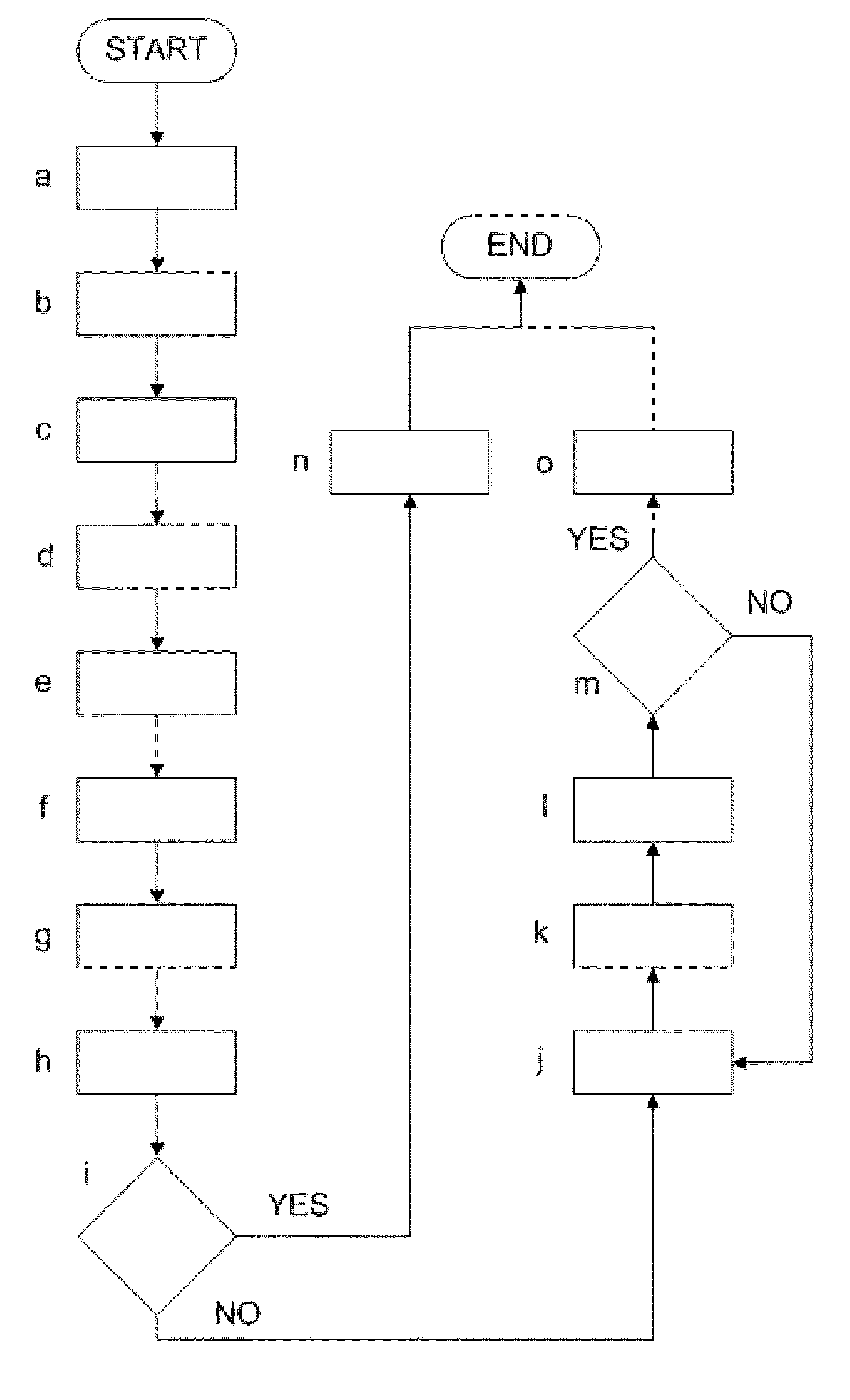
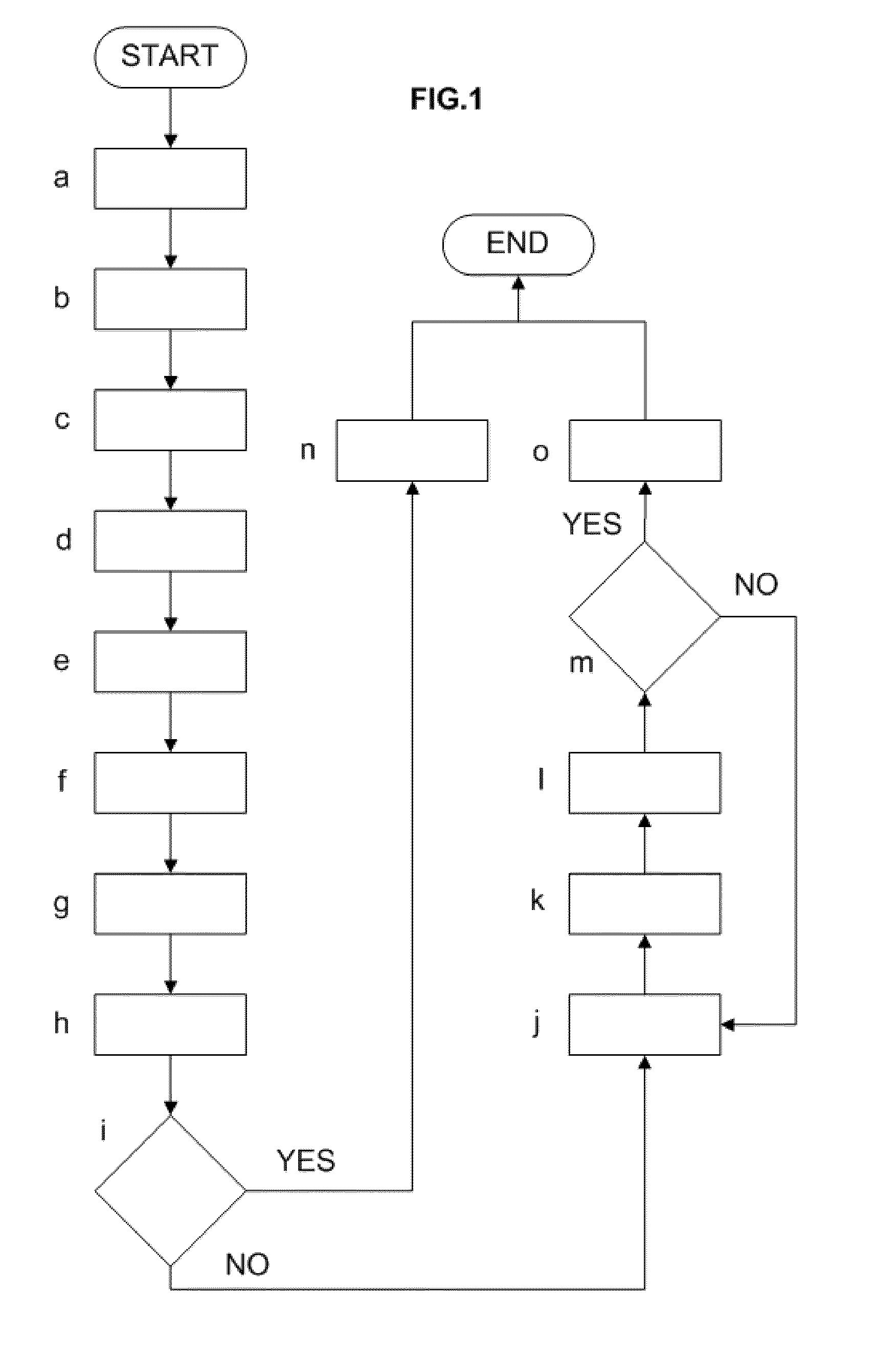
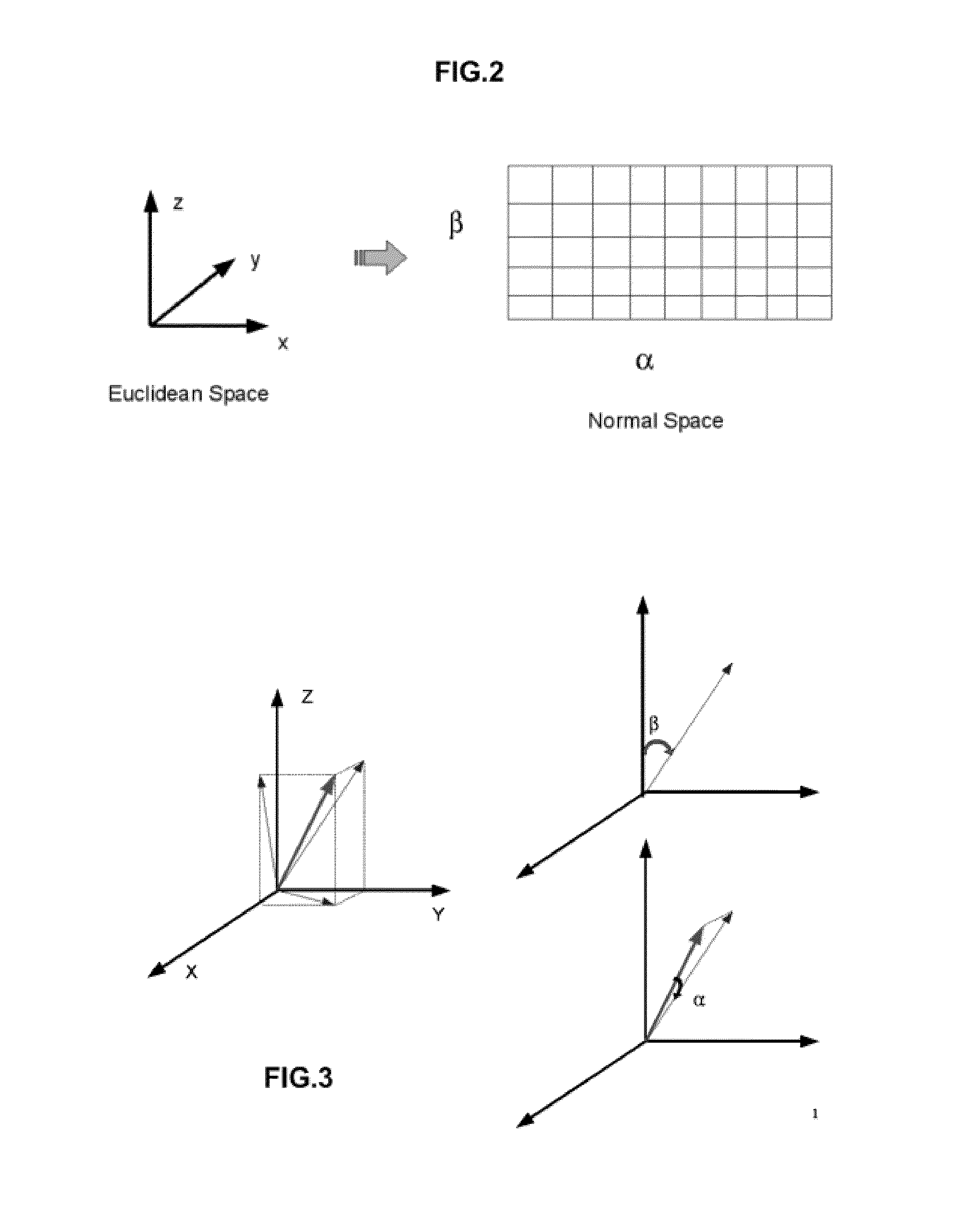
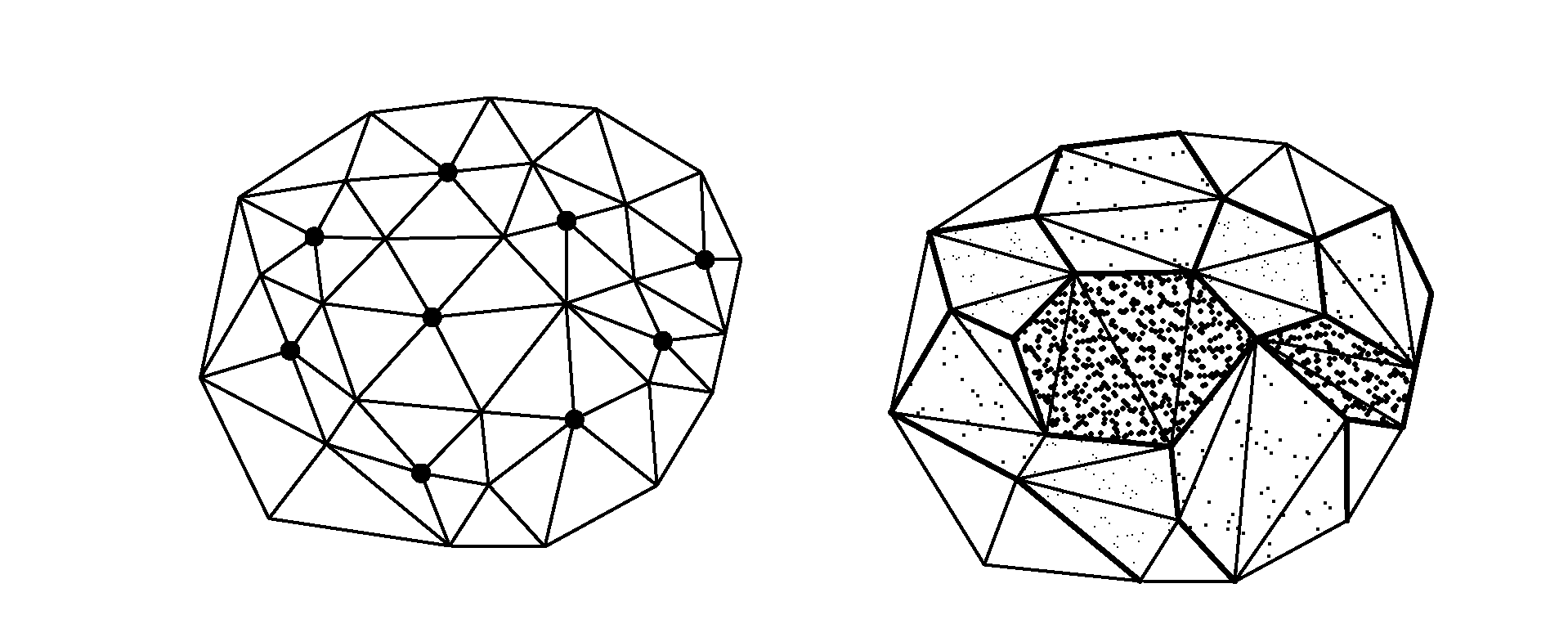
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
851 results about "Control point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer-aided geometric design a control point is a member of a set of points used to determine the shape of a spline curve or, more generally, a surface or higher-dimensional object. For Bézier curves, it has become customary to refer to the d-vectors pᵢ in a parametric representation ∑ᵢ pᵢϕᵢ of a curve or surface in d-space as control points, while the scalar-valued functions ϕᵢ, defined over the relevant parameter domain, are the corresponding weight or blending functions.
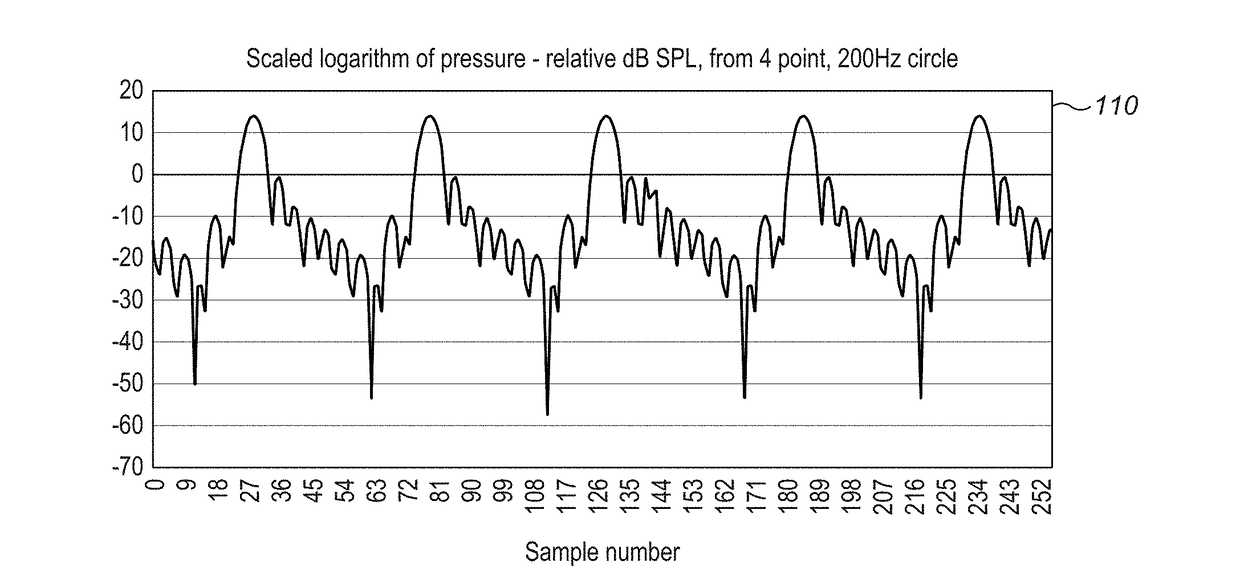
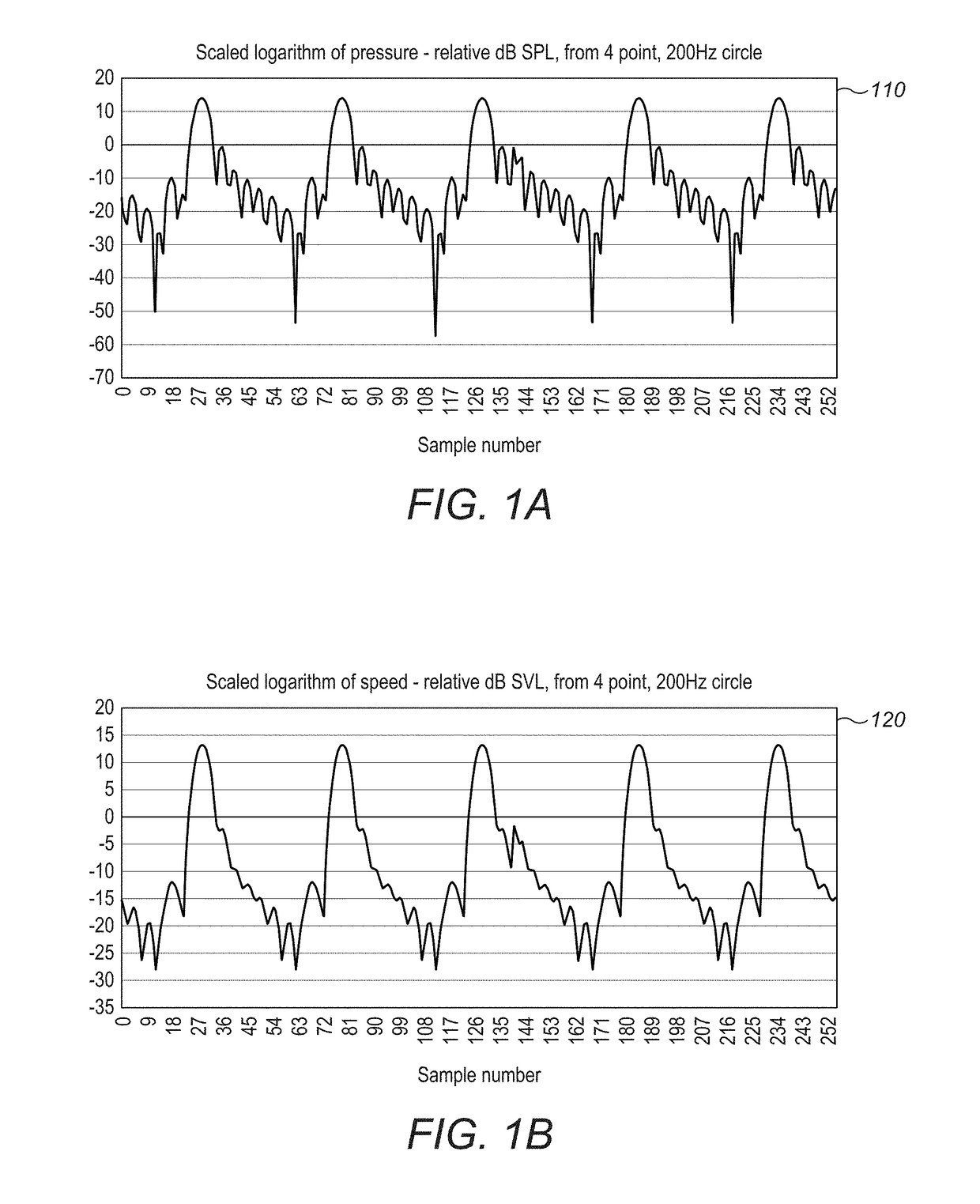
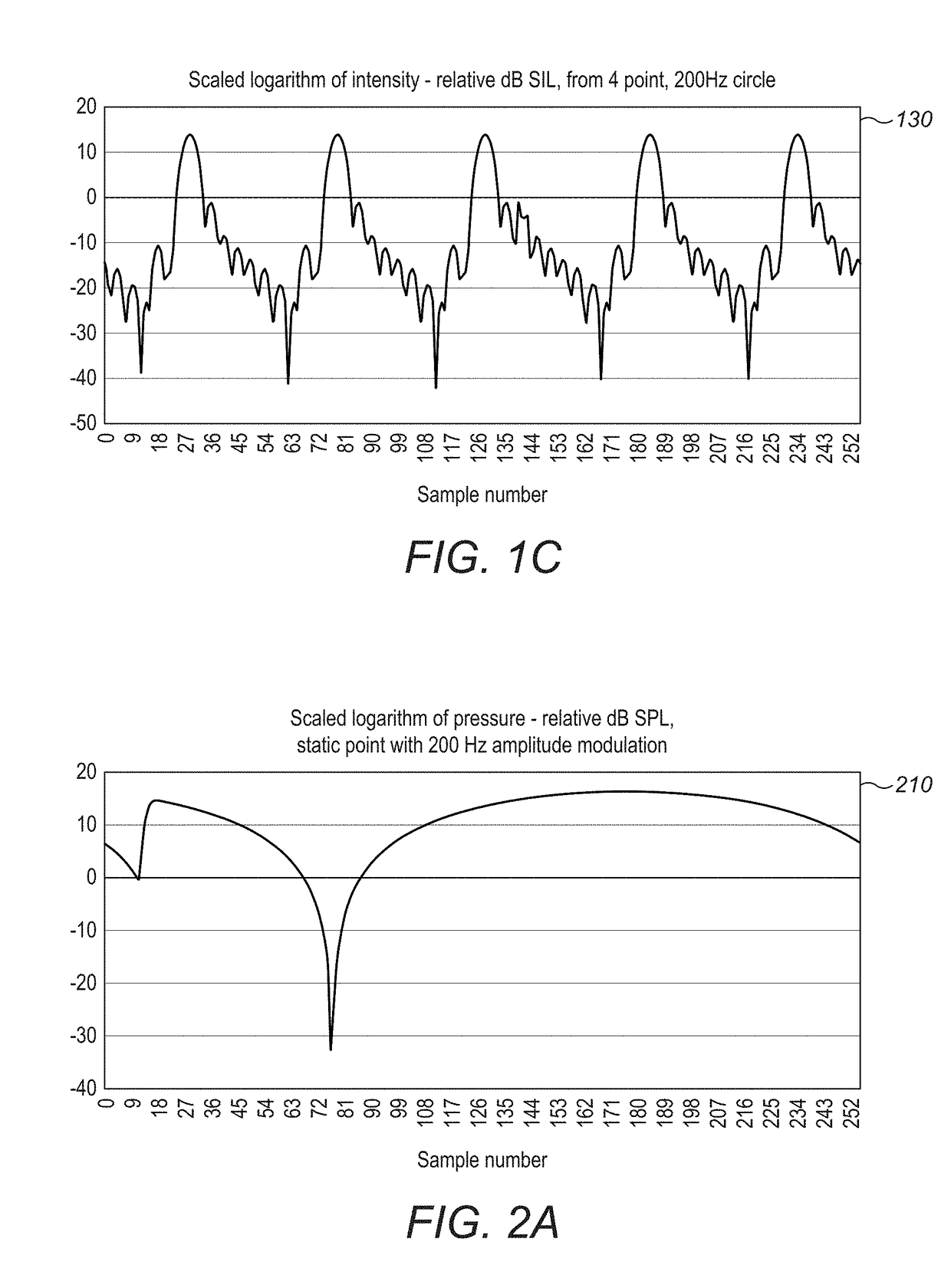
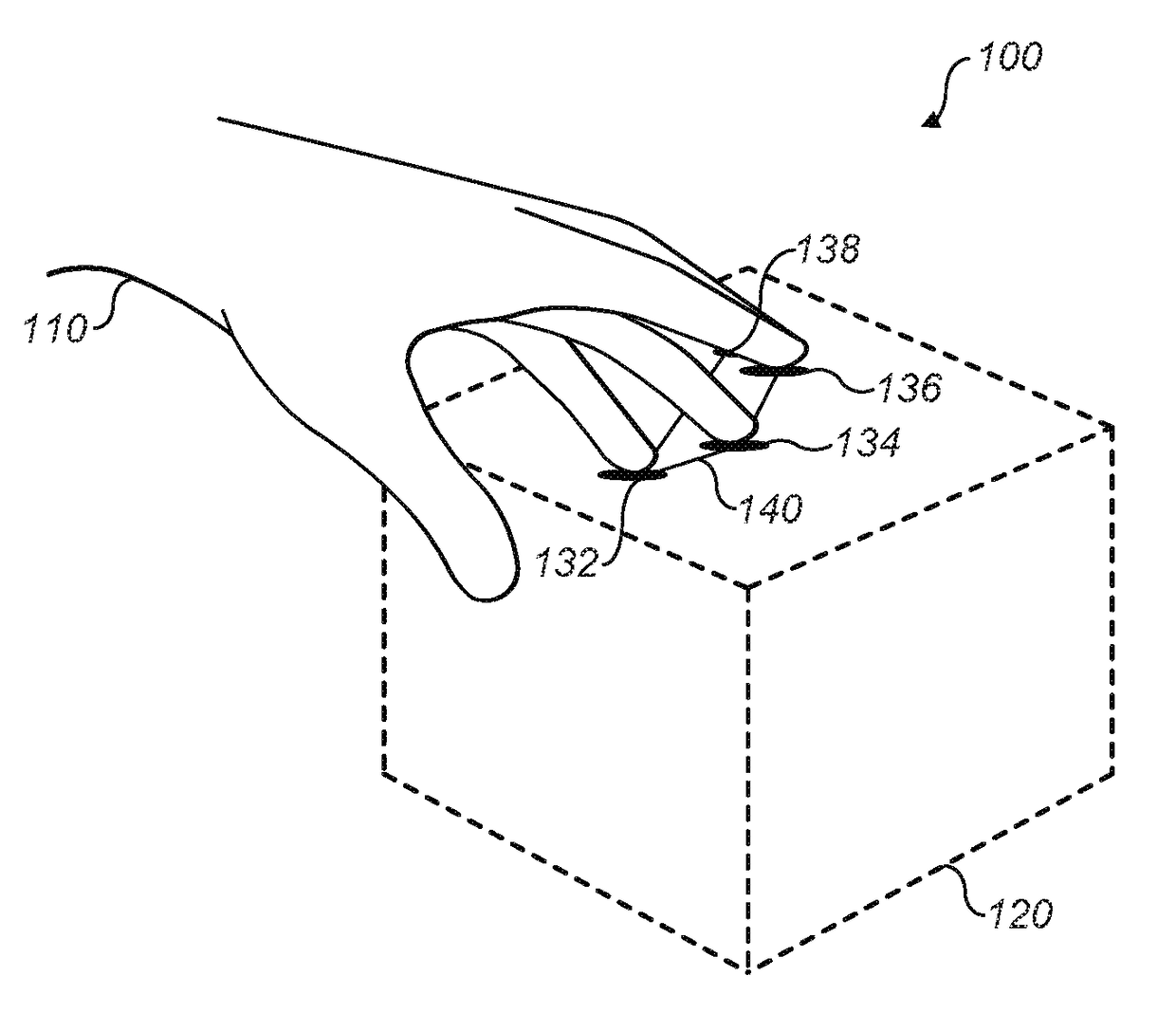
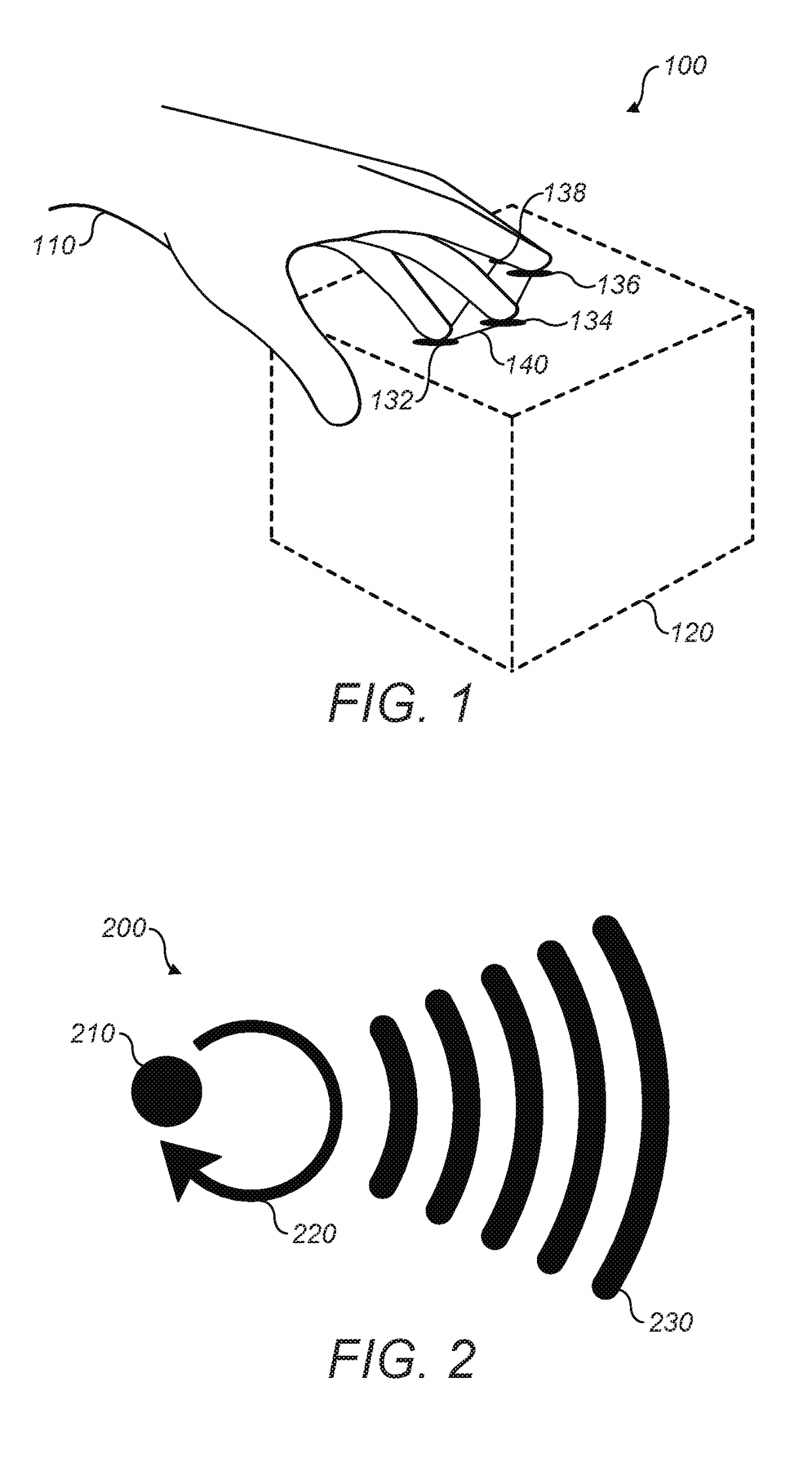
Method and apparatus for producing an acoustic field
ActiveUS20160124080A1Improve power output efficiencyEasily specified matrix augmentationSound producing devicesStereophonic systemsFeature vectorRelative magnitude
A plurality of control points are defined having a known spatial relationship relative to an array of transducers. An amplitude is assigned to each control point. A matrix is produced containing elements which represent, for each of the control points, the effect that producing a modeled acoustic field having the assigned amplitude with a particular phase at the control point has on the consequential amplitude and phase of the modeled acoustic field at the other control points. Eigenvectors of the matrix are determined, each eigenvector representing a set of phases and relative amplitudes of the modeled acoustic field at the control points. One of the sets is selected and the transducer array is operated to cause one or more of the transducers to output an acoustic wave each having an initial amplitude and phase such that the phases and amplitudes of the resultant acoustic field at the control points correspond to the phases and relative amplitudes of the selected set.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
