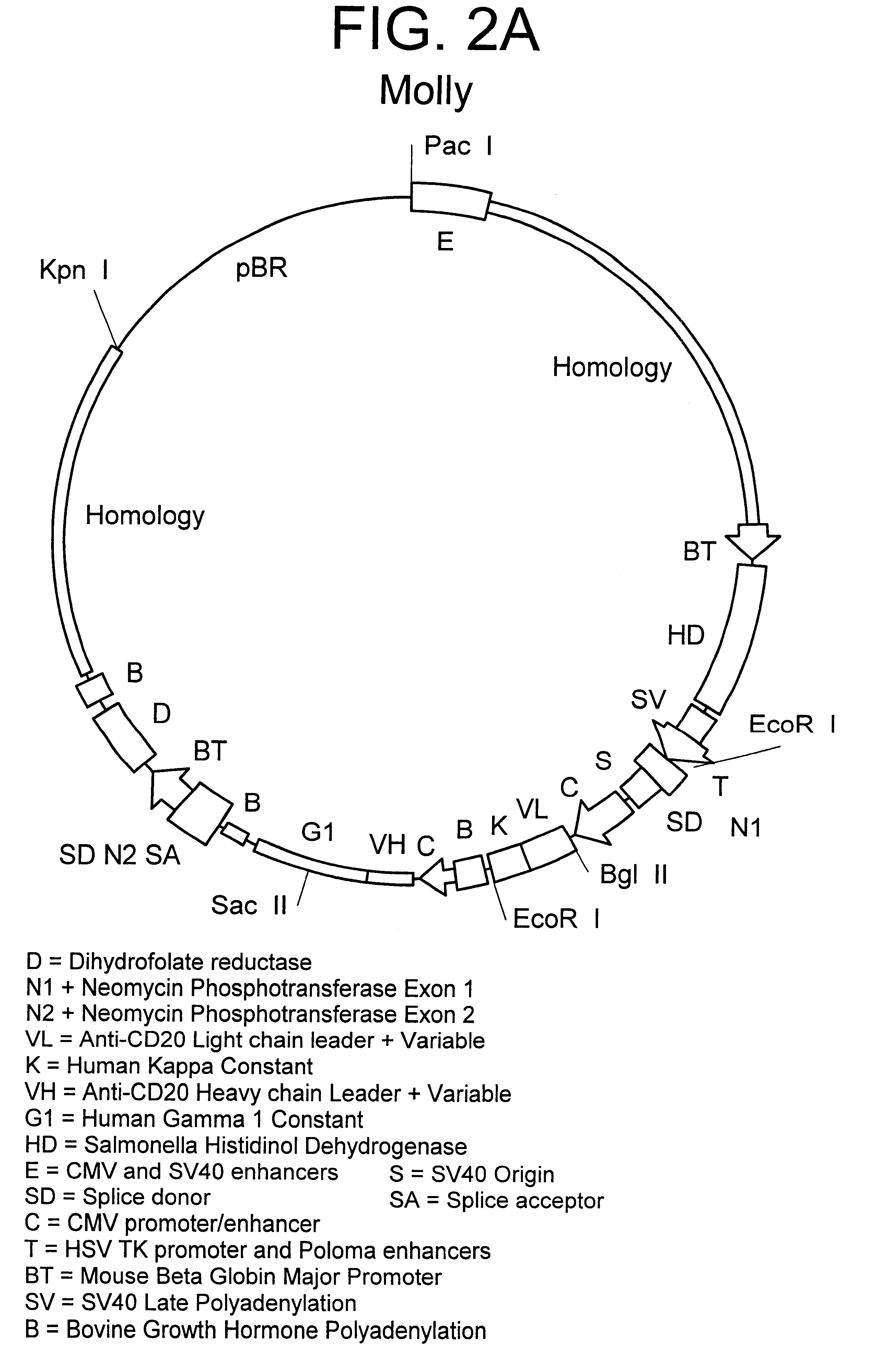
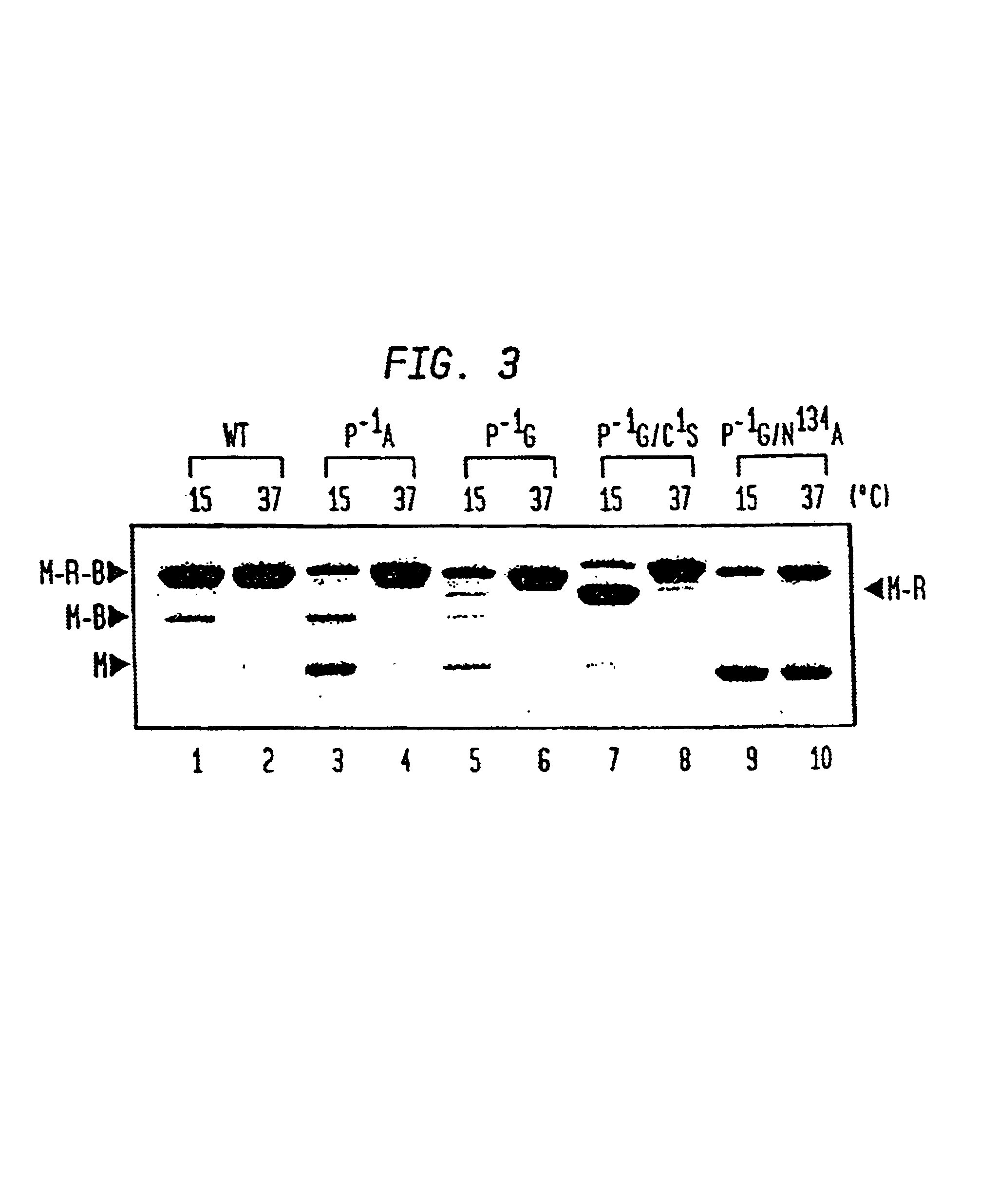
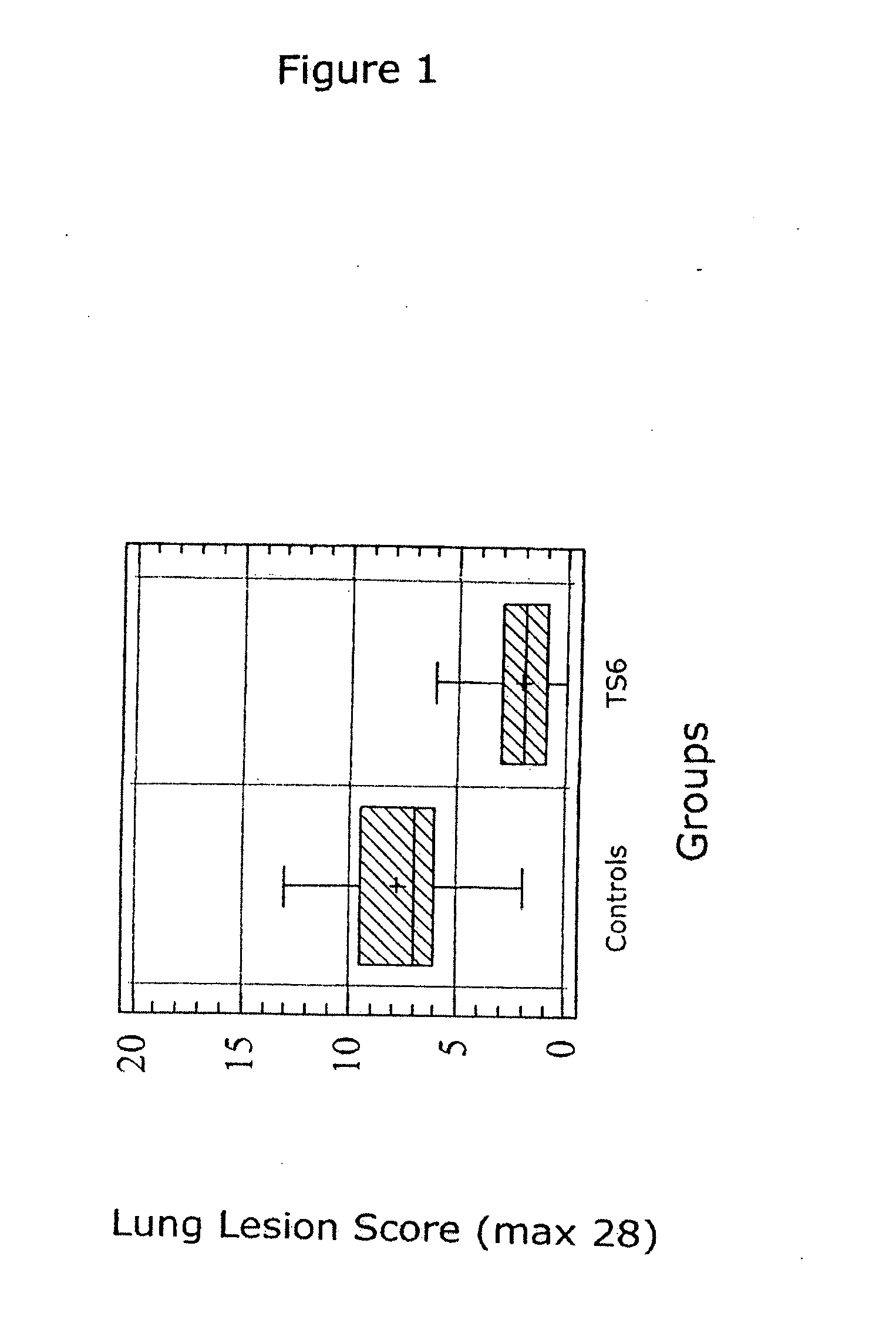
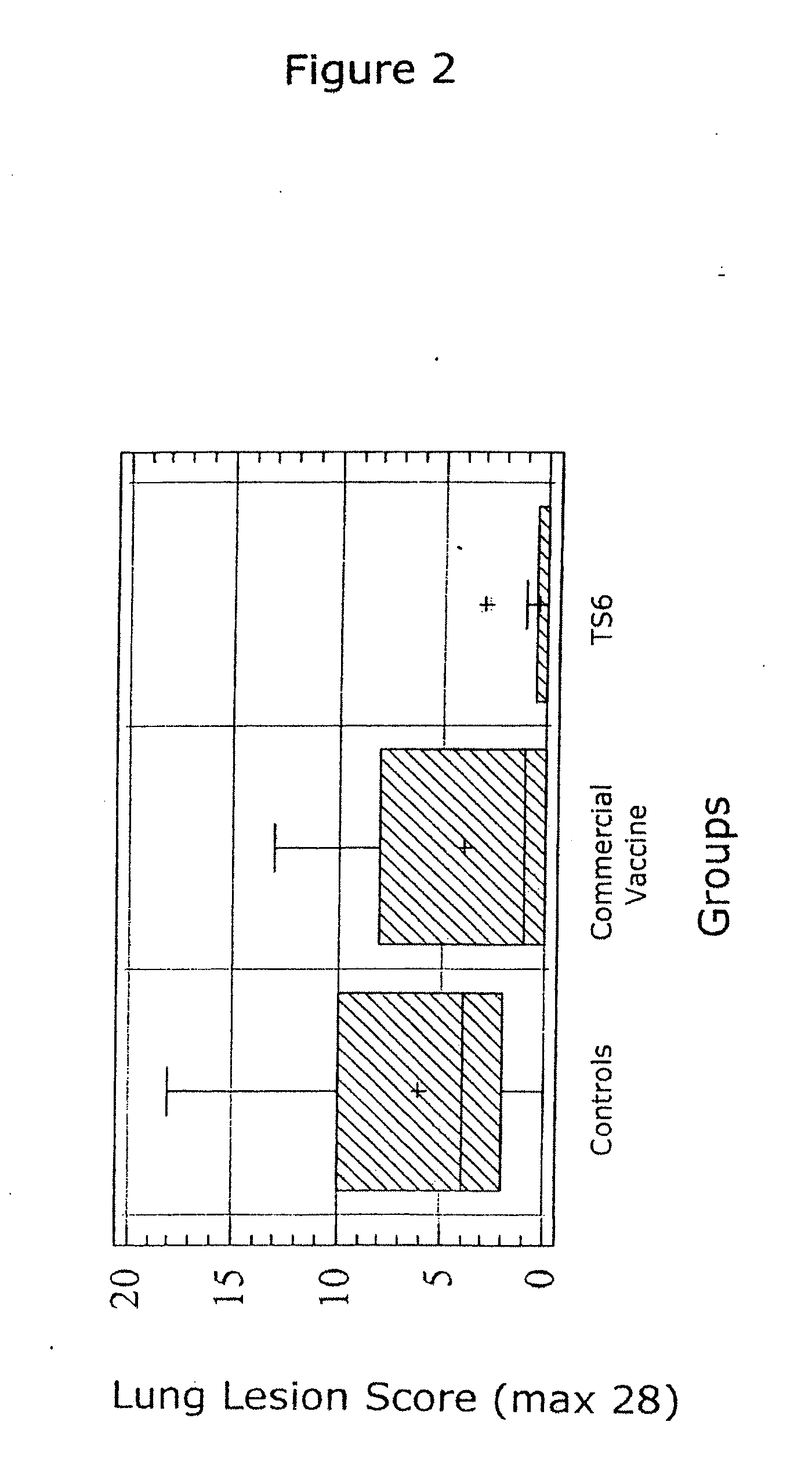
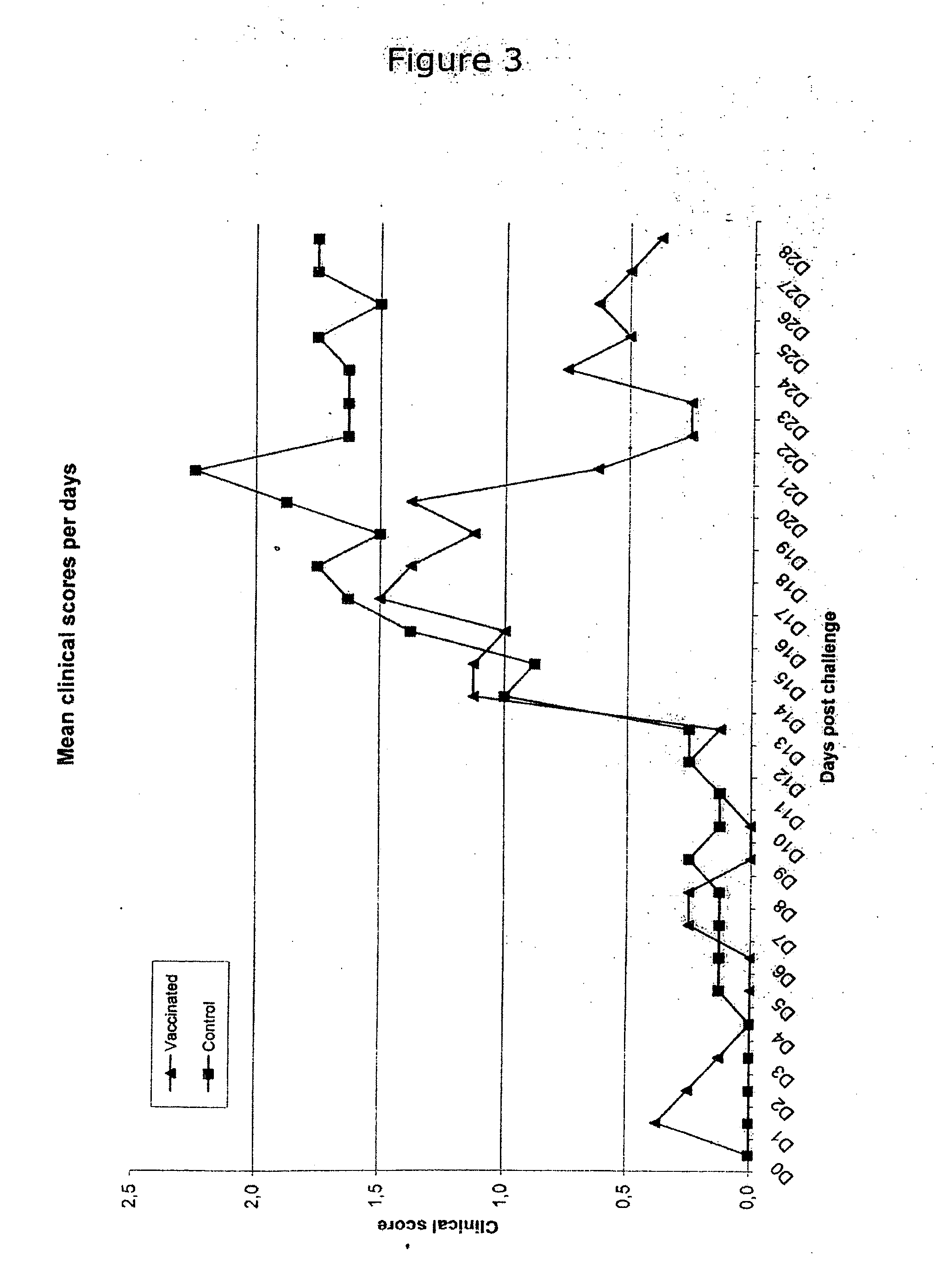
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8730 results about "Plasmid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A plasmid is a small DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism, such as by providing antibiotic resistance. While the chromosomes are big and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids usually are very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation.
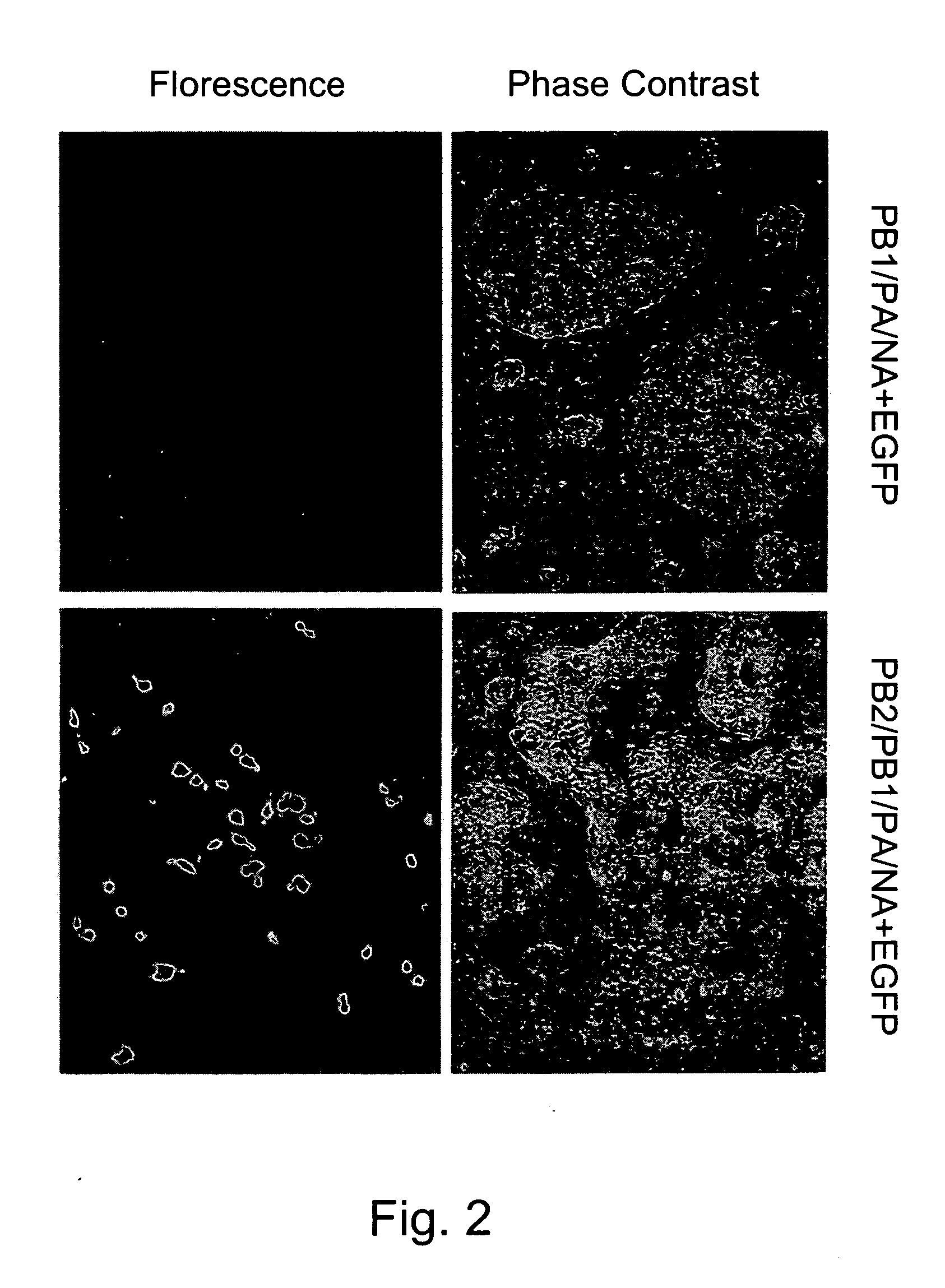
Multivalent antibody constructs
InactiveUS7129330B1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsVariable domainPlasmid
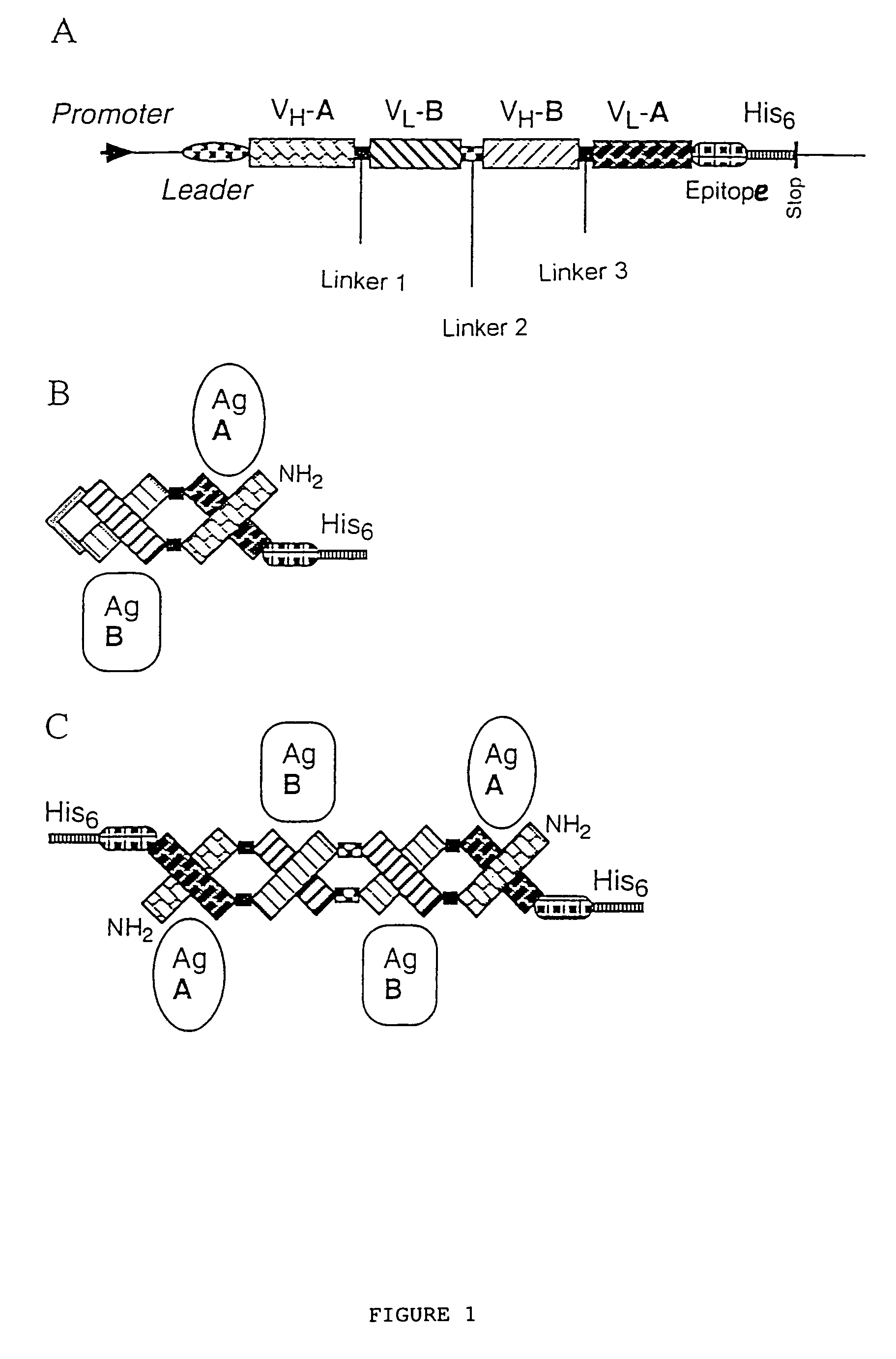
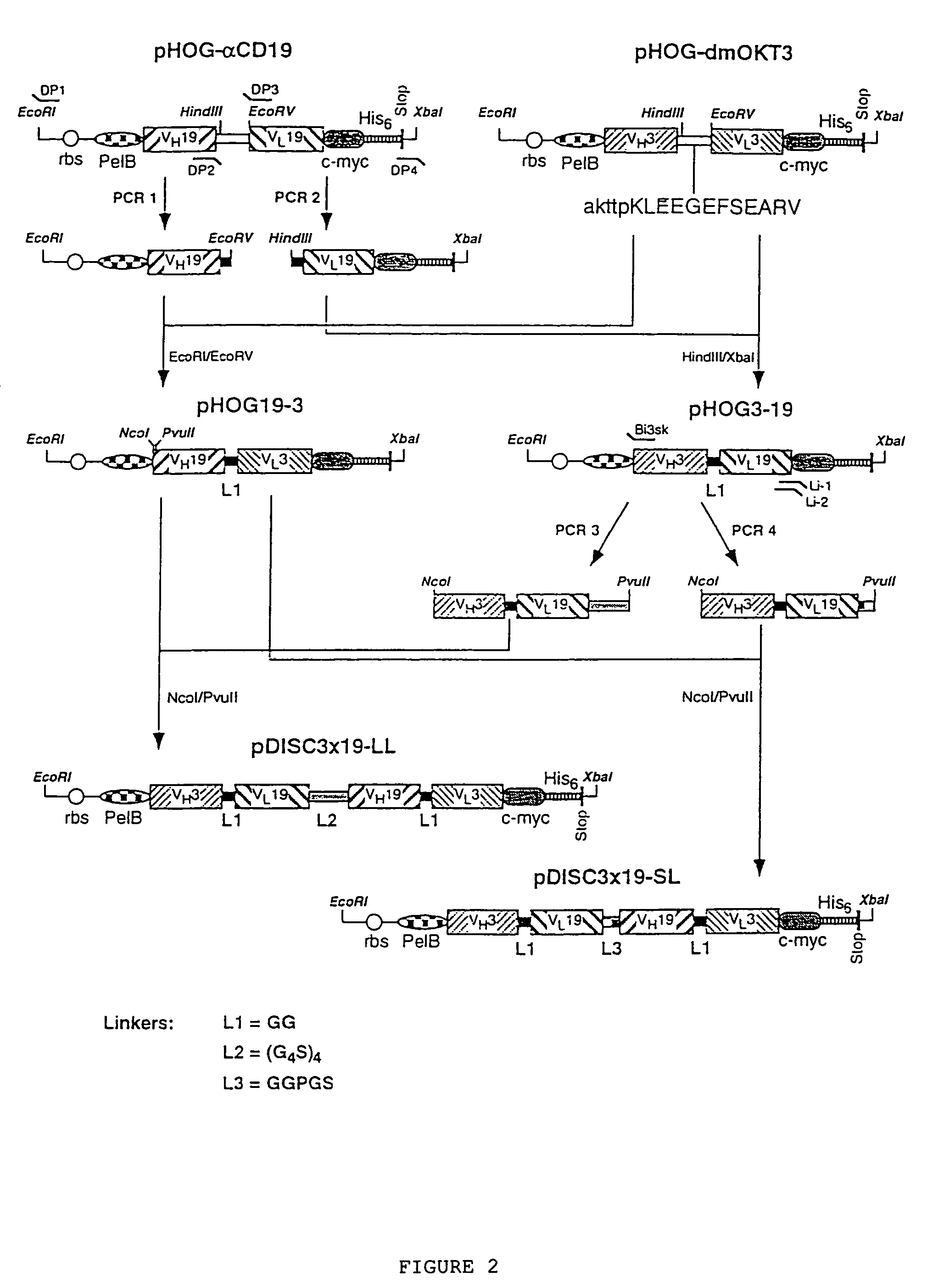
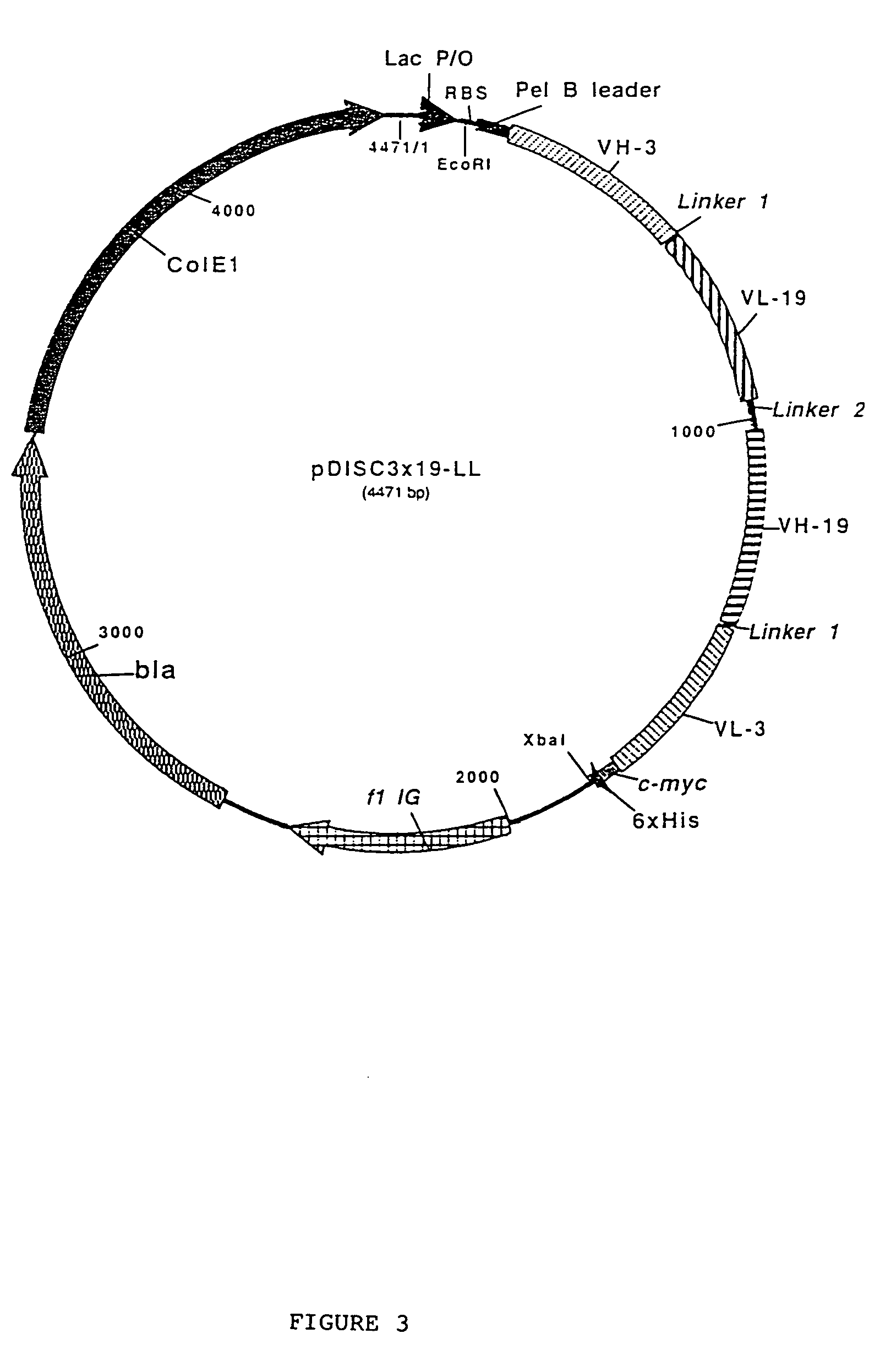
The present invention relates to multivalent Fvantibody construct having at least four variable domains which are linked with each over via the peptide linkers 1, 2 and 3. The invention also concerns expression plasmids which code for such an Fvantibody construct and a method of producing the Fvantibody constructs as well as their use.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Glycosylation analogs of erythropoietin
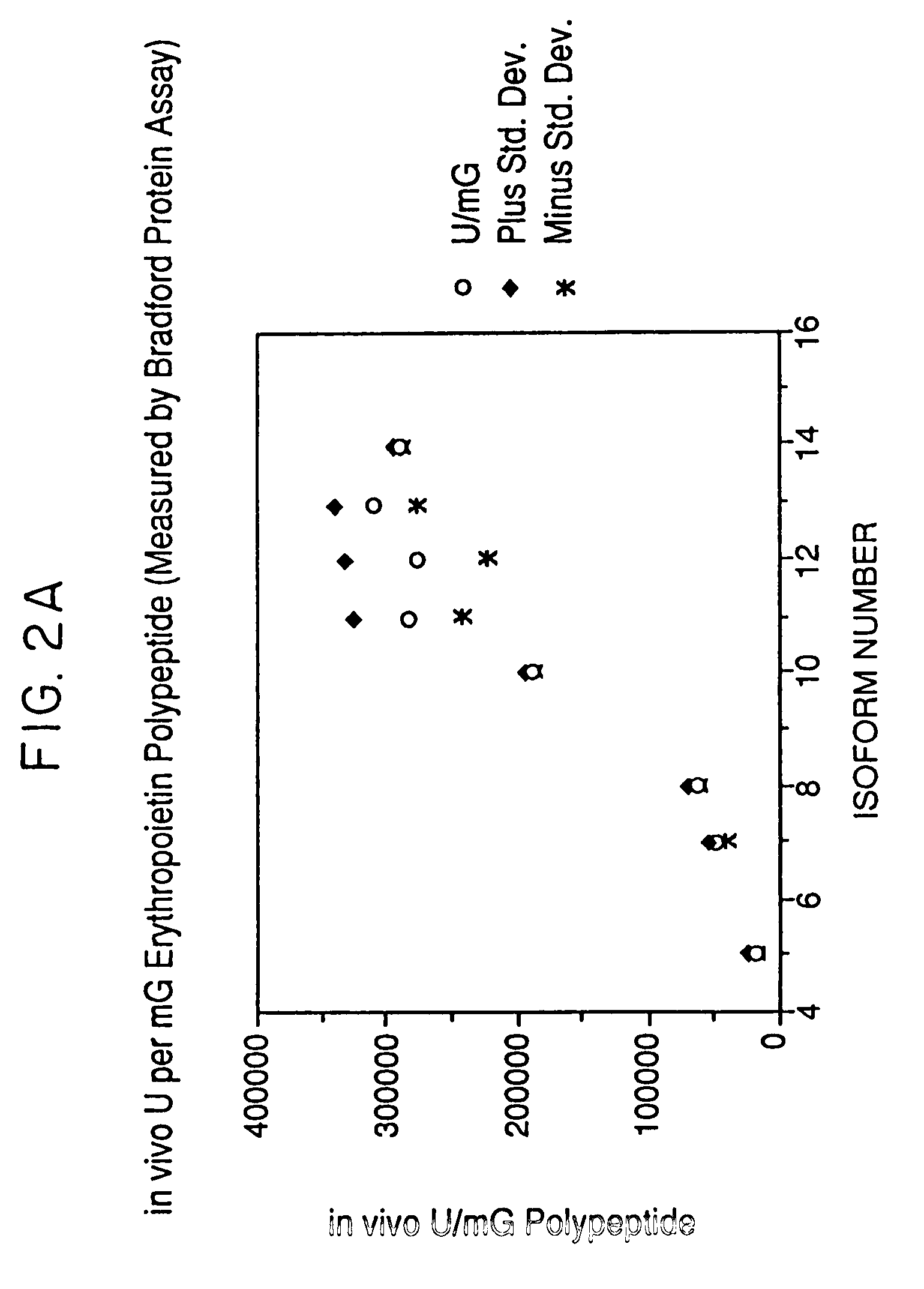
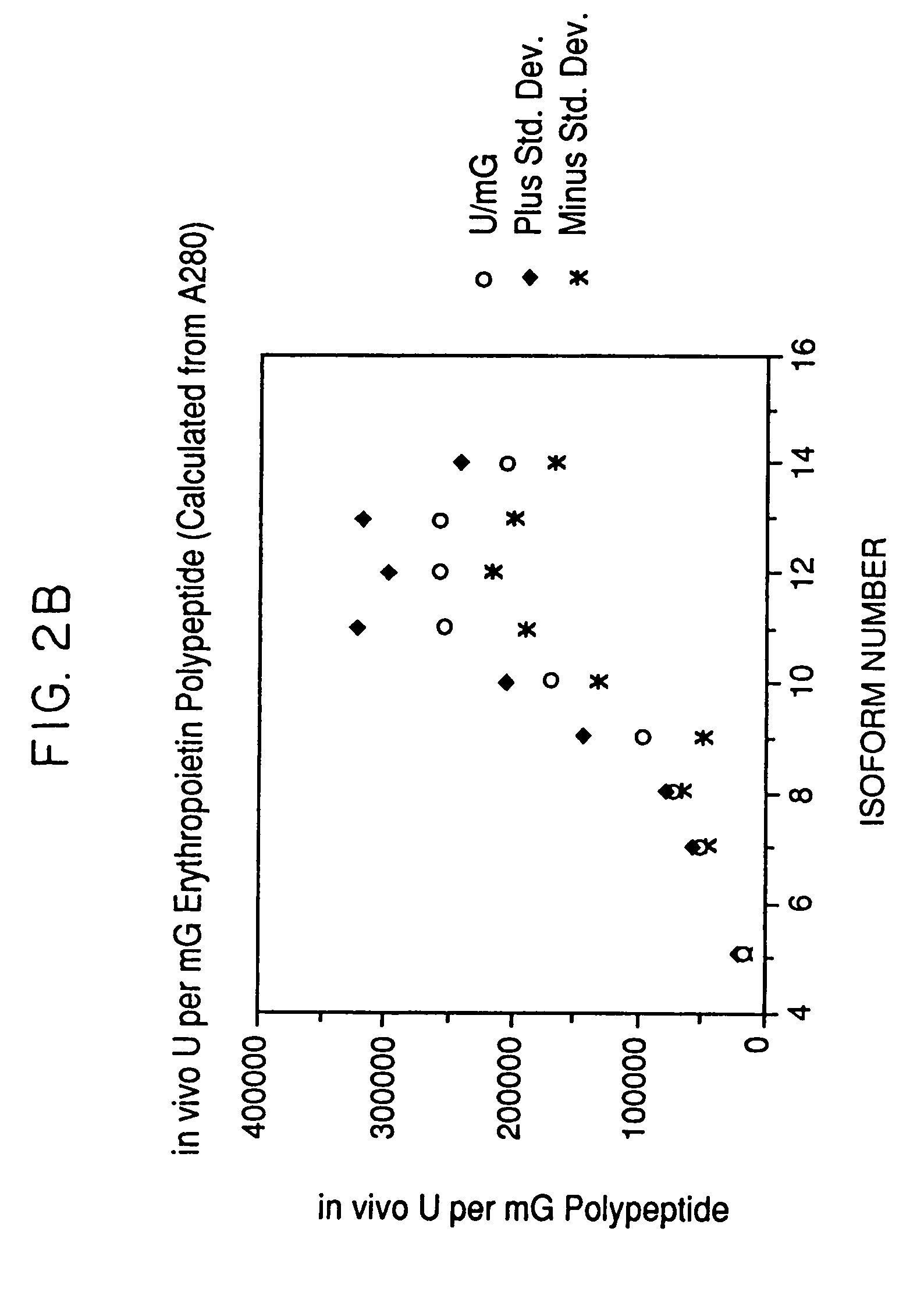
ActiveUS7217689B1Increase the number ofHigh sialic acid contentPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue culturePlasmidDNA
Erythropoietin analogs having at least one additional site for glycosylation, or a rearrangement of at least one site for glycosylation are disclosed. The invention also relates to DNA sequences encoding said erythropoietin analogs, and recombinant plasmids and host cells for analog expression.
Owner:AMGEN INC
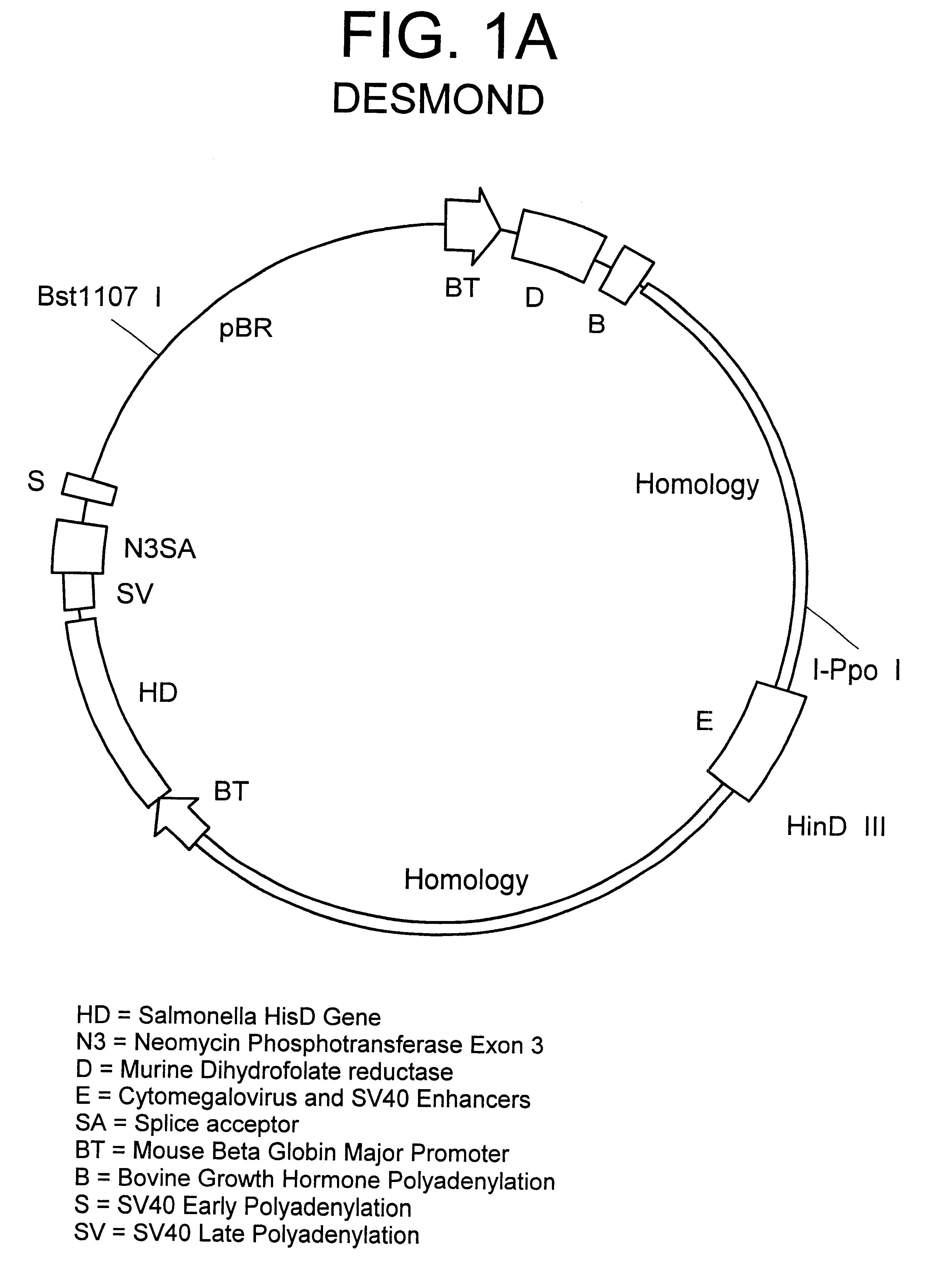
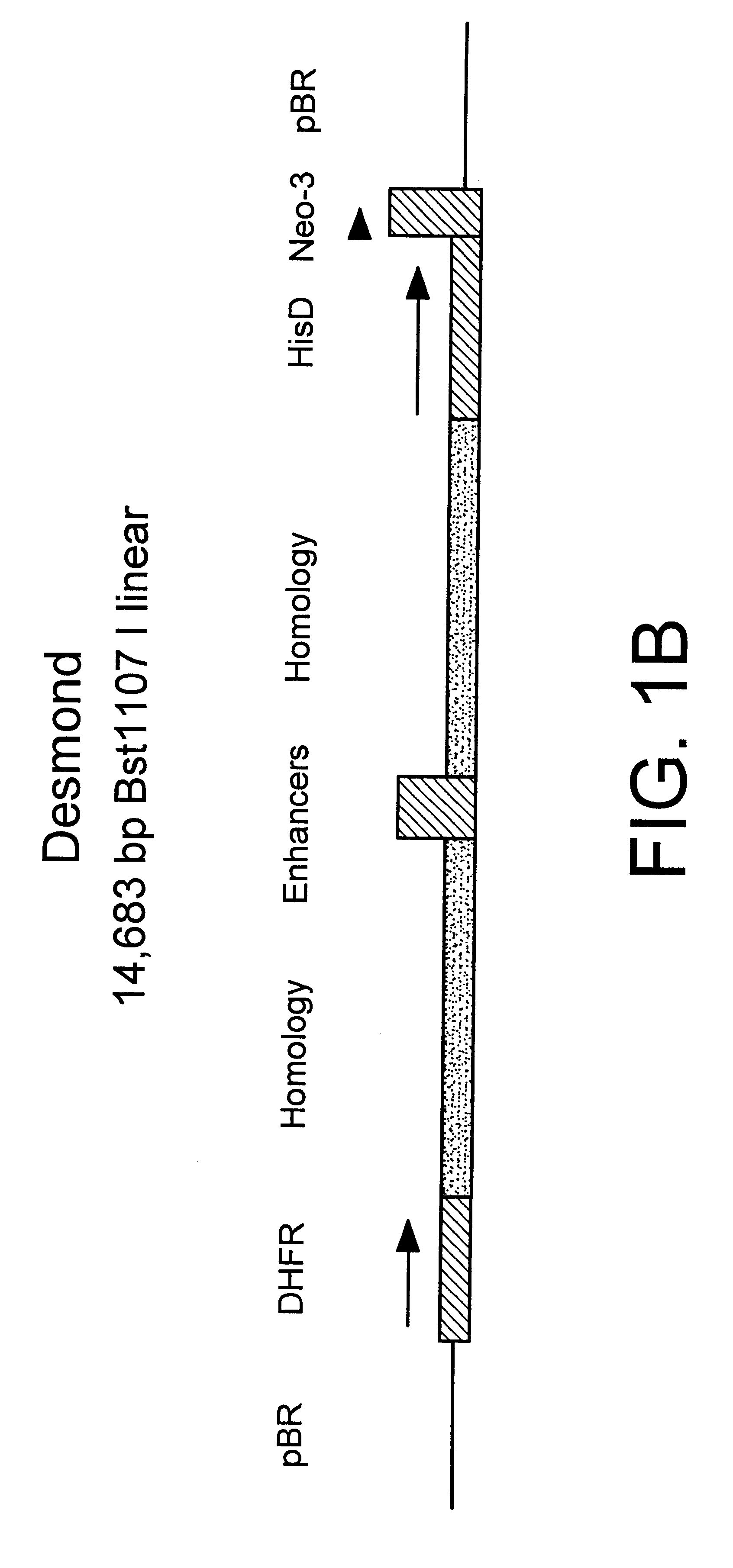
Method for integrating genes at specific sites in mammalian cells via homologous recombination and vectors for accomplishing the same
InactiveUS6413777B1Reduce in quantityImprove the level ofPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMammalReactive site
A method for achieving site specific integration of a desired DNA at a target site in a mammalian cell via homologous recombination is described. This method provides for the reproducible selection of cell lines wherein a desired DNA is integrated at a predetermined transcriptionally active site previously marked with a marker plasmid. The method is particularly suitable for the production of mammalian cell lines which secrete mammalian proteins at high levels, in particular immunoglobulins. Novel vectors and vector combinations for use in the subject cloning method are also provided.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Recombinant canine adenoviruses, method for making and uses thereof
