Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1352 results about "Ephemeris" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In astronomy and celestial navigation, an ephemeris (plural: ephemerides) gives the trajectory of naturally occurring astronomical objects as well as artificial satellites in the sky, i.e., the position (and possibly velocity) over time. The etymology is from Latin ephemeris, meaning 'diary' and from Greek ἐφημερίς (ephemeris), meaning 'diary, journal'. Historically, positions were given as printed tables of values, given at regular intervals of date and time. The calculation of these tables was one of the first applications of mechanical computers. Modern ephemerides are often computed electronically, from mathematical models of the motion of astronomical objects and the Earth. However, printed ephemerides are still produced, as they are useful when computational devices are not available.
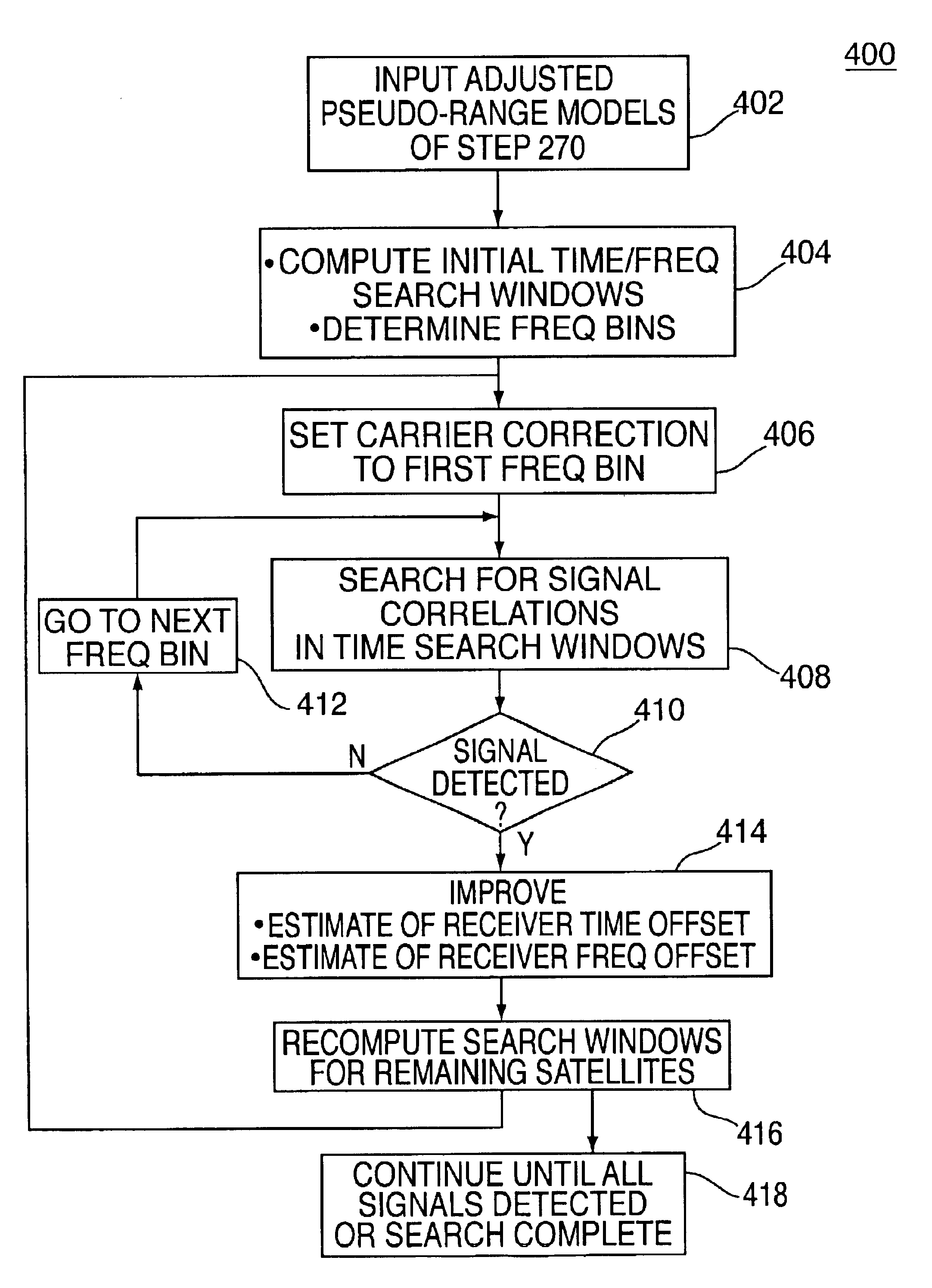
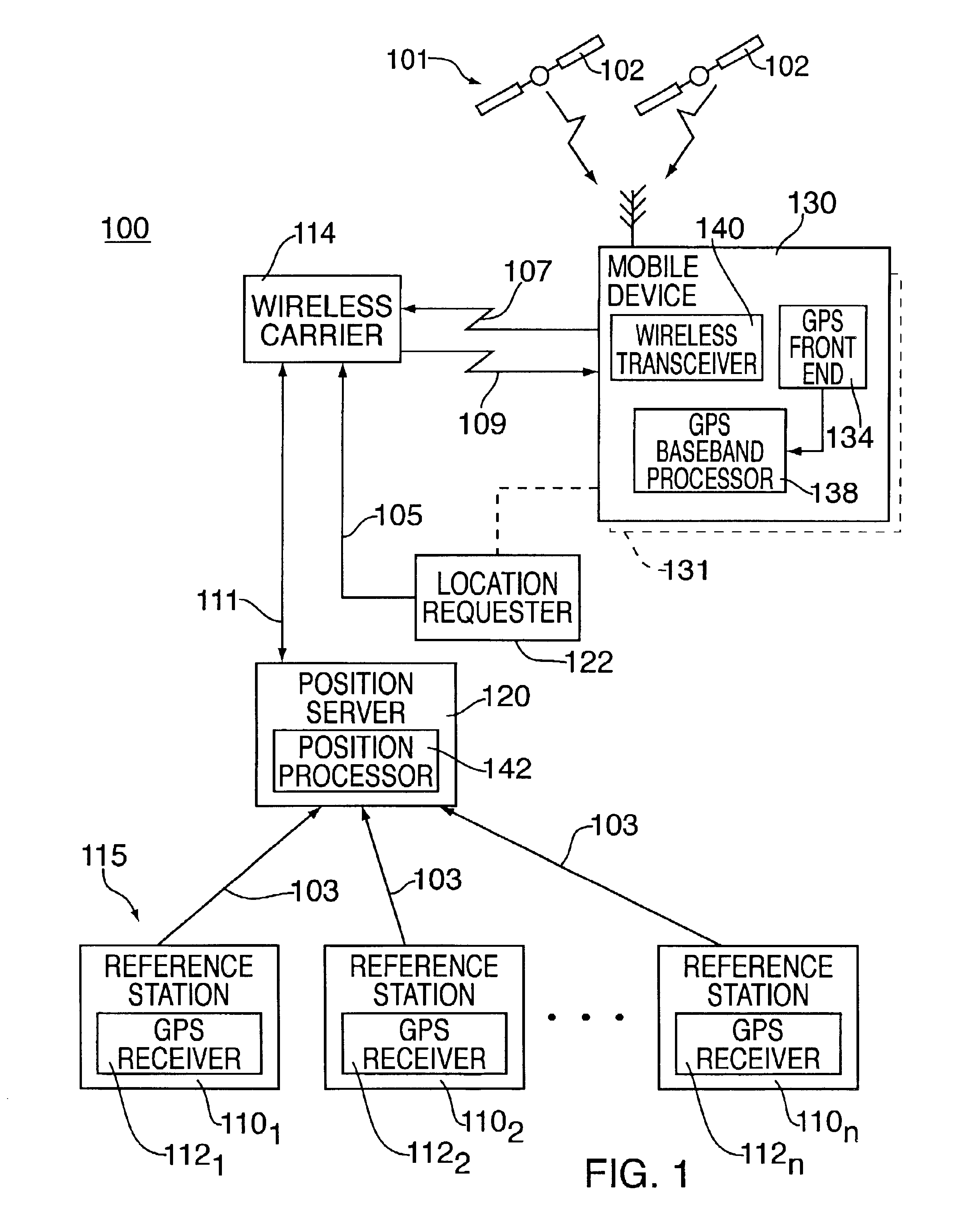
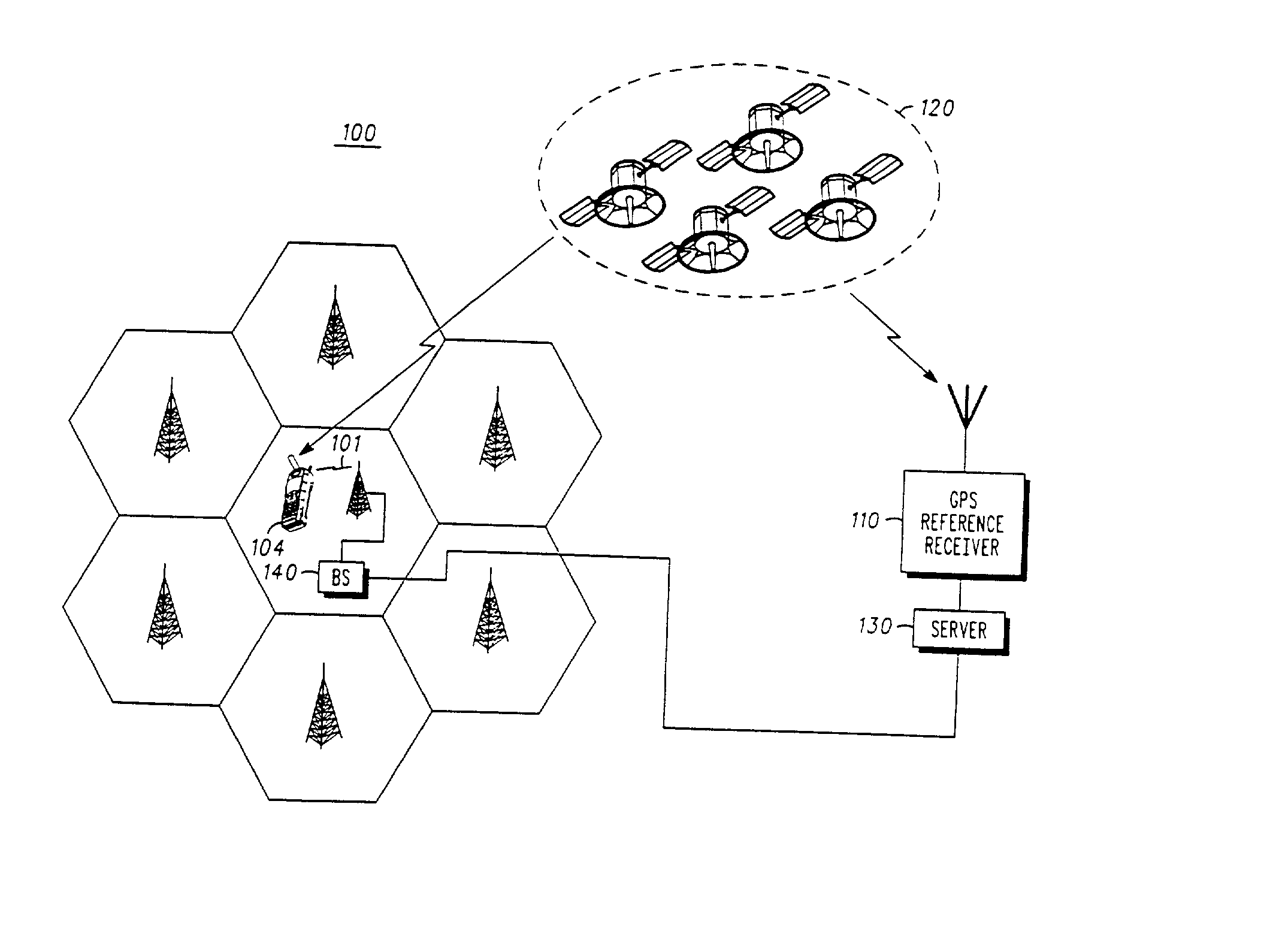
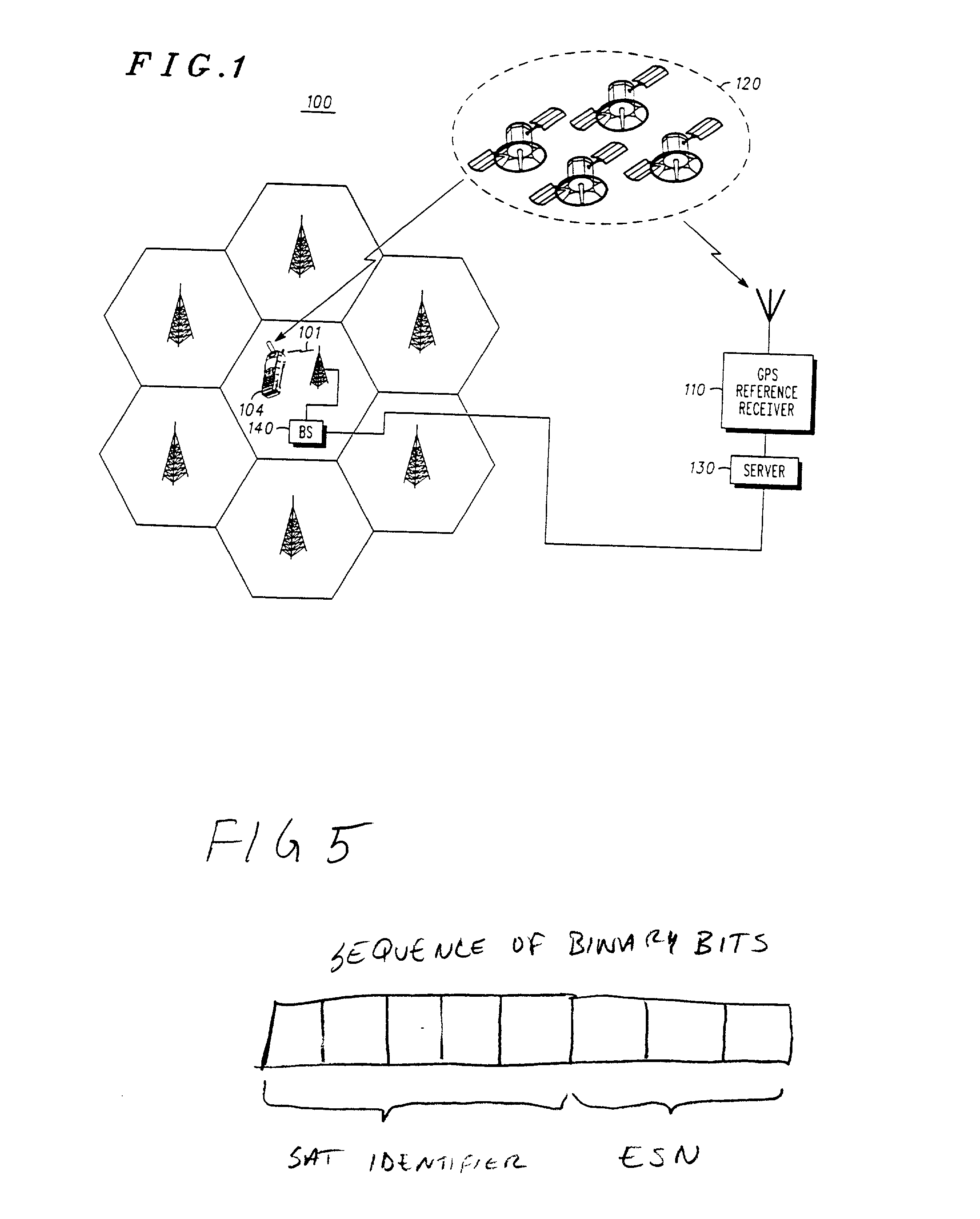
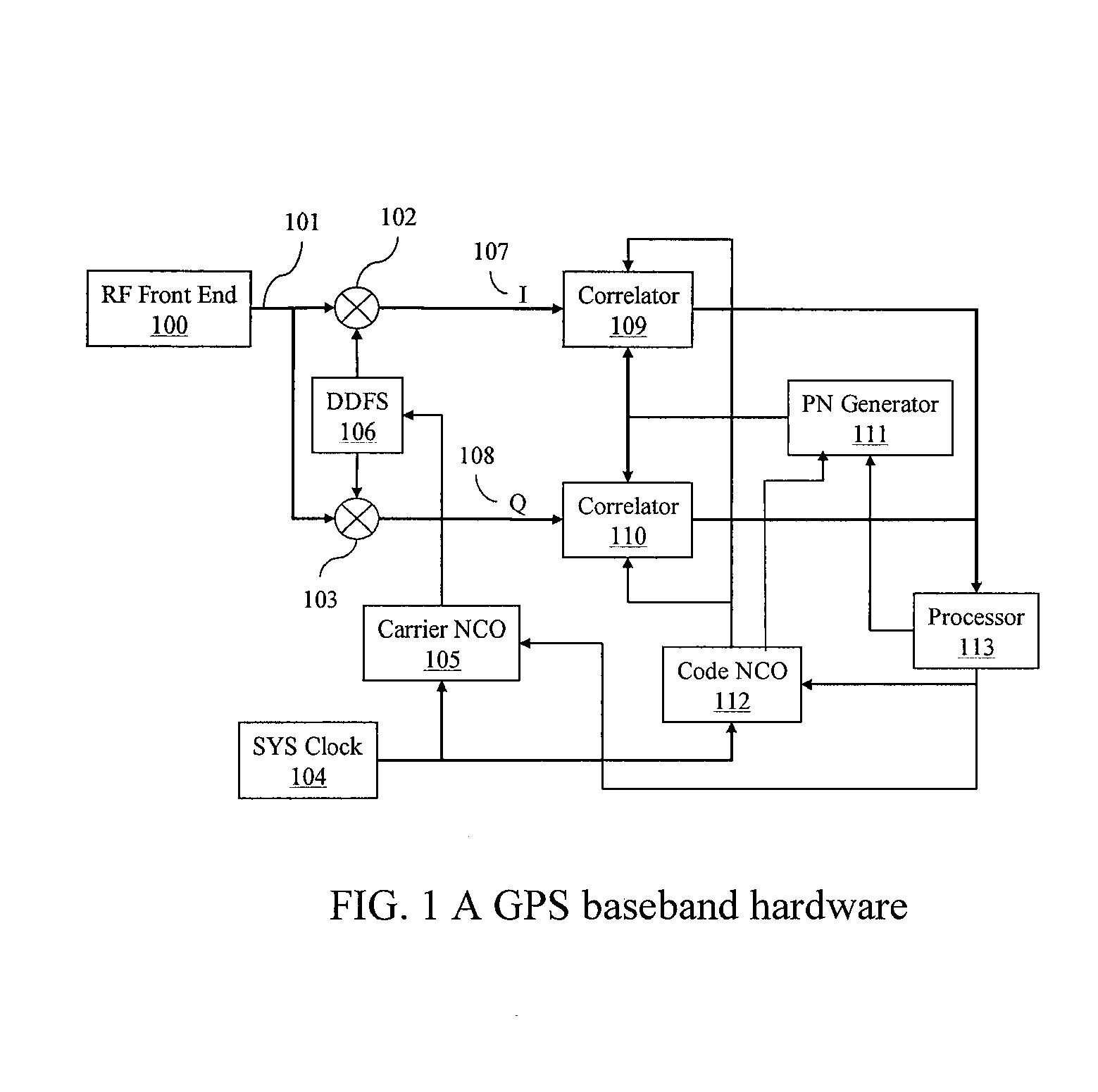
Method and apparatus for forming a pseudo-range model
InactiveUS6853916B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTelecommunications linkSignal on
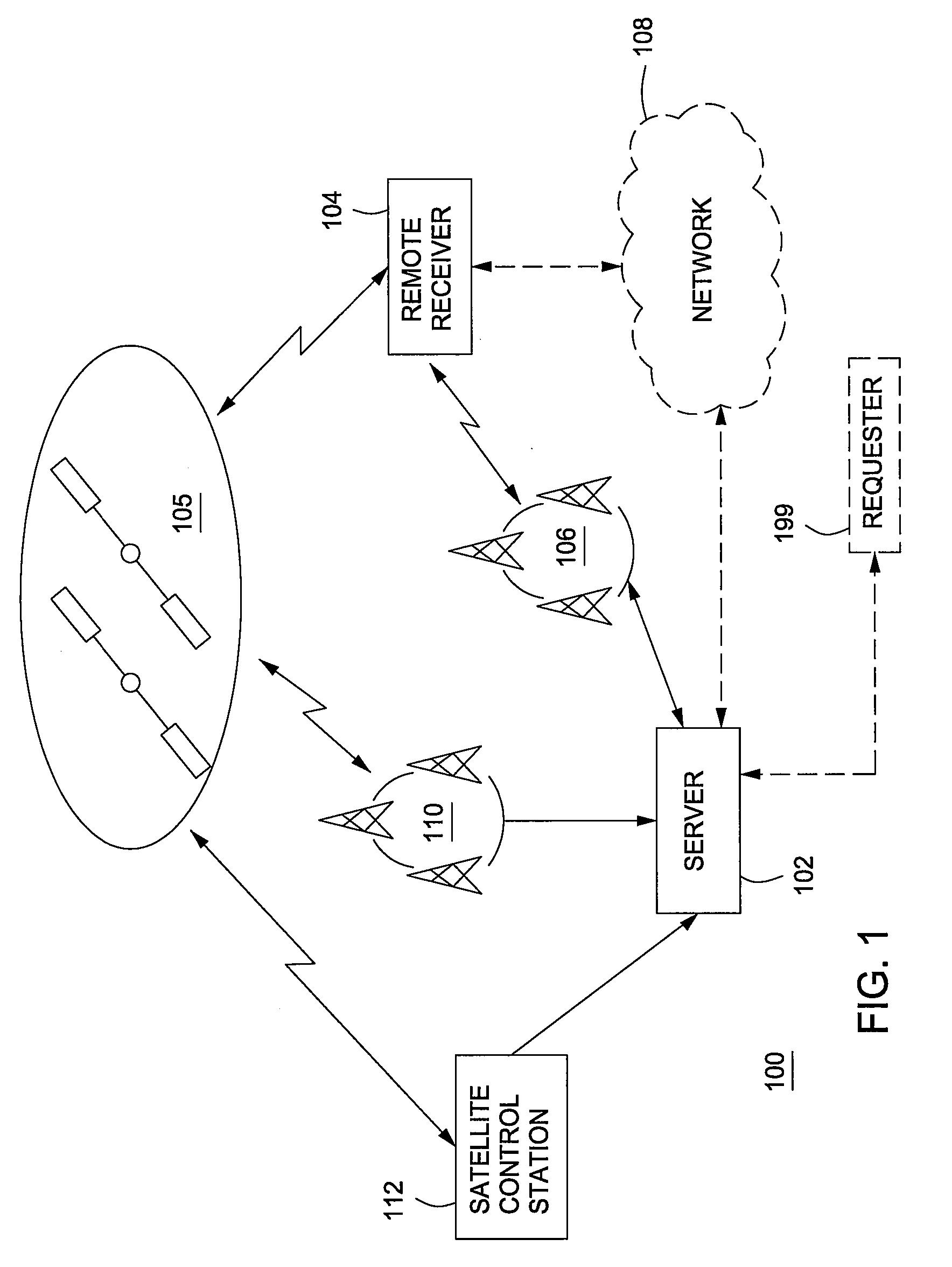
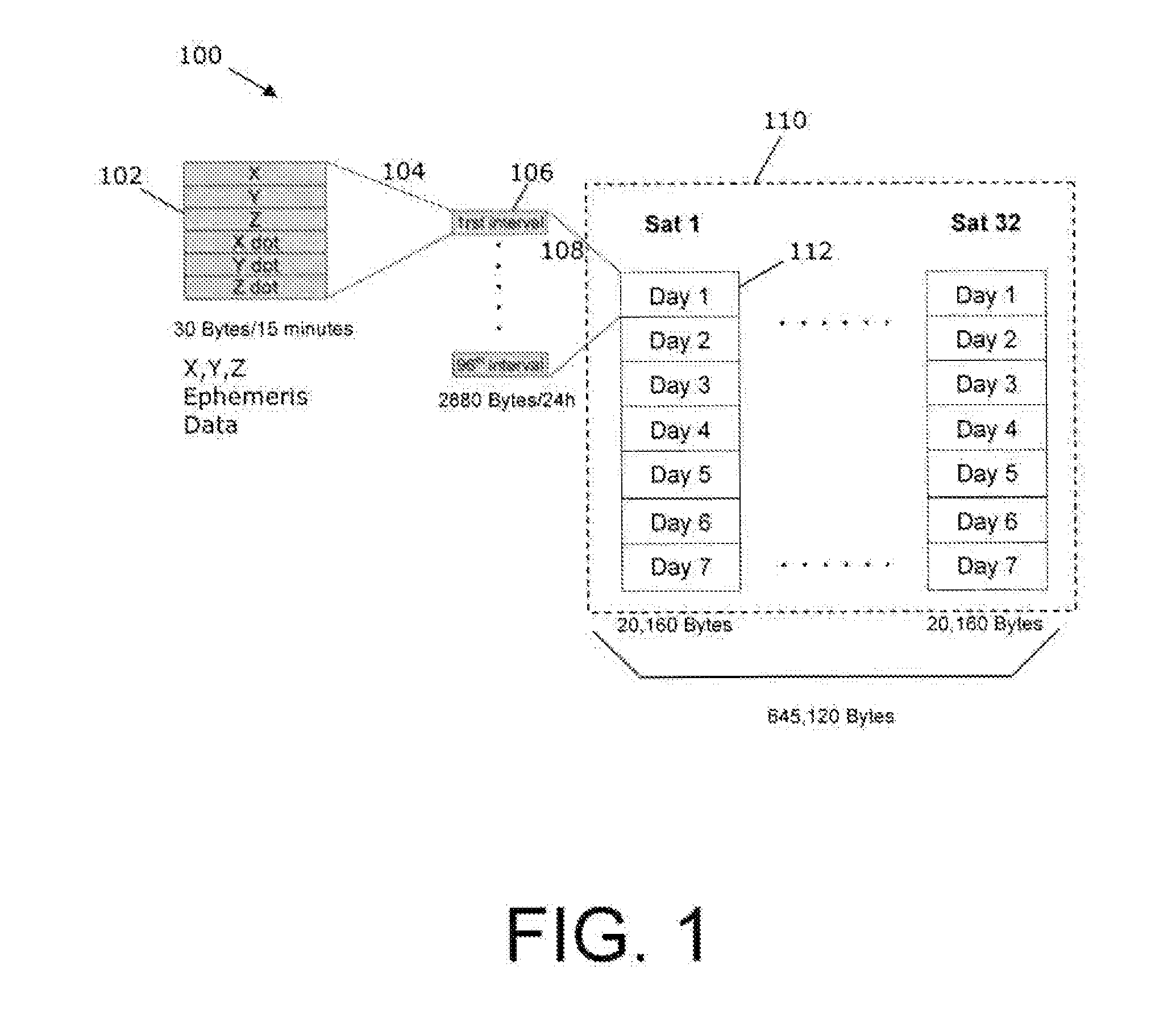
A method and apparatus for locating mobile device over a broad coverage area using a wireless communications link that may have large and unknown latency. The apparatus comprises at least one mobile device, a reference network, a position server, a wireless carrier, and a location requester. The mobile device is in communication with the wireless carrier and receives global positioning system (GPS) signals from a plurality of satellites in the GPS satellite constellation. The reference network is coupled to the position server and provides GPS data. The mobile receiver receives GPS signals, performs rudimentary signal processing and transmits the processed signals to the wireless carrier. The wireless carrier passes the signals on to the position server. The position server processes the mobile receiver's GPS data and the reference network ephemeris data to identify the location of the mobile receiver. The location is sent to the location requester.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
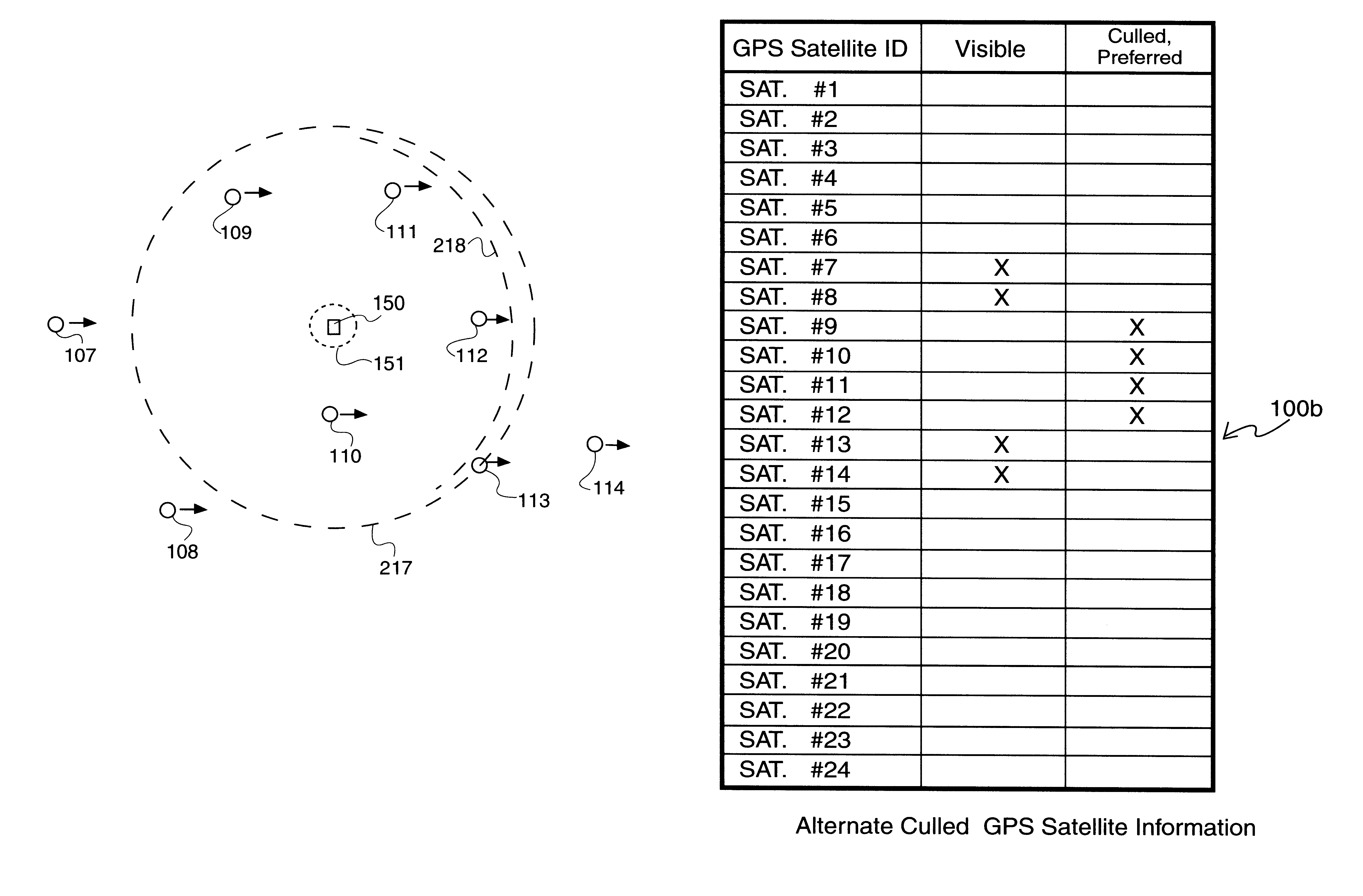
Culled satellite ephemeris information for quick assisted GPS location determination
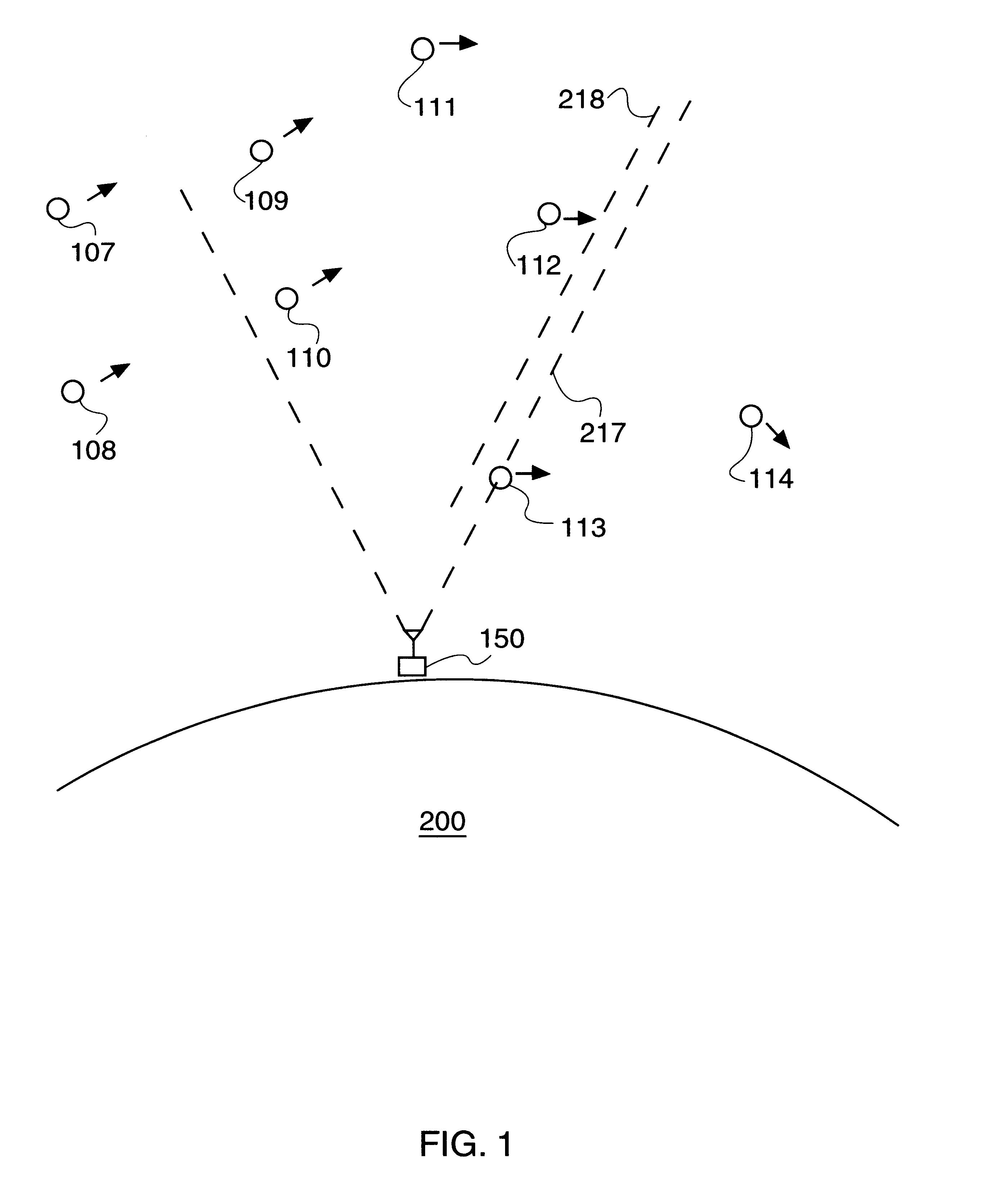
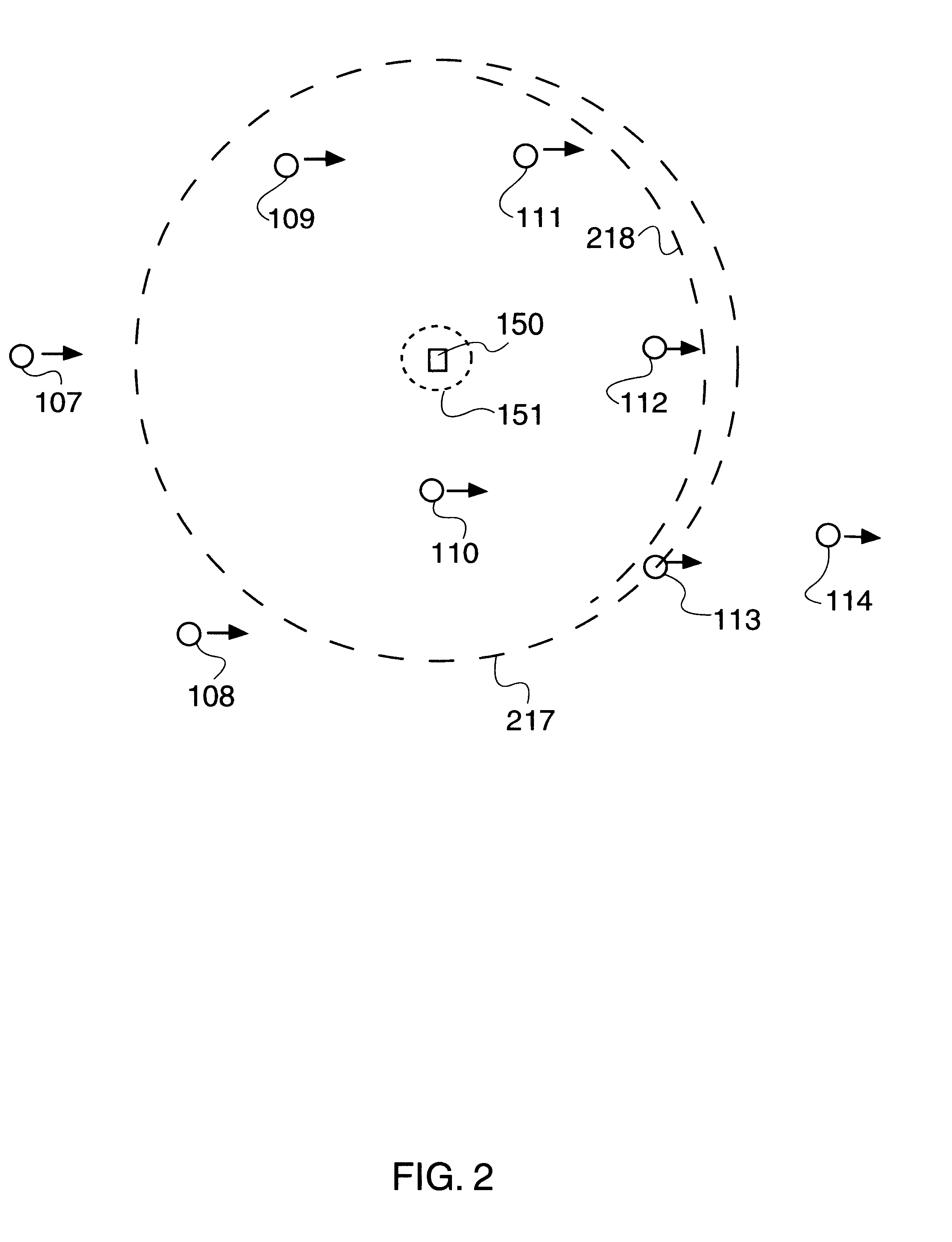
