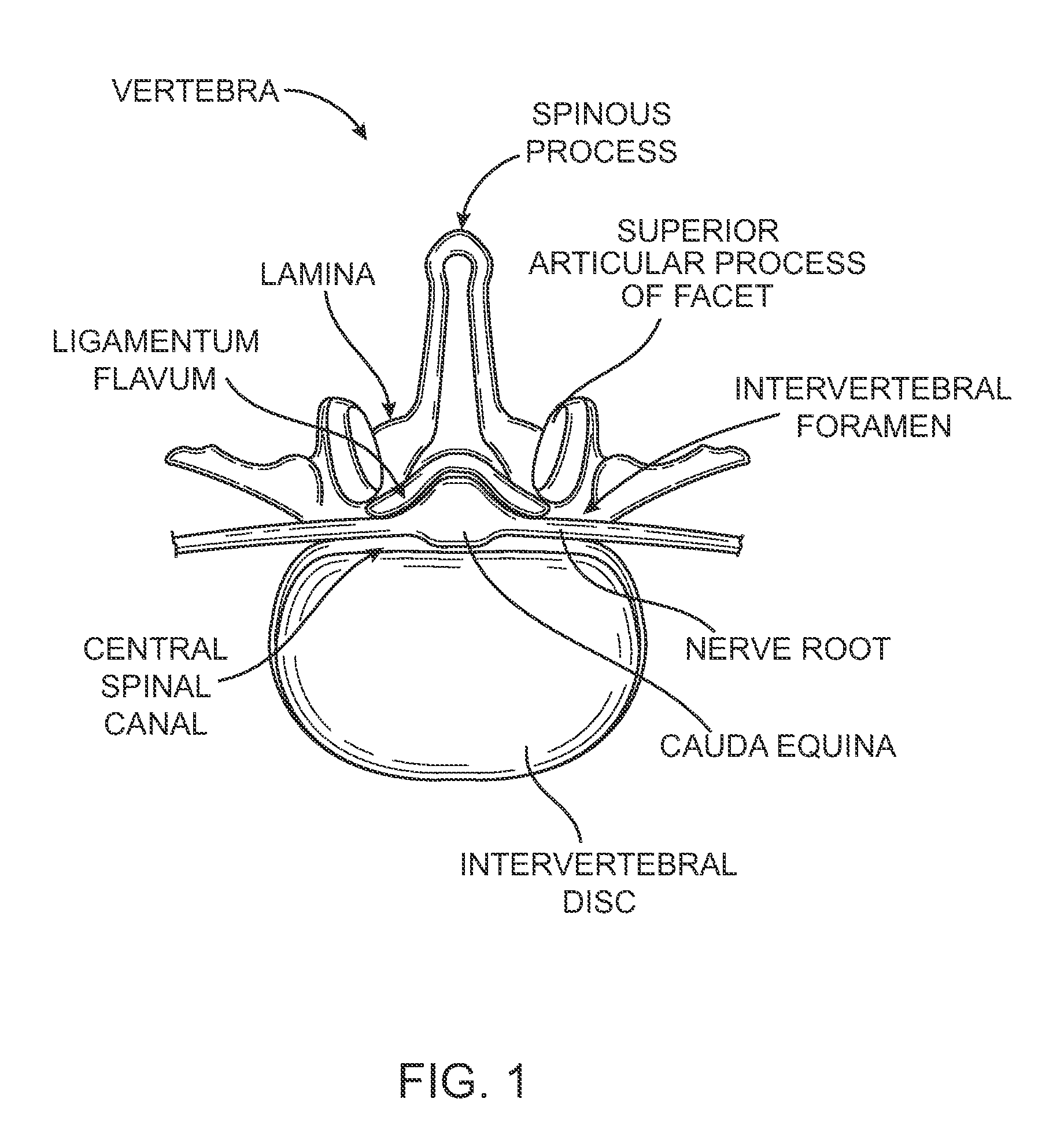
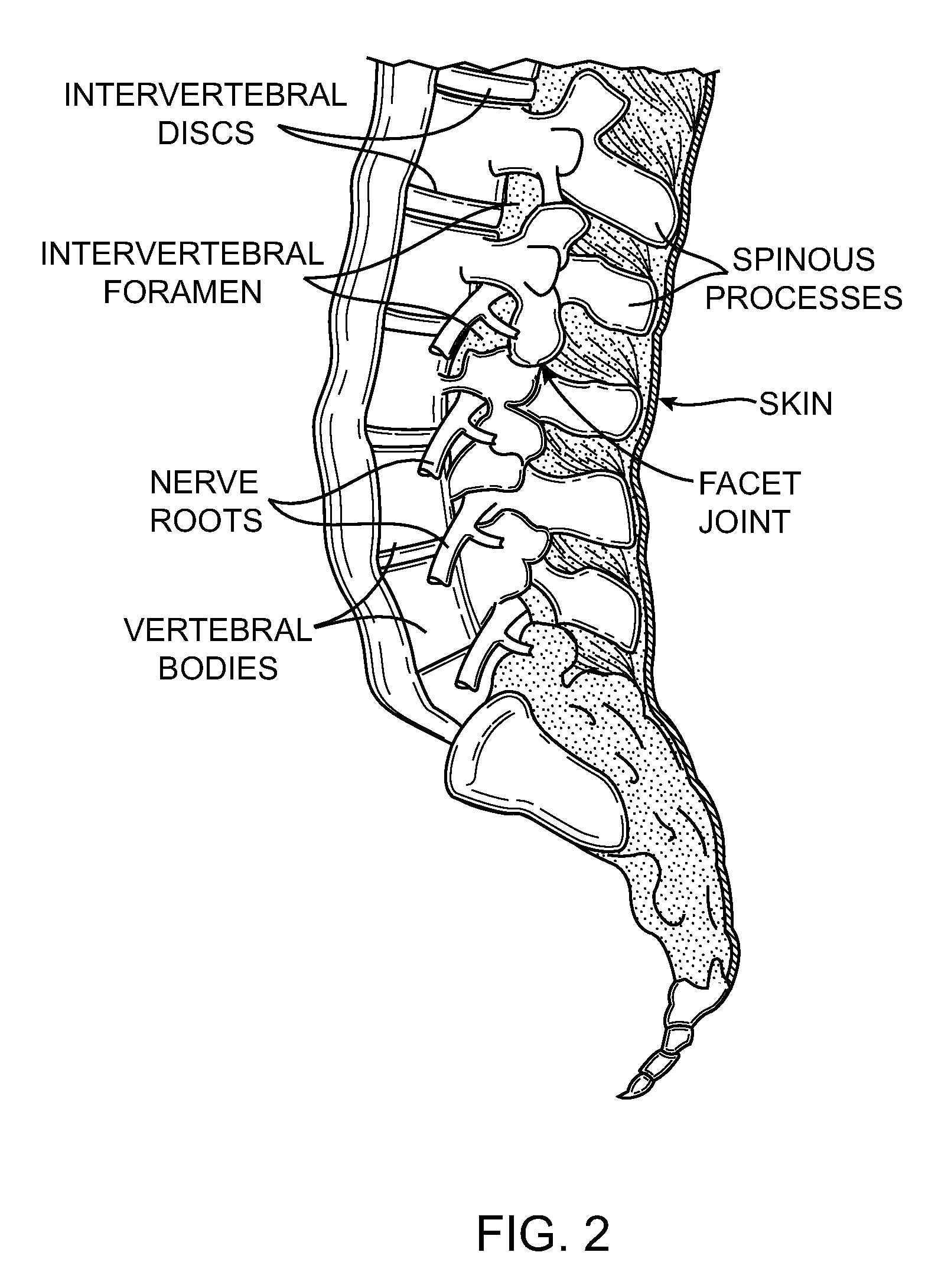
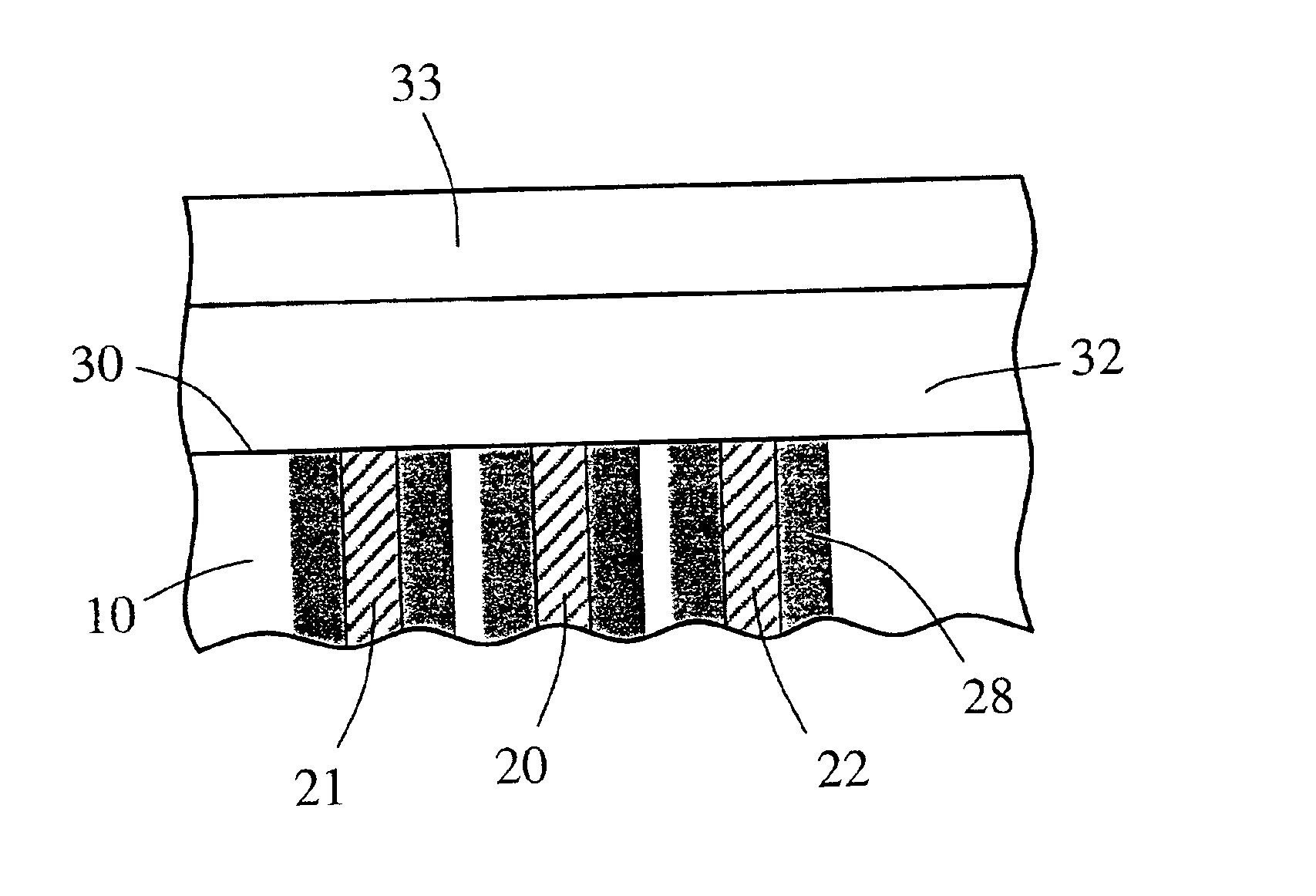
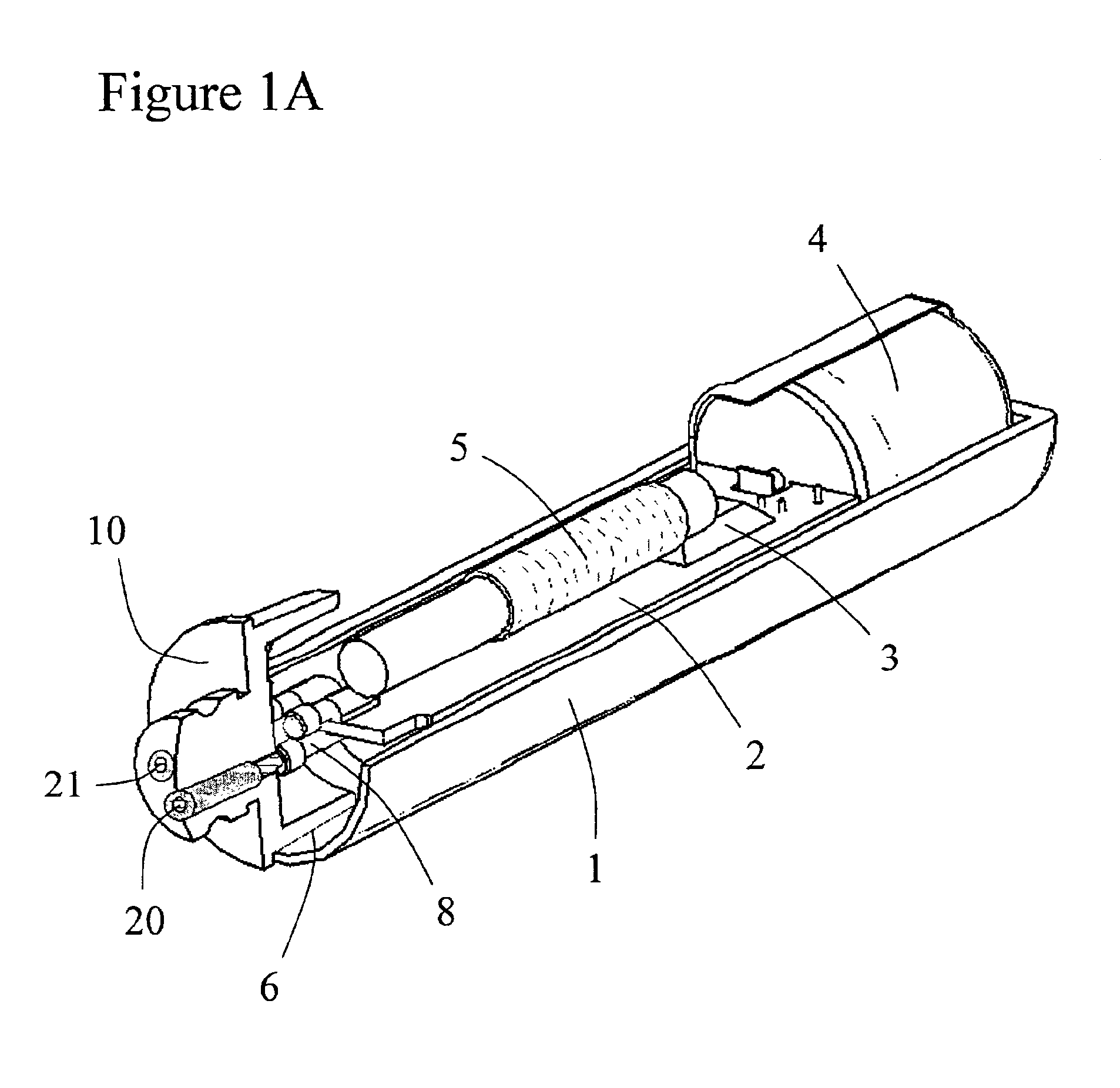
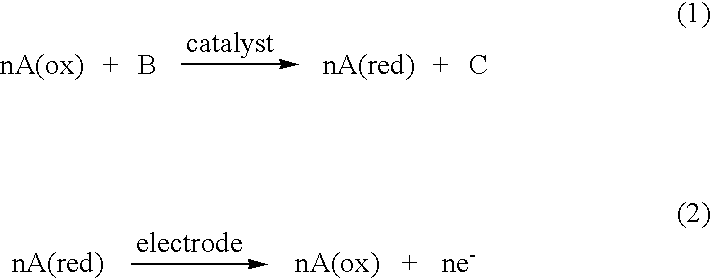Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
92215results about "Diagnostic recording/measuring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
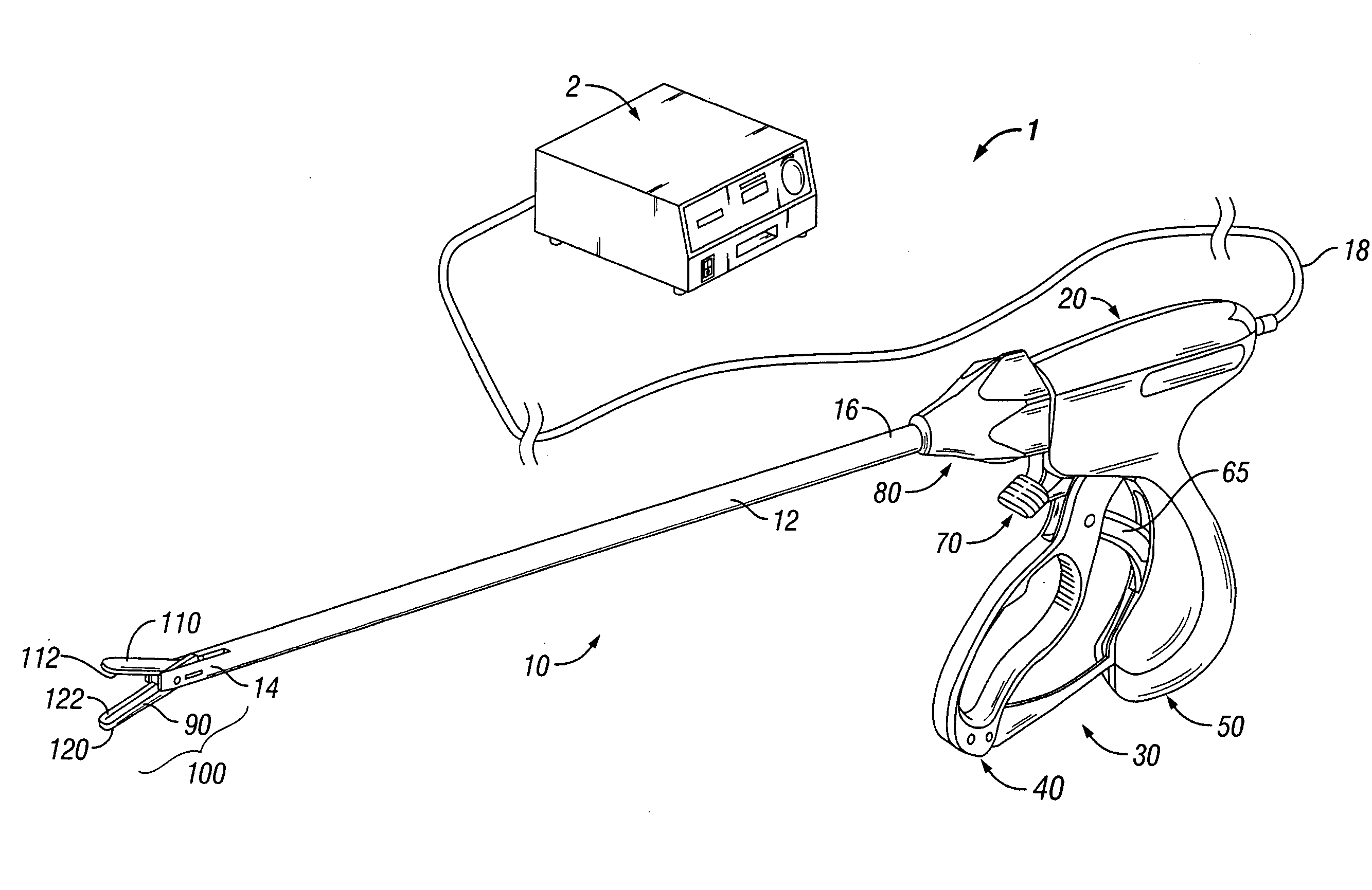
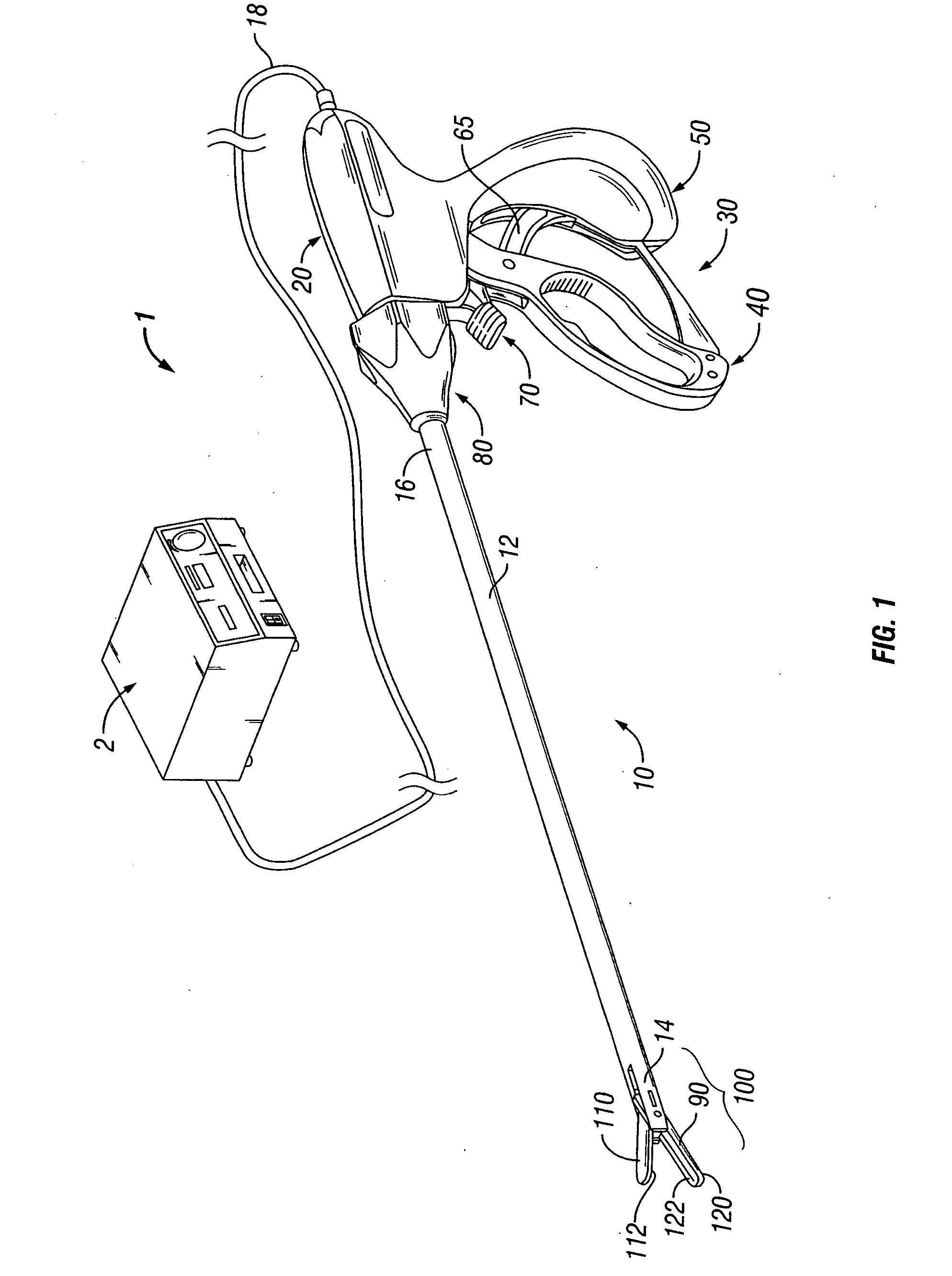
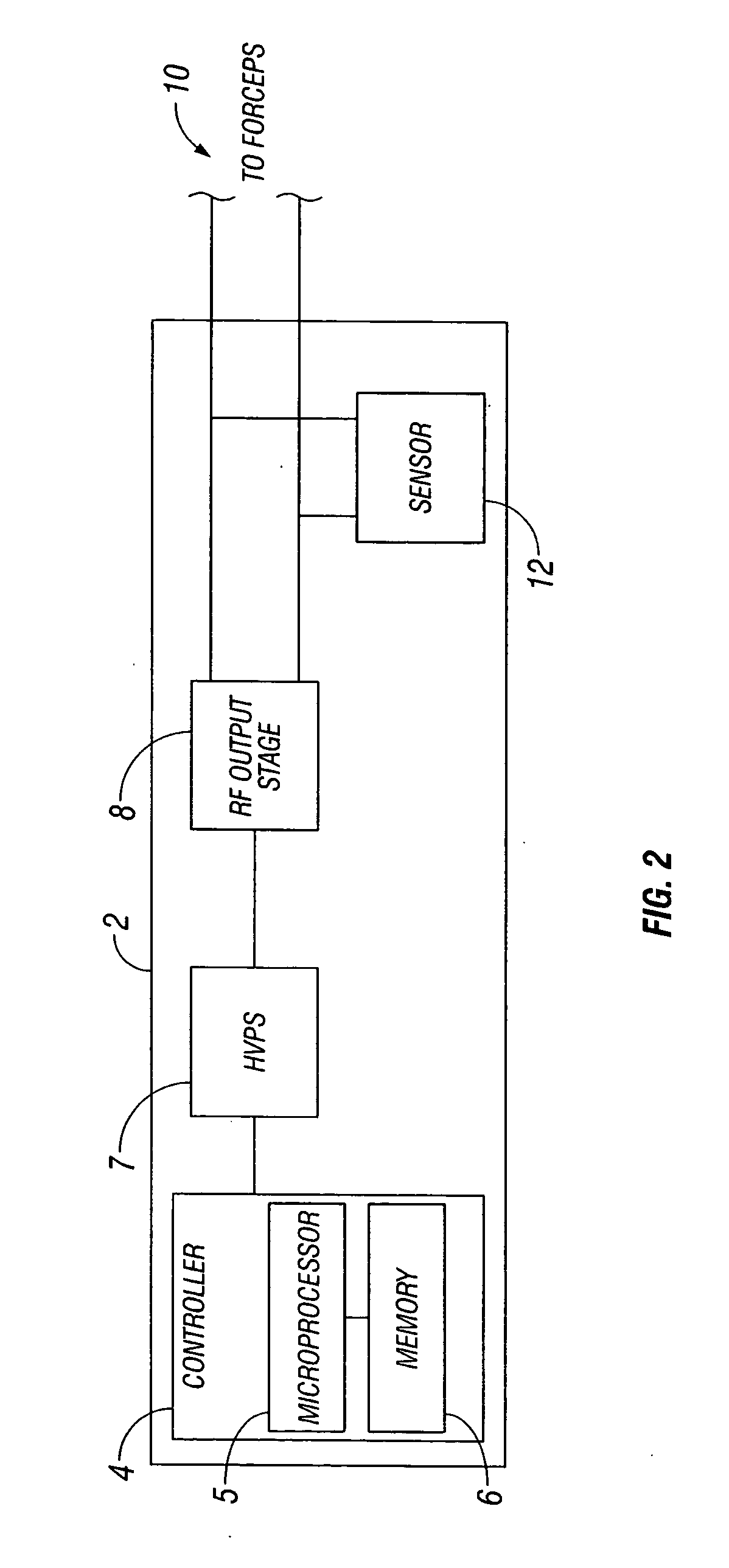
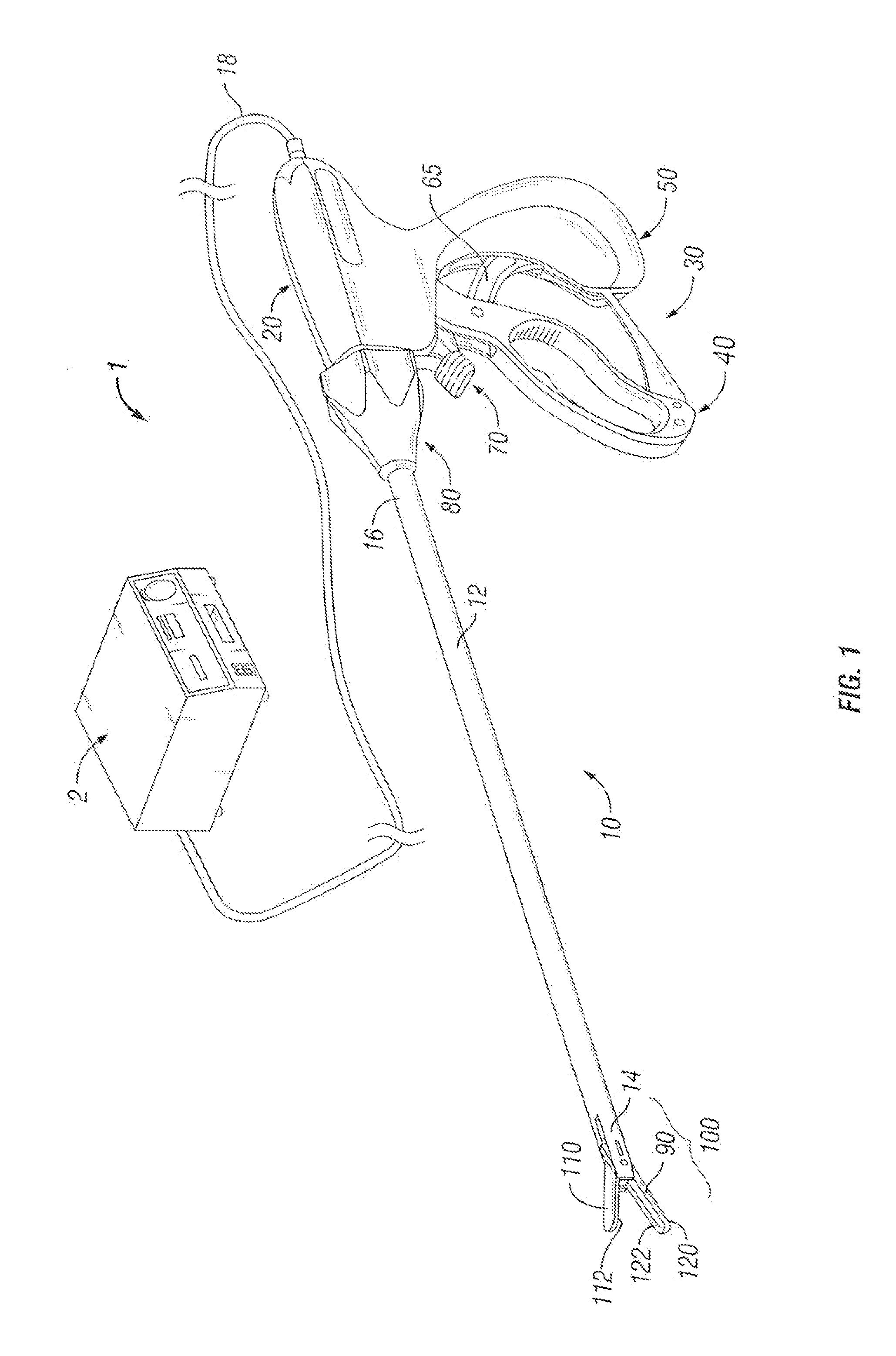
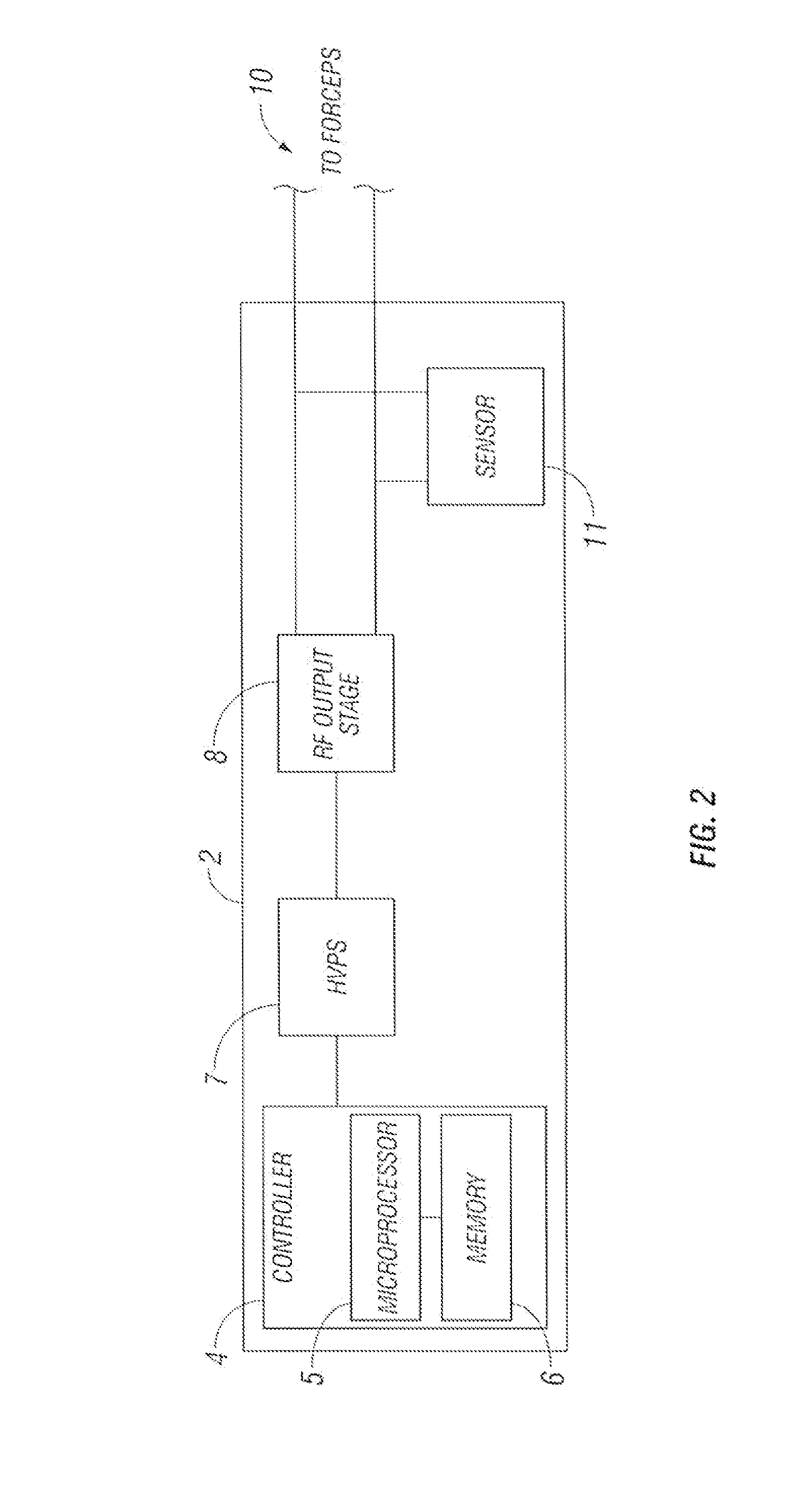
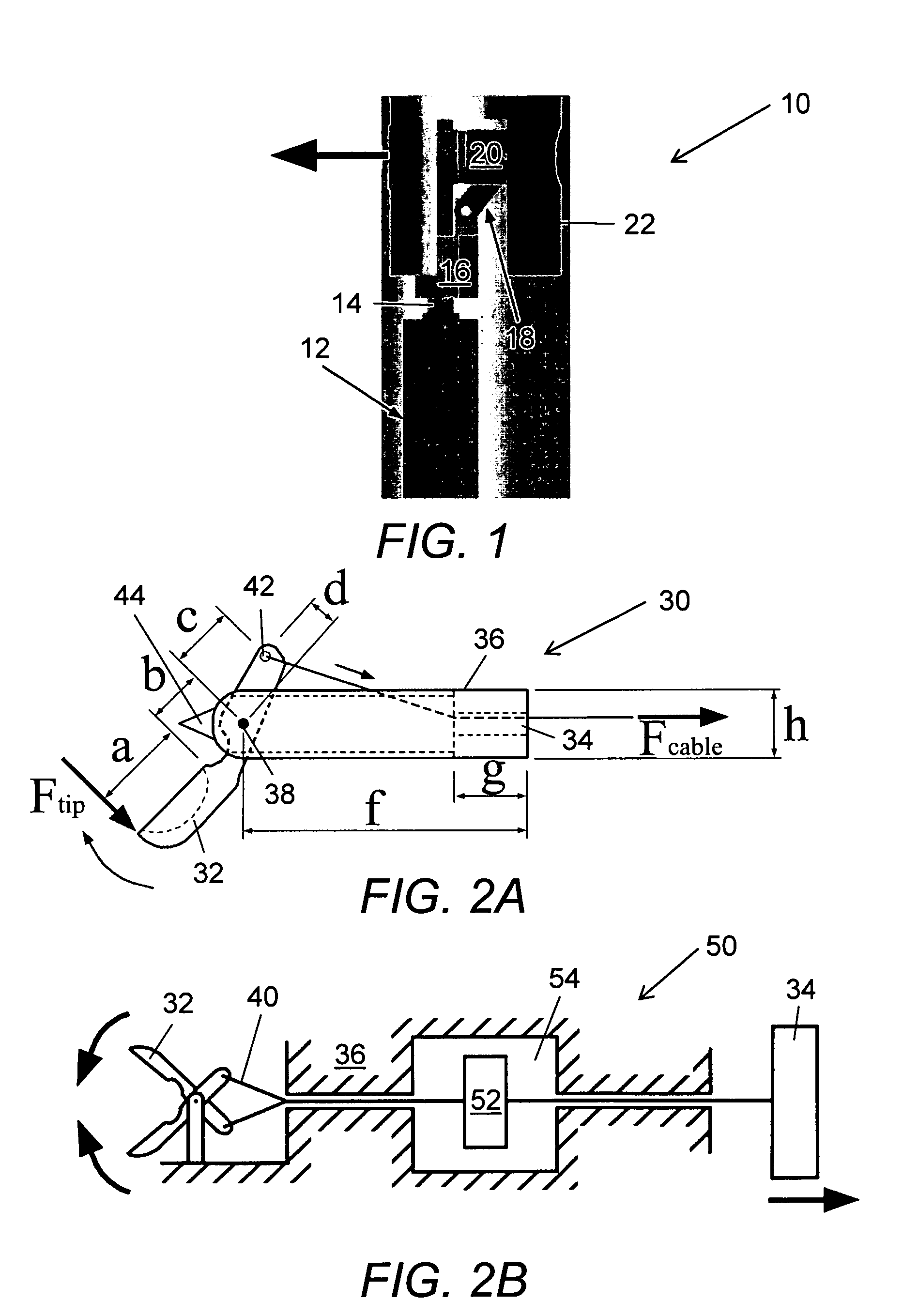
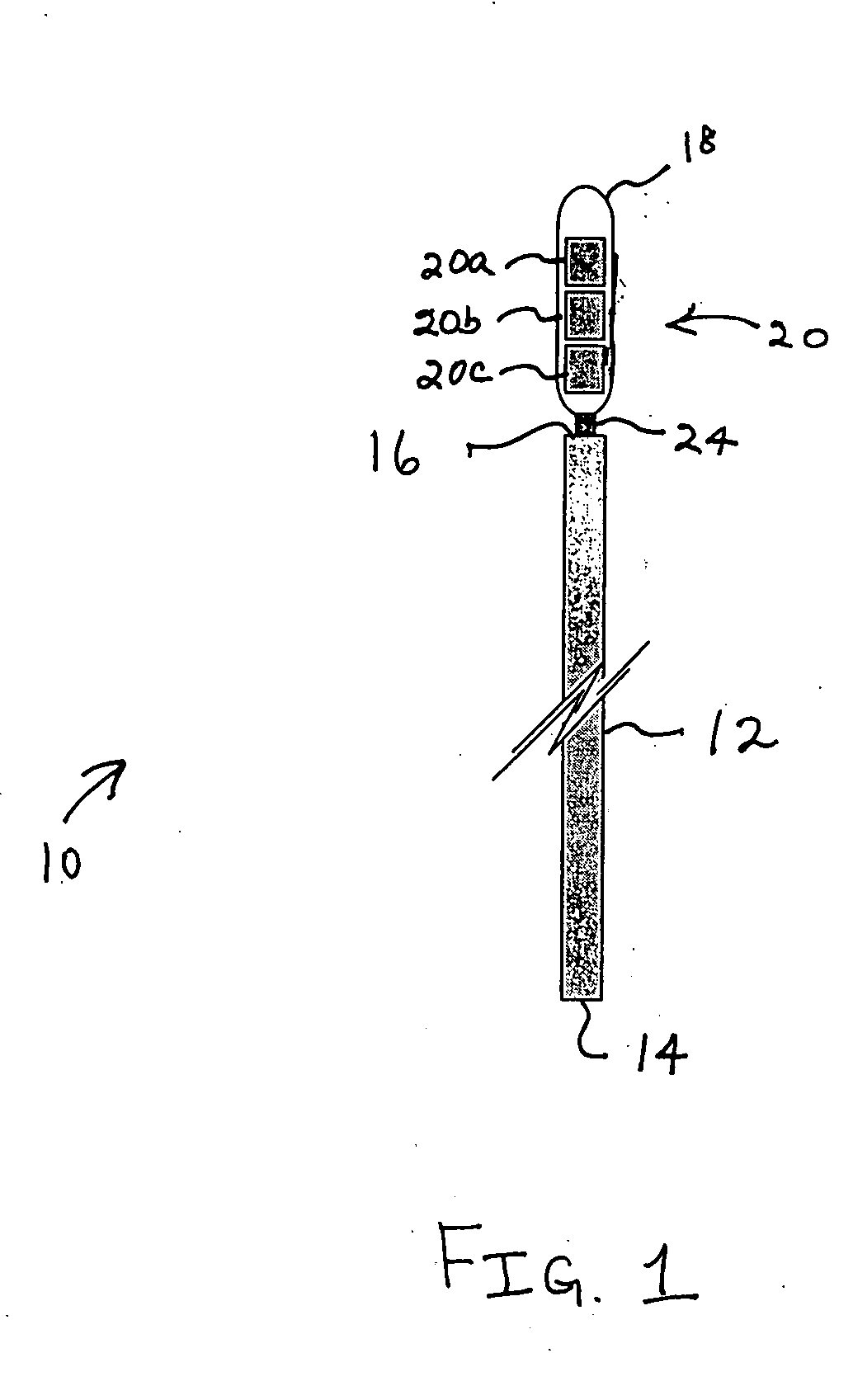
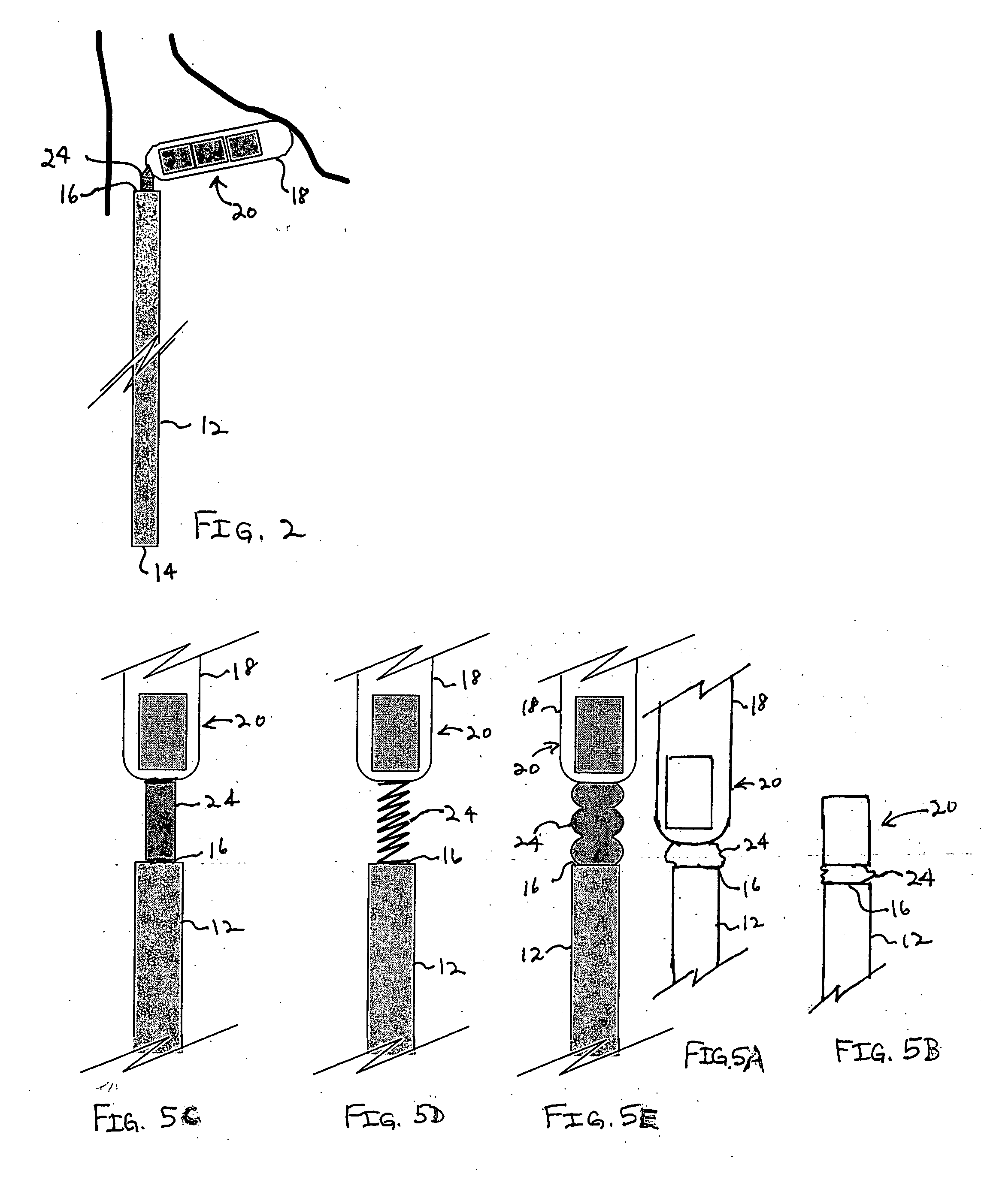
Bipolar or ultrasonic surgical device
ActiveUS8292888B2Reduce in quantityLess mechanical forceUltrasound therapySurgical needlesAmpullaSurgical device
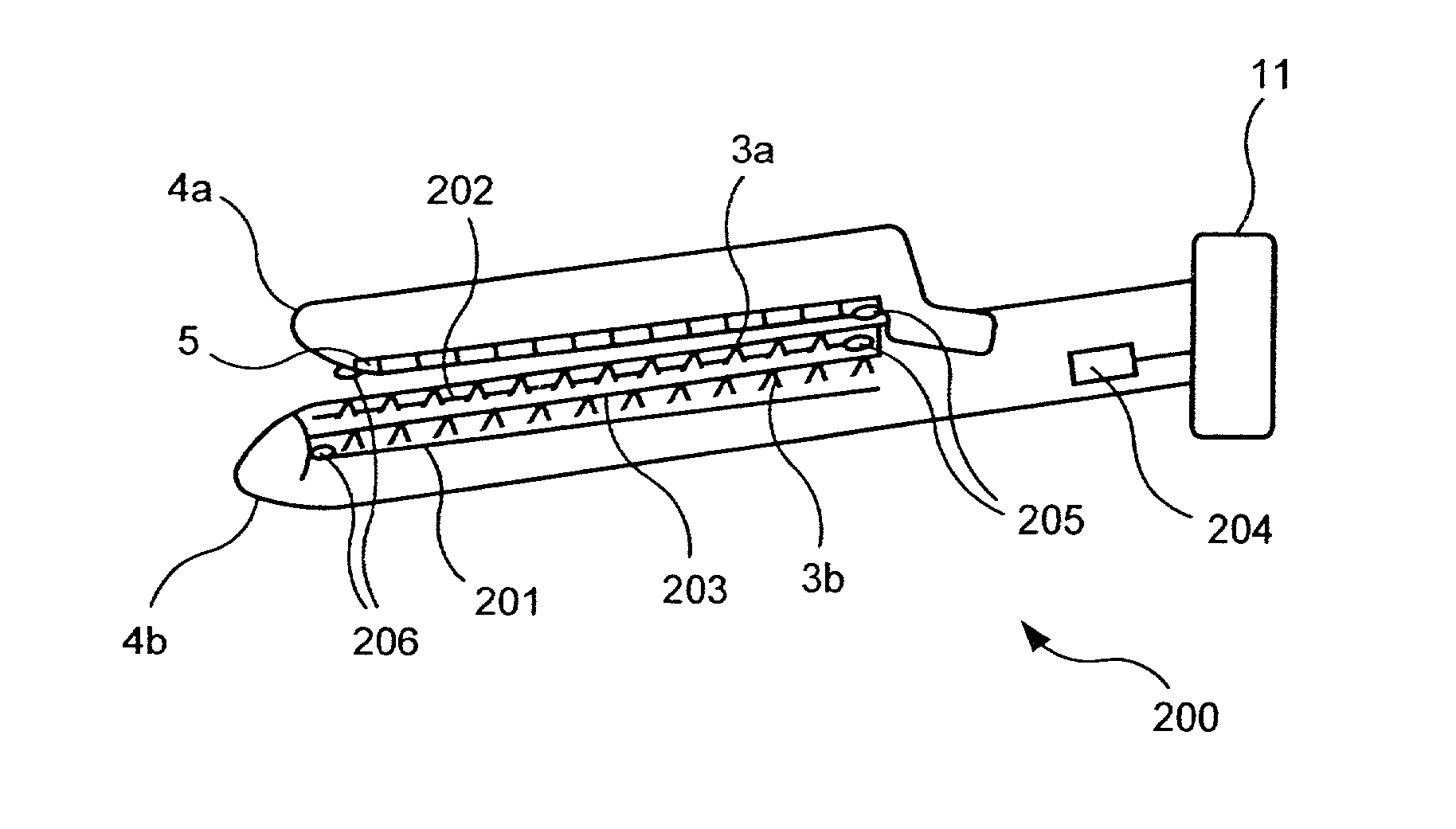
An electro-mechanical surgical device, system and / or method may include a housing, at least two opposing jaw, and at least one electrical contact associated with at least one of the jaws. The electrical contact may include at least one of a bipolar electrical contact and an ultrasonic electrical contact. The electrical contact may be a row of electrodes located on one or all of the jaws. A sensor may also be associated with any tissue located between the jaws to sense and report the temperature of that tissue. A piercable ampulla containing fluid may also be placed on at least one of the jaws so that the fluid is releasable when the jaws are in closed position and the electrode(s) pass through the tissue into the piercable ampulla.