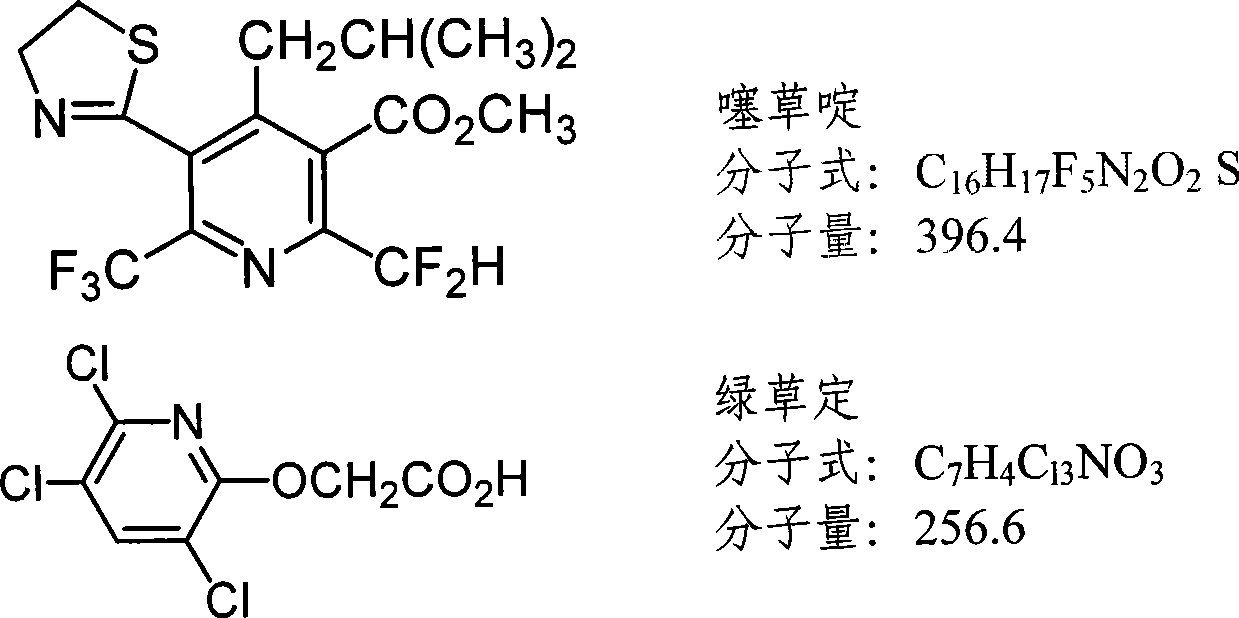
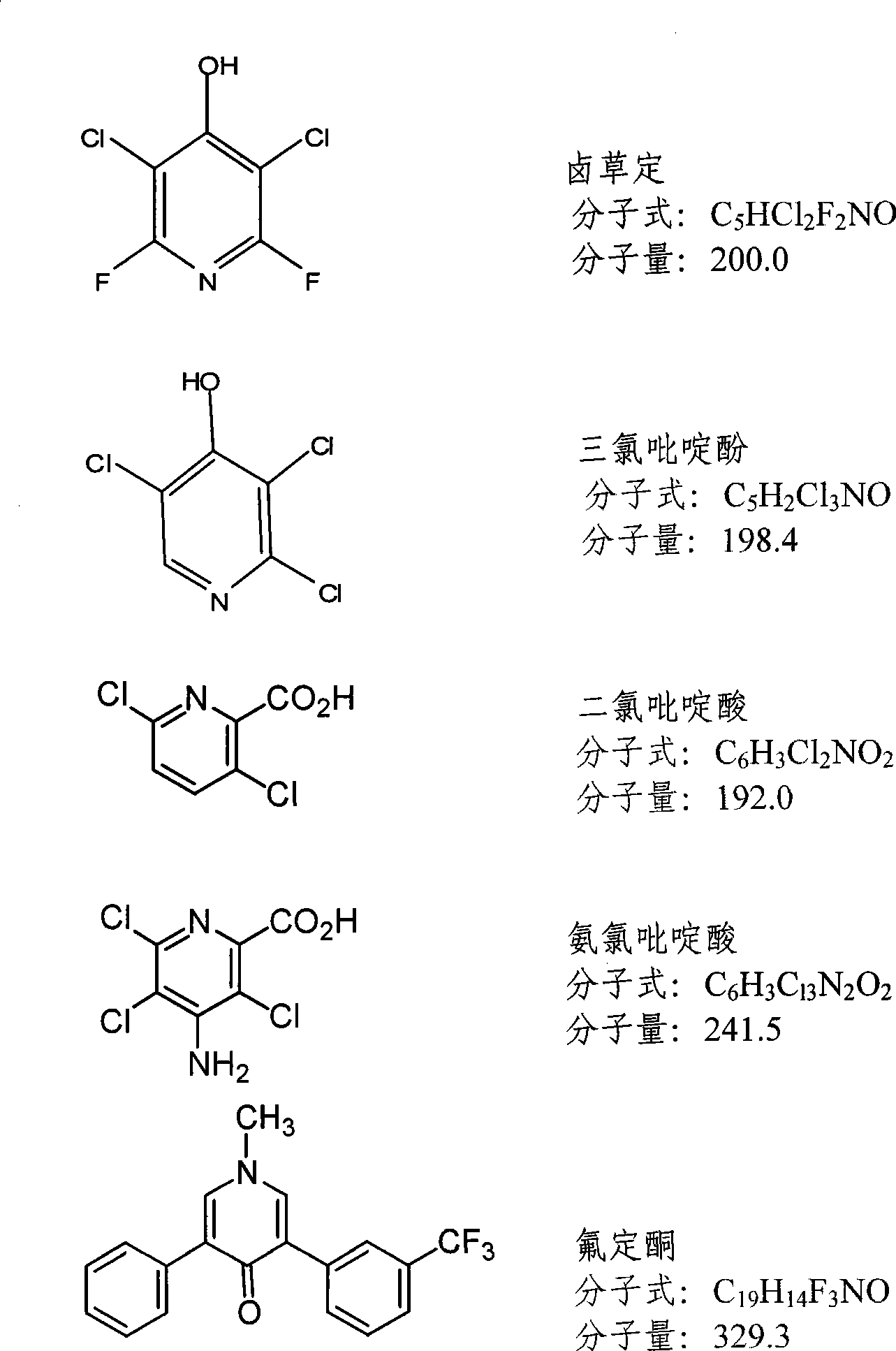
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10469 results about "Weed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, "a plant in the wrong place". Examples commonly are plants unwanted in human-controlled settings, such as farm fields, gardens, lawns, and parks. Taxonomically, the term "weed" has no botanical significance, because a plant that is a weed in one context is not a weed when growing in a situation where it is in fact wanted, and where one species of plant is a valuable crop plant, another species in the same genus might be a serious weed, such as a wild bramble growing among cultivated loganberries. In the same way, volunteer crops (plants) are regarded as weeds in a subsequent crop. Many plants that people widely regard as weeds also are intentionally grown in gardens and other cultivated settings, in which case they are sometimes called beneficial weeds. The term weed also is applied to any plant that grows or reproduces aggressively, or is invasive outside its native habitat. More broadly "weed" occasionally is applied pejoratively to species outside the plant kingdom, species that can survive in diverse environments and reproduce quickly; in this sense it has even been applied to humans.
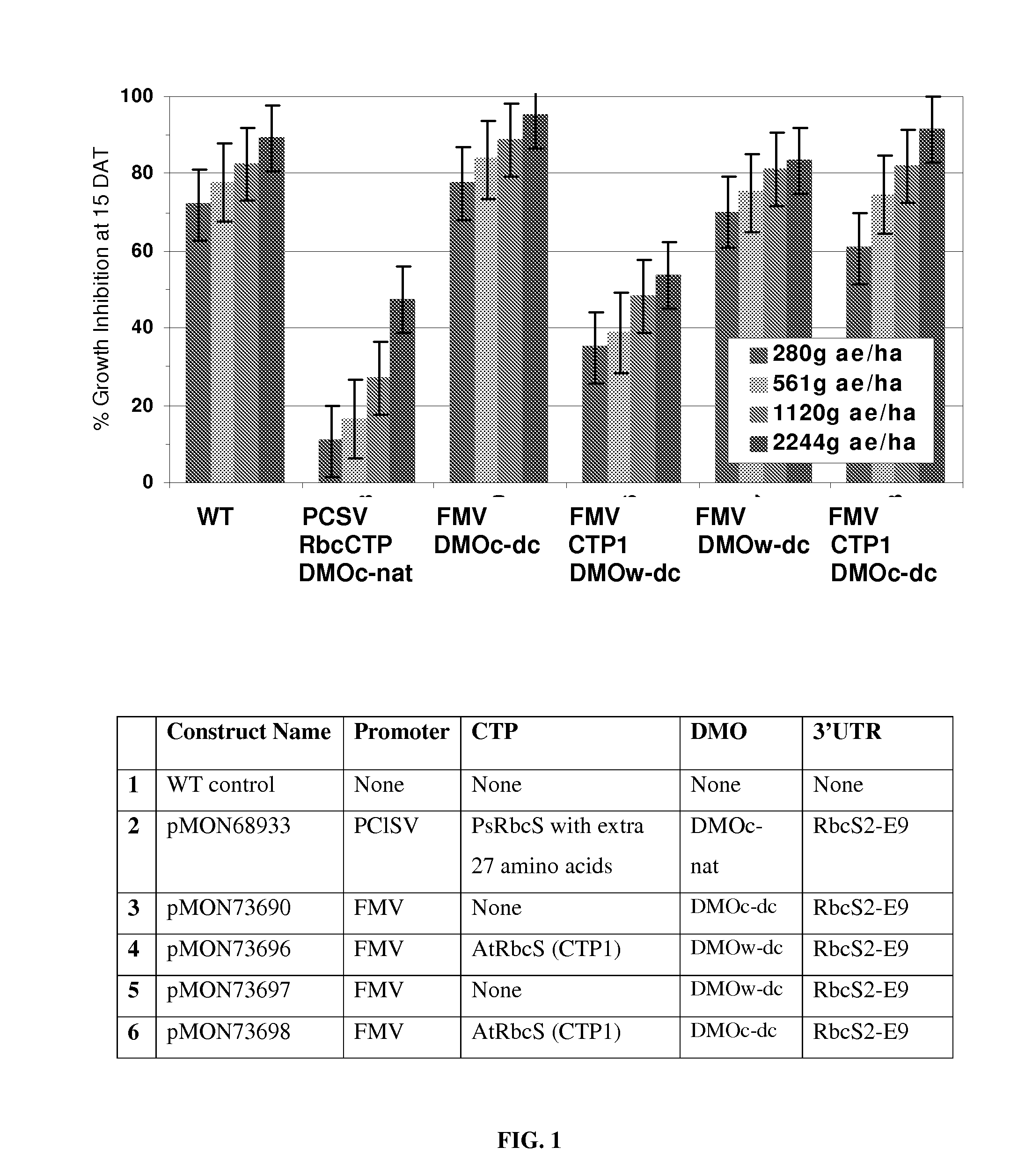
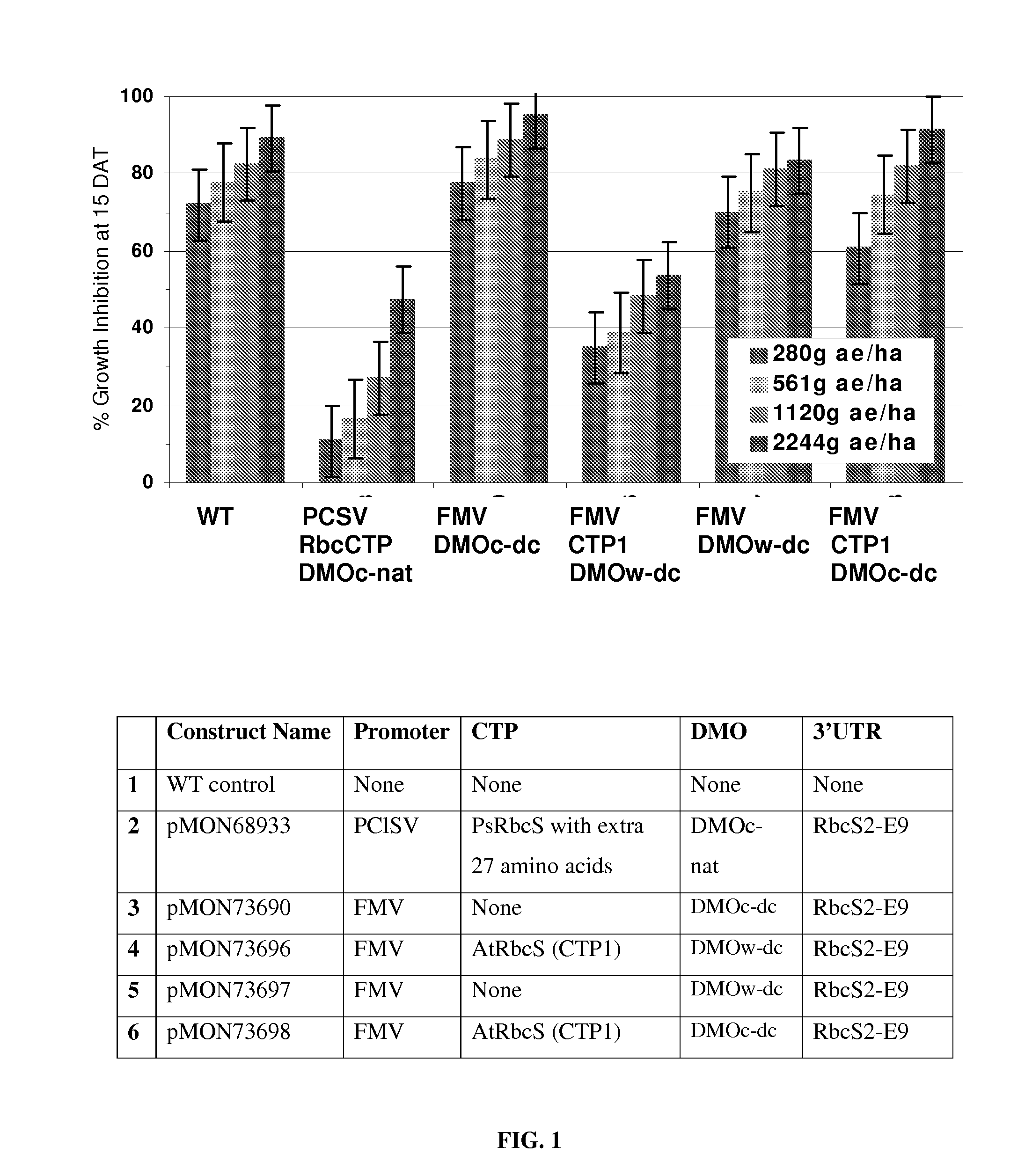
Chloroplast transit peptides for efficient targeting of DMO and uses thereof
ActiveUS7838729B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesMonooxygenaseGMO Plants
The invention provides for identification and use of certain chloroplast transit peptides for efficient processing and localization of dicamba monooxygenase (DMO) enzyme in transgenic plants. Methods for producing dicamba tolerant plants, methods for controlling weed growth, and methods for producing food, feed, and other products are also provided, as well as seed that confers tolerance to dicamba when it is applied pre- or post-emergence.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for weed control using plants having dicamba-degrading enzymatic activity
