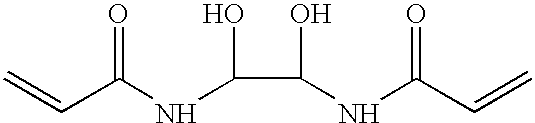
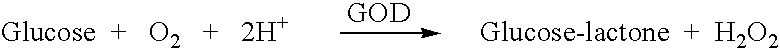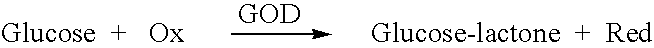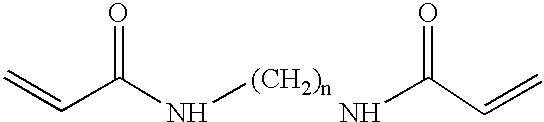Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1659 results about "Electrochemical detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrochemical detection (ECD) for HPLC or uHPLC is an extremely selective and sensitive detection technique that is applied in a number of analyses such as the neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin and noradrenalin. In combination with the proper electronics, ECD has an enormous linear dynamic range of more then 6 orders of magnitude.
Analyte measurement
InactiveUS20040096959A1Low viscosityMore suitedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrochemical detectorAnalyte
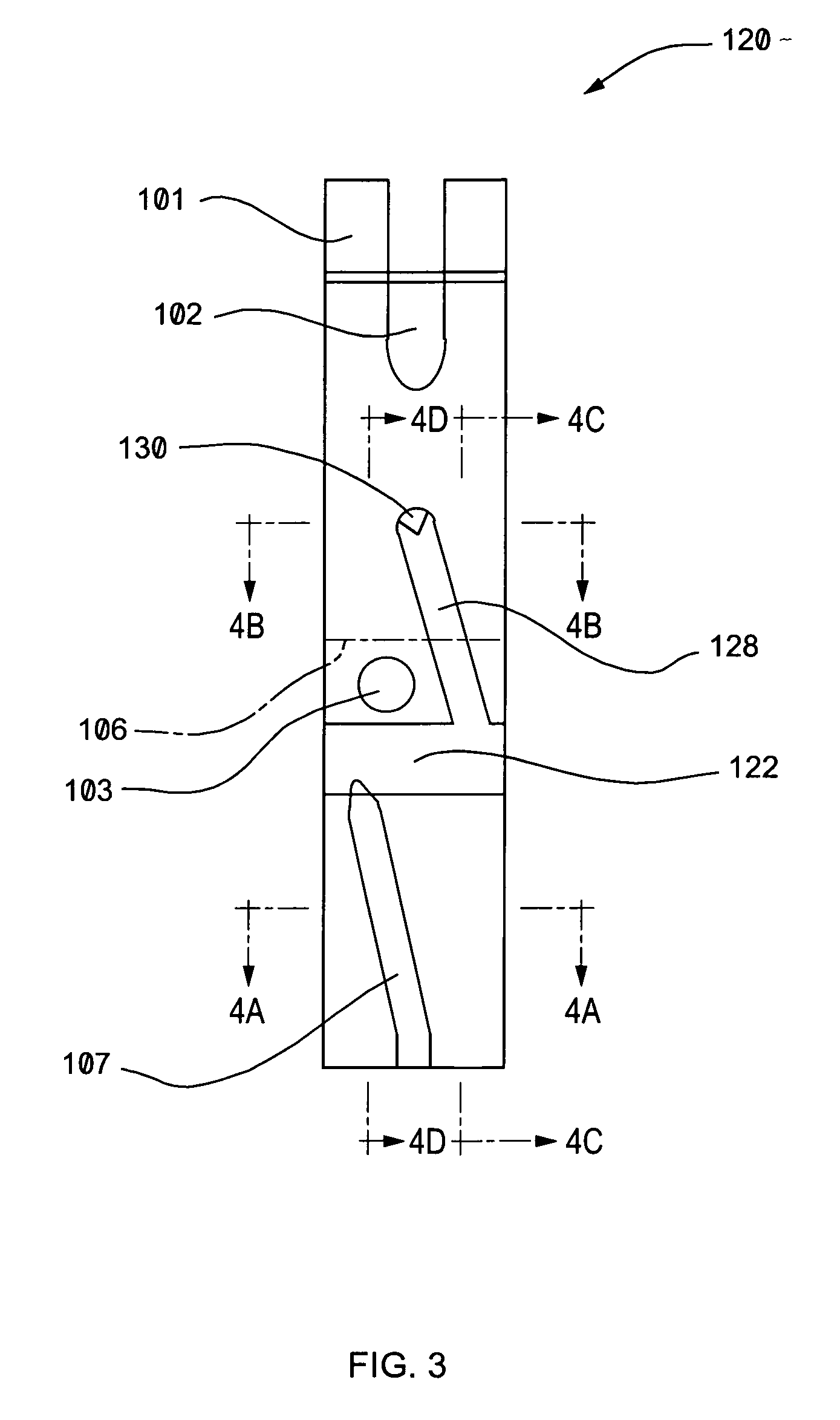
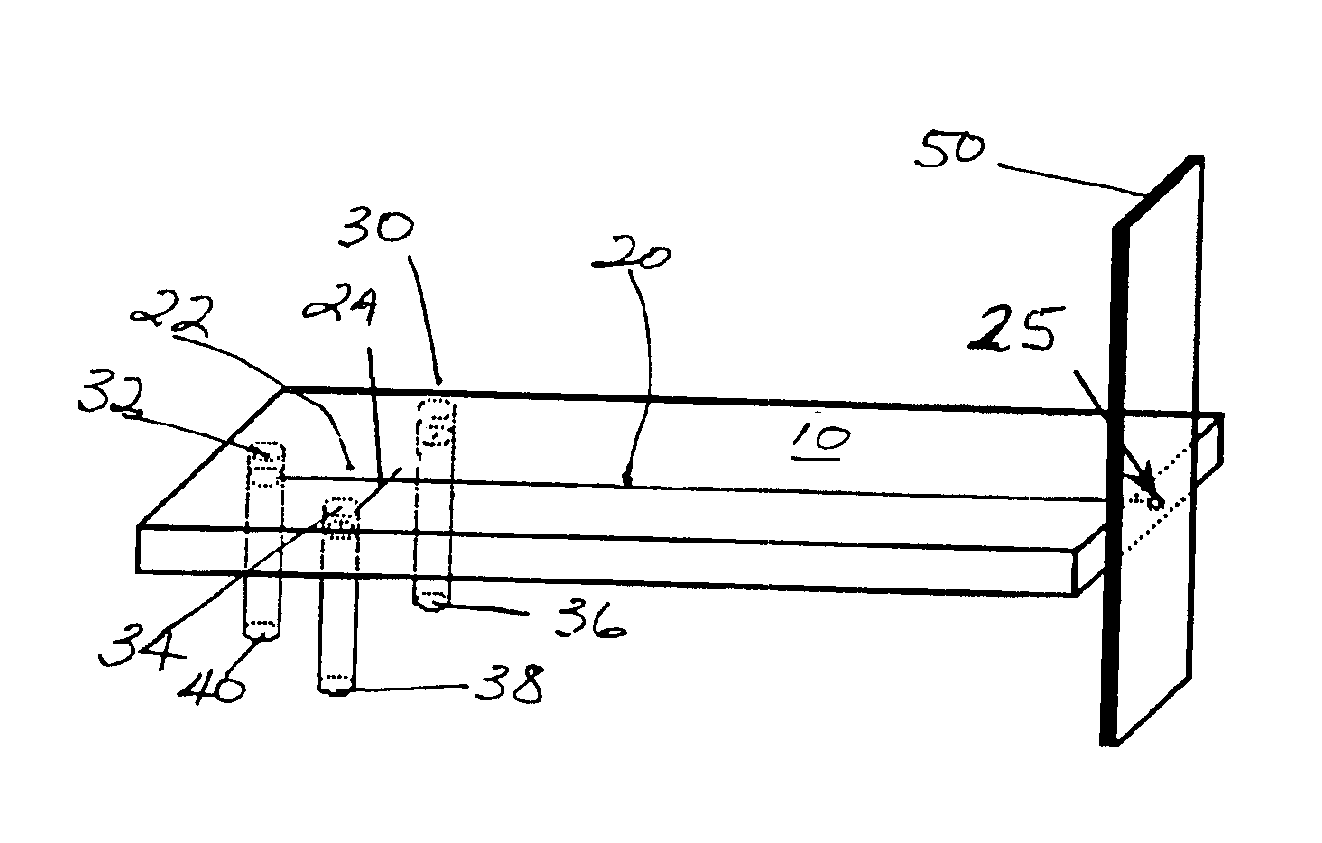
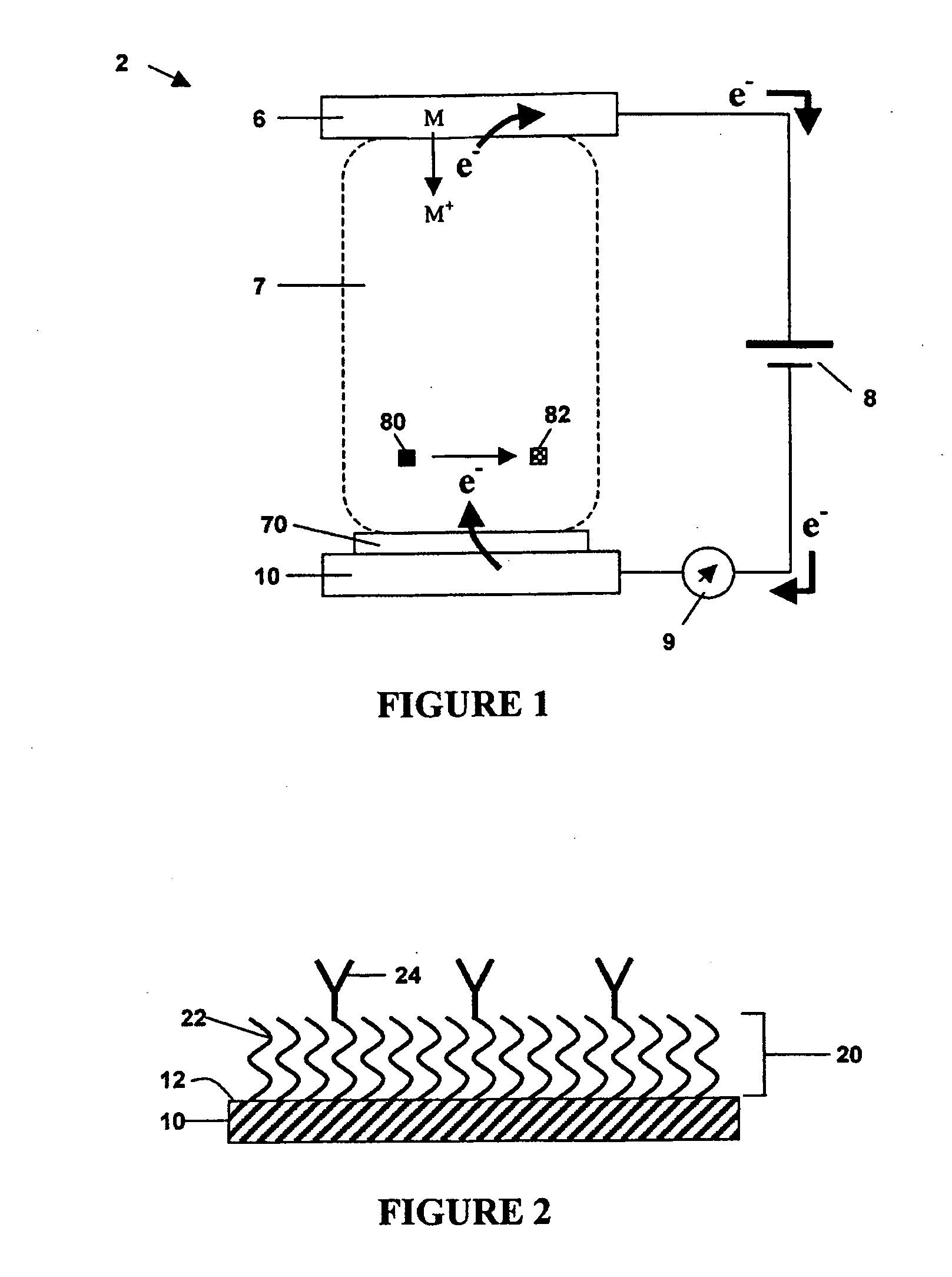
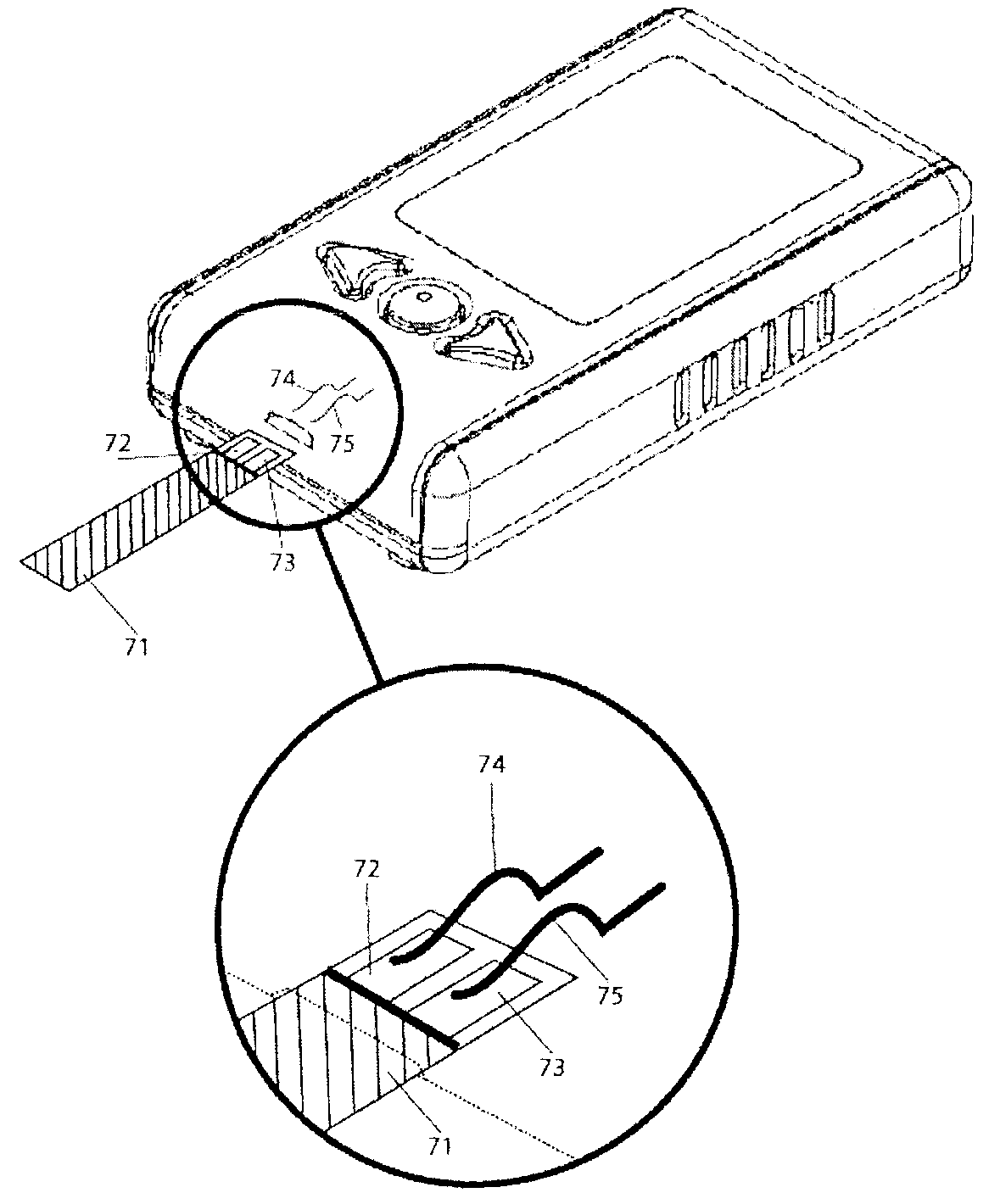
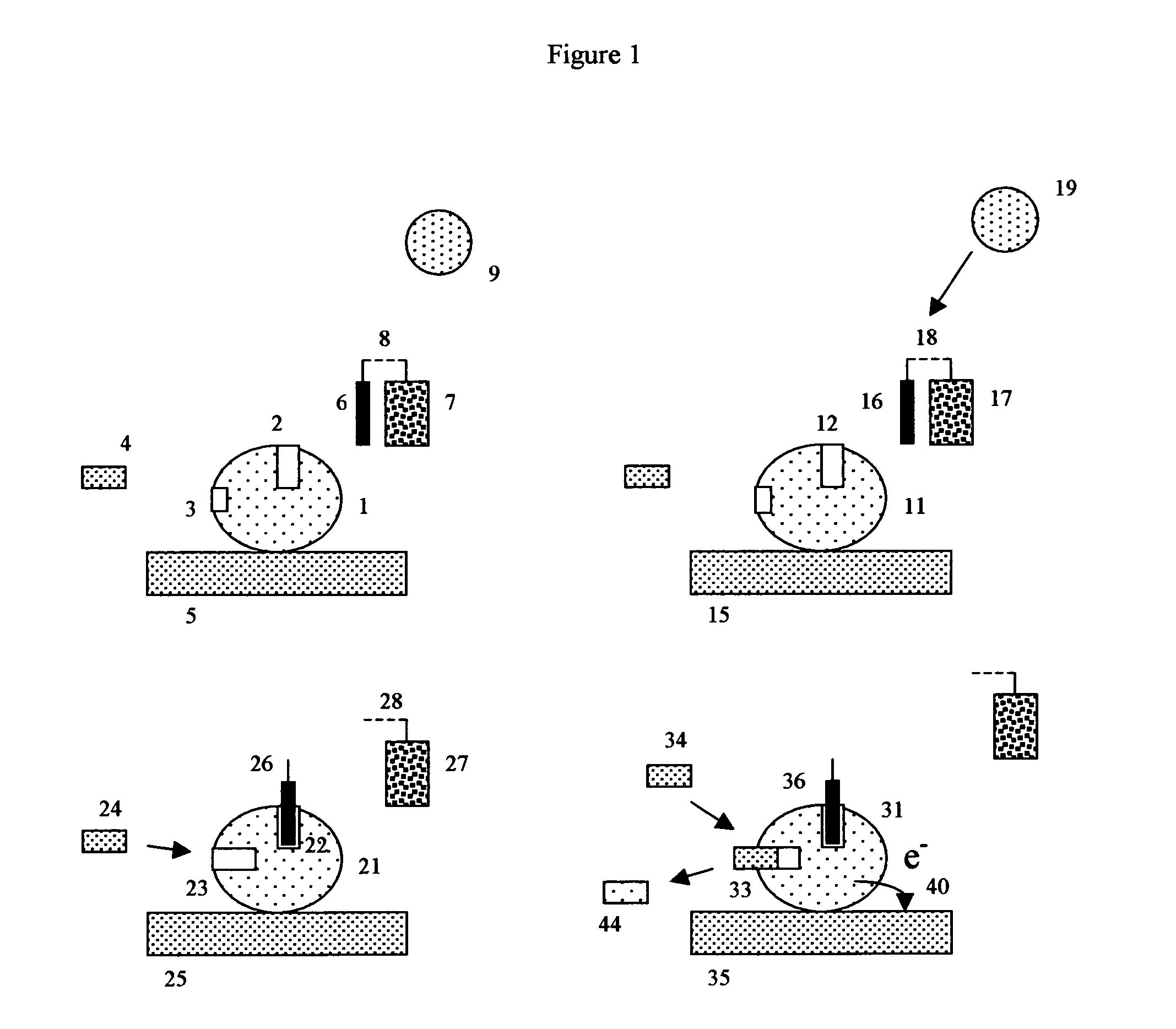
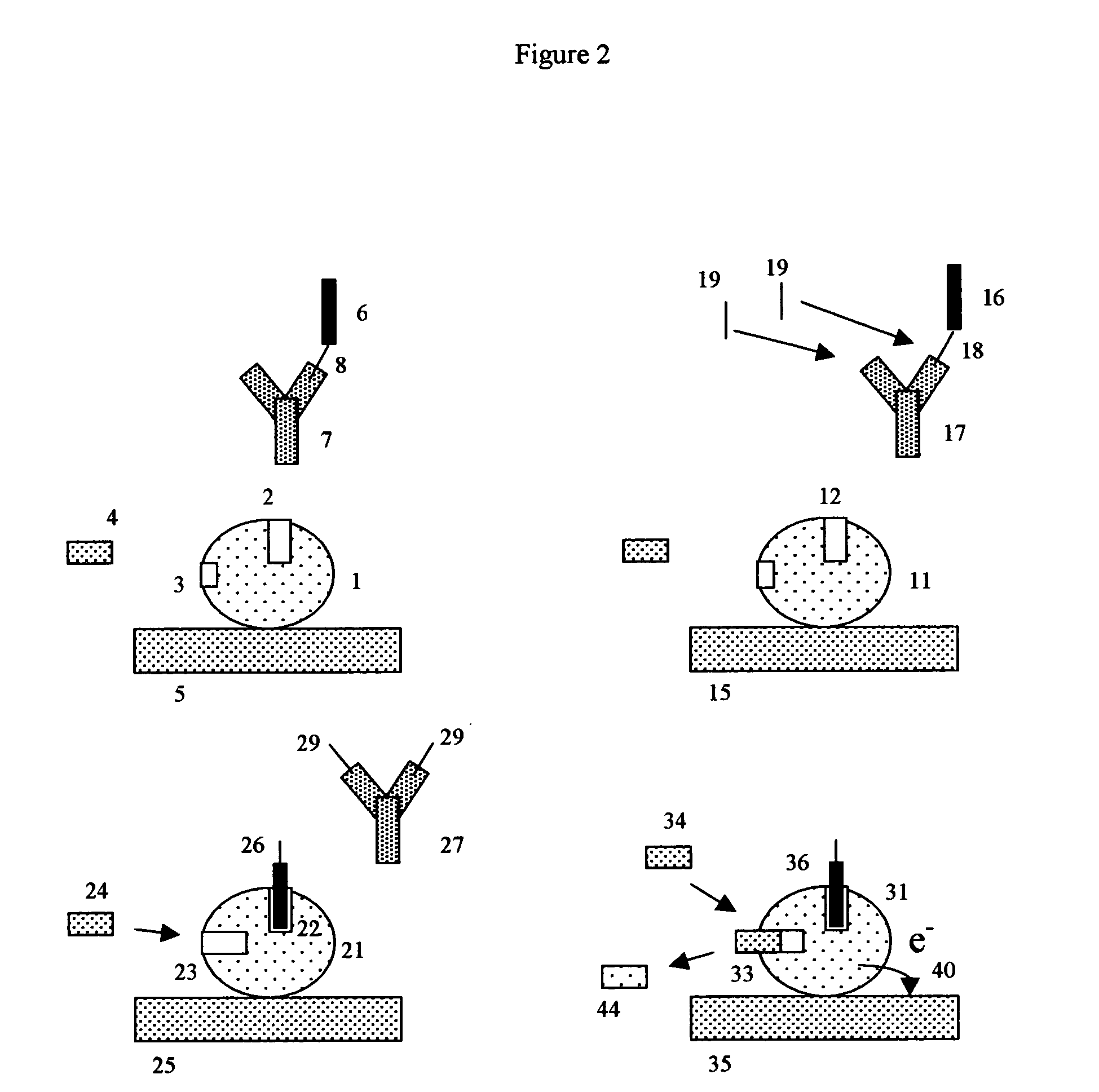
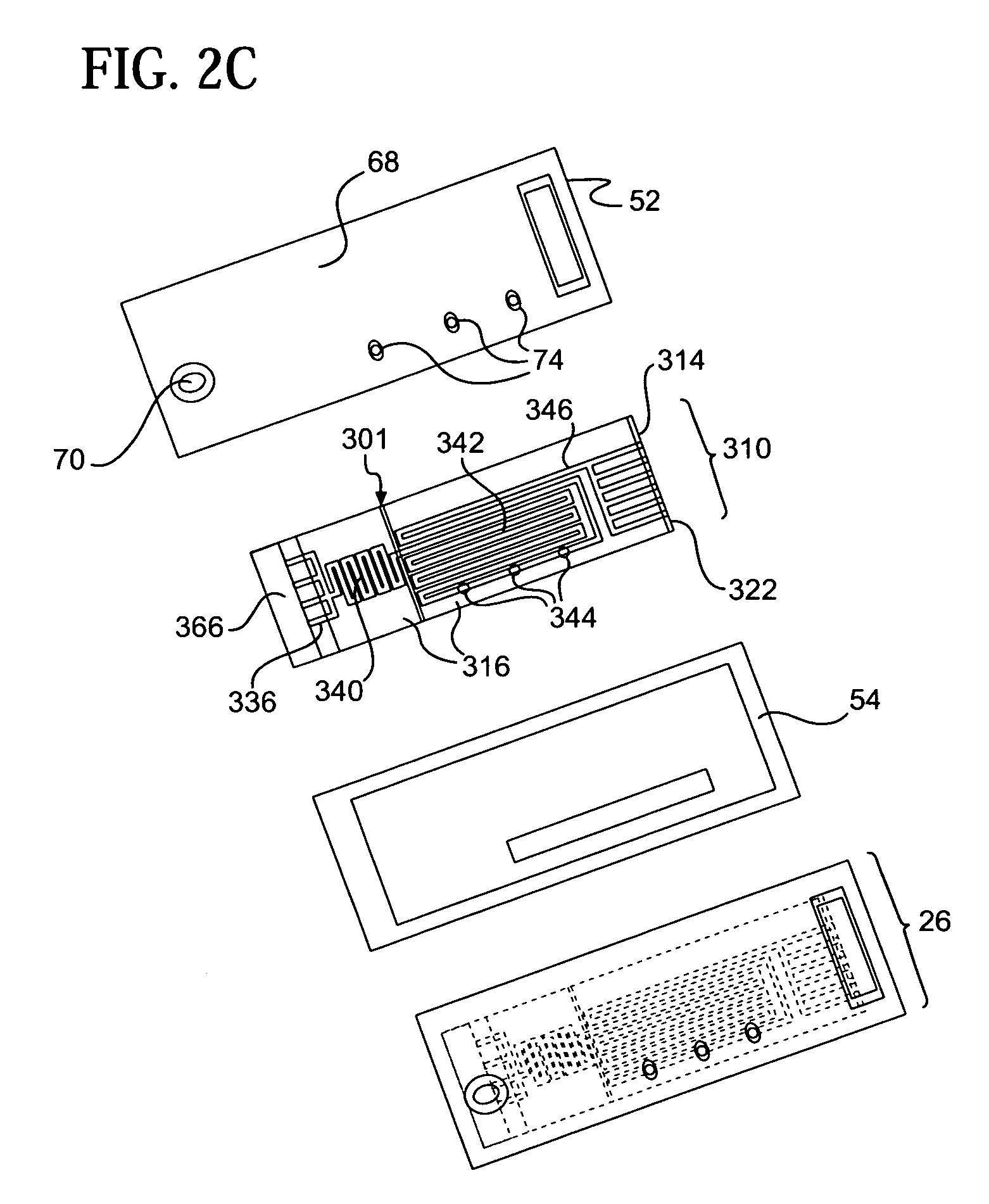
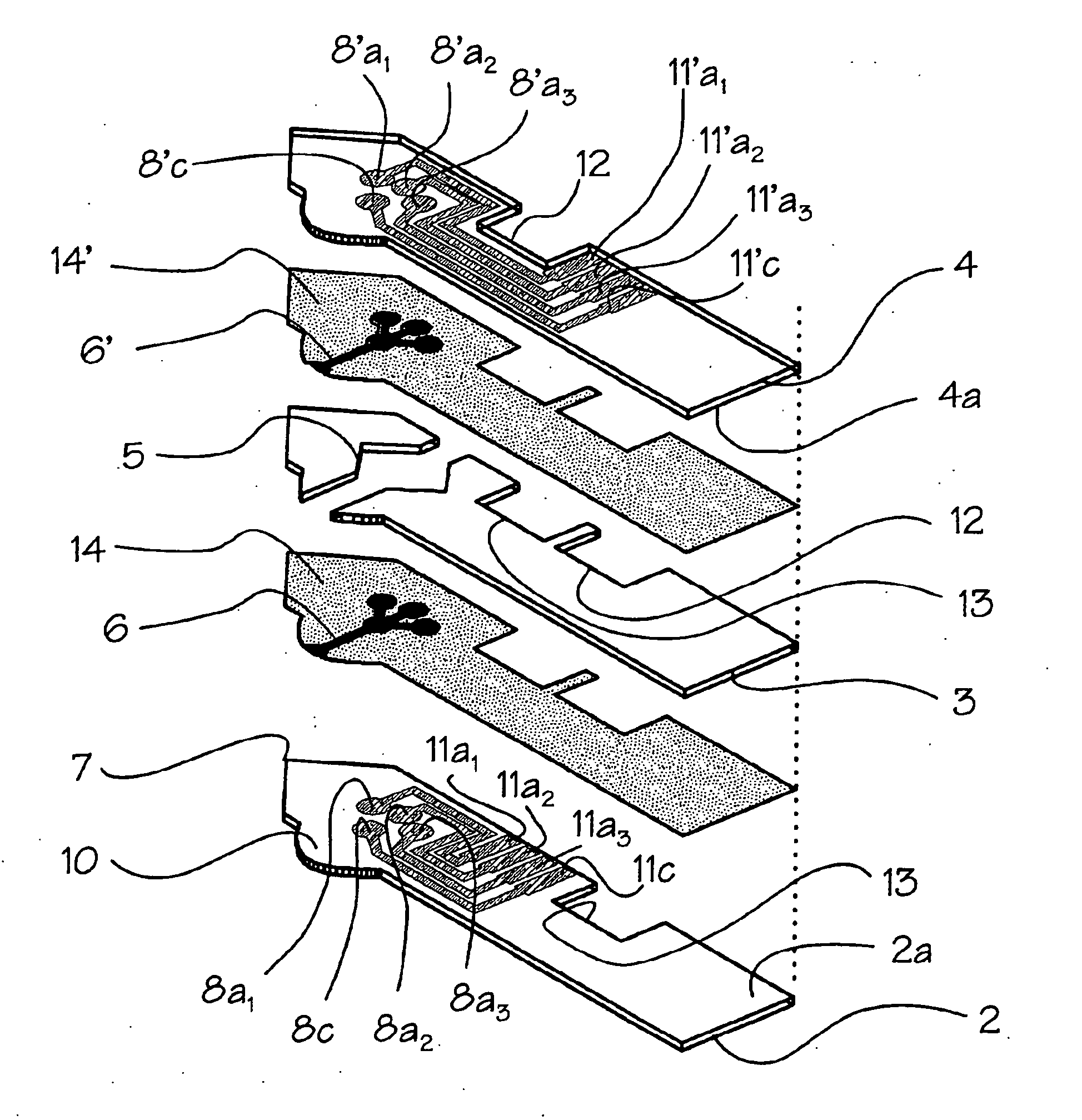
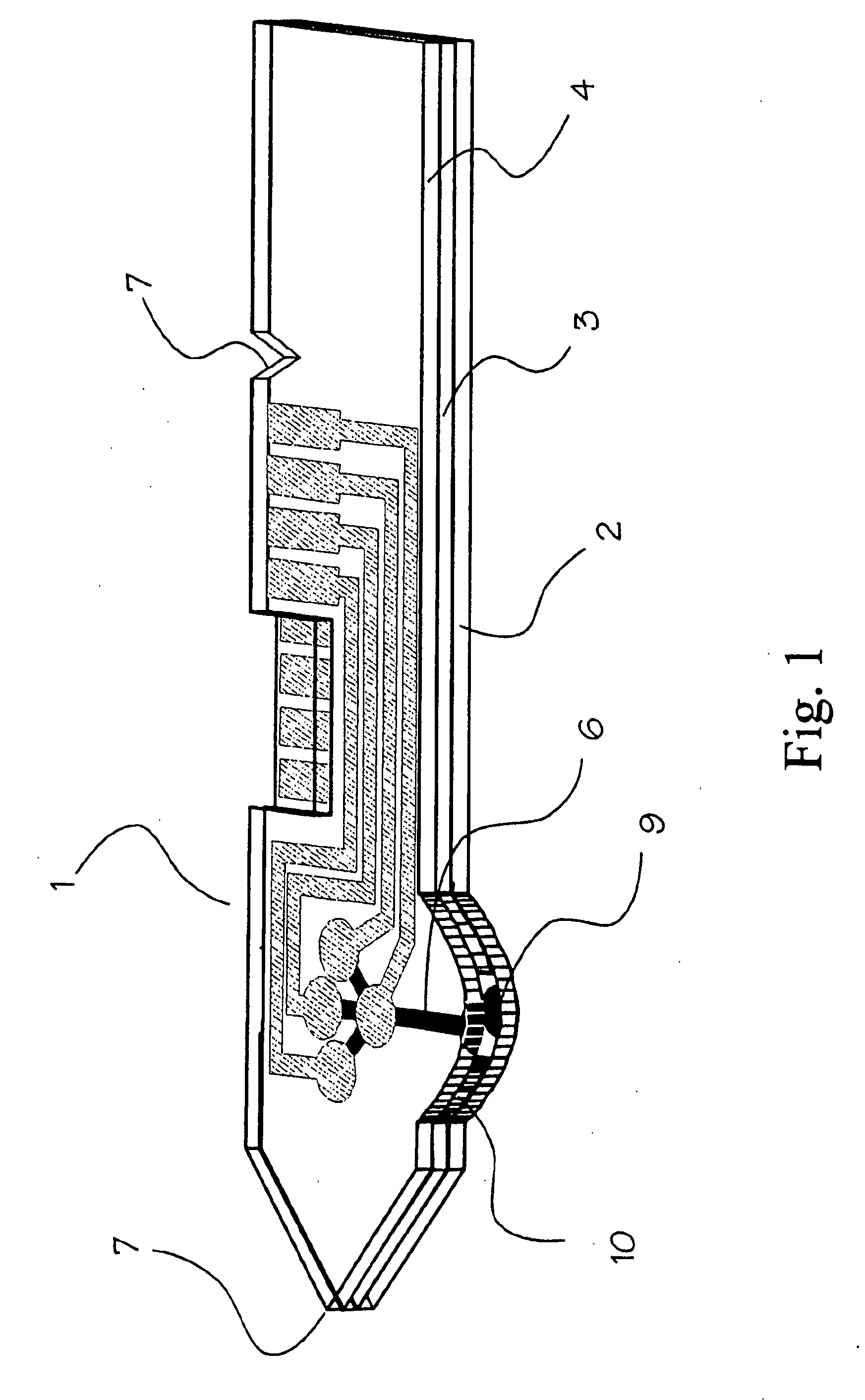
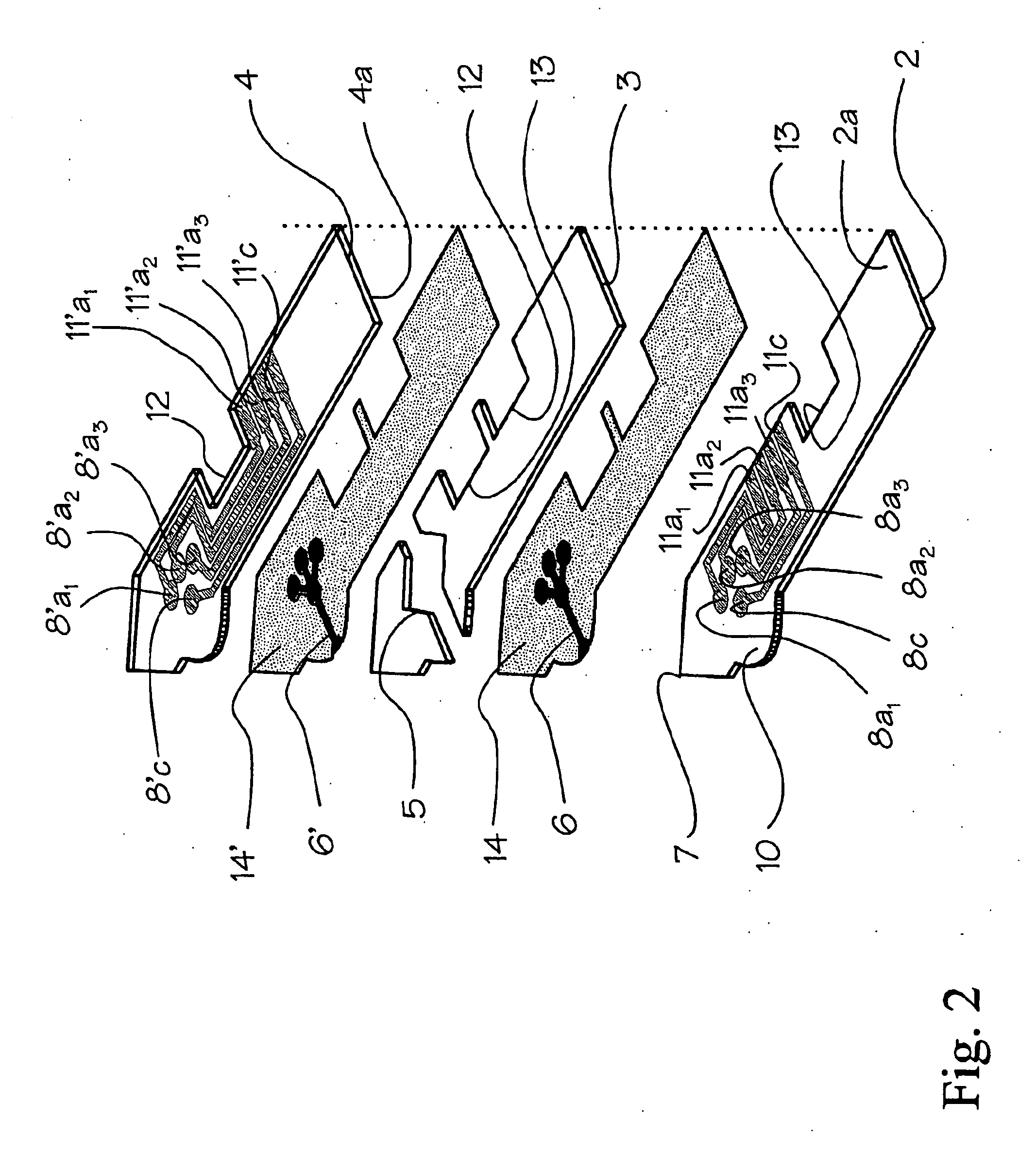
A glucose sensor in the form of a skin patch 2 has a microneedle 4 which painlessly penetrates the skin to draw out interstitial fluid. The interstitial fluid passes to a common entrance port 7. A series of microchannels 8 is provided on the skin patch. The fluid drawn onto the patch is selectively switched between a number of microchannels 8 by means of electro-osmotic pumps 10 and hydrophobic gates 12. Each microchannel 8 has an electrochemical detector 11 for sensing gluocse concentration. Also disclosed is a monlithic device with an integrated lance 83.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
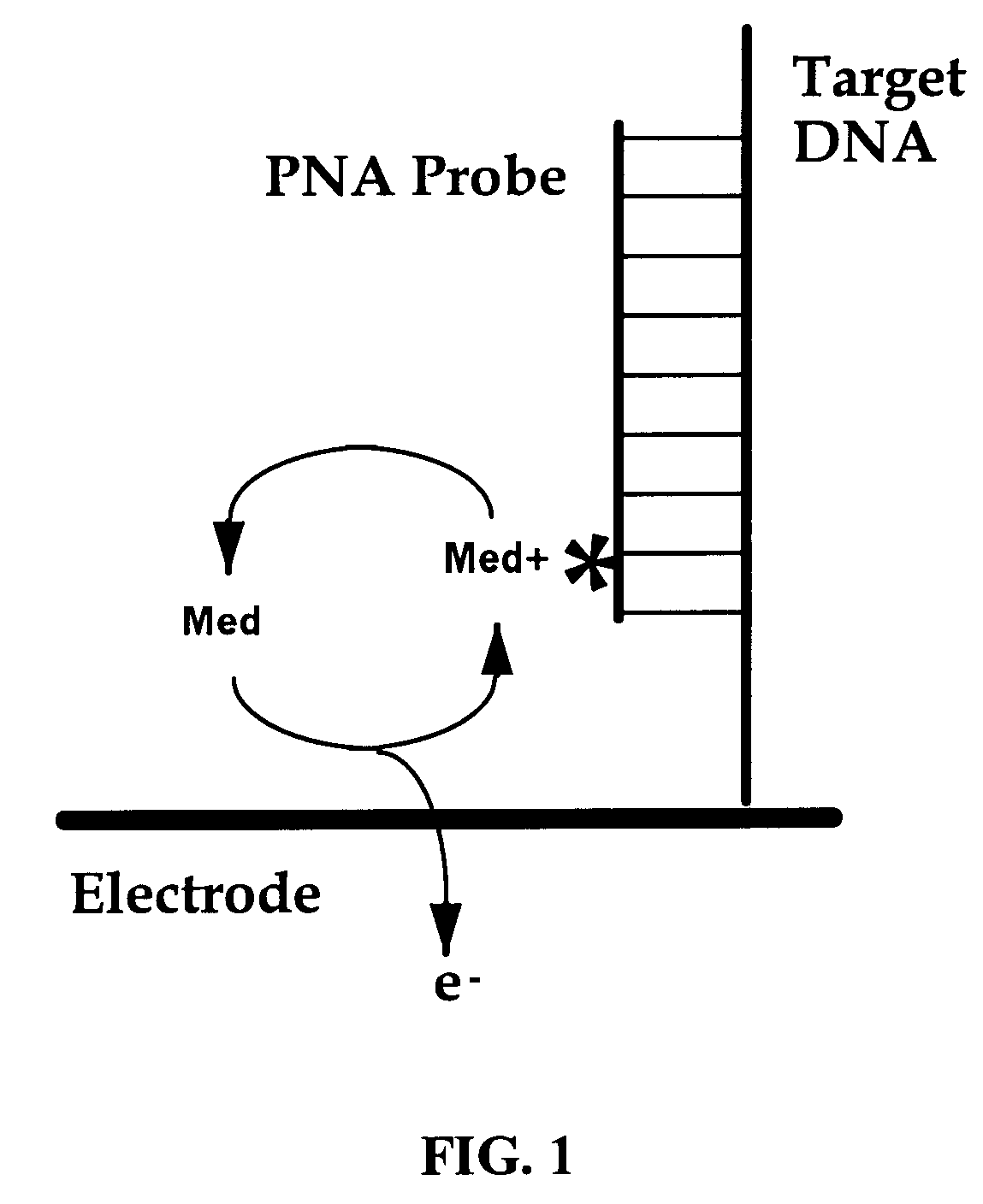
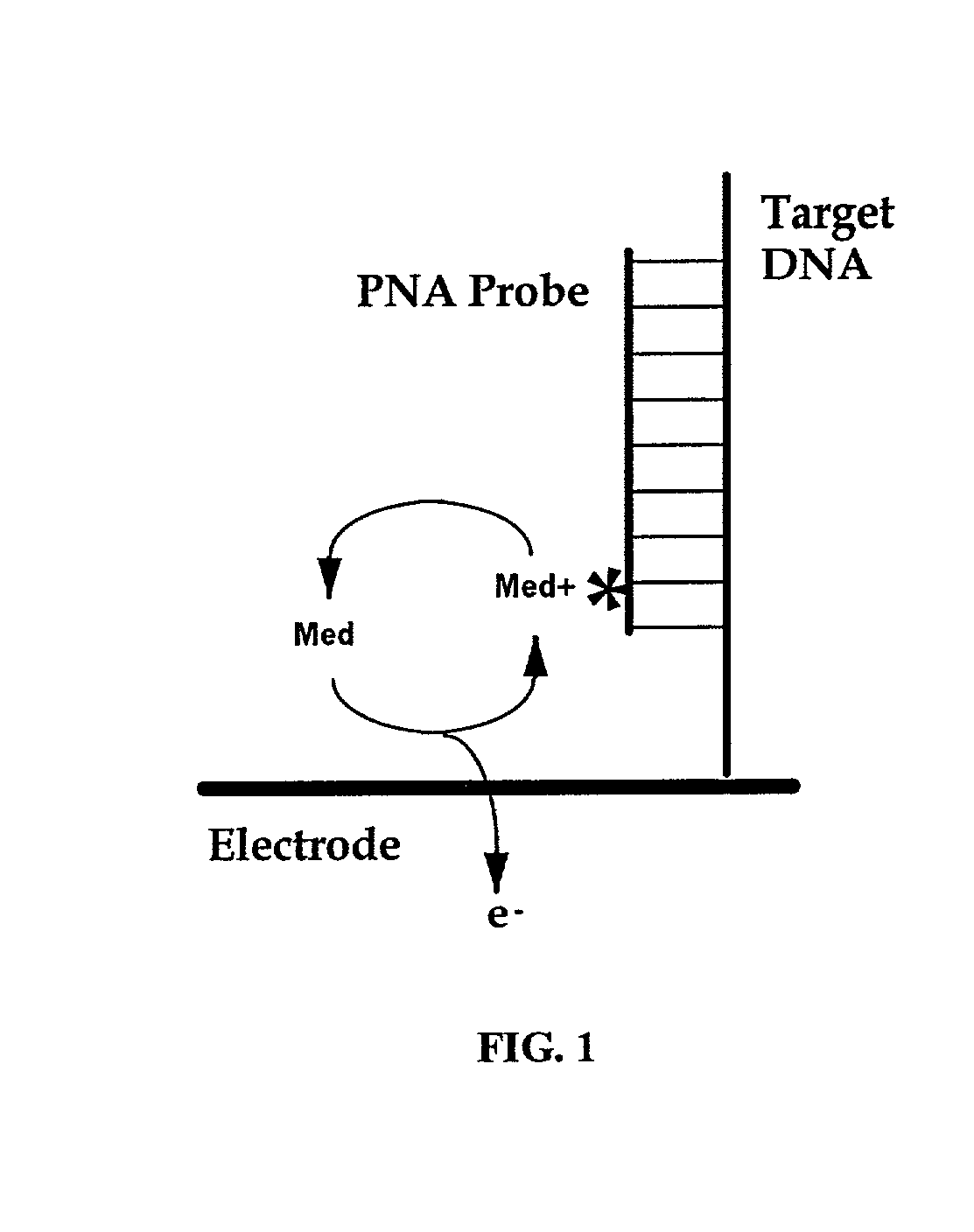
Electrochemical detection of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6391558B1Quick checkComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
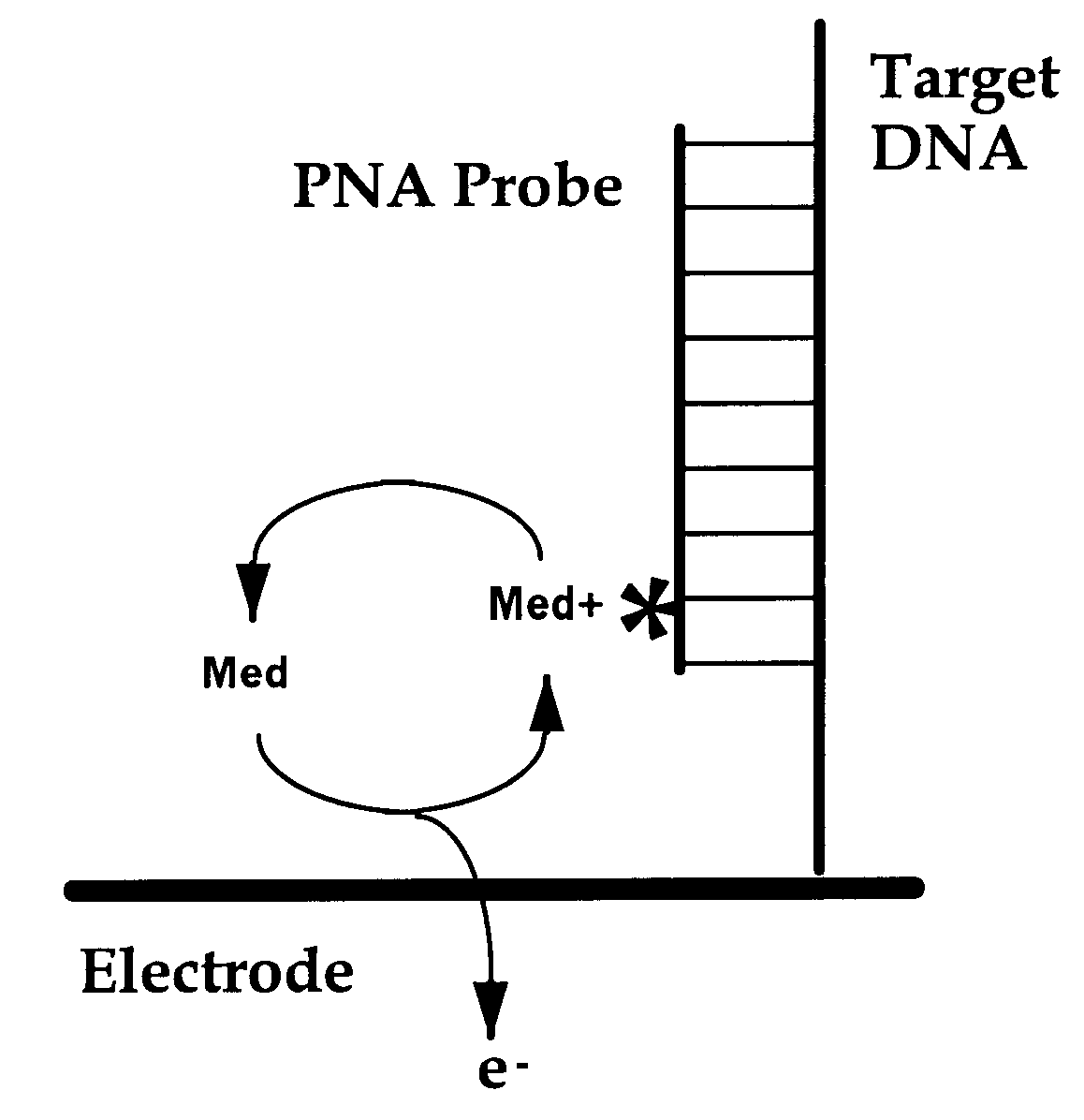
An electrochemical detection system which specifically detects selected nucleic acid segments is described. The system utilizes biological probes such as nucleic acid or peptide nucleic acid probes which are complementary to and specifically hybridize with selected nucleic acid segments in order to generate a measurable current when an amperometric potential is applied. The electrochemical signal can be quantified.
Owner:MAGELLAN DIAGNOSTICS
Biosensor apparatus and methods of use
InactiveUS20060134713A1Increase in the amount of probe boundReduce the amount requiredBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrochemical responseAnalyte
Disclosed herein are methods and devices for detecting the presence of an analyte of interest. A biosensor device can include a reaction chamber and an electrochemical detection chamber. The reaction chamber can include at least one immobilized binding site and a probe conjugate adapted to bind to at least one of the target analyte and the immobilized binding site, while the detection chamber can include electrodes for detecting an electrochemical reaction. If present, the target analyte in the fluid sample results in a change in the amount of probe conjugate bound in the reaction chamber, which can be detected electrochemically in the detection chamber.