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
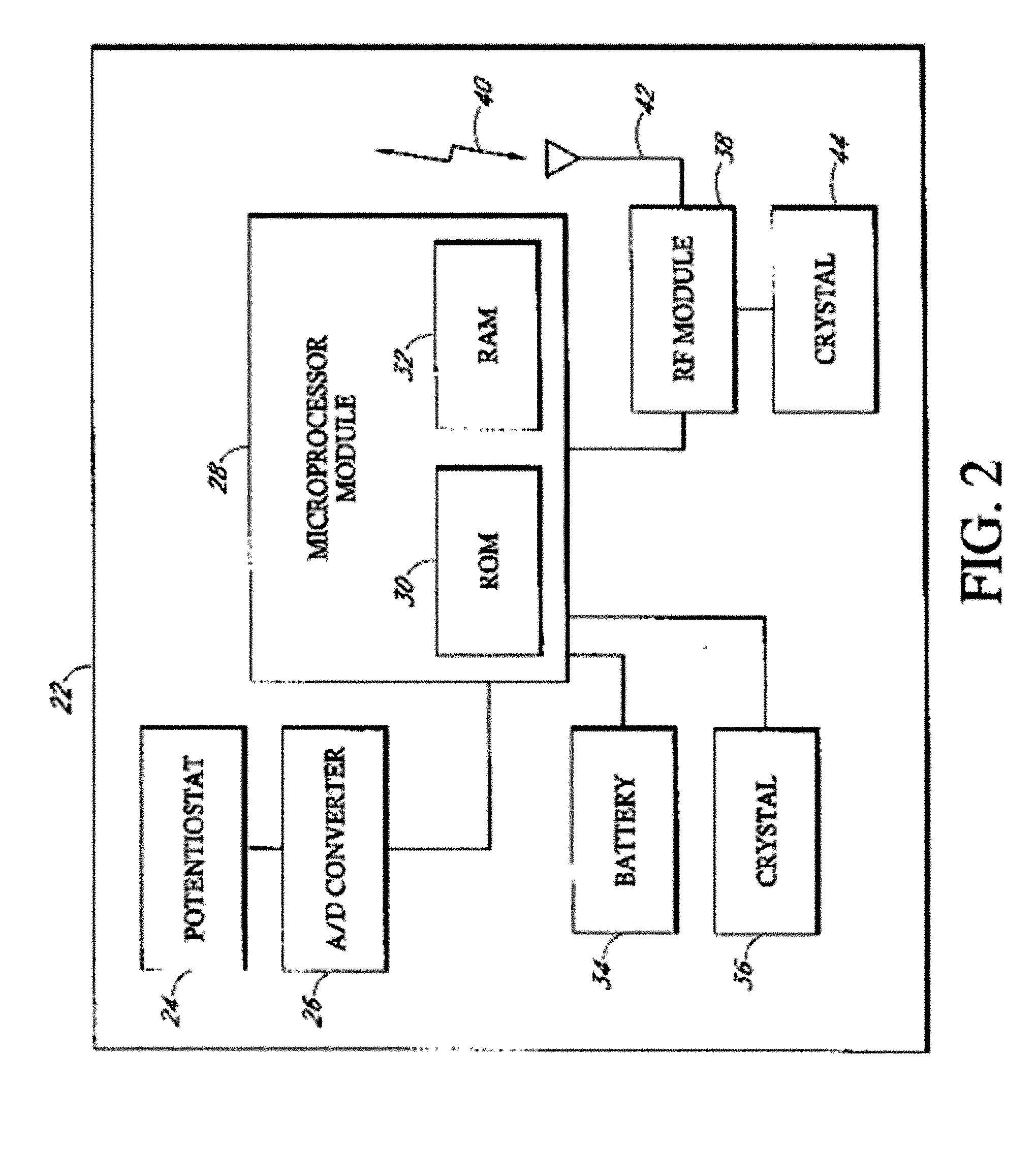
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS6484046B1Avoid and reduce corrosionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteElectrolysis
An electrochemical analyte sensor having conductive traces on a substrate is used to determine a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
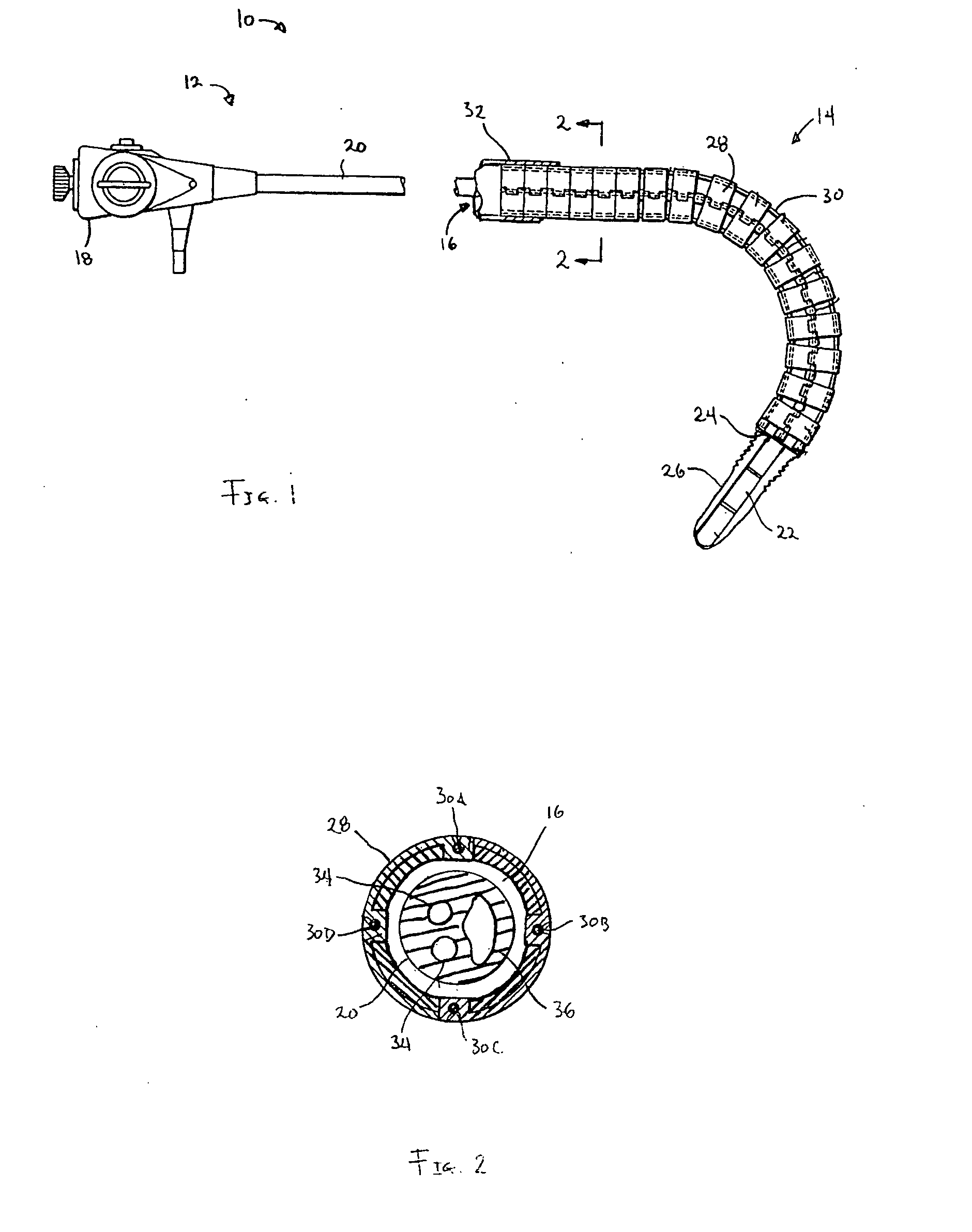
Endoscope with adjacently positioned guiding apparatus
InactiveUS6984203B2Desirable column strengthPrevent bucklingEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringAutomatic controlDistal portion
An endoscope with guiding apparatus is provided. The endoscope has an elongate body with a steerable distal portion, an automatically controlled portion, a flexible and passively manipulated proximal portion, and an externally controlled and manipulatable guiding apparatus. The guiding apparatus may be positioned within the endoscope or may be positioned adjacent to the endoscope. An interlocking device is provided to slidably interlock the guiding apparatus and the endoscope. When the guide is in a flexible state, it can conform to a curve or path defined by the steerable distal portion and the