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
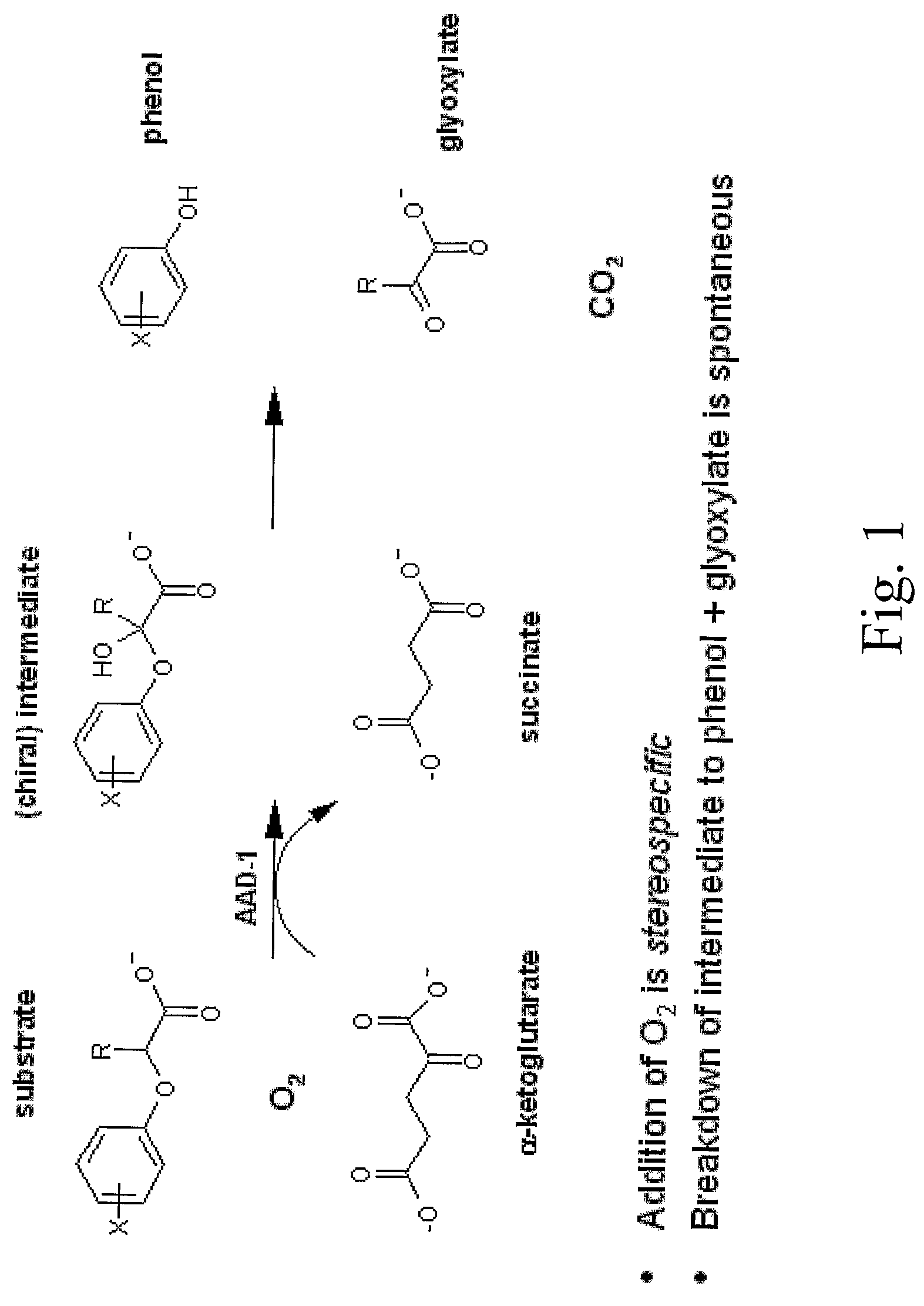
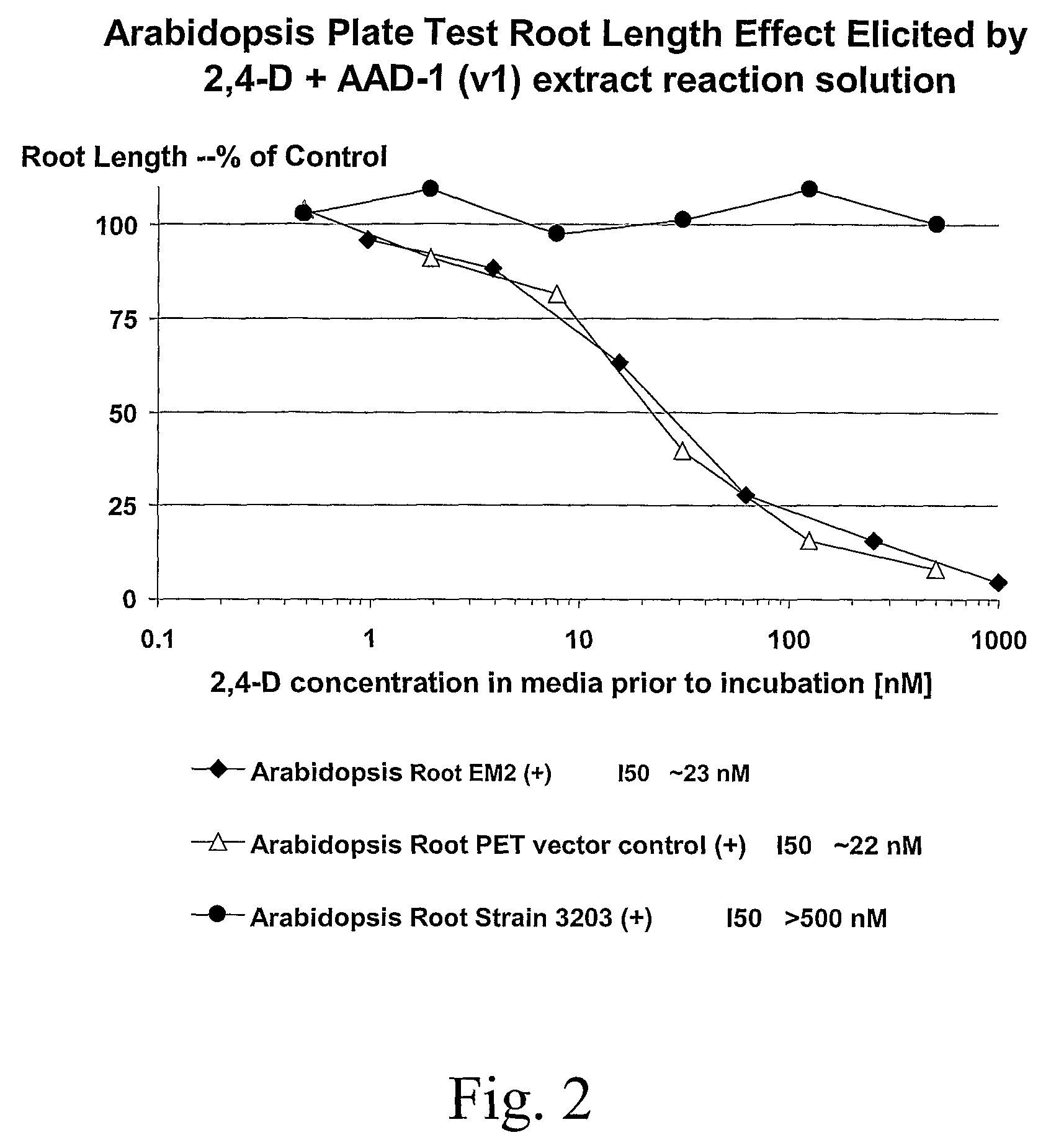
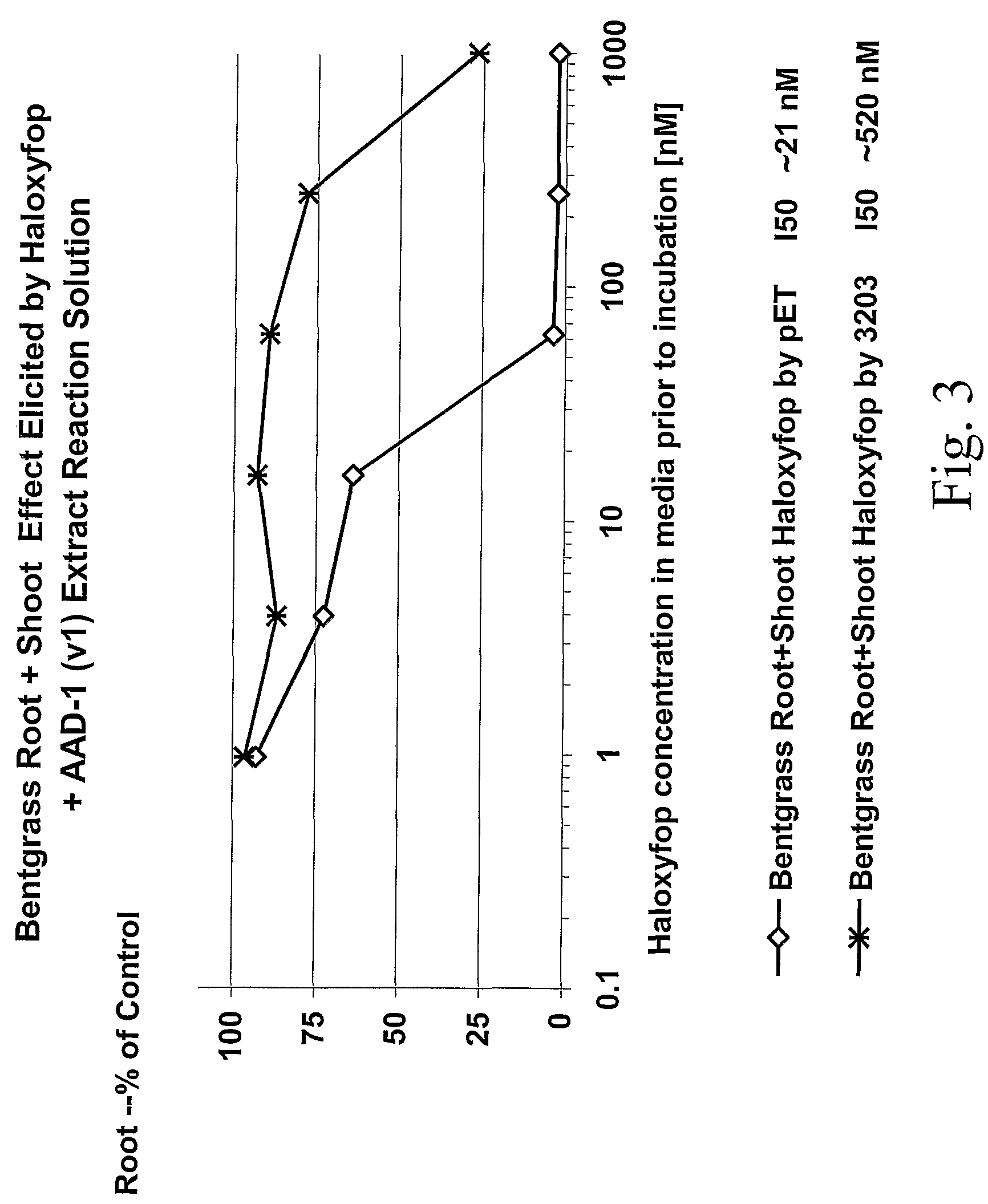
Herbicide resistance genes
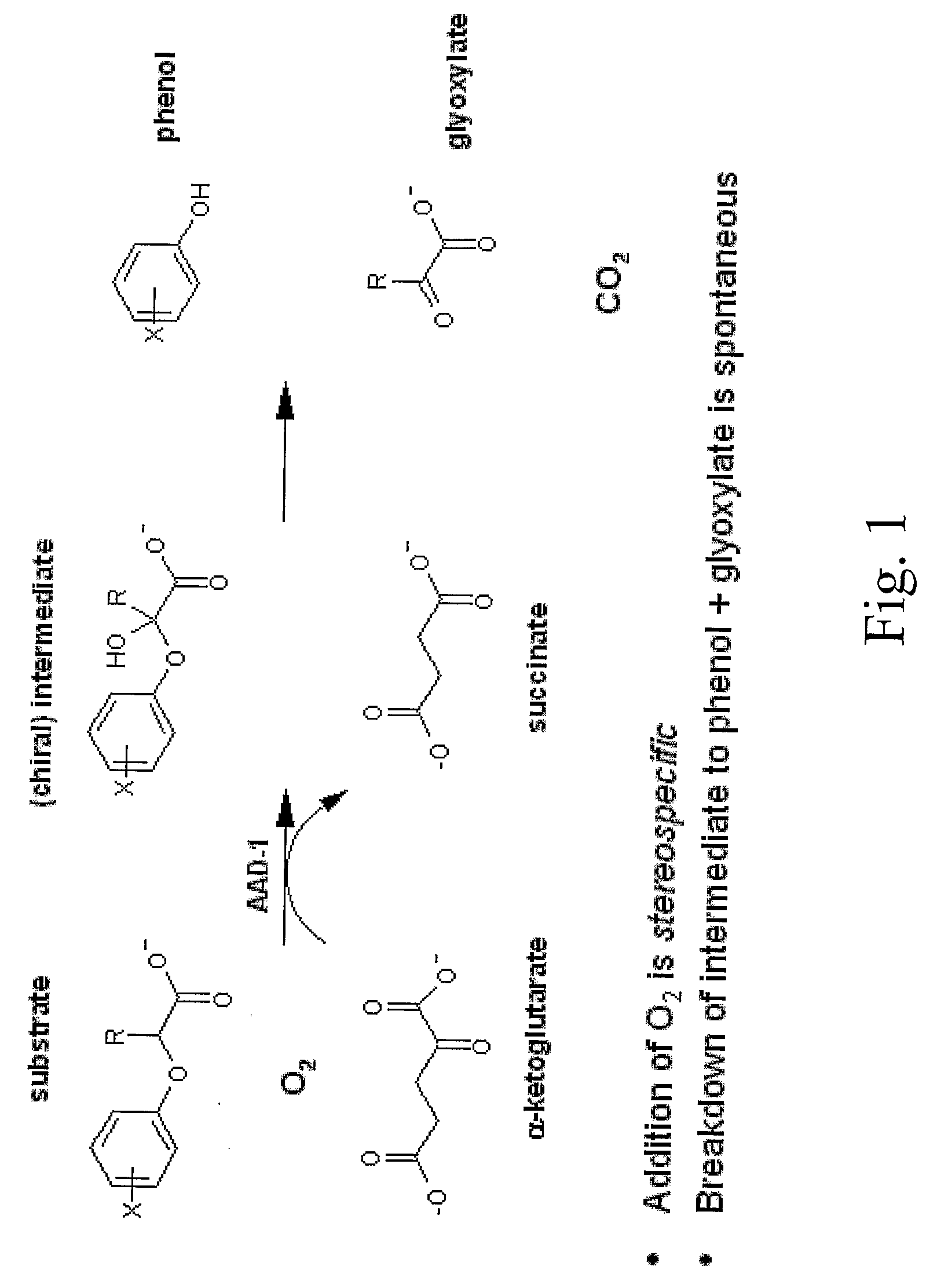
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D and other phenoxy auxin herbicides, but also to aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention alone or “stacked” together with another herbicide resistance gene, preferably a glyphosate resistance gene, so as to provide broader and more robust weed control, increased treatment flexibility, and improved herbicide resistance management options. More specifically, preferred enzymes and genes for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD (aryloxyalkanoate dioxygenase) genes and proteins. No α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase enzyme has previously been reported to have the ability to degrade herbicides of different chemical classes and modes of action. This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait opportunities as well as development of selectable marker technology. The subject invention also includes related methods of controlling weeds. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the formation of, and controlling, weeds that are resistant (or naturally more tolerant) to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Novel Herbicide Resistance Genes
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D and other phenoxy auxin herbicides, but also to aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention alone or “stacked” together with another herbicide resistance gene, preferably a glyphosate resistance gene, so as to provide broader and more robust weed control, increased treatment flexibility, and improved herbicide resistance