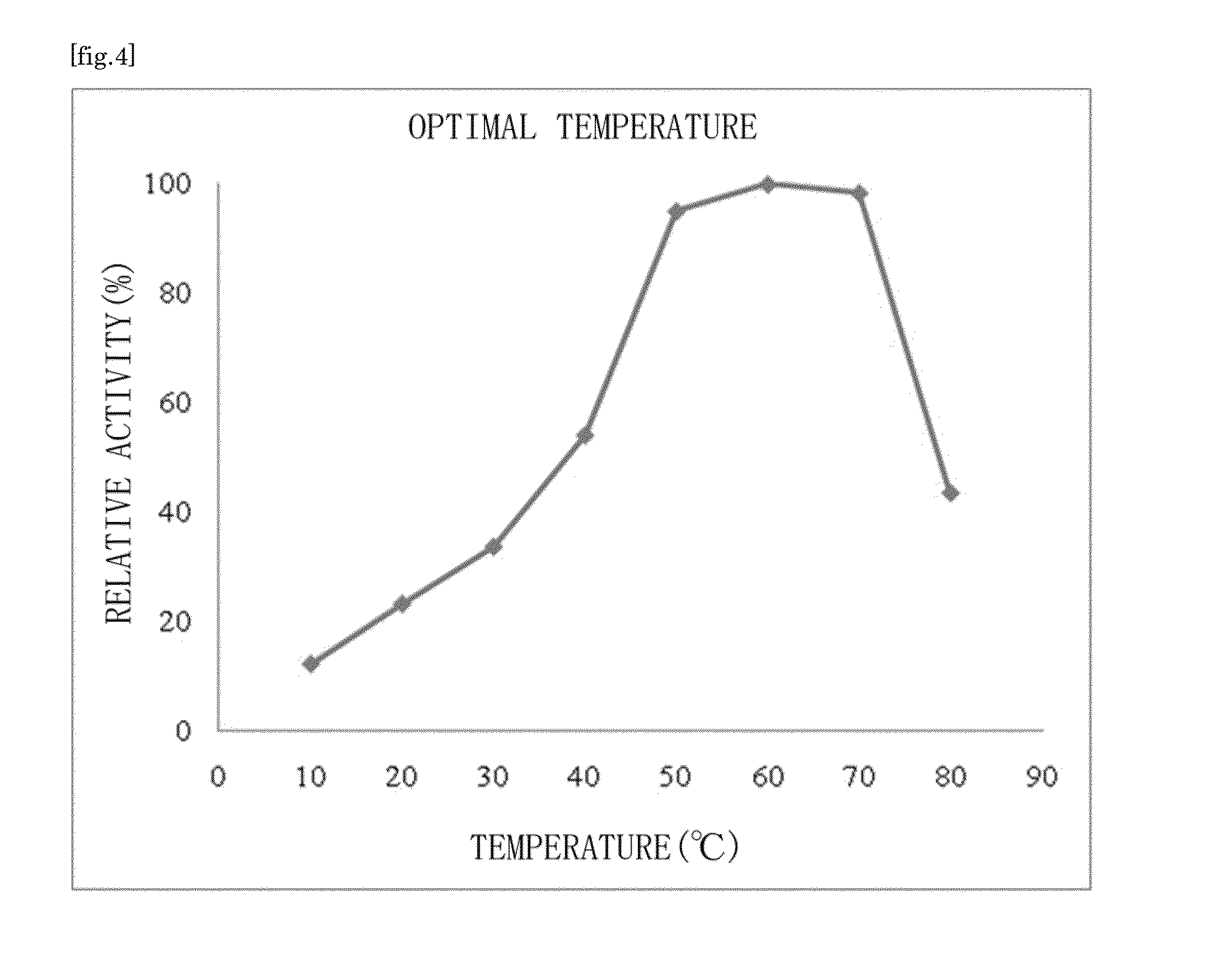
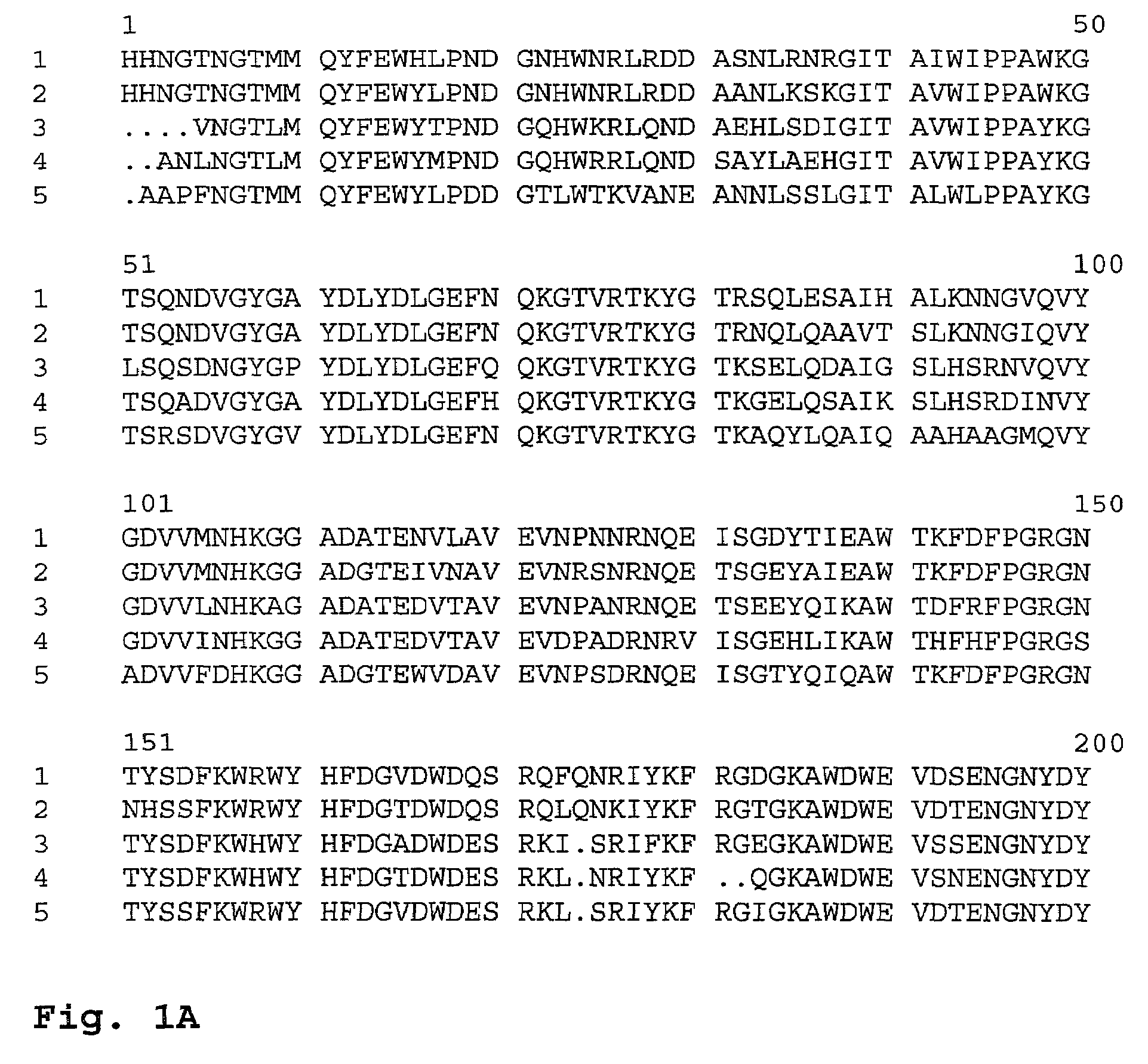
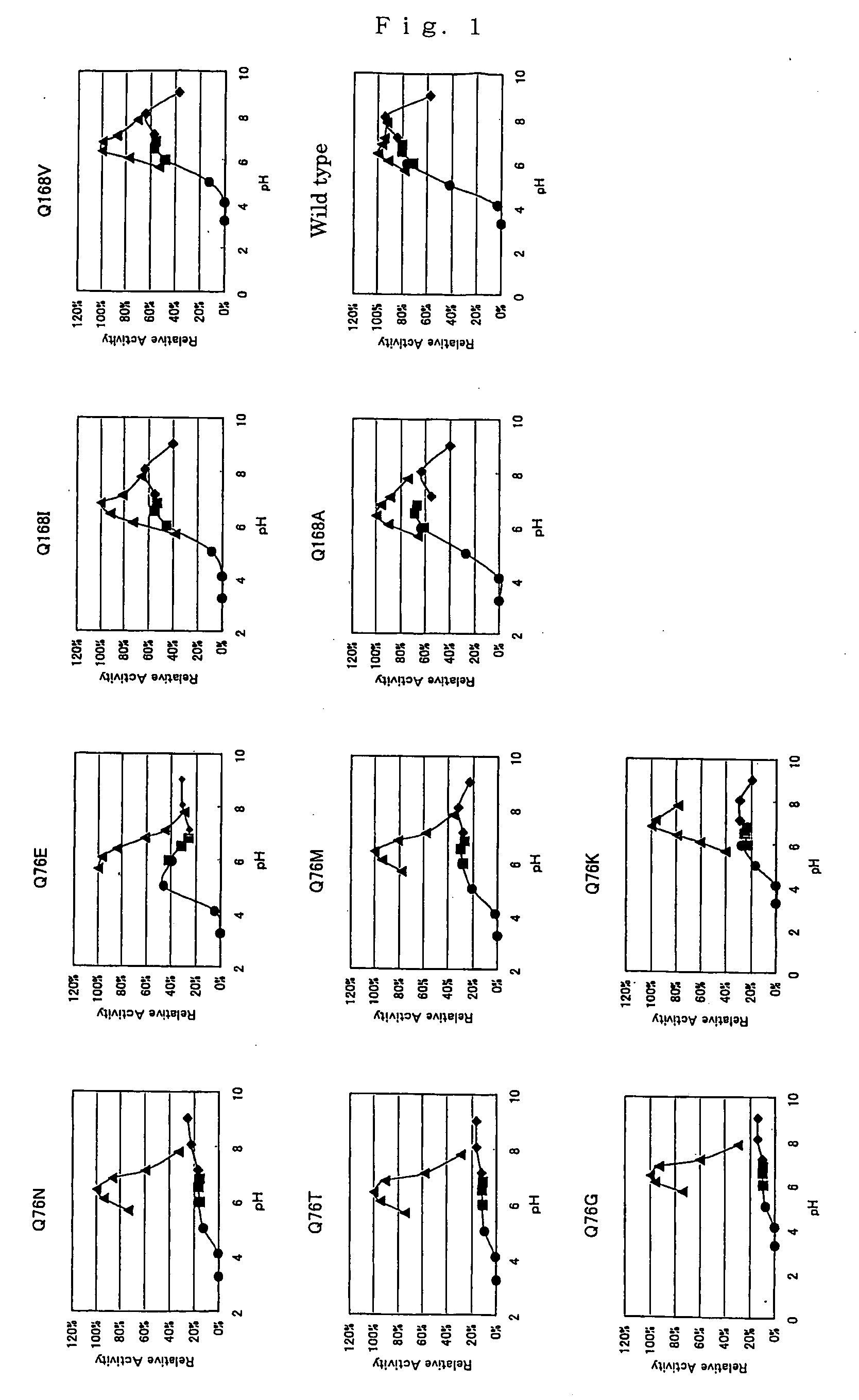
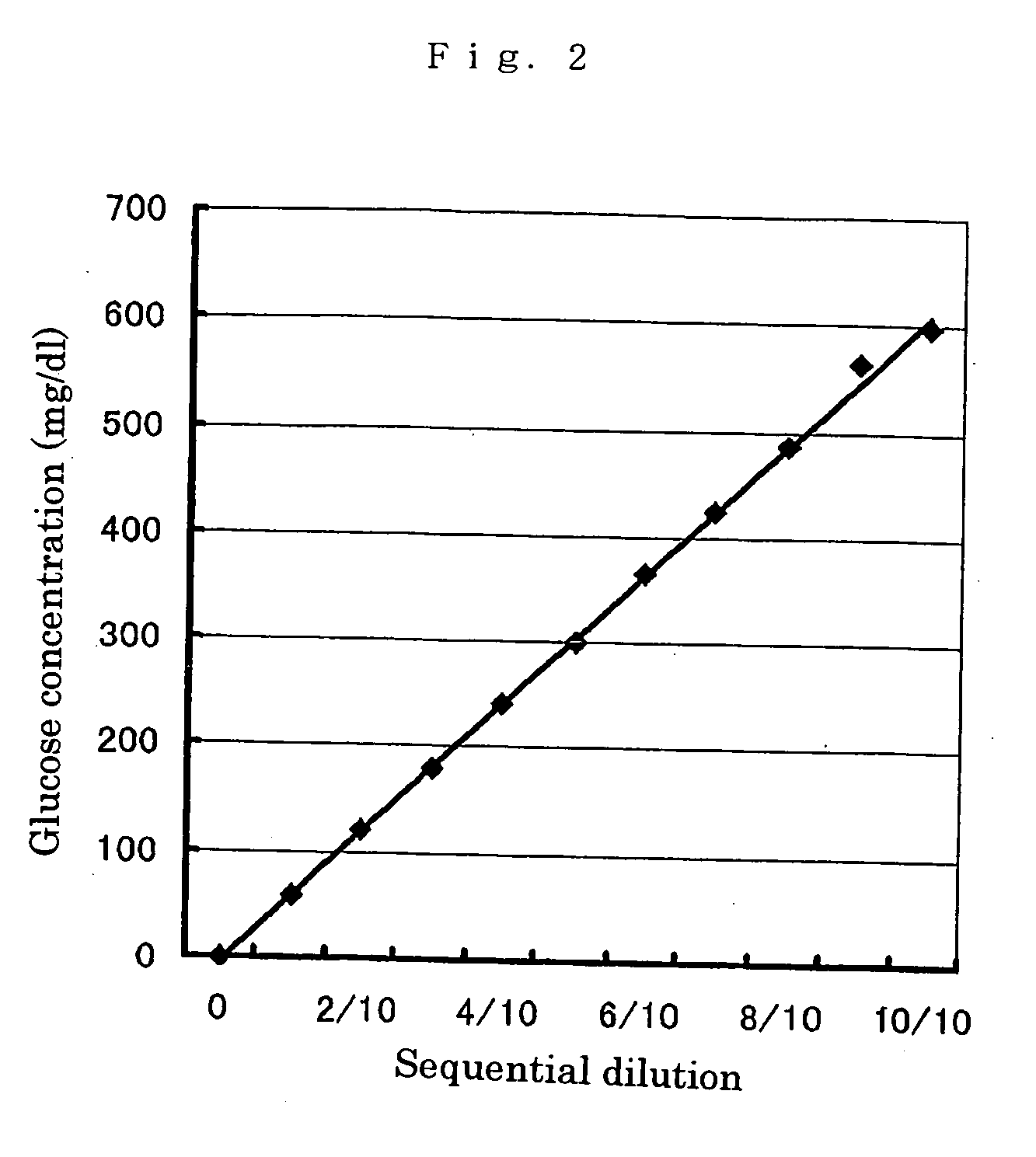
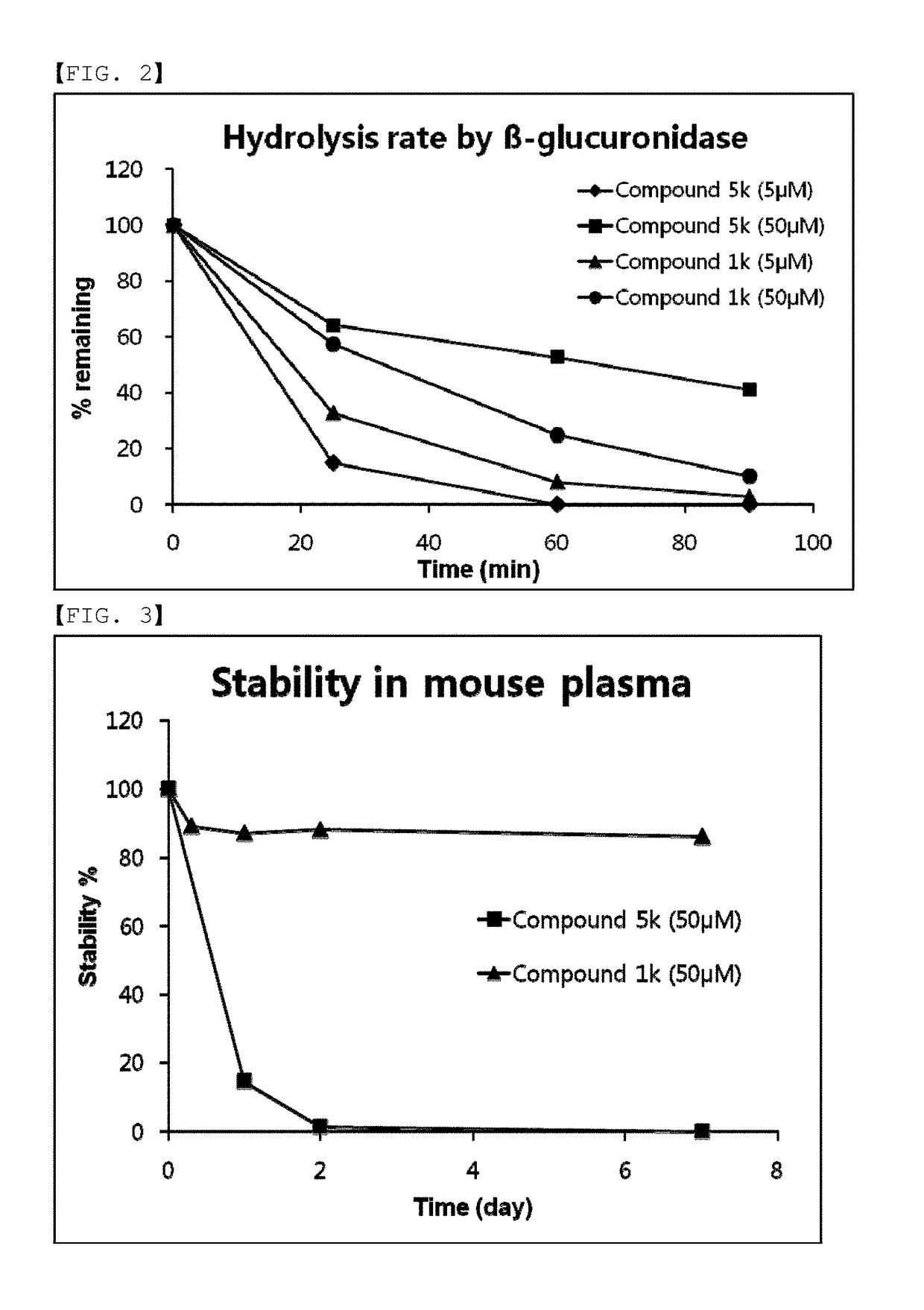
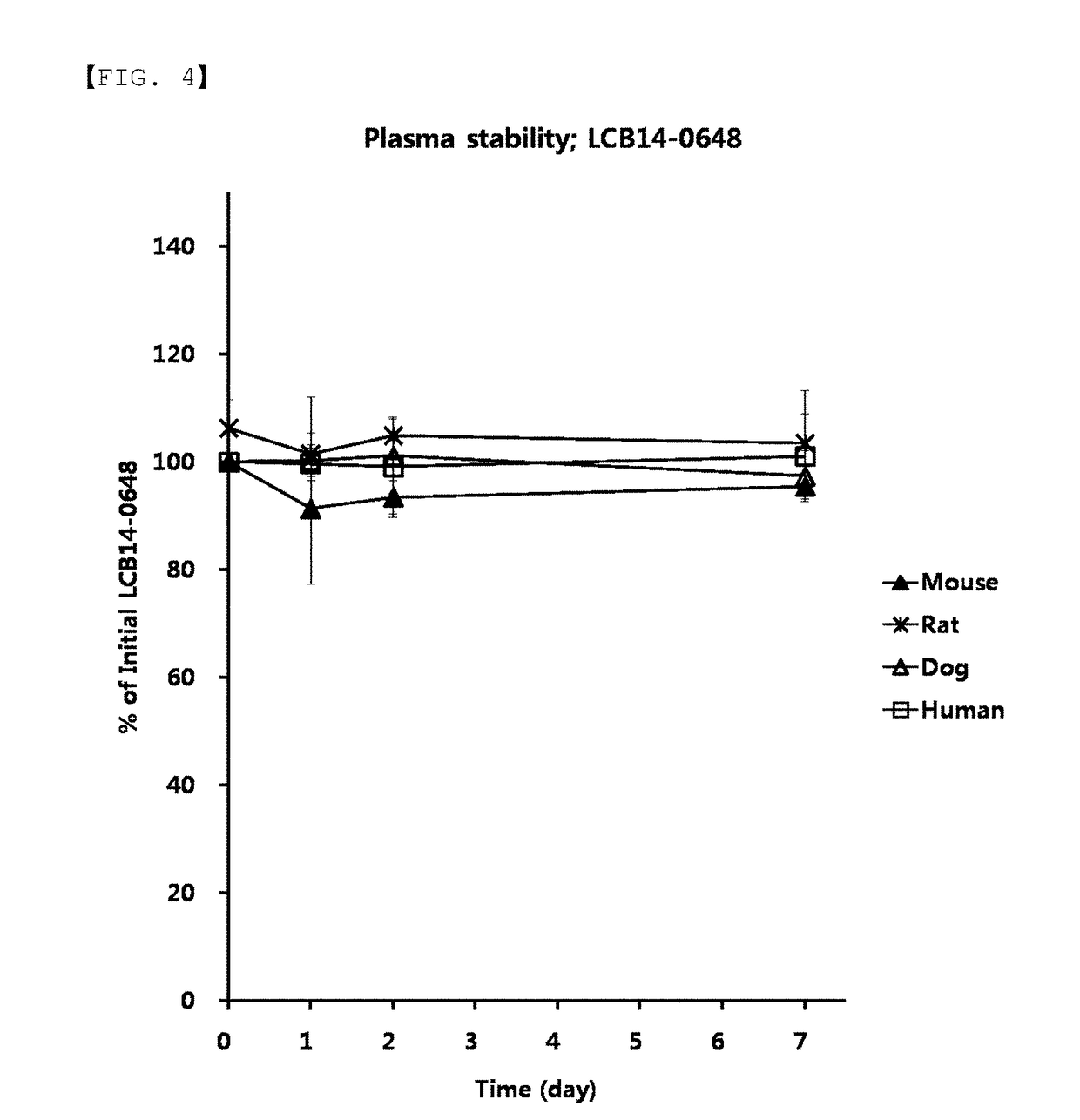
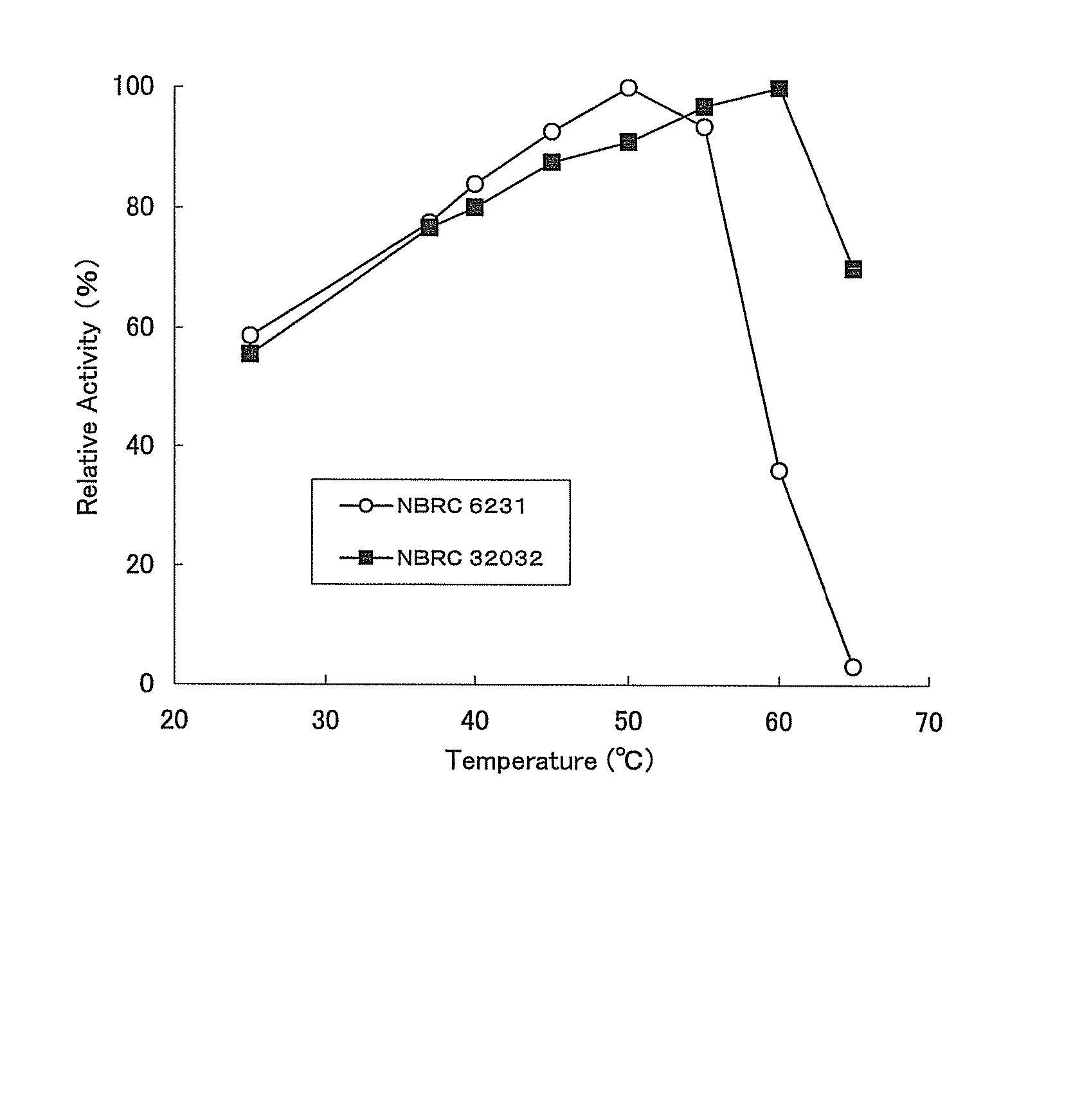
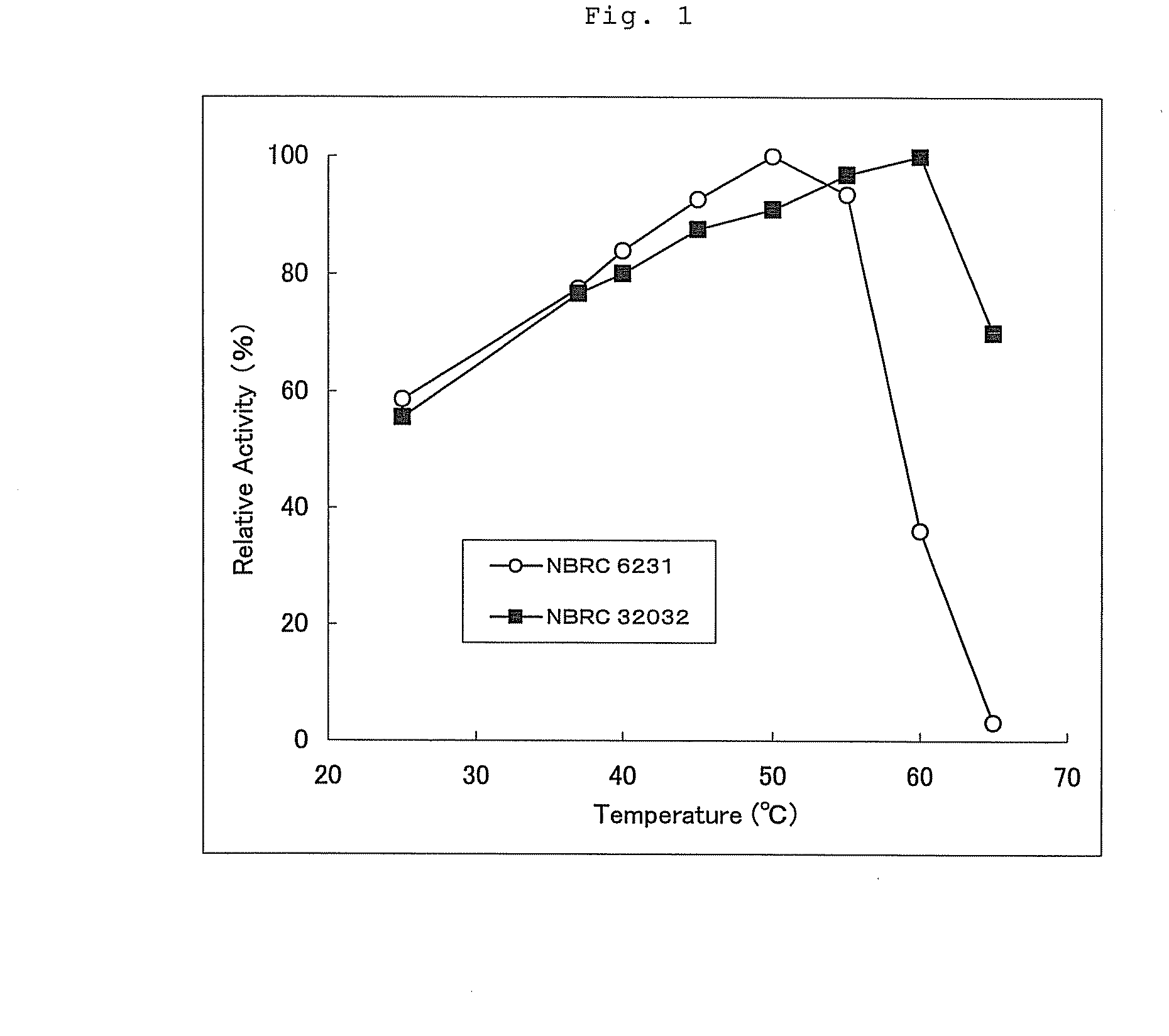
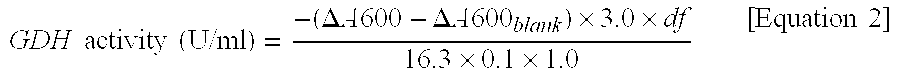Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
376 results about "Substrate specificity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