automatically controlled portion. The guide can then be selectively rigidized to assume that curve or path. Once rigidized, the endoscope can be advanced along the guide in a monorail or “piggy-back” fashion so that the flexible proximal portion follows the curve held by the guide until the endoscope reaches a next point of curvature within a body lumen.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
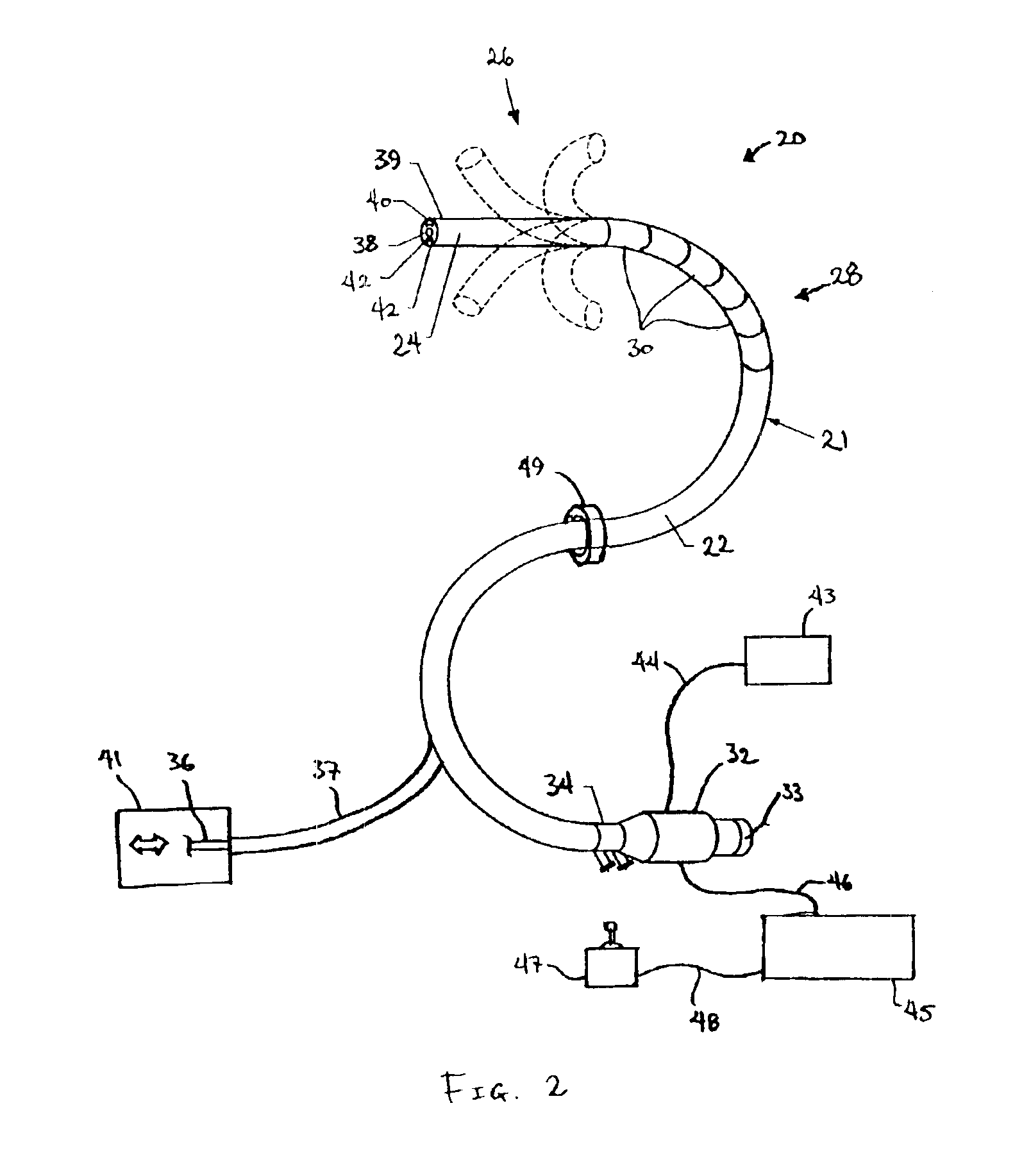
System and method for tissue sealing
An electrosurgical bipolar forceps for sealing is disclosed. The forceps includes one or more shaft members having an end effector assembly disposed at the distal end. The end effector assembly includes two jaw members movable from a first position to a closed position wherein the jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue at constant pressure. Each of the jaw members includes an electrically conductive sealing plate connected to a first energy source which communicates electrosurgical energy through the tissue held therebetween. The electrosurgical energy is communicated at constant voltage. The electrically conductive sealing plates are operably connected to sensor circuitry which is configured to measure initial tissue impedance and transmit an initial impedance value to a controller. The controller determines the constant pressure and the constant voltage to be applied to the tissue based on the initial impedance value.
