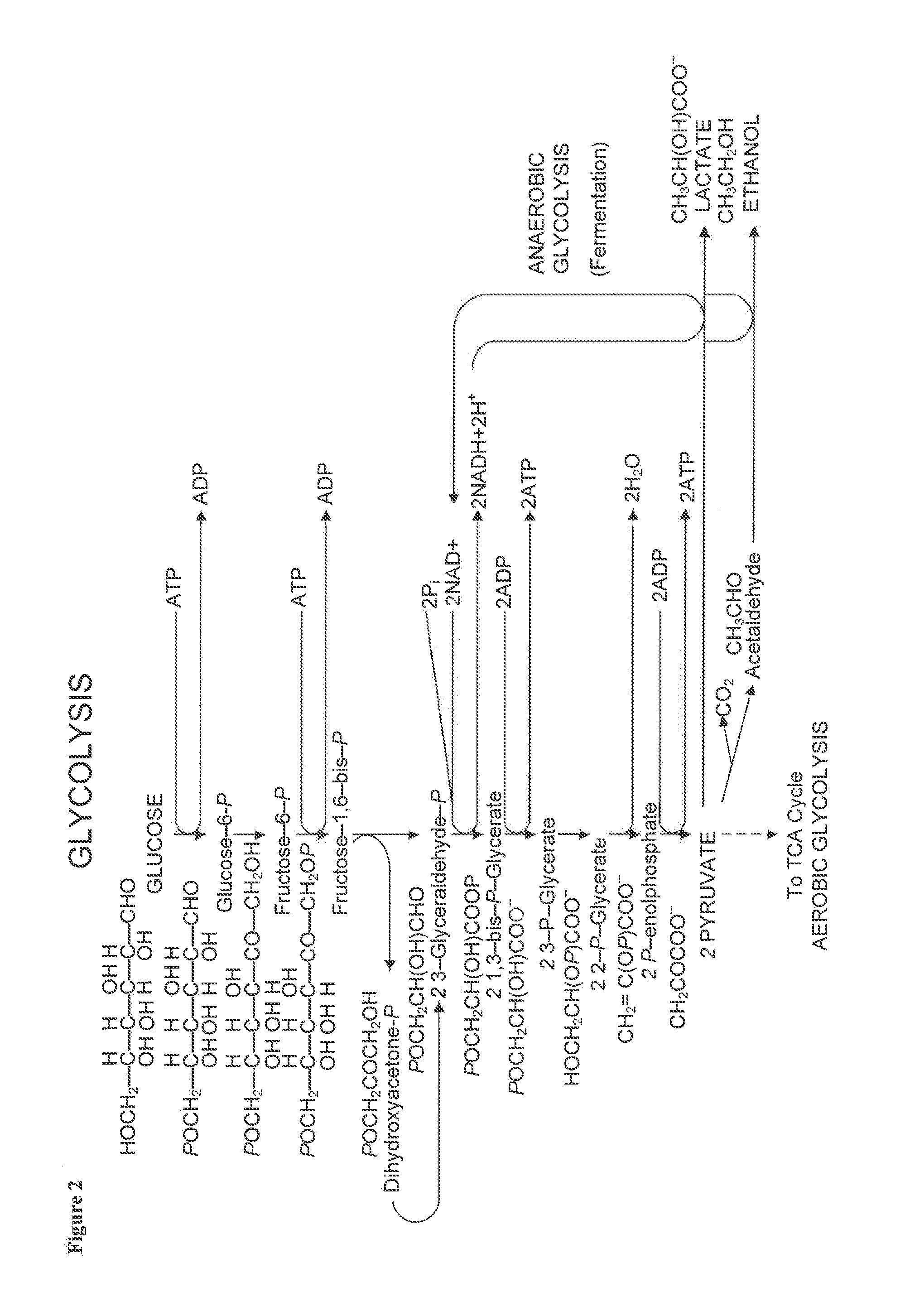
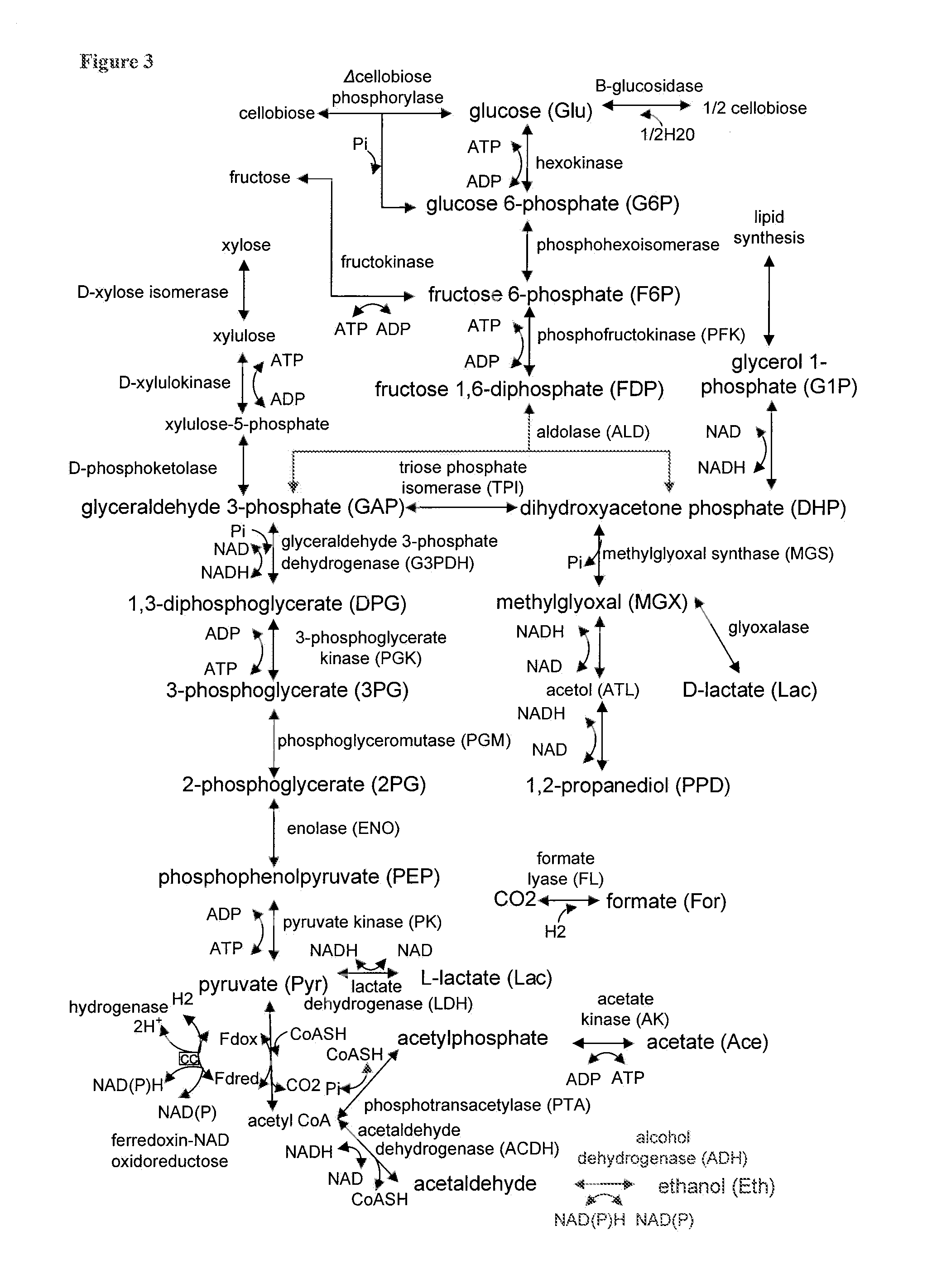
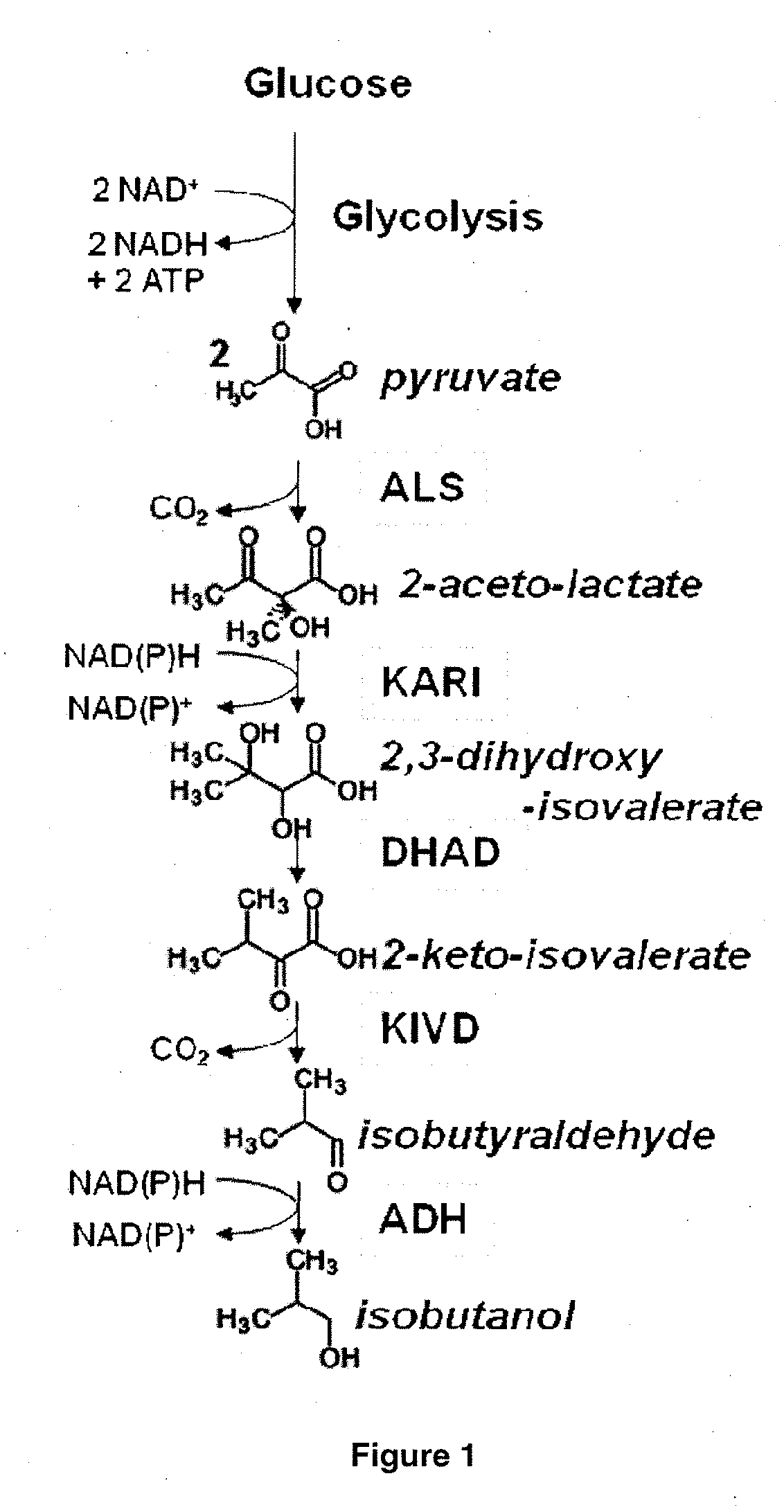
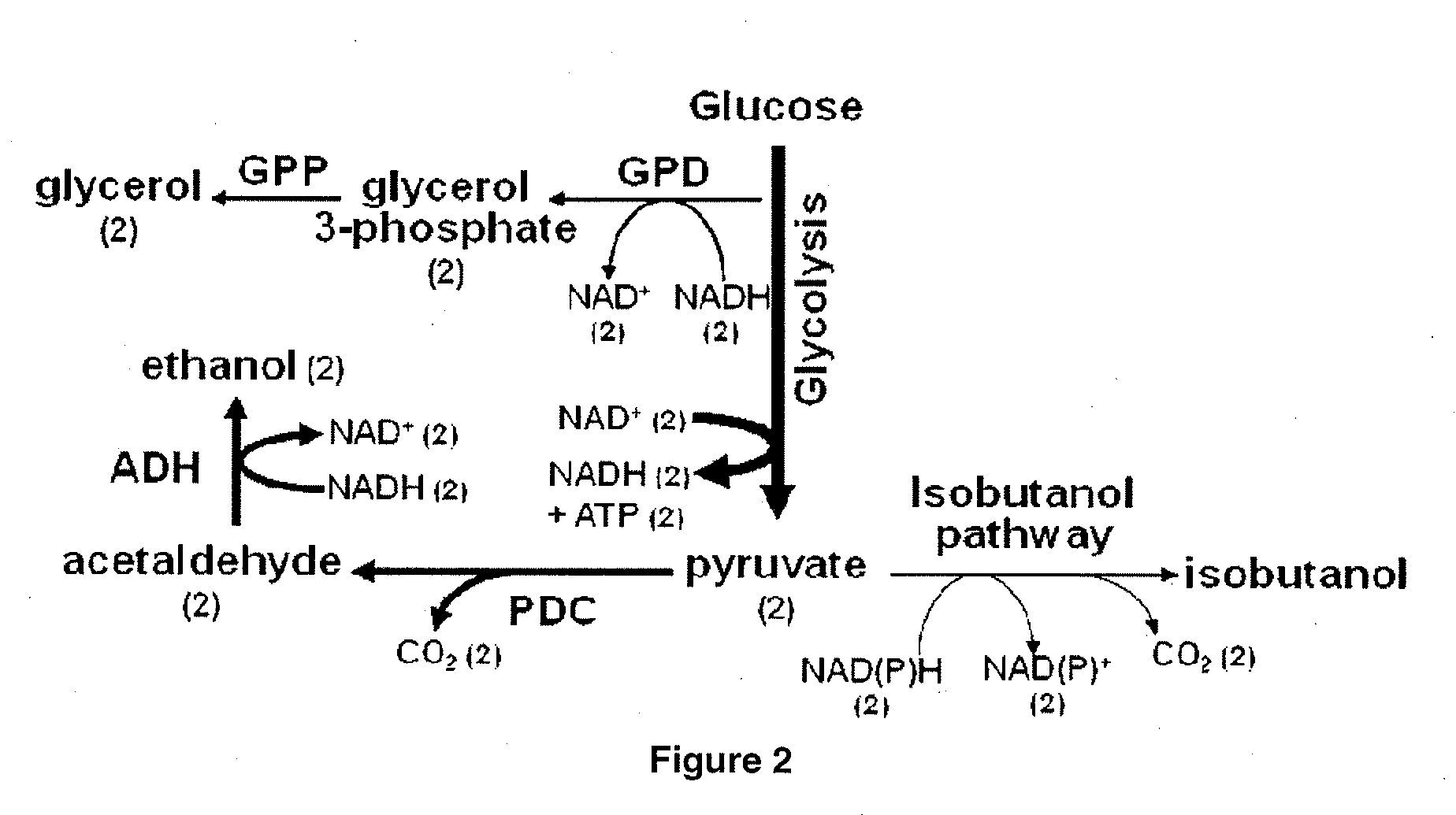
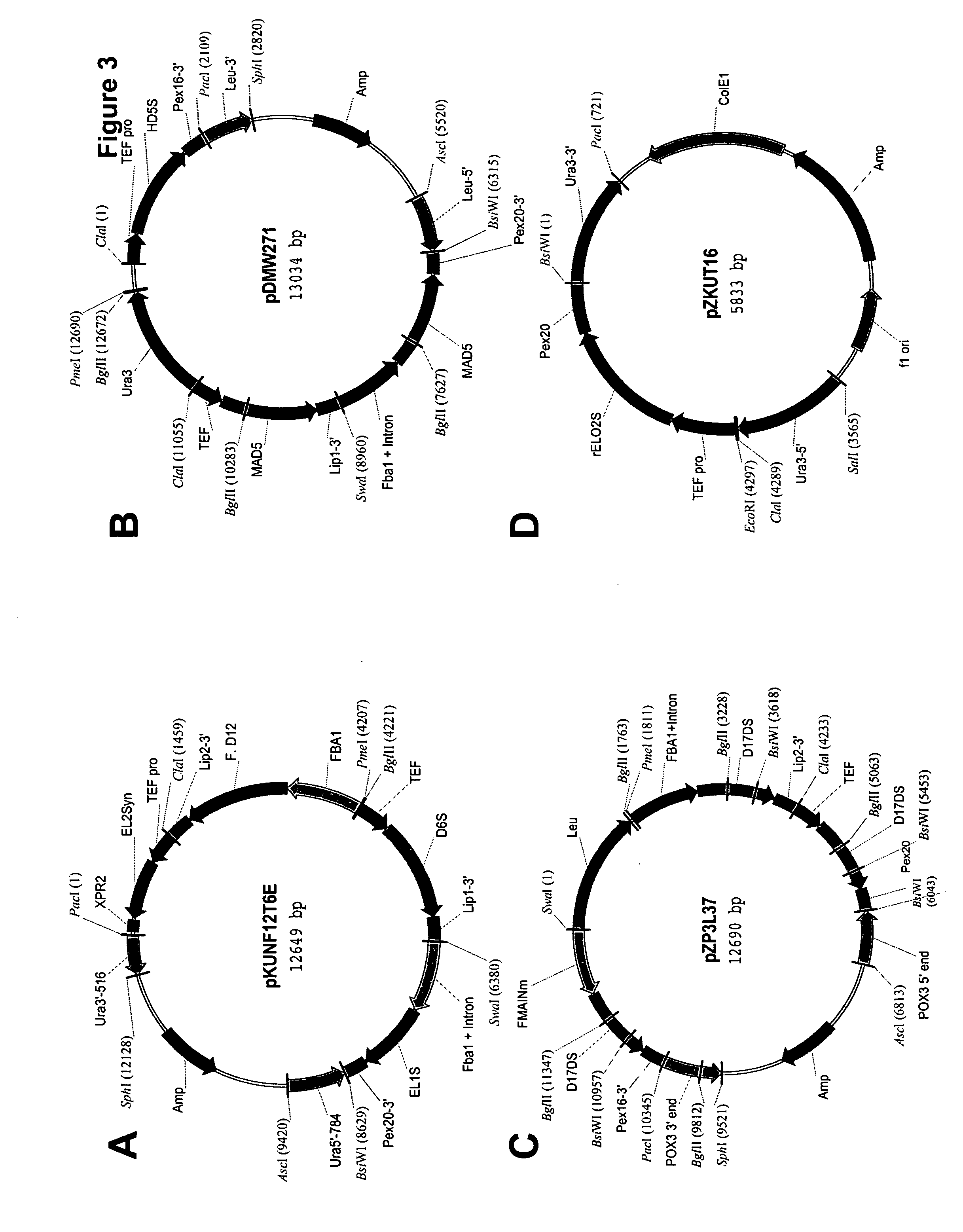
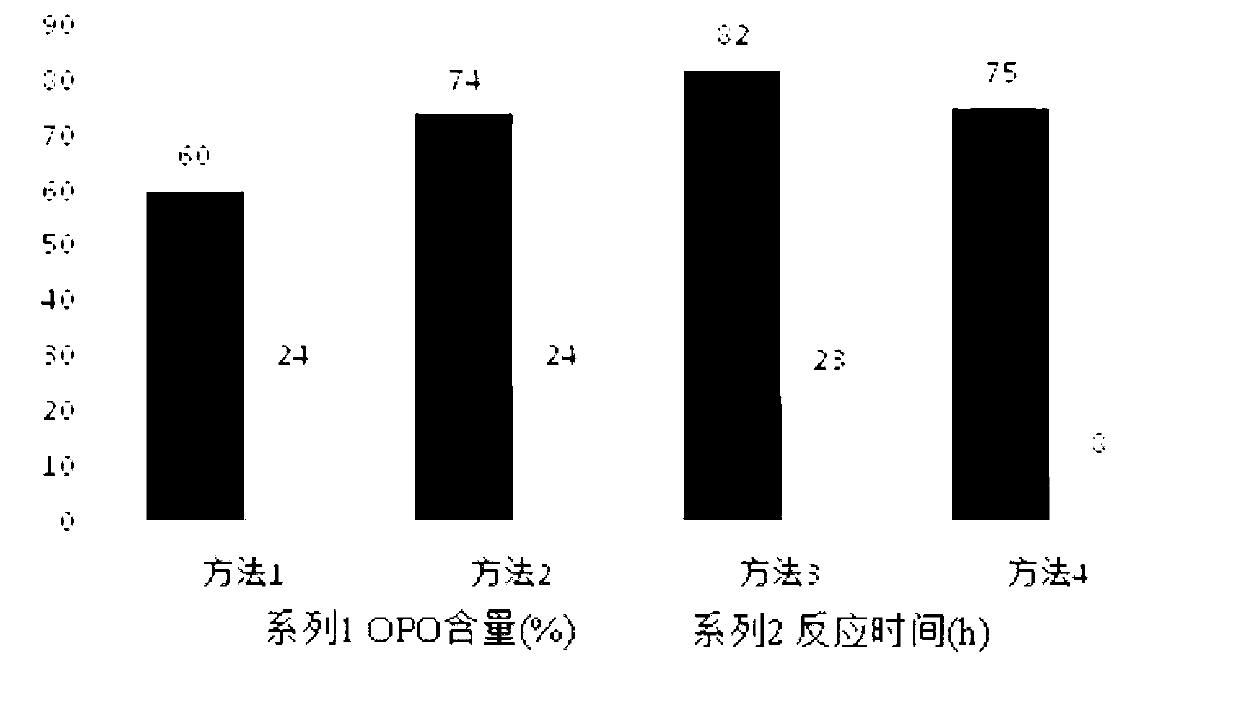
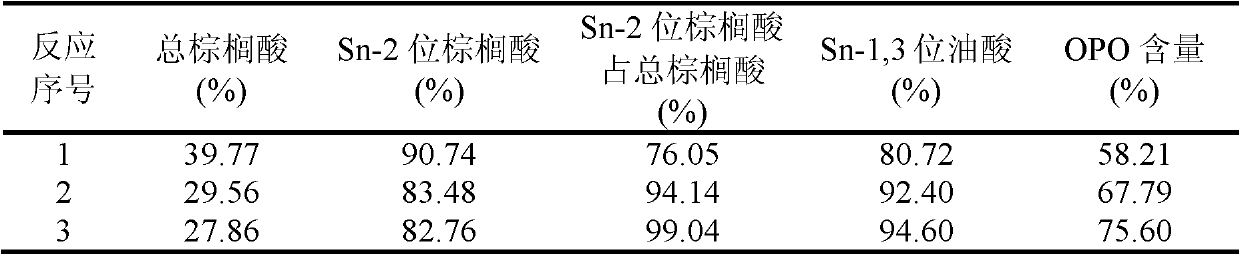
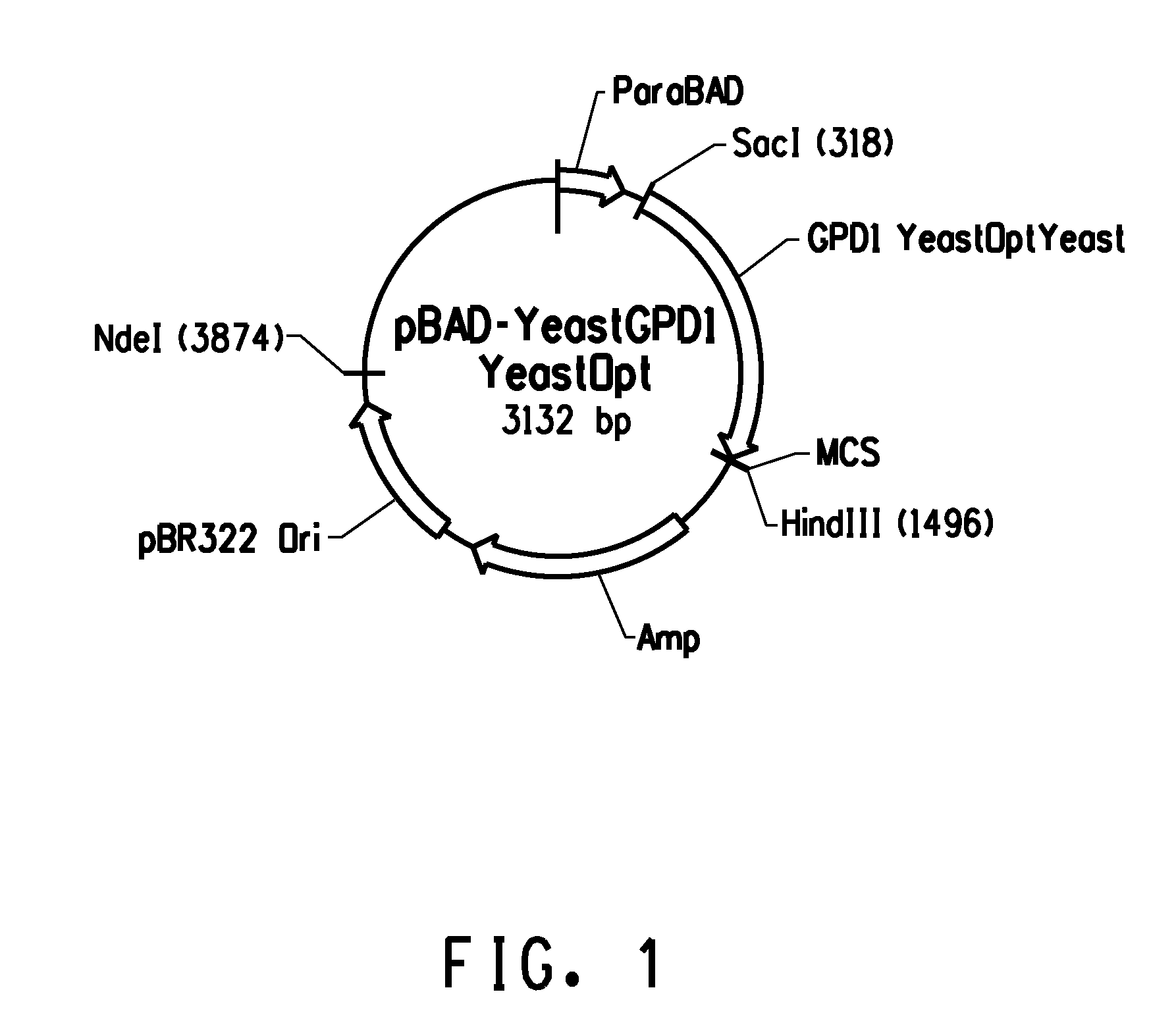
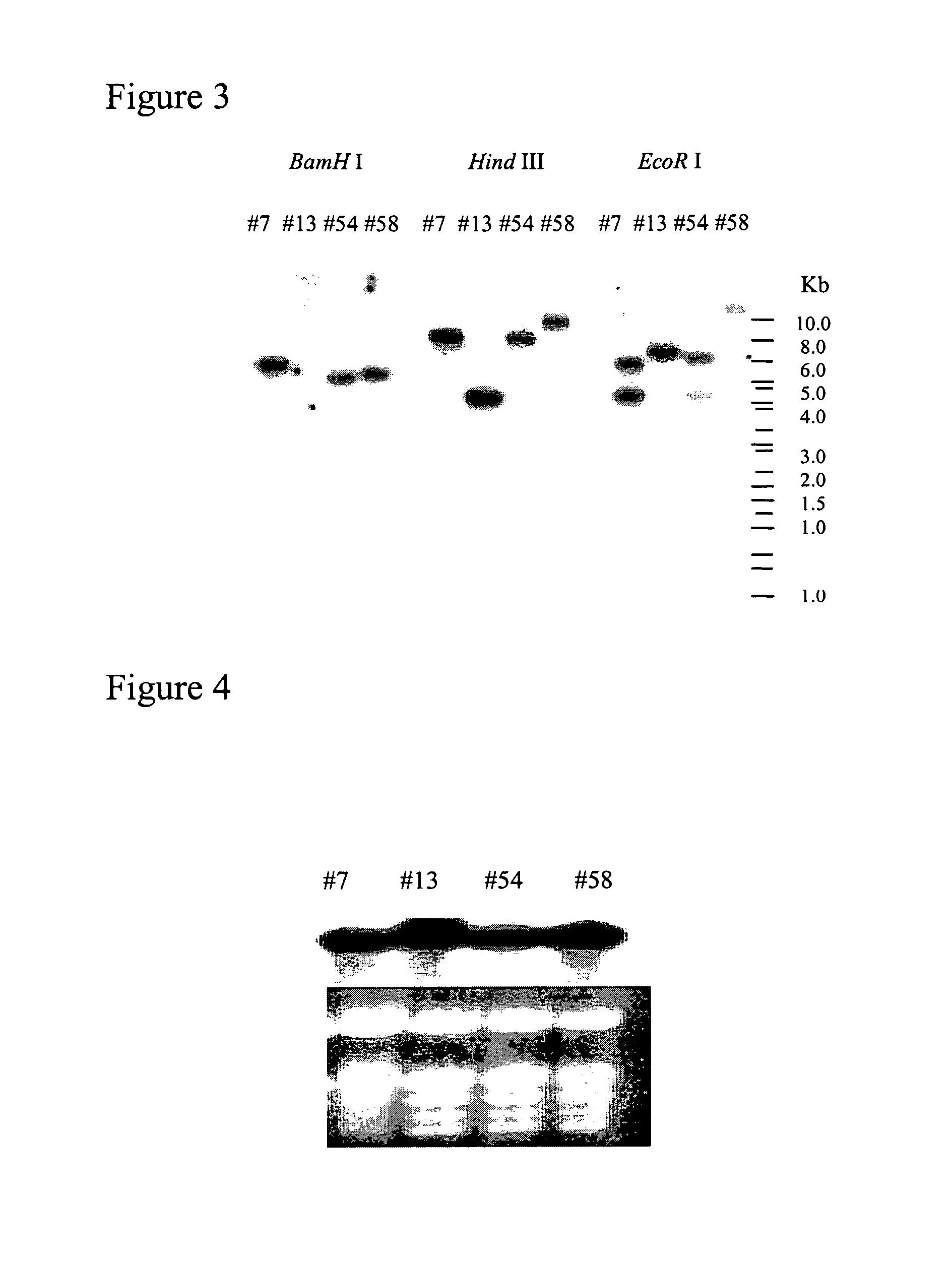
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
337 results about "Glyceollin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
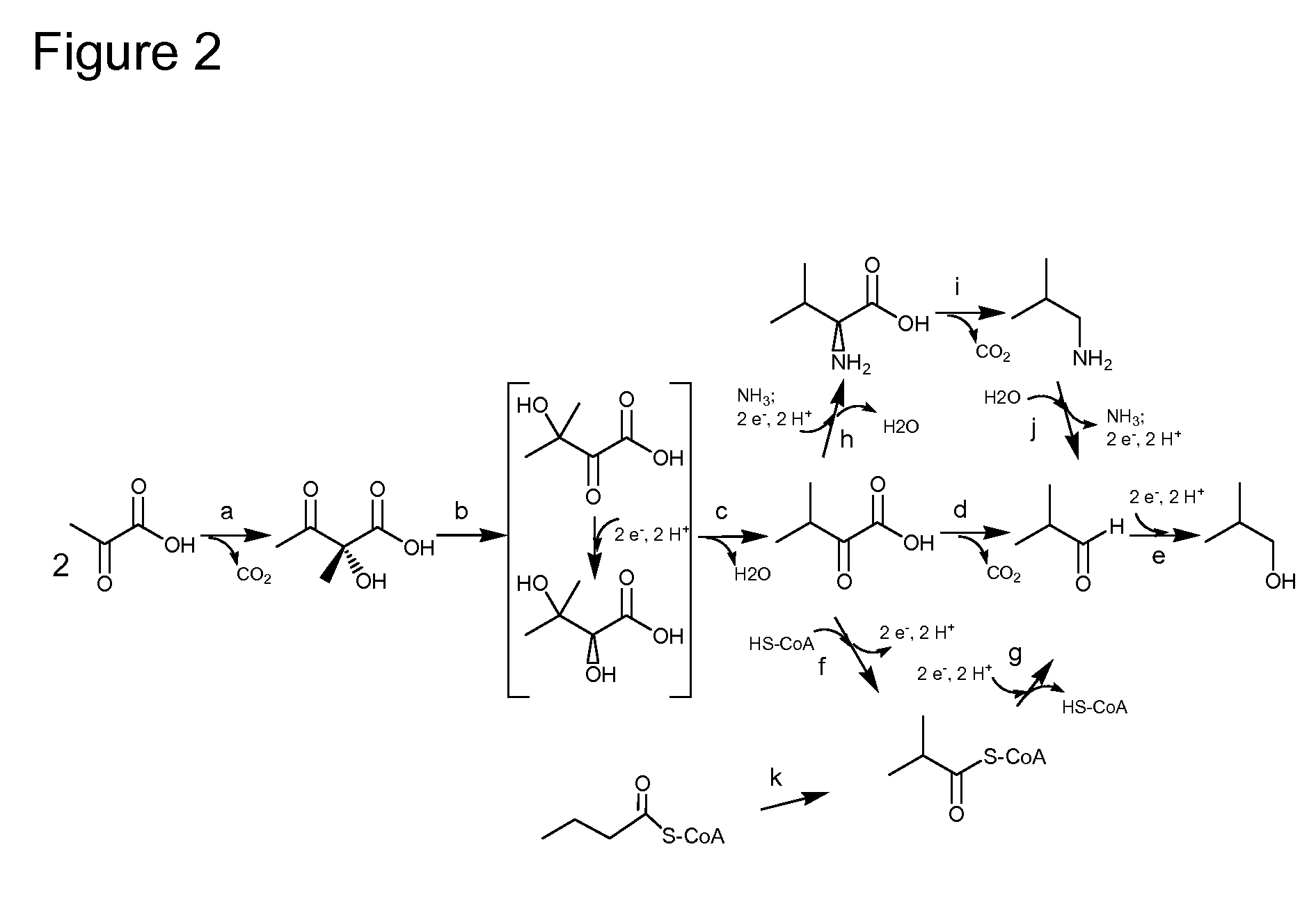
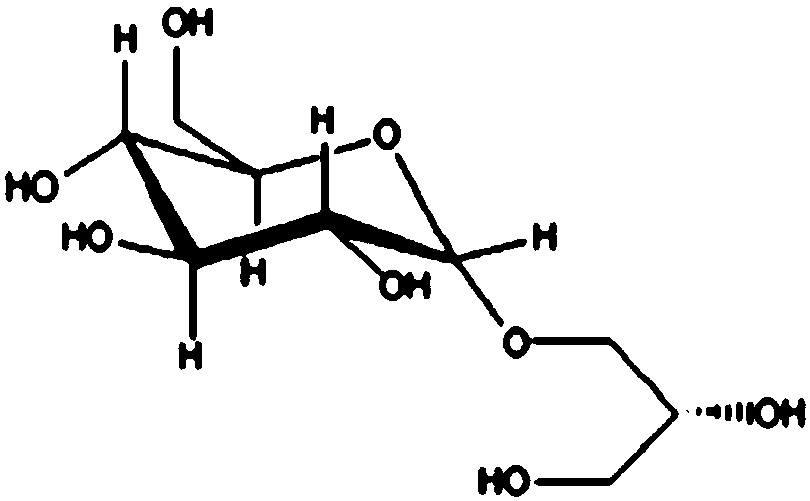
