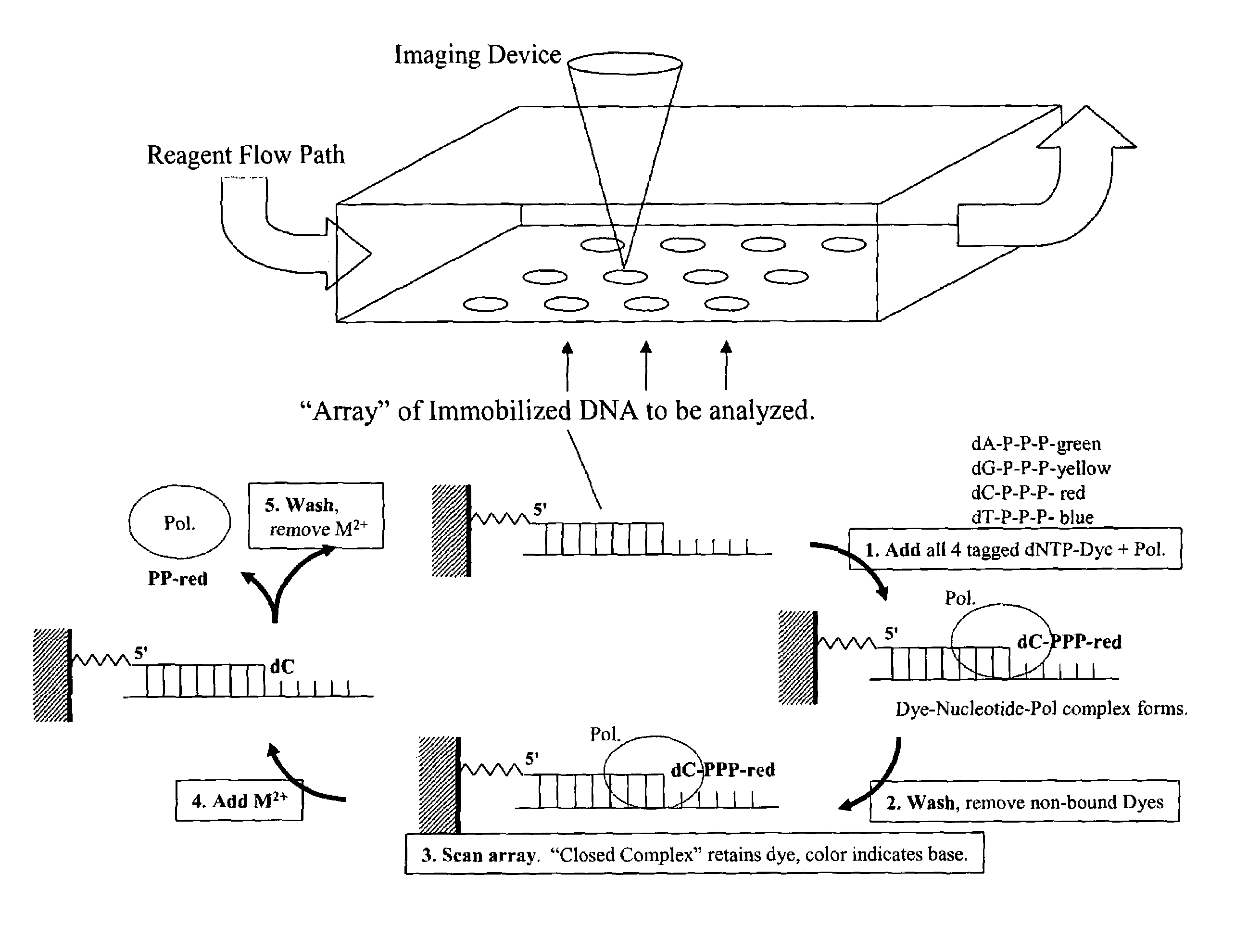
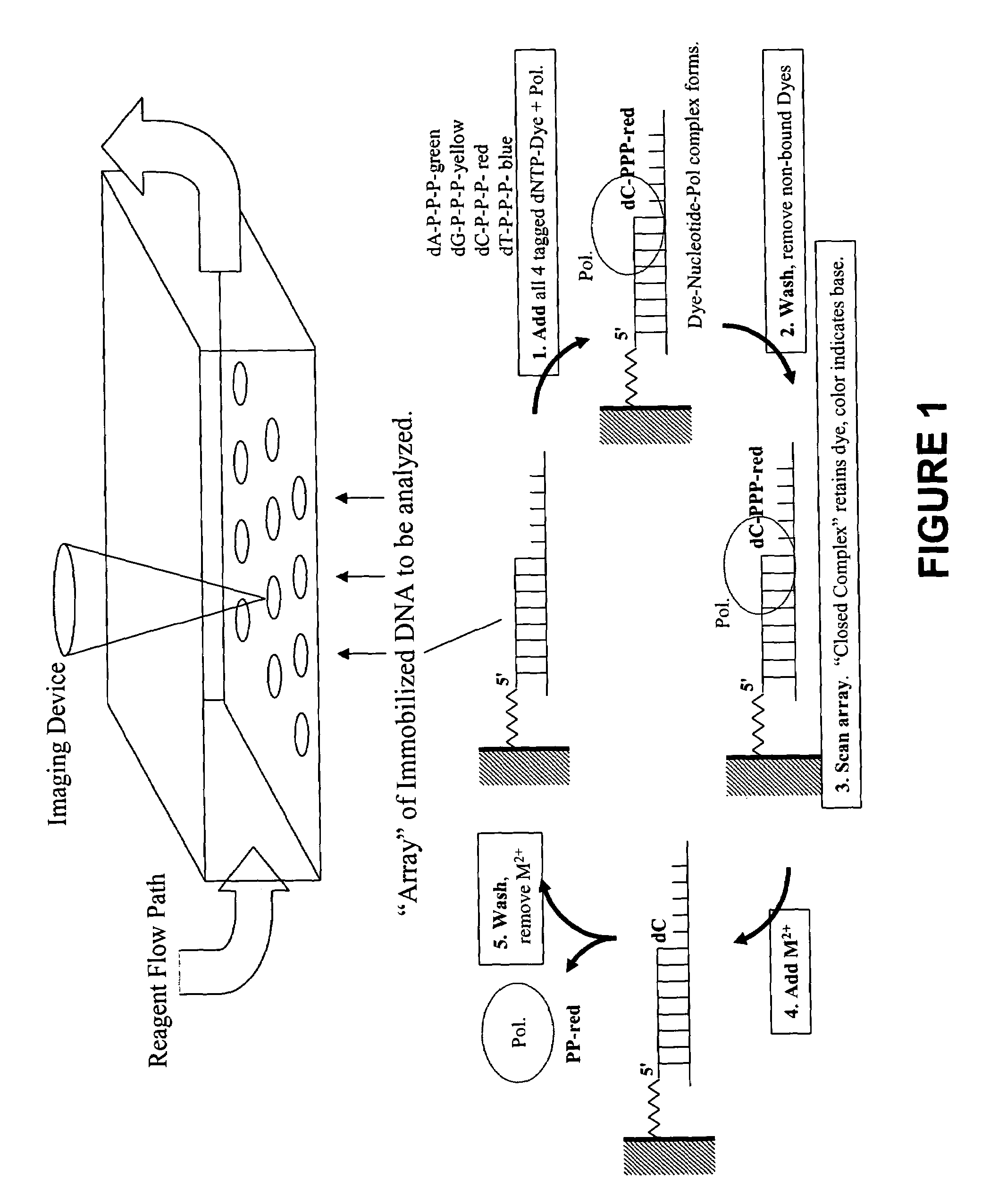
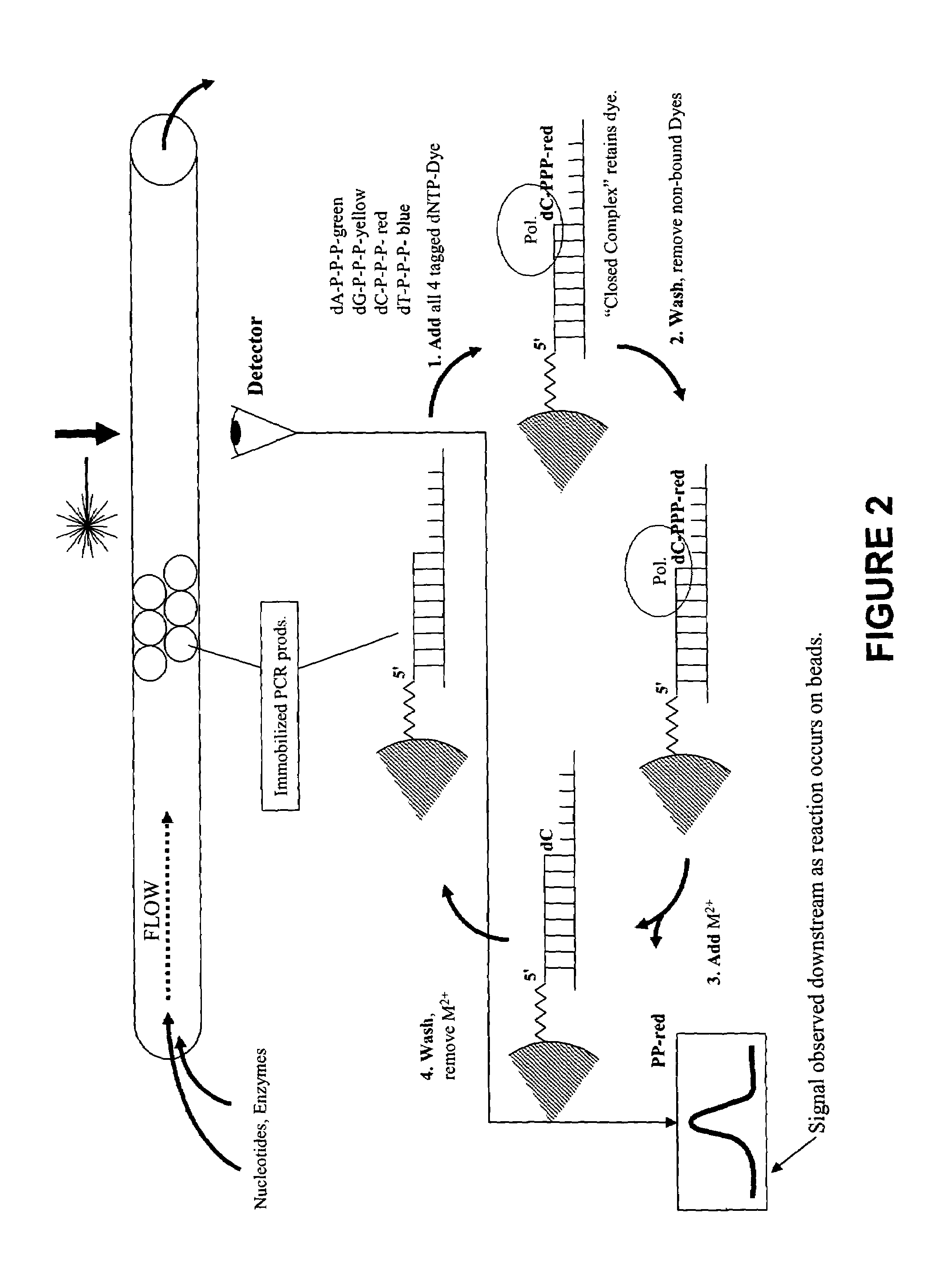
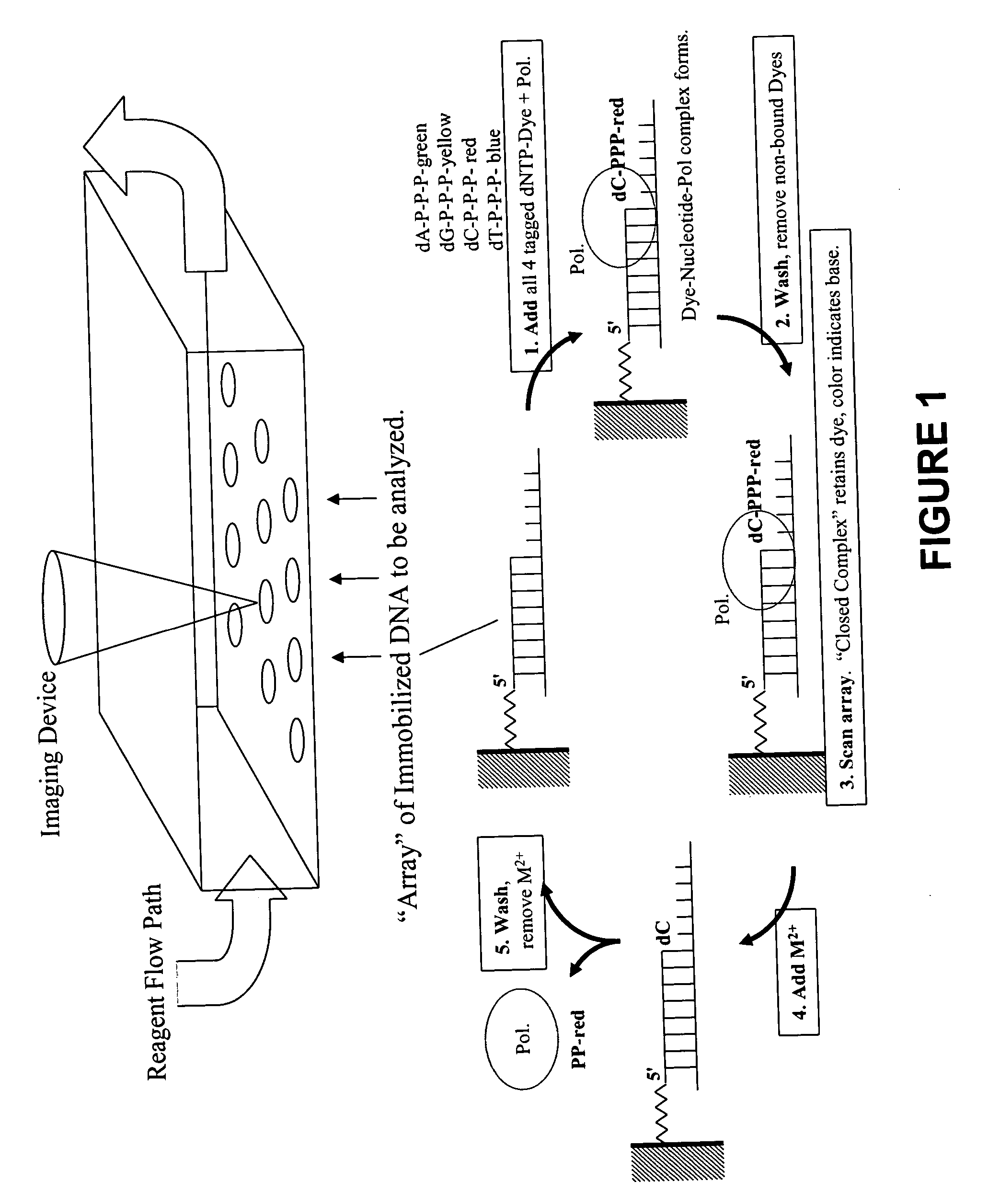
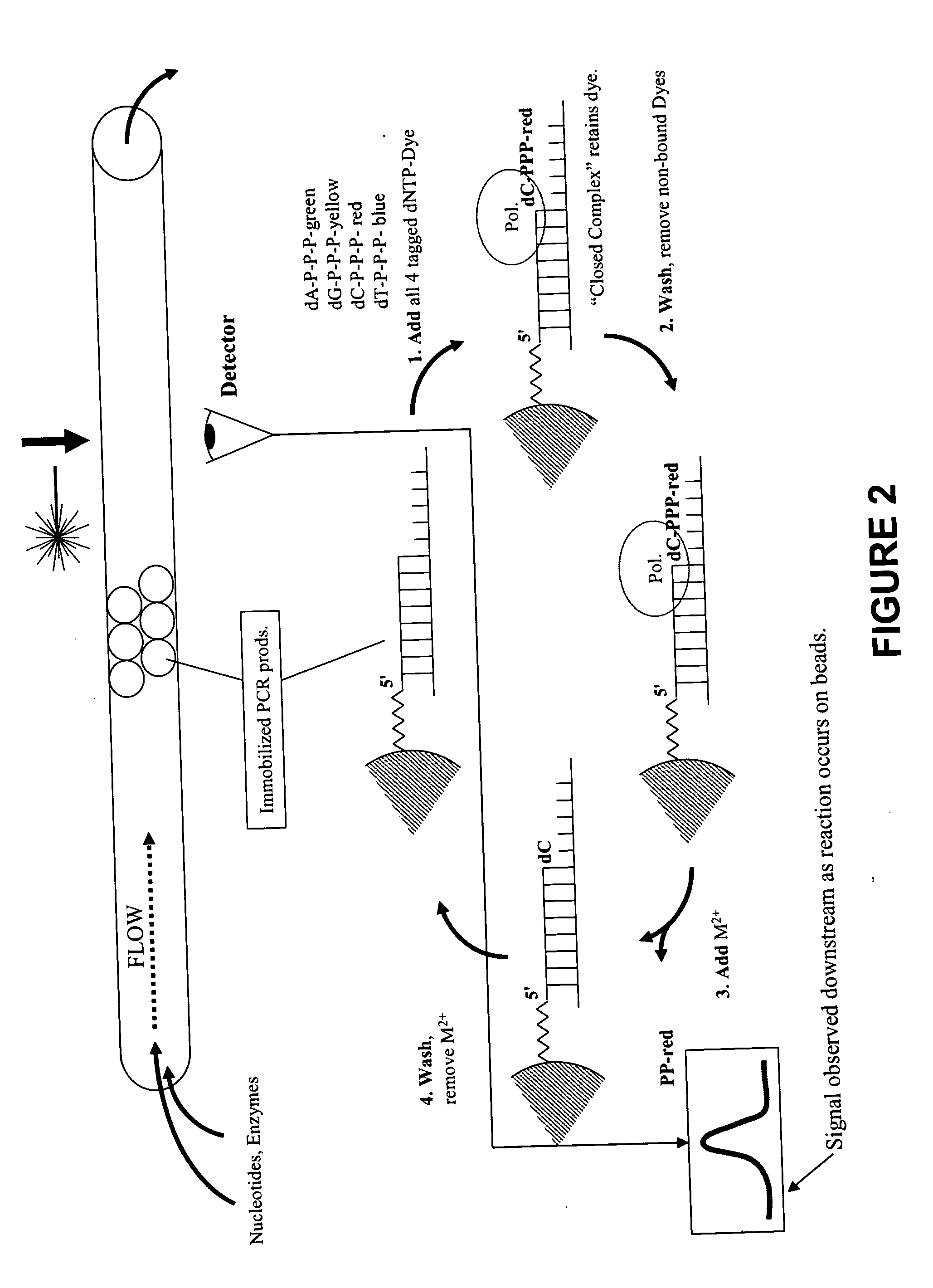
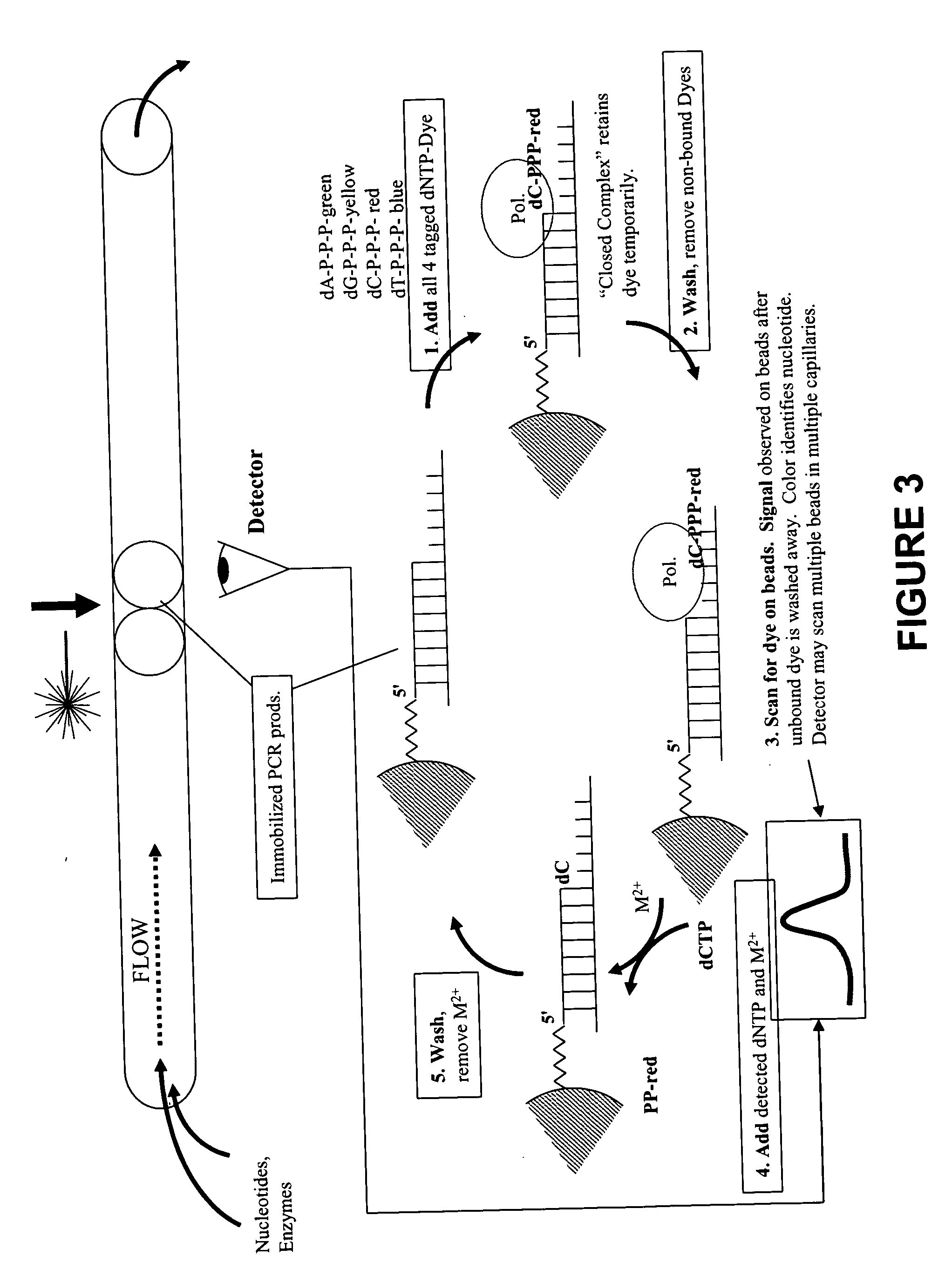
This invention provides methods for massive parallel nucleic acid analysis. A closed complex of nucleic acid template, nucleotide and polymerase can be formed during polymerase reaction, absent divalent metal ion. This is used to trap the nucleotide complementary to the next template nucleotide in the closed complex. Detection of the trapped nucleotide allows determination of the sequence of this next correct nucleotide. In this way, sequential nucleotides of a nucleic acid template can be identified, effectively determining the sequence. This method is applied to sequence multiple templates in parallel, particularly if they are immobilized on a solid support.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Single nucleotide amplification and detection by polymerase
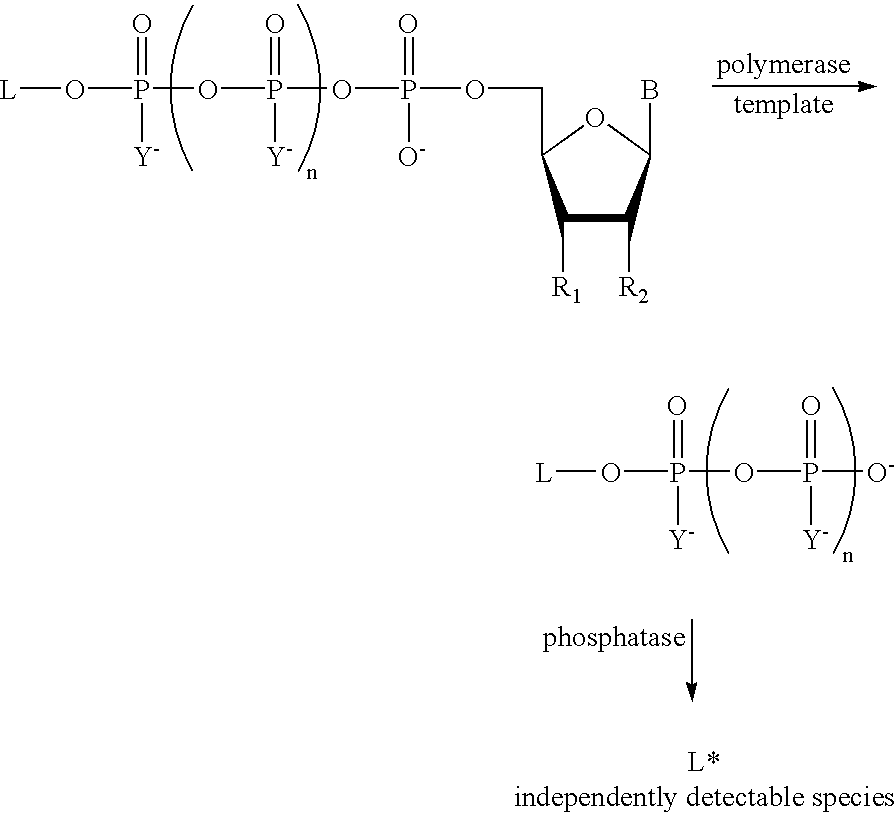
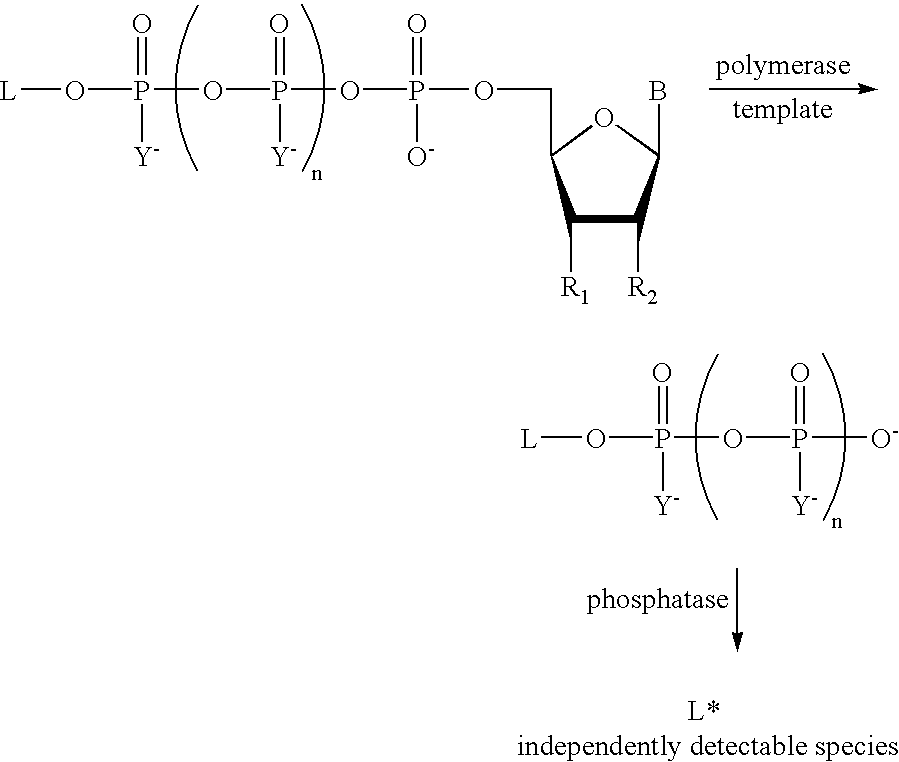
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Field-switch sequencing
ActiveUS7462452B2Low costImprove reuseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphatePolymerase L