Owner:SHERWOOD SERVICES AG
Tendon-driven endoscope and methods of insertion
InactiveUS6858005B2Limit motionPrevent unintended tensionEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringAutomatic controlDistal portion
A steerable, tendon-driven endoscope is described herein. The endoscope has an elongated body with a manually or selectively steerable distal portion and an automatically controlled, segmented proximal portion. The steerable distal portion and the segment of the controllable portion are actuated by at least two tendons. As the endoscope is advanced, the user maneuvers the distal portion, and a motion controller actuates tendons in the segmented proximal portion so that the proximal portion assumes the selected curve of the selectively steerable distal portion. By this method the selected curves are propagated along the endoscope body so that the endoscope largely conforms to the pathway selected. When the endoscope is withdrawn proximally, the selected curves can propagate distally along the endoscope body. This allows the endoscope to negotiate tortuous curves along a desired path through or around and between organs within the body.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
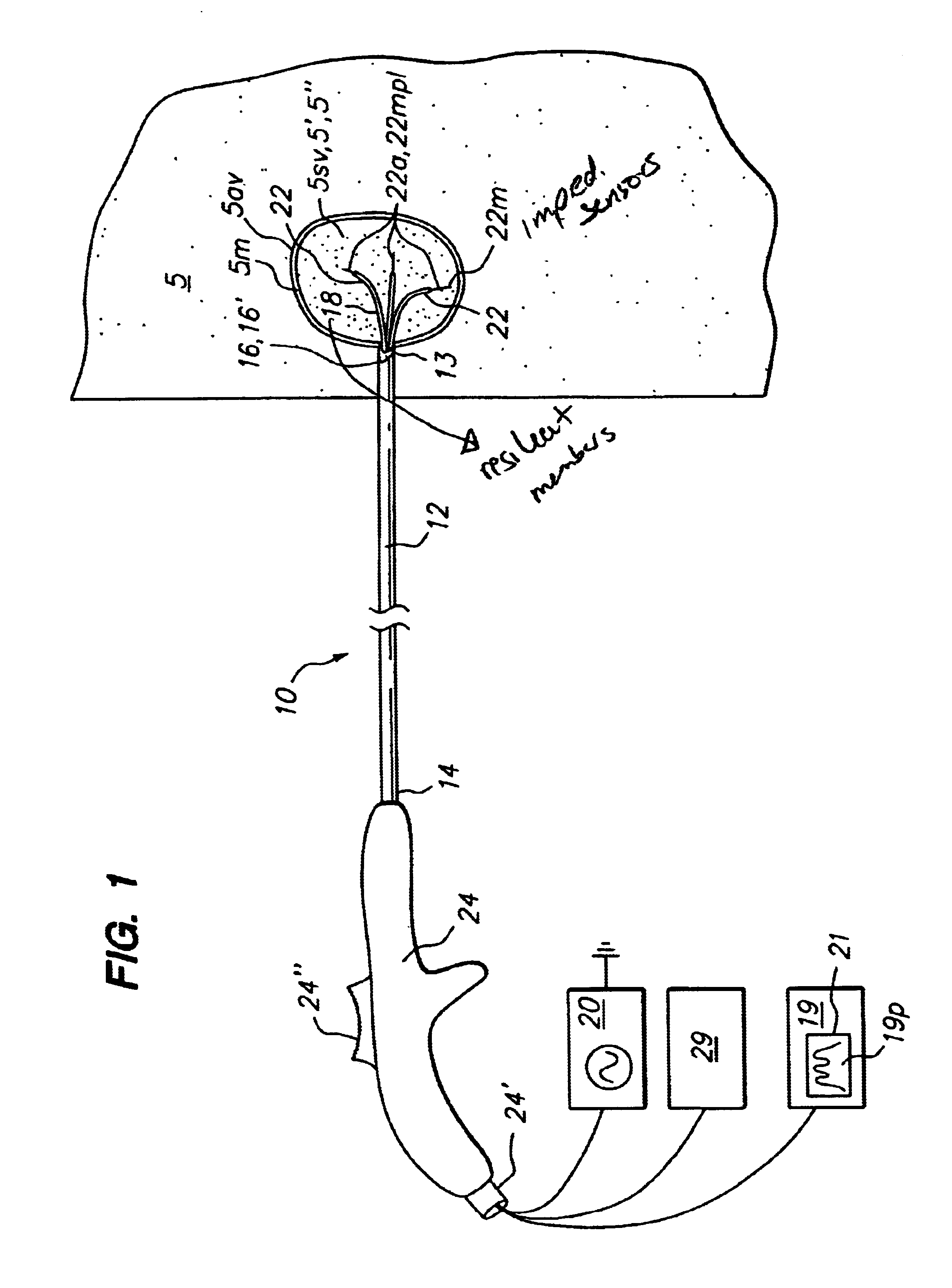
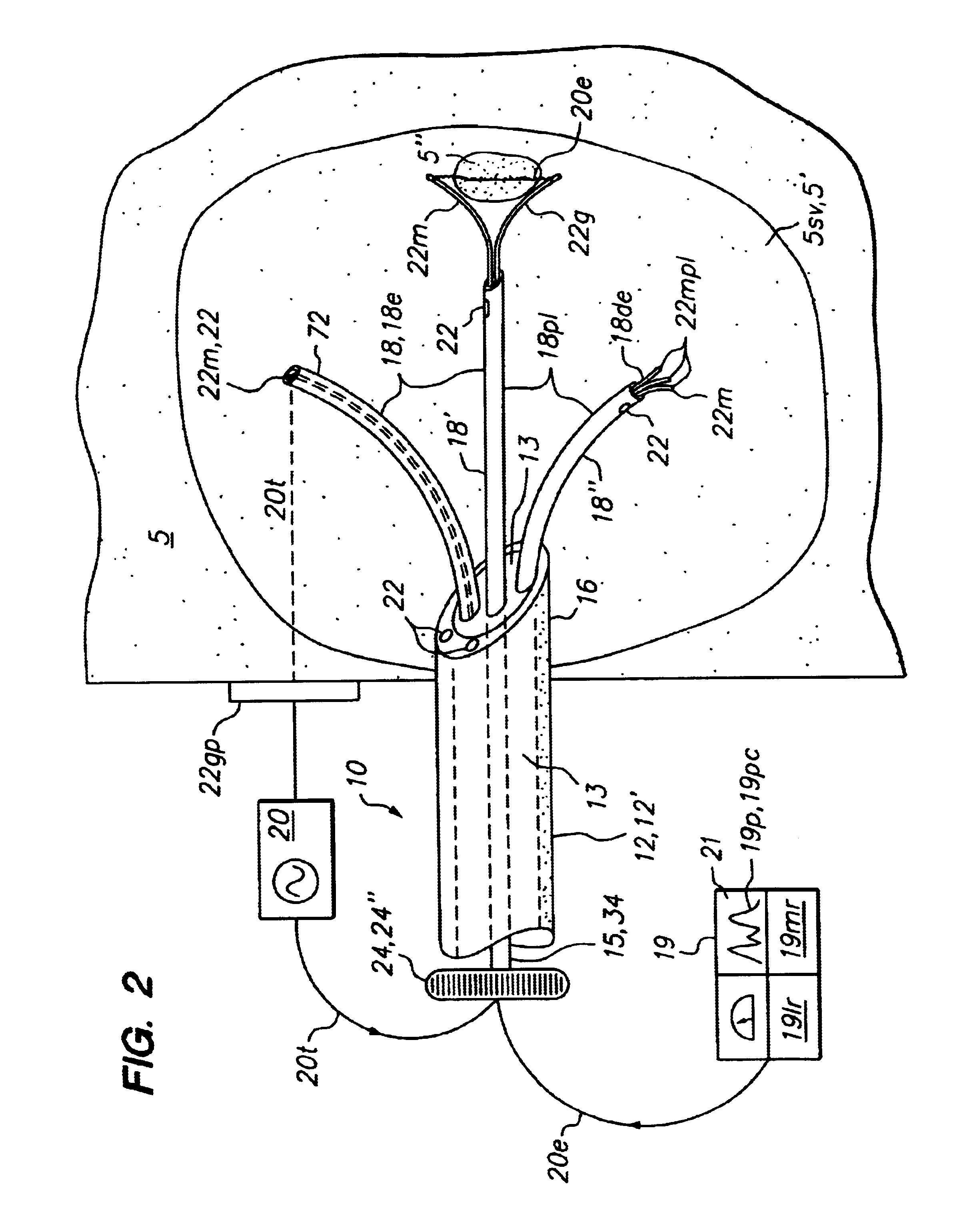
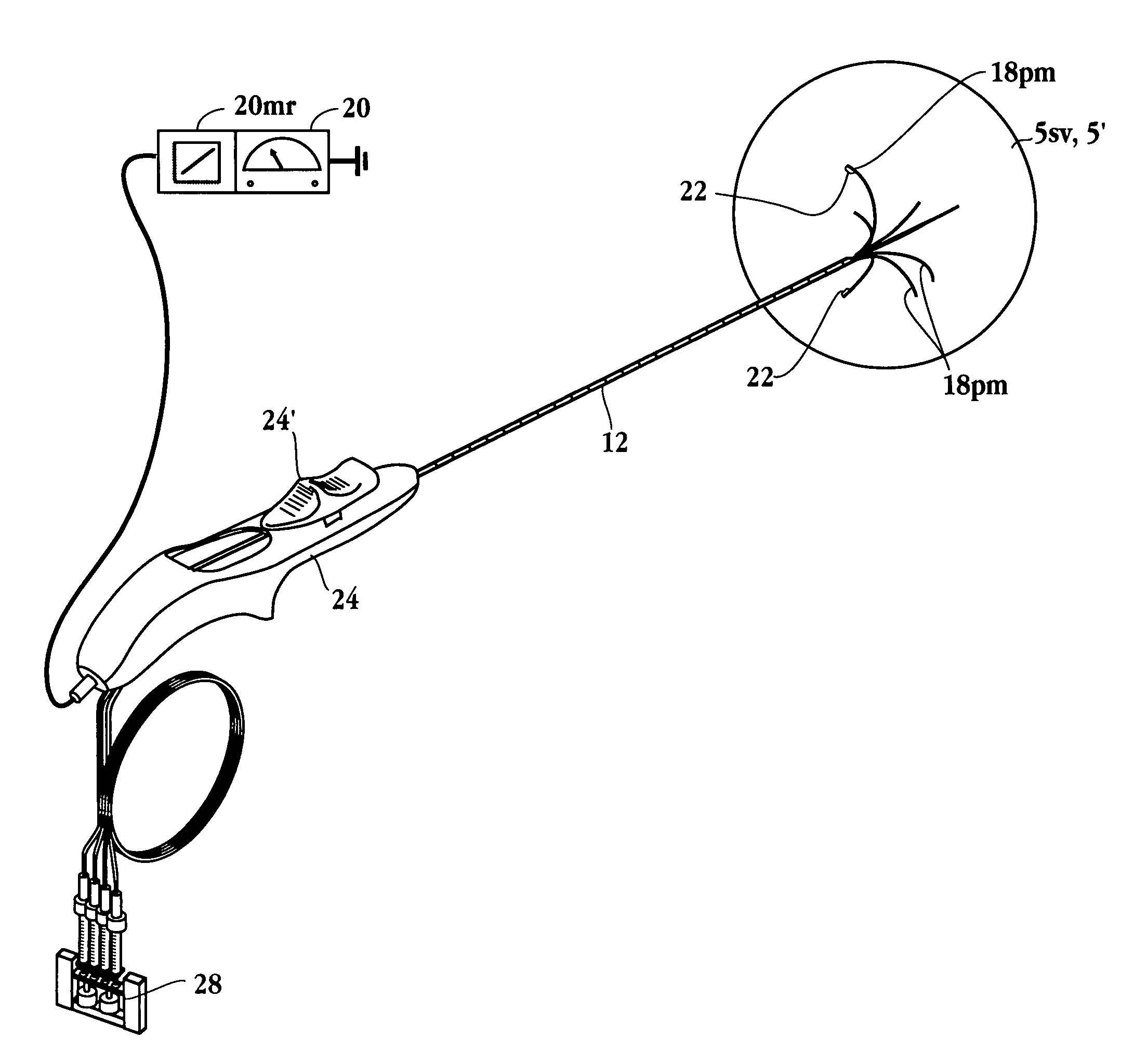
Method for detecting and treating tumors using localized impedance measurement
InactiveUS6962587B2Precise positioningEasy to monitorSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringAbnormal tissue growthEngineering
An embodiment of the invention provides a method for detecting and treating a tumor using tissue localized volumetric impedance measurement. The method includes providing an impedance measurement apparatus having a plurality of resilient members deployable with curvature and configured to sample tissue impedance through a plurality of conductive pathways. The apparatus is configured to be coupled to at least one of an energy delivery device, a power supply, a switching device or logic resources. The apparatus is then positioned at a selected tissue site and the impedance array deployed to define a sample volume. The impedance array is then utilized to make impedance measurements through a plurality of conductive pathways. Information from the impedance measurements is then utilized to determine a tissue condition of the sample volume. Energy is then delivered from the energy delivery device to ablate or necrose at least a portion of the tumor.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
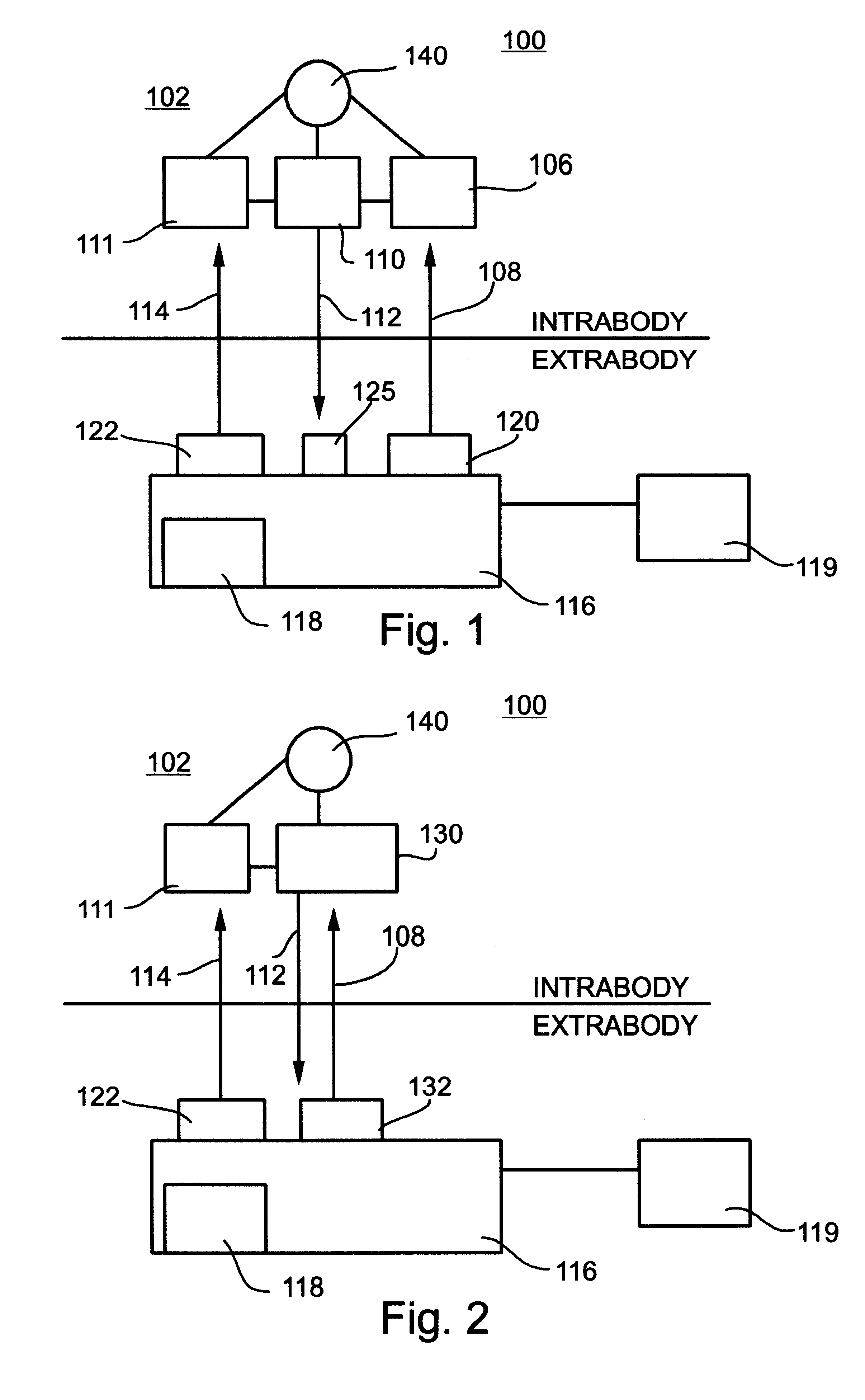
System and method for telemetrically providing intrabody spatial position
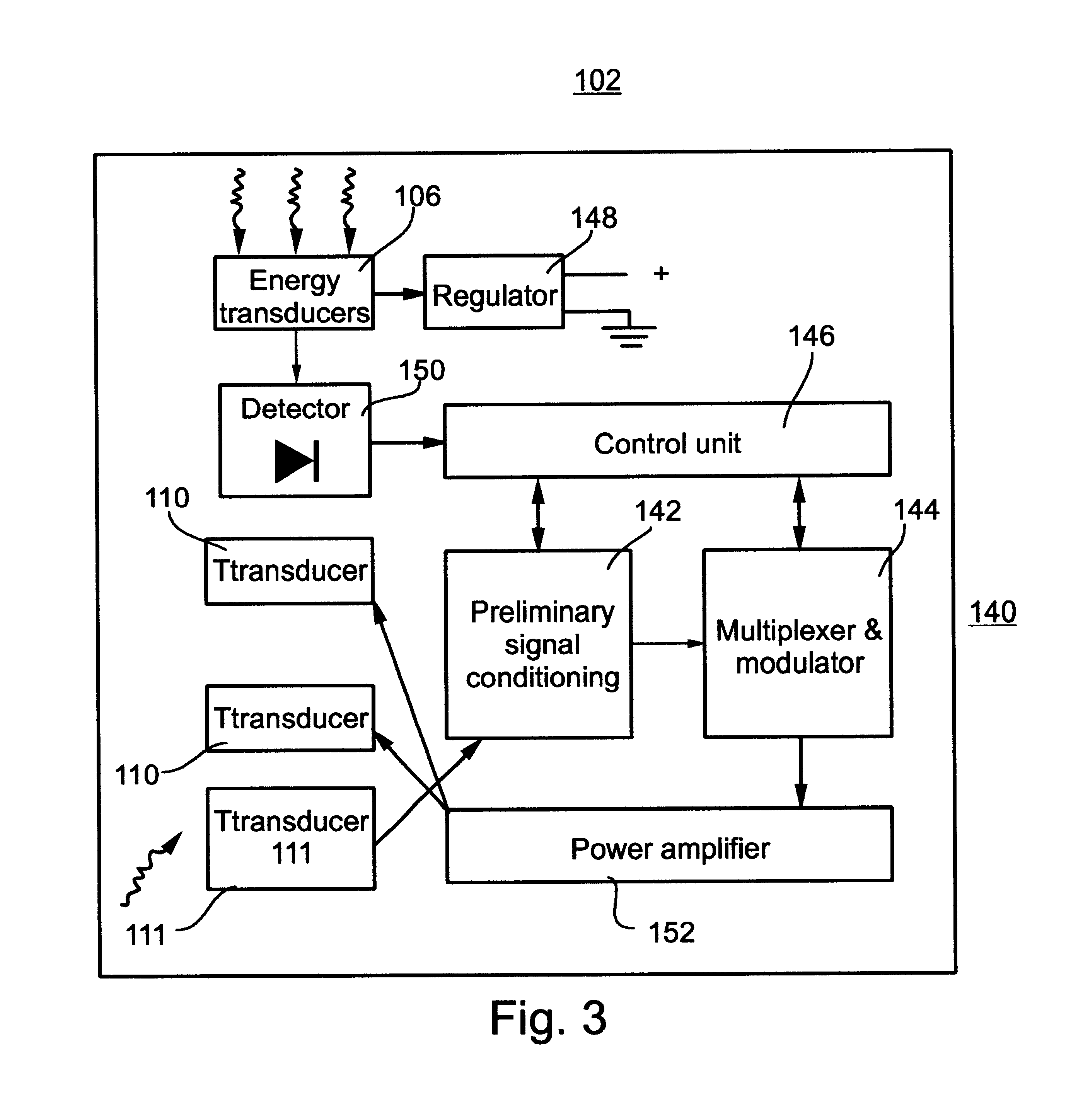
A telemetry system and method for providing spatial positioning information from within a patient's body are disclosed. The system includes at least one implantable telemetry unit which includes (a) at least one first transducer being for converting a power signal received from outside the body, into electrical power for powering the at least one implantable telemetry unit; (b) at least one second transducer being for receiving a positioning field signal being received from outside the body; and (c) at least one third transducer being for transmitting a locating signal transmittable outside the body in response to the positioning field signal.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
