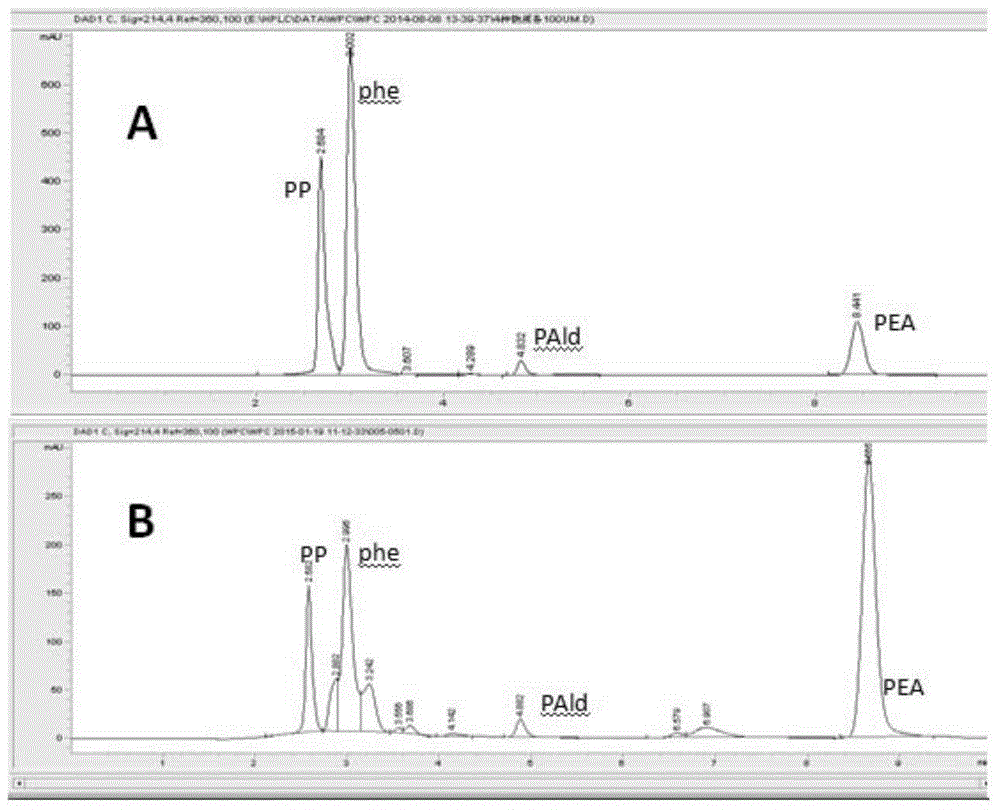
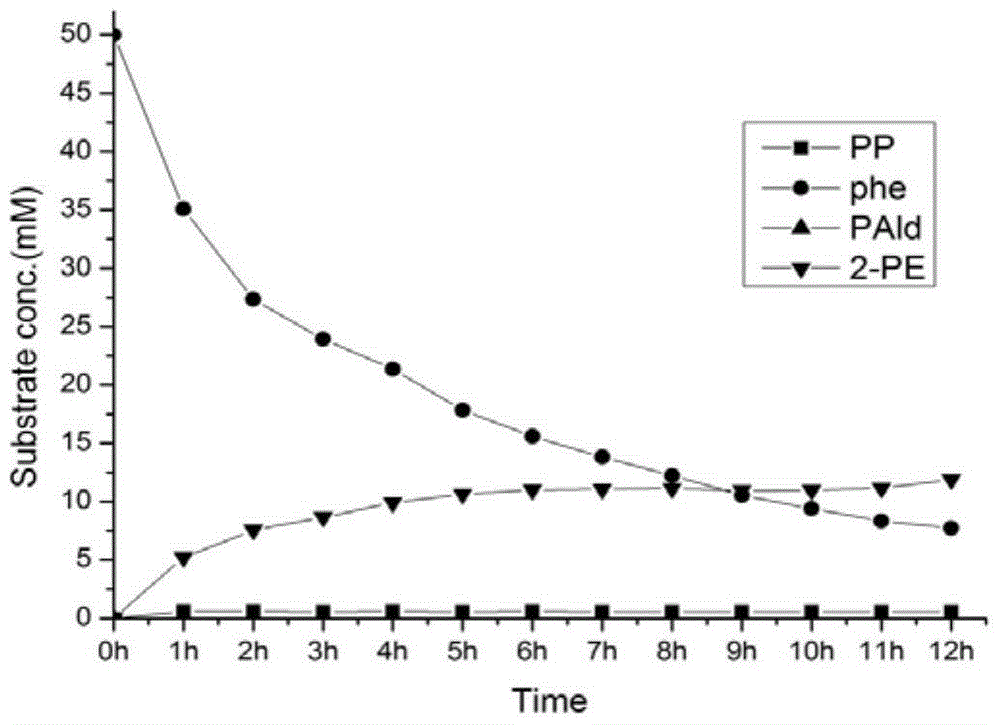
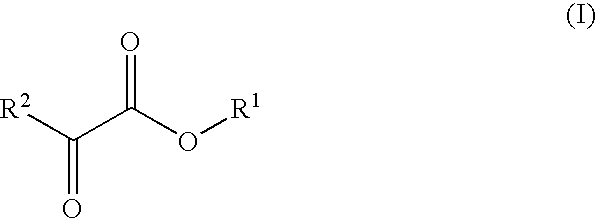
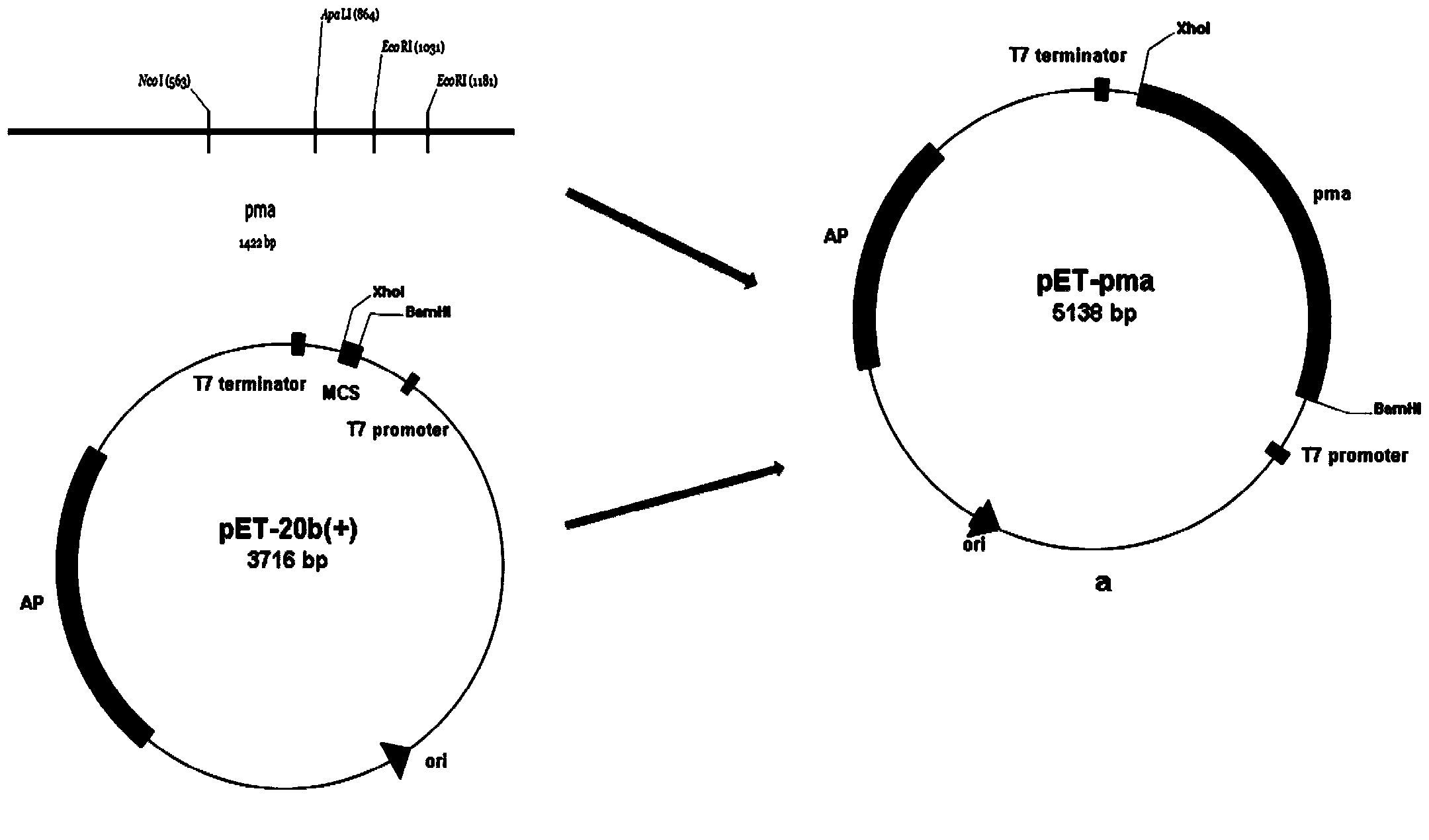
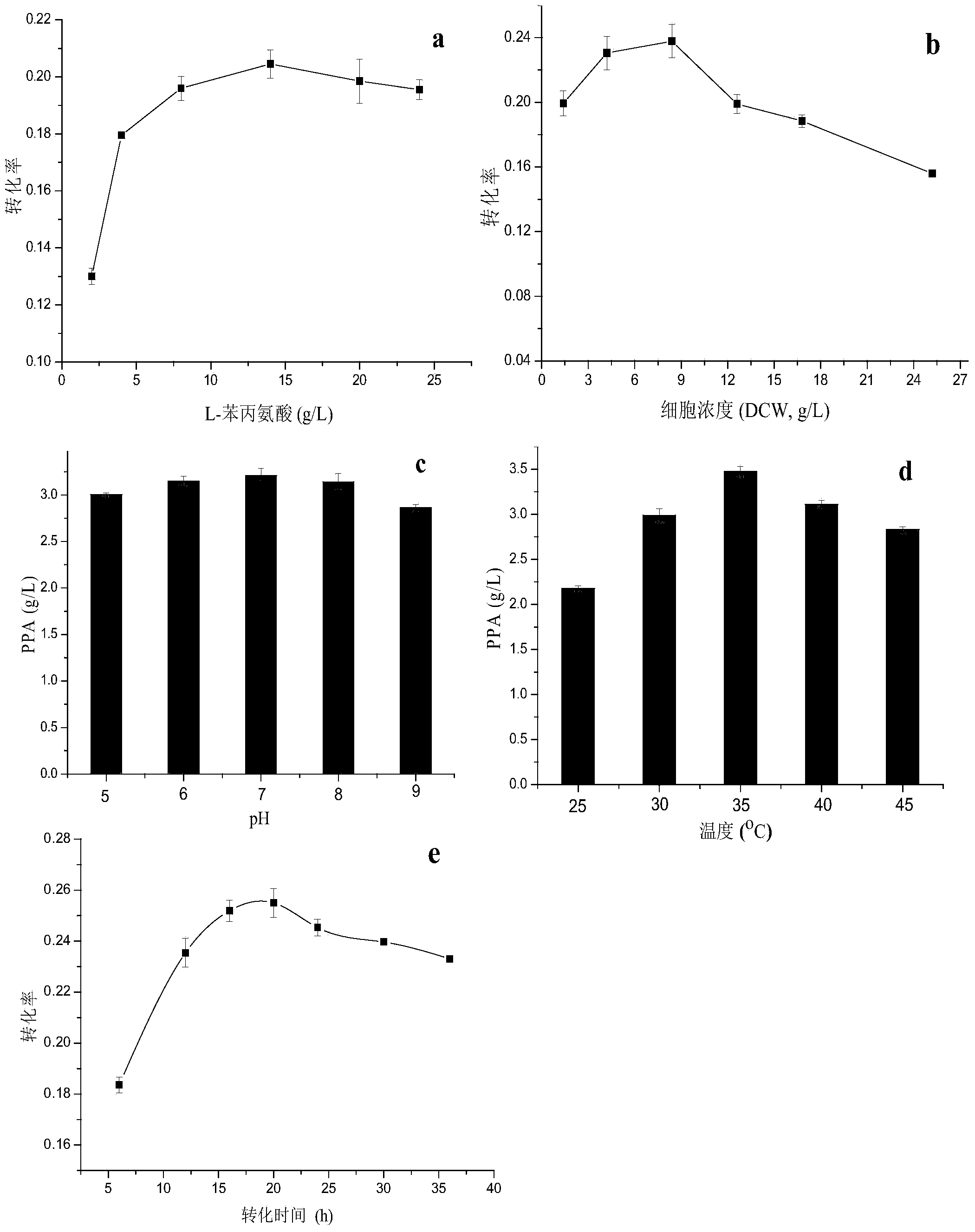
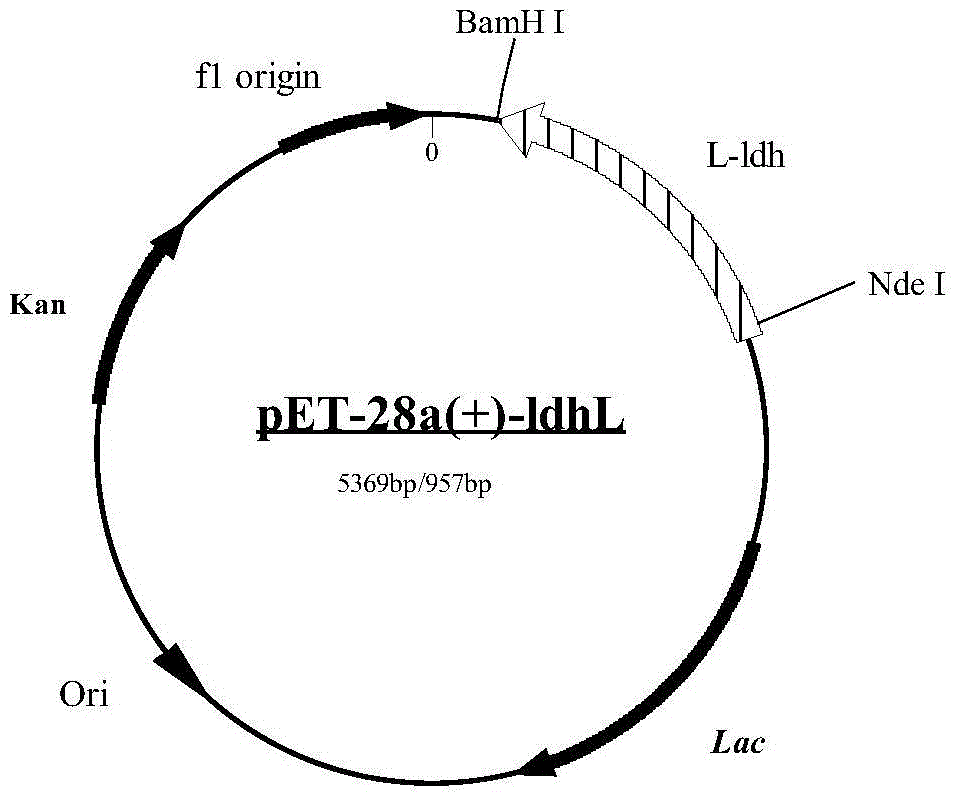
