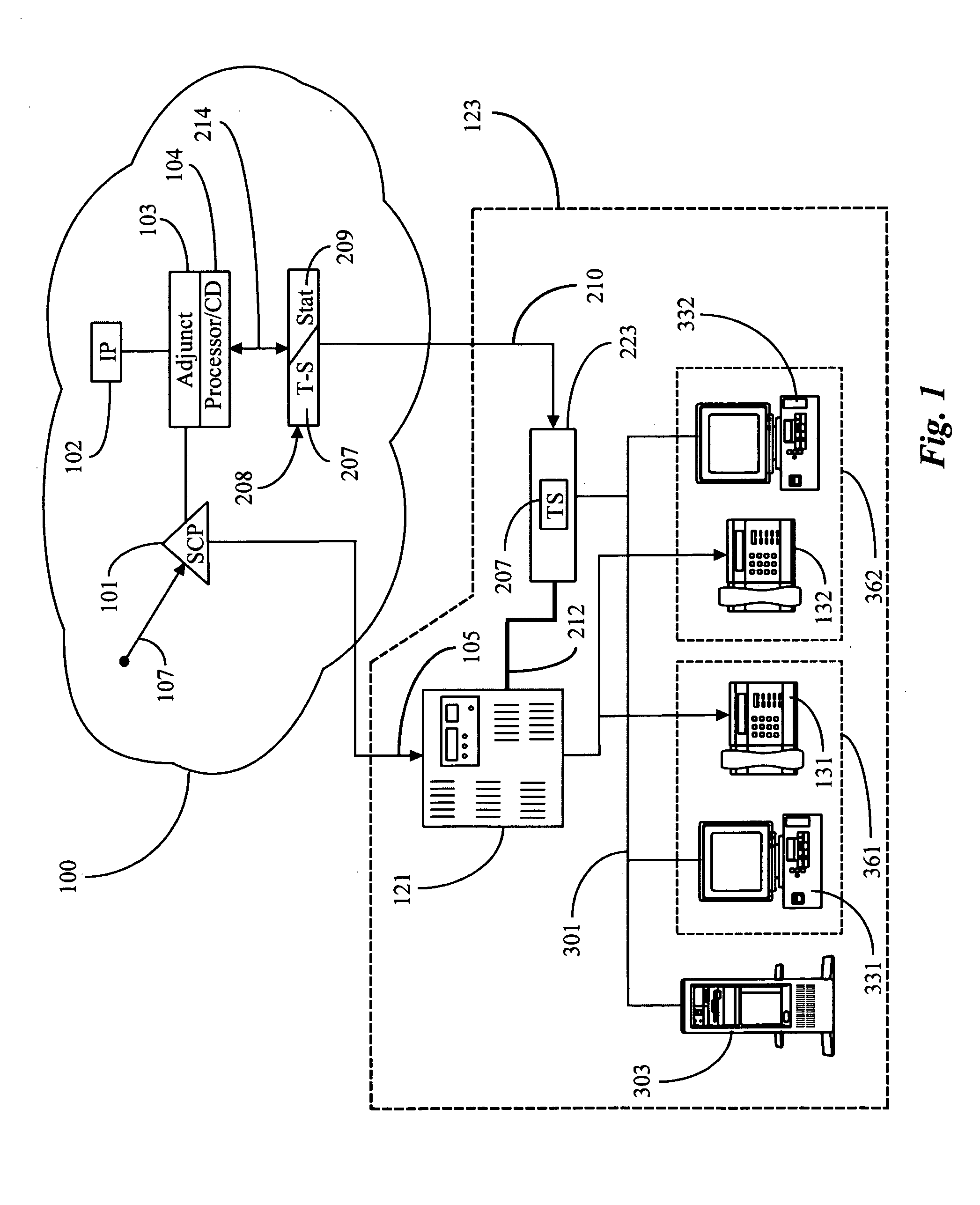
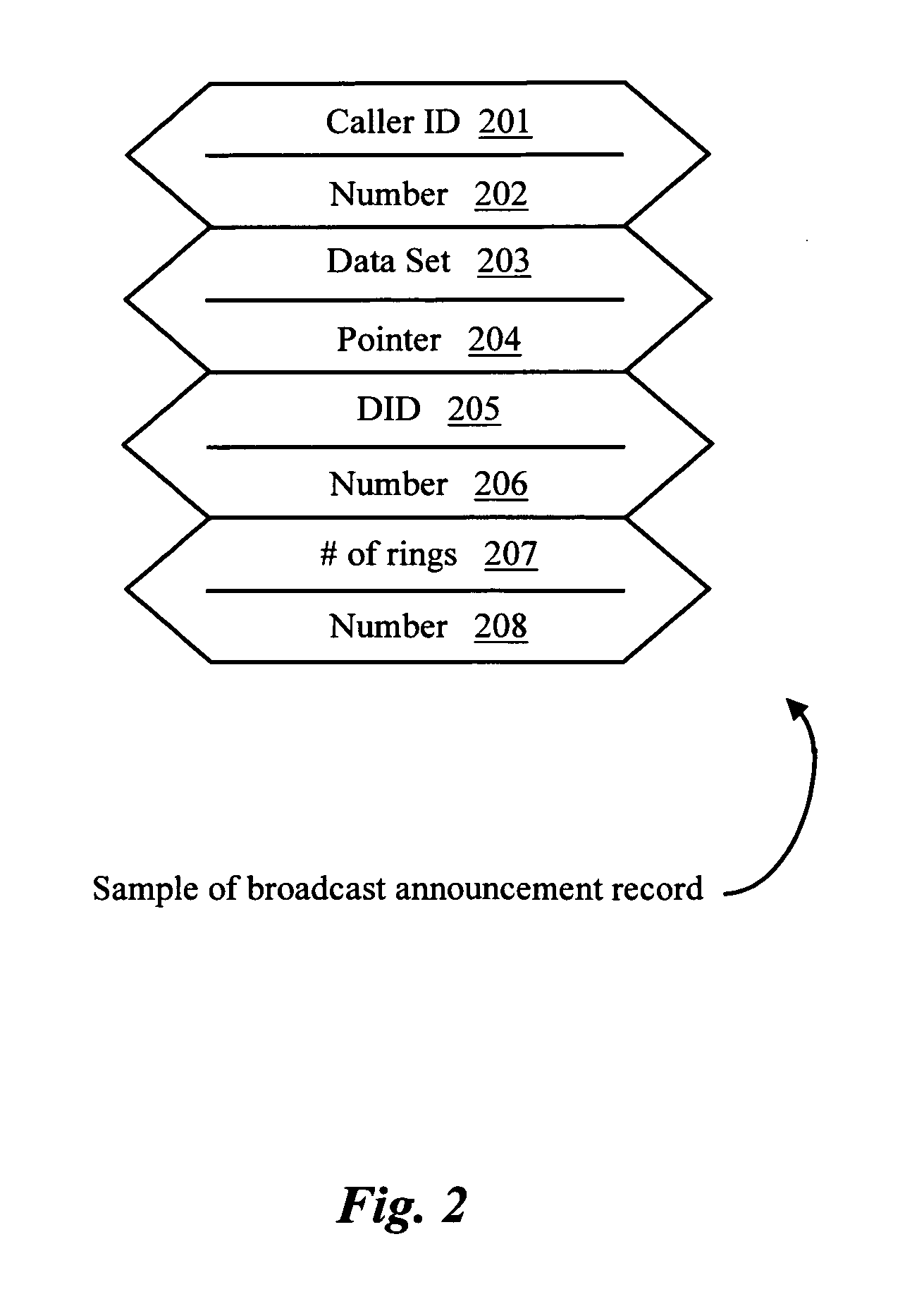
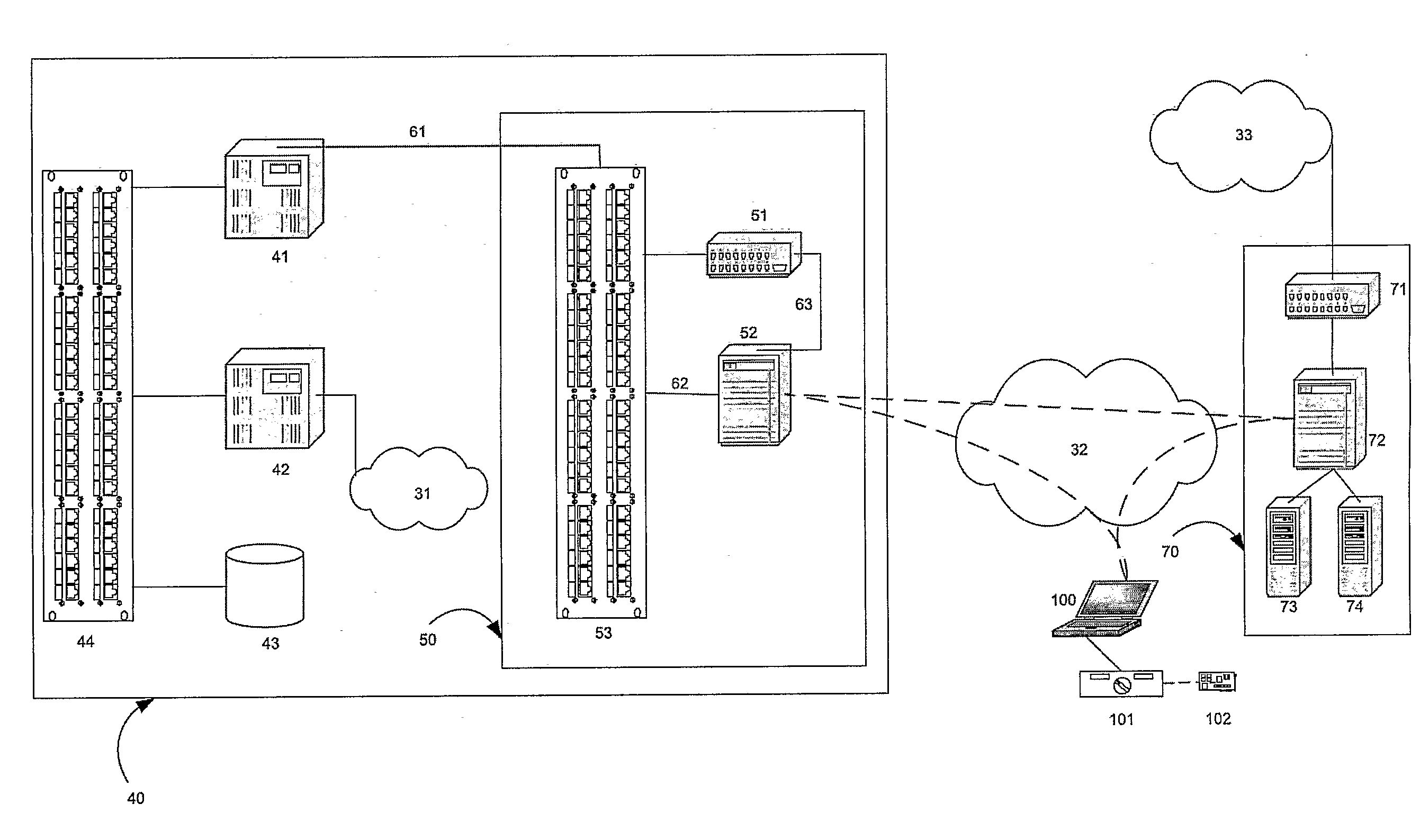
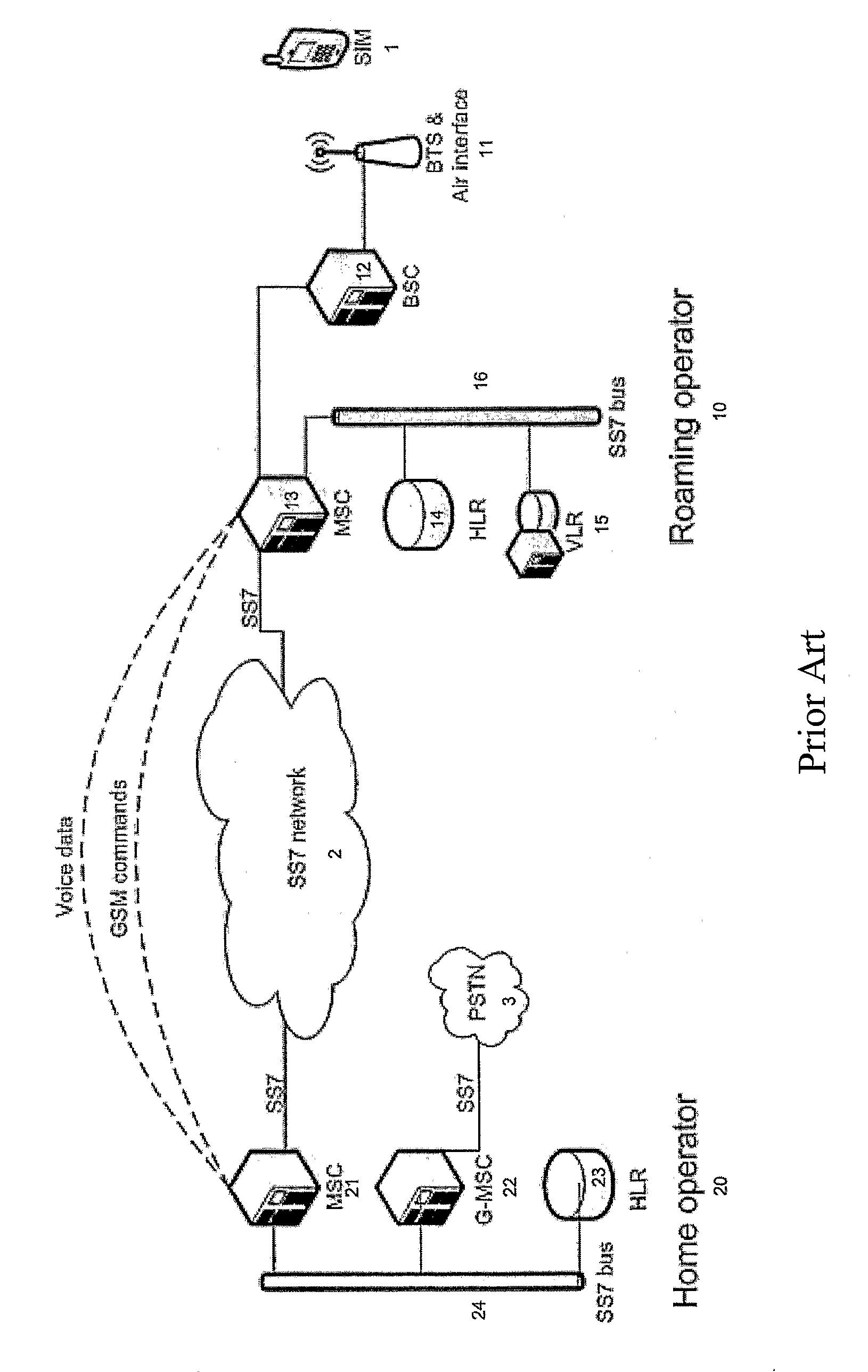
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
522 results about "Telephone switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
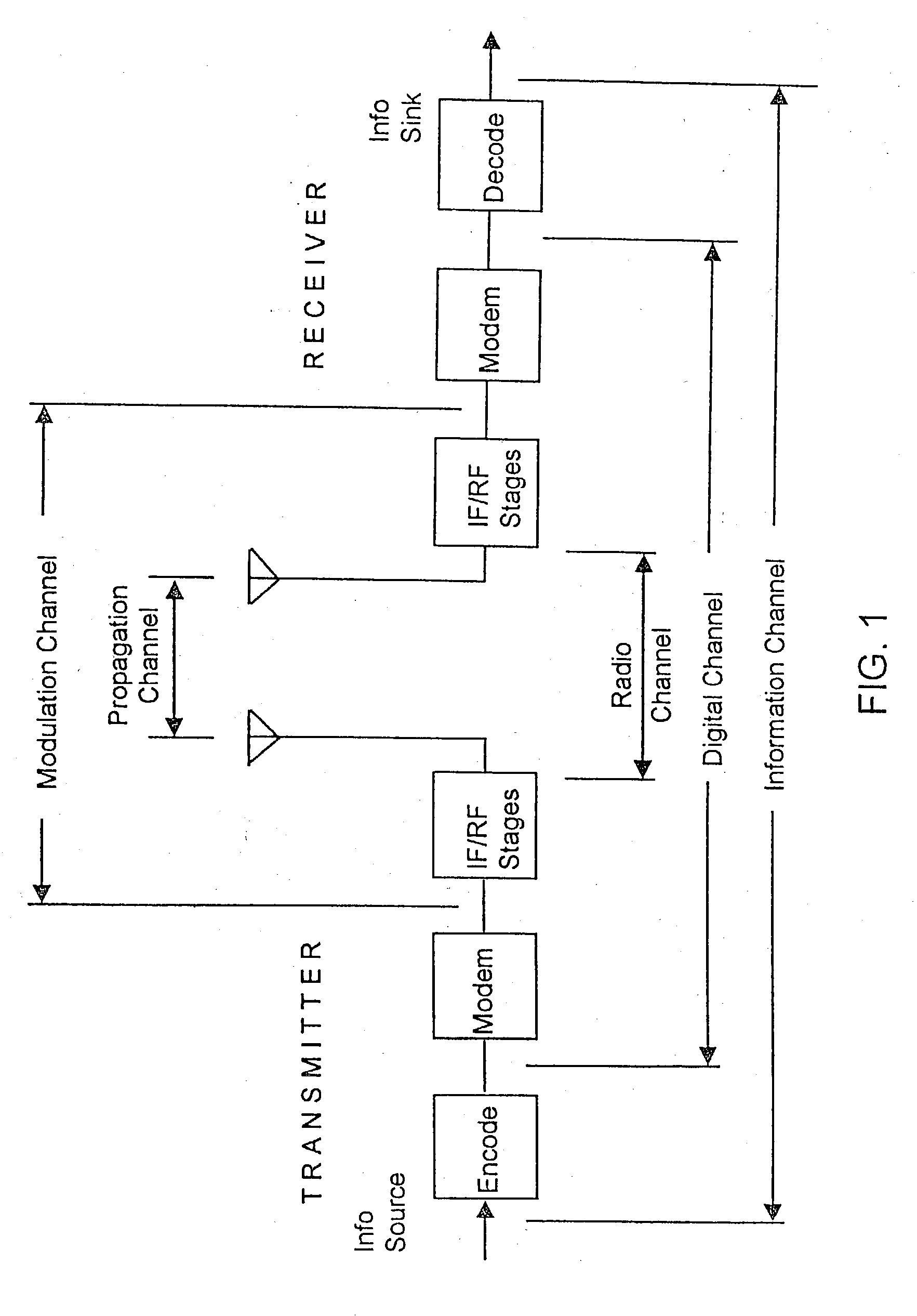
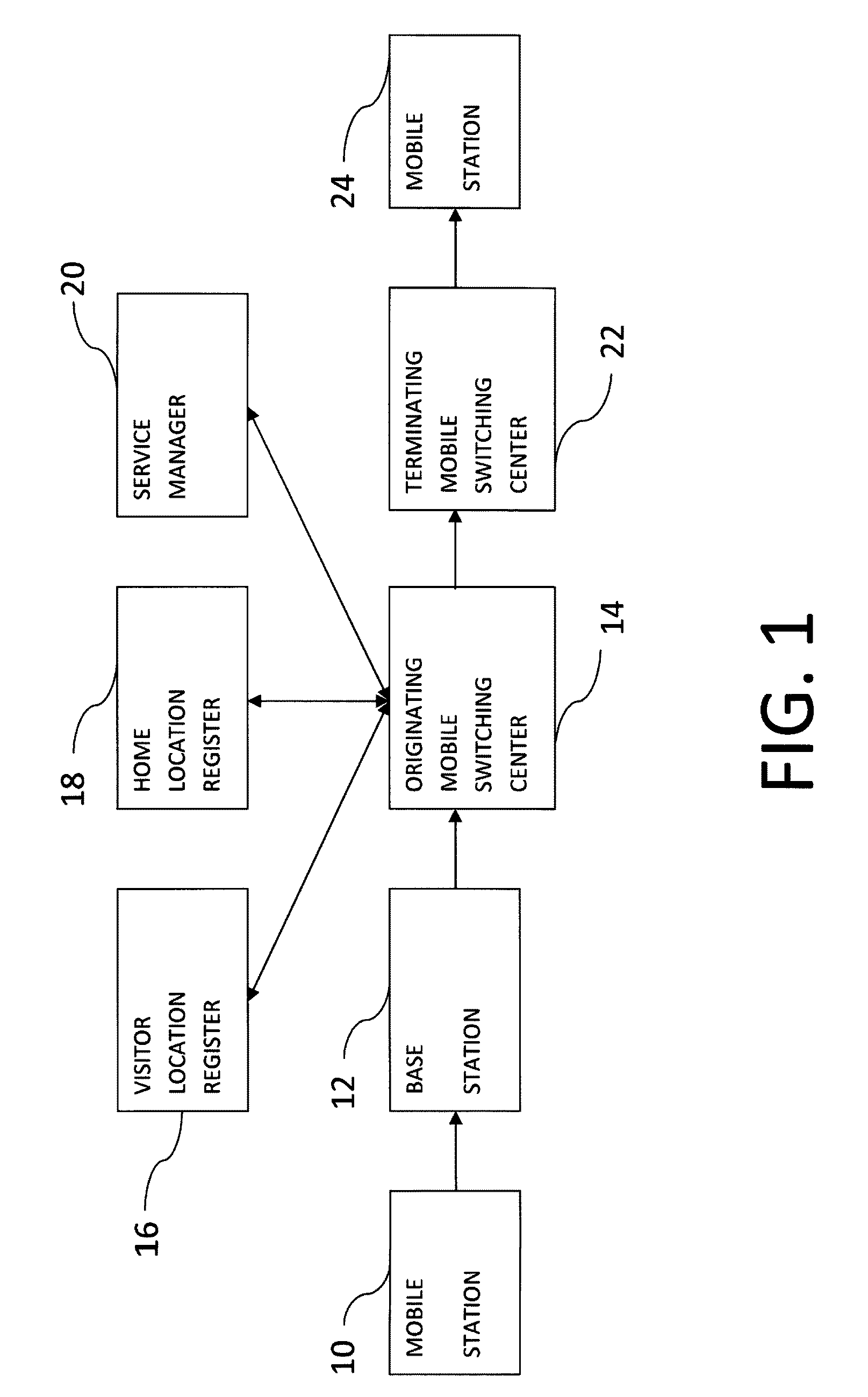
Bell Canada operated NE-1ESS 2 wire switches (some of which also provided Centrex services) in Toronto, Ottawa and Montreal. A 4W NE-1ESS was installed in Thunder Bay to provide telephone switching services (SAGE and AUTOVON)for USA and Canadian bases in that part of North America. The #1ESS was implemented using discrete diode transistor logic.