User interfaces for electrosurgical tools in robotic surgical systems
A method for a minimally invasive surgical system is disclosed including capturing camera images of a surgical site; generating a graphical user interface (GUI) including a first colored border portion in a first side and a second colored border in a second side opposite the first side; and overlaying the GUI onto the captured camera images of the surgical site for display on a display device of a surgeon console. The GUI provides information to a user regarding the first electrosurgical tool and the second tool in the surgical site that is concurrently displayed by the captured camera images. The first colored border portion in the GUI indicates that the first electrosurgical tool is controlled by a first master grip of the surgeon console and the second colored border portion indicates the tool type of the second tool controlled by a second master grip of the surgeon console.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Insertable device and system for minimal access procedure
ActiveUS7066879B2Limited mobilityWide field of viewEndoscopesLaproscopesAbdominal cavityProcedure Indication
The present invention provides a system and single or multi-functional element device that can be inserted and temporarily placed or implanted into a structure having a lumen or hollow space, such as a subject's abdominal cavity to provide therewith access to the site of interest in connection with minimally invasive surgical procedures. The insertable device may be configured such that the functional elements have various degrees of freedom of movement with respect to orienting the functional elements or elements to provide access to the site from multiple and different orientations / perspectives as the procedure dictates, e.g., to provide multiple selectable views of the site, and may provide a stereoscopic view of the site of interest.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
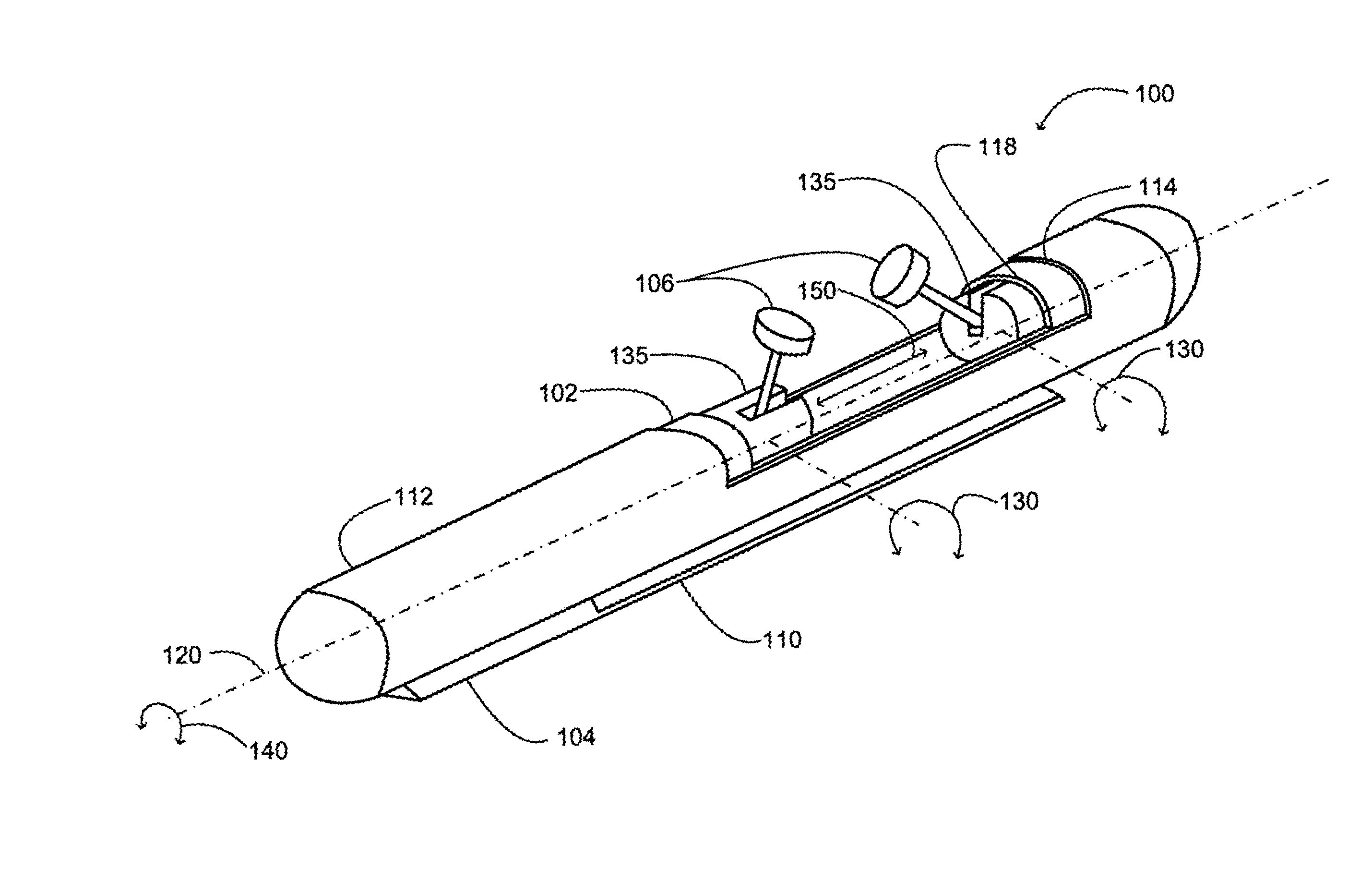
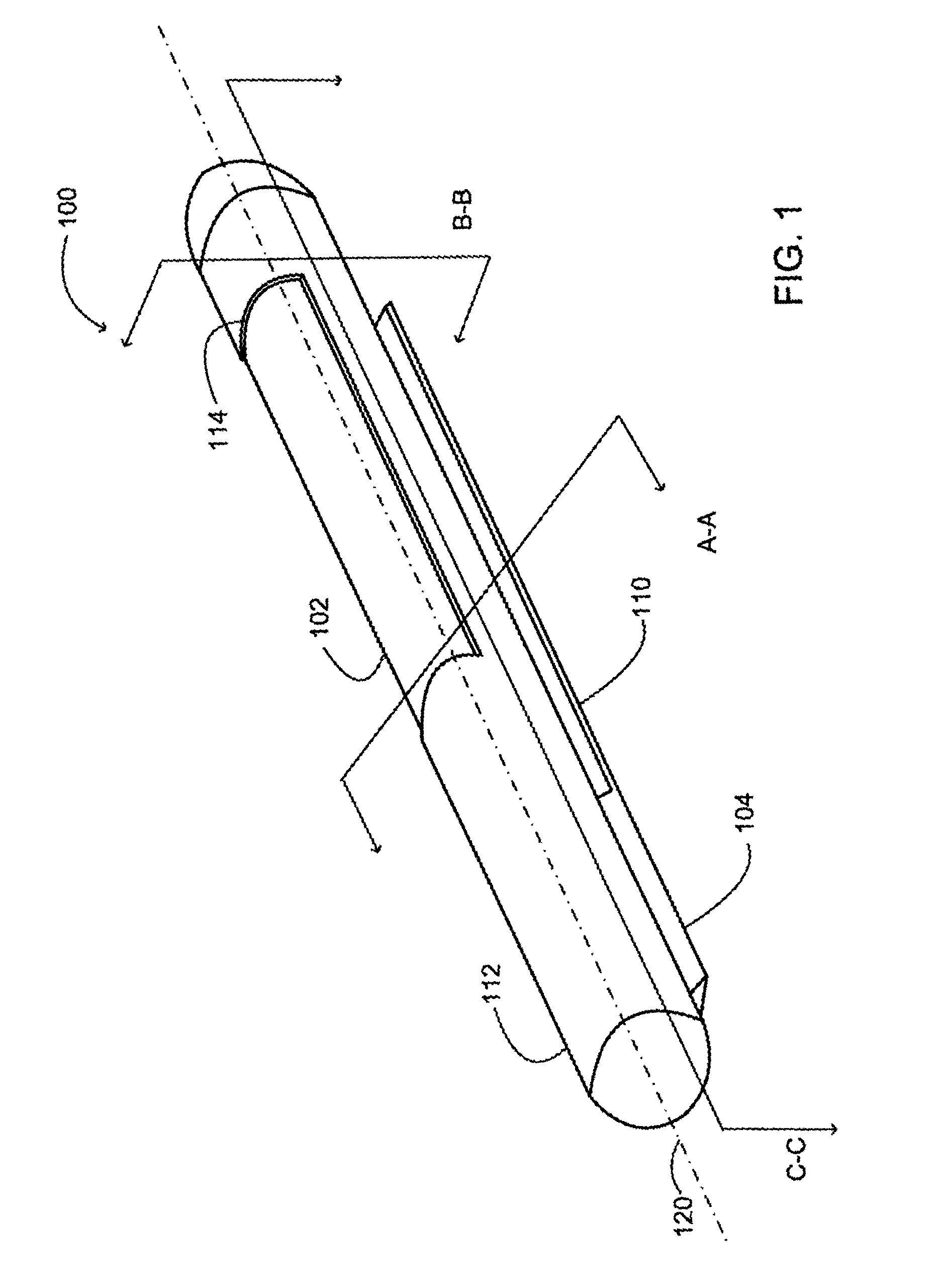
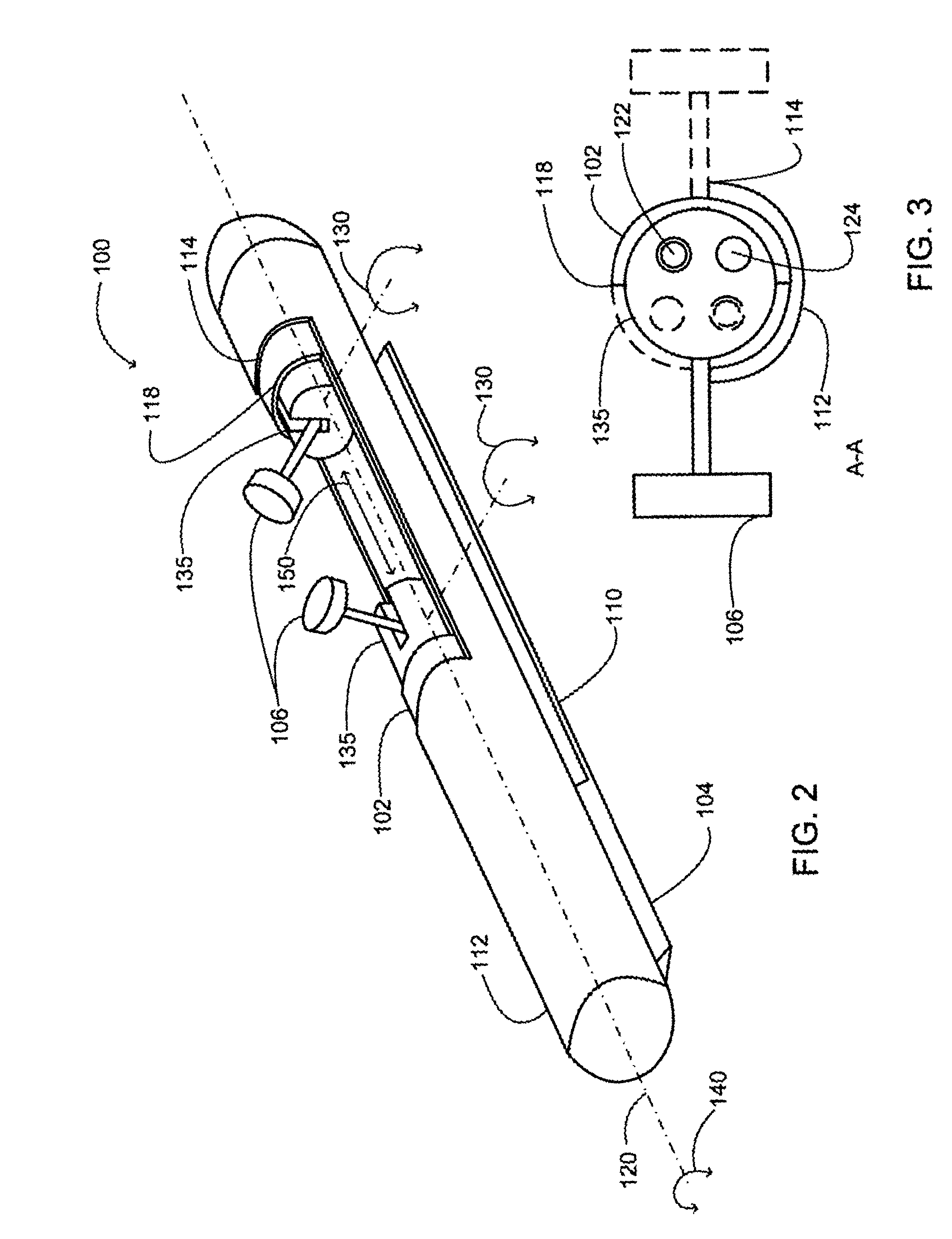
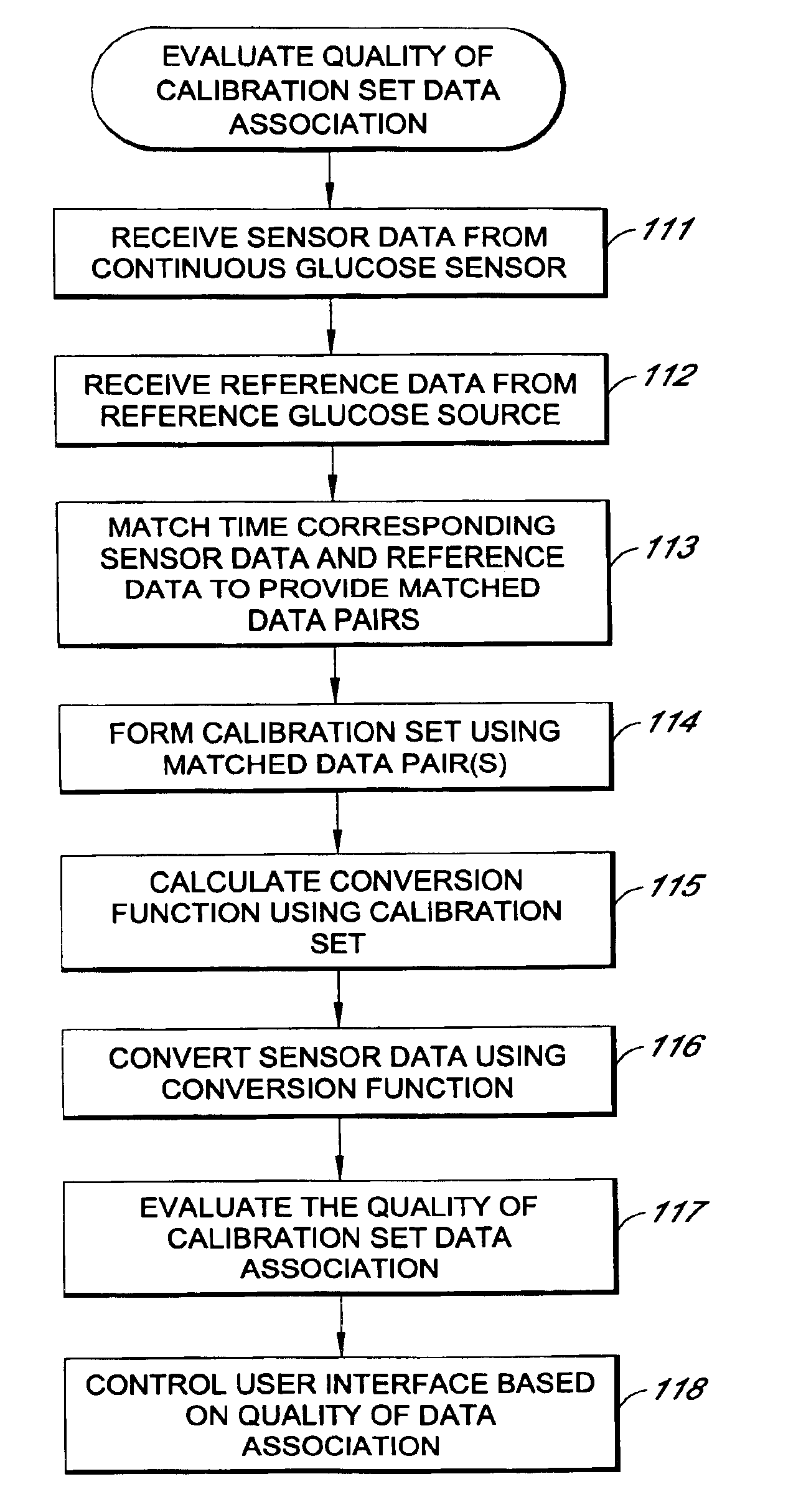
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
Systems and methods for manufacture of an analyte-measuring device including a membrane system
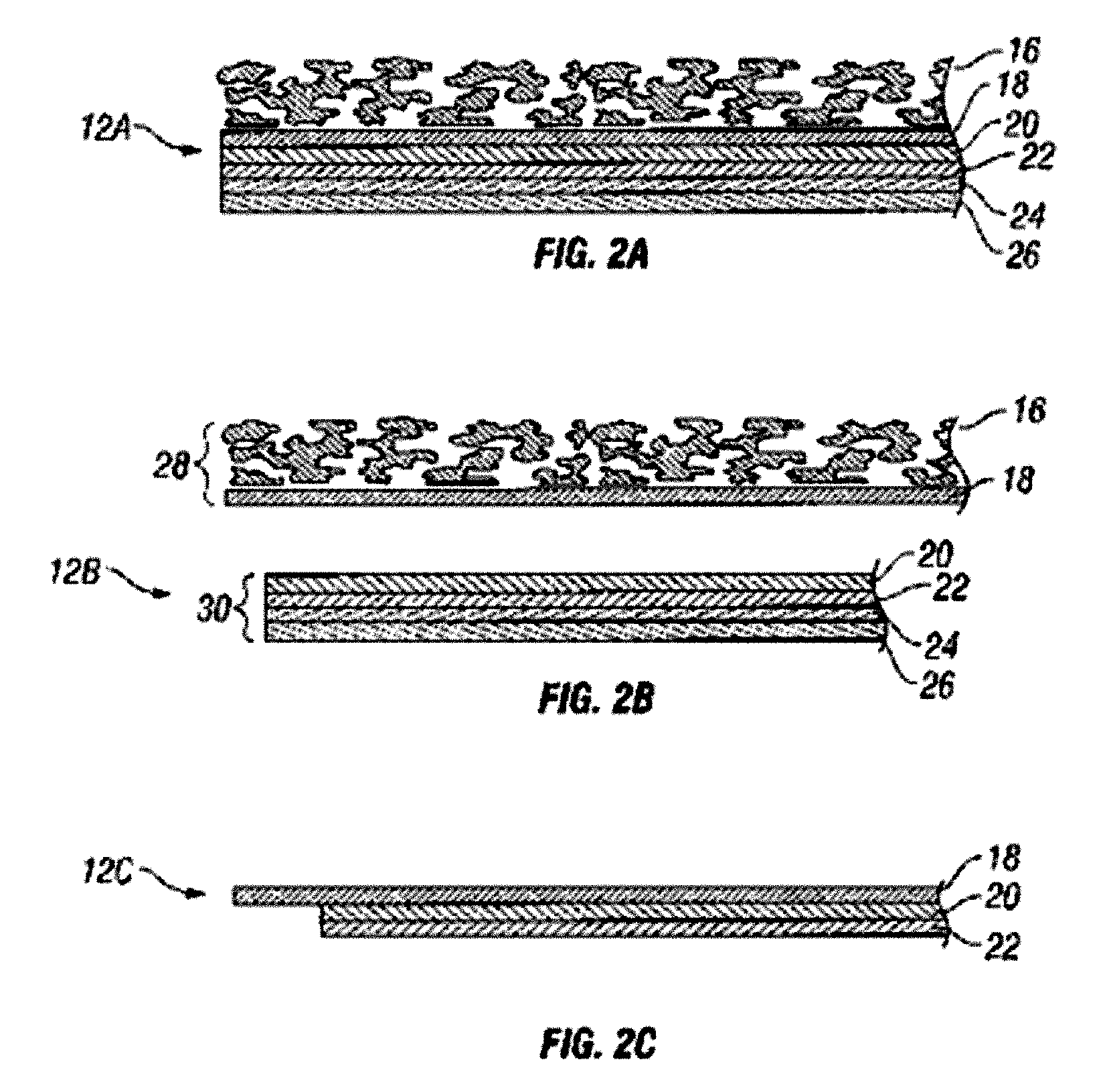
InactiveUS20060015020A1Minimized in sizeMaximize adhesionLaminationLamination apparatusAnalyteBiomedical engineering
Abstract of the DisclosureSystems and methods for manufacture of an analyte-measuring device, including adhering a membrane system that allows the passage of the analyte therethrough to a sensing mechanism. The implantable analyte-measuring device includes a body formed from a material that is substantially similar to the membrane system so as to enable sufficiently strong adhesion therebetween, which enables a sufficiently strong adhesive joint capable of withstanding in vivo cellular forces. In some embodiments, the device body includes an insert to which the membrane system is adhered, wherein the insert is formed from a material substantially similar to the membrane system to enable strong adhesion therebetween. The analyte-measuring device is designed with optimized device sizing and maximum membrane adhesion and longevity to enable controlled transport of analytes through the membrane system in vivo with improved device performance.
