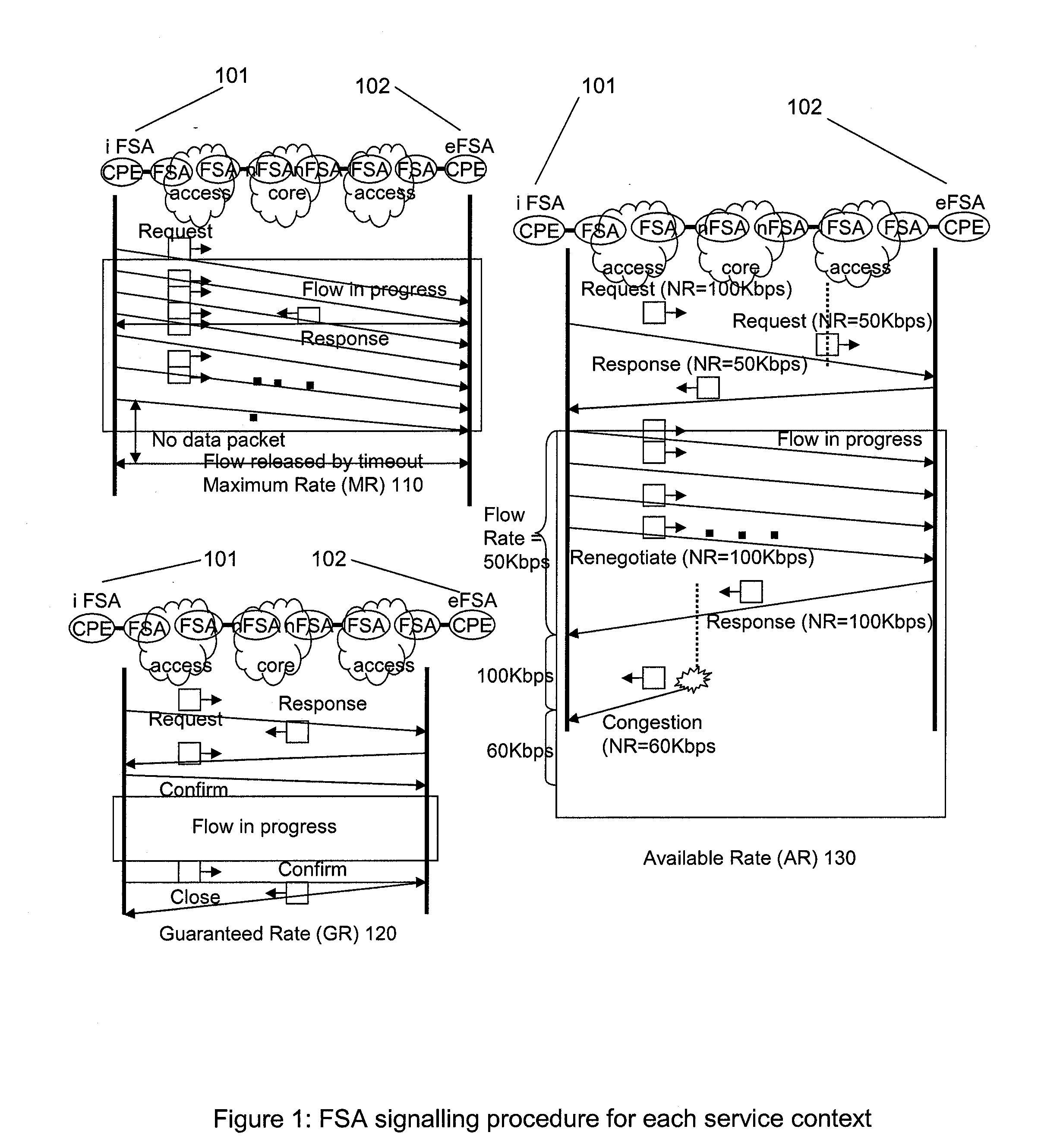
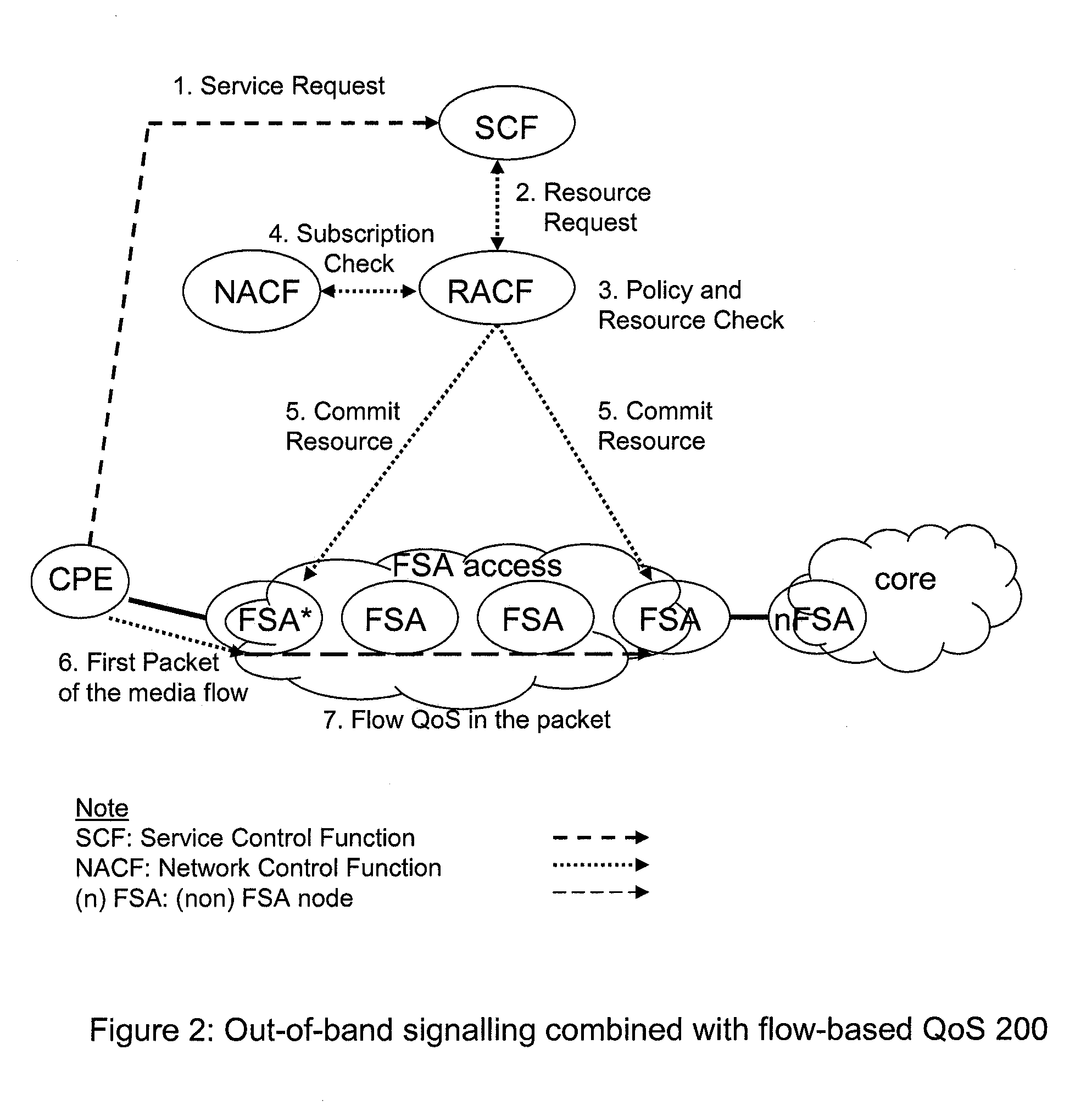
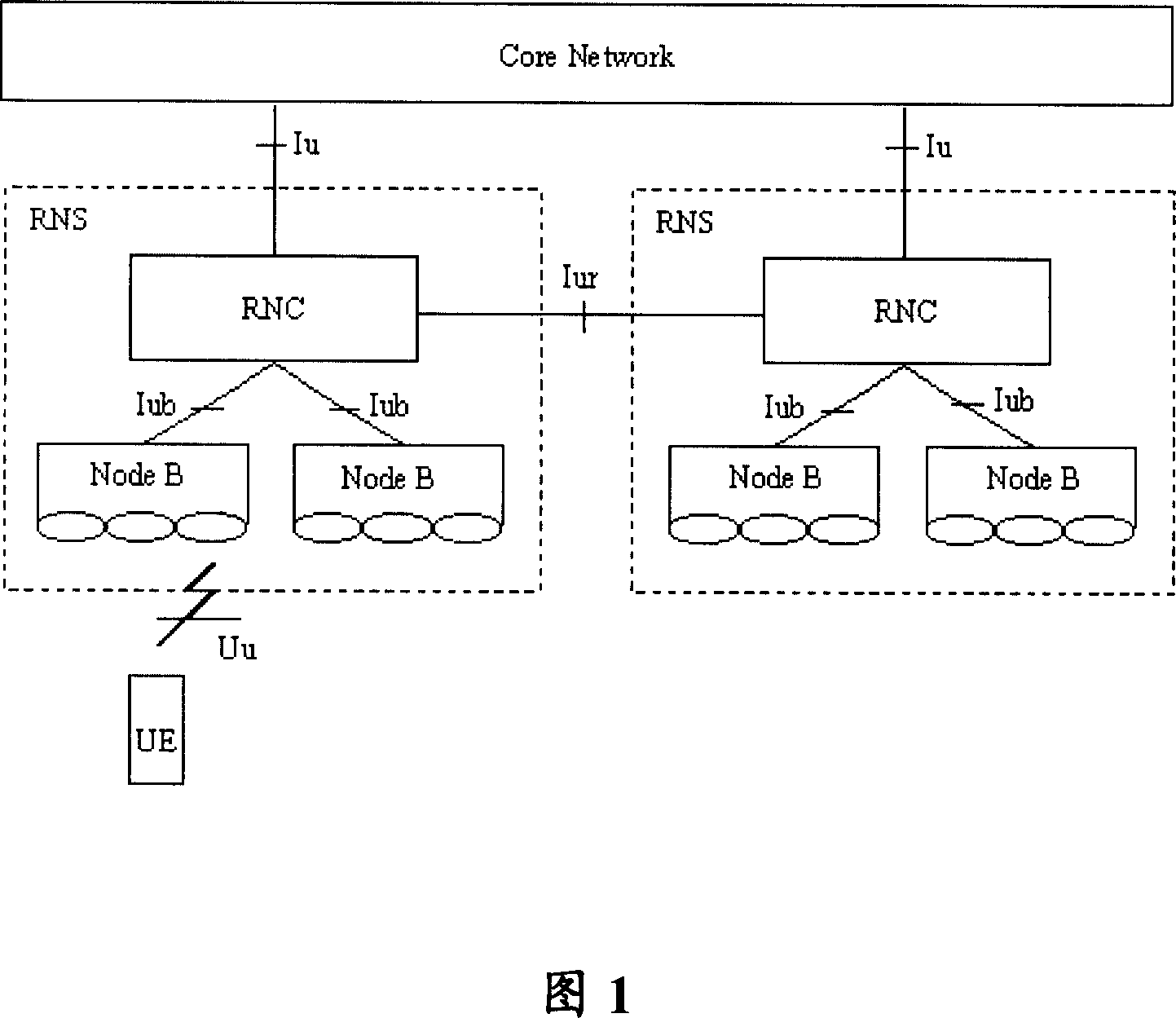
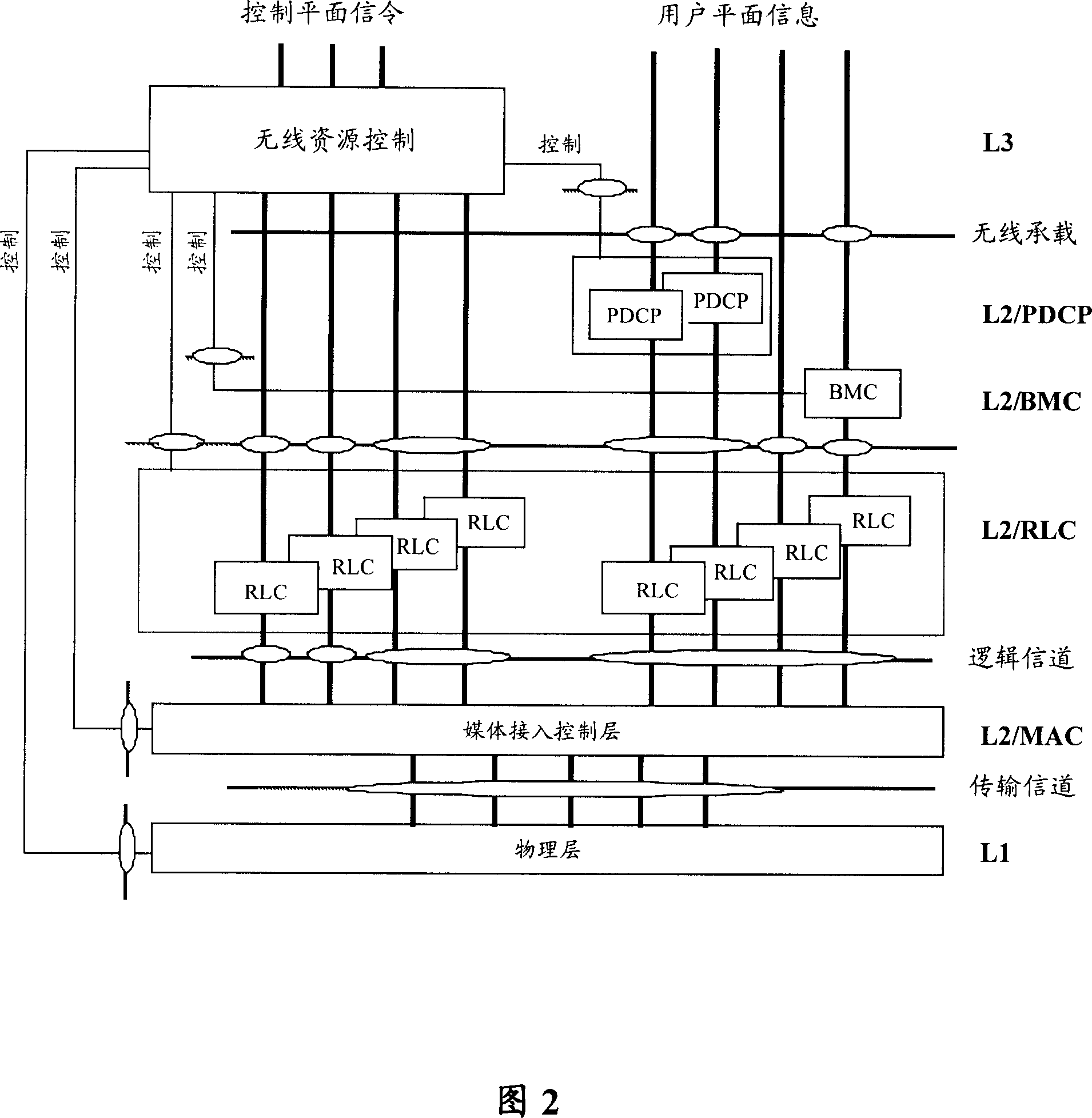
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
170 results about "Qos management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quality of service (QoS) refers to any technology that manages data traffic to reduce packet loss, latency and jitter on the network. QoS controls and manages network resources by setting priorities for specific types of data on the network.
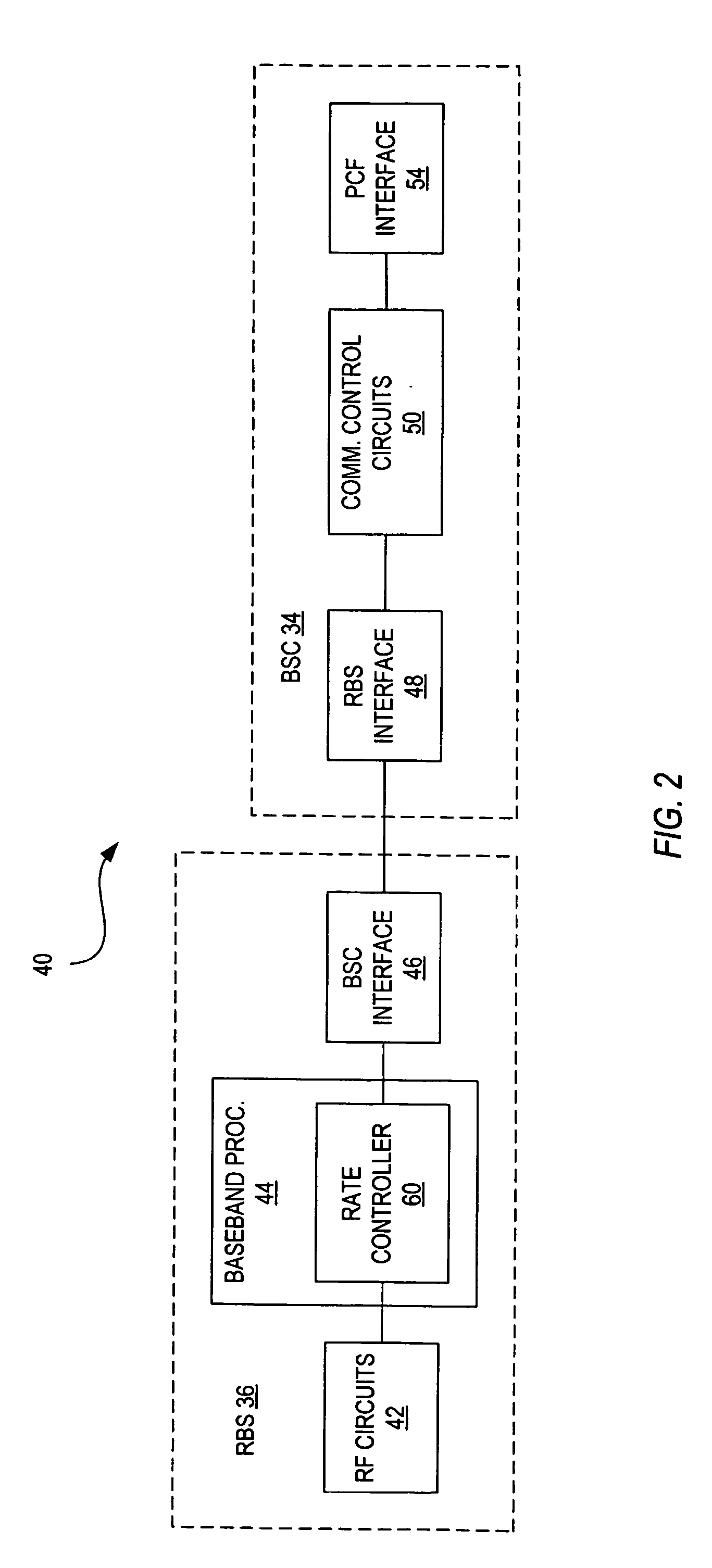
Method and system for wireless QOS agent for all-IP network
A wireless quality of service (QoS) agent for an all-Internet Protocol (IP) network. The QoS agent couples to an all-IP network. The coupling means includes communication means for transfer of information between the agent and a QoS manager of the all-IP network. The agent is also able to seamlessly extend QoS support for multimedia applications from wireline to wireless and control QoS of the multimedia applications sent over wireless connections on the all-IP network.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
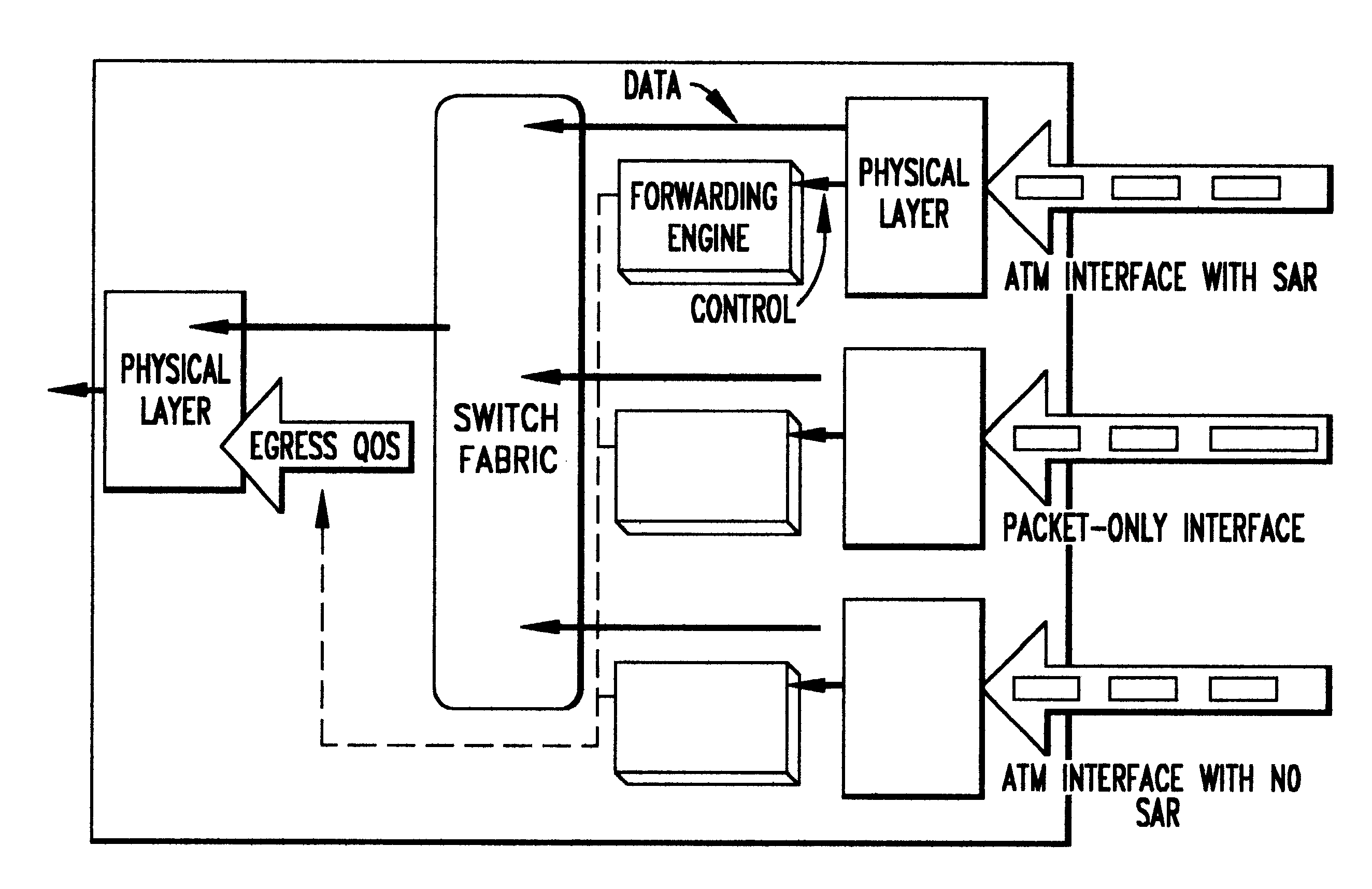
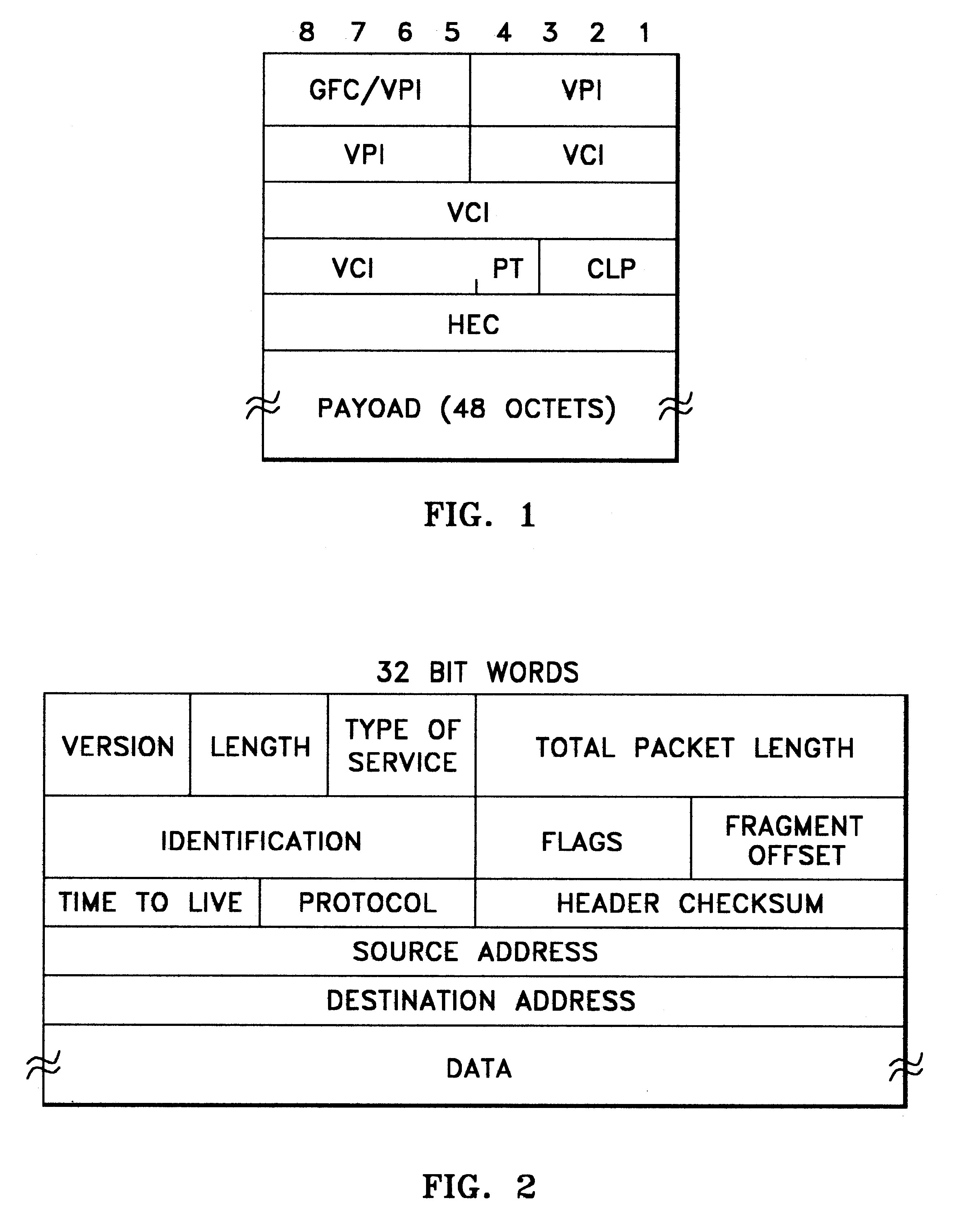
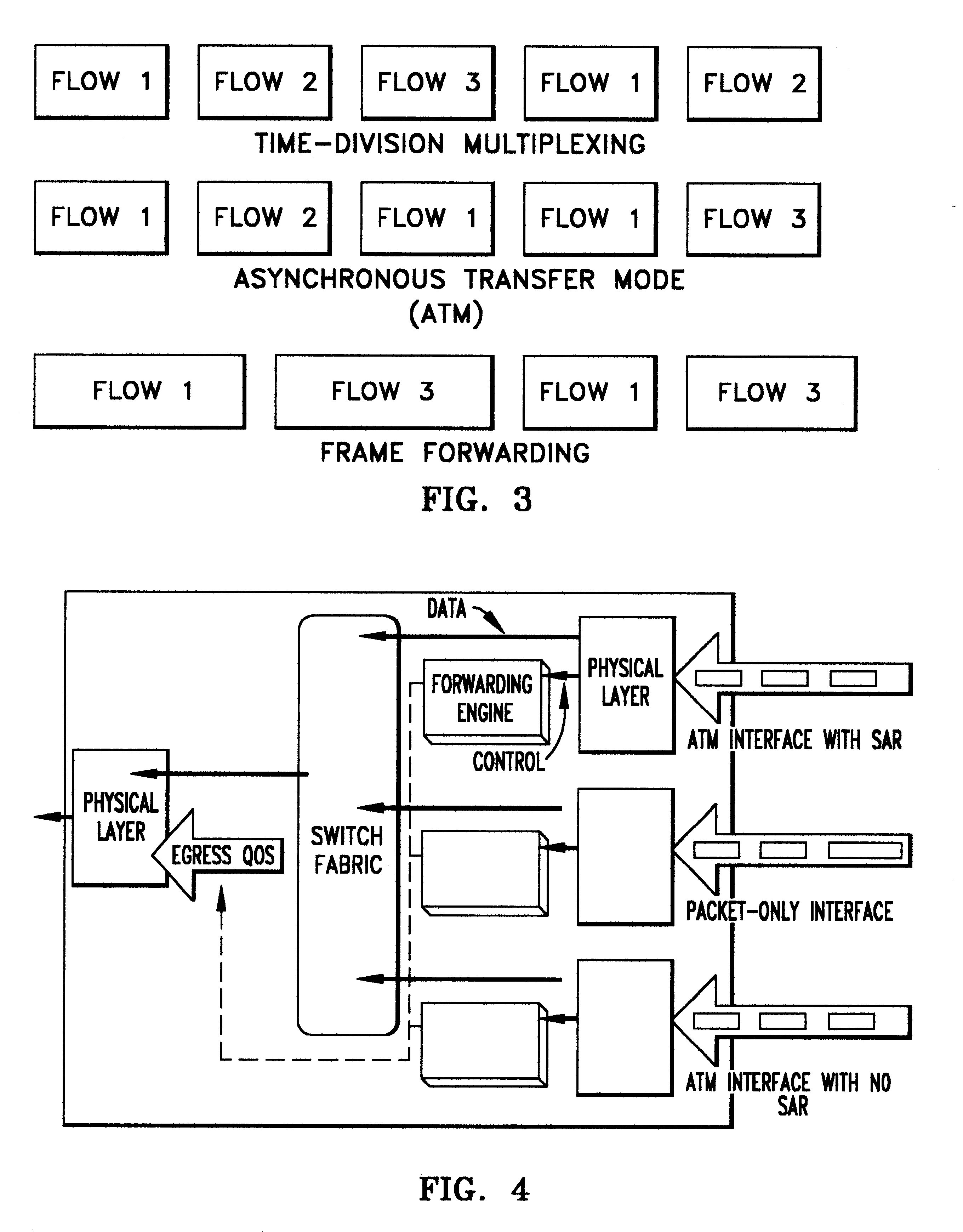
System architecture for and method of processing packets and/or cells in a common switch
InactiveUS6259699B1Without impacting performance aspectPromote resultsData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsAtm switchingQos management
A novel networking architecture and technique for transmitting both cells and packets or frames across a common switch fabric, effected, at least in part, by utilizing a common set of algorithms for the forwarding engine (the ingress side) and a common set of algorithms for the QoS management (the egress part) that are provided for each I / O module to process packet / cell information without impacting the correct operation of ATM switching and without transforming packets into cells for transfer across the switch fabric.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
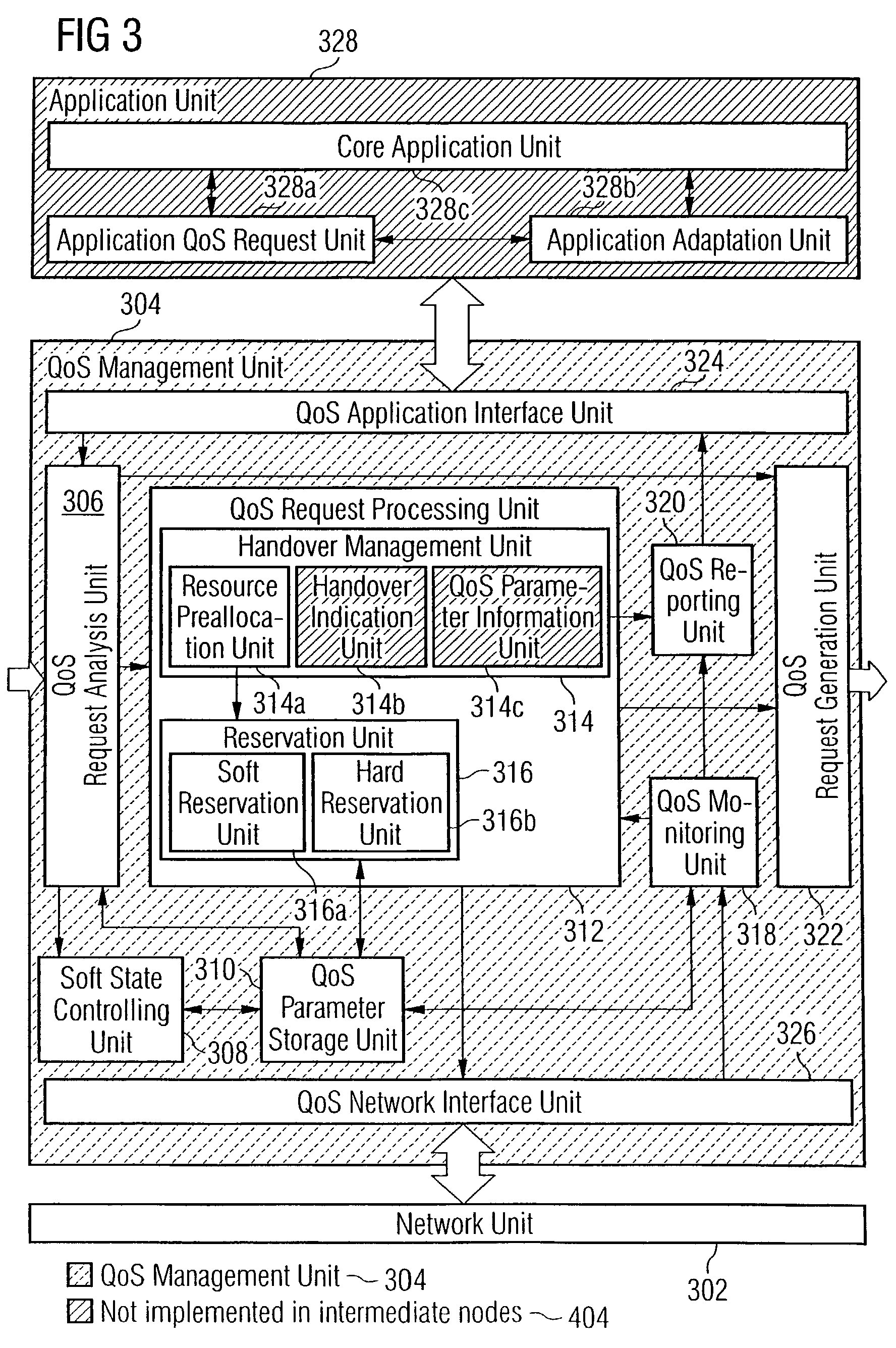
Adaptive quality-of-service reservation and pre-allocation for mobile systems
ActiveUS7289453B2Minimize impactDelay minimizationError preventionTransmission systemsAdaptive servicesQos management
In the field of Quality-of-Service (QoS) management for adaptive real-time services running on mobile devices which support different access technologies in dynamic wireless Internet Protocol (IP) networks, the connectivity of the applied nodes is unpredictable time-varying. In this context, a QoS management unit (304) is proposed that allows adaptive applications with real-time requirements in typical mobile wireless scenarios—e.g. a radio link with a changing transmission quality and handover procedures (2900)—to adaptively and responsively react to a time-varying network topology and different radio link characteristics. Said QoS management unit (304) provides methods of pre-allocating, reserving, monitoring and adapting QoS-related parameters in a dynamic mobile environment.The QoS management unit (304) comprises at least one analysis unit (306) which evaluates QoS requests received from other nodes (402a / b, 404) to inform the application unit (328) of said mobile terminal (208) about the current QoS situation, at least one processing unit (312) that manages request messages (1200, 2000, 2400) for each type of QoS request, at least one monitoring unit (318) which monitors the current QoS situation within said mobile node (208) and initiates requests by activating the processing unit (312), and at least one generation unit (322) which is responsible for generating QoS requests or passing them on to the QoS management units (304) of other nodes (402a+b, 404).
