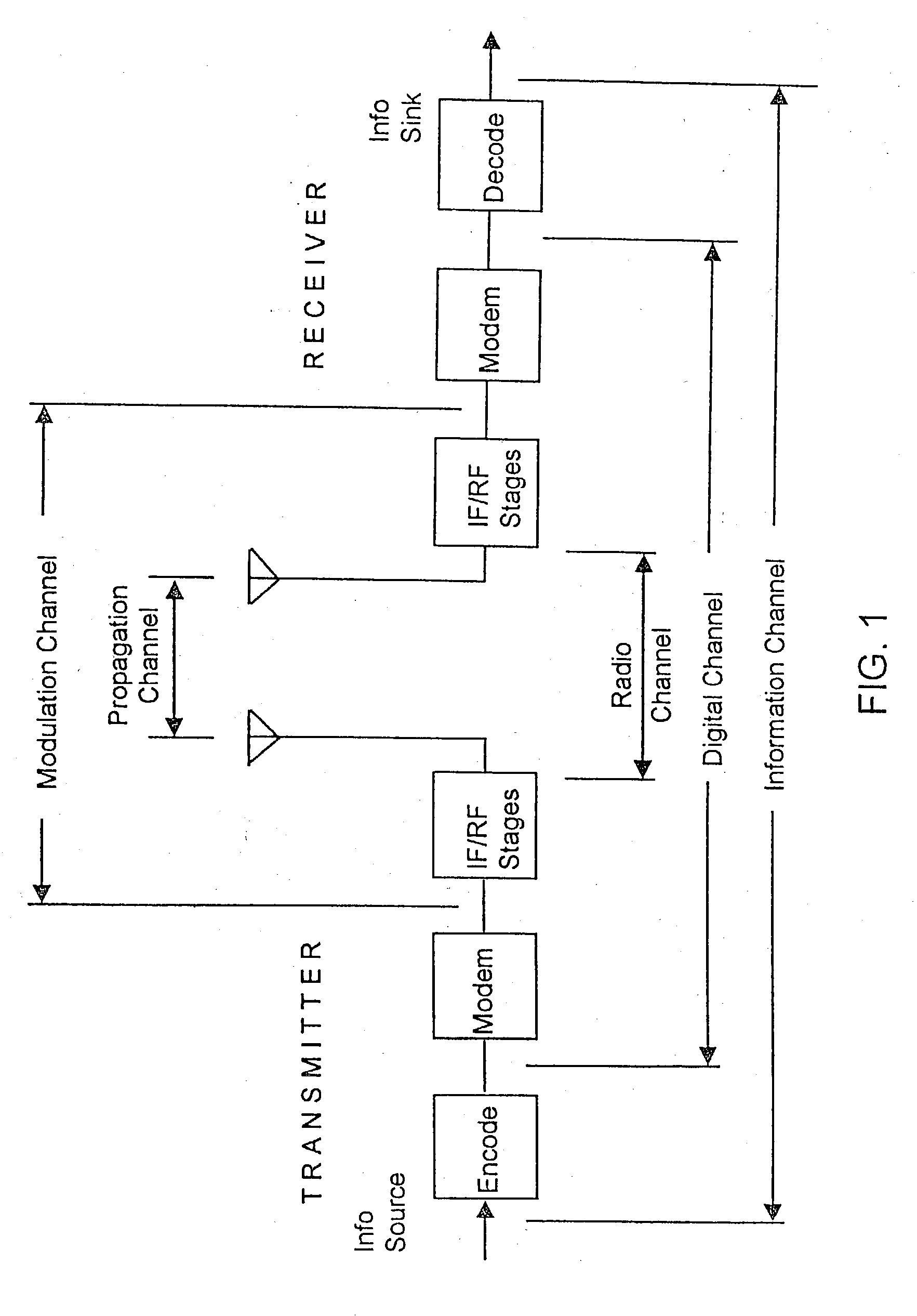
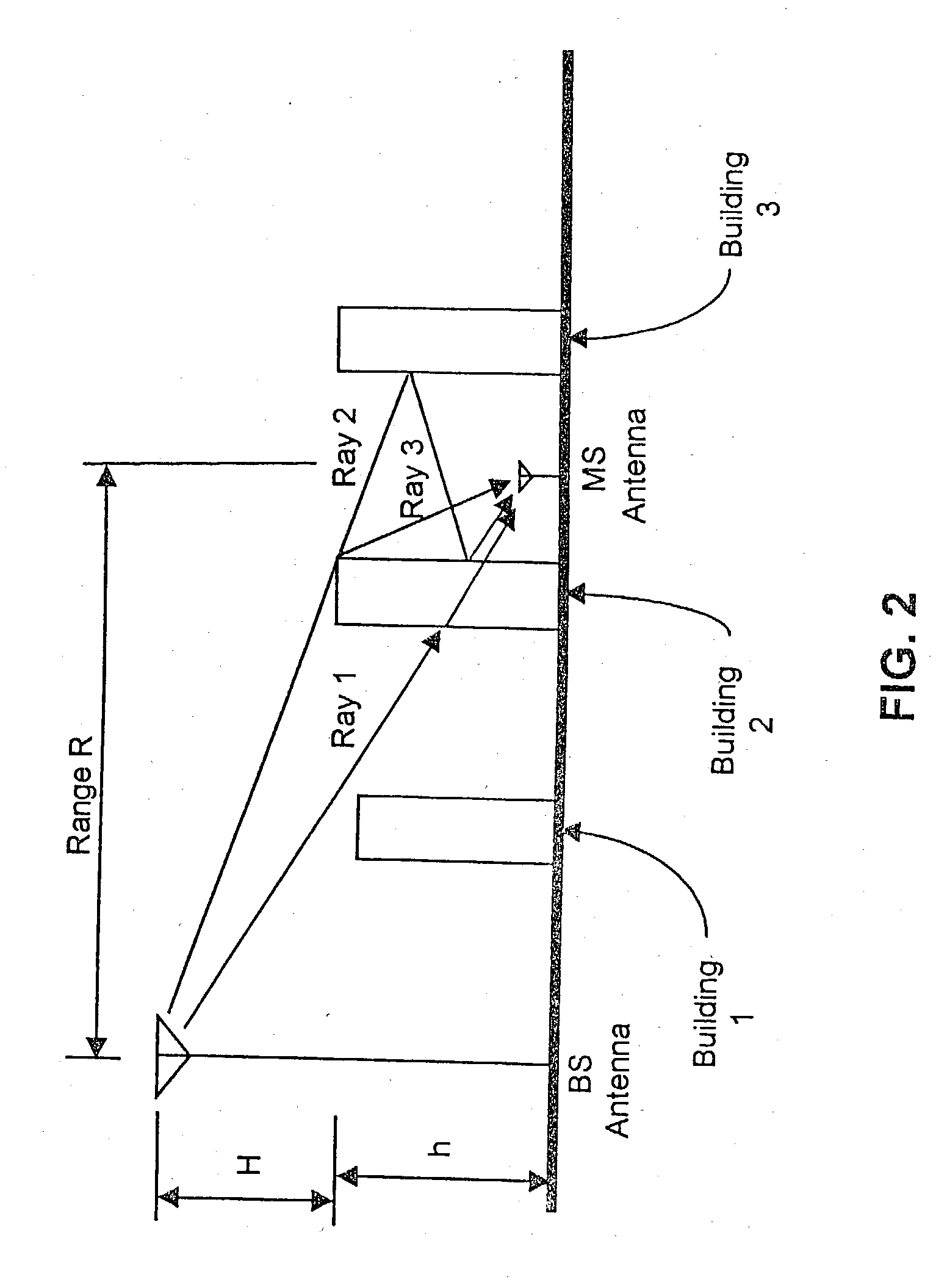
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2831 results about "GPS signals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
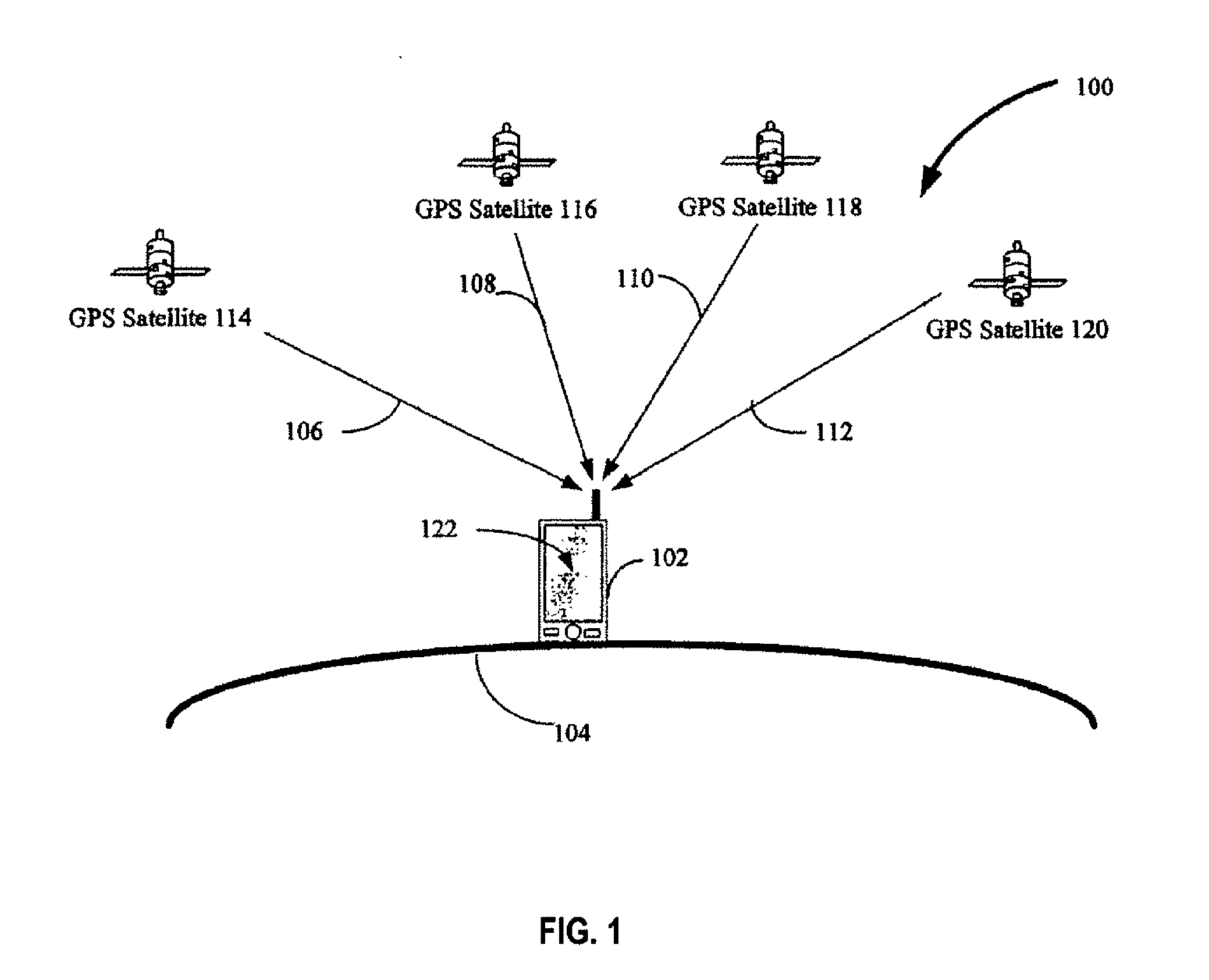
Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites broadcast microwave signals to enable GPS receivers on or near the Earth's surface to determine location and time, and to derive velocity. The system is operated by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) for use by both the military and the general public.
Wireless location using multiple location estimators
InactiveUS6249252B1Effectively and straightforwardly resolvedAmbiguity and conflictDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesTerrainHeuristic
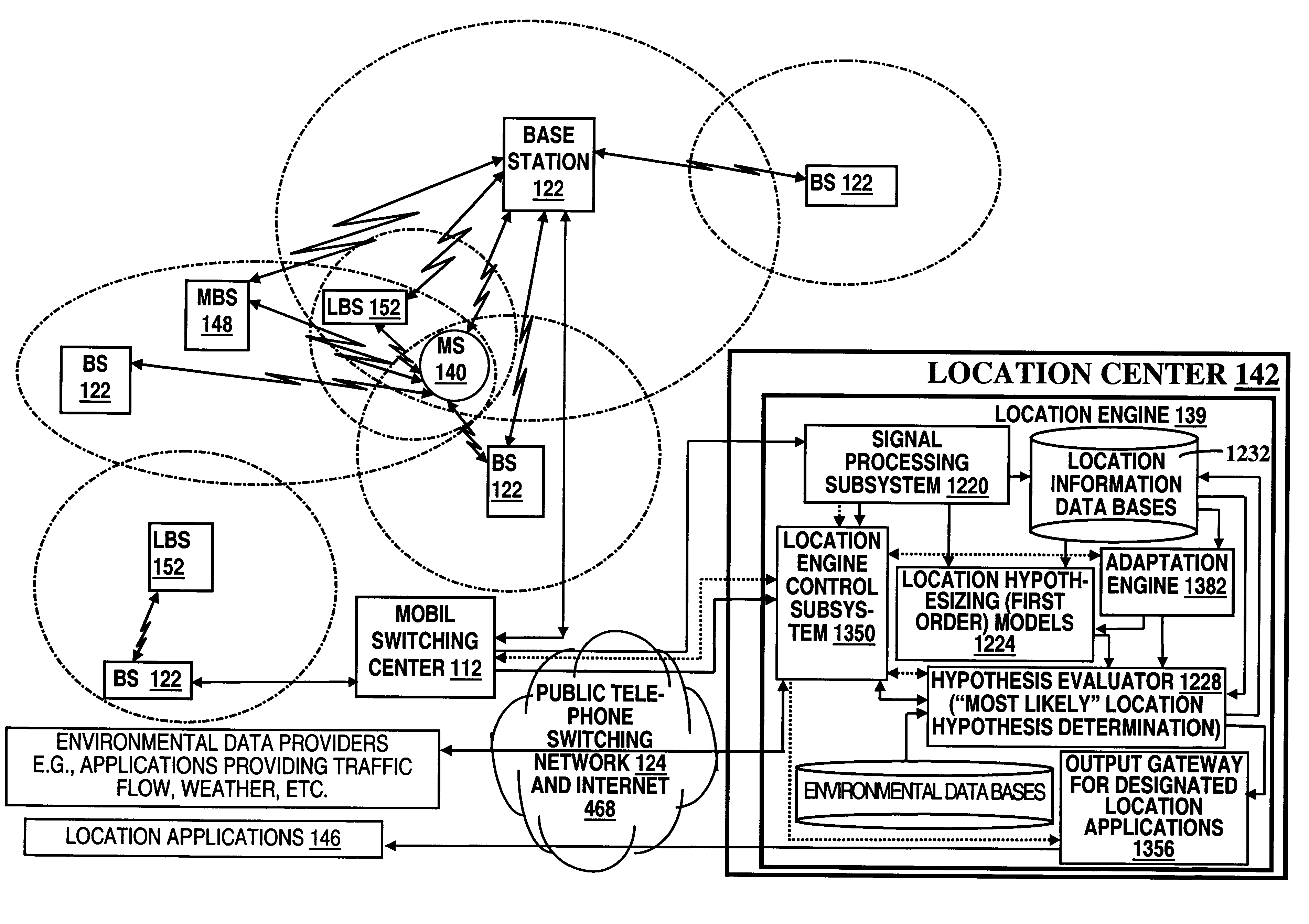
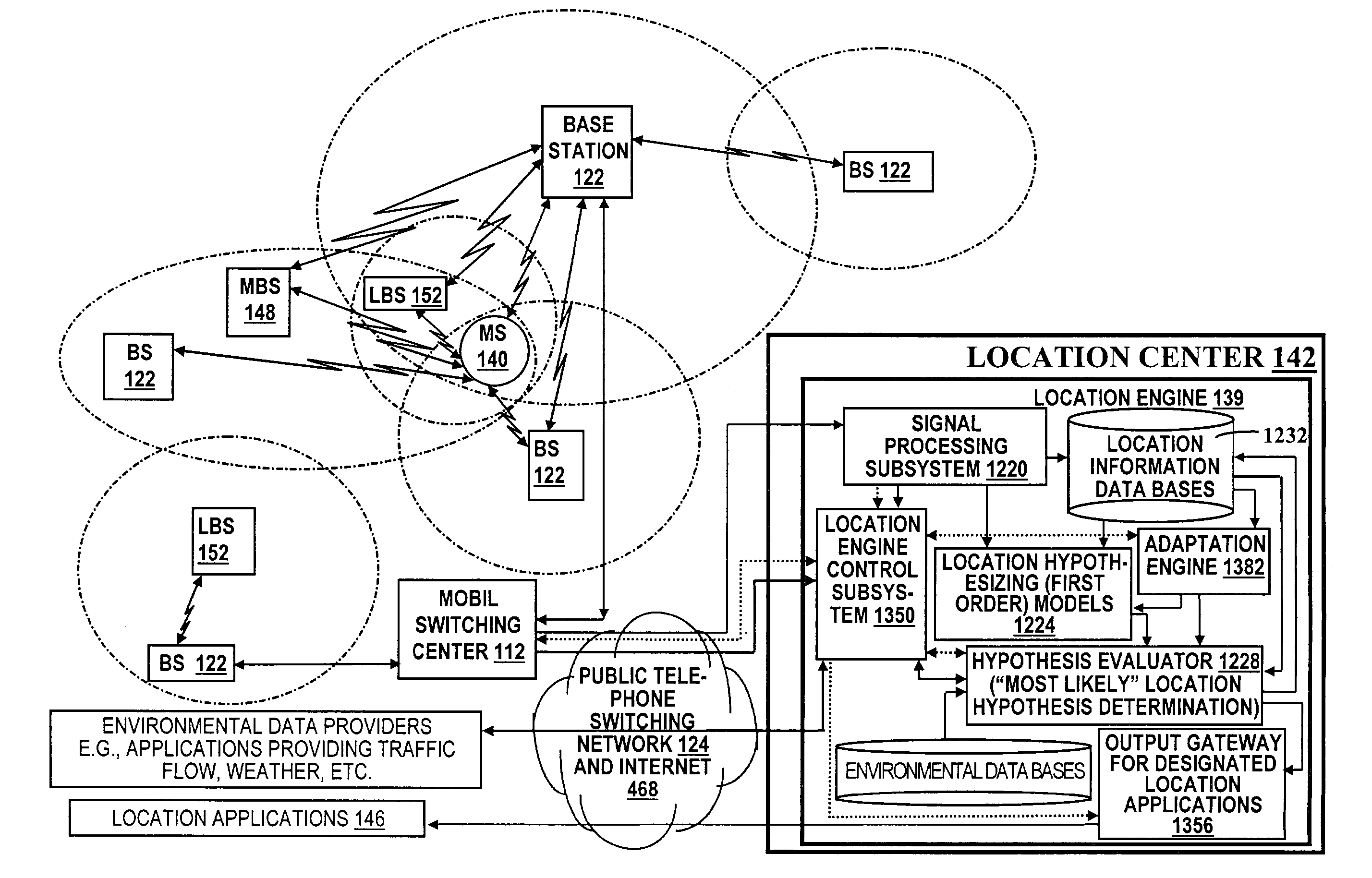
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; (5) GPS signals, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signing environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:TRACBEAM
Applications for a wireless location gateway
InactiveUS20040198386A1Easy to implementEffectively and straightforwardly resolvedPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTerrainInternet communication
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; (5) GPS signals, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:DUPRAY DENNIS J
Wireless mobile indoor/outdoor tracking system
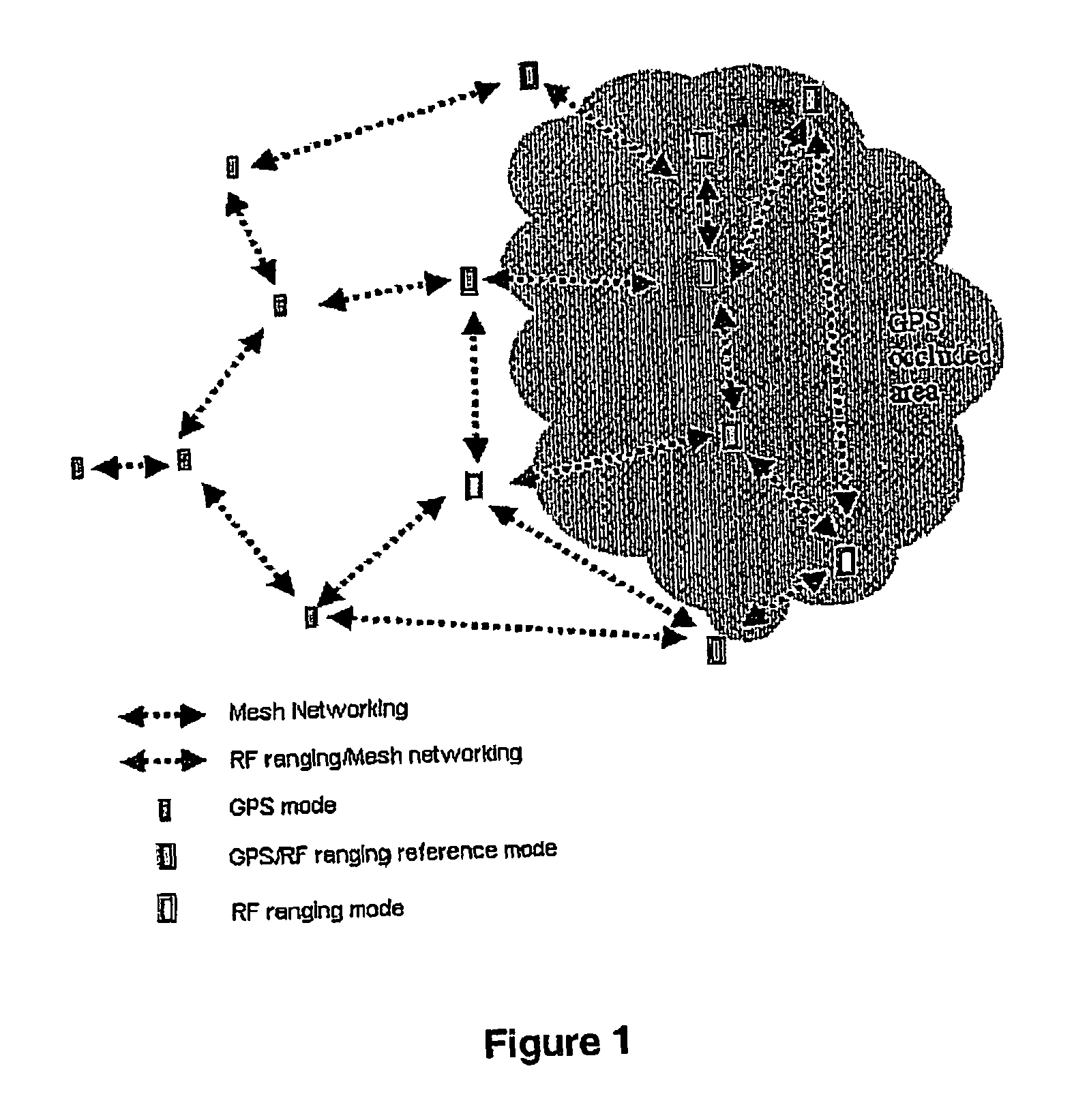
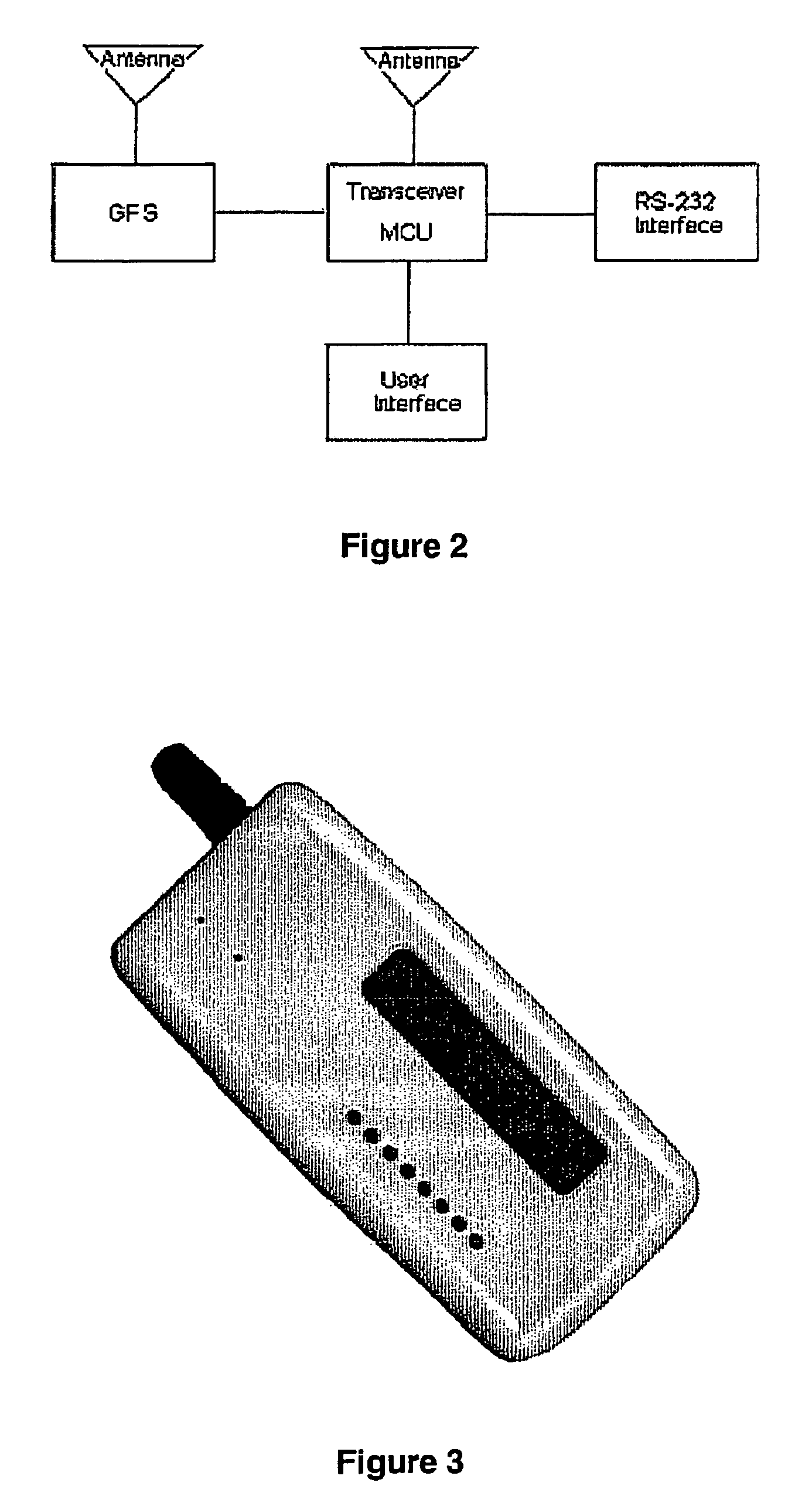
This invention is a wireless mobile indoor / outdoor tracking system. It is designed to track the absolute position of all nodes in a network indoors and outdoors. The system uses GPS positioning when a signal is available and RF ranging when it is unavailable. When indoors, a minimum of three network nodes must receive a GPS signal to determine absolute position. A mesh network is used to make the system mobile and to create an avenue for data to be transmitted to a remote base station.
