Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Pyrophosphatase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pyrophosphatases, also known as diphosphatases, are acid anhydride hydrolases that act upon diphosphate bonds.
Method of detecting primer extension reaction, method of discriminating base type, device for discriminating base type, device for detecting pyrophosphate, method of detecting nucleic acid and tip for introducing sample solution
InactiveUS20050032075A1Decrease of H+ concentrationImprove concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBase JNucleotide
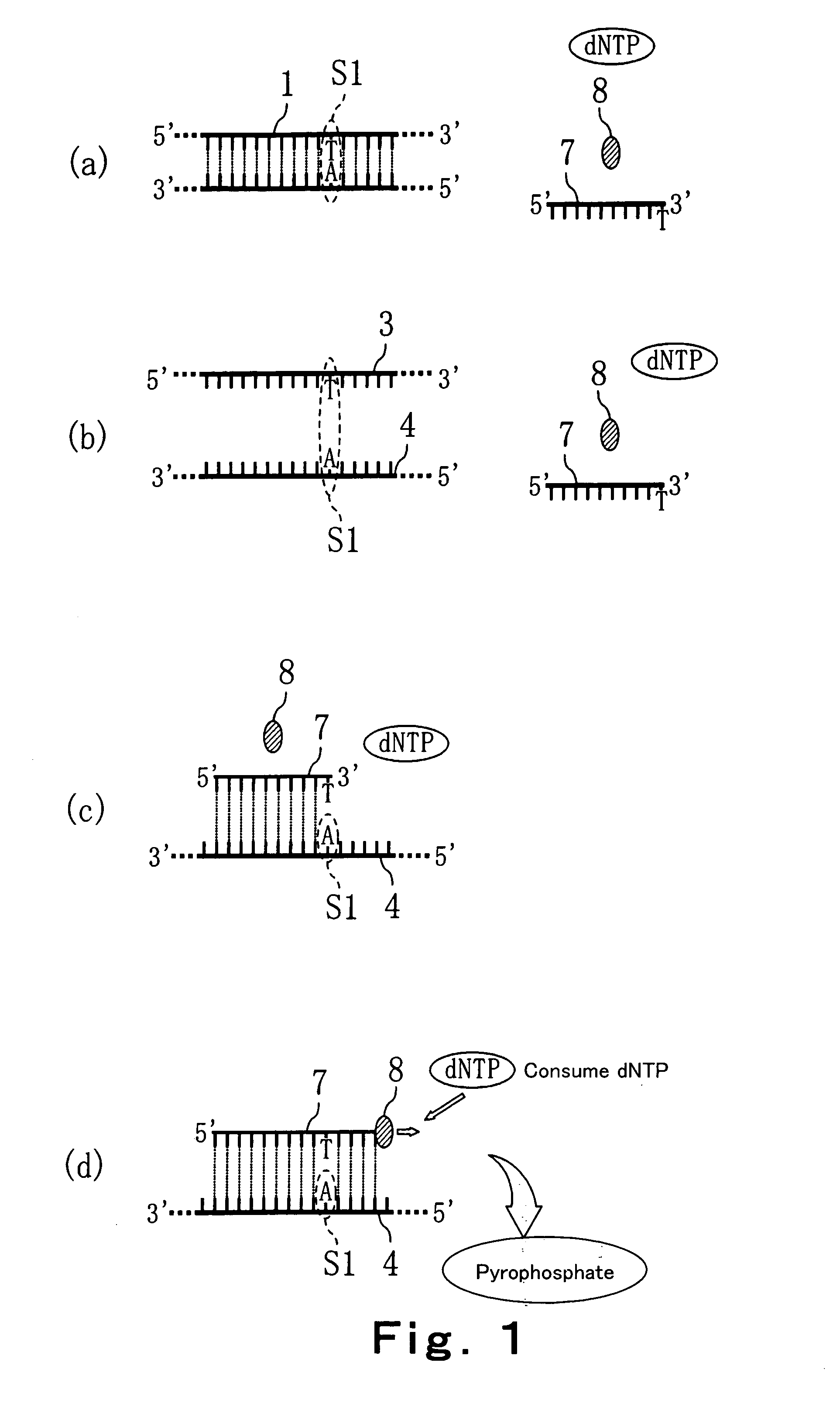
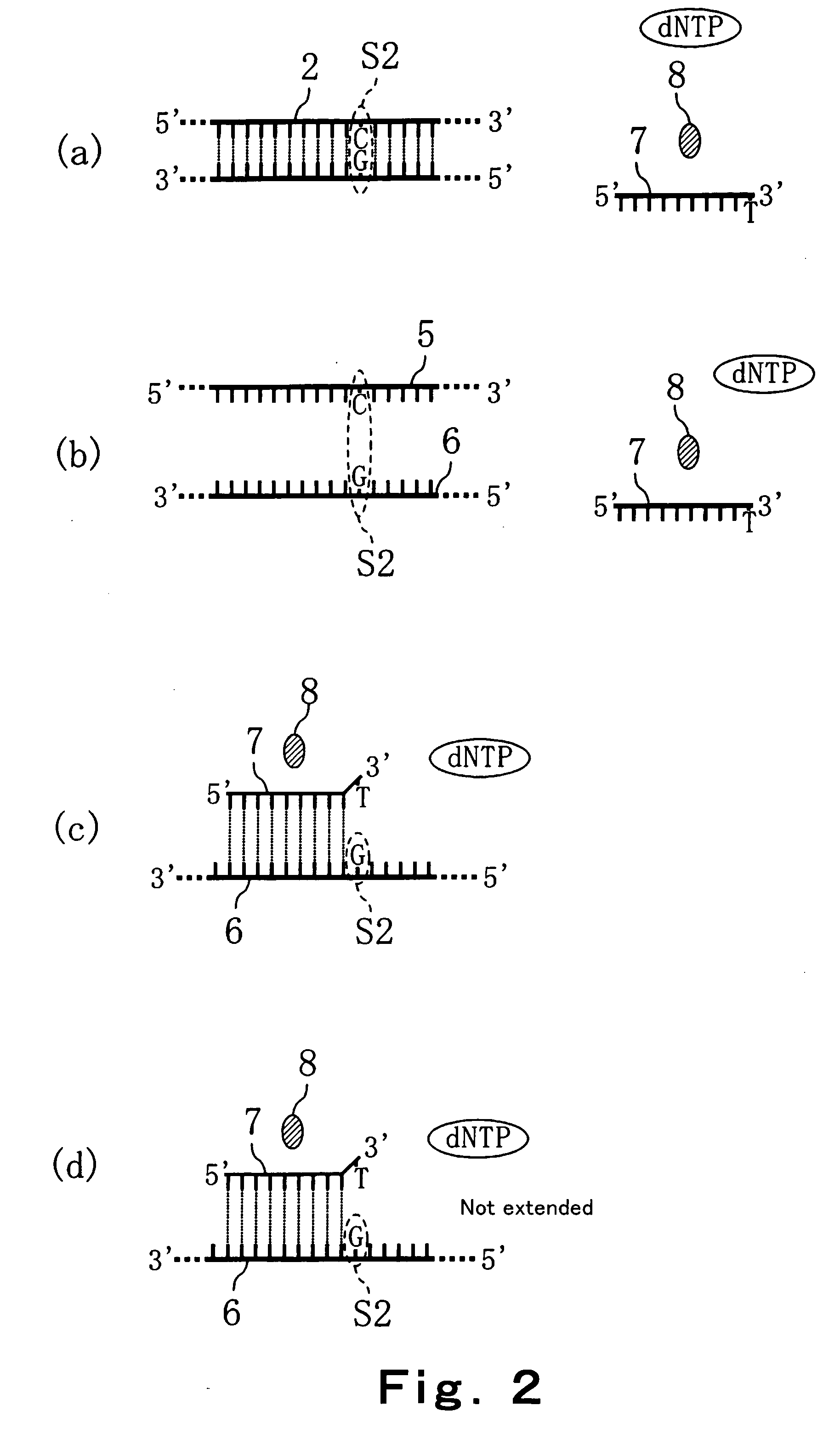
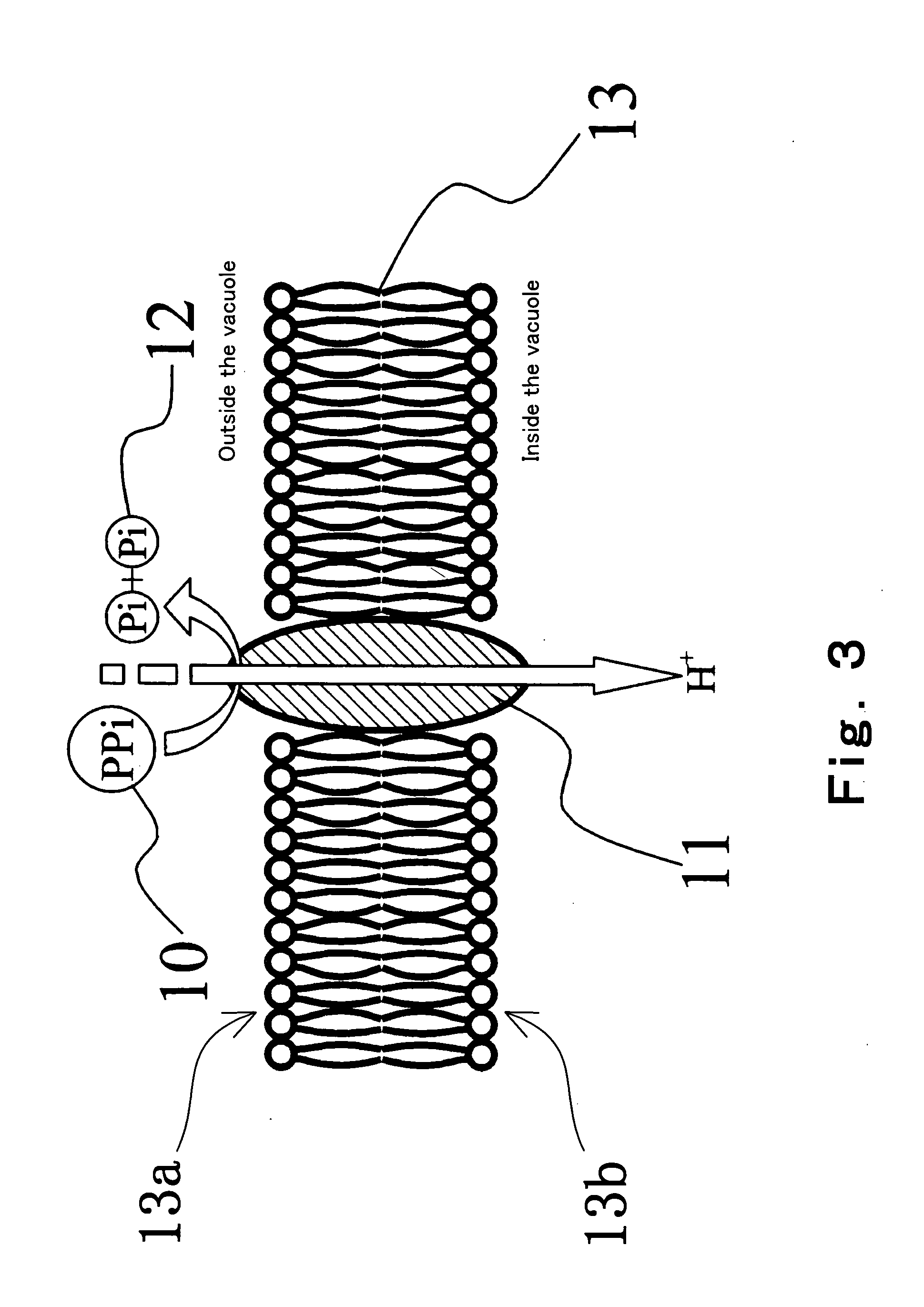
Convenient techniques for discriminating the base type in a base sequence of a nucleic acid are provided. The technique includes the step (a) of preparing a sample solution containing a nucleic acid, a primer having a base sequence that includes a complementary binding region which complementarily binds to the nucleic acid, and a nucleotide; the step (b) of allowing the sample solution to stand under a condition to cause an extension reaction of the primer, and producing pyrophosphate when the extension reaction is caused; the step (c) of bringing the sample solution into contact with the front face of a H+ hardly permeable membrane having H+-pyrophosphatase, which penetrates from front to back of the membrane, of which active site that hydrolyzes pyrophosphate being exposed to the front face; the step (d) of measuring the H+ concentration of at least either one of the solution at the front face side of the H+ hardly permeable membrane or the solution at the back face side of the H+ hardly permeable membrane, in a state where the H+-pyrophosphatase is immersed in the solution; the step (e) of detecting the extension reaction on the basis of the result of measurement in the step (d) ; and the step (f) of discriminating the base type in the base sequence of the nucleic acid on the basis of the result of detection in the step (e).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules and its application
InactiveUS6605428B2Improved and rapid and reliable methodReduction of initial amountSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
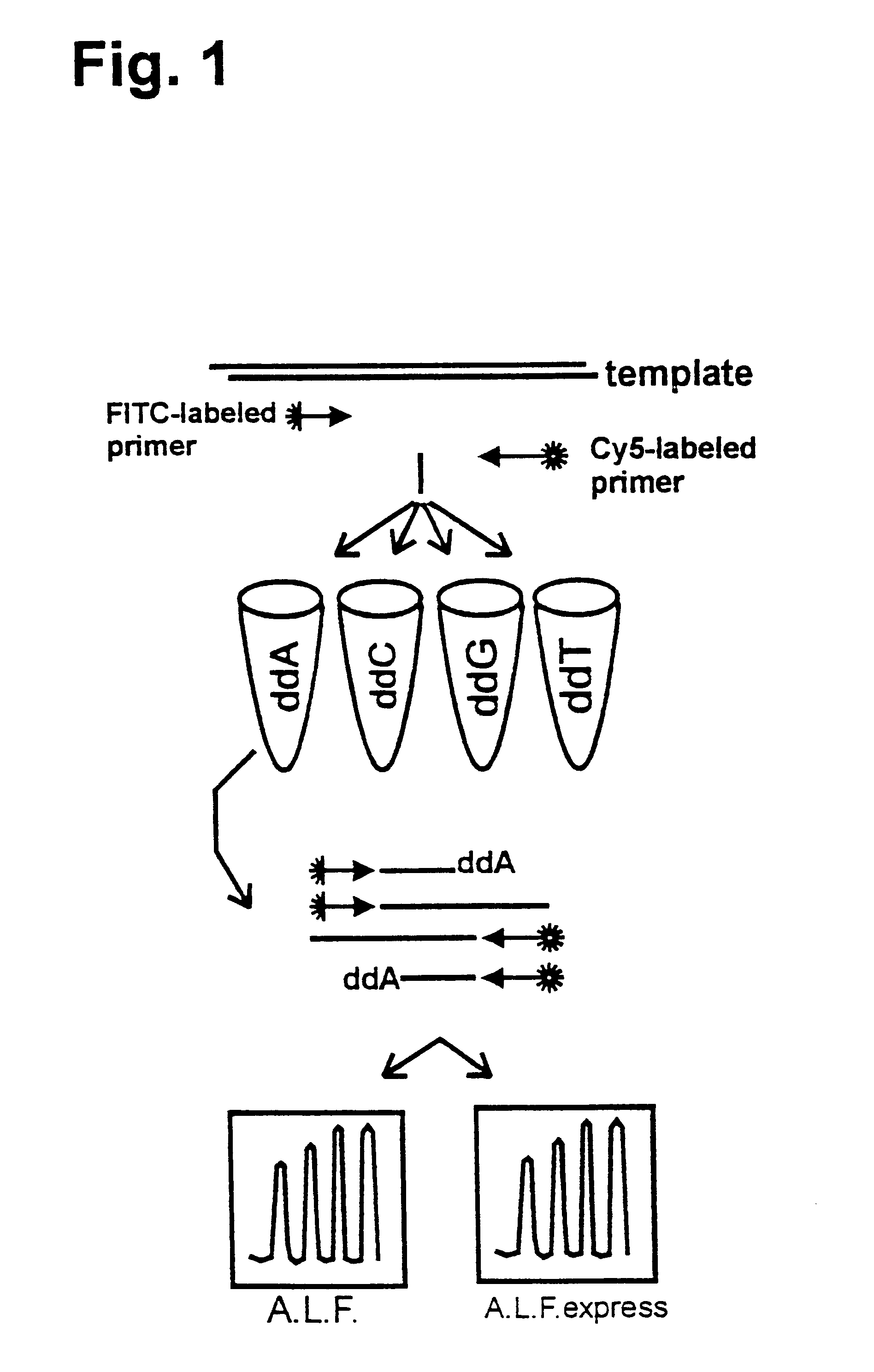
A method is described for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing ("DEXAS") of a DNA molecule from a complex mixture of nucleic acids, wherein truncated DNA molecules as well as DNA molecules of full length are synthesized simultaneously and exponentially between two positions on the said DNA molecule, which initially contains a DNA molecule in a thermocycling reaction, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a thermostable DNA polymerase, a thermostable pyrophosphatase (optionally), deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed using one polymerase having a Tabor-Richardson mutation, or a functional derivative thereof, and reverse transcriptase activity. In a more preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed in one step, in one vessel.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Plant cells and plants overexpressing vacuolar proton pyrophosphatases
InactiveUS8058515B2Increase planting yieldIncrease in sizeBryophytesClimate change adaptationHalotoleranceLeaf cell
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which increases expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plants grown from seed are also described. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cells, leaf cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which increases expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cells are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. The present invention also relates to a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, and a method of producing a transgenic plant with increased salt tolerance.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
Method for the uncoupled, direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules with the addition of a second thermostable DNA polymerase and its application
InactiveUS20020034792A1Increases exponential amplificationReduction of initial amountMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesDNA
Method for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule in a thermocycling reaction which initially comprises a nucleic acid molecule, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a first thermostable DNA polymerase, (optionally) a thermostable pyrophosphatase, deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or a derivative thereof and which is characterized in that the thermocycling reaction additionally contains a second thermostable DNA polymerase which, in comparison to the said first thermostable DNA polymerase, has a reduced ability to incorporate dideoxynucleotides as well as the use of the said method.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Methods and compositions for the treatment of diseases characterized by pathological calcification
InactiveUS20060069068A1Good curative effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth retardantCalcification
Methods and compositions are provided which contains preparations of calcium chelators, bisphosphonates, antibiotics, antimicrobial agents, cytostatic agents, calcium ATPase and pyrophosphatase pump inhibitors, calcium phosphate-crystal dissolving agents, agents effective against calcium phosphate-crystal nucleation and crystal growth, and / or a combination of supportive agents and which may be used for treating and or reducing pathological calcifications, the growth of Nanobacterium and calcification-induced diseases including, but not limited to, Arteriosclerosis, Atherosclerosis, Coronary Heart Disease, Chronic Heart Failure, Valve Calcifications, Arterial Aneurysms, Calcific Aortic Stenosis, Transient Cerebral Ischemia, Stroke, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Vascular Thrombosis, Dental Plaque, Gum Disease (dental pulp stones), Salivary Gland Stones, Chronic Infection Syndromes such as Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Kidney and Bladder Stones, Gall Stones, Pancreas and Bowel Diseases (such as Pancreatic Duct Stones, Crohn's Disease, Colitis Ulcerosa), Liver Diseases (such as Liver Cirrhosis, Liver Cysts), Testicular Microliths, Chronic Calculous Prostatitis, Prostate Calcification, Calcification in Hemodialysis Patients, Malacoplakia, Autoimmune Diseases. Erythematosus, Scleroderma, Dermatomyositis, Antiphospholipid Syndrome, Arteritis Nodosa, Thrombocytopenia, Hemolytic Anemia, Myelitis, Livedo Reticularis, Chorea, Migraine, Juvenile Dermatomyositis, Grave's Disease, Hypothyreoidism, Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, Addison's Disease, Hypopituitarism, Placental and Fetal Disorders, Polycystic Kidney Disease, Glomerulopathies, Eye Diseases (such as Corneal Calcifications, Cataracts, Macular Degeneration and Retinal Vasculature-derived Processes and other Retinal Degenerations, Retinal Nerve Degeneration, Retinitis, and Iritis), Ear Diseases (such as Otosclerosis, Degeneration of Otoliths and Symptoms from the Vestibular Organ and Inner Ear (Vertigo and Tinnitus)), Thyroglossal Cysts, Thyroid Cysts, Ovarian Cysts, Cancer (such as Meningiomas, Breast Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Thyroid Cancer, Serous Ovarian Adenocarcinoma), Skin Diseases (such as Calcinosis Cutis, Calciphylaxis, Psoriasis, Eczema, Lichen Ruber Planus), Rheumatoid Arthritis, Calcific Tenditis, Osteoarthritis, Fibromyalgia, Bone Spurs, Diffuse Interstitial Skeletal Hyperostosis, Intracranial Calcifications (such as Degenerative Disease Processes and Dementia), Erythrocyte-Related Diseases involving Anemia, Intraerythrocytic Nanobacterial Infection and Splenic Calcifications, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Broncholiths, Bronchial Stones, Neuropathy, Calcification and Encrustations of Implants, Mixed Calcified Biofilms, and Myelodegenerative Disorders (such as Multiple Sclerosis, Lou Gehrig's and Alzheimer's Disease) in humans and animals. The method comprises administering the various classes of compositions of the present invention, which together effectively inhibit or treat the development of calcifications in vivo.