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
System and method for nucleic acid sequencing by polymerase synthesis
InactiveUS7229799B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
This invention relates to improved methods for sequencing and genotyping nucleic acid in a single molecule configuration. The method involves single molecule detection of fluorescent labeled PPi moieties released from NTPs as a polymerase extension product is created.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
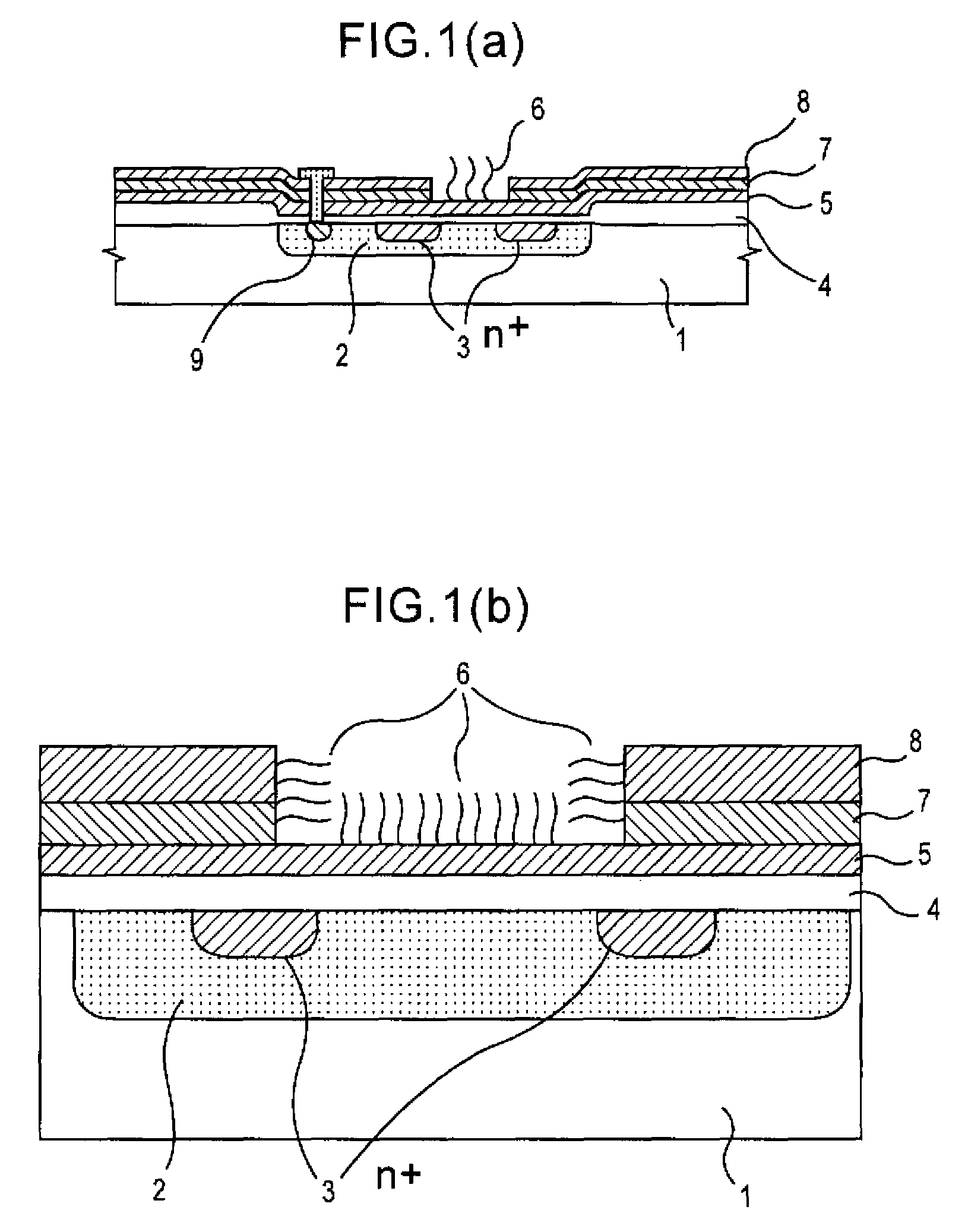
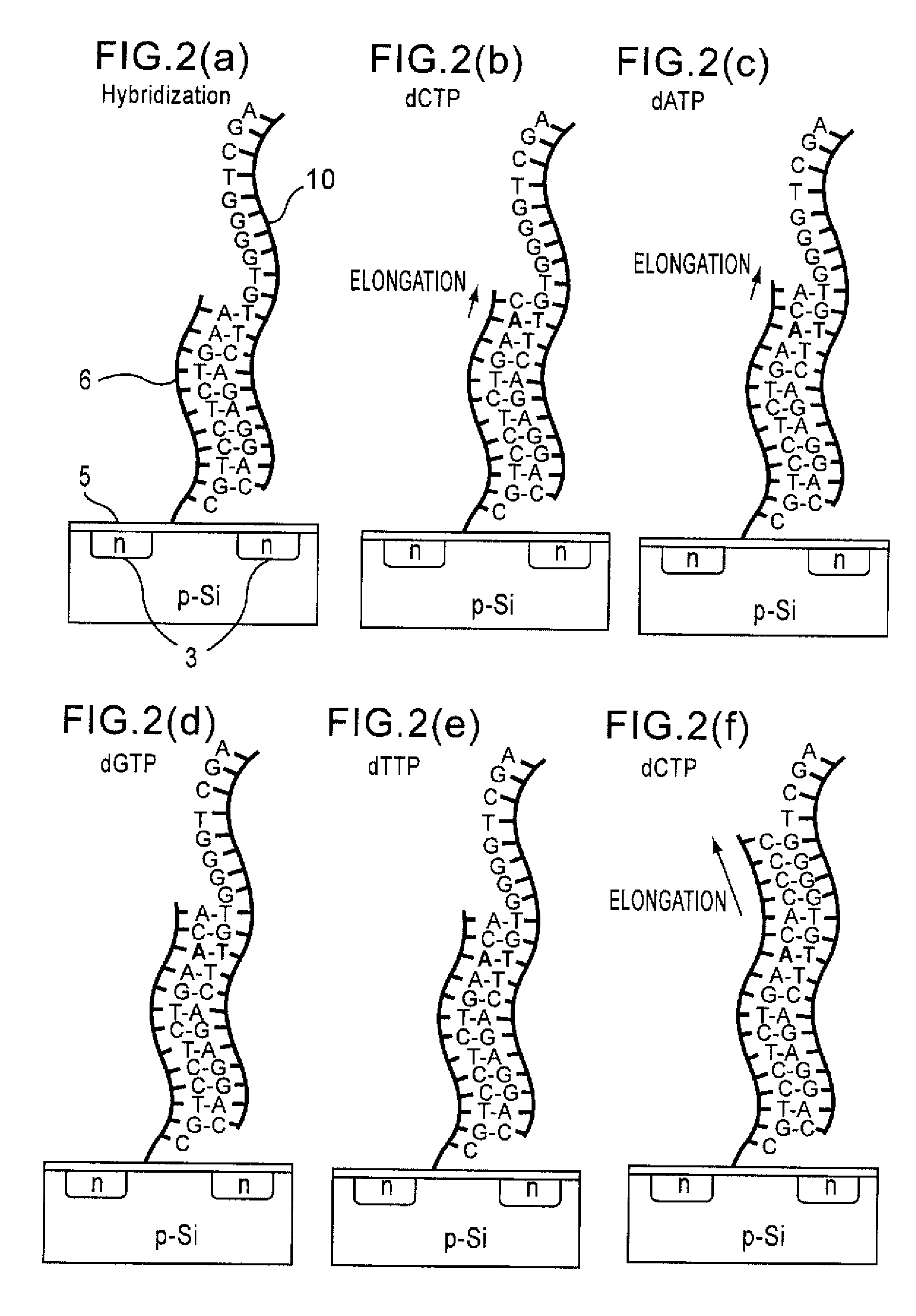
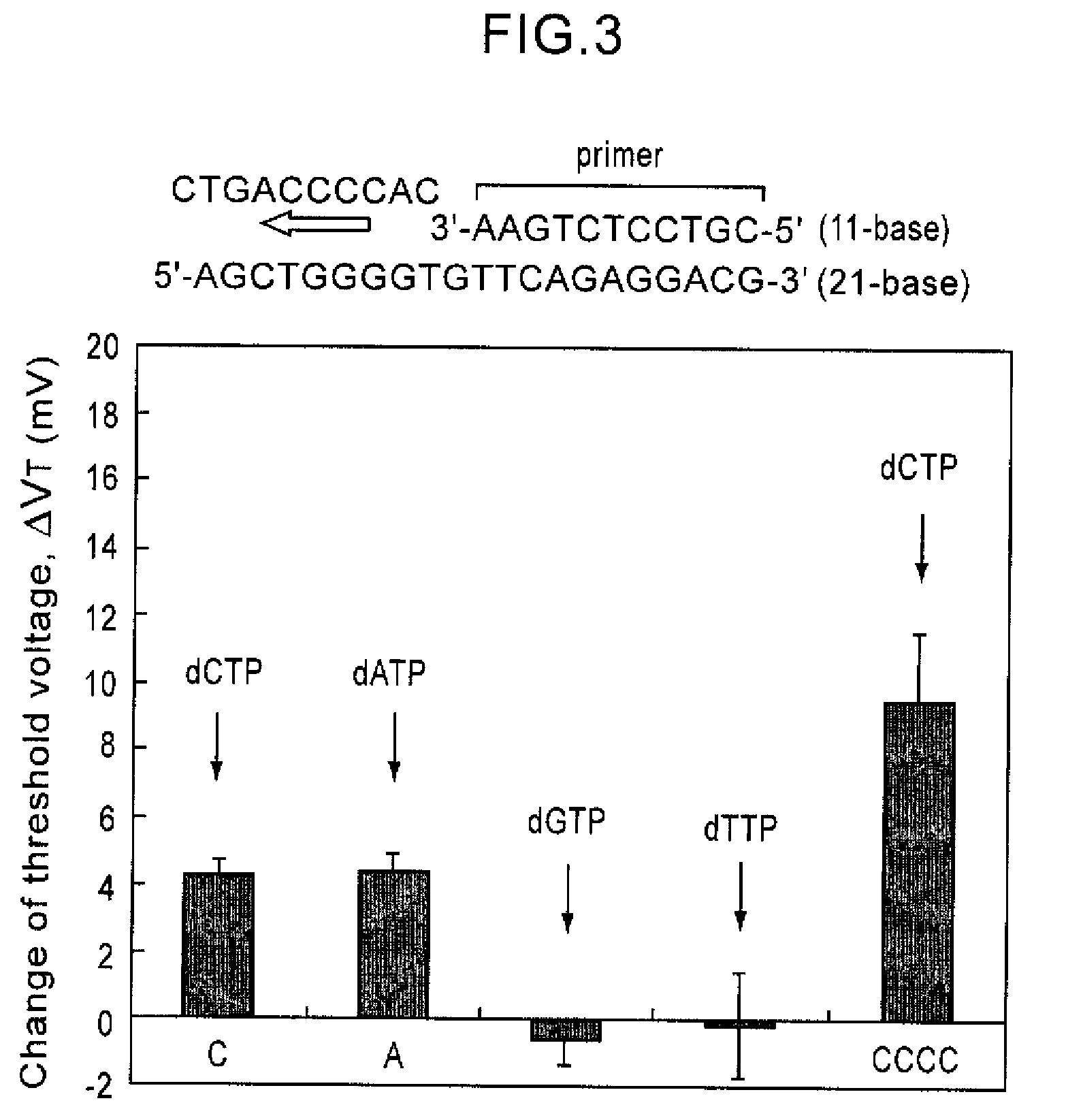
Method of analyzing DNA sequence using field-effect device, and base sequence analyzer
ActiveUS7888013B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Molecular redundant sequencing
ActiveUS20090029385A1Improve accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
Methods, systems and compositions where a target nucleic acid includes a registration sequence disposed therein for identification of the number or relative position of determined sequence from the template sequence. Particularly preferred aspects include a registration sequence in