InactiveUS6090393AProvide securityIncrease capacitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsBiotechnologyImmunogenicity
Disclosed and claimed are recombinant adenoviruses, methods of making them, uses for them (including in immunological, immunogenic, vaccine or therapeutic compositions, or, as a vector for cloning, replicating or expressing DNA and methods of using the compositions and vector), expression products from them, and uses for the expression products. More particularly, disclosed and claimed are recombinant canine adenoviruses (CAV) and methods of making them, uses for them, expression products from them, and uses for the expression products, including recombinant CAV2 viruses. Additionally, disclosed and claimed are truncated promoters, expression cassettes containing the promoters, and recombinant viruses and plasmids containing the promoters or expression cassettes.
Owner:VIROGENETICS +1
Vaccine formulations
ActiveUS7371395B2Improve stabilityStable and safe and easily administrableSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsPlasmidBacilli
Owner:MERIAL INC
Eukaryotic use of non-chimeric mutational vectors
The invention is based on the reaction of Duplex Mutational Vector in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Non-Chimeric Mutational Vector, having no RNA:DNA hybrid-duplex is shown to be an effective substrate for eukaryotic enzymes. The invention concerns the use of Non-Chimeric Mutational Vectors protected from 3' exonuclease attack in eukaryotic cells. Such protection can be conferred by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the recombinagenic oligonucleobase.
Owner:VALIGEN US +1
Methods and compositions for cellular and metabolic engineering
InactiveUS7105297B2Improve abilitiesExcellent catalytic performanceImmunoglobulinsFermentationIndividual geneOrganism
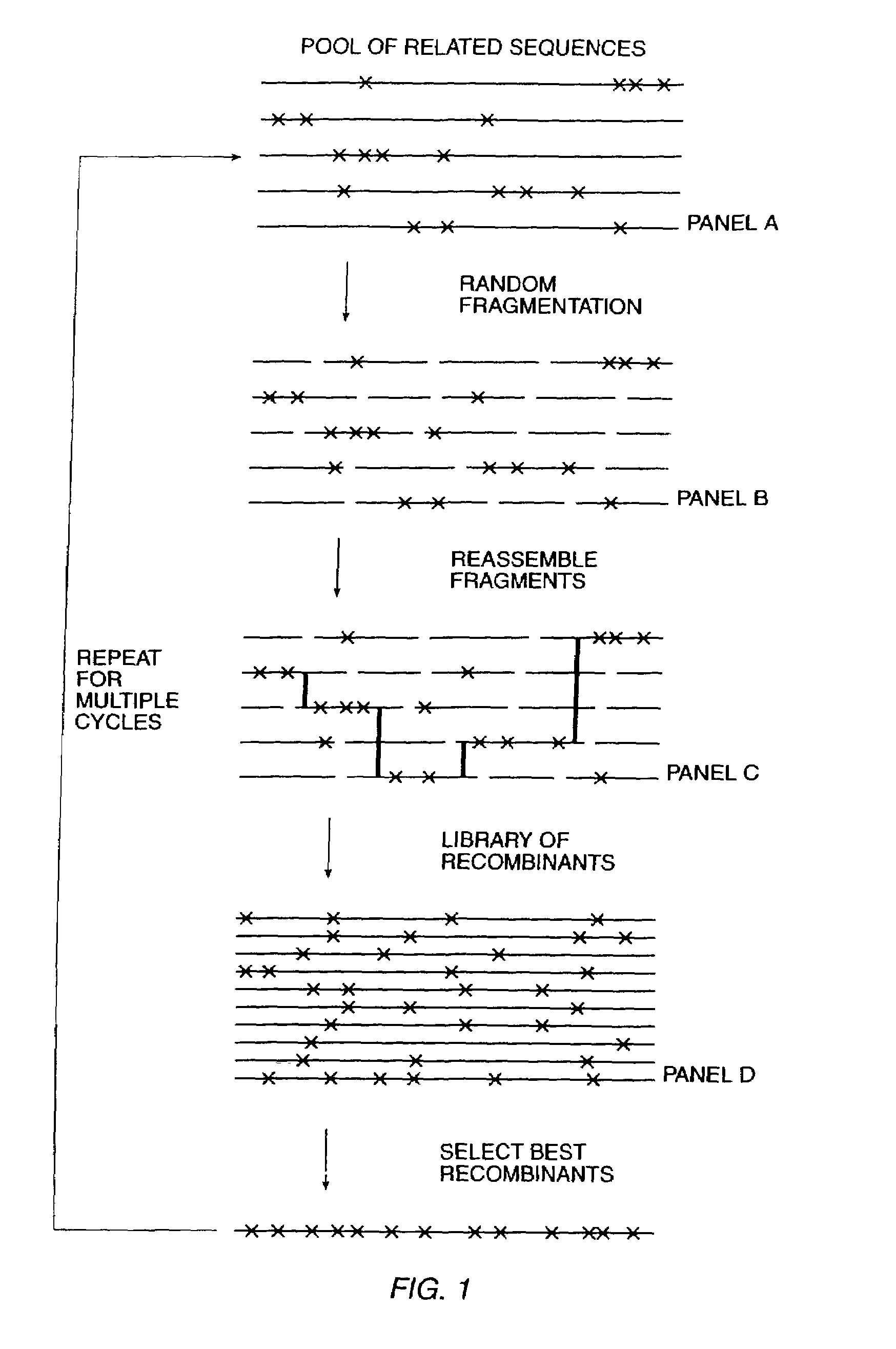
The present invention is generally directed to the evolution of new metabolic pathways and the enhancement of bioprocessing through a process herein termed recursive sequence recombination. Recursive sequence recombination entails performing iterative cycles of recombination and screening or selection to “evolve” individual genes, whole plasmids or viruses, multigene clusters, or even whole genomes. Such techniques do not require the extensive analysis and computation required by conventional methods for metabolic engineering.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Genetically modified cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, the constructs and method thereof
The invention provides a genetically modified Cyanobacteria having a construct comprising DNA fragments encoding pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase (adh) enzymes obtained from the Zymomonas mobilis plasmid pLOI295. The Cyanobacteria are capable of producing ethanol in recoverable quantities of at least 1.7 mumol ethanol per mg of chlorophyll per hour.
