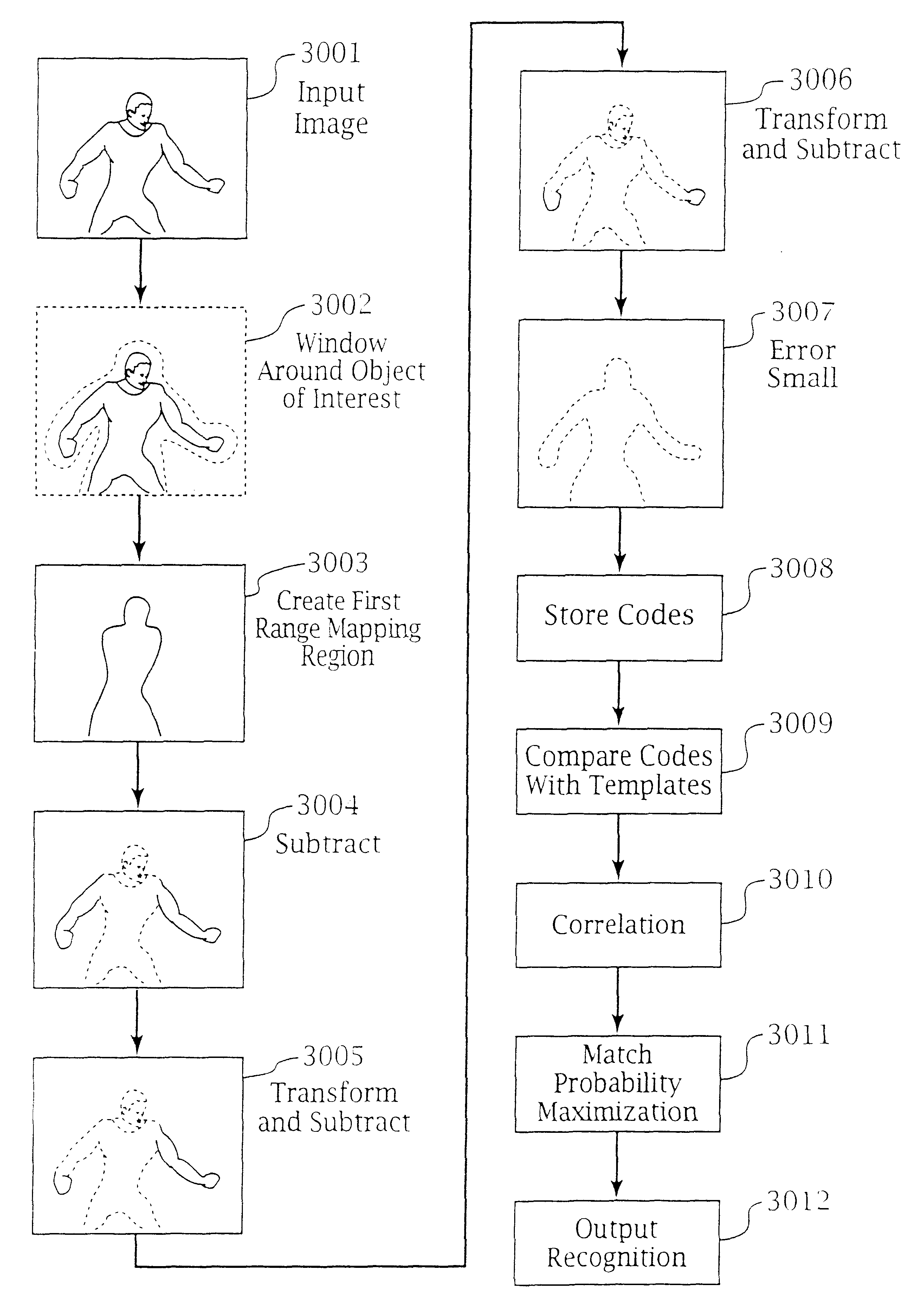
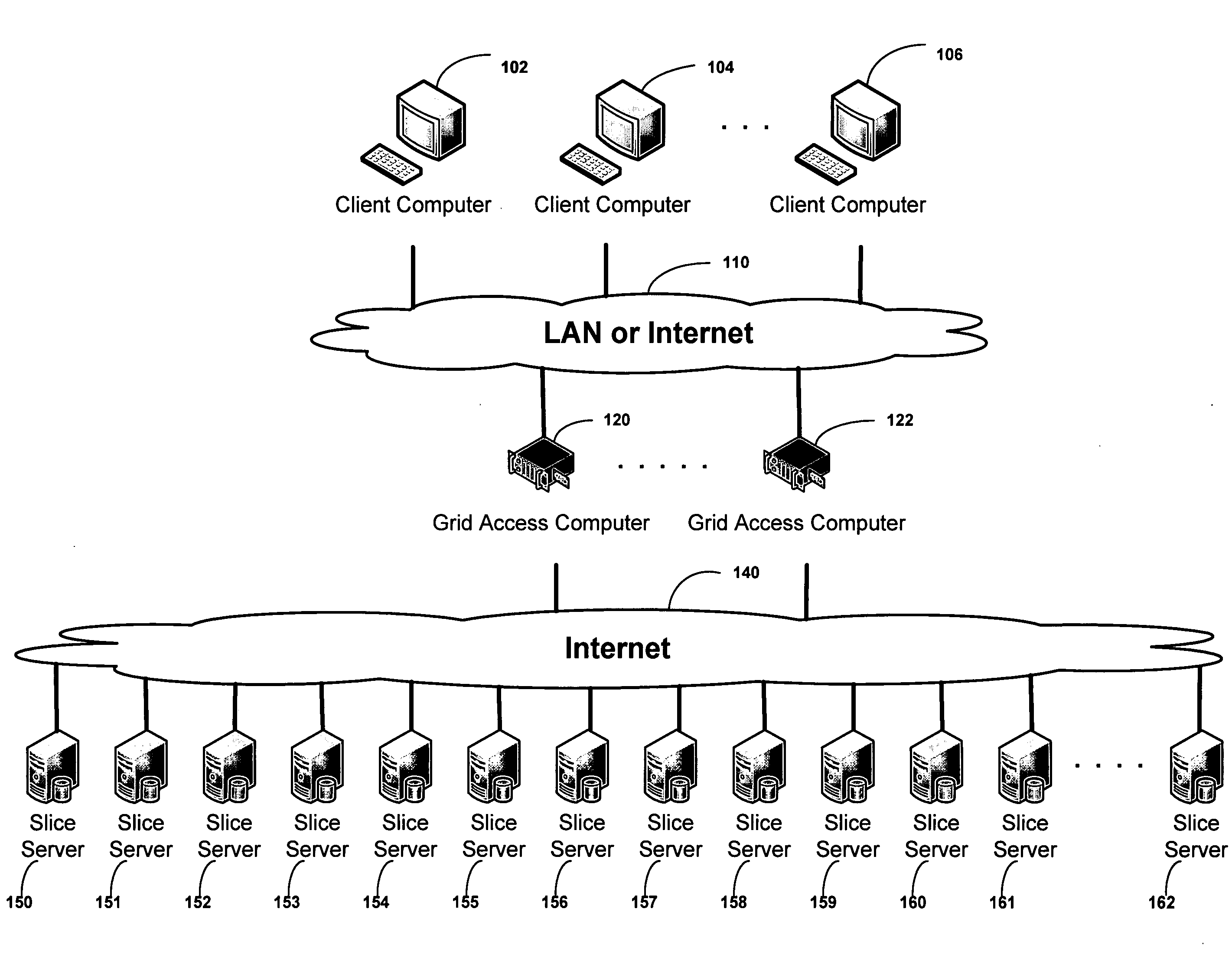
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35197results about "Fault location" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adaptive pattern recognition based control system and method
InactiveUS6400996B1Minimize timeEasy to implementError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData streamSmart house
An adaptive interface for a programmable system, for predicting a desired user function, based on user history, as well as machine internal status and context. The apparatus receives an input from the user and other data. A predicted input is presented for confirmation by the user, and the predictive mechanism is updated based on this feedback. Also provided is a pattern recognition system for a multimedia device, wherein a user input is matched to a video stream on a conceptual basis, allowing inexact programming of a multimedia device. The system analyzes a data stream for correspondence with a data pattern for processing and storage. The data stream is subjected to adaptive pattern recognition to extract features of interest to provide a highly compressed representation that may be efficiently processed to determine correspondence. Applications of the interface and system include a video cassette recorder (VCR), medical device, vehicle control system, audio device, environmental control system, securities trading terminal, and smart house. The system optionally includes an actuator for effecting the environment of operation, allowing closed-loop feedback operation and automated learning.
Owner:BLANDING HOVENWEEP
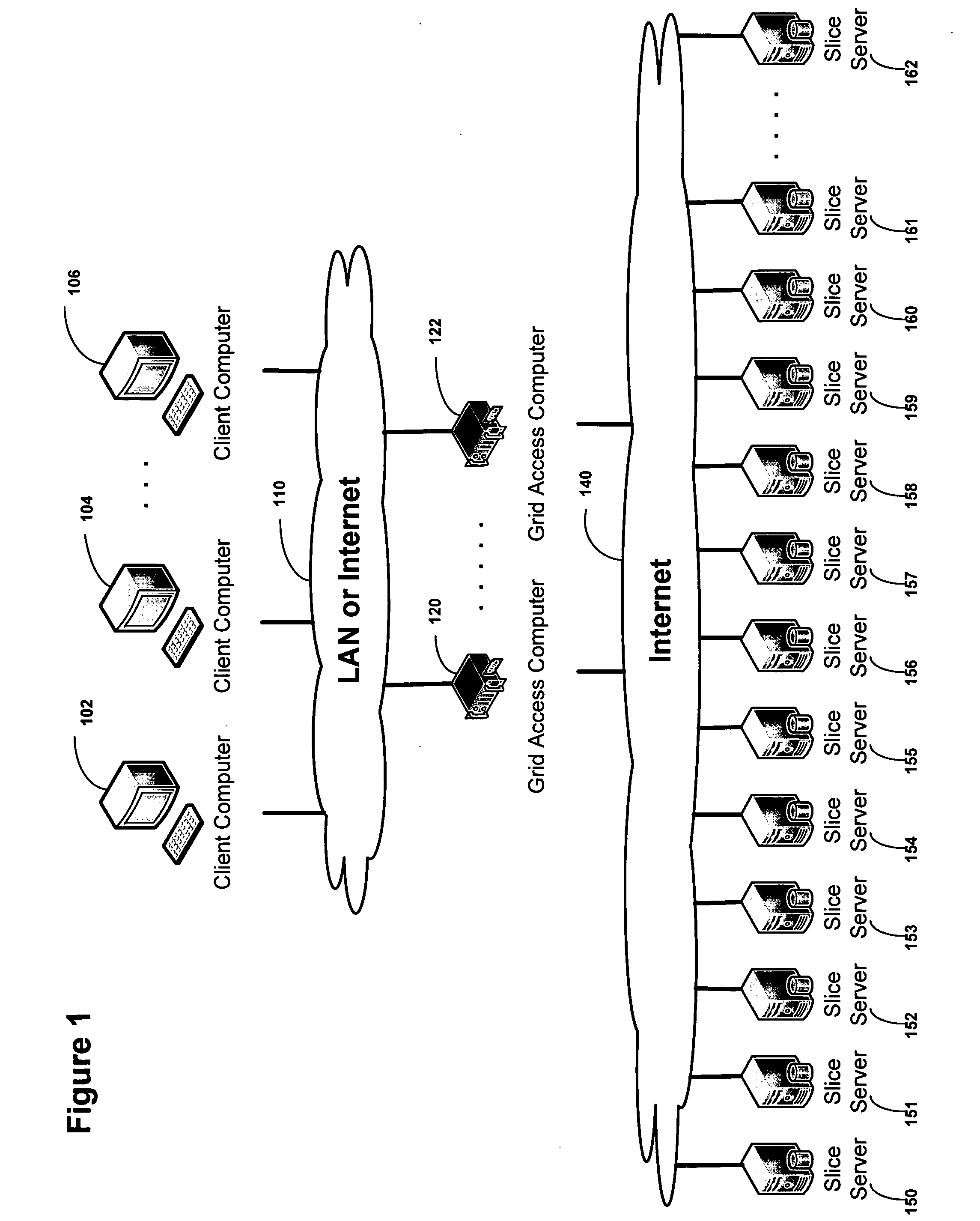
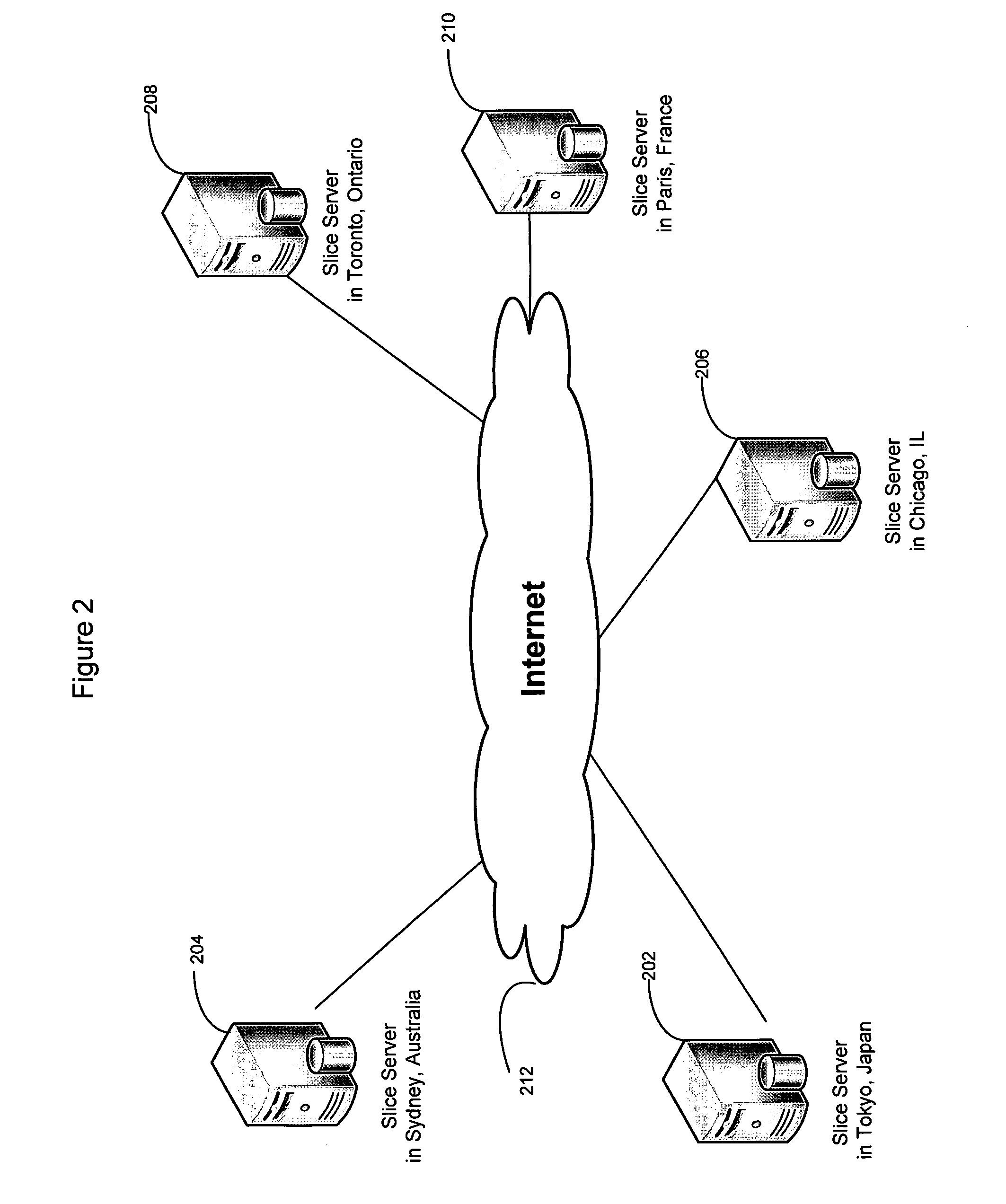
Smart access to a dispersed data storage network
ActiveUS20090094318A1Efficient accessImprove network performanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData segmentRanking
An improved system for accessing data within a distributed data storage network (“DDSN”) is disclosed. In a system implementing the disclosed invention, traffic is routed to individual slice servers within the DDSN in accordance with objective criteria as well as user-defined policies. In accordance with one aspect of the disclosed invention, when a data segment is written to a DDSN, the segment is divided into multiple data slices, which are simultaneously transmitted to different slice servers. In accordance with another aspect of the disclosed invention, when a data segment is read from a DDSN, a list of slice servers, each containing a data slice that could be used to reconstruct the requested data segment, is assembled, and sorted in accordance with a preference rating assigned to each of the slice servers. Sufficient data slices to reconstruct the data segment are then read in accordance with the preference ranking of the slice servers.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
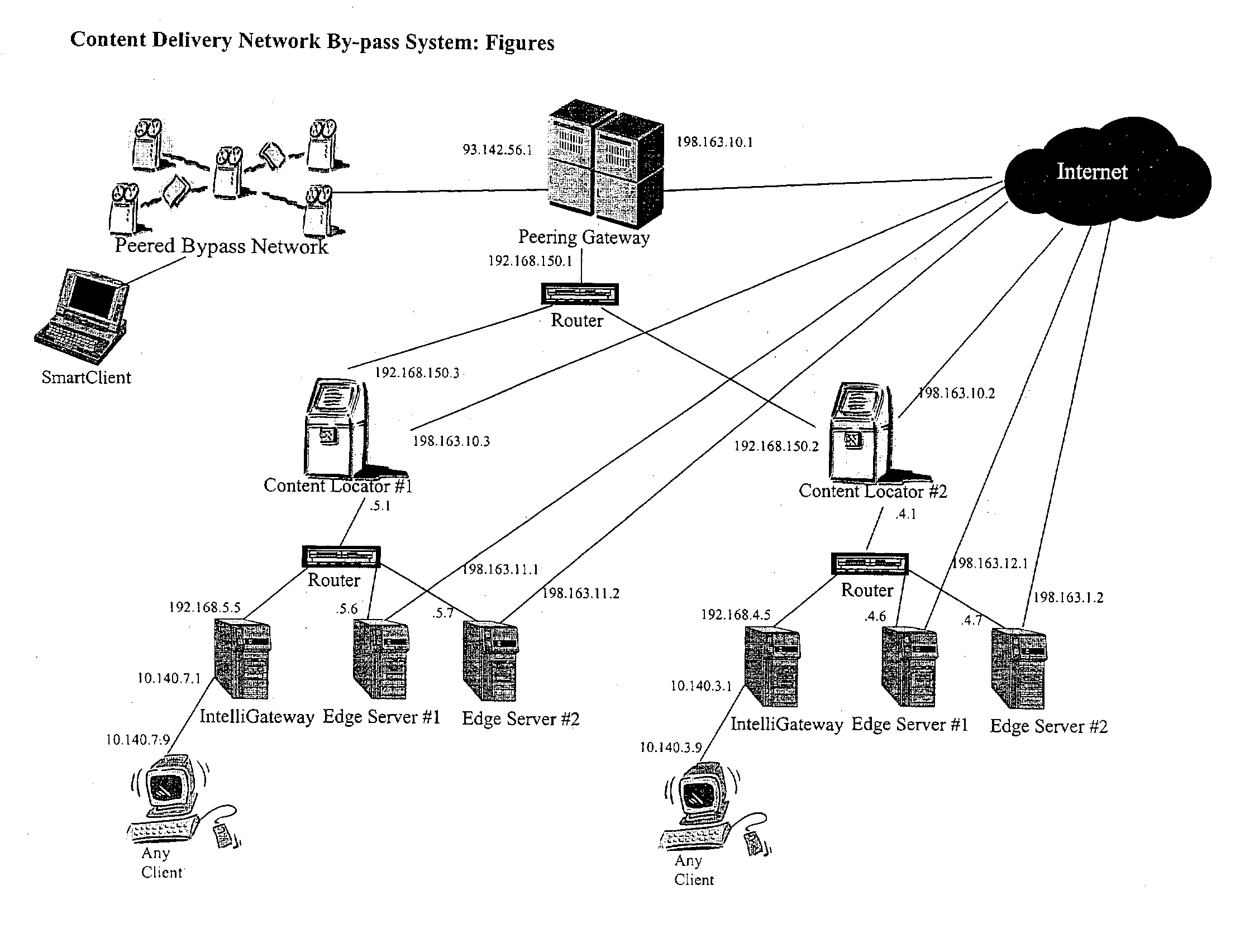
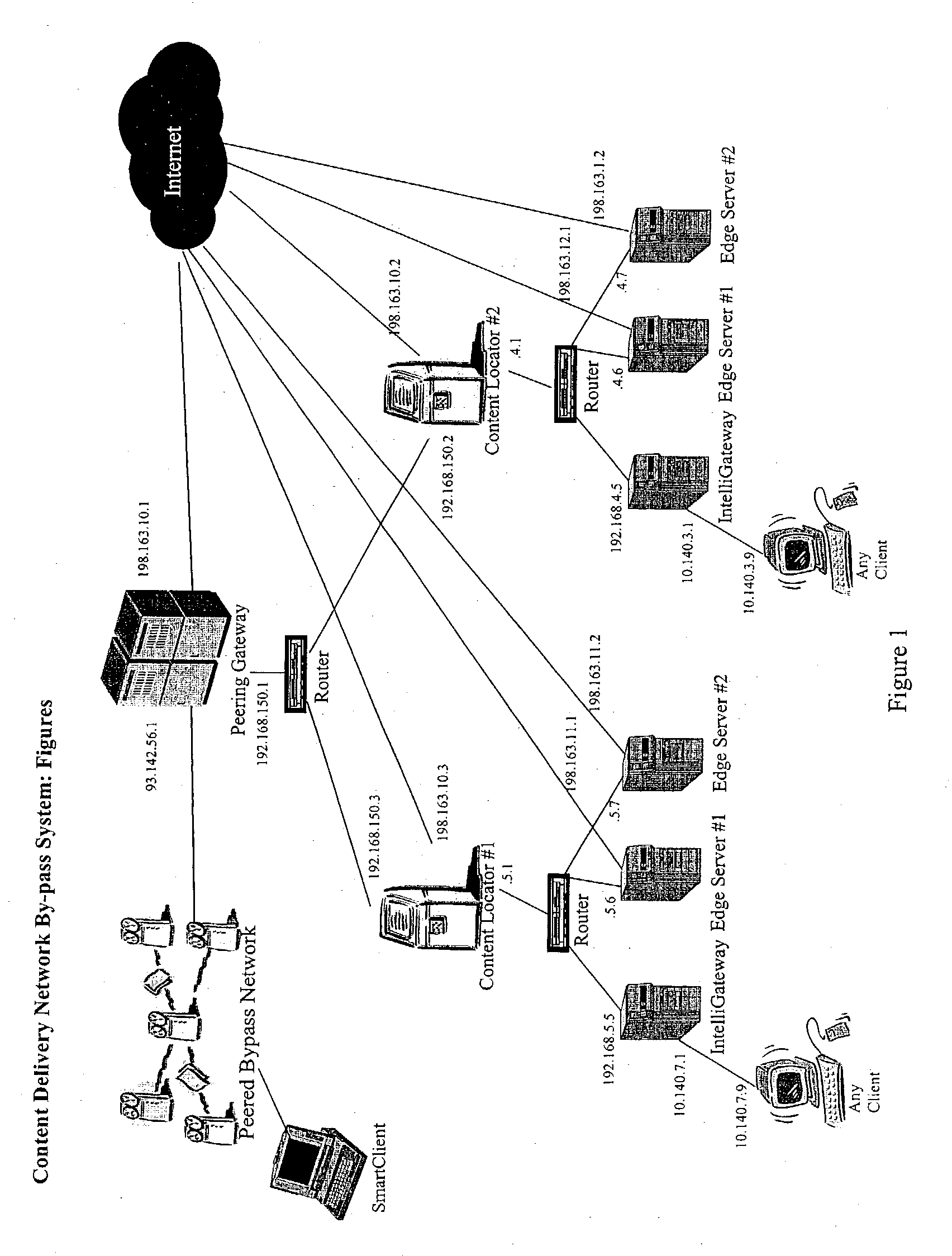
Content delivery network by-pass system
InactiveUS20030174648A1Increase capacityIncrease in sizeError preventionTransmission systemsWeb sitePeering
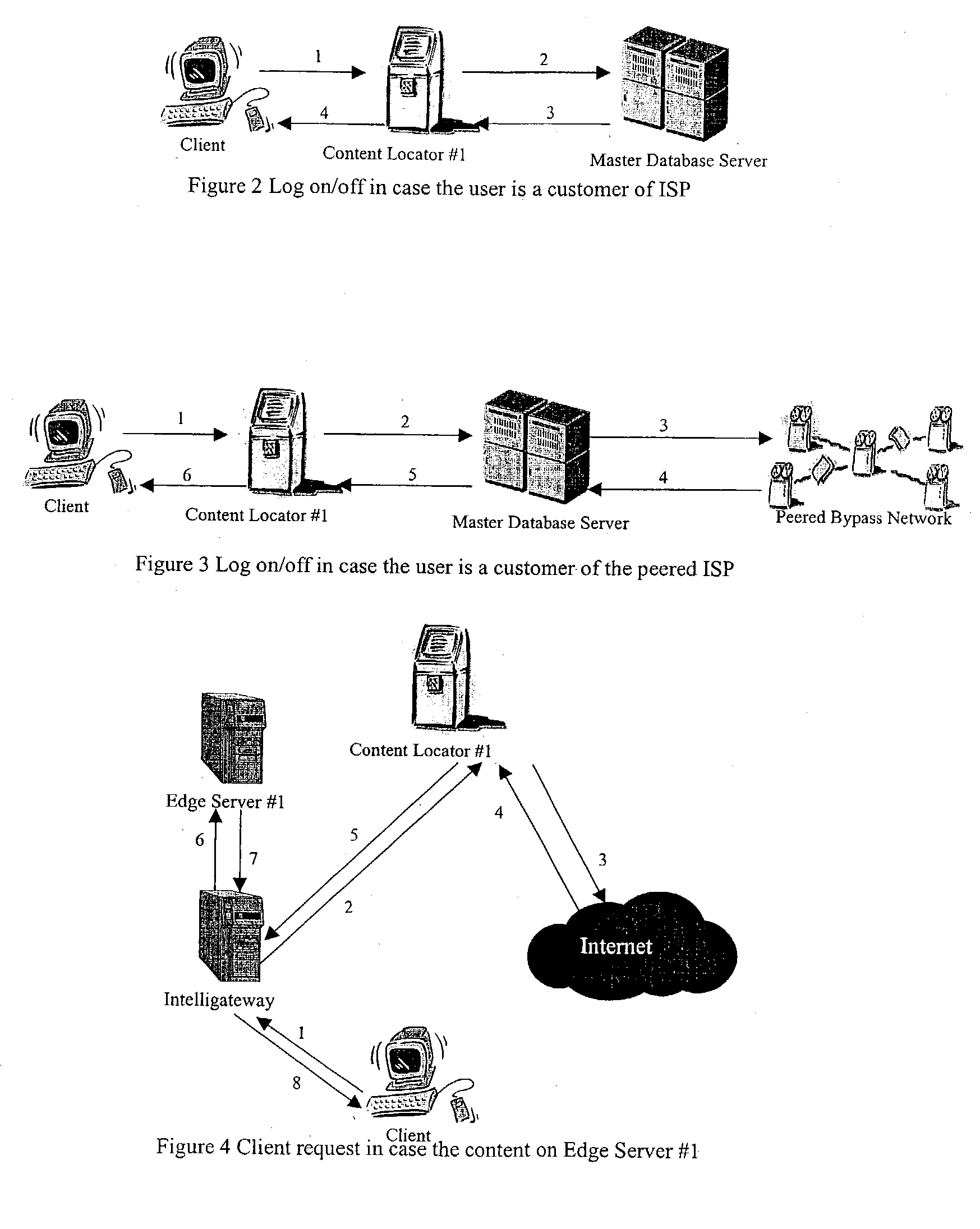
The bypass network is designed to provide fast access and high quality streaming media services anywhere anytime. There are five major components including Peering Gateway, Content Locator, Edge Server, Gateway and Client. The whole bypass network is divided into number of self-managed sub-networks, which are referred as local networks in this document. Each local network contains Edge Servers, gateways, and a Content Locator. The Edge Servers serve as cache storage and streaming servers for the local network. The gateways provide a connection point for the client computers. Each local network is managed by a Content Locator. The Content Locator handles all client requests by communicating with the Peering Gateway and actual web sites, and makes the content available on local Edge Servers. The Content Locator also balances the load on each Edge Server by monitoring the workload on them. One embodiment is designed for home users whose home machine does not move around frequently. A second embodiment is designed for business users who travel around very often where the laptops would self-configure as a client of the network.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
System, method and article of manufacture for selecting a gateway of a hybrid communication system architecture