Wireless location using multiple location estimators
InactiveUS6249252B1Effectively and straightforwardly resolvedAmbiguity and conflictDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesTerrainHeuristic
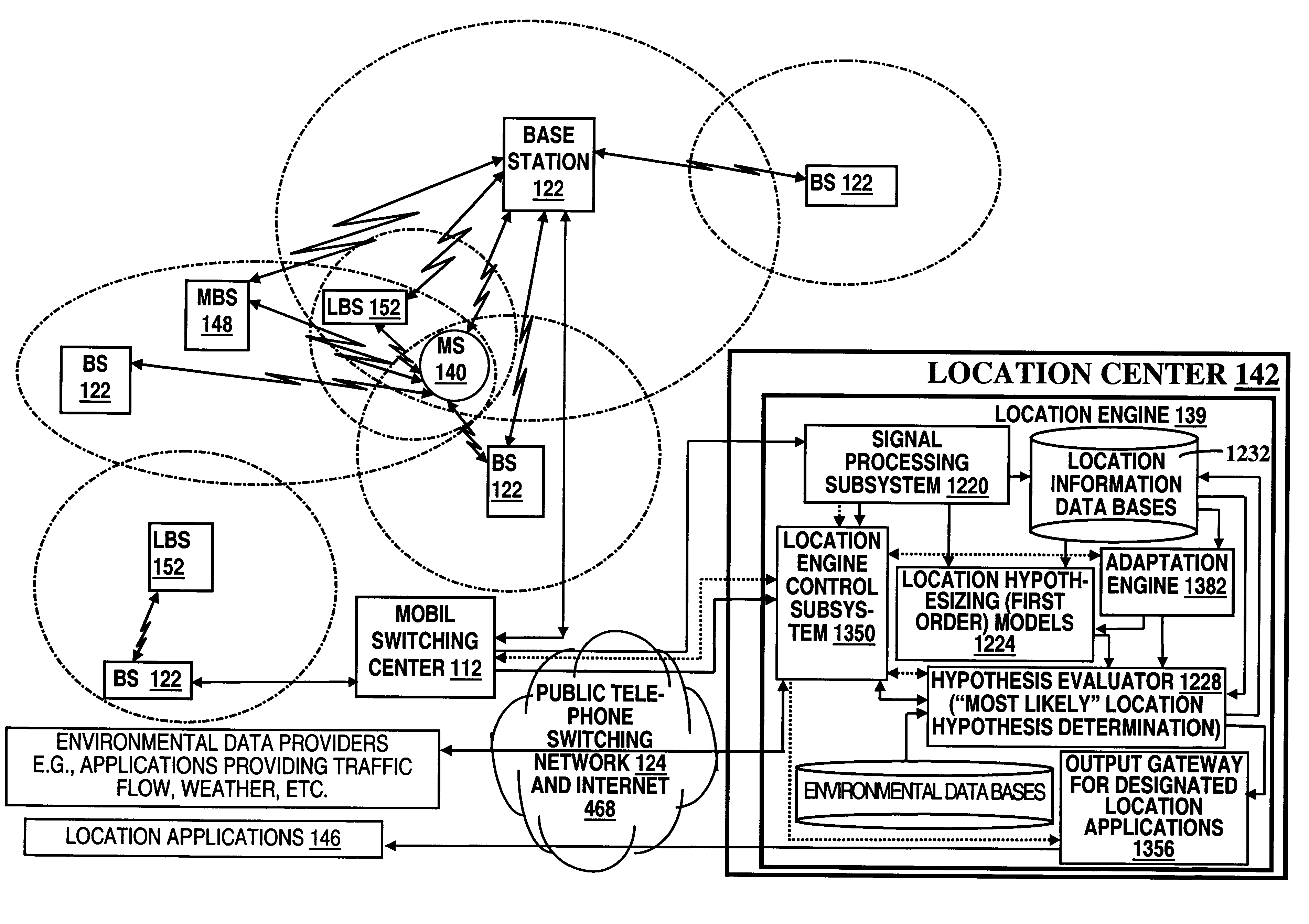
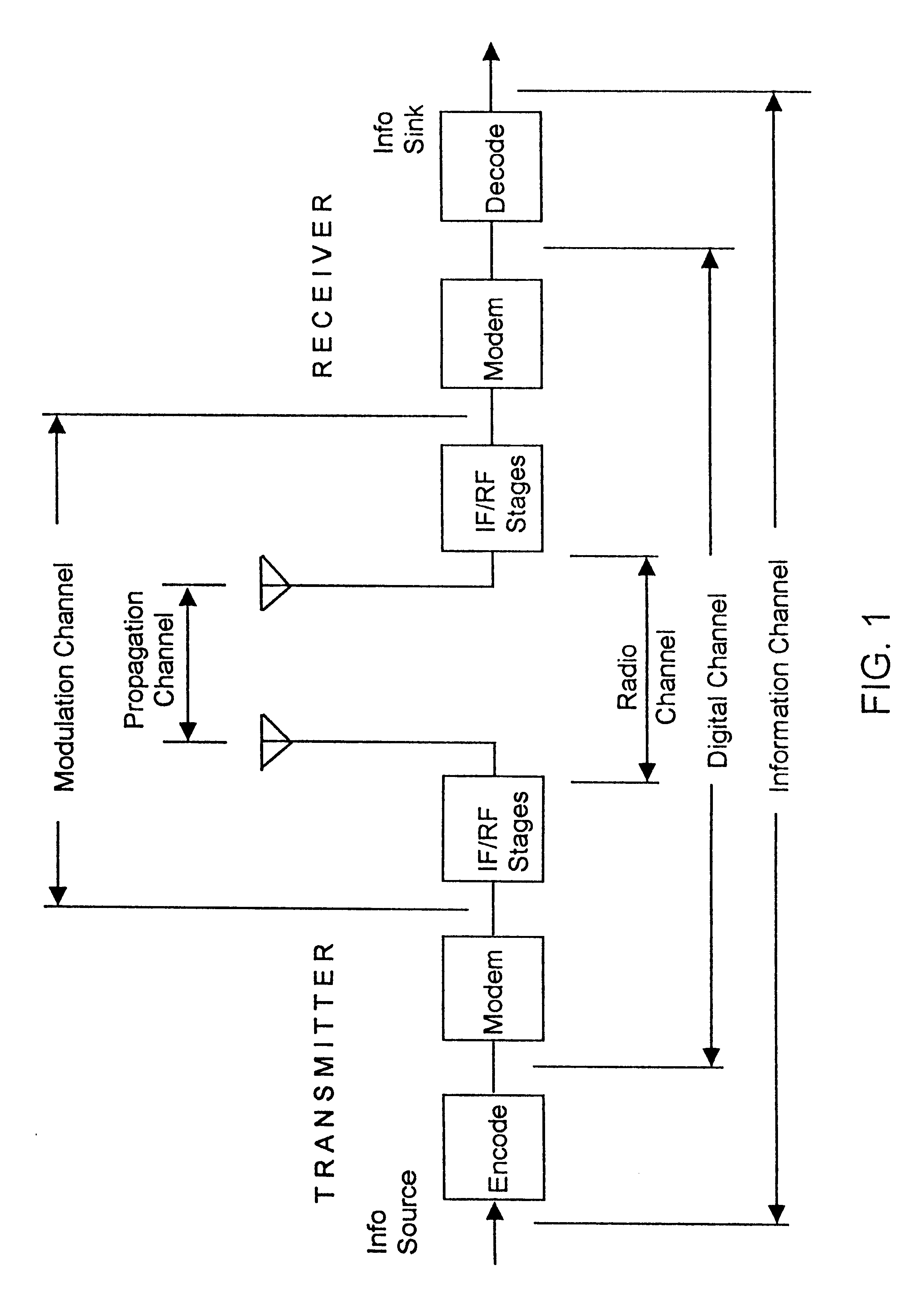
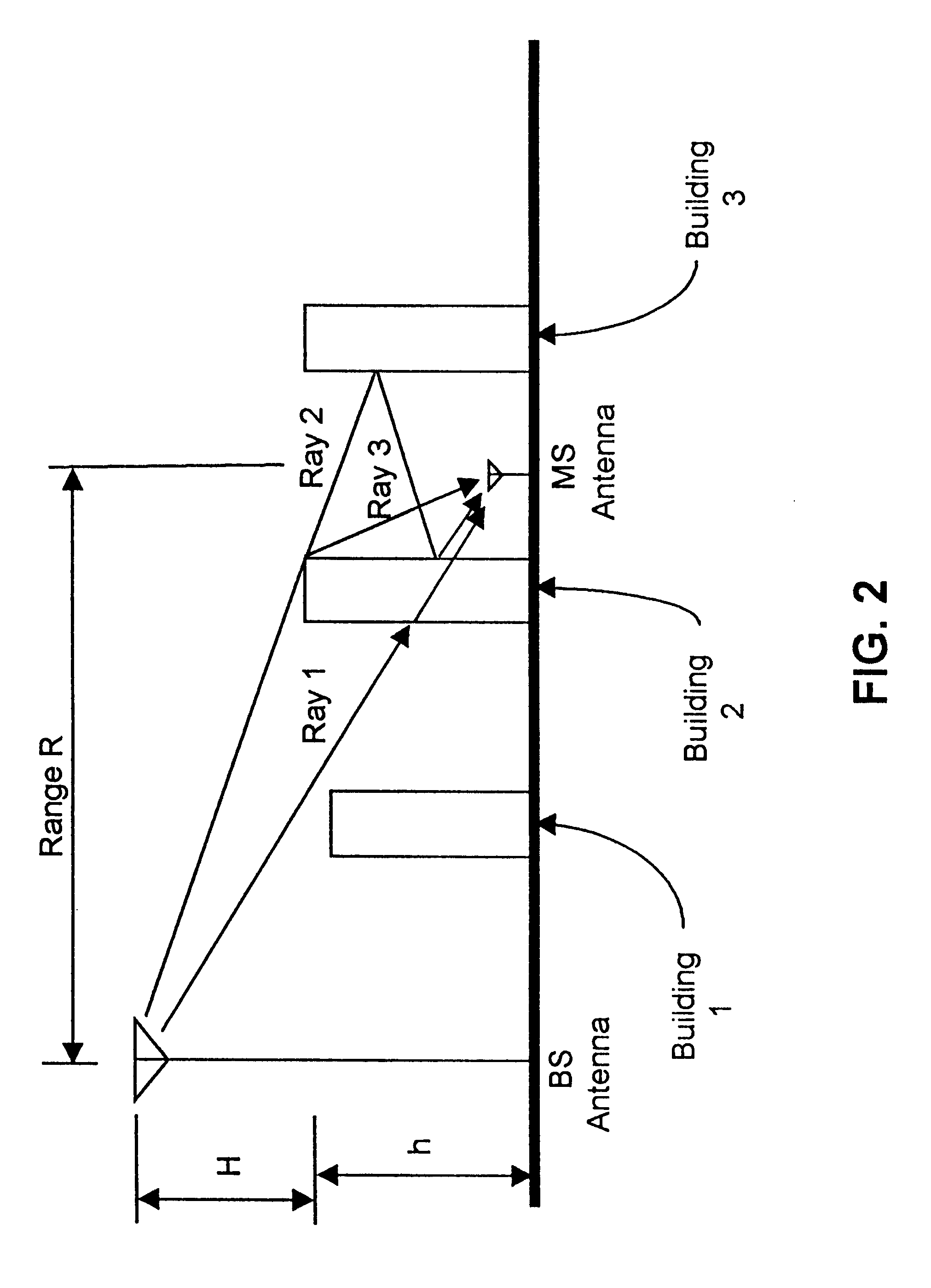
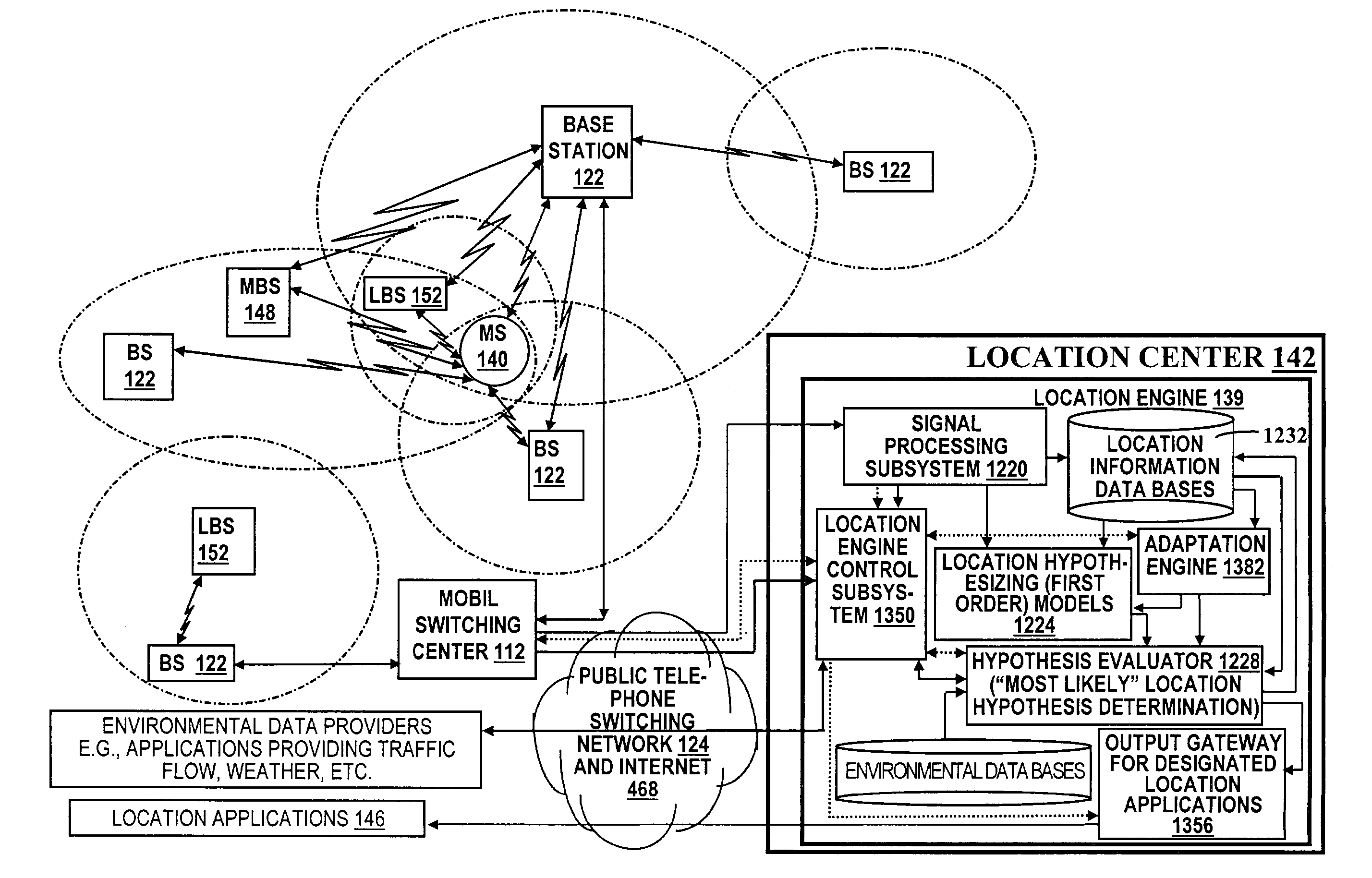
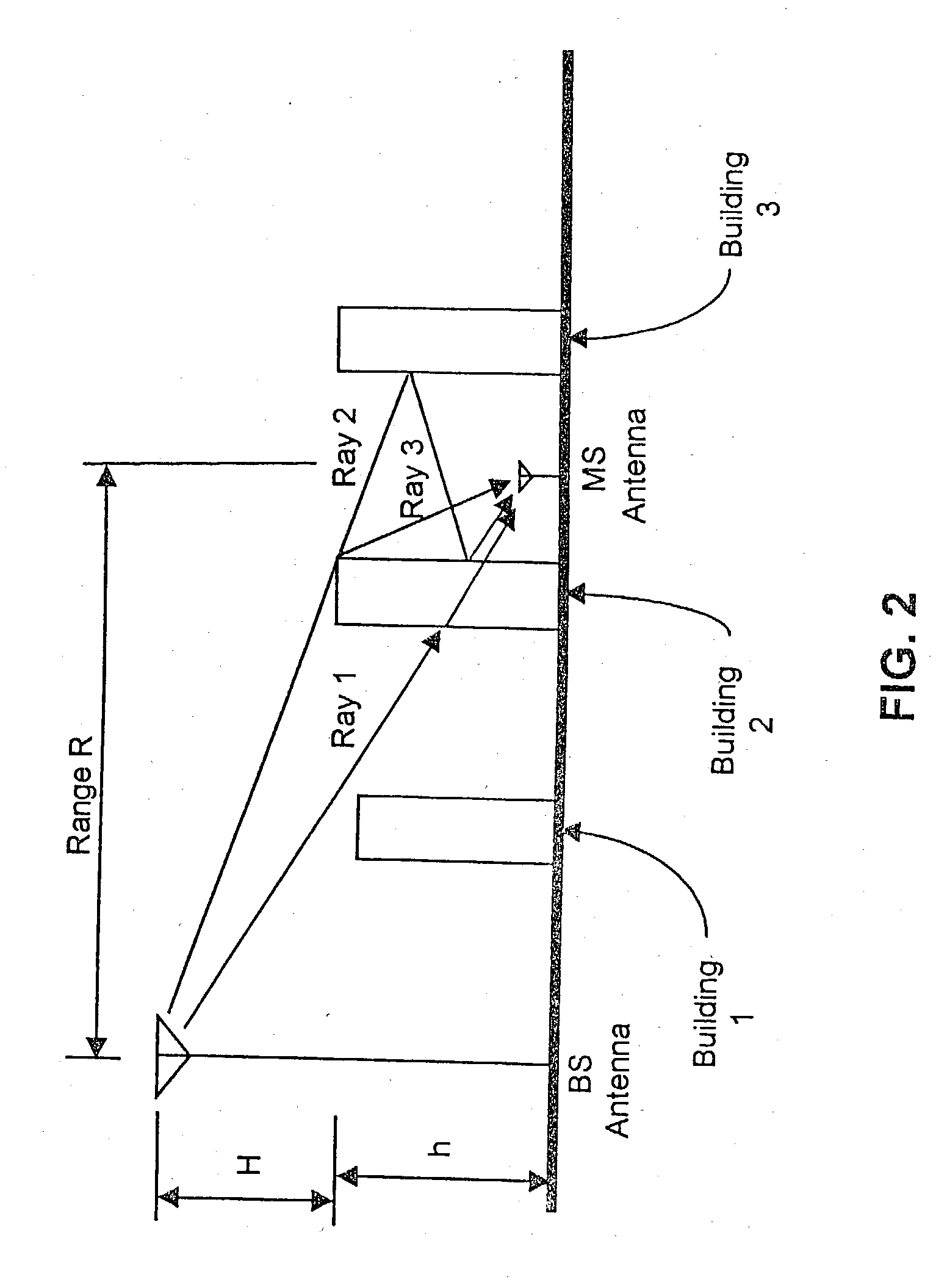
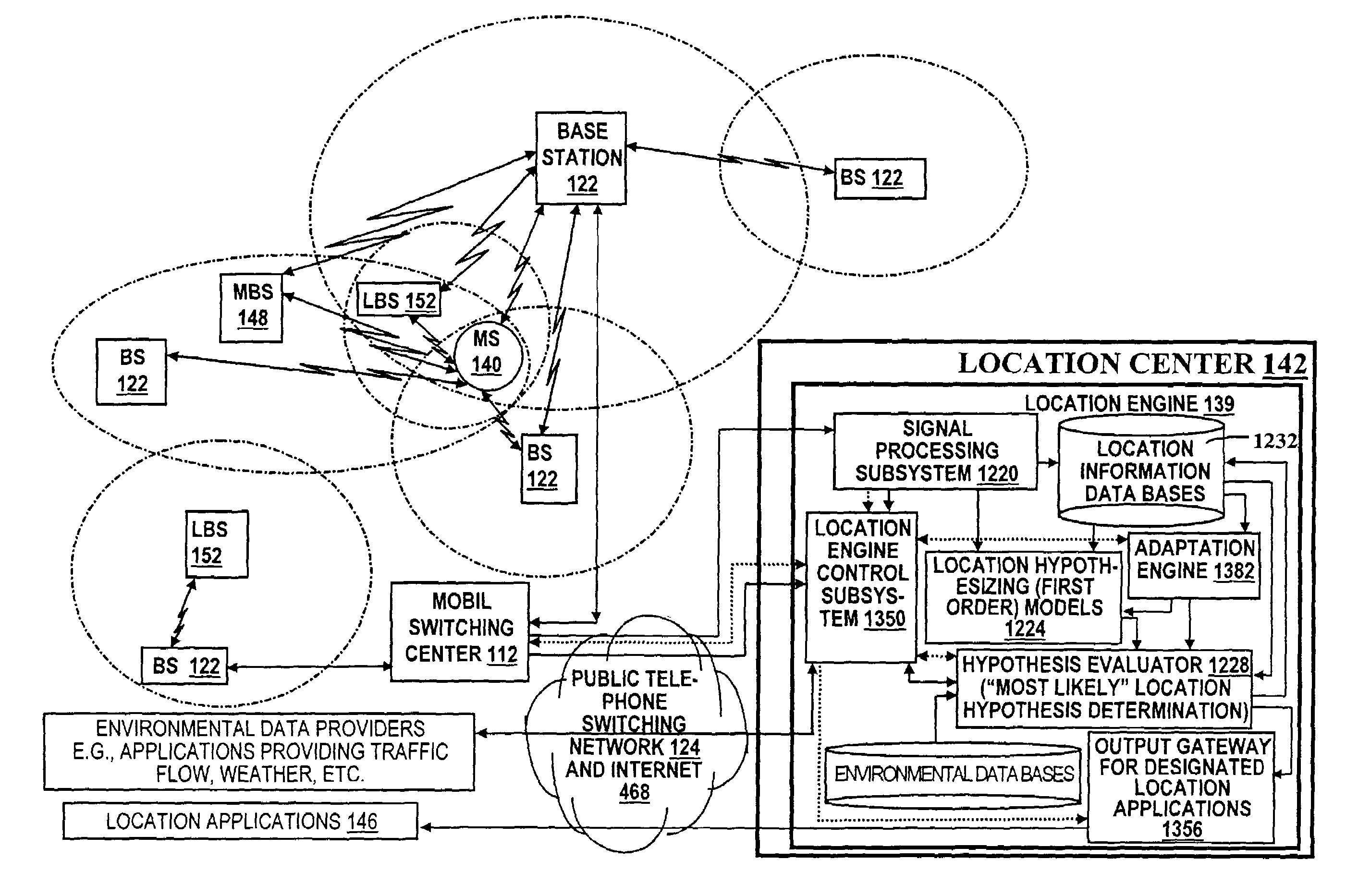
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; (5) GPS signals, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signing environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:TRACBEAM
Applications for a wireless location gateway
InactiveUS20040198386A1Easy to implementEffectively and straightforwardly resolvedPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTerrainInternet communication
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; (5) GPS signals, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:DUPRAY DENNIS J
Systems and Methods to Target Predictive Location Based Content and Track Conversions
ActiveUS20080248815A1Particular environment based servicesDevices with GPS signal receiverCommunications systemMobile device
Methods and systems that record the location of a user and transmit targeted content to a user based upon their current and past location information. A network is configured to include a server programmed with a database of targeted content, a database of location information, a database of user information, a database searching algorithm, and a wireless communication system capable of communicating with the user's mobile device. The location of the mobile device is ascertained and recorded. The location information is analyzed to determine the routes taken by the user, businesses visited by the user, and other behaviors of the user. Targeted content is sent to the mobile device of the user and whether the user visits the physical locations associated with the targeted content is monitored. Payment systems, phone exchange systems, and other features may also be integrated to provide detailed conversion tracking to producers of targeted content and business owners.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Wireless location using signal fingerprinting
InactiveUS20010022558A1Low costSpectrum efficiencyDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesInternet communicationCall tracing
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; and (4) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:TRACBEAM
Geographic location using multiple location estimators
InactiveUS7298327B2Overcome inaccurate recognitionThe result is accurate and reliableDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesTerrainHeuristic
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; and (4) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:TRACBEAM
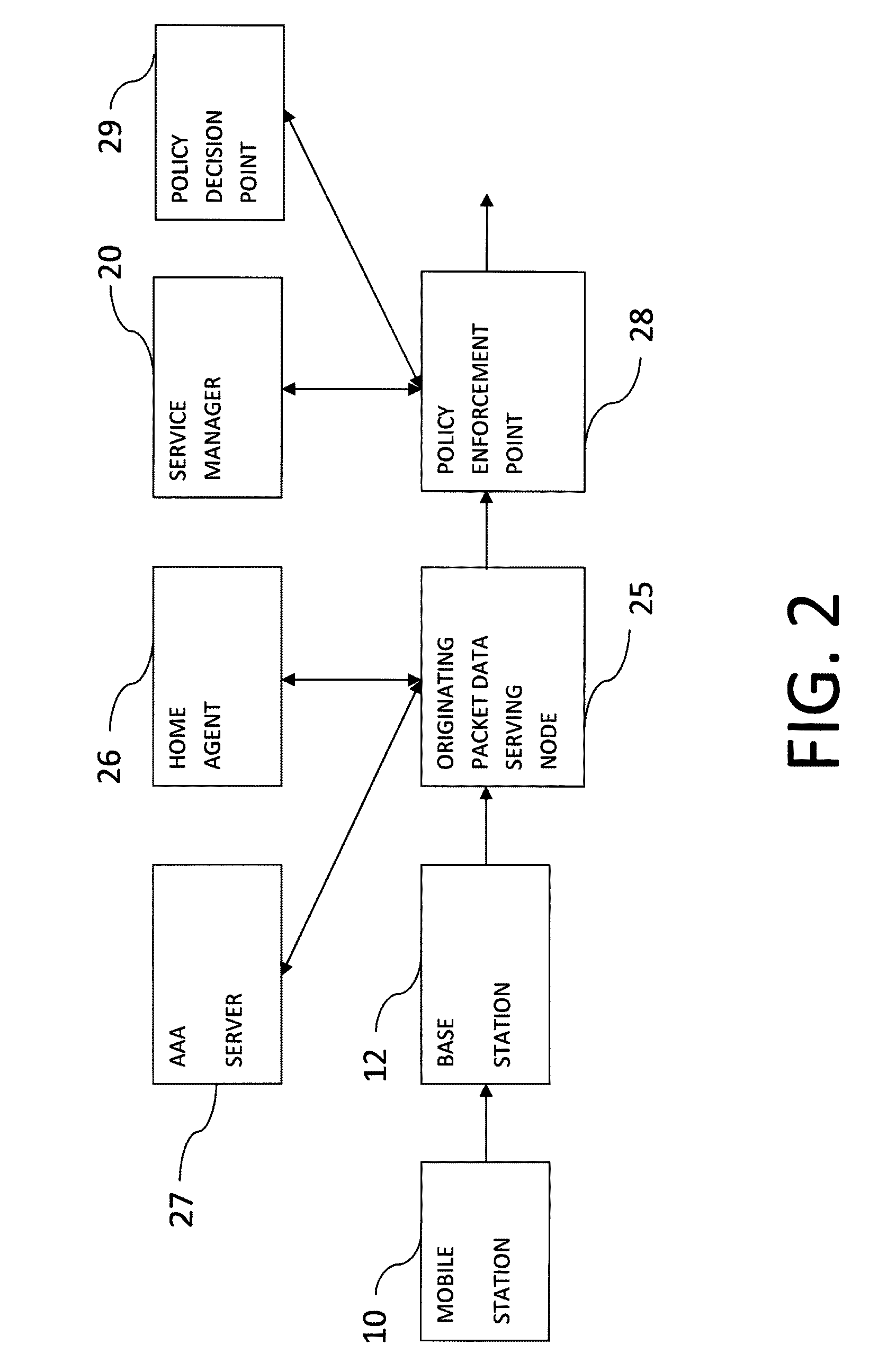
Feature management of a communication device
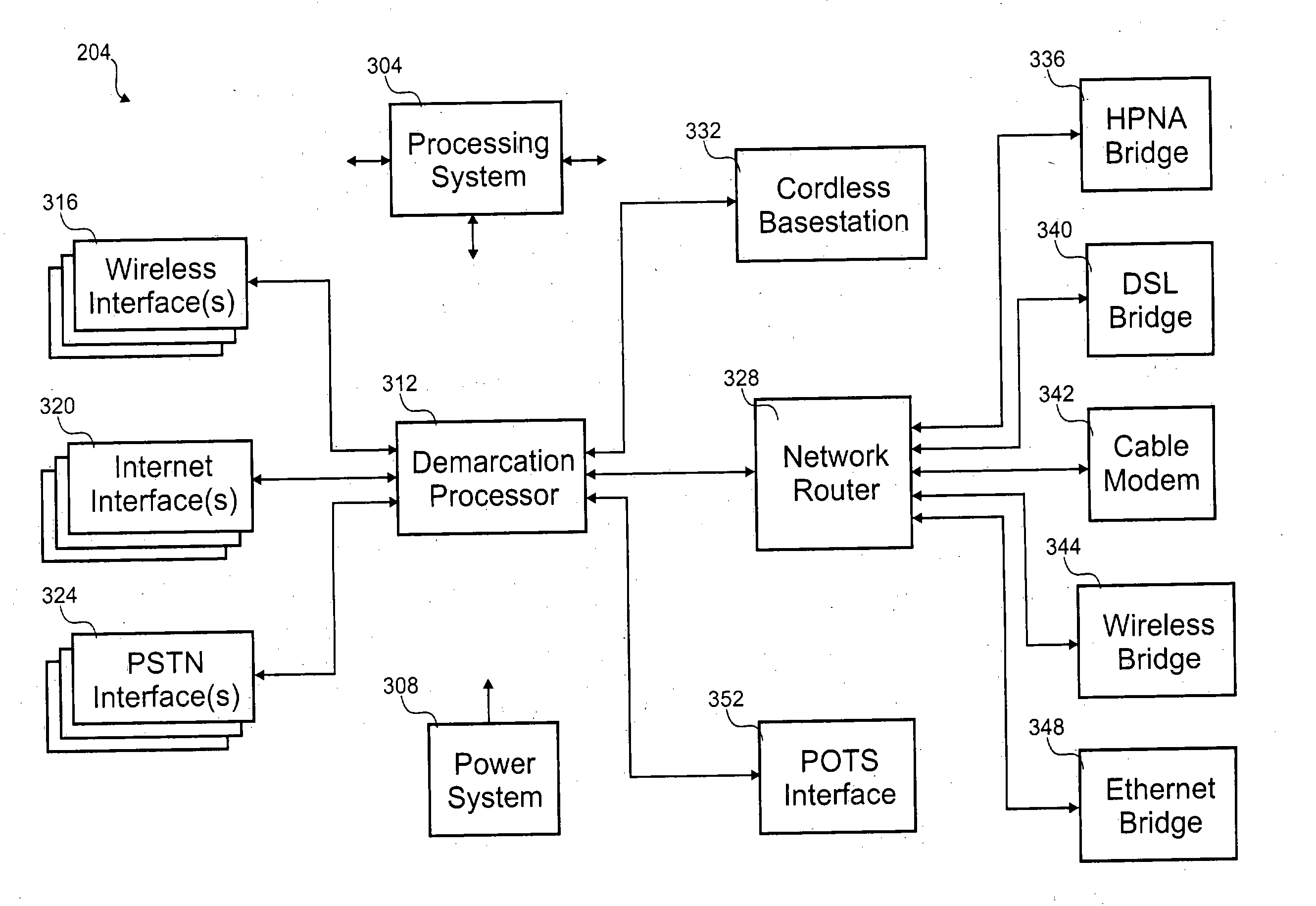
A system and method for the real-time management of a device, and more particularly to the establishment and enforcement of policies or rules associated with the feature or functions that may be performed with the device. Modern communication devices are capable of many things, including making and receiving calls, exchanging data, playing games and music, sending and receiving email, accessing web sites, and paying for goods and services. Depending on who is using the communication device, such as a child or an employee, there may be a need or desire to regulate how that communication device can be used and to determine who will pay for what goods or services. In addition to providing all of the features associated with a device, service providers need to be able to establish and enforce rules (policies) regulating how and when that device can be used and who will pay for a good or service requested by the user of the device.
Owner:KAJEET
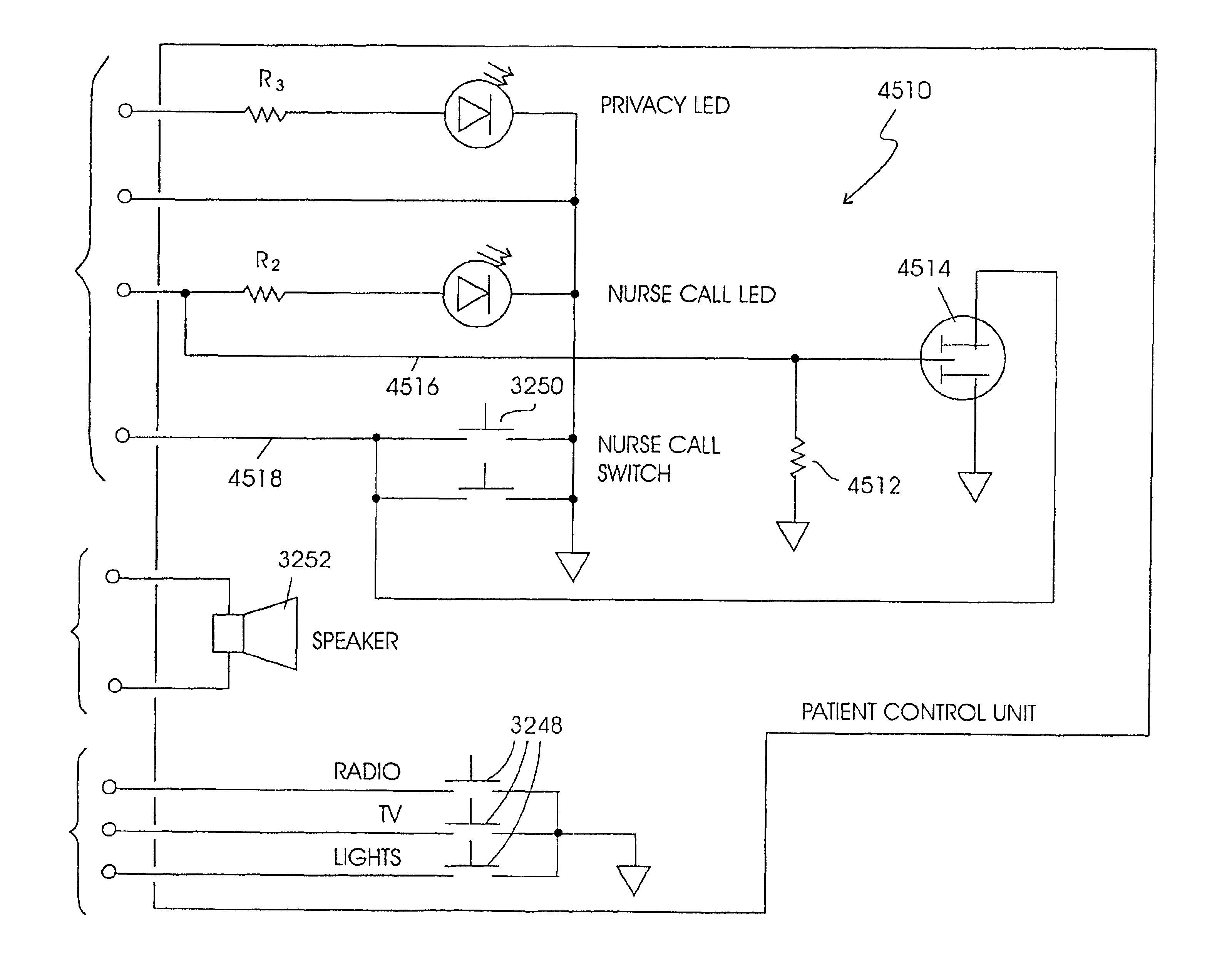
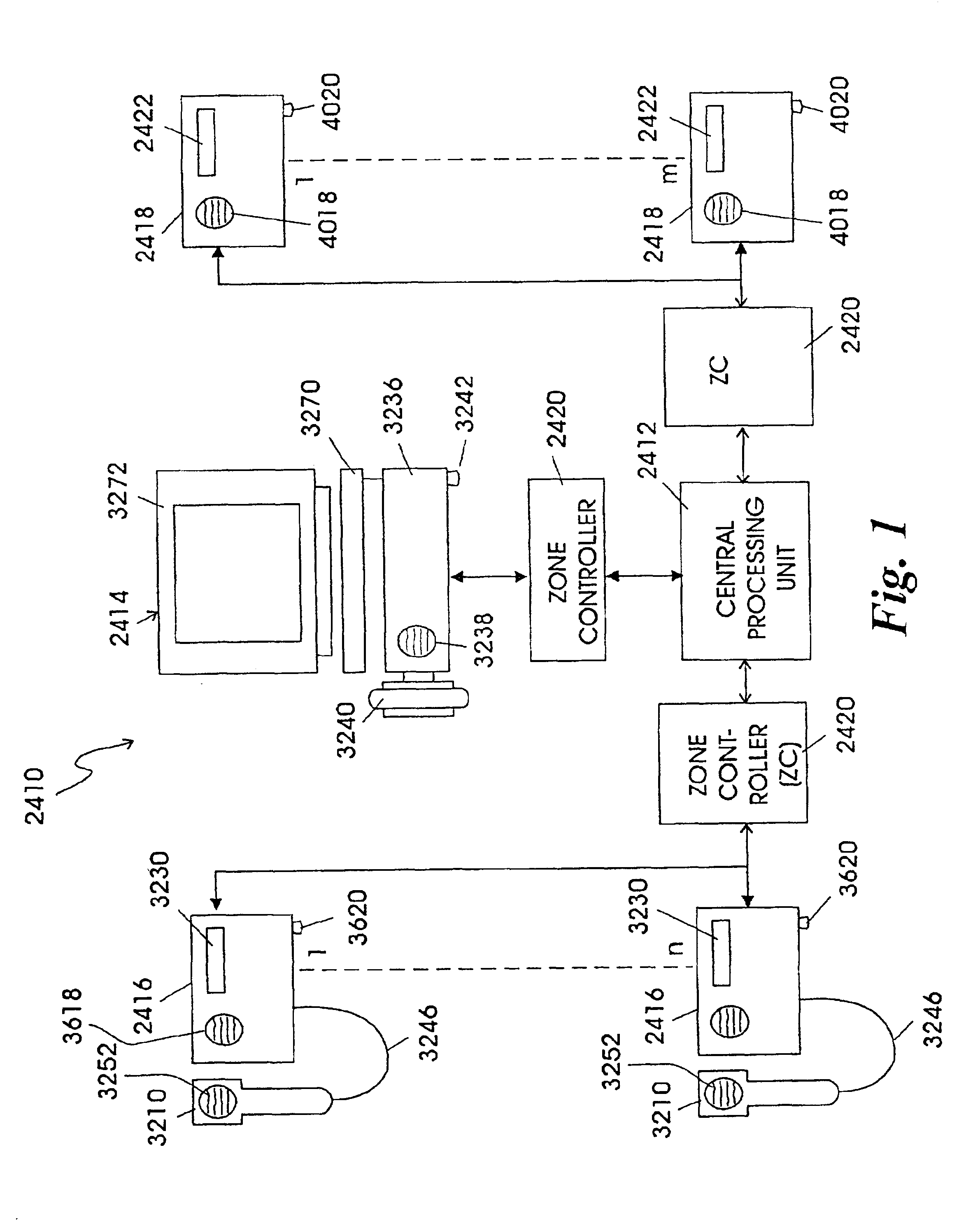
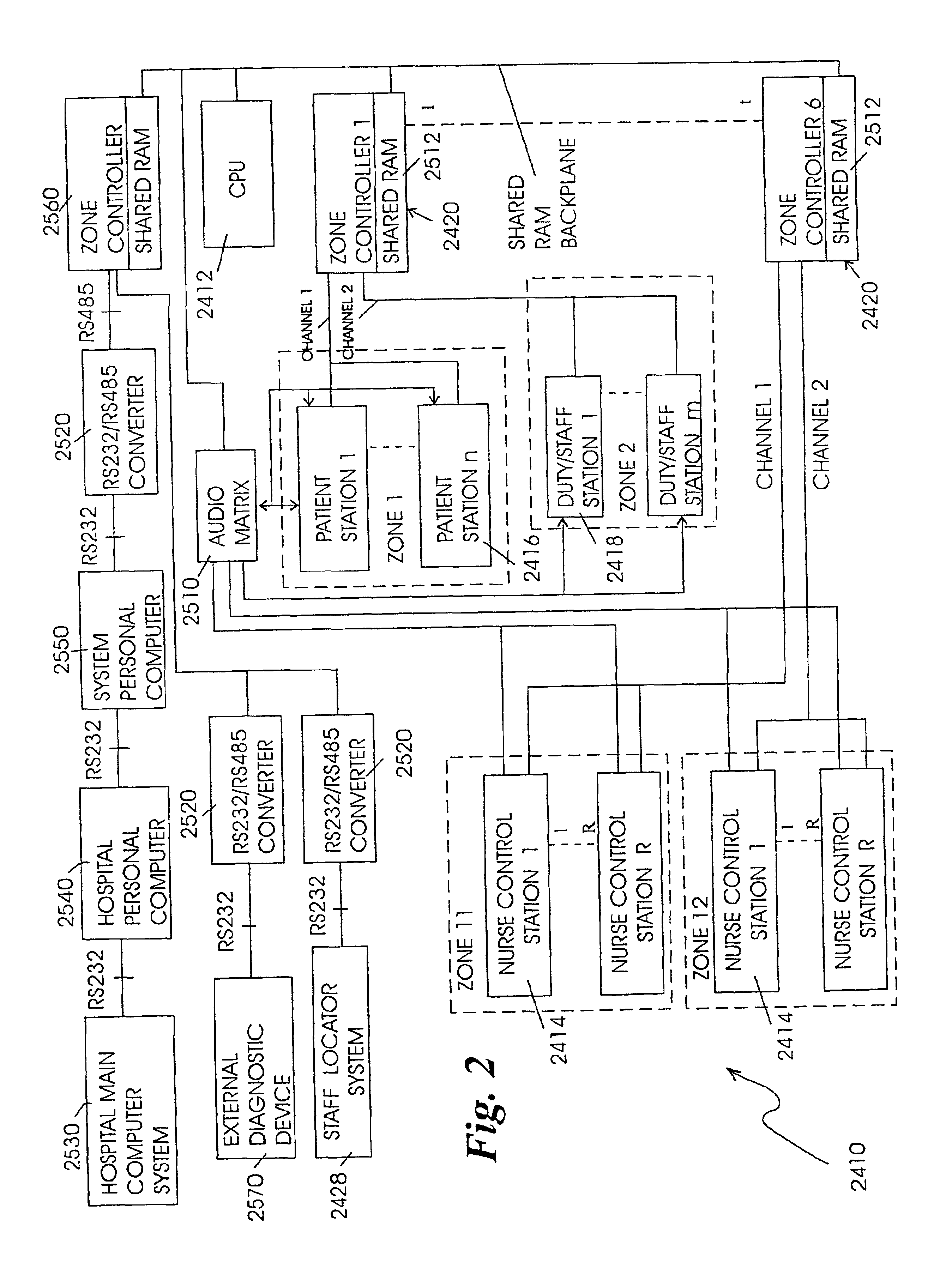
Patient care and communication system
InactiveUS6958706B2Facilitate visualFacilitate dataElectric signal transmission systemsSurgeryTelecommunications linkDisplay device
The present invention relates to a patient care and communication system which utilizes a central processing system and a plurality of remote stations electrically connected to the central processing system to facilitate visual and data communications. Each remote station includes telephone circuitry which is connected to a private branch exchange for telephone communications between stations. In addition, the private branch exchange is connected to a telephone exchange and a plurality of telephones for facilitating telephone communication therebetween. The central processing system facilitates the visual and data communications between the plurality of remote stations, and includes a system for determining which of the plurality of remote stations are transmitting the visual and data communications and which of the plurality of remote stations are to receive the visual and data communications. The central processing system also includes a system which establishes a communication link between the transmitting stations and the receiving stations. The remote stations include a processing system which also facilitates the visual, data and telephone communications and a display for displaying the visual communications. The present invention also includes a staff and / or patient locator system, in which each remote station includes an infrared receiver that receives infrared transmissions from a portable transmitter worn by a staff member or patient. The infrared transmissions include identity information associated with the person wearing the transmitter. The identity information is then transferred to the central processing system which determines the identity and location of each person wearing a portable transmitter.