Owner:ENOL ENERGY
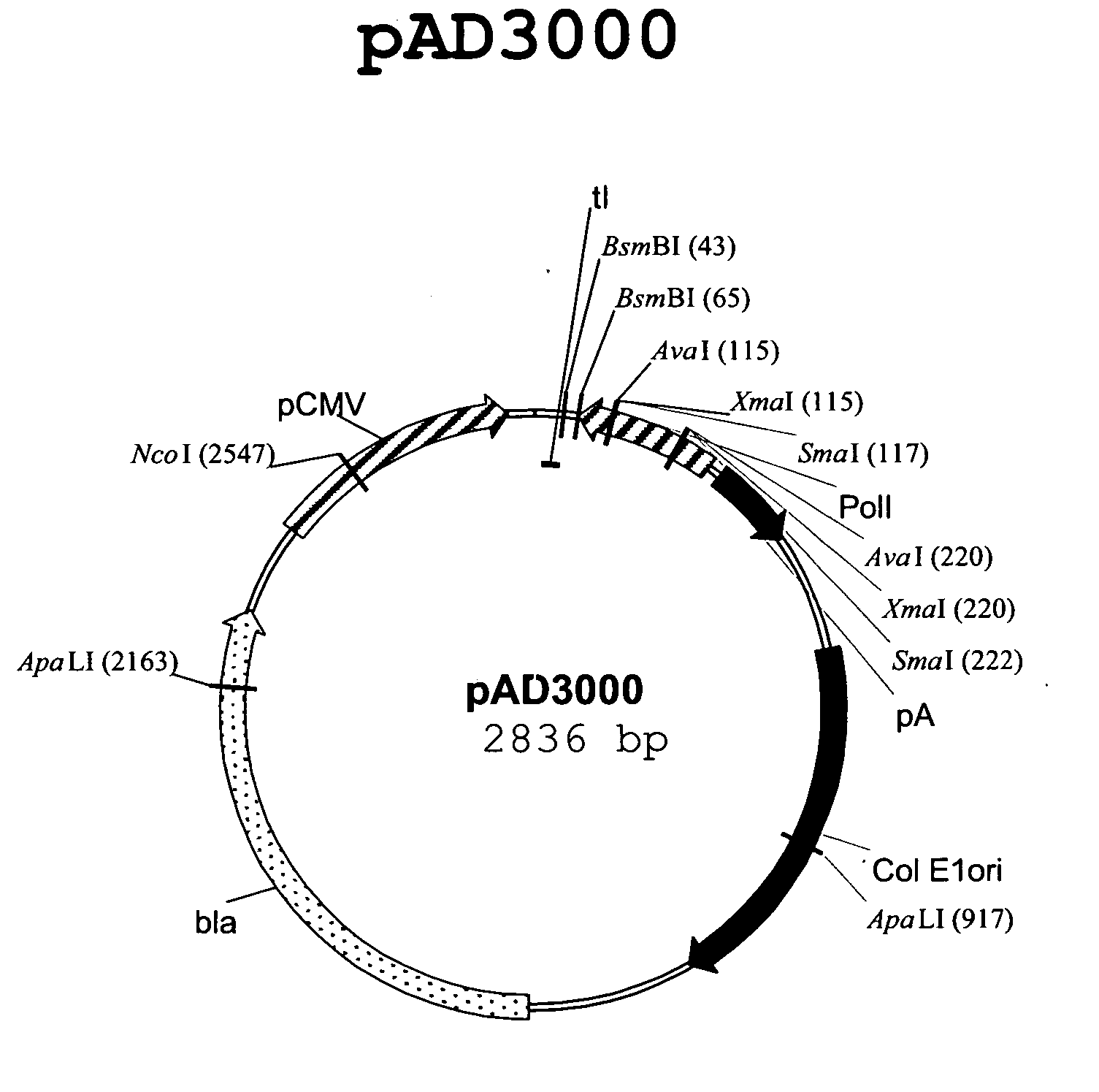
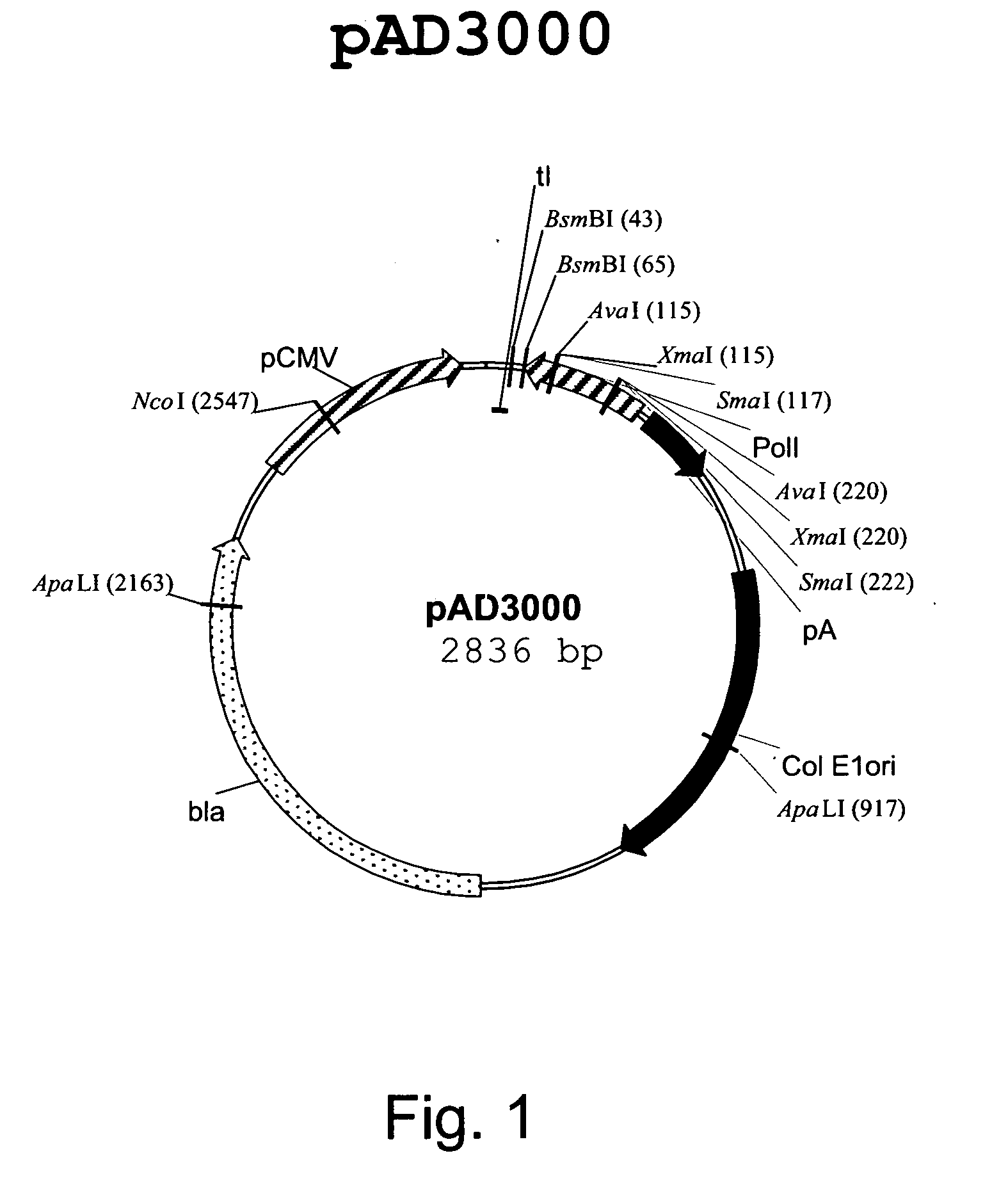
Multi plasmid system for the production of influenza virus
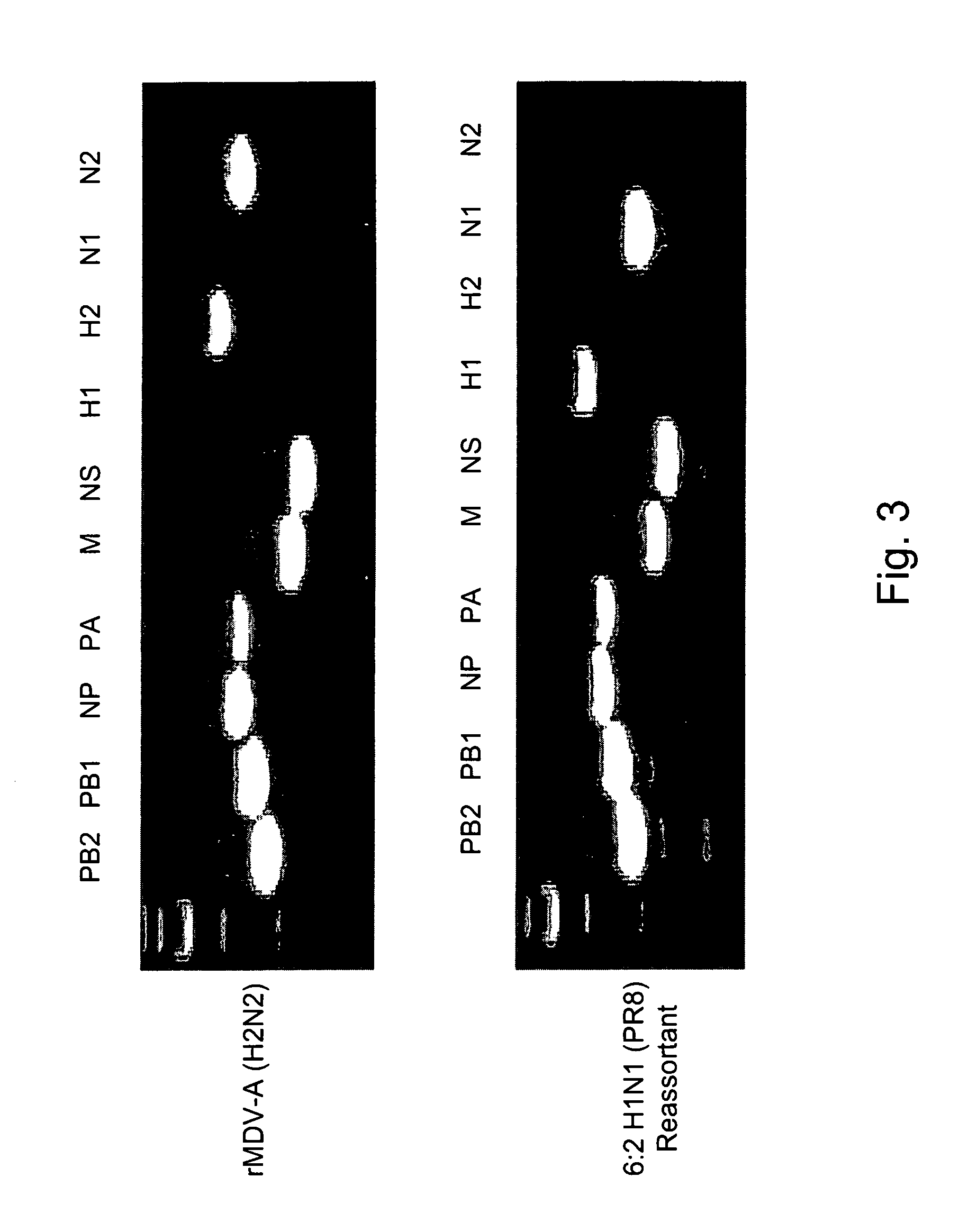
InactiveUS20050266026A1Easy to copyEnhanced ability to replicateSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsEmbryonated chicken eggCold adapted
Vectors and methods for the production of influenza viruses suitable as recombinant influenza vaccines in cell culture are provided. Bi-directional expression vectors for use in a multi-plasmid influenza virus expression system are provided. Additionally, the invention provides methods of producing influenza viruses with enhanced ability to replicate in embryonated chicken eggs and / or cells (e.g., Vero and / or MDCK) and further provides influenza viruses with enhanced replication characteristics. A method of producing a cold adapted (ca) influenza virus that replicates efficiently at, e.g., 25° C. (and immunogenic compositions comprising the same) is also provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
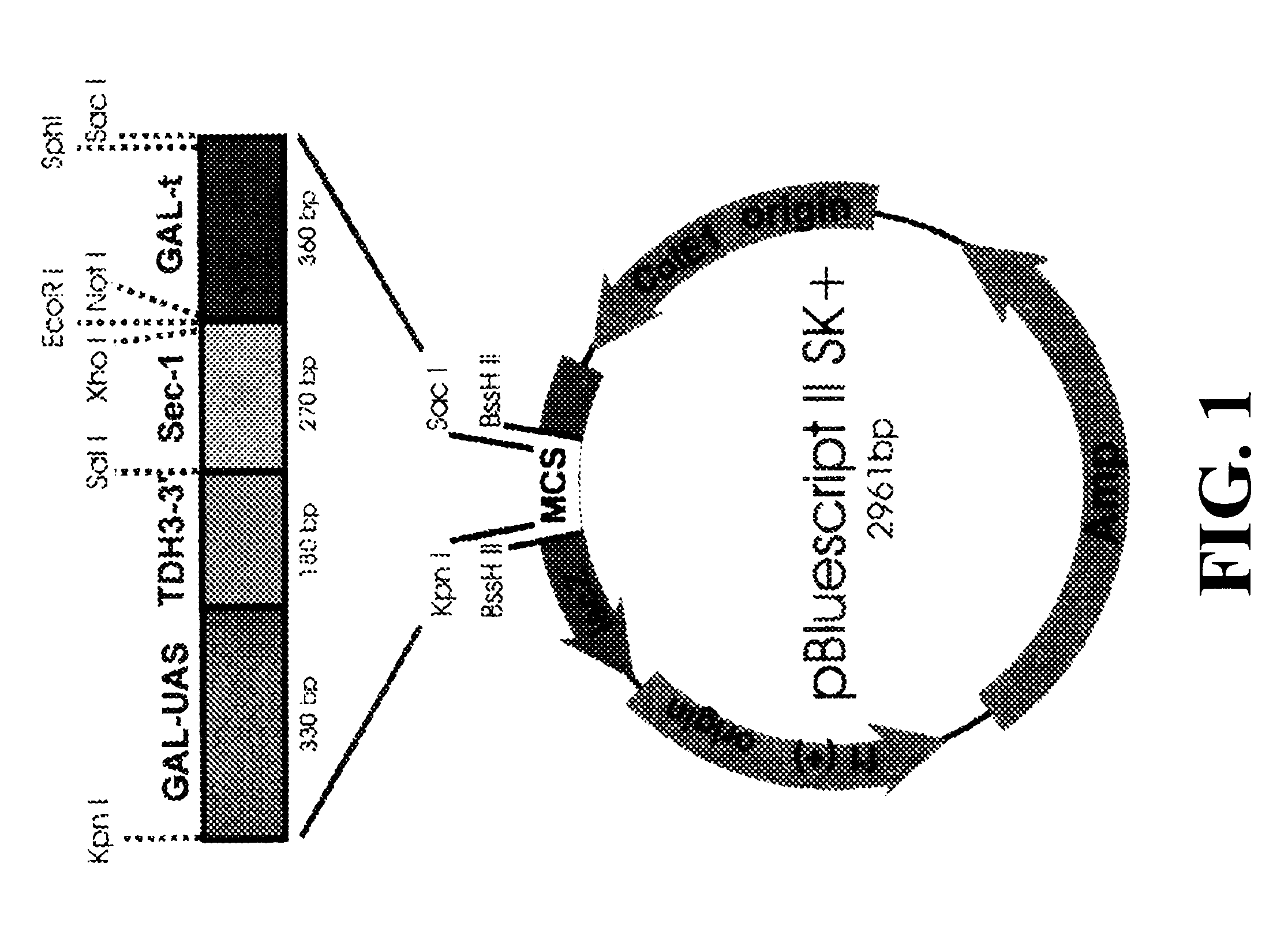
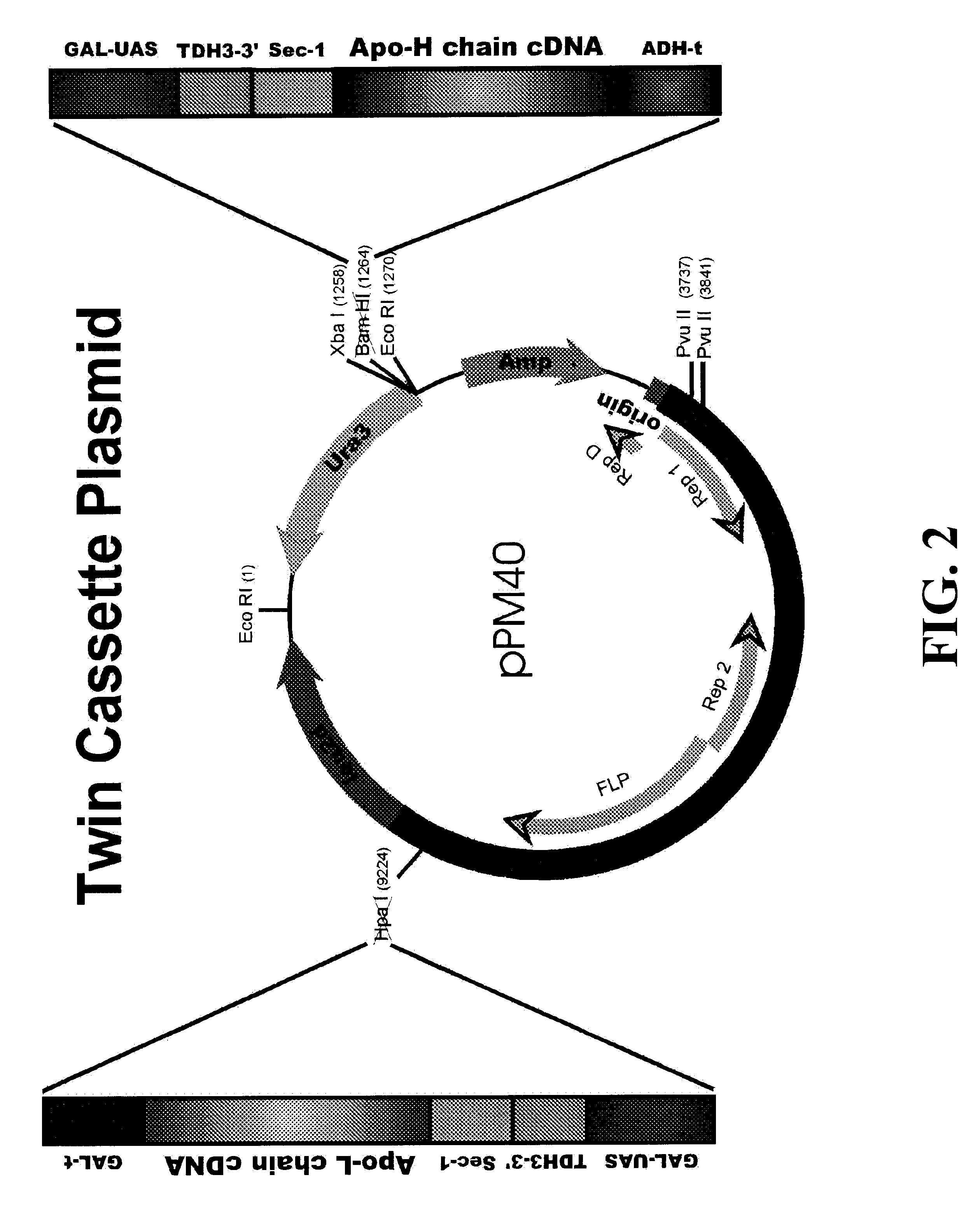
Expression of heterologous multi-domain proteins in yeast
InactiveUS6358733B1Increase productionCost effective productionSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsYeastSingle-Chain Antibodies
This invention demonstrates the utility of a yeast expression system for the expression of functional heterologous multi-domain proteins in yeast. The yeast expression system allows for the inclusion of a plurality of (up to three) modular expression cassettes which may encode multiple polypeptide chains of a heterologous multi-domain protein on a single plasmid (Twin Cassette). Because multiple polypeptide chains may be encoded for by the expression cassettes of the present invention in a single vector, the system can produce equivalent amounts of the multiple polypeptide chains, thereby enhancing the yield of a functional heterologous multi-domain protein. For example, functional monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) comprising a heavy chain and a light chain of an immunoglobulin (IgG), and functional immunotoxins comprising an antibody domain and an oxidase toxin may be produced using the Yeast expression system of the present invention. In addition, functional single chain antibodies, antibody fragments and chimeric antibodies may also be produced.
Owner:APOLIFE
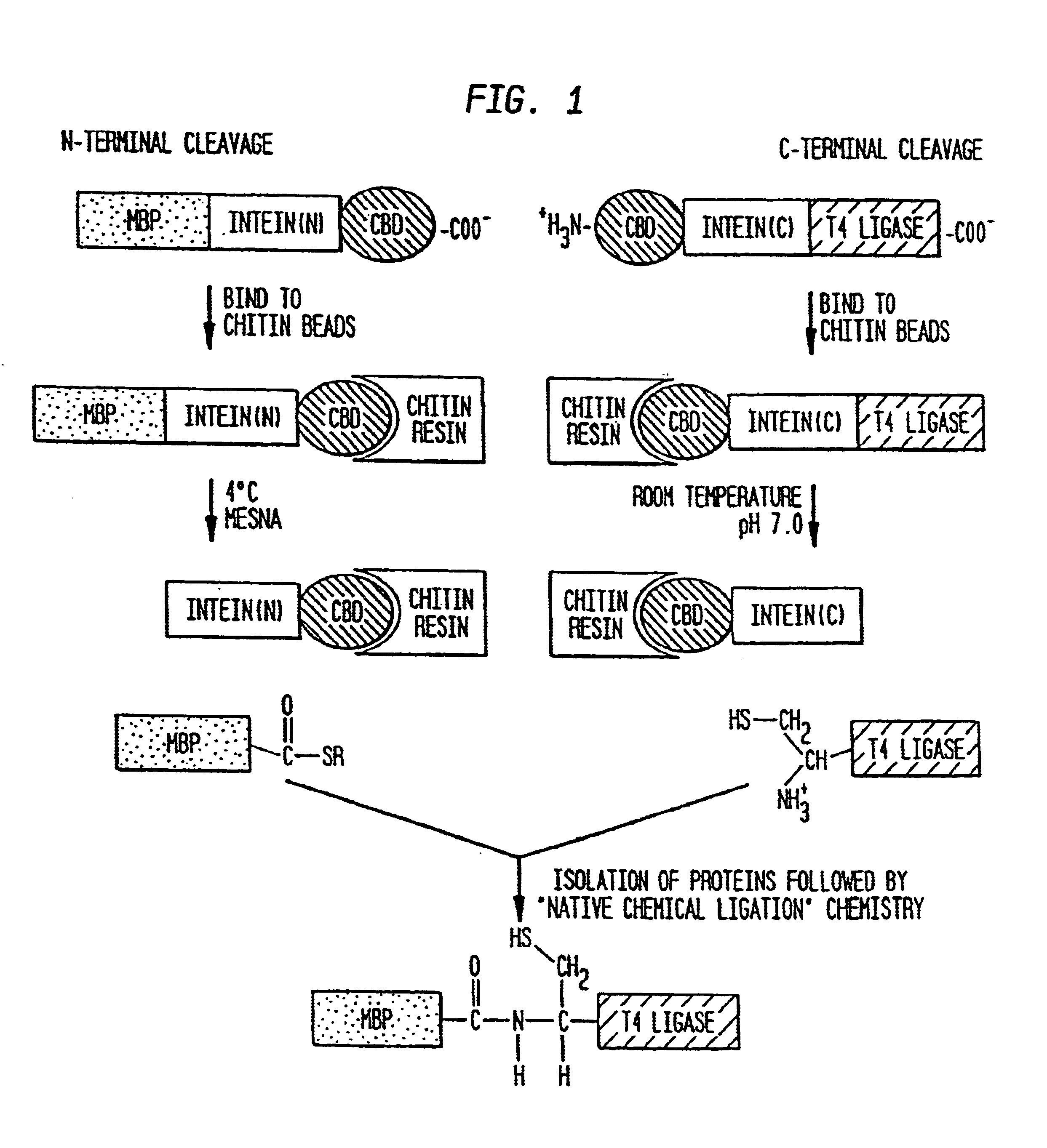
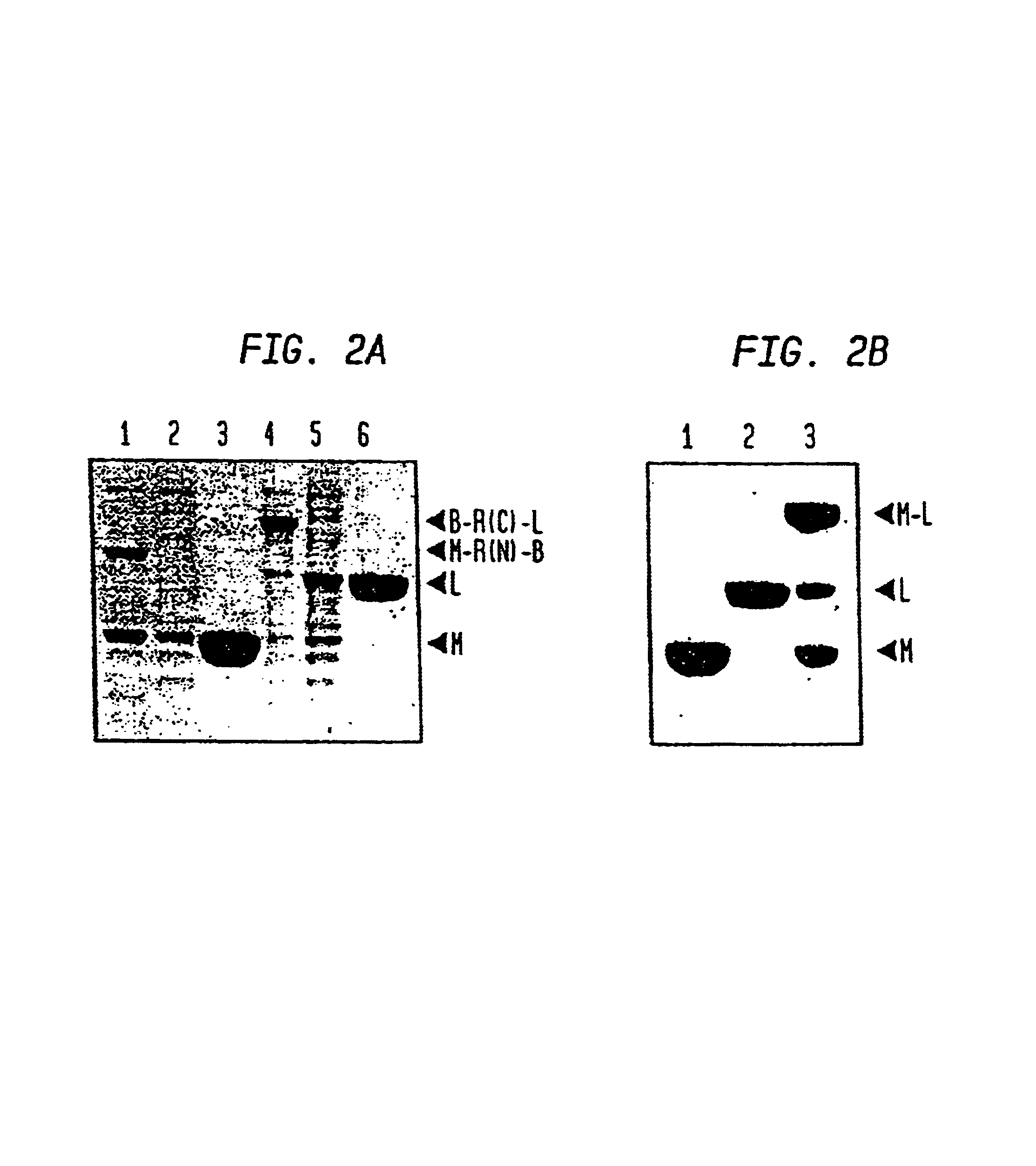
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
InactiveUS6849428B1Eliminate needBacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifProtein targetIntein
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum, is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Method for making linear, covalently closed DNA constructs
InactiveUS6451563B1Bulking digestionHigh processivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructGenomic DNA
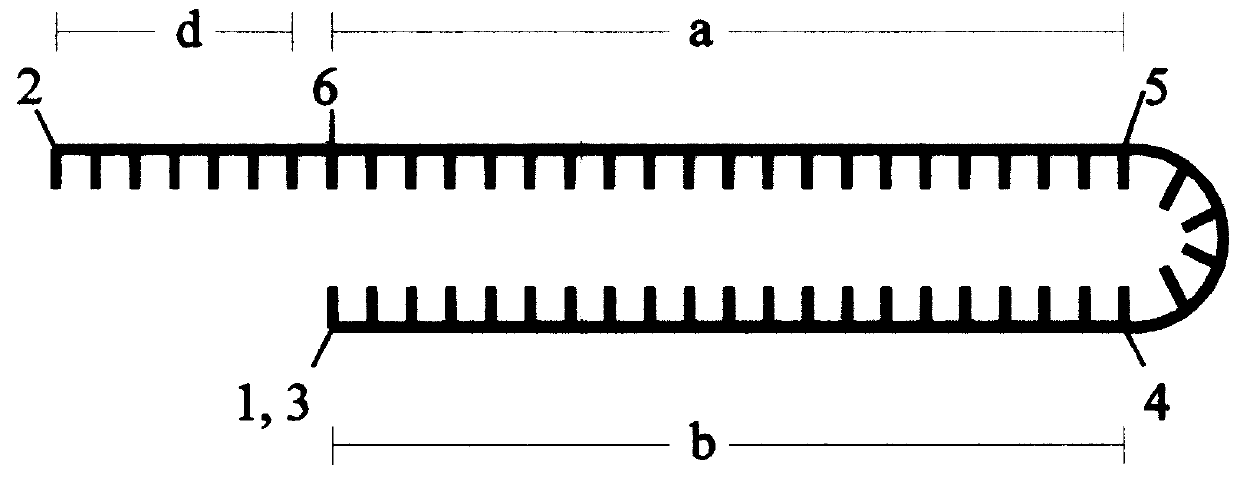
A process to obtain linear double-stranded covalently closed DNA "dumbbell" constructs from plasmids by restriction digest, subsequent ligation with hairpin oligodesoxyribonucleotides, optionally in the presence of restriction enzyme, and a final digestion with endo- and exonucleolytic enzymes that degrade all contaminating polymeric DNA molecules but the desired construct. The invention also provides a process to obtain said dumbbell constructs employing endonuclease class II enzymes. Furthermore, the invention provides a process to obtain linear, covalently closed DNA molecules, such as plasmids, free from contamination by genomic DNA, by submitting the DNA preparation to a facultative endonucleolytic degradation step and an obligatory exonucleolytic degradation step.
