Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1046 results about "Percutaneous" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In surgery, a percutaneous procedure is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using an "open" approach where inner organs or tissue are exposed (typically with the use of a scalpel).
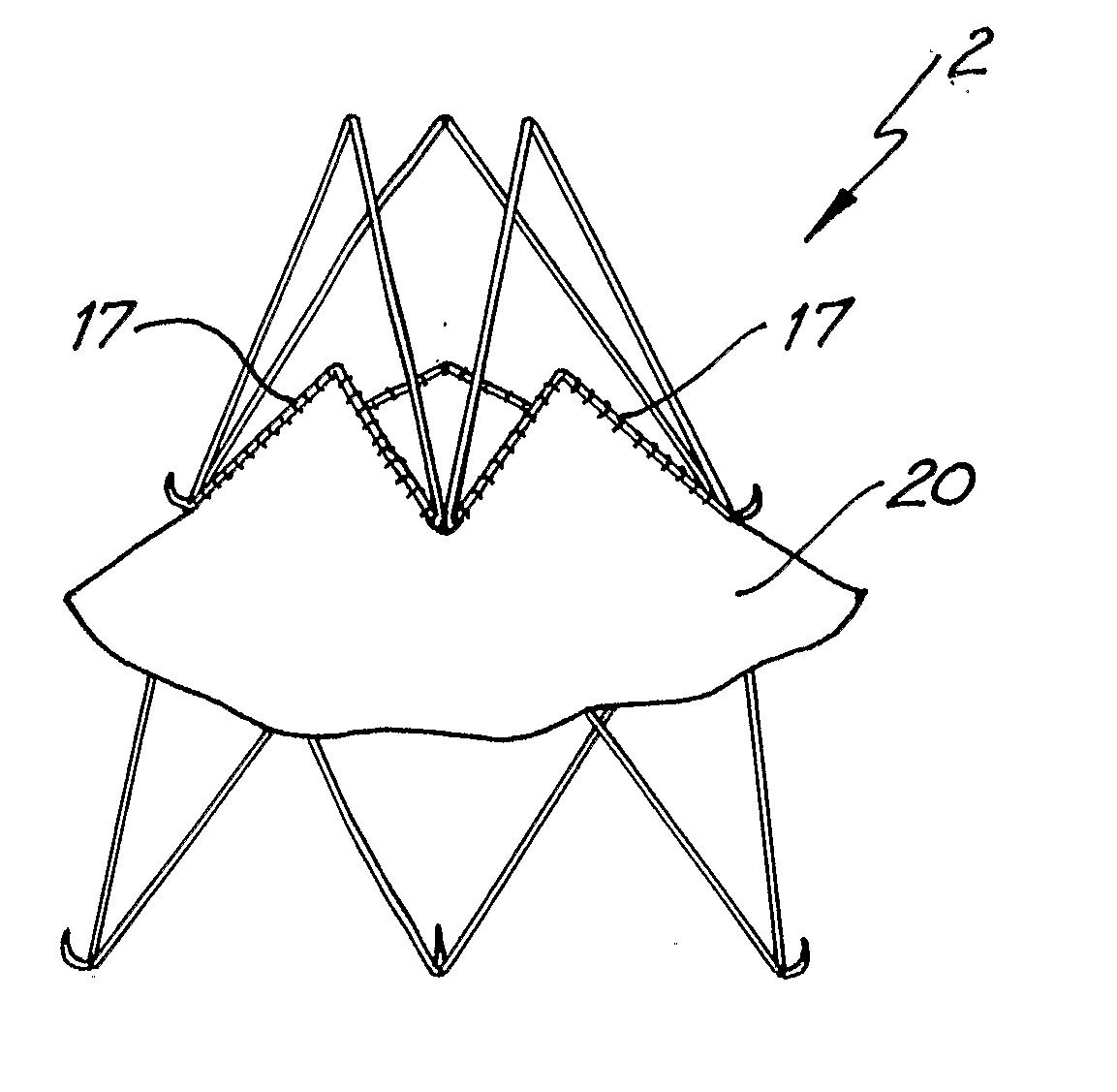
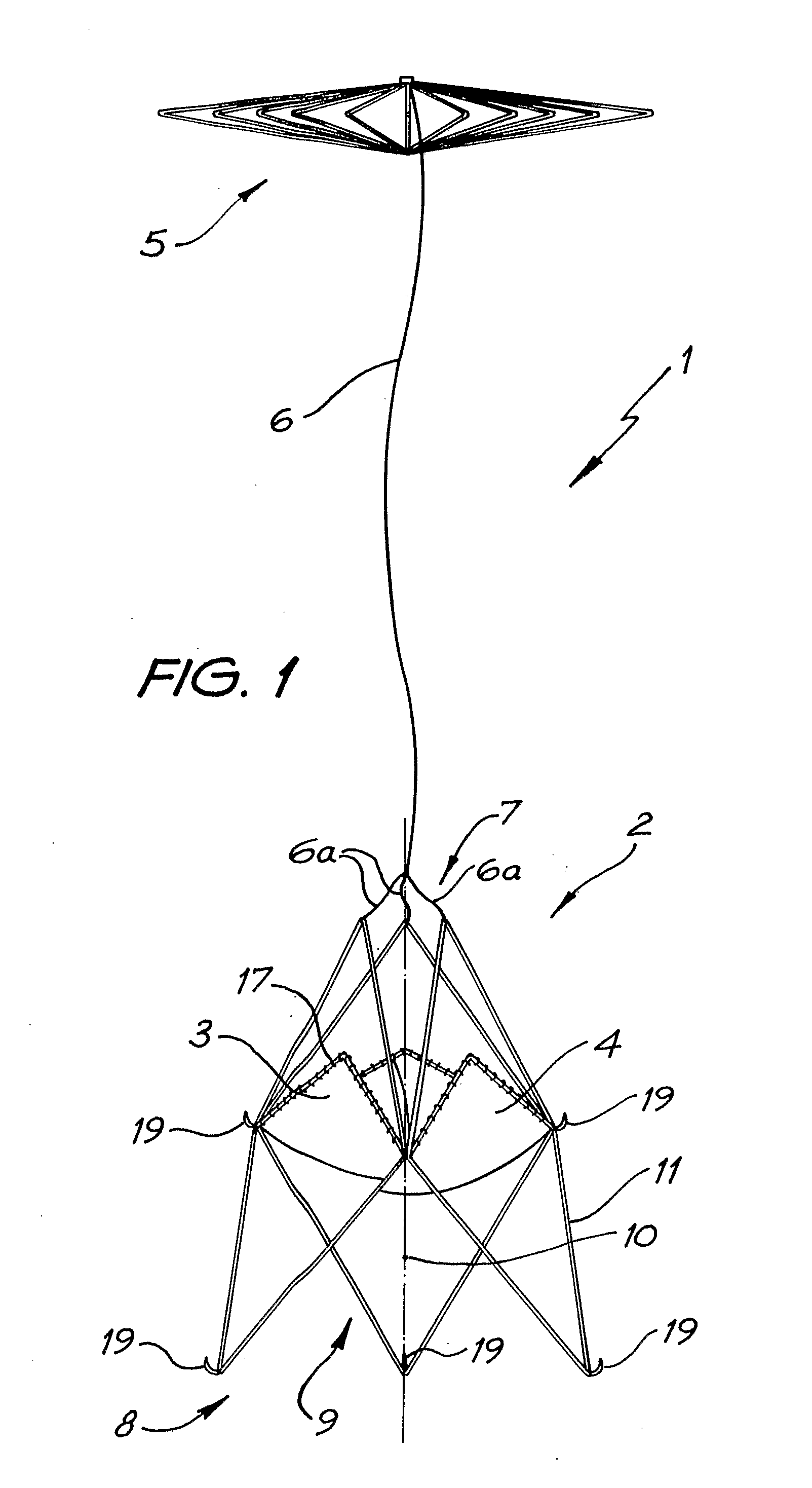
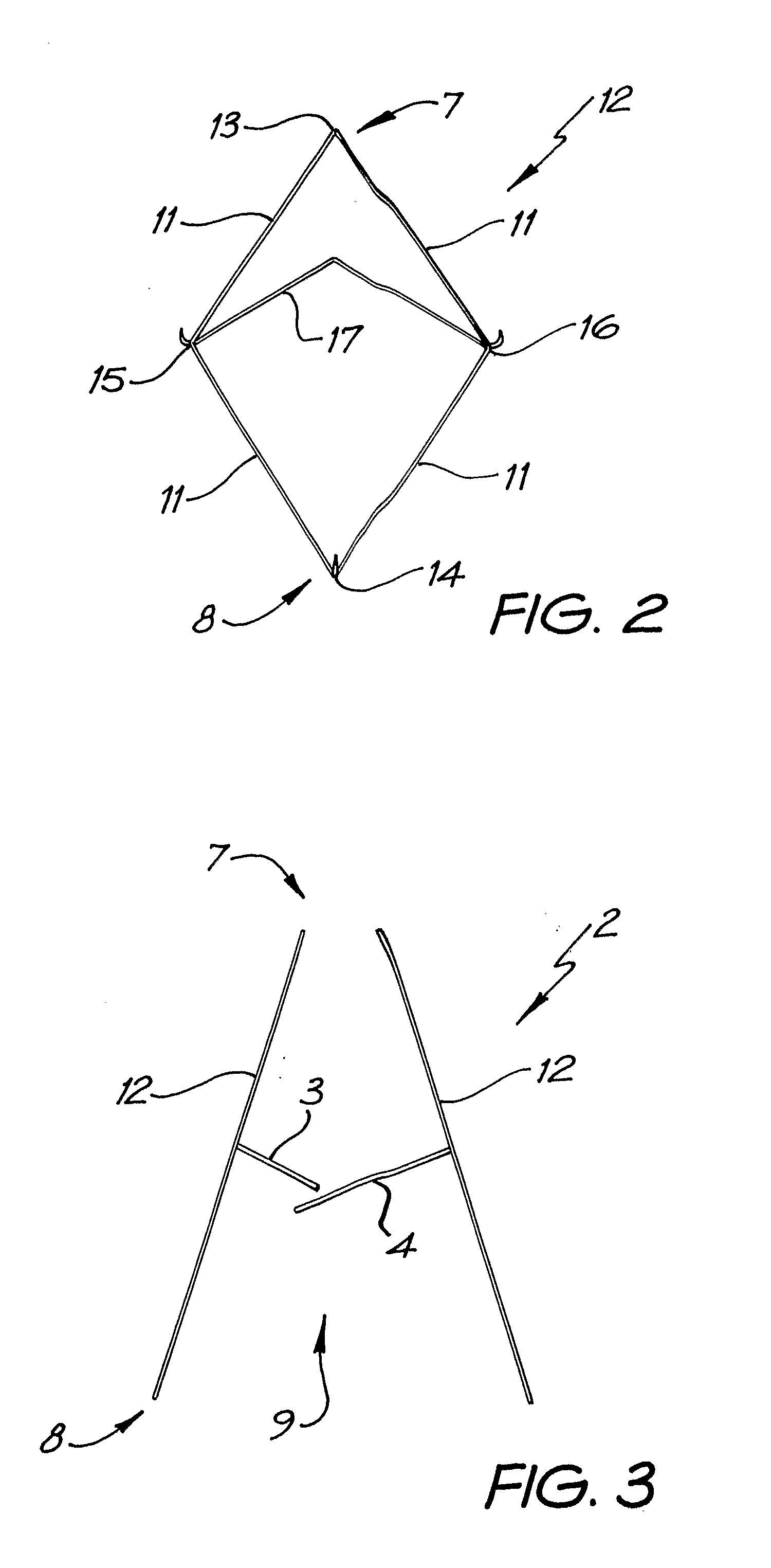
