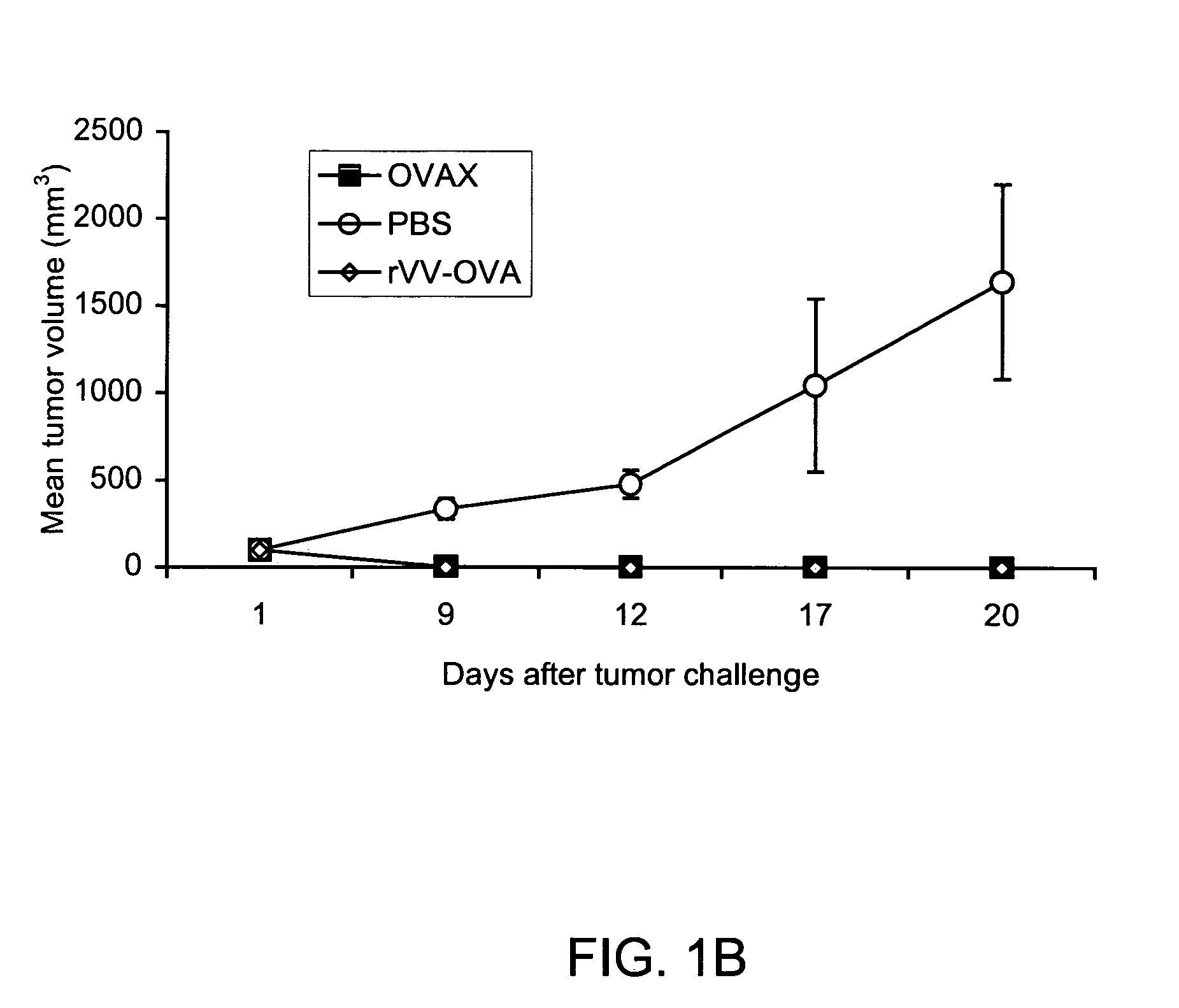
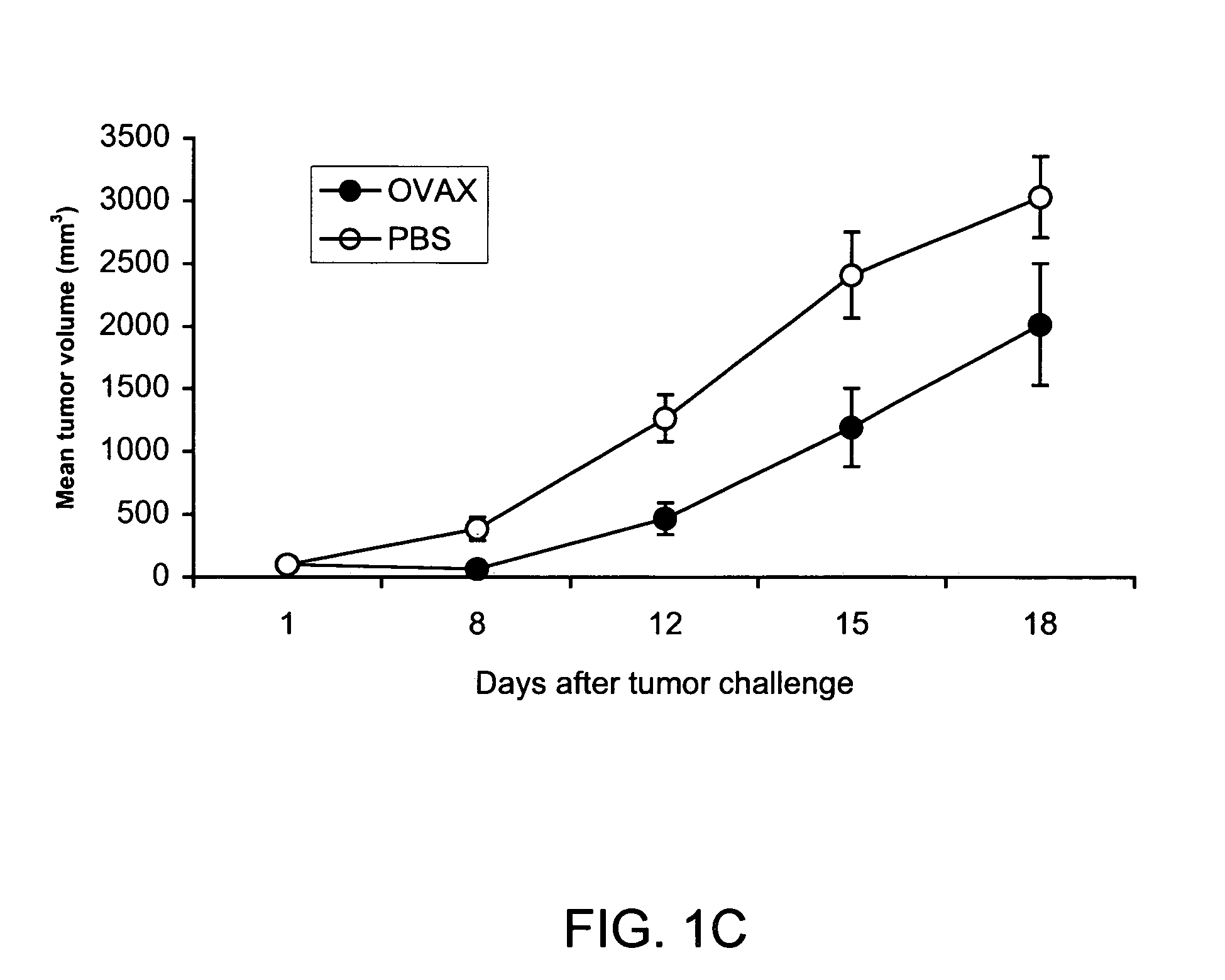
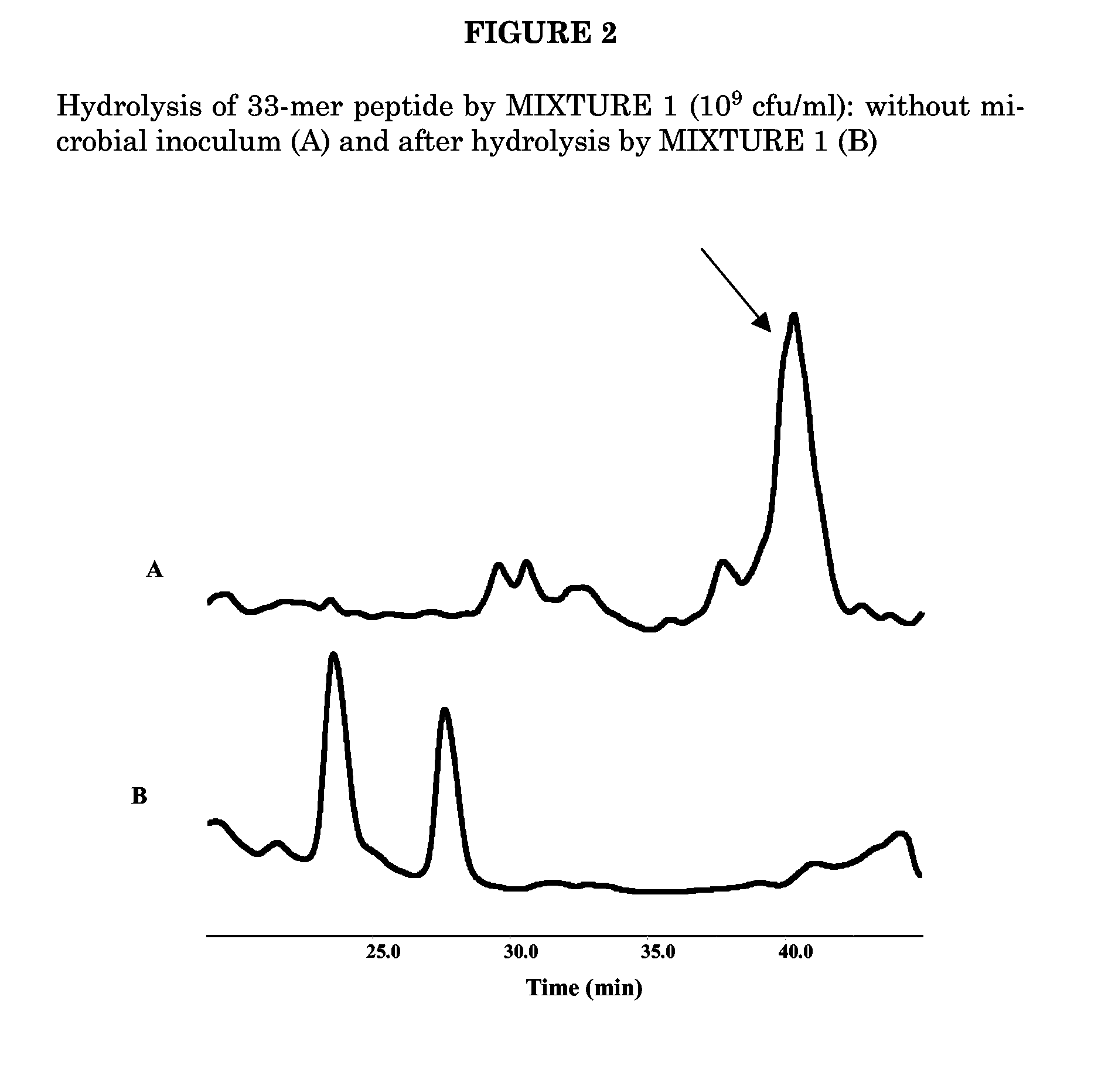
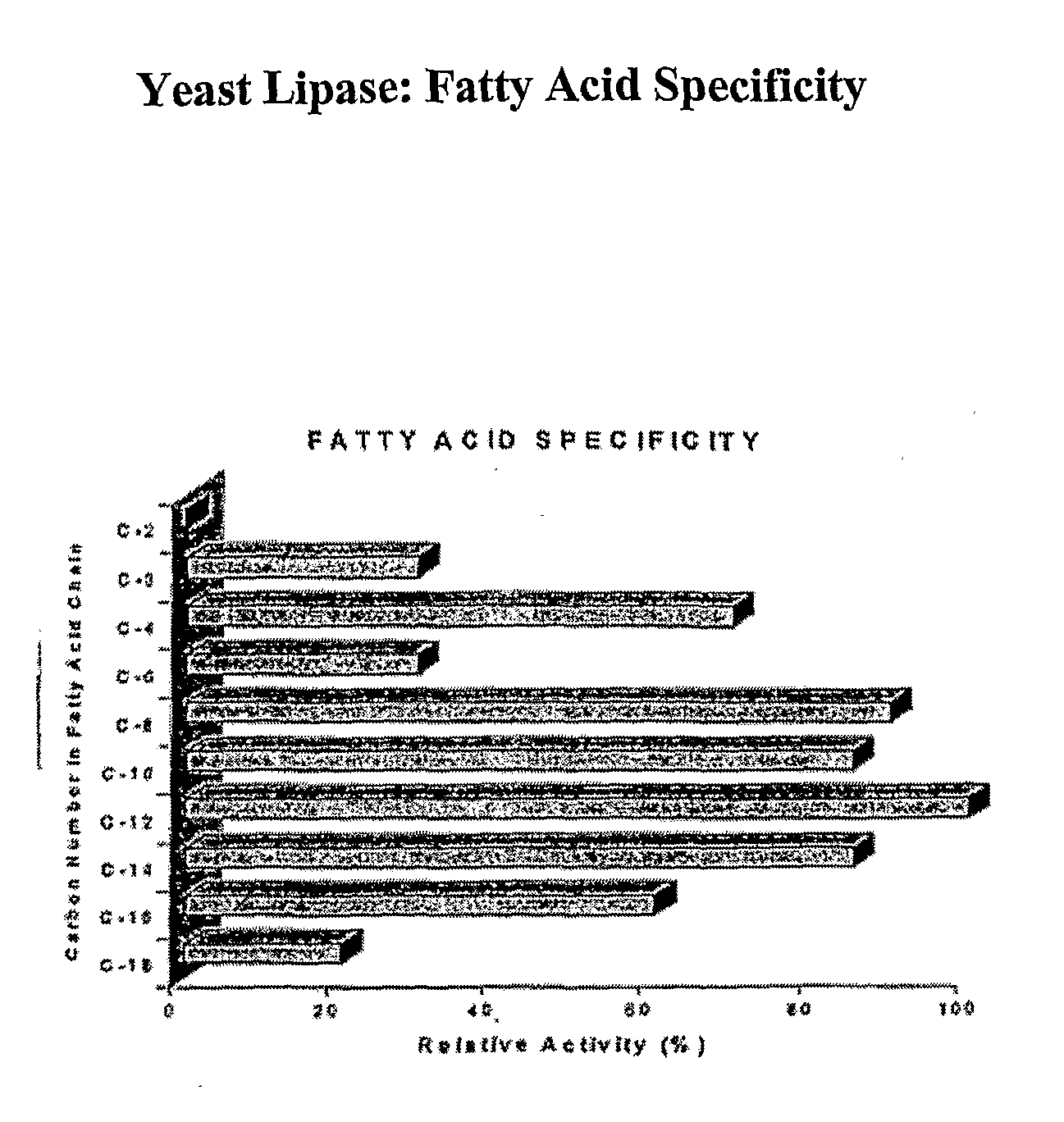
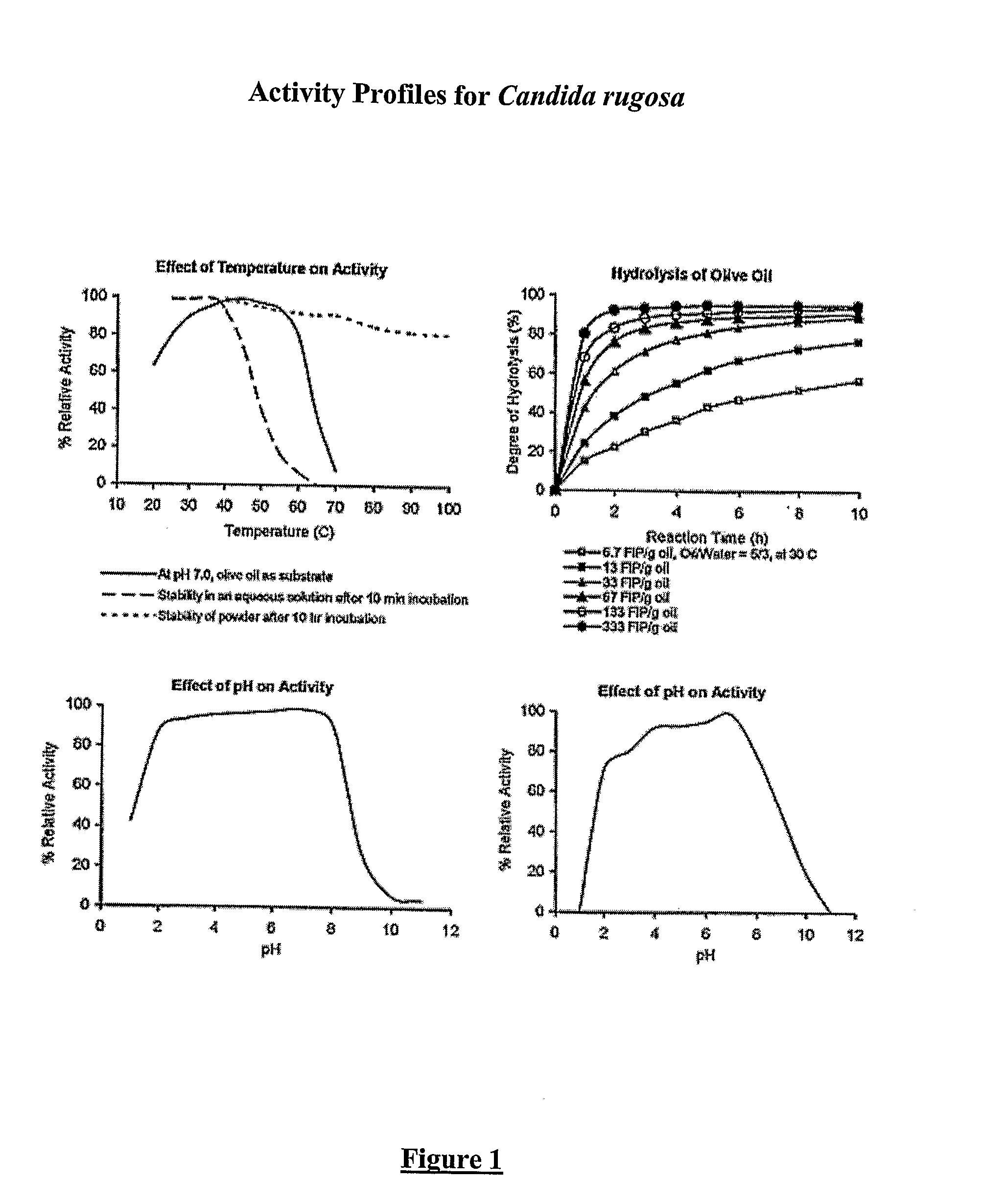
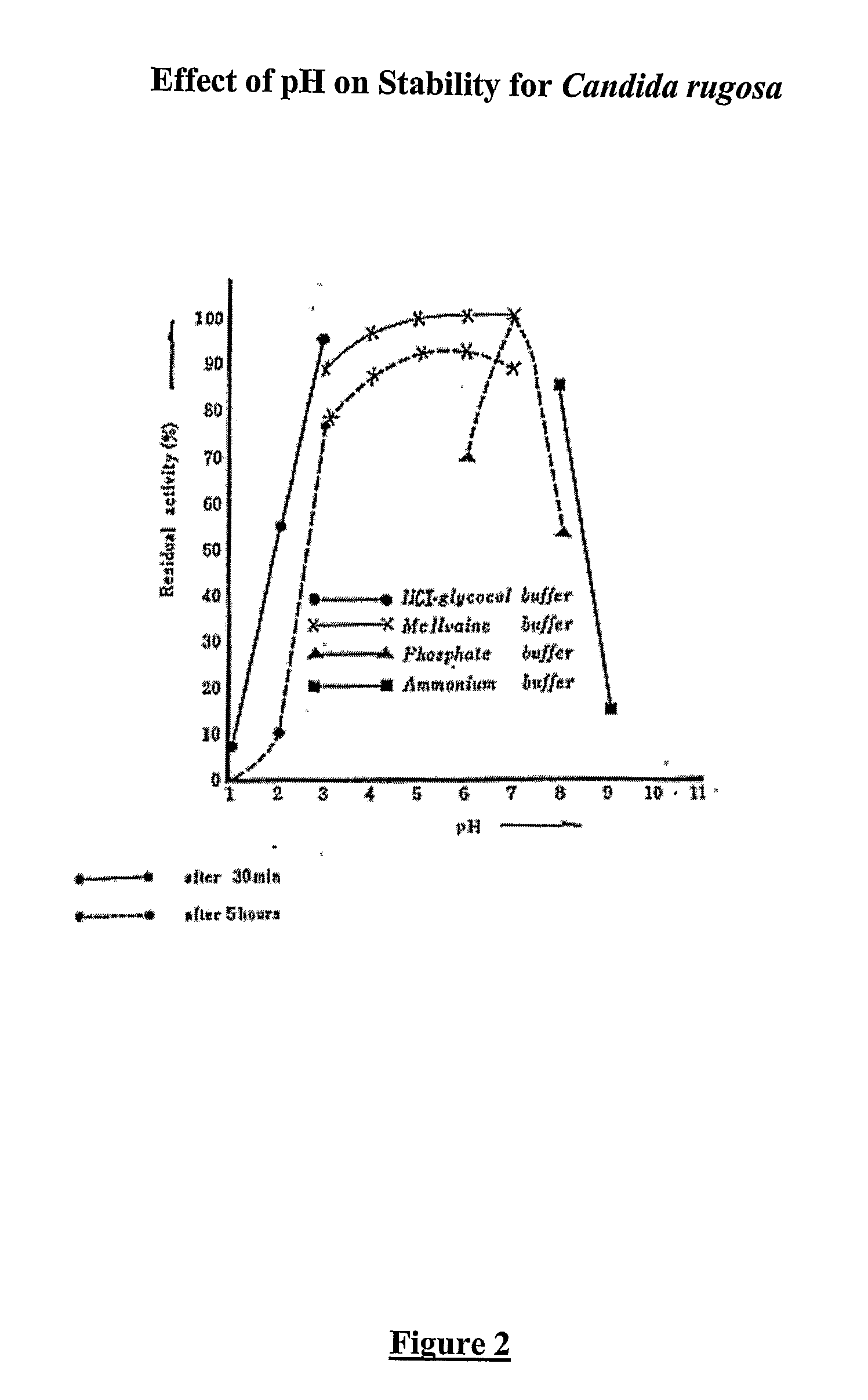
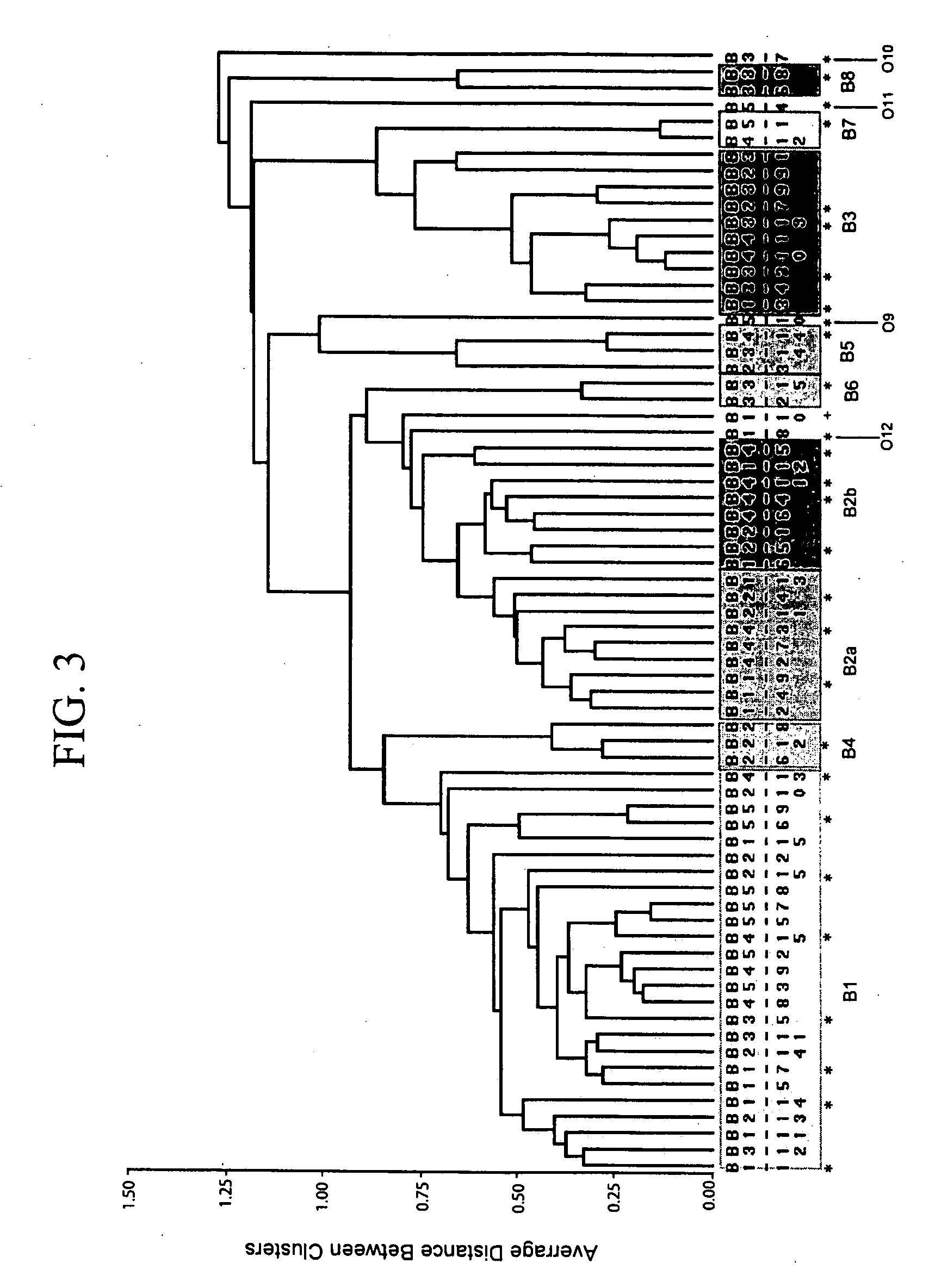
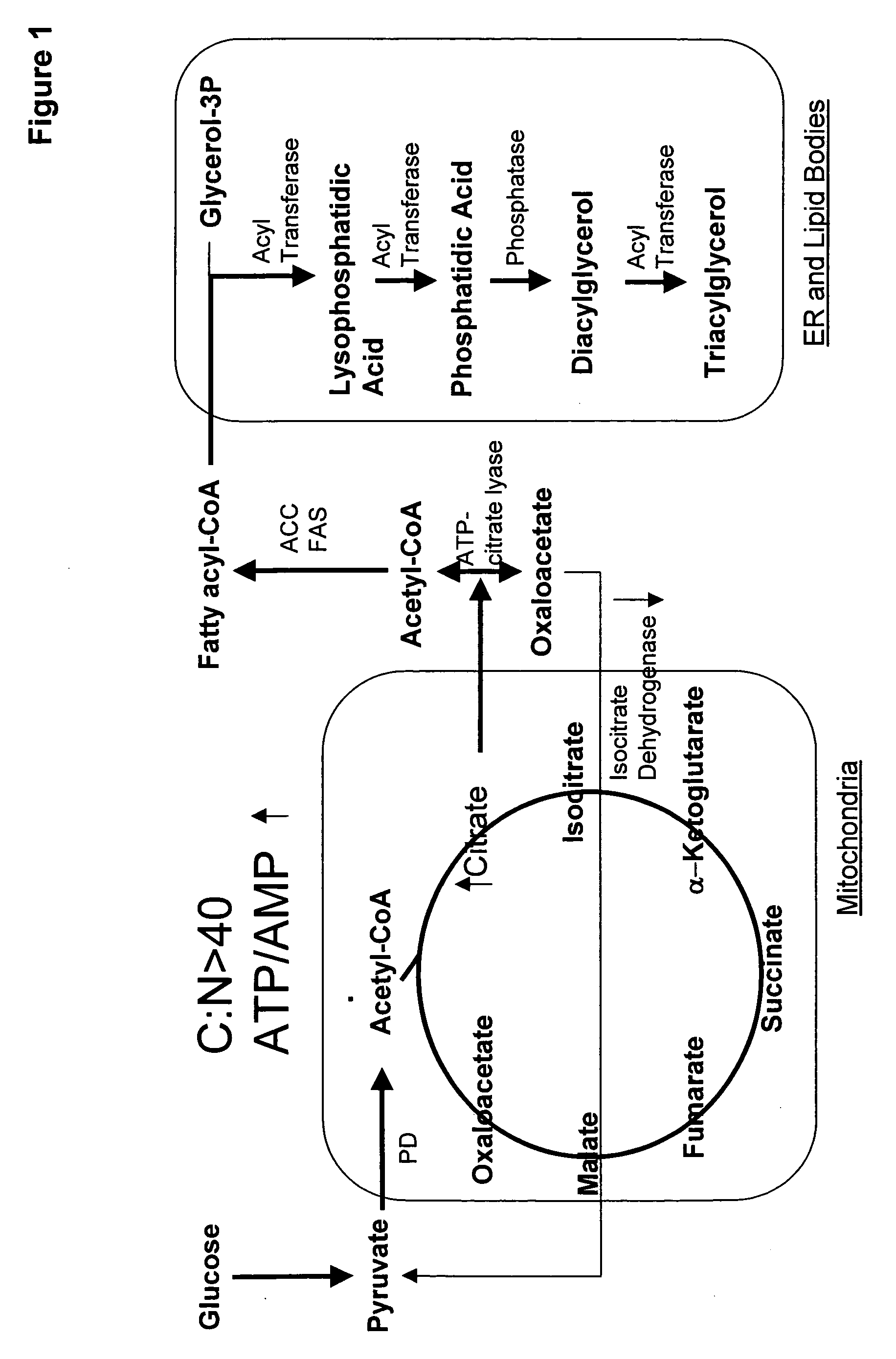
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
19605 results about "Yeast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Yeasts are eukaryotic single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and 1,500 species are currently identified. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding.