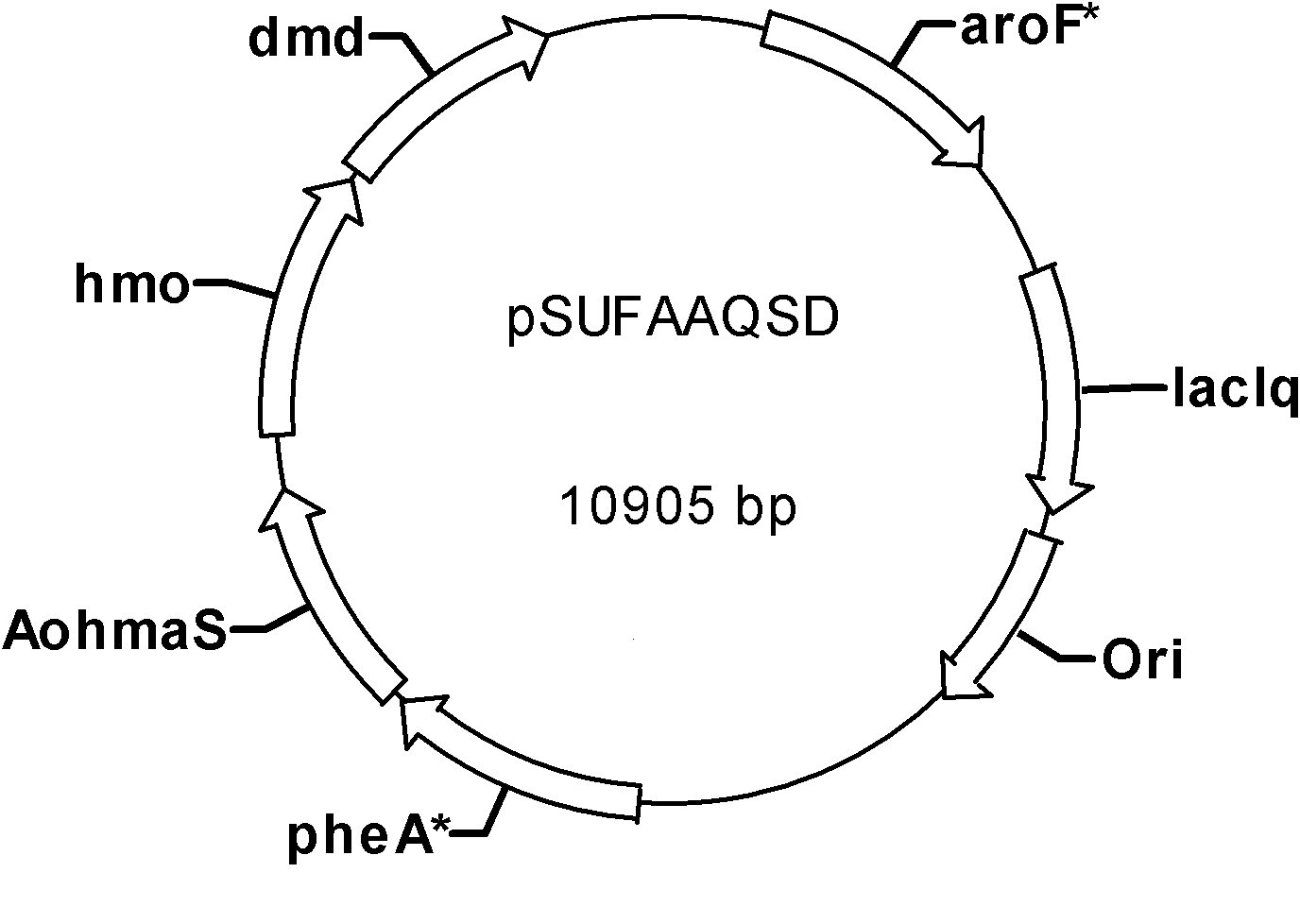
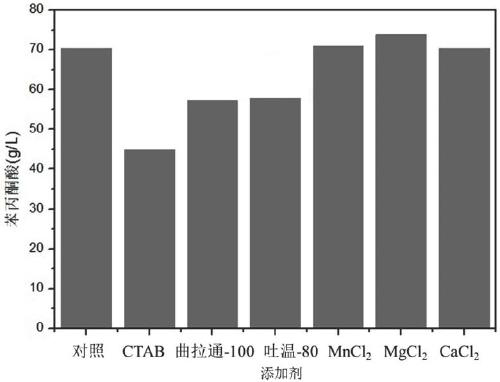
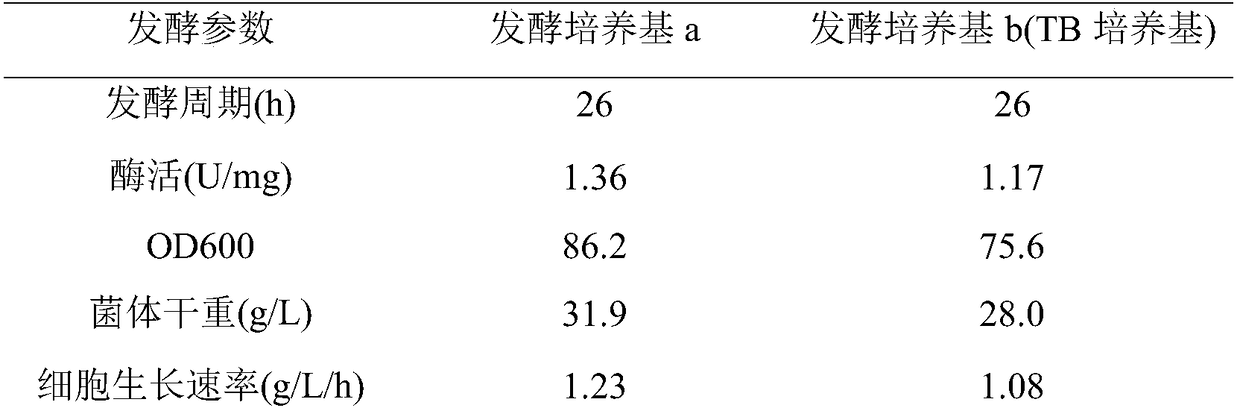
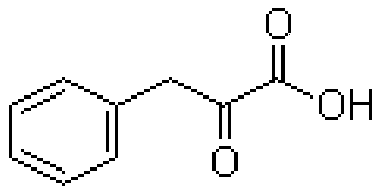
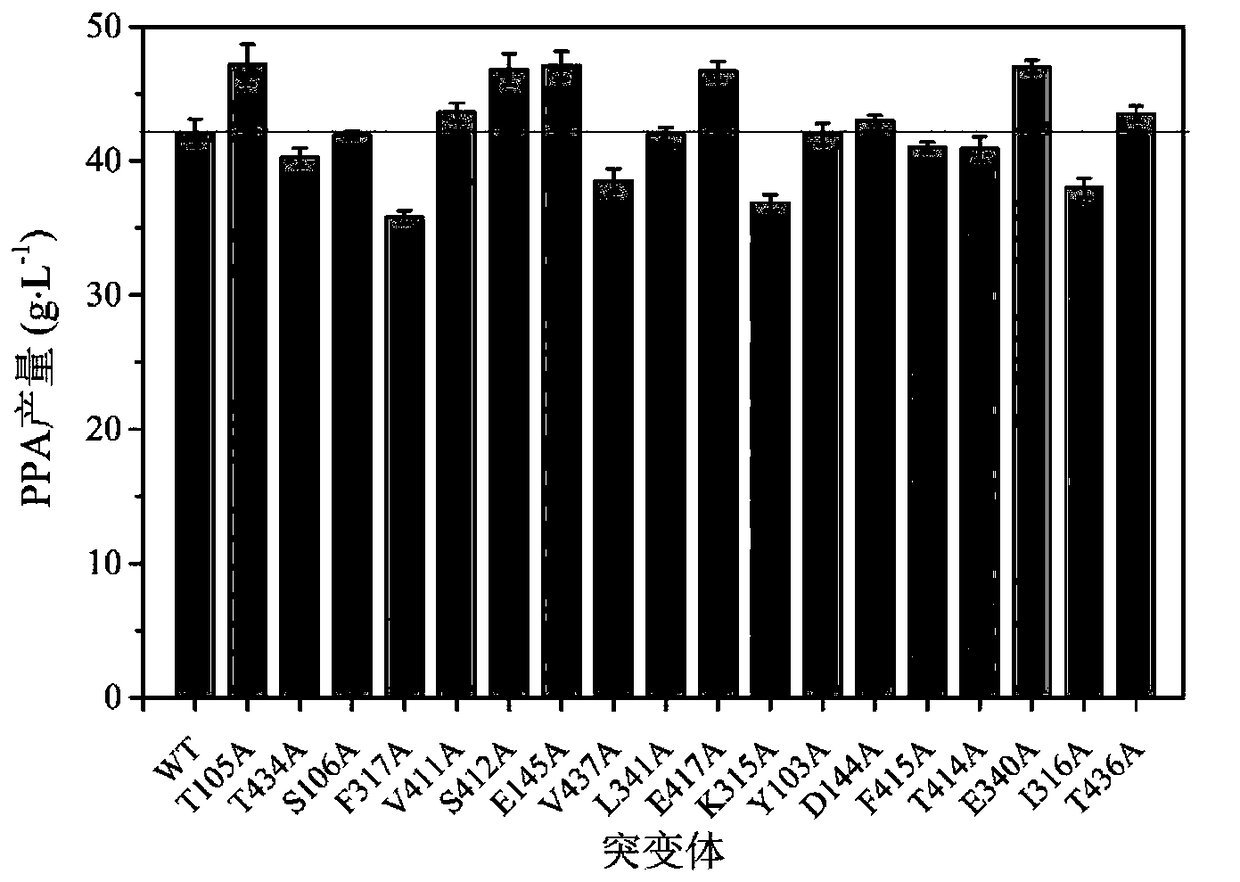
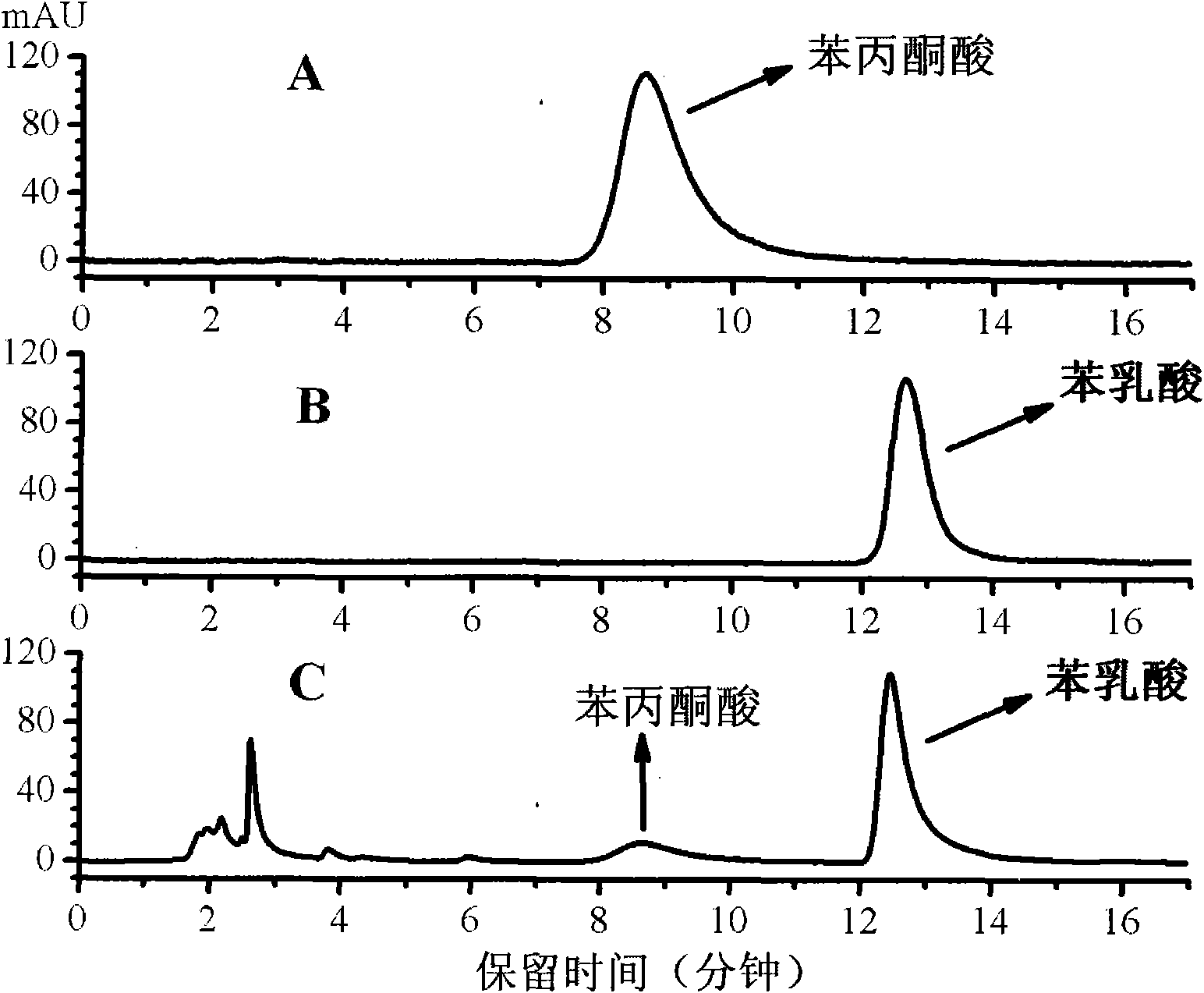