Telephone calls, data and other multimedia information is routed through a hybrid network which includes transfer of information across the internet utilizing telephony routing information and internet protocol address information. A media order entry captures complete user profile information for a user. This profile information is utilized by the system throughout the media experience for routing, billing, monitoring, reporting and other media control functions. Users can manage more aspects of a network than previously possible, and control network activities from a central site. A directory service that supports a hybrid communication system architecture is provided for routing traffic over the hybrid network and the internet and selecting a network proximal to the origination of the call.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
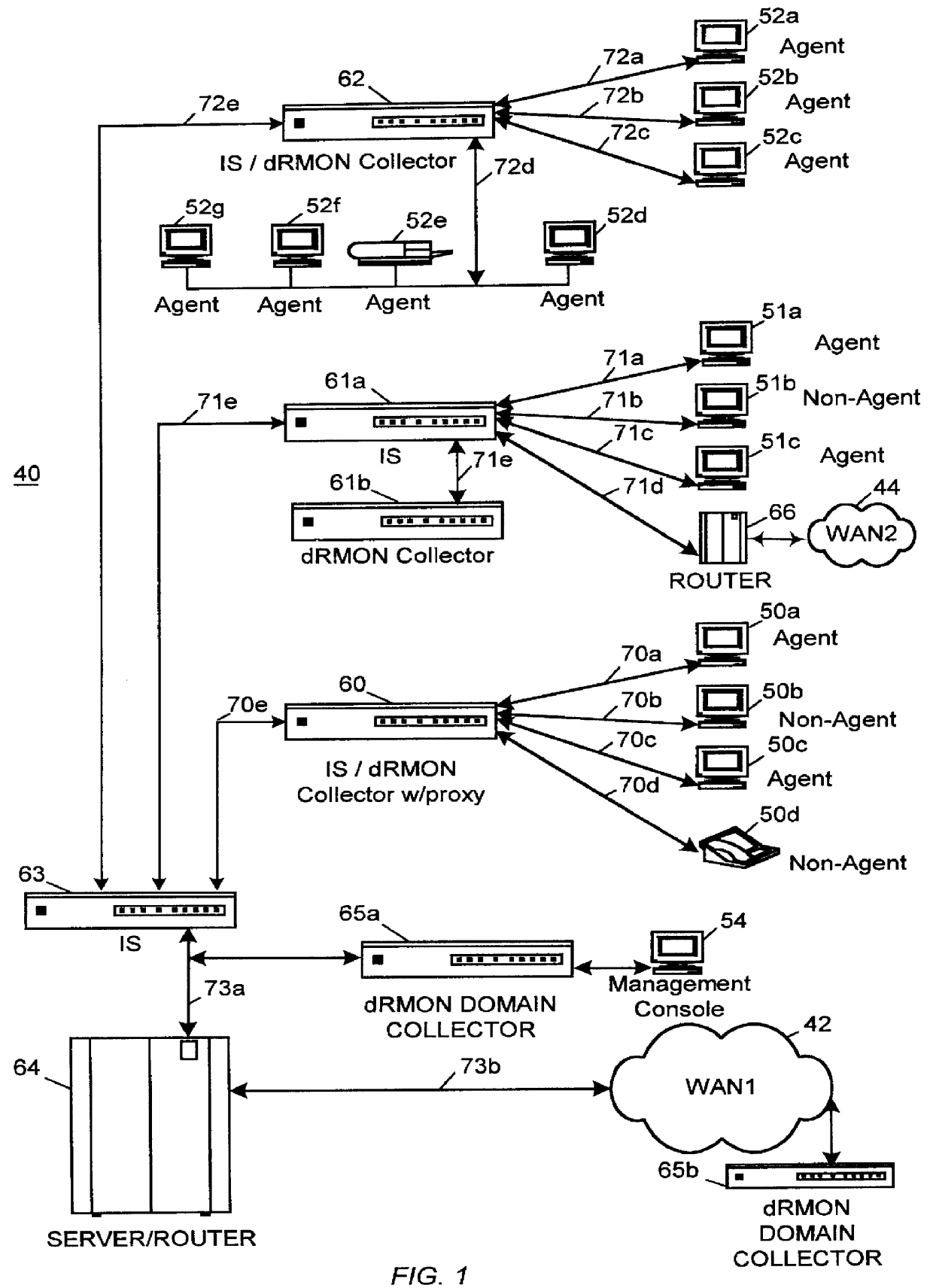
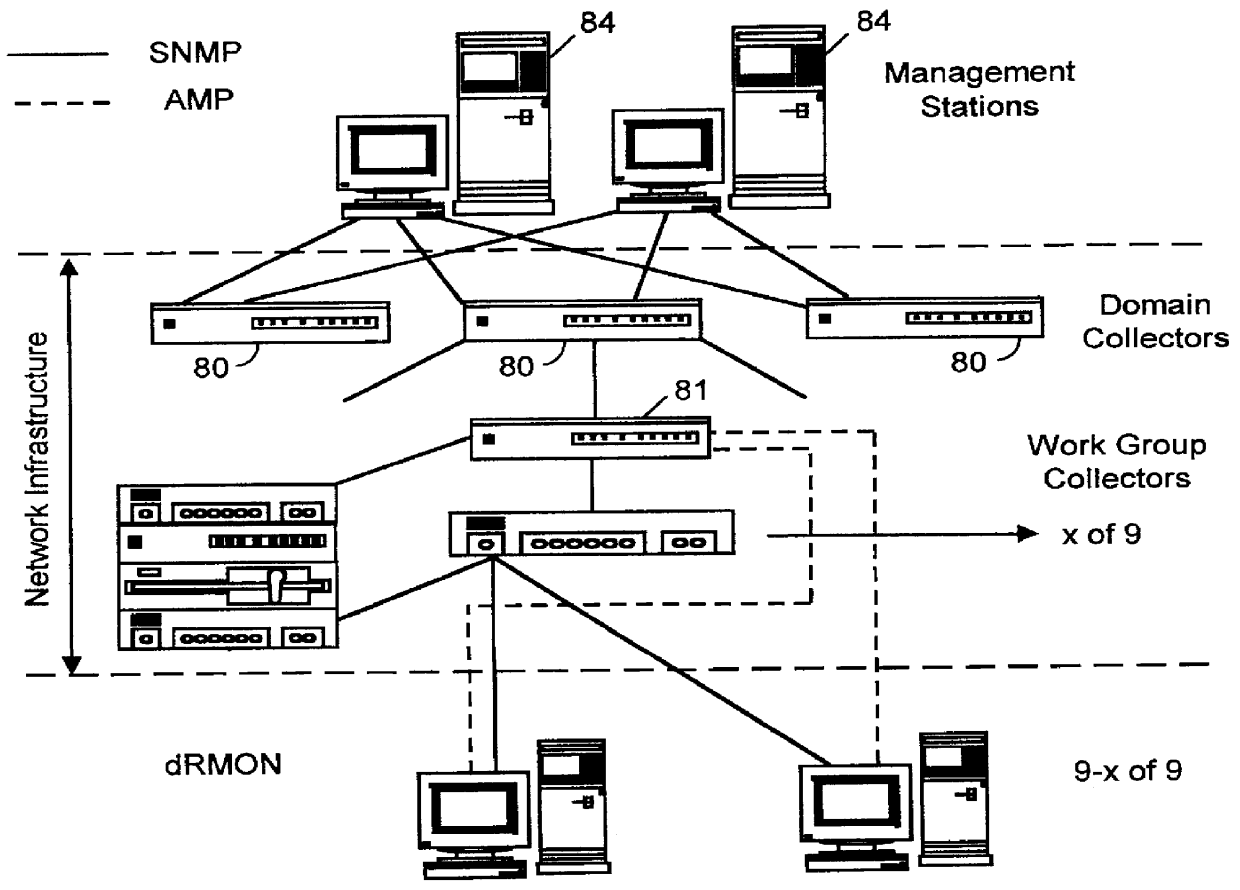
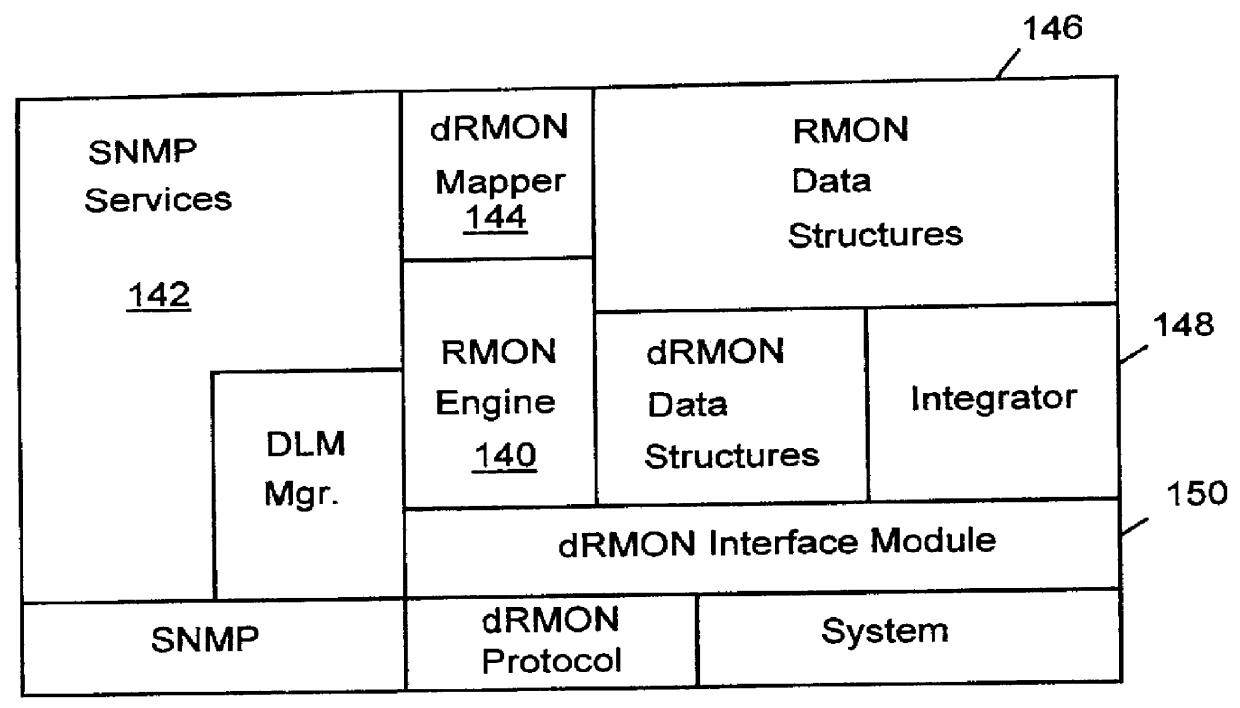
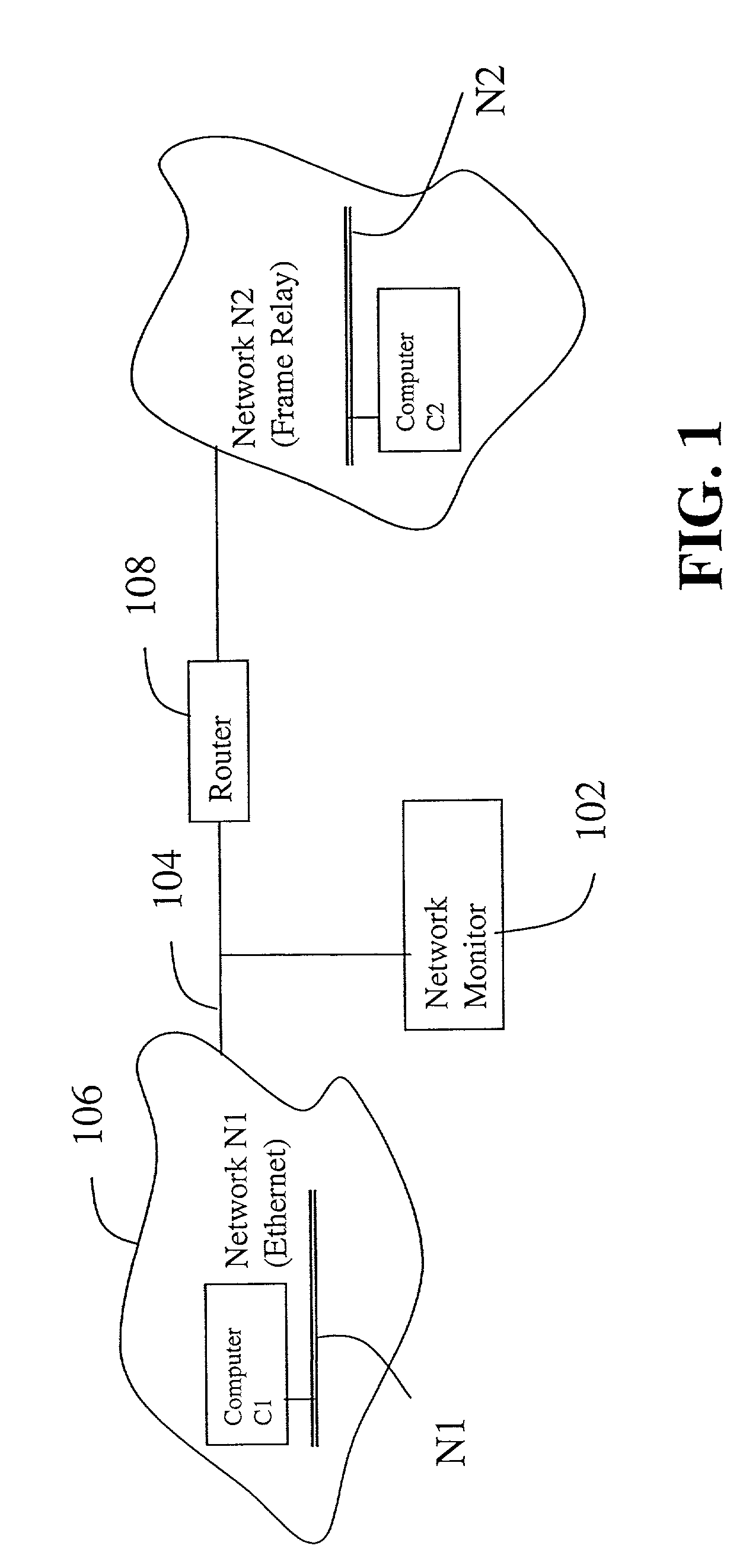
Distributed remote monitoring (dRMON) for networks
InactiveUS6108782AError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork operating systemOperational system
Distributed remote monitoring (dRMON) of network traffic and performance uses distributed nodes to collect traffic statistics at distributed points in the network. These statistics are forwarded to collectors which compile the statistics to create combined views of network performance. A collector may mimic a prior art, non-distributed, network probe and may interact with network management software as though it were a stand alone network probe thereby simplifying a user's interaction with the distributed system. The invention is designed to work in accordance with a variety of standard network management protocols including SNMP, RMON, and RMON2 but is not limited to those environments. The invention has applications in a variety of communication system environments including local area networks, cable television distribution systems, ATM systems, and advanced telephony systems. A specific embodiment of the invention solves is particularly optimized to work in LAN environments with end systems running under Windows-compatible network operating systems.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
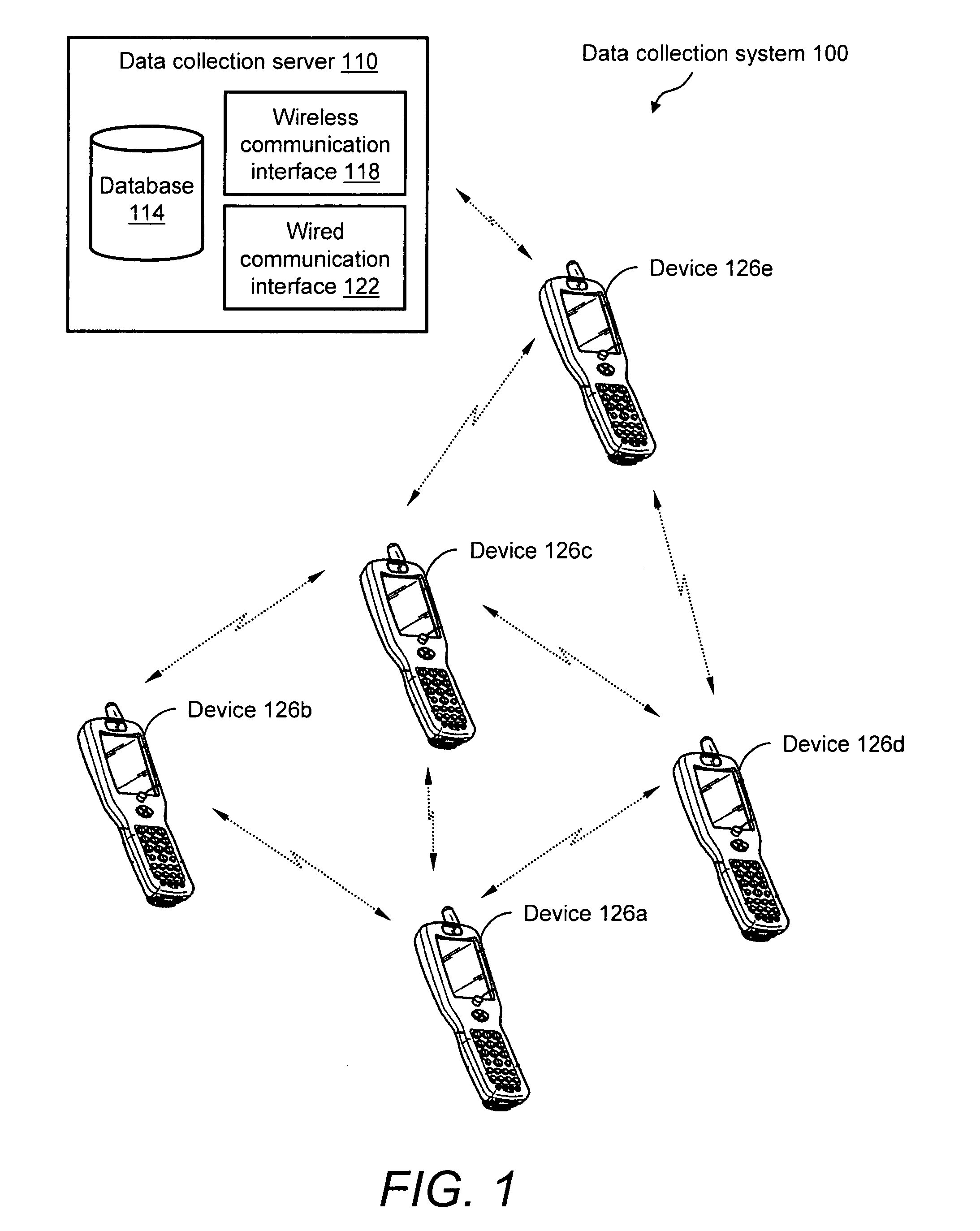
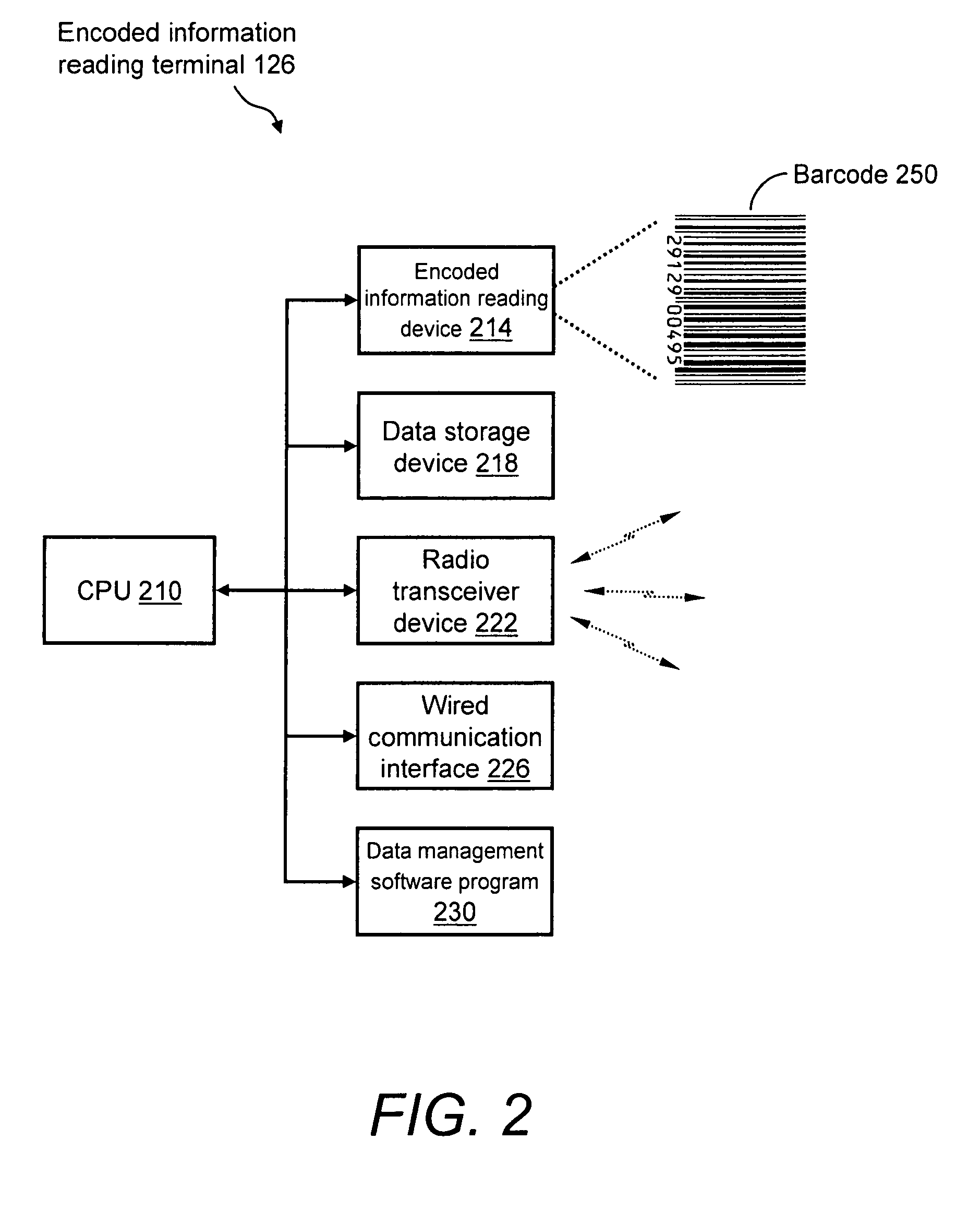
System and method for reliable store-and-forward data handling by encoded information reading terminals
InactiveUS8971346B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsStore and forwardComputer terminal
A data collection system for, and methods of, providing reliable store-and-forward data handling by encoded information reading terminals can utilize ad-hoc peer-to-peer (i.e., terminal-to-terminal) connections in order to store data that is normally stored on a single terminal only, in a redundant manner on two or more terminals. Each portable encoded information reading terminal can be configured so that when it captures data, a software application causes the terminal to search out nearby peer terminals that can store and / or forward the data to other peer terminals or to a data collection server, resulting in the data having been stored by one or more peer terminals that are immediately or not immediately accessible by the data-originating terminal.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Systems and methods for processing packets
InactiveUS7215637B1Minimize occurrenceSize of output is increasedError preventionTransmission systemsPacket filteringTraffic analysis
Methods and devices for processing packets are provided. The processing device may include an input interface for receiving data units containing header information of respective packets; a first module configurable to perform packet filtering based on the received data units; a second module configurable to perform traffic analysis based on the received data units; a third module configurable to perform load balancing based on the received data units; and a fourth module configurable to perform route lookups based on the received data units.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Dynamic parameter adjustment for LTE coexistence
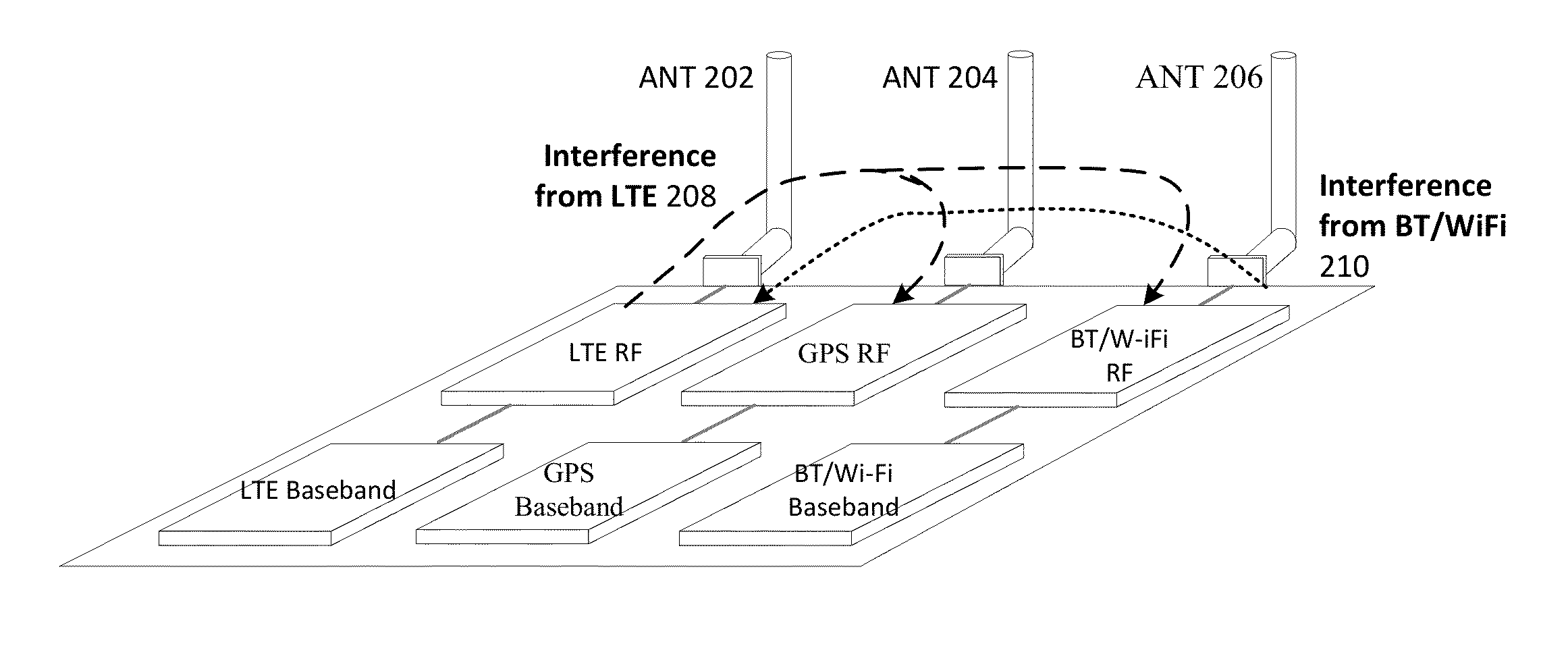
Coexistence gaps may permit one radio access technology (RAT) to coexists with another RAT by providing period in which one RAT may be silent and another may transmit. Methods may account for the RAT traffic and for the presence of other secondary users in a channel. Methods may be provided to dynamically change the parameters of a coexistence gap pattern, such as the duty cycle, to adapt to both the RAT traffic and the presence of other secondary users. Methods may include PHY methods, such as synchronization signal (PSS / SSS) based, MIB based, and PDCCH based, MAC CE based methods, and RRC Methods. Measurements may be provided to detect the presence of secondary users, and may include reporting of interference measured during ON and OFF durations, and detection of secondary users based on interference and RSRP / RSRQ measurements.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Software control plane for switches and routers