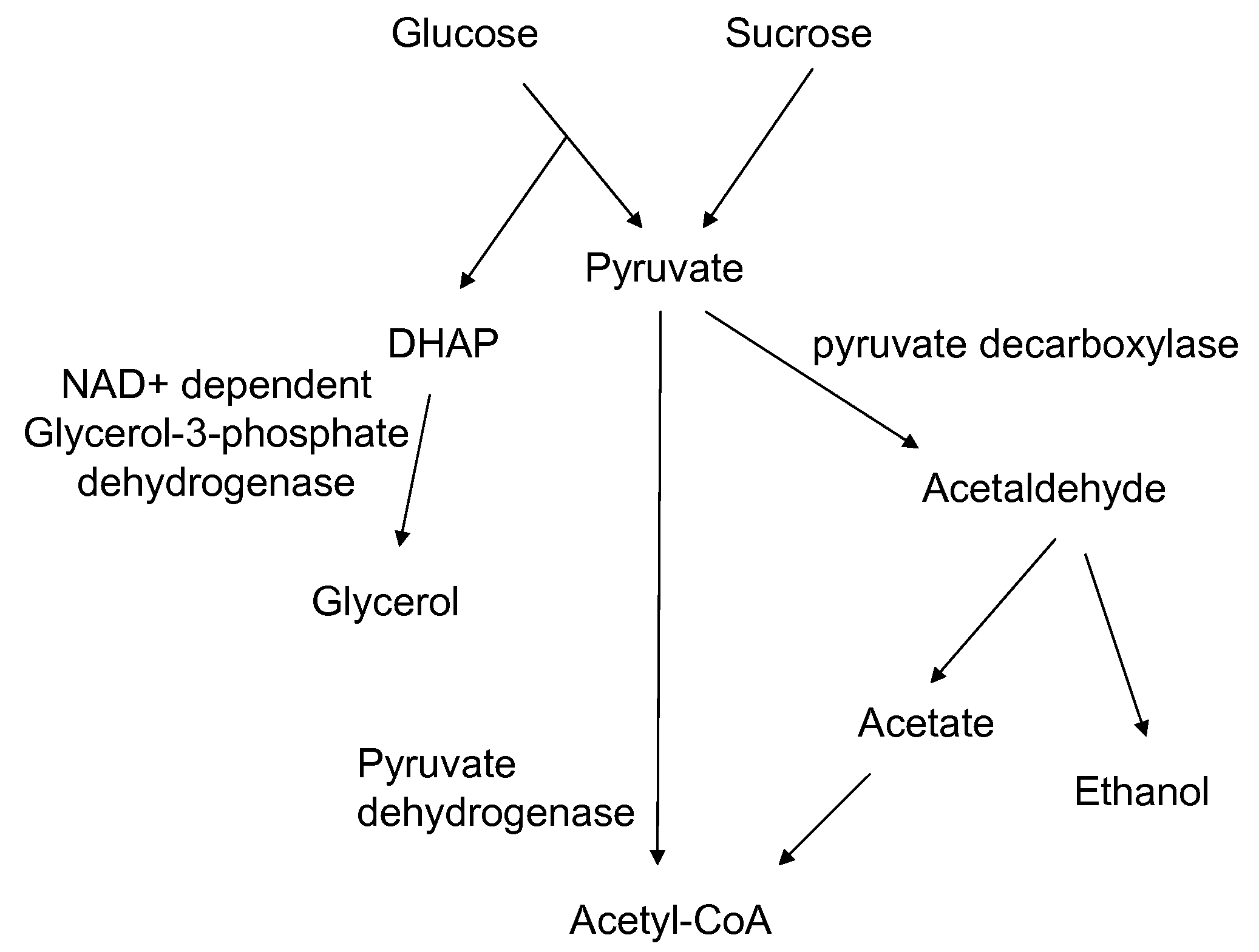
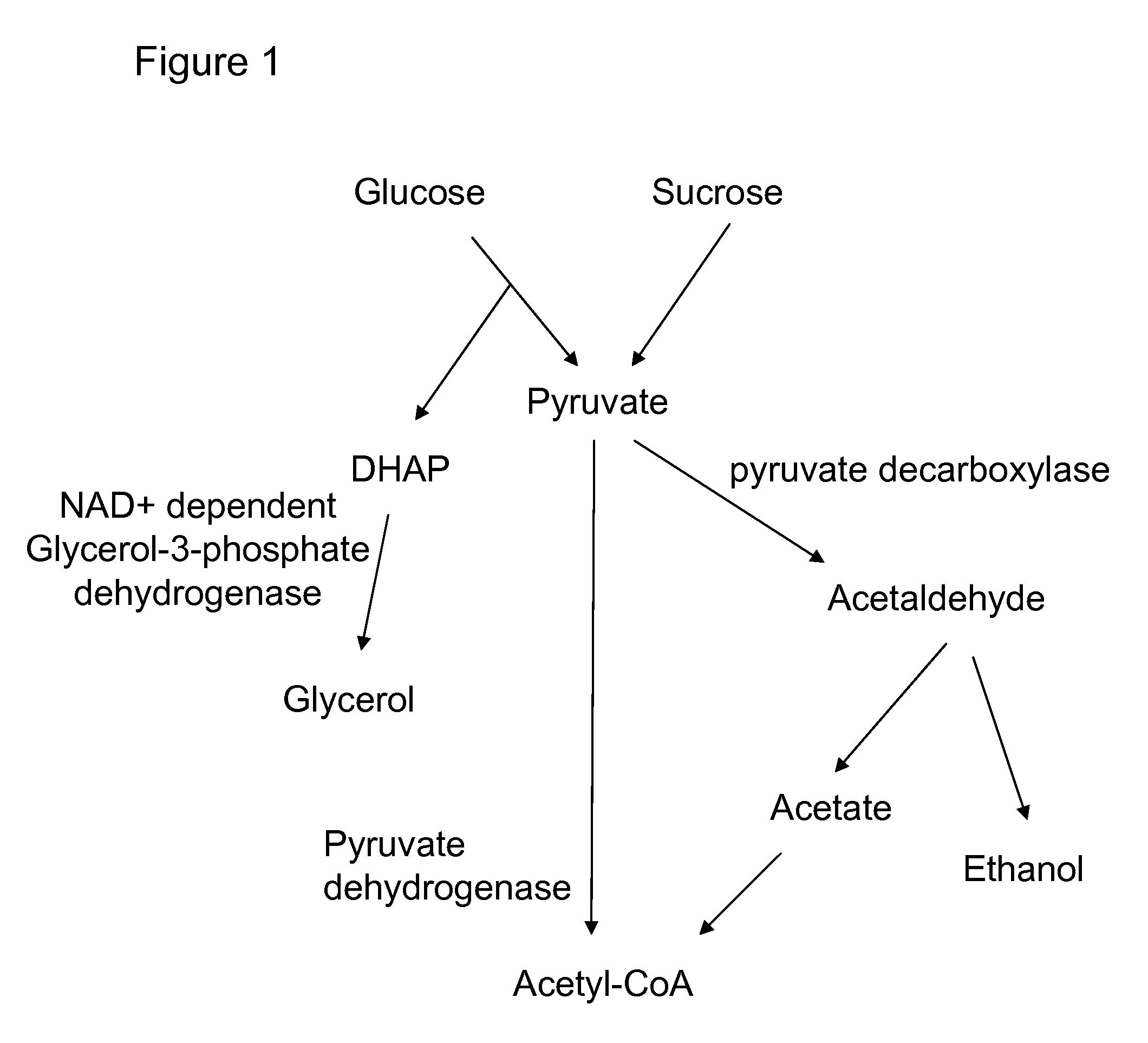
Enhanced pyruvate to acetolactate conversion in yeast
ActiveUS20090305363A1Improve throughputReduction of pyruvate decarboxylase activityFungiTransferasesYeastCytosol
A high flux in conversion of pyruvate to acetolactate was achieved in yeast through expression of acetolactate synthase in the cytosol in conjunction with reduction in pyruvate decarboxylase activity. Additional manipulations to improve flux to acetolactate are reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and reduced glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. Production of compounds having acetolactate as an upstream intermediate benefit from the increased conversion of pruvate to acetolactate in the described strains.
Owner:GEVO INC
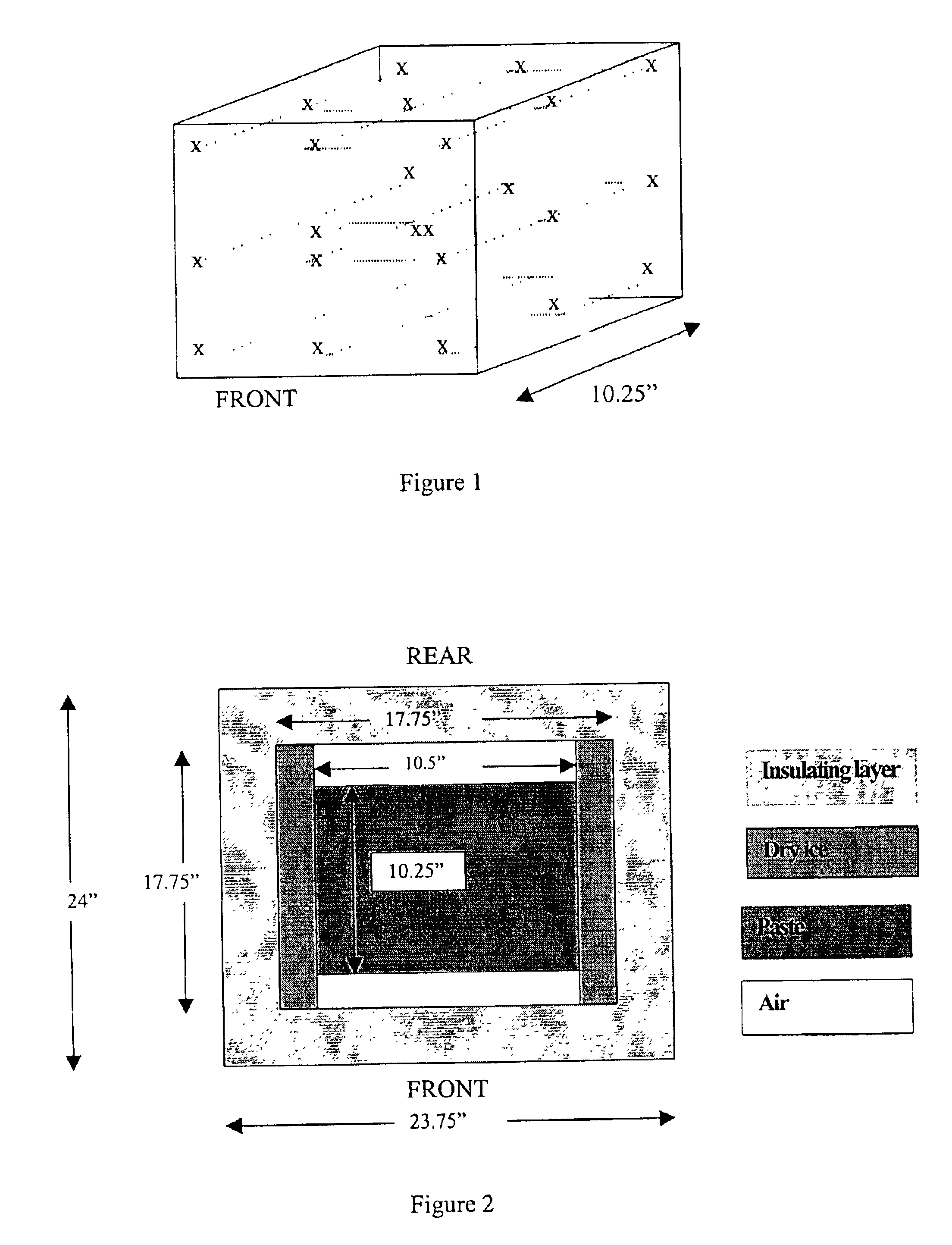
Methods for sterilizing biological materials by irradiation over a temperature gradient
InactiveUS6908591B2Effective sterilizationImprove permeabilityDead animal preservationLavatory sanitoryBiological materialsBiology
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing tissue to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria, (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, spores, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. The methods involve sterilizing one or more tissues with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Expression of heterologous proteins
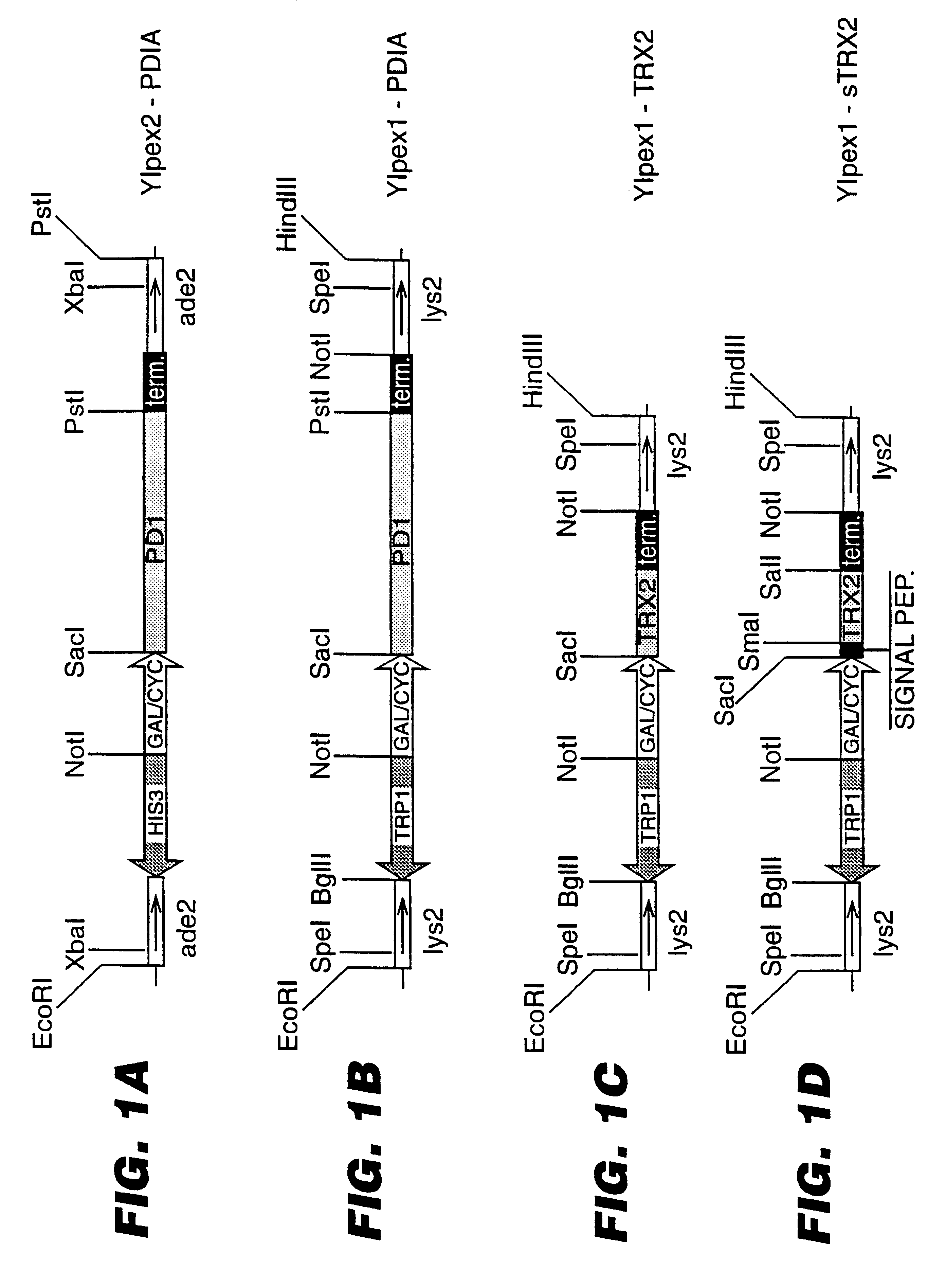
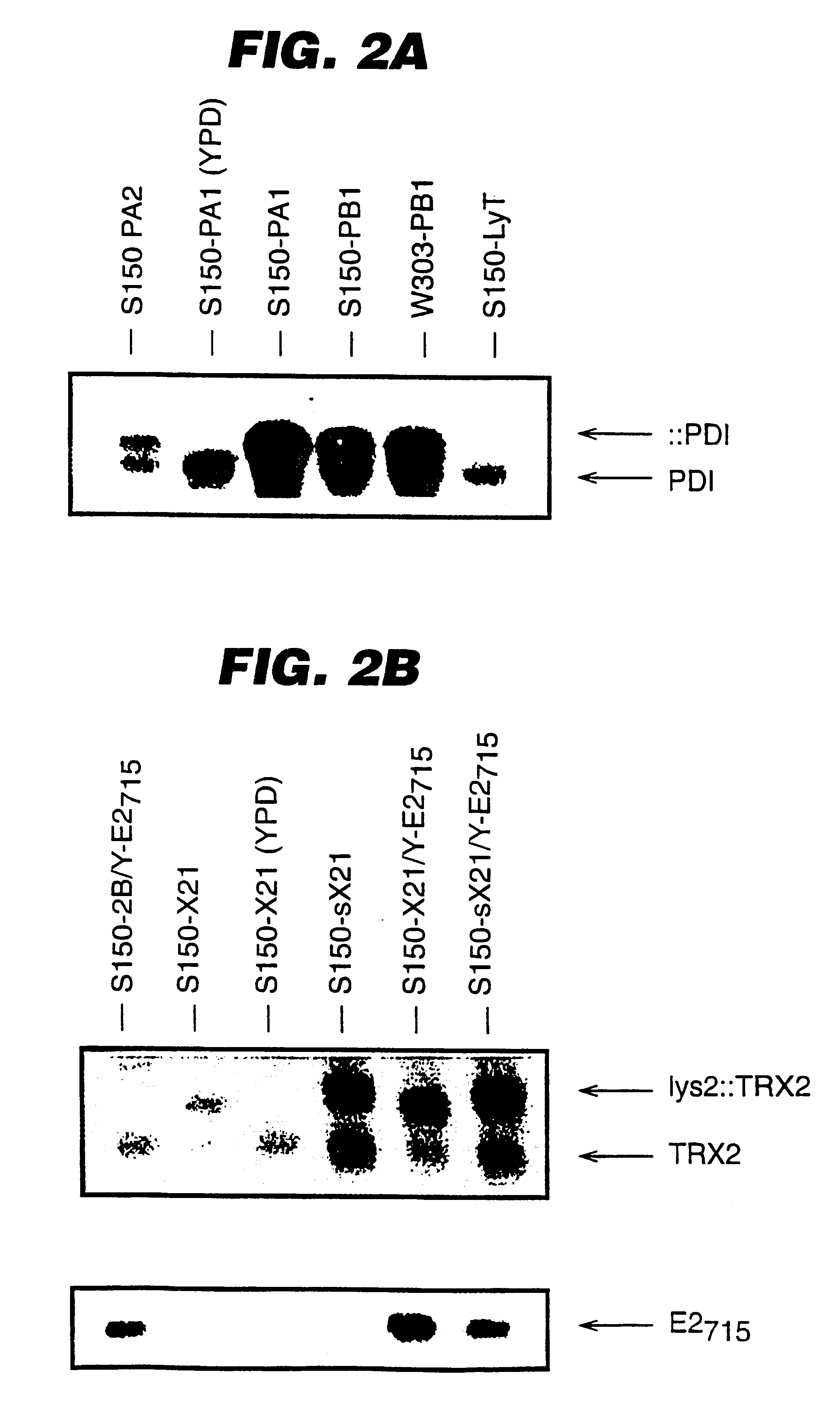
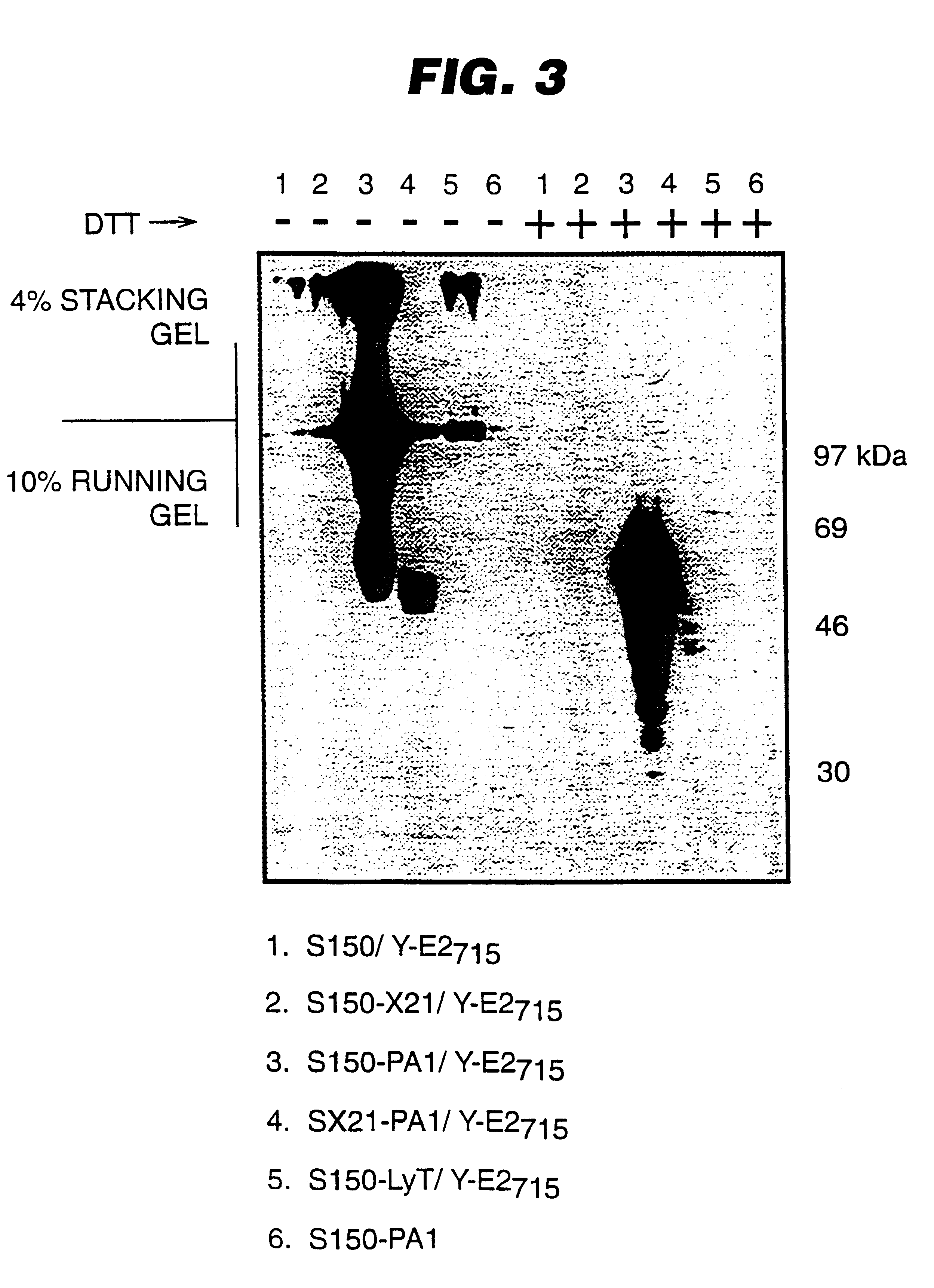
An expression system which provides heterologous proteins expressed by a non-native host organism but which have native-protein-like biological activity and / or structure. Disclosed are vectors, expression hosts and methods for expressing the heterologous proteins. The expression system involves co-expression of protein factor(s) which is / are capable of catalyzing disulphide bond formation and desired heterologous protein(s). The expression system is presented using yeast cells as the preferred host, protein disulphide isomerase (PDI) and thioredoxin (TRX) as the preferred examples of the protein factors and HCV-E2715 envelope glycoprotein and human FIGF as the preferred examples of the heterologous proteins.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
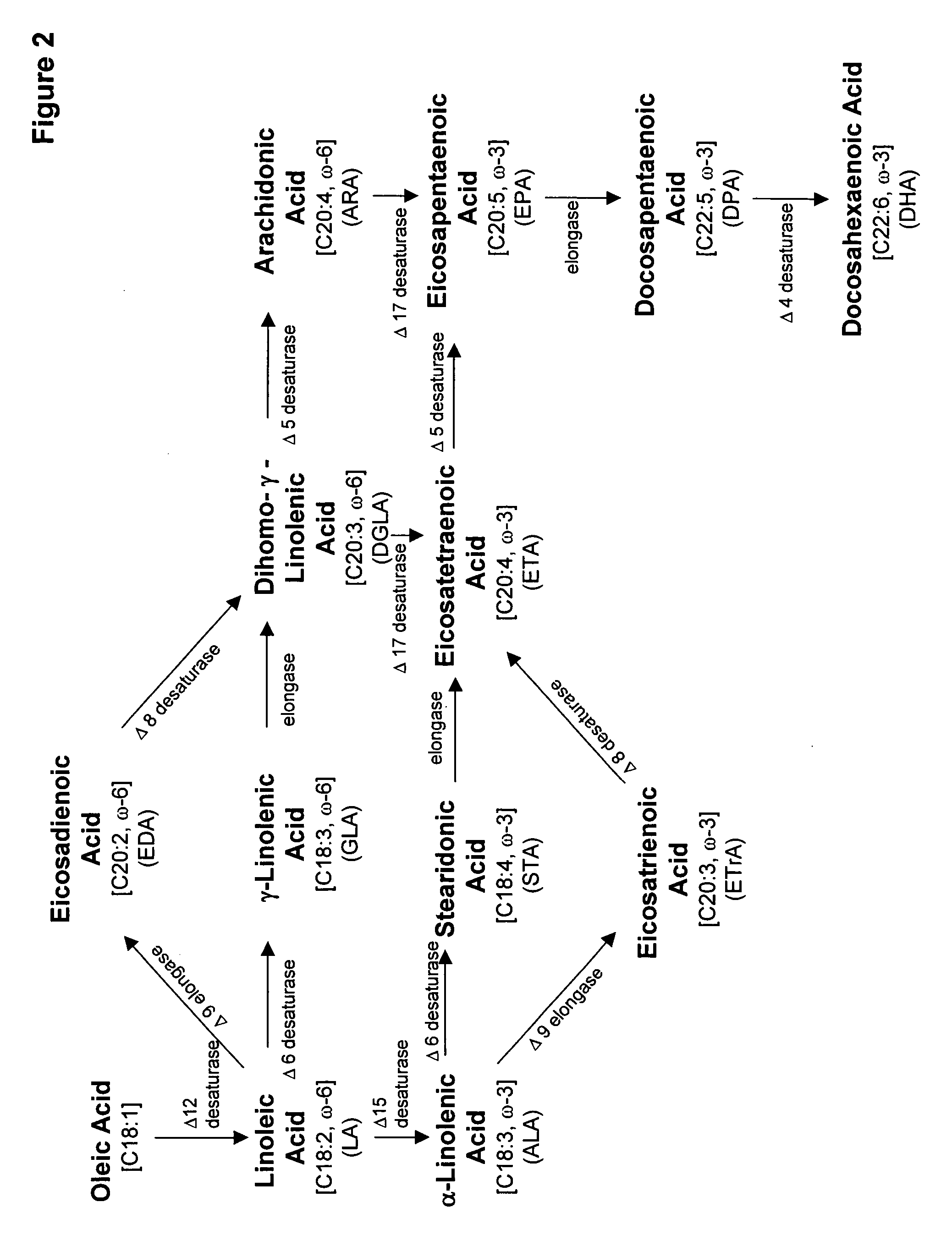
Codon-optimized genes for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
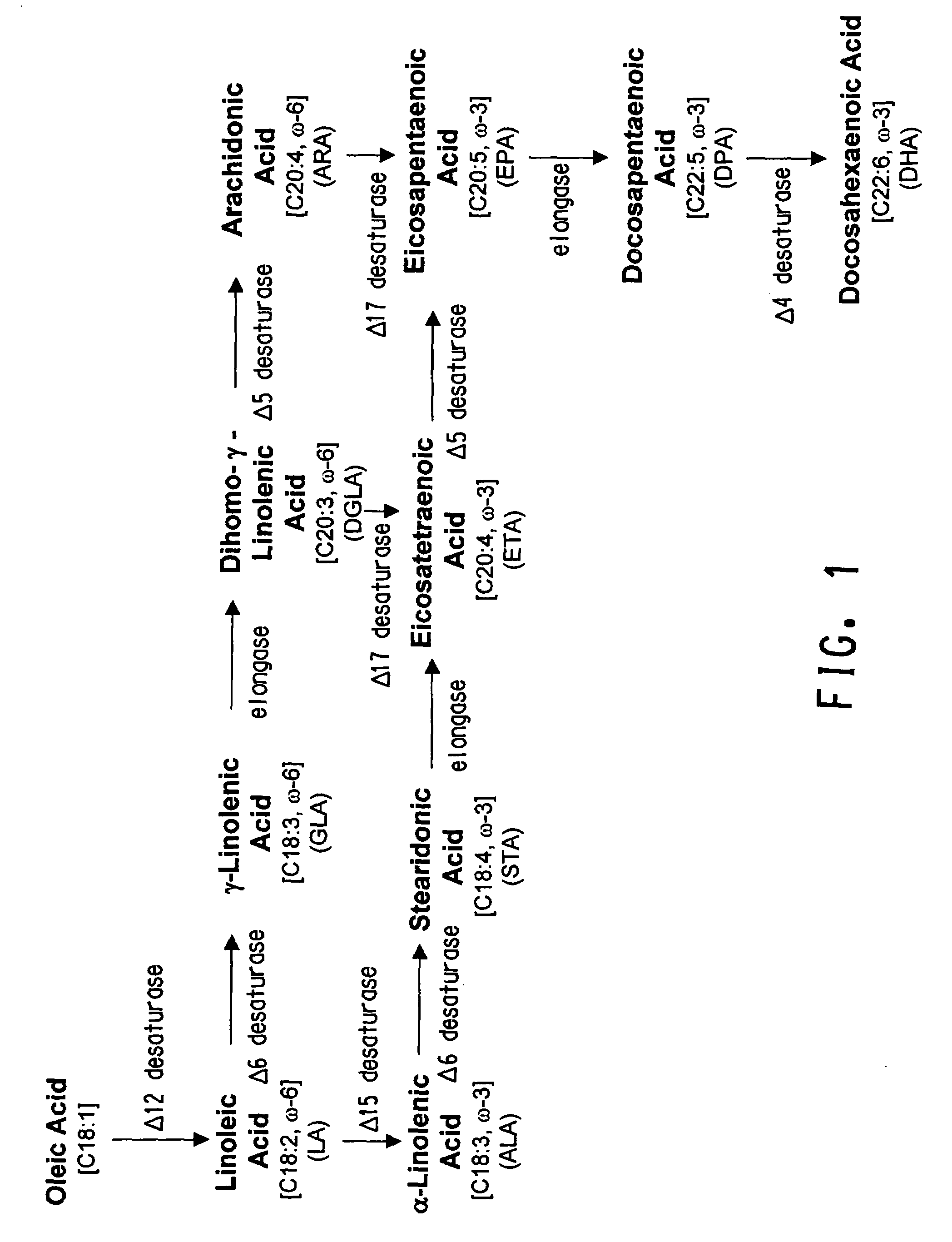
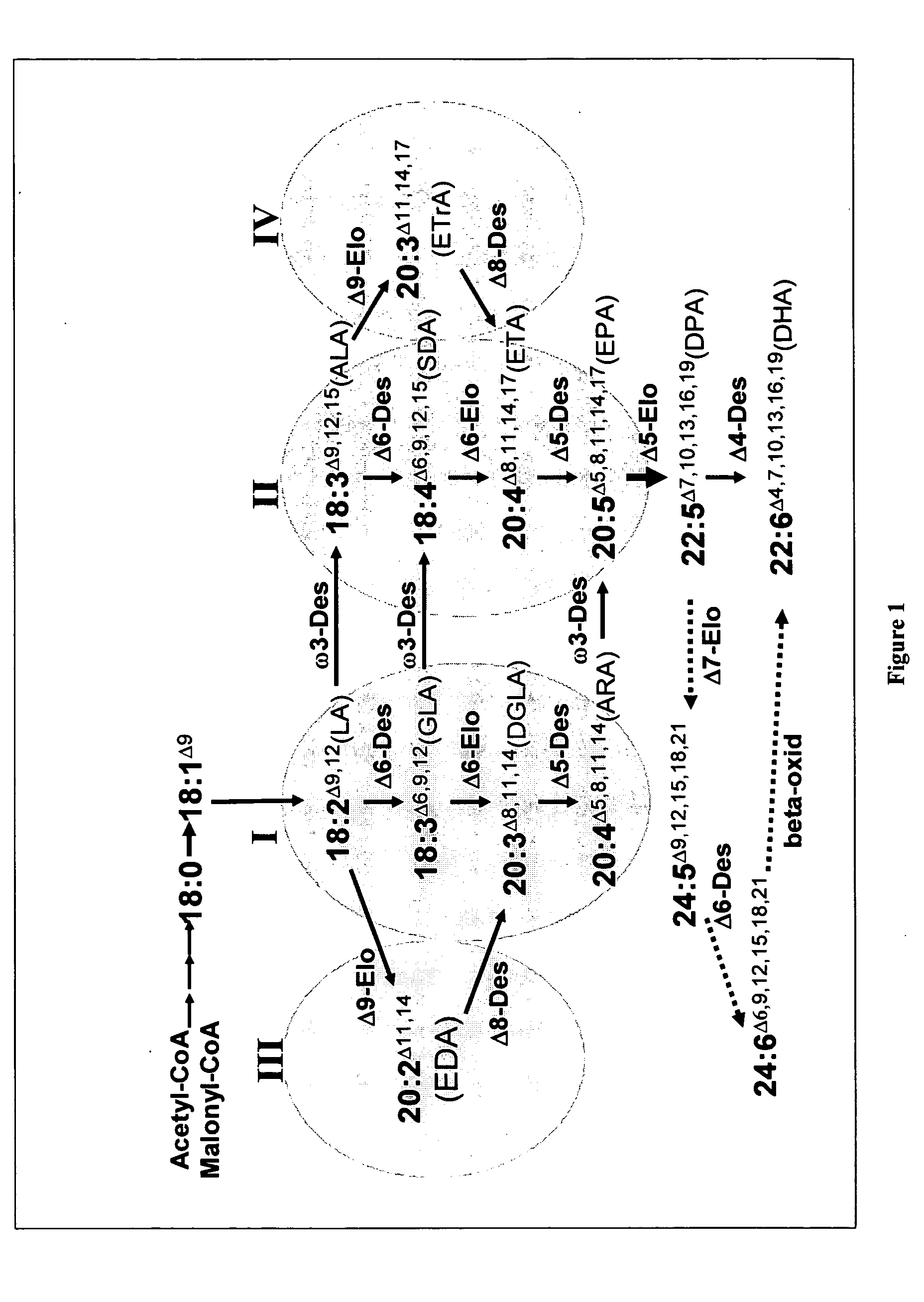
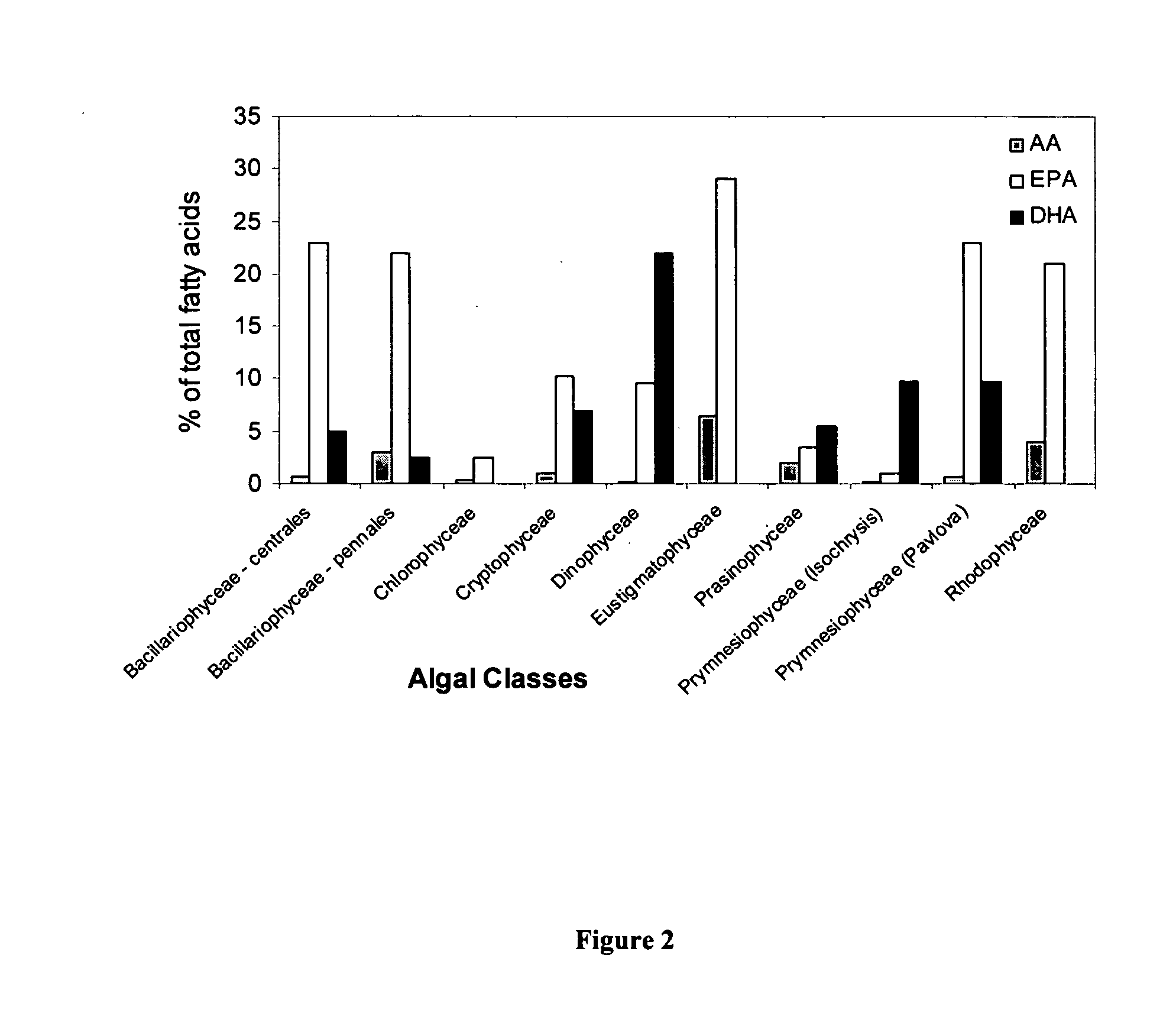
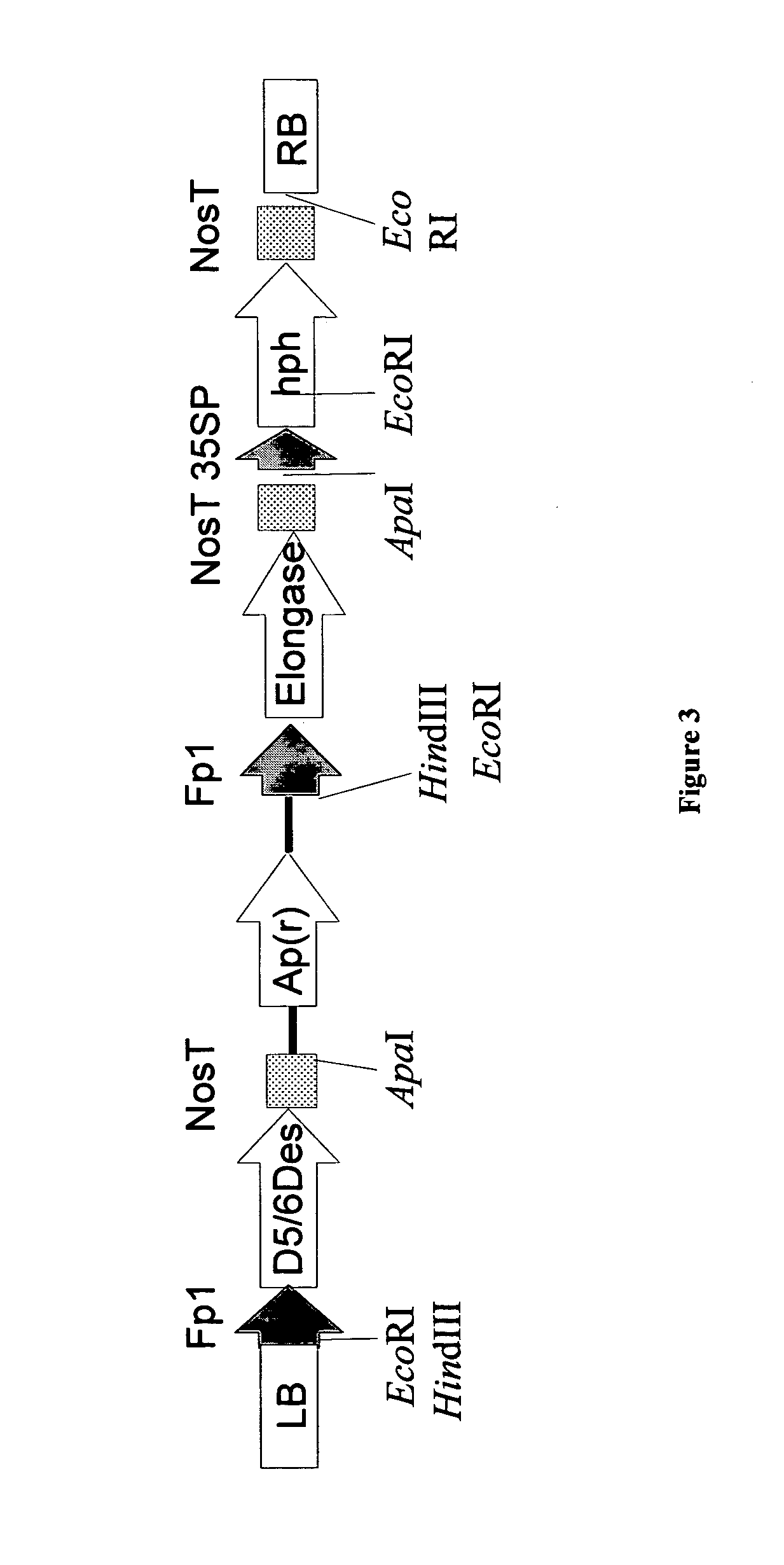
The present invention relates to fatty acid desaturases and elongases able to catalyze the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) to γ-linolenic acid (GLA); α-linoleic acid (ALA) to stearidonic acid (STA); GLA to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid (DGLA); STA to eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA); DGLA to ETA; eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to docosapentaenoic acid (DPA); and arachidonic acid (ARA) to EPA. Nucleic acid sequences encoding codon-optimized desaturases and elongases, nucleic acid sequences which hybridize thereto, DNA constructs comprising the codon-optimized desaturase or elongases, and recombinant host microorganisms expressing increased levels of desaturase or elongase are described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Yeast-dendritic cell vaccines and uses thereof
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Synthesis of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids by recombinant cells
ActiveUS20050273885A1Reduce enzyme activityImprove efficiencyNervous disorderAntipyreticYeastPlant cell