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
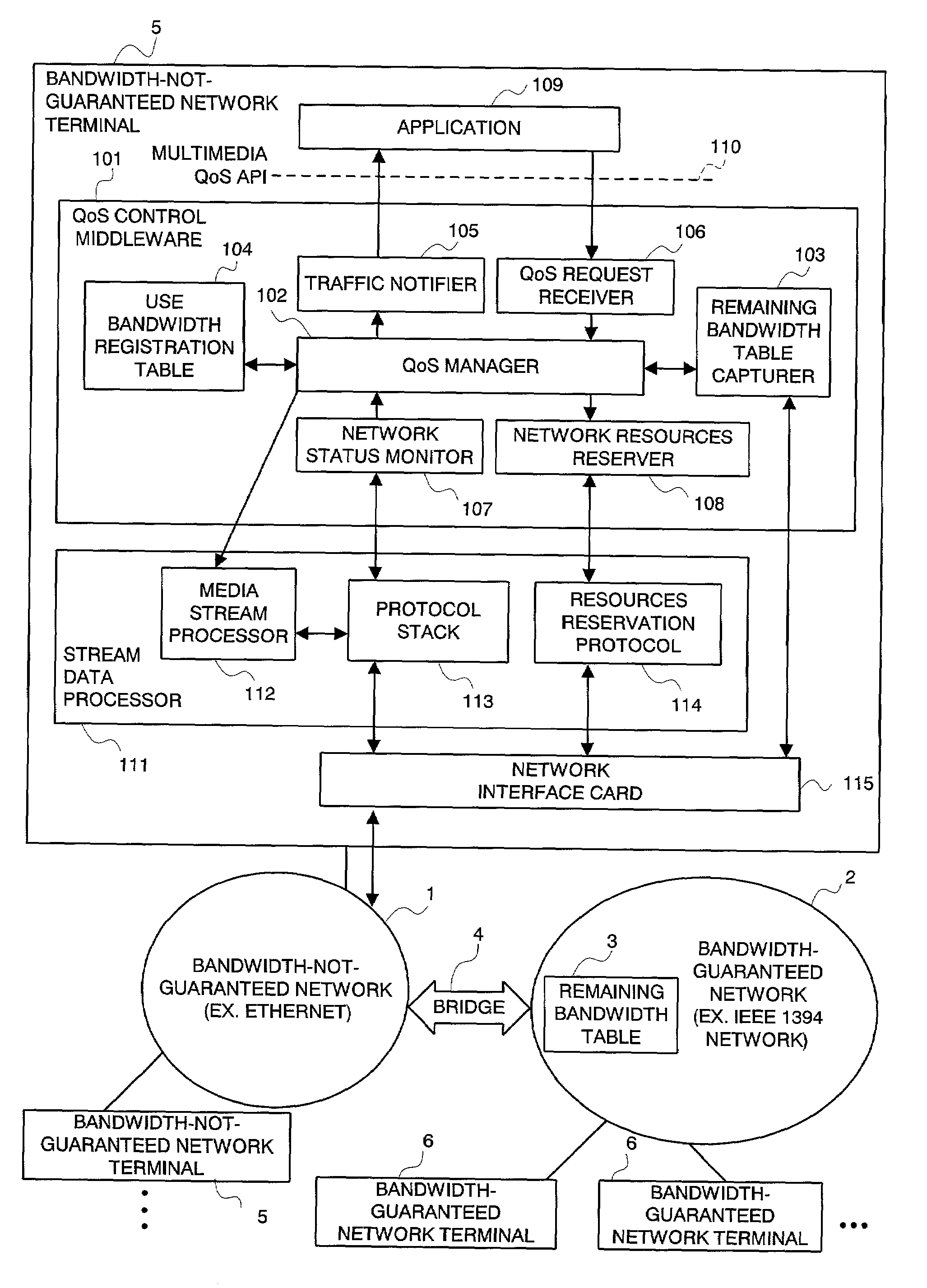
QoS control middleware in integrated network, QoS control method, and the program for the same
InactiveUS7212491B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityQuality of service
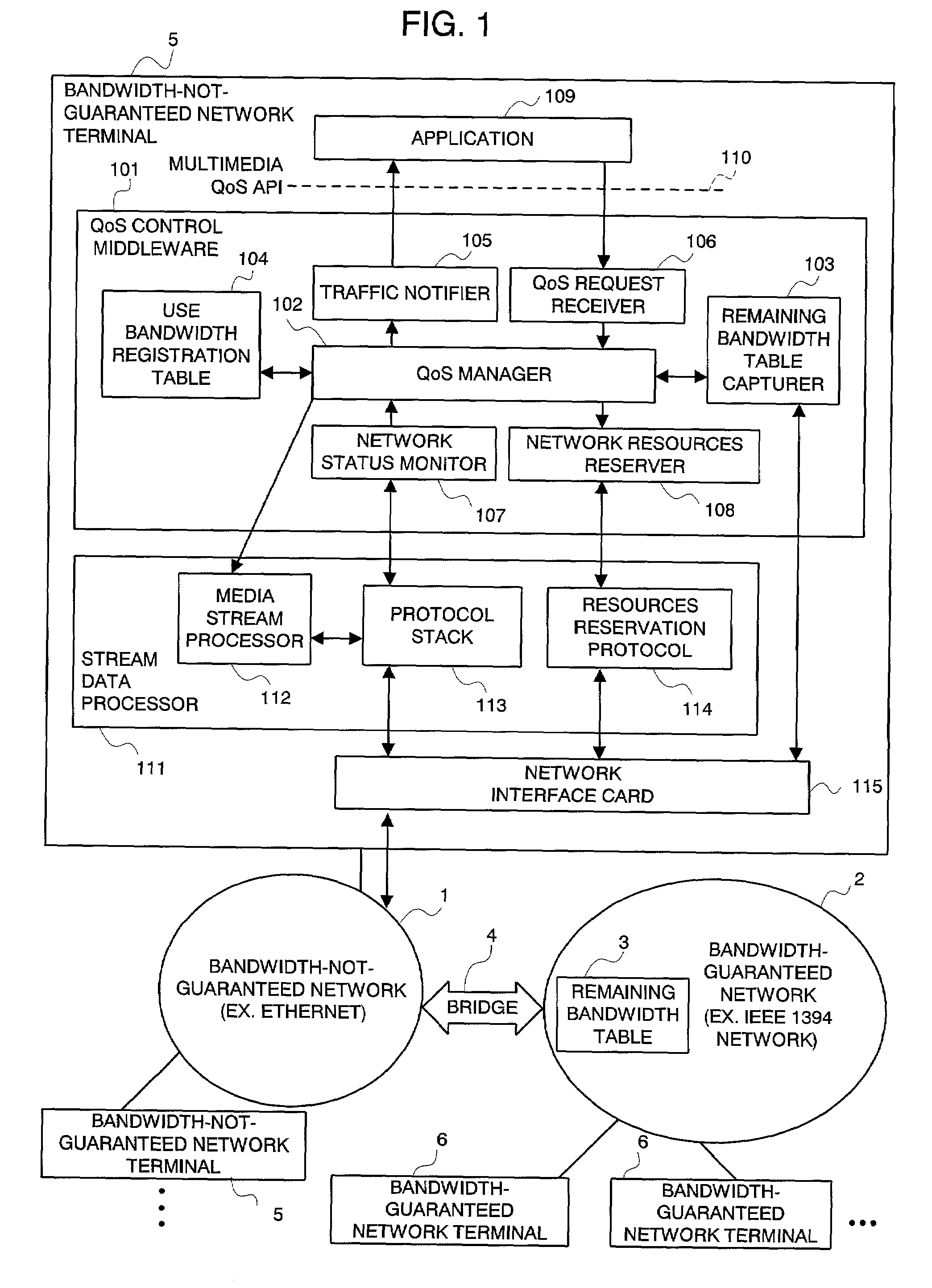
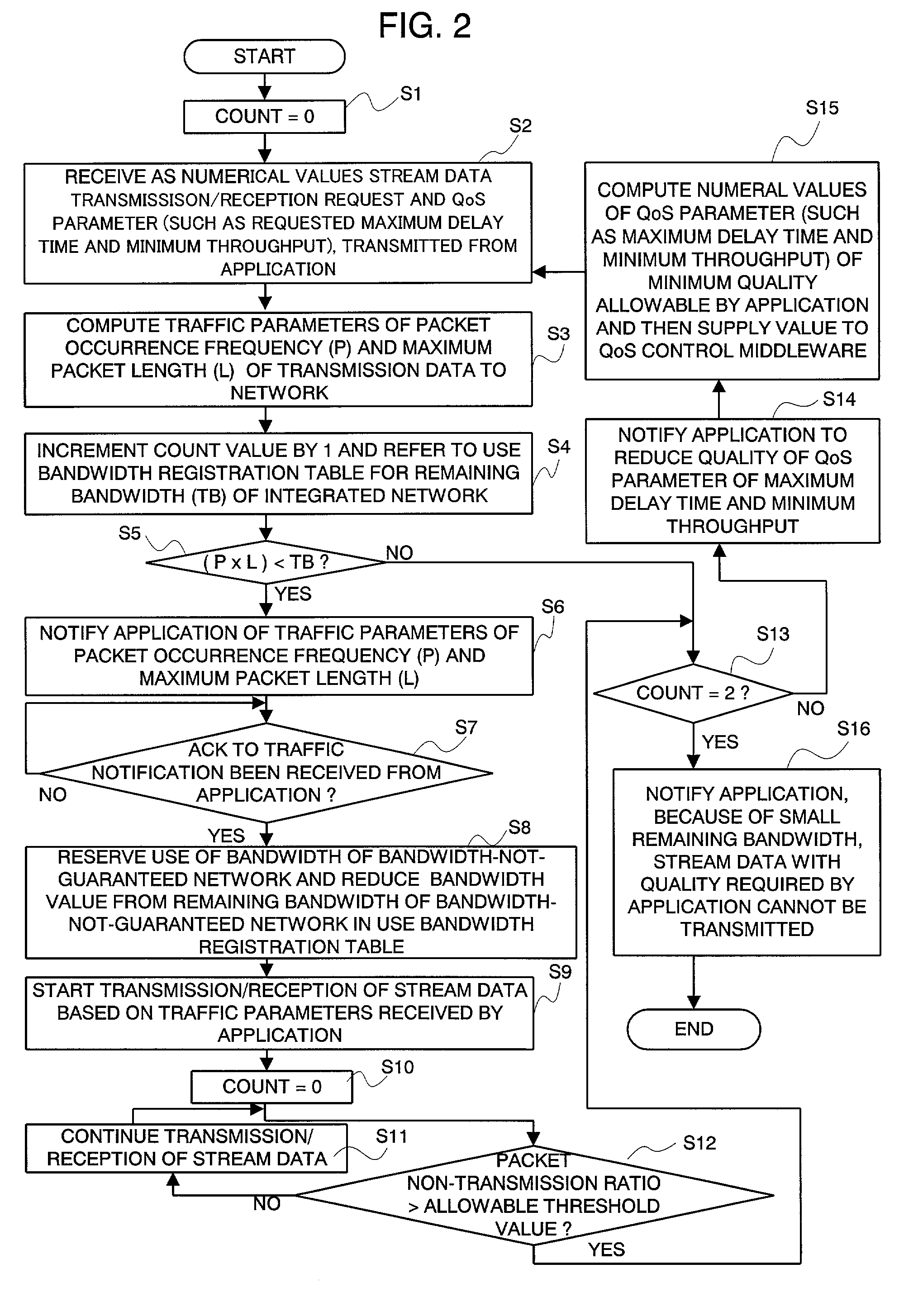
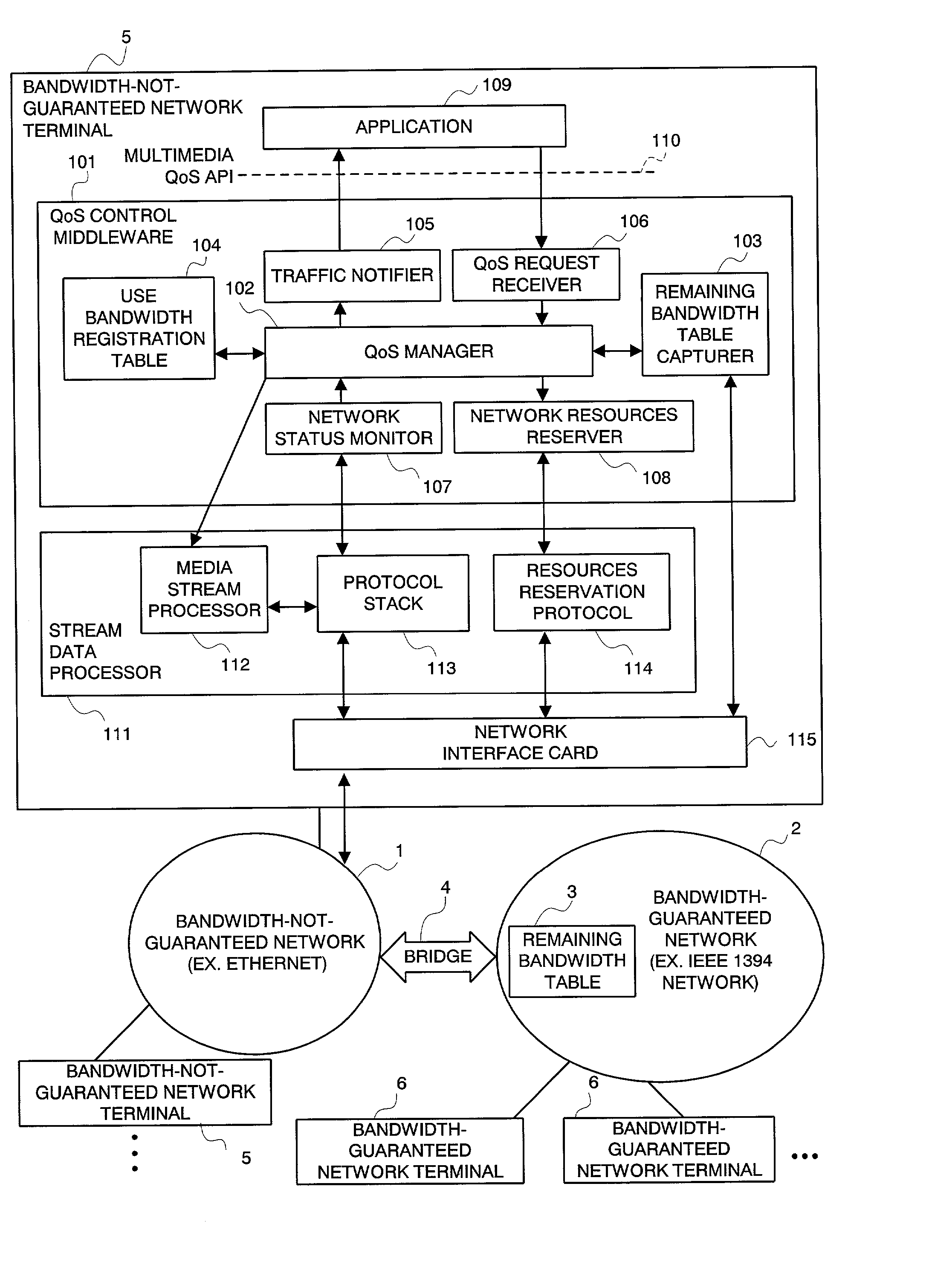
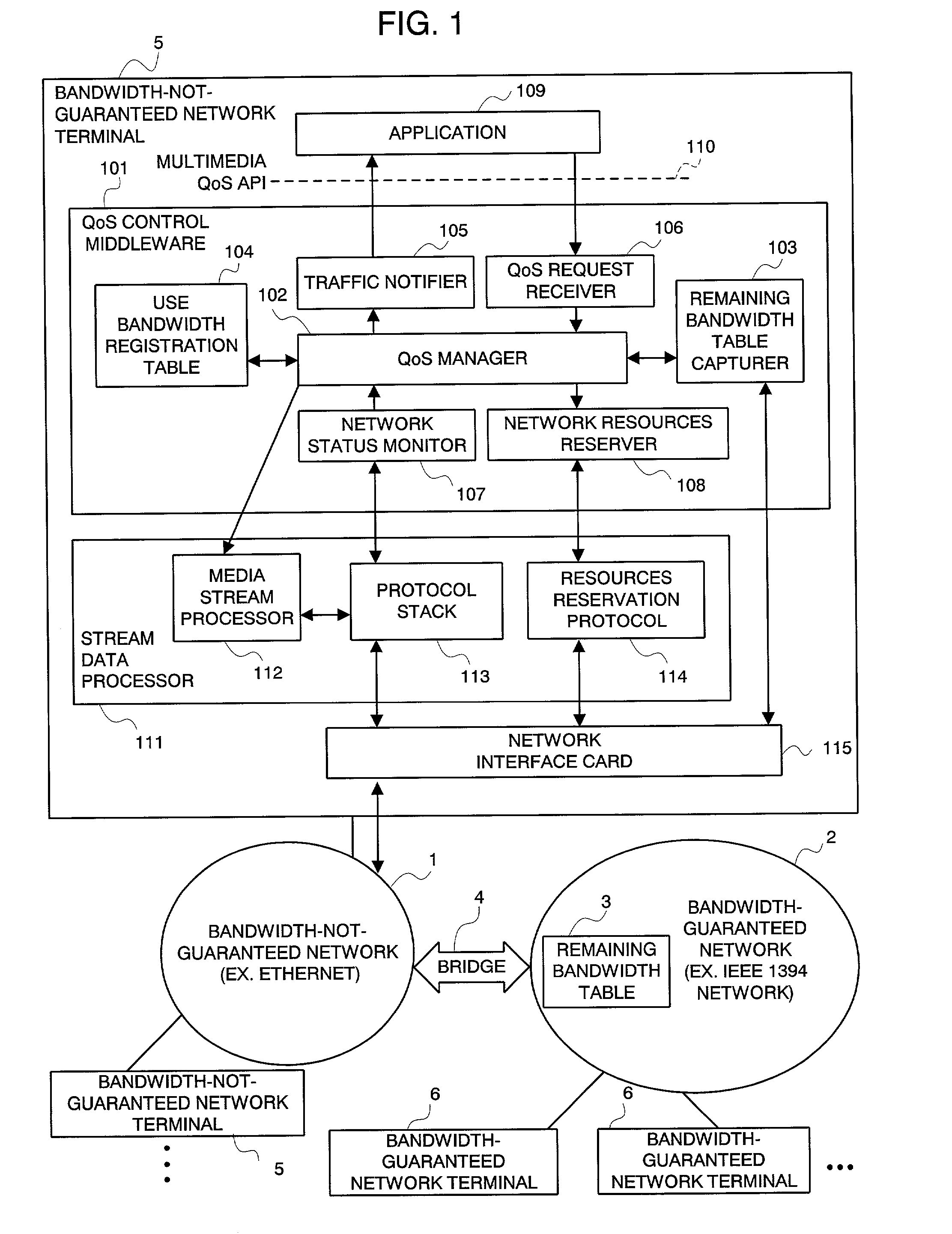
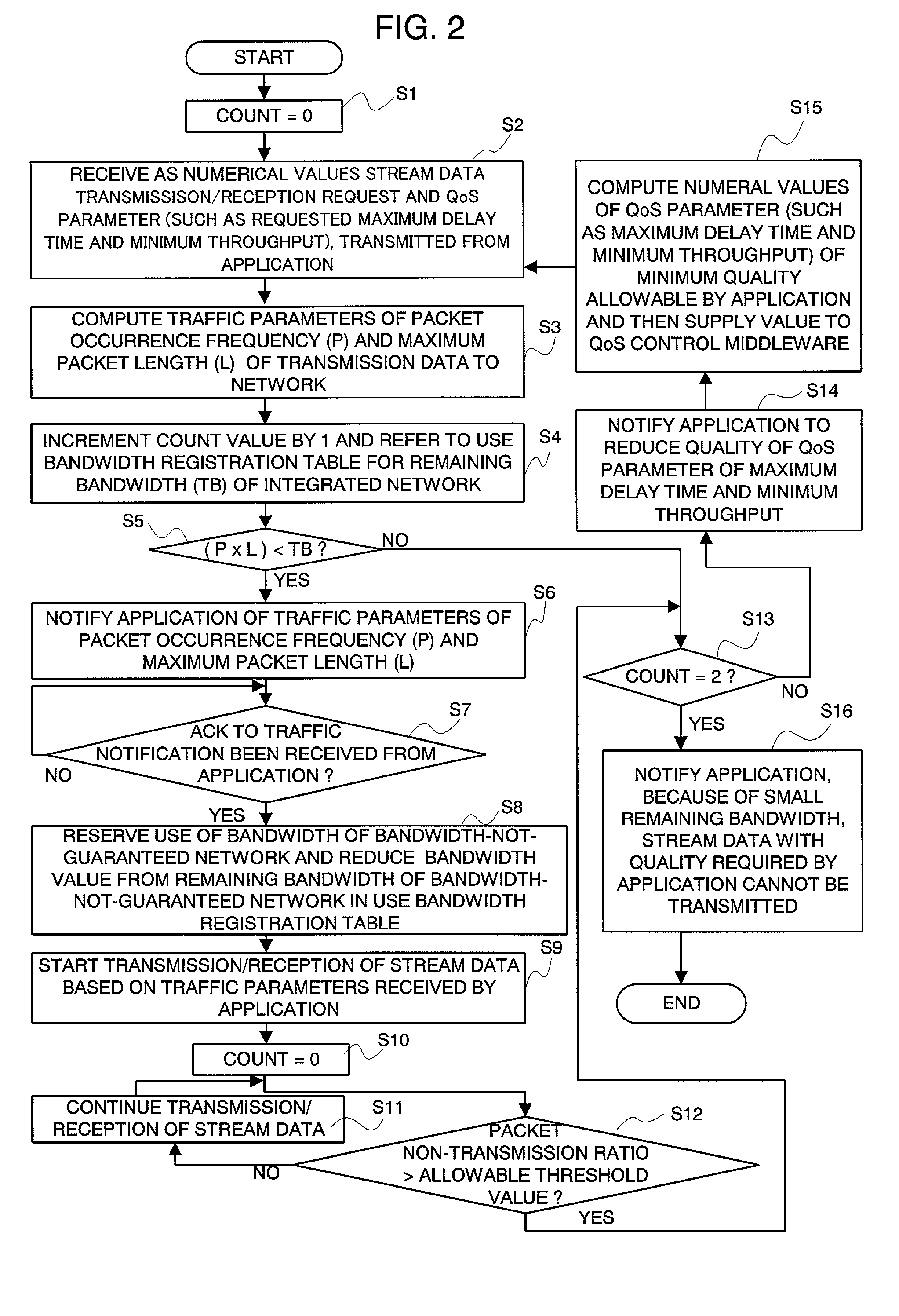
An integrated QoS control system is provided that transmits, in real time, the stream data between a bandwidth-guaranteed network and a bandwidth-not-guaranteed network. The QoS manager 102 records the remaining bandwidth of the bandwidth-guaranteed network 2 captured by the remaining bandwidth table capturer 103 and the remaining bandwidth of the bandwidth-not-guaranteed network 1 calculated with traffic information notified by the network status monitor 107 on the use bandwidth registration table 104 (for comprehensively managing the bandwidth of an integrated network). The Qos manager 102 converts a QoS parameter received via the QoS request receiver 106 into a traffic parameter and controllably adapts the value of the traffic parameter to a service quality required by the application 109.