a circular template nucleic acid sequence which is, in turn, used in sequence by incorporation processes that rely upon template dependent, polymerase mediated primer extension in the identification of the sequence of the template.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Helicase-dependent amplification of RNA
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Double ended sequencing
InactiveUS20060134633A1Heating or cooling apparatusSugar derivativesPolymerase LComputational biology
This invention relates to methods of sequencing DNA. More specifically, this invention relates to methods of sequencing both the sense and antisense strands of DNA through the use of blocked and unblocked sequencing primers. In brief, these methods include the steps of annealing an unblocked primer to a first strand of nucleic acid; annealing a second blocked primer to a second strand of nucleic acid; elongating the nucleic acid along the first strand with a polymerase; terminating the first sequencing primer; deblocking the second primer; and elongating the nucleic acid along the second strand.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
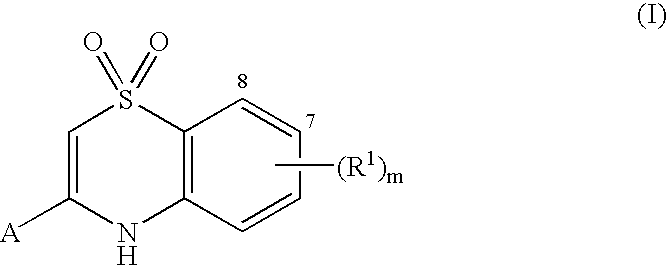
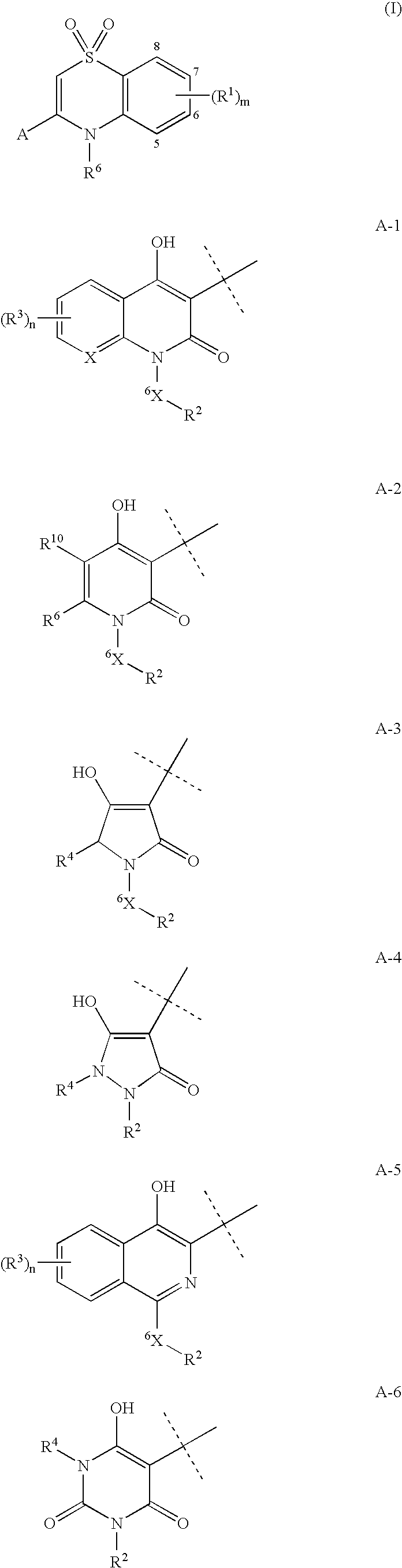