Owner:HILL ROM SERVICES
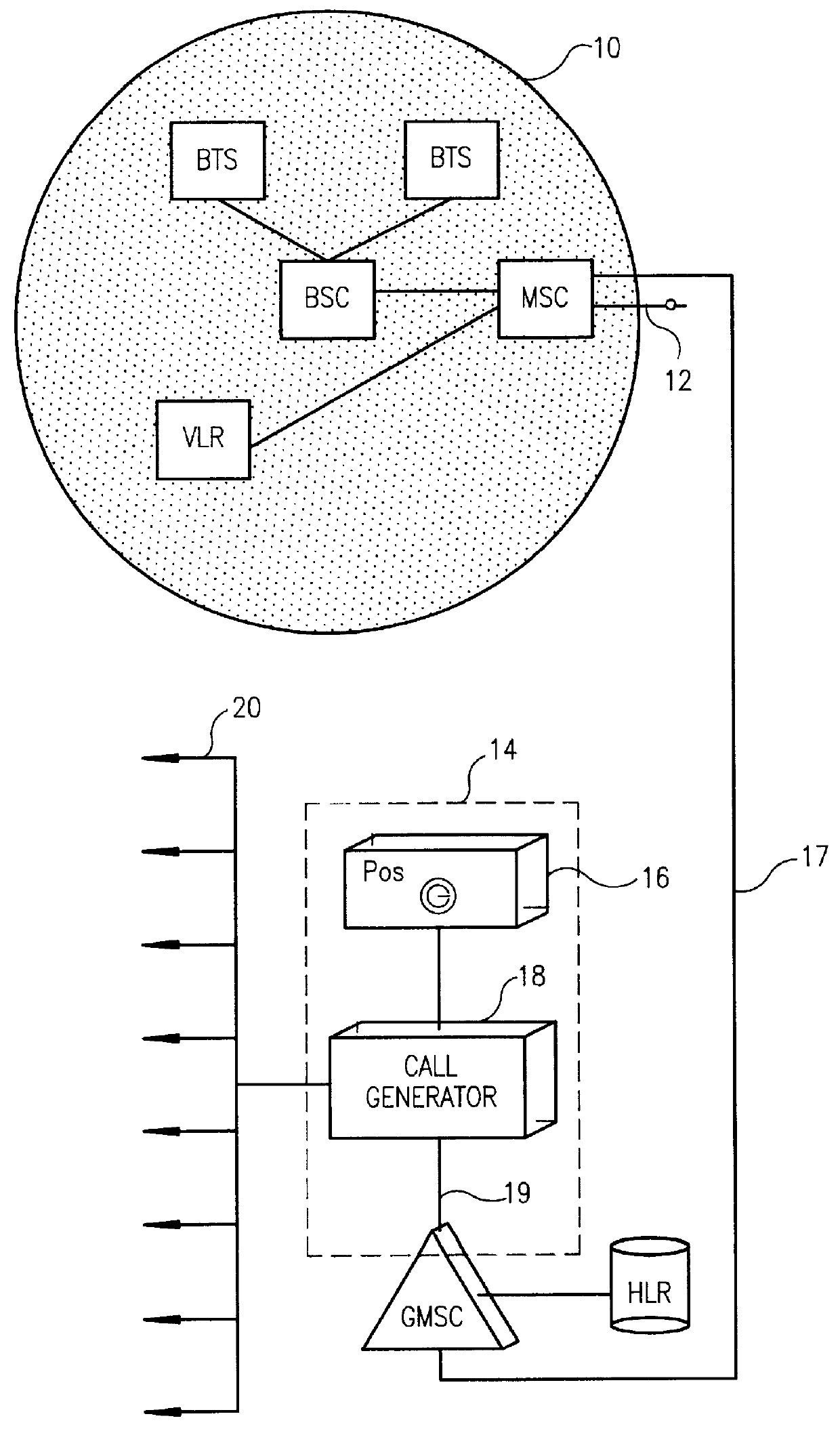
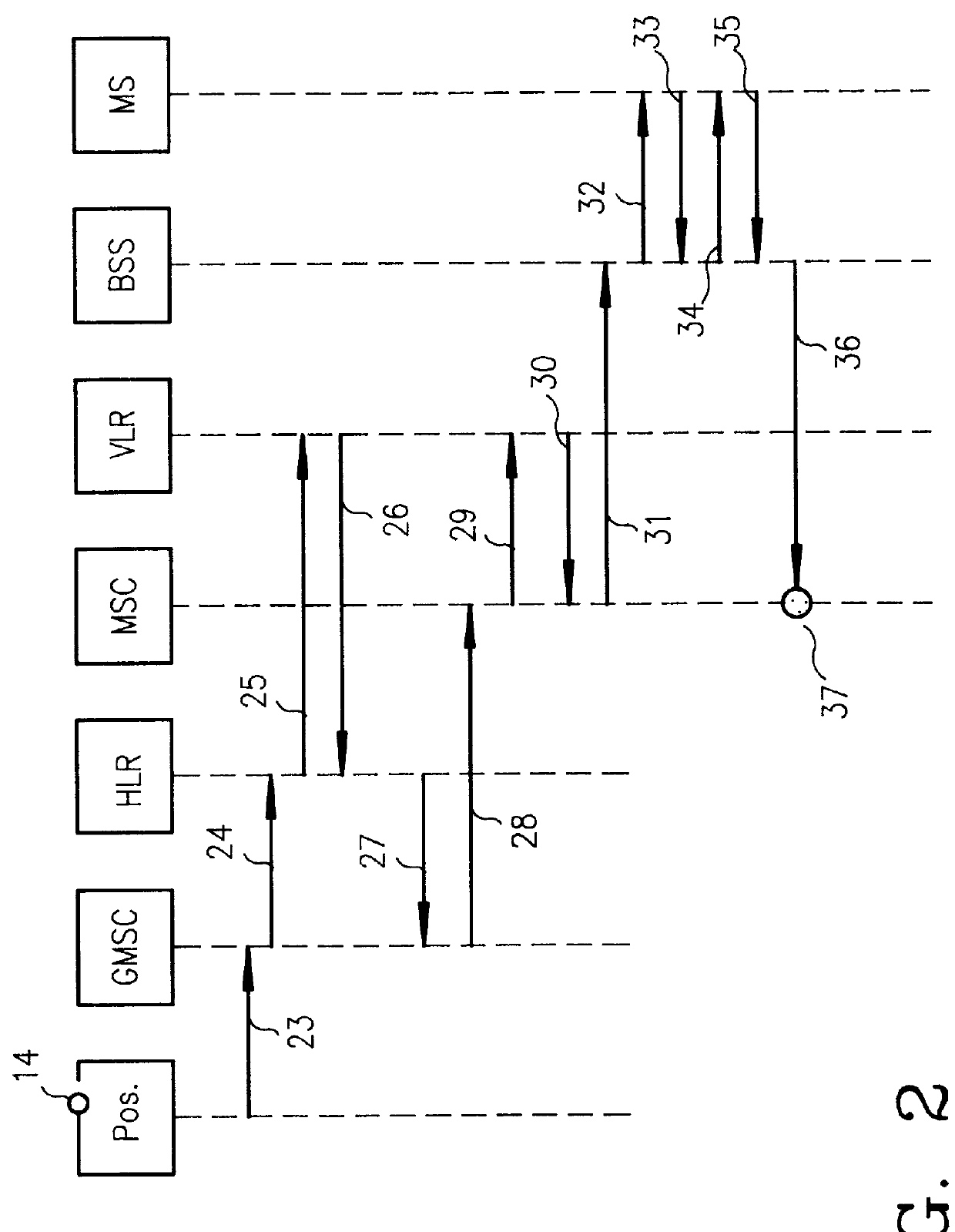
Short message service initiated cellular mobile positioning system
InactiveUS6052597ADirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationMobile Telephone ServiceGeolocation
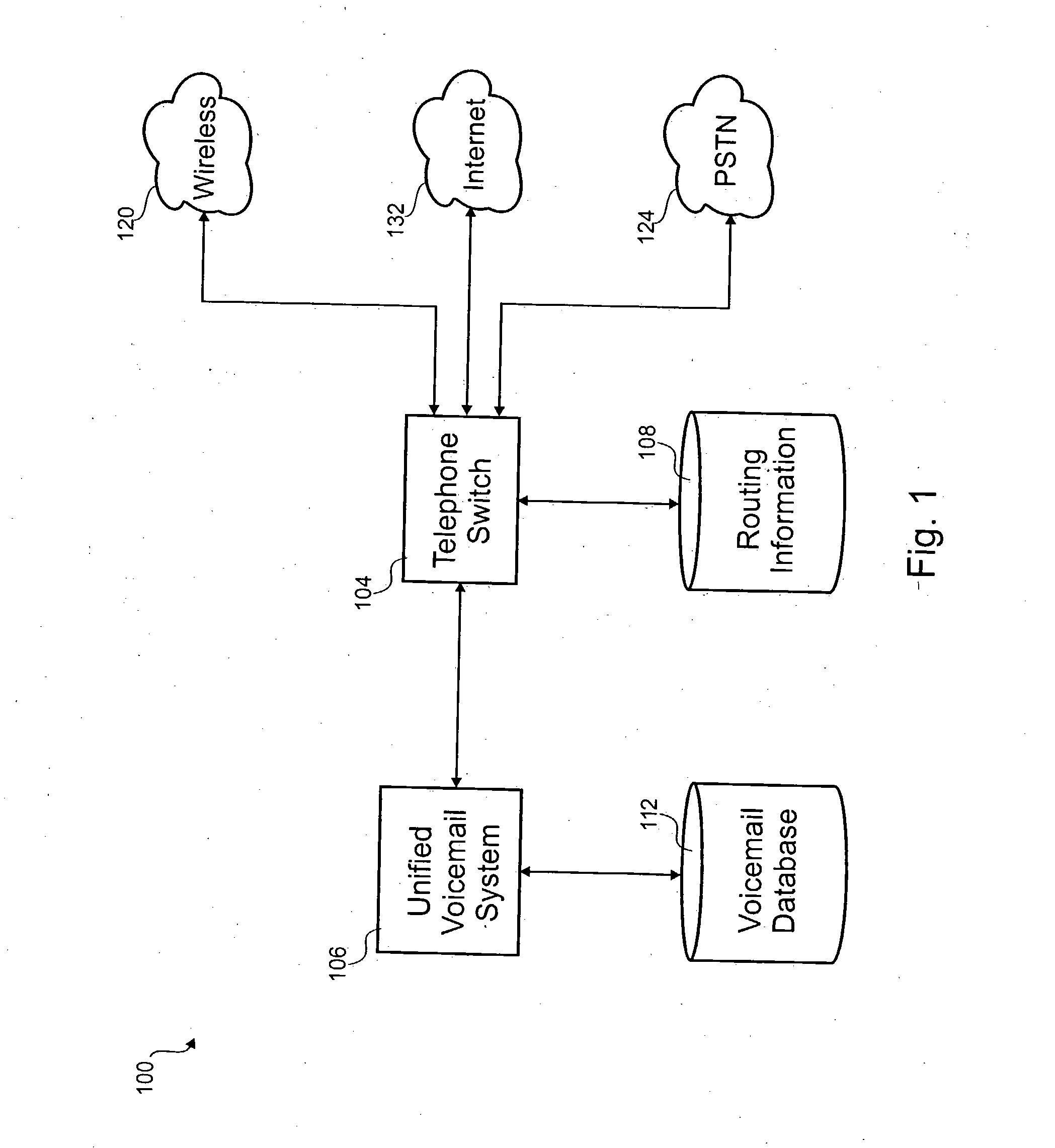
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00210 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 15, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 15, 1997 PCT Filed Feb. 16, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 25830 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 22, 1996The position of a mobile station in a cellular mobile telephone system, particularly a GSM system, is determined by carrying out a simulated call setup, i.e., the call setup is interrupted subsequent to a telephone switching center (MSC) having received a paging response containing the identity of the cell and, optionally, a timing advance. The simulated call setup is initiated by generating a modified short message signal (SMS) which is not registered in the SMS catalogue of the mobile station and which is not shown to the user of the mobile station. The SMS commands the mobile station to carry out a position determining sequence in order to establish parameters for use in establishing the position of the mobile station, for example by commanding the mobile station to connect itself to a base station contained in its neighbor list, analyze the geographical position of the base station, and subsequently send the position determining parameters to a position handler. The geographical position of the base station is analyzed from the cell identity and, if available, the timing advance, the position of the mobile station being presented graphically on a picture screen and constantly updated after each call setup. The call setups are generated by the position handler.
Owner:EUROPOLIGRAFICO
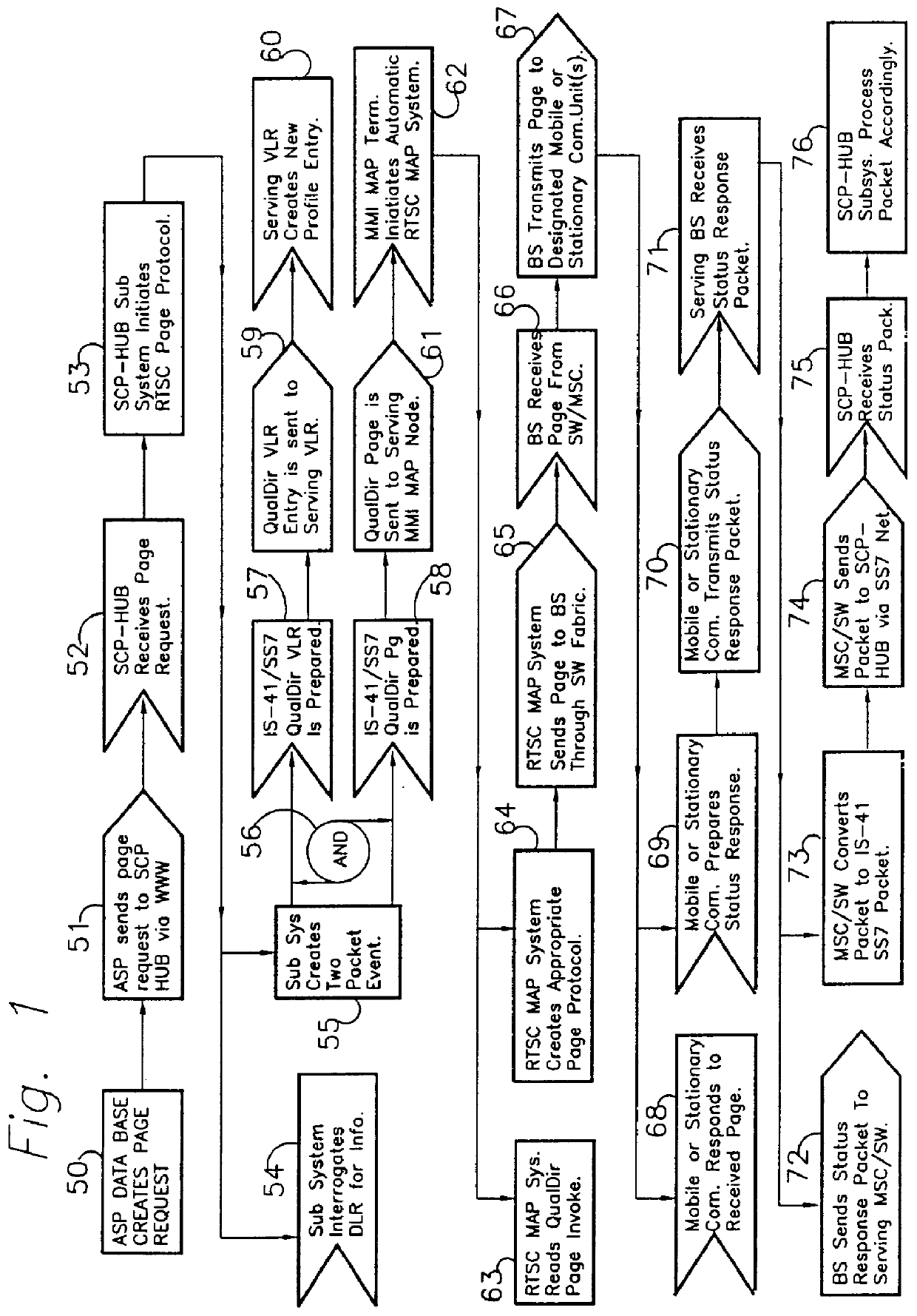
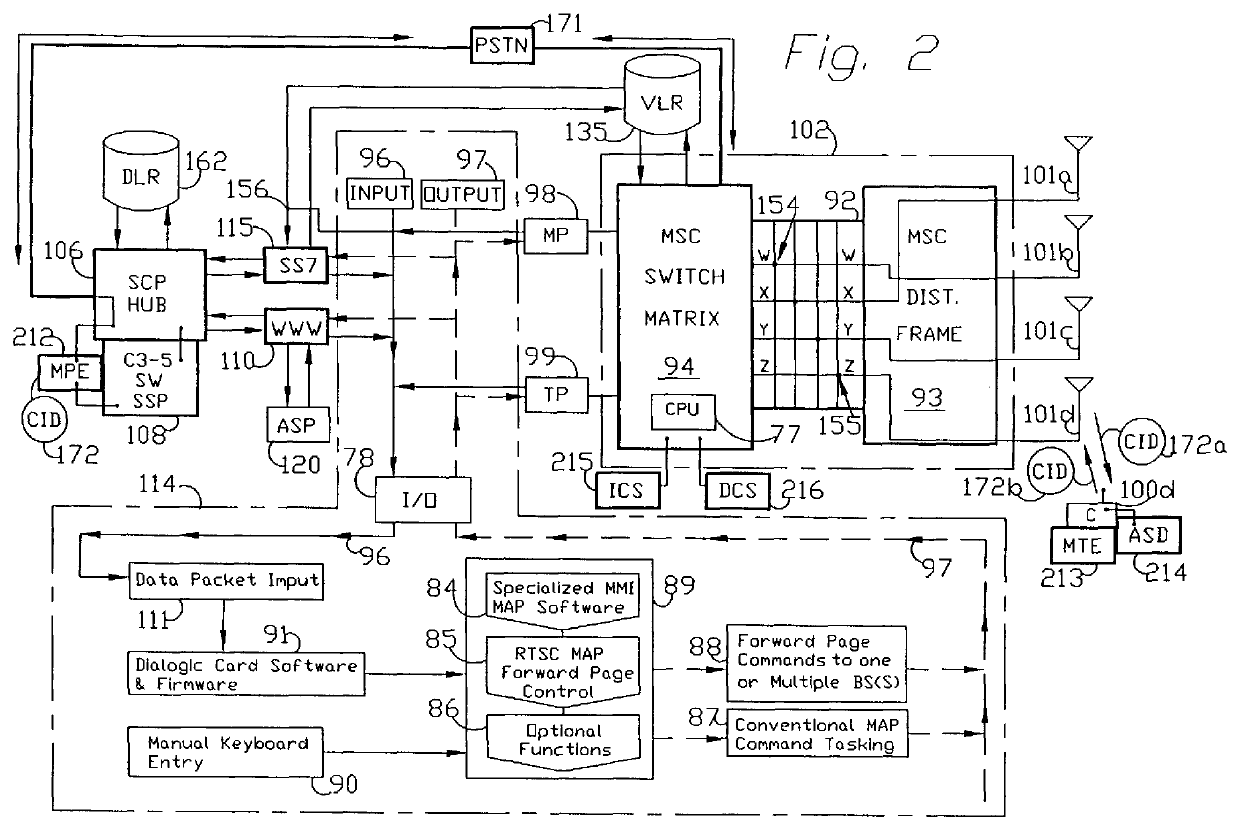
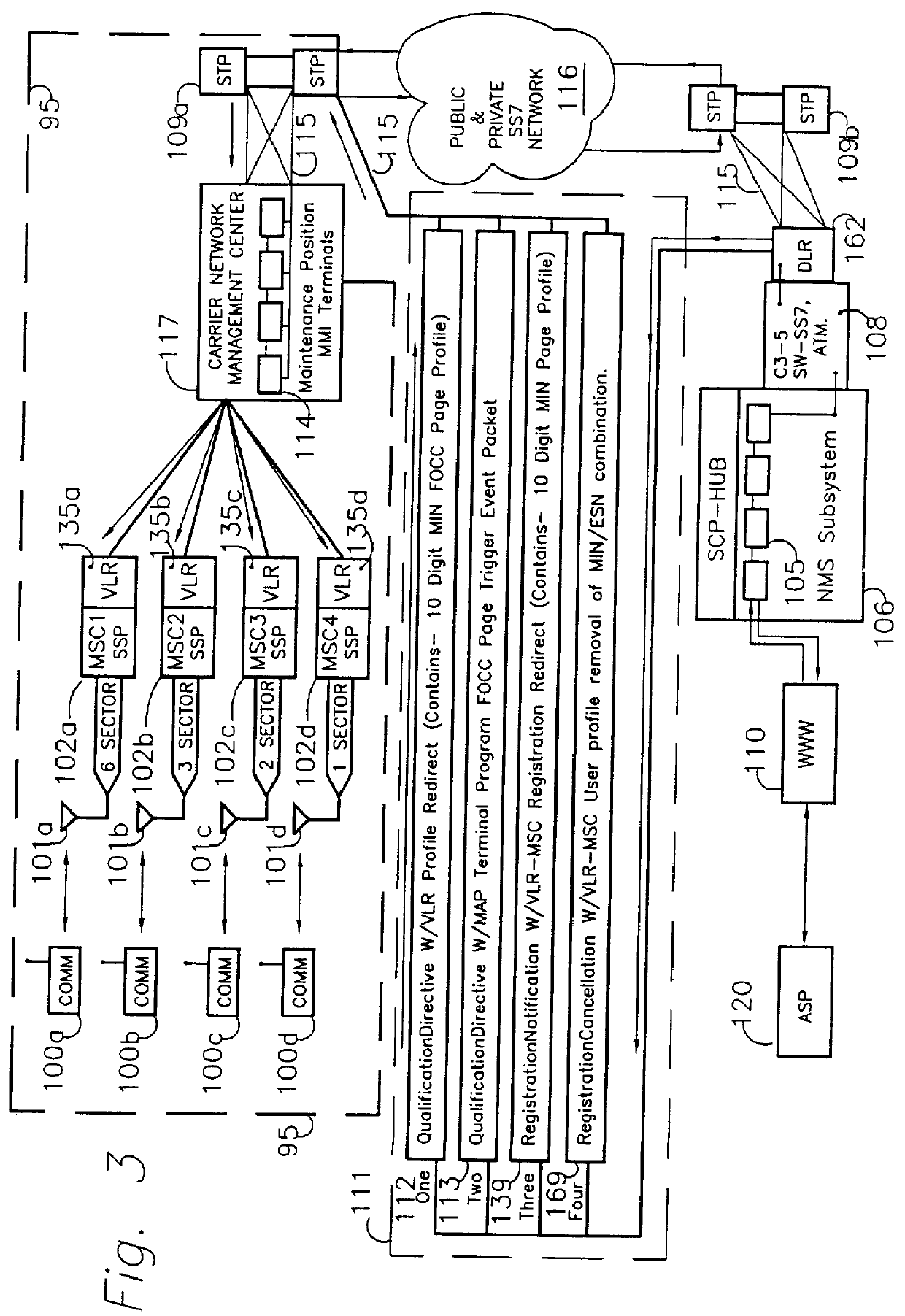
Method and apparatus for remote telephony switch control
InactiveUS6070070AEnabling message/page call delivery (MPCDMultiplex system selection arrangementsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsMobile identification numberElectronic serial number
A command, such as an application specific command, is communicated from a central host to a remote station via a cellular mobile radio network. The station may be a fixed or roaming device. The central host sends the command a network switch, such as an SS7 SSP, wherein the command comprises a mobile identification number (MIN) and an electronic serial number (ESN). The network switch queries an associated HLR database to locate the remote station, the query specifying the MIN and the ESN. If the HLR does not recognize the MIN / ESN combination, it so informs the network switch, as well as the VLR associated with the MSC serving a remote station identified by the ESN. In response to the notification from the HLR, the VLR removes any entry in its database relating to the ESN and updates its database with the new MIN / ESN combination transmitted by the HLR to the VLR. The VLR confirms with the HLR that it has taken these steps and then sends the command to the remote station by calling the station using the new MIN / ESN.