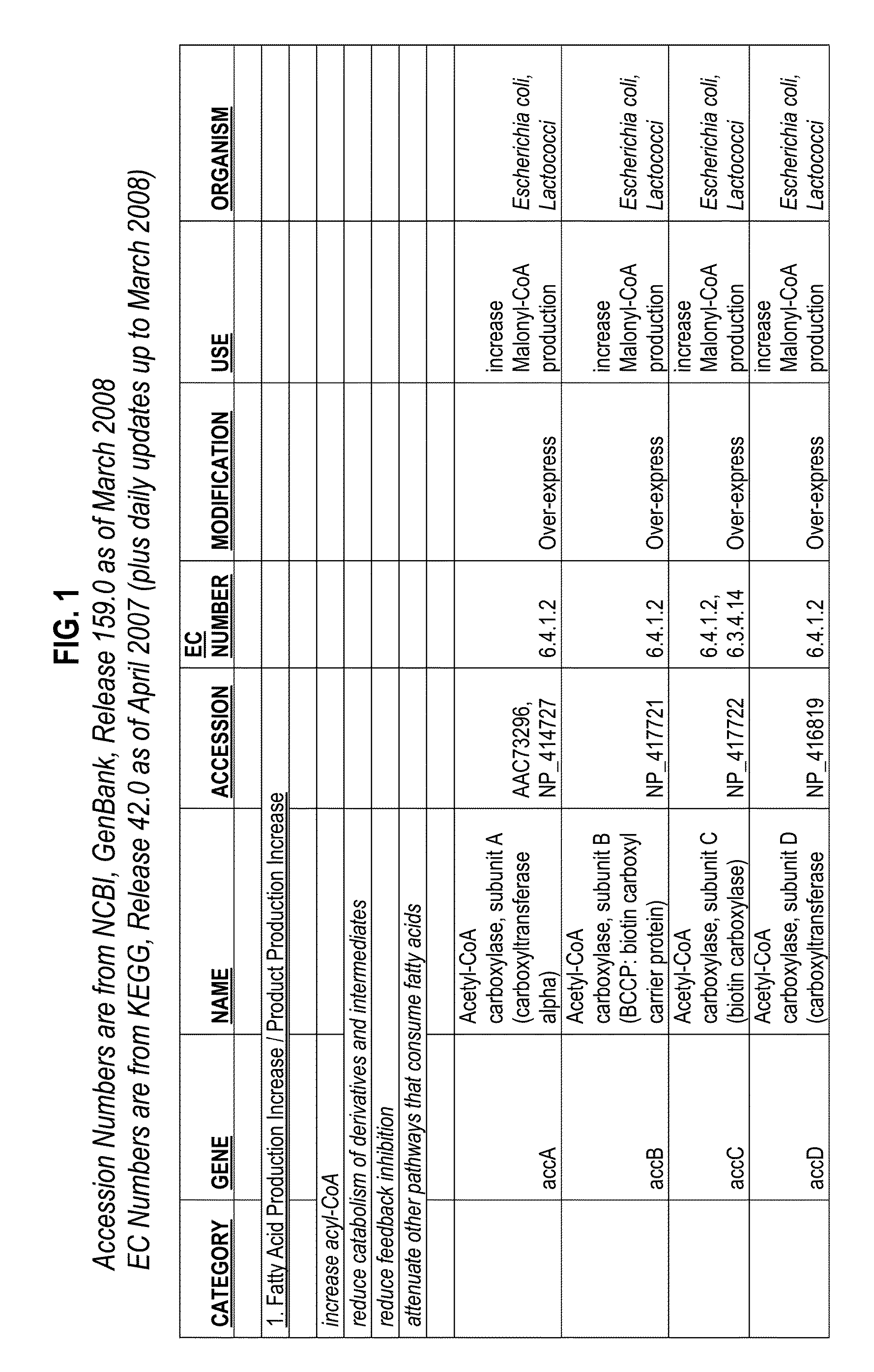
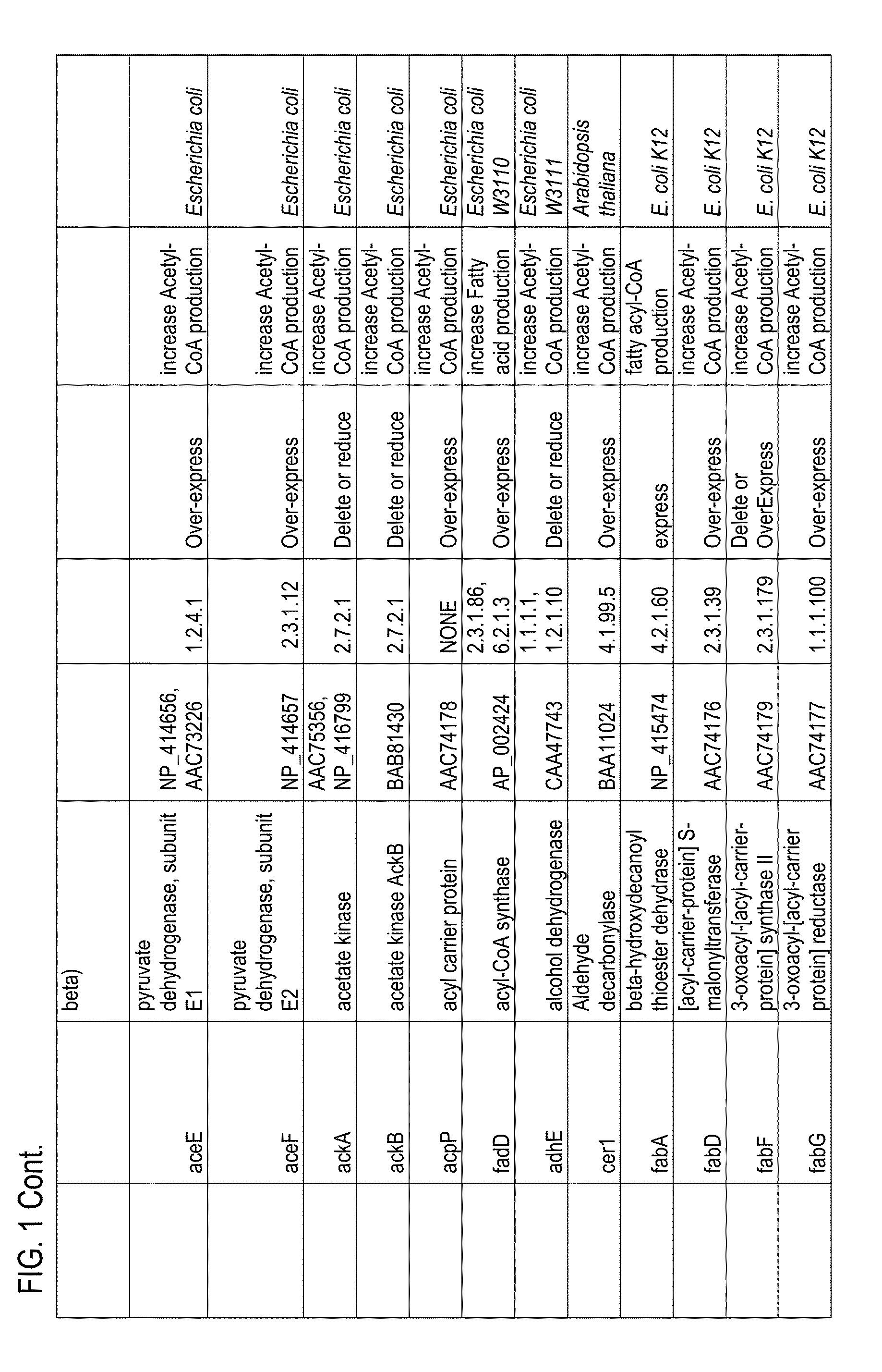
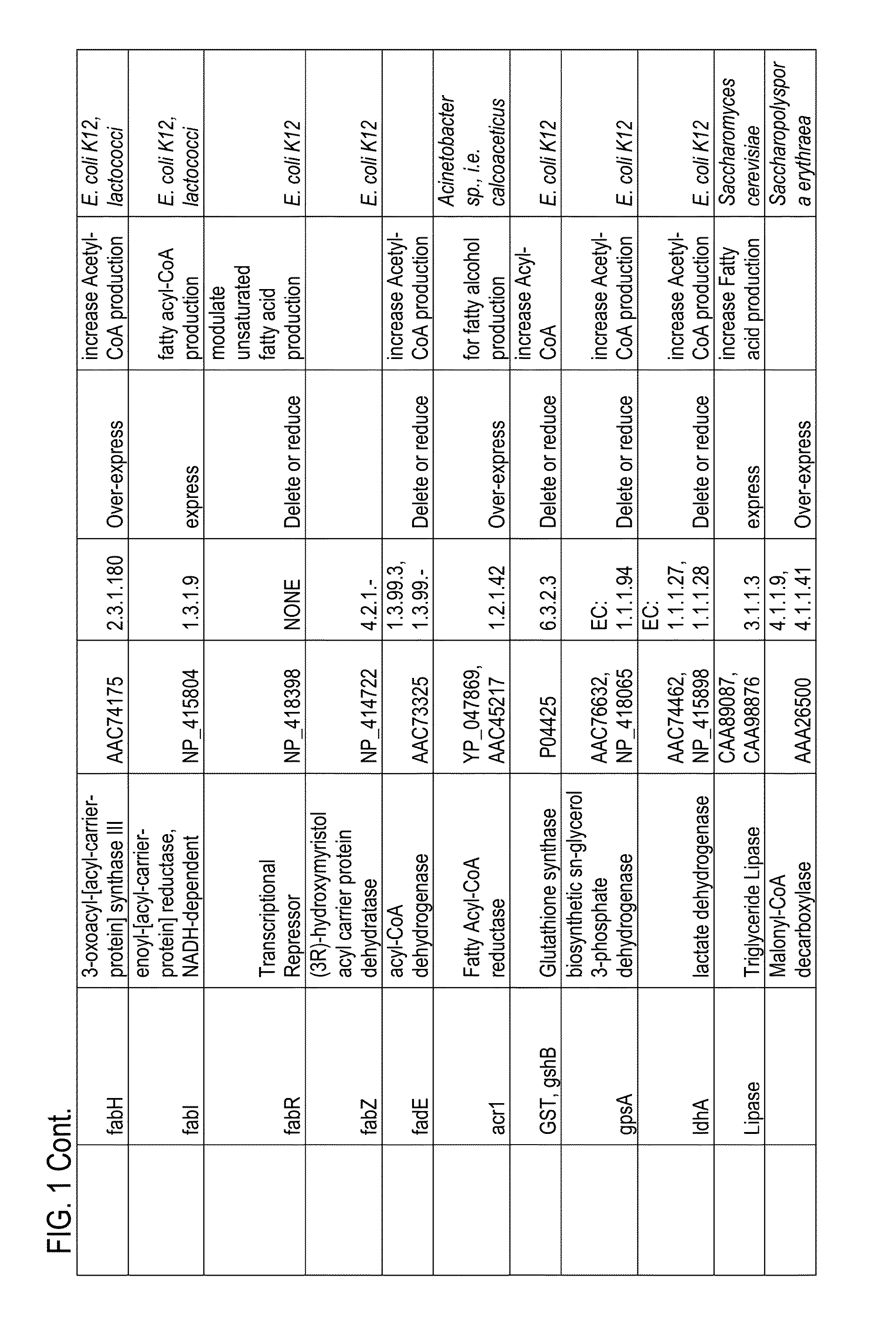
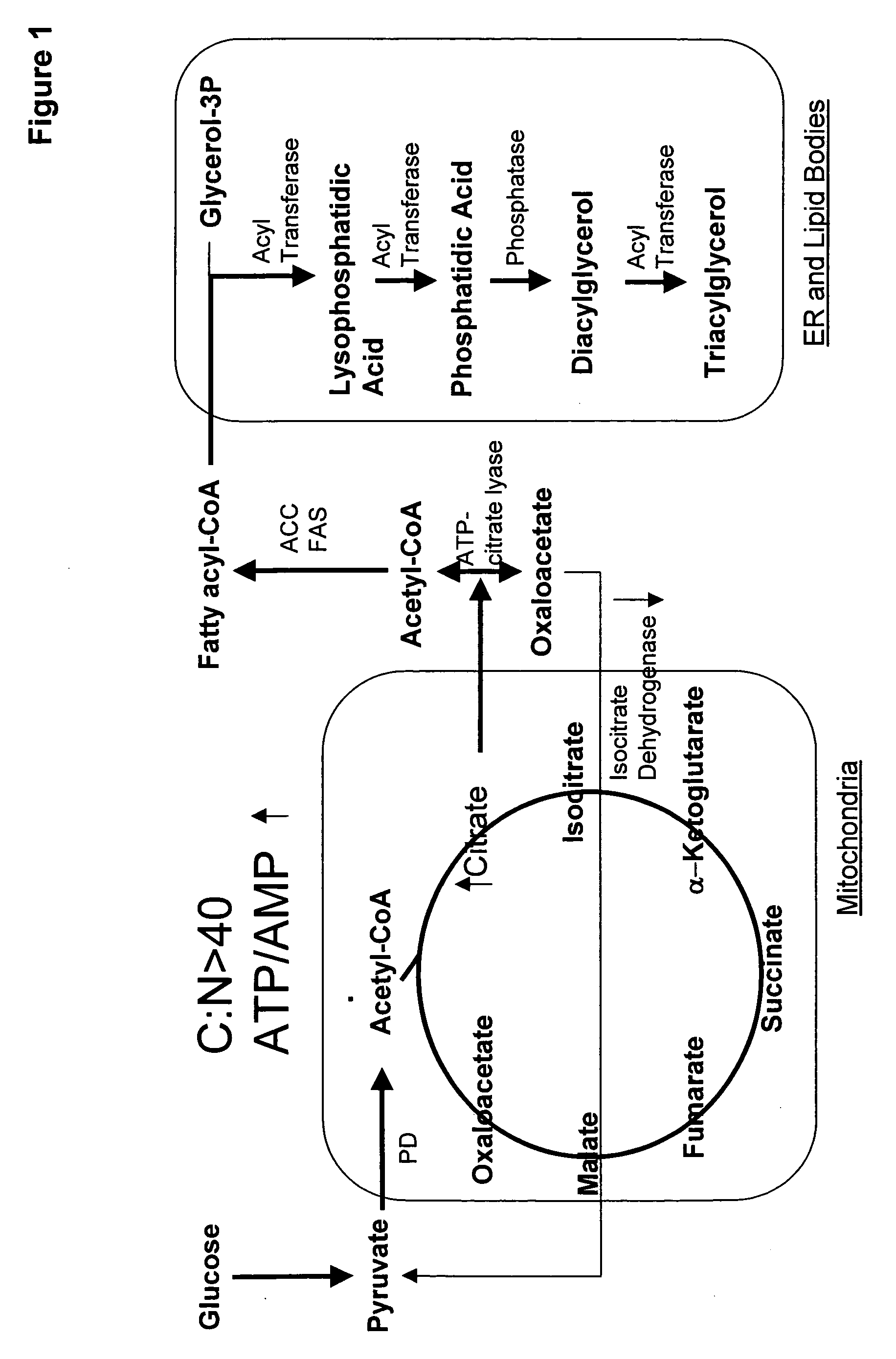
Substrate specificity. In an enzyme activity, the substrate must bind with the enzyme to become a catalyst of a chemical reaction. And most enzymes are highly specific particularly to the nature of the substrate they bind to. Substrate specificity is one of the most essential distinctive features of enzymes.