Owner:NEC PERSONAL COMPUTERS LTD
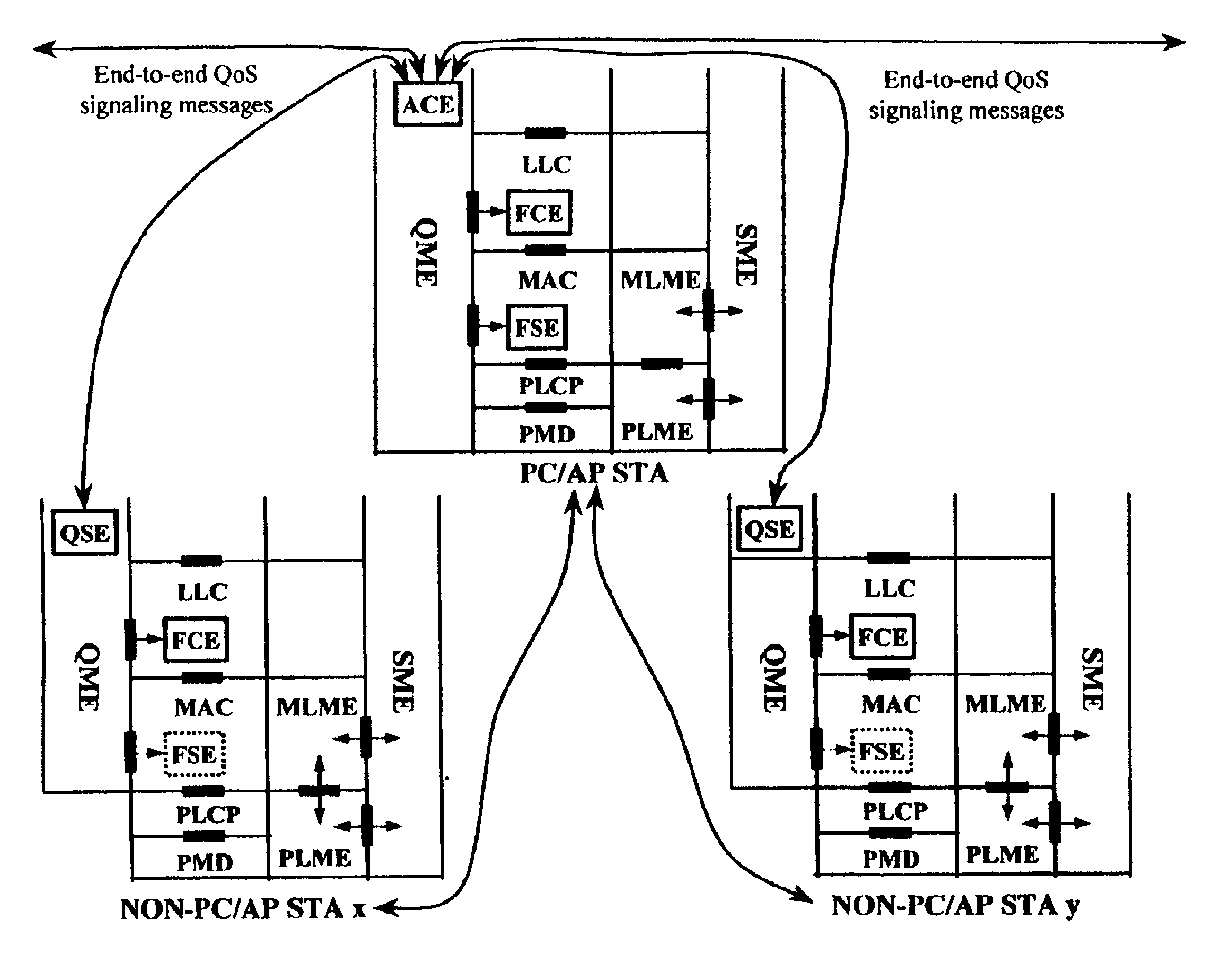
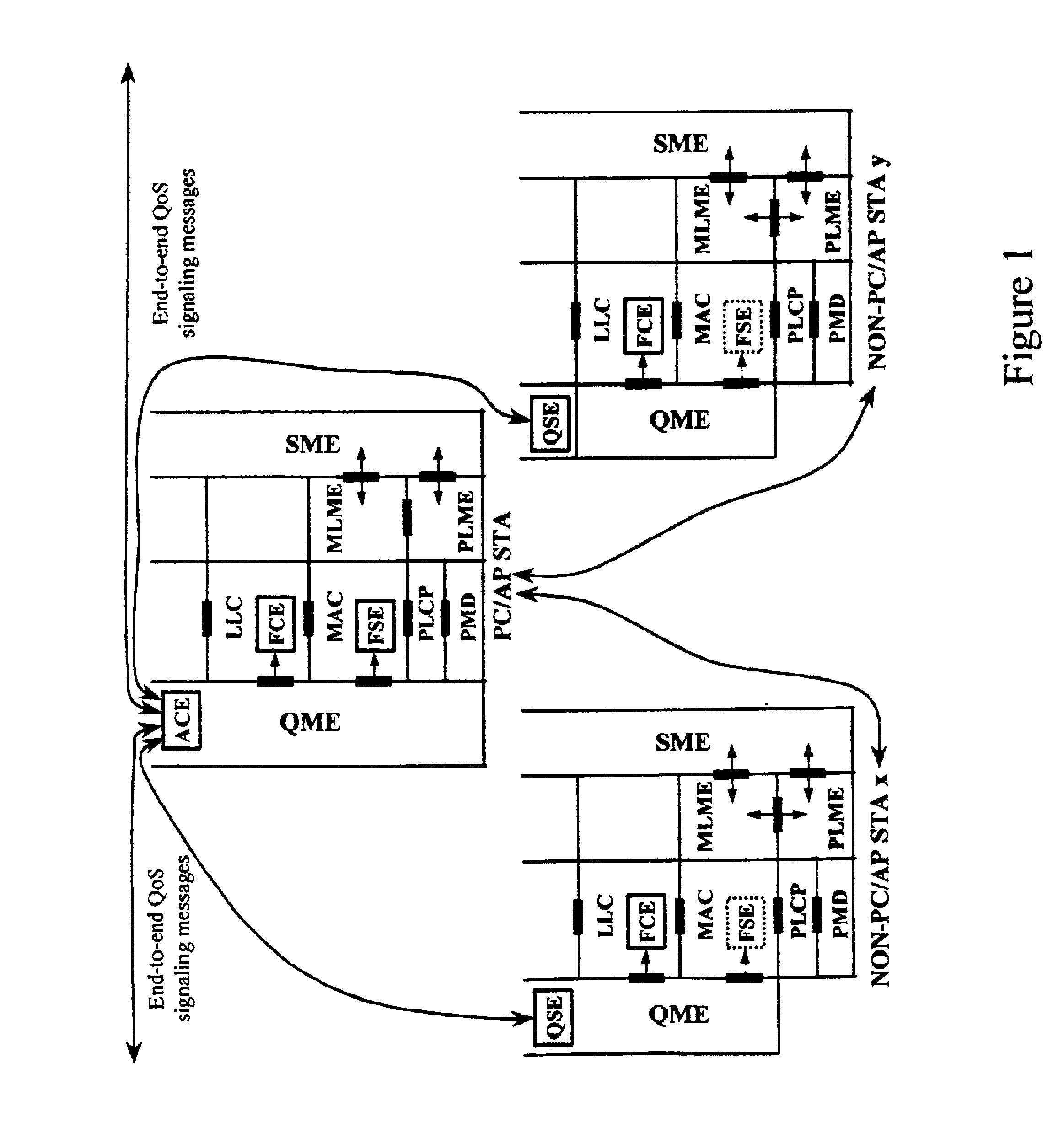
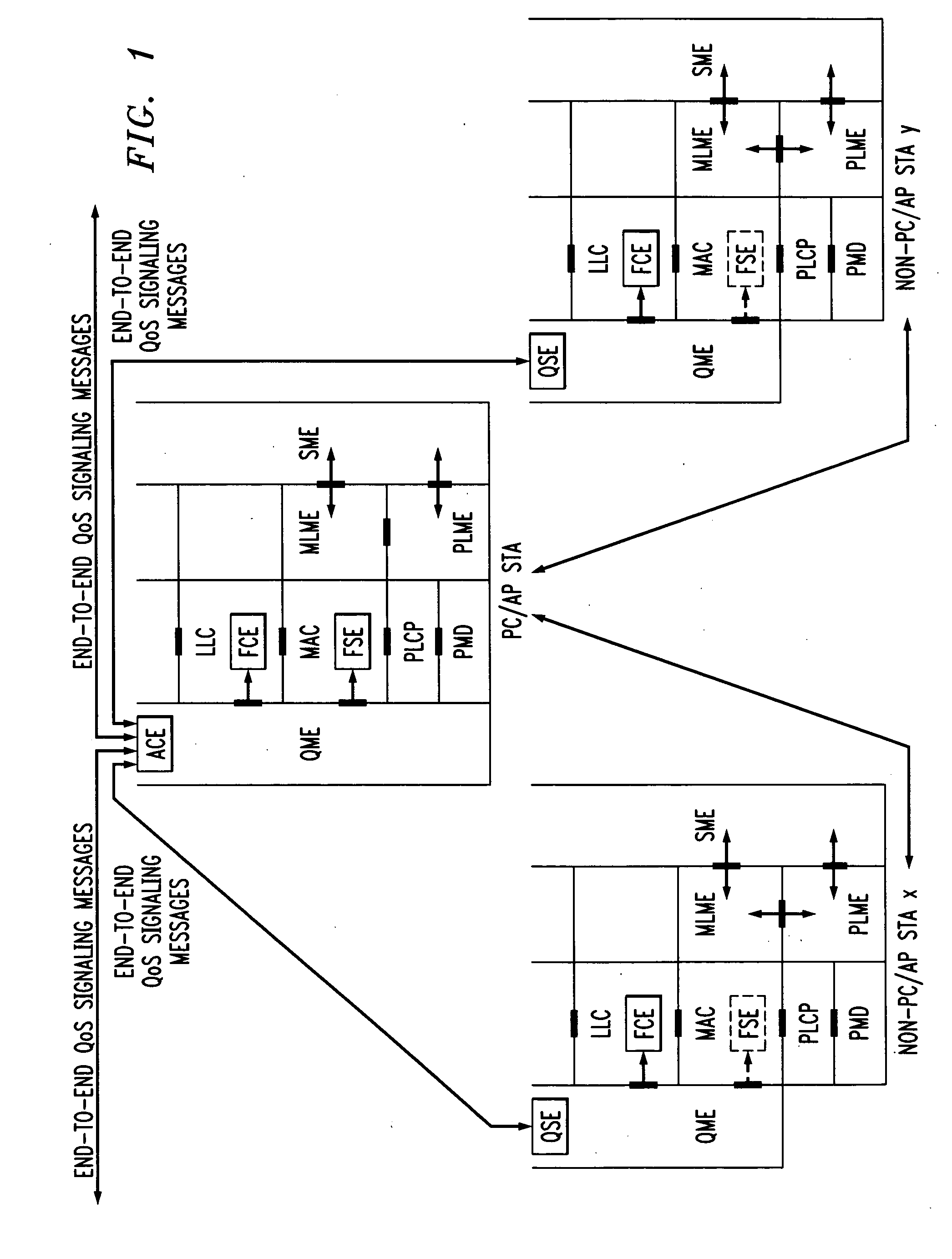
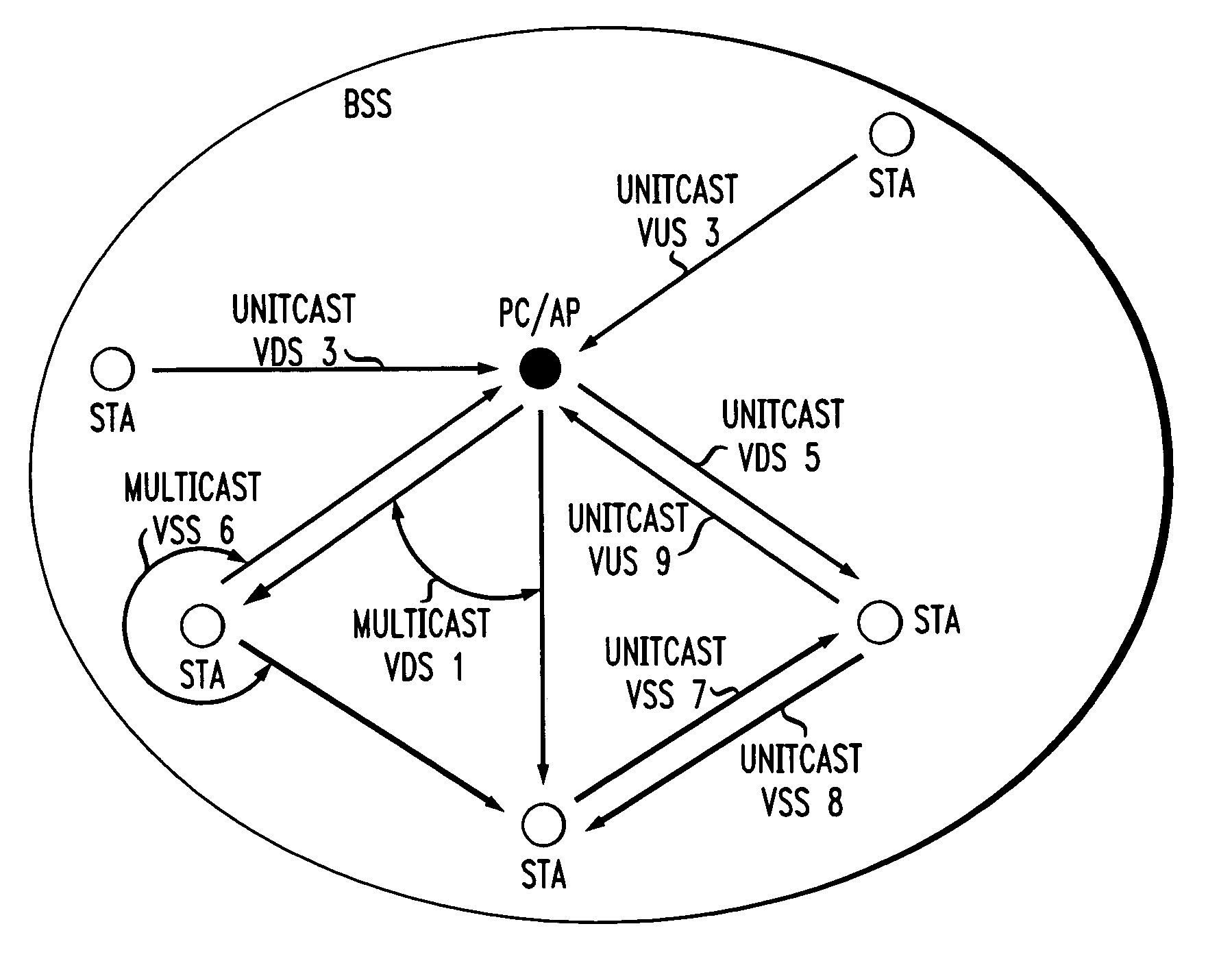
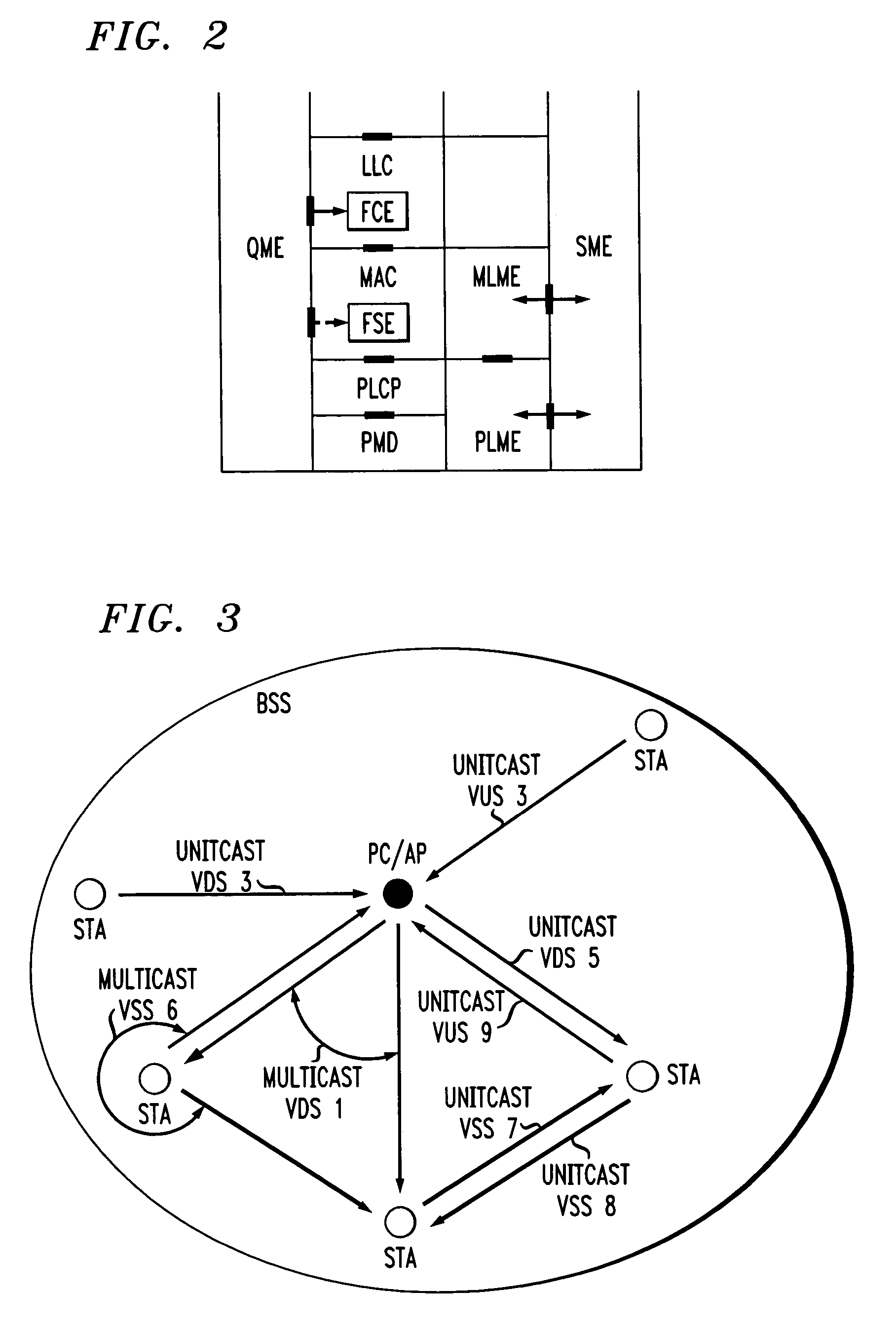
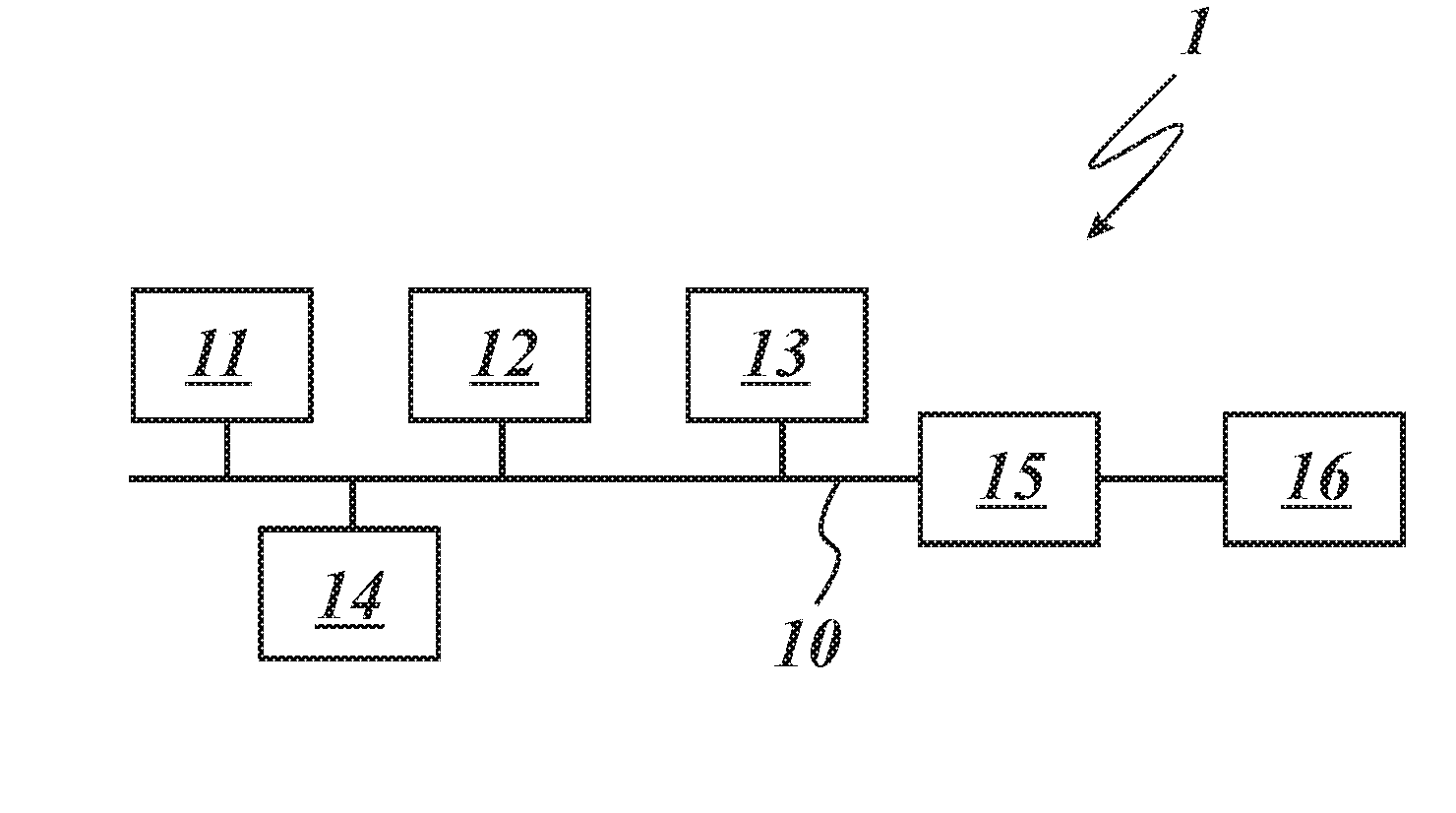
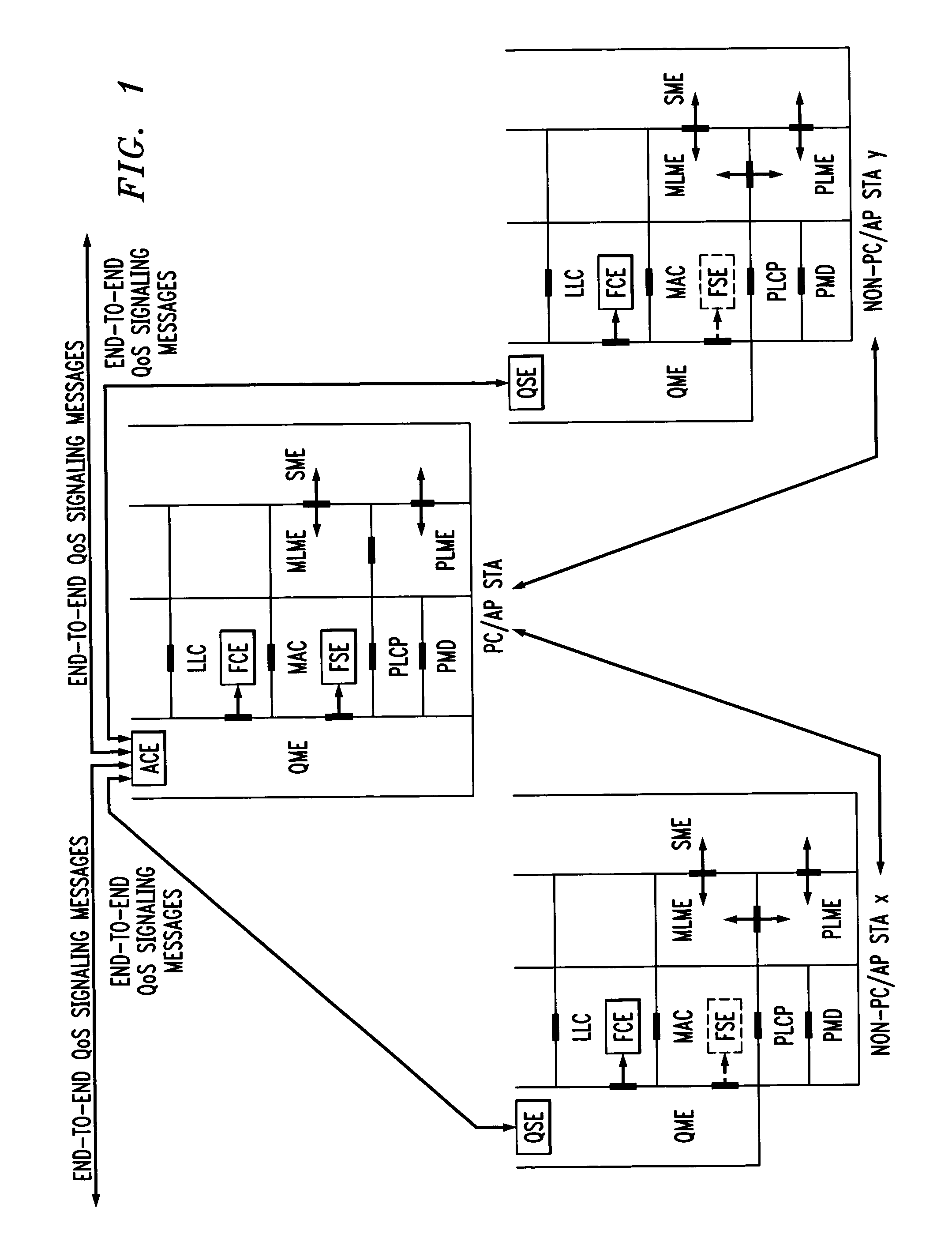
Architectural reference model for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS6862270B1Enhanced channel accessImprove bandwidth utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesOpen Systems InterconnectionEnd to end qos
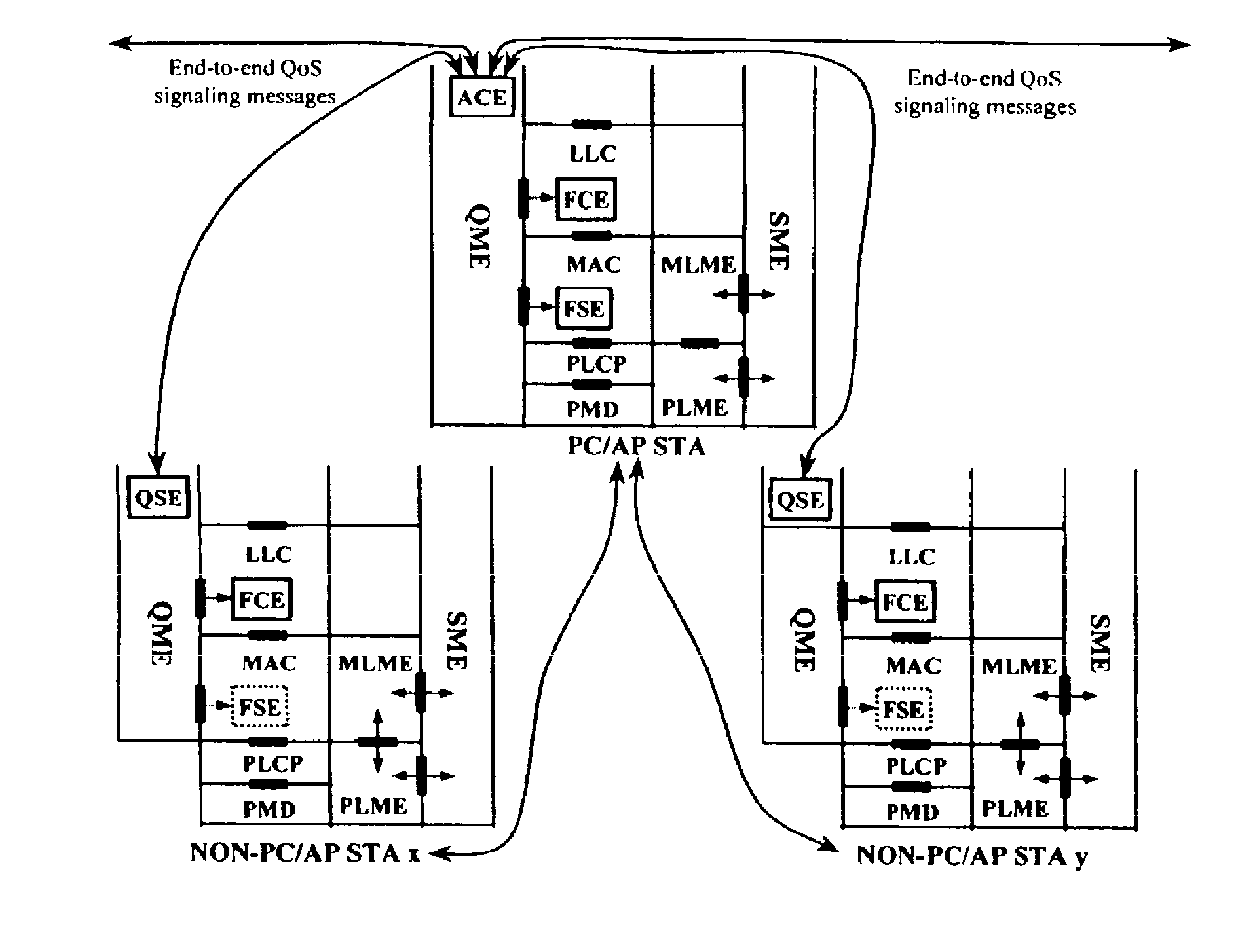
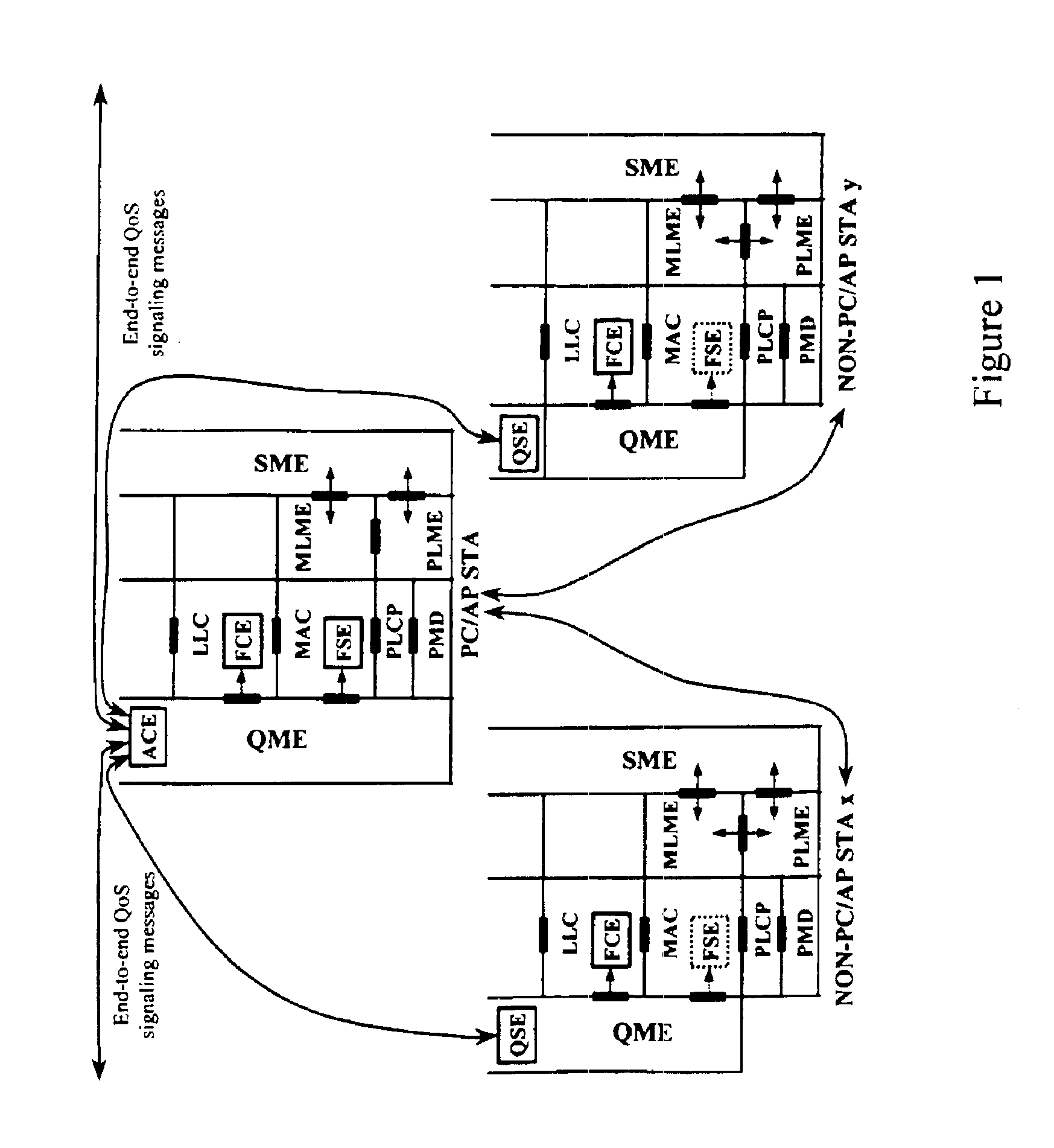
A quality of service (QoS) station is disclosed containing a point coordinator (PC) for a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless LAN. The PC station includes a QoS management entity (QME) and an admission control entity (ACE). The QME receives at least one end-to-end QoS message that characterizes a user application, such as a voice call, a video call, a data call and a multimedia call. The at least one end-to-end QoS message includes at least one QoS parameter set that is expressed at layer 3 and higher of an ISO / IEC basic reference model of Open Systems interconnection (OSI) (ISO / IEC 7498-1) and is to be passed down to layer 2 of the PC-station for enabling QoS traffic transport of the application. The ACE performs an admission control decision relating to the application based on the at least one end-to-end QoS message characterizing the application. The ACE reserves a resource based on a QoS parameter set contained in the end-to-end QoS message. The ACE can be part of the QME and can include a resource control module that performs at least one admission control decision based on resource permission, and a policy control module that performs at least one admission control decision based on policy permission.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Admission control for QoS-Driven Wireless LANs
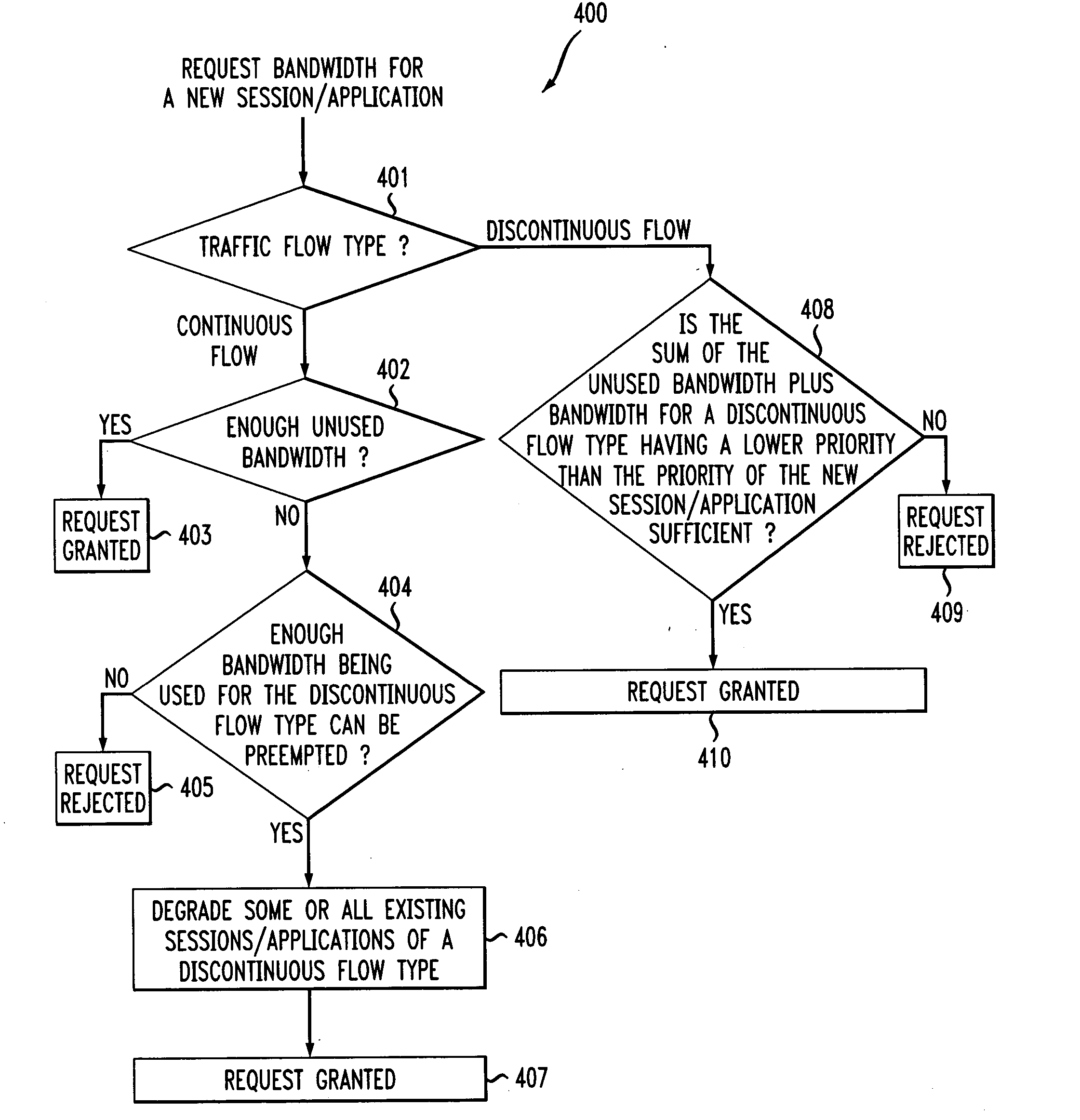
A method and a system for a quality of service (QoS) point coordinator (PC) for a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The PC includes a QoS management entity (QME) and an admission control entity (ACE). The QME receives at least one reservation request message that characterizes one of a QoS session and a QoS application (session / application) that can be of a continuoustperiodic flow type that is time sensitive, or can be of a discontinuous / bursty flow type that is time tolerant. The reservation request message contains at least one QoS parameter set and requests a resource of a communication channel in the BSS for the QoS session / application. The communication channel is organized into superframes, such that each superframe includes a contention-free period (CFP) and a contention-period (CP). The reservation request message requests apredetermined bandwidth of each CFP of the communication channel in the BSS. The ACE performs macro bandwidth management for QoS traffic transport of the session / application over a medium access control (MAC) sublayer for the communication channel by determining whether to grant the reservation request based on at least one QoS parameter set associated with the session / application.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Method and system for providing a mobile IP network with non-path dependent intra domain quality of service
InactiveUS7269657B1Improve abilitiesImprove efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsDomain nameQuality of service
A system and method for providing quality of service (QoS) service over a mobile IP network with dynamic domains, multiple or distributed QoS managers per domain and / or with network congestion feedback being used to establish an estimated total domain bandwidth which is used for regulating access to a domain.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Communication system and communication method