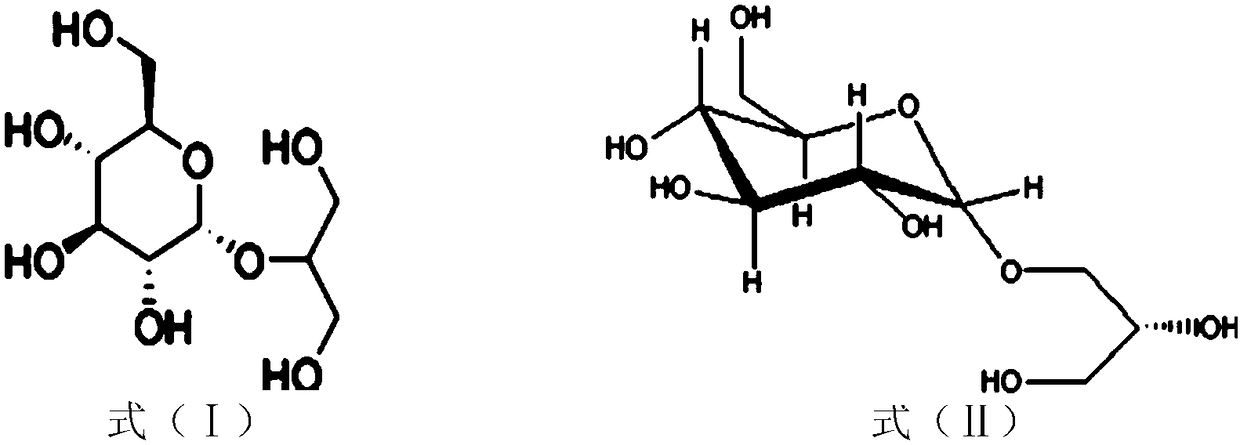
Glyceollins are a family of prenylated pterocarpan found in ineffective types of nodule in soybean in response to symbiotic infection. It possesses two chiral centers and can be asymmetrically synthesized chemically at a gram level scale.
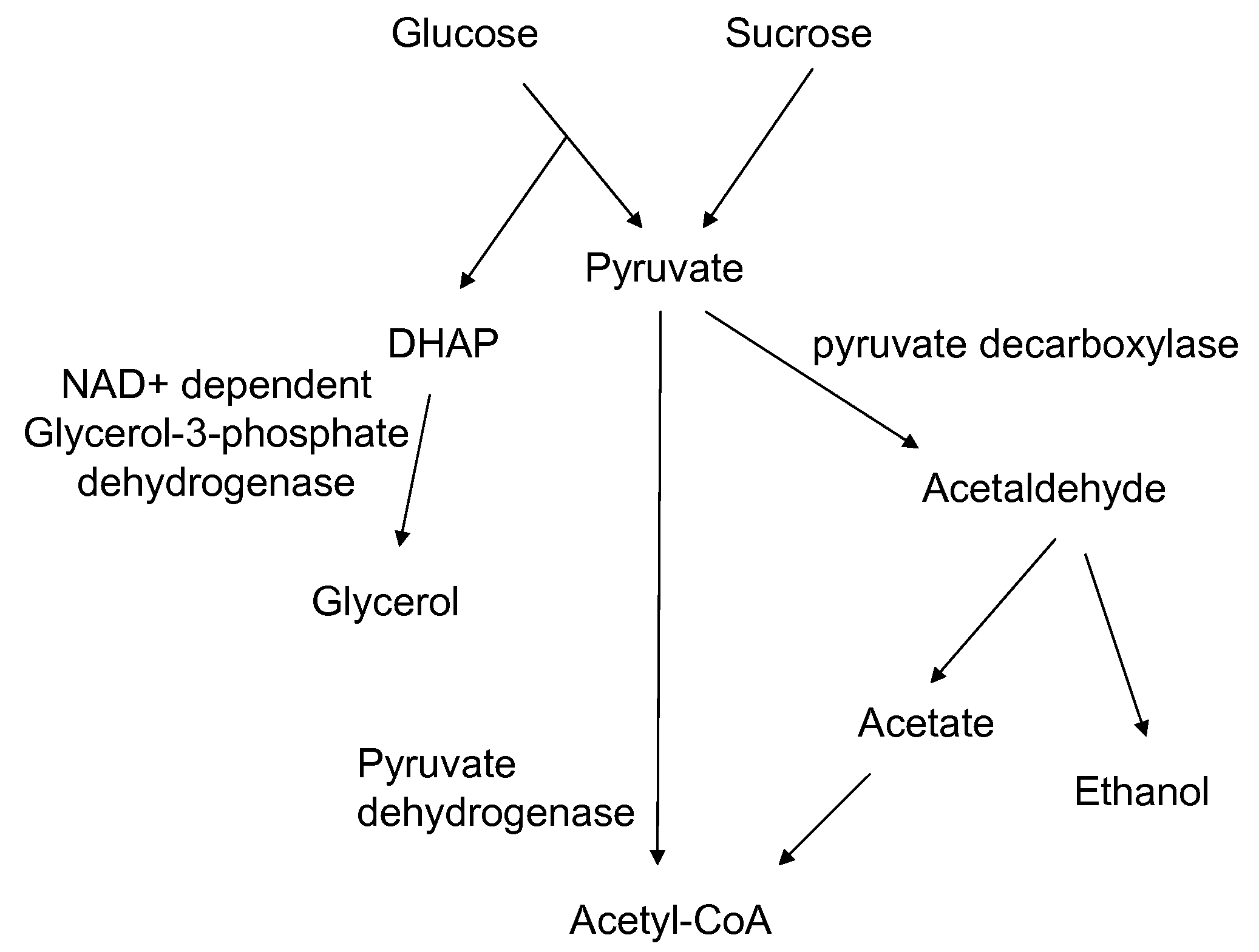
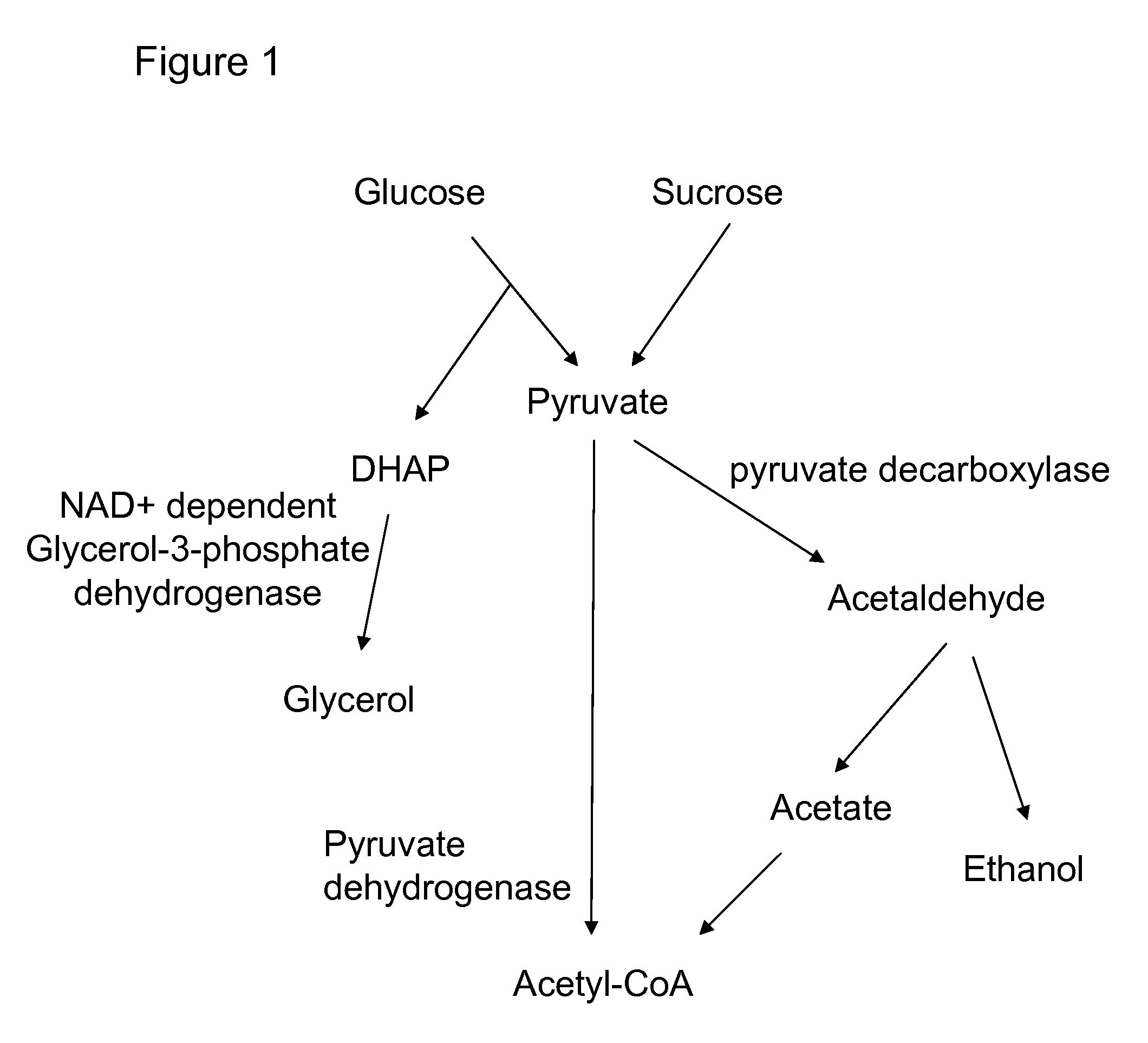
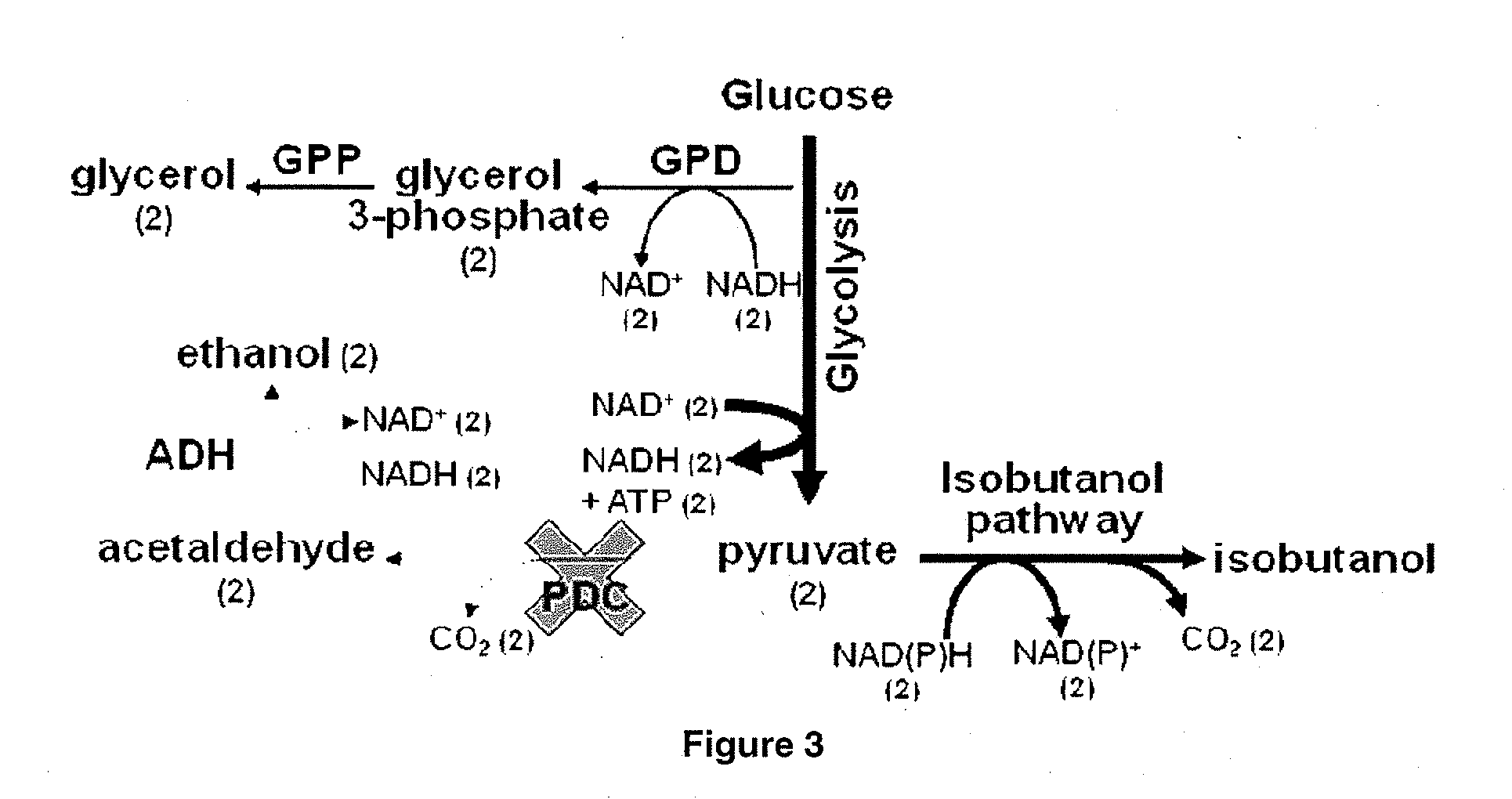
Enhanced pyruvate to acetolactate conversion in yeast
ActiveUS20090305363A1Improve throughputReduction of pyruvate decarboxylase activityFungiTransferasesYeastCytosol
A high flux in conversion of pyruvate to acetolactate was achieved in yeast through expression of acetolactate synthase in the cytosol in conjunction with reduction in pyruvate decarboxylase activity. Additional manipulations to improve flux to acetolactate are reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and reduced glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. Production of compounds having acetolactate as an upstream intermediate benefit from the increased conversion of pruvate to acetolactate in the described strains.