Owner:CIFTCIOGLU NEVA
Preparation method of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
The invention relates to a preparation method of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, which comprises the following steps of: with 1,2,3,5-tetraacetyl-beta-D-ribofuranose as a starting raw material, preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide through sequentially a condensation reaction, an ammonolysis reaction and a phosphorylation reaction; and then mixing the prepared nicotinamide mononucleotide with adenosine triphosphate, generating an enzymic catalytic reaction in the presence of nicotinamide adenosine nucleotide transferase and pyrophosphatase to prepare the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the invention has the advantage that the whole process is simplified and optimized by combination of a chemical method and an enzymic method.
Owner:SYNCOZYMES SHANGHAI
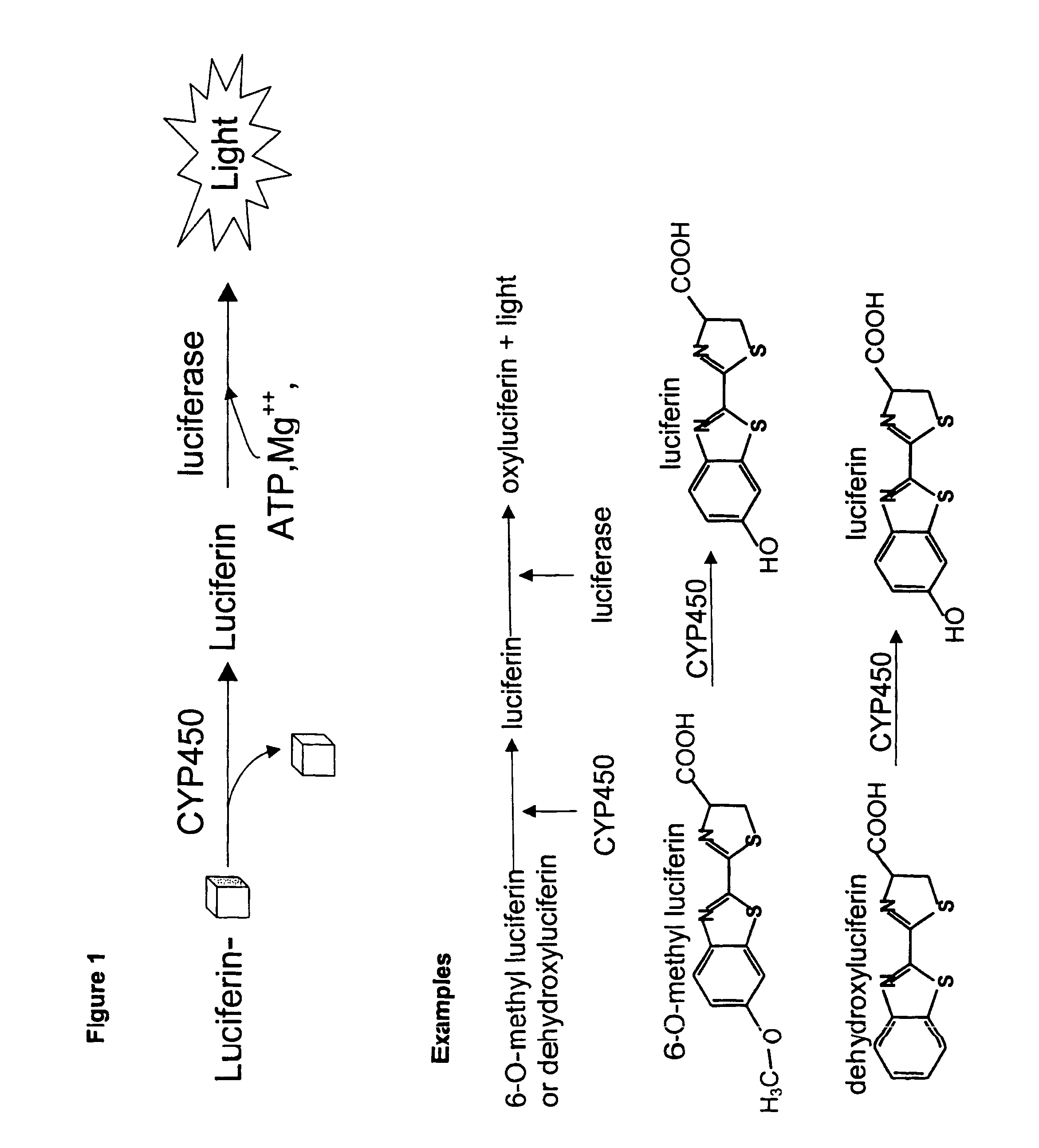
Luminescence-based methods and probes for measuring cytochrome P450 activity
ActiveUS7692022B2Improve stabilityExtended service lifeCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningMetabolitePresent method
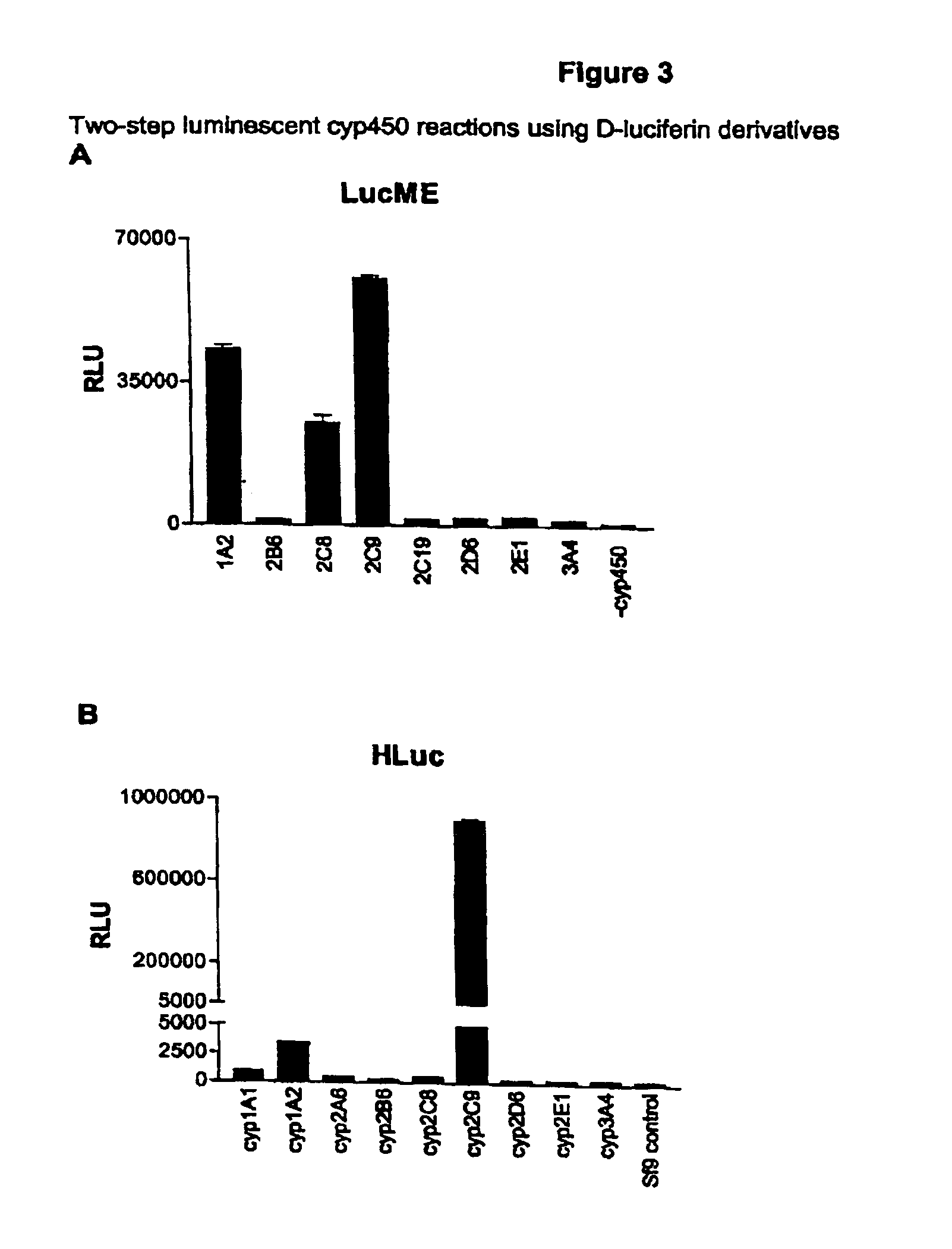
The present invention provides methods, compositions, substrates, and kits useful for analyzing the metabolic activity in cells, tissue, and animals and for screening test compounds for their effect on cytochrome P450 activity. In particular, a one-step and two-step methods using luminogenic molecules, e.g. luciferin or coelenterazines, that are cytochrome P450 substrates and that are also bioluminescent enzyme, e.g., luciferase, pro-substrates are provided. Upon addition of the luciferin derivative or other luminogenic molecule into a P450 reaction, the P450 enzyme metabolizes the molecule into a bioluminescent enzyme substrate, e.g., luciferin and / or luciferin derivative metabolite, in a P450 reaction. The resulting metabolite(s) serves as a substrate of the bioluminescent enzyme, e.g., luciferase, in a second light-generating reaction. Luminescent cytochrome P450 assays with low background signals and high sensitivity are disclosed and isoform selectivity is demonstrated. The present invention also provides an improved method for performing luciferase reactions which employs added pyrophosphatase to remove inorganic pyrophosphate, a luciferase inhibitor which may be present in the reaction mixture as a contaminant or may be generated during the reaction. The present method further provides a method for stabilizing and prolonging the luminescent signal in a luciferase-based assay using luciferase stabilizing agents such as reversible luciferase inhibitors.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
Method for the uncoupled, direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules with the addition of a second thermostable DNA polymerase and its application
InactiveUS6828094B2Increases exponential amplificationReduction of initial amountMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesDNA
Method for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule in a thermocycling reaction which initially comprises a nucleic acid molecule, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a first thermostable DNA polymerase, (optionally) a thermostable pyrophosphatase, deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or a derivative thereof and which is characterized in that the thermocycling reaction additionally contains a second thermostable DNA polymerase which, in comparison to the said first thermostable DNA polymerase, has a reduced ability to incorporate dideoxynucleotides as well as the use of the said method.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Pyrophosphatase of ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and coding gene and application thereof
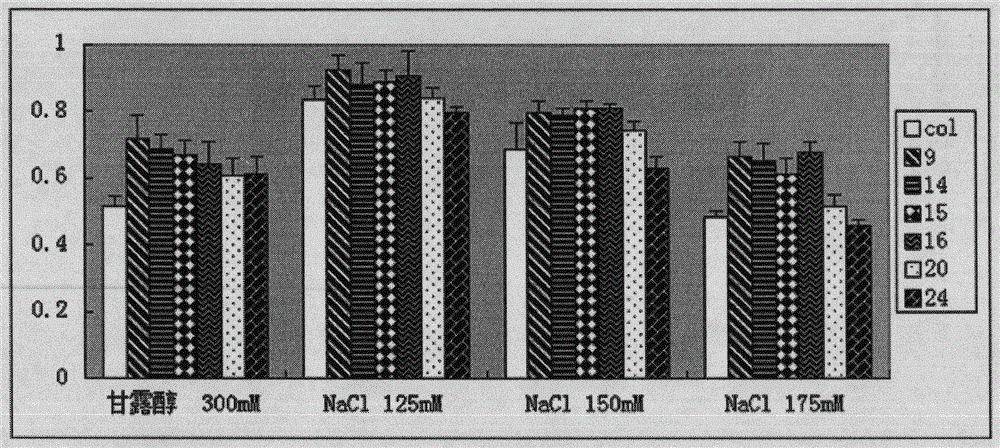
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and in particular relates to pyrophosphatase of ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and a coding gene and application thereof. The pyrophosphatase provided by the invention comes from the ammopiptanthus mongolicus, named AmVP1, wherein the amino acid sequence of the pyrophosphatase is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The coding gene of the pyrophosphatase of the ammopiptanthus mongolicus is one of the following nucleotide sequences: SEQ ID NO.1 and polynucleotide with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The gene of the invention can be applied to the research of the salt-resisting and drought-enduring molecular mechanism of the ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and is used for improving the salt-resisting and drought-enduring property of plants.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Dried composition for hot-start PCR with long-term stability
ActiveUS20100209973A1Avoid inefficiencyPreventing error mixingHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementHot start PCRPyrophosphate
The present invention relates to a dried composition for hot-start PCR, more precisely a dried composition for hot-start PCR with improved stability and long-term storagability which is characteristically prepared by the steps of preparing a reaction mixture by mixing an aqueous solution containing reaction buffer, MgCl2, 4 types of dNTPs, DNA polymerase with pyrophosphate and pyrophosphatase in a reaction tube; and drying the reaction mixture prepared above, a preparation method of the same and a method for amplifying nucleic acid using the same. The dried composition for hot-start PCR is added with pyrophosphate and pyrophosphatase together before drying, so that it can have improved stability and long-term storagability as well as convenience in use, compared with the conventional compositions for hot-start PCR. Therefore, this composition can be effectively used for hot-start PCR, multiplex PCR or real-time quantitative PCR.