ActiveUS20080219268A1Bridging the gapImprove convenienceError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceAbstraction layer
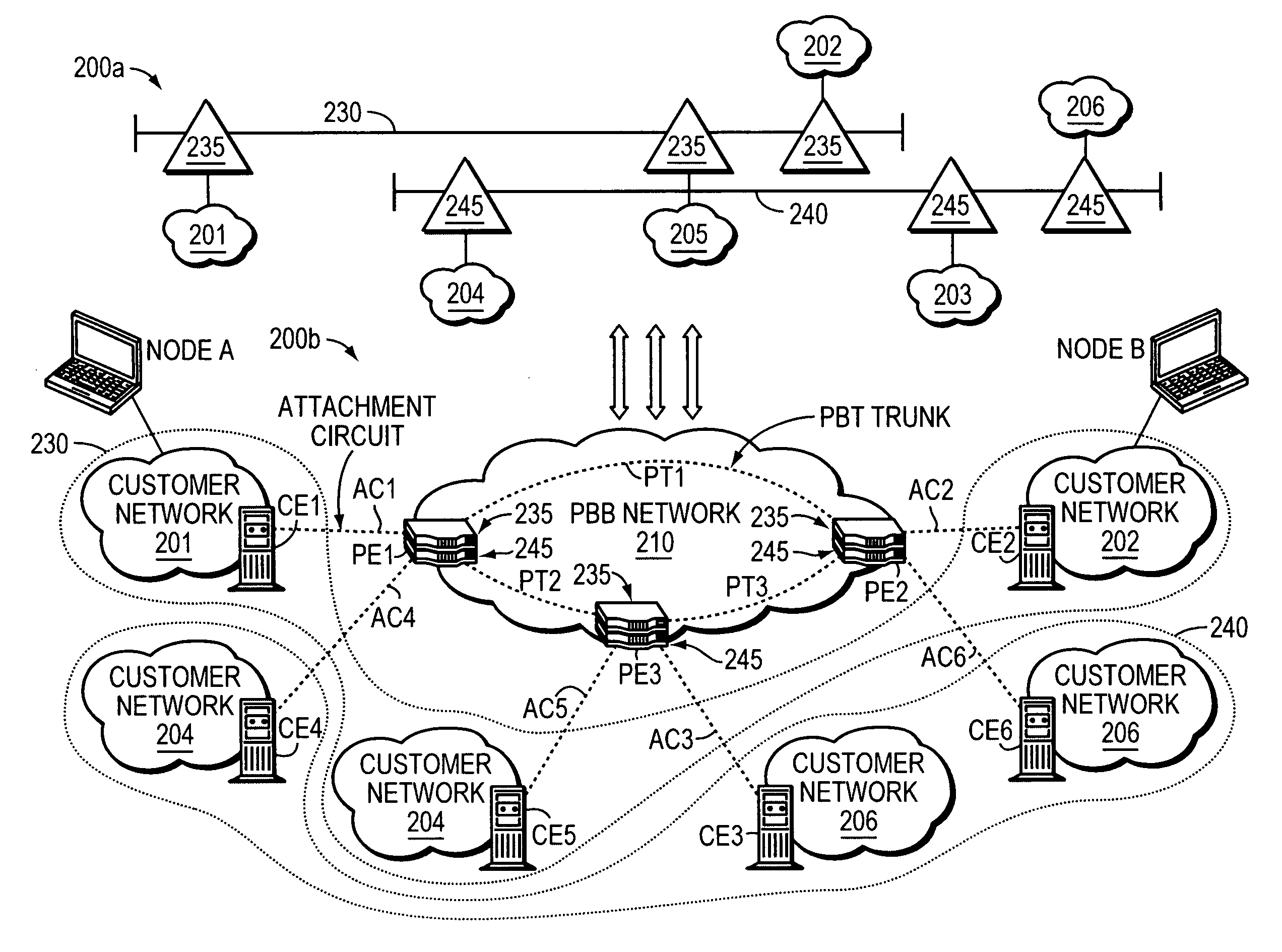
A Provider Network Controller (PNC) addresses the challenges in building services across Next Generation Network (NGN) architectures and creates an abstraction layer as a bridge, or glue, between the network transport and applications running over it. The PNC is a multi-layer, multi-vendor dynamic control plane that implements service activation and Layer 0-2 management tools for multiple transport technologies including Carrier Ethernet, Provider Backbone Transport (PBT), Multi-protocol Label Switching (MPLS), Transport MPLS (T-MPLS), optical and integrated networking platforms. Decoupling transport controls and services from the network equipment simplifies service creation and provides options for carriers to choose best-in-class equipment that leverages the PNC to enable rapid creation and management of transports and services. The PNC provides Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) interfaces to abstract transport objects expressly designed to support both wholesale and retail services, and supports service offerings with varied bandwidth and Quality of Service (QoS) requirements, thus achieving enterprise Ethernet economics.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
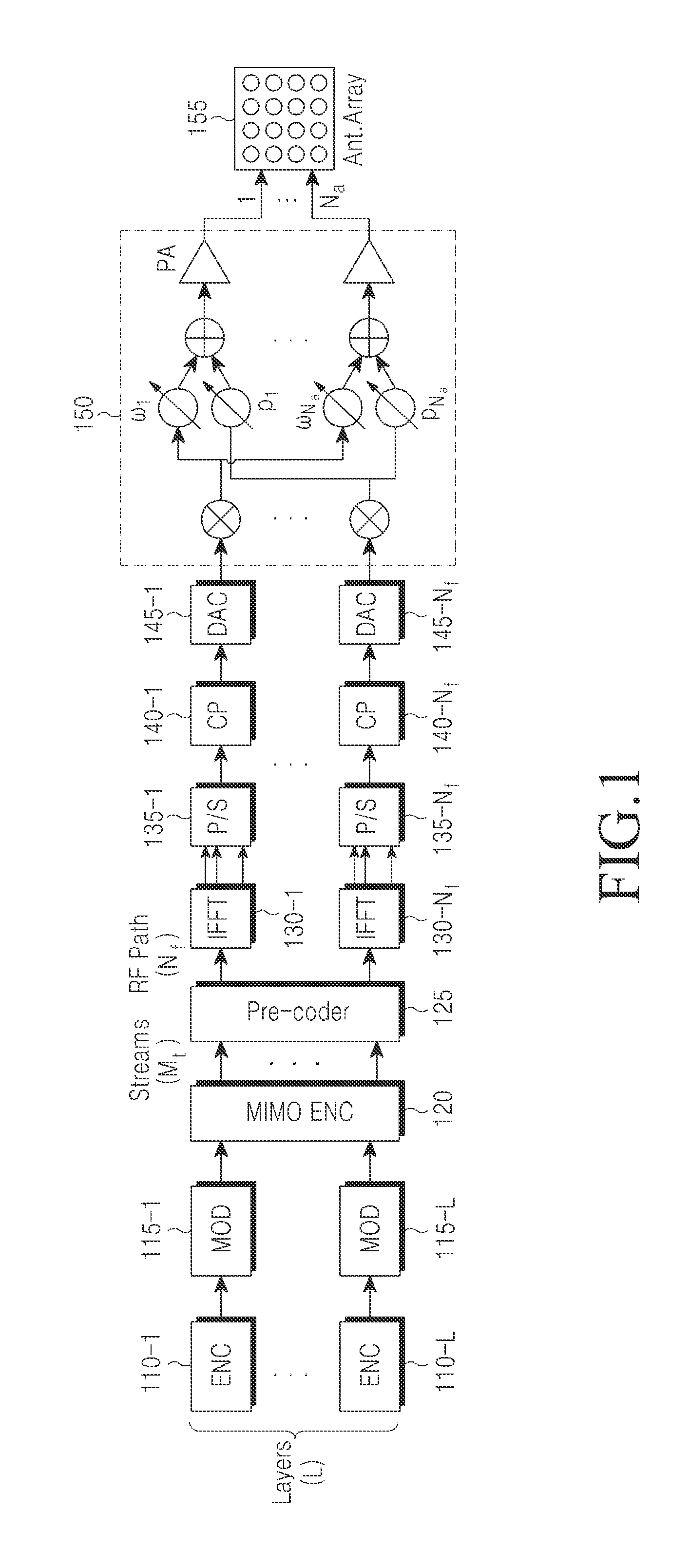
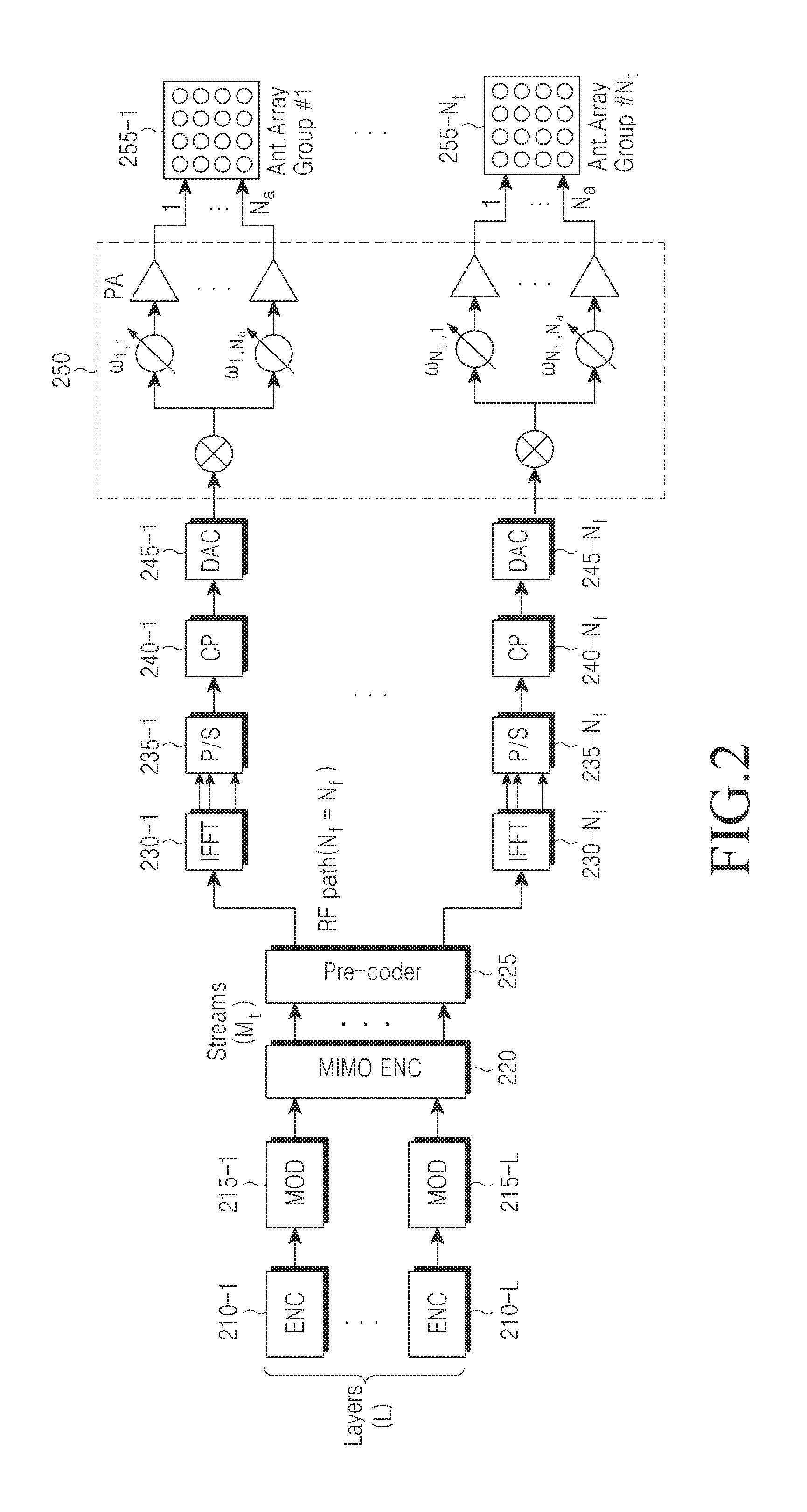
Communication method and apparatus using analog and digital hybrid beamforming
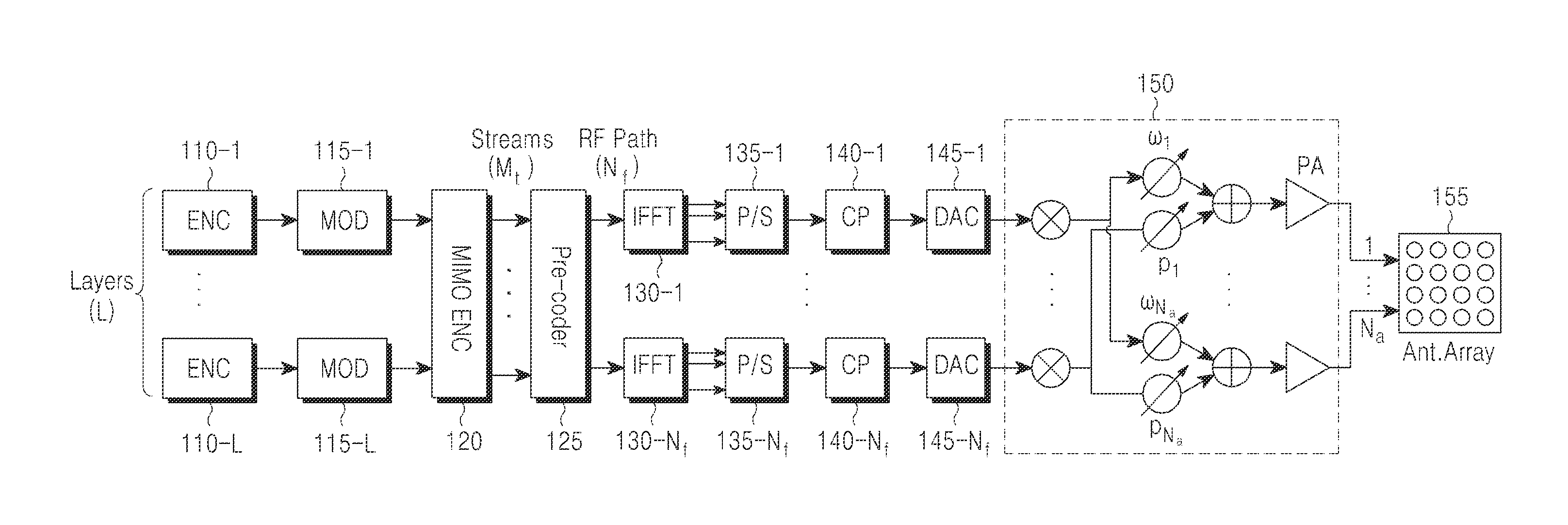
ActiveUS20130301454A1Efficient executionSpatial transmit diversityTransmission systemsHybrid beamformingEngineering
A communication method and apparatus using analog and digital hybrid beamforming are provided. The method includes receiving a first message including a measurement and selection condition for hybrid beamforming from a Base Station (BS), measuring channels of a plurality of BS transmission beams, selecting at least one BS transmission beam based on channel measurements, transmitting report information about the selected at least one BS transmission beam to the BS, receiving from the BS a second message, estimating an effective channel matrix for the selected final BS transmission beam according to the measurement and report condition, determining feedback information for digital beamforming of the BS based on the effective channel matrix, transmitting the determined feedback information to the BS, and receiving a data burst from the BS according to a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) mode and / or a configuration scheduled based on the feedback information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
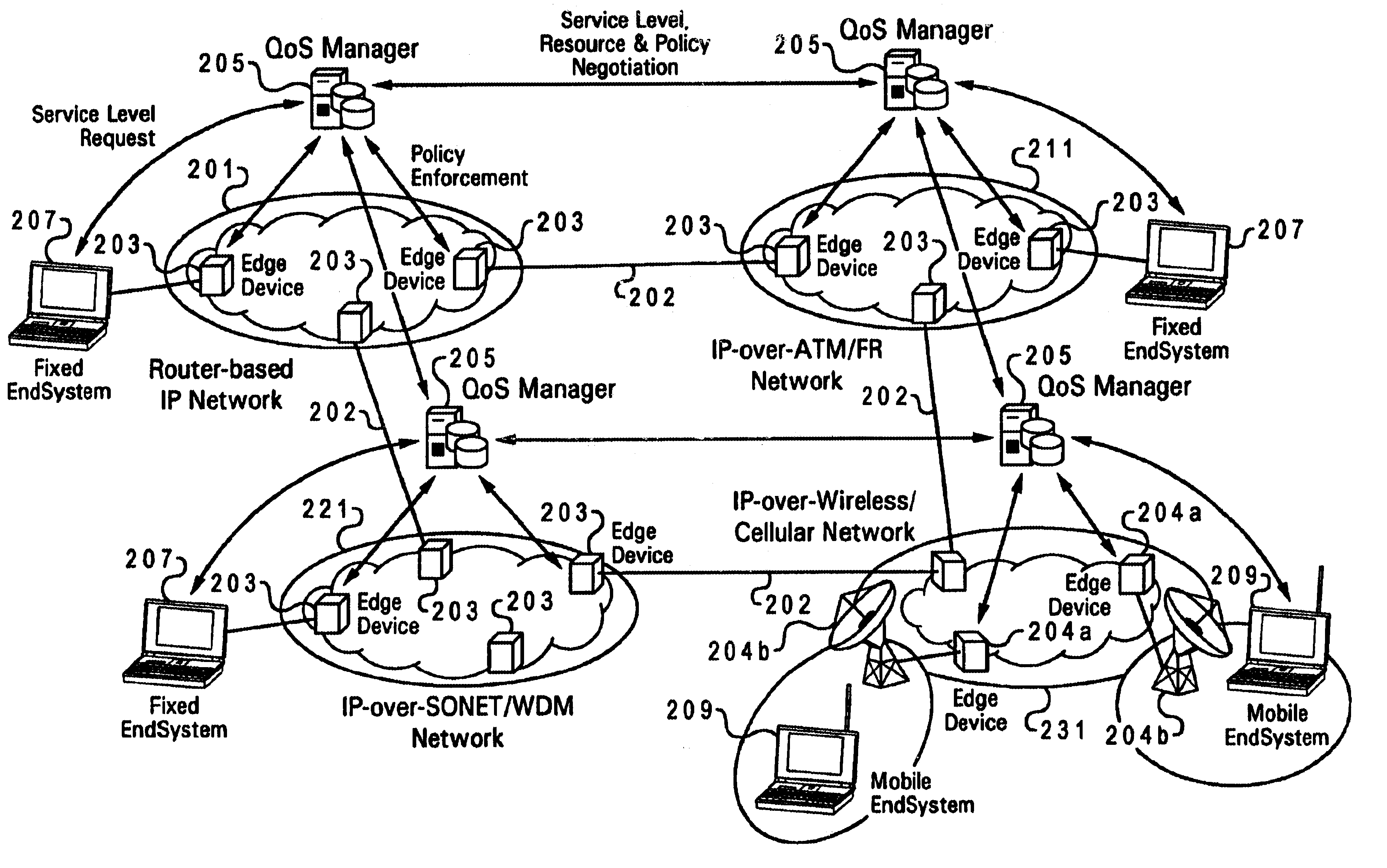
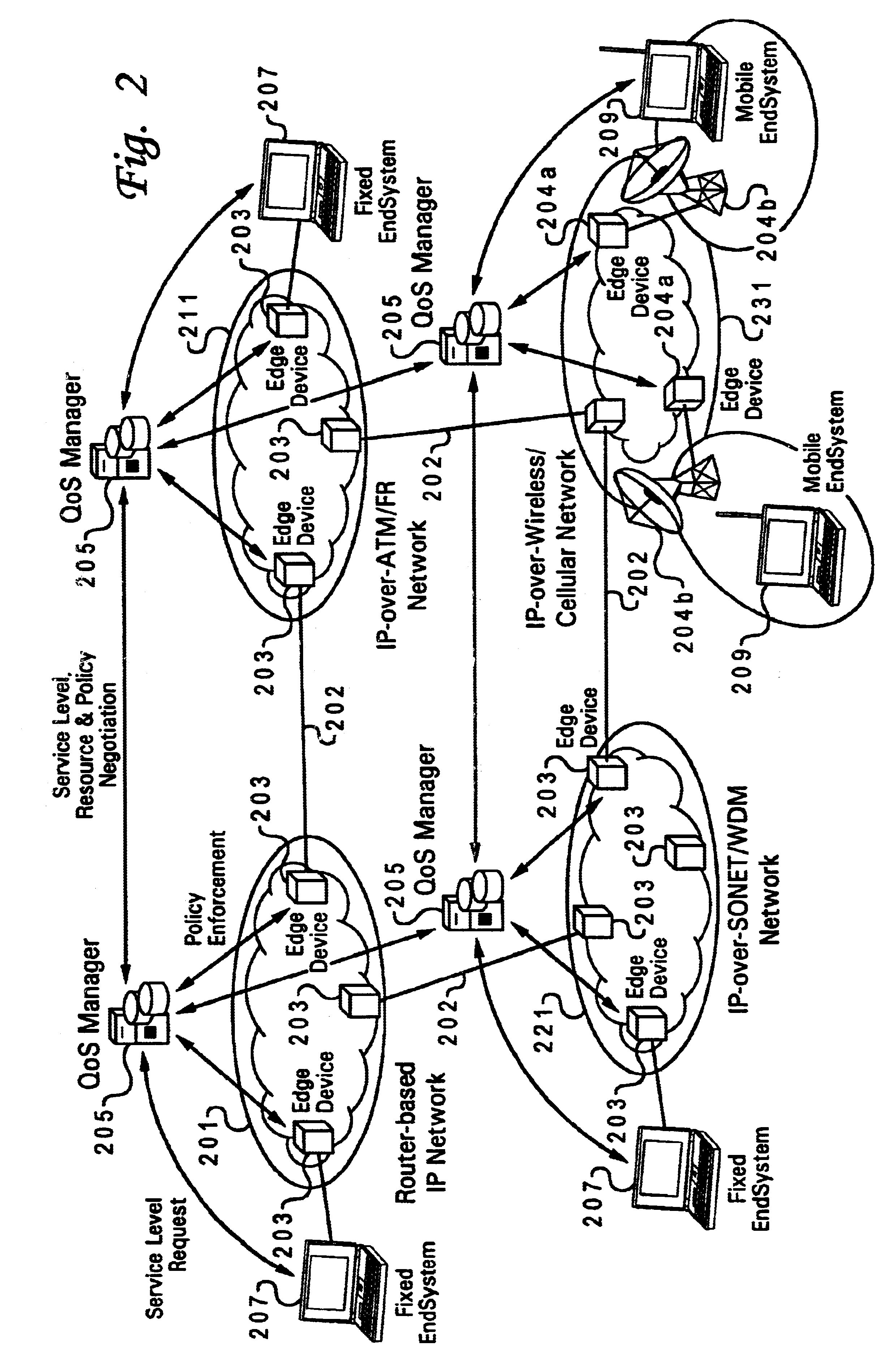
Method and system for wireless QOS agent for all-IP network
A wireless quality of service (QoS) agent for an all-Internet Protocol (IP) network. The QoS agent couples to an all-IP network. The coupling means includes communication means for transfer of information between the agent and a QoS manager of the all-IP network. The agent is also able to seamlessly extend QoS support for multimedia applications from wireline to wireless and control QoS of the multimedia applications sent over wireless connections on the all-IP network.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
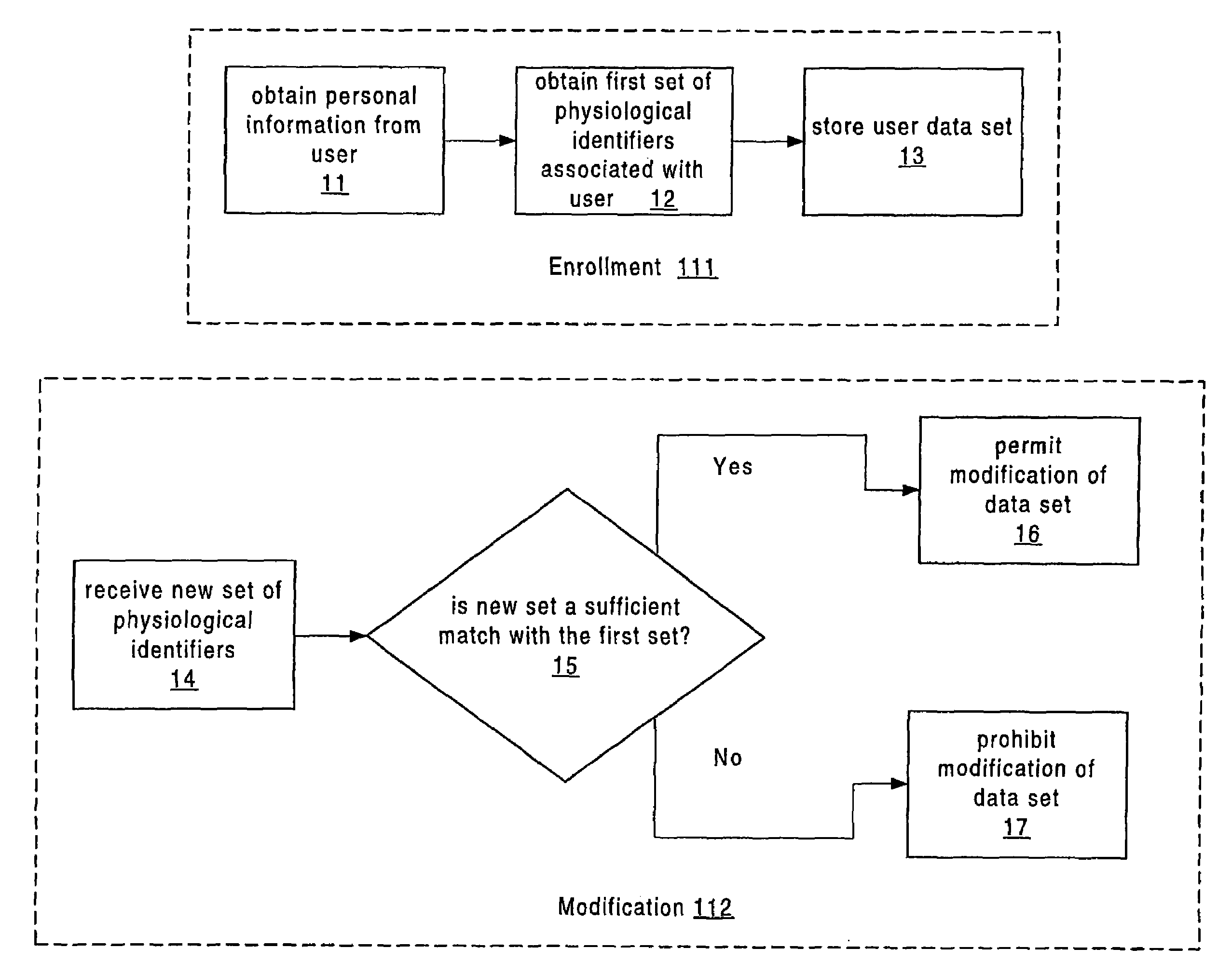
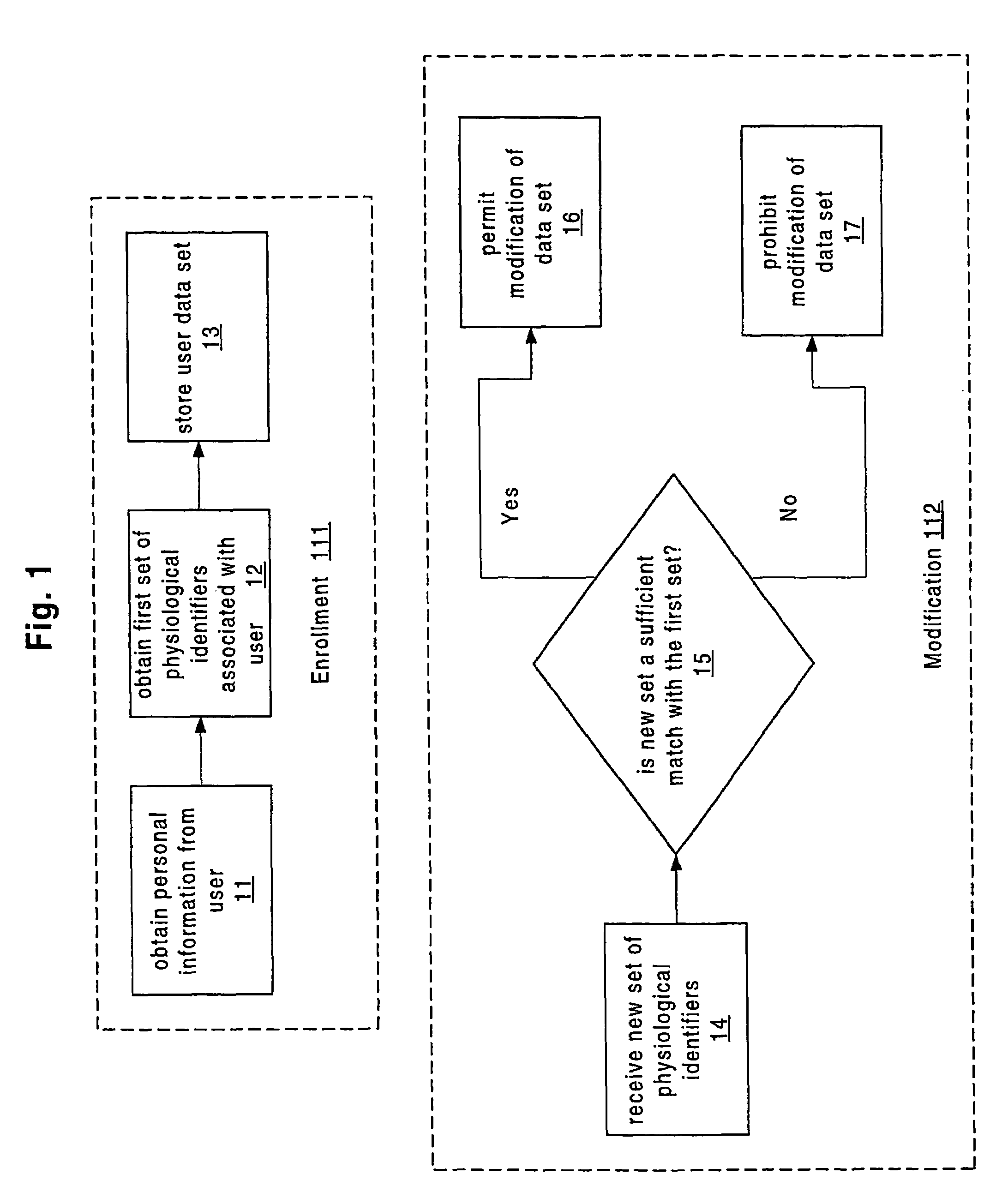
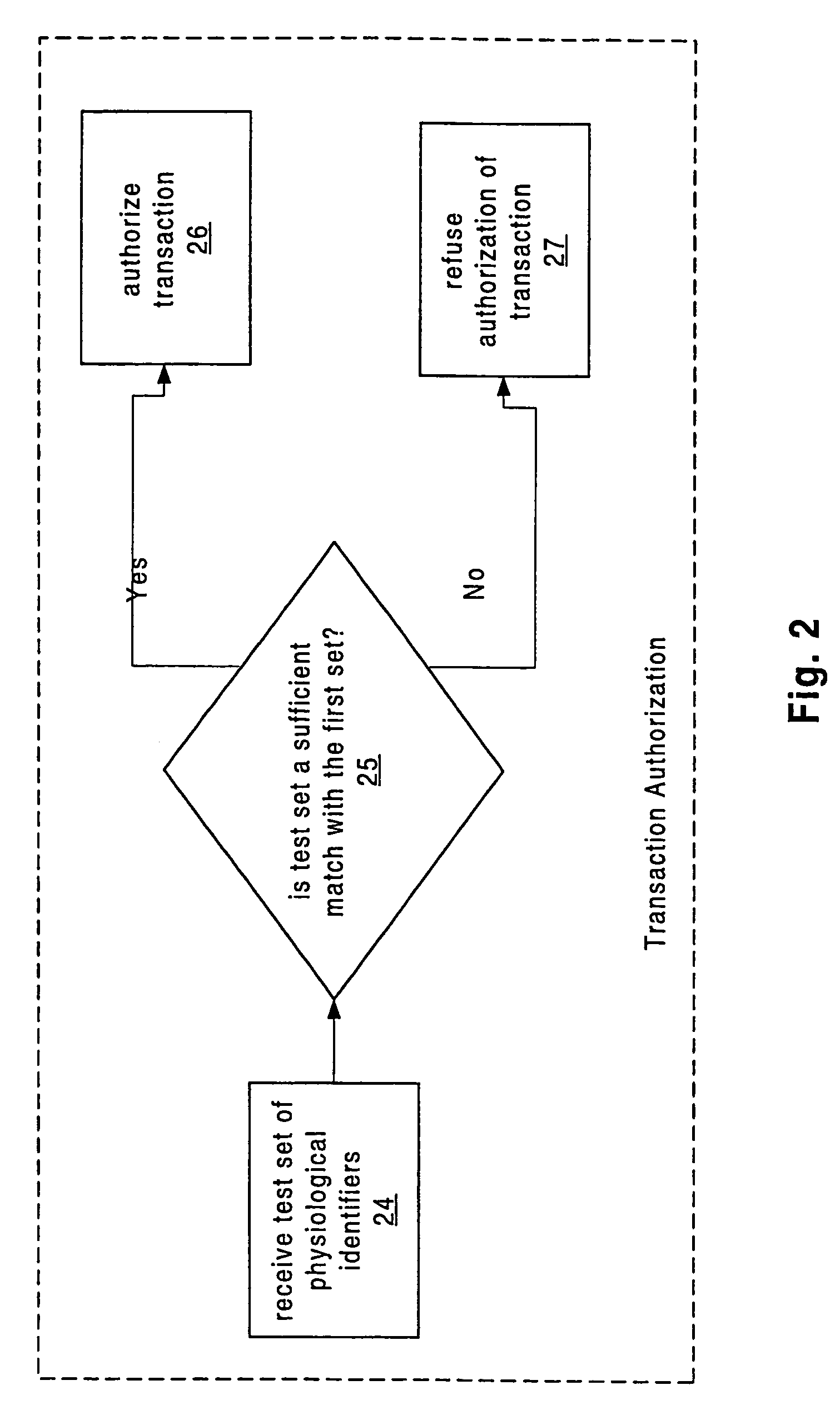
Apparatus and method for authenticated multi-user personal information database
InactiveUS6985887B1Improve reliabilityLower level of reliabilityStampsError preventionInternet privacyMulti-user
Owner:GOLD STANDARD TECH
Immediate ready implementation of virtually congestion free guaranteed service capable network: external internet nextgentcp (square waveform) TCP friendly san
InactiveUS20080037420A1Guaranteed service qualityGood serviceFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsSquare waveformThe Internet
Various techniques of simple modifications to TCP / IP protocol and other susceptible protocols and related network's switches / routers configurations, are presented for immediate ready implementations over external Internet of virtually congestion free guaranteed service capable network, without requiring use of existing QoS / MPLS techniques nor requiring any of the switches / routers softwares within the network to be modified or contribute to achieving the end-to-end performance results nor requiring provision of unlimited bandwidths at each and every inter-node links within the network.
Owner:TANG BOB
Method and apparatus for performing effective feedback in wireless communication system supporting multiple antennas