Owner:UNIVERSAL BIOSENSORS
Combined lancet and electrochemical analyte-testing apparatus
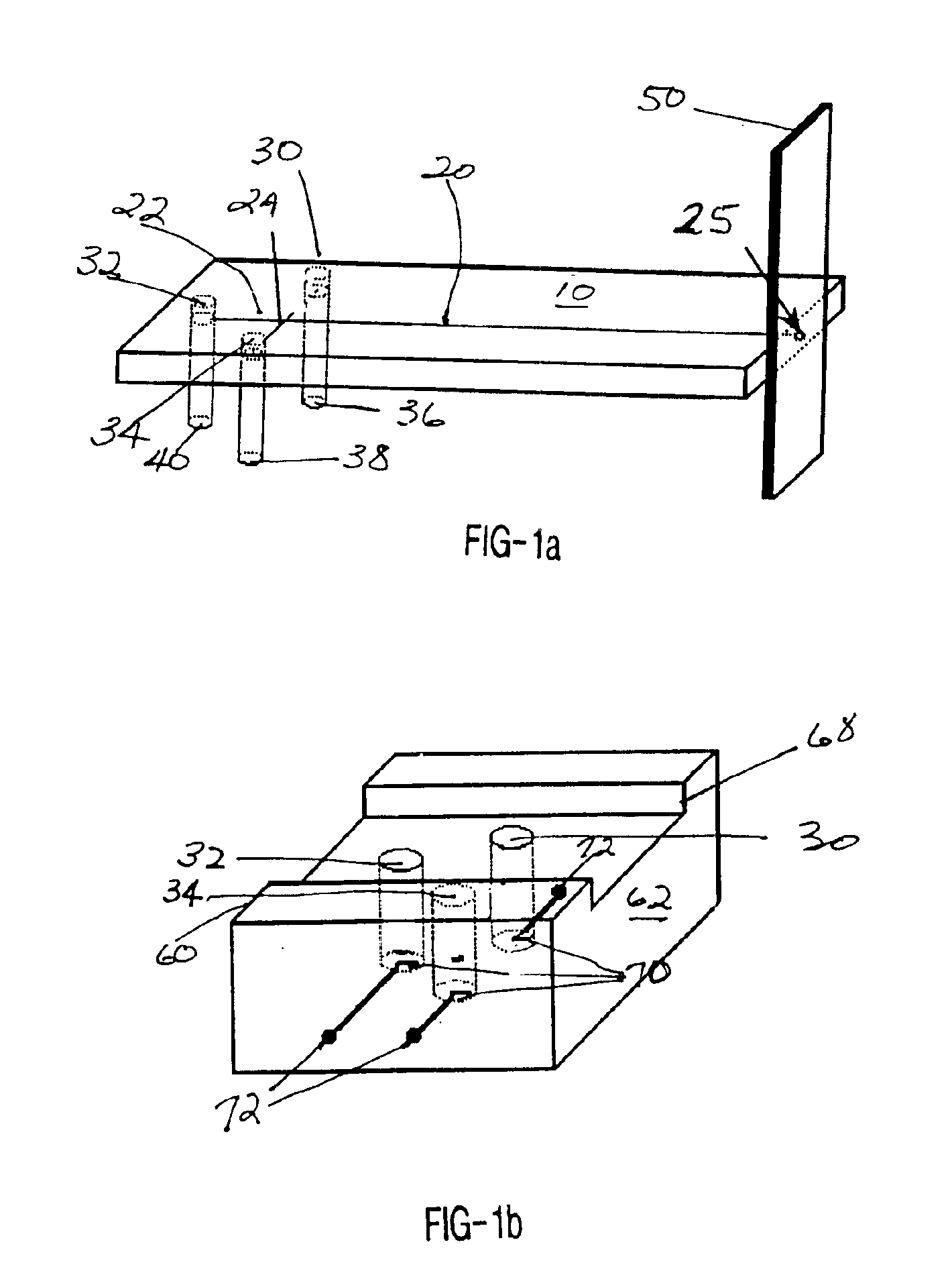
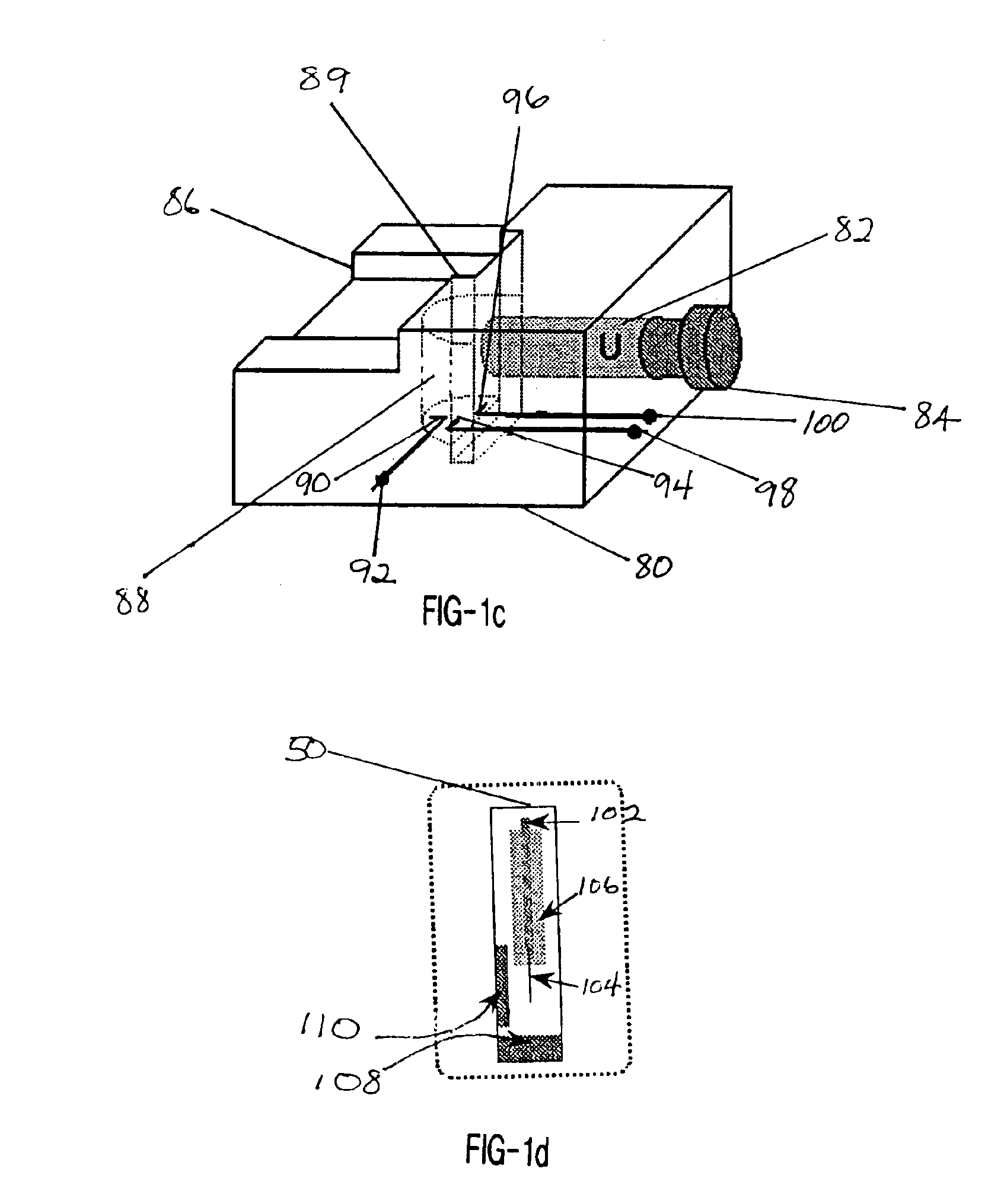
InactiveUS20050011759A1Easy to takeReduces and eliminates disposal issueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTissue fluidDisplay device
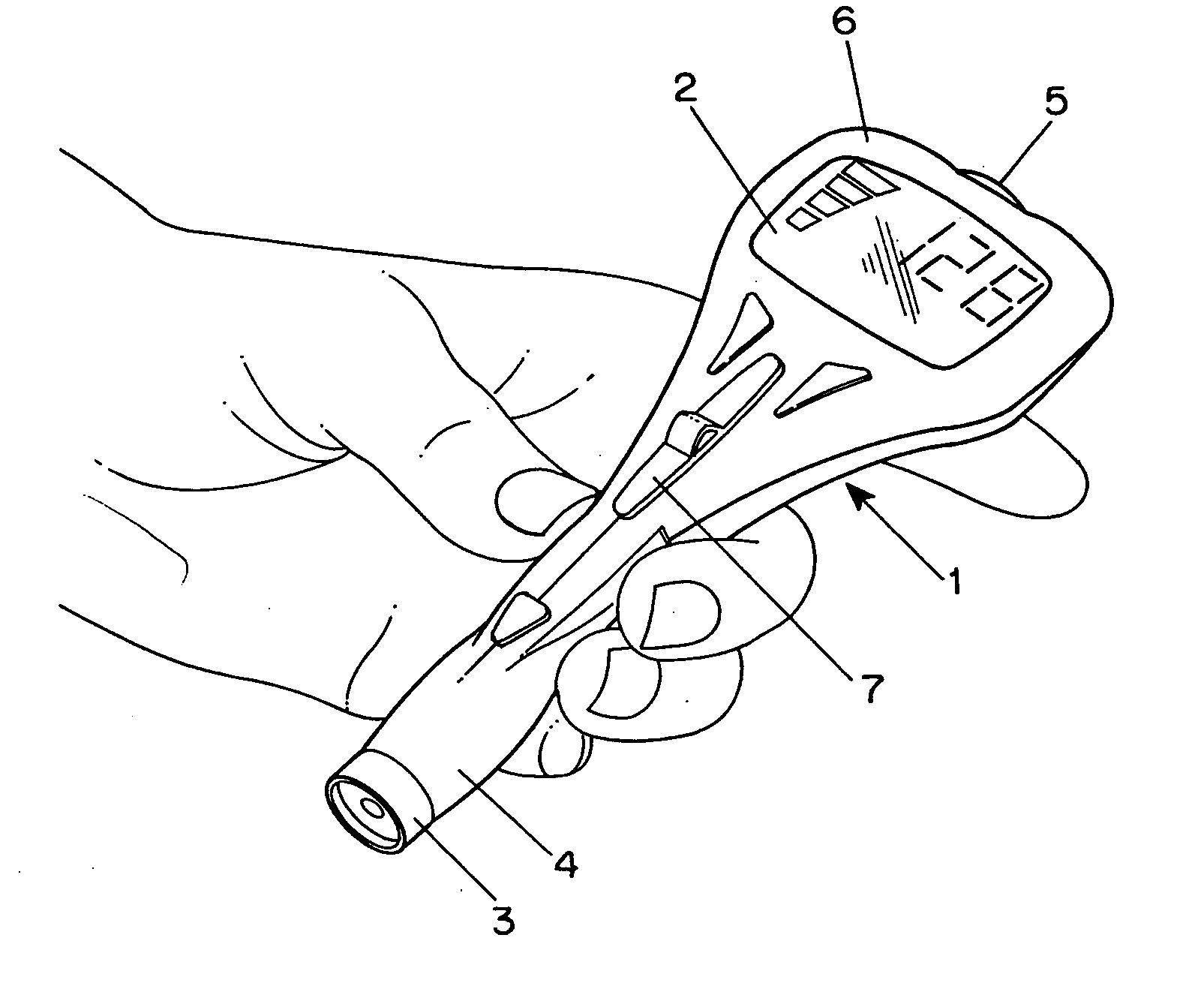
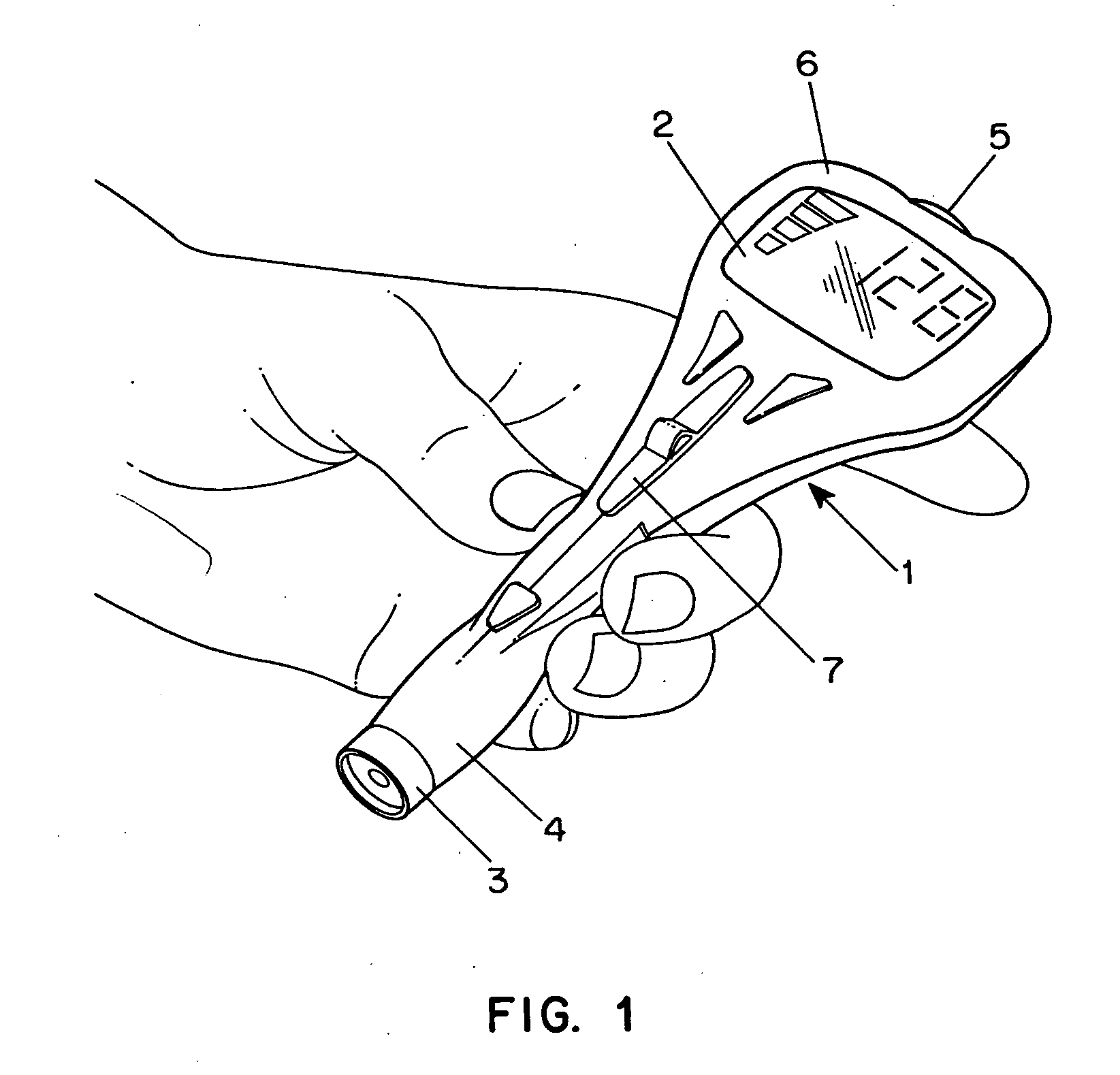
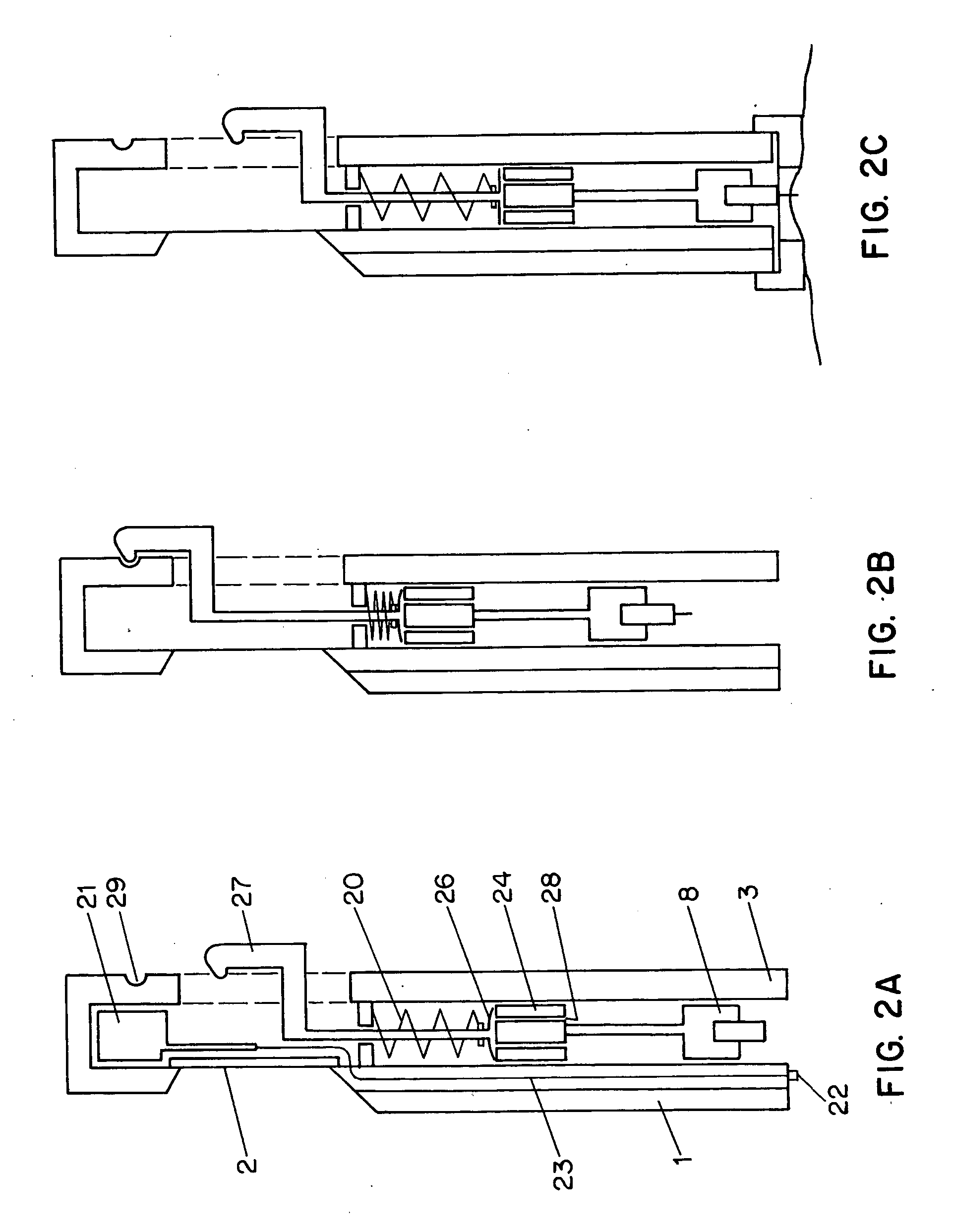
An apparatus for detection and quantitation of an electrochemically-detectable analyte, such as glucose, in blood or interstitial fluid includes a meter unit, a lancet and an electrochemical sensor. Of these components, the meter is preferably reusable, while the lancet and the electrochemical sensor are preferably incorporated in assemblies intended for single-use. The meter unit has a housing, within which a lancet is engaged with a mechanism for moving then lancet; a connector disposed within the housing for engaging an electrochemical sensor specific for the analyte and transmitting a signal indicative of the amount of analyte, and a display operatively-associated with a connector for displaying the amount of the analyte to user. The electrochemical sensor is adapted for detection of a particular analyte. In addition, the electrochemical sensor has an absorptive member for uptake of a sample of blood or interstitial fluid. In one version, the lancet moves from a initial position to a piercing position in which skin of the user is pierced and optionally back to a retracted position. The electrochemical sensor is disposed such that the absorptive member takes up a sample from the pierced skin of the user when it is pierced by the lancet without movement of the apparatus. In an alternative version, the lancet is a hollow cannula through which blood or interstitial fluid is transported from the puncture site to an absorbent portion of the electrochemical sensor. In either version, the apparatus provides single-step operation in which sample acquisition and analysis occur as a result of the single action of pressing, the apparatus against the users skin.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Microfluidic devices with thick-film electrochemical detection
InactiveUS6878255B1Reduce usageCost advantageSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteMicrofluidic channel
An apparatus for conducting a microfluidic process and analysis, including at least one elongated microfluidic channel, fluidic transport means for transport of fluids through the microfluidic channel, and at least one thick-film electrode in fluidic connection with the outlet end of the microfluidic channel. The present invention includes an integrated on-chip combination reaction, separation and thick-film electrochemical detection microsystem, for use in detection of a wide range of analytes, and methods for the use thereof.
