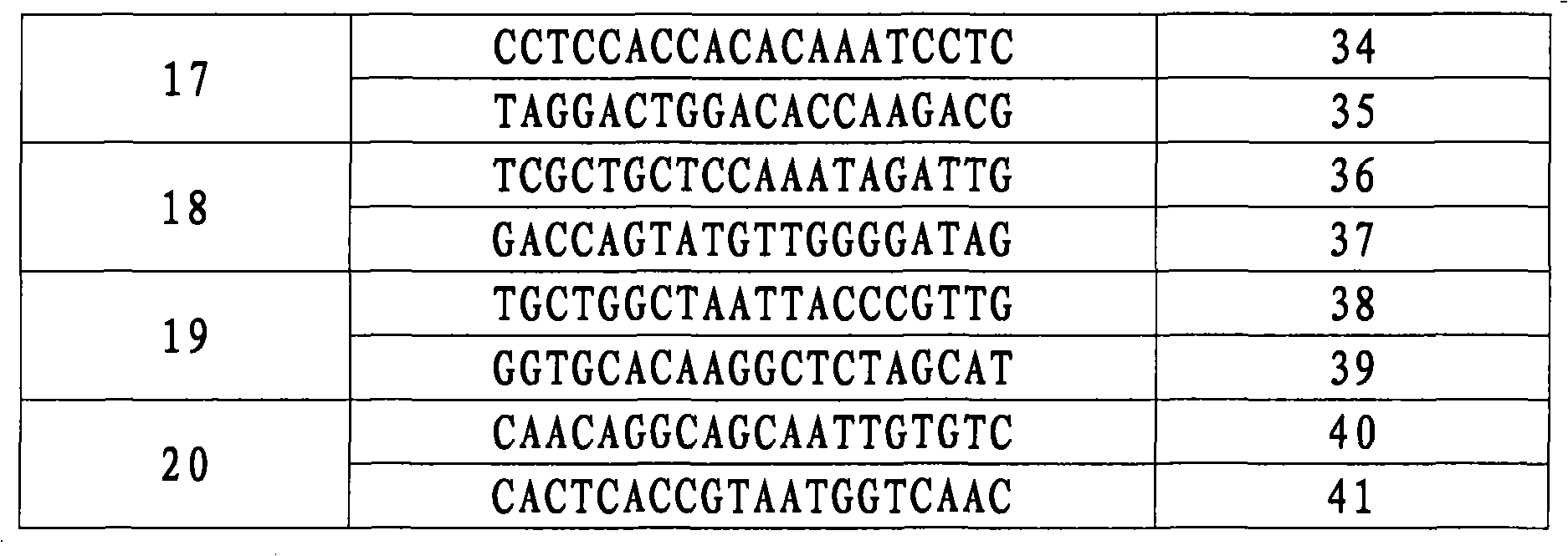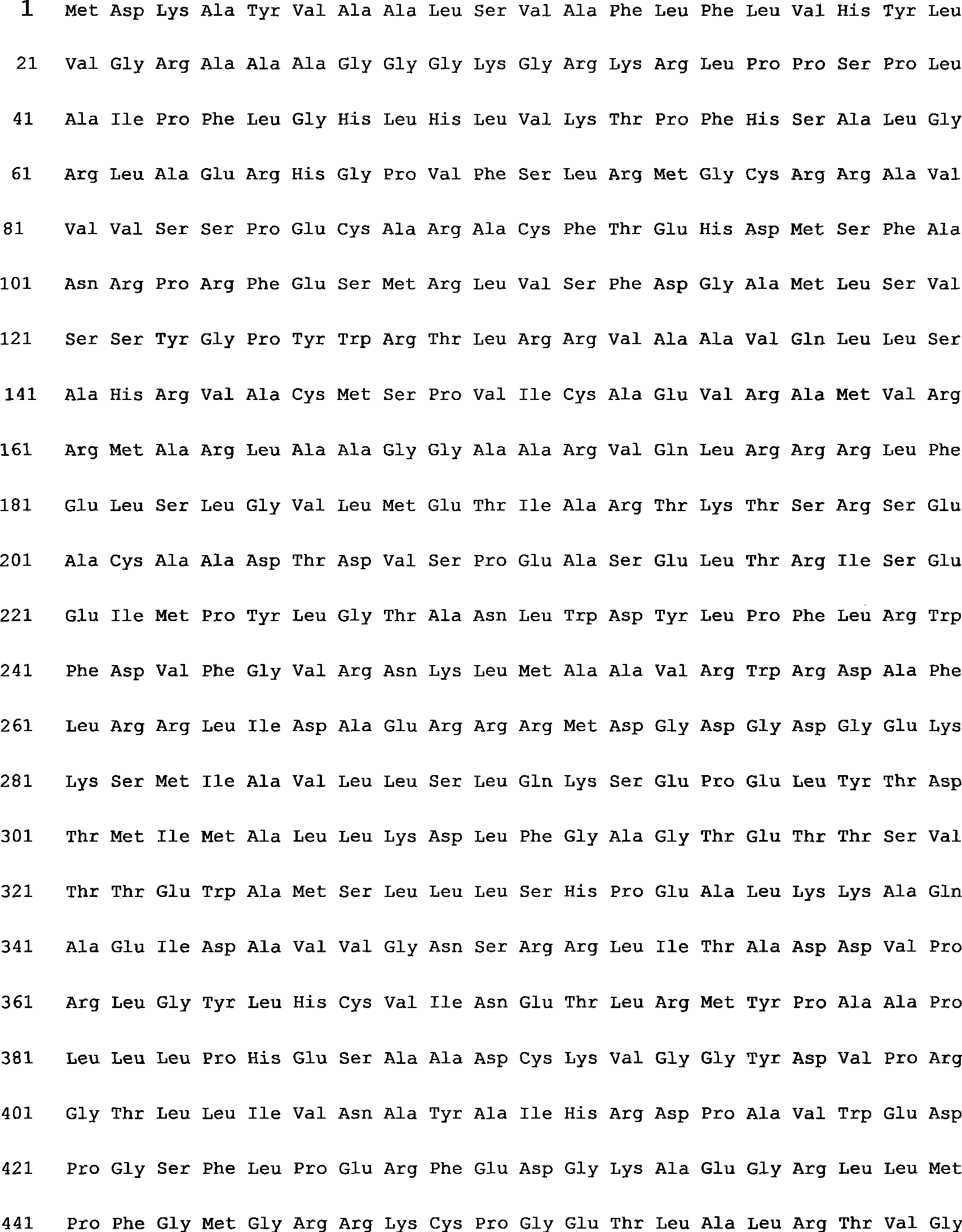Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
306 results about "Herbicide resistant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Herbicide resistance. Herbicide resistance is the inherited ability of an individual plant to survive a herbicide application that would kill a normal population of the same species. Herbicide resistance does not equate to poor performance of a herbicide.
Cropping systems for managing weeds
The invention provides cropping systems for managing weeds in crop environments. The cropping systems comprise, in one embodiment, transgenic plants that display tolerance to an auxin-like herbicide such as dicamba. Method for minimizing the development of herbicide resistant weeds are also provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
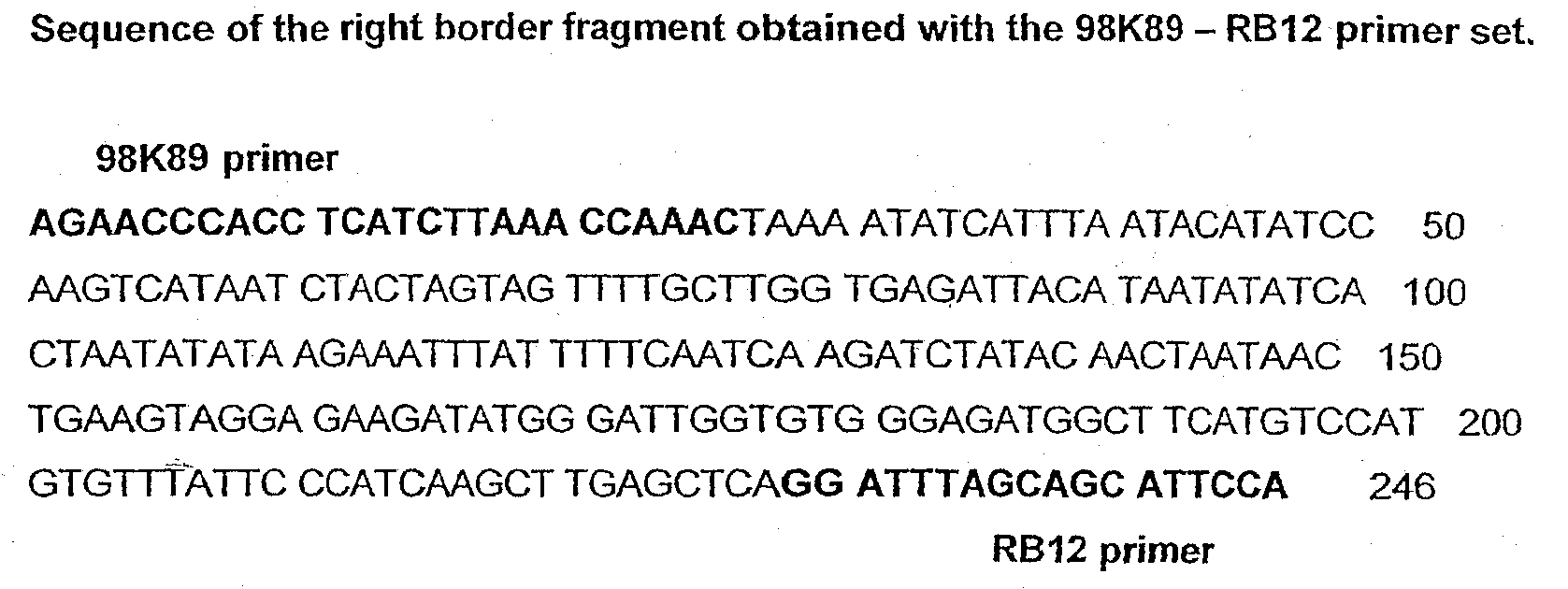
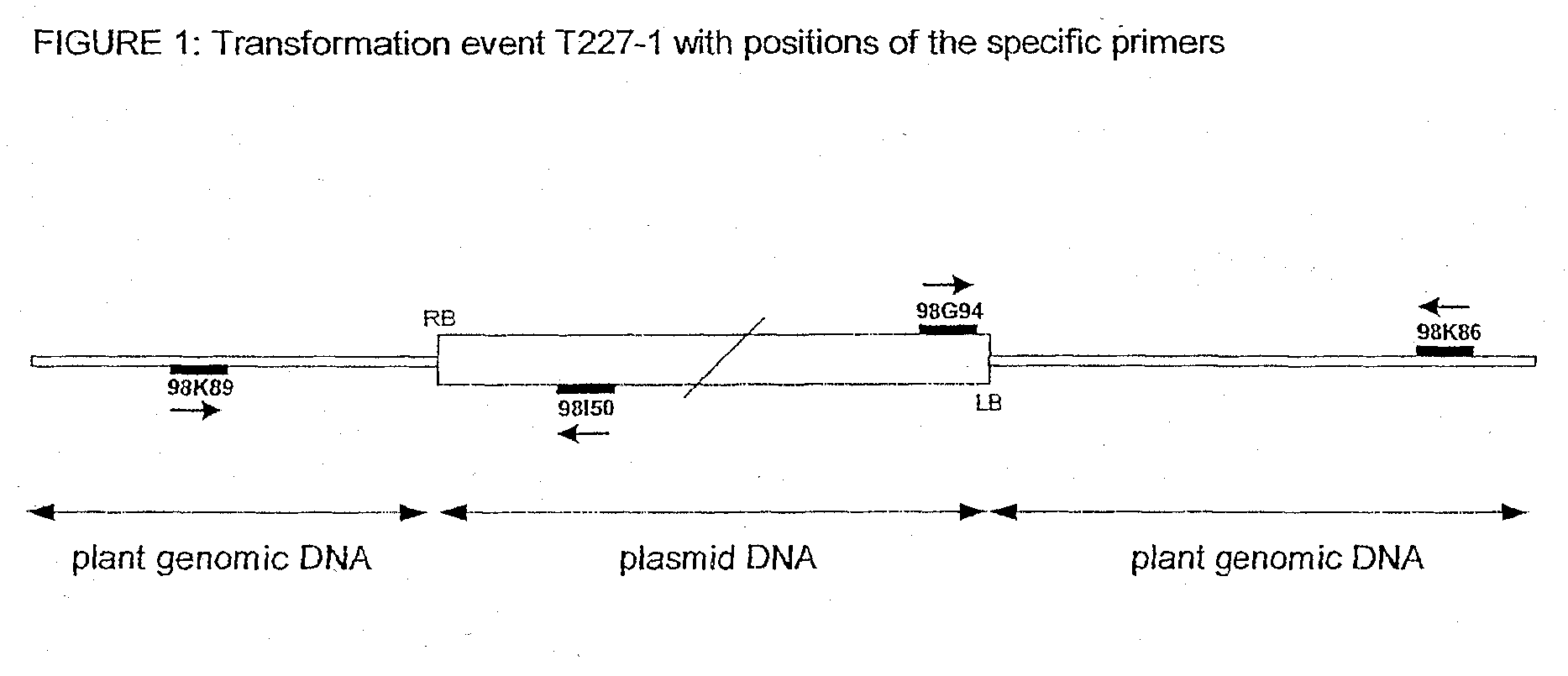
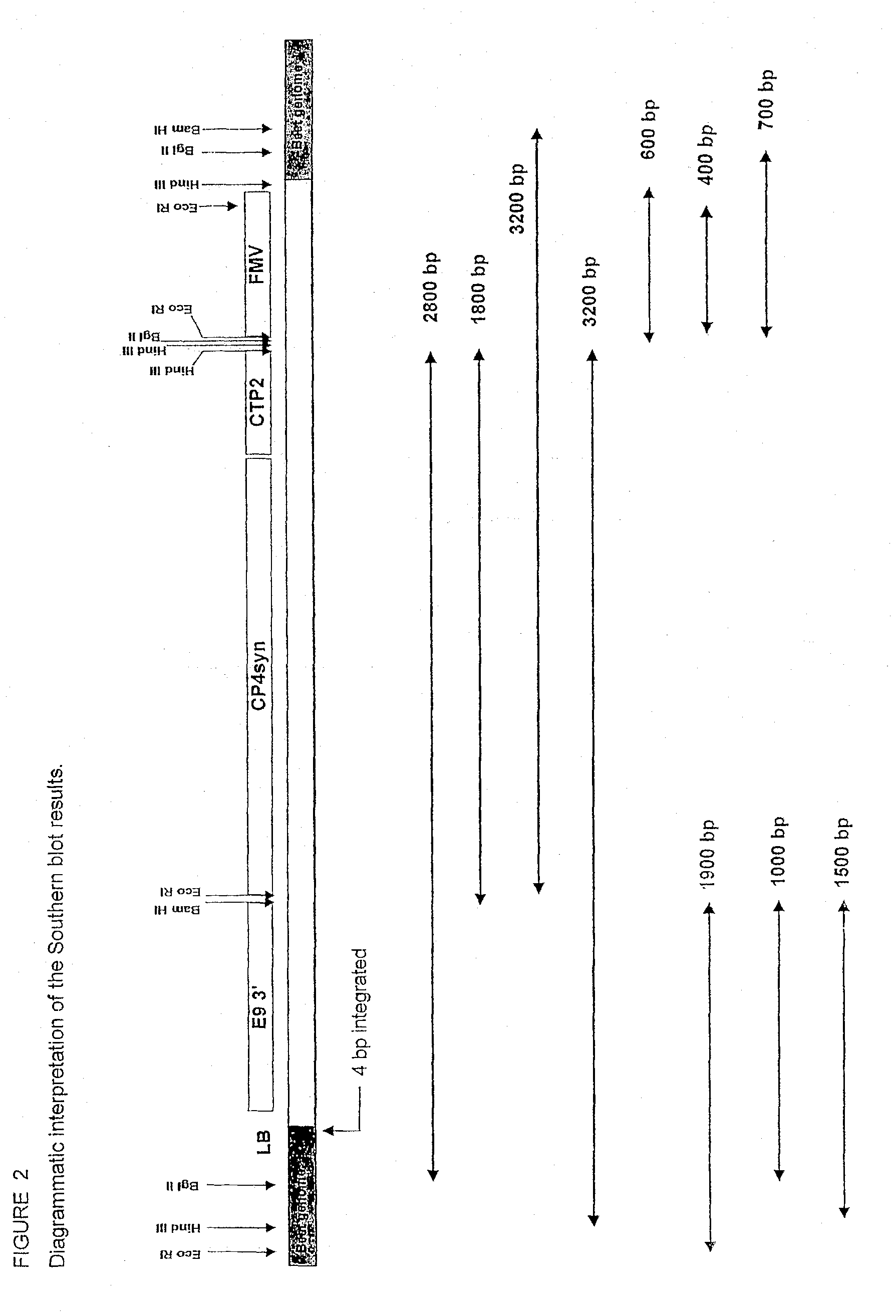
T227-1 flanking sequence