ActiveUS20120076028A1Easy to operateModulated-carrier systemsTransmission systemsChannel state informationCommunications system
A method for transmitting channel status information (CSI) of downlink multi-carrier transmission includes generating the CSI including at least one of a rank indicator (RI), a first precoding matrix index (PMI), a second PMI and a channel quality indicator (CQI) for one or more downlink carriers, the CQI being calculated based on precoding information determined by a combination of the first and second PMIs, determining, when two or more CSIs collide with one another in one uplink subframe of one uplink carrier, a CSI to be transmitted on the basis of priority, and transmitting the determined CSI over a uplink channel. If a CSI including an RI or a wideband first PMI collides with a CSI including a wideband CQI or a subband CQI, the CSI including a wideband CQI or a subband CQI has low priority and is dropped.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for the assessment and optimization of network traffic
A system for the assessment of network performance criteria, and applying this criteria to the classification of network addresses into appropriate ranges, using these ranges to consolidate performance measurements for the associated addresses, and applying these metrics toward the optimization of the network towards performance or policy objectives.
Owner:AVAYA INC
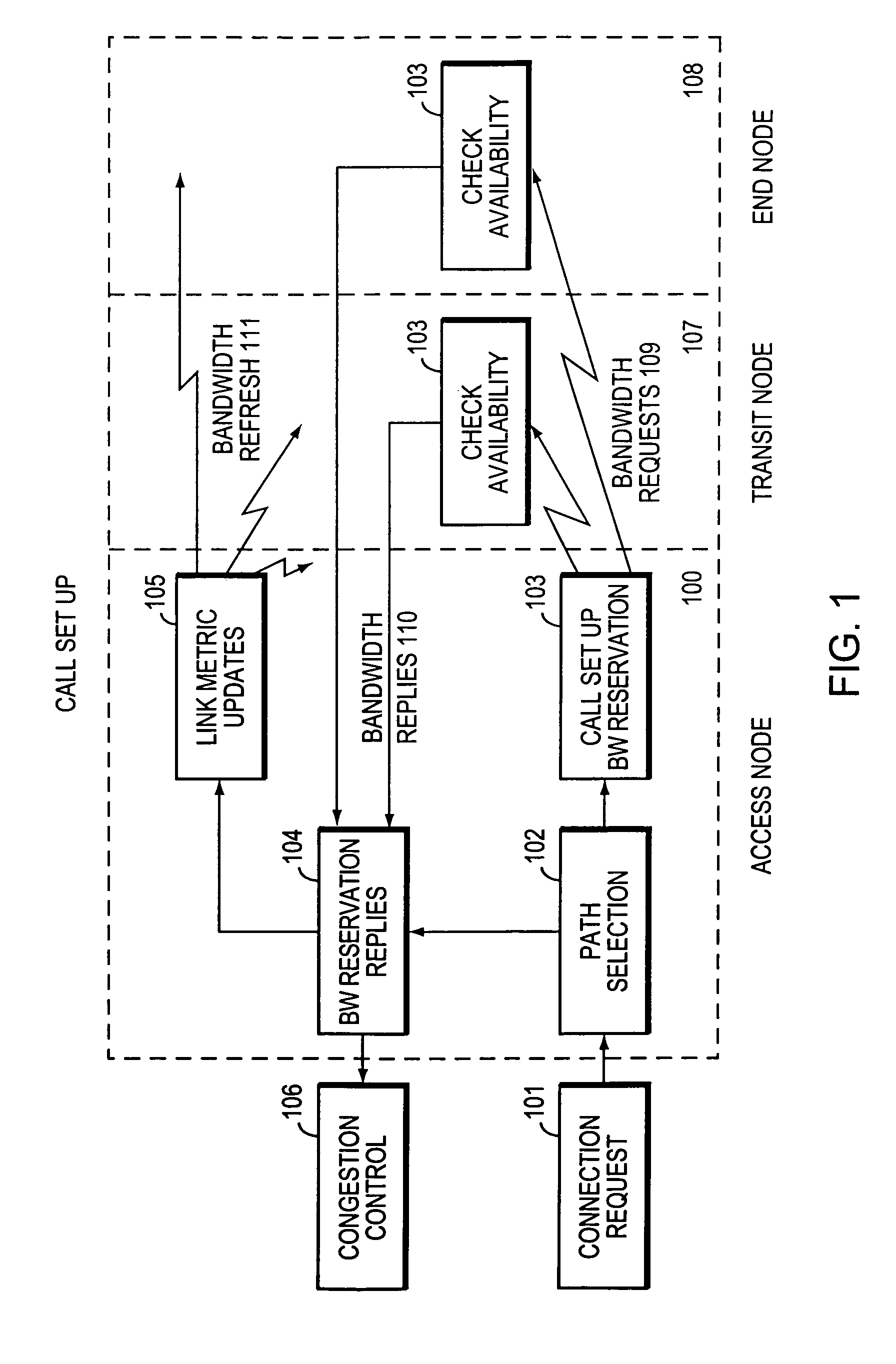
Method and system for minimizing the connection set up time in high speed packet switching networks
InactiveUS6934249B1Minimize delayMinimize in in to selectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket switched
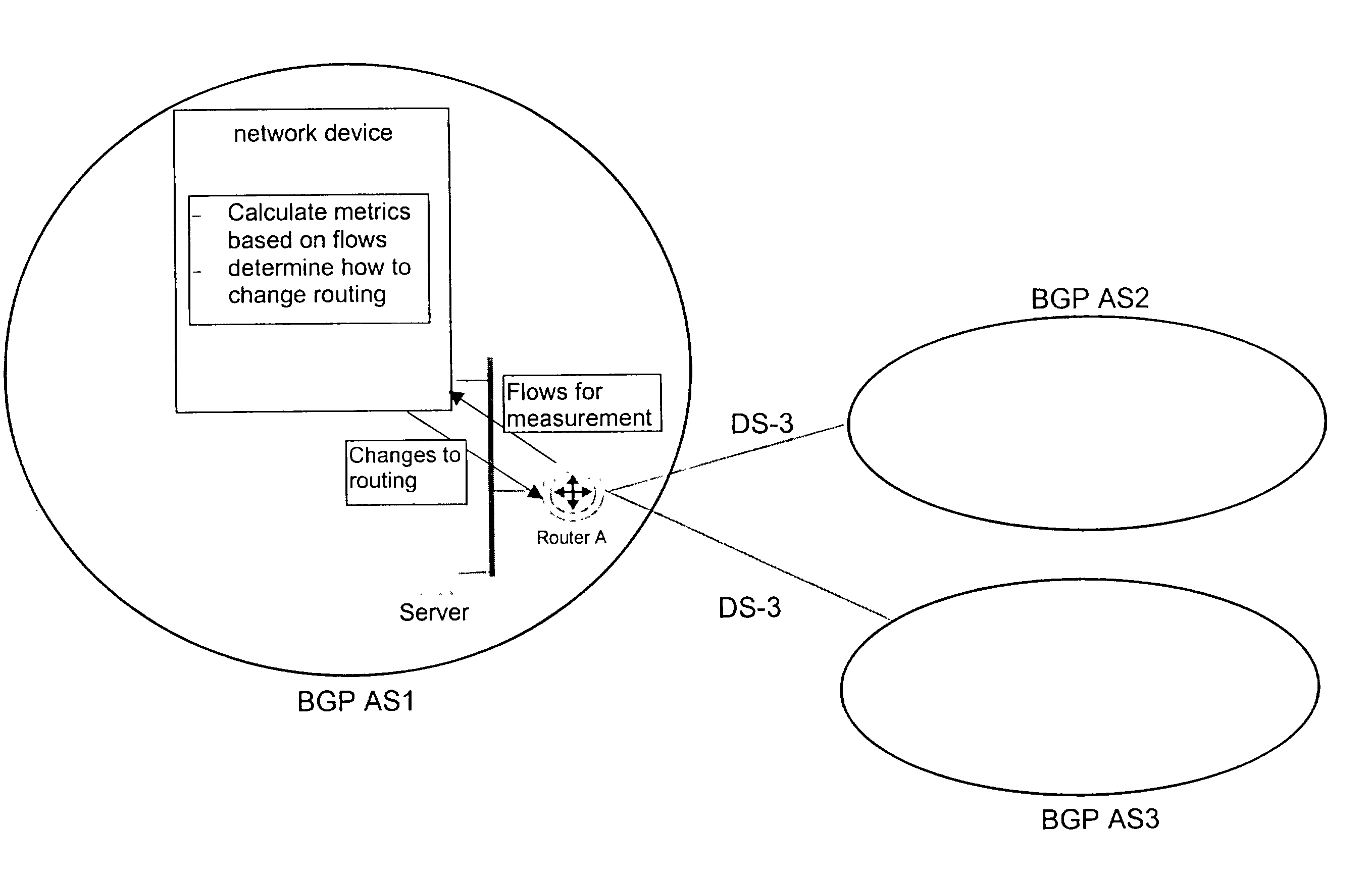
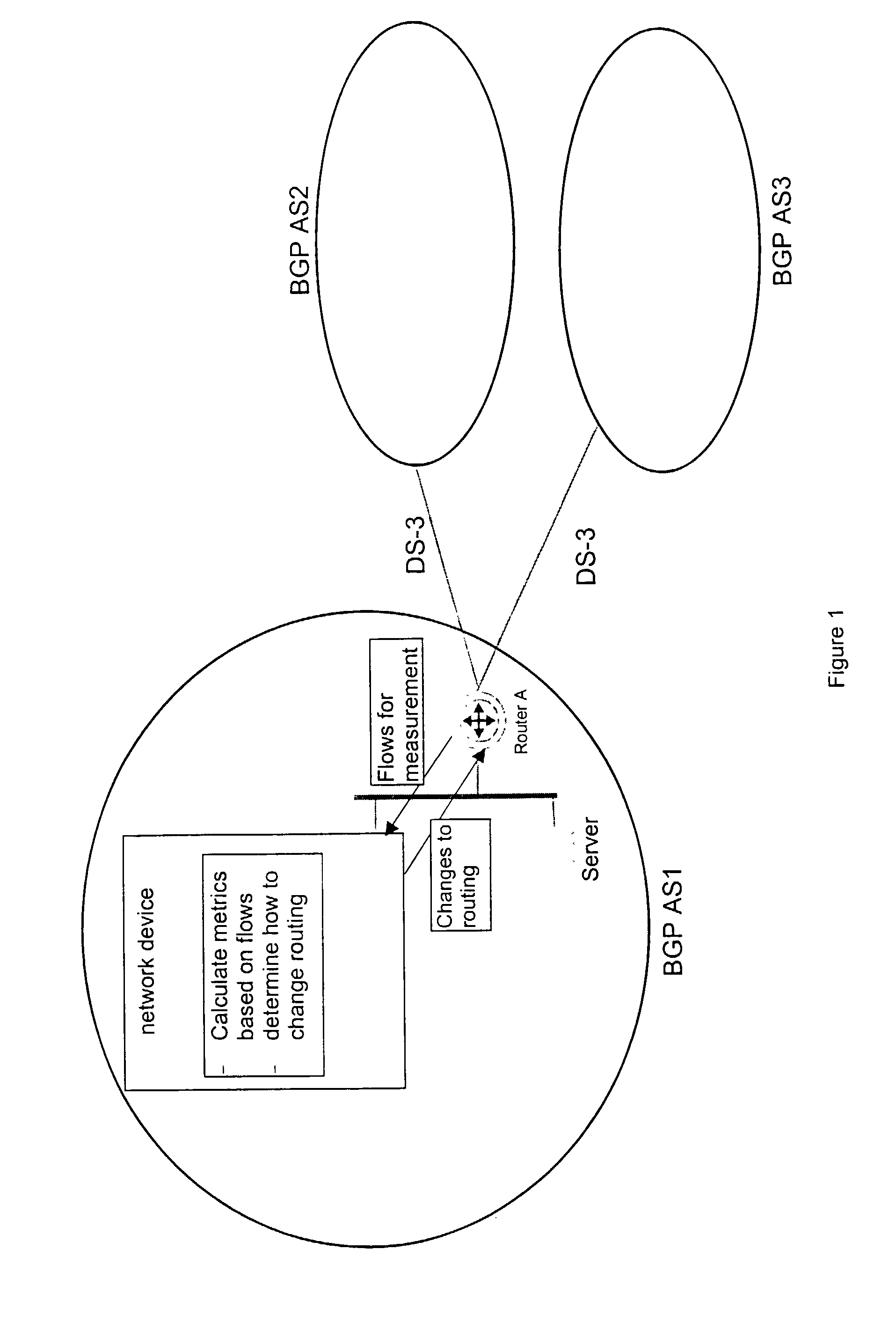
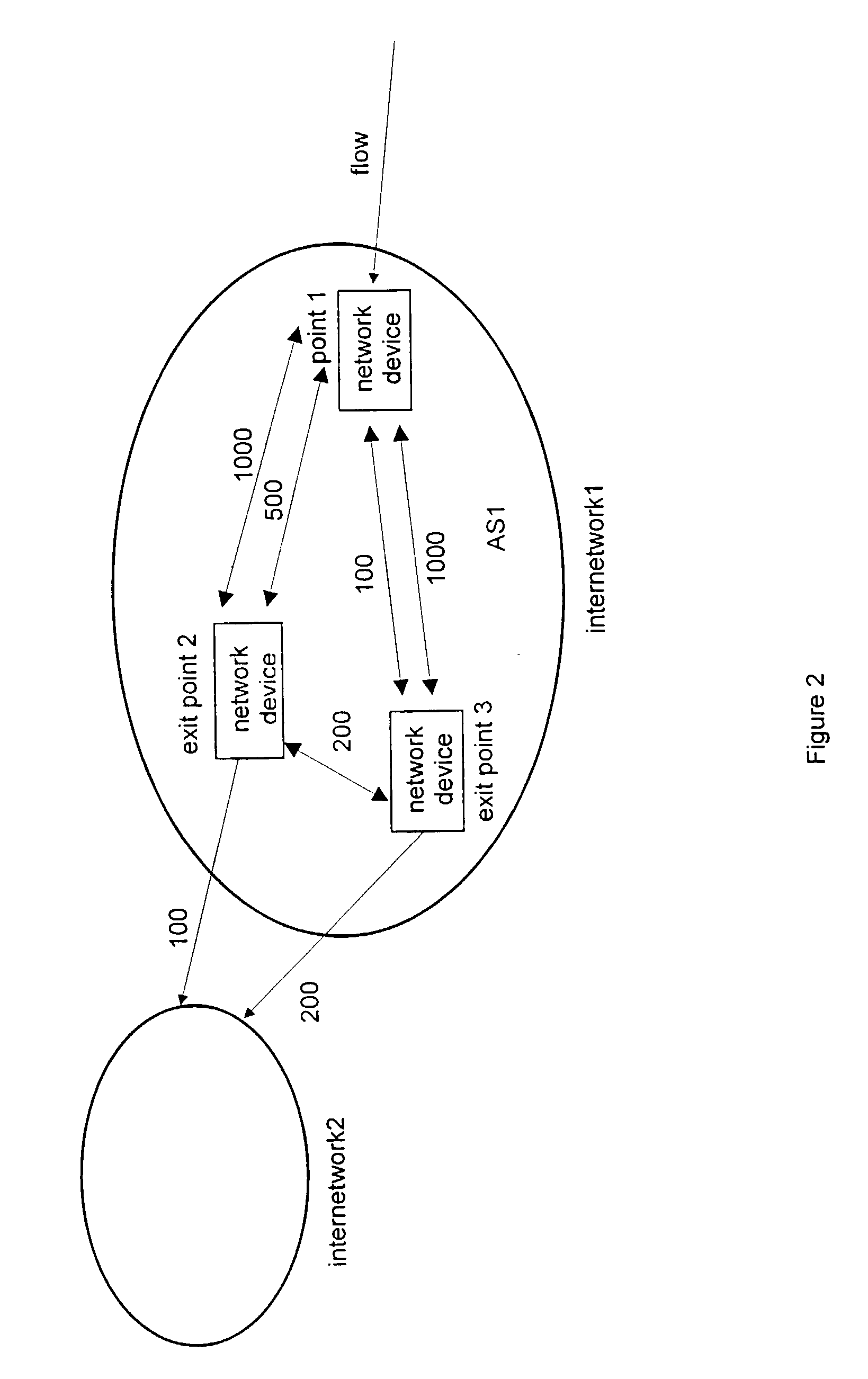
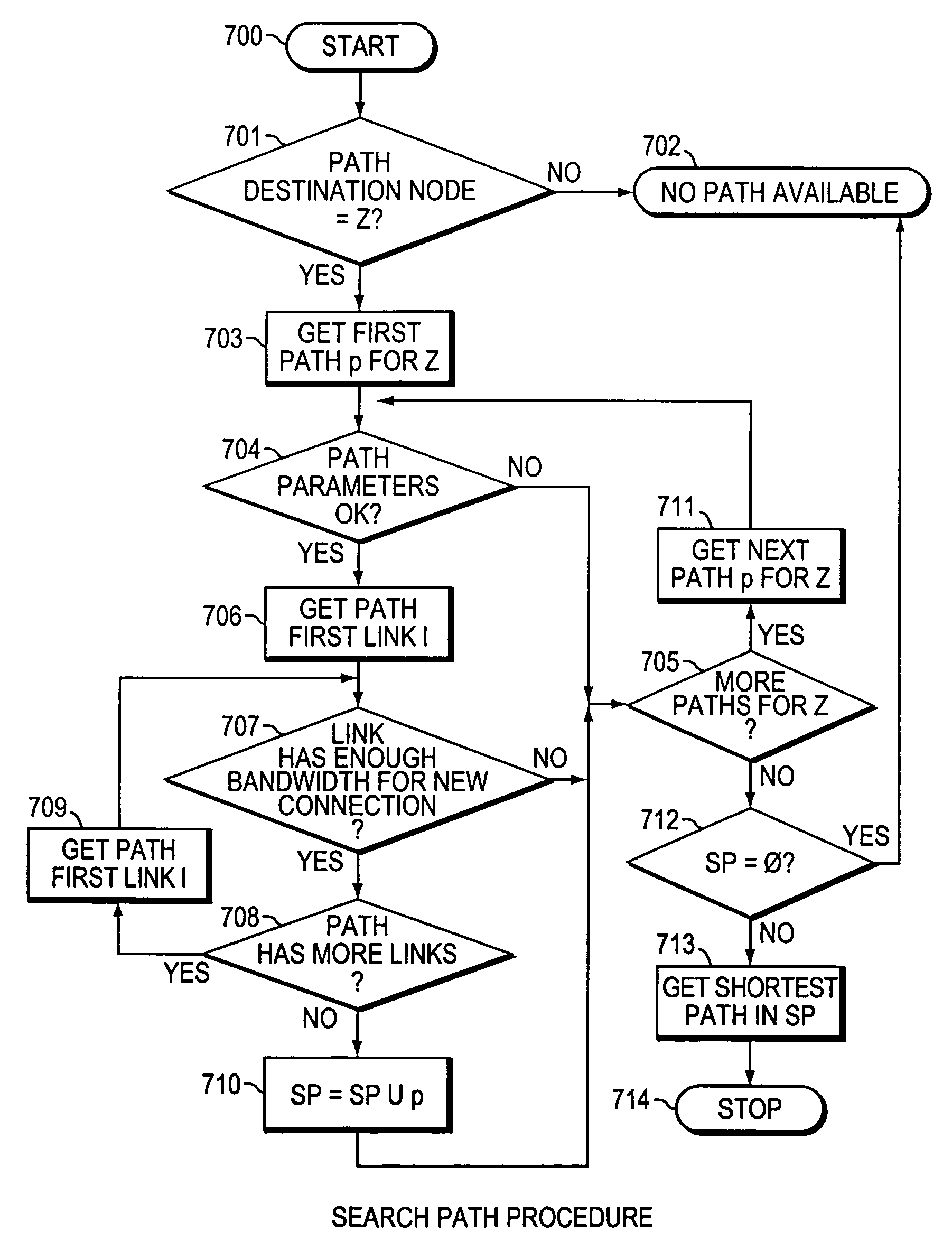
The present invention is directed to a high speed packet switching network and, in particular to a method and system for minimizing the time to establish a connection between an origin and a destination node. Due to high dynamicity of the traffic on transmission links, it is important to select a routing path according to a fully up-to-date information on all network resources. The simpler approach is to calculate a new path for each new connection request. This solution may be very time consuming because there are as many path selection operations as connection set up operations. On another hand, the calculation of paths based on an exhaustive exploration of the network topology, is a complex operation which may also take an inordinate amount of resources in large networks. Many of connections originated from a network node flow to the same destination network node. It is therefore possible to take a serious benefit in reusing the same already calculated paths for several connections towards the same node. The path calculated at the time the connection is requested is recorded in a Routing Database and updated each time a modification occurs in the network. Furthermore, alternate paths for supporting non-disruptive path switch on failure or preemption, and new paths towards potential destination nodes can be calculated and stored when the connection set up process is idle. These last operations are executed in background with a low processing priority and in absence of connection request.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information for carrier aggregated spectrums
InactiveUS20100271970A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
Methods and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information (UCI) in carrier aggregated spectrums are disclosed. UCI may include, but is not limited to, Precoding Matrix Indicator (PMI), Rank Indication (RI), Channel Quality Indicator (CQI), Acknowledge / Not Acknowledge (ACK / NACK) and Scheduling Request (SR). For symmetric carrier aggregation, uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) component carriers may be paired and use physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) in each UL component carrier to send UCI for the corresponding DL component carrier. For asymmetric carrier aggregation, methods are provided for UCI transmission and resource allocation depending on component carrier configuration or assignment. Methods are provided for multiple and single component carrier configurations that may further provide backward compatibility.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Quality of service for device assisted services
Quality of Service (QoS) for Device Assisted Services (DAS) are provided. In some embodiments, QoS for DAS includes providing a wireless communications device configures to determine a QoS request for a service over a wireless network; and verify the QoS request for the service over the wireless network using one or more verification techniques.