Owner:GEVO INC
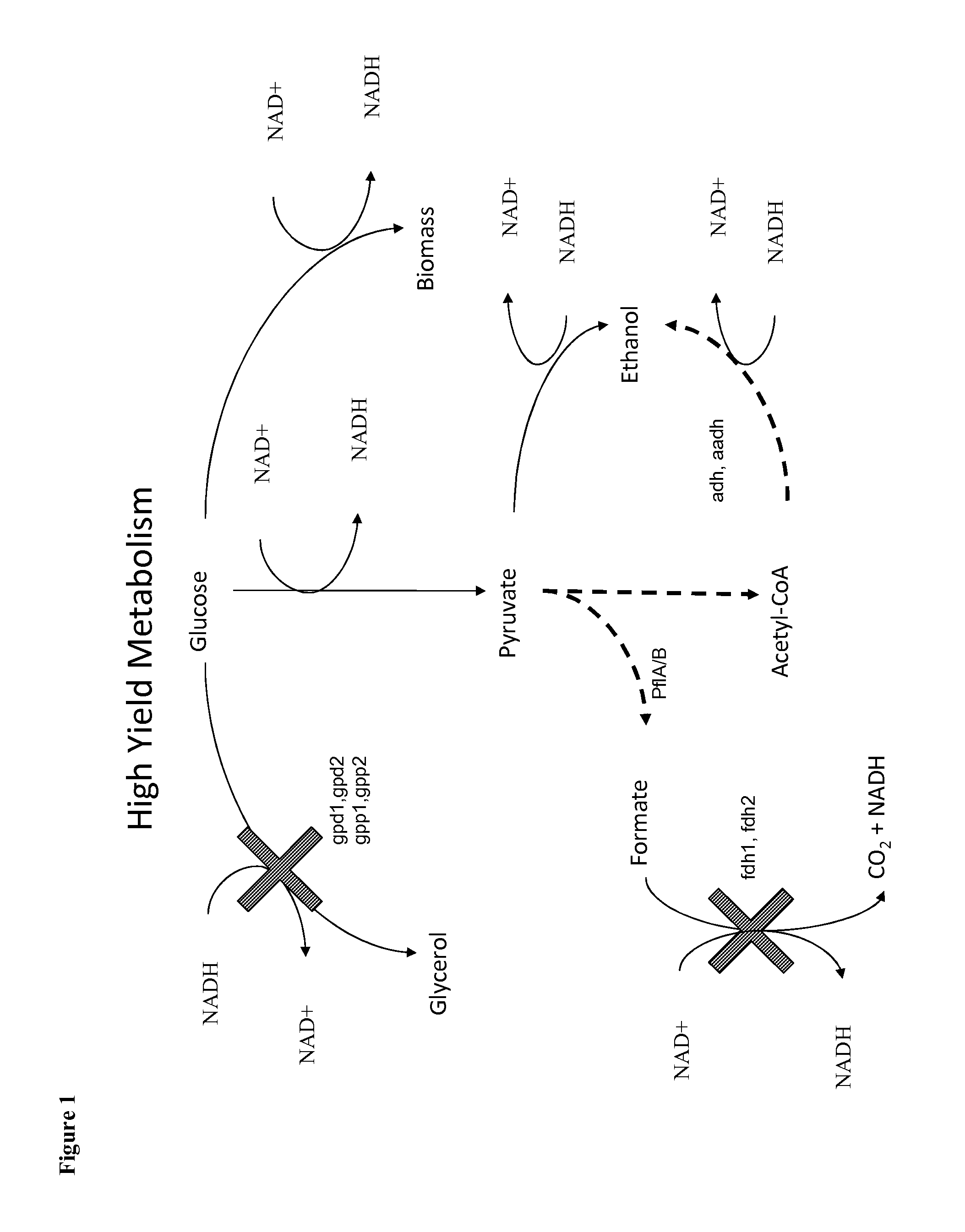
Methods for the improvement of product yield and production in a microorganism through the addition of alternate electron acceptors
ActiveUS8956851B2Reduce formationSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyHeterologous
The present invention provides for novel metabolic pathways to reduce or eliminate glycerol production and increase product formation. More specifically, the invention provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising a deletion of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol and / or regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source, such as lignocellulose, to a product, such as ethanol, wherein the one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, or downregulated. The invention also provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising one or more heterologous enzymes that function to regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source to ethanol, wherein said one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated or downregulated.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Yeast organism producing isobutanol at a high yield
The present invention provides recombinant mircoorganisms comprising an isobutanol producing metabolic pathway and methods of using said recombinant microorganisms to produce isobutanol. In various aspects of the invention, the recombinant microorganisms may comprise a modification resulting in the reduction of pyruvate decarboxylase and / or glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. In various embodiments described herein, the recombinant microorganisms may be microorganisms of the Saccharomyces clade, Crabtree-negative yeast microorganisms, Crabtree-positive yeast microorganisms, post-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, pre-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, and non-fermenting yeast microorganisms.
Owner:GEVO INC
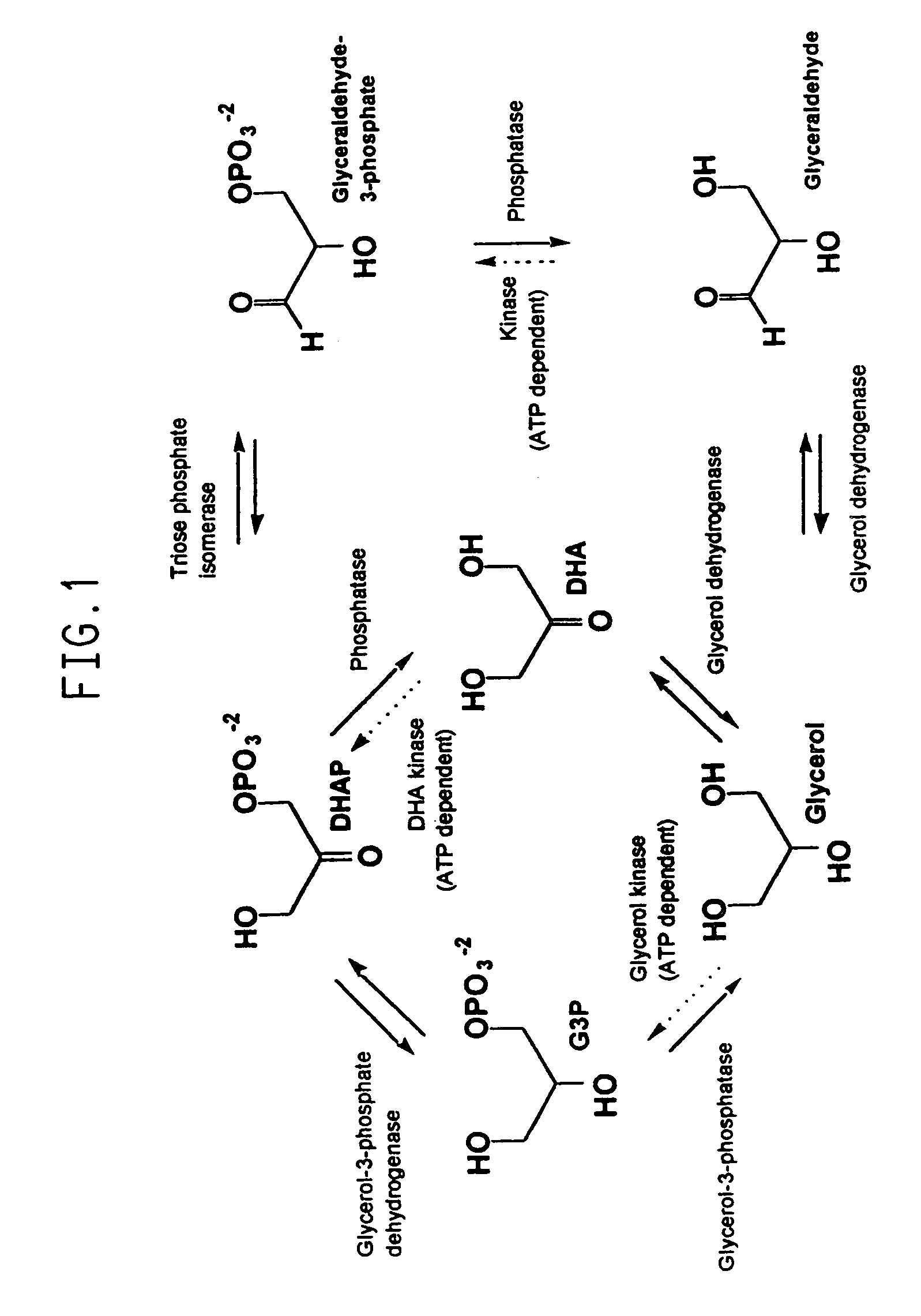
Transformed microorganisms and genes useful in the production of glycerol and 1,3-propanediol
Recombinant organisms are provided comprising genes encoding a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and / or a glycerol-3-phosphatase activity useful for the production of glycerol from a variety of carbon substrates. The organisms further contain disruptions in the endogenous genes encoding proteins having glycerol kinase and glycerol dehydrogenase activities.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
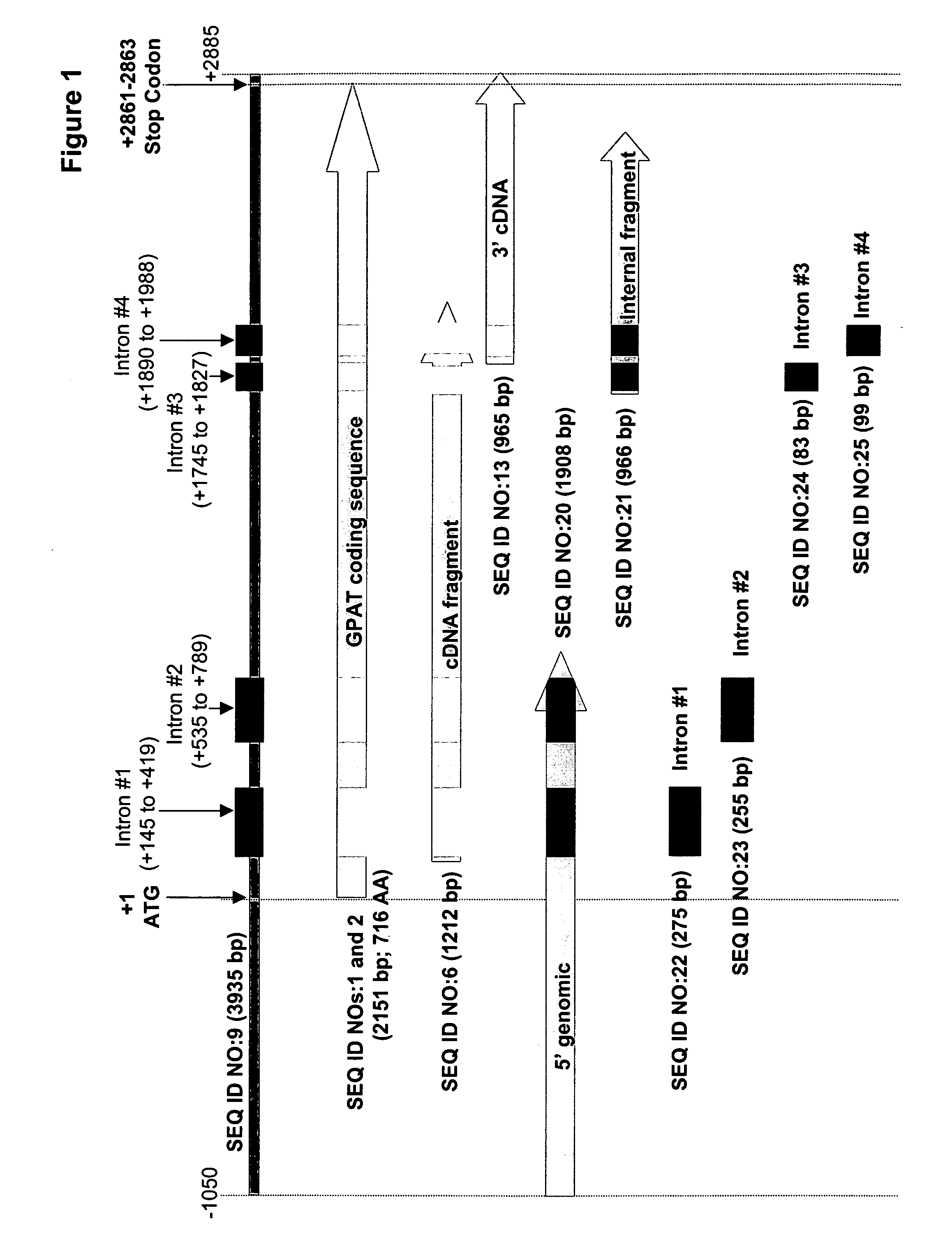
Mortierella alpina glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
Glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase (GPAT) participates in the first step of oil biosynthesis and is expected to play a key role in altering the quantity of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) produced in oils of oleaginous organisms. The present application provides a nucleic acid fragment isolated from Mortierella alpina encoding a GPAT that is suitable for use in the manufacture of oils enriched in omega fatty acids in oleaginous organisms. Most desirably, the substrate specificity of the instant GPAT will be particularly useful to enable accumulation of long-chain PUFAs having chain lengths equal to or greater than C20 in oleaginous yeast, such as Yarrowia lipolytica.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Preparation method of 1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoyl triglyceride
ActiveCN102757988AMild process conditionsShort reaction timeFermentationOleic Acid TriglycerideON-glycerol
The invention discloses a preparation method of 1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoyl triglyceride, which comprises the following steps: carrying out esterification reaction on glycerol and palmitinic acid under the action of a catalyst to obtain tripalmitin; carrying out ester exchange reaction on the tripalmitin and oleic acid or oleate under the action of 1,3-specific lipase until the ester exchange rate reaches 30-60%, and removing free fatty acids or fatty acid esters in the reaction system; and adding oleic acid or oleate into the reaction system, continuing the reaction until the ester exchange rate reaches 60-90%, and separating and purifying the 1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoyl triglyceride from the reaction products. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of wide raw material sources, high economy, high safety, mild technological conditions, short reaction time, low energy consumption and low enzyme consumption; and the method can be used for preparing high-yield high-purity 1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoyl triglyceride, and can be used as a food nutrient reinforcer for blending infant formula milk powder.