Heterocyclic antiviral compounds
Compounds having the formula I wherein A, m and R1 are herein defined are Hepatitis C virus polymerase inhibitors. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for treating diseases mediated by HCV and for inhibiting hepatitis replication. Also disclosed are processes for making the compounds and synthetic intermediates used in the process
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Analyte detection
A method of characterizing an analyte sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) anchoring the analyte to a nucleic acid template of known sequence; (b) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (c) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (d) detecting the detectable species. The method may include the step of characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection. Also provided are methods of analyzing multiple analytes in a sample, and kits for characterizing analyte samples.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Active surface coupled polymerases
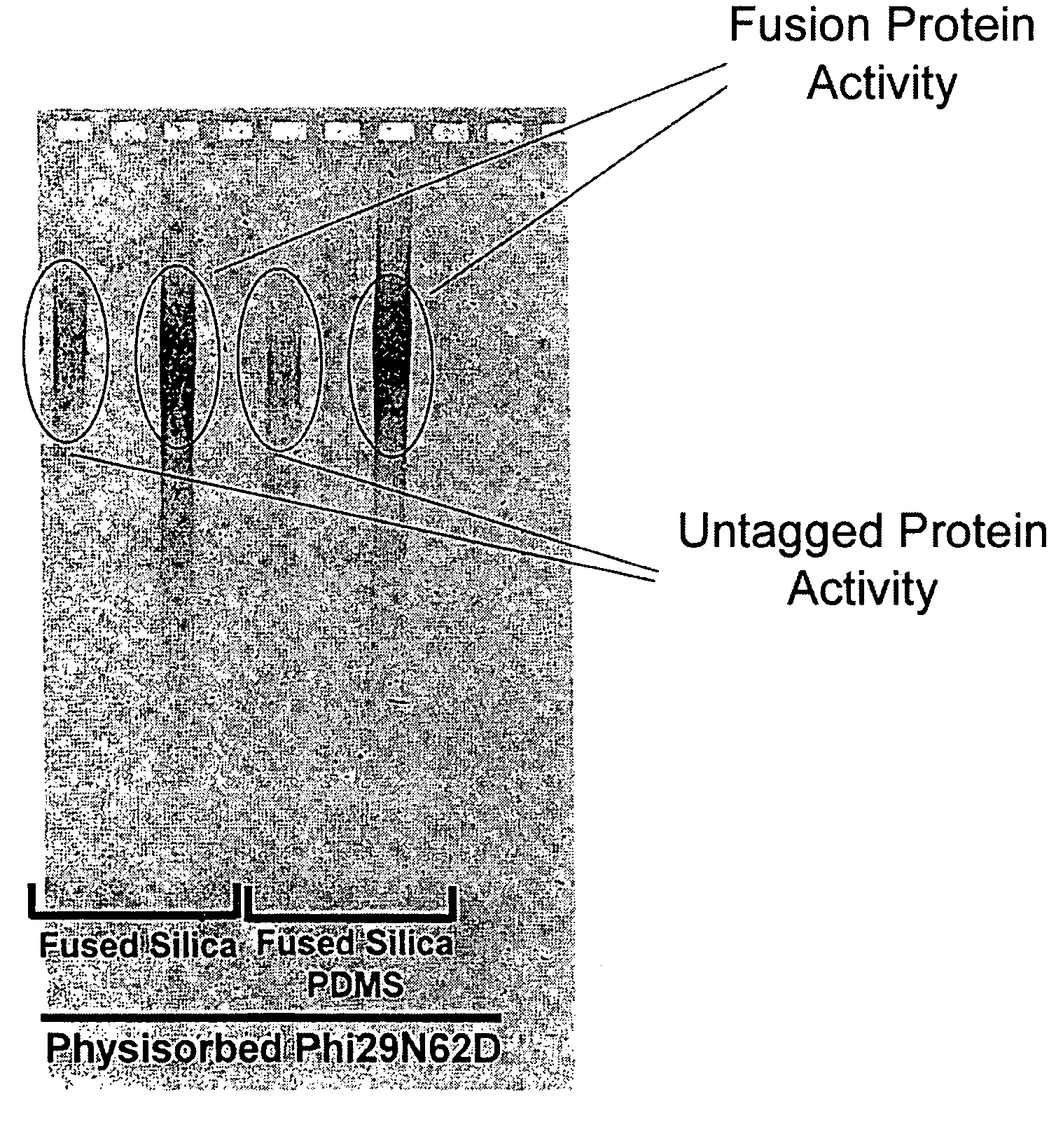
ActiveUS20080199932A1Without substantial loss of activityHigh binding affinityMicrobiological testing/measurementOn/in organic carrierPolymerase LBiomedical engineering