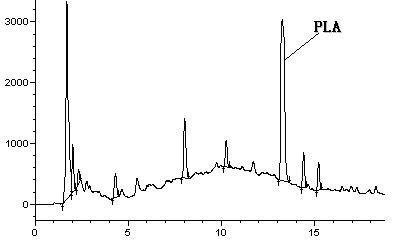
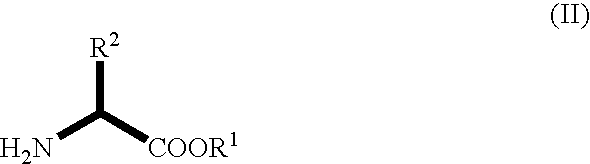Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Phenylpyruvic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
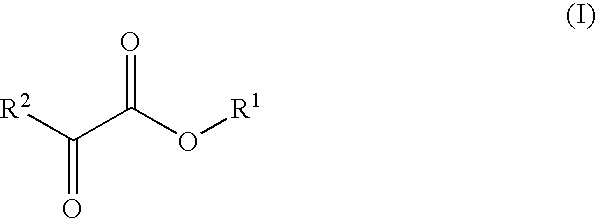
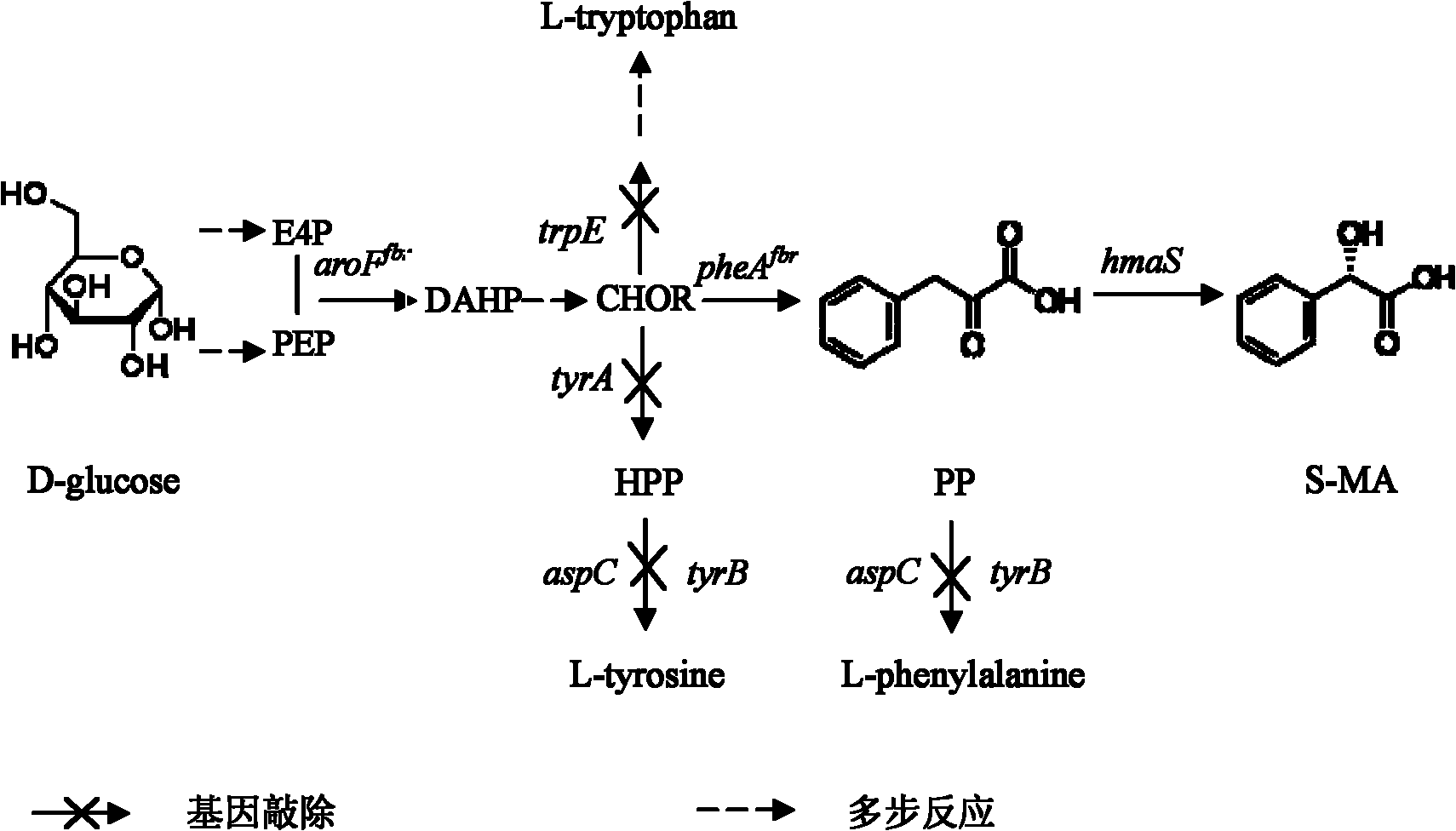
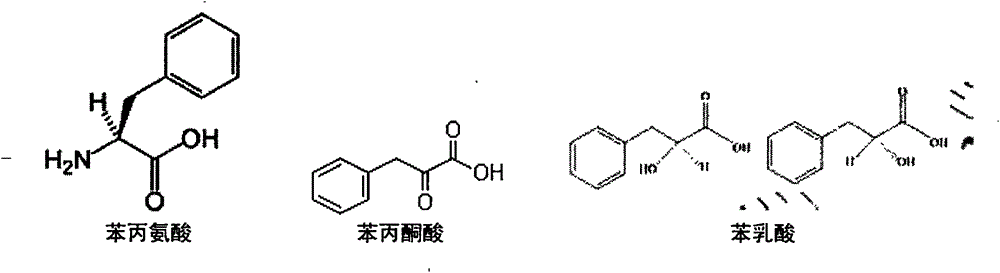
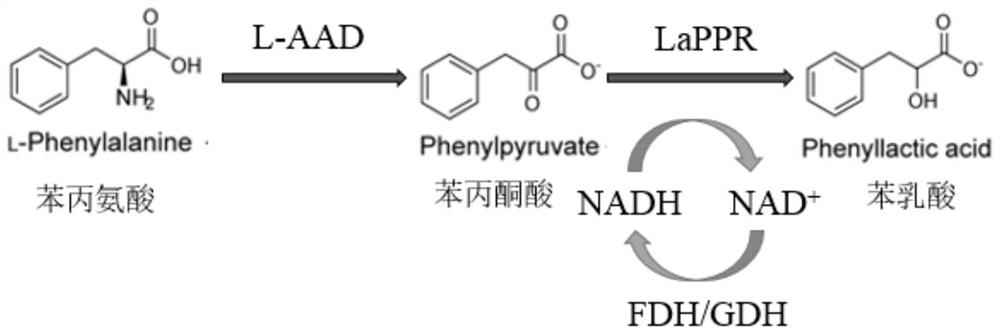
Phenylpyruvic acid is the organic compound with the formula C₆H₅CH₂C(O)CO₂H. It is a keto acid.