Owner:DEXCOM
Systems and methods for processing analyte sensor data
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for measuring an analyte in a host. More particularly, the present invention relates to systems and methods for processing sensor data, including calculating a rate of change of sensor data and / or determining an acceptability of sensor or reference data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Method and apparatus for performing stereotactic surgery
A stereotactic navigation system for navigating an instrument to a target within a patient may include a stereotactic head frame, an imaging device, a tracking device, a controller and a display. The stereotactic head frame is coupled to the patient and is used to assist in guiding the instrument to the target. The imaging device captures image data of the patient and of the stereotactic head frame. The tracking device is used to track the position of the instrument relative to the stereotactic head frame. The controller receives the image data from the imaging device and identifies the stereotactic head frame in the image data and automatically registers the image data with navigable patient space upon identifying the stereotactic head frame, while the display displays the image data.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
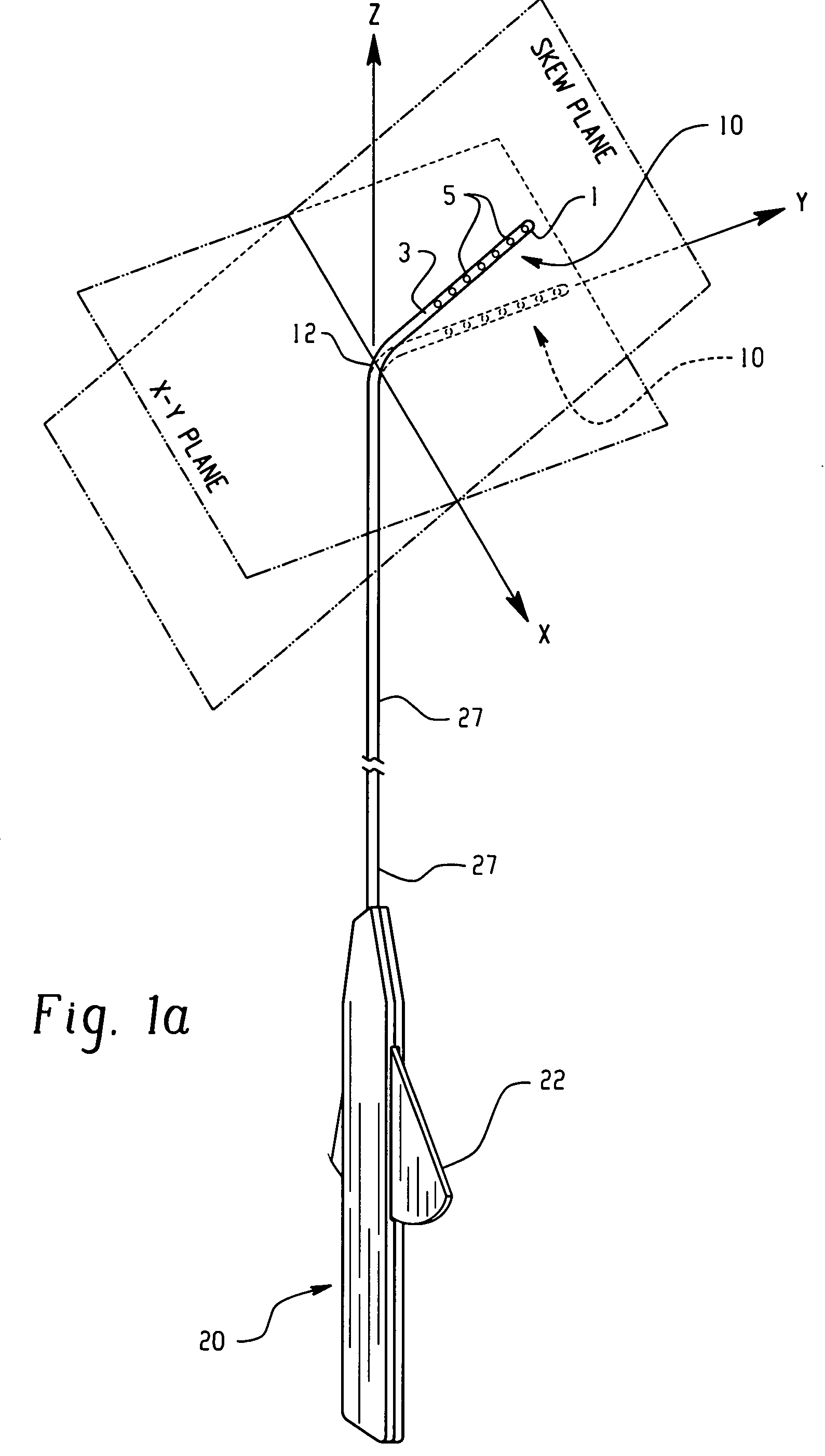
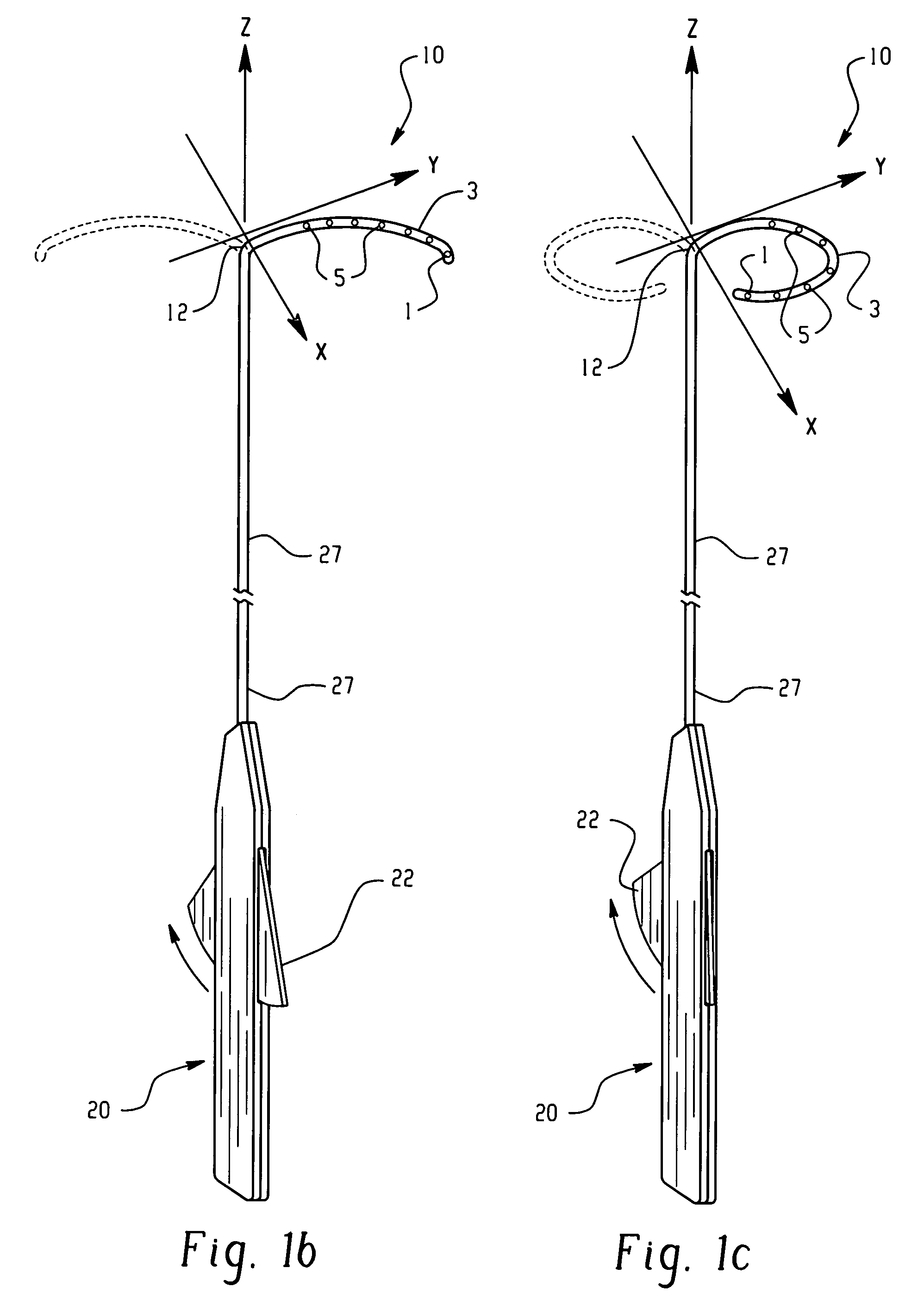
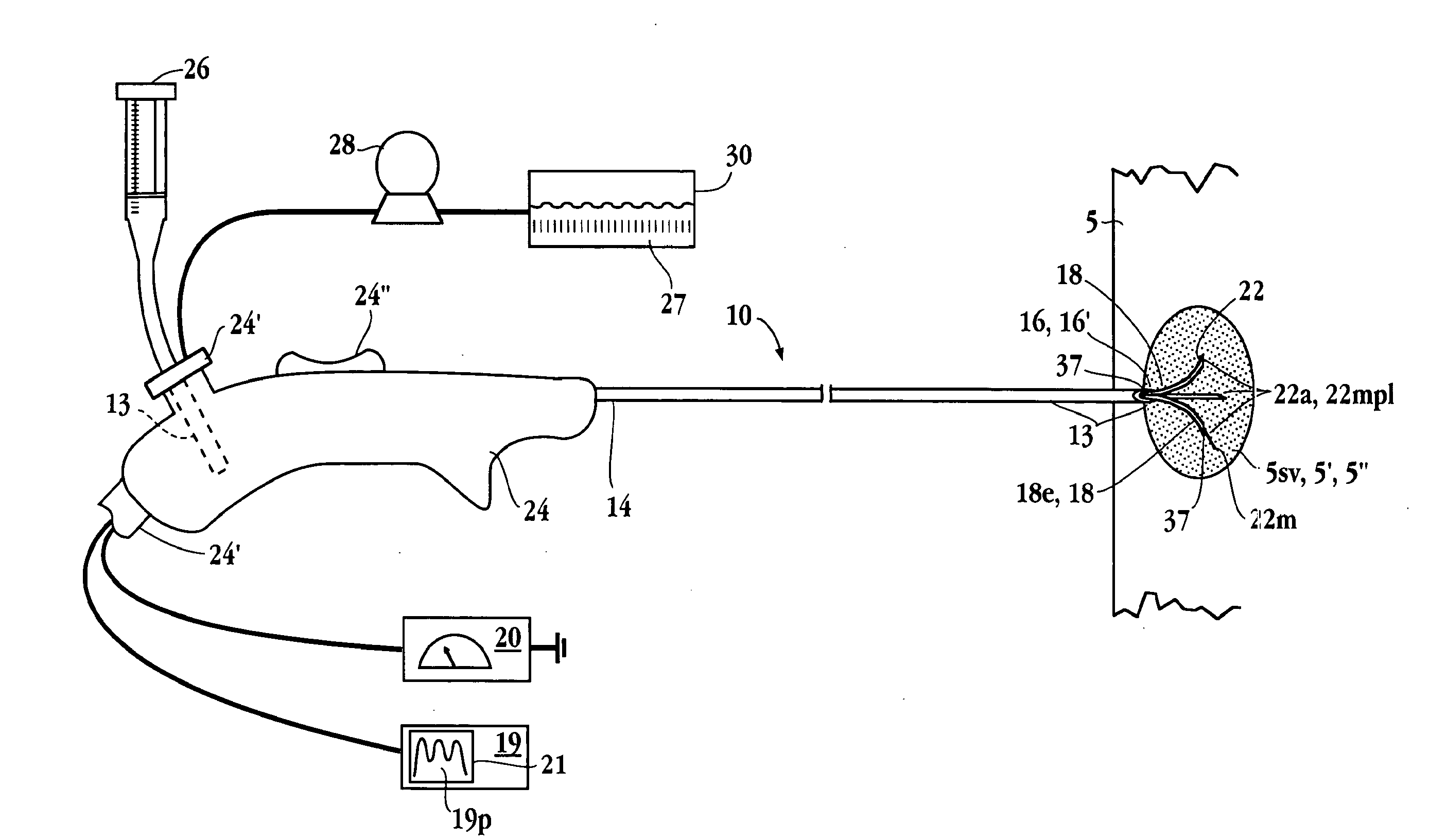
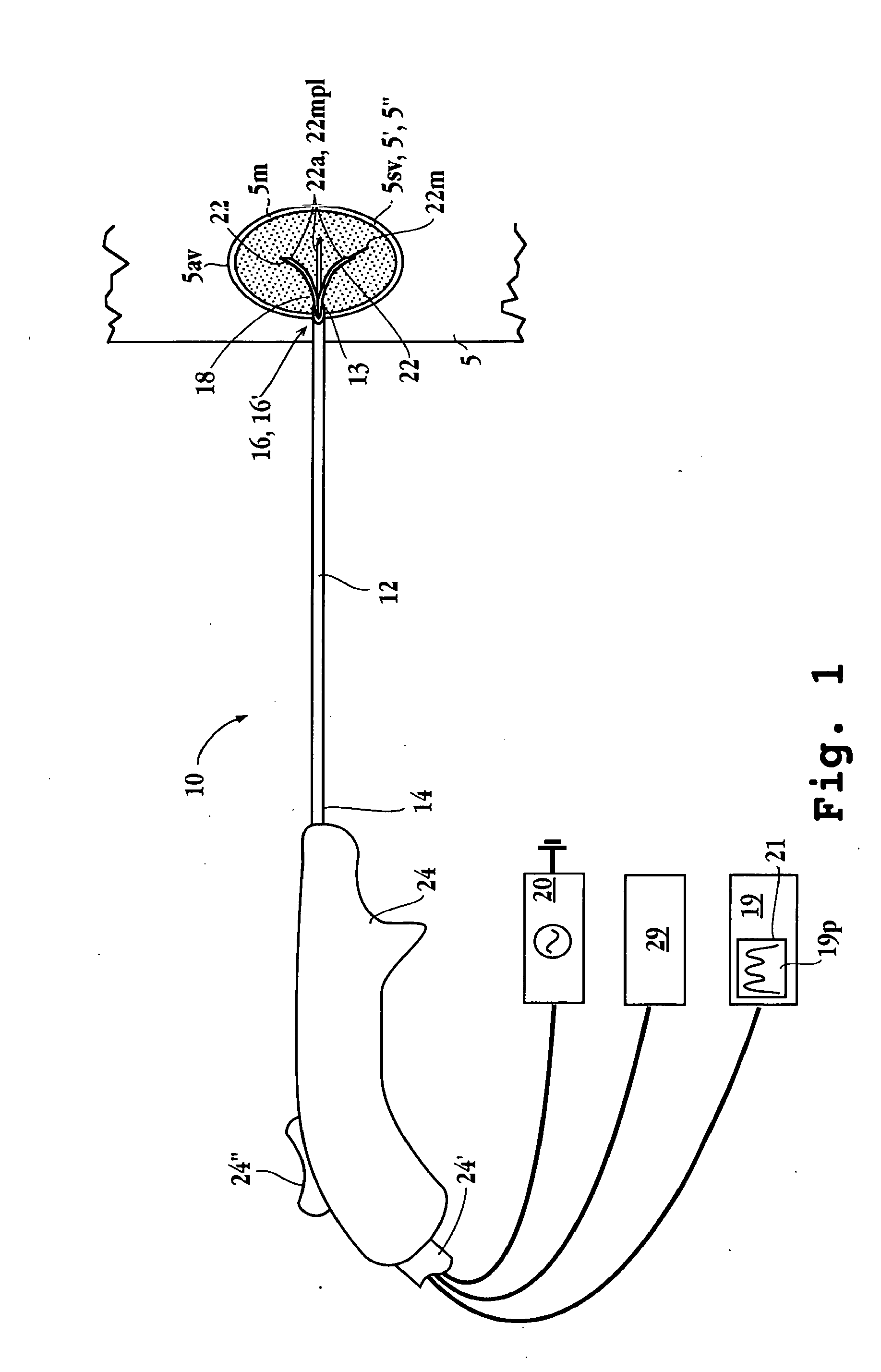
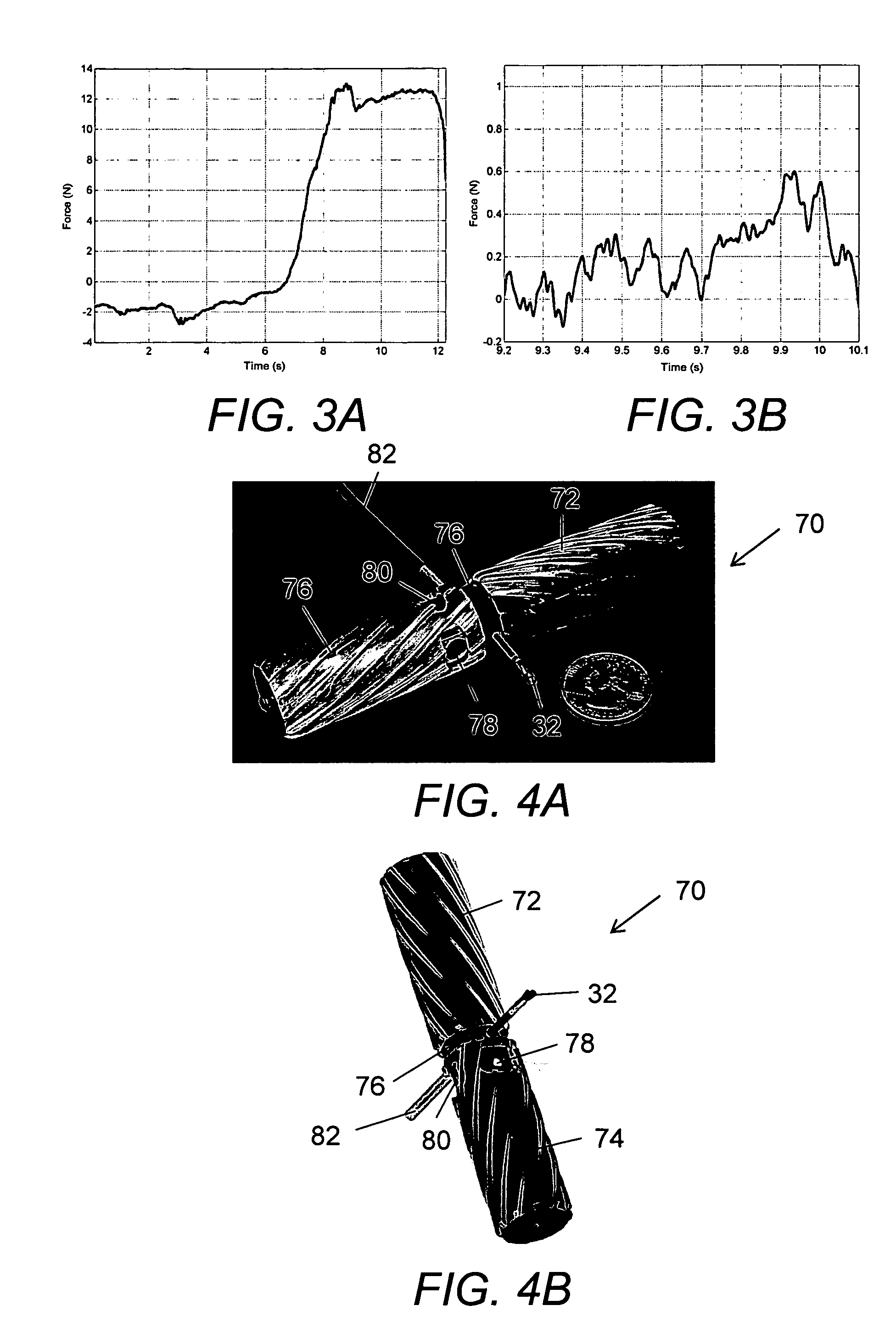
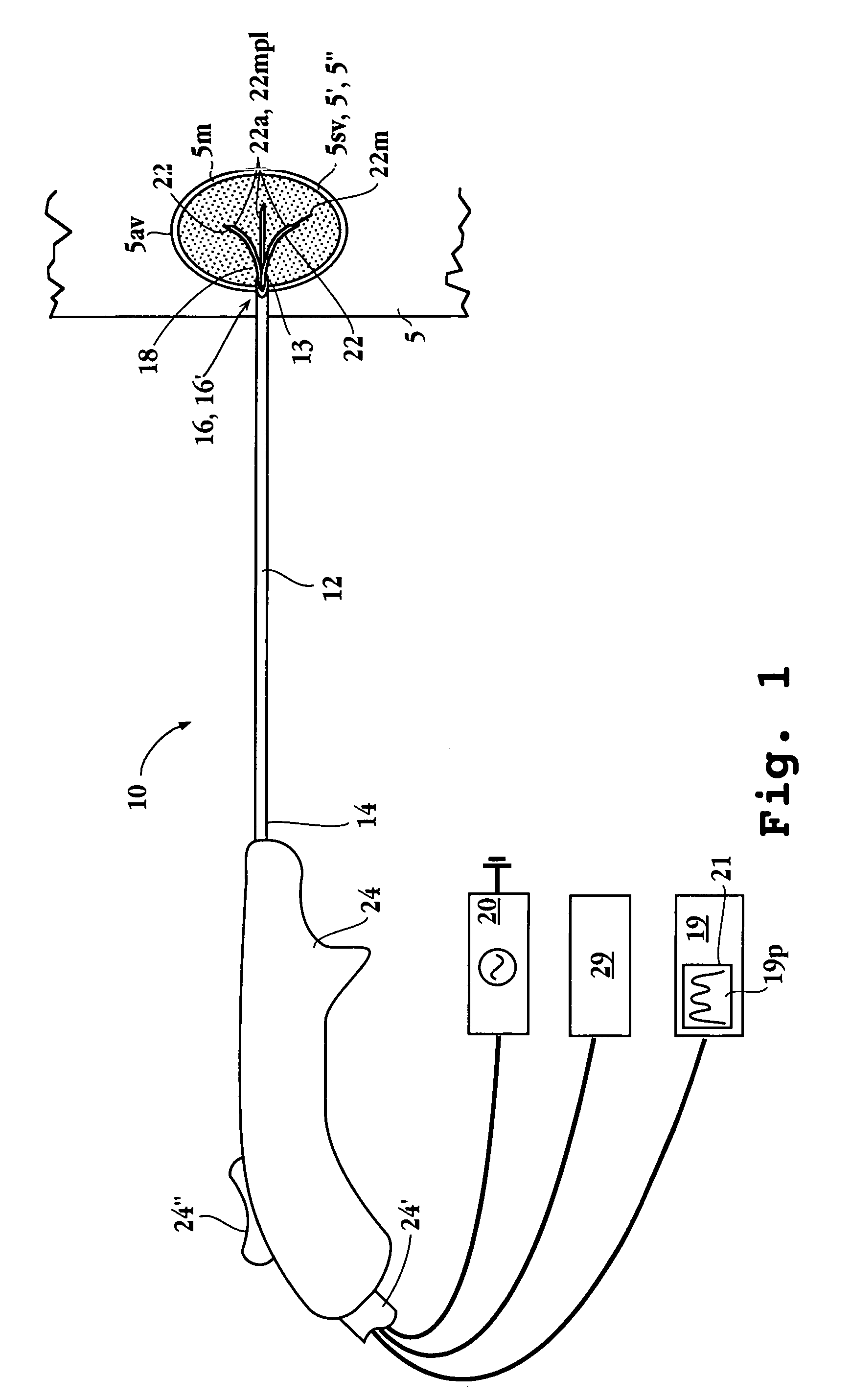
Electrophysiology/ablation catheter having lariat configuration of variable radius
InactiveUS7081114B2Easy to curlReduced radiusElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringDistal portionElectrophysiology
A remotely deflectable electrophysiology / ablation catheter of the type intended for placing into an interior passage of the heart is disclosed. The distal end of this elongated tubular catheter has a pair of tension / compression members each with a flattened end portion connected to the distal electrode and extending through the catheter casing and attached to a user moveable actuator for effecting the tension / compression thereon for remotely curling the distal end of the catheter. Spaced ring electrodes are provided adjacent the distal electrode. A permanent bend is pre-formed in the casing and tension / compression members adjacent the ring electrodes about an axis perpendicular to the elongated tension / compression members. Movement of the remote actuator causes the distal portion of the catheter to curl into a lariat in a plane perpendicular to the axis along the elongated catheter casing, thus permitting electrical mapping or ablation with the distal and / or ring electrodes about the inner surface of the heart passage into which the lariat is formed and situated. The lariat can achieve a curvature greater than 360 degrees and at a significantly reduced radius to allow insertion of the catheter distal end into passages of reduced dimension.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
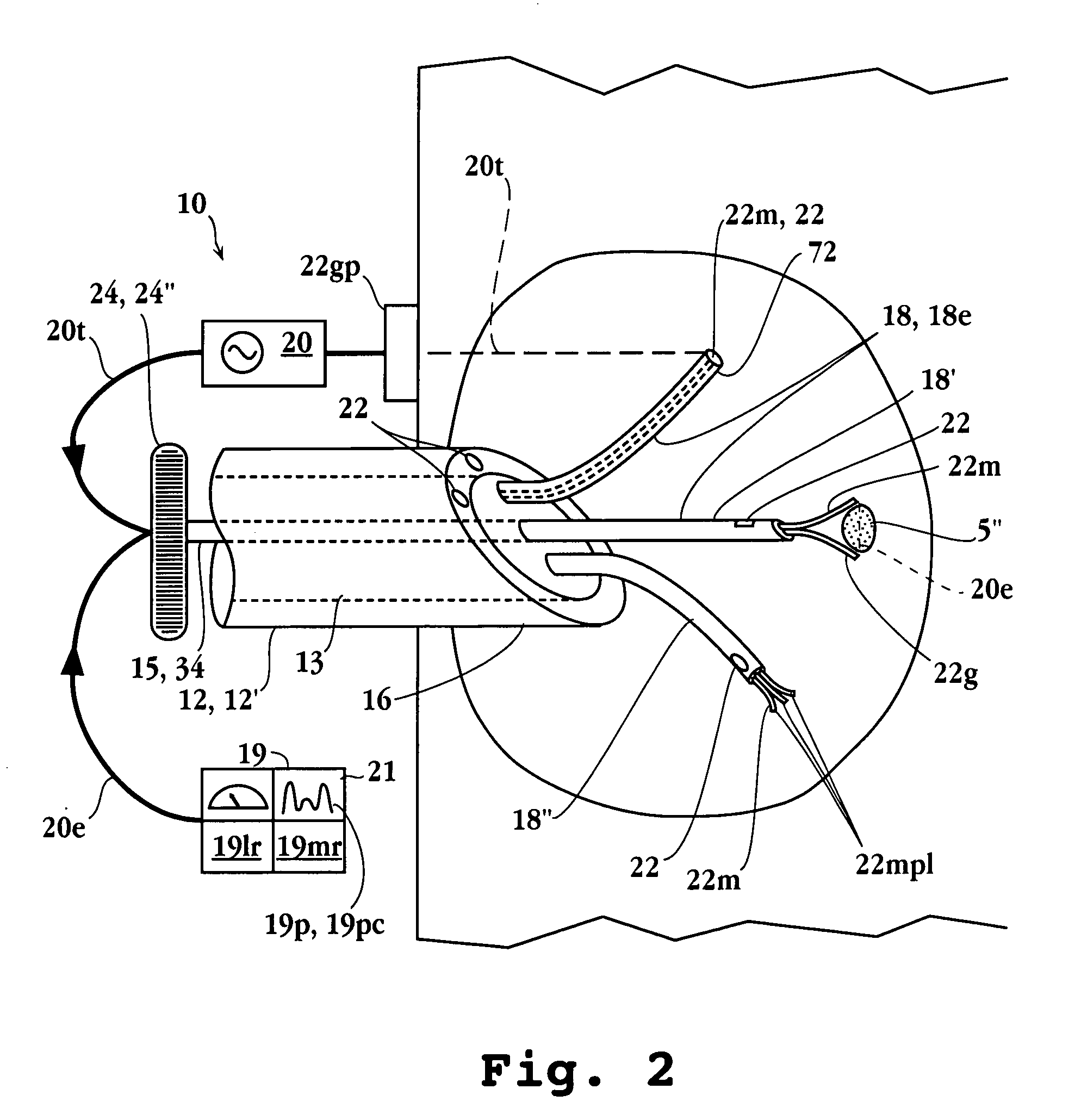
Tissue ablation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080287944A1Improve the level ofIncrease in sizeSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringRf ablationTarget tissue
A method and apparatus for carrying our thermal ablation of target tissue is disclosed. The apparatus includes an RF ablation device having a multi-electrode electrode assembly designed to be deployed in target tissue, defining a selected-volume tissue region to be ablated, and having infusion channels for infusing a liquid into the target tissue during the ablation process. A control unit in the apparatus is operably connected to an RF energy source, for controlling the RF power level supplied to the electrodes, and to an infusion device, for controlling the rate of infusion of a liquid through the device into the tissue. During both electrode deployment and tissue ablation, impedance and or temperature measurements made within the tissue are used to control the RF source and infusion device, for optimizing the time and extent of tissue ablation.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
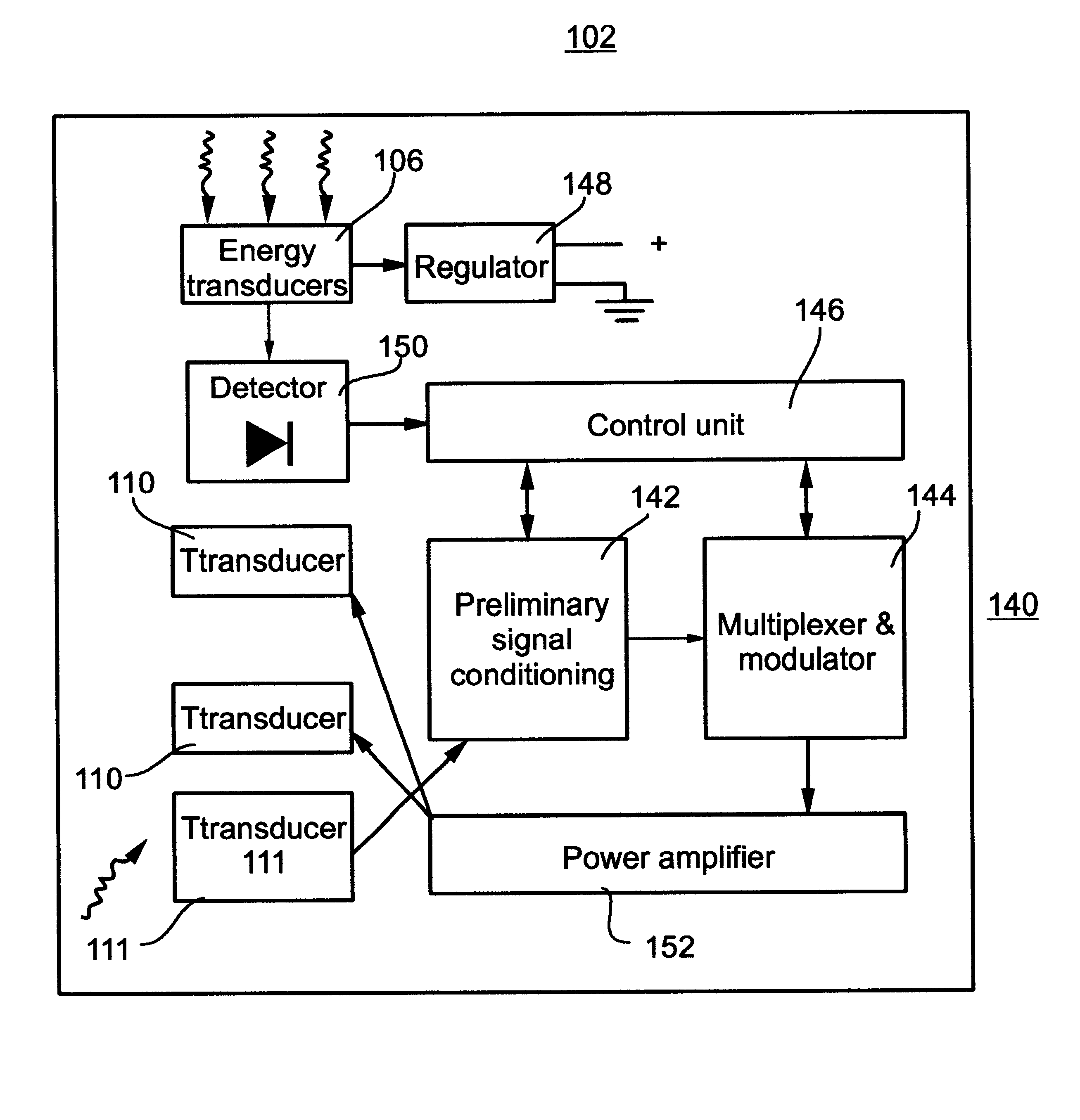
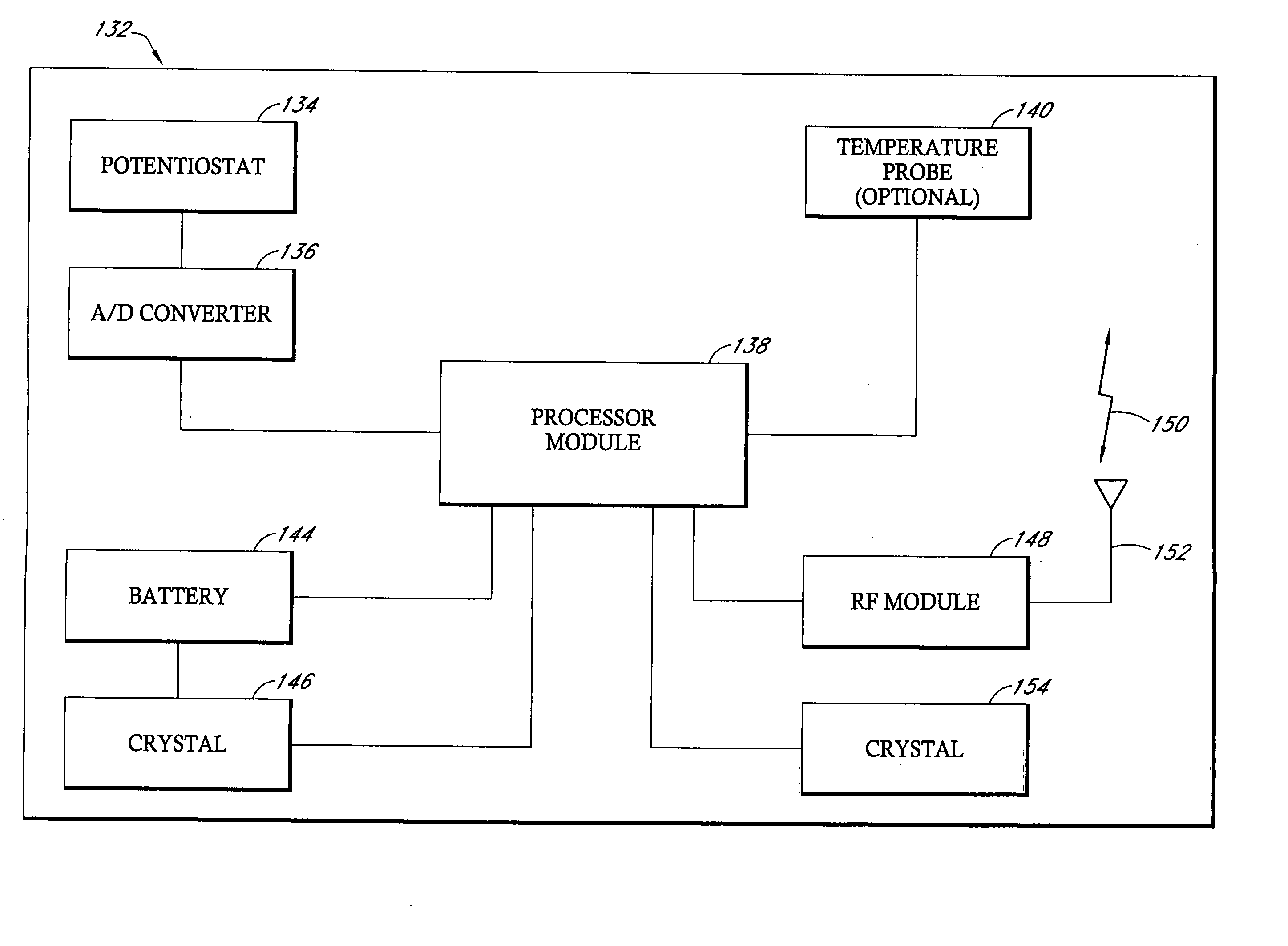
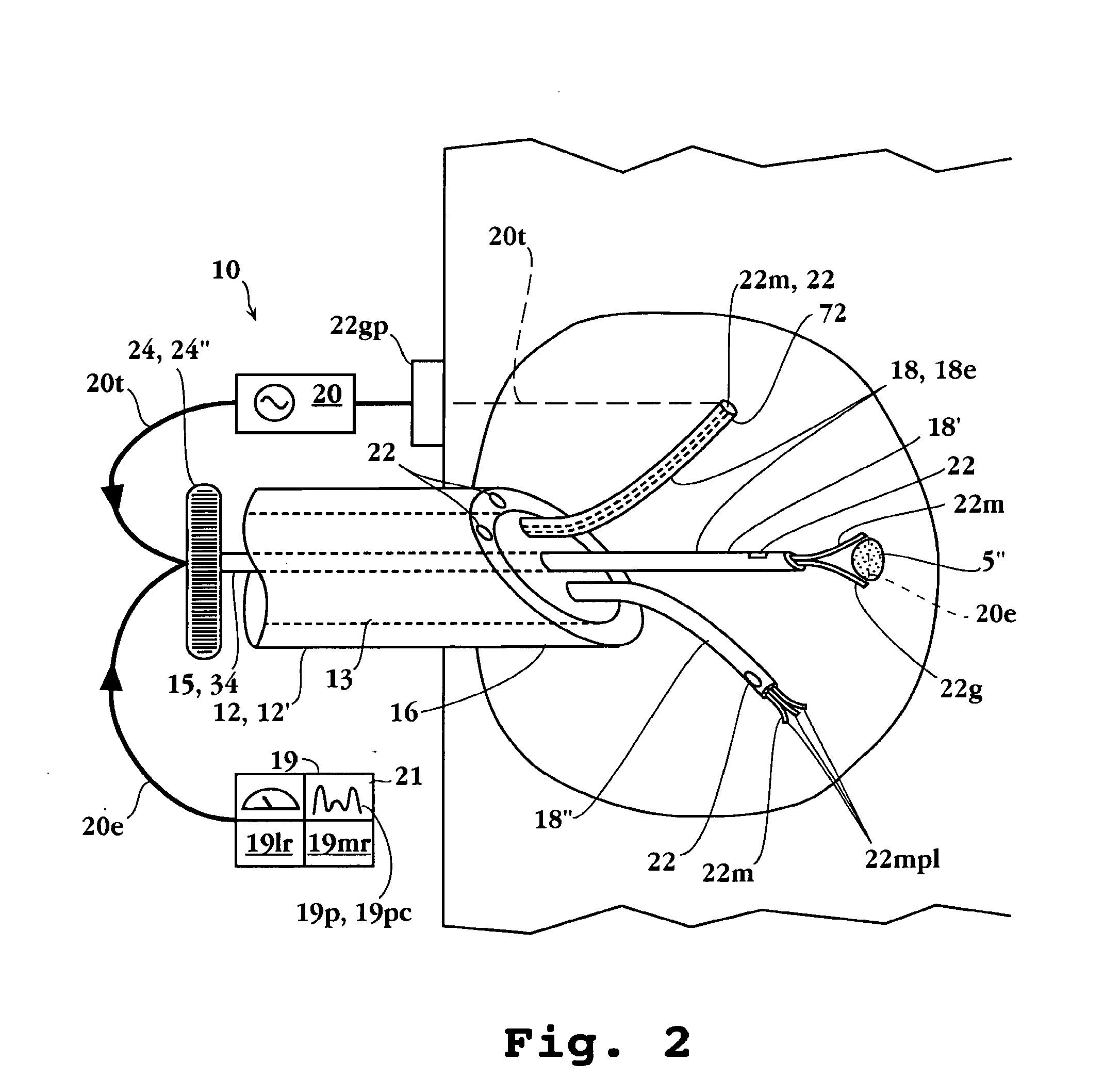
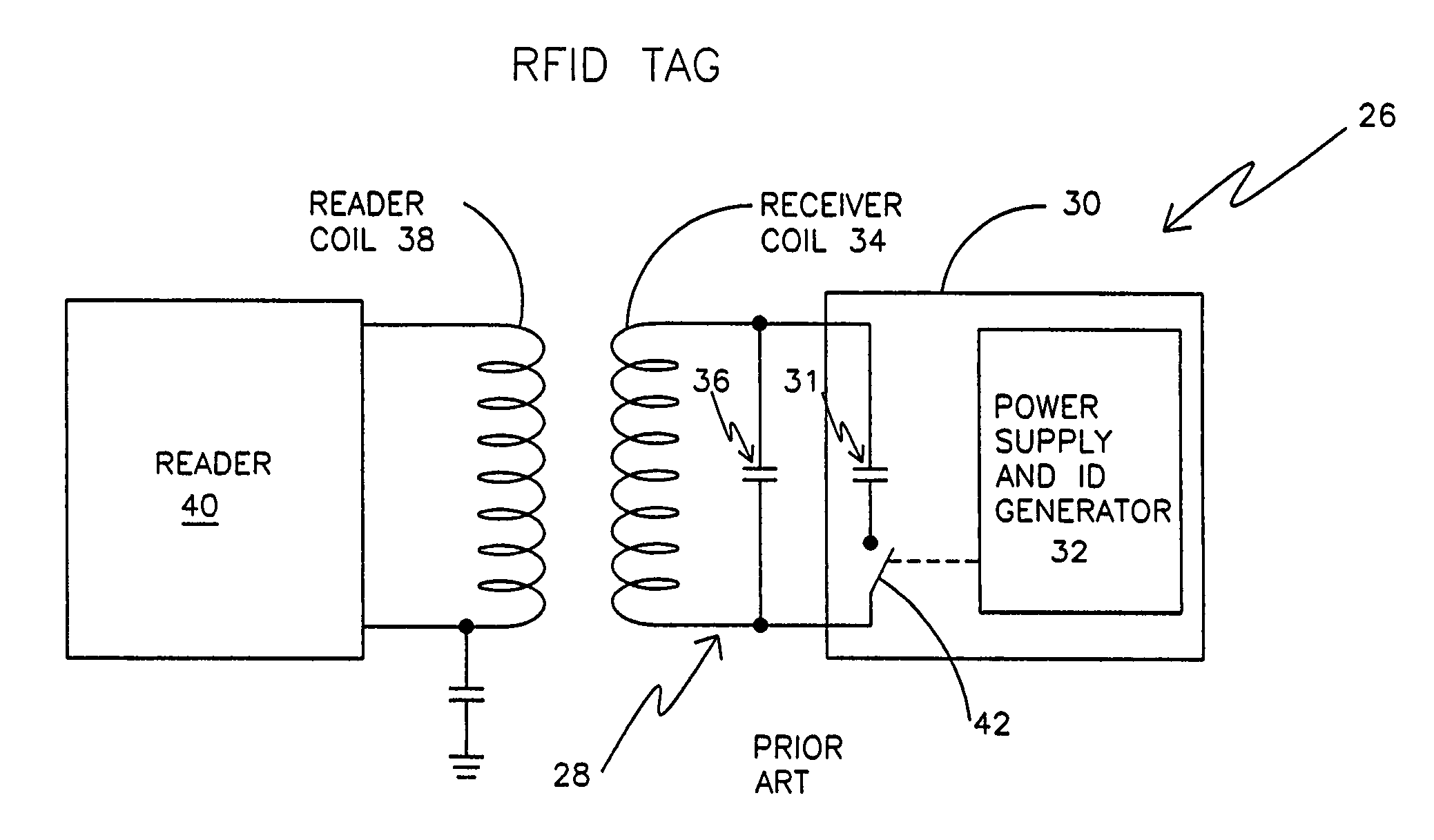
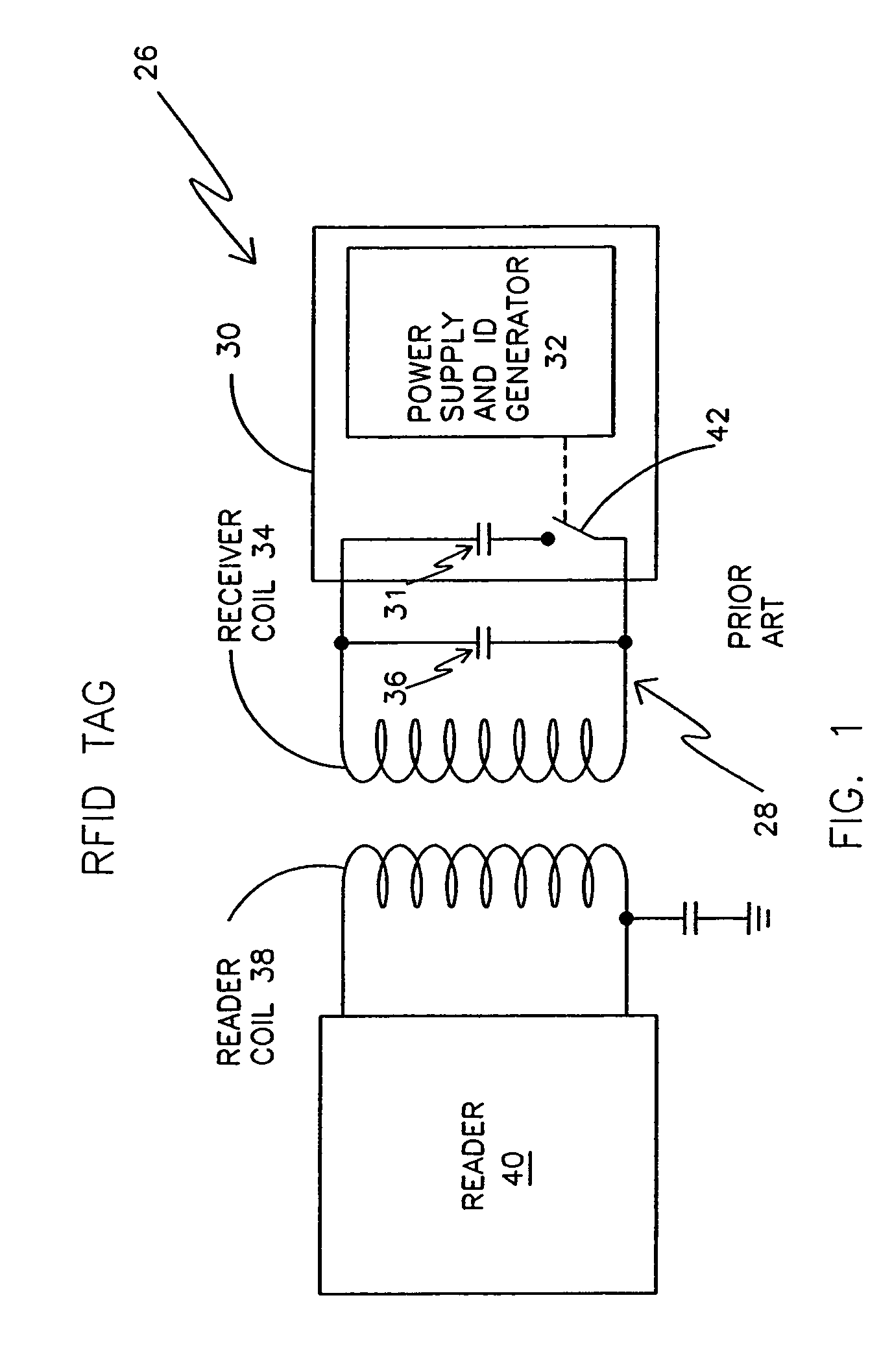
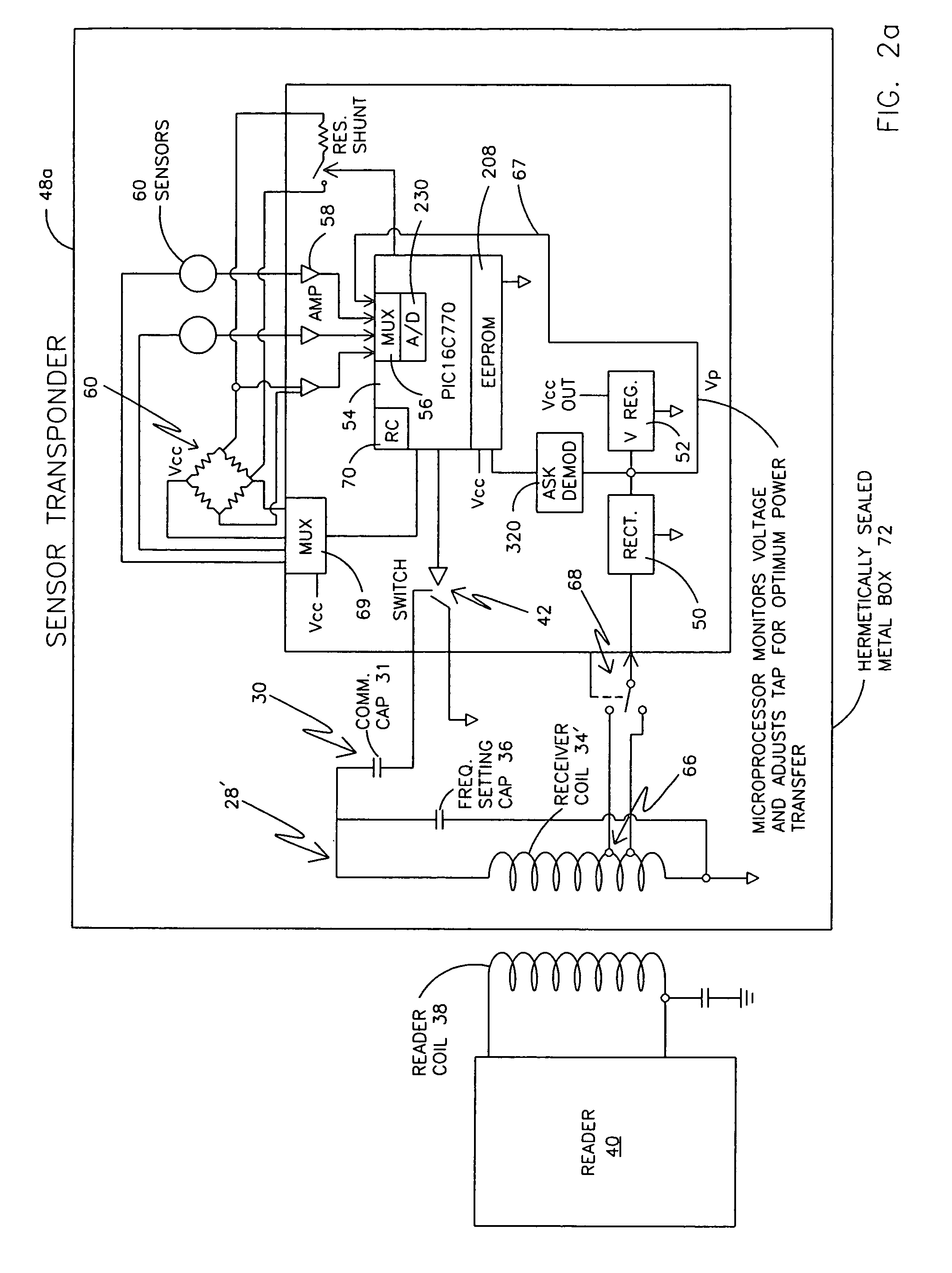
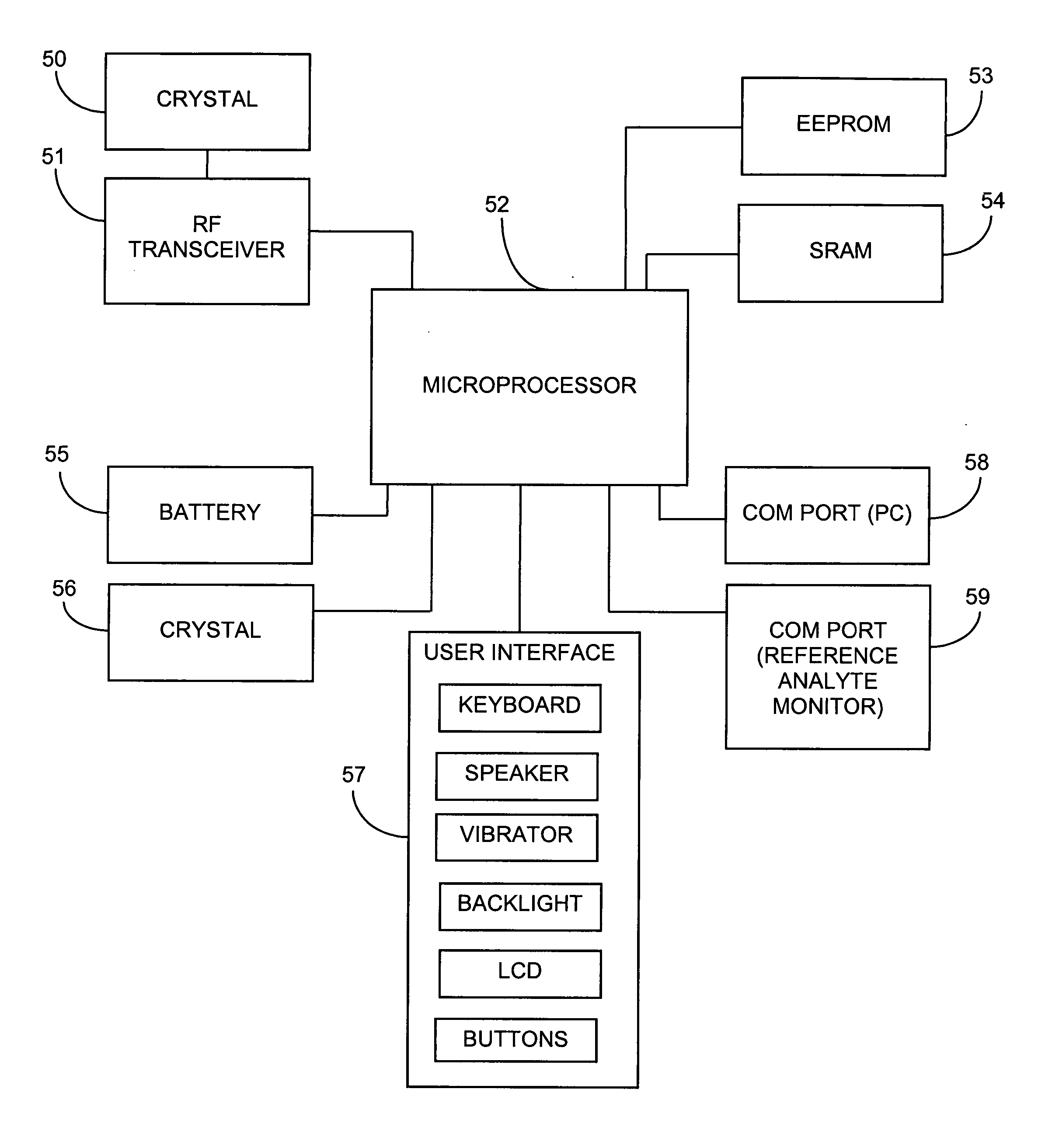
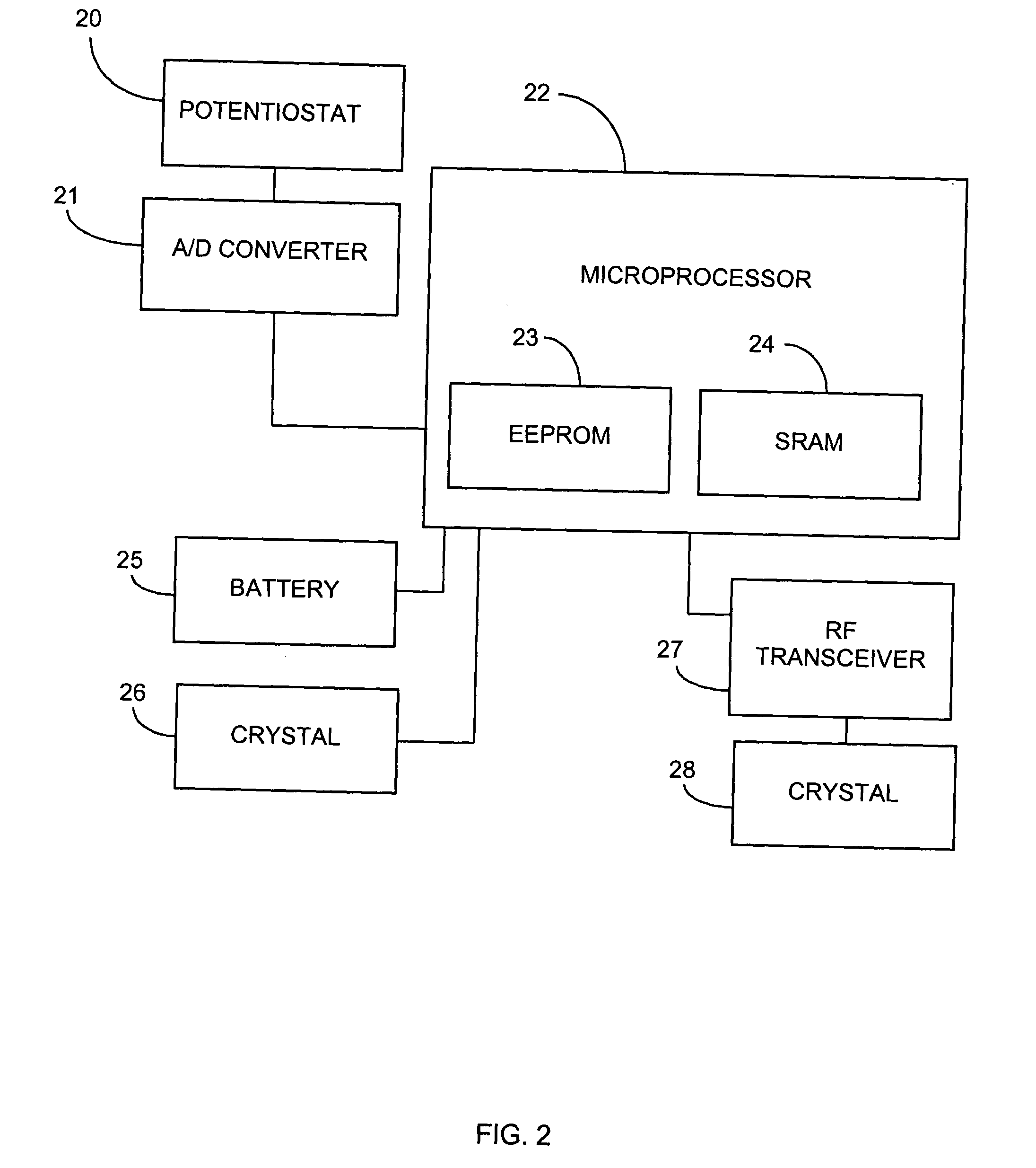
Remotely powered and remotely interrogated wireless digital sensor telemetry system
ActiveUS7256695B2More powerElectric signal transmission systemsElectrotherapyElectronic systemsPower flow
An electronic system includes a reader and a remotely powered and remotely interrogated sensor transponder. The sensor transponder includes a coil or an antenna, a switched reactance circuit, a processor, and a sensor. The sensor transponder receives power radiated from the reader to the coil or antenna. The sensor uses the power for sensing. The sensor transponder is capable of processing sensor data in the processor and transmitting the sensor data to the reader using the switched reactance circuit. In one embodiment, the receiver coil or antenna is part of a resonant tank circuit which includes an impedance matching circuit. The impedance matching circuit is connected to the receiver coil or antenna to provide greater current to the sensor or other power-using device than would be available to the sensor or other power-using device if the sensor or other power-using device were connected between the first and second end. The impedance matching circuit can be two or more taps to the coil or antenna.