The present invention relates to methods of synthesizing long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially eicosapentaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, in recombinant cells such as yeast or plant cells. Also provided are recombinant cells or plants which produce long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a group of new enzymes which possess desaturase or elongase activity that can be used in methods of synthesizing long-chain poly unsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
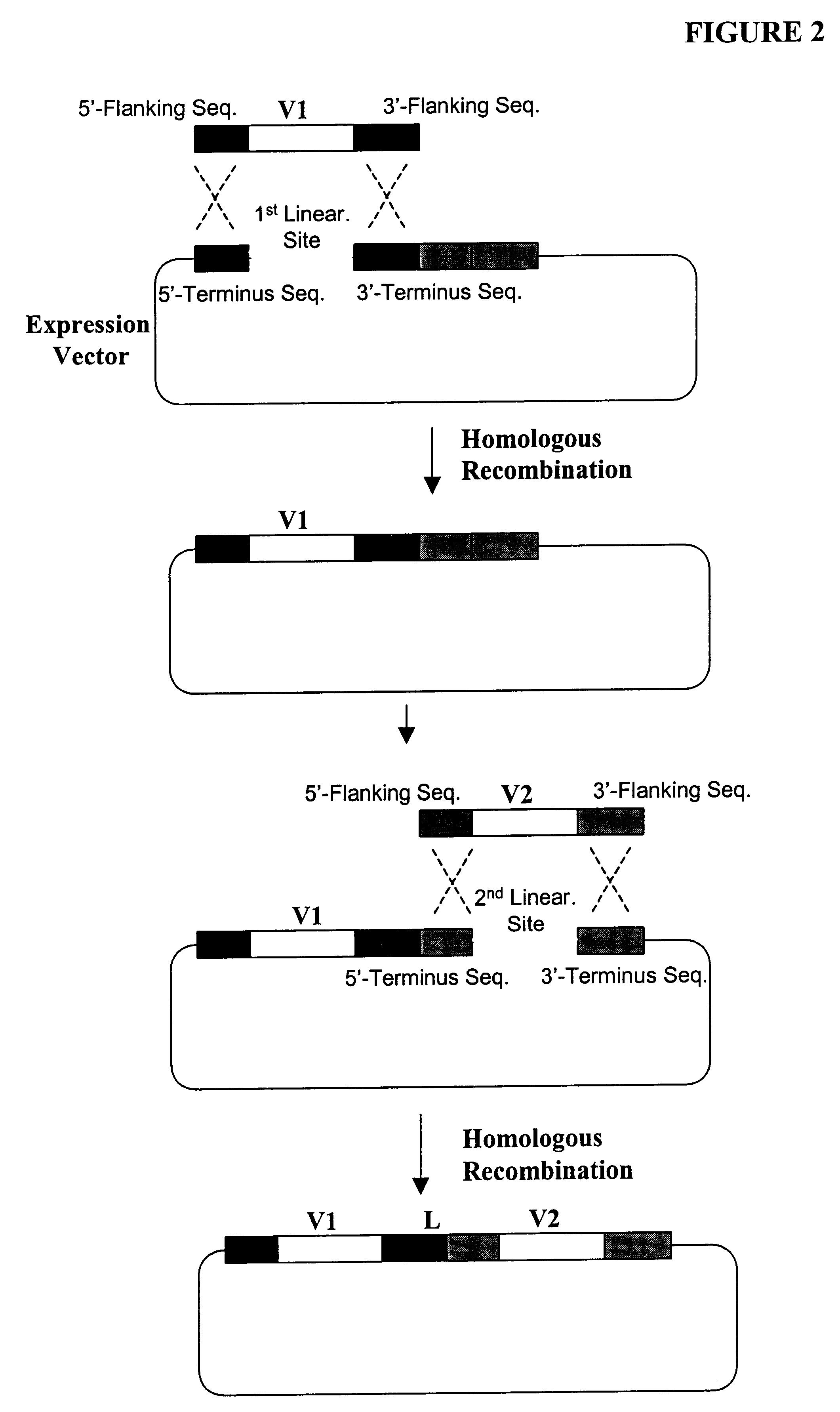
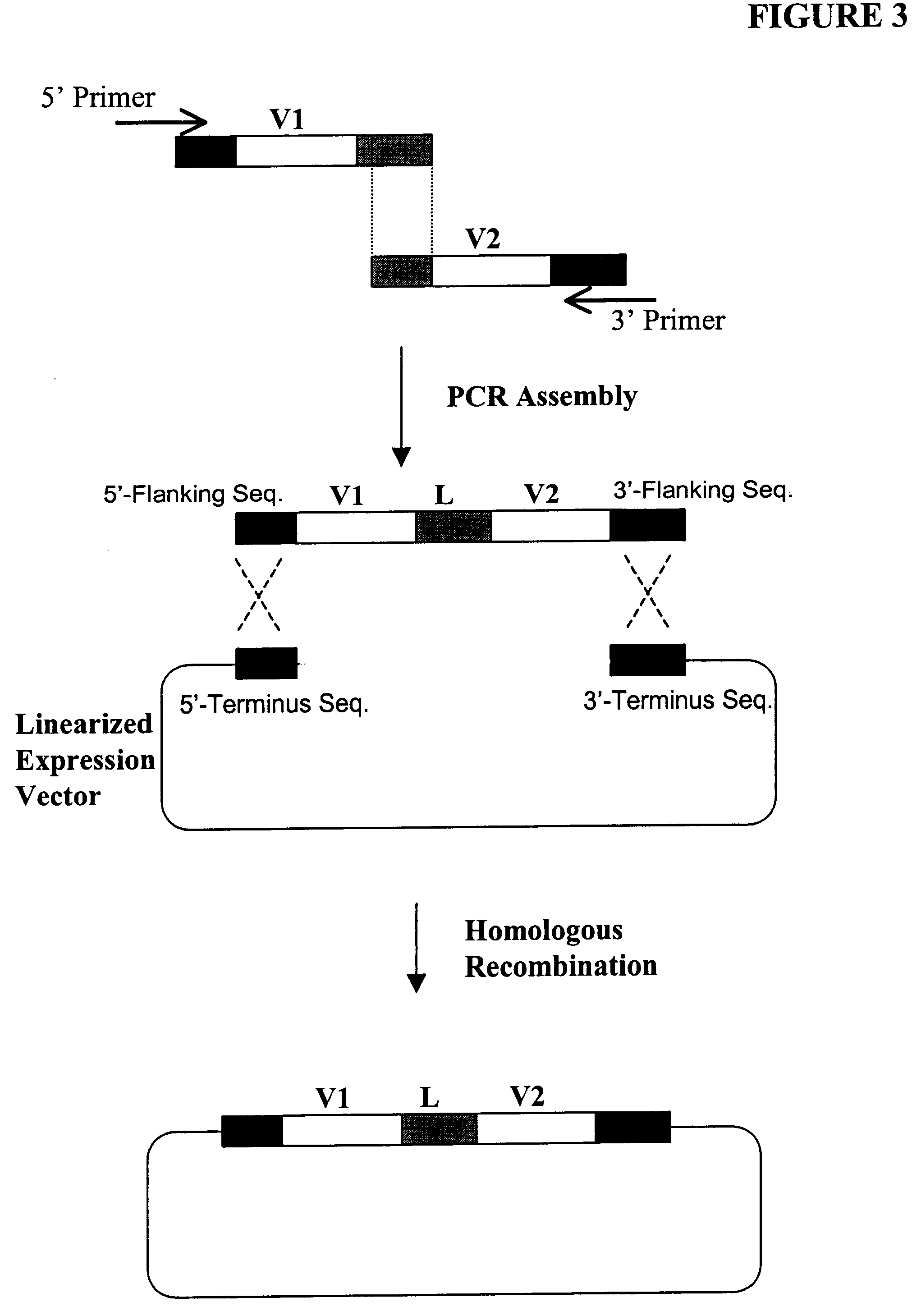
Expression of heterologous multi-domain proteins in yeast
InactiveUS6358733B1Increase productionCost effective productionSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsYeastSingle-Chain Antibodies
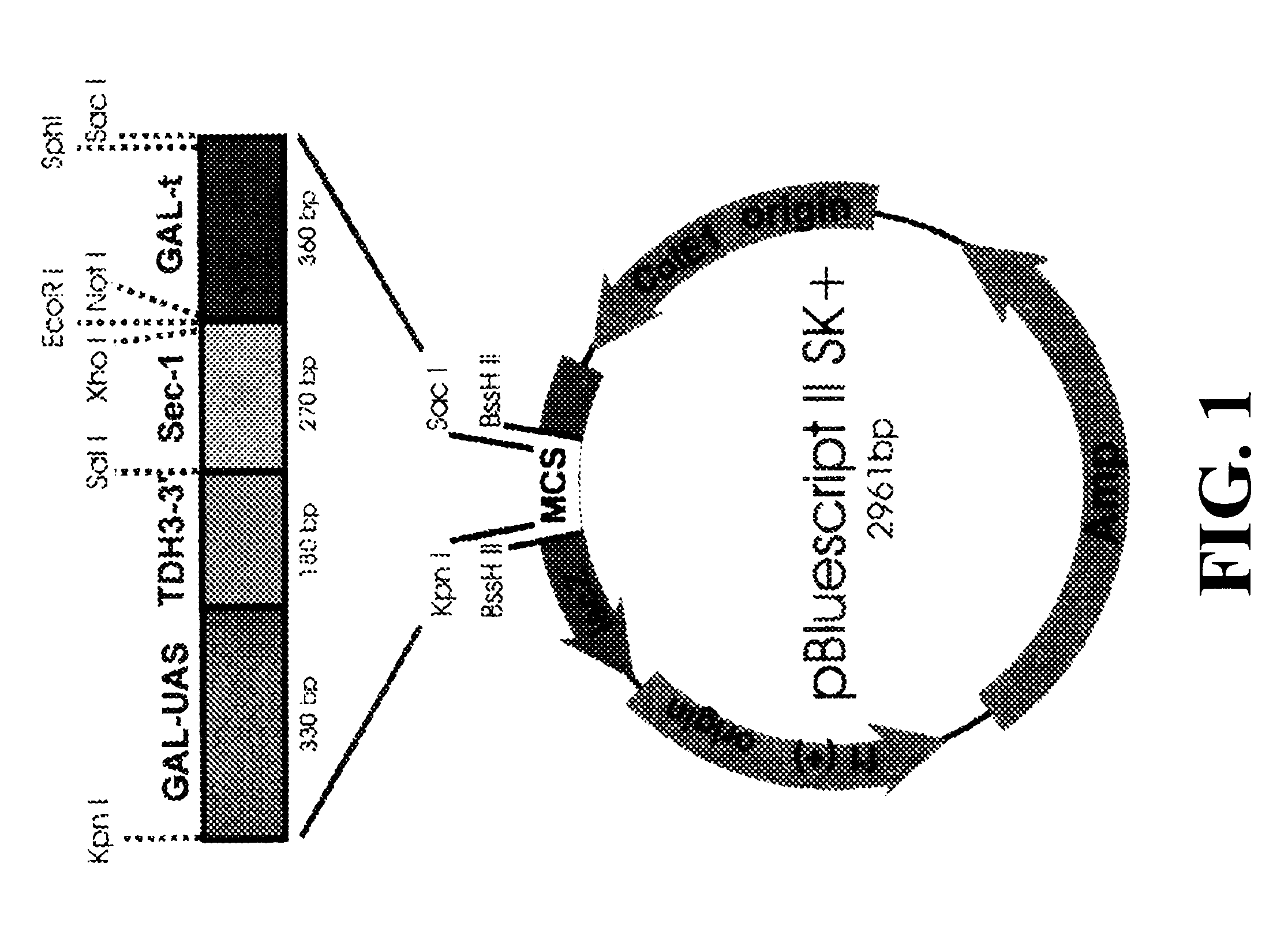
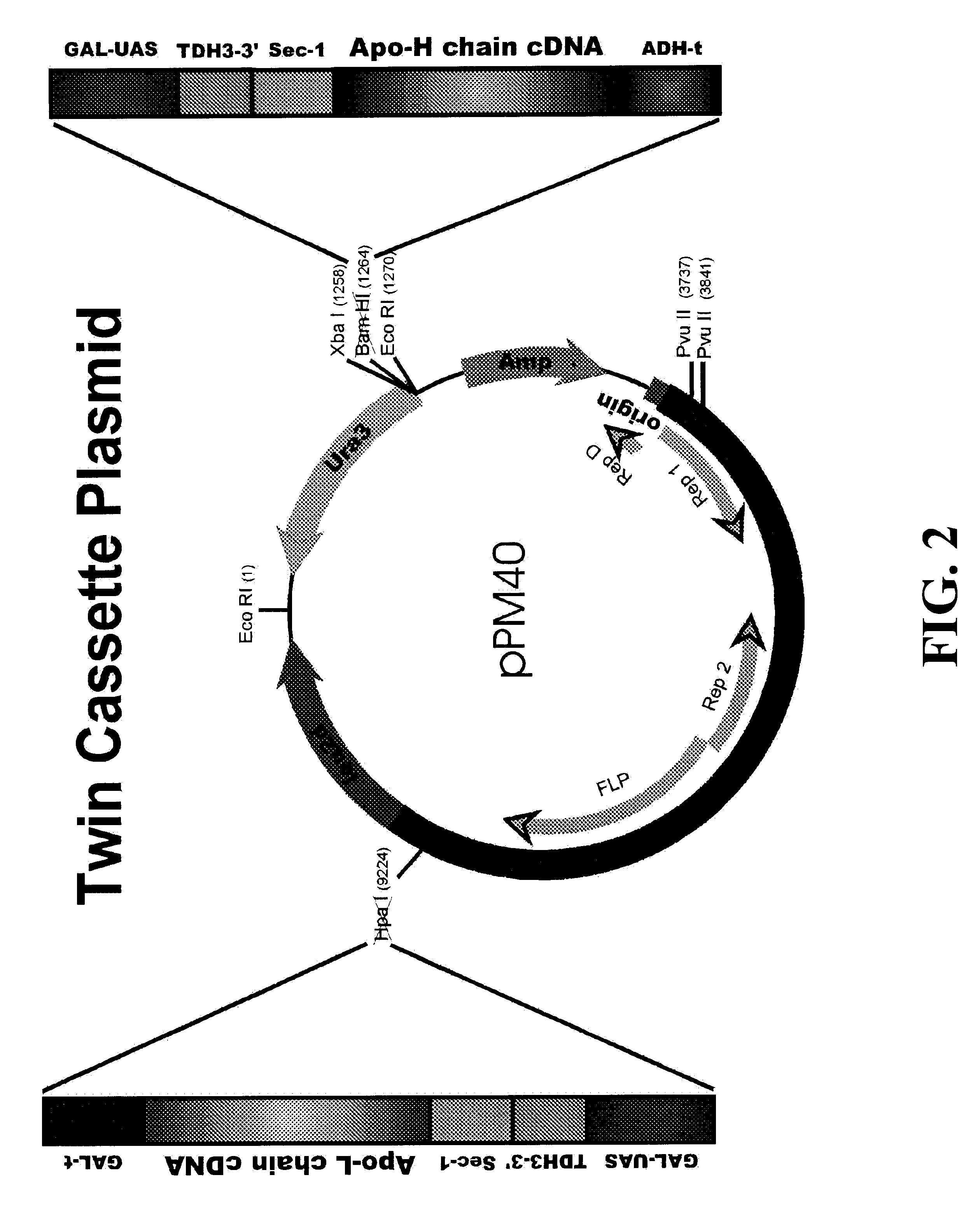
This invention demonstrates the utility of a yeast expression system for the expression of functional heterologous multi-domain proteins in yeast. The yeast expression system allows for the inclusion of a plurality of (up to three) modular expression cassettes which may encode multiple polypeptide chains of a heterologous multi-domain protein on a single plasmid (Twin Cassette). Because multiple polypeptide chains may be encoded for by the expression cassettes of the present invention in a single vector, the system can produce equivalent amounts of the multiple polypeptide chains, thereby enhancing the yield of a functional heterologous multi-domain protein. For example, functional monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) comprising a heavy chain and a light chain of an immunoglobulin (IgG), and functional immunotoxins comprising an antibody domain and an oxidase toxin may be produced using the Yeast expression system of the present invention. In addition, functional single chain antibodies, antibody fragments and chimeric antibodies may also be produced.
Owner:APOLIFE
Mixture of at Least 6 Species of Lactic Acid Bacteria and/or Bifidobacteria in the Manufacture of Sourdough
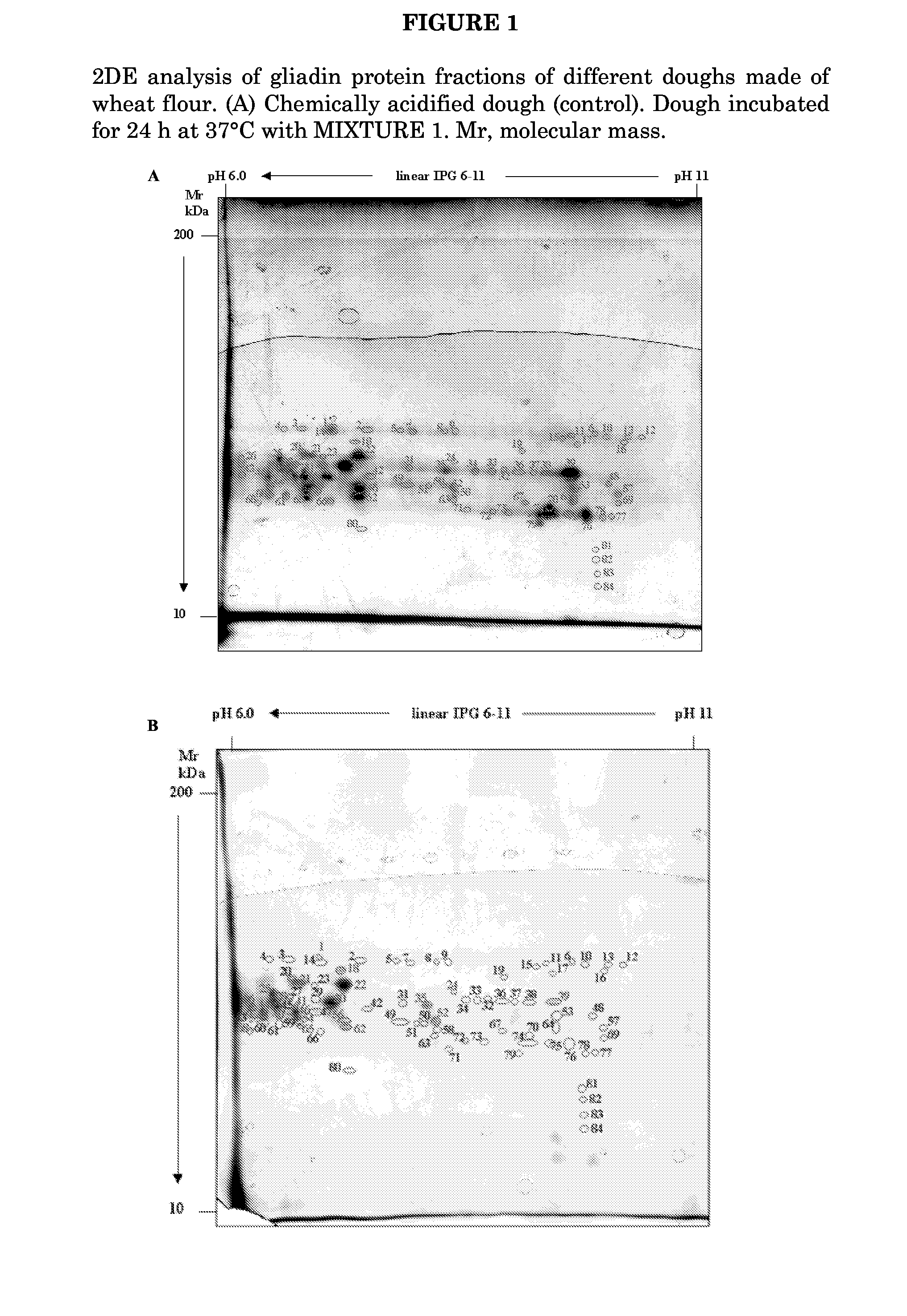
A mixture of at least 6 species of lactic acid bacteria and / or Bifidobacteria is disclosed for use in bakery and medical field. The preferred mixture comprises Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium infantis, Bifidobacterium longum, Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Said mixture is useful for a sourdough, a leavening composition. Baked goods and other food products obtained therefrom are disclosed. These goods have low or no gluten content and are suitable for the integration of the diet of a subject suffering from celiac disease, for decreasing the risk of allergies due to wheat flour albumins and globulins, for the treatment of schizophrenic symptoms, in the preparation of products for enteric diet.
Owner:VSL PHARMA INC
Process for the production of ethanol from algae
The present invention describes a process for the production of ethanol by harvesting starch-accumulating filament-forming or colony-forming algae to form a biomass, initiating cellular decay of the biomass in a dark and anaerobic environment, fermenting the biomass in the presence of a yeast, and the isolating the ethanol produced. The present invention further relates to processing of the biomass remaining after ethanol production to recovering biodiesel starting materials and / or generation of heat and carbon dioxide via combustion.
Owner:PROPULSION LOGIC
Composition With a Fungal (Yeast) Lipase and Method For Treating Lipid Malabsorption in Cystic Fibrous as Well as People Suffering From Pancreatic Lipase Insufficiency
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating pancreatic enzyme insufficiency, such as the pancreatic enzyme insufficiency associated with cystic fibrosis. The invention also provides compositions comprising lipase from Candida cylindracea, alone or in combination with amylase or amyloglucosidase, protease and / or lactase. Furthermore, the invention discloses methods for treating pancreatic enzyme insufficiency comprising administering compositions to patients in need thereof.