Owner:AERIS COMM
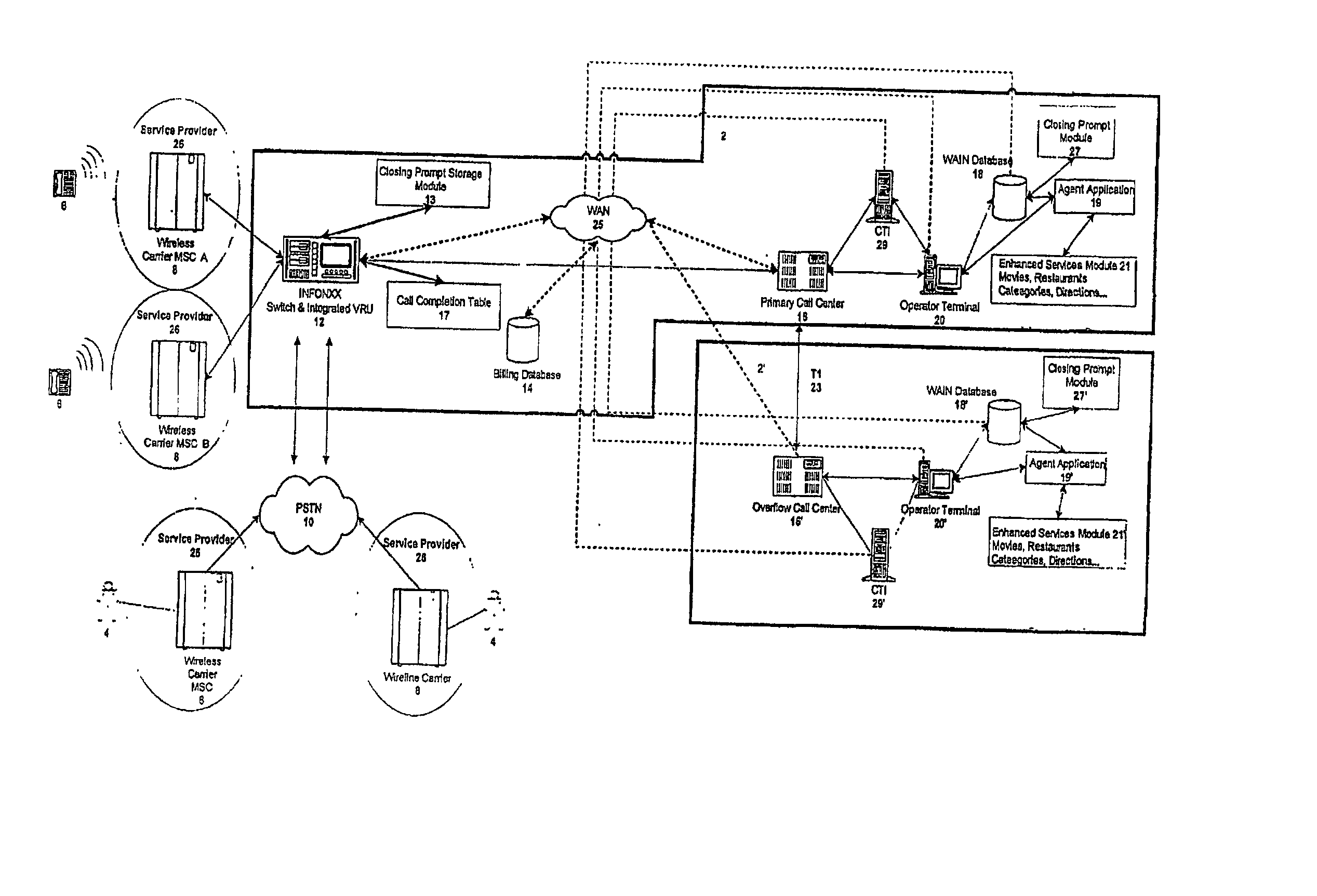
Communication assistance system and method
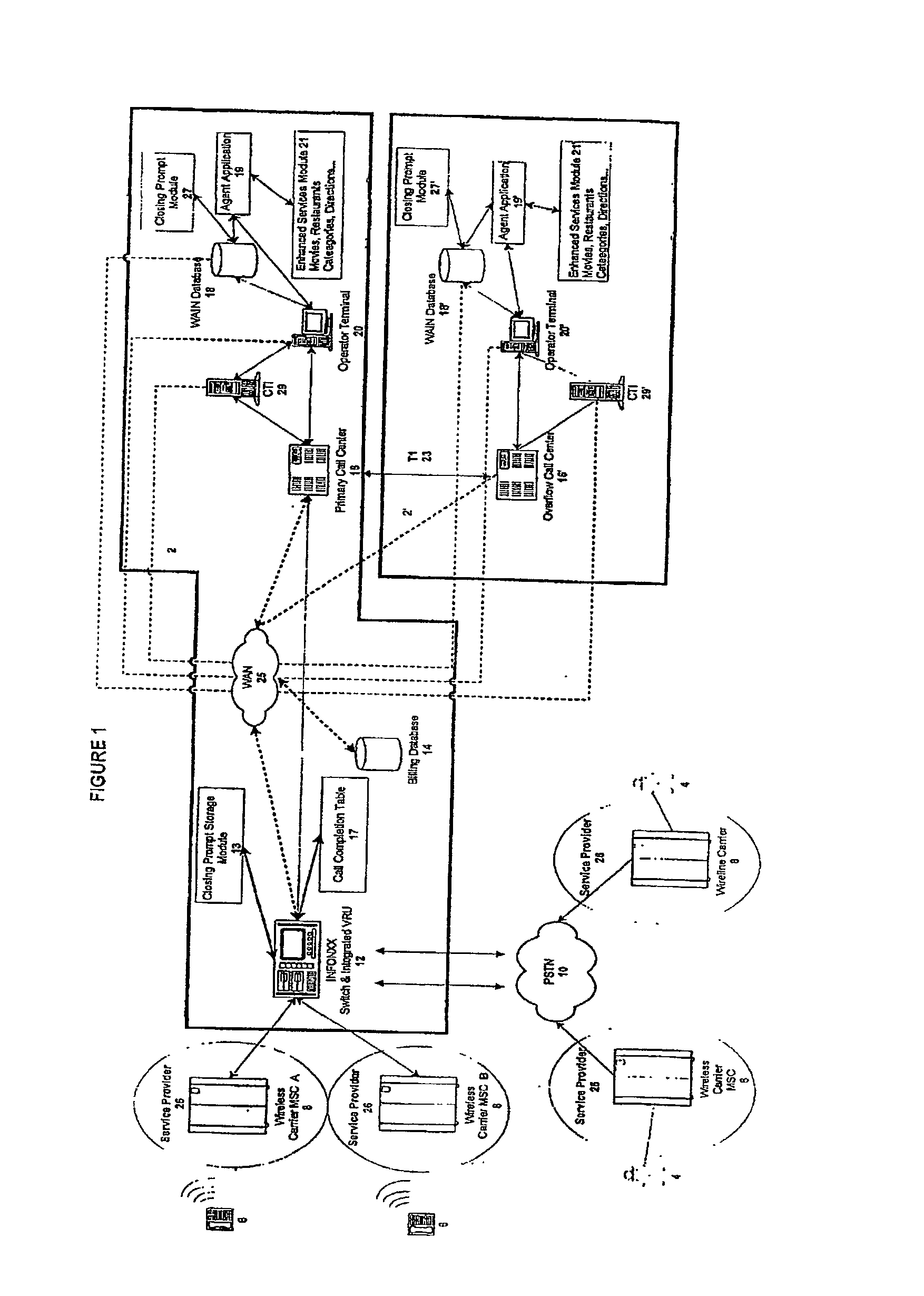
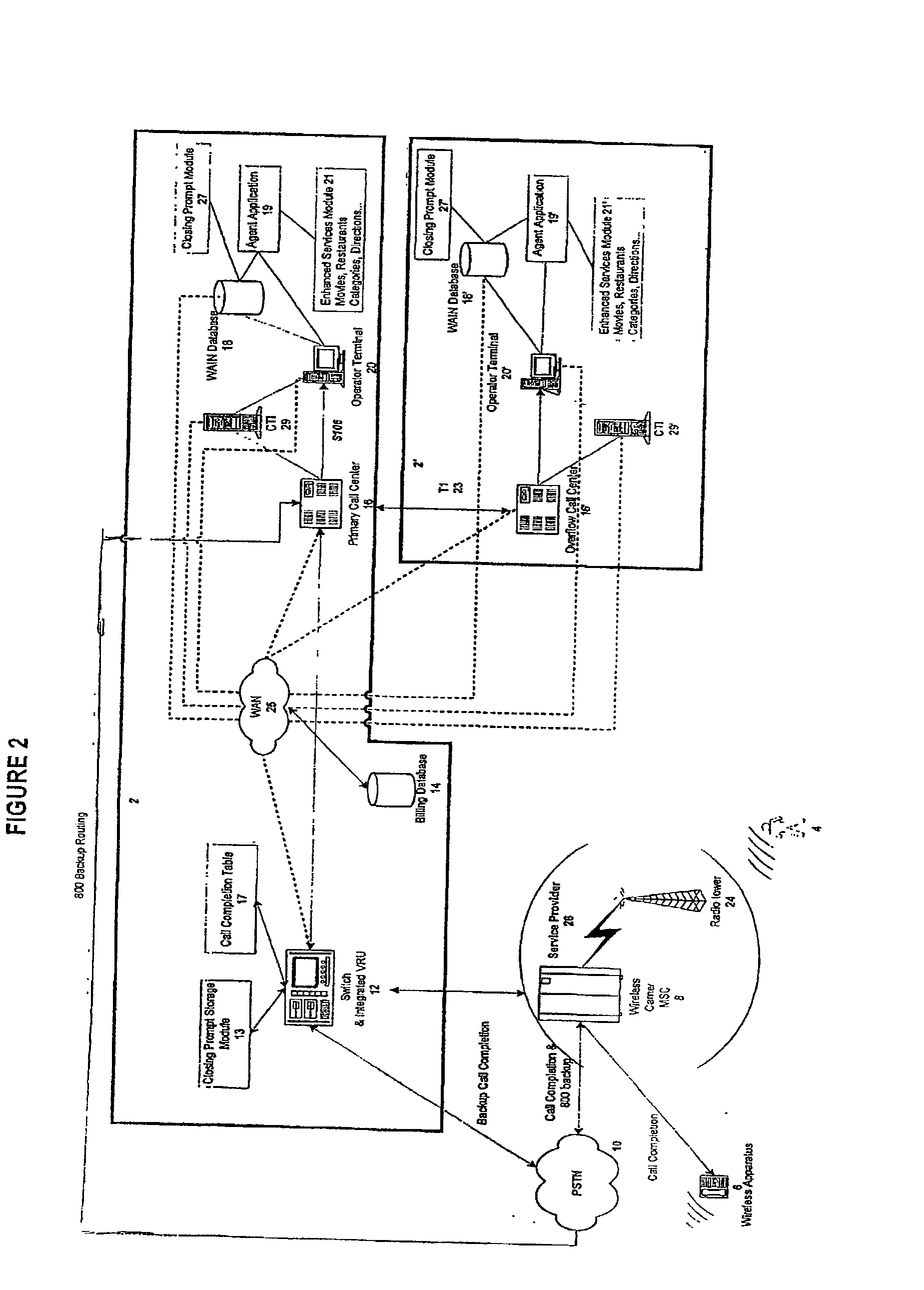
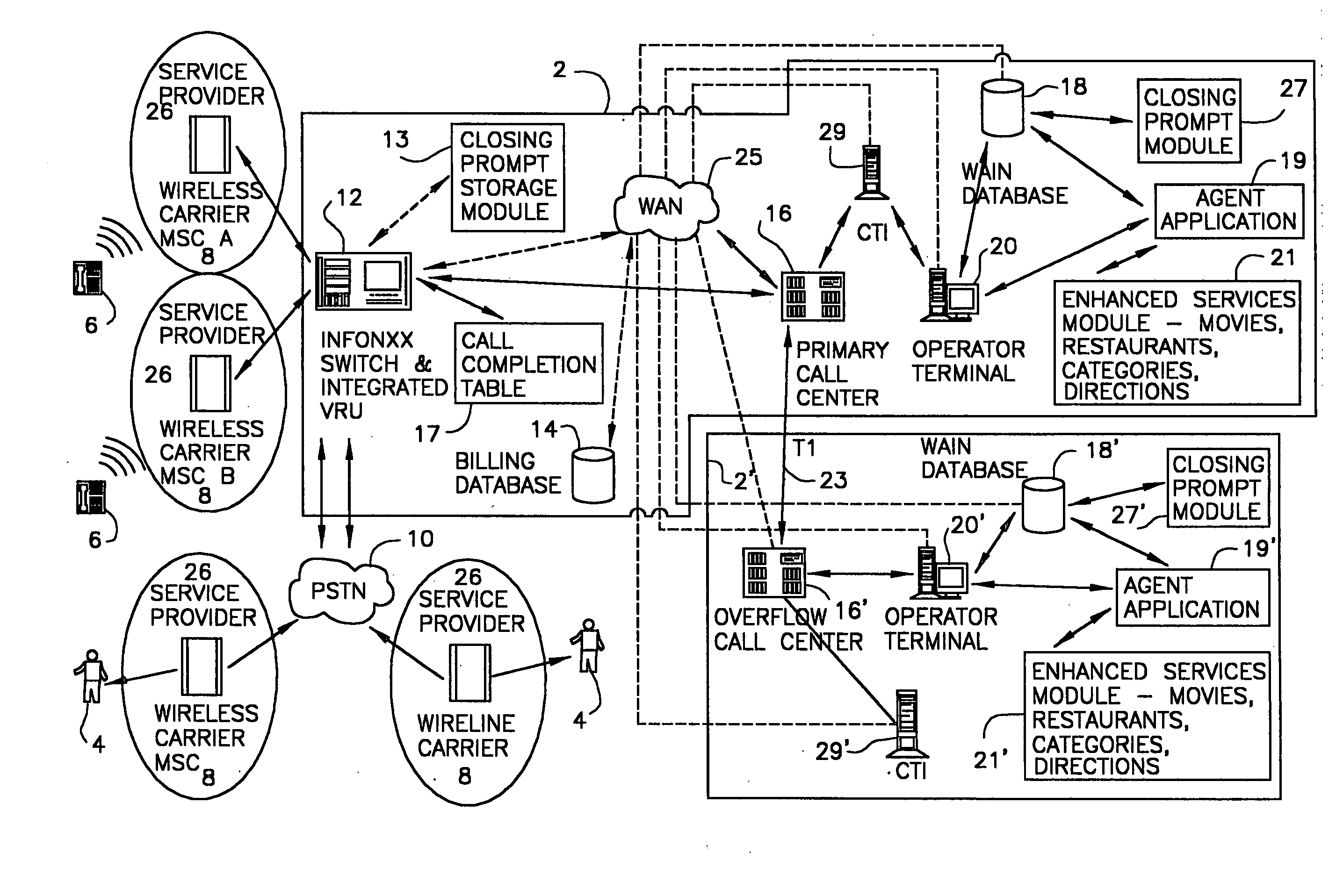
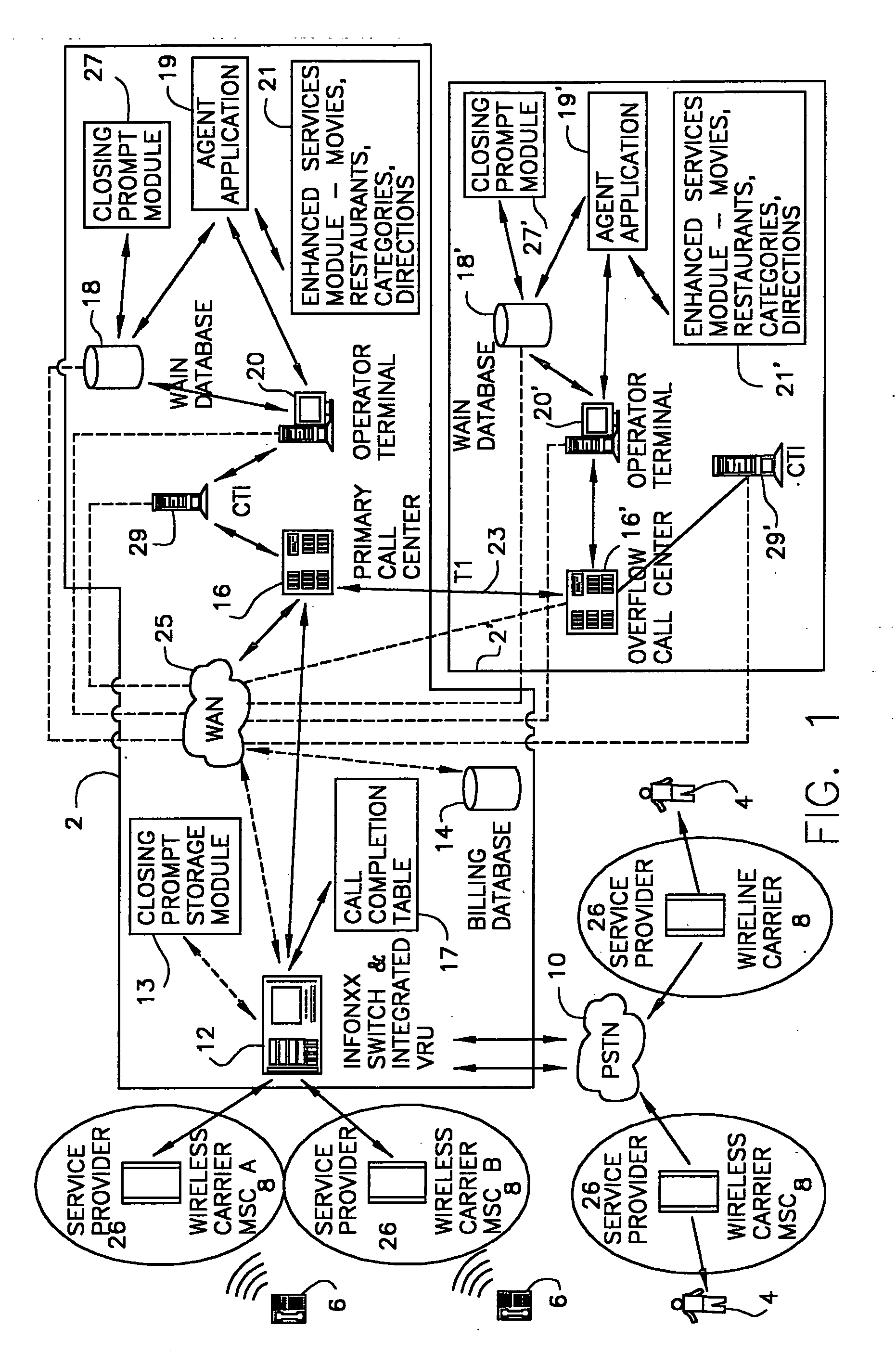
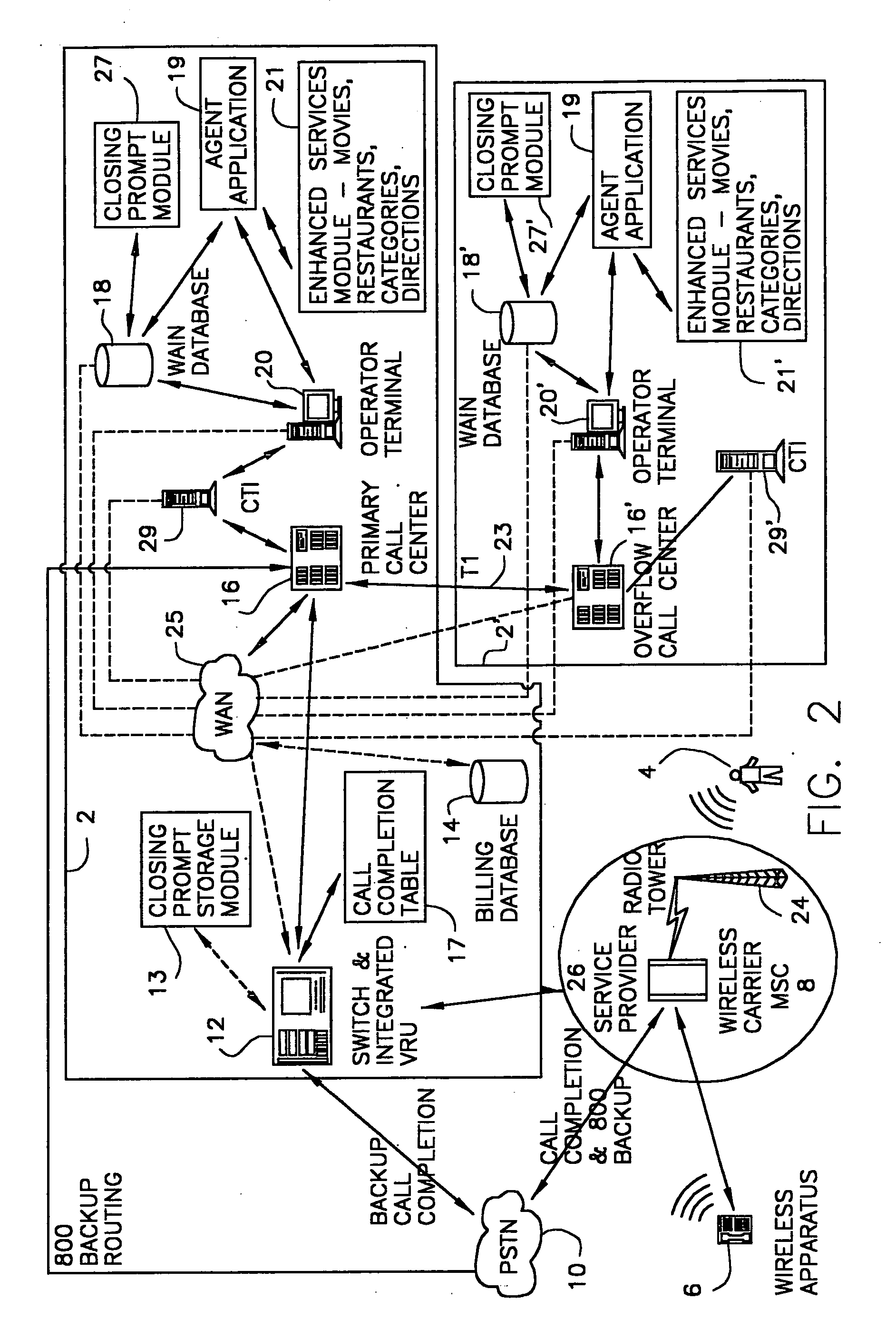
InactiveUS20030007625A1Convenient and efficient accessImprove securitySynchronisation arrangementInterconnection arrangementsMobile Telephone NumberAuxiliary system
A communication assistance system (2) is provided for accessing information corresponding to a plurality of subscribers (6). This system is comprised of a telephone switch (12) for receiving calls from a plurality of requesters (4), a call center (16) for routing each of said received calls to an operator terminal (20), and a first database (18) configured to store said information corresponding to each of said subscribers (6). The system (2) provides: a dynamically controlled closing prompt; an interface feature allowing subscribers (6) to update their own information; a dial string translator for identifying service provider of the requester (4); a billing database (14) for transferring call charges of the subscriber (6) to the requester (4); a processor to notify subscribers (6) to update their information; the ability to store license plate numbers of the subscribers (6); a masking feature that allows system (32) to connect requester (4) to subscriber (6) without revealing subscriber's (6) mobile telephone number, a searchable database of subscriber (6) information based on particular information found in the subscriber (6) listing.
Owner:GRAPE TECH GROUP
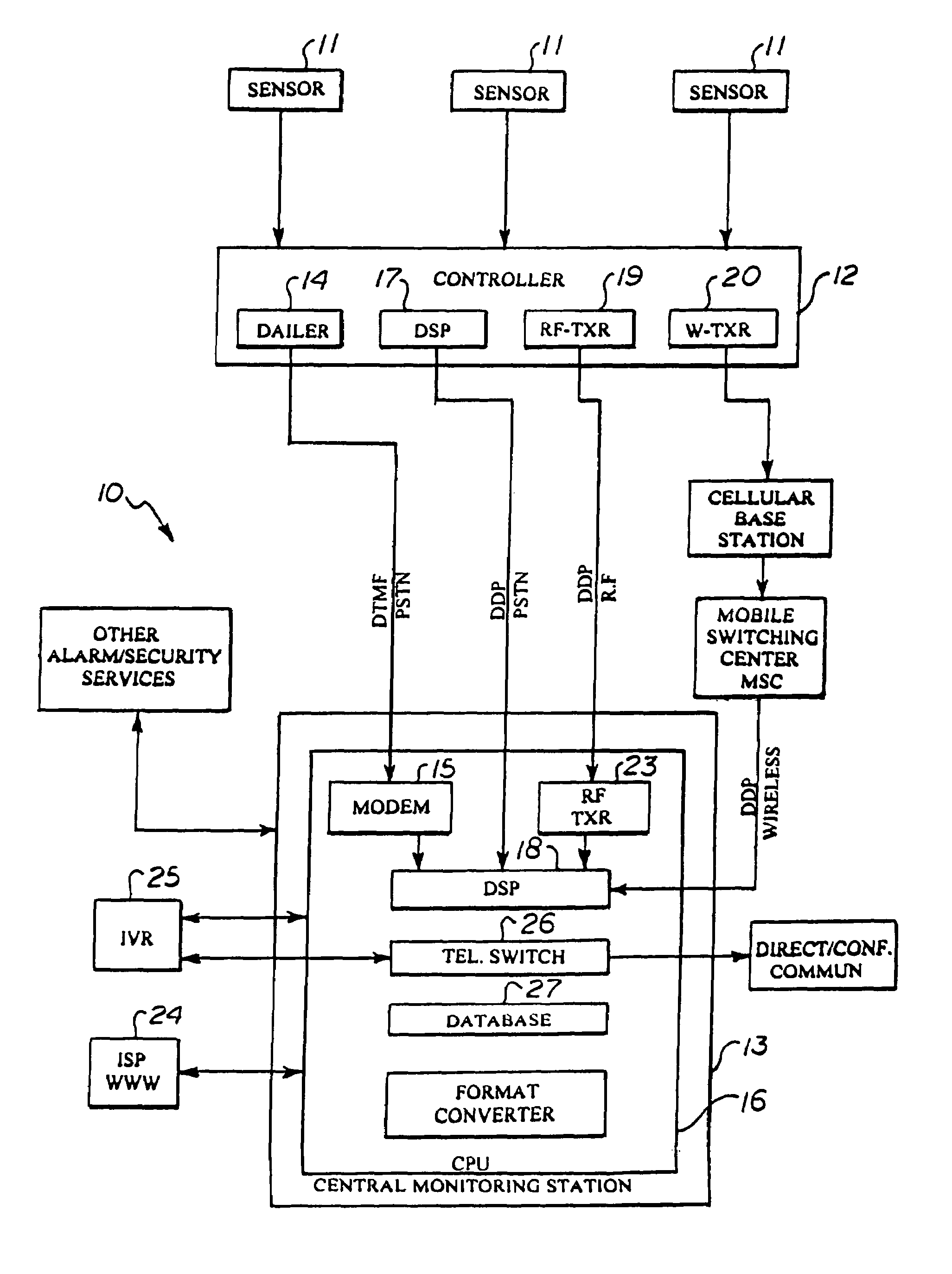
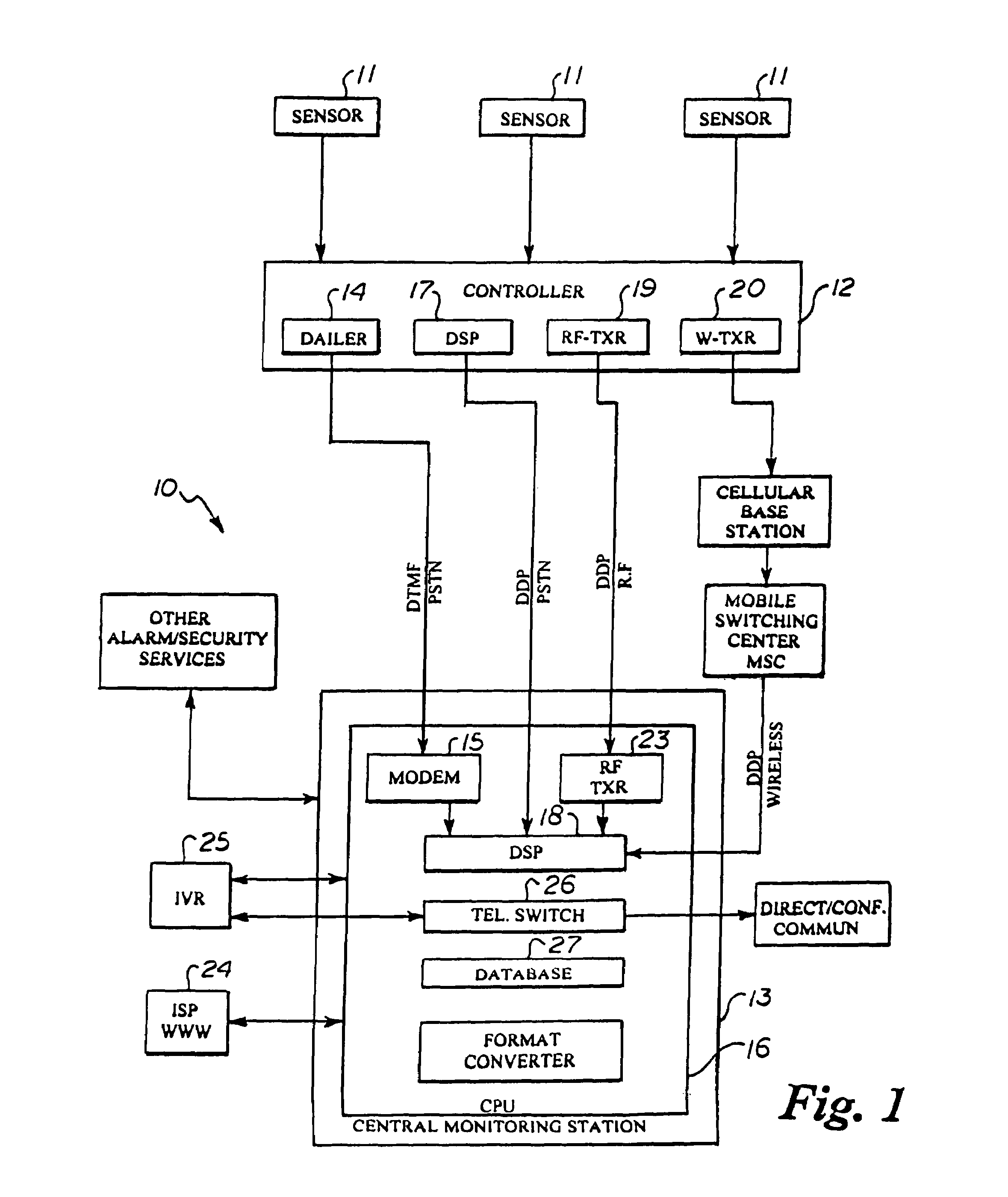
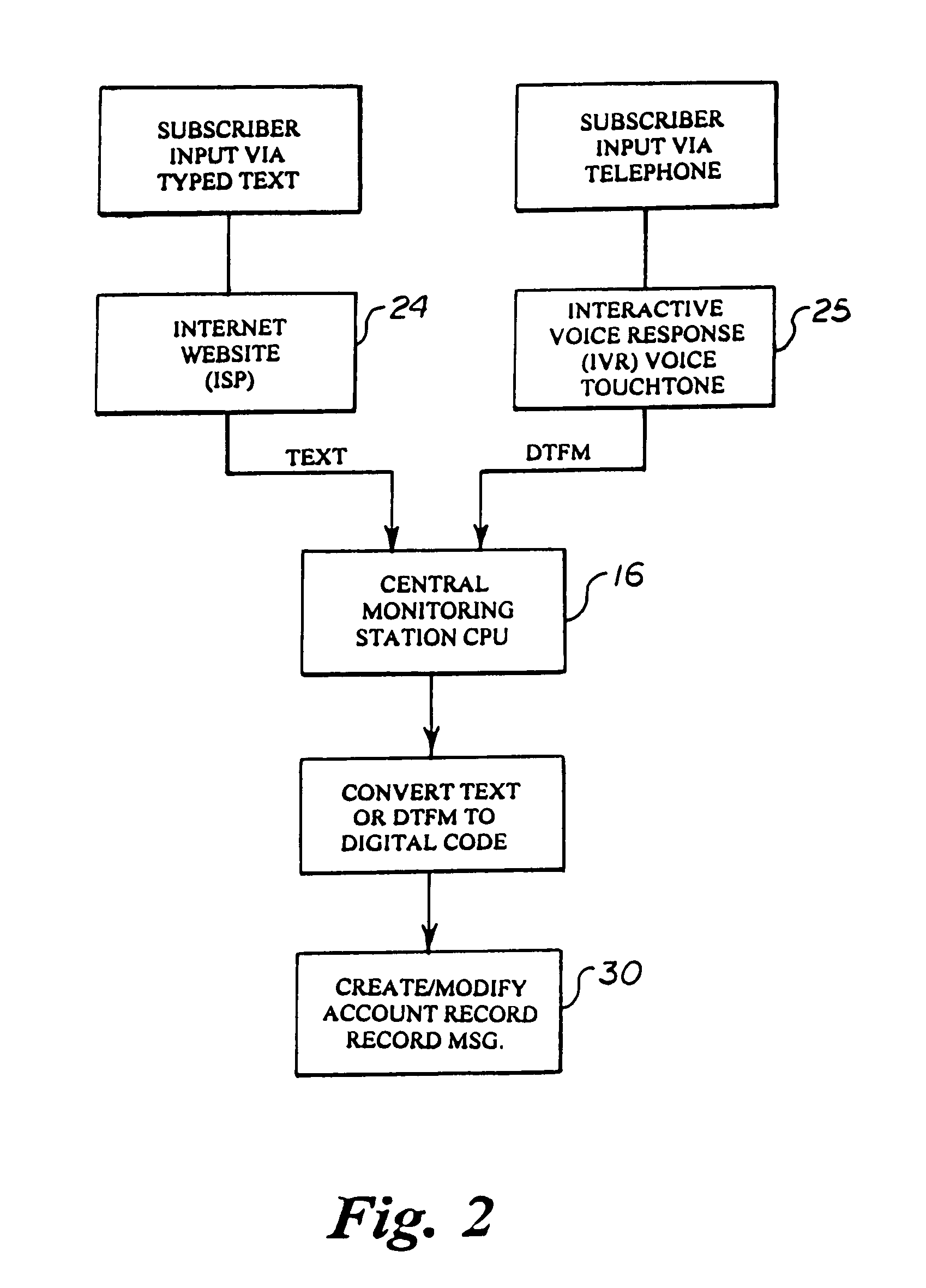
Automated parallel and redundant subscriber contact and event notification system
An automated parallel and redundant subscriber contact and event notification system capable of being triggered by the change in status of any sensing device or process including the sensor of an alarm system or other event. The system enables automated simultaneous contact of one or more persons over a plurality of telephonic and electronic communication channels and provides parallel event-specific notification via voice, pager, voice mail, fax and email to the recipient(s) that are identified by electronic or speech recognized entry of a PIN and then provides them with a detailed message including the date and time of a specific event which has occurred with respect to a monitored sensor. A telephone switching or conferencing feature allows the recipient(s) to communicate directly with a predetermined or pre-programmed location or person or select from a menu based upon the type of event that has occurred and the pre-programmed selection list. The system may be custom programmed by the authorized subscriber via a telephone interactive voice response system or Internet web page that offers specific programming, reporting, contact numbers, and message options. The system may also be triggered or programmed to perform its notification based upon the failure to receive a anticipated input, input of a timer, pre-programmed to operate at a specific time, or triggered by another CPU.