A herbicide resistant transformed sugar beet that is detectable by the specific primers developed to match the DNA sequences that flank the left and / or right border region of the inserted transgenic DNA and the method of identifying primer pairs containing plant genomic DNA / plasmid DNA. More specifically, the present invention covers a specific glyphosate resistant sugar beet plant having an insertion of the transgenic material identified as the T227-1 event. The present invention additionally covers primer pairs: plant genomic DNA / Plasmid DNA that are herein identified. Additionally, these primer pairs for either the left or the right flanking regions make an event specific test for the T227-1 insert of transgenic material.
Owner:SES EURO N V
Methods of making non-transgenic herbicide resistant plants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide.
Owner:CIBUS
Cropping systems for managing weeds
The invention provides cropping systems for managing weeds in crop environments. The cropping systems comprise, in one embodiment, transgenic plants that display tolerance to an auxin-like herbicide such as dicamba. Method for minimizing the development of herbicide resistant weeds are also provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
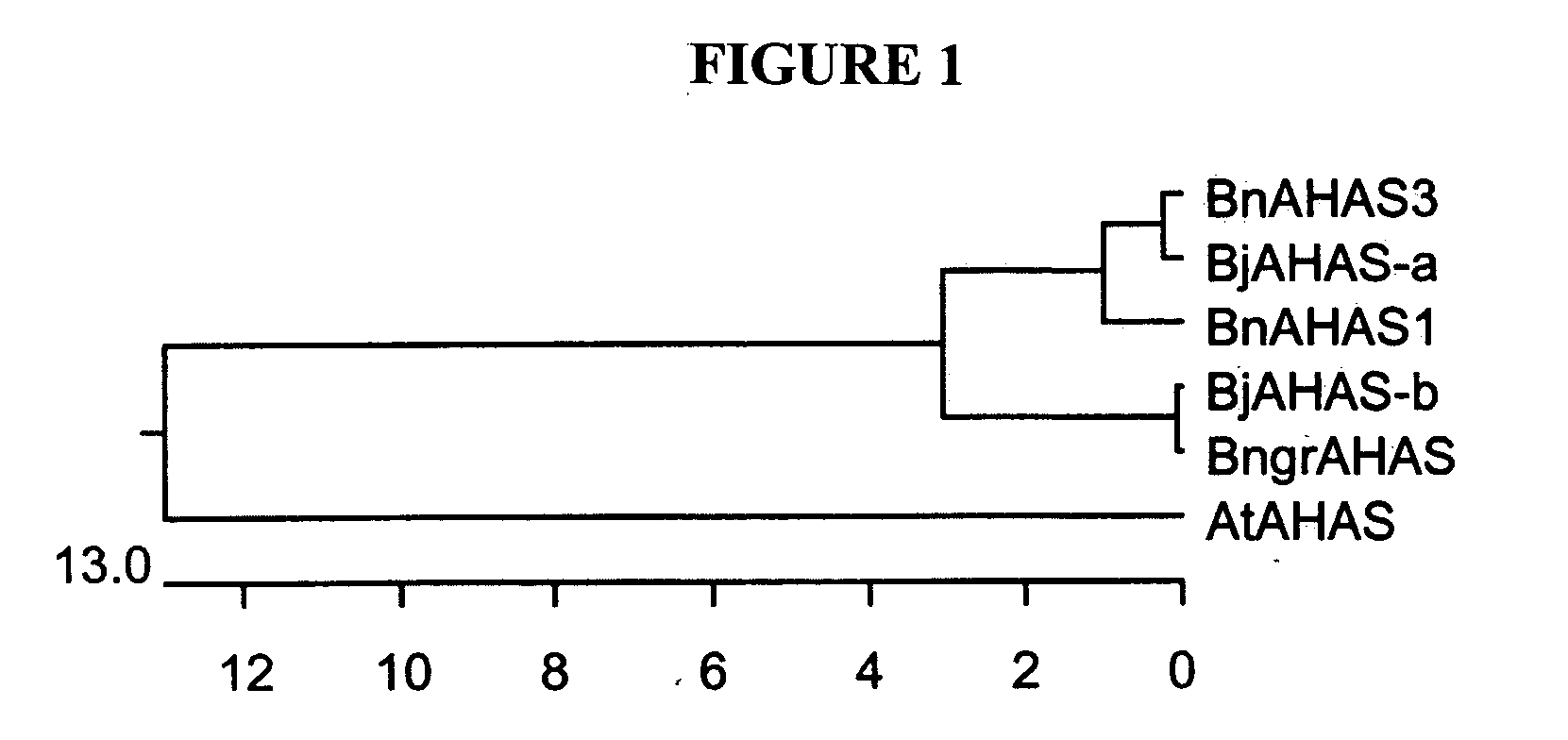
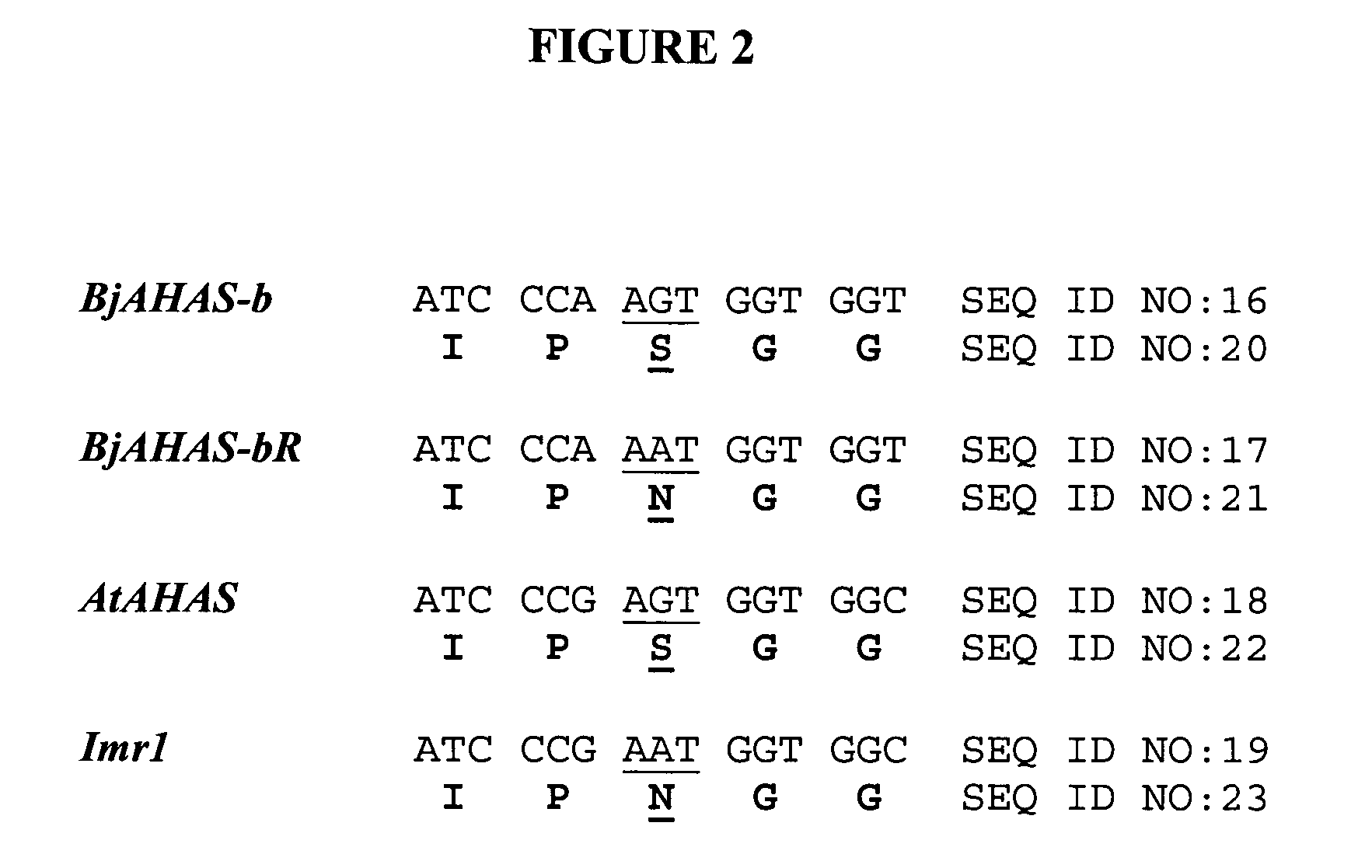
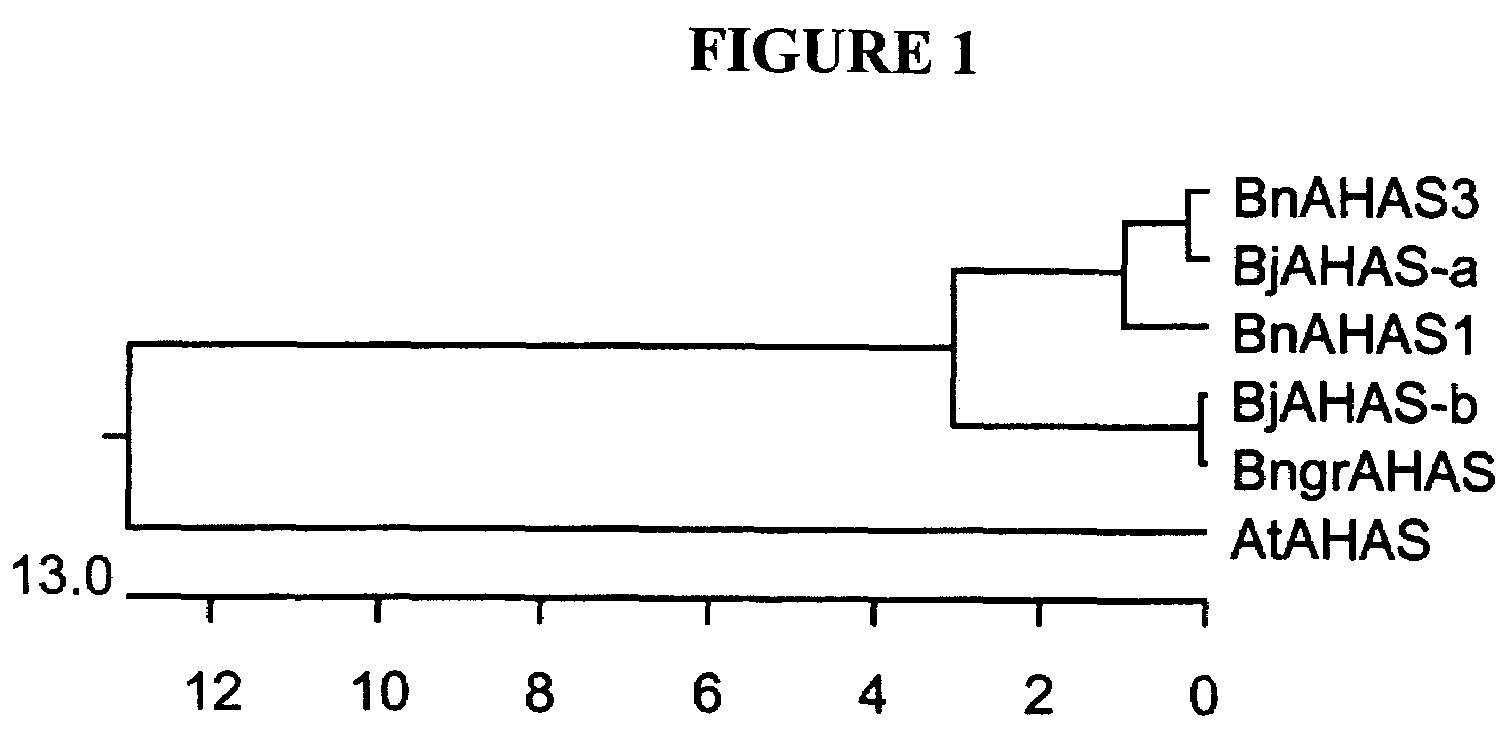
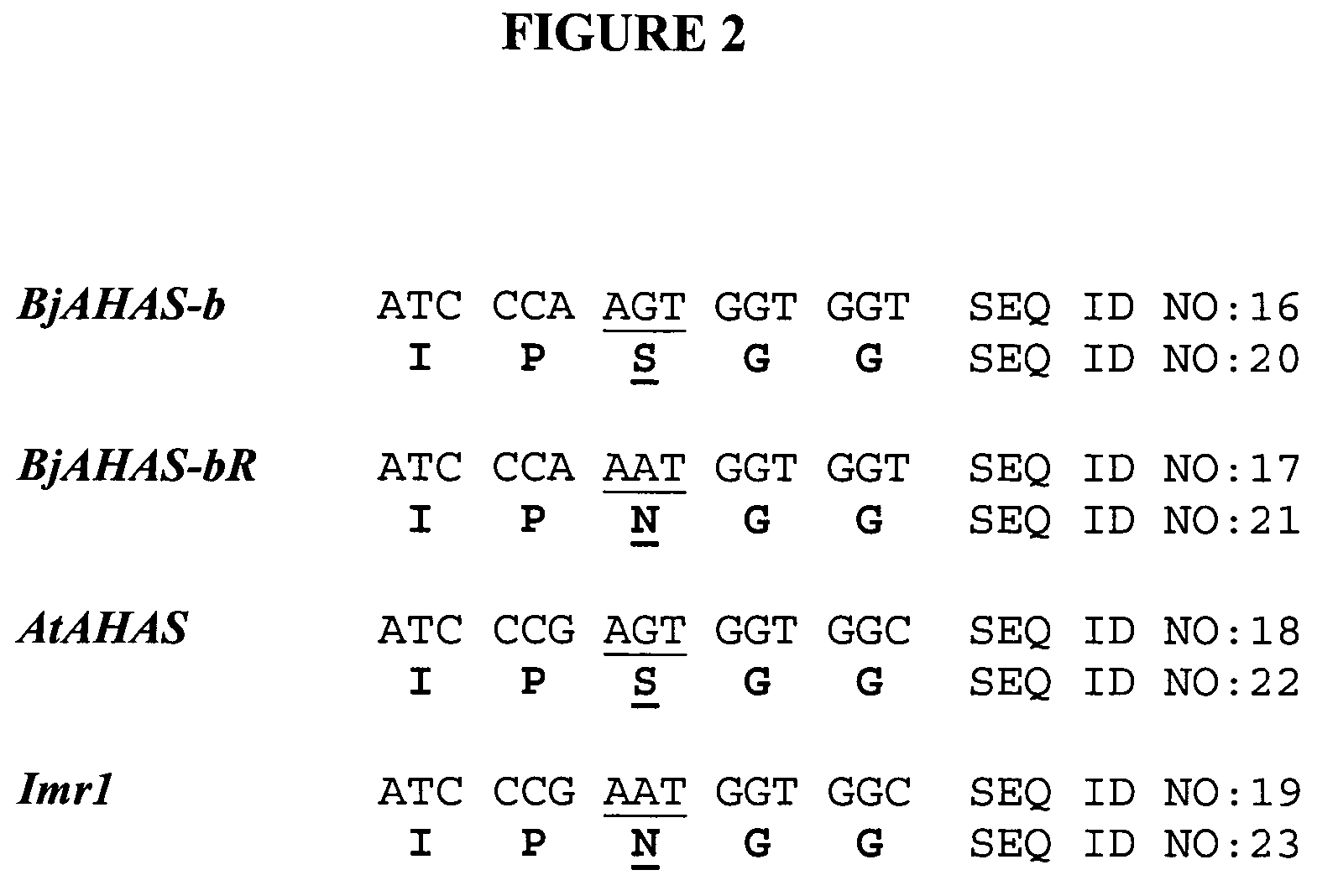
Brassica AHAS genes and gene alleles that provide resistance to imidazolinone herbicides
Plants, plant parts and plant seeds that are resistant to imidazolinone herbicides are provided. Plants are disclosed that contain a mutation in an AHAS gene. Specifically, plants are disclosed that contain a mutant AHAS gene allele of the Brassica juncea B genome. Two B. juncea AHAS gene sequences (BjAHAS-a and BjAHAS-b) and one B. nigra AHAS gene sequence (BngrAHAS) are disclosed. The sequence of the mutant allele, BjAHAS-bR, is also disclosed. Various methods are disclosed that include creation of mutant B. juncea lines, selection for herbicide resistant lines and determining the presence of the BjAHAS-bR mutant allele after crosses.