Owner:BIO CAT
Pet food compositions comprising two components
Pet food compositions comprising a first component comprising a source of protein, a source of fat, and a source of carbohydrate, and a second component comprising a biologic selected from the group consisting of a probiotic component; yeast; enzymes; antibodies; immunoglobulins; cytokines; and combinations thereof are useful for providing pet food compositions that are sufficiently stable such that effective amounts of the biologic are present in the pet food compositions at the time of ingestion by a pet.
Owner:IAMS
Method for the production of polypeptides
The present invention relates to a novel method for the production of short chain polypeptides, including polypeptides having up to 3 disulfide bonds and / or structures rich in basic amino acid residues, and open structured short chain polypeptides, e.g. glucagon, glucagon like peptides and their functional analogues, in genetically modified yeast cells, said genetically modified yeast cells, and a method for the preparation of said yeast cells.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
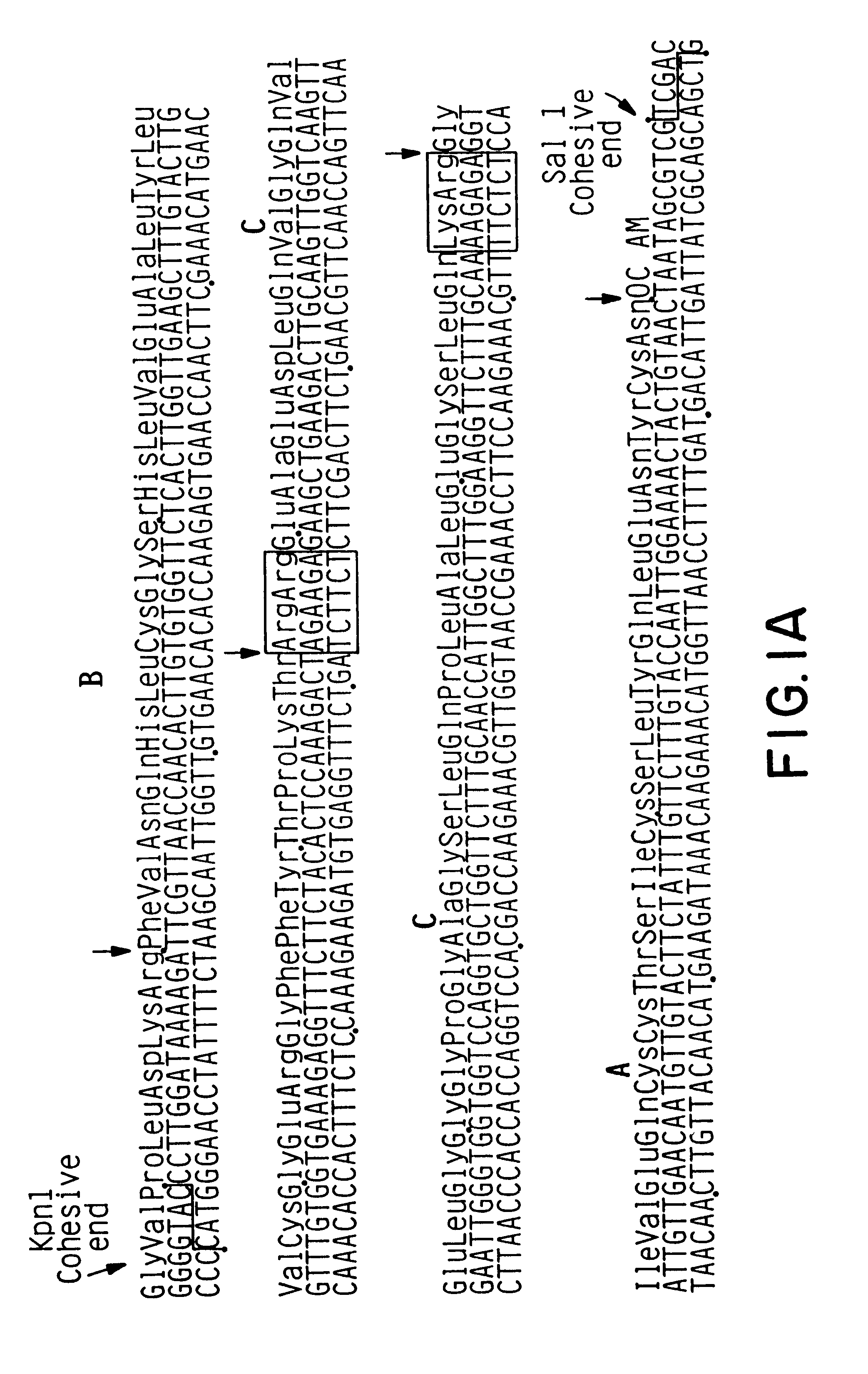
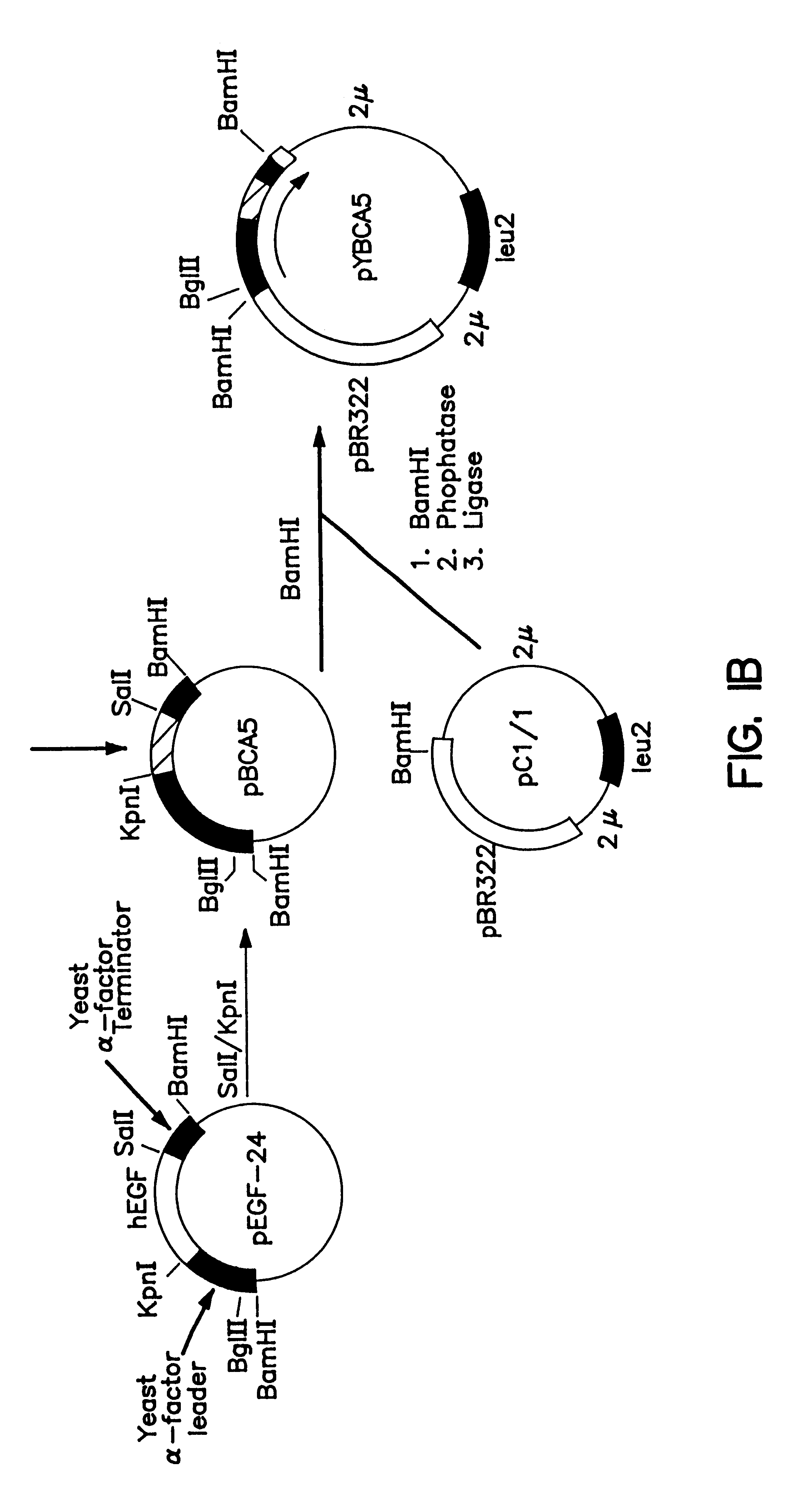
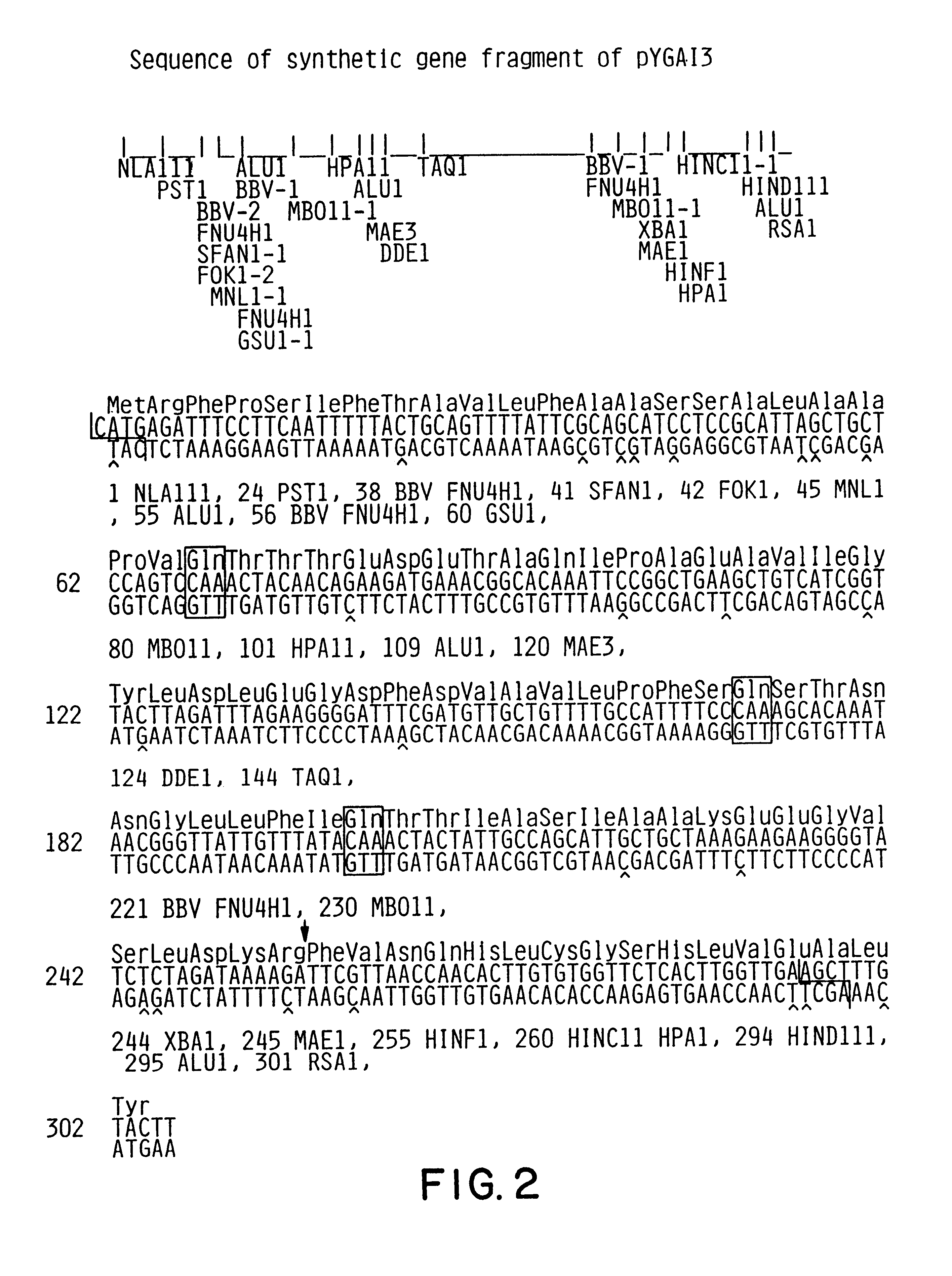
Expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in yeast employing truncated alpha-factor leader sequences
InactiveUSRE37343E1Efficiently direct expressionEfficient secretionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiHeterologousBiotechnology
A yeast alpha-factor expression system is provided comprised of a truncated leader sequence, containing the alpha-factor signal peptide and one glycosylation site, linked by a processing site to a non-yeast protein-encoding sequence.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
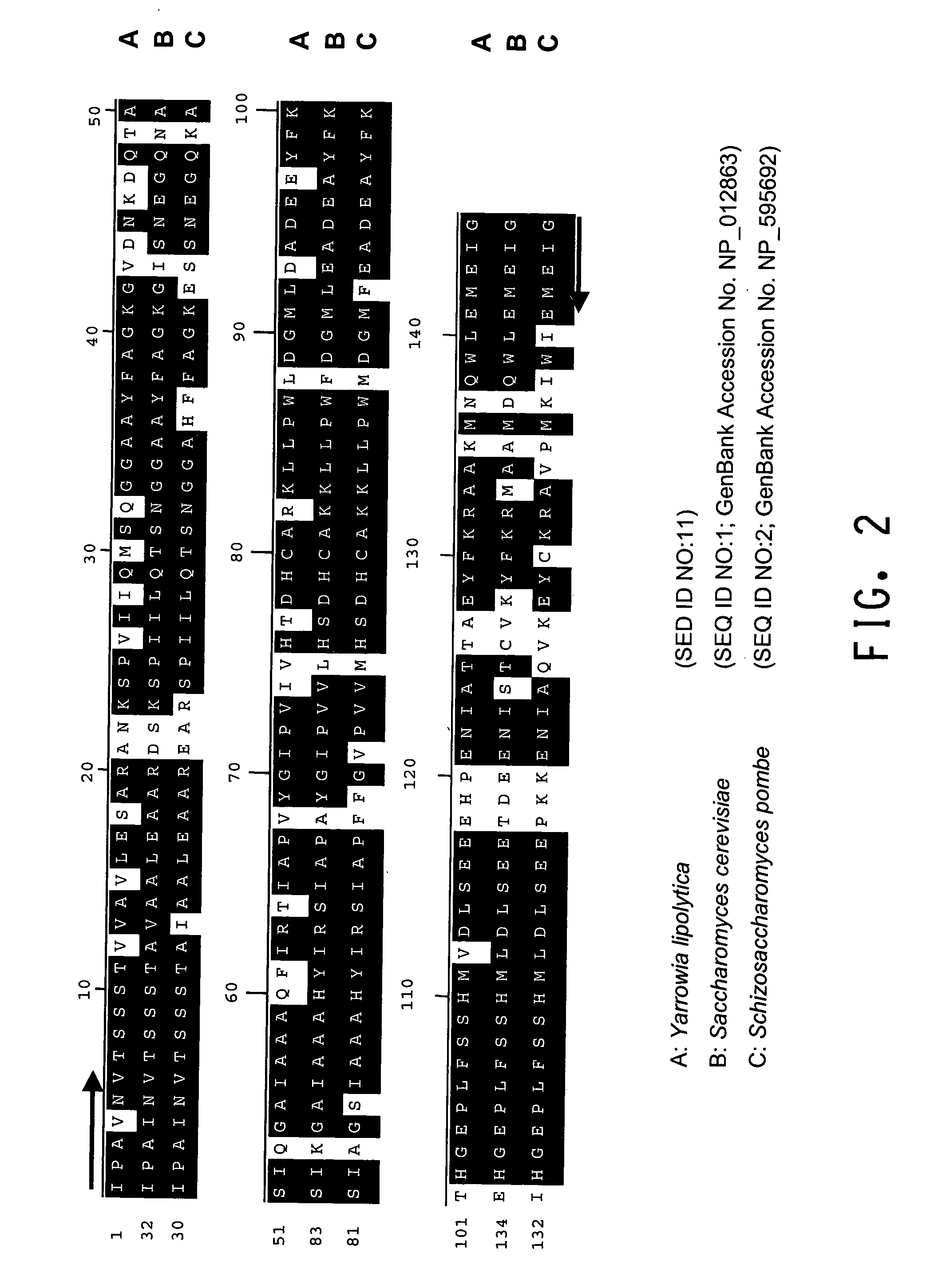
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
The regulatory sequences (i.e., promoter regions, introns and enhancers) associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica gene encoding fructose bis-phospate aldolase (FBA1) have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologus genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Ethanol production with dilute acid hydrolysis using partially dried lignocellulosics
InactiveUS20030199049A1Increase sugar yieldImprove digestibilityBiofuelsWaste based fuelCelluloseGrowth phase
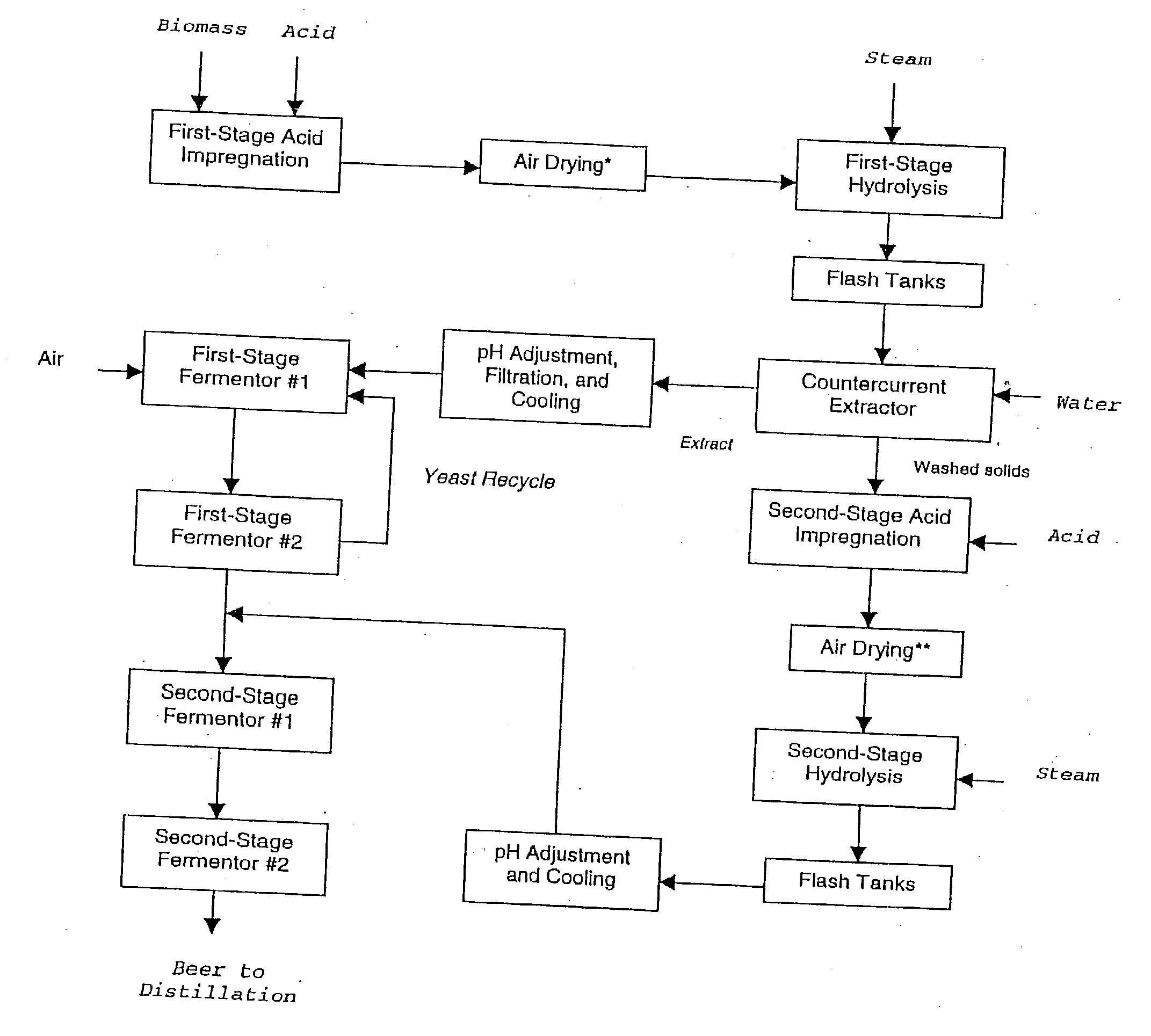
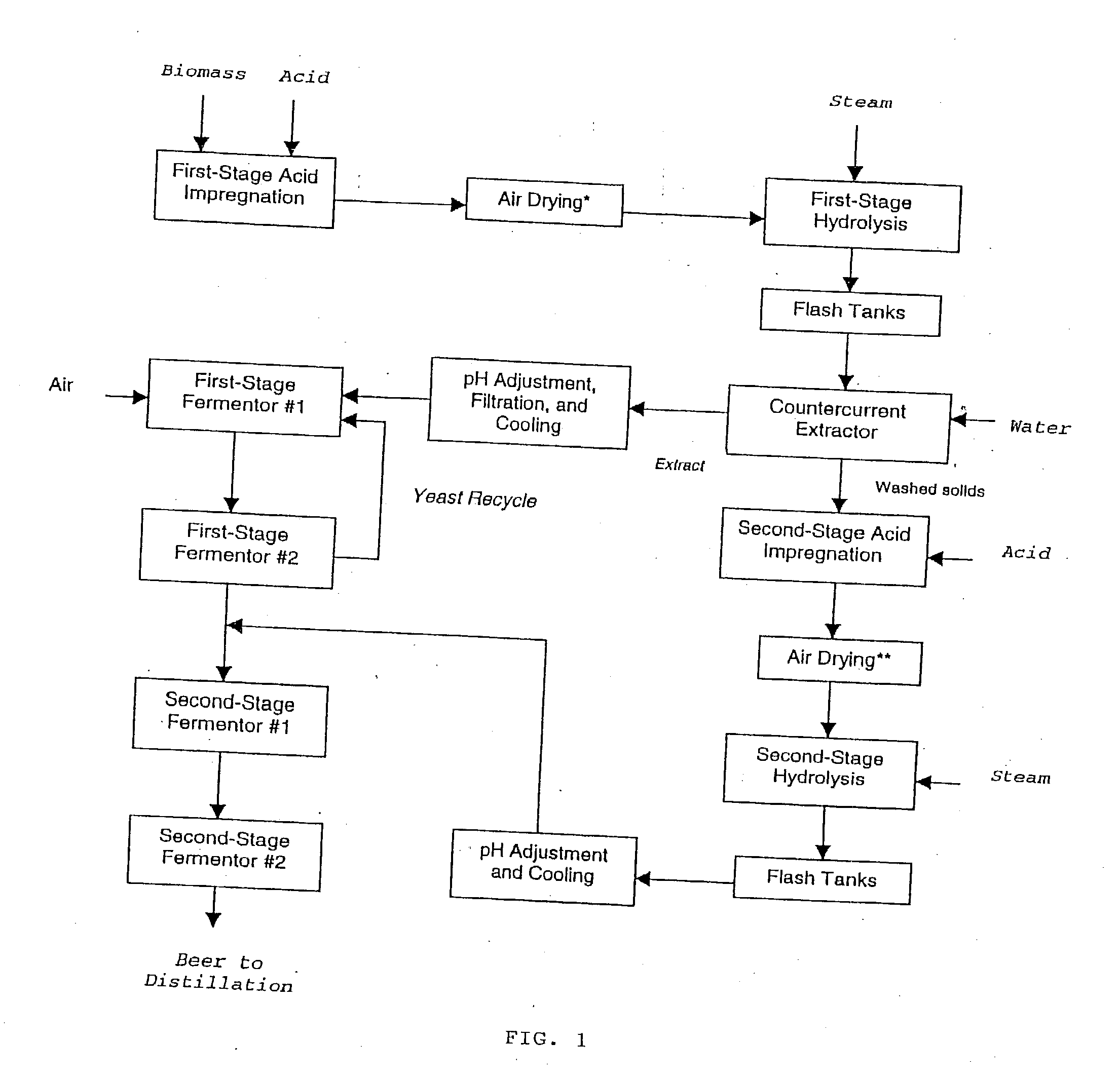
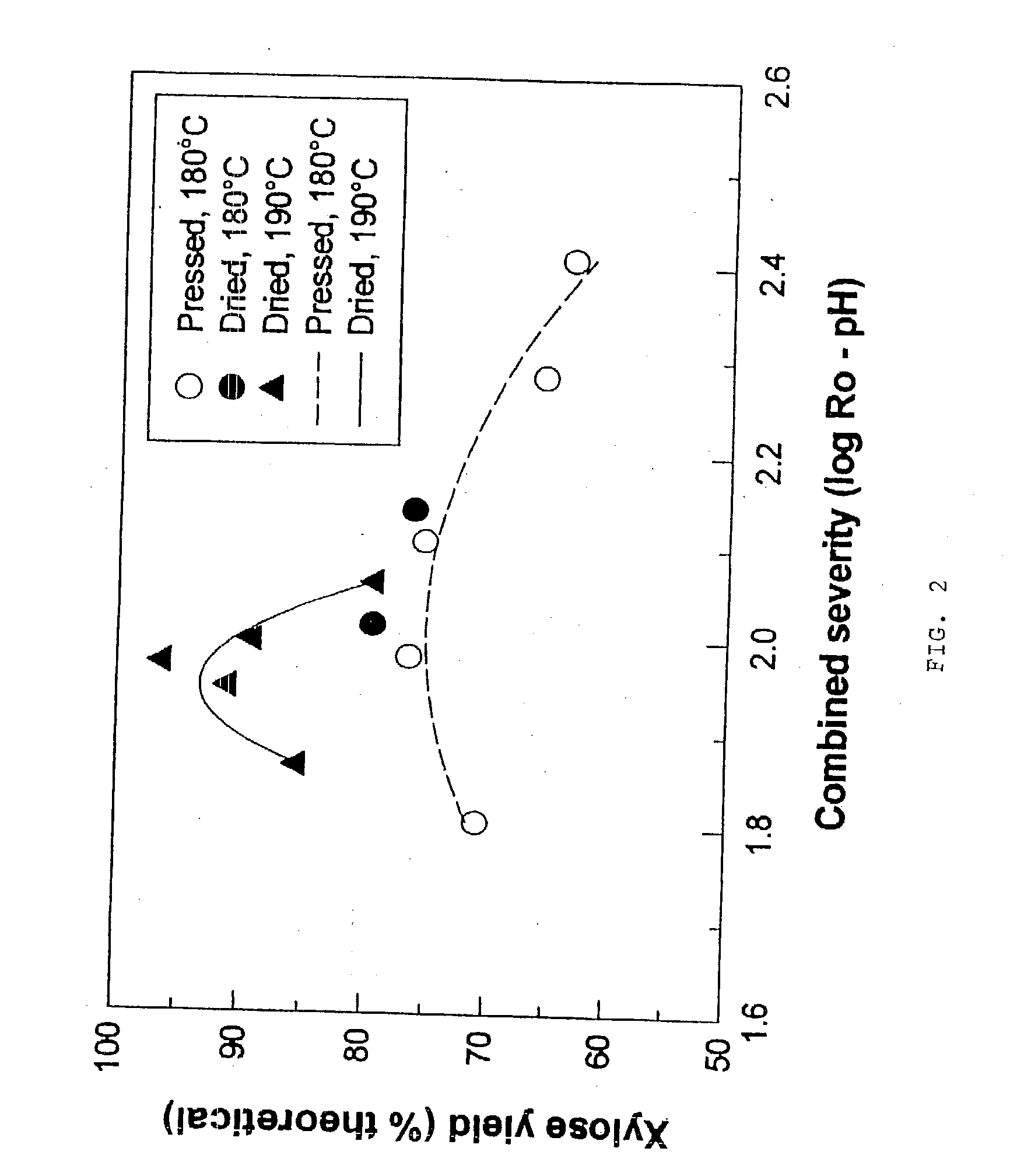
In a process for converting lingnocellulosic biomass to ethanol, the improvement of obtaining higher fermentable soluble sugar yields by drying acid impregnated biomass particles, comprising: a) feeding moist lignocellulosic biomass into an acid impregnator to render it acid-soaked and draining the acid-soaked biomass to about 30% to 35% by weight solids; b) dewatering the acid-soaked biomass by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of the biomass and arrive at about 40% to 60% by weight solids; c) subjecting the acid-impregnated biomass to a first-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature of from 130° C. to 220° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars, and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank-the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for a counter-current extractor; d) washing the hydrolysate, adjusting the pH of the sugar extract to about 5, and recovering more than 95% of the soluble sugars in the first-stage hydrolysate slurry by a counter-current extractor; e) subjecting remaining washed-first stage solids of pretreated biomass to a second-stage