Owner:CYBERNET SYST
System using leo satellites for centimeter-level navigation
InactiveUS6373432B1Improve reliabilityEasy accessPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNatural satelliteAmbiguity
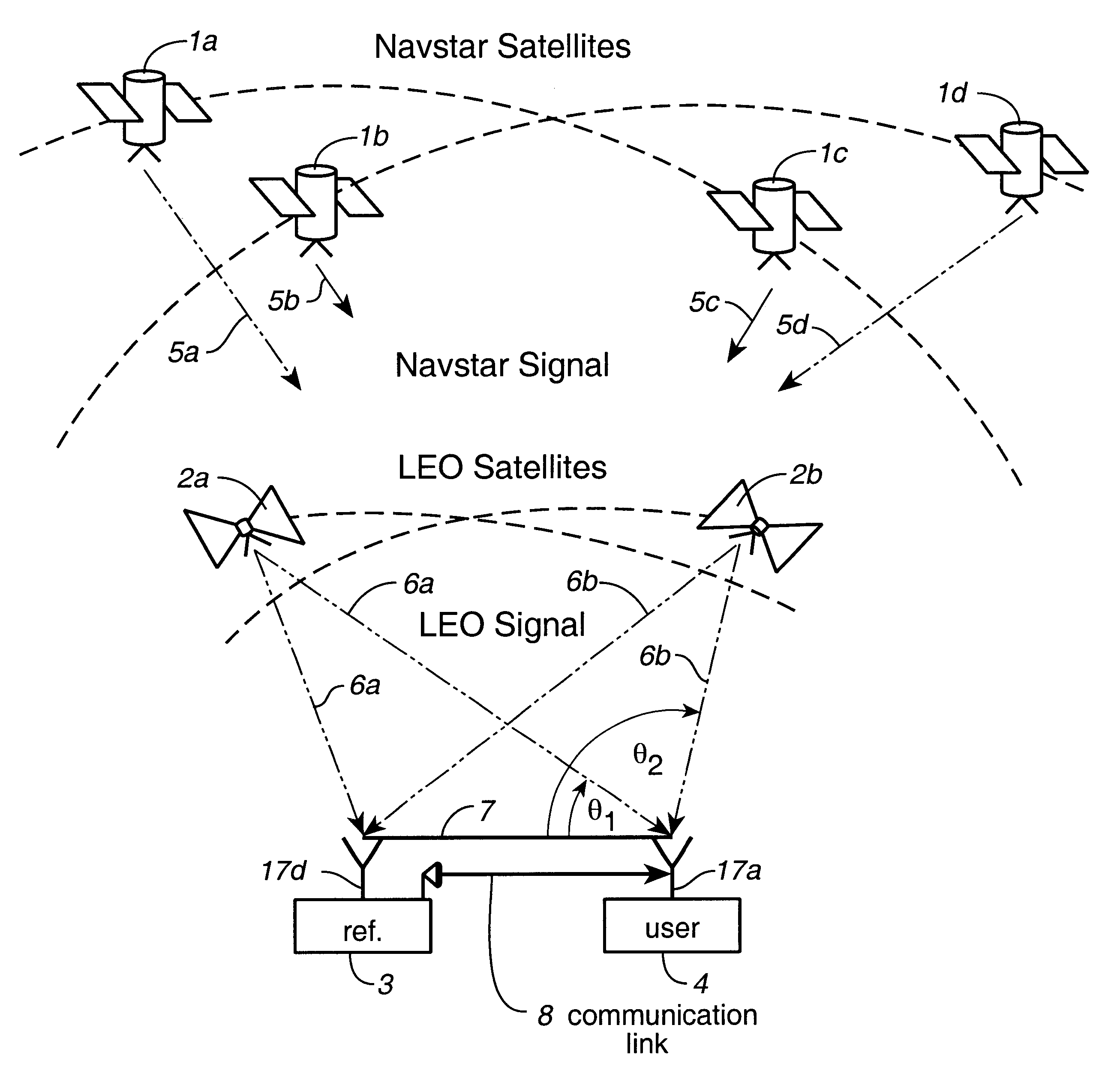
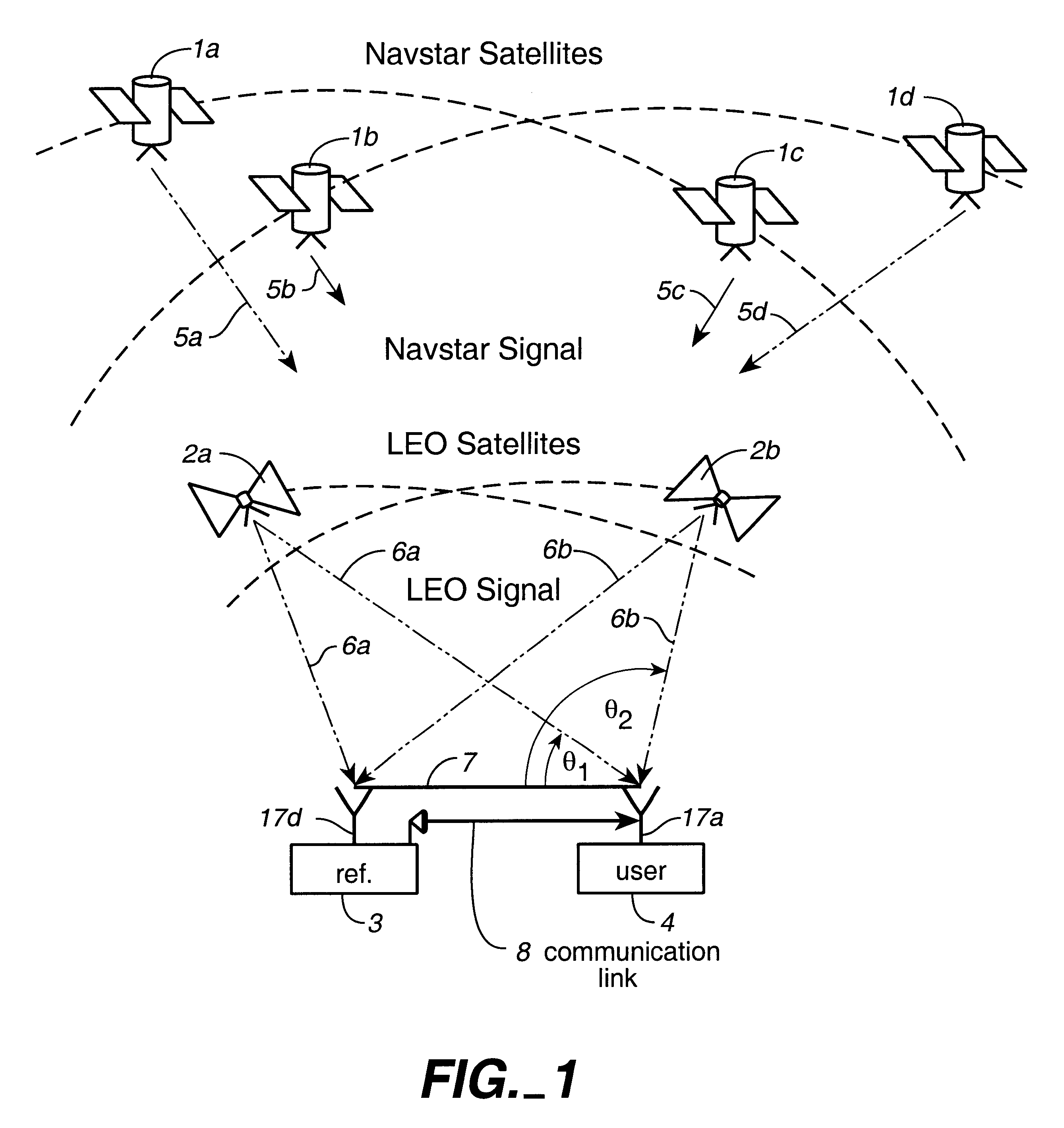
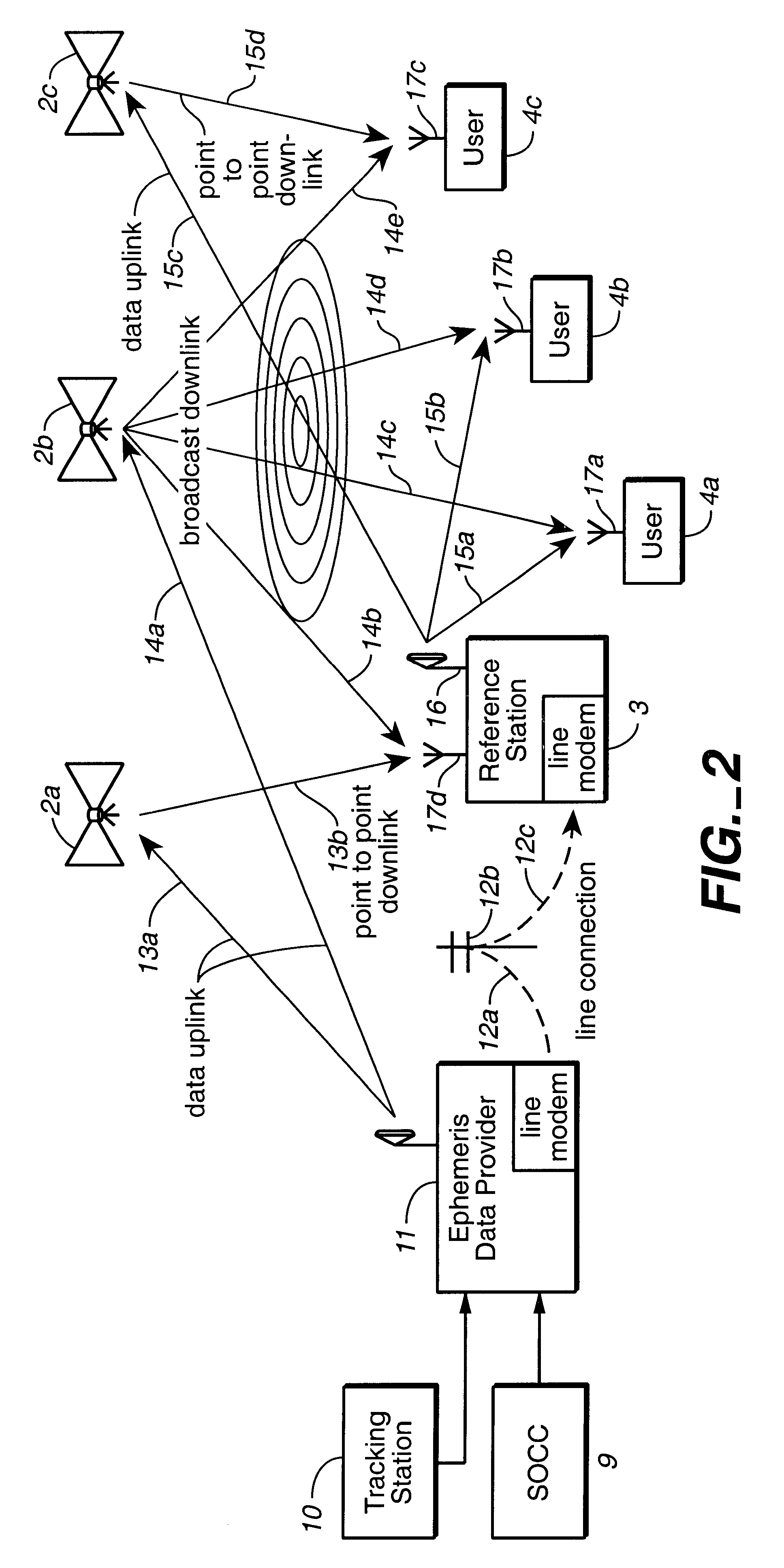
Disclosed herein is a system for rapidly resolving position with centimeter-level accuracy for a mobile or stationary receiver [4]. This is achieved by estimating a set of parameters that are related to the integer cycle ambiguities which arise in tracking the carrier phase of satellite downlinks [5,6]. In the preferred embodiment, the technique involves a navigation receiver [4] simultaneously tracking transmissions [6] from Low Earth Orbit Satellites (LEOS) [2] together with transmissions [5] from GPS navigation satellites [1]. The rapid change in the line-of-sight vectors from the receiver [4] to the LEO signal sources [2], due to the orbital motion of the LEOS, enables the resolution with integrity of the integer cycle ambiguities of the GPS signals [5] as well as parameters related to the integer cycle ambiguity on the LEOS signals [6]. These parameters, once identified, enable real-time centimeter-level positioning of the receiver [4]. In order to achieve high-precision position estimates without the use of specialized electronics such as atomic clocks, the technique accounts for instabilities in the crystal oscillators driving the satellite transmitters, as well as those in the reference [3] and user [4] receivers. In addition, the algorithm accommodates as well as to LEOS that receive signals from ground-based transmitters, then re-transmit frequency-converted signals to the ground.
Owner:INTEGRINAUTICS
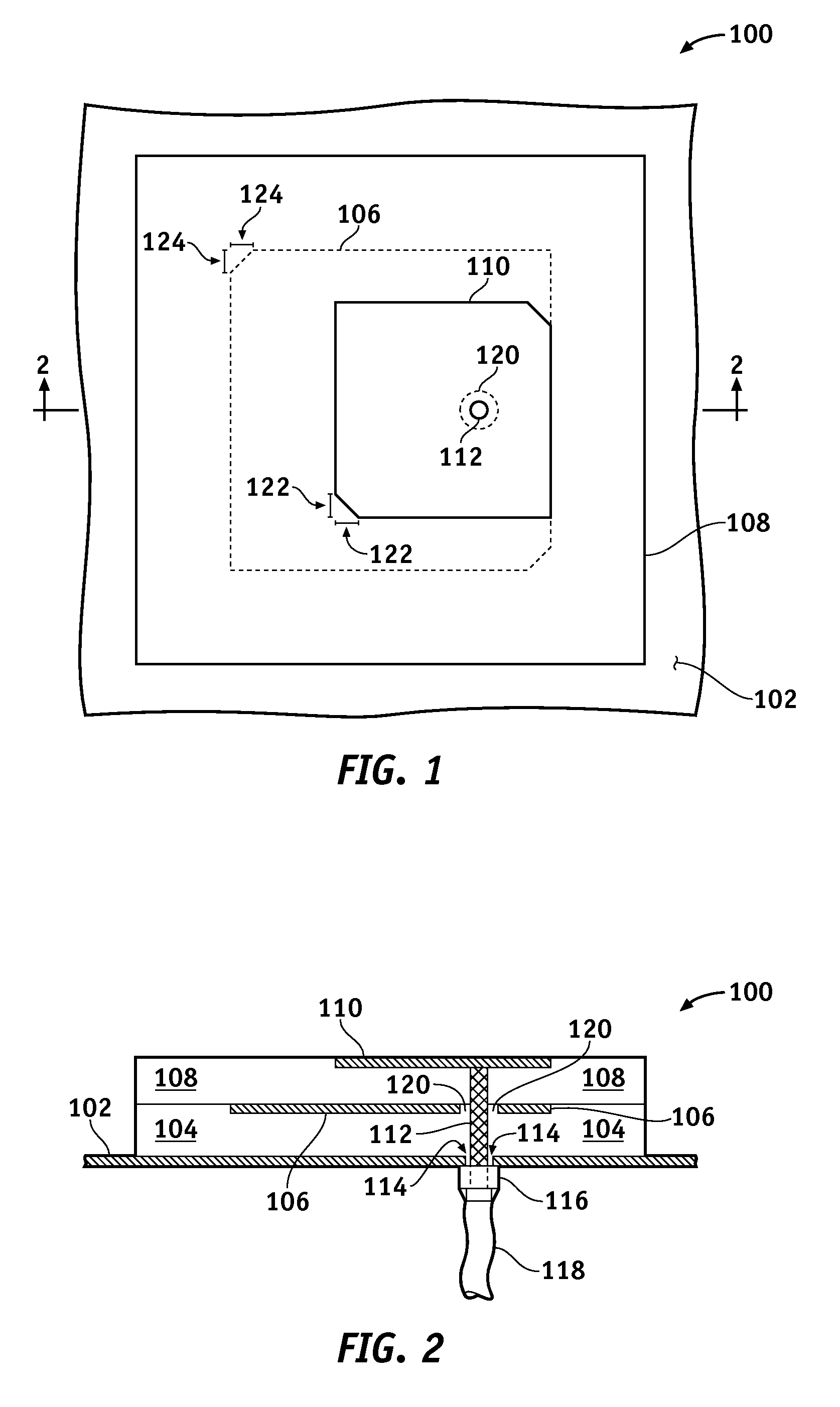
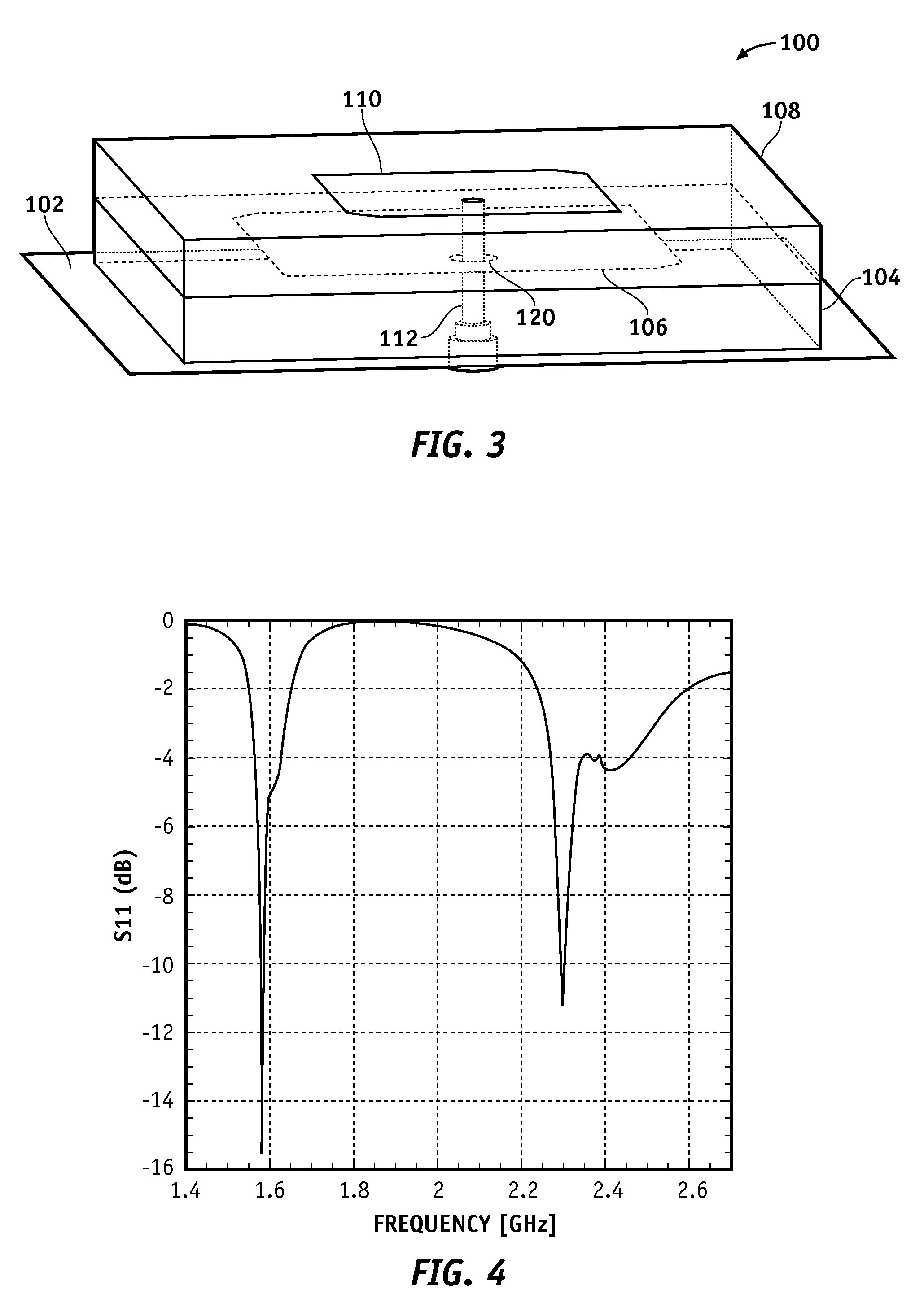
Dual Band Stacked Patch Antenna
InactiveUS20090058731A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDual frequencyDual band antenna
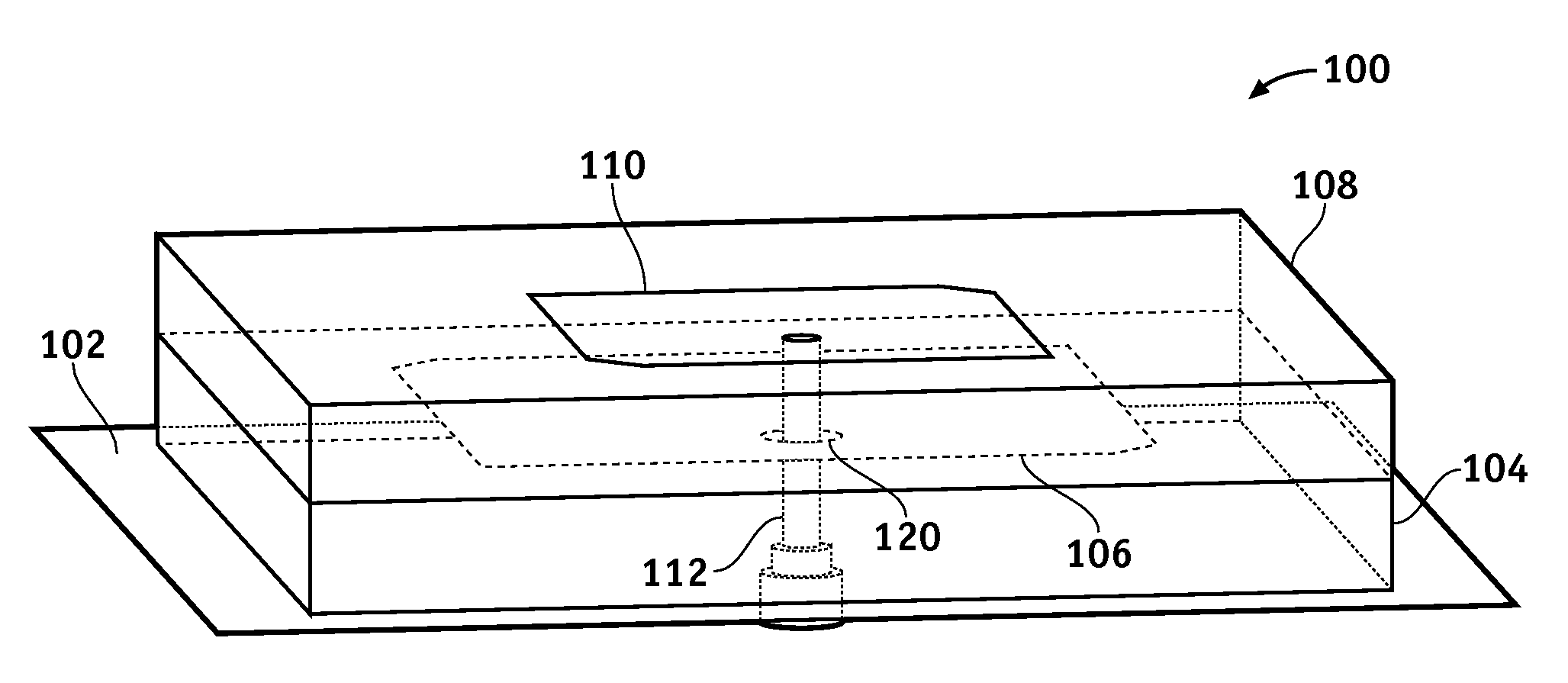
One or more of the embodiments of a dual band stacked patch antenna described herein employ an integrated arrangement of a global positioning system (GPS) antenna and a satellite digital audio radio service (SDARS) antenna. The dual band antenna receives right hand circularly polarized GPS signals in a first frequency band, left hand circularly polarized SDARS signals in a second frequency band, and vertical linear polarized SDARS signals in the second band. The dual band antenna includes a ground plane element, an upper radiating element (which is primarily utilized to receive SDARS signals), dielectric material between the ground plane element and the upper radiating element, and a lower radiating element (which is primarily utilized to receive GPS signals) surrounded by the dielectric material. The dual band antenna uses only one conductive signal feed to receive both GPS and SDARS signals.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
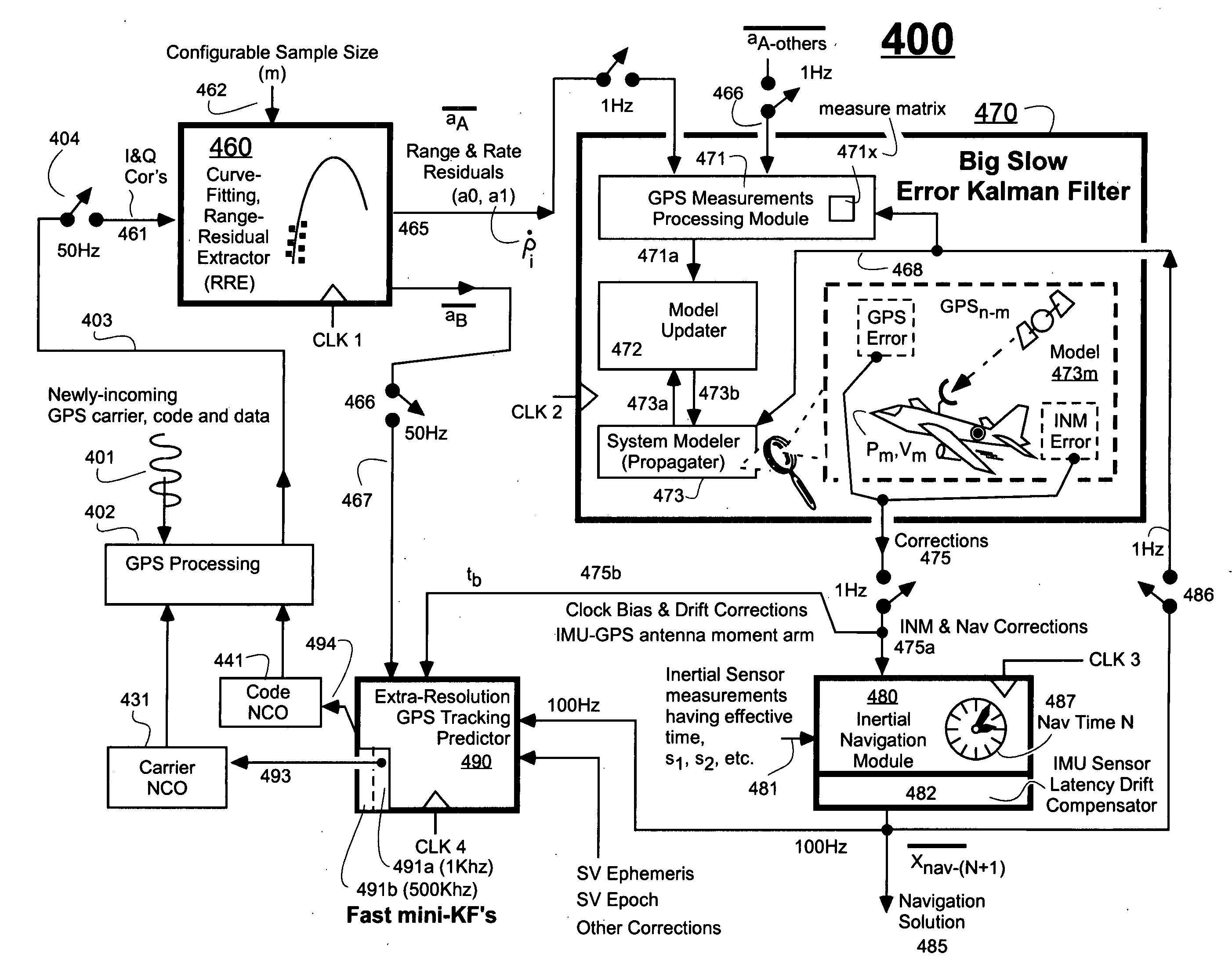
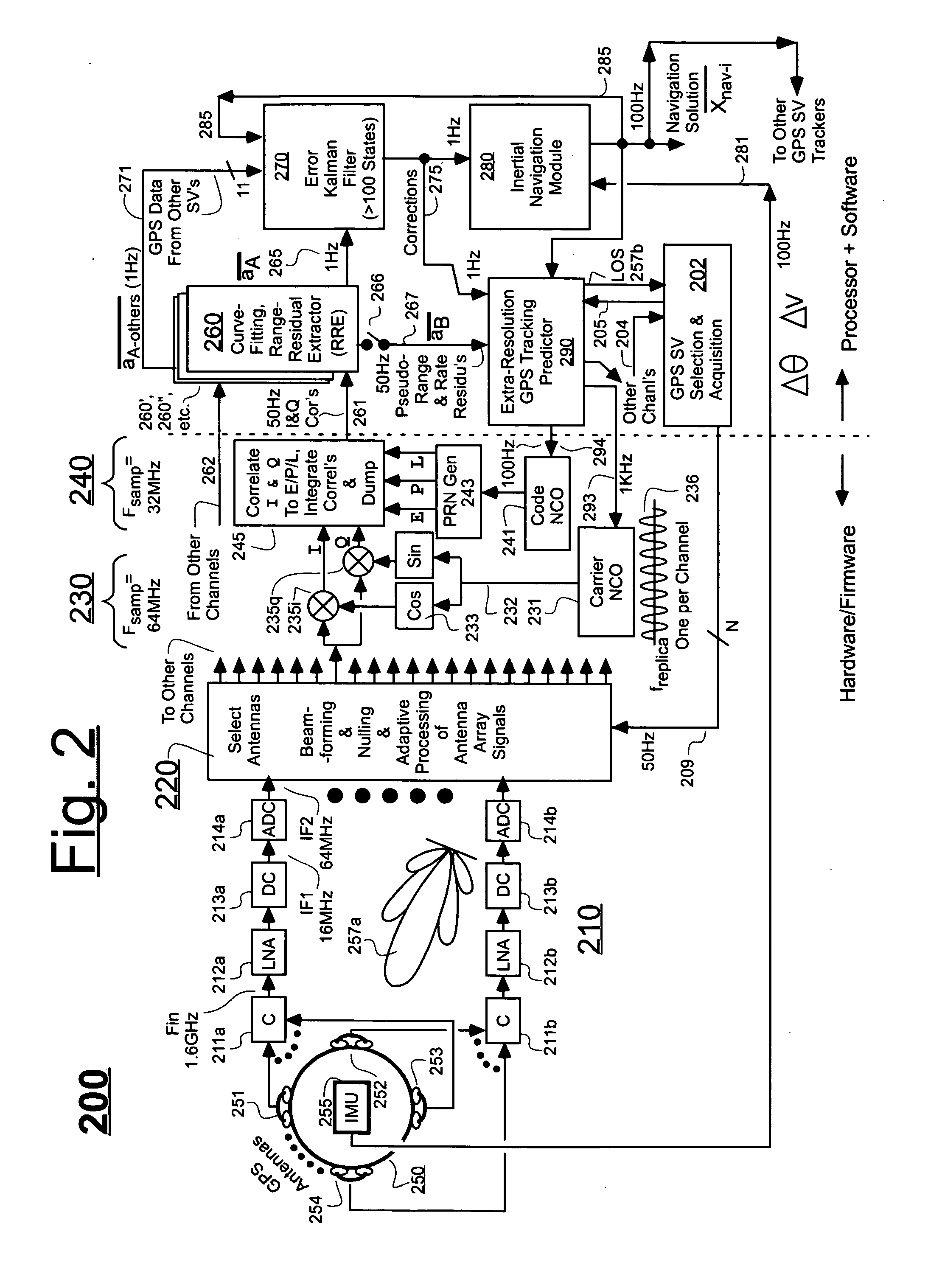
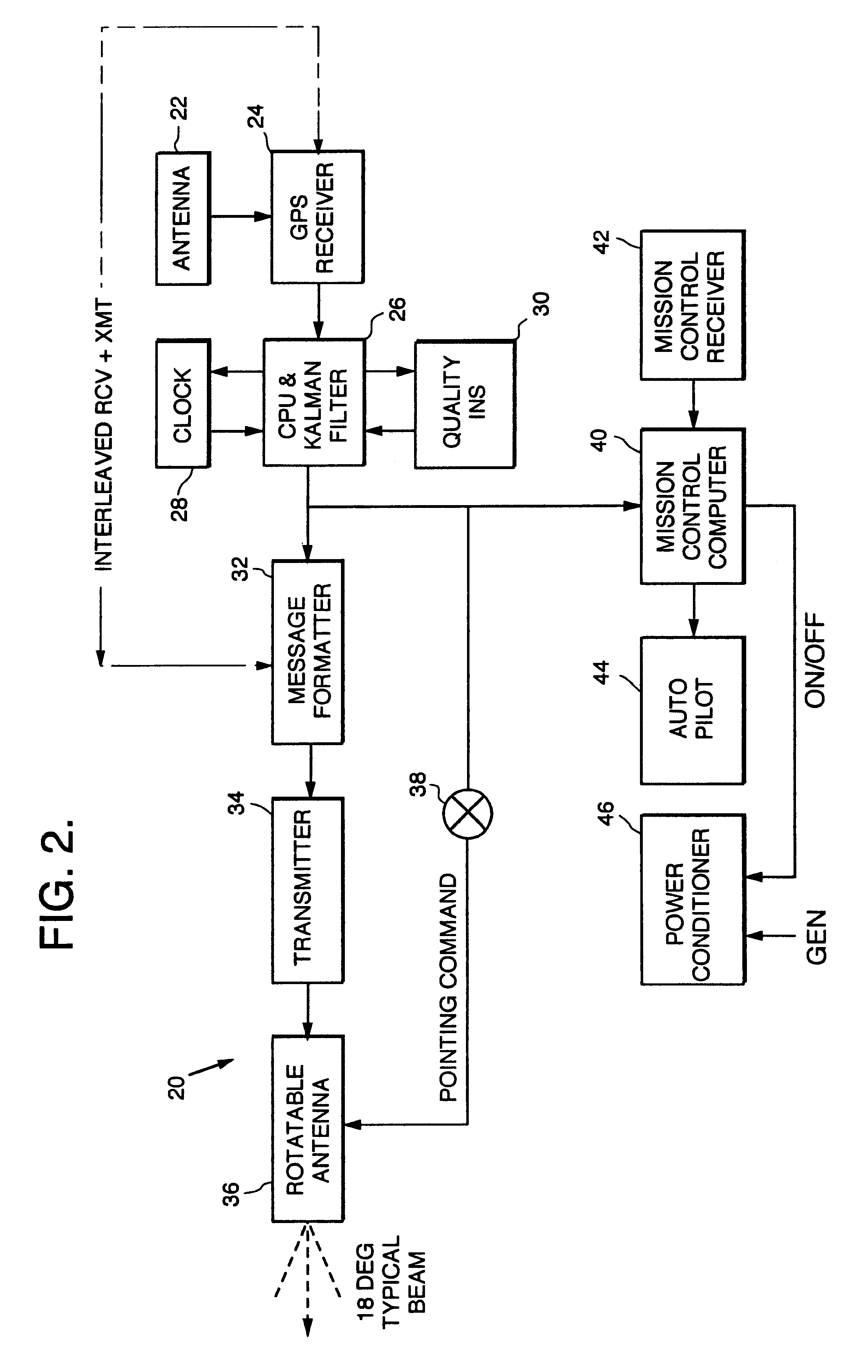
Ultra-tightly coupled GPS and inertial navigation system for agile platforms
InactiveUS20070118286A1Cancel noiseReduce computing timeDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCurve fittingCarrier signal
An Ultra-Tightly Coupled GPS-inertial navigation system for use in a moving agile platform includes a range residual extractor that uses best curve fitting of a third order polynomial for estimating range residual. The curve-fitted residual is used to update an error Kalman filter. The error Kalman filter includes correction for navigation solution, and IMU and GPS parameters. The navigation solution together with GPS parameter corrections are used in a Tracking Predictor to generate high-sampling-rate carrier and code replicas. The curve-fitting error covariance indicates signal to noise ratio for the tracked GPS signal and may be used for early indication of interference or jamming.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
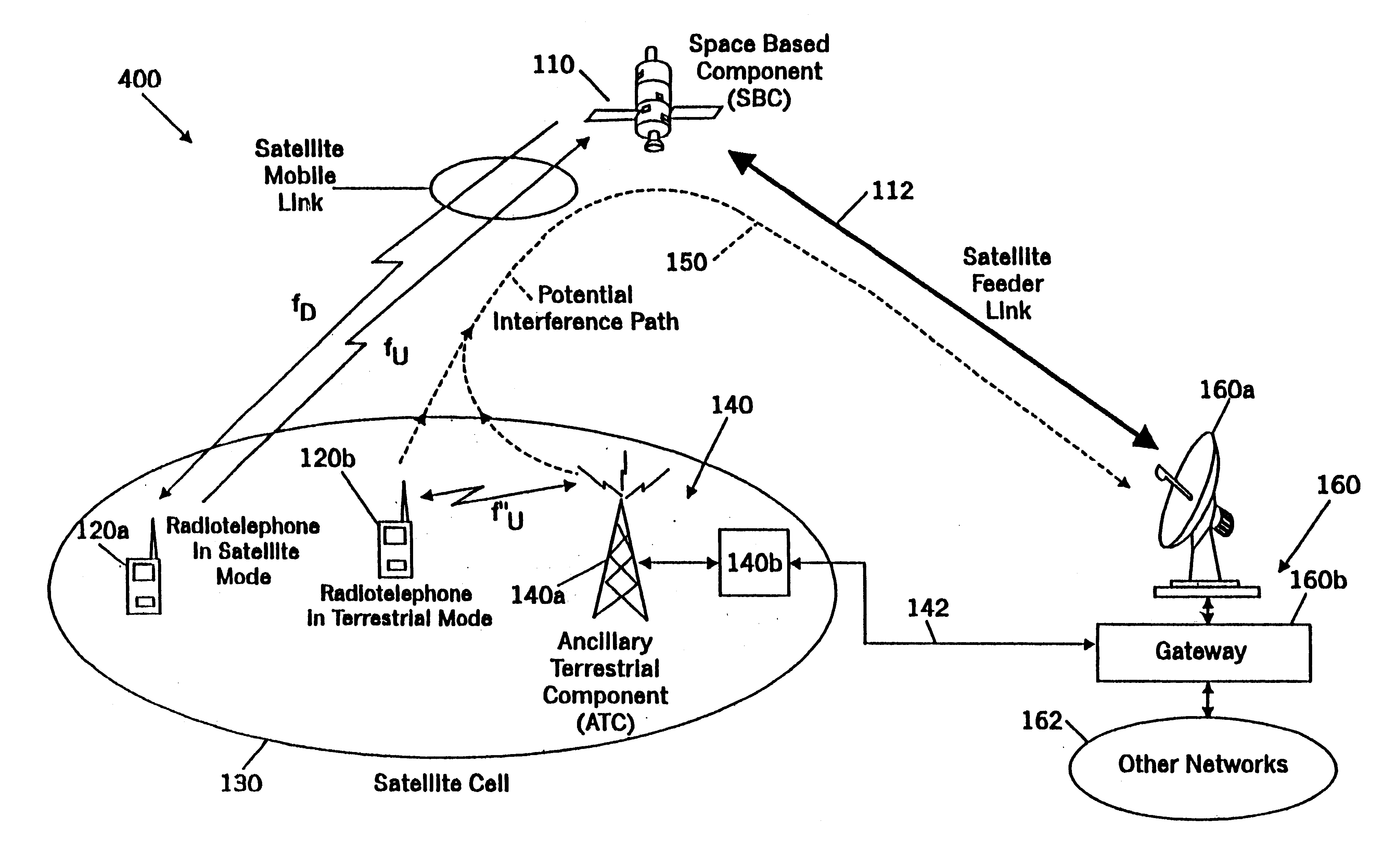
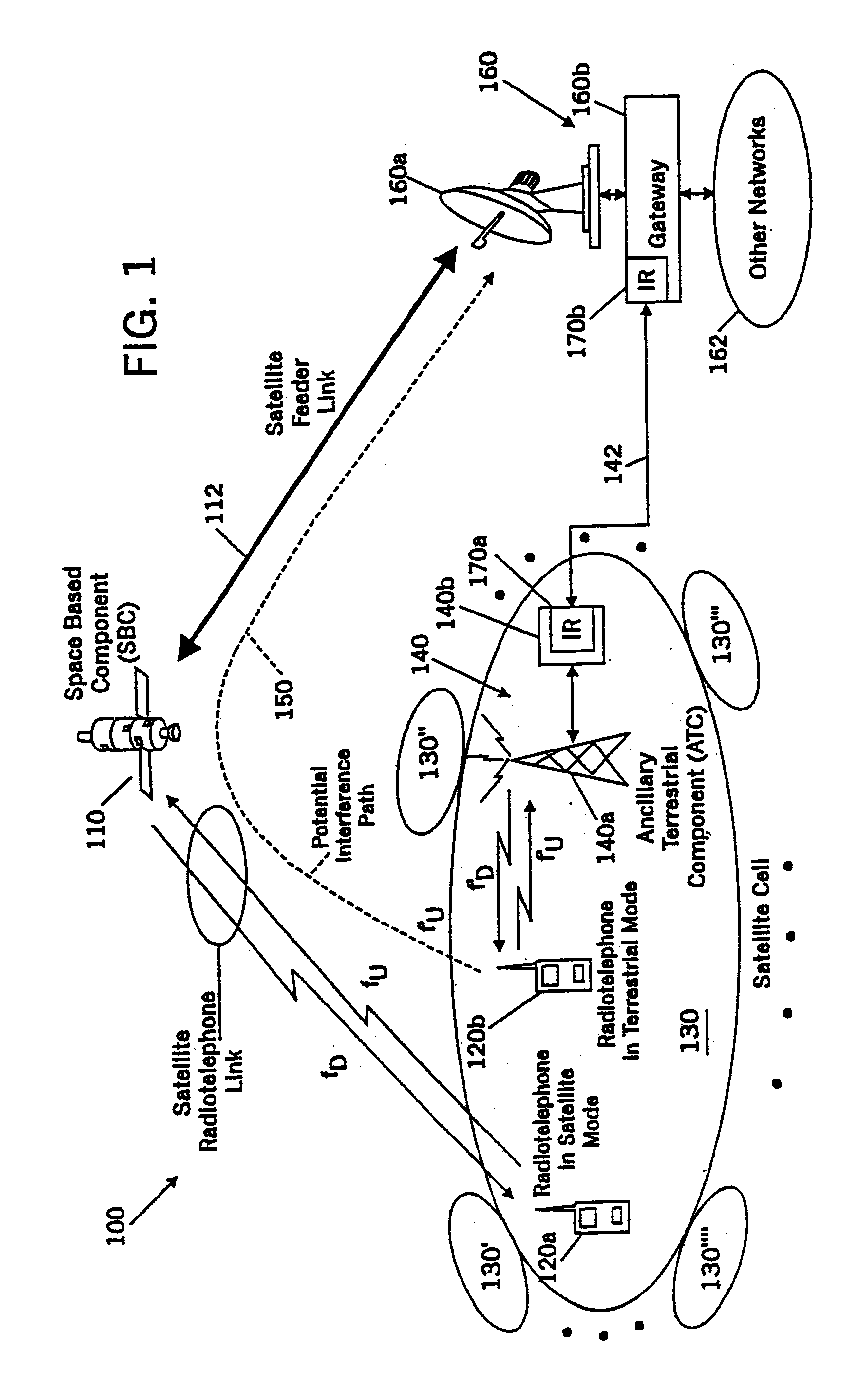
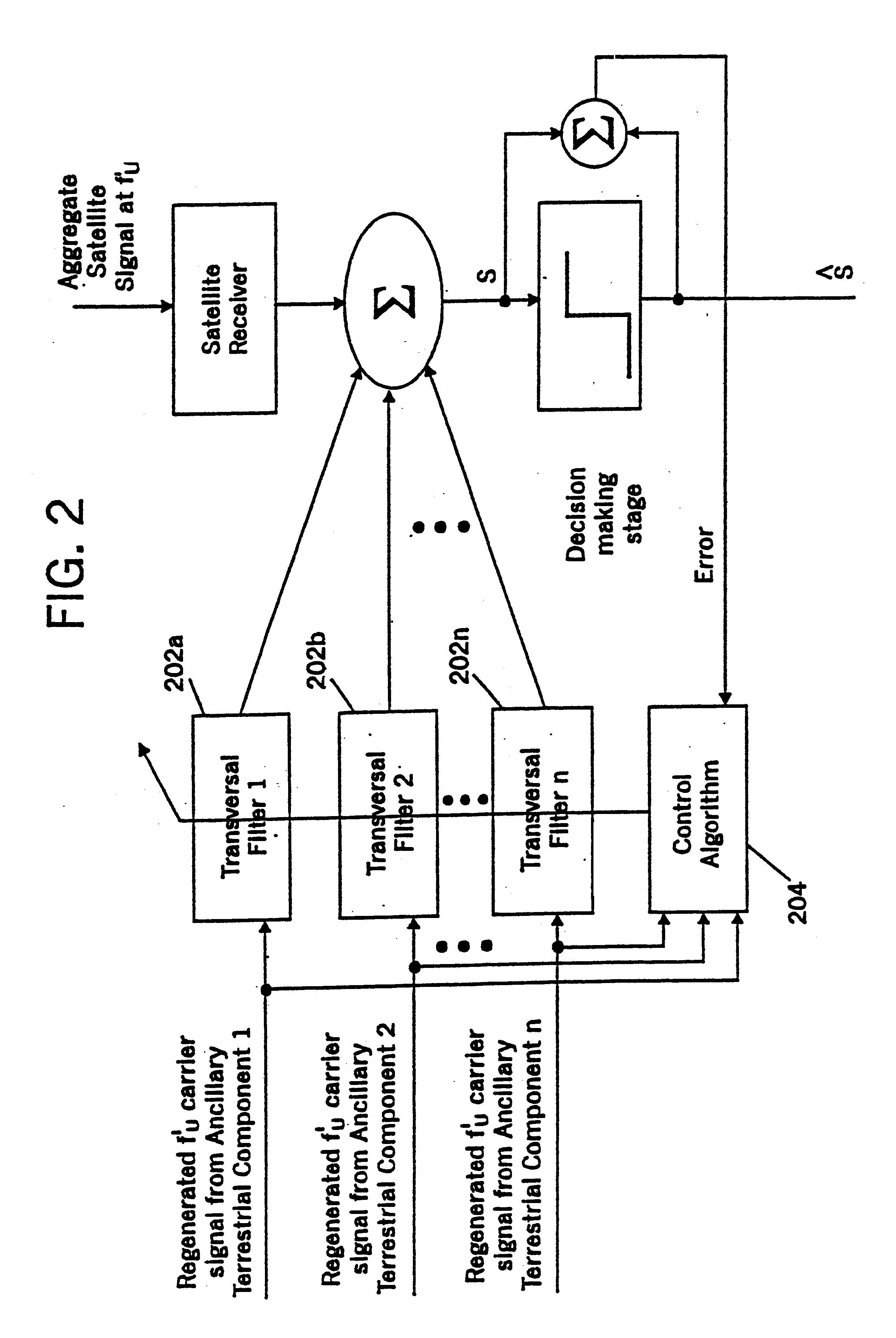
Filters for combined radiotelephone/GPS terminals
A satellite radiotelephone system includes a space-based component, a plurality of ancillary terrestrial components, and a plurality of radiotelephones. The space-based component is configured to provide wireless radiotelephone communications using satellite radiotelephone frequencies. The plurality of ancillary terrestrial components include a plurality of ancillary terrestrial component antennas configured to provide wireless radiotelephone communications using at least one of the satellite radiotelephone frequencies in a radiation pattern that increases radiation below the horizon compared to above the horizon. The plurality of radiotelephones are configured to communicate with the space-based component and with the plurality of ancillary terrestrial components. Each radiotelephone also includes a GPS signal processor and a GPS mode filter that is configured to suppress energy at (1575.42-.DELTA.) MHz, where 0<.DELTA..ltoreq.16.42 MHz. Related radiotelephones and methods are also discussed.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
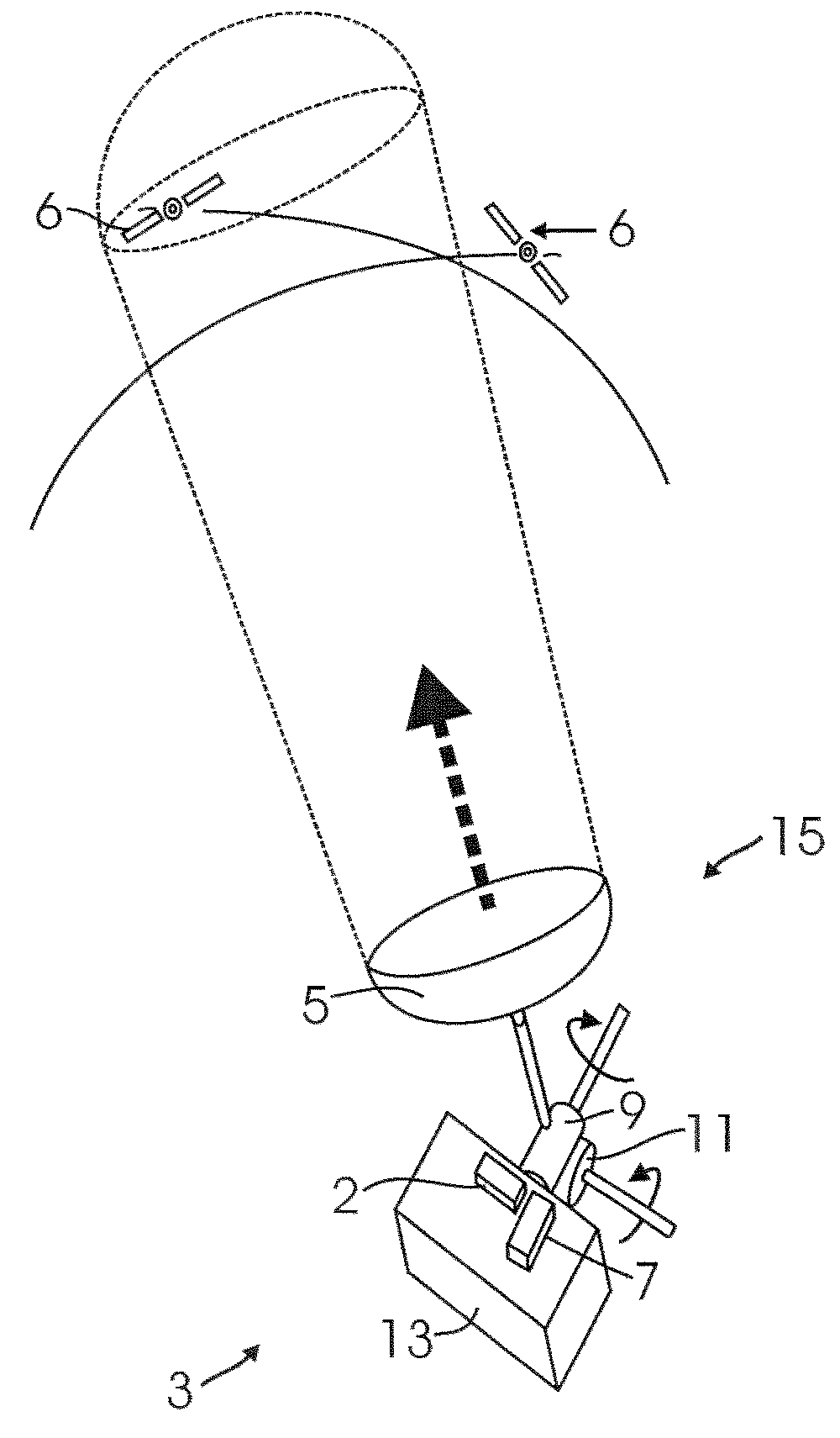
Method and system for attitude determination of a platform using global navigation satellite system and a steered antenna