Owner:ZANYU TECH GRP CO LTD
Infant formula milk powder with the fatty acid structure adjusted
InactiveCN101061819AAvoid exposureDelayed Post OxidationMilk preparationWhey manufactureDocosahexaenoic acidVegetable oil
The invention provides an infant milk powder with adjusted structure of aliphatic acid, which comprises the following raw materials (by weight portion in tons): dry matter of fresh milk 276, desalinized whey powder 450, structured fatty oil 105, lactose 50, fructooligosaccharide 20, alpha-lactalbumin 10, docosahexaenoic acid 5, arachidonic acid 6, nucleic acid 0. 42, taurine 0. 45, choline 0. 42, L-carnitine 0. 06, beta-carotene 0. 012, composite vitamin 2. 5, composite microelement 3. 5 and balancing refined vegetable oil.
Owner:SANLU GROUP
Glycerol 3- phosphate dehydrogenase for butanol production
ActiveUS20140273129A1Improved and increased production of butanolReduced and decreased production of glycerolBacteriaBiofuelsHeterologousMicroorganism
Provided herein are glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD) enzymes with increased KM for NADH and GPD enzymes with substantially the same affinity for NADH and NADPH and / or are feedback inhibited by glycerol-3-phosphate. Also provided herein are recombinant microorganisms comprising a heterologous gene encoding GPD and a deletion or disruption in an endogenous gene encoding GPD. Also provided are recombinant microorganisms comprising a heterologous gene encoding GPD and a butanol biosynthetic pathway. Further provided are methods of producing butanol comprising providing the recombinant microorganisms described herein and contacting the recombinant microorganism with at least one fermentable carbon substrate under conditions wherein butanol is produced.
Owner:GEVO INC
Process for preparing nutritional, therapeutic or organoleptic products from crude glycerol
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a nutritional, therapeutic or organoleptic product by growing non-recombinant yeast under aerobic conditions, in a medium that includes crude glycerol, as one possible carbon source to produce a yeast product. The yeast product can be processed to obtain such nutritional, therapeutic or organoleptic products as yeast paste, yeast metabolites, carbohydrates, proteins, functional proteins, nucleotides, yeast autolysates, yeast extract, yeast cell walls, beta-glucans, mannans or a product derived from a mineralized yeast product.
Owner:BIO PROCESSING AUSTRALIA
Modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in the treatment of tuberous sclerosis
InactiveUS20100022495A1Promote apoptosisReduce and prevent ER stressOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseHAMARTOMATOUS DISEASES
Endoplasmic reticulum stress has been found to be associated with the genetic disease tuberous sclerosis. Tuberous sclerosis is cause by defects in the two genes, TSC1 and TSC2. Agents that modulate ER stress may be used to treat tuberous sclerosis and other hamartomatous diseases. In particular, 4-phenyl butyric acid (PBA) has been shown to reduce ER stress is TSC-deficient cells. Other compounds useful in reducing ER stress are chemical chaperones such as trimethylamine N-oxide arid glycerol may also be useful in treating tuberous sclerosis. The present invention provides methods of treating a subject suffering from tuberous sclerosis using ER stress reducers such as PBA, TUDCA, UDCA, and TMAO. Methods of screening for ER stress reducers by identifying agents that reduce levels of ER stress markers in TSC-deficient cells are also provided. These agents may find use in methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating tuberous sclerosis.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Coenzyme Q10- Containing Composition
ActiveUS20080248013A1Excellent stability and bioavailabilitySuperior coenzymeOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsOrganic acidMonoglyceride
There is provided a coenzyme Q10-containing composition having a high coenzyme Q10 content and excellent stability and bioavailability of coenzyme Q10, without using synthetic emulsifiers such as glycerin fatty acid esters, polyglycerin fatty acid esters, organic acid monoglycerides or sucrose fatty acid esters.The coenzyme Q10-containing liquid composition is obtained by dispersing and emulsifying coenzyme Q10 in an aqueous liquid containing a water-soluble substance consisting of octenylsuccinate starch and dextrin, and glycerin. The liquid composition may be dried to prepare a coenzyme Q10-containing solid composition.
Owner:NISSHIN PHARMA INC
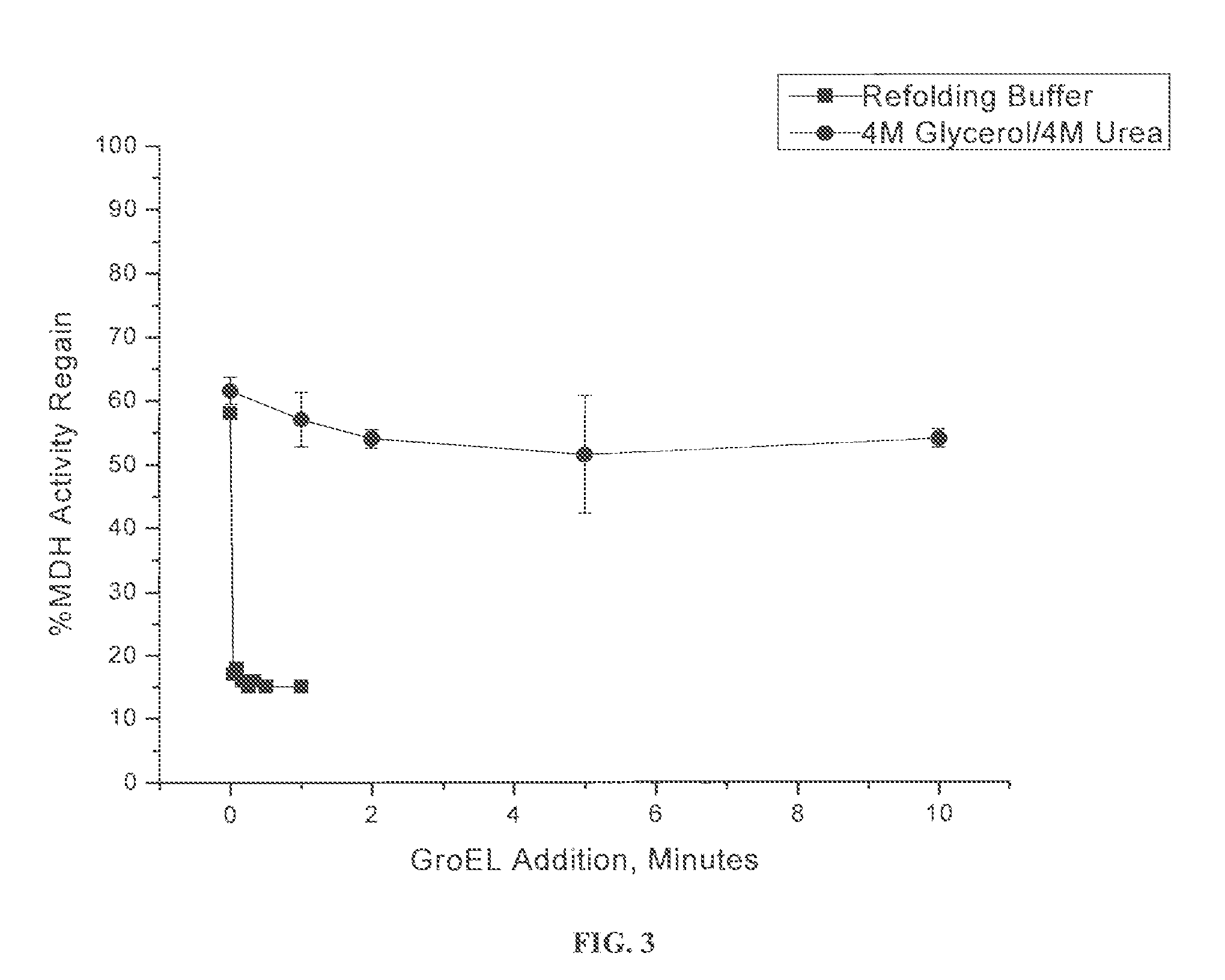
Osmolyte Mixture for Protein Stabilization
ActiveUS20110053795A1Speed up the processInhibit aggregationLibrary screeningEnzyme stabilisationProtein insertionOsmolyte
An osmolyte composition comprising 4 M glycerol and 4M urea for stabilizing previously transient protein folding intermediates as long-lived stable forms. A method to search for other possible stabilizing osmolyte mixtures using a screening array is also provided. These additional osmolyte mixtures may complement or augment the successful 4M glycerol / 4 M urea mixture.
Owner:UNIV KANSAS MEDICAL CENT
Method for preparing freeze-dried powder containing bacillus natto and nattokinase
InactiveCN101214263AReduce purification costsKeep alivePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSucroseFreeze-drying
The present invention relates to freeze-dried powder containing bacillus natto and nattokinase and a preparation method thereof, the process of which comprises that: firstly, culture medium is confected and sterilized, wherein, the culture medium components with the weight percentage are 8 percent to 15 percent of soybean flour, 1 percent to 5 percent of sucrose, 0.4 percent to 0.6 percent of NaCl and the water with the rest quantity, the pH value of which is 6.8 to 7.2; secondly, the bacillus natto is inoculated, and the inoculation quantity is 2 percent to 8 percent; thirdly, the bacillus natto after the inoculation is cultured and fermented for 20 to 28 hours under the temperature of 36 DEG C to 38 DEG C; fourthly, fermentation liquid is frozen and dried in vacuum, the glycerin with 1 percent to 7 percent of the weight of the fermentation liquid is used protecting agent to be added into the fermentation liquid, which is frozen under the temperature of subzero 18 DEG C in advance to be frozen and dried in vacuum for 12 to 20 hours and then is resolved under the temperature lower than 30 DEG C. The method has low cost and is in favor of the industrial production. Under the precondition of maintaining the nattokinase activity, the freeze-dried process also holds other nutrient component in the bacillus natto and the fermentation liquid, which reduces the nattokinase purification cost.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Polyene phosphatidyl choline injection and method for preparing the same
The invention discloses a polyene phosphatidyl choline injection and the preparation method. The components and the ratio (portion) of the polyene phosphatidyl choline injection of the invention is: 465 portion of polyene phosphatidyl choline injection, 88 portion of benzyl zlcohol, 50 to 800 portion of glycocholic acid, cholic acid or tween-80, 50 to 80 portion of alcohol, propanediol or glycerin, 15 to 200 portion of sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate, 0.5 to 5 portion of 2,6-D-itert-butyl-p-cresol, 0.8 to 8 portion of Tertiary butyl-4-hydroxyl anisole, 3 to 25 portion of Vitamin E by weight. The polyene phosphatidyl choline injection of the invention has good clarity, high stability, simple preparation process and easy operation.