Owner:PIONEER OVERSEAS
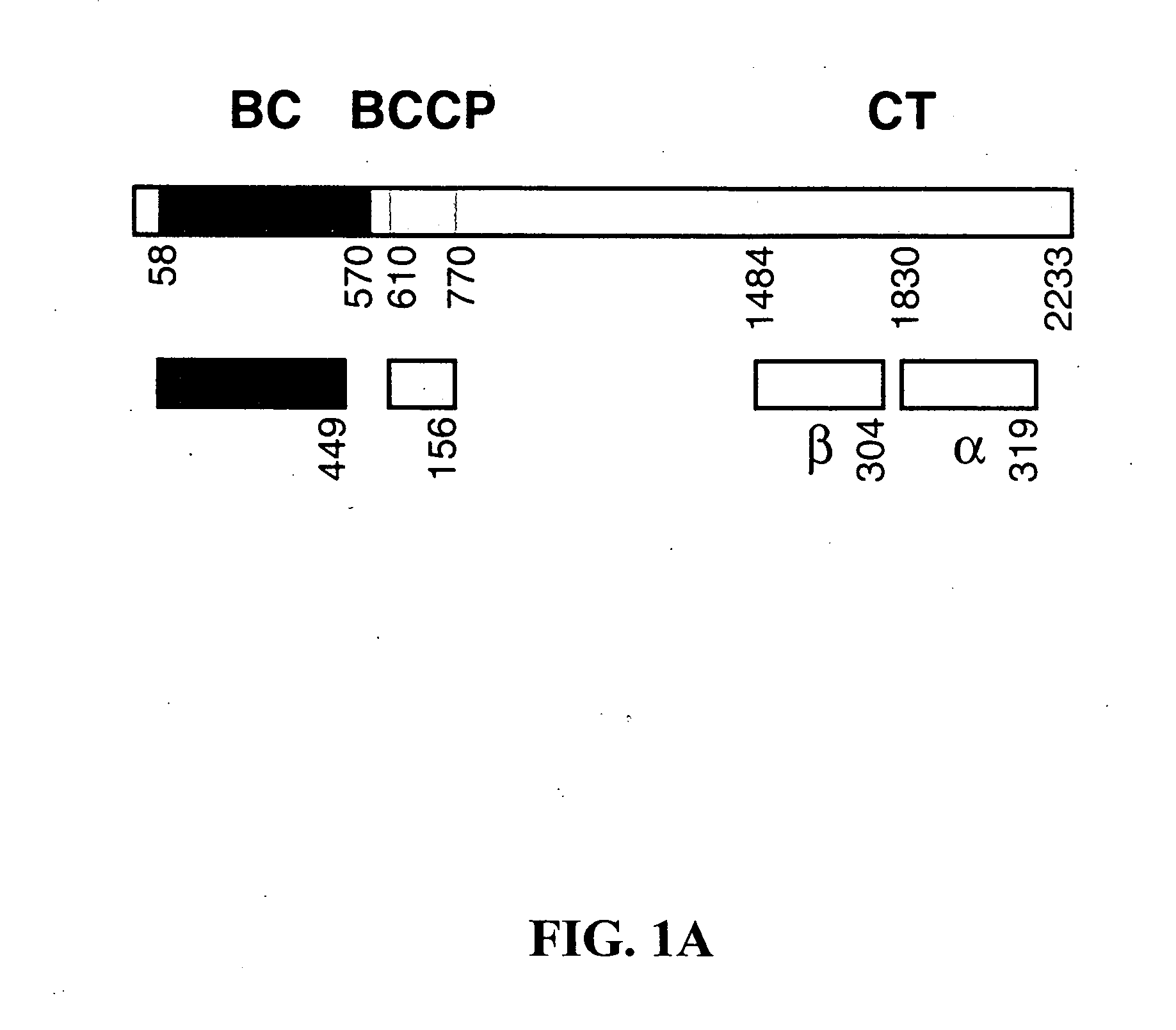
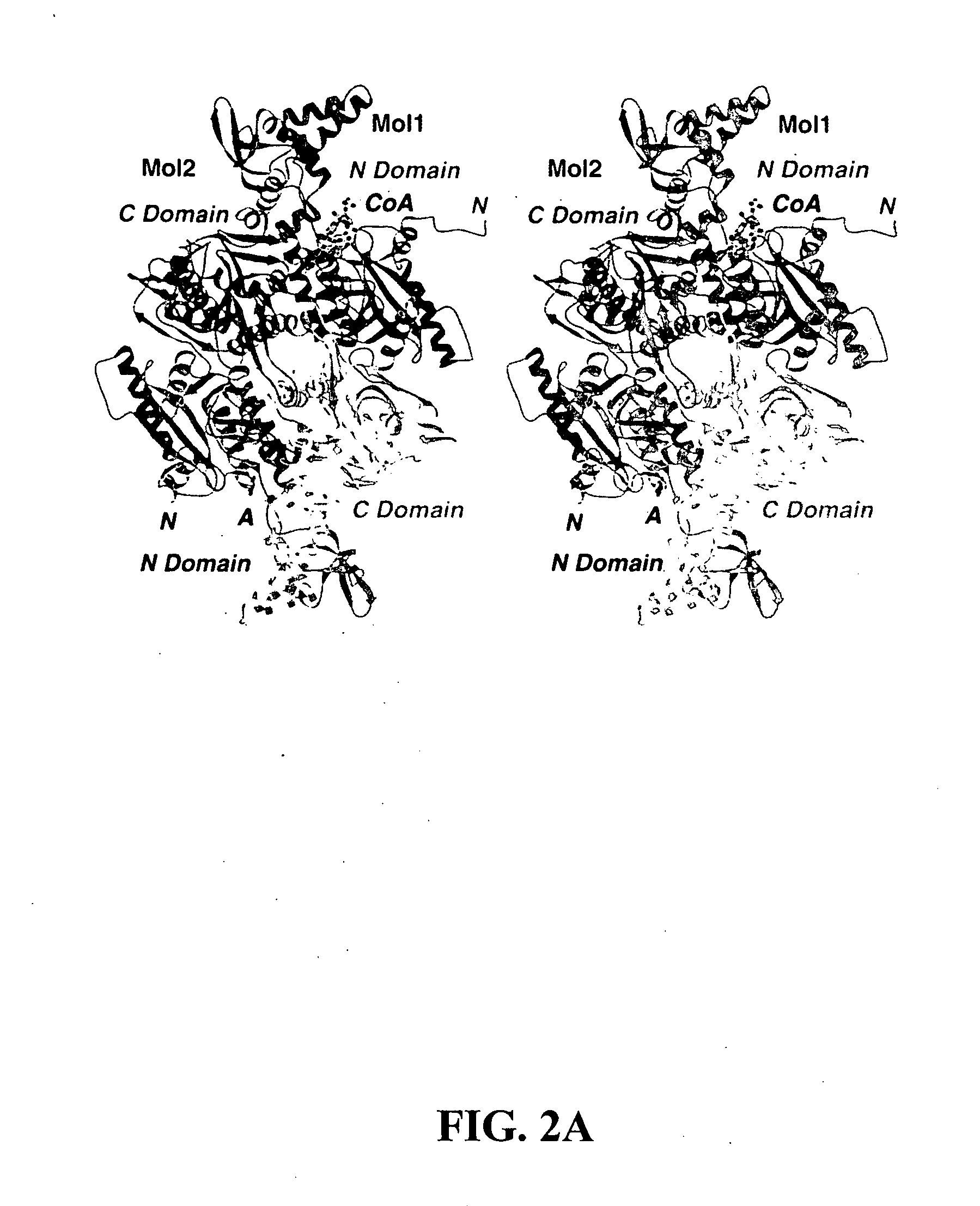
Methods of using crystal structure of carboxyltransferase domain of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, modulators thereof, and computer methods
InactiveUS20050009163A1Increase and decreases acetyl-CoA carboxylase activityTransferasesPeptide preparation methodsX-rayCrystal structure
The present invention provides compositions and crystals of the carboxyltransferase (CT) domain (the C-terminal ˜90 kDa fragment) of various acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) proteins, including yeast, mouse and human ACCs. Further, the present invention provides methods for identifying and designing compounds that can modulate ACC activity. These methods are based, in part, on the X-ray crystallographic structures of the CT domain of yeast ACC, either alone or bound to acetyl-CoA or a CT inhibitor, such as haloxyfop or diclofop or CP-640186. Thus, the present invention relates to the crystal structures of the carboxyltransferase (“CT”) domain of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (“ACC”), and to the use of these structures in the design of anti-obesity compounds, anti-diabetes compounds, antibiotic compounds, herbicide compounds, and in the design of herbicide resistant plants.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Herbicide-Resistant Plants, And Polynucleotides And Methods For Providing Same
Described are polynucleotides having nucleotide sequences encoding mutant plant phytoene desaturase proteins that are resistant the bleaching herbicides that act on phytoene desaturase, and related nucleic acid constructs, plants and methods.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Gene site-directed mutation vector as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106834341ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionCytosine deaminaseCytosine
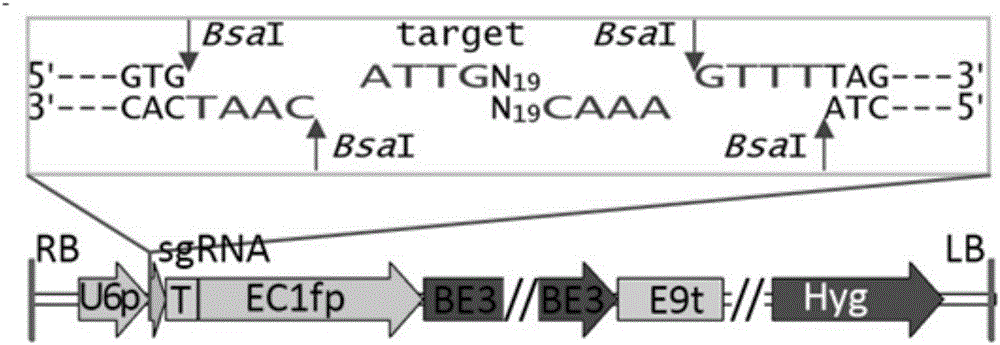