Owner:BIONEER
Method for heightening salt tolerance and drought tolerance of cotton by polymeric stress-resistant gene
InactiveCN101624604AImprove salt and drought toleranceVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationEscherichia coliAgricultural science
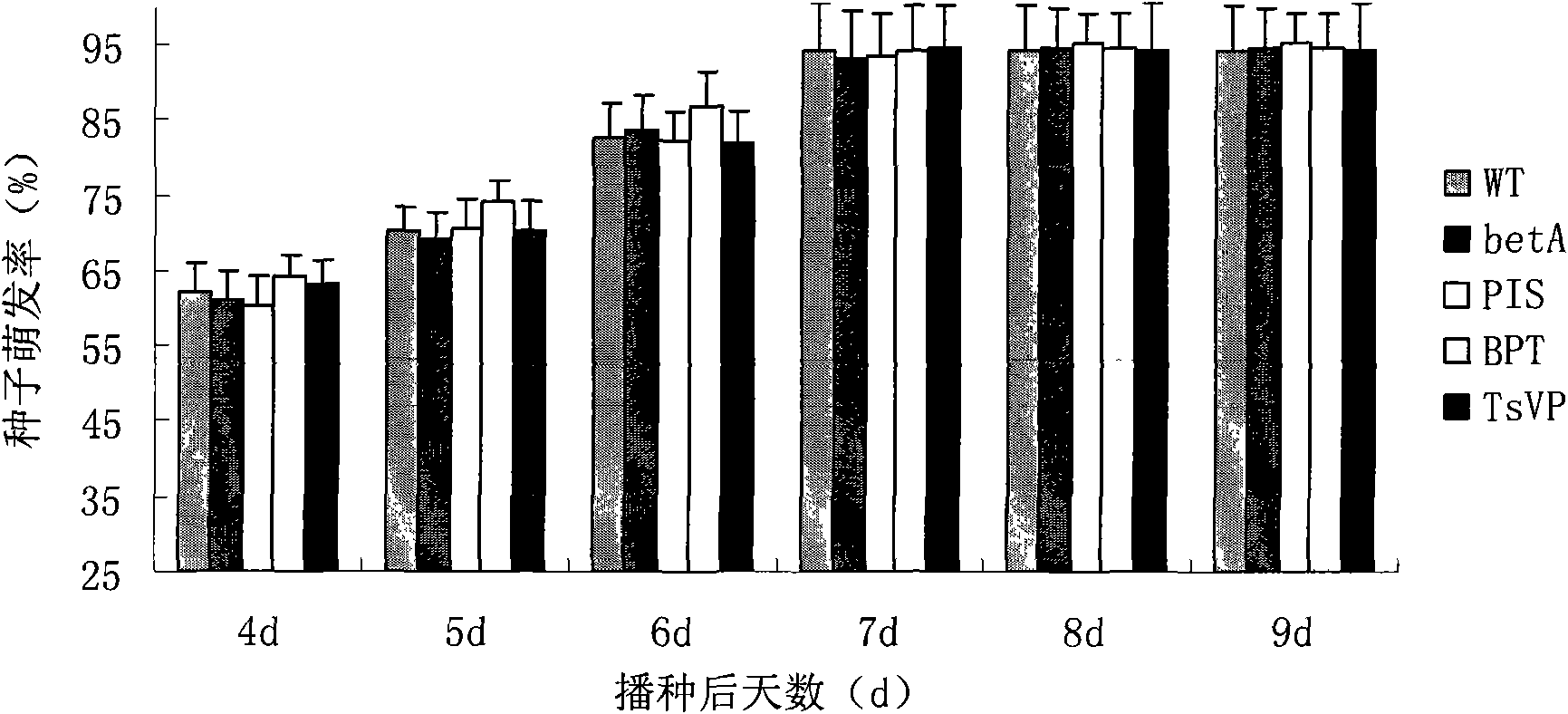
The invention discloses a method for heightening the salt tolerance and the drought tolerance of cotton by polymeric stress-resistant gene, comprising the following steps of: recombining phosphatidyl inositol synthetase gene PIS from a signal transduction pathway of a plant, tonoplast pyrophosphatase gene Ppase isolated from an ion region, and choline dehydrogenase gene betA which is from colon bacillus and gives glycine betaine synthesis capability into a plant expression carrier; transplanting the recombinant into cotton cells to be effectively expressed; regenerating transgene plantlet; selecting transgene homozygote with the obviously heightened salt tolerance and drought tolerance from the transgene plantlet and filial generation thereof; and breeding out new cotton germplasm with good salt tolerance and salt tolerance, so as to create new material for breeding the cotton with good salt tolerance and salt tolerance for breeding the conventional variety or hybrid variety of the cotton.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Selective 5' Ligation Tagging of RNA
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
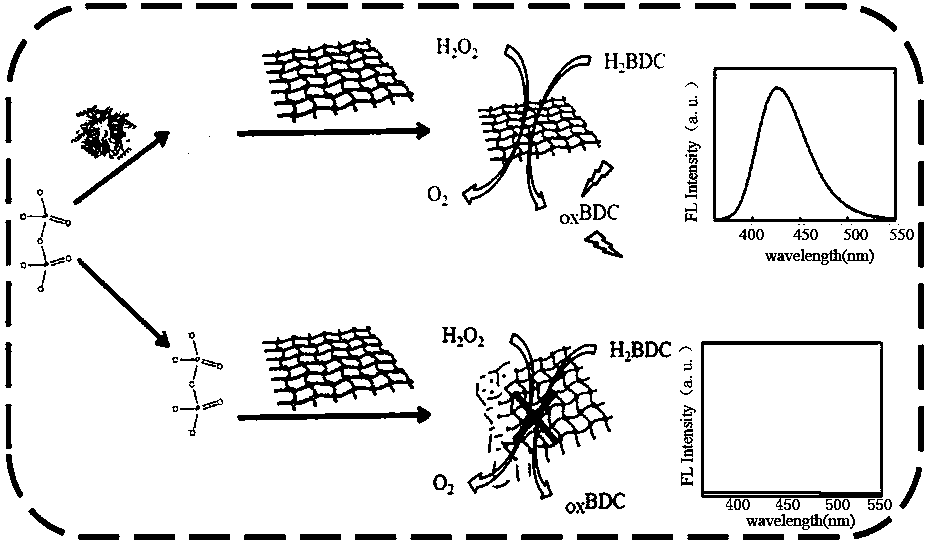
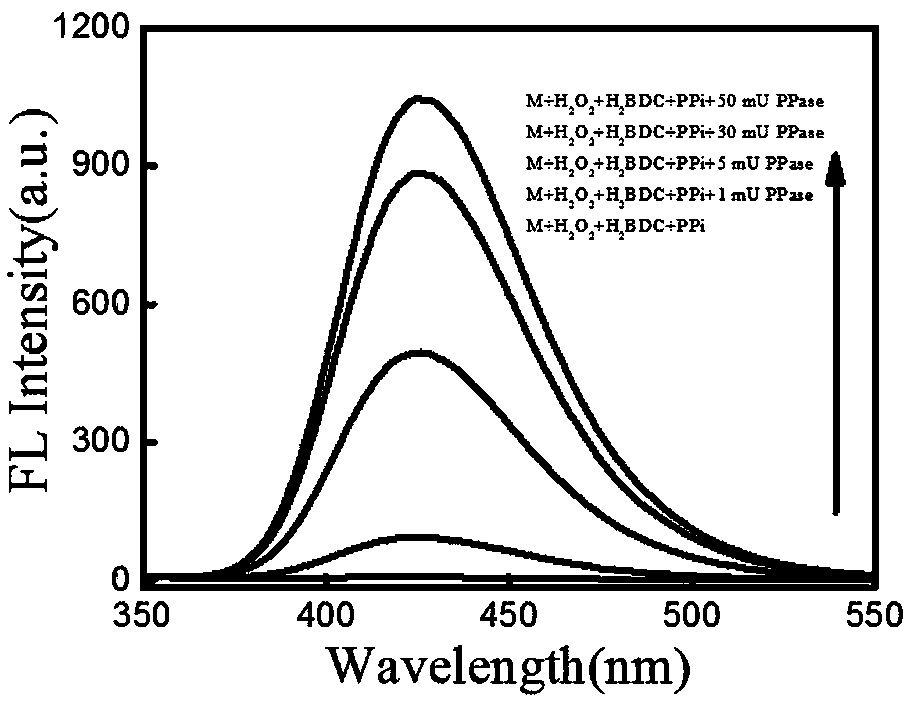
Fluorescent sensor for detecting inorganic pyophosphatase and its preparation method
ActiveCN108051418AFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsDiseaseMetal-organic framework
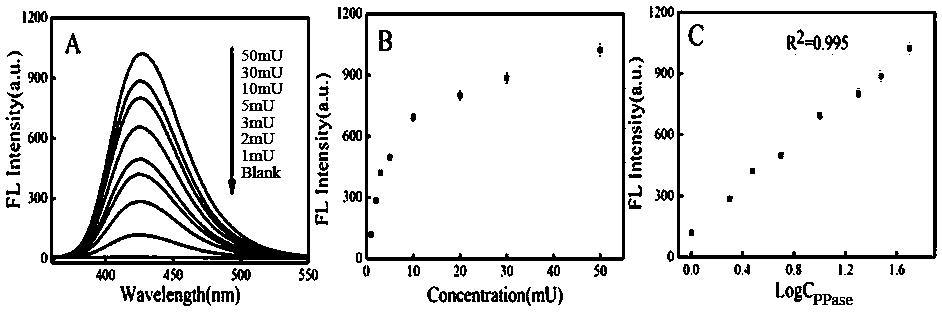
The invention belongs to the field of applying a metal organic framework to analysis and detection of a disease marker, and particularly relates to a fluorescent sensor for detecting inorganic pyophosphatase and its preparation method. Through reacting different concentrations of inorganic pyophosphatase solution with pyrophosphate, Cu-BDC-MOF nanosheet solution, hydrogen peroxide solution and terephthalic acid solution are added and incubated at 37 DEG C for 30 minutes; fluorescent signals of inorganic pyophosphatase with different concentrations is detected, a working curve is structured, and the fluorescent sensor is prepared. The fluorescent signal of the inorganic pyophosphatase in a sample is detected by the fluorescent sensor, and then corresponding to the working curve, thus the quantitative analysis of the inorganic pyophosphatase in the sample is realized. The detection method is high in selectivity, fast, sensitive and high-efficient.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Real time PCR with the addition of pyrophosphatase
InactiveUS20060051796A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationHybridization probeFluorescence
The present invention is directed to a method and a kit for amplifying and detecting a target nucleic acid, wherein the composition containing reagents to perform and monitor nucleic acid amplification in real time comprises at least a first hybridization probe labeled with a first fluorescent entity and a pyrophosphatase.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS
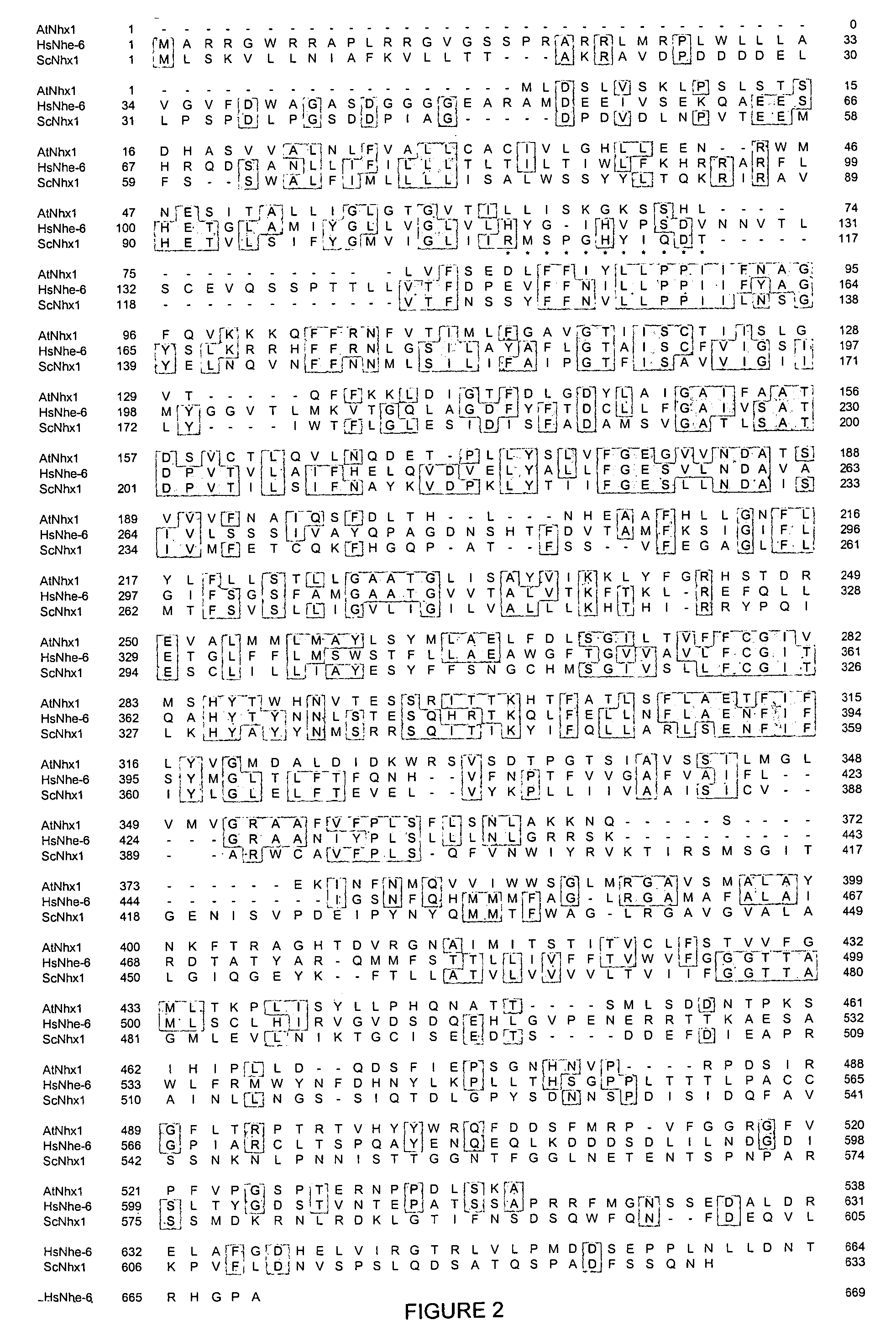
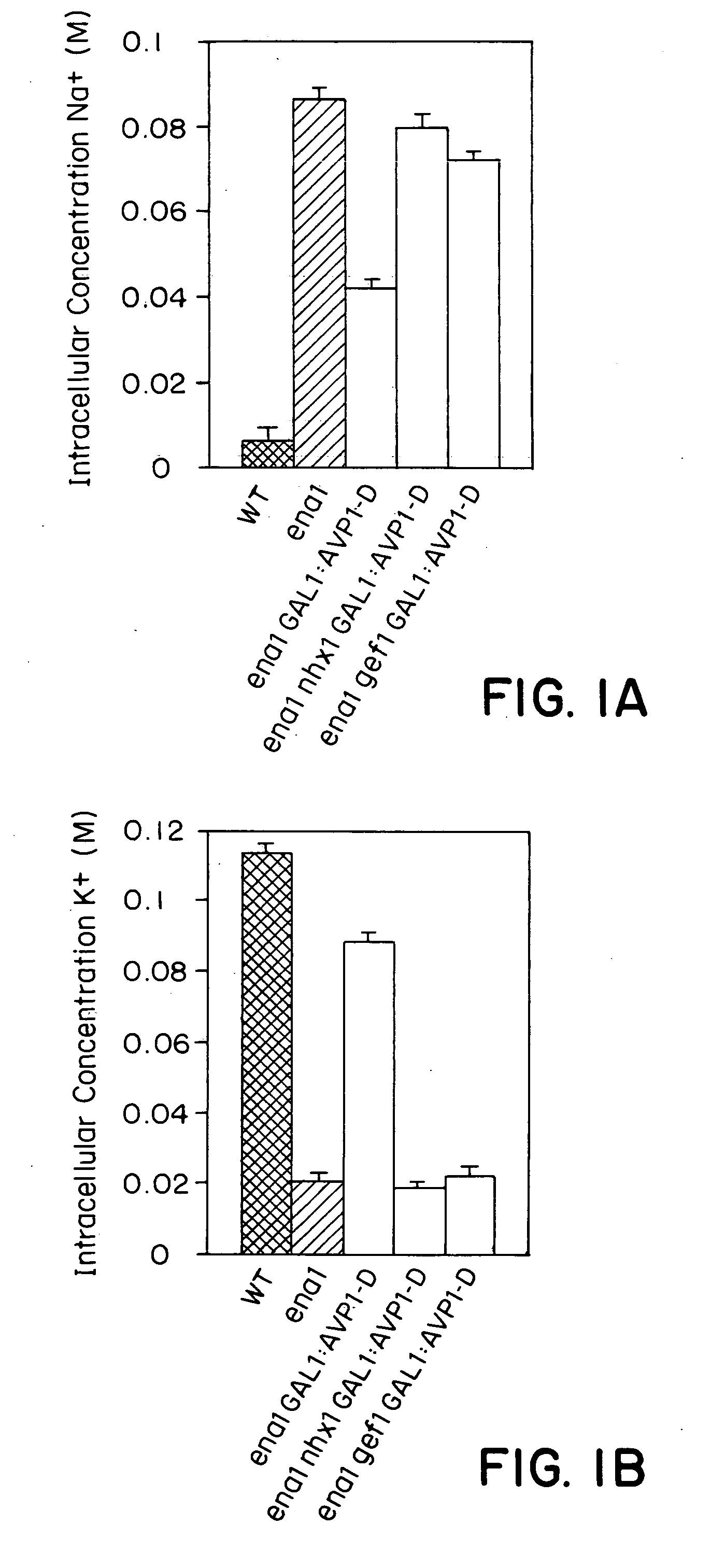
Proton transporters and uses in plants
InactiveUS20050262598A1Increase planting yieldIncreased flower sizeBryophytesClimate change adaptationPlant cellWild type
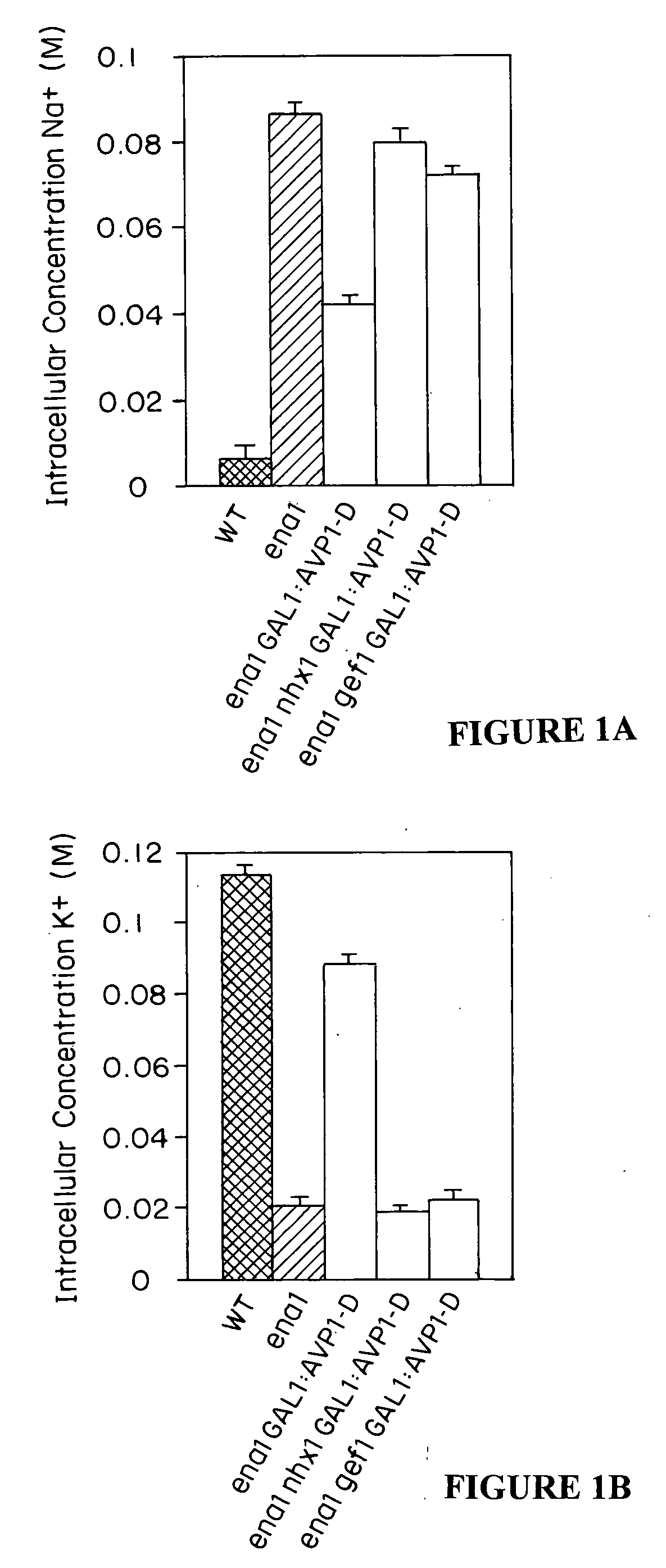