acid and metal salt impregnator and dewatering by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of biomass to arrive at 40% to 60% by weight solids; f) subjecting the acid and metal salt-impregnated biomass to a second-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature from 190° C. to 240° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank, at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank, the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for second-stage fementors; g) cooling pH-adjusted extract from the counter-current extractor, feeding the extract to a first-stage fermentor and air sparging the first-stage fermentor at a rate sufficient to promote enough yeast growth to compensate for loss through second-stage fermentors; h) pH adjusting second-stage hydrolysate slurry to 4.5, cooling the slurry and adding it into the top of the first fermentor of a two-fermentor train in the second stage fermentors, pumping broth from the bottom of the first stage fermentors to the second stage fermentors while the yeast is in the growth phase for a period sufficient to consume over 95% of fermentable sugars; and i) recovering ethanol.
Owner:MIDWEST RES INST
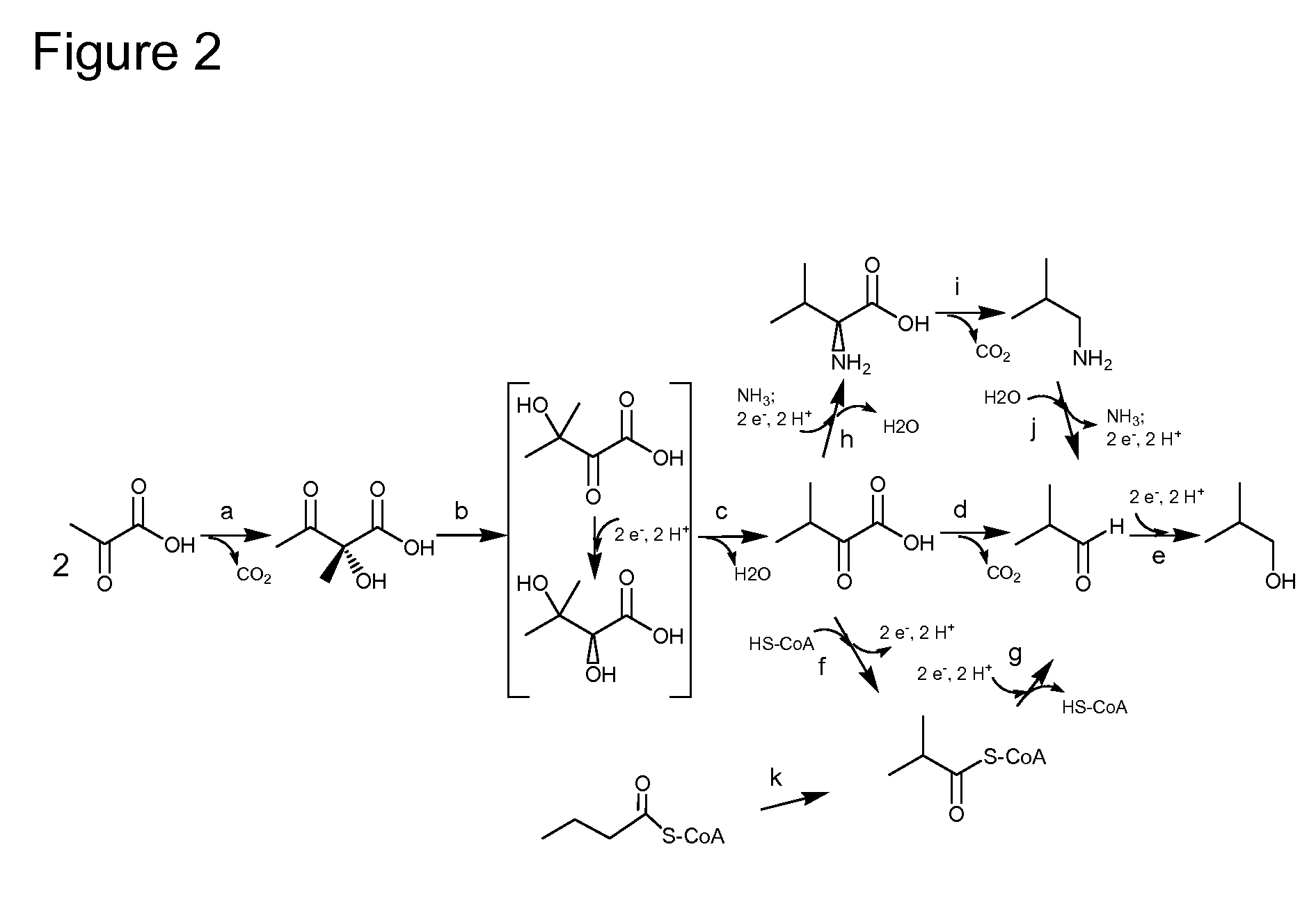
Methods and materials for the synthesis of organic products
This invention provides biocatalysts that are recombinant yeast cells comprising recombinant expression vectors encoding heterologous lactate dehydrogenase genes for producing lactate.
Owner:RAJGARHIA VINEET +4
Categorization of microbial communities
ActiveUS20060172330A1Special deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic microorganismYeast
The present disclosure provides embodiments of a method for characterizing microbial populations. Exemplified by methods for characterizing microbiota in vaginal samples, the methods provided herein are widely applicable to the characterization of microbial communities. Also provided are probiotic regimens and methods for selecting appropriate probiotic regimens based on the normal vaginal microbiota of a subject. Reagents and kits for detecting normal vaginal microbiota and diagnosing pathogenic microorganisms in the vagina are also provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY +1
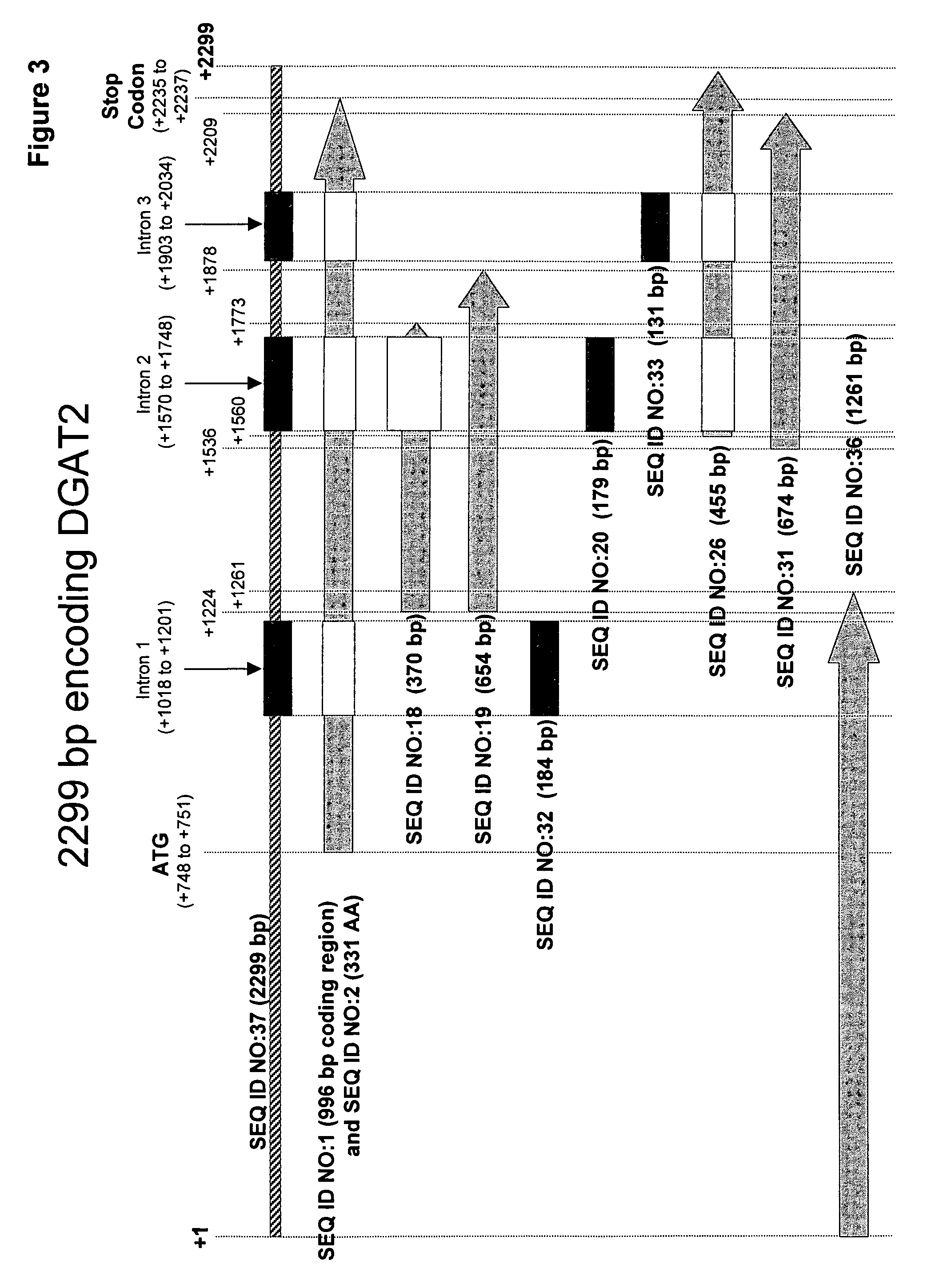
Mortierella alpina diacylglycerol acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
An acyltransferase is provided, suitable for use in the manufacture of microbial oils enriched in omega fatty acids in oleaginous organisms. Specifically, the gene encoding diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT2) has been isolated from Mortierella alpina. This gene encodes an enzyme that participates in the terminal step in oil biosynthesis in fungi and yeast and is expected to play a key role in altering the quantity of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids produced in oils of oleaginous organisms. Most desirably, the substrate specificity of the instant DGAT2 will be particularly useful to enable accumulation of long-chain PUFAs having chain lengths equal to or greater than C20 in oleaginous yeast, such as Yarrowia lipolytica.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Biological fertilizer based on yeasts
The present invention provides biological fertilizer compositions that comprise yeast cells that have an enhanced ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, decompose phosphorus minerals and compounds, decompose potassium minerals and compounds, decompose complex carbon compounds, over produce growth factors, and over produce ATP. The biological fertilizer composition of the invention can replace mineral fertilizers in supplying nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to crop plants. Methods of manufacturing the biological fertilizer compositions and methods of uses are also encompassed.