InactiveUS20060218302A1Not unnecessarily trafficError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemQos management
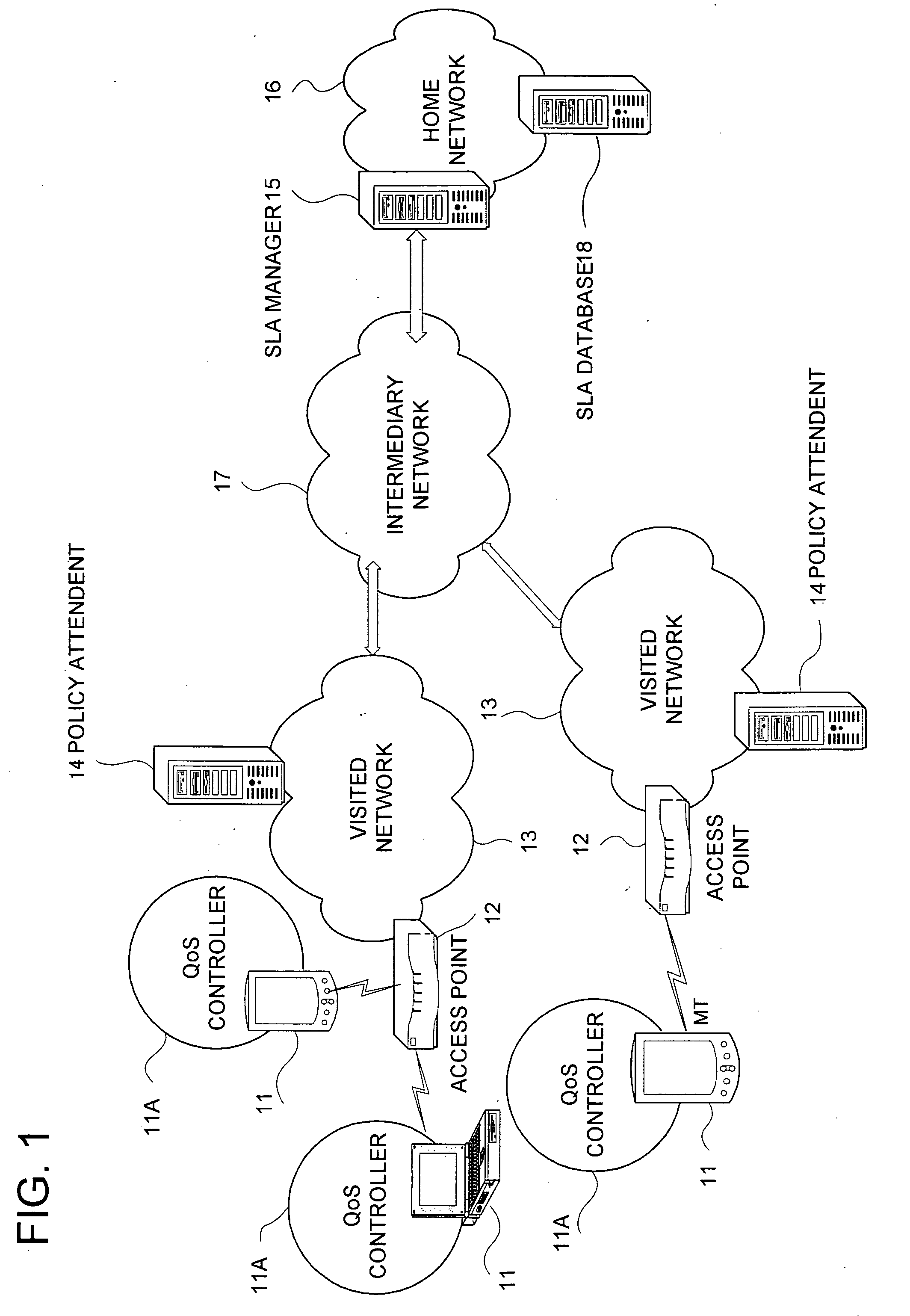
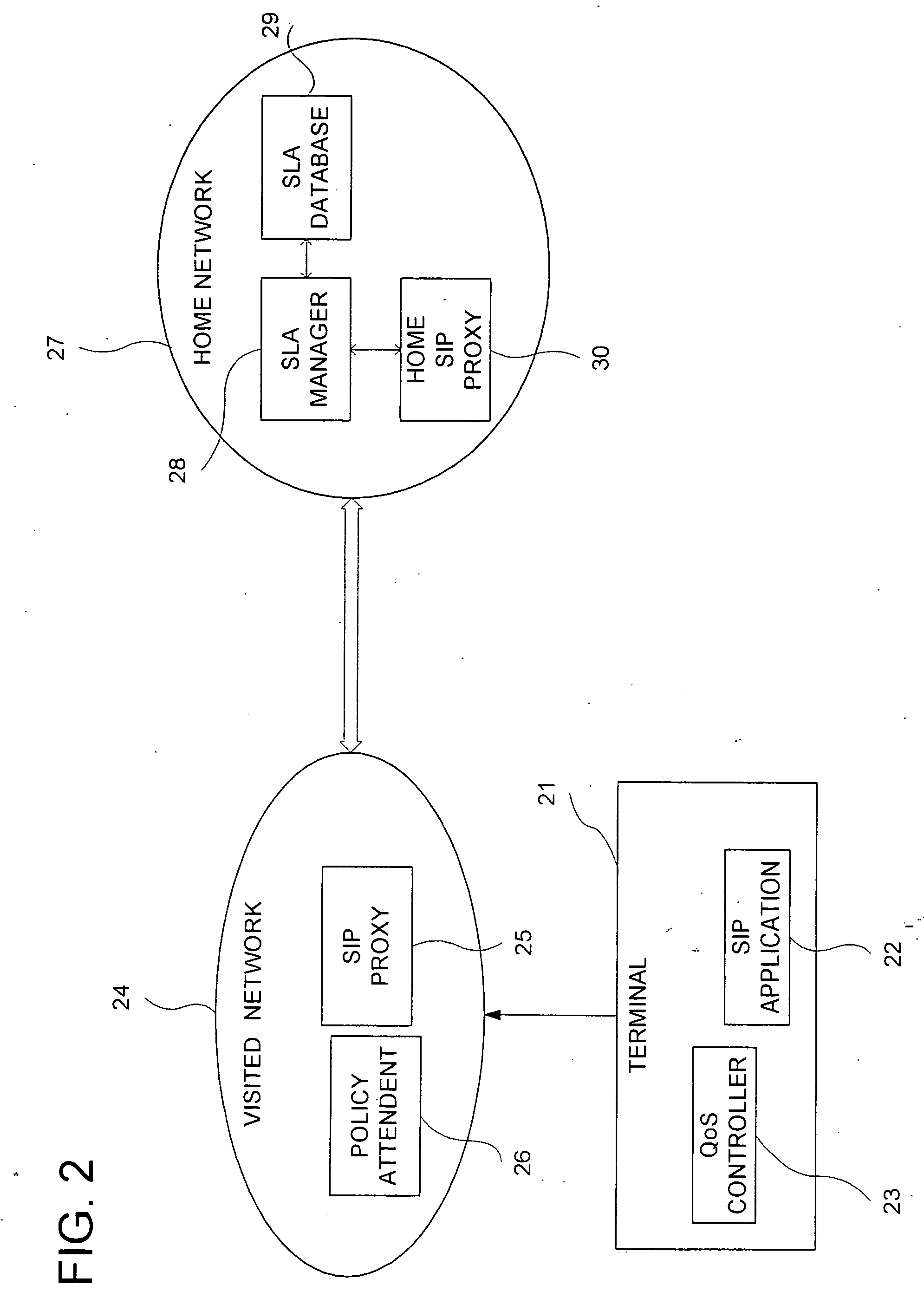
A technique for the end terminal provided with services to handle QoS process is disclosed. According to this technique, a terminal based QoS management scheme is implemented to achieve end-to-end QoS wherein the end terminal 21 is responsible for handling of the QoS related functions. In order for QoS management to be handled at terminal, the terminal needs to know the network conditions and external state of entities in order to know what action to be taken. For example, the terminal performs monitoring and usage collection. These performance data are then reported to a central server (SLA manager 28). The central server collects these data from all terminals within its administration domain. The central server also has access to information on the QoS to be given to individual terminals, such as service level. Based on the information, the central server decides what action to be taken by individual terminal and enforces these actions into the affected terminals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods And Systems For Dynamic Bandwidth Management For Quality Of Service In IP Core And Access Networks
InactiveUS20080130495A1Easy to useStringent qualityError preventionTransmission systemsPresent methodKey issues
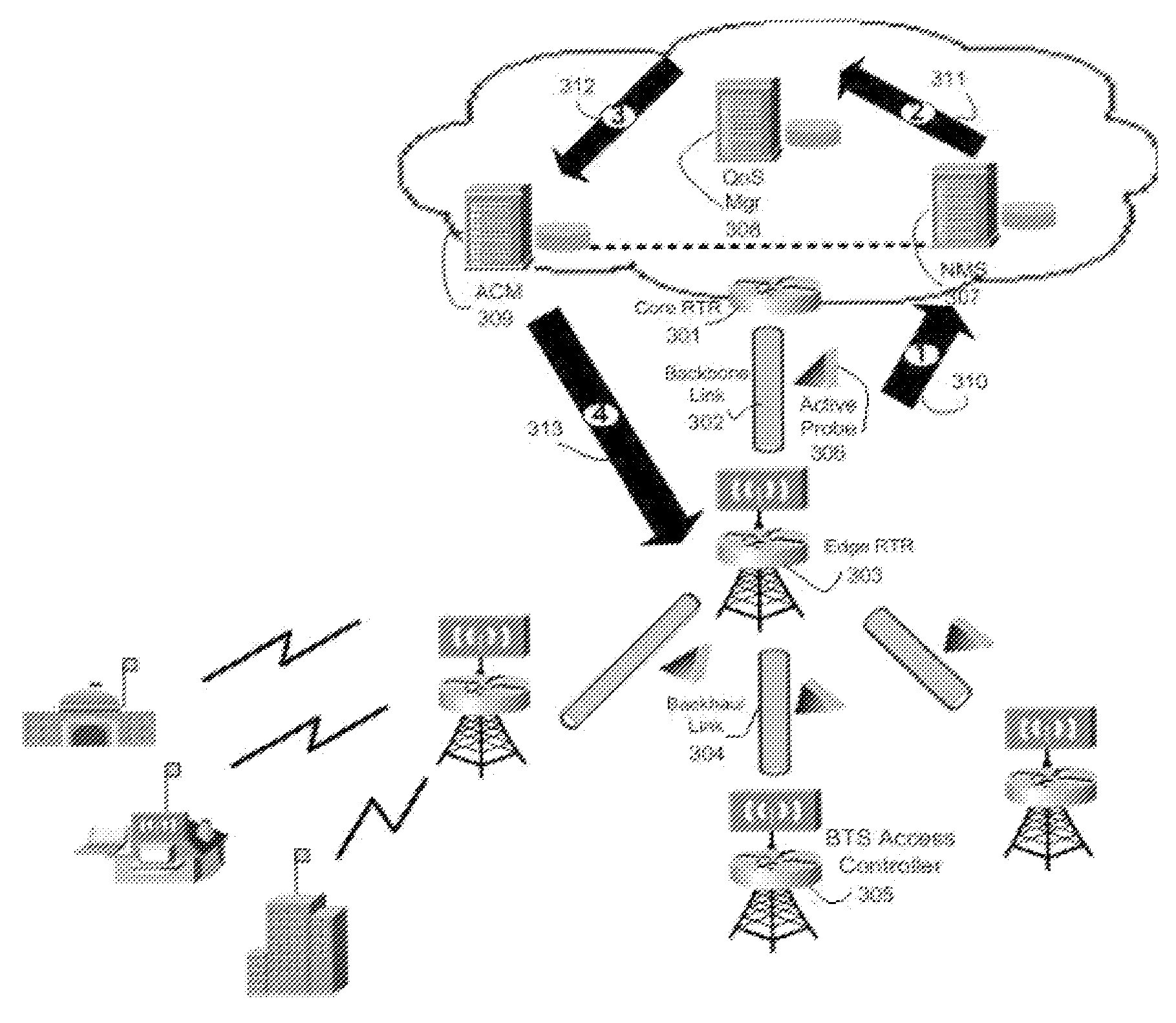
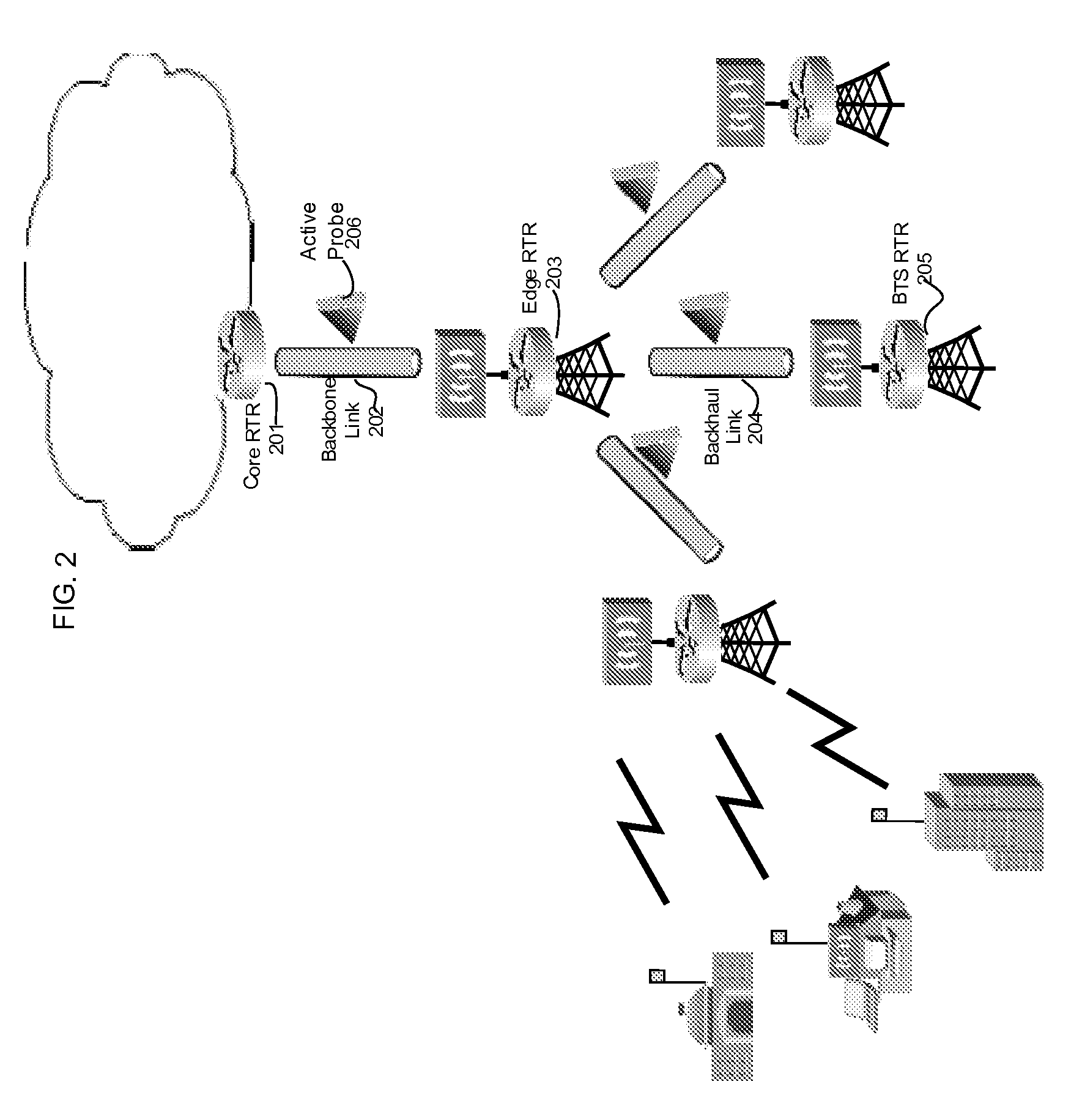
Proper allocation of network bandwidth is a crucial issue in rendering certain performance guarantees to meet the growing customer demands. Hence, allocation methodologies must explicitly be carried out for these guarantees to be given as efficiently as possible since the shared resources are limited. This invention presents methods and systems for Dynamic Bandwidth Management (DBM) and Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based networks. DBM is an algorithm that dynamically adjusts the resource allocation in the IP Access Networks based upon measured QoS at the IP Core Network through an implementation of a Feedback Control Mechanism to manage available core transport bandwidth. Such a Feedback Control Mechanism is capable of maintaining a condition of non-congestion, a sufficient and necessary condition to meet end-to-end QoS requirements in a Next Generation Network (NGN). The emphasis is given on the system implementation of QoS policies for the fair distribution of network resources through a scalable architecture comprising key Resource and Admission Control Functional (RACF) entities, namely: a Network Management System (NMS), a QoS Manager, an Access Controller Manager (ACM), the Access Controllers, and the active probes.
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
Network quality of service management
InactiveUS7609637B2Fast response timeEfficient and reliableError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceQos management
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
QoS control middleware in integrated network, QoS control method, and the program for the same
An integrated QoS control system is provided that transmits, in real time, the stream data between a bandwidth-guaranteed network and a bandwidth-not-guaranteed network. The QoS manager 102 records the remaining bandwidth of the bandwidth-guaranteed network 2 captured by the remaining bandwidth table capturer 103 and the remaining bandwidth of the bandwidth-not-guaranteed network 1 calculated with traffic information notified by the network status monitor 107 on the use bandwidth registration table 104 (for comprehensively managing the bandwidth of an integrated network). The Qos manager 102 converts a QoS parameter received via the QoS request receiver 106 into a traffic parameter and controllably adapts the value of the traffic parameter to a service quality required by the application 109.