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant which is tolerant to a salt, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plant grown from seed are also described. The present invention also relates to a construct comprising an AVP1 gene operably linked to a chimeric promoter designed to overexpress AVP1 or designed to down regulate endogenous pyrophosphatase. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cell, leaf cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cell are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. Transgenic plants produced by the methods of making a transgenic plant as described herein are also a subject of the present invention. The present invention also relates to a method of bioremediating soil, a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, and a method of producing a transgenic plant which grows in salt water comprising introducing into one or more cells of a plant nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. The transgenic plants of the present invention can also be used to produce double transgenic plants which are tolerant to a salt.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
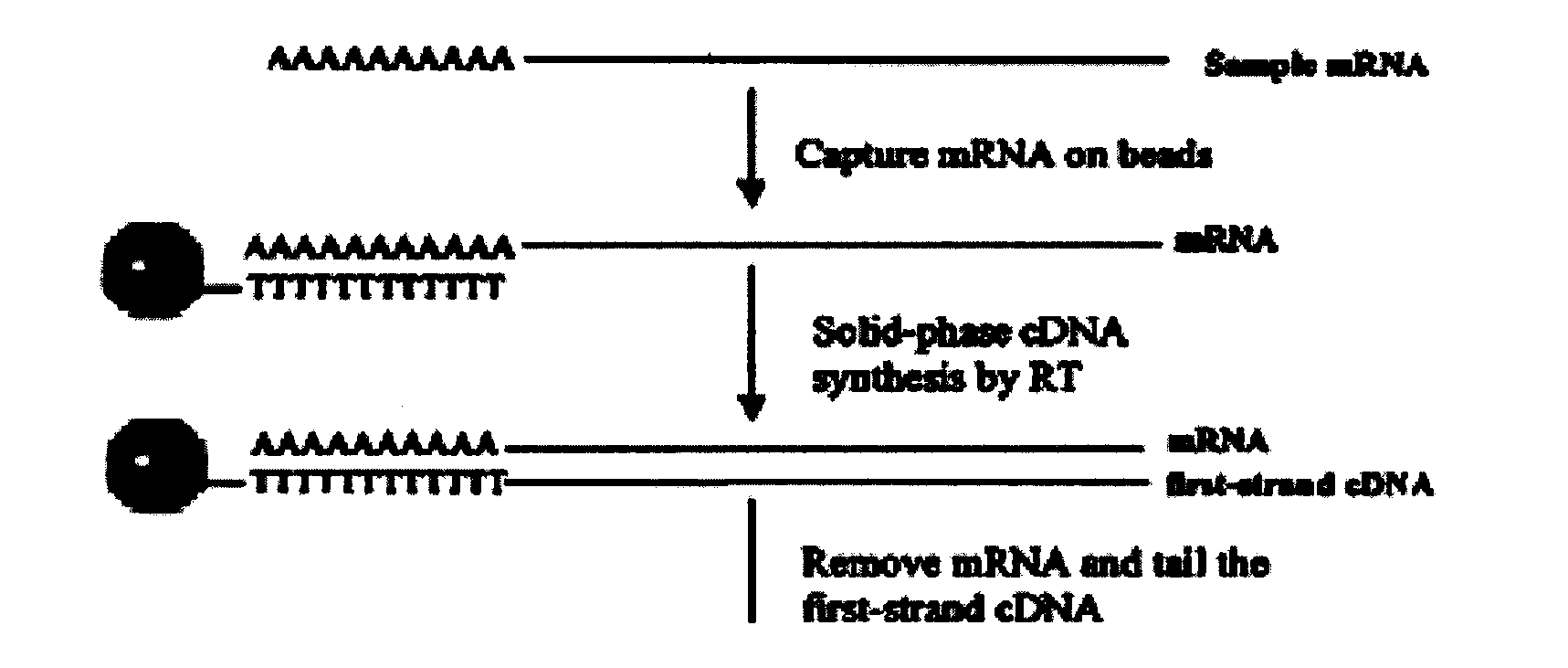
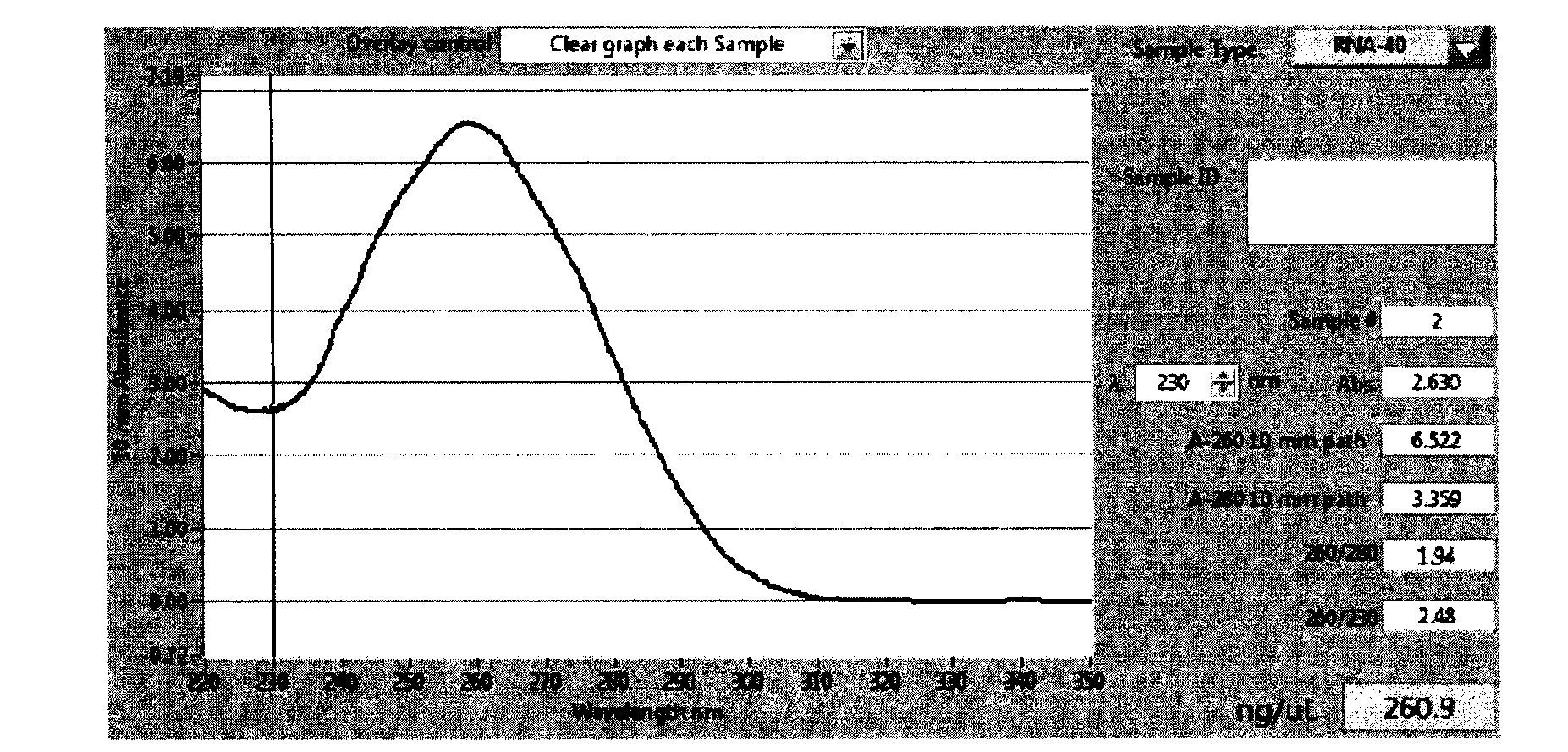
Fast and efficient construction method of normalized full-length cDNA library
ActiveCN102797044AAchieve captureConcise and efficient full-length mRNA screening functionLibrary creationProtein nucleotide librariesPhosphateNucleotide
The invention relates to a fast and efficient construction method of a normalized full-length cDNA library. The method consists of: using specific 5-OH oligonucleotide to close non-full-length mRNA, then employing tobacco acid pyrophosphatase to remove a cap structure from the mRNA5' end to make a phosphate group at the cap structure of the mRNA5' end exposed, adopting an efficient RNA connection system to connect a section of optimized oligomeric RNA to the mRNA 5' end to serve as a primer binding site for triggering synthesis of second strand cDNA, finally conducting reverse transcription, two-strand synthesis as well as graded purification, and cloning the double-stranded DNA into a vector. The method can concisely and efficiently screen full-length mRNA, and realizes full-length mRNA capture of eukaryotes. The mRNA5' tail end contains a biotin label, which can be used for full-length mRNA separation. The used oligonucleotide primer contains optimized modification method and a nucleotide sequence, thus being able to realize full-length mRNA capture of eukaryotes, reverse transcription and DNA synthesis.
Owner:BEIJING VJT BIO CO LTD
Method for improving beet salt-resistance, draught-resistance and anti-herbicide chlorsulfuron characteristics by multi-gene transformation and application
InactiveCN1768575AImprove salt and drought toleranceImprove featuresPlant phenotype modificationPlant genotype modificationEscherichia coliTransgene
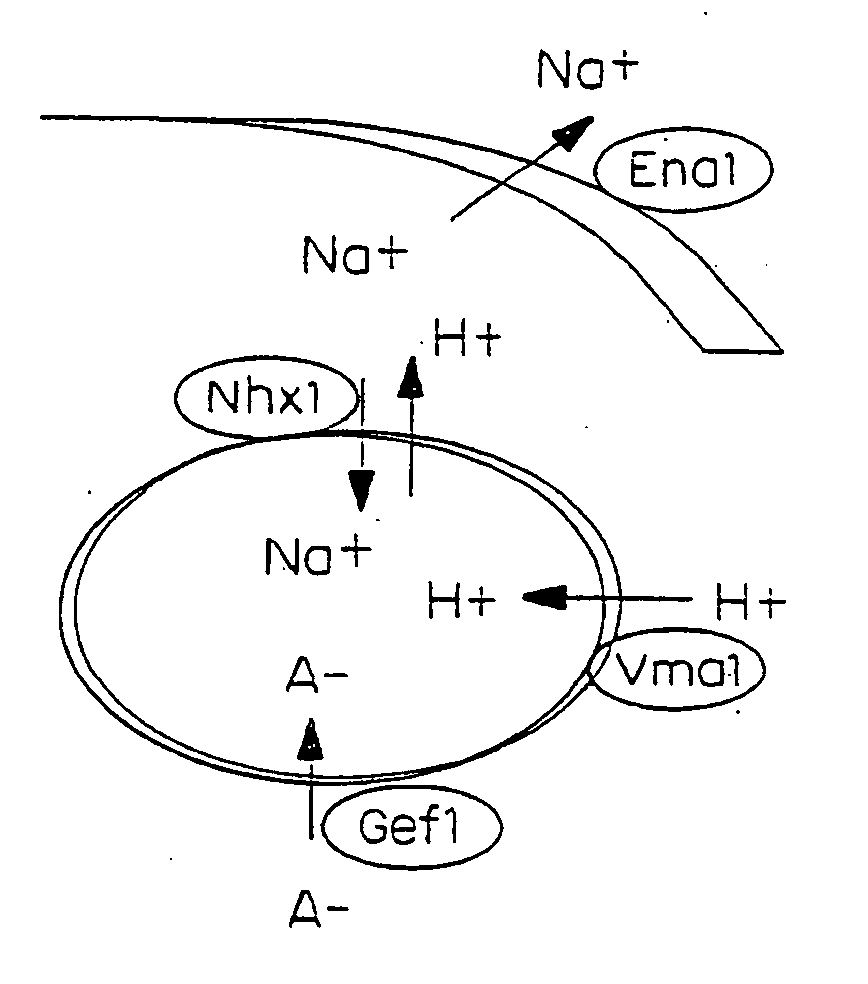
The invention provides a method of improving the sugar beet property of salt and drought resistance and weedicide resistance of green-yellow ron through polygene inversion and the application; recombining gene NHX1 of sodium hydrogen inversing transferring protein from the plant racuolar membrane, gene Ppase of racuolar membrane pyrophosphatase , gene beta of choline dehydrogenase from bacillus coli and gene als of acetolactate synthetase resisting the accident mutation of weed killer of green-yellow ron from quasi-mustard in the plant expression carrier, transferring into the sugar beet cell for high effective expression and getting trans genetic plant; choosing trans plants of salt and drought resistance and weedicide resistance of green-yellow ron dramatically increased from the trans genetic plants and their generations; getting the trans genetic plants with 3-4 target genes by a second conversion or making the plants with different trans genes mate with each other; choosing individuals with outstanding properties of salt and drought resistance and weedicide resistance of green-yellow ron from generations of polygenetic inversed plants, and then producing the sugar beet of new strain with properties of salt and drought resistance and weedicide resistance of green-yellow ron.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
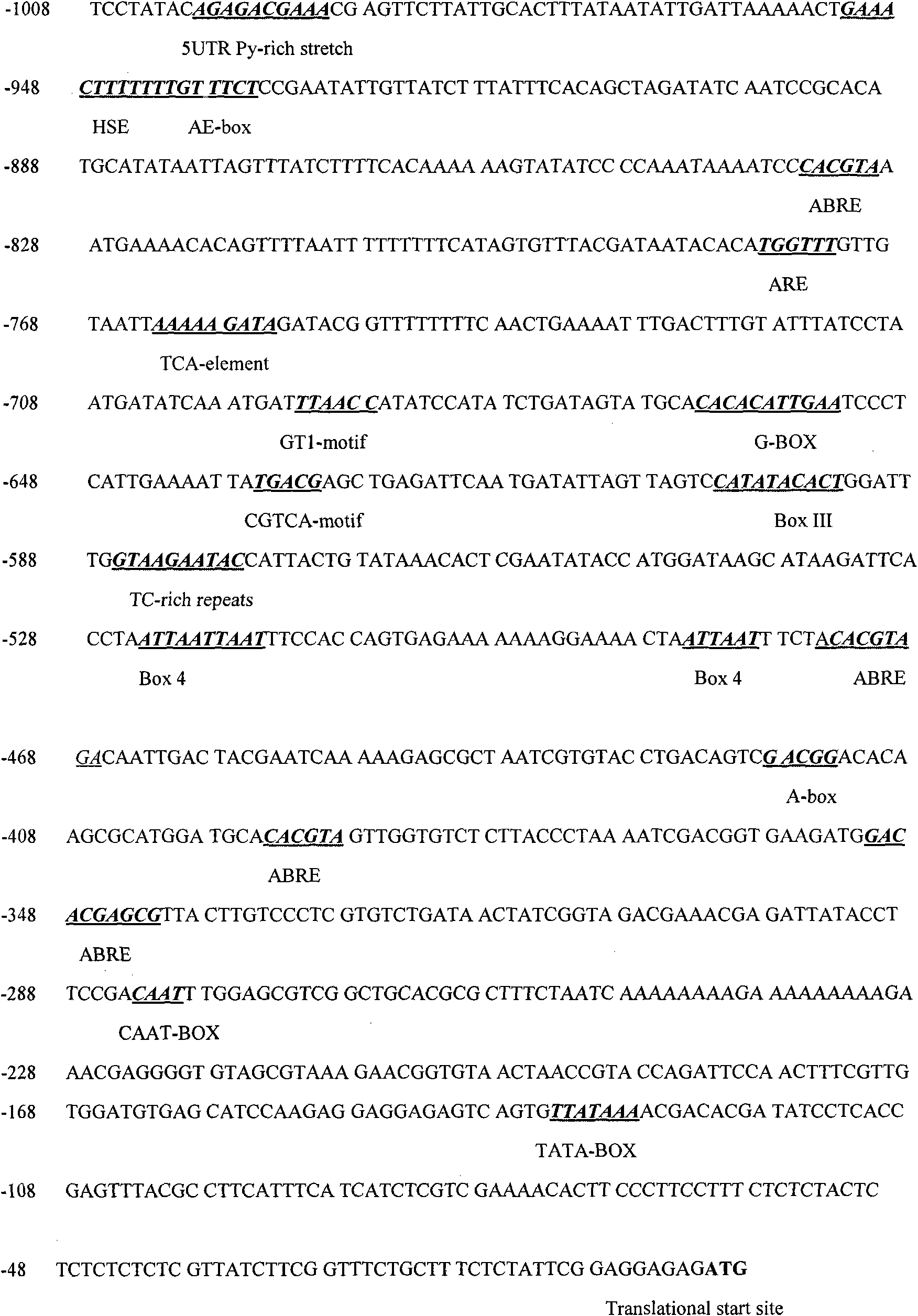
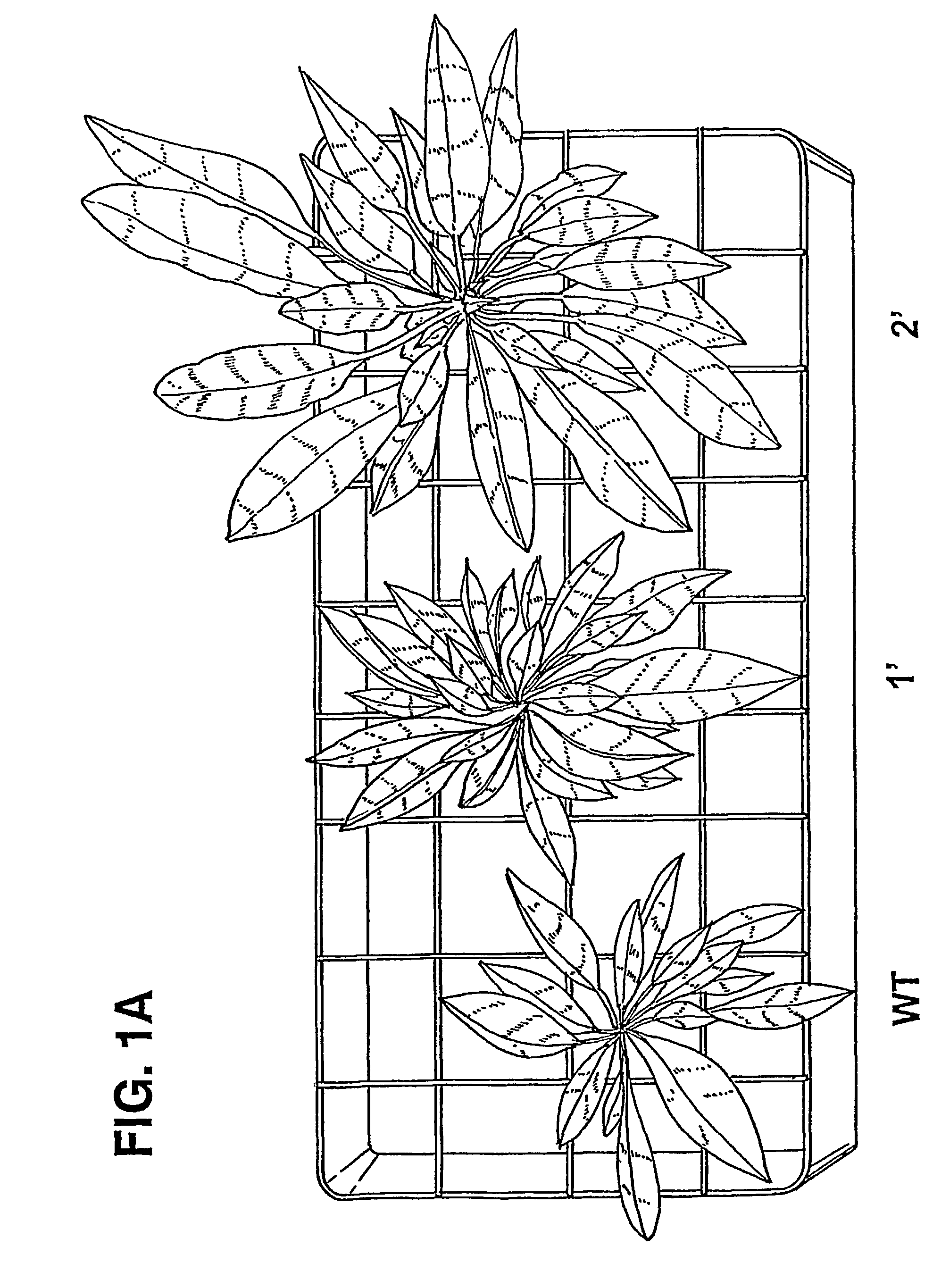
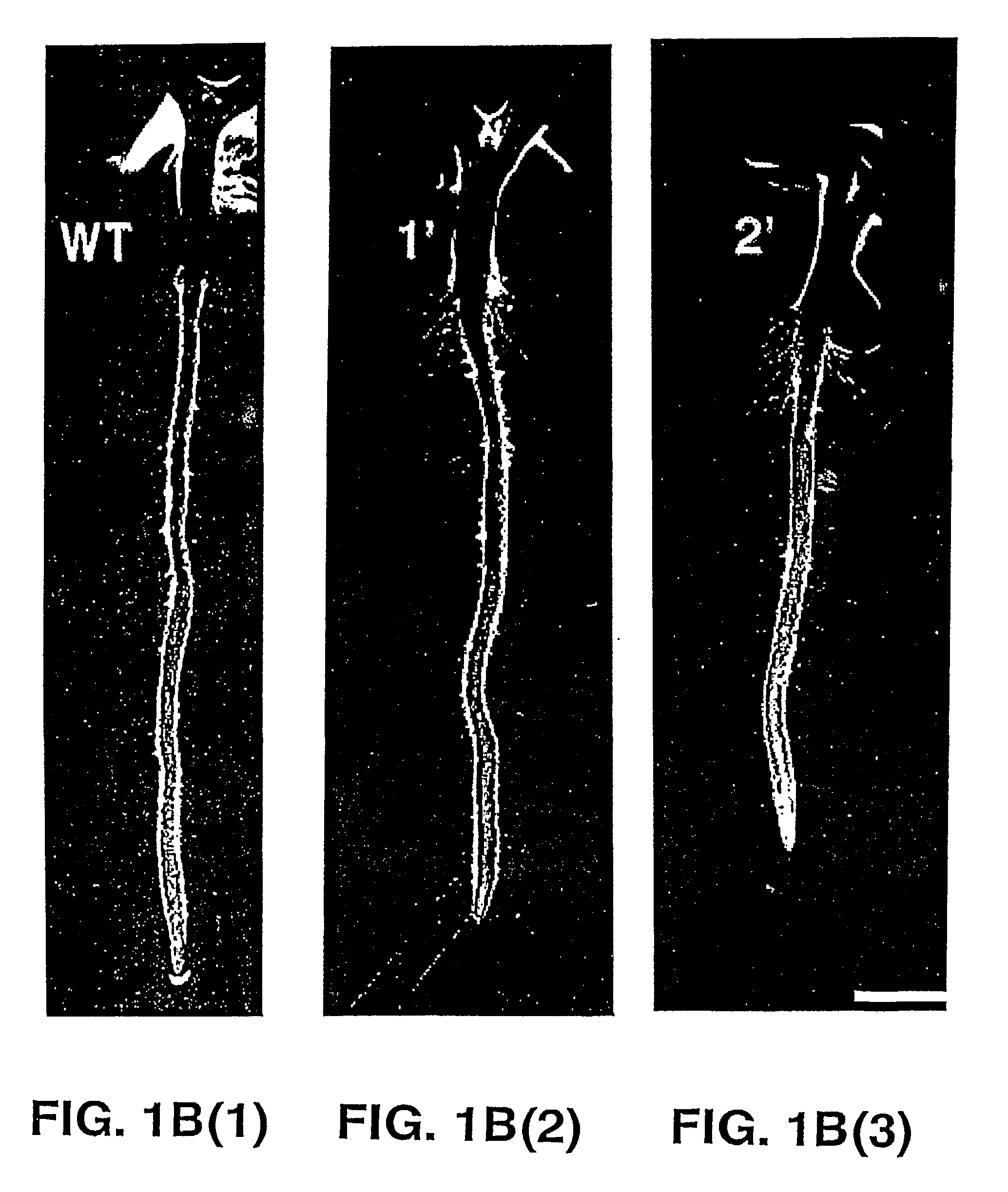
Thellungiella V-pyrophosphatase gene (TsVPI) promoter sequence and application of deletion mutant thereof