GPS satellites are culled into a minimum, preferred group having a longest dwell time within a cone of space, and communicated to mobile devices or subscribers within a particular region (e.g., serviced by a particular base station). The culling may initially be a list of GPS satellites visible to a particular base station at a particular time. As a preferred culling, only those GPS satellites currently within a cone of space above the relevant base station are selected for communication by a mobile device within the service area of the relevant base station. As an ultimate culling, a minimum set of GPS satellites may be selected based on, e.g., being not only within an arbitrary cone of space normal to the base station, but also projected to remain within that cone of space for the longest period of time, i.e., having the longest dwell time.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Enhanced location based services
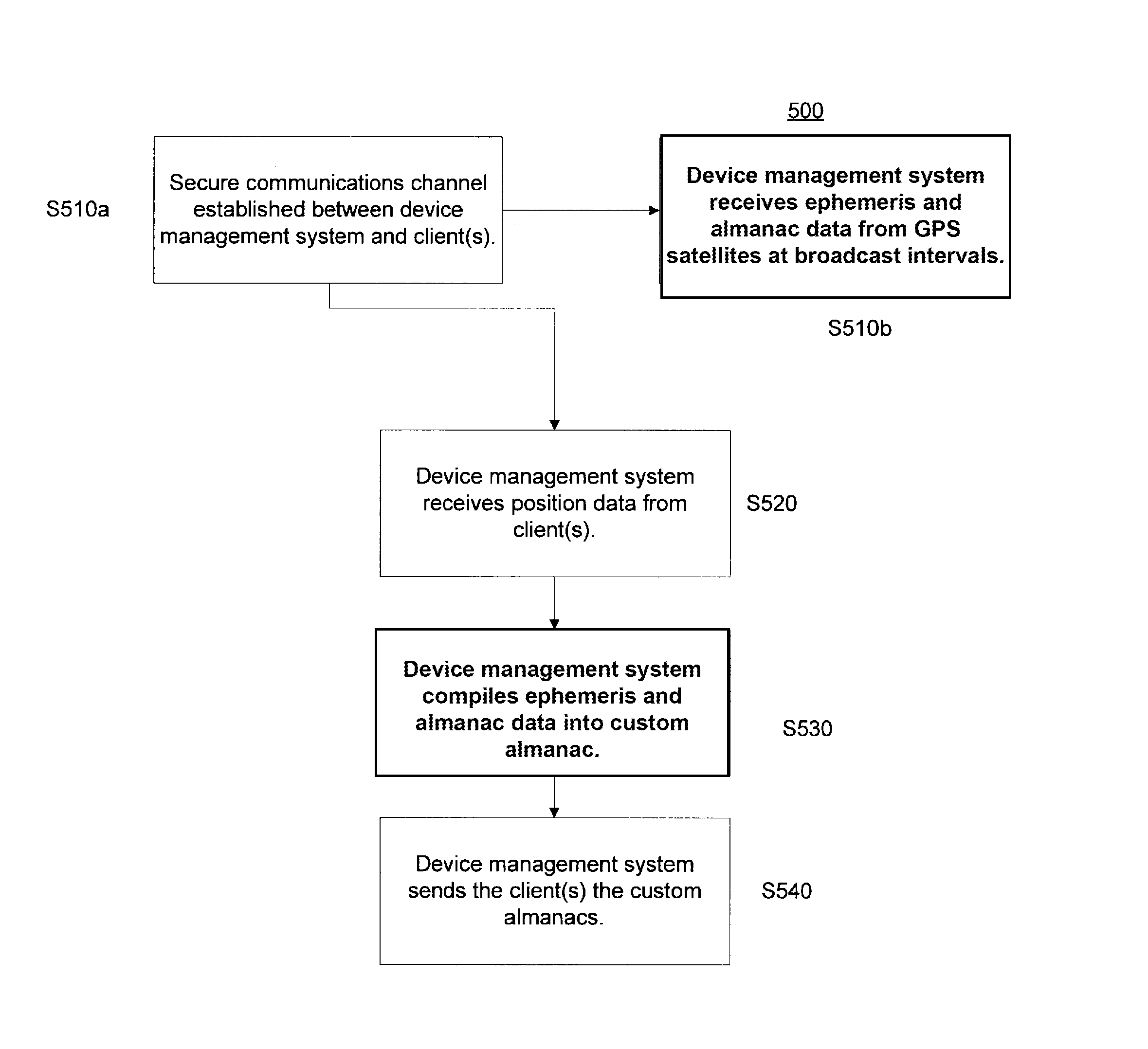
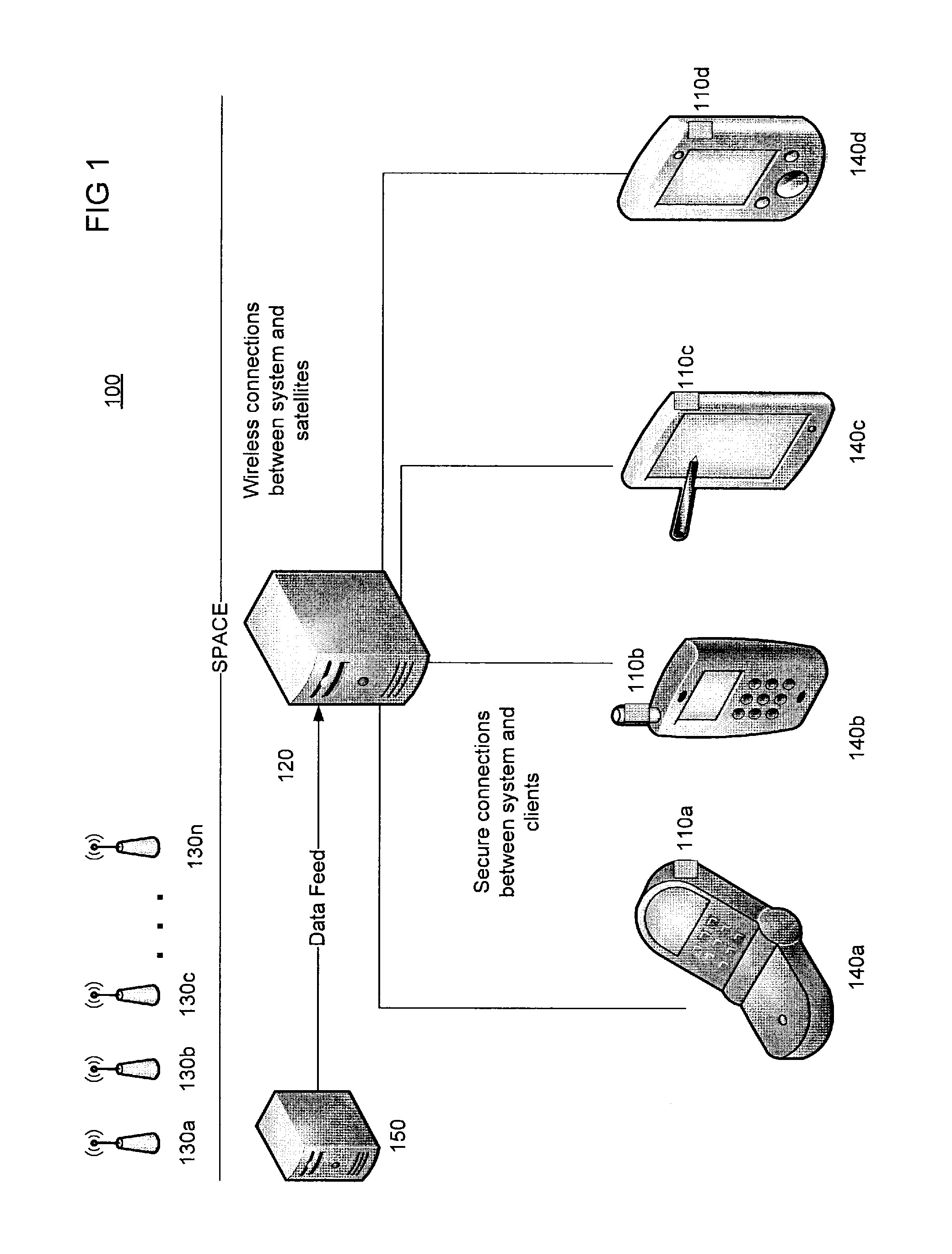
ActiveUS9158000B2The process is fast and efficientHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingPosition dependentEphemeris
A device management system is comprised of a server-side proxy component and at least one back-end computer. The server-side proxy component is configured to receive ephemeris and almanac data from a source and information from at least one client describing the geographic location of the client. The server-side proxy component is configured to send the ephemeris and almanac data and the information from the client to a back-end computer. Responsive to receiving this data and information, the computer compiles it into GPS data relevant to the location of the client.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Reduced global positioning system receiver code shift search space for a cellular telephone system
InactiveUS6070078APosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime informationGps receiver
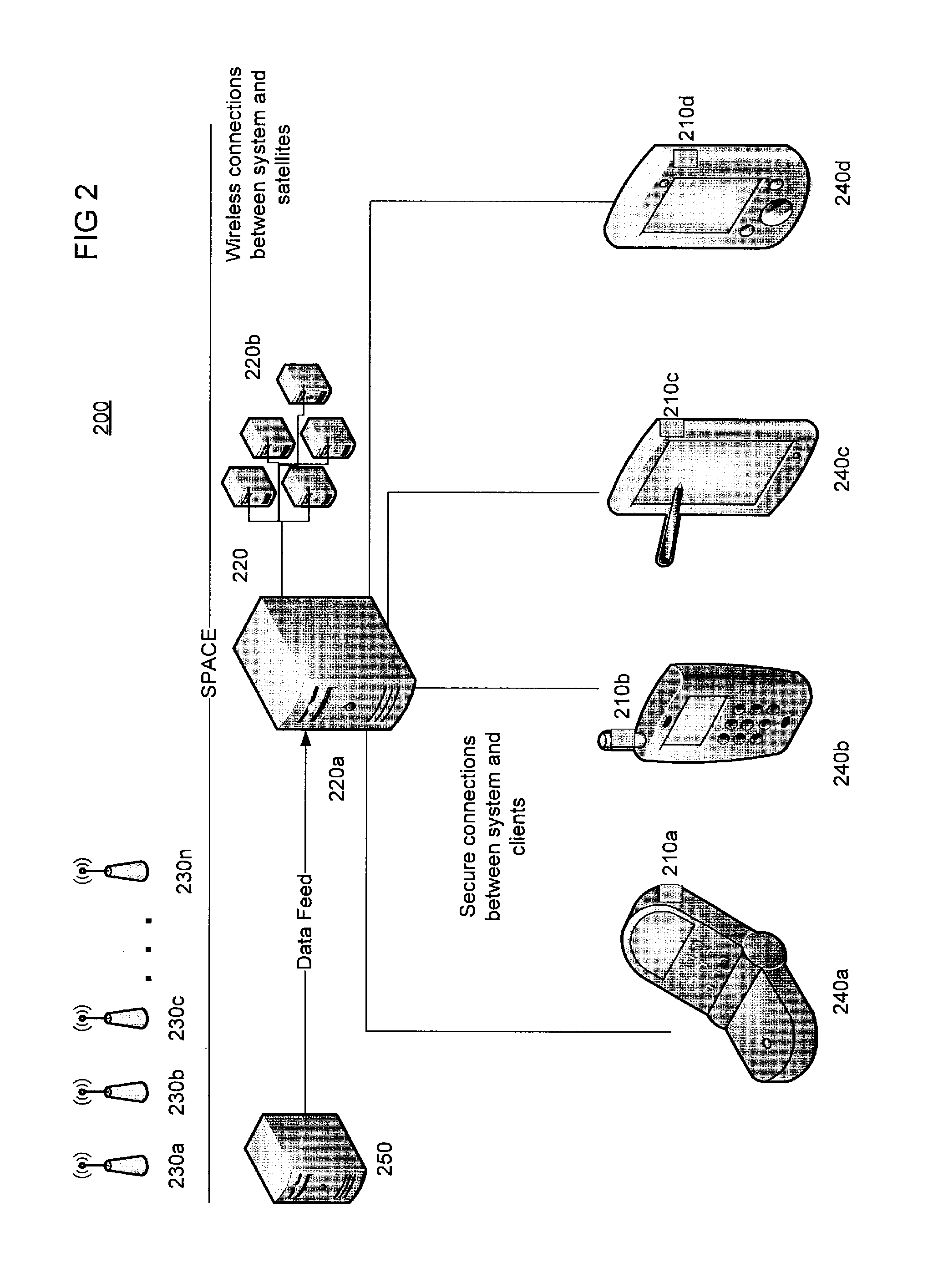
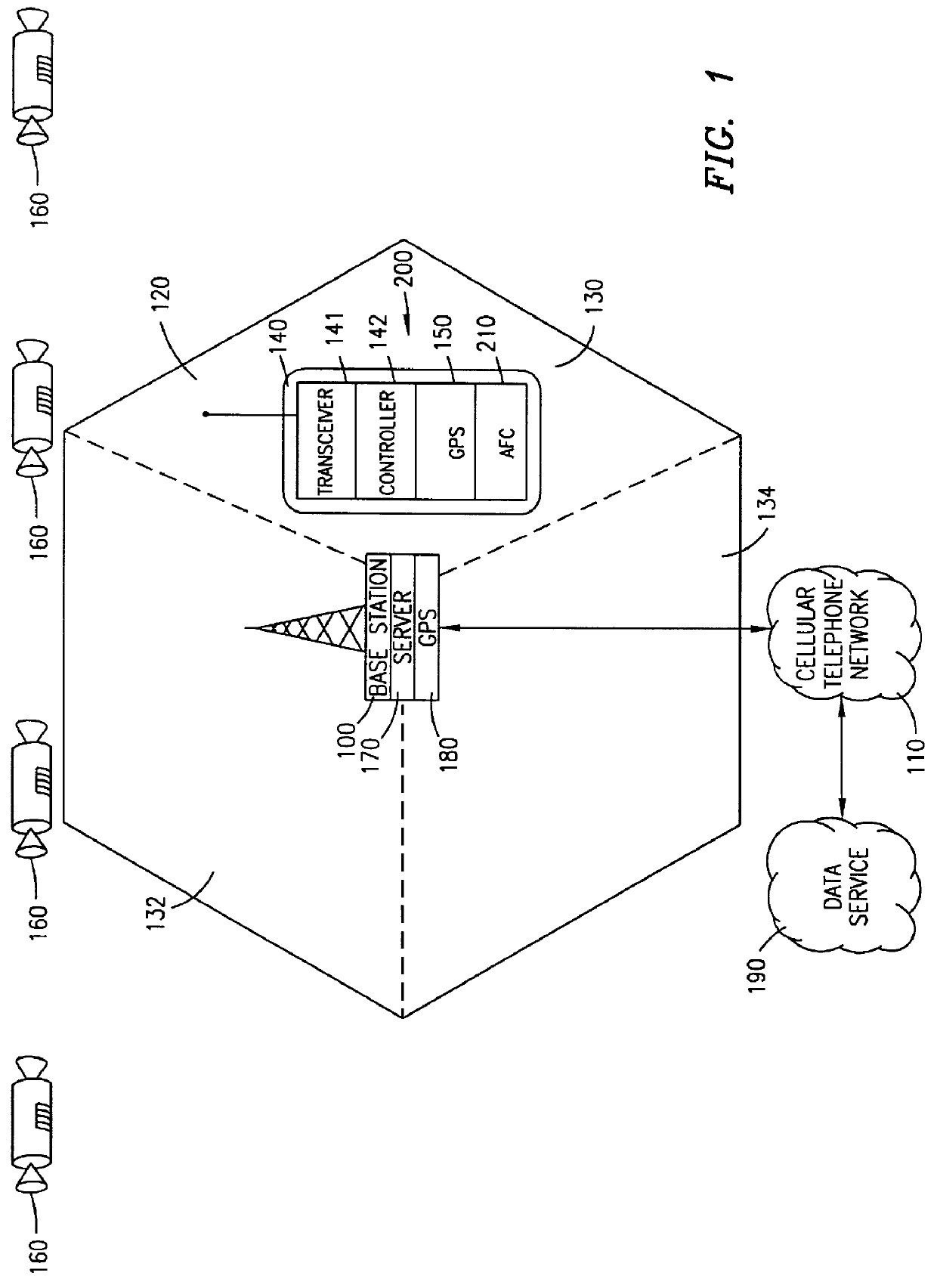
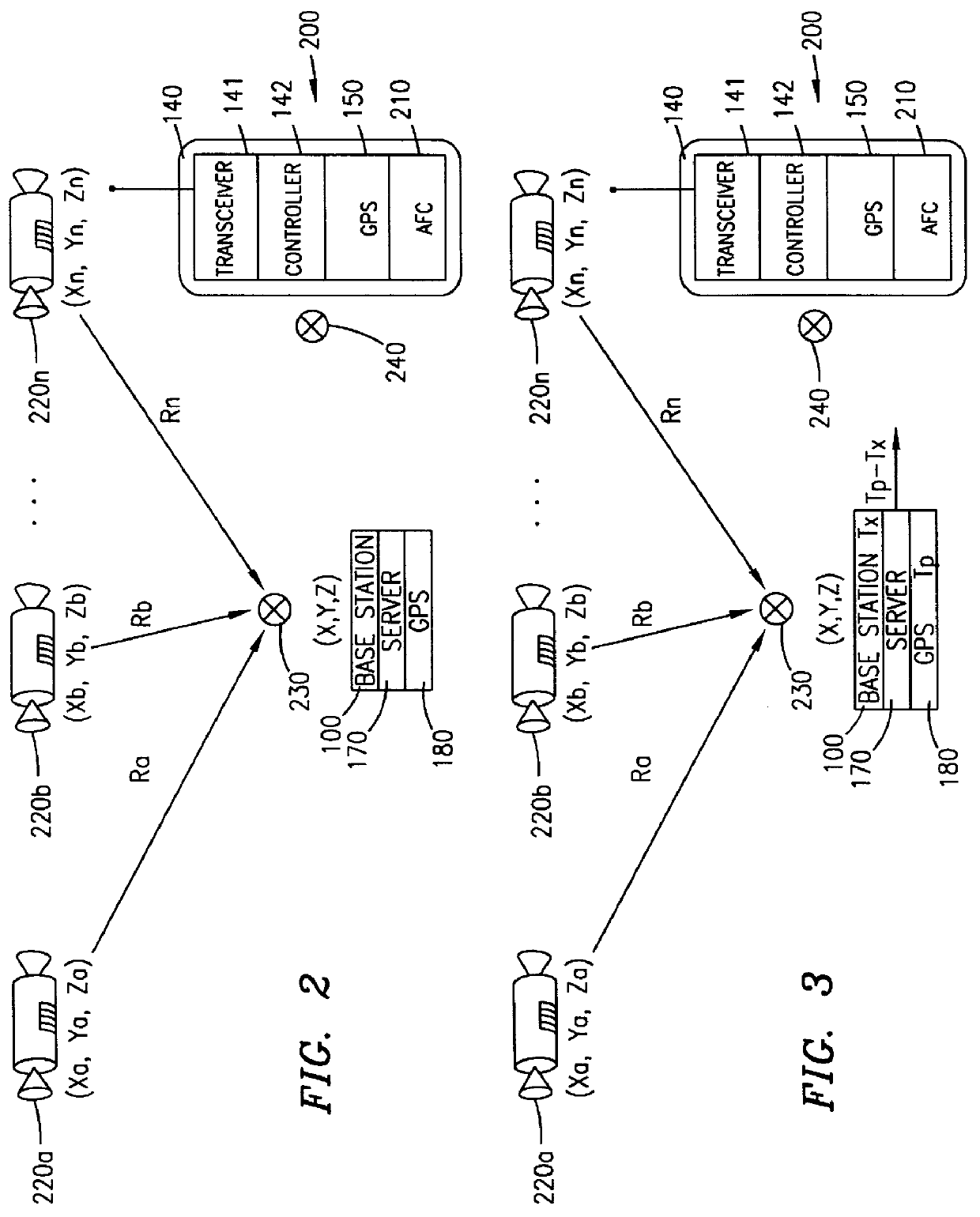
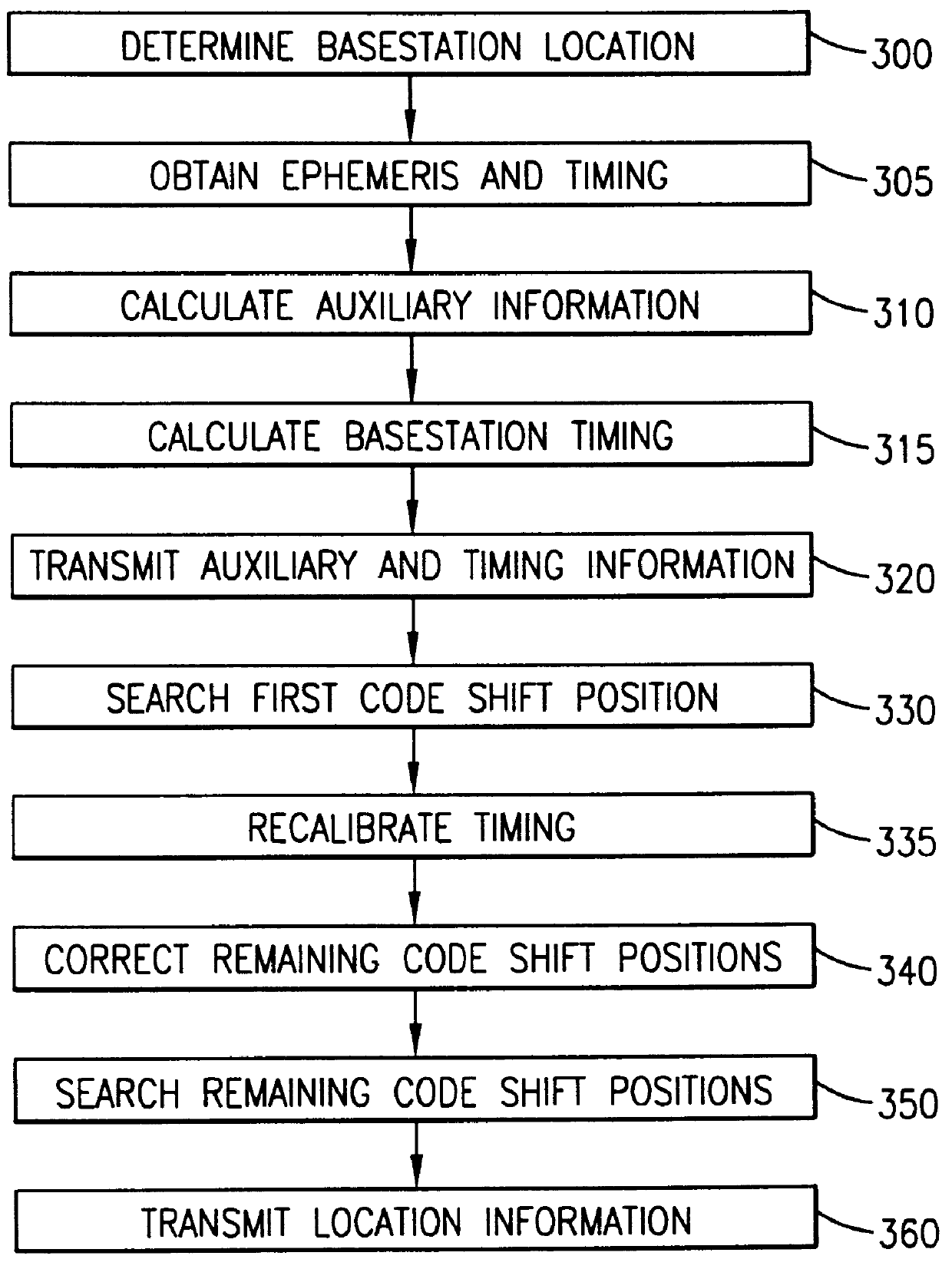
A Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver located at a base station of a cellular telephone network determines the location of the base station and obtains GPS ephemeris and, if available, timing information. A server uses the obtained information to calculate auxiliary information for use by a GPS receiver. The base station transmits the auxiliary information to the GPS receiver which is located within a cellular telephone operating within the service area of the base station. The cellular telephone GPS receiver uses the auxiliary information to determine the location of the cellular telephone and transmits location information to the cellular telephone network via the cellular telephone and the base station.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