Methods and compositions related to thioesterase enzymes
ActiveUS20100154293A1Improved fuel characteristicGood suitSugar derivativesHydrolasesNucleotidePolynucleotide
The present invention relates to novel mutant thioesterase enzymes and naturally-occurring equivalents thereof, compositions made from such enzymes and uses of thioesterase enzymes. In particular, the present invention provides mutant thioesterase enzymes that have altered properties, for example, altered substrate specificity, altered activity, altered selectivity, and / or altered proportional yields in the product mixtures. The present invention also provides polynucleotides encoding such mutant thioesterase enzymes, and vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotides. The invention further provides for novel uses of thioesterases in the production of various fatty acid derivatives, which are useful as, or as components of, industrial chemicals and fuels.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
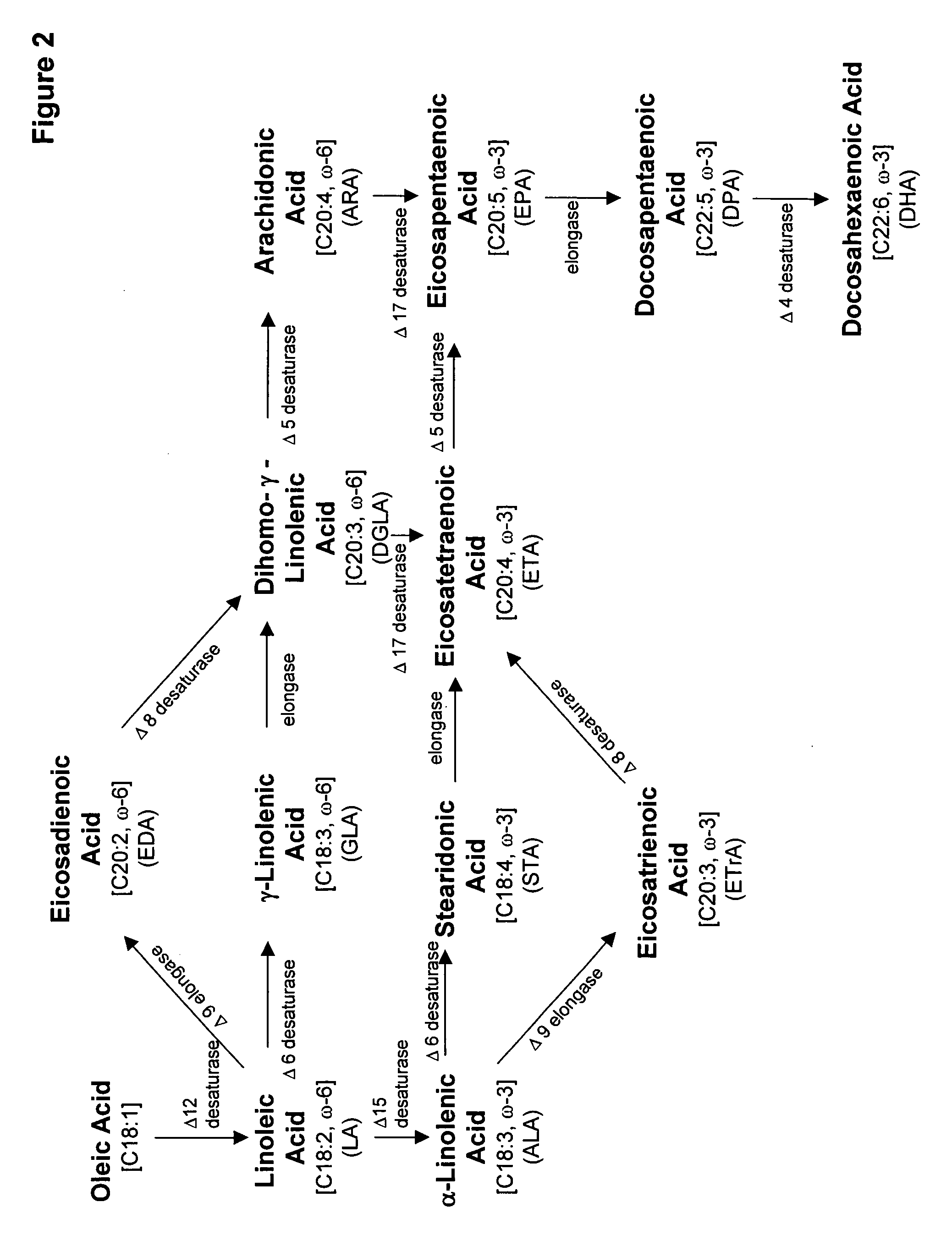
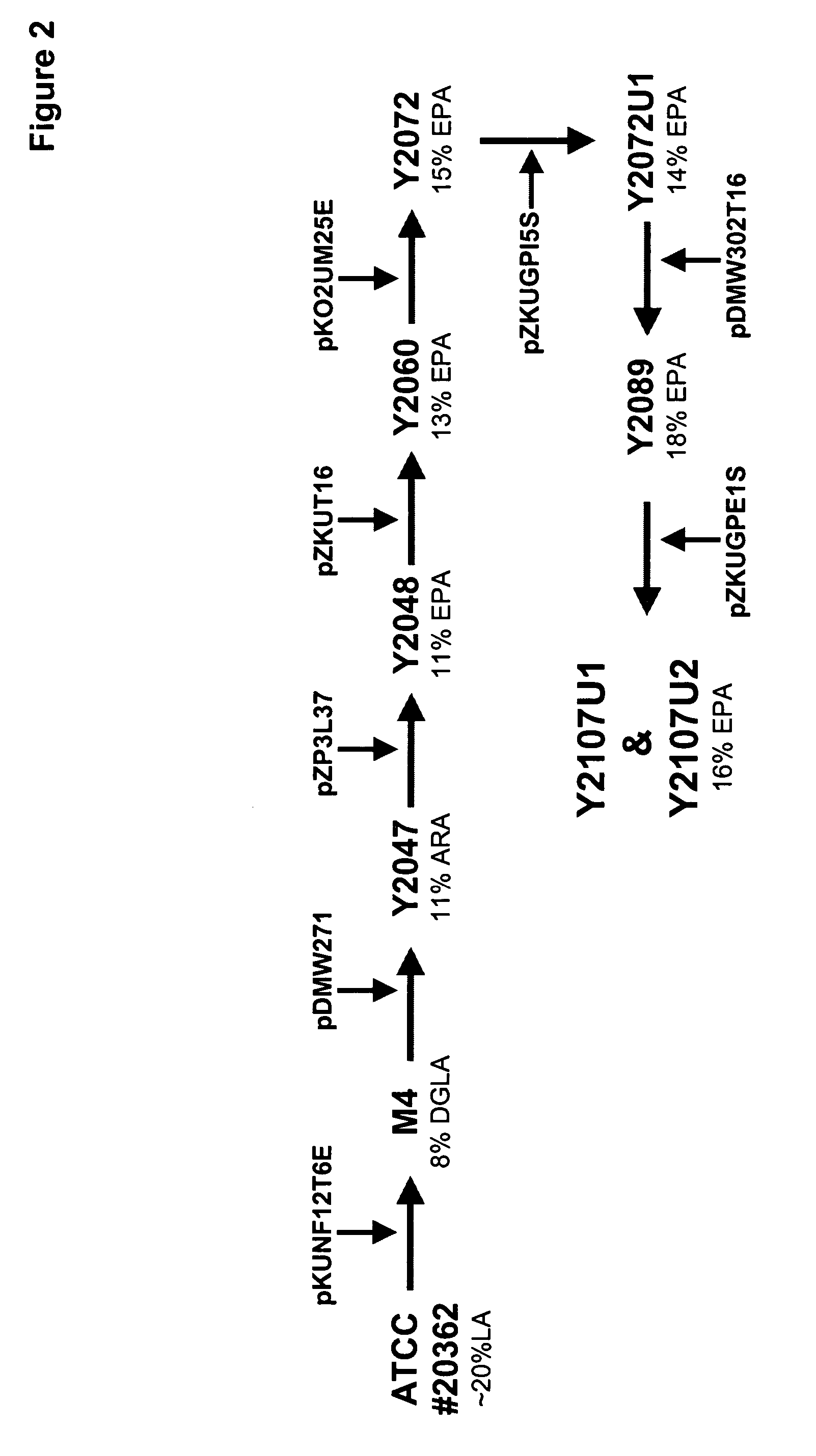
Mortierella alpina diacylglycerol acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
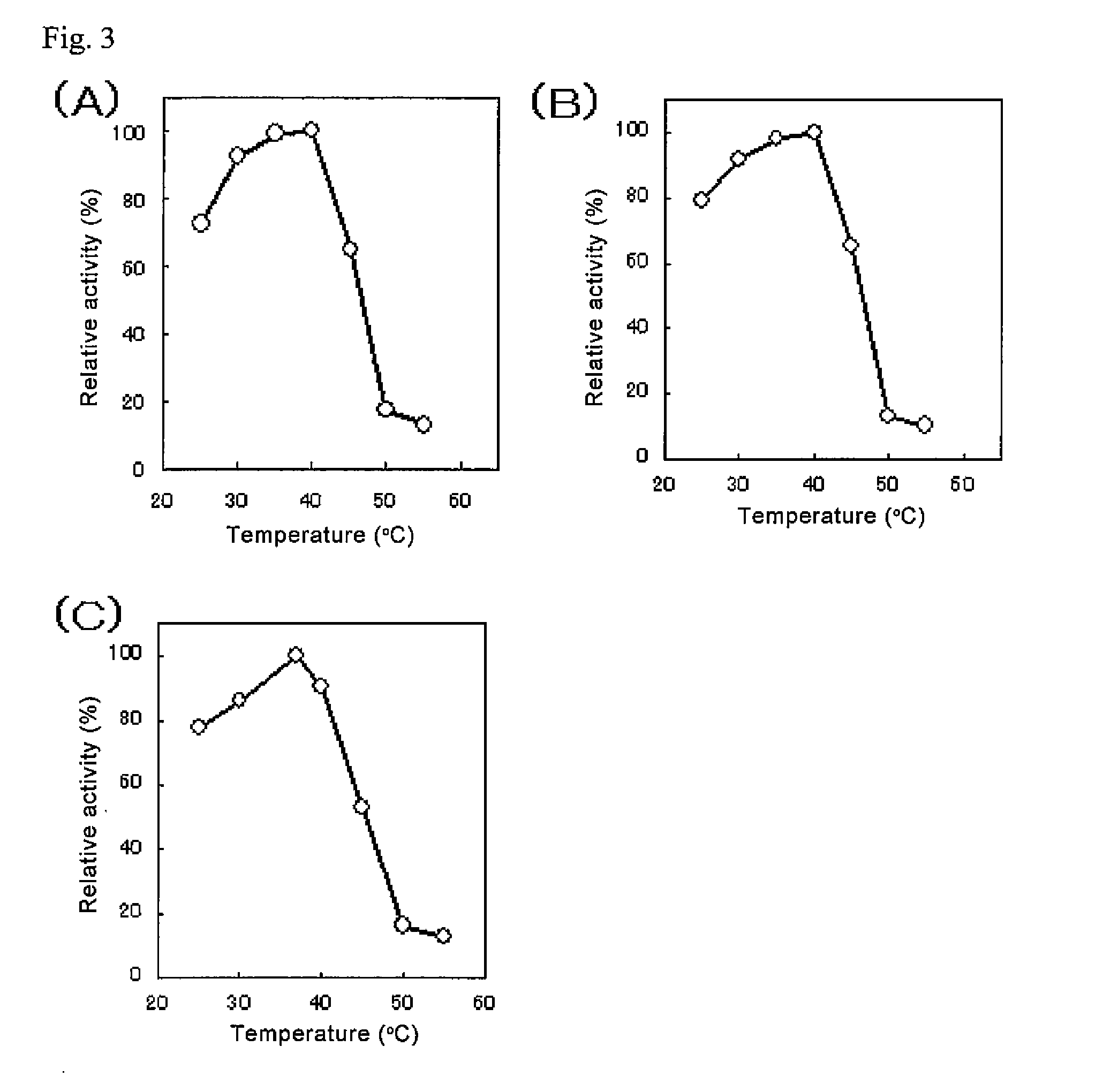
An acyltransferase is provided, suitable for use in the manufacture of microbial oils enriched in omega fatty acids in oleaginous organisms. Specifically, the gene encoding diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT2) has been isolated from Mortierella alpina. This gene encodes an enzyme that participates in the terminal step in oil biosynthesis in fungi and yeast and is expected to play a key role in altering the quantity of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids produced in oils of oleaginous organisms. Most desirably, the substrate specificity of the instant DGAT2 will be particularly useful to enable accumulation of long-chain PUFAs having chain lengths equal to or greater than C20 in oleaginous yeast, such as Yarrowia lipolytica.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Polypeptide having activity of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and use thereof
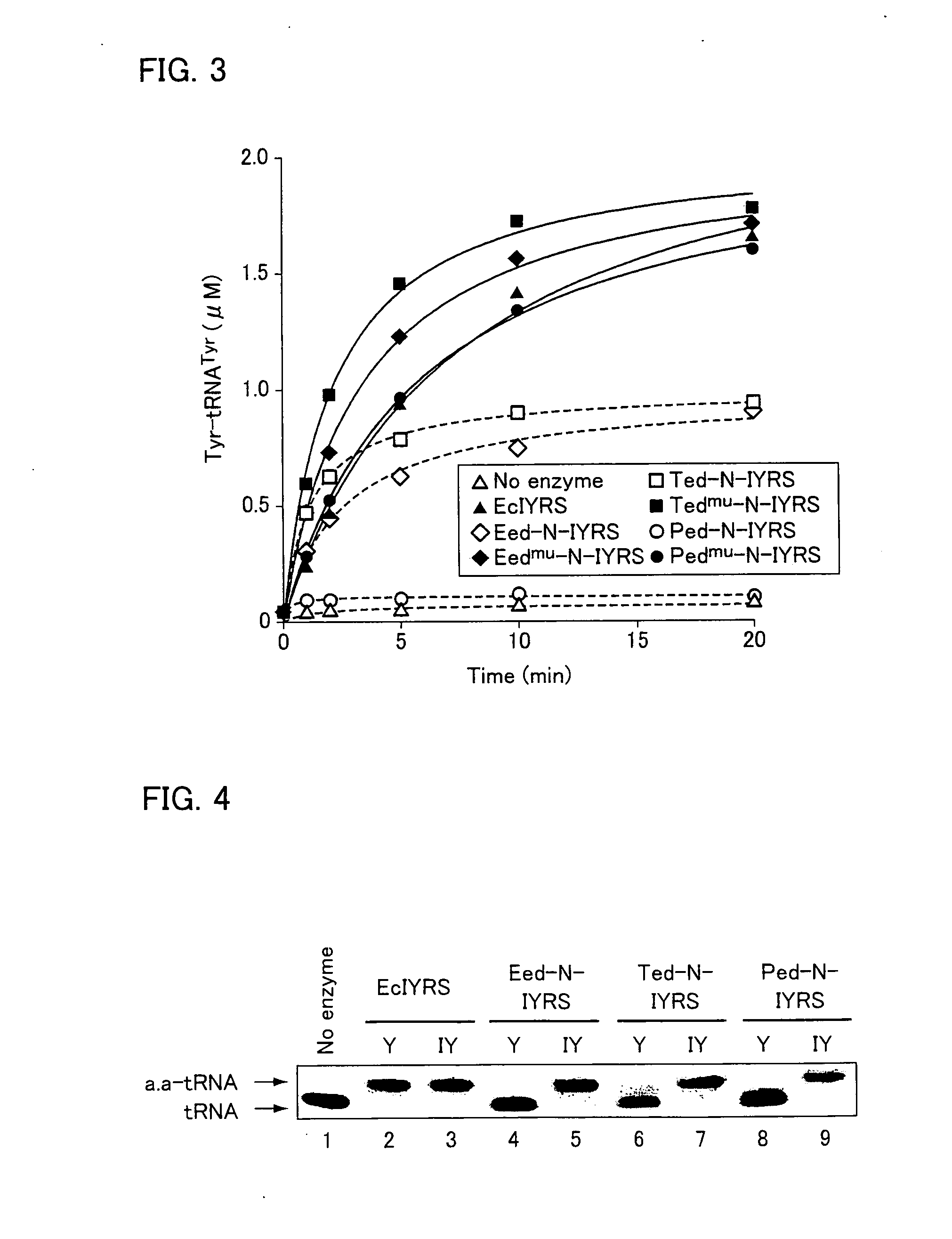
A polypeptide according to the present invention includes: an altered polypeptide obtained by altering an ArgRS, a CysRS, a MetRS, a GlnRS, a GluRS, a LysRS, a TyrRS, or a TrpRS so that an unnatural amino acid is recognized; and an editing polypeptide derived from a PheRS, a LeuRS, an IleRS, a ValRS, an AlaRS, a ProRS, or a ThrRS, the editing polypeptide having been either inserted between a Rossman-fold N domain and a Rossman-fold C domain that exist in the altered polypeptide, or bound to an N terminal of the altered polypeptide. Thus provided are a new aaRS that exhibits high substrate specificity to an unnatural amino acid and a technique that involves the use of such an aaRS.
Owner:RIKEN
Mortierella alpina glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Assay tools and methods of use
InactiveUS20120129248A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalysis toolsImproved method
The present invention provides assay tools for the detection of biological or chemical activity in a sample. The assay tools of the invention provide direct detection using a positive signal generated on a surface of the assay tool. These assay tools provide improved methods for detection and / or identification of multiple agents (e.g., enzymes) in a sample, analysis of substrate specificity of such agents, and binding affinities and specificities of such agents. Upon activity a component is released from a first immobilised construct and then captured by a capture surface. At least two different immobilised constructs are used.
Owner:PROGNOSYS BIOSCI
Compositions and methods for use in targeting vascular destruction
Treatment of warm-blooded animals having a tumor or non-malignant hypervascularation, by administering a sufficient amount of a cytotoxic agent formulated into a phosphate prodrug form having substrate specificity for microvessel phosphatases, so that microvessels are destroyed preferentially over other normal tissues, because the less cytotoxic prodrug form is converted to the highly cytotoxic dephosphorylated form.
Owner:MATEON THERAPEUTICS INC
Forms of soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase
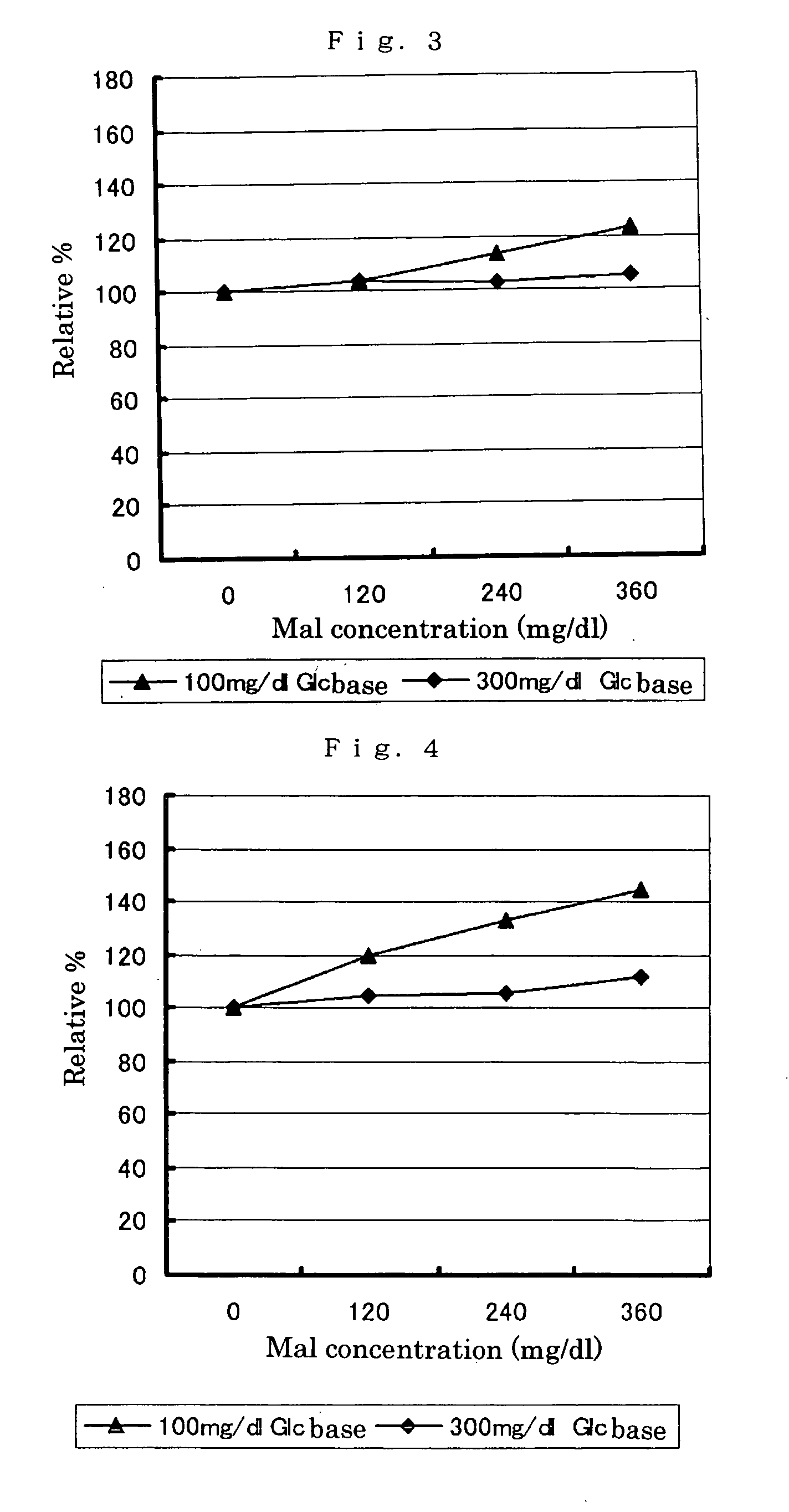
InactiveUS7132270B2Increased substrate specificityImprove propertiesFungiBacteriaMutated proteinGlucose polymers
The present invention relates to improved variants of soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ)-dependent glucose dehydrogenases (s-GDH), to genes encoding mutated s-GDH, to mutant proteins of s-GDH with improved substrate specificity for glucose, and to different applications of these s-GDH variants, particularly for determining concentrations of sugar, especially of glucose in a sample.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
E. coli transformant, method for producing flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase using the same, and mutant flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20130309750A1Accurate measurementEfficiently obtainedBacteriaOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
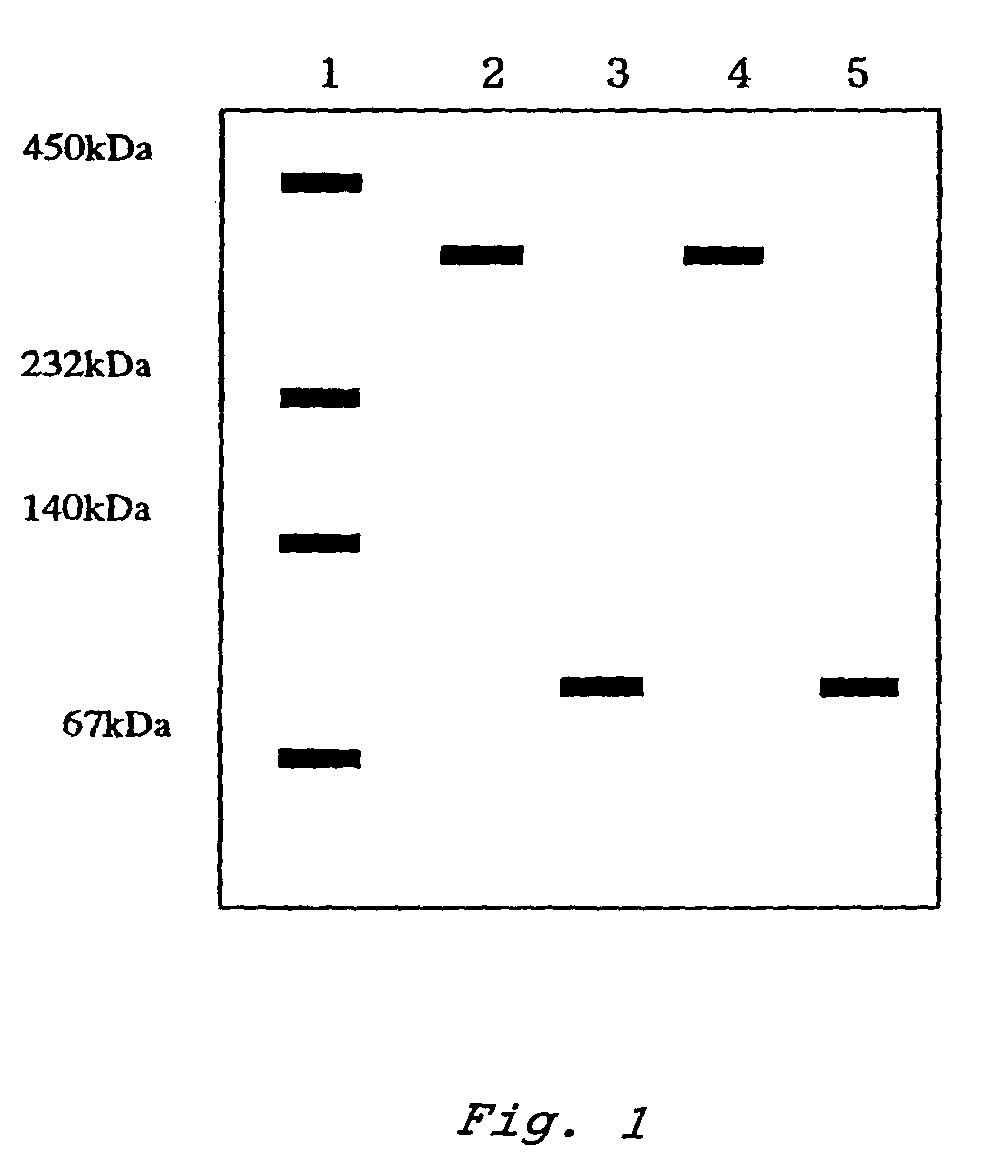
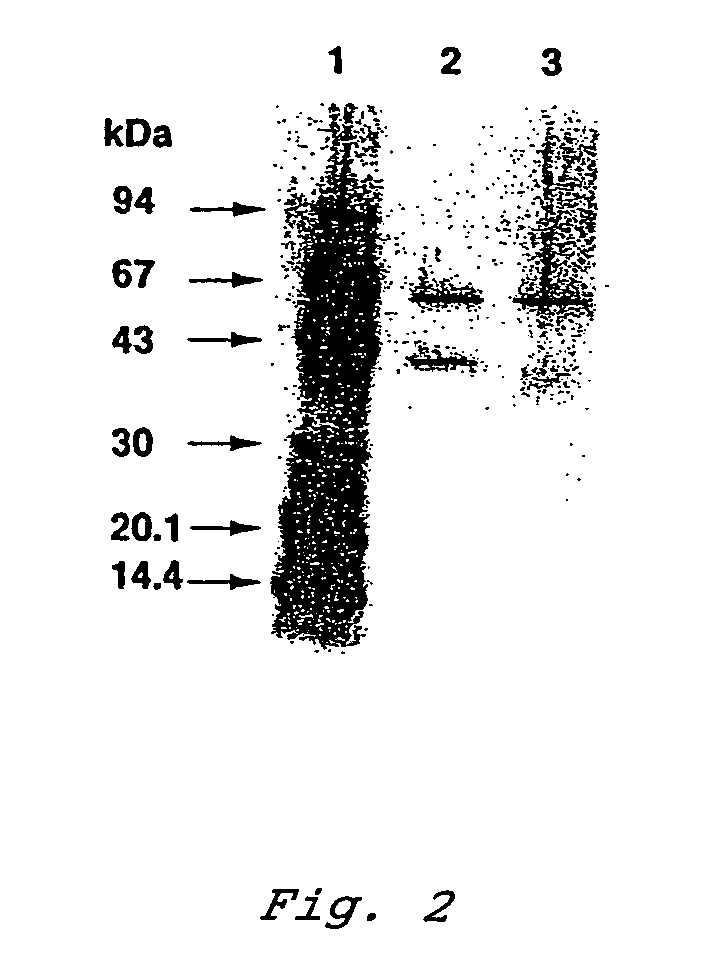
A flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH) with high substrate specificity for D-glucose. A gene encoding a mutant FAD-GDH with its N-terminal region, containing an amino acid sequence corresponding to MKITAAIITVATAFASFASA that exists in the N-terminal region, deleted from the amino acid sequence of a wild-type FAD-GDH derived from Mucor is introduced into E. coli to obtain an E. coli transformant. Subsequently, this E. coli transformant is cultured to obtain an FAD-GDH with a specific N-terminal region deleted. The transformant allows the production of a large amount of GDH in a short time as compared with the original microorganism. An FAD-GDH that is less susceptible to the effects of dissolved oxygen and allows accurate measurement of glucose even in the presence of sugar compounds other than glucose in a sample.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
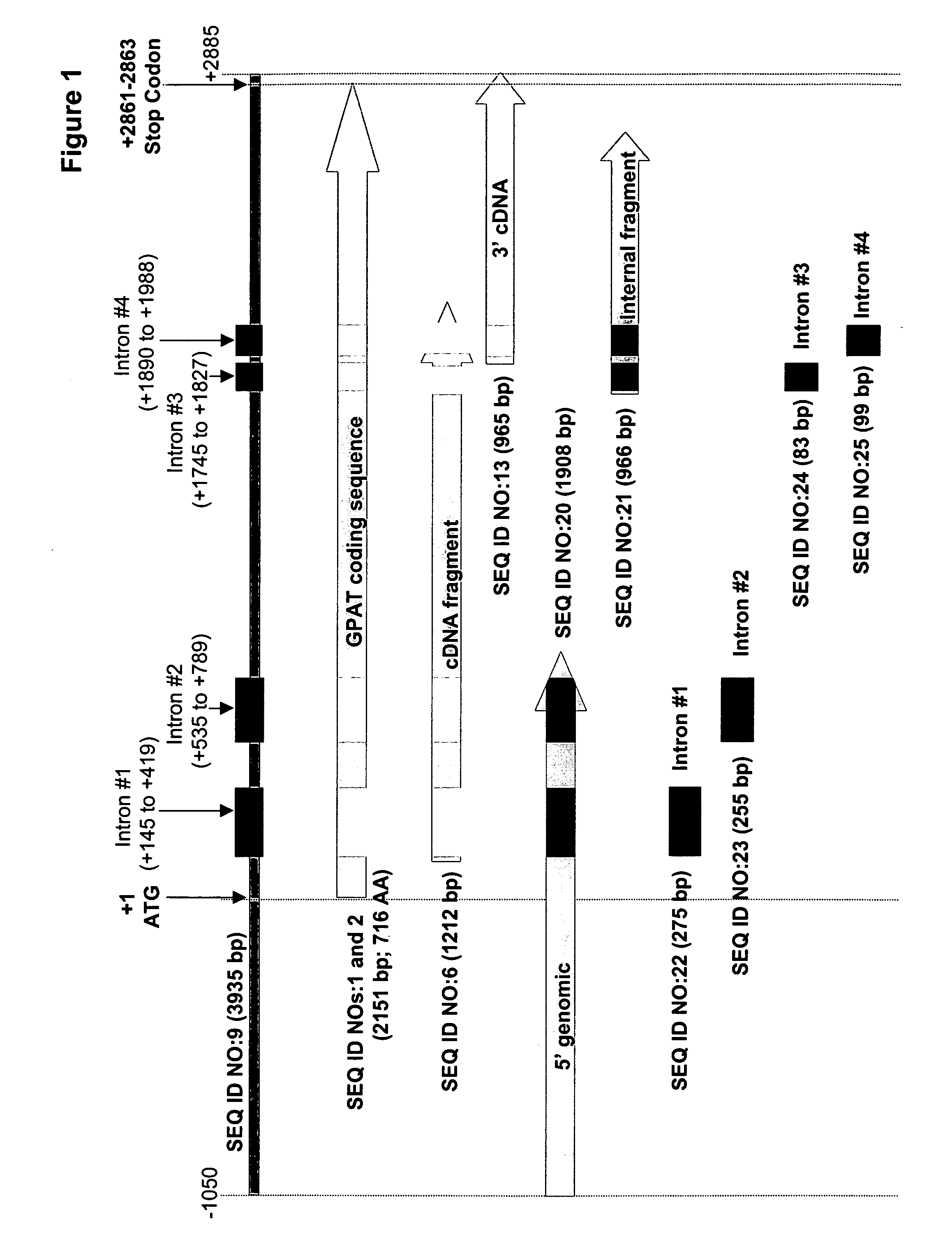
Mortierella alpina glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
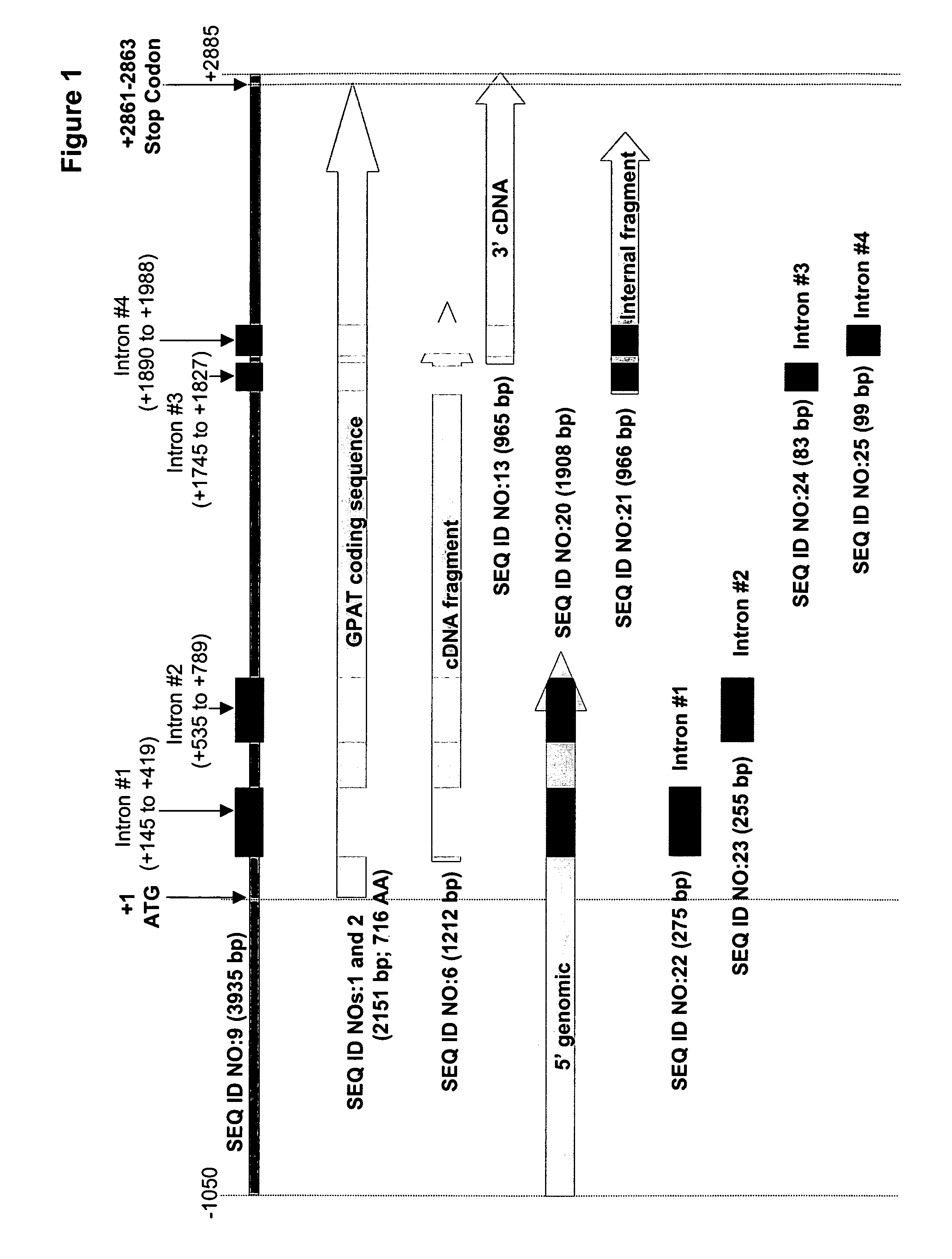
Glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase (GPAT) participates in the first step of oil biosynthesis and is expected to play a key role in altering the quantity of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) produced in oils of oleaginous organisms. The present application provides a nucleic acid fragment isolated from Mortierella alpina encoding a GPAT that is suitable for use in the manufacture of oils enriched in omega fatty acids in oleaginous organisms. Most desirably, the substrate specificity of the instant GPAT will be particularly useful to enable accumulation of long-chain PUFAs having chain lengths equal to or greater than C20 in oleaginous yeast, such as Yarrowia lipolytica.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenases, a method for producing a flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase, and yeast transformant used for the same
A heat-resistant flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase having a high substrate specificity for D-glucose, an method for producing the same, and a transformant used for the same. A flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase gene encoding a flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase derived from Mucor is introduced into yeast, Zygosaccharomyces, to obtain a transformant. Subsequently, the yeast transformant is cultured to obtain a flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase from the culture. The heat-resistant flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase is less susceptible to the effects of dissolved oxygen and allows accurate measurement of glucose even in the presence of sugar compounds other than glucose in a sample.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
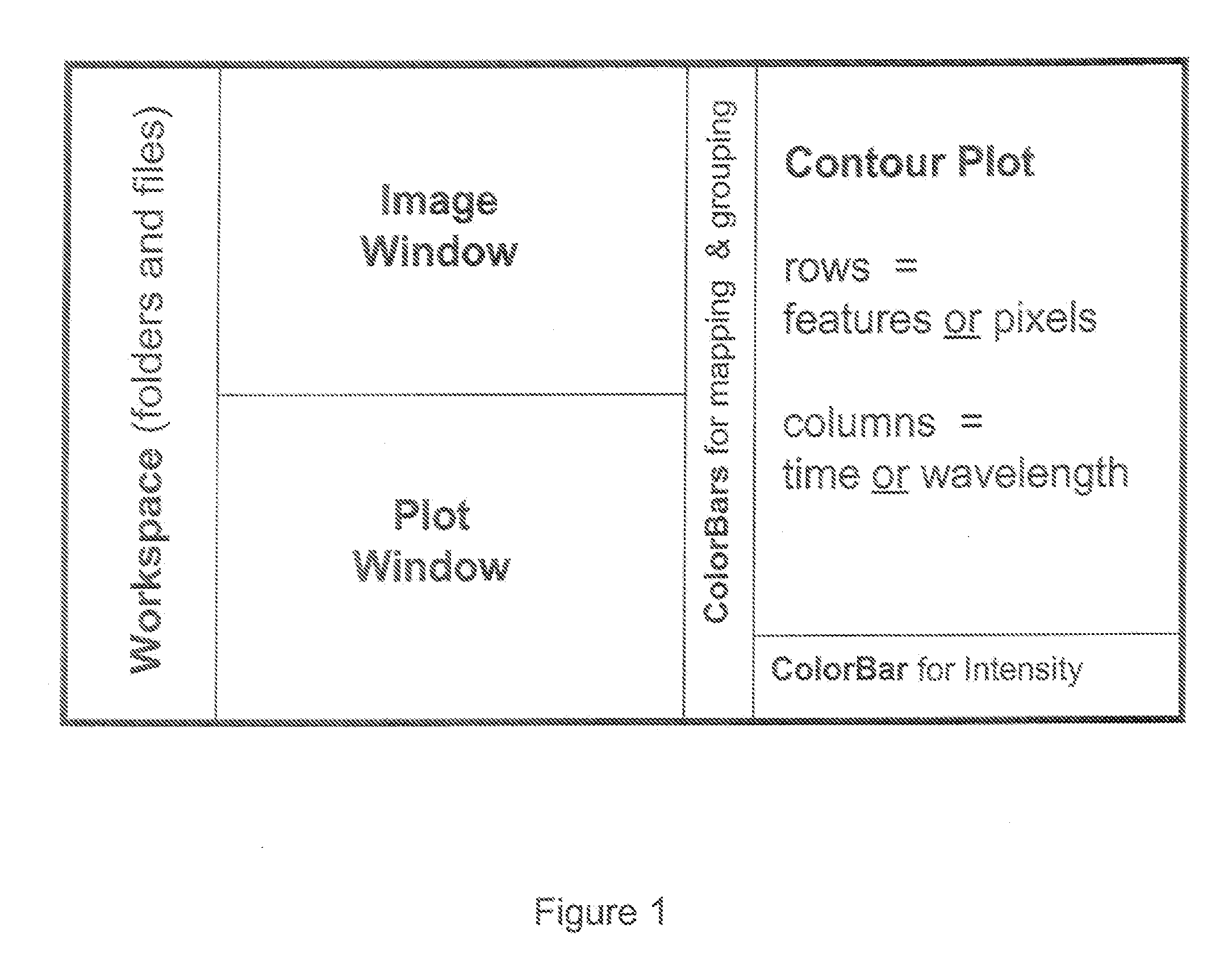
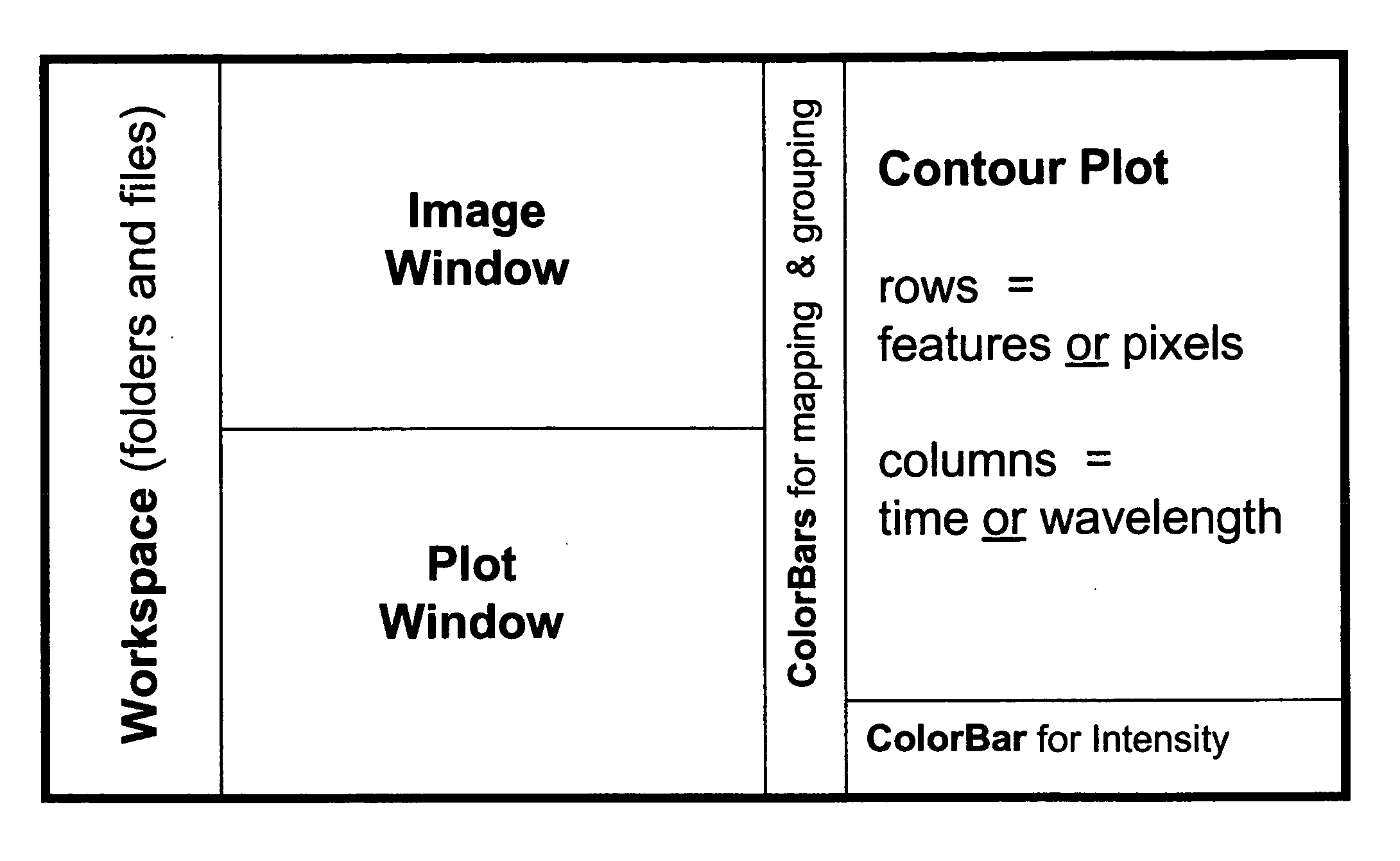
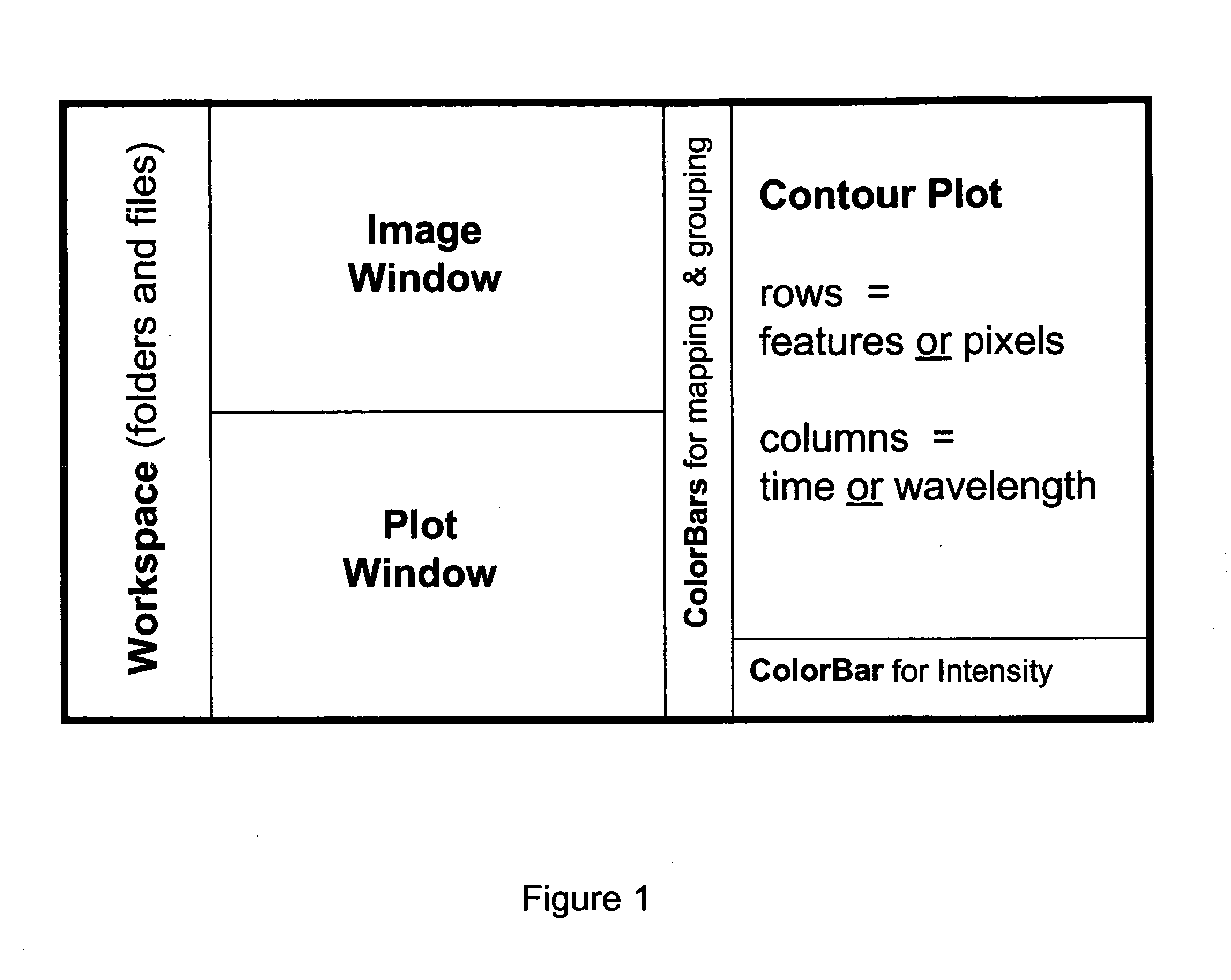
Visualization and Processing of Multidimensional Data Using Prefiltered and Sorting Criteria
InactiveUS20070217689A1Rapidly and efficiently extracting useful informationFacilitates independent sorting backcoloringImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imagingSorting algorithm
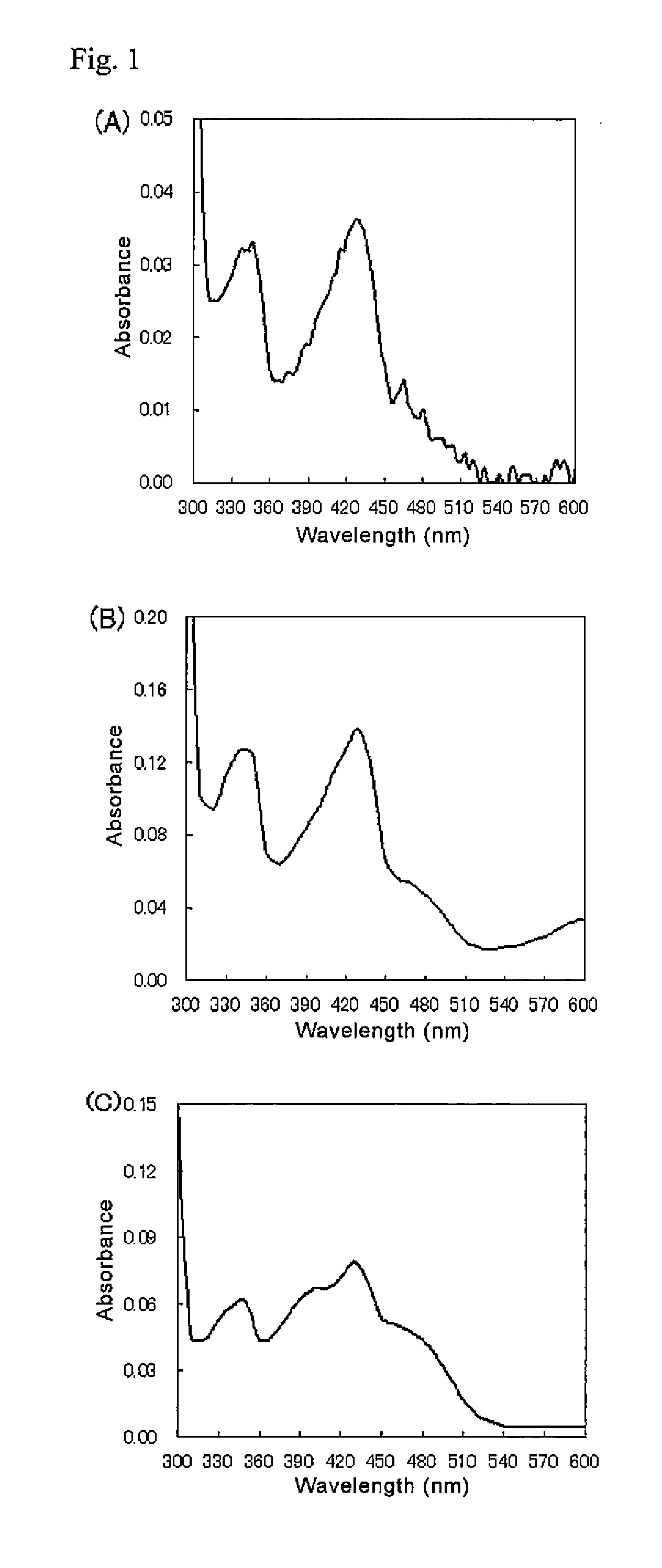
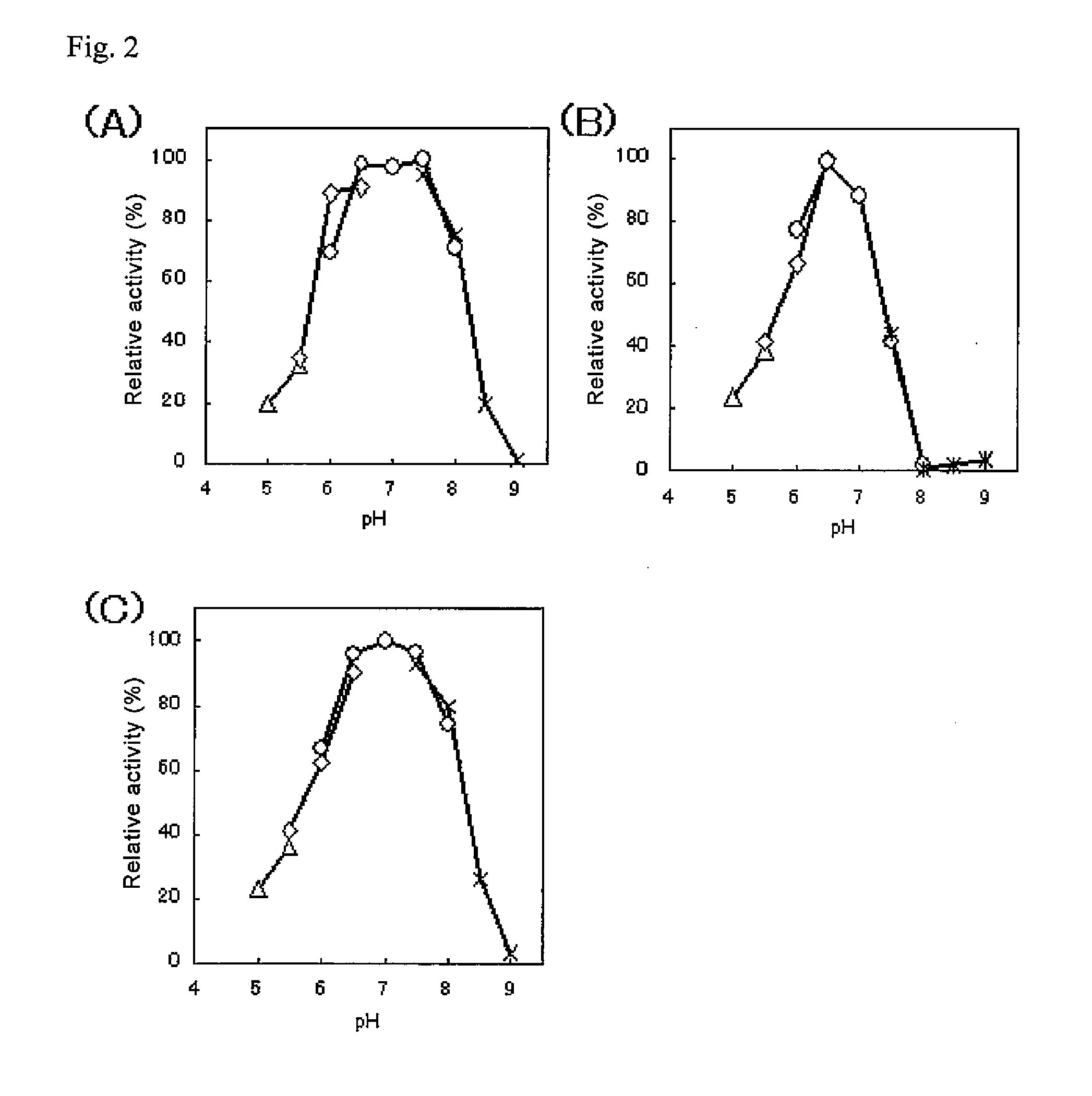