InactiveCN101643745AHigh strengthFacilitate genetic recombinationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a thellungiella V-pyrophosphatase gene (TsVPI) promoter sequence and the application of a deletion mutant thereof. A clone carrying a TsVPI promoter is screened from a genomiclibrary of halophyte thellungiella, a 2200 nucleotide sequence positioned on the upstream of a TsVPI coding frame 5' is truncated as an overall-length promoter, promoter snippets with different lengths are obtained through PCR amplification, and then the promoter snippets are respectively blended with gus genes to be recombined into a plant expression vector to be converted into Arabidopsis; the TsVPI promoter and a part of the deletion mutant thereof are determined as salt-stress inducible type promoters by detecting the GUS enzymatic activity of transgenic plants, wherein a T5 promoter not only has a short sequence (667bp) but also has root specificity, and the TsVPI promoter and the T5 promoter are respectively connected with betA genes from colibacillus to be transmitted into tobaccosand corns so as to determine that the TsVPI promoter and the T5 promoter can normally exert functions in the transgenic tobaccos and the transgenic corns, are salt-stress inducible type strong promoters and have important application value in the industrialization development of plant gene engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Enzymatic preparation method of oxidized coenzyme II
ActiveCN102605027AMild reaction conditionsEfficient reaction conditions under mild conditionsFermentationAdenosinePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to an enzymatic preparation method of an oxidized coenzyme II. Nicotinamide nucleotide (NR) and adenosine triphosphate disodium salt (ATP-Na2) are used as the raw material and subjected to one-pot reaction with nicotinamide nucleoside kinase (NRK), inorganic pyrophosphatase, NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) kinase and poly-pyrophosphokinase in a buffer solution with pH being 4.0-8.5 and at the temperature being 10-40 DEG C to obtain the oxidized coenzyme II. With the adoption of the enzymatic preparation method, the technical problems that in the existing enzymatic preparation method, the nicotinamide nucleotide is expensive and not easily obtained, the reaction time is long, the technical cost is relatively high and the technical conditions are not suitable for the industrialized scale-up production are solved; and the oxidized coenzyme II can be obtained with high efficiency and low lost in an industrialized scale-up production way.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
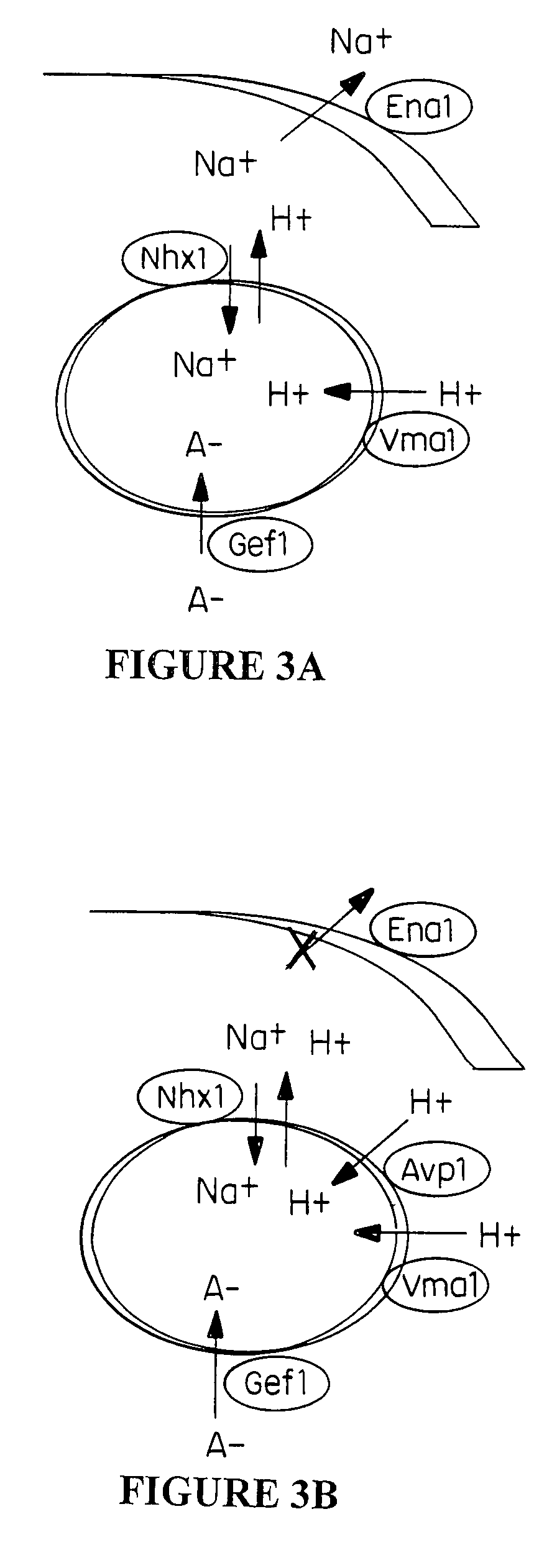
Transgenic plants overexpressing a plant vacuolar H + (proton) pyrophosphatase
InactiveUS7534933B2Increased tolerance to saltIncrease resistanceSugar derivativesHydrolasesNicotiana tabacumProton
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT +2
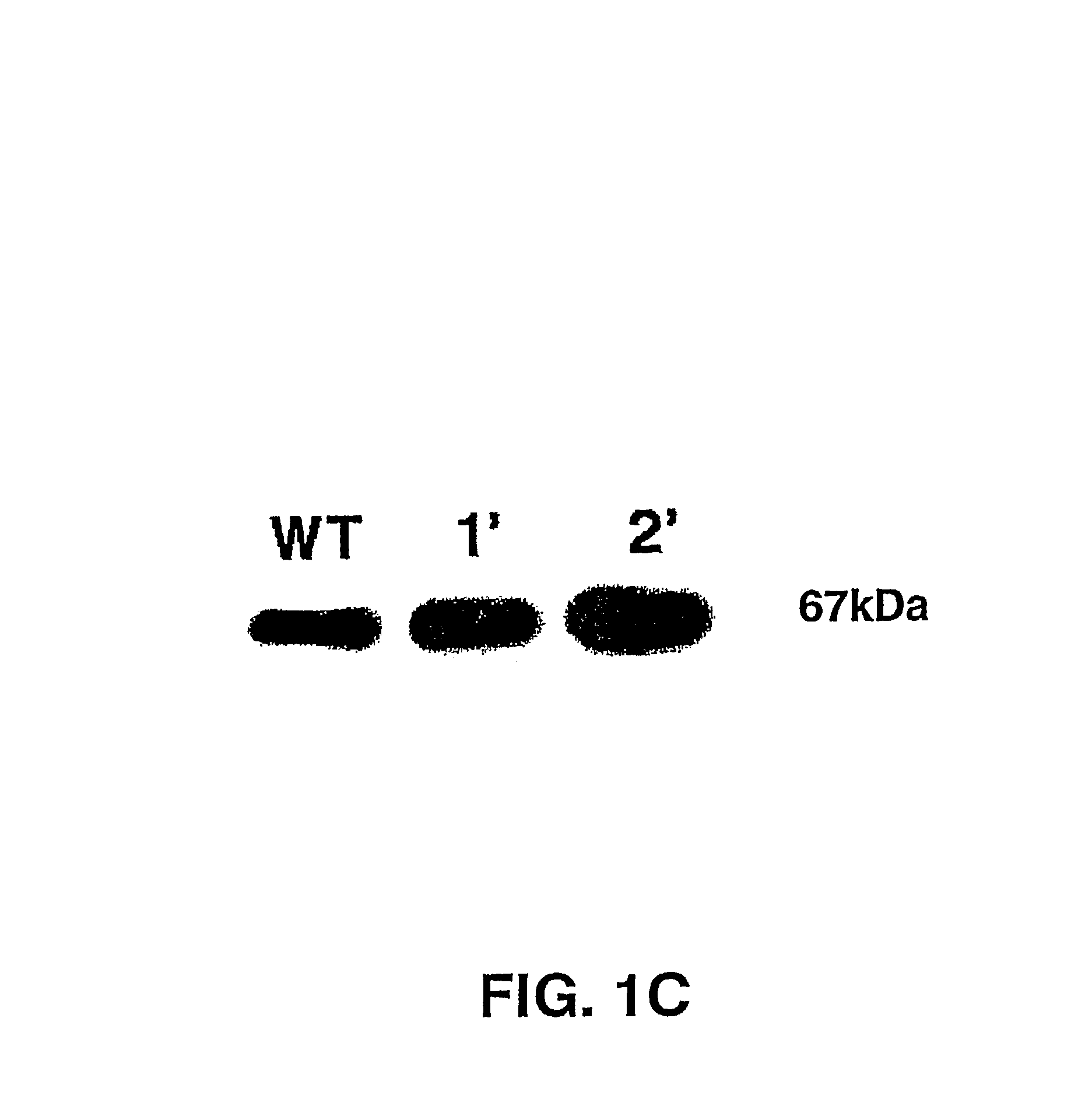
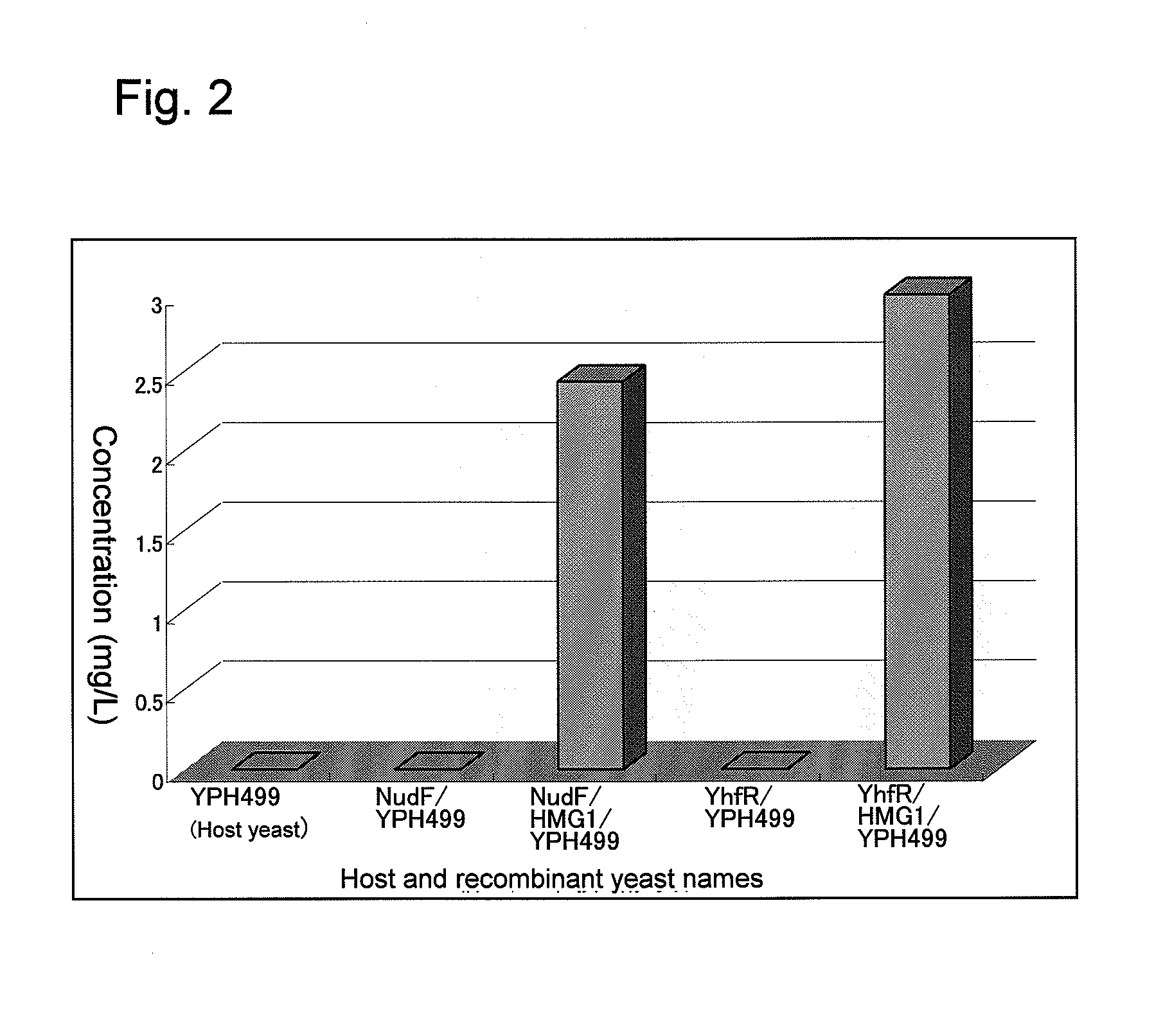
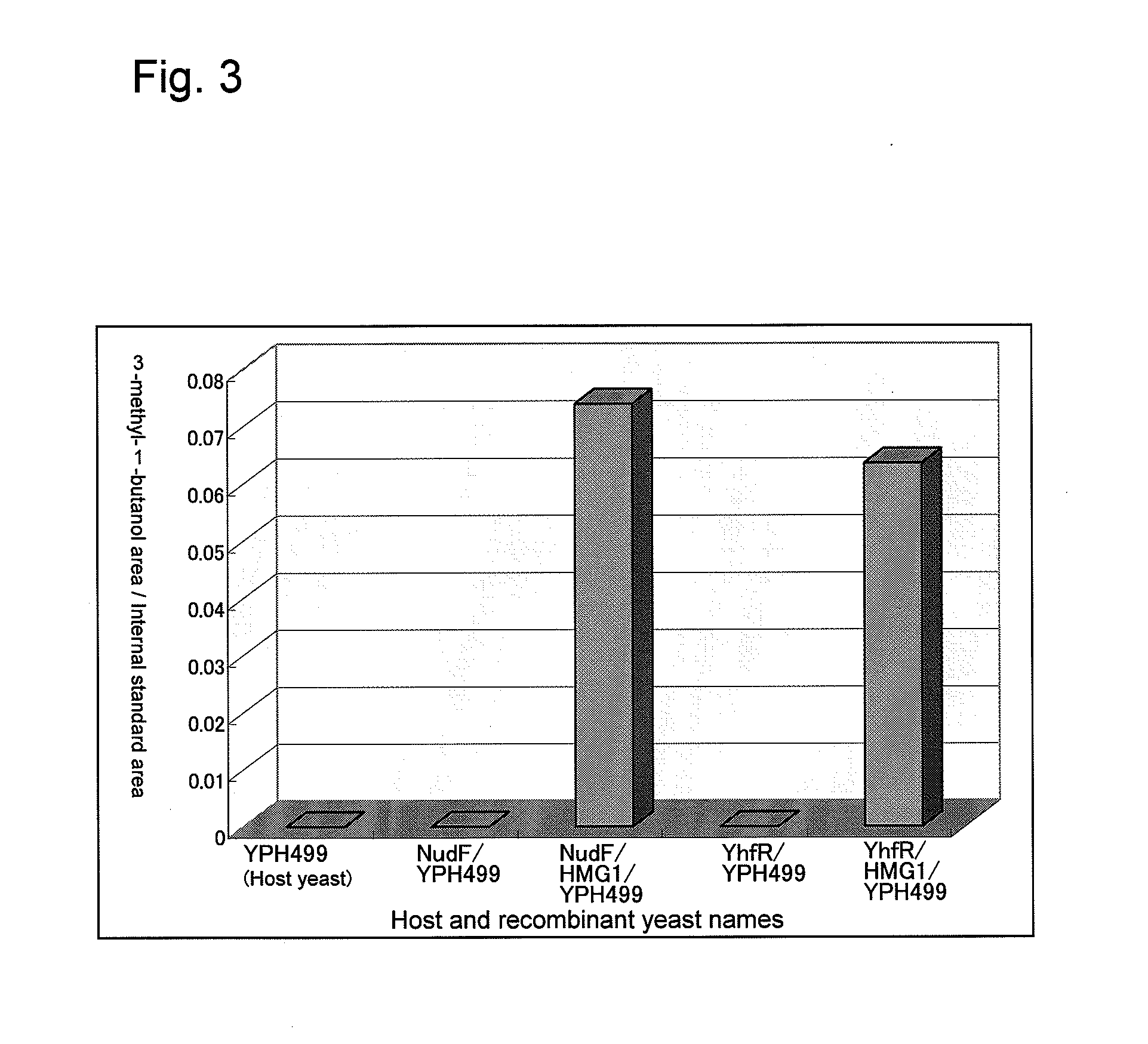
Recombinant yeast and branched alcohol production method using recombinant yeast
This invention provides a recombinant yeast that can produce branched alcohol appropriate for automotive fuel and the like and a branched alcohol production method whereby branched alcohol can be produced at low cost with the use of the recombinant yeast.A recombinant yeast in which a hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA reductase gene has been expressed to a high degree and the ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase gene and / or the yhfR gene are introduced so as to be expressed therein is provided.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
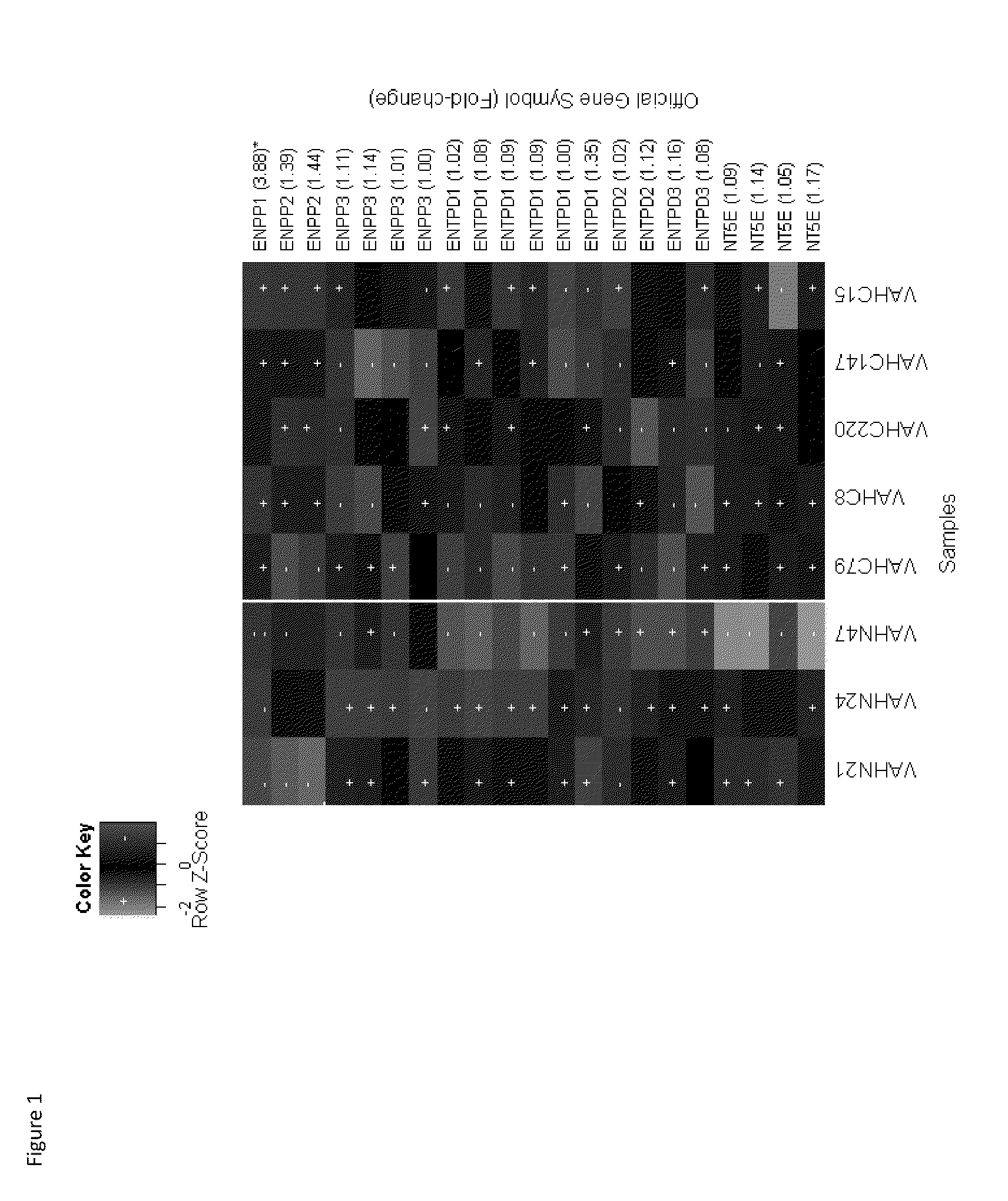
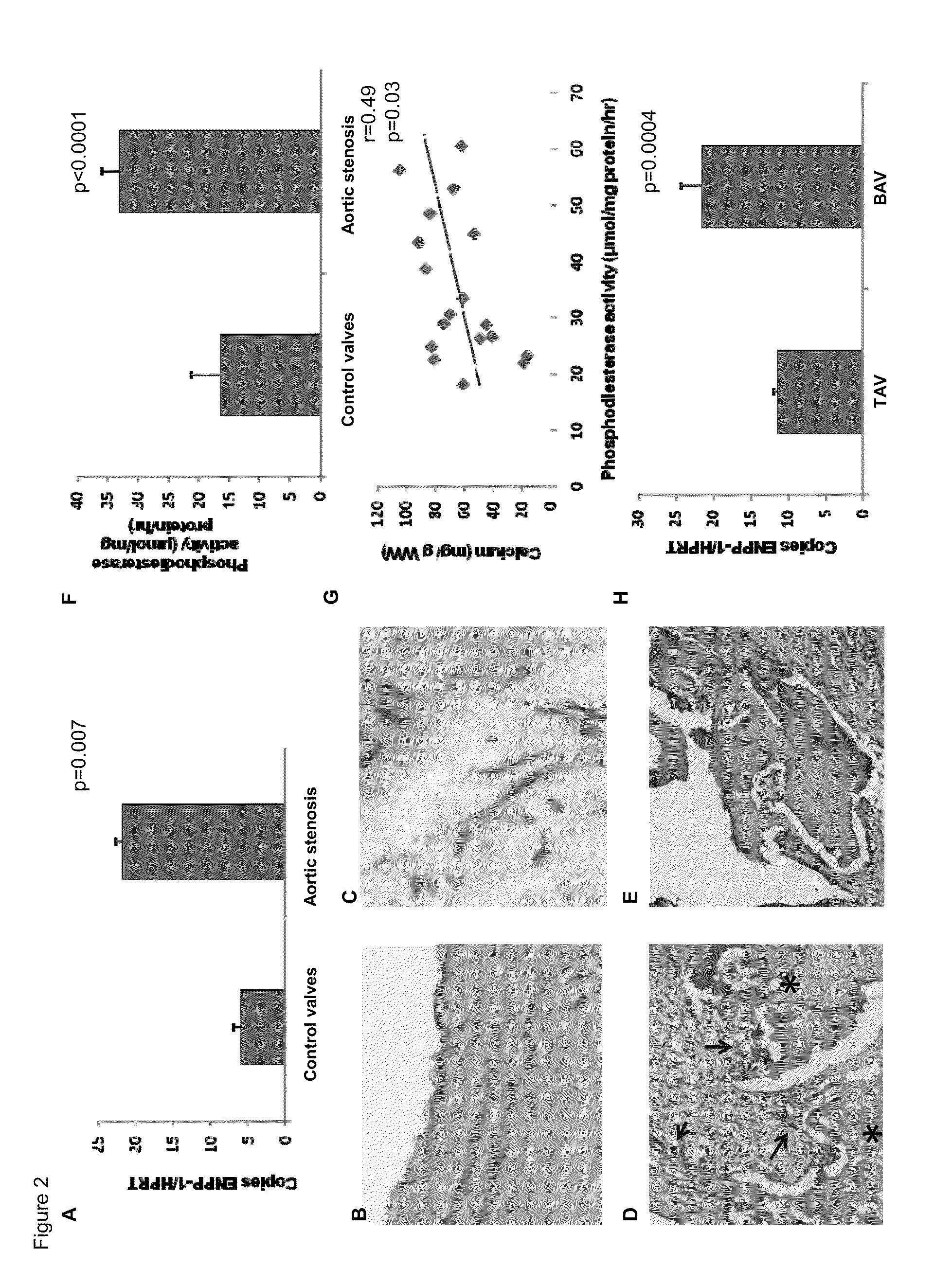
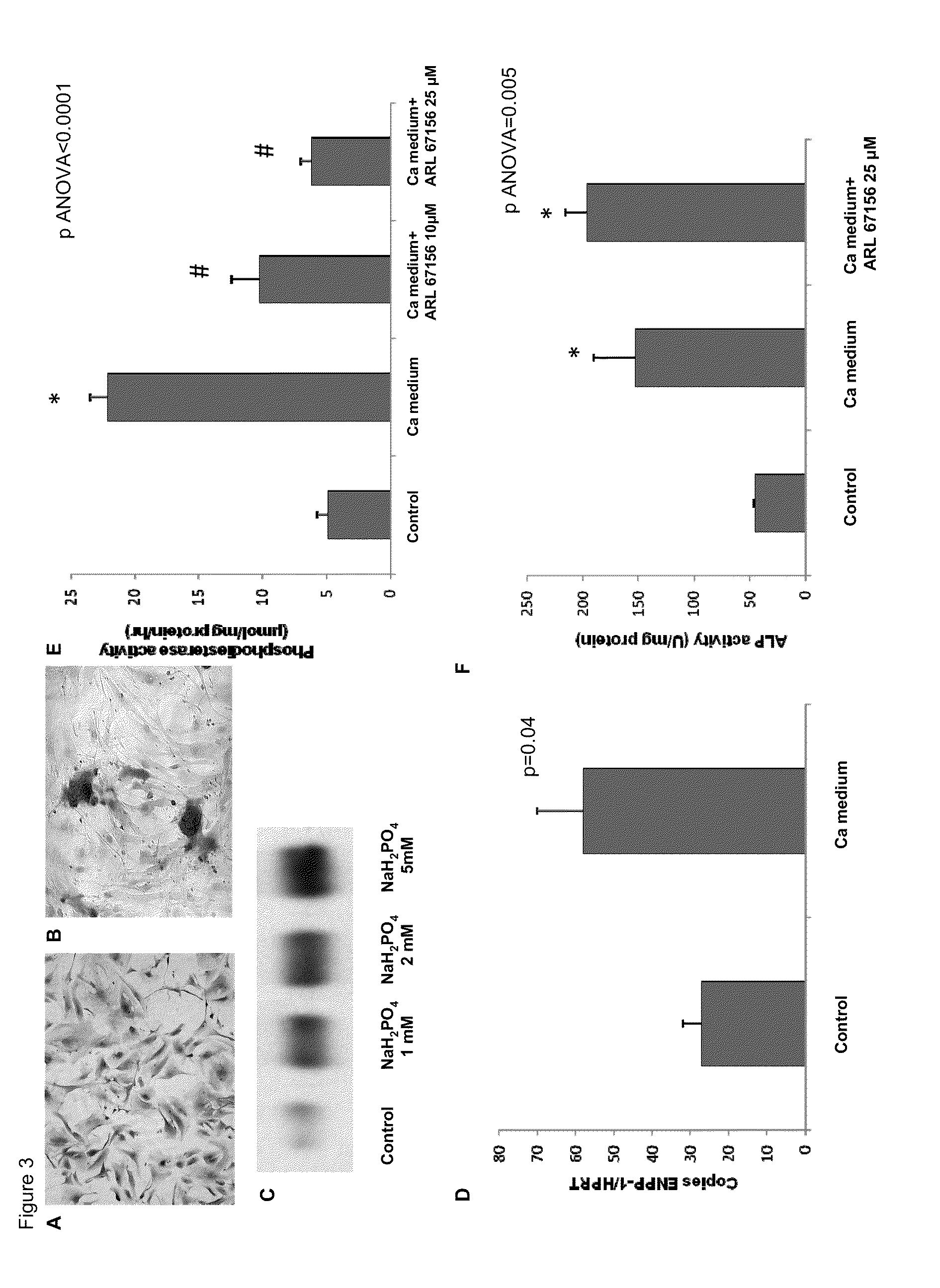
Ectonucleotidase pyrophosphate/phosphodiesterase-1 (enpp-1) as a target for the treatment of aortic valve stenosis and cardiovascular calcification
InactiveUS20110098243A1Elevated level of ENPP-High magnitudeBiocideSugar derivativesPhosphodiesteraseEctonucleotidase