Owner:ULTRA BIOTECH
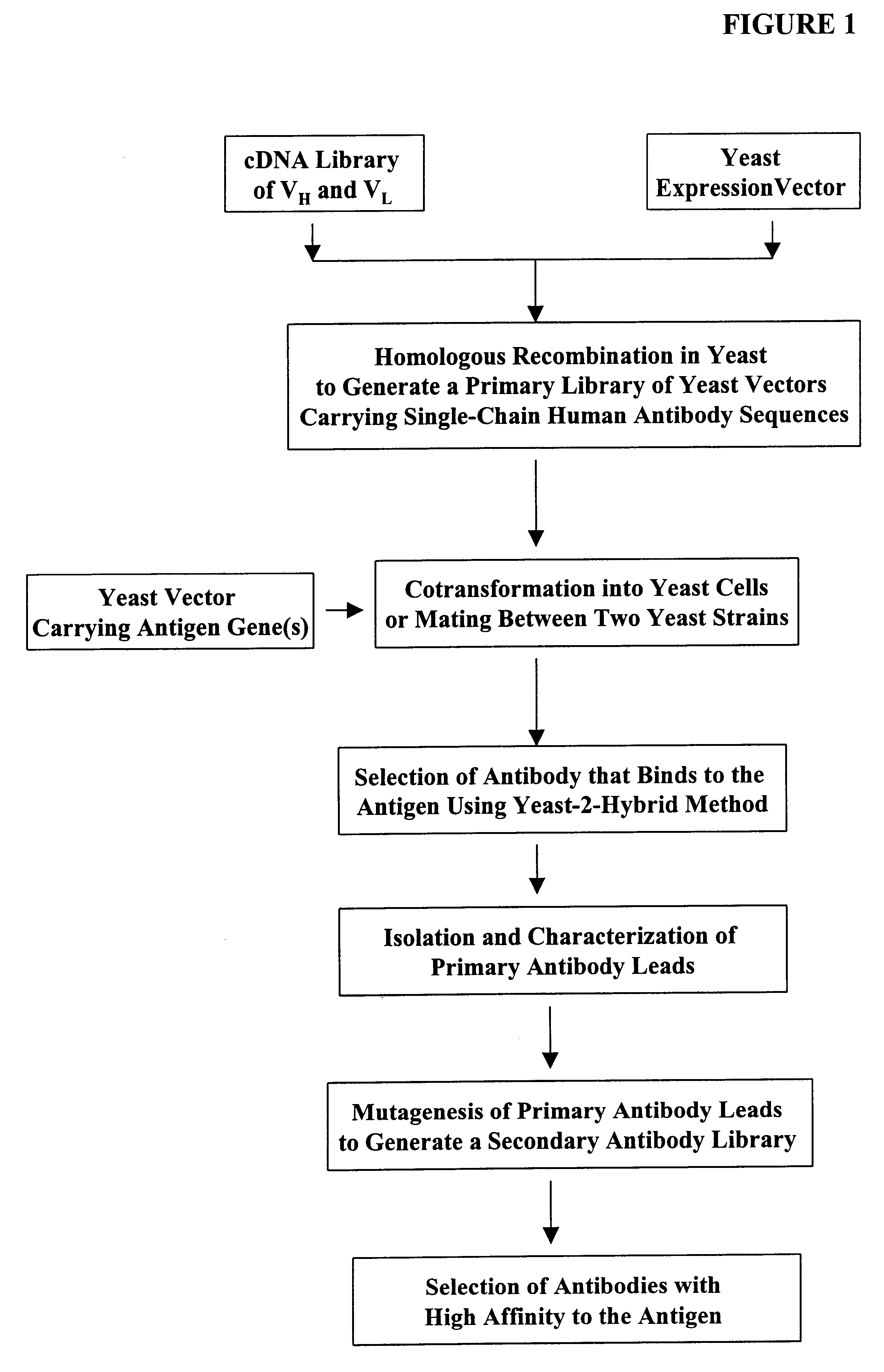
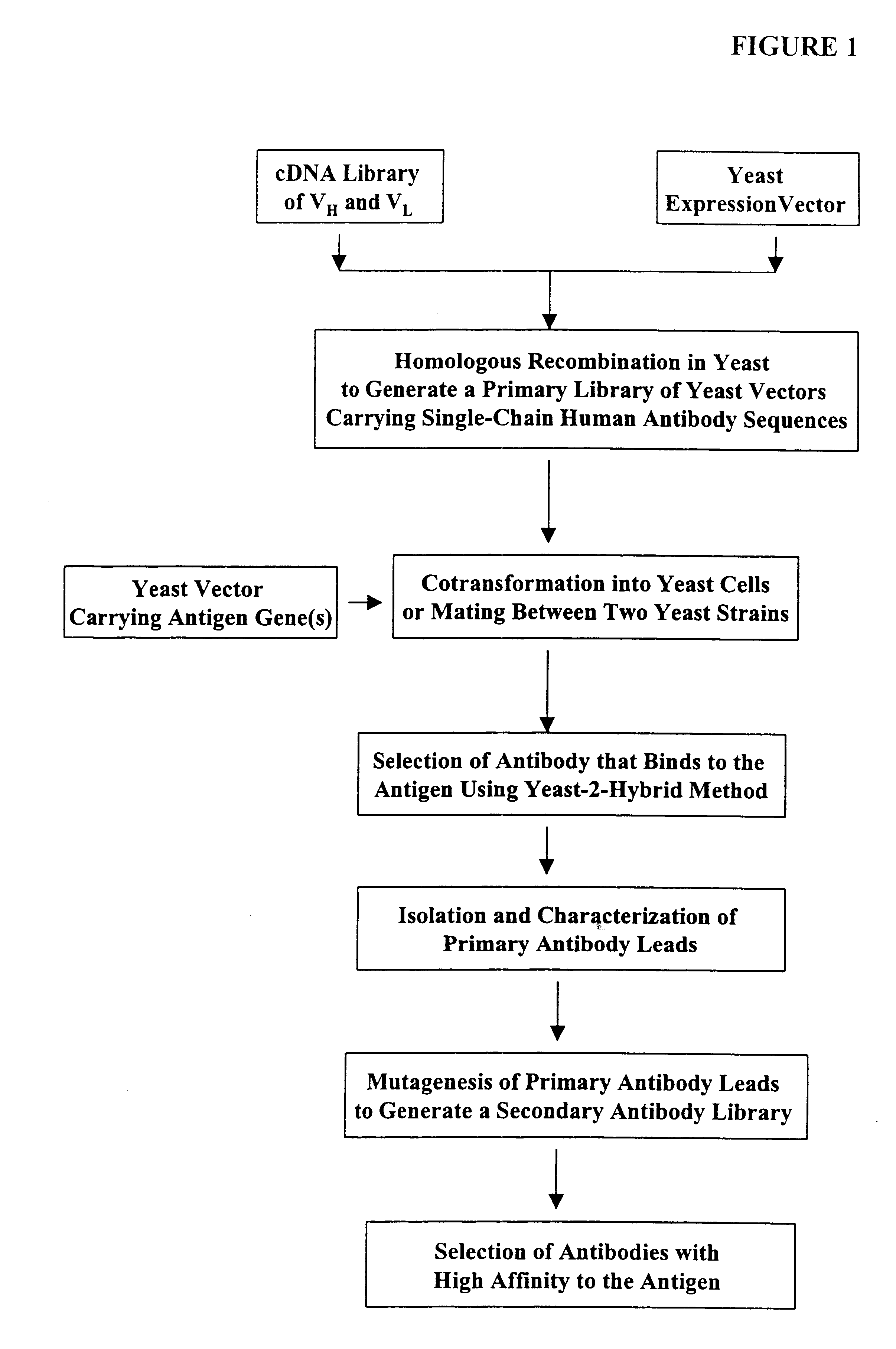
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6406863B1High affinityEasy to assembleMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsTarget peptideIn vivo
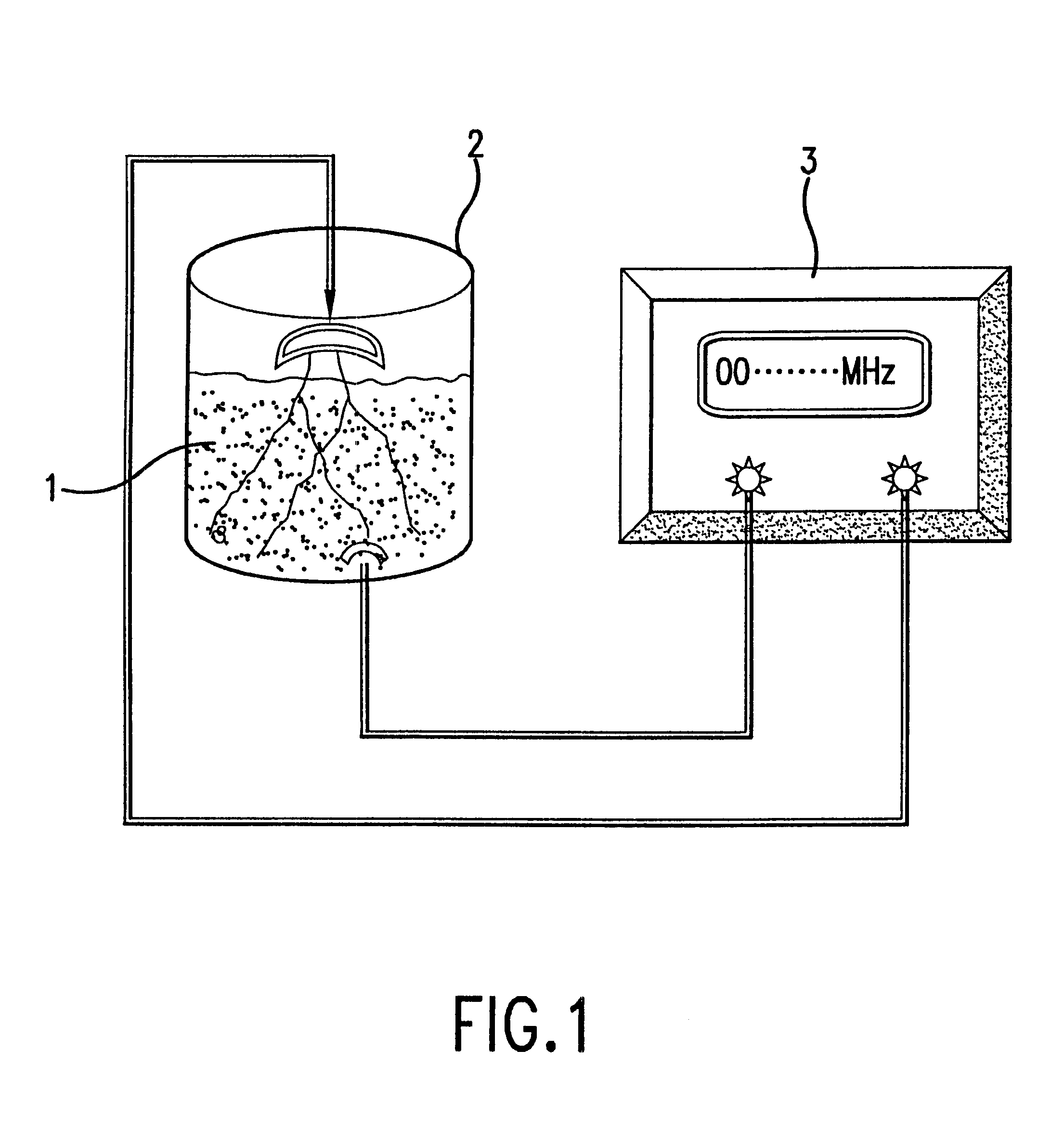
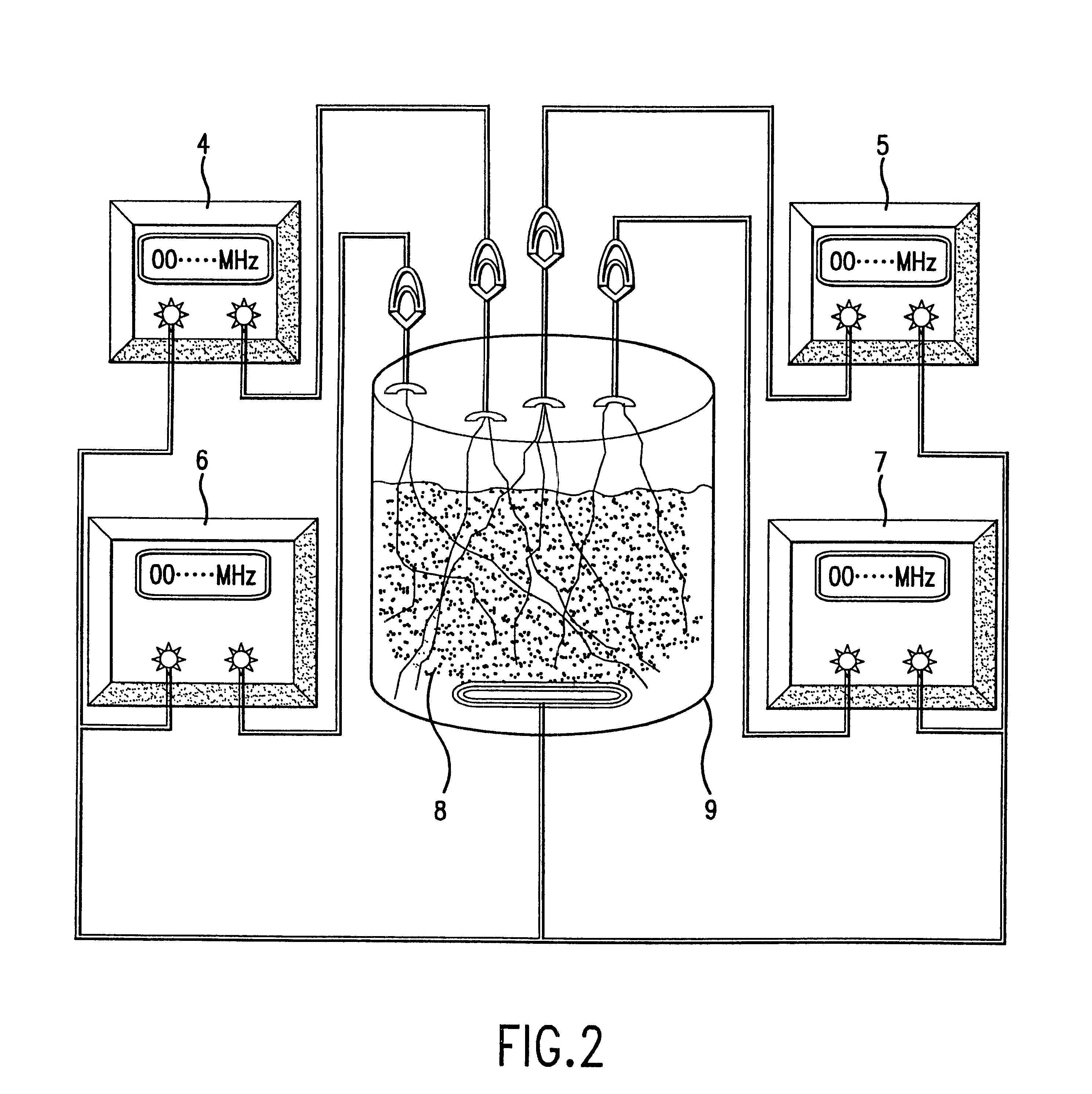
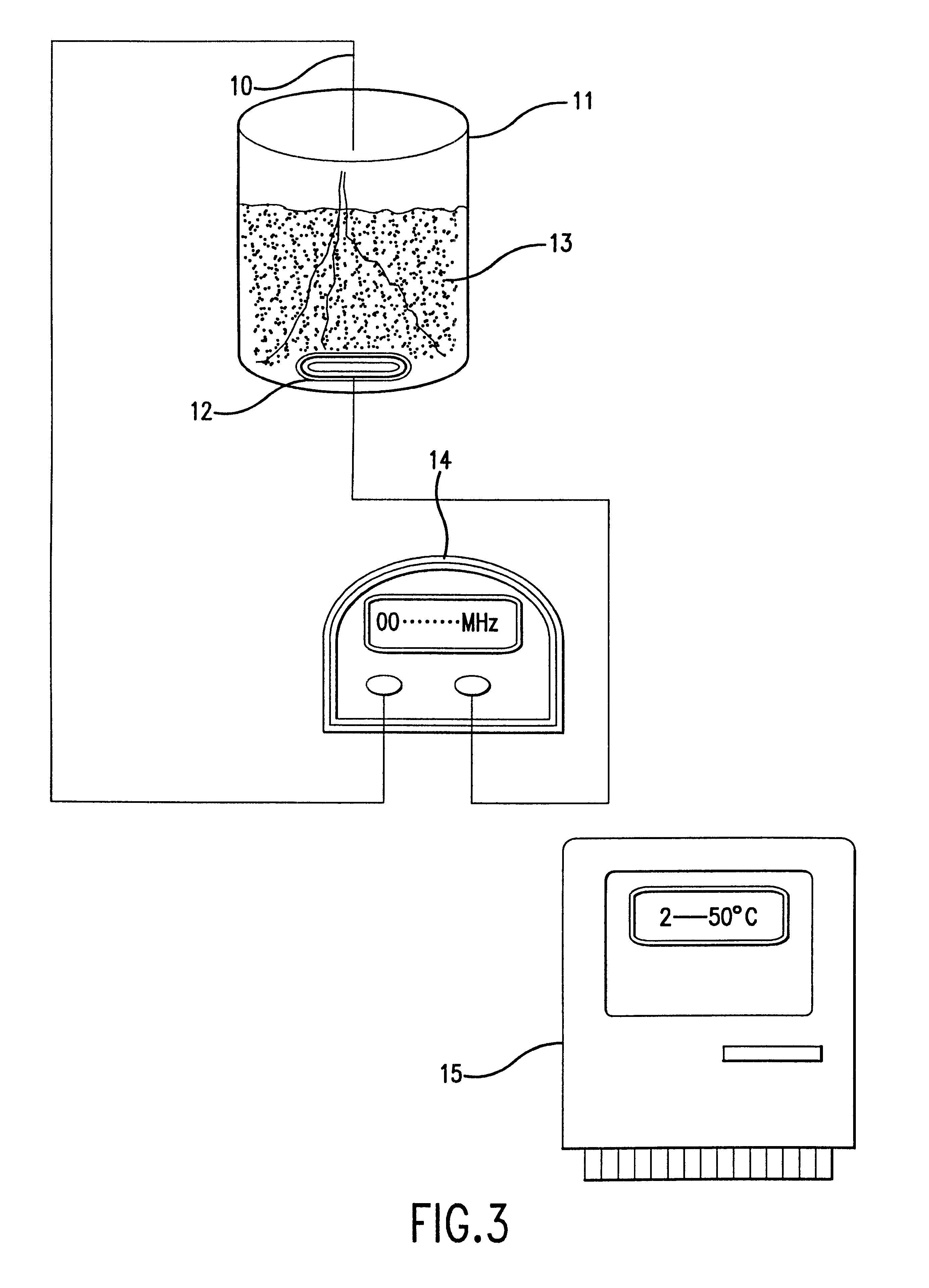
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES WITH ALTERED AFFINITIES FOR HUMAN FCyRI, FCyRIIIa, AND C1q PROTEINS
InactiveUS20130149300A1Good curative effectLow toxicitySugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsDiseaseFc-Gamma Receptor
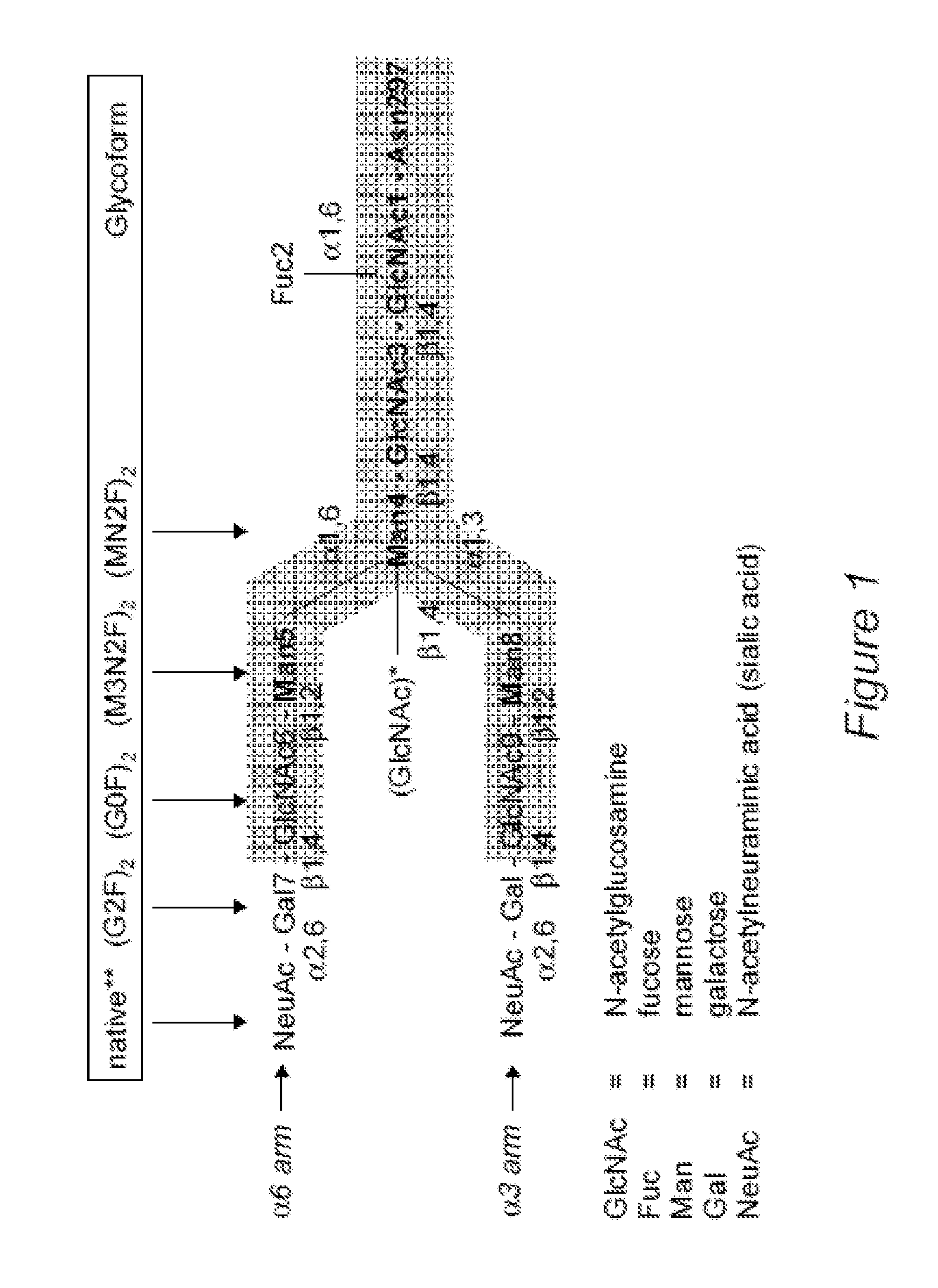
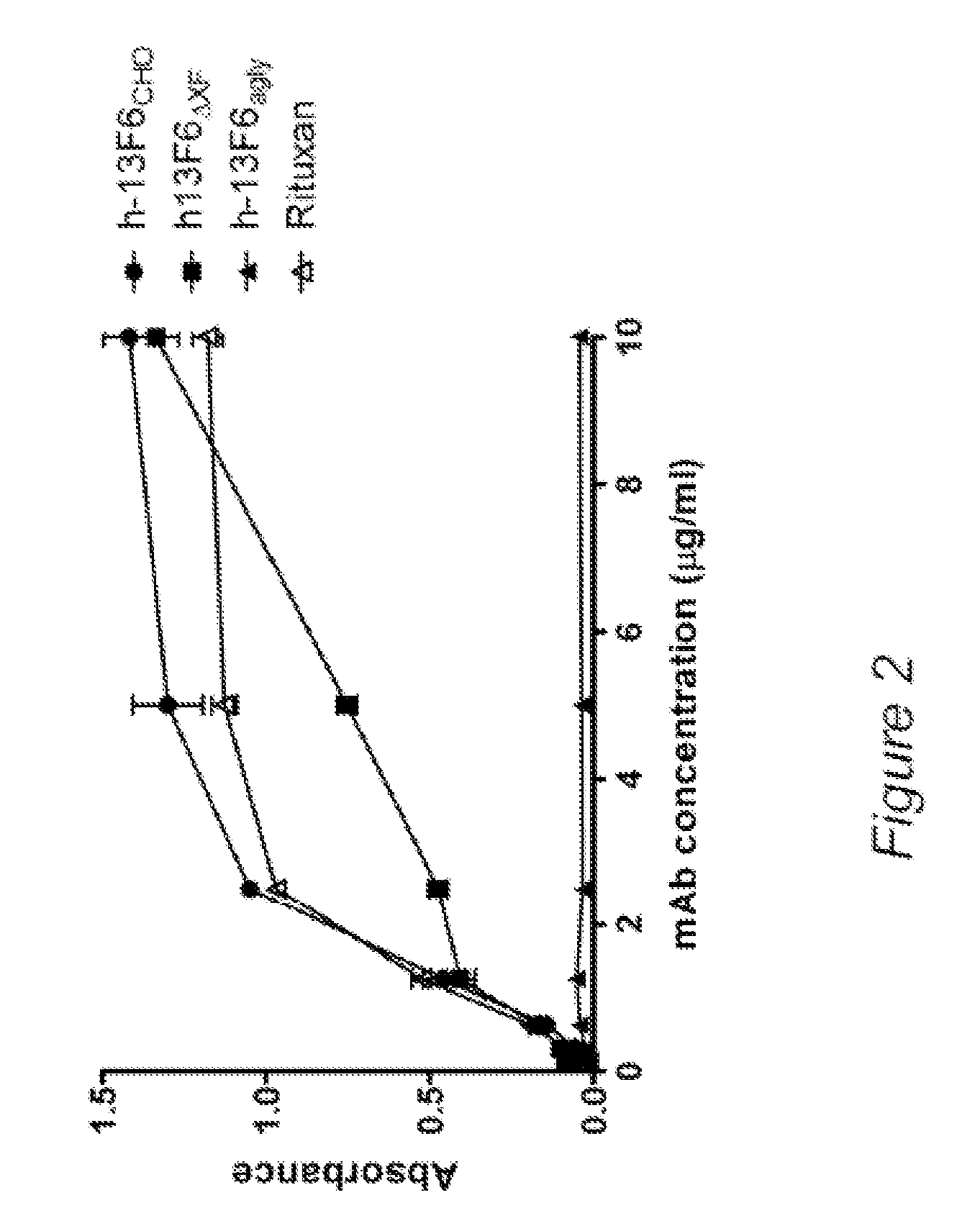
Disclosed herein are GNGN and G1 / G2 antibodies that recognize and bind various FcRs and C1q. Also disclosed herein are glycan-optiminzed antibodies, predominantly of the GNGN or G1 / G2 glycoform, with enhanced Fcγ receptor binding achieved through CHO, Nicotiana benthamiana and yeast manufacturing systems. Nucleic acids encoding these antibodies, as well as expression vectors and host cells including these nucleic acids are also disclosed herein. Methods and pharmaceutical compositions including the monoclonal antibodies are provided herein for the prevention and / or therapeutic treatment of viral infections, cancers and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:MAPP BIOPHARM +1
Natural fruit and vegetable ferment beverage, and preparation method thereof
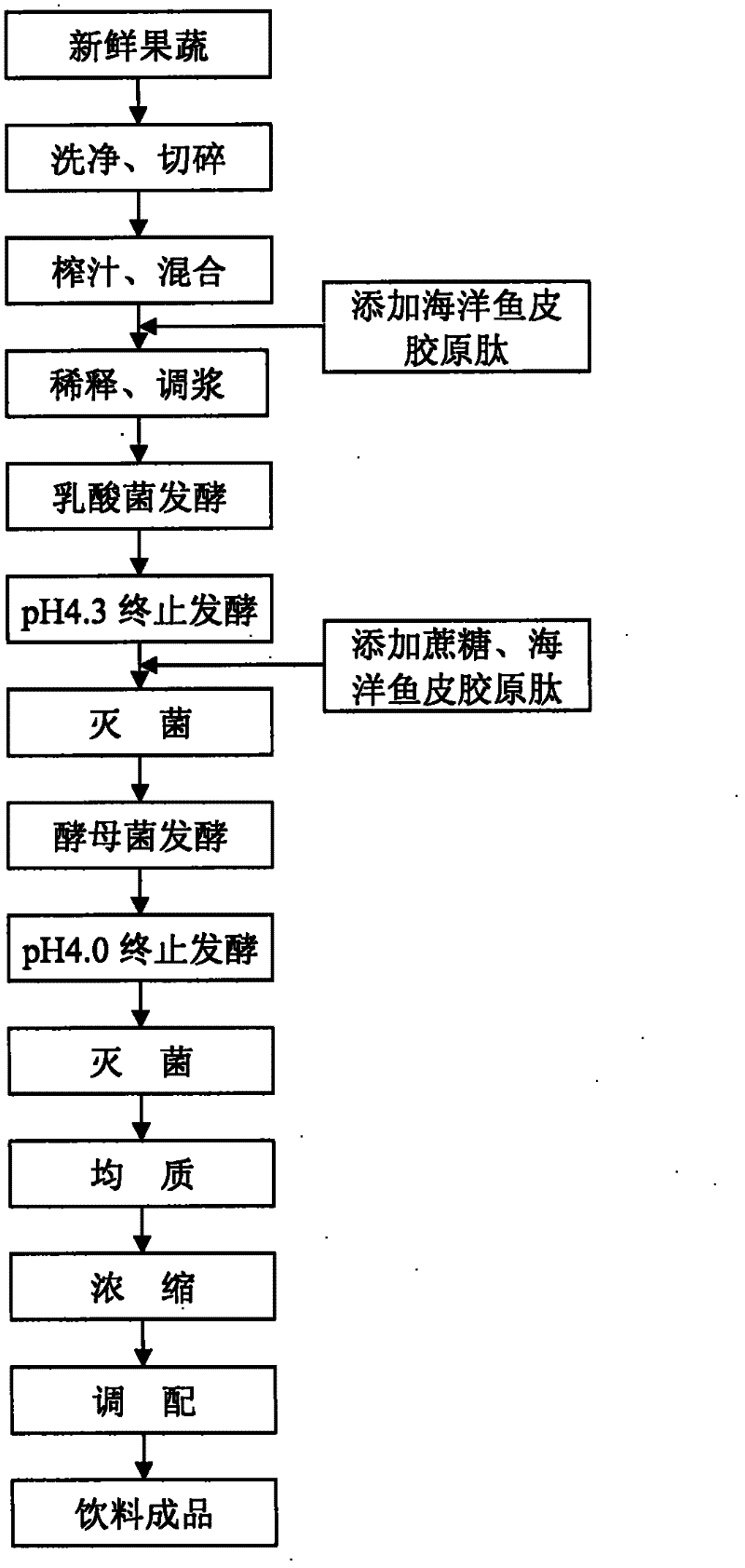
ActiveCN102356899AWith health functionPrevent diseaseYeast food ingredientsLactobacillusMetaboliteFreeze-drying
The present invention discloses a natural fruit and vegetable ferment beverage, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method for the ferment beverage comprises: adding freshly-squeezed fruit and vegetable juice to marine fish skin collagen peptide; adopting the resulting mixture as a fermentation substrate; carrying out dilution, slurry mixing and sterilization, and then adopting a direct vat and freeze-dried type lactic acid starter to carry out fermentation; stopping the fermentation after 7-11 days until the pH value is 4.3; adding a supplementary feed and carrying out sterilization; then adding high-activity dried yeast to carry out fermentation; stopping the fermentation after 5-7 days until the pH value is 4.0; after storing the fermentation broth at the low temperature, carrying out homogenization, concentration, centrifugation, blending, sterilization and bulking to finally prepare the novel natural fruit and vegetable ferment beverage. According to the ferment beverage of the present invention, the stepwise fermentation is adopted for the freshly-squeezed fruit and vegetable juice by using the lactic acid bacteria and the yeast; the marine fish skin collagen peptide is added to promote the growth and the metabolism of fermentation bacteria, such that metabolic products of nutritional ingredients in the natural fruits and vegetables are rich so as to provide a beneficial nutrition and health effect.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
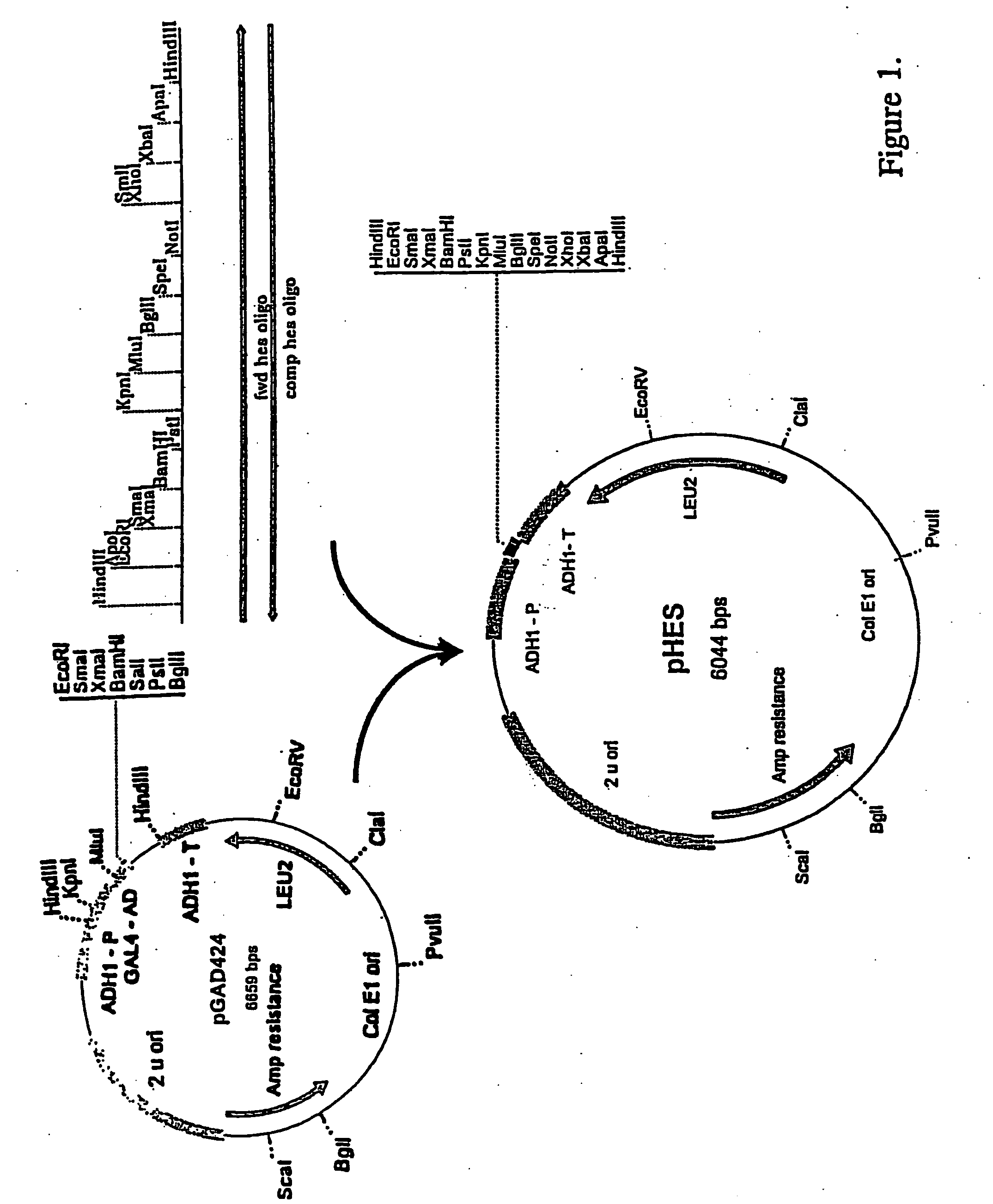
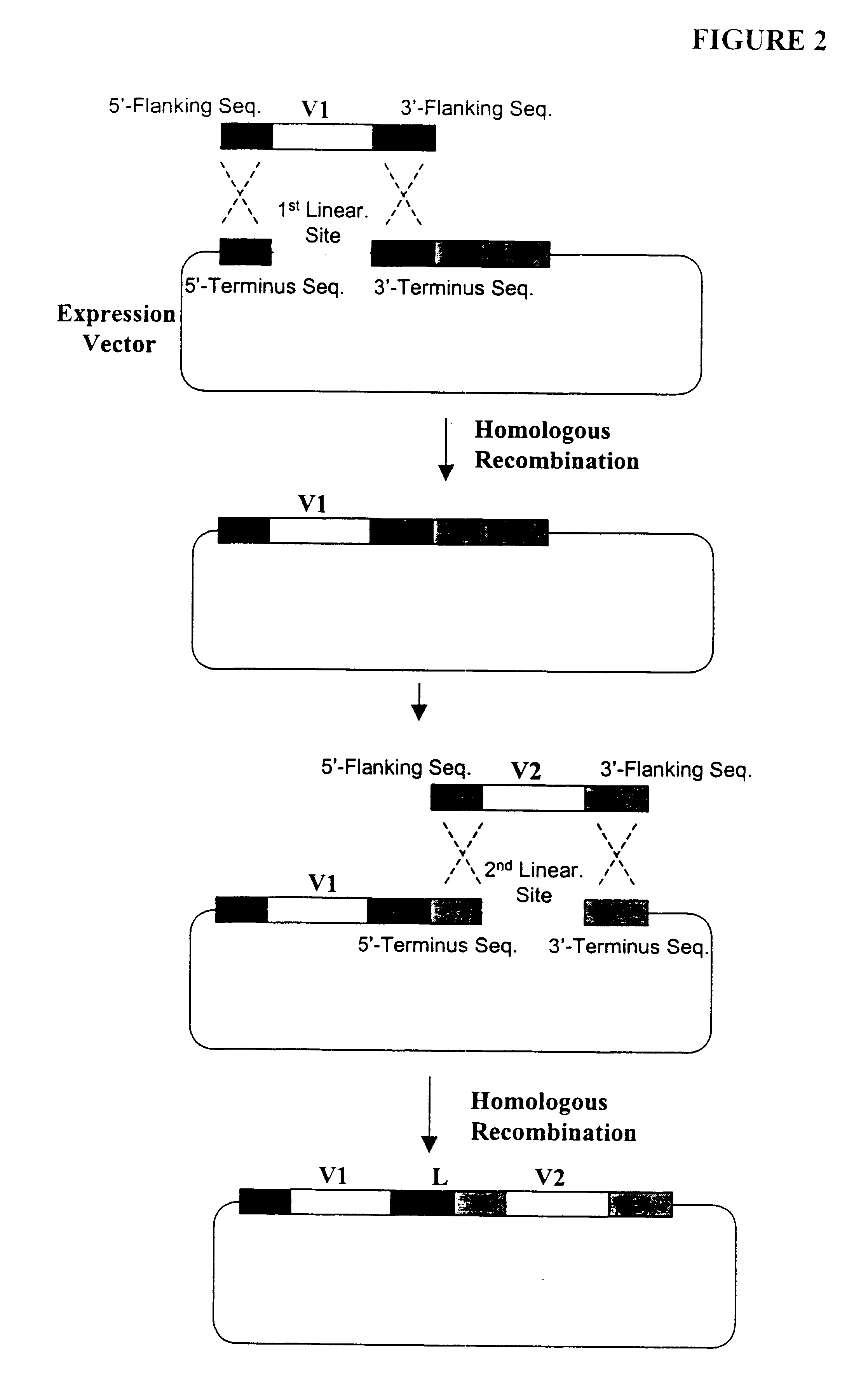
Highly diverse library of yeast expression vectors