GPS with aiding from ad-hoc peer-to-peer bluetooth networks
InactiveUS20110163914A1Reduce the possibilityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingTime informationEphemeris
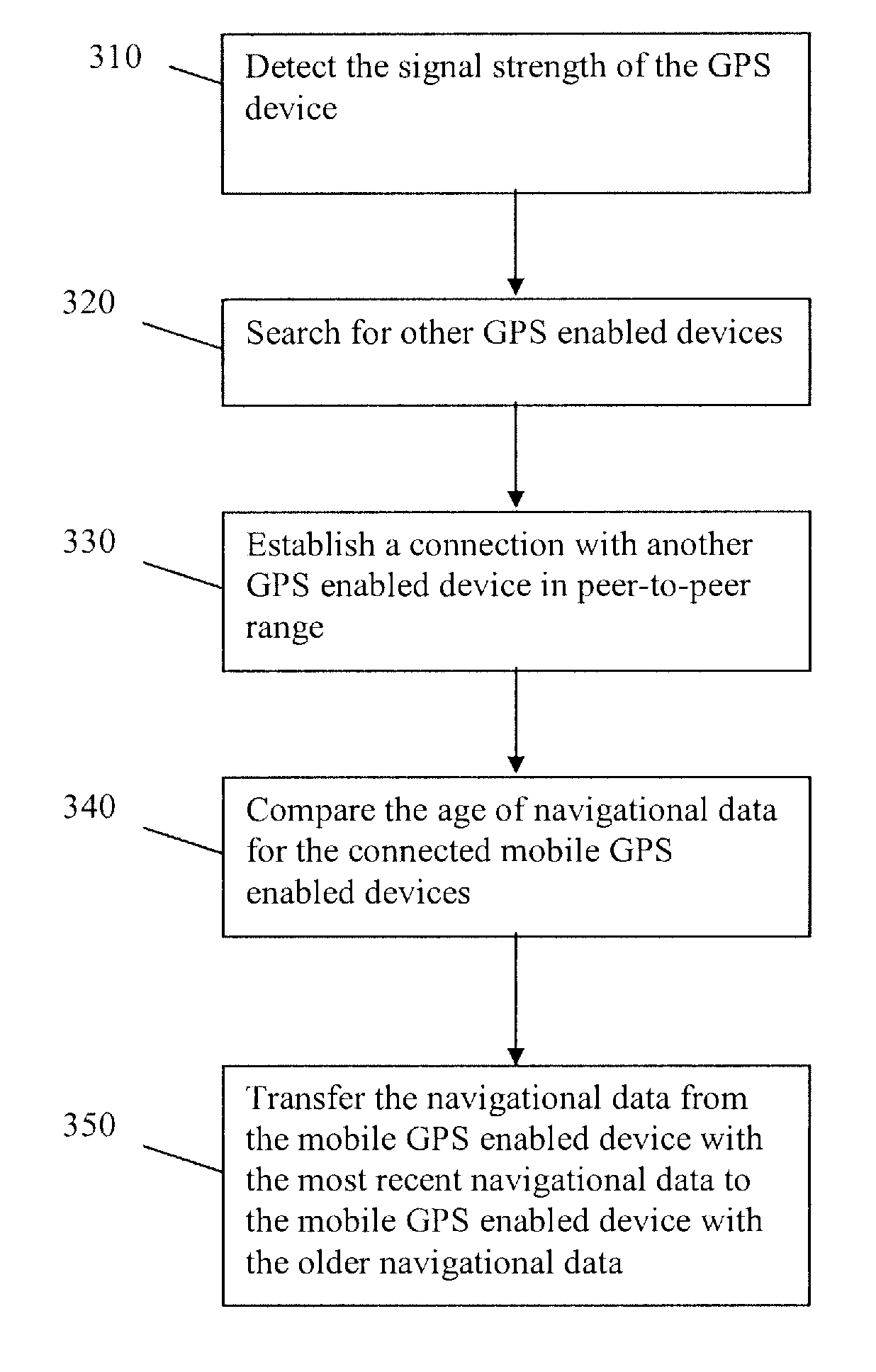
The present invention is related to location positioning systems, and more particularly, to a method and apparatus for providing an update of ephemeris information. According to one aspect, GPS enabled devices in the signal unavailable area monitors the state of its ephemeris data and time information. When the ephemeris data and time information become out of date, the GPS enable device uses an ad hoc Bluetooth network to retrieve ephemeris data and time information from another GPS enabled device with more current data. According to further aspects, a map of a deep hole region in which GPS and other cellular signals are not available, is generated to enable power reduction and cost saving measures.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
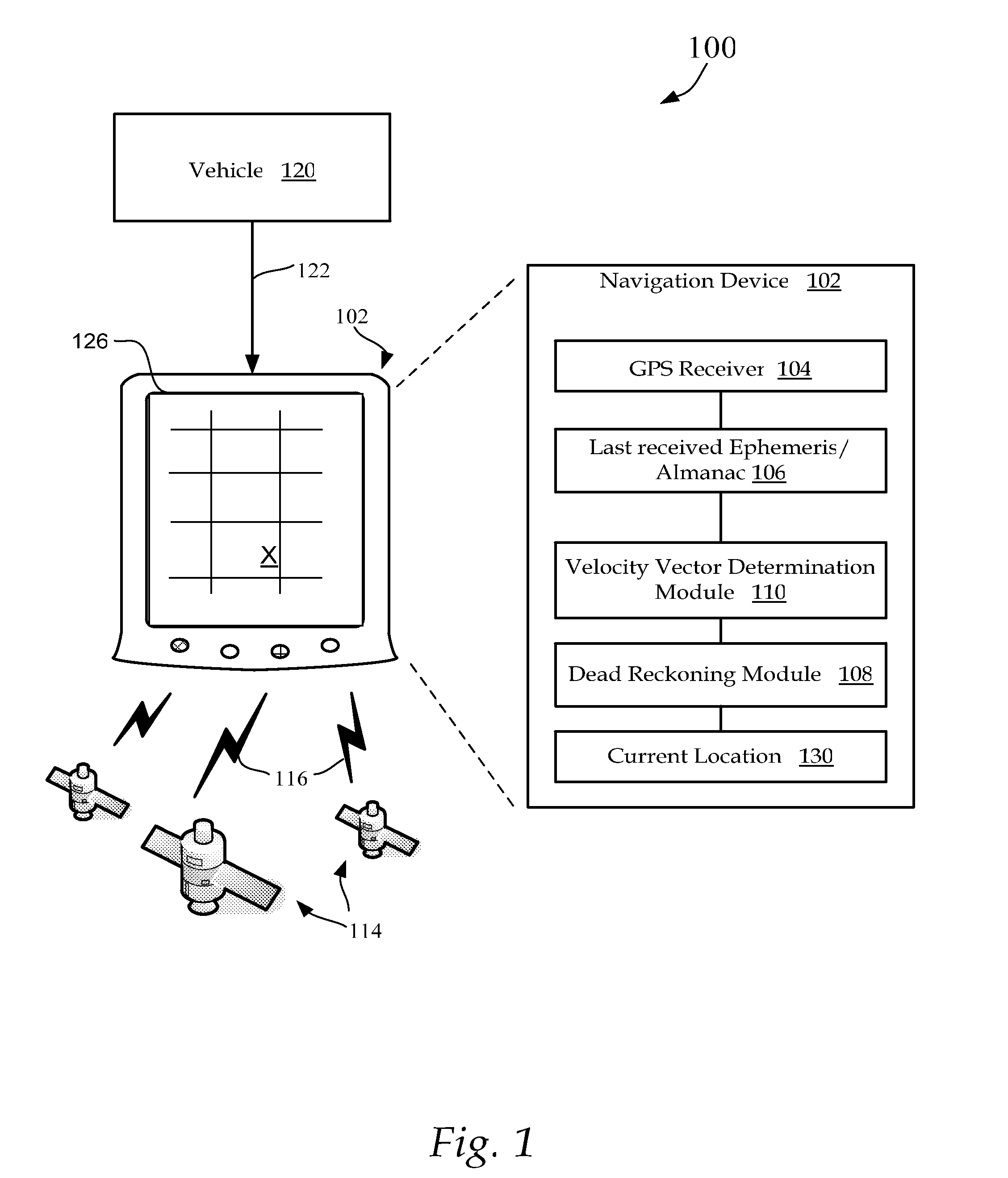
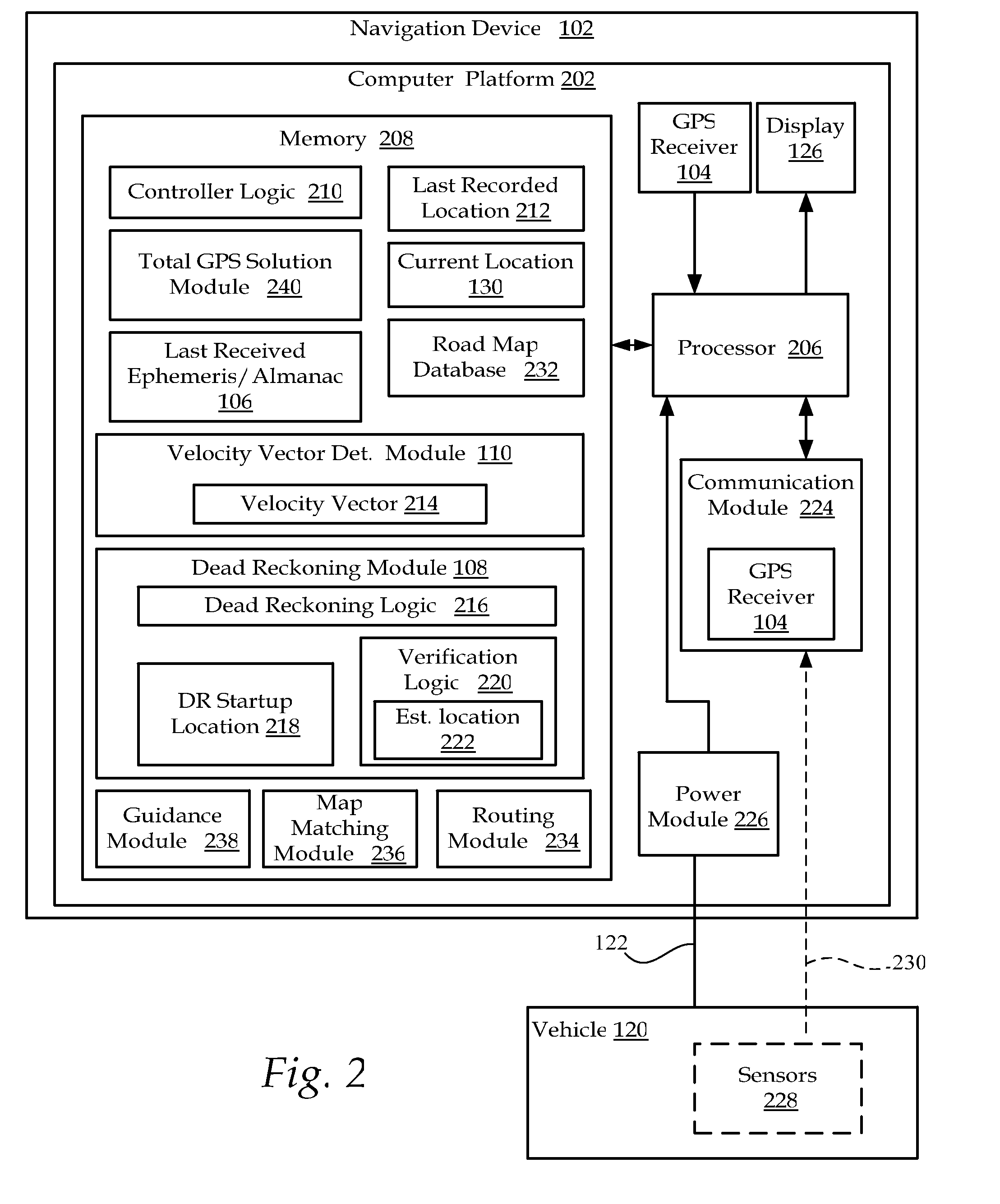
Method and system for navigation using GPS velocity vector
ActiveUS20080262728A1Accurate calculationPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsCurrent velocityEphemeris
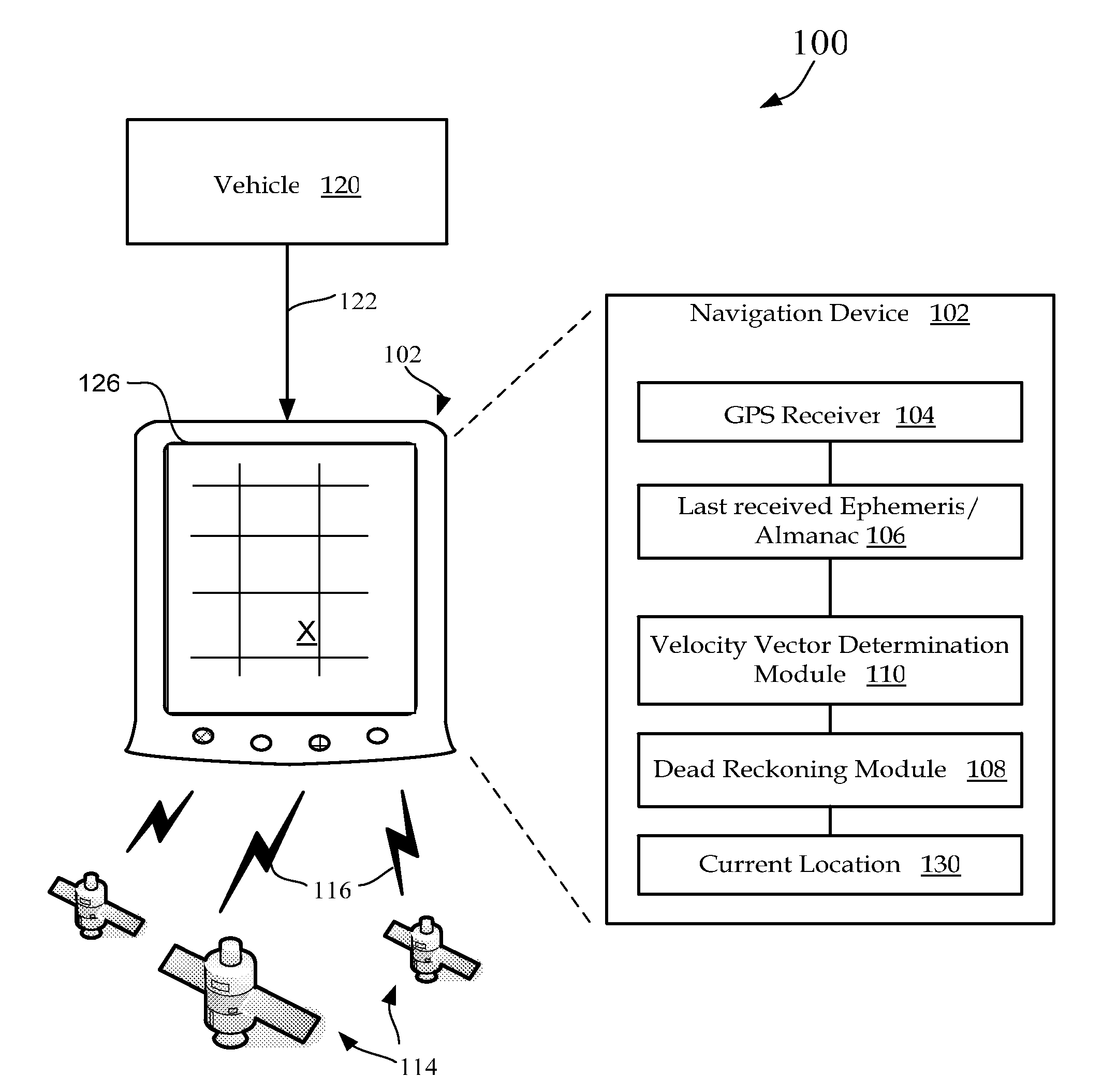
A navigation device includes a computer platform that includes a global positioning system (GPS) receiver operable to acquire and track a GPS signal, a processor assembly, and a memory. The memory includes at least one of last recorded Ephemeris and Almanac information, and a GPS velocity vector determination module operable to generate a velocity vector output in the absence of current Ephemeris based upon the tracked GPS signal and the last recorded GPS information. A method of vehicle navigation in the absence of current Ephemeris includes acquiring and tracking a GPS signal, retrieving from a memory a last recorded location of a vehicle, setting a dead reckoning startup location equal to the last recorded location, retrieving from a memory at least one of a last recorded Ephemeris and Almanac, determining a current velocity vector and determining a current location based upon the velocity vector and the dead reckoning startup location.