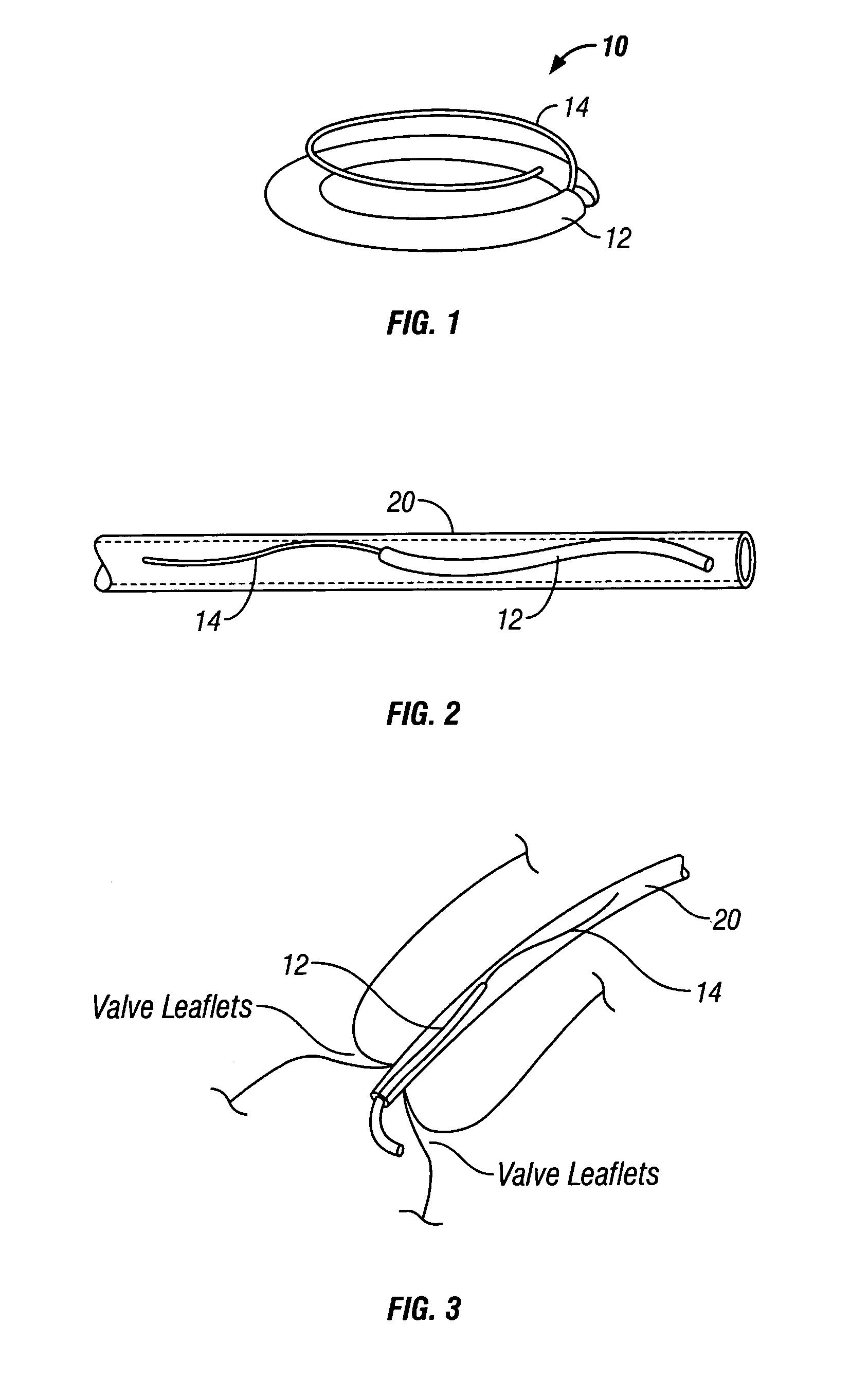
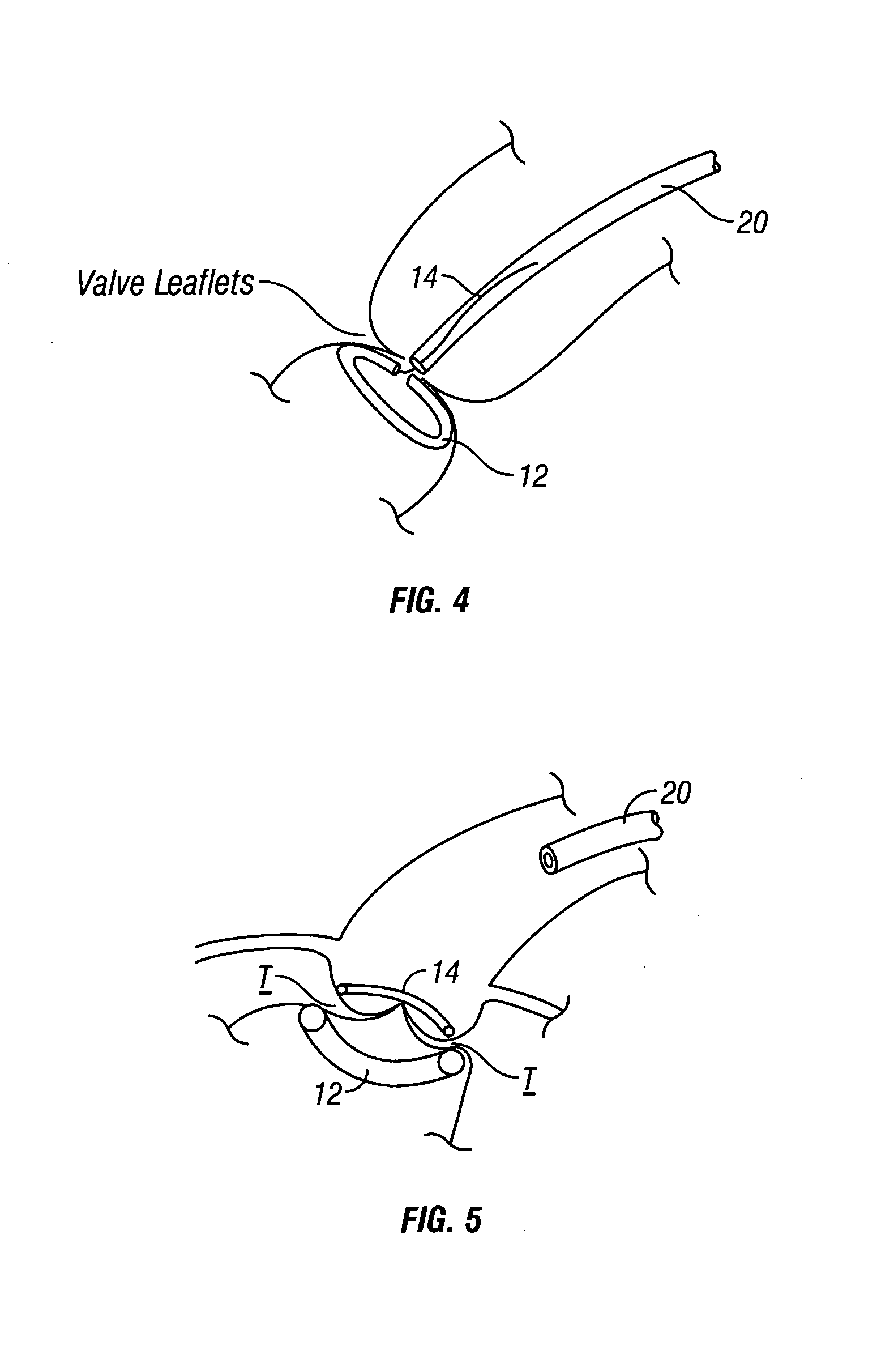
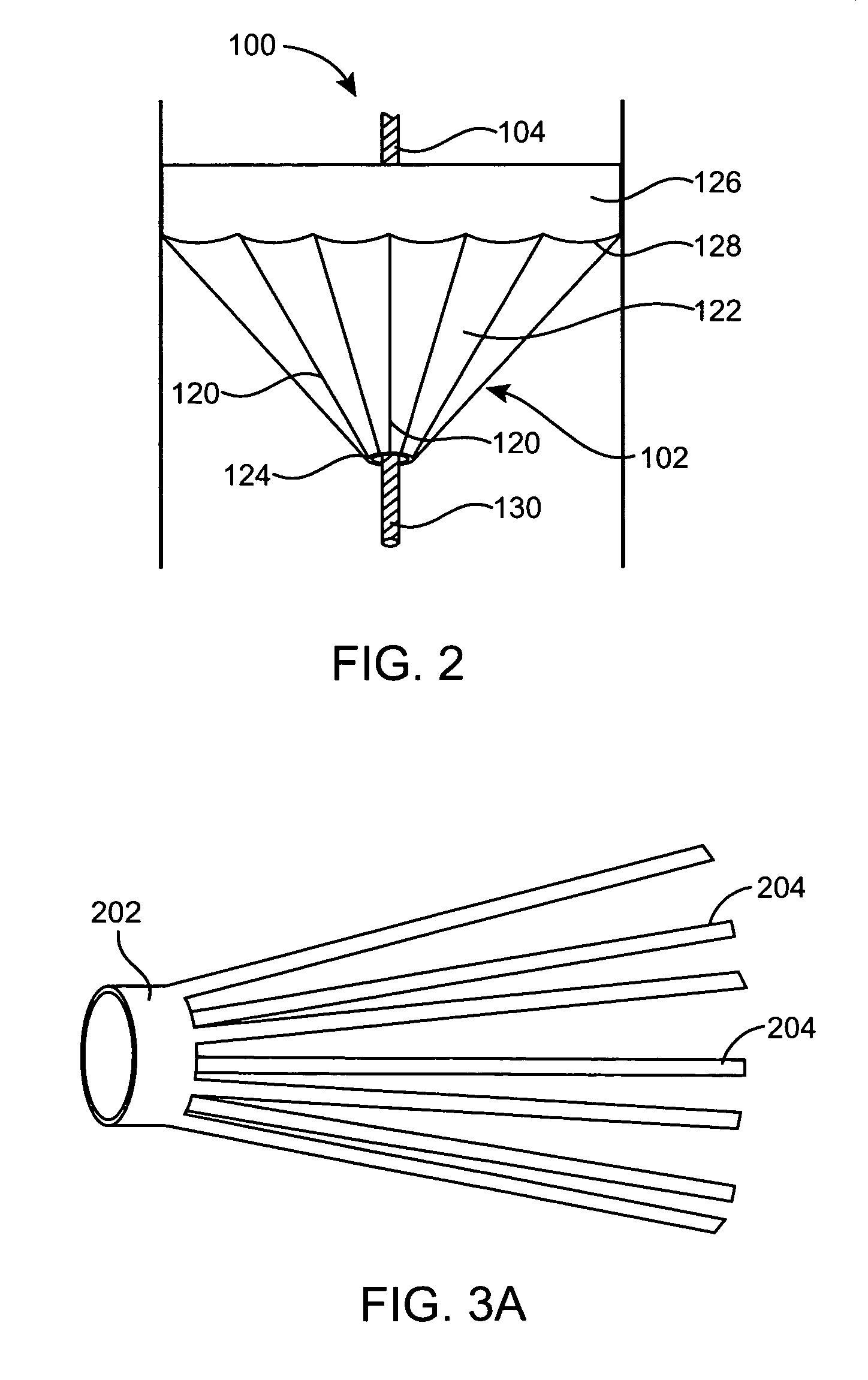
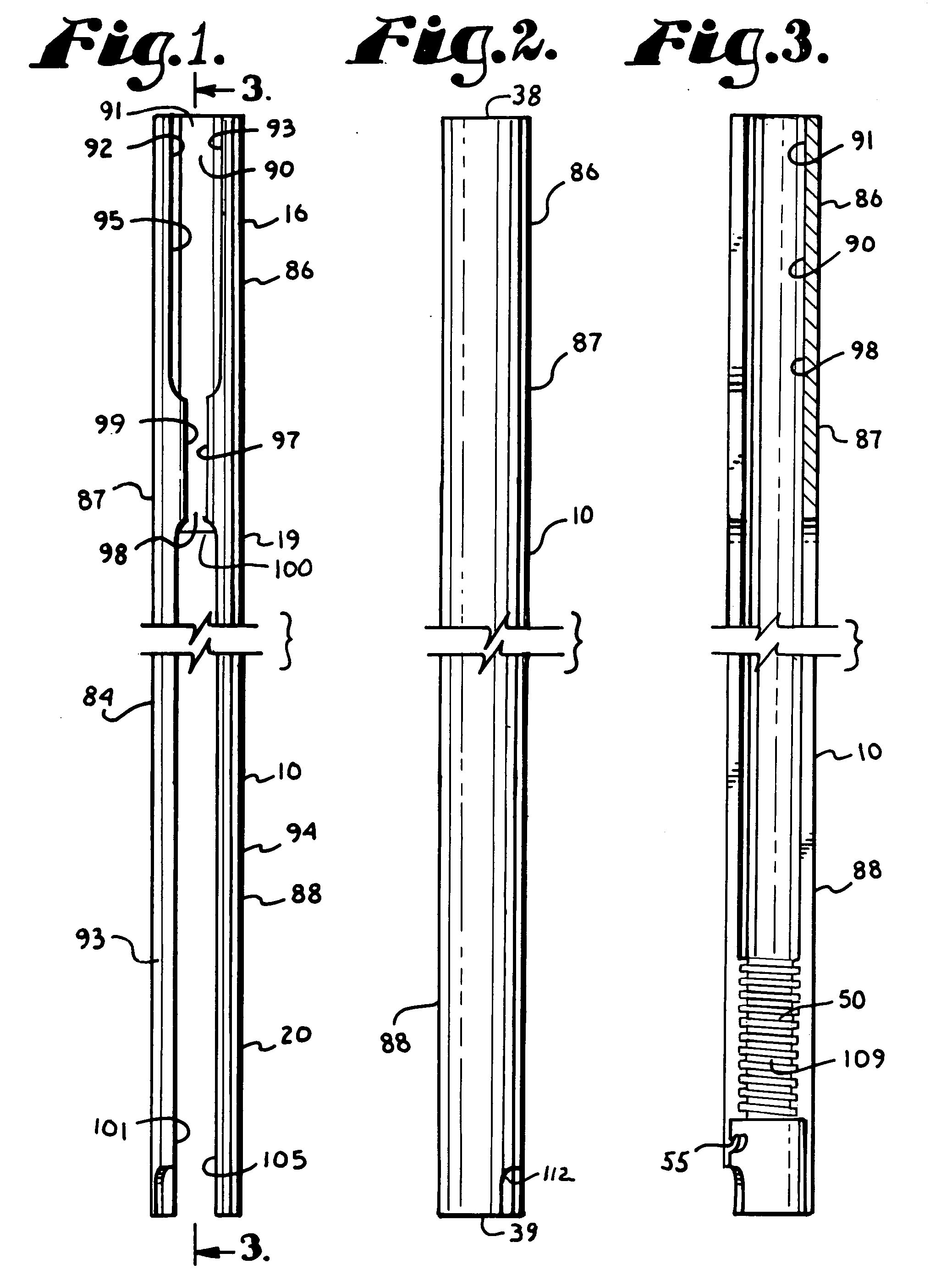
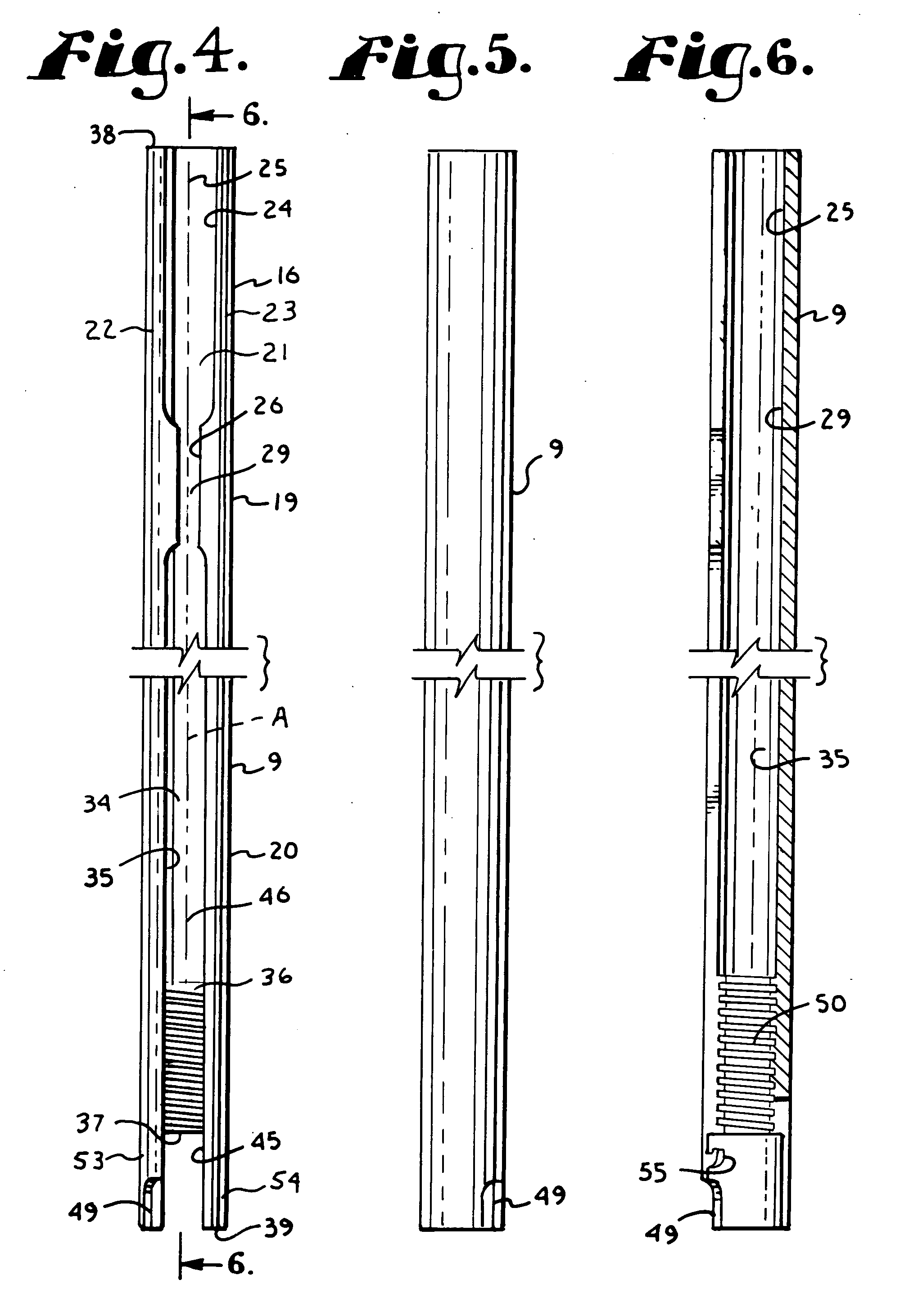
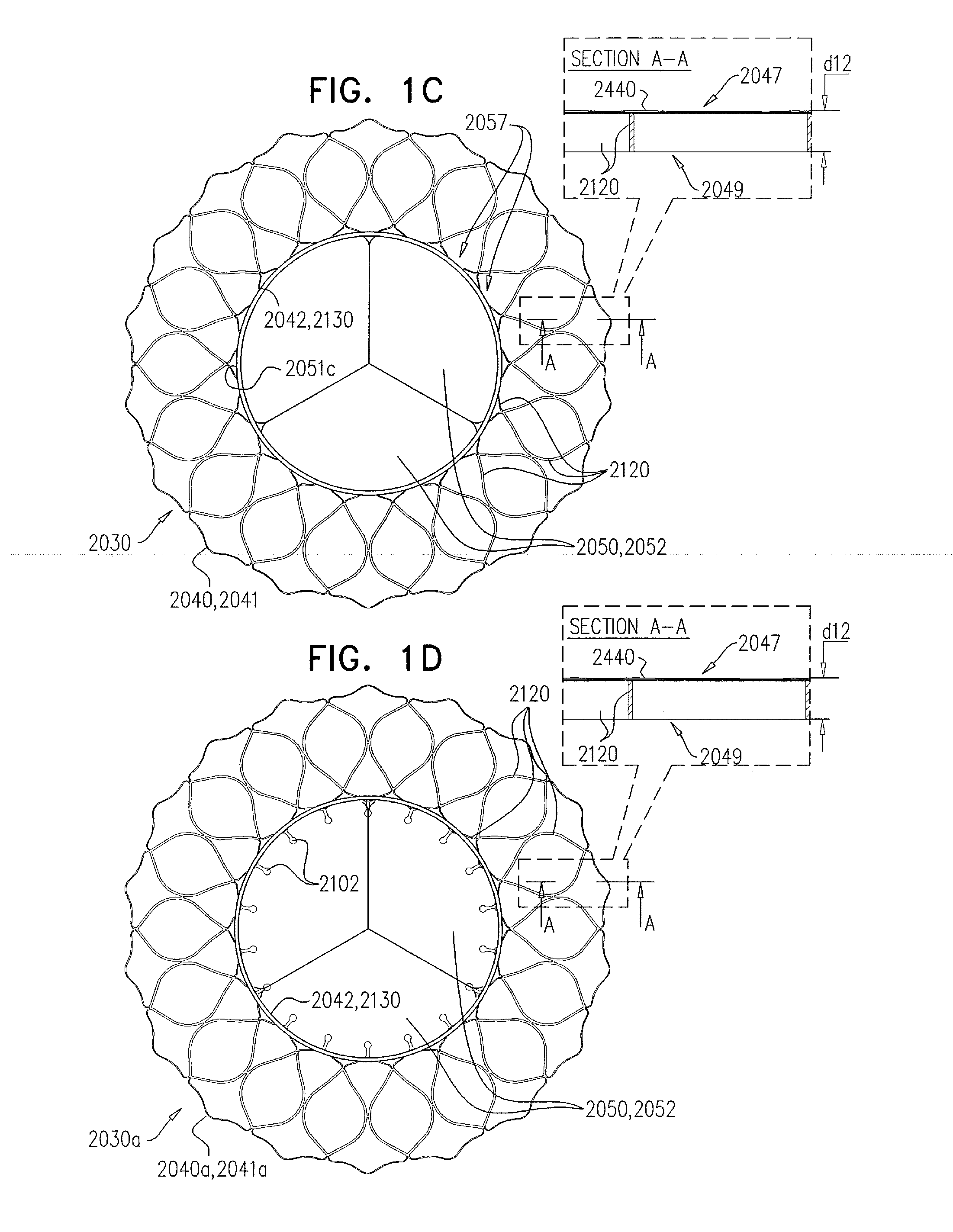
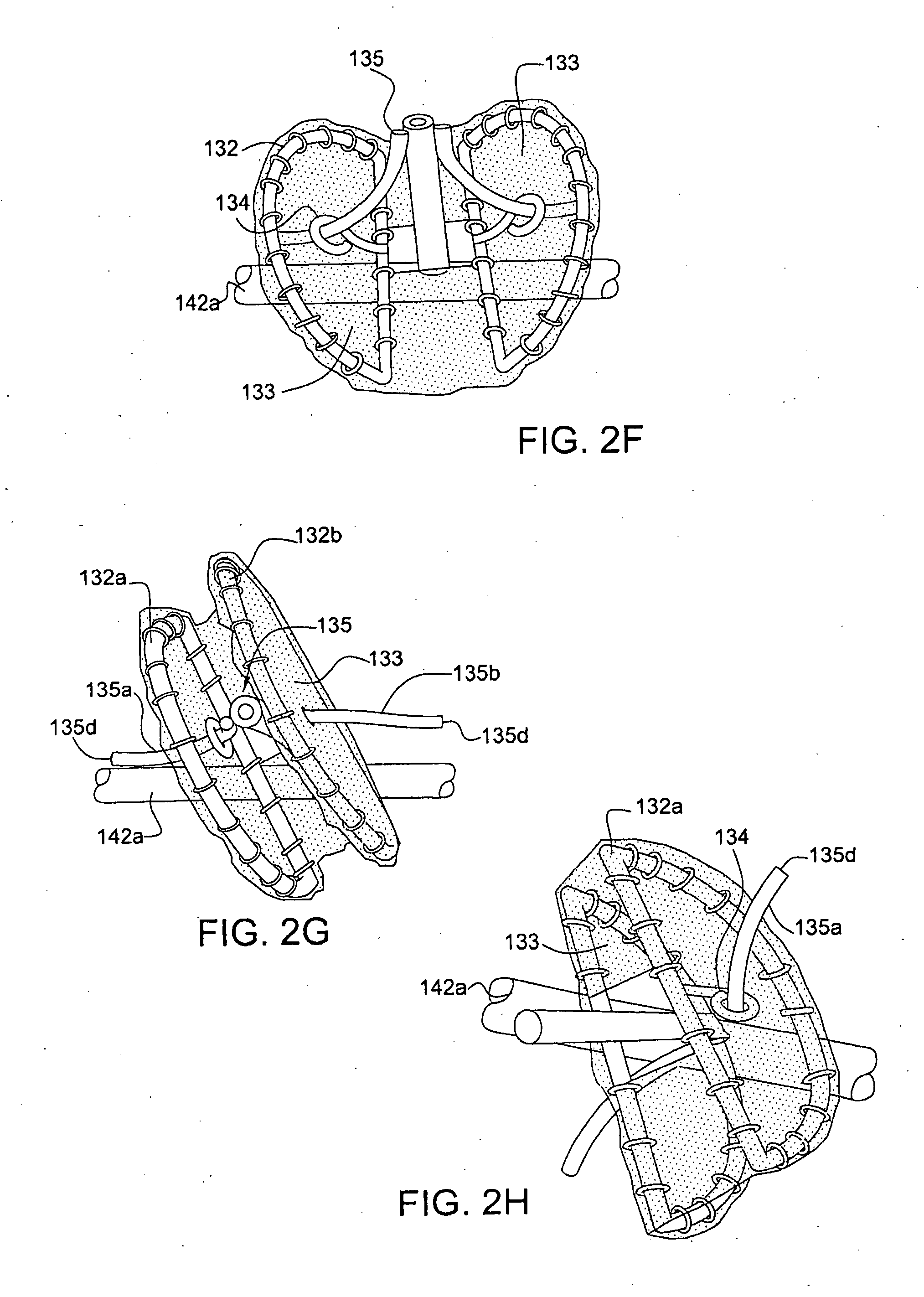
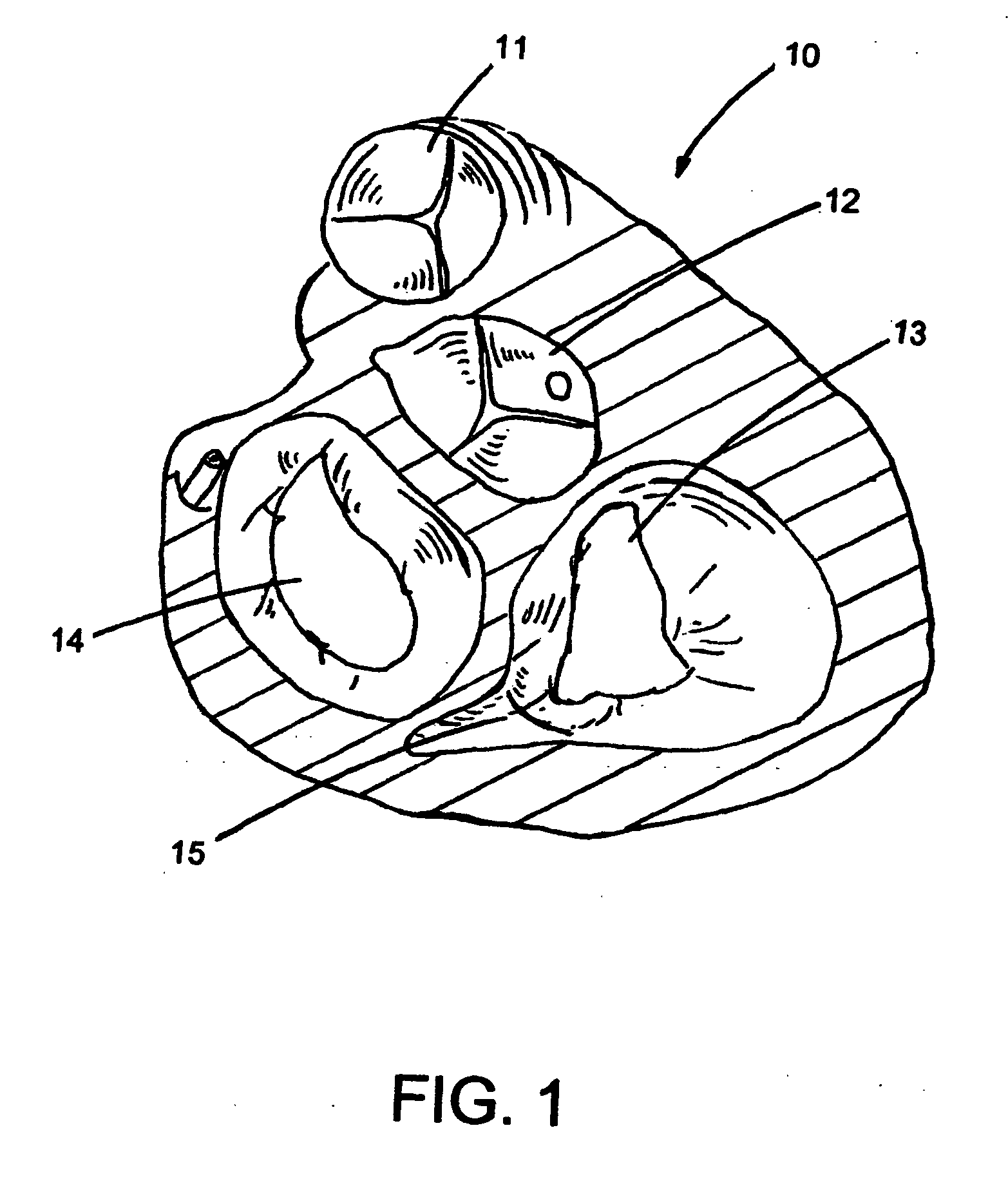
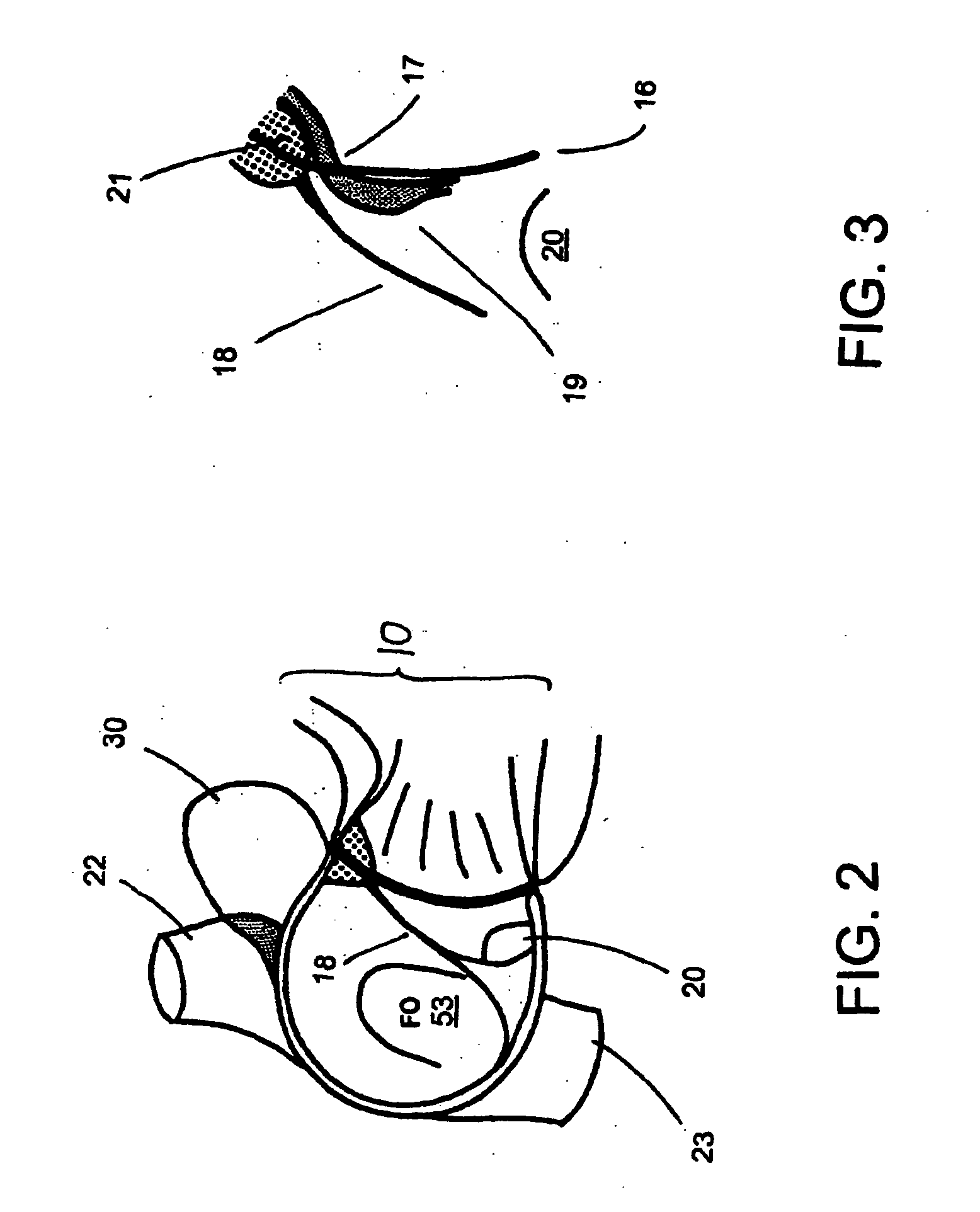
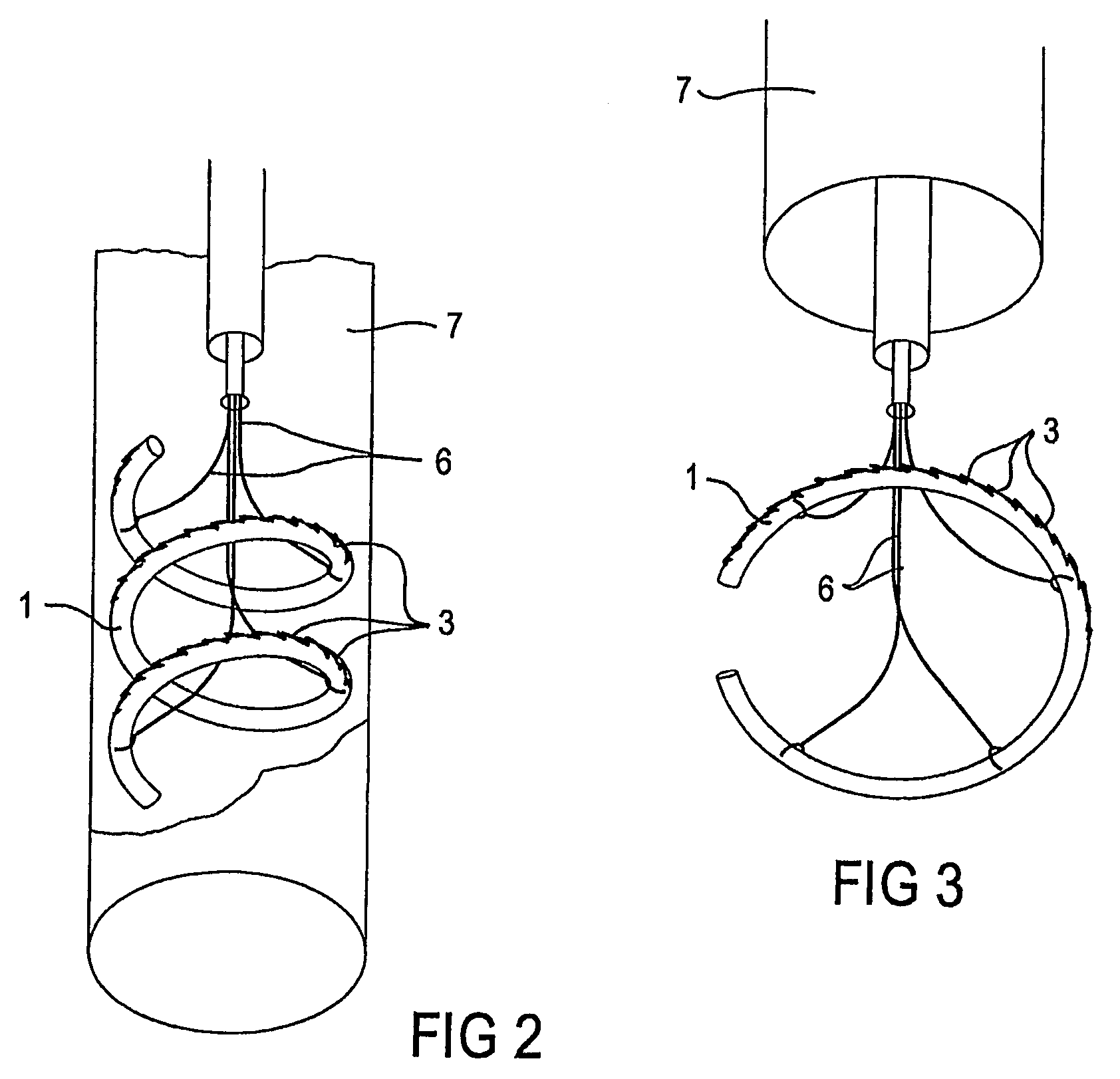
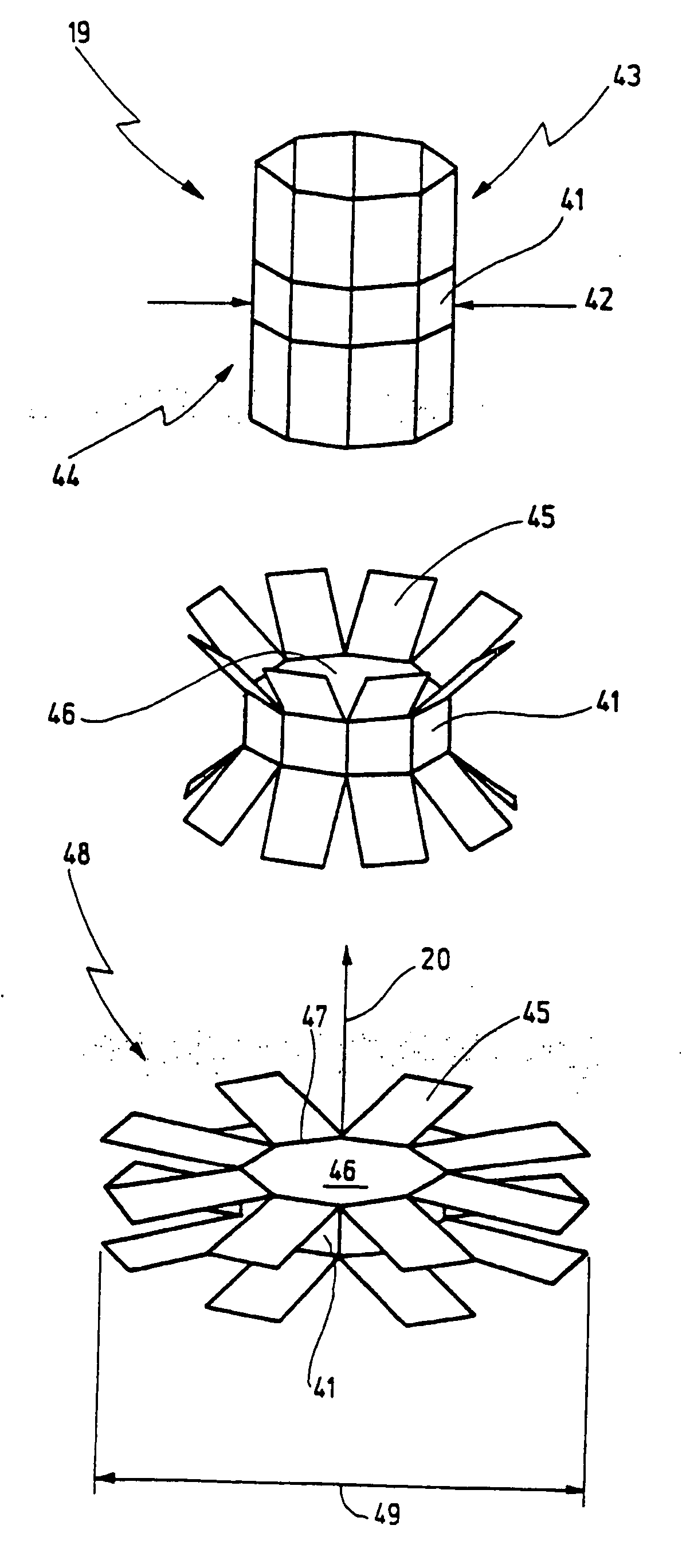
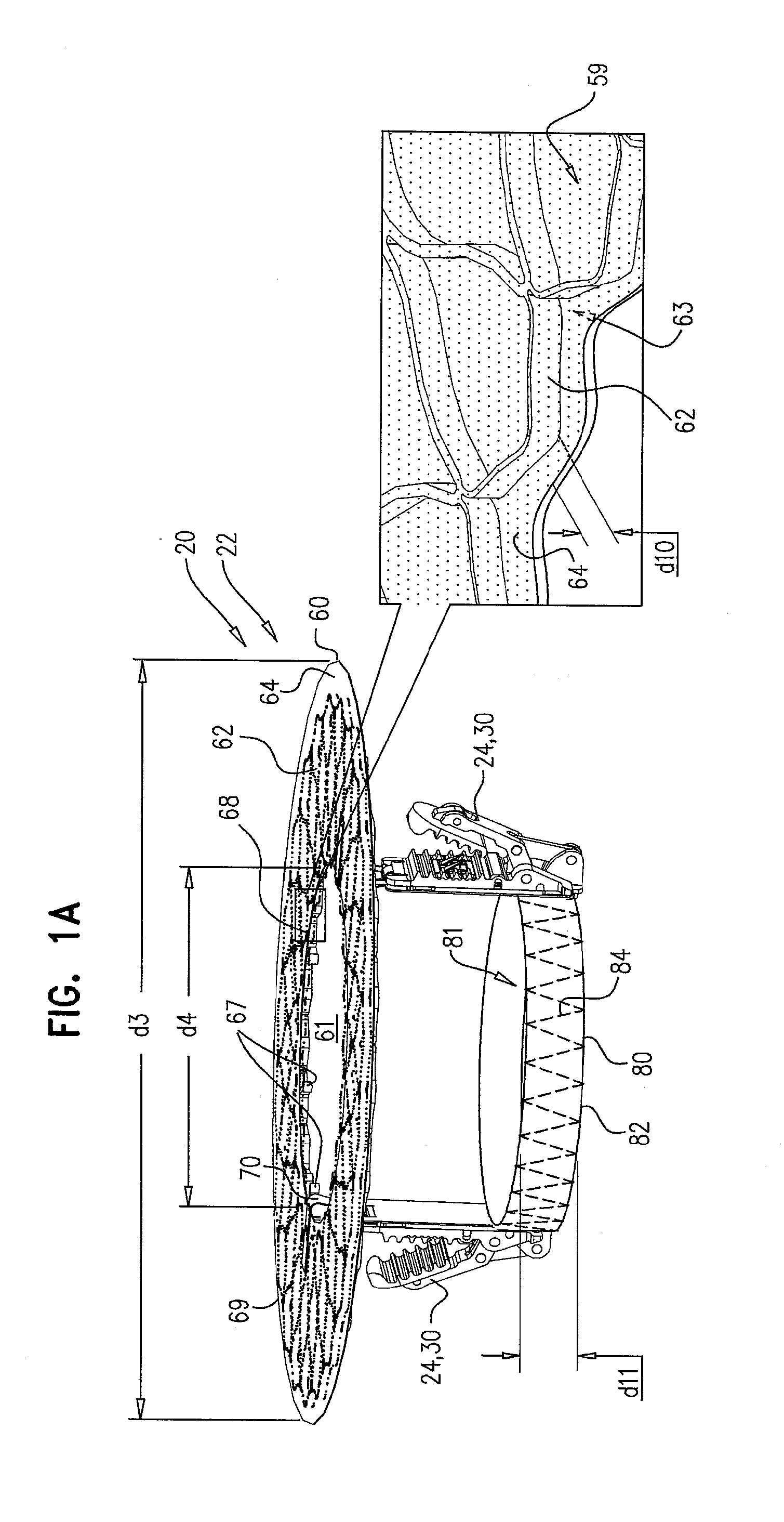