Owner:MOLOGEN AG +1
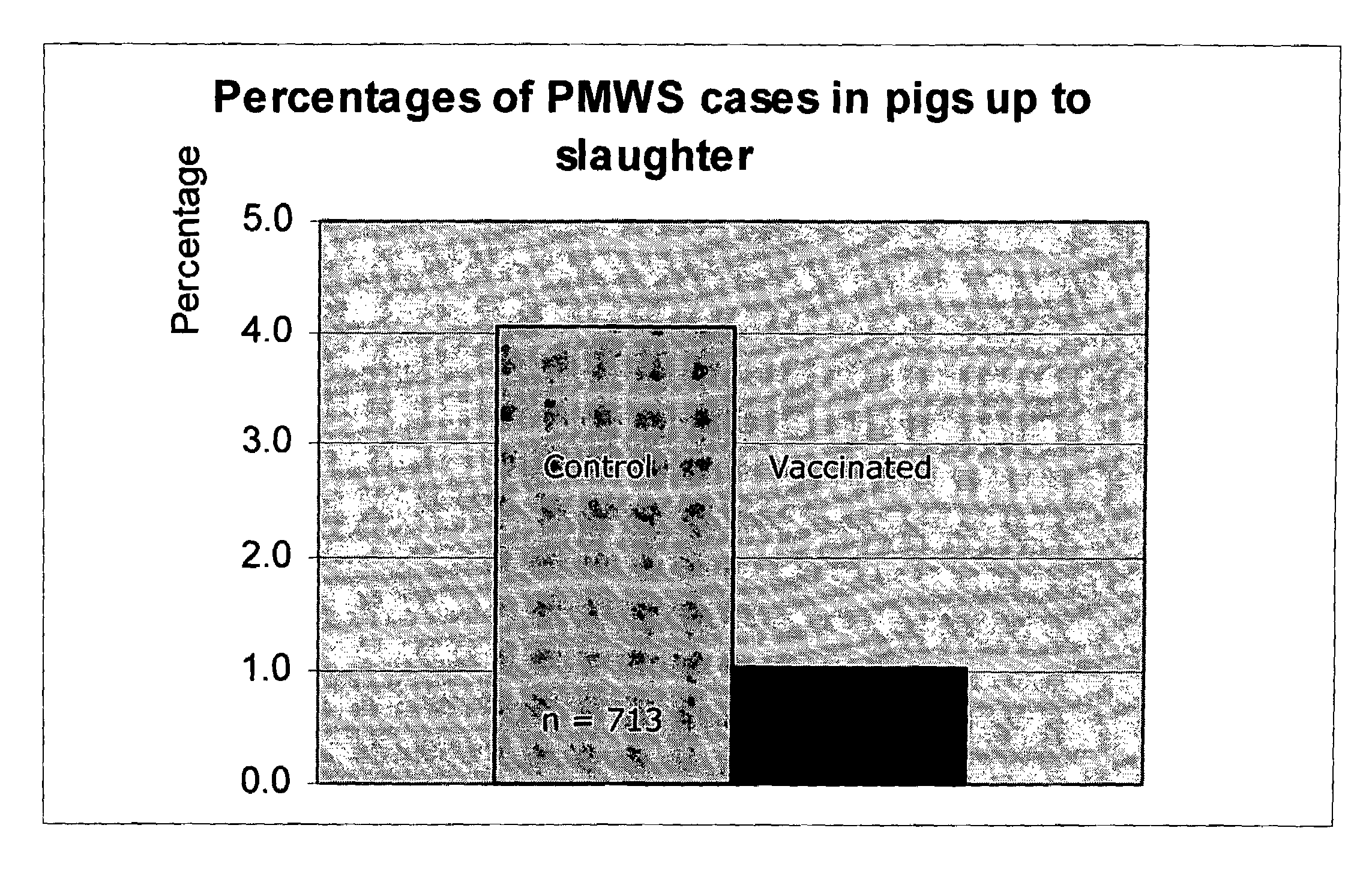
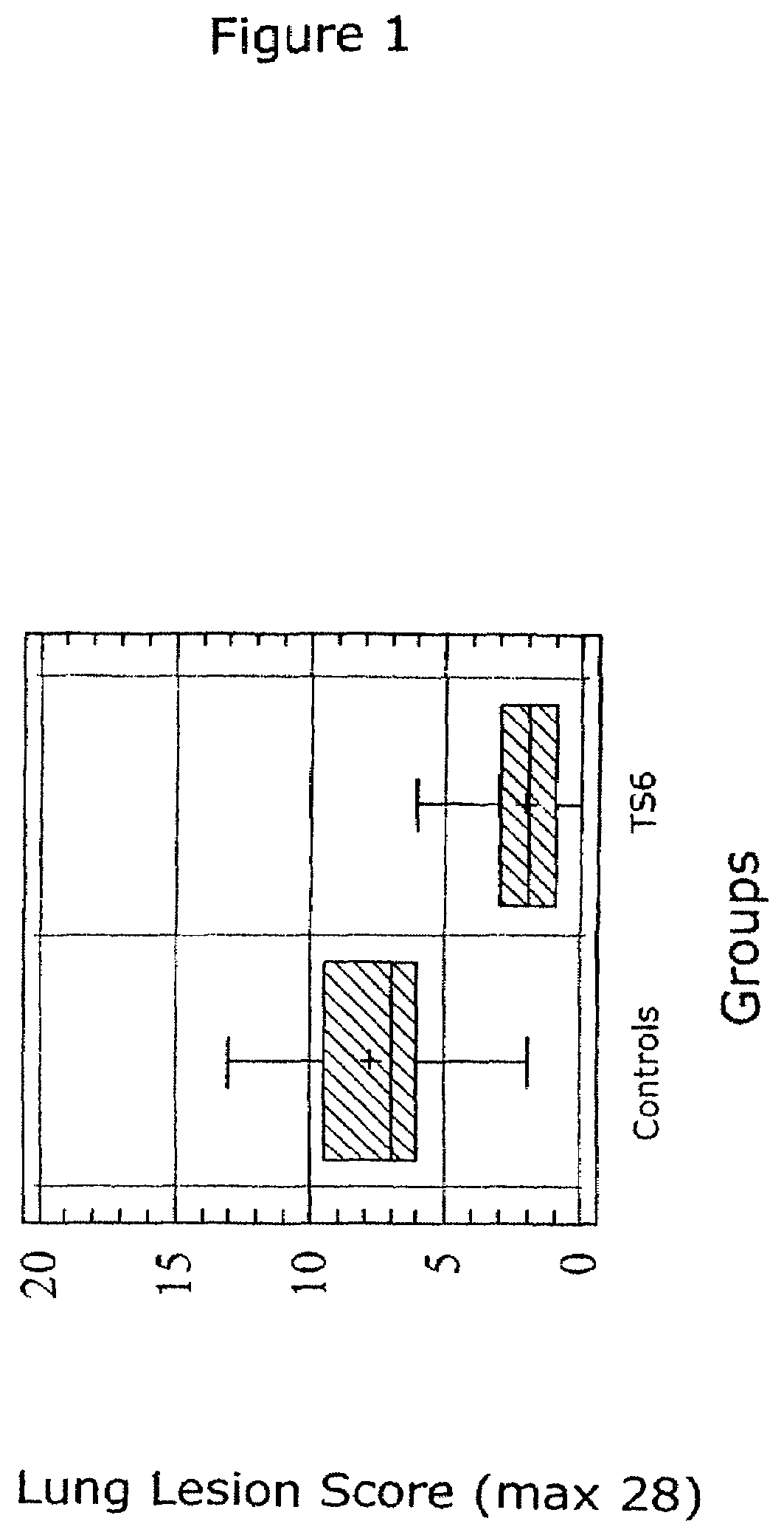
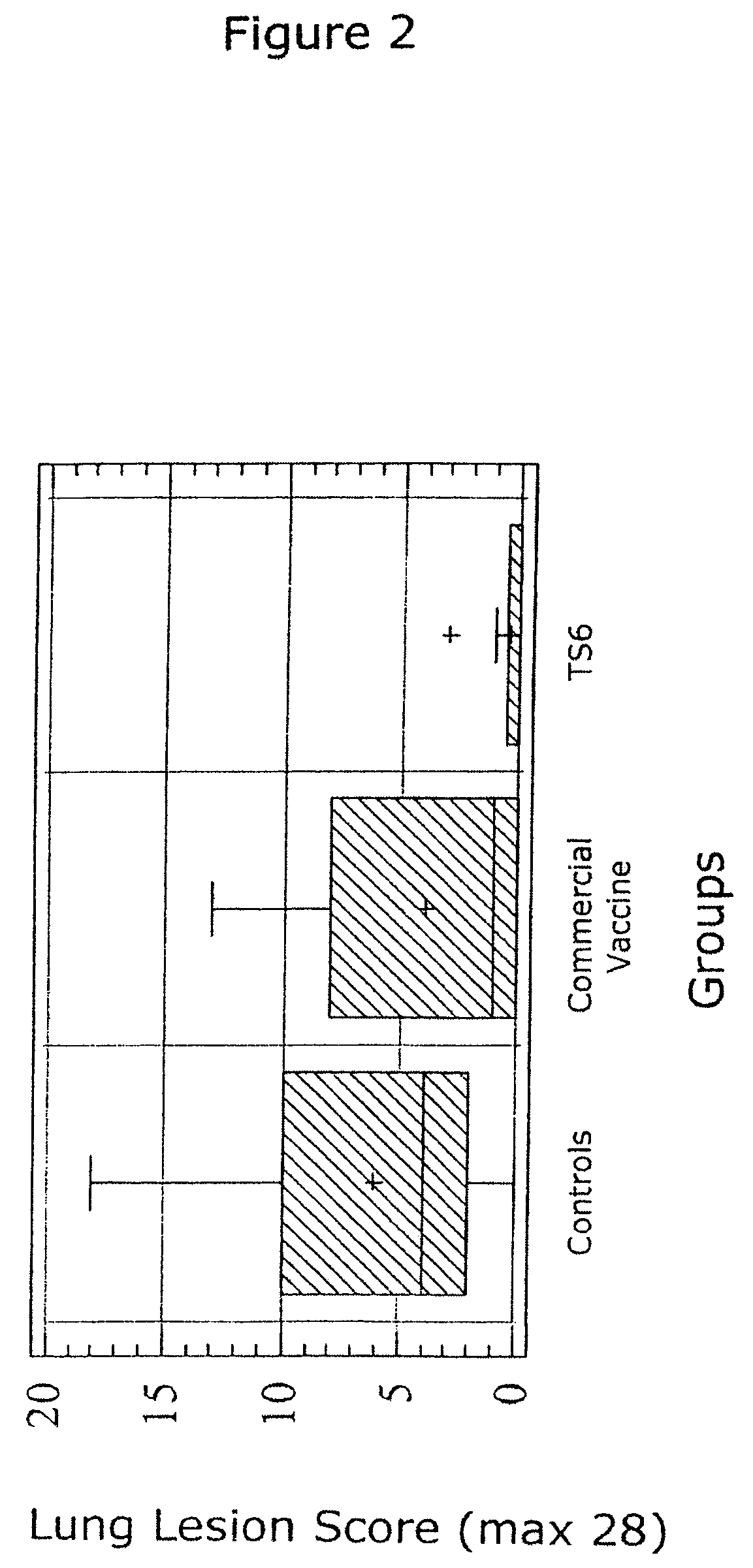
Vaccine formulations
ActiveUS20050079185A1Improve stabilityStable and safe and easily administrableAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseEukaryotic plasmidsNon ionic
The present invention provides for a novel oil-in-water (O / W) emulsion, with increased stability in the presence of bacterial or viral suspensions, especially those concentrated and non-purified or weakly purified. The emulsion of the present invention can act as vehicle for the delivery of a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one immunogen and, in particular, an immunogen selected from the group comprising an inactivated pathogen, an attenuated pathogen, a subunit, a recombinant expression vector, and a plasmid or combinations thereof. In one embodiment, the present invention provides for an injectable oil-in-water (O / W) emulsion comprising: (1) an aqueous solution containing an immunogen, said immunogen selected from the group comprising an inactivated Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae bacterium, an inactivated porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV-2) virus or combinations thereof; (2) a mineral oil; (3) a non-ionic lipophilic surfactant; and (4) a non-ionic hydrophilic surfactant having a low HLB value which comprises ethoxylated fatty acid diesters of sorbitan (generally having HLB value between 11 and 13). In another preferred embodiment, the present invention provides for an injectable oil-in-water (O / W) emulsion comprising: (1) an aqueous solution containing an immunogen; (2) a non-ionic hydrophilic surfactant having a high hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) value greater than 13 and less than 40, in particular HLB≧13.5, and preferably HLB≧14; (3) a mineral oil; (4) a non-ionic lipophilic surfactant; and (5) a non-ionic hydrophilic surfactant having a low HLB value (HLB value of about 9 to about 13).
Owner:MERIAL INC
Microbial production of nuclease resistant DNA, RNA, and oligo mixtures
Owner:FRAYNE CONSULTANTS
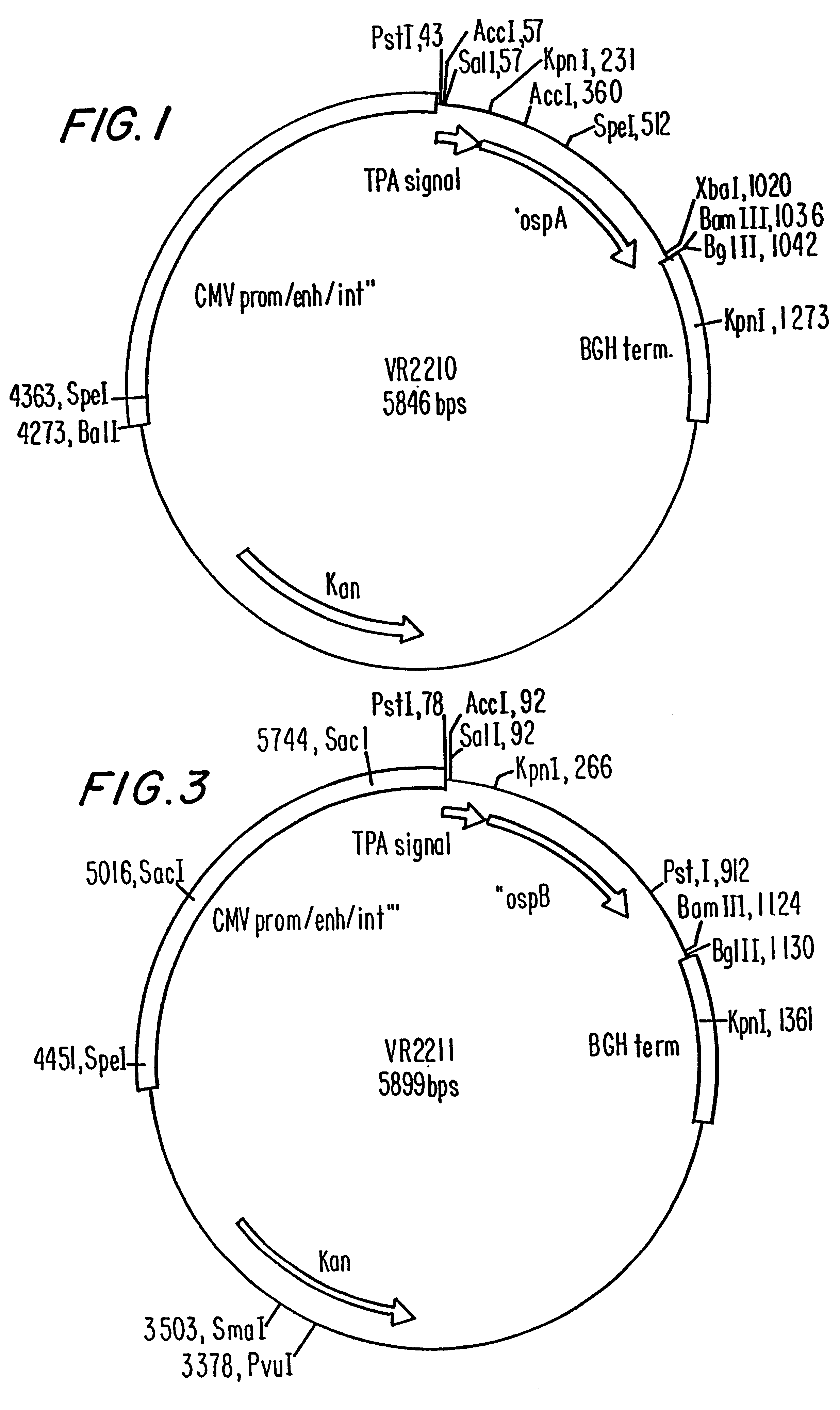
Compositions and methods for administering Borrelia DNA
Disclosed is a vaccine against Lyme Disease or its causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto or sensu lato) containing a plasmid a DNA encoding a promoter for driving expression in a mammalian cell, DNA encoding a leader peptide for facilitating secretion / release of a prokaryotic protein sequence from a mammalian cell, a DNA encoding Borrelia OspA or OspB, and a DNA encoding a terminator. Disclosed too is an immunogenic composition against Lyme Disease or its causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto or sensu lato) containing a plasmid comprising a DNA encoding a promoter for driving expression in a mammalian cell, DNA encoding a leader peptide for facilitating secretion / release of a prokaryotic protein sequence from a mammalian cell, a DNA encoding a Borrelia OspC, and a DNA encoding a terminator. And, methods for making and using such vaccines and the immunogenic composition are also disclosed.
Owner:PASTEUR MERIEUX SERUMS & VACCINS SA
Sequence specific antimicrobials