management options. More specifically, preferred enzymes and genes for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD (aryloxyalkanoate dioxygenase) genes and proteins. No α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase enzyme has previously been reported to have the ability to degrade herbicides of different chemical classes and modes of action. This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait opportunities as well as development of selectable marker technology. The subject invention also includes related methods of controlling weeds. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the formation of, and controlling, weeds that are resistant (or naturally more tolerant) to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Herbicide resistance genes
ActiveUS8283522B2Prevent shifting or shiftingAvoid developmentBiocideSugar derivativesGlyphosateDioxygenase
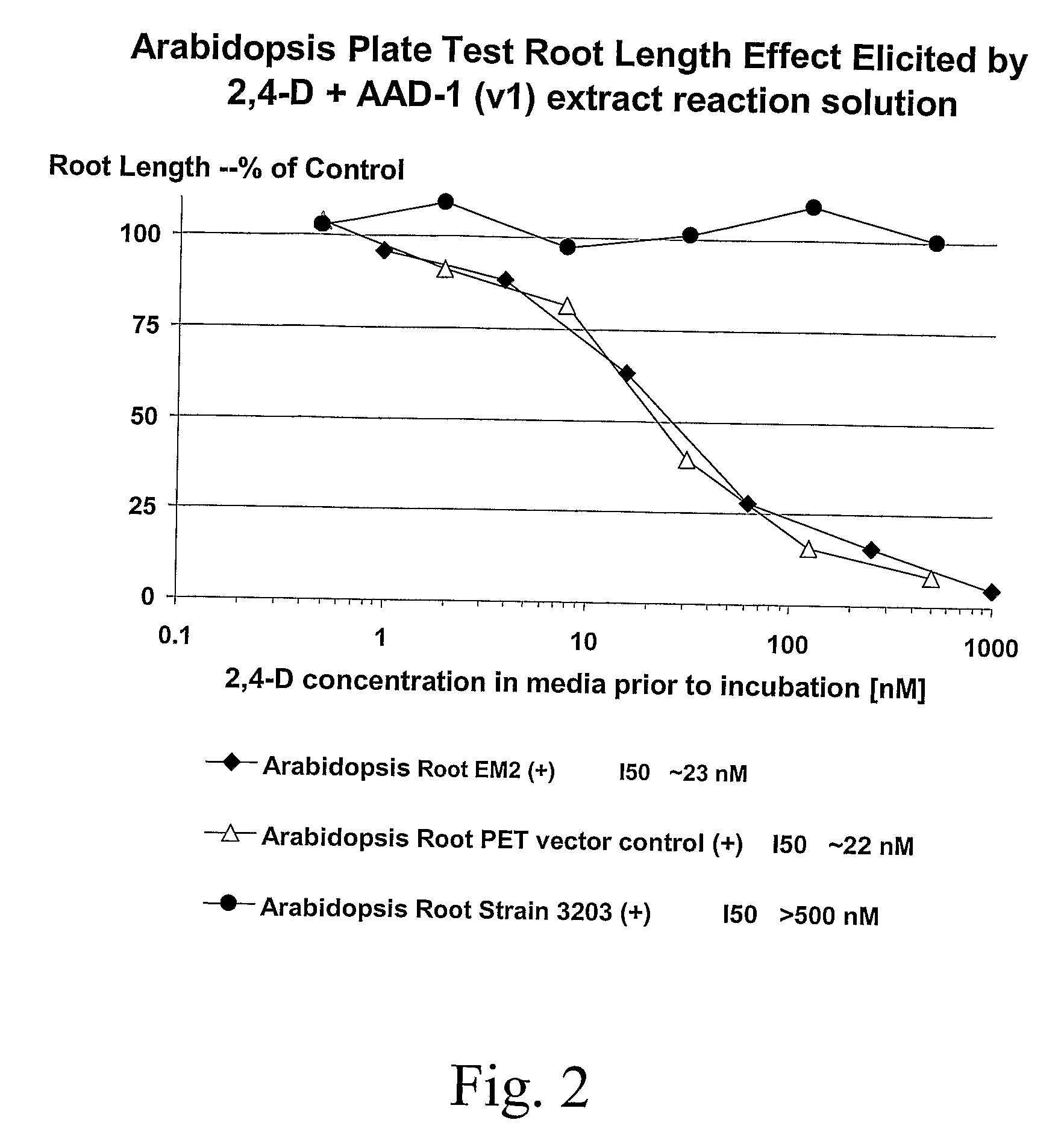
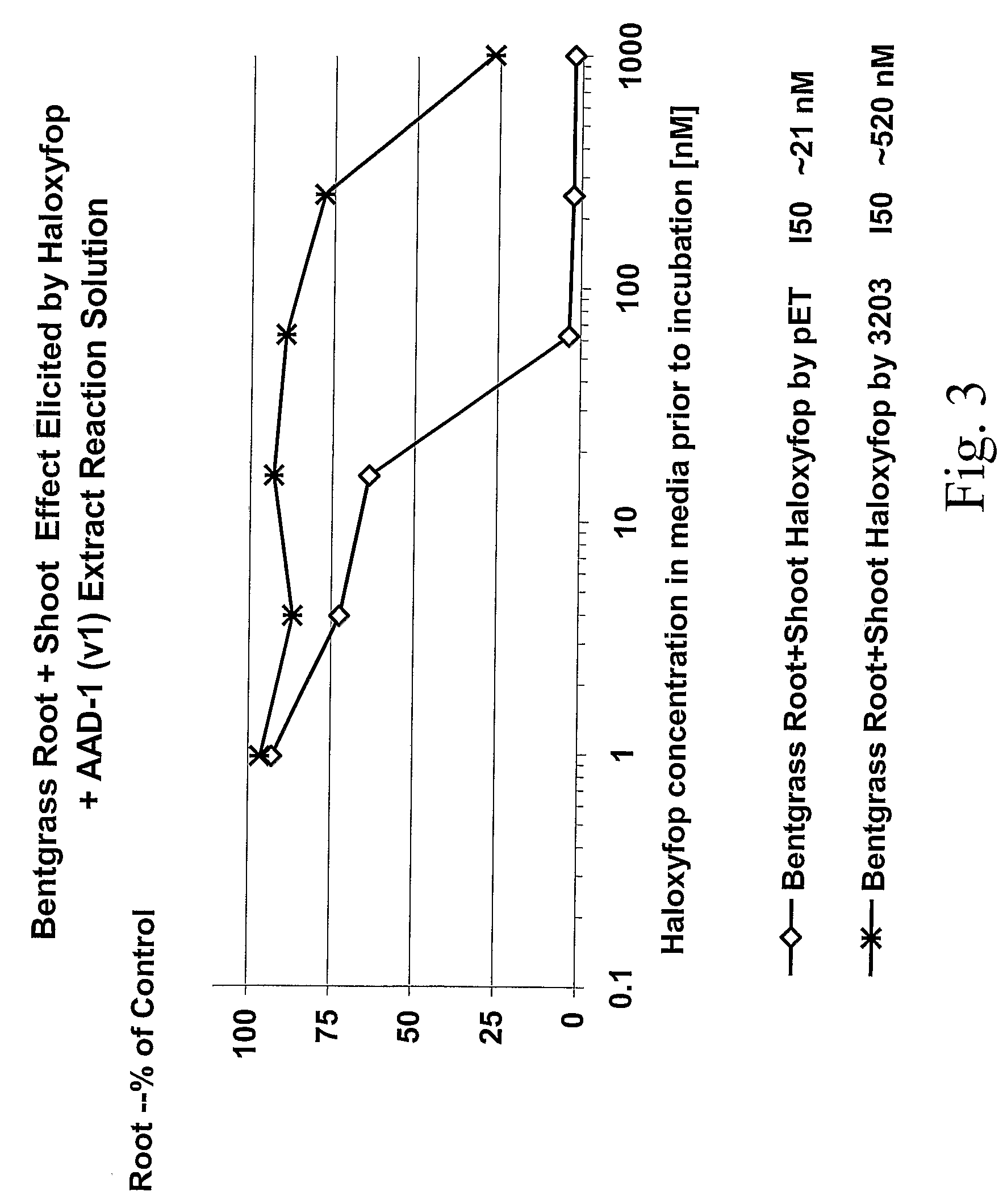
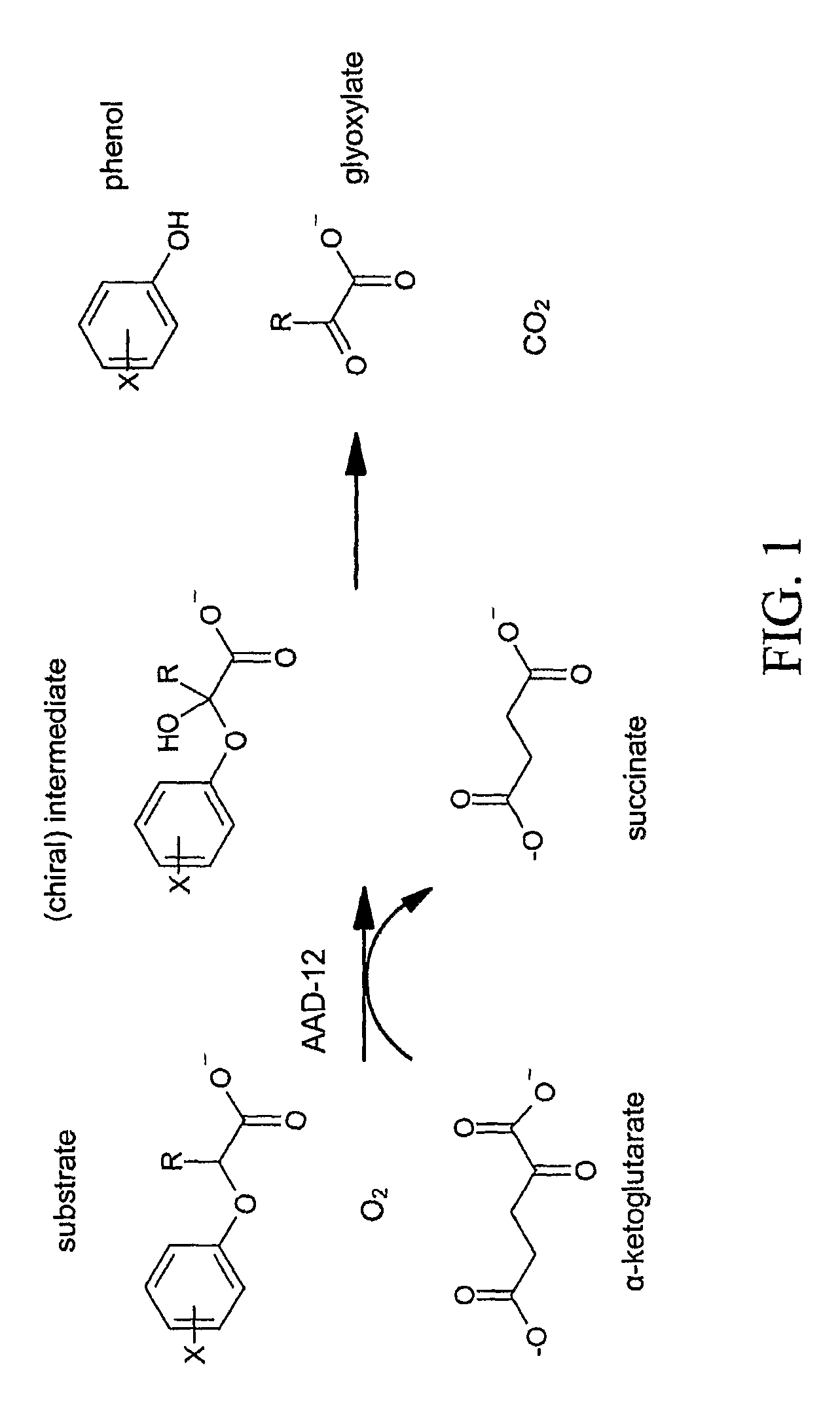
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D, but also to pyridyloxyacetate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention “stacked” together with one or more other herbicide resistance genes. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the development of, and controlling, strains of weeds that are resistant to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate. The preferred enzyme and gene for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD-12 (AryloxyAlkanoate Dioxygenase). This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait and selectable marker opportunities.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
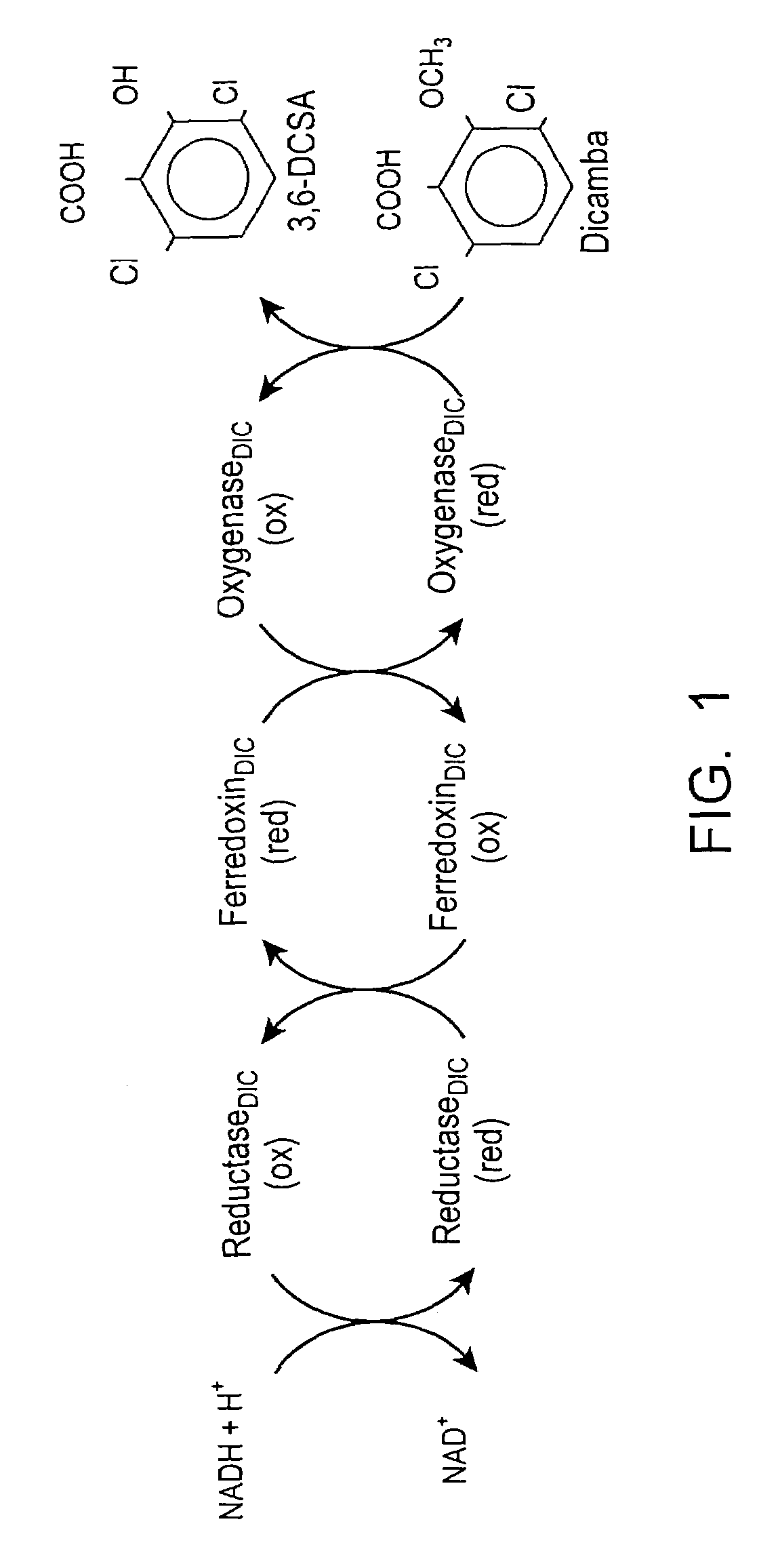
Methods and materials for making and using transgenic dicamba-degrading organisms
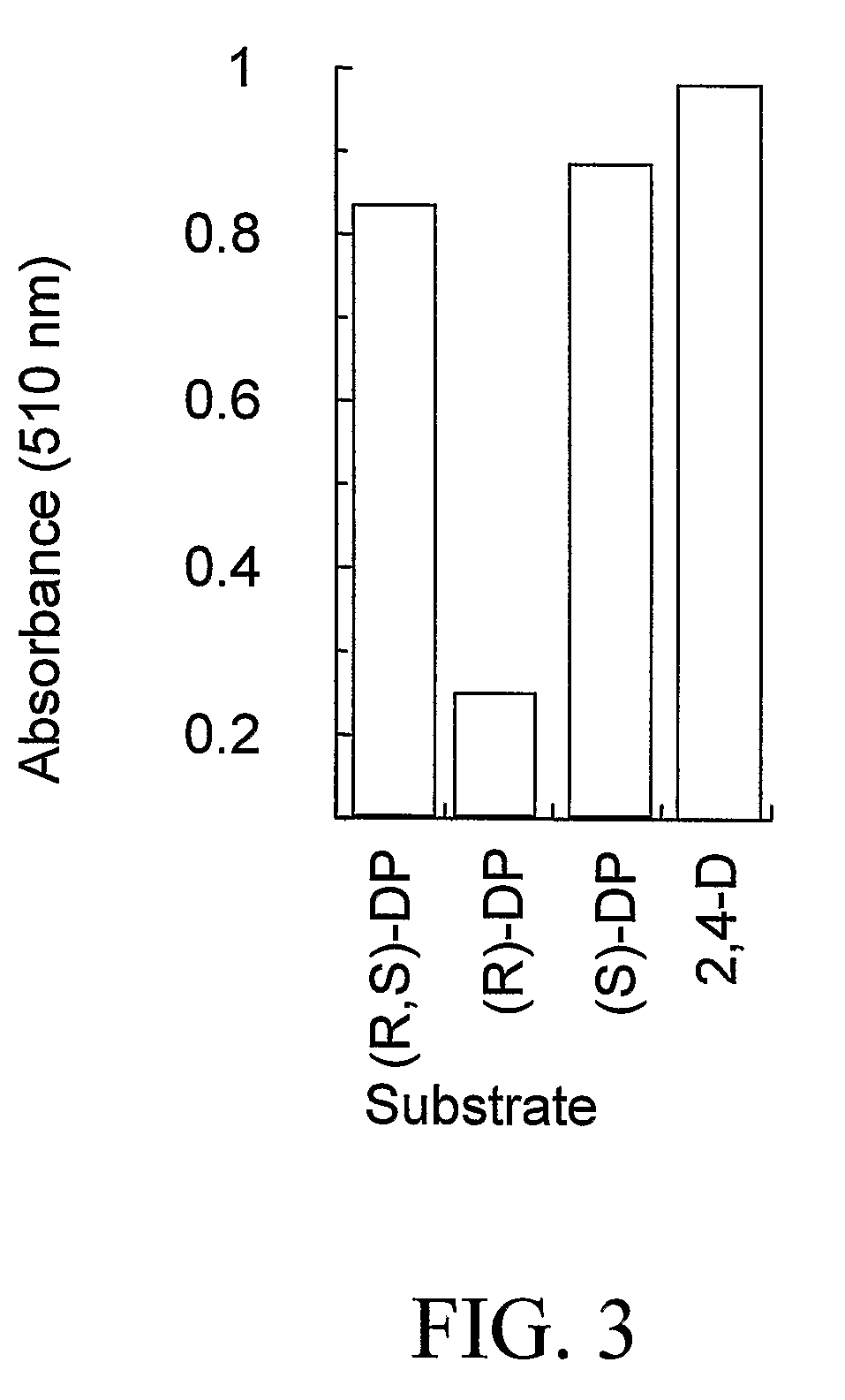
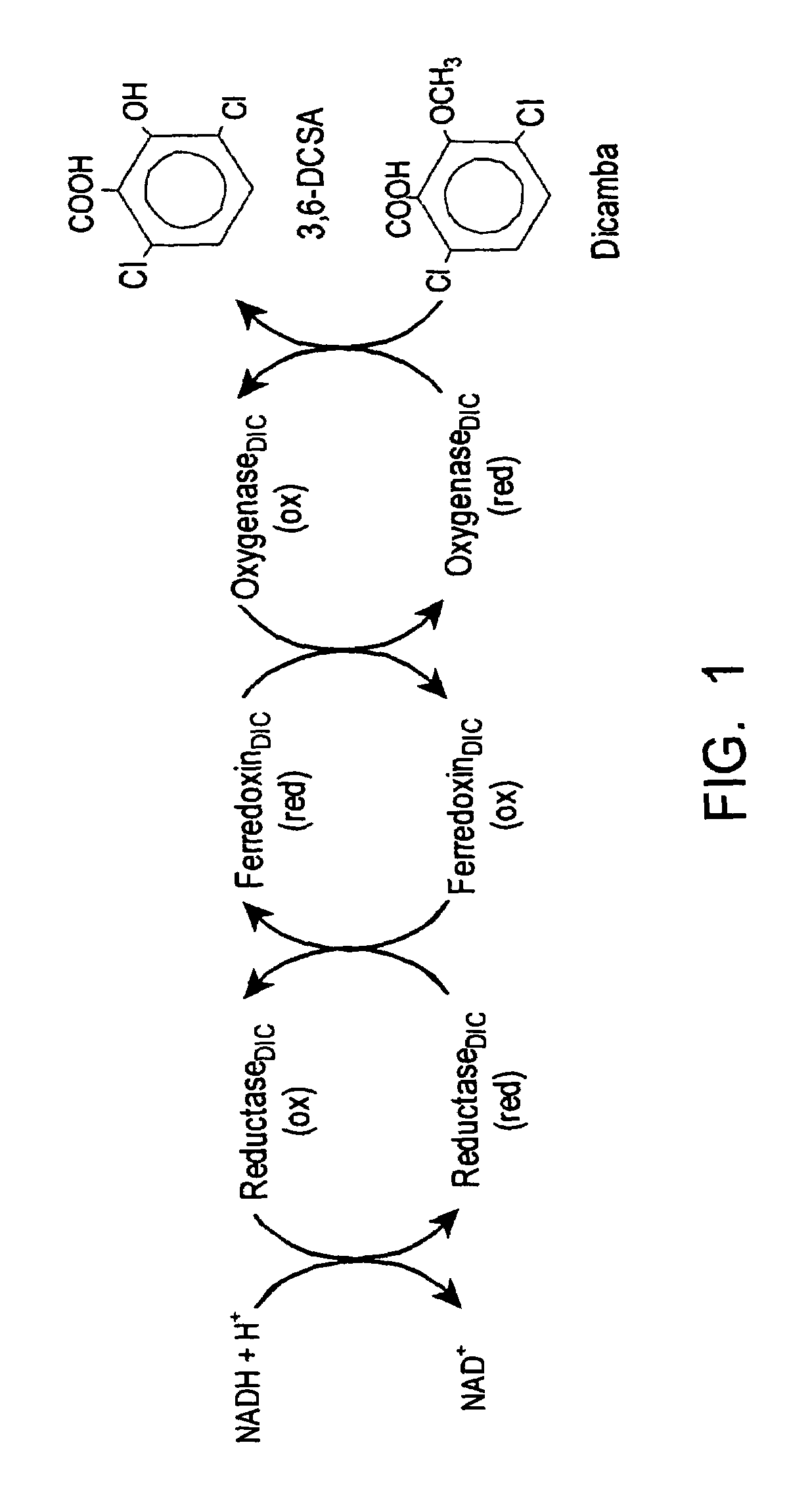