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and in particular relates to a gene site-directed mutation vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The invention provides the gene site-directed mutation vector due to lots of optimizations, cytosine deaminase is guided to be close to cytosine through a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) system, the cytosine is changed into uracil, then uracil is changed into thymine through self-repair in plant cells, and finally, site-specific mutagenesis from C to T is realized in plants so as to generate resistance to herbicides. In addition, point mutation can be produced in a non-sgRNA targeted area, and novel herbicide-resistant great agronomic traits are brought.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Nucleic acid segments encoding wheat acetyl-CoA carboxylase
InactiveUS6306636B1Reduce the amount requiredAlter fatty acid biosynthesisSugar derivativesBacteriaCarboxysomePolynucleotide
The present invention provides isolated and purified polynucleotides that encode plant polypeptides that participate in the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA. Also provided are methods for identifying such nucleic acid segments and polypeptides. Processes for altering acetyl-CoA carboxylation, increasing herbicide resistance of plants and identifying herbicide resistant variants of acetyl-CoA carboxylase are also provided.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Canola Plants with High Oleic and Low Linolenic
ActiveUS20090093367A1DegreeQuantitative precisionBiocideAnimal repellantsHigh oleic acidOleic Acid Triglyceride
Canola plants with high oleic acid and low linolenic acid content are disclosed. In addition, the canola plants of the invention are resistant to imidazolinone herbicides and are resistant to blackleg. The canola plants of the invention also have low total glucosinolate content. There is also provided a method for controlling weeds in a field of canola plants wherein the canola plants are herbicide resistant.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Molecular marker SIsv0372 in close linkage with foxtail millet herbicide resistant gene
ActiveCN101974521AEasy Assisted BreedingAssisted Breeding FastMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideDNA fragmentation