A highly diverse library of yeast expression vectors encoding a library of fusion proteins such as antibodies is provided. The yeast expression vector formed in the library comprises: a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first polypeptide subunit; a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second polypeptide subunit; and a linker sequence encoding a linker peptide that links the first nucleotide sequence and the second nucleotide sequence. The first polypeptide subunit, the second polypeptide subunit, and the linker polypeptide are expressed as a single fusion protein within the library of fusion proteins. The first and second nucleotide sequences each independently varies within the library of expression vectors. The library of fusion proteins expressed by the library expression vectors can be used for screening against target molecules such as proteins, peptides, DNAs and small molecules in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Microbial ecological traditional Chinese medicine preparation for livestock and poultry from fermentation production of multiple bacterials and fermentation method thereof
ActiveCN101401921ALow costImmunity exceedsFungiAnthropod material medical ingredientsHouttuyniaLactobacillus acidophilus
The invention relates to micro-ecological Chinese medicine preparation for livestock and poultry by adoption of multi-strain fermentation production and a fermentation method. The compositions of traditional Chinese medicines in a culture medium of the fermentation preparation include: radix astragali, radix codonopsitis, Atractylodes macrocephala, Poria cocos, liquorice, medicated leaven, hawkthorn, angelica, Chinese rhubarb, Scutellaria baicalensis, radix isatidis, cordate houttuynia, sicklesenna seeds, Schisandra chinensis, Gynostemma pentaphylla, phellodendron, dried orange peel, radix bupleuri, curcuma, honeysuckle, Chinese gall, purslane and Quisqualis indica. The fermentation method is as follows: a multi-strain solid state fermentation strain is adopted for fermentation; bacillus subtilis, bacillus natto, bacillus licheniformis, beer yeast, Candida wtilis, Aspergillus niger, lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus acidophilus and bifidobacteria are purified and subjected to anaerobic fermentation under the conditions of a rotating speed of 180 revolutions per minute at a temperature is 32 DEG C for 48 to 72 hours till the pH value reaches 4.0. The micro-ecological Chinese medicine preparation has the advantages that the micro-ecological Chinese medicine preparation uses probiotics to ferment different Chinese medicine compositions, and is micro-ecological Chinese medicine preparation which completely replaces antibiotics and has the advantages of no residual medicine, disease prevention, growth promotion and low cost.
Owner:河南省龙腾高科实业有限公司
Methods for eliminating mannosylphosphorylation of glycans in the production of glycoproteins
The present invention relates to the elimination of mannosylphosphorylation on the glycans of glycoproteins in the yeast genus Pichia. The elimination of mannosylphosphorylated glycoproteins results from the disruption of the PNO1 gene and the newly isolated P. pastoris MNN4B gene. The present invention further relates to methods for producing modified glycan structures in host cells that are free of glycan mannosylphosphorylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
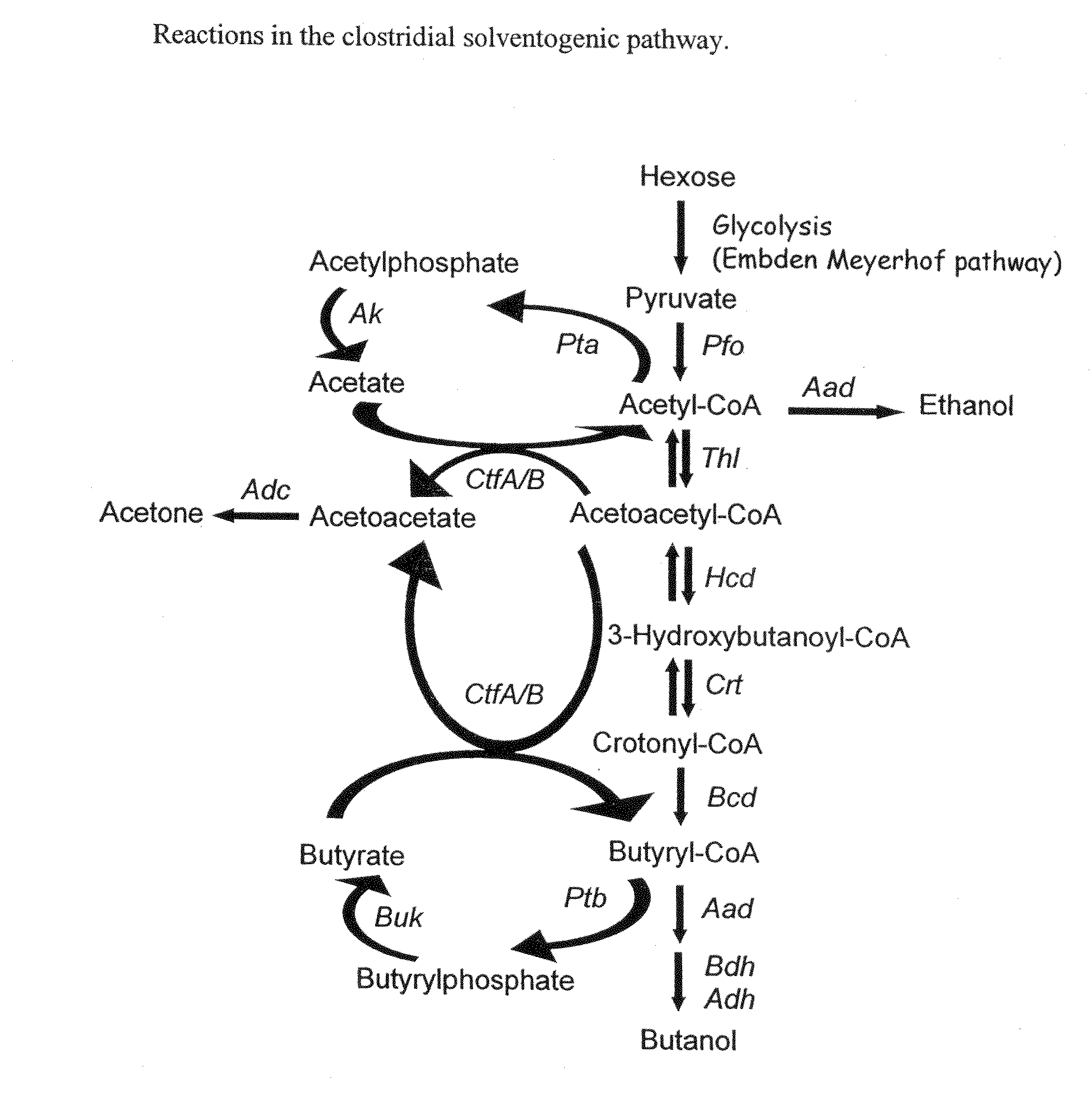
Methods and compositions for producing solvents
Described herein are methods, compositions and synthetic biology approaches for solvent production, including but not limited to butanol production. Described herein are recombinant bacteria and yeast strains which may be used in production of a solvent, including but not limited to butanol, from lignocellulosic and other plant-based feedstocks. Described herein are methods of producing solvents, including but not limited to butanol, using bacteria and yeast strains. Described herein are methods of producing organisms that display highly efficient butanol production.