Active surface coupled polymerases, surfaces that include such polymerases, and methods of making and using surface-attached polymerases are provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Rapid parallel nucleic acid analysis
ActiveUS20060051807A1Efficiently determinedEliminates non-specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LDivalent metal ions
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
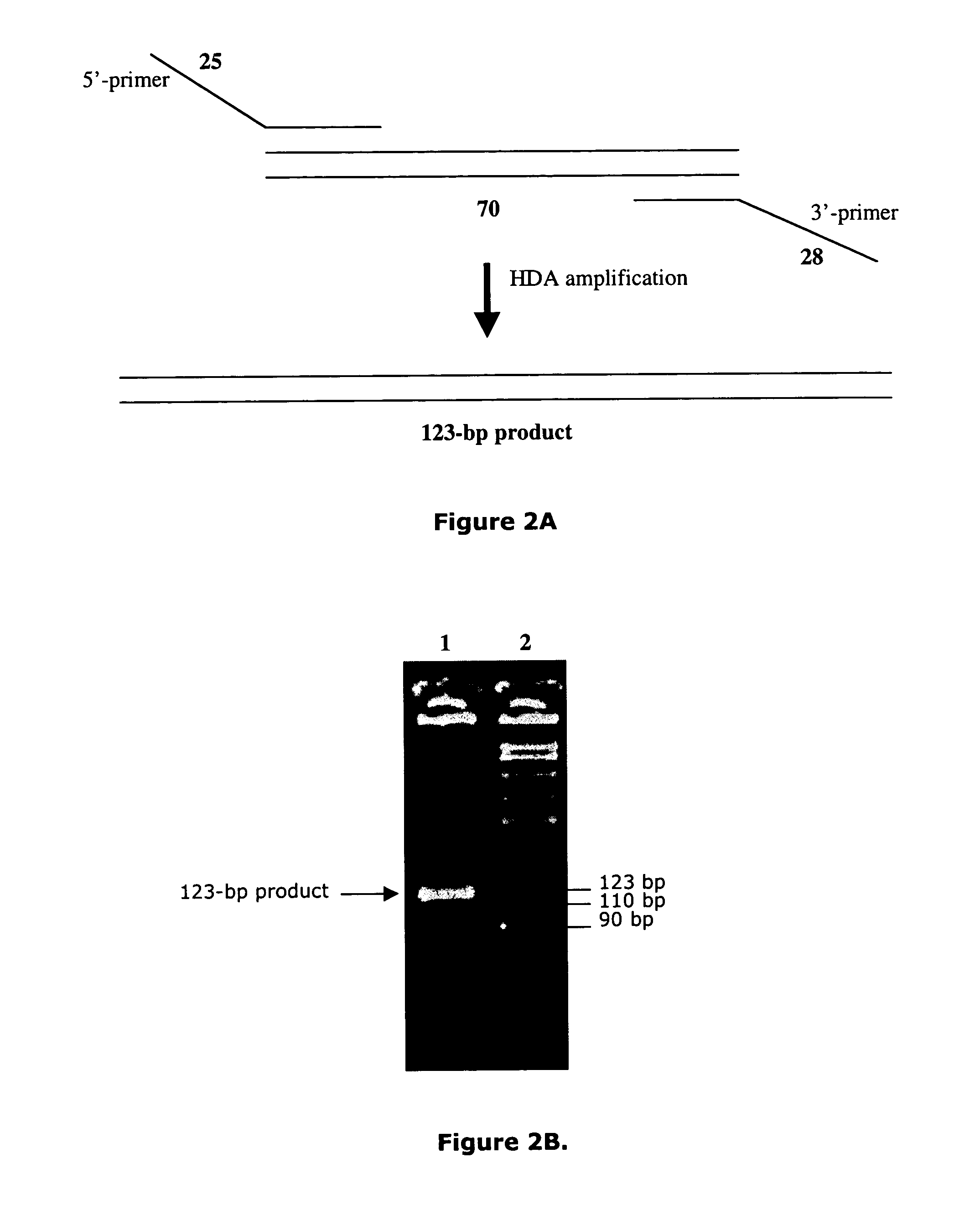
Method for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules and its application
InactiveUS6605428B2Improved and rapid and reliable methodReduction of initial amountSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
A method is described for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing ("DEXAS") of a DNA molecule from a complex mixture of nucleic acids, wherein truncated DNA molecules as well as DNA molecules of full length are synthesized simultaneously and exponentially between two positions on the said DNA molecule, which initially contains a DNA molecule in a thermocycling reaction, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a thermostable DNA polymerase, a thermostable pyrophosphatase (optionally), deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed using one polymerase having a Tabor-Richardson mutation, or a functional derivative thereof, and reverse transcriptase activity. In a more preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed in one step, in one vessel.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Parallel polymorphism scoring by amplification and error correction
InactiveUS20070009954A1Easy to processFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesPolymerase LBinding domain
This invention provides a method of detecting polymorphisms, e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), by amplification and error correction. The invention encompasses methods of performing amplification and error correction using an improved generation of nucleic acid polymerases, and methods of multiplexing the assay. The improvement to the polymerases is the joining of a sequence-non-specific nucleic-acid-binding domain to the enzyme in a manner that enhances the ability of the enzyme to bind and catalytically modify the nucleic acid.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Field-switch sequencing
ActiveUS20050266456A1Low costSolve the lack of resolutionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphatePolymerase L
The present invention provides novel compositions, methods and apparatus for DNA sequencing that can be performed, e.g., in a two-electrode chamber. The present invention also provides a method for sequencing a nucleic acid comprising immobilizing a plurality of complexes comprising a target nucleic acid, a primer nucleic acid, and a polymerase onto a surface, contacting the surface with a plurality of charged particles comprising a nucleotide phosphate by applying an electric field, reversing the electric field to transport unbound charged particles away from the surface, and detecting the incorporation of a nucleotide phosphate into a single molecule of the primer nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
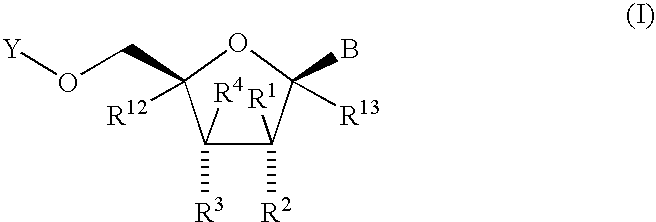
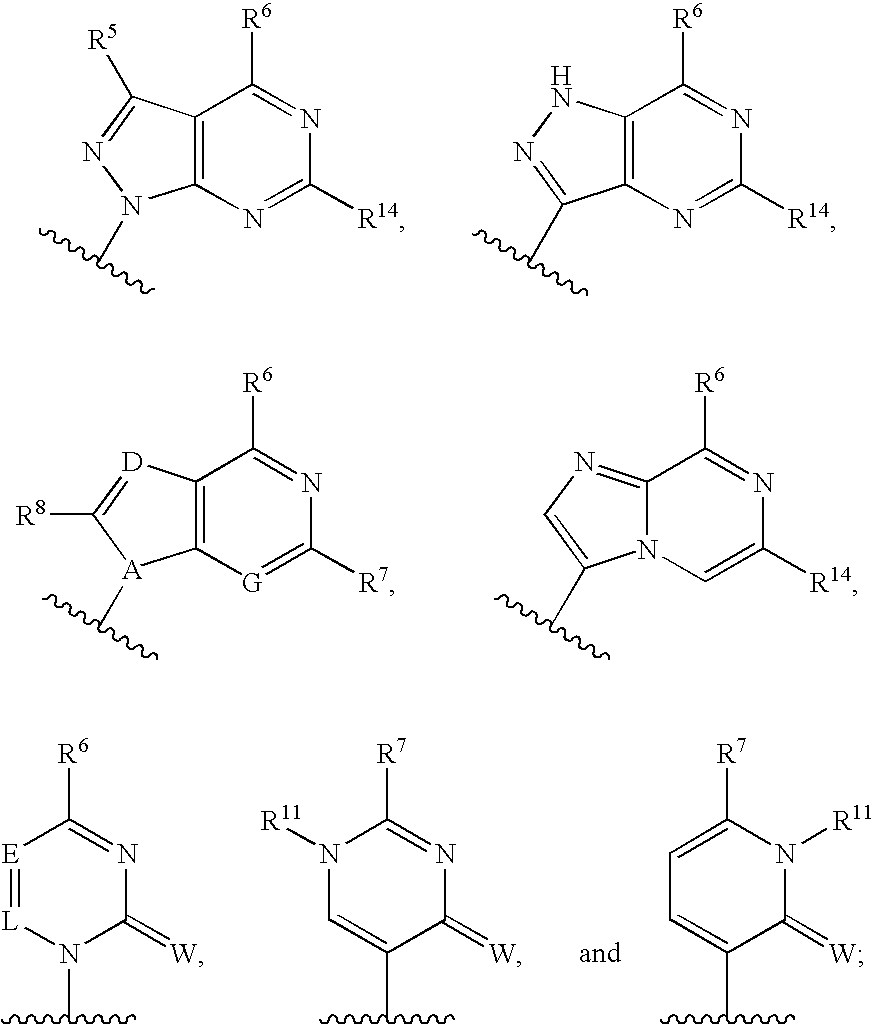
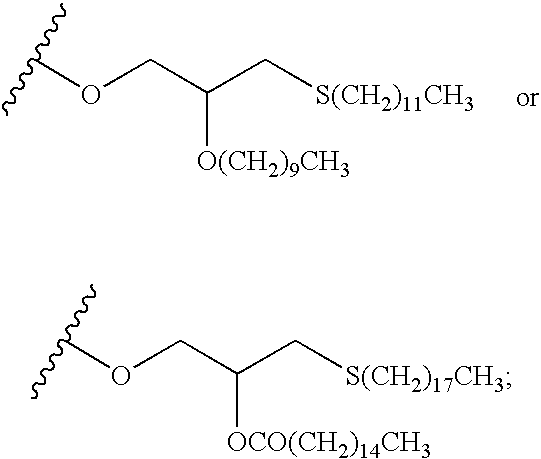
Substituted nucleosides, preparation thereof and use as inhibitors of RNA viral polymerases
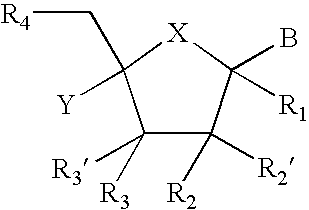
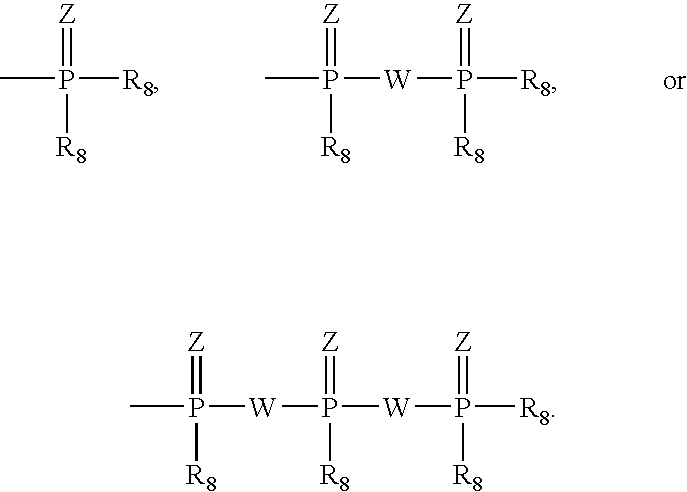
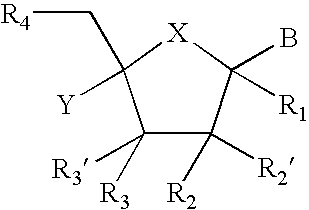
Provided are compounds represented by: X is O, S or NR6, R1 is H or (CH2)mR5, R2, R2', R3 and R3' are independently NO2, N3 or (CH2)mR5, OH R4 is H, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)nR7, R5 is H, halo, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)mR7, R6 and R6a are individually H, alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, aryl or substituted aryl, R7 is: R8 is H, F, SR9 or OR9, R9 is H, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl or hydroxyprotecting group, Y is H, CH3 or (CH2)mR5, Z is O or S W is CH2, CF2, CHF or O, m is 0-4, B is adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil, thymine, modified purines and pyrimidines substituted pyridines, five membered heterocycles substituted by at least one of amines, substituted amines, amides, substituted amides, esters, halogens, alkyls, ethers; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and prodrugs thereof. These ring systems may be substituted.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS20030124576A1Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, charcterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have calorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
System and methods for nucleic acid sequencing of single molecules by polymerase synthesis
InactiveUS20090082212A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com