Owner:MITAC INT CORP
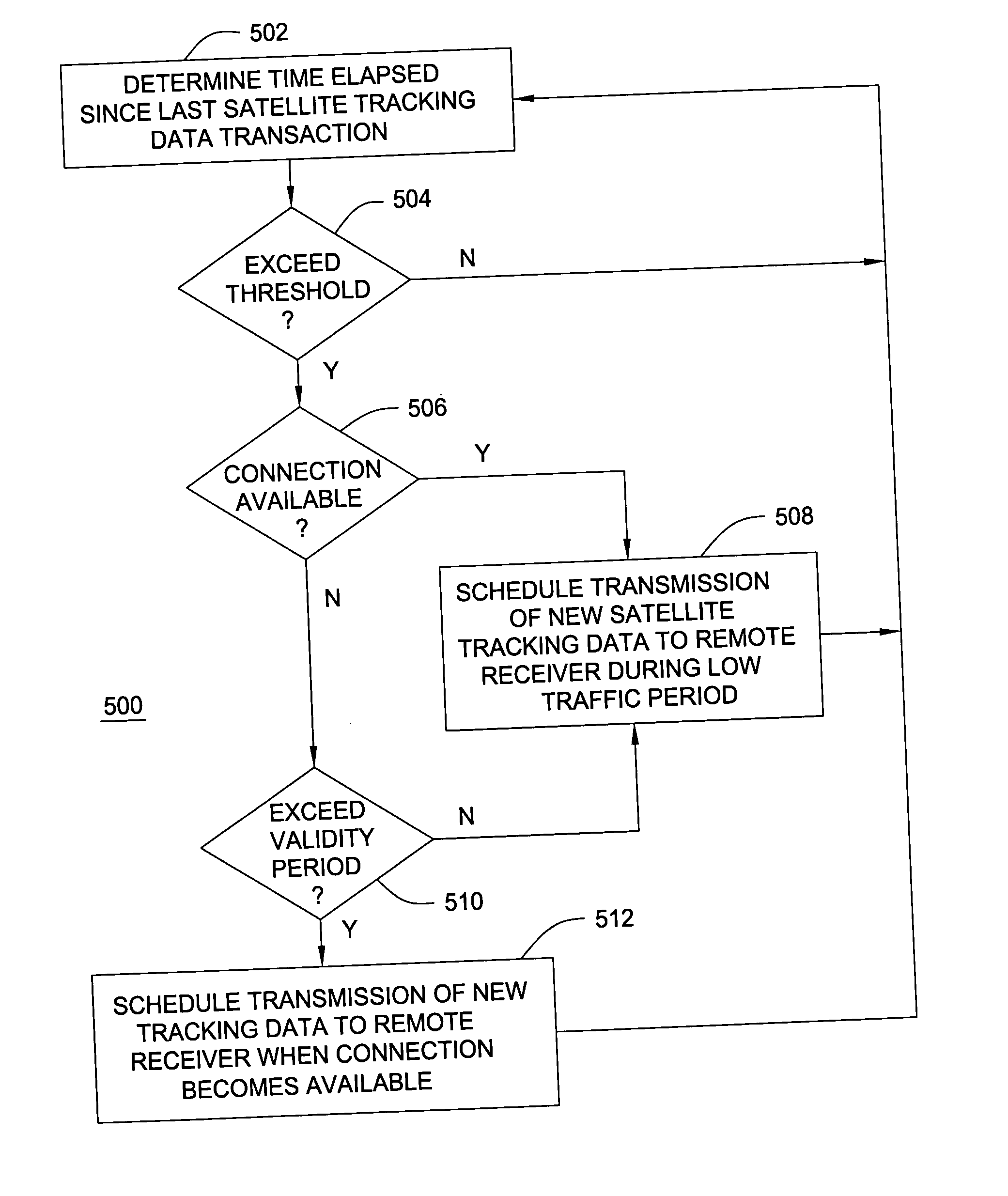
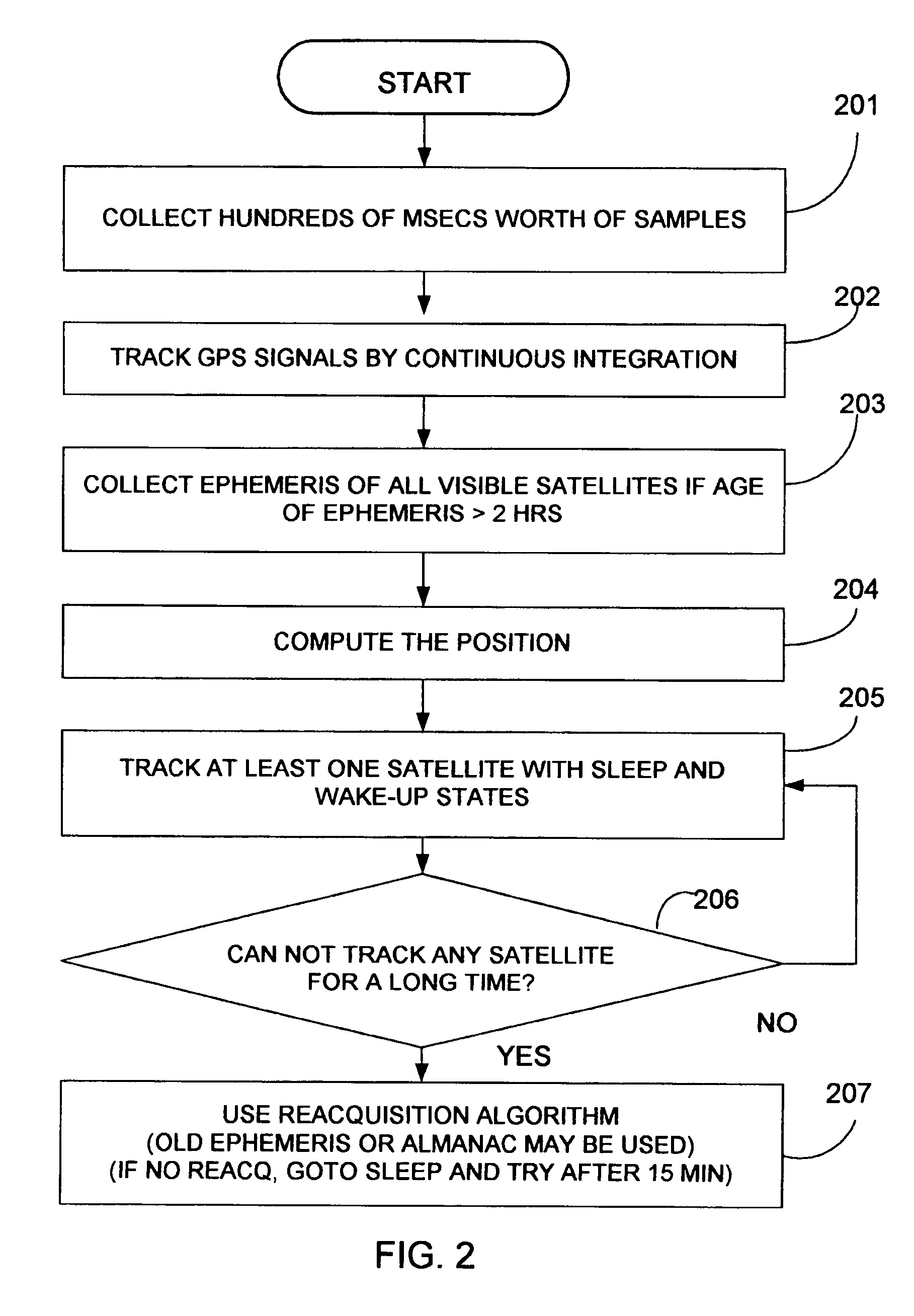
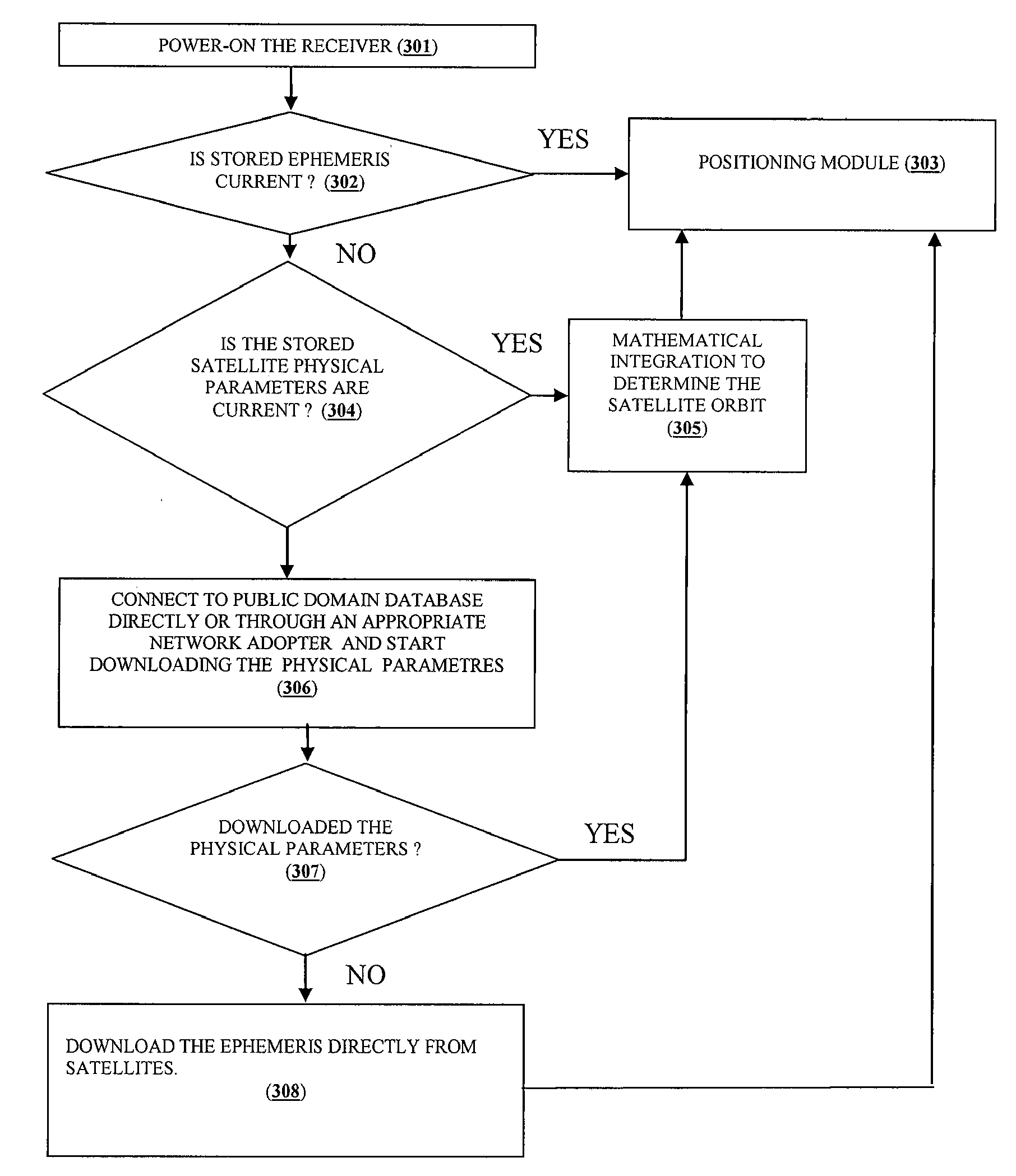
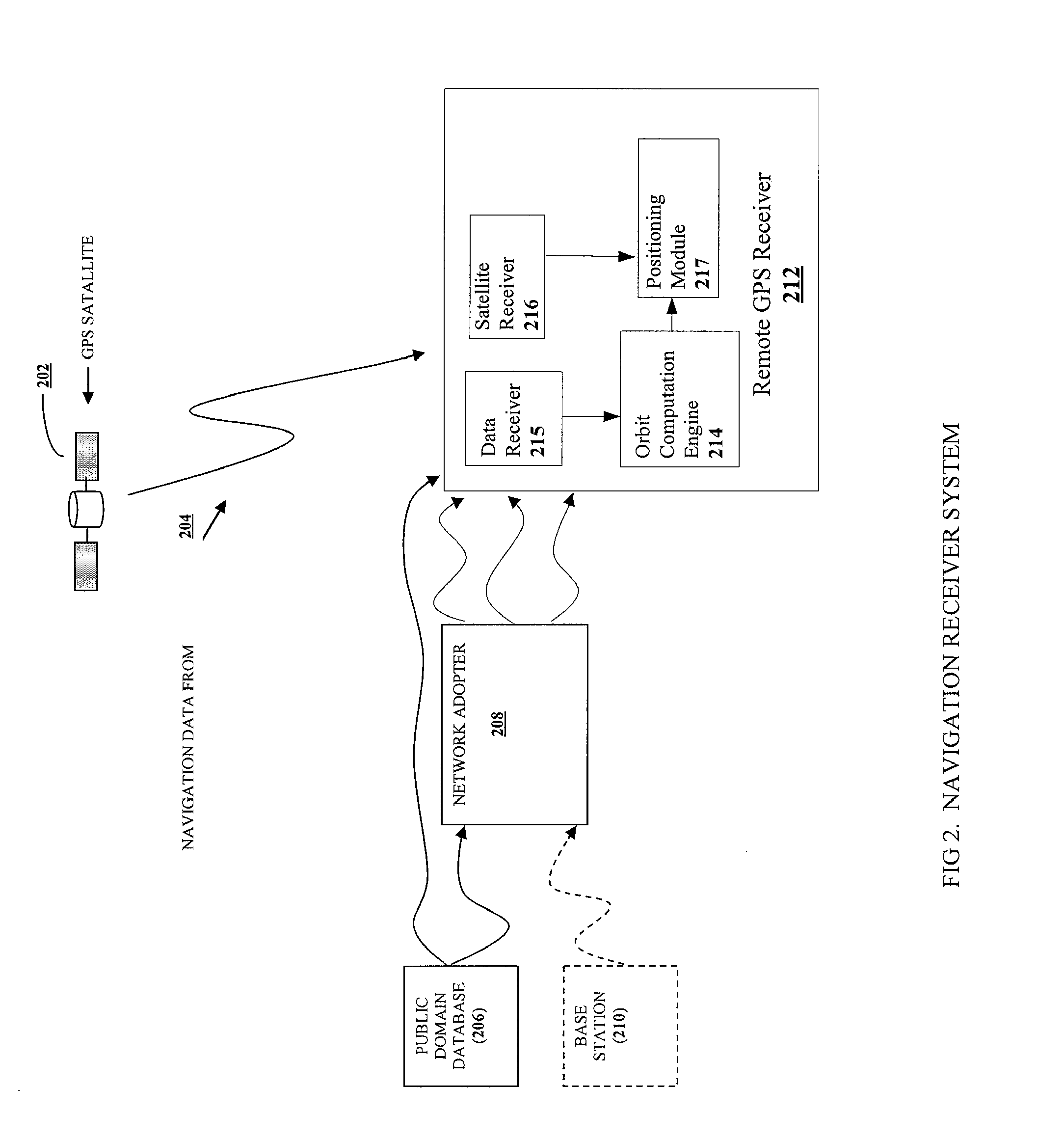
Background ephemeris download in navigational receivers
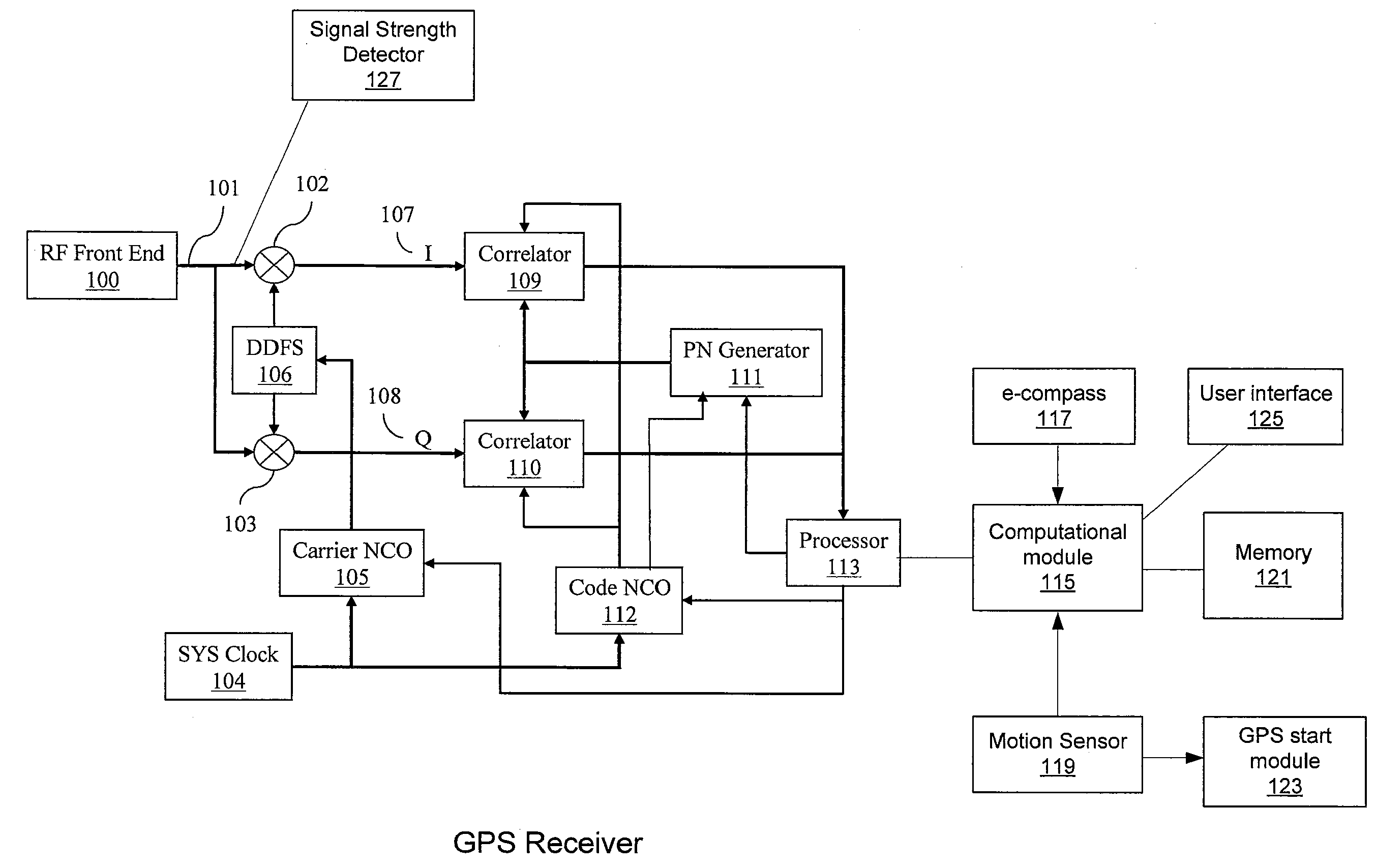
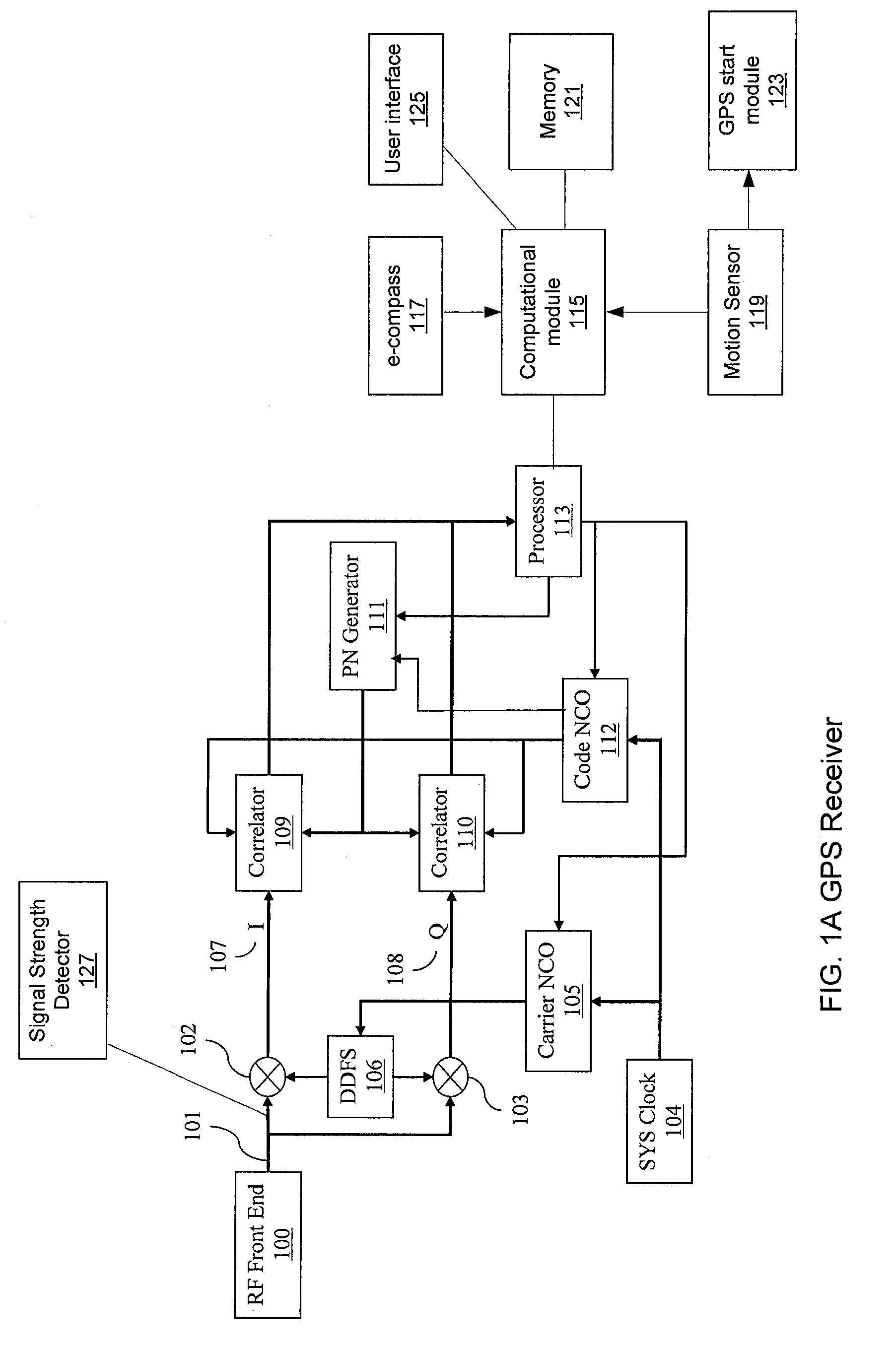
The present invention provides methods and systems for keeping the ephemeris in a navigational receiver current to achieve fast TTFF without the need for connecting to an aiding network or remote server. In an embodiment, the receiver keeps the ephemeris current by downloading the ephemeris in the background. In the preferred embodiment, the receiver uses a background sleep / wake up process to download current ephemeris with minimal power drain. In this embodiment, the receiver alternates between a sleep mode and a wake up mode. During the wake up mode, the receiver attempts to download current ephemeris. The receiver then goes back to the sleep mode until the next wake up to conserve power. The receiver may wake up from the sleep mode to download the ephemeris when the stored ephemeris is no longer current or the ephemeris broadcasted from a satellite has been updated or based on receiver usage patterns.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
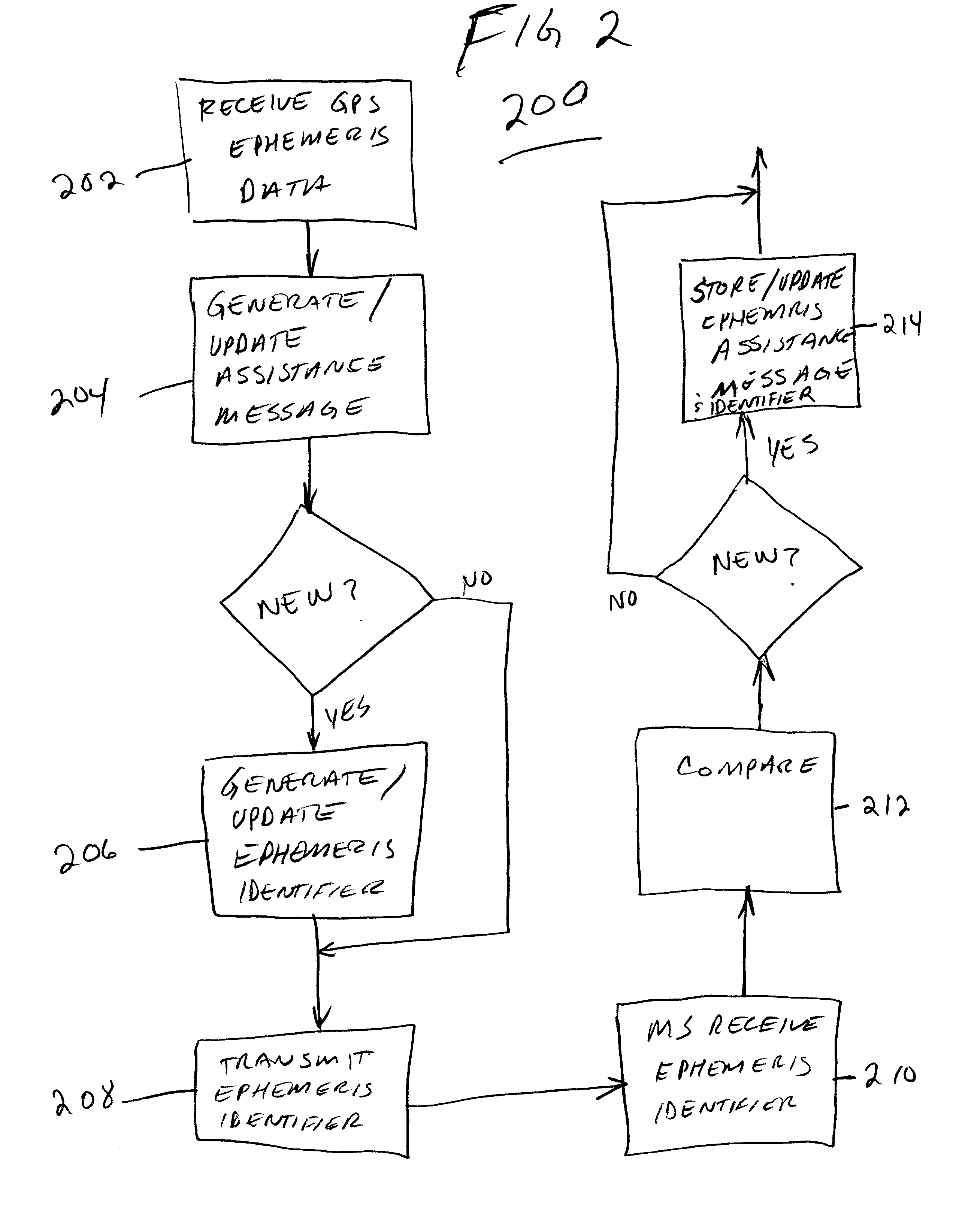
GPS assistance messages in cellular communications networks and methods therefor
InactiveUS20020168985A1Energy efficient ICTRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEphemerisMobile station
GPS assistance message and data issue identifiers for transmission to GPS enabled mobile stations in cellular communications networks and methods therefor. The GPS data issue identifiers indicate whether GPS data, for example corresponding ephemeris and almanac data, stored at the mobile station requires updating. In the exemplary 3rd generation (W-CDMA / UMTS) architecture, the GPS assistance message is a System Information Block (SIB), and the GPS ephemeris data identifier and corresponding satellite identifier is encoded in a value tag included in a Master Information Block (MIB).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Ephemeris extension method for GNSS applications