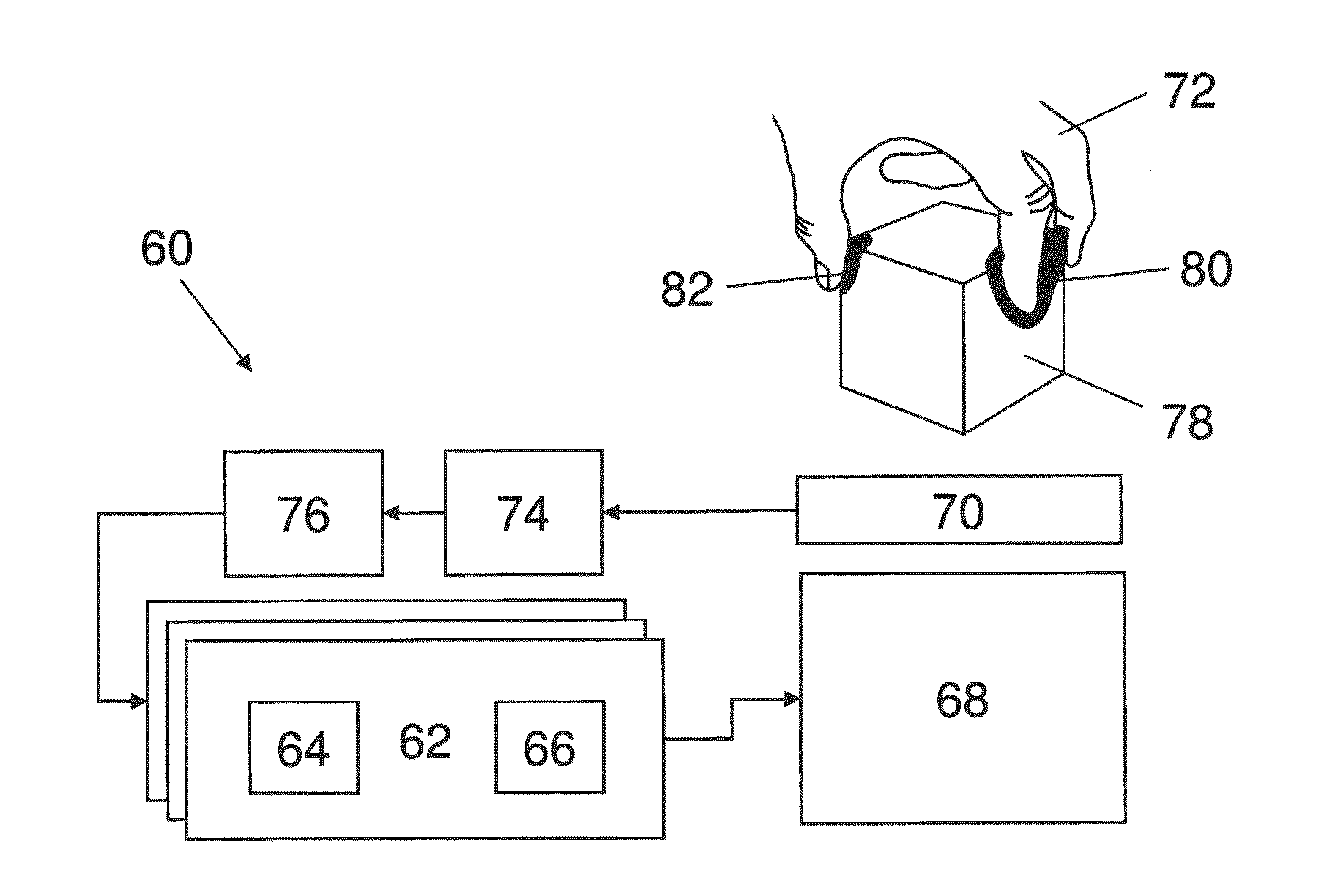
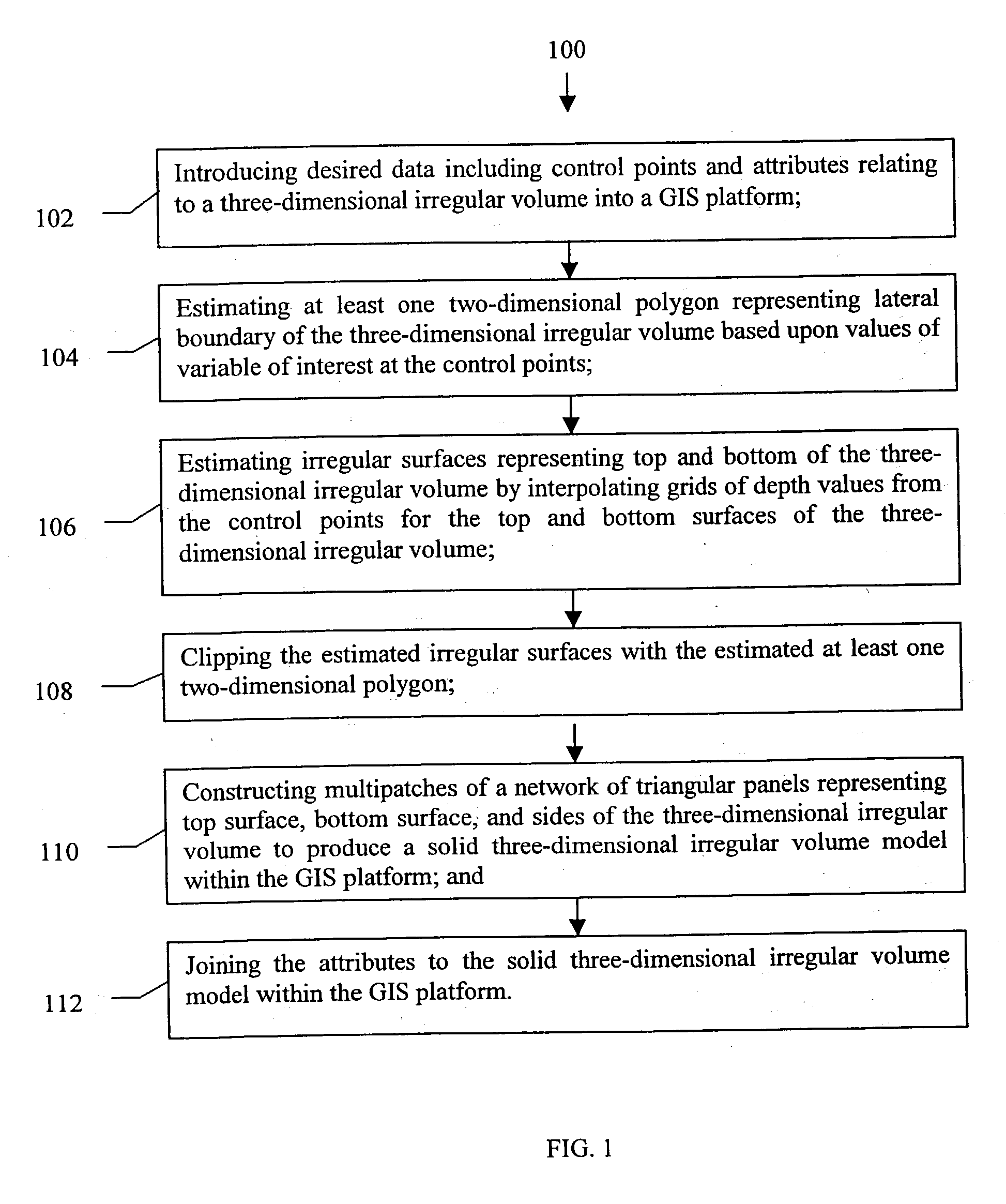
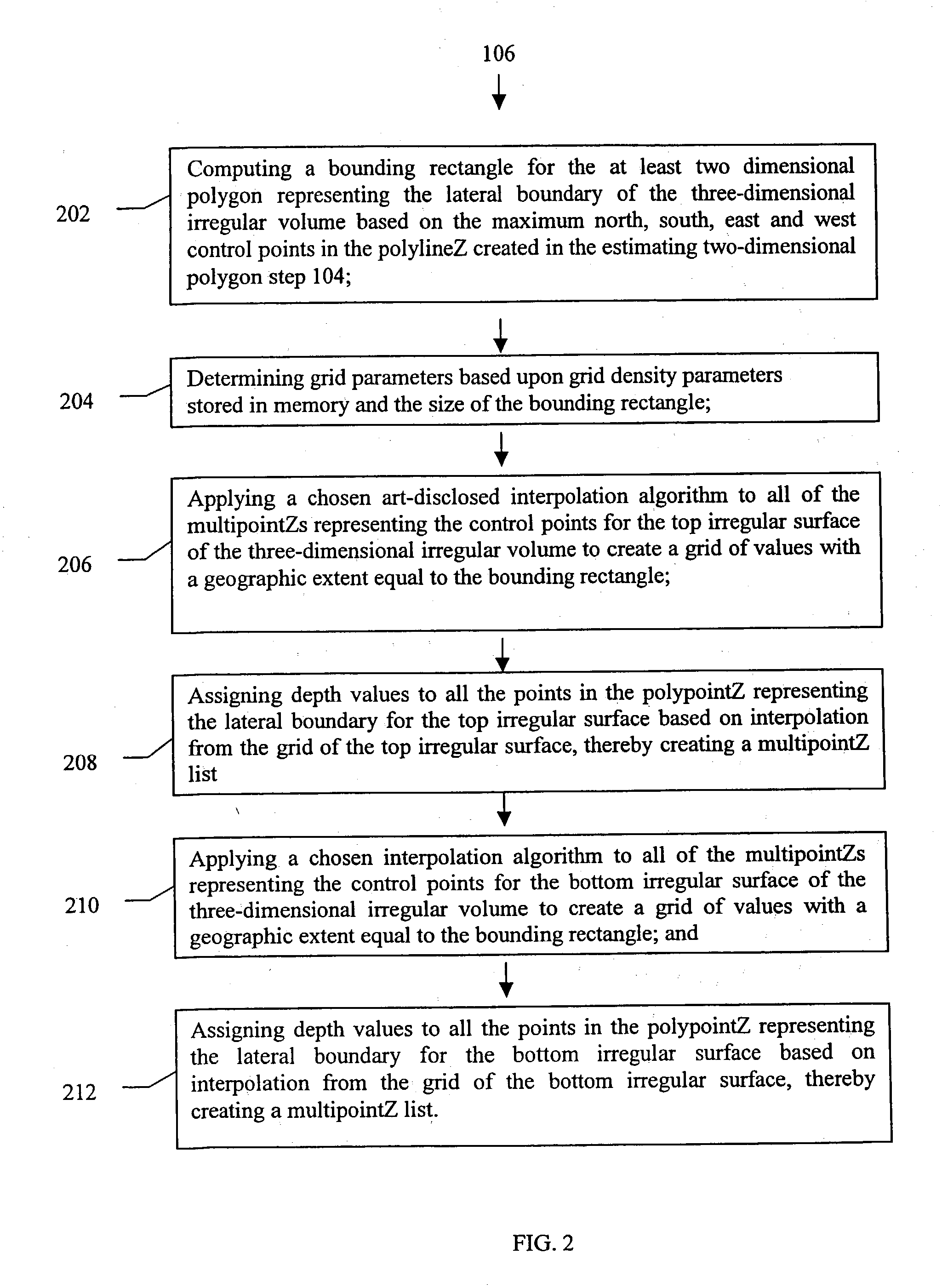
Method and system for creating irregular three-dimensional polygonal volume models in a three-dimensional geographic information system
InactiveUS20030112235A1Maps/plans/chartsSeismic signal processingWire frameGeographic information system
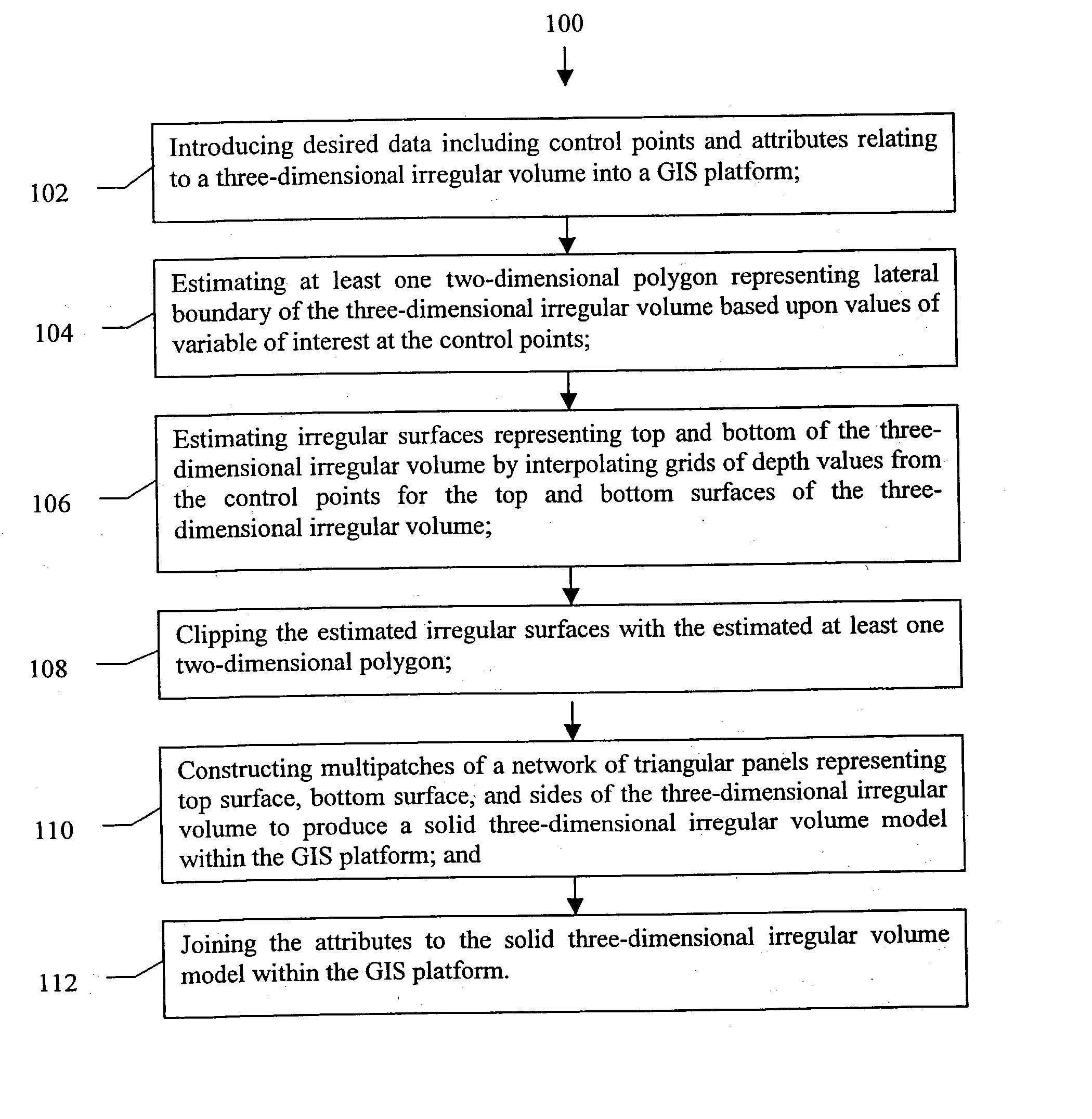
A method to construct a solid three-dimensional polygonal model of a three-dimensional irregular volume within a GIS platform comprising of: (1) introducing desired data including control points and attributes relating to the three-dimensional irregular volume into the GIS platform; (2) estimating at least one two-dimensional polygon representing a lateral boundary of the three-dimensional irregular volume based upon values of variable of interest at the control points; (3) estimating irregular surfaces representing top and bottom of the three-dimensional irregular volume by interpolating grids of depth values from the control points for the top and bottom surfaces of the three-dimensional irregular volume; (4) clipping the estimated irregular surfaces with the estimated at least one two-dimensional boundary polygon; (5) constructing multipatches of a network of triangular panels representing top surface, bottom surface, and sides of the three-dimensional irregular volume to produce a solid three-dimensional irregular volume model within the GIS platform; and (6) joining the attributes to the solid three-dimensional irregular volume model within the GIS platform. A method to construct a wire-frame three-dimensional polygonal model of a three-dimensional irregular volume within a GIS platform comprising of the same steps 1-4 and 6 as described above and the step of constructing a grid of regularly spaced polylineZs representing top surface, bottom surface, and sides of the three-dimensional irregular volume to produce the wire frame three-dimensional irregular volume model within the GIS platform. A system comprising of a computer system and processing software using the method of the present invention to construct a three-dimensional polygonal model of a three-dimensional irregular volume within a GIS platform.