Bacterial strain for preparing phenyllactic acid and method for preparing phenyllactic acid through bacterial strain fermentation
InactiveCN102604858AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood additiveBacterial strain
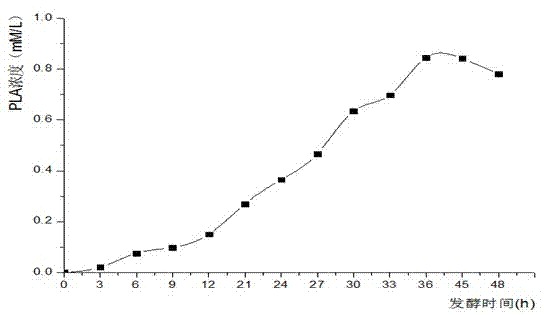
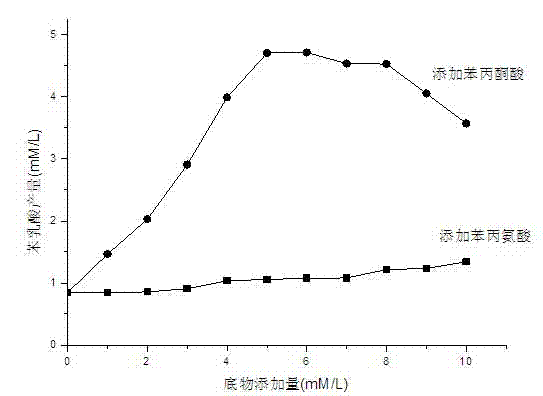
The invention provides a bacterial strain for preparing a phenyllactic acid and a method for preparing phenyllactic acid through bacterial strain fermentation, belonging to the food biotechnology. The invention discloses a pediococcus lactobacillus for preparing phenyllactic acid and particularly relates to Pediococcus pentosaceus SK25 capable of preparing phenyllactic acid, which is preserved inthe China center for type culture collection with a collection number of CCTCC NO: M2011360. According to the method provided by the invention, the pediococcus is used as a starting bacterial strain.In an MRS (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus) culture medium fermentation liquor, the content of phenyllactic acid reaches 0.8 mmol / L. At present, the reported maximum yield of wild bacterial strains in the MRS culture medium fermentation liquor is only 0.57 mmol / L. When phenylalanine or phenylpyruvic acid is added to the MRS culture medium, the yield of phenyllactic acid is improved. If the phenylpyruvic acid is added in the MRS culture medium, the improvement of the yield of the phenyllactic acid is obvious, and the optimal addition quantity is determined to be 5-6 mmol / L. The product obtained by the invention is safe and reliable, can be used as a medicinal intermediate and a food additive, and has a very strong antibacterial and antiseptic function.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A genetically engineered bacterium producing 2-phenylethanol and an applying method thereof
ActiveCN106566794AImprove cycle efficiencyDisinhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenethyl alcoholPhenylpyruvate decarboxylase
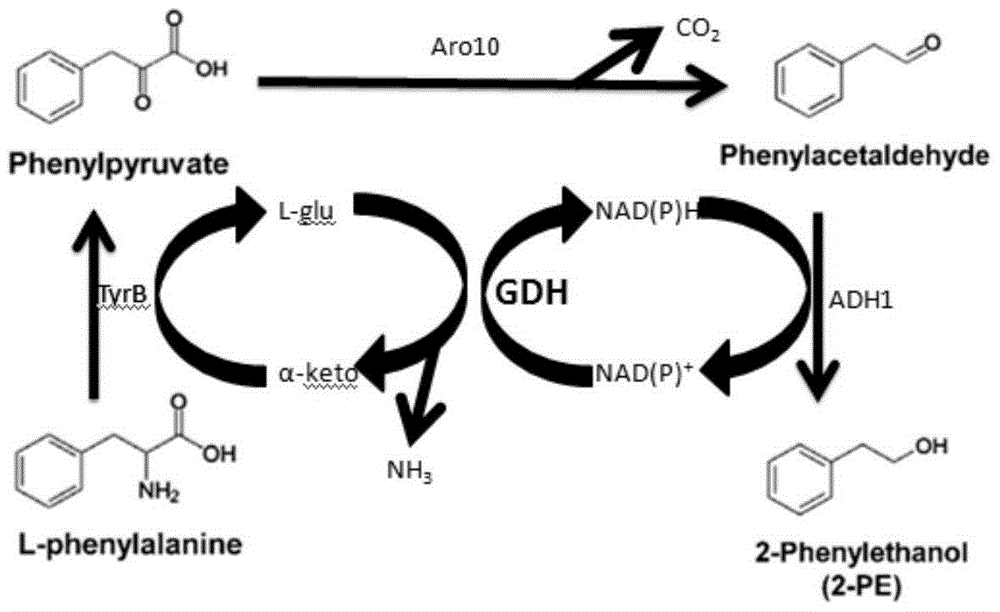
A genetically engineered bacterium producing 2-phenylethanol and an applying method thereof are disclosed. The recombinant bacterium is constructed by coexpressing aromatic amino acid aminotransferase and exogenous phenylpyruvate decarboxylase (Aro10) (or indole-3-pyruvic acid decarboxylase), phenylethanol dehydrogenase or phenylacetaldehyde reductase in escherichia coli to obtain the recombinant bacterium producing the 2-phenylethanol. Glutamate dehydrogenase is coexpressed on this basis to achieve self-balancing cofactor circulation, thus increasing the yield of the 2-phenylethanol. The conversion ratio of the 2-phenylethanol prepared through the recombinant bacterium is high. The bacterium and the method have important application value in production of the 2-phenylethanol in the future.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel dehydrogenase and a gene encodign the same
InactiveUS20060205045A1High yieldProduced industrially and inexpensivelyFungiSugar derivativesPhenylpyruvic acidSubstrate specificity
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Production of biological antiseptic agent phenyllactic acid
InactiveCN1940078AImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationAntiseptic AgentMaltose
Production of biological antiseptic benzyl lactic acid is carried out by taking lactic acid as bacteria, taking phenylalanine, phenyl-pyruvic acid or sodium phenyl-pyruvic acid as conversion substrate, adding into fermentation culture medium with carbon source, nitrogen source and inorganic salt, preparing benzyl lactic acid by biological conversion, culturing lactic acid in MRS culture medium at 25-40degree and inspecting. The fermentation culture medium carbon source is selected from glucose, maltose, lactose or cane sugar; nitrogen source is selected from corn liquor, yeast cream, protein peptone and soy mill cake. The concentration of benzyl lactic acid reaches to 50-150mg / 100ml. It's safe, reliable and has excellent sterilizing function.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Use of keto acids to enhance the flavor of cheese products
Process for enhancing the flavour of a cheese or of a cheese-flavoured food product whose preparation comprises a maturation step in the presence of lactic acid bacteria, characterized in that a preparation additive comprising at least one keto acid chosen from the group consisting of alpha-ketoglutaric acid, alpha-ketoisocaproic acid ketoisovaleric acid and phenylpyruvic acid is used to increase the catabolism of the amino acids in the cheese or food product by the said bacteria.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE
Novel dehydrogenase and a gene encoding the same
InactiveUS20050124040A1Generate efficientlyEfficient productionFungiBacteriaPhenylpyruvic acidPyruvic acid acetal
The object of the present invention is to provide a novel dehydrogenase having a property which is different from that of known dehydrogenases. The present invention provides a dehydrogenase having the following physicochemical properties: (1) effect: to produce N-alkyl-L-alanine from pyruvic acid and alkylamine or dialkylamine using NADPH and / or NADH as coenzyme; (2) substrate specificity: to show activity to alkylamine or dialkylamine but not to ammonium; (3) optimal pH when using phenylpyruvic acid and methylamine as substrates is around 10; and (4) when treated at 30° C. for 30 minutes, the enzyme is stable at around pH 5 to 10.5.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Escherichia coli engineering strain having high phenethyl alcohol yield and application thereof
InactiveCN102851253APromote productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEthanol dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli engineering strain having high phenethyl alcohol yield and application thereof. An Escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium capable of substantially accumulating phenylalanine (L-Phe) is used as an original strain (the fermentation level of the shake flask fermented phenylalanine can be up to 6.0g / L); phenylpyruvic acid decarboxylase (KDC) and alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH1) are subjected to independent expression and appropriate gene combination to co-express two key enzyme genes so as to construct a recombinant strain; the recombinant strain capable of co-expressing phenylpyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase can produce 130mg / L of beta-phenethyl alcohol, and the phenylalanine yield is 5.0g / L; and the accumulation of phenethyl alcohol can not be detected in the whole fermentation process of the Escherichia coli having high L-Phe yield of the original strain used as a control strain. The invention provides a method for enabling Escherichia coli to directly produce phenethyl alcohol through the fermentation of glucose used as a unique carbon source by means of a metabolic engineering means by using enzyme genes which can realize over-expression and are derived from anabolic pathways of different hosts.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing alpha-phenylpyruvic acid efficiently through whole cell transformation