Systems, methods and devices for improving the performance of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers are disclosed. In particular, the improvement of the ability to calculate a satellite position or a receiver position where a receiver has degraded ability to receive broadcast ephemeris data directly from a GNSS satellite is disclosed. Correction terms can be applied to an approximate long-term satellite position model such as the broadcast almanac.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
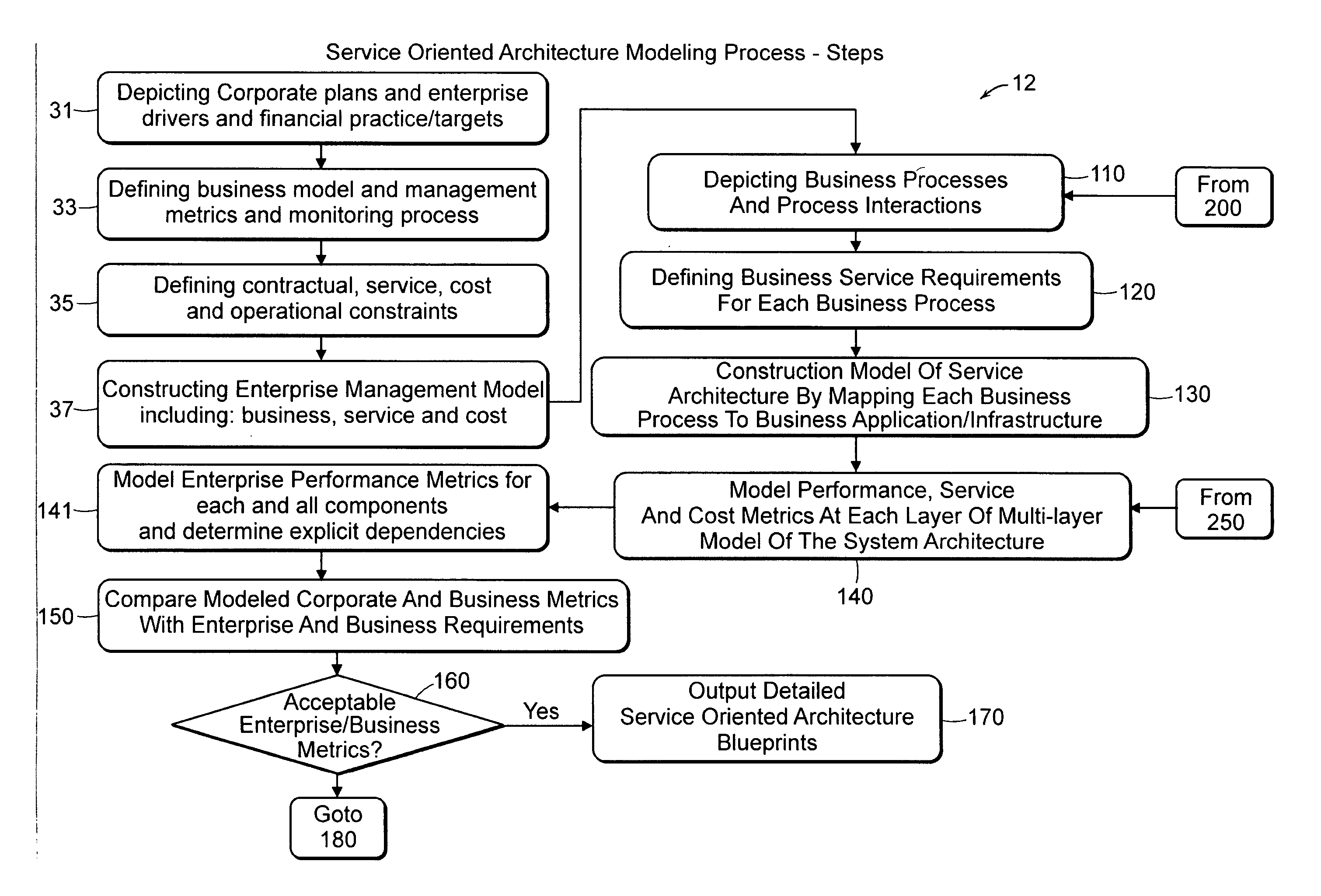
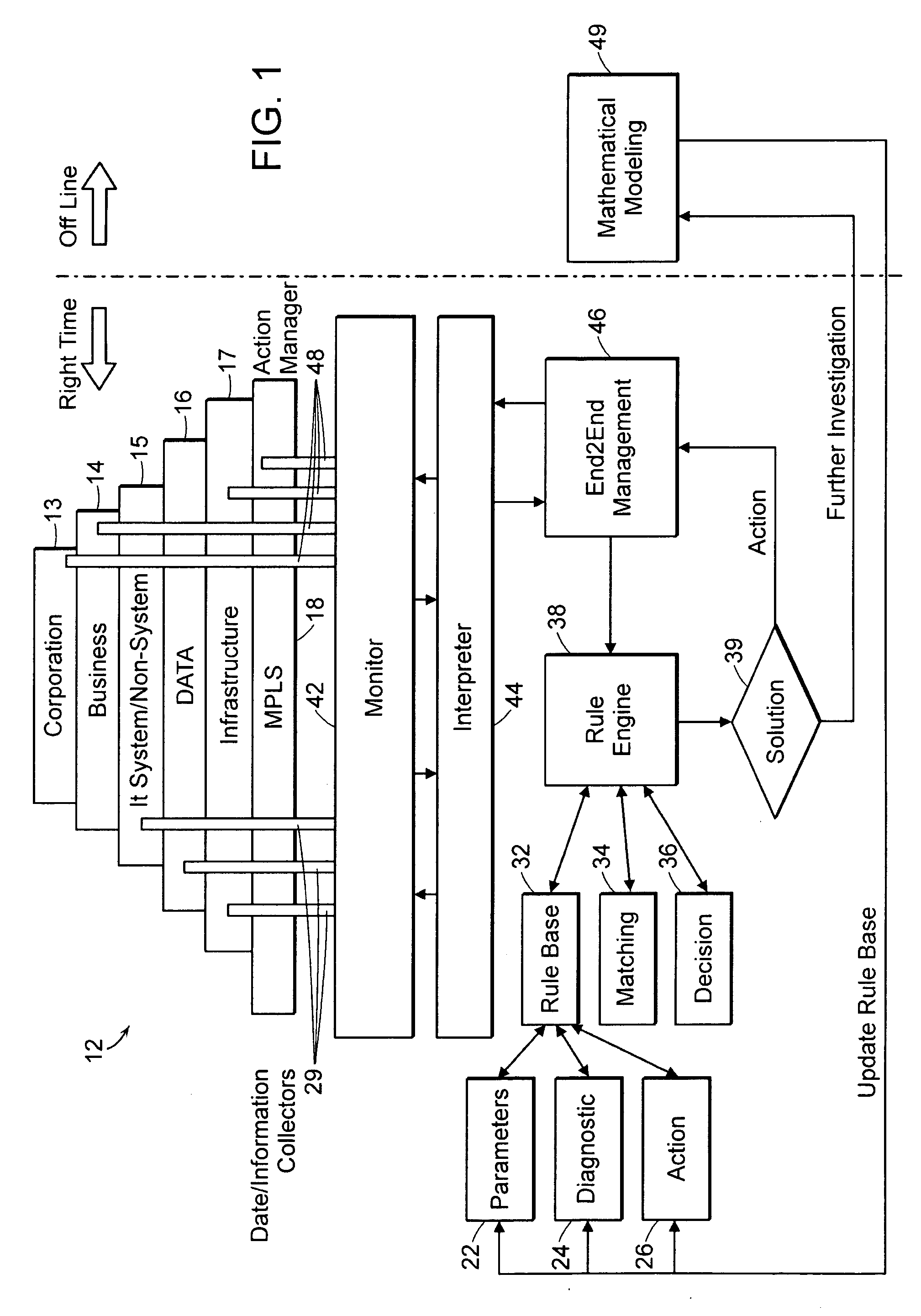
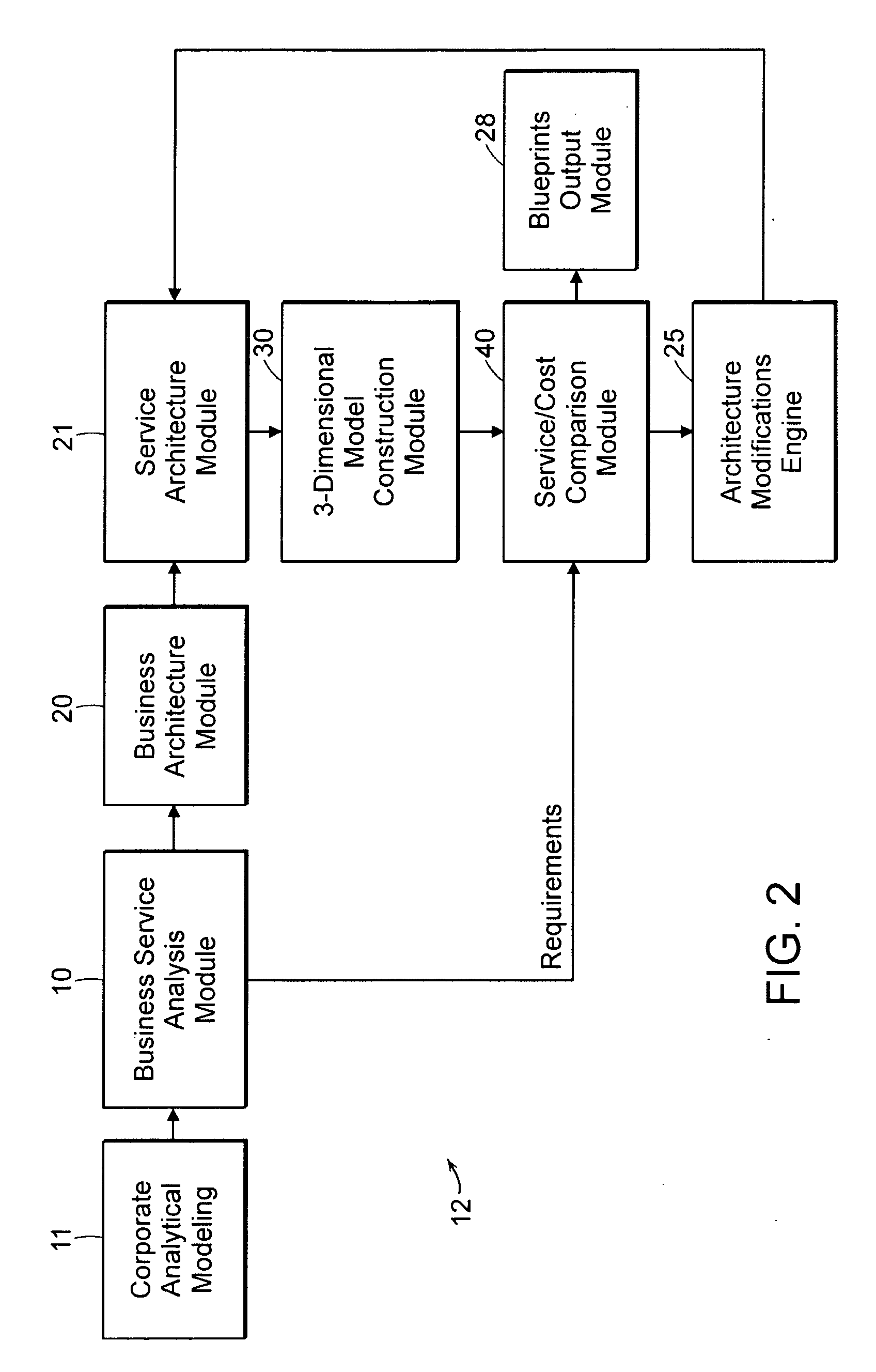
Automated system and method for service and cost architecture modeling of enterprise systems
An automated system and method is provided for system architects to model enterprise-wide architectures of information systems. From an initial model of a proposed system architecture, performance metrics are modeled and compared against a set of user-defined corporate and business requirements. The performance metrics include cost, quality of service and throughput. For unacceptable metrics, modifications to the system architecture are determined and proposed to the system architect. If accepted, the model of the system architecture is automatically modified and modeled again. Once the modeled performance metrics satisfy the corporate and business requirements, a detailed description of the system architecture derived from the model is output. The model of the system architecture also enables a business ephermeris or precalculated table cross referencing enterprise situation and remedy to be formed. A rules engine employs the business ephemeris and provides indications to the enterprise user for optimizing or modifying components of the enterprise system architecture. Off line a mathematical modeling member provides feedback to further update the business ephemeris and rules base for the rules engine.