Owner:EARTH SCI ASSOCS
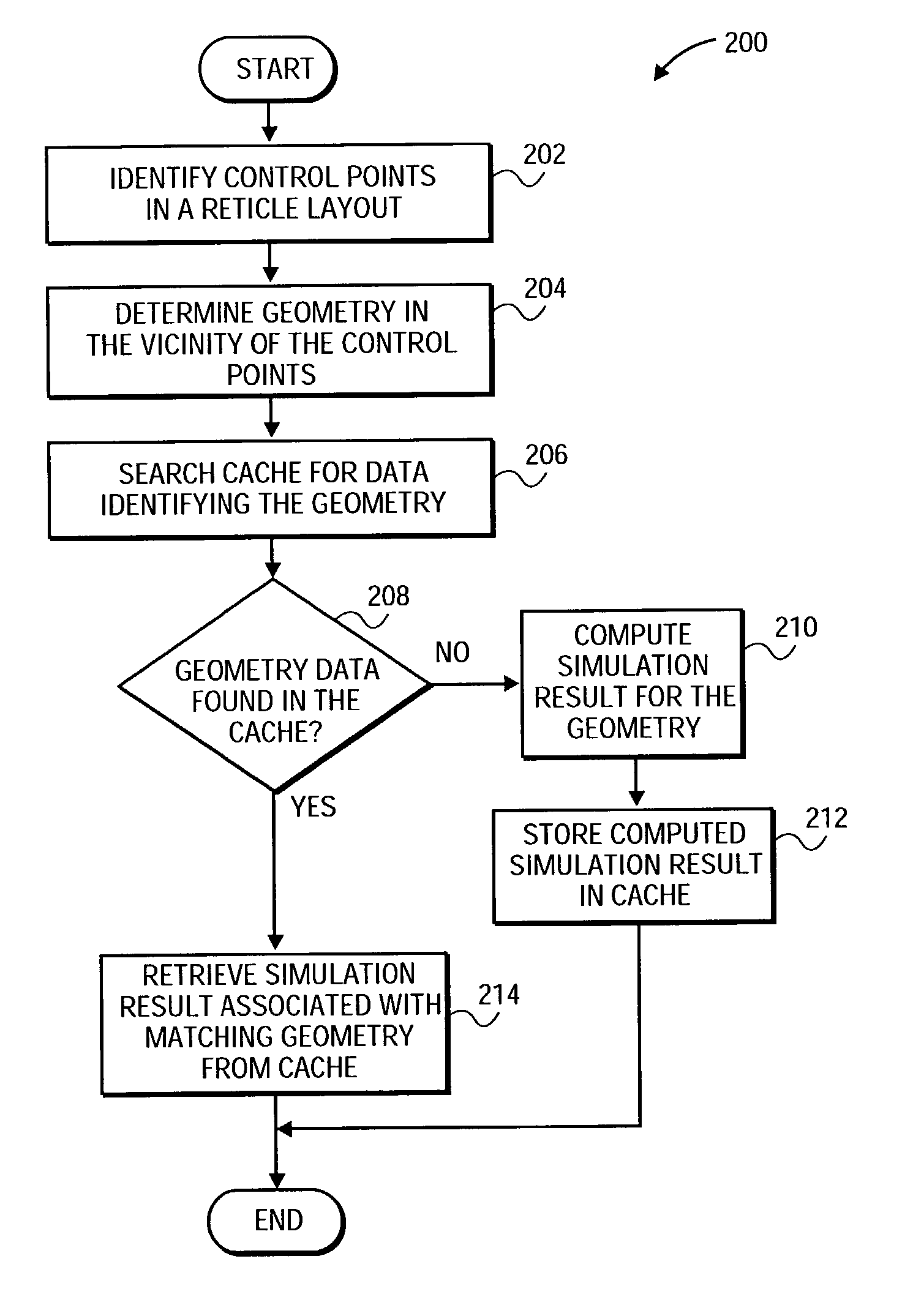
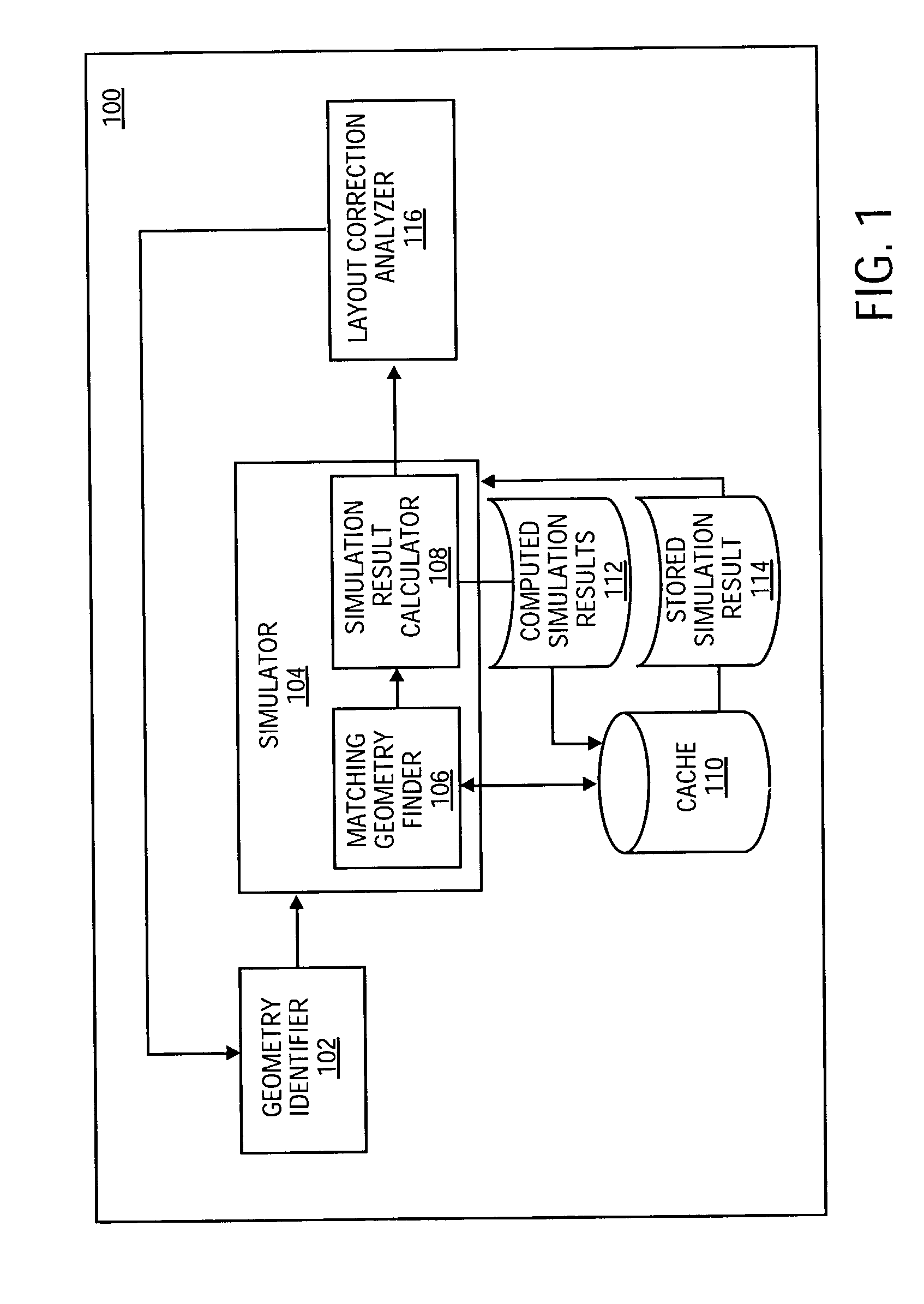
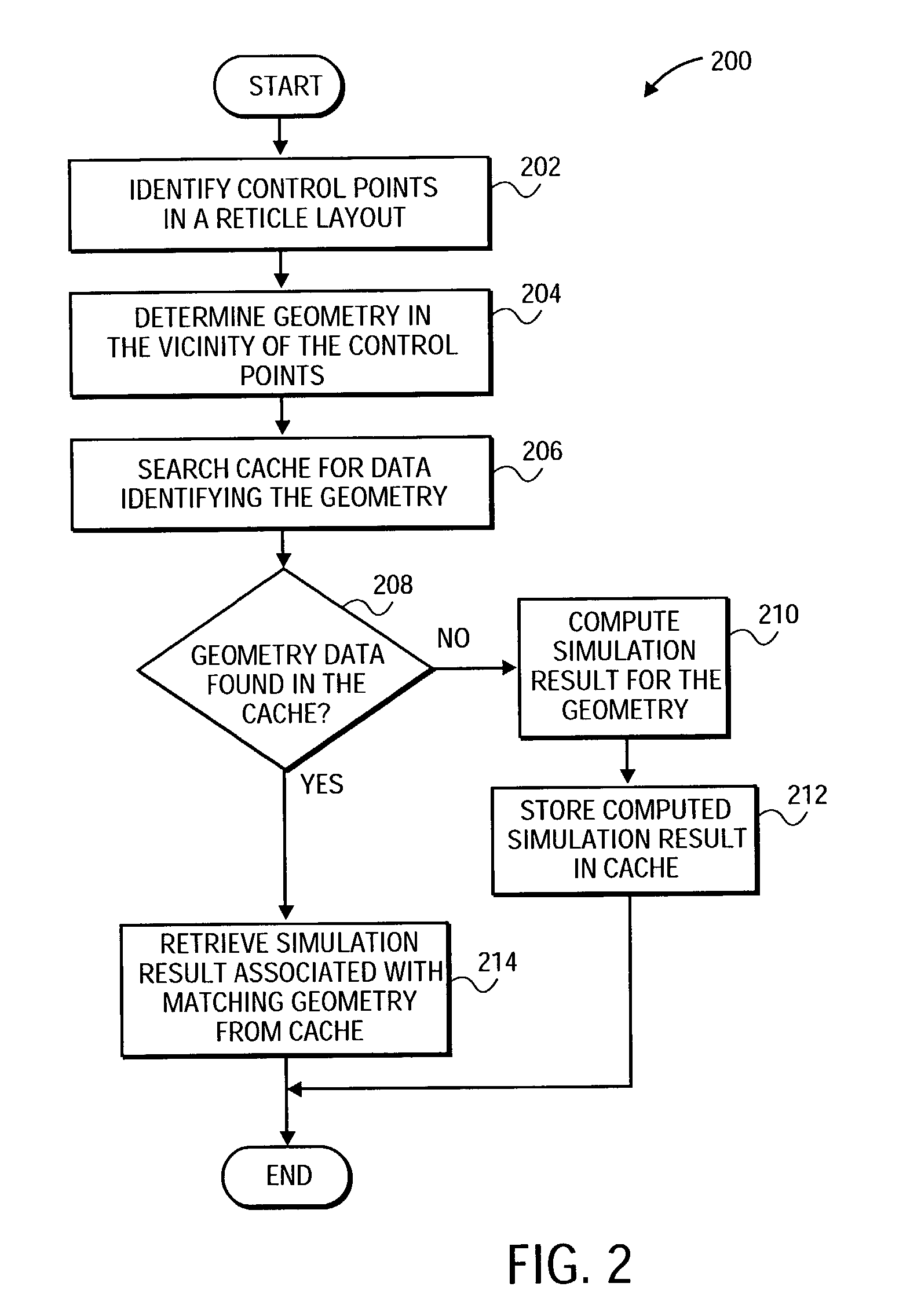
Caching of lithography and etch simulation results
InactiveUS6973633B2CAD circuit designOriginals for photomechanical treatmentDesign patternIntegrated devices
One or more control points are identified within a reticle layout that is used in a simulation of a manufacturing process for an integrated device layer. Further, a current geometrical layout pattern is determined in the vicinity of the control points, and a cache is searched for a matching geometrical layout pattern. If the search is successful, a simulation result associated with the matching geometrical layout pattern is retrieved from the cache and reused for the current geometrical layout pattern. Alternatively, if the search is unsuccessful, a simulation result associated with the current geometrical design pattern is computed and stored in the cache for future reuse.
Owner:SIEMENS PRODUCT LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
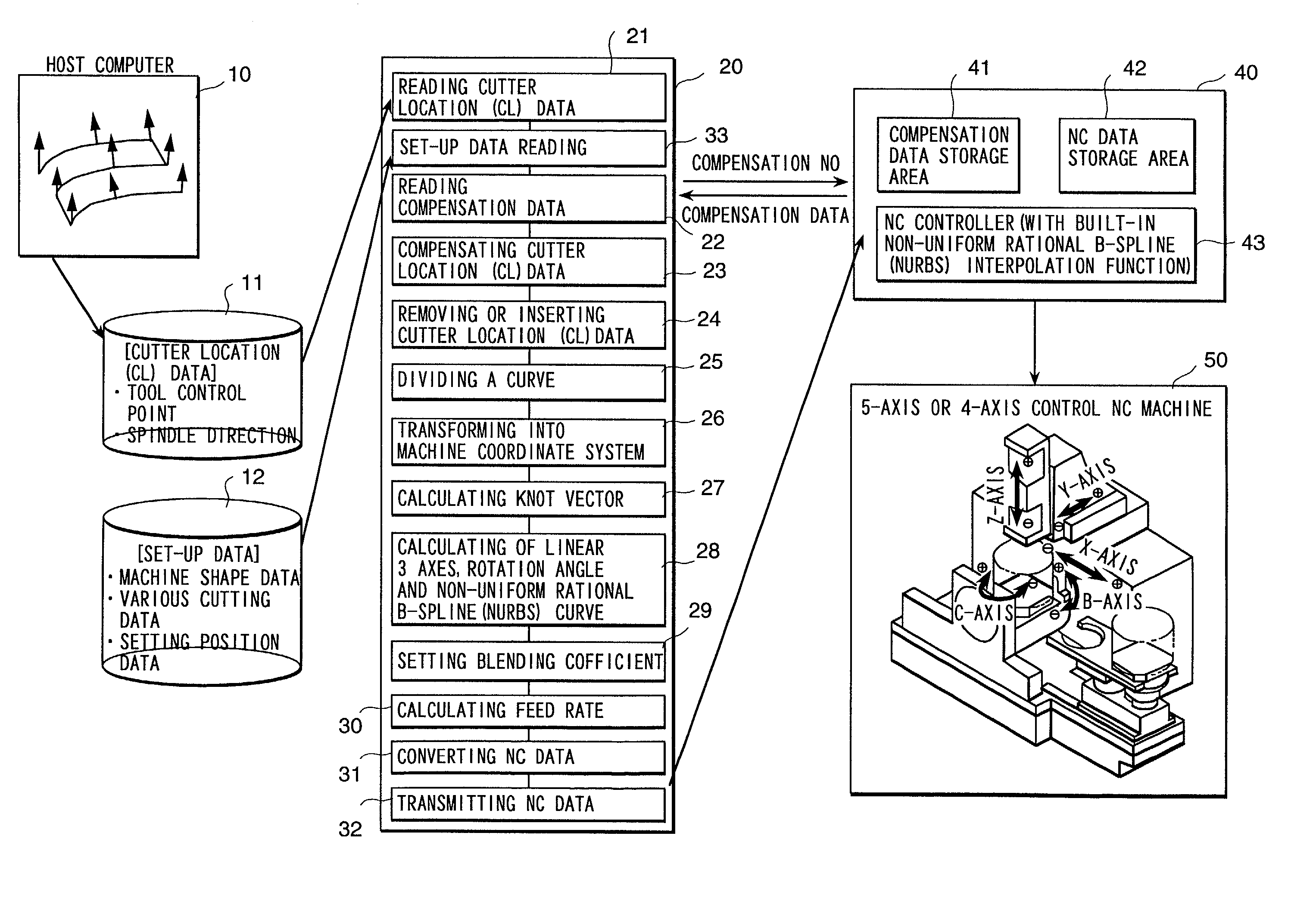
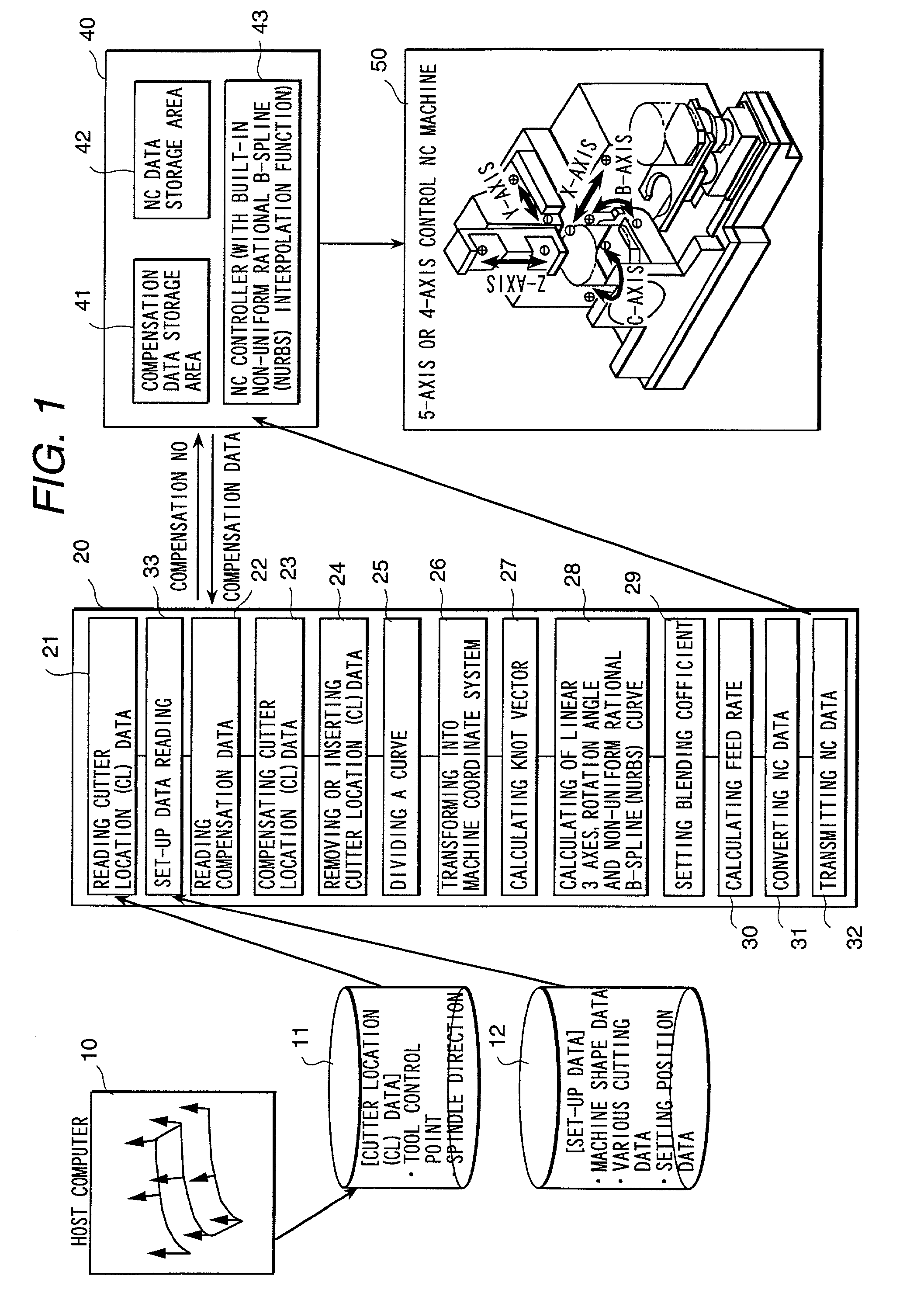
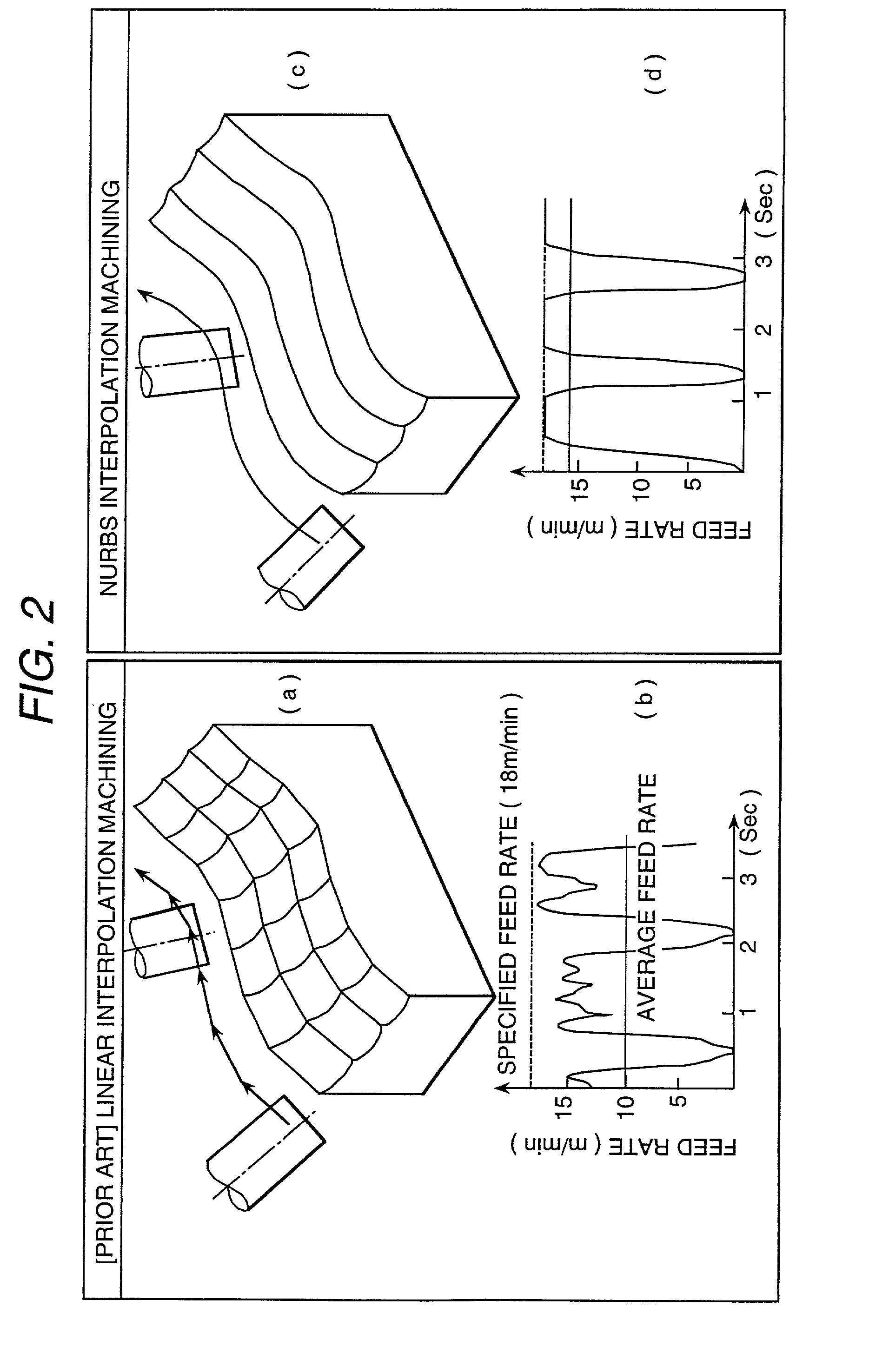
Numerically controlled curved surface machining unit
InactiveUS20020002420A1Automatic control devicesDrawing from basic elementsCutter locationSurface roughness
To provide a numerically controlled curved surface machining unit, and a method or program thereof, which, by moving a tool smoothly along a NURBS (non-uniform rational B-spline) curve, enables not only to improve the machining surface roughness and machining surface accuracy but to achieve high-speed machining so as to be able to eliminate hand finishing and reduce machining steps drastically. Performing NURBS (non-uniform rational B-spline) interpolation machining by a machine equipped with a means for reading cutter location (CL) data consisting of a tool control point vector and a tool axis vector on a workpiece coordinate system, a means for converting the CL data into a position vector of three linear axes and a rotation angle on a machine coordinate system in accordance with the machine configuration of a simultaneous multiple-axis NC machine, a means for calculating knot vectors of a NURBS curve with the most suitable chord length on the basis of a position vector of the three linear axes and a rotation angle, a means for calculating NURBS curve of the three linear axes and one rotary axis using the knot vectors, a means for converting the NURBS curve into NURBS interpolation NC data, a means for converting the feed rate on a workpiece coordinate system into the feed rate per minute on a machine coordinate system, and a means for transmitting NC data to a NC machine.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG +1
Algorithm Enhancements for Haptic-Based Phased-Array Systems
InactiveUS20180310111A1Reduce complexityReduction in fidelityInput/output for user-computer interactionSpeech analysisSonificationPattern perception
Improved algorithm techniques may be used for superior operation of haptic-based systems. An eigensystem may be used to determine for a given spatial distribution of control points with specified output the set of wave phases that are the most efficiently realizable. Reconstructing a modulated pressure field may use emitters firing at different frequencies. An acoustic phased-array device uses a comprehensive reflexive simulation technique. There may be an exchange of information between the users and the transducer control processors having the ability to use that information for optimal haptic generation shadows and the like. Applying mid-air haptic sensations to objects of arbitrary 3D geometry requires that sensation of the object on the user's hand is as close as possible to a realistic depiction of that object. Ultrasonic haptics with multiple and / or large aperture arrays have high-frequency update rates required by the spatio-temporal modulation. More efficient haptic systems require the prevention of a channel of audio unintentionally encoding phase information that may distort its perception.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Three-Dimensional Perceptions in Haptic Systems
ActiveUS20180039333A1Input/output for user-computer interactionSound input/outputHuman bodyPhysics engine
An acoustic field may be produced from a transducer array having known relative positions and orientations In this acoustic field, one or more control points may be defined. An amplitude may be assigned to the control point. Mid-air haptic effect for a virtual object on a human body part may be generated by moving the control point in a single closed curve comprising a plurality of curve segments. The single closed curve traverses at least one location where the human body part intersects with the virtual object. Additionally, a user may interact with virtual three-dimensional content using the user's hands while a tracking system monitoring the user's hands, a physics engine updates the properties of the virtual three-dimensional content and a haptic feedback system provides haptic information to the user.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
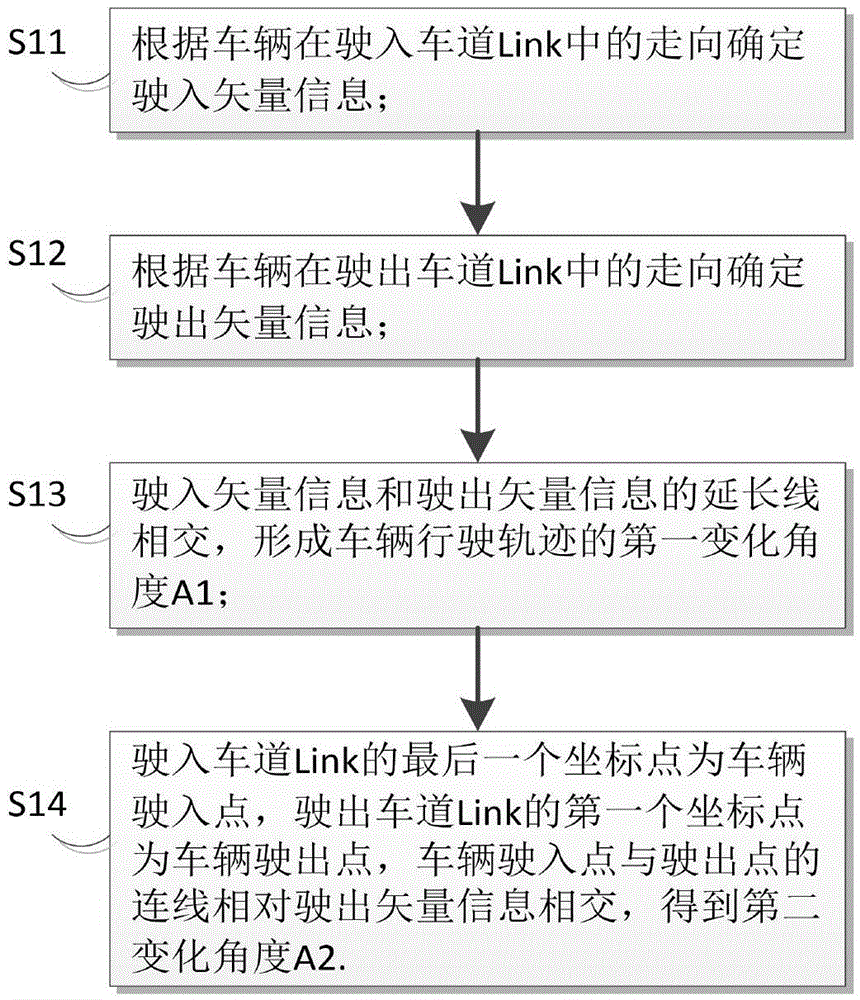
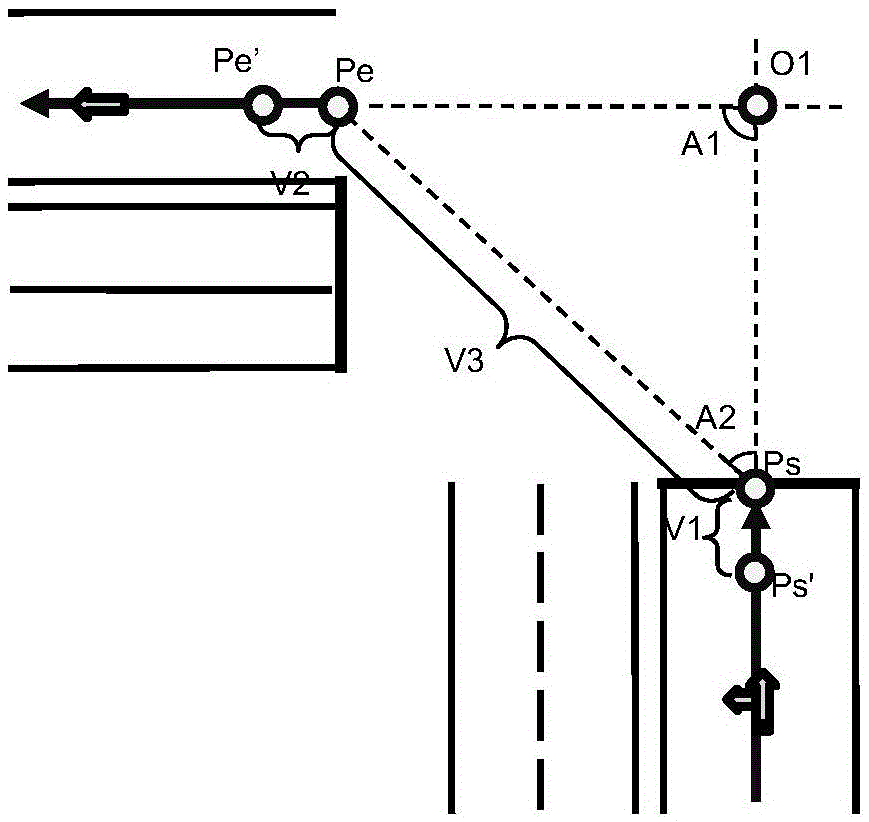
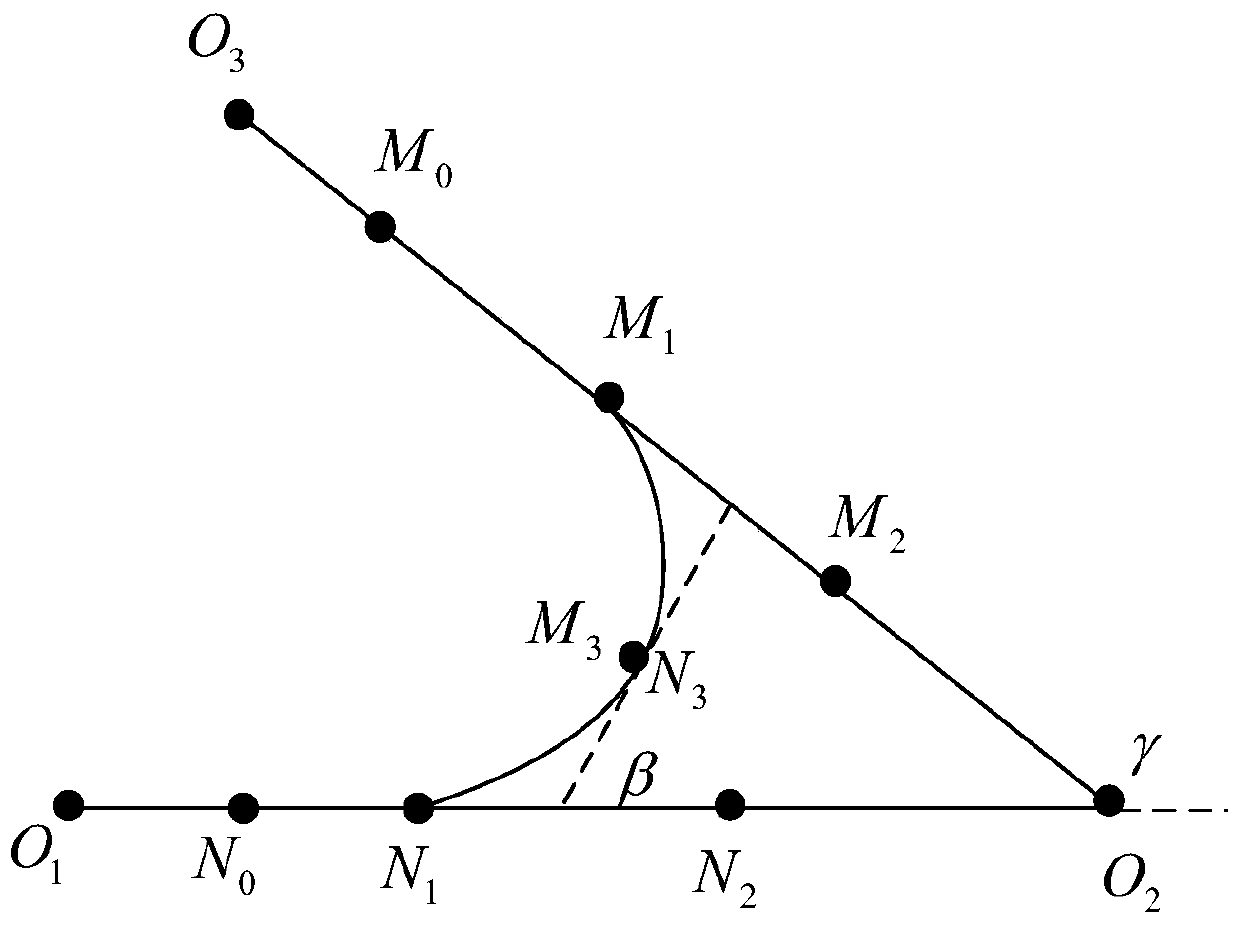
Connection curve algorithm for constructing intersection entry and exit lane Links based on Bezier curve
InactiveCN105651295AAvoid security issuesAvoid the situationInstruments for road network navigationReference lineComputer science
The invention discloses a connection curve algorithm for constructing intersection entry and exit lane Links based on a Bezier curve. It can be ensured that the curve is tangent to the entry lane Link and the exit lane Link through characteristics of the Bezier curve, meanwhile, the through region of the curve can be safely controlled by means of the position of a middle control point, the phenomena of passing through an intersection safety island and a road edge are avoided, and the generated curve fits a safe wheelpath line. Accordingly, the safe wheelpath reference line can be provided for an unmanned car when the car passes through the intersection. According to characteristics of the Bezier curve, the algorithm for connecting wheelpath curves of the intersection entry and exit lane Links is built, the algorithm meets the fitness and safety demand of the actual wheelpaths, the algorithm is unified and convenient to obtain, and the algorithm can be used for different moving direction connecting relations.