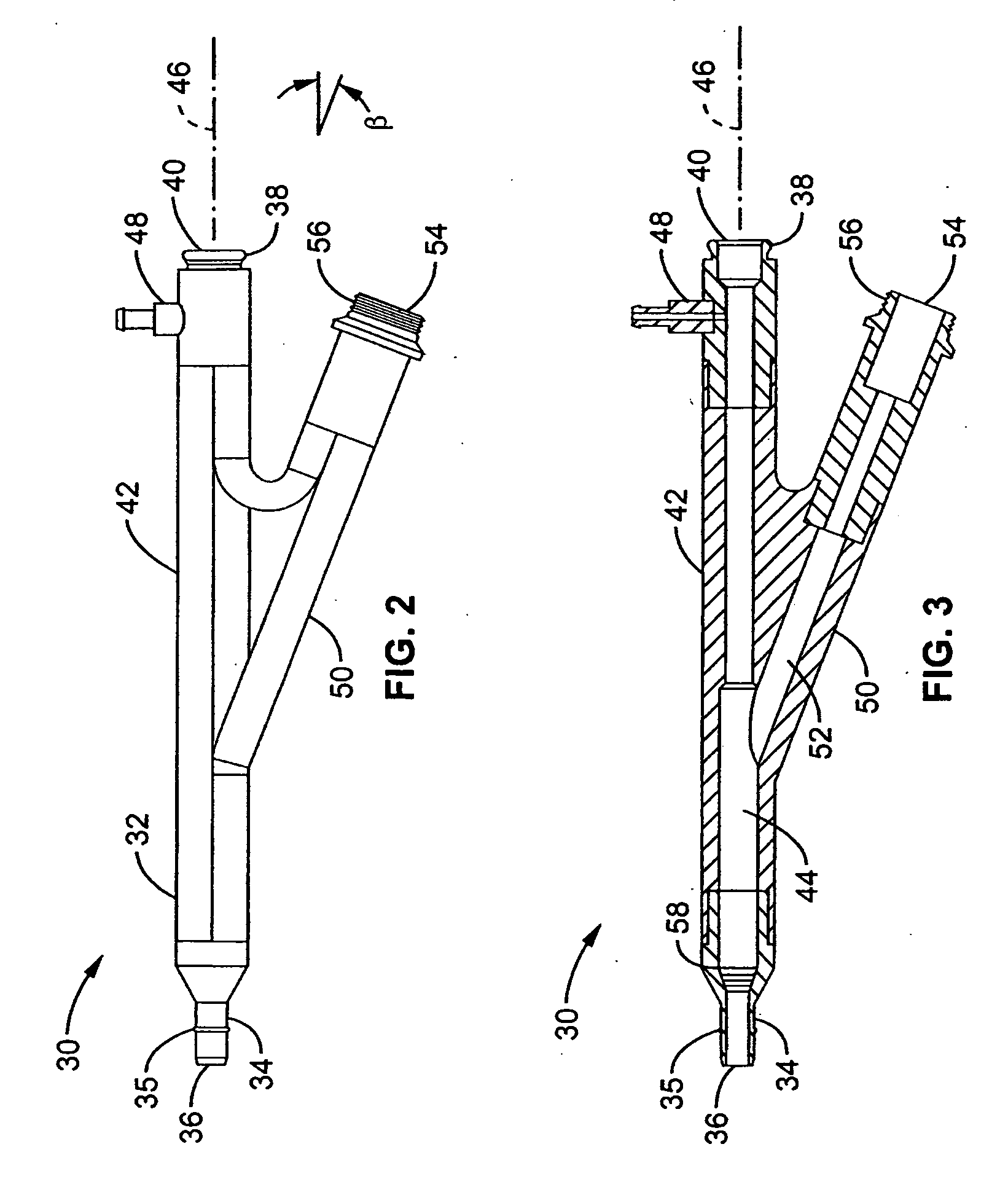
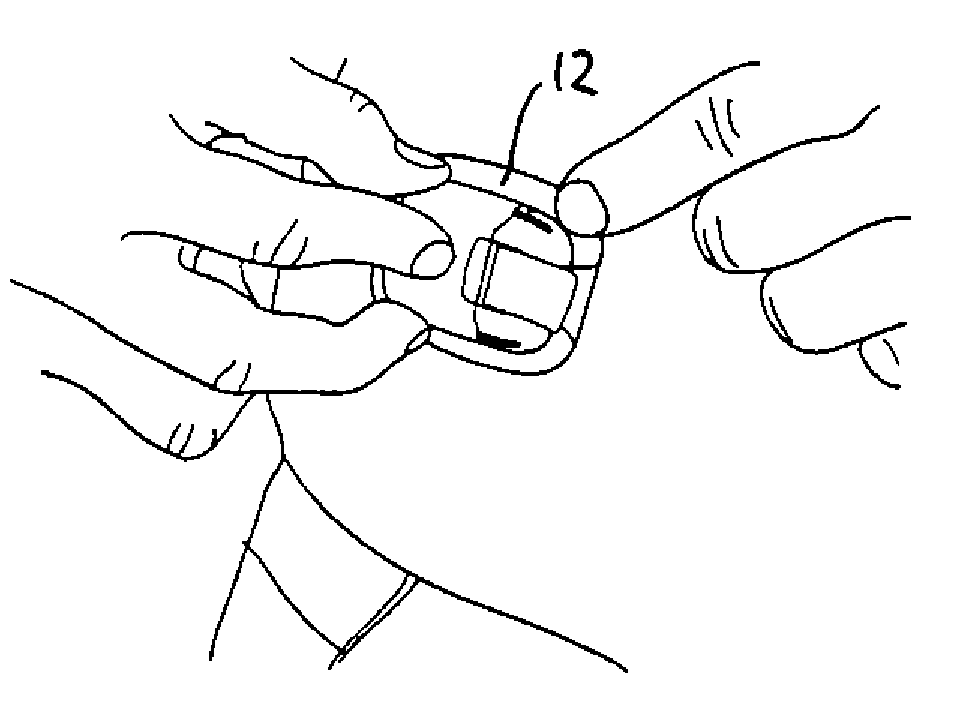
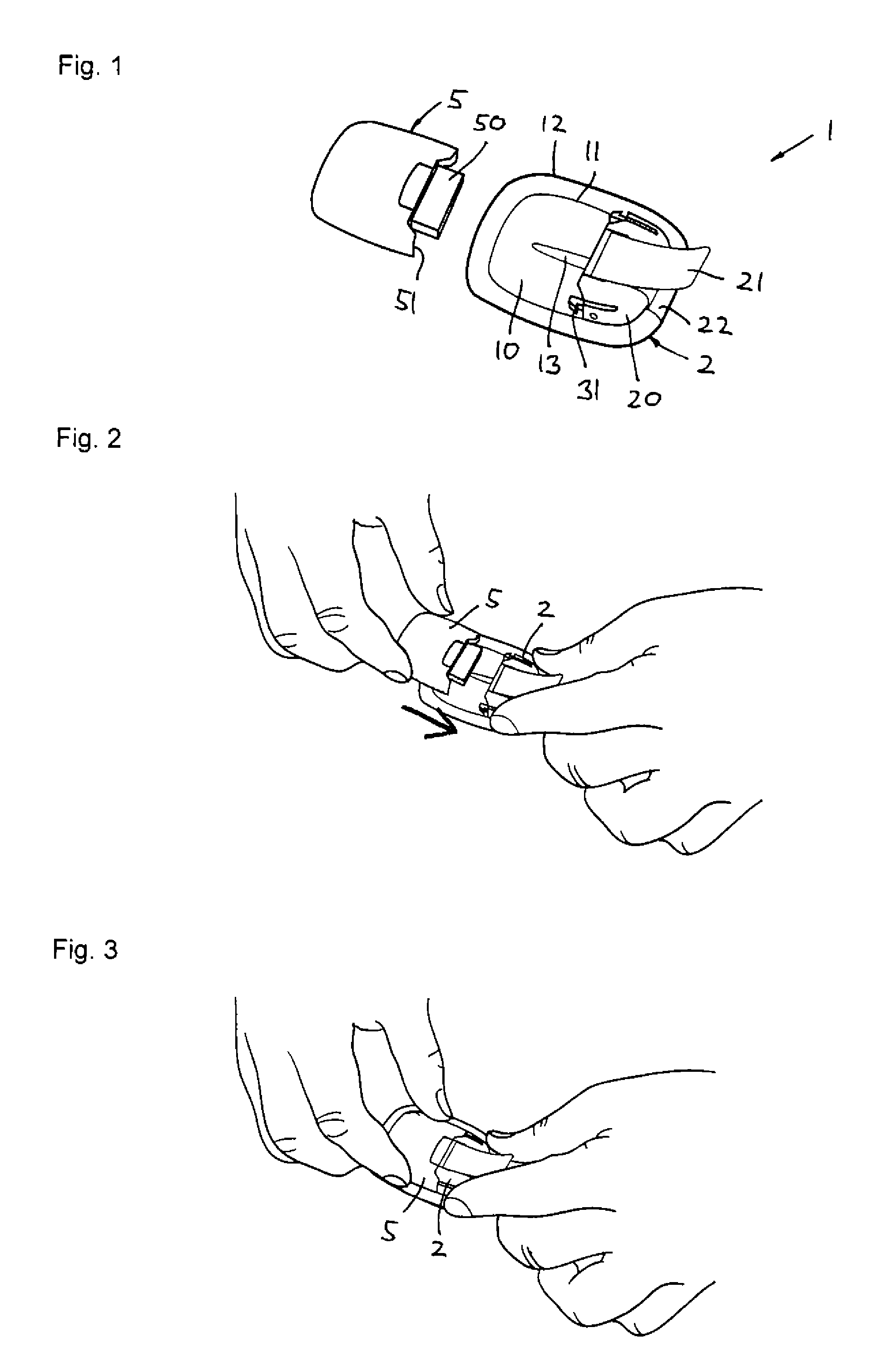
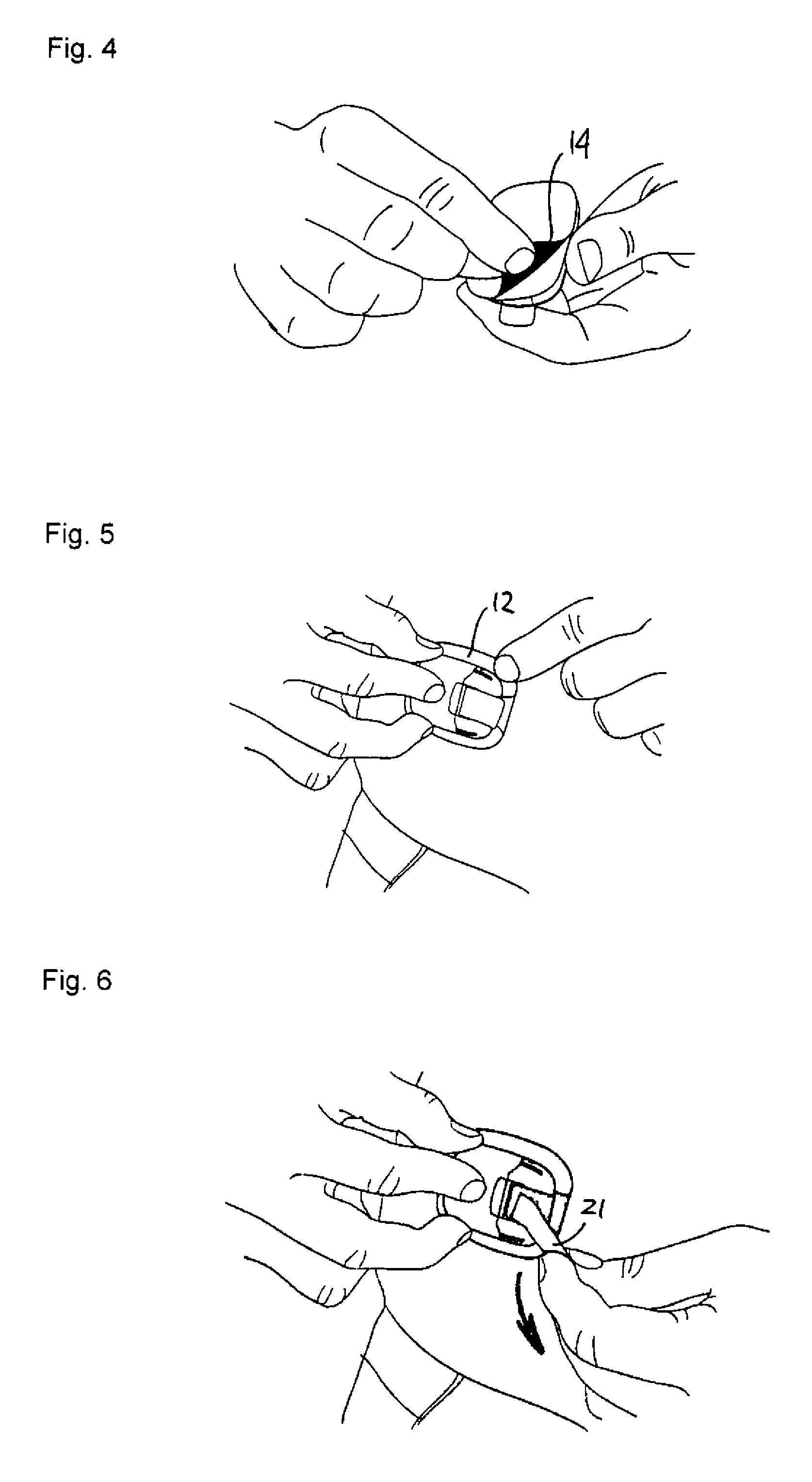
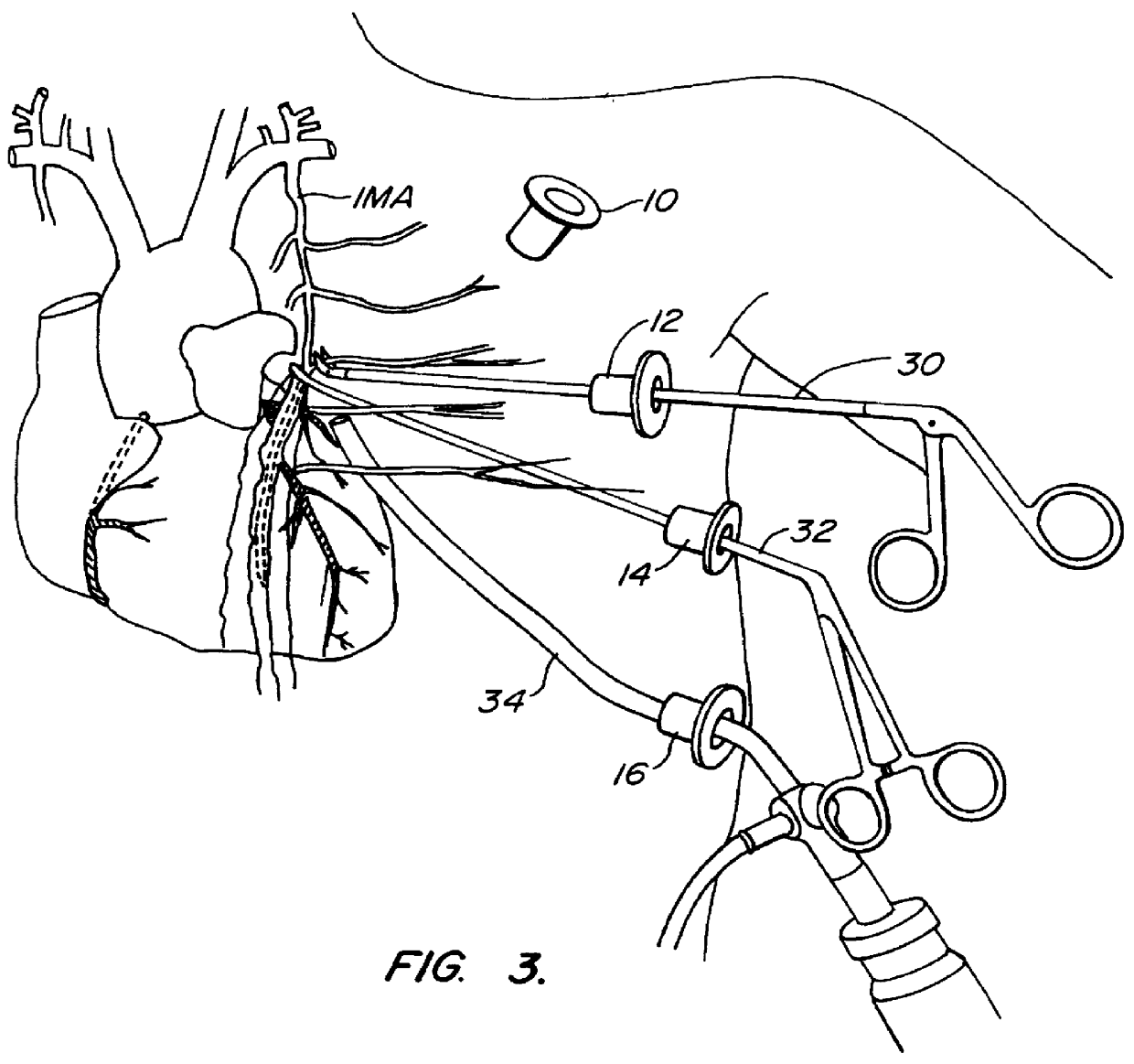
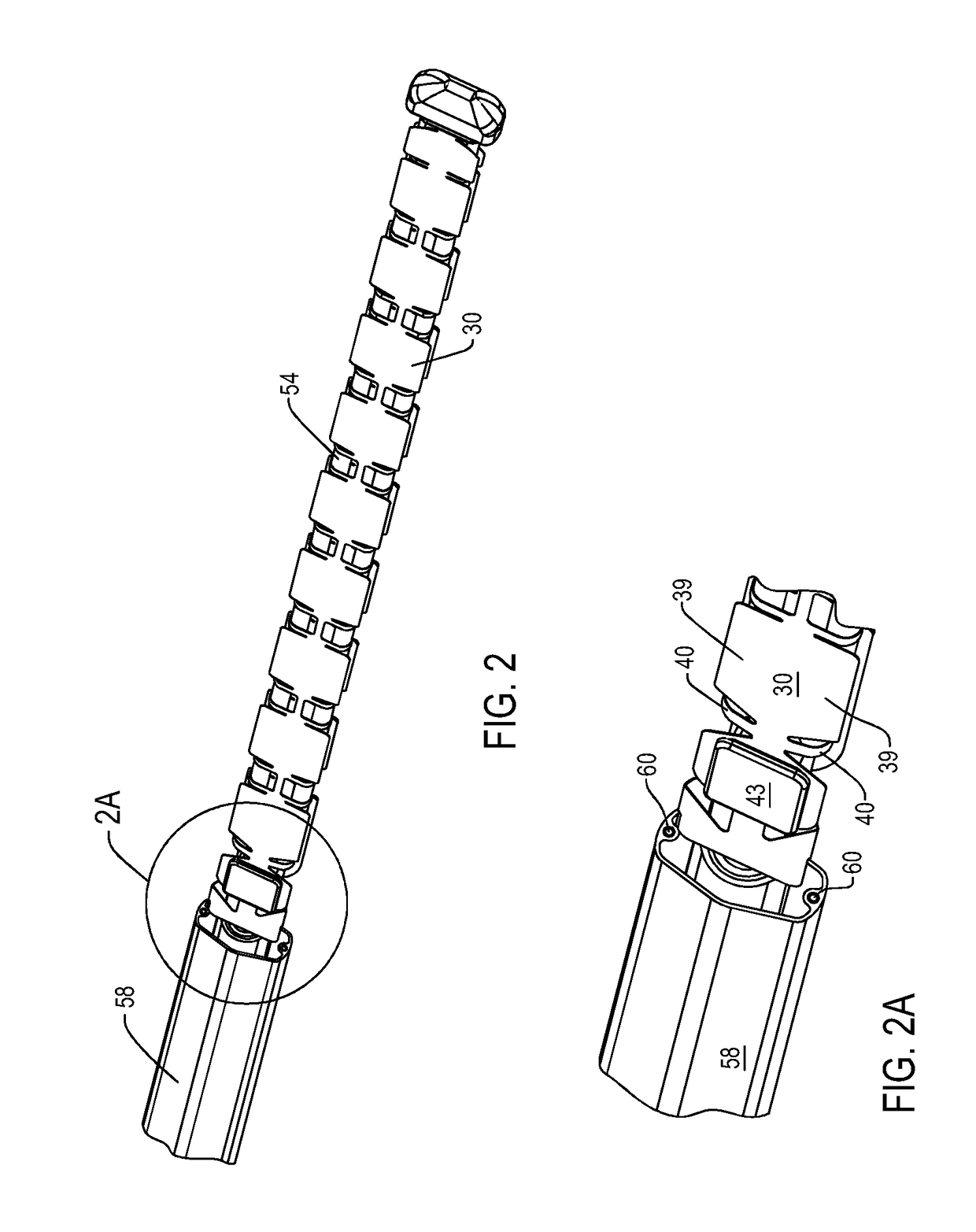
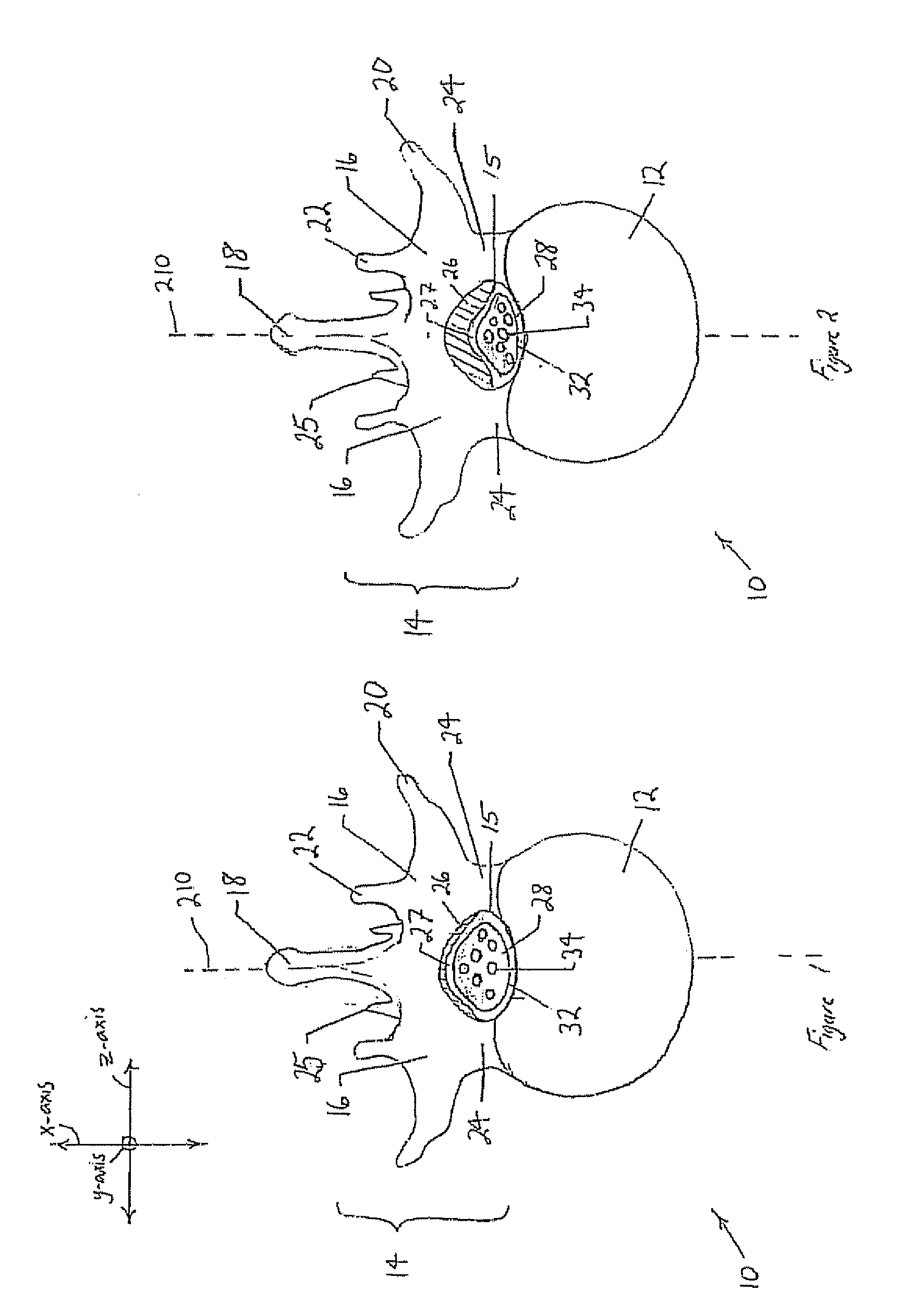
Percutaneous Heart Valve Prosthesis
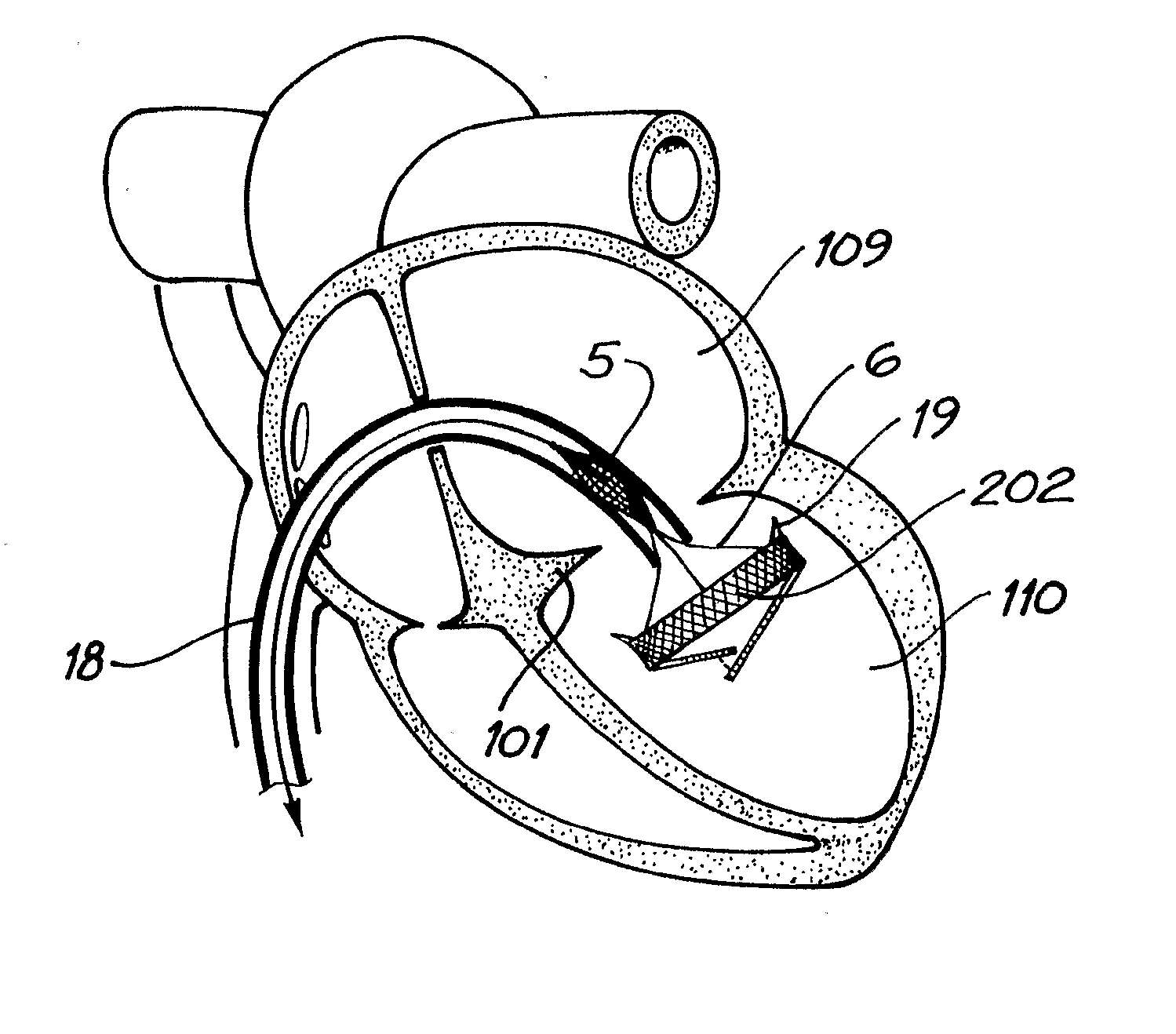
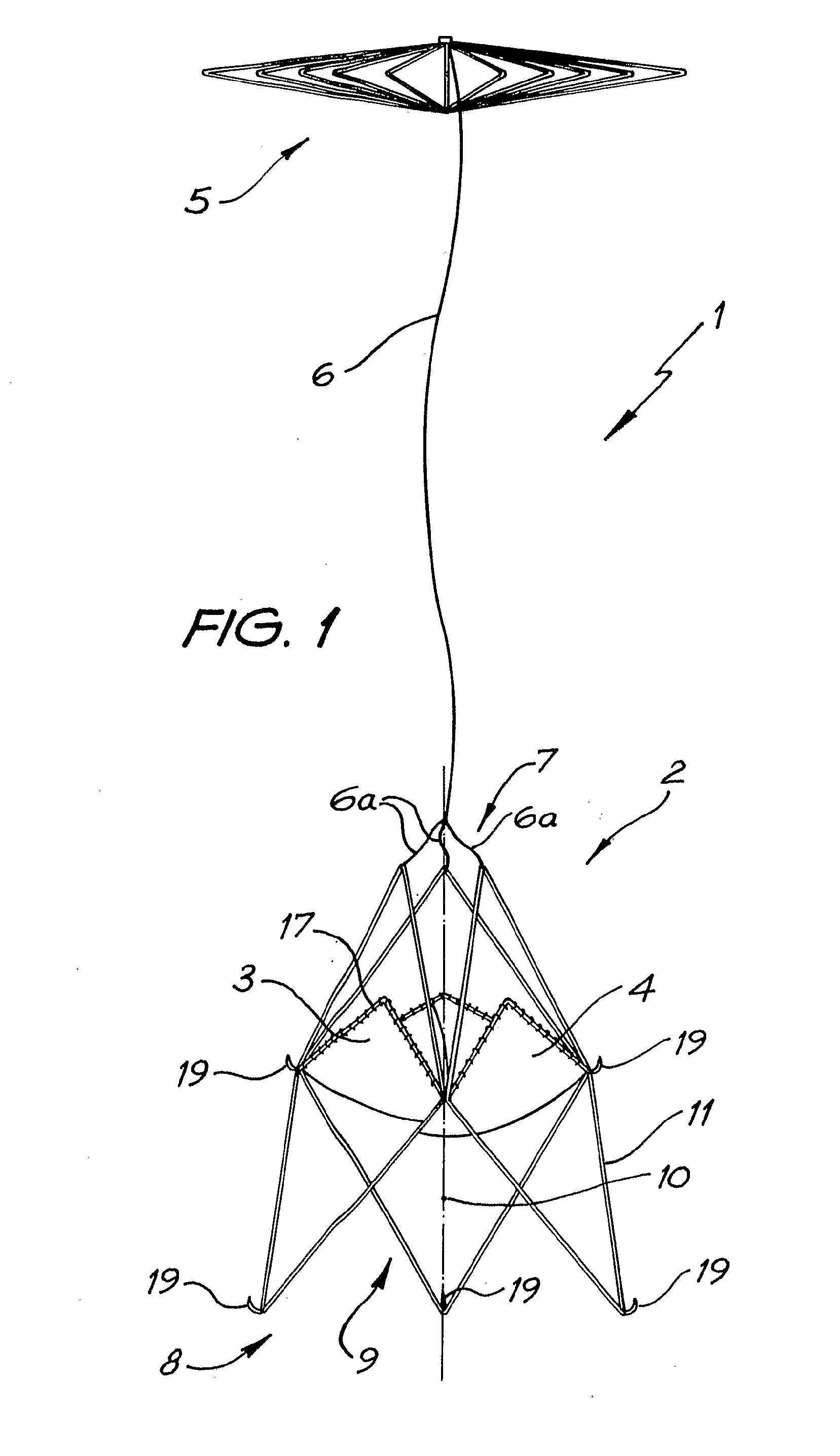
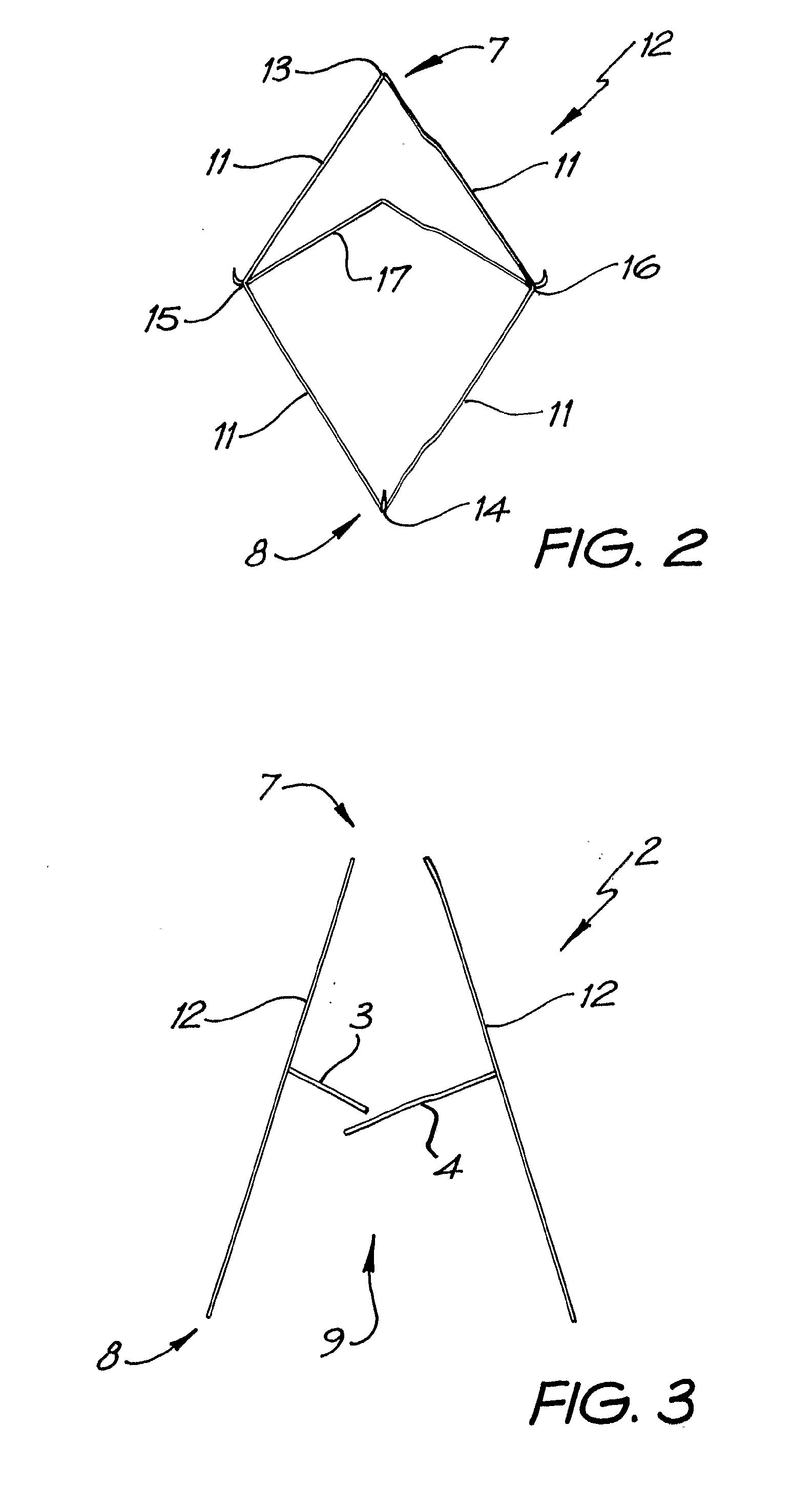
