Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
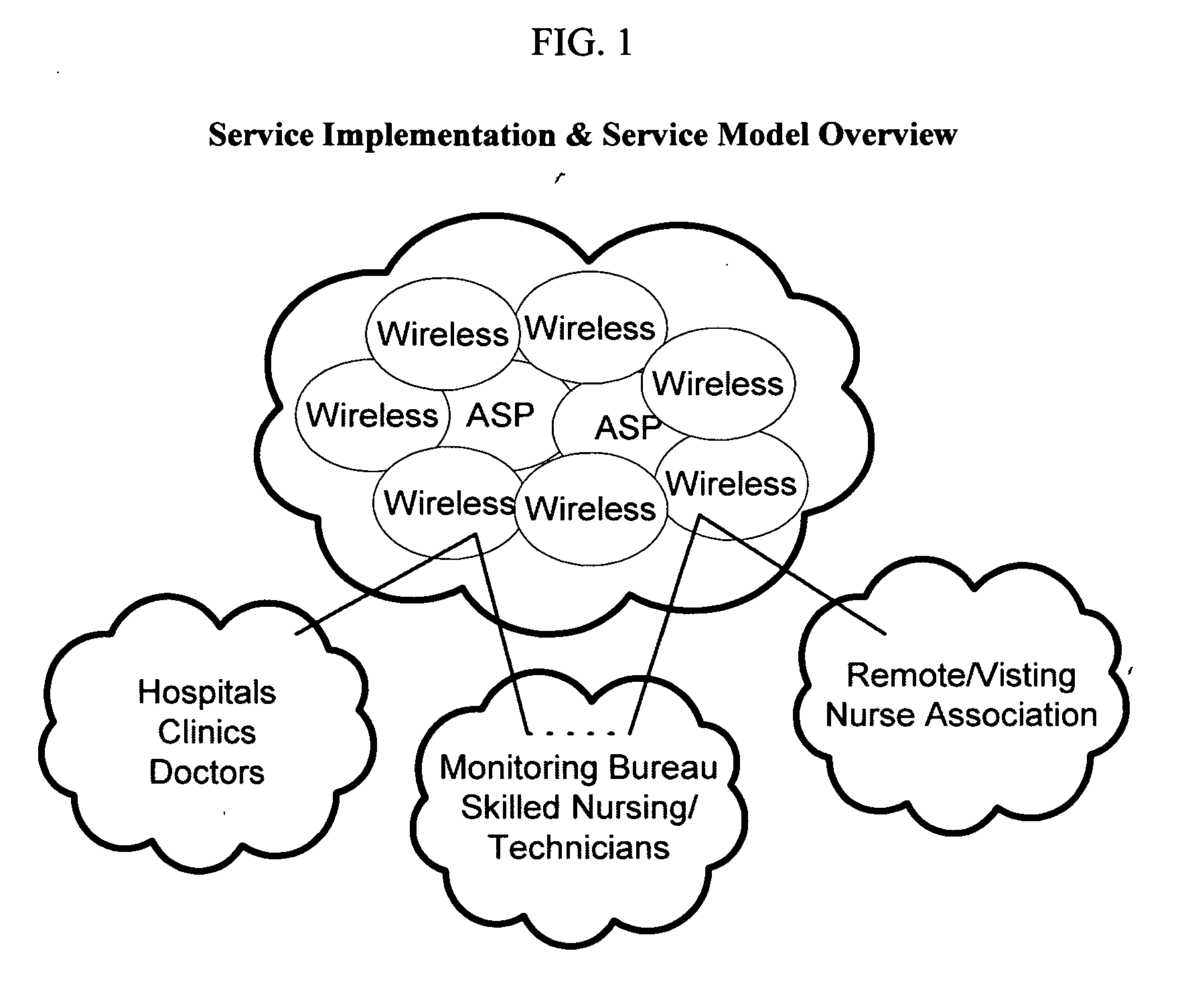
755 results about "Patient care" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
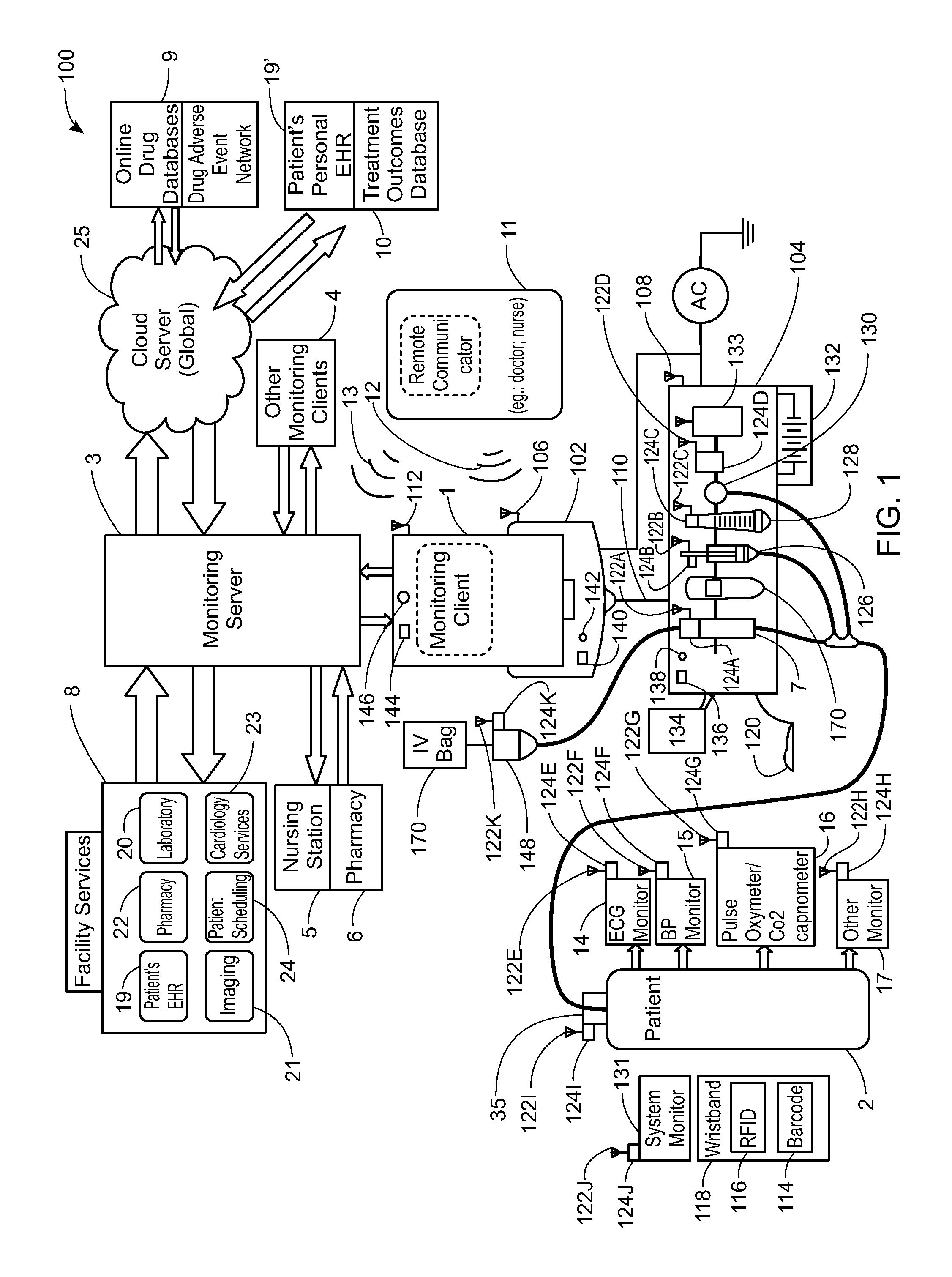
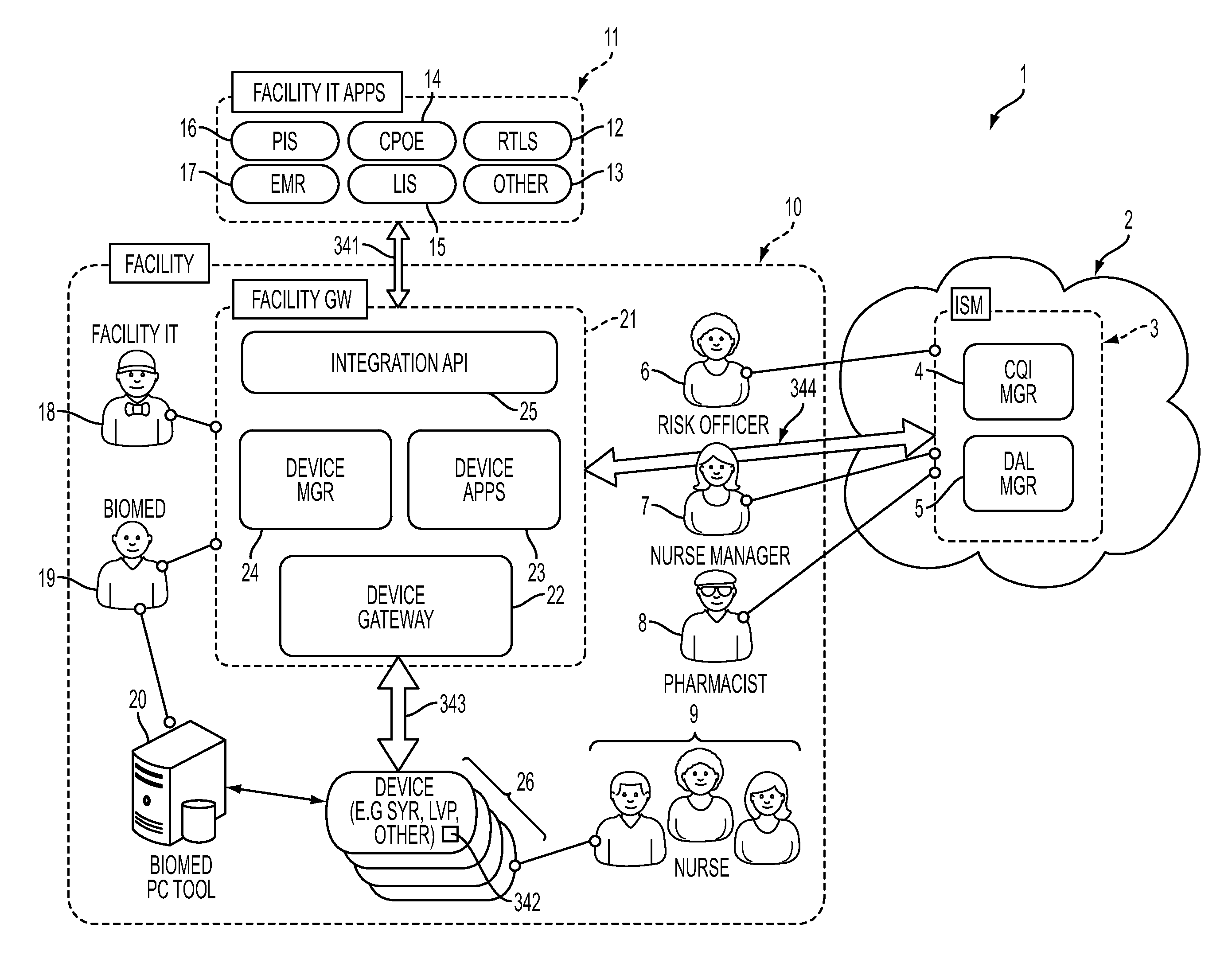
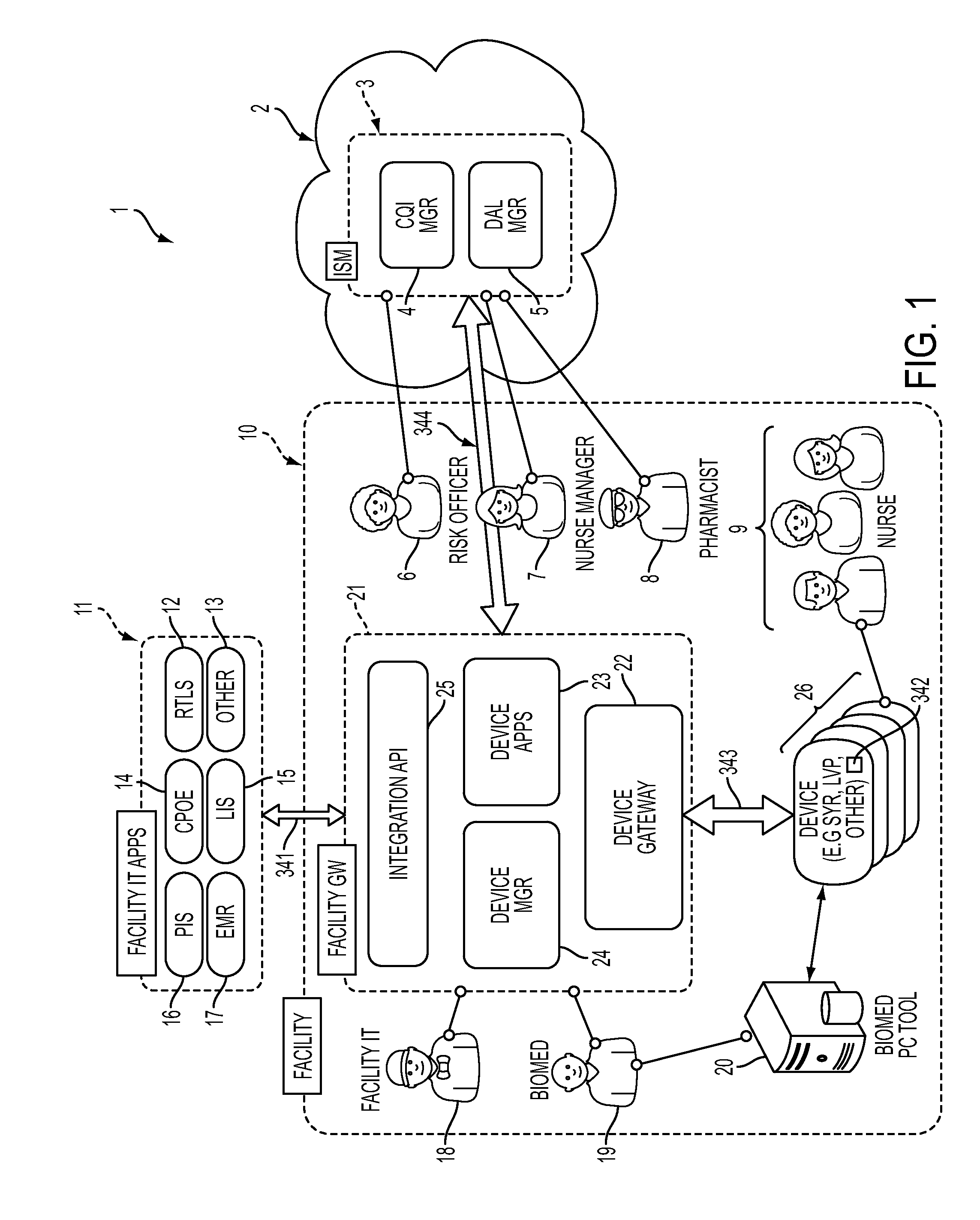
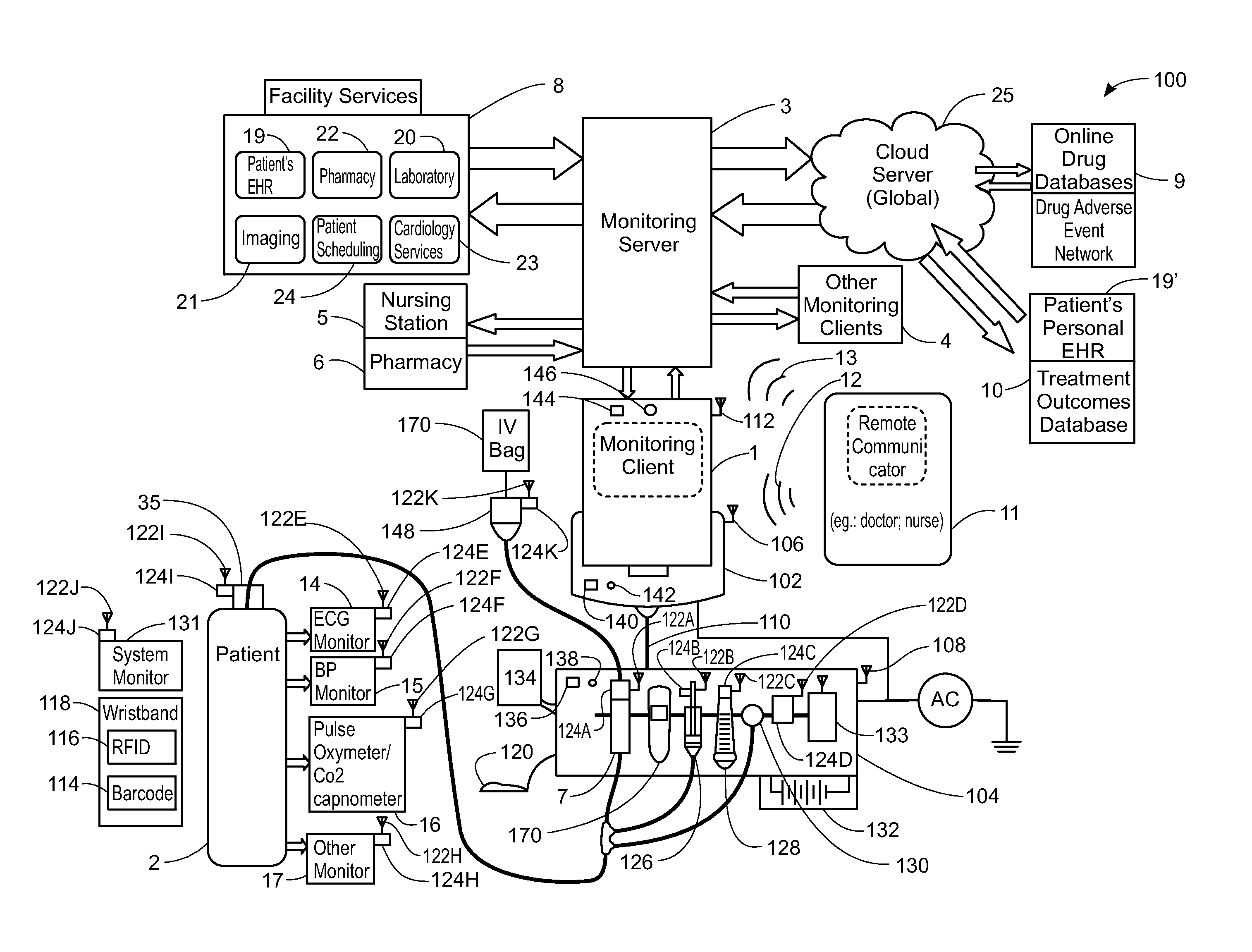
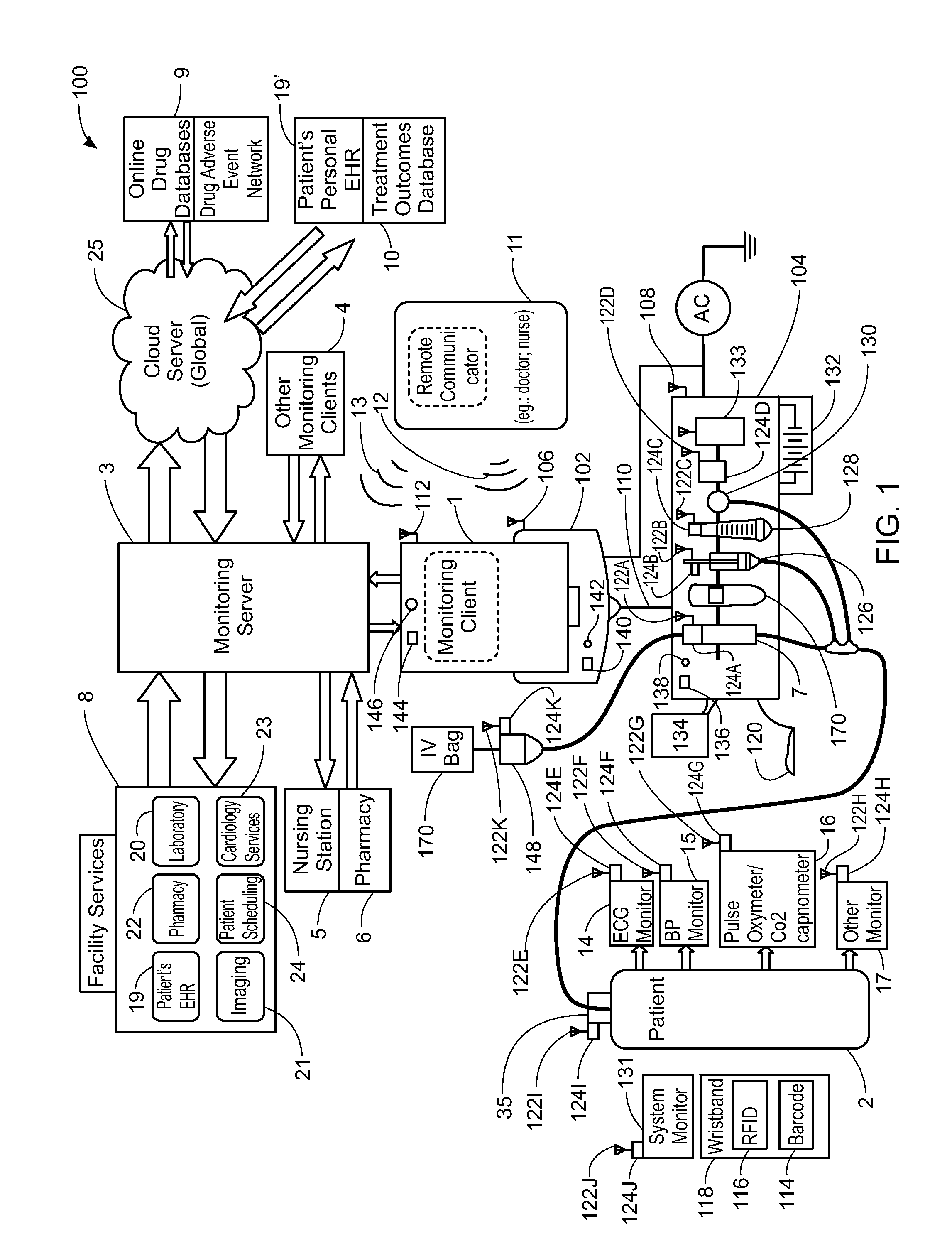
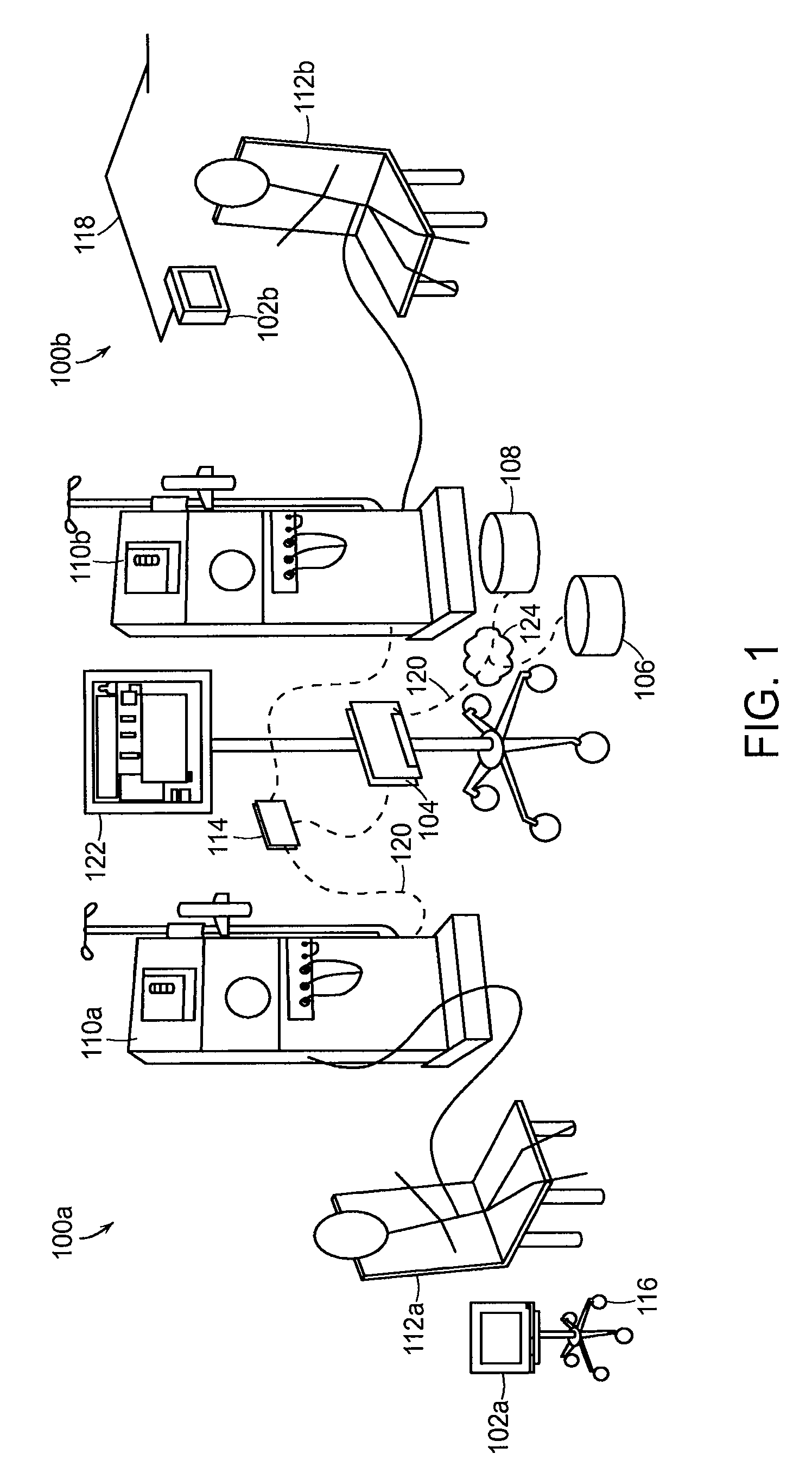
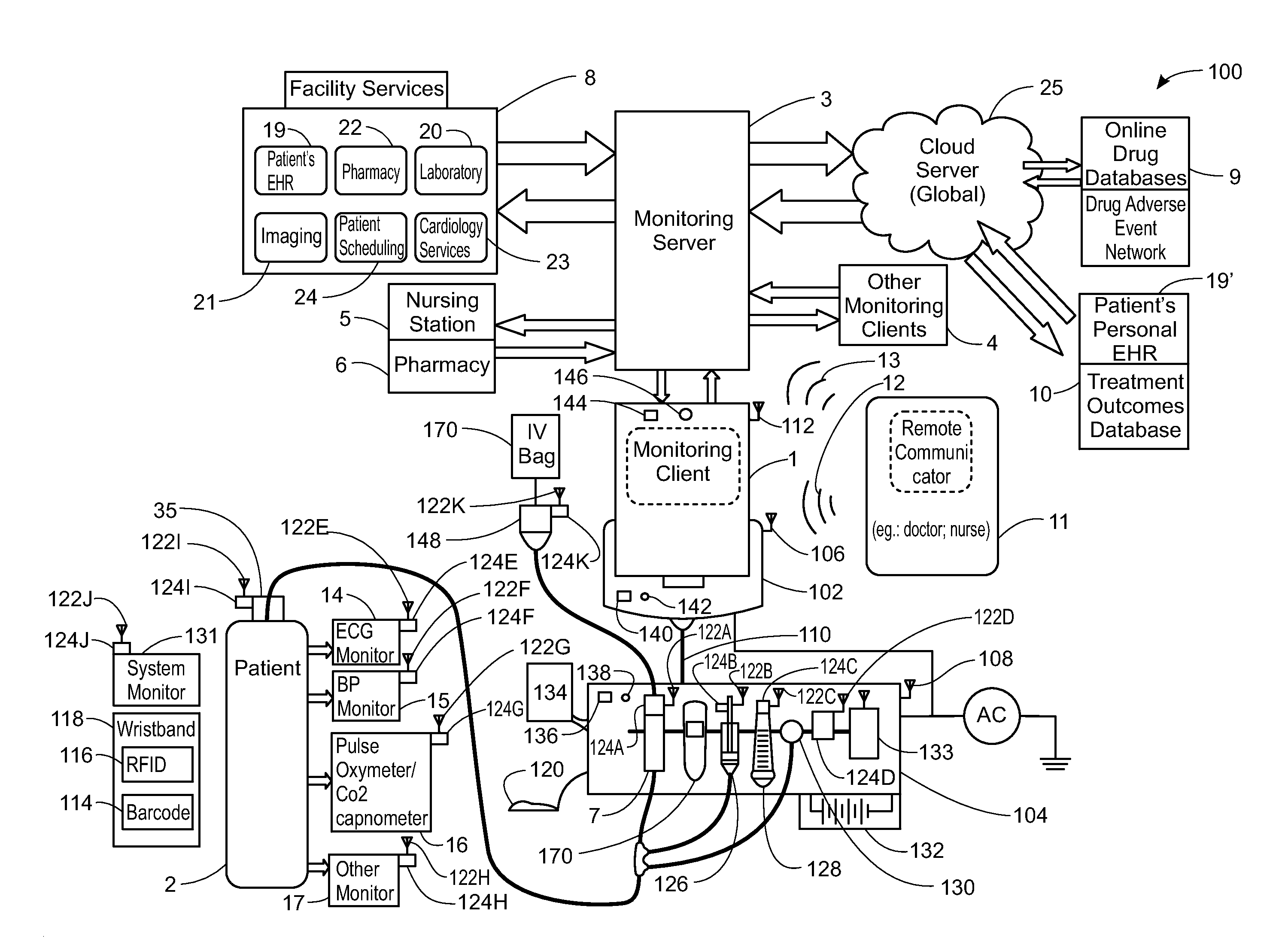
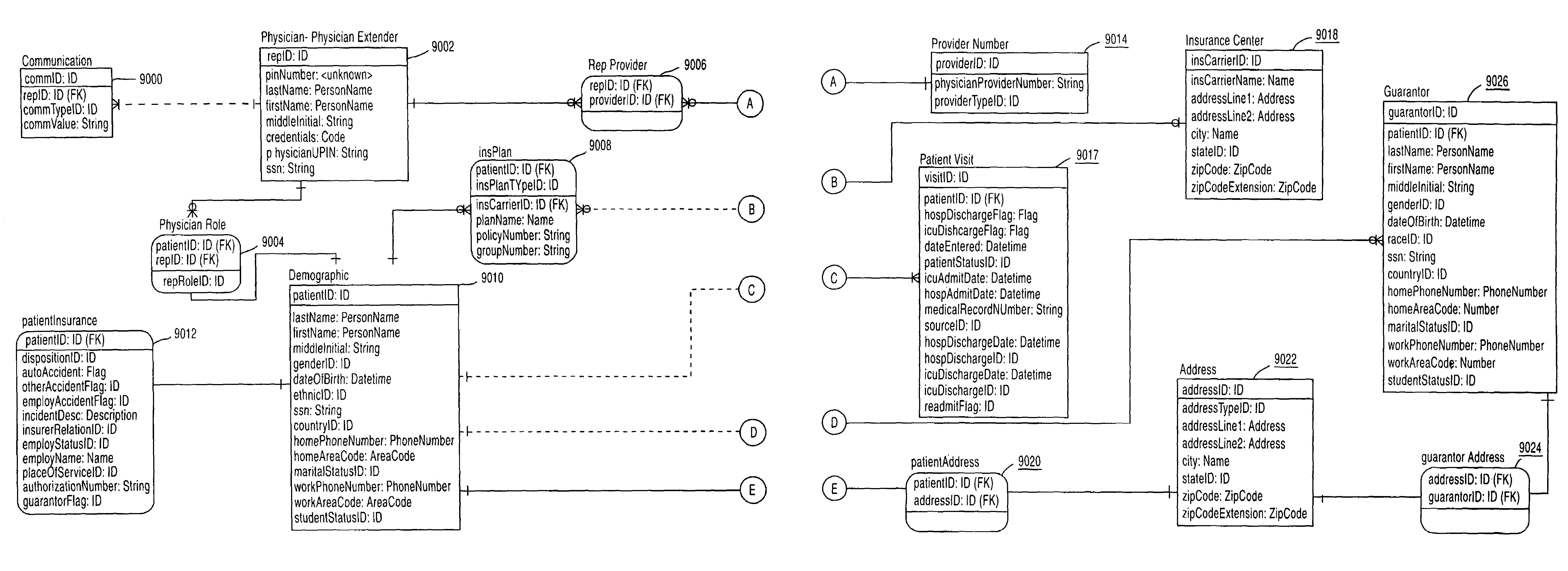
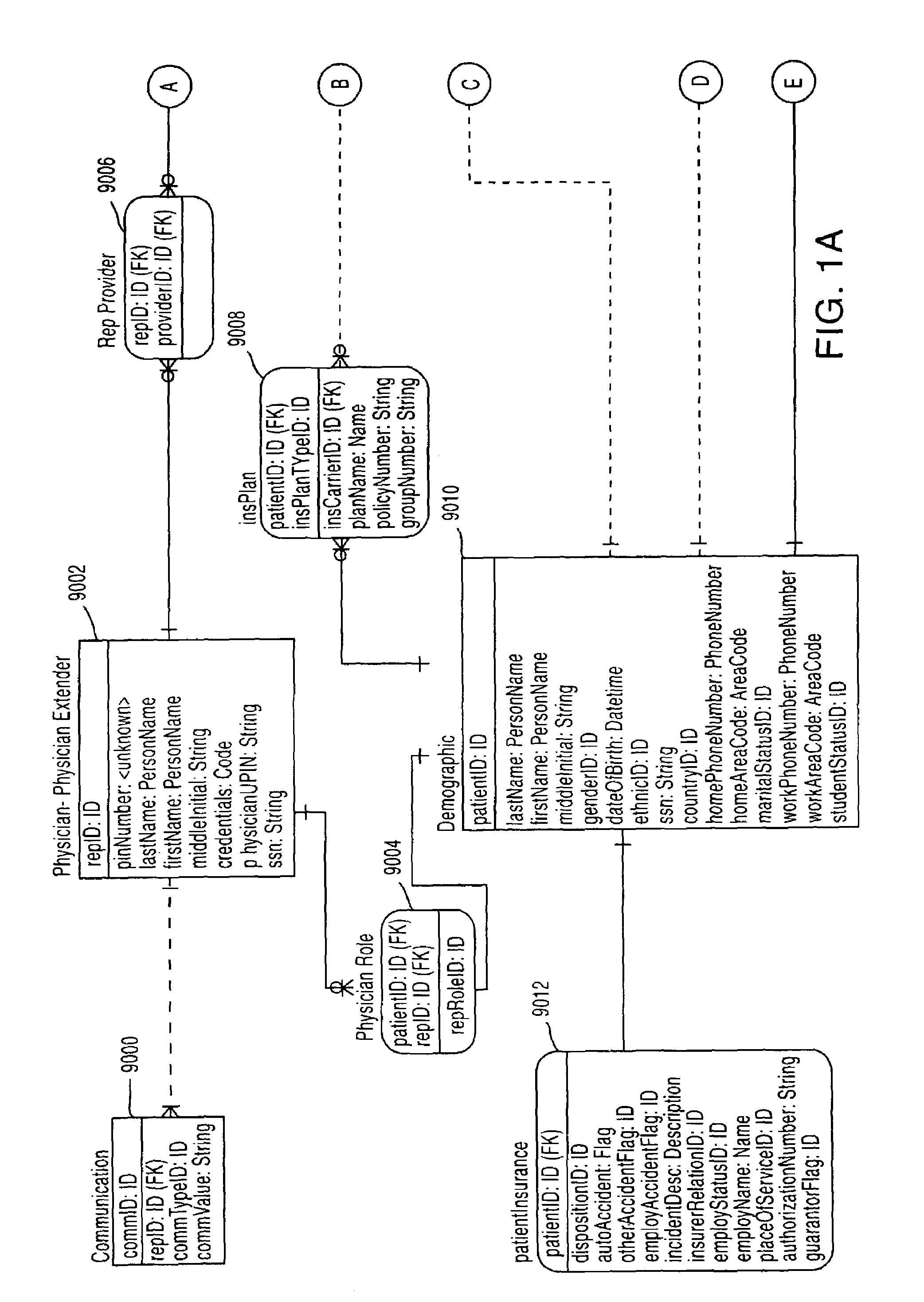
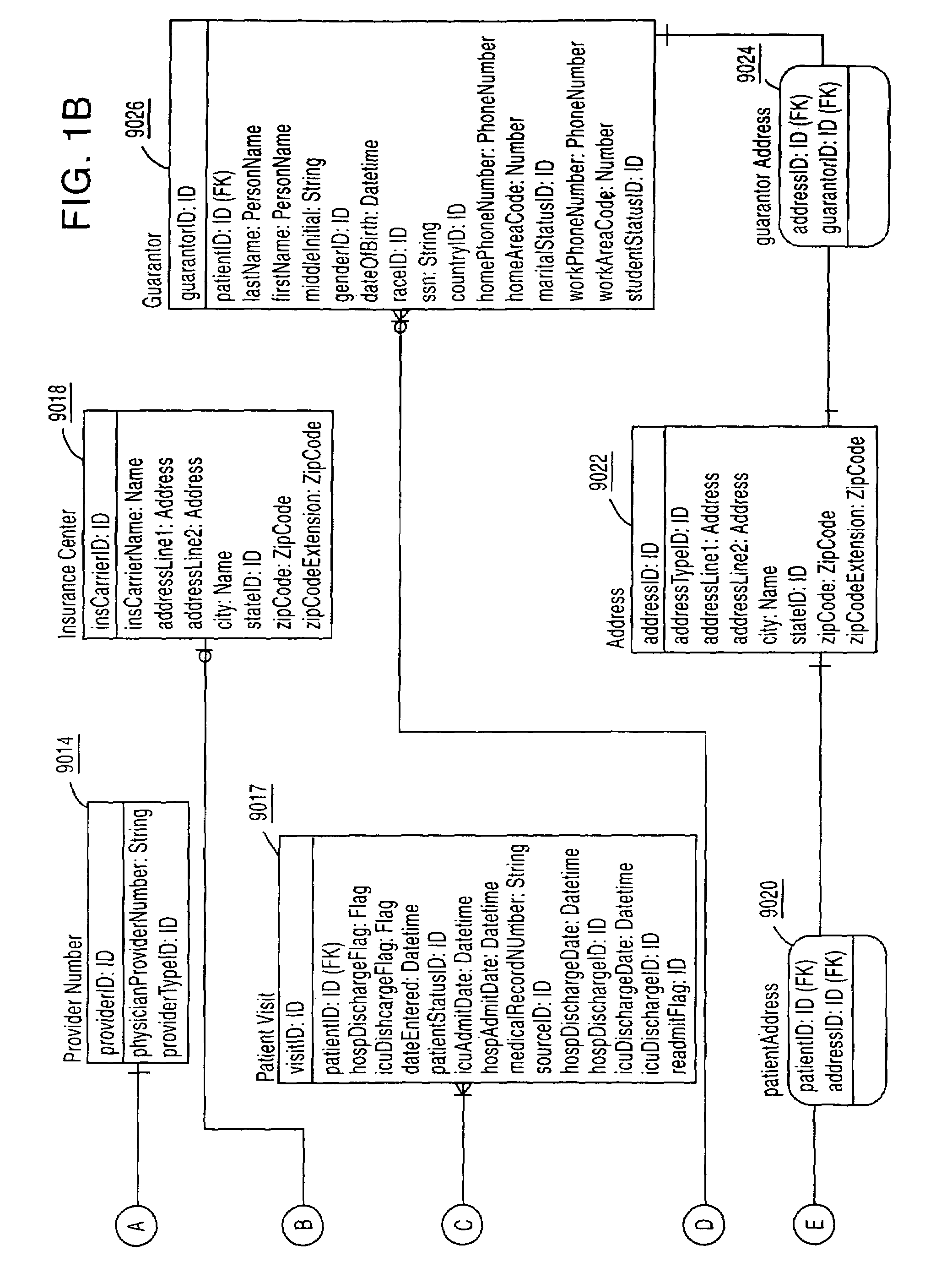
System, Method, and Apparatus for Electronic Patient Care
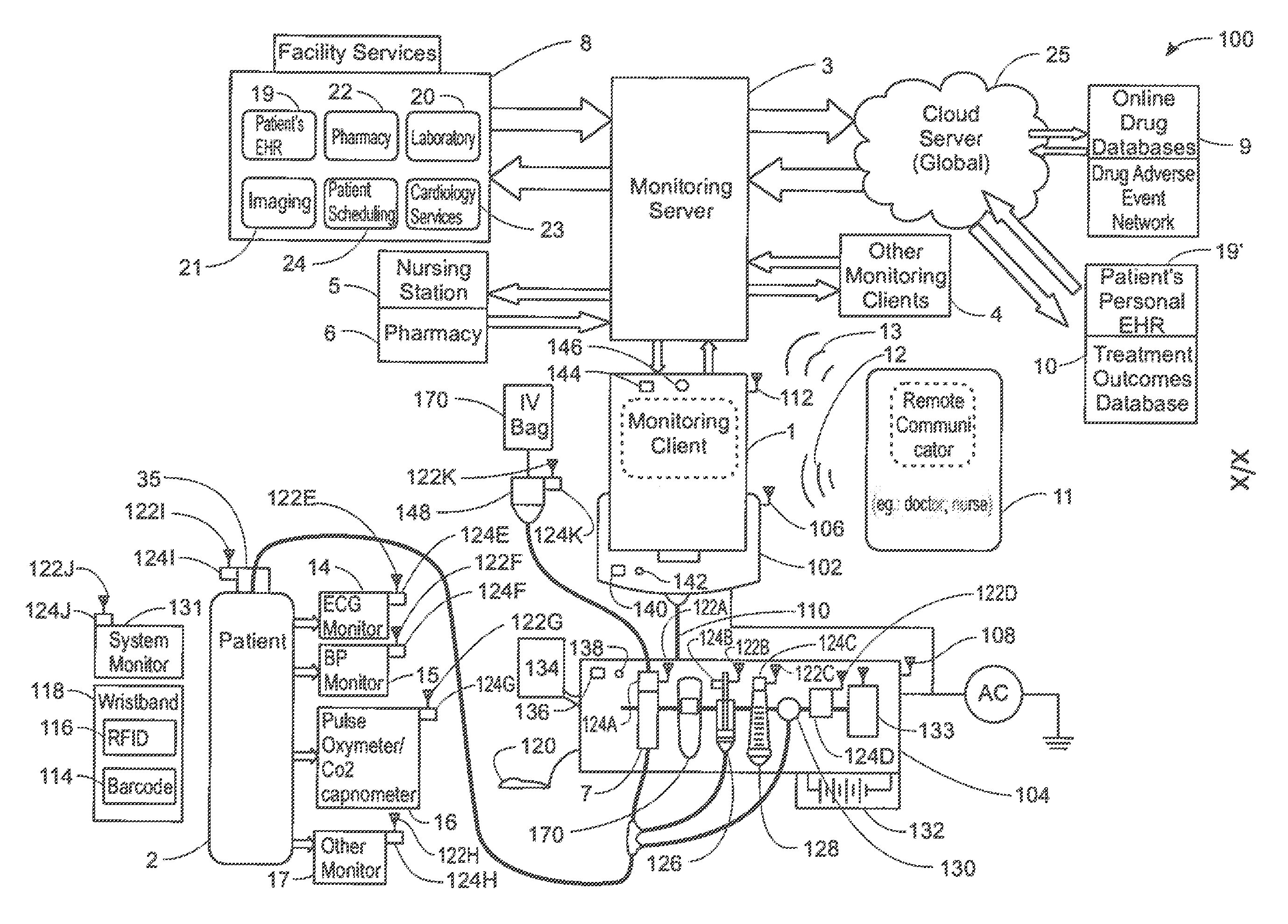
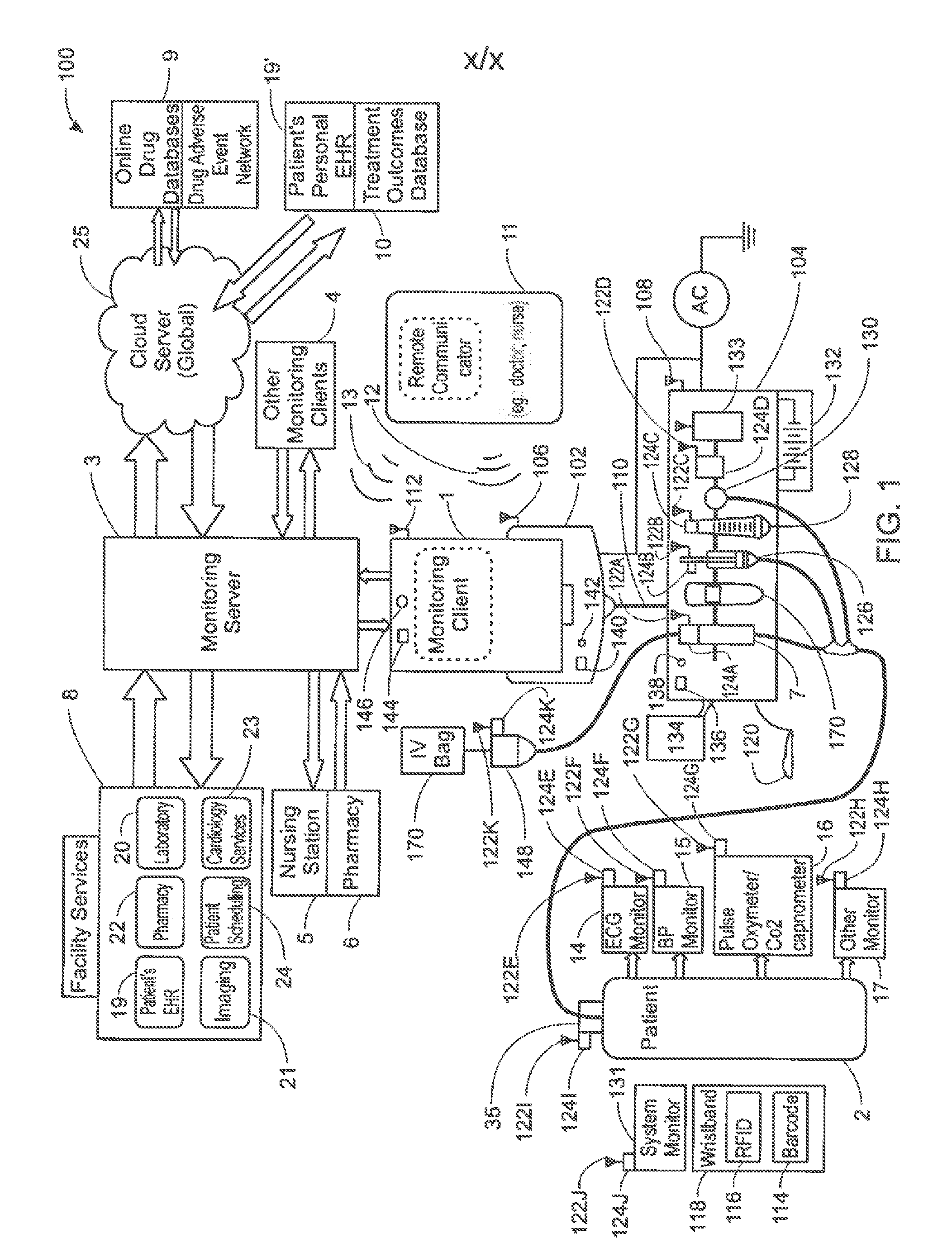
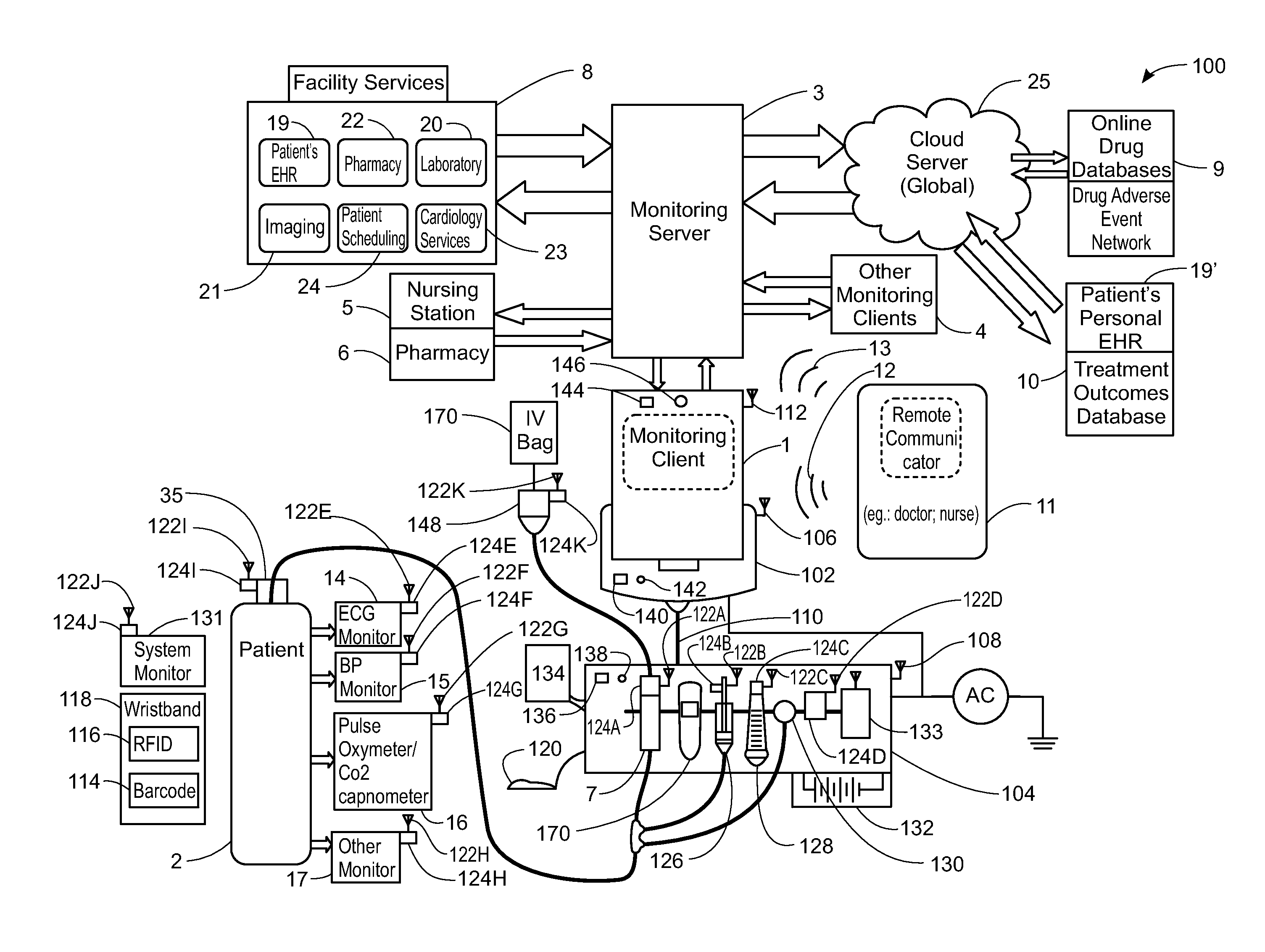
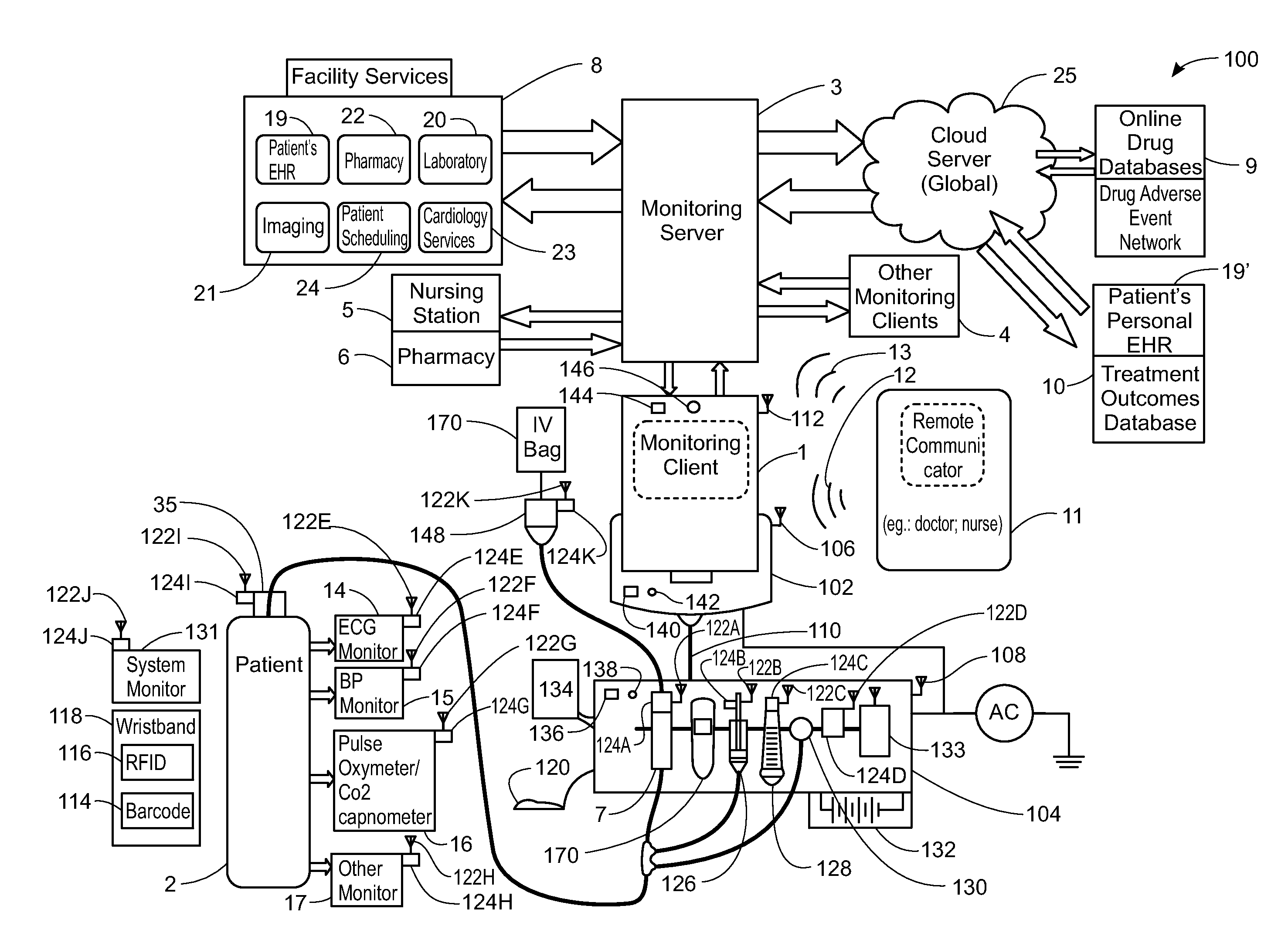
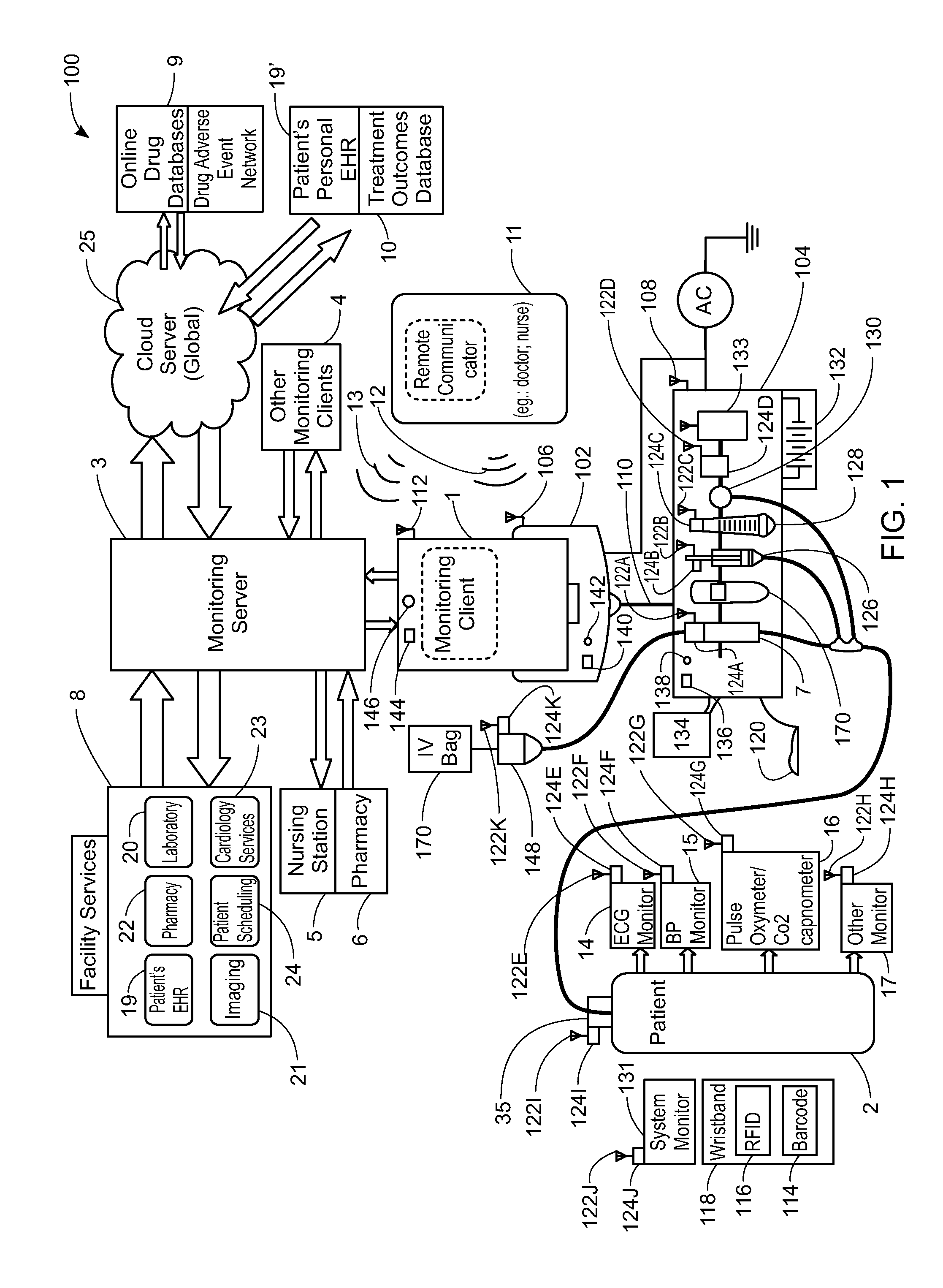
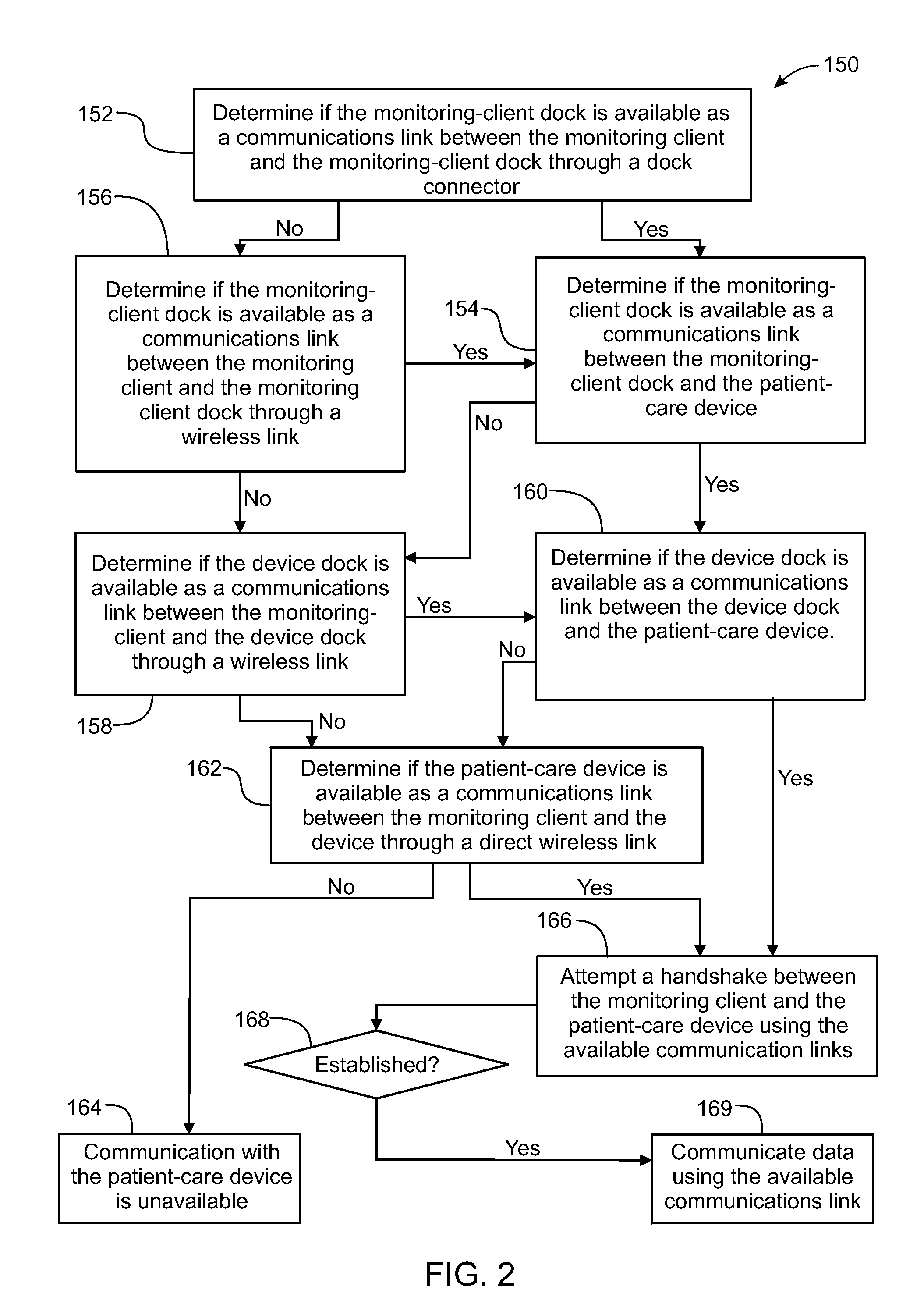
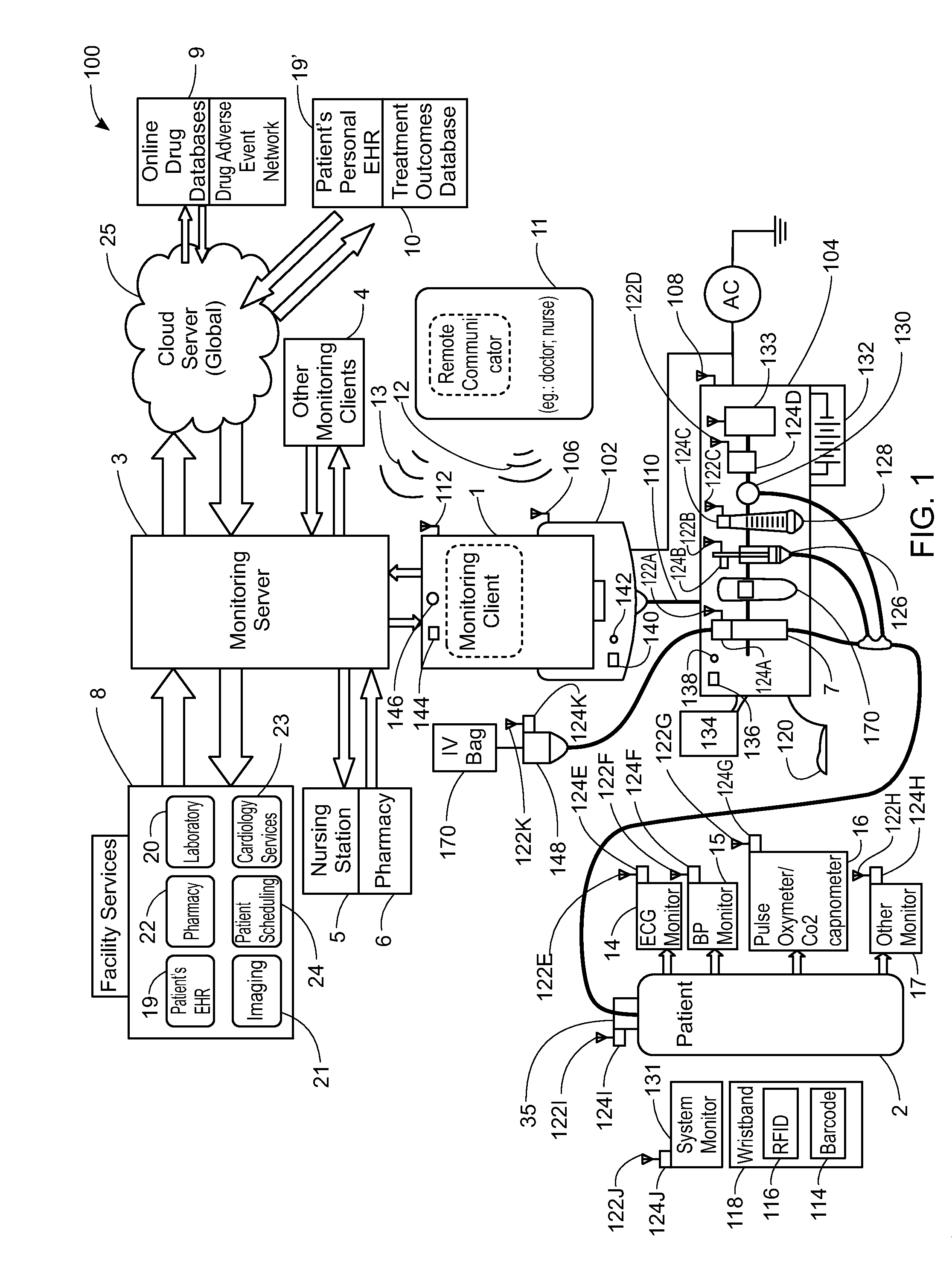
ActiveUS20130317753A1Quantity minimizationPerson identificationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareCommunication link
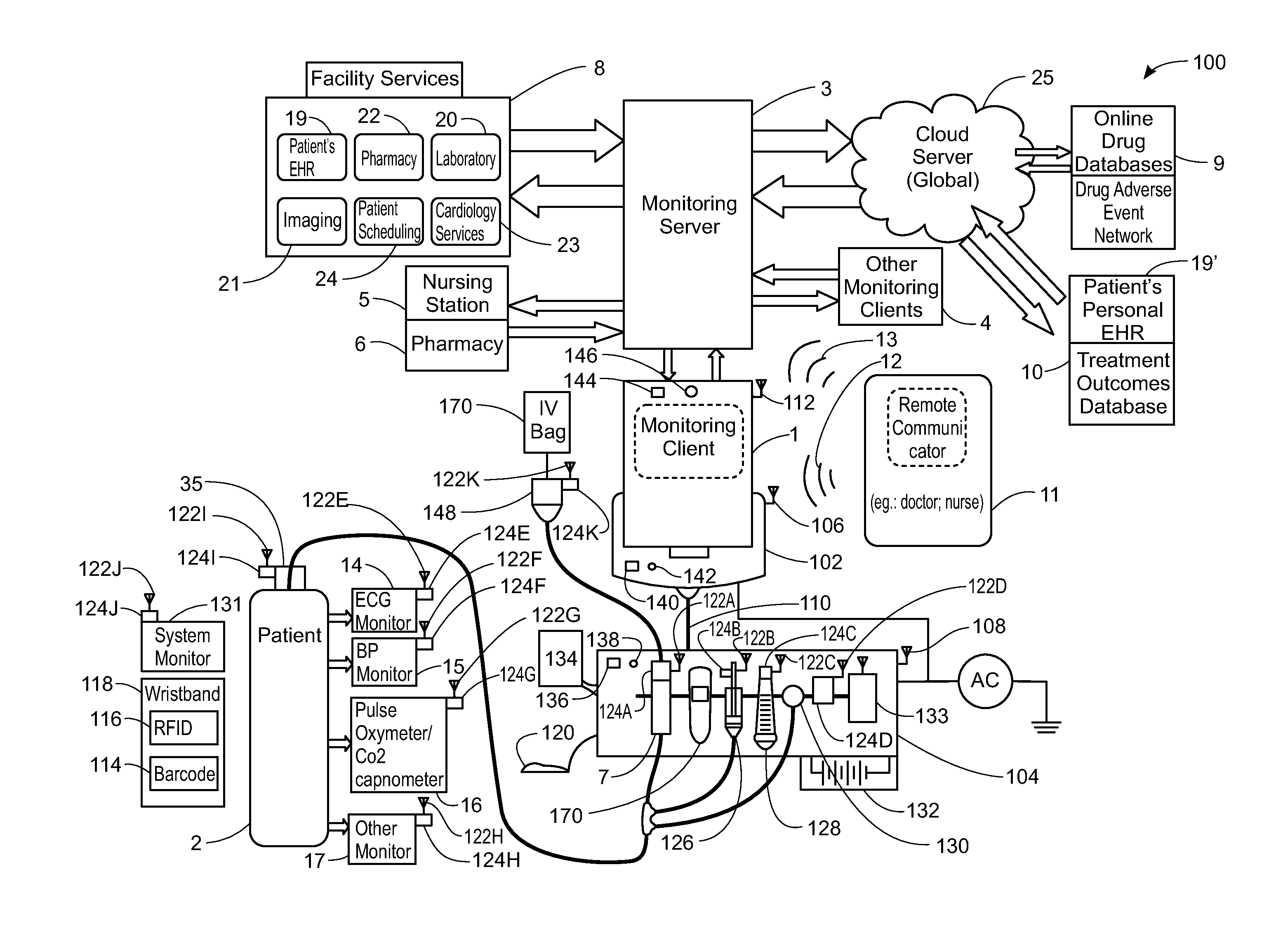
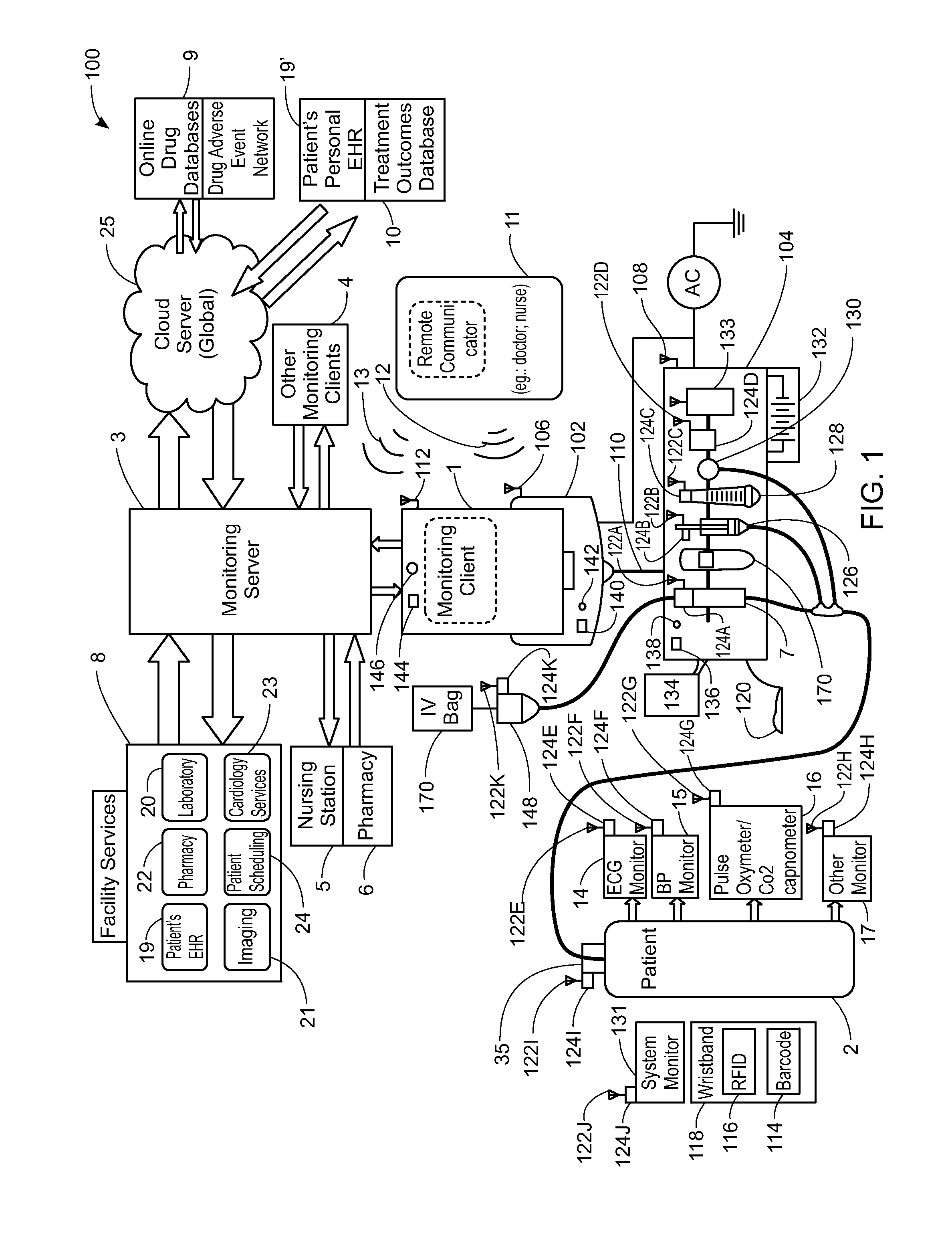
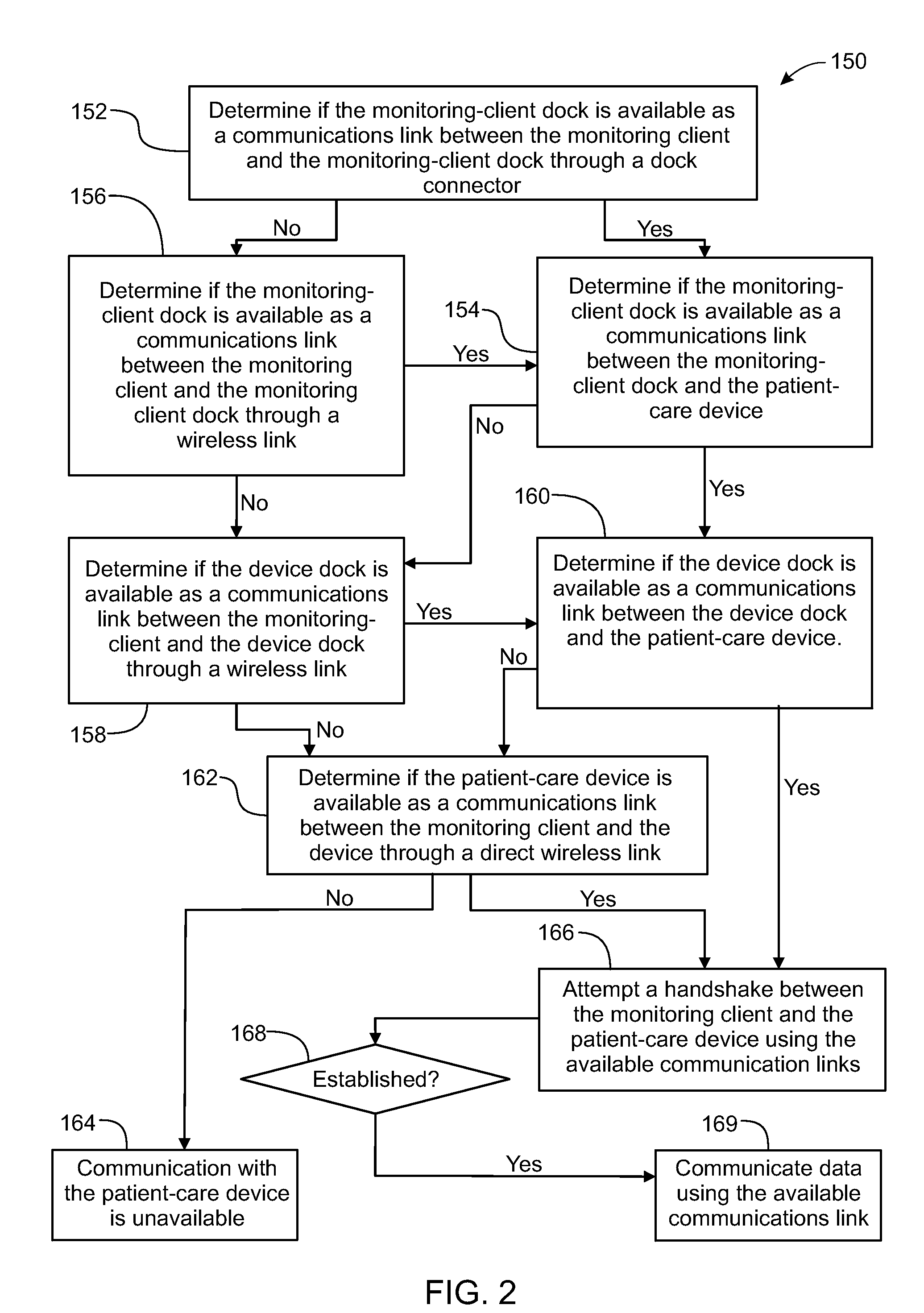
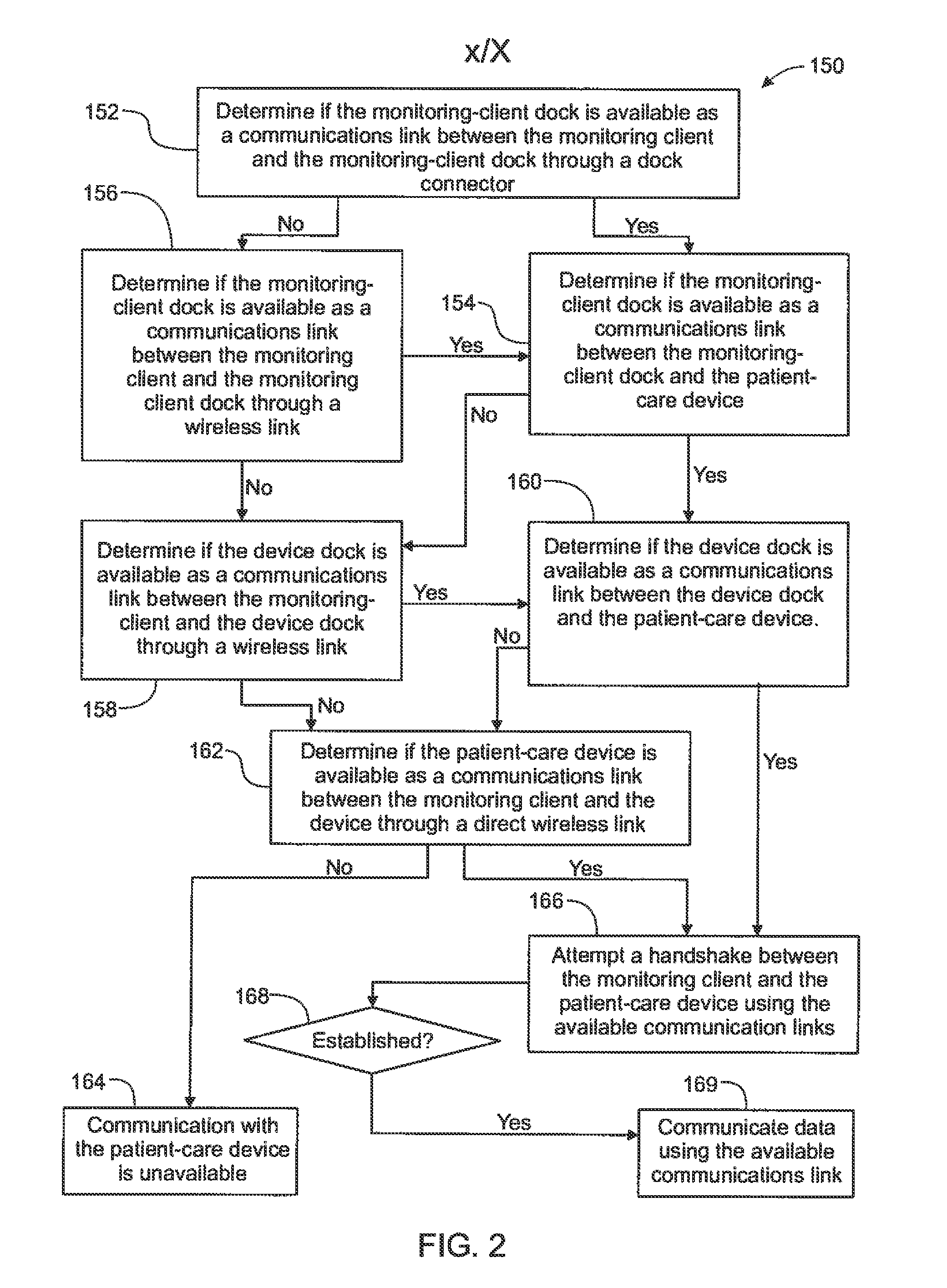
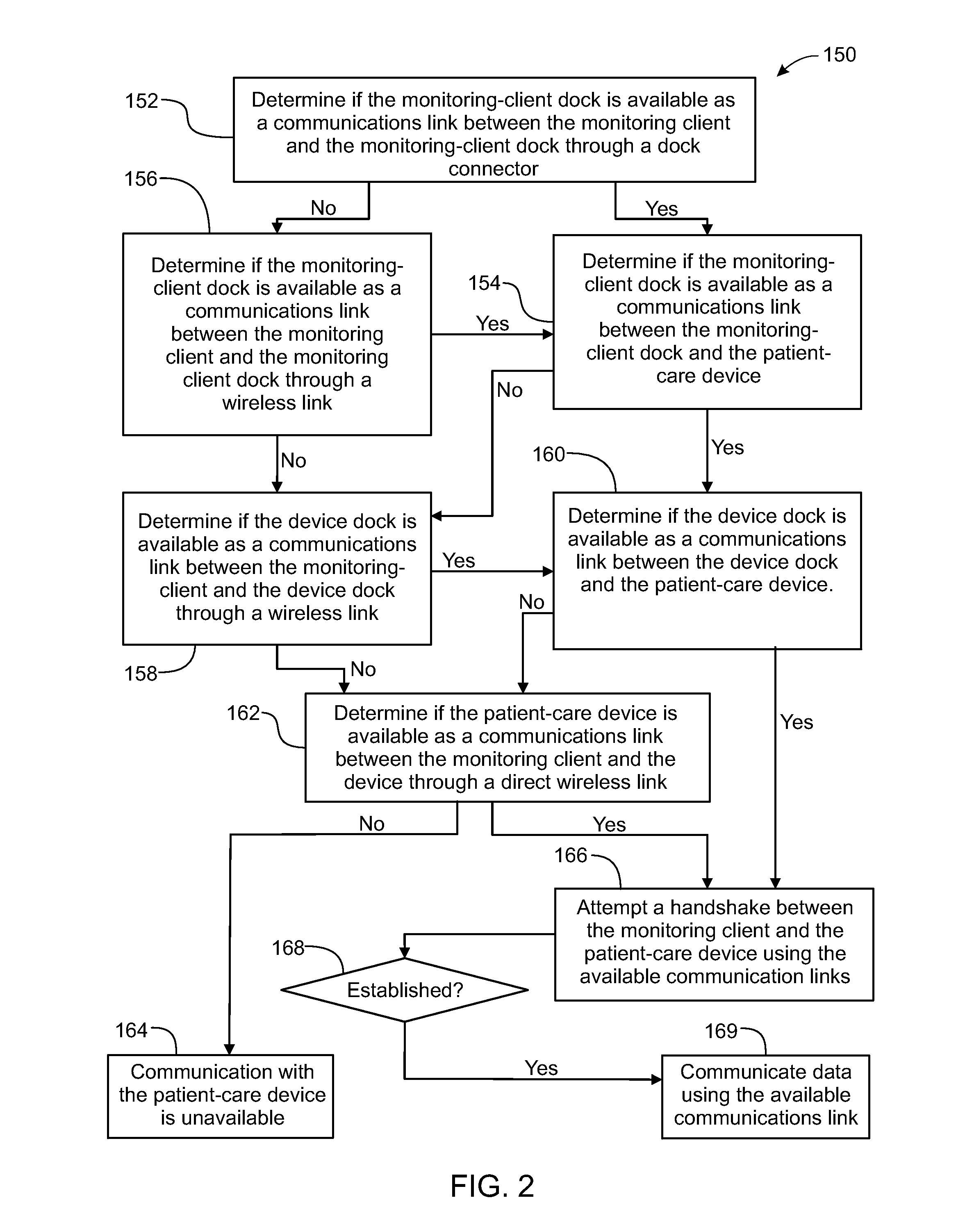