Owner:WUHAN ZHONGHAITING DATA TECH CO LTD
Cutter spacing optimizing method for cydariform knife tool multiple coordinates line width processing
InactiveCN101063880AAvoid Artificial Adjustment WorkIncrease programming automationTotal factory controlNumerical controlProcess optimizationLine width
This invention relates to one bump knife tool multi-coordinate wide row process optimization method, which comprises the following steps: isolating the tool into one set of intense latitude lines according to its process type; through computation on each latitude line distance to process design curve to get error distribution function; accordingly establishing wide computation method and restrains to form tool optimization module. To avoid backward adjust, the part is selected with one control point and to determine one point beyond for one relative initial position from one point in program public error and the selection point.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
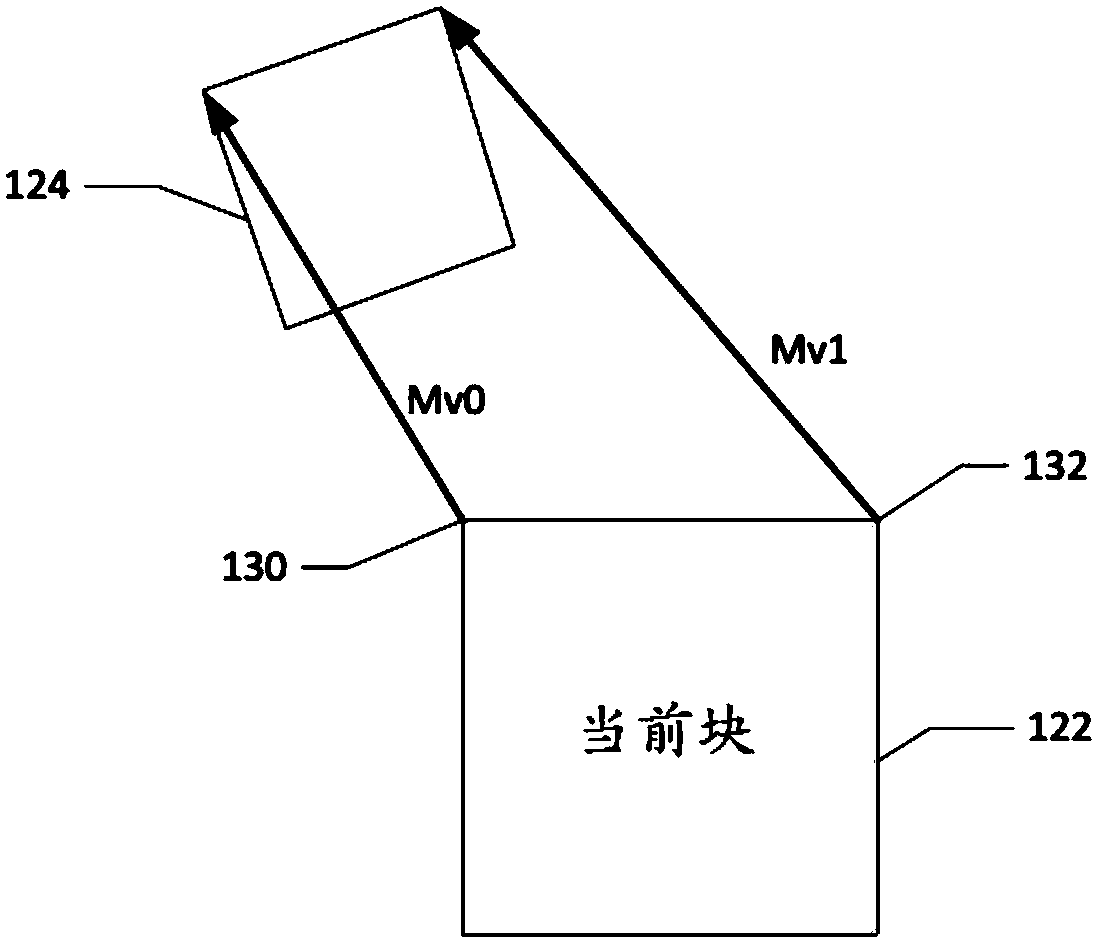
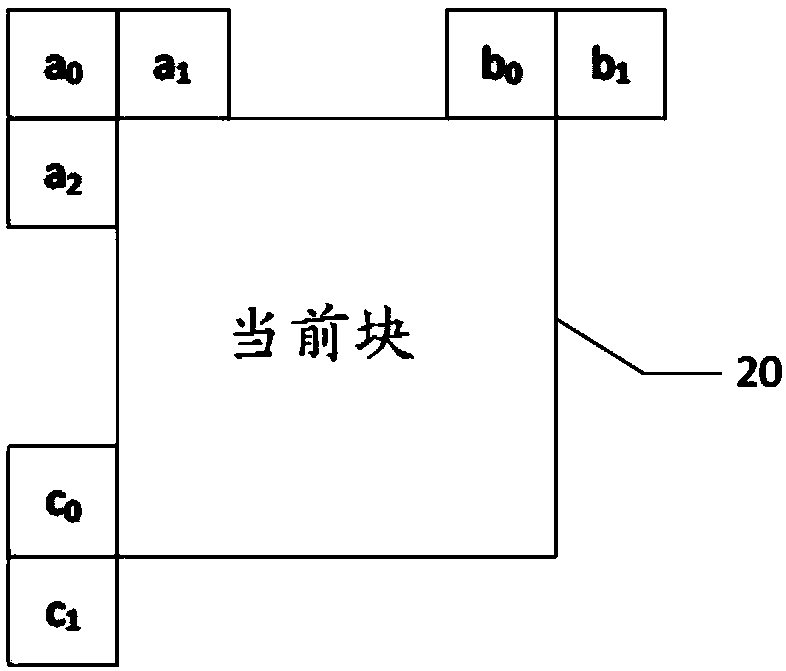
Method and apparatus of video coding with affine motion compensation
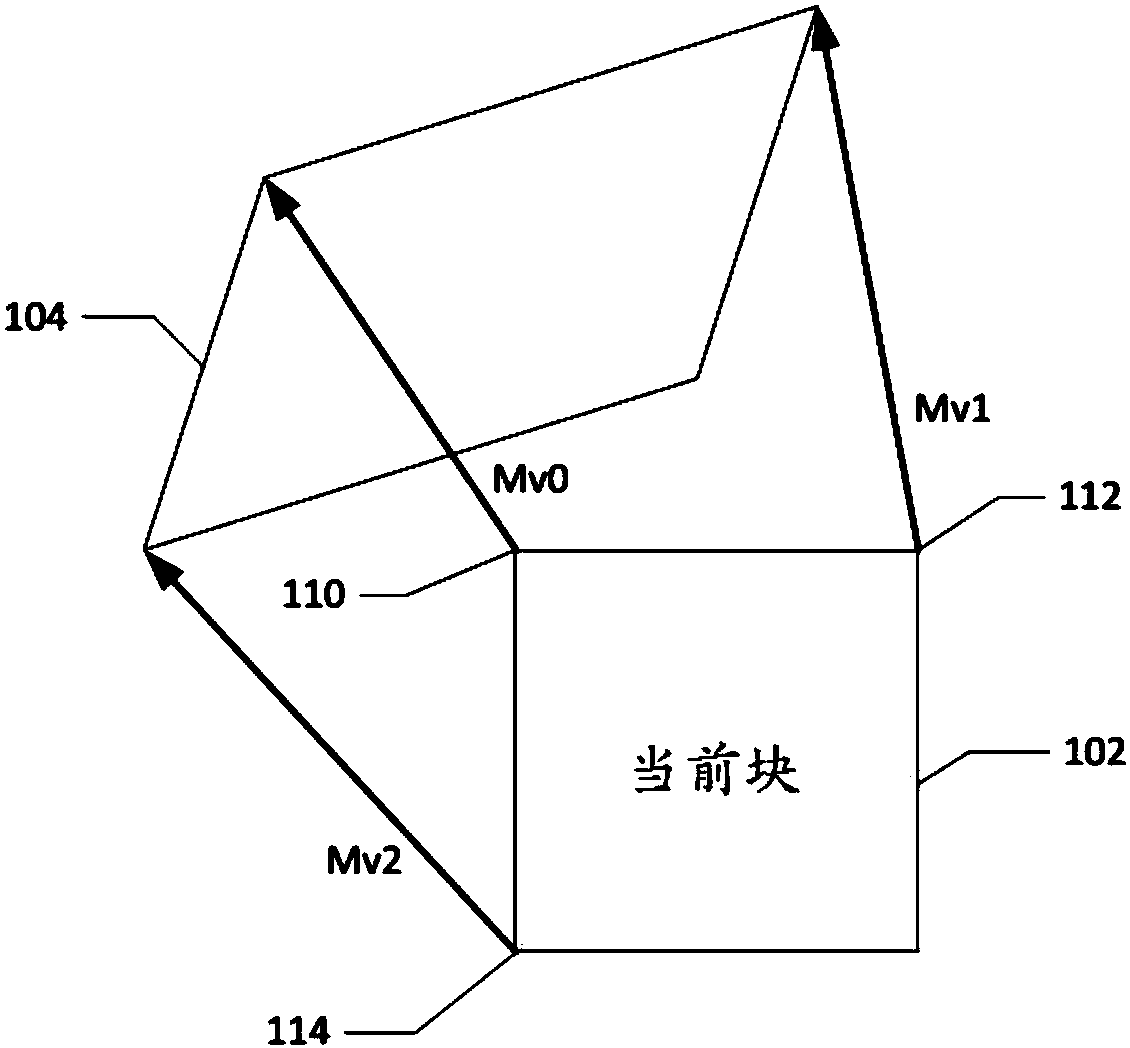
An encoding or decoding method with affine motion compensation includes receiving input data associated with a current block in a current picture, and deriving a first affine candidate for the currentblock including three affine motion vectors for predicting motion vectors at control points of the current block if the current block is coded or to be coded in affine Merge mode. The affine motion vectors are derived from three different neighboring coded blocks of the current block. An affine motion model is derived according to the affine motion vectors if the first affine candidate is selected. Moreover, the method includes encoding or decoding the current block by locating a reference block in a reference picture according to the affine motion model. The current block is restricted to becoded in uni-directional prediction if the current block is coded or to be coded in affine Inter mode.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
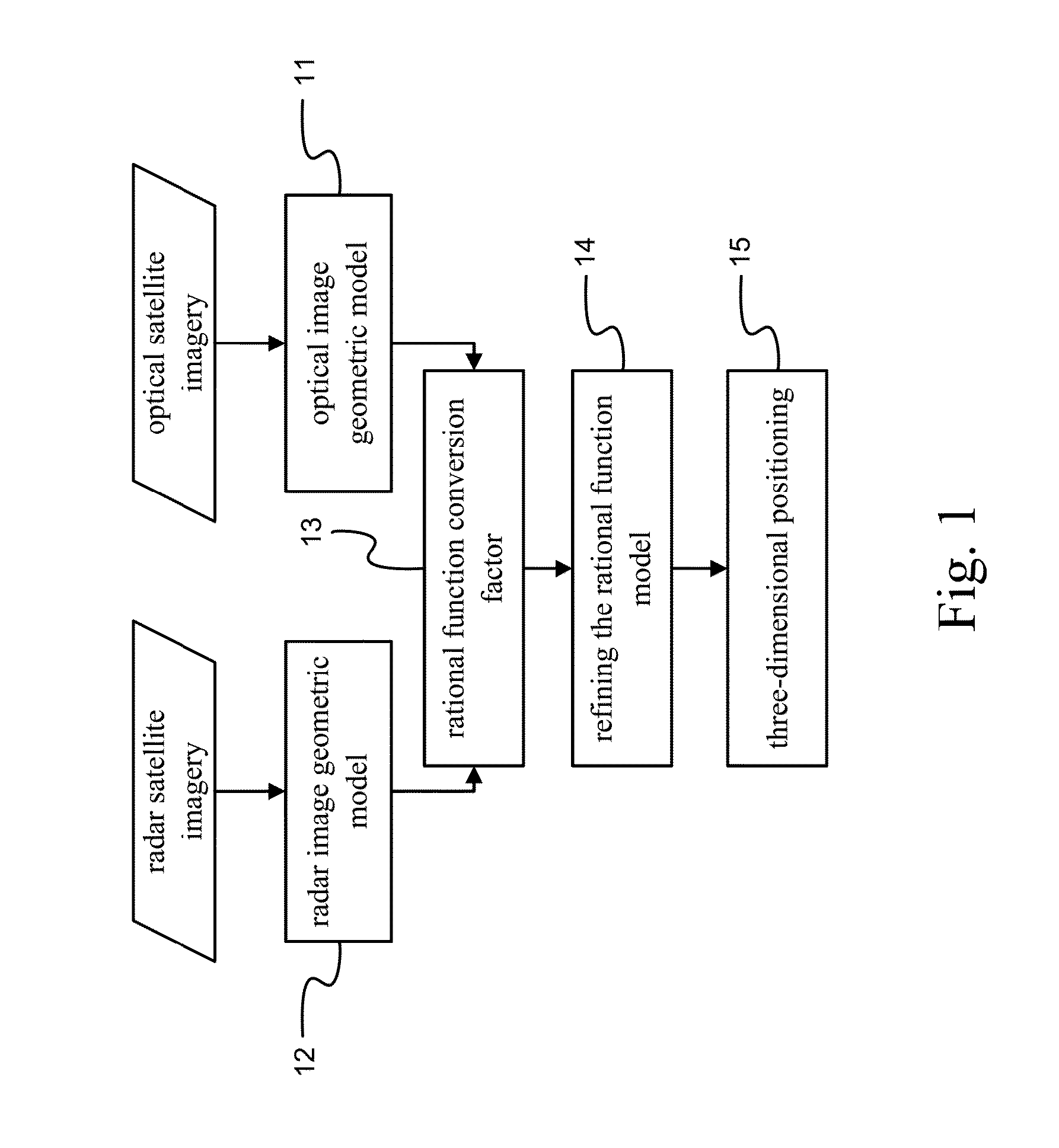
Three-dimensional positioning method
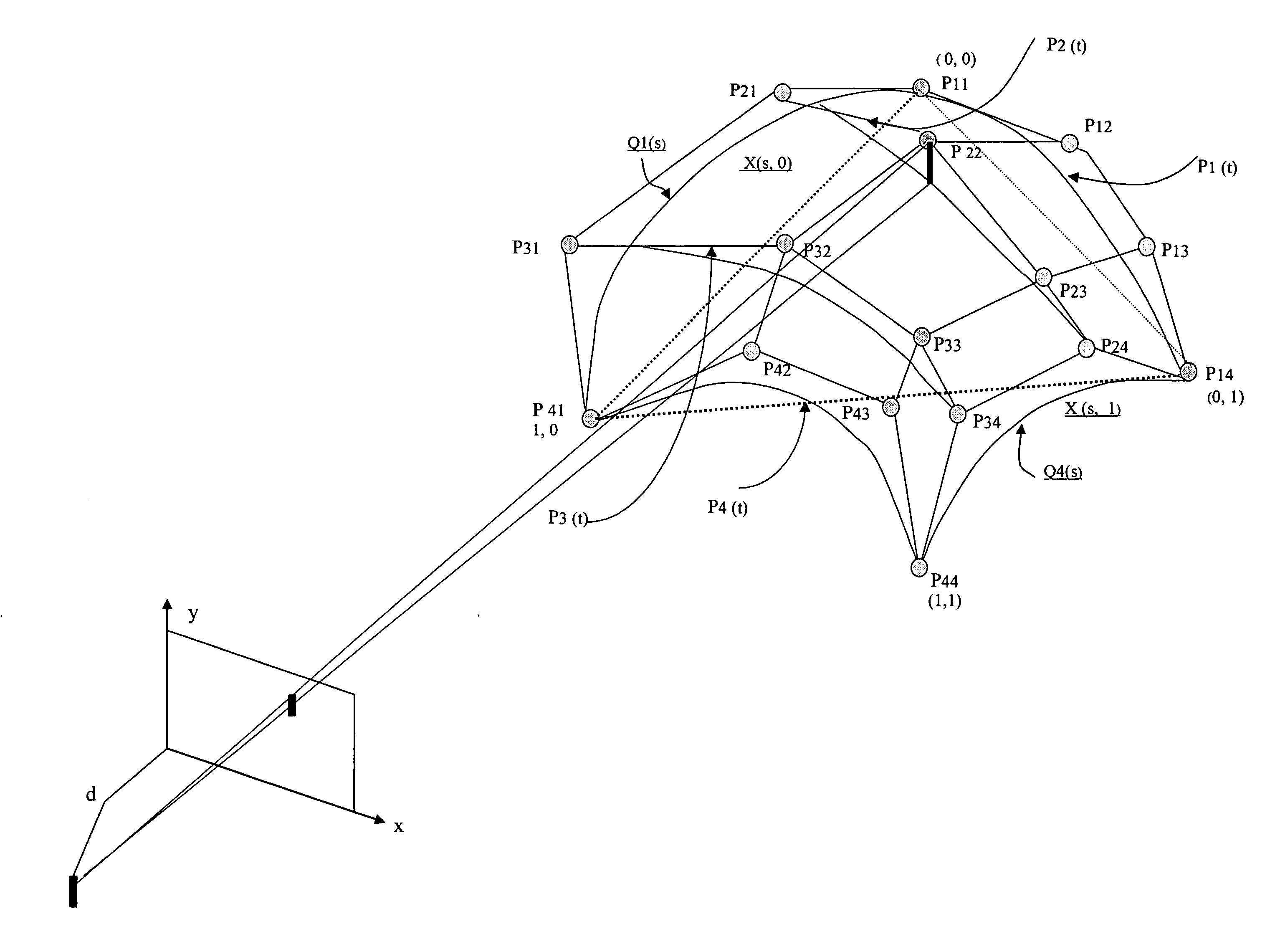
InactiveUS20140191894A1Improve shortcomingsImage enhancementImage analysisRadarConversion coefficients
A three-dimensional positioning method includes establishing the geometric model of optical and radar sensors, obtaining rational function conversion coefficient, refining the rational function model and positioning the three-dimensional coordinates. Most of the radar satellite companies and part of the optical satellite only provide satellite ephemeris data, rather than the rational function model. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain the rational polynomial coefficients from the geometric model of optical and radar sensors; followed by refining the rational function model by the ground control points, so that object image space intersection is more serious; and then followed by measuring the conjugate point on the optical and radar images. Finally, the observation equation is established by the rational function model to solve the three-dimensional coordinates. It is obvious from the above results that the integration of optical and radar images does achieve the three-dimensional positioning.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Method and apparatus for producing an acoustic field
ActiveUS9977120B2Faster andFaster and more solution timeSound producing devicesStereophonic systemsRelative magnitudeFeature vector
A plurality of control points are defined having a known spatial relationship relative to an array of transducers. An amplitude is assigned to each control point. A matrix is produced containing elements which represent, for each of the control points, the effect that producing a modeled acoustic field having the assigned amplitude with a particular phase at the control point has on the consequential amplitude and phase of the modeled acoustic field at the other control points. Eigenvectors of the matrix are determined, each eigenvector representing a set of phases and relative amplitudes of the modeled acoustic field at the control points. One of the sets is selected and the transducer array is operated to cause one or more of the transducers to output an acoustic wave each having an initial amplitude and phase such that the phases and amplitudes of the resultant acoustic field at the control points correspond to the phases and relative amplitudes of the selected set.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