Owner:ARROWHEAD CENT
Dual glucose-hydroxybutyrate analytical sensors
InactiveUS6984307B2Diffusion fastMinimize cross-talkImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical detectionD-Glucose
Diagnostic dry reagent tests capable of reacting with a single drop of whole blood and reporting both glucose and beta-hydroxybutyrate levels are taught. Such dry reagent tests may employ electrochemical detection methodologies, optical detection methodologies, or both methodologies. These tests help facilitate the early detection of the onset of ketoacidosis in diabetes.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Methods for microdispensing patterened layers
InactiveUS6306594B1Efficient couplingShort response timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBurettes/pipettesAnalyteClinical settings
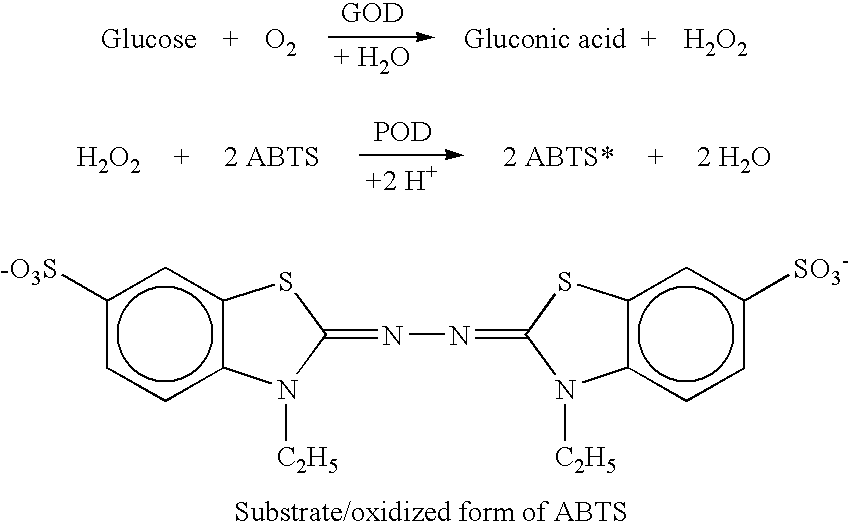
An efficient method for the microfabrication of electronic devices which have been adapted for the analyses of biologically significant analyte species is described. The techniques of the present invention allow for close control over the dimensional features of the various components and layers established on a suitable substrate. Such control extends to those parts of the devices which incorporate the biological components which enable these devices to function as biological sensors. The materials and methods disclosed herein thus provide an effective means for the mass production of uniform wholly microfabricated biosensors. Various embodiments of the devices themselves are described herein which are especially suited for real time analyses of biological samples in a clinical setting. In particular, the present invention describes assays which can be performed using certain ligand / ligand receptor-based biosensor embodiments. The present invention also discloses a novel method for the electrochemical detection of particular analyte species of biological and physiological significance using an substrate / label signal generating pair which produces a change in the concentration of electroactive species selected from the group consisting of dioxygen and hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:I STAT CORP
Enzymatic electrochemical detection assay using protective monolayer and device therefor
InactiveUS20060160100A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
There is provided an electrochemical assay method for detecting a target molecule, for example a protein, in a sample, which involves the use of a protective monolayer and a redox polymer to form a bilayer immobilized on an electrode. The monolayer protects the electrode from non-specific adherence of reagents, particular proteins, to the electrode while simultaneously providing a surface that can be functionalized to immobilize a capture molecule and that can interact with the redox polymer.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method and apparatus for detection of abnormal traces during electrochemical analyte detection