A method implemented by an operative set of processor executable instructions configured for execution by a processor includes: determining if a monitoring client is connected to a base through a physical connection; establishing a first communications link between the monitoring client and the base through the physical connection; updating, if necessary, the interface program on the monitoring client and the base through the first communications link; establishing a second communications link between the monitoring client and the base using the first communications link; and communicating data from the base to the monitoring client using the second communications link.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
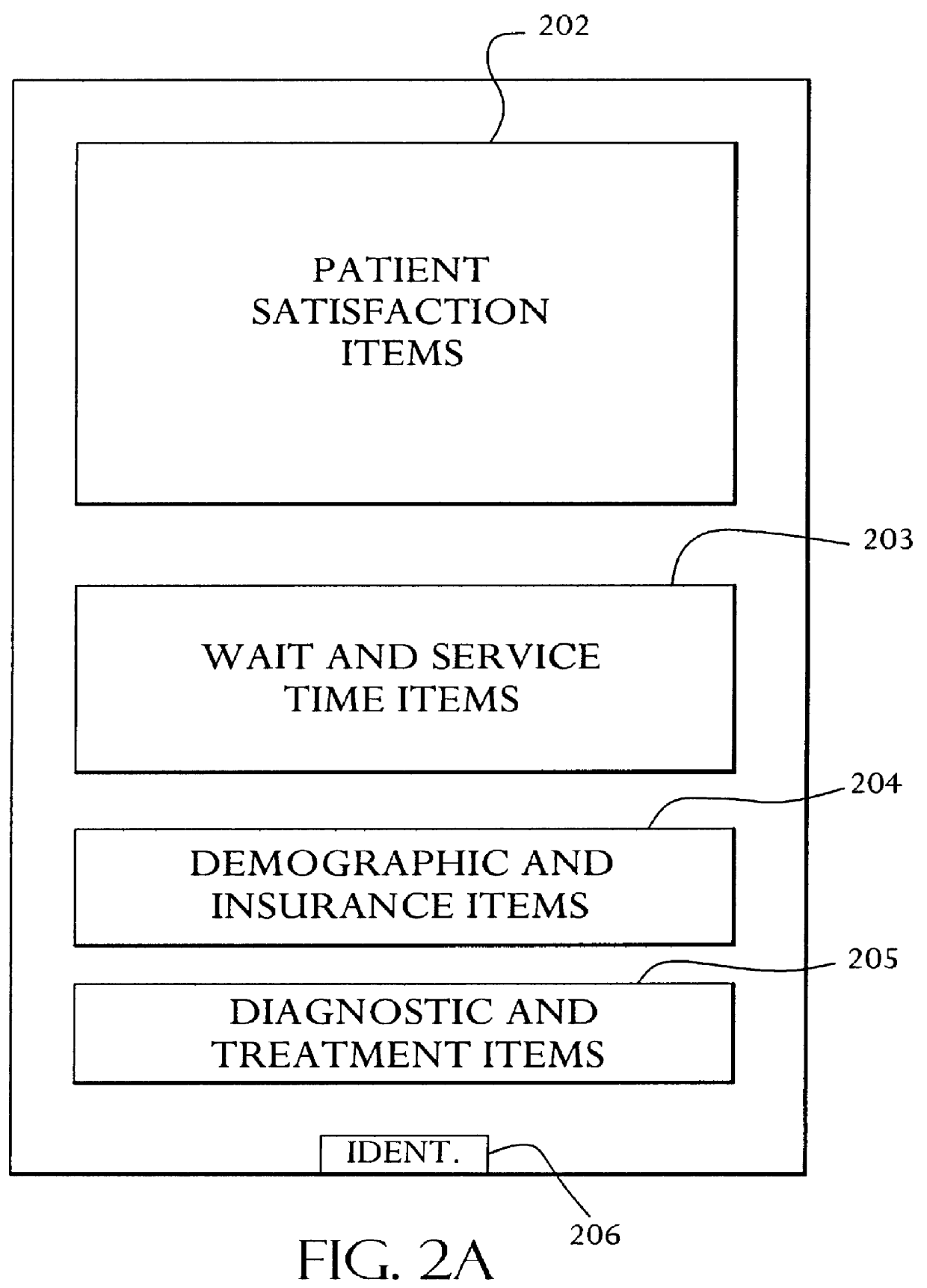
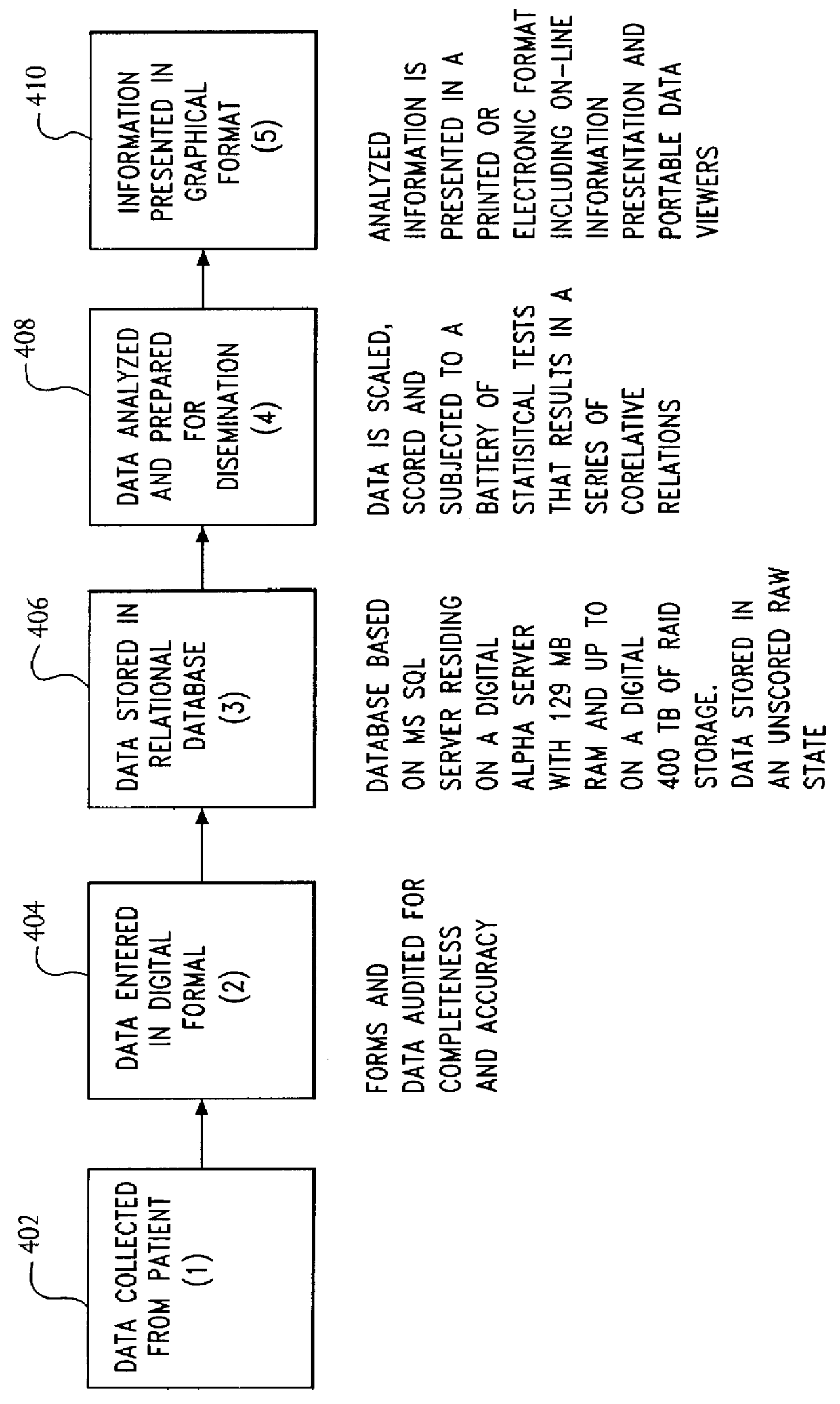
System for and method of collecting and populating a database with physician/patient data for processing to improve practice quality and healthcare delivery
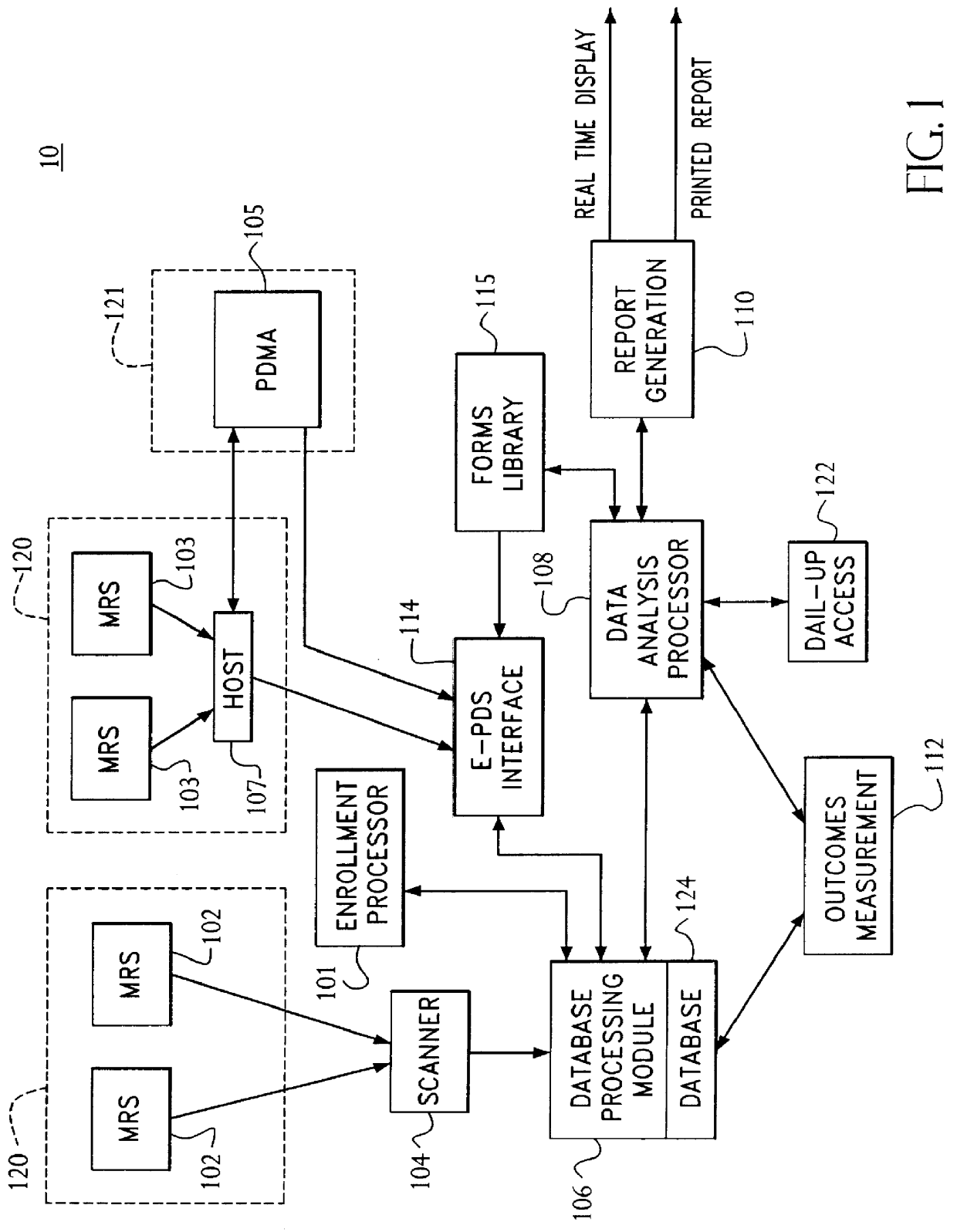
A system and method relates to the field of building and administrating a patient management and health care management database containing data relevant to the clinical care of patients, to the management of the practices to which the patients belong, and to outcomes of that health care and practice management. The disclosed system encompasses (i) designing and administering paper and pen and hand held computer survey instruments; (ii) administering and collecting completed surveys (iii) building and managing a database of information collected from the surveys; (iv) analyzing data collected from the surveys; (v) and providing clinical practices with summary information. Summary information may be used to improve patient care, health outcomes, and the management of physician practices.