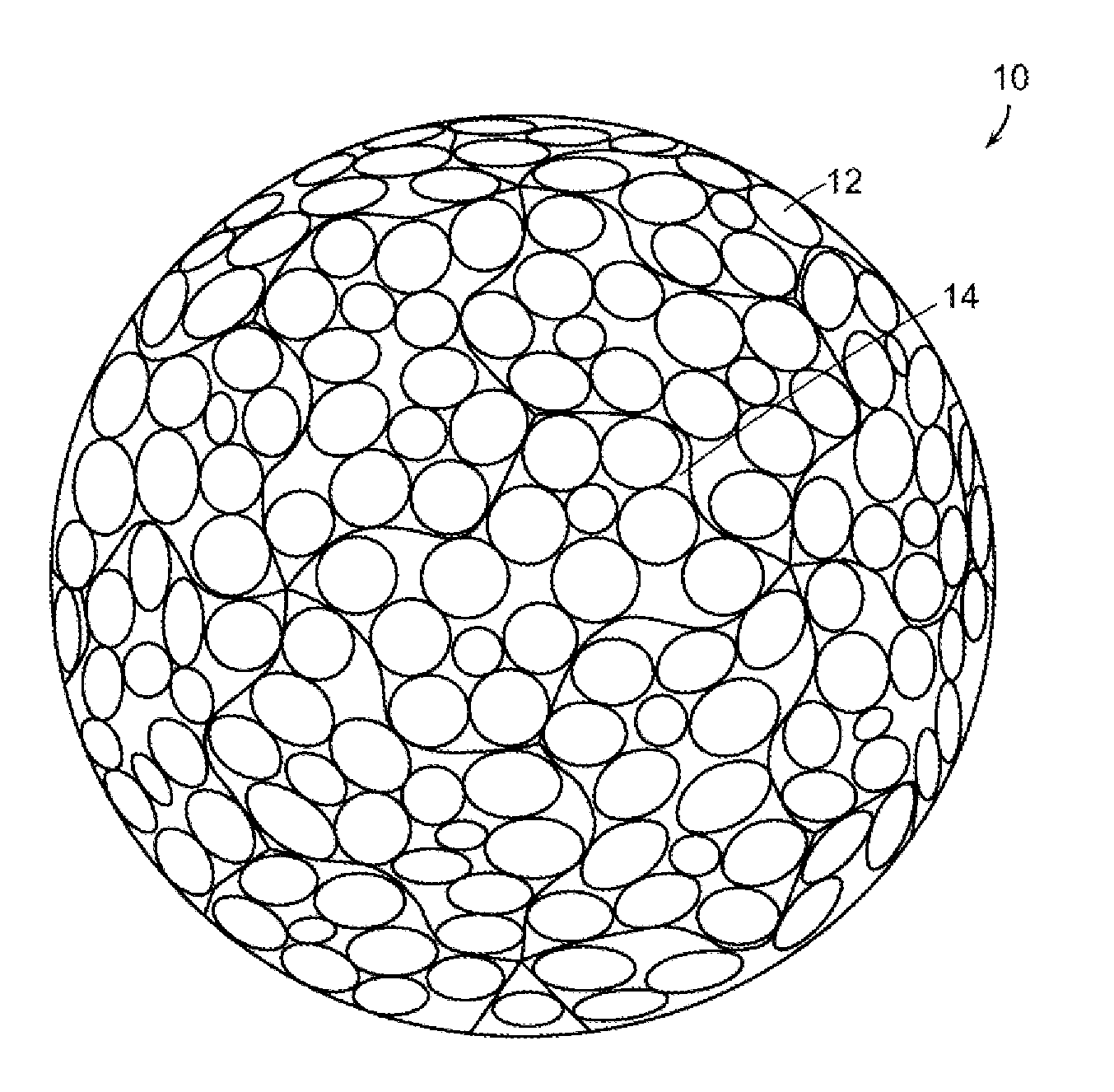
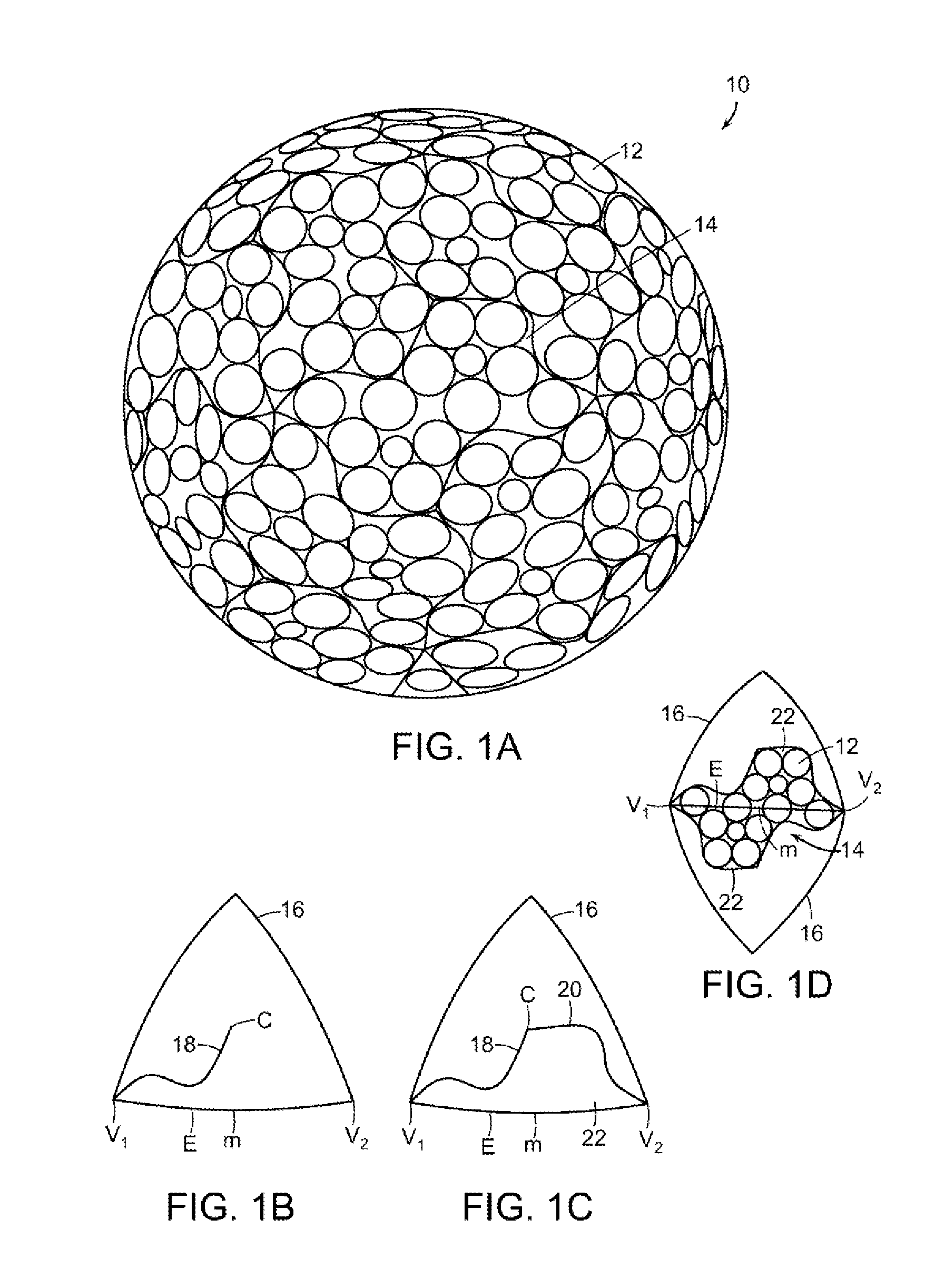
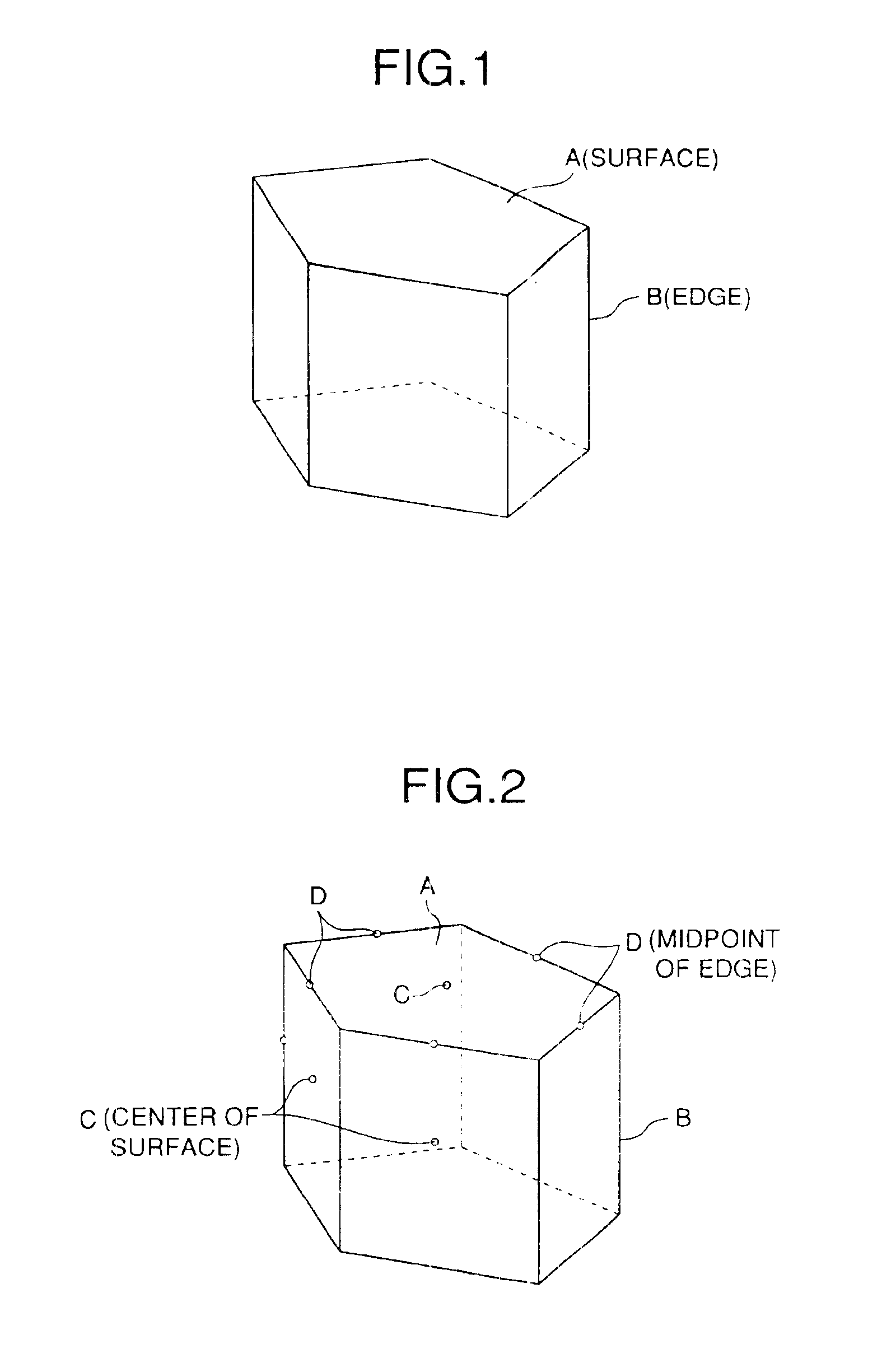
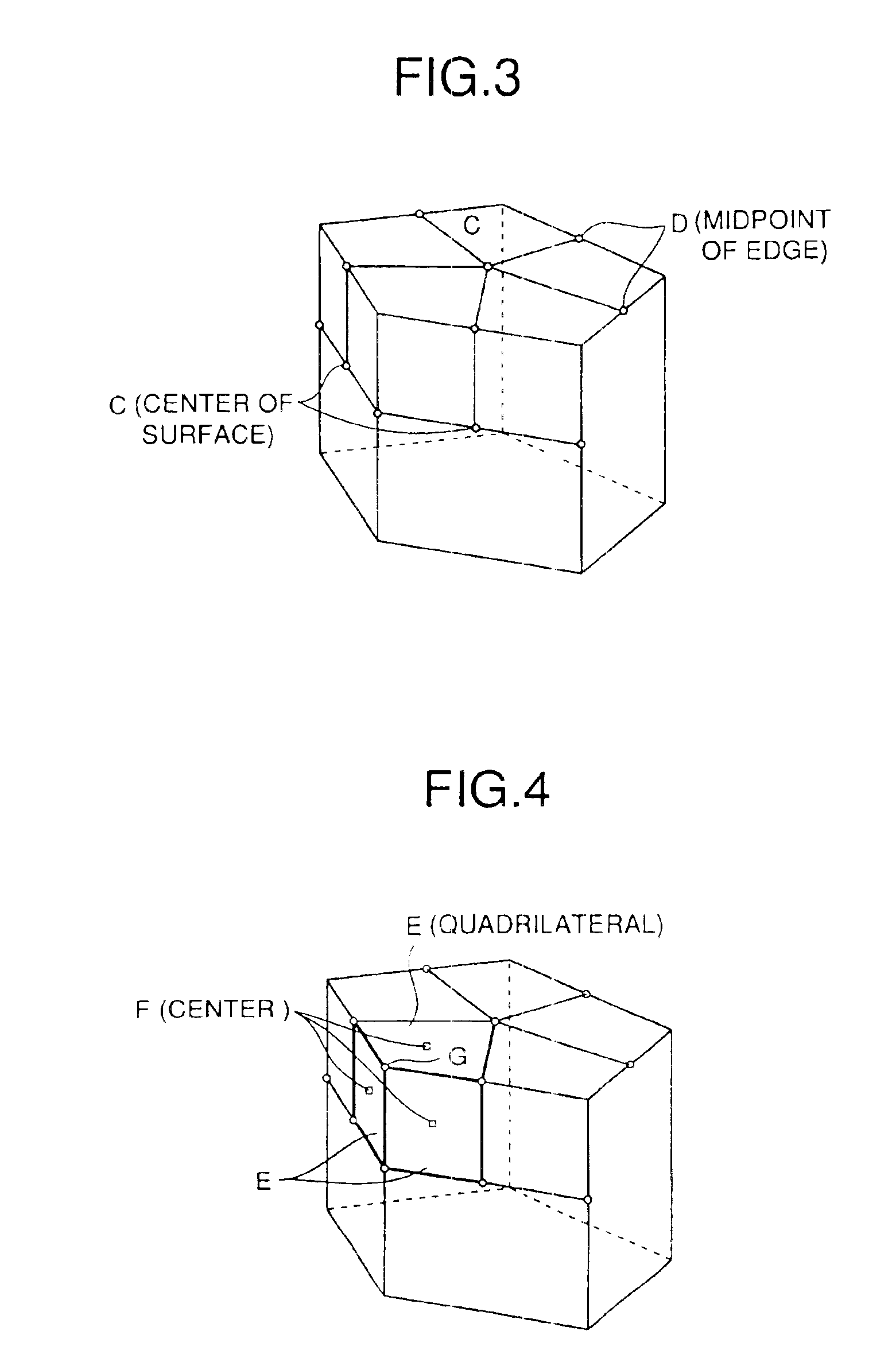
Dimple patterns for golf balls
The present invention provides a method for arranging dimples on a golf ball surface in which the dimples are arranged in a pattern derived from at least one irregular domain generated from a regular or non-regular polyhedron. The method includes choosing control points of a polyhedron, generating an irregular domain based on those control points, packing the irregular domain with dimples, and tessellating the irregular domain to cover the surface of the golf ball. The control points include the center of a polyhedral face, a vertex of the polyhedron, a midpoint or other point on an edge of the polyhedron and others. The method ensures that the symmetry of the underlying polyhedron is preserved while minimizing or eliminating great circles due to parting lines.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
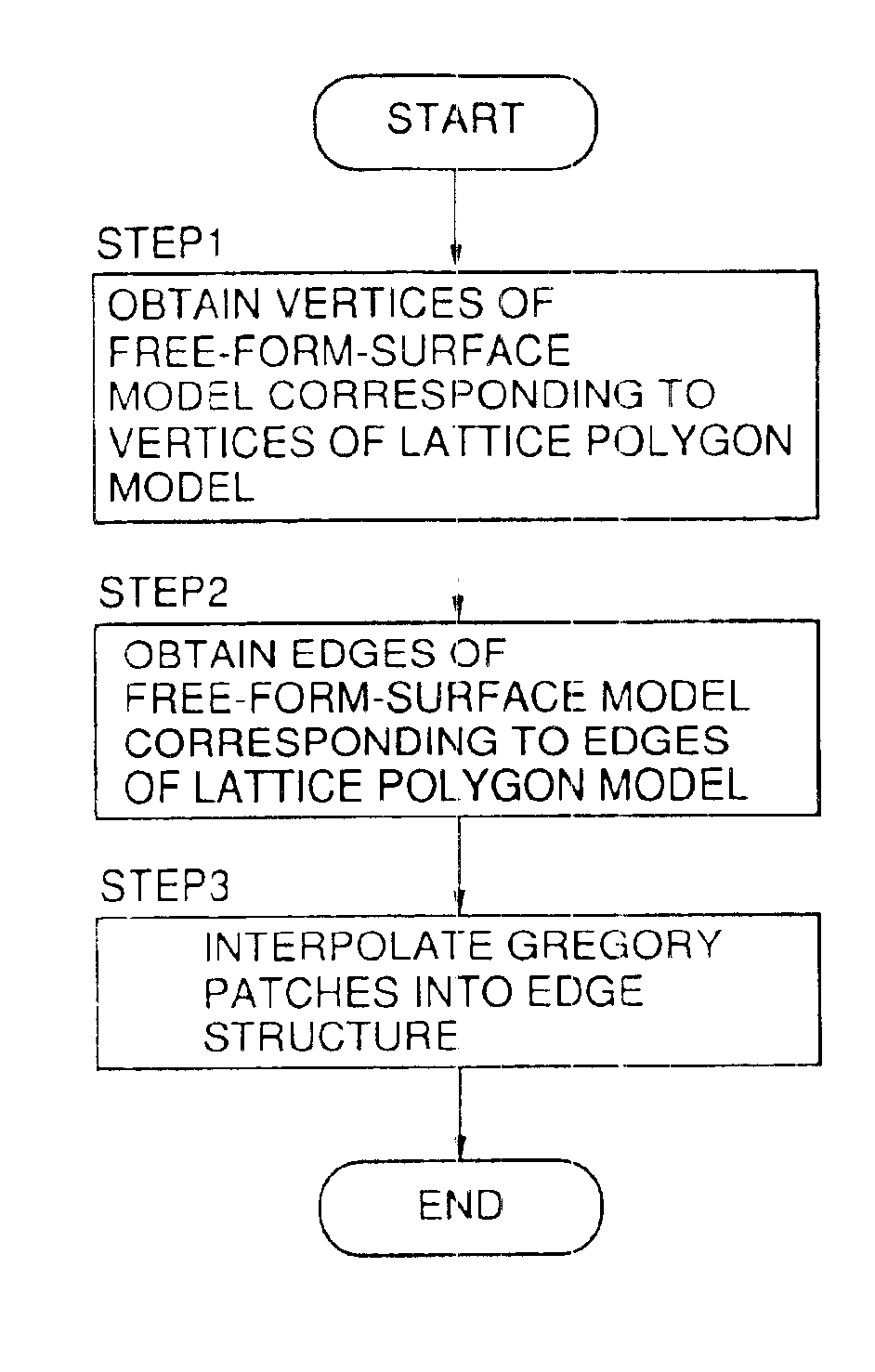
Generation of free-form surface model by reversible rounding operation
InactiveUS6867769B1Drawing from basic elementsSpecial data processing applicationsFree formLinear transform
Owner:RICOH KK +1
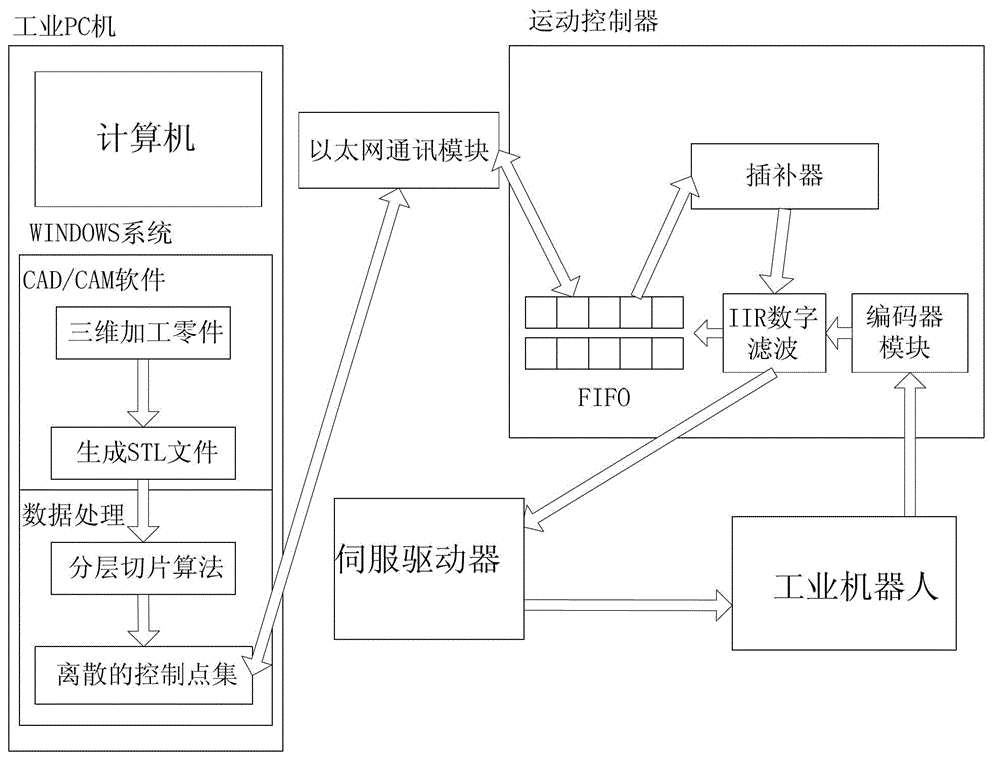
Track generating method facing toward complex curved surface processing and track generating system thereof
InactiveCN103064343AOvercoming the inability to resolve model voidsReduce the number of timesProgramme controlComputer controlIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineMotion controller
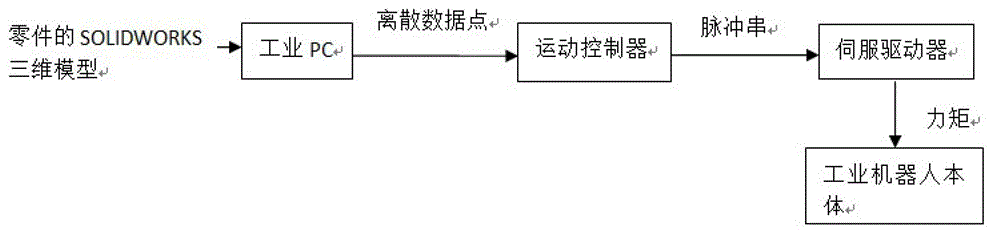
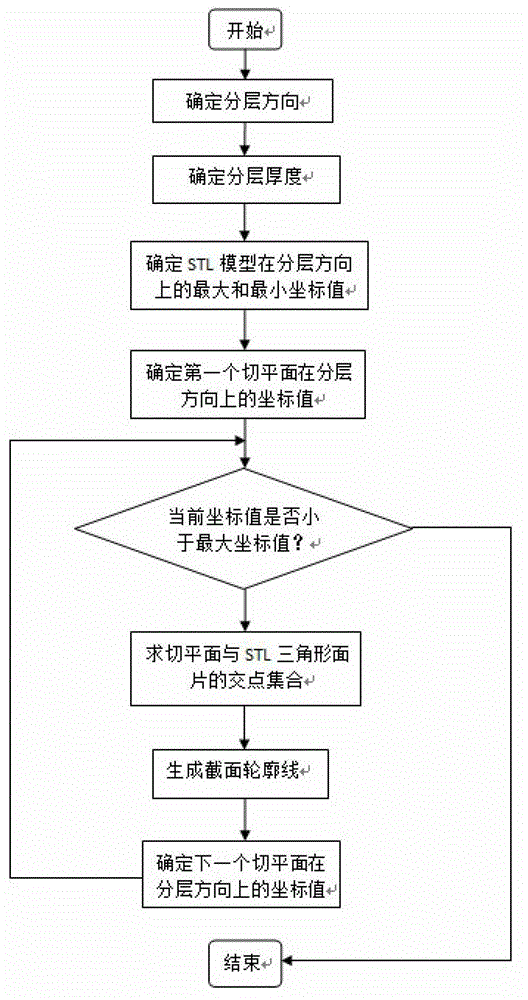
The invention discloses a track generating method facing toward complex curved surface processing and a track generating system thereof. The track generating method includes that a to-be-processed complex curved surface is chosen and a standard template library (STL) file is generated; layer dividing direction and layer dividing thickness are determined; group dividing is conducted on a triangular patch; the point of intersection is obtained by an incremental method; a coordinate minimum value point of each section point of intersection gather in the direction of being vertical to the layer dividing direction is found out, another point of intersection of the same triangular patch is searched and connected with the minimum value point, and the process continues until the outline of each tangent plane is obtained and eventually the generating route track is obtained. The track generating system comprises an industrial personal computer (PC), a motion controller, a servo driver and an industrial robot body. The industrial PC generates three-dimensional to-be-processed components into a scattered control point set and transmits the control point set to the motion controller. The motion controller conducts an interpolation calculation on the control point set and outputs pulse trains to the servo driver, and drives the industrial robot body to conduct coordinated movement in a torque control mode. The track generating method facing toward complex curved surface processing and the track generating system thereof have the advantages of small calculation quantity, short calculation time, and high calculation efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
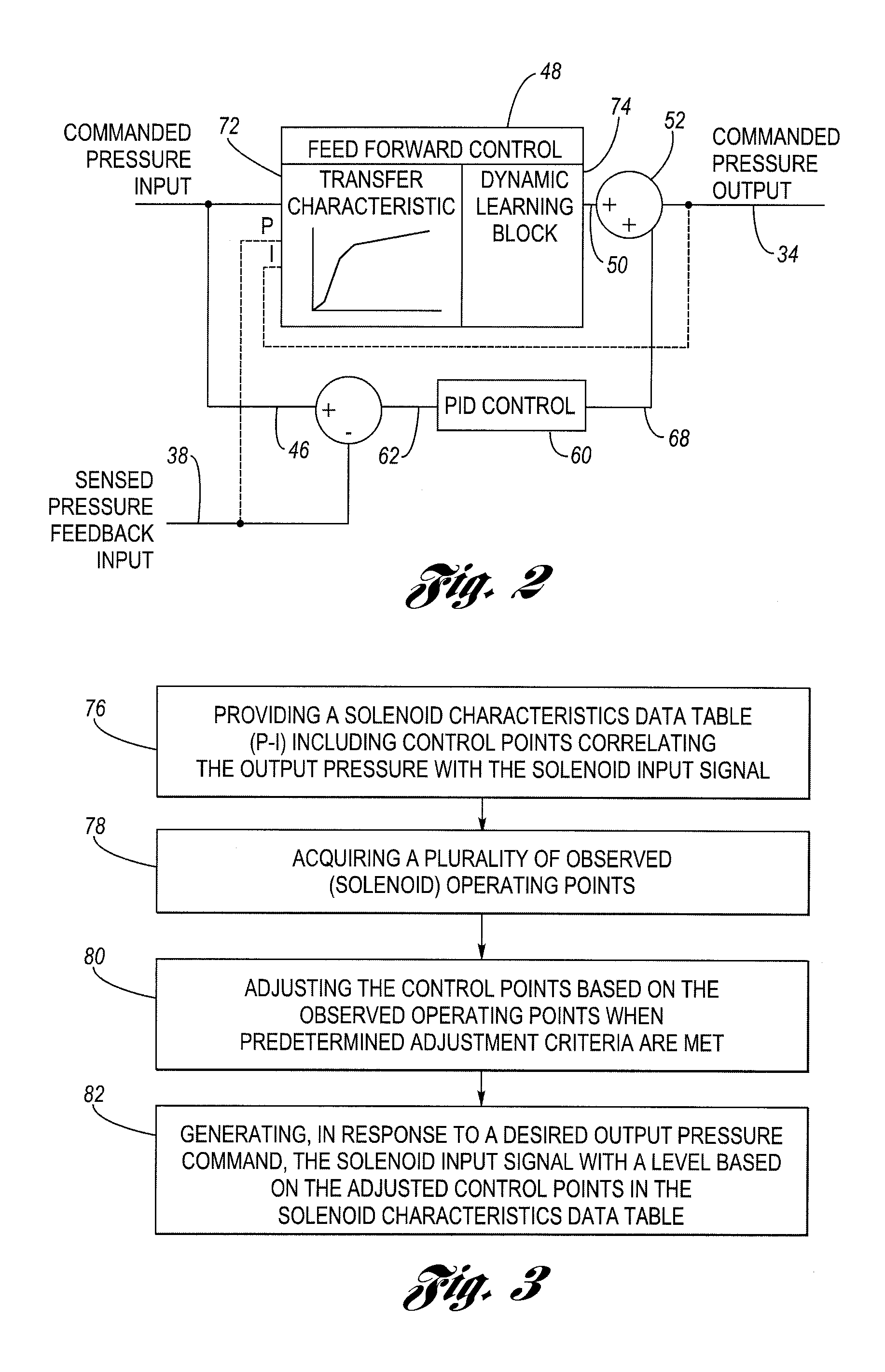
Method for real-time learning of actuator transfer characteristics
ActiveUS20090222180A1Increase variation amountImprove effectivenessValve arrangementsDigital data processing detailsReal time learningOperating point
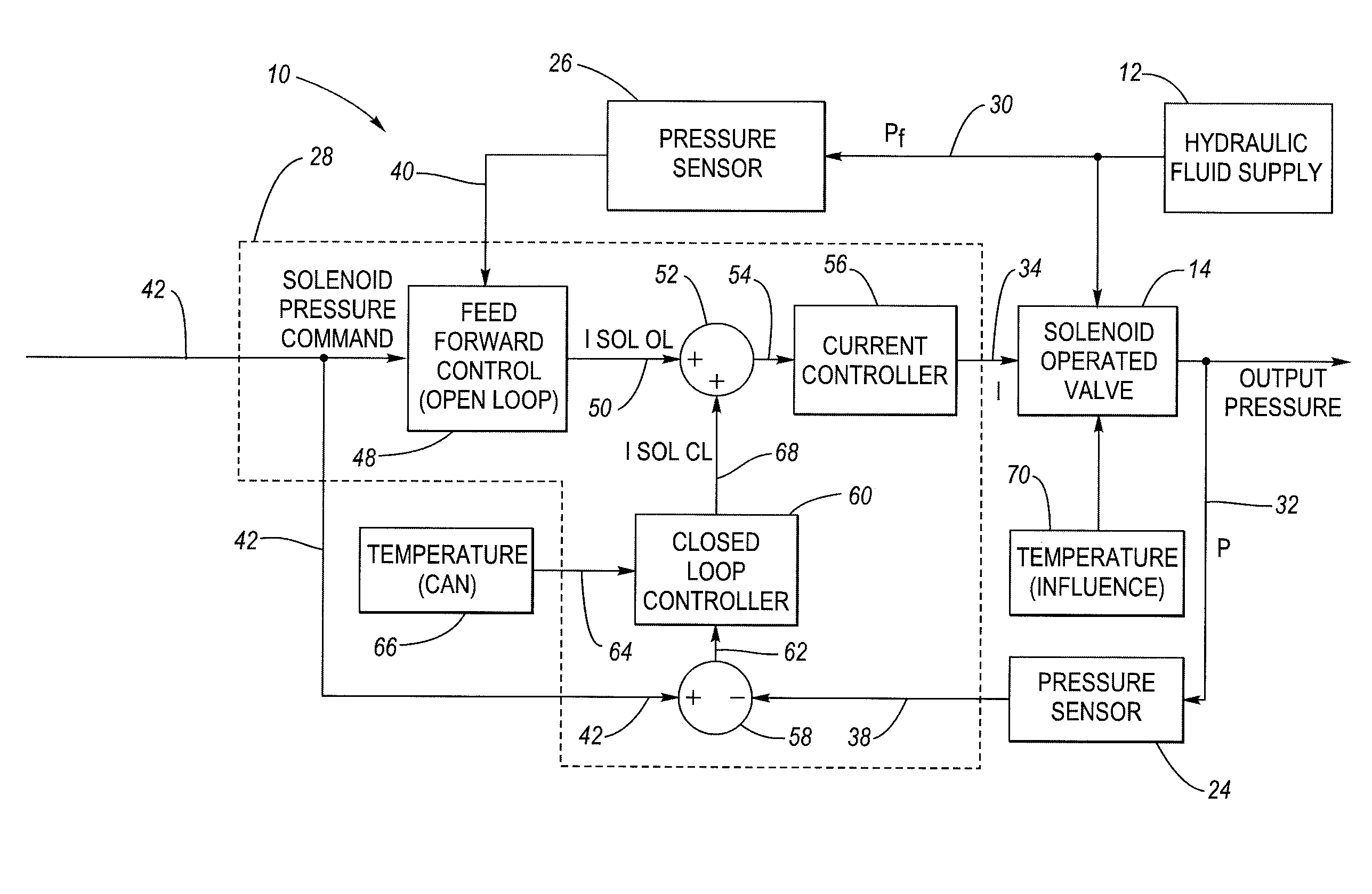
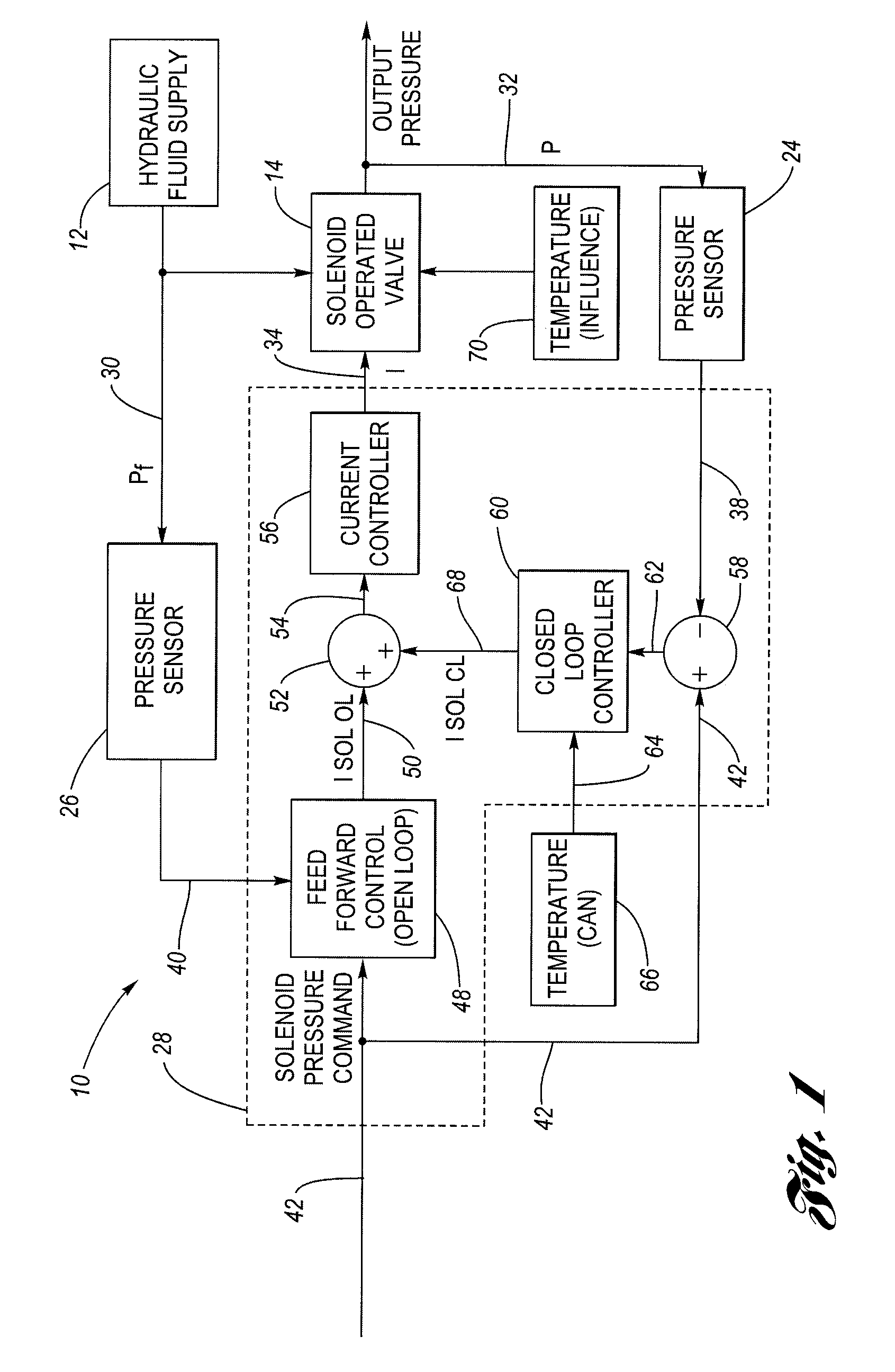
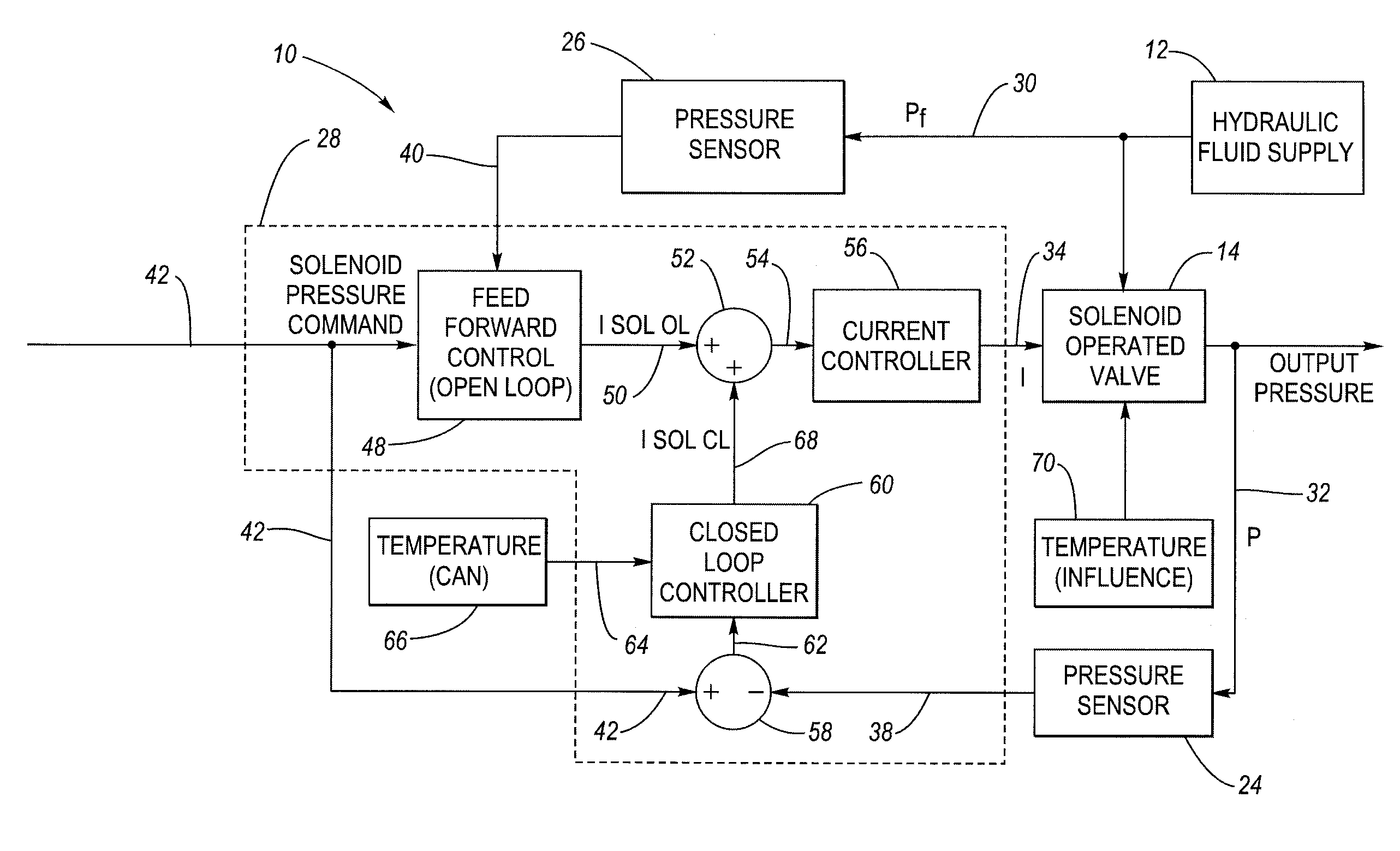
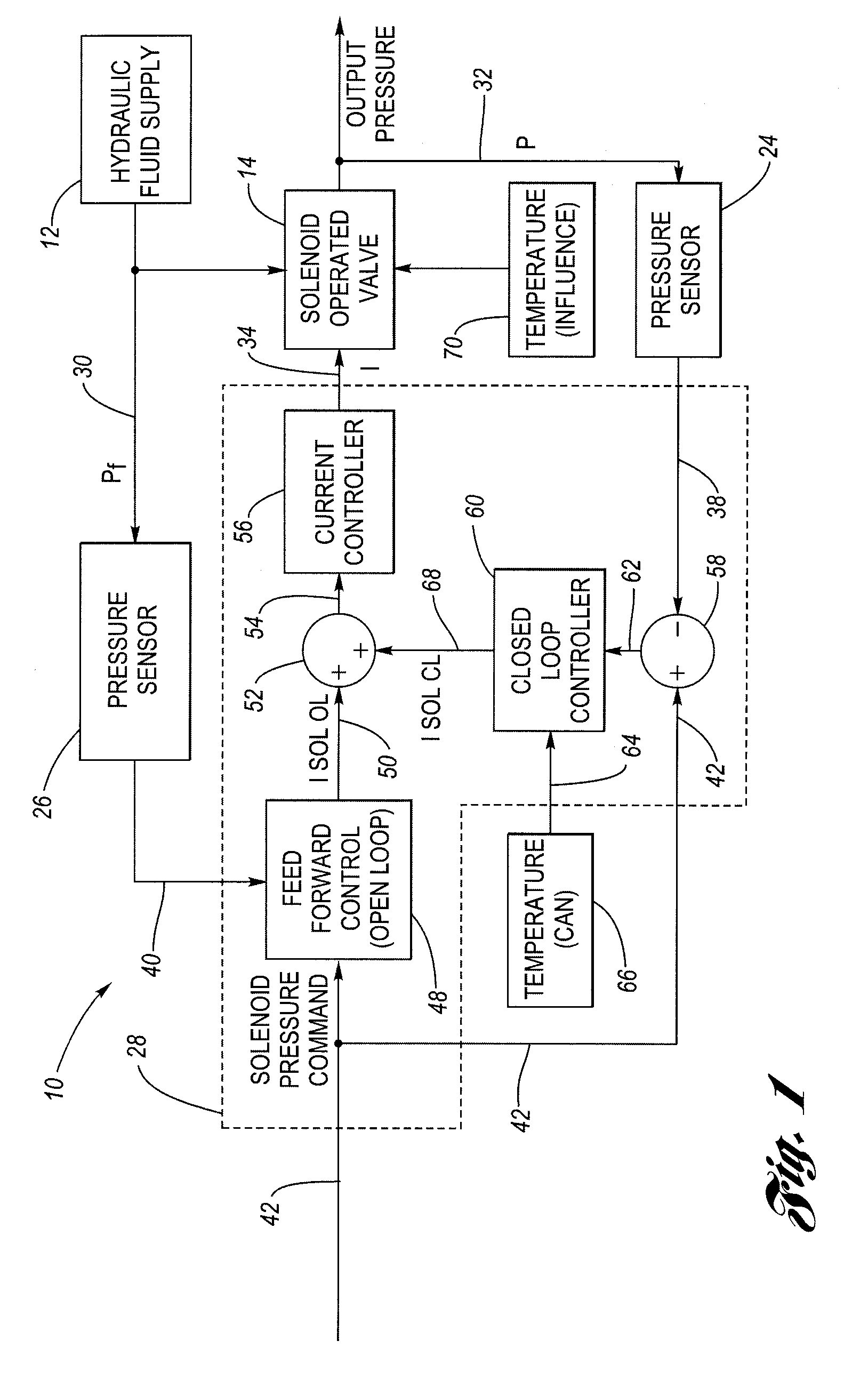
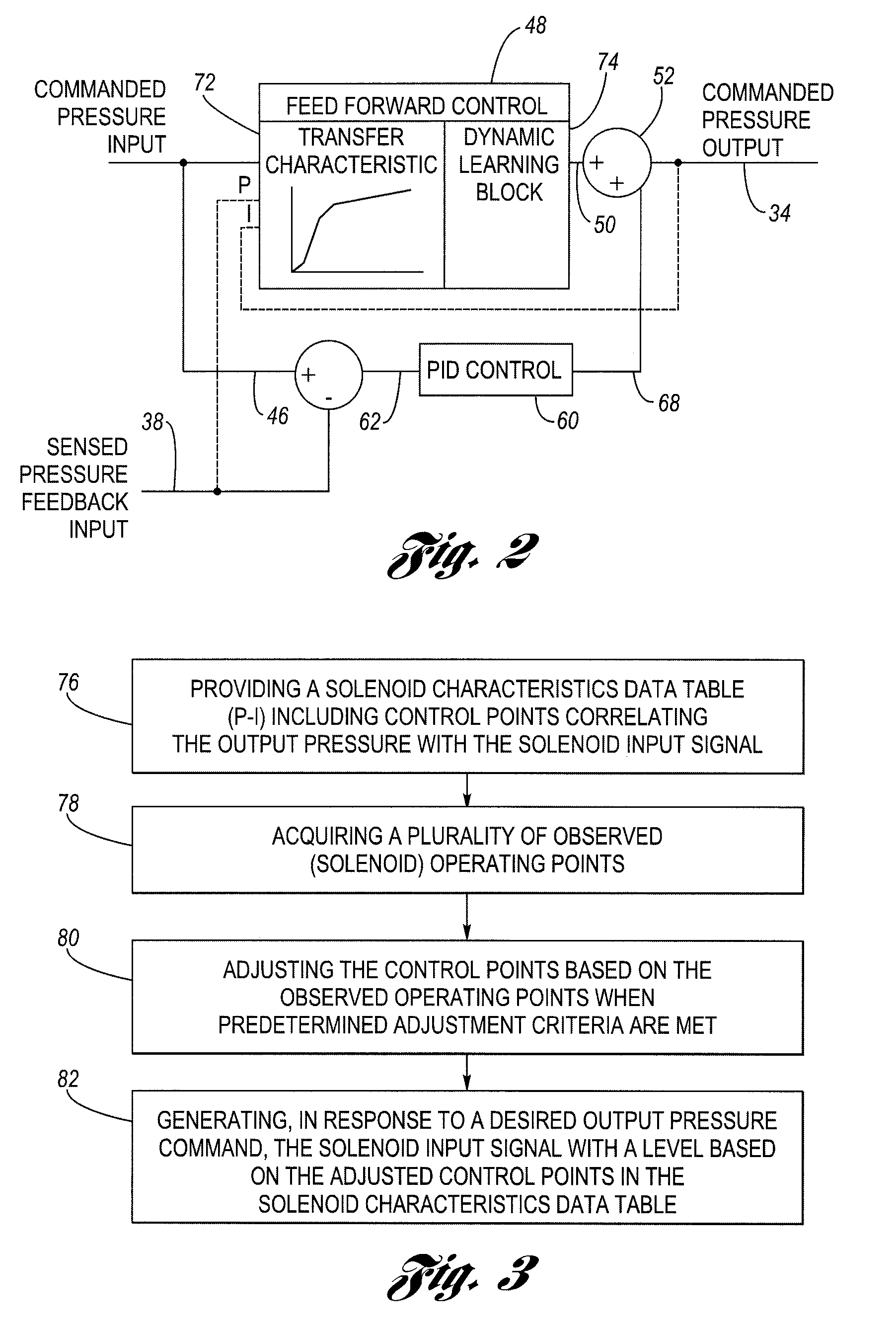
In a pressure control system having a solenoid-operated fluid valve that has an output hydraulic pressure which varies in accordance with a solenoid input signal, a dynamic learning block is configured to adjust the initial, default values for control points stored in a pressure-current (P-I) data table based on observed (measured) operating points that reflect the solenoid's actual transfer characteristic. A feed forward control block is configured to generate the solenoid input signal having a level based on the adjusted control points in the data table, which improves the accuracy of the solenoid input signal. An adjustment method uses a plurality of circular buffers each configured to store observed operating points falling within a respective range, and provides a mechanism to allow adjustment of the control points based on only partial data.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