InactiveUS7397422B2Reduce noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingDirectional antennaMarine navigation
A system and method for determining the attitude of a platform is provided. The method includes: (a) Searching and scanning for one or more GPS satellite(s) to determine initial platform position; wherein a single directionally steered antenna scans for the GPS / GNSS satellite; (b) pointing and scanning the antenna to GPS / GNSS satellite to determine a first angular measurement of a direction of a GPS / GNSS signal; (c) measuring carrier to noise ratio of the GPS / GNSS satellite; (d) dithering the single directionally steered antenna to obtain an angular measurement relative to an antenna pattern bore-sight reference; (e) repeating steps (b)-(d) to determine a second angular measurement of the direction of a second GPS signal; (f) determining the attitude error of the platform using the first and second angular measurements; (g) updating the platform position and attitude.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
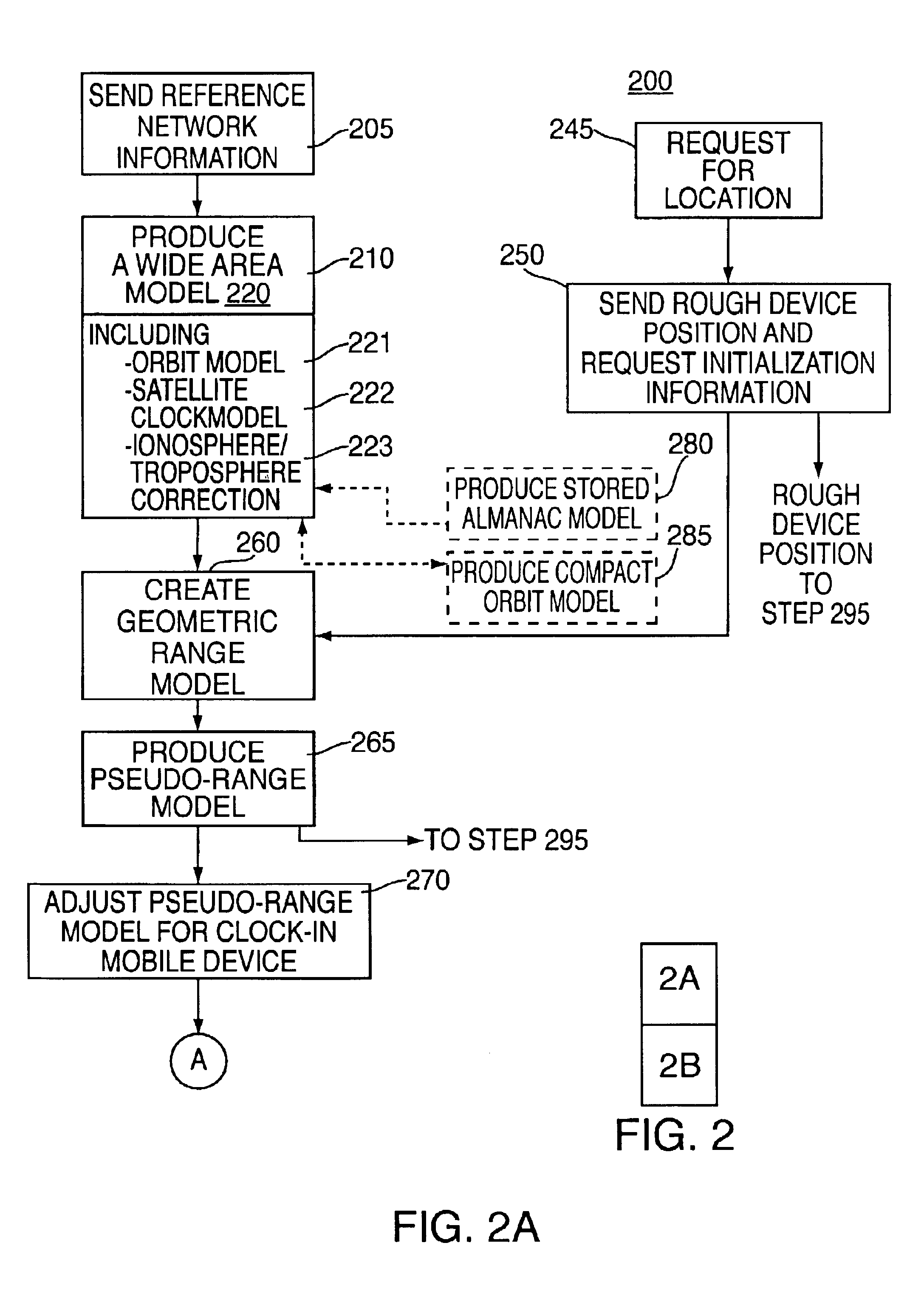
Method and apparatus for forming a pseudo-range model
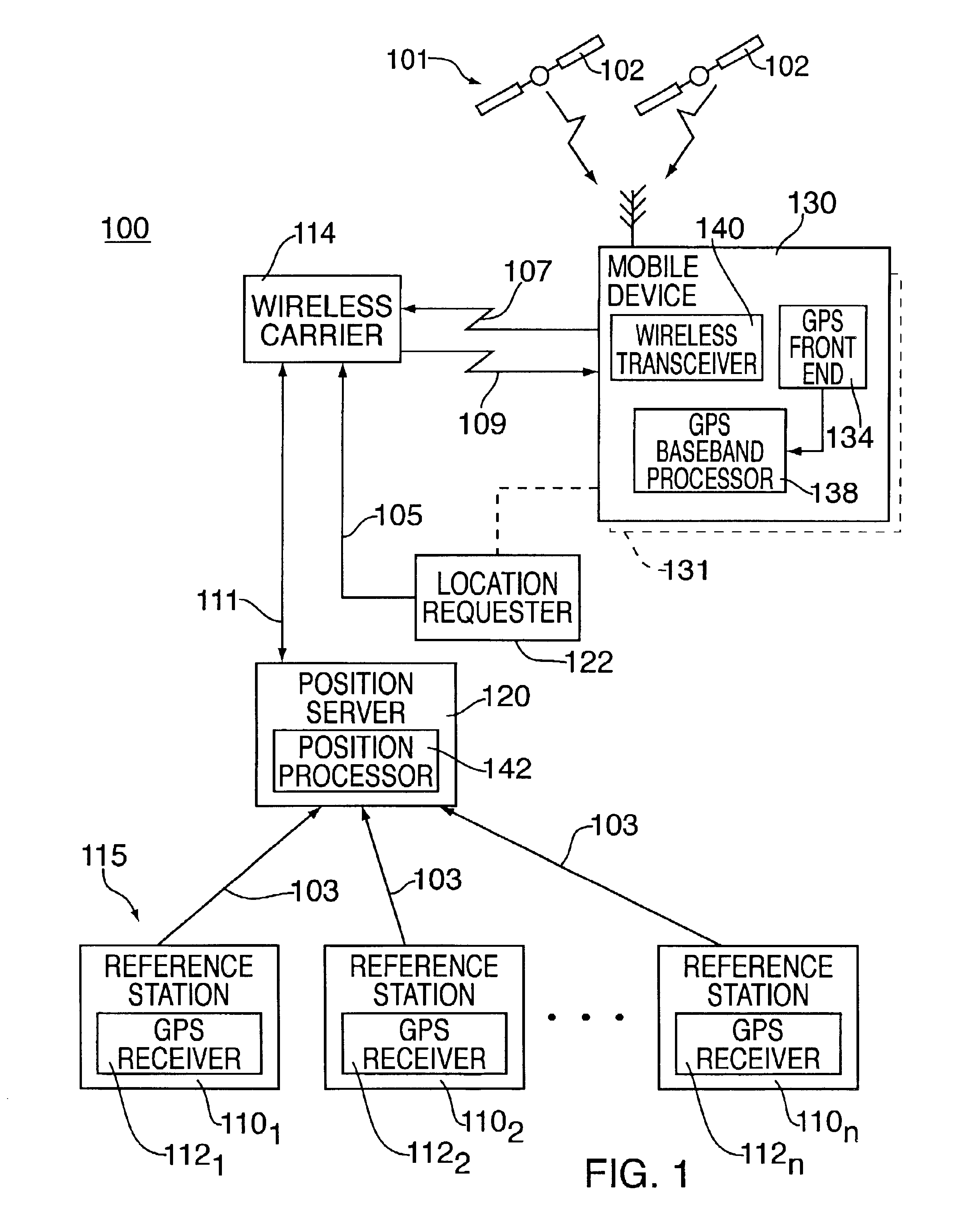
InactiveUS6853916B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTelecommunications linkSignal on
A method and apparatus for locating mobile device over a broad coverage area using a wireless communications link that may have large and unknown latency. The apparatus comprises at least one mobile device, a reference network, a position server, a wireless carrier, and a location requester. The mobile device is in communication with the wireless carrier and receives global positioning system (GPS) signals from a plurality of satellites in the GPS satellite constellation. The reference network is coupled to the position server and provides GPS data. The mobile receiver receives GPS signals, performs rudimentary signal processing and transmits the processed signals to the wireless carrier. The wireless carrier passes the signals on to the position server. The position server processes the mobile receiver's GPS data and the reference network ephemeris data to identify the location of the mobile receiver. The location is sent to the location requester.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
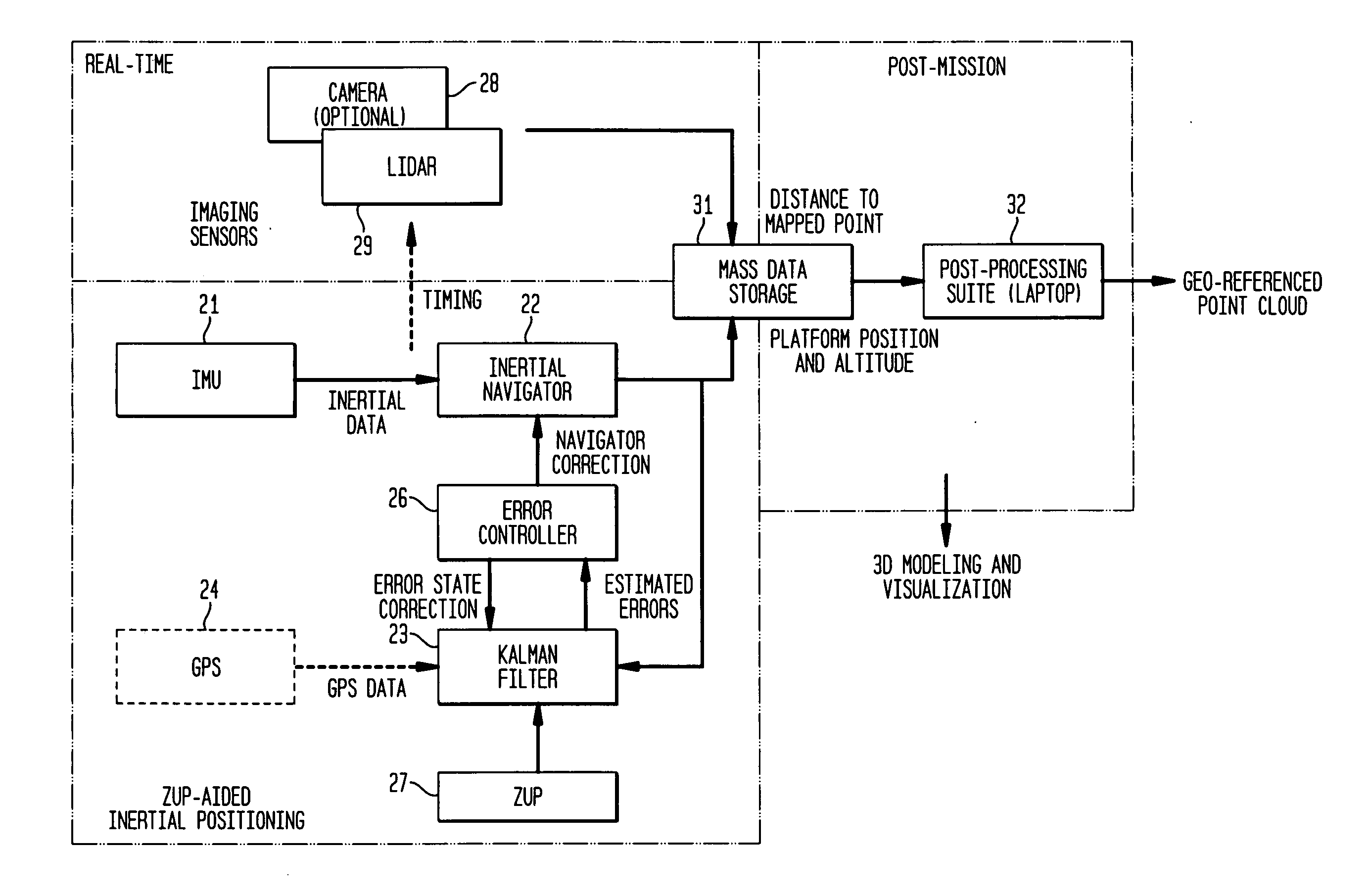
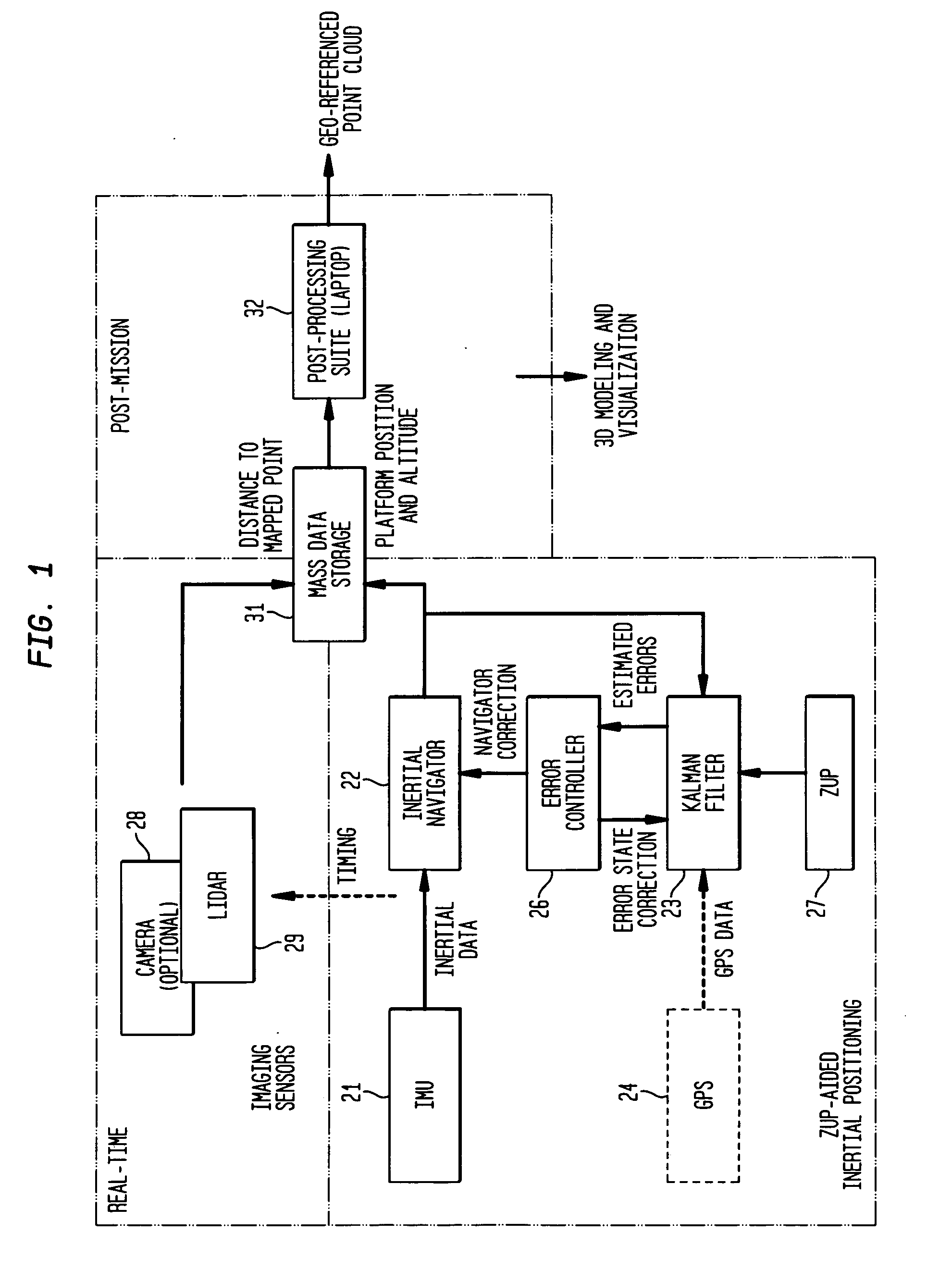
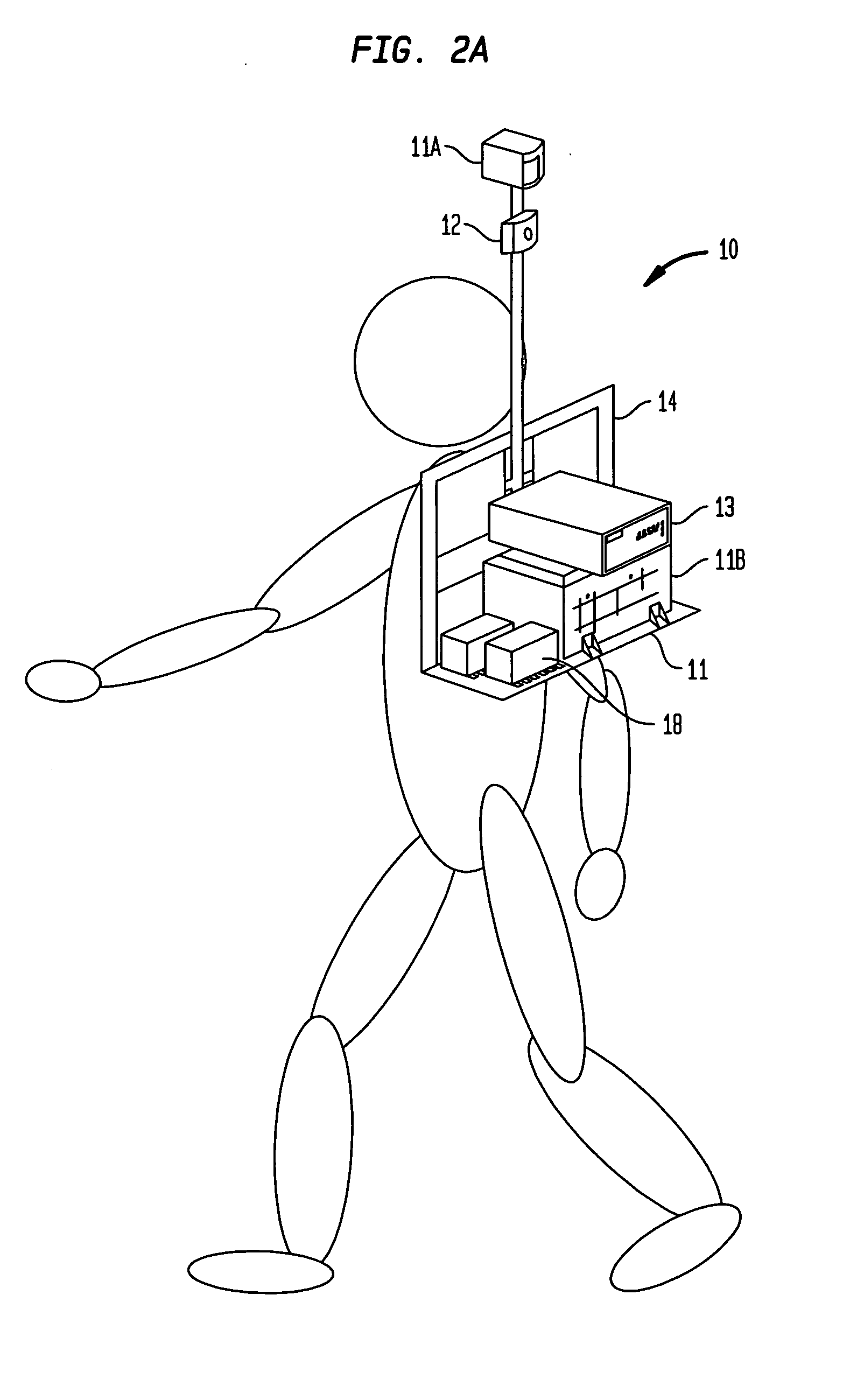
System and method for obtaining georeferenced mapping data
InactiveUS20090262974A1Visually enhancedMinimize the numberImage analysisOptical rangefindersSpatial mappingGeolocation
A system and method for acquiring spatial mapping information of surface data points defining a region unable to receive effective GPS signals, such as the interior of a building, includes an IMU for dynamically determining geographical positions relative to at least one fixed reference point, a LIDAR or camera for determining range of the IMU to each surface data point, and a processor to determine position data for each surface data point relative to the at least one reference point. A digital camera obtains characteristic image data, including color data, of the surface data points, and the processor correlates the position data and image data for the surface data points to create an image of the region.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
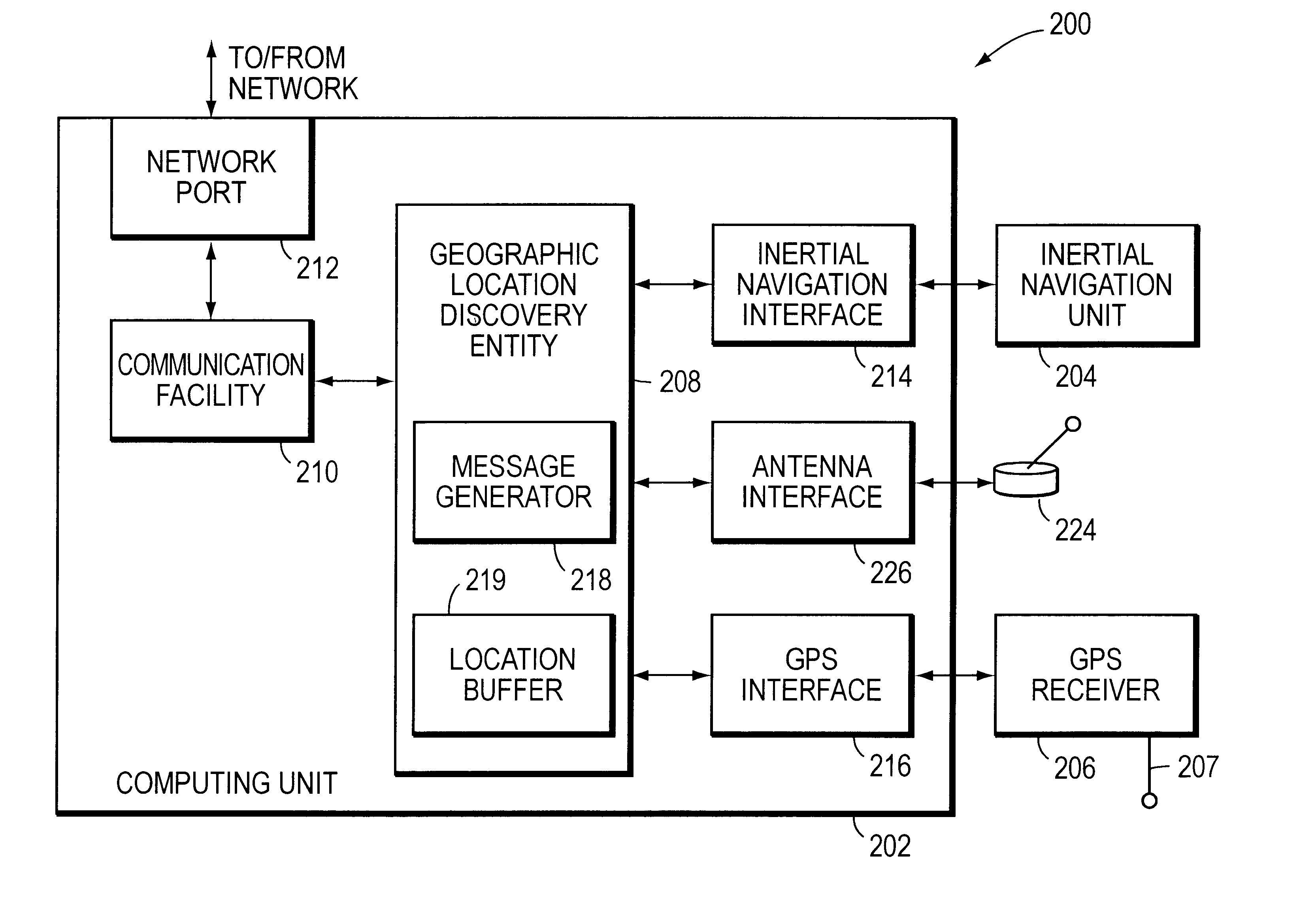
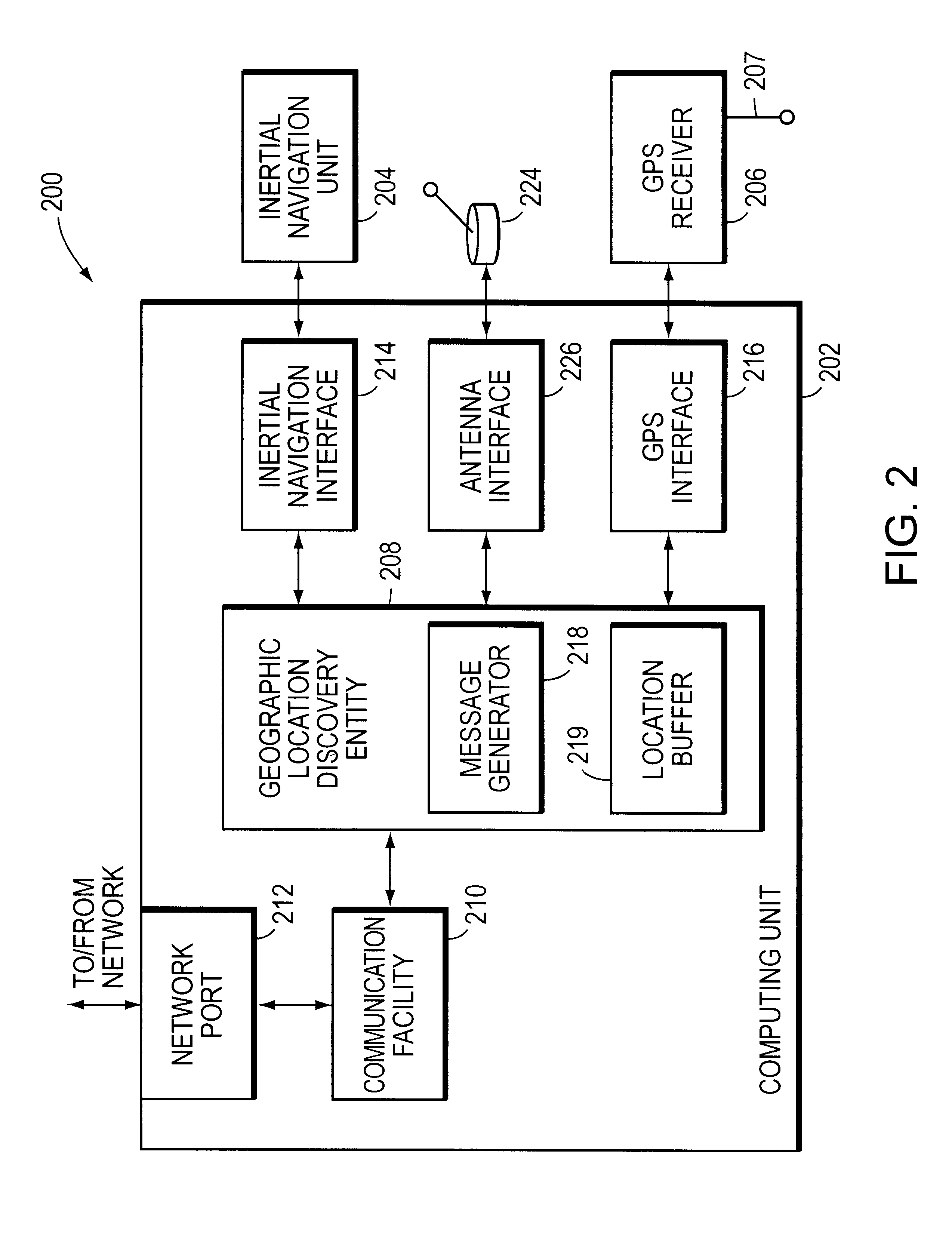
System for discovering and maintaining geographic location information in a computer network to enable emergency services
InactiveUS6665611B1Promote generationPosition fixationTelephonic communicationGps receiverGeolocation
A system automatically discovers and maintains geographic location information for entities and devices making up a computer network. The system preferably includes a computing unit and a geographic location generator, such as a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver. The computing unit includes a location discovery entity and a message generator. The GPS receiver, which is mounted to and in communication with the computing unit, may be augmented with an inertial navigation unit to facilitate the generation of location information inside of buildings where GPS signals can be difficult to receive. The computing unit further includes a network communications facility so that it can communicate with one or more network devices, such as a network switch. The switch includes a location recording / reporting entity and a location database. Physical coordinates of network entities or devices are obtained by the GPS receiver and / or-inertial navigation unit and transmitted to the network switch, and the recording / reporting entity stores the physical coordinates at the location database.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
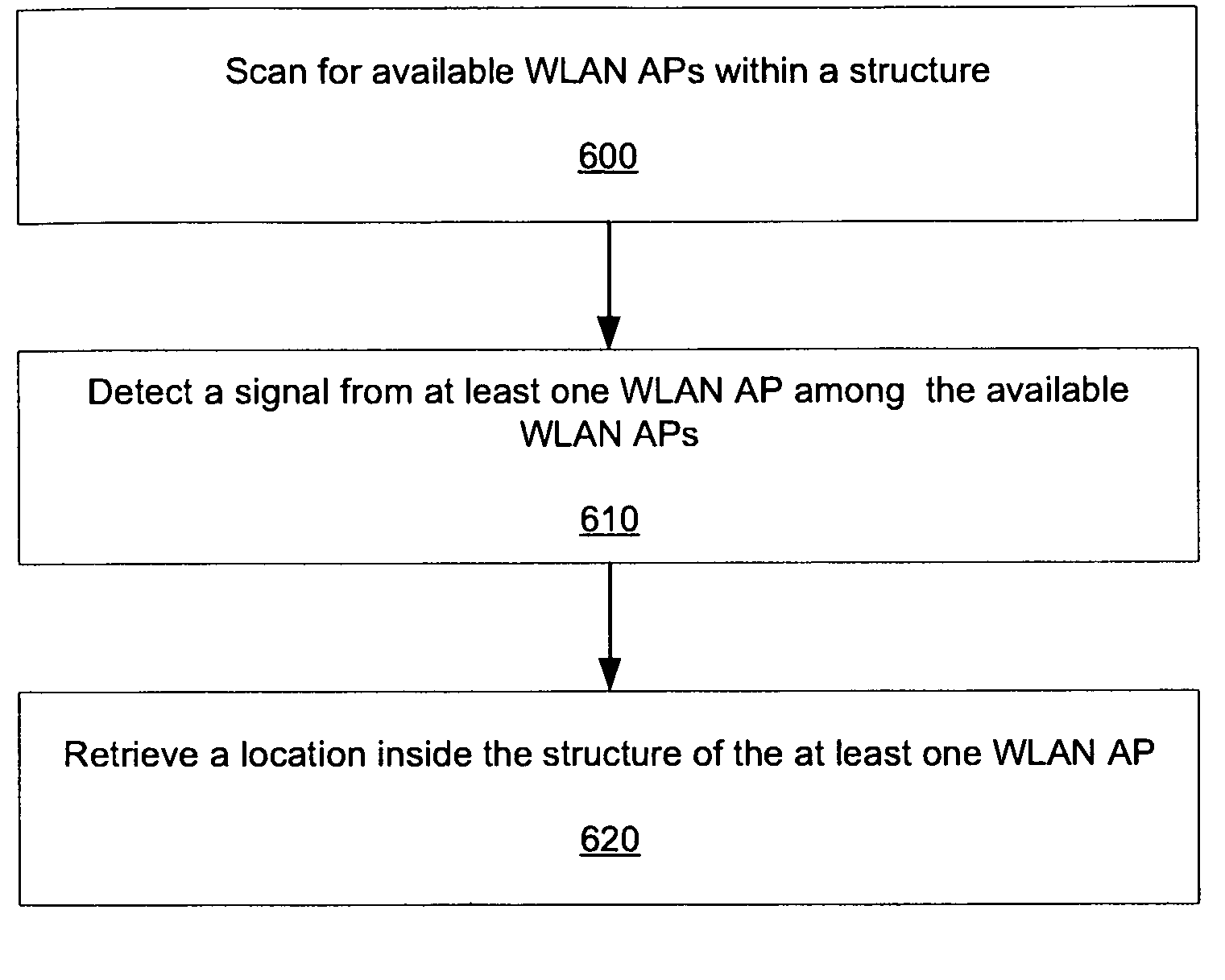
Method providing positioning and navigation inside large buildings
ActiveUS20100008337A1Particular environment based servicesNetwork topologiesNative QueriesMedia access control