Aortic valve stenosis (AS) is a chronic process related to a progressive mineralization of the aortic root and valve cusps. We found in human AS valves a high level of expression and enzymatic activity of ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase / phosphodiesterase-1 (ENPP-1), which correlated to the degree of mineralization. In vitro, inhibition of ENPP activity with ARL 67156 significantly reduced calcification of isolated valve interstitial cells. In a rat model of cardiovascular calcification, ARL 67156 significantly reduced calcification of the aortic root and valve cusps. This is the first study to demonstrate that increased expression and activity of ENPP-1 promotes the mineralization process in AS valves. Hence, inhibition of ectonucleotidase may represent a novel target of therapy for this frequent and serious cardiovascular disease.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Application of pyrophosphatase gene
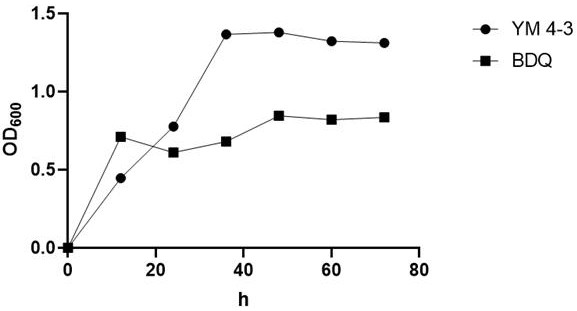
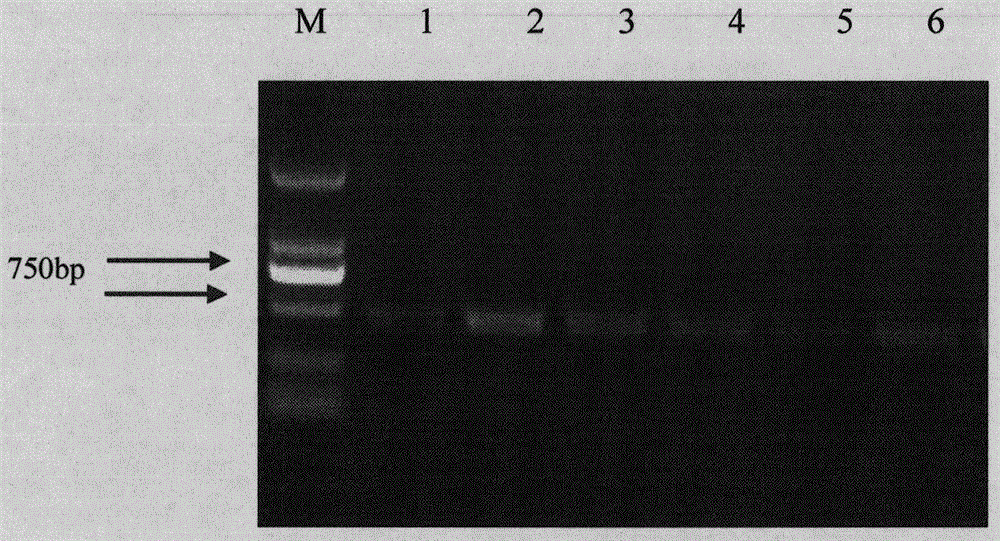
The invention discloses application of a pyrophosphatase gene and application of pyrophosphatase gene folQ in improvement of lactobacillus plantarum folic acid synthesis. The nucleotide sequence of the pyrophosphatase gene folQ is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The application comprises the following steps of carrying out enzyme digestion connection on the gene folQ and a constitutive vector pMG36e to obtain a recombinant expression vector, transferring the recombinant expression vector into lactobacillus plantarum YM-4-3, and realizing overexpression of the gene folQ in a YM-4-3 strain body to obtain an overexpression strain. An LC-MS method is adopted to measure the folic acid producing capacity of the strain, it is found that compared with a wild type strain, the content of folic acid monoglutamic acid produced by the BDQ strain is increased, the folQ gene plays a key role in folic acid synthesis, and therefore the pyrophosphatase gene has huge potential in the fields of folic acid biosynthesis research and application.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Vacuole proton pyrophosphatase as well as encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103602644ARaise the level of resilienceHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyFunctional identification
The invention discloses vacuole proton pyrophosphatase as well as an encoding gene and application thereof and relates to the technical field of molecular biology and biology. A wheat TAVP gene is cloned, the functional identification is carried out in arabidopsis thaliana, a drought-relief and antisalt gene of the wheat is explored, and a foundation can be set for obtaining a good novel wheat strain. The vacuole proton pyrophosphatase has great significance in knowing the resistance mechanism of a plant, and a theoretical direction can be provided to assemble molecules, improve the crop stress resistance and improve the crop yield in the future.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Vacuolar pyrophosphatases and uses in plants
InactiveUS20080104733A1Improve toleranceLarge plant sizeClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesWild typePlant cell
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant which is tolerant to a salt, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. The present invention also relates to a transgenic plant with increased Pi uptake, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plant grown from seed are also described. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cell, leaf cells, flower cells, fruit cells and seed cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cell are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. Transgenic plants produced by the methods of making a transgenic plant as described herein are also a subject of the present invention. The present invention also relates to a method of bioremediating soil, a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, a method of producing a transgenic plant which grows in salt water, and a method of producing a transgenic plant with increased Pi uptake. The transgenic plants of the present invention can also be used to produce double transgenic plants which are tolerant to a salt, or have increased Pi uptake.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