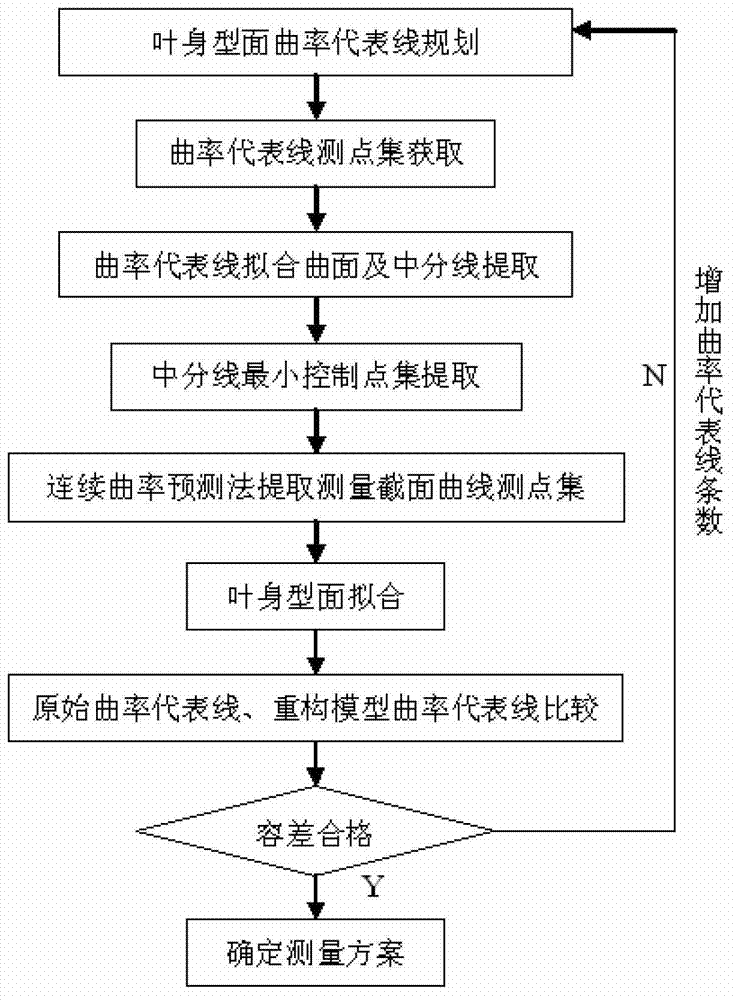
Measuring method for unknown aviation engine blade profile of CAD model
InactiveCN103486996AAvoid Measuring SectionsAvoid the pitfalls of cross-section measurement pointsMeasurement devicesAviationMeasurement point
The invention discloses a measuring method for an unknown aviation engine blade profile of a CAD model, wherein the measuring method is used for solving the technical problem that an existing aviation engine blade profile three-coordinate measuring method is low in precision. According to the technical scheme, multiple curves reflecting distribution states of curvature in the main shaft direction and located on the multiple blade profile are measured and analyzed, control points of the curves are figured out on the basis of curvature and allowance control, and then blade measuring sections are determined; on the basis of a curvature continuous prediction method, a measuring point set of each measuring section is planned, and three-coordinate measuring carried out on the unknown aviation engine blade profile of the CAD model is achieved. Because the blade measuring sections are selected according to blade profile curvature distribution characteristics, measuring point planning is carried out on the measuring sections on the basis of the continuous curvature prediction method, and the continuous curvature prediction method has better robustness, so extraction of molded line redundant points is reduced, meanwhile the situation that extraction points are fit with changes of measuring section molded line curvature is guaranteed, measuring efficiency is improved, and measuring precision can be guaranteed.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method and system for aligning three-dimensional surfaces
ActiveUS20110200248A1Shorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionThree dimensional surface
A method for associating a three-dimensional surface representing a real object and a three-dimensional reference surface, said reference surface being represented by a set of reference points, the method comprising: obtaining a set of real points representing the real surface, determining the normal vector of each point of said obtained set of real points, selecting, among the set of real points, control points according to the determined normal vector by converting the set of real points to a bi-dimensional space of normal vectors, generating sets of points having similar normal vector among the points of the set of real points and selecting, for each set of points with similar normal vector, one point that is a control point of the real surface, determining correspondence points close to the set of reference points that are determined to correspond to the control points of the real surface, and determining the motion that minimizes the distances between the control points of the real surface and the correspondence points.
Owner:AQSENSE
Method for compressing/decompressing a three-dimensional mesh
ActiveUS20130114910A1Lower the volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
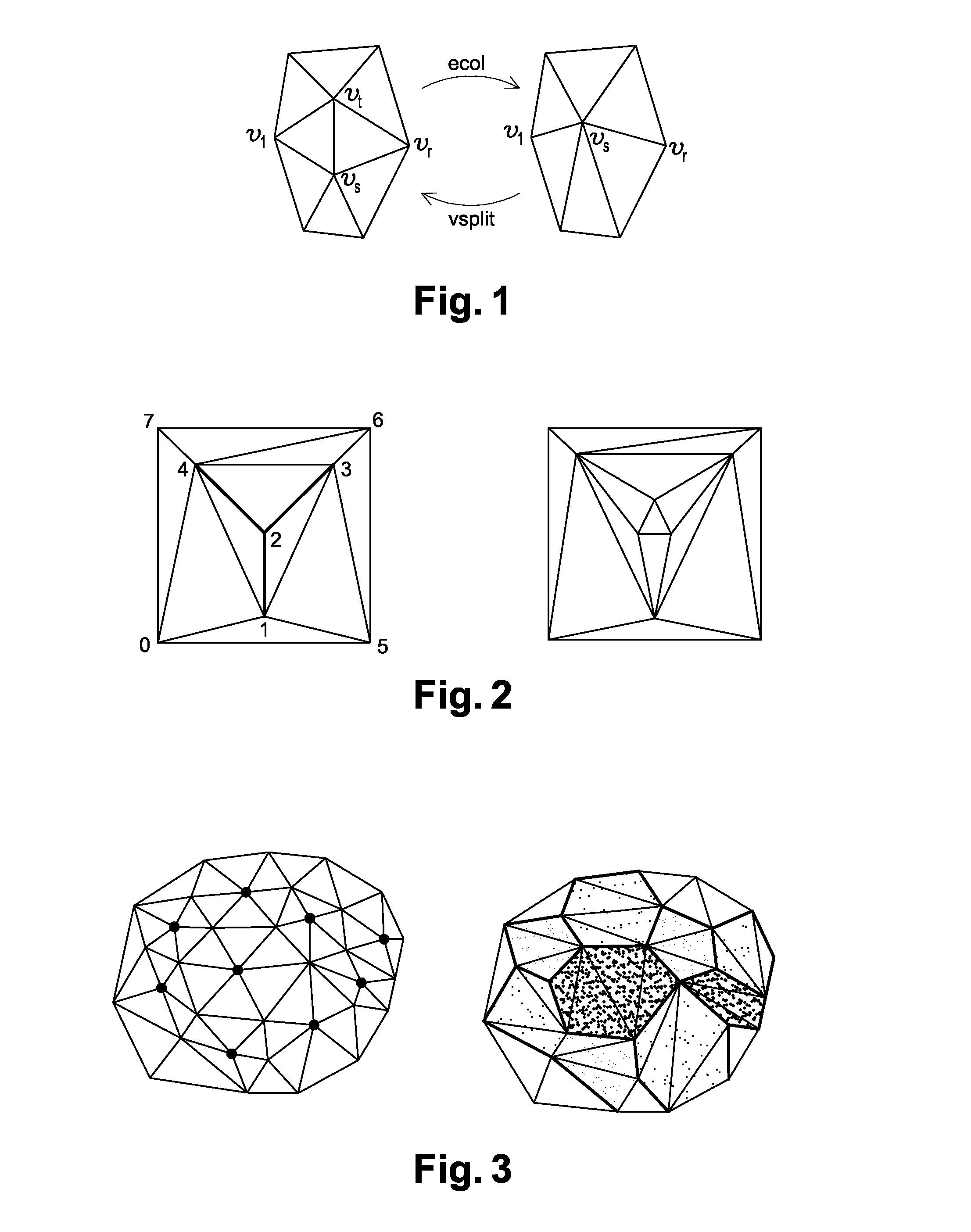
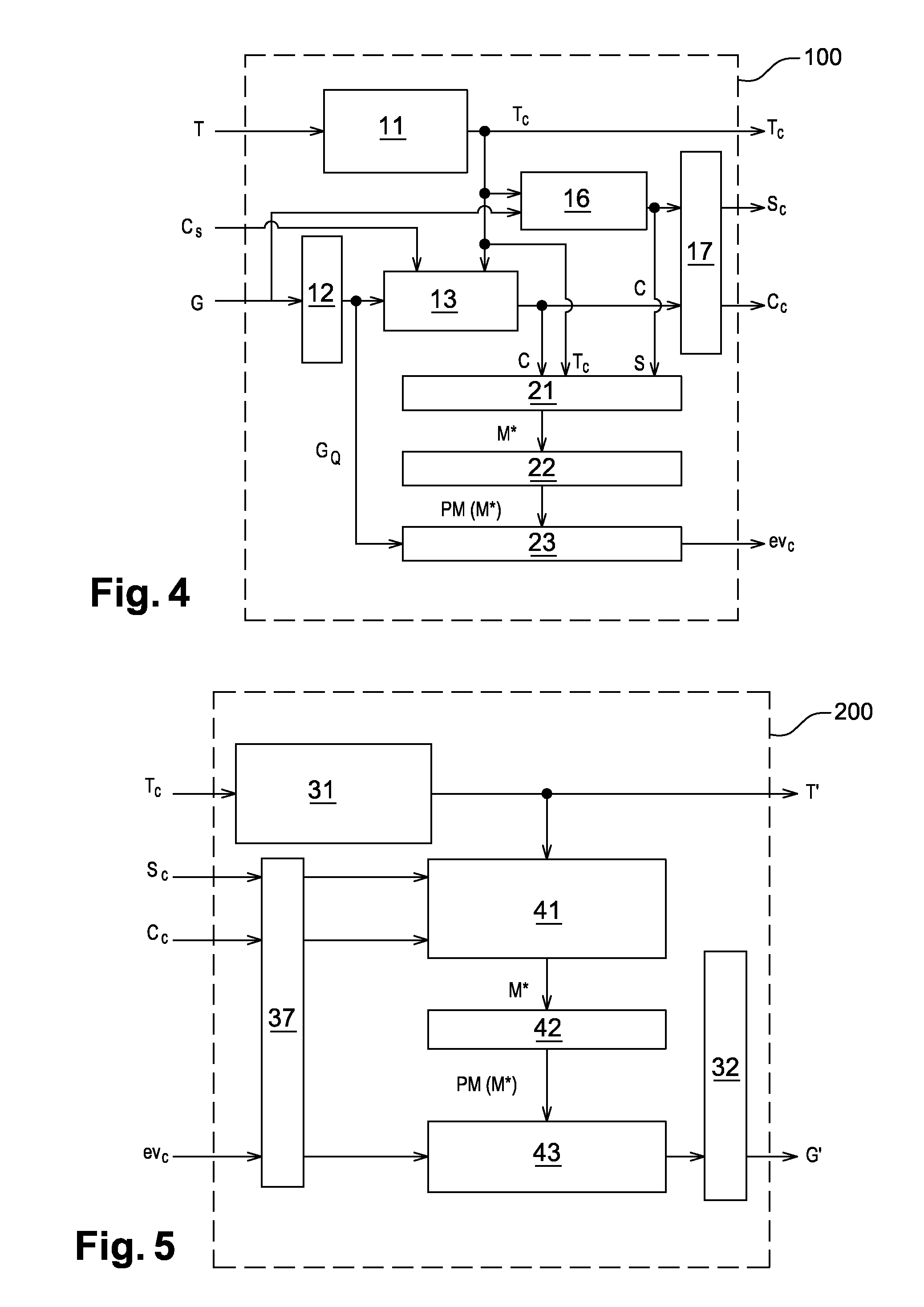
The method for encoding / decoding three-dimensional meshes of dots or vertices connected in the form of facets delimited by edges; the mesh M is defined by connectivity data T and geometry data G includes the steps of:lossless encoding of the connectivity data T into encoded connectivity data Tc,iteratively generating a progressive mesh hierarchy, i.e. a set of meshes with progressive levels of detail, PM (M*),generating a piecewise smooth approximation M* of the original mesh M, from the mesh connectivity T; this smooth approximation M* being described as follows:a. compressed connectivity data Tc;b. a small number N of control dots andc. a number of indexes S of edges called protruding edges of the mesh M, identified beforehand,using the progressive mesh hierarchy PM(M*) to calculate a prediction of approximation errors in M* compared with the original mesh M.