Positioning and / or navigation of an electronic device within a building when GPS signals are unavailable is provided. The electronic device scans for available Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) Access Points (APs) upon, e.g., entering a building. The electronic device detects a signal (e.g., beacon) from at least one available WLAN AP, whereupon the electronic device retrieves the indoor location of the available WLAN AP. The location information can be directly downloaded from the WLAN AP while in state-1 via, e.g., a Native Query Protocol which includes an extension to currently defined Native Query info elements that returns location information. Alternatively, the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the WLAN AP can be read from the beacon signal, which is then used to retrieve the location of the WLAN AP from an associated database. Additionally, various embodiments may be implemented with or via a mapping application or service, where the mapping application is able to display any floor's floor plan of a building and determine / obtain the position of the electronic device inside the building relative to the floor plan.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
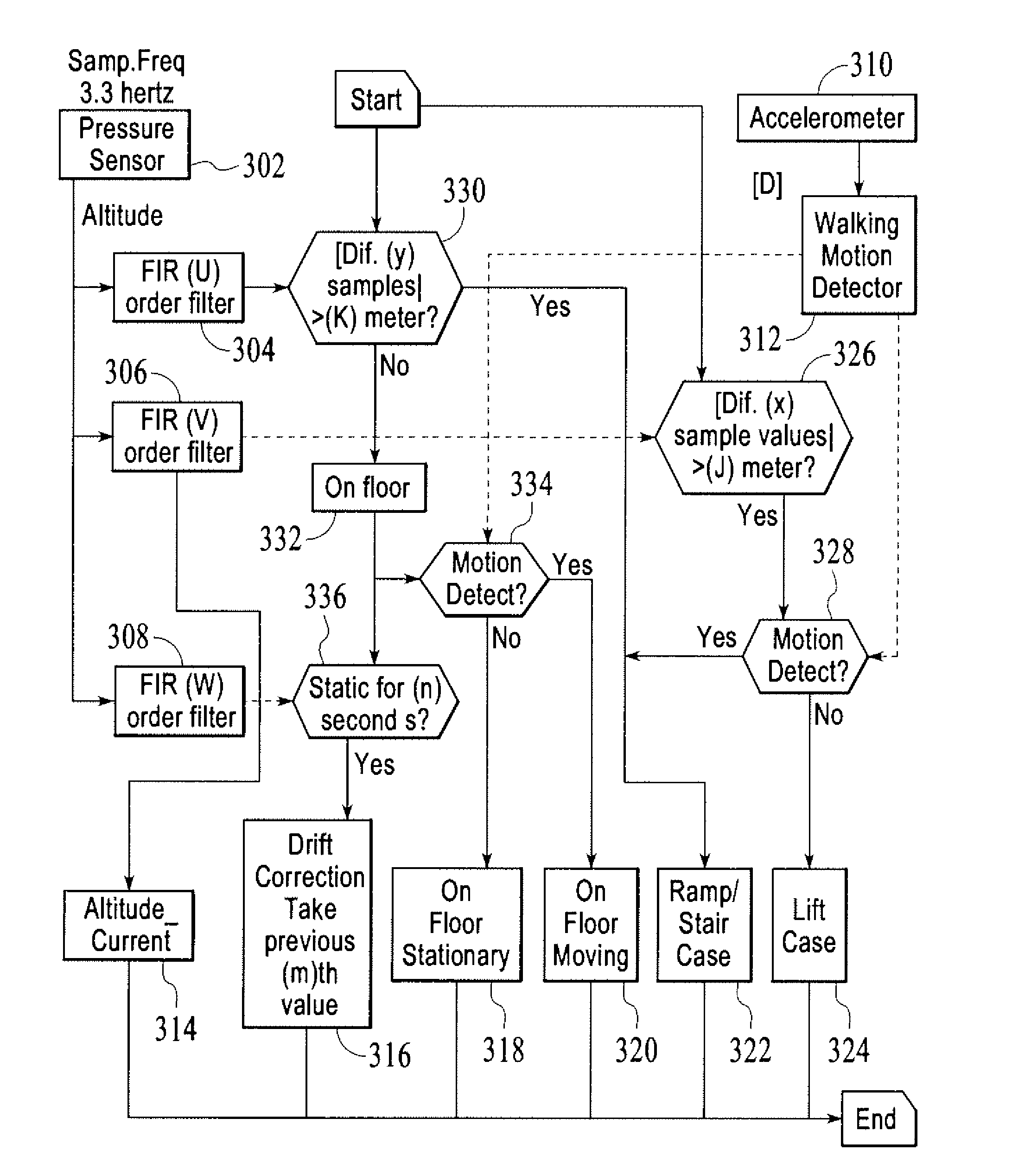
Methods and applications for altitude measurement and fusion of user context detection with elevation motion for personal navigation systems
InactiveUS20110106449A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficOpen skiesCanyon
Methods and apparatuses for estimating a user's altitude with respect to the mean sea level are provided. According to some aspects, the present invention is able to estimate altitude in both open sky as well as in degraded GPS signal environments such as dense urban canyon environments where GPS performance is affected by fewer available satellites and / or multipath error. According to other aspects, the present invention uses data from a pressure sensor to estimate altitude, either with or without the use of GPS aiding data. According to further aspects, estimated altitude is integrated with other types of dead reckoning data to provide user context detection pertaining to changes of altitude.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Athletic ball telemetry apparatus and method of use thereof
An athletic ball includes a receiver, a processor, a transmitter, a power source and / or a multiplexing signal relay. The athletic ball receives GPS signal date from earth-orbiting satellites in order to determine the location of the ball. An output device is utilized to display the ball location and / or provide analytical data pertaining to movement of the athletic ball.
Owner:STARK DAVID A
Method providing positioning and navigation inside large buildings
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
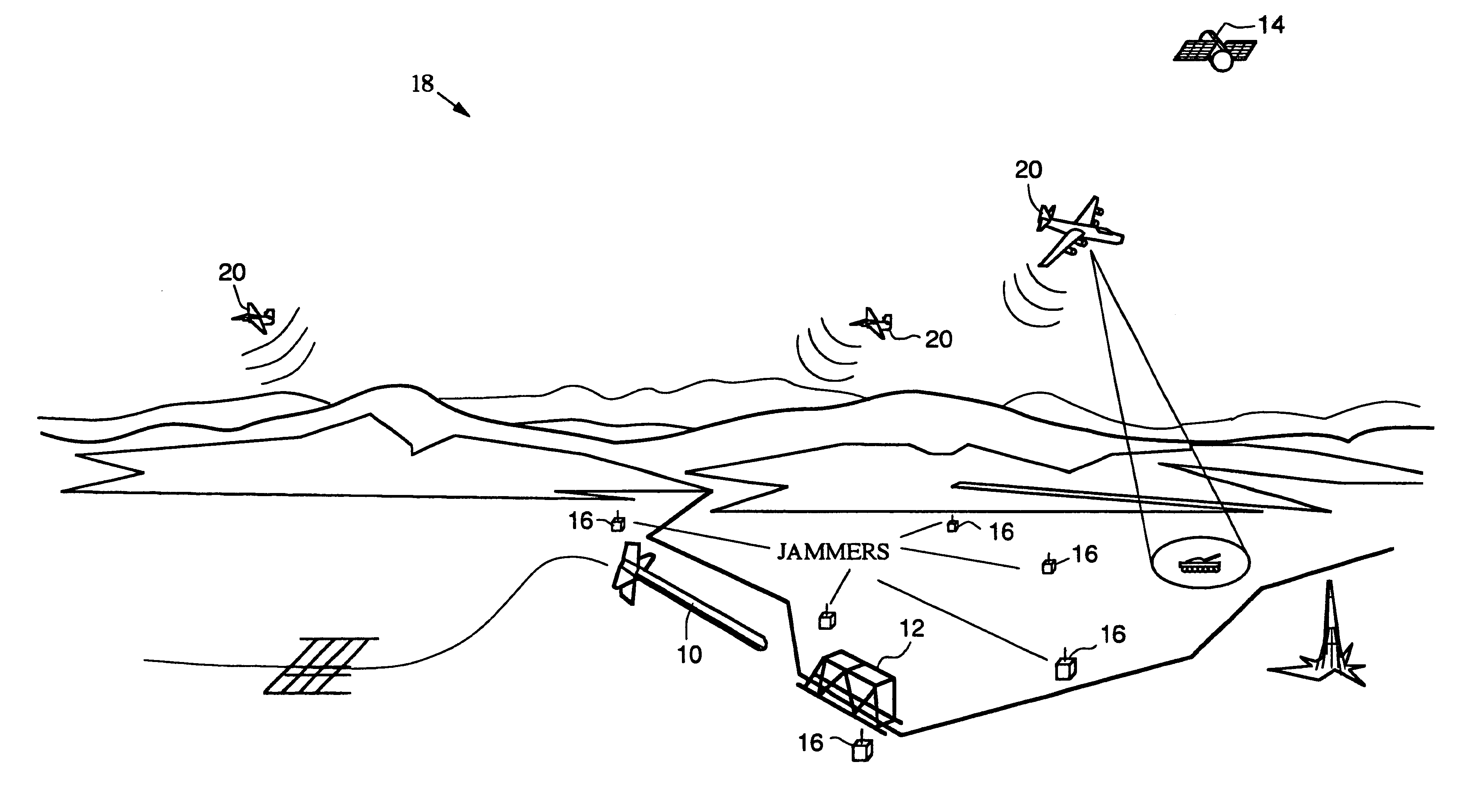
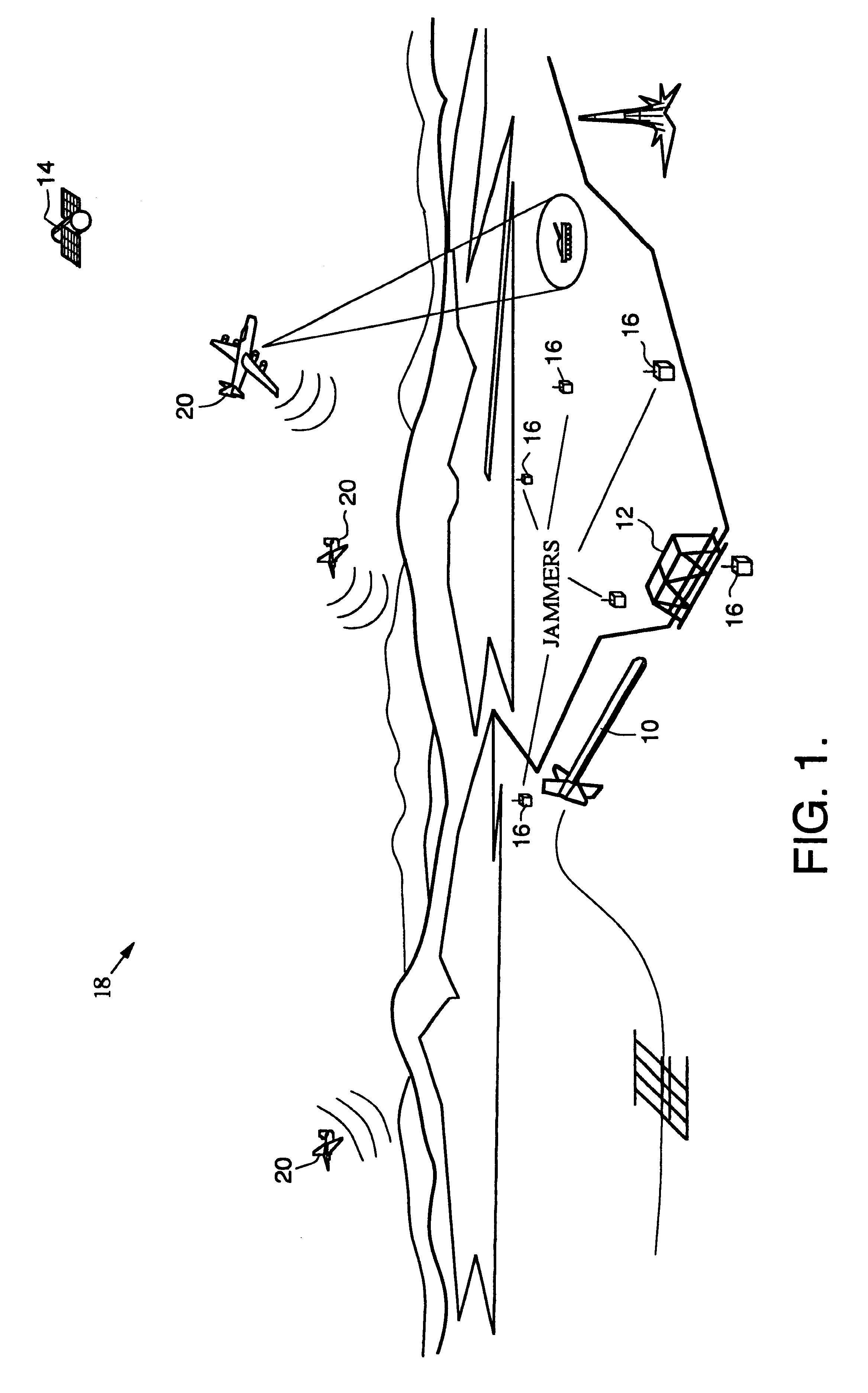
Airborne GPS guidance system for defeating multiple jammers
InactiveUS6300898B1Eliminate the effects ofDirection controllersBeacon systemsGuidance systemAnti jamming
A missile guidance system designed to operate on GPS signals in an anti-jamming environment. The inventive system includes first, second and third airborne vehicles (20). A GPS receiver (24) is mounted on each of the three vehicles (20) to receive signals transmitted from spaceborne satellites (14). Each vehicle (20) acts as a pseudo-satellite or "pseudolite'. The received GPS signals are processed by a processor (26) to provide a first intermediate signal indicating the position of the vehicle (20). This signal is retransmitted from each vehicle and received by a GPS receiver mounted on a missile. The received intermediate signal is processed on the missile to provide an output signal indicating the position thereof. The pseudolites would be airborne in the vicinity of a target area. Because the pseudolites are relatively close to the targets compared to a satellite in high altitude orbit and because the pseudolites would be able to transmit a kilowatt or more power, the signal strength may be improved significantly. To succeed as a jammer, a jammer, successful against GPS satellites, would need considerably more power to succeed against aircraft carried pseudolites. The pseudolite system delivers GPS signals into the target area 40-70 dB stronger than signals coming directly from GPS satellites. By timing the signals for 100% time coverage, enemy C / A code receivers will be jammed because they are limited to a J / S capability of 30 dB.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ARTHUR J +1
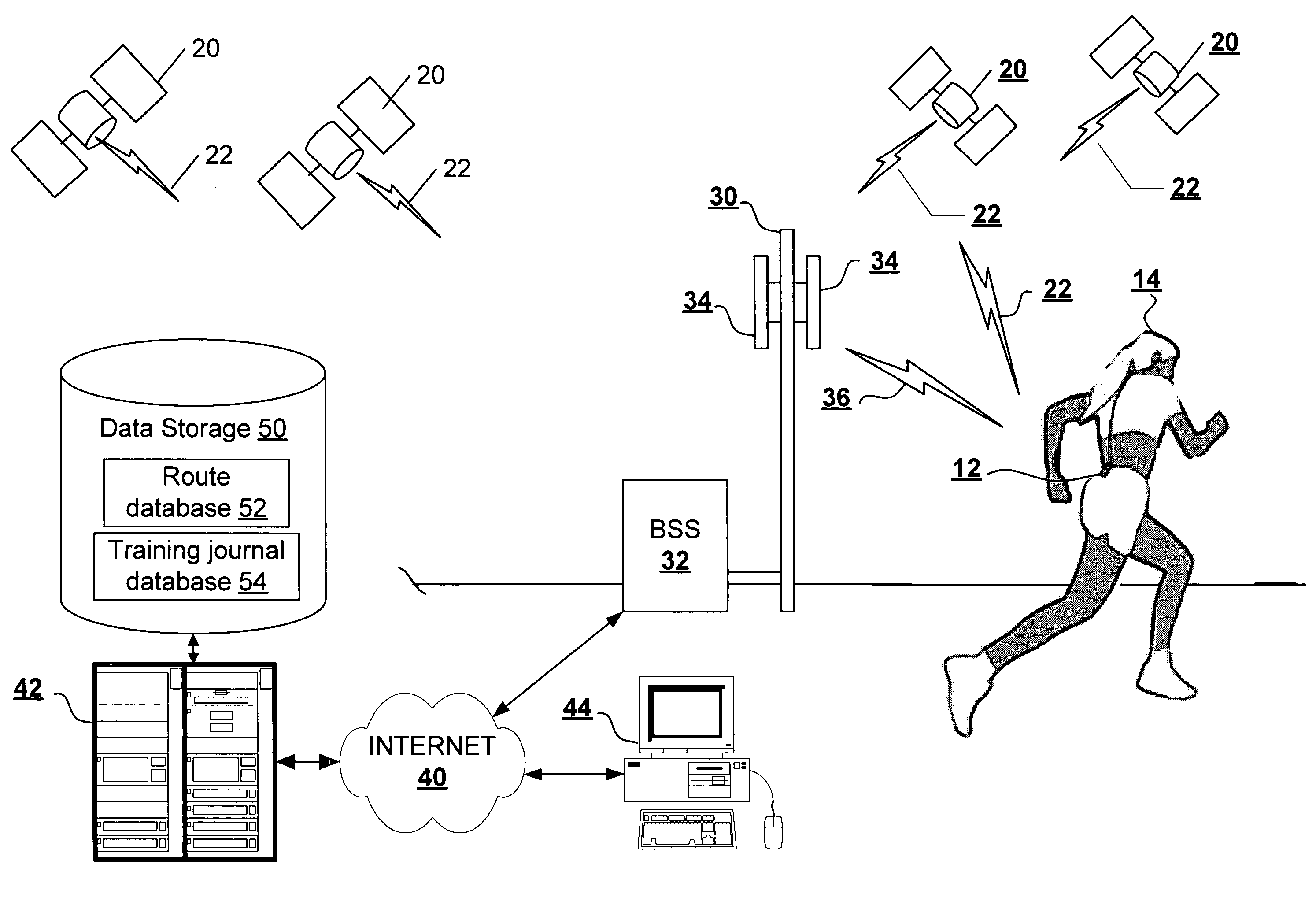
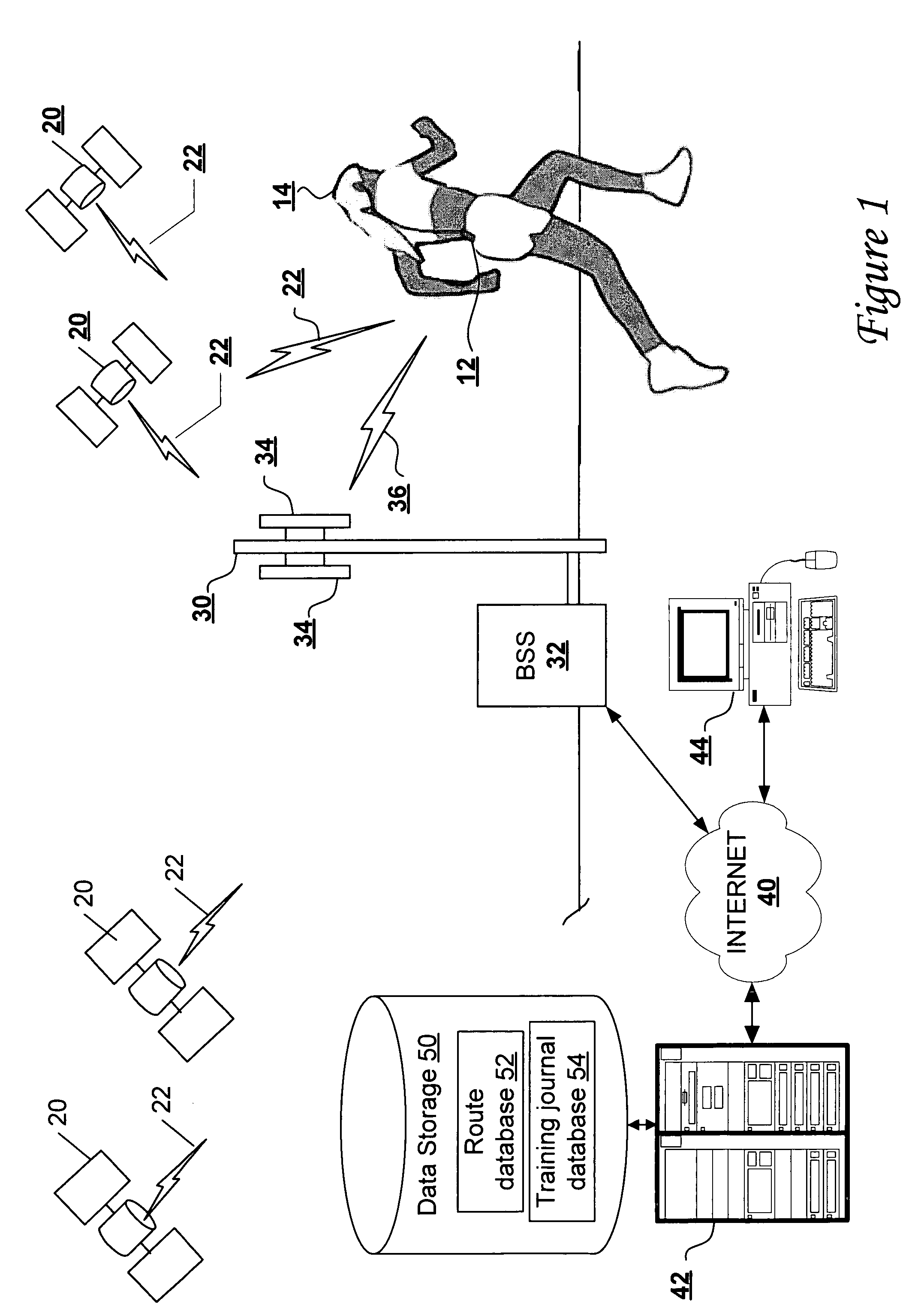
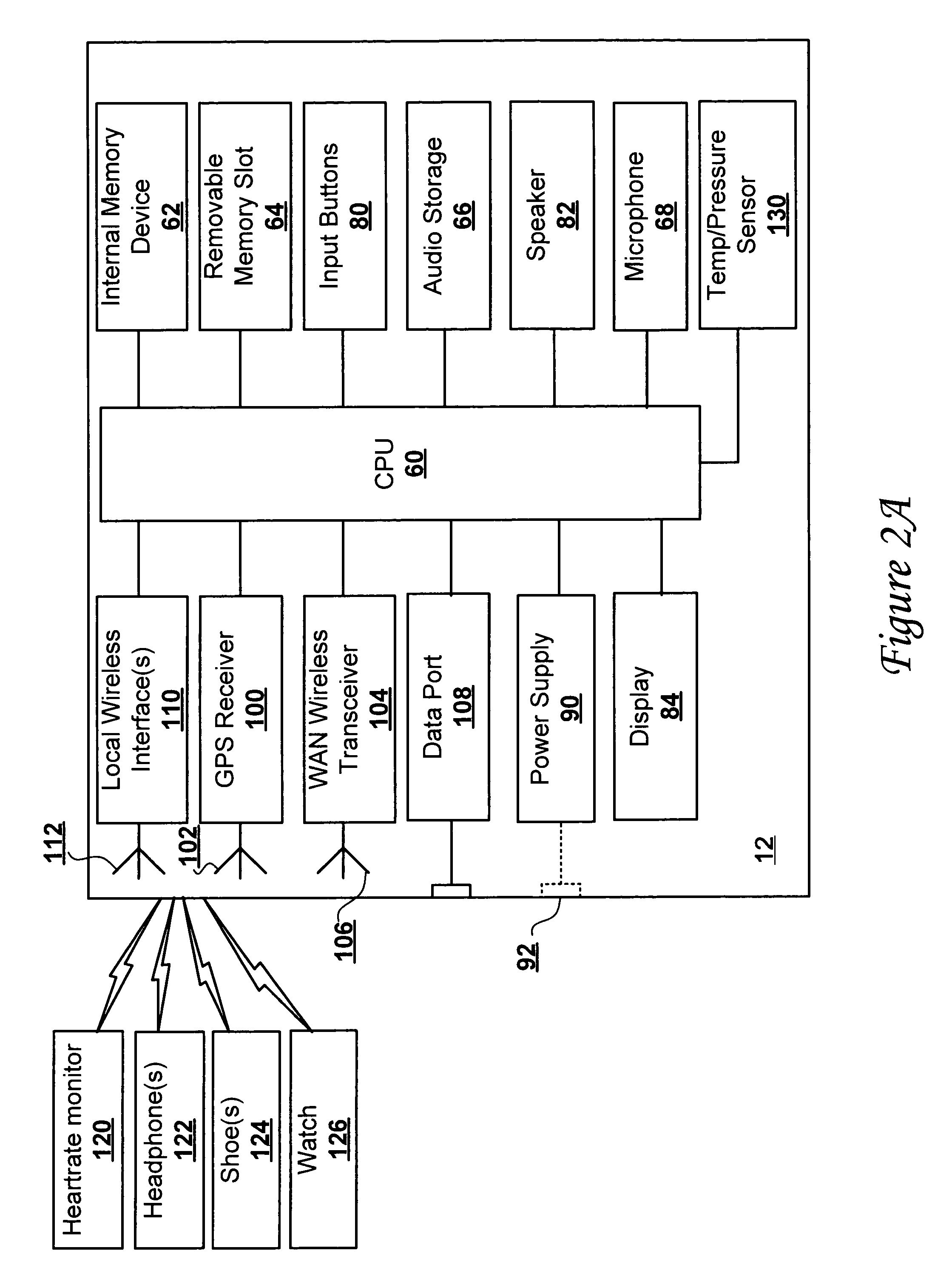
Location-aware fitness training device, methods, and program products that support real-time interactive communication and automated route generation
ActiveUS20040209600A1Resonant long antennasAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAutomatic routingGps receiver
A portable fitness device includes a global positioning system (GPS) receiver that receives GPS signals, a wireless wide-area network transmitter supporting communication over-the-air to a wireless communication network, and a processing unit coupled to the GPS receiver and the wireless wide-area network transmitter. The processing unit receives the time-stamped waypoints from the GPS receiver and determines athletic performance information and route information from the time-stamped waypoints. The processing unit further outputs at least one of the athletic performance information and the route information to the wireless communication network during a human fitness activity via the wireless wide-area network transmitter.