Owner:NEC PERSONAL COMPUTERS LTD
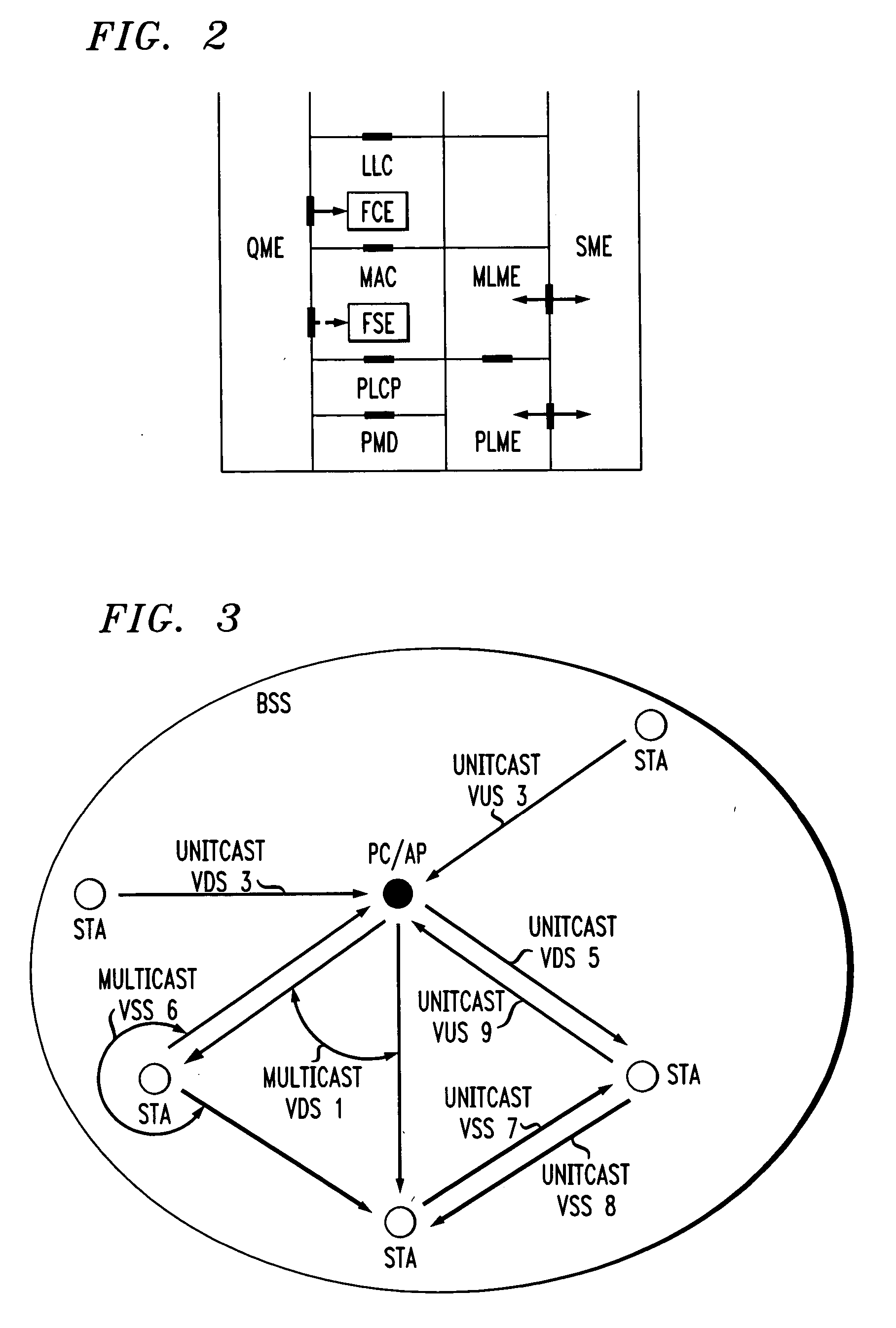
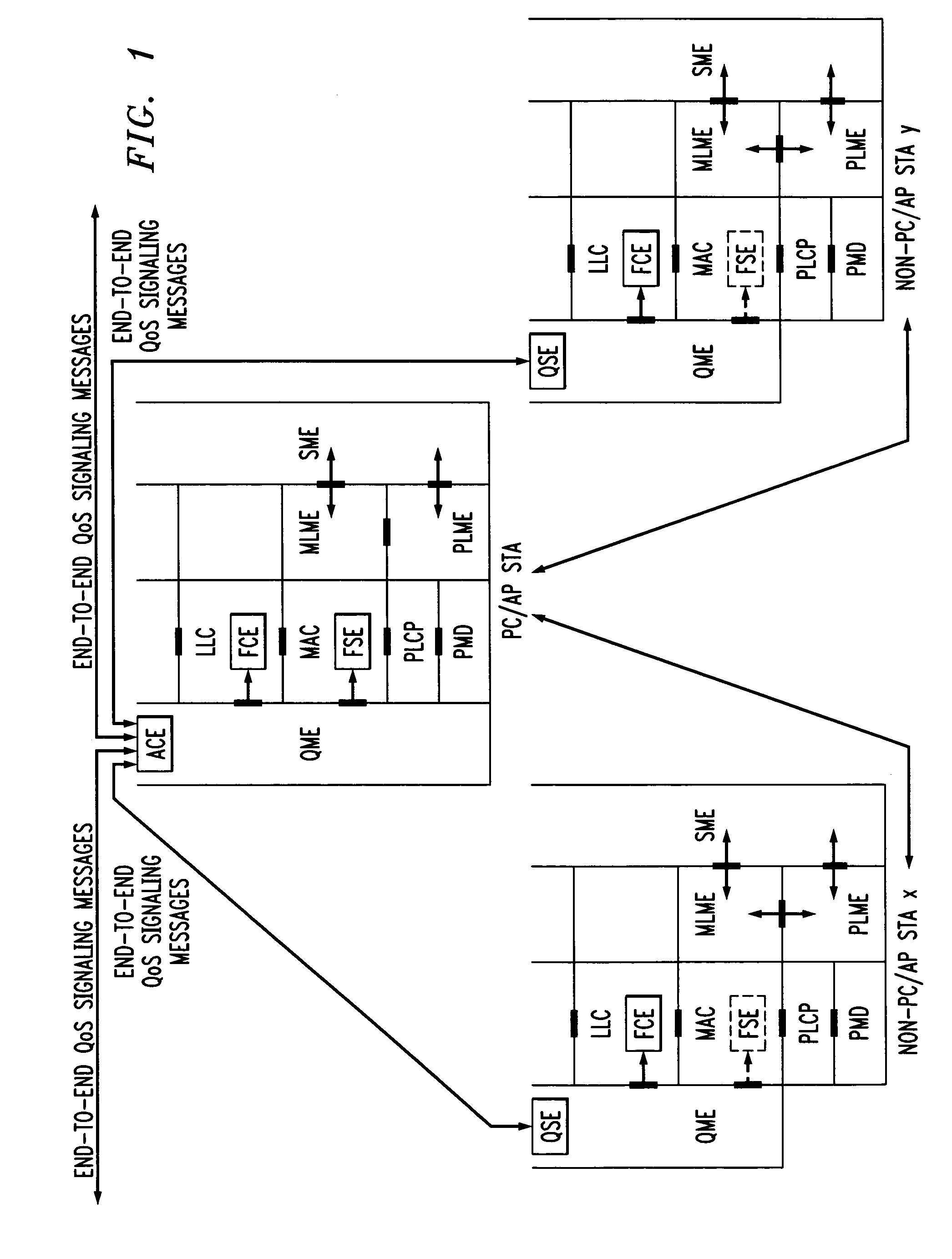
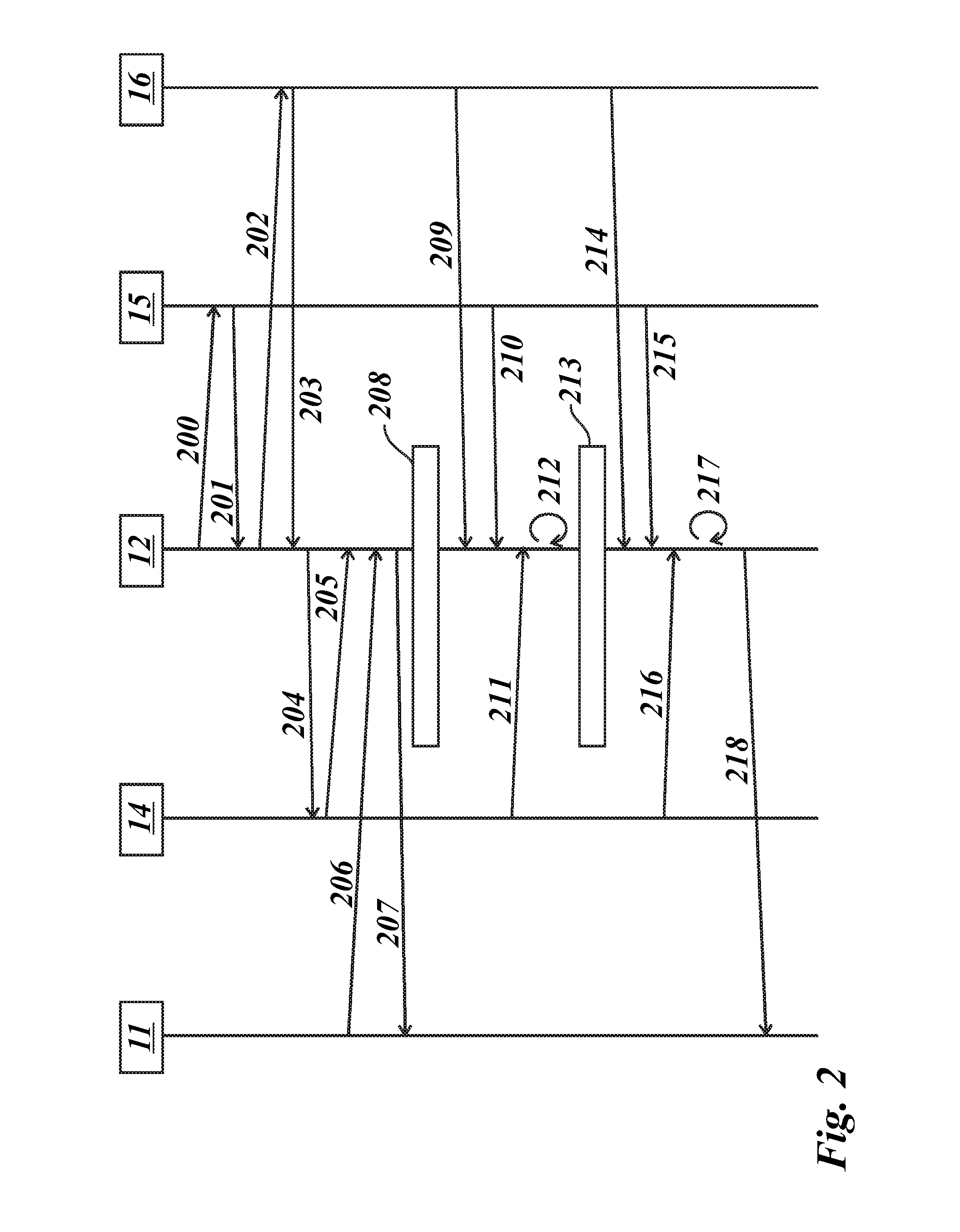
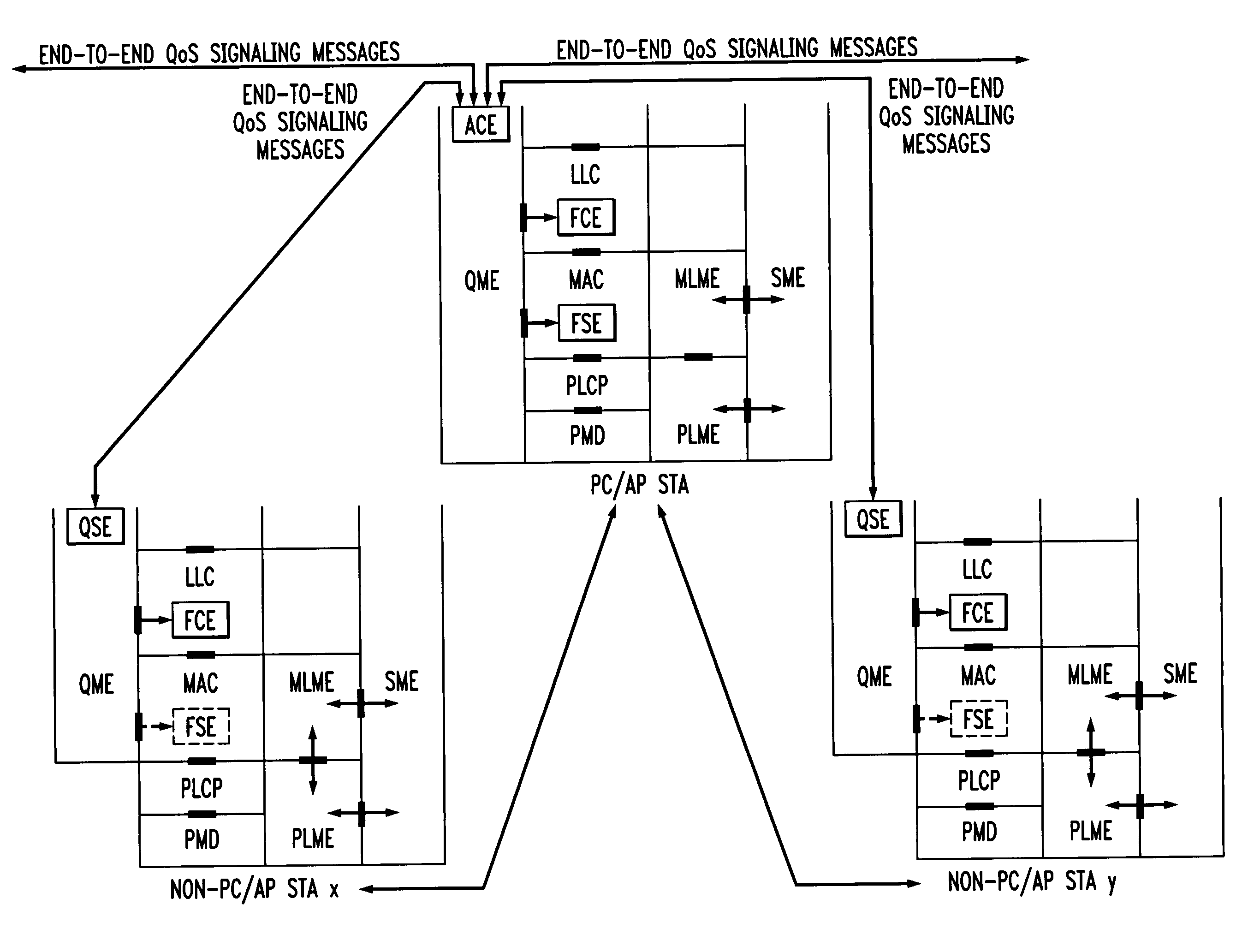
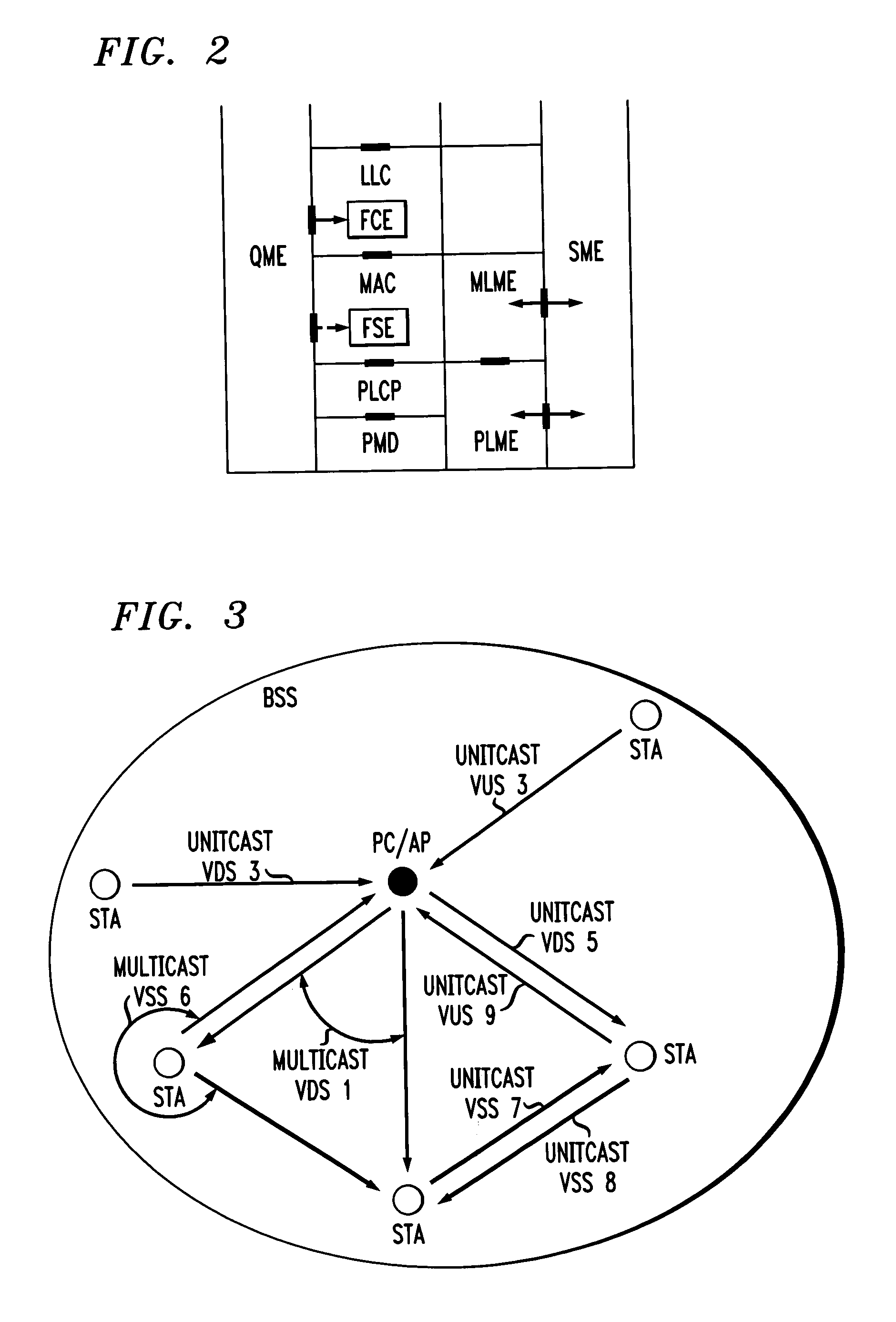
In-band QoS signaling refernce model for QoS-driven wireless lans
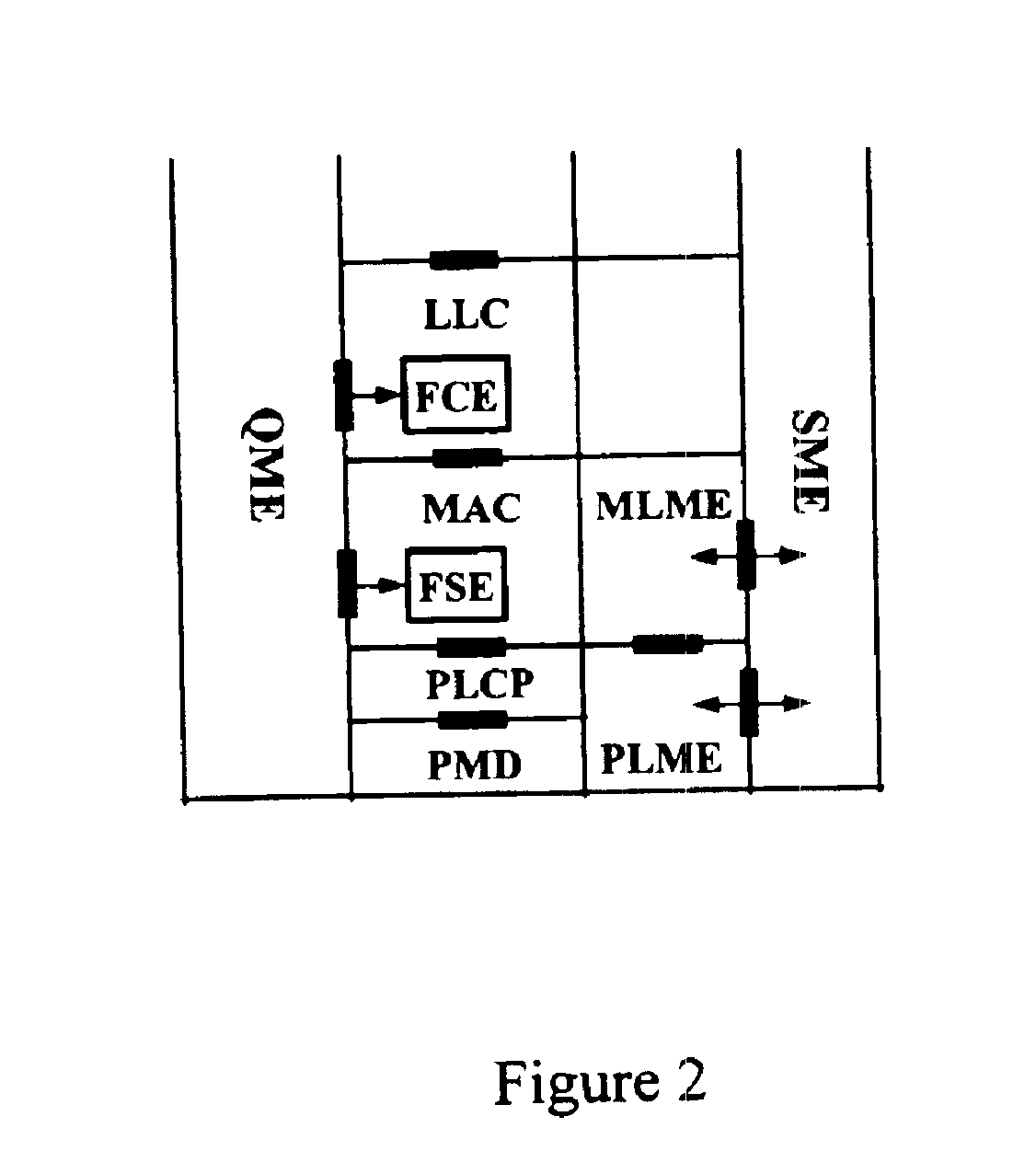
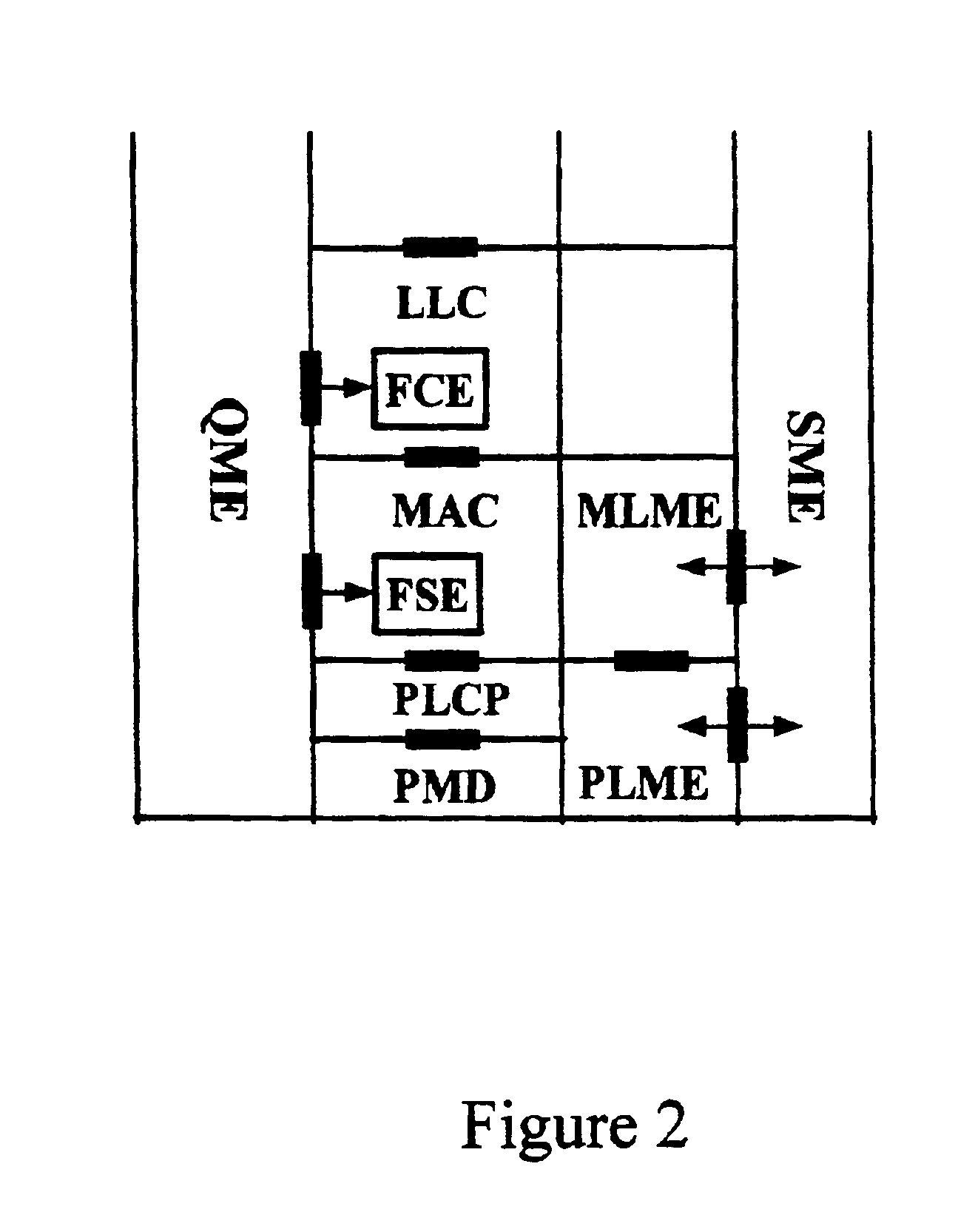
InactiveUS20050041670A1Function increaseError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceFrame based
A station, such as a point coordinator (PC) or a non-PC station, in a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The station includes a frame classification entity (FCE), a frame scheduling entity (FSE) and a QoS management entity (QME). The FCE is logically located in a logical link control (LLC) layer of the station and has a classification table containing at least one classifier entry. Each classifier entry contains a virtual stream identifier (VSID) and a frame classifier associated with a user session. The FCE receives a data frame associated with the user session, which can be one of a voice session, a video session, a data session and a multimedia session. The data frame contains in-band quality of service (QoS) signaling information for the user session. The FCE classifies the received data frame to a selected VSID contained in a classifier entry in the classification table based on a match between an in-band frame classification information contained in the received frame and the frame classifier contained in the classifier entry. The FSE is logically located in a medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the station and has a frame scheduling table containing at least one entry. Each entry in the frame scheduling table contains a VSID and a QoS parameter set associated with a user session identified by the VSID. The FSE is responsive to the classified data frame by scheduling a transmission opportunity (TO) for the classified data frame based on the at least one QoS parameter value associated with the VSID and characterizing the user session. The QME interfaces with the FCE and The FSE.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Wireless network having link-condition based proxies for QoS management
ActiveUS7068599B1Reduce decreaseReduce contentTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsQos managementWireless mesh network
A wireless network includes a plurality of proxy servers located at various locations to selectively transform data based upon network conditions, such as link congestion. A queueing model for the network can be used to determine optimal operating parameters for the network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
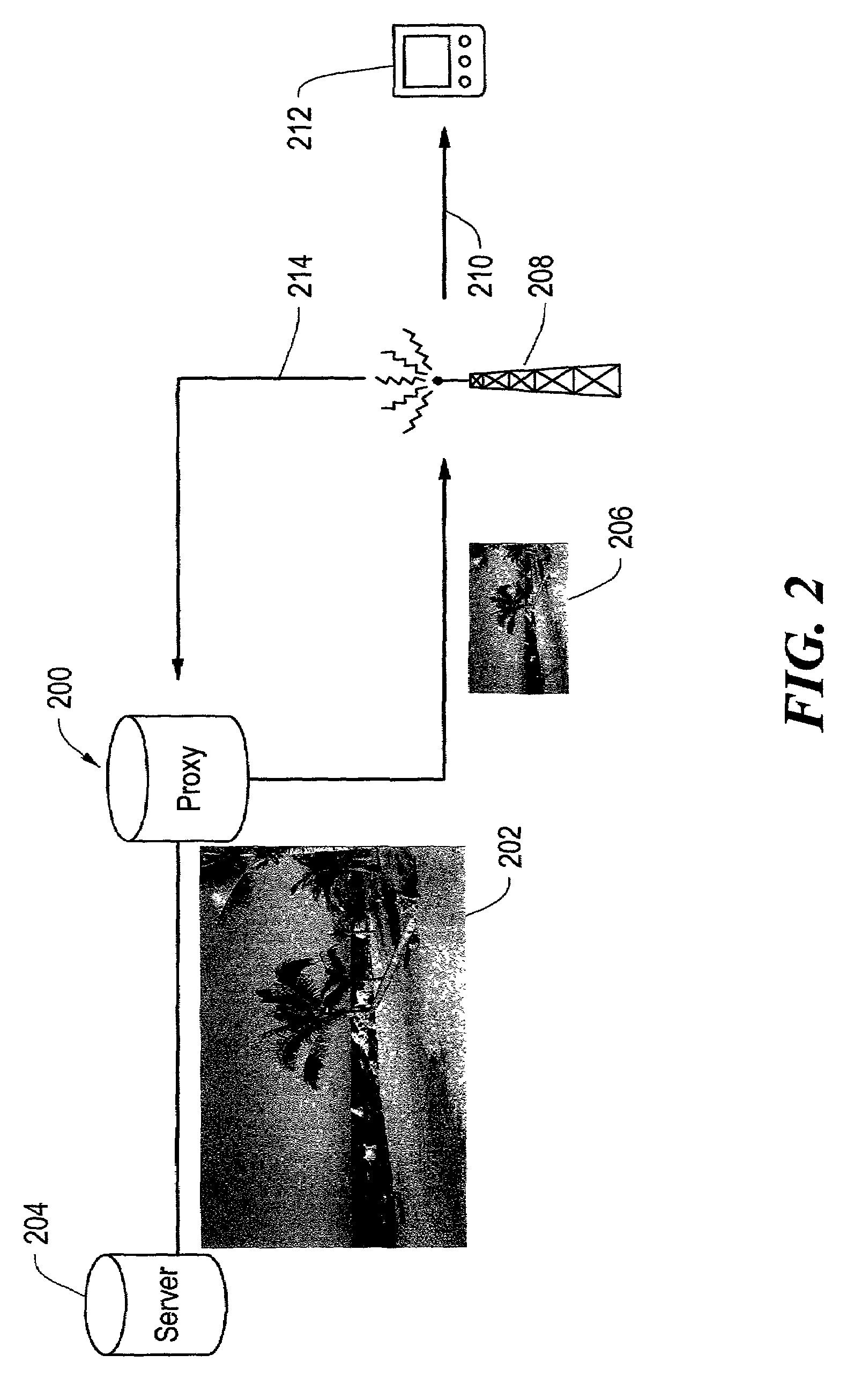
Videoconference application user interface with messaging system
InactiveUS20050010638A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsQos managementControl system
There is provided a playback control system for a videoconference system, the latter spanning a wide area network. The playback control system includes a user interface having multiple display windows that alow different resolutions and frame rates, and a messaging system for managing display and transport characteristics with a policy and QoS manager in accordance with individual display requirements.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
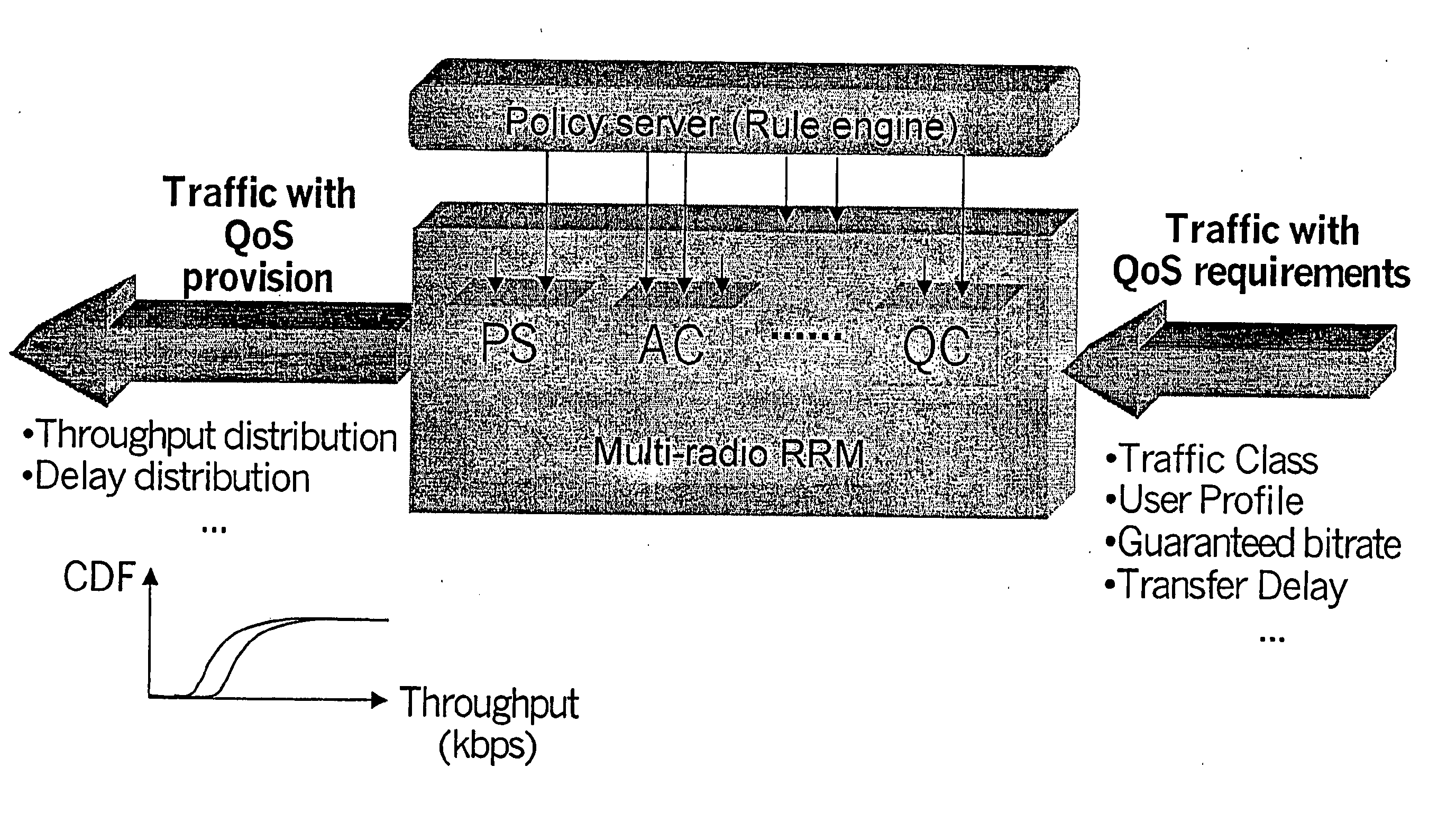
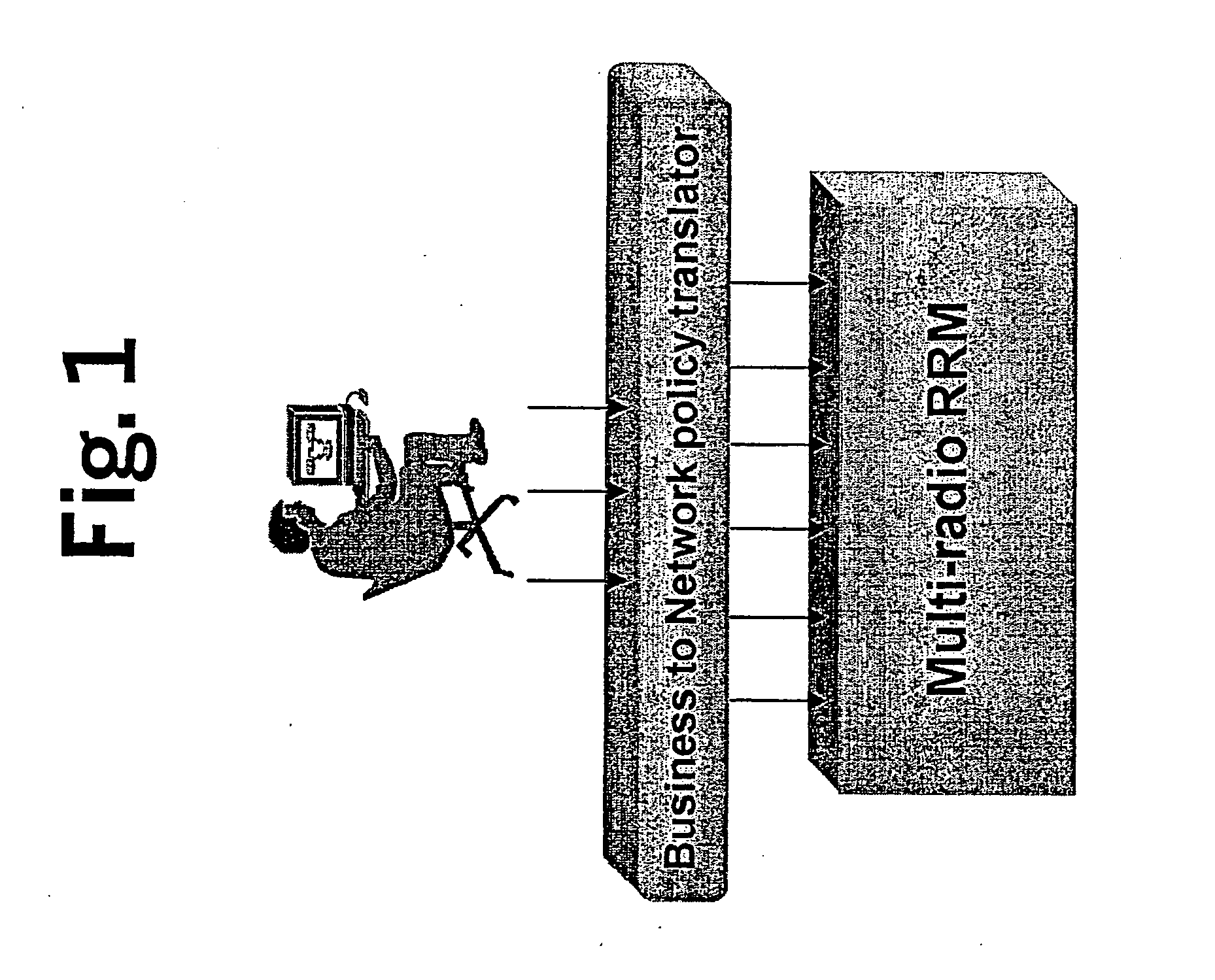
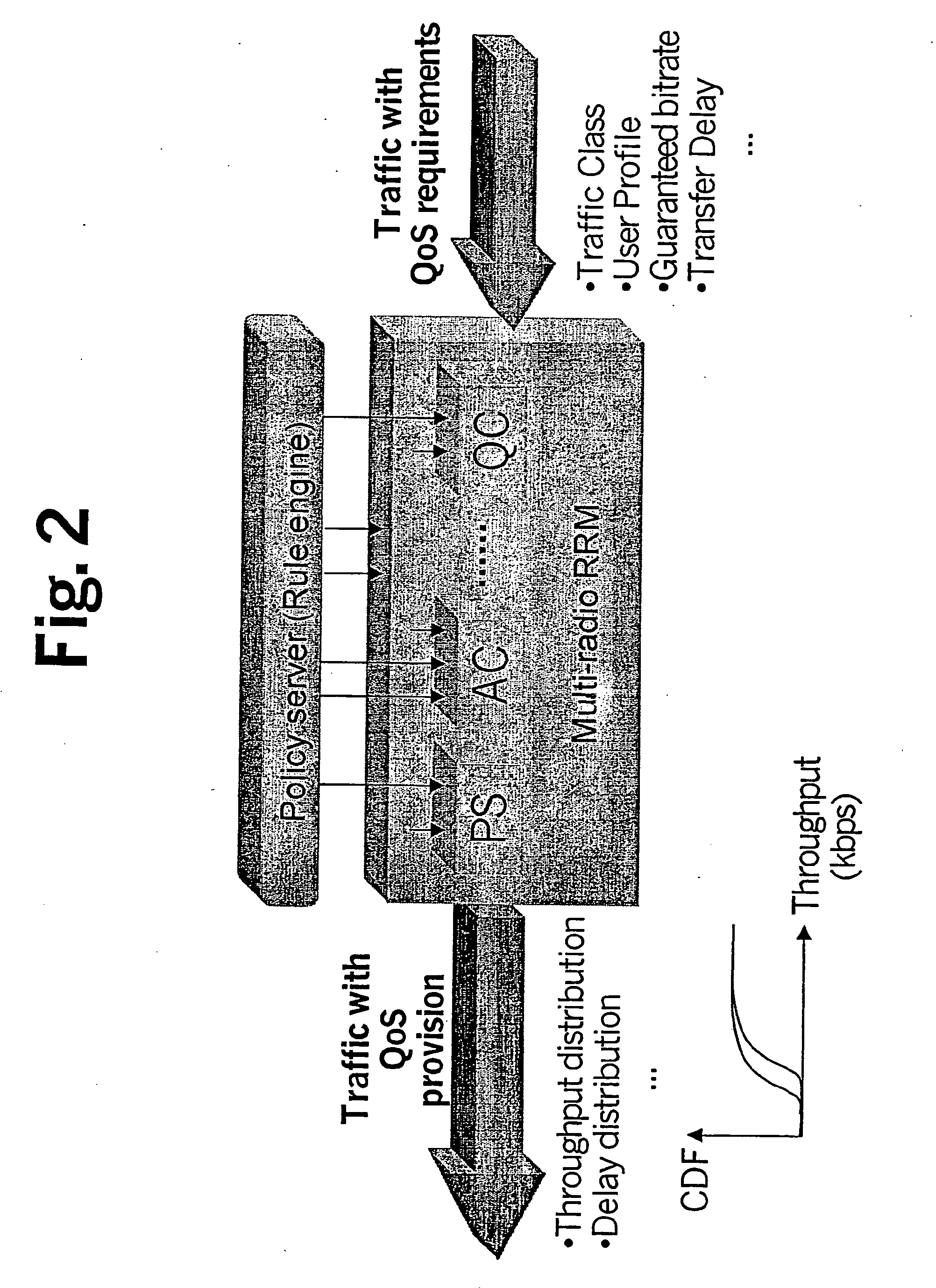
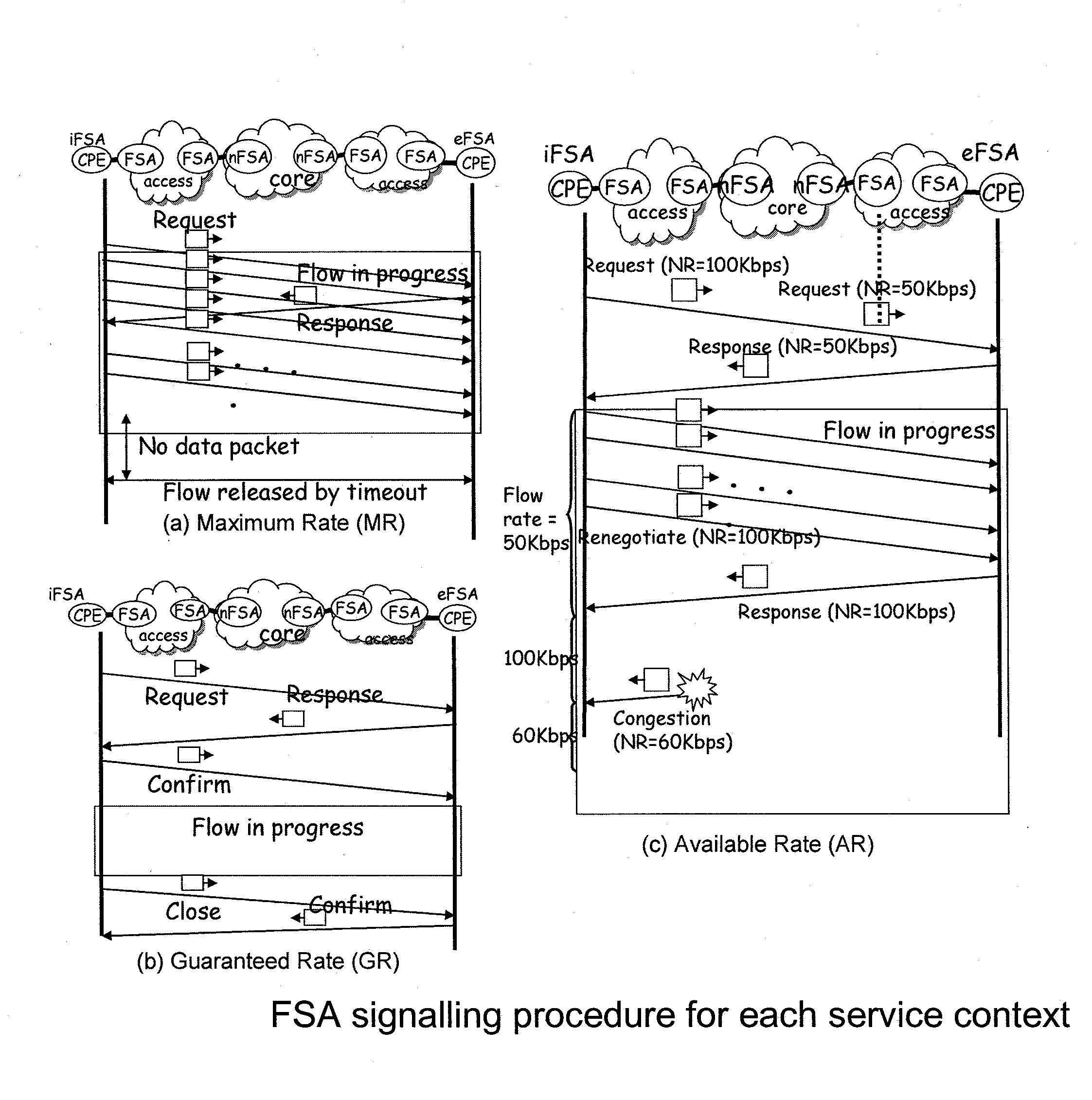
Policy-based qos management in multi-radio access networks
A system for providing a policy based Quality-of-Service management in multi-radio access mobile networks, comprising: control center means for administrating said radio access networks, thereby controlling the behavior thereof, wherein information model is implemented in said control center means which describes different Quality-of-Service mechanisms including attributes which are involved in each function under policy thus representing the manageable parameters of specific network implementations, and wherein said information model forms the basis of a set of policy rules defining actions to be executed in dependency of the occurrence of conditions; and a policy based management device adapted to receive said set of rules for the implementation thereof, said device having a plurality of policy based radio resource management means each adapted for managing said parameters of specific network implementations, and a translation function means adapted to translate said rules in a form executable by said plurality of policy based radio resource management means.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
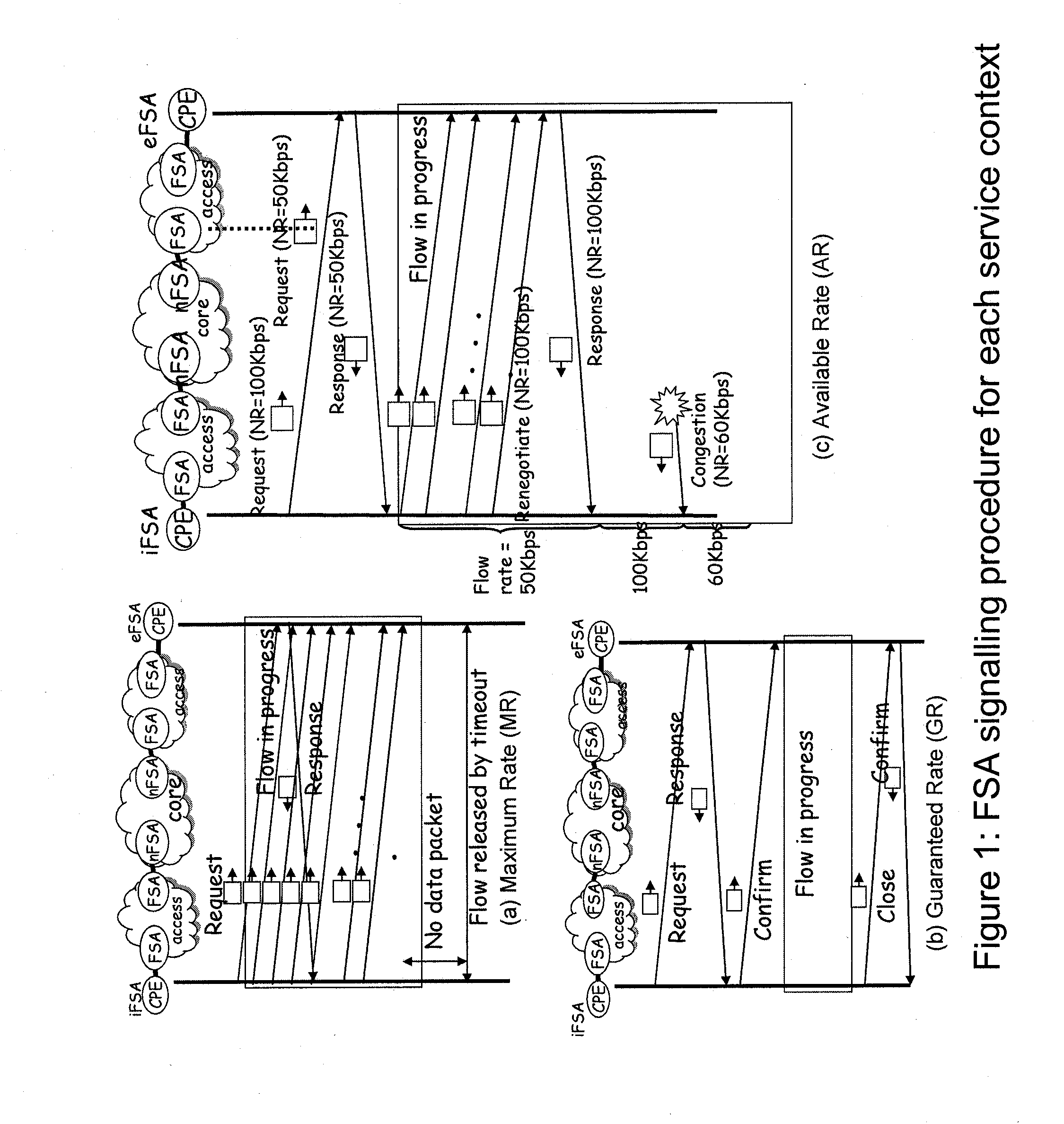
FLOW STATE AWARE MANAGEMENT OF QoS THROUGH DYNAMIC AGGREGATE BANDWIDTH ADJUSTMENTS
InactiveUS20100329118A1Shorten the durationReduce frequencyError preventionTransmission systemsQos managementLower priority
A packet network node and method of operating a packet network node are disclosed. Conventional packet network nodes react to congestion in the packet network by dropping packets in a manner which is perceived by users to be indiscriminate. In embodiments of the present invention, indiscriminate packet discards are prevented by causing packets to be discarded on lower priority flows and flow aggregates. A further action is taken to reduce the likelihood of packet discards. When an aggregate set of flows raises a congestion alarm action is taken to try to increase the capacity of the aggregate through taking capacity from pre-assigned donor aggregates. A donor aggregate may be carrying flows, for example flows classified as best effort. Another type of donor capacity is donor re-assignable unused capacity. Aggregates may have capacity added either up to a defined limit or, temporarily, exceeding any limit provided there is free capacity available, but removable back to the defined limit when other aggregates need increased capacity and are below their defined limits.