Owner:SICHUAN HAISCO PHARMA CO LTD +1
Method for improving glycerol microbial fermentation production of 1,3-propanediol by constructing gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN102199570APromote conversionPromote circulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTricarboxylic acid
The invention provides a method for improving the microbial production of 1,3-propanediol by constructing a gene engineering bacterium. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an expression vector with the inserted malic enzyme gene; delivering the expression vector in host bacteria generating 1,3-propanediol; adding an inducer to induce the overexpression of the malic enzyme gene in the fermentation and culture process; and adopting the aerobic fermentation means and performing the fed batch of substrate glycerol to produce 1,3-propanediol. The method is characterized in that the constructed gene engineering bacterium can express more malic enzyme than the original strain in the fermentation process, thus the convertion from pyruvic acid to malic acid can be promoted, the circulation of tricarboxylic acid can be promoted, the bacterium can generate more nicotinamide adenine dinueleotide (NADH) and energy (ATP), the activity of 1,3-propanediol oxidation-reduction enzymein the bacterium and the glycerol conversion rate can be increased. The invention has the following advantages: the substrate glycerol utilization rate of the producing bacterium can be increased, the concentration and production strength of the fermented 1,3-propanediol can be obviously increased, the yield of 1,3-propanediol can be increased and the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
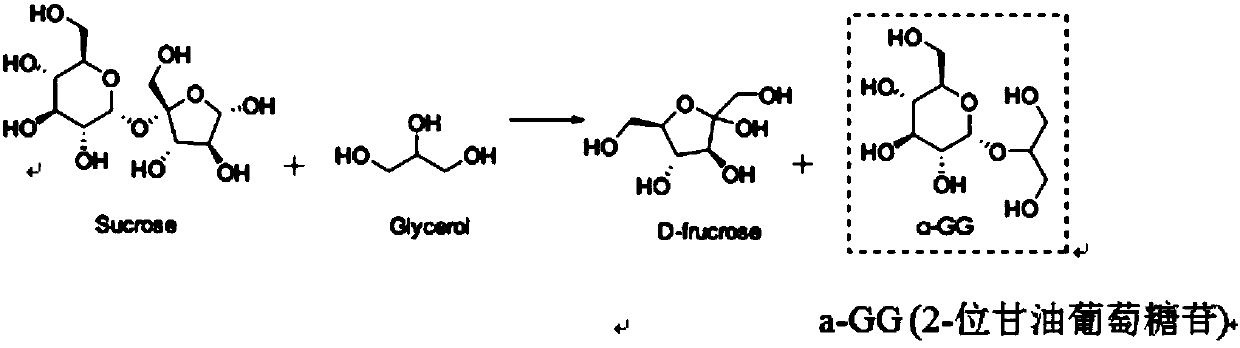
Sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof in production of glycerol glucoside
ActiveCN107858335AReduce outputStrong specificityGenetic engineeringFermentationSucrose phosphorylaseGlycerol
The invention aims to provide a sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof in the production of glycerol glucoside. The sucrose phosphorylase mutant which is protein is obtained by replacingthe 341st-site amino acid residue, which is leucine, of sucrose phosphorylase with other amino acid residues. The protein can be BaSP / L341W protein obtained by replacing the 341st-site amino acid residue, which is the leucine, of the sucrose phosphorylase with tryptophan. The sucrose phosphorylase mutant has the advantages that by the primer point mutation of the 341st-site amino acid residue ofthe wild sucrose phosphorylase derived from bifidobacterium adolescentis, the specificity of 2-glycerol glucoside produced by using the sucrose phosphorylase mutant, sucrose and glycerin as the raw materials, and the yield of the byproduct 1-glycerol glucoside is lowered; the sucrose phosphorylase mutant has an important application value in the field of the production of the 2-glycerol glucoside.
Owner:NANJING HUASHI NEW MATERIAL
Method for eliminating capability of klebsiella pneumoniae in synthesizing 2,3-butanediol and acetoin
ActiveCN102952826AEliminate generationReduce separation and extraction stepsBacteriaStable introduction of DNA2,3-ButanediolGlycerol
The invention discloses a method for eliminating capability of klebsiella pneumoniae in synthesizing 2,3-butanediol and acetoin, comprising the following step of inactivating acetolacetate decearboxylase gene in a synthesis route of 2,3-butanediol by lebsiella pneumoniae to cut off the catalytic reaction that acetolactic acid is converted into acetoin. According to the method, when 1,3-propylene glycol is synthesized from glycerol by the klebsiella pneumoniae, the synthesis of byproducts, i.e. 2,3-butanediol and acetoin, can be eliminated, and the conversation rate of glycerol to 1,3-propylene glycol can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN109423485AStrong specificityReduce outputFermentationGenetic engineeringSucrose phosphorylaseArginine
The present invention discloses a sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is obtained by replacing leucine of the amino acid residue at the number 341 site of sucrose phosphorylase with other amino acid residues. The protein can be BaSP / L341D protein obtained by replacing leucine of the amino acid residue at the number 341 site of sucrose phosphorylase with aspartic acid, and can be BaSP / L341R protein obtained by replacing leucine of the amino acid residue at the number 341 site of sucrose phosphorylase with arginine. Through single-point mutation at the amino acid residue at the number 341 site of wild sucrose phosphorylase derived from Bifidobacterium adolescentis with primers, specificity for producing 2-glycosylglycerol from sucrose and glycerin is significantly improved, and the yield of 1-glycosylglycerol that is a byproduct is reduced. The sucrose phosphorylase mutant has great application value in the field of production of the 2-glycosylglycerol.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
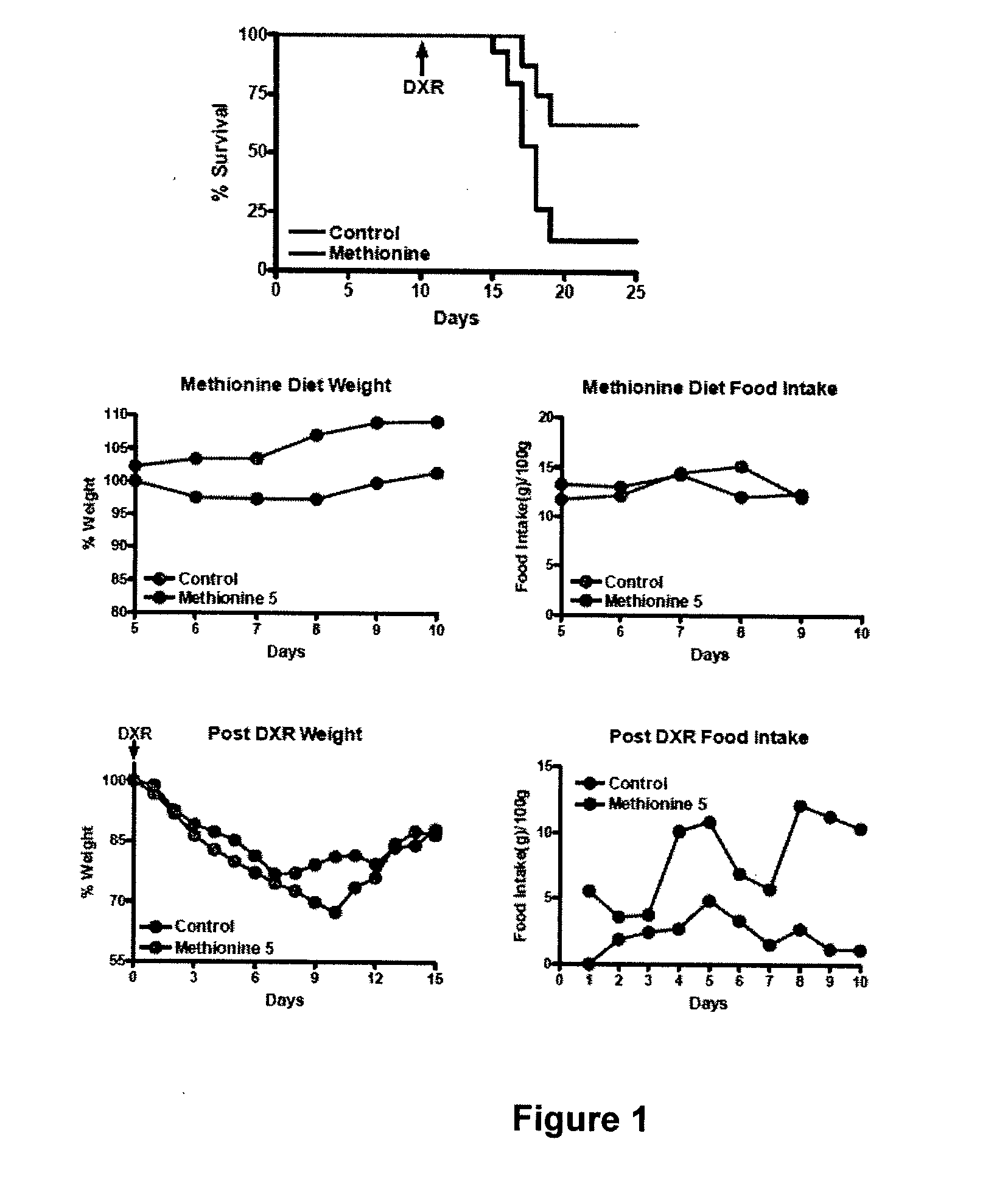
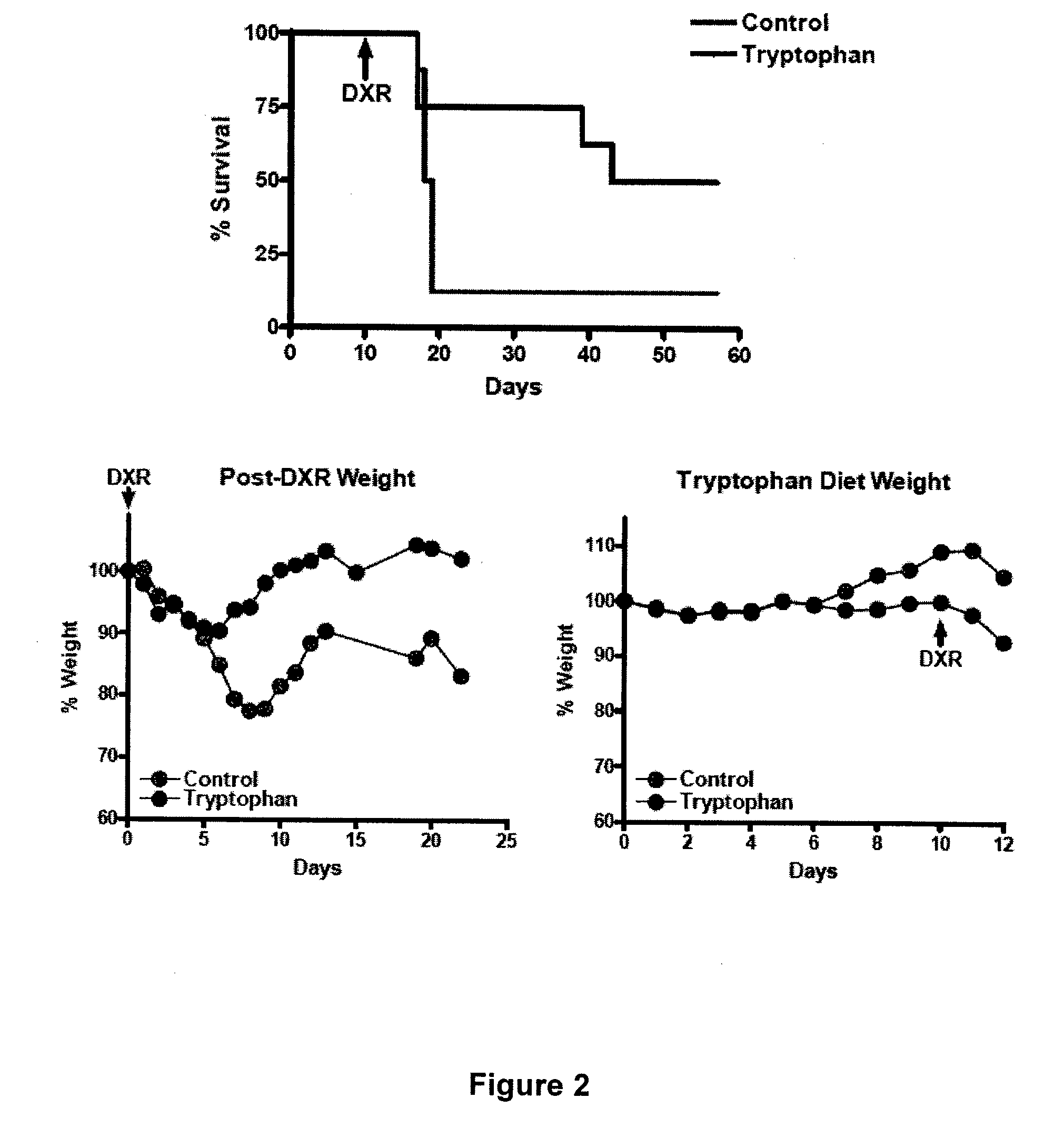
Dietary Compositions and Methods for Protection Against Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy, Oxidative Stress, and Aging
The present invention relates to dietary compositions comprising reduced level of methionine, tryptophan, all amino acids, or protein, dietary compositions comprising glycerol as a substitute for monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, and hypocaloric or calorie free diets with reduced level of energy, carbohydrates, or protein. Also disclosed are methods of using these compositions and diets, as well as fasting, to protect subjects against chemotherapy, radiotherapy, oxidative stress, or aging.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
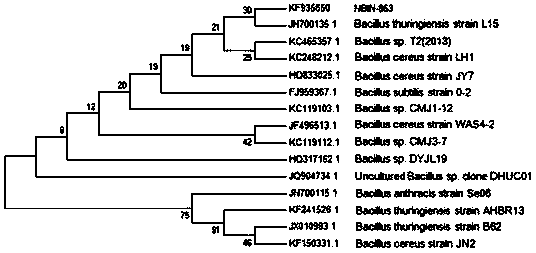
Bacillus thuringiensis for killing meloidogyn incognita and culture method of bacillus thuringiensis
The invention relates to bacillus thuringiensis for killing meloidogyn incognita and a culture method of the bacillus thuringiensis. The bacillus thuringiensis NBIN-863 for killing meloidogyn incognita is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University in Wuhan China on 29th November, 2013, the survival date is 29th November, 2013, and the serial number in the Center is CCTCC NO: M2013612. A culture method of the Bacillus thuringiensis comprises the following steps: taking soil at 117 degrees and 29 minutes east longitude and 30 degrees and 39 minutes north latitude near the Jiuhuashan in Anhui province, suspending in sterile water, diluting according to gradient concentration, coating on a flat plate, culturing by using an LB (Lusso-Brillante) solid culture medium, diluting, drawing a line on an LB flat plate for culture, inoculating a single colony to a shake flask for culture, mixing with glycerin, preserving in a refrigerator, transferring the single colony into a liquid culture medium for culture, smearing and observing and confirming by using a crystal violet staining optical microscope.