Owner:ADIDAS
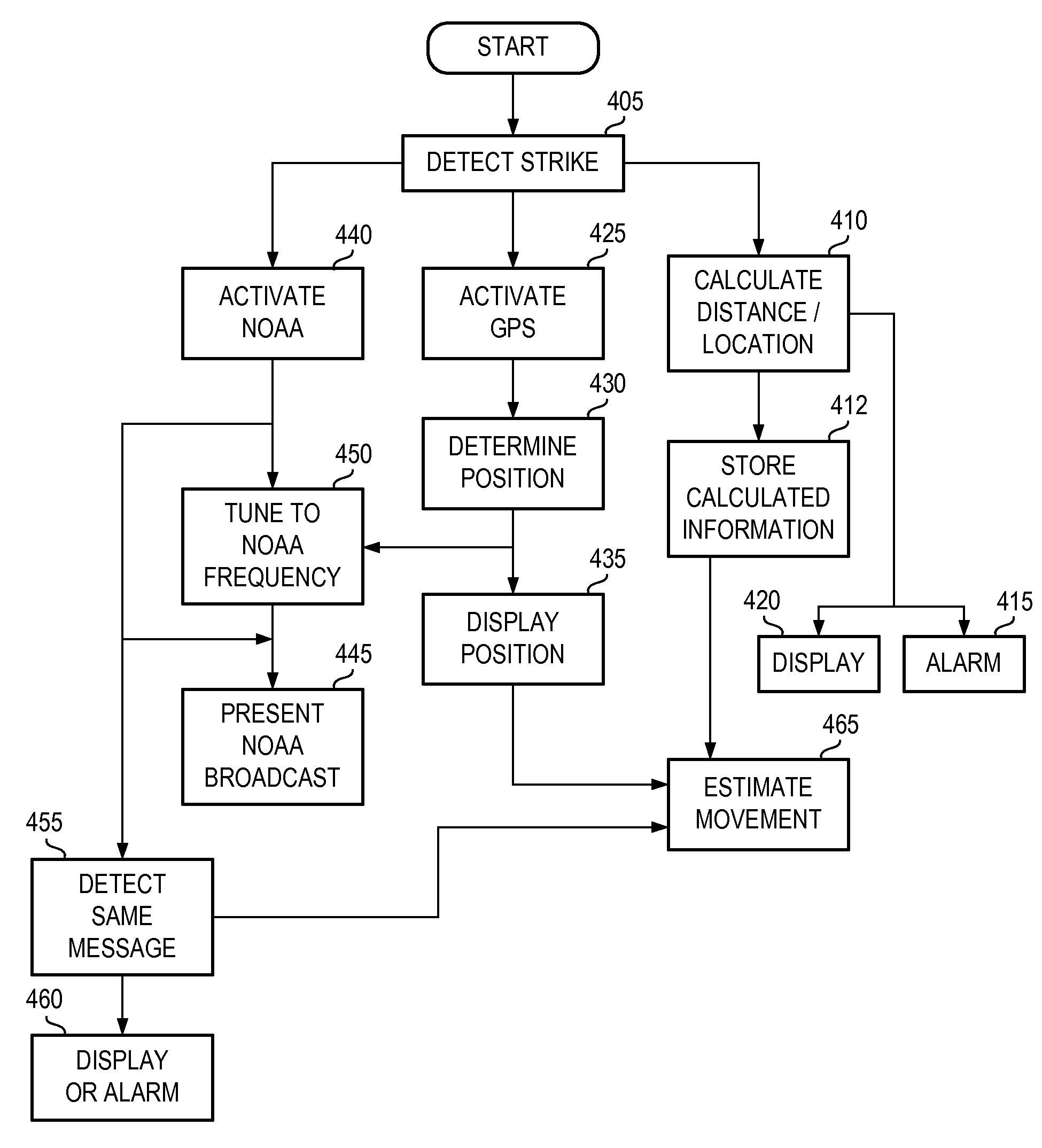
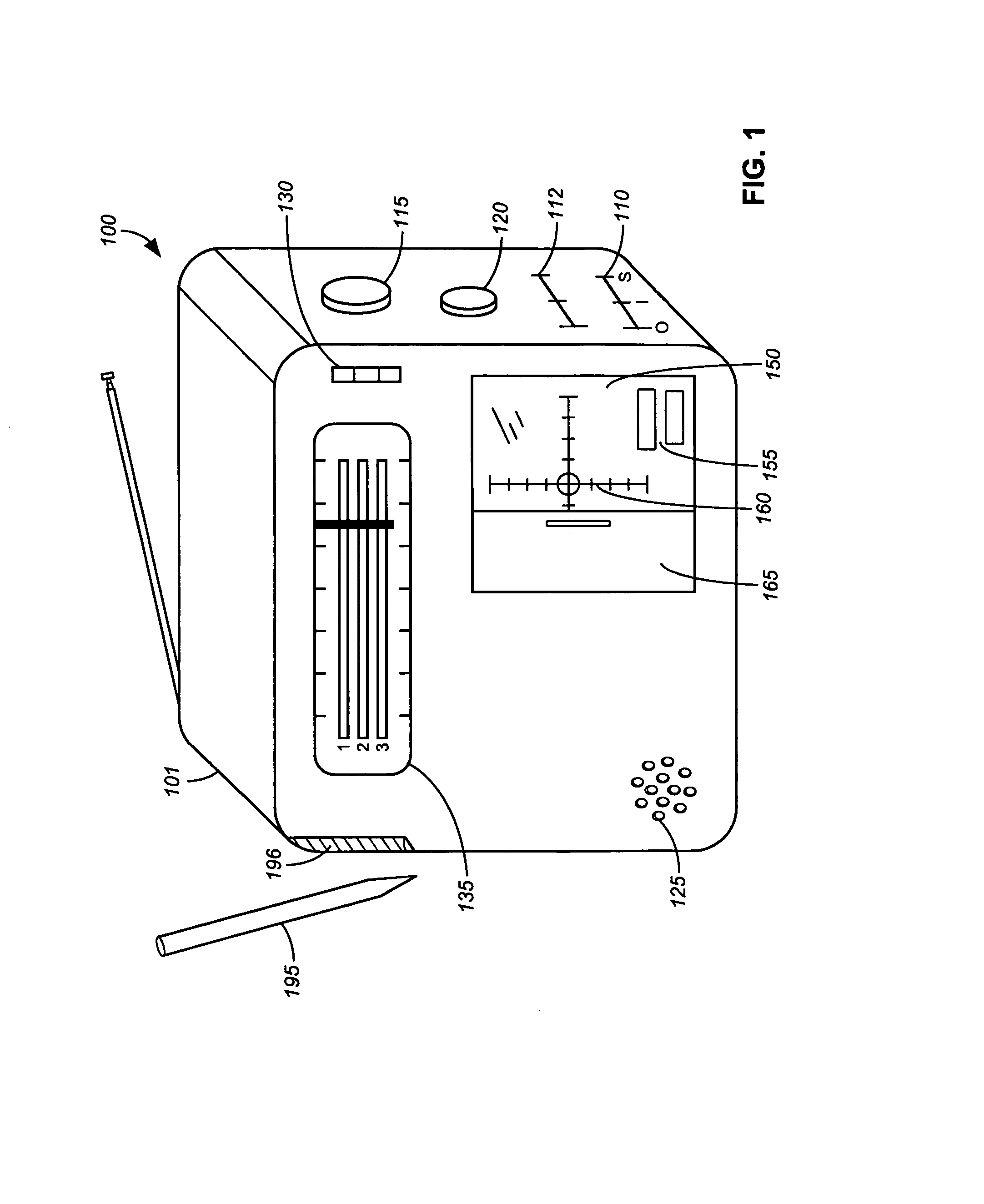
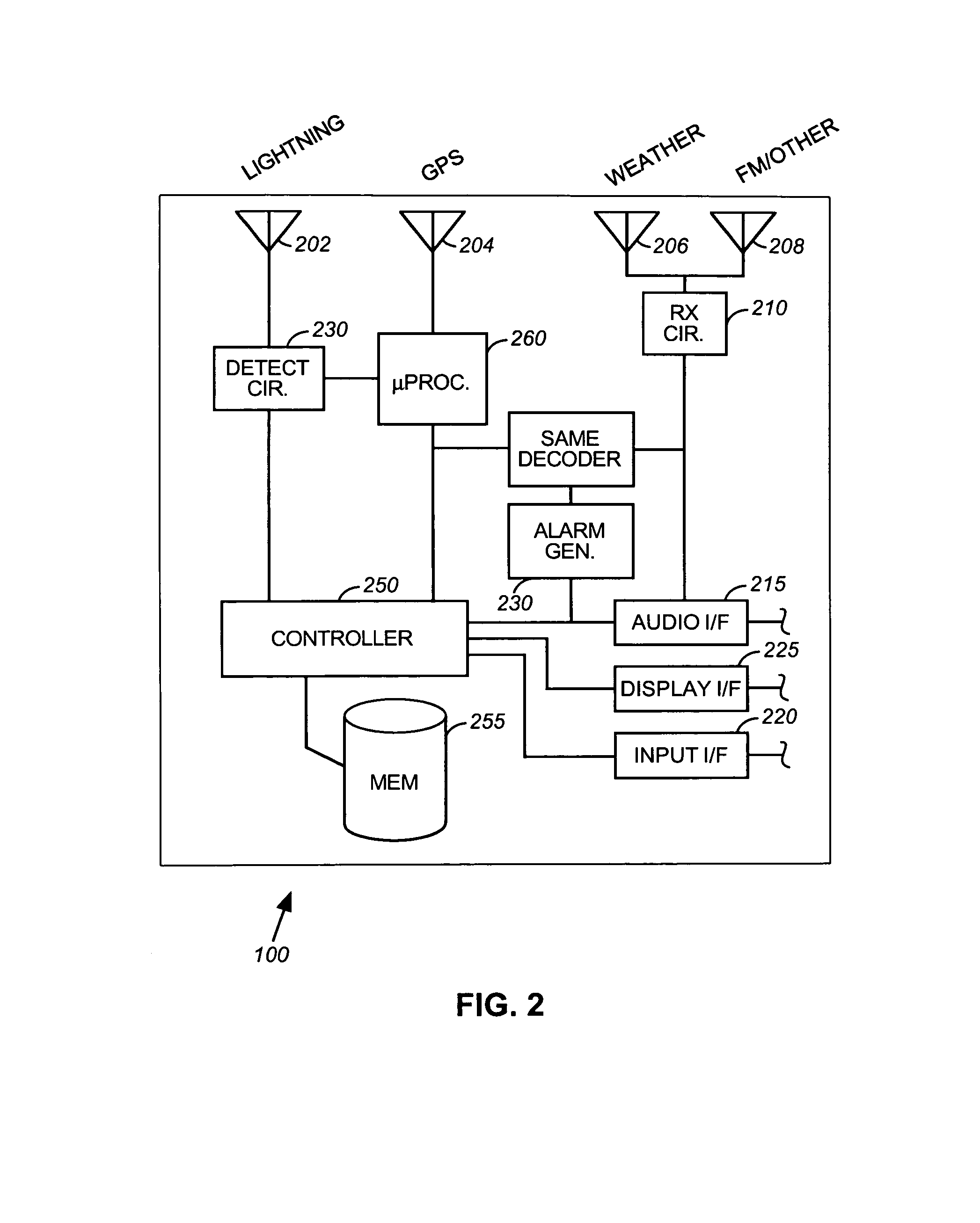
Weather station
ActiveUS7171308B2Special data processing applicationsAtmospheric potential difference measurementLightning strikeThunderstorm
A weather station for providing weather information to a user, especially weather information related to lightning and severe thunderstorm activity. In accordance with the present invention, the weather station includes one or more antennas for receiving GPS transmissions, weather radio transmissions, and a separate radio band, such as the AM radio band for use in detecting lightning strikes. The GPS signal is used to determine the position of the user. A lightning detector coupled to the antenna for receiving the AM (or other band) signal calculates the proximity of any detected lightning strikes. The national weather radio band antenna receives information from NOAA and similar organizations and presents it to the user in the normal fashion. In accordance with the present invention, the weather station may take storm data from NOAA and compare it to lightning proximity data that it has already obtained at a particular location and present to the user an indication of the relative location of the severe thunderstorm activity and its direction of movement.
Owner:RADIOSHACK ONLINE IPCO LLC +1
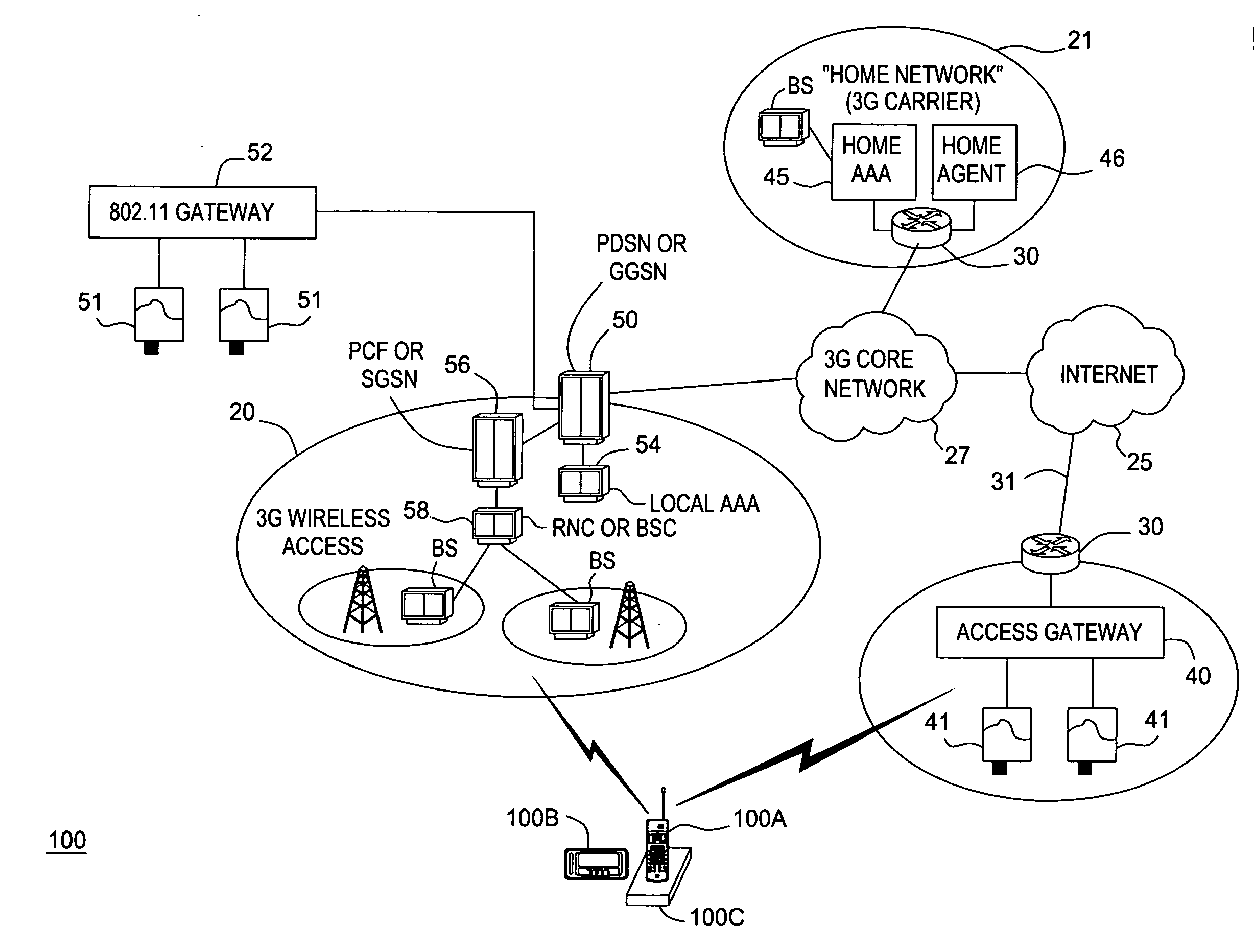
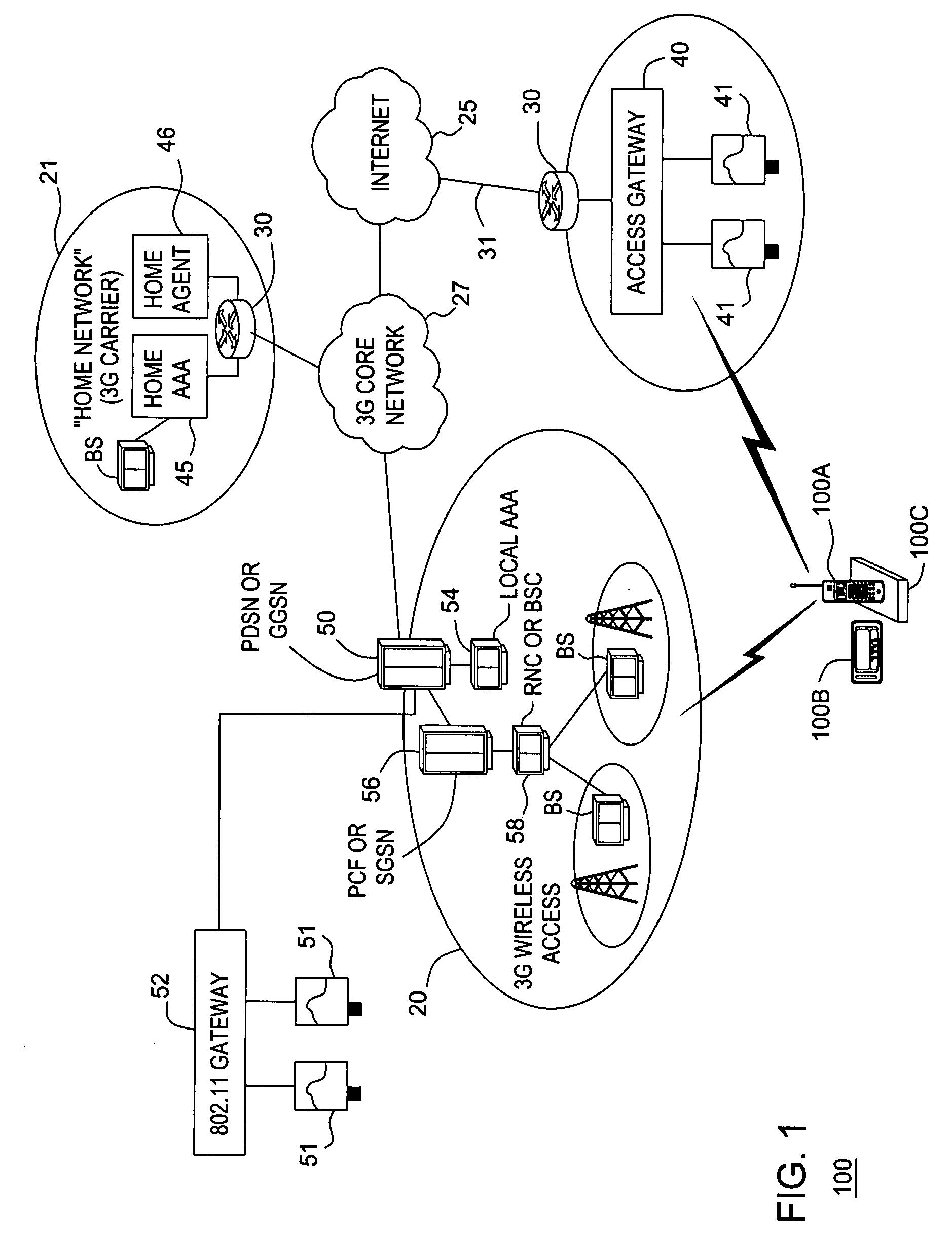
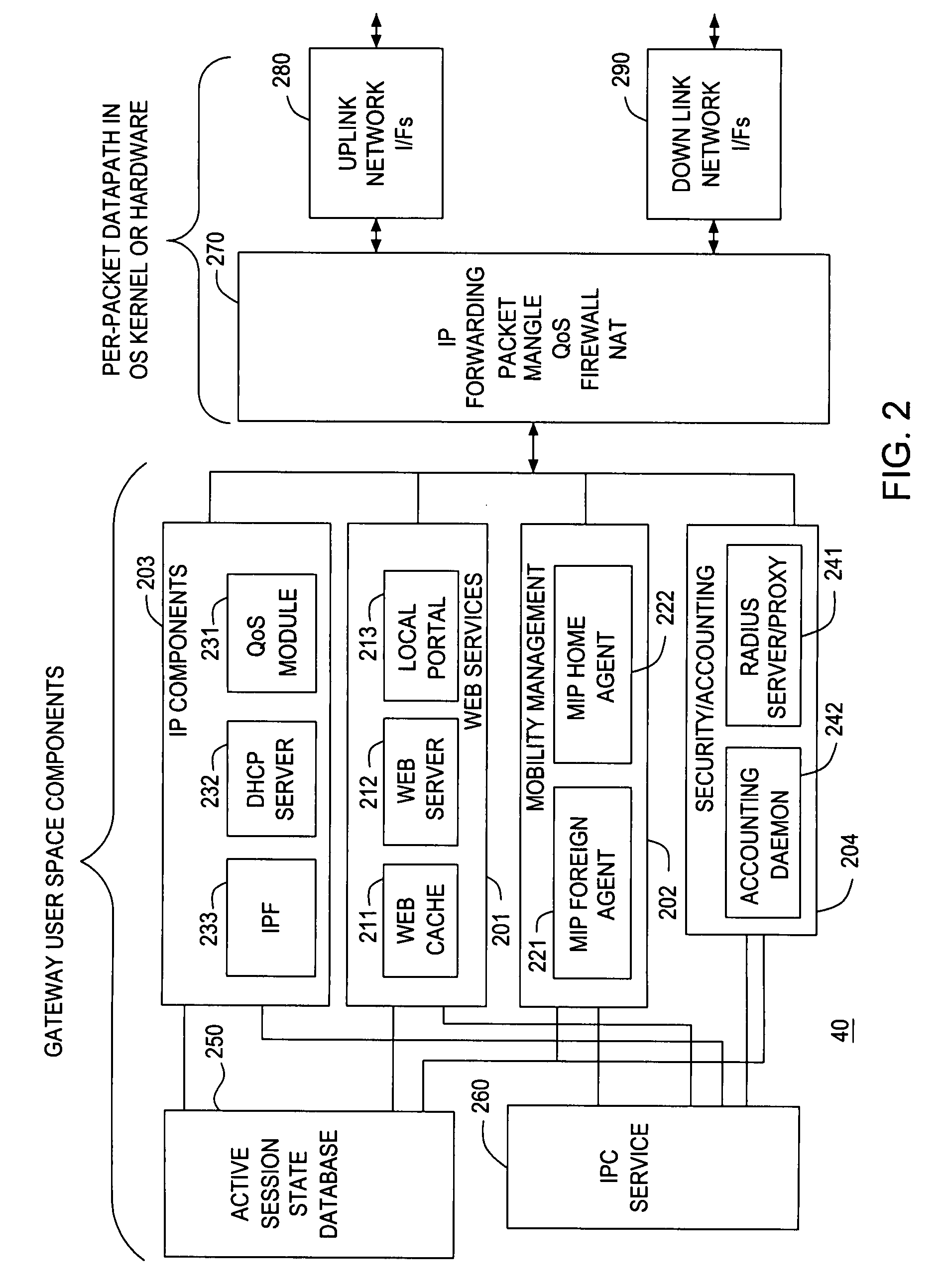
Mobility access gateway
InactiveUS20070208864A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsCable Internet accessForeign agent
A gateway for mobile access includes a foreign agent that receives user profile data and session state data from a home authentication, authorization and accounting (AAA) system of a mobile node, and a dynamic packet filter that performs multi-layer filtering based on the user profile data. The foreign agent transfers a session from a first network to a second network without session interruption, using the session state data, when the mobile node moves from the first network to the second network. The packet filter permits Internet access by the mobile node without passing Internet data requested by the mobile node through the first network. The mobility access gateway may be used in combination with a GPS signal receiver to provide Internet access to passengers of a mass transit vehicle and to propagate GPS location data to the Internet for tracking the mass transit vehicle.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
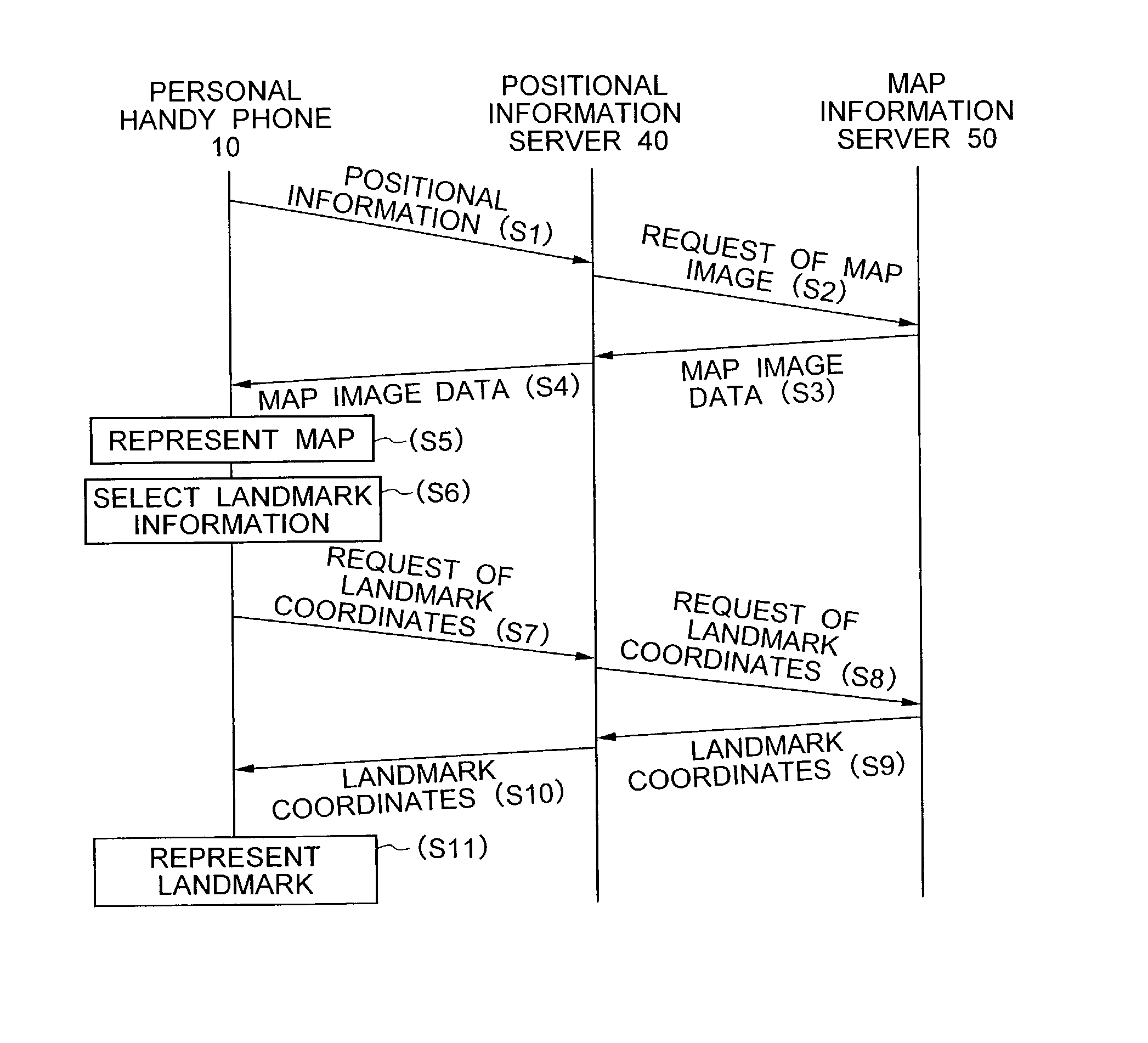
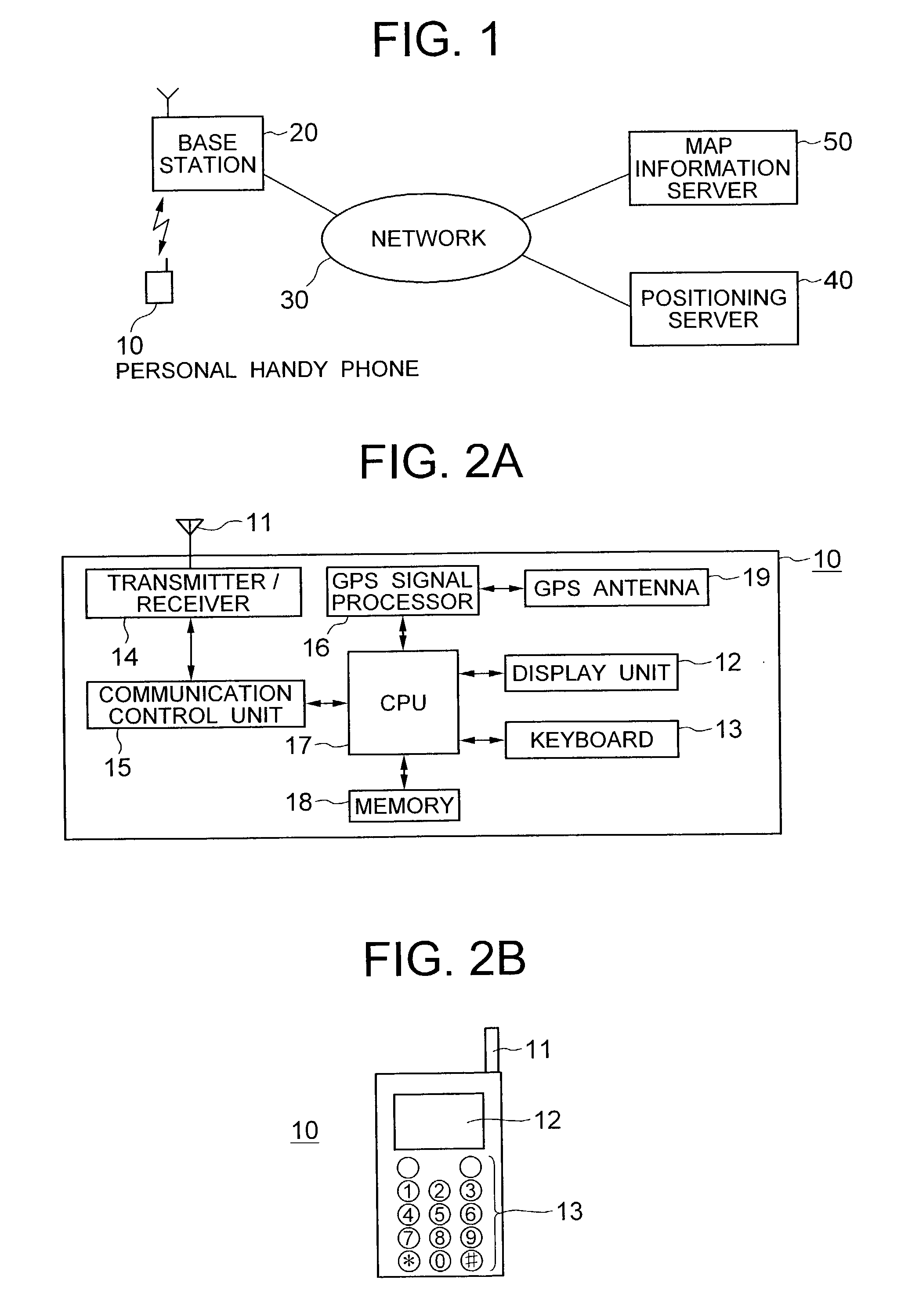
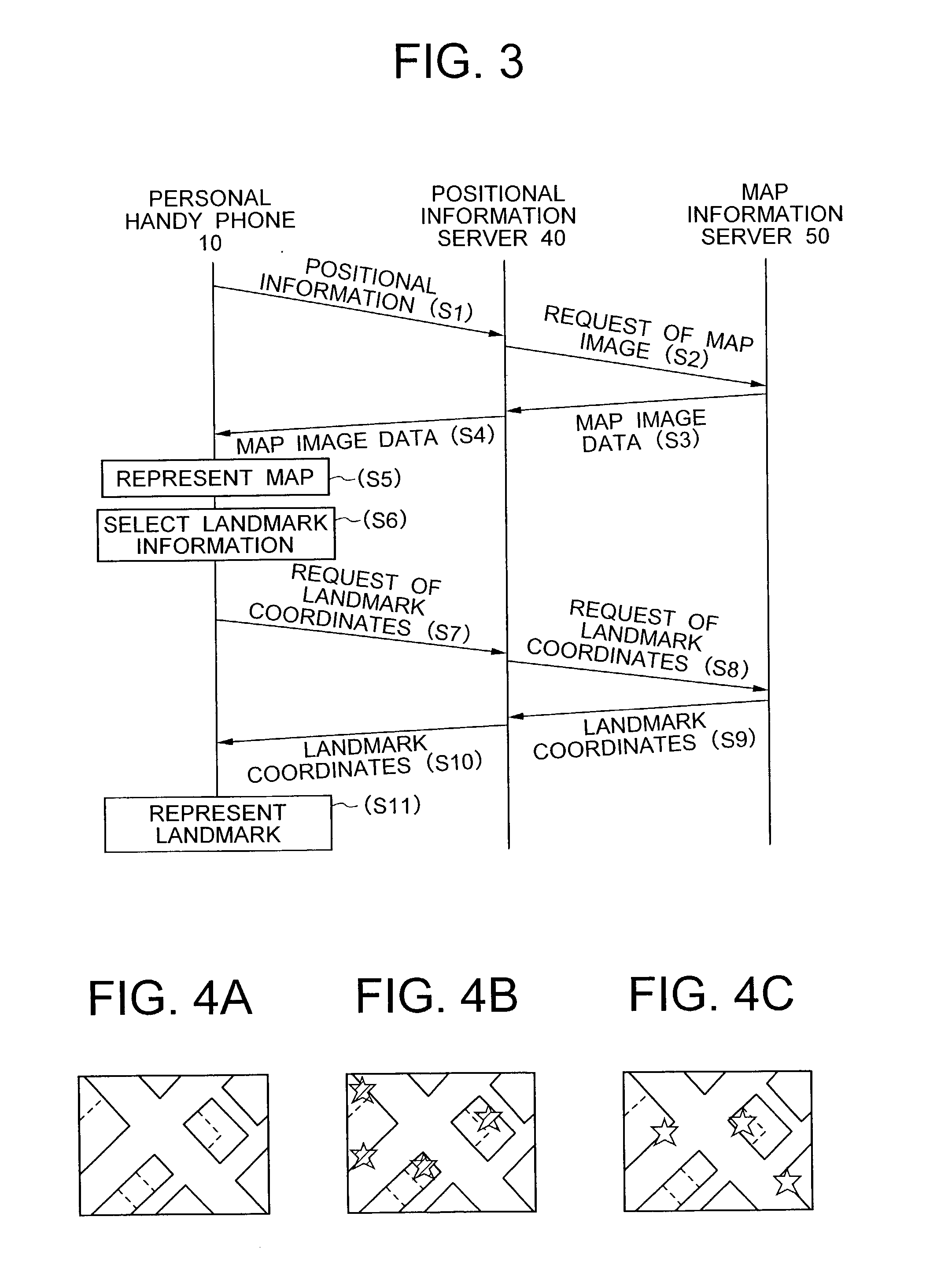
Map information display system
InactiveUS20030100316A1Low costNetwork can be lowMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpecial service for subscribersInformation display systemsComputer terminal
A portable radio terminal includes a GPS signal processor for determining the position of the portable radio terminal, and requests a system server to transmit map image data and landmark data in the vicinity of the portable radio terminal. The system server transmits the map image data and landmark data separately to allow the display unit of the portable radio terminal to represent desired landmarks overlapped with the map image on the display unit.