Owner:HEADWATER RES LLC
Systems and Methods for Providing Dynamic Spillover of Virtual Servers Based on Bandwidth
The present solution provides a spillover management technique for virtual servers of an appliance based on bandwidth. A network administrator may configure a bandwidth threshold for one or more virtual servers, such as virtual servers providing acceleration or load balancing for one or more services. The bandwidth threshold may be specified as a number of bytes transferred via the virtual server. The bandwidth threshold may also be specified as a round trip time or derivative thereof. A user may specify the bandwidth threshold via a configuration interface. Otherwise, the appliance may establish the bandwidth threshold. The appliance monitors the bandwidth used by a first virtual server. In response to detecting the bandwidth reaching or exceeding the bandwidth threshold, the appliance dynamically directs client requests to a second virtual server.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
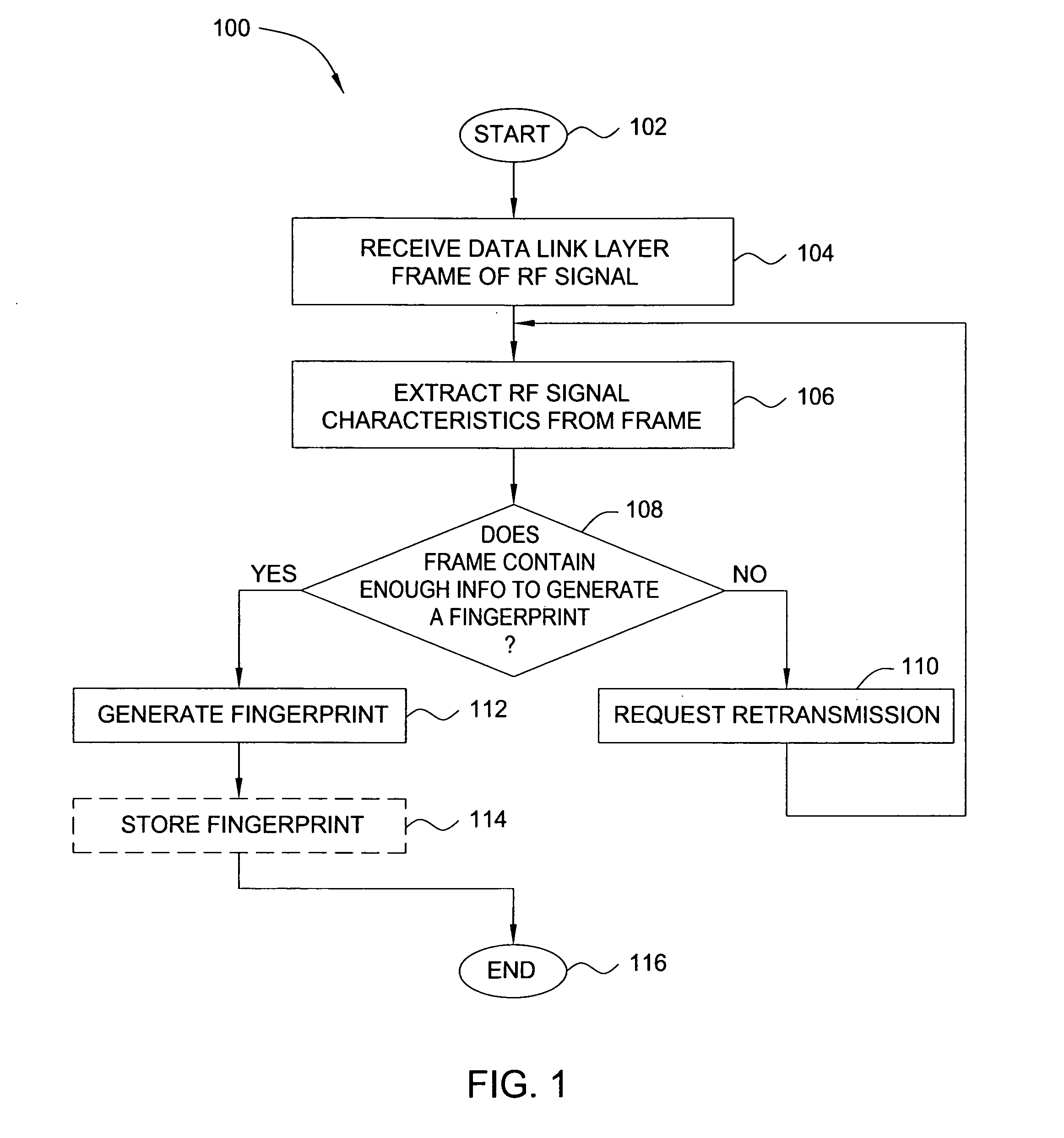
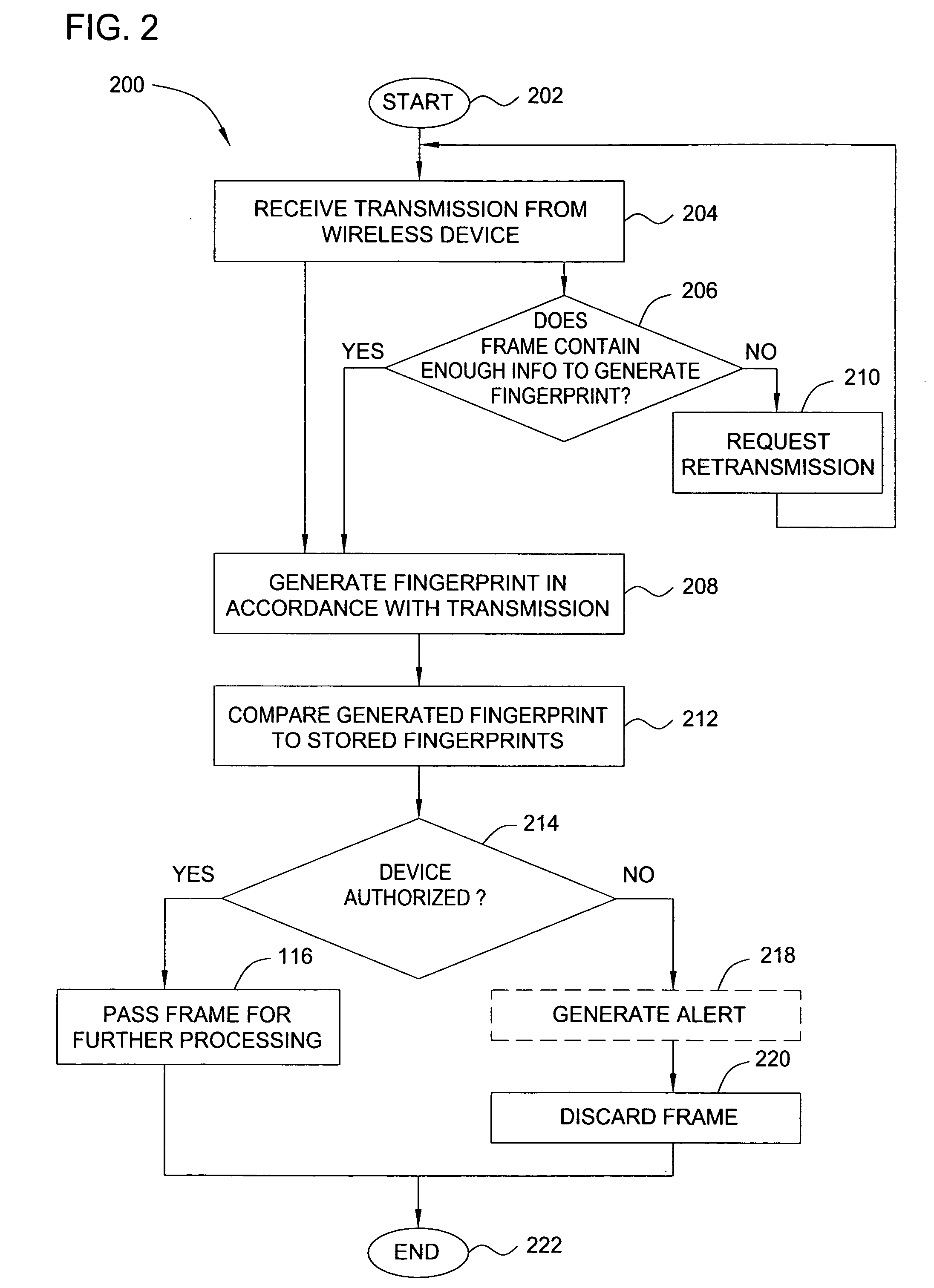
Method and apparatus for wireless network security
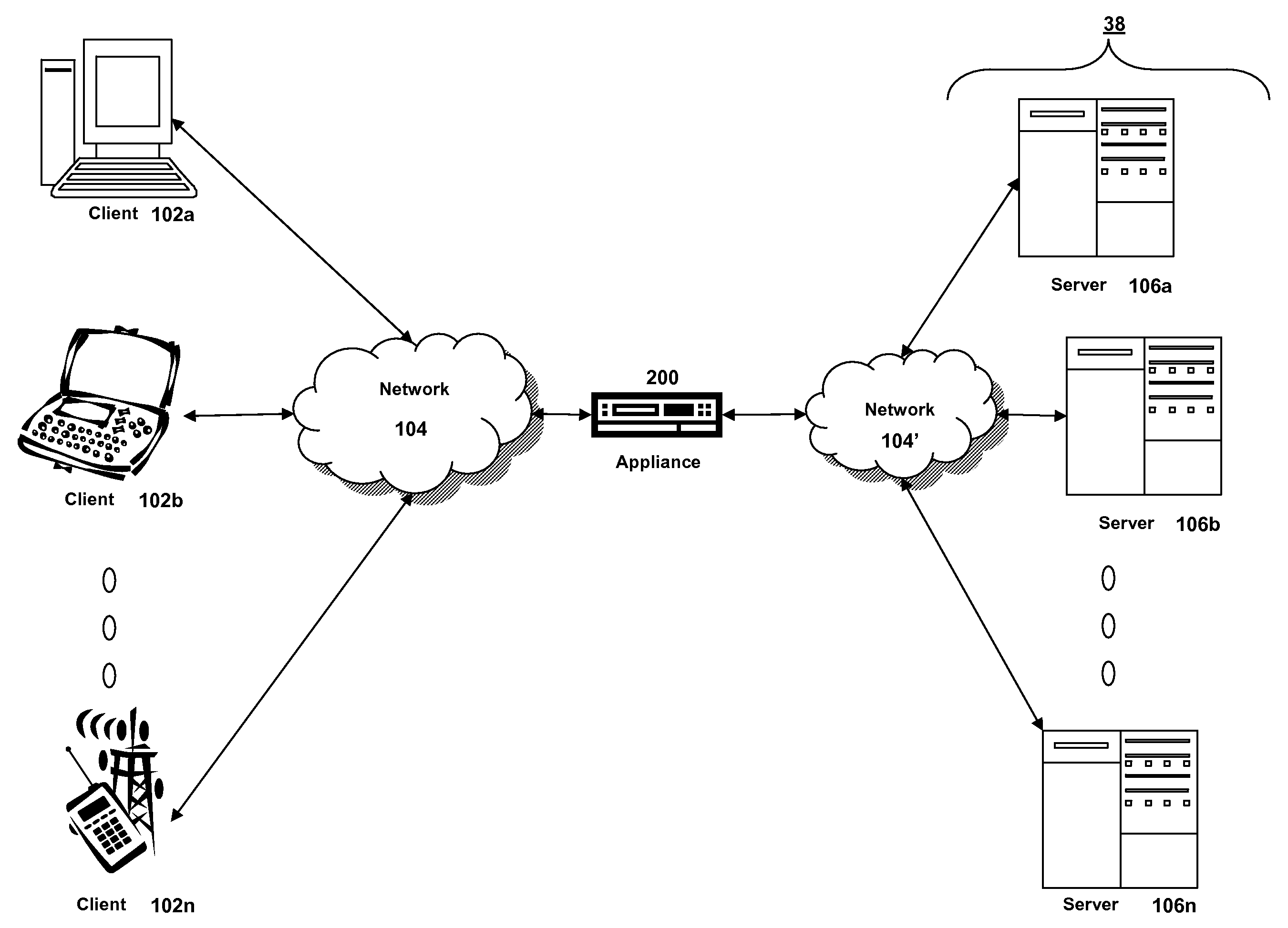
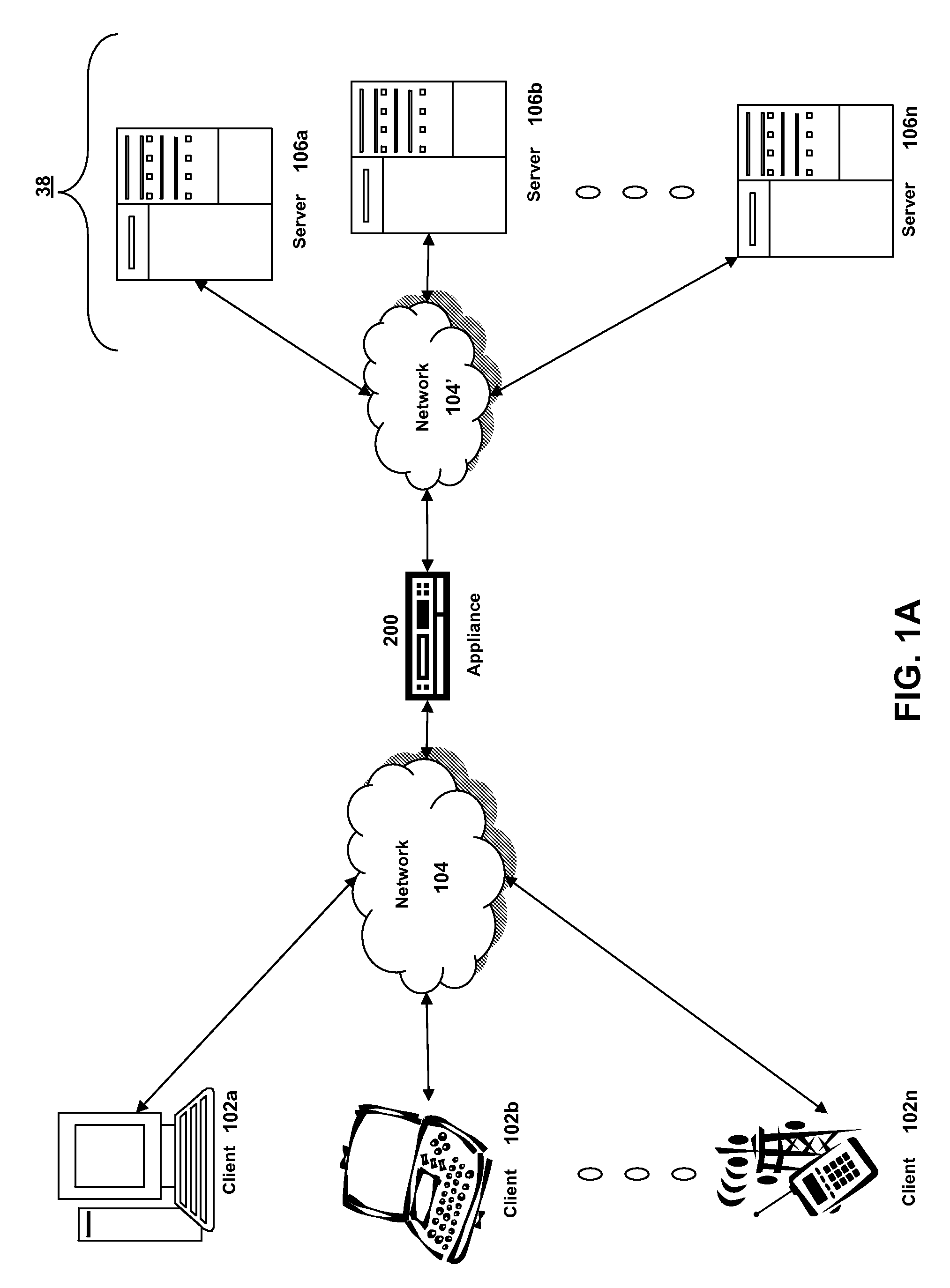
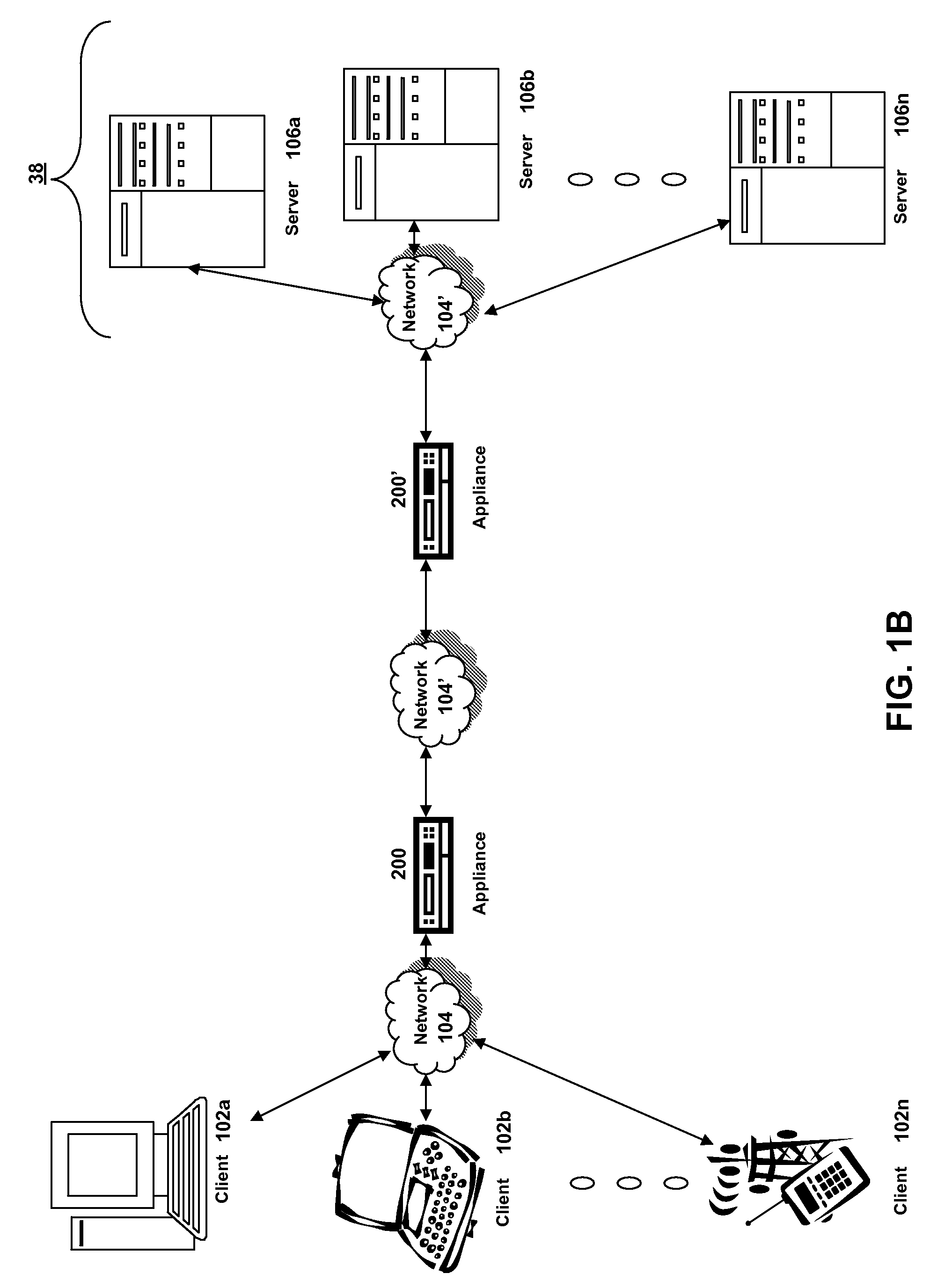
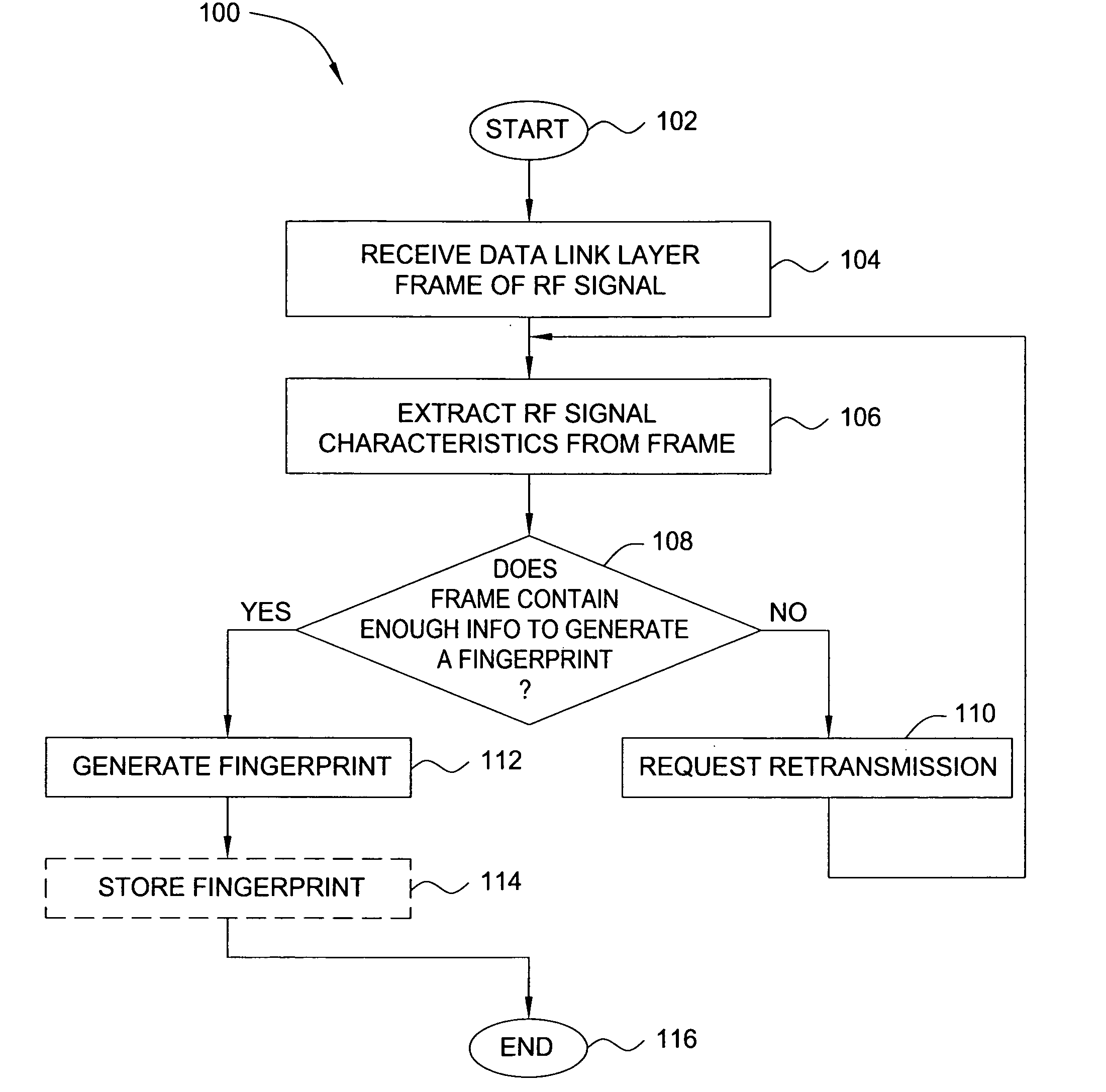
ActiveUS20070025265A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRadio frequency signalEngineering
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method and apparatus for wireless network security. In one embodiment, a method for securing a wireless computing network includes receiving a communication from an unidentified transmitter, identifying the transmitter in accordance with a fingerprint generated from one or more radio frequency signal characteristics extracted from the communication, and taking action in response to an identity of the transmitter.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
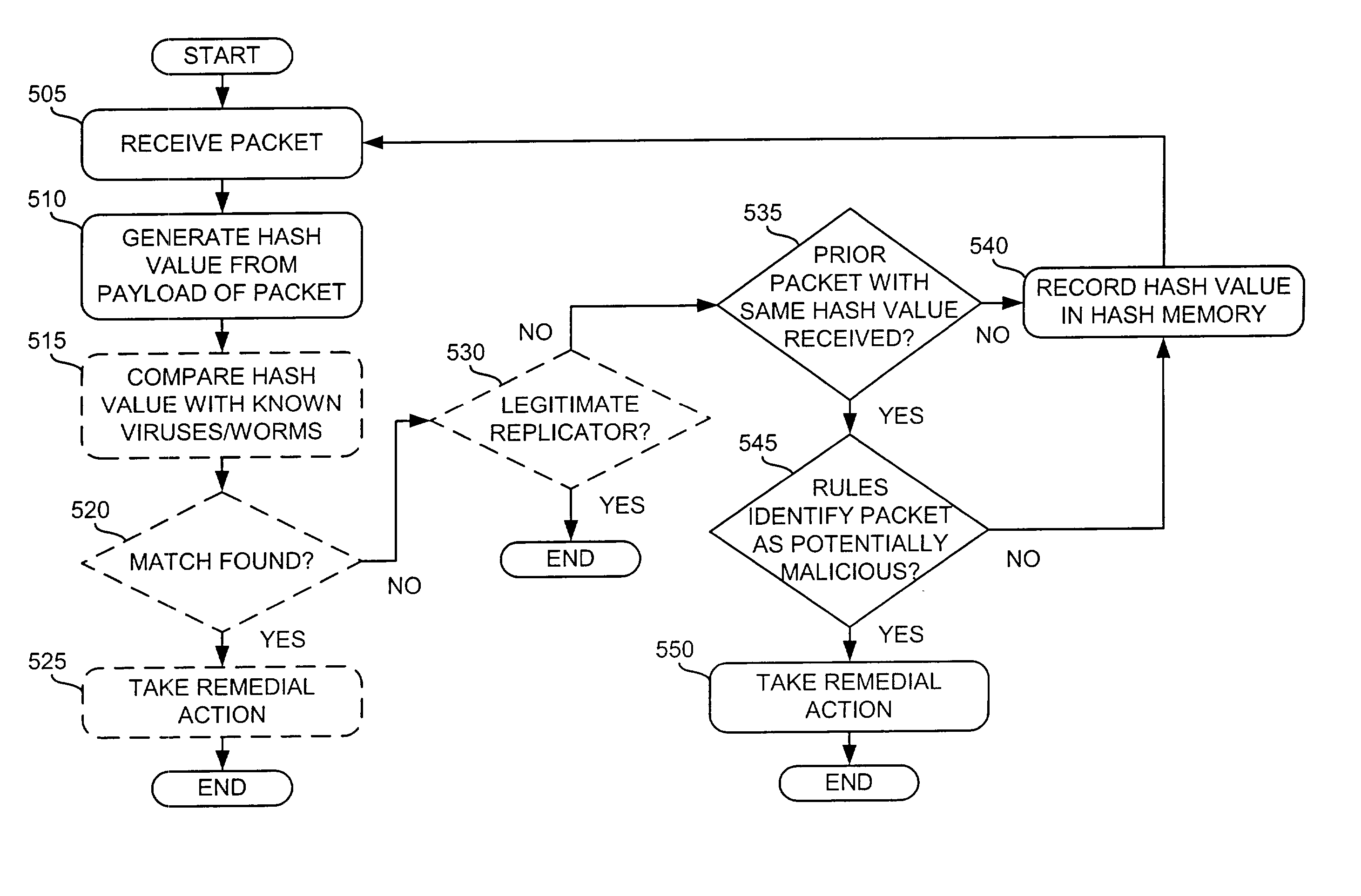
Hash-based systems and methods for detecting, preventing, and tracing network worms and viruses
A system (126-129) detects transmission of potentially malicious packets. The system (126-129) receives packets and generates hash values corresponding to each of the packets. The system (126-129) may then compare the generated hash values to hash values corresponding to prior packets. The system (126-129) determines that one of the packets is a potentially malicious packet when the generated hash value corresponding to the one packet matches one of the hash values corresponding to one of the prior packets and the one prior packet was received within a predetermined amount of time of the one packet. The system (126-129) may also facilitate the tracing of the path taken by a potentially malicious packet. In this case, the system (126-129) may receive a message that identifies a potentially malicious packet, generate hash values from the potentially malicious packet, and determine whether one or more of the generated hash values match hash values corresponding to previously-received packets. The system (126-129) may then identify the potentially malicious packet as one of the previously-received packets when one or more of the generated hash values match the hash value corresponding to the one previously-received packet.