The invention provides isolated and at least partially-purified dicamba-degrading enzymes, isolated DNA molecules coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, DNA constructs coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, transgenic host cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, and transgenic plants and plant parts comprising one or more cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes. Expression of the dicamba-degrading enzymes results in the production of dicamba-degrading organisms, including dicamba-tolerant plants. The invention further provides a method of controlling weeds in a field containing the transgenic dicamba-tolerant plants of the invention and a method of decontaminating a material containing dicamba comprising applying an effective amount of a transgenic microorganism or dicamba-degrading enzyme of the invention to the material. Finally, the invention provides a method of selecting transformed plants and plant cells based on dicamba tolerance and a method of selecting or screening transformed host cells, intact organisms and parts of organisms based on the fluorescence of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid produced as a result of dicamba degradation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
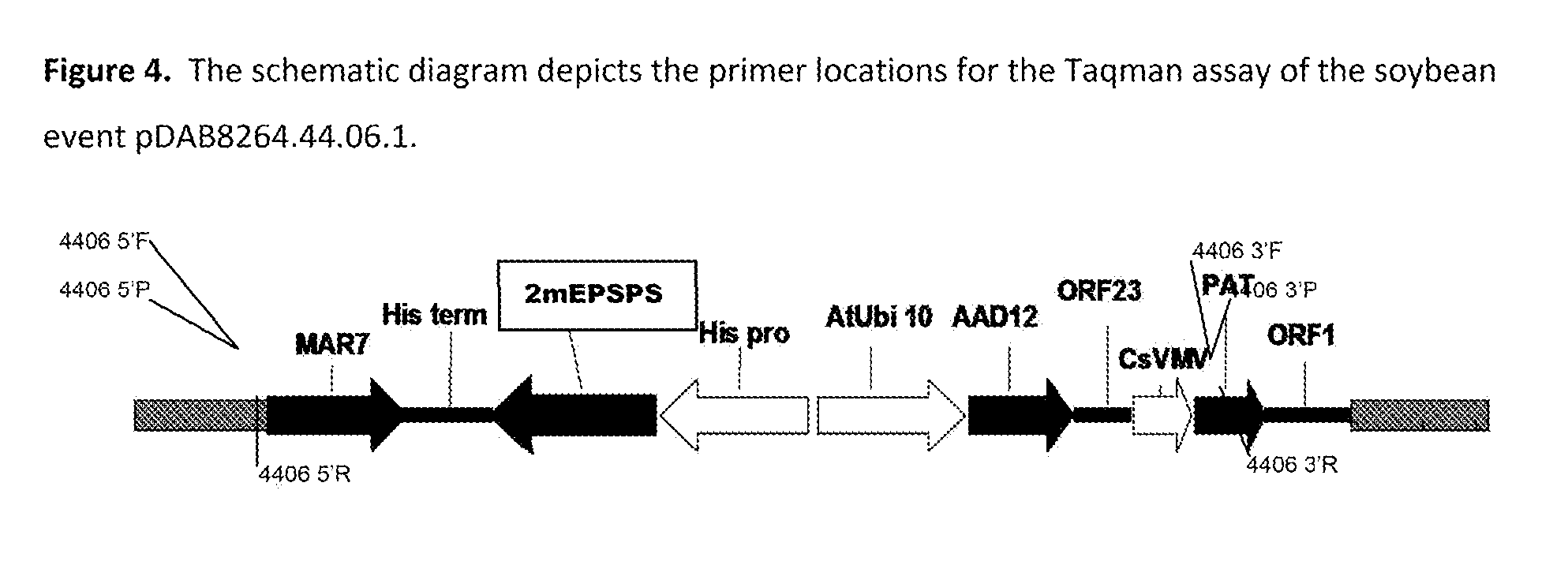
Stacked herbicide tolerance event 8264.44.06.1, related transgenic soybean lines, and detection thereof
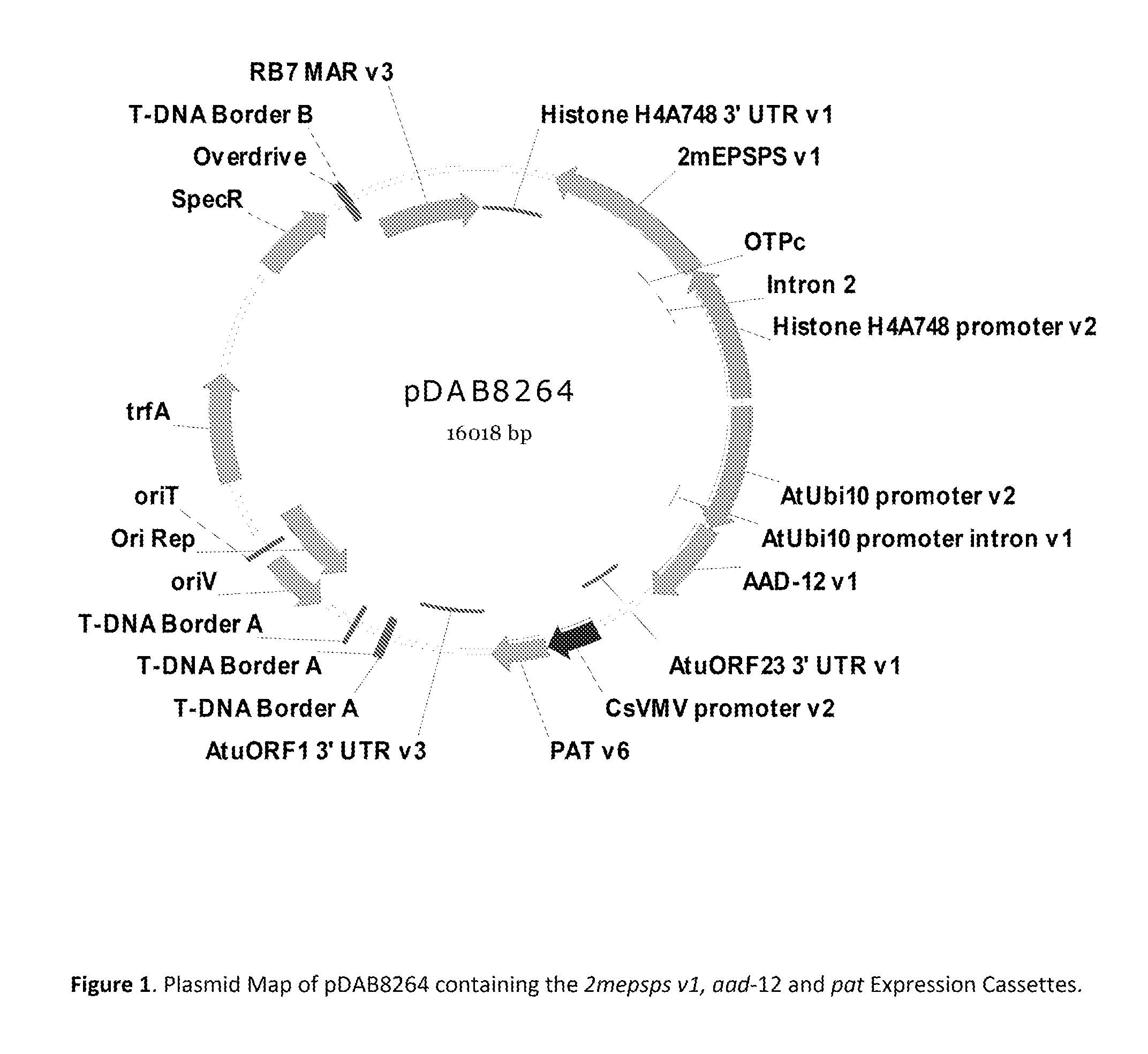
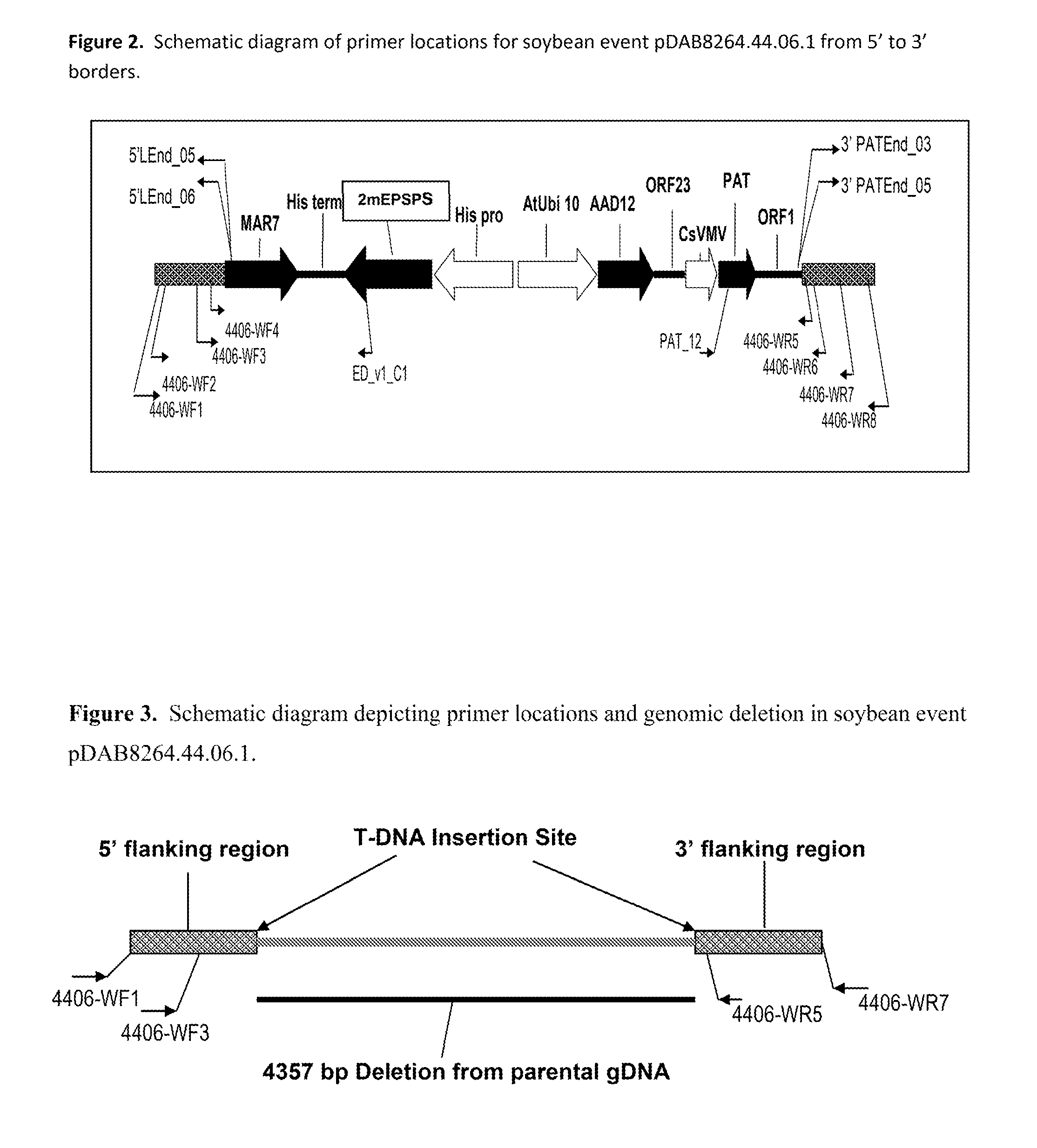
ActiveUS9540655B2Preserve usefulnessIncrease flexibilityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayMultiple traits
Owner:M S TECH +1
Method of controlling weeds in transgenic crops
The invention relates to a method for the control of weeds at a crop locus, said method comprising the application of an effective amount of: (a) a glyphosate herbicide which is glyphosate or a derivative thereof; and (b) at least one HPPD-inhibiting herbicide; wherein the crop is tolerant to glyphosate and optionally the HPPD-inhibiting herbicide.