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to a molecular marker, in particular to a molecular marker in close linkage with a foxtail millet herbicide resistant gene, with a nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker shown as SEQID NO:1, or a DNA fragment containing the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO:1 in a foxtail millet genome. The invention also relates to primers of the molecular marker, application of the molecular marker in the positioning of the foxtail millet herbicide resistant gene or in foxtail millet inheritance breeding, a foxtail millet herbicide resistant gene positioning method, and a foxtail millet breeding method. The invention finds the molecular marker SIsv0372 which is in close linkage with the foxtail millet herbicide resistant gene, associates the foxtail millet genome DNA sequence and the foxtail millet herbicide resistant gene, and better benefits the establishment of a foxtail millet molecular marker assisted breeding system.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
Non-transgenic herbicide resistant plants
InactiveUS20030084473A1High sensitivityAlignment score can be increasedTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesMutated proteinPlant cell
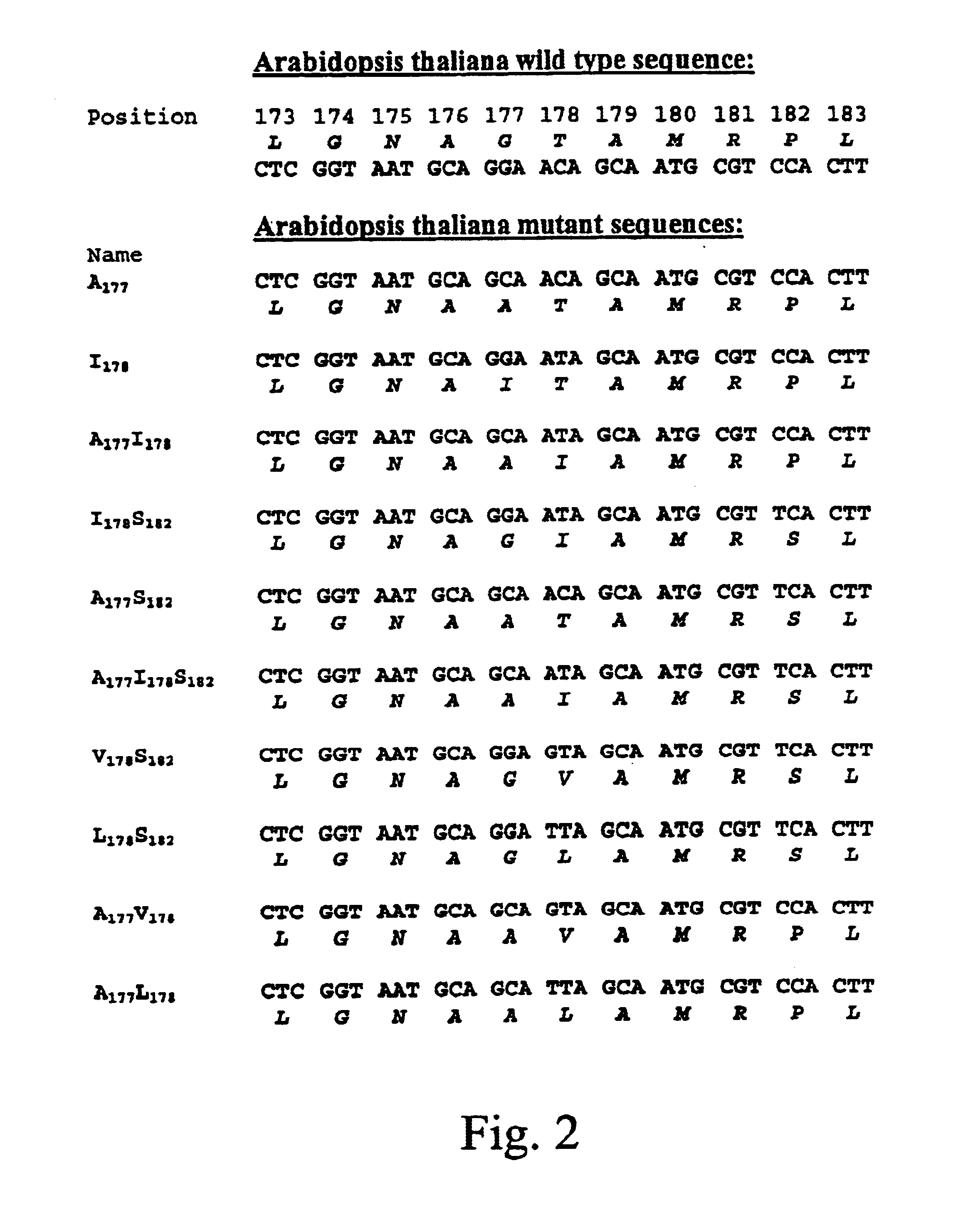
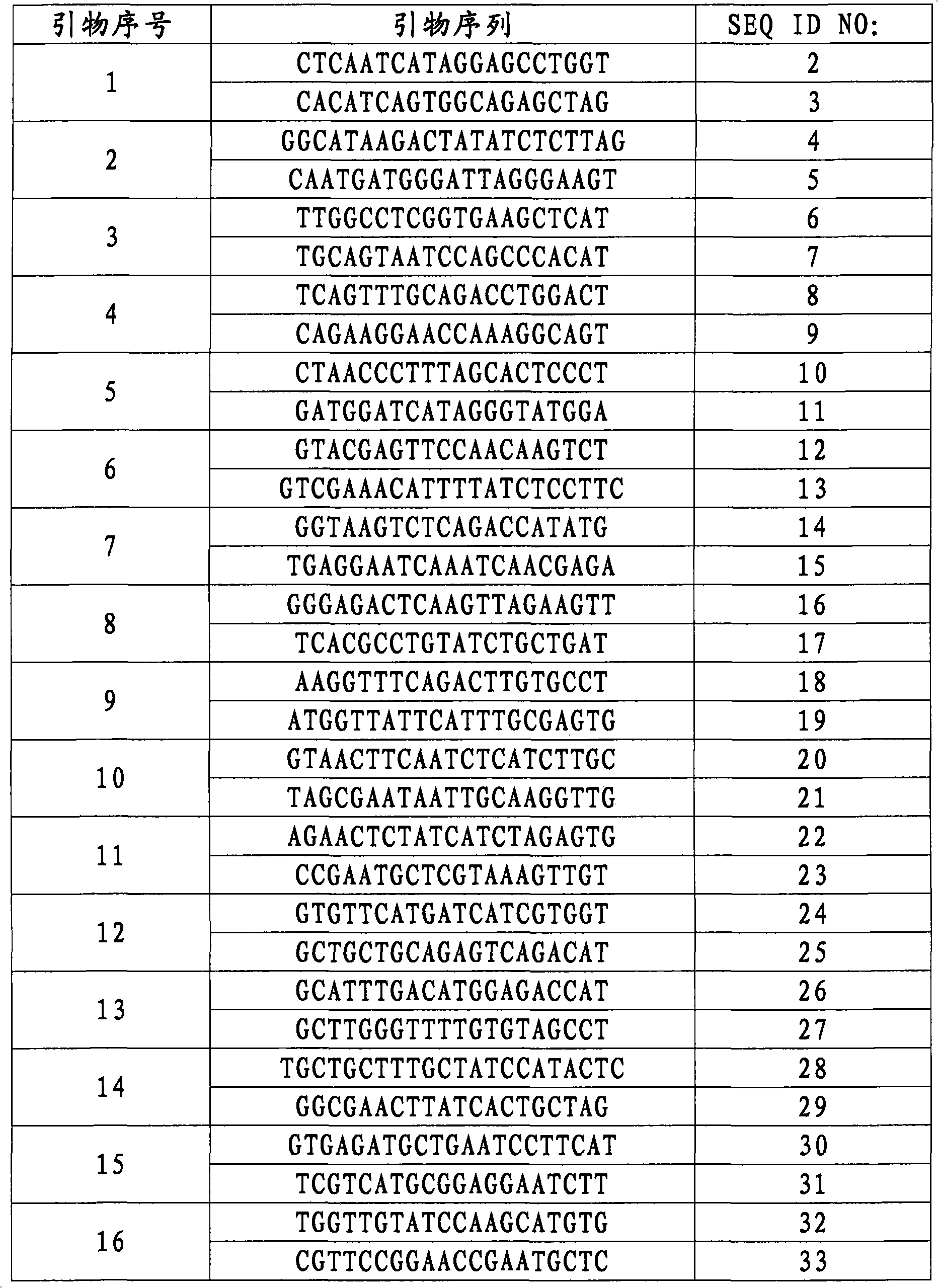
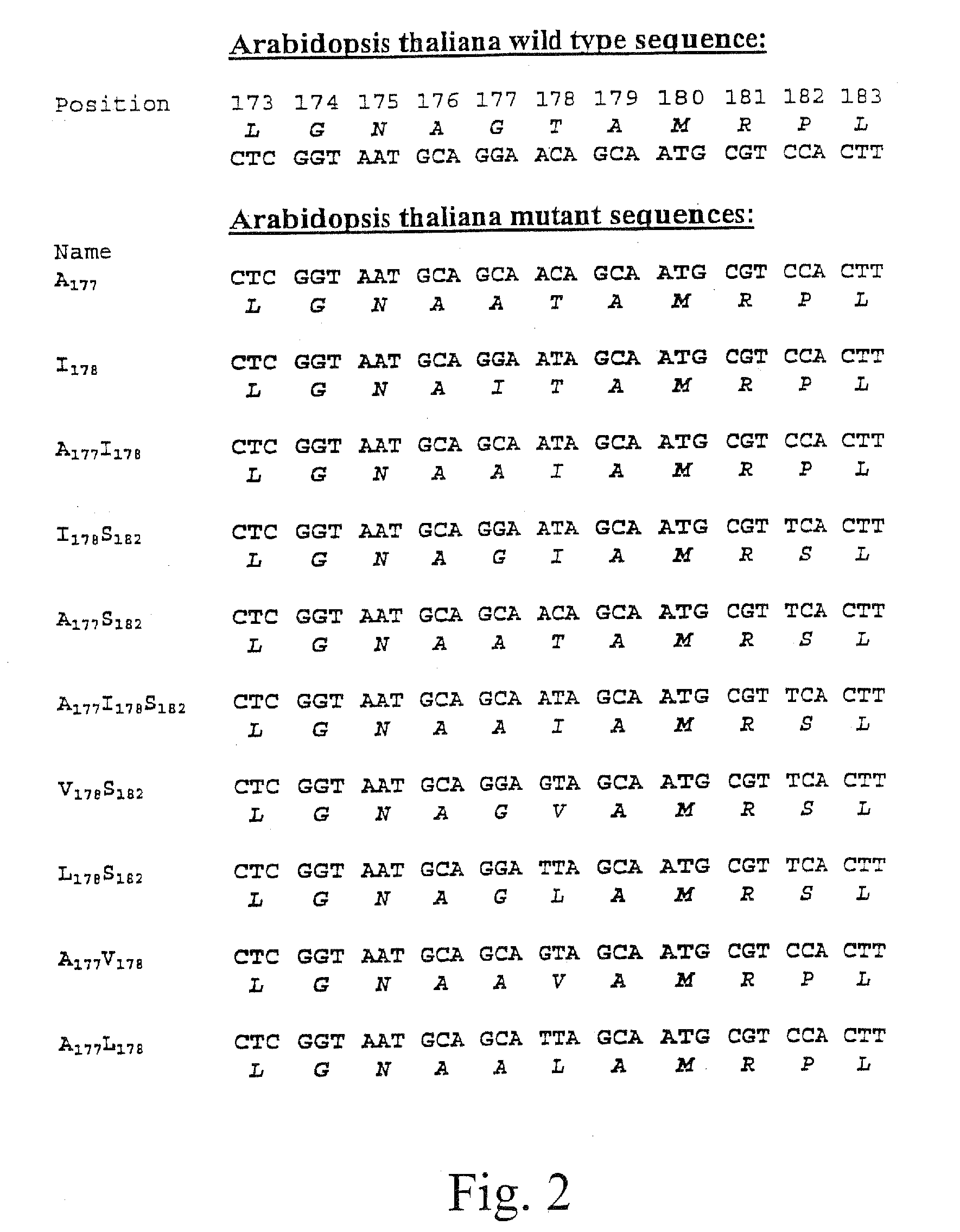
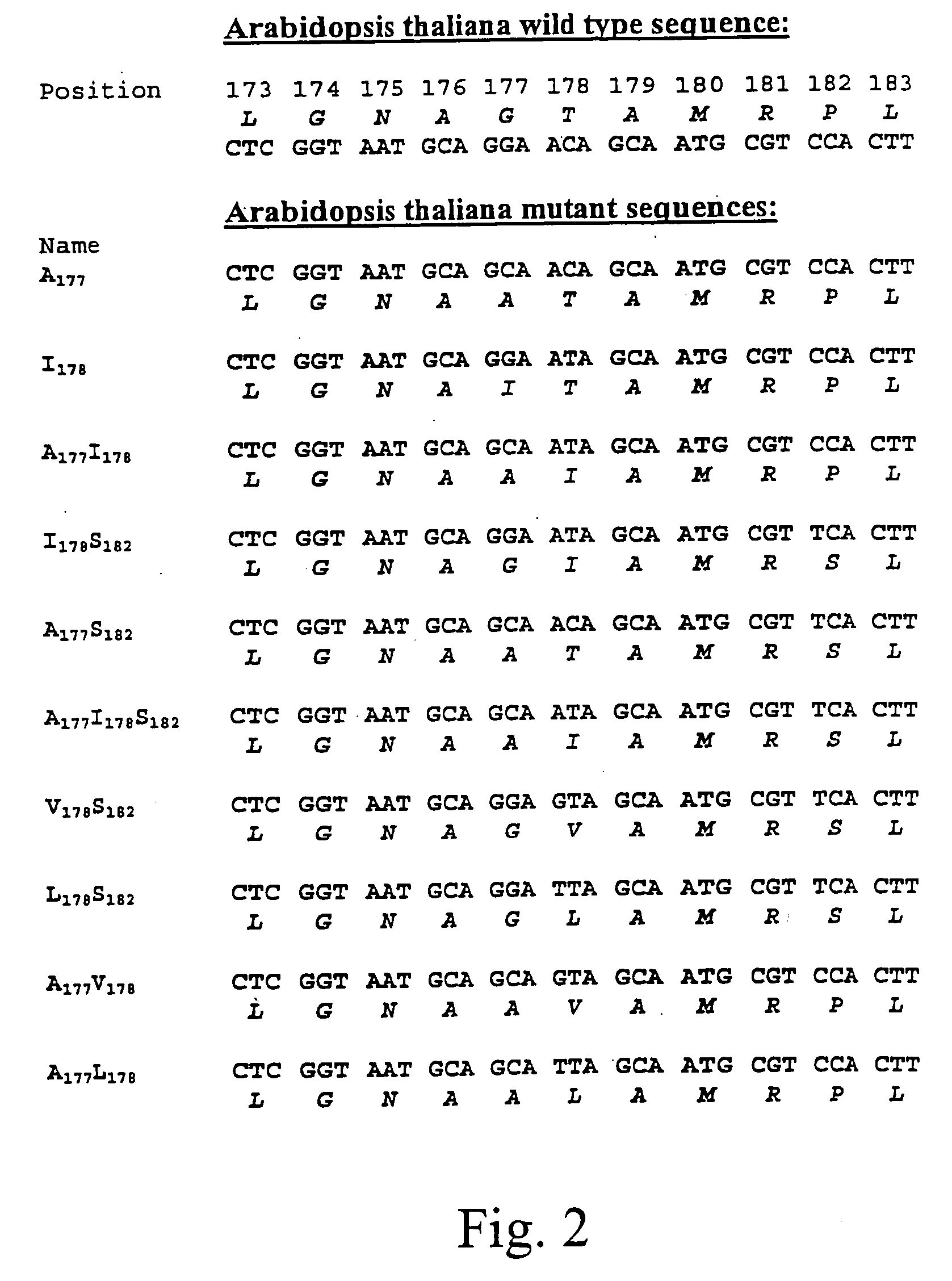
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide. The present invention also relates to a non-transgenic plant cell in which the EPSPS gene has been mutated, a non-transgenic plant regenerated therefrom, as well as a plant resulting from a cross using a regenerated non-transgenic plant having a mutated EPSPS gene. The amino acids at the positions 126, 177, 207, 438, 479, 480 and / or 505 are changed tp produce a mutant EPSPS gene product.
Owner:VALIGEN US
Herbicide-resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase isolated from Nicotiana tabacum
A protoporphyrinogen oxidase tolerant to photobleaching herbicide and derivatives thereof, comprising a polypeptide having the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 2 or mutated peptides derived therefrom by deletion, addition, substitution, etc. of one or more amino acids in the above amino acid sequence and having an activity substantially equivalent to that of the protoporphyrinogen oxidase. The acquisition of the novel protoporphyrinogen oxidase, which is highly tolerant to photobleaching herbicide and originates in plant, make it possible to construct plants highly tolerant to photobleaching herbicide via the expression of this enzyme in host plants.