Owner:STRAGENT
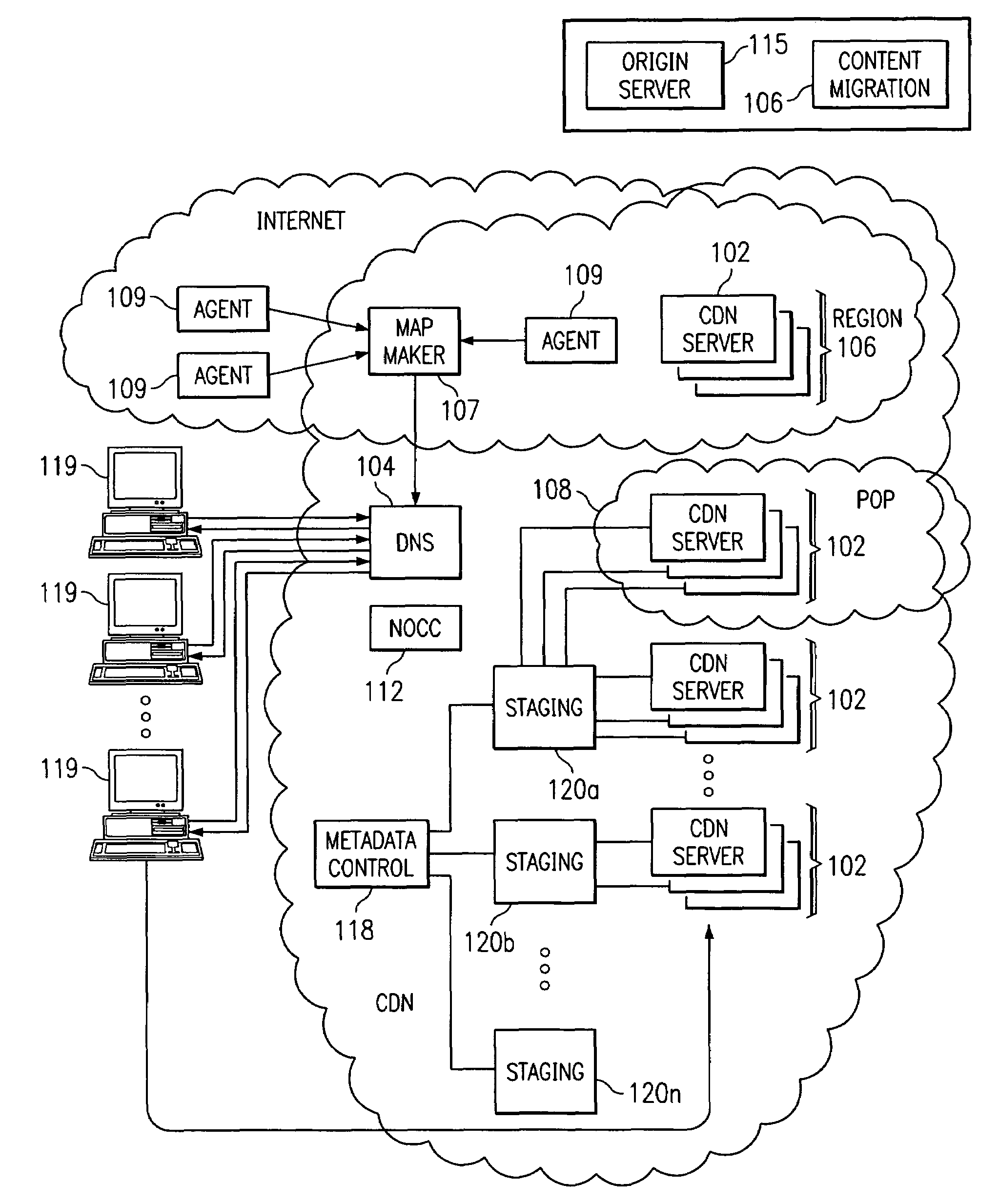
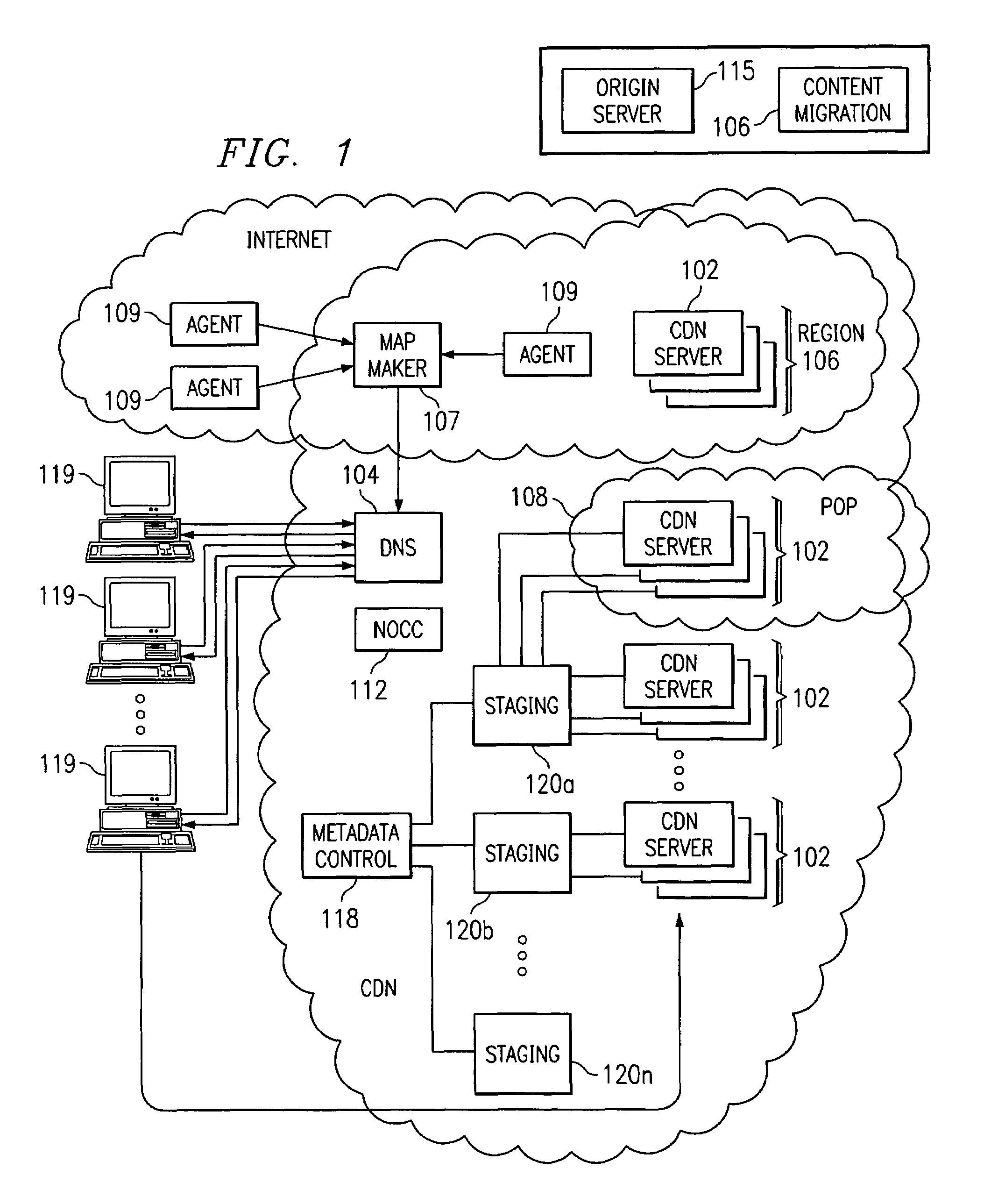
Optimal route selection in a content delivery network
InactiveUS20080008089A1Improve speed and reliabilityRetrieve content (cacheableError preventionTransmission systemsFile area networkPeer-to-peer
A routing mechanism, service or system operable in a distributed networking environment. One preferred environment is a content delivery network (CDN) wherein the present invention provides improved connectivity back to an origin server, especially for HTTP traffic. In a CDN, edge servers are typically organized into regions, with each region comprising a set of content servers that preferably operate in a peer-to-peer manner and share data across a common backbone such as a local area network (LAN). The inventive routing technique enables an edge server operating within a given CDN region to retrieve content (cacheable, non-cacheable and the like) from an origin server more efficiently by selectively routing through the CDN's own nodes, thereby avoiding network congestion and hot spots. The invention enables an edge server to fetch content from an origin server through an intermediate CDN server or, more generally, enables an edge server within a given first region to fetch content from the origin server through an intermediate CDN region.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
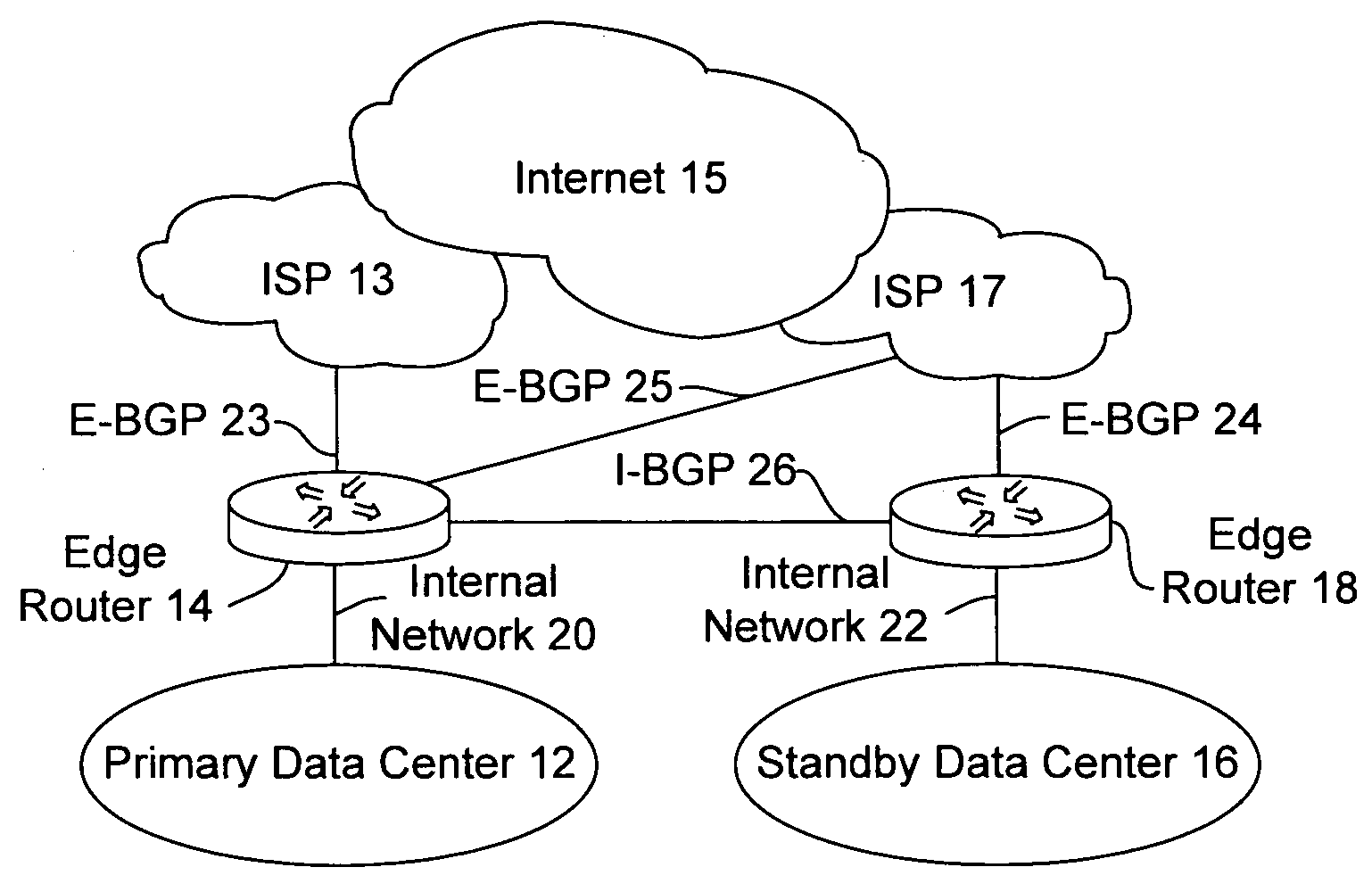
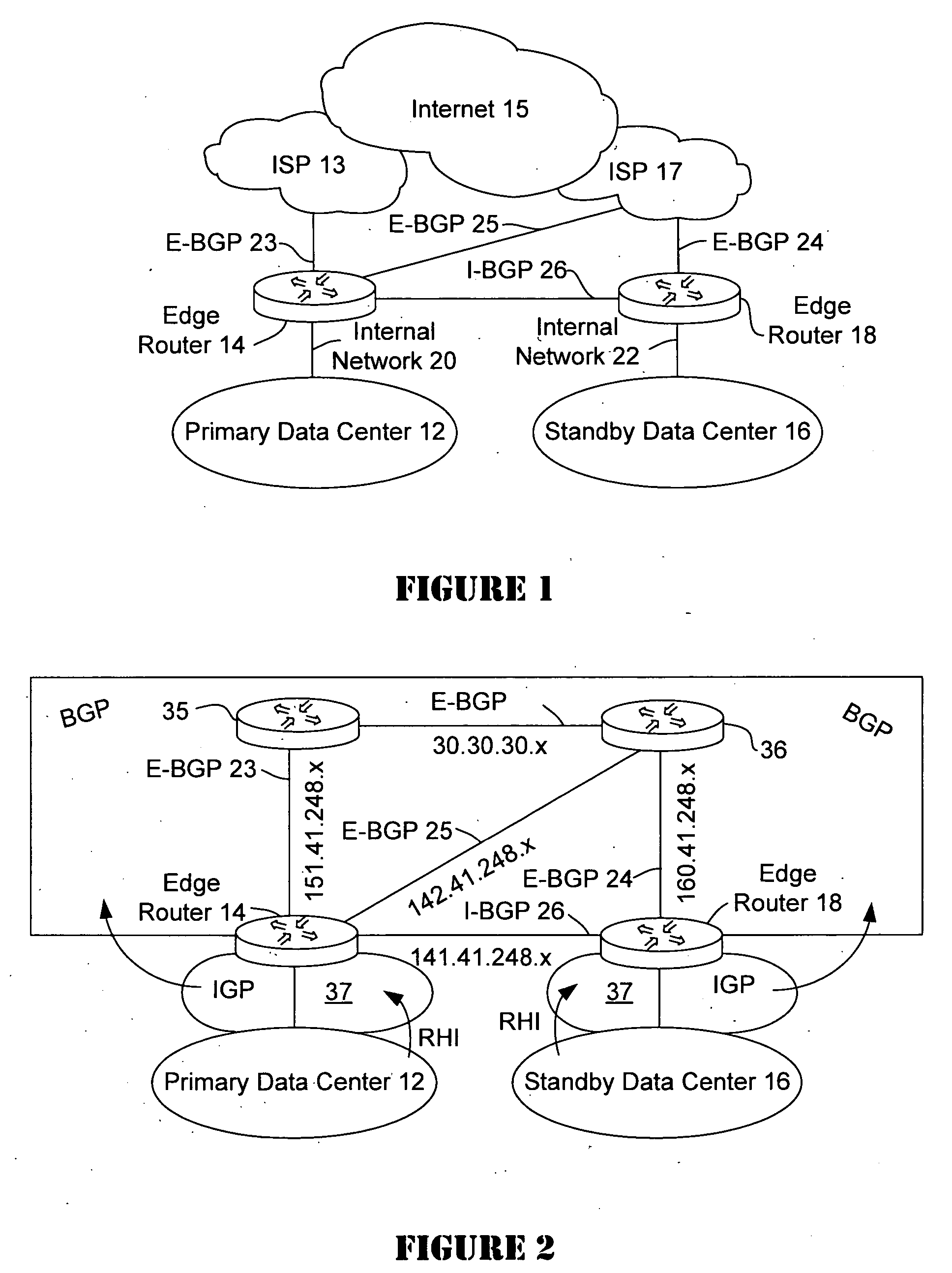
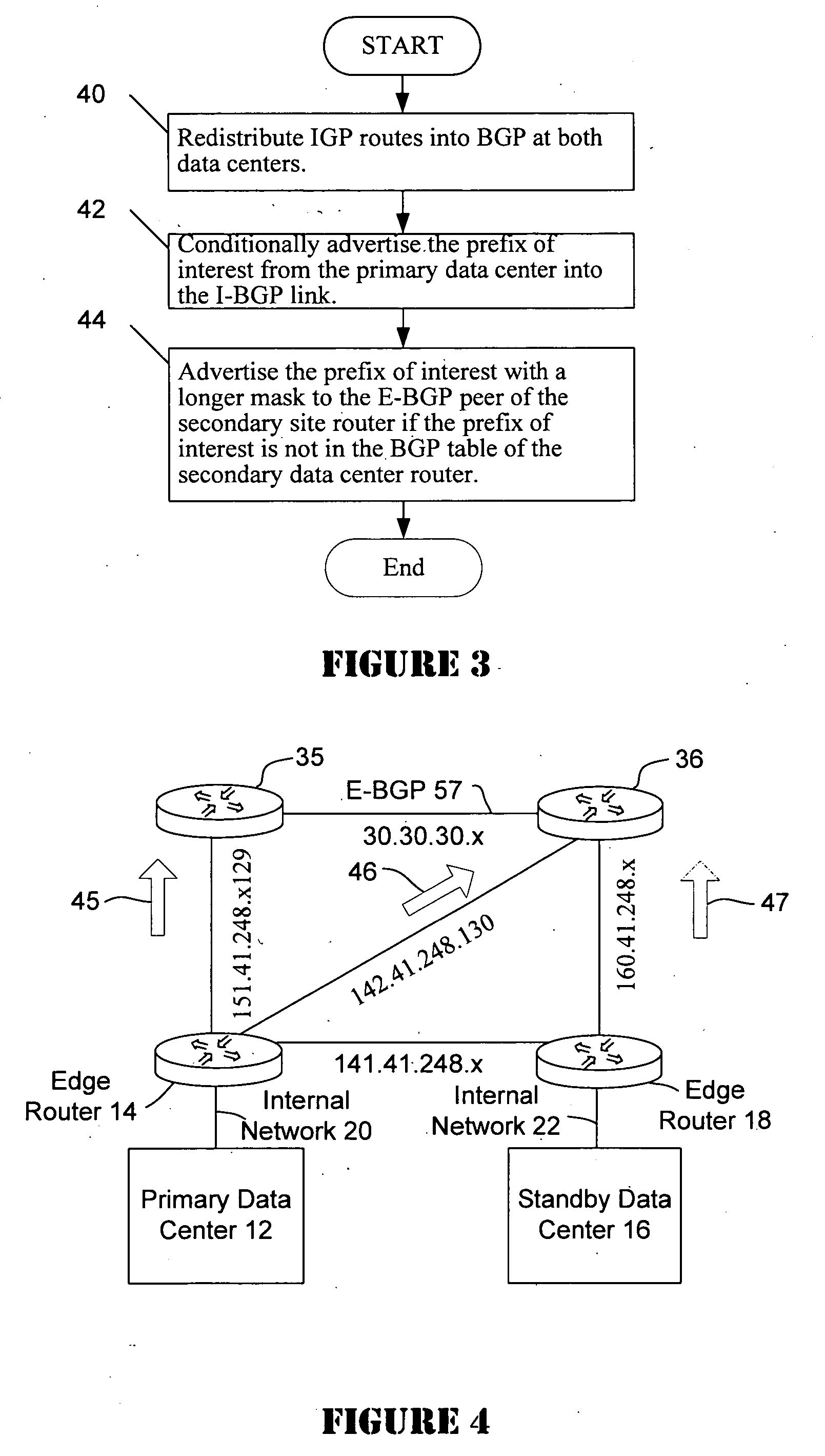
Disaster recovery for active-standby data center using route health and BGP
The present invention provides an active / standby data center that avoids the delay associated with a cached DNS entry to switch from the active data center to the standby data center. When the active data center becomes unavailable, the standby data center advertises the same address as the primary data center so the change over occurs quickly. When the IP address of the primary data center is no longer visible to the standby data center, the standby data center begins to advertise.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
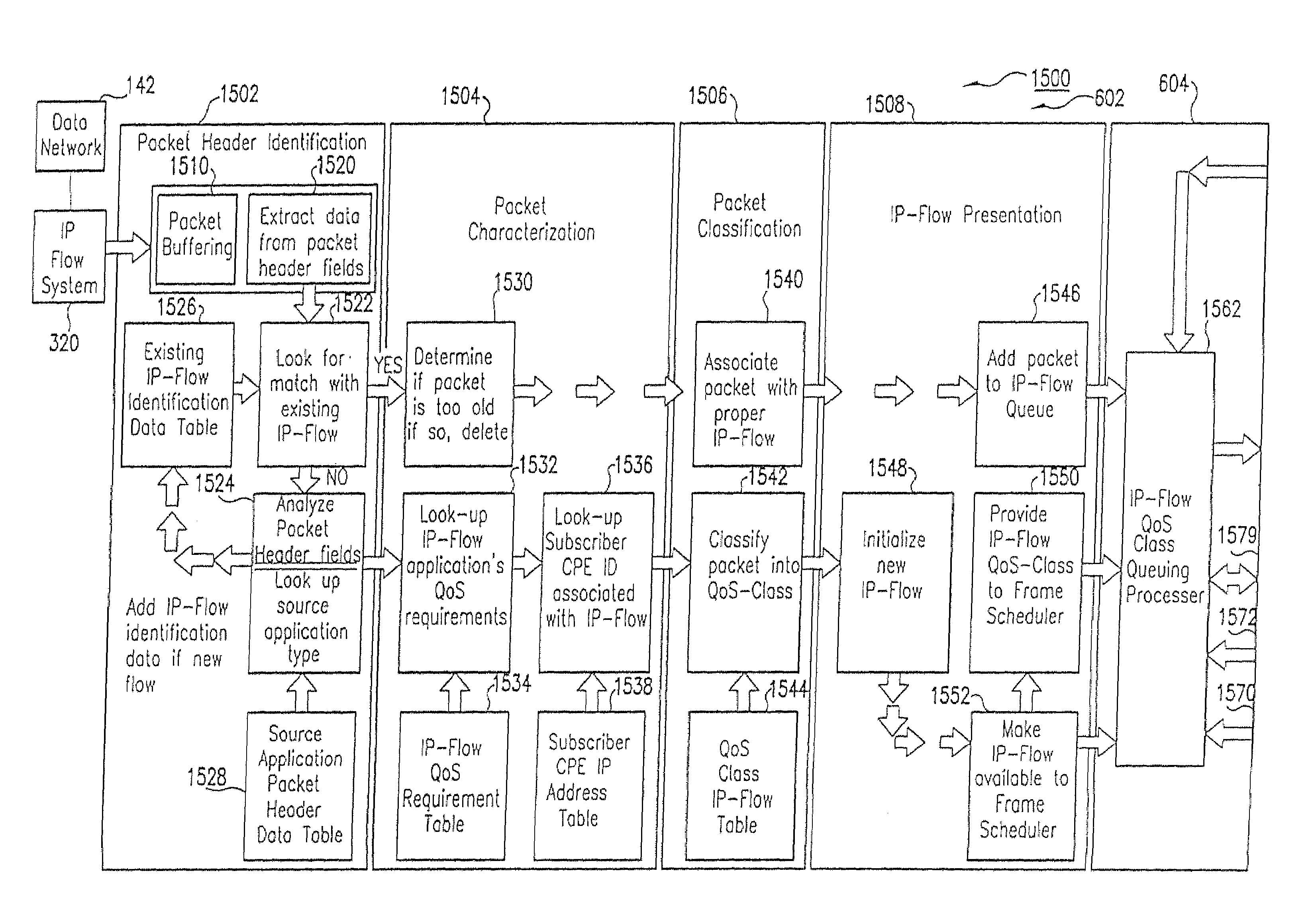
Method and computer program product for internet protocol (IP)-flow classification in a wireless point to multi-point (PtMP) transmission system
InactiveUS7251218B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorQuality of serviceWireless access point