Owner:BAYER SAS
Methods and materials for making and using transgenic dicamba-degrading organisms
The invention provides isolated and at least partially-purified dicamba-degrading enzymes, isolated DNA molecules coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, DNA constructs coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, transgenic host cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, and transgenic plants and plant parts comprising one or more cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes. Expression of the dicamba-degrading enzymes results in the production of dicamba-degrading organisms, including dicamba-tolerant plants. The invention further provides a method of controlling weeds in a field containing the transgenic dicamba-tolerant plants of the invention and a method of decontaminating a material containing dicamba comprising applying an effective amount of a transgenic microorganism or dicamba-degrading enzyme(s) of the invention to the material. Finally, the invention provides a method of selecting transformed plants and plant cells based on dicamba tolerance and a method of selecting or screening transformed host cells, intact organisms and parts of organisms based on the fluorescence of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid produced as a result of dicamba degradation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Methods for weed control
The invention provides methods for weed control with dicamba and related herbicides. It was found that pre-emergent applications of dicamba at or near planting could be made without significant crop damage or yield loss. The techniques can be combined with the herbicide glyphosate to improve the degree of weed control and permit control of herbicide tolerant weeds.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Compositions providing tolerance to multiple herbicides and methods of use thereof
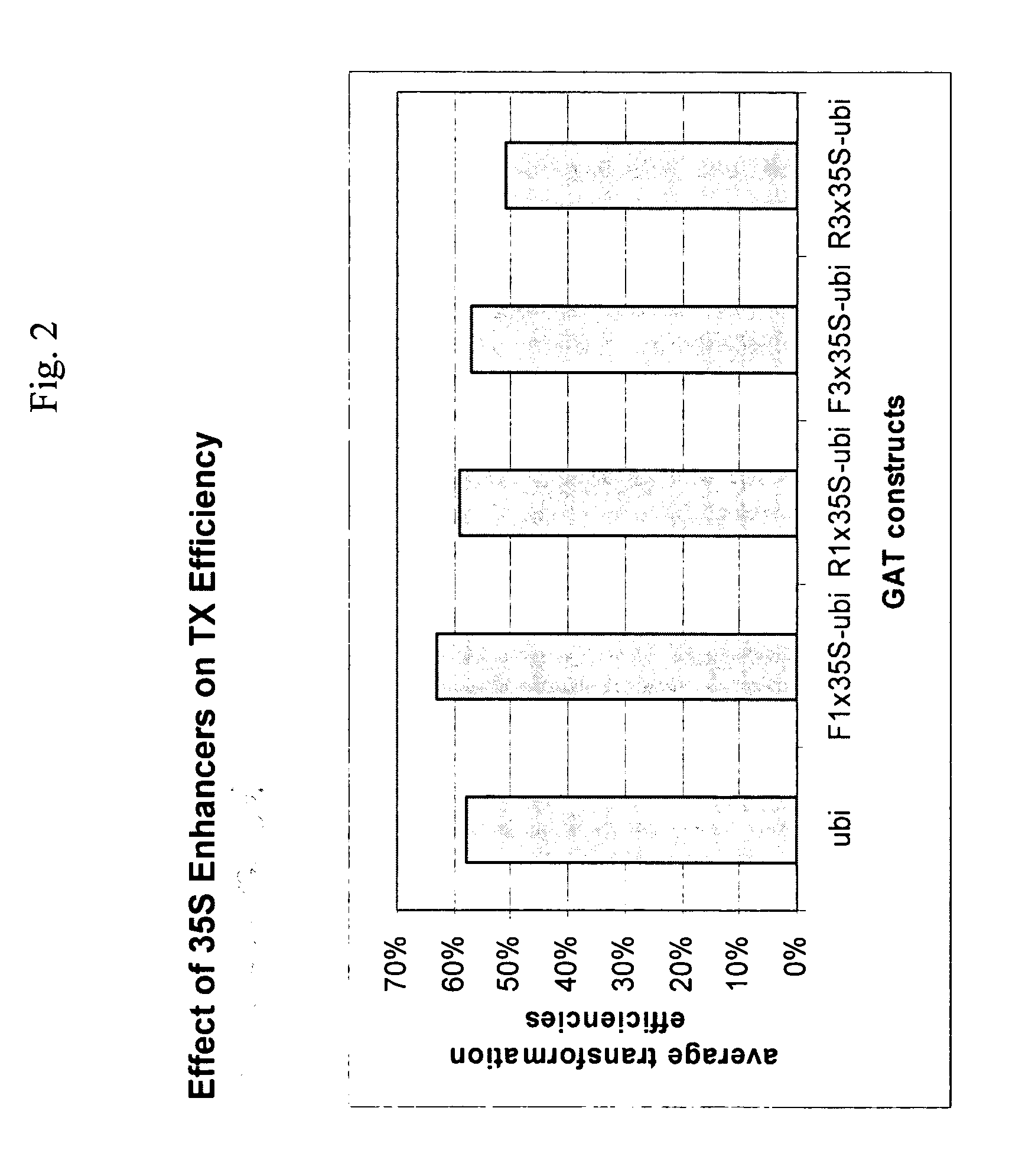
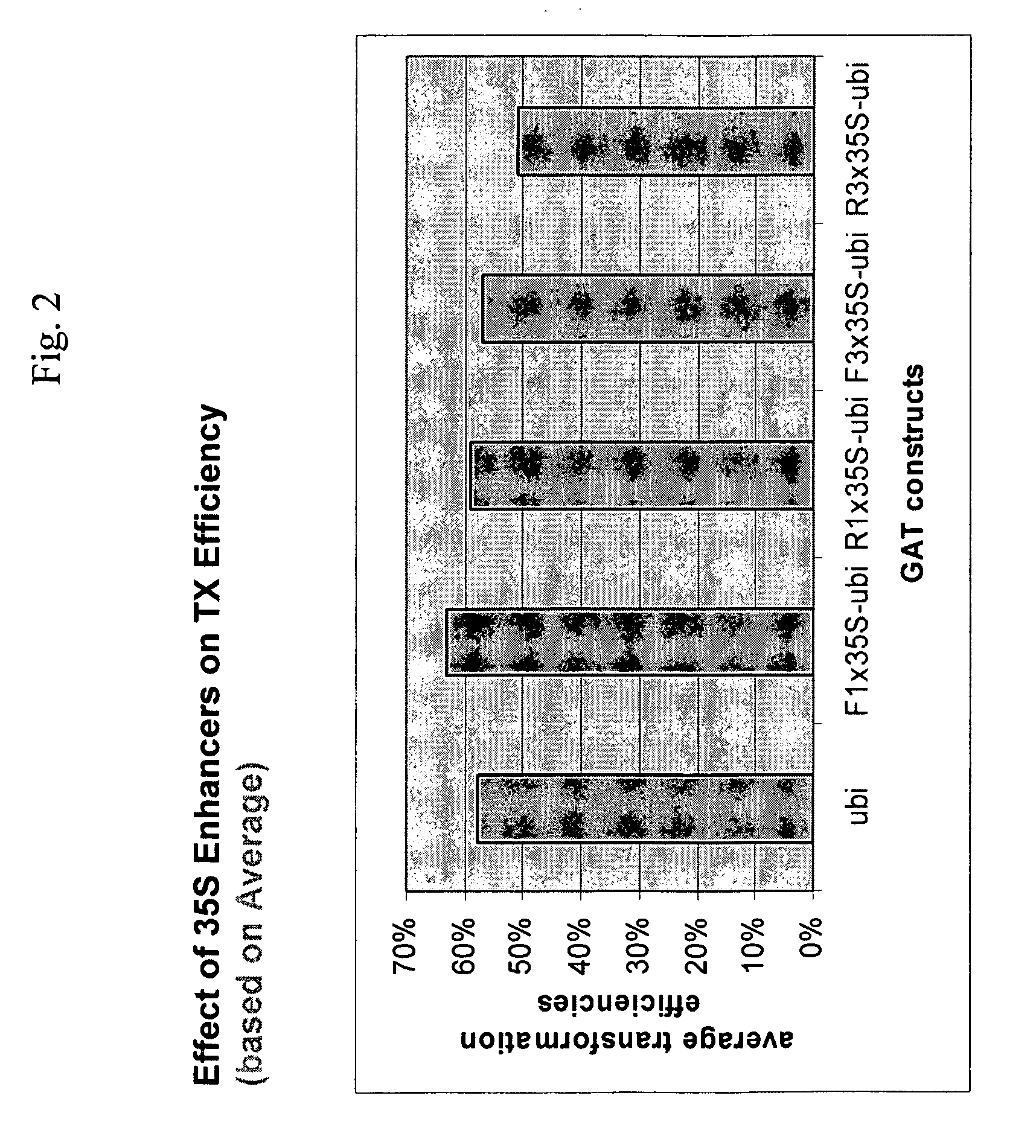
Methods and compositions are provided related to improved plants that are tolerant to more than one herbicide. Particularly, the invention provides plants that are tolerant of glyphosate and are tolerant to at least one ALS inhibitor, and methods of use thereof. The glyphosate / ALS inhibitor-tolerant plants comprise a polynucleotide that encodes a polypeptide that confers tolerance to glyphosate and a polynucleotide that encodes an ALS inhibitor-tolerant polypeptide. In specific embodiments, a plant of the invention expresses a GAT polypeptide and an HRA polypeptide. Methods to control weeds, improve plant yield, and increase transformation efficiencies are provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Light sensor with modulated radiant polychromatic source
ActiveUS20050098713A1Increase costImprove performancePhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryDetector arrayAnalytical control
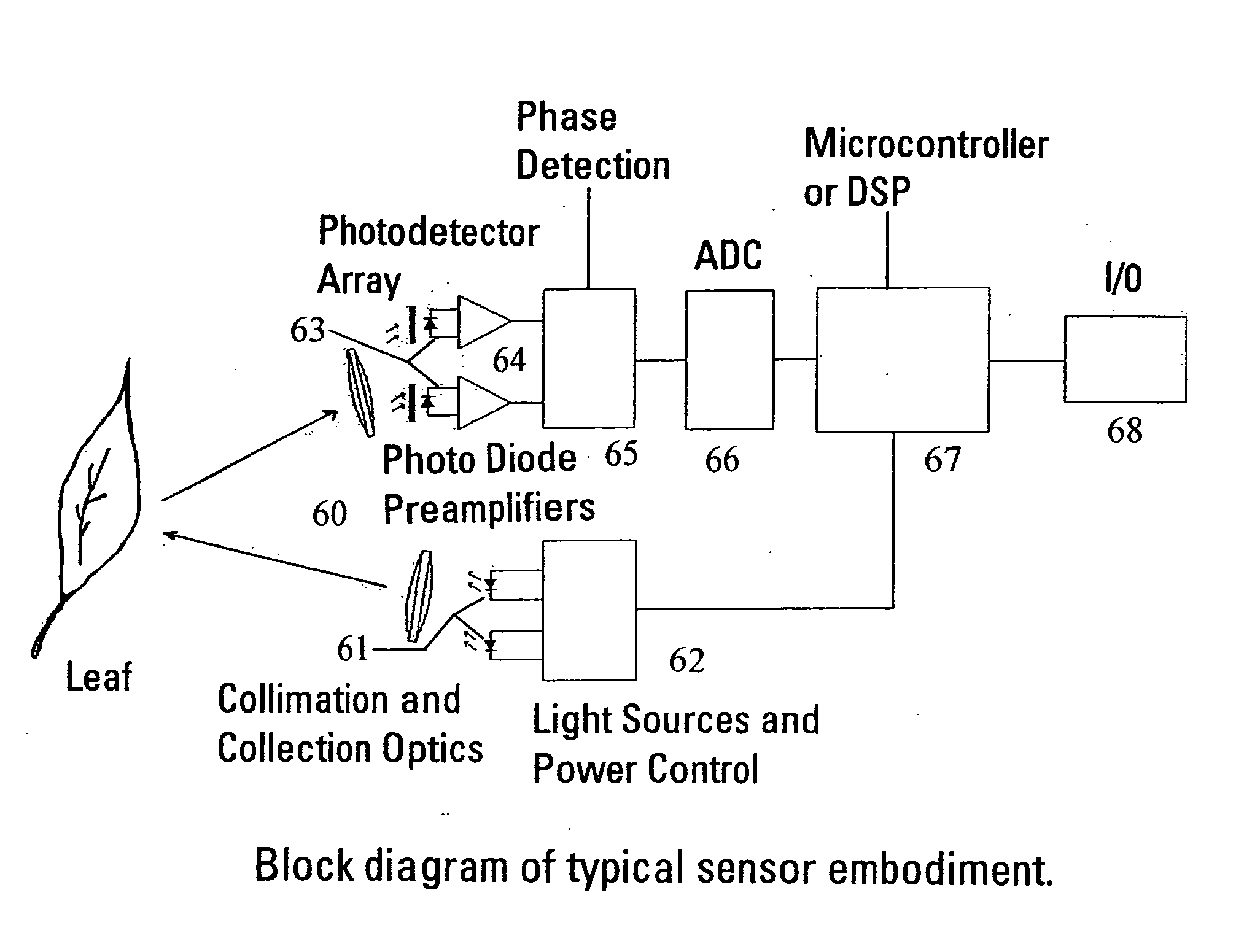
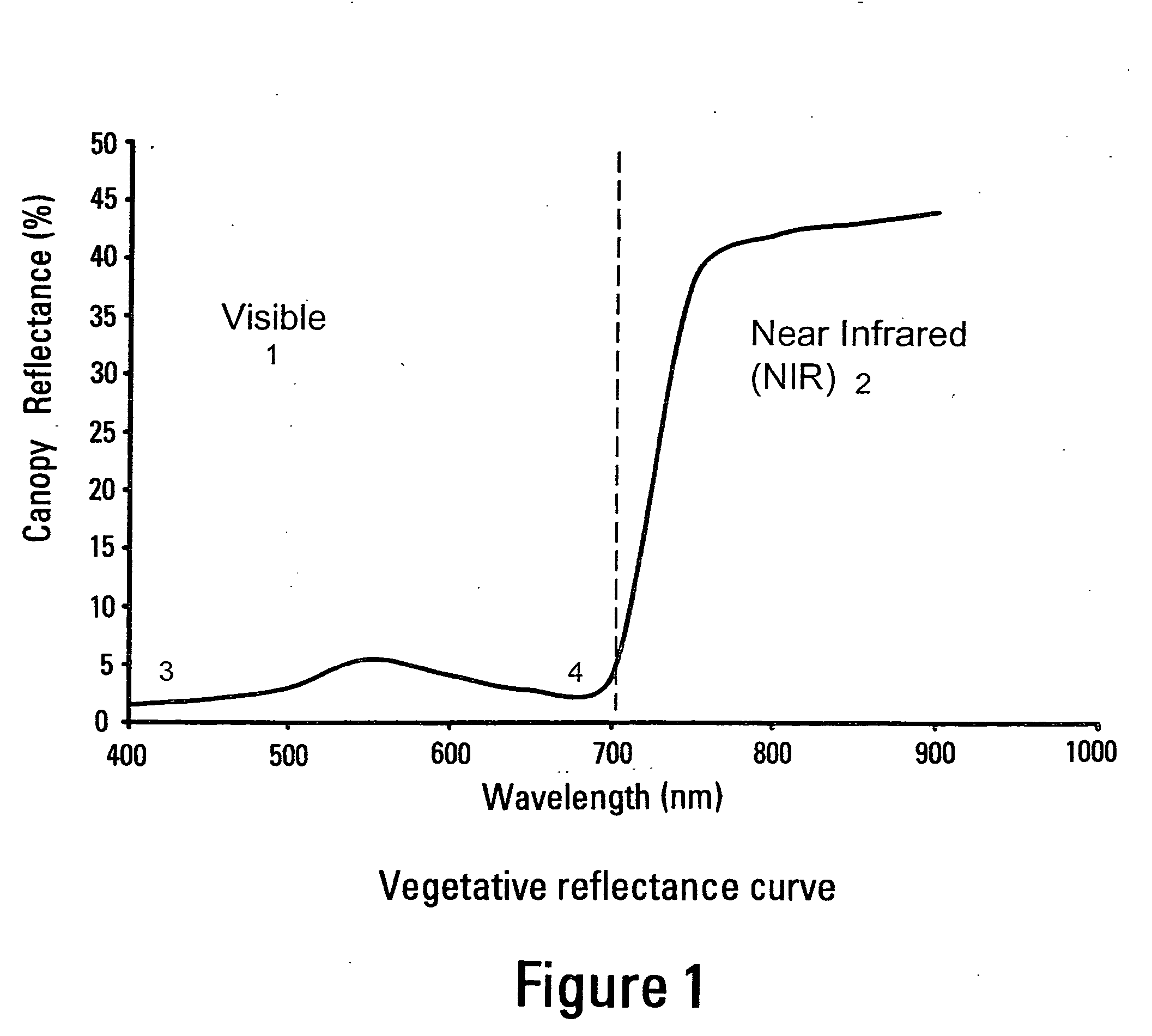
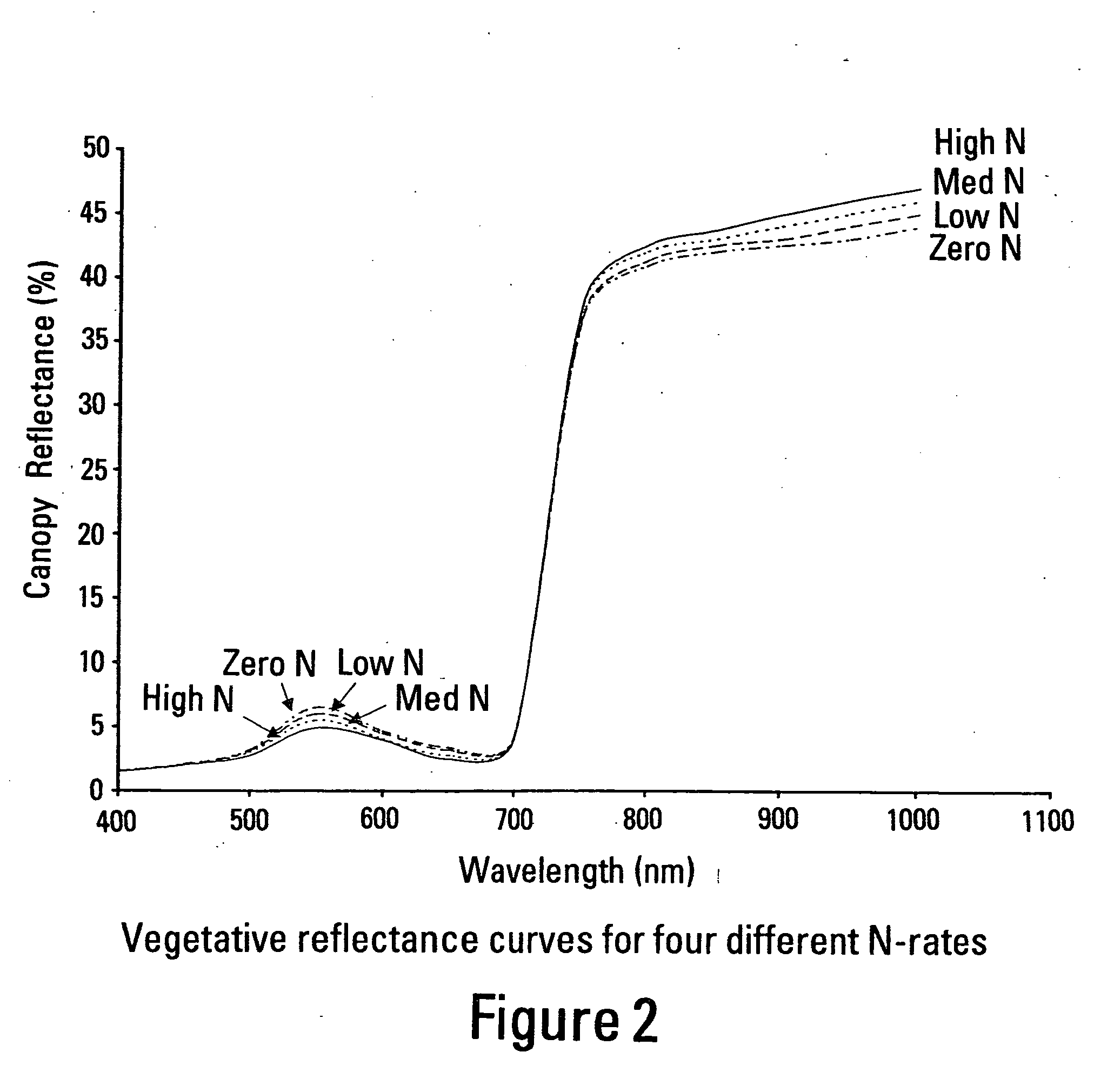
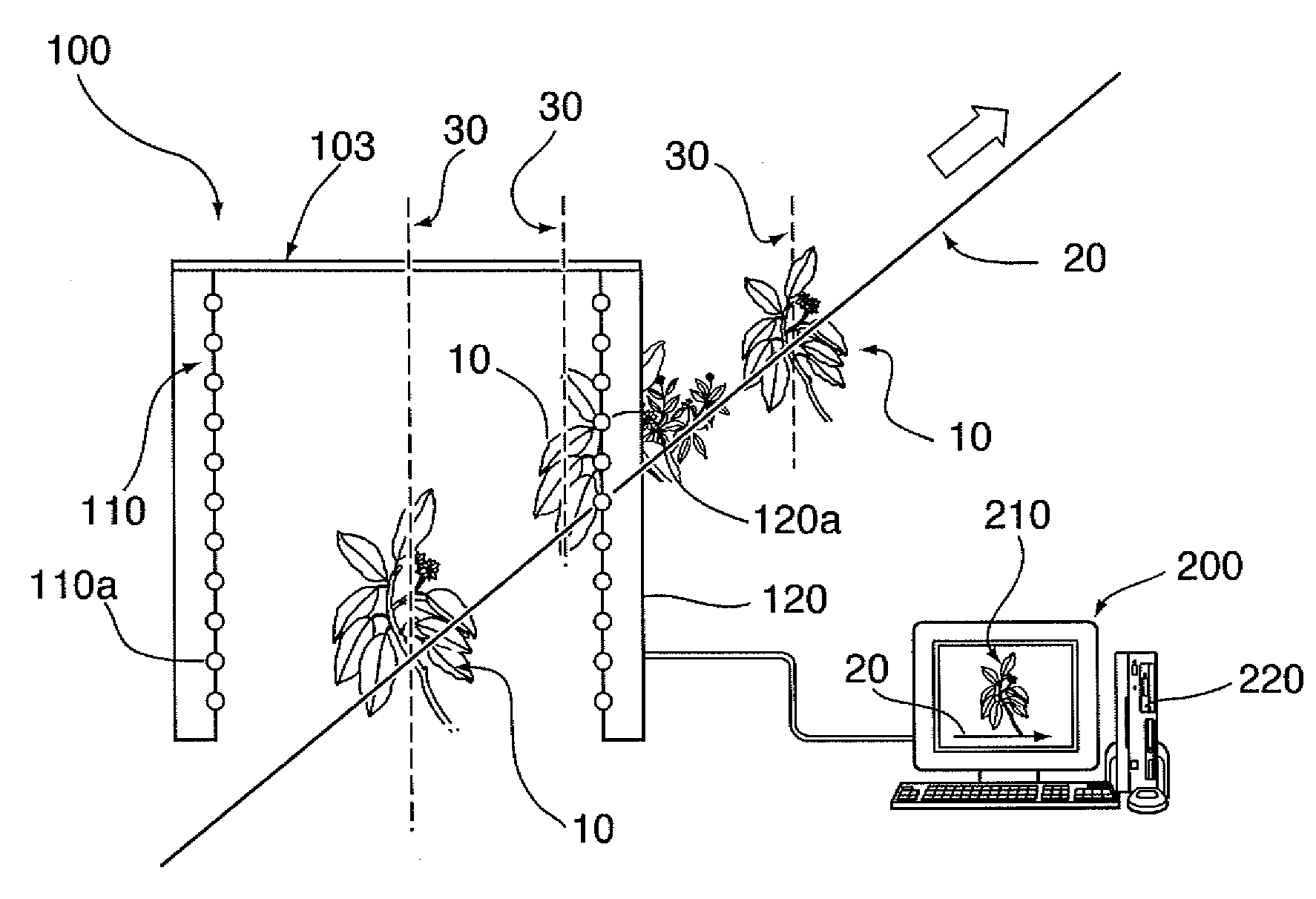
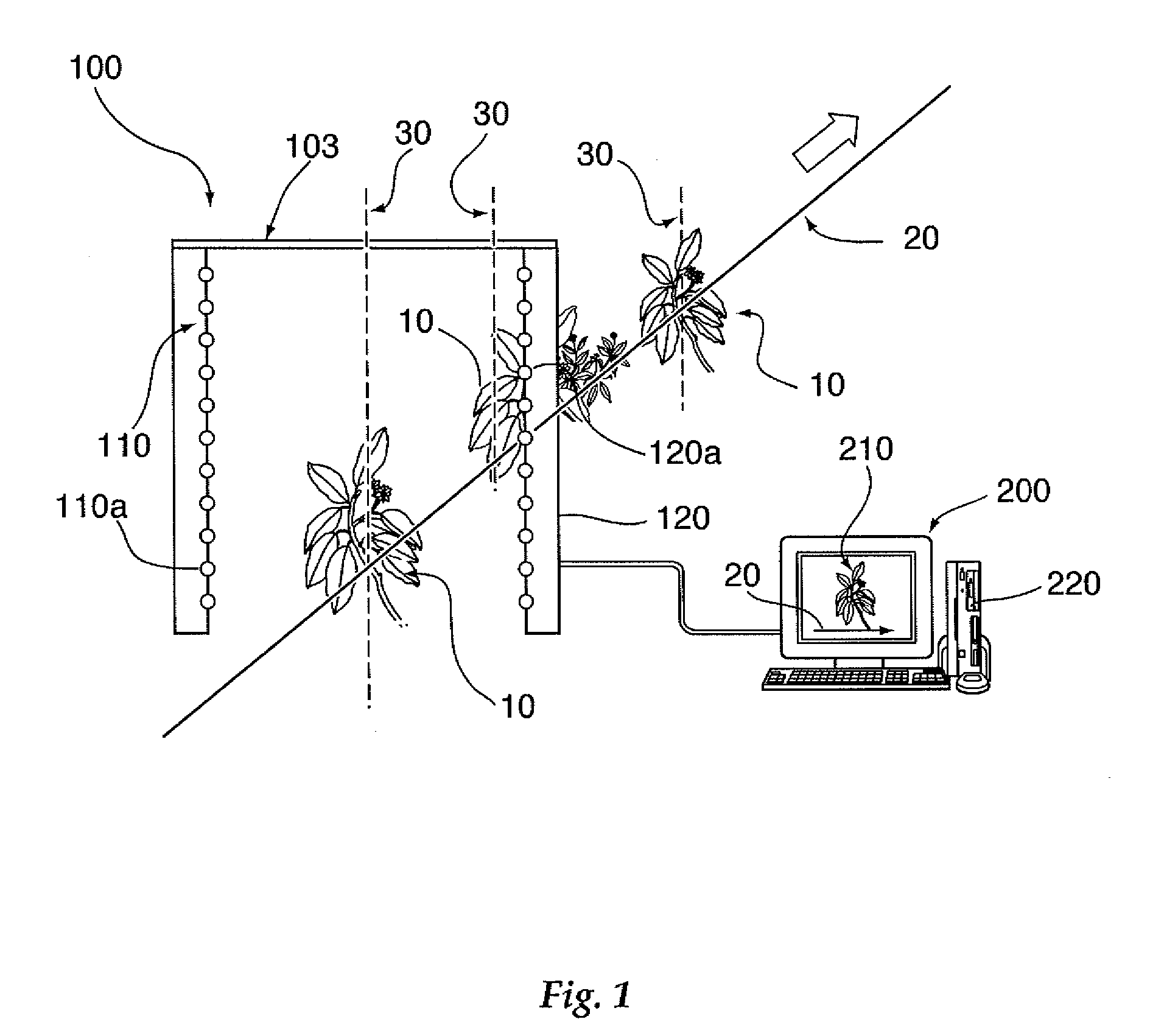
An apparatus is described for assessing plant status using biophysical and biochemical properties of the plant remotely sensed by the invention thereby allowing selective monitoring, elimination or treatment of individual plants. In a preferred embodiment, a single polychromatic emitter provides coincident light beams; one beam substantially in the visible portion of the spectrum (400 nm to 700 nm) and the other in the near infrared (NIR) portion of the spectrum (700 nm to 1100 nm). This light beam illuminates a small surface area on the ground, which may be bare ground, desired plants or undesired weeds. The beam of light may be focused, collimated or non-focused. A detector array, usually composed of a visible detector and a NIR detector, detects portions of this polychromatic light beam reflected by the surface area and provides a signal indicative of whether the detected light was reflected by a plant or by some non-plant object such as soil. A controller analyzes this signal and, assuming a plant is detected, responds by activating a device to take some action with respect to the plant or stores the analyzed signal with corresponding DGPS position in the controller's memory for later analysis. A number of actions may be taken by the controller. For instance, if the plant is a weed, the desired action might be to spray herbicide on the weed. Or, if the plant is a crop that is determined to be lacking in nutrient, the desired action may be to apply fertilizer. Additionally, if the plant under test is a turf landscape, such as found on golf courses and sporting fields, plant biomass may be mapped and geo-located using GPS for later, comparative analysis.
Owner:KYLE H HOLLAND TRUSTEE OF THE MARANATHA TRUST DATED JULY 30 2013
Glyphosate-tolerant 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthases
InactiveUSRE39247E1Reduce amount of overproductionGlyphosate toleranceSugar derivativesTransferasesPhosphateGenetically modified crops
Genes encoding Class II EPSPS enzymes are disclosed. The genes are useful in producing transformed bacteria and plants which are tolerant to glyphosate herbicide. Class II EPSPS genes share little homology with known, Class I EPSPS genes, and do not hybridize to probes from Class I EPSPS's. The Class II EPSPS enzymes are characterized by being more kinetically efficient than Class I EPSPS's in the presence of glyphosate. Plants transformed with Class II EPSPS genes are also disclosed as well as a method for selectively controlling weeds in a planted transgenic crop field.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Sensor system, method, and computer program product for plant phenotype measurement in agricultural environments
ActiveUS20070044445A1Easy to operateAccurate locationMowersUsing optical meansEngineeringReady to use
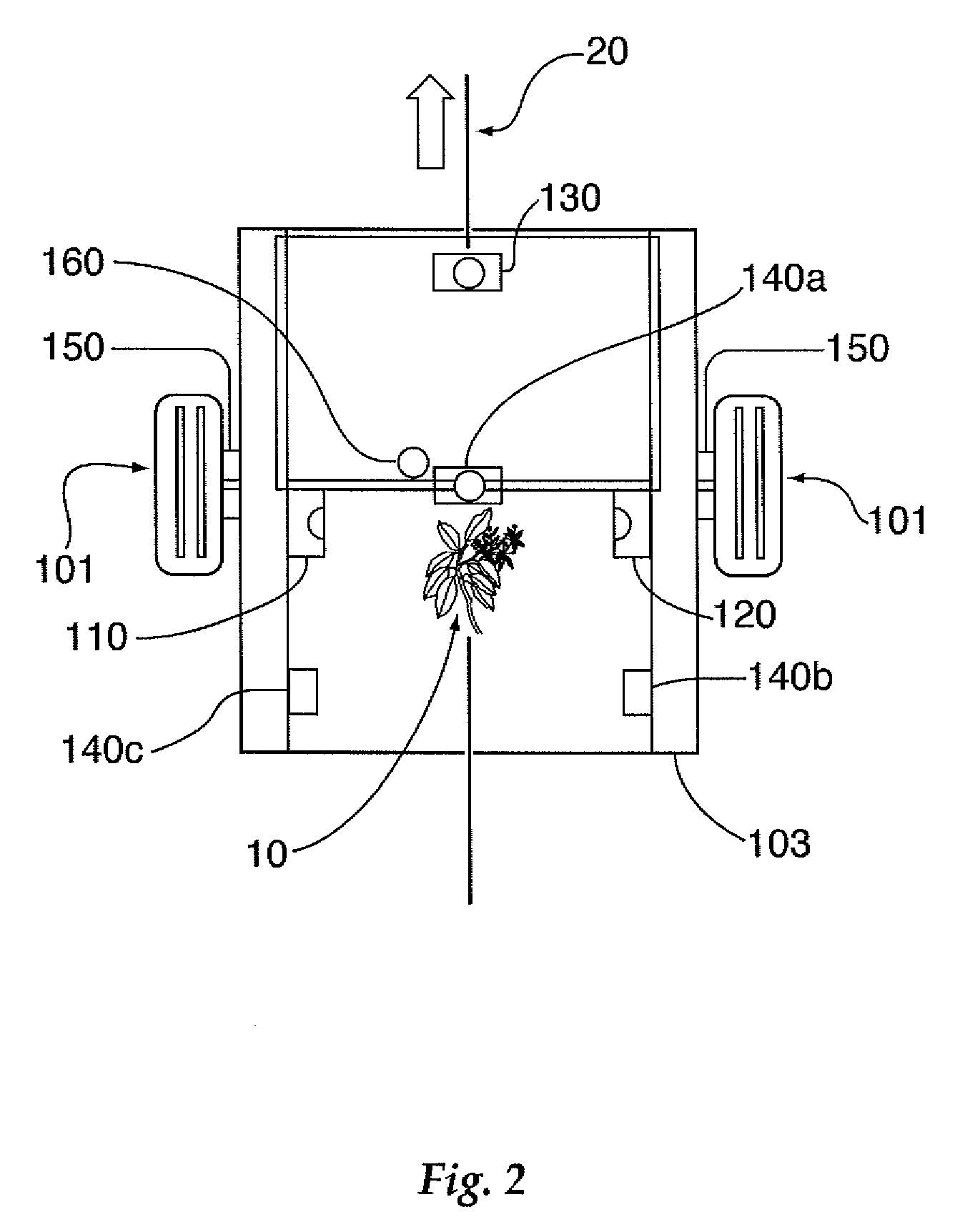
A sensor system, method, and computer program product for determining physical characteristics of individual plants within a row located in an agricultural environment is provided. Embodiments of the present invention include, but are not limited to, a sensor assembly including a plurality of emitters and a corresponding plurality of receivers disposed substantially opposite one another such that the receivers may receive a plurality of signals emitted by said emitters to generate a binary profile image of each plant within a row of plants positioned along a row axis. Embodiments of the present invention also include supplementary sensors for determining other plant characteristics including leaf pattern and plant location along the row axis. The method and computer program product embodiments of the present invention may also differentiate selected plants of interest from invasive or weed species using the outputs of the sensor device of the present invention.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Adherent biologically active ingredient carrier granule
InactiveUS20070280981A1Reduce total usageEasy to useBiocideAnimal repellantsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTMoisture
A composition is provided that includes an inventive biologically active ingredient carrier granule that adheres to the surface of plants, grasses, and weeds using a moisture-active coating, illustratively including gum Arabic, guar gum, gum karaya, gum tragacanth and locust bean gum. Upon application of the inventive granule onto a plant surface, water from precipitation, irrigation, dew, co-application with the granules from special application equipment, or guttation water from the plant itself, provides sufficient moisture for adherence of the granule to the plant surface.
Owner:THE ANDERSONS
Clear-white gold needle mushroom cultivation method
InactiveCN101366346AAvoid pollutionNo diseaseBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationSucroseSaccharum
The invention discloses a method for cultivating pure white needle mushrooms. The method comprises the following steps: a strain is prepared; a culture material is prepared; bagging and sterilization are carried out; inoculation is carried out; a mycelium is cultured; nutrition, humidity, temperature, light, air and other culture conditions are strictly controlled during a fruiting period; and harvesting is carried out in an optimum period. the formulation of the culture material is 0 to 32 percent of weed tree sawdust, 0 to 93 percent of cotton seed hulls or wheat straw, straw, corncob and other crop straw, 0 to 20 percent of wheat bran, 0 to 10 percent of corn meal, 0 to 10 percent of soybean meal, 0 to 1 percent of calcium carbonate, 0 to 0.2 percent of monopotassium phosphate, 0 to 0.2 percent of magnesium sulfate, 1 to 1.2 percent of sucrose, 0 to 10 percent of rice bran, 0 to 1 percent of plaster and 0 to 0.02 percent of urea. Quicklime and wettable carbendazim are added during the preparation of the culture material so as to prevent the pollution of undesired bacteria. The technical proposal aims to select proper breeds, popularize local large scale planting and improve cultivation benefit.
Owner:WUHU YESHULIN BIOTECH
Herbicide resistant rice
InactiveUS6274796B1Growth inhibitionGood flexibilityBiocideMutant preparationRice plantsAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
Rice plants are disclosed with two separate, but synergistic mechanisms for resistance to herbicides that normally inhibit a plant's acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) enzyme. The herbicide resistance of plants with both resistance mechanisms is substantially greater than one would expect from a simple combination of the two types of resistance. The first of the two resistance mechanisms is a metabolic pathway that is not fully understood, but that does not itself involve a mutant AHAS enzyme. The second resistance mechanism is a mutant AHAS enzyme, an enzyme that shows direct resistance to levels of herbicide that normally inhibit the enzyme, in both in vivo and in vitro assays. Besides controlling red rice, many AHAS-inhibiting herbicides also effectively control other weeds that are common in rice fields. Several of these herbicides have residual activity, so that a treatment controls both existing weeds as well as weeds that sprout later. No herbicide currently available for use on rice has residual activity against a broad spectrum of weeds including red rice. With effective residual activity against red rice and other weeds, rice producers now have a weed control system superior to those currently used.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Spin milling type multifunctional machine for deeply ploughing and crushing ridges
InactiveCN101971723AImprove permeabilityIncrease productionSpadesTilling equipmentsGear wheelAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a spin milling type multifunctional machine for deeply ploughing and crushing ridges, which is based on a tractor. A hydraulic mechanism and a linking spin milling drill bit device or a cultivation component is arranged on a rear frame of the tractor; the linking spin milling drill bit device is provided with one or more drill bit shafts; spiral hinges are arranged on the drill bit shafts and provided with apical teeth; the linking spin milling drill bit device is provided with a device for preventing a straw from being wound; the hydraulic mechanism drives a spin milling drill bit to move up and down; and a gearbox drives the spin milling drill bit by a connecting rod and a gear. According to the spin milling type multifunctional machine, the drill bit enters intosoil and then vertically cuts, spin mills and crushes the soil and ensures that the soil is automatically suspended to form the ridges; the soil crushing section of the crushed ridge is T-shaped; thelower part of the compacted soil on the ground is in a U-shaped groove, so that the whole layer of the soil is in a loosing state during cultivation; and in addition, the invention plays roles of covering and replacing the soil, increases an active layer, improves the capabilities of preserving moisture and fertility and the permeability of the soil, benefits the utilization of deep growing of the crop root system to water and fertilizer, relatively reduces pests and weeds and ensures that the crop is easy to obtain high and stable yield.
Owner:GUANGXI WUFENG MACHINERY CO LTD
Precise targeted spraying and weeding device
InactiveCN101961003AReduce dosageReduce pollutionInsect catchers and killersPollutionElectromagnetic valve
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural plant protection machinery, and provides a precise targeted spraying and weeding device. The spraying and weeding device comprises a farmland information acquisition and processing system, a spraying system and a control system. The spraying and weeding device finishes acquisition and processing of images in real time and identifies crops and weeds; a DSP (digital signal processor) sends weed positions and density information acquired after the images are processed to an ARM (advanced RISC machine) processor; and the ARM processor realizes combination of different spray heads and opening of an electromagnetic valve by combining the received speed, flow and pressure information and controlling so as to perform precise targeted spraying on the weeds. By adopting a targeted spraying weedicide mode, the device reduces weeding labor and consumption of pesticide, saves the cost and relieves the pollution of the pesticide to the environment.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Controlled-release pesticide fertilizer and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105061084AThe effect of increasing production is obviousLow input costFertilizer mixturesPotassiumInsect pest
The invention discloses controlled-released pesticide fertilizer and preparing method thereof. The controlled-released pesticide fertilizer comprises, by mass, 0.001-15% of effective component A, 4%-45% of nitrogen, 1%-15% of phosphorus, 1%-25% of potassium, 0.1%-5% of microelement, 0.01%-10% of coagulator, 0.01%-10% of binder, 0.15-10% of surfactant and the balance packing. The preparing method of the controlled-released pesticide fertilizer comprises is simple and comprises the steps of preparing of liquid materials, preparing of powder materials and fluidized bed granulating. The controlled-released pesticide fertilizer can control the occurrence of damage caused by diseases, insect pests and weeds can be controlled in all the seasons of crop growth and meet the supply of nutrient substances needed in all the seasons of crop growth, production and use are safe, labor and cost are reduced, and the application amount and the use frequency of pesticides and the fertilizer in the period of crop growth can be reduced.