Detection of abnormal signal traces in electrochemical measurements generated using an electrochemical test strip to which a potential is applied allows for an indication of an erroneous analyte determination. The current trace has an expected shape in which a peak current is observed a time tpeak after which there is a decrease in current. To detect abnormal signal traces, the time tpeak is determined experimentally and compared with an expected value, t′peak, and if the difference between the two values to over a predetermined threshold, an error message is provided to the user instead of a test result. The value of t′peak is determined as a function of a mobility term that is determined during a potentiometry phase following the amperometric measurements.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050164322A1Lower the volumeAccurate and efficient measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectron transferPolymer
A sensor designed to determine the amount and concentration of analyte in a sample having a volume of less than about 1 μL. The sensor has a working electrode coated with a non-leachable redox mediator. The redox mediator acts as an electron transfer agent between the analyte and the electrode. In addition, a second electron transfer agent, such as an enzyme, can be added to facilitate the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the analyte. The redox mediator is typically a redox compound bound to a polymer. The preferred redox mediators are air-oxidizable. The amount of analyte can be determined by coulometry. One particular coulometric technique includes the measurement of the current between the working electrode and a counter or reference electrode at two or more times. The charge passed by this current to or from the analyte is correlated with the amount of analyte in the sample. Other electrochemical detection methods, such as amperometric, voltammetric, and potentiometric techniques, can also be used. The invention can be used to determine the concentration of a biomolecule, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum. An enzyme capable of catalyzing the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the biomolecule is provided as a second electron transfer agent.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Apoenzyme reactivation electrochemical detection method and assay
InactiveUS7166208B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorAssay
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
System and method of microdispensing and arrays of biolayers provided by same
InactiveUS20020090738A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReal time analysisClinical settings
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
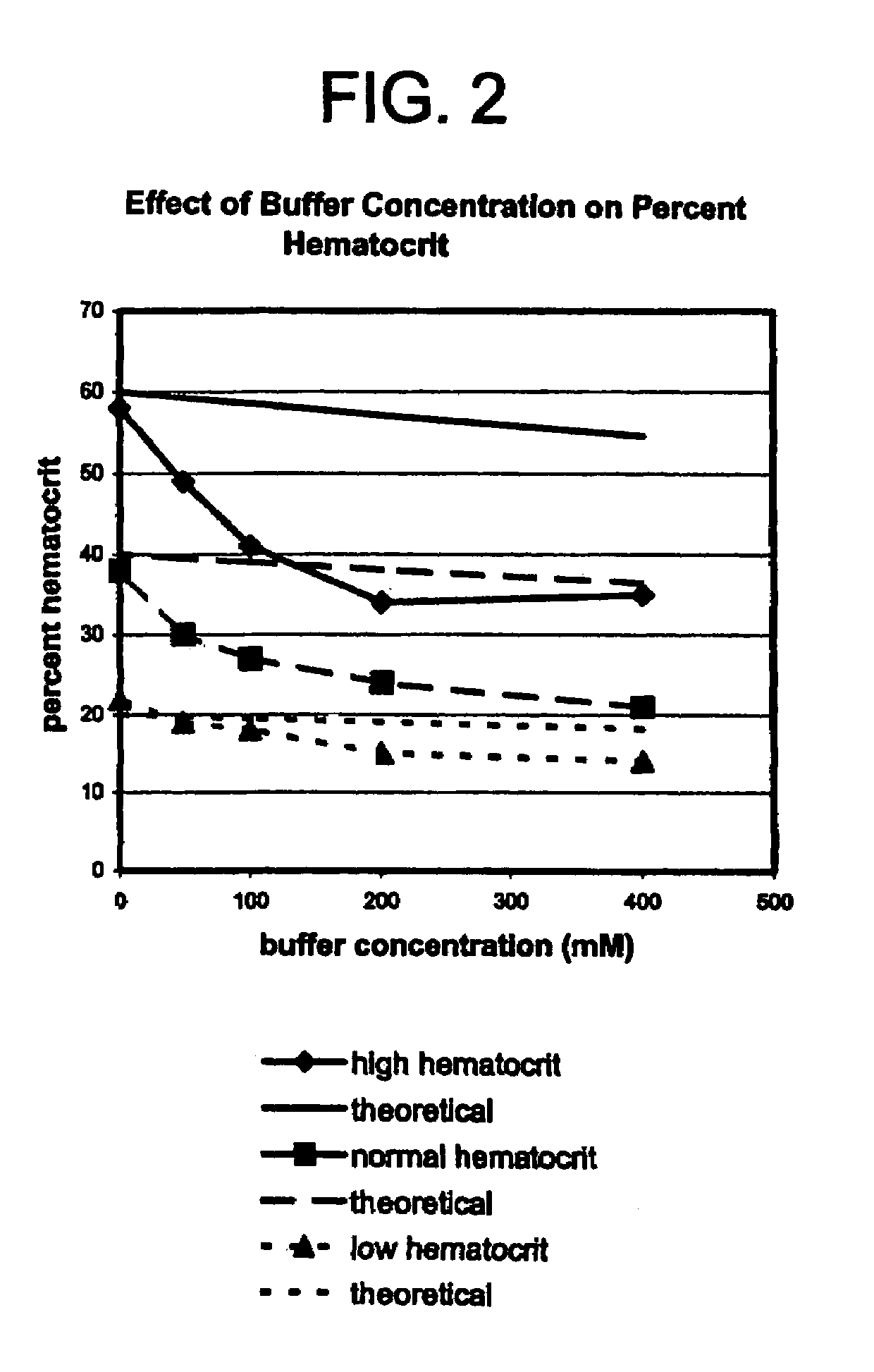
Method for reducing effect of hematocrit on measurement of an analyte in whole blood
ActiveUS7323315B2Microbiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsDiffusionErythrocyte production