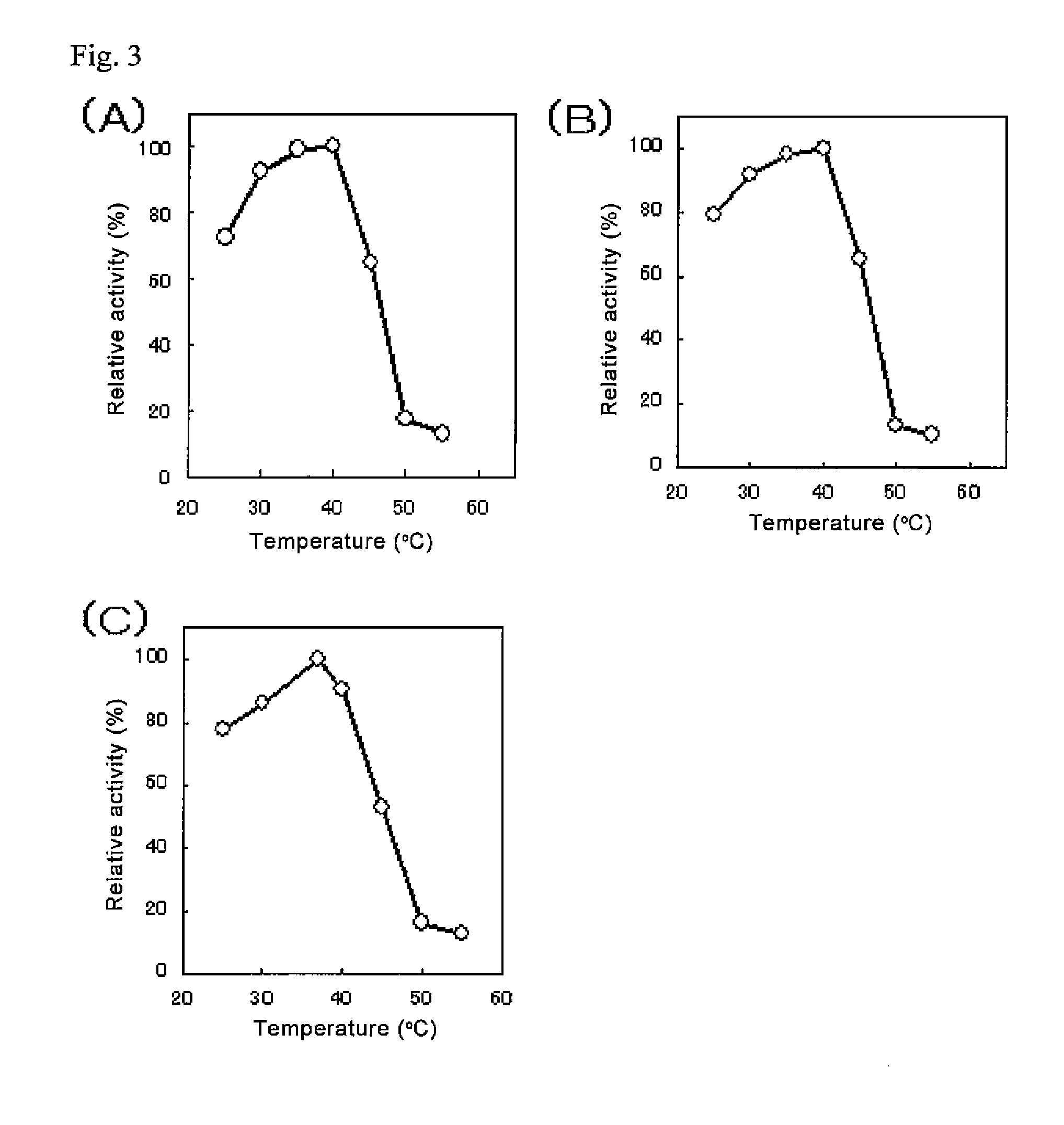
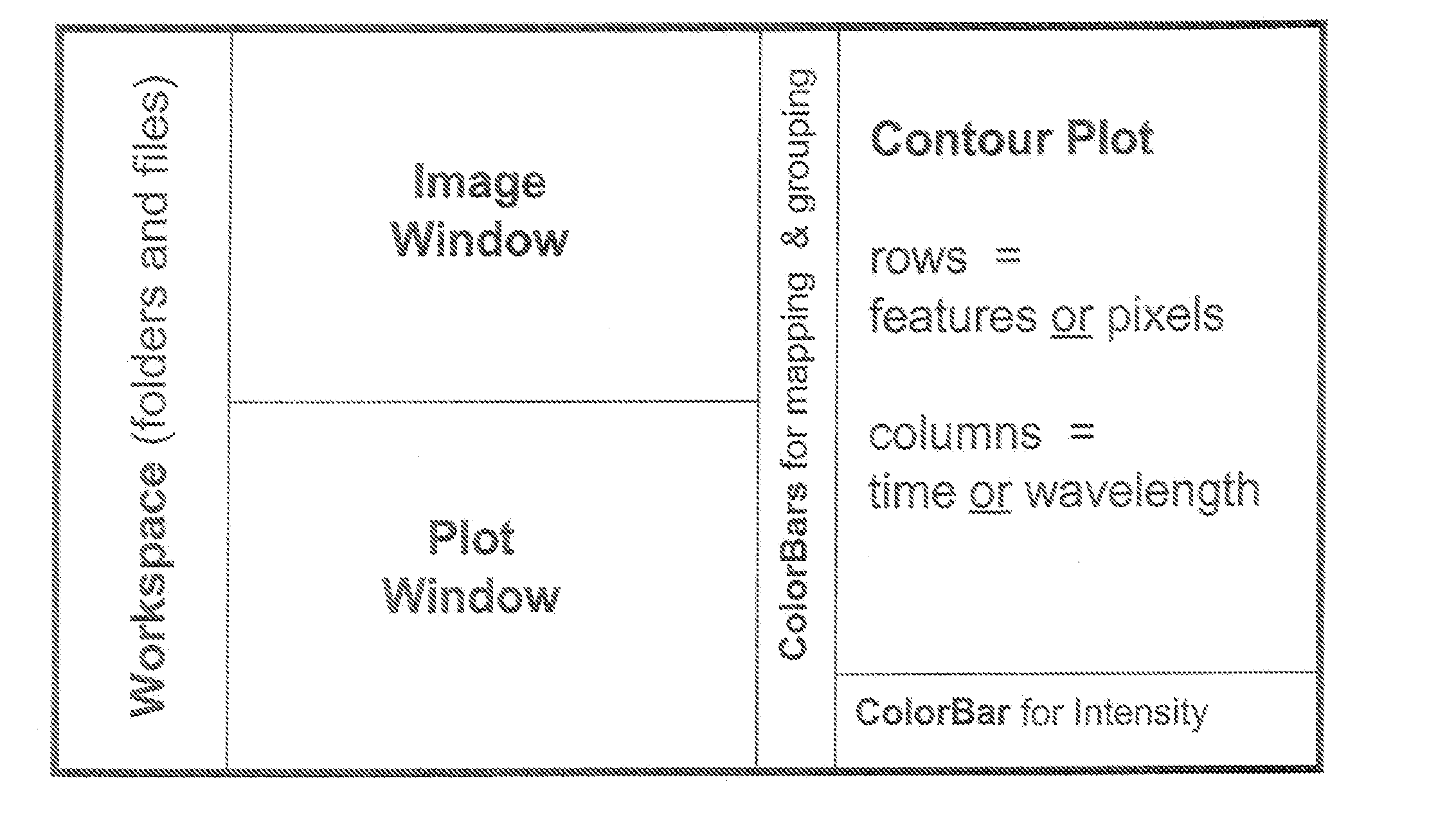
Complex multidimensional datasets generated by digital imaging spectroscopy can be organized and analyzed by applying software and computer-based methods comprising sorting algorithms. Combinations of these algorithms to images and graphical data, allow pixels or features to be rapidly and efficiently classified into meaningful groups according to defined criteria. Multiple rounds of pixel or feature selection may be performed based on independent sorting criteria. In one embodiment sorting by spectral criteria (e.g., intensity at a given wavelength) is combined with sorting by temporal criteria (e.g., absorbance at a given time) to identify microcolonies of recombinant organisms harboring mutated genes encoding enzymes having desirable kinetic attributes and substrate specificity. Restriction of the set of pixels analyzed in a subsequent sort based on criteria applied in an earlier sort (“sort and lock” analyses) minimize computational and storage resources. User-defined criteria can also be incorporated into the sorting process by means of a graphical user interface that comprises a visualization tools including a contour plot, a sorting bar and a grouping bar, an image window, and a plot window that allow run-time interactive identification of pixels or features meeting one or more criteria, and display of their associated spectral or kinetic data. These methods are useful for extracting information from imaging data in applications ranging from biology and medicine to remote sensing.
Owner:KAIROS SCI
Visualization and processing of multidimensional data using prefiltering and sorting criteria
InactiveUS20050114801A1Rapidly and efficiently extracting useful informationFacilitates independent sortingImage enhancementDrawing from basic elementsSorting algorithmDigital imaging
Complex multidimensional datasets generated by digital imaging spectroscopy can be organized and analyzed by applying software and computer-based methods comprising sorting algorithms. Combinations of these algorithms to images and graphical data, allow pixels or features to be rapidly and efficiently classified into meaningful groups according to defined criteria. Multiple rounds of pixel or feature selection may be performed based on independent sorting criteria. In one embodiment sorting by spectral criteria (e.g., intensity at a given wavelength) is combined with sorting by temporal criteria (e.g., absorbance at a given time) to identify microcolonies of recombinant organisms harboring mutated genes encoding enzymes having desirable kinetic attributes and substrate specificity. Restriction of the set of pixels analyzed in a subsequent sort based on criteria applied in an earlier sort (“sort and lock” analyses) minimize computational and storage resources. User-defined criteria can also be incorporated into the sorting process by means of a graphical user interface that comprises a visualization tools including a contour plot, a sorting bar and a grouping bar, an image window, and a plot window that allow run-time interactive identification of pixels or features meeting one or more criteria, and display of their associated spectral or kinetic data. These methods are useful for extracting information from imaging data in applications ranging from biology and medicine to remote sensing.
Owner:YANG MARY M +5
Substrates specific to von willebrand factor cleaving protease and method of assaying the activity
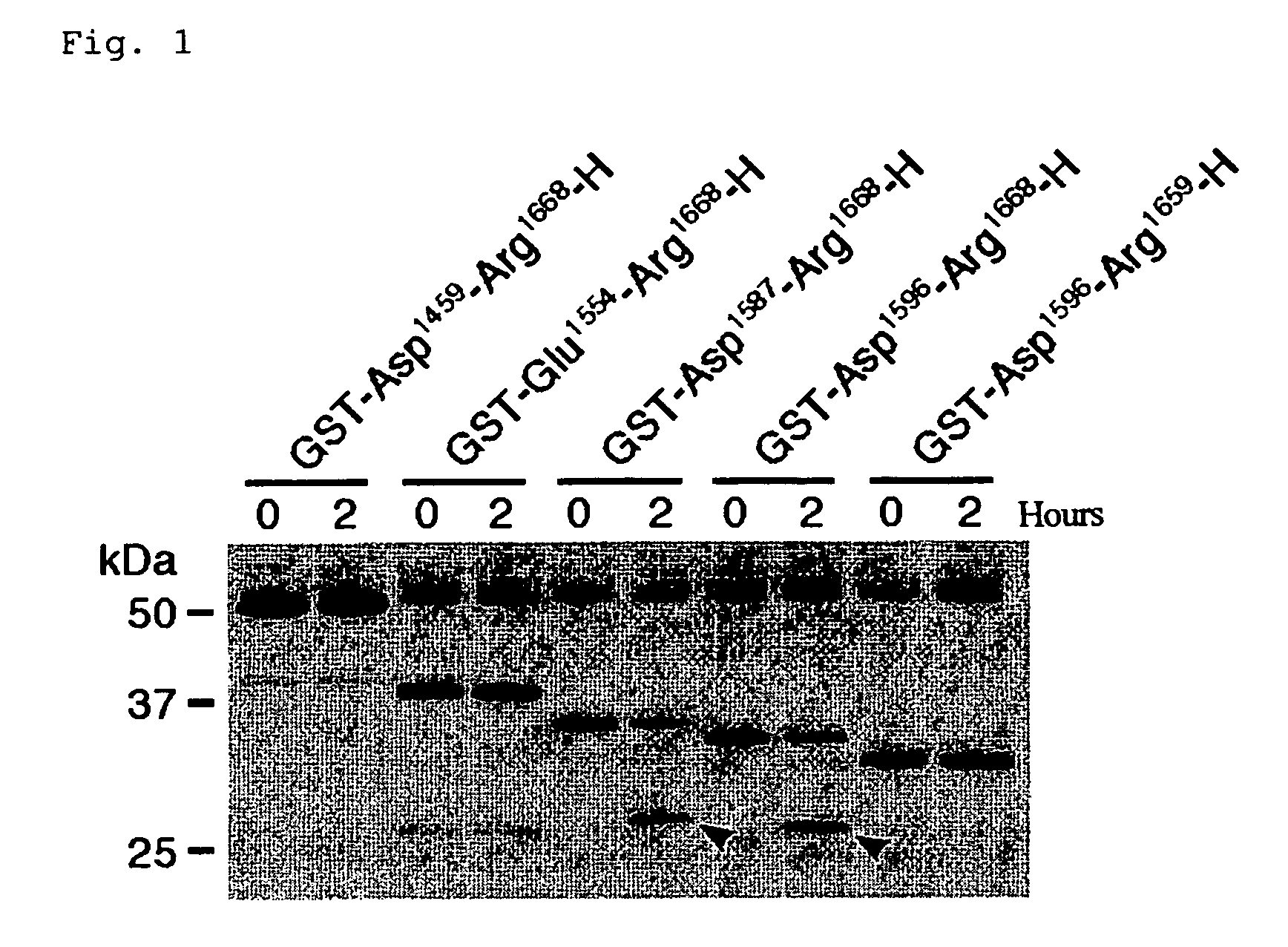
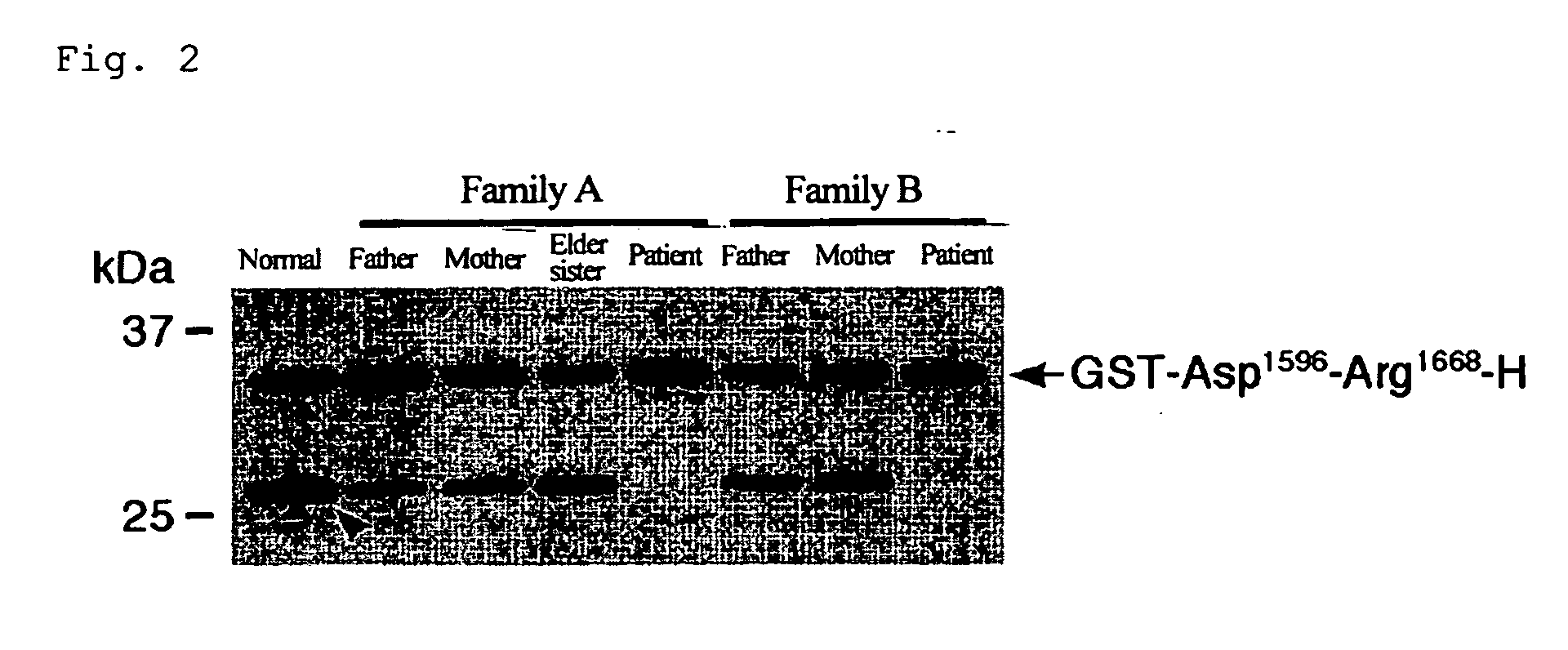
The present invention relates to specific substrates for a von Willebrand factor cleaving enzyme, ADAMTS-13, as well as to diagnosis of ADAMTS-13 deficient patients, diagnostic compositions, and kits employing the substrates. Particularly preferable substrate polypeptides for ADAMTS-13 are the polypeptide which begins at amino acid 1587 and ends at amino acid 1668 of SEQ ID NO: 1 in the Sequence Listing, and the polypeptide which begins at amino acid 1596 and ends at amino acid 1668 of SEQ ID NO: 1 in the Sequence Listing. These substrate polypeptides for ADAMTS-13 have high substrate specificity and also superior quantitativeness, and a suitable size for production by recombinant methods.