Owner:PULSEGROUP
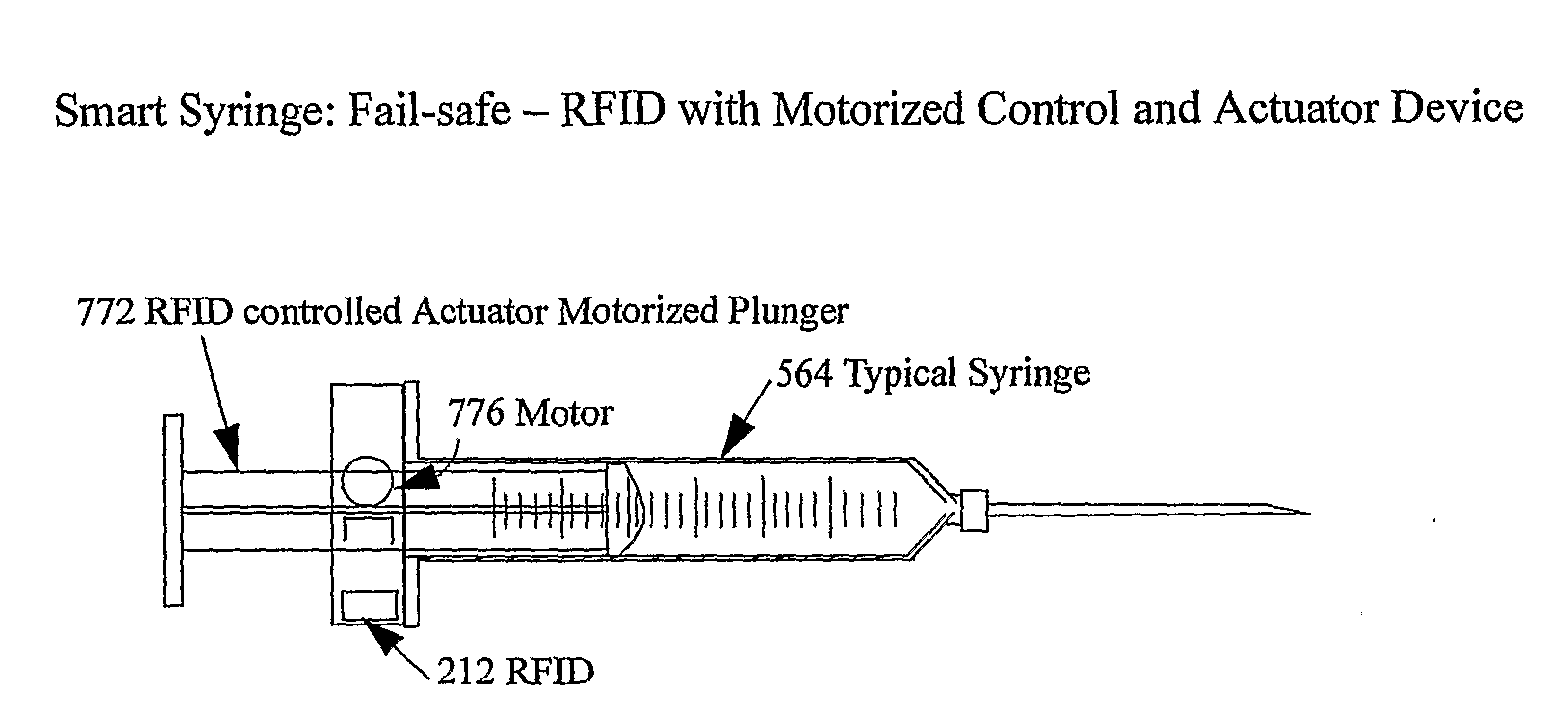
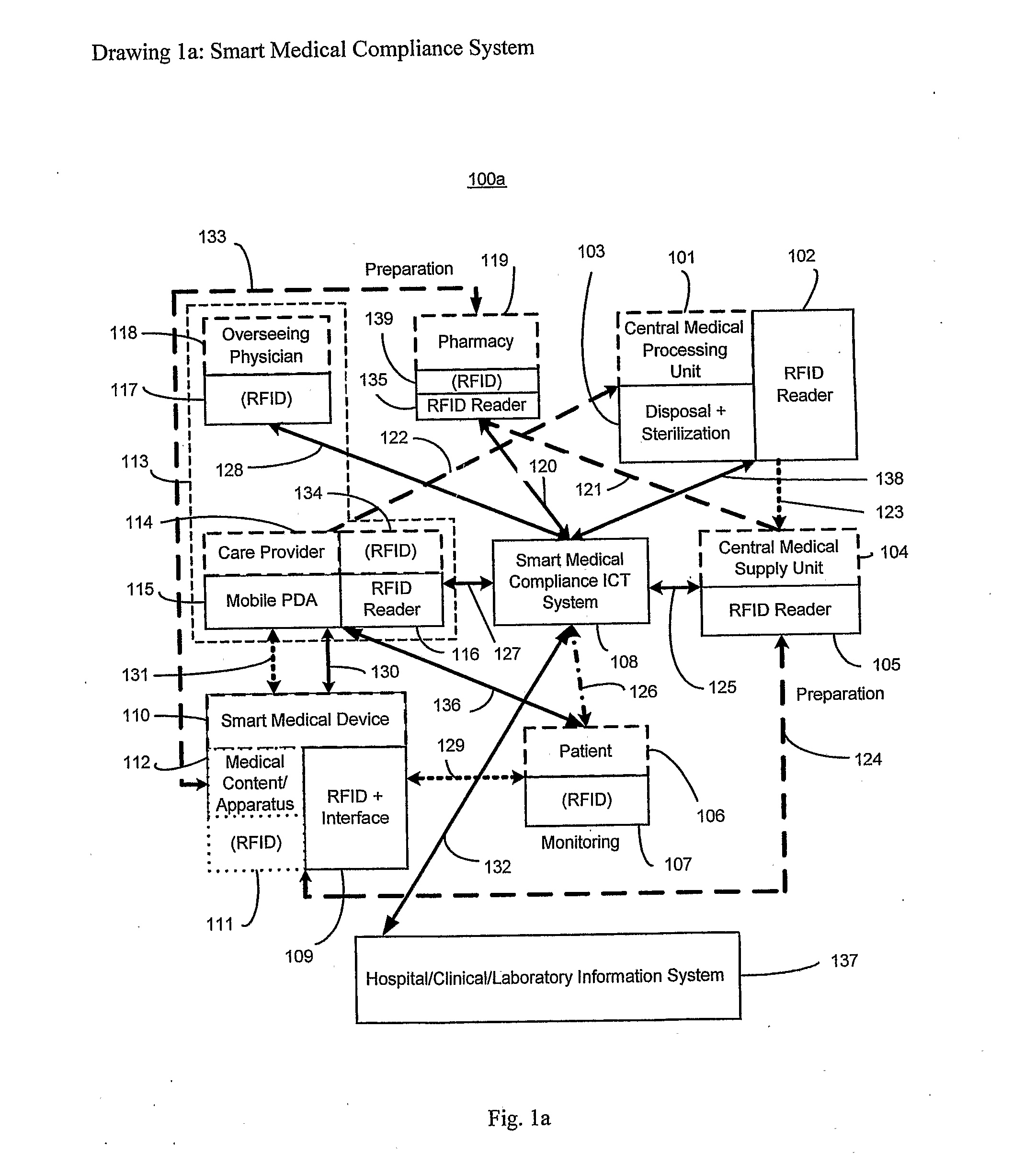
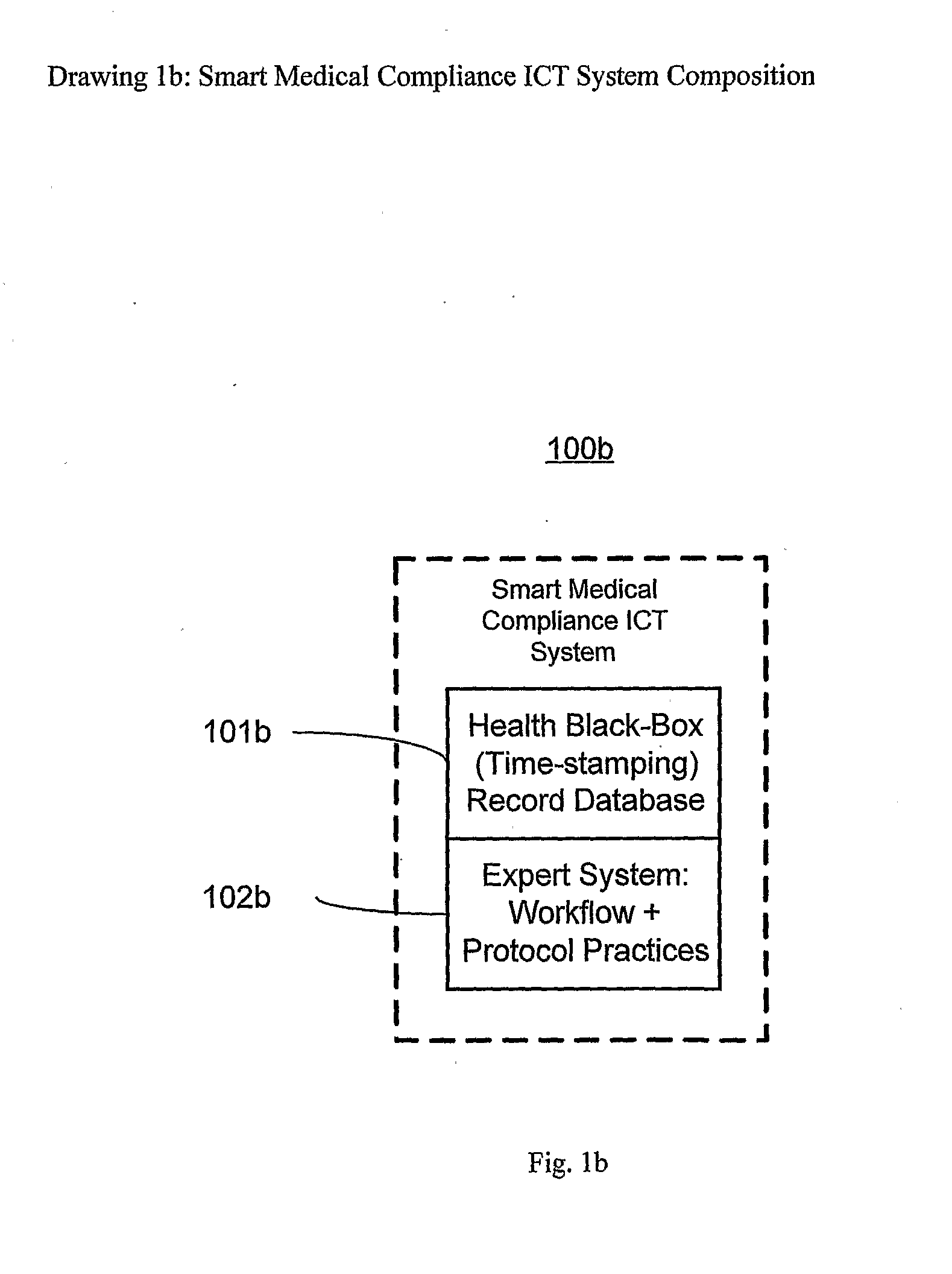
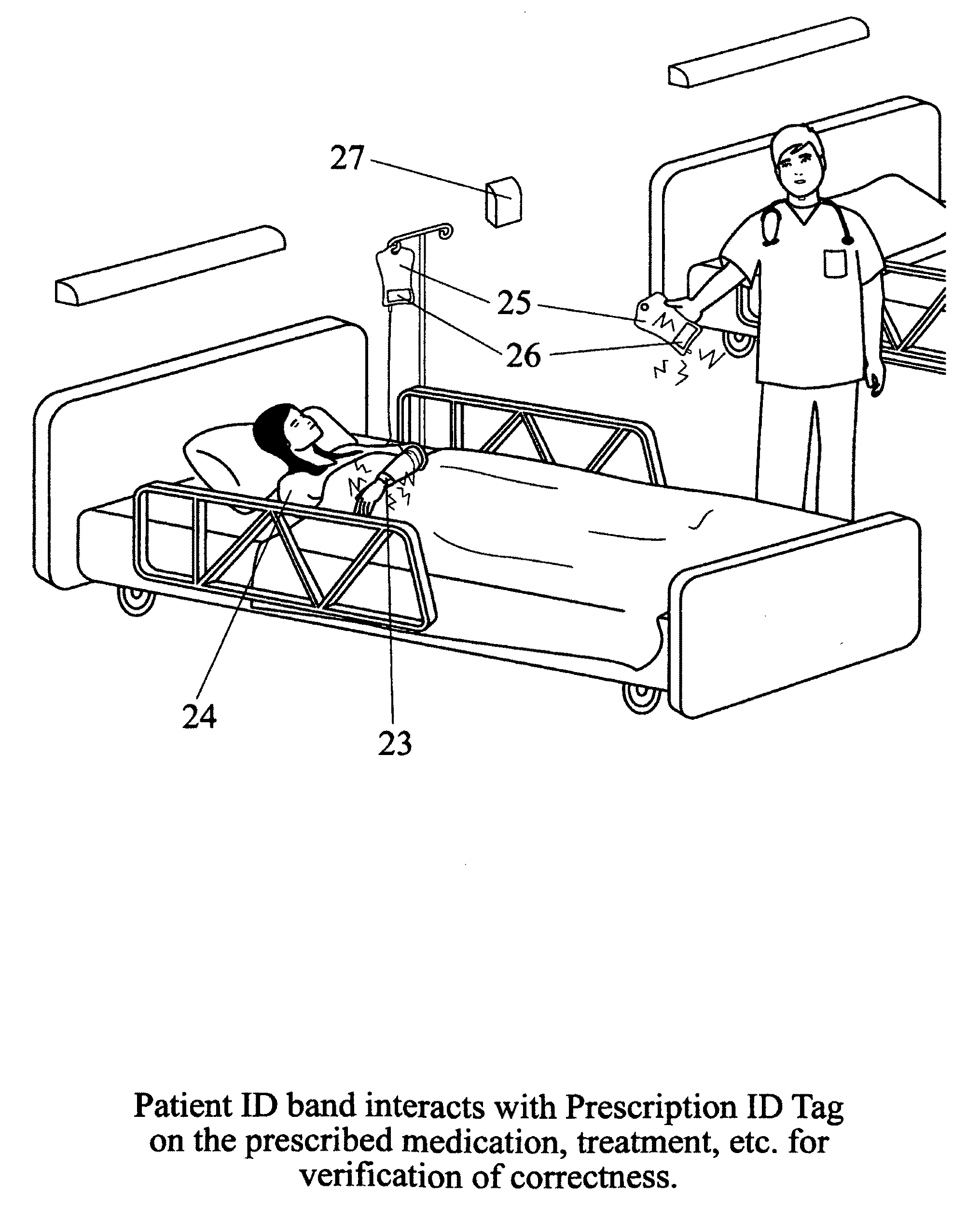
Smart medical compliance method and system
The smart medical compliance method and system invention prevents adverse drug events through the use of protocols that uniquely identifies the patient, care provider, medication and / or medical device that is to be used with radio frequency identification (RFID). The RFID devices incorporate fail-safe locks or indicators that prevent the inadvertent or unauthorized use of medication, medical devices, or medical supplies. The system corroborates, patient, the care provider, the medical device, and the manner in which it is to be used, and authorizes the action to be undertaken through an interface on a personal digital assistant PDA over a wireless communication channel. The system also timestamps events in the equivalent of a medical black box such that records may be kept to further improve patient care and allow an analysis of procedures. In addition, the system includes interfaces to medication preparation and safe disposal. A number of smart devices that interact with the system are also described. These include smart medical containers, smart clamps, smart valves, smart syringes, smart couplers, smart pipettes, and a host of other point of care devices.