A method for determining the presence and / or amount of an analyte in a sample of whole blood comprises the step of treating the sample with a nonlytic hypertonic salt composition to reduce the hematocrit by reducing the size of the red blood cells. In optical detection systems, the smaller red blood cells create greater scatter, which allows a more accurate correction to be applied in a dual-wavelength detection system. In electrochemical detection systems, as well as in optical detection systems, the smaller red blood cells provide less obstruction to the diffusion of analyte and reagents in the sample, to facilitate the reactions thereof.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Sensor arrangement with electrically controllable arrays
InactiveUS7208077B1Eliminating undesired binding eventAvoid polarizationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSensor arrayMicroelectrode
An electric sensor array which is provided with several sensor positions that each have at least two microelectrodes. Molecular substances can be detected electrochemically and charged molecules can be transported or handled using the array. Measuring procedures can be effected, especially using two addressing procedures, in which sensor positions can be individually addressed and electrochemically or electrically controlled by pairing or in groups for voltage or impedance measurements. For biomolecular assays, affinity-binding molecules can be immobilized at the sensor positions, between the microelectrodes, or on auxiliary surfaces.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
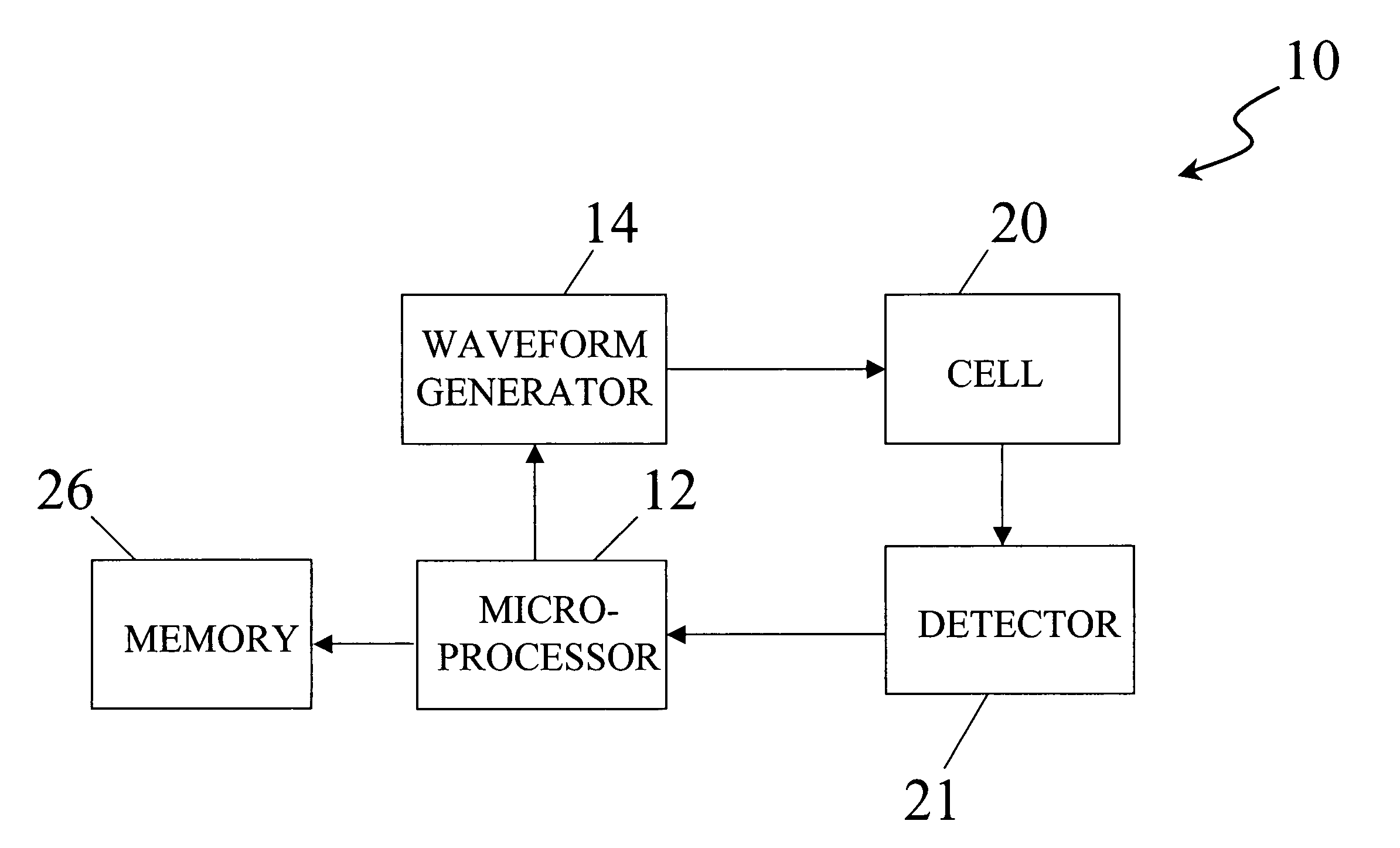
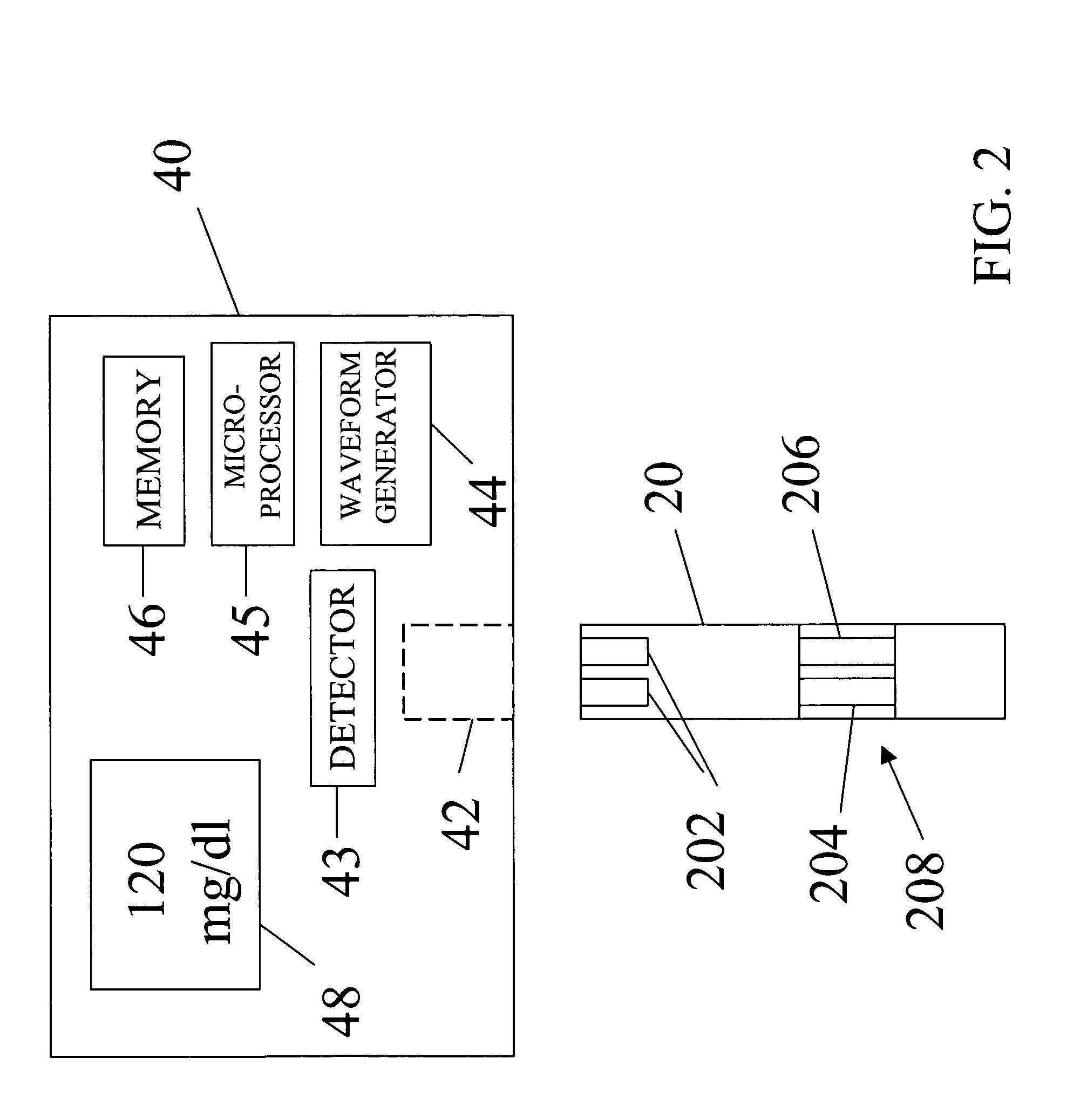
Method and apparatus for electrochemical detection
InactiveUS20060016698A1Enhance electrochemical reactionHigh signal resolutionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteQuantitative determination
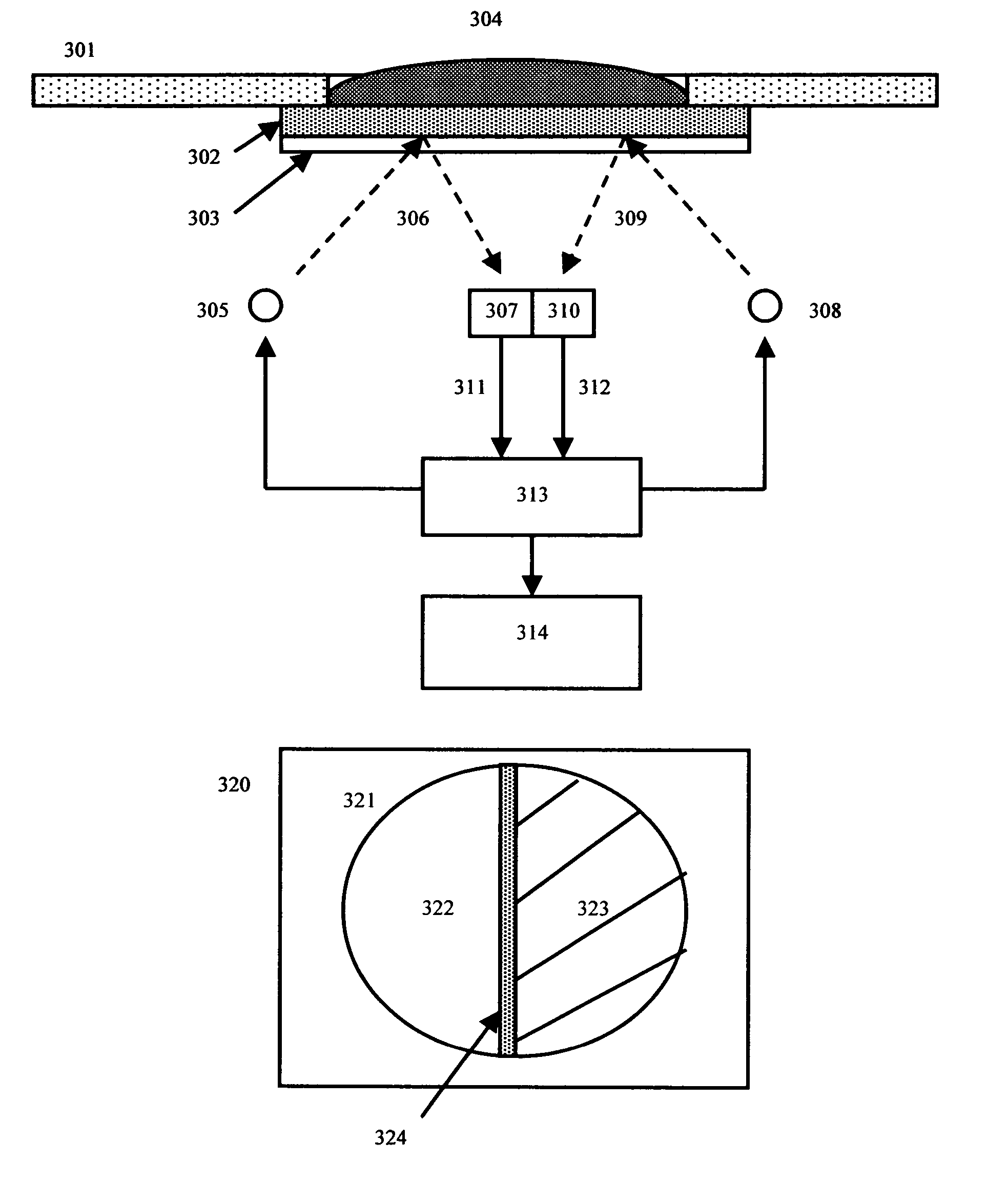
An apparatus for quantitatively determining an analyte in a sample fluid includes a holder for holding an electrochemical cell that includes a catalyst, a waveform generator for generating a potential profile having a voltage bias and an alternating part, a detector for detecting a current signal for a period of measuring time through the electrochemical cell, a memory for storing the current signal, and a processor for correlating the current signals with the concentration of the analyte.
Owner:LEE CHIH KUNG +1
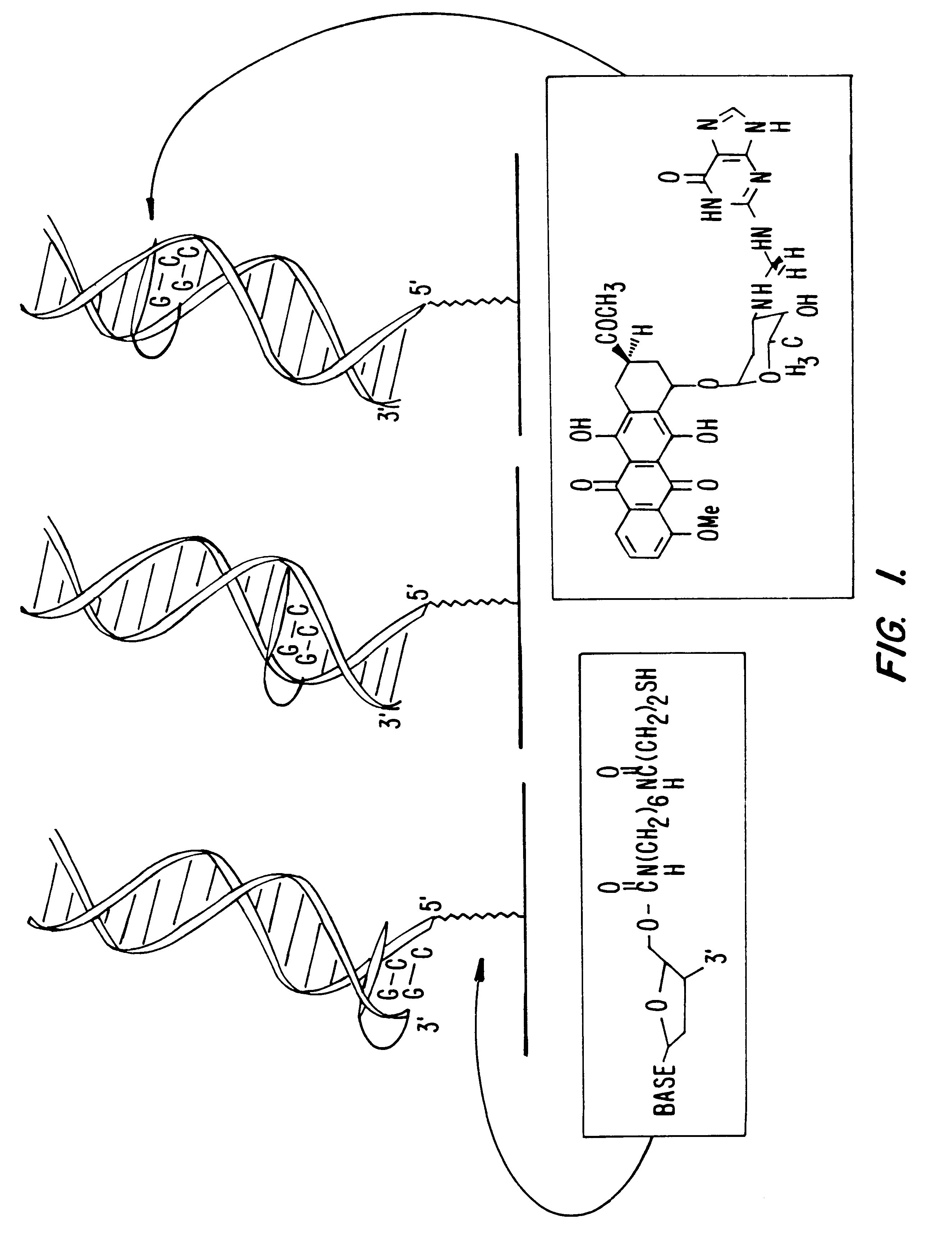
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
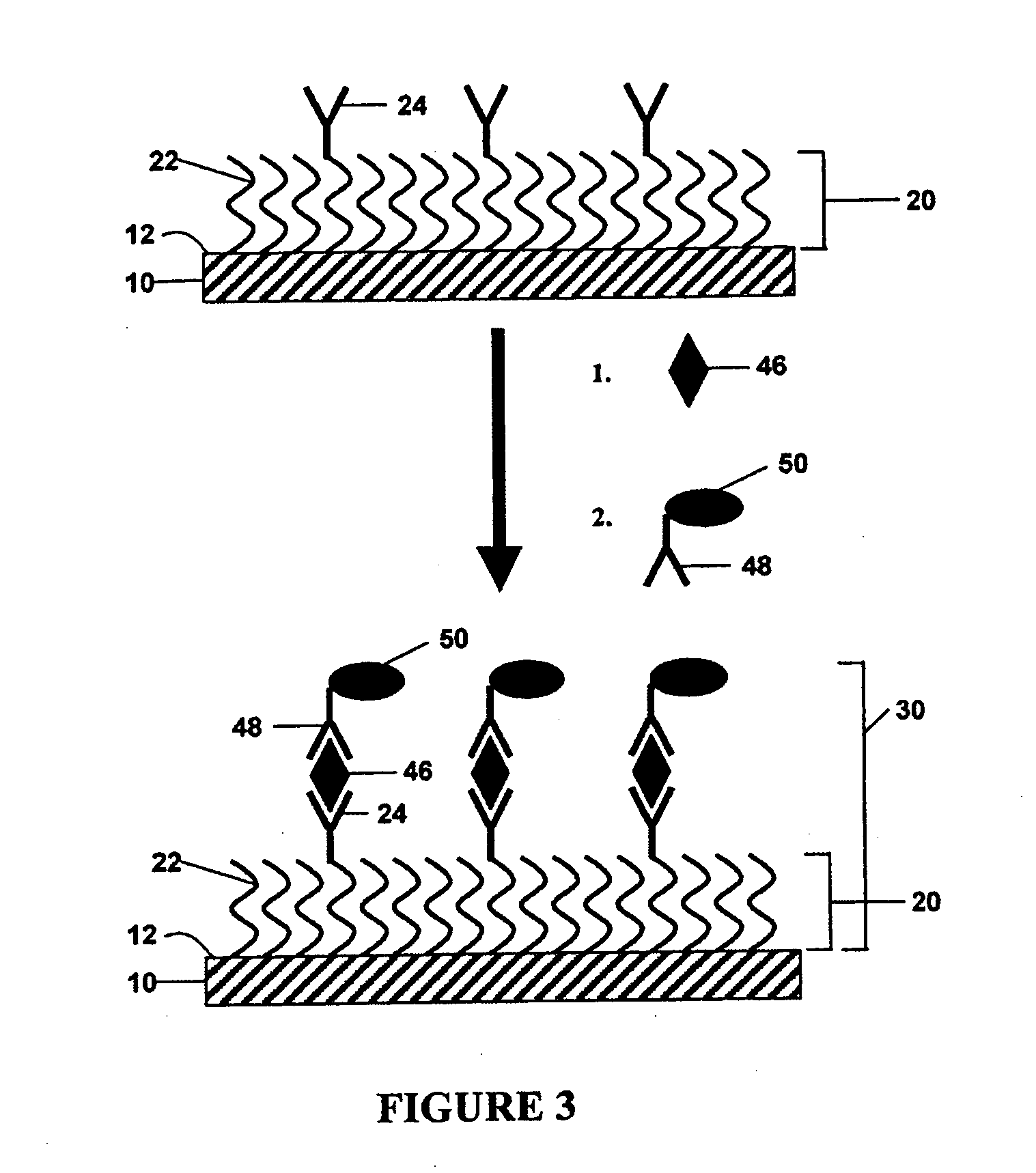
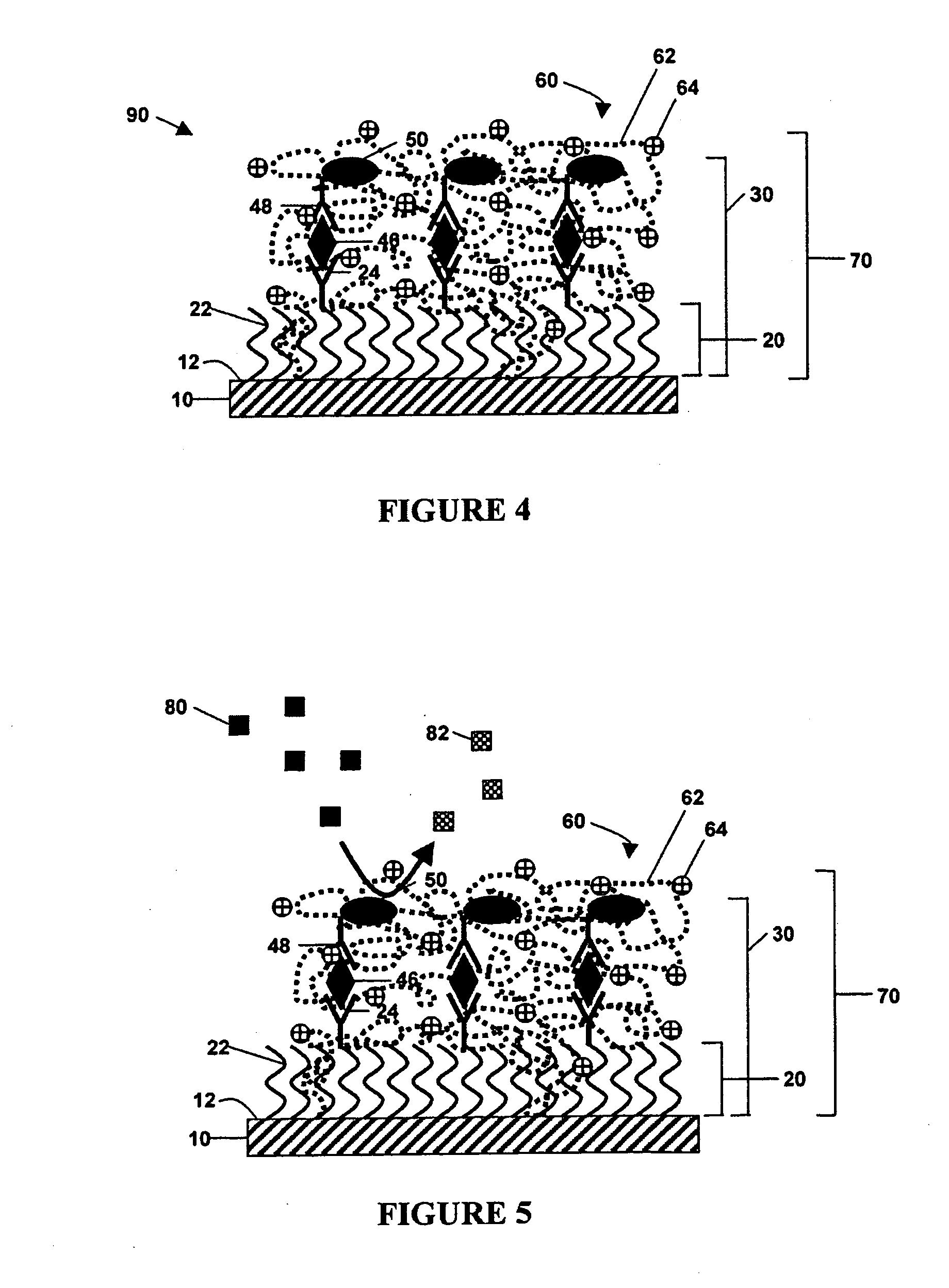
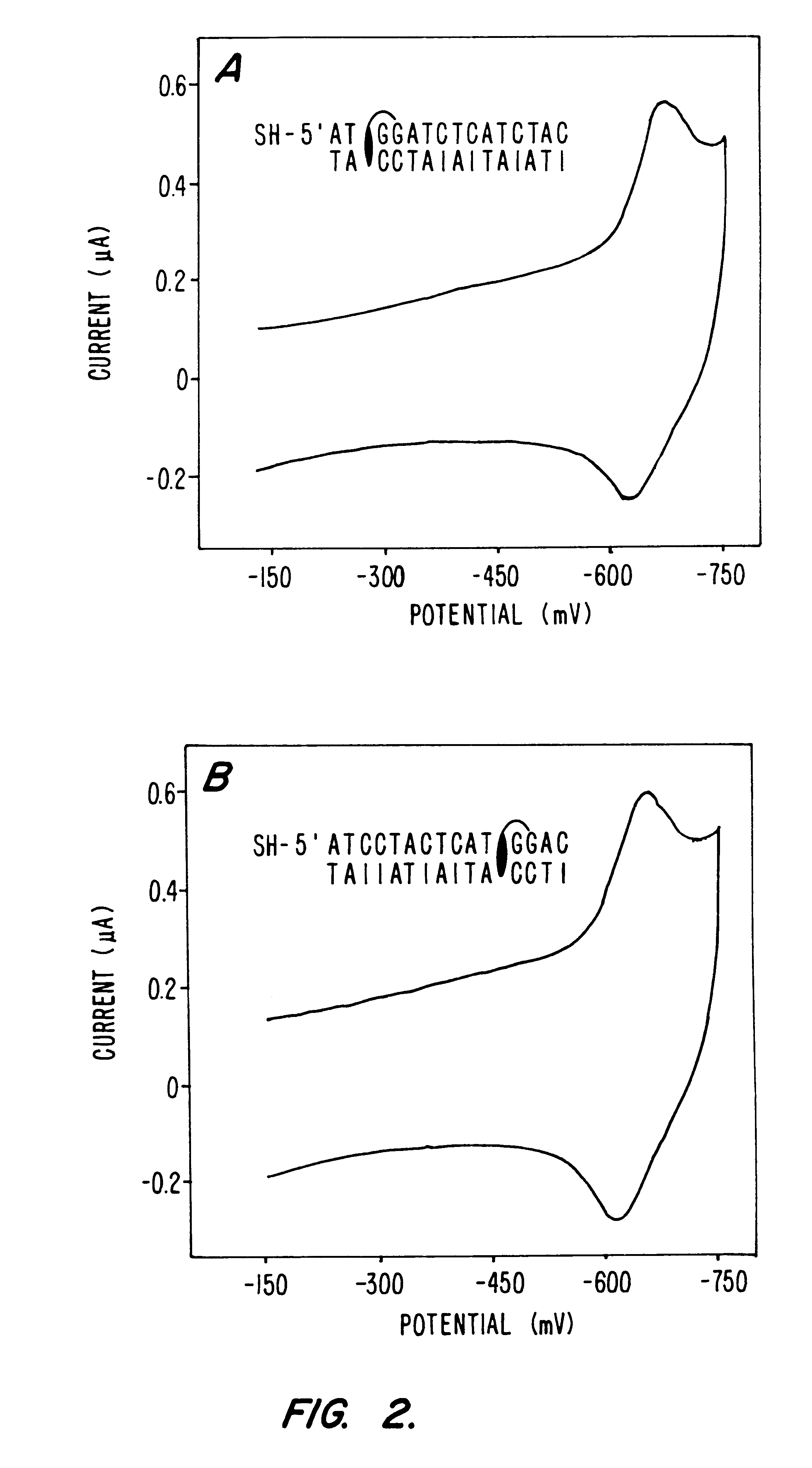
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Electrochemical Analyte Detection Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20090026075A1Easy to useLow costImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesAnalyte
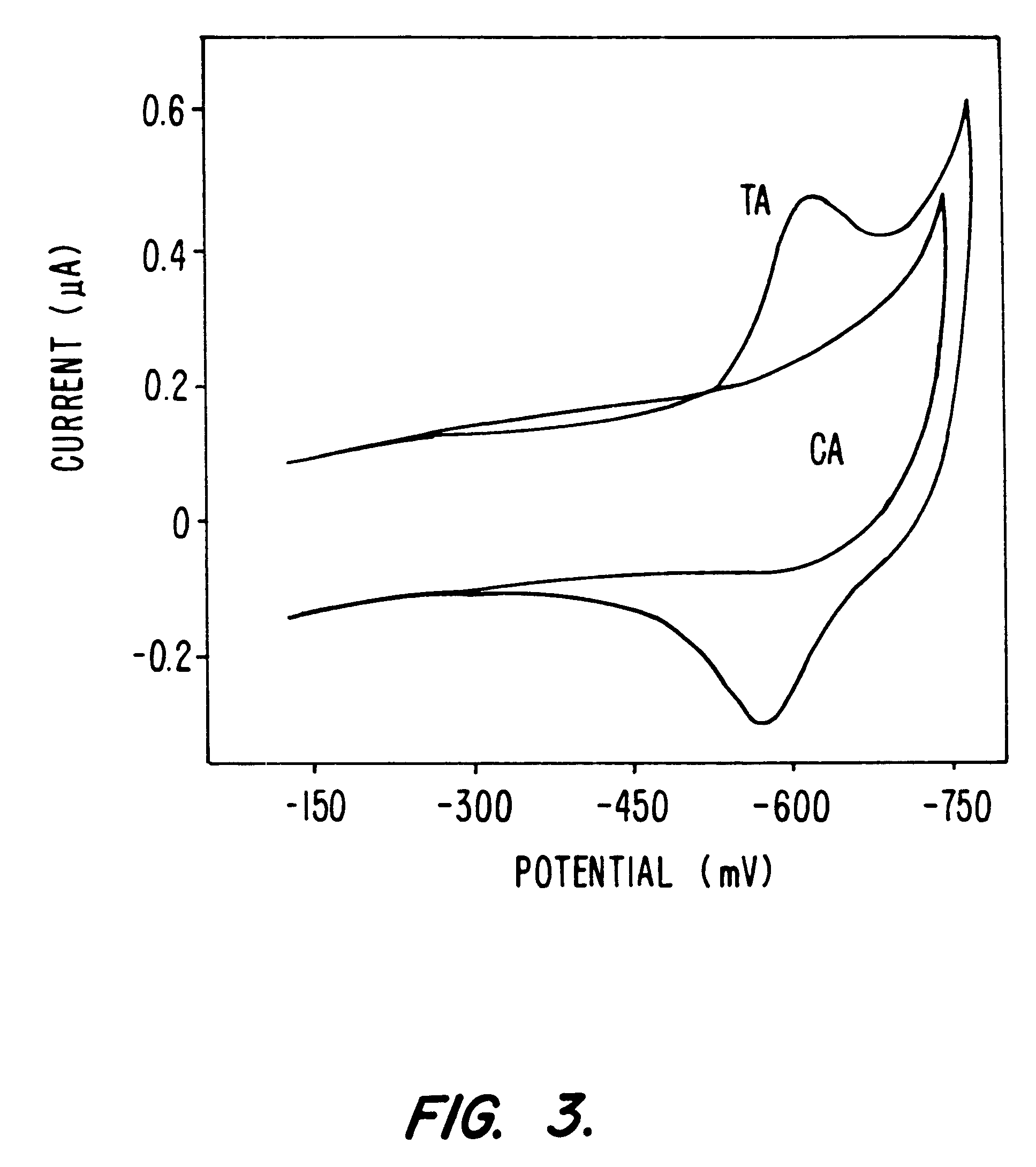
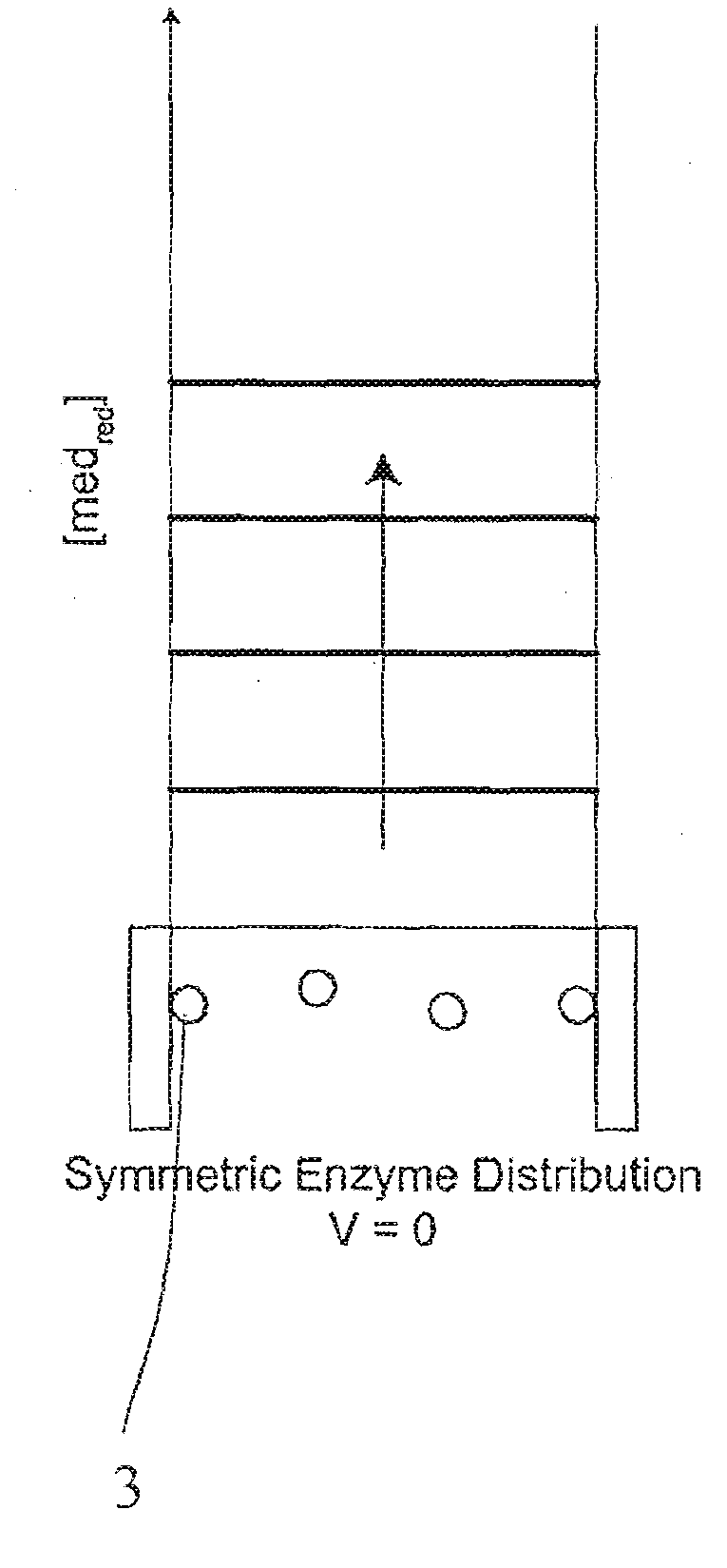
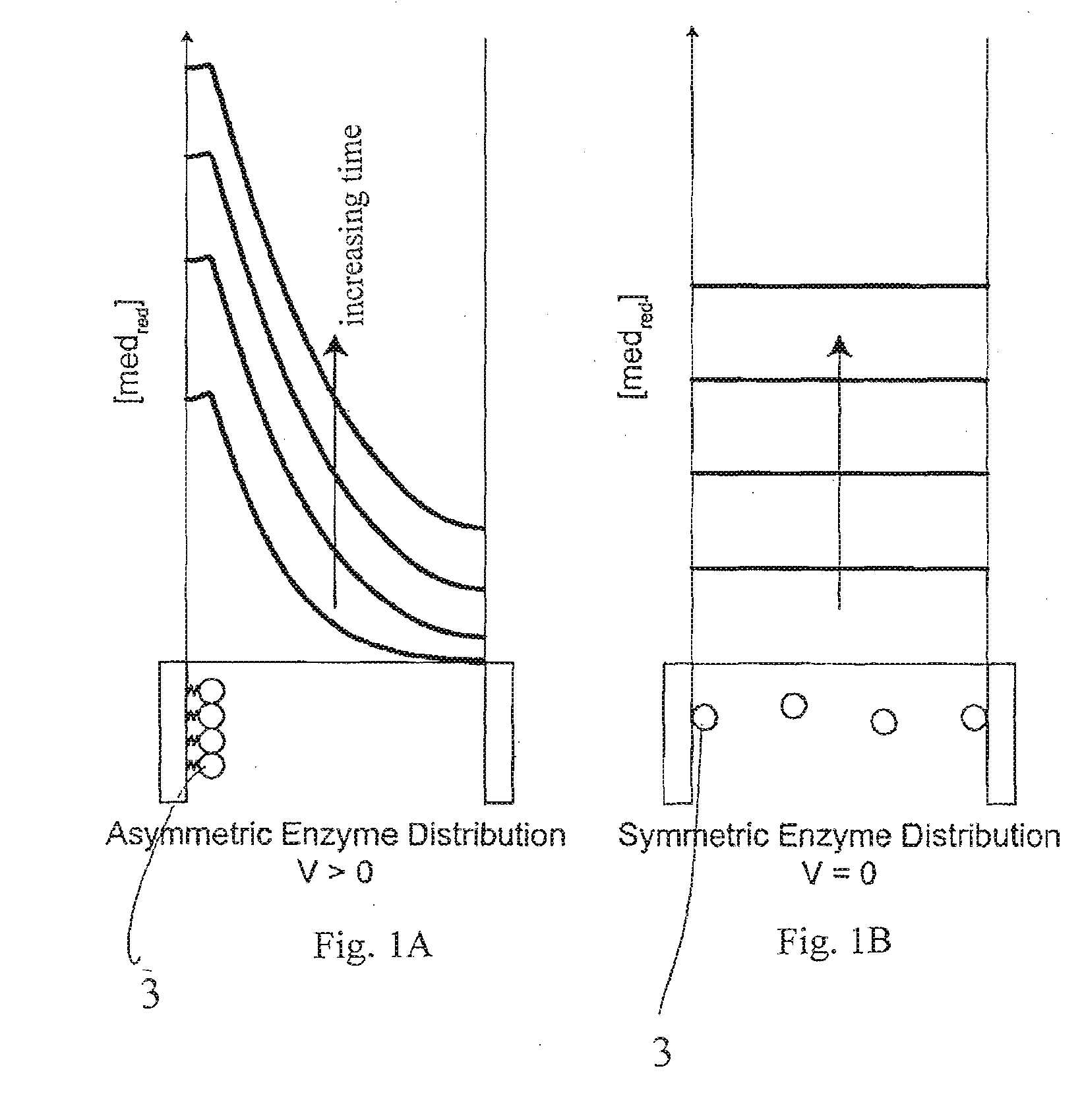
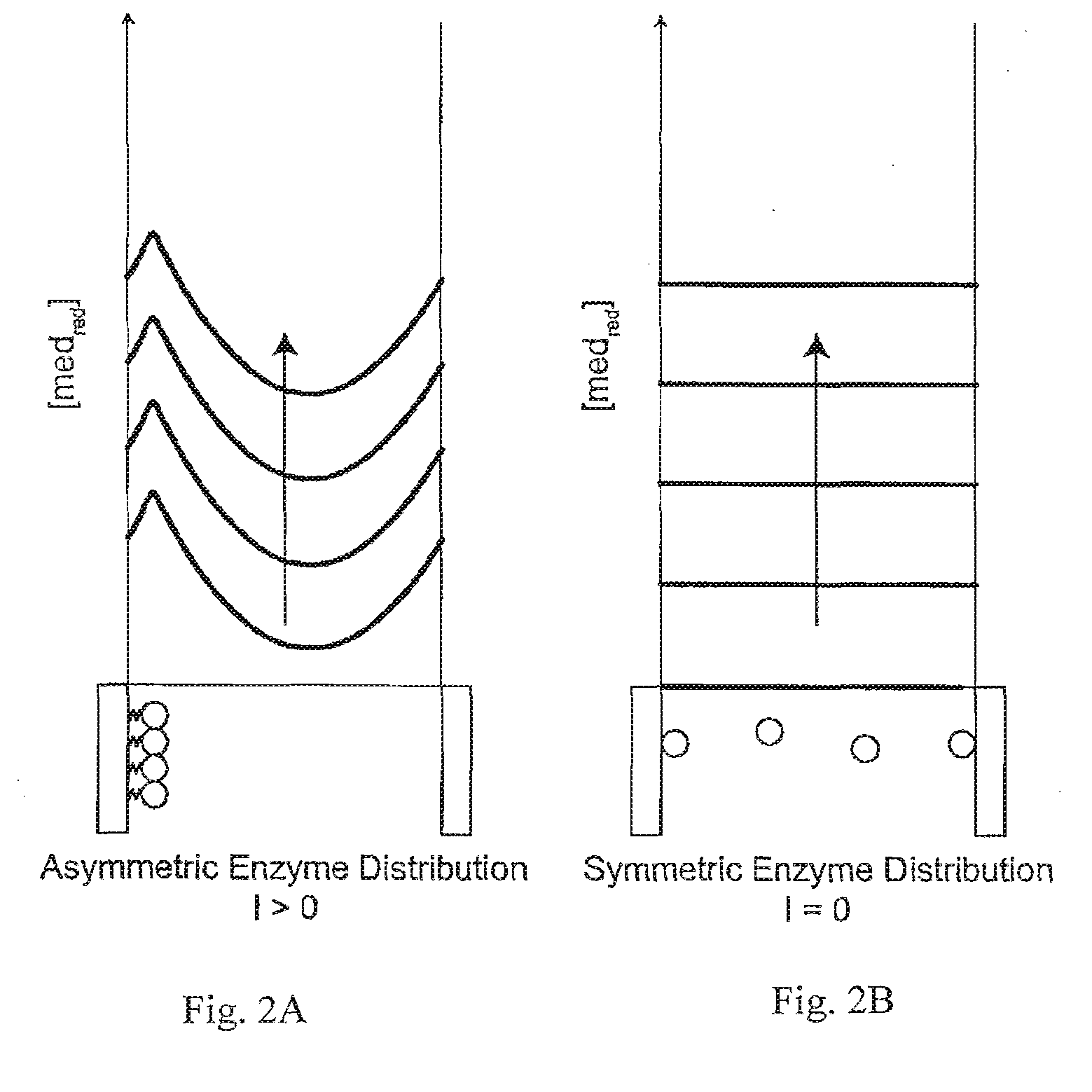