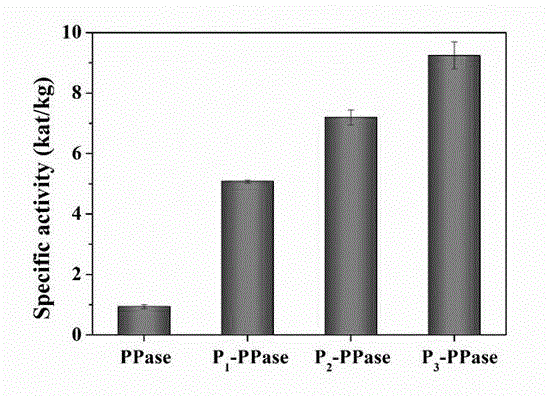
Novel temperature-response inorganic pyrophosphatase conjugate synthesis and application of conjugate to enhanced polymerase chain reaction
ActiveCN104862288AIncrease temperatureImprove heat resistanceHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementTemperature responseHeat stability
The invention relates to novel temperature-response inorganic pyrophosphatase conjugate synthesis and application of the conjugate to enhanced polymerase chain reaction, belongs to the field of polymer-protein coupling techniques and application of the polymer-protein coupling techniques to biology, and provides a strategy of enhancing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) efficiency. By the aid of the polymer-protein coupling techniques, temperature-response PNIPAM (polymer N-isopropylacrylamide) is modified in a site-directed manner near the active center of inorganic PPase (pyrophosphatase), heat stability of protein is enhanced to adapt to the condition of PCR high-temperature long-time circulation, and PCR is enhanced by the aid of the capacity of catalytic decomposition of pyrophosphoric acid.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Room-temperature phosphorescence detection method of alkaline phosphatase and application thereof
PendingCN110982873AImprove performanceGood biocompatibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCyclodextrinPyrophosphate
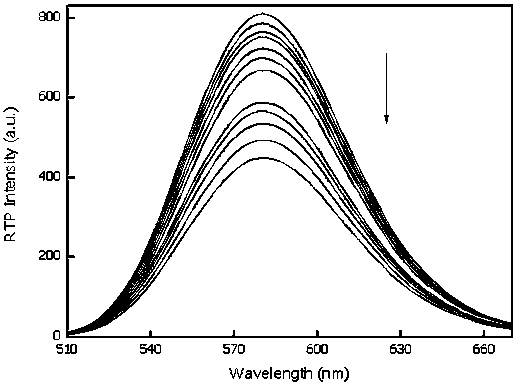
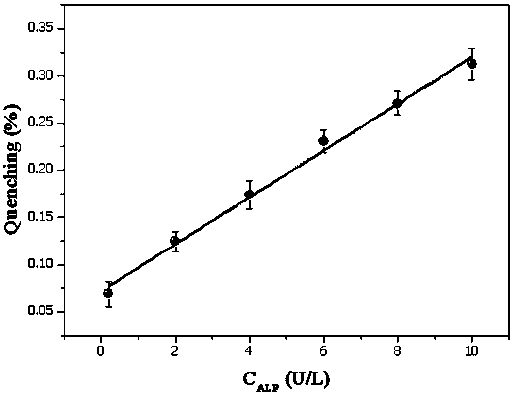
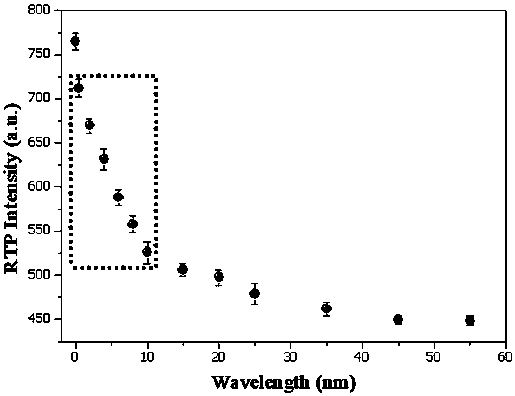
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of alkaline phosphatase detection, discloses a room-temperature phosphorescence detection method of alkaline phosphatase and application thereof, thereby solving problems of complex detection process, high cost and large interference of the existing alkaline phosphatase. At a room temperature, a prepared beta-cyclodextrin-modified Mn: ZnS room-temperature phosphorescent quantum dot is used as a phosphorescent probe and pyrophosphate is used as a molecular recognition unit; and analysis and detection of pyrophosphatase are realized by detecting room-temperature phosphorescence changes of a system after alkaline phosphatase is added. The response range of the phosphorescence detection system to pyrophosphatase is 0.22-10.4 U / L, and the detection limit is 0.045 U / L. The method can be used for detecting alkaline phosphatase in serum; and a complex sample pretreatment process is not needed during measurement. A deoxidant and an inducer donot need to be added for generation of room-temperature phosphorescent, and interference of background fluorescence and scattered light of an actual sample can be avoided.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
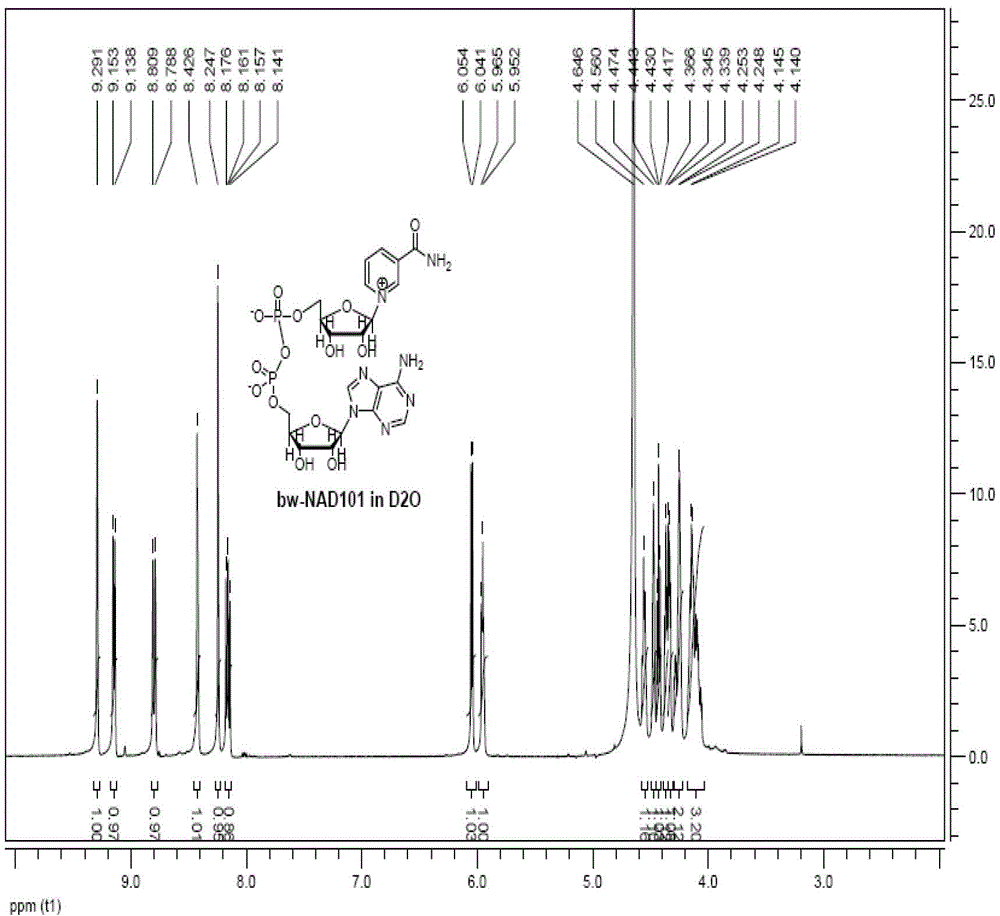
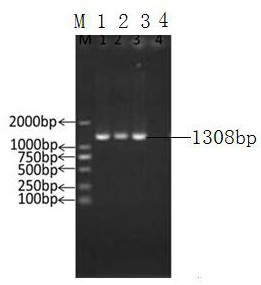
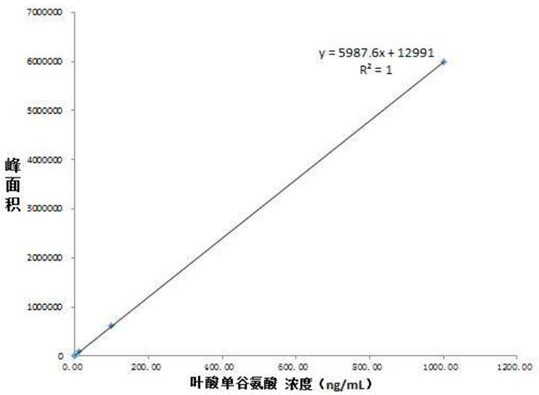
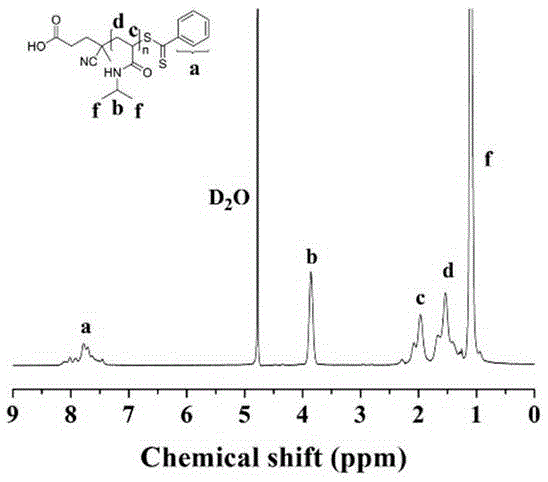
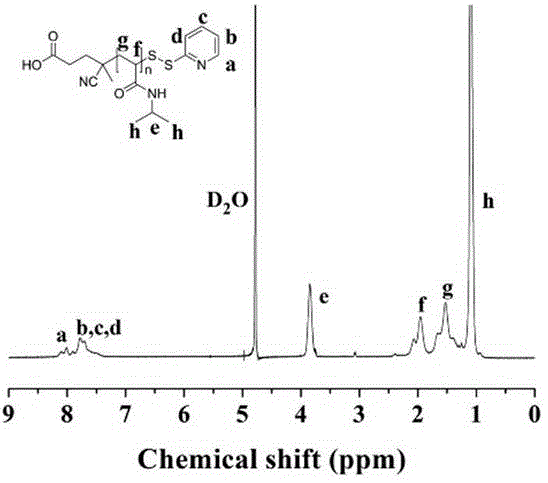
Method for preparing [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide
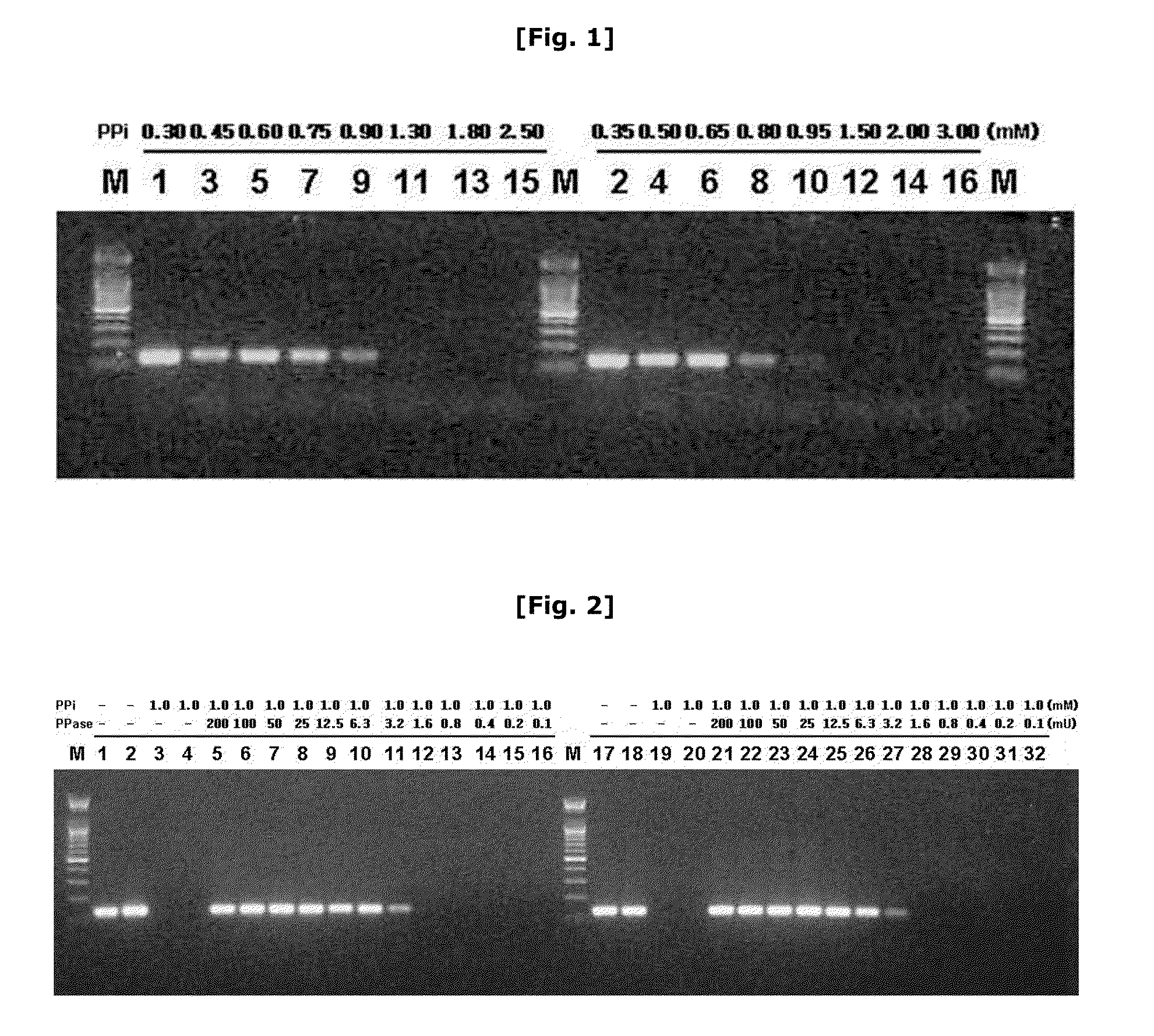
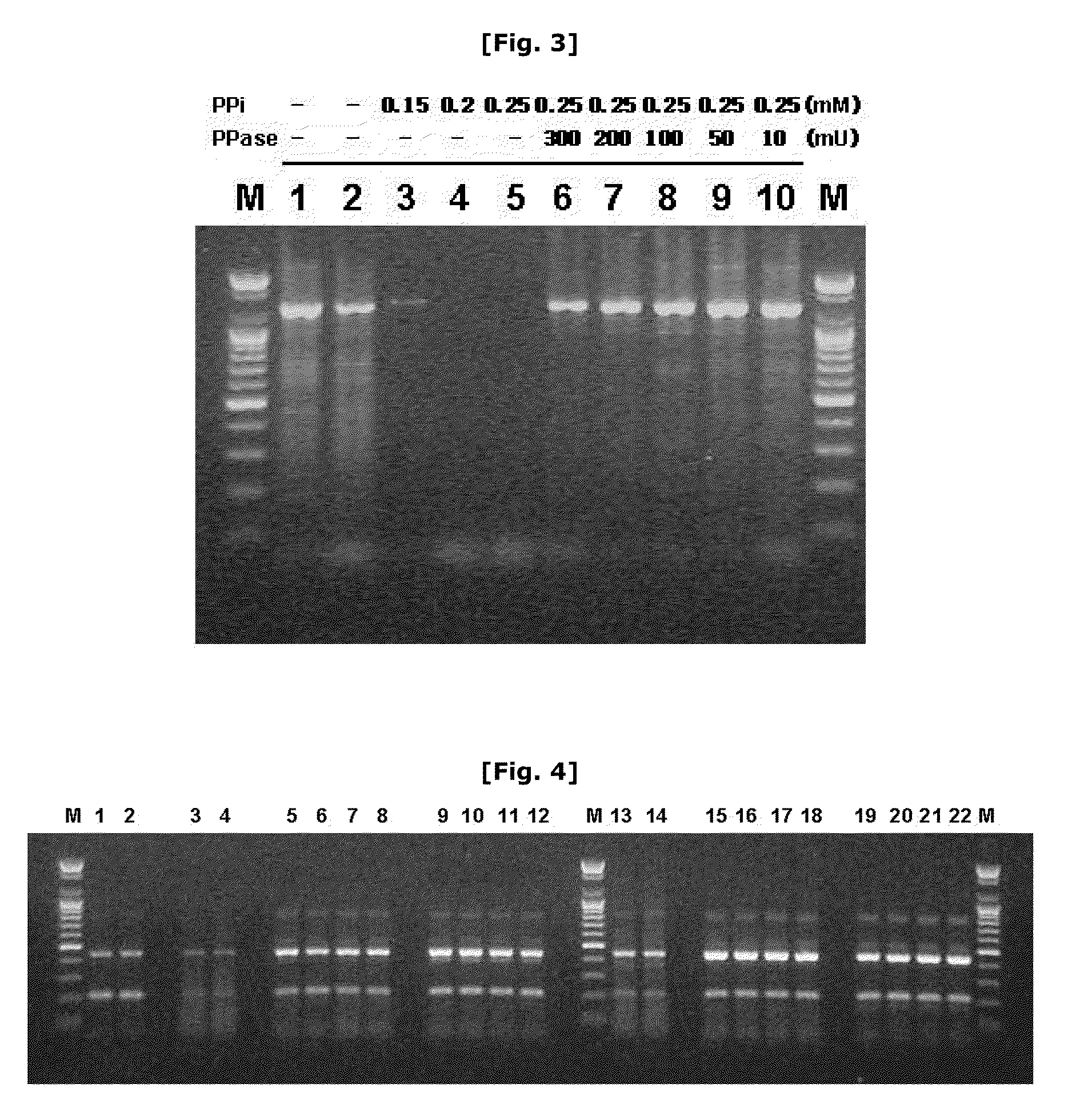
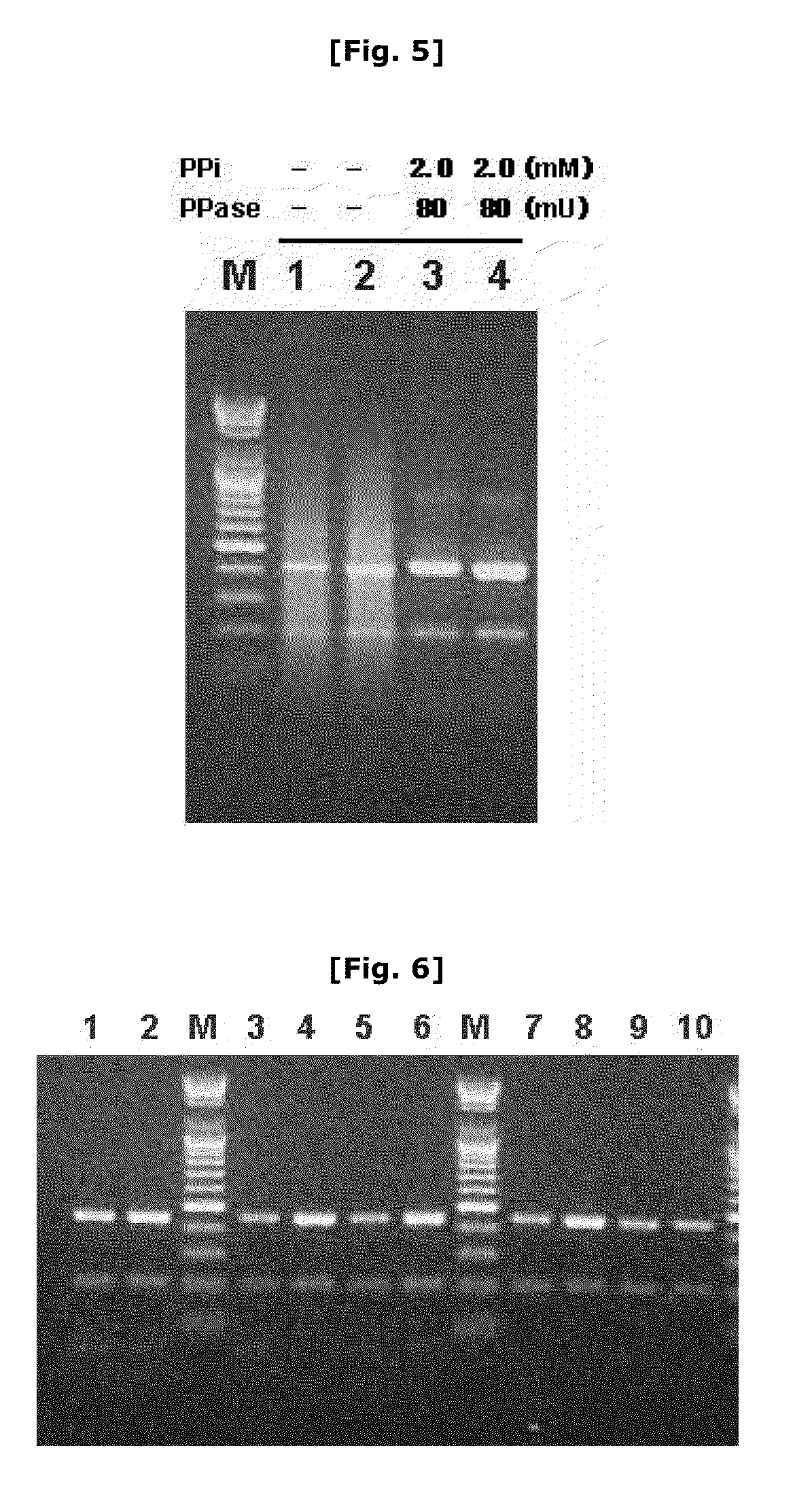
The invention puts forward a method for preparing [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide. In the method, [beta]-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is taken as a substrate, and reacts under a catalytic function of [beta]-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide pyrophosphatase and / or a recombinant cell containing the [beta]-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide pyrophosphatase to generate the [beta]-nicotinamidemononucleotide. Compared with an existing preparation method for the [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide, the method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, is efficient, has a short production period, is environmentally-friendly, is low in cost and has an important application value in fields, including health care products, biological medicines and the like, and a product can be easily purified.