Owner:NEC CORP
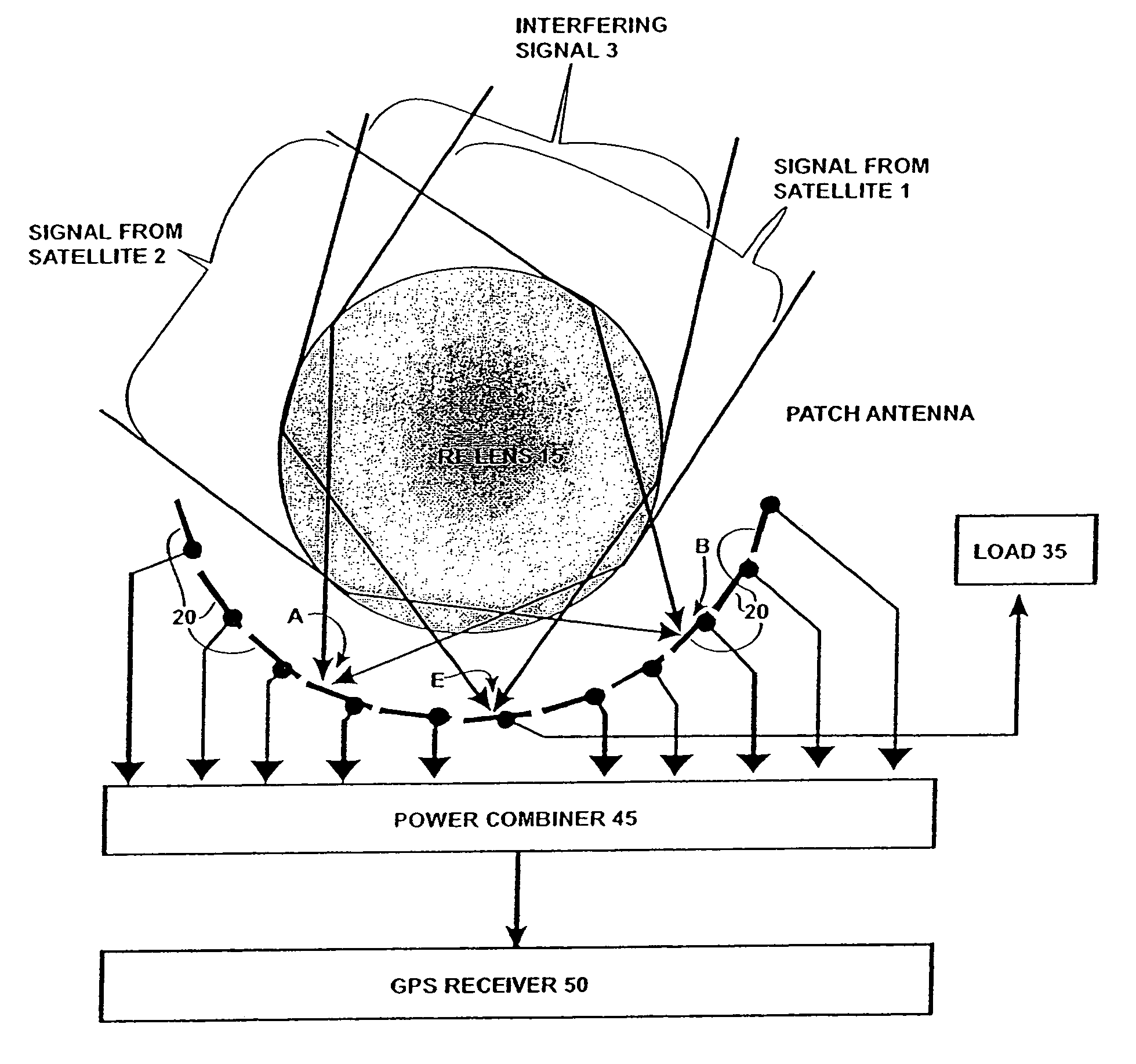
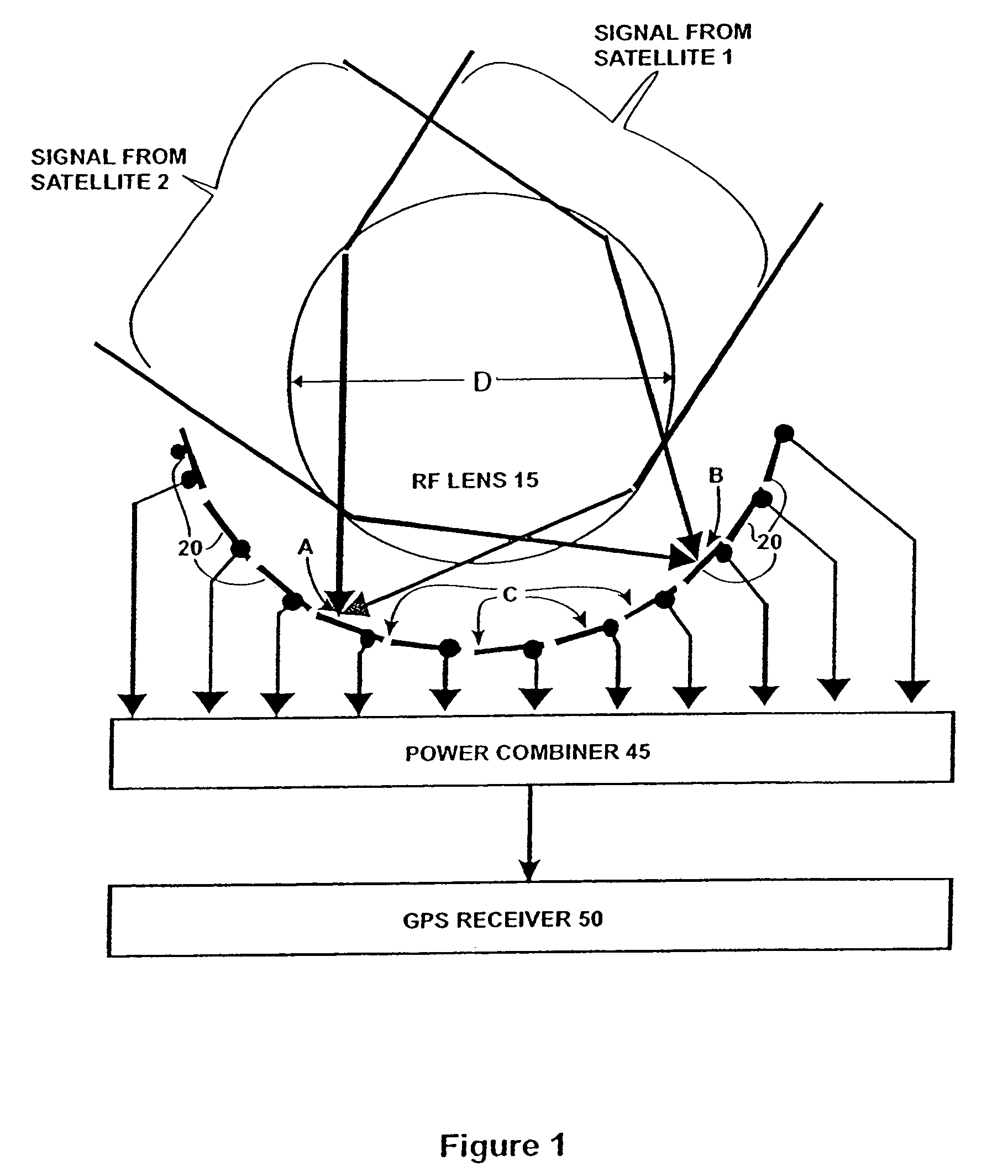
Antenna system and RF signal interference abatement method
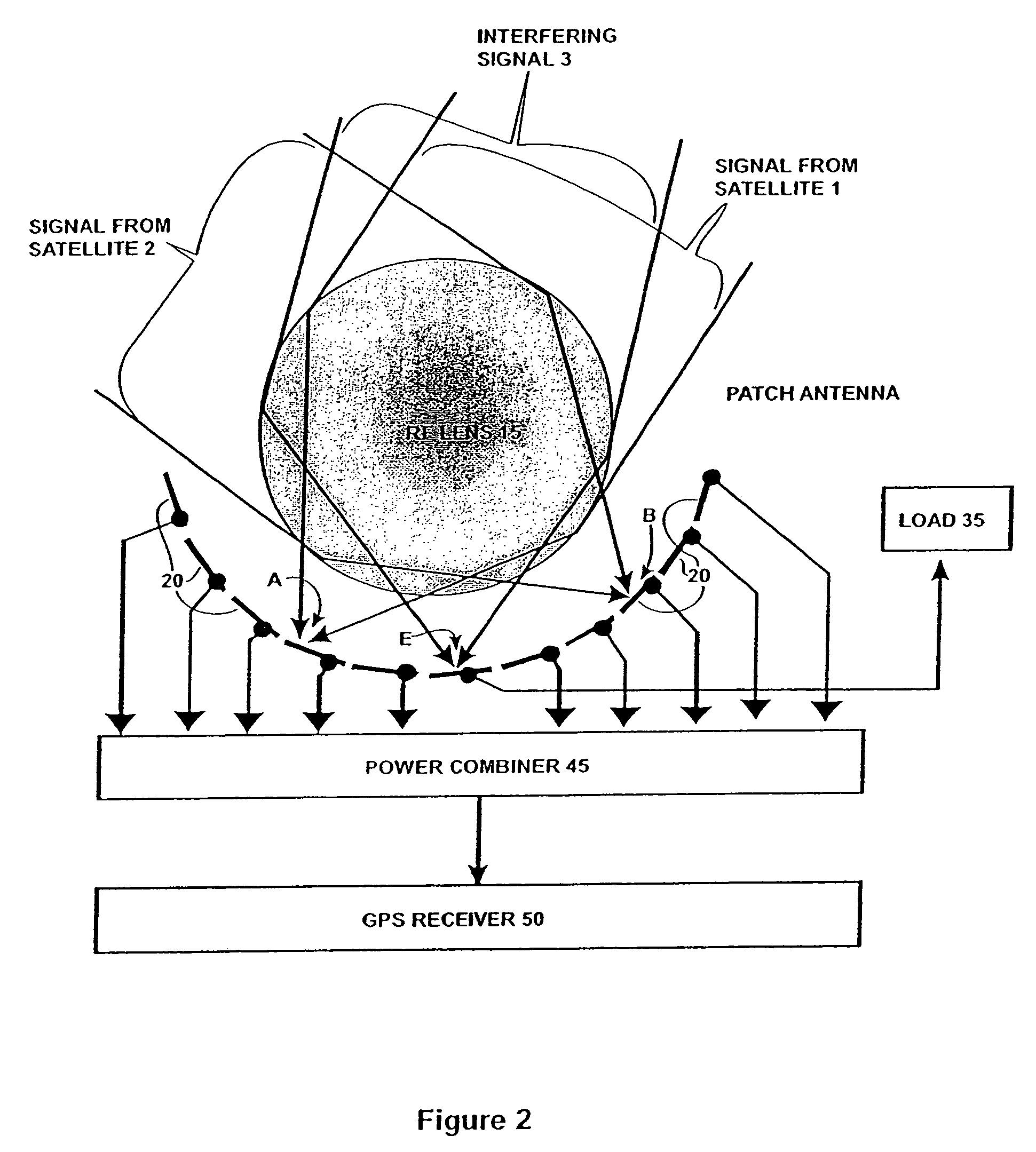
InactiveUS7151508B2Reduce distractionsSimultaneous aerial operationsPosition fixationPower combinerGps receiver
Disclosed is an antenna system including a Luneberg Lens having a spherically shaped outer surface and a spherically shaped focal surface spaced from its outer surface with a plurality of patch antenna elements disposed along the focal surface of the Luneberg Lens; and a power combiner for combining signals received by said plurality of patch antenna elements. The disclosed antenna system may be used a part of a robust GPS system having a plurality of GPS satellites each transmitting a GPS signal; a plurality of airborne GPS platforms, each GPS platform including a GPS transmitter for transmitting its own GPS signal, the GPS signals being transmitted from the plurality of airborne GPS platforms being differentiated from the GPS signals transmitted by visible GPS satellites; and at least one terrestrially located GPS receiver for receiving the GPS signals transmitted by visible ones of the GPS satellites and by visible ones of said airborne GPS platforms.
Owner:HRL LAB
Systems and Methods For Tracking the Transportation of Passengers
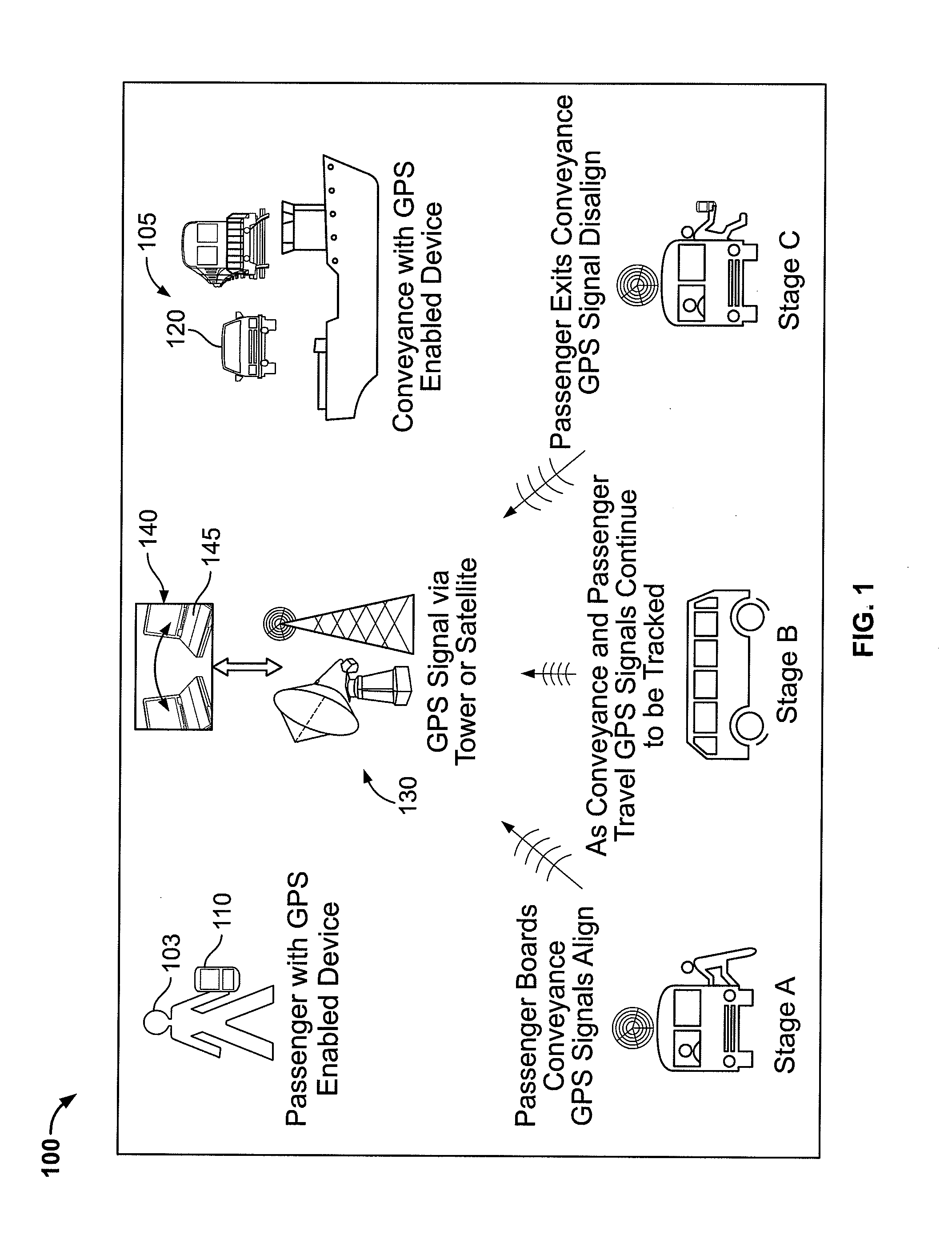
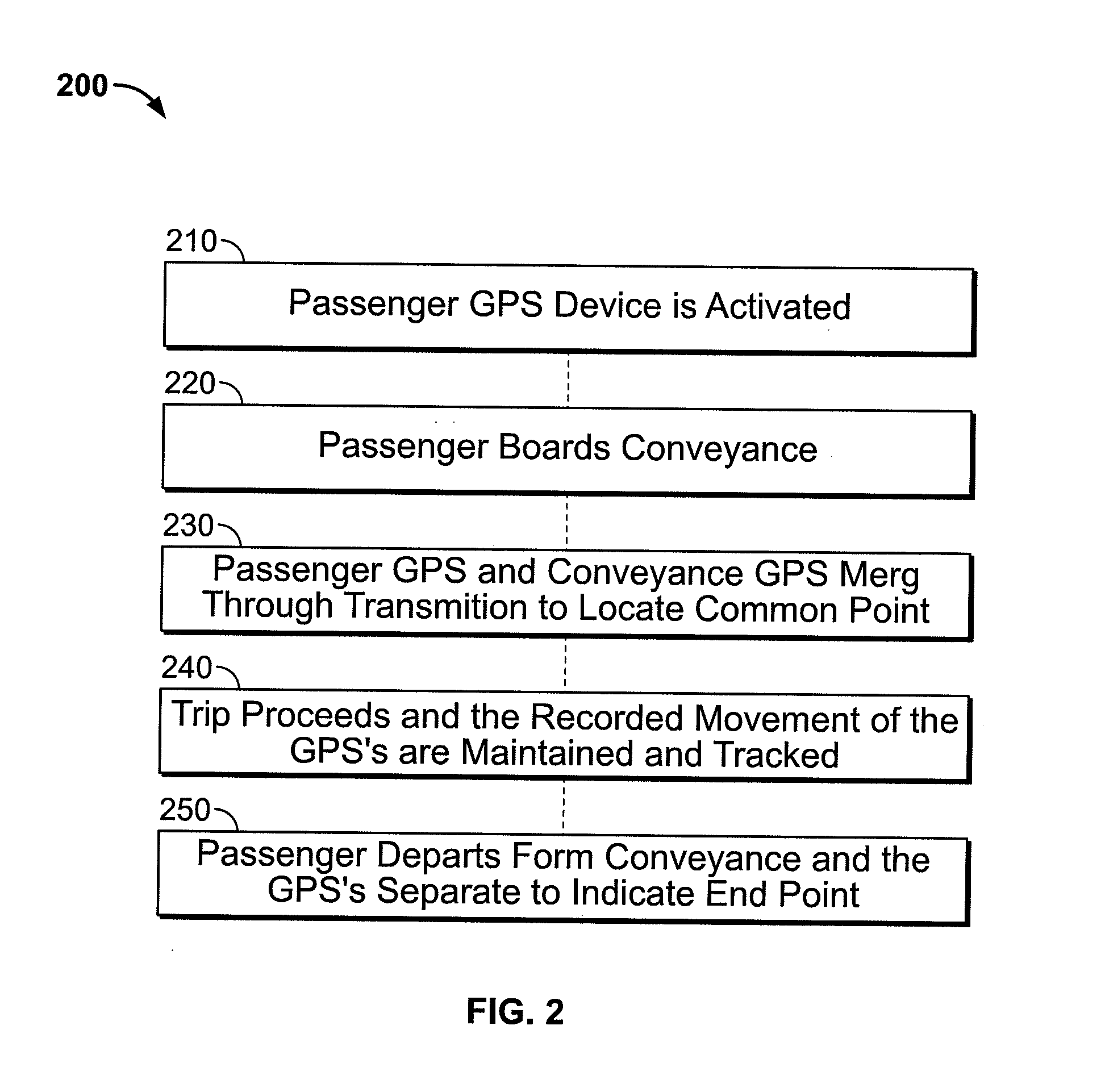
InactiveUS20110060600A1Facilitate ticketingTicket-issuing apparatusData processing applicationsTrip distanceComputer science
Advantageous systems and methods are provided for tracking the transportation of passengers. In general, the systems and methods utilize GPS signals associated with each of a passenger and a transportation vehicle to determine at least one of: (i) a start point for the passenger traveling via the transportation vehicle and (ii) an end point for the passenger traveling via the transportation vehicle. The determination of the start and / or end points for the passenger traveling via the transportation vehicle may advantageously facilitate ticketing, e.g., by automatically validating / calculating trip cost, trip duration, trip distance, etc.
Owner:TRANSITTIX
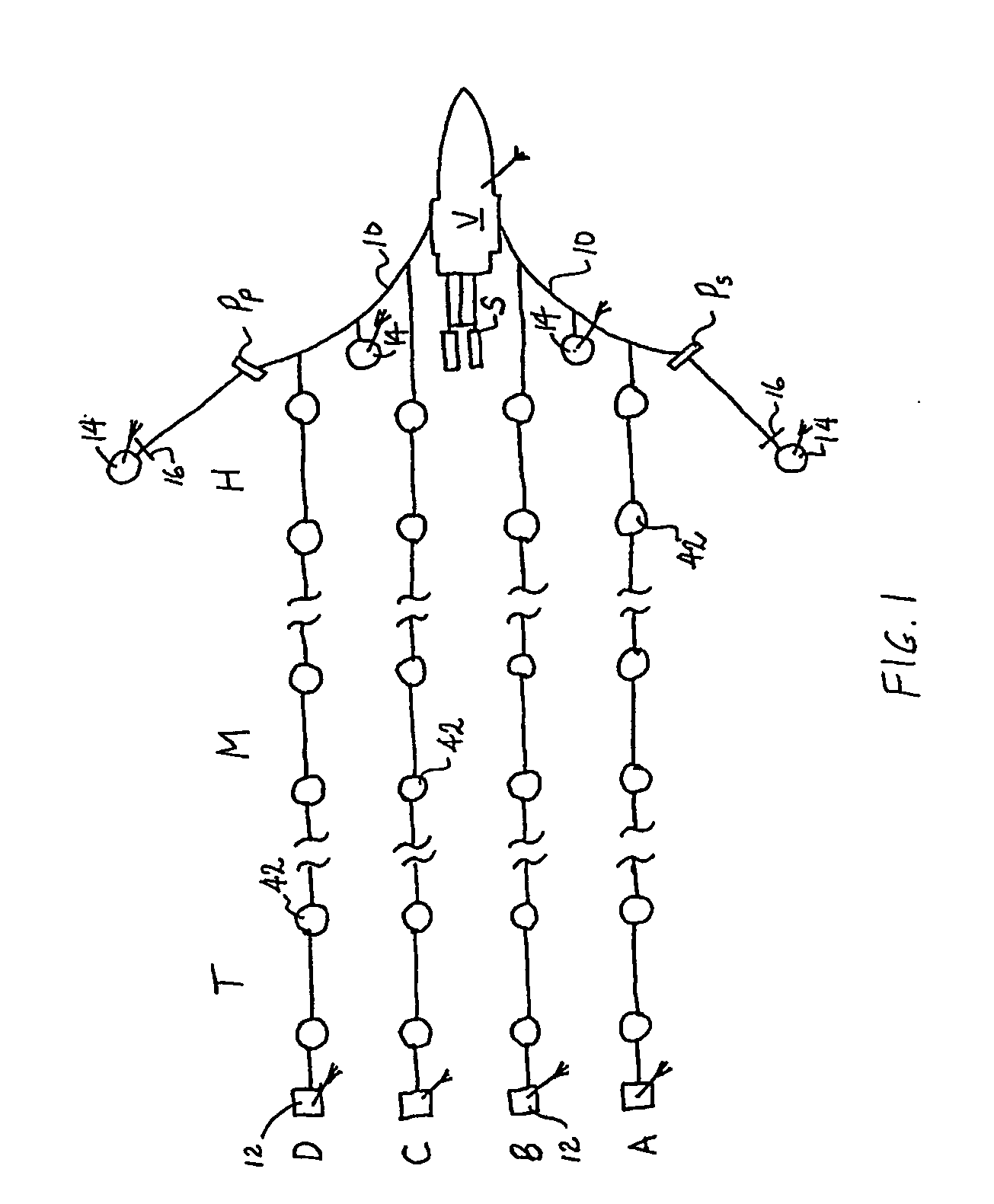
Gps-based underwater cable positioning system
ActiveUS20050180263A1Improve positioning geometryEnhanced signalBeacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesHydrophoneTransceiver
A GPS-based underwater cable positioning system for use in determining the shape and position of hydrophone streamers towed underwater behind survey vessels involved in marine seismic prospecting. The system includes a plurality of surface units towed behind the vessel. Each surface unit includes a GPS receiver to receive radio frequency GPS signals and to determine its positions. Each surface unit also has an acoustic transmitter to transmit an acoustic message signal representing its position and an optional time stamp into the water. Acoustic receiver units, attached spaced apart locations along one or more streamer cables, each include an acoustic receiver to receive the acoustic message signals from the surface units and to determine its position from the message signals. To augment the message signals from the surface units at locations distant from the surface units, acoustic transceiver units may be used. The acoustic transceiver units are attached to the streamer cables at ranges between the surface units and distant acoustic receiver units. The acoustic transceiver units each include an acoustic receiver that performs as the receivers in the acoustic receiver units and an acoustic transmitter to transmit acoustic message signals representing its position and an optional time stamp into the water to be received by the acoustic receiver units. In this way, the positions and shapes of towed streamer cables can be determined.