Owner:KYAB LULEA
System and method for integrated learning and understanding of healthcare informatics
InactiveUS20070118399A1Data processing applicationsPatient personal data managementCrowdsData entity
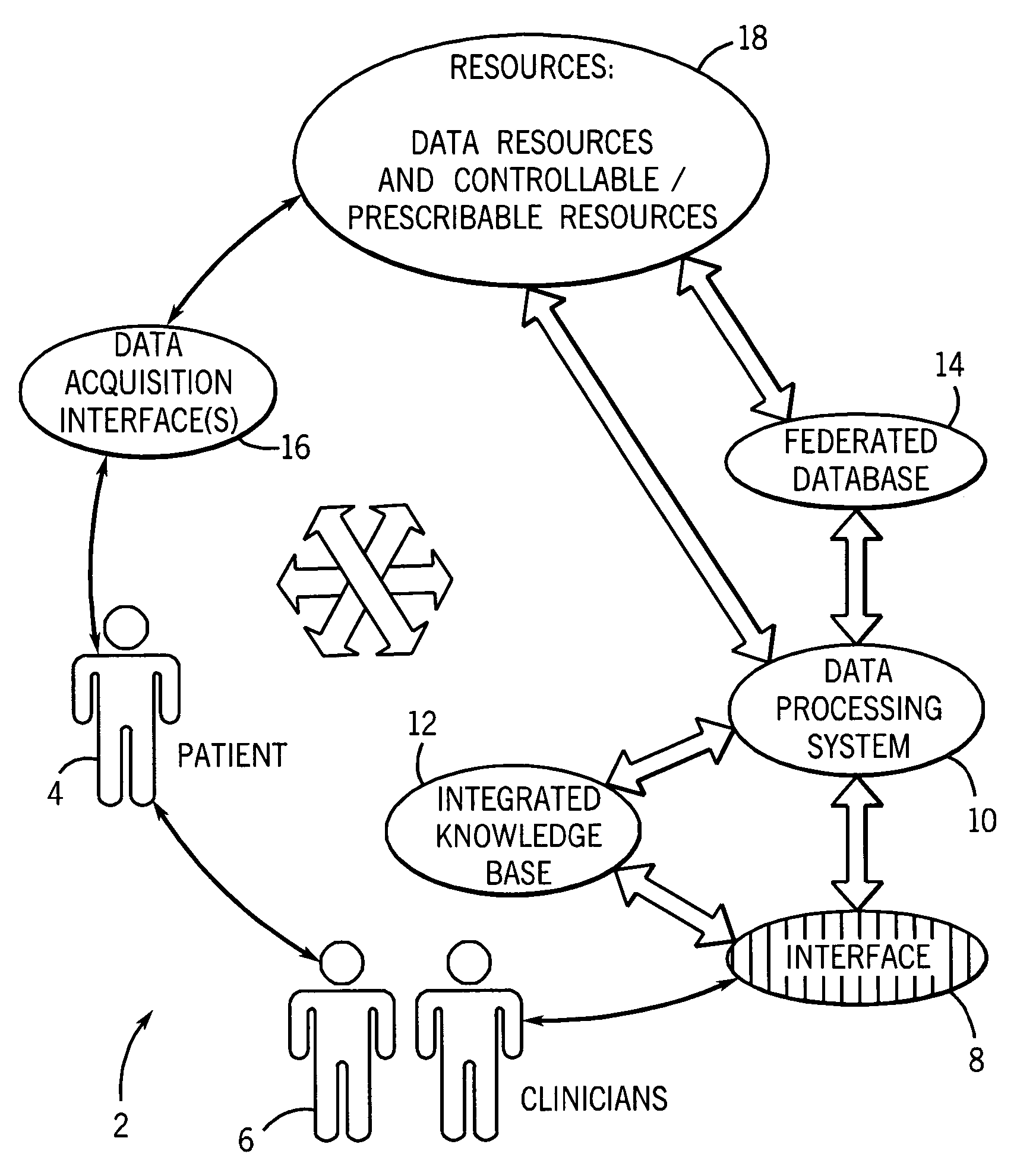
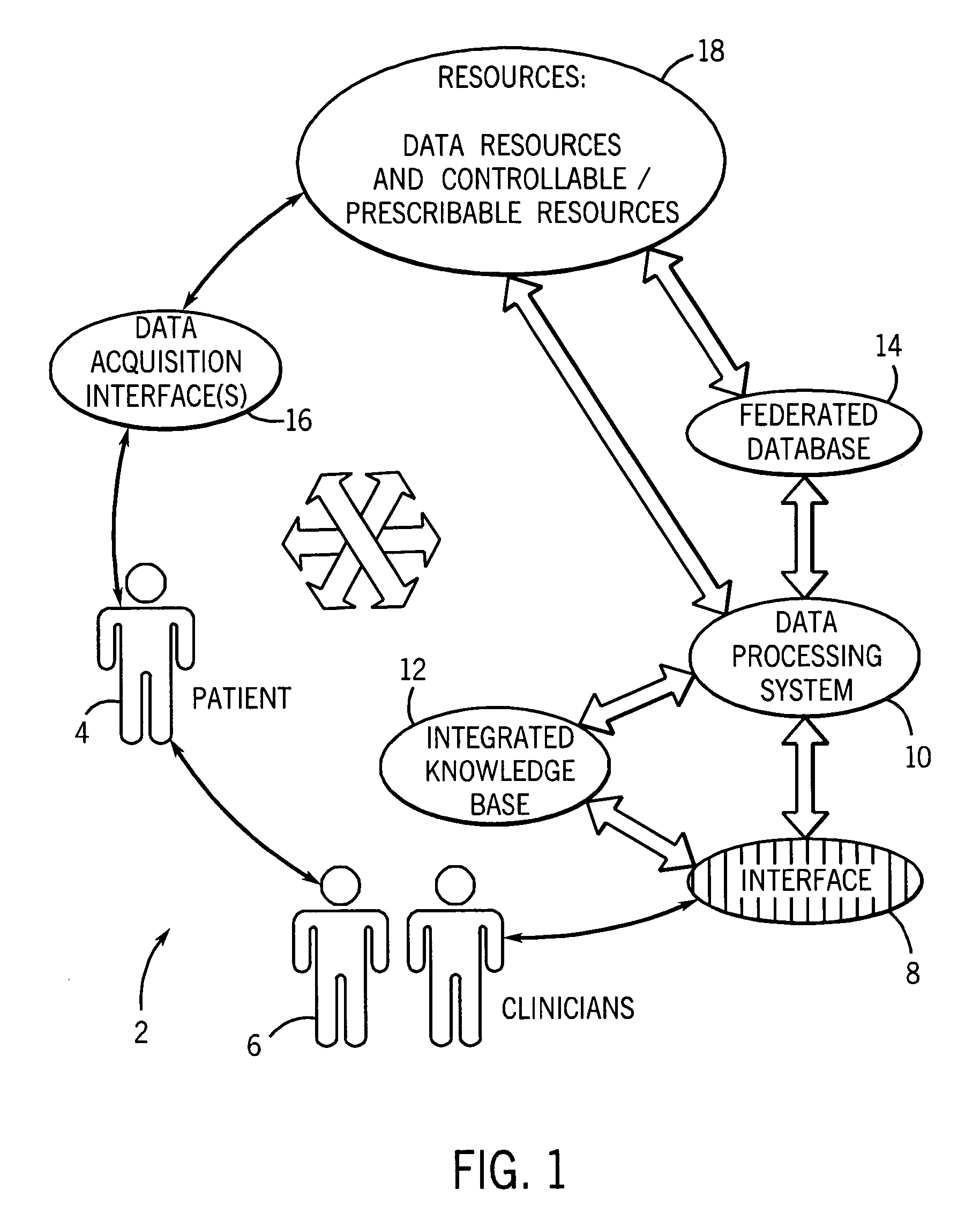
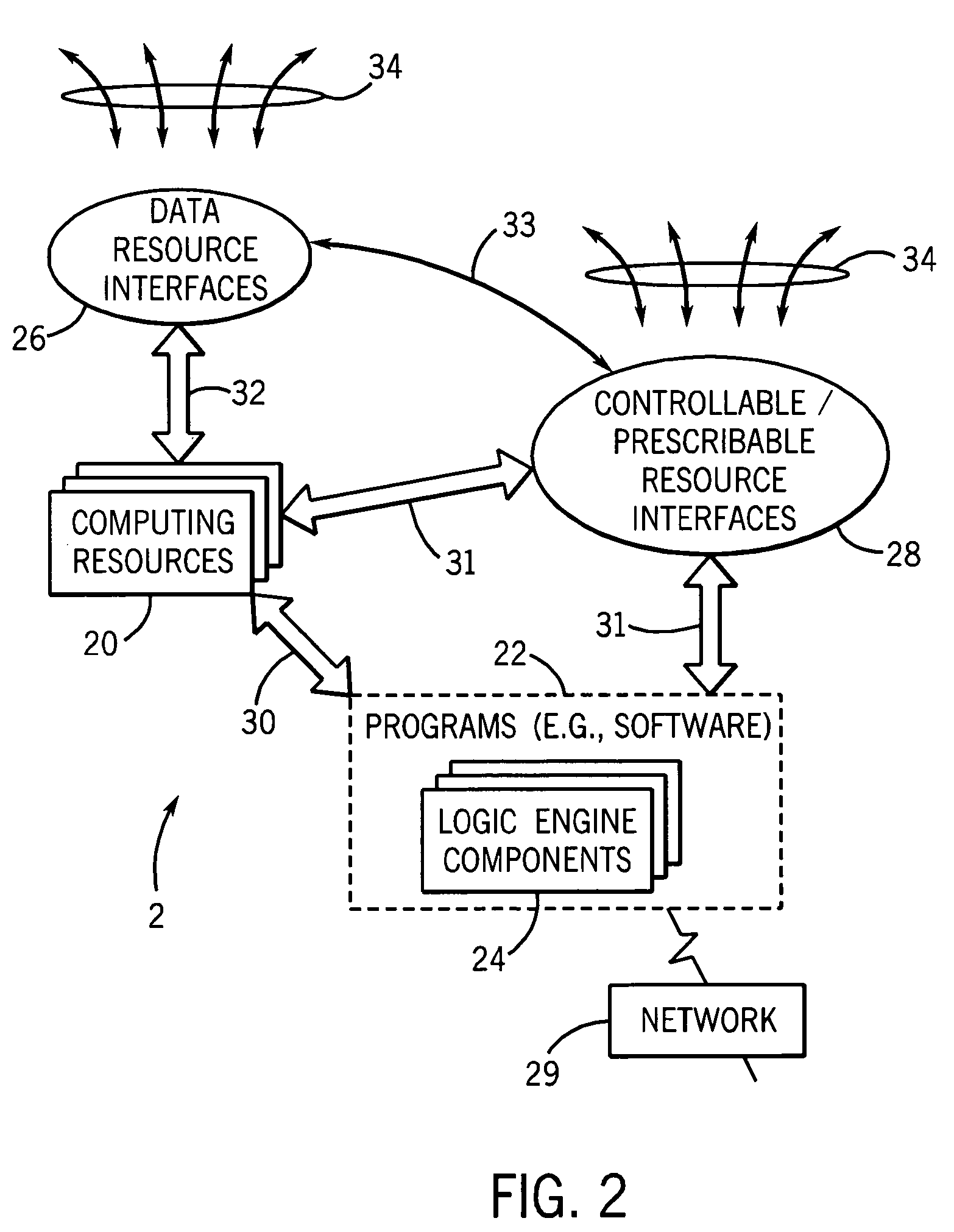
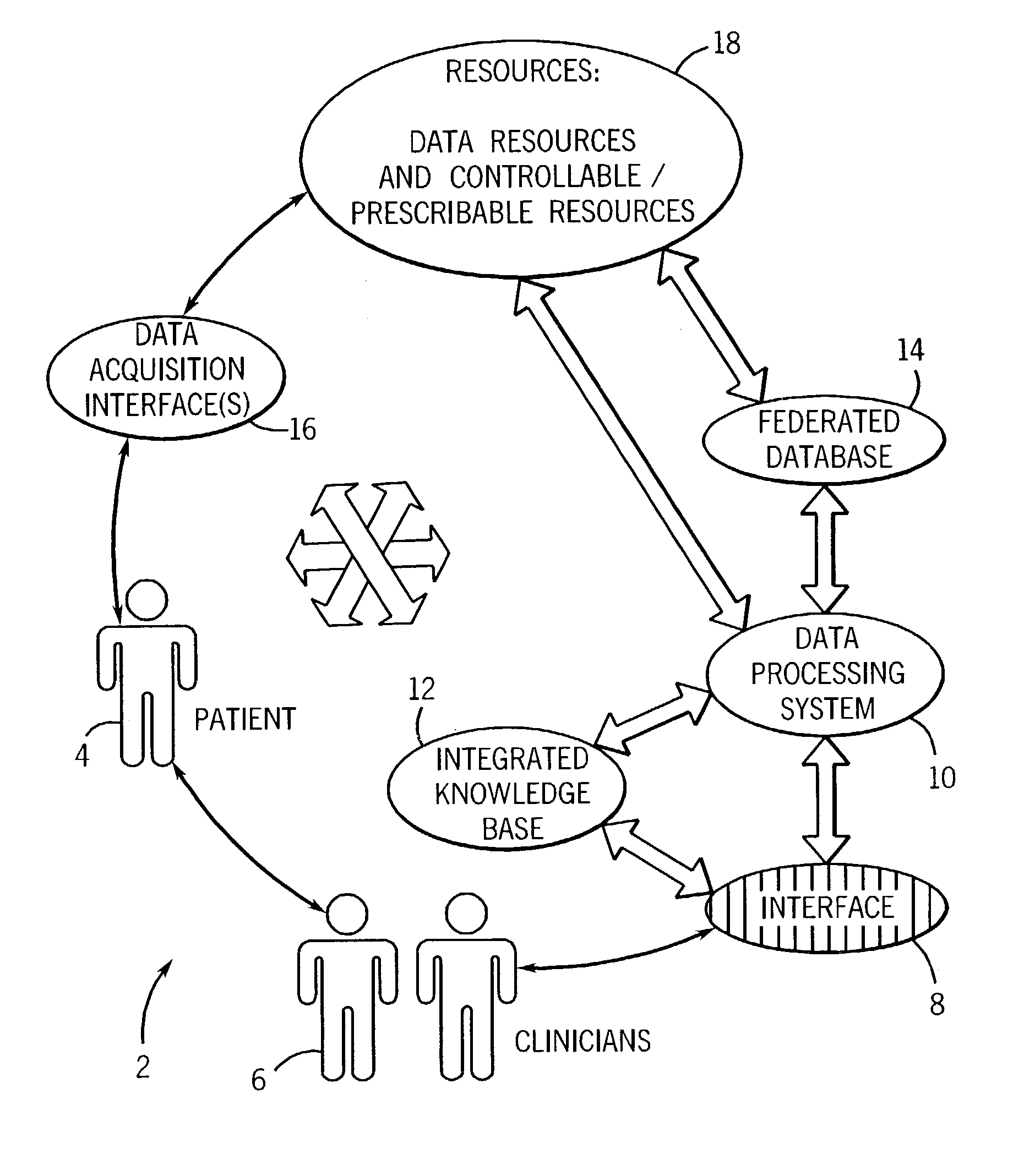
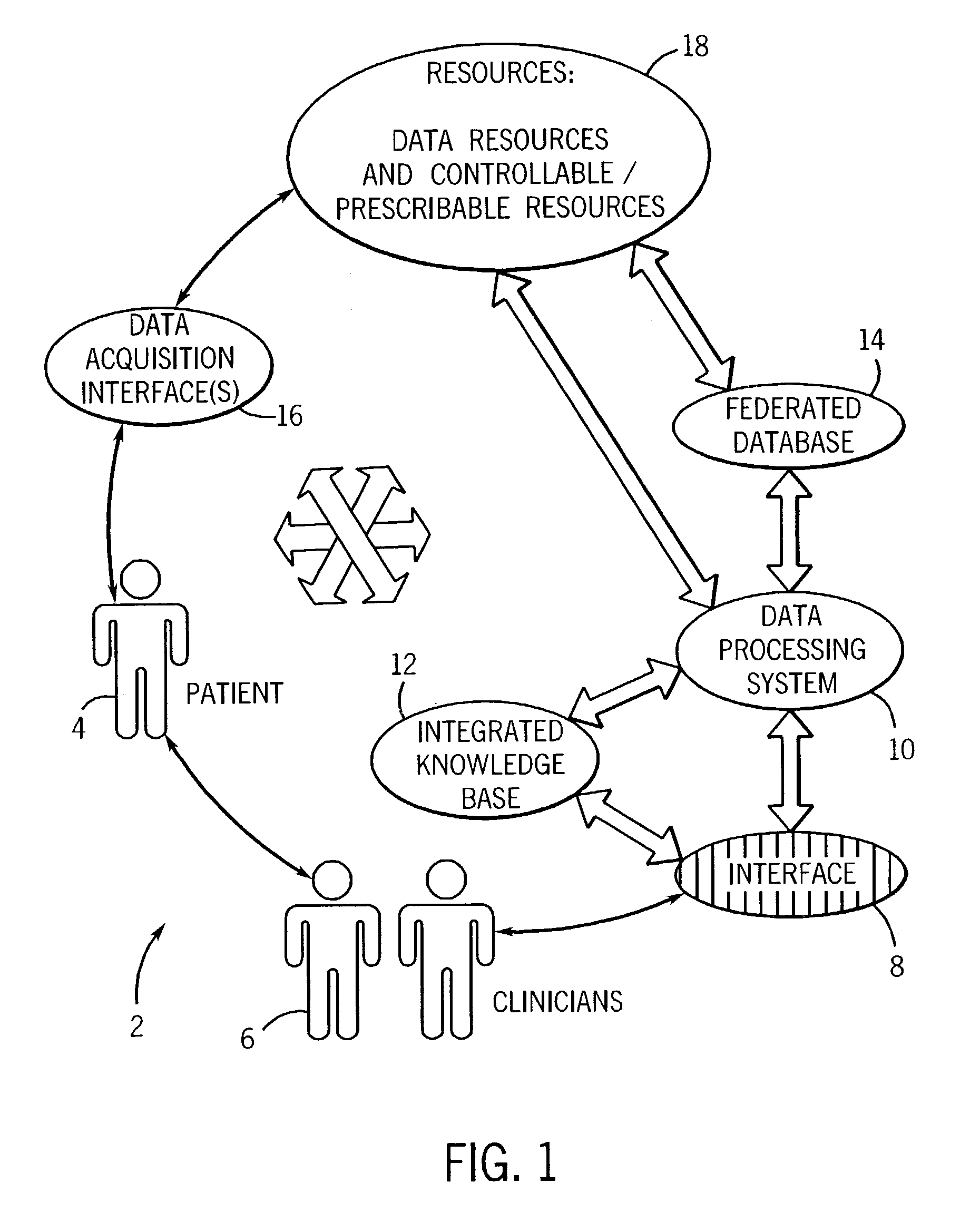
An informatics system permits data entities from a wide range of data sources to be accessed and evaluated. The sources of the data entities may be simply data sources, such as for articles and other non-patient or population specific information, as well as controllable and prescribable sources, such diagnostic imaging, clinical and other sources forming part of the patient care path. The entities are organized, analyzed in accordance with a domain framework, which may be altered by a user to focus on factors and informational components of interest. Holistic and integrated understanding of such factors are there fore available, and refinement of healthcare processes can be made to provide improved care in a more time and cost effective manner.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
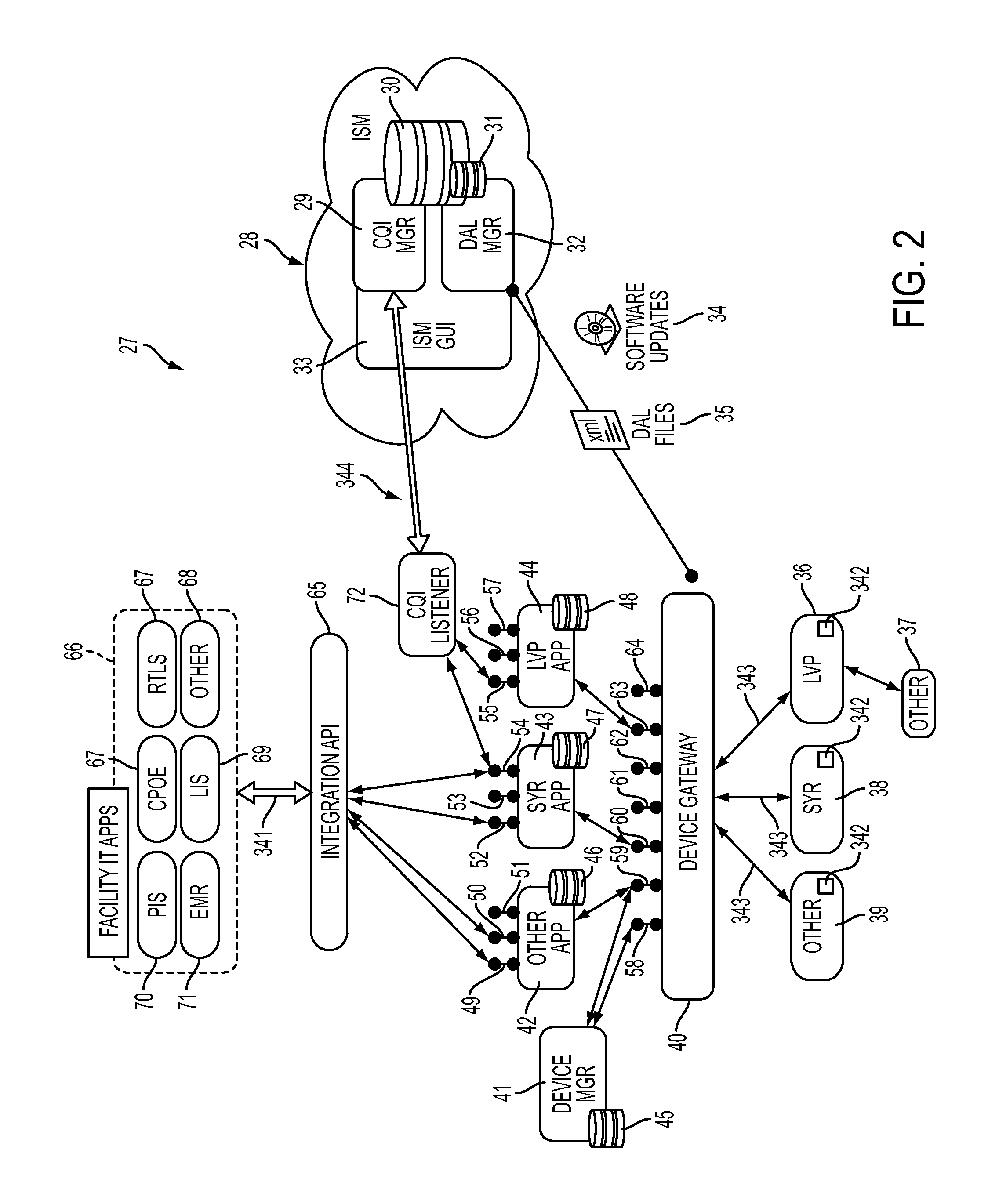
System, Method, and Apparatus for Electronic Patient Care
ActiveUS20120185267A1Quantity minimizationData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsApplication softwareEmbedded system
A system for electronic patient care includes a hub. The hub is configured to monitor a patient-care device. The sandbox may be configured to control access to at least one of a hardware resource and a software resource. The hub is further configured to identify the patient-care device and execute an application to monitor the patient-care device. The hub executes the application within the sandbox component such that the application accesses the at least one of the hardware resource and the software resource through the sandbox component. The hub may be further configured to control the patient-care device. The hub may be further configured to receive an identification from the patient-care device and download the application from a server associated with the identification. The hub may be further configured to receive an identification from the patient-care device and update the application from a server associated with the identification.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
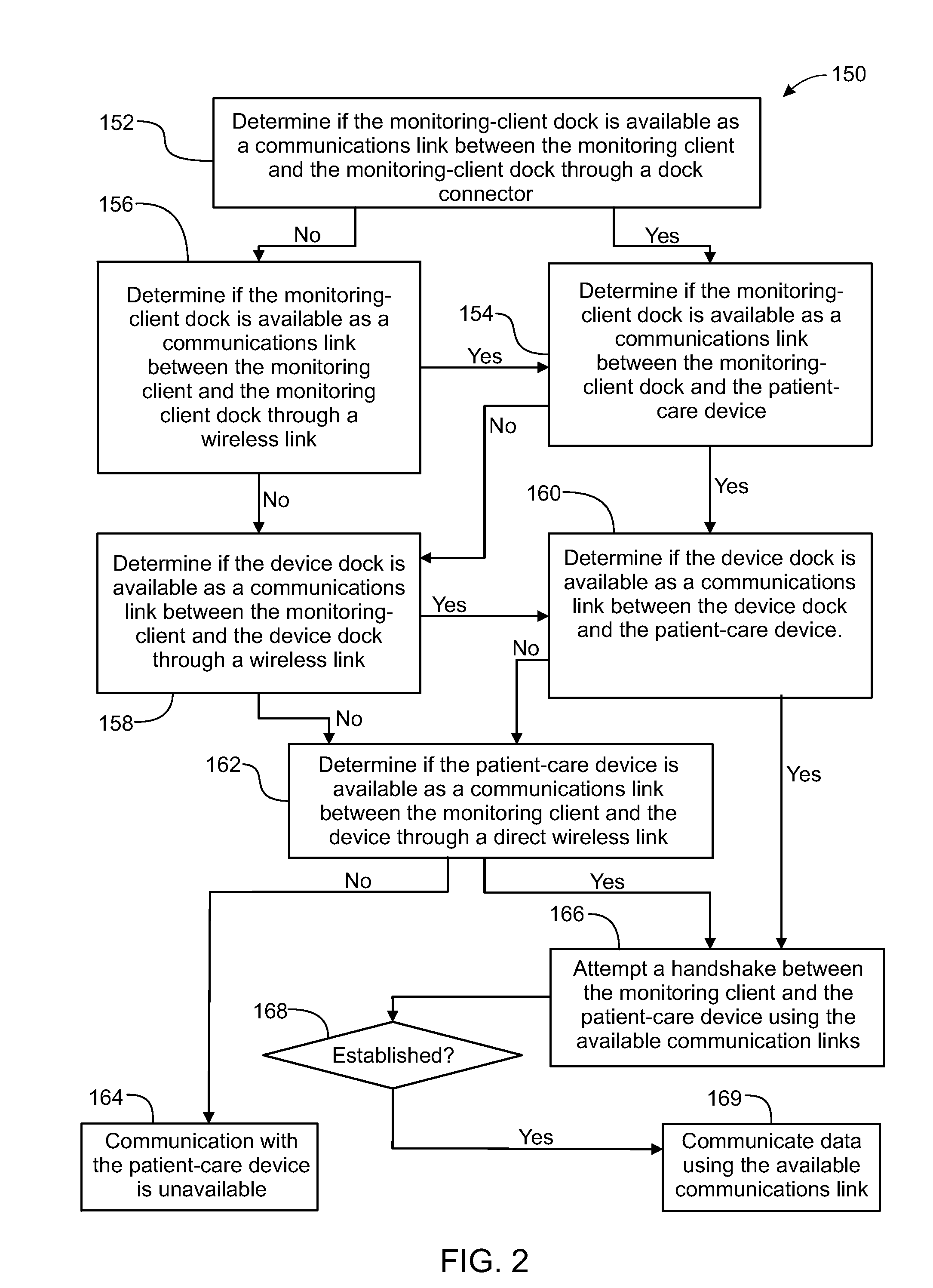
System, Method, and Apparatus for Electronic Patient Care
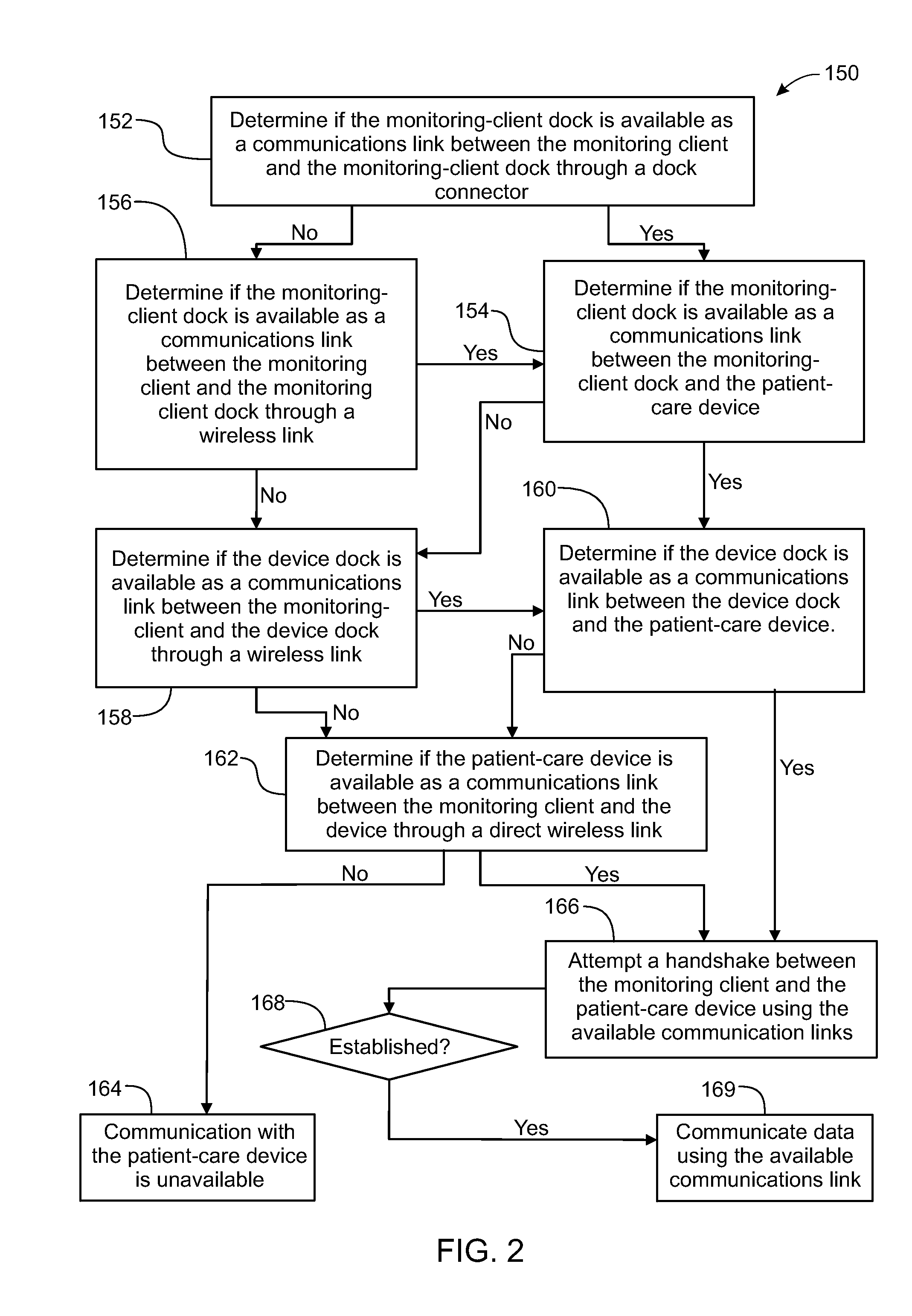
PendingUS20130317837A1Quantity minimizationData processing applicationsLocal control/monitoringComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A method, related system and apparatus are disclosed. The method is implemented by an operative set of processor executable instructions configured for execution by a processor. The method includes the acts of: determining if a monitoring client is connected to a base through a physical connection; establishing a first communications link between the monitoring client and the base through the physical connection; updating, if necessary, the interface program on the monitoring client and the base through the first communications link; establishing a second communications link between the monitoring client and the base using the first communications link; and communicating data from the base to the monitoring client using the second communications link.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Antimicrobial silver compositions
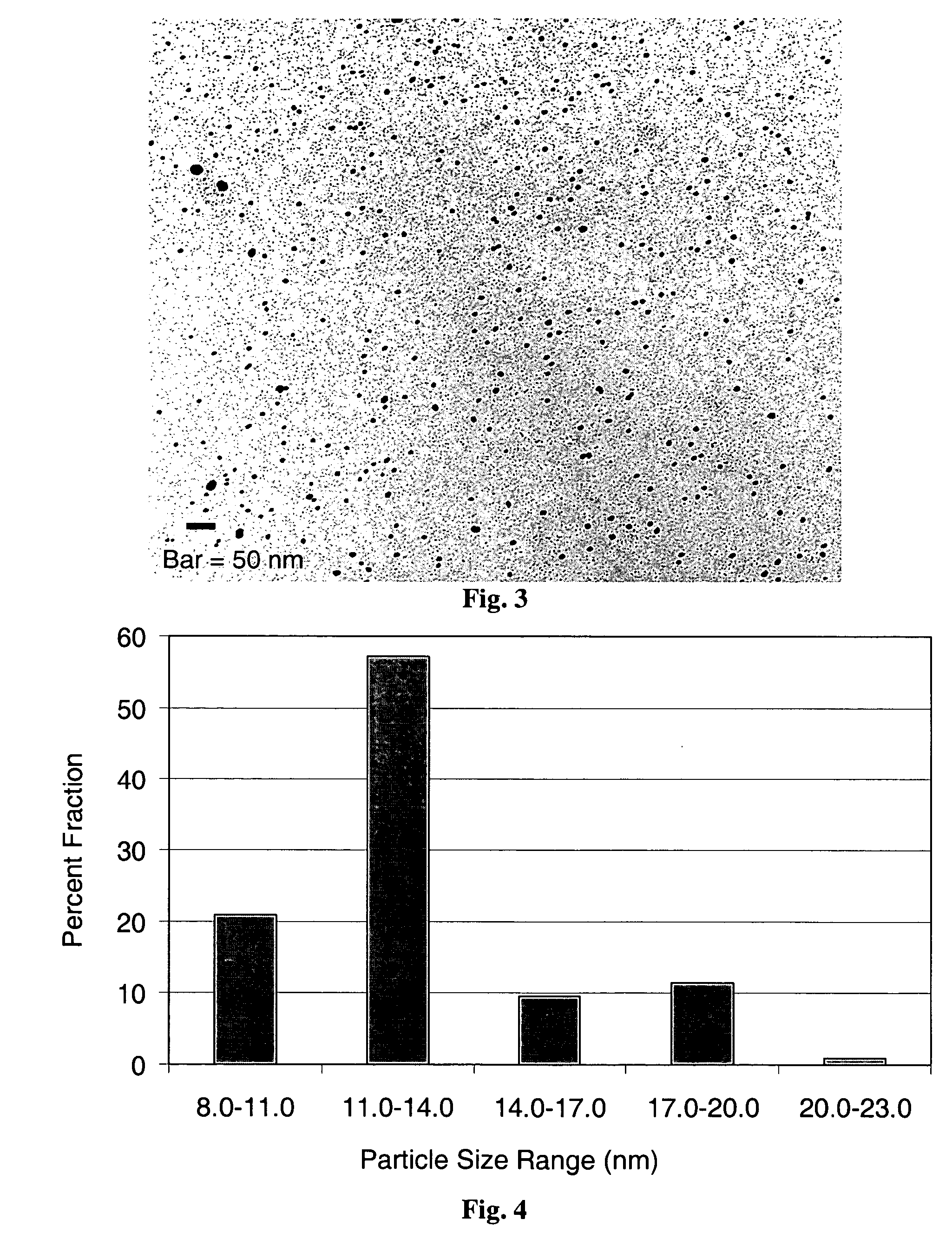
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for antimicrobial silver compositions comprising silver nanoparticles. The present invention further comprises compositions for preparing silver nanoparticles comprising at least one stabilizing agent, one or more silver compounds, at least one reducing agent and a solvent. In one aspect, the stabilizing agent comprises a surfactant or a polymer. The polymer may comprise polymers such as polyacrylamides, polyurethanes, and polyamides. In one aspect, the silver compound comprises a salt comprising a silver cation and an anion. The anion may comprise saccharinate derivatives, long chain fatty acids, and alkyl dicarboxylates. The methods of the present invention comprise treating devices with the silver nanoparticle compositions, including, but not limited to, such devices as woven wound care materials, catheters, patient care devices, and collagen matrices. The present invention further comprises treatment of humans and animals wacr6ith the antimicrobial devices described herein.
Owner:AVENT INC
Apparatus and method for mobile medical services
A mobile personal computing and communications device provides for secure, reliable, accurate and up-to-date point-of-care medical information for rendering sound medical care to a patient. The mobile personal device may be used by either the patient and / or by caregivers to furnish, access and / or acquire and store the patient's medical records using wireless communications, to provide a treatment, to facilitate compliance with a treatment plan, to facilitate patient care, to facilitate collaboration on treatment for the patient's condition, and to proffer an authenticated medical directive, among other mobile medical services.