Owner:X ACT SCI INC
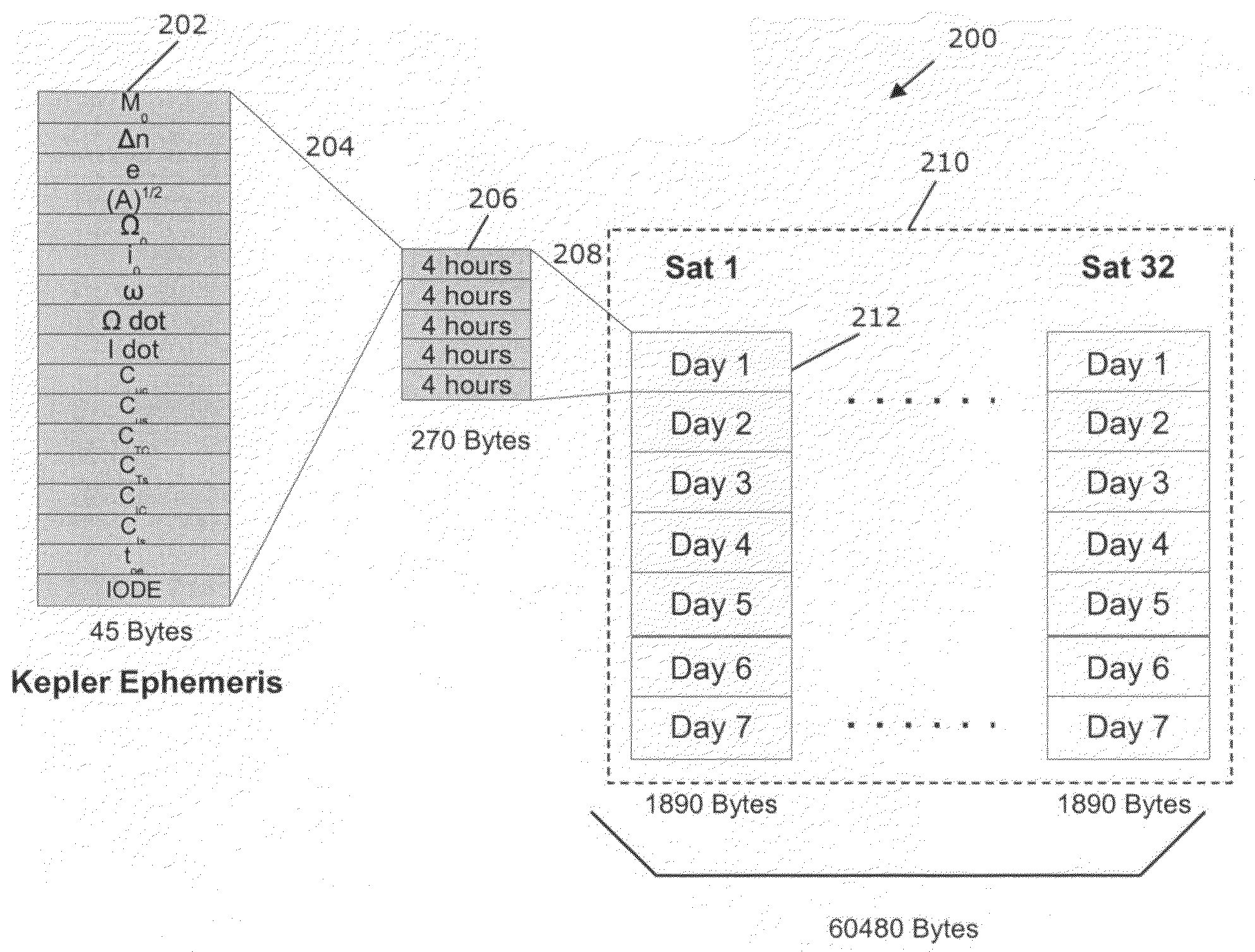
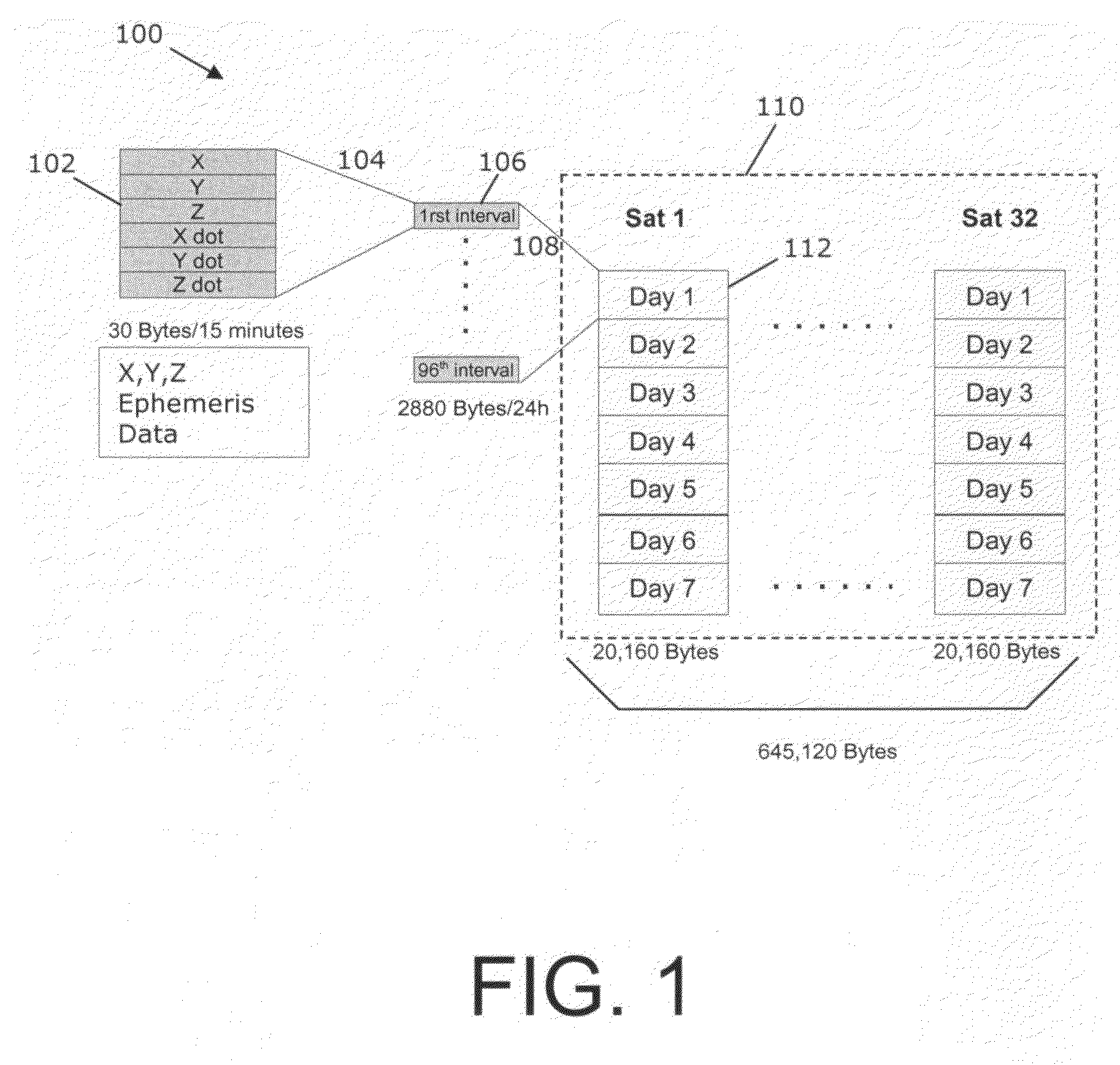
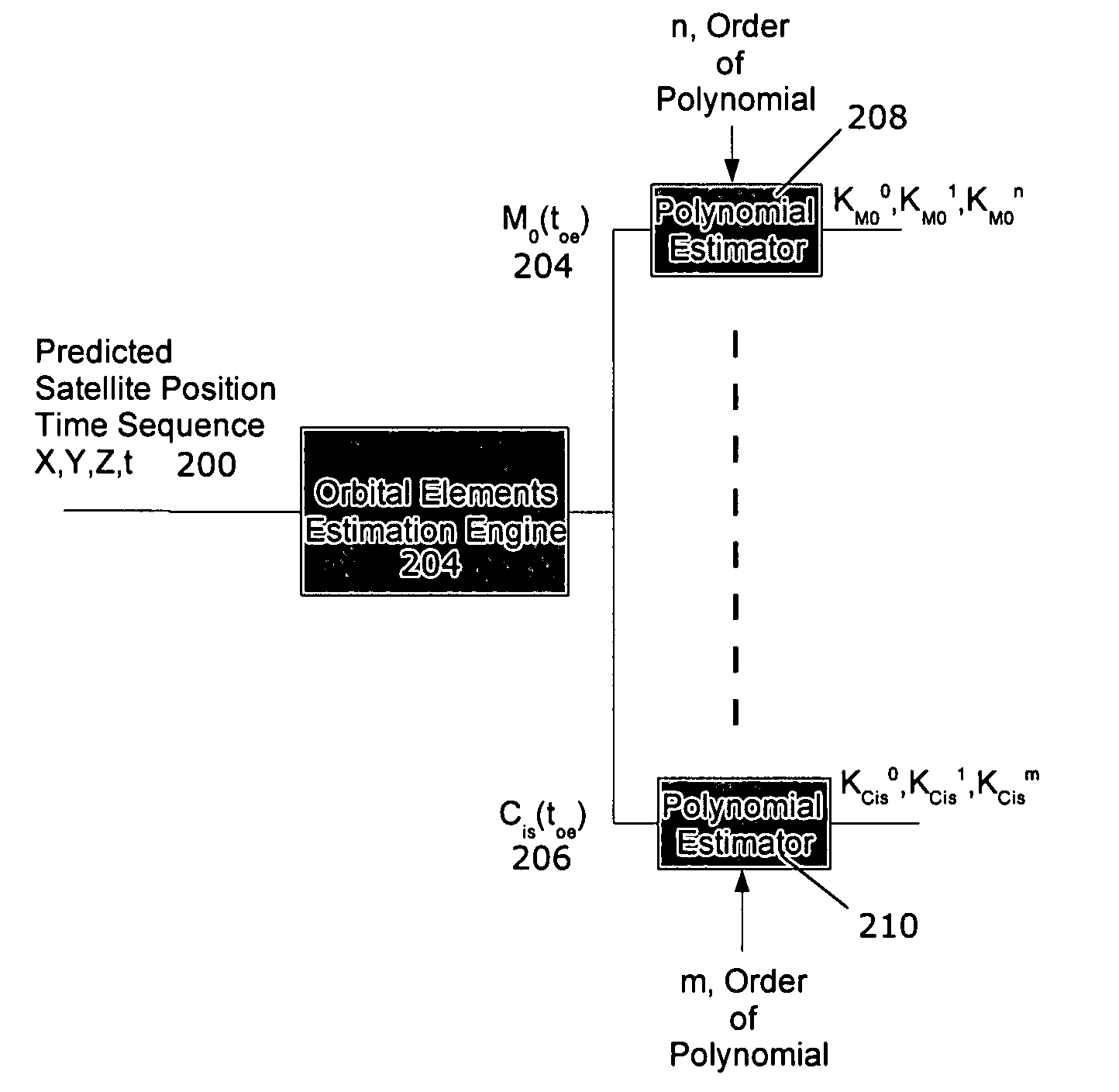
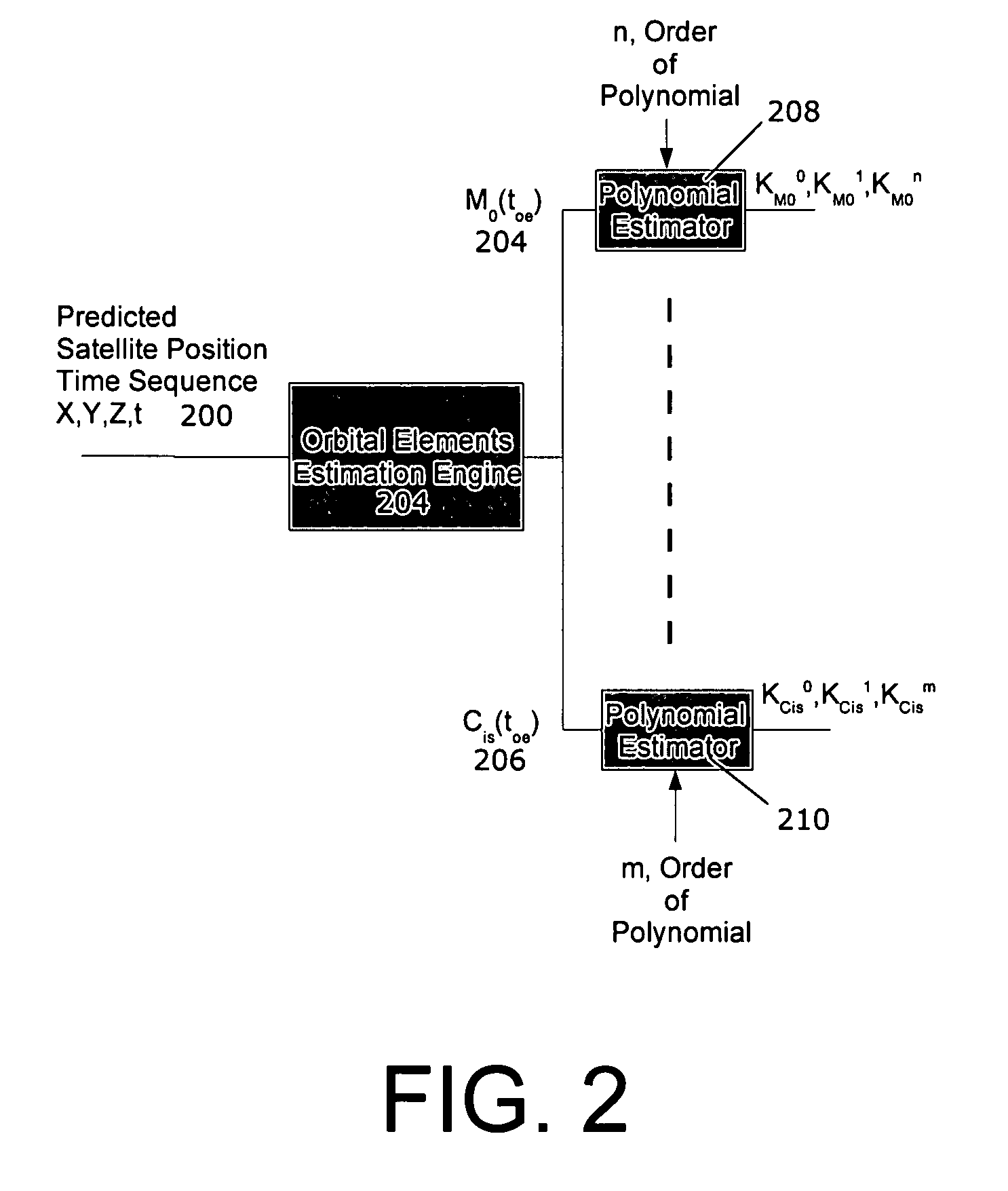
System and method for model-base compression of GPS ephemeris
InactiveUS20070273581A1Lower requirementQuick initializationPosition fixationRadio transmissionEphemerisOrbit
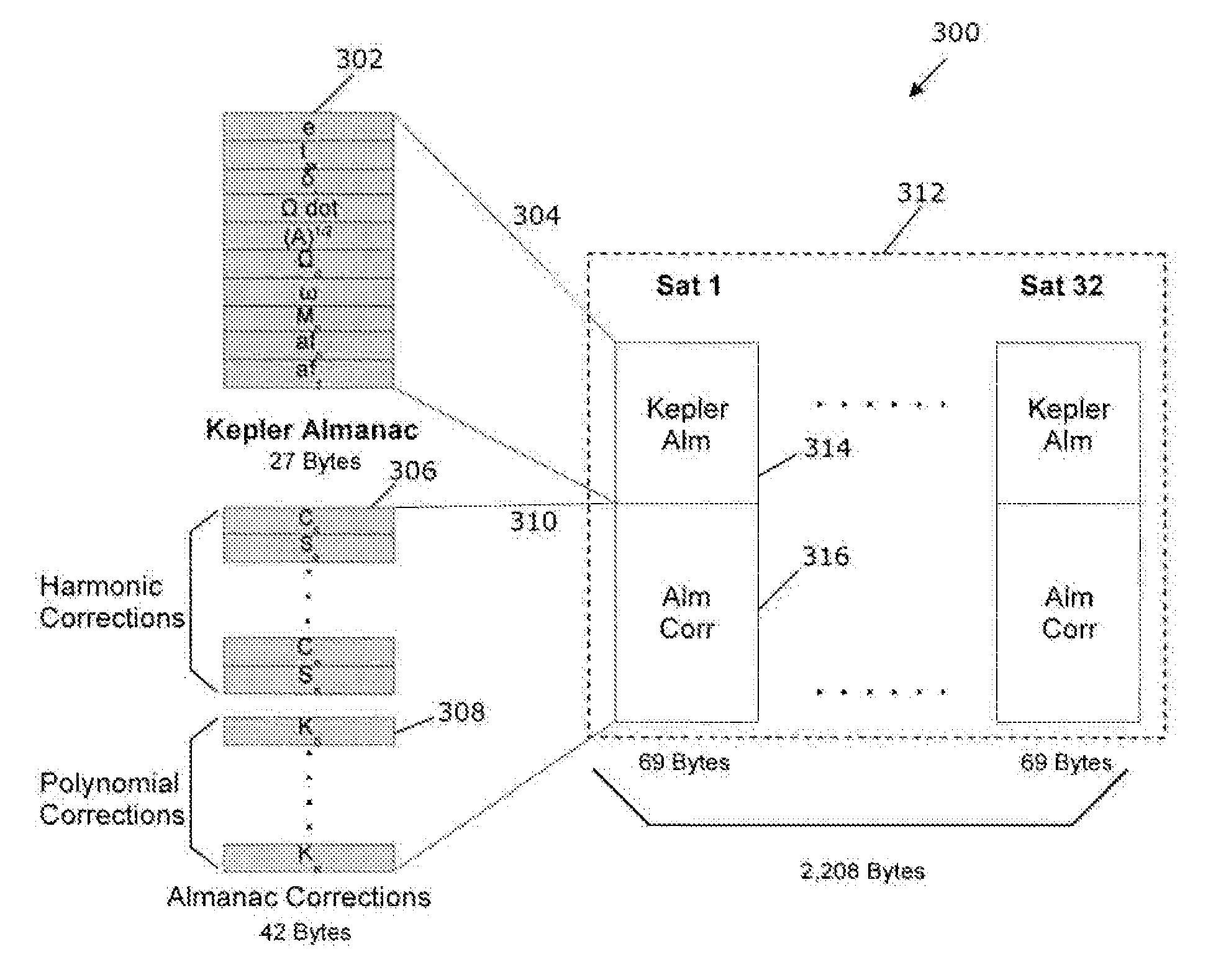
A method for propagating ephemeris data for a satellite in Earth orbit is provided. The method includes the steps of receiving orbital positional data for a first time period of a satellite's Earth orbit, propagating orbital positional data for the satellite's Earth orbit during a second time period extending beyond the first time period, fitting a Keplerian ephemeris model to the propagated orbital positional data to estimate model coefficients, and sending the estimated model coefficients to receivers for determination of receiver position at a time during the second time period.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Wireless communication apparatus method and system for vehicle
InactiveUS20070290920A1Reduce power consumptionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlCommunications systemEngineering
A wireless communication system for a vehicle includes a navigation apparatus and an emergency report apparatus. When a vehicle accessory switch is in an on position, the navigation apparatus performs a GPS synchronization to receive assistance data including almanac and ephemeris from a GPS satellite and outputs the assistance data to the emergency report apparatus. The emergency report apparatus stores the assistance data in a memory. In a case where an abnormal condition of the vehicle occurs when the accessory switch is in an off position, the emergency report apparatus determines whether the assistance data stored in the memory is valid for a GPS positioning. When the assistance data is valid, the emergency report apparatus starts to perform the GPS positioning to calculate a current location of the vehicle by using the assistance data stored in the memory.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and system for ephemeris extension for GNSS applications
InactiveUS20070299609A1Avoid receivingPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsPhysical modelData file
Methods and devices for calculating long-validity satellite prediction data, compacting such data and providing the data GNSS receivers are presented. The data are compacted using a multistage compaction approach which takes physical models into account and produces an extremely low-memory satellite prediction data file size for transmission to remote receivers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
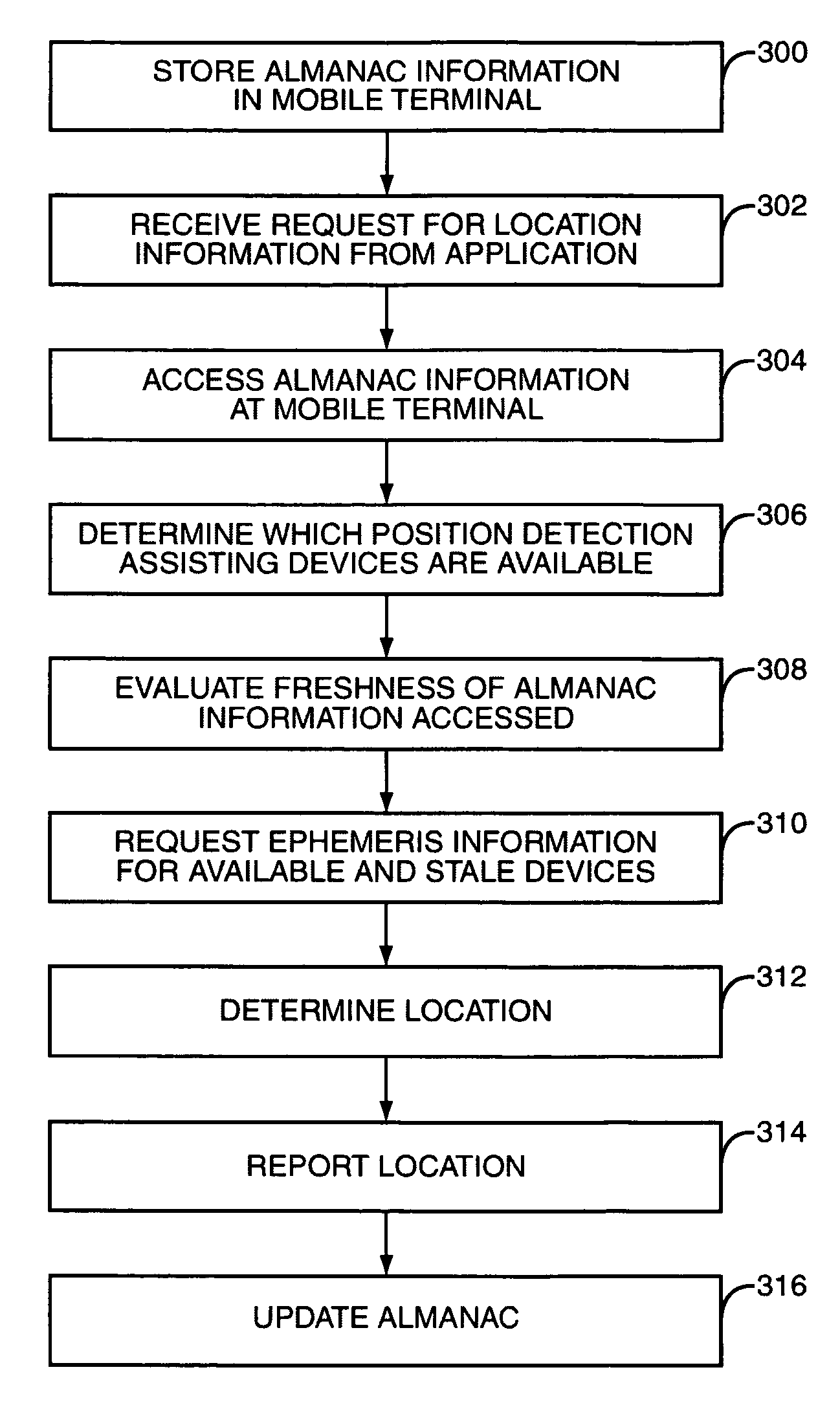
Position detection system integrated into mobile terminal
InactiveUS6937865B1Save bandwidthReduce the amount of informationSpecial service for subscribersPosition fixationLocation detectionEphemeris
A wireless communications mobile terminal conserves bandwidth by determining which position detection assisting devices within a position detection system are available for use and limiting ephemeris information inquiries to only those devices that are available. To make this determination, mobile terminals are provided with an almanac of position information relating to the position detection system. Once the ephemeris information is provided to the mobile terminal, the mobile terminal may determine its location relatively quickly and with a minimal imposition on the mobile network.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Method and apparatus for enhanced autonomous GPS
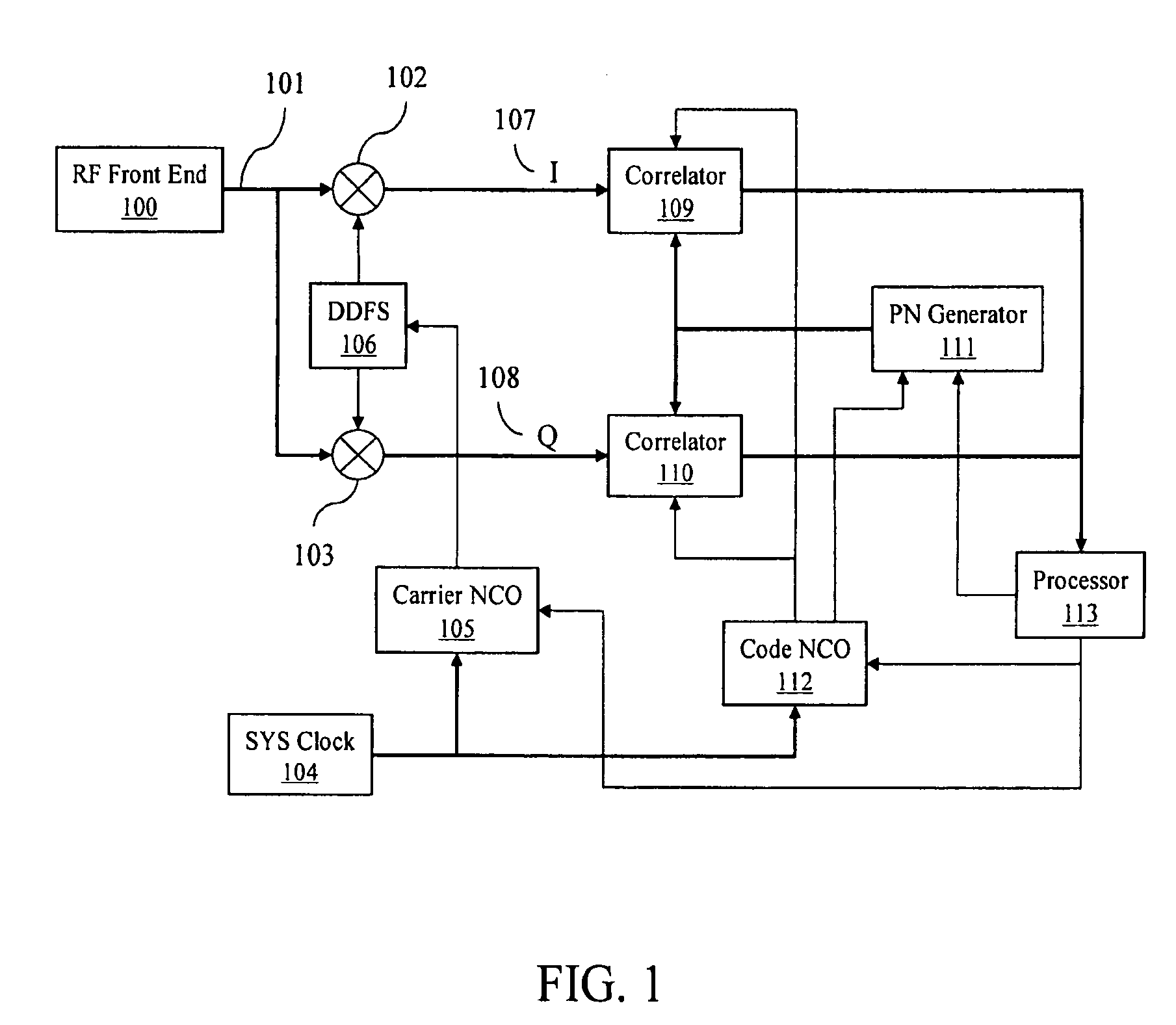
Method and apparatus for locating position of a remote receiver is described. In one example, long term satellite tracking data is obtained at a remote receiver. Satellite positioning system (SPS) satellites are detected. Pseudoranges are determined from the remote receiver to the detected SPS satellites. Position of the remote receiver is computed using the pseudoranges and the long term satellite tracking data. SPS satellites may be detected using at least one of acquisition assistance data computed using a previously computed position and a blind search. Use of long term satellite tracking data obviates the need for the remote receiver to decode ephemeris from the satellites. In addition, position of the remote receiver is computed without obtaining an initial position estimate from a server or network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
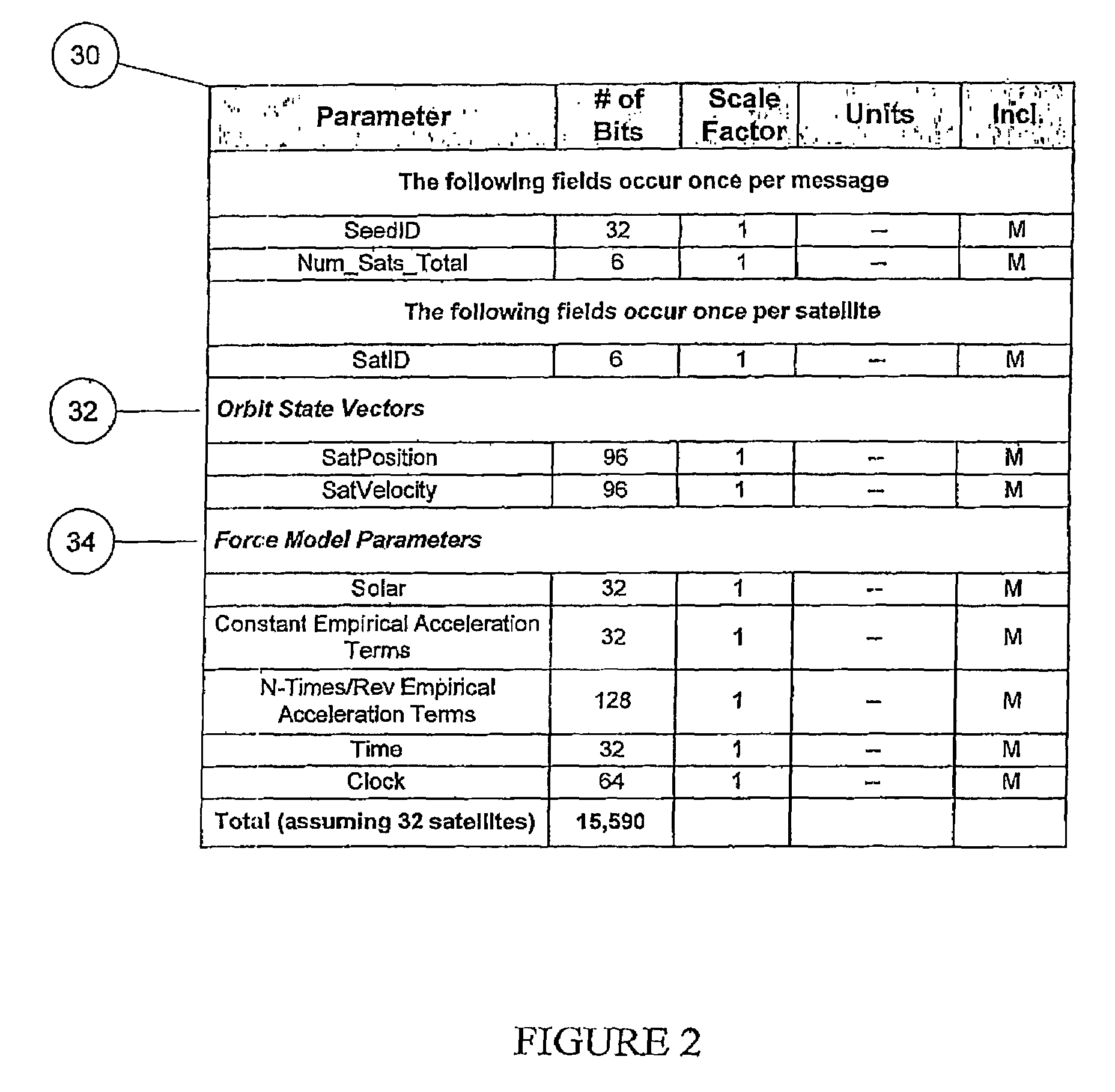
Distributed orbit modeling and propagation method for a predicted and real-time assisted GPS system
ActiveUS7612712B2Easy to integrateNavigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingData setTime to first fix
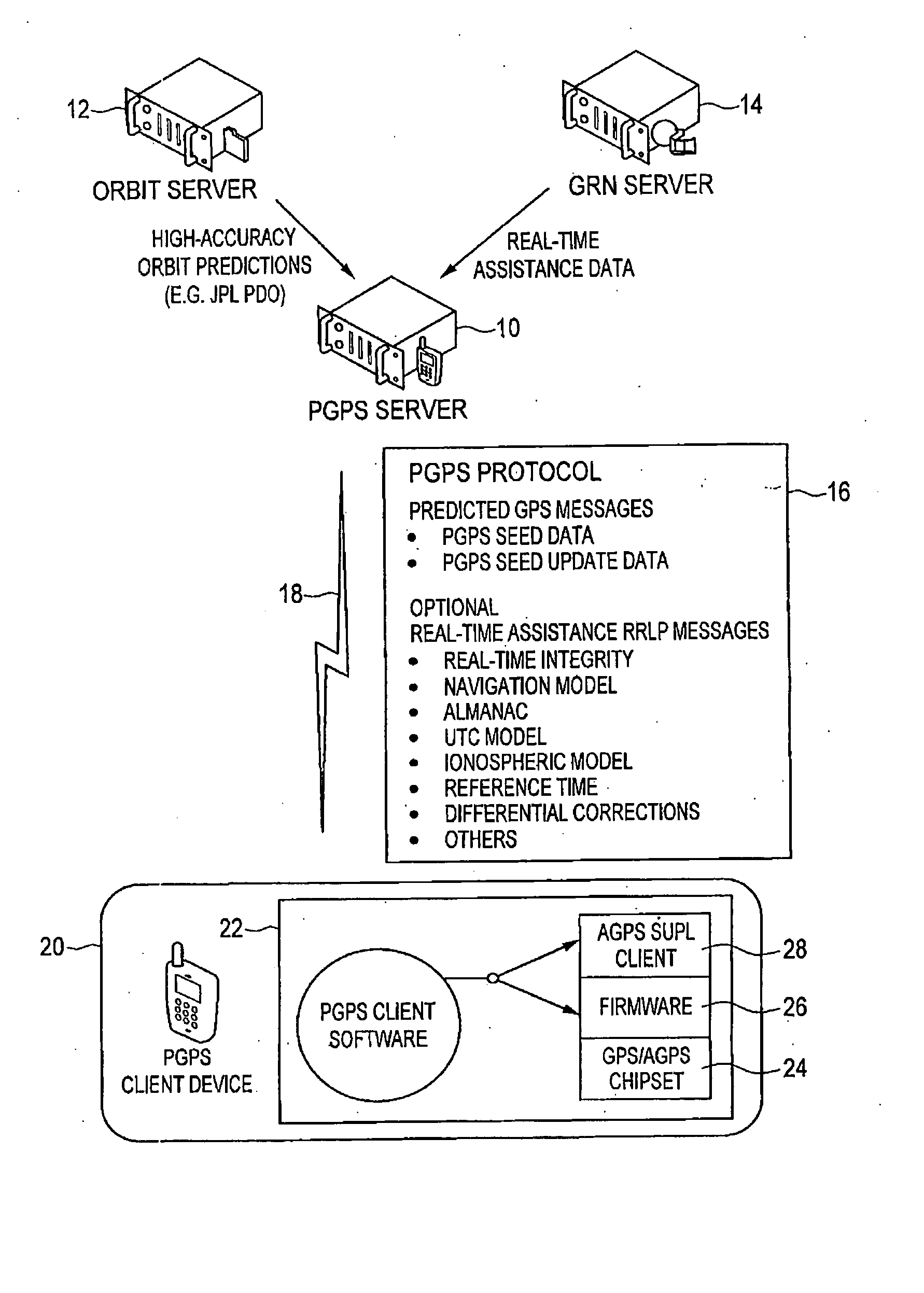
A distributed orbit and propagation method for use in a predicted GPS or GNSS system, which includes a predicted GPS server (PGPS Server), a source of high accuracy orbit predictions (Orbit Server), a global reference network (GRN Server) providing real-time GPS or GNSS assistance data to the PGPS Server, a predicted GPS client (PGPS Client) running on a device equipped with a GPS or AGPS chipset. In response to requests from the PGPS Client, the PGPS Server produces and disseminates an initial seed dataset consisting of current satellite orbit state vectors and orbit propagation model coefficients. This seed dataset enables the PGPS Client to locally predict and propagate satellite orbits to a desired future time. This predictive assistance in turn helps accelerate Time To First Fix (TTFF), optimize position solution calculations and improve the sensitivity of the GPS chip present on, or coupled with, the device. In contrast with other conventional predicted GPS systems that forward large volumes of predicted orbits, synthetic ephemeris or synthetic almanac data, this method optimally reduces data transfer requirements to the client, and enables the client to locally synthesize its own predicted assistance data as needed. This method also supports seamless notification of real-time satellite integrity events and seamless integration of predicted assistance data with industry standard real-time assistance data.