Owner:INPUT OUTPUT INC
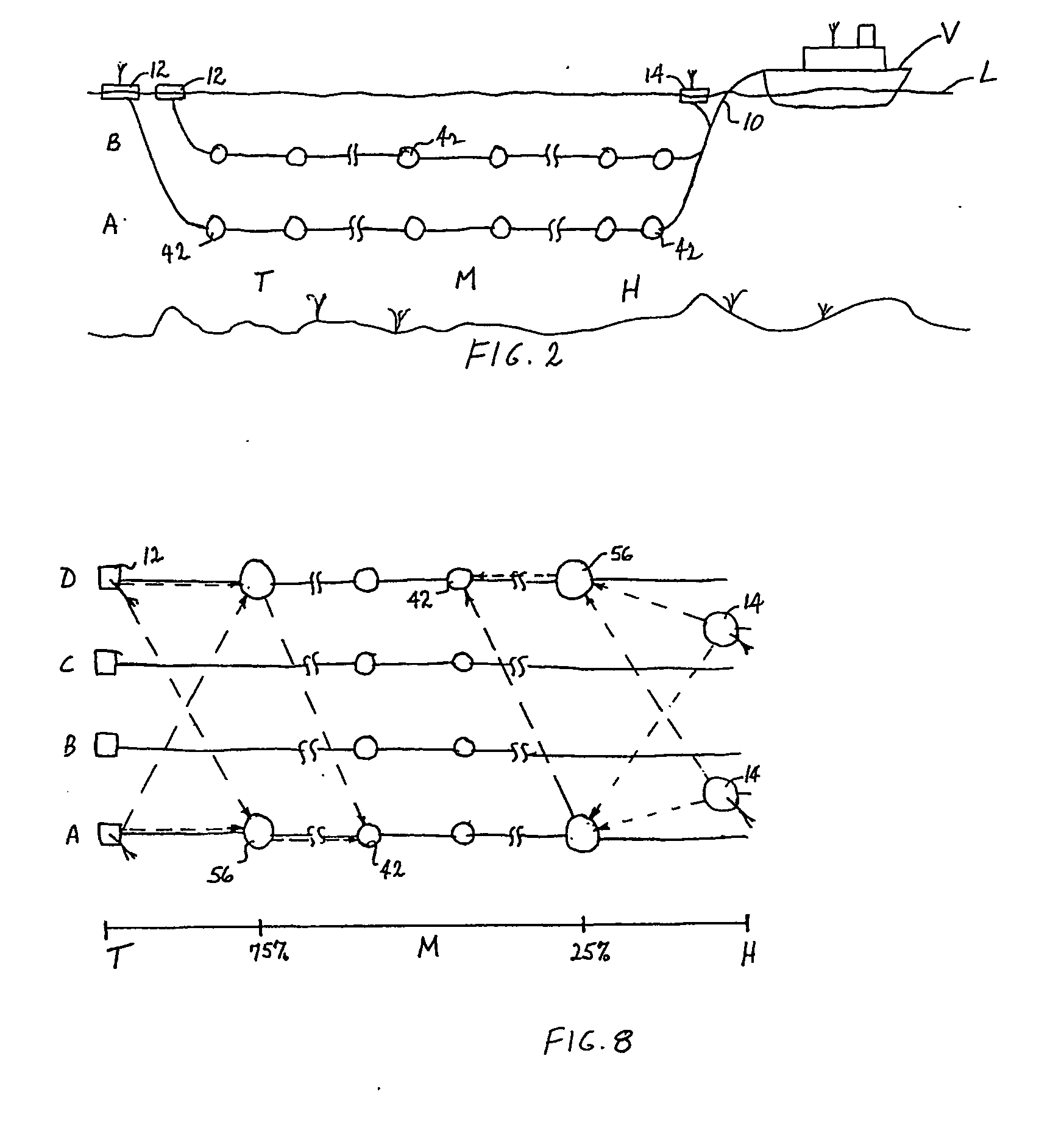
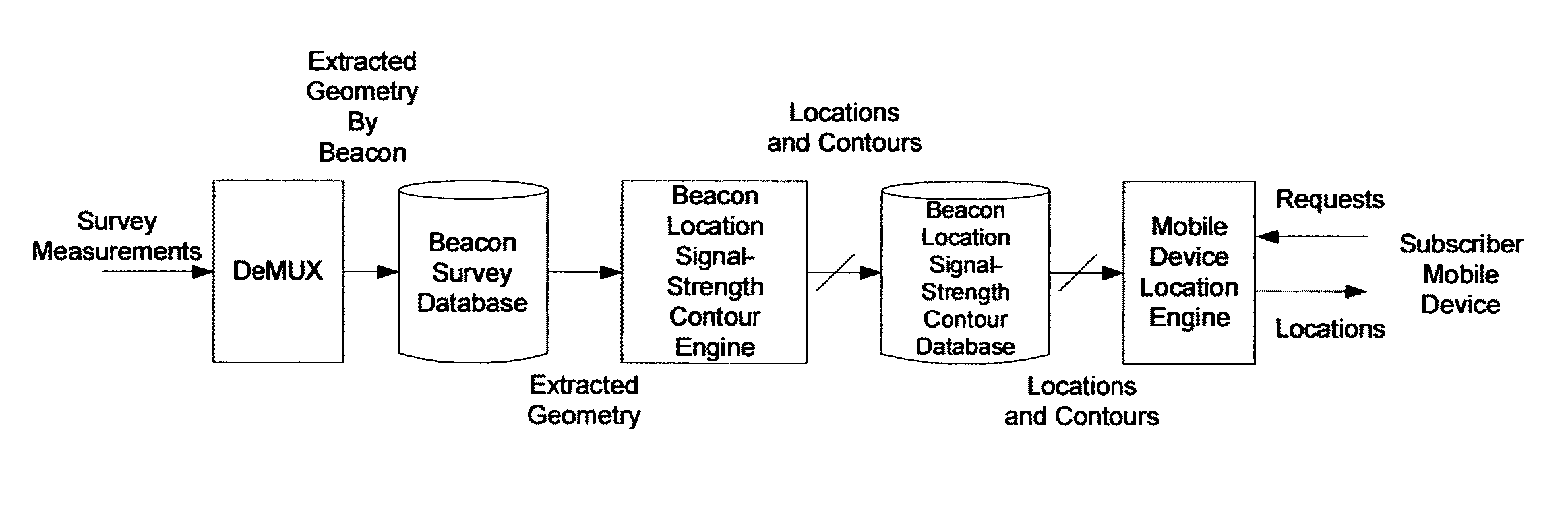
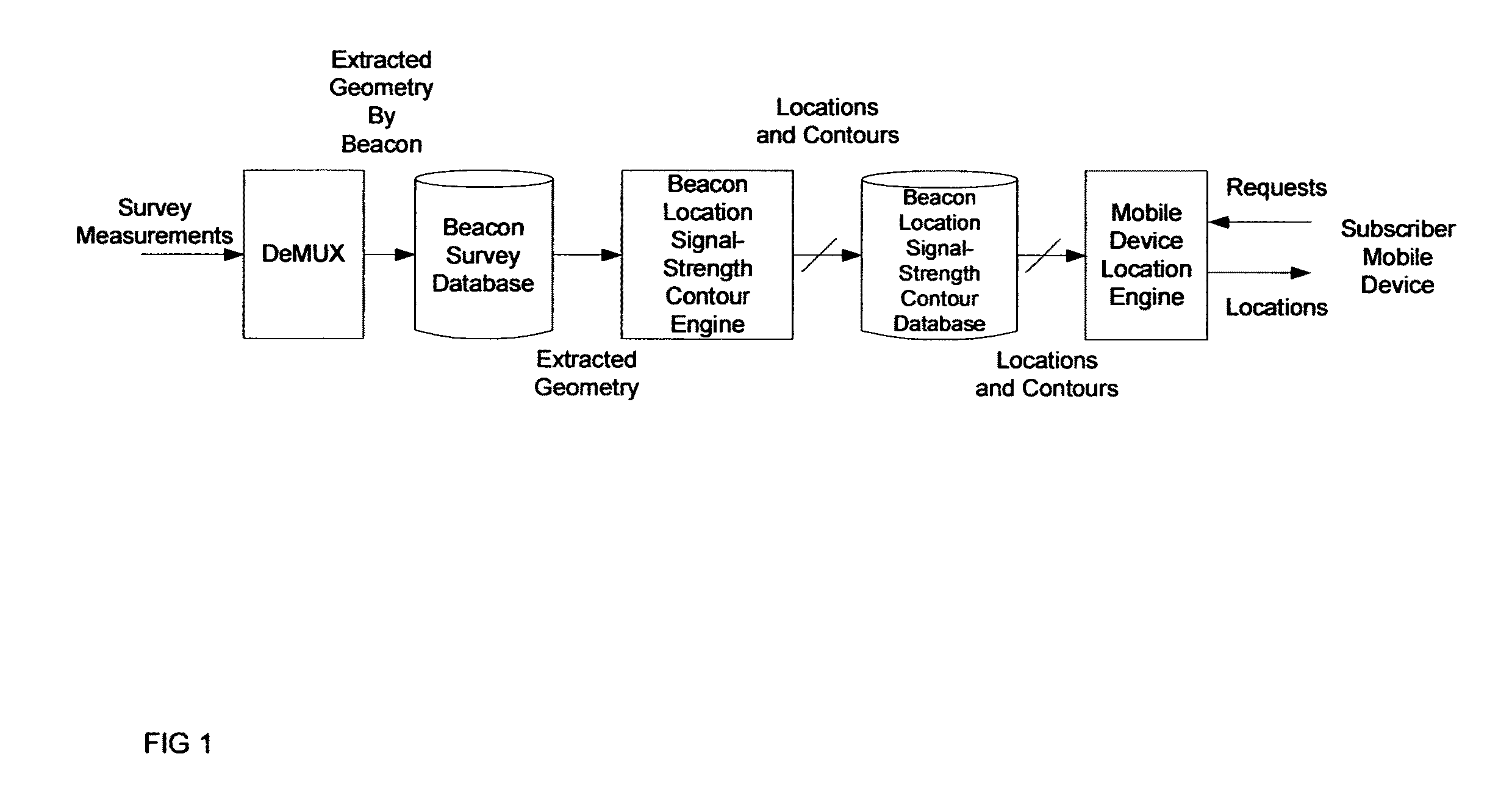
System framework for mobile device location
ActiveUS7994981B1Rapid and inexpensive compilationRapid and inexpensive and maintenanceBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationMobile deviceUltimate tensile strength
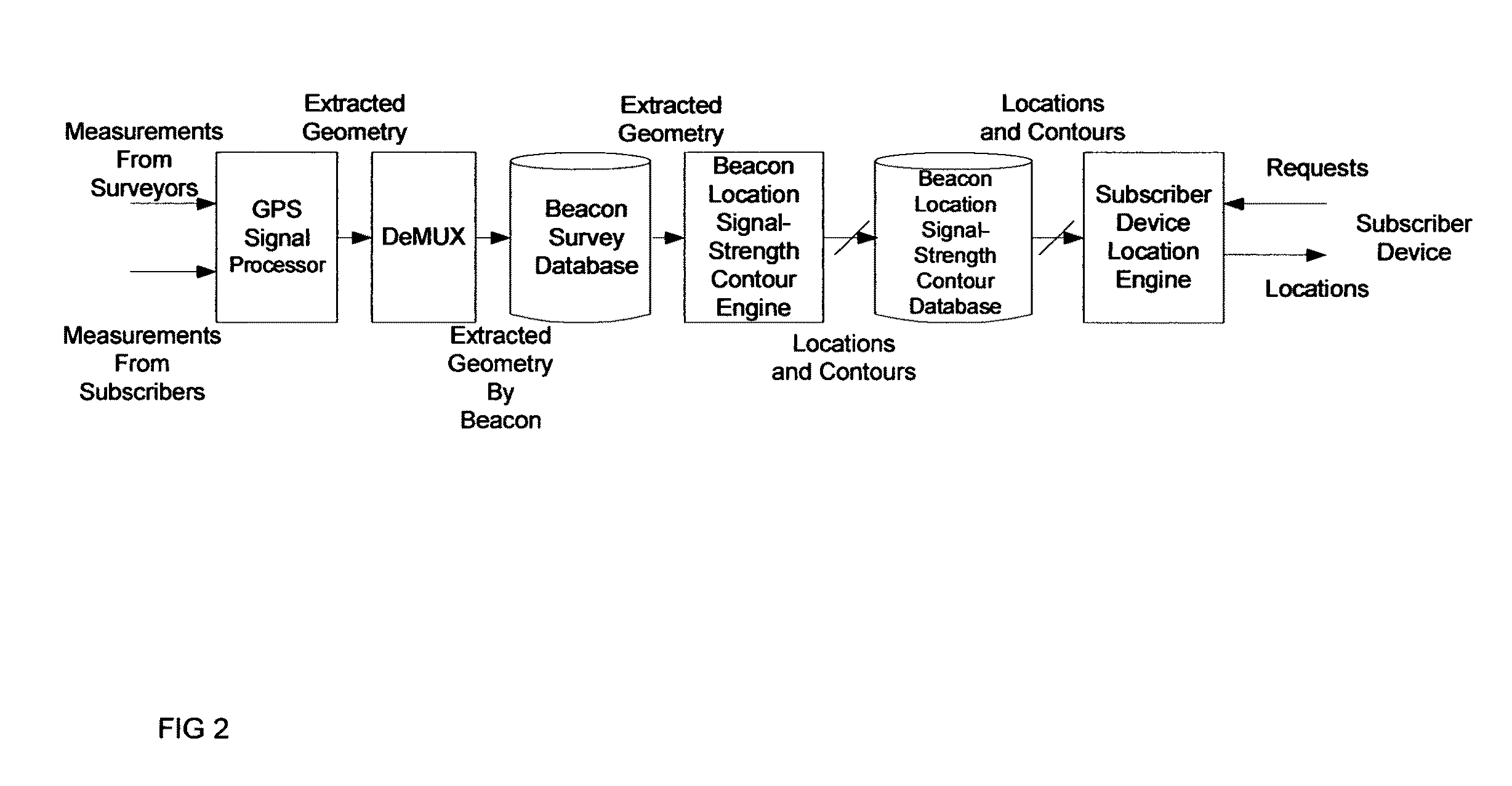
A method for estimating the location of a beacon from an ensemble of measurements associated with said beacon, where, contained in each measurement, are GPS data from which surfaces of location may be extracted, together with the ID's of beacons detectable at the point of measurement, is disclosed. The method comprises extracting the canonical set of surfaces of location implicit in each of the associated measurements, and determining the estimate of the location of the beacon as the point for which the sum of the squares of the distances to each of the surfaces so extracted is minimized. A system for the compilation of a database of beacon locations from measurements containing a time-stamped recording of the composite GPS signal (which recording is referred to as a datagram), together with the ID's and associated signal strengths of beacons detectable at the point of measurement, is also disclosed. The system comprises GPS signal processing means for extracting, from each time-stamped datagram, the canonic set of surfaces of location, and beacon location estimation means for estimating the location of a beacon from an ensemble of surfaces of location associated with said beacon.
Owner:ETHERWHERE CORP
Durable global asset-tracking device and a method of using the same
InactiveUS7072668B2Maintain durabilityIncrease in sizePosition fixationSubstation equipmentConstant powerCommunications system
A communication system for tracking an asset globally accesses multiple communication networks and switches among them, choosing the most economic, available communication mode without need for a constant power supply. An integrated motion sensor uses a combination of GPS updating and dynamic movement calculation to obtain the most reliable position estimation. Current location is identified within a small radius at all times. While taking advantage of the GPS system to obtain accurate location information, direct exposure to GPS satellites is not required at all times. The system obtains position information from GPS satellites whenever valid GPS signals are available, and provides its own location tracking capability when GPS signals are not accessible. The position accuracy of the device is preferably within a 20-meter radius from the exact location.
Owner:GEOSPATIAL TECH
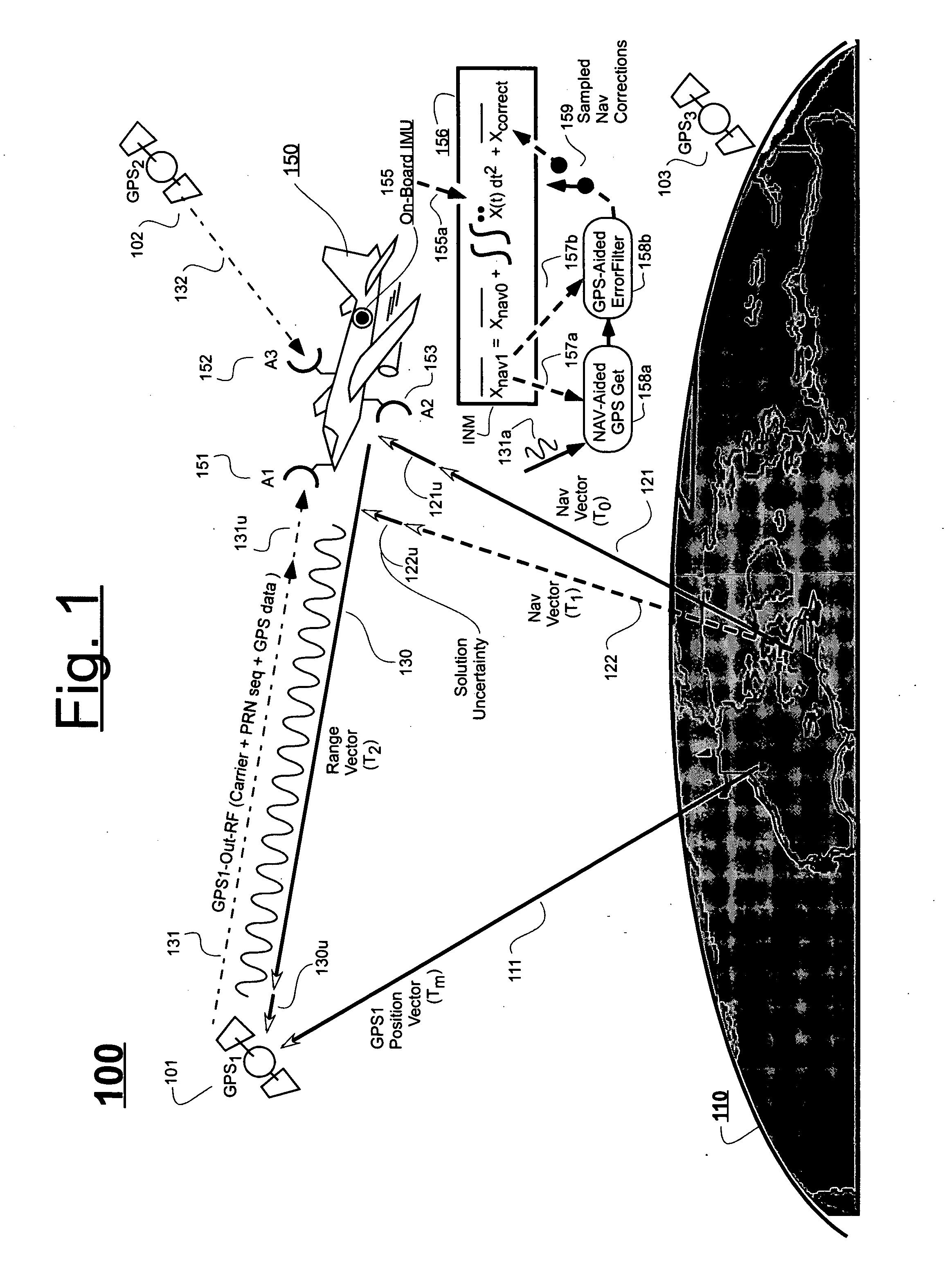
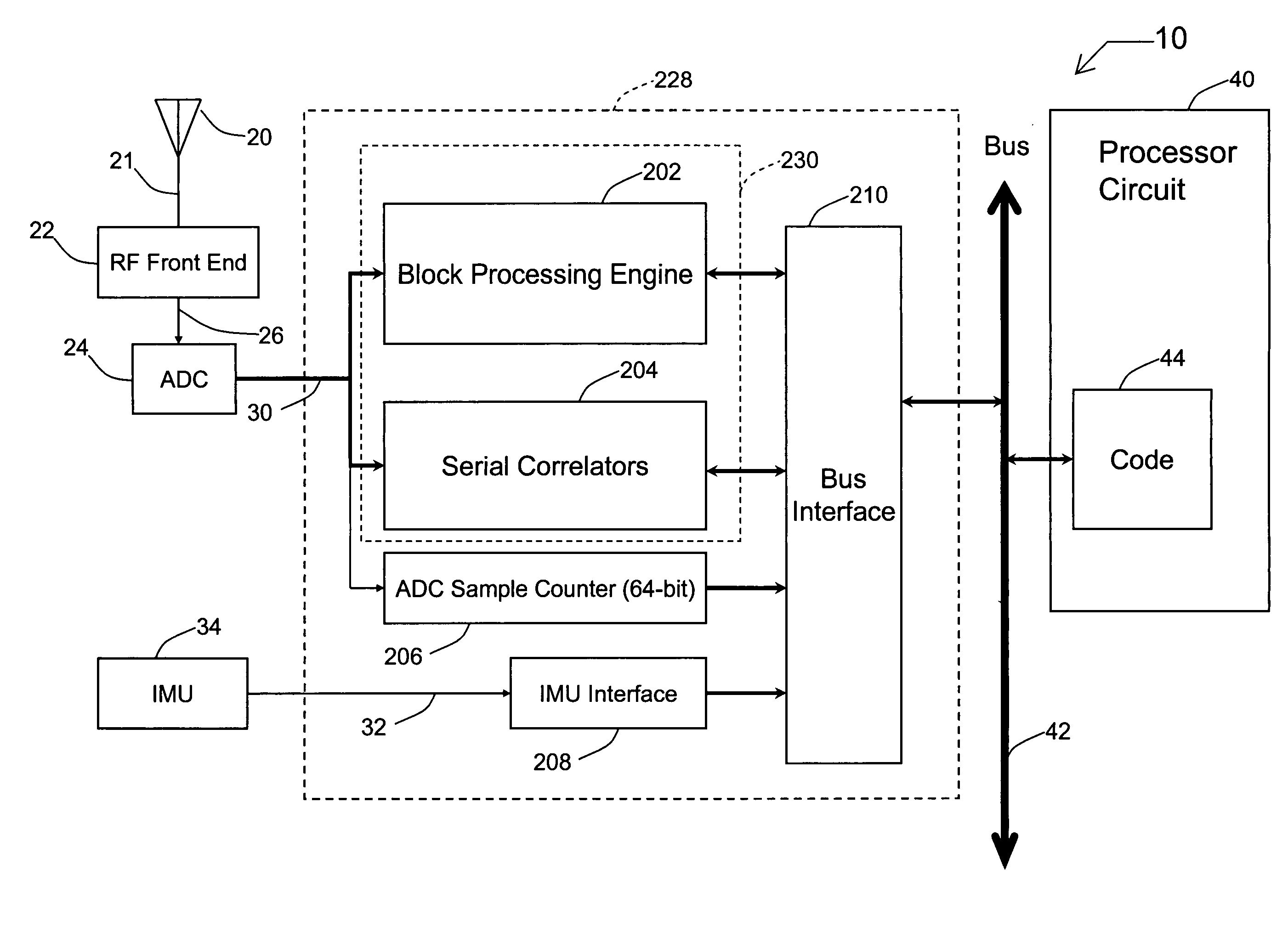
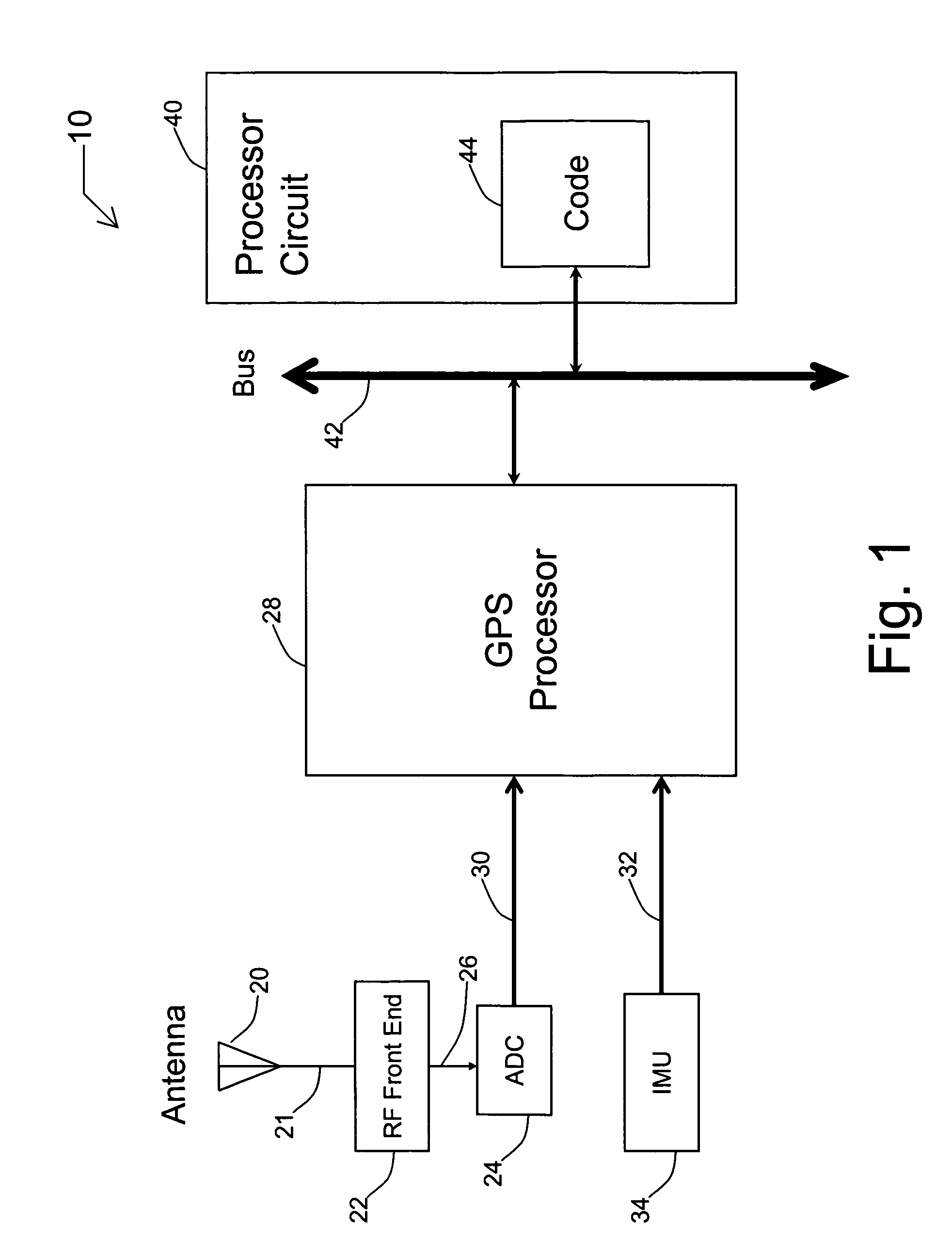
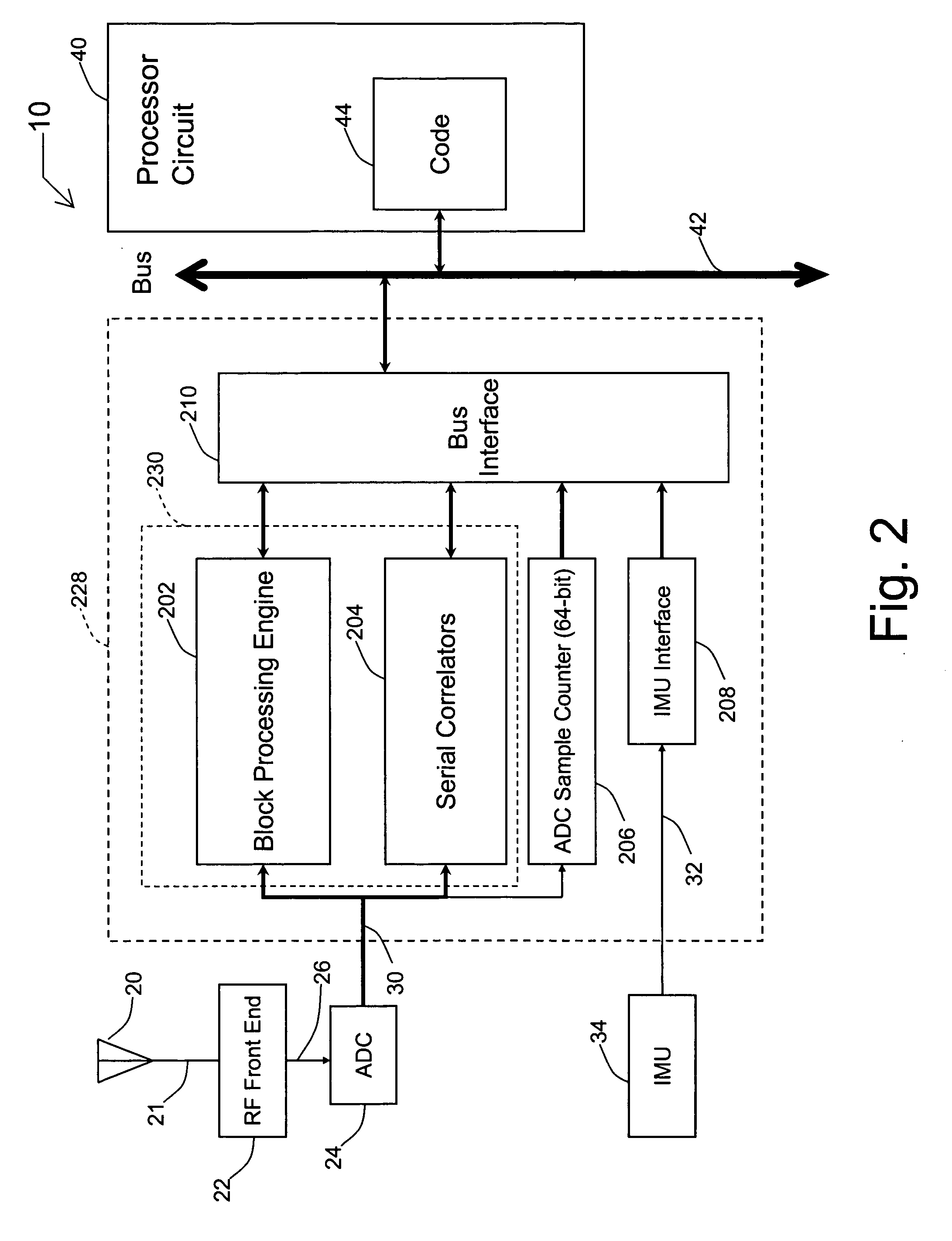
Systems and methods for acquisition and tracking of low CNR GPS signals
A receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low carrier-to-noise ratio (“CNR”) signals from a plurality of radio navigation satellites while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may have: a radio frequency (RF) front-end that provides satellite data corresponding to signals received from the plurality of radio navigation satellites; an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that provides inertial data; and a processor circuit in circuit communication with the RF front end and the IMU, the processor circuit being capable of using satellite data from the RF front-end and inertial data from the IMU to perform continuous carrier phase tracking of low CNR radio navigation satellite signals having a CNR of about 20 dB-Hz, while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may be a GPS receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low-CNR GPS signals.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Self-charging power controlled system for locating animals by GPS
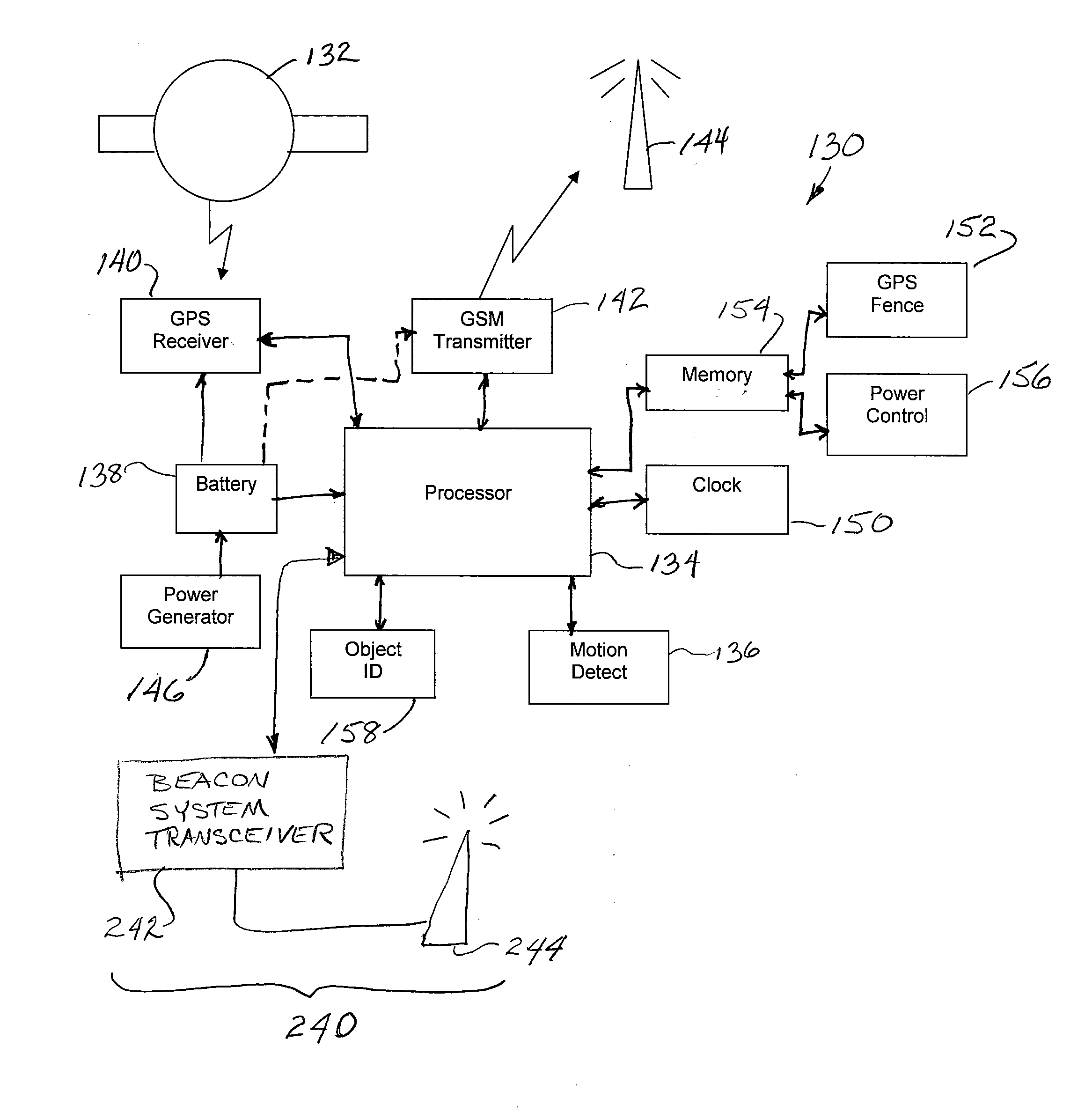
InactiveUS20120206296A1Reduce weightReduce energy consumptionSatellite radio beaconingAlarmsMotion detectorPower control system
A portable tracking unit attached to a movable object, such as an animal's collar, includes a GPS receiver to receive GPS signals from multiple satellites for use in multilateration calculations in determining the current position of the tracking unit. A processor in the tracking unit processes the GPS data signals to determine the tracking unit's position, and a GSM mobile wireless transmitter is used to transmit the geographic coordinates of the tracking unit to a remote monitoring unit. The tracking unit also includes a motion detector that outputs a motion signal when the animal is on the move. A motion signal “wakes up” the processor that wakes up the GPS receiver and the GSM transmitter to begin calculating and transmitting the geographic coordinates of the tracking unit. The tracking unit also includes electrical generators configured to transduce mechanical motion of the tracking unit into electrical energy to recharge a battery and power devices. The portable tracking unit is fabricated monolithically in silicon with circuitry integrated with silicon micro-machined motion sensor, as well as power generators, and packaged through silicon wafer bonding. A remote computing device receives the geographic coordinates of the tracking device and indicates to a user the position of the tracking device in relation to a map. An alert may also be provided if the location of the tracking device is outside a programmed safe zone.