A percutaneous heart valve prosthesis (1) has a valve body (2) with a passage (9) extending between the first and second ends (7, 8) of the valve body (2). The valve body (2) is collapsible about a longitudinal axis (10) of the passage (9) for delivery of the valve body (2) via a catheter (18). One or more flexible valve leaflets (3, 4) are secured to the valve body (2) and extend across the passage (9) for blocking bloodflow in one direction through the passage (9). An anchor device (5), which is also collapsible for delivery via catheter (18), is secured to the valve body (2) by way of an anchor line (6). A failed or failing mitral heart valve (101) is treated by percutaneously locating the valve body (2) in the mitral valve orifice (102) with the anchor device (5) located in the right atrium (107) and engaging the inter-atrial septum (103), such that the taught anchor line (6) acts to secure the valve body (2) within the mitral valve orifice (102).
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS CARDIOVASCULAR SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for valve repair
InactiveUS7125421B2Minimize traumaLow costAnnuloplasty ringsTubular organ implantsLinear configurationBiomedical engineering
A tissue connection device is provided for use on a patient at a treatment site. The device comprises an elongate member having a distal end and a proximal end. The elongate member has a first, substantially linear configuration during delivery through an elongate delivery device, wherein the first configuration is sufficient to allow said member to be delivered percutaneously into the patient to the treatment site. The elongate member has a second, substantially circular configuration when said member disengages from the delivery device, wherein the second configuration is sufficient to support tissue at the treatment site. The elongate member in the second configuration defines a single ring.