Owner:NIHON NOHYAKU CO LTD
Rice herbicide resistant protein and application thereof in plant bleeding
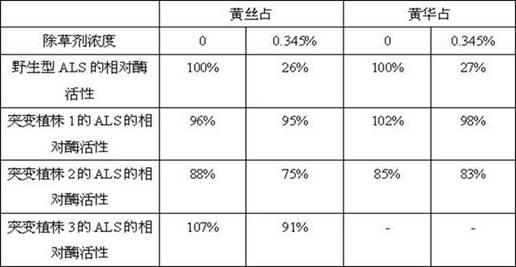
The invention discloses rice herbicide resistant protein and application thereof in plant bleeding. The ALS (acetolactate synthase) protein provided by the invention realizes that a plant has the herbicide resistance, and is derived from rice varieties Huangsizhan and Huanghuazhan, and carries Trp548, Ala96 or Ser627mutation. Furthermore, the invention also provides corresponding nucleic acid, expression cassettes, carriers, cells, plants, and method for obtaining the plants with herbicide resistance and application of the plants, as well as a method for identifying the plants in the invention.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINGWANG BIOLOGICAL SEED IND +1
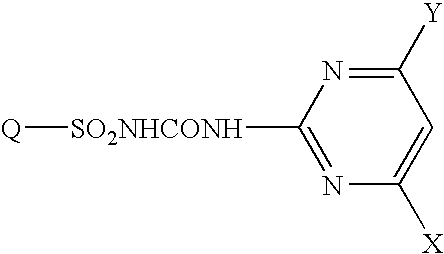
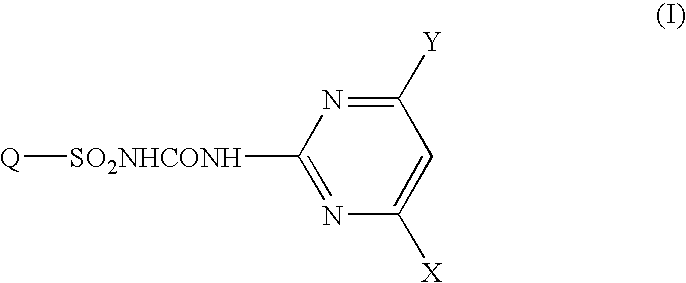
Fused heterocyclic sulfonylurea compound herbicide containing the same and method of controlling weed with the same
InactiveUS20050032650A1Broad weeding spectrumHigh weeding effectBiocideOrganic chemistryAlkoxy groupBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention provides a compound represented by the formula: wherein Q represents a fused heterocyclic group, X and Y are the same or different and each represent an optionally halogenated lower alkyl group, an optionally halogenated lower alkoxy group, etc., or a salt thereof, as well as a herbicide comprising the compound or a salt thereof, which exhibits a significant effect for control of sulfonylurea herbicide-resistant weeds in paddy fields and can reduce the number of active ingredients in a combined preparation and a method of controlling sulfonylurea herbicide-resistant weeds which comprises using the same.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Herbicide resistant rice
InactiveUS7019196B1Seed and root treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementRice plantsResidual activity
Rice plants are disclosed with multiple sources of resistance to herbicides that normally inhibit a plant's acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) enzyme. Besides controlling red rice, many AHAS-inhibiting herbicides also effectively control other weeds that are common in rice fields. Several of these herbicides have residual activity, so that one treatment can control both existing weeds and weeds that sprout later. With effective residual activity against red rice and other weeds, rice producers now have a weed control system superior to those that are currently available commercially.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Non-Transgenic Herbicide Resistant Plants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphoniorethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phophonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide. The present invention also relates to a non-transgenic plant cell in which the EPSPS gene has been mutated, a non-transgenic plant regenerated therefrom, as well as a plant resulting from a cross using a regenerated non-transgenic plant having a mutated EPSPS gene.
Owner:CIBUS
Preparation method of glyphosate resistant transgenic rice
InactiveCN104004781AReduce the number of copiesShort processPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMolecular identificationGenetically modified rice
The invention provides a preparation method of glyphosate resistant transgenic rice. The method comprises the following steps: converting an expression vector containing glyphosate resistant gene into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, invading rice calluses by the Agrobacterium tumefaciens, transferring the calluses to a selective aluminum containing glyphosate for screening, choosing resistant calluses, differentiating, rooting, hardening-seedling, and transplanting to obtain glyphosate resistant transgenic rice. A molecular identification result shows that an exogenous gene is stably expressed. The obtained glyphosate resistant transgenic rice contains glyphosate herbicide resistant gene, contains no other screening marker genes, and can be used as a commercial herbicide resistant rice kind to reduce the reduce the later process and accelerate the breeding pace. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low copy number of transgenic plants, stable heredity properties, and good market application prospect.
Owner:CHINA NAT SEED GRP
Applications of ALS (acetolactate synthase) mutant type protein based on gene editing technology and ALS mutant type protein gene in plant breeding
ActiveCN109097346ANo significant change in basic agronomic traitsImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAgricultural scienceAcetolactate synthase
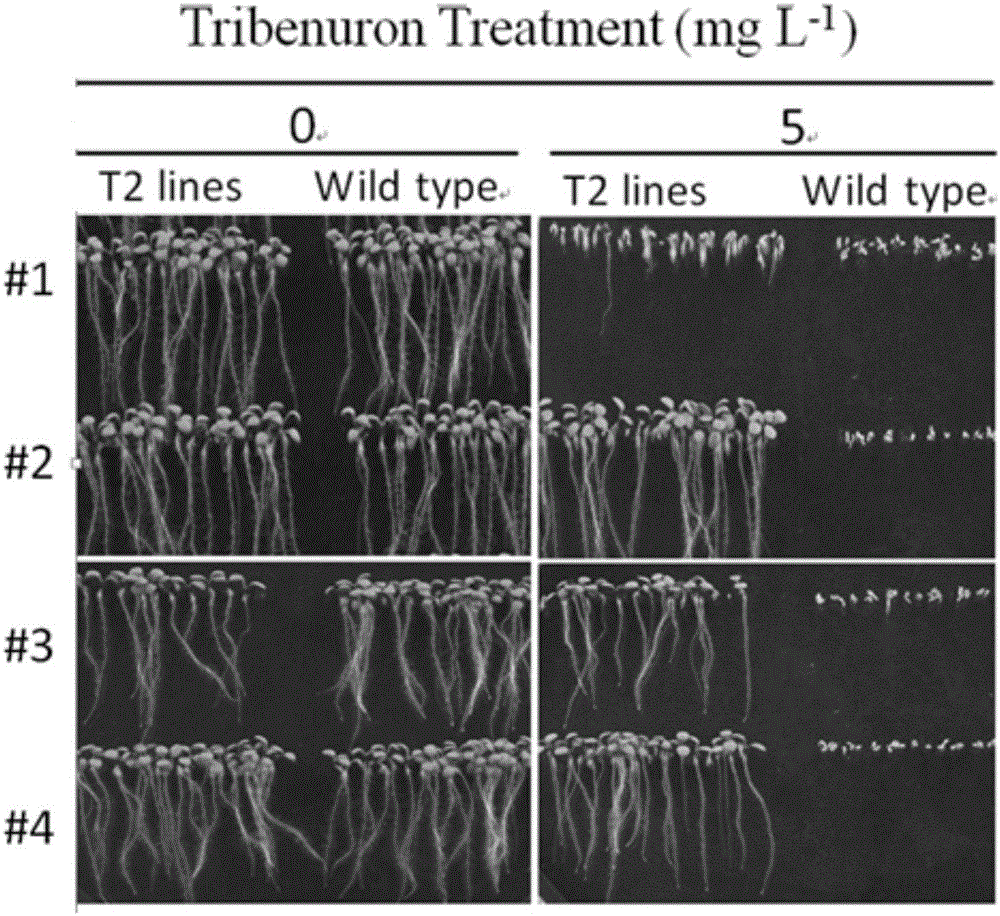
The invention discloses a rice ALS (acetolactate synthase) mutant type protein, a mutant type gene and applications of the rice ALS mutant type protein and the mutant type gene. The amino acid sequence of the ALS mutant type protein has following mutation: the 628-poisiton amino acid corresponding to the amino acid sequence of rice ALS has the mutation. The invention further discloses a breeding method of creating herbicide-resistant rice by gene editing. The CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology is used for editing the ALS gene for the first time, a T-DNA-knockout new material with the stably inherited herbicide resistant characteristic can be obtained in the T2 generation through offspring screening, and basic agronomic traits of the new material have no obvious change. Compared with breeding based on chemical mutagenesis, hybrid transform breeding and the like, the orderly improved molecular breeding technology based on gene editing has the advantages of being rapid, accurate, efficient and the like, and by means of combination with gene function marked genotype selection, breeding efficiency can be greatly increased and breeding progress is substantially accelerated.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Brassica AHAS genes and gene alleles that provide resistance to imidazolinone herbicides
Owner:PIONEER OVERSEAS
Herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase
InactiveCN103070068AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce chanceSeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention provides a herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase, which belongs to a plant trait breeding method. The method comprises the following steps of selecting materials needed by production of rape or breeding of the rape, processing seeds with ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS), mutagenizing the seeds to be isolated and propagated to a M2 generation, and directionally screening herbicide-resistant mutant characters in a large group under the selection pressure of the herbicide adopting the ALS as the target esterase. In order to increase the probability for acquiring the mutant characters, the directive screening can be continuously conducted in multiple years, or conducted in multiple places in the same year or conducted in multiple places in multiple years until the needed mutant material is screened out.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Herbicidal Compositions Comprising Flufenacet
Herbicidal compositions are disclosed comprising an effective amount of flufenacet, diflufenican and metribuzin. A method of controlling harmful plants is disclosed. The compositions may be used flexibly, e.g, in post-emergent and / or pre-emergent applications. The compositions may be used prior to sowing a crop. The compositions may provide enhanced compatibility with crops. The compositions may be used on different soil types, e.g., with high-organic matter soils and / or at different soil depths, e.g., at shallow soil depths. The compositions may be used against herbicide-resistant plant species, for example EMR and TSR-resistant species and / or may be used for resistance management. The compositions may be used with various irrigation techniques.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Corn chloroplast transgene expression vector containing herbicide resistant gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102533844AStrong resistanceSmall molecular weightVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsChloroplastTransgene
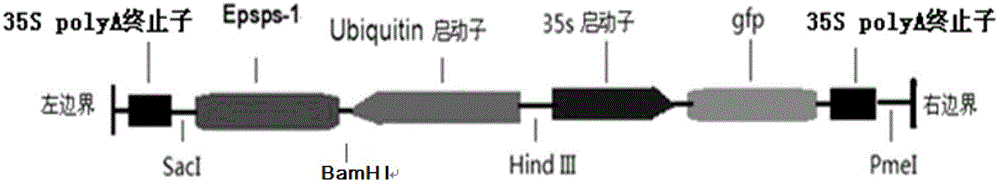
The invention provides a corn chloroplast transgene expression vector containing herbicide resistant gene and application thereof. The transgene expression vector comprises an expression box of 5-enol form acetone shellokimic acid-3-phosphate synthase (EPSP) gene, a homologous recombination fragment atpB in a corn chloroplast gene group and a homologous recombination fragment rbcL, wherein the expression box of the EPSP synthase gene is positioned between the homologous recombination fragment atpB and the homologous recombination fragment rbcL. The invention further provides a construction method of the chloroplast transgene expression vector. The invention also provides application of the chloroplast transgene expression vector in improving corn glyphosate resistance, which comprises leading the expression vector to convert callus or cells of corns, and screening to obtain resistant callus or cells; and inducing resistant callus or cells to differentiate, and regenerating to achieve corn resistance plants. The corn chloroplast transgene expression vector containing herbicide resistant gene can remarkably improve corn glyphosate resistance and has the advantages of being high in biological safety, capable of saving time, efficient, little in energy consumption, low in cost and the like.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cropping systems for managing weeds
The invention provides cropping systems for managing weeds in crop environments. The cropping systems comprise, in one embodiment, transgenic plants that display tolerance to an auxin-like herbicide such as dicamba. Method for minimizing the development of herbicide resistant weeds are also provided.