Owner:HUBEI BIOPESTICIDE ENG RES CENT
Transgenic manipulation of sn-glycerol-3-phosphate and glycerol production with a feedback defective glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenese gene
InactiveUS7112724B1Enhanced production of glycerolIncrease productionOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesWild typePhosphoric acid
The invention provides a method for genetically transforming a plant so that it expresses a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase that is feedback-defective. The feedback-defective enzyme raises levels of glycerol and glycerol-3-phosphate in comparison to the wild-type, leading to increased osmotic stress tolerance, and altered fatty acid content in glycerolipids.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
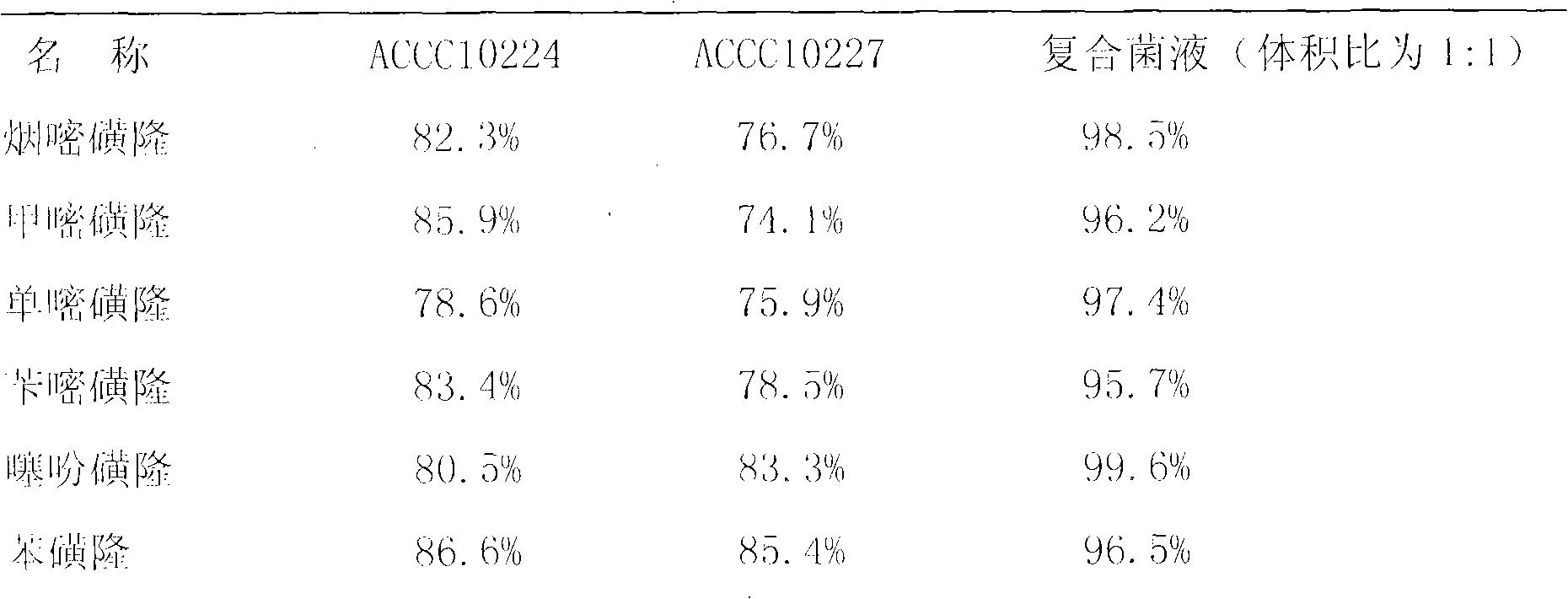
Fermentation and preparation of composite microbial agent for degrading sulfonylurea herbicide with high efficiency
The invention relates to a fermentation and preparation method of a composite microbial agent for degrading sulfonylurea herbicides in soil and water with high efficiency, and the composite microbial agent is fermented compositely by using bacillus benzoevorans ACCC 10244 and bacillus chitinivorous ACCC 10227 as bacterial sources. After fermentation, a carrier substance of alginic acid (in a form of micro-colloid in aqueous solutions), a electrolyte (potassium nitrate) and an antifreeze agent (glycerin) are added into the fermented bacterial liquid; the bacterial number ratio of bacillus benzoevorans ACCC 10244 and bacillus chitinivorous ACCC 10227 in the prepared bacterial agent is 1:1, and the bacterial number contents of both bacteria in the bacterial agent are up to above 1 billion / ml. The bacterial agent can degrade the followings with high efficiency: nicosulfuron, suifometuron-methyl, monosulfuron, bensulfuron-methyl, thifensulfuron-methyl, tribenuron-methyl, metsulfuron-methyl, chlorsulfuron, methyl sulfuron, etc.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
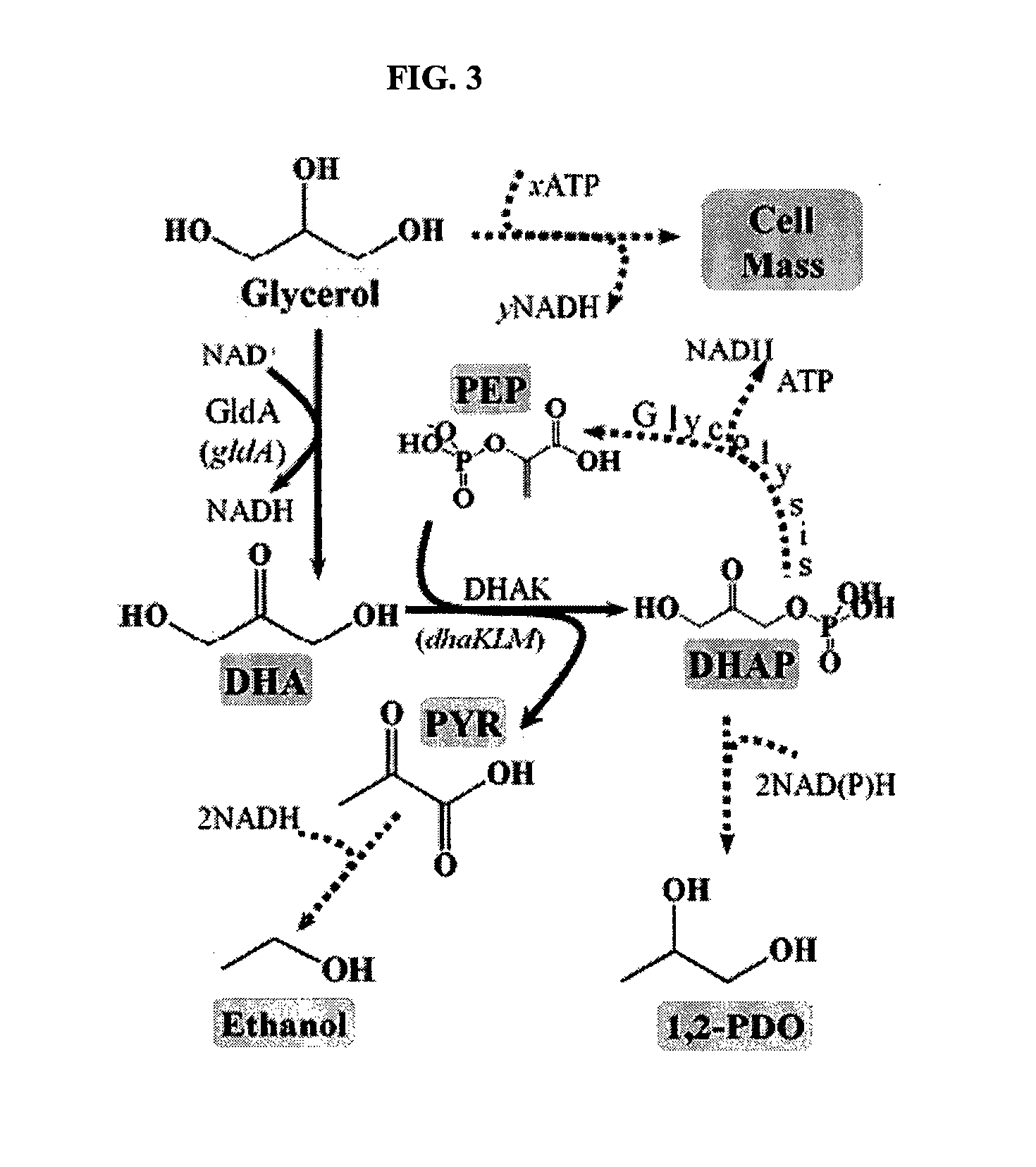
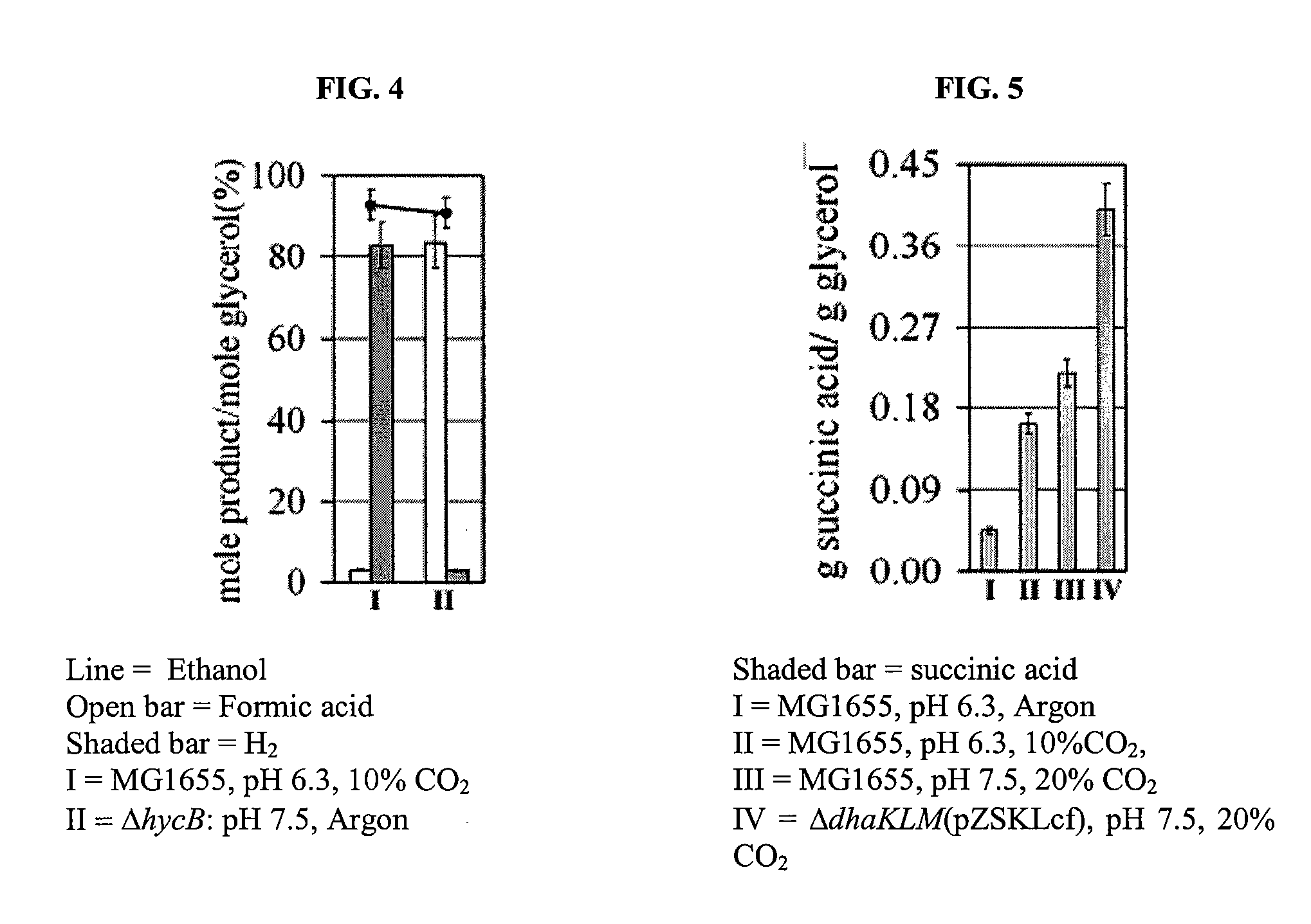
Anaerobic Fermentation of Glycerol
InactiveUS20090186392A1Reduce negative impactImprove filtering effectBiofuelsHybrid cell preparationHigh concentrationBacteroides
The invention relates to the development of appropriate cultivation conditions for a bacteria to grow anaerobically (fermentatively) on a glycerol substrate. The method requires culturing bacteria having a functional 1,2-propanediol pathway and a functional type II glycerol dehydrogenase-dihydroxyacetone kinase pathway in a culture medium containing high concentrations of glycerol, a neutral to mildly acidic pH, low levels of potassium and phosphate, and high levels of CO2, such that glycerol is thus converted into a desirable product, such as ethanol, —hydrogen, formate, succinate, or 1,2-propanediol.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Gene engineering bacterium for producing 1,3-propanediol and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101260379AImprove stabilityHigh final concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsozymeGlycerol
The invention belongs to the biochemical field and discloses a 1, 3-propylene glycol genetic engineering bacterium and a preparation method and application thereof. The strain is classified and named as Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955-pUC18-yqhD-Tet<R>, and is obtained by connection of a 3-propylene redoxase isozyme gene yqhD from Escherichia coli and a tetracycline resistant gene Tet<R> from a plasmid pHY300PLK, insertion of a carrier pUC18 and conversion of Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955. The bacterium can obviously improve the capacity for conversion of glycerol into 1, 3-propylene glycol, improve the utilization ability and the conversion rate of the substrate glycerol and the final concentration of the final offspring 1, 3-propylene glycol, simultaneously shorten the fermentation time, and is convenient for industrial production of the 1, 3-propylene glycol through the microbial fermentation method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Polypeptide compound for removing wrinkles in eyes and preparation method of polypeptide compound
ActiveCN105232352AAvoid formingSpeed up circulationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWrinkle skinDipeptide
The invention provides a polypeptide compound for removing wrinkles in eyes. The polypeptide compound, in percentage by mass, consists of the following components: 0.02-0.035% of acetyl hexapeptide-3, 0.001-0.01% of palmitoyl pentapeptide-3, 0.025-0.035% of palmitoyl tetrapeptide-7, 0.025-0.035% of tripeptide, 0.08-0.12% of dipeptide-2, 0.1-0.2% of acetyl tetrapeptide-5, 4-6% of glycerol, 0.2-0.4% of sodium hyaluronate, 0.3-0.5% of 1,2-hexanediol and the balance of purified water. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a preparation method of the compound. The polypeptide compound for removing wrinkles in eyes provided by the invention, applied to volunteers, is capable of taking a significant effect of relieving wrinkles in eyes, so that the average quantity of the wrinkles in eyes is reduced, the depth of the wrinkles in eyes is reduced, the smoothness of eye skin is enhanced, the coverage area of the wrinkles in eyes is reduced and the phenomenon of the wrinkles in eyes is significantly improved.