Owner:SEAGUARD TECH
Hierarchical data collection network supporting packetized voice communications among wireless terminals and telephones
InactiveUS20040264442A1Efficient communication pathwayEfficient communicationDevices with card reading facilityError preventionVoice communicationThe Internet
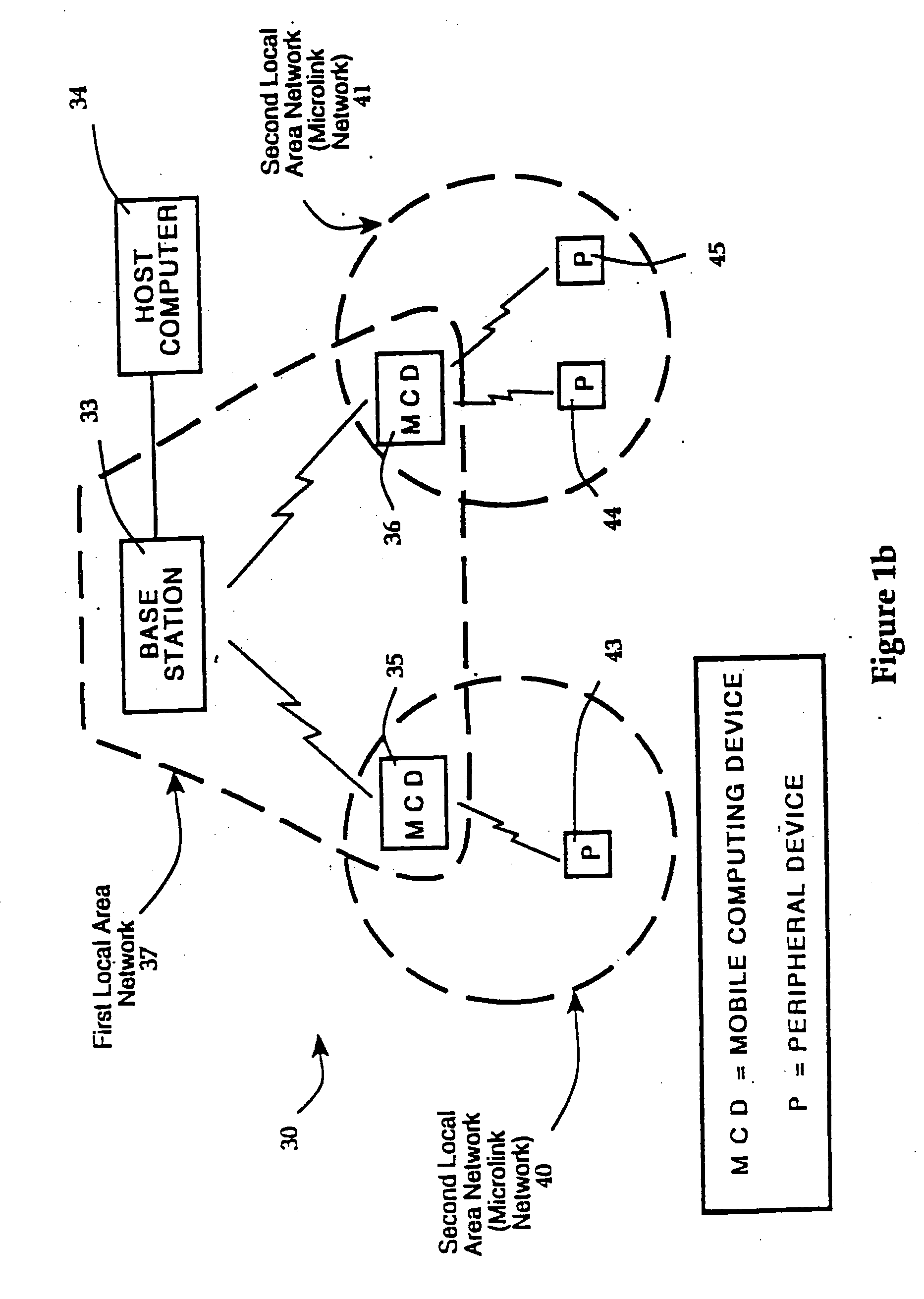
A packet-based, hierarchical communication system, arranged in a spanning tree configuration, is described in which wired and wireless communication networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed in an overall scheme to link portable or mobile computing devices. The network accommodates real time voice transmission both through dedicated, scheduled bandwidth and through a packet-based routing within the confines and constraints of a data network. Conversion and call processing circuitry is also disclosed which enables access devices and personal computers to adapt voice information between analog voice stream and digital voice packet formats as proves necessary. Routing pathways include wireless spanning tree networks, wide area networks, telephone switching networks, internet, etc., in a manner virtually transparent to the user. A voice session and associate call setup simulates that of conventional telephone switching network, providing well-understood functionality common to any mobile, remote or stationary terminal, phone, computer, etc.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
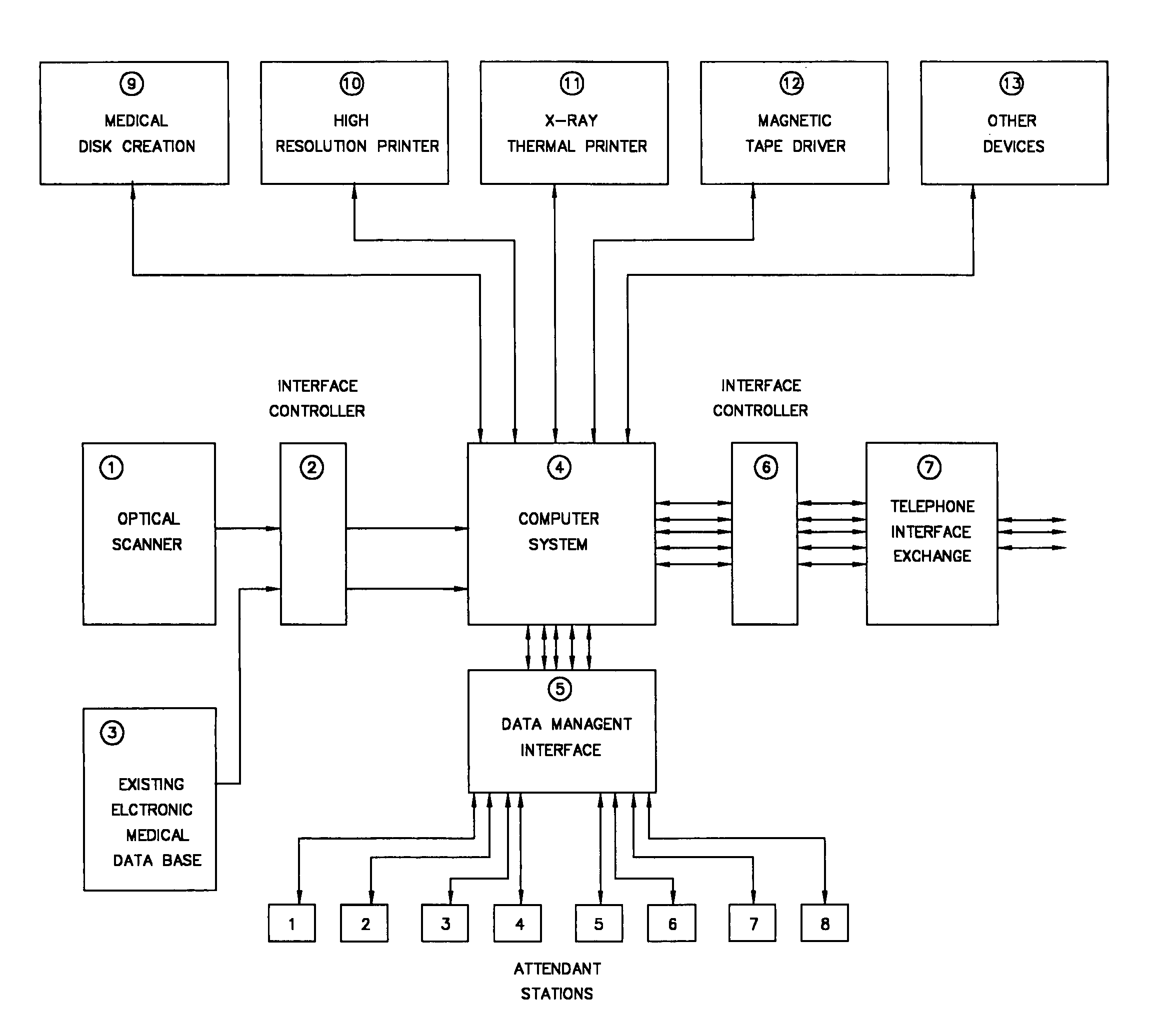
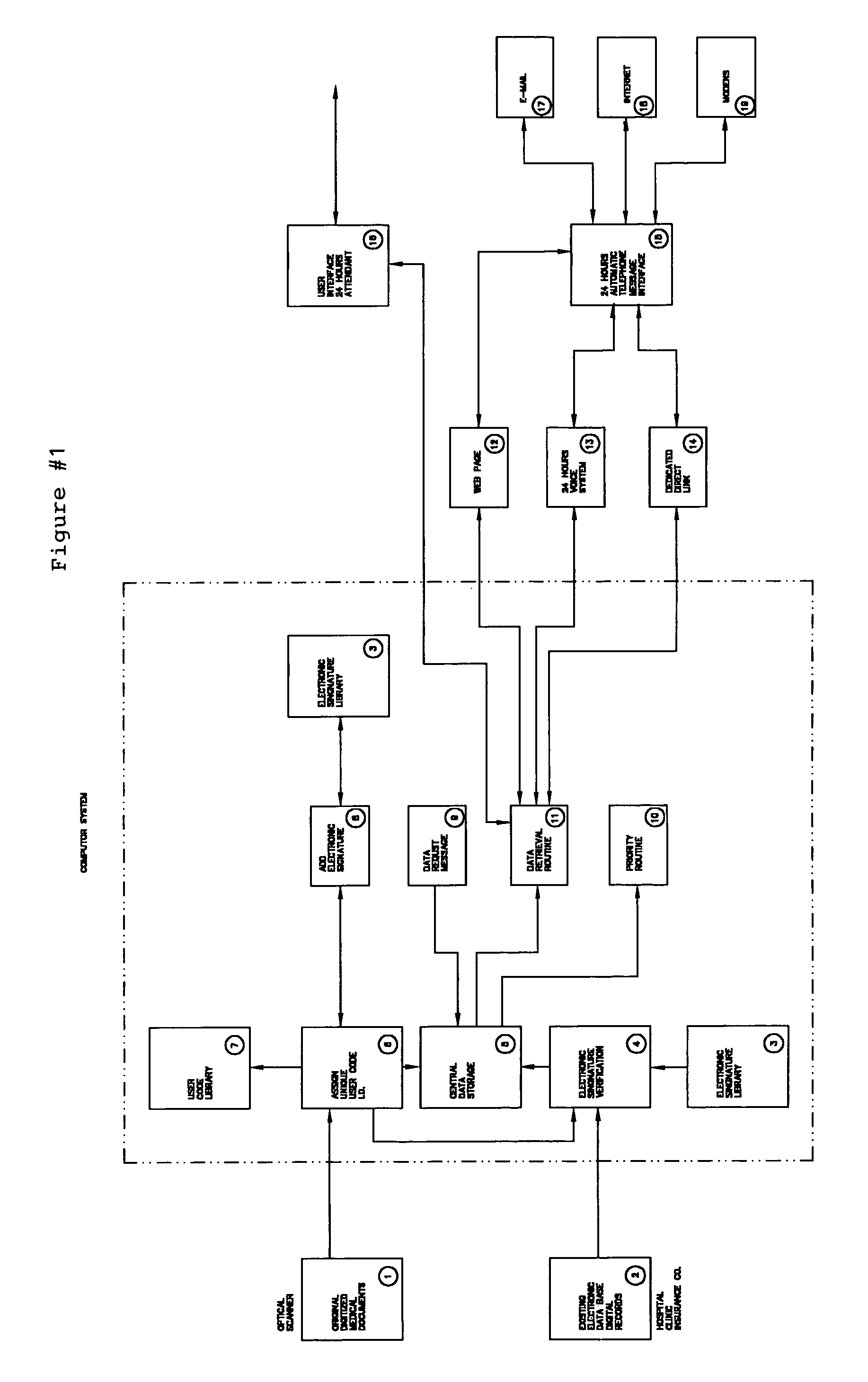
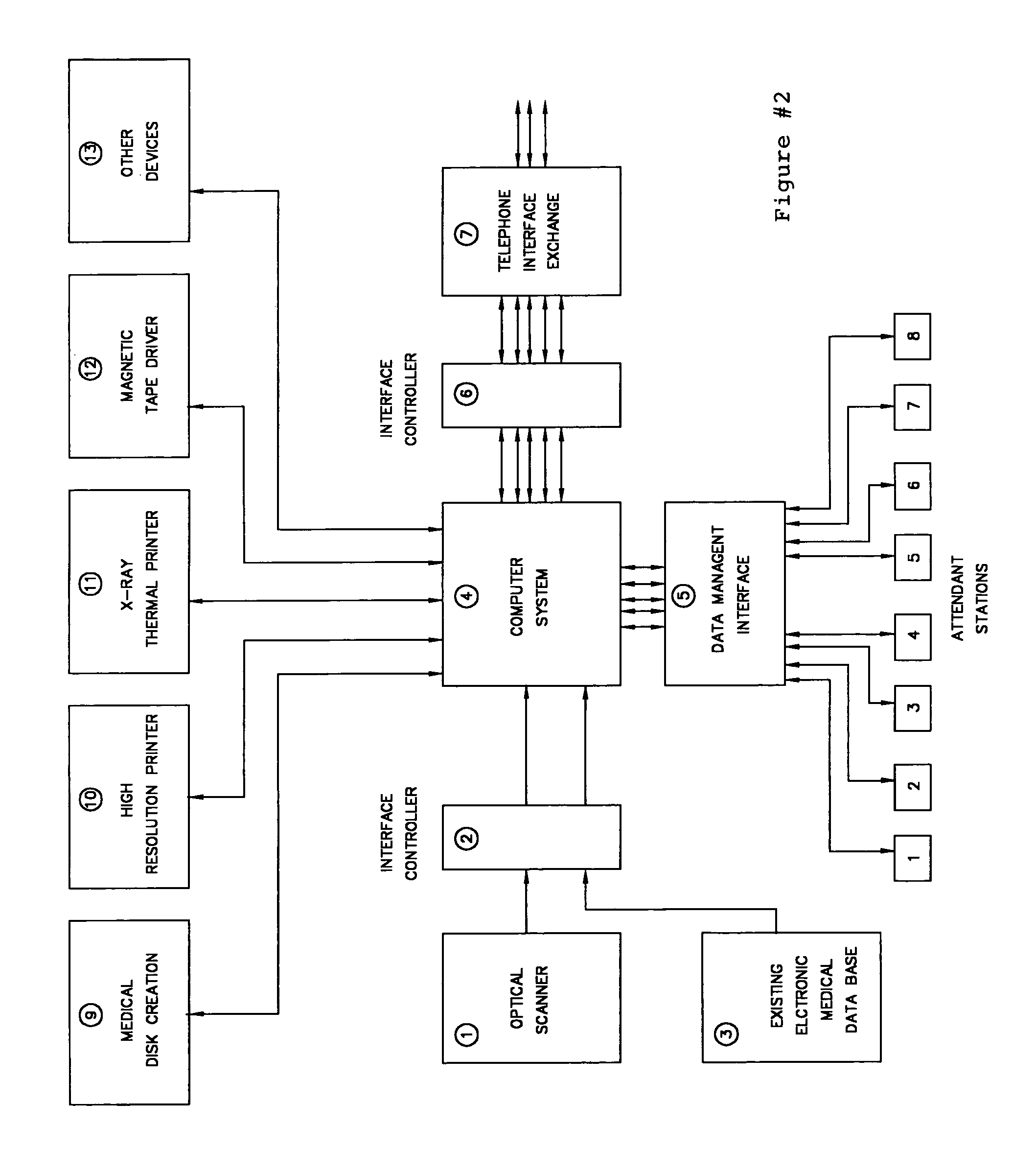
Computer system for optical scanning, storage, organization, authentication and electronic transmitting and receiving of medical records and patient information, and other sensitive legal documents
InactiveUS7295988B1Data processing applicationsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical recordOptical scanning
The invention disclosed herein relates to an improved method and system for the optically scanning, storage, management, retrieval and electronic mailing of a persons medical records and identification information on a 24 hour a day basis, primarily for use in a medical emergency of other medical scenario. The invention disclosed also encompasses unique and novel methods of verifying the authenticity of original medical records via a unique physicians digital signature embedded into the documents, a means for standardizing and prioritizing the history and prior medical records of a patient so as to provide an edited or abbreviated medical chart for emergencies which is current and clinically significant, a means of encrypting medical records for security, and a means of providing a unique alpha numerical identified code for each patient and digitally embedding the identifier into said patient records within the system and a means of 24 hour a day electronic access, transmission and updating of said records using a unique telephone exchange system, Internet, wesbite Intranet or other appropriate electronic or wireless means.
Owner:MED DATANET
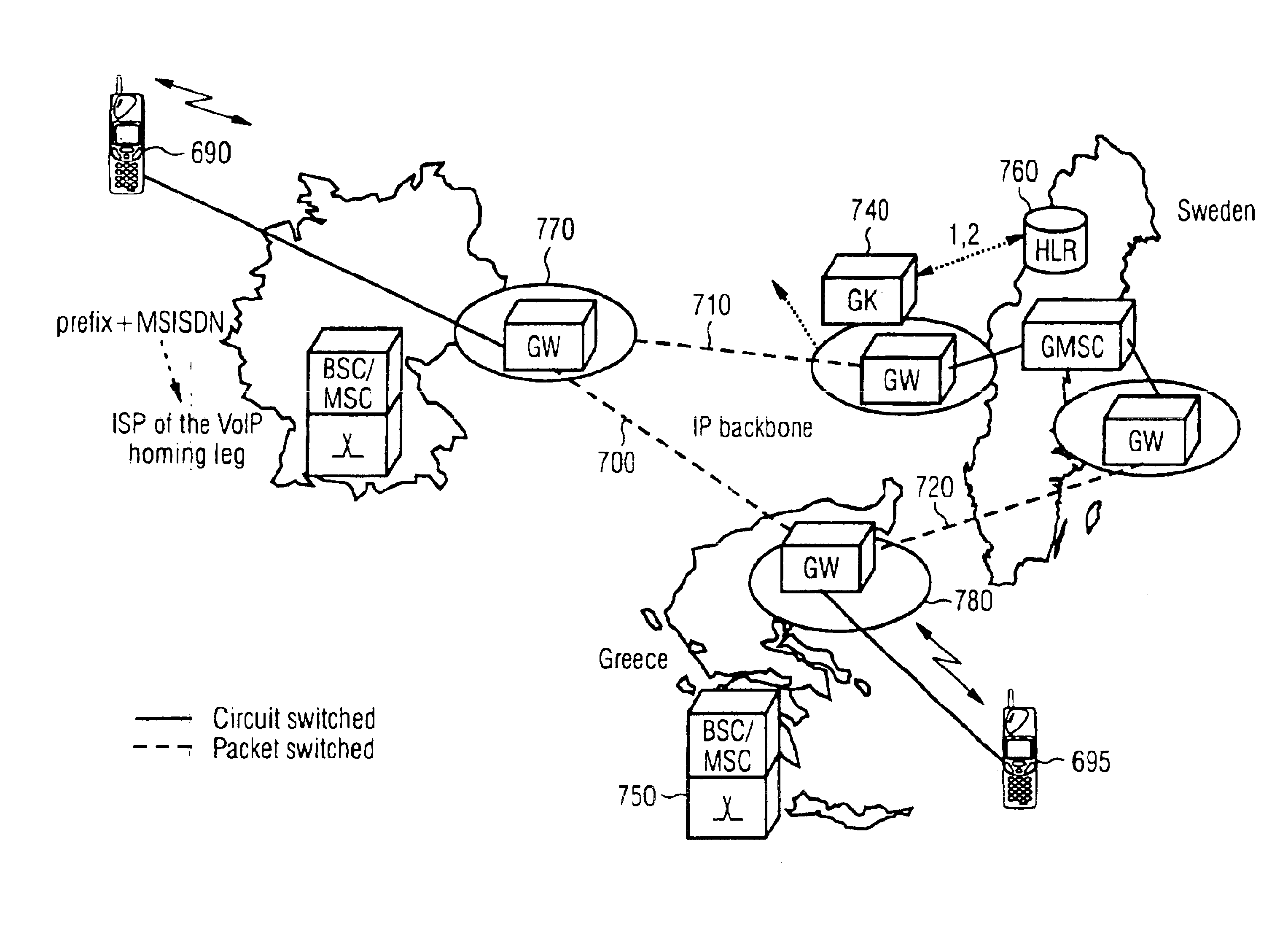
Methods and systems for call routing and codec negotiation in hybrid voice/data/internet/wireless systems
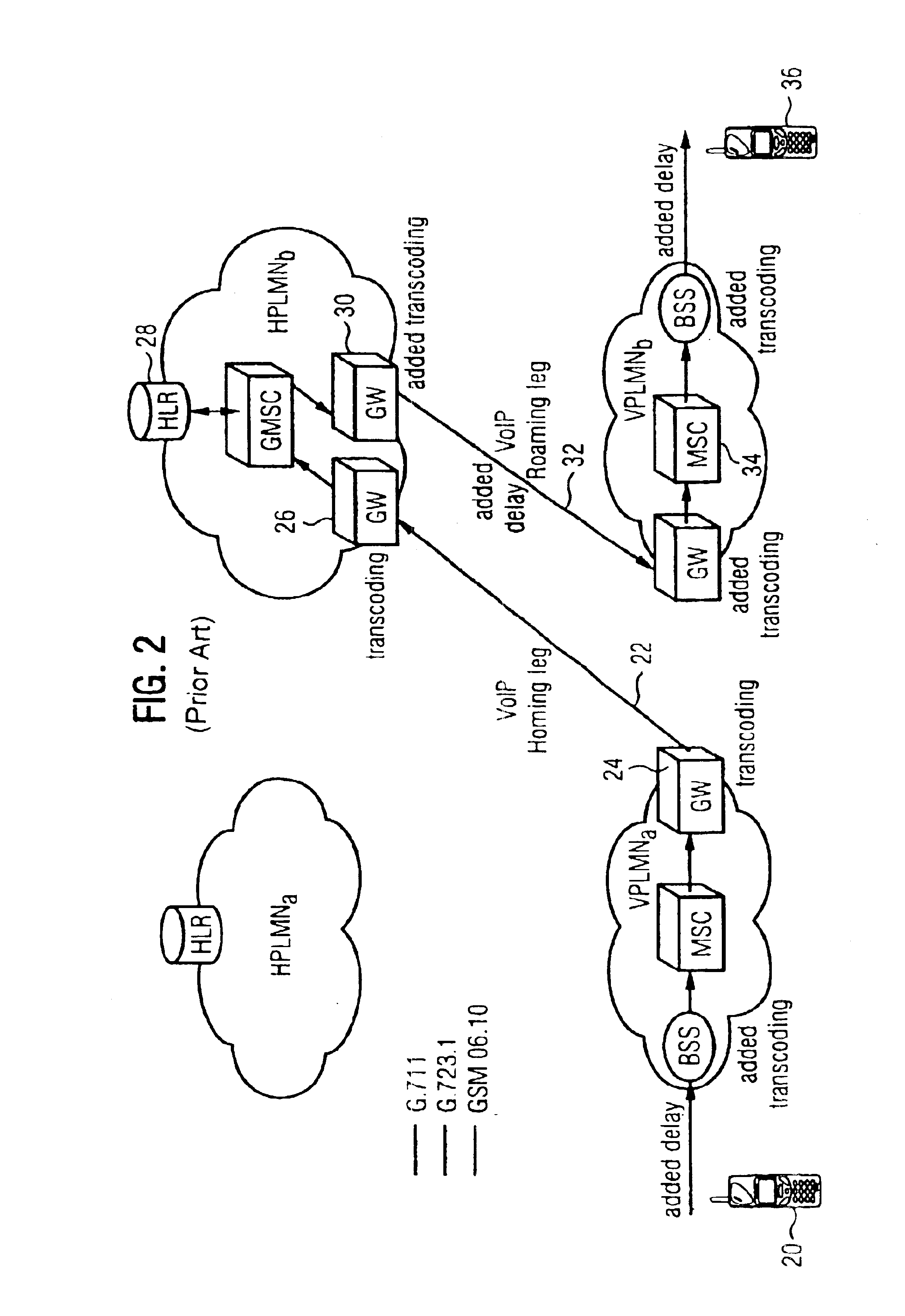
InactiveUS6856612B1Minimize delayMinimize the numberInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsThe InternetTranscoding
A method and system for communicating information includes evaluation regarding routing of calls performed at a call control point in an ITSP and / or wireless network. A PIC identity associated with another party's preferences is acquired and sent to the call control point. The PIC identity identifies the type of the carrier network (e.g., circuit switched or VoIP) and is used to make further routing decisions. If a circuit-switched carrier is identified, the IP homing leg is terminated at the voice gateway in the recipient's HPLMN and information is sent over to the GMSC where normal, circuit-switched routing procedures. If a VoIP carrier is identified then the called user's roaming number is retrieved from the HLR, and the call is further routed directly over the IP domain towards a voice gateway at the visited network minimizing the number of transcodings. Additional transcoding steps can be avoided if a single encoding is agreed upon according to “tandem free operation” (TFO). Combining inband signaling through the telephony exchanges and out-of-band signaling in the IP network it is possible to achieve, for a mobile subscriber, one encoding and one decoding of a voice.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
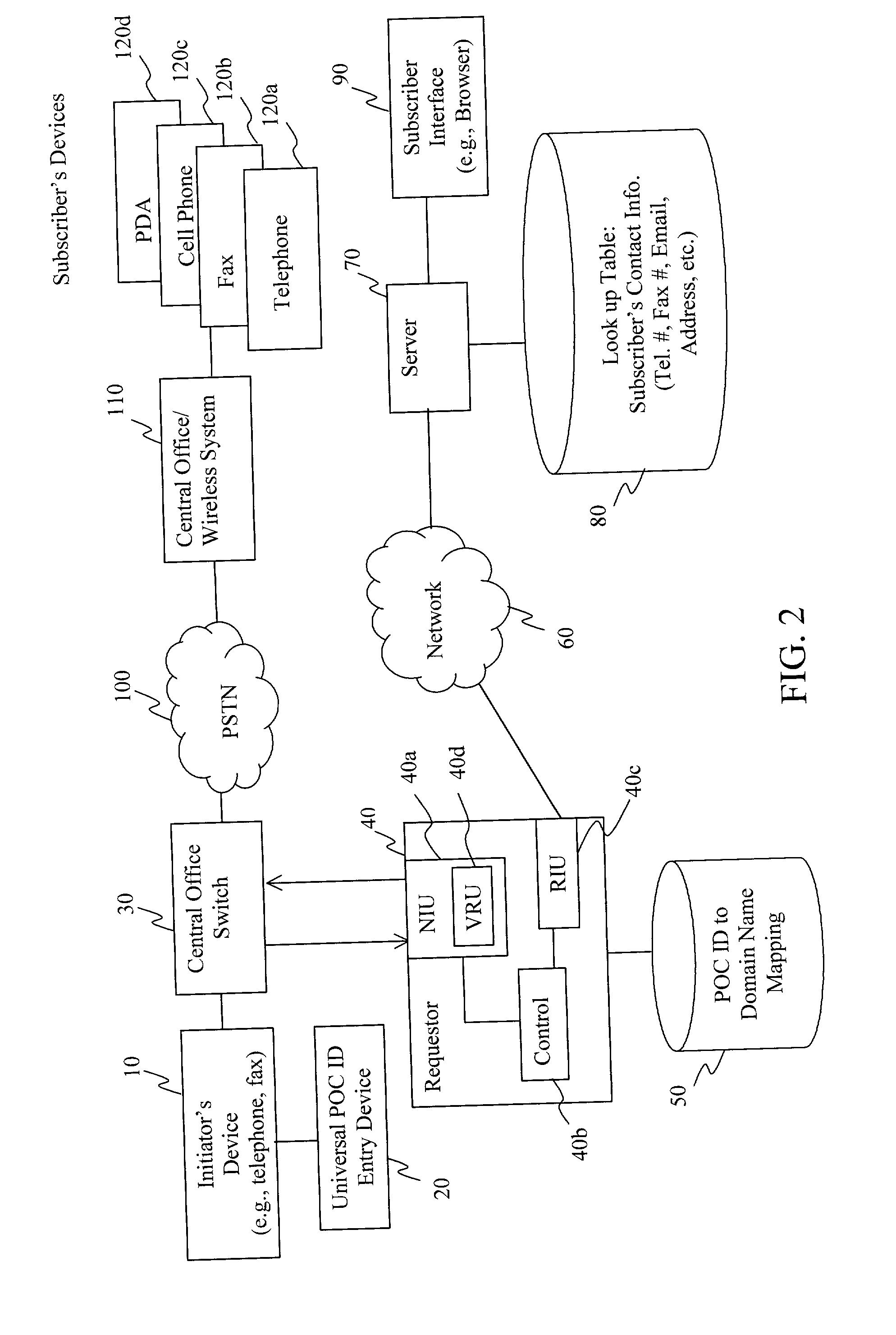
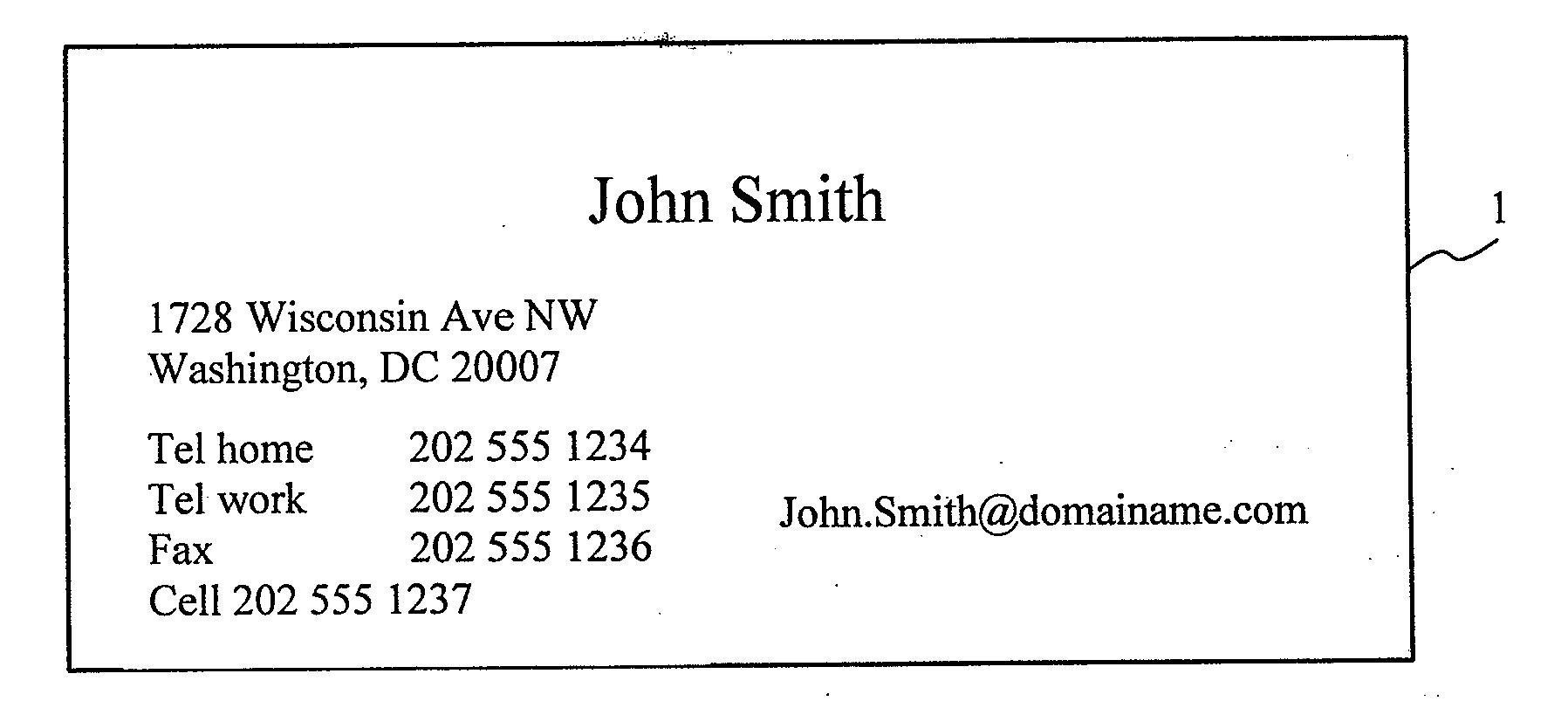
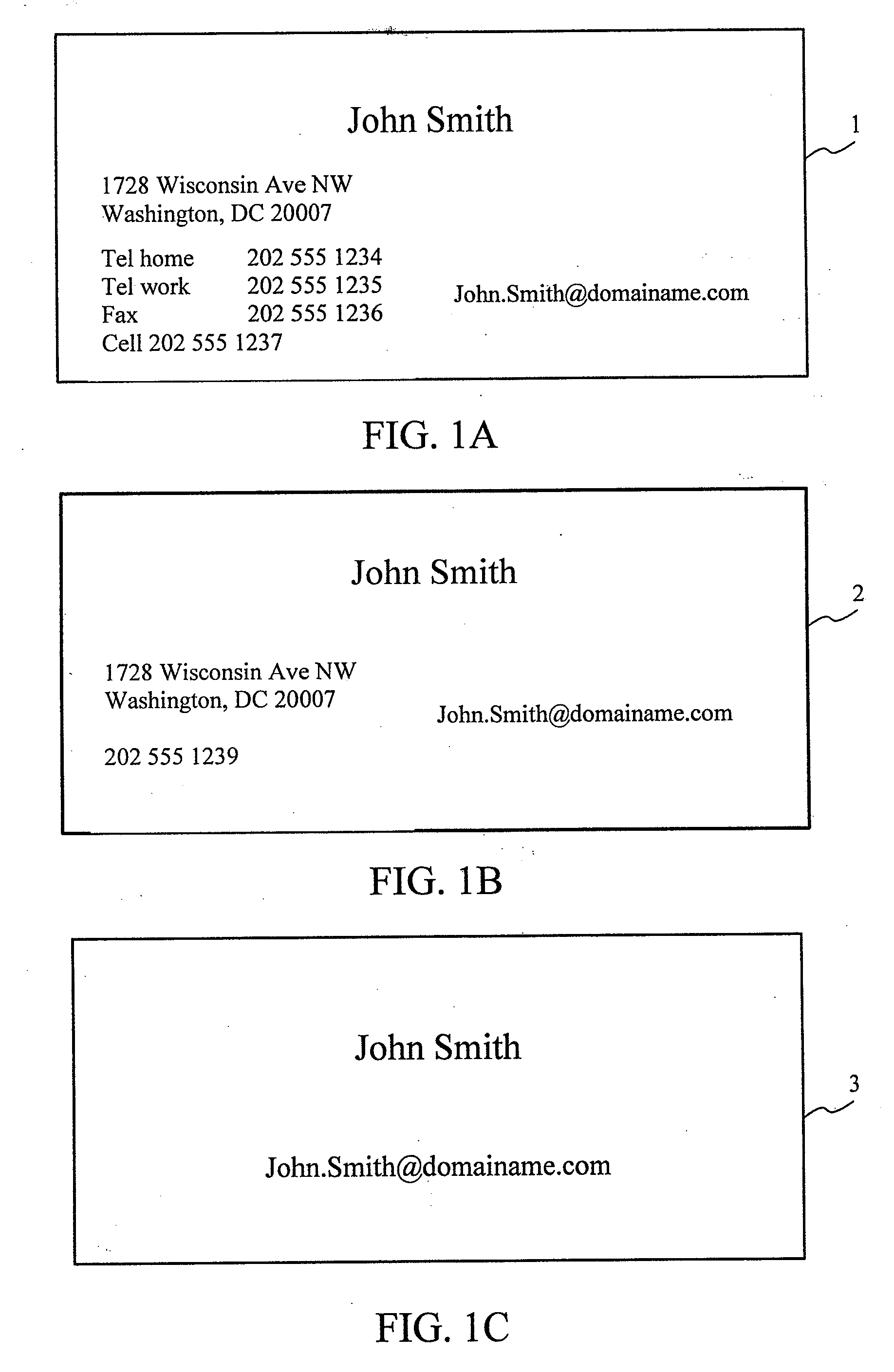
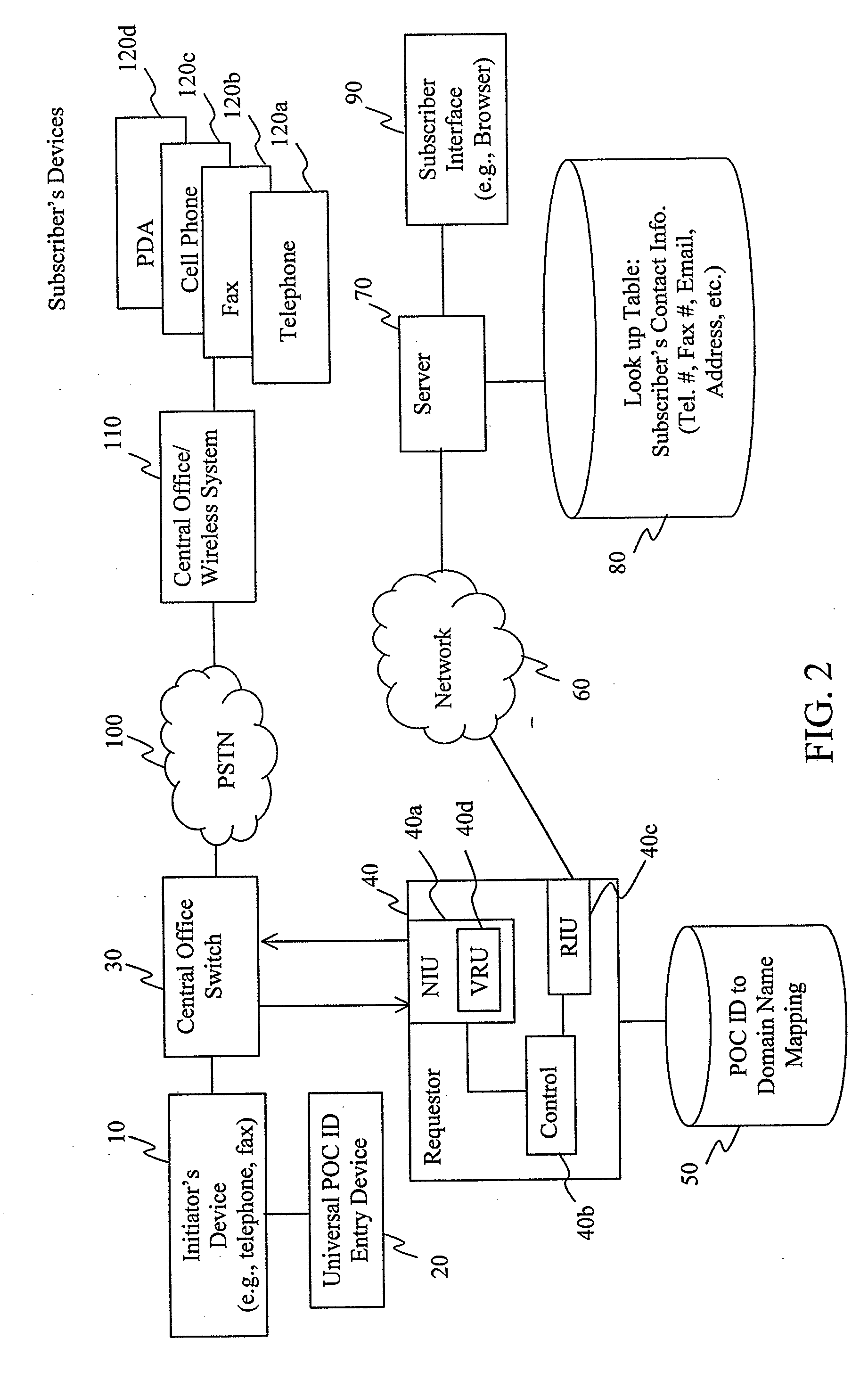
Universal point of contact identifier system and method
ActiveUS20020126817A1Telephone data network interconnectionsSpecial service for subscribersEmail addressElectronic mail
A subscriber to a universal point of contact service designates a preferred point of contact at which a communication initiator, such as a telephone caller, can contact the subscriber. Such an initiator desiring to contact the subscriber uses the subscriber's email address to establish a communication session with a device associated with the subscriber's preferred point of contact. The subscriber's email address is input to an initiating device, preferably a telephone or facsimile machine, using an entry device capable of entering an email address. A requestor unit, receiving the email address, locates a repository of the subscriber's point of contact information, and requests that information. The repository sends the point of contact information the subscriber has designated as preferred, and the requester unit uses that information to control a telephone switch to establish a communication session between the initiating device and the subscriber's preferred point of contact device.