InactiveCN103642743ASolve the problem of energy consumptionThe solution steps are cumbersomeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for producing alpha-phenylpyruvic acid efficiently through whole cell transformation and belongs to the fermentation engineering field. Heterologous expression of P. mirabilis amino acid deaminases is carried out in colibacillus. L-phenylalanine is transformed by utilization of the strains to produce alpha-phenylpyruvic acid. The transformation conditions are optimized, and efficient production of alpha-phenylpyruvic acid through whole cell transformation is achieved. Compared with traditional chemical methods, the method is advantaged by low cost, simple operation, environmental protection, and lays the foundation for industrial biotransformation production of alpha-phenylpyruvic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for adopting whole-cell conversion to efficiently produce alpha-phenylpyruvic acid
ActiveCN104830815AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenylpyruvic acidFermentation
The invention discloses a method for adopting whole-cell conversion to efficiently produce alpha-phenylpyruvic acid and belongs to field of fermentation engineering. The method includes that L-amino acid deaminase is modified to obtain an L-amino acid deaminase mutant with activity improved; L-phenylpyruvic acid is converted by recombinant strain whole-group cells containing the L-amino acid deaminase mutant to produce PPA, and conversion rate when L-phenylpyruvic acid is used to produce PPA is increased remarkably. A whole-cell conversion system is established in the method, so that the problems of troublesomeness in step, low yield and environment pollution when a chemical method is adopted to synthesize PPA and the problem of low conversion rate when PPA is produced through enzymatic conversion are solved, one-step PPA production which is pollution-free and high in yield is realized, and a certain theoretical foundation is laid for subsequent industrialized production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for producing phenyl-lactic acid by controlling pH value, feeding and fermenting
InactiveCN101333547AReduce pollutionPromote growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationHigh concentrationPhenylpyruvic acid
Disclosed is a method for producing phenyllactic acid by controlling pH value and fed-batch fermentation, which belongs to the food biotechnology field. The method uses lactobacillus as a strain which is inoculated in a fermentation tank with the volume of liquid ranging from 1 to 10L, the agitation speed is between 50 and 150 rpm, 6 to 10mol / L of sodium hydroxide is added after 6 to 12h, and the pH value is controlled at between 5.5 and 6.5; and glucose and substrate phenylpyruvic acid are supplemented to the fermentation tank in batch at the period between 12 to 54h in the fermentation process, and a fermentation broth containing phenyllactic acid is obtained after the cultivation for 70 to 90h. The method has the advantages that: the high-concentration substrate inhibition is eliminated and nutritive materials are also supplemented through controlling the pH value in the fermentation environment and supplementing a carbon source and the substrate, so the thalli can grow in the suitable environment, the content of phenyllactic acid reaches 6 to 20g / L after the fermentation, the process is simple, the environmental pollution is less, the operation is convenient, and the output of phenyllactic acid is high.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant Escherichia coli construction and (S)-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropionic acid synthesis method
InactiveCN104878024ASimple cultivation conditionsImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacillus megaterium
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing chiral monomer mandelic acid
InactiveCN102086462AIn line with the development directionImprove sustainabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenylpyruvic acidPara-hydroxymandelic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing S-mandelic acid or R-mandelic acid and a method for converting S-mandelic acid into R-mandelic acid. The method comprises the following steps: catalyzing phenylpyruvic acid by using p-hydroxymandelic acid synthetase or mandelic acid synthetase to obtain S-mandelic acid; and catalyzing the S-mandelic acid by using p-hydroxymandelic acid oxidase or mandelic acid oxidase or mandelic acid dehydrogenase, and D-mandelic acid dehydrogenase or D-mandelic acid reductase to obtain R-mandelic acid. The method provided by the invention can be used for in-vitro preparation of single-configuration S-mandelic acid or R-mandelic acid; meanwhile, the enzymes can be combinedly over-expressed to ferment glucose, thereby obtaining S-mandelic acid or R-mandelic acid; and the method can be used for chirally splitting DL-mandelic acid to generate R-mandelic acid or S-mandelic acid, or converting S-mandelic acid into R-mandelic acid. When being used for synthesizing S-mandelic acid or R-mandelic acid by fermentation and culture, the method is sustainable and can lower the cost; and in addition, the method is mild, and friendly to environment and human.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
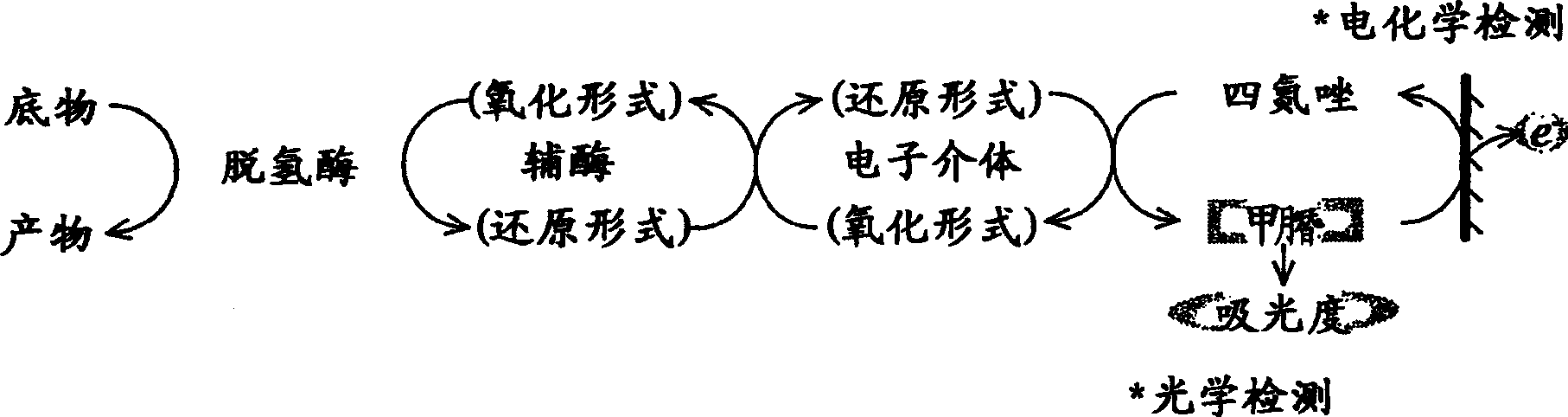
Method and apparatus for examining diseases with inborn errors of metabolism
InactiveCN1461347AEasy to operateAvoid the need to prepare reagentsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTert-leucinePhenylalanine
A method of conveniently and quickly quantitating subject substances which comprises using as reaction reagents at least dehydrogenases specific respectively to branched amino acids containing D-galactose and L-leucine and phenylalanine, which are the substances contained in biological samples to be assayed, coenzymes, an electron mediator and a tetrazolium salt and detecting formazan, which has been finally formed depending on the concentrations of the subject substances by the enzymatic reactions and oxidation reactions of the biological samples with the reaction reagents, by using both or one of an optical detection procedure and an electrochemical detection procedure, thereby embodying a convenient and quick examination of three diseases with inborn errors of metabolism, i.e., galactosemia, maple syrup urine disease and phenylketonuria.