Owner:EASTMAN RENEWABLE MATERIALS LLC +1
Adjuvant combinations comprising a microbial tlr agonist, a cd40 or 4-1bb agonist, and optionally an antigen and the use thereof for inducing a synergistic enhancement in cellular immunity
InactiveUS20080241139A1Enhanced T cell responseImprove responseAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseYeast
Adjuvant combinations comprising at least one microbial TLR agonist such as a whole virus, bacterium or yeast or portion thereof such a membrane, spheroplast, cytoplast, or ghost, a CD40 or 4-1BB agonist and optionally an antigen wherein all 3 moieties may be separate or comprise the same recombinant microorganism or virus are disclosed. The use of these immune adjuvants for treatment of various chronic diseases such as cancers and HIV infection is also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Method for the production of a fermentation product from a pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock
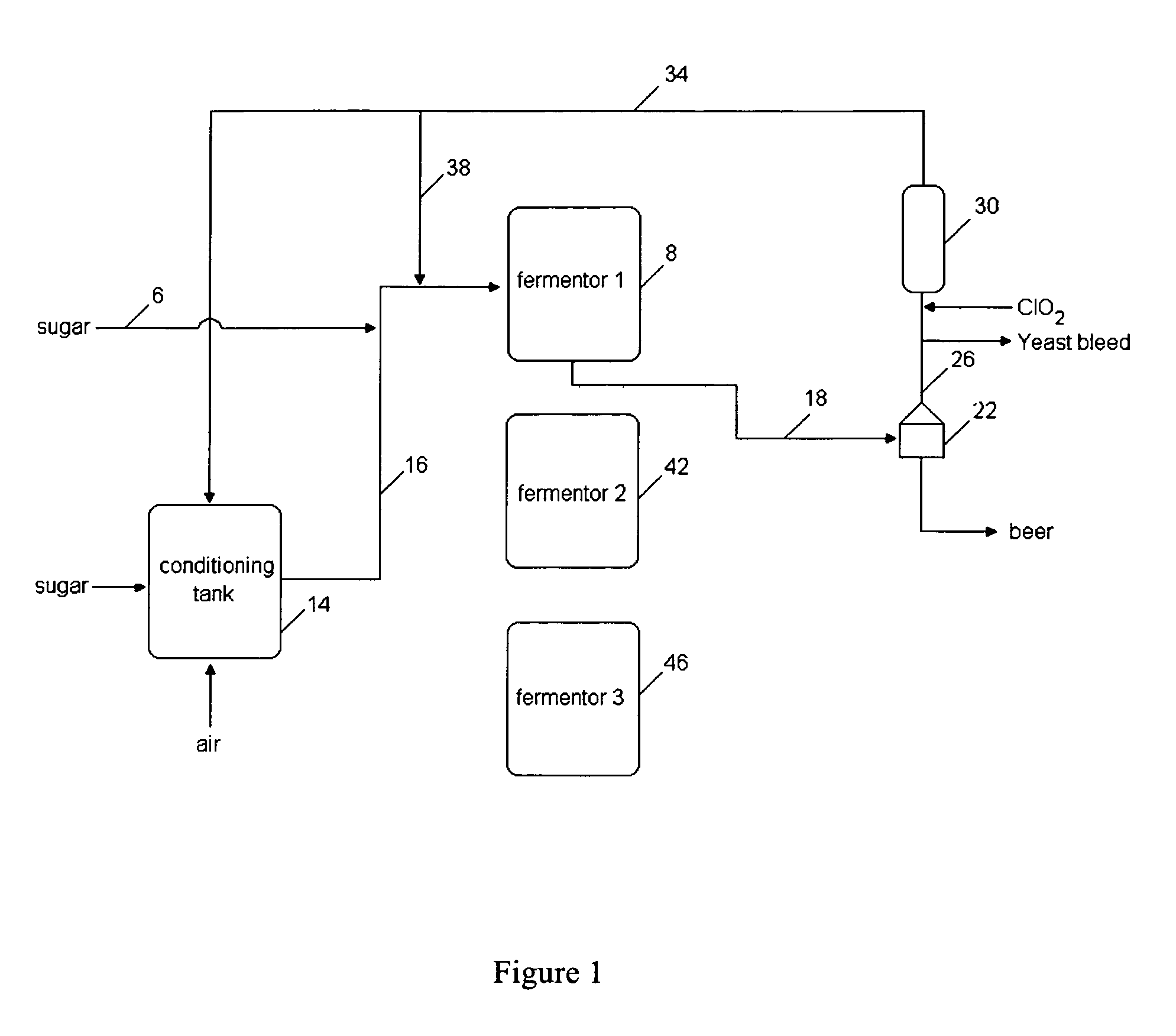
A method for obtaining a fermentation product from a sugar hydrolysate obtained from a feedstock containing hemicellulose, by (i) removing suspended fiber solids from said sugar hydrolysate to obtain a clarified sugar solution; (ii) fermenting xylose in the clarified sugar solution in a fermentation reaction with yeast to produce a fermentation broth comprising the fermentation product; (iii) separating the yeast from the fermentation broth to produce a yeast slurry; (vi) treating the yeast slurry thus obtained with an oxidant to kill microbial contaminants, thereby an oxidant-treated yeast slurry; (v) re-introducing at least a portion of the oxidant-treated yeast back to step (ii) to increase the concentration of yeast in said fermentation reaction; and (vi) recovering the fermentation product.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
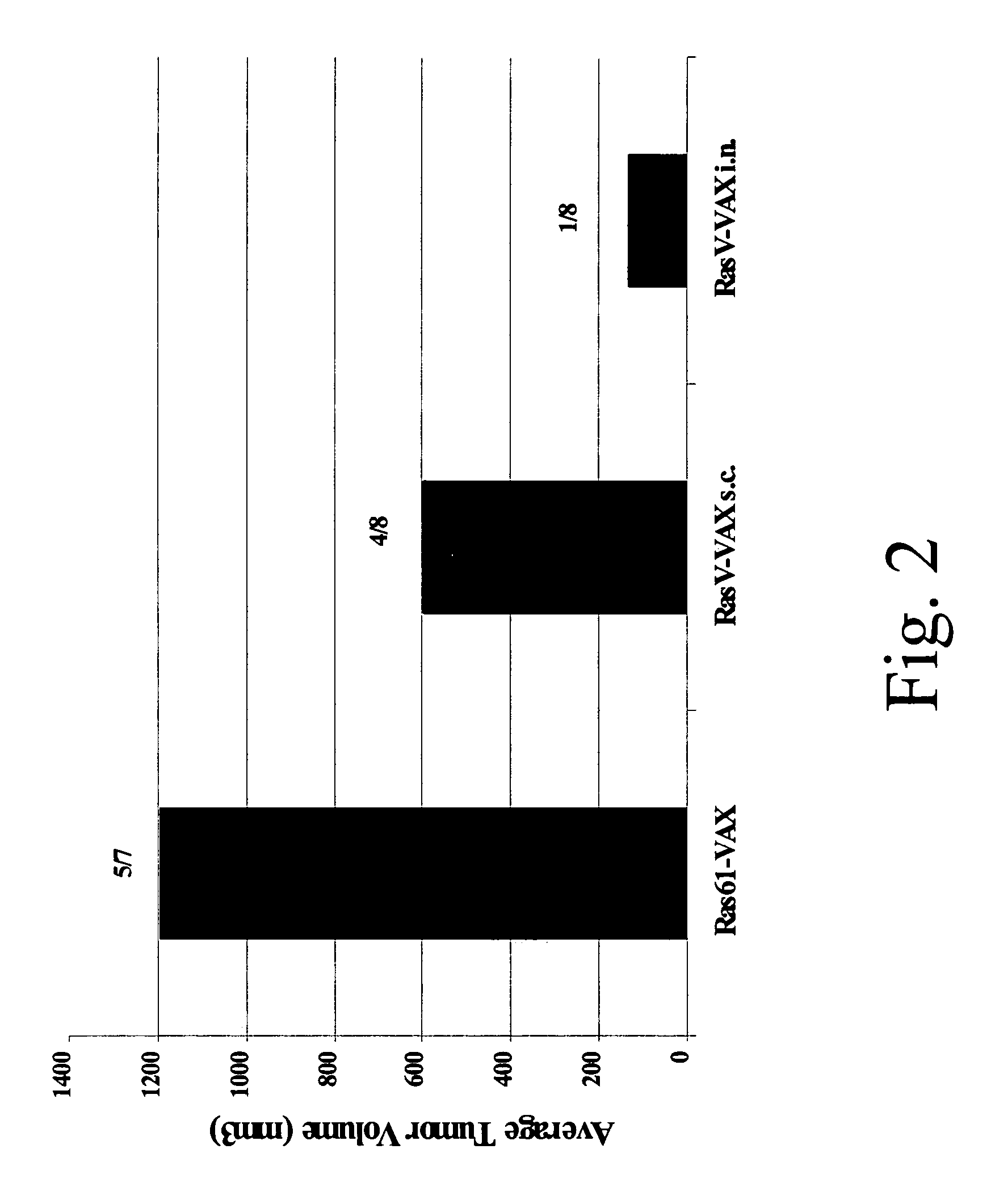
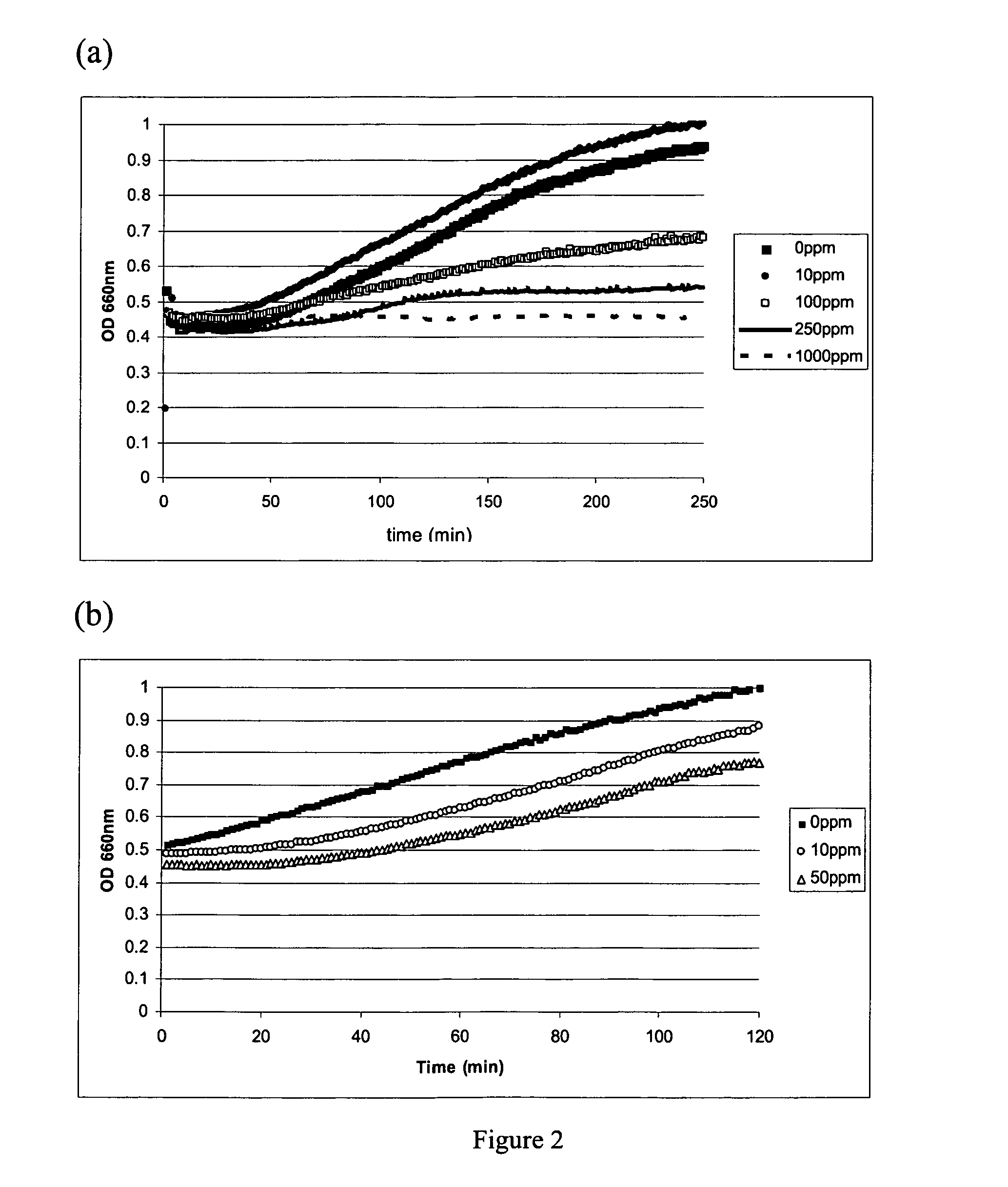
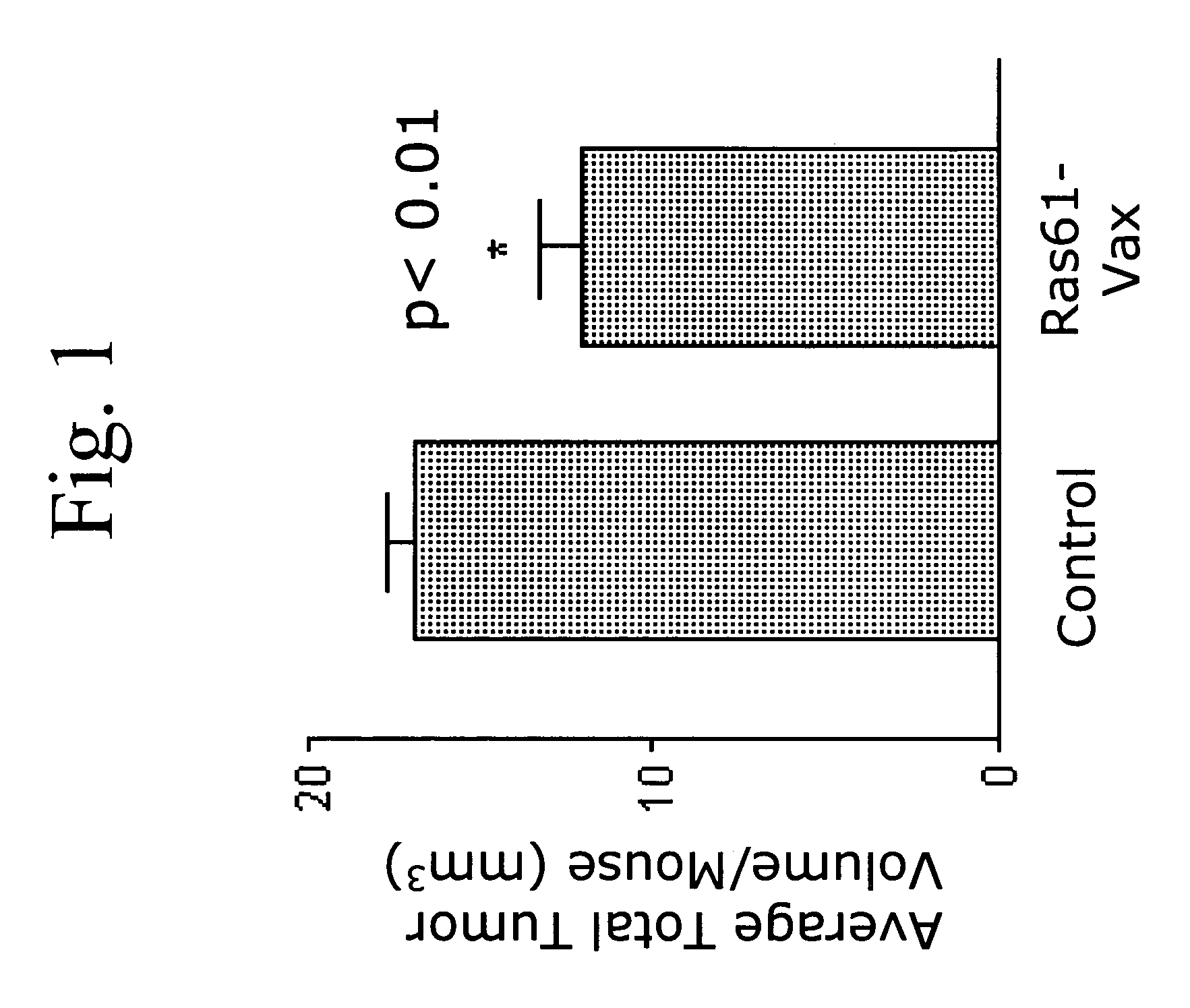
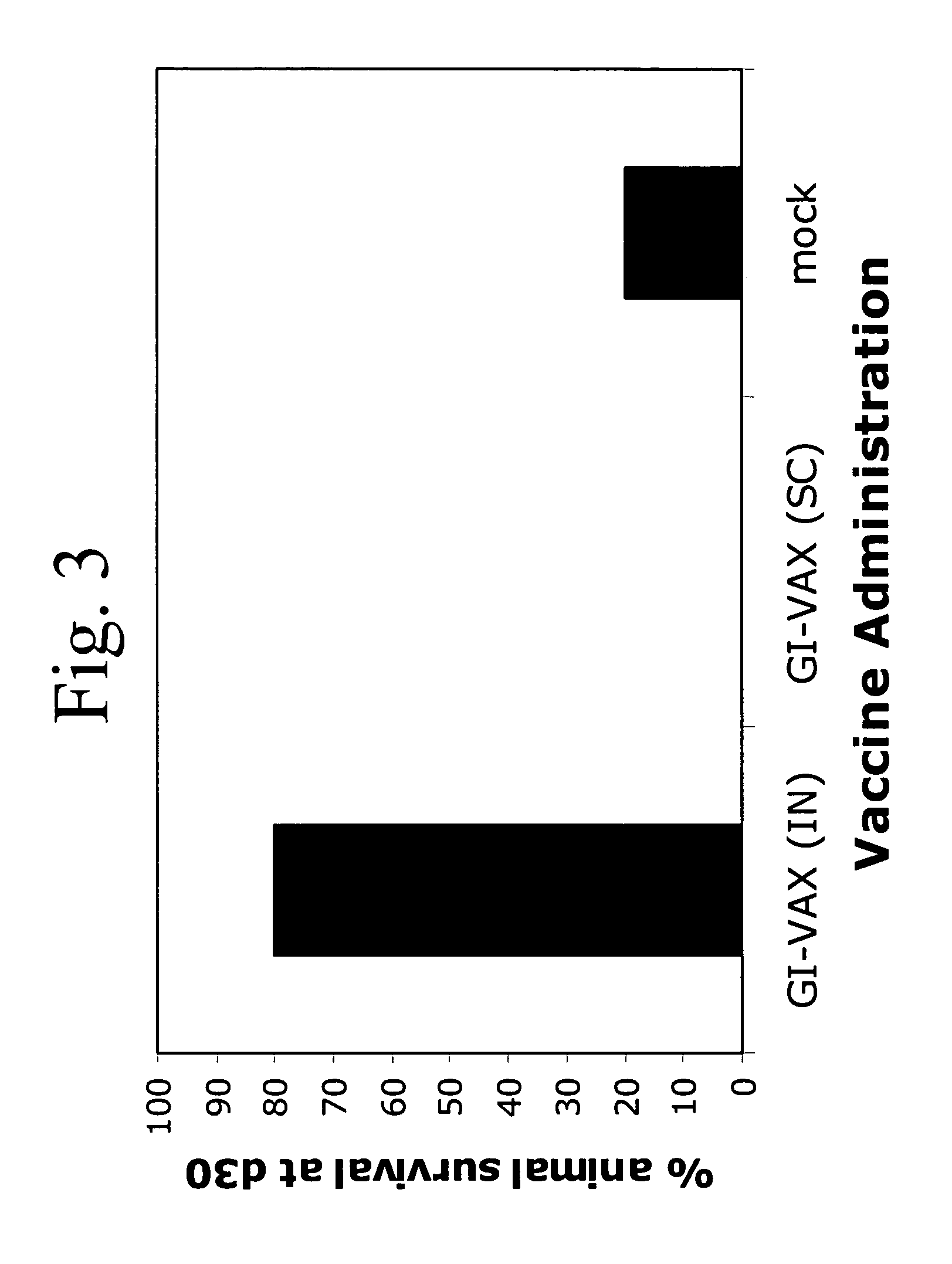
Yeast-based vaccines as immunotherapy
InactiveUS7465454B2Enhance immune responseExtended half-lifeBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsYeastDisease
Compositions and methods for treating and / or preventing a variety of diseases and conditions that are amenable to immunotherapy and, in one particular embodiment, compositions and methods for treating and / or preventing cancer in an animal are described. Specifically improvements related to the use of a yeast-based vaccine comprising a yeast vehicle and an antigen that is selected to elicit an antigen-specific cellular and humoral immune response in an animal, for use in prophylactic and / or therapeutic vaccination and the prevention and / or treatment of a variety of diseases and conditions are disclosed.
Owner:GLOBE IMMUNE INC
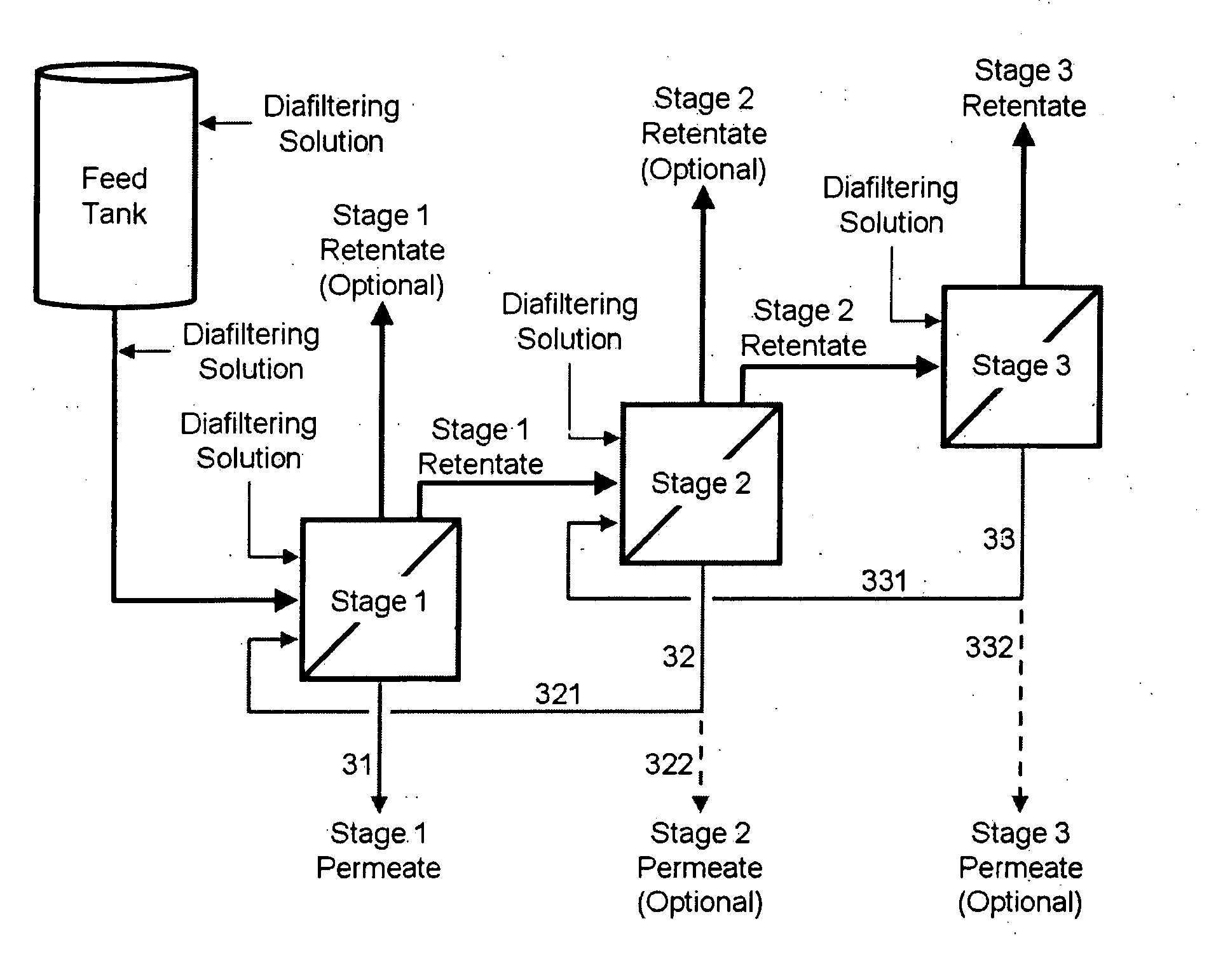
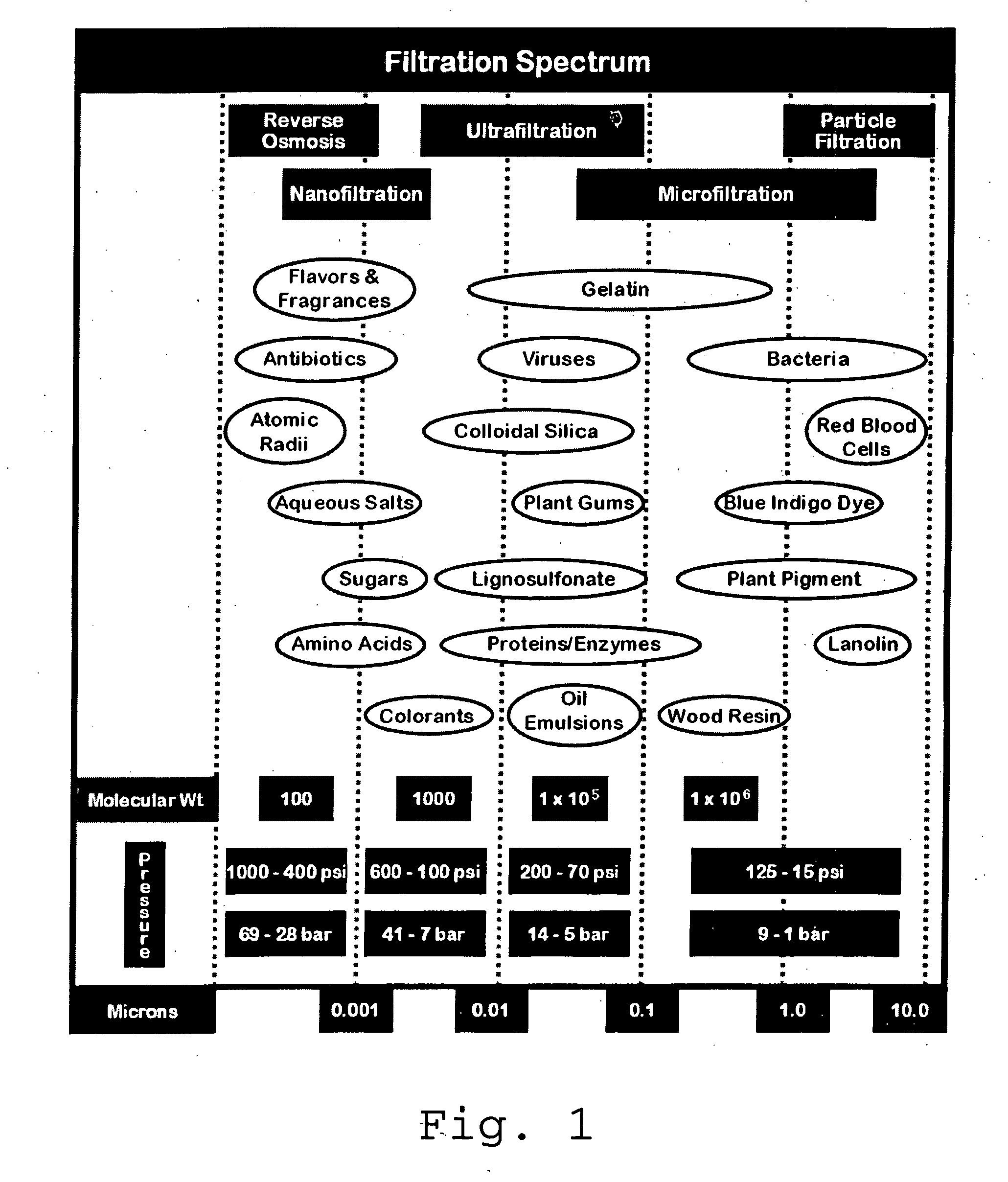
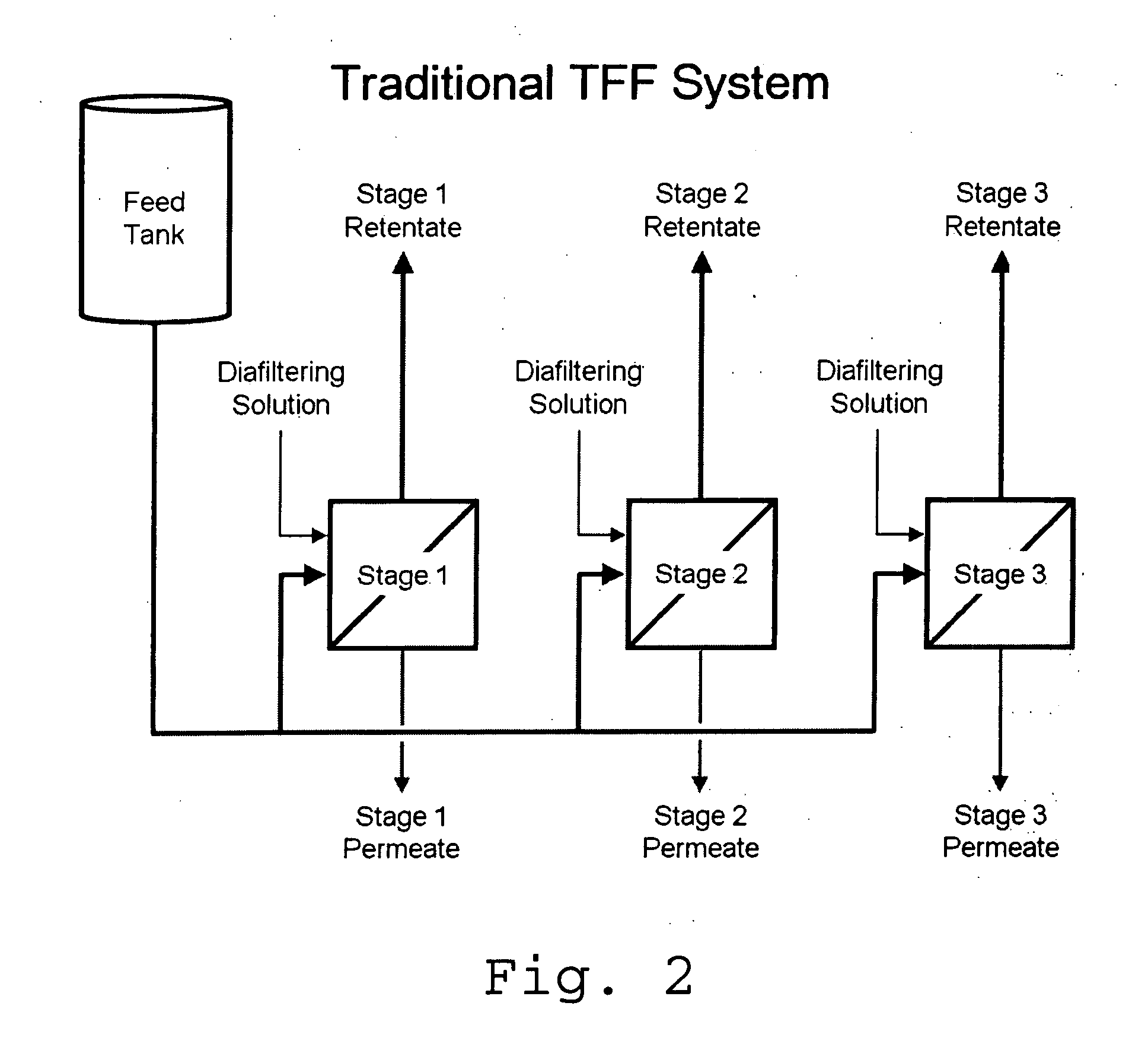
Tangential flow filtration apparatuses, systems, and processes for the separation of compounds
InactiveUS20070246406A1Precise and predictable control of process parameter and product qualityConstantMembranesUltrafiltrationYeastFiltration
The invention relates to apparatuses, machines, systems and methods for the recovery and purification of proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, biologically produced polymers and other compounds from aqueous fluids. The aqueous fluids can comprise enzyme concentrates and or a fermentation broth with or without cells or other starting material. The fermentation broth can be produced by fermentations of fungal, yeast, bacterial, mammalian, insect or plant cells.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com