Owner:NAT CEREBRAL & CARDIOVASCULAR CENT
Ketose 3-epimerase produced by arthrobacter globiformis
There are provided a highly safe epimerase usable in food industry, and a method for producing a ketose. The epimerase is a ketose 3-epimerase obtainable from a microorganism of the genus Arthrobacter, and having the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 of the Sequence Listing, and (1) substrate specificity whereby a D- or L-ketose is epimerized at position 3 to produce a corresponding D- or L-ketose, and (2) the highest substrate specificity for D-fructose and D-psicose among D- and L-ketoses. The ketose 3-epimerase is also represented by SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4 of the Sequence Listing, and epimerizes a D- or L-ketose at position 3 to produce a corresponding D- or L-ketose.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD +1
Amylase variants
The present invention relates to variants (mutants) of polypeptides, in particular Termamyl-like alpha-amylases, which variant has alpha-amylase activity and exhibits an alteration in at least one of the following properties relative to said parent alpha-amylase: substrate specificity, substrate binding, substrate cleavage pattern, thermal stability, pH / activity profile, pH / stability profile, stability towards oxidation, Ca2+ dependency, specific activity, and solubility, in particular under production conditions.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
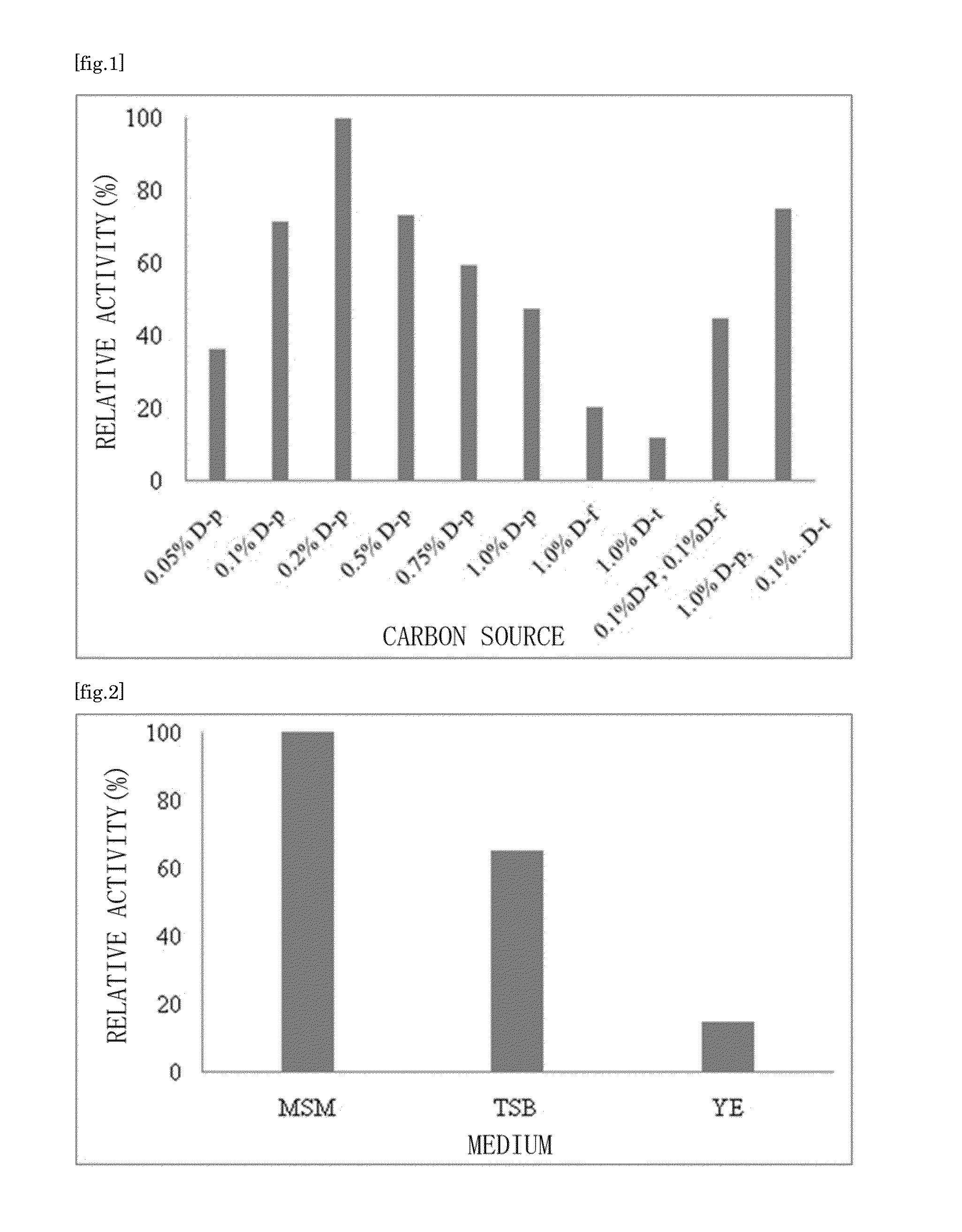
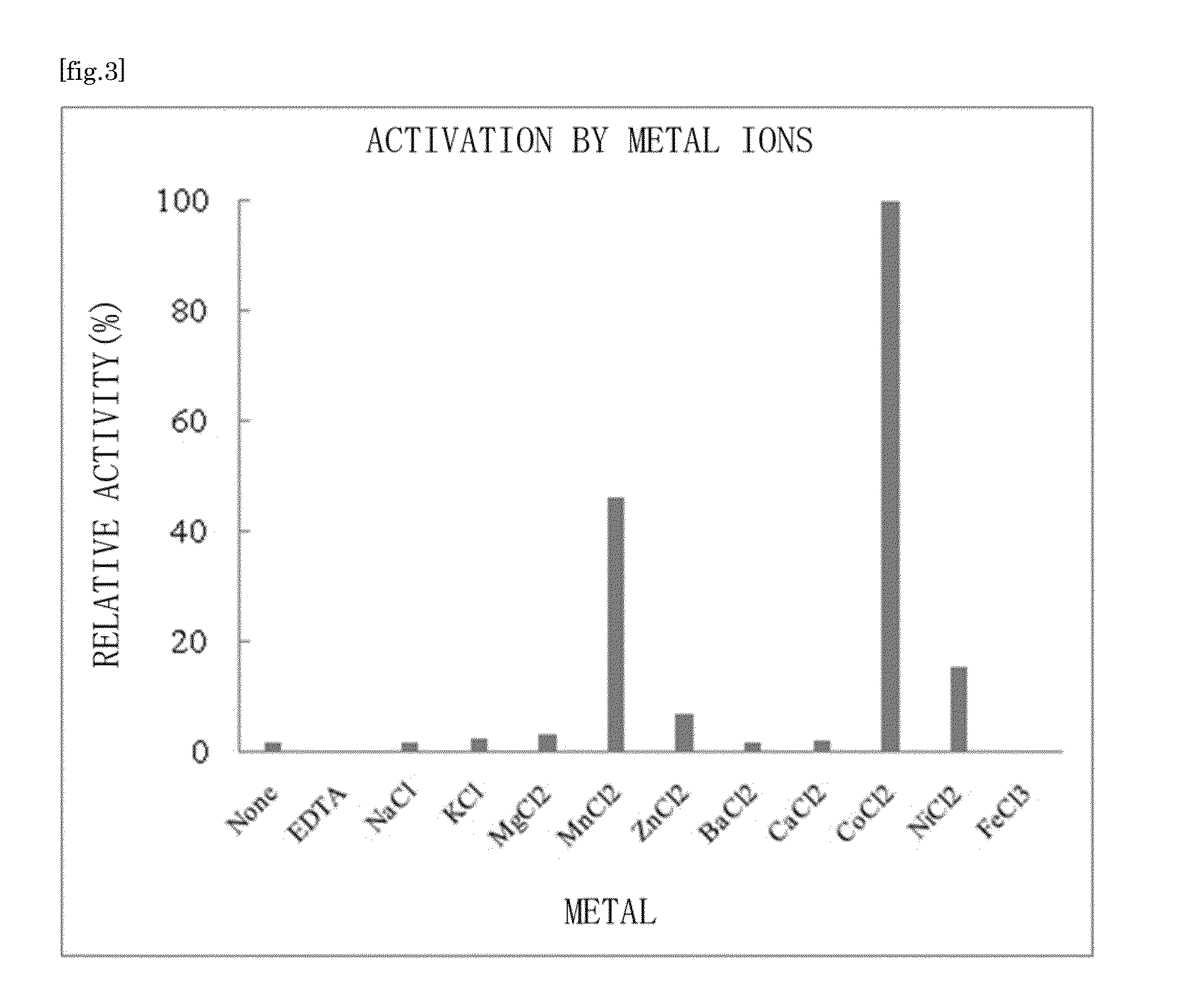
Modified pyrroloquinoline quinone (pqq) dependent glucose dehydrogenase excellent in substrate specificity
InactiveUS20070105173A1Action propertyProcess stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiWild typePyrroloquinoline quinone
PQQGDH having an improved substrate specificity or having an improved specific activity in an assay system using ferricyanide ion as a mediator is provided. Modified PQQGDH having the enhanced substrate specificity by introducing an amino acid mutation in a particular region of PQQGDH, and a method of enhancing the specific activity compared with a wild type in the assay system using the ferricyanide ion as the mediator by deleting, substituting, or adding one or more amino acids in an amino acid sequence of the wild type pyrroloquinoline quinone dependent glucose dehydrogenase.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Glucose dehydrogenase and process for producing the dehydrogenase
InactiveUS7741090B2Increased substrate specificityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
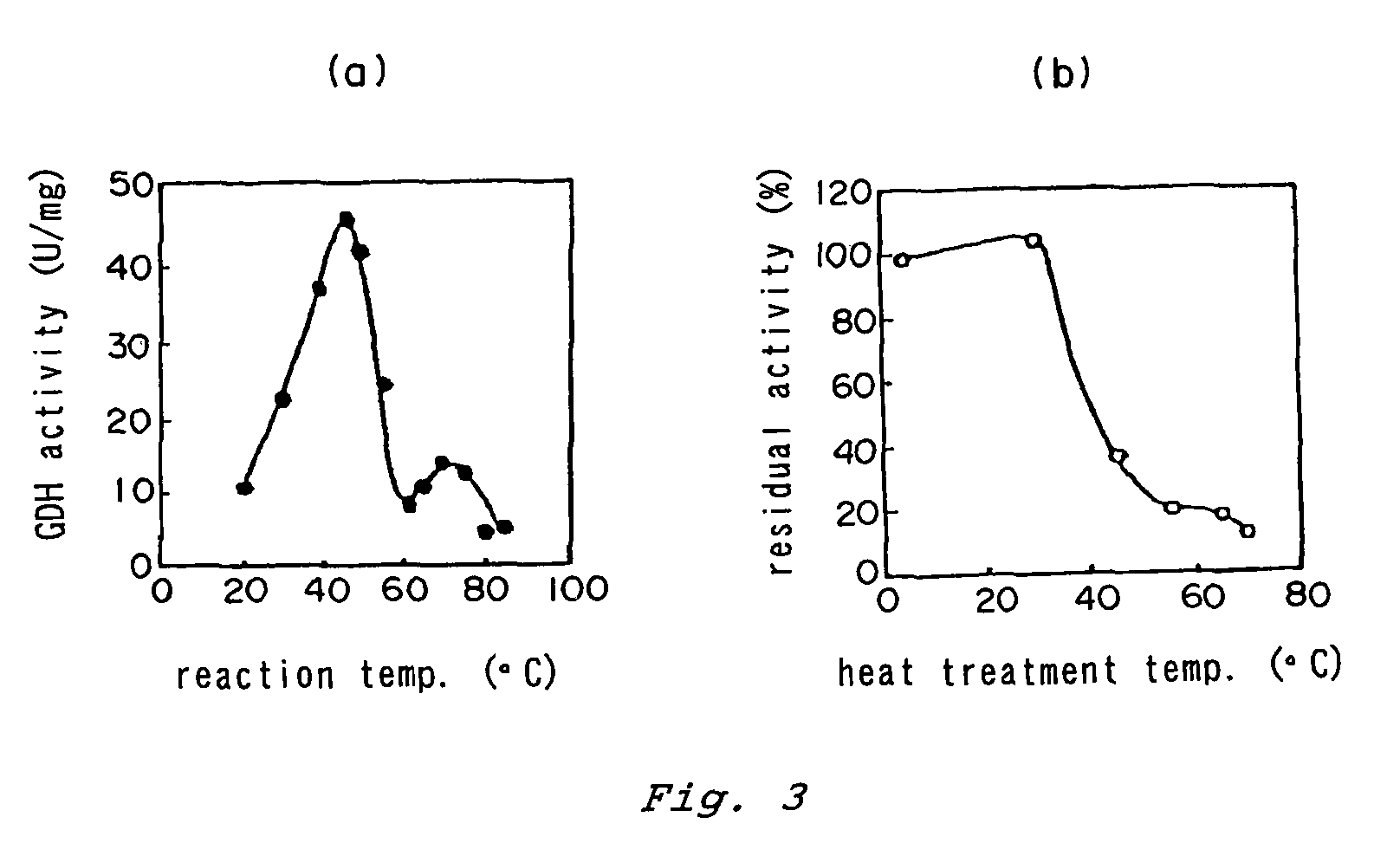
A novel glucose dehydrogenase, which is an enzyme that has high substrate specificity, can be produced at a low cost, is not affected by oxygen dissolved in a measurement sample and, in particular, has superior thermal stability is obtained by culturing a microorganism belonging to the genus Burkhorderia and having glucose dehydrogenase producing ability in a medium and collecting glucose dehydrogenase from the medium and / or cells of the microorganism.
Owner:SODE
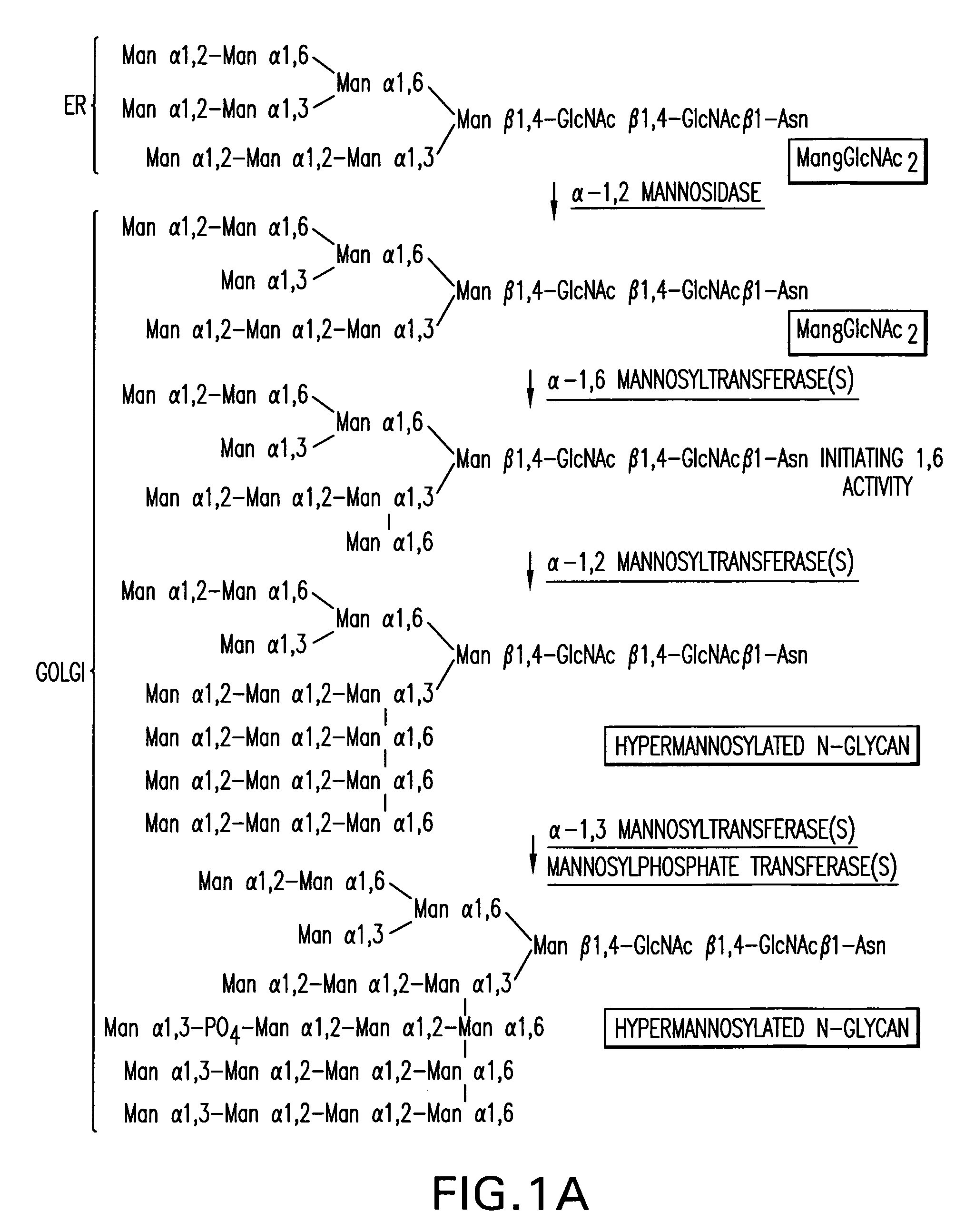
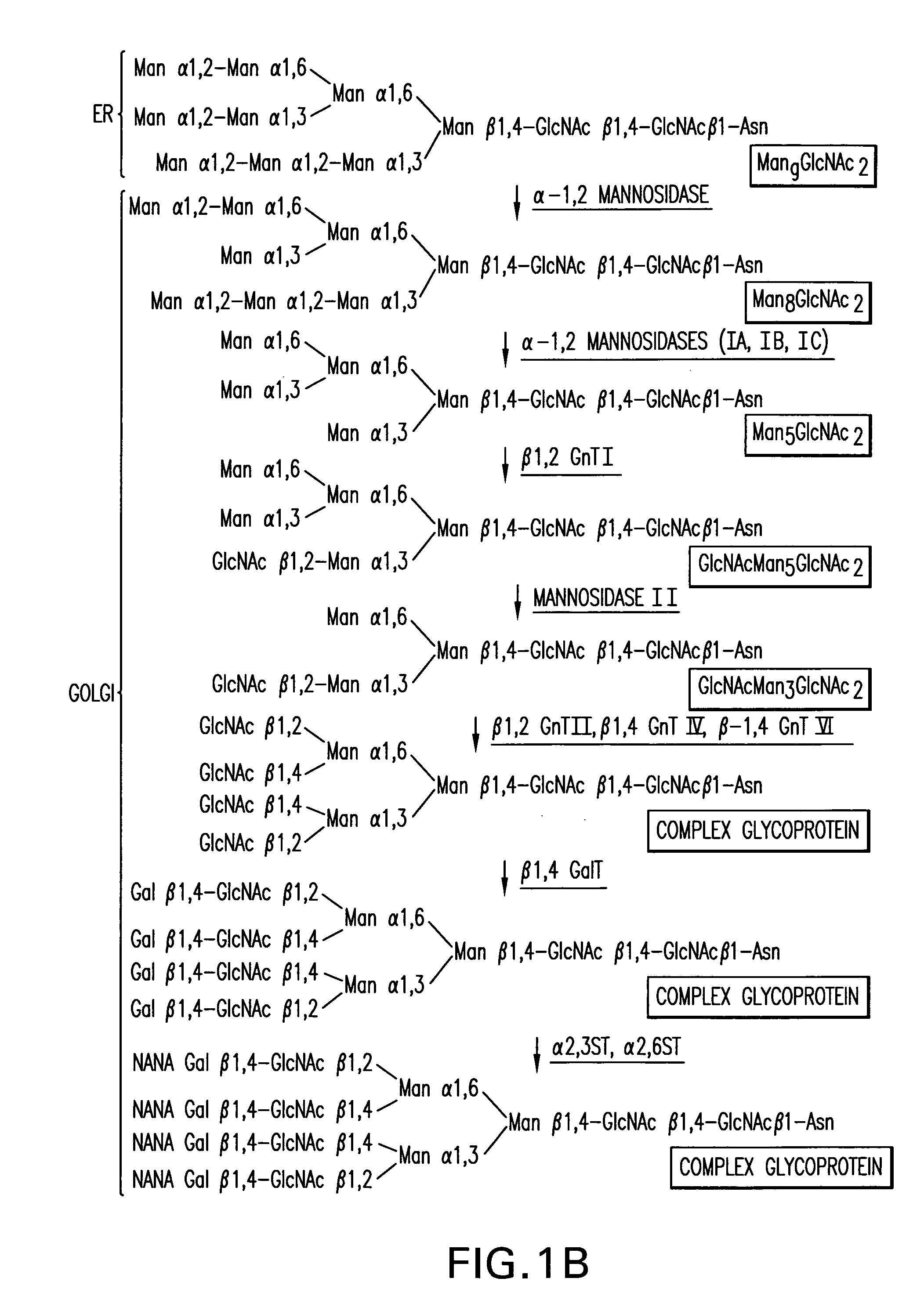
Expression of class 2 mannosidase and class III mannosidase in lower eukaryotic cells
A method for producing human-like glycoproteins by expressing a Class 2 α-mannosidase having a substrate specificity for Manα1,3 and Manα1,6 glycosidic linkages in a lower eukaryote is disclosed. Hydrolysis of these linkages on oligosaccharides produces substrates for further N-glycan processing in the secretory pathway.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Amino acid racemase having low substrate specificity and process for producing racemic amino acid
InactiveUS20050095670A1Improve productivityAnimal cellsFungiAmino-acid racemase activityDna encoding
The present invention provides a protein having low-substrate-specific amino acid racemase activity; DNA encoding the protein; a recombinant DNA comprising the DNA; a transformant carrying the recombinant DNA; a process for producing the protein by using the transformant; and a process for producing a racemic amino acid which comprises allowing a culture of the transformant or a treated matter thereof as an enzyme source and an amino acid to be present in an aqueous medium to racemize the amino acid in the aqueous medium, and recovering the racemic amino acid from the aqueous medium.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
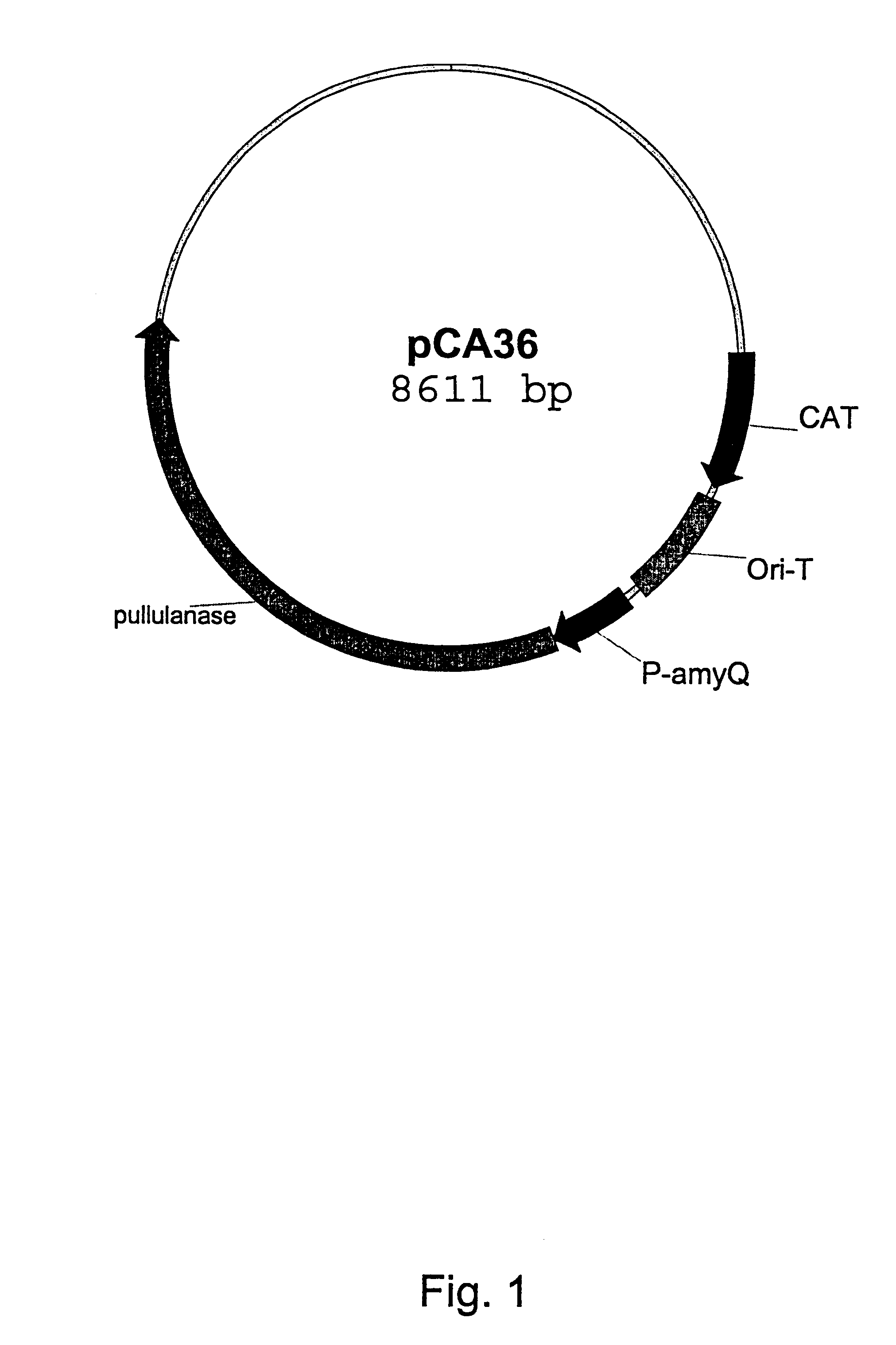
Pullulanase variants and methods for preparing such variants with predetermined properties
InactiveUS6350599B1Improve propertiesAltered physicochemical propertySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPullulanaseSubstrate specificity