Owner:NEW RENAISSANCE TECH & INTPROP
In-band QoS signaling reference model for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS7298724B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceReference model
A station, such as a point coordinator (PC) or a non-PC station, in a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The station includes a frame classification entity (FCE), a frame scheduling entity (FSE) and a QoS management entity (QME). The FCE is logically located in a logical link control (LLC) layer of the station and has a classification table containing at least one classifier entry. Each classifier entry contains a virtual stream identifier (VSID) and a frame classifier associated with a user session. The FCE receives a data frame associated with the user session, which can be one of a voice session, a video session, a data session and a multimedia session. The data frame contains in-band quality of service (QoS) signaling information for the user session. The FCE classifies the received data frame to a selected VSID contained in a classifier entry in the classification table based on a match between an in-band frame classification information contained in the received frame and the frame classifier contained in the classifier entry. The FSE is logically located in a medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the station and has a frame scheduling table containing at least one entry. Each entry in the frame scheduling table contains a VSID and a QoS parameter set associated with a user session identified by the VSID. The FSE is responsive to the classified data frame by scheduling a transmission opportunity (TO) for the classified data frame based on the at least one QoS parameter value associated with the VSID and characterizing the user session. The QME interfaces with the FCE and The FSE.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
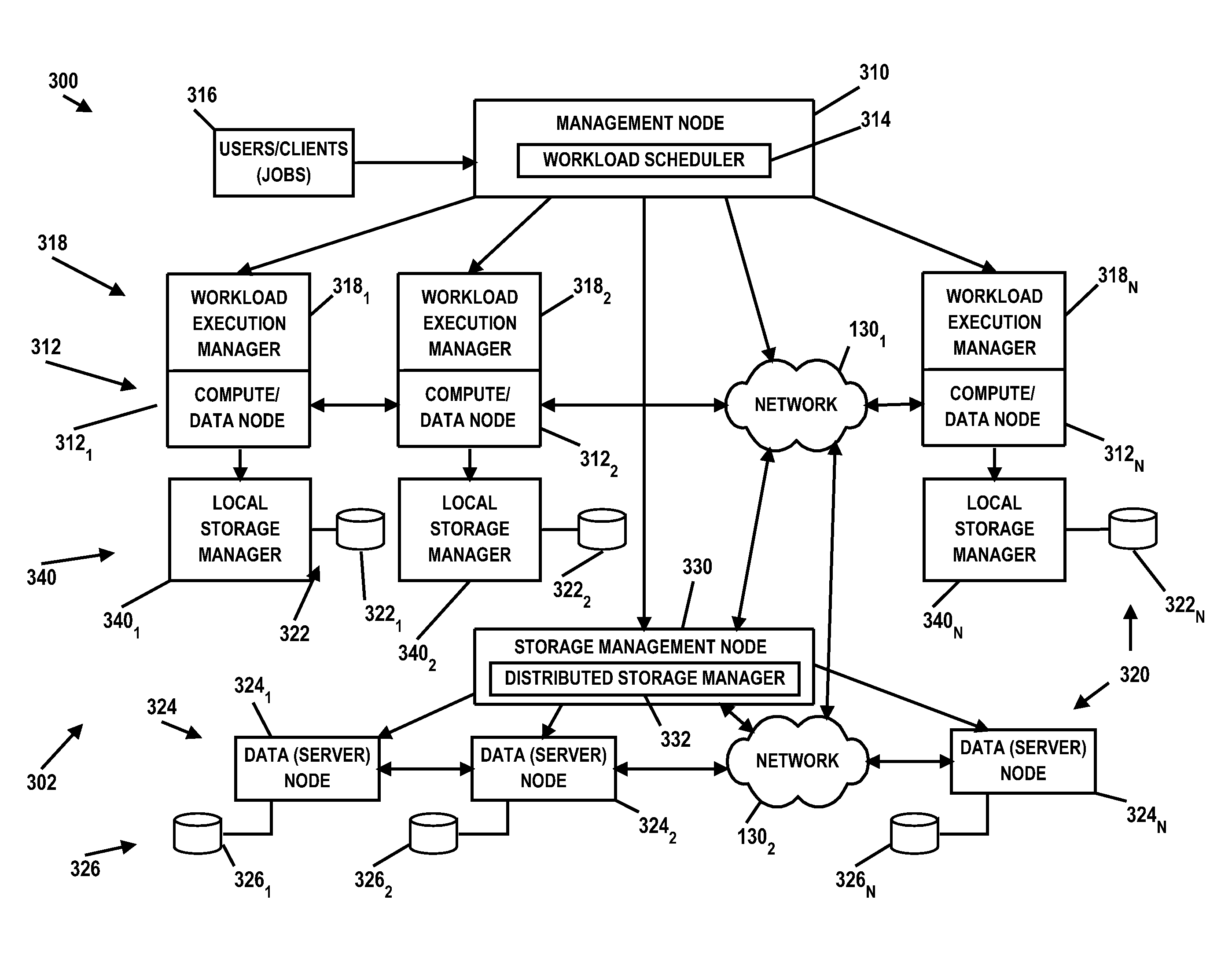
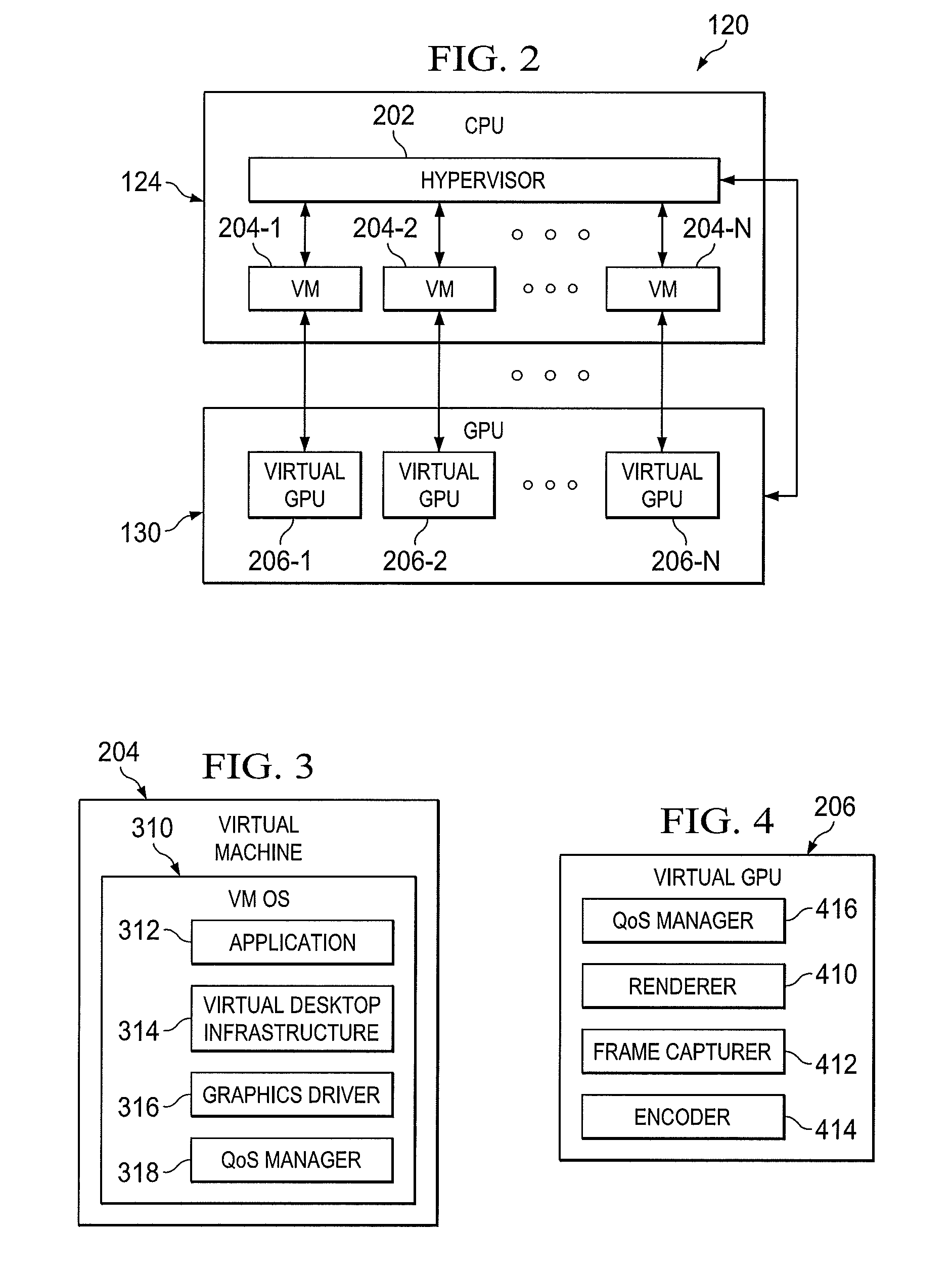
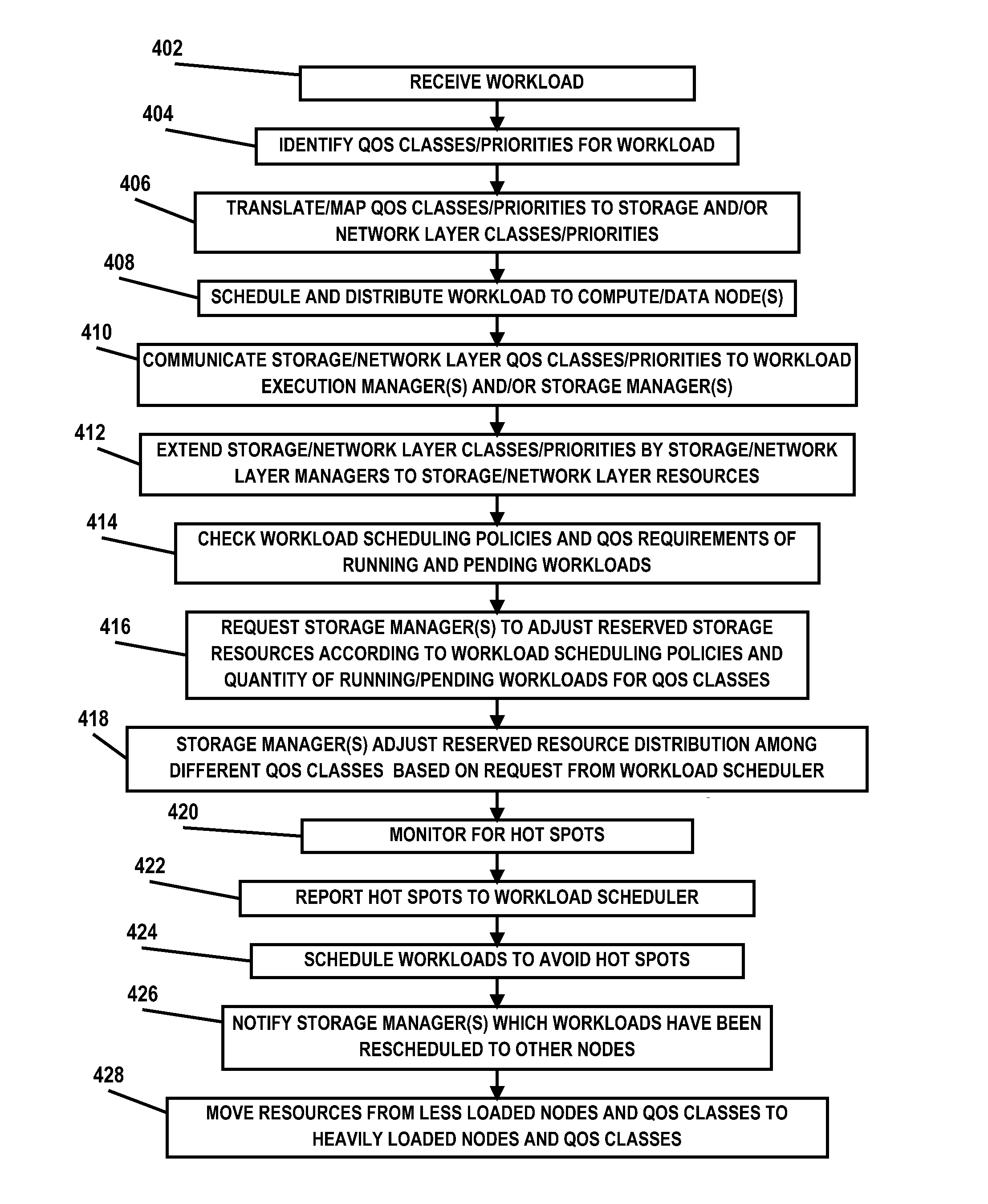
Multi-layer QOS management in a distributed computing environment
ActiveUS20160062795A1Program initiation/switchingResource allocationQuality of serviceQos management
A technique for multi-layer quality of service (QoS) management in a distributed computing environment includes: receiving a workload to run in a distributed computing environment; identifying a workload quality of service (QoS) class for the workload; translating the workload QoS class to a storage level QoS class; scheduling the workload to run on a compute node of the environment; communicating the storage level QoS class to a workload execution manager of the compute node; communicating the storage level QoS class to one or more storage managers of the environment, the storage managers managing storage resources in the environment; and extending, by the storage managers, the storage level QoS class to the storage resources to support the workload QoS class.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and Methods for QoS Provisioning and Assurance for Point-to-Point SIP Sessions in DiffServ-enabled MPLS Networks
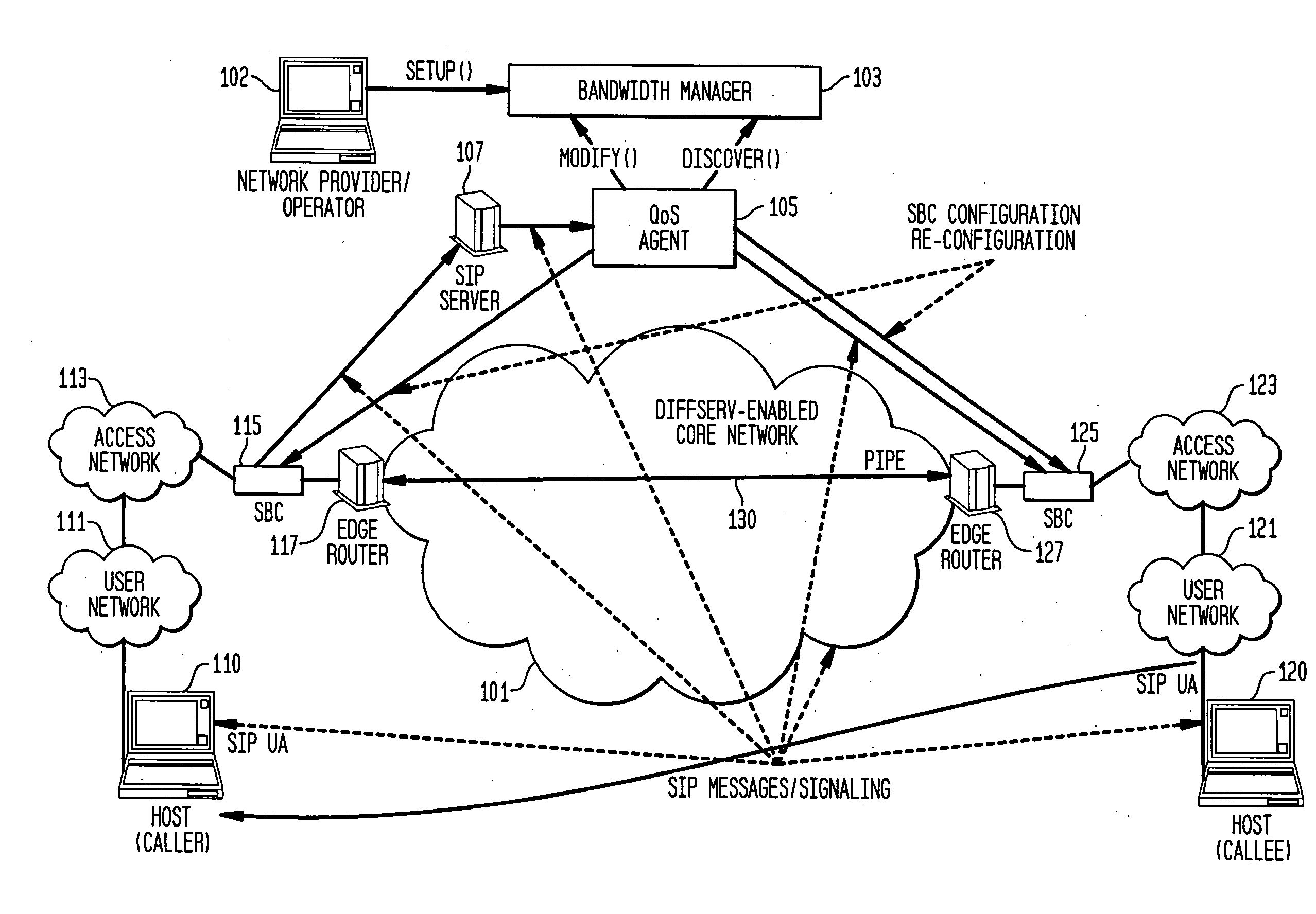
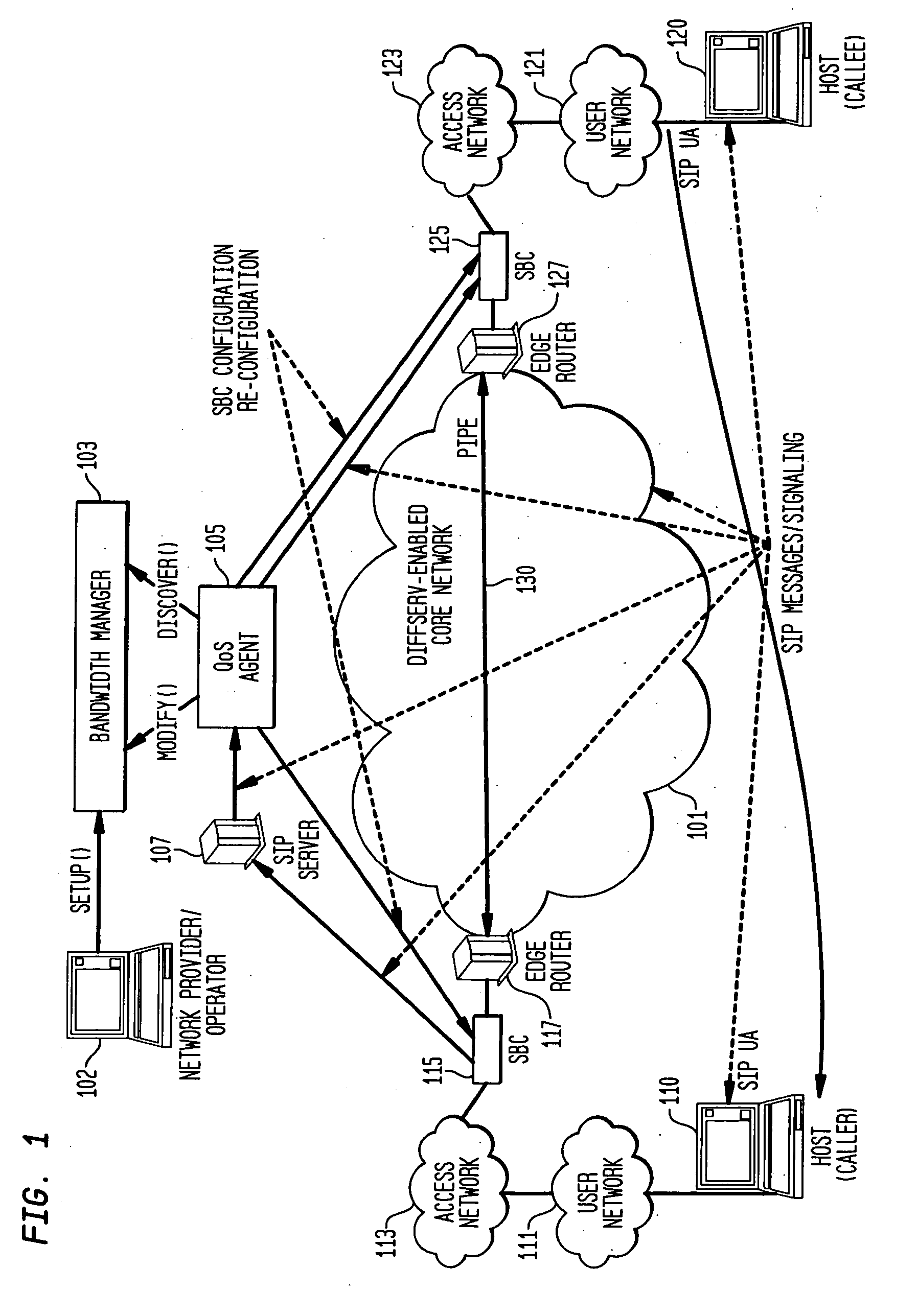
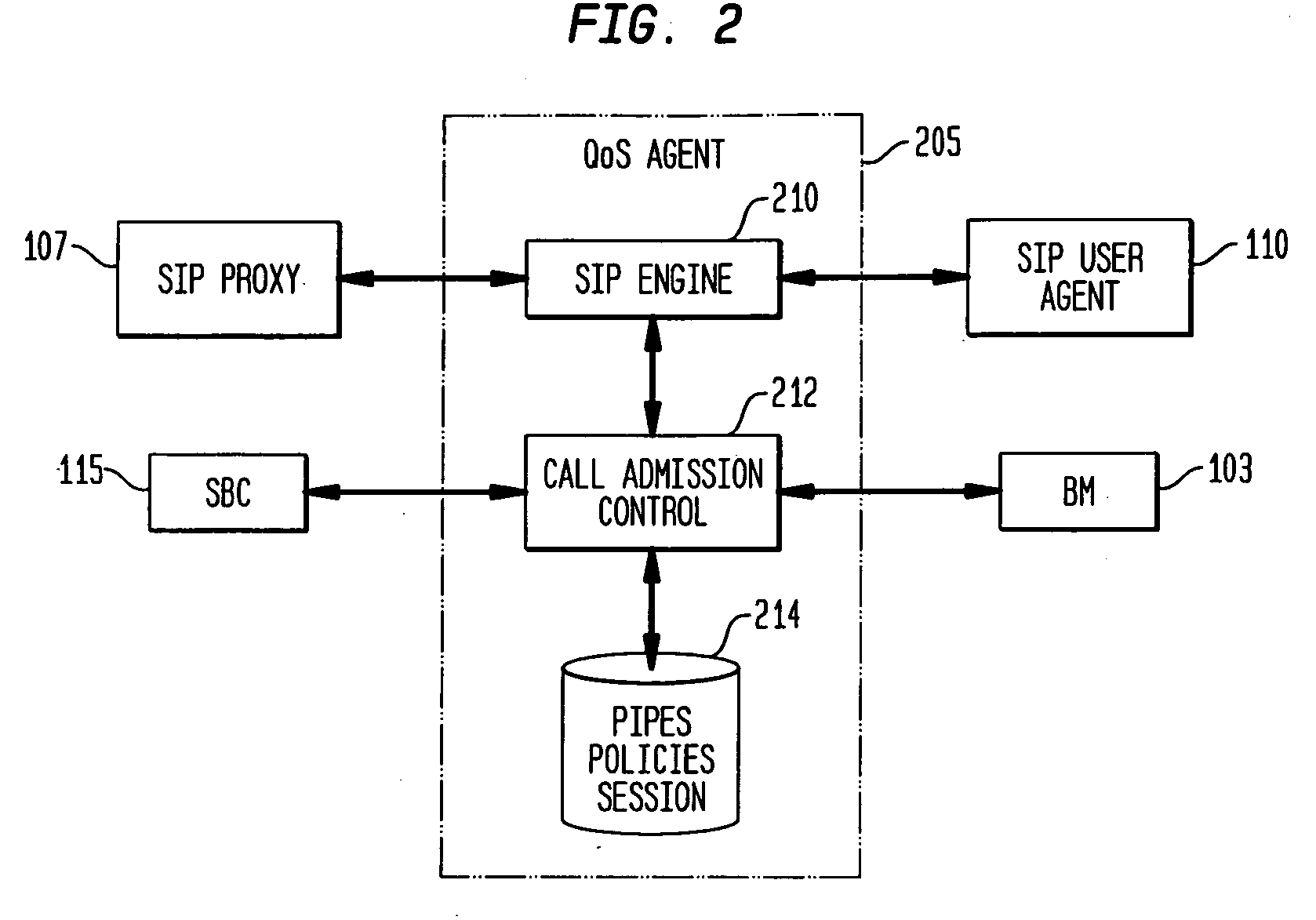
Systems and methods for efficiently provisioning and assuring Quality of Service (QoS) between user networks communicating over a DiffServ-enabled network, with QoS management transparency to SIP user agents. The system comprises user networks communicating via a core network, each user network having a source and destination SIP user agent respectively, a SIP proxy server between the source SIP user agent and destination SIP user agent, a Bandwidth Manager to provision a pipe between the source user network and the destination user network, wherein the pipe has a specified bandwidth, and a QoS Agent for accepting and / or rejecting a SIP session based on availability of bandwidth in the pipe; wherein the SIP proxy server is configured to forward an incoming SIP request to the QoS Agent. The method comprises provisioning a pipe between the SIP user agents or their respective user networks, and allowing / rejecting incoming SIP sessions based on the available bandwidth in the pipe.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Flow State Aware QoS Management Without User Signalling
InactiveUS20100135158A1Improve service qualityFacilitate communicationEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityQos management
Conventional packet network nodes react to congestion in the packet network by dropping packets in a manner which is perceived by users to be indiscriminate. In embodiments of the present invention, indiscriminate packet discards are prevented by causing packets to be discarded according to bandwidth allocations that intelligently track flow sending rates. Flows are allocated bandwidth based on policy information. Where such policy information indicates that the flow should be treated as delay-sensitive, the present invention includes means to allocate an initial minimum rate that will be guaranteed and such flows will also have the use of an additional capacity that varies depending on the number of such flows that currently share an available pool of capacity. This provides a congestion alleviation method which is less annoying to users since communications that have been in existence for longer are less susceptible to component packets being deleted.