Owner:江苏易诺维生物医学研究院有限公司
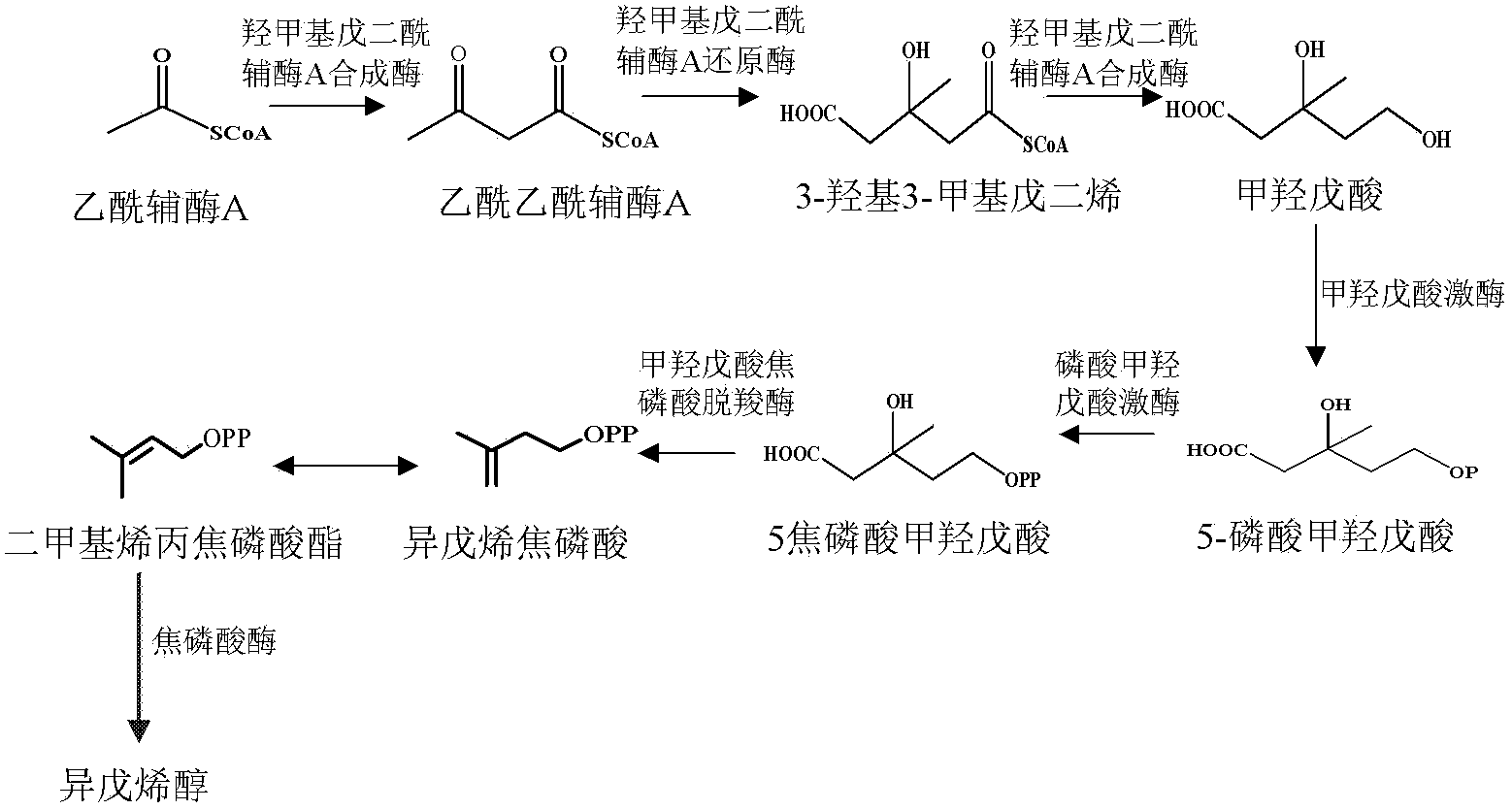
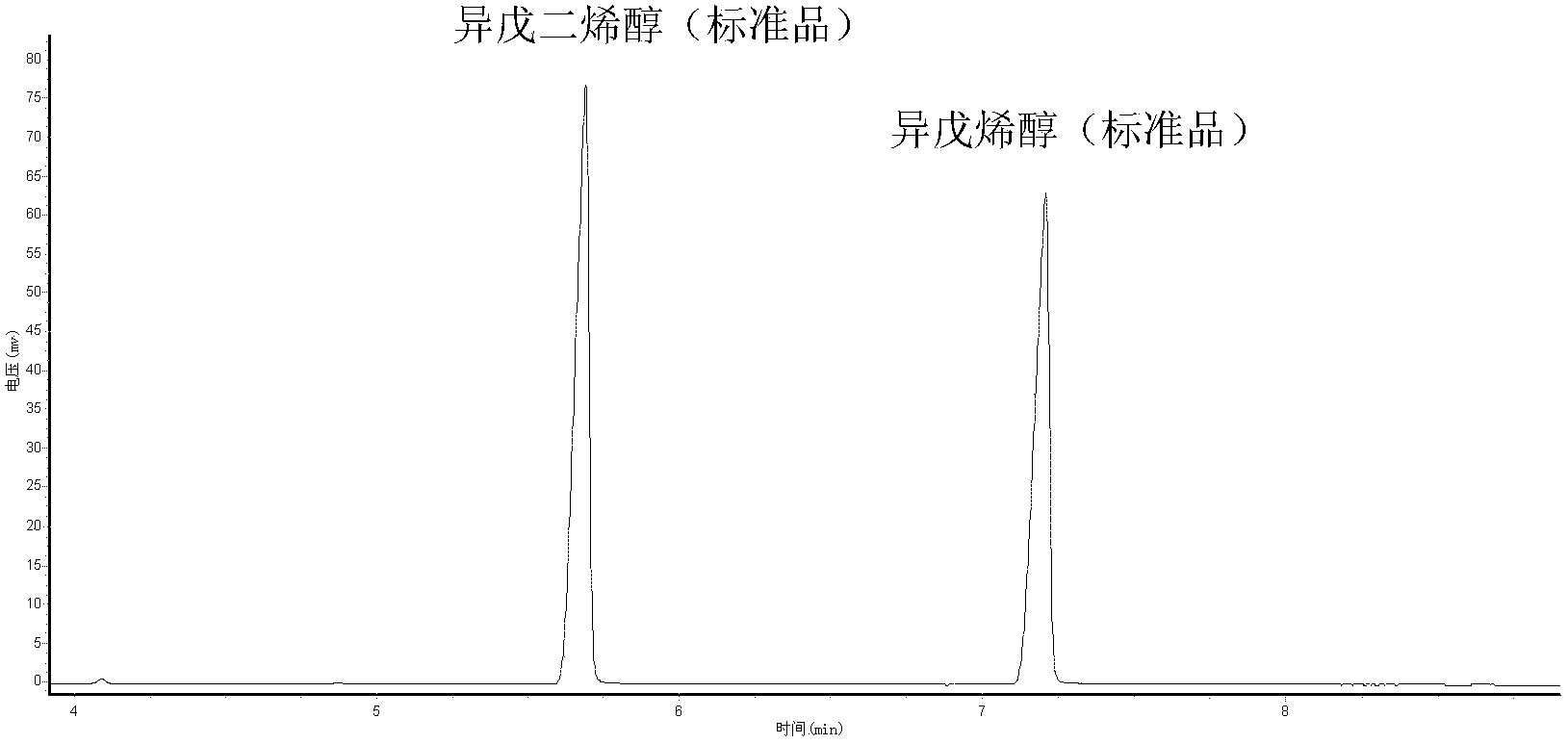
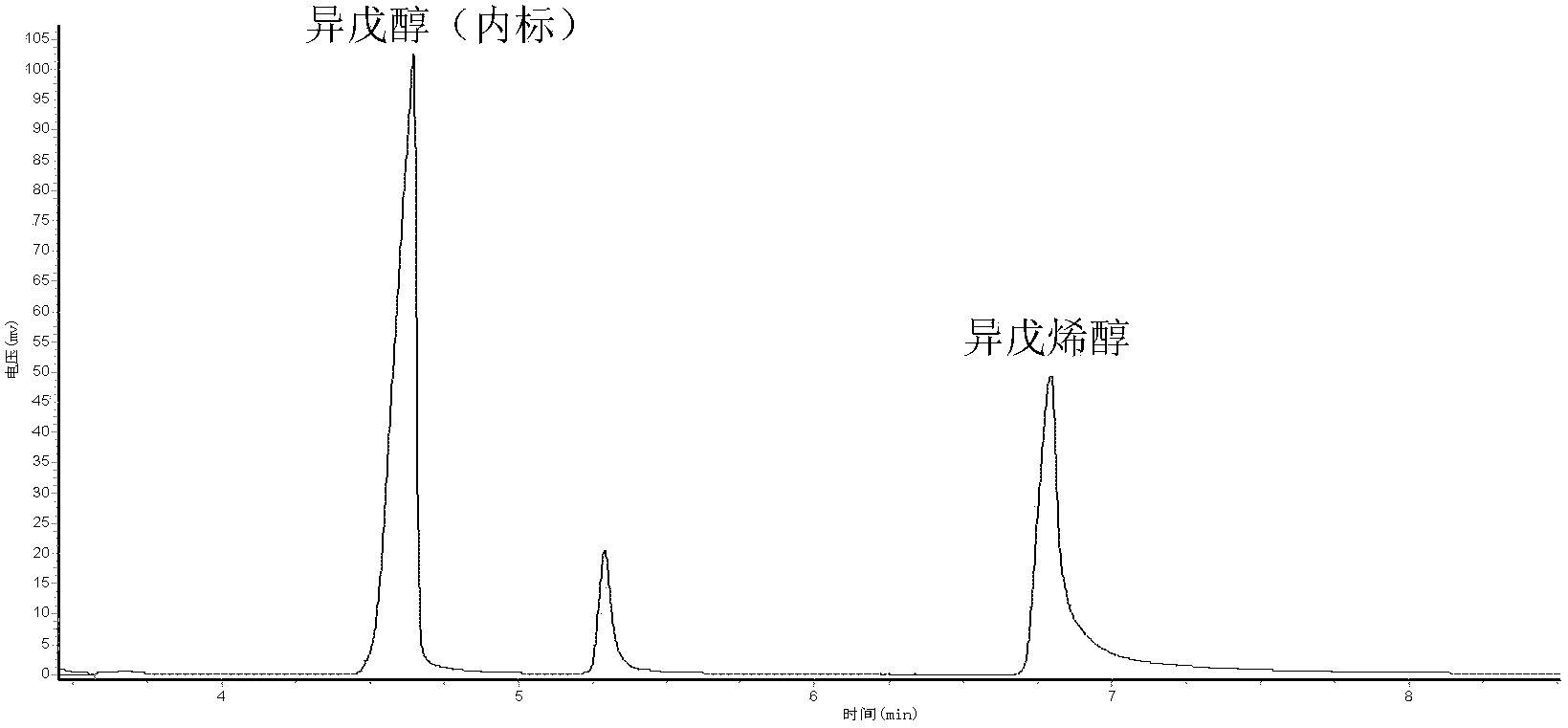
Method for synthesizing isopentenol by biological methods
The invention provides a recombinant Escherichia coli strain, a preparation method thereof and a method for synthesizing isopentenol therefrom by biological methods. According to the method, through an (MVA (Mevalonic Acid) way) for constructing and transforming mevalonic acid in an Escherichia coli body and pyrophosphatase for over-expressing Escherichia coli, a product, of which the composition contains over 80% of isopentenol, can be synthesized from engineering Escherichia coli strains in a high specificity manner.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
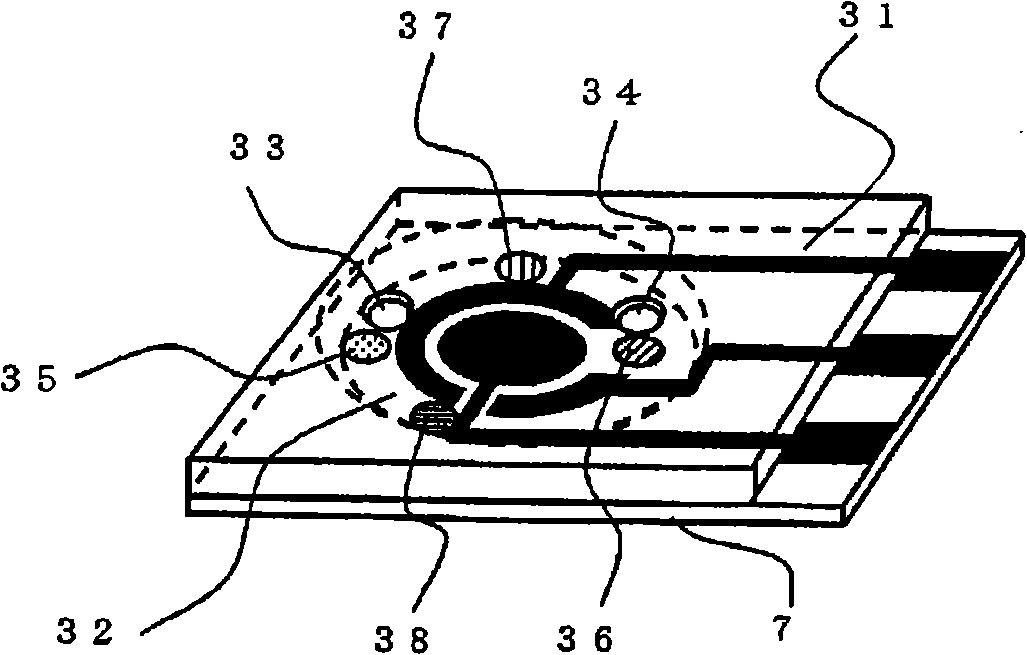
Pyrophosphoric acid sensor and snp typing sensor utilizing the same
ActiveCN101360993ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnesium saltGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
A pyrophosphoric acid sensor that in the method of measuring pyrophosphoric acid in SNP typing making use of primer extension reaction, realizes convenient detection of pyrophosphoric acid with high sensitivity. There is provided a pyrophosphoric acid sensor composed of insulating substrate (1); formed thereon, an electrode group consisting of measuring electrode (2) and counter electrode (3); and superimposed on the substrate (1), multiple reaction reagent layers consisting of pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, electron mediator, magnesium salt and buffer solution components wherein reaction reagent layer (35) containing buffer solution components is separated from enzyme-containing reaction reagent layer (36), characterized in that reaction reagent layer (37) containing glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is separated from the reaction reagent layer (35) containing buffer solution components.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com













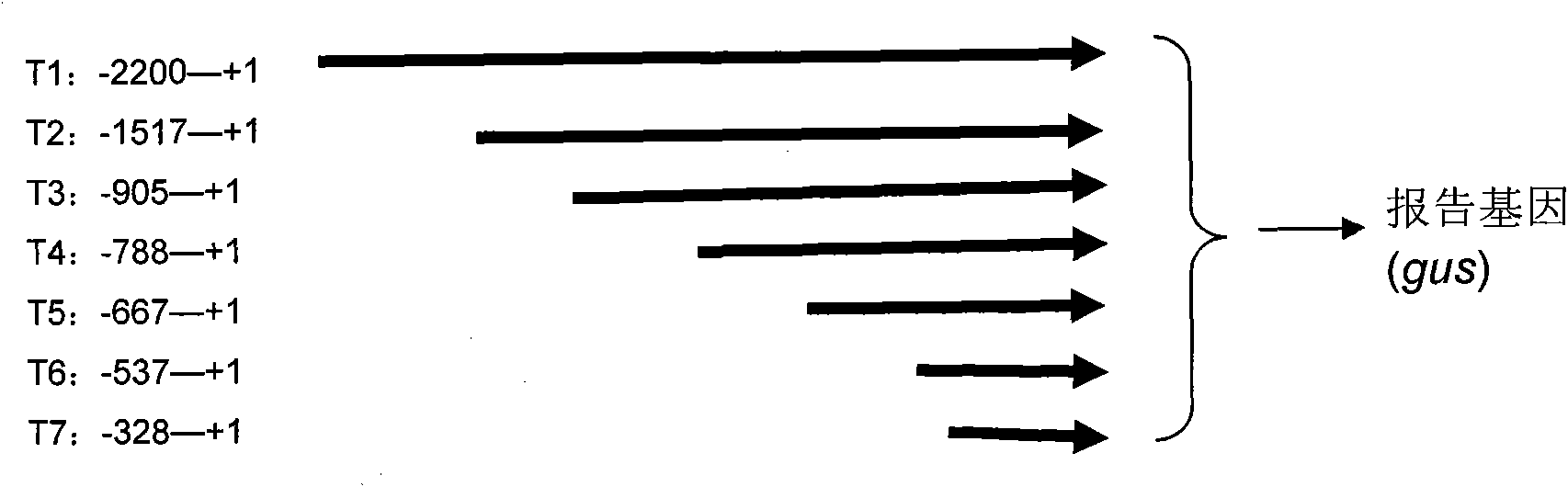



![Method for preparing [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide Method for preparing [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/8466951b-adb7-49b3-80b1-bf4d591031ee/HDA0002515530550000011.png)
![Method for preparing [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide Method for preparing [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/8466951b-adb7-49b3-80b1-bf4d591031ee/HDA0002515530550000012.png)
![Method for preparing [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide Method for preparing [beta]-nicotinamide mononucleotide](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/8466951b-adb7-49b3-80b1-bf4d591031ee/HDA0002515530550000021.png)