Owner:LORD CORP
Method and system for integrated medical tracking
InactiveUS20090099876A1Thorough and integrated and accurate data collectionAccurate data collectionMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDiagnostic recording/measuringPatient dataComputer science
A system for processing data provided by medical devices. The system includes a medical device having a memory device configured to store medical device information. The system also includes an information system connected to the medical device. The information system includes at least a server configured to receive at least a portion of the medical device information from the memory device of the medical device. The server is also configured to employ the medical device information to process at least one of patient data, prescription data and inventory / ordering data. The medical device information may include serial number data, device identifier data, operation data and / or usage data for the medical device. The patient data may include at least one of patient tracking data, patient recordkeeping data and patient billing data. The prescription data may include prescription issuance data, prescription filling data and prescription tracking data. The inventory / ordering data may include at least one of maintenance and replacement schedule data, administrator notification data, and automatically-generated medical device order data.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
System and method for tissue sealing
InactiveUS20090292283A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingActuatorBipolar forceps
An electrosurgical bipolar forceps for sealing is disclosed. The forceps includes one or more shaft members having an end effector assembly disposed at the distal end. The end effector assembly includes two jaw members movable from a first position to a closed position wherein the jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue at constant pressure. Each of the jaw members includes an electrically conductive sealing plate connected to a first energy source which communicates electrosurgical energy through the tissue held therebetween. The electrosurgical energy is communicated at constant voltage. The electrically conductive sealing plates are operably connected to sensor circuitry which is configured to measure initial tissue impedance and transmit an initial impedance value to a controller. The controller determines the constant pressure and the constant voltage to be applied to the tissue based on the initial impedance value.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Endoscope having a guide tube
InactiveUS20050124855A1Facilitates advancement and withdrawalPreventing tissue from being pinchedGuide needlesCannulasDistal portionCatheter
An endoscope having a guide tube is described herein. The assembly has an endoscope which is slidably insertable within the lumen of a guide tube. The guide tube is configured to be rigidizable along its entire length from a relaxed configuration. The endoscope has a steerable distal portion to facilitate the steering of the device through tortuous paths. In the relaxed configuration, a portion of the guide tube is able to assume the shape or curve defined by the controllable distal portion of the endoscope. Having assumed the shape or curve of the endoscope, the guide tube may be rigidized by the physician or surgeon to maintain that shape or curve while the endoscope is advanced distally through the tortuous path without having to place any undue pressure against the tissue walls.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
Biointerface membranes incorporating bioactive agents
InactiveUS20050031689A1Improve performancePowder deliveryAdditive manufacturing apparatusBiointerfaceActive agent
A biointerface membrane for an implantable device including a nonresorbable solid portion with a plurality of interconnected cavities therein adapted to support tissue ingrowth in vivo, and a bioactive agent incorporated into the biointerface membrane and adapted to modify the tissue response is provided. The bioactive agents can be chosen to induce vascularization and / or prevent barrier cell layer formation in vivo, and are advantageous when used with implantable devices wherein solutes are transported across the device-tissue interface.
Owner:DEXCOM
Biopsy system having a single use loading unit operable with a trocar driver, a knife driver and firing module
InactiveUS7189207B2Reduce resistanceIncrease speedSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTissue sampleEngineering
A biopsy system for retrieving biopsy tissue samples from different regions of the body is disclosed. The biopsy system includes a single use loading unit having a trocar assembly and a knife assembly. A trocar driver is operably connected to the trocar assembly and is actuable to move a trocar between retracted and advanced positions. The trocar driver is disengaged from the trocar assembly prior to firing the trocar into a target tissue mass to reduce drag on the trocar during firing. A knife driver is operably connected to the knife assembly such that when actuated, a knife is both rotatably and axially advanced about the trocar.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Tissue access guidewire system and method