The inventors have modified the amino acid sequence of a pullulanase to obtain variants with improved properties, based on the three-dimensional structure of the pullulanase Promozyme(R). The variants have altered physicochemical properties, e.g. an altered pH optimum, improved thermostability, altered substrate specificity, increased specific activity or an altered cleavage pattern.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
L-d-glutamic oxidase with substrate specificity and alpha-oxoglutarate produced by catalysis of same
InactiveCN102994467ANo pollution in the processSimple production processMicroorganism based processesEnzymesSodium GlutamateIsopropyl alcohol
The invention discloses L-d-glutamic oxidase with substrate specificity and alpha-oxoglutarate produced by catalysis of the same, and belongs to the field of enzyme-method catalytic production of fine chemicals. The invention has the advantages that the L-d-glutamic oxidase which only has the substrate specificity to L-glutamic acid, L-sodium glutamate and glutamine is utilized, 20g / L L-sodium glutamate solution is added in fermented liquid which is fermented for 60 hours and contains the L-d-glutamic oxidase, carrying out conversion for 12 hours under the ventilating condition and the conditions that the temperature is 30 DEG C, the pH is 8.5 and the 5% (v / v) isopropyl alcohol, and measured by a high-performance liquid chromatography, the content of alpha-oxoglutarate reaches 14.5g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel dehydrogenase and a gene encodign the same
InactiveUS20060205045A1High yieldProduced industrially and inexpensivelyFungiSugar derivativesPhenylpyruvic acidSubstrate specificity
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
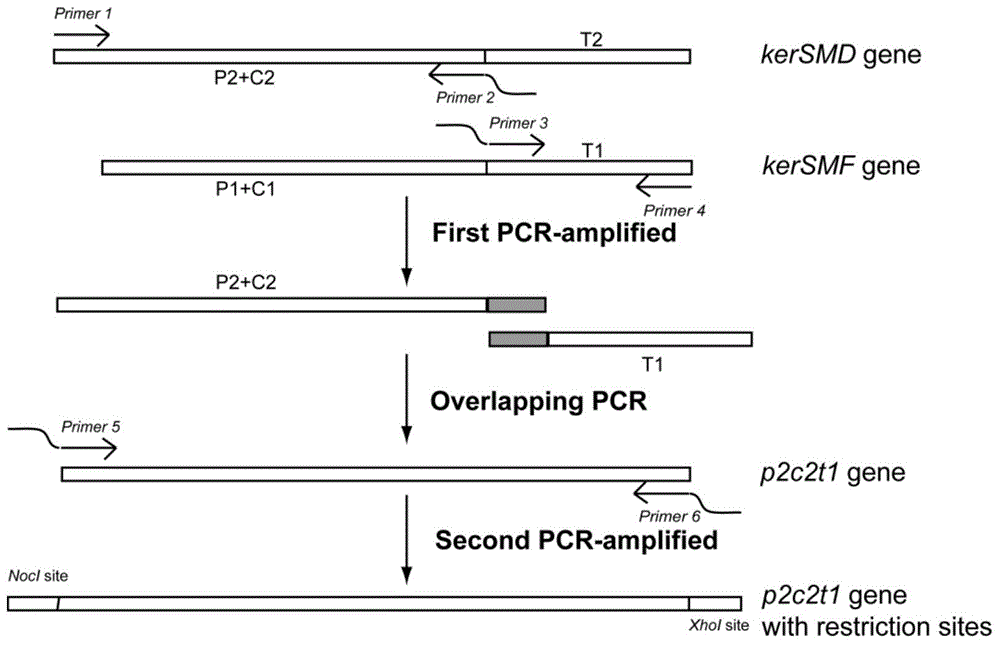
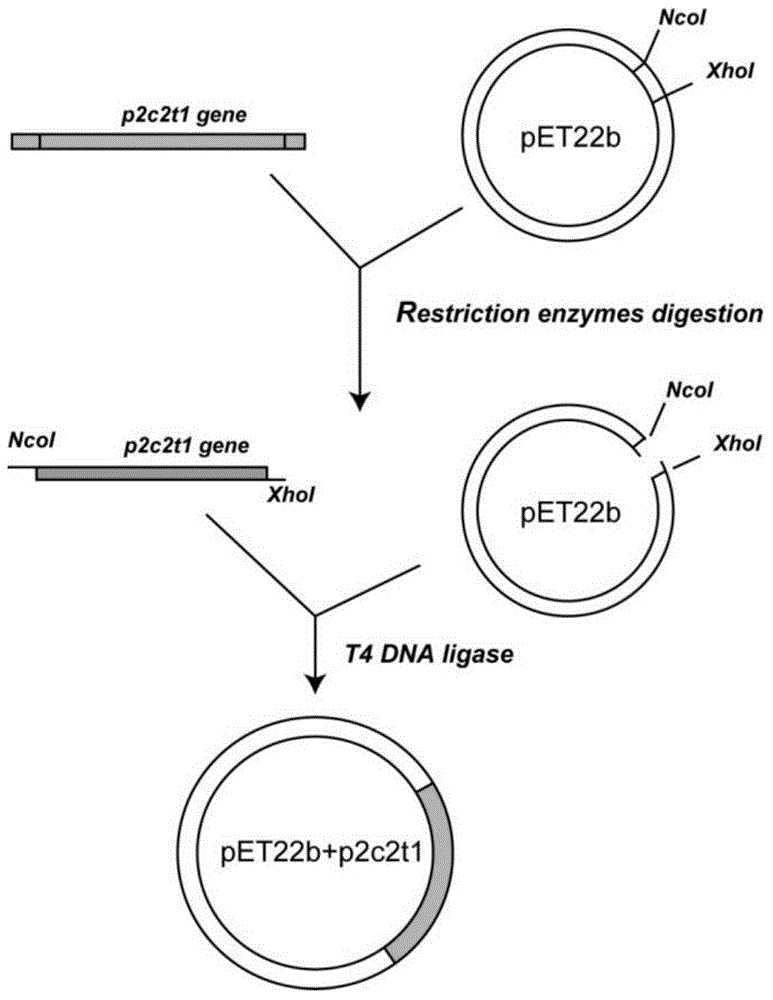
Keratinase mutant with improved thermal stability and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104017791AImprove thermal stabilityIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesWater insolubleHigh homology
The invention discloses a keratinase mutant with improved thermal stability and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. Thermal stability and substrate specificity of the keratinase are improved by interchanging N ends or C ends of two different keratinases with higher homology from the same bacterial strain. The keratinase and the mutant thereof can effectively hydrolyze water-insoluble keratinase substrates such as feathers, wools, and the like, and can be used for leather spinning industry and feed industry.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20110318810A1Accurate measurementAccurate blood glucose levelSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismLactose
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase with a high substrate specificity for D-glucose. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase which is derived from a microorganism belonging to the genus Mucor. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has a low reactivity for maltose, D-galactose and D-xylose compared to its reactivity for D-glucose, and therefore is relatively unaffected by these saccharide compounds. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase is also relatively unaffected by dissolved oxygen, and allows accurate measurement of glucose amounts even in the presence of saccharide compounds other than glucose in samples.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
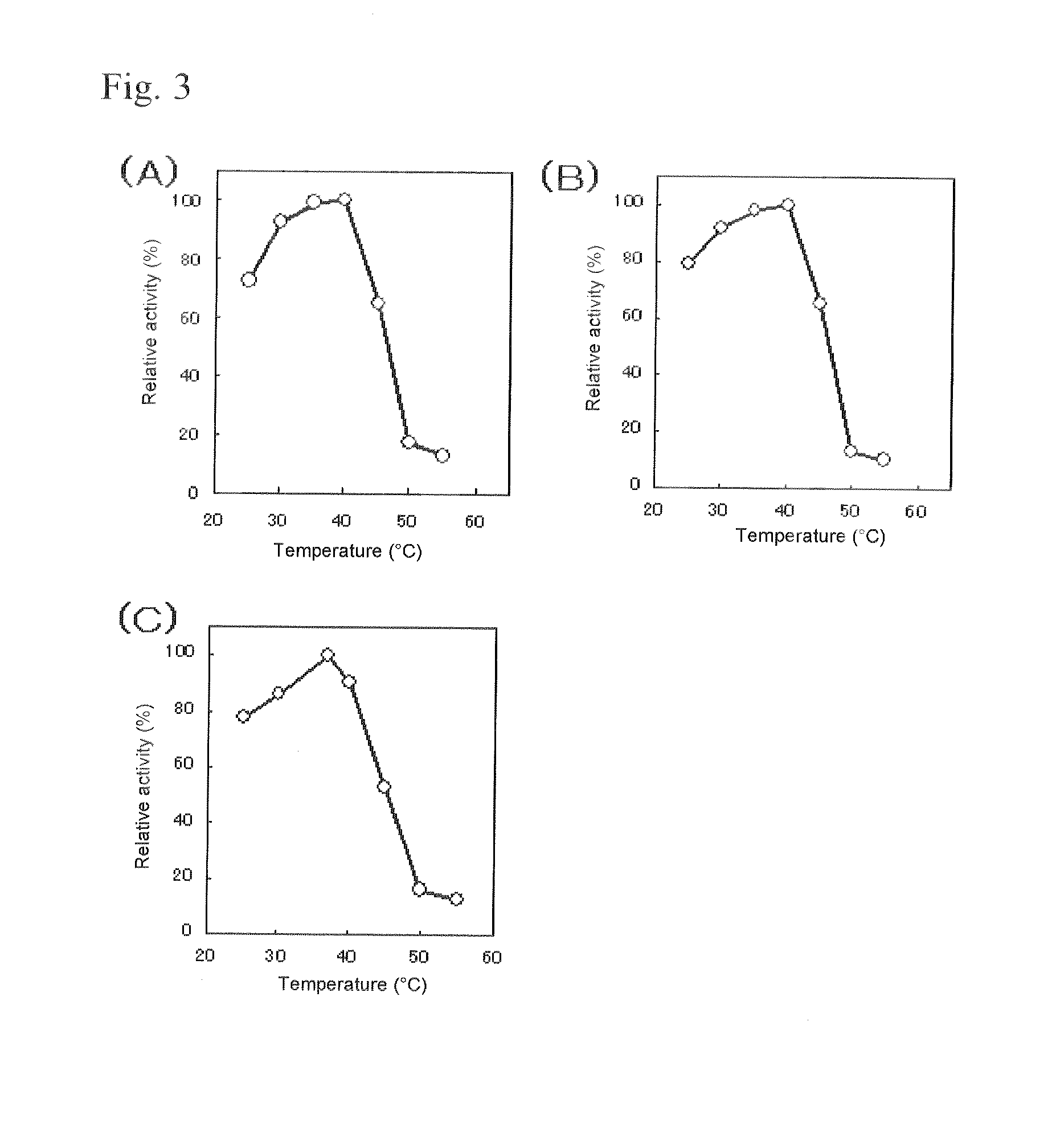
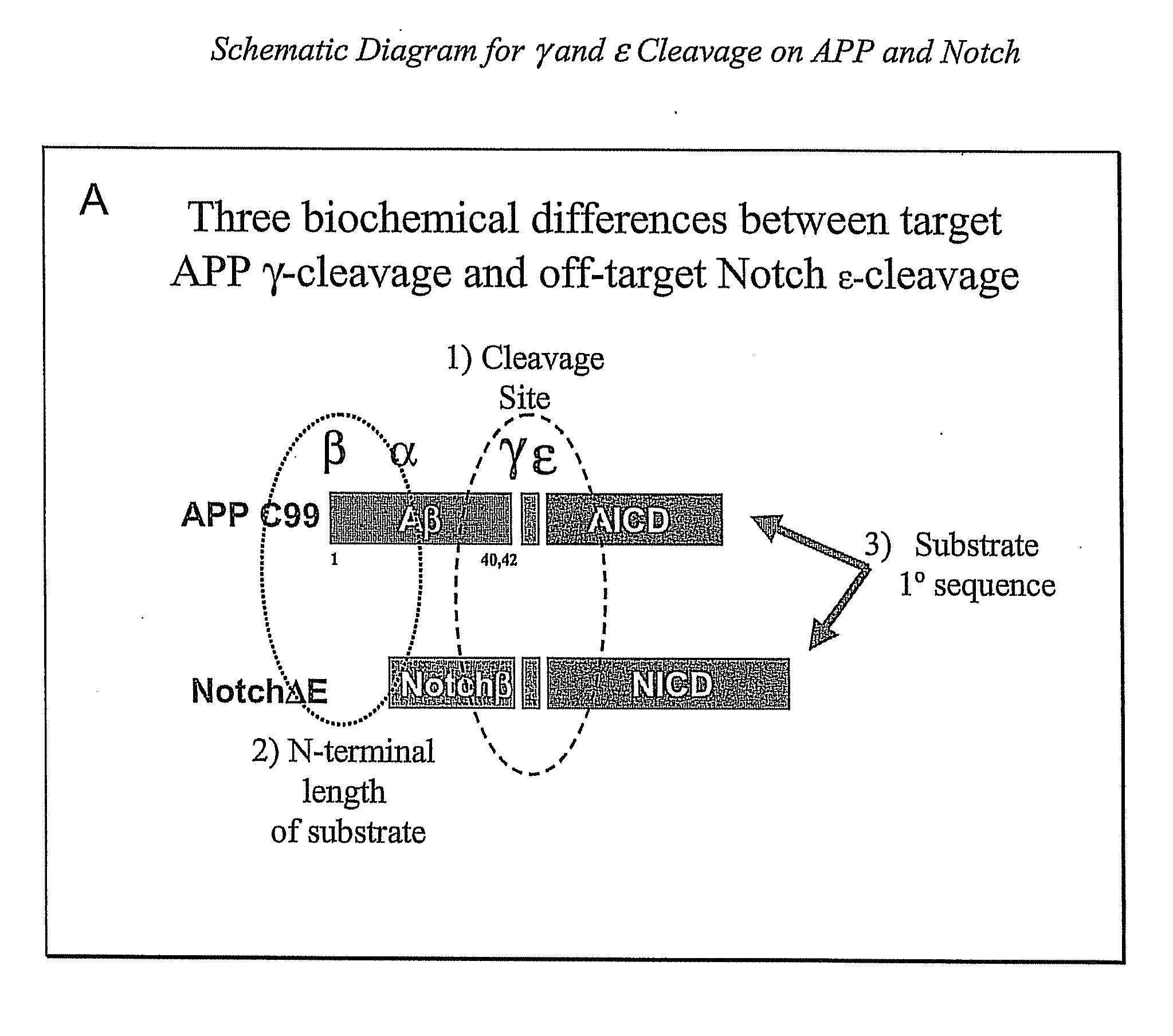
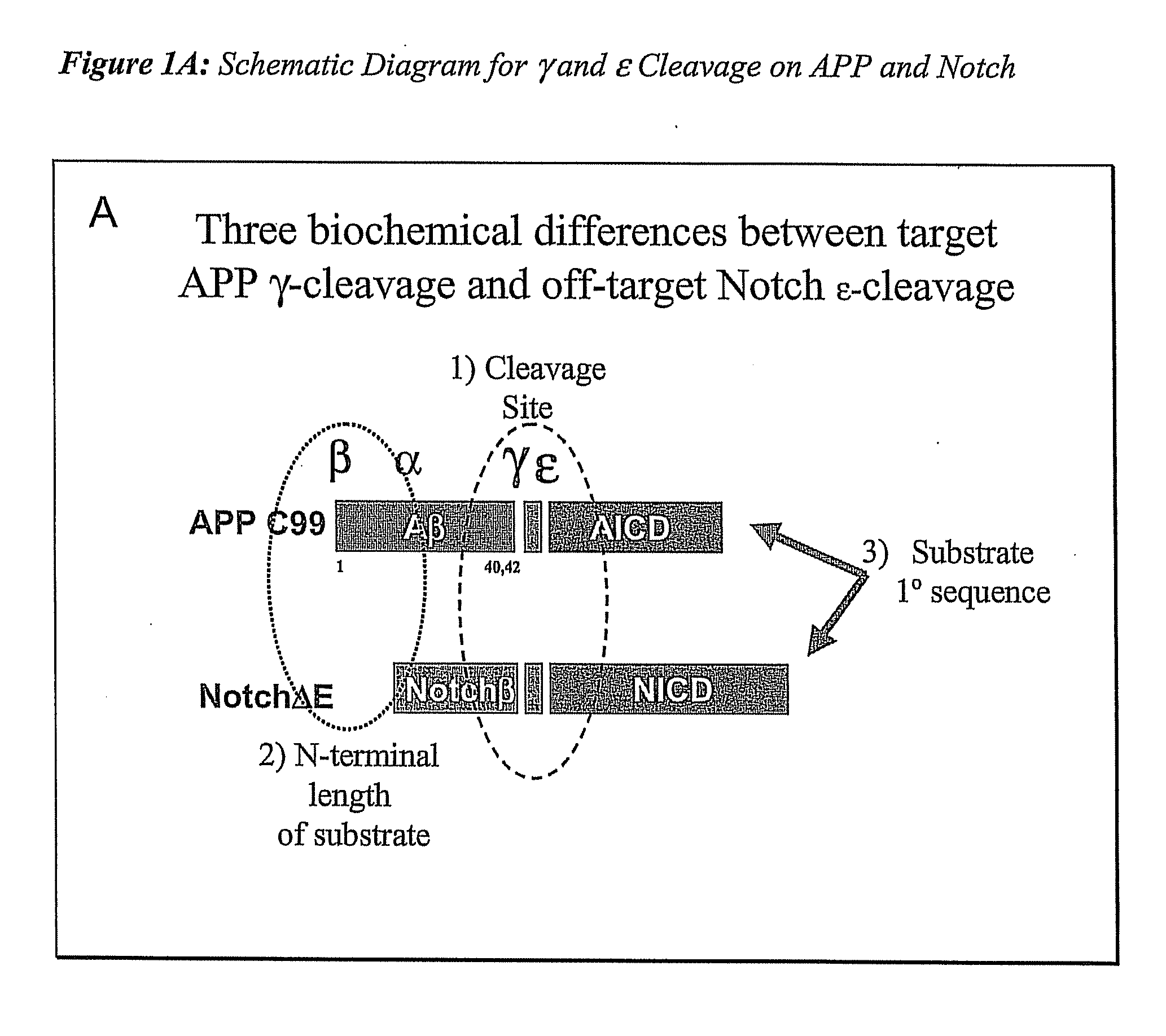
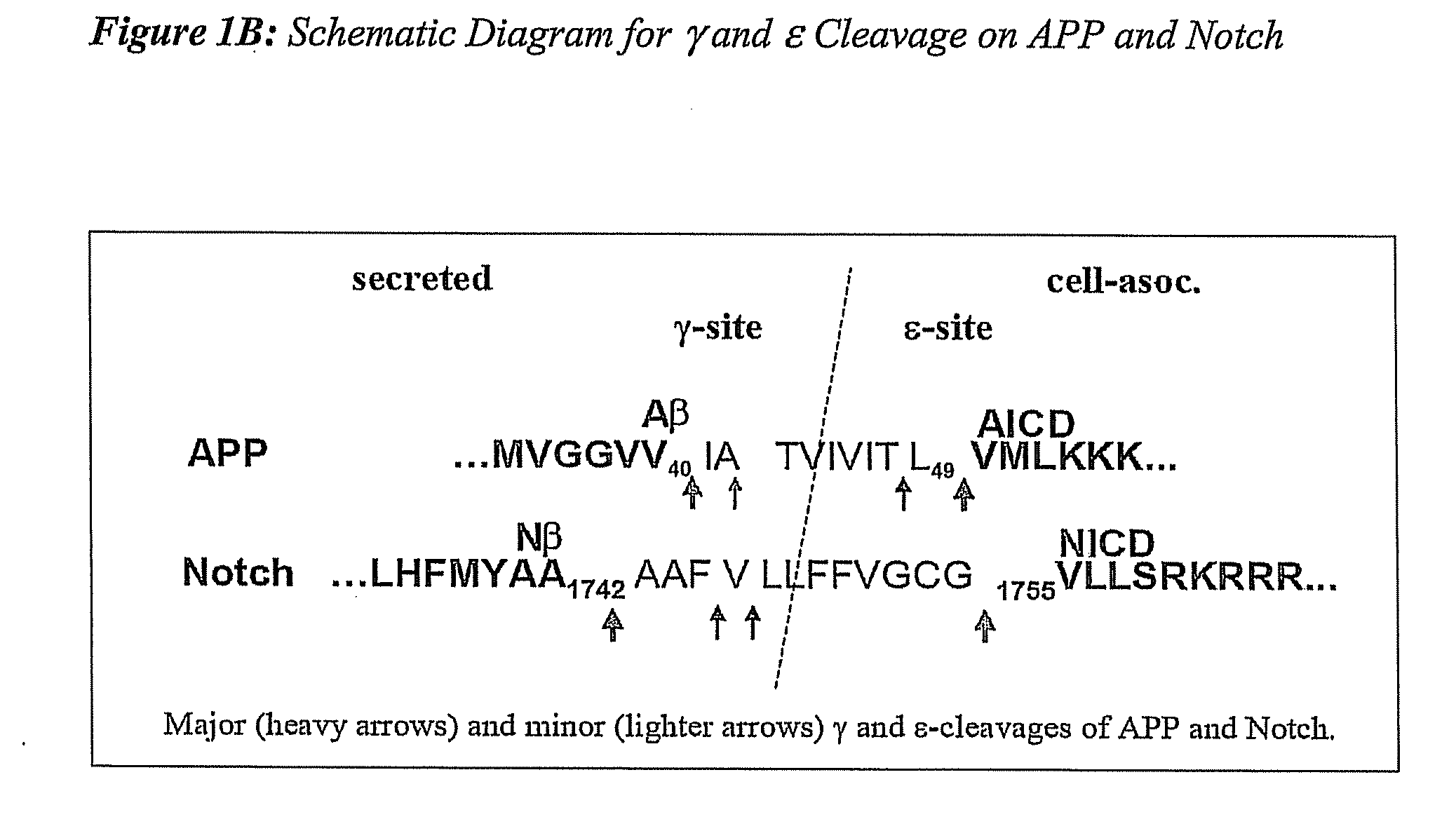
Compositions and Methods for Identifying Substrate Specificity of Inhibitors of Gamma Secretase
The invention provides assays and methods for determining the substrate specificity of gamma secretase inhibitors and for identifying substrate-selective (and substrate isoform-selective) inhibitors of gamma secretase. The invention provides assays and methods for determining whether a compound inhibits gamma secretase in a site specific or substrate specific manner. The invention provides isolated polypeptide sequences comprising modified gamma secretase substrates, and polynucleotide sequences encoding the polypeptide sequences. The invention also provides compounds that inhibit gamma secretase, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and methods of treating Alzheimer's disease using such compounds.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, method for producing flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, and glucose measurement method using thereof