A method and apparatus for electrochemical detection of analyte in a sample makes use of a binding interaction and relies on the discovery that asymmetric distribution of a redox enzyme between two electrodes that occurs when a redox enzyme-containing reagent is immobilized at the surface of one electrode can be detected as a chemical potential gradient arising from an asymmetry, in the distribution of oxidized or reduced redox substrate. This chemical potential gradient can be detected potentiometrically by observing the potential difference between the electrodes in an open circuit, or amperometrically by observing the current flow between the electrodes when the circuit is closed. In both cases, the observation of asymmetry can be done without the application of an external potential or current to the electrodes.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
Microvolume immunoabsorbant assays with amplified electrochemical detection
InactiveUS6887714B2Preventing phsysiabsorptionEasy to detectSequential/parallel process reactionsFixed microstructural devicesAssayChemical compound
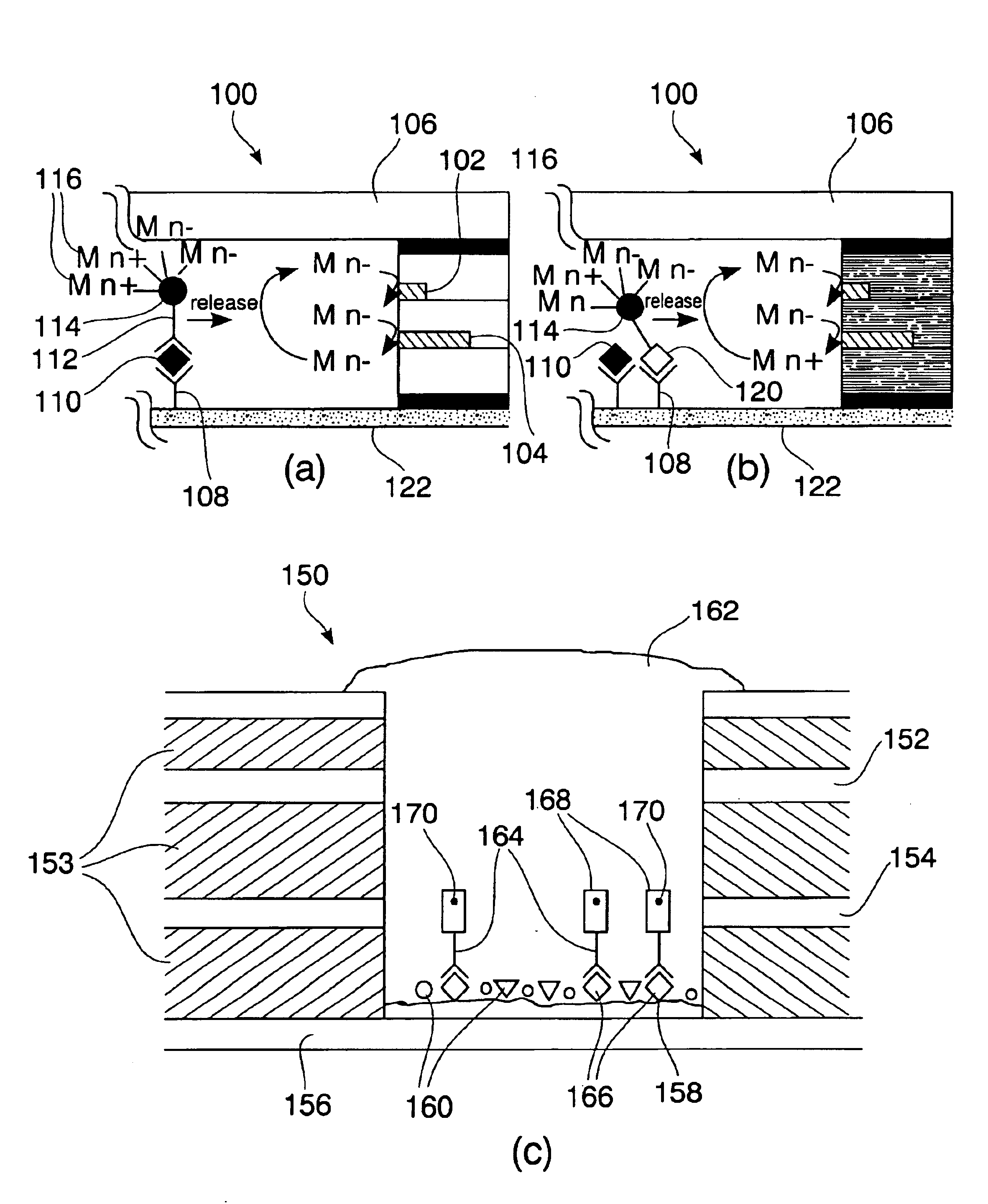
A structure and method for chemical sensing utilizing microassays. Microcavities or micropores are combined with assay techniques to provide a very fast and very sensitive means of detecting chemical compounds. Assay techniques are modified to include a metal ion binding carrier species especially suitable for use in conjunction with the electrochemical detection. This allows assays to be combined with electrochemical analysis, thus allowing the high speed ease and hypersensitivity available in the invention disclosed herein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
High-specific-surface-area boron-doped diamond electrode and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106435518AHigh activityLarge electrochemical reaction interfaceWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentElectrochemical biosensorDiamond electrodes
The invention discloses a high-specific-surface-area boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrode which comprises an electrode substrate. A boron-doped diamond layer is arranged on the surface of the electrode substrate. Or, a transition layer is arranged on the surface of the substrate, and then a boron-doped diamond layer is arranged on the surface of the transition layer. Metal particles are distributed in the diamond layer, and tiny holes and / or pointed cones are distributed on the surface of the diamond layer. Compared with a traditional plate electrode, the boron-doped diamond electrode contains a large number of tiny holes and pointed cones and has the extremely high specific surface area, and the large current intensity is provided through the low current intensity; and meanwhile, due to the different electrode configurations of the substrate and modification of surface graphene and / or carbon nano tubs (CNT), the mass transfer process can be greatly improved, the current efficiency and the electrochemical property are greatly improved, and the BDD electrode with high electrocatalytic activity and high using efficiency is prepared. The electrode can be widely applied in the fields of electrochemical wastewater purification treatment, electrochemical biosensors, strong oxidant electrochemical synthesis, electrochemical detection and the like.