Owner:SAPPORO IMMUNO DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Technology for producing phenylpyruvic acid by phenylalanine through enzymatic conversion
ActiveCN109022338AThe conversion system is simpleEasy to purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenylpyruvic acidBio engineering
The invention discloses a technology for producing phenylpyruvic acid by phenylalanine through enzymatic conversion and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the technology disclosed by the invention, a proteus mirabilis derived amino acid deaminase mutant is subjected to codon optimization and fermentation condition optimization and the enzyme activity of amino acid deaminase is remarkably improved. Furthermore, a conversion condition is optimized and the yield of the phenylpyruvic acid is remarkably improved; when the adding amount of wet strains is 25 to 30g / L, the yield of the phenylpyruvic acid can reach 81.1 to 83.0g / L and the mol conversion rate of the phenylpyruvic acid reaches 98.0 percent or mor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Lactobacillus casei and application thereof
ActiveCN106399195AHigh biosecurityHigh product concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenylpyruvic acidMicroorganism
The invention provides Lactobacillus casei and an application thereof in transforming and synthesizing microorganisms into phenyllactic acid. The Lactobacillus casei is named Lactobacillus casei HR S67 and is preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC No. M 2016216. With a bacterial strain of the Lactobacillus casei as an original strain, the phenyllactic acid can be synthesized by fermentation and cultivation, concentration of the fermented liquor can reach 20mg / L; with thallus of the Lactobacillus casei as a whole-cell catalyst, a converted solution containing the phenyllactic acid can be obtained by conducting microbial conversion on a substrate solution containing phenylpyruvic acid, wherein the concentration of the phenyllactic acid can reach 11.2g / L. The bacterial strain of the Lactobacillus casei is separated from pickle food and is a typical probiotics. As a catalyst for fermentation microorganisms or whole-cell microorganisms, the bacterial strain has not only good biosecurity but also the advantages of mild conditions for fermentation and transformation, high product concentration and easy product amplification in the converted solution and good industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for efficiently producing phenylpyruvic acid
ActiveCN108841844AIncrease productionIncrease production intensityBacteriaHydrolasesPhenylpyruvic acidThallus
The invention discloses a method for high-yield production of phenylpyruvic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the method provided by the invention, amino acid deaminase from proteus mirabilis is modified by a conformational dynamics engineering method, and the gene of the modified amino acid deaminase is connected to a pET 20b carrier and expressed in E. coliBL21 (DE3). A recombinant strain is cultured in a fermentation tank, and wet thallus converted alanine is collected to produce phenylpyruvic acid; and when the amount of wet thalli is 30g / L, the yield of phenylpyruvic acid can reach 72.5 g / L and the mol conversion rate of phenylalanine can reach 96.7% after 12h of conversion.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Hydrocarbon oil demetalization agent and method for hydrocarbon oil demetalization
ActiveCN105733657AHigh removal rateWeak corrosiveRefining with non-metalsDewatering/demulsification with chemical means2-ketobutyric acidKeto acid
The invention relates to a hydrocarbon oil demetalization agent and a method for hydrocarbon oil demetalization. The hydrocarbon oil demetalization agent is a keto acid, wherein the keto acid is any of alpha-keto acid, beta-keto acid and gamma-keto acid, and the alpha-keto acid is one of pyruvic acid, 2-ketobutyric acid, phenylpyruvic acid and benzoyl formic acid; the beta-keto acid is acetoacetic acid; and the gamma-keto acid is 4-ketovaleric acid. The method comprises the steps of carrying out mixed contact on hydrocarbon oil, water, the keto acid, which serves as the demetalization agent, and a demulsifier, and then, carrying out electric desalting, so as to achieve oil-water separation and remove metals from the hydrocarbon oil. A molecule of the demetalization agent disclosed by the invention contains a difunctional group, can be in chelation with the metals and can also be in complexation with the metals, so that the demetalization agent has a high removal ratio to the metals in the hydrocarbon oil; according to the demetalization agent, the acidity is between the acidity of organic acids and the acidity of inorganic acids, the corrosiveness is lower than that of the inorganic acids, and the demetalization rate is higher than that of the organic acids; and meanwhile, the demetalization agent is free of elements such as phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen and thus cannot cause adverse effects on subsequent processing.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Composition for preventing or/and treating insulin resistance and related diseases
The invention relates to metabolism of enteric microorganisms and phenylalanine and phenylpyruvic acid of the enteric microorganisms, and provides a composition containing phenyllactic acid or salts of phenyllactic acid and phenylpyruvic acid or salts of phenylpyruvic acid and used for preventing or / and treating insulin resistance and related diseases, use of the composition in preparation of a medicine or food for improving, preventing or treating insulin resistance and related diseases, and a method for preventing or treating insulin resistance and related diseases. The related diseases include intestinal dysbacteriosis, metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, podagra and tumors.
Owner:萧湘
Application of phenylpyruvate decarboxylase mutant M538A in biological fermentation production of phenethyl alcohol
ActiveCN110331173AIncrease enzyme activityReduced catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenethyl alcoholFermentation
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Microbial cell cryogel, preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN108384729ALarge apertureMicron-sized ultra-large poresBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPorosityPhenylpyruvic acid
The invention discloses a microbial cell cryogel for conversion synthesis of phenyllactic acid, a preparation method and application thereof. The microbial cell cryogel is an integral porous material,the matrix skeleton is a cross-linked Lactobacillus casei microbial cell, the pore size ranges from 1 to 50 micrometers, the porosity is 36.9-95.2%, and the water permeability is 1*10<-15>-3*10<-13>m<2>. Serving as a biocatalyst, the cryogel can achieve conversion synthesis of a phenylpyruvic acid key substrate into phenyllactic acid, and the maximum conversion yield can reach 75%. The microbialcell integral cryogel provided by the invention has the advantages of large pore size, high porosity, fast substrate and product mass transfer, good bio-safety, reusability, simple preparation method, and low cost, and has broad application prospects in the biochemical synthesis field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Heat-resistant bacillus and application thereof in preparing phenyl lactic acid
ActiveCN101831394ASimple ingredientsShorten the growth cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenylpyruvic acidPreservative
The invention discloses a heat-resistant bacillus, which has a name of Bacillus sp.SDM, is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on January 18, 2010, and has a preservation registration number of CCTCC No.M 2010012. The invention simultaneously discloses application of the heat-resistant bacillus in preparing phenyl lactic acid through biological transformation of phenylpyruvic acid, which comprises the steps of (1) slant cultivation, (2) seed culture, (3) preparation of a cell suspension, (4) transformation, (5) sample processing and detection and the like. The method for preparing the phenyl lactic acid by using the heat-resistant bacillus has the characteristics of simple operation, high substrate transformation efficiency, high speed and high yield of the product of the phenyl lactic acid, and has a great application prospect in preparing a biological preservative namely the phenyl lactic acid.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
Lactobacillussp.W2 strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101906392APromote growthEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhenylpyruvic acid
The invention relates to Lactobacillussp.W2. The preservation number of the Lactobacillussp.W2 is CCTCCM209318. The invention also relates to application of the Lactobacillussp.W2 in biologically transforming phenylpyruvic acid substrate and extracting phenyllactic acid from fermentation solution by using ethyl acetate. The Lactobacillussp.W2 is from the traditional fermented food, belongs to an acknowledged safe strain and can be applied to food; the strain grows well on an MRS culture medium and is easily cultured and stored; and the content of the phenyllactic acid obtained by fermentation can reach 1.038 grams per liter, and the phenyllactic acid has strong capability of inhibiting putrefactive bacteria in the food.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for synthetizing D-phenyllactic acid through recombinant Escherichia coli