ActiveUS20160024510A1Reduce the amount requiredUnwanted amountOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBacteroidesMicrobial agent
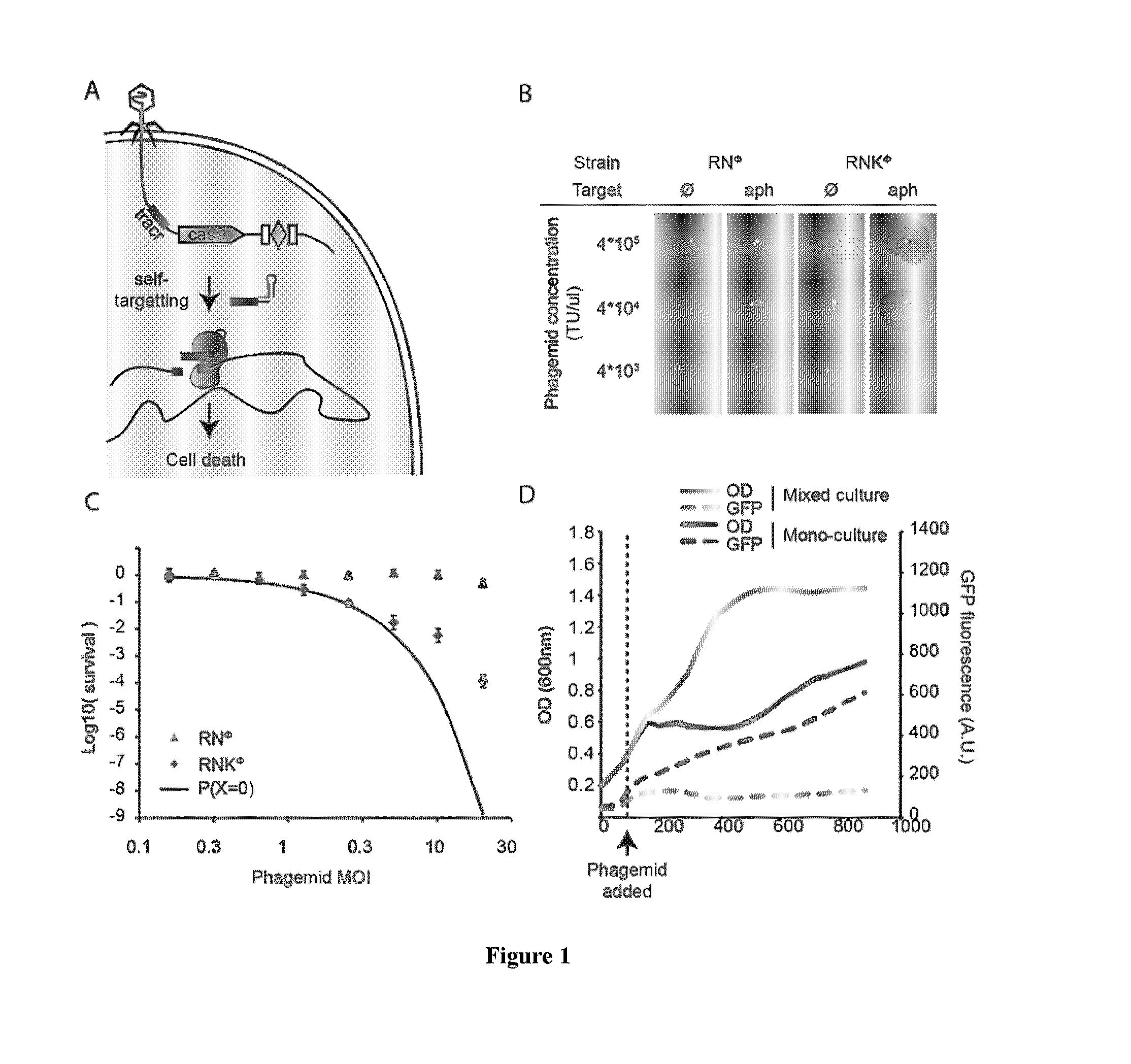
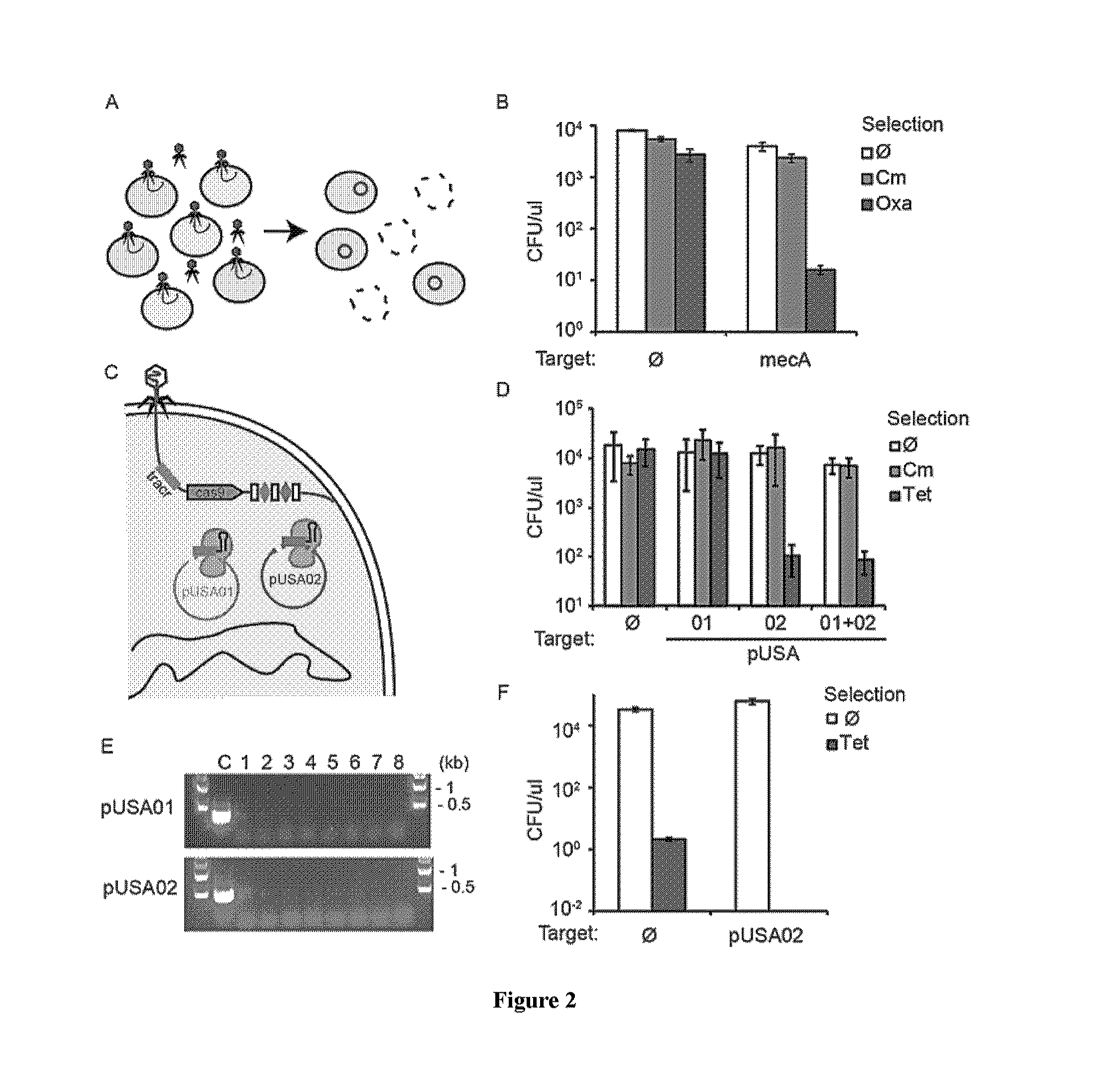
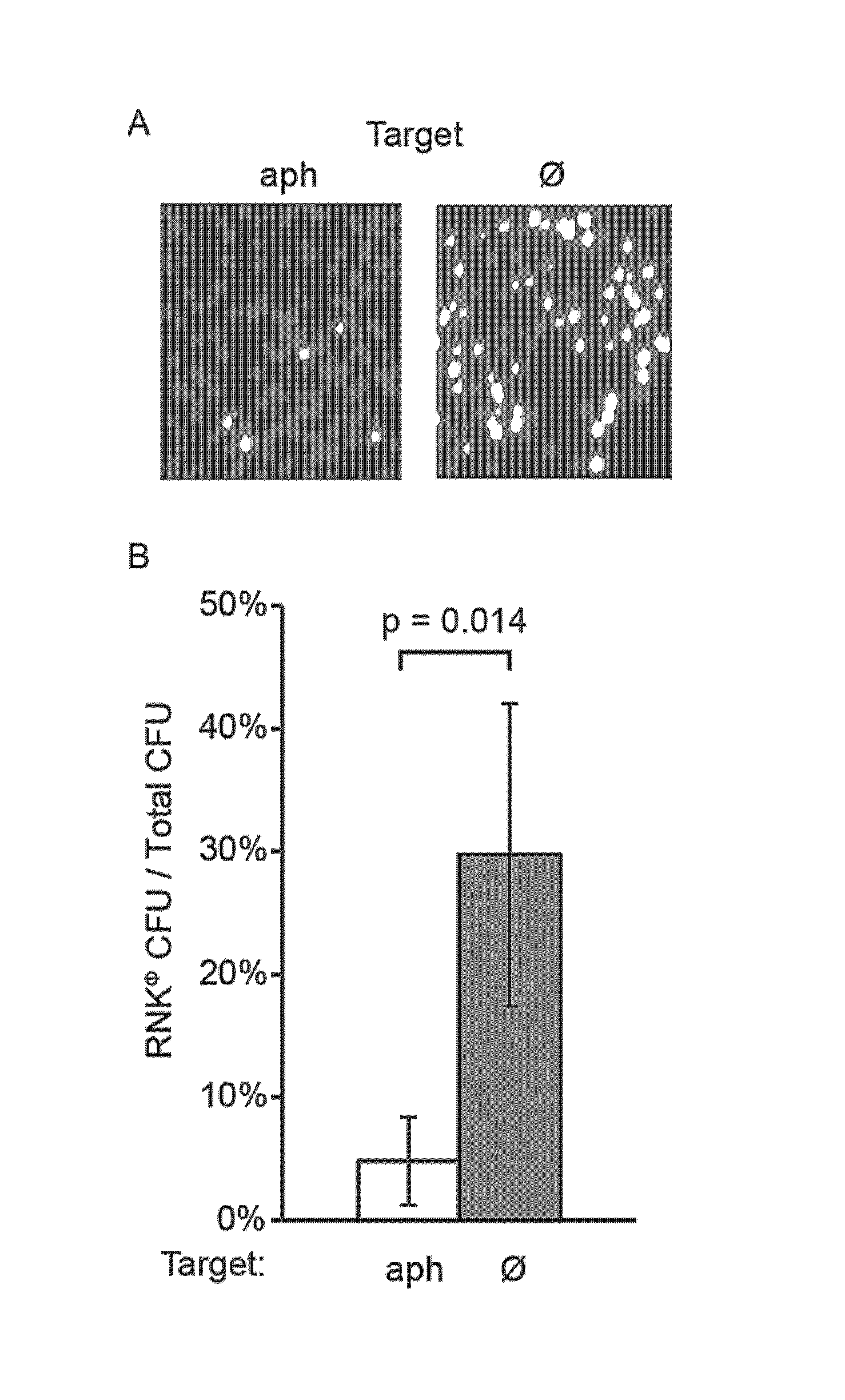
Provided are compositions and methods for selectively reducing the amount of antibiotic resistant and / or virulent bacteria in a mixed bacteria population, or for reducing any other type of unwanted bacteria in a mixed bacteria population. The compositions and methods involve targeting bacteria that are differentiated from other members of the population by at least one unique clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) targeted DNA sequence. The compositions and methods can be readily adapted to target any bacteria or any bacteria plasmid, or both.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Multi plasmid system for the production of influenza virus
InactiveUS20050158342A1Easy to copyEnhanced ability to replicateSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsEmbryonated chicken eggEukaryotic plasmids
Vectors and methods for the production of influenza viruses suitable as recombinant influenza vaccines in cell culture are provided. Bi-directional expression vectors for use in a multi-plasmid influenza virus expression system are provided. Additionally, the invention provides methods of producing influenza viruses with enhanced ability to replicate in embryonated chicken eggs and / or cells (e.g., Vero and / or MDCK) and further provides influenza viruses with enhanced replication characteristics. In addition, the present invention includes an improved method of rescue, wherein animal cells (e.g., SF Vero cells) are electroporated with plasmids and vectors of the invention.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
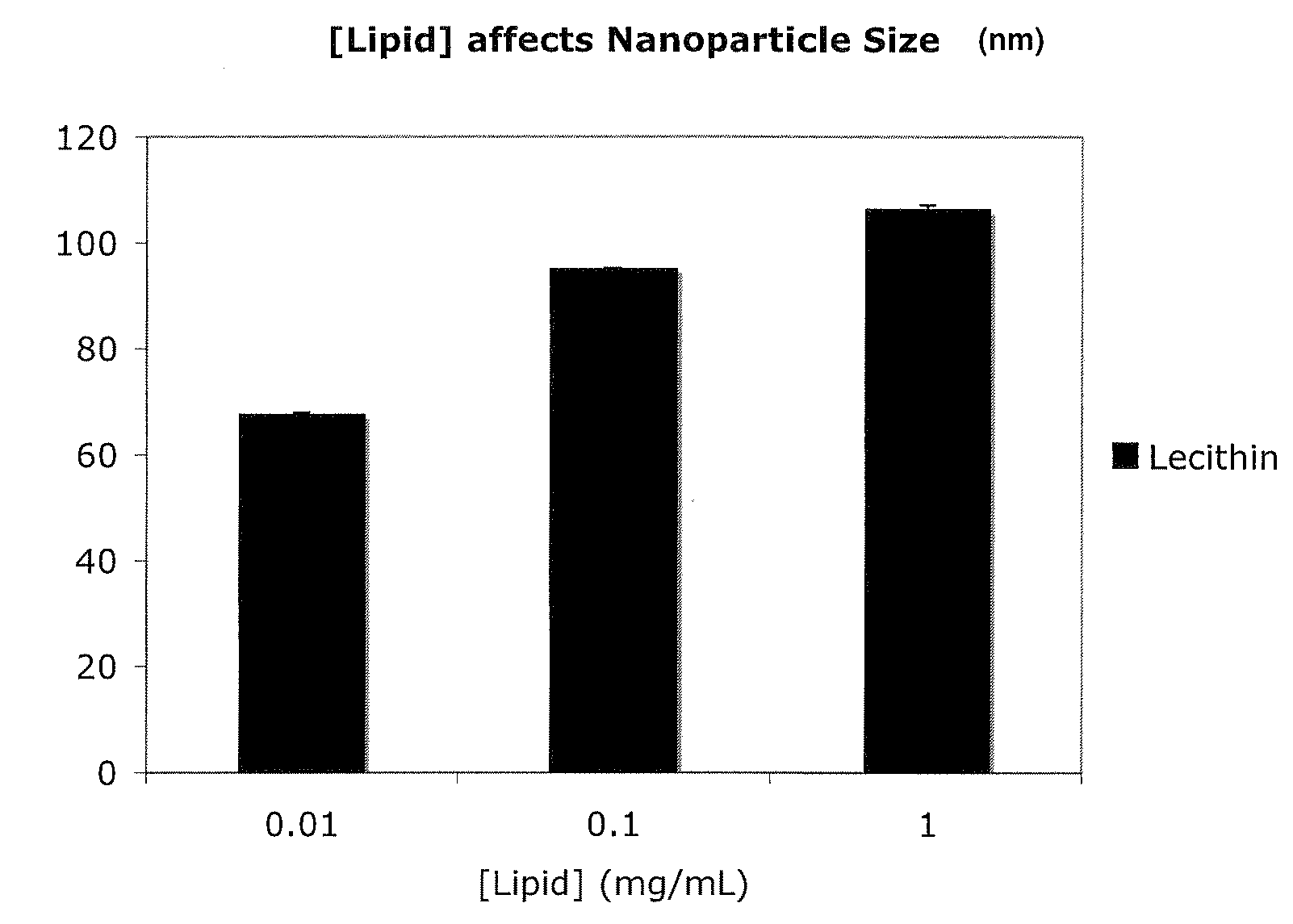
Polymer-encapsulated reverse micelles
ActiveUS20100196482A1Efficient packagingConvenience to mergePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationNanoparticle
A method for encapsulating nucleic acids, particularly siRNAs, shRNAs, microRNAs, gene therapy plasmids, and other oligonucleotides in biodegradable polymers is disclosed, whereby the nucleic acids are formulated into reverse micelles composed of non-toxic and / or naturally-occurring lipids prior to nanoparticle formation by nanoprecipitation. This method can be coupled to other techniques that improve intracellular drug targeting, ultimately enhancing intracellular delivery of the aforementioned nucleic acids.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Hydrogel bioscaffoldings and biomedical device coatings
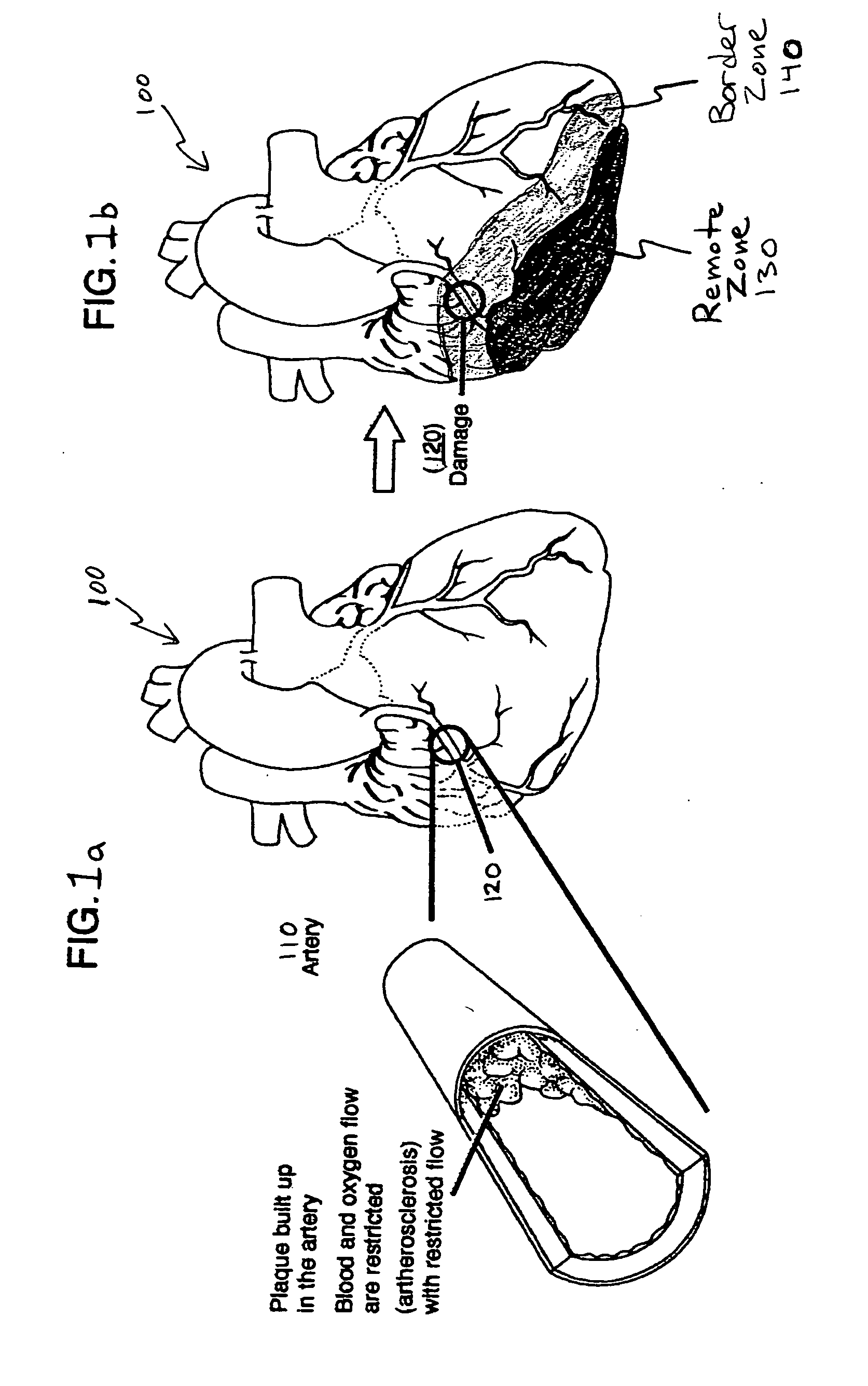
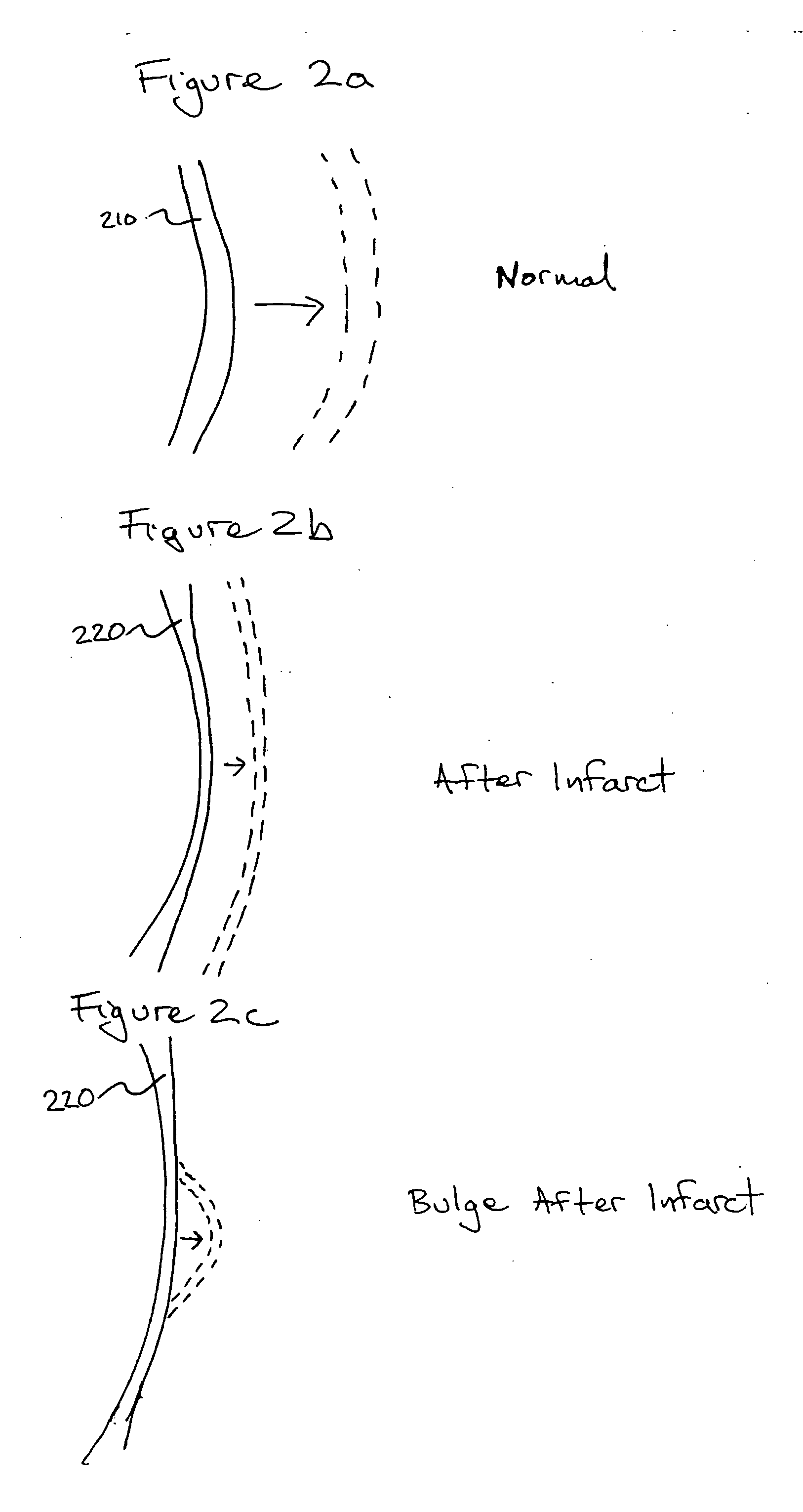
Bioscaffoldings formed of hydrogels that are crosslinked in situ in an infarcted region of the heart (myocardium) by a Michael's addition reaction or by a disulfide bond formed by an oxidative process are described. Each of the bioscaffoldings described includes hyaluronan as one of the hydrogel components and the other component is selected from collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-l-lysine, and fibrin. The bioscaffolding may further include an alginate component. The bioscaffoldings may have biofunctional groups such as angiogenic factors and stem cell homing factors bound to the collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-l-lysine, or fibrinogen hydrogel component. In particular, the biofunctional groups may be PR11, PR39, VEGF, bFGF, a polyarginine / DNA plasmid complex, or a DNA / polyethyleneimine (PEI) complex. Additionally, the hydrogel components may be injected into the infarct region along with stem cells and microspheres containing stem cell homing factors. The bioscaffolding may be formed on a stent or a cardiac medical device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Insect resistant plants
InactiveUS6943282B1Stably replicatedEliminating instanceClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacteroidesAureobasidium sp.
A method for expressing insecticidal protein structural genes in plant genomes is provided. In the preferred embodiments this invention comprises placing a structural gene for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein under control of a plant or a T-DNA promoter and ahead of a polyadenylation site followed by insertion of said promoter / structural gene combination into a plant genome by utilizing an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-based transformation system. The modified Ti plasmid is then used to transform recipient plant cells. Also provided are the plants and tissues produced by this method and bacterial strains, plasmids, and vectors useful for execution of this invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Plasmid system for multigene expression
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
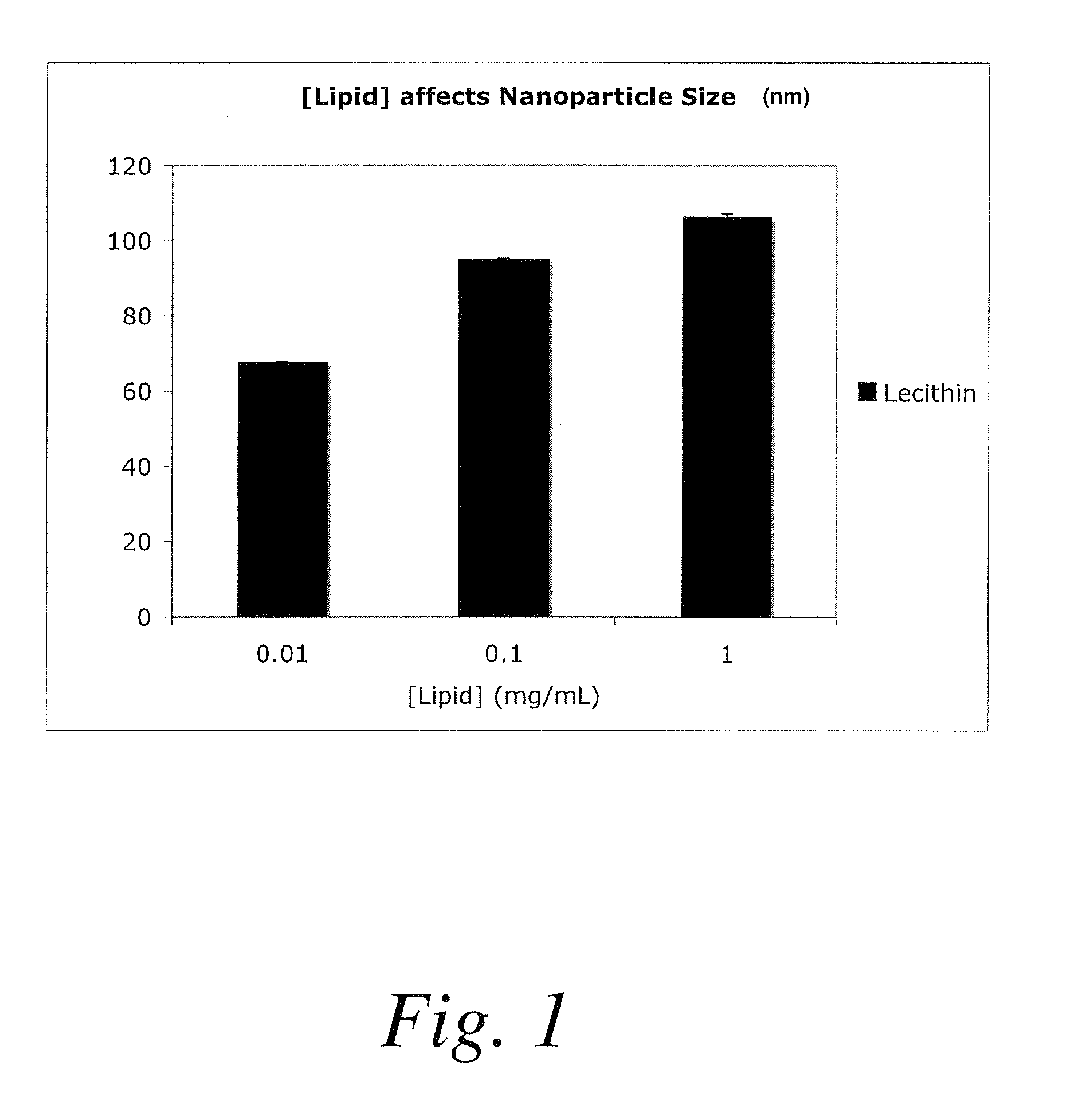
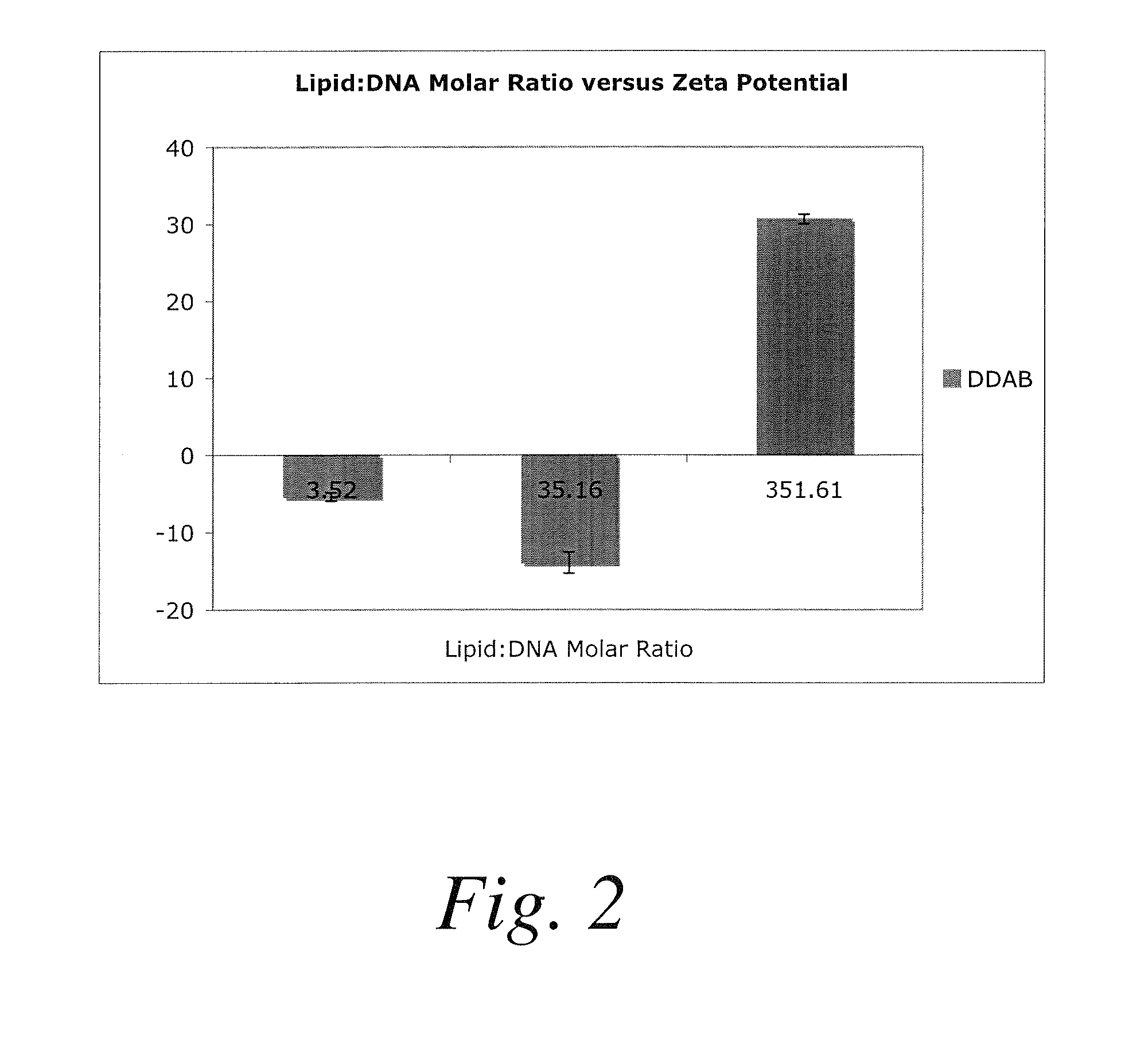
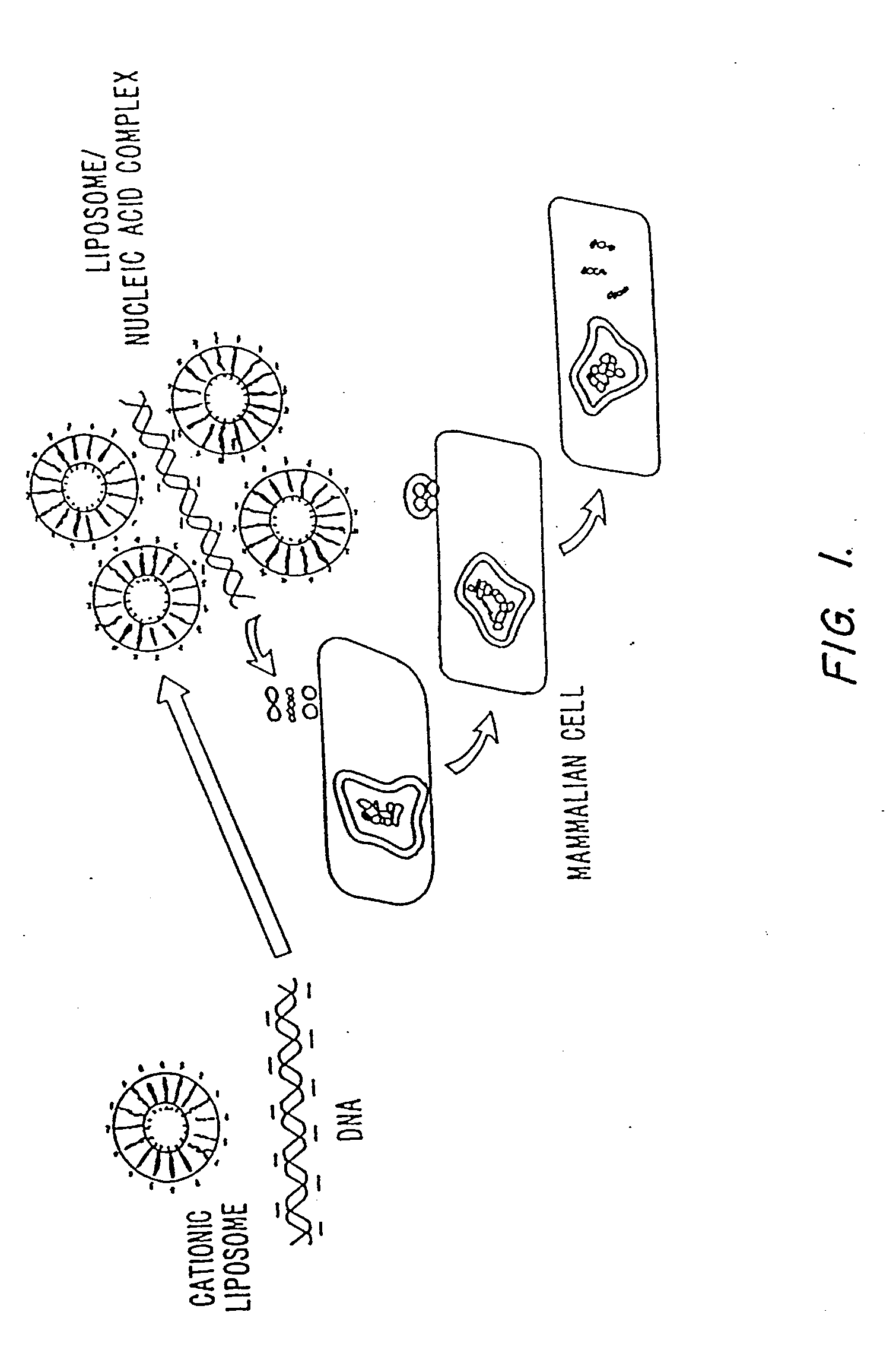
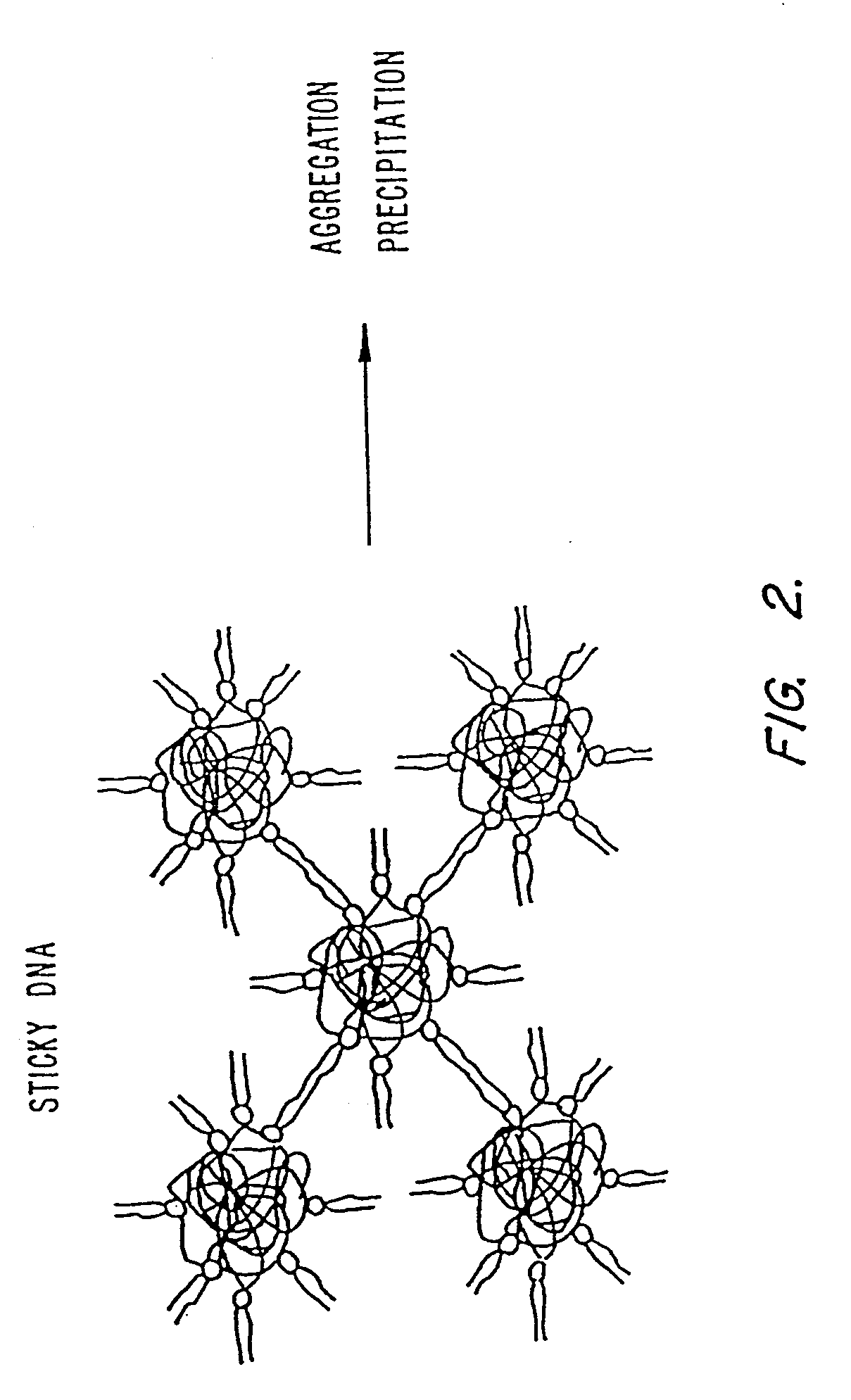
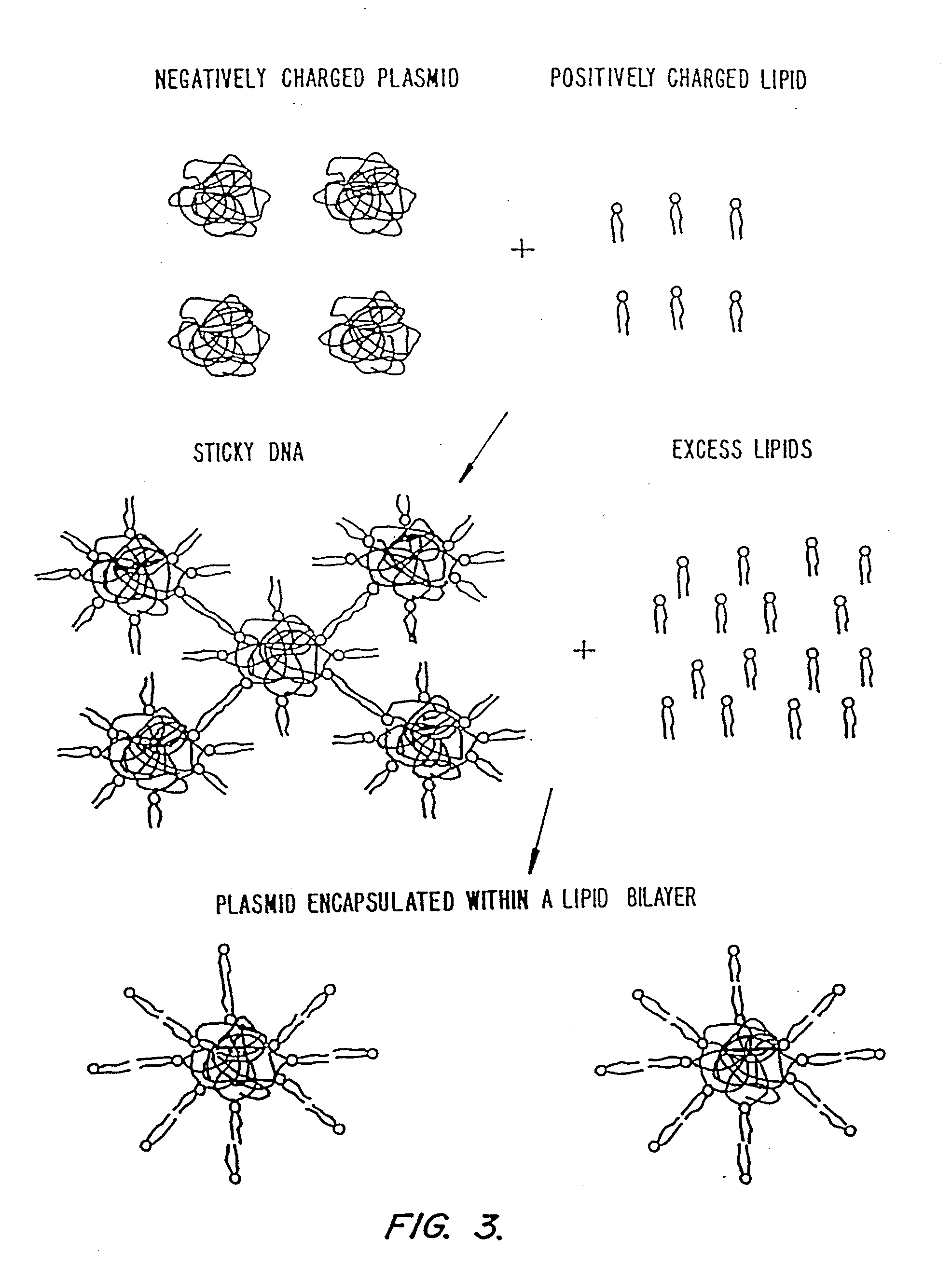
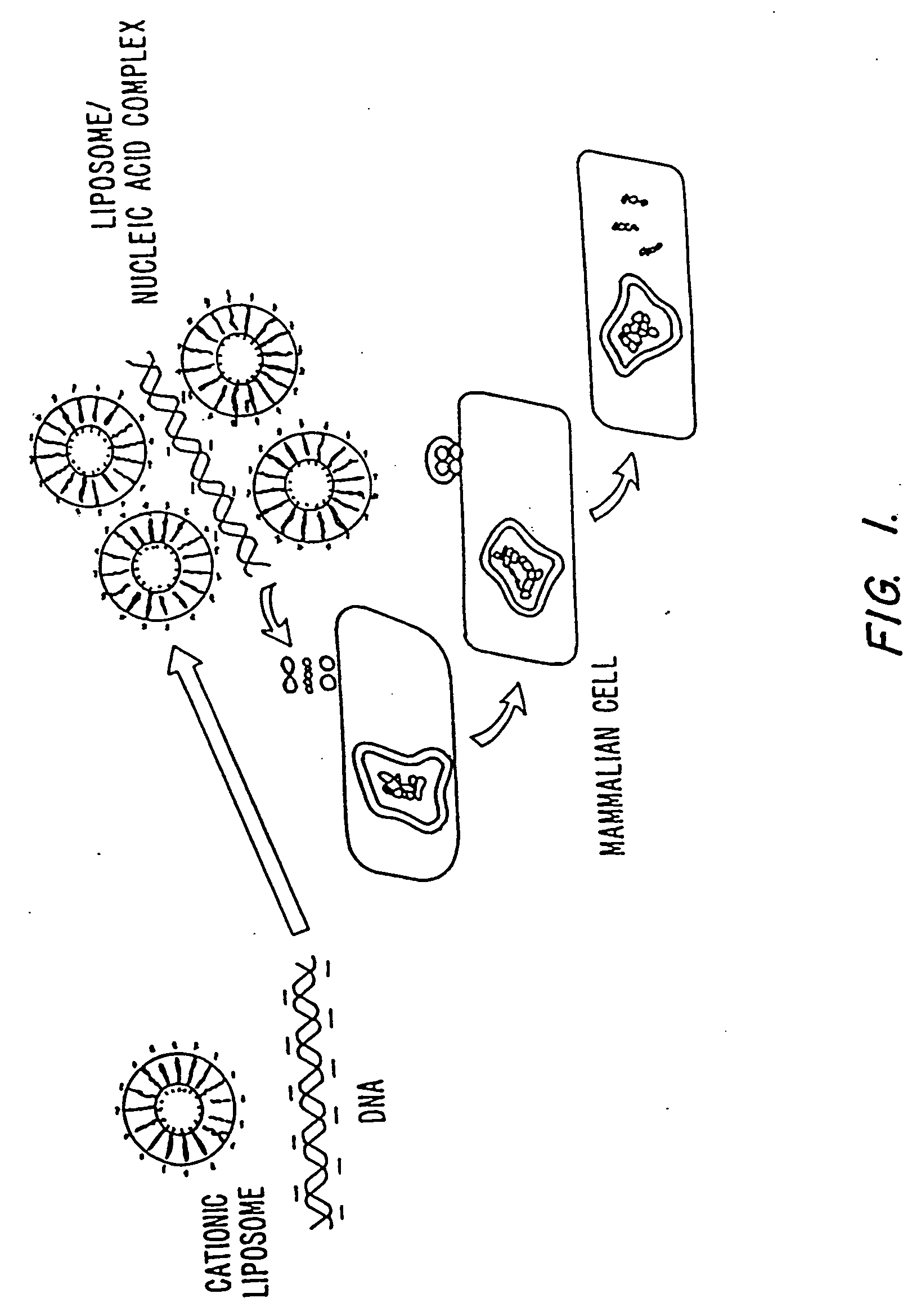
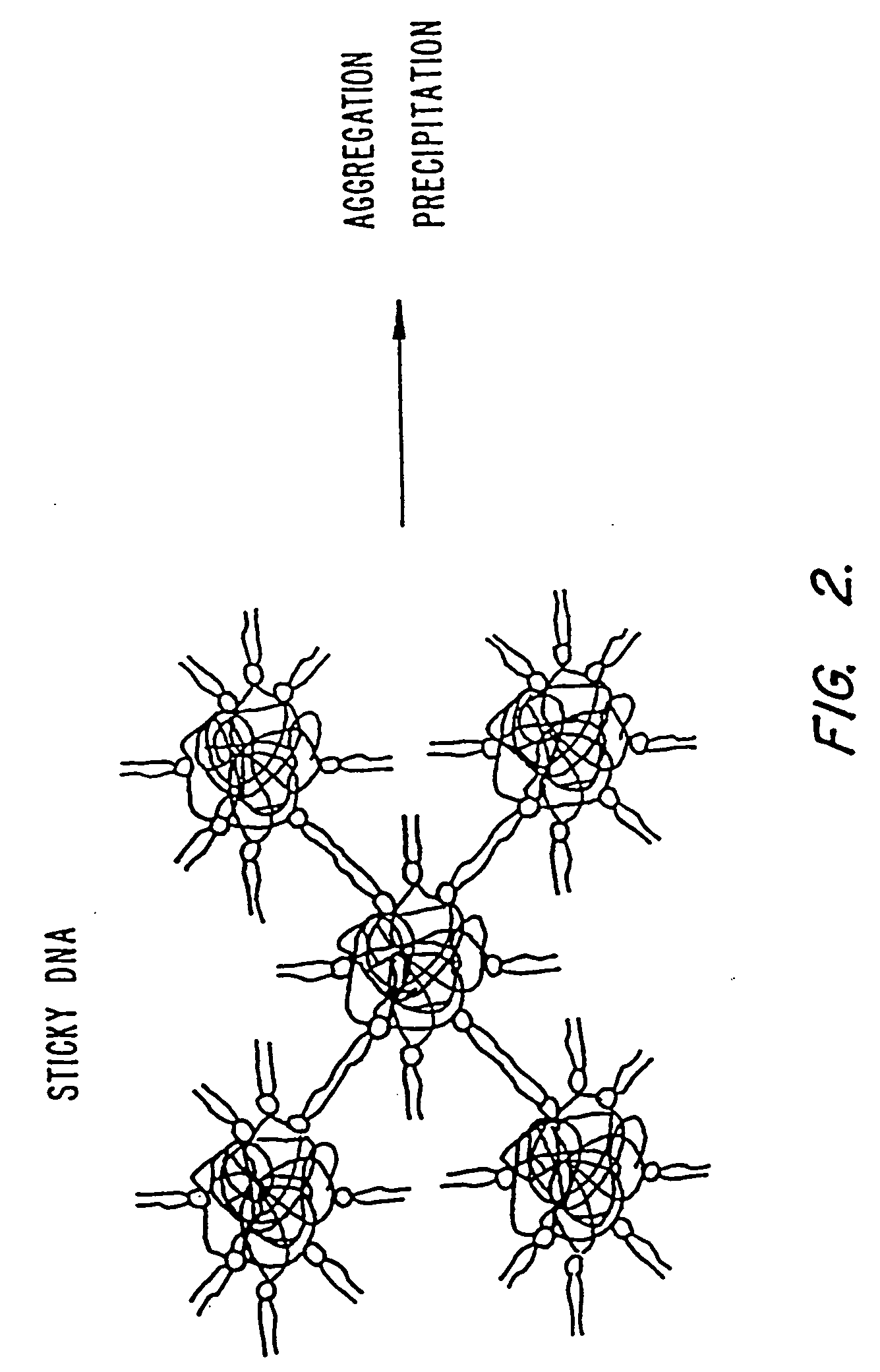
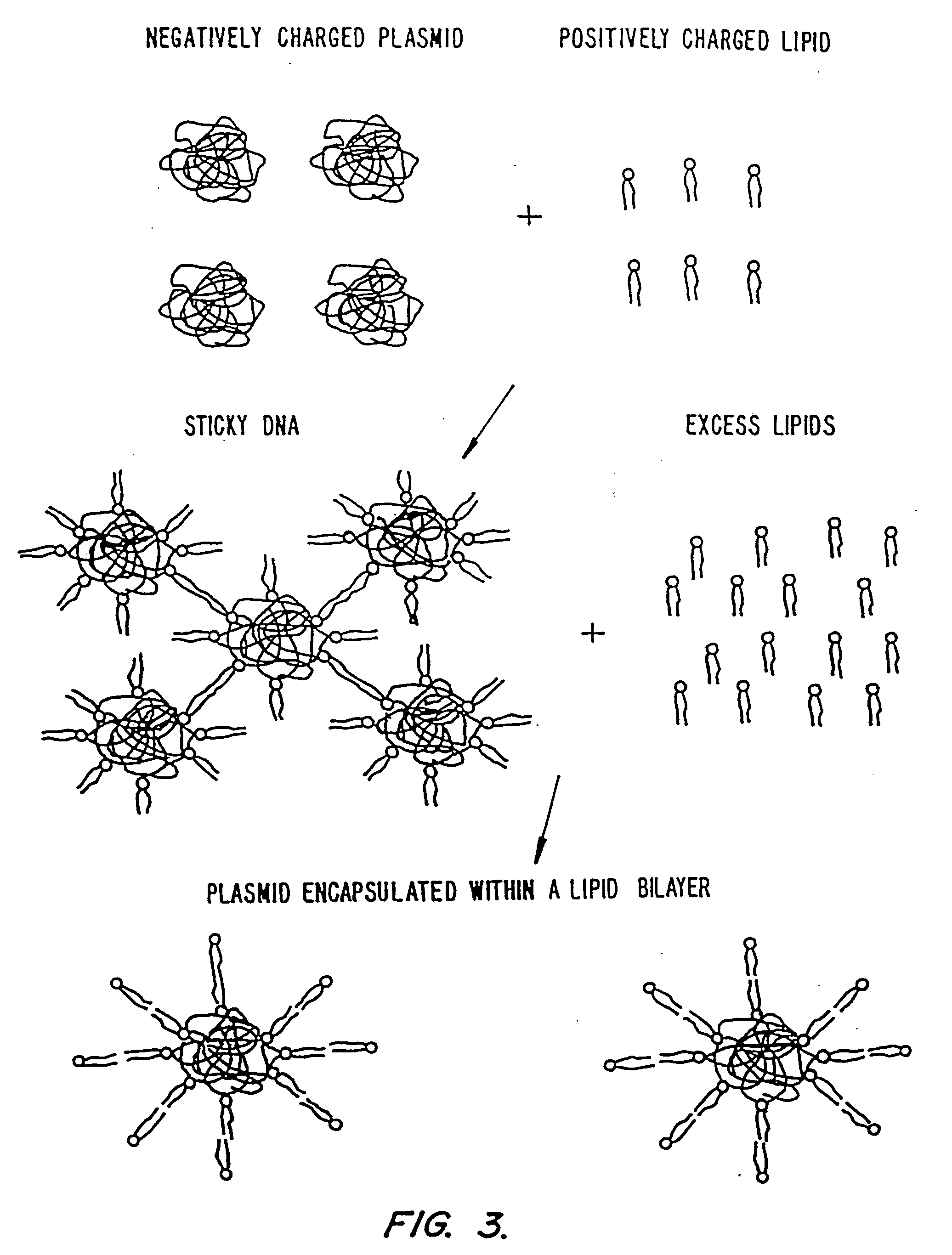
Methods for encapsulating plasmids in lipid bilayers
Plasmid-lipid particles which are useful for transfection of cells in vitro or in vivo are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. The particles are typically 65-85 nm, fully encapsulate the plasmid and are serum-stable.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
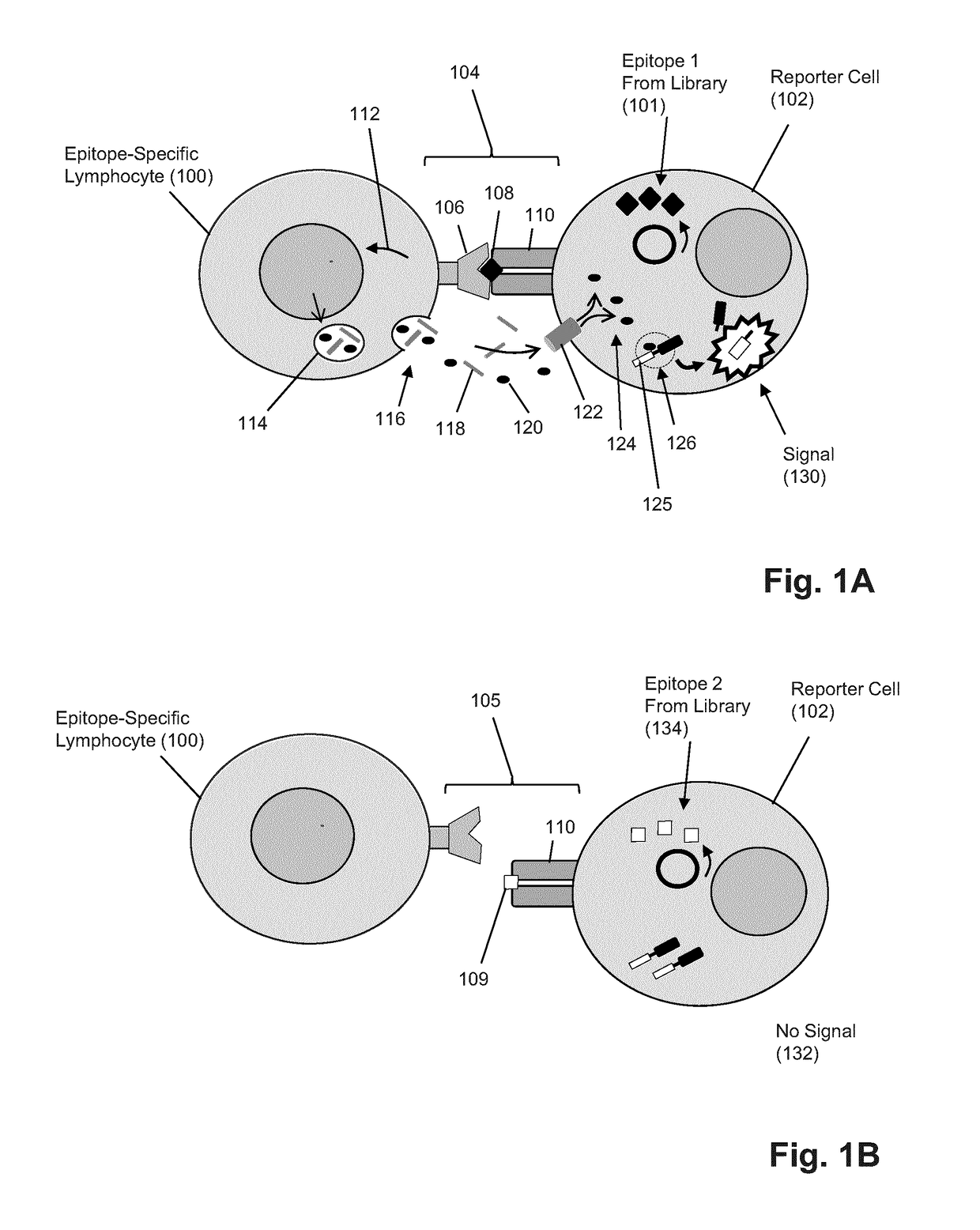
T-cell epitope identification
ActiveUS20180052176A1Efficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideMembrane bound
The present invention is a method for determining the identity of the epitopes recognized by T-cells. The method consists of expressing an encoded library of candidate epitope sequences in a recipient reporter cell capable of providing a detectable signal upon cytotoxic attack from a single cognate T-cell followed by contacting the reporter cells with T-cells of interest. The reporter cells with a single indicating cytotoxic attack from a T-cell are isolated and then analyzed by next-generation sequencing in order to identify the epitope sequences. Specifically disclosed is a method in which a library of candidate epitope-encoding nucleic acids are expressed in cells which feature a membrane-bound major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein, said library produced by transfection of plasmids featuring both a nucleotide encoding the candidate epitope and a nucleotide encoding a FRET-based fluorescent protein cleaved by granzyme.