Owner:NANJING DAIMONTE TECH CO LTD
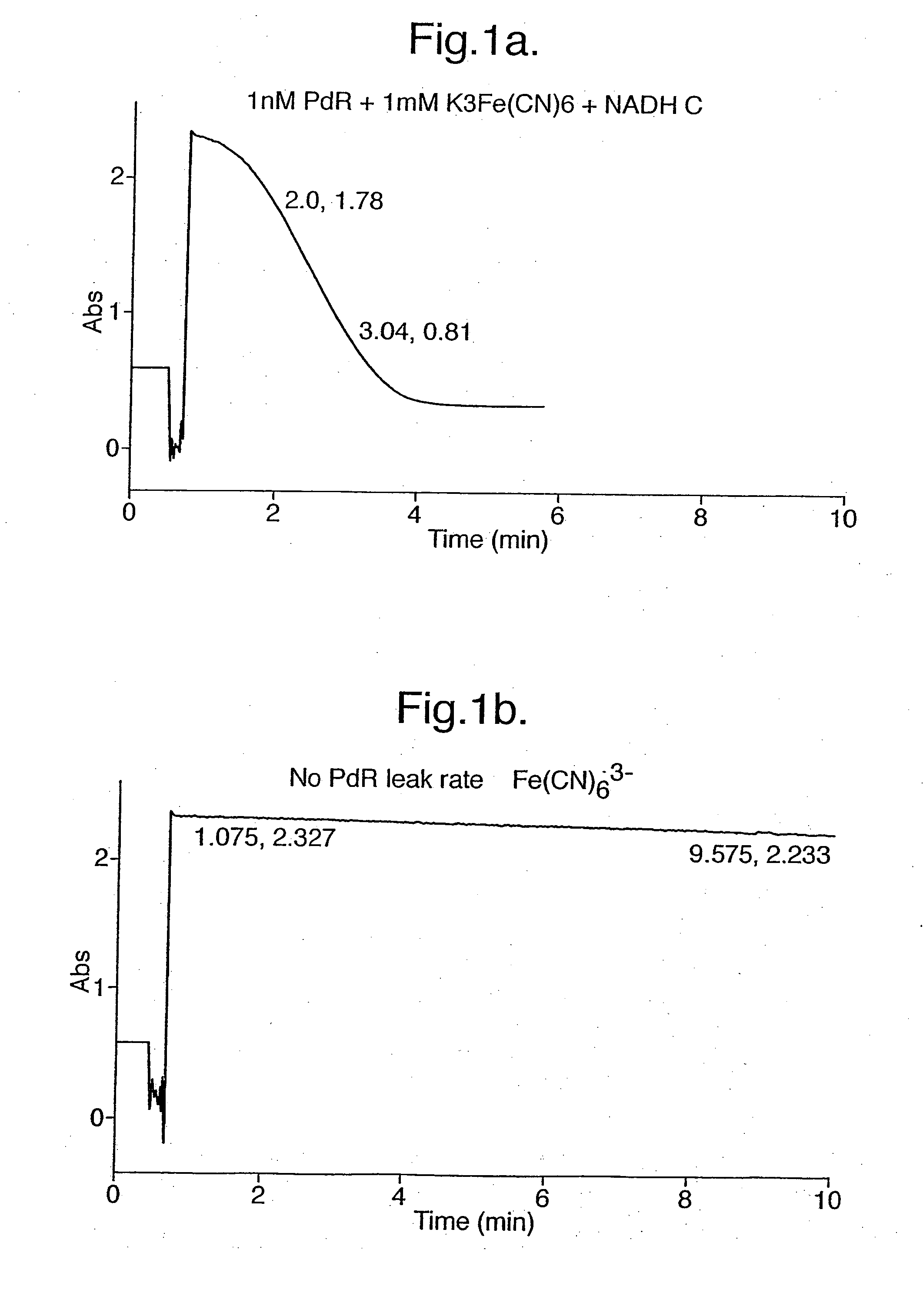
Electrochemical detection of nadh or naph
InactiveUS20050067303A1Easy to carryFast electron transfer rateImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidoreductaseReductase
A method for detecting the presence or absence of, or for determining the concentration of, NADH or NADPH in a sample is provided, wherein the method comprises contacting a reductase and a redox active agent to said sample; and measuring the quantity of reduced redox active agent produced by the reductase, by electrochemical means. The method may be used to quantify the amount or activity of a redox enzyme or its substrate, wherein the redox enzyme uses NAD+, NADP+, NADPH or NADP as a cofactor.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Electrochemical detection of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20040072158A1Conveniently accomplishedEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingOrganic chemistry
An electrochemical detection system which specifically detects selected nucleic acid segments is described. The system utilizes biological probes such as nucleic acid or peptide nucleic acid probes which are complementary to and specifically hybridize with selected nucleic acid segments in order to generate a measurable current when an amperometric potential is applied. The electrochemical signal can be quantified.
Owner:MAGELLAN DIAGNOSTICS
Electrochemical detection of single molecules using abiotic nanopores having electrically tunable dimensions
InactiveUS20090283412A1Decreases electrically tunable diameterIncreases electrically tunable diameterElectrolysis componentsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElectricityConductive polymer
A barrier structure for use in an electrochemical stochastic membrane sensor for single molecule detection. The sensor is based upon inorganic nanopores having electrically tunable dimensions. The inorganic nanopores are formed from inorganic materials and an electrically conductive polymer. Methods of making the barrier structure and sensing single molecules using the barrier structure are also described.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Detection of analytes using electrochemistry
InactiveUS6100045ALow costReduce lossesImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseMatrix solution
The present invention relates to diagnostic assays whereby the detection means is based on electrochemical reactions. This means that the label to be detected provides an electric signal. Preferred labels are enzymes giving such a signal. Provided is a flow cell whereby a solid phase is provided in a flow stream of the sample, in close proximity to a working electrode to detect any electrical signal. In a typical embodiment, a sample is mixed with molecule having specific binding affinity for an analyte of which the presence in the sample is to be detected, whereby said specific binding molecule is provided with a label. The conjugate of labelled specific binding molecule and analyte is then immobilized on the solid phase in the vicinity of the working electrode, the flow cell is rinsed with a solution and afterwards a substrate solution for the label (an enzyme) is provided upon which an electrical signal is generated and can be detected by the working electrode. The methods and devices of the present invention are particular useful for liquids which comprise many substances that may disturb measurement in conventional assays. The design of the flow cell allows for removal of said interfering substances before measurement. In a preferred embodiment at least part of the solid phase is provided in the form of magnetic beads. In this embodiment the solid phase can be mixed with the sample thereby creating a longer reaction time, a better sensitivity and a higher speed of the assay.
Owner:DSM NV
Multi-layered electrochemical microfluidic sensor comprising reagent on porous layer
InactiveUS20060141469A1Enabling detectionEnhanced detection signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteFrit
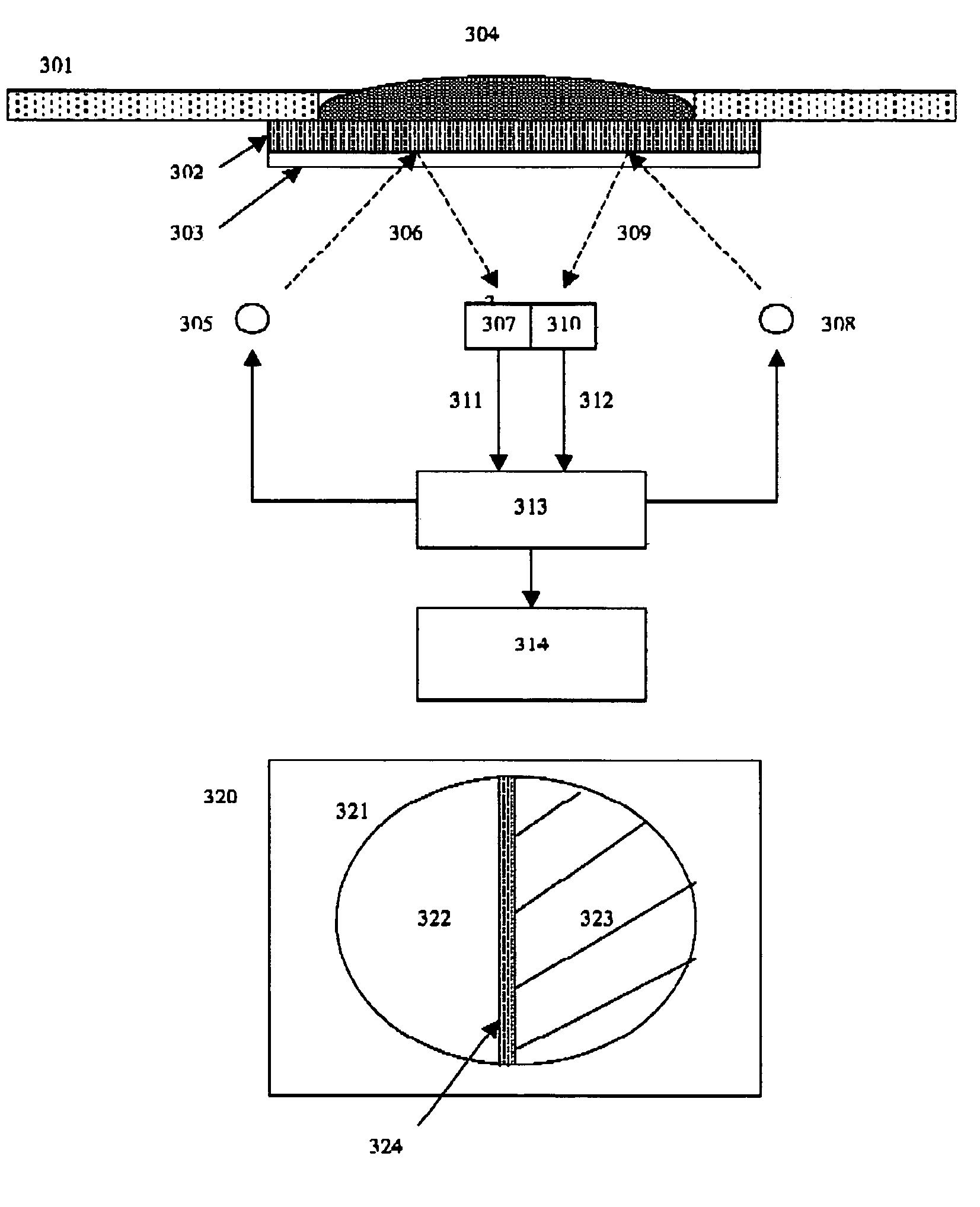
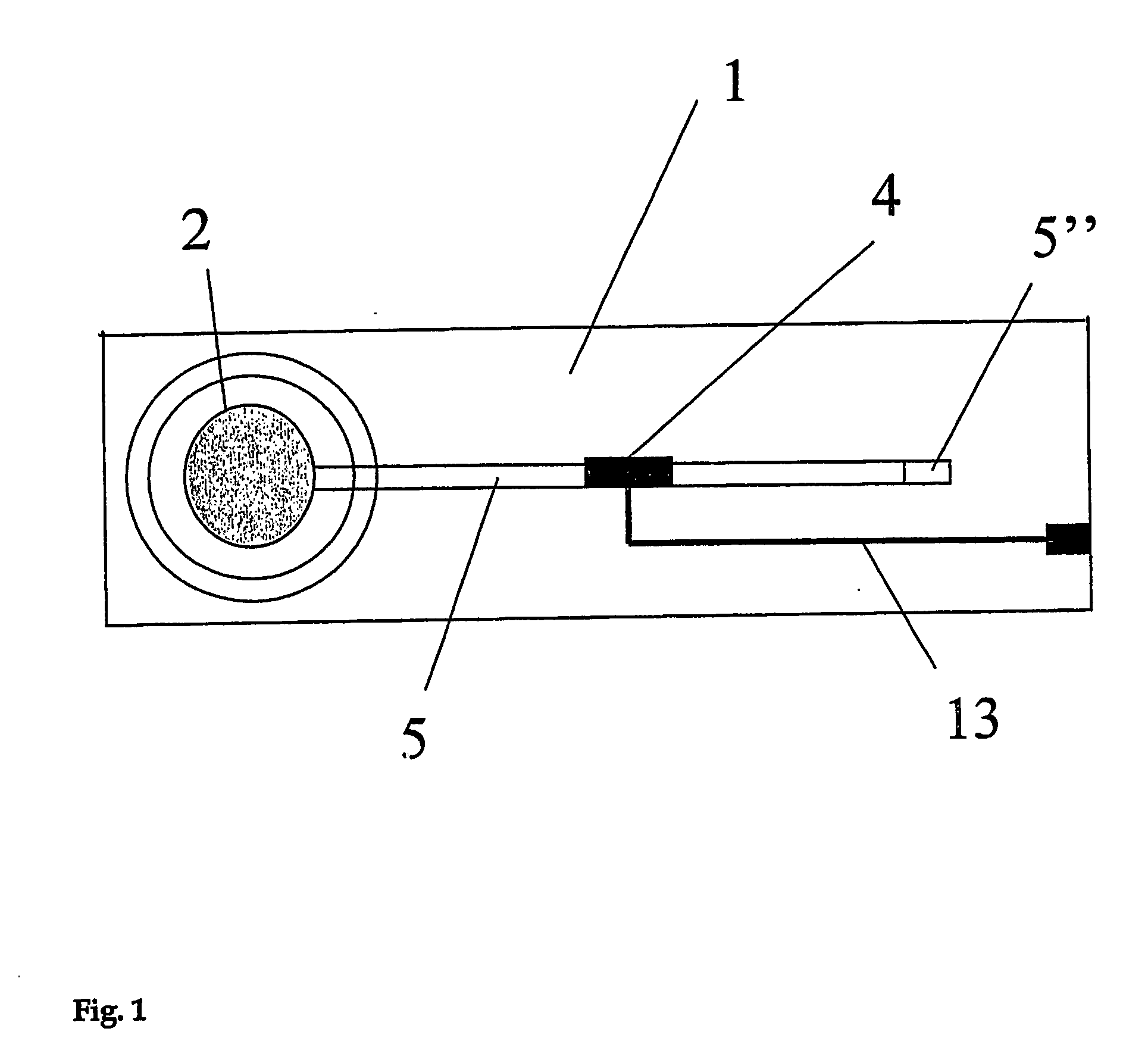
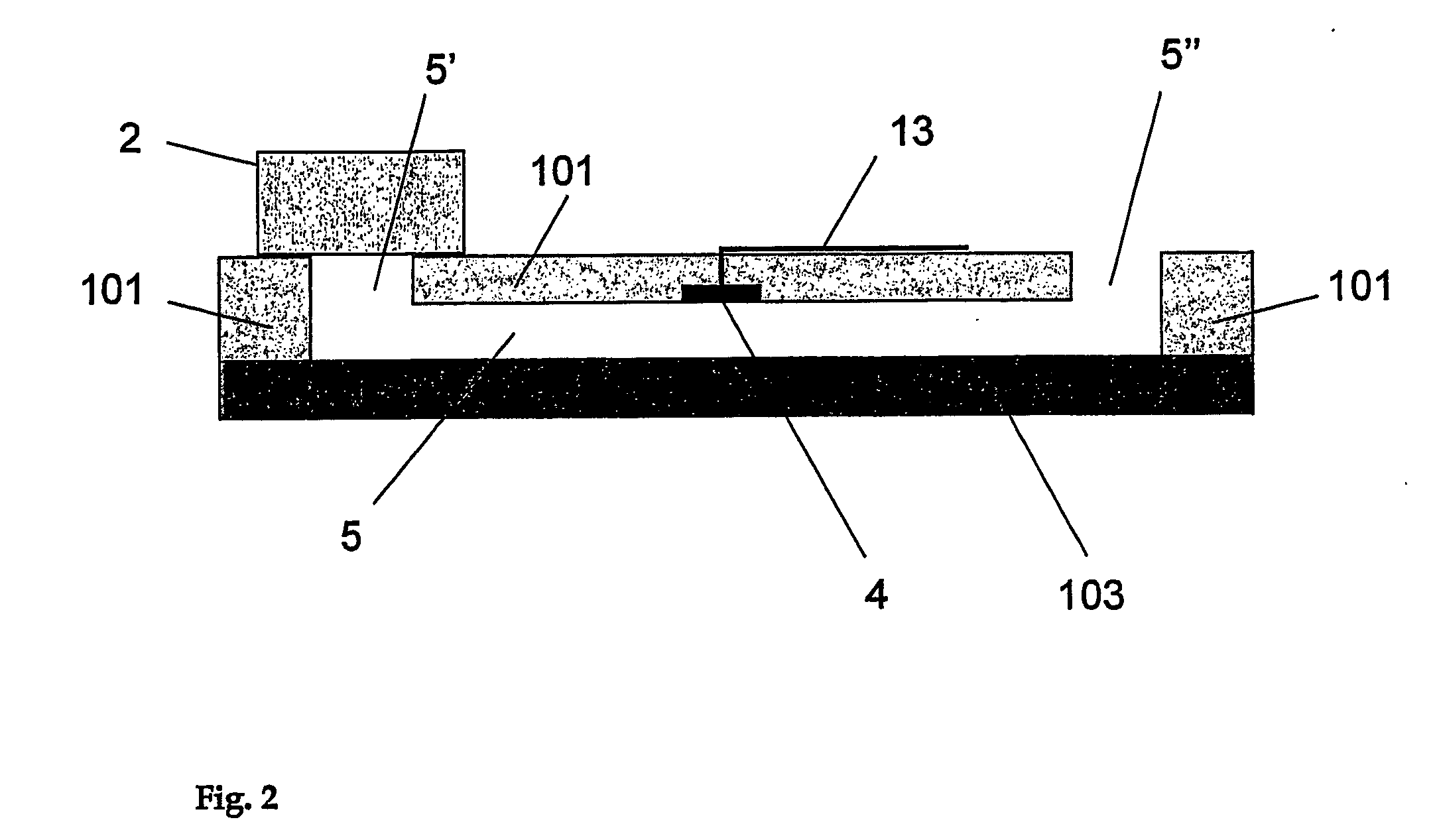
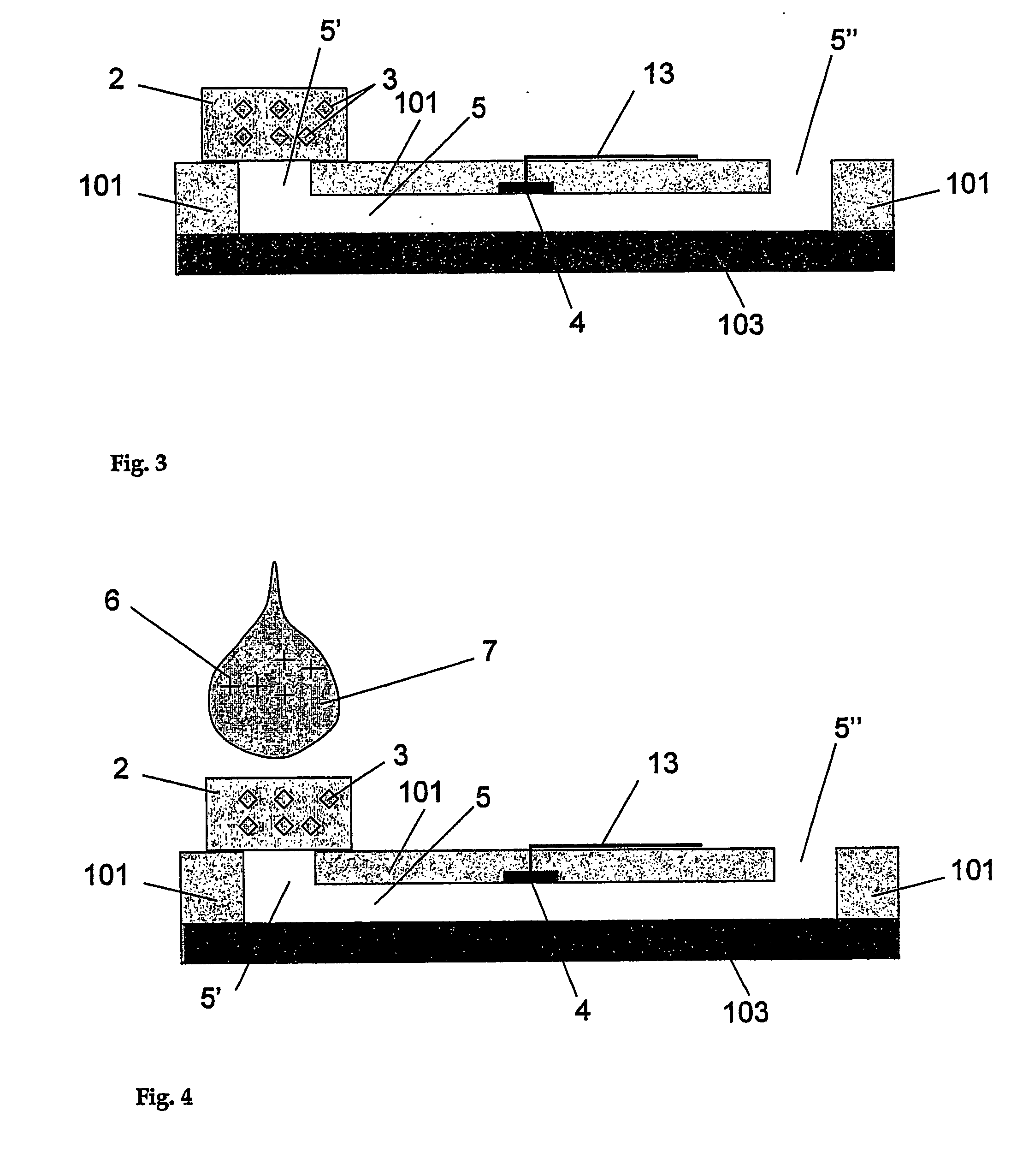
The present invention relates to a microfluidic electrochemical sensor apparatus and a method for conducting analytical tests with said apparatus for multi-reactant assays. The apparatus of this invention is a multi-layer body made of at least three layers, the first one being a polymer layer (1) comprising a microstructure (5) with at least one integrated microelectrode (4) and conductive tracks (13) for connection to an external electrochemical unit, the second one being a non-porous material serving to cover said microstructure so as to enable microfluidic manipulations and the third one being a porous layer (2) such as a membrane or a glass frit, said porous layer comprising at least one reagent (3) to be solubilized upon contact with a test solution (7) and reacting with an analyte (6) present in said solution to form a product that is transported along said microstructure so as to enable electrochemical detection of said analyte. The invention notably enables the performance of multi-reactant assays in a reduced number of steps.
Owner:DIAGNOSWISS
Apoenzyme reactivation electrochemical detection method and assay