InactiveCN104099350AIncrease productionHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to a recombinant lactate dehydrogenase gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, and tyrosine is mutated into any one of alanine, valine and leucine in the 52 position of the sequence. The invention further relates to recombinant Escherichia coli containing the recombinant lactate dehydrogenase gene and a method for synthetizing D-phenyllactic acid through the recombinant Escherichia coli. According to the method, the tyrosine on a substrate recognition site of D-LDH is replaced by smaller hydrophobic amino acid residue-valine with a site-directed mutagenesis technology, so that the affinity and the catalytic efficiency of the D-LDH to substrate phenylpyruvic acid are improved, after conversion of an expression host, the yield of phenyllactic acid is significantly increased when being compared with that of un-mutated strains, and after whole-cell conversion for 6 h, the yield of the phenyllactic acid is increased from 18 g / L to 24.6 g / L.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Recombinant bacterium providing improved efficiency in convertive production of Alpha-phenylpyruvic acid
ActiveCN105647846AImprove regeneration efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium providing improved efficiency in convertive production of Alpha-phenylpyruvic acid and belongs to the field of biotechnology. Co-expression of L-amino acid deaminase and halogenase in Escherichia coli is successfully implemented herein, coenzyme regeneration is improved, and PPA yield is up to 18.3 g / L. By establishing this whole-cell conversion system, the problems of step complexity, low yield, environmental pollution and the like in chemical synthesis of PPA are solved, the problem that enzymatic convertive production of PPA is low in conversion efficiency is solved, pollution-free, high-yield and one-step PPA production is implemented, and certain theoretical basis is laid for following industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
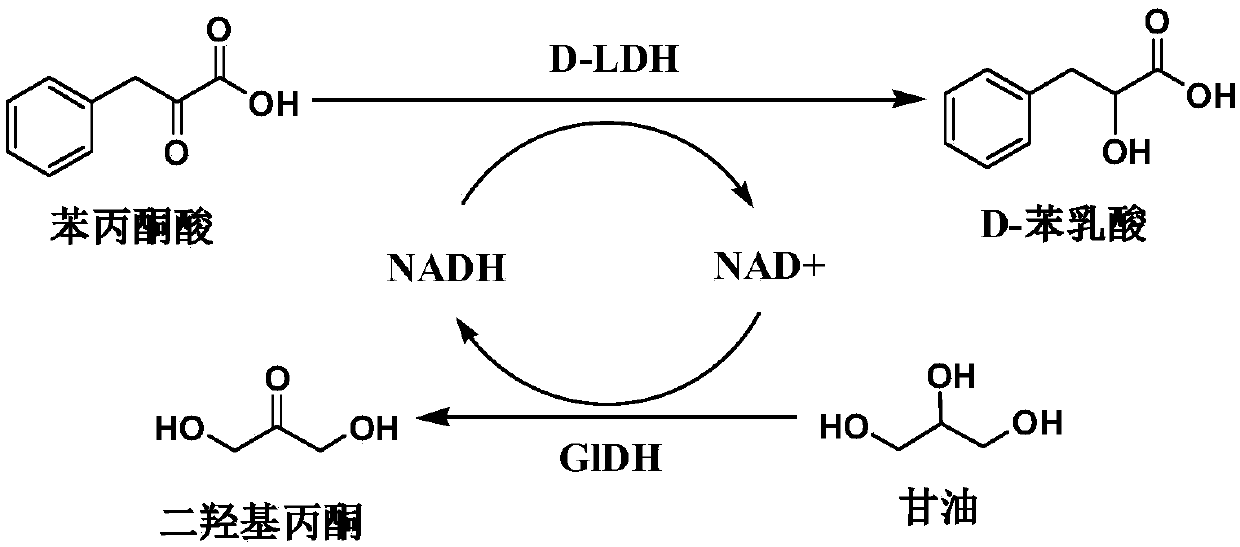
Difunctional fusion protein and method for producing D-phenyllactic acid from same
InactiveCN109628419AEasy to synthesizeReduce usageBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLactate dehydrogenaseChemical synthesis
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation, particularly relates to D-lactic dehydrogenase and glycerol dehydrogenase fusion protein, and relates to a method for generatingD-phenyllactic acid through whole-cell catalysis of engineering bacteria containing the fusion protein. A gene fusion strategy is utilized, D-lactic dehydrogenase (D-LDH) and glycerol dehydrogenase (GlDH) are subjected to fusion expression and introduced into a D-phenyllactic acid anabolism means for the first time, and in the reaction of asymmetric synthesis of the D-phenyllactic acid (D-PLA) with phenylpyruvic acid as a substrate, regeneration of coenzyme factors and production of the high-yield D-phenyllactic acid are achieved. The cost is low, the safety is high, glycerol is converted into dihydroxy acetone, and the fusion protein can serve as an important medicine and chemical synthesis intermediate, is widely applied to fine chemical industry, food industry and cosmetic industry andis high in additional value.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Construction and expression of D-LDH-FDH fusion gene capable of improving D-phenyllactic acid yield
ActiveCN104845988AKeep aliveHigh activityOxidoreductasesFermentationLactate dehydrogenaseEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a cDNA sequence of a D-LDH-FDH fusion gene capable of improving D-phenyllactic acid yield, wherein the cDNA sequence is formed by a D-LDH gene, a DNA sequence of connecting peptide and an FDH gene through serial connection. The invention further provides a construction method and an expression method for the fusion gene. By serially connecting lactic dehydrogenase and formic dehydrogenase through the connecting peptide to obtain fusion protein, activities of two enzymes are kept after the protein is expressed in colon bacillus, the enzyme activity of lactic dehydrogenase in the fusion protein is higher than the activity during single expression and is higher than the activity during separate expression of lactic dehydrogenase and formic dehydrogenase in the same cell, and a stronger catalytic effect is reflected when phenylpyruvic acid is catalytically converted into phenyllactic acid.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Lactobacillus buchneri 8-2N and application thereof in preparation of phenyllactic acid
ActiveCN106399181AHigh biosecuritySynthetic conversion is goodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenylpyruvic acidMicroorganism
The invention discloses lactobacillus buchneri 8-2N and application thereof in preparation of phenyllactic acid. A strain provided by the invention is used as an original strain for synthesizing phenyllactic acid through metabolism by virtue of a microbial fermentation method; and a bacterial cell of the fermented strain is taken as a whole-cell catalyst, phenylpyruvic acid is taken as a key substrate, and synthesized phenyllactic acid can be converted by virtue of a microbial conversion method. The strain is separated from traditional pickles, has good biosecurity and very good capacity of producing phenyllactic acid through synthesis conversion, can grow relatively rapidly in a conventional MRS fermentation culture solution and has a moderate fermentation cycle; when the bacterial cell is used for converting synthesized phenyllactic acid, the conversion reaction time is short, the conversion rate is high, the concentration of phenyllactic acid in a conversion solution can reach above 9g / L, and the conversion rate can reach 80%-90%; and lactobacillus buchneri 8-2N has a relatively good application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for synthesizing L-phenyllactic acid through whole-cell catalysis of recombinant microorganisms
PendingCN113025544ASolve the problem of expensive and poor stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing L-phenyllactic acid through whole-cell catalysis of recombinant microorganisms, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and genetic engineering. The invention provides an effective conversion system for synthesizing L-phenyllactic acid through whole-cell catalysis of phenylalanine by multi-enzyme tandem recombinant escherichia coli. According to the system, L-amino acid deaminase and phenylpyruvate reductase are used for catalyzing phenylalanine to synthesize L-phenyllactic acid for the first time, so that L-amino acid deaminase is successfully realized; a phenylpyruvate reductase and glucose dehydrogenase co-expression strain are constructed. The final yield reaches 21.39 g / L, and the molar conversion rate is 71.33%. Whole-cell catalytic synthesis of phenyllactic acid is adopted, the operation process is convenient, the conversion efficiency is superior to that of a previous L-phenyllactic acid biosynthesis method, theoretical and practical foundations are laid for industrial production and application of L-phenyllactic acid, and certain guiding significance is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
L-lactic dehydrogenase derived from Lactobacillus casei and application of L-lactic dehydrogenase
The invention discloses L-lactic dehydrogenase derived from Lactobacillus casei and application of L-lactic dehydrogenase, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The invention provides the L-lactic dehydrogenase, and realizes heterologous expression of the gene of the L-lactic dehydrogenase. A recombinant plasmid pET-22b(+)-Lcldh1 containing the gene is constructed, and is converted into escherichia coli to obtain recombinant escherichia coli E.coli / Lcldh1 containing the expression plasmid pET-22b(+)-Lcldh1. By taking 10mmol / L of phenylpyruvic acid as a substrate, whole-cell catalysis is performed on recombinant LcLDH1 engineering bacteria, and reaction lasts for 1h to obtain L-PLA (D-phenyllactic acid), wherein concentration of L-PLA is 8.59mmol / L; the yield is 85.9 percent, and eep is greater than 99 percent. Purified LcLDH1 reaches 294.2U / mg in specific activity; the L-lactic dehydrogenase shows relatively high catalytic activity and enantioselectivity, and has obvious application potentiality and economic value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Herbicide-resistant hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenases
ActiveUS10619138B2Improved and increased and resistanceImproved and increased toleranceBiocideFused cellsBiotechnologyPlant tissue
The present invention refers to method for producing a transgenic plant with increased herbicide tolerance or resistance as compared to a corresponding non-transformed wild type plant, comprising transforming a plant cell or a plant cell nucleus or a plant tissue with a nucleic acid molecule encoding a HPPD polypeptide, as well as to the nucleic acid, and plants with increased HPPD-inhibiting herbicide tolerance or resistance comprising the nucleic acid of the invention.
Owner:BASF SE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com