Owner:PROVINCIAL HEALTH SERVICES AUTHORITY
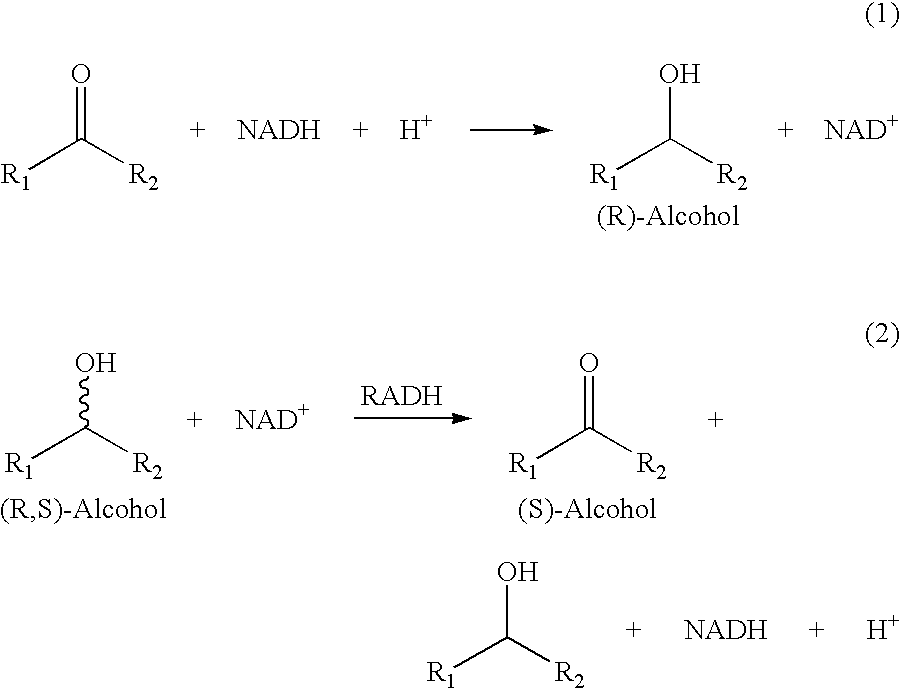
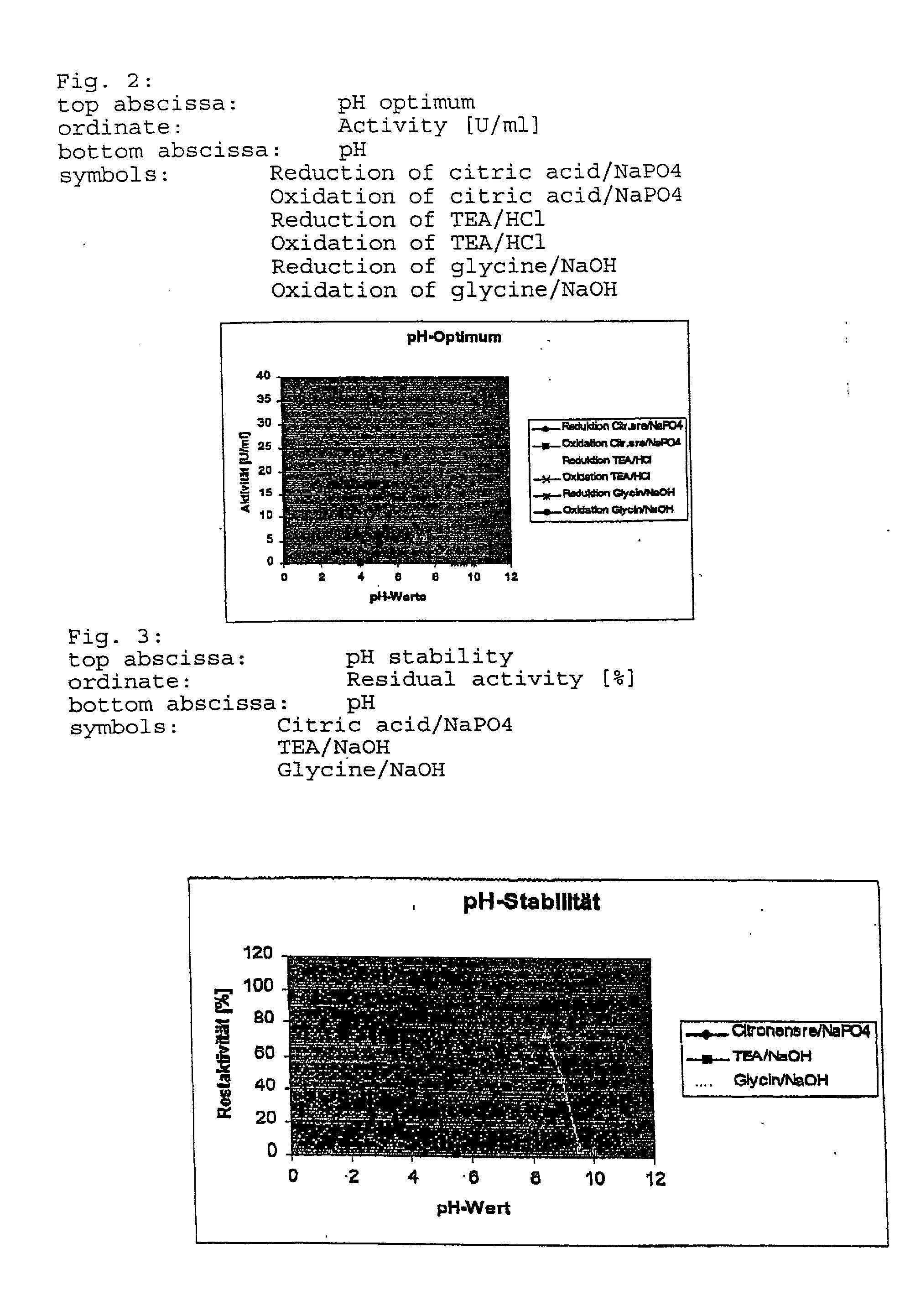
Recombinant enzymes having improved NAD (H) affinity
The present invention relates to recombinantly modified enzymes, which exhibit increased NAD(H) affinity compared to a unmodified or wildtype enzyme, gene sequences or polynucleotides that code for the recombinantly modified enzymes, plasmids and microorganisms that contain these gene sequences; as well as, methods of making and methods of using the enzymes of the present invention.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
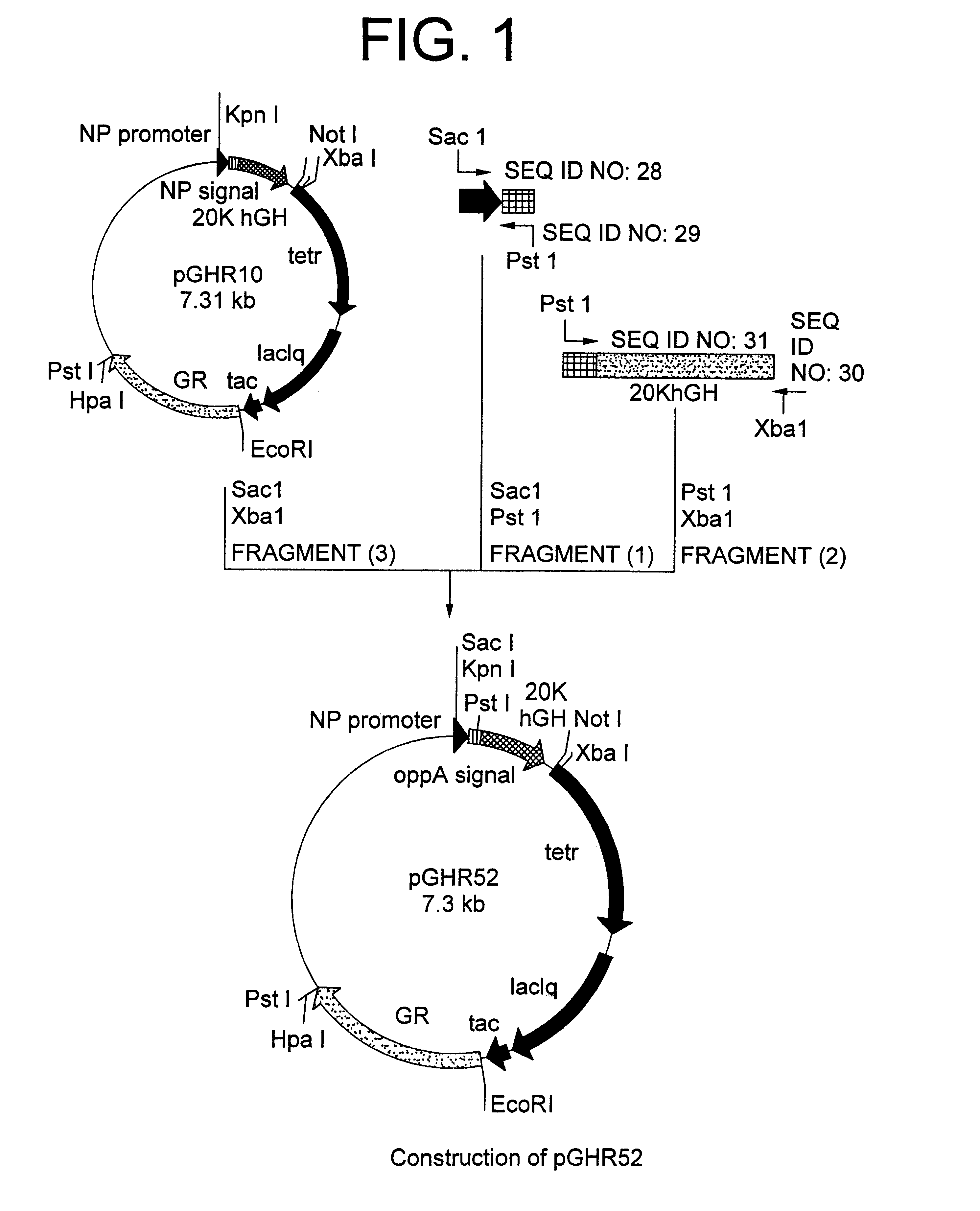
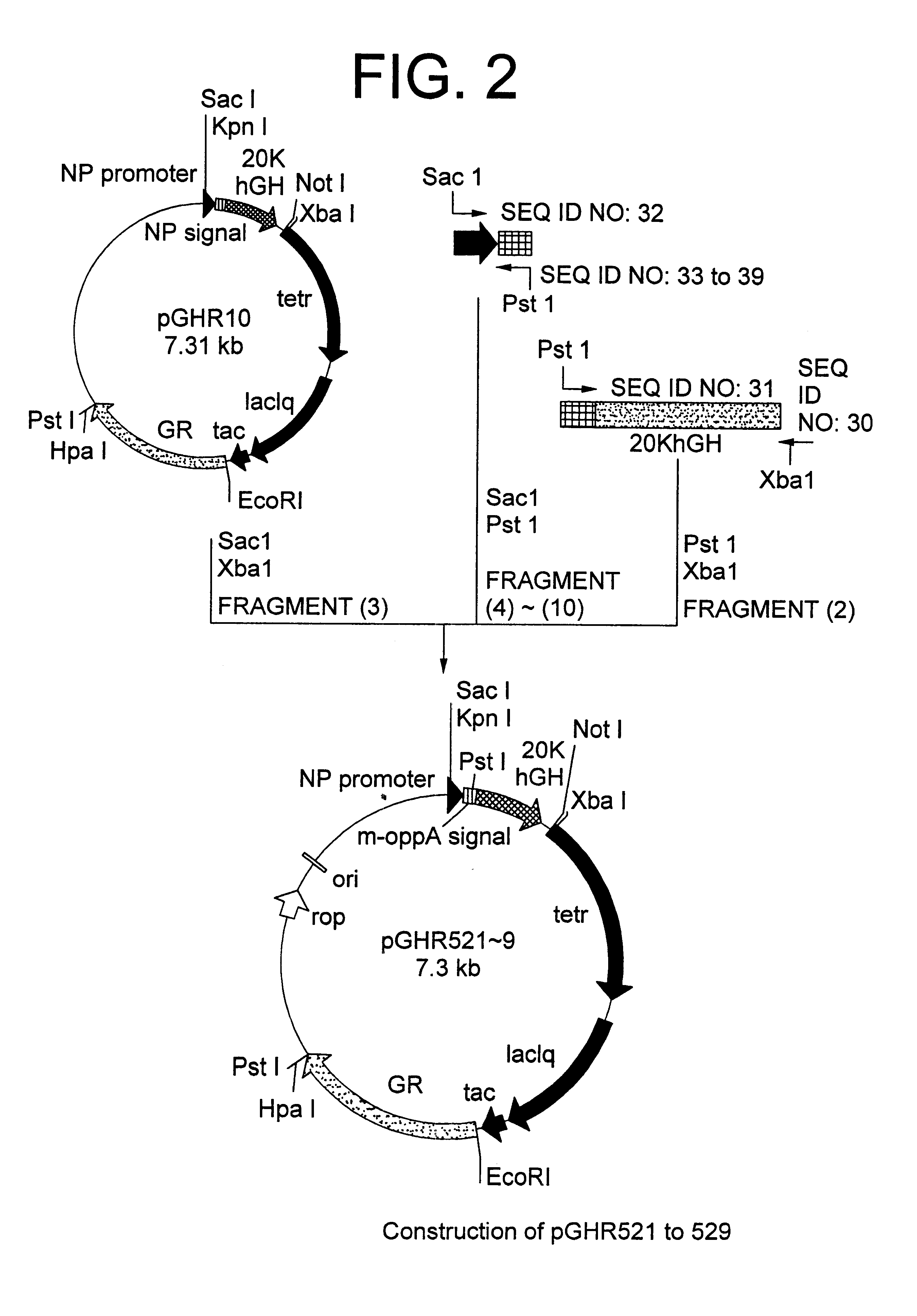
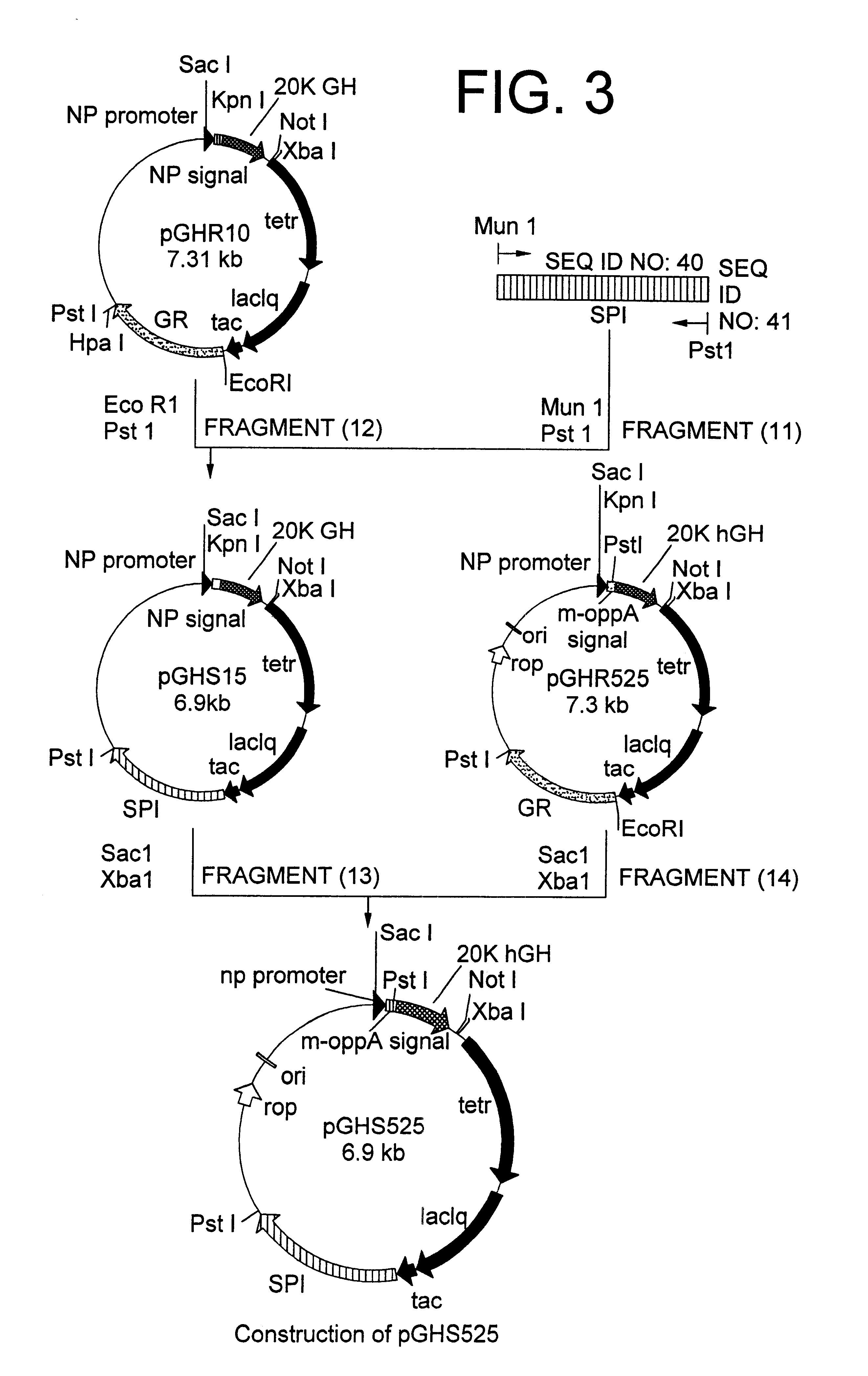
Method for secretory production of human growth hormone
InactiveUS6436674B1Increase productionDecreased tendency for lysisBacteriaHydrolasesHuman growth hormoneA-DNA
A DNA encoding 20K hGH is connected directly to a gene encoding Escherichia coli OppA protein secretion signal, or a modified form thereof, and a DNA encoding signal peptidase 1 to construct a recombinant plasmid, E. coli is transformed by the plasmid and cells of the resulting E. coli transformant strain are cultured for secretory production of the 20K hGH in the E. coli periplasm. This method enables efficient secretory production of 20K hGH and easy isolation and purification of 20K hGH from the periplasm fraction because the level of impure proteins in the E. coli periplasm is low.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
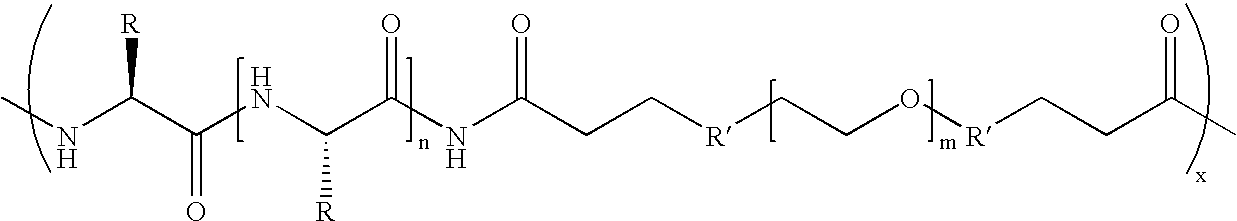
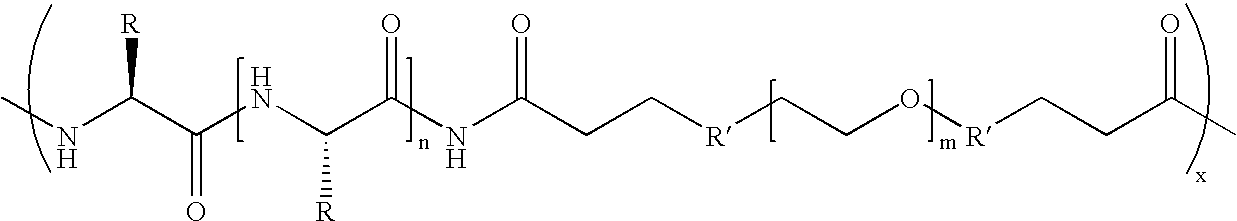
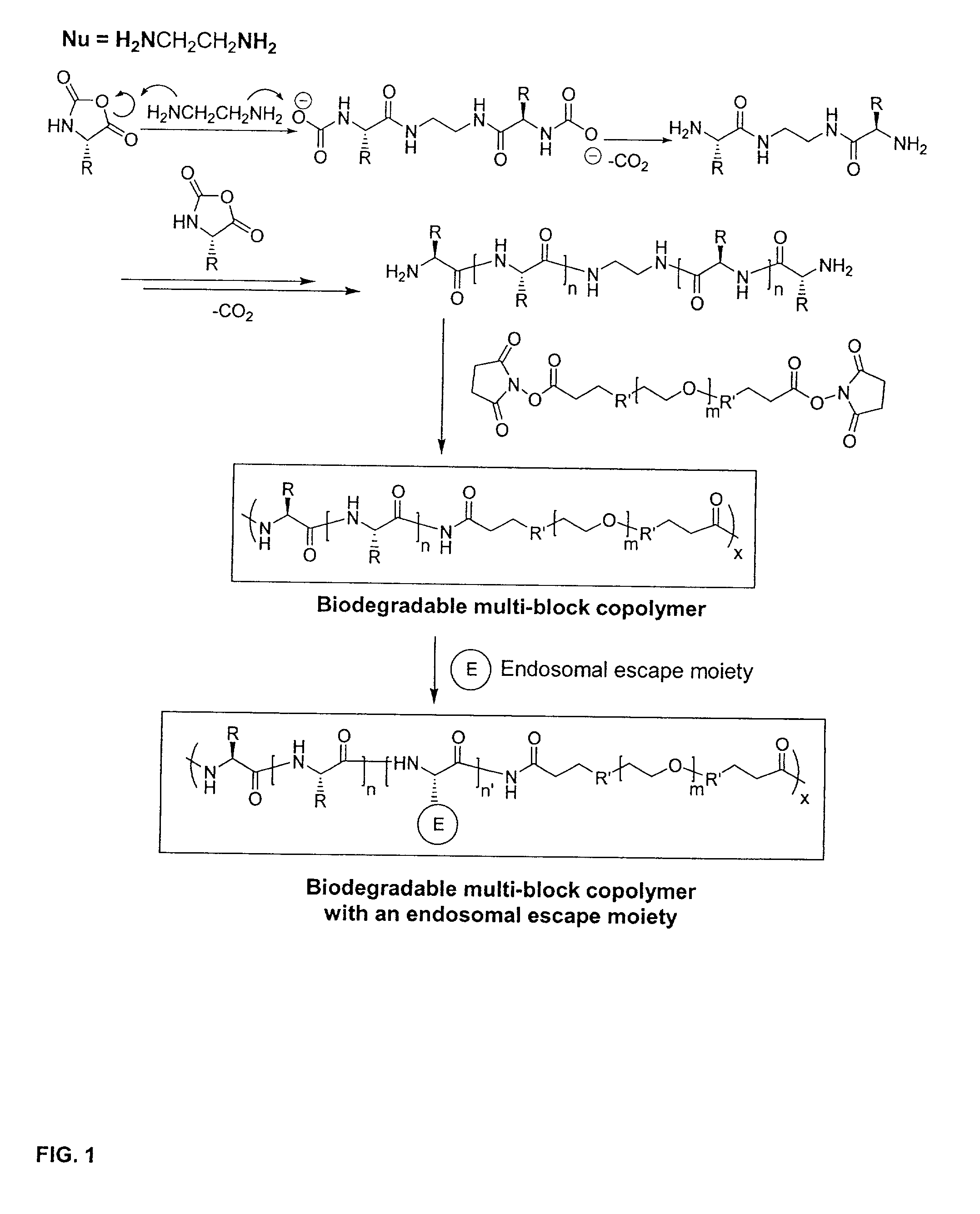
Biodegradable multi-block copolymers of poly(amino acid)s and poly(ethylene glycol) for the delivery of bioactive agents
InactiveUS20030147958A1Easy to chargeSmall sizePowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsCarbamateHydrophilic polymers
This patent discloses the synthesis of a multi-block copolymer containing poly(amino acids) (PAA) and a hydrophilic polymer which are degradable under physiological conditions. Control over the degradation rate of the obtained copolymers is achieved by introducing ester, amide or urethane groups as a biodegradable linkage connecting the PAA and the hydrophilic polymer. The biodegradable multi-block copolymers display high transfection efficiency in plasmid delivery with low cytotoxicity.
Owner:EXPRESSION GENETICS INC
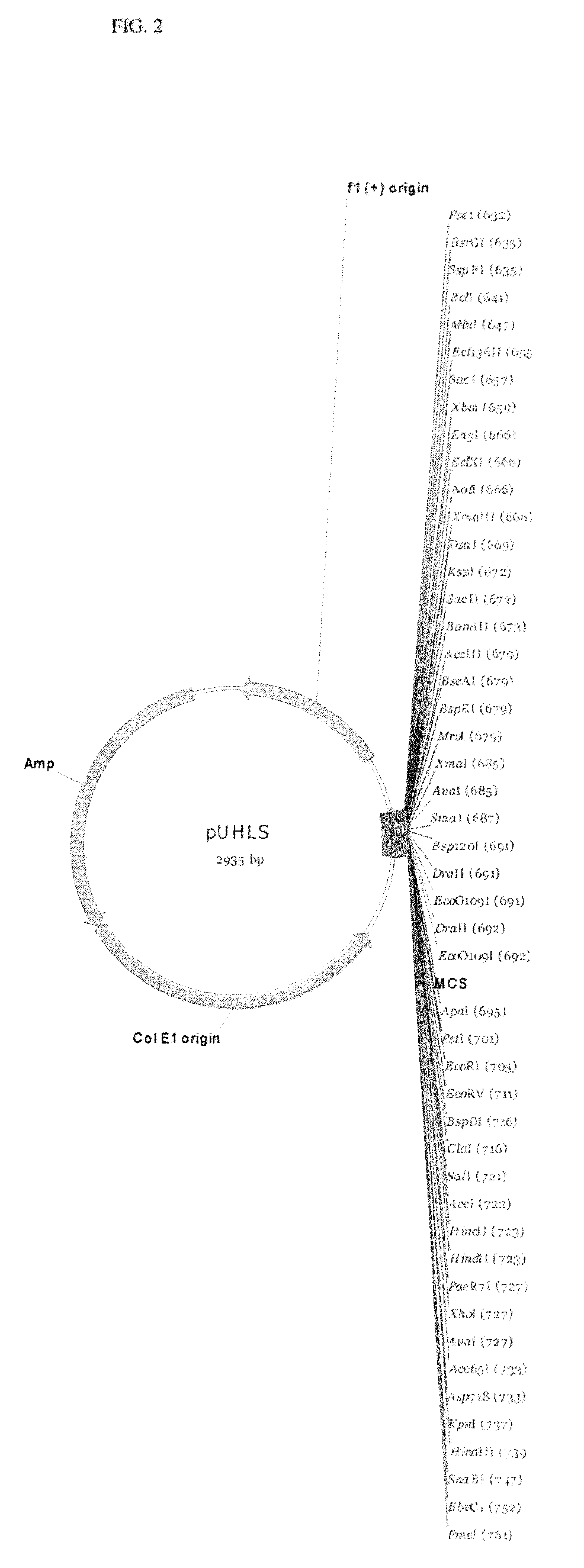
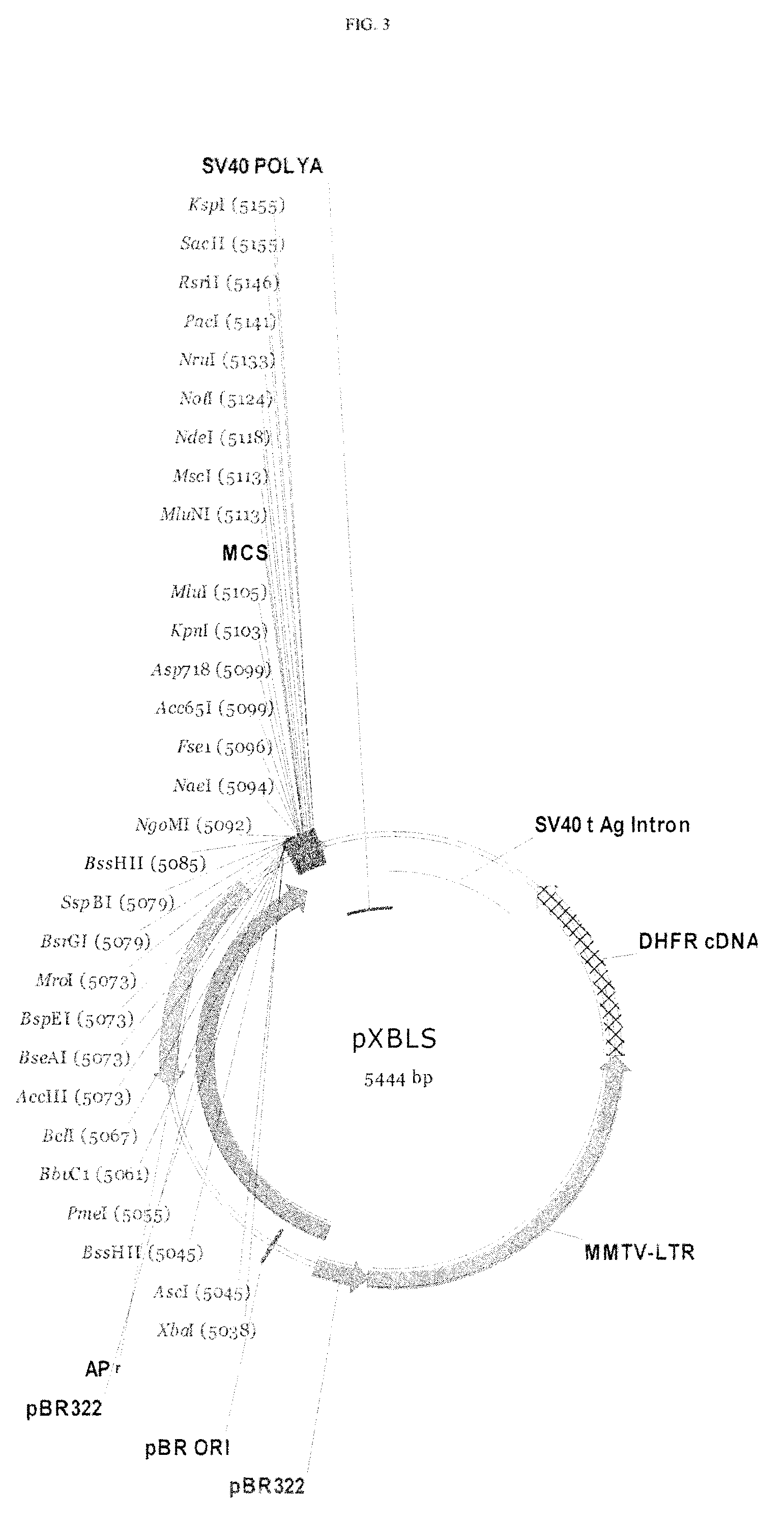
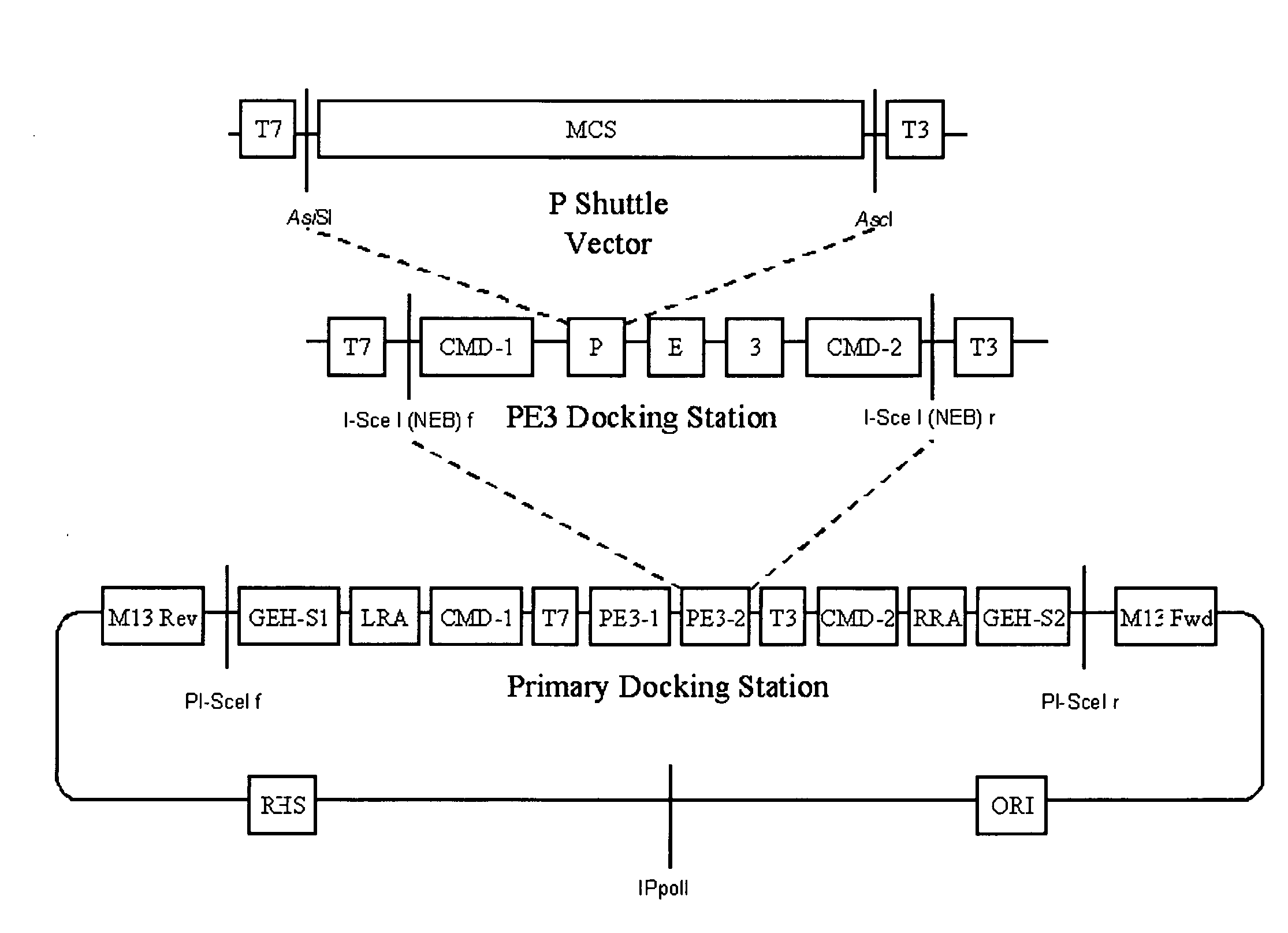
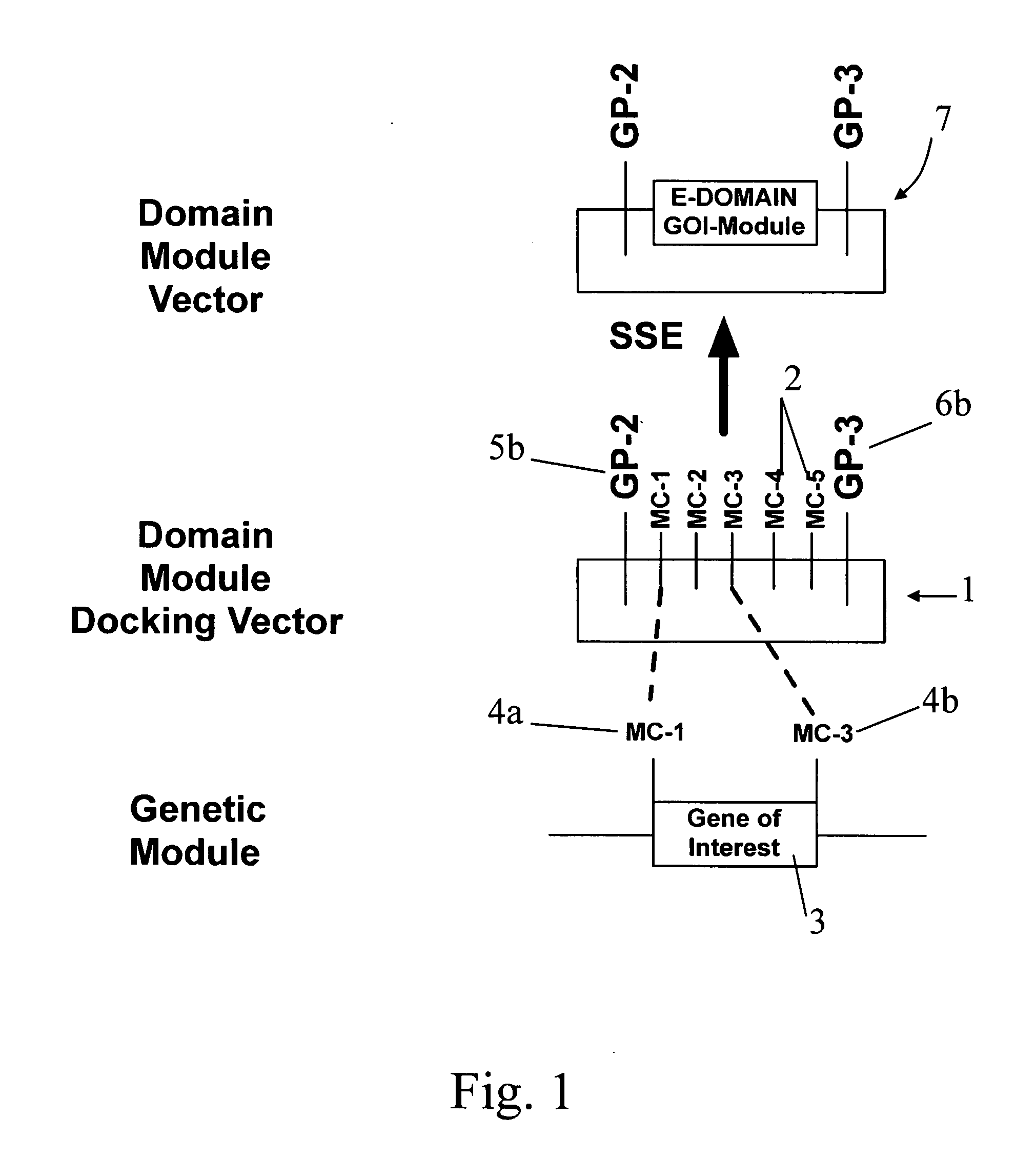
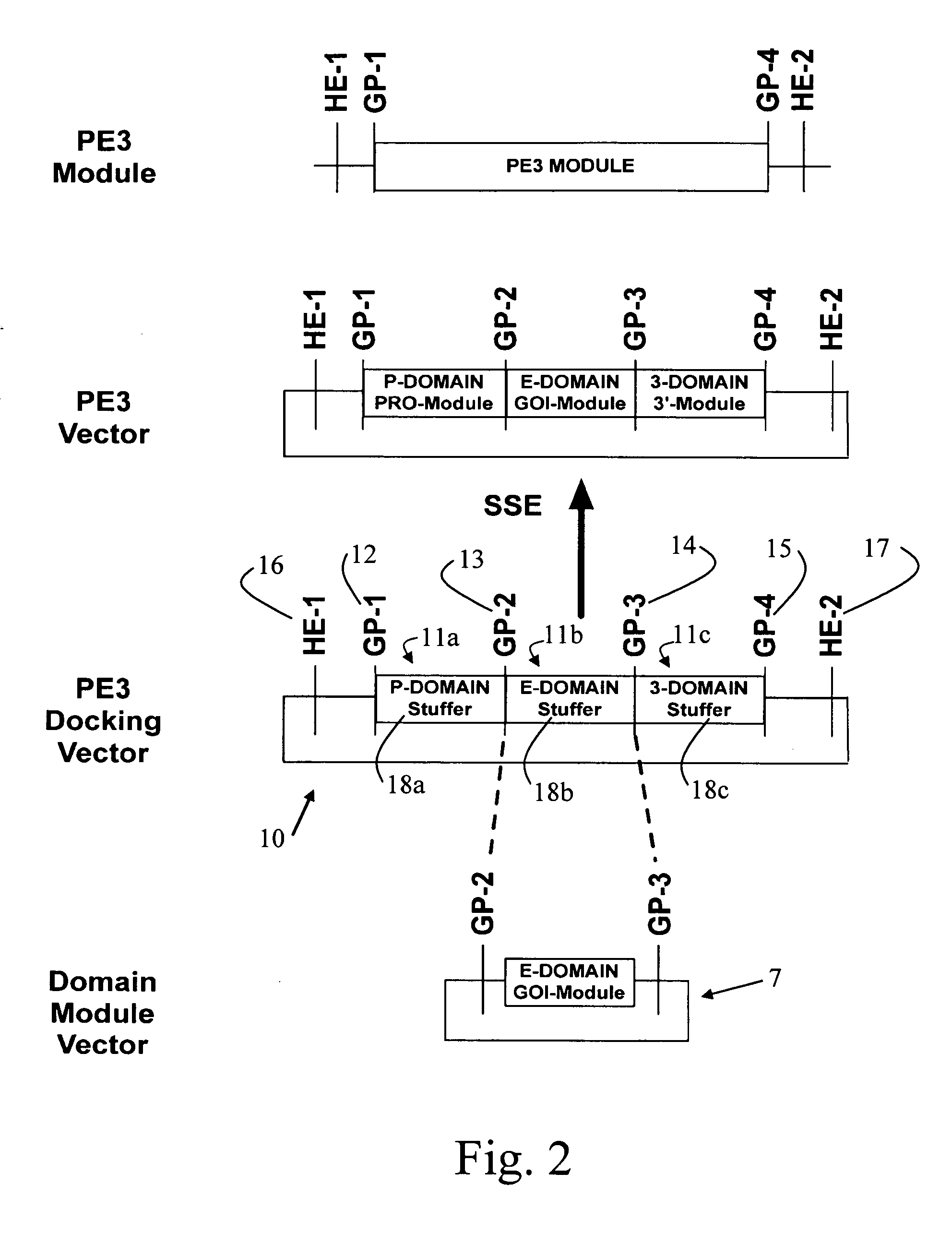
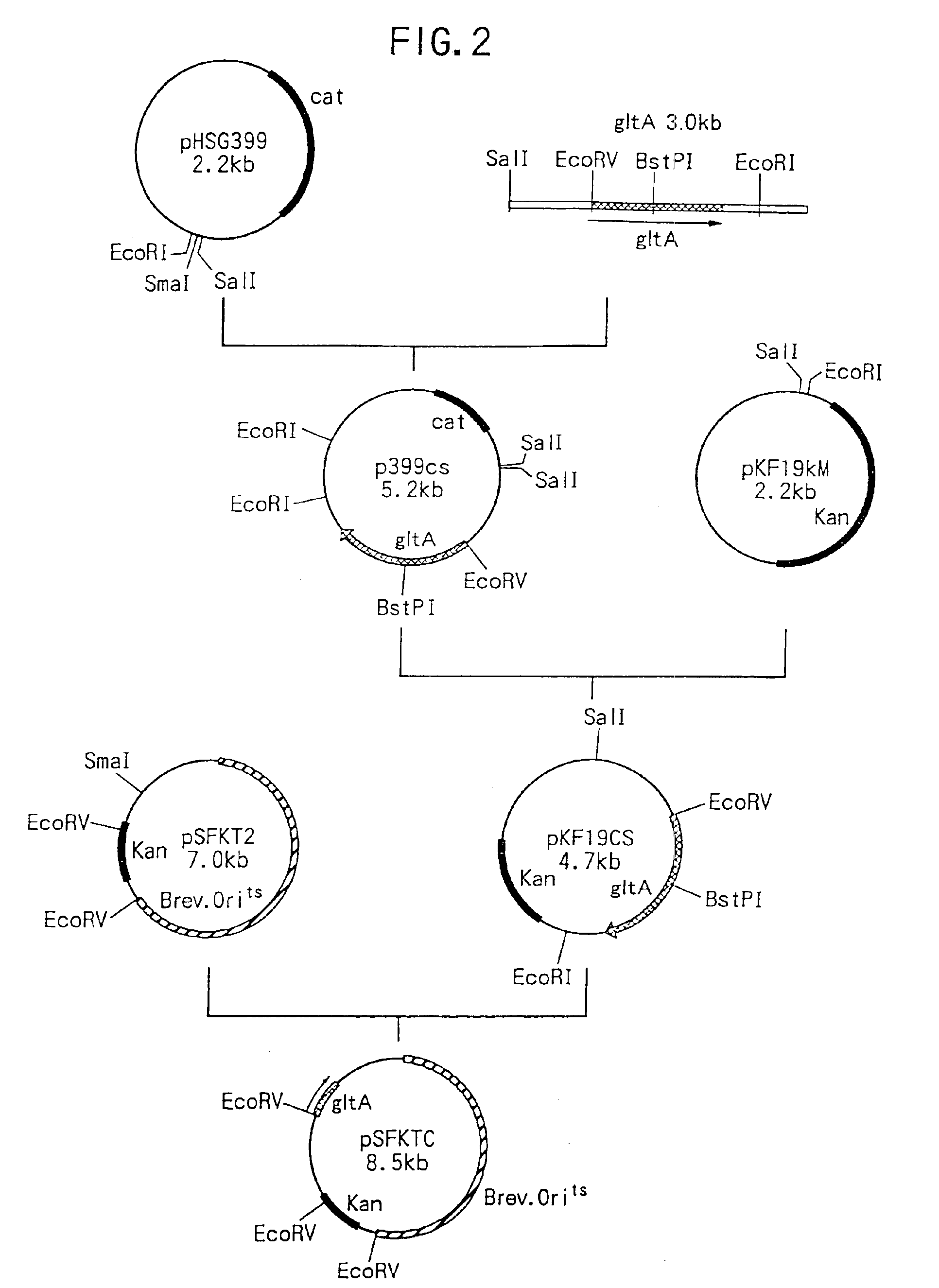
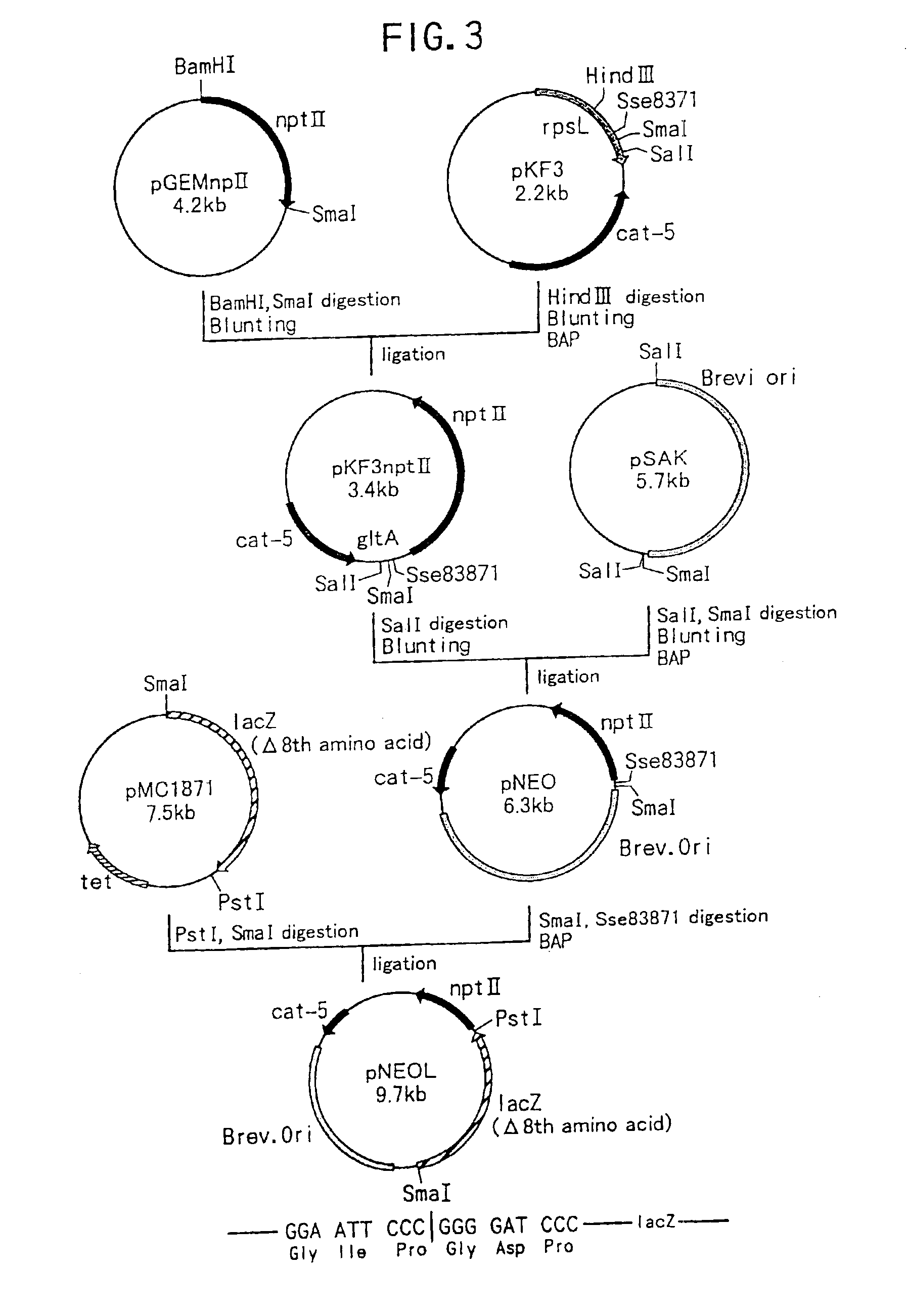
DNA modular cloning vector plasmids and methods for their use