InactiveUS20050196820A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorAnalyte
The invention discloses a methods in which dry reagent enzyme based electrochemical biosensors, which are in a relatively mature form due to the extensive amount of development pioneered by the blood glucose monitoring industry, may be simply adapted to perform tests for blood coagulation, enzymatic activity, or immunochemical assays for antigens present in a fluid sample. In particular, the utility of combining apoenzyme based dry reagent electrochemical biosensors with apoenzyme reactivation technology is taught. This combination creates a novel combination dry reagent test technology capable of detecting a wide range of different analytes.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Microfluidic devices and methods of preparing and using the same
InactiveUS20100261286A1Constant flowAccurate samplingMaterial nanotechnologyComponent separationFluorescenceCapillary action
Microfluidic devices include a photoresist layer in which an inlet chamber, an optional reaction chamber and at least one detection chamber are in fluid contact, a support arranged under the photoresist layer and a cover arranged above the photoresist layer. The devices further include a set of absorbent channels downstream of the last detection chamber. Biogenic or immunoreactive substances are placed in the reaction chamber and detection chamber(s). When a liquid sample is dropped into the inlet chamber, the sample liquid is drawn through the devices by capillary action. Detection methods include electrochemical detection, colorimetric detection and fluorescence detection.
Owner:NANO DITECH CORP
Dual glucose-turbidimetric analytical sensors
InactiveUS20060051738A1Simple data analysisImprove compatibilityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceChylomicronTurbidity
Diagnostic dry reagent tests capable of reacting with a single drop of whole blood and reporting both glucose and light-scattering analytes, such as chylomicrons, are taught. Such dry reagent tests may employ electrochemical detection methodologies, optical detection methodologies, or both methodologies. These tests alert diabetics to excessive levels of postprandial lipemia caused by meals with excessive amounts of fat, and thus can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Analyte Test System for Determining the Concentration of an Analyte in a Physiological or Aqueous Fluid
InactiveUS20070287191A1Inexpensive and usableCheap productionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPretreated surfacesAnalyteDistribution system
An analyte test element for determining the concentration of at least one analyte in a physiological sample fluid having a first and a second surface in a predetermined distance opposite from each other, said both surfaces are provided with two substantially equivalent patterns forming areas of high and low surface energy which are aligned mostly congruent, whereby the areas with high surface energy create a sample distribution system with at least two detection areas, characterized in that the detection areas of first and second surface are also provided with two corresponding patterns of working and reference electrodes of electrochemical detection means.
Owner:EGOMEDICAL TECH
Biosensor Apparatus and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20100006452A1Increase in the amount of probe boundReduce the amount requiredImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical reactionAnalyte
Disclosed herein are methods and devices for detecting the presence of an analyte of interest. A biosensor device can include a reaction chamber and an electrochemical detection chamber. The reaction chamber can include at least one immobilized binding site and a probe conjugate adapted to bind to at least one of the target analyte and the immobilized binding site while the detection chamber can include electrodes for detecting an electrochemical reaction. If present, the target analyte in the fluid sample results in a change in the amount of probe conjugate bound in the reaction chamber, which can be detected electrochemically in the detection chamber.
Owner:UNIVERSAL BIOSENSORS
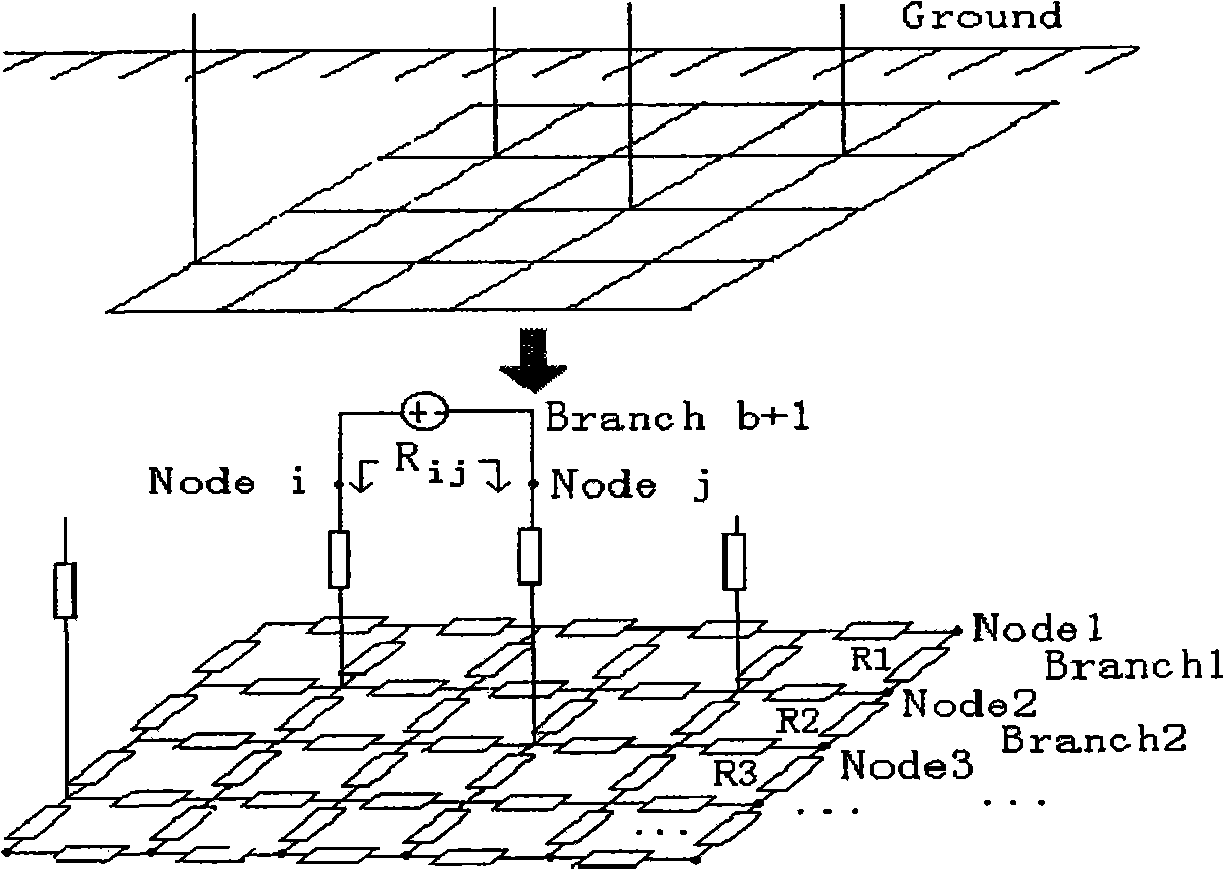
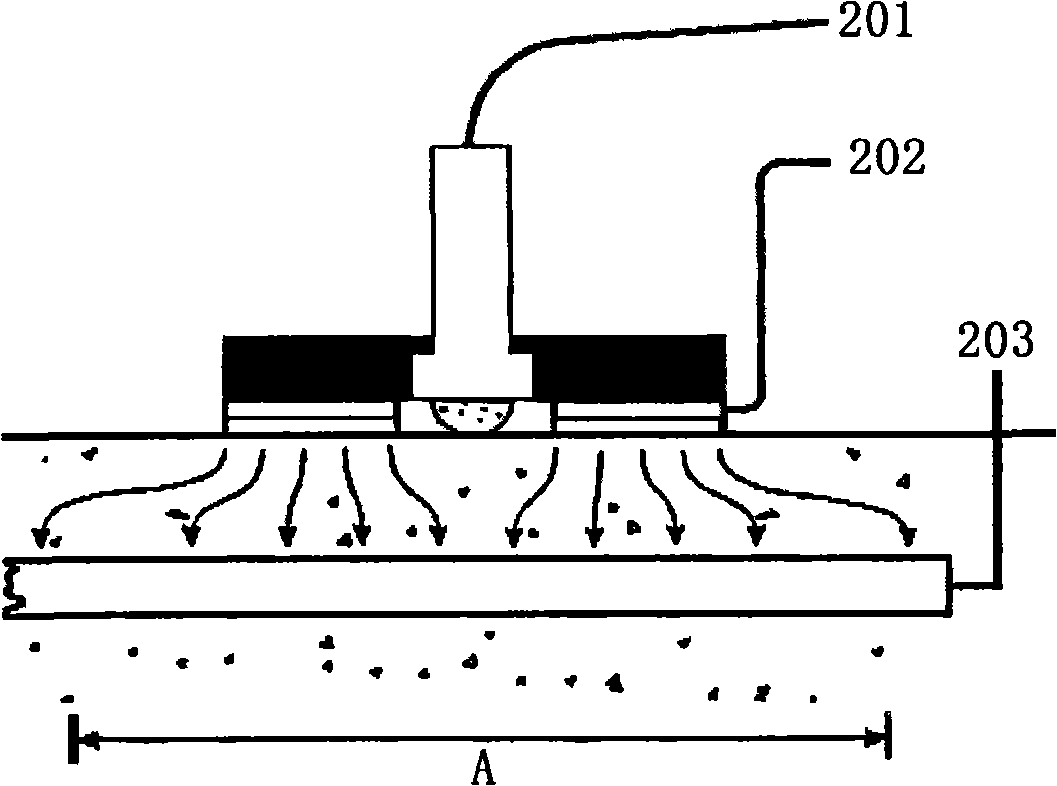
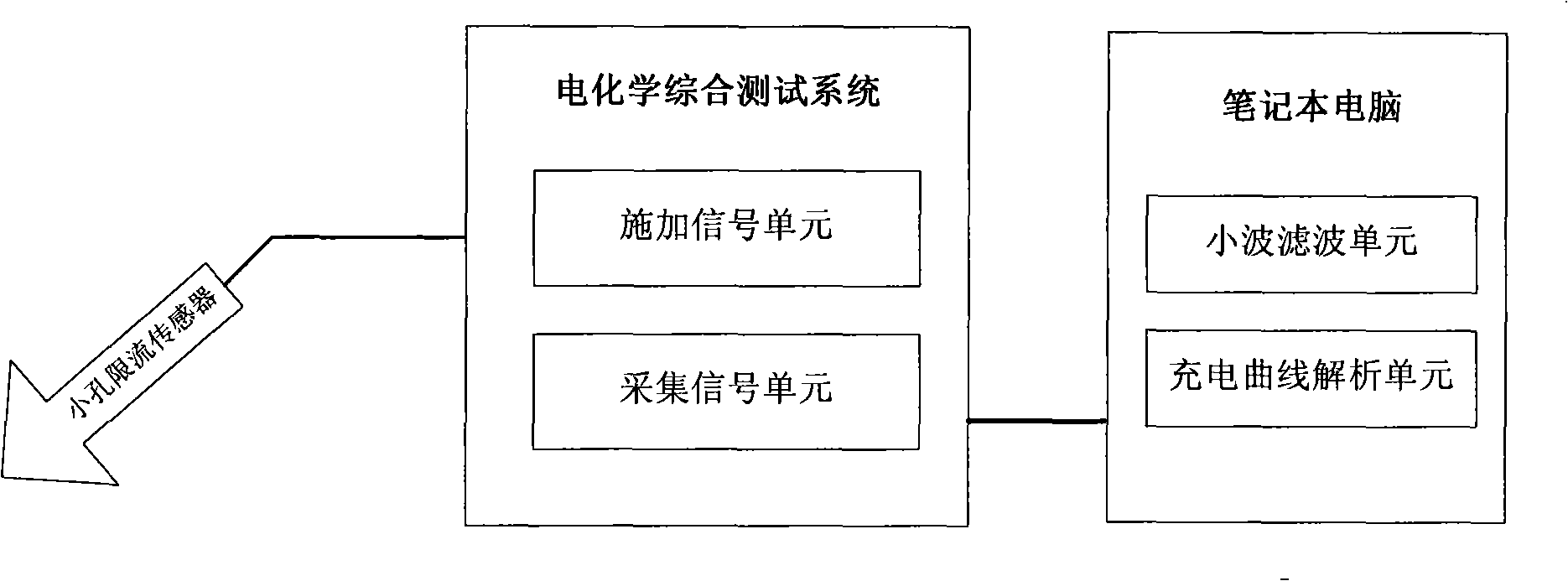
Ground net corrosion detection method and system
ActiveCN101315403AEasy to measureQuick testWeather/light/corrosion resistanceFault locationStep responseMetal
The invention provides a corrosion detection method for a grounding net, as well as a system. The method comprises the steps as follows: the corrosion potential of detected grounding net metal is measured, constant current step signals are applied to the detected grounding net metal, and the constant current step response signals are collected; the wavelet filter treatment is performed to the collected grounding net soil corrosion electrochemical detection data; and the corrosion electrochemical parameter analysis processing is performed to the grounding net soil corrosion electrochemical detection data after the wavelet filter treatment, thereby generating the grounding net soil corrosion detection result. The grounding net corrosion status is detected accurately and conveniently by the electrochemical detection method.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRICAL POWER RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com