Owner:RAZOOM
Wireless access loaded packet data service QoS management method.
InactiveCN1968198ASend quicklyMeet performance requirementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData switching networksTraffic capacitySupport group
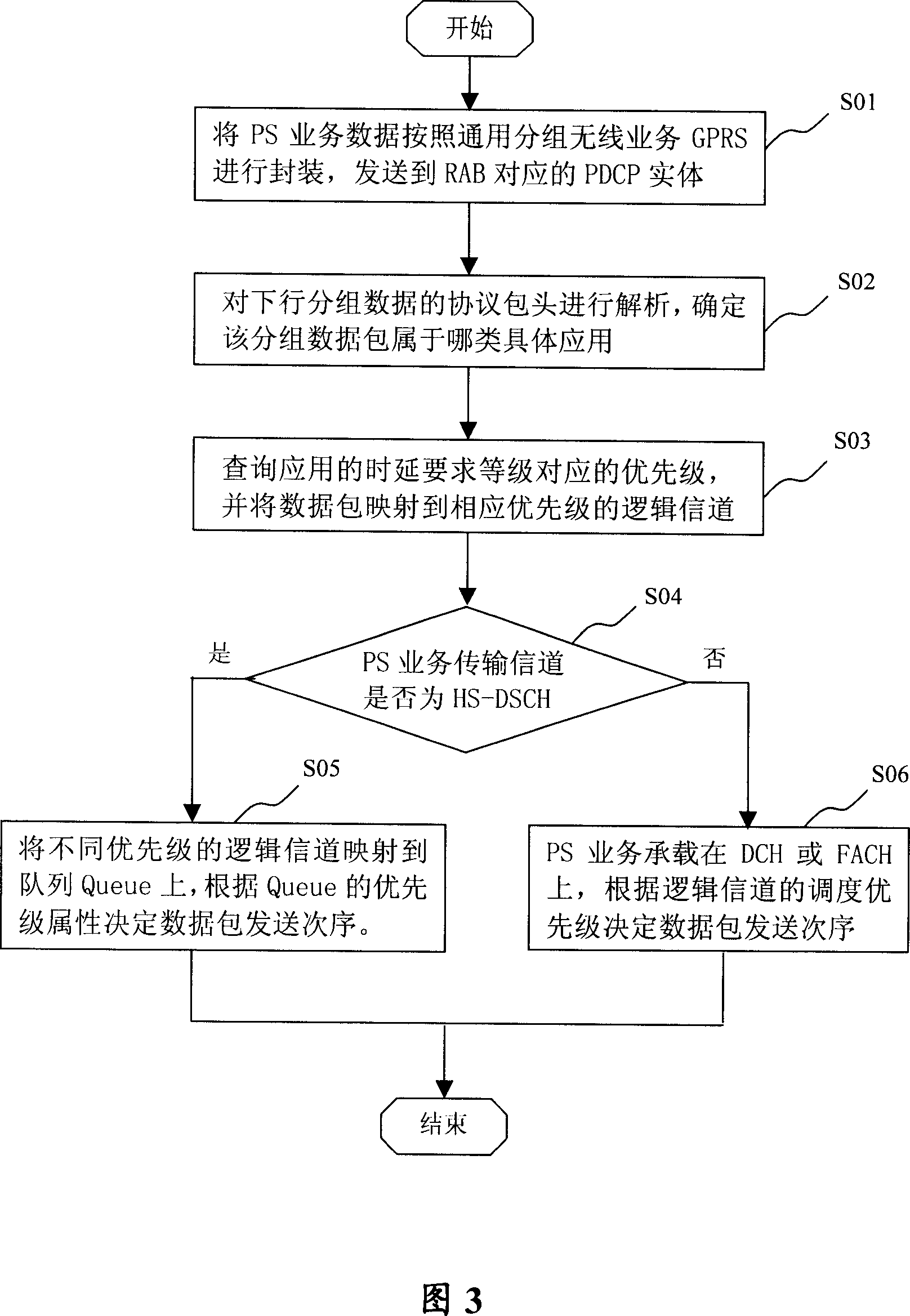
The invention relates to a QoS manage method of wireless access support group data service, wherein it comprises that: judging the service type of data supported by wireless access; based on said type, finding the sending priority of data pack; projecting the data pack with high priority to the channel with high priority, to be sent out. When the time delay demand of application service, based on the data flux of target address, classifying the priorities; projecting the data pack with low data flux to the logic channel with high priority, to confirm the application data pack with high time delay demand to be sent quickly, to meet the service quality QoS of different application services.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Quality of service management server and method of managing streaming bit rate
InactiveUS20140286438A1Increase bitrateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuality of serviceQos management
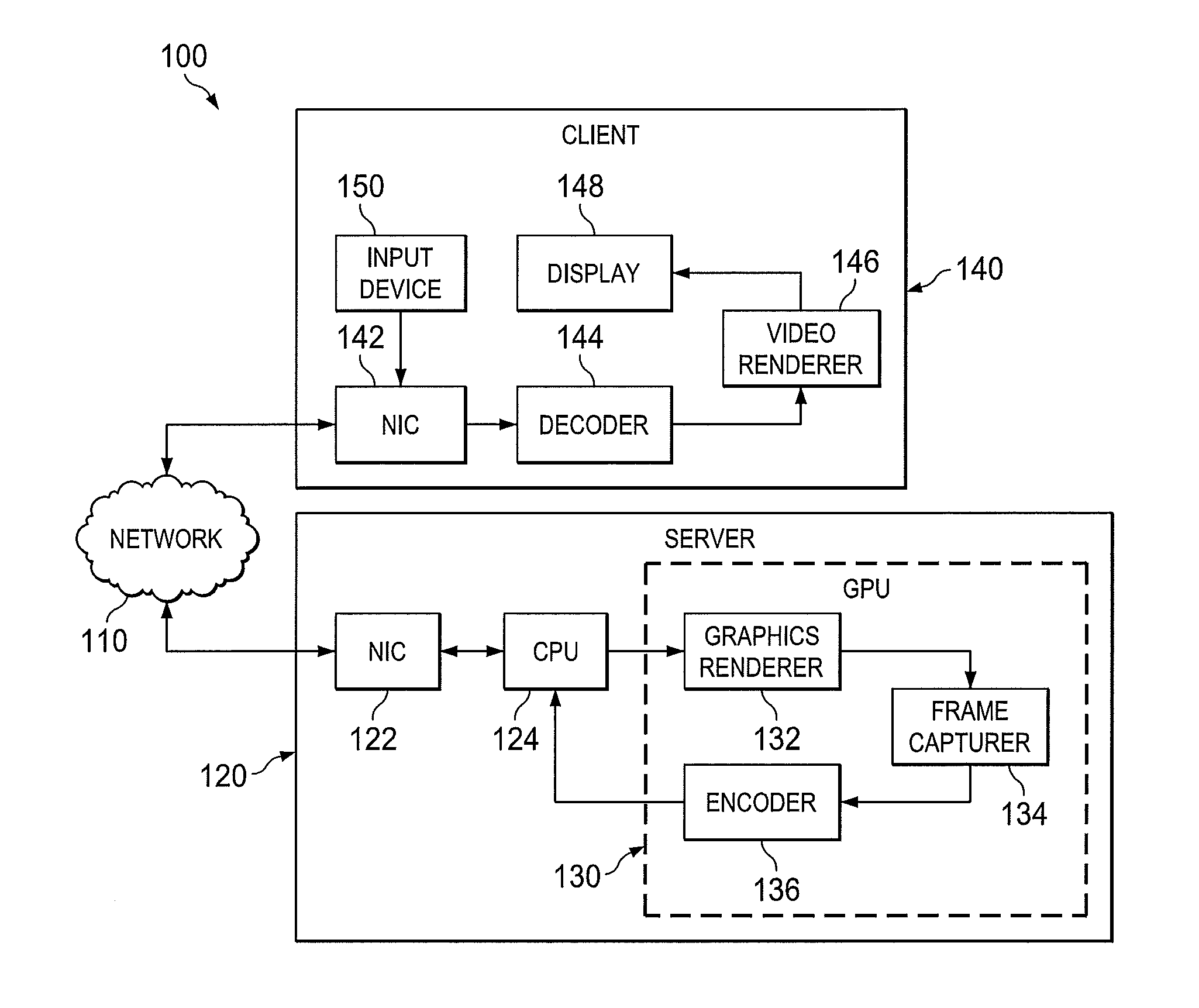
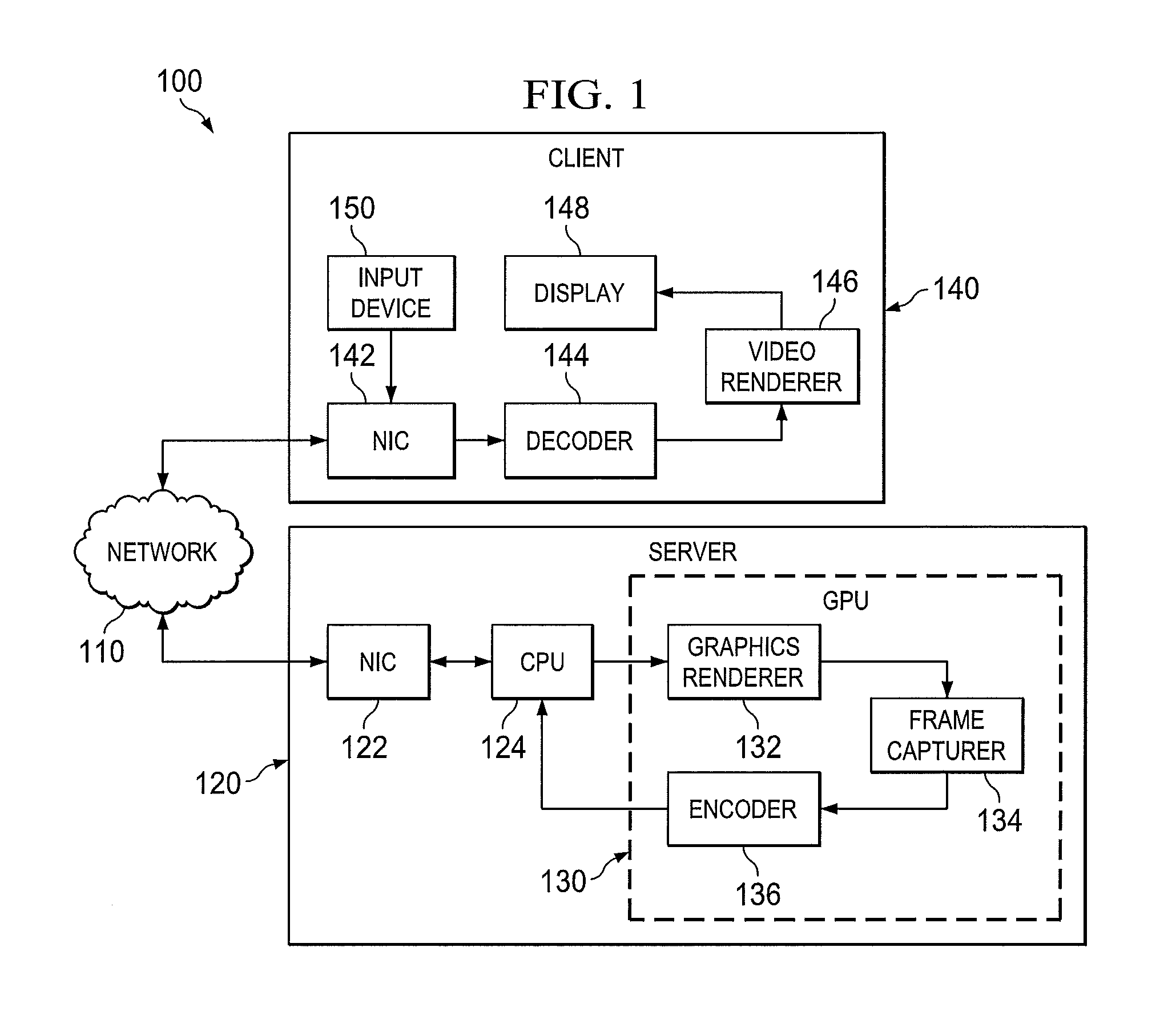
A quality of service (QoS) management server and a method of managing a streaming bit rate. One embodiment of a QoS management server includes: (1) an encoder operable to encode a video stream at a current bit rate for transmission via a network interface controller (NIC) and (2) a processor operable to receive QoS statistics regarding the video stream via the NIC, employ the QoS statistics to determine a new bit rate and cause the encoder to encode the video stream at the new bit rate.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
METHOD OF PROVIDING QoS FOR A FLOW
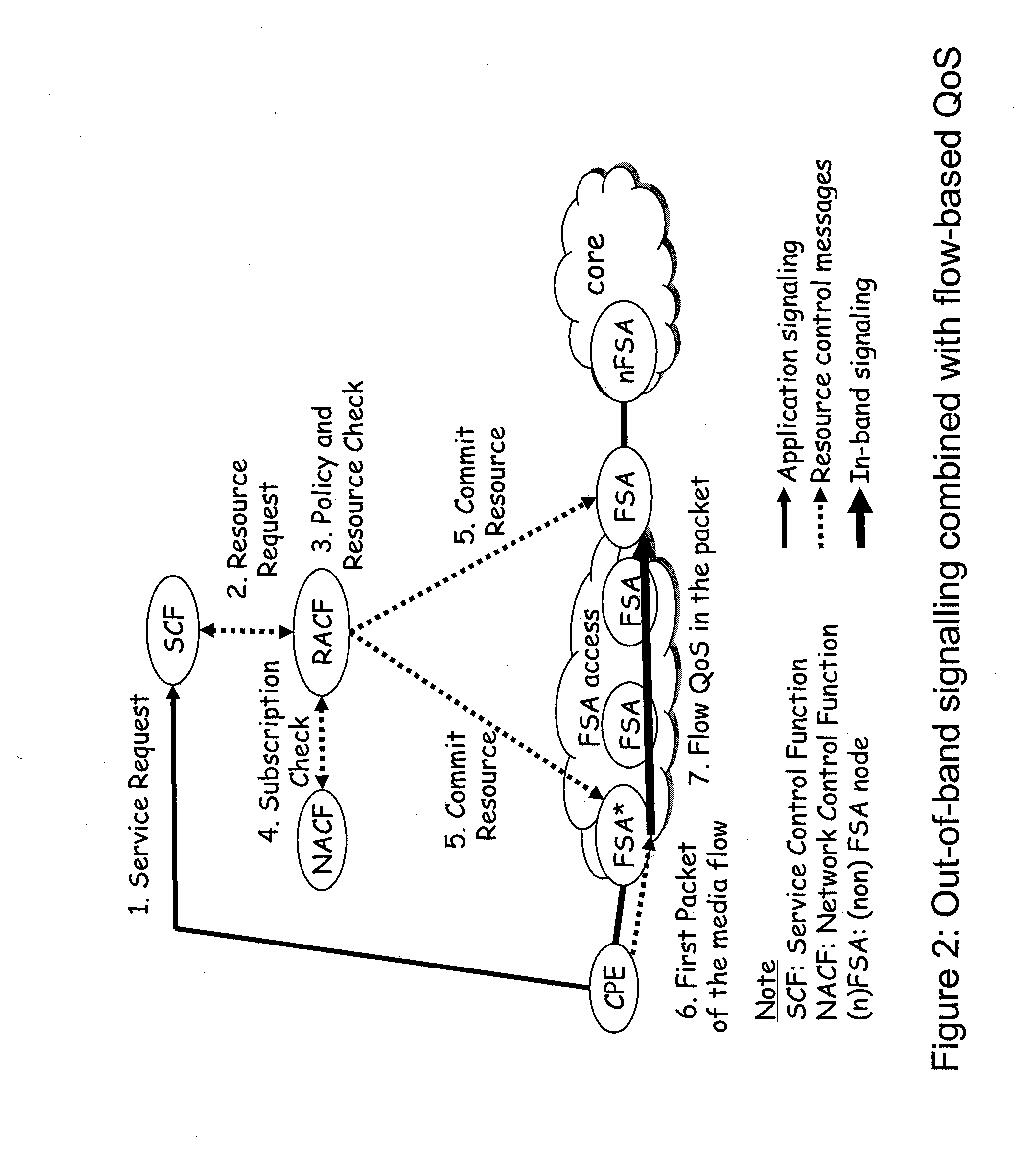
InactiveUS20080181117A1Thinner and less complex client applicationIncrease its OPEXError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQos managementNetwork on
A method of providing QoS for a flow associated with a client application in a network, and a QoS manager to execute this method. The network comprises said QoS manager, a QoS policy holder, one or more QoS devices, and a control point associated with the client application. Moreover, the network supports a Universal Plug and Play QoS service. The QoS manager calculates a topology of the network on flow setup and requests traffic policy data from the QoS policy holder. The QoS manager submits traffic descriptor data based on said traffic policy data to the one or more QoS devices for configurating said QoS devices for handling the flow. The QoS manager subscribes to events of the one or more QoS devices. The control point subscribes to events of the QoS manager. On detection of a QoS device event by the QoS manager, the topology of the network is re-calculates by the QoS manager for determining a topology change. The QoS manager checks whether the topology change affects the flow. If the flow is affected by the topology change, the QoS manager triggers suitable measures.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Admission control for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS7450504B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQos quality of serviceEngineering
A method and a system for a quality of service (QoS) point coordinator (PC) for a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The PC includes a QoS management entity (QME) and an admission control entity (ACE). The QME receives at least one reservation request message that characterizes one of a QoS session and a QoS application (session / application) that can be of a continuous / periodic flow type that is time sensitive, or can be of a discontinuous / bursty flow type that is time tolerant. The reservation request message contains at least one QoS parameter set and requests a resource of a communication channel in the BSS for the QoS session / application. The communication channel is organized into superframes, such that each superframe includes a contention-free period (CFP) and a contention-period (CP). The reservation request message requests a predetermined bandwidth of each CFP of the communication channel in the BSS. The ACE performs macro bandwidth management for QoS traffic transport of the session / application over a medium access control (MAC) sublayer for the communication channel by determining whether to grant the reservation request based on at least one QoS parameter set associated with the session / application.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
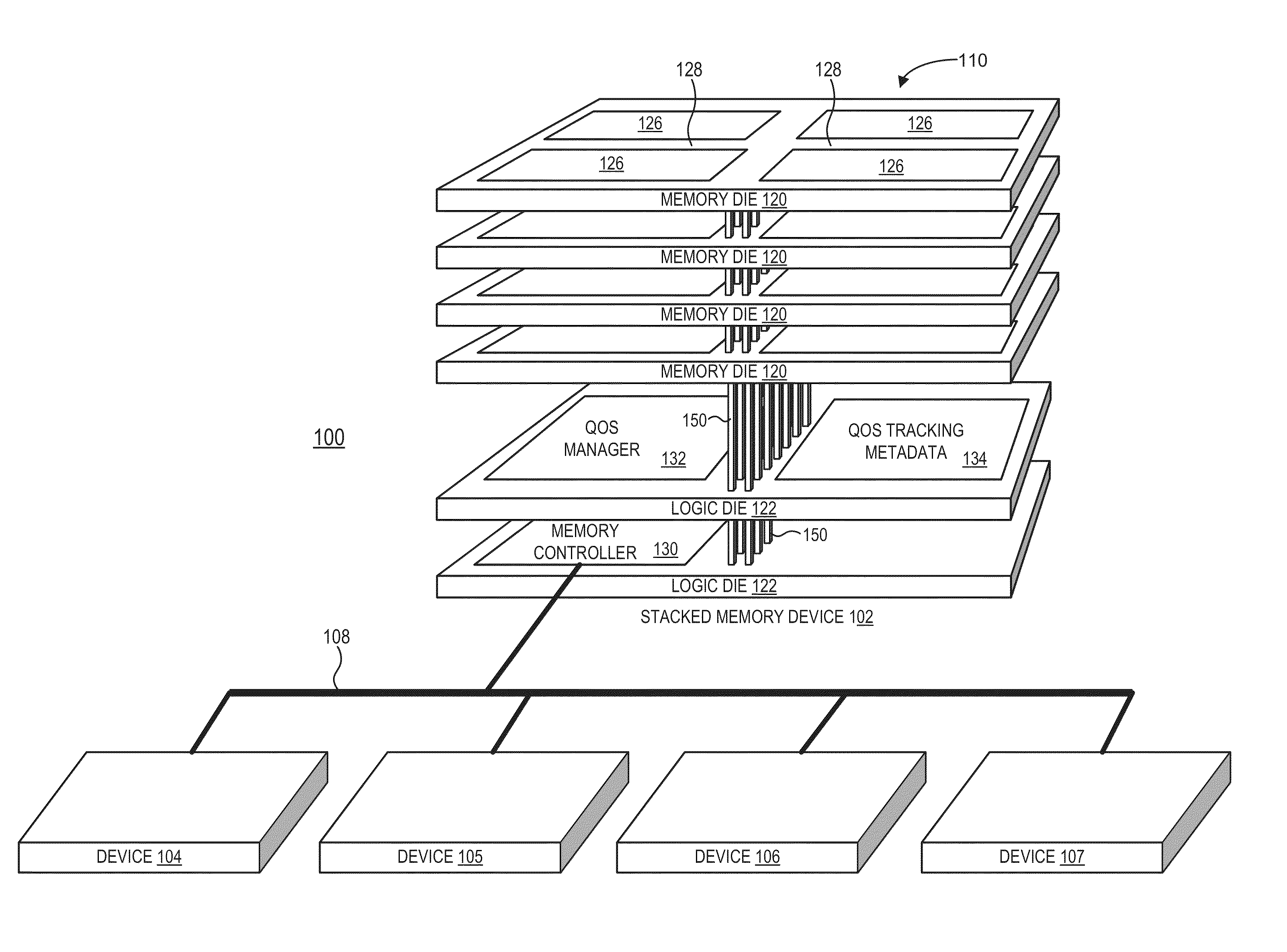
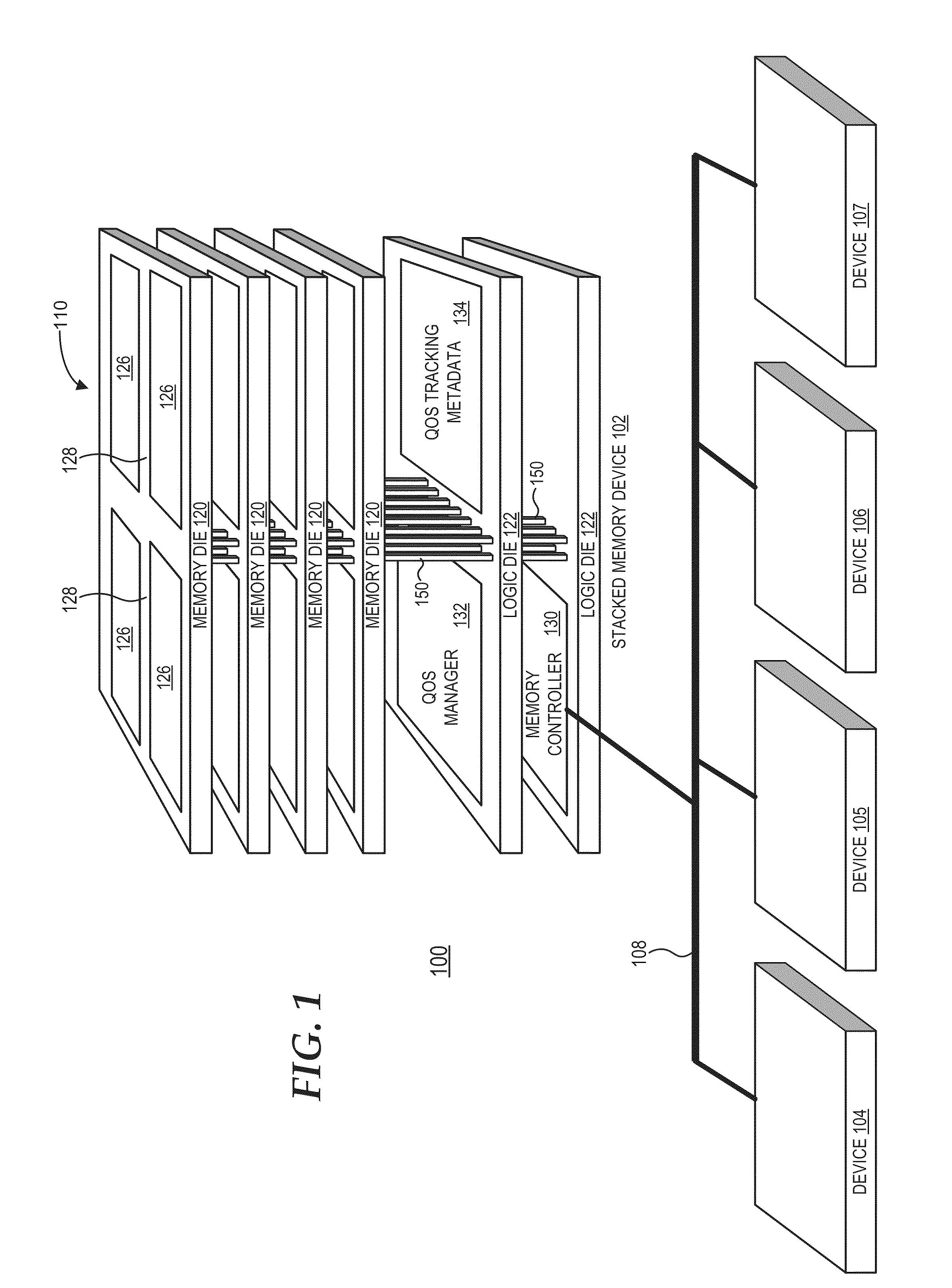
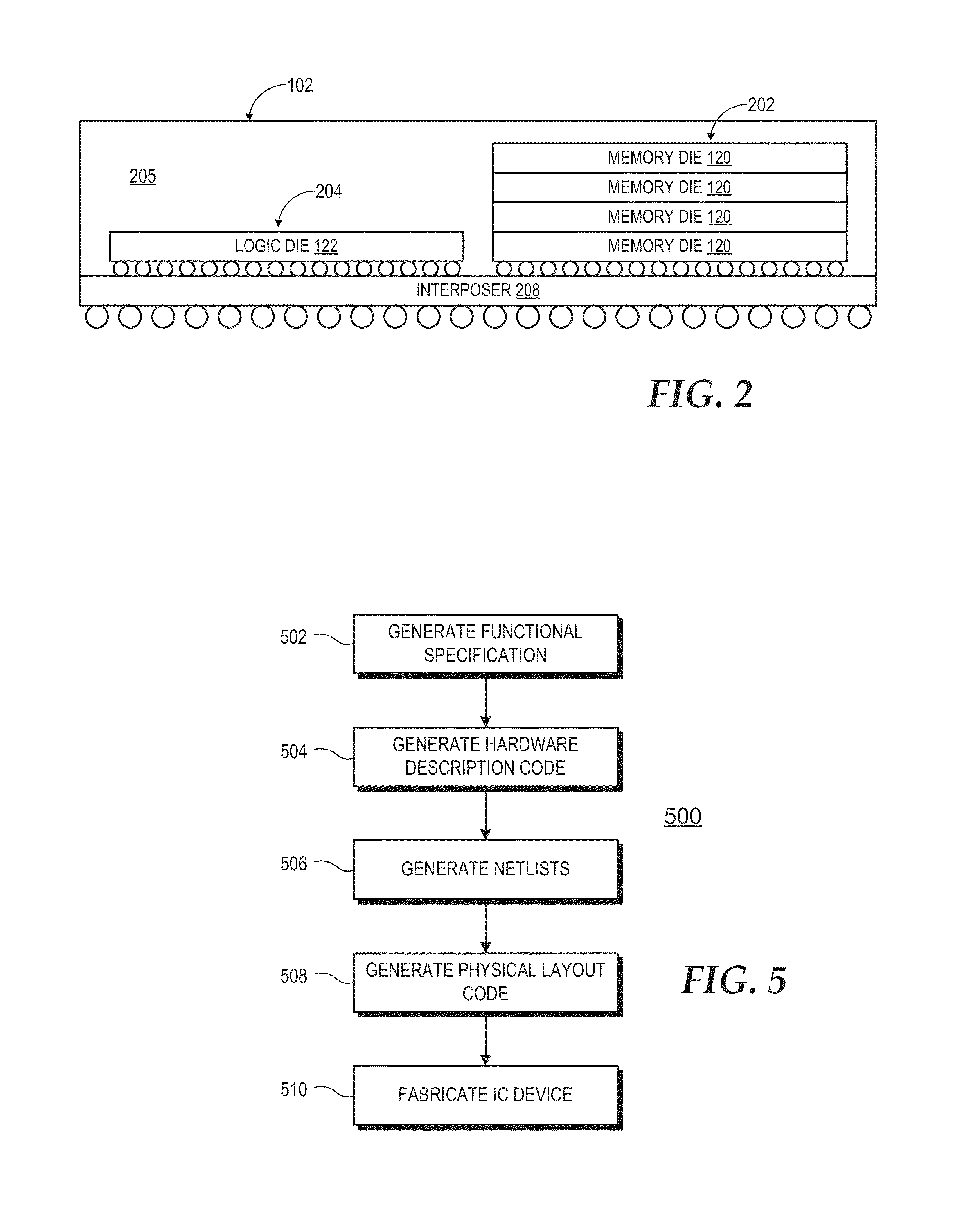
Quality of service support using stacked memory device with logic die