ActiveUS20140287445A1Increased substrate specificityImprove stabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEscherichia coliHeat stability
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH), which in addition to having high substrate specificity and adequate desirable heat stability, is suitable for efficient production, preferably using E. coli, yeast or molds and the like as host cells. The FAD-GDH has amino acid substitutions at positions equivalent to one or more locations selected from the group consisting of position 213, position 368 and position 526 in the amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 8. The FAD-GDH is acquired from a culture by inserting a gene encoding the FAD-GDH into host cells such as E. coli. A preferable example of the FAD-GDH is FAD-GDH, in which a signal peptide region present in an N-terminal region has been deleted from the amino acid sequence of Mucor-derived FAD-GDH, and which has the aforementioned amino acid substitutions. The FAD-GDH can be preferably used in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
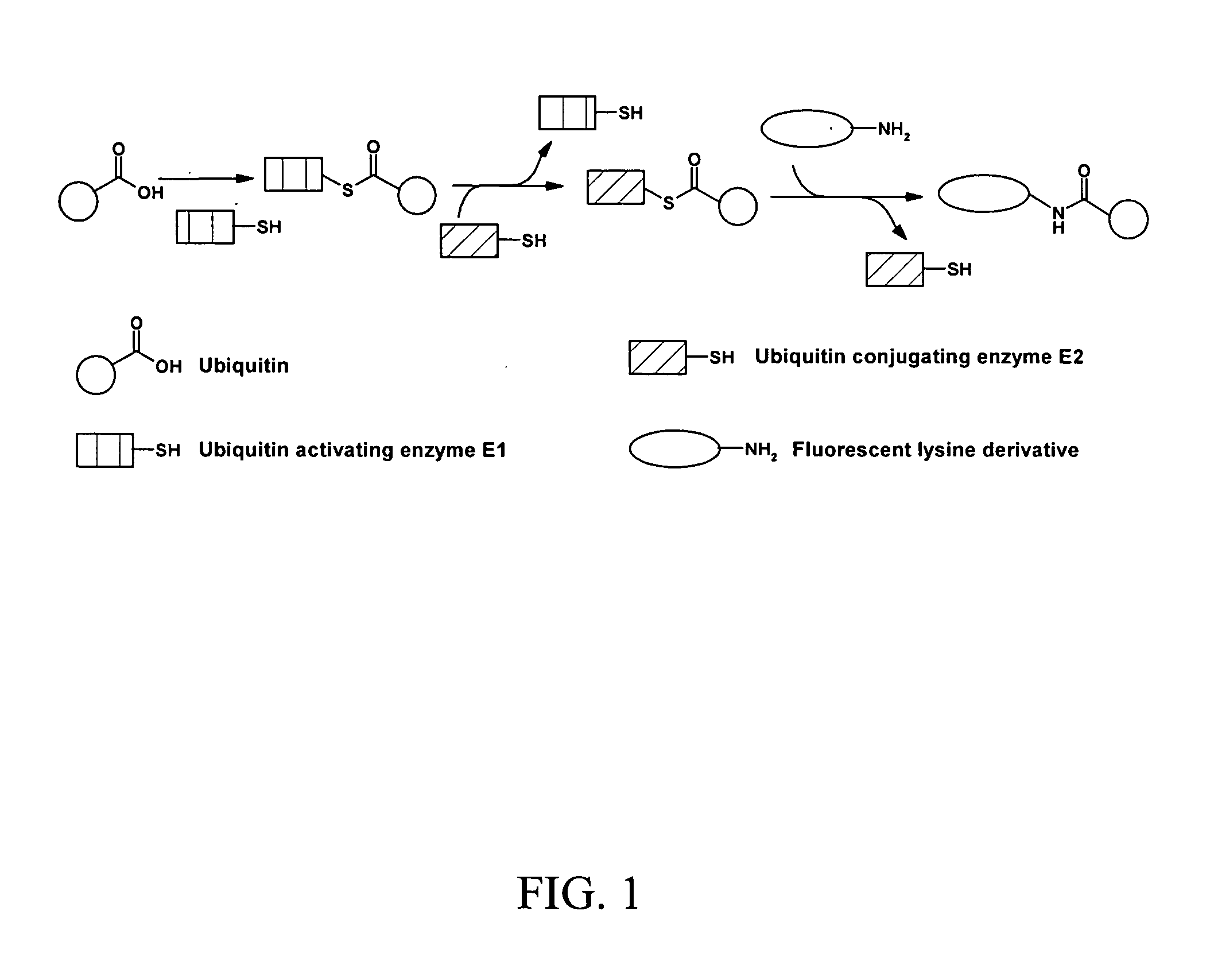
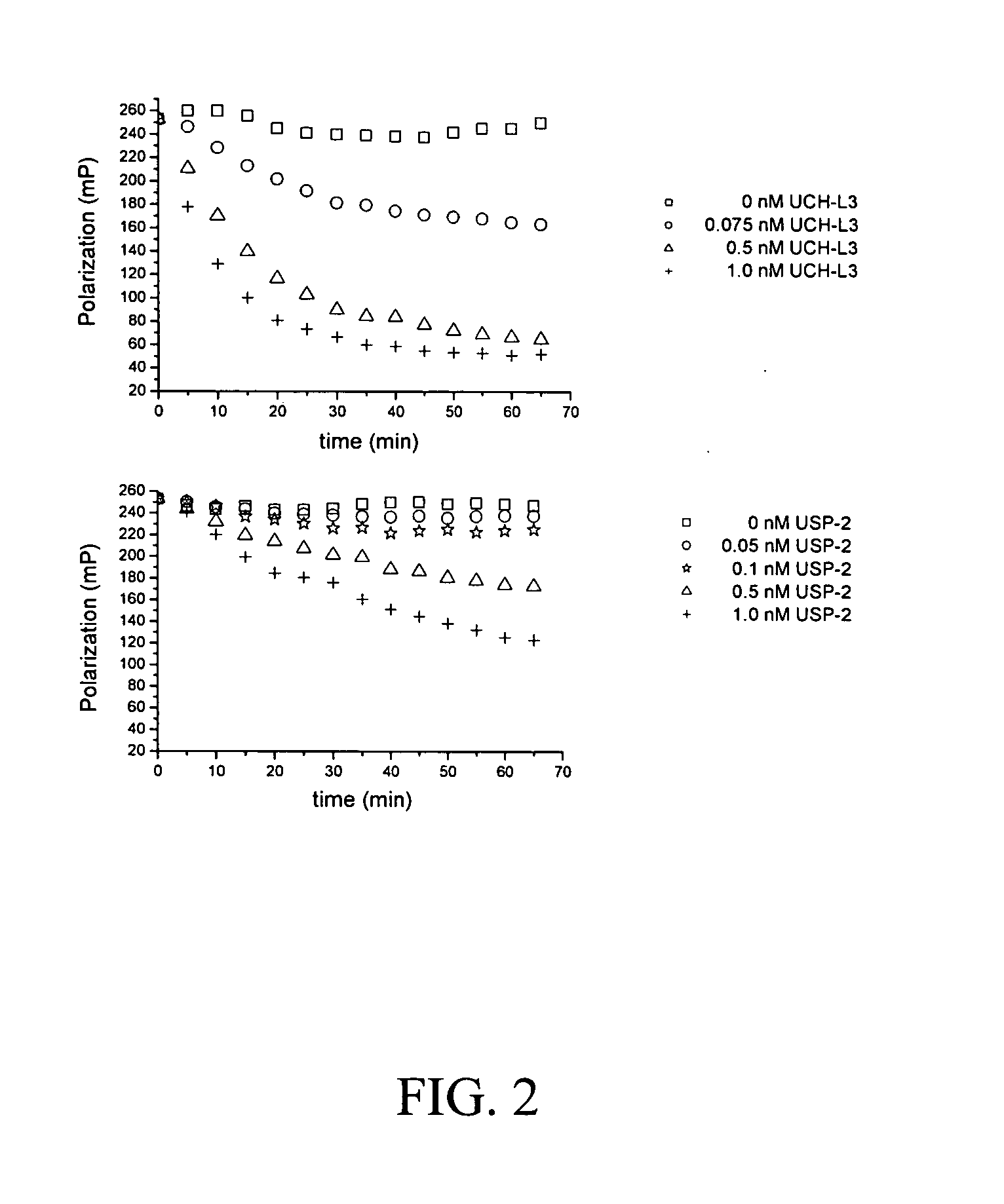
Assay for ubiquitin mediated proteolysis
InactiveUS20080038768A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFluorescenceDeubiquitination
The present invention provides methods and compositions useful in the screening for agents that modulate activity of a deubiquitinating enzyme. In one embodiment, the invention relates to methods for measuring a deubiquitination activity comprising combining a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) with a substrate comprising a ubiquitin moiety and a fluorescently labeled compound under conditions allowing for deubiquitinating activity and measuring an altered fluorescence polarization and / or fluorescence lifetime of the released fluorescently labeled compound The invention also relates to a substrate library comprising peptides of the formula (Z)a(X)mK(X)n(Z)b useful e.g. for the determination of the substrate specificity of a deubiquitinating enzyme.
Owner:FILIPUZZI IREOS +2
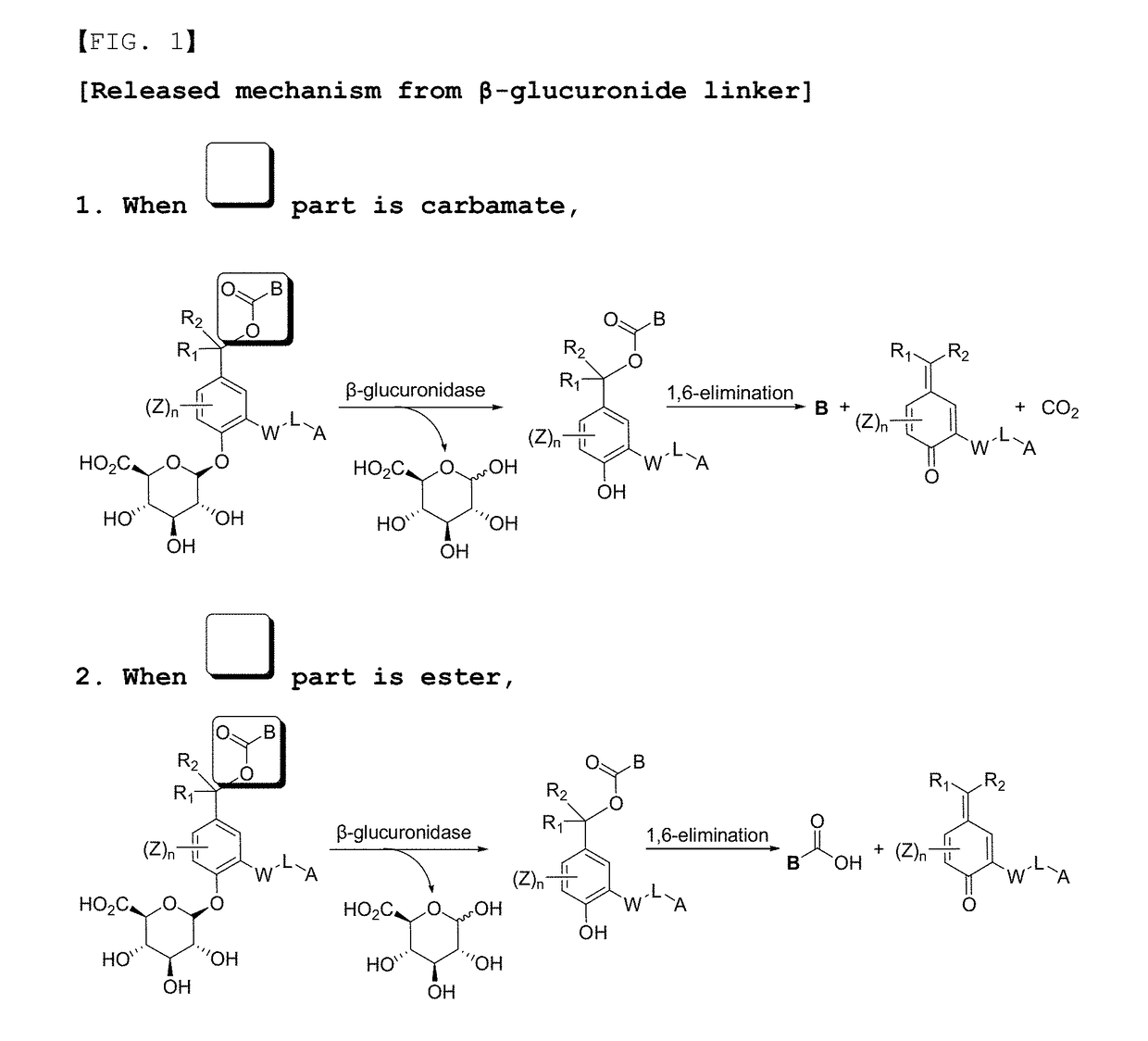
Compounds comprising self-immolative group
Provided are compounds comprising a self-immolative group, and the compounds comprising a self-immolative group according to the present invention may include a protein (for example, an oligopeptide, a polypeptide, an antibody, or the like) having substrate-specificity for a target and an active agent (for example, a drug, a toxin, a ligand, a detection probe, or the like) having a specific function or activity.
Owner:LEGOCHEM BIOSCIENCES INC
Novel glucose dehydrogenase
The present invention provides glucose dehydrogenase which is excellent in heat resistance and substrate specificity and is not affected by dissolved oxygen. Specifically, the present invention relates to glucose dehydrogenase characterized by being derived from an eukaryotic organism and keeping 90% or more activity after being treated with heat at 55° C. for 15 minutes in a liquid form compared with the activity before being treated.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
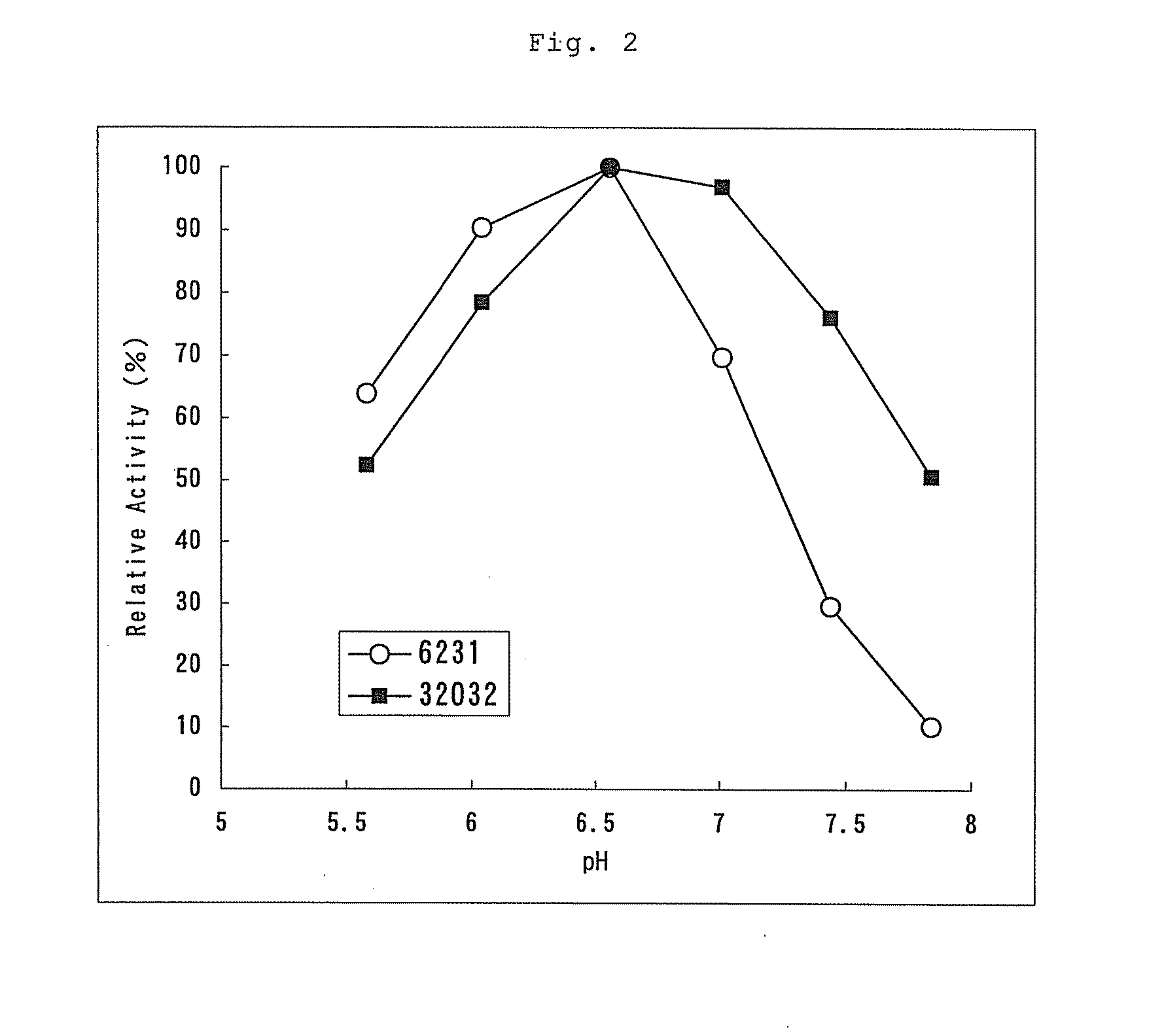
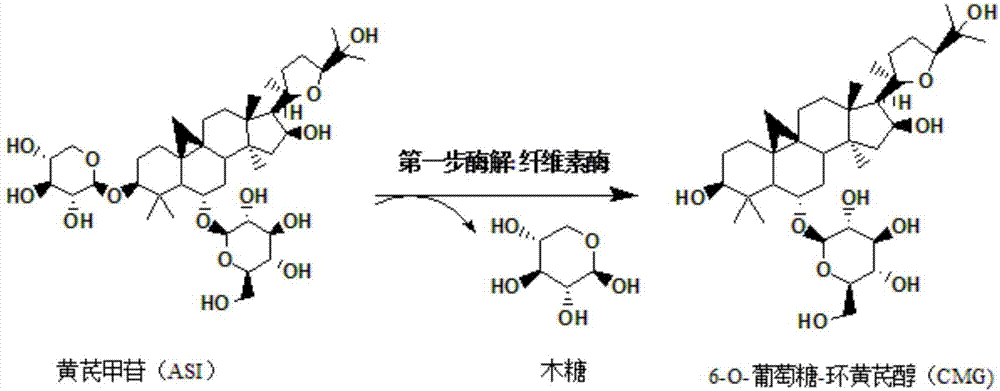
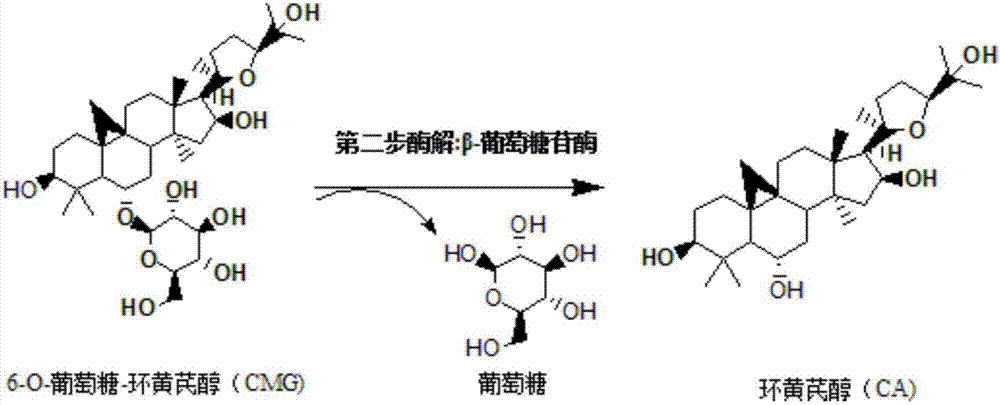
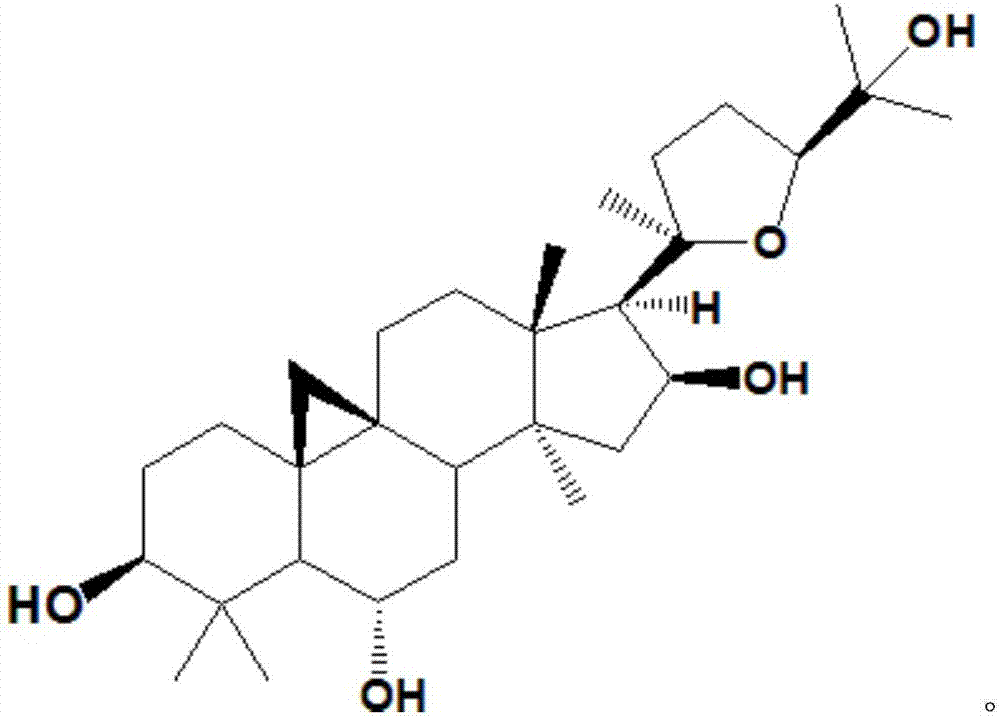
Method for converting astragalosides to prepare cycloastragenol by two-step enzymolysis
The invention discloses a method for converting astragalosides to prepare cycloastragenol by two-step enzymolysis; the method comprises the specific steps of using astragalosides as a substrate, using two different hydrolases to hydrolyze and break beta-xyloside bond at site C3 of the astragalosides and beta-glucoside bond at the site C6 respectively to obtain aglycone cycloastragenol of the astragalosides, extracting, performing silica-gel column chromatography, recrystallizing with ethanol, and purifying to obtain the finished cycloastragenol up to 95% and higher in purity. The problem that damage of three-membered ring structure of astragalosides during the preparation of cycloastragenol by a chemical process causes massive byproducts is solved, the defects of traditional cycloastragenol preparation methods, such as low substrate conversion rate, step complexity and environmental pollution, are overcome. The method has the advantages that substrate specificity is high, the substrate astragalosides is completely converted, the steps are simple, the conditions are mild, the cost is low, and the method is a mild biological preparation method, has no environmental pollution and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com