Owner:XIAN LEAD LIGHT BIOTECH CO LTD
Penoxsulam as a turfgrass, vineyard and orchard floor herbicide
Penoxsulam, 2-(2,2-difluoroethoxy)-N-(5,8-dimethoxy [1,2,4]-triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonamide, is useful in controlling broadleaf weeds and sedges in turfgrass and in vine and orchard floors.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
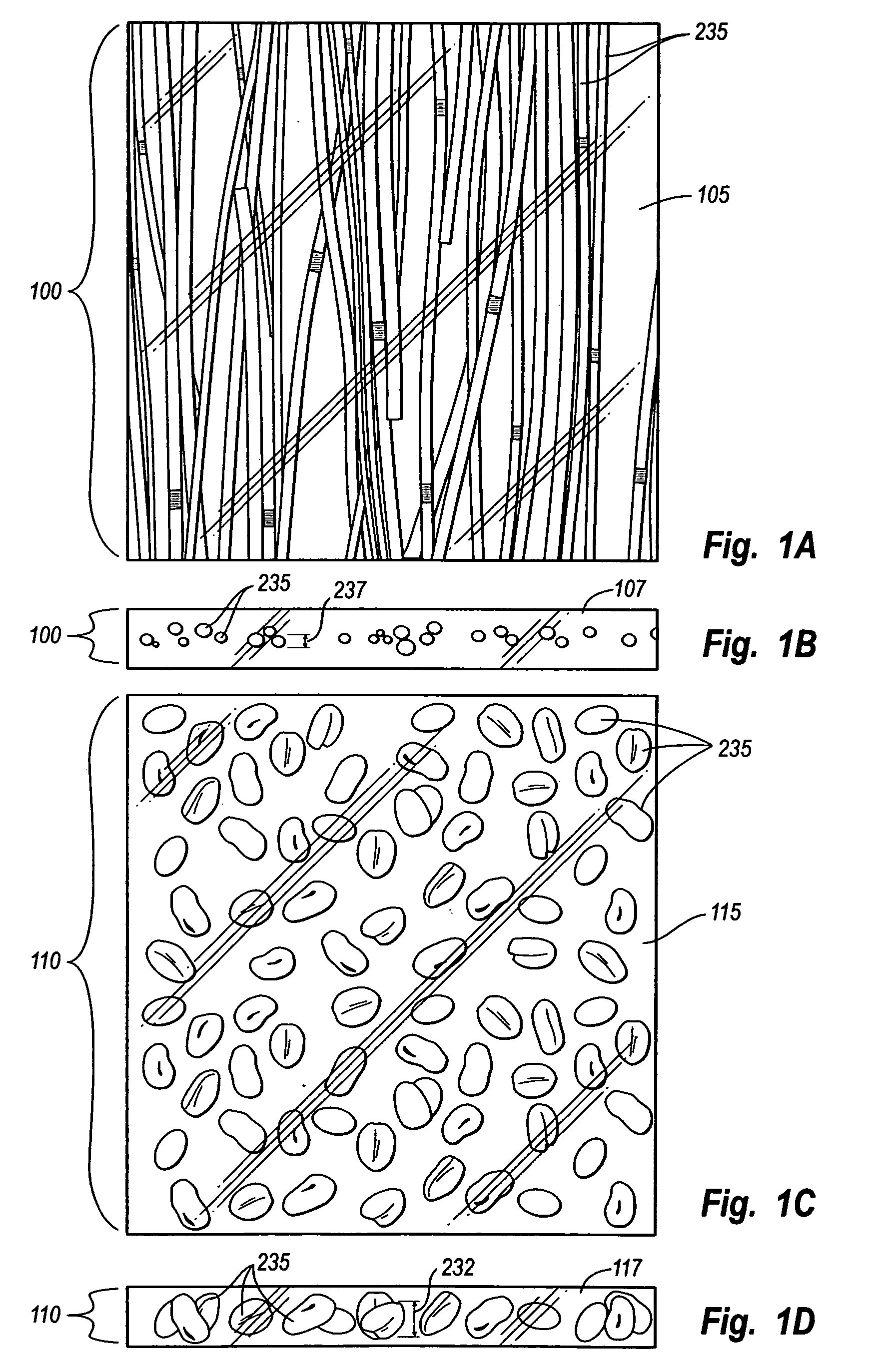
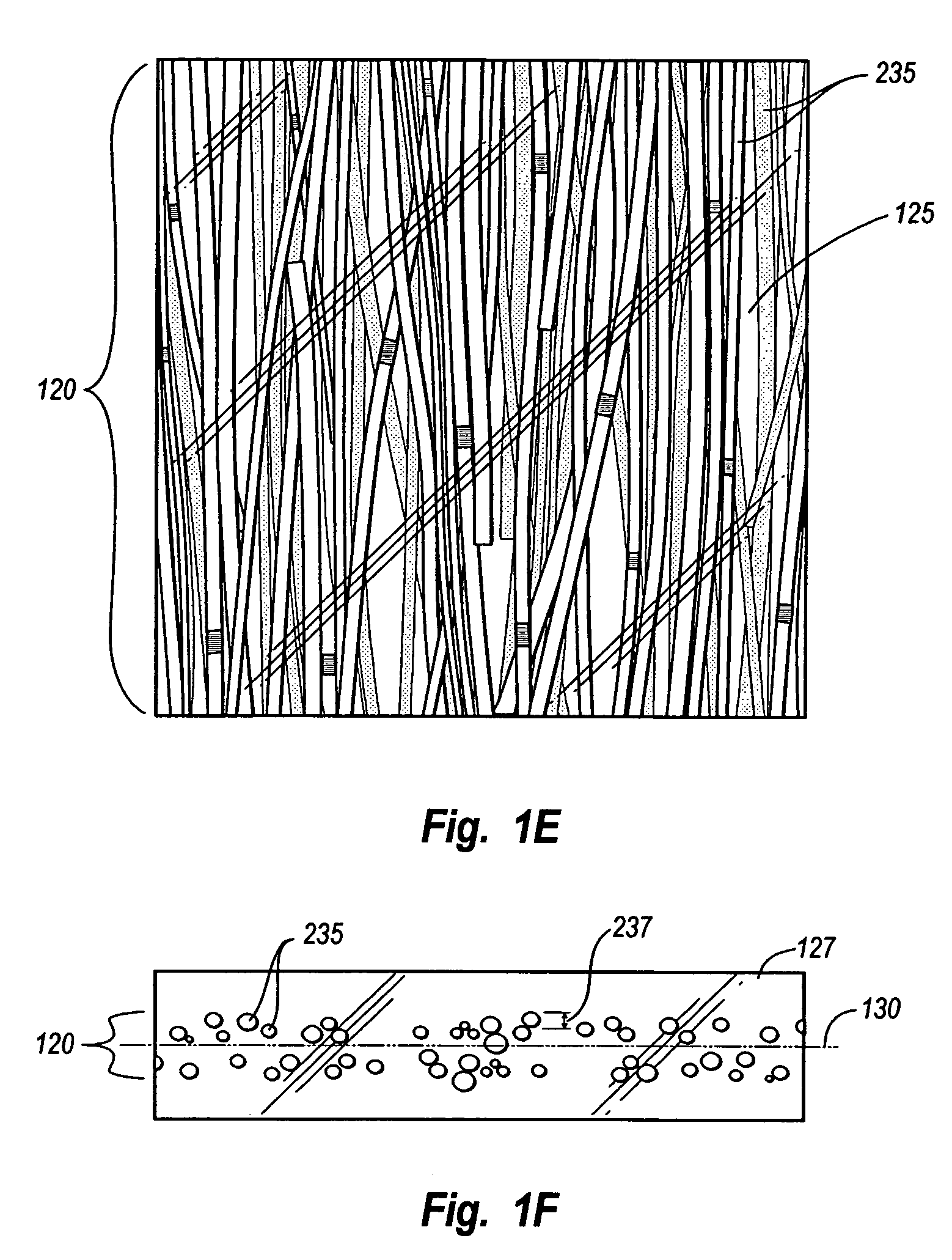
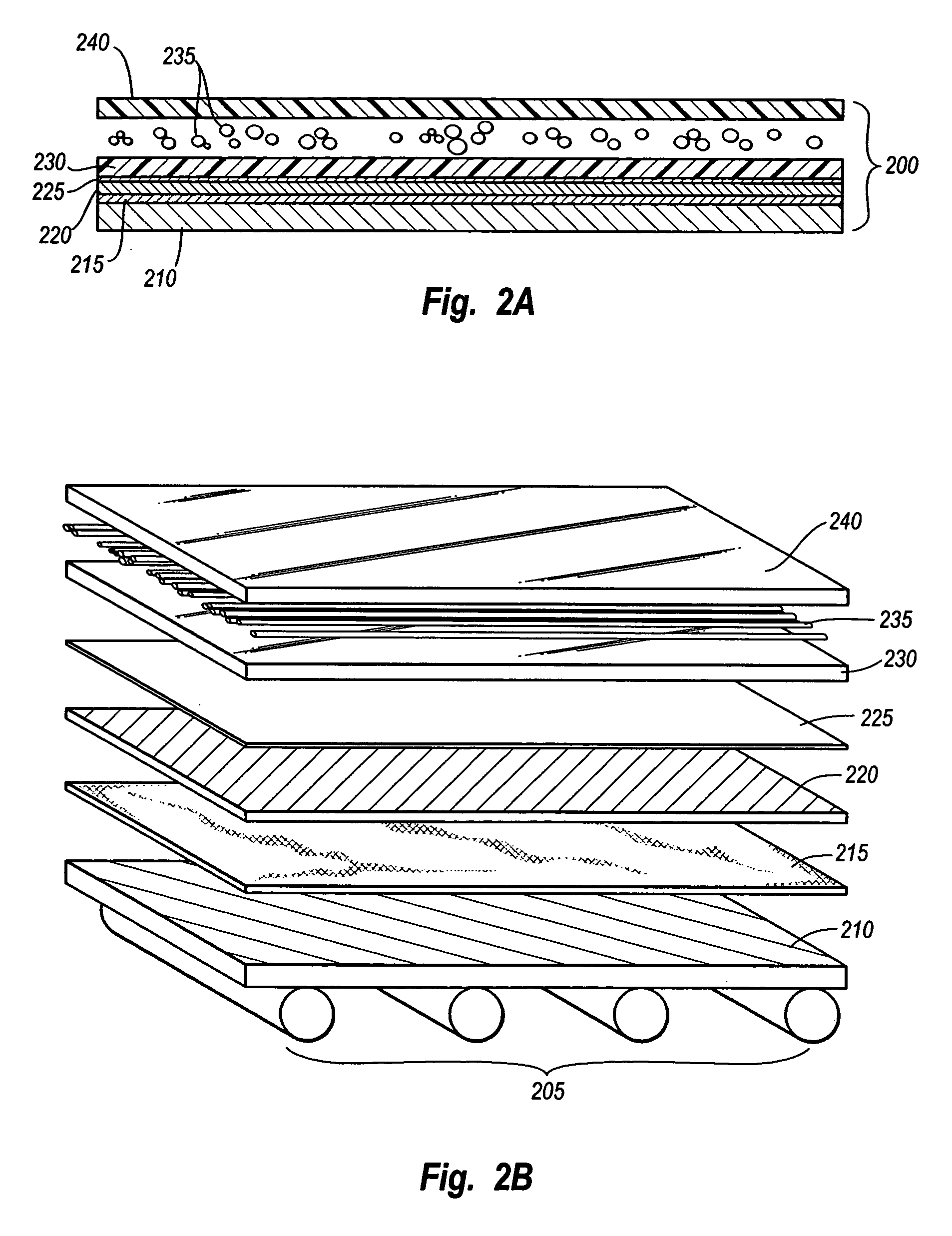
Architectural laminate panel with embedded compressible objects and methods for making the same
InactiveUS7008700B1Significantly trapping airPicture framesDecorative surface effectsCompressible materialEngineering
A decorative laminate panel comprises compressible objects embedded inside, wherein the compressible objects would be flattened in unnatural shapes under conventional processes. For example, an exemplary decorative laminate product comprises thatch reed, willow reed, bamboo, weeds, grasses, twigs and branches of a tree or bush, beans, and so forth. In at least one exemplary implementation of the present invention, an extruded sheet, such as PETG or polycarbonate, is softened and melted around the compressible materials such that the compressible materials do not deform. Imperfections in the decorative laminate panel can be easily removed, thereby allowing for producing a high quality decorative laminate panel with high efficiency and relatively low cost compared with conventional methods and materials.
Owner:3FORM
4-benzoyl pyrazole compound with herbicidal activity
ActiveCN103980202AGood choiceImprove securityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsHydrogenStructural formula
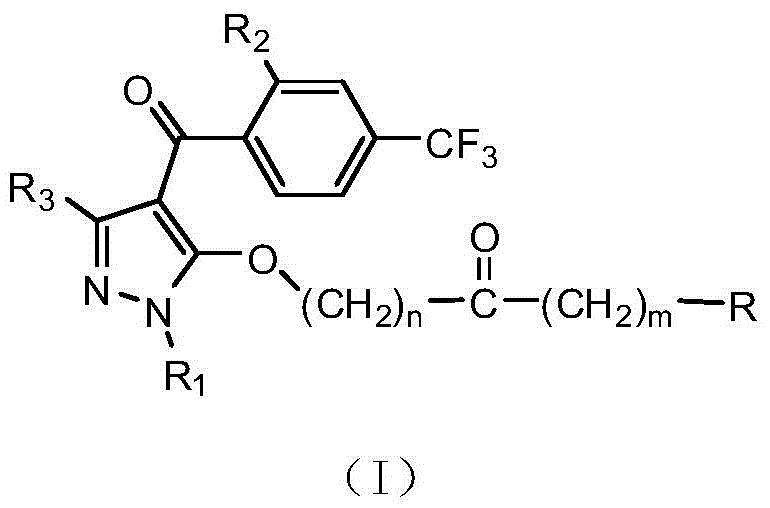
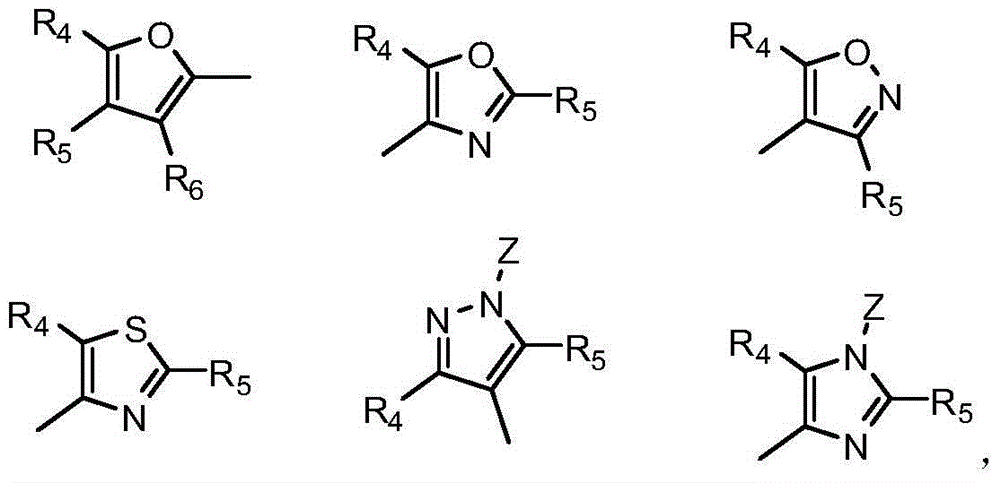
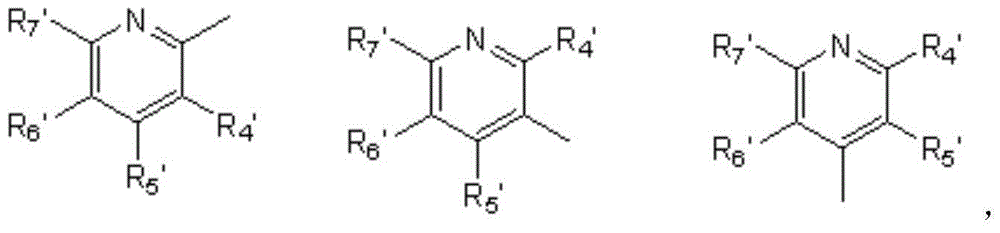
The invention relates to a 4-benzoyl pyrazole compound with herbicidal activity. The structural formula of the 4-benzoyl pyrazole compound with the herbicidal activity is as shown in specifications, wherein R1 in the structural formula is selected from hydrogen, methyl or ethyl, R2 in the structural formula is selected from methylsulfonyl, methoxyl, methylthio, fluorine, chlorine or cyan, R3 in the structural formula is selected from hydrogen, methyl, methyl fluoride, difluoromethyl or trifluoromethyl, R in the structural formula is selected from a five-membered heteroaromatic ring, a six-membered heteroaromatic ring, C1-C6 alkoxyl, aromatic hetero-oxy, six-membered aryloxy or six-membered aromatic amino, and hydrogen in the C1-C6 alkoxyl can be replaced by fluorine or chlorine; m and n are selected from 0 or 1 and cannot be 1 at the same time. A series of relatively efficient weed killers and plant growth regulators with relative good selectivity and safety are synthesized by introducing a fluorine-containing functional group to a pyrazole 3-site and chemically modifying a pyrazole 5-site.
Owner:QINGDAO KINGAGROOT CHEM COMPOUNDS CO LTD
Methods and compositions for controlling weeds
ActiveUS20070074303A1Simple methodBiocideClimate change adaptationGlyphosateTransformation efficiency
Methods and compositions are provided related to improved plants that are tolerant to more than one herbicide. Particularly, the invention provides plants that are tolerant of glyphosate and are tolerant to at least one ALS inhibitor, and methods of use thereof. The glyphosate / ALS inhibitor-tolerant plants comprise a polynucleotide that encodes a polypeptide that confers tolerance to glyphosate and a polynucleotide that encodes an ALS inhibitor-tolerant polypeptide. In specific embodiments, a plant of the invention expresses a GAT polypeptide and an HRA polypeptide. Methods to control weeds, improve plant yield, and increase transformation efficiencies are provided.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
Herbicide composition containing sulfonylurea, pyridine and cyhalofop-butyl and use thereof
ActiveCN101530104AGood synergyImprove weed control effectBiocideAnimal repellantsSulfonylureaBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a herbicide composition, containing sulfonylurea or salt thereof, pyridine and cyhalofop-butyl as active ingredients with the weight ratio of 0.1 to 5: 0.1 to 10: 0.1 to 10. Compared with herbicides with single dose, the weed control effect of the herbicide composition of the invention is obviously improved, thereby reducing the using dosage, reducing the influence degreefor the environment while reducing the pesticide cost, simultaneously enlarging weed control spectrum, and having good control efficiency for Gramineae and broadleaf weeds in rice paddy fields.