Owner:MODULAR COMPUTING & COMM CORP
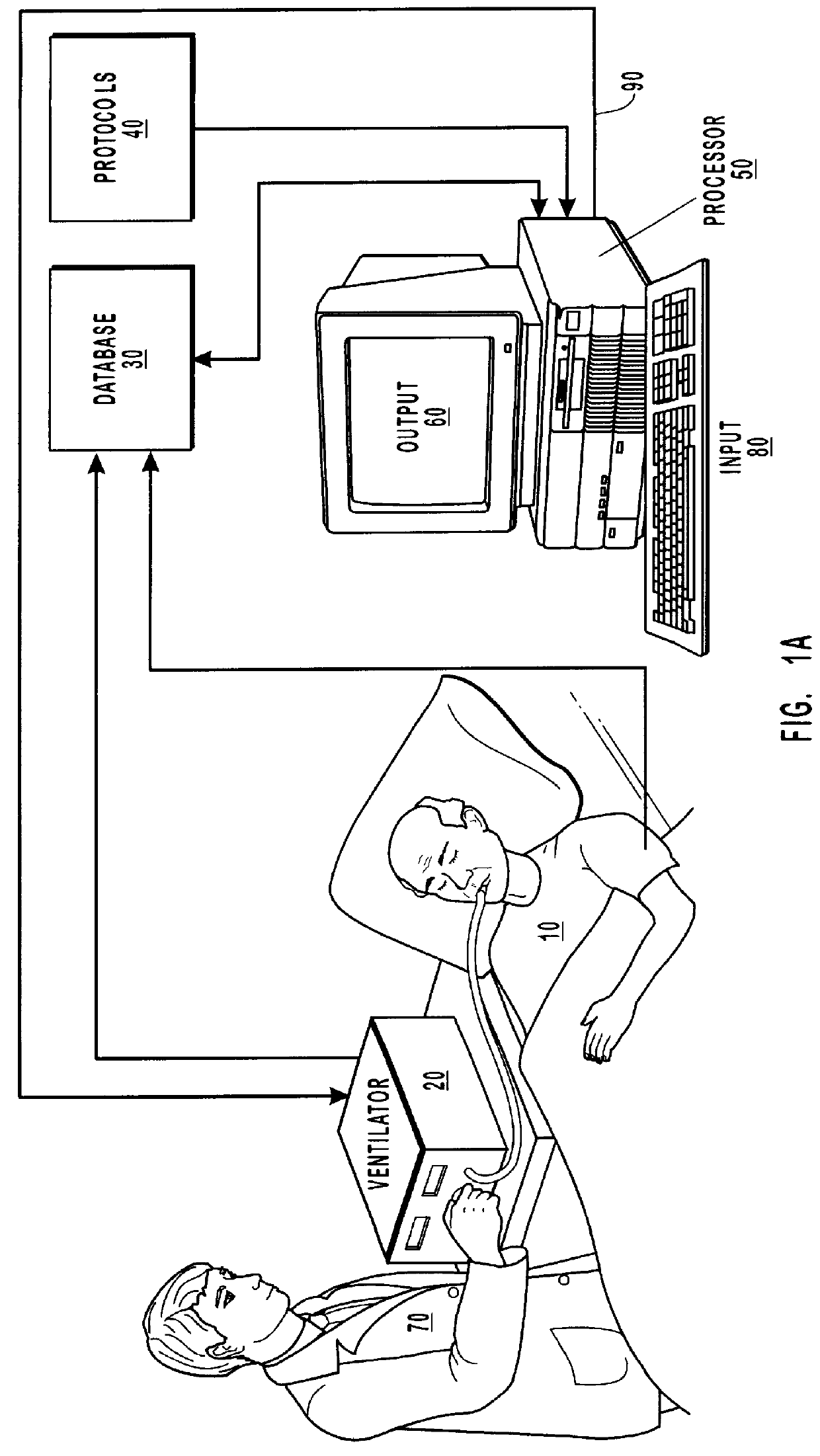
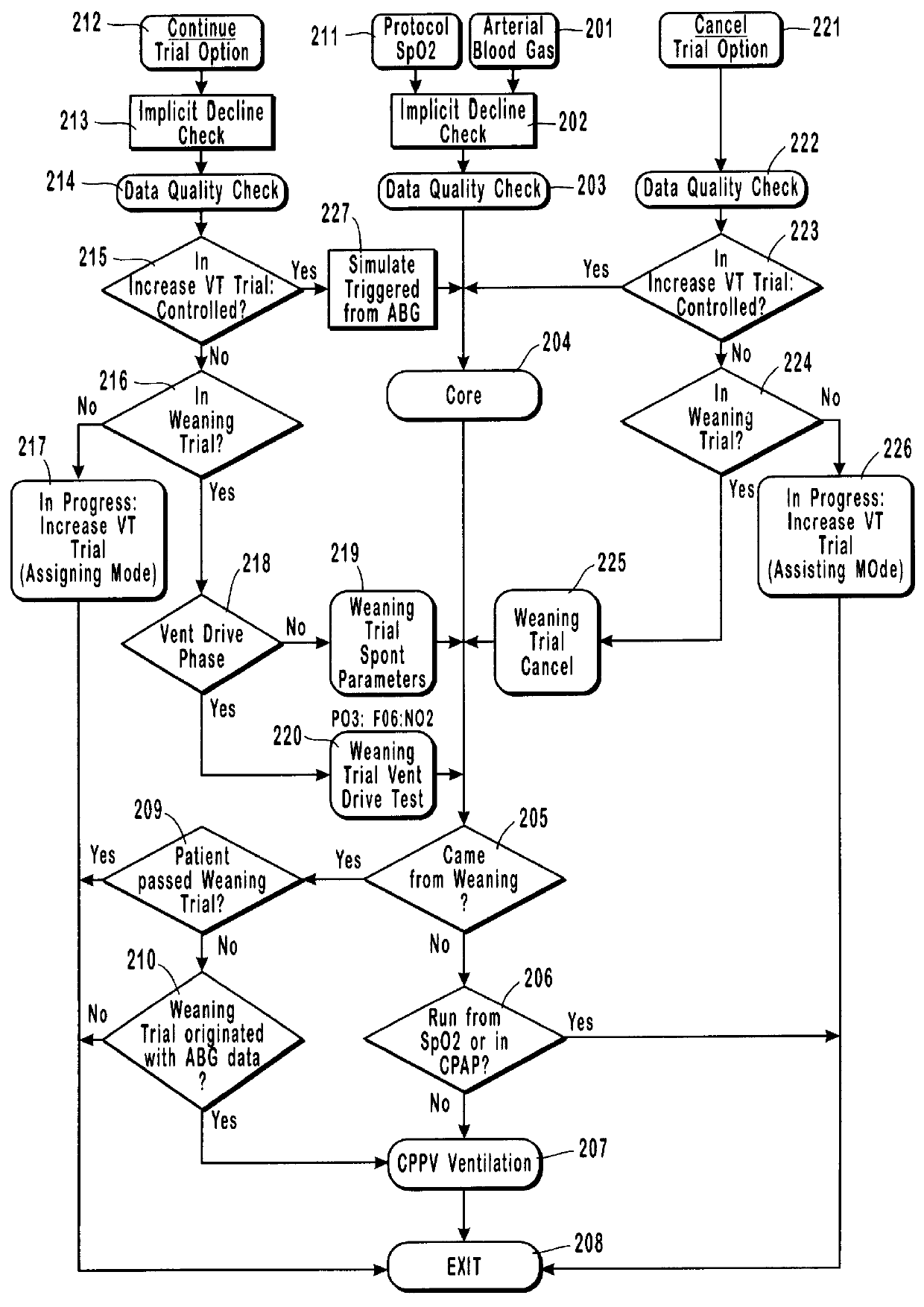
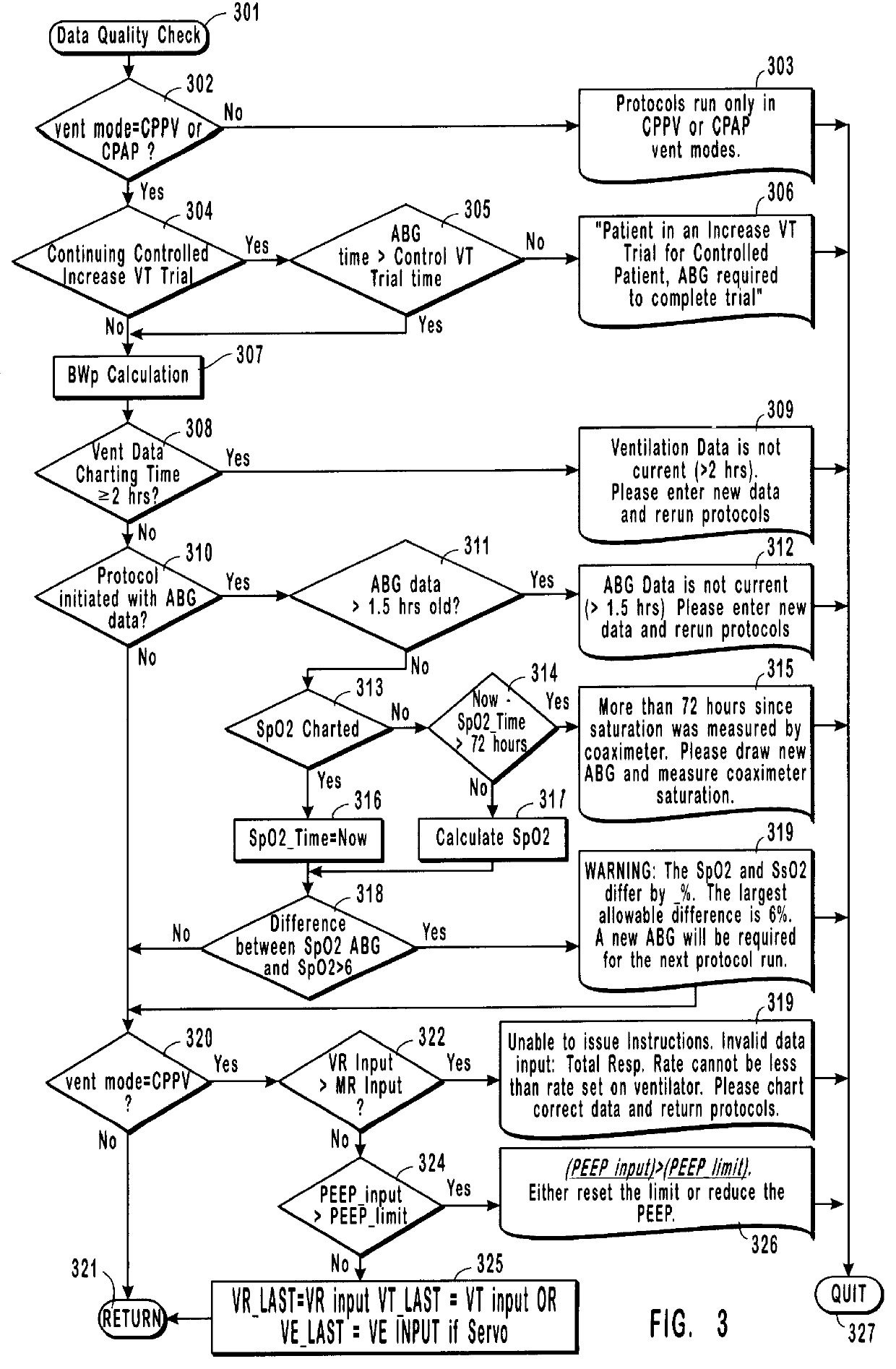
Method and system for patient monitoring and respiratory assistance control through mechanical ventilation by the use of deterministic protocols
InactiveUS6148814AReducing ventilator rateRelieve pressureRespiratorsBreathing masksDiseaseClinical staff
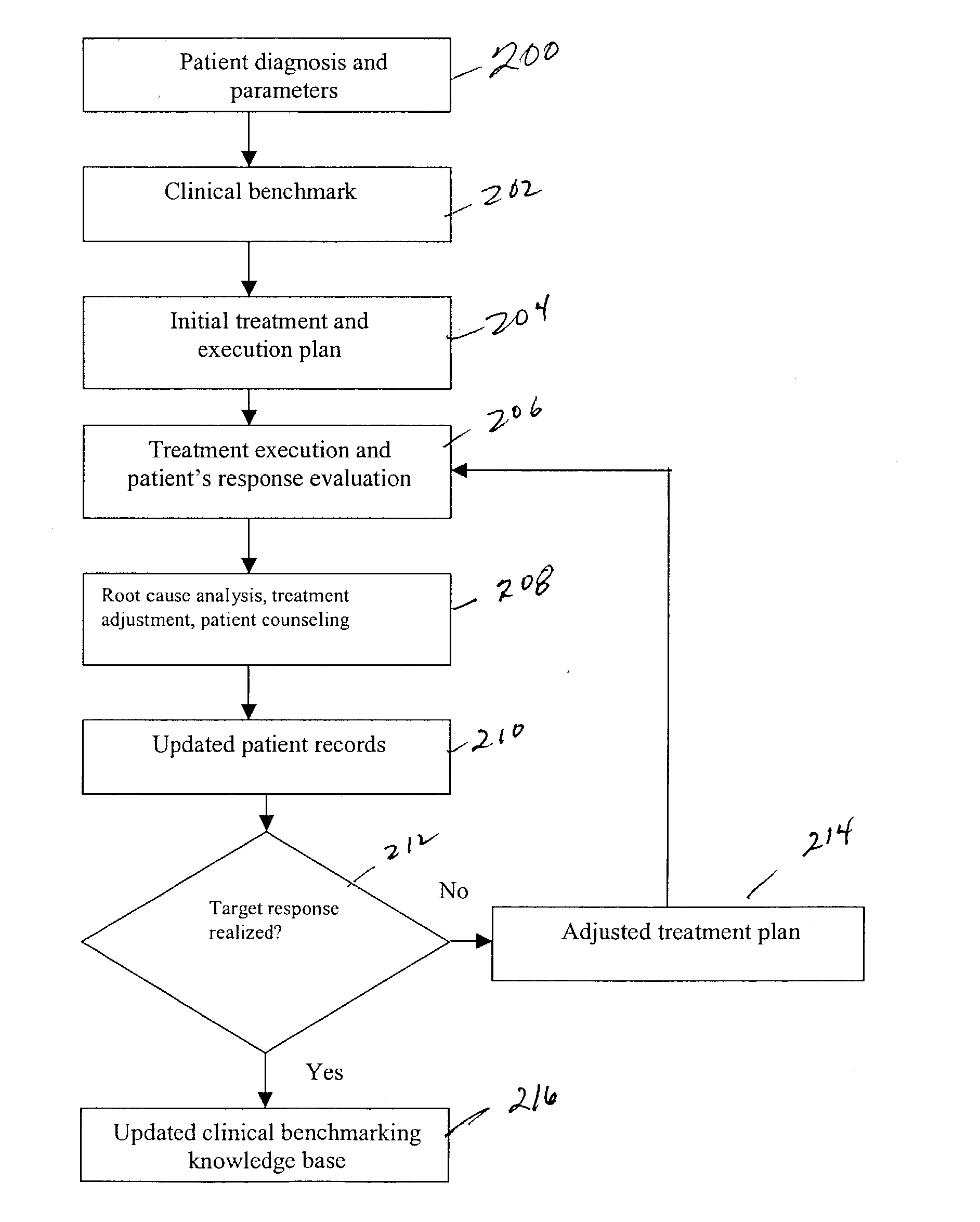
A method and system for managing mechanical ventilation of patients with respiratory disorders is described. The main objective of the system is to generate executable instructions for patient care which take into account a large number of parameters of patient condition and ventilation. Data regarding the state of the patient are stored in a database. Patient data are processed according to a set of protocols which contain rules for patient care decisions arranged in a logical sequence to generate detailed, executable instructions for patient care. Instructions are updated when new data are entered into the database. The data can be acquired in an automated fashion, or the clinician can be instructed to collect and enter new data into the clinical database. Likewise, patient care instructions can be carried out automatically or manually, but it is preferred that instructions are carried out manually as a safety check. The preferred embodiment of the invention includes a computer system, software for processing patient data, and a display device for presenting patient care instructions to the clinician. The system maintains a record of patient data, patient care instructions, whether instructions were followed by the clinical staff, and if not, a reason why.
Owner:INTERMOUNTAIN INTELLECTUAL ASSET MANAGEMENT LLC
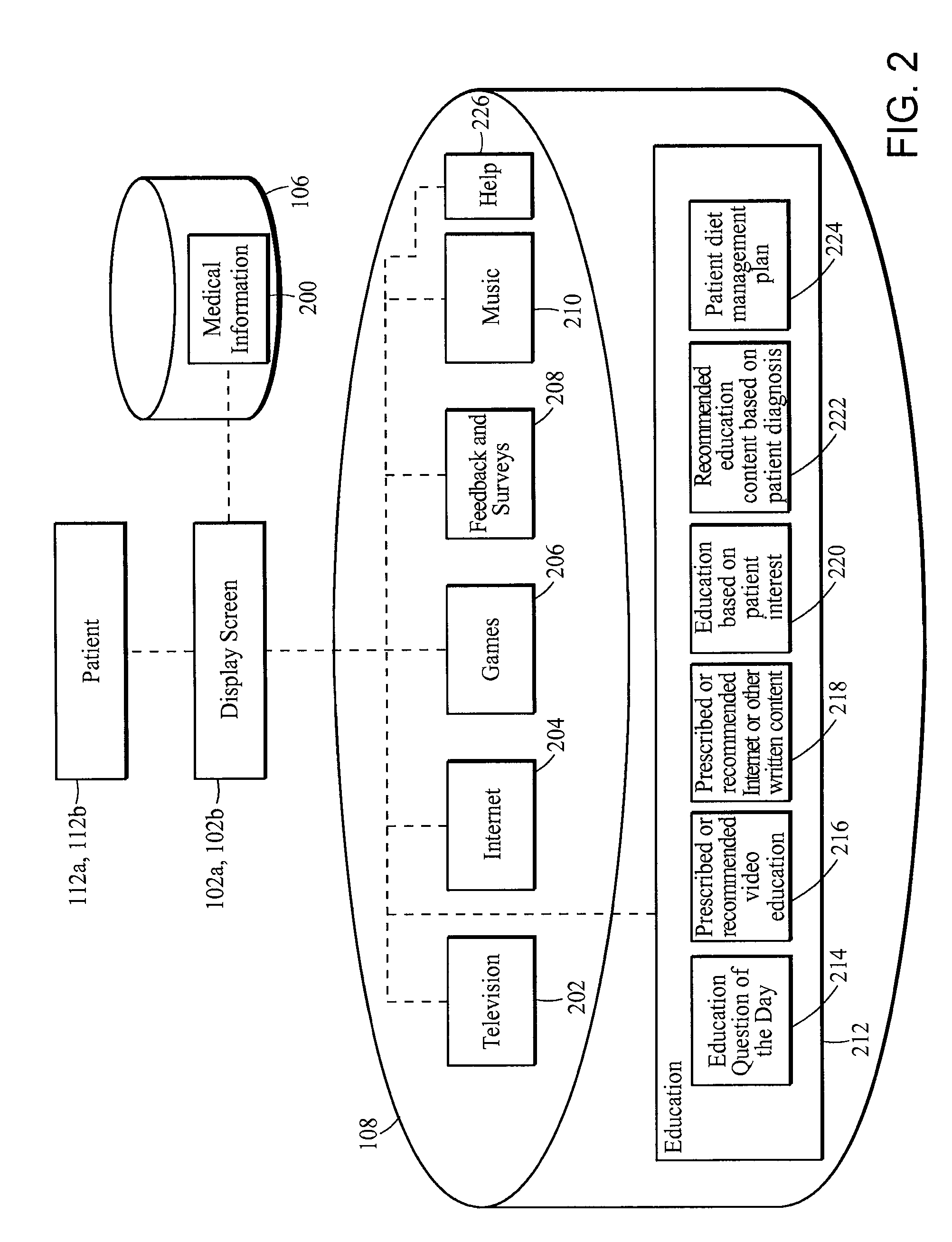
Computer-Implemented Method, System, and Apparatus for Electronic Patient Care
A medical error reduction system may include a medical error reduction software for use in creating and revising at least one drug library. The software configured to provide one of a plurality of sets of privileges to each of a plurality of sets of users. Each of the plurality of sets of privileges arranged to allocate a degree of software functionality to one of the plurality of sets of users. The degree of software functionality configured to define the ability of a user to alter the at least one drug library. The medical error reduction system may include at least one server. The medical error reduction system may include at least one editor computer each of the at least one editor computer comprising a processor in communication with a display. The at least one editor computer and at least one server may be configured to communicate via a network in a client-server based model. Each of the at least one drug library may be for use in at least one medical device.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
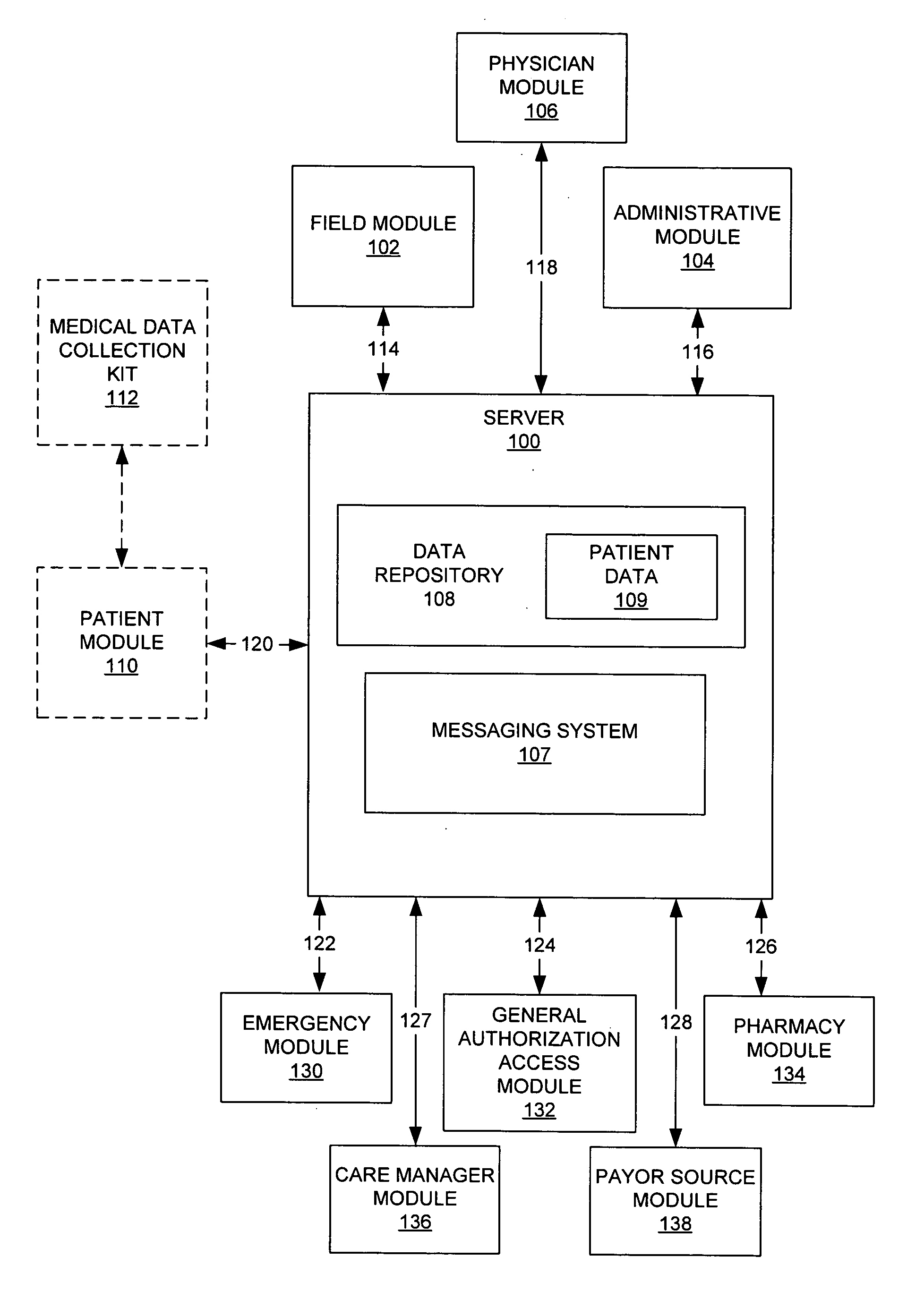
System and method for health care data collection and management
A health care system including a field module configured to gather a first portion of patient data and to send the first portion of patient data to a server, an administrative module configured to perform a plurality of functions on patient data, and a physician module configured to display patient data and perform a patient care function.
Owner:TAHA AMER JAMIL
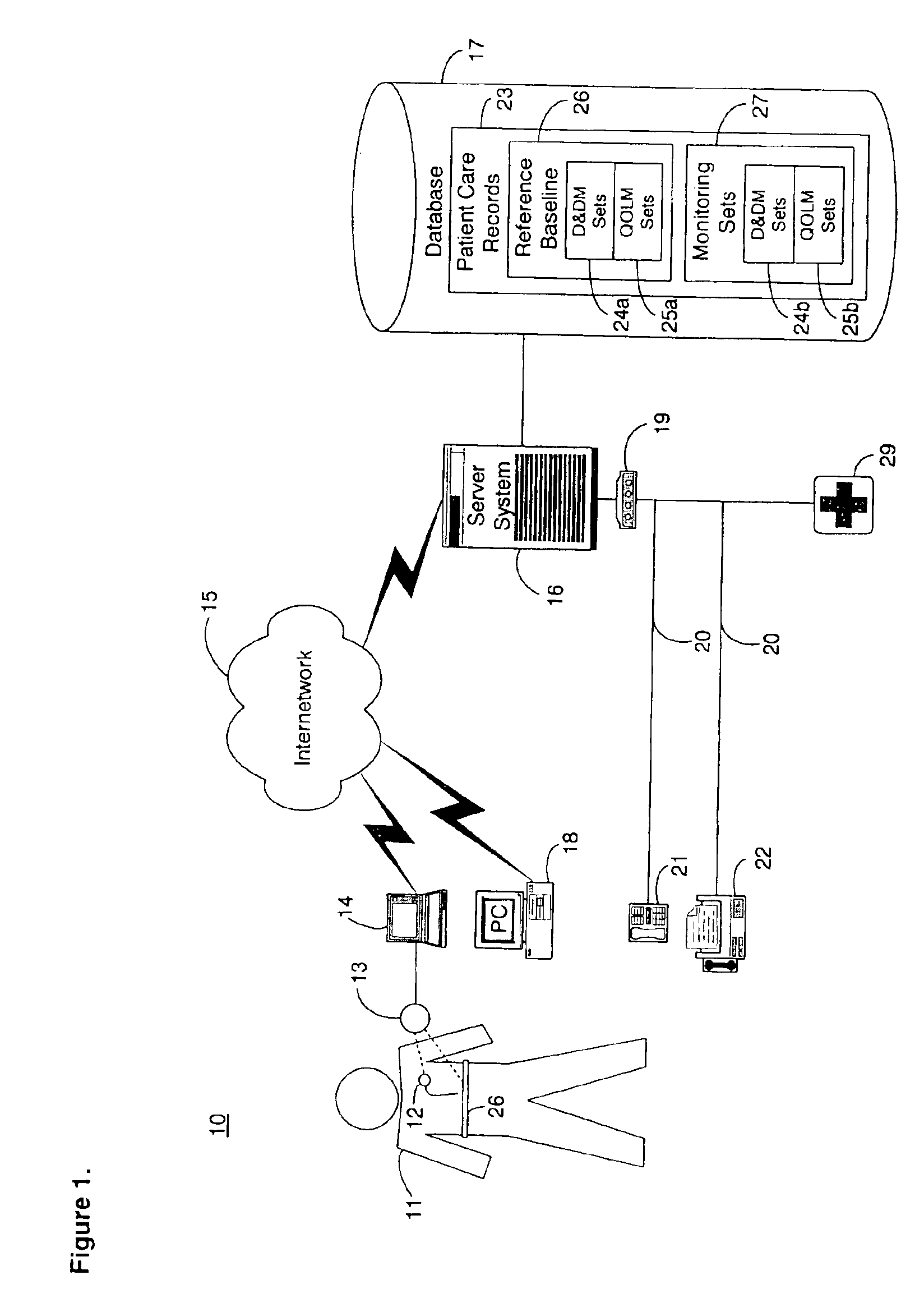
System and method for collection and analysis of patient information for automated remote patient care
InactiveUS7134996B2Easy to gatherEasy to storePhysical therapies and activitiesElectrotherapyDatabase serverPatient status
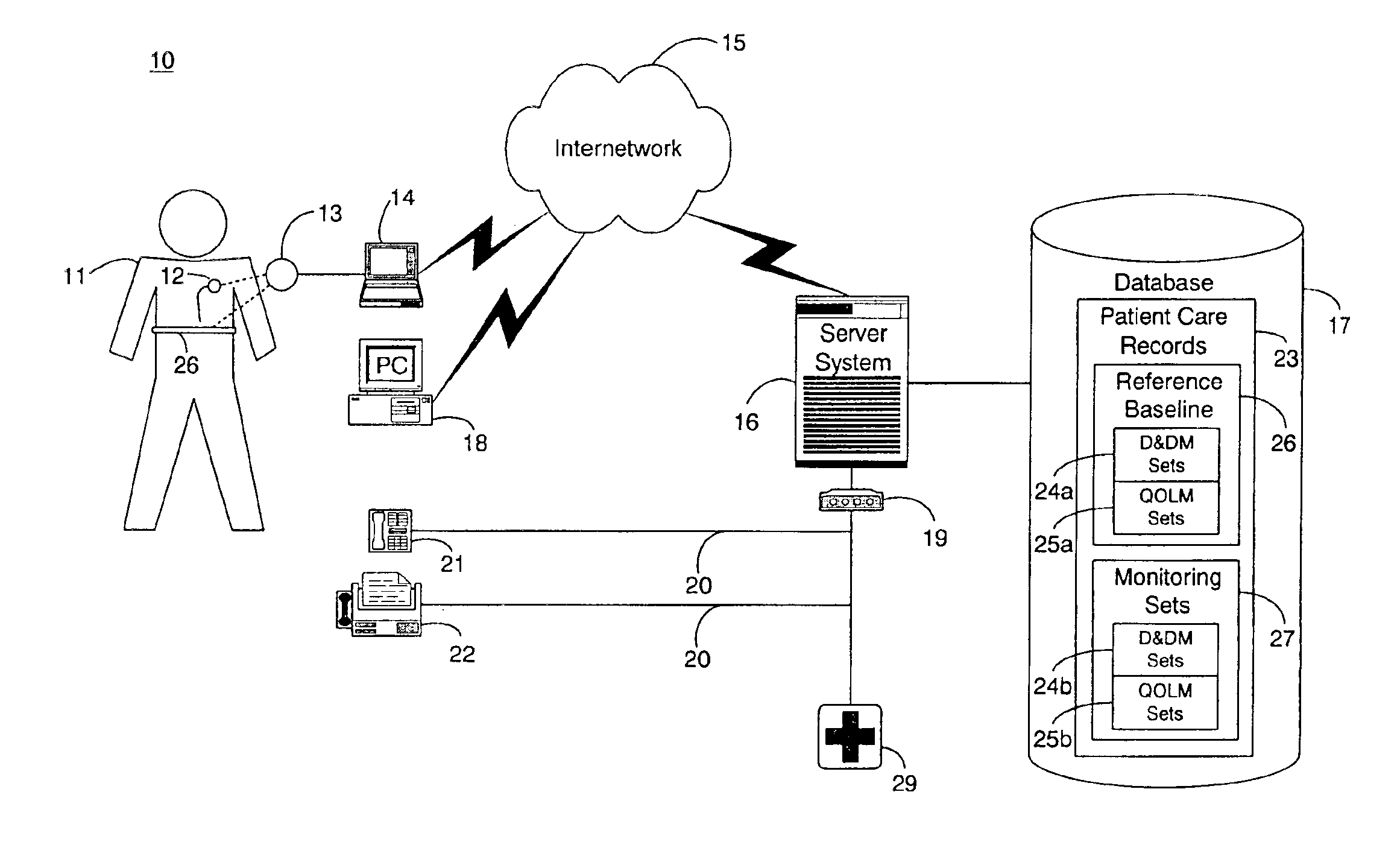
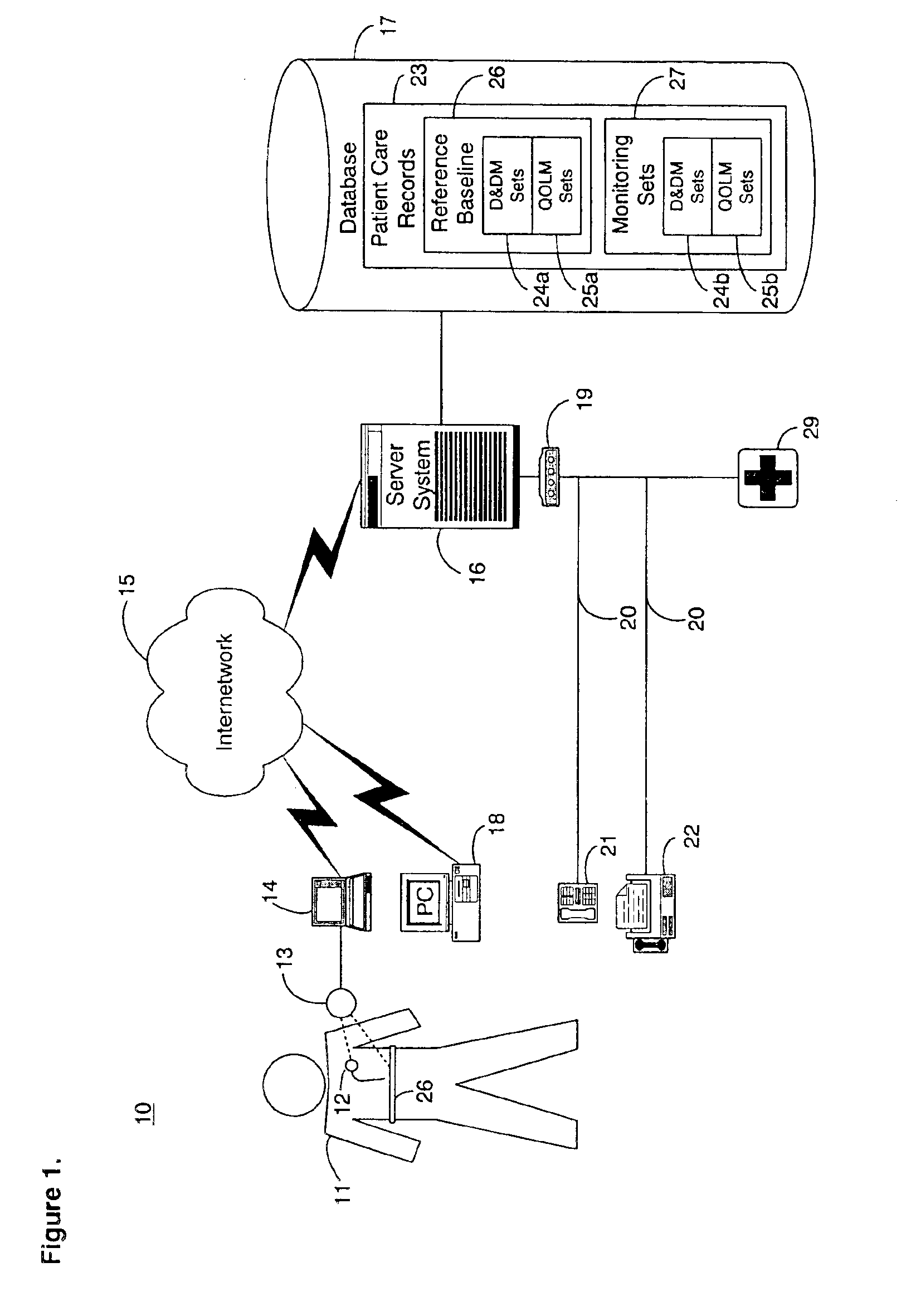
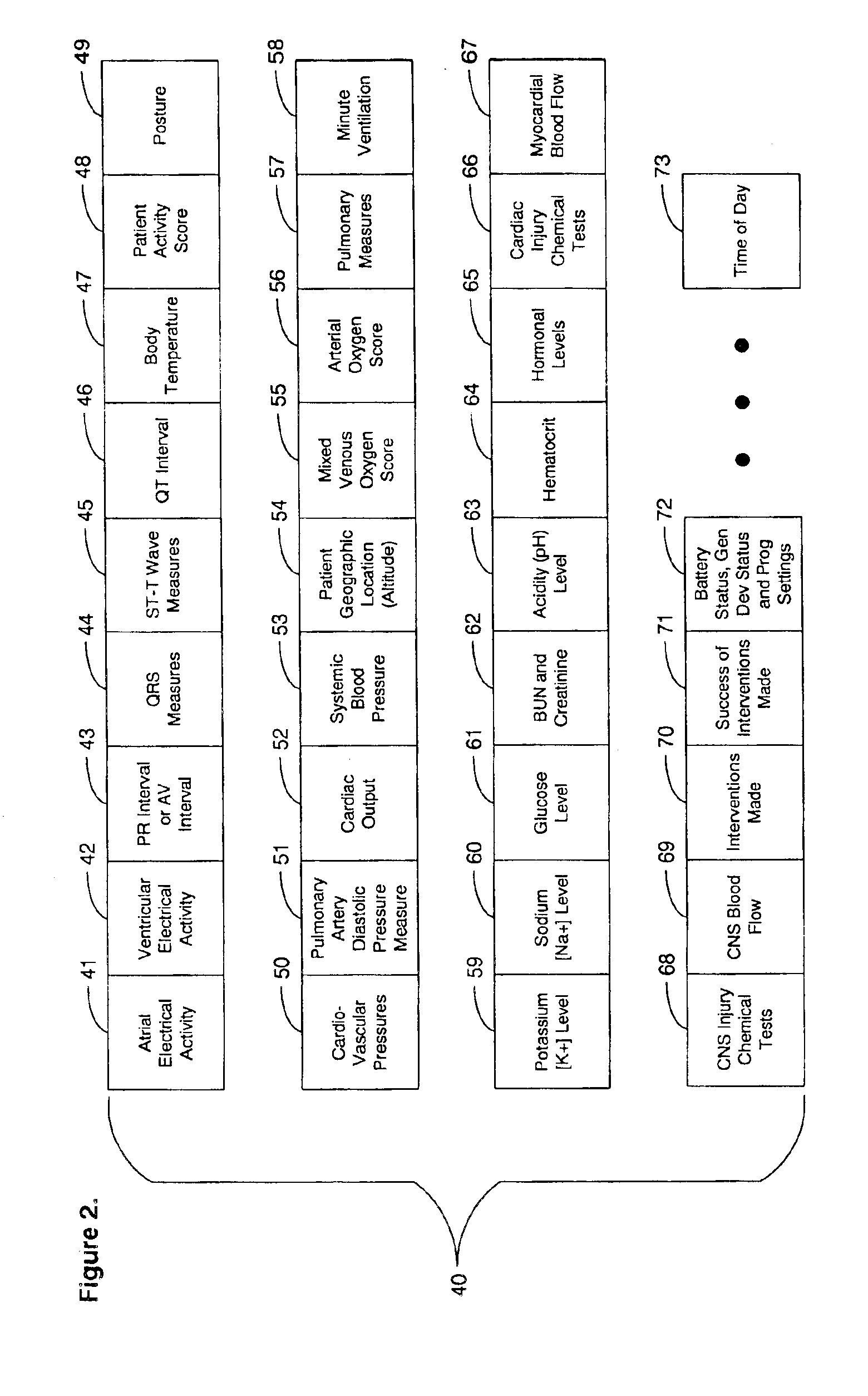
A system for collection and analysis of patient information for automated remote patient care is presented. A medical device adapted to be implanted for an individual patient regularly records and stores measures sets containing individual measures which each relate to patient information. A database collects one or more patient care records organized to include a plurality of the collected measures sets, and stores the collected measures set into a patient care record for the individual patient within a database. A server periodically receives a set of the collected measures from the medical device adapted to be implanted, and analyzes one or more of the collected measures sets in the patient care record for the individual patient relative to one or more other collected measures sets stored in the database server to determine a patient status indicator.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
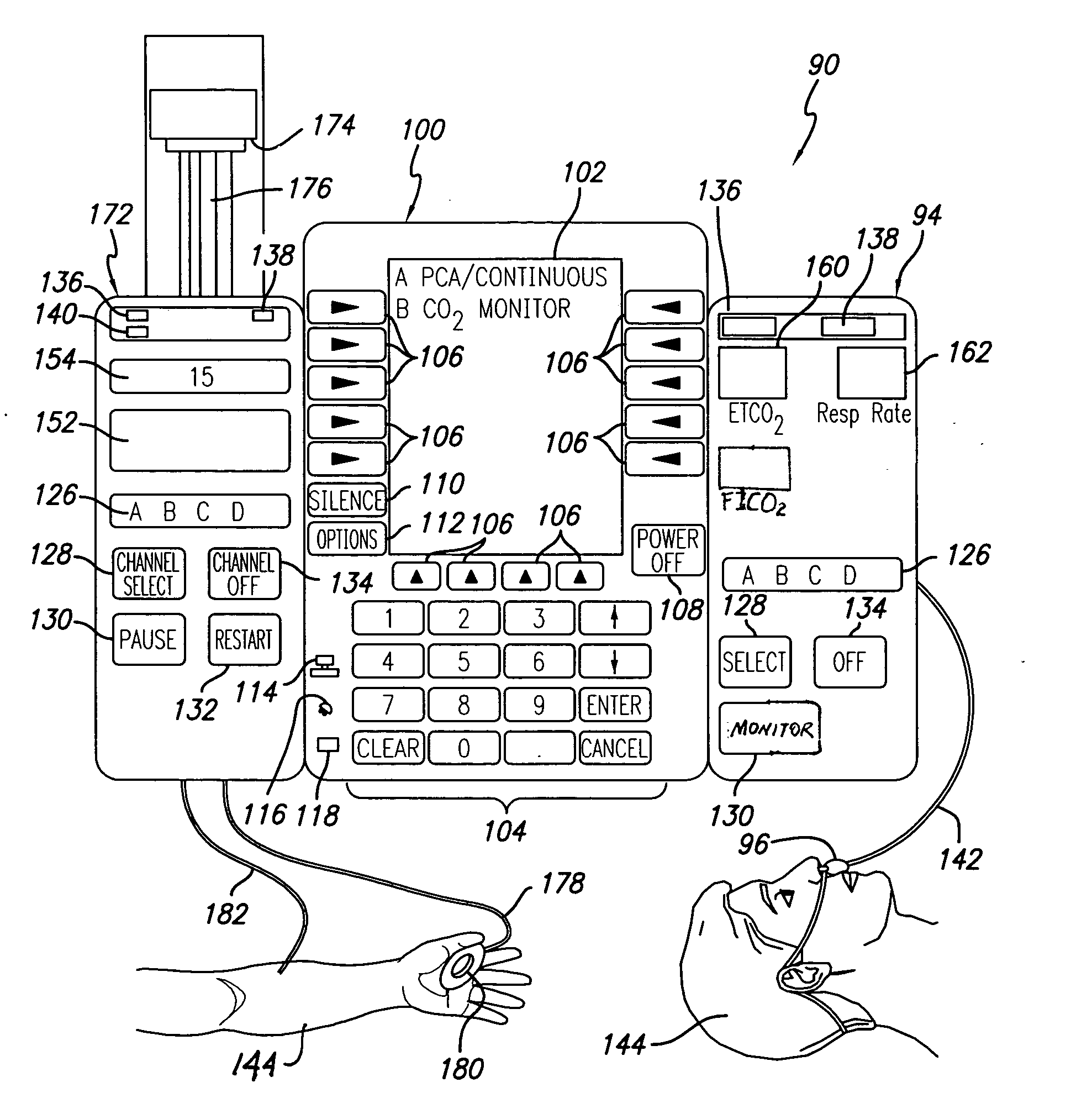
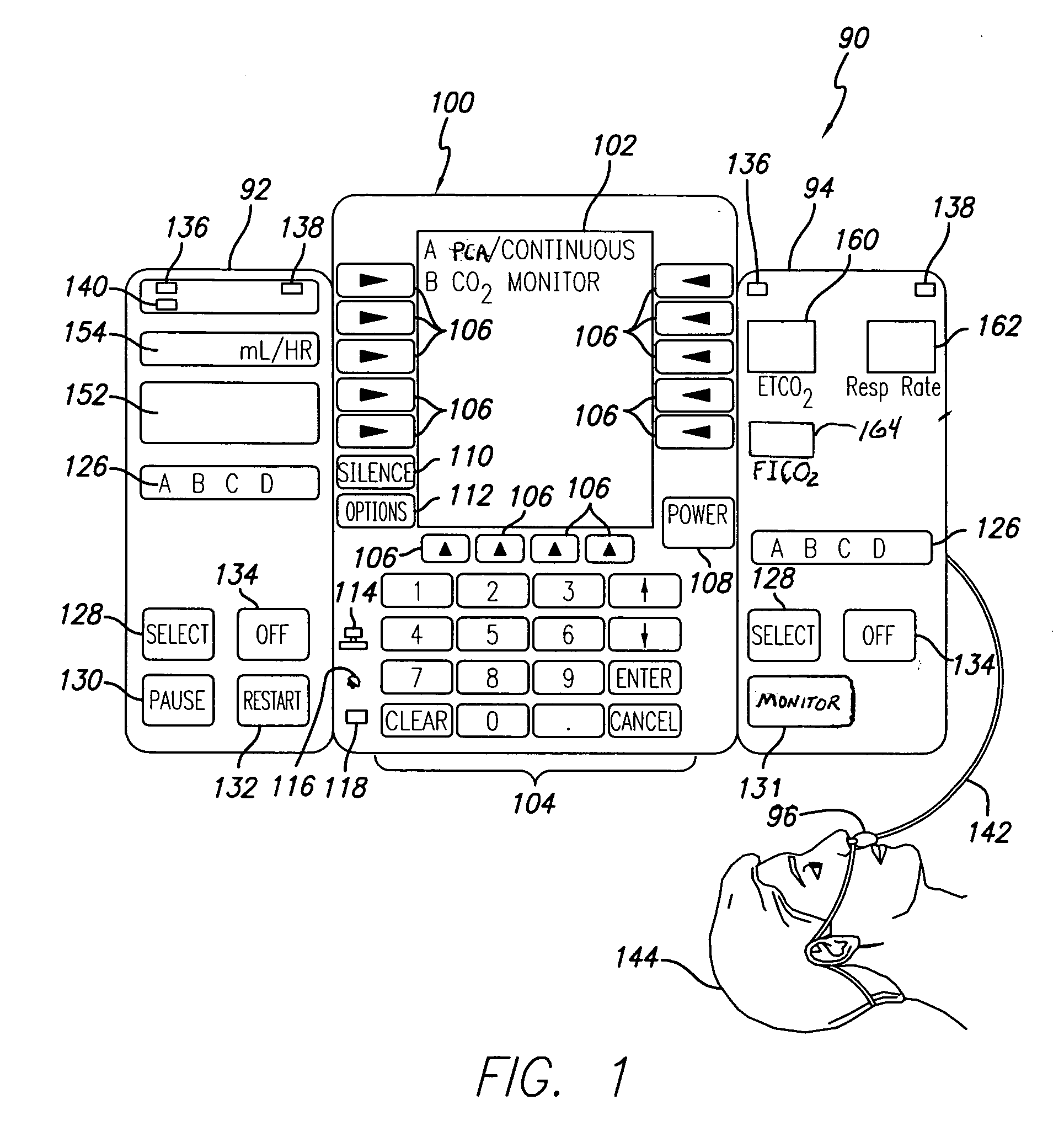
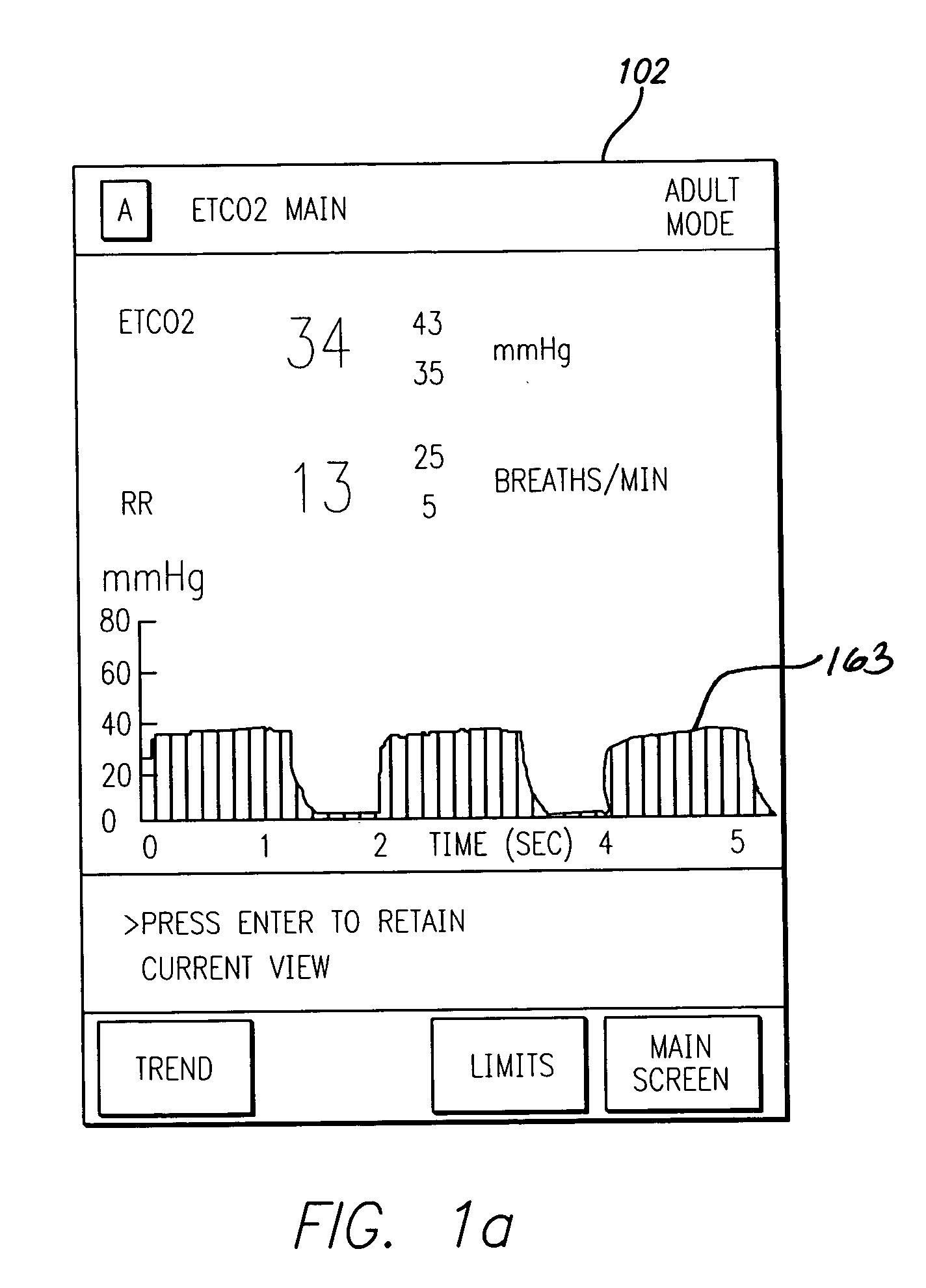
Patient-controlled analgesia with patient monitoring system and method
A patient care system in which a physiological parameter of a patient is monitored while the patient self-administers analgesic. A display presents a trend of the patient's physiological parameter along with the time of self-administration of the analgesic (“PCA”—patient controlled analgesic) such that the effect of the analgesic on the physiological parameter can be seen over selectable time periods. The physiological parameter may be ETCO2 or SpO2 or other. Also included is a drug library having acceptable pumping parameters as well as other PCA specific data. Should the operator program a pumping parameter that is outside an acceptable range, or should the patient attempt to self-administer more analgesic than the acceptable range permits, or should a patient's physiological parameter change during infusion such that a pumping parameter becomes outside an acceptable range, an indication of such will be given and action, such as stopping the pump, will be taken.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
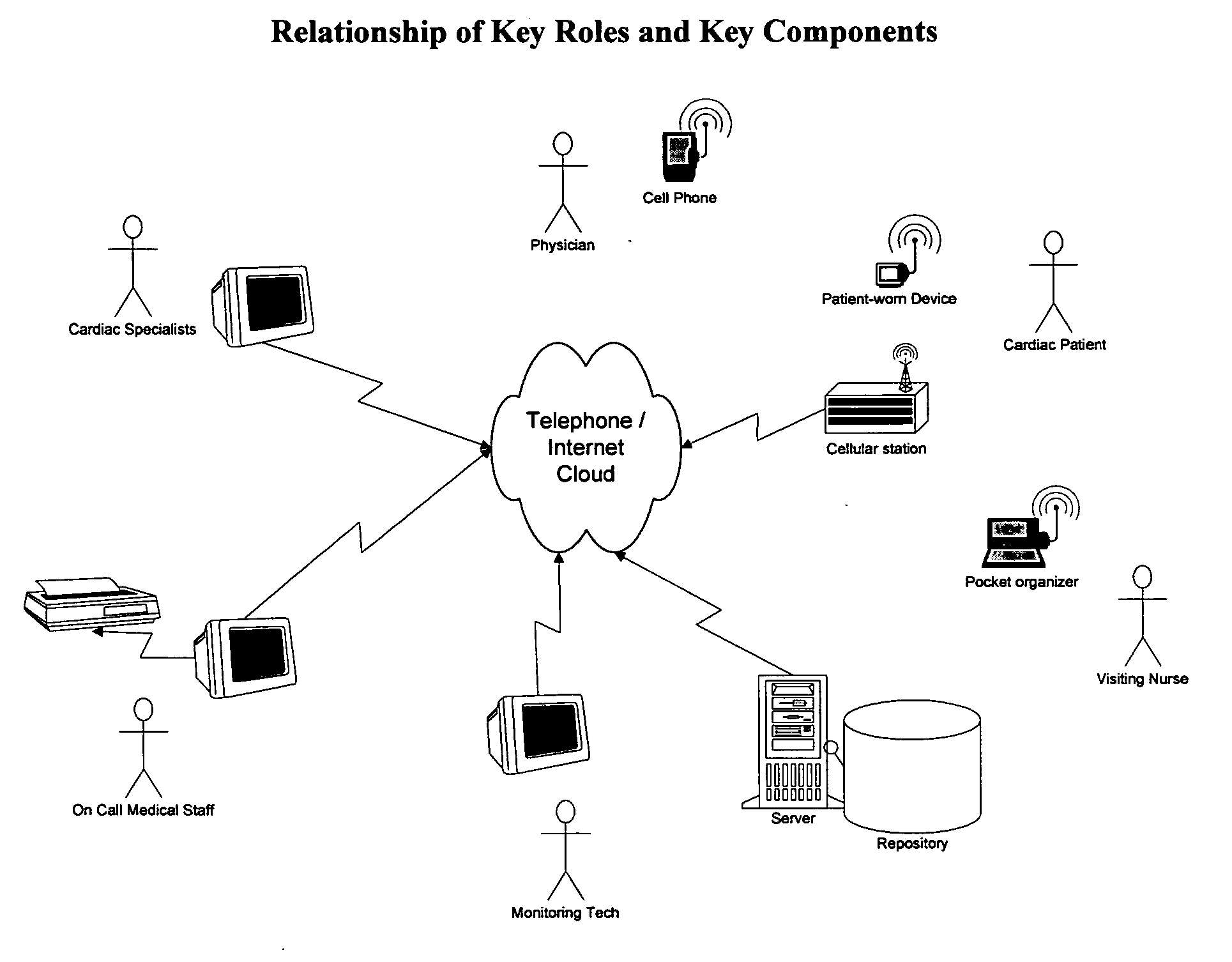
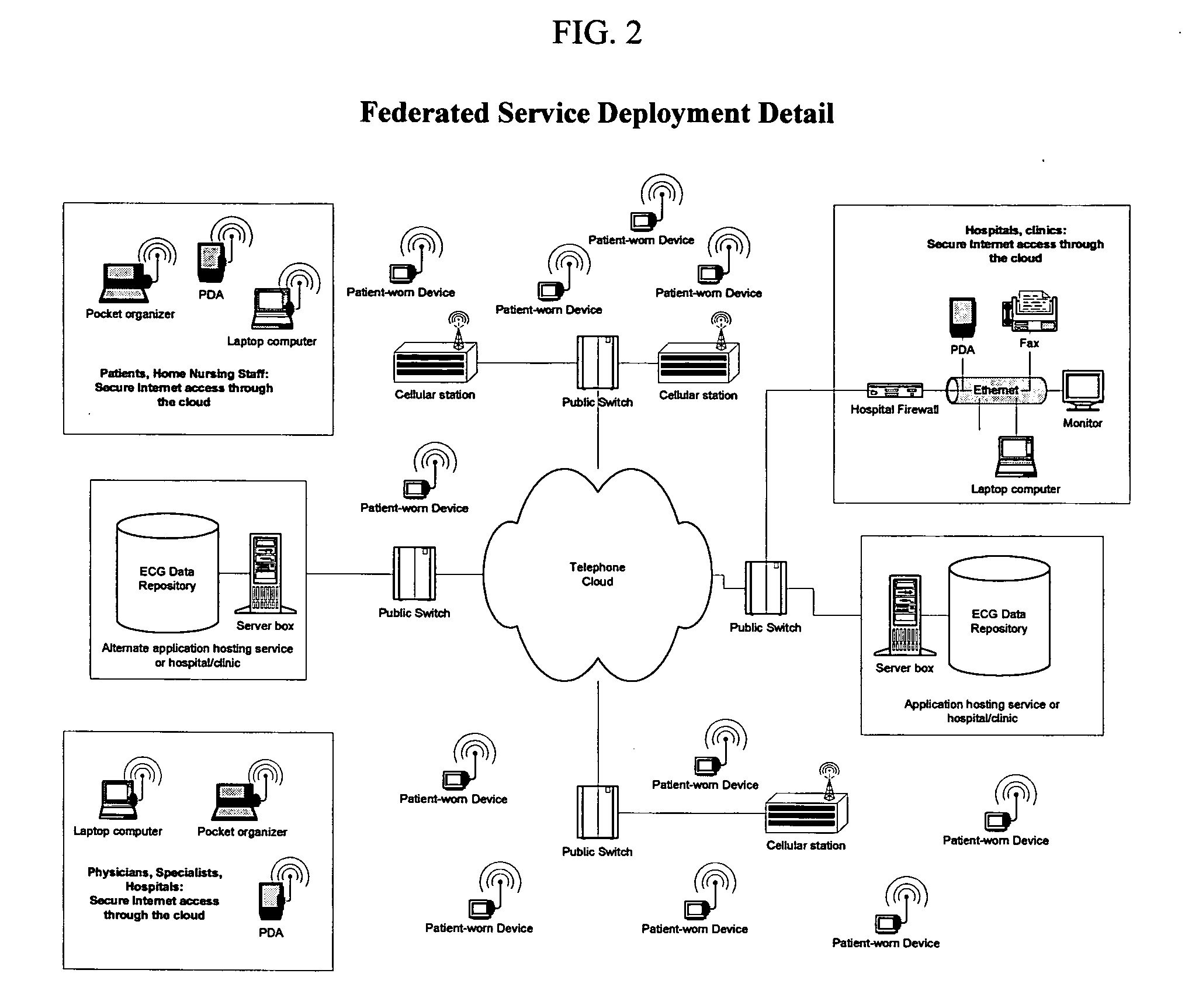
Remote medical monitoring system
InactiveUS20060122469A1Improve scalabilityEffective step-down patient careSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringMonitoring systemEmergency medicine
A medical monitoring system that brings the hospital-campus telemetry experience to the patient home. This system is designed to enable effective step-down patient care in the home setting while providing the patient with the freedom to go anywhere and remain “logically” tethered to the system. The system achieves this by being distributed in nature, globally accessible, highly scalable, with near real-time concurrent reporting and analysis of multiple physiological parameters, and making this information real-time accessible to healthcare practitioners.
Owner:MARTEL NORMAND M
System, Method, and Apparatus for Electronic Patient Care