A method and system for guiding at least a portion of a surgical device to a desired position between two tissues in a patient's body involves coupling a guidewire to the device and pulling the distal end of the guidewire to guide at least a portion of the surgical device to a desired position between the two tissues. The surgical device generally includes one or more guidewire coupling members and may comprise a tissue access device. A system may include a guidewire and a surgical device. In some embodiments, a guidewire, a tissue access device, and one or more additional devices to use with the access device may be provided. Methods, devices and systems may be used in open, less-invasive or percutaneous surgical procedures, in various embodiments.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC +1
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS6862465B2Reduce in quantityControl volumeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteImplanted device
Devices and methods for determining analyte levels are described. The devices and methods allow for the implantation of analyte-monitoring devices, such as glucose monitoring devices that result in the delivery of a dependable flow of blood to deliver sample to the implanted device. The devices include unique architectural arrangement in the sensor region that allows accurate data to be obtained over long periods of time.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
ActiveUS20050027463A1Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteData system
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
Robot for surgical applications
The present invention provides a micro-robot for use inside the body during minimally-invasive surgery. The micro-robot includes an imaging devices, a manipulator, and in some embodiments a sensor.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Implantable analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050245799A1Improved patient convenienceConvenient careCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteMiniaturization
Abstract of the DisclosureAn implantable analyte sensor including a sensing region for measuring the analyte and a non-sensing region for immobilizing the sensor body in the host. The sensor is implanted in a precisely dimensioned pocket to stabilize the analyte sensor in vivo and enable measurement of the concentration of the analyte in the host before and after formation of a foreign body capsule around the sensor. The sensor further provides a transmitter for RF transmission through the sensor body, electronic circuitry, and a power source optimized for long-term use in the miniaturized sensor body.
Owner:DEXCOM
Impedance controlled tissue ablation apparatus and method
InactiveUS7344533B2Improve the level ofIncrease in sizeSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringRf ablationControl cell
A method and apparatus for carrying our thermal ablation of target tissue is disclosed. The apparatus includes an RF ablation device having a multi-electrode electrode assembly designed to be deployed in target tissue, defining a selected-volume tissue region to be ablated, and having infusion channels for infusing a liquid into the target tissue during the ablation process. A control unit in the apparatus is operably connected to an RF energy source, for controlling the RF power level supplied to the electrodes, and to an infusion device, for controlling the rate of infusion of a liquid through the device into the tissue. During both electrode deployment and tissue ablation, impedance and or temperature measurements made within the tissue are used to control the RF source and infusion device, for optimizing the time and extent of tissue ablation.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Electrode systems for electrochemical sensors
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for improved electrochemical measurement of analytes. The preferred embodiments employ electrode systems including an analyte-measuring electrode for measuring the analyte or the product of an enzyme reaction with the analyte and an auxiliary electrode configured to generate oxygen and / or reduce electrochemical interferants. Oxygen generation by the auxiliary electrode advantageously improves oxygen availability to the enzyme and / or counter electrode; thereby enabling the electrochemical sensors of the preferred embodiments to function even during ischemic conditions. Interferant modification by the auxiliary electrode advantageously renders them substantially non-reactive at the analyte-measuring electrode, thereby reducing or eliminating inaccuracies in the analyte signal due to electrochemical interferants.
Owner:DEXCOM
Method and apparatus for indicating an encountered obstacle during insertion of a medical device
A technique for detecting and indicating an internal anatomical obstacle encountered during insertion of a medical device into the body of a patient, comprising an elongated member such as a tube, catheter, guidewire, or other device, having a location indicating element, such as a permanent magnet, flexibly coupled to its distal end, and an external detector that tracks and displays the location and orientation of the location indicating element. The flexible coupling has sufficient stiffness to maintain the orientation of the location indicating element against the forces from both gravity and flowing blood within a patient's vasculature, but allows the location indicating element to change orientation if it encounters an obstacle during insertion. The medical caregiver monitors the detector's display and determines encounters with obstacles by observing changes in the orientation of the location indicating element.
Owner:LUCENT MEDICAL SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com