A die-stacked memory device implements an integrated QoS manager to provide centralized QoS functionality in furtherance of one or more specified QoS objectives for the sharing of the memory resources by other components of the processing system. The die-stacked memory device includes a set of one or more stacked memory dies and one or more logic dies. The logic dies implement hardware logic for a memory controller and the QoS manager. The memory controller is coupleable to one or more devices external to the set of one or more stacked memory dies and operates to service memory access requests from the one or more external devices. The QoS manager comprises logic to perform operations in furtherance of one or more QoS objectives, which may be specified by a user, by an operating system, hypervisor, job management software, or other application being executed, or specified via hardcoded logic or firmware.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Multi-layer QOS management in a distributed computing environment
A system for multi-layer quality of service (QoS) management in a distributed computing environment includes: a management node hosting a workload scheduler operable to receive a workload and identify a workload QoS class for the workload; and a plurality of distributed compute nodes, the workload scheduler operable to schedule running of the workload on the compute nodes. The workload scheduler is operable to: translate the workload QoS class to a storage level QoS class; communicate the storage level QoS class to a workload execution manager of the compute nodes; and communicate the storage level QoS class to one or more storage managers, the storage managers managing storage resources. The storage managers are operable to extend the storage level QoS class to the storage resources to support the workload QoS class.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for providing a mobile IP network with non-path dependent intra domain quality of service
InactiveUS20080056178A1Improve abilitiesEfficient changeRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesDomain nameQuality of service
A system and method for providing quality of service (QoS) service over a mobile IP network with dynamic domains, multiple or distributed QoS managers per domain and / or with network congestion feedback being used to establish an estimated total domain bandwidth which is used for regulating access to a domain.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
QUALITY OF SERVICE MANAGEMENT METHOD, DEVICE AND SYSTEM (Amended)
InactiveUS20110222399A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceQos management
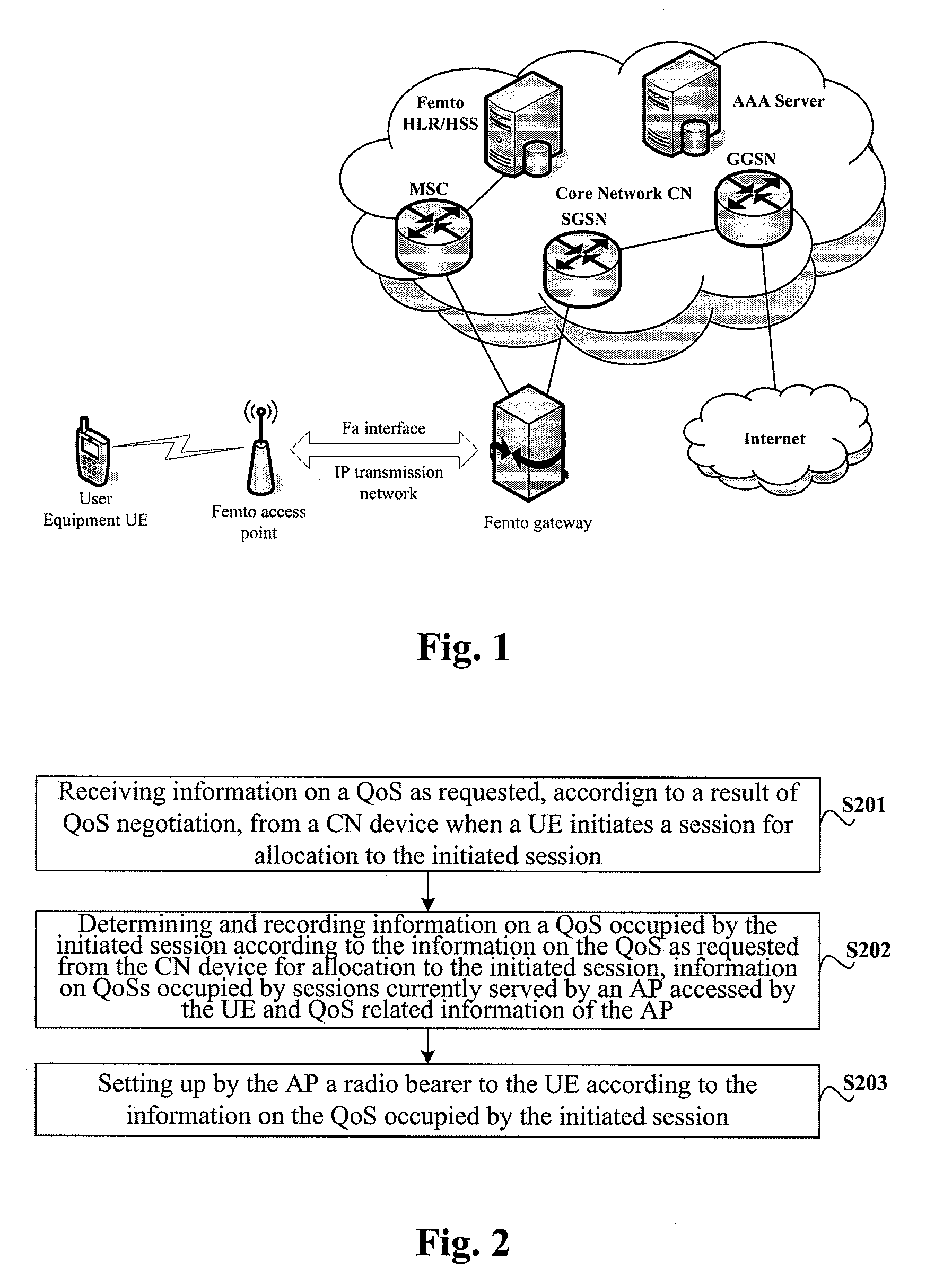
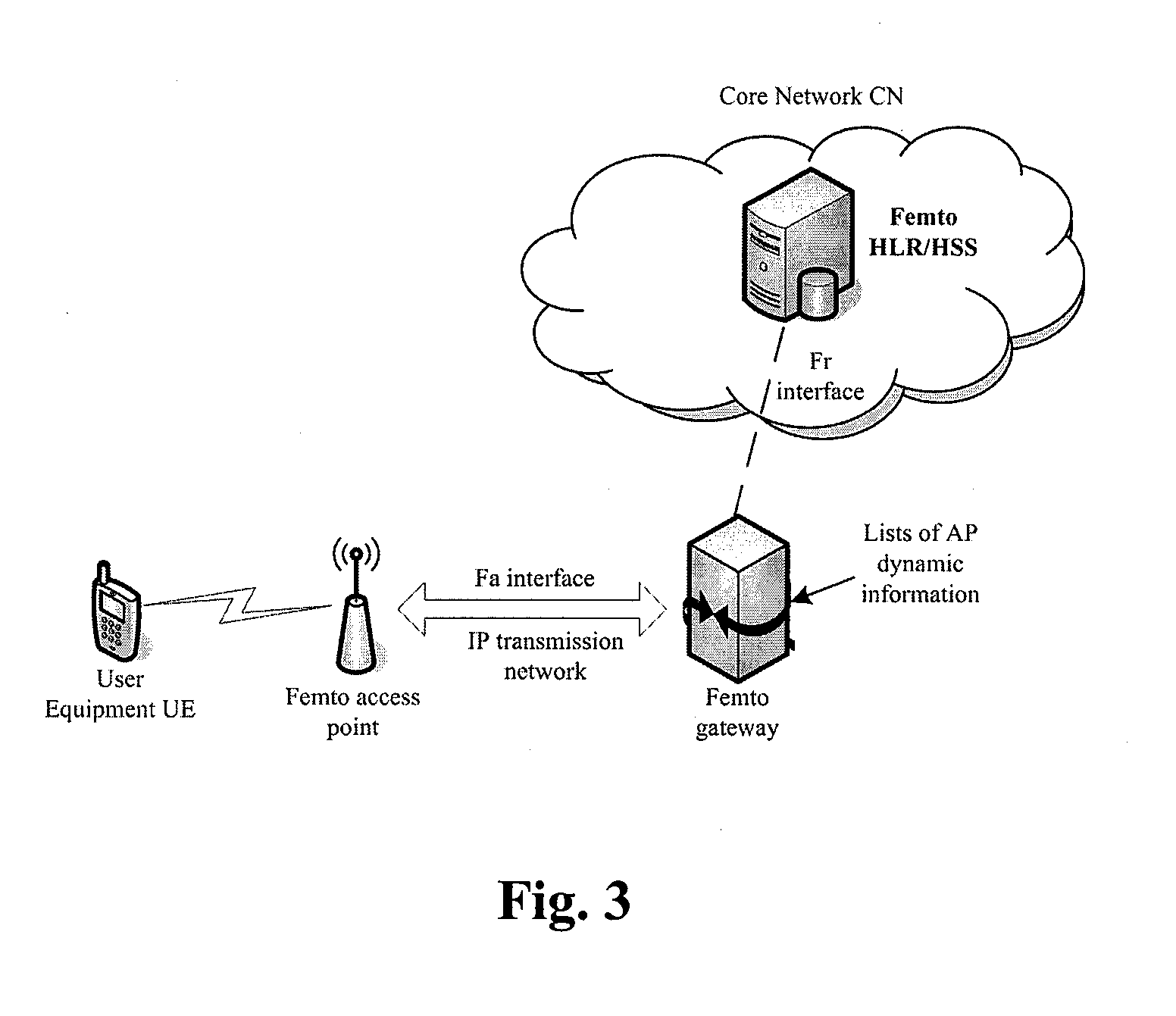
A quality of service QoS management method, apparatus and system are disclosed. The method includes: receiving Qos information requested by a core network device, wherein the Qos information is assigned to a current originated session according to a Qos negotiation result during a user equipment UE session origination phase; according to the requested Qos information assigned to the current originated session, Qos information occupied by a current serving session of an access point AP accessed by the UE, and Qos associated information of the AP, determining and recording the Qos information occupied by the current originated session; and the AP establishing a wireless bearer with the UE according to the QoS information occupied by the current originated session.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SHAIHAI
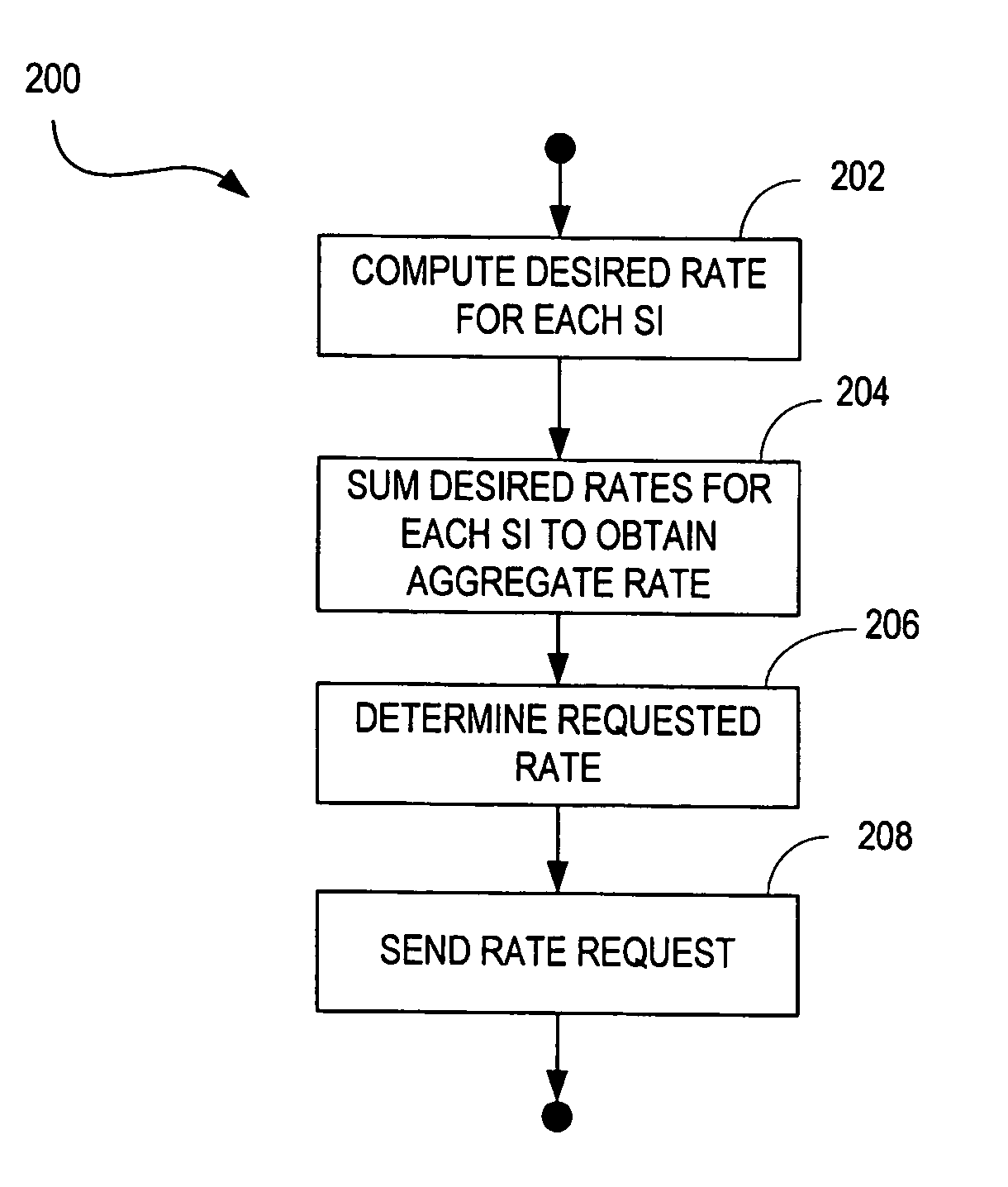
QoS management for multiple service instances
InactiveUS20050185583A1Satisfactory qualityError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceQos management
In a mobile communication network, a desired rate needed to maintain a desired quality of service for each service instance is computed and the individual rates for all service instances are summed to get an aggregate rate needed to maintain the desired quality of service for all service instances. A rate determination is made based on the aggregate rate.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and wireless network system for providing QoS on wireless network communicating via point-to-point network
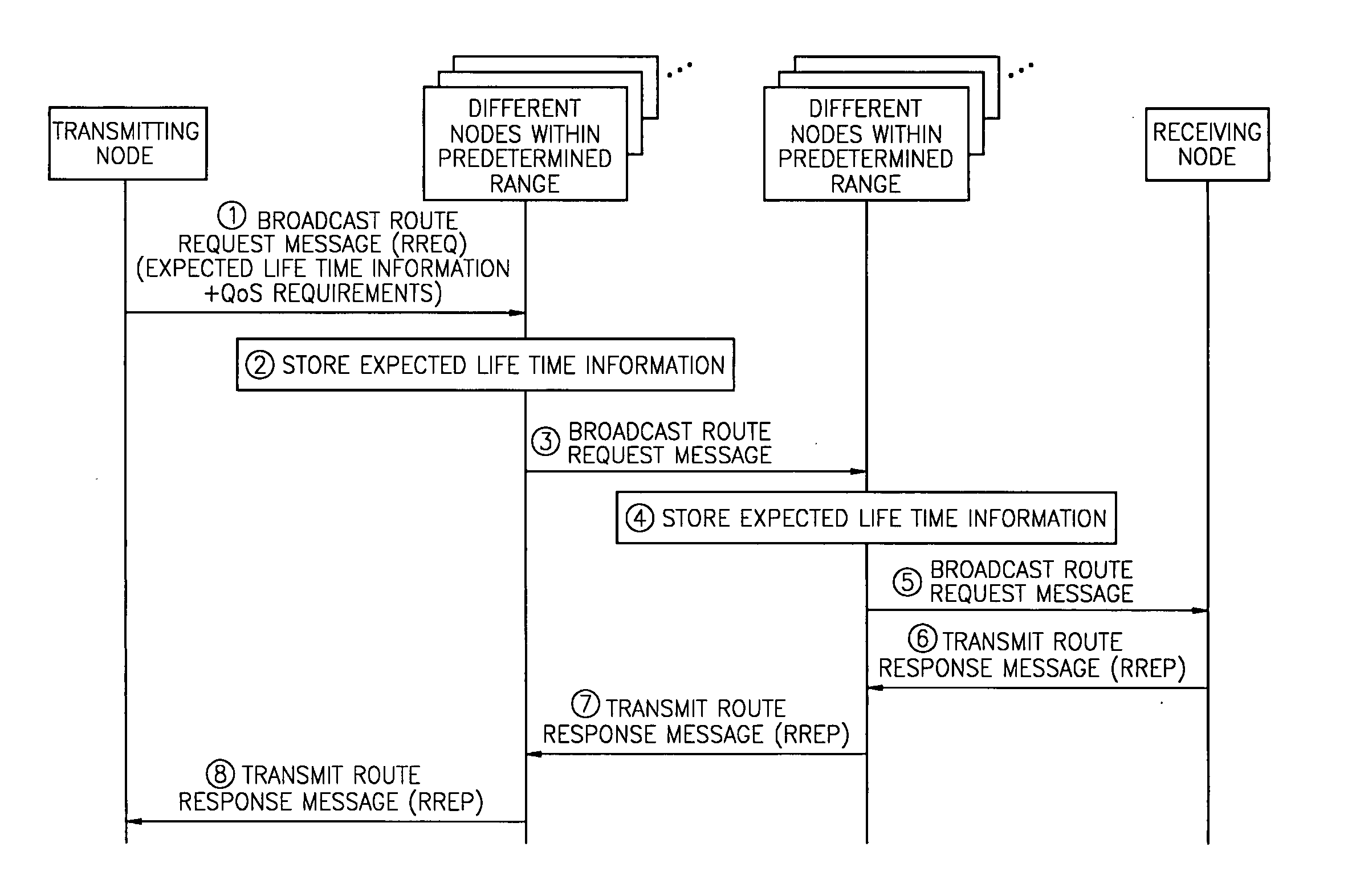
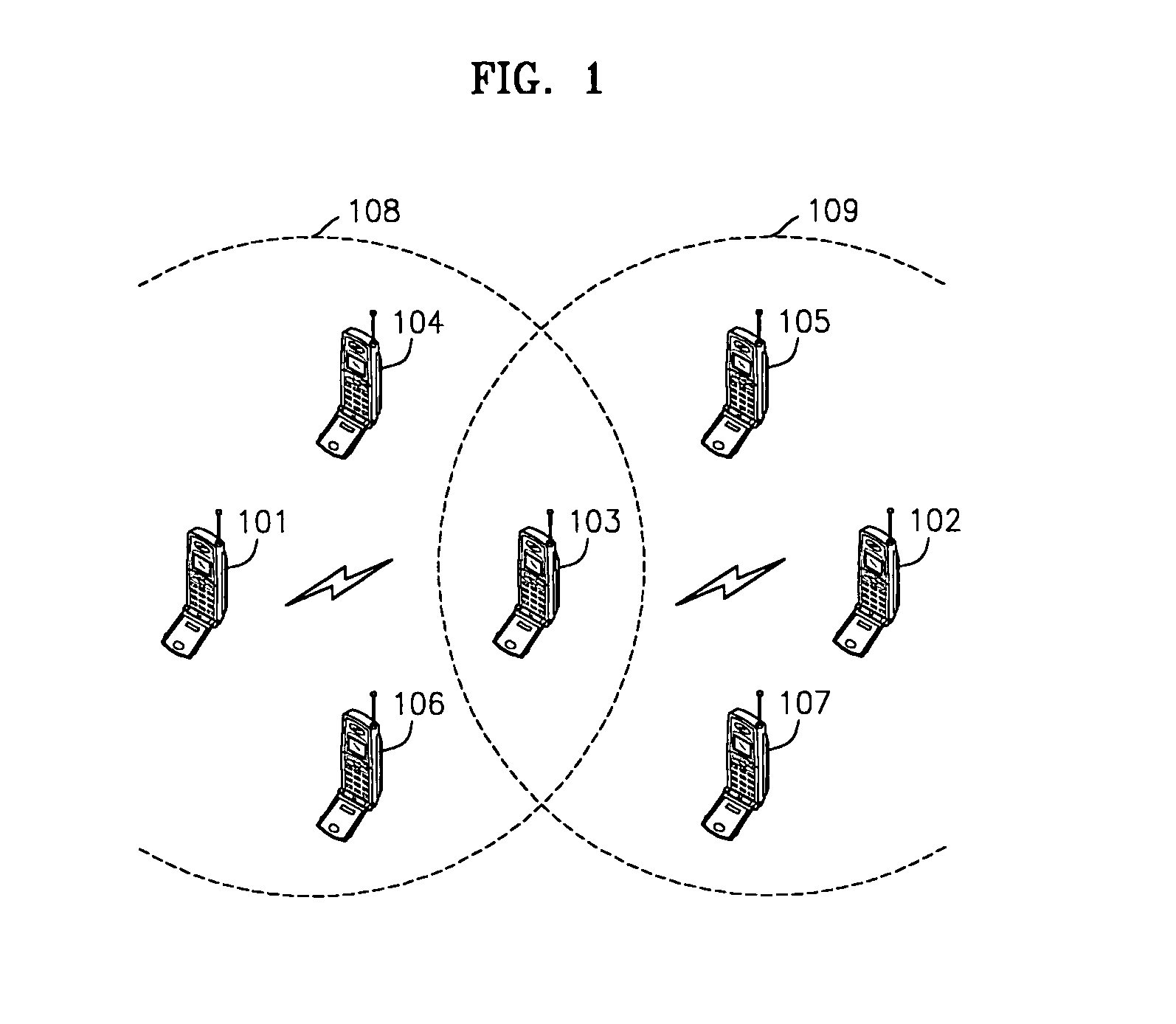
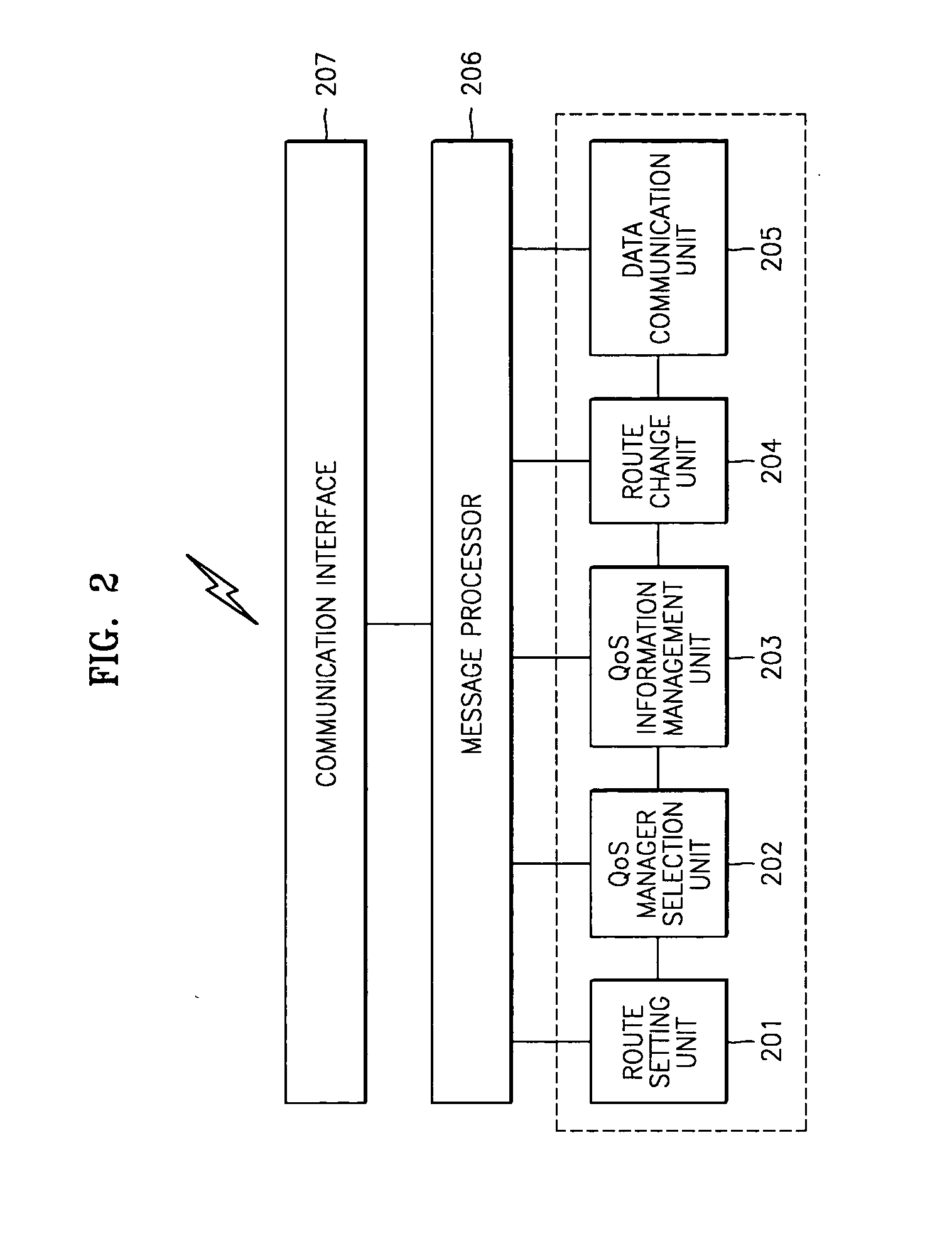
InactiveUS20050014510A1Data switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemQos management
A method and wireless communication system for providing QoS in a wireless network communicating through a point-to-point network are provided. The method includes: (a) at least one of intermediate nodes and a receiving node, selecting at least one QoS management node among different nodes within a predetermined range which are not included on a forwarding route, the forwarding route reaching from a transmitting node to the receiving node via at least one intermediate node satisfying QoS requirements; (b) the selected QoS management node, managing QoS management information of the different nodes which are not included on the forwarding route; and (c) the QoS management node, changing the forwarding route on the basis of the QoS management information so that the changed forwarding route passes through a different node satisfying the QoS requirements, if it is expected that at least one intermediate existing on the forwarding route will not satisfy the QoS requirements. Therefore, it is possible to reduce end-to-end delay and route discontinuity and provide QoS in a wireless communication system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com