ActiveUS20130191513A1Quantity minimizationData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A method implemented by an operative set of processor executable instructions configured for execution by a processor includes: determining if a monitoring client is connected to a base through a physical connection; establishing a first communications link between the monitoring client and the base through the physical connection; updating, if necessary, the interface program on the monitoring client and the base through the first communications link; establishing a second communications link between the monitoring client and the base using the first communications link; and communicating data from the base to the monitoring client using the second communications link.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Data processing and feedback method and system
ActiveUS7187790B2Patient care can be improvedQuick identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionOffice automationComputer-aidedHuman operator
A technique is provided for offering feedback, including feedback for patient care and for training purposes for medical professionals and human operators. The technique includes accessing data, such as image data, for evaluation by a human operator. The data is then analyzed via a computer-assisted data operating algorithm, and the analysis may further include analysis of supplemental data accessed from an integrated knowledge base. Based upon the analysis feedback is provided to the operator, such as for completing or complementing the evaluation, correcting analysis by the human operator, or otherwise informing the human operator of similarities or differences between the analyses.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Methods and systems for patient care
InactiveUS20100137693A1Improve clinical outcomesEasy to participateMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDialysis systemsPeritoneal dialysisHemodialysis
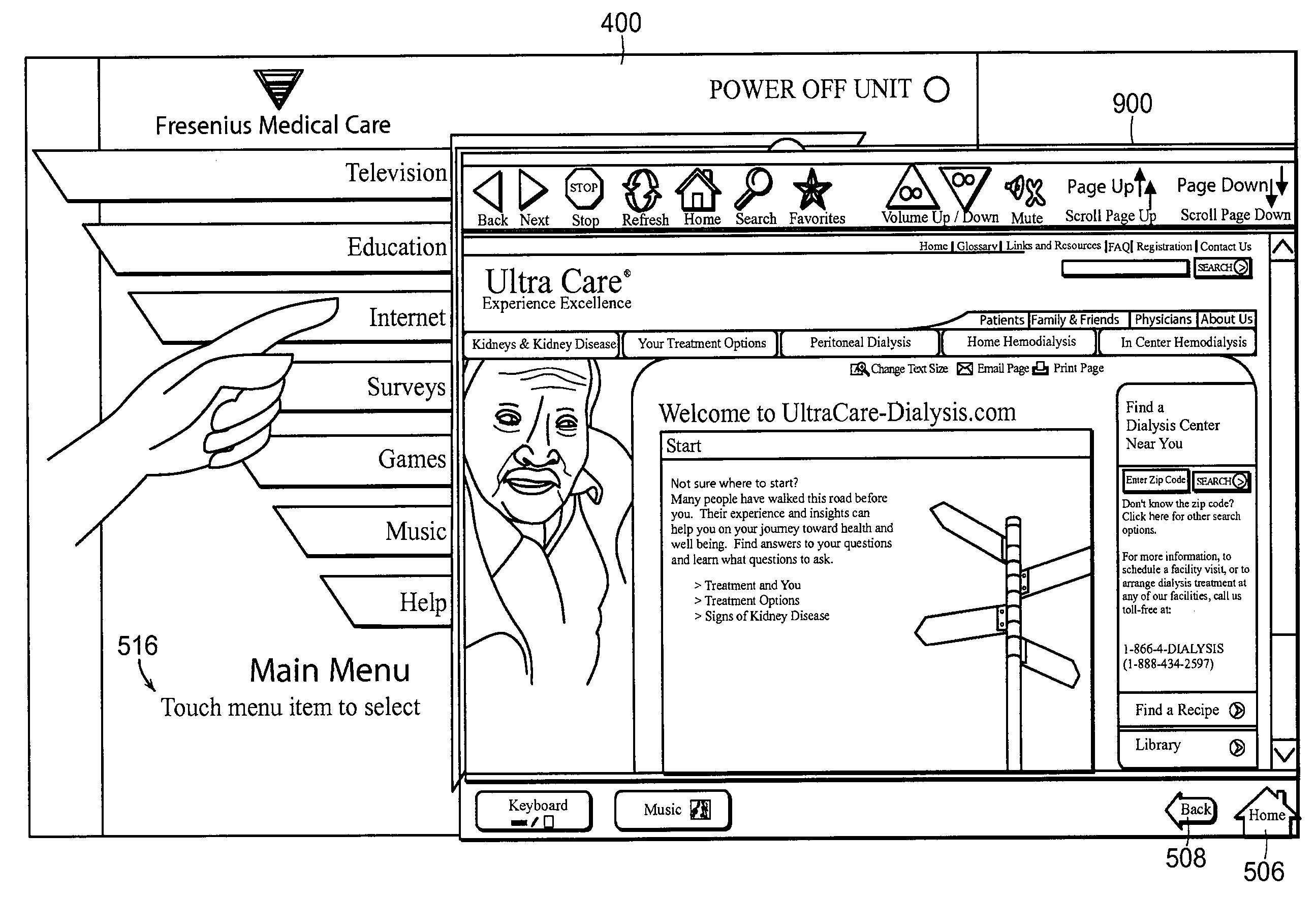
Methods and apparatus for patient care detect a current medical condition of a patient receiving medical treatment, e.g., by sensing blood pressure, heart rate, weight, glucose level, hemoglobin level, and / or blood potassium level (all by way of example) and transmit information regarding that medical condition to a digital data processing system disposed remotely from the medical treatment apparatus. The medical treatment apparatus can be, for example, one for peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis, and the medical condition can be sensed by sensors coupled to or otherwise utilized in connection with such apparatus.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
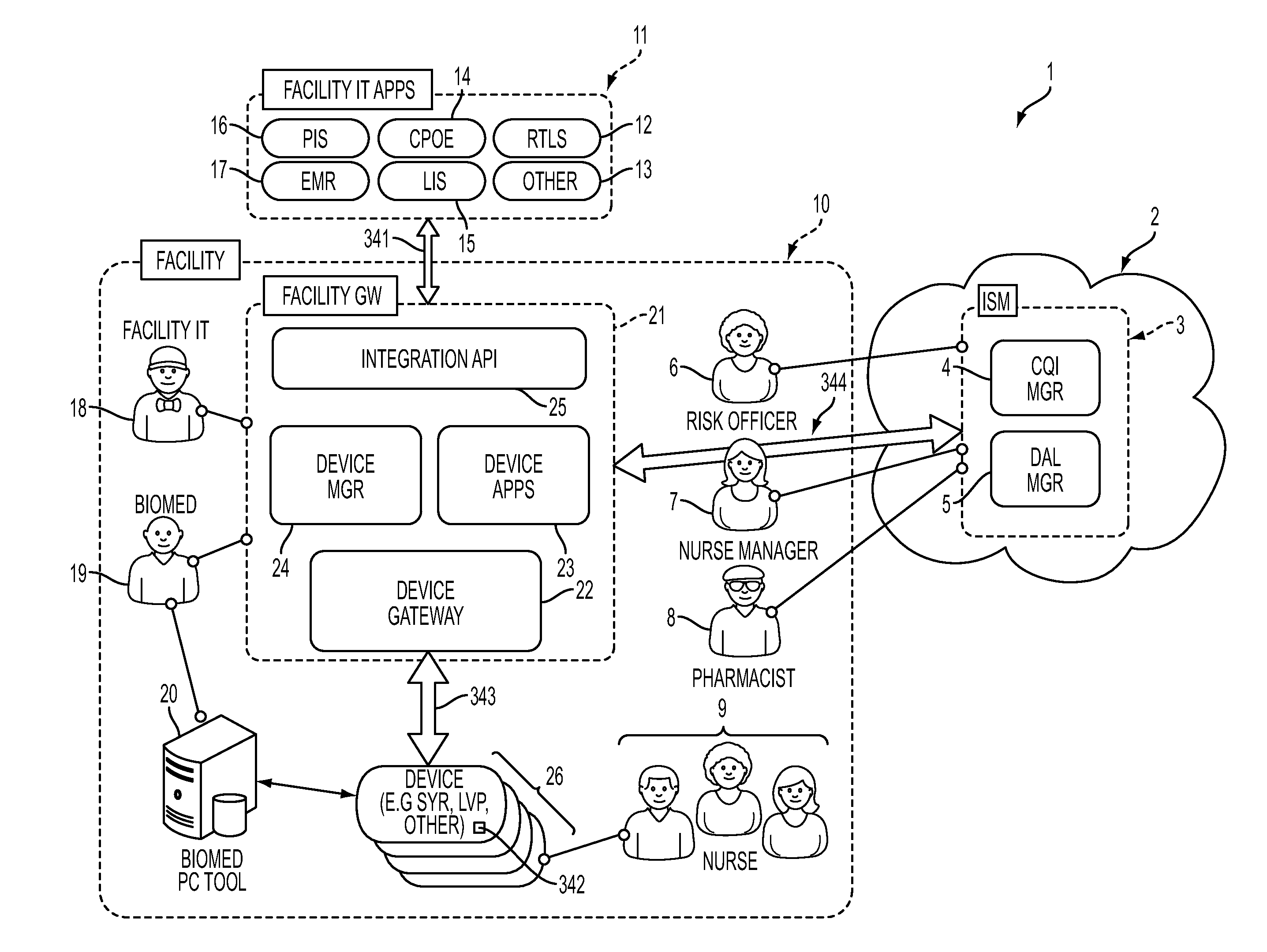
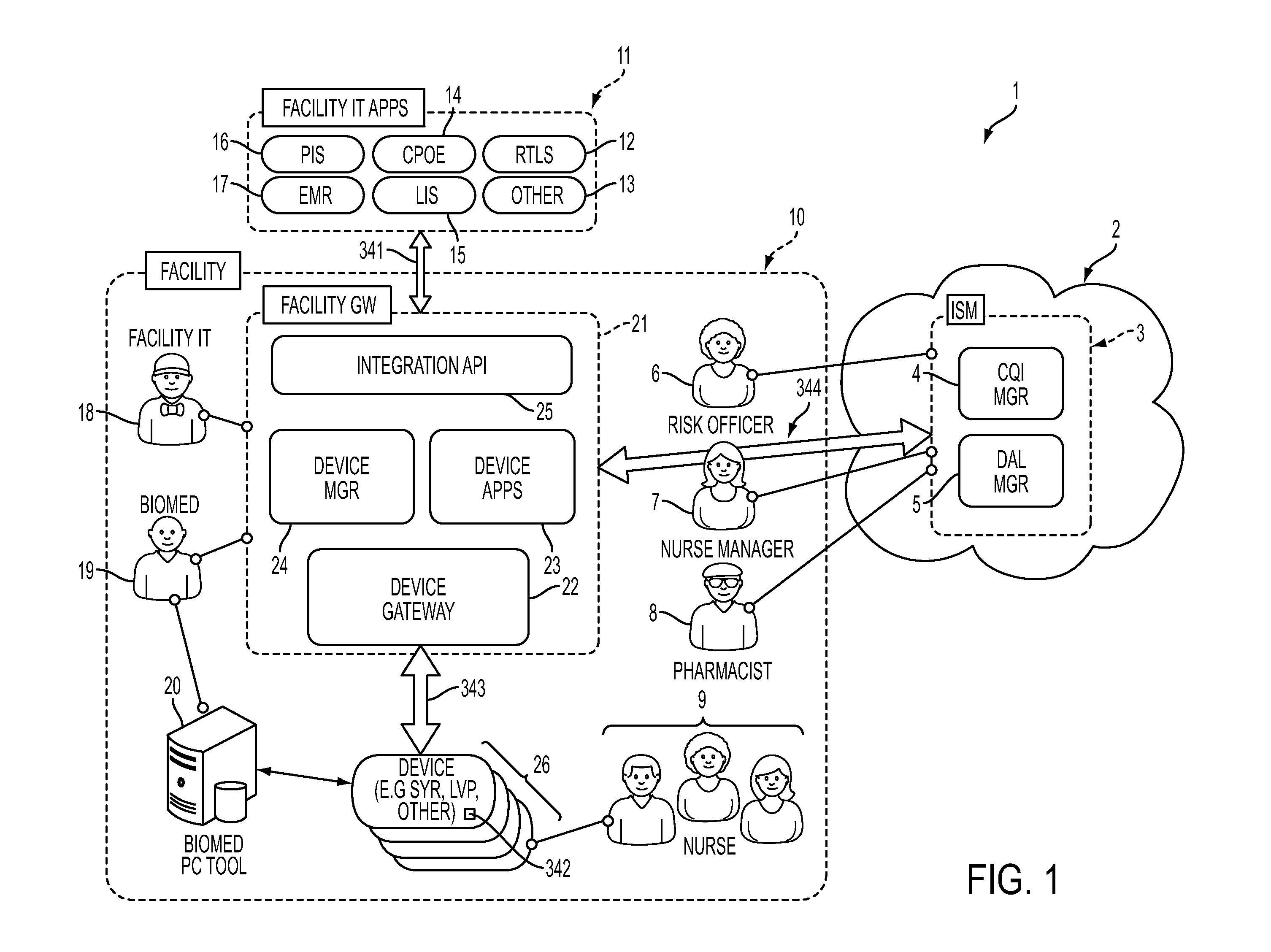
System and Apparatus for Electronic Patient Care
ActiveUS20130346108A1Data processing applicationsDrug and medicationsWeb serviceApplication software
A system for electronic patient care includes a network, a facility gateway, a device gateway application and a medical device. The facility gateway is configured to provide a publish-subscribe service for an application. The device gateway application is configured for execution by the facility gateway. The device gateway is configured to communicate via the network by providing a web service. The medical device is in operative communication with the network. The medical device is configured to communicate with the device gateway using the web service.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
System, Method, and Apparatus for Electronic Patient Care
ActiveUS20140188516A1Quantity minimizationData processing applicationsLocal control/monitoringComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A method, related system and apparatus are disclosed. The method is implemented by an operative set of processor executable instructions configured for execution by a processor. The method includes the acts of: determining if a monitoring client is connected to a base through a physical connection; establishing a first communications link between the monitoring client and the base through the physical connection; updating, if necessary, the interface program on the monitoring client and the base through the first communications link; establishing a second communications link between the monitoring client and the base using the first communications link; and communicating data from the base to the monitoring client using the second communications link.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
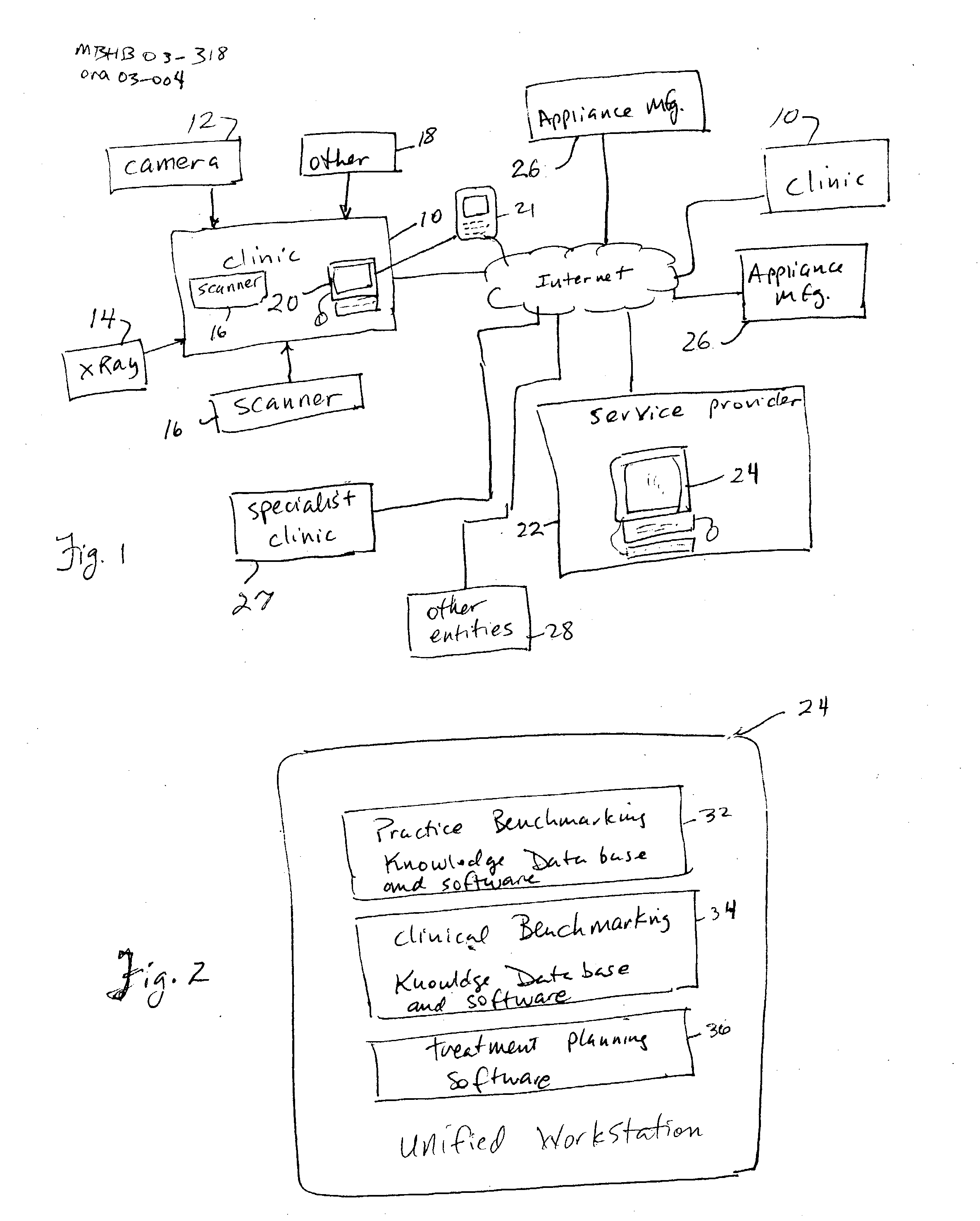
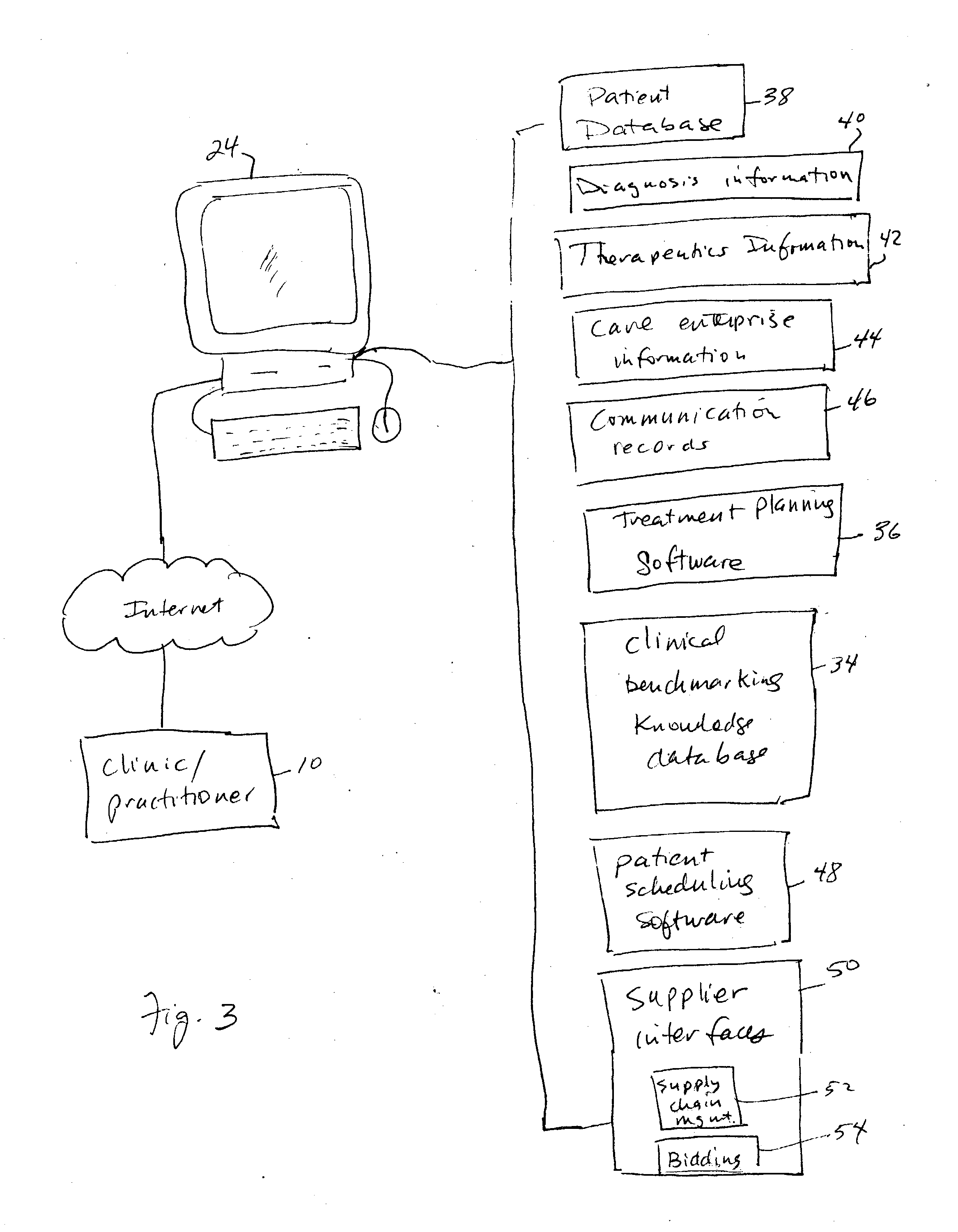
Interactive unified workstation for benchmarking and care planning
InactiveUS20050038669A1Reduce deliveryFunctional integrationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDental toolsBusiness practiceWorkstation
An interactive, unified workstation is described that unifies in a single system multitude of functions pertaining to a practitioners practice that would otherwise require disjointed, more expensive, and less efficient individual workstations dedicated to a specific, limited task or a sub-set of tasks. The invention is directed towards benchmarking for a practitioner's business practice, and for clinical aspects of treatment planning; and integrating overall patient care planning functions. The unified workstation further facilitates access to archived database resources and facilitates both knowledge base services to practitioners and also hybrid treatment planning, wherein different types of appliance systems (fixed, such as brackets and wires, or removable, such as aligning shells) may be used during the course of treatment.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
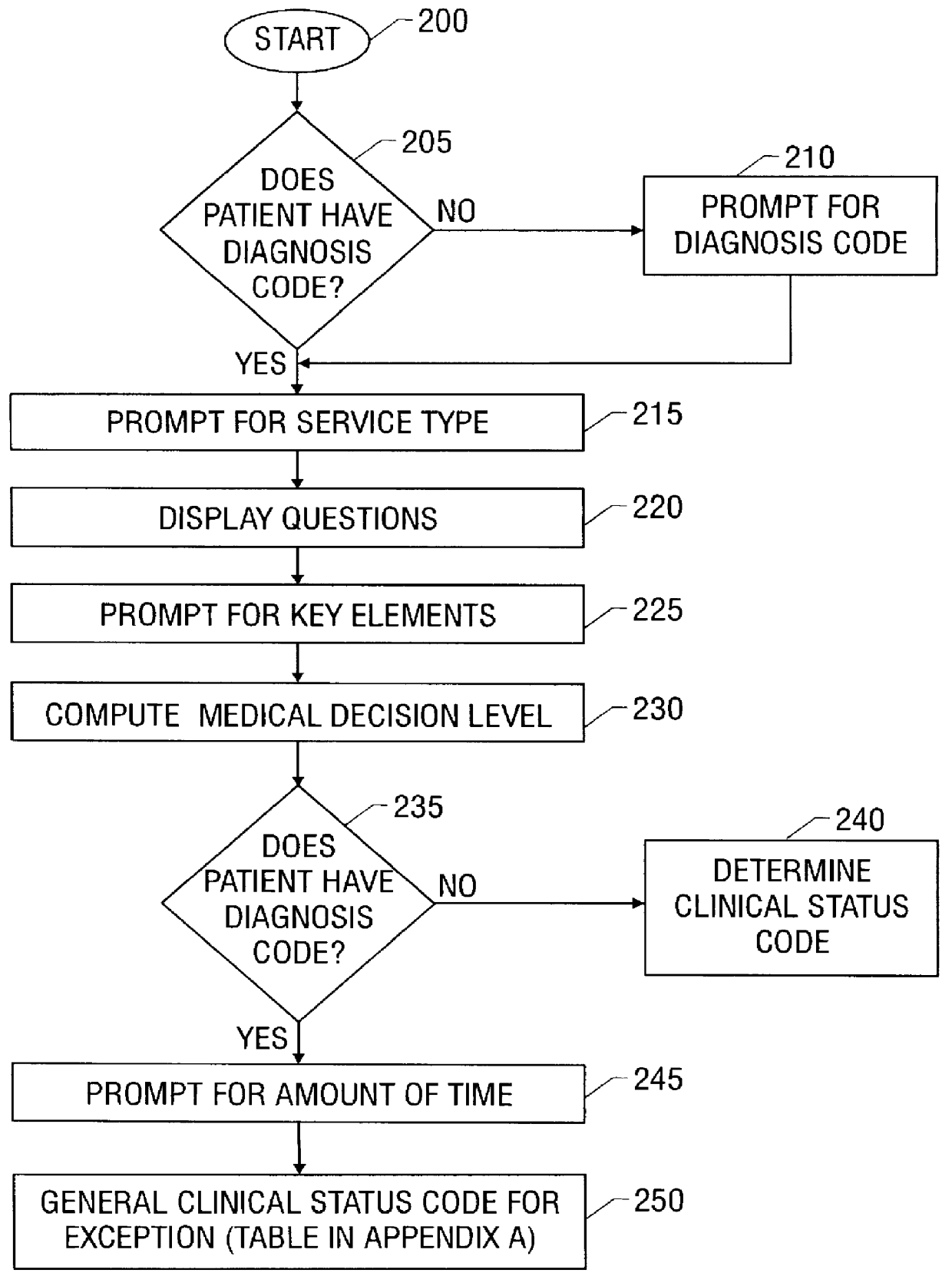
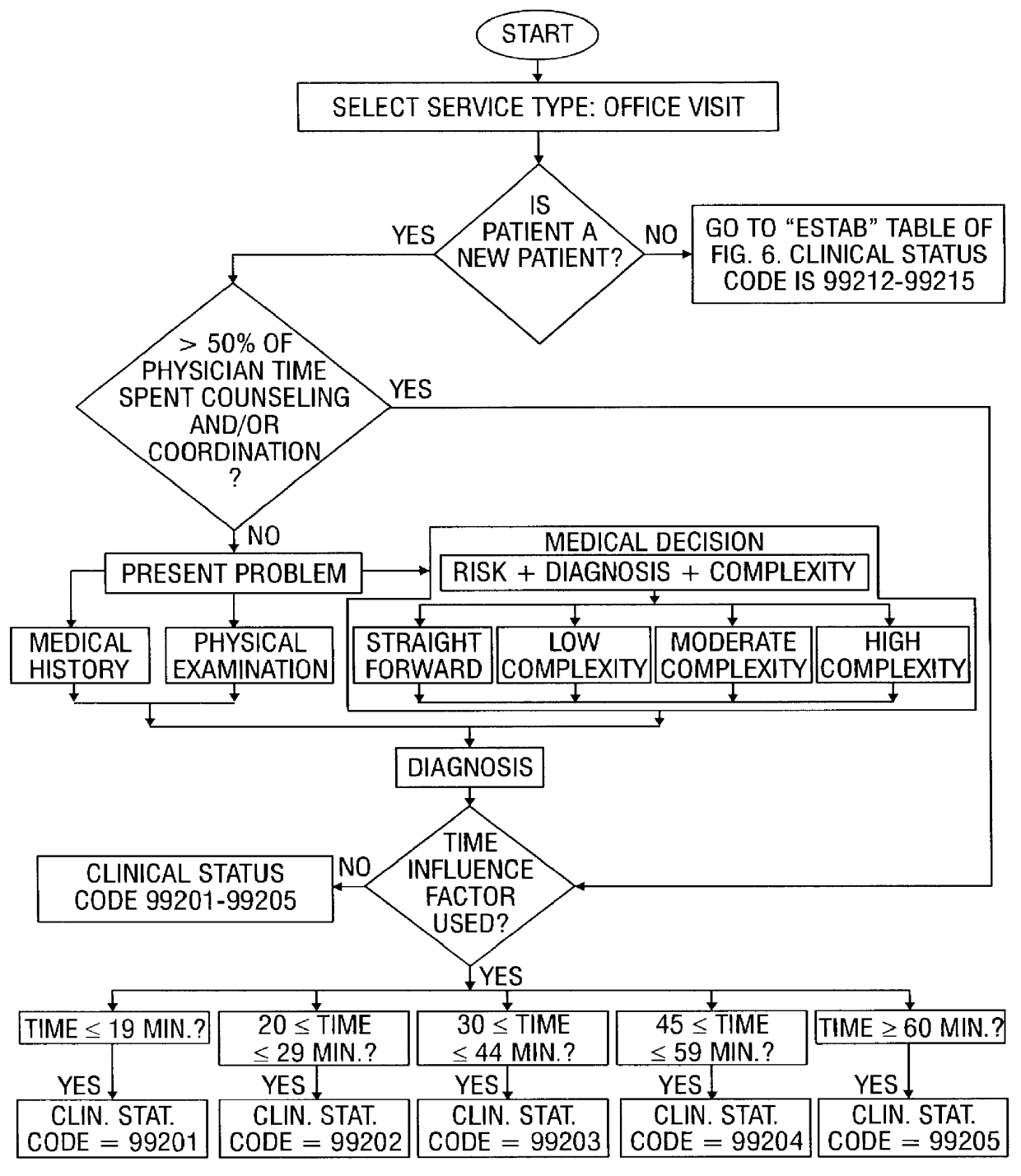
System and method for recording patient history data about on-going physician care procedures
InactiveUS6154726AConvenient recordingOptimize schedulingData processing applicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionStaff timeEfficacy
A system and method for processing patient data permits physicians and other medical staff personnel to record, accurately and precisely, historical patient care information. An objective measure of a physician's rendered level of care, as described by a clinical status code, is automatically generated. Data elements used in the determination of the generated clinical status code include a level of history of the patient, a level of examination of the patient, a decision-making process of the physician treating the patient, and a "time influence factor." The quantity and quality of care information for a particular patient is enhanced allowing future care decisions for that patient to be based on a more complete medical history. Enhanced care information can be used in outcome studies to track the efficacy of specific treatment protocols. Archiving of patient information is done in a manner which allows reconstruction of the qualitative aspects of provided medical services. The medical care data can be recorded, saved, and transferred from a portable system to a larger stationary information or database system. Considerable physician and staff time are saved and precision and accuracy are significantly enhanced, by generating these clinical status codes automatically (at the point of service by the care-provider without any intermediary steps) from information recorded simultaneously with the provision of services.