Owner:AYMAN
Method and system for establishing voice communications using a computer network
InactiveUS20050074108A1Easily and convenientlyMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersVoice communicationHome page
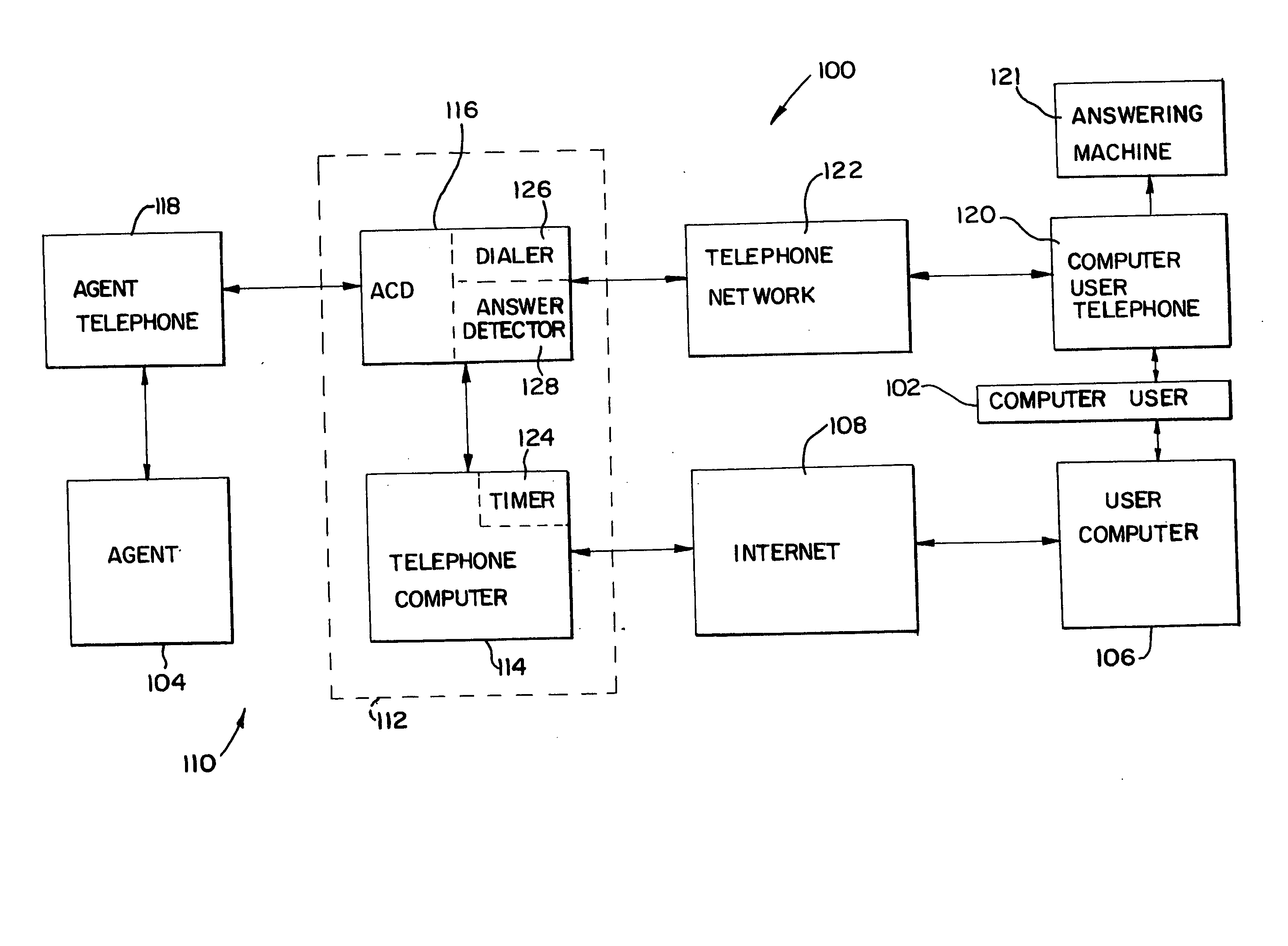
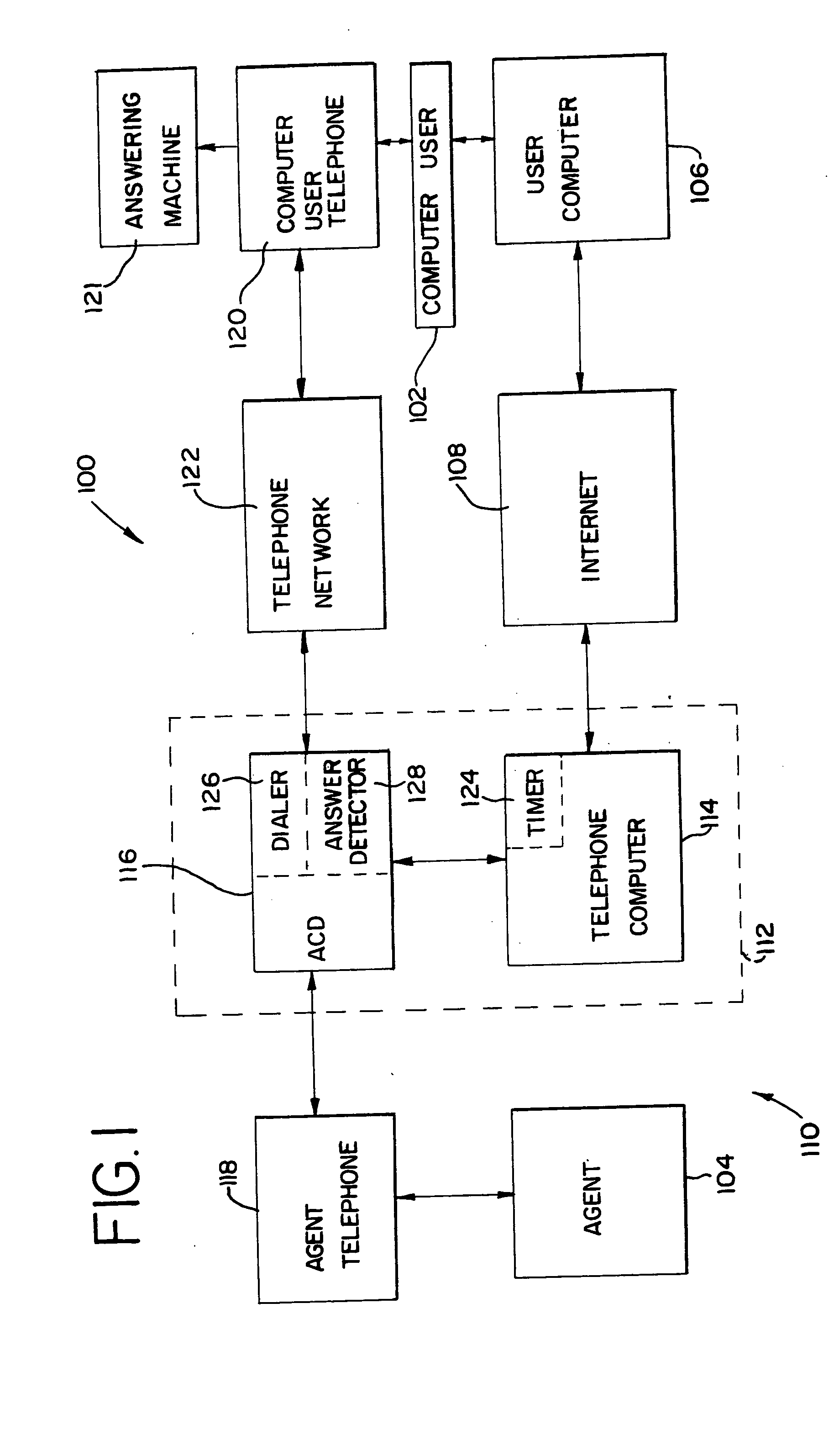
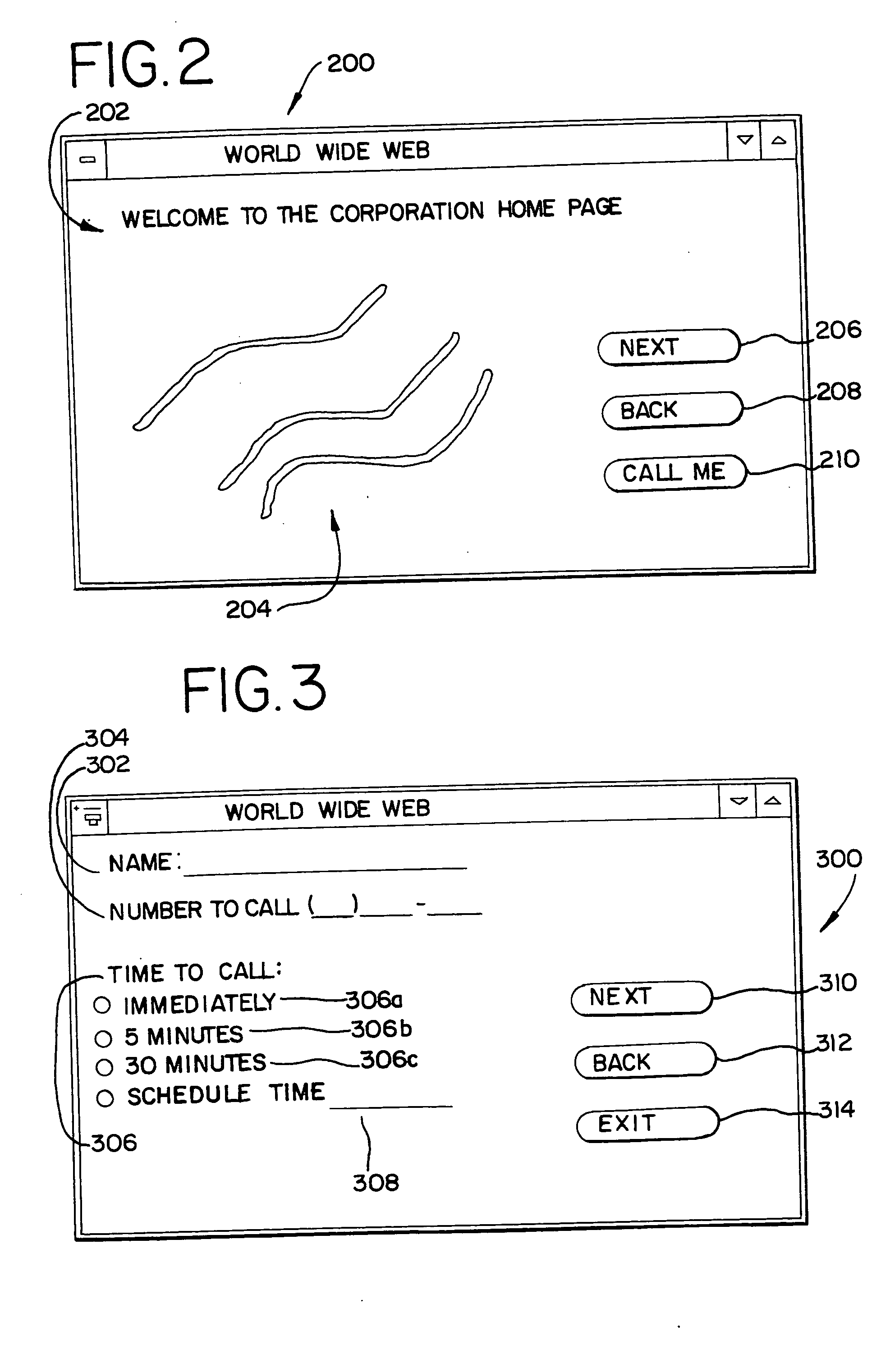
A method and system (100) establishes voice communications between a computer operator (102) and an agent (104) of a business over a computer network, such as the Internet (108). Using an operator computer (106), the computer operator (102) views advertisements of the business' products or services on the Internet (108) via customized home pages (200). When the operator (102) wishes to order a product or ask additional questions about a product, the operator (102) activates a “call me” button (210). A return call screen (300) is then presented to the operator (102) with areas to insert a name (302), a telephone number (304) and a time to call (306). This information is packetized in a call request which is transmitted over the Internet (108) to a telephone switching system (112) associated with the business. The telephone switching system (112) subsequently dials the telephone number (304) at the time to call (306). When the operator (102) answers an operator telephone (120), the telephone switching system (112) connects the operator (102) with the agent (104) via an agent telephone (118). The telephone switching system (112) may be comprised of a telephone computer (114) and an automatic call distributor (116).
Owner:WILMINGTON TRUST NAT ASSOC AS ADMINISTATIVE AGENT +1
Hierarchical data collection network supporting packetized voice communications among wireless terminals and telephones
InactiveUS20050013266A1Modulated-carrier systemsDevices with card reading facilityVoice communicationThe Internet
A packet-based, hierarchical communication system, arranged in a spanning tree configuration, is described in which wired and wireless communication networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed in an overall scheme to link portable or mobile computing devices. The network accommodates real time voice transmission both through dedicated, scheduled bandwidth and through a packet-based routing within the confines and constraints of a data network. Conversion and call processing circuitry is also disclosed which enables access devices and personal computers to adapt voice information between analog voice stream and digital voice packet formats as proves necessary. Routing pathways include wireless spanning tree networks, wide area networks, telephone switching networks, internet, etc., in a manner virtually transparent to the user. A voice session and associate call setup simulates that of conventional telephone switching network, providing well-understood functionality common to any mobile, remote or stationary terminal, phone, computer, etc.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Enhanced directory assistance system
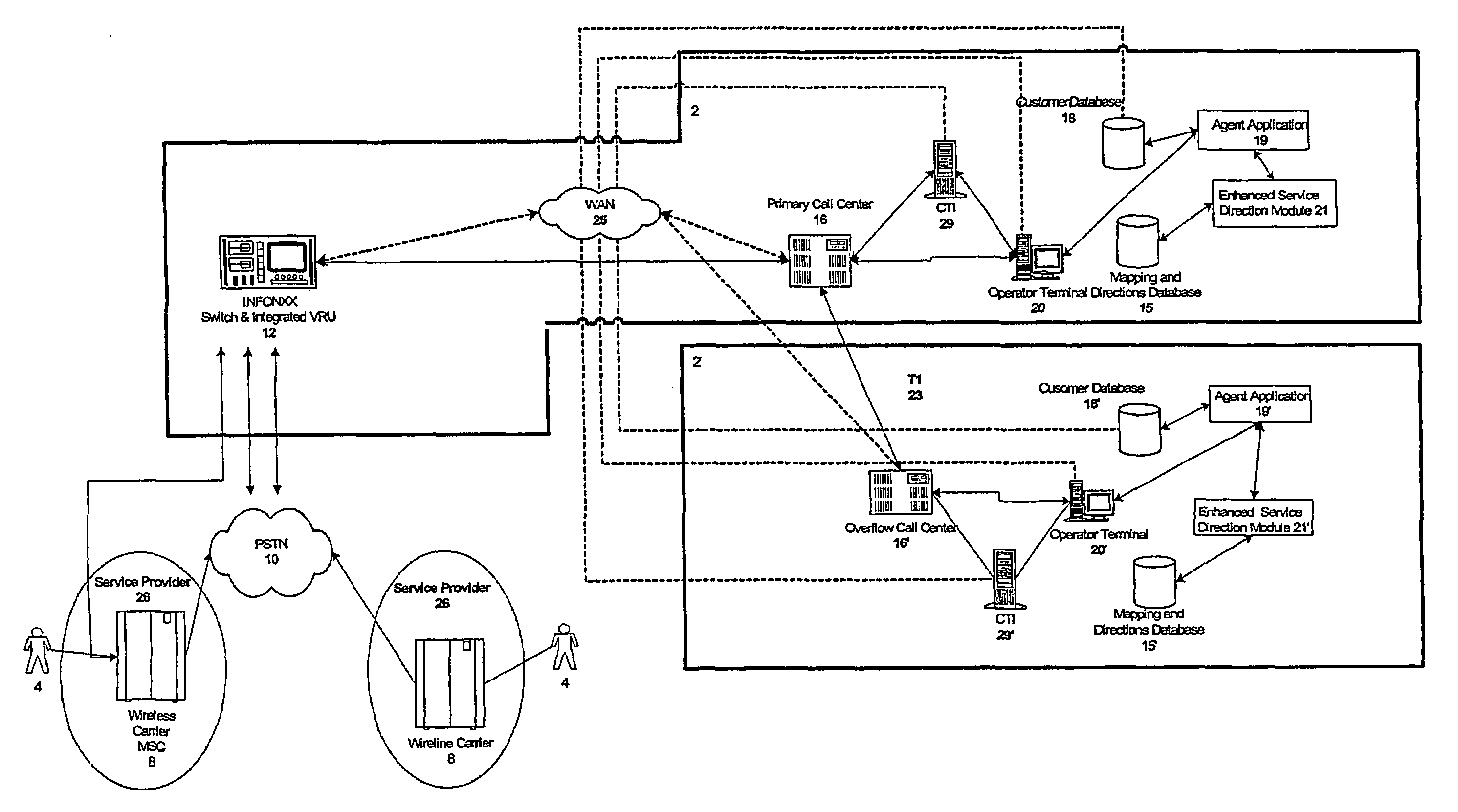
InactiveUS7130406B2Special service for subscribersLocation information based serviceDirection informationEnhanced service
Owner:GRAPE TECH GROUP
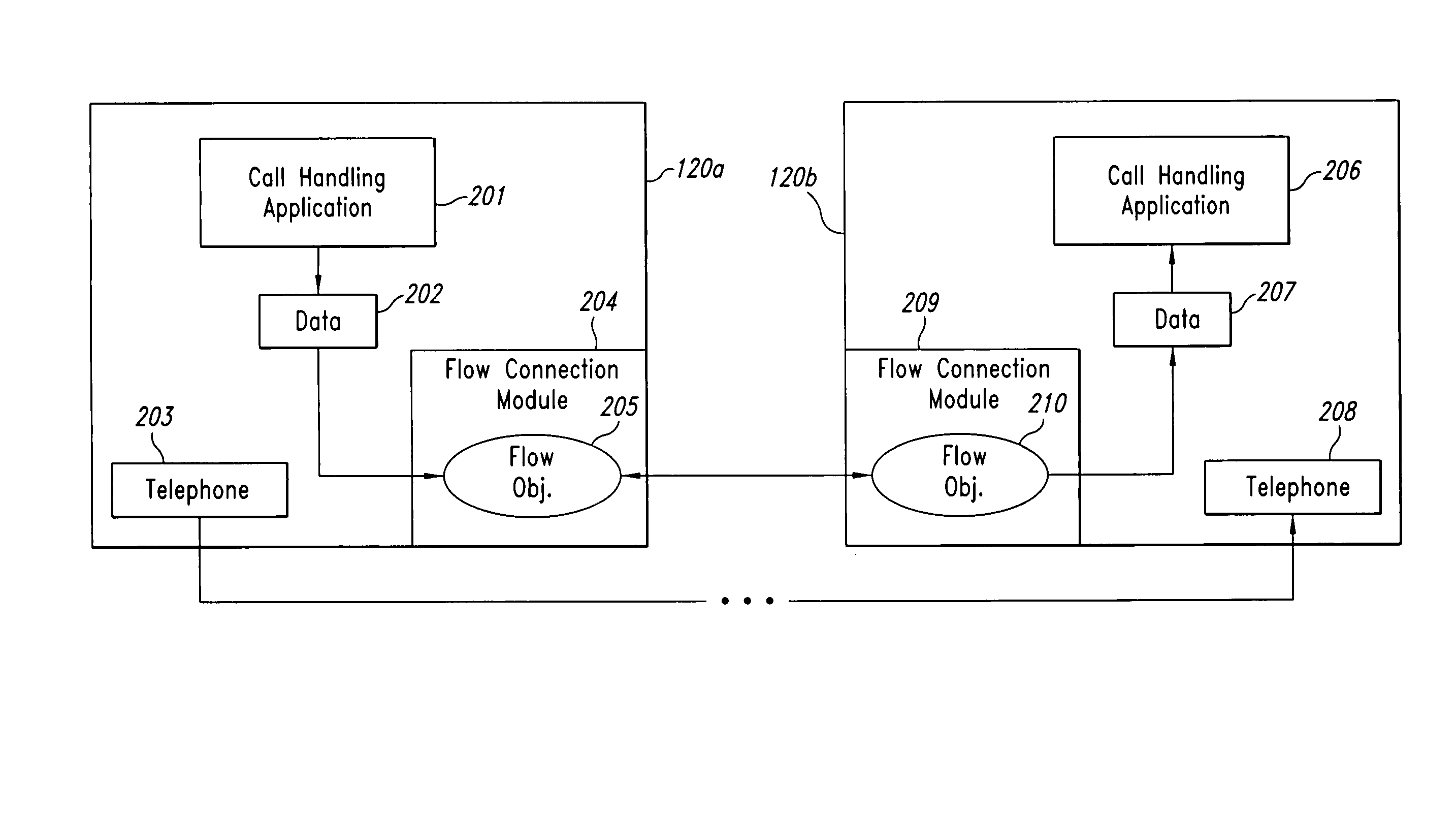
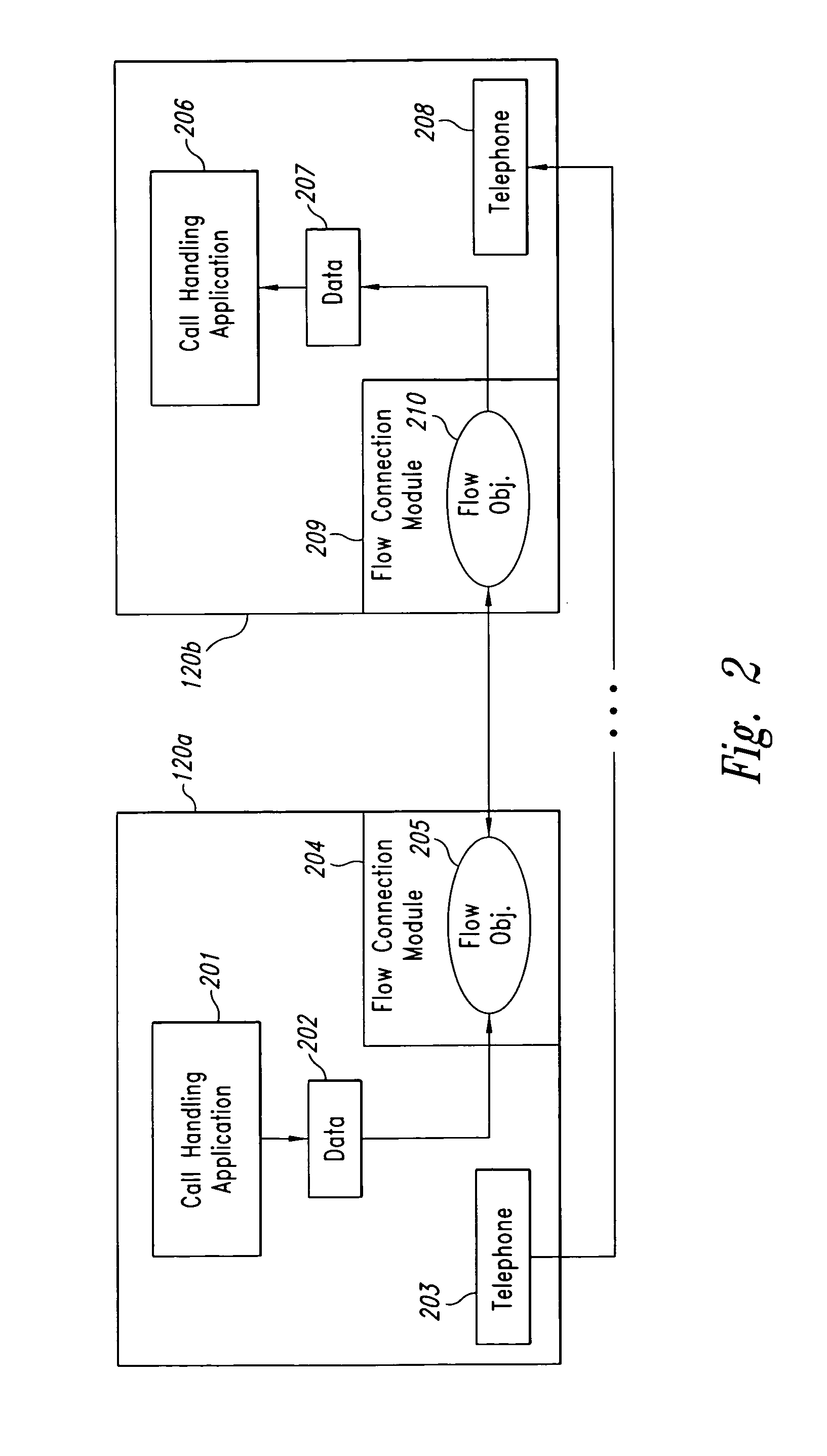
Call center telephone and data flow connection system
InactiveUS7295669B1Low costIncreased and decreasedSpecial service for subscribersManual exchangesData connectionData stream
A method and system for transferring telephone calls and data between computer programs in a call center. Flow connection modules associated with call center application programs allow data and telephone calls to be transferred from one computer program to another in the call center. The flow connection modules may be combined with a locator program such that the combination replaces the automatic call distributor (“ACD”) in a call center. The flow connection modules enable development of modular call centers, allowing call center agent workstations to be easily increased or decreased. In operation, an application notifies its flow connection module that a call on a telephone in the workstation should be transferred to another application. The flow connection module establishes a data connection with a flow connection module associated with the other application. The flow connection module sends call-related data to the other flow connection module which then returns the telephone extension associated with the other application. The flow connection module requests a computer telephony interface (“CTI”) link associated with a phone switch to transfer the call to the other application's telephone. The CTI link directs the phone switch to transfer the telephone call from the original application's workstation to the telephone of the other workstation. Having received notification of the transferred call, the other flow connection module informs the original flow connection module that the call has been successfully transferred, and the original flow connection module then disconnects the data connection.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Dispatch call origination and set up in a CDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS7099291B2Reduce delaysNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexCommunications systemRadio access network