Owner:CARBON GLOBAL
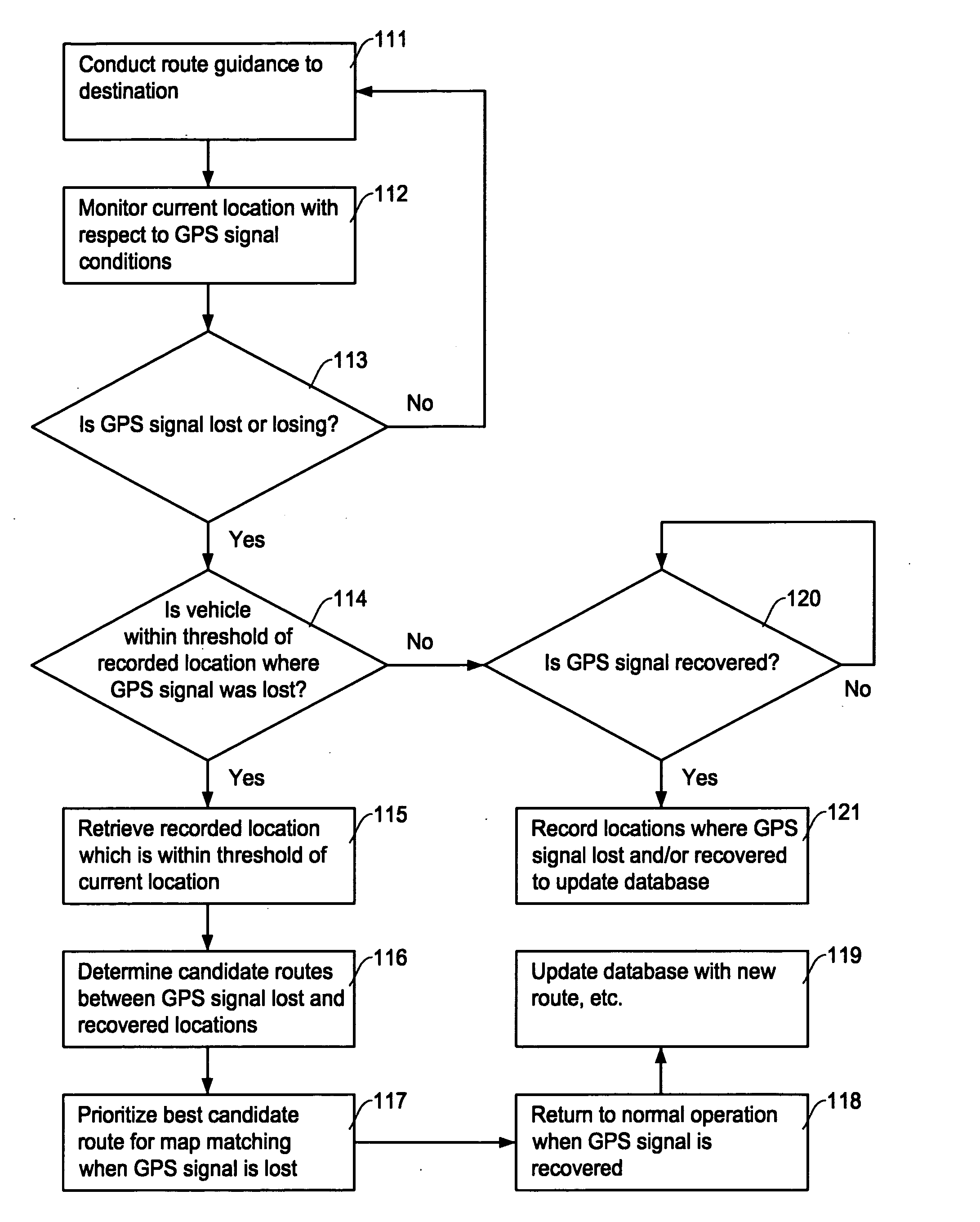
Map matching method and apparatus for navigation system
ActiveUS20080091347A1Exact matchAvoid false displayInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation systemAccessibility
A map matching method and apparatus for a navigation system estimates a location of the navigation system on a correct road segment when a GPS signal is invalid. The map matching method creates a database of pairs of locations at which the navigation system encountered GPS signal loss and recovery in the first time. The navigation system conducts a map matching processing when the GPS signal is lost in the second time at the recorded location by incorporating various additional factors to match the current position with a correct road segment. The various additional factors, in addition to the measured data by a dead reckoning process, include road class, road accessibility, road angle, proximity to candidate road, etc.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
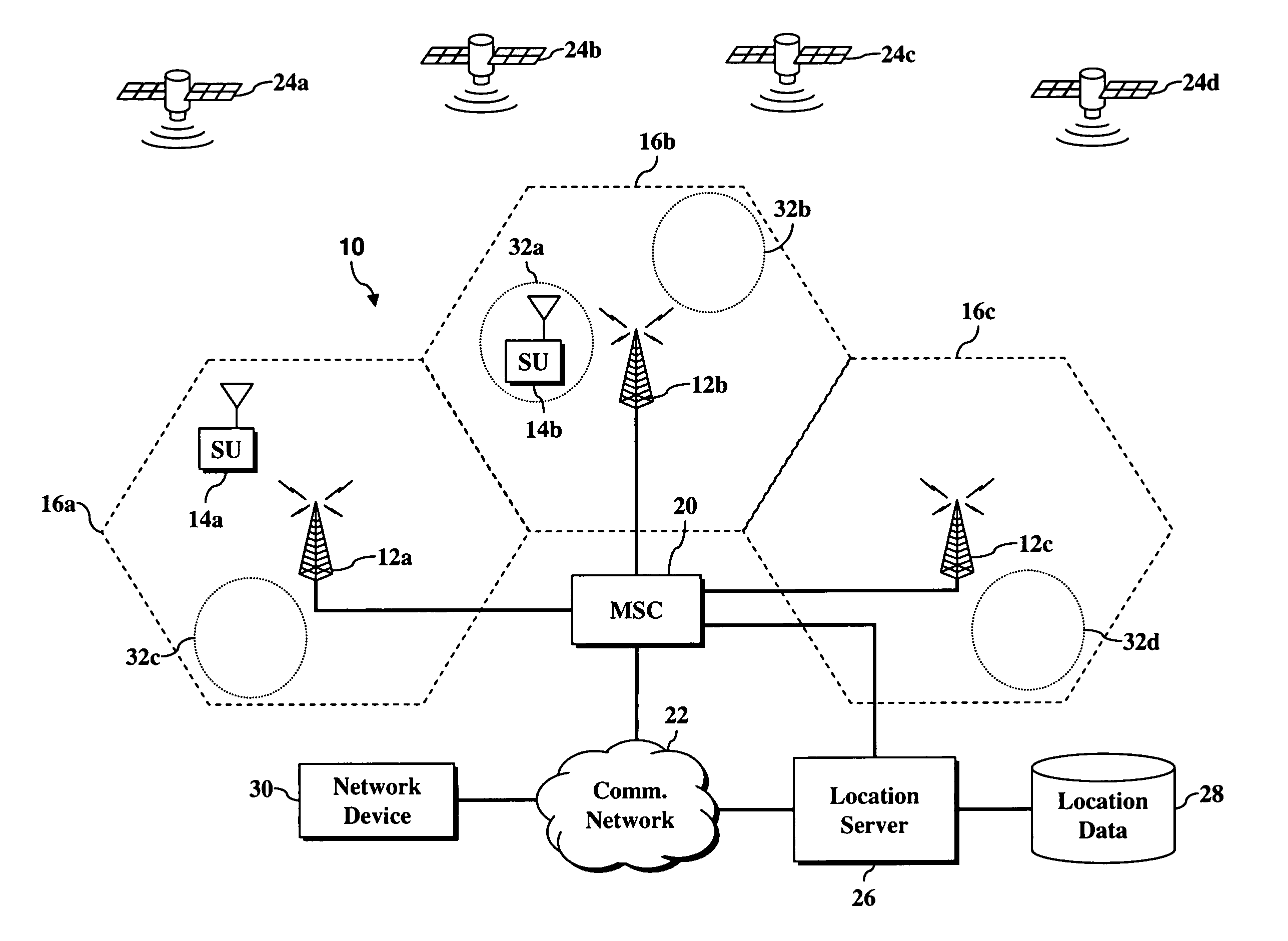
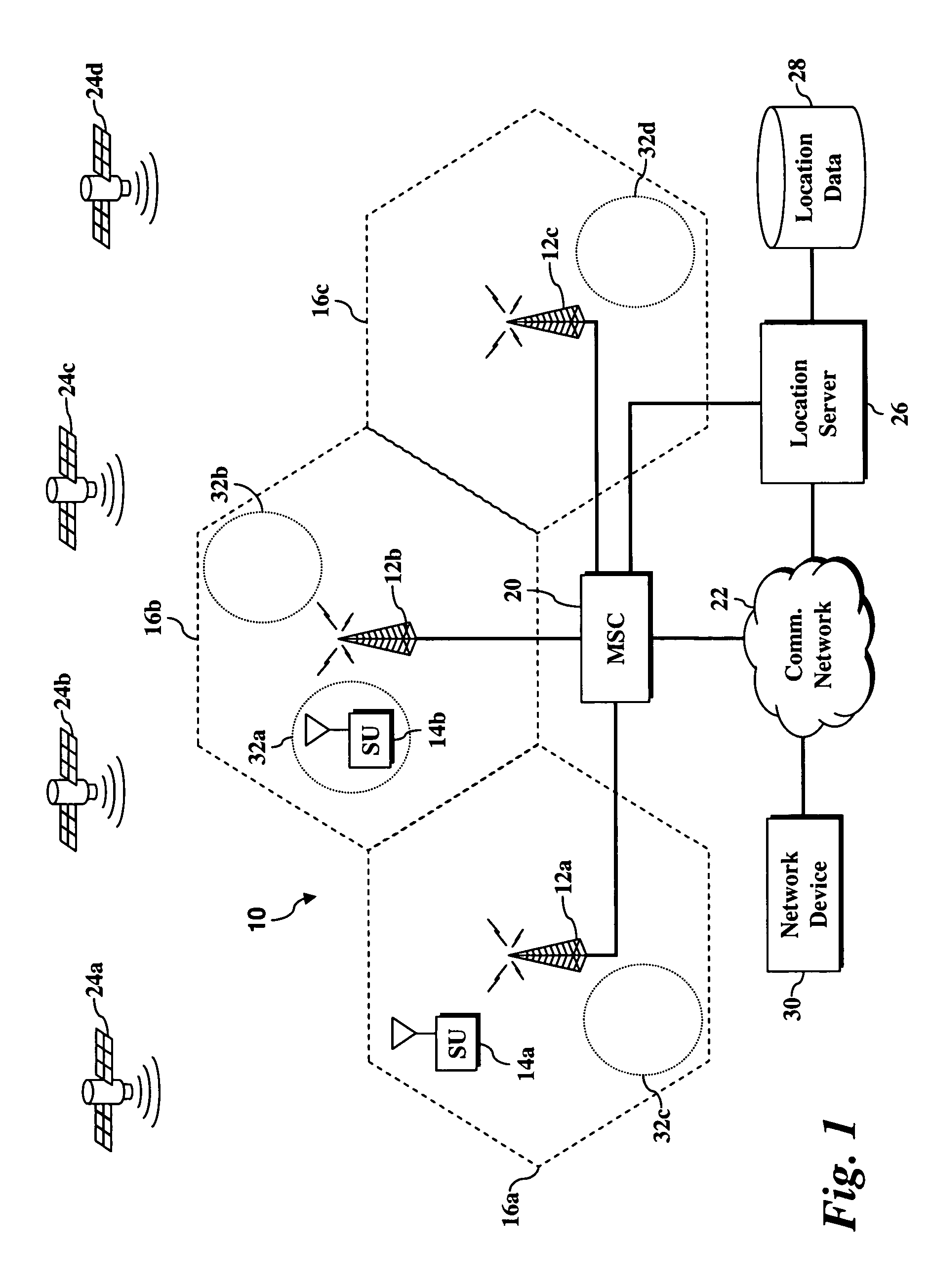
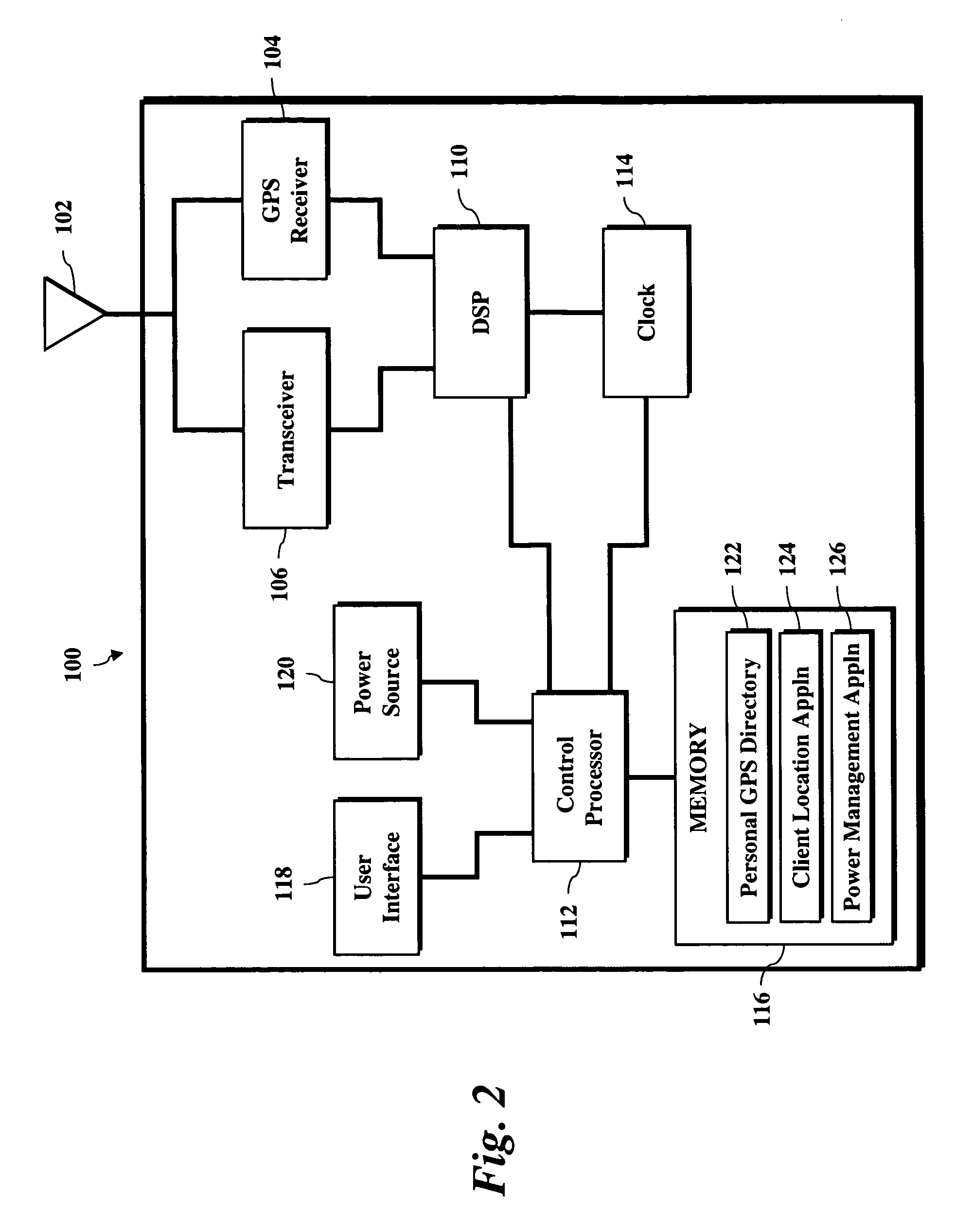
System and method for recovering a lost or stolen wireless device
ActiveUS20070072620A1Complete understandingEnhanced advantageRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsLocation information based serviceGps receiverClient-side
A user may locate a missing wireless device through a location server storing user-associated location information. A wireless device includes a client location application adapted to determine a current geographic location and transmit location data to a location server, a power source, and a power management application adapted to detect a low power level and instruct the client location application to determine the current geographic location. The wireless device further includes a GPS receiver adapted to receive and decode GPS signals and a personal GPS directory storing location information associated with the subscriber unit.
Owner:NEXTEL COMMUNICATIONS
Method and apparatus for global positioning system based cooperative location system
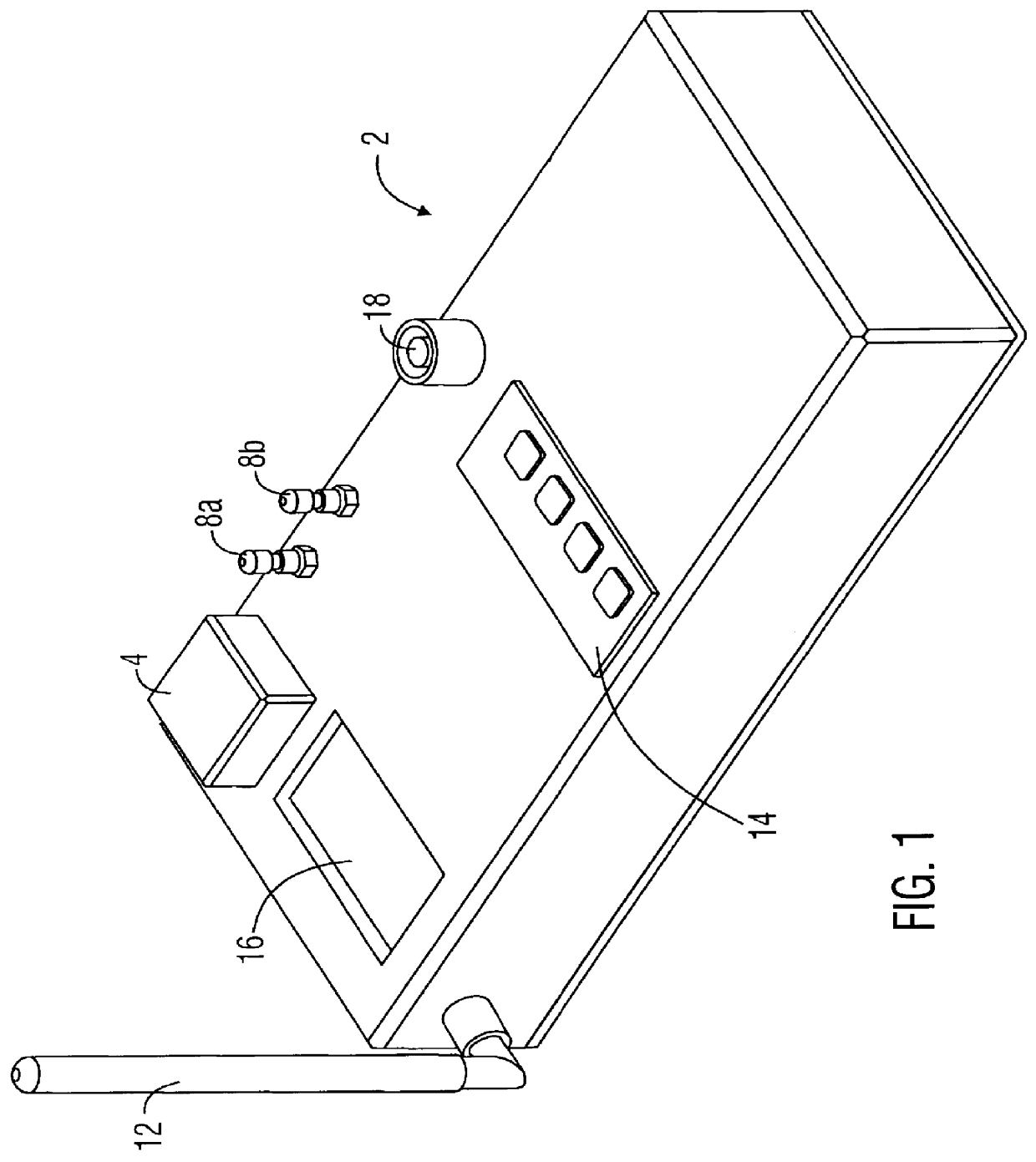
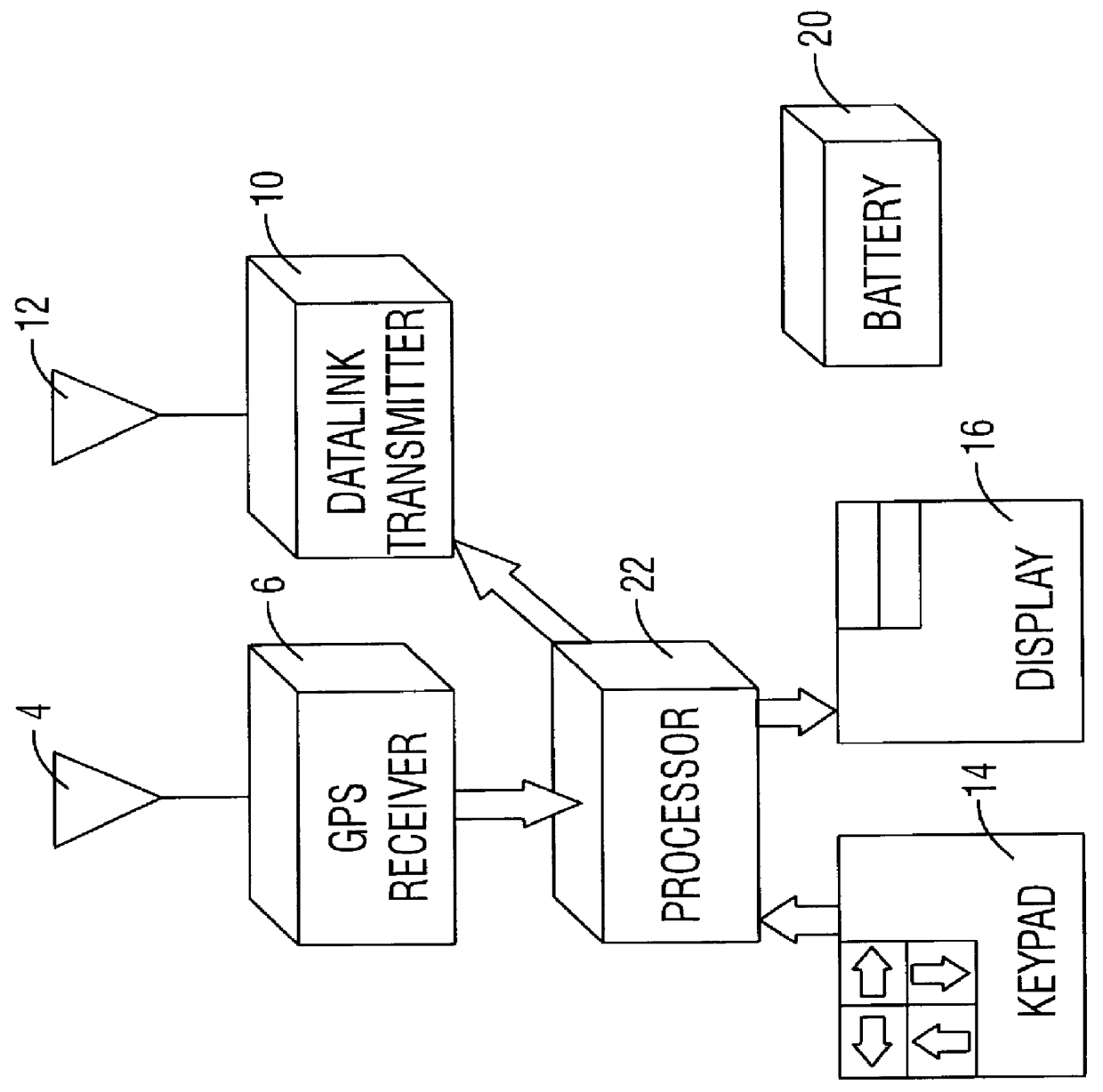
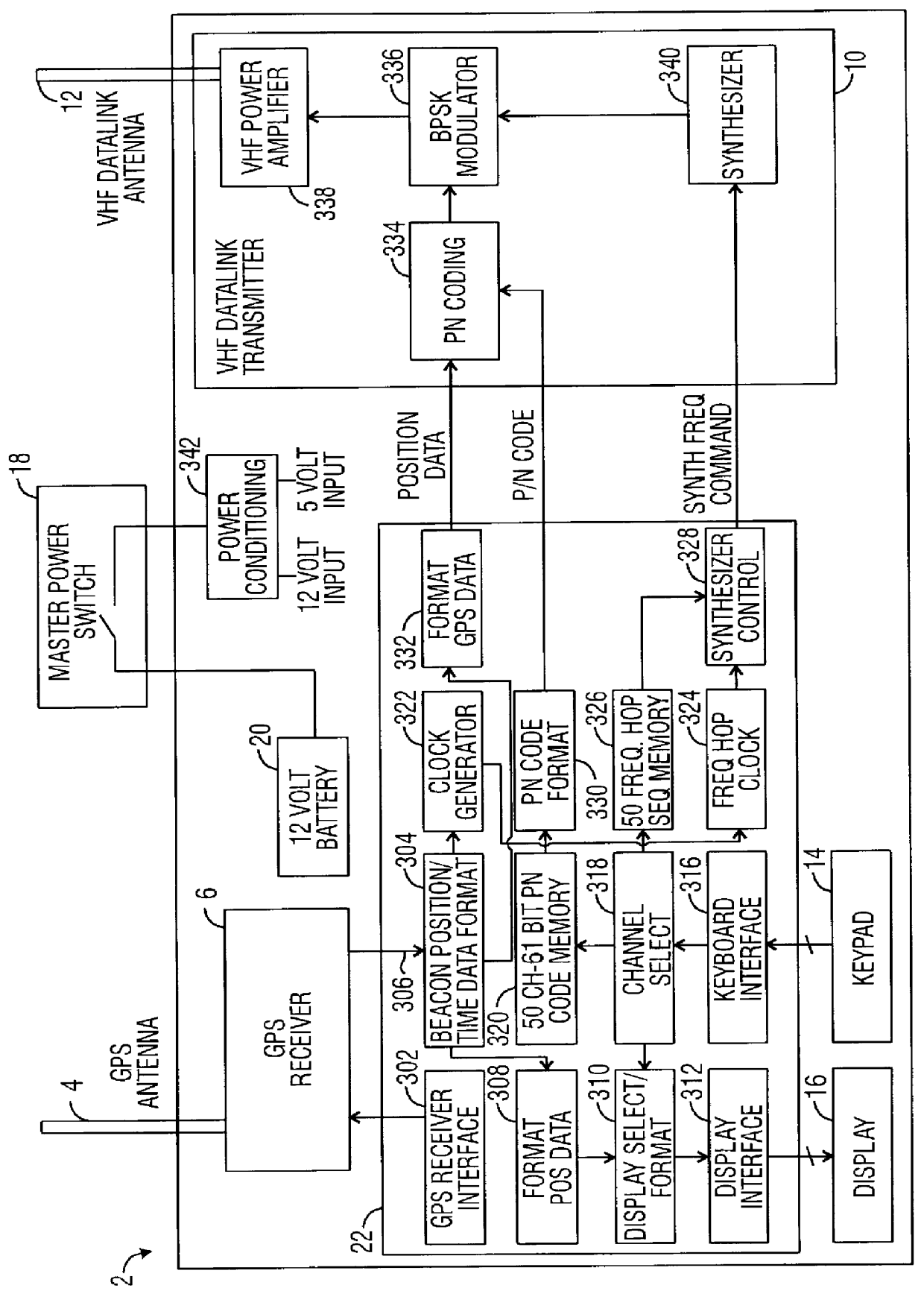
A cooperative location system for use with a Global Positioning System ("GPS"). The system includes a beacon that receives GPS signals and transmits GPS data representing the location of the beacon to a remote locator. The locator receives the beacon's GPS data from the beacon. Based on the beacon's GPS data, a reference direction provided by a compass, and the locator's own GPS data, the locator calculates range and direction information to the beacon.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com