Owner:RX NETWORKS INC
Distributed orbit modeling and propagation method for a predicted and real-time assisted GPS system
ActiveUS20080018527A1Easy to integrateNavigational calculation instrumentsRadio transmissionData setTime to first fix
A distributed orbit and propagation method for use in a predicted GPS or GNSS system, which includes a predicted GPS server (PGPS Server), a source of high accuracy orbit predictions (Orbit Server), a global reference network (GRN Server) providing real-time GPS or GNSS assistance data to the PGPS Server, a predicted GPS client (PGPS Client) running on a device equipped with a GPS or AGPS chipset. In response to requests from the PGPS Client, the PGPS Server produces and disseminates an initial seed dataset consisting of current satellite orbit state vectors and orbit propagation model coefficients. This seed dataset enables the PGPS Client to locally predict and propagate satellite orbits to a desired future time. This predictive assistance in turn helps accelerate Time To First Fix (TTFF), optimize position solution calculations and improve the sensitivity of the GPS chip present on, or coupled with, the device. In contrast with other conventional predicted GPS systems that forward large volumes of predicted orbits, synthetic ephemeris or synthetic almanac data, this method optimally reduces data transfer requirements to the client, and enables the client to locally synthesize its own predicted assistance data as needed. This method also supports seamless notification of real-time satellite integrity events and seamless integration of predicted assistance data with industry standard real-time assistance data.
Owner:RX NETWORKS INC
Integrity of differential GPS corrections in navigation devices using military type GPS receivers
A method and apparatus for calculating corrections to a navigation solution based on differential GPS data includes receiving GPS ephemeris from at least three GPS satellites. A PVT solution is resolved from the GPS ephemeris. The PVT solution includes a Circular Error Probable (CEP). Differential GPS data for calculating the corrections to the PVT solution is received. A corrected PVT solution is then based upon the differential GPS data. The corrected PVT solution is compared to an area defined by the CEP. Where the corrected PVT solution is not within the area, the corrected PVT solution is rejected in favor of the PVT solution for determining an accurate navigational solution.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
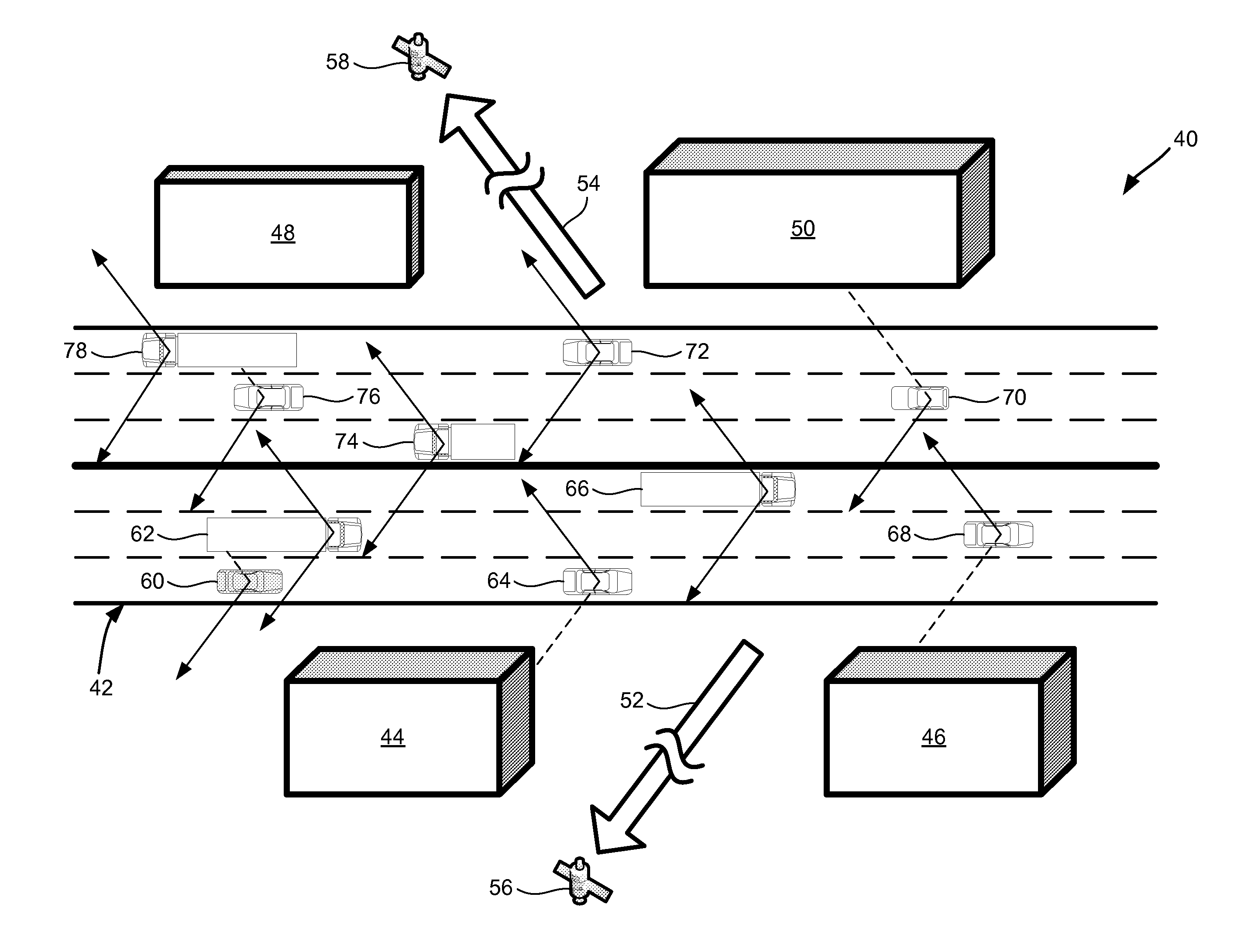
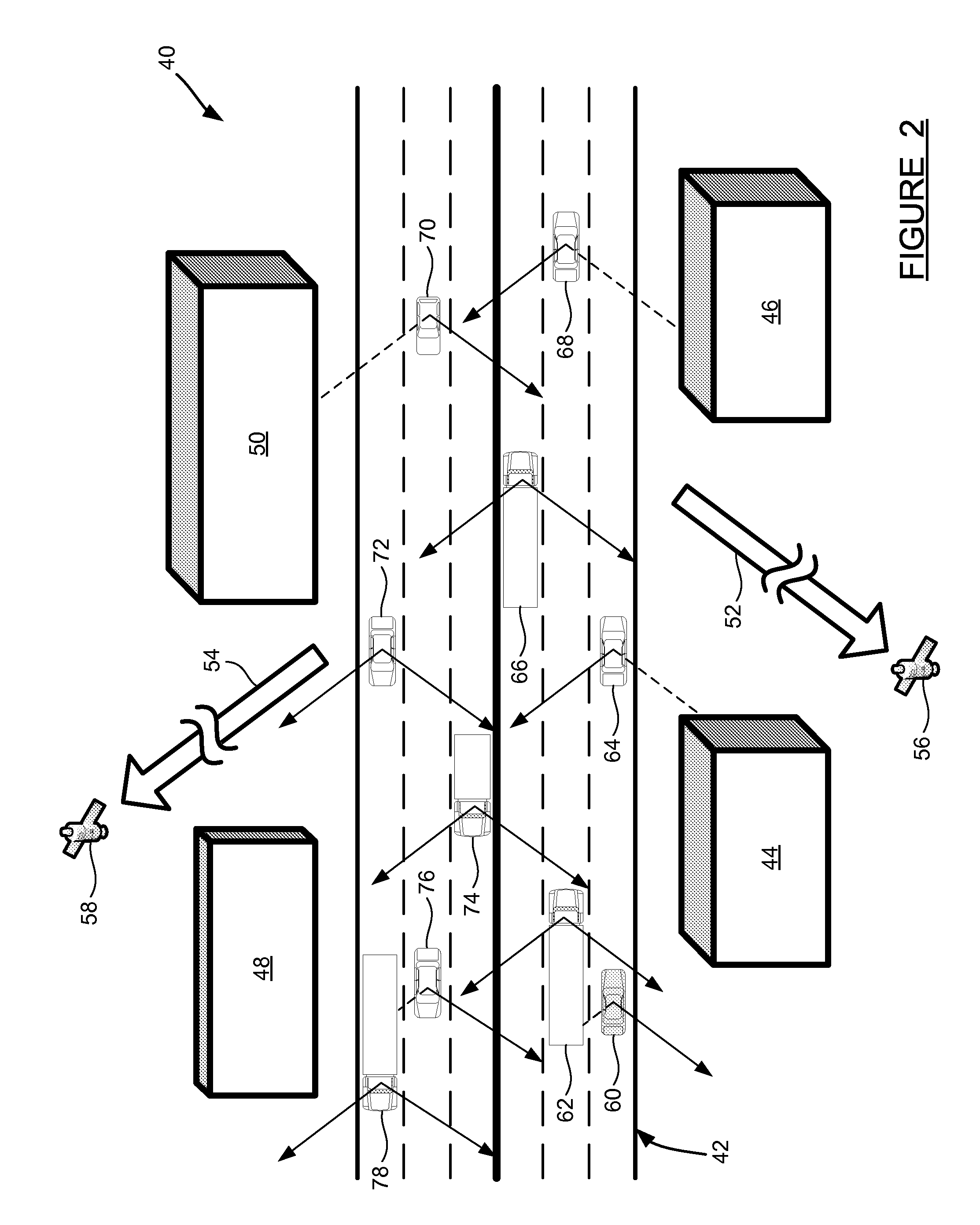
Use of self and neighboring vehicle gps/gnss data to estimate current and approaching sky visibility changes
ActiveUS20120209519A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlElevation angleSignal quality
A method and system for creating a sky visibility map, using data from a vehicle and its neighbors. A host vehicle with satellite-based navigation capability measures the quality of signals it receives from available satellites, where azimuth and elevation angles of the satellites are known from an ephemeris or almanac. The host vehicle also receives satellite signal data from surrounding vehicles via vehicle-to-vehicle communication. Using data from all of the vehicles, a sky visibility map is constructed, indicating where obstructions to satellite visibility exist for different locations. The sky visibility map is used to anticipate satellite signal quality. A driving environment classification can be used to configure other vehicle systems. The sky visibility map can also be constructed without using data from surrounding vehicles; the host vehicle can store its satellite signal data long-term and use it to estimate satellite visibility when returning to a location previously visited.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and Apparatus for Monitoring Satellite-Constellation Configuration To Maintain Integrity of Long-Term-Orbit Information In A Remote Receiver
A method and apparatus for monitoring a configuration of satellites to maintain integrity of LTO information in a GNSS receiver of a GNSS or other positioning system is described. The method may include obtaining broadcast ephemeris transmitted from at least one satellite of a constellation of satellites; comparing the broadcast ephemeris to long-term-orbit information available to a global-navigation-satellite receiver; and causing the global-navigation-satellite receiver to not use the long-term-orbit information when the long-term-orbit information does not correspond to the broadcast ephemeris.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Navigation signal receiver trajectory determination
The present invention provides methods and systems that enable a mobile navigation receiver to accurately determine its trajectory with non-current ephemeris in stand-alone mode. In an embodiment, the receiver computes the position for the same location using non-current ephemeris and current ephemeris at different time instances. The receiver then determines a position correction by finding the difference between these two computed positions, and applies this correction to the trajectory generated with non-current ephemeris to obtain a more accurate trajectory. In another embodiment, the receiver computes an initial position of the receiver using non-current ephemeris and finds the difference between the computed initial position and an accurate approximation of the initial position. The receiver then shifts the subsequent receiver trajectory computed using non-current ephemeris by the difference to obtain a more accurate trajectory.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Ephemeris extension method for GNSS applications
ActiveUS20070247354A1Improve accuracyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingEphemerisSystems approaches
Systems, methods and devices for improving the performance of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers are disclosed. In particular, the improvement of the ability to calculate a satellite position or a receiver position where a receiver has degraded ability to receive broadcast ephemeris data directly from a GNSS satellite is disclosed. Correction terms can be applied to an approximate long-term satellite position model such as the broadcast almanac.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Unassisted indoor GPS receiver
ActiveUS20070152878A1Shorten the timeSave powerPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingElectricitySleep state
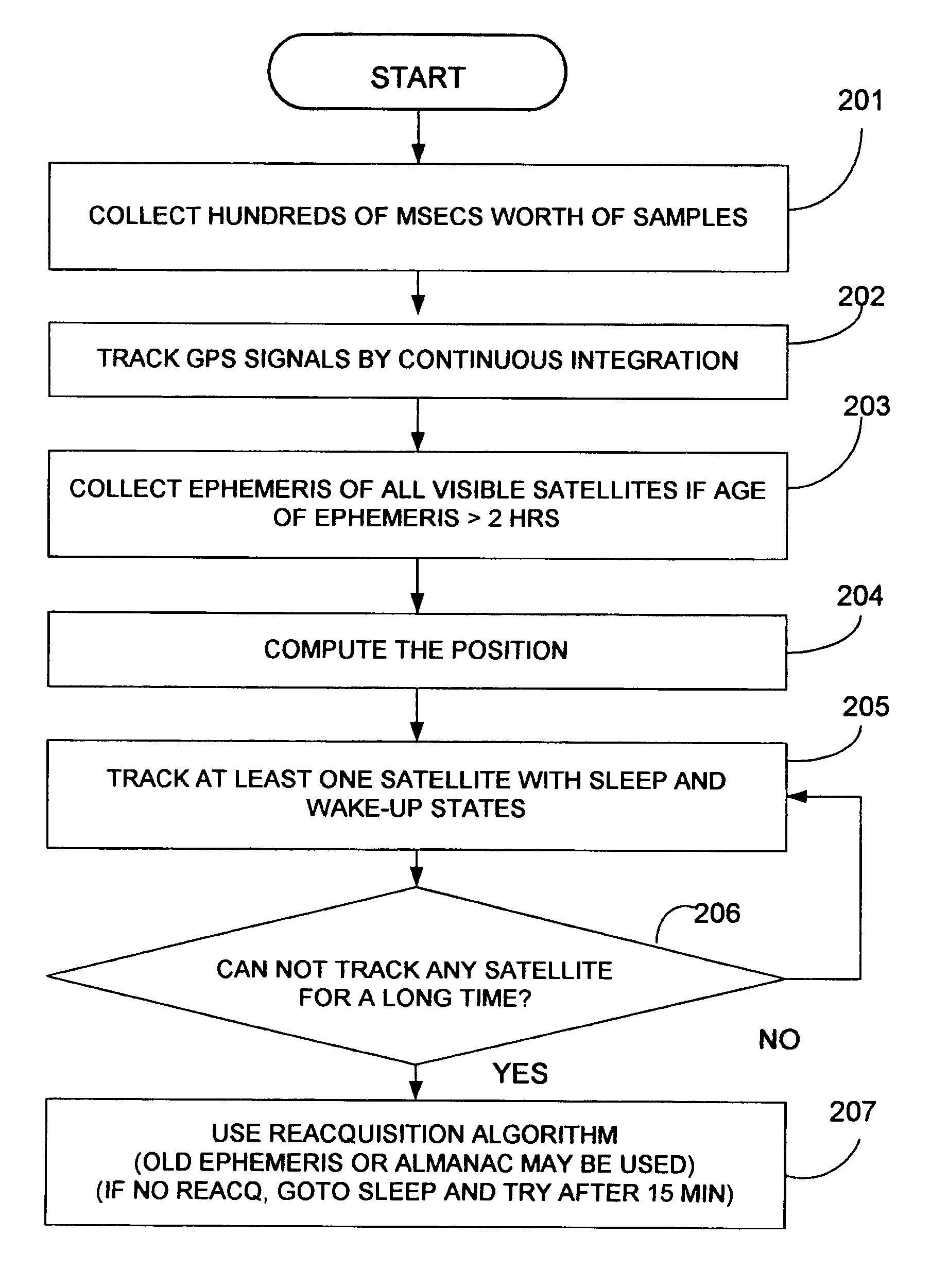
The present invention provides GPS receivers capable of tracking very weak GPS signals particularly in an indoor environment without assistance from an external server or a network. In a preferred embodiment, a GPS receiver initially acquires and locks onto GPS satellite signals to compute receiver position outdoors. The GPS receiver then tracks at least one satellite signal indoors to maintain acquisition parameters for quick acquisition of GPS signals. To save power, the receiver automatically goes to the sleep state and periodically wakes up, i.e., powers up, to maintain the at least one satellite signal tracking. During the wakeup state, the receiver collects ephemeris data from the at least one satellite signal when the ephemeris data needs to be updated for quick acquisition of GPS signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
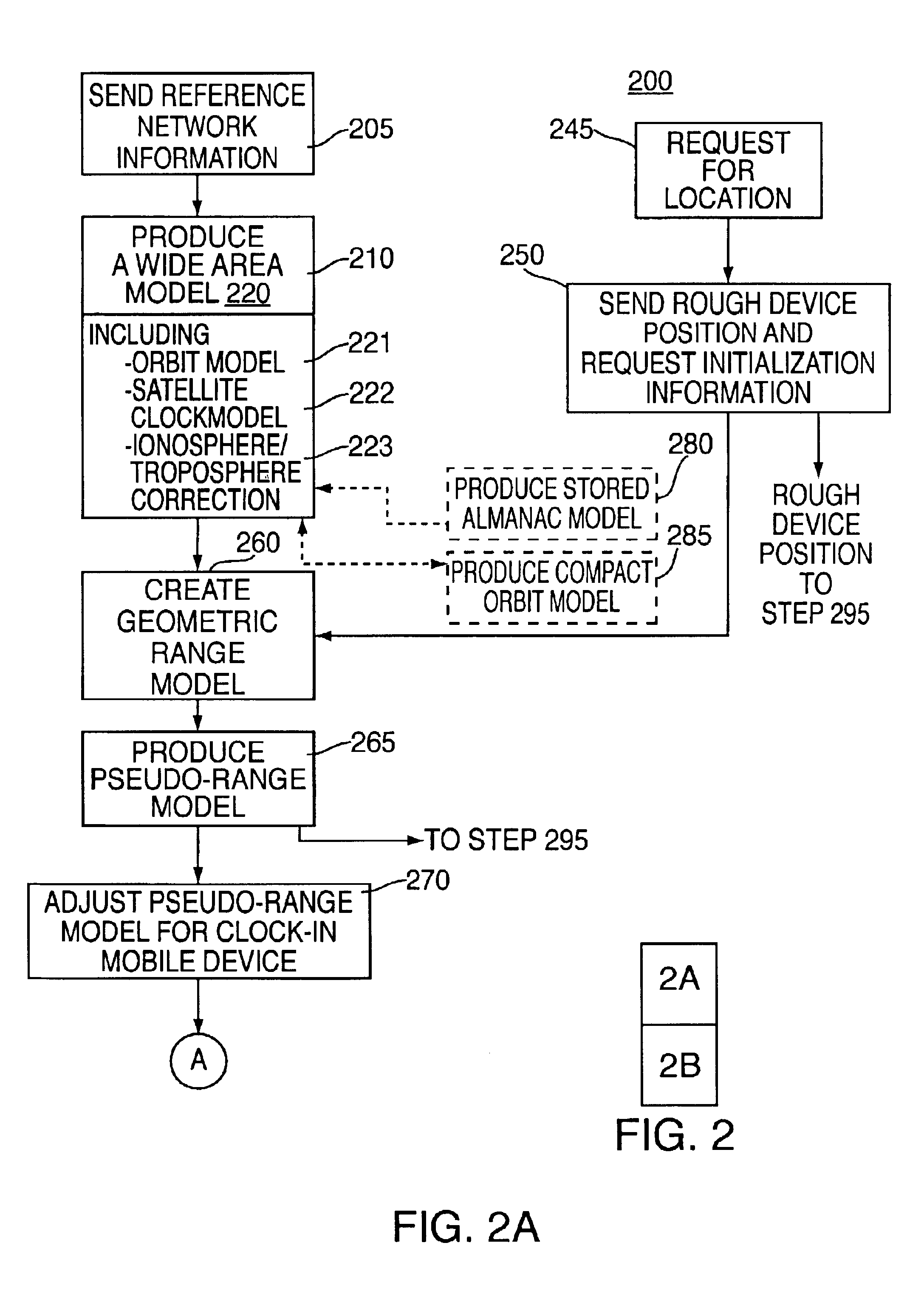
Correction of a pseudo-range model from a GPS almanac
InactiveUS20020072854A1Message being delayedKeep for a long timeInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationTelecommunications linkSignal on
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A method and apparatus for locating mobile device over a broad coverage area using a wireless communications link that may have large and unknown latency. The apparatus comprises at least one mobile device, a reference network, a position server, a wireless carrier, and a location requester. The mobile device is in communication with the wireless carrier and receives global positioning system (GPS) signals from a plurality of satellites in the GPS satellite constellation. The reference network is coupled to the position server and provides GPS data. The mobile receiver receives GPS signals, performs rudimentary signal processing and transmits the processed signals to the wireless carrier. The wireless carrier passes the signals on to the position server. The position server processes the mobile receiver's GPS data and the reference network ephemeris data to identify the location of the mobile receiver. The location is sent to the location requester.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus in positioning without broadcast ephemeris