Owner:SHANGYU NUTRICHEM
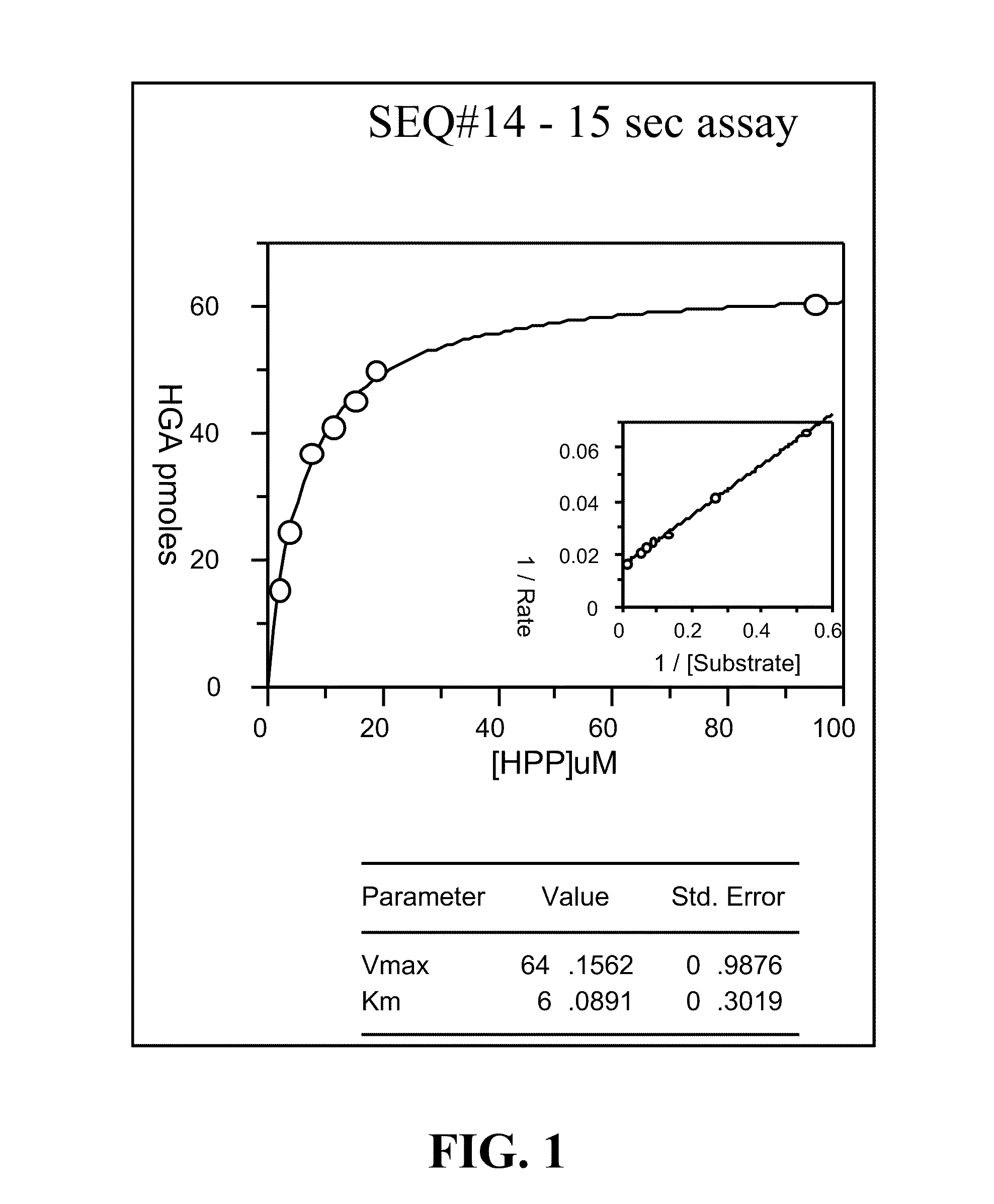
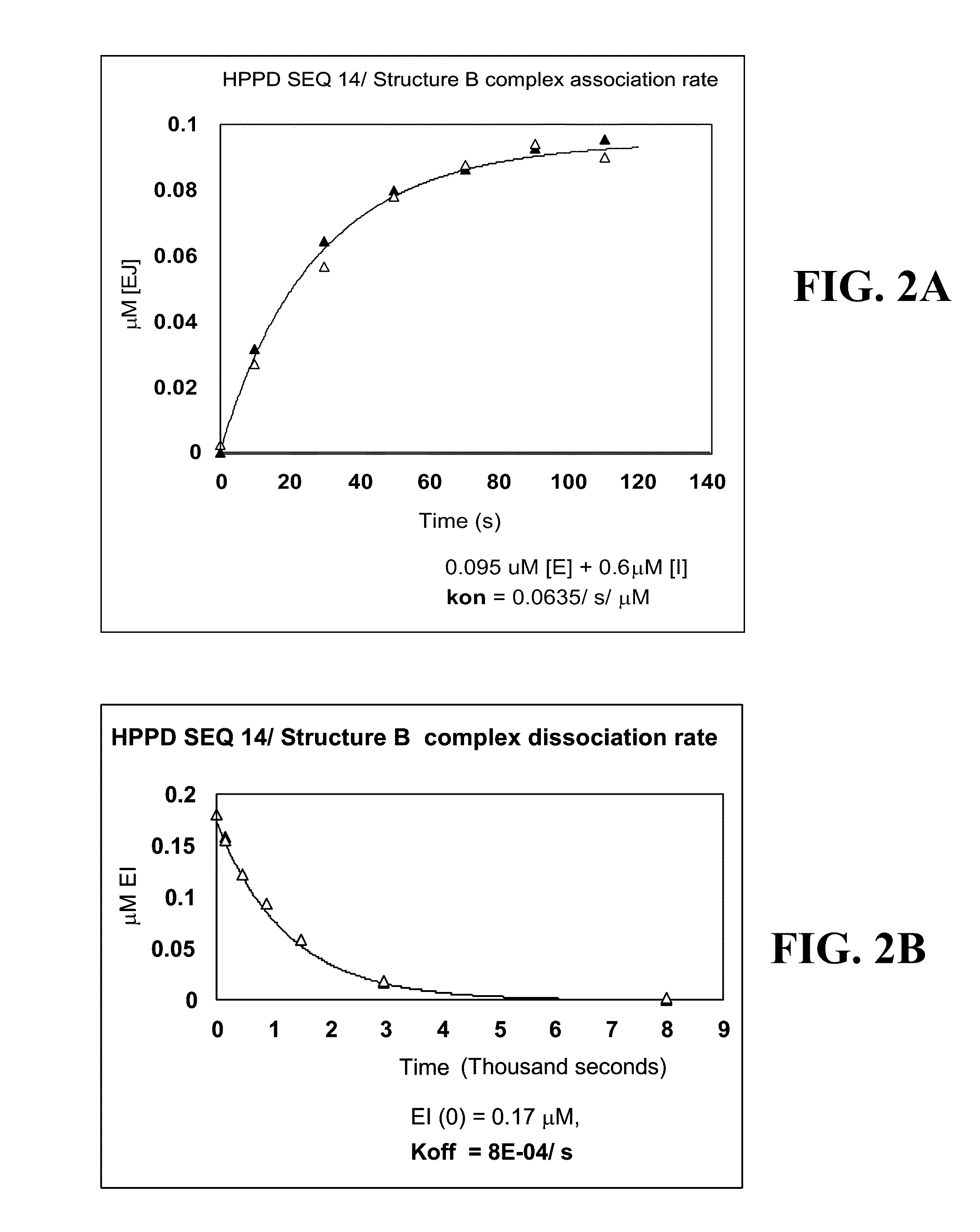
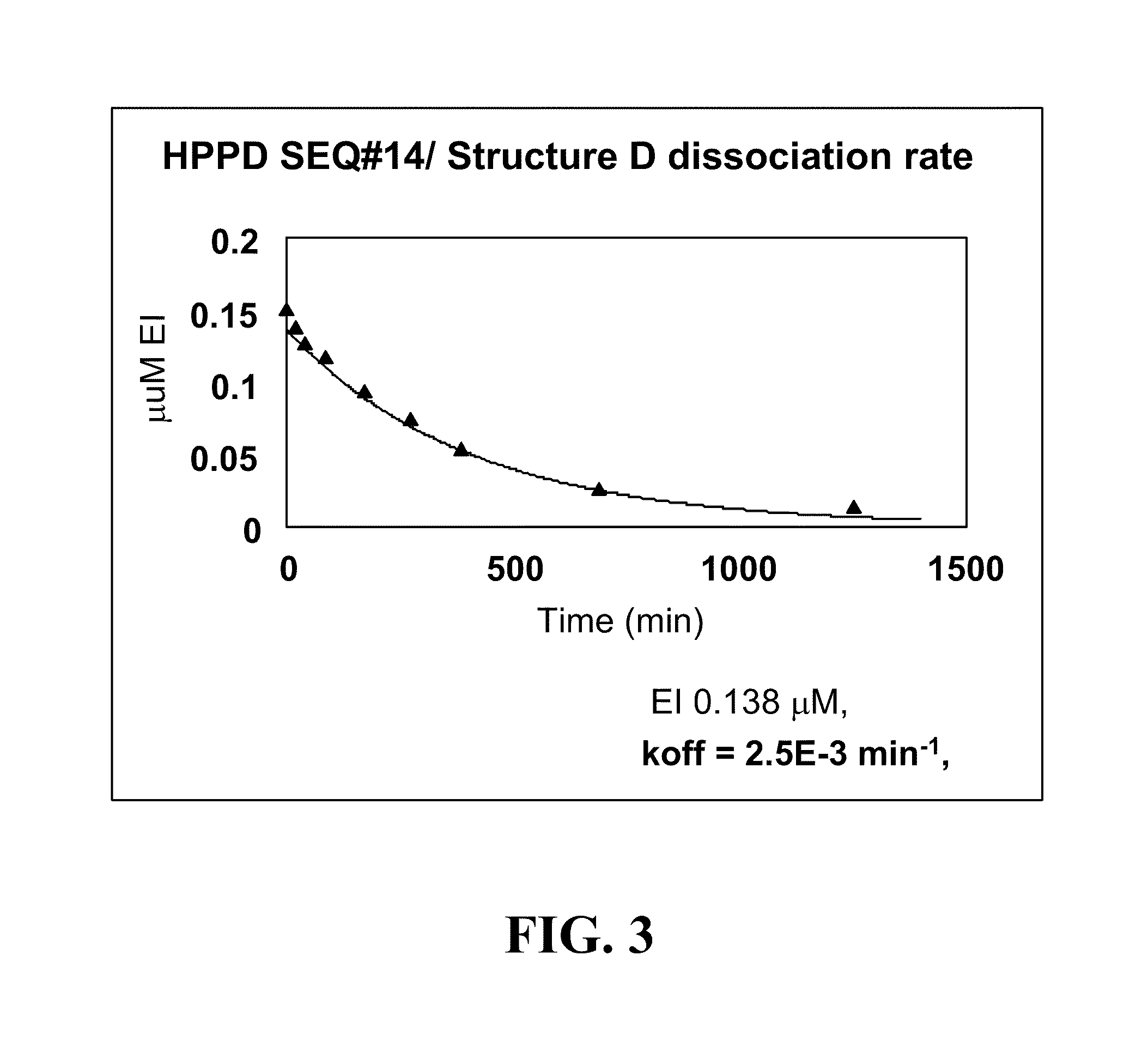
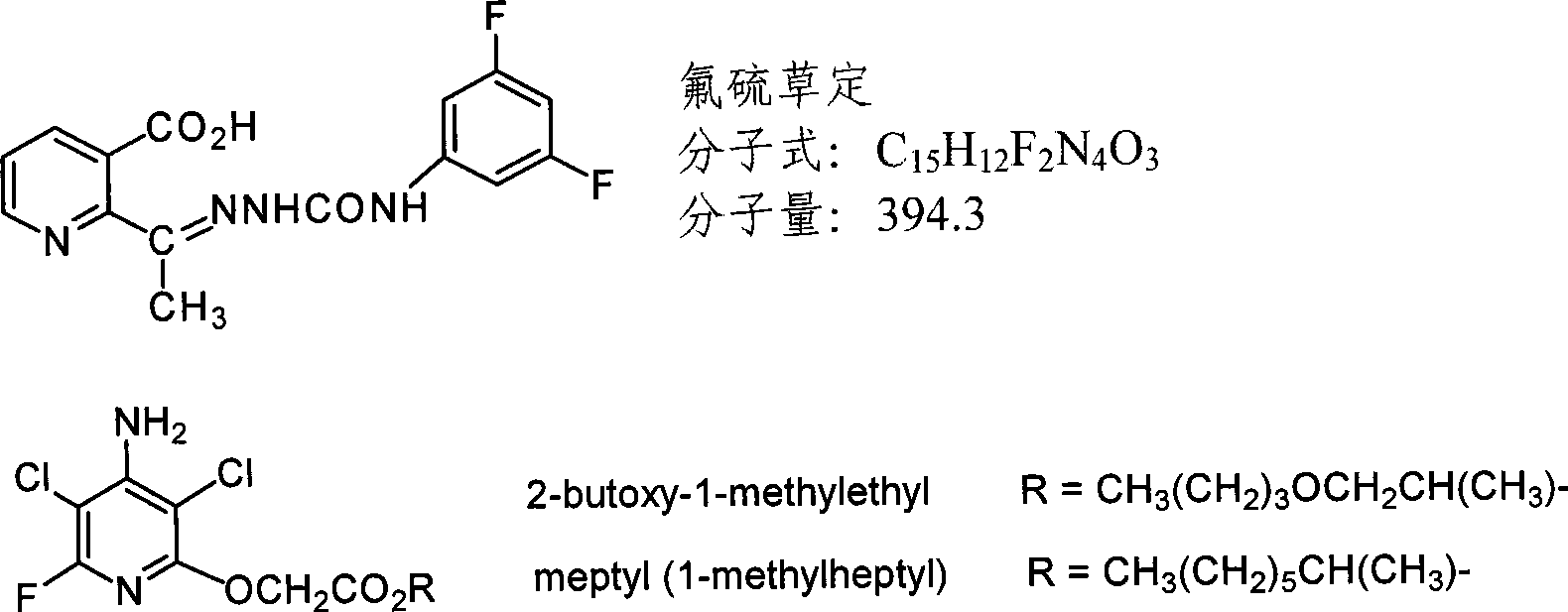
Mutant Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Polypeptides and Methods of Use
Compositions and methods for conferring hydroxyphenyl pyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) herbicide resistance or tolerance to plants are provided. Compositions include amino acid sequences, and variants and fragments thereof, for mutant HPPD polypeptides. Nucleic acids that encode the mutant HPPD polypeptides are also provided. Methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance, particularly resistance or tolerance to certain classes of herbicides that inhibit HPPD, in plants are further provided. Methods are also provided for selectively controlling weeds in a field at a crop locus and for the assay, characterization, identification and selection of the mutant HPPDs of the current invention that provide herbicide tolerance.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Herbicide composition containing sulfonylurea, pyridine and penoxsulam and use thereof
InactiveCN101530105AGood synergyImprove weed control effectBiocideAnimal repellantsEnvironment effectSulfonylurea
The invention relates to a herbicide composition, containing sulfonylurea or salt thereof, pyridine and penoxsulam as active ingredients with the weight ratio of 0.1 to 5: 0.1 to 10: 0.1 to 10. Compared with herbicides with single dose, the weed control effect of the herbicide composition of the invention is obviously improved, thereby reducing the using dosage, reducing the influence degree for the environment while reducing the pesticide cost, simultaneously enlarging weed control spectrum, and having good control efficiency for Gramineae and broadleaf weeds in rice paddy fields.
Owner:NUTRICHEM LAB CO LTD
Chloroplast transit peptides for efficient targeting of dmo and uses thereof
The invention provides for identification and use of certain chloroplast transit peptides for efficient processing and localization of dicamba monooxygenase (DMO) enzyme in transgenic plants. Methods for producing dicamba tolerant plants, methods for controlling weed growth, and methods for producing food, feed, and other products are also provided, as well as seed that confers tolerance to dicamba when it is applied pre- or post-emergence.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plantation method for tea tree
ActiveCN103947422ANutritional balancePromote absorptionBio-organic fraction processingFertilising methodsSoil propertiesDry season
The invention discloses a plantation method for a tea tree. The plantation method comprises the steps of soil preparation, soil pH value adjustment, plantation, tea garden management, weed and pest killing, dressing and pruning. The plantation method comprises the following specific steps: adjusting the soil pH value to 4.5-6.5 according to the soil property after soil preparation; after the tea tree is planted, filling gaps with seedlings and thinning the seedlings under the condition of missing of tea tree seedling plants, and performing shallow tillage and ridging before the dry season comes; when weeds grow at the ridge edges, shortening the weeds, dressing an organic fertilizer on a young tea garden according to the growth situation of the tea tree, and properly pruning the tea tree to contribute to the growth of lateral branches of the tea tree. The tea tree planted by using the plantation method is pollution-free, and no pesticides, no chemical fertilizers and no selenium-rich elements are used.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LOHAS BIOLOGICAL TECH
Cropping systems for managing weeds
The invention provides cropping systems for managing weeds in crop environments. The cropping systems comprise, in one embodiment, transgenic plants that display tolerance to an auxin-like herbicide such as dicamba. Method for minimizing the development of herbicide resistant weeds are also provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com