In a CDMA wireless communication system (200) a dispatch call can be established between two CDMA mobile stations (202, 226), or between other mobile stations and the CDMA mobile station, or between a CDMA mobile station and a computer (236) located outside of the wireless system. To reduce the delay normally association with call set up in a CDMA system, a dispatch processing network (128, 144) is provided in addition to a telephony switch (118). Dispatch calls and call set up requests are routed to the dispatch processing network from the radio access network (110) which includes base stations (204, 206). Once a dispatch call request is made, while the dispatch processing network begins setting up a traffic channel for the originating mobile communication device, the target is also paged, and upon responding, set up on a traffic channel. The concurrence of establishing radio links with the target and originating communication devices substantially reduces dispatch call set up time.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
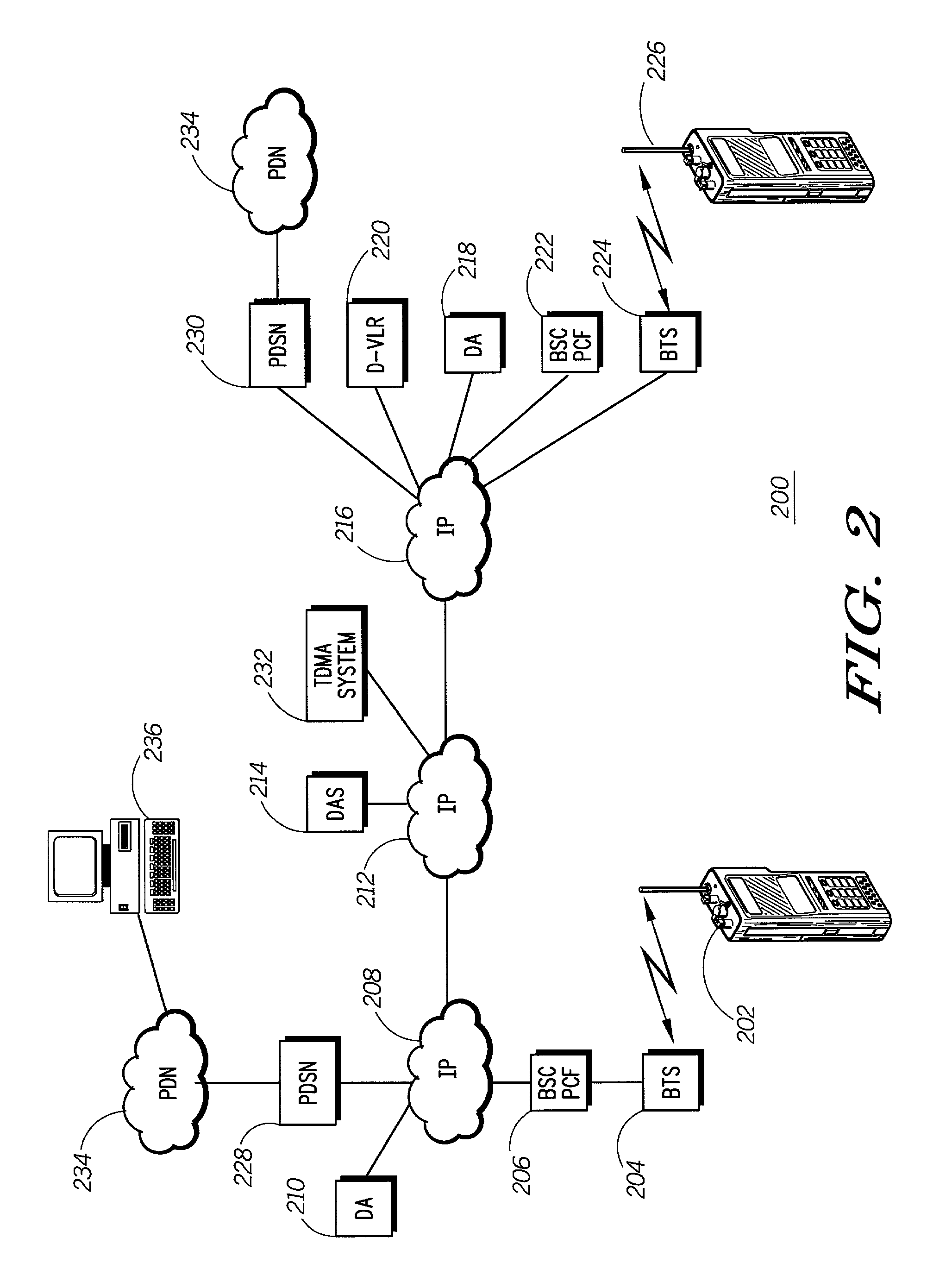
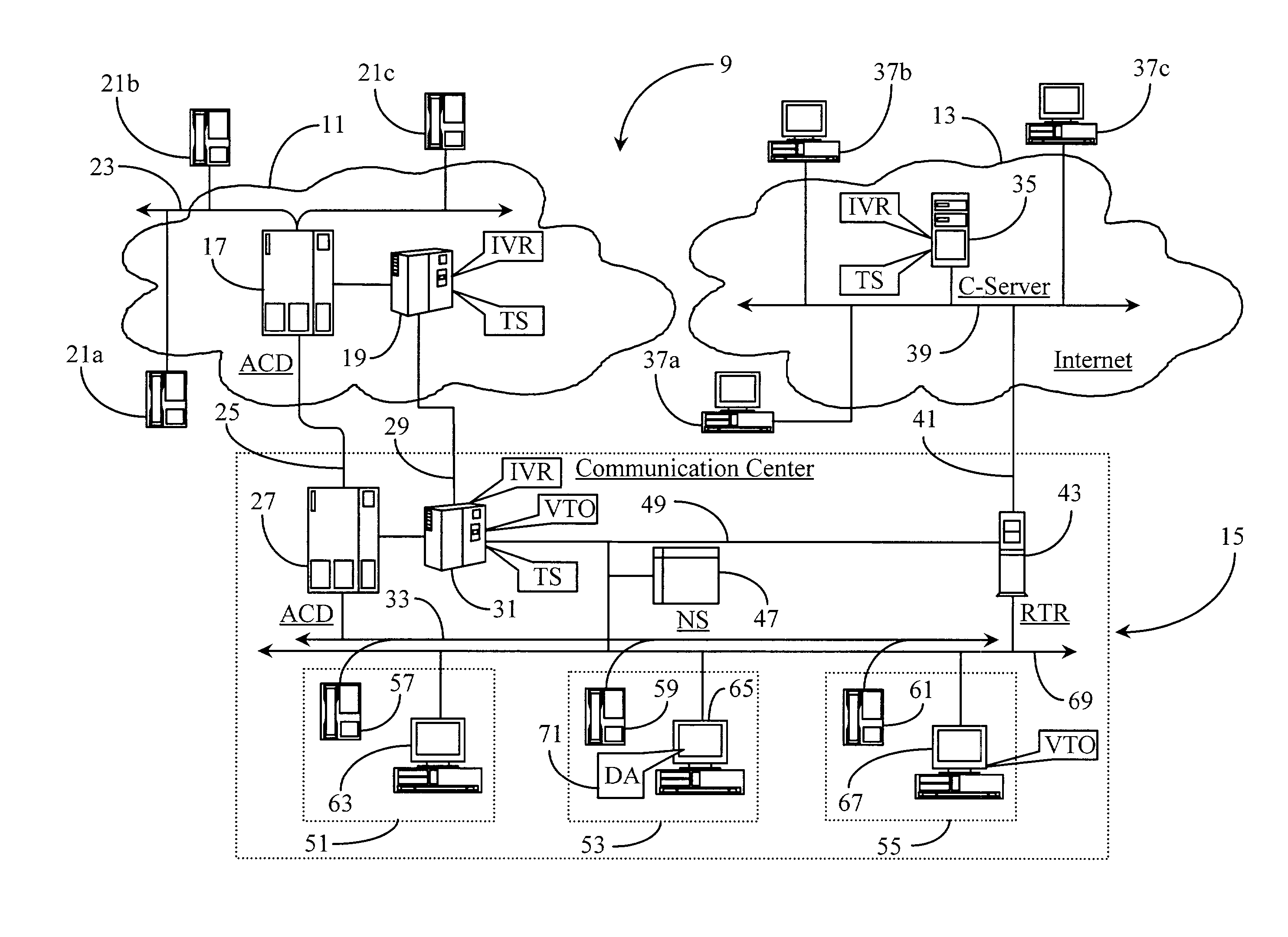
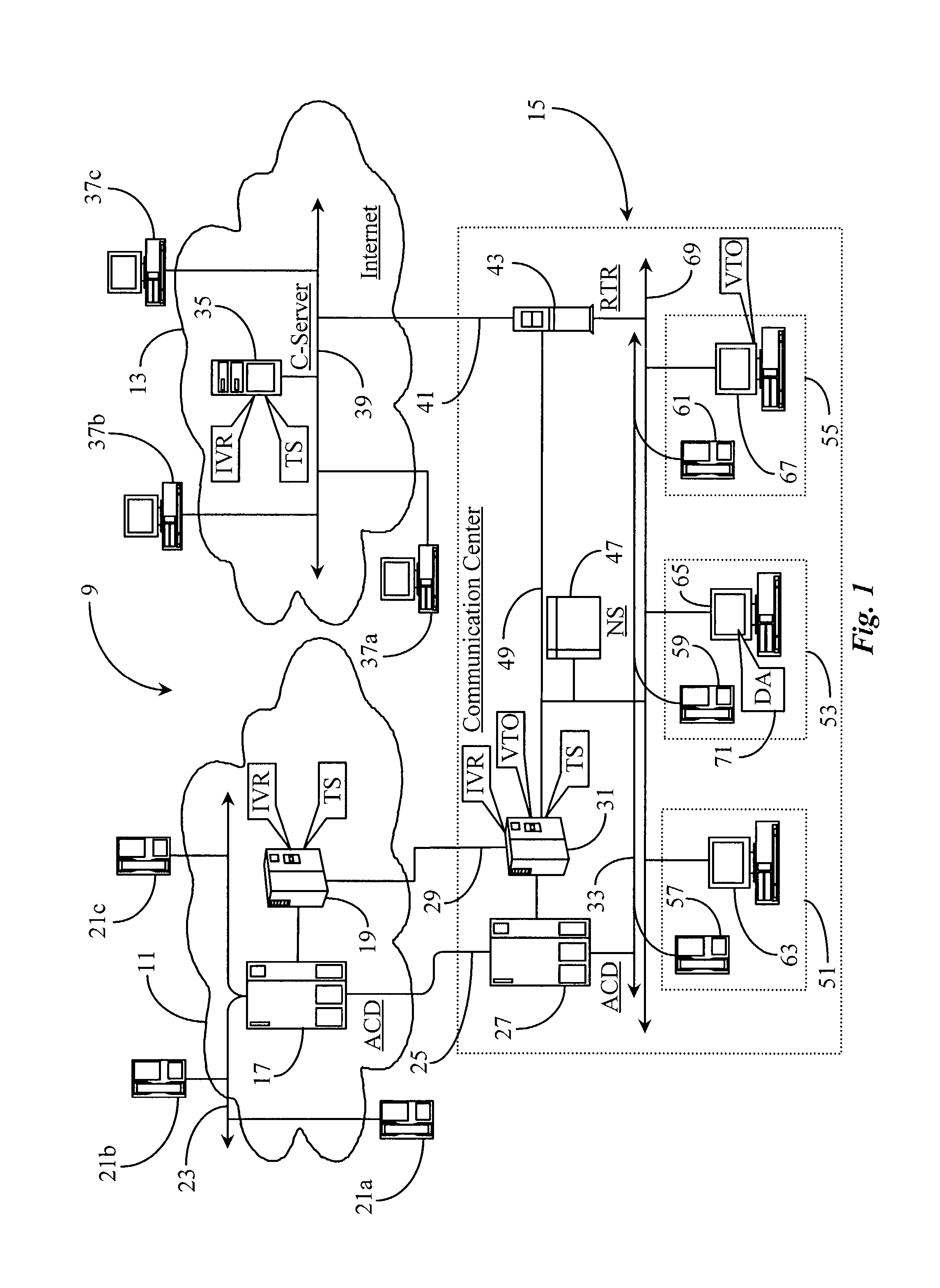
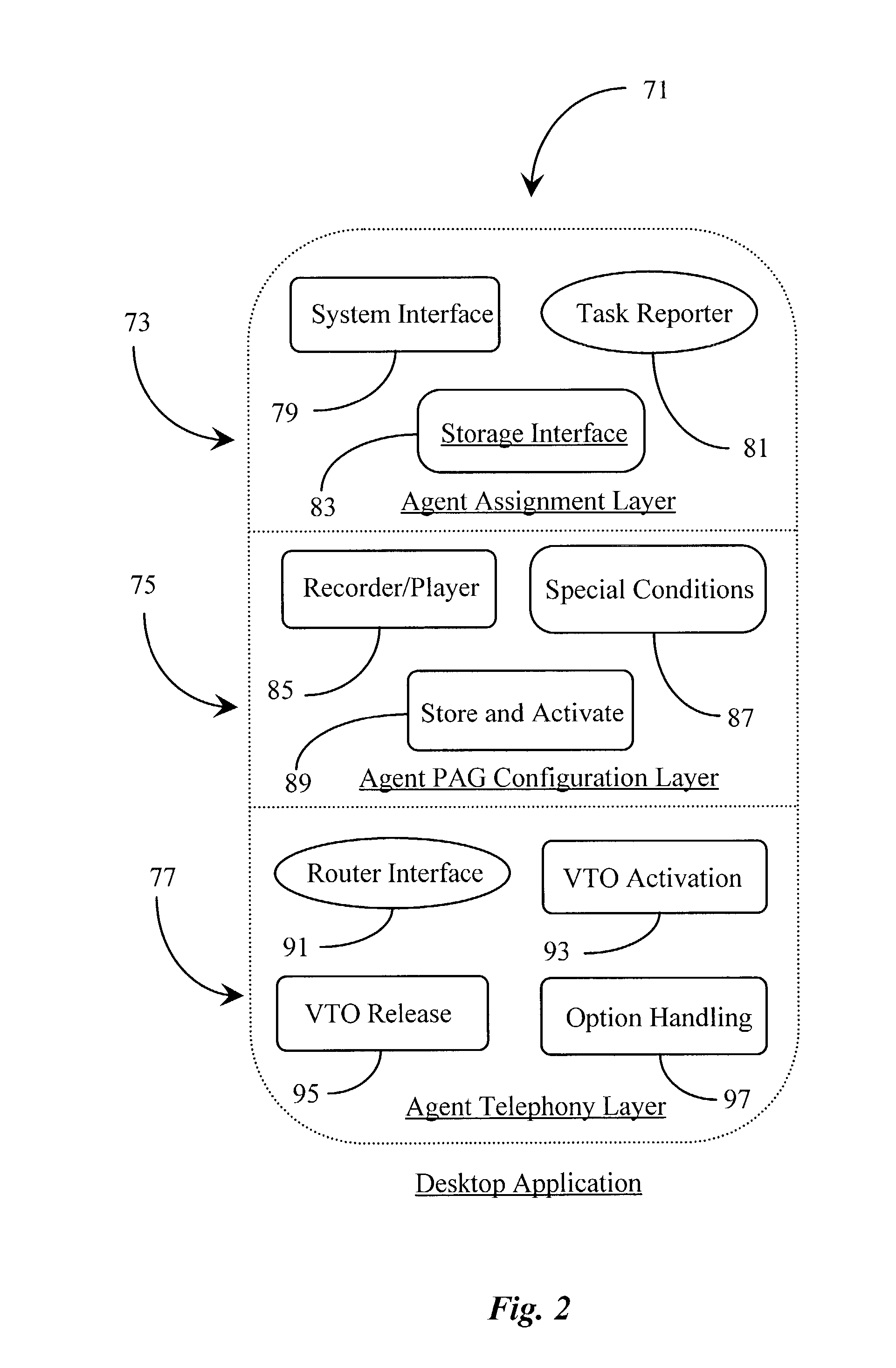
Method and apparatus for recording and automated playback of personal agent greetings in a communication-center environment
InactiveUS7006607B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersThe InternetCall routing
A system for presenting a recorded message on behalf of an agent receiving a call at an agent station in a call center, the agent station having a telephony interface for receiving calls and a personal computer with a video display unit (PC / VDU), has a telephony switching apparatus enhanced by a computer-telephony integration (CTI) processor, an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system executing a voice treatment option (VTO) software, coupled to the telephony switching apparatus and the CTI processor; and a data repository having recorded messages stored on behalf of the agent and accessible to the CTI processor. The CTI processor routes incoming calls to the telephony interface for the agent, uses data associated with the calls for selecting appropriate recorded messages, and causes, by controlling the IVR, a retrieved recorded message to be played to a caller upon the agent picking up the routed call. The system is useful with both conventional telephone systems and data network telephony, such as over the Internet.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORIES INC
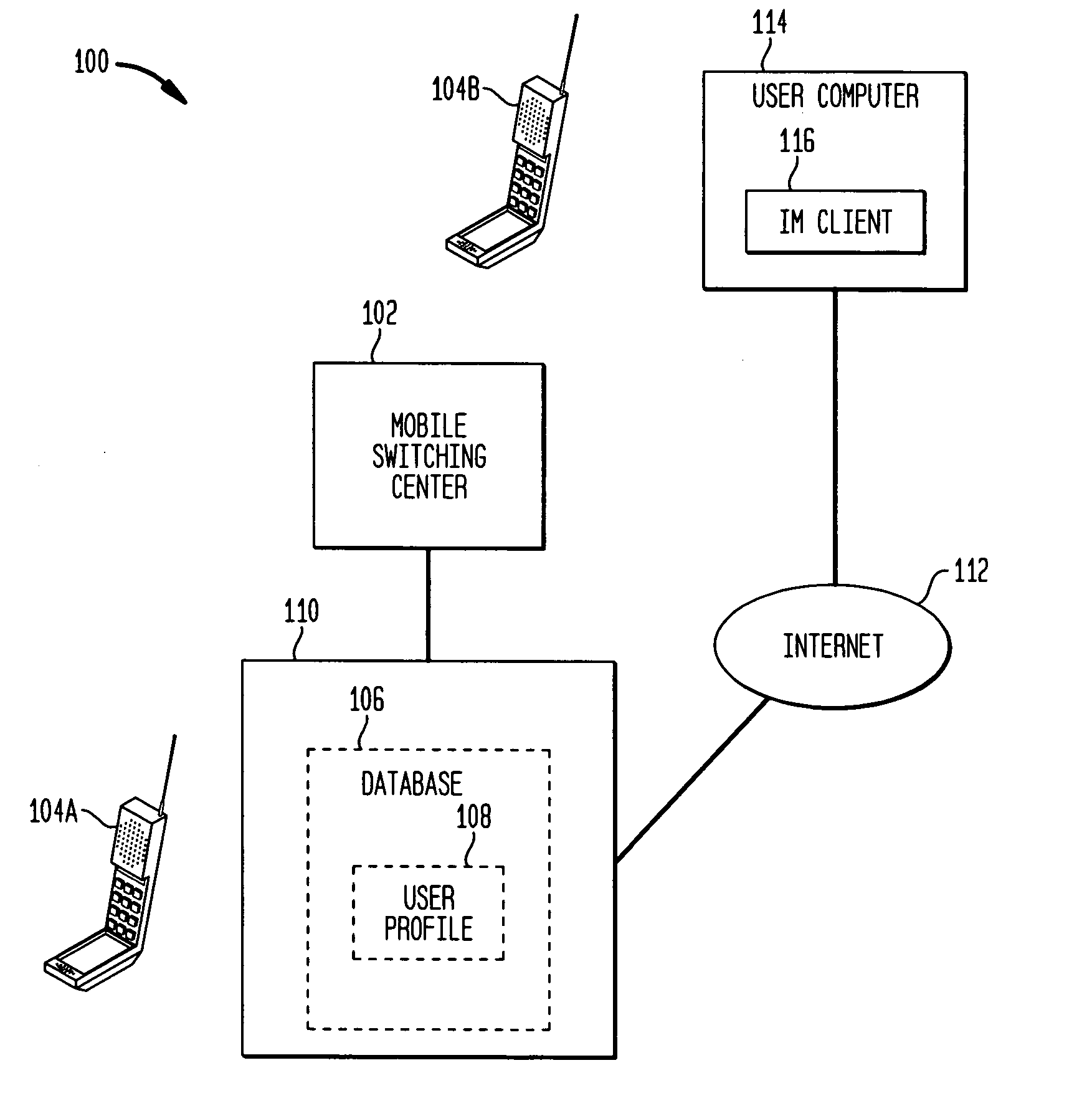
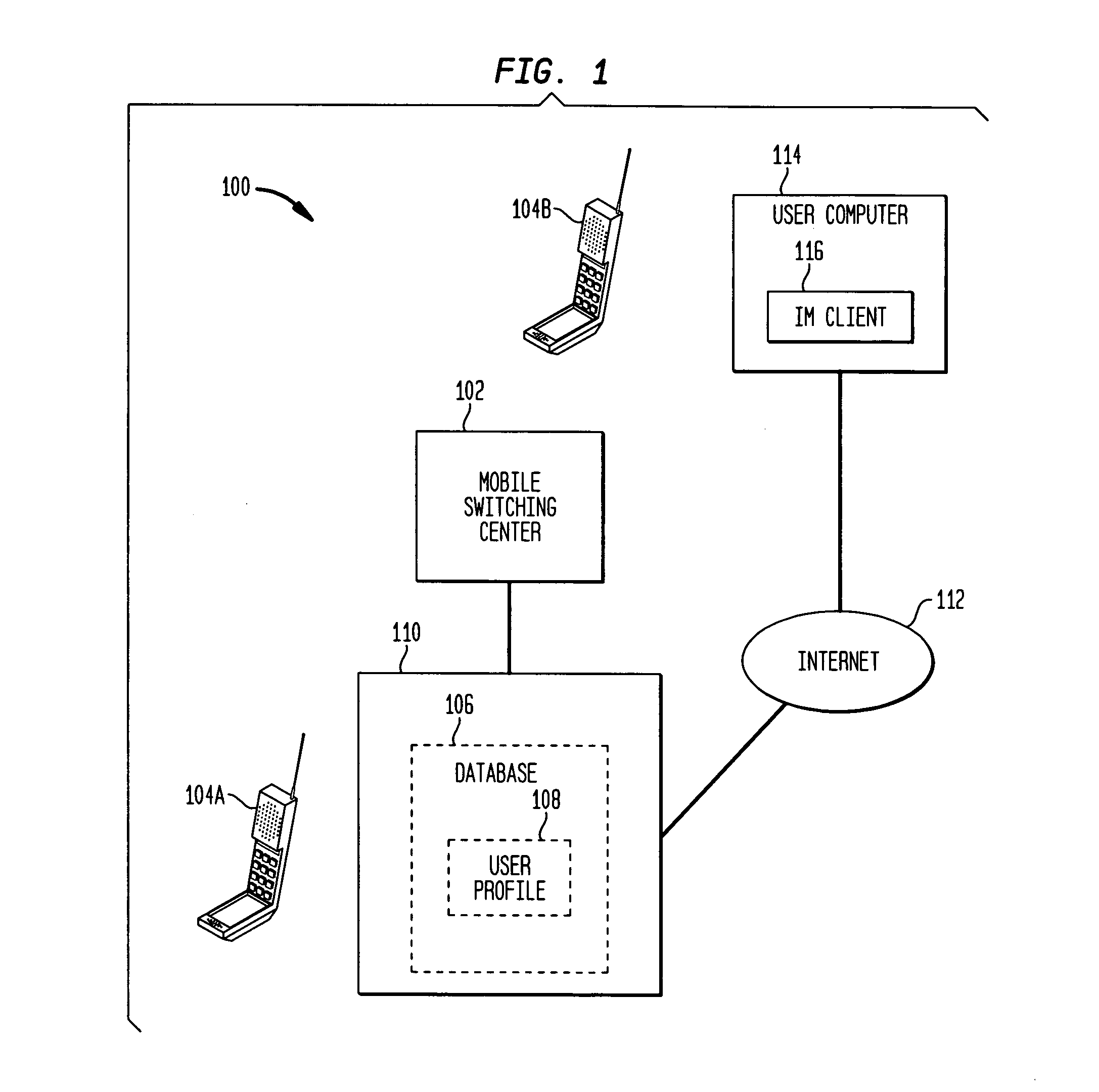
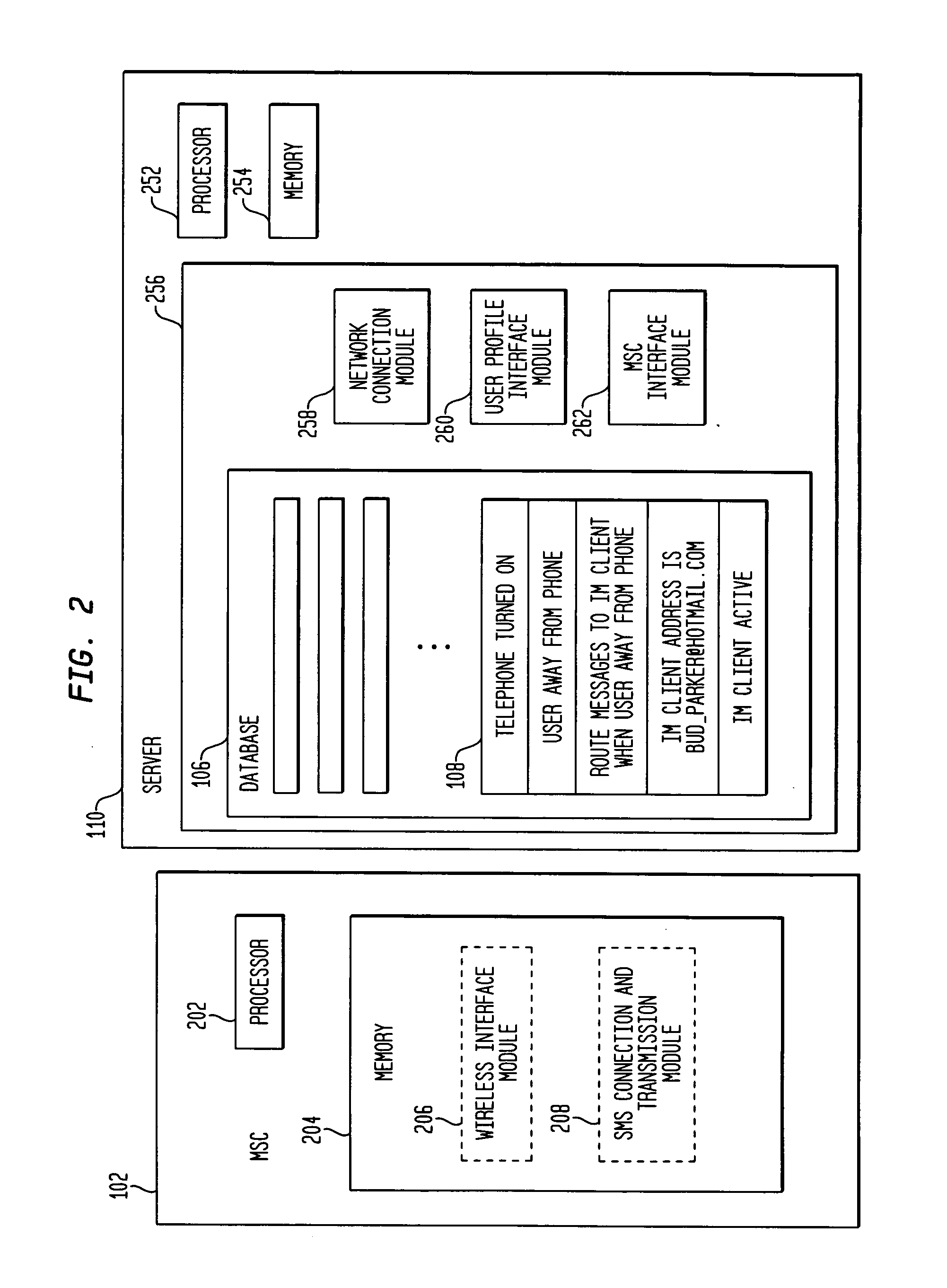
Methods and apparatus for alternative routing of text based messages on a cellular telephone network
InactiveUS20050037762A1Telephonic communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsShort Message ServiceThe Internet
Systems and techniques for routing and transmission of short message service messages are described. A user profile associated with a wireless telephone includes conditions relating to a user's need or desire to receive a text message through a device other than the wireless telephone and the user's preferences in the event of each of the conditions. The conditions include whether a user's instant messaging client is active. If the client is active, the user profile include the address of the client. When a text message arrives for the user at a wireless telephone switching center, the switching center determines if the message is to be sent to the user through the wireless telephone network, through the internet messaging client or both. Depending on the desired routing of the message, the message is transmitted through the wireless network or formatted and sent as an instant messaging message, or both.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Methods and apparatus for personal routing in computer-simulated telephony
A client-server telephone call router system as part of a customer premises system has a client-server router adapted to execute on a telephony switch, such as a public branch exchange (PBX) or other telephony switch, or on a processor connected by CTI link to a telephony switch. The telephony switch or processor executing the router is connected to a local area network (LAN) that also interconnects computer workstations proximate to telephones connected to the telephony switch. Client user interface applications run on the computer workstations, allowing clients to edit routing rules for the router, which has a list of routing rules keyed to users and workstations of the customer premises system. The editing rules are kept by the router in portions dedicated to individual users. With this system a user can edit at a workstation on the LAN his\her own routing rules, and transmit the edits to the client-server router where the rules will be followed to route calls for that user and protocol.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORIES INC
Method and system to enable mobile roaming over ip networks and local number portability
InactiveUS20090129371A1Overcomes additional integration costMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTraffic capacityThe Internet
A method and system for creating a virtual roaming solution for a MSISDN using a softphone over an IP network. The system involves (i) implementation of a novel virtual mobile network (VMN) comprising virtual visitor location register (vVLR), virtual home location register (vHLR) and virtual multiple switching centre (vMSC) on an IP server responsible for managing IP call traffic administration, and (ii) implementation of a novel mobile to internet gateway (MIG) comprising an VoIP gateway for diverting call traffic from the mobile network to the IP network, and an IP server with vMSC functionality to translate routing information from the VMN to GSM network so as to appear to the GSM network as a traditional mobile operator. The system dynamically registers the subscriber to the IP network, and provides valid routing information to the MSC (Mobile Switching Centre) or public telephone switch to route the call over to the NGN (next generation network) operator in the IP space.