ActiveUS20080270026A1Reduce the amount of calculationGood receiver position accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationEphemerisSatellite orbit
Provided herein are methods and system for enabling a navigation receiver to generate receiver specific satellite orbital models based on relatively small sets of parameters obtained from a server. In an embodiment, a set of parameters for a satellite includes a force parameter (e.g., solar radiation pressure), initial condition parameters (e.g., satellite position and velocity at a time instance) and time correction coefficients, which the receiver uses in a numerical integration to predict the position of the satellite. The set of parameters needed for the integration is small compared to current methods which require transmission of a complete set of ephemeris and other parameters for each satellite. Since the set of parameters is relatively small, it requires less communication resources to transmit compared to current methods. Further, the integration based on the small set of parameters enables the receiver to predict satellite orbits with low computational load.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Relative positioning device for satellite navigation and carrier phase cycle-slip repairing method of device
InactiveCN104570011AHigh frequencyReduce resource requirementsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceInformation processing
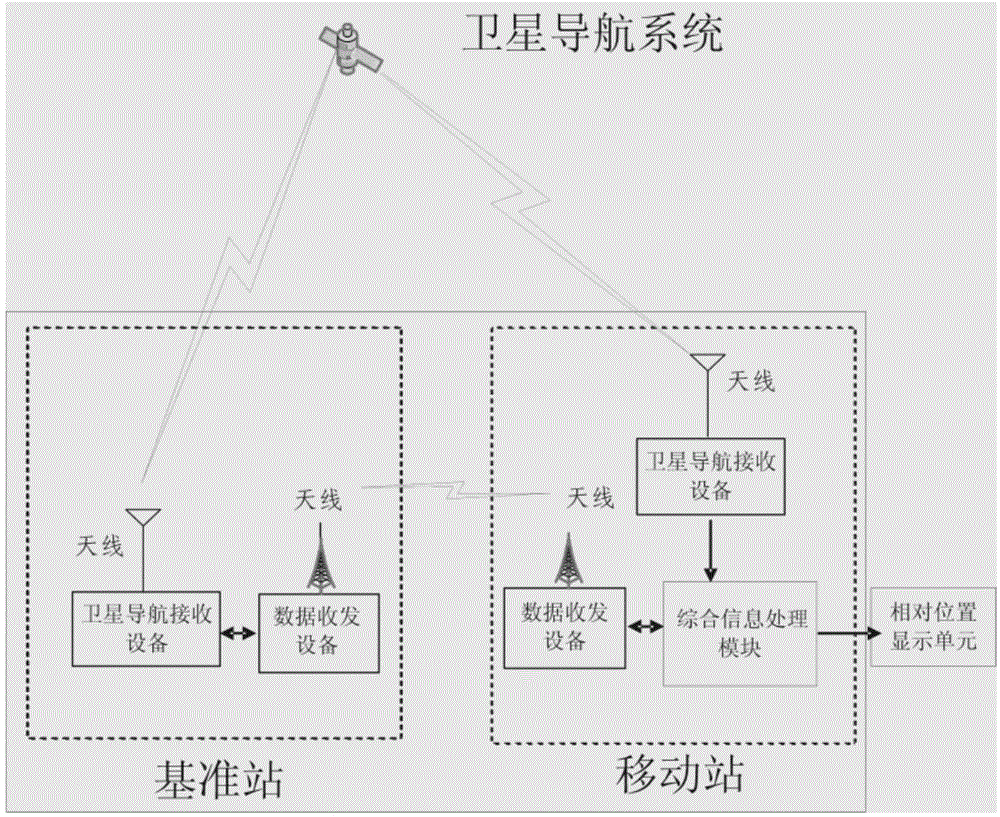
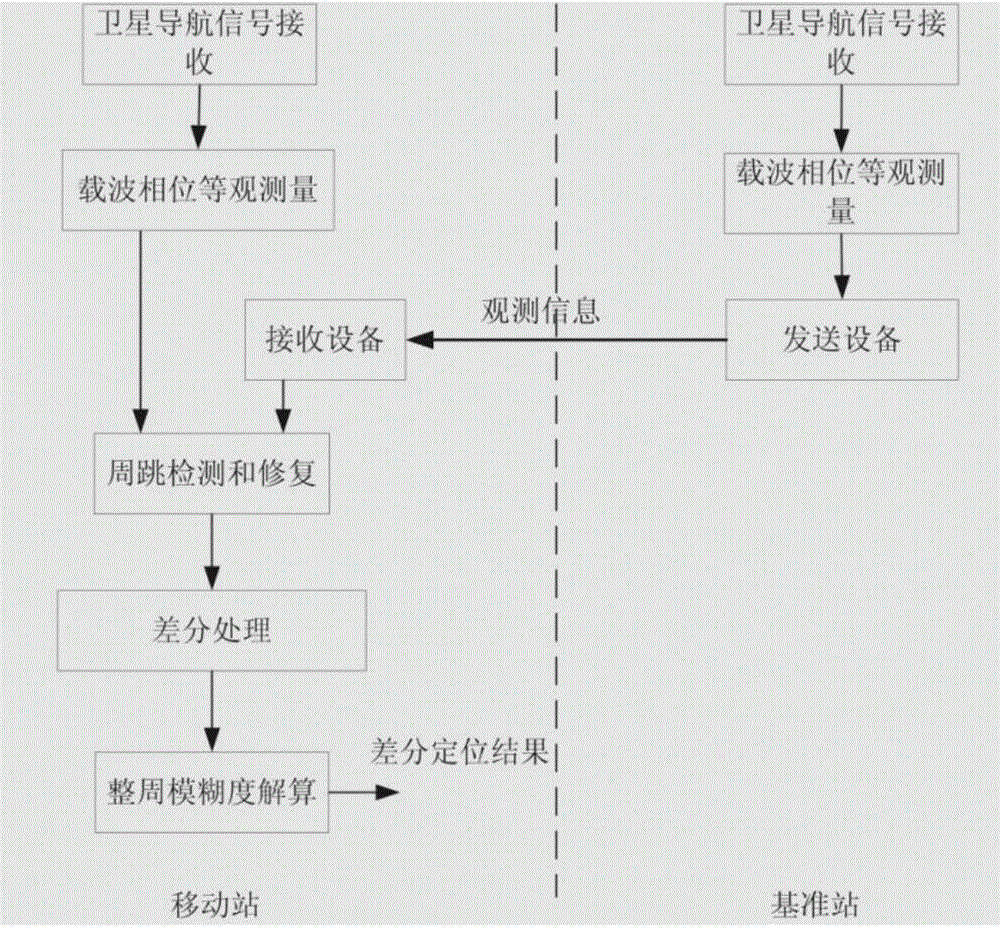
The invention provides a relative positioning device for satellite navigation and a carrier phase cycle-slip repairing method of the device. A satellite navigation antenna on a base station receives a navigation signal, outputs ephemerides and observed quantities of all satellites through a satellite navigation receiver and sends the ephemerides and the observed quantities to a mobile station; the mobile station receives data sent by the base station and outputs the data to a comprehensive information processing module, a satellite navigation antenna on the mobile station receives the navigation signal and outputs the ephemerides and the observed quantities of all the satellites through the satellite navigation receiver, the comprehensive information processing module performs gross error processing on data output by the base station and the mobile station, carrier phase cycle-slip detection and repairing are finished, a double-difference observation equation is established through carrier phase double-difference processing, the whole-cycle ambiguity is resolved, and relative positioning information is output. With the adoption of the device and the method, the cycle-slip can be detected and repaired in real time, outliers can be marked out in real time, meanwhile, the cycle-slip occurrence frequency can be determined, high-precision relative positioning can be realized, and the availability of a system is guaranteed.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
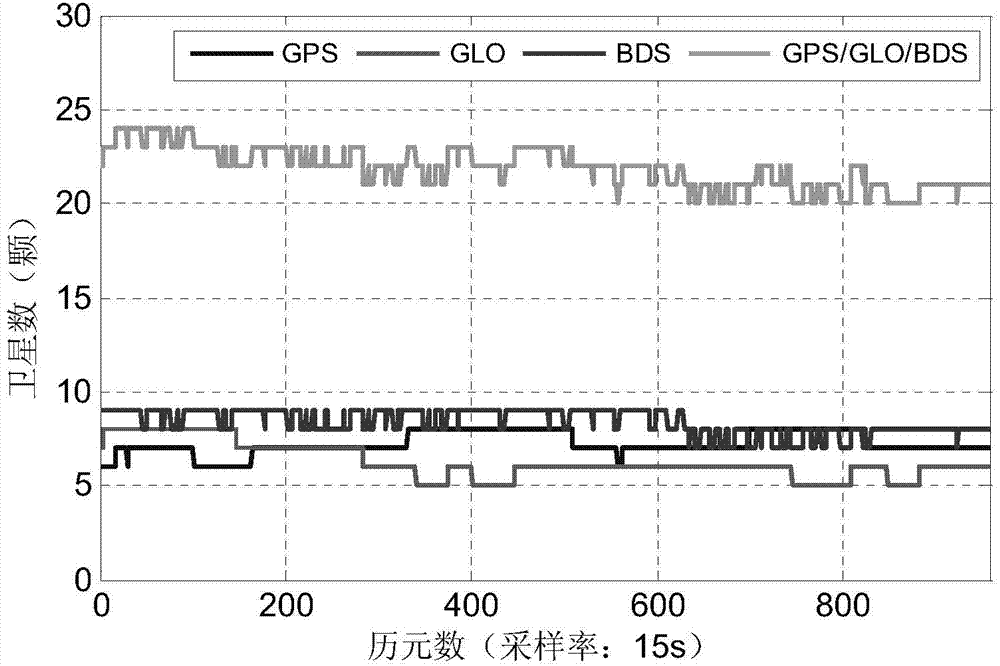
Multi-system dynamic PPP resolving method based on robust self-adaption Kalman smoothing
ActiveCN104714244AAvoid divergenceImprove noise anomaliesSatellite radio beaconingDynamic noiseObservation data
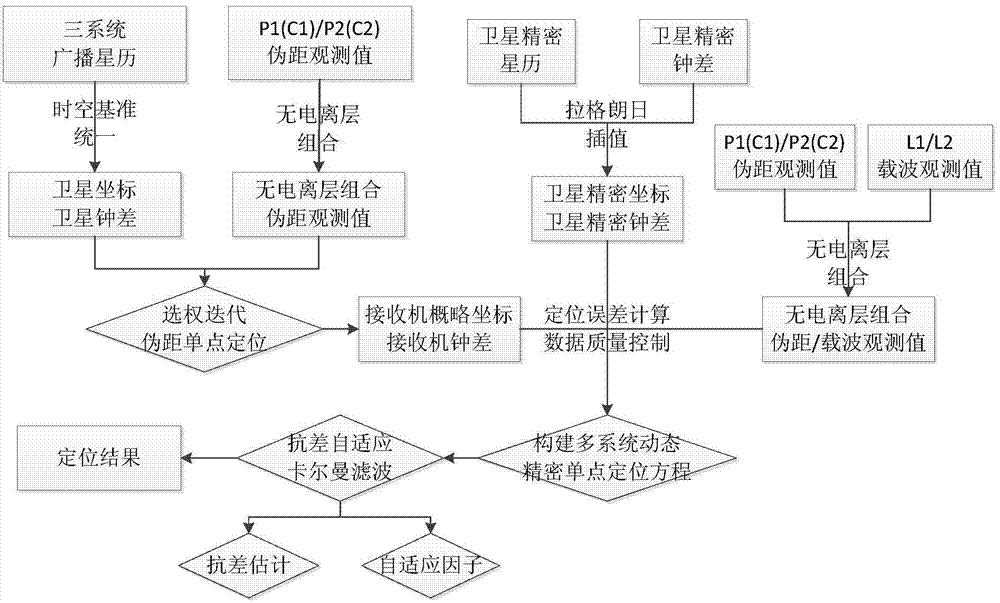
The invention discloses a multi-system dynamic PPP resolving method based on robust self-adaption Kalman smoothing. The method includes the steps that receiving machine outline coordinates and receiving machine clock bias of all systems are solved through selecting-weight-iteration pseudo-range single-point positioning, and accordingly all positioning error correction values are calculated according to an error correction model in combination with the satellite precise ephemeris and satellite precise clock bias; strict data quality control is conducted on observation data. Due to the fact that dynamic PPP accuracy is easily affected by undetected small cycle slips or the gross error and the like, an observation equation weight matrix is adjusted according to the observation value residual vectors, and the undetected small cycle slips or the gross error and other influence factors are removed; self-adaption factors are determined according to the state predictive information, and thus the influence on parameter estimation of the predictive information is controlled. By means of the method, when multi-system dynamic PPP is conducted through a single receiving machine, the feature that the number of multi-system satellites is increased greatly, on the basis that the stability of the satellite structure is guaranteed, the influence of the gross error is weaken effectively, the dynamic noise abnormity in dynamic positioning is improved, and finally the high-precision and high-stability multi-system dynamic PPP result is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
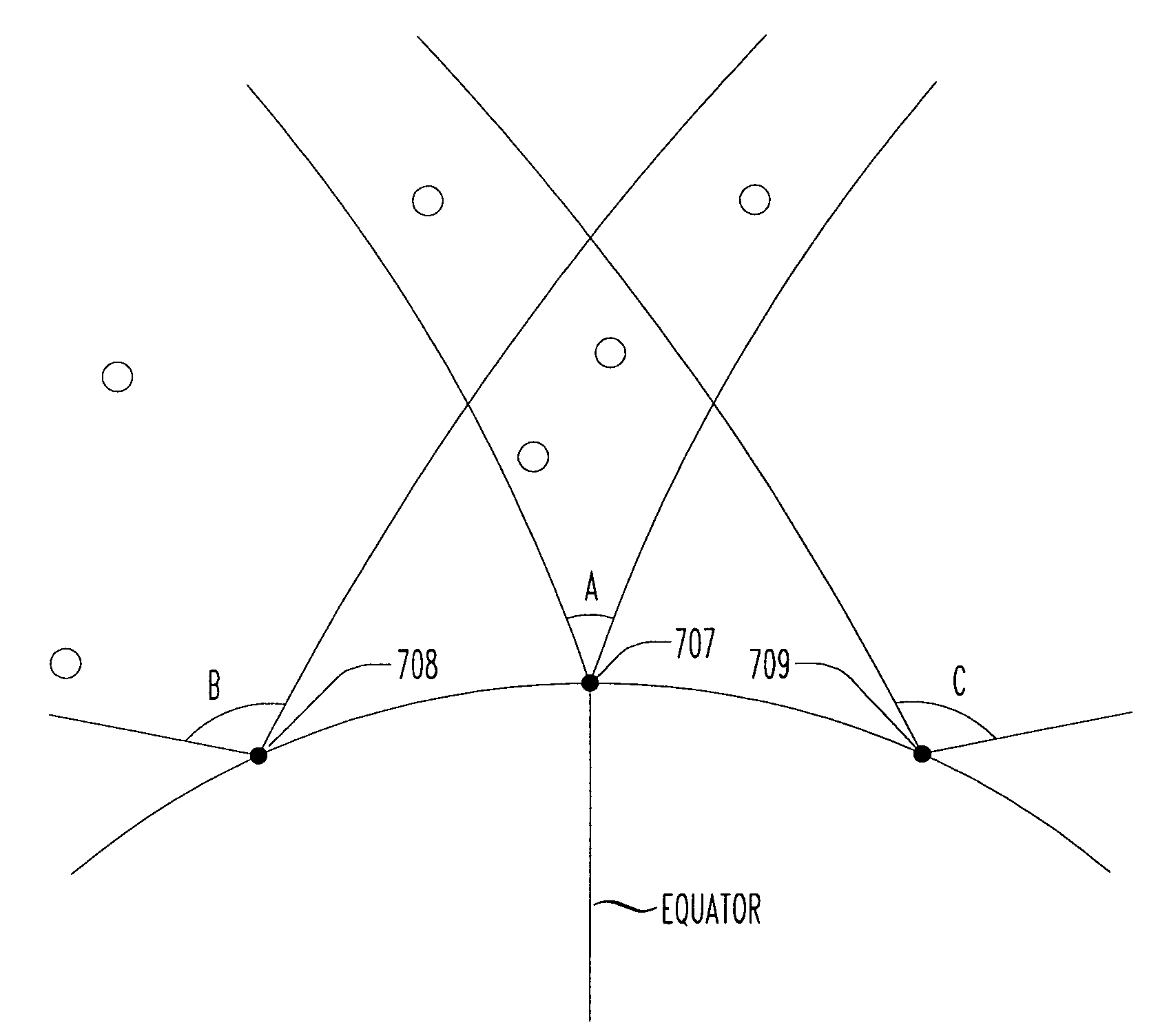
Culled satellite ephemeris information based on limiting a span of an inverted cone for locating satellite in-range determinations
Locating satellites (e.g., GPS) are culled into a sub-plurality based largely on dwell time within an inverted cone above a relevant site in communication with a wireless device. A first inverted cone having a first base angle is defined above a first site, a second inverted cone having a second base angle is defined above a second site. If the second site is farther from an equator of Earth than the first site, then the second inverted cone is made to have a base angle larger than a base angle of the first inverted cone. If the first site is farther from the equator of Earth than the second site, then the first inverted cone is made to have a base angle larger than a base angle of the second inverted cone. The span of the inverted cone over the site closest to the equator may be limited.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
BDS/GPS high-accuracy positioning method
InactiveCN105929424AOvercome the safety hazards of leakageSolve potential safety hazardsSatellite radio beaconingObservation dataSatellite observation
The invention discloses a BDS / GPS high-accuracy positioning method, relating to the field of satellite navigation. The method includes establishing a virtual reference station, acquiring the common-view satellite ephemeris and the satellite observation data received by a reference station Bi and a roving station M, and acquiring the geometry distance between the satellite and the reference station Bi; acquiring the pseudo range correction number of the reference station Bi; interpolating the pseudo range correction number of the virtual reference station by means of an algorithm of inverse distance to a power; interpolating the pseudo range correction number of the roving station by the roving station by means of an algorithm of inverse distance to a power; correcting the satellite pseudo range observation data received by the roving station by means of the pseudo range correction number of the roving station; and establishing a roving station satellite pseudo range observation equation to obtain the accurate coordinate of the roving station to complete the positioning. According to the invention, the safety hidden troubles of information leakage of the reference station because a multi-reference difference positioning method in the prior art must use the accurate coordinate of the reference station can prevented, and high-accuracy positioning is obtained.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
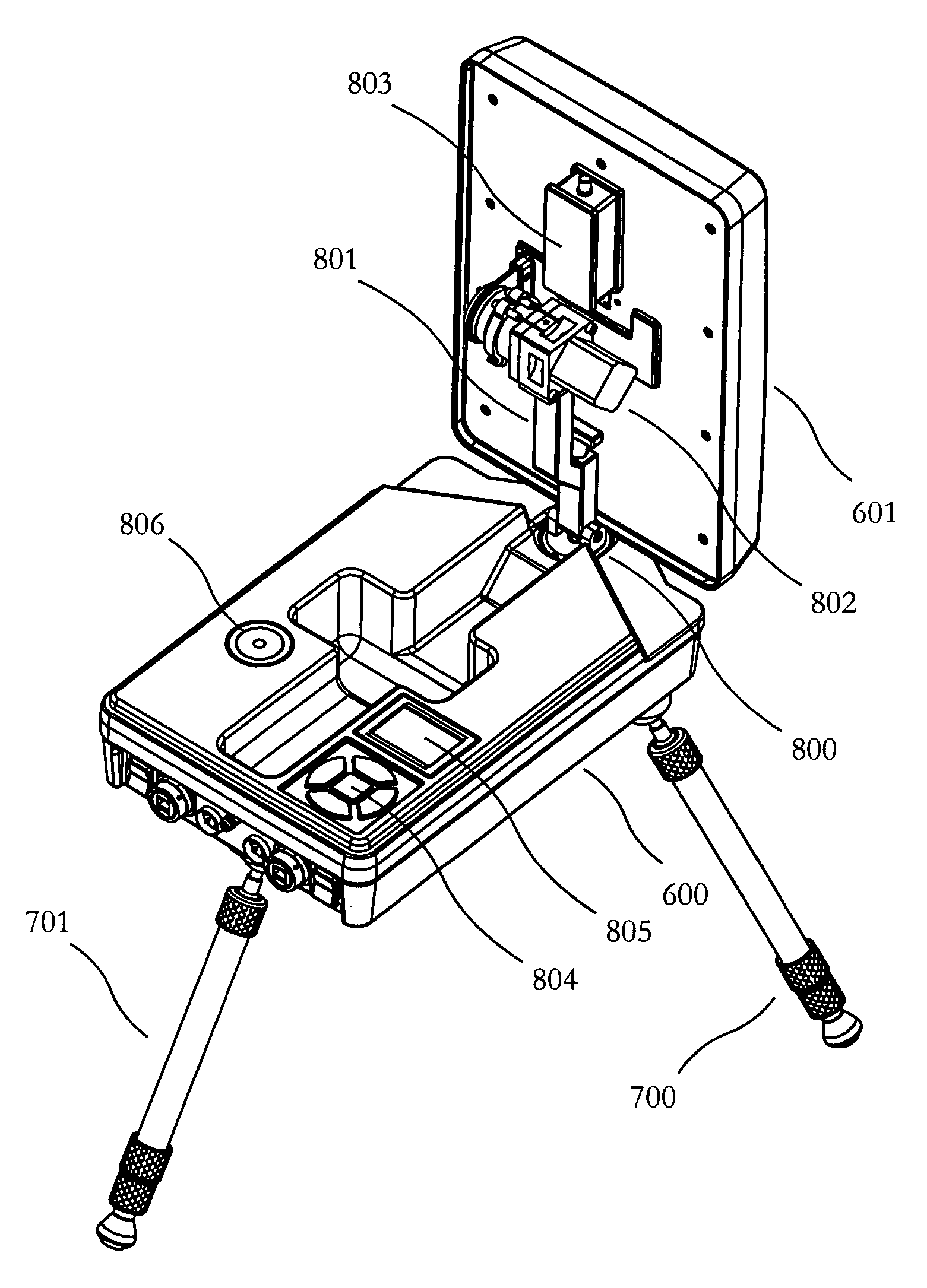
Portable antenna positioner apparatus and method
ActiveUS20070001920A1Easy to carryLow costPivotable antennasAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringEphemeris
A low power, lightweight, collapsible and rugged antenna positioner for use in communicating with geostationary, geosynchronous and low earth orbit satellite. By collapsing, invention may be easily carried or shipped in a compact container. May be used in remote locations with simple or automated setup and orientation. Azimuth is adjusted by rotating an antenna in relation to a positioner base and elevation is adjusted by rotating an elevation motor coupled with the antenna. Manual orientation of antenna for linear polarized satellites yields lower weight and power usage. Updates ephemeris or TLE data via satellite. Algorithms used for search including Clarke Belt fallback, transponder / beacon searching switch, azimuth priority searching and tracking including uneven re-peak scheduling yield lower power usage. Orientation aid via user interface allows for smaller azimuth motor, simplifies wiring and lowers weight. Tilt compensation, bump detection and failure contingency provide robustness.
Owner:AQYR TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com