Owner:卡丝生物(广东)科技有限公司
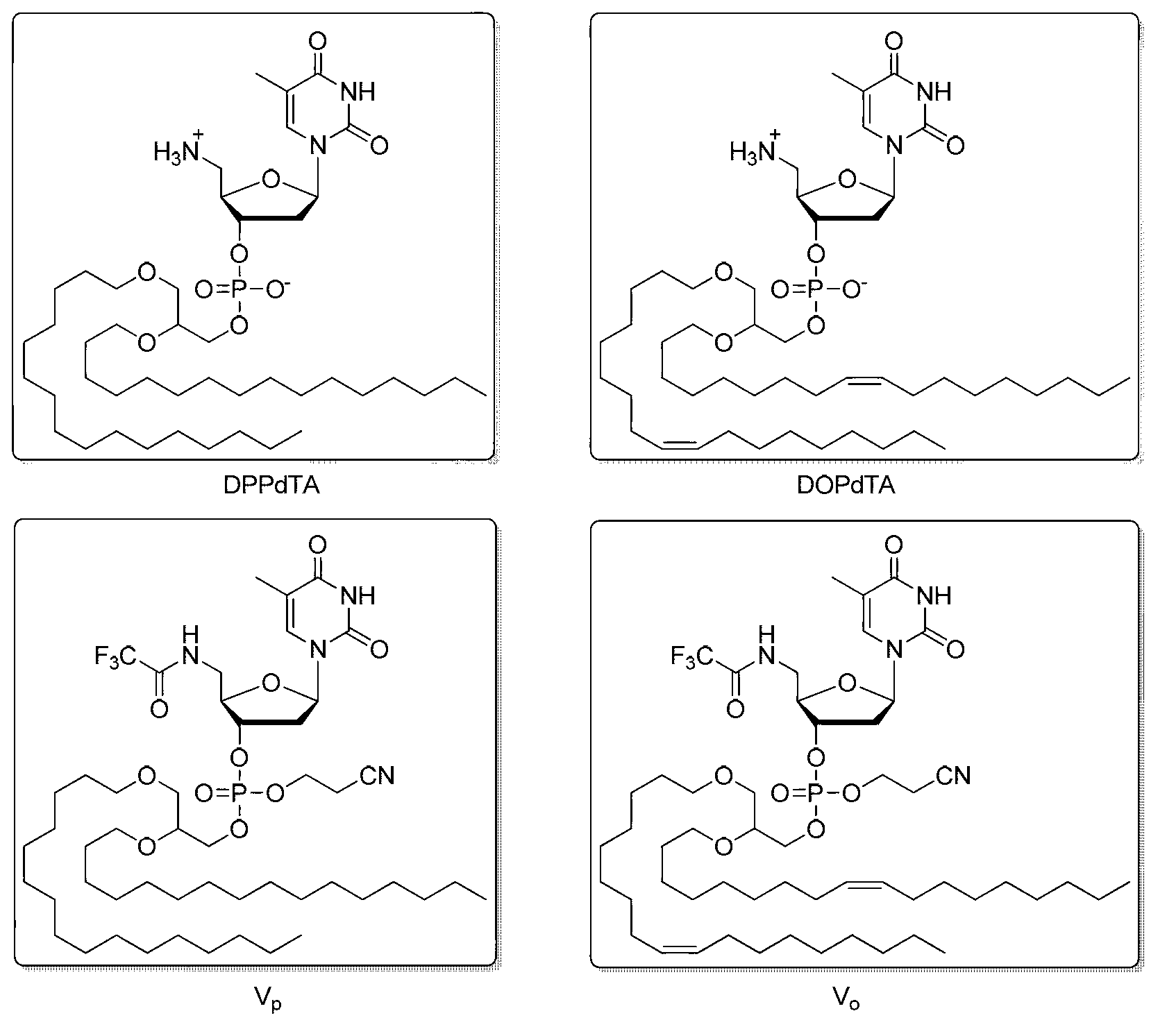
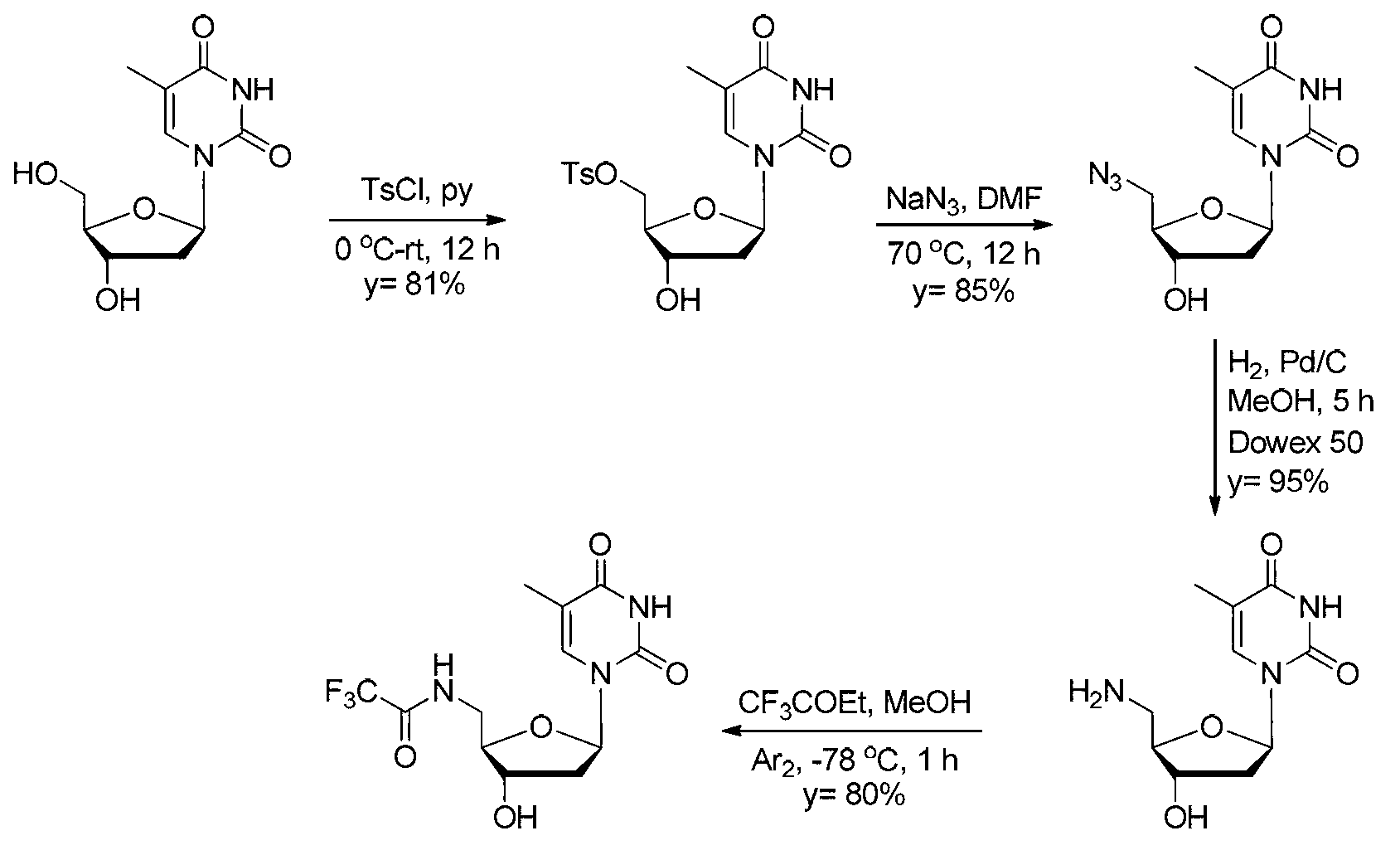
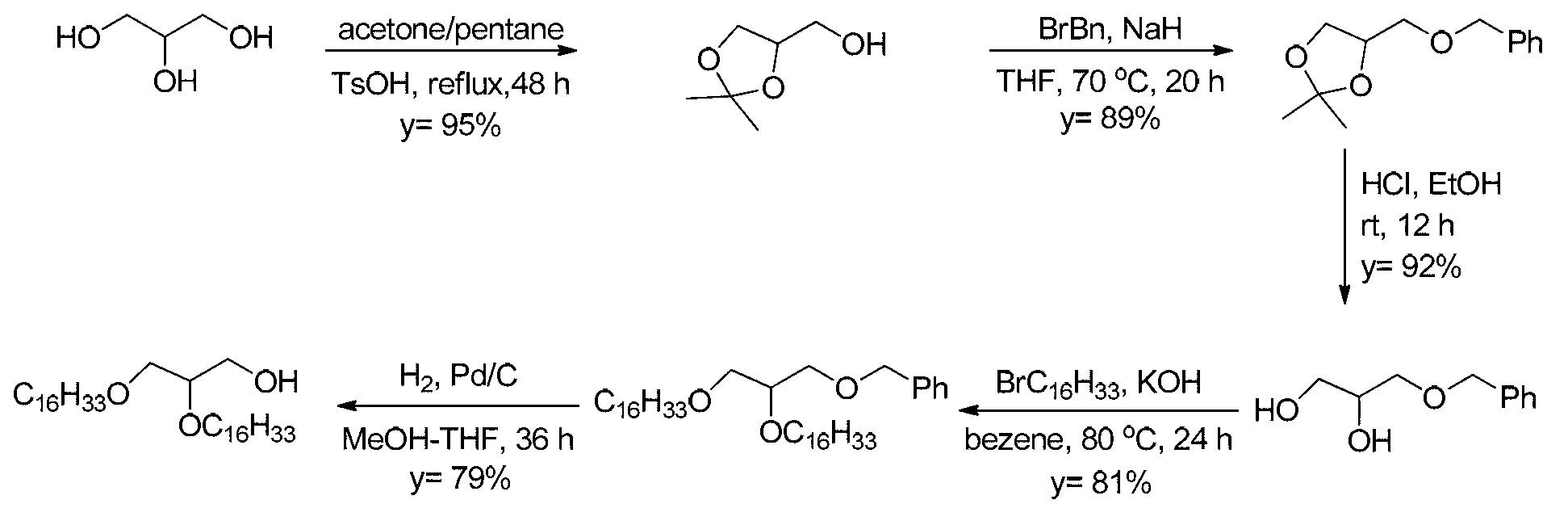
5'-amino-2',5'-dideoxynucleotide phospholipid molecules, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103232510AThe synthesis method is simpleEasy to prepareSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesSolventPyrimidine
The invention discloses 5'-amino-2',5'-dideoxynucleotide phospholipid molecules, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The 5'-amino-2',5'-dideoxynucleotide phospholipid molecules provided by the invention have an amphiphilic structure represented by the formula (I). 5'-amino-2',5'-dideoxynucleoside is adopted as a hydrophilic head, and glycerol fatty ether connected by using a phosphate bond is adopted as a hydrophobic tail, such that an amphiphilic molecule is formed. The Base group is common purine and pyrimidine bases, and R group is saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbon chain. In a water-phase solvent, the dideoxynucleotide phospholipid molecule can form a plurality of supramolecular structures including multi-layer film structure, lipid structure, fibrous structure, and hydrogel. Therefore, 5'-amino-2',5'-dideoxynucleotide phospholipid molecules have certain potential to be used as aggregation, trapping, loading, or carrying type nucleic acid medicines, and can be used as a high-efficiency biological material for mediating transmembrane of nucleic acid medicines.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Recombinant bacteria for producing glycerol and glycerol-derived products from sucrose
Recombinant bacteria capable of producing glycerol and glycerol-derived products from sucrose are described. The recombinant bacteria comprise in their genome or on at least one recombinant construct: a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide having sucrose transporter activity; a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide having fructokinase activity; and a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide having sucrose hydrolase activity. These nucleotide sequences are each operably linked to the same or a different promoter. These recombinant bacteria are capable of metabolizing sucrose to produce glycerol and / or glycerol-derived products such as 1,3-propanediol and 3-hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Application of gluconobacter oxydans in preparing 1,3-dioxyacetone
InactiveCN101948878AStrong dehydrogenation reaction abilityEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses application of gluconobacter oxydans in preparing 1,3-dioxyacetone. The gluconobacter oxydans is named gluconobacter oxydans NH-10, and preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the number of CGMCC No.2709 and the preservation data of October 14, 2008. The gluconobacter oxydans NH-10 can convert glycerol in high efficiency under a condition of high concentration glycerol to produce the 1,3-dioxyacetone. Under the technical condition of the application, the conversion rate of the glycerol can reach 99.7 percent (w / w), and the yield of the 1,3-dioxyacetone can reach 97 percent, the concentration of the 1,3-dioxyacetone in the conversion solution reaches 166.2g / L, and other components are scarcely contained in the conversion solution. The microorganism strain is applicable to industrial production of dioxyacetone.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveCN103898034AWide variety of sourcesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
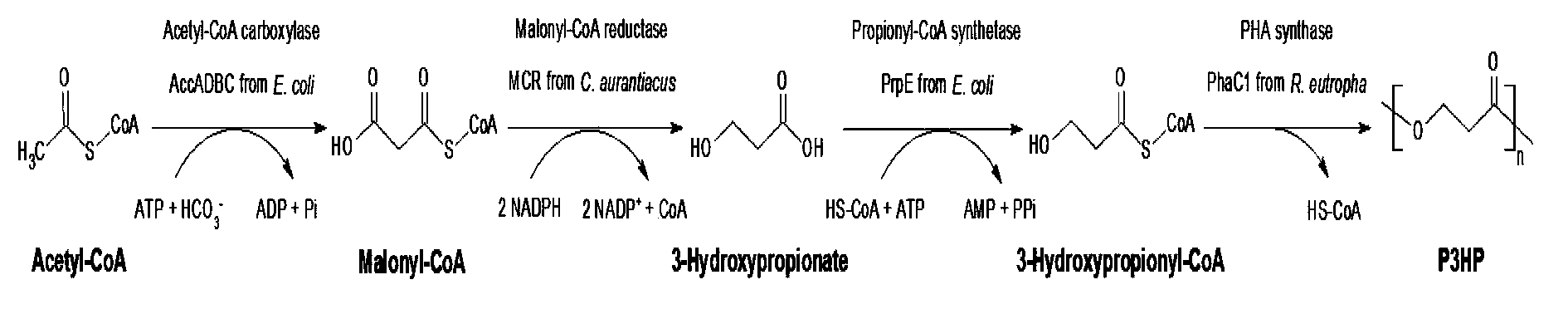
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli strain, a preparation method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain and a method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid from acetyl coenzyme A. The method comprises the following steps: with glucose or glycerin and the like as carbon sources, commonly over-expressing endogenous or exogenous acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase genes (acc) and propionyl coenzyme A synthetase genes (prpE) as well as exogenous malony coenzyme A reductase genes (mcr) and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase genes (phaC) in proper host cells (such as escherichia coli), and degrading intermediate products by virtue of glucose so as to biologically synthesize the poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid, wherein acetyl coenzyme A is finally obtained from simple starting materials such as the glucose and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Whitening sunscreen cream containing marine oligosaccharides
InactiveCN106176319AImprove water retentionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSkin repairGlycerol
The invention relates to the field of daily cosmetics, in particular to whitening sunscreen cream containing marine oligosaccharides. The whitening sunscreen cream comprises raw materials in weight proportion as follows: 1%-2% of an emulsifier, 20%-40% of pure water, 5%-20% of alginate oligosaccharides, 10%-20% of olive oil, 5%-10% of glycerin, 10%-20% of butylene glycol, 5%-20% of chitosan oligosaccharides, 1%-10% of chitosan, 10%-20% of collagen, 5%-10% of vitamins and 0.5%-1% of an antibacterial agent. According to the whitening sunscreen cream, hydroxyl groups, amino groups and other polar groups in all molecules of the chitosan oligosaccharides and the chitosan can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, and the hydrogen bonds are combined with a large amount of water; further, sugar chains of the chitosan oligosaccharides and the chitosan can be interwoven mutually to form a net, and a higher water retention function is realized; finally, by means of the antibacterial and antioxidation functions of the chitosan oligosaccharides and the ultraviolet ray absorption function of the alginate oligosaccharides, the sunscreen and skin repair functions can be realized effectively.
Owner:QINGDAO BZ OLIGO BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com