Owner:RENSIMER ENTERPRISES
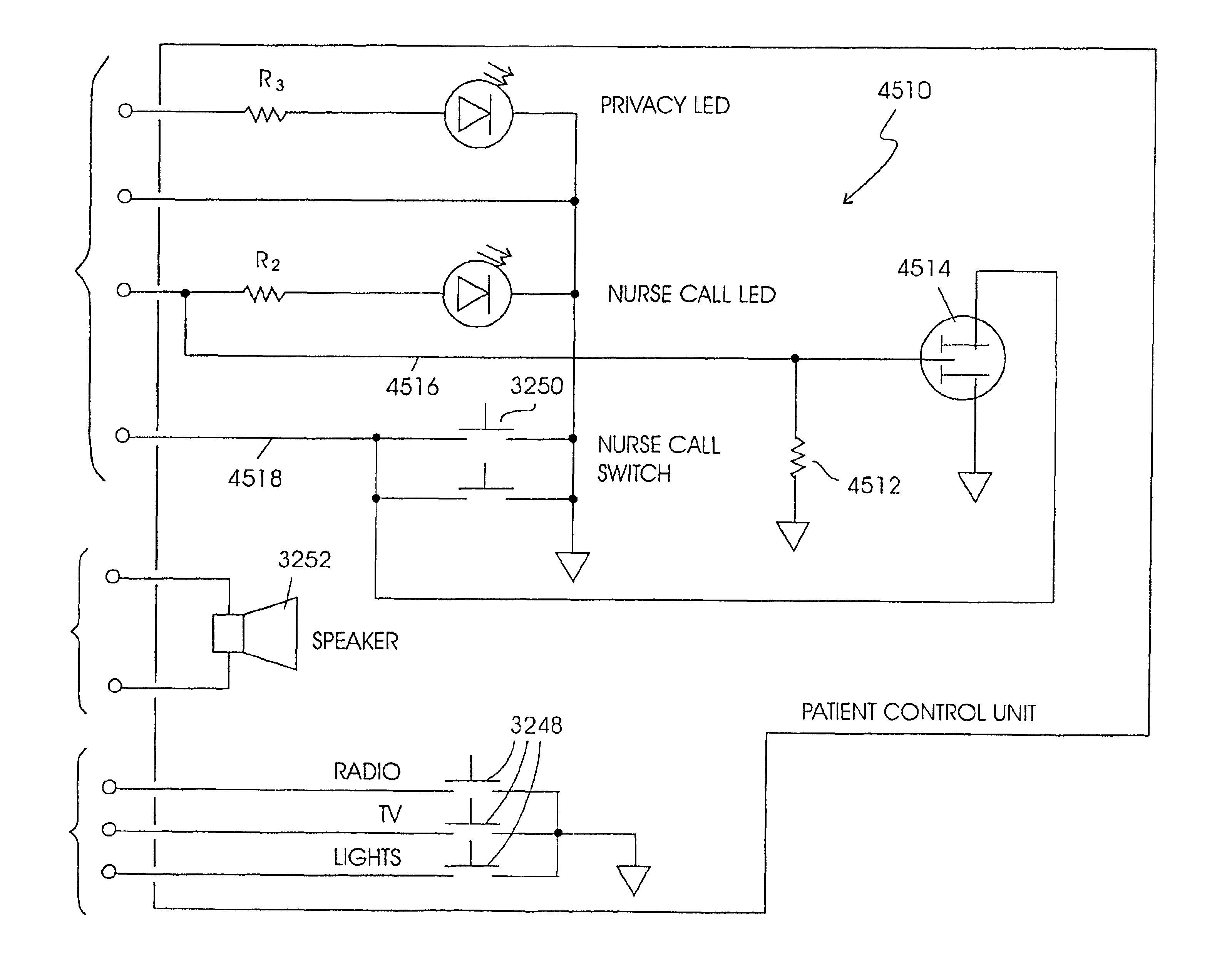
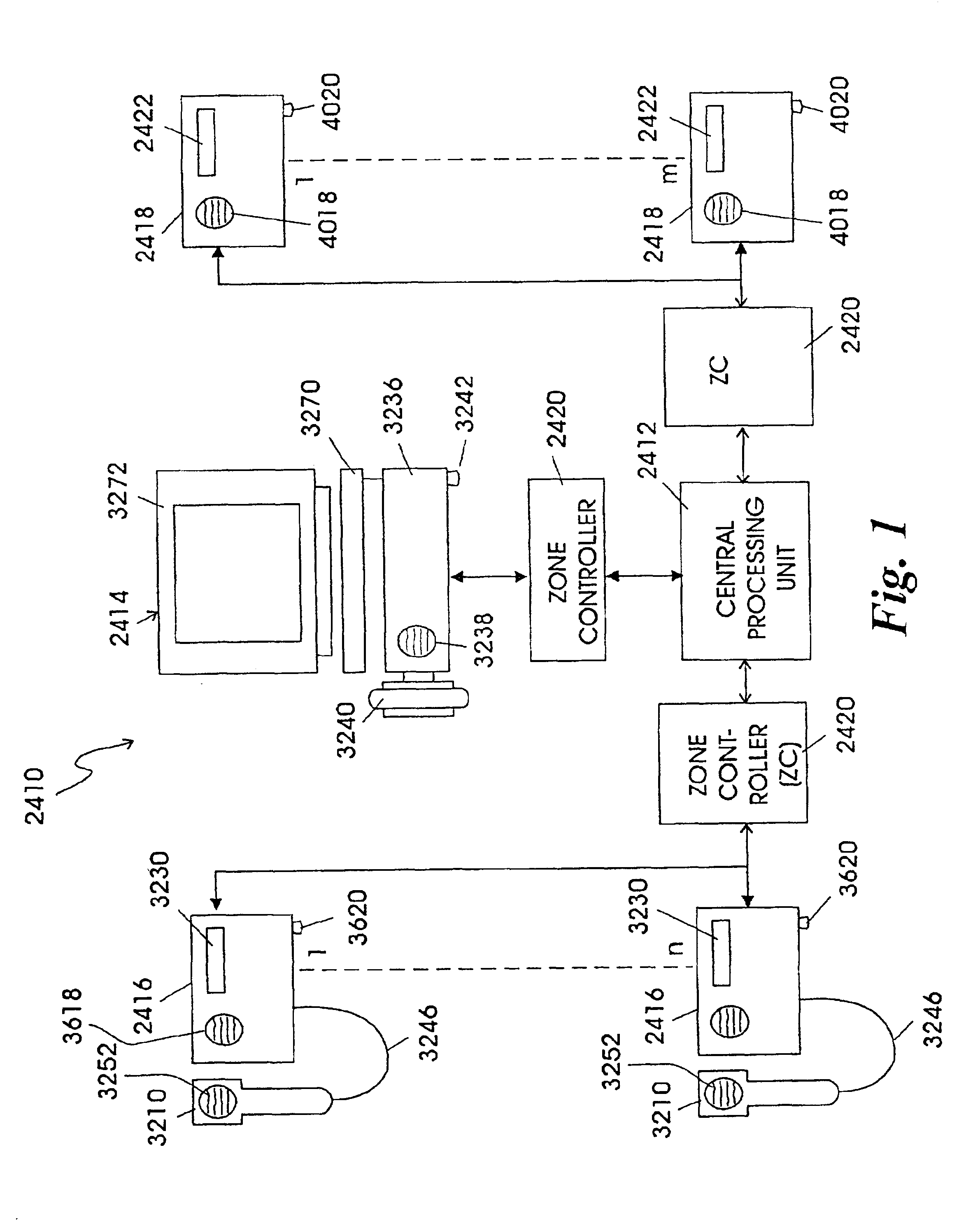
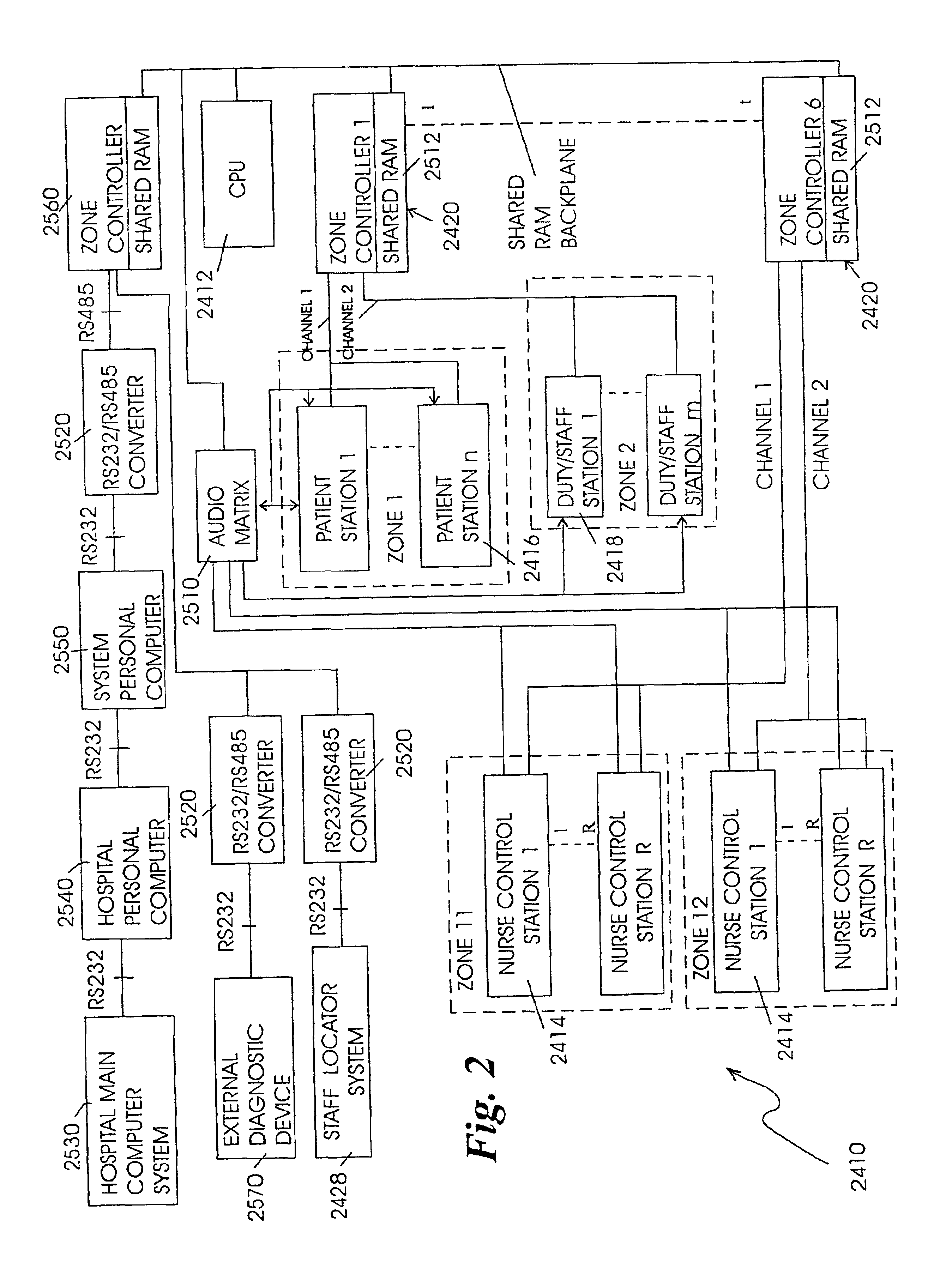
Patient care and communication system
InactiveUS6958706B2Facilitate visualFacilitate dataElectric signal transmission systemsSurgeryTelecommunications linkDisplay device
The present invention relates to a patient care and communication system which utilizes a central processing system and a plurality of remote stations electrically connected to the central processing system to facilitate visual and data communications. Each remote station includes telephone circuitry which is connected to a private branch exchange for telephone communications between stations. In addition, the private branch exchange is connected to a telephone exchange and a plurality of telephones for facilitating telephone communication therebetween. The central processing system facilitates the visual and data communications between the plurality of remote stations, and includes a system for determining which of the plurality of remote stations are transmitting the visual and data communications and which of the plurality of remote stations are to receive the visual and data communications. The central processing system also includes a system which establishes a communication link between the transmitting stations and the receiving stations. The remote stations include a processing system which also facilitates the visual, data and telephone communications and a display for displaying the visual communications. The present invention also includes a staff and / or patient locator system, in which each remote station includes an infrared receiver that receives infrared transmissions from a portable transmitter worn by a staff member or patient. The infrared transmissions include identity information associated with the person wearing the transmitter. The identity information is then transferred to the central processing system which determines the identity and location of each person wearing a portable transmitter.
Owner:HILL ROM SERVICES
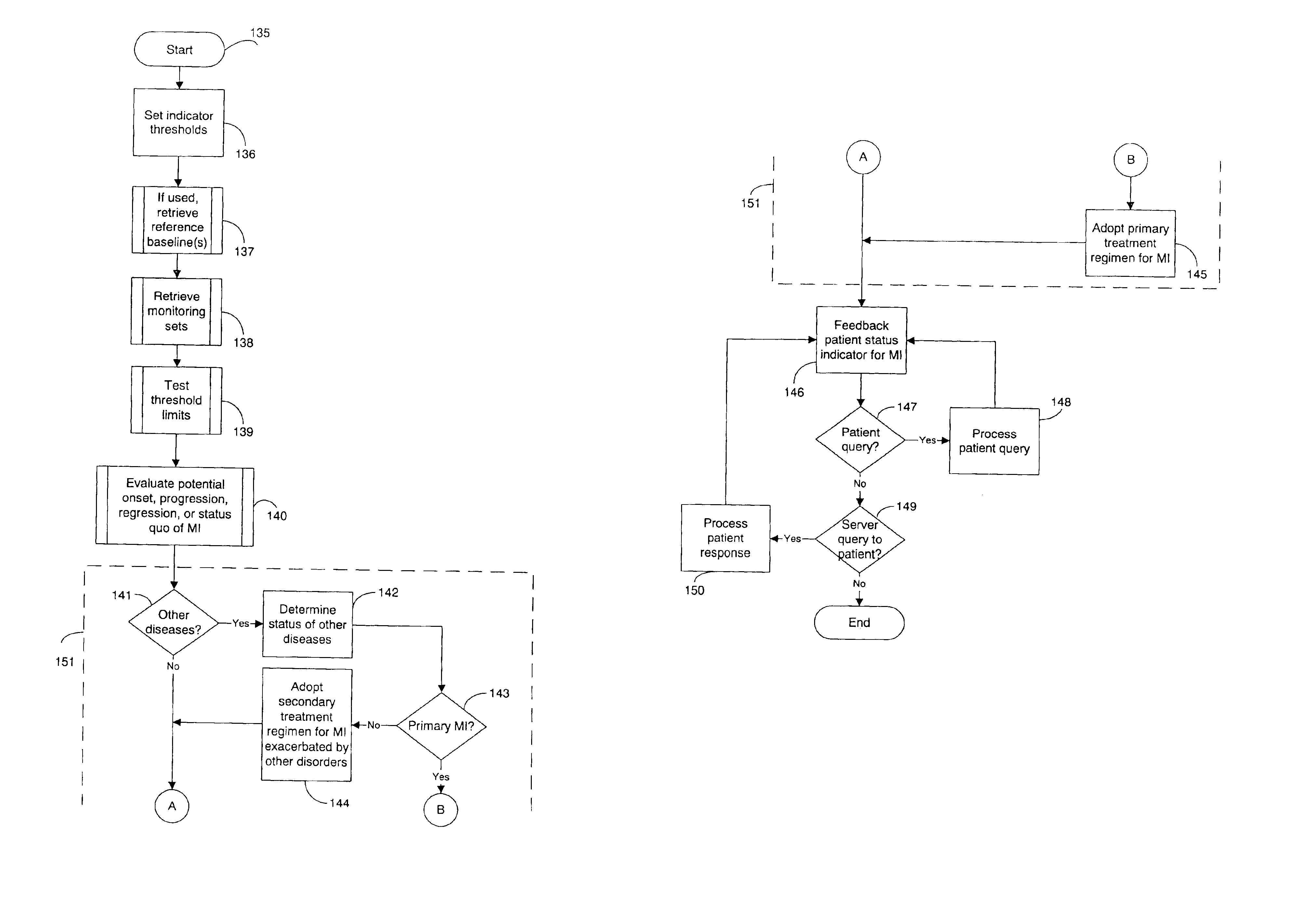
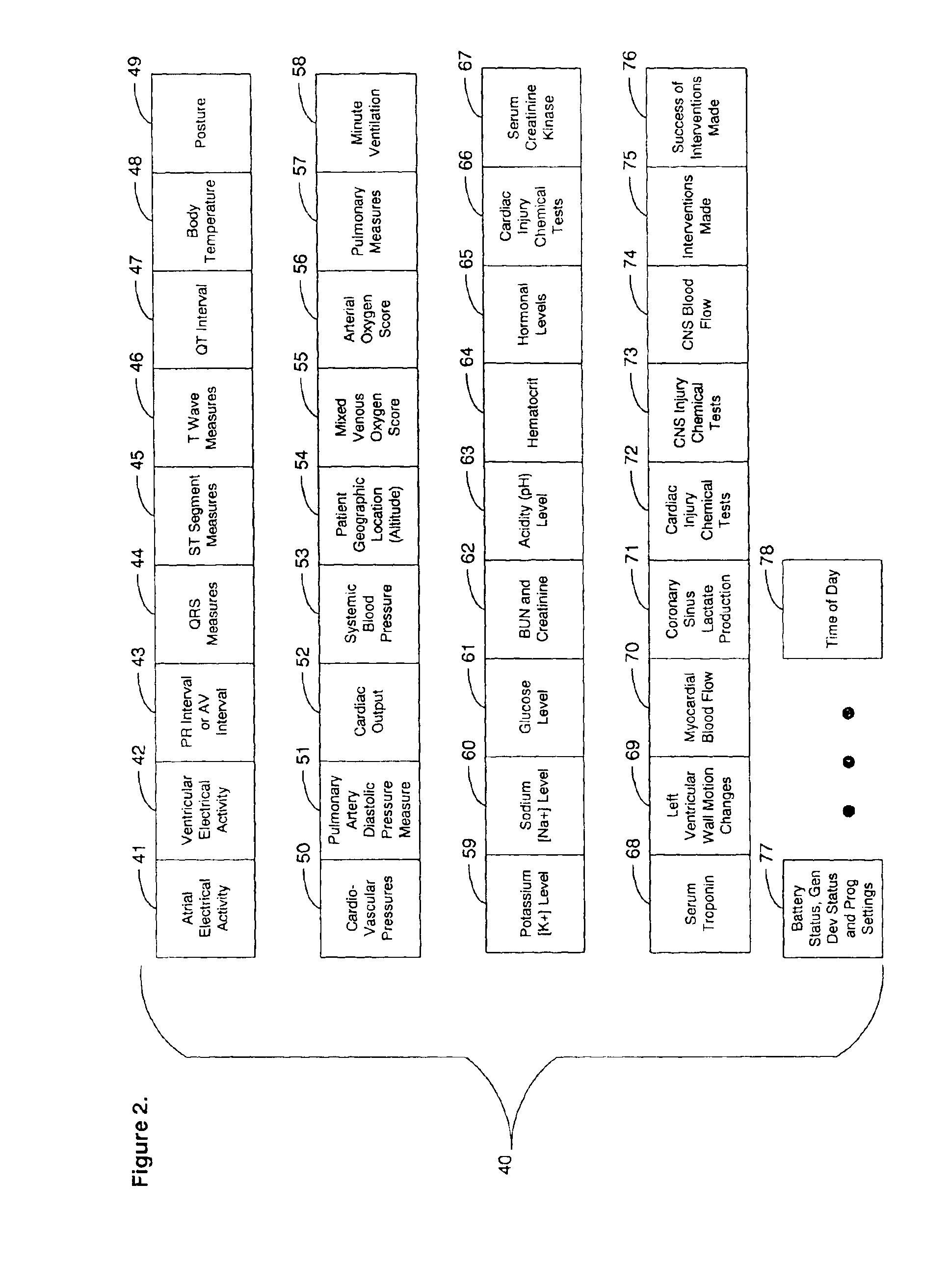
System and method for diagnosing and monitoring myocardial ischemia for automated remote patient care
InactiveUS6913577B2Increase productionIncreased serum creatinine kinaseElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHysteresisHeart muscle extract
A system for diagnosing and monitoring myocardial ischemia for automated remote patient care is presented. A database stores monitoring sets containing recorded measures relating to patient information recorded on a substantially continuous basis. A server retrieving and processing the monitoring sets includes a comparison module determining a patient status change by comparing recorded measures and time from each of the monitoring sets to other recorded measures and time from another monitoring set with both recorded measures relating to a same type of patient information recorded at different times, and an analysis module testing each patient status change for, an onset, a progression, a regression, and a status quo of myocardial ischemia against a predetermined indicator threshold, including hysteresis threshold, corresponding to same type of patient information as the compared recorded measures.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
System, Method, and Apparatus for Electroinic Patient Care
ActiveUS20130297330A1Quantity minimizationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDrug and medicationsOrder formMonitoring system
An electronic patient monitoring system includes first and second modules. The first module is configured to receive and store information pertaining to a patient, said information including data related to a first parameter of the patient measured by a device connected to the patient, and data related to a second parameter of the patient received from a first database containing information about the patient. The second module is configured to receive a medication order from a user via a user interface associated with the second module, said second module being further configured to transmit said treatment order to the first module.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
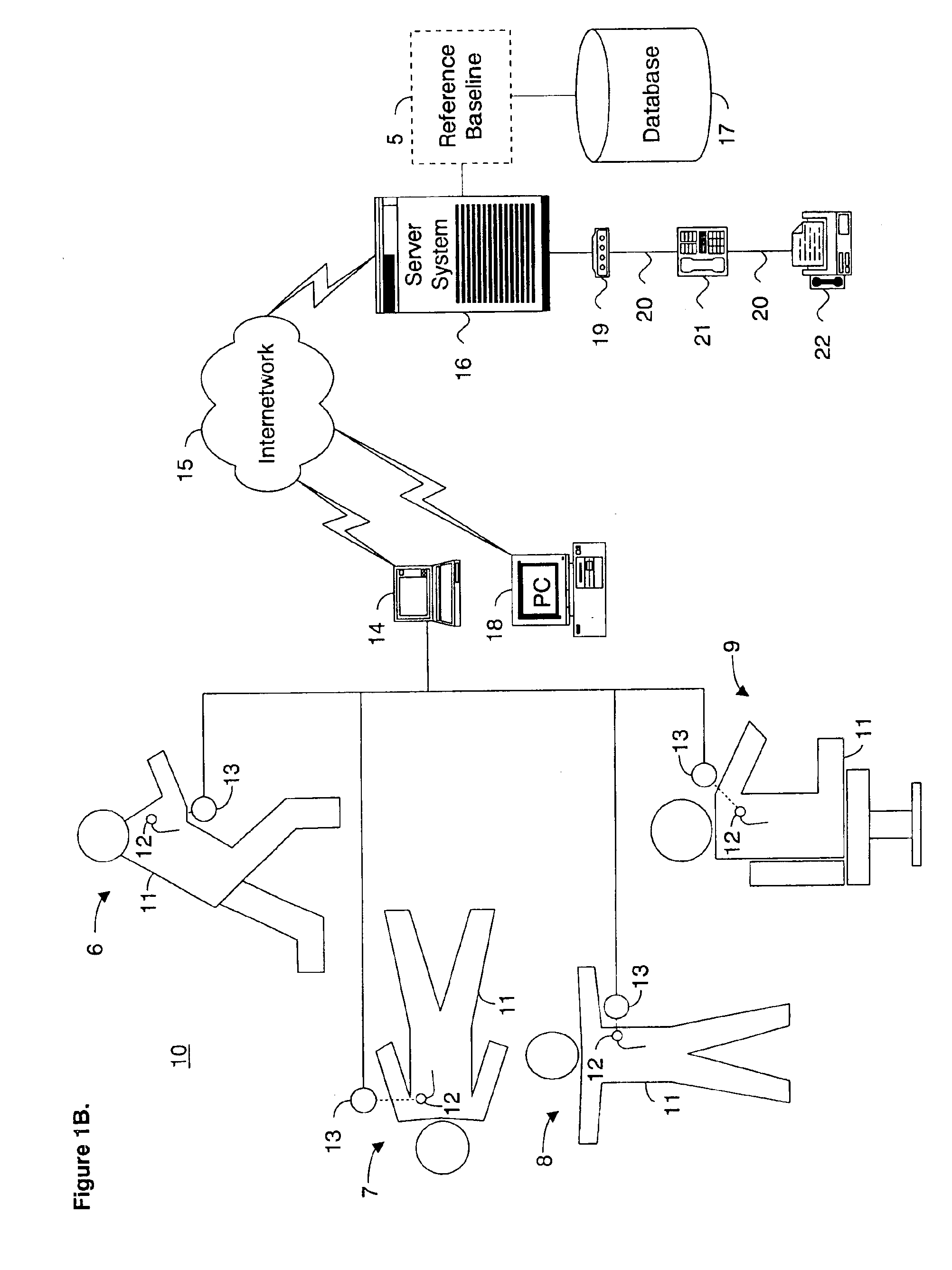
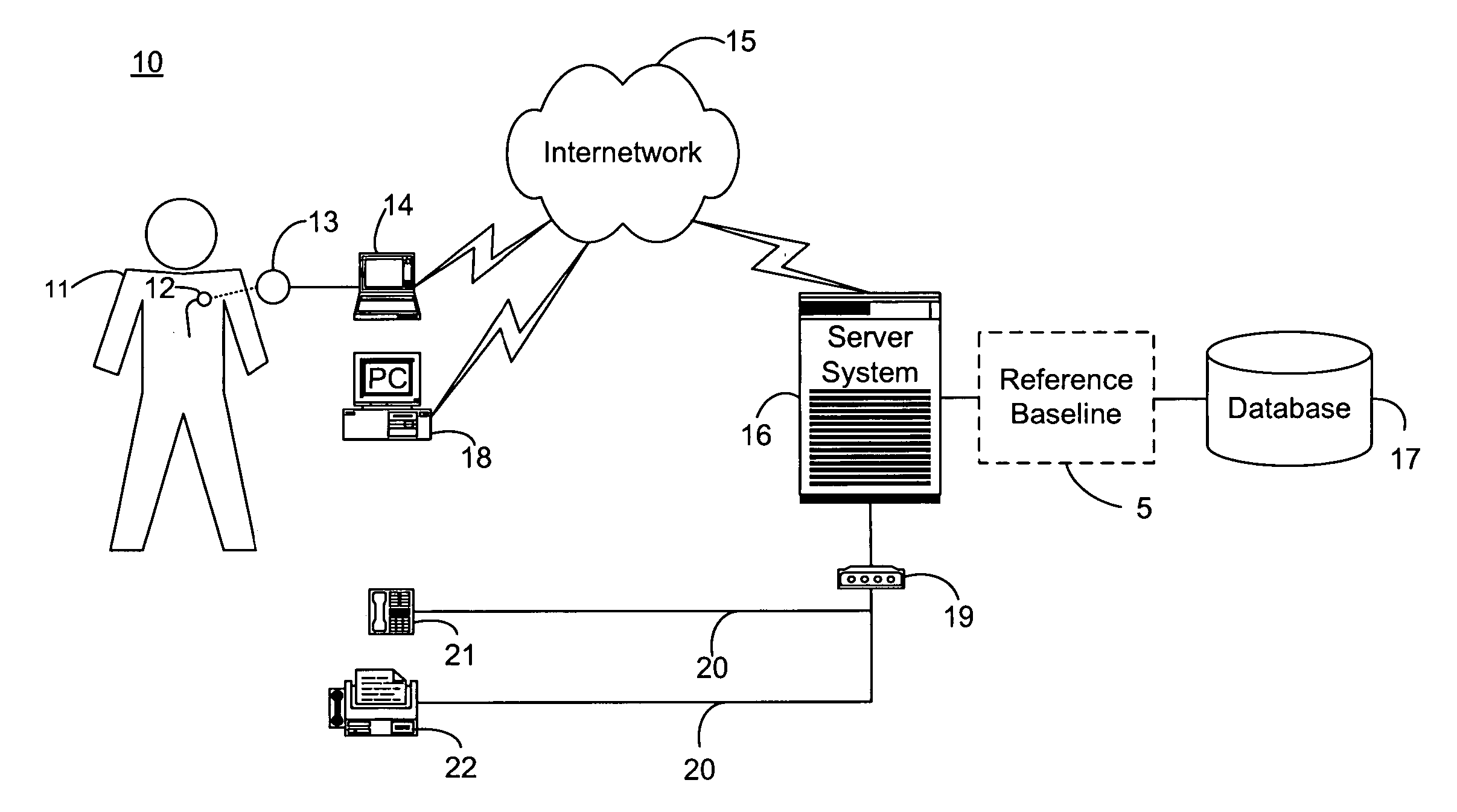
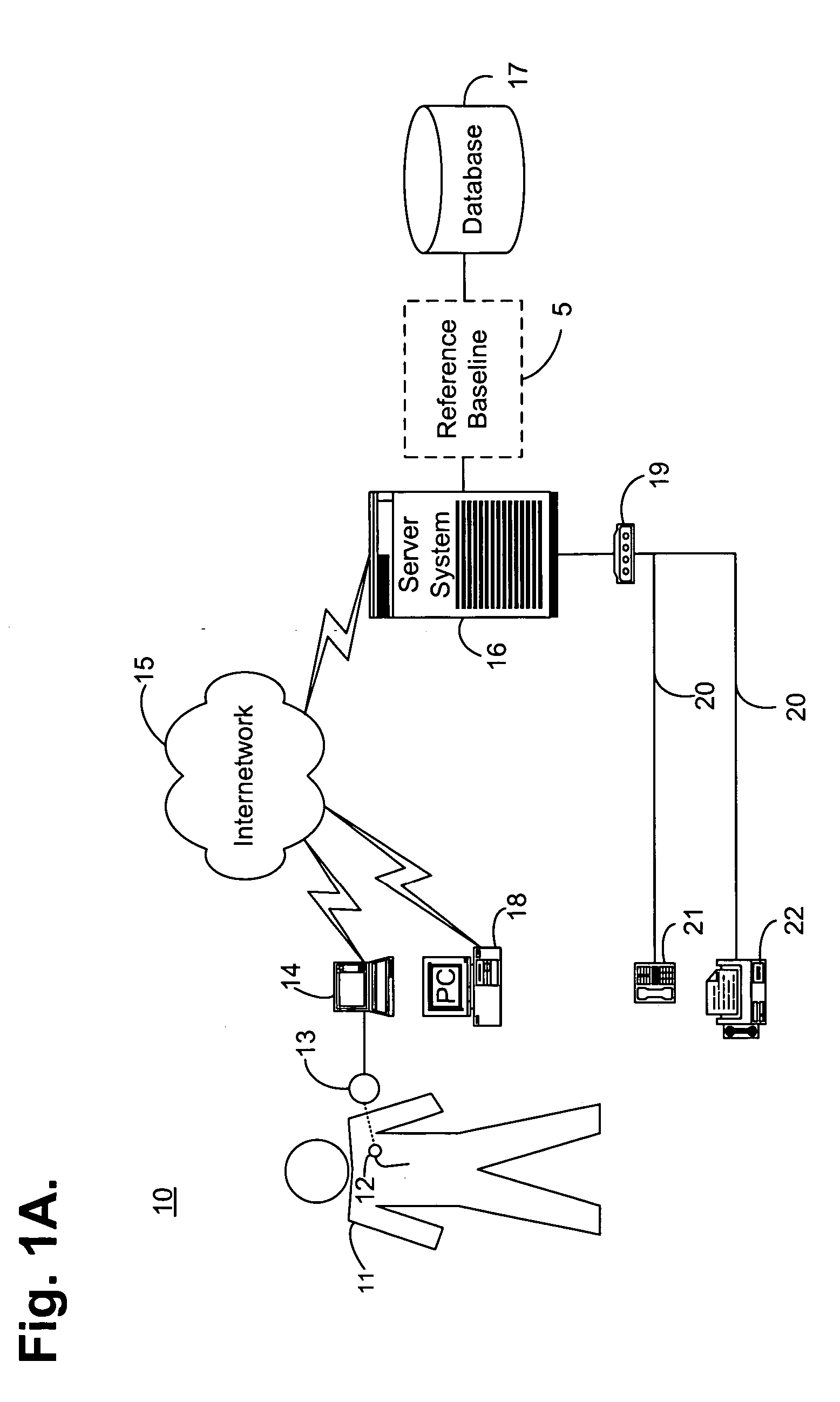
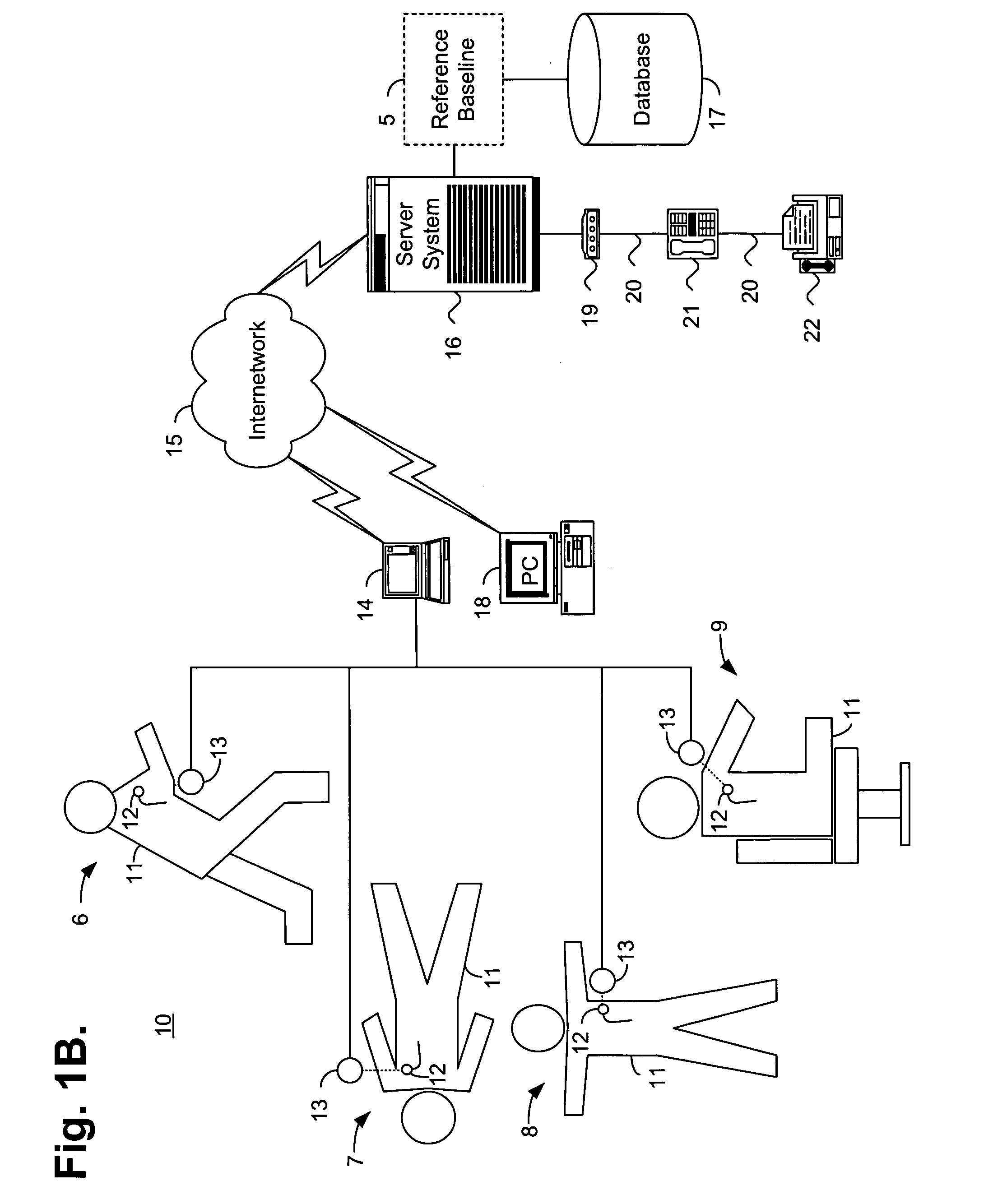
System and method for determining a reference baseline of regularly retrieved patient information for automated remote patient care
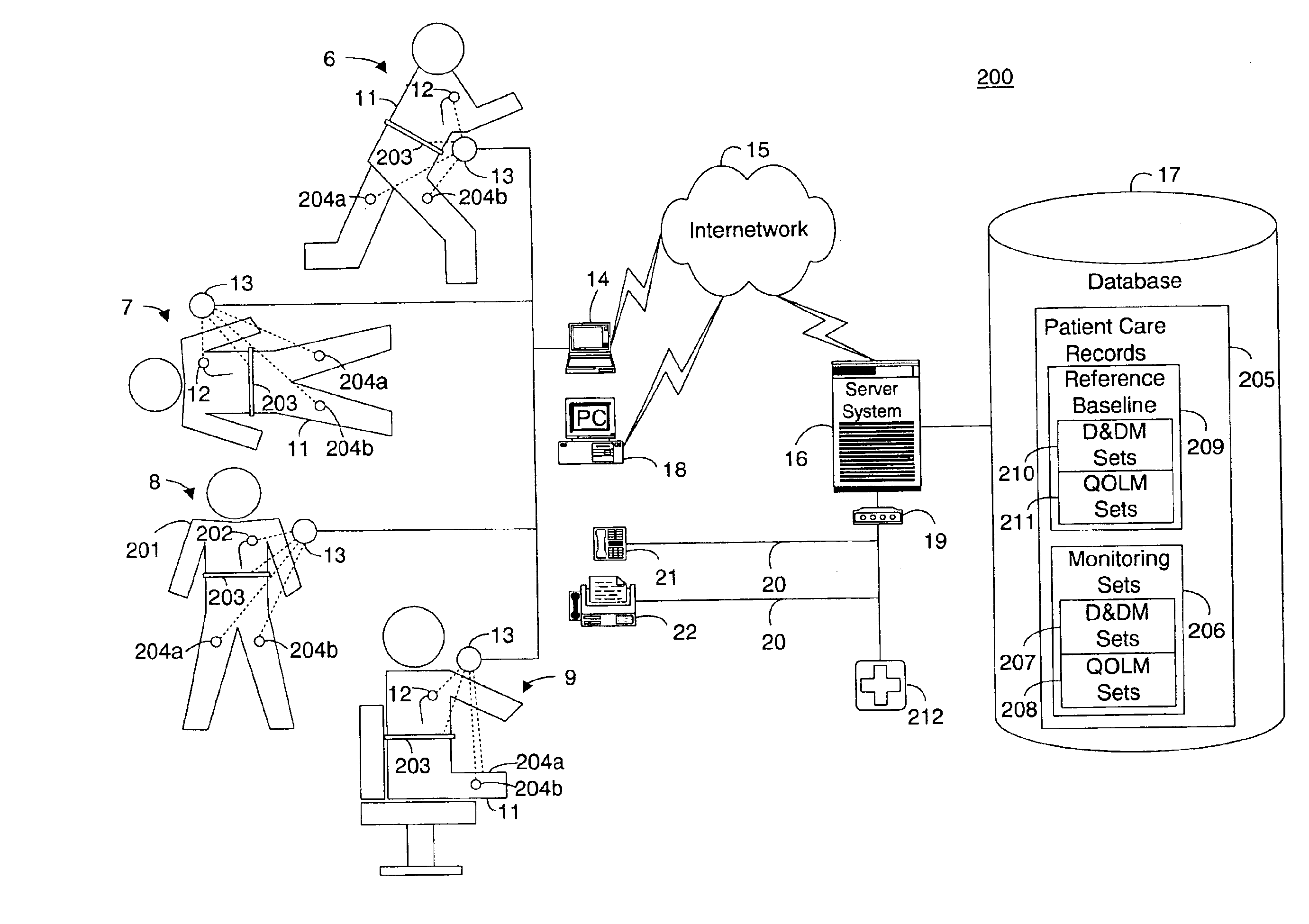
InactiveUS6887201B2Improve accuracyImproves chroniclingElectrotherapyHealth-index calculationEmergency medicinePatient status
A system for determining a reference baseline of regularly retrieved patient information for automated remote patient care is presented. A medical device having a sensor for monitoring at least one physiological measure of an individual patient regularly records and stores measures sets relating to patient information during an initial time period. A database collects one or more patient care records by organizing one or more patient care records and storing the collected measures set into such a patient care record for the individual patient. A server receives the collected device measures set from the medical device, processes the collected device measures set into a set of reference measures representative of at least one of measured or derived patient information, and stores the reference measures set into the patient care record as data in a reference baseline indicating an initial patient status.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
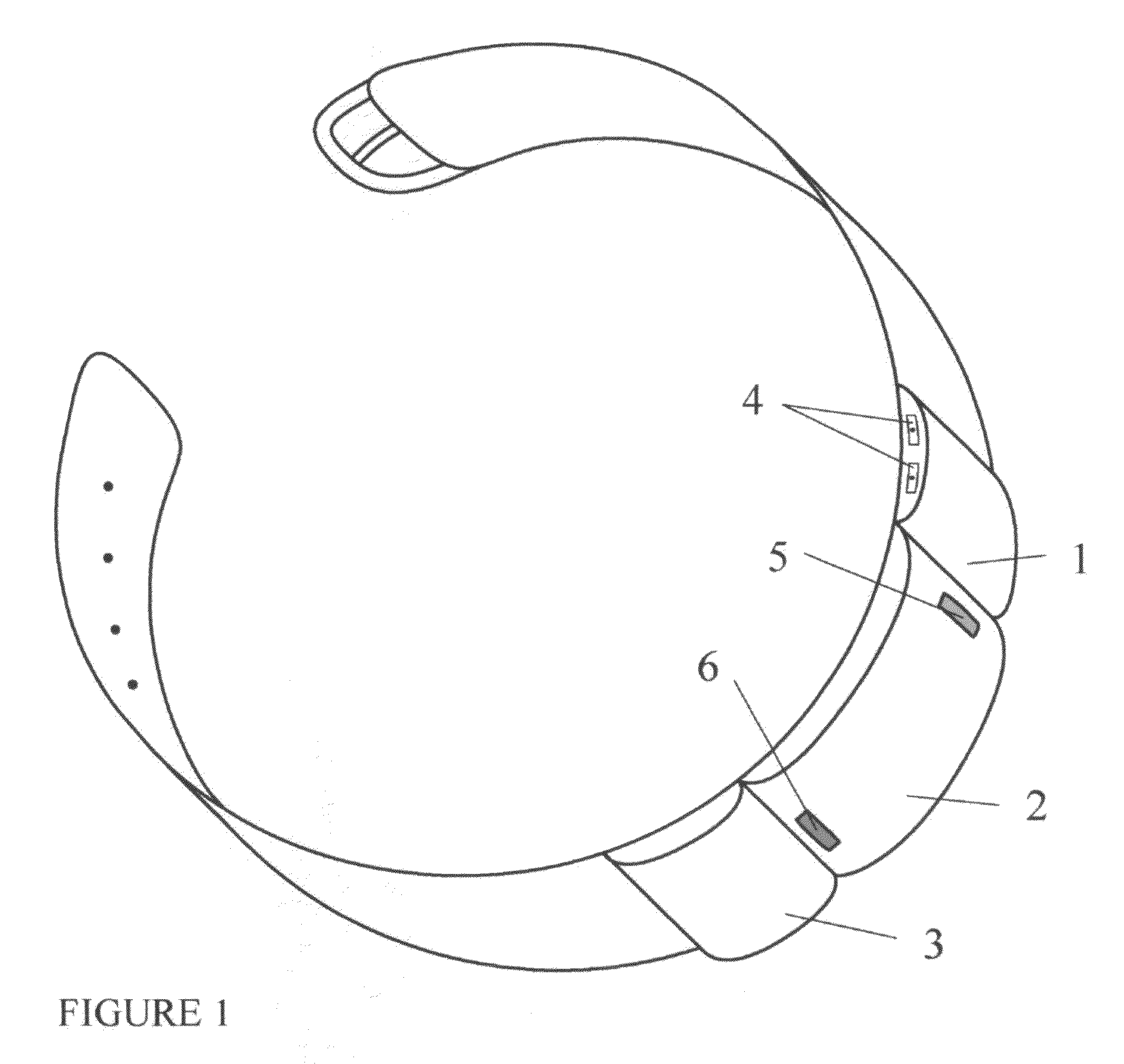