Owner:BISHAY SAMER
Personal communication service network interface device
ActiveUS20050018653A1Commmunication supplementary servicesData switching by path configurationCommunications systemCable telephony
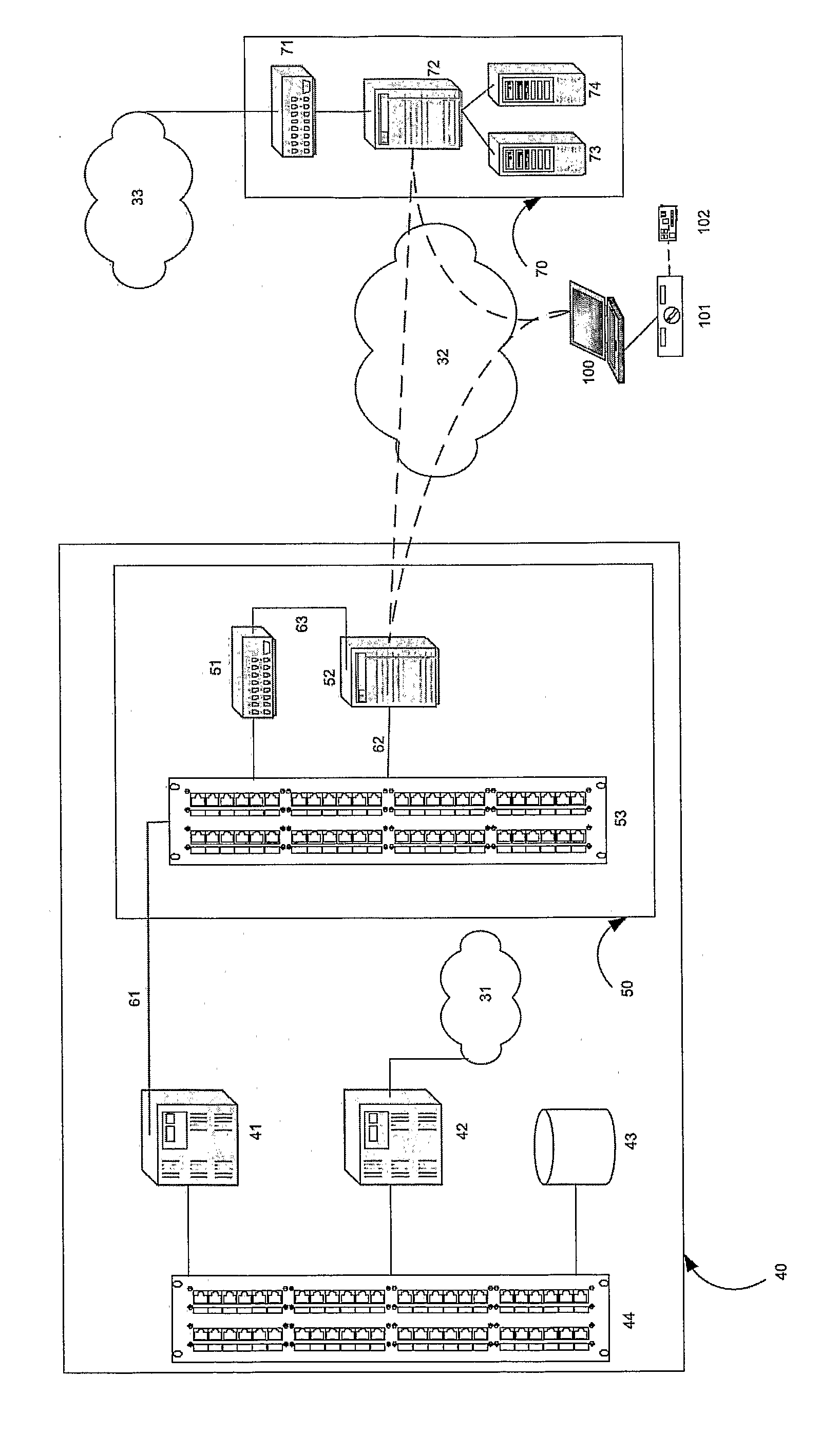
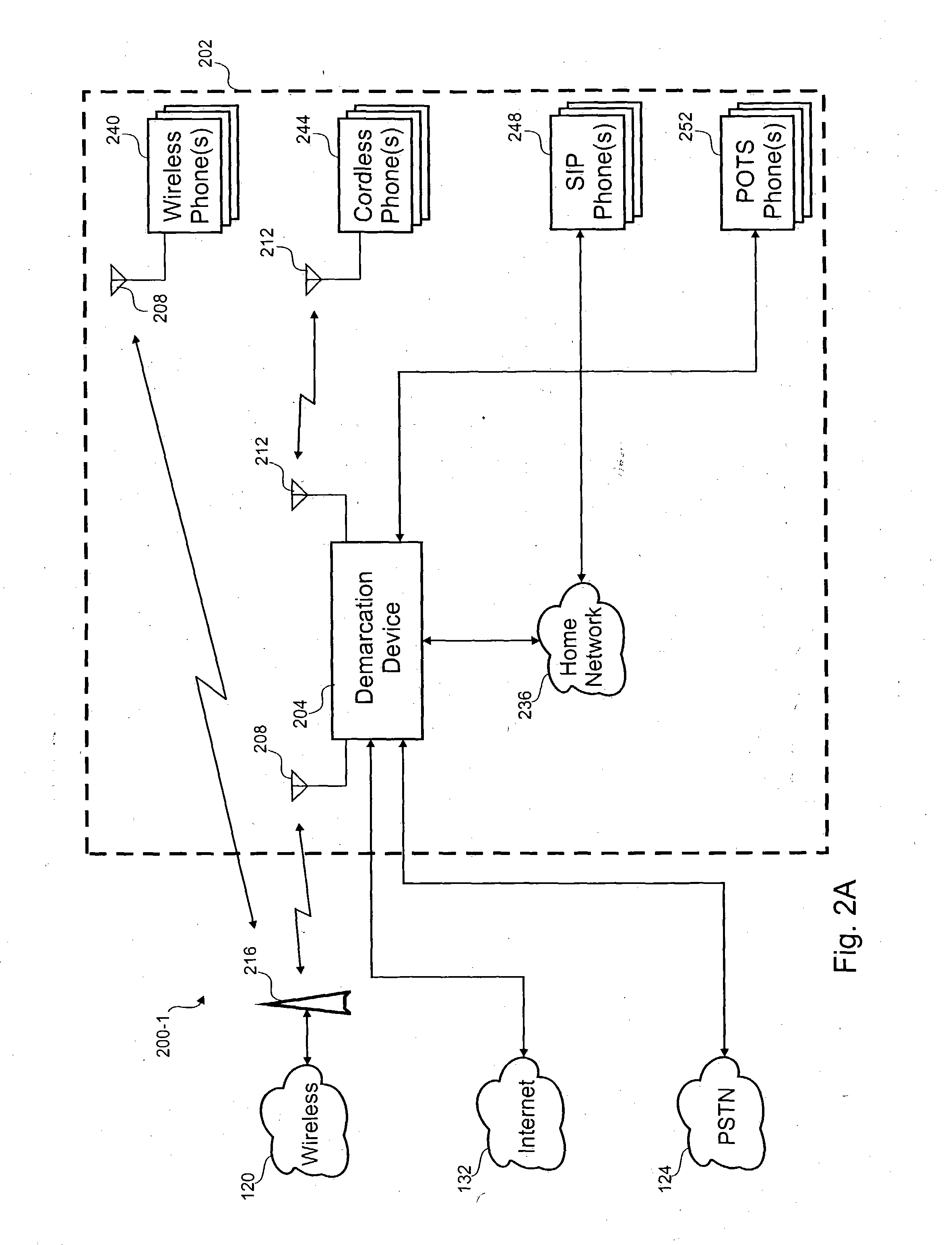
According to the invention, a telephonic communication system for integrating wireless phone service with home phone service is disclosed. The telephone communication system includes a first communication and second communication channels and a telephone switch. The first communication channel is coupled to a wireless phone and the second communication channel is coupled to an interface that is coupled to one or more wired phones at a user location. The first and second communication channels are accessible with a single telephone number. The telephone switch is coupled to the first and second communication channels and determines if the first and second communication channels should be simultaneously sent an incoming phone call directed to the telephone number.
Owner:QWEST
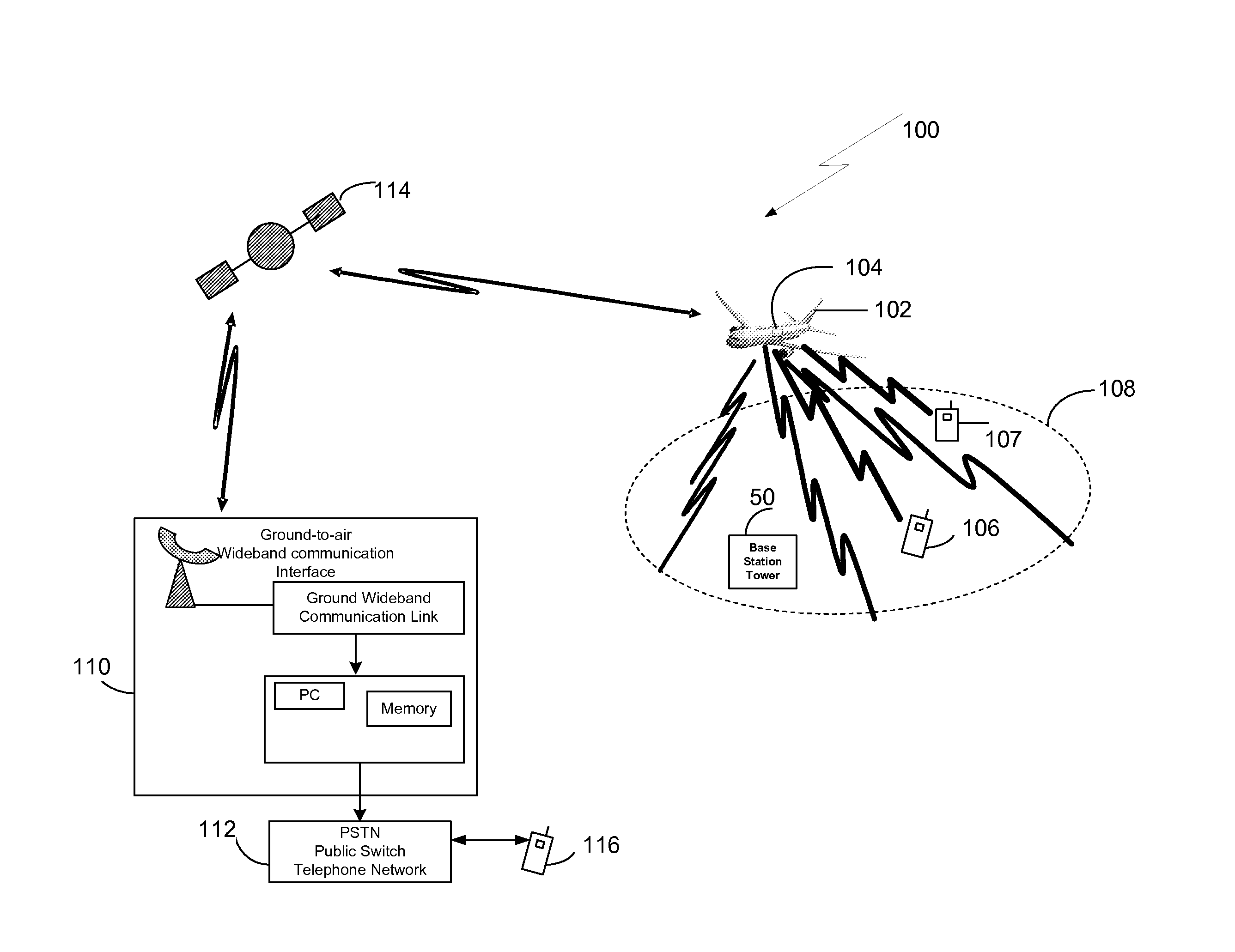
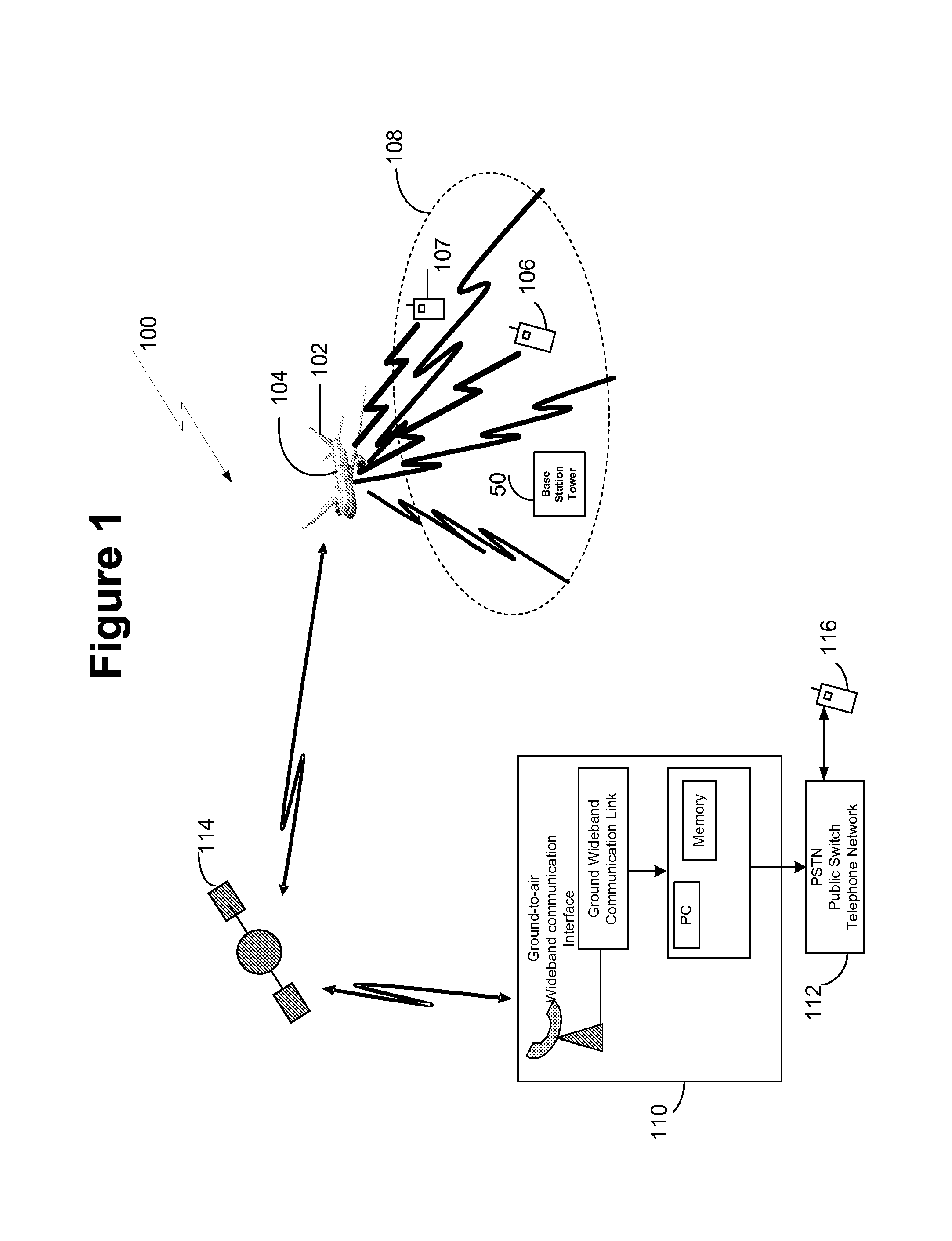
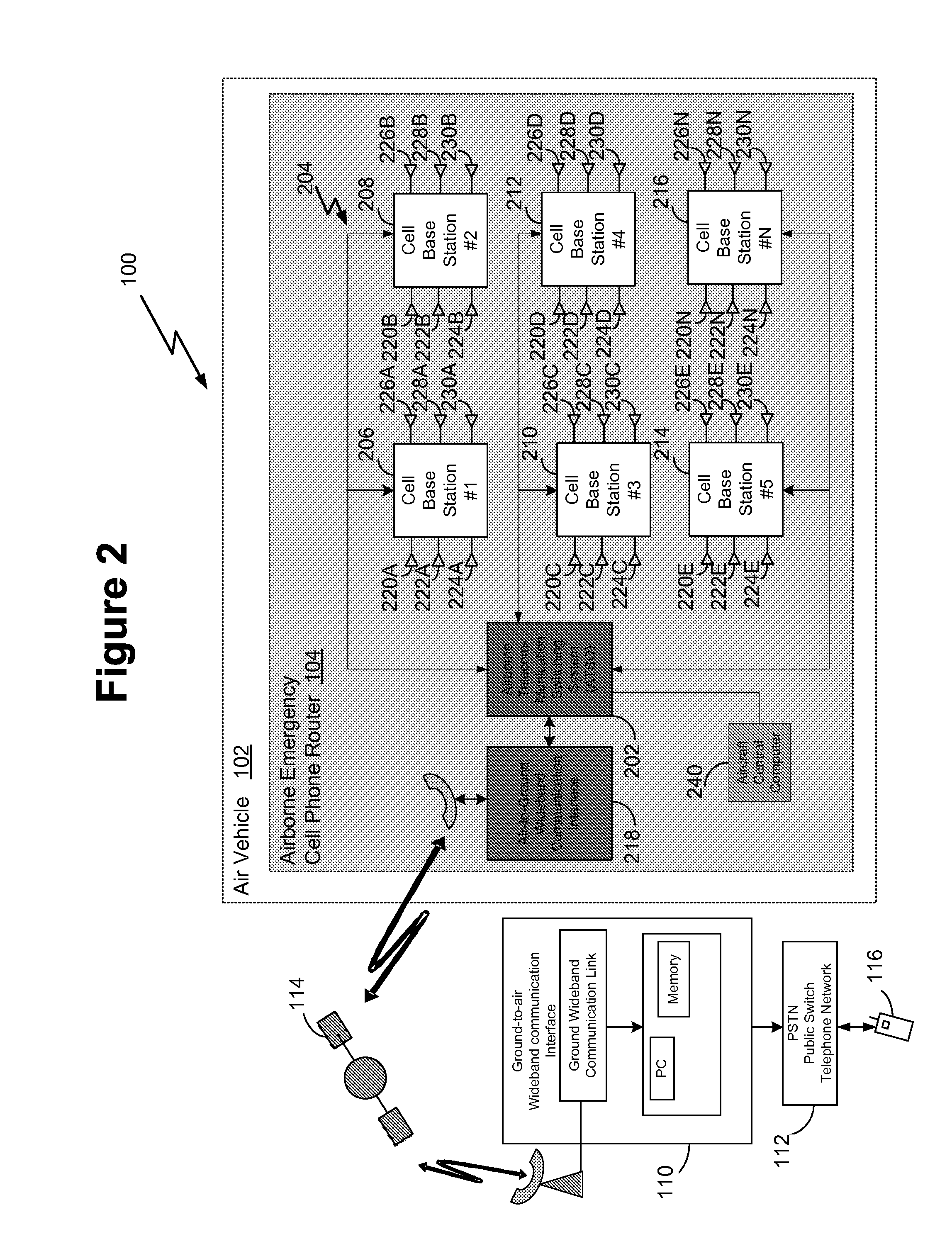
Airborne Emergency Cell Phone Router
Methods, systems, and articles of manufacture enable routing a communication from a cell phone associated with a service provider in which the cell phone is located in a predetermined area in which the service provider does not have an operational base station or in which routing assistance is required. A cell base station having one or more antennas is provided in an aircraft. Each of the antennas is configured to monitor a respective sector of the predetermined area for a cell phone communication when the aircraft is flown in proximity to the predetermined area. A registration request from a first cell phone in the predetermined is detected via the cell base station and an ID and location associated with the first cell phone is routed to a ground based telephone switching office, such as the mobile telephone switching office associated with the service provider of the detected cell phone.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
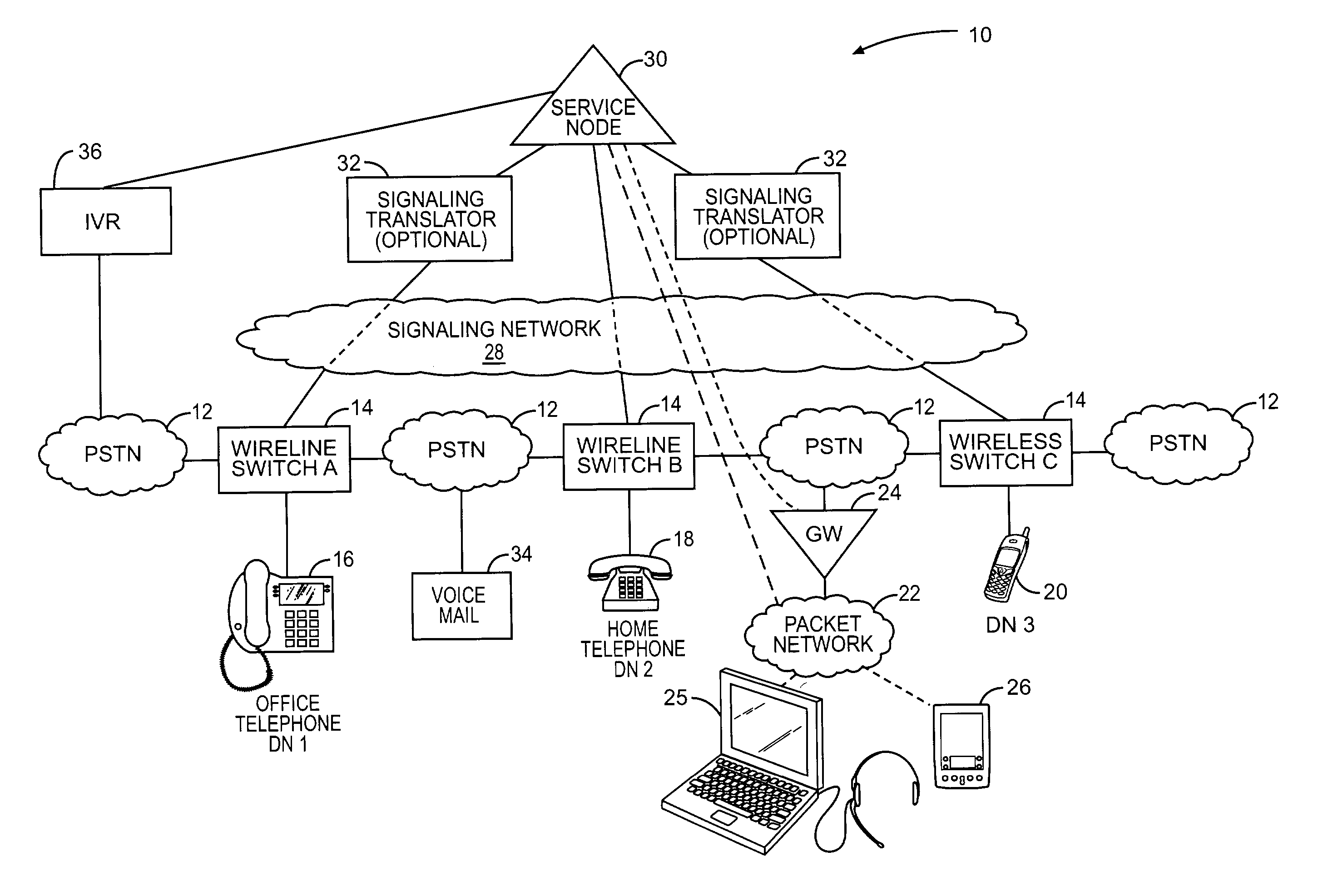
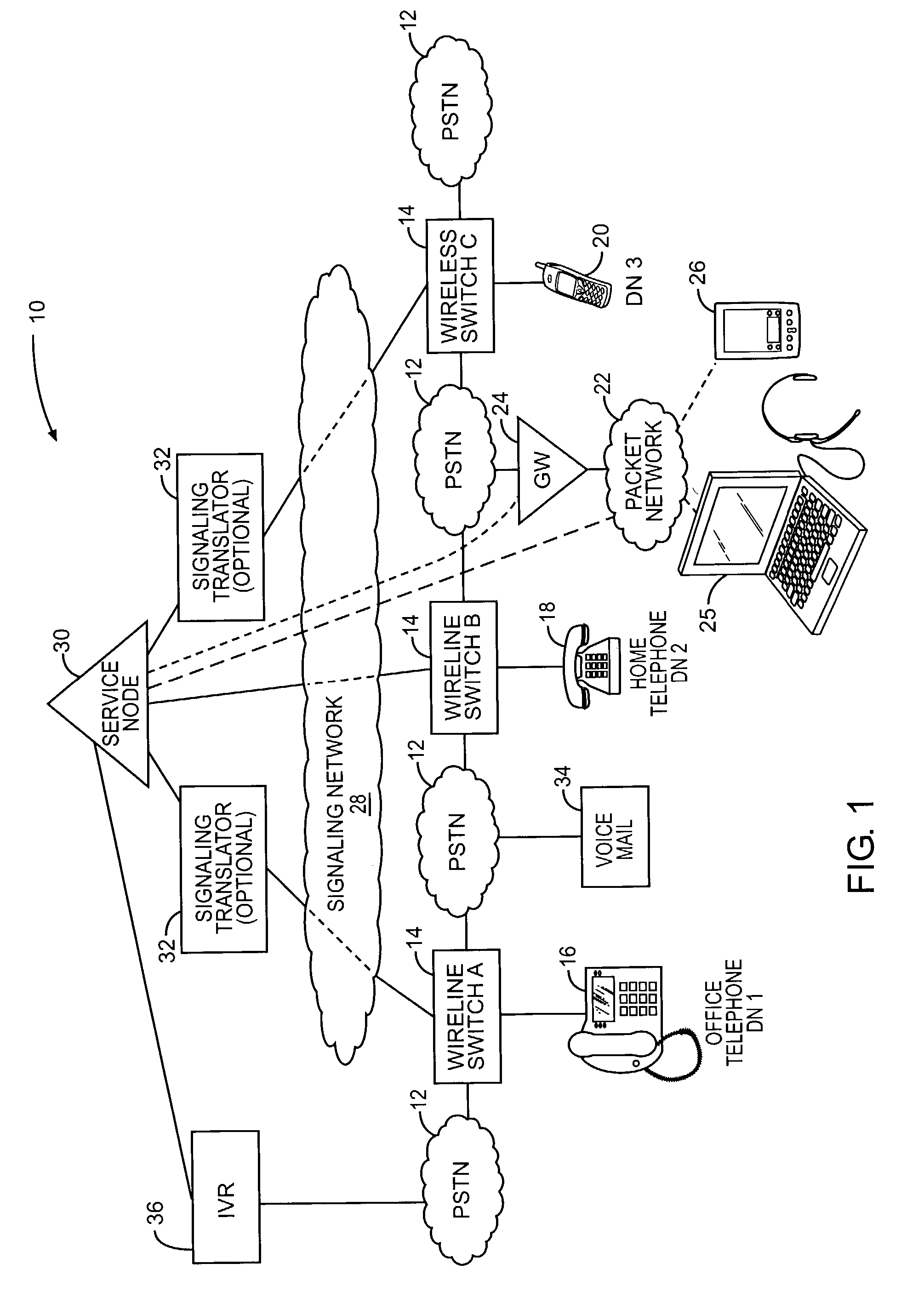
User controlled call routing for multiple telephony devices
InactiveUS7035390B2Interconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersCall routingUser control
The present invention provides a service node capable of coordinating call processing for incoming calls intended for any one of multiple telephony devices of a given entity, such as a business or individual user. Switching devices, such as traditional telephony switches or internetworked gateways controlling call routing, are configured to interact with the service node to determine how to handle incoming calls to the telephony devices that they serve. Through a variety of techniques, the entity can dynamically instruct the service node how to route incoming calls, and preferably, upon putting those instructions into effect, the service node will send an alert to the entity. The instructions are used by the service node to create call processing rules for the switching devices to apply to an incoming call intended for any of the entity's telephony devices.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
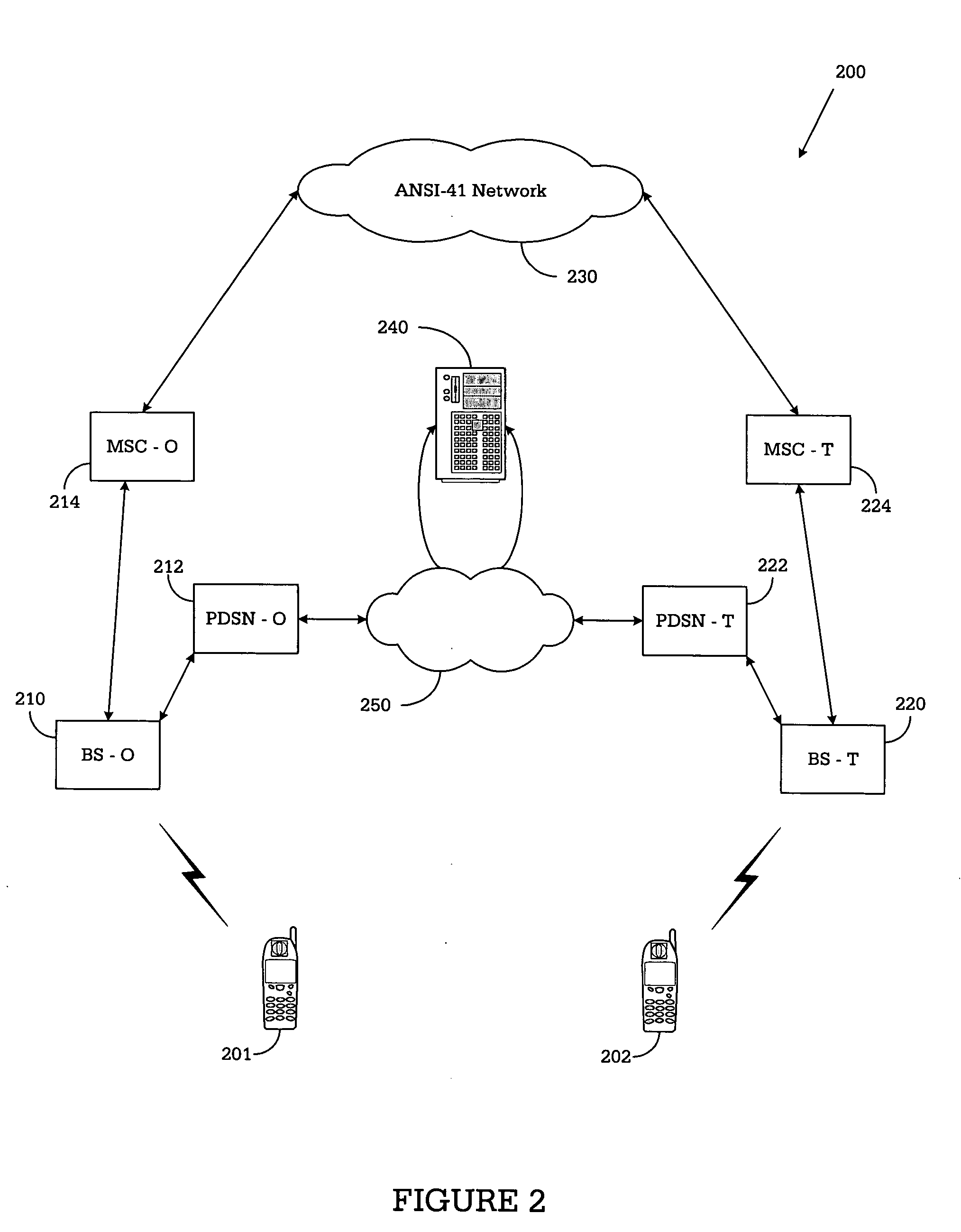
System and method for establishing mobile station-to-mobile station packet data calls between mobile stations in different wireless networks
InactiveUS20050099998A1Quick connectionAssess restrictionData switching by path configurationData connectionTelephone network
A method of establishing a packet data session from an originating mobile station (MS) to a terminating mobile station (MS). The method comprises the steps of: i) receiving in an originating base station (BS) of a first wireless network a packet data connection request transmitted by the originating MS; ii) transmitting the terminating MS phone number from the originating BS to an originating mobile switching center (MSC) of the first wireless network; iii) transmitting a first message containing the terminating MS phone number from the originating MSC to a terminating mobile switching center (MSC) of a second wireless network via a switched telephone network; and iv) transmitting a second message from the terminating MSC to the terminating MS via a terminating base station of the second wireless network, the second message informing the terminating MS that a packet data session with the originating mobile station is being established.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Communication assistance system and method
InactiveUS20050136899A1Improve securityIncrease capacitySynchronisation arrangementAccounting/billing servicesCommunication interfaceData synchronization
A directory assistance system is provided for providing subscriber information to requesters communicating with the assistance system. A telephone switch receives calls from a plurality of requesters desiring to access the information corresponding to subscribers. A first database stores the information corresponding to each of the subscribers, including their phone numbers. A communications interface for database clean-up receives instructions from the subscribers so as to allow the subscribers to modify their corresponding information in the first database, where the communications interface is coupled to a carrier customer care representative system configured to receive phone calls from the subscribers. A carrier clean-up database is coupled to the customer care representative system and configured to store the modified information received from the subscribers. The communications interface unit further comprises a synchronization technology unit coupled to the clean-up database unit, and is further coupled to the first database, and configured to synchronize the subscriber modifications with data stored in the first database.
Owner:INFONXX
Universal point of contact identifier system and method
ActiveUS20080144791A1Telephone data network interconnectionsSpecial service for subscribersEmail addressElectronic mail
A subscriber to a universal point of contact service designates a preferred point of contact at which a communication initiator, such as a telephone caller, can contact the subscriber. Such an initiator desiring to contact the subscriber uses the subscriber's email address to establish a communication session with a device associated with the subscriber's preferred point of contact. The subscriber's email address is input to an initiating device, preferably a telephone or facsimile machine, using an entry device capable of entering an email address. A requestor unit, receiving the email address, locates a repository of the subscriber's point of contact information, and requests that information. The repository sends the point of contact information the subscriber has designated as preferred, and the requester unit uses that information to control a telephone switch to establish a communication session between the initiating device and the subscriber's preferred point of contact device.
Owner:AYMAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com