A system and method for Internet Protocol (IP) flow classification group IP flows in a packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system is disclosed. The method comprises analyzing an IP flow in a packet-centric manner, classifying the IP flow, scheduling the IP flow for transmission over a shared wireless bandwidth between a wireless base station and at least one subscriber customer premises equipment (CPE) station, allocating the shared wireless bandwidth to a communication of the IP flow between the wireless base station and a subscriber CPE station so as to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS) associated with the IP flow.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
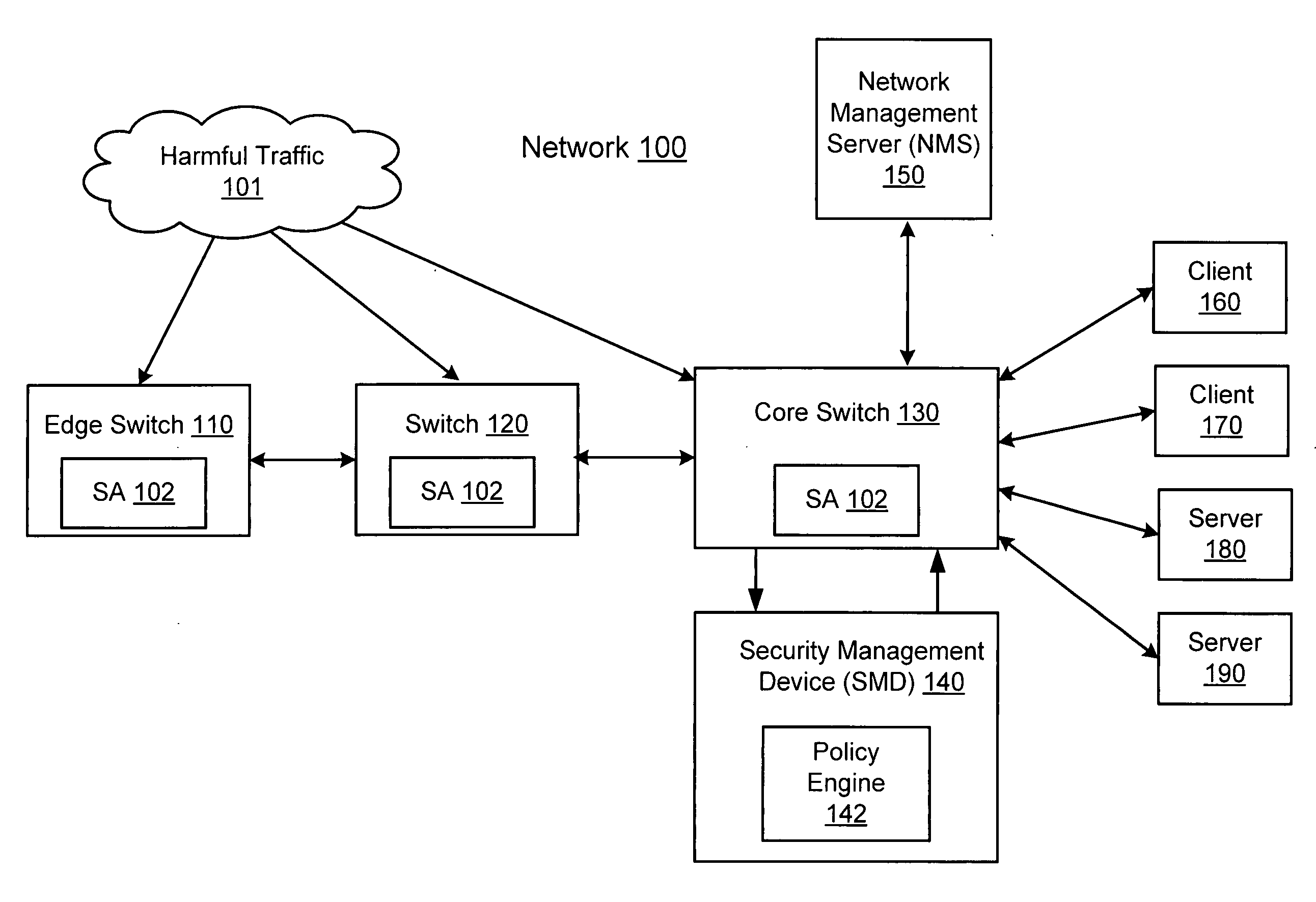
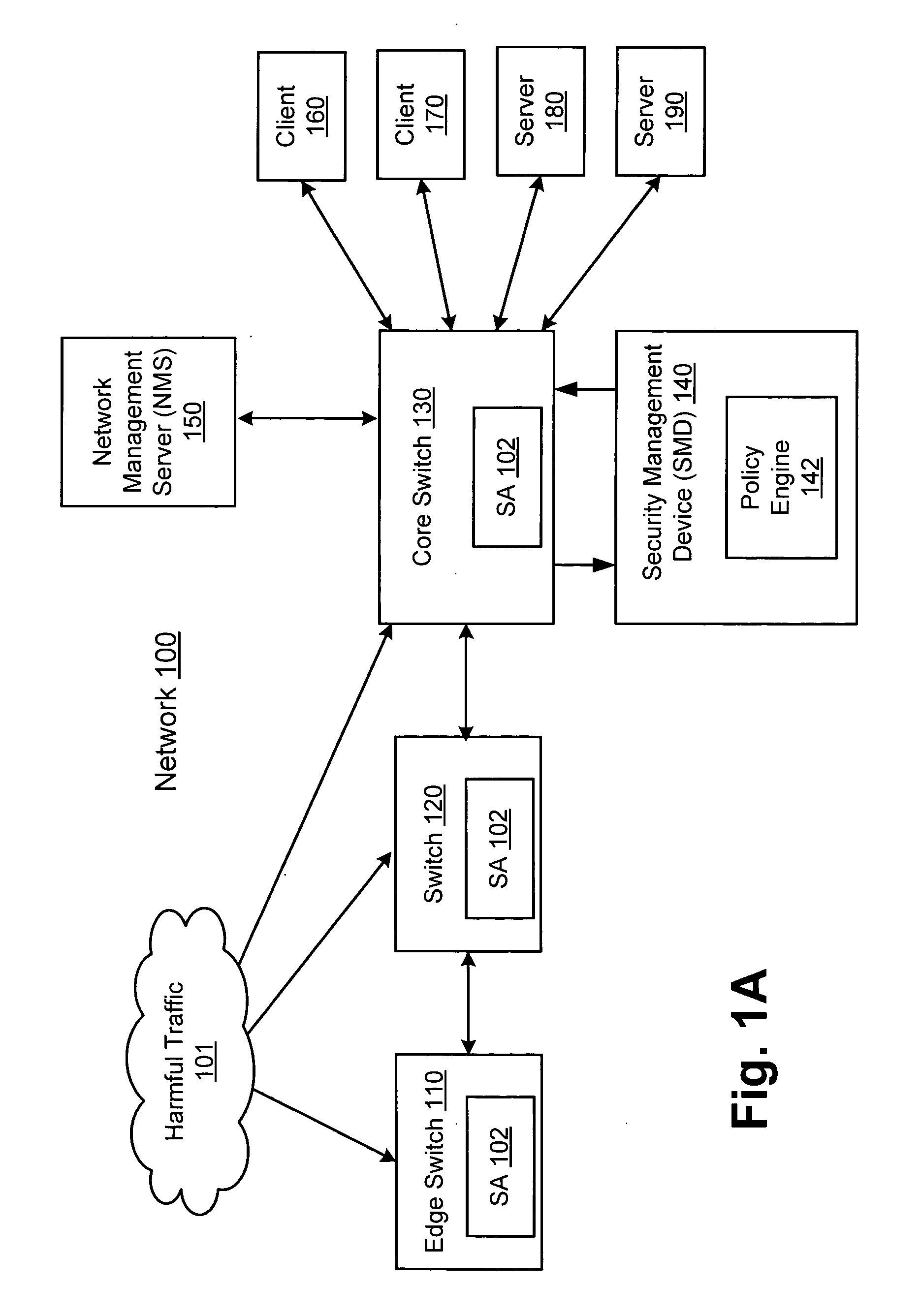
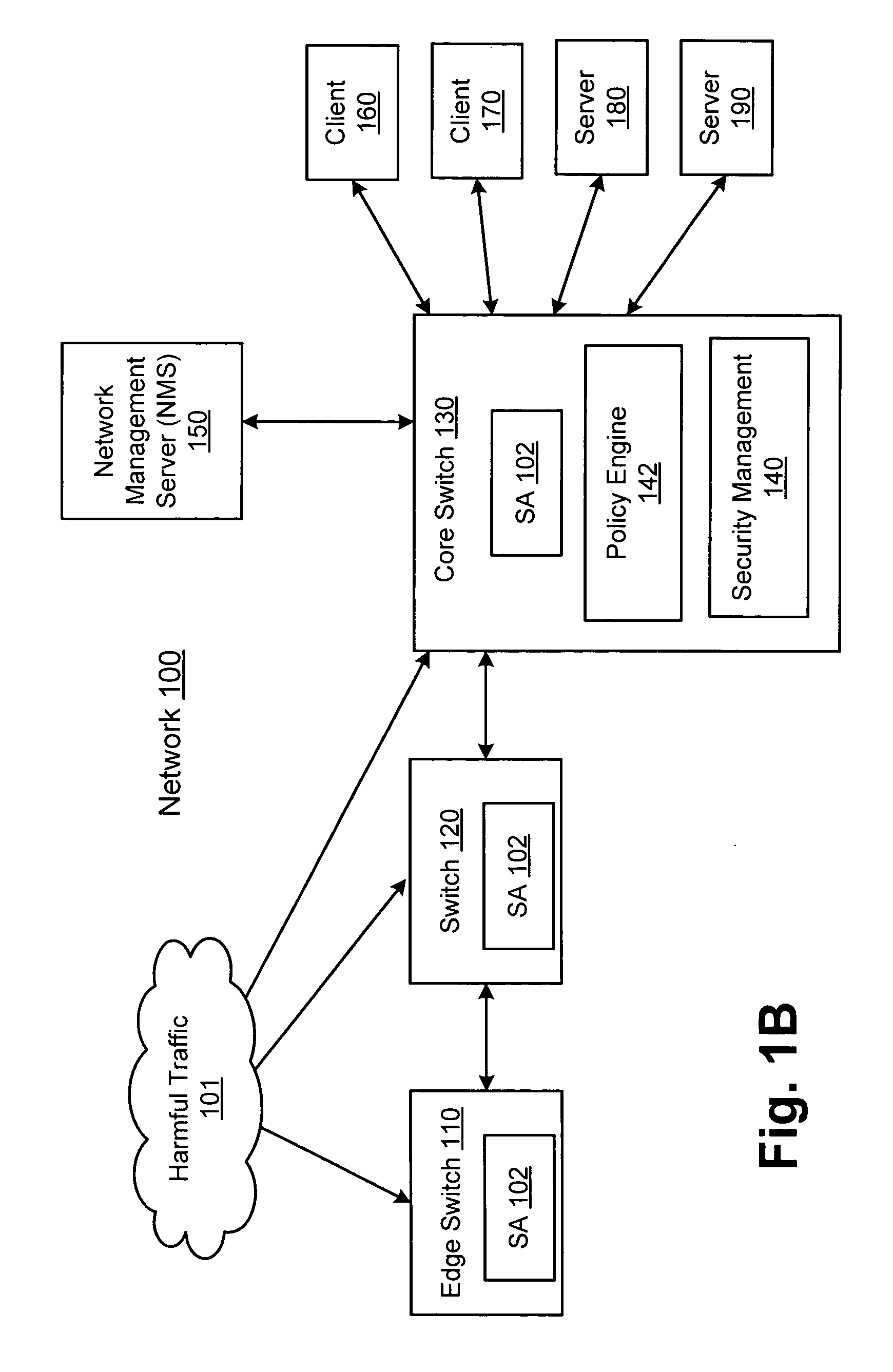
Network threat detection and mitigation
ActiveUS20070157306A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInternet trafficNetwork switch
A network switch automatically detects undesired network traffic and mirrors the undesired traffic to a security management device. The security management device determines the source of the undesired traffic and redirects traffic from the source to itself. The security management device also automatically sends a policy to a switch to block traffic from the source.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
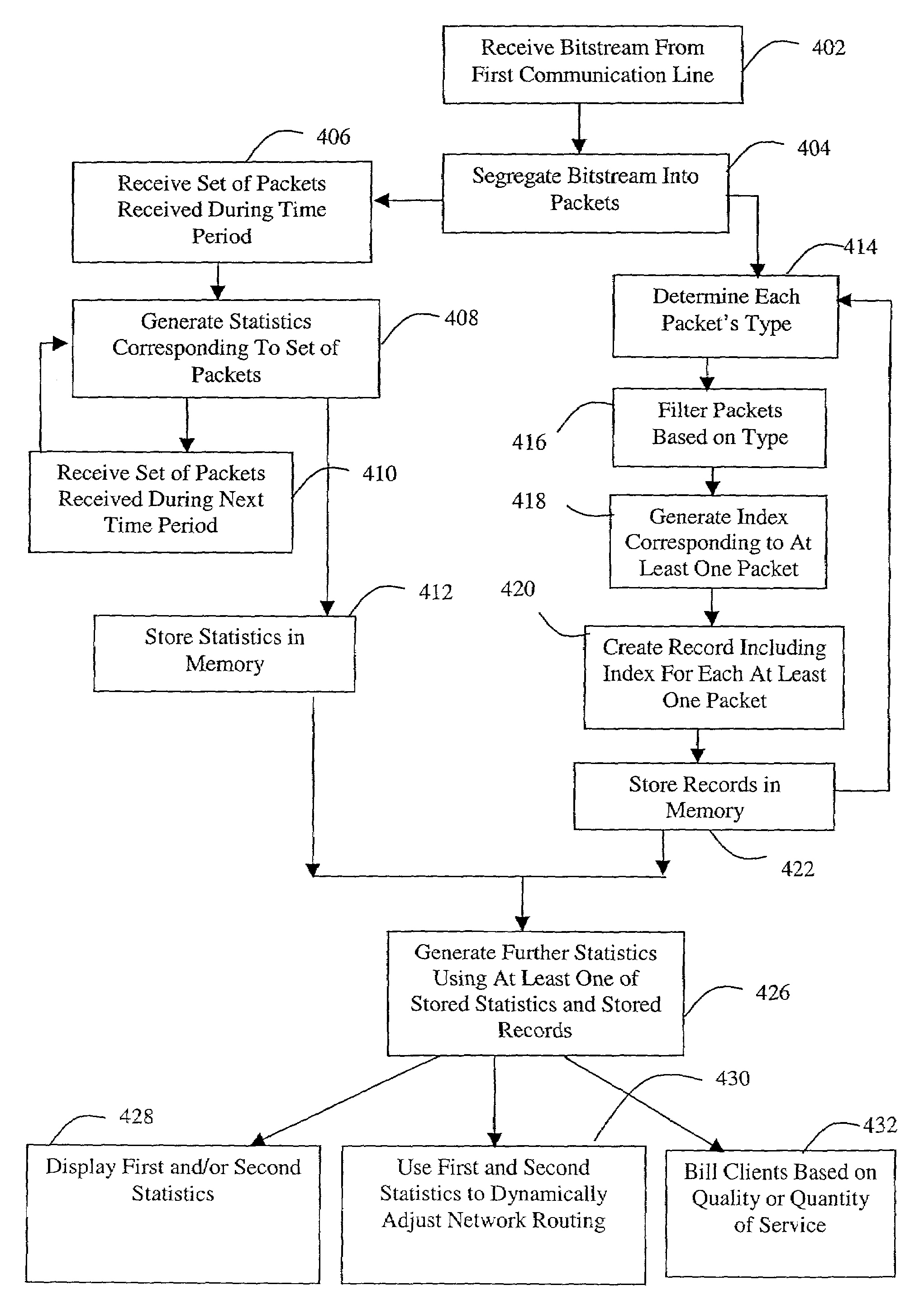
Apparatus and method for collecting and analyzing communications data
InactiveUS7492720B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMonitoring dataReal-time computing
A method for monitoring data on a first communication line. Data is received from the first communication line and a plurality of packets are extracted from the data. Statistics are then recursively generated, the statistics corresponding to the plurality of packets.
Owner:NIKSUN
Media module apparatus and method for use in a network monitoring environment
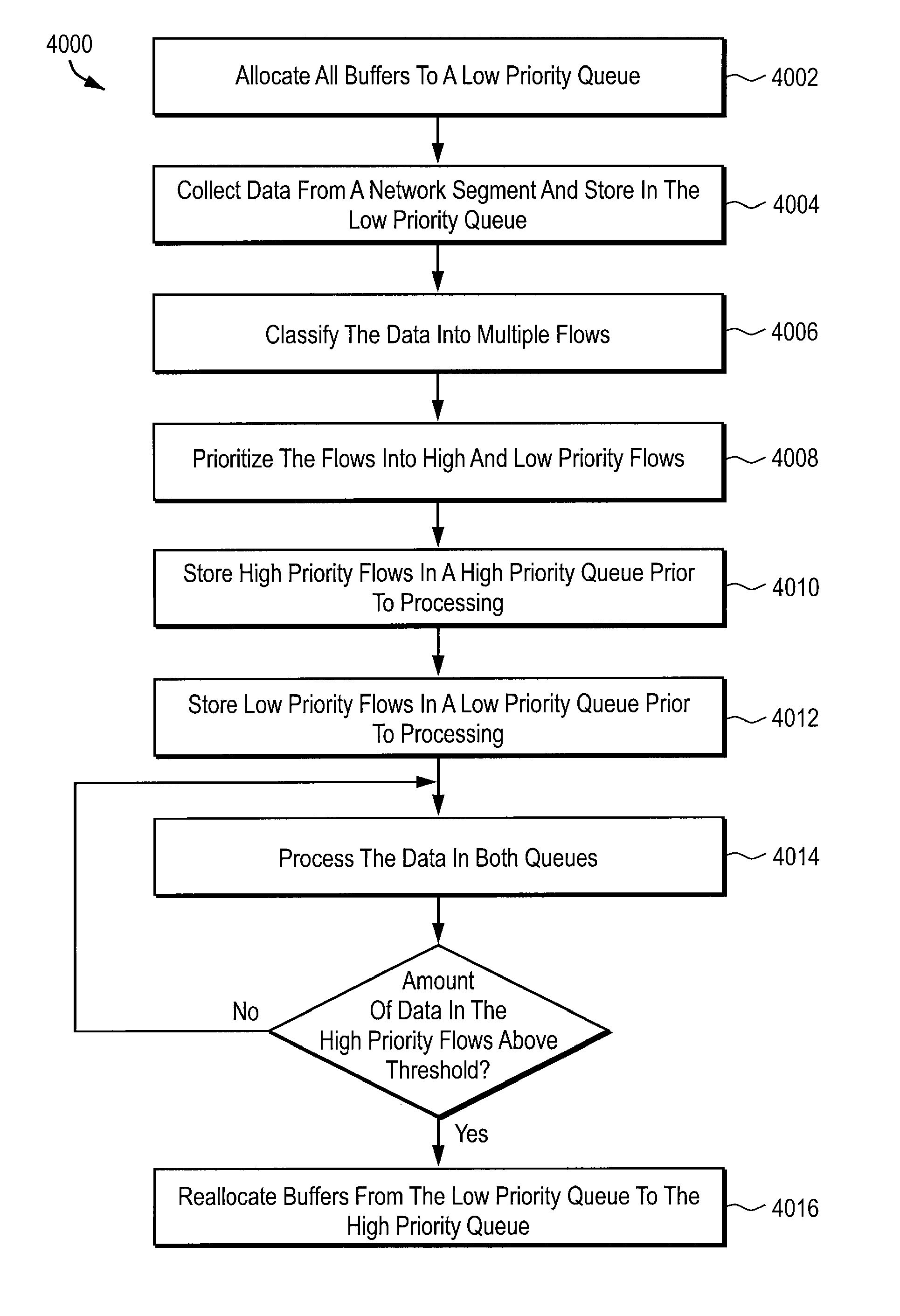
InactiveUS7299277B1Avoid data lossReduce probabilityError preventionTransmission systemsApplication softwareMaster processor
A probe apparatus, method and computer program product for application monitoring are provided. A data collection module collects data from a network segment. A flow processor coupled to the data collection module classifies the collected data into a plurality of flows. A capture system coupled to the flow processor filters and buffers the collected data. A main processor processes the filtered data.