Owner:FITTINGBOX
Rapid zippering for real time tesselation of bicubic surfaces
InactiveUS20060125824A1Minimize the numberReduce in quantity3D-image rendering3D modellingLine segmentComputer graphics (images)
A method and system is provided for rendering bicubic surfaces of an object on a computer system. Each bicubic surface is defined by sixteen control points and bounded by four boundary curves, each corresponding to an edge, and each boundary curve is formed by boundary box of line segments formed between four of the control points. The method and system of include transforming only the control points of the surface given a view of the object, rather than points across the entire bicubic surface, and using the four boundary edges for purposes of subdivision. Next, a pair of orthogonal boundary curves to process is selected. After the boundary curves have been selected, each of the curves is iteratively subdivided and the pair of orthogonal internal curves, wherein two new curves are generated with each subdivision. The subdivision of each of the curves is terminated when the curves satisfy a flatness threshold expressed in screen coordinates, whereby the number of computations required to render the object is minimized.
Owner:3D SURFACES LLC
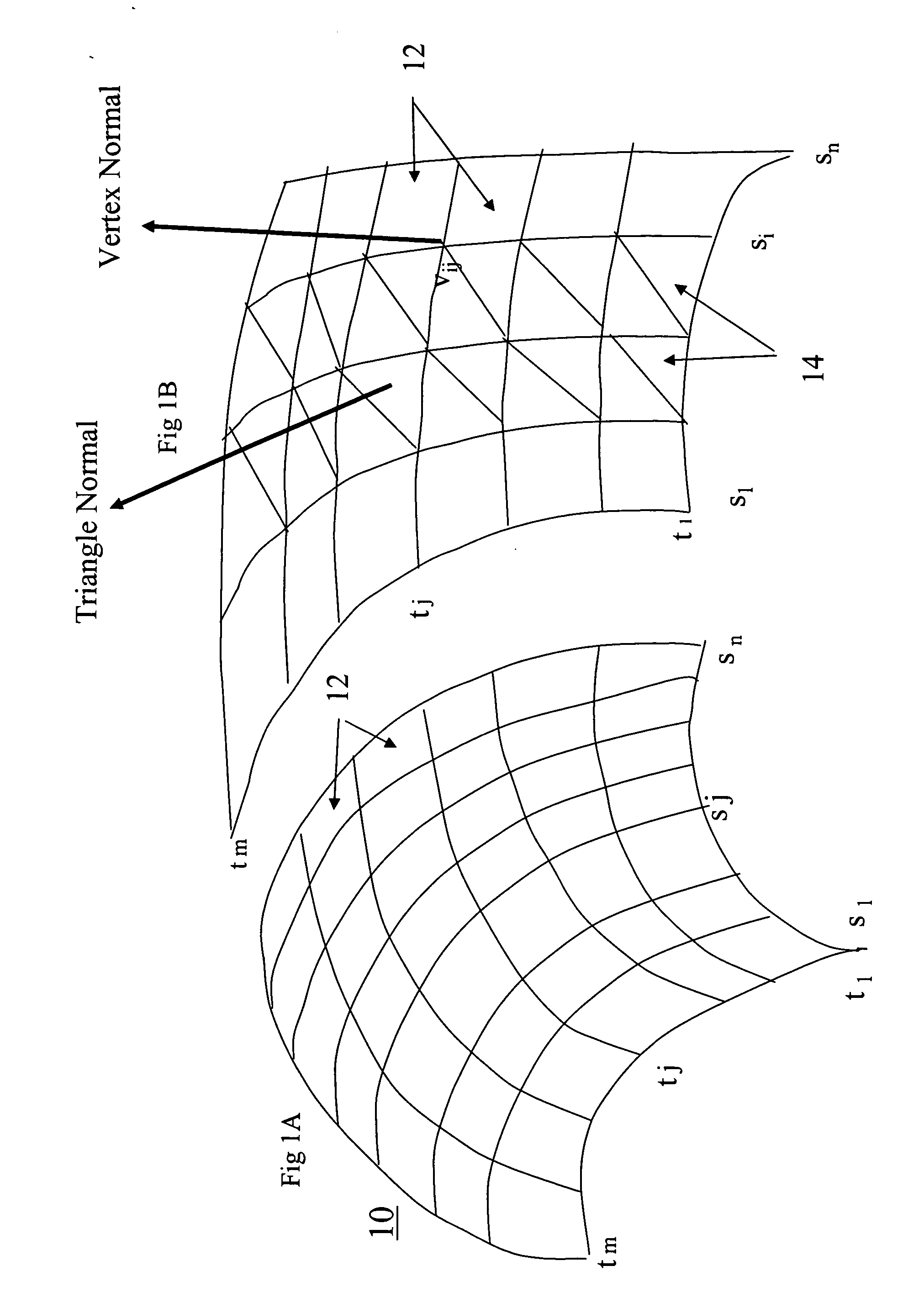
Interpolation processing method, interpolation processing device, shape evaluation method, and shape evaluation device
InactiveUS20090303235A1Additional processing stepsHigh precisionDrawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionShortest distanceTime segment
An initial polygon obtained from a point group is used as a control polygon, and a control point of the control polygon is offset in a normal direction by the shortest distance from a limit surface generated by the control polygon, so that the position of new control point is determined to allow a subdivision surface to interpolate the initial polygon, thereby generating the subdivision surface which interpolates the point group. A first process to determine the point on the subdivision surface at the shortest distance from each control point, and a second process to move and offset the control point in the normal direction from the surface by the distance between the point on the surface and the initial control point, are iterated until the distance between the initial point group and the point on the surface satisfies the threshold or becomes smaller than the threshold, thereby generating the subdivision surface interpolating the initial polygon. Consequently, the subdivision surface interpolating the point group is generated within a short operation time period, without solving a linear system.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA NAT UNIV
AUV path planning method in ocean current environment based on population super-heuristic algorithm
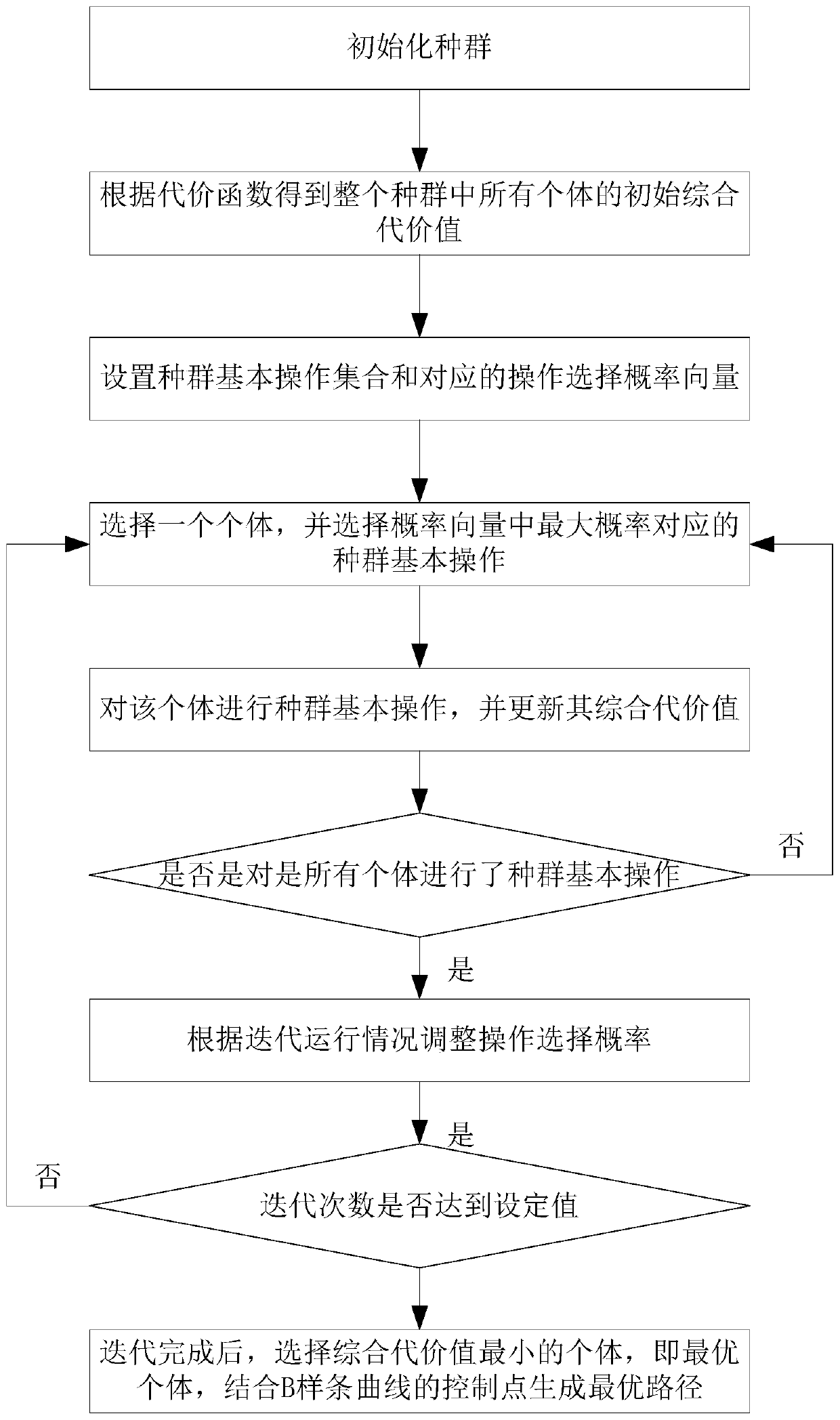
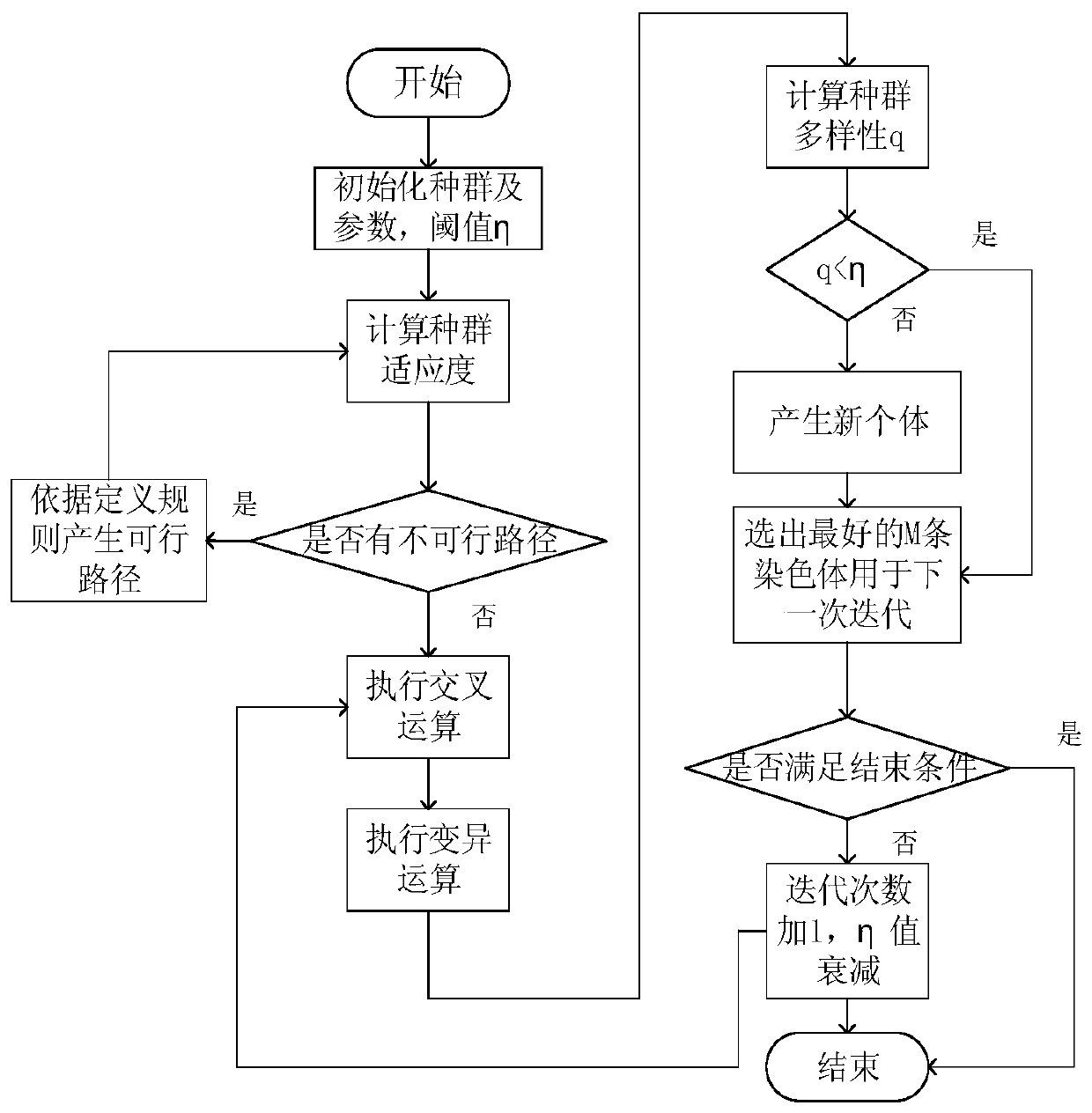
ActiveCN109782779AReduce difficultySatisfy constraintsAltitude or depth controlEntire populationPath plan
The invention, which belongs to the field of underwater robots, discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle path planning method in an ocean current environment based on a population super-heuristic algorithm. A population is initialized and initial comprehensive cost values of all individuals in the whole population are obtained according to the cost function; a population basic operation set and a corresponding operation selection probability vector are set; one individual in the population and a population basic operation corresponding to the maximum probability in the operation selection probability vector are selected, the individual is operated, the basic operation of the population is repeated until the entire population is traversed, so that the iteration is completed; the operation selection probability vector is adjusted again and next iteration is carried out until the iteration number reaches a set value; and after iteration completion, an individual with the lowest cost value isselected, one group of control points is formed by combining a starting point, an end point and a fixed control point of a B-spline curve, and an optimal path is generated. Therefore, problems that the path planned based on the existing AUV path planning method is not smooth and is tracked difficultly, and the tracking energy consumption is high are solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
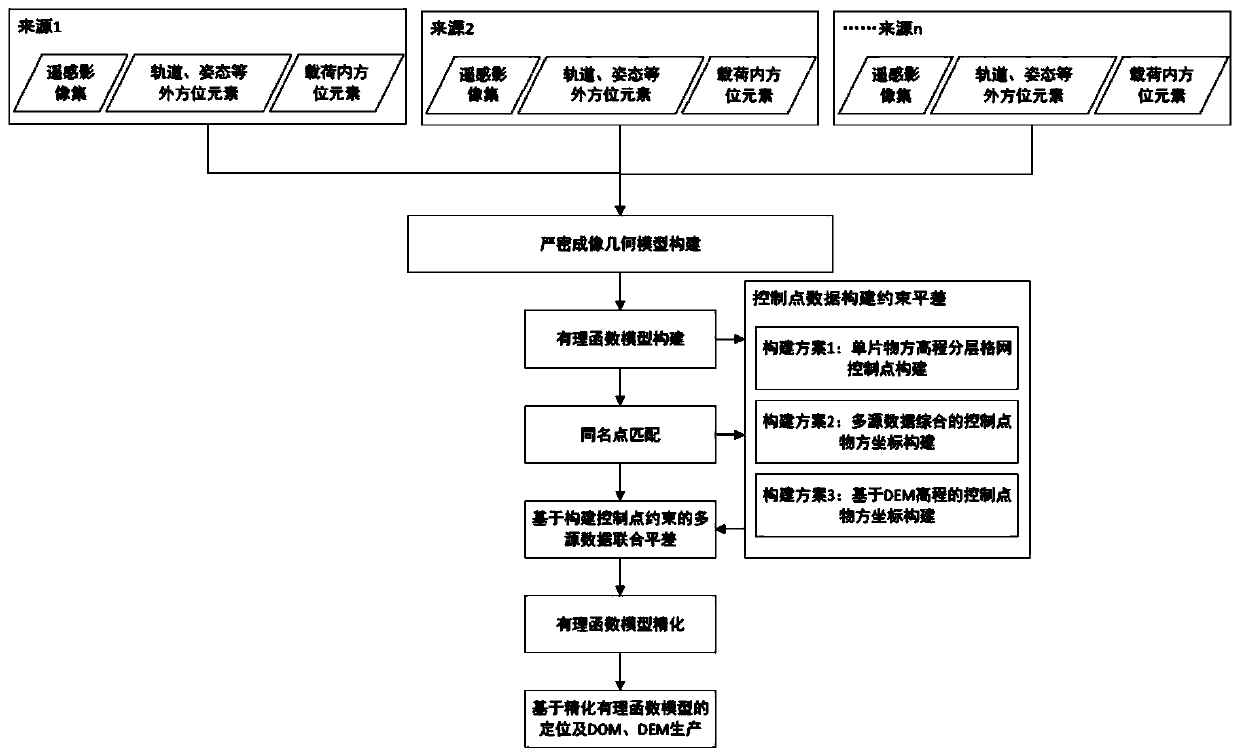
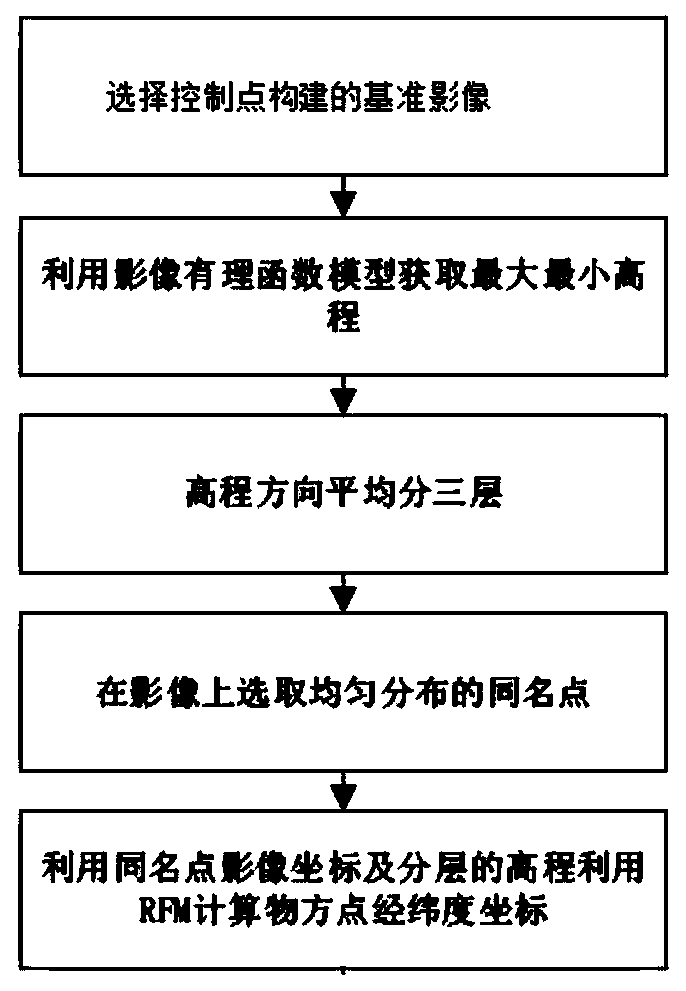
Constructing virtual control point constrained multi-source multi-coverage remote sensing image adjustment method
ActiveCN110388898AImprove stabilityAvoid huge deviationsImage enhancementImage analysisGeometric modelingVirtual control
The invention relates to a constructing virtual control point constrained multi-source multi-coverage remote sensing image adjustment method that comprises the following steps: S1, constructing an image imaging geometric model; S2, performing image matching on a stereo remote sensing image pair to obtain homonymous points of the remote sensing images; S3, constructing control points based on imagecharacteristics of different sensors; S4, performing multi-source data joint adjustment based on control point constraint; and S5, outputting refined parameters of a rational function model, and completing the multi-source block adjustment based on the RFM. According to the calculation method of the virtual control points, object space three-dimensional coordinates of the control points can be adaptively determined according to an intersection result of the homologous three-dimensional model, so that the adjustment solving stability and precision are remarkably improved.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
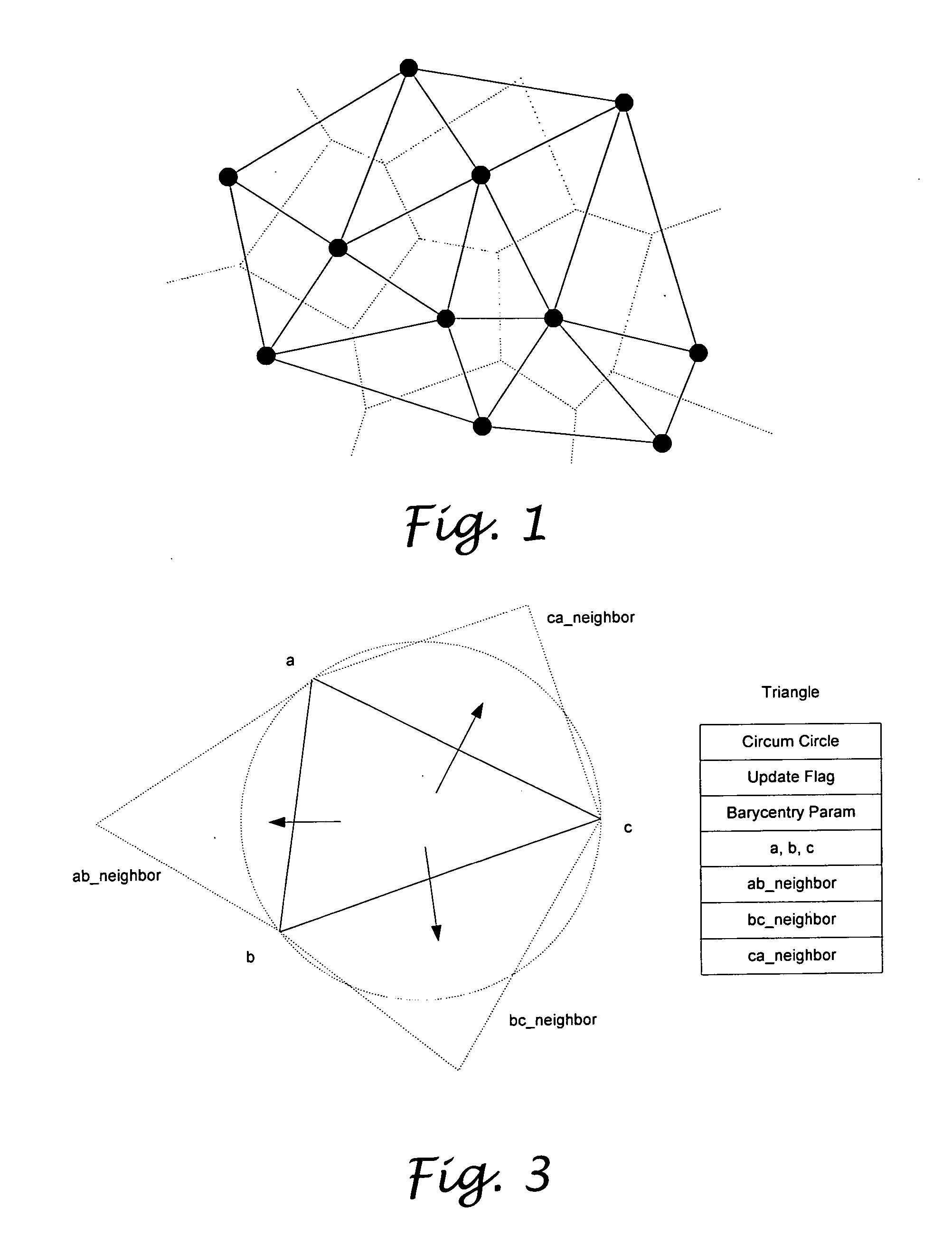
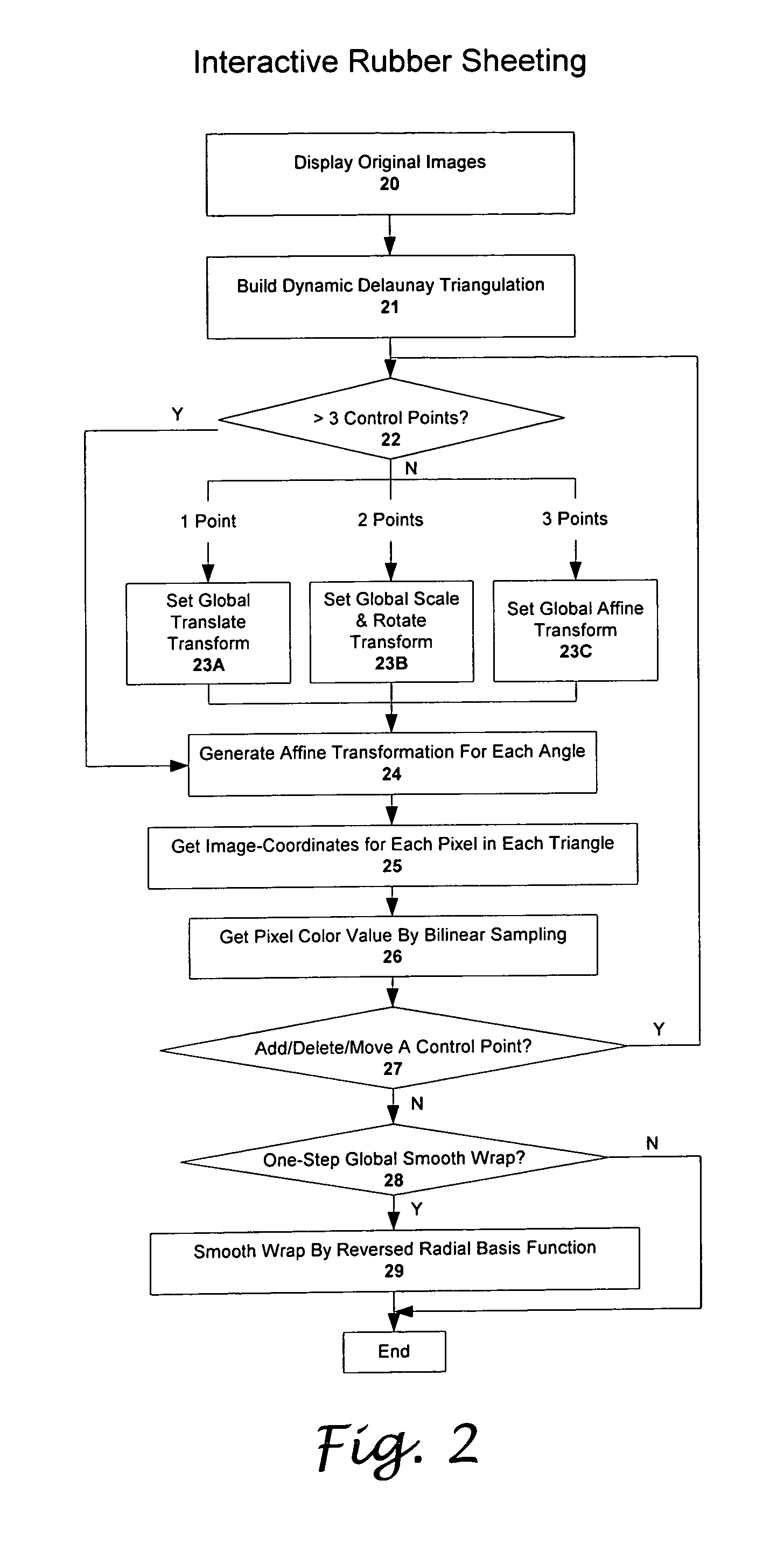
Real-time interactive rubber sheeting using dynamic delaunay triangulation
InactiveUS20070182762A1Geometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsTriangulationDecomposition
A novel, easy to use, and computational efficient rubber sheeting algorithm is designed for interactive image registration in a web-based application environment. The algorithm has two steps, including a piece-wise linear interpolation step to interactively find a suitable set of control points and displacement vectors, and a following optional global radial basis wrap step to generate smoother result using the final control point set. A dynamic Delaunay triangulation method is designed to efficiently update the decomposition of the image. Natural and intuitive wrapping result will be dynamically generated in real-time while the user interactively insert, delete or drag a control point. The number of control points is not limited, and a large number of control points can be used if necessary without compromising the performance of the algorithm. With enough control points specified using the piece-wise rubber-sheeting step, the wrapping result can be further smoothed by using the optional, click-button poly-quadric global wrapping method in the second step. The algorithm is implemented as a Java Applet and able to run as a cross-platform web-based application.