A group of modular cloning vector plasmids for the synthesis of a transgene or other complicated DNA construct, by providing a backbone having docking points therein, for the purpose of gene expression or analysis of gene expression. The invention is useful for assembling a variety of DNA fragments into a de novo DNA construct or transgene by using cloning vectors optimized to reduce the amount of manipulation frequently needed. The module vector contains at least one multiple cloning site (MCS) and multiple sets of rare restriction and / or unique homing endonuclease (“HE”) sites, arranged in a linear pattern. This arrangement defines a modular architecture that allows the user to place domain modules or inserts into a PE3 transgene vector construct without disturbing the integrity of DNA elements already incorporated into the PE3 vector in previous cloning steps. The PE3 transgenes produced using the invention may be used in a single organism, or in a variety of organisms including bacteria, yeast, mice, and other eukaryotes with little or no further modification.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
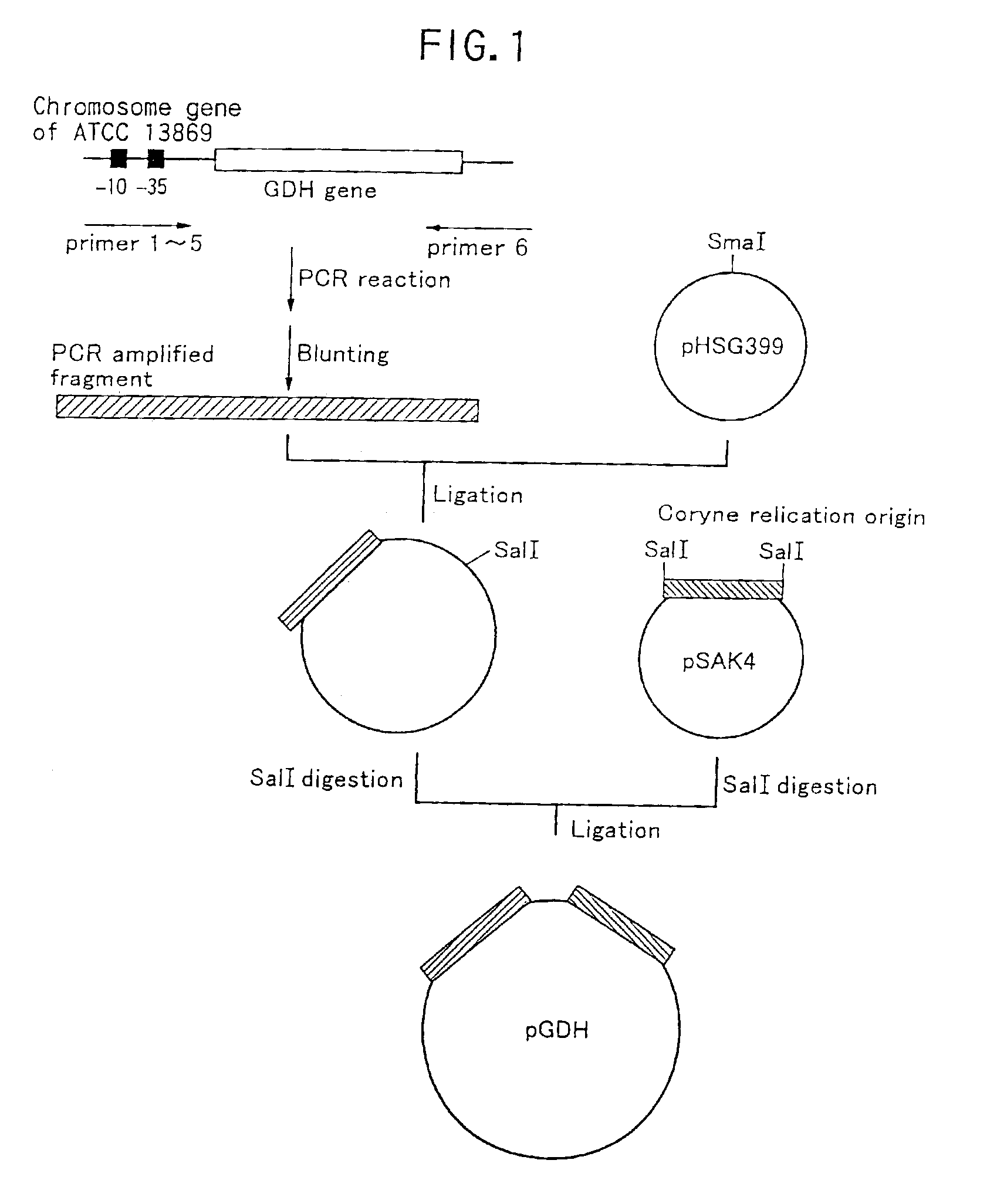
Method of constructing amino acid producing bacterial strains, and method of preparing amino acids by fermentation with the constructed amino acid producing bacterial strains
A method of producing coryneform bacteria having improved amino acid or nucleic acid productivity comprising the steps of introducing a mutation in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium to make it close to a consensus sequence, or introducing a change in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium by gene recombination to make it close to a consensus sequence, to obtain mutants of the coryneform amino acid- or nucleic acid-producing microorganism, culturing the mutants and selecting a mutant capable of producing the intended amino acid or nucleic acid in a large amount. This method allows the construction of a mutant capable of enriching or controlling the expression of an intended gene without using a plasmid and to promote production of amino acids in a high yield by recombination or mutation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Methods for encapsulating plasmids in lipid bilayers
Plasmid-lipid particles which are useful for transfection of cells in vitro or in vivo are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. The particles are typically 65-85 nm, fully encapsulate the plasmid and are serum-stable.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
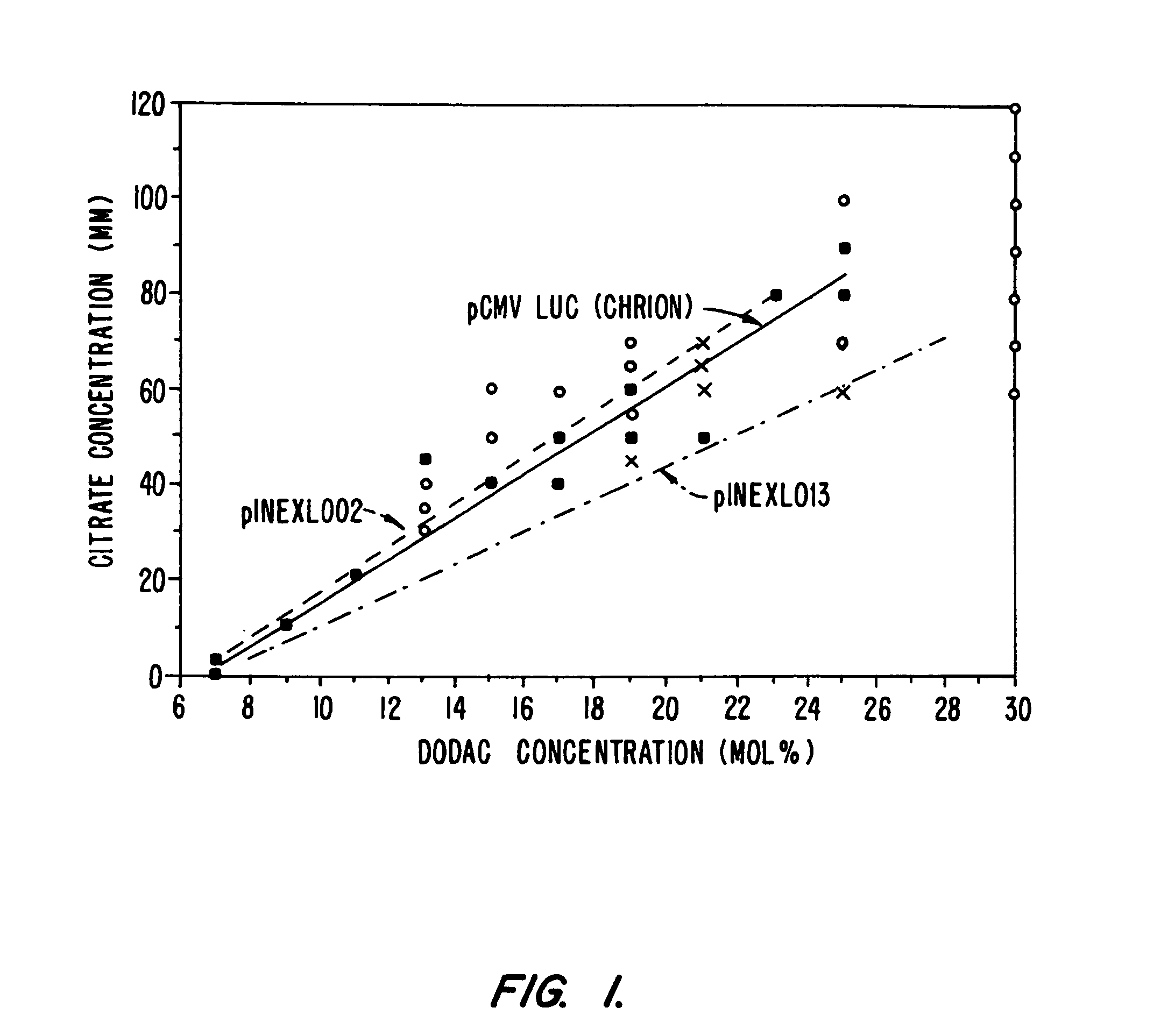
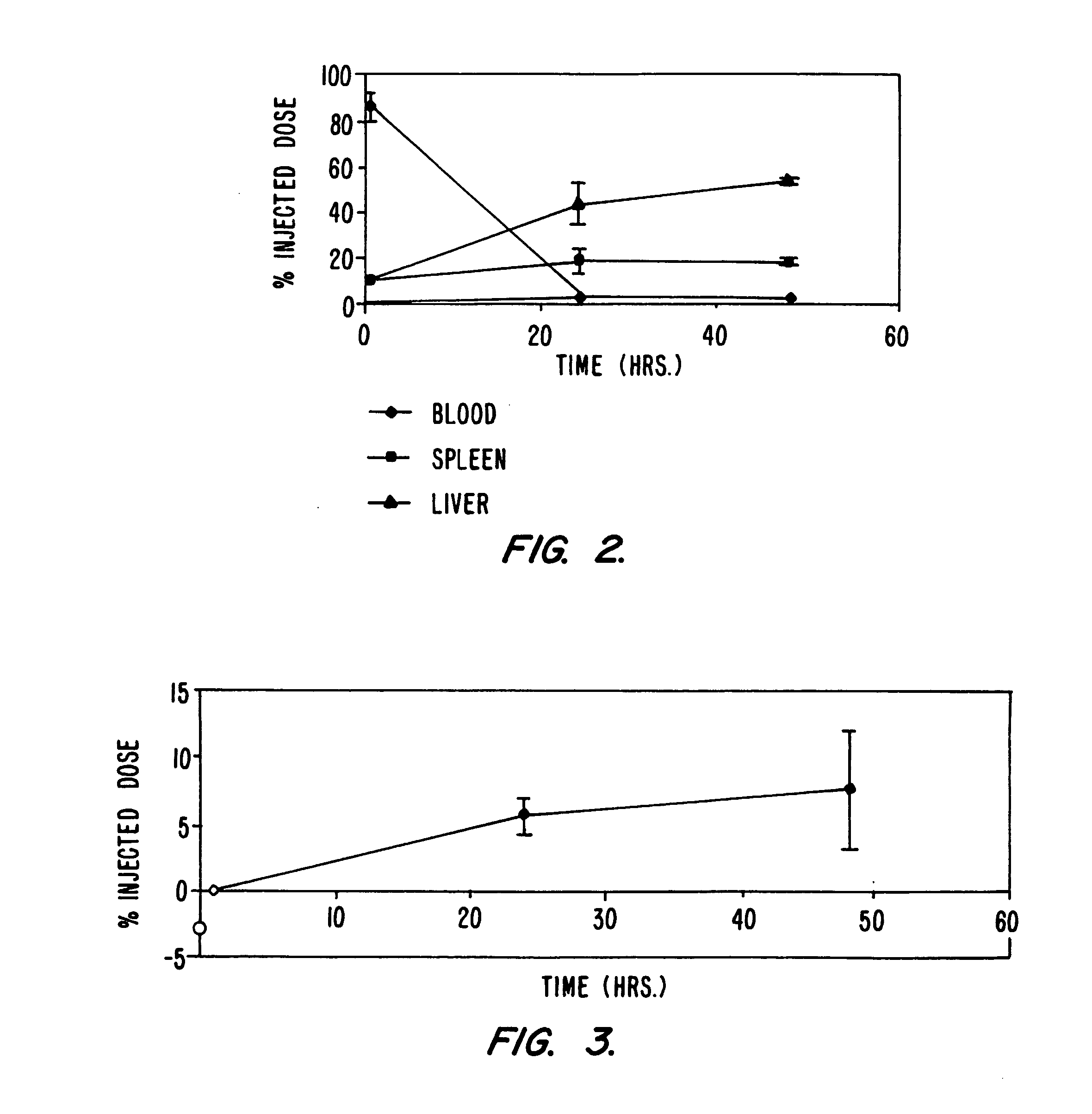
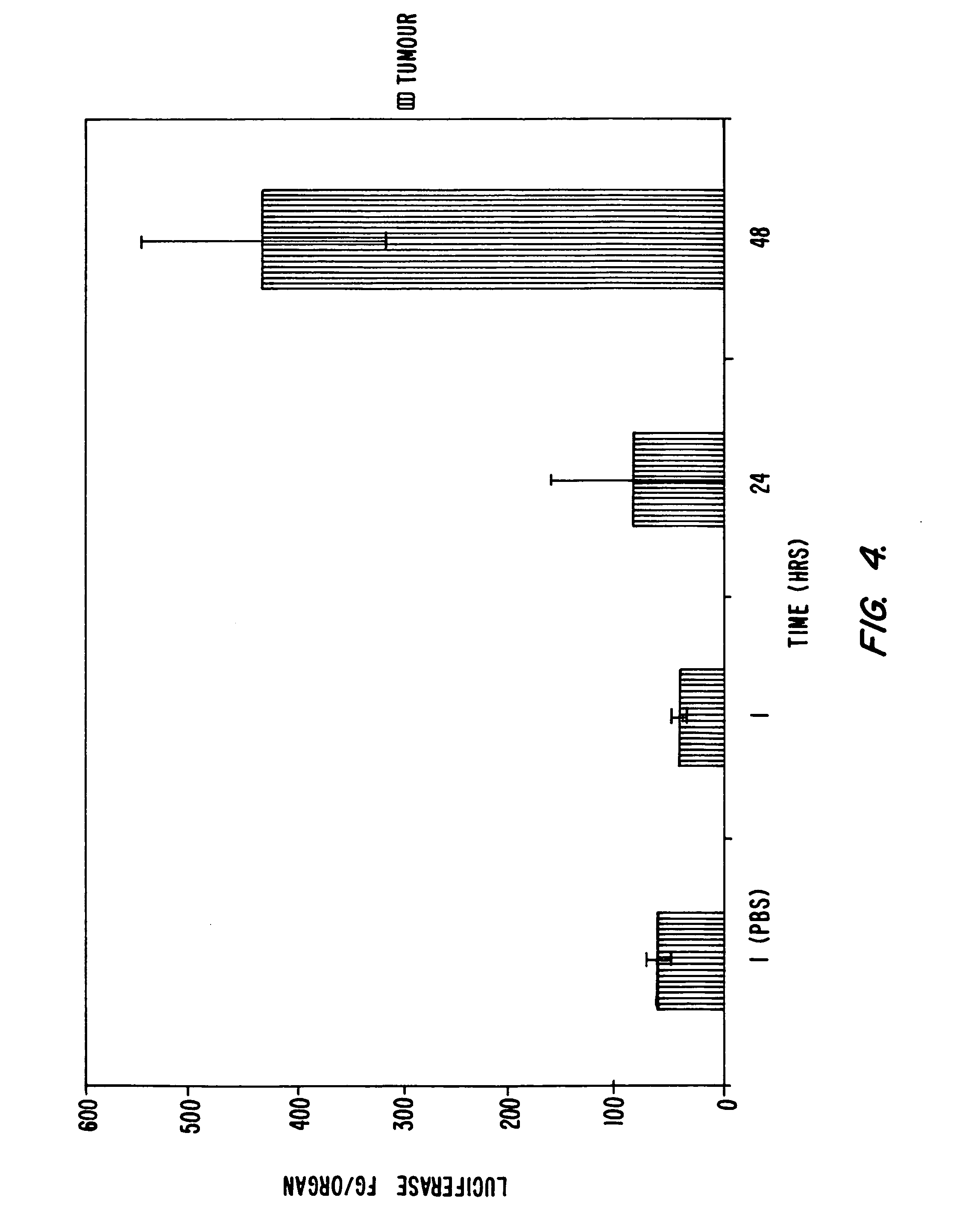
Systemic delivery of serum stable plasmid lipid particles for cancer therapy
InactiveUS20050118253A1Improve propertiesExcellent characteristicsPowder deliveryNanotechLipid particleMedicine
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com