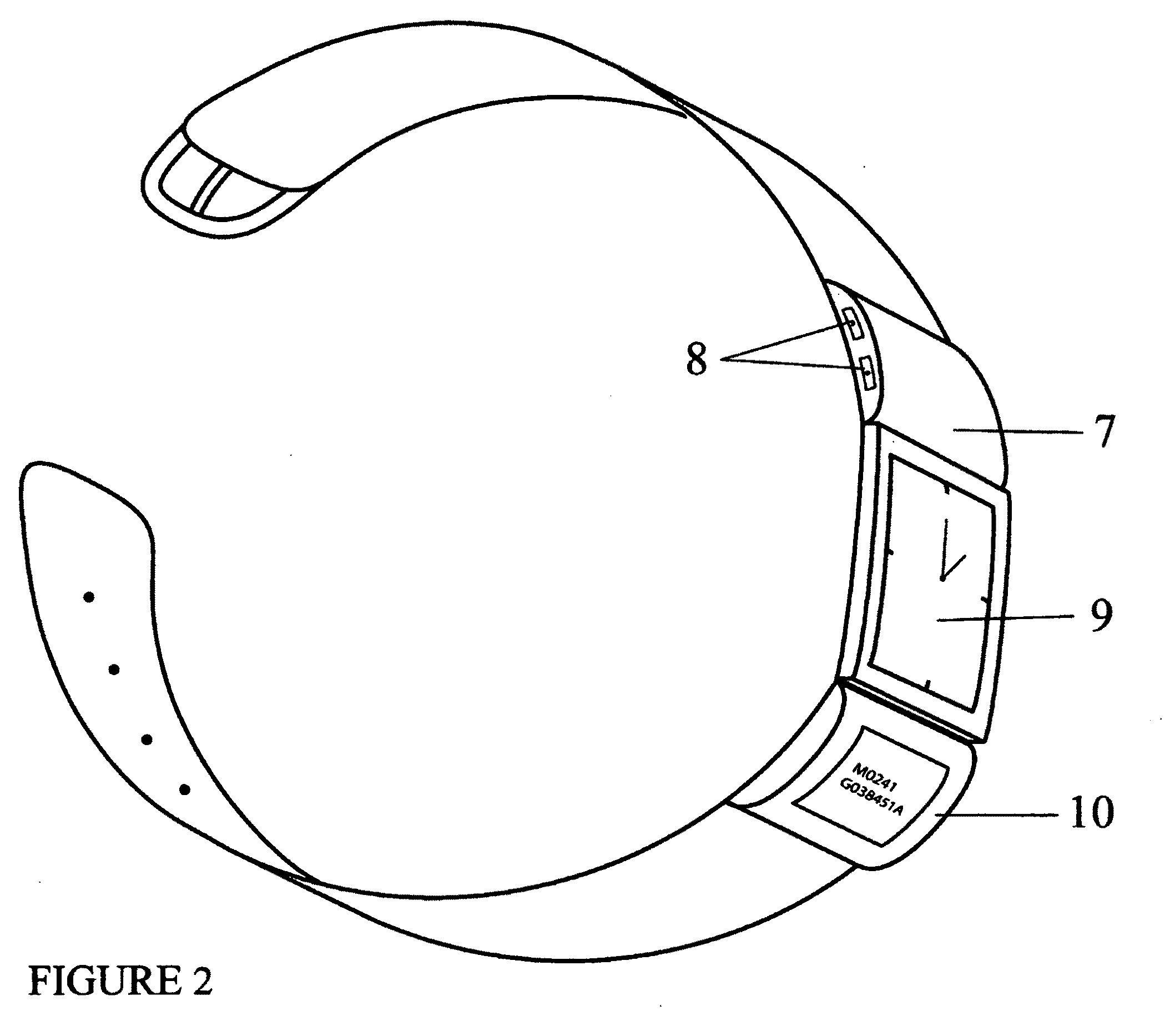
Monitoring system and method for patient care
A patient care monitoring system and method employ active RFID devices integrated with digital processing, memory and timing circuitry for patient identification, care giver identification and for identification of each prescribed treatment, procedure, medication and general and / or special care action. At the point-of-care, each care action identity device will match directly with the targeted patient identity device or issue an error warning to prevent mistakes. The patient identity device will also interact with an associated sensor network to proactively prompt care givers to provide general care actions, such as altering a patient's laying position, changing bed pan / clothing / bed sheet, etc. for invalid patients. Also the patient identity tag will furnish periodic records of every care action, mistakes, remedies, care givers' identities and time and date for a central processor of a healthcare facility to monitor the quality of patient care. Such record can also be potentially accessed via the Internet by the responsible regulatory agencies, accreditation associations, insurance firms and even patients' families to ensure patient care is meeting the standards as well as medical billing accuracy.
Owner:HUANG CHING CHING +4
System and method for video observation of a patient in a health care location
InactiveUS7307543B2Minimizing adverse eventsMinimize complicationsElectric signal transmission systemsBilling/invoicingVisual monitoringPatient data
A system and method for observing patients in geographically dispersed health care locations. A patient is assigned to a health care location comprising a patient visual monitoring system, a patient audio receiver, and a patient controller. The visual monitoring system is responsive tri-axially to command signals received via a patient controller connected to the network. The patient controller sends patient imaging data and patient audio data to a remote command center via the network. A computerized patient care management system comprising the remote command center monitors patient data, patient imaging data, and patient audio data determines from the patient data, the patient imaging data, and the patient audio data if intervention with the selected patient is warranted.
Owner:VISICU +1
System and method for determining a reference baseline record
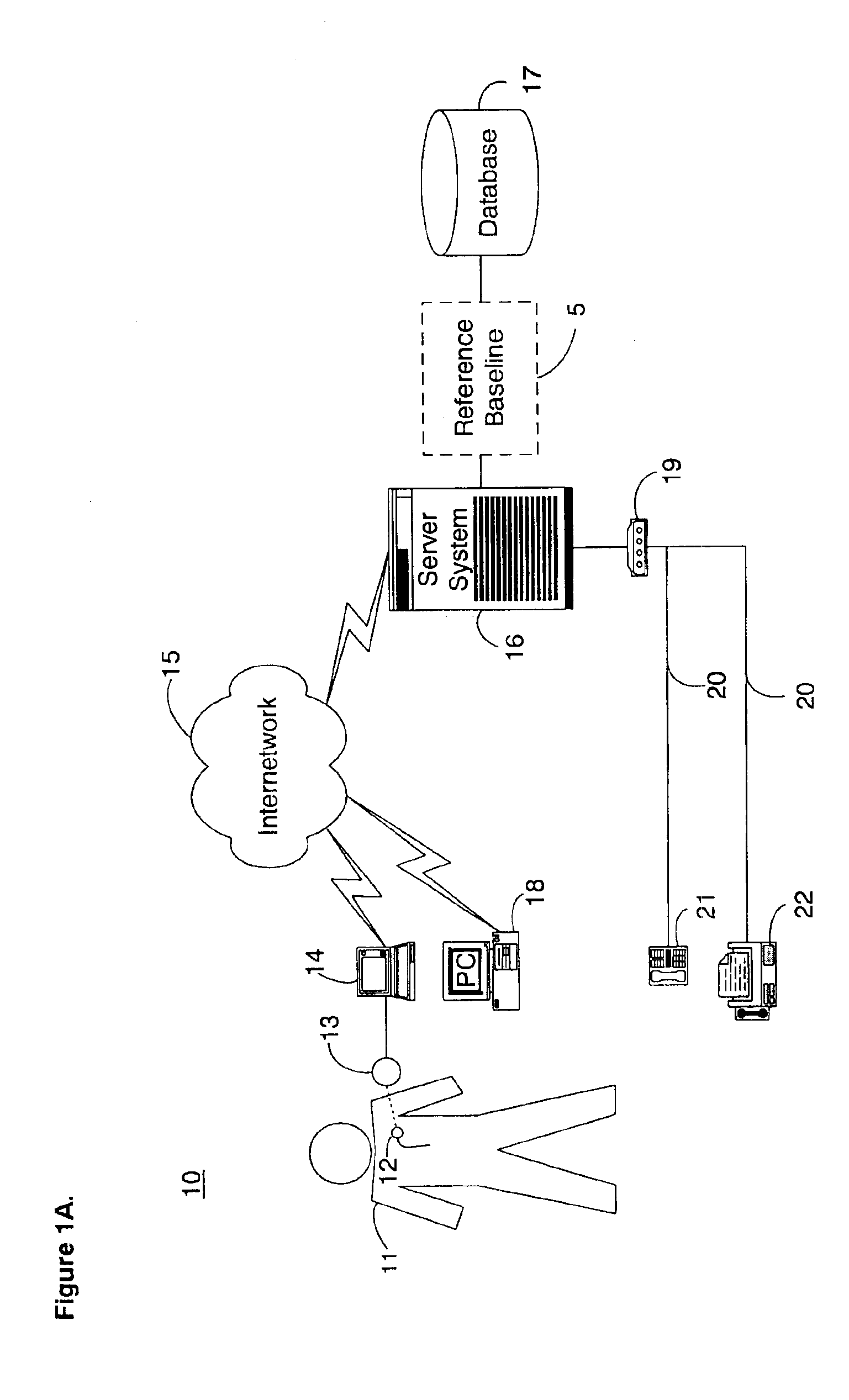
InactiveUS20050182308A1Improve accuracyElectrotherapyHealth-index calculationEmergency medicinePatient status
A system and method for determining a reference baseline record for use in automated patient care. One or more physiological measures are retrieved. Each of the measures relates to individual patient information recorded during an initial observation period from a patient care record. One or more reference measures are determined from the physiological measures. Each reference measure is representative of at least one of measured and derived patient information. The reference measures are stored into the patient care record indicating a reference baseline patient status.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
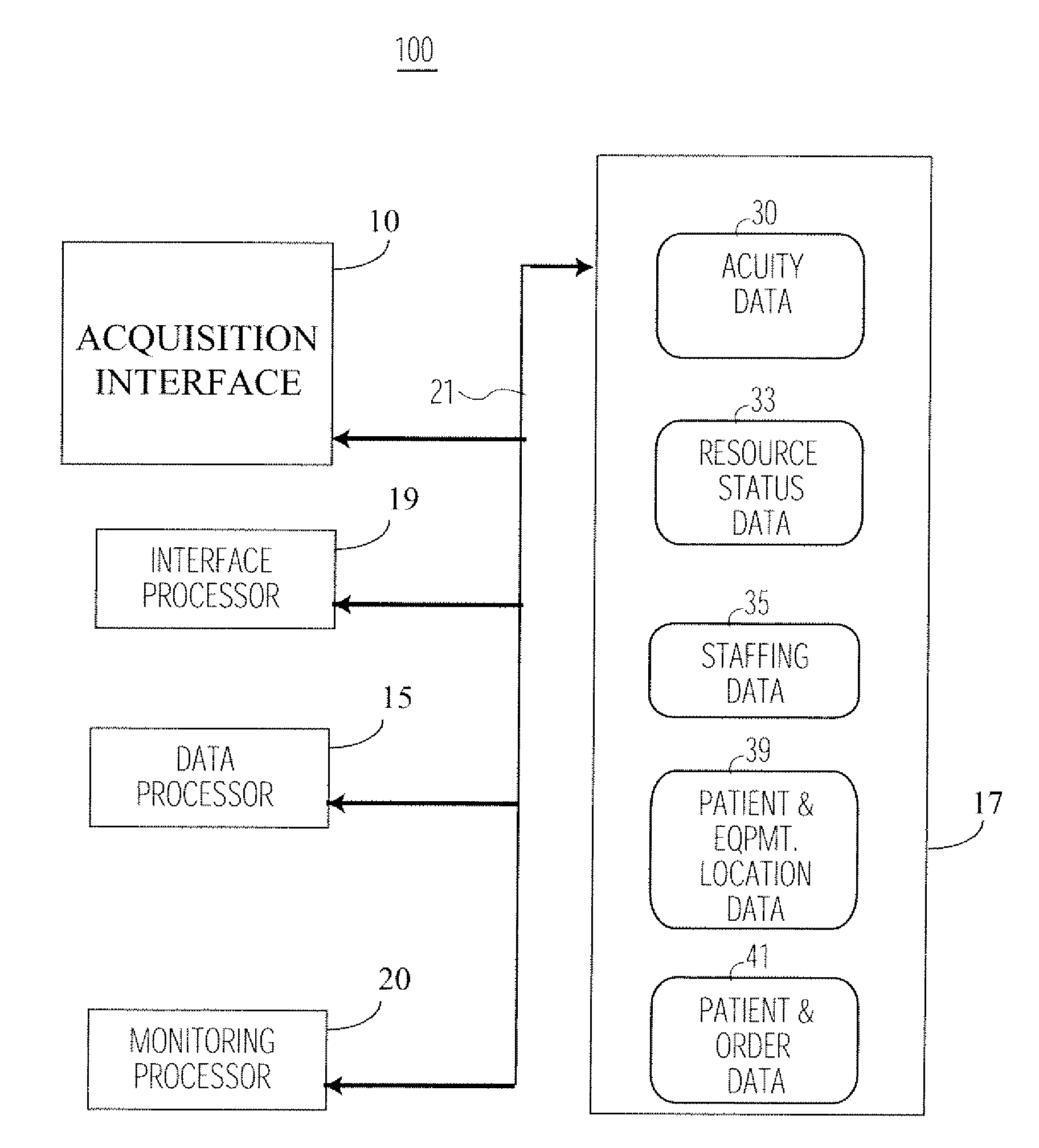
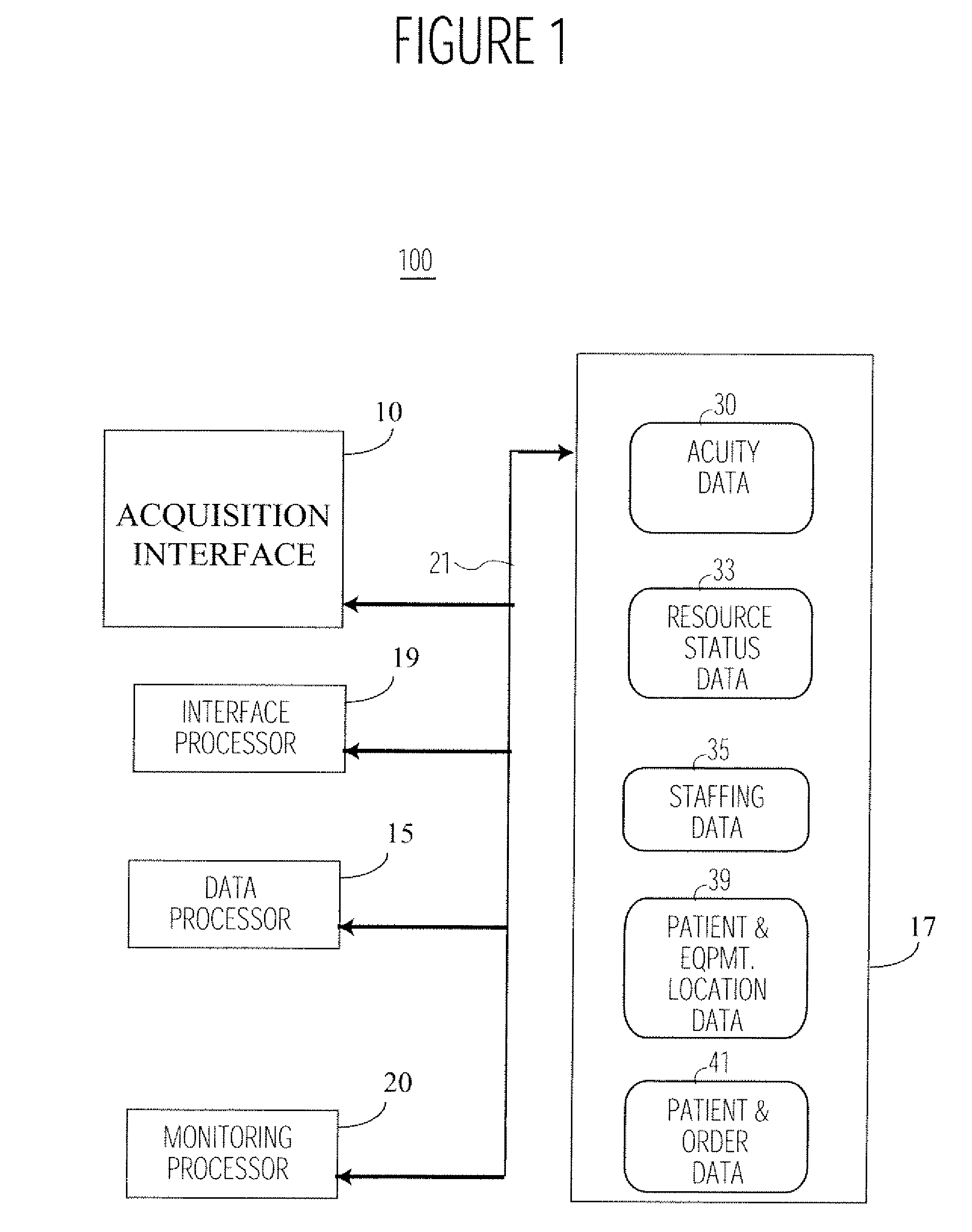
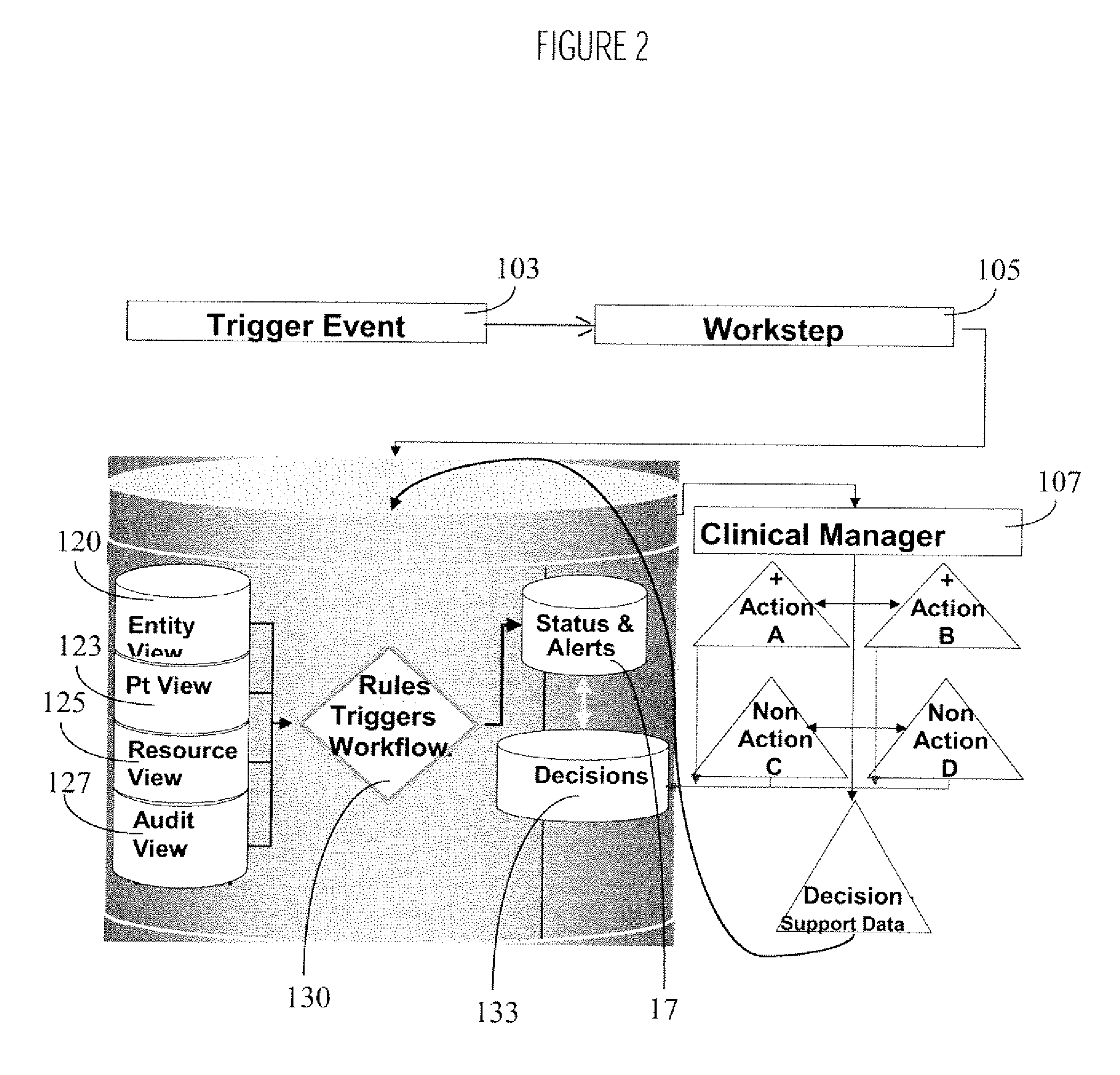
System for Monitoring Healthcare Related Activity In A Healthcare Enterprise
A system provides comprehensive patient and resource status information (manpower and equipment required to maintain optimal patient care) in an organization (e.g., a hospital) for use in adjusting resources to meet existing and future conditions. A system for monitoring activity in a healthcare enterprise includes an acquisition interface for acquiring acuity data representative of severity of medical condition of an individual patient, for multiple different patients. A monitoring processor monitors data identifying orders initiated for treatment to be provided to an individual patient and data identifying laboratory test results received for an individual patient, for multiple different patients. A data processor generates data representing status of healthcare activity for multiple patients in response to the data identifying orders and laboratory test results and the acuity data, for multiple different patients. An interface processor provides the data representing status of healthcare activity to a healthcare worker.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS HEALTH SERVICES CORPORAT
System and method for diagnosing and monitoring outcomes of atrial fibrillation for automated remote patient care
A system for diagnosing and monitoring outcomes of atrial fibrillation for remote patient care is presented. A database stores monitoring sets containing recorded measures relating to patient information recorded on a substantially continuous basis. A server retrieving and processing a plurality of the monitoring sets includes a comparison module receiving a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and determining patient status changes in response to the atrial fibrillation diagnosis by comparing periodically recorded measures from each of the monitoring sets to other recorded measures from another of the monitoring sets with both recorded measures relating to a same type of patient information; and an analysis module evaluating on a periodic basis each patient status change for an absence, an onset, a progression, a regression, and a status quo of atrial fibrillation against a predetermined indicator threshold corresponding to the same type of patient information as the recorded measures which were compared.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com