Owner:MITRAL INTERVENTIONS INC
Percutaneously delivered temporary valve assembly
The percutaneously delivered temporary valve assembly of the present invention, and method of using the same, provides an elongate element and a temporary valve disposed on the elongate element. The temporary valve can comprise struts and a membrane attached to the struts. The elongate element can include at least one lumen. The percutaneously delivered temporary valve assembly can be used to replace an aortic valve by locating a temporary valve in a patient's ascending aorta; deploying the temporary valve; removing the native aortic valve past the temporary valve; implanting the prosthetic aortic valve past the temporary valve; collapsing the temporary valve; and removing the temporary valve from the patient. The temporary valve can be sized to the patient and can be left in place while the prosthetic aortic valve heals in.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
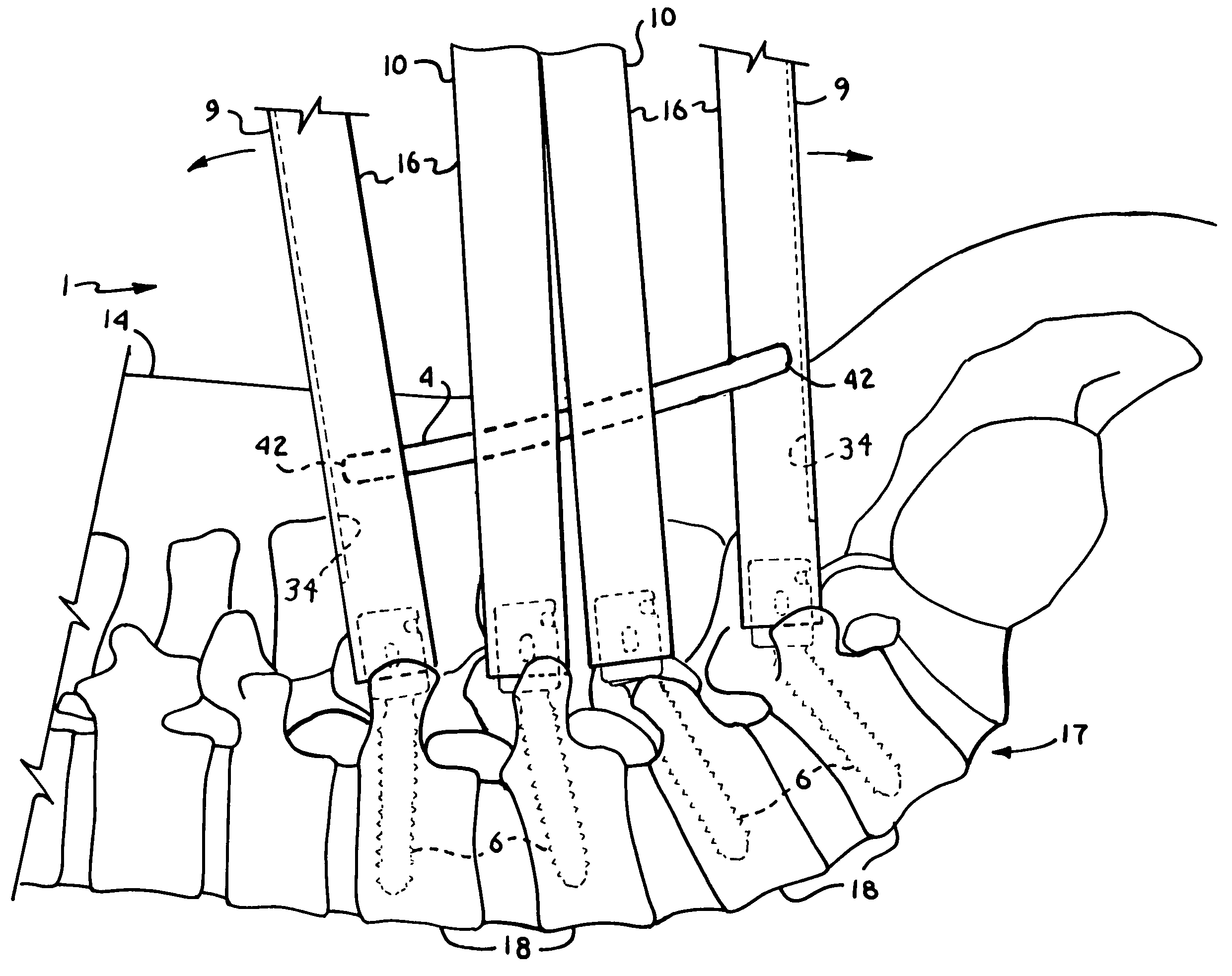
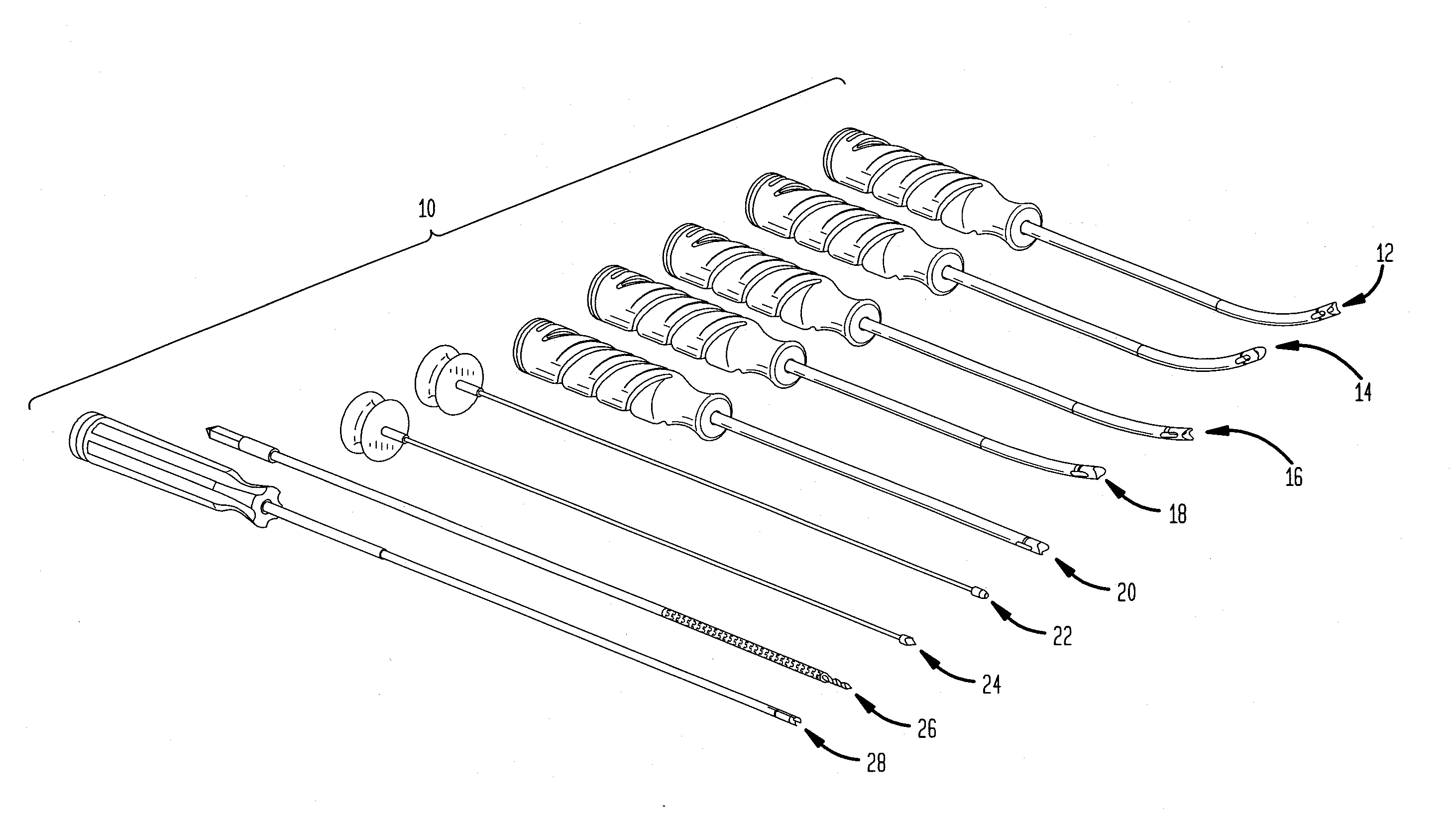
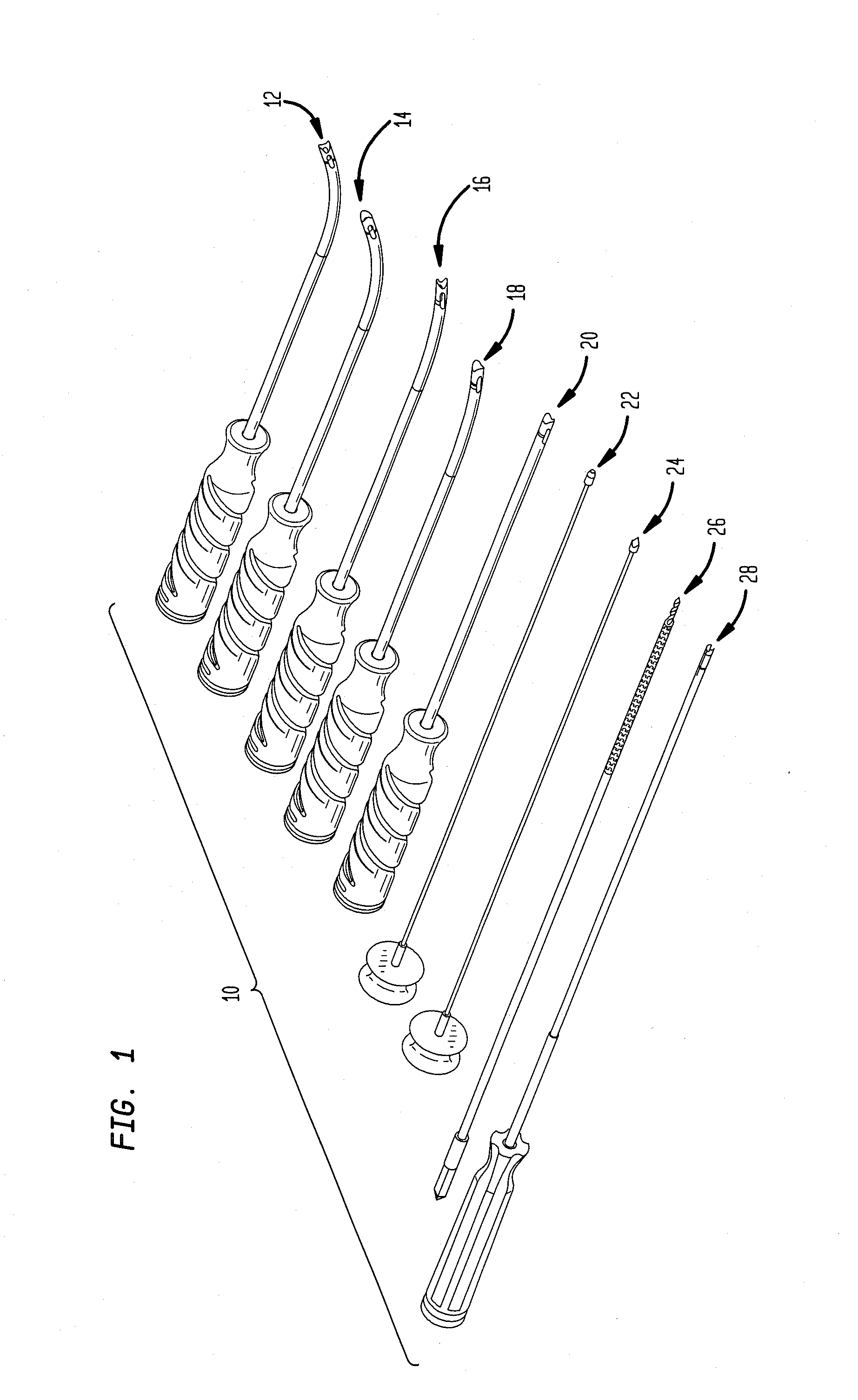
Orthopedic implant rod reduction tool set and method
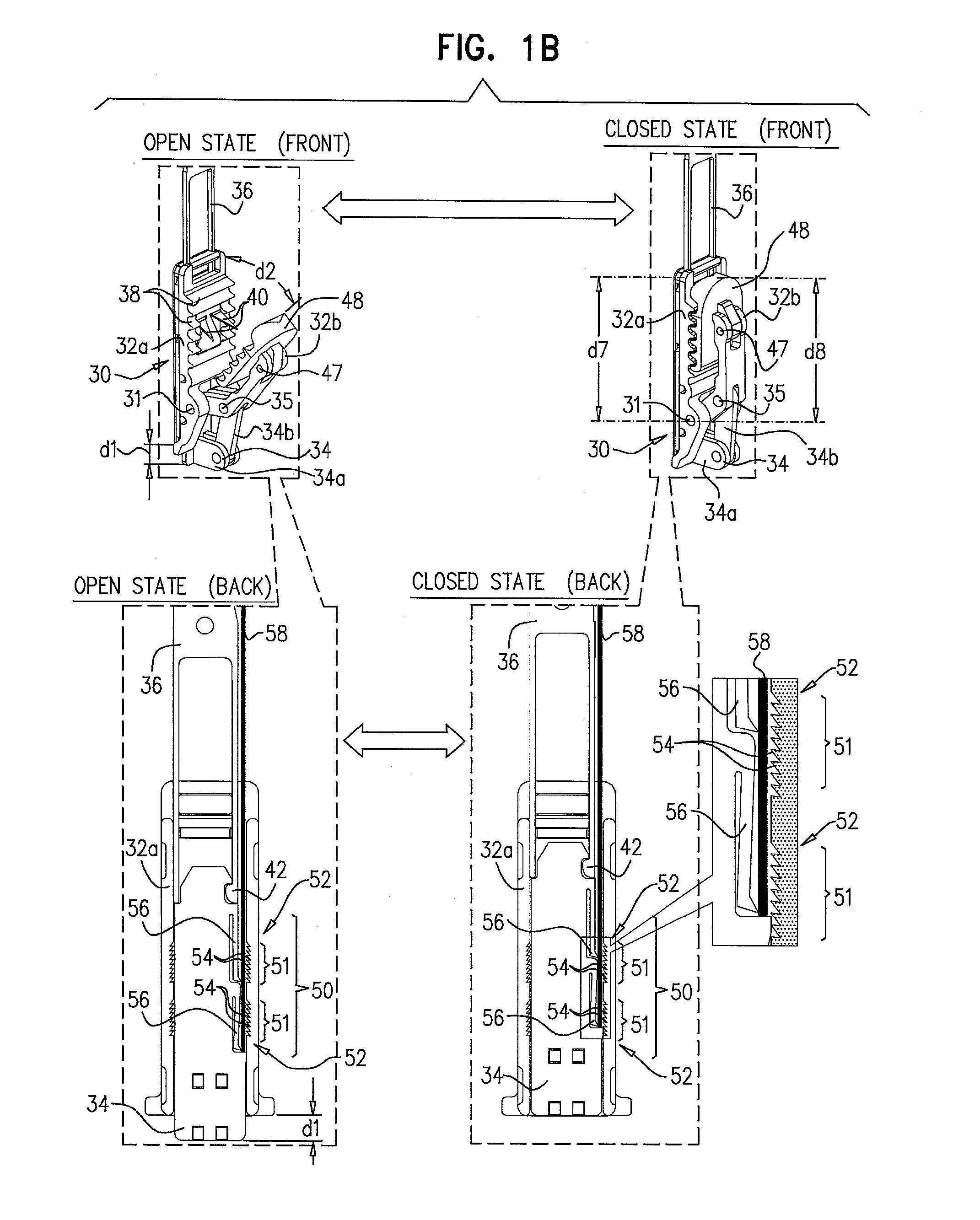