Owner:WU XIAQING +2
Deformable 2d-3d registration
A method for deformable registration including determining a vector field from a two-dimensional matching of a volume of an object of interest and a two-dimensional image of the object of interest, providing a deformation profile, and finding a volume deformation that maps to a state of the two-dimensional image, wherein the deformation is parameterized by the vector field and control points of the deformation profile to find a control point configuration of the volume deformation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Path planning method based on mobile robot
PendingCN110865642ASatisfy the requirement of path rationalityShort time spentPosition/course control in two dimensionsControl theoryRobot path planning
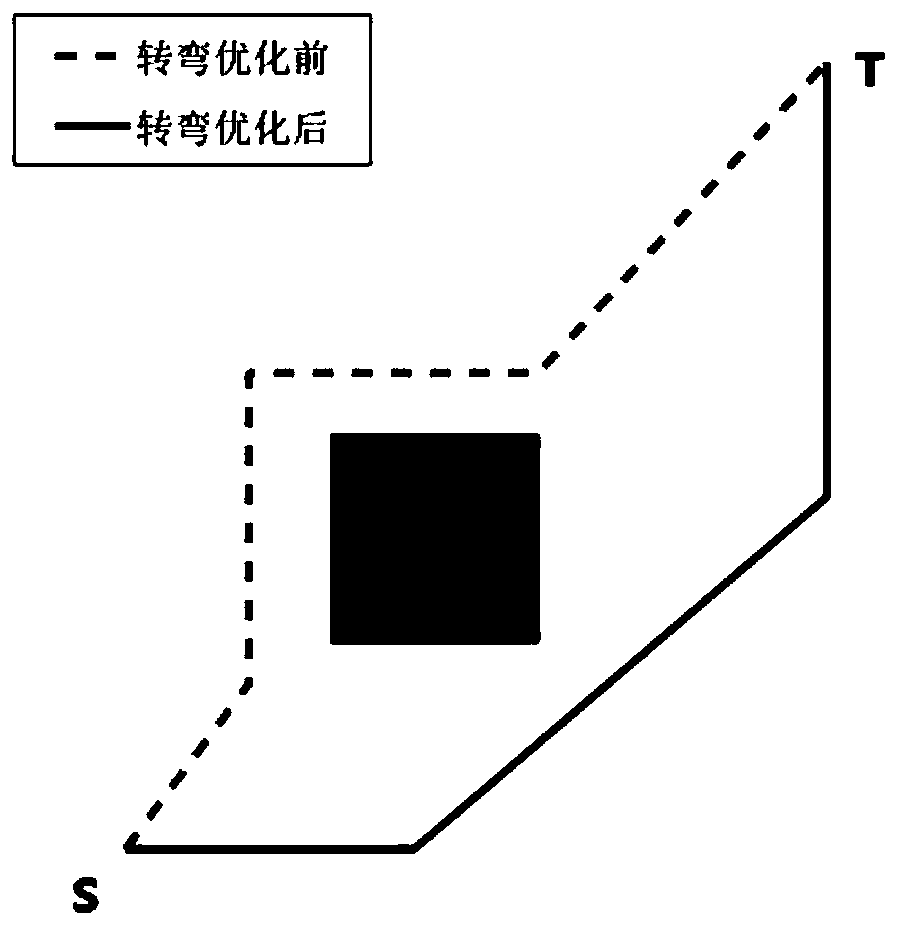
The invention discloses a path planning method based on a mobile robot. The method comprises the steps that based on a polygonal barrier planar model, Q-IGA is utilized to collaboratively search for the most appropriate control point P which serves as a control point of a Bezier curve, and the control point is utilized to generate an optimal path; the difference between difference paths in a population in each iteration is calculated, a judgment criterion is added to a selection operator for optimization, and the diversity of feasible solutions in the population is guaranteed; and a fitness function considering a barrier distance, a turning angle and a robot volume is constructed with the optimization objective of a maximum fitness function value. Through the method, the situation that steps are tedious when the optimal path is obtained through direct fitting search by use of the Bezier curve in robot path planning is avoided, it is guaranteed that the path planning process is completed efficiently, consumed time is short, and path planning efficiency is higher.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
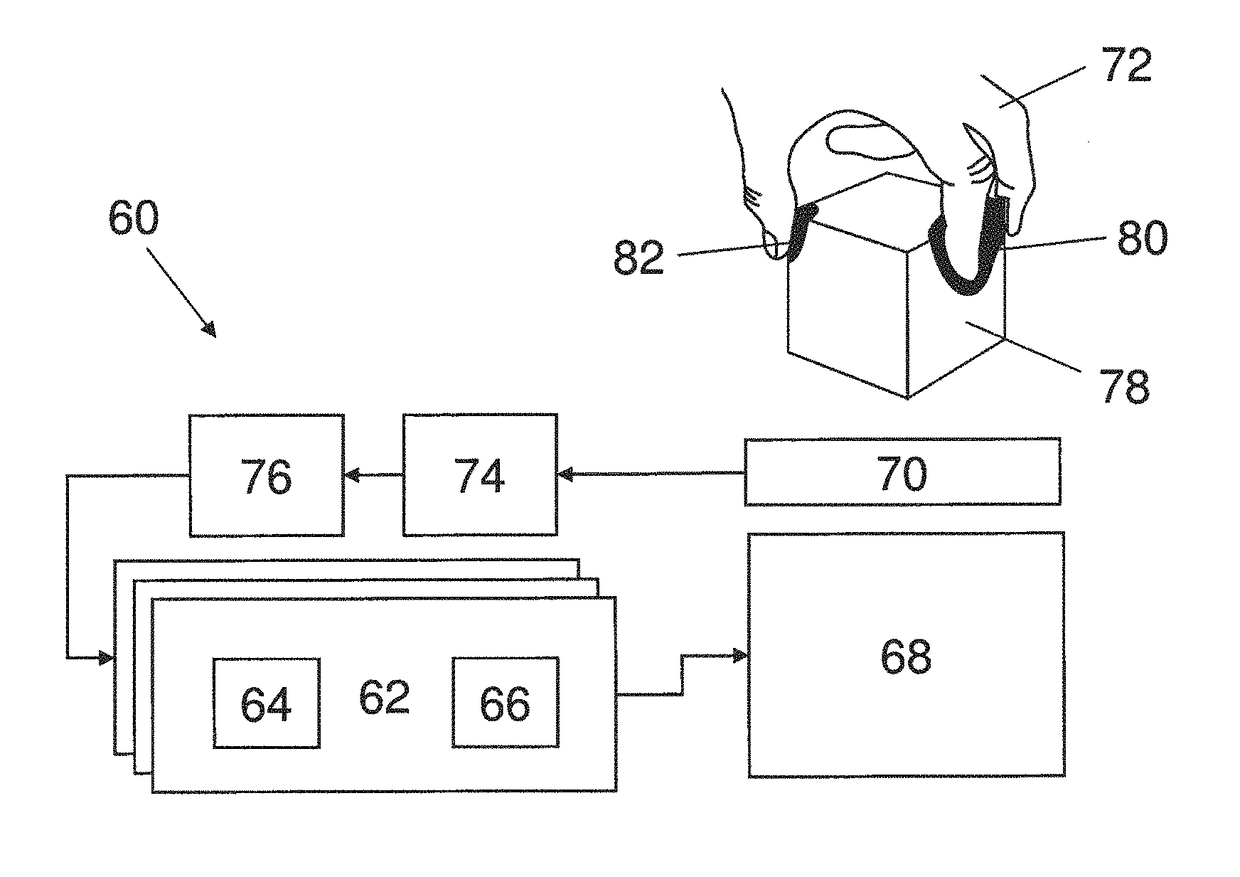
Calibration techniques in haptic systems
ActiveUS10818162B2Input/output for user-computer interactionRepeater circuitsClassical mechanicsTransducer
A system providing various improved calibration techniques for haptic feedback is described. An acoustic field is defined by one or more control points in a space within which the acoustic field may exist. Each control point is assigned an amplitude value equating to a desired amplitude of the acoustic field at the control point. Because complete control of space is not possible, controlling the acoustic field at given points yields erroneous local maxima in the acoustic field levels at other related positions. In relation to mid-air haptic feedback, these can interfere in interactions with the space by creating secondary effects and ghost phenomena that can be felt outside the interaction area. The level and nature of the secondary maxima in the acoustic field is determined by how the space is controlled. By arranging the transducer elements in different ways, unwanted effects on the acoustic field can be limited and controlled.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Stand column perpendicularity measuring method
InactiveCN111174771AEasy to measureFast measurementFixed angles setting outSlant angleAzimuth direction
The invention discloses a stand column perpendicularity measuring method and adopts a prism-free distance measurement total station for measurement. The method comprises steps of preparing more than two control points with known three-dimensional coordinates and a centering rod in advance, erecting the total station at one control point, and leveling, centering and orientating the total station; determining an upper section and a lower section on a stand column, measuring azimuth angles on left and right sides of the upper section by using the total station, taking an average value of the twoazimuth angles as a central azimuth angle of the upper section, measuring a horizontal distance from the total station to a surface of the central azimuth angle of the upper section without a prism, and calculating central three-dimensional coordinates of the upper section according to the horizontal distance, a radius of the stand column and a vertical angle from the total station to the surfaceof the central azimuth angle of the upper section; measuring and calculating the lower section according to the same method to obtain the central three-dimensional coordinates of the lower section; and calculating an inclination angle and an inclination azimuth angle of the stand column by utilizing the central three-dimensional coordinates obtained by calculating the upper section and the lower section, and finally obtaining perpendicularity of the stand column.
Owner:CHINA MCC17 GRP
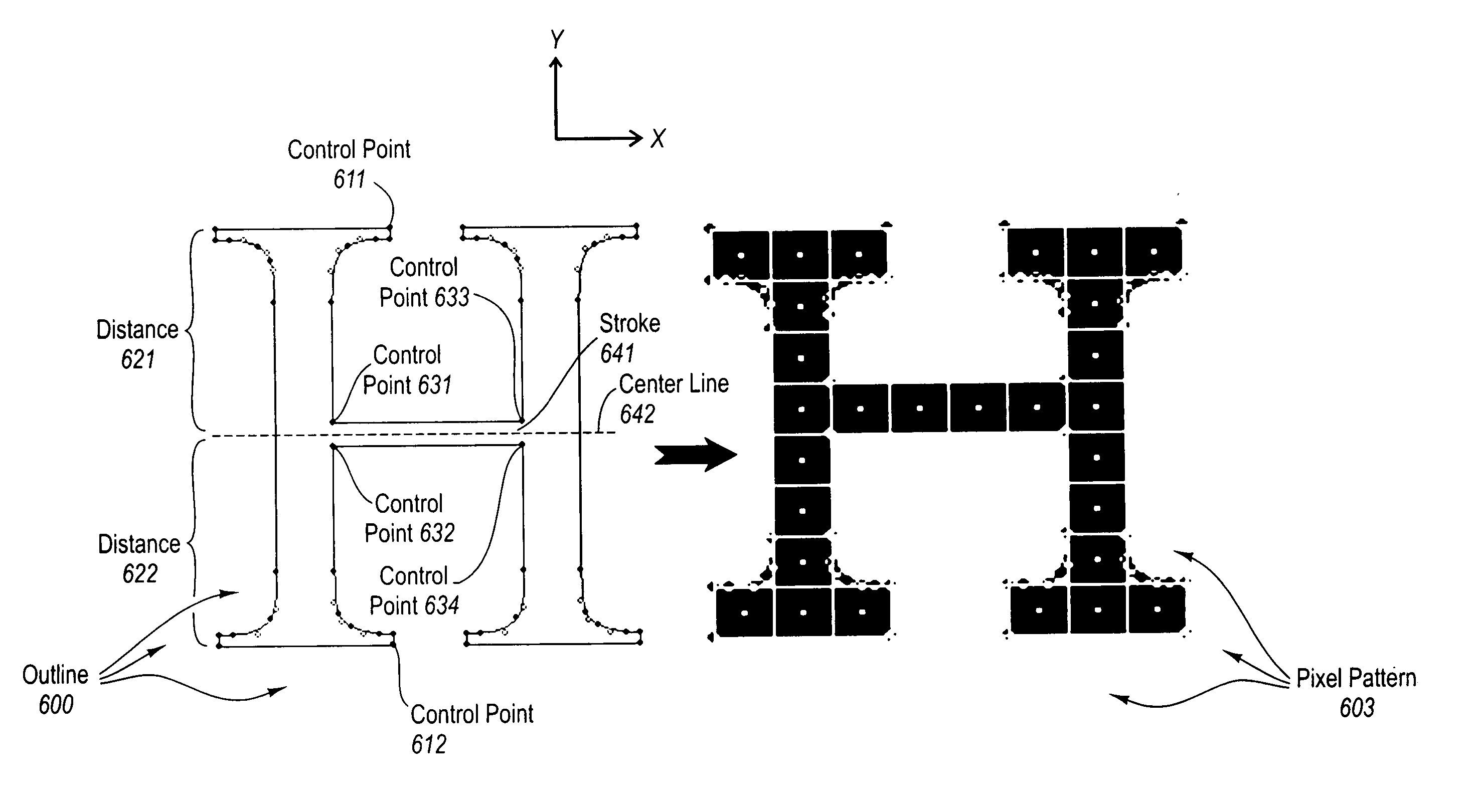
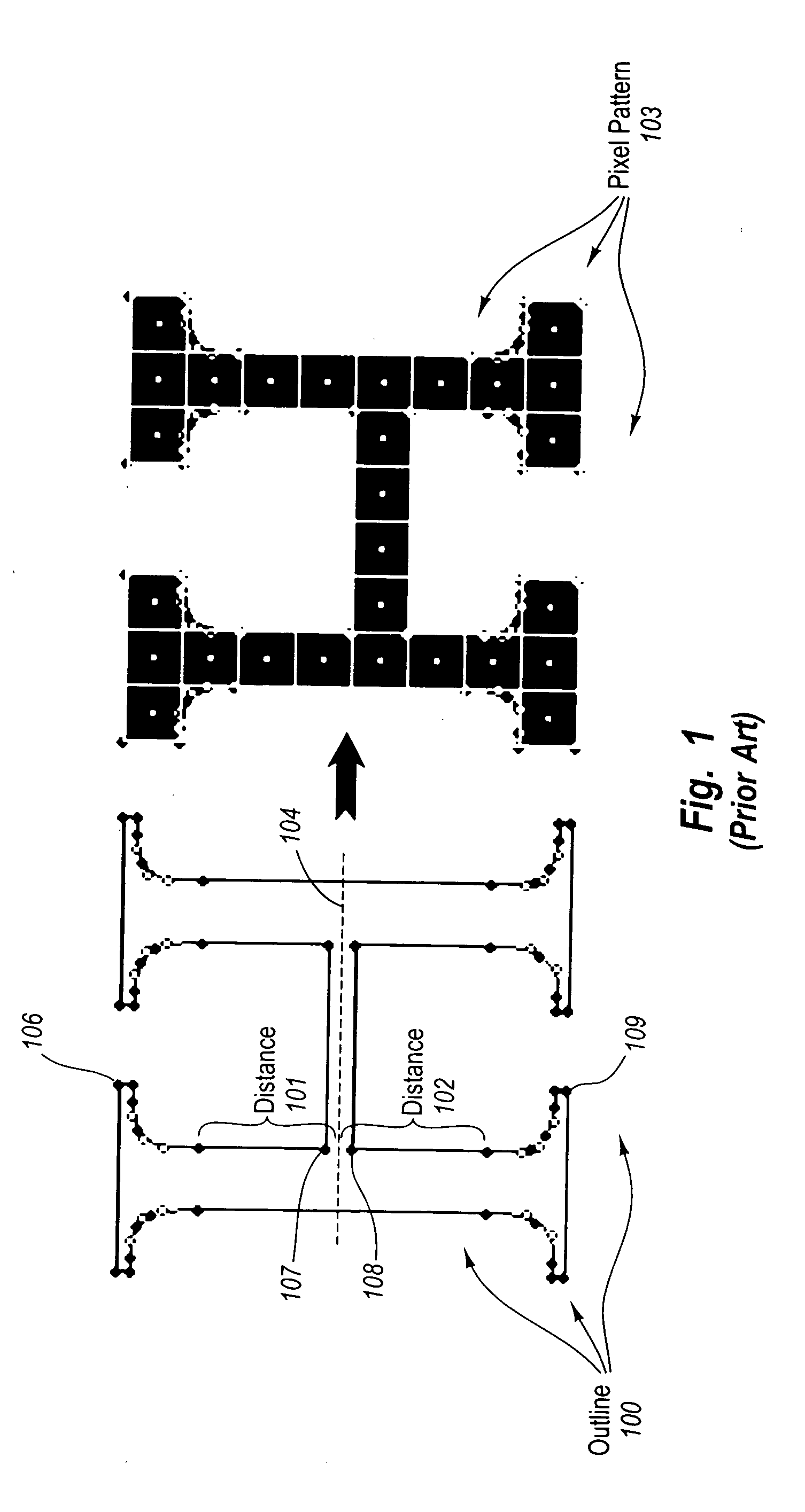
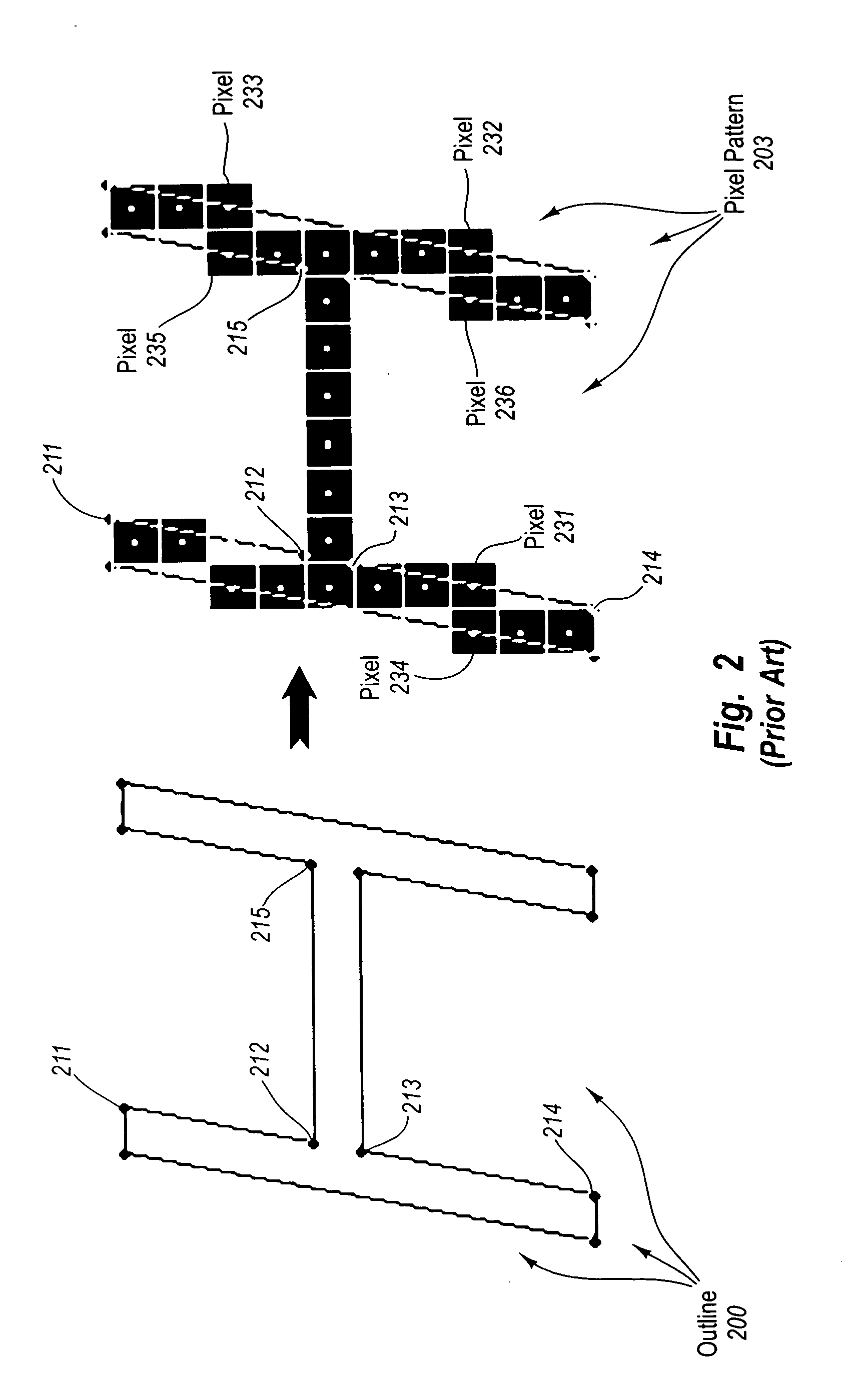
Appropriately rendering a graphical object when a corresponding outline has exact or inexact control points
InactiveUS20050264570A1Overcome problemsFilling planer surface with attributesGraphicsComputer science
The principles of the present invention relate to appropriately rendering a graphical object when a corresponding outline has exact or inexact control points. Based on the positions of control points on an outline it is calculated, that between a first parent control point and a second parent control point, the outline passes approximately though the center of a grid location. The positions of the first and second parent control points are adjusted by a first and second fraction of the size of a grid location respectively. The position of the child control point is realigned along a second axis of the grid space based on the positions of the first and second parent control points. The child control point position is rounded by a fraction of the size of a grid location based on the positions of the first and second parent control points.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Design method of stretch bending loading trace of novel stretch bender
The invention provides a design method of the stretch bending loading trace of a novel stretch bender, comprising the following steps of: dispersing the bending trace curve of a profile into subtense substituted sections, dispersing the bending process in forming into bending steps, establishing a formula relationship among the elongation, profile length and bending radius of the profile in each bending step, and acquiring the elongations of the profile parts in each bending step; simulating the bending process, establishing the geometrical relationship between the coordinates of bending control points in each bending step to obtain the coordinates of the control points in each bending step; and introducing the coordinates of the control points in each bending step into simulation software to make calculation. According to the invention, a circular arc is dispersed and substituted with subtense, the profile is bent on the control points when moving along the subtense, and the stretching amount is applied in the bending process, thereby well averaging the internal strain of a large profile, reducing wrinkling and distortion and improving the dimensional accuracy; and because stretching is performed in the bending process, a supplementary stretching process can be saved, thus improving the production efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Dynamic learning of solenoid p-i curves for closed loop pressure controls
InactiveUS20090222179A1Increase the amount of changeAccurate forward control signalDigital data processing detailsFluid pressure controlOperating pointControl system
In a pressure control system having a solenoid-operated fluid valve that has an output hydraulic pressure which varies in accordance with a solenoid input signal, a dynamic learning block is configured to adjust the initial, default values for control points stored in a pressure-current (P-I) data table based on observed (measured) operating points that reflect the solenoid's actual transfer characteristic. A feed forward control block is configured to generate the solenoid input signal having a level based on the adjusted control points in the data table, which improves the accuracy of the solenoid input signal. An adjustment method uses a plurality of circular buffers each configured to store observed operating points falling within a respective range, and provides a mechanism to allow adjustment of the control points based on only partial data.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com