Owner:ARNEVIK CINDY L +6
Anti-herbicide gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101451143APrevent accidental transmissionAvoid spreadingOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a herbicide-resistant gene, wherein a nucleotide sequence of the gene is SEQ ID NO: 1 or has more than 90 percent of identity with the SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses herbicide-resistant protein encoded by the herbicide-resistant gene, wherein an amino acid sequence of the protein is SEQ ID NO: 2 or has more than 90 percent of identity with the SEQ ID NO: 2. The gene can be used for preparing a transgenic plant which increases the resistance to a herbicide, or obtaining a method which utilizes the herbicide to selectively kill transgenic corn.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Rice ACCase mutant gene and application thereof in herbicide resistance of plants
The invention discloses a rice ACCase mutant gene and an application thereof in herbicide resistance of plants. The amino acid sequence of the encoding protein of the ACCase mutant gene has the following mutation: the 1731st siteor / and 2276th site of the amino acid sequence corresponding to the wild type rice ACCase is subjected to mutation. The ACCase mutant gene is introduced into herbicide-sensitive rice genome by a transgenic method and is expressed; and receiver plants can have resistance to acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor herbicide. The ACCase mutant gene can be widely applied to the breeding of plants with the herbicide resistance.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method and kit of ALS (acetolactate synthetase) inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia
ActiveCN103923996AImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAcetolactate synthaseNucleotide
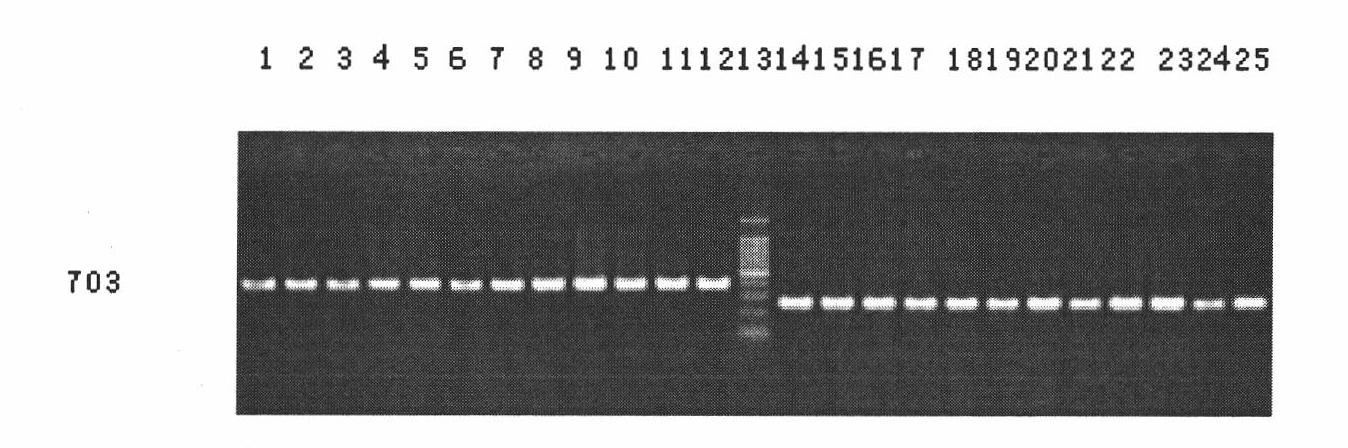
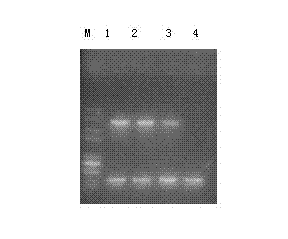
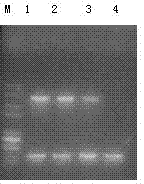
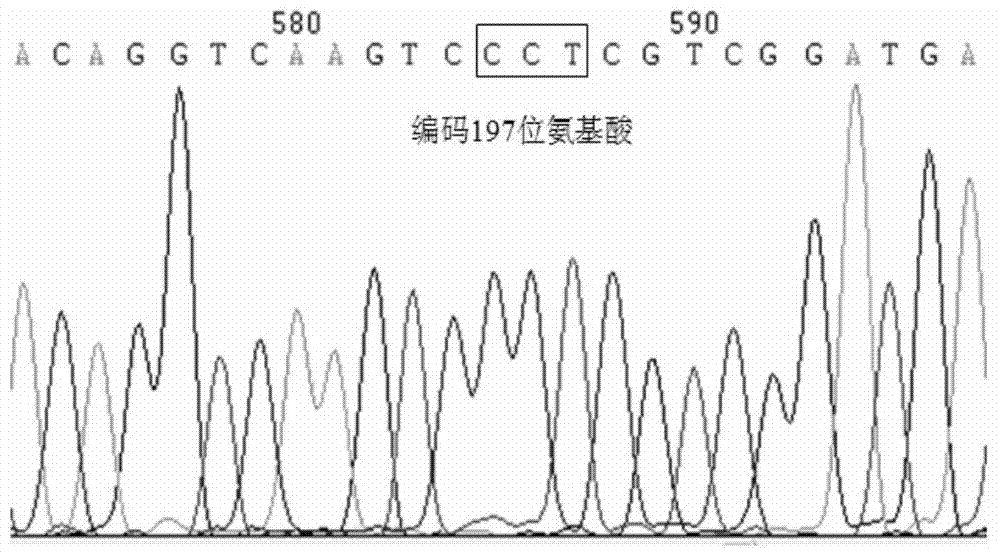
The invention provides a specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer pair for detecting ALS (acetolactate synthetase) inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia. The primer pair comprises a primer pair (Seq ID No.1-2) for specific amplification of a B-ALS-1 gene of the descurainia sophia and a primer pair (Seq ID No.3-4) for specific amplification of a B-ALS-2 gene of the descurainia sophia. A PCR detection method adopting the primer pair is excellent in specificity and sensitivity, and a specificity test proves that the two ALS genes of the descurainia sophia can be amplified (figures 1 and 2). As the PCR method is simple, convenient and quick to operate, the sampling detection can be carried out in season based on nucleotide detection, and only 2-4 days are required for a process from sampling to results. The sensitivity and specificity of the method can realize quick identification of suspended ALS inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia in the field and confirmation of mutation sites, thus the scientific control of resistant weeds in production practice is guided.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Weeding composition containing pyrazolone compounds and application of weeding composition
ActiveCN106106506AReduce the amount of applicationSignificantly active aloneBiocideDead animal preservationCompound cHerbicide resistant
Owner:QINGDAO KINGAGROOT RESISTANT WEED MANAGEMENT CO LTD
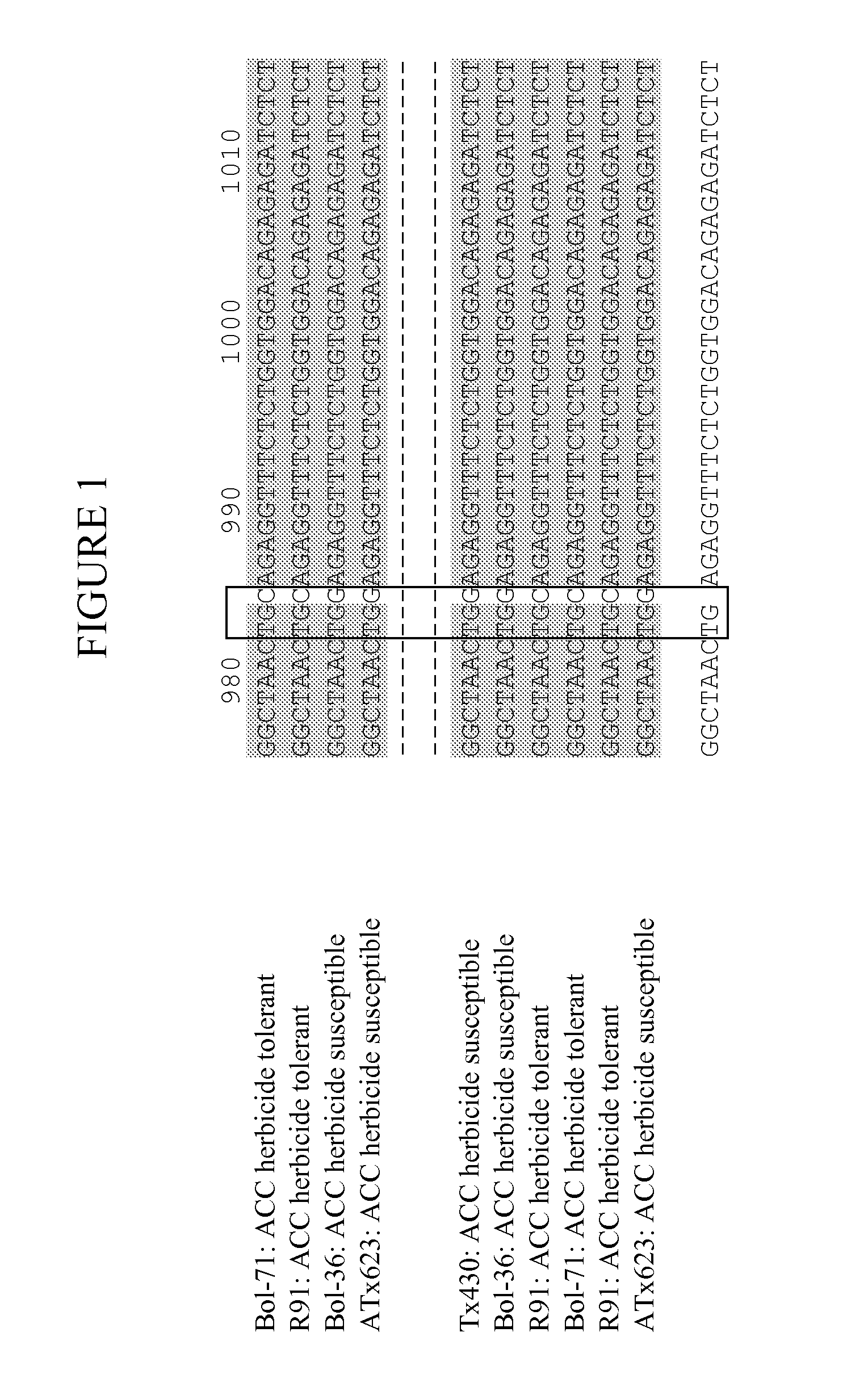
ACETYL-CoA CARBOXYLASE HERBICIDE RESISTANT SORGHUM
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for producing crop plants that are resistant to herbicides. In particular, the present invention provides for sorghum plants, plant tissues and plant seeds that contain altered acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) genes and proteins that are resistant to inhibition by herbicides that normally inhibit the activity of the ACC protein.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Non-transgenic herbicide resistant plants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide. The present invention also relates to a non-transgenic plant cell in which the EPSPS gene has been mutated, a non-transgenic plant regenerated therefrom, as well as a plant resulting from a cross using a regenerated non-transgenic plant having a mutated EPSPS gene.
Owner:BEETHAM PETER +3
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com