Owner:NETWORK GENERAL TECH
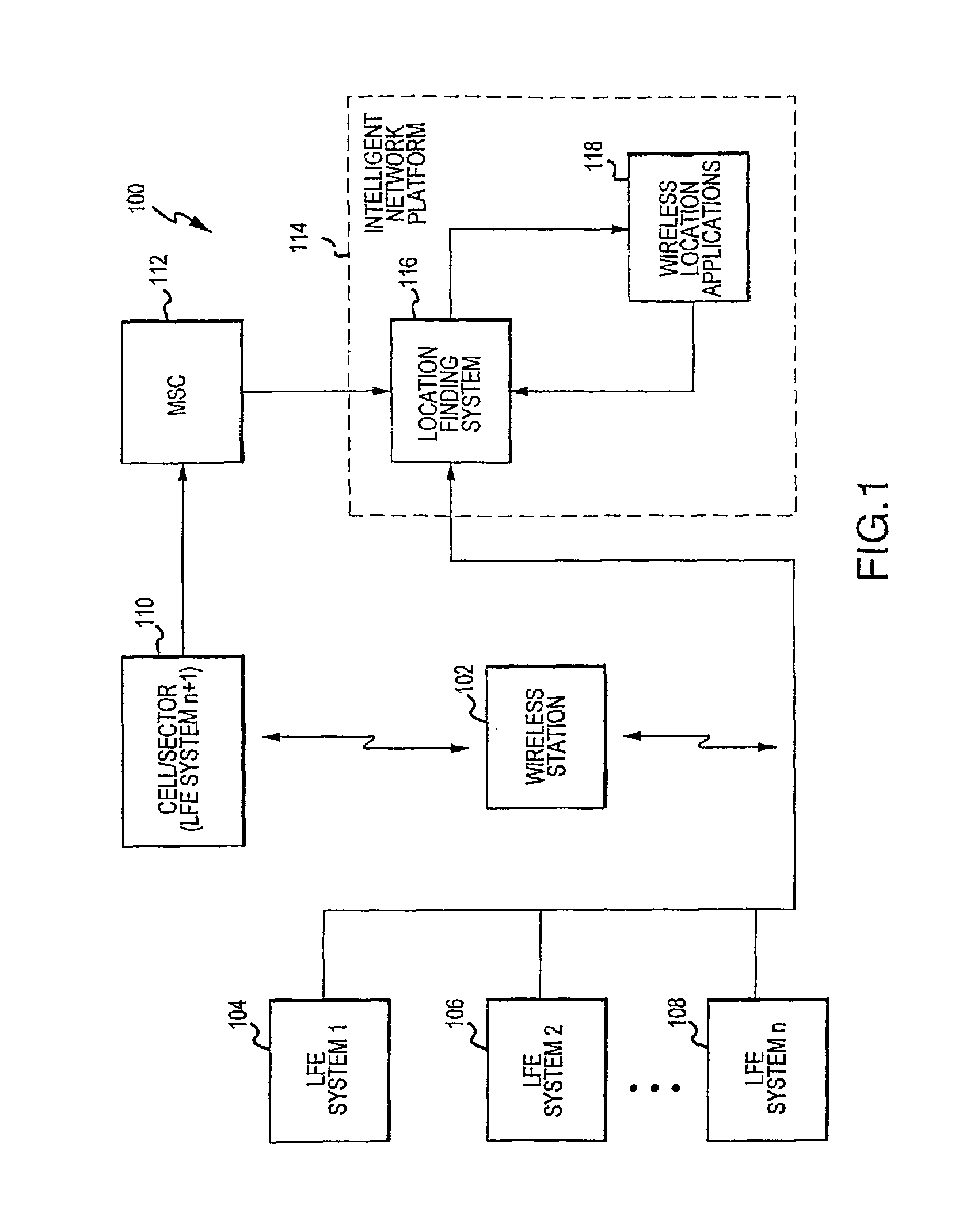
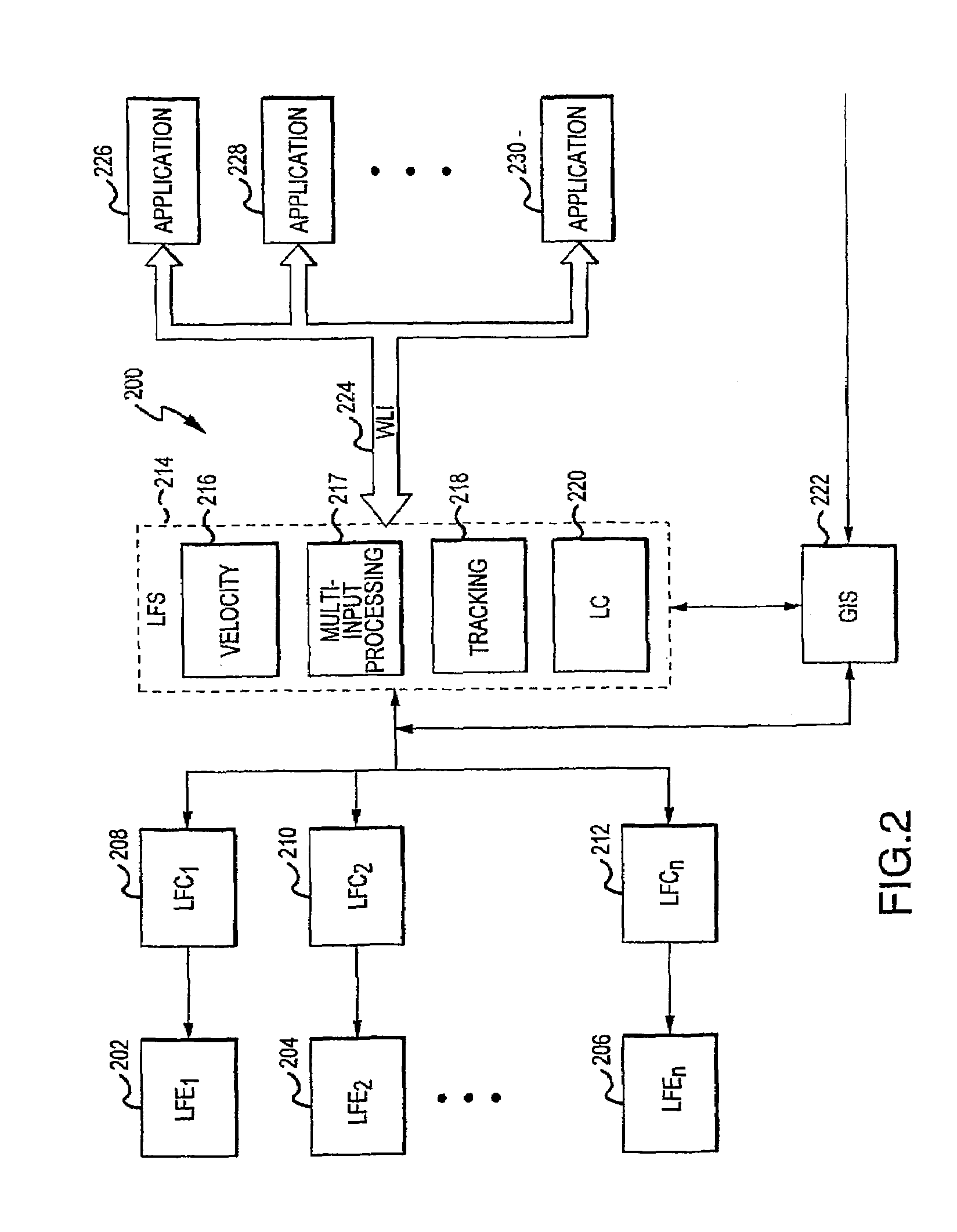
Interface for wireless location information
InactiveUS7522927B2Enhanced informationEnhancing timeliness and accuracy and reliabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLocation EquipmentComputer science
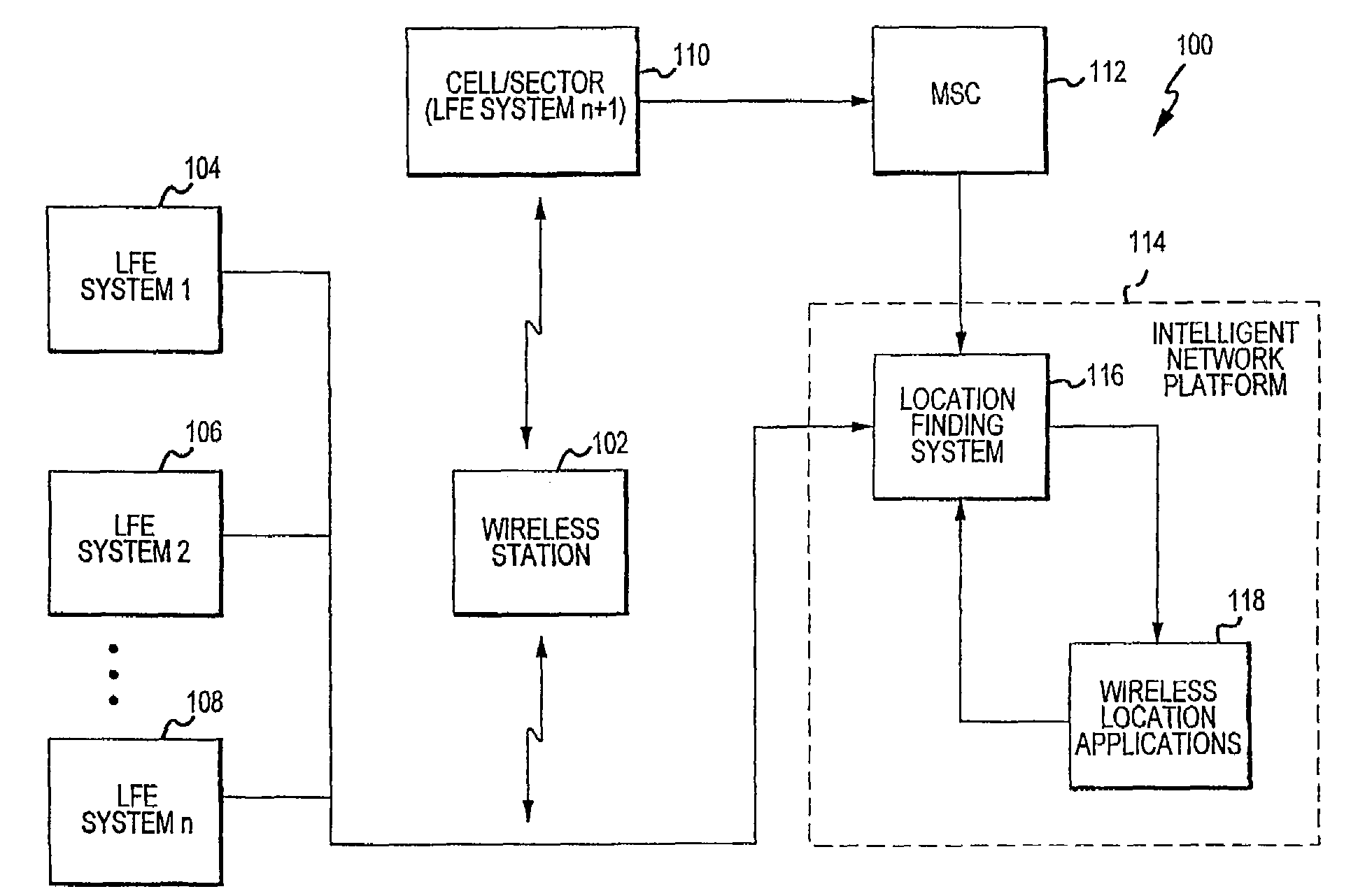
Multiple location finding equipment (LFE) inputs are used to enhance location information made available to wireless location-based applications. A wireless network utilizes a mobile switching center to route communications between wireless stations, a network platform, and a variety of LFE systems. A Location Finding System (LFS), resident on the network platform, receives location information from the LFEs and provides location information to wireless location based applications. In this regard, the LFS can receive input information at varying time intervals of varying accuracies and in various formats, and can provide standardized outputs to the applications, for example, depending on the needs of the applications. Multiple inputs may also be co-processed for enhanced accuracy. A specification can be used to ensure that location information at least meets certain minimum criteria, such as geographical accuracy, allowable age, acceptable response time, and confidence.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Optimal route selection in a content delivery network
ActiveUS7274658B2Improve speed and reliabilityRetrieve content (cacheableError preventionTransmission systemsFile area networkPeer-to-peer
A routing mechanism, service or system operable in a distributed networking environment. One preferred environment is a content delivery network (CDN) wherein the present invention provides improved connectivity back to an origin server, especially for HTTP traffic. In a CDN, edge servers are typically organized into regions, with each region comprising a set of content servers that preferably operate in a peer-to-peer manner and share data across a common backbone such as a local area network (LAN). The inventive routing technique enables an edge server operating within a given CDN region to retrieve content (cacheable, non-cacheable and the like) from an origin server more efficiently by selectively routing through the CDN's own nodes, thereby avoiding network congestion and hot spots. The invention enables an edge server to fetch content from an origin server through an intermediate CDN server or, more generally, enables an edge server within a given first region to fetch content from the origin server through an intermediate CDN region. As used herein, this routing through an intermediate server, node or region is sometimes referred to as “tunneling.”
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
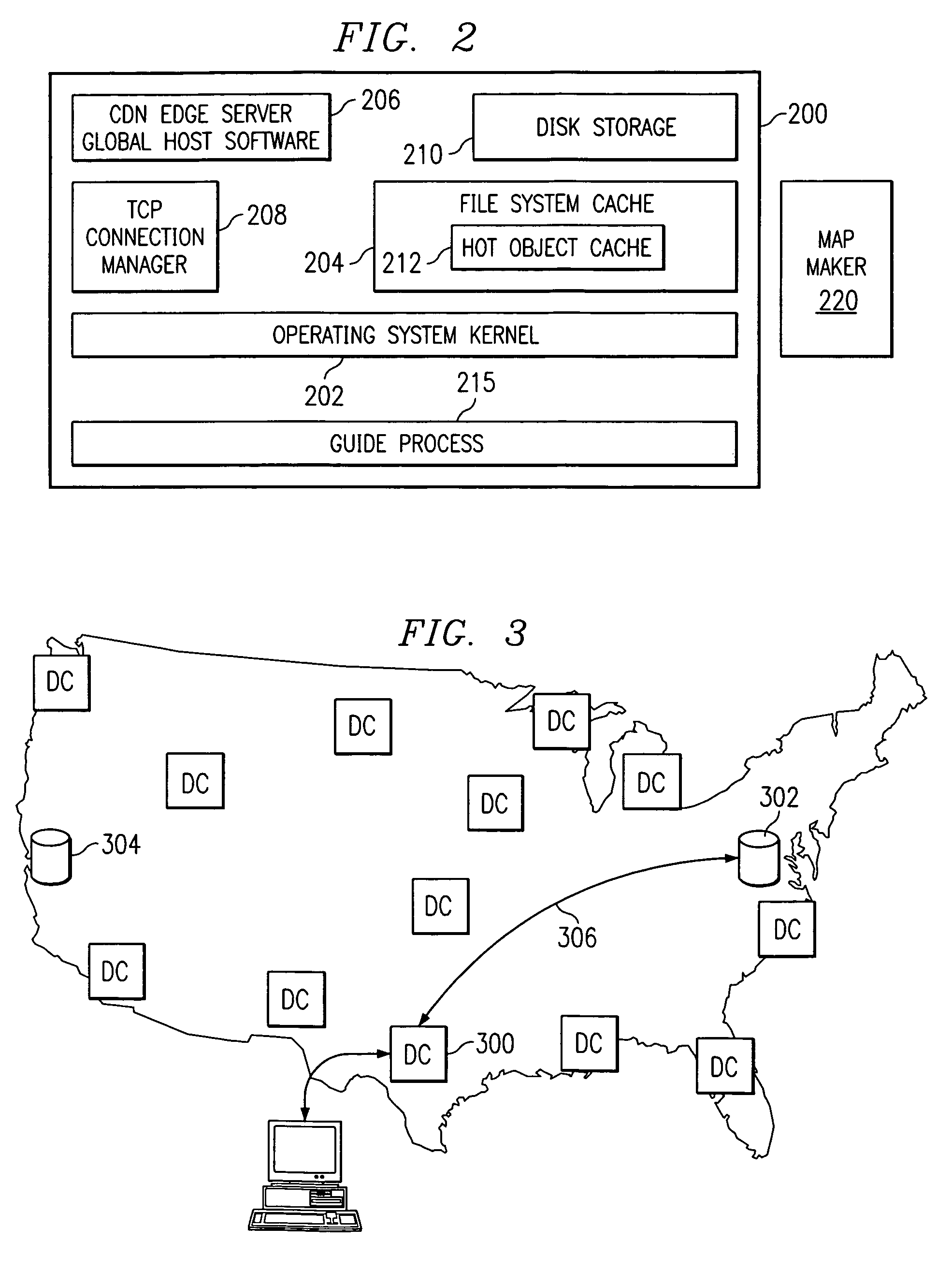
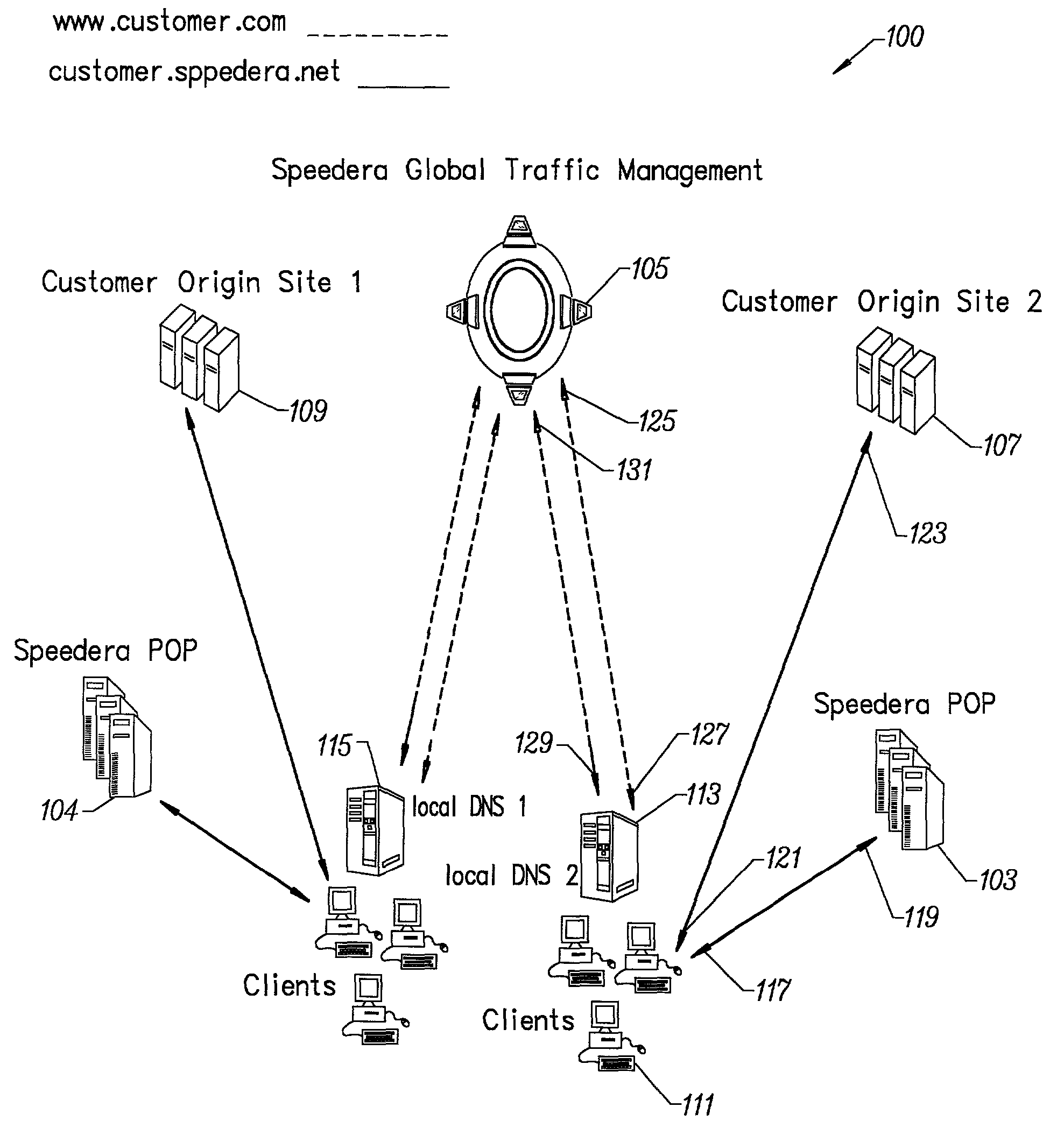
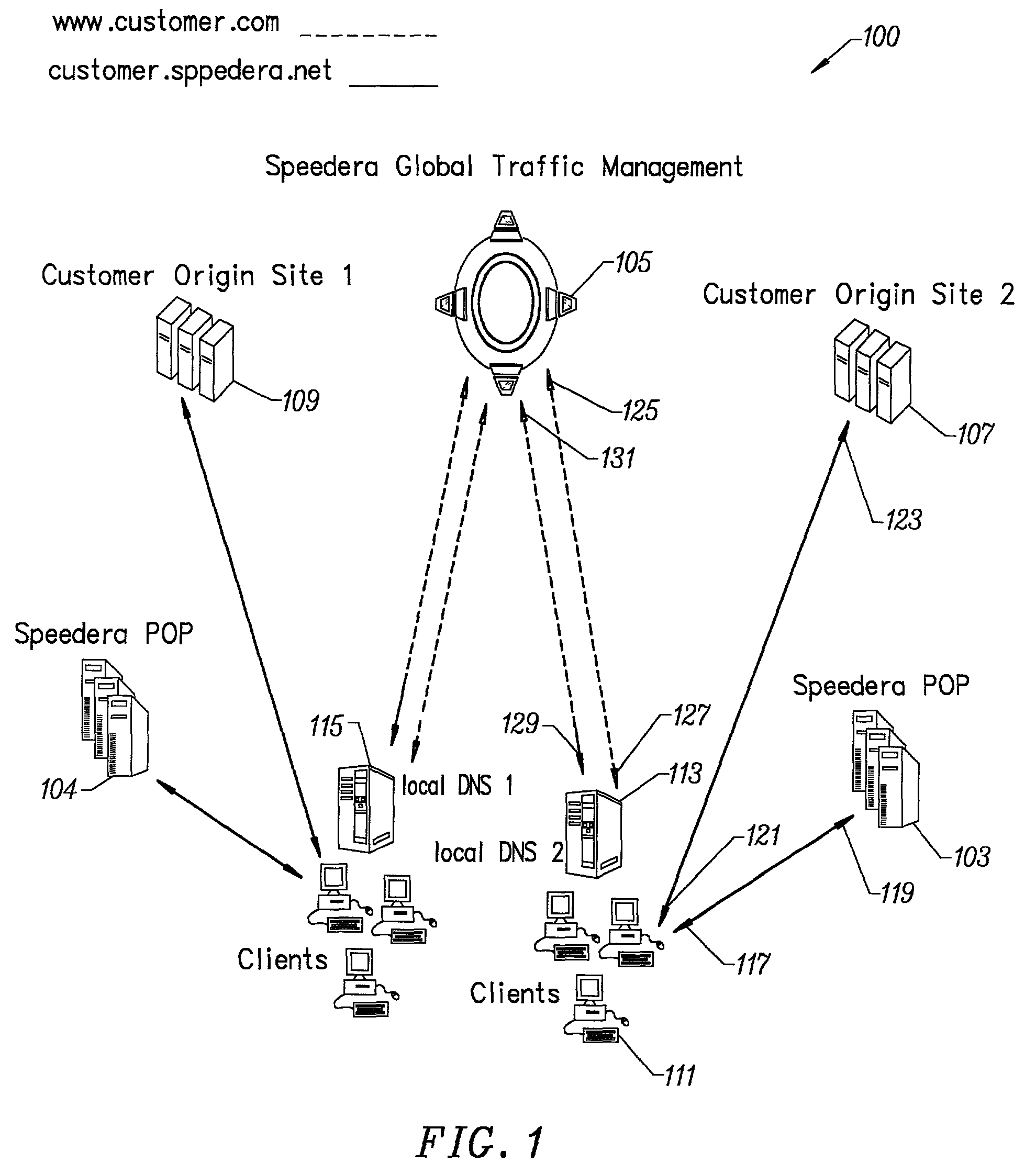
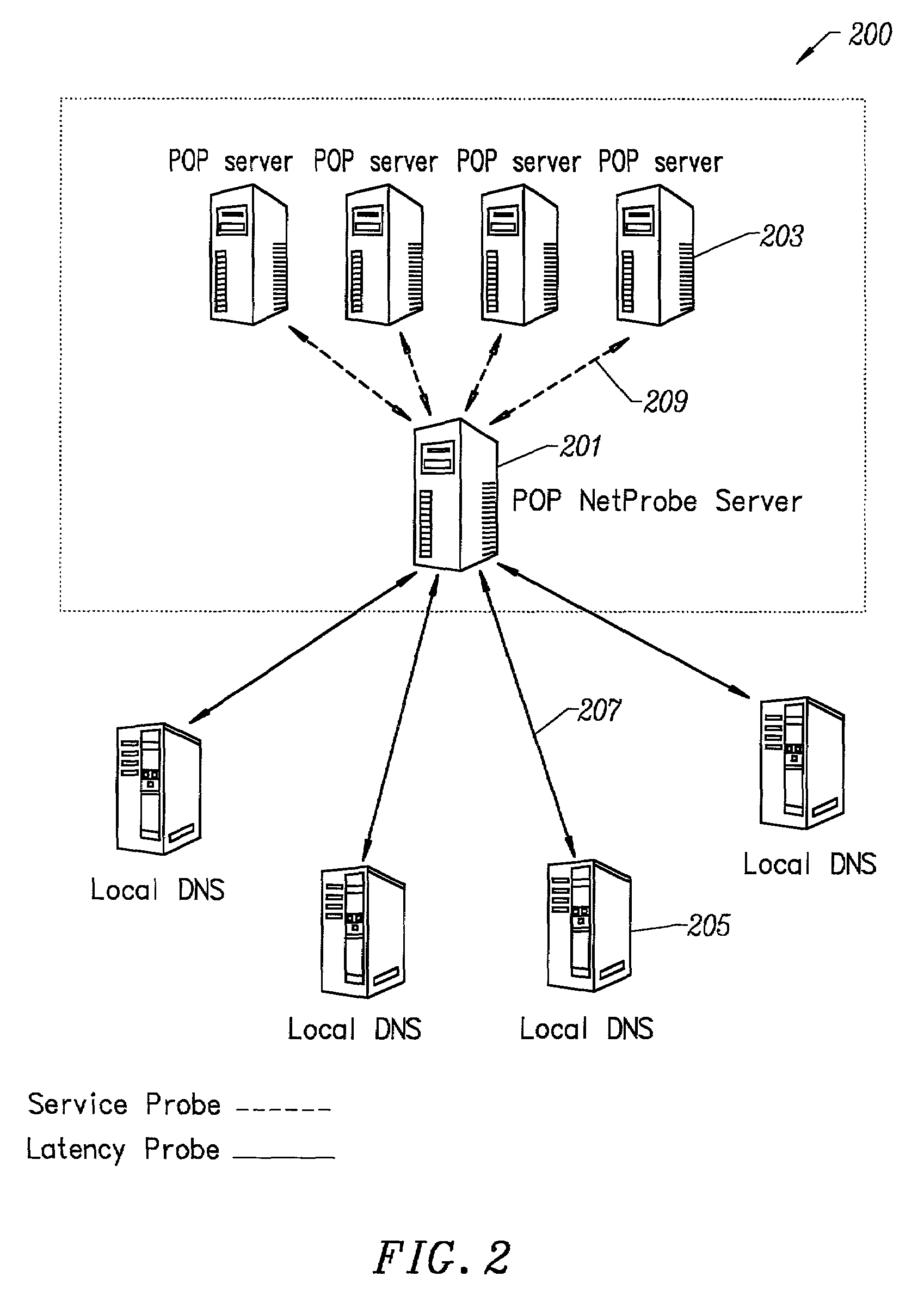
Method for determining metrics of a content delivery and global traffic management network
ActiveUS7523181B2Efficient executionMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsError preventionData packConfigfs
A method for determining metrics of a content delivery and global traffic management network provides service metric probes that determine the service availability and metric measurements of types of services provided by a content delivery machine. Latency probes are also provided for determining the latency of various servers within a network. Service metric probes consult a configuration file containing each DNS name in its area and the set of services. Each server in the network has a metric test associated with each service supported by the server which the service metric probes periodically performs metric tests on and records the metric test results which are periodically sent to all of the DNS servers in the network. DNS servers use the test result updates to determine the best server to return for a given DNS name. The latency probe calculates the latency from its location to a client's location using the round trip time for sending a packet to the client to obtain the latency value for that client. The latency probe updates the DNS servers with the clients' latency data. The DNS server uses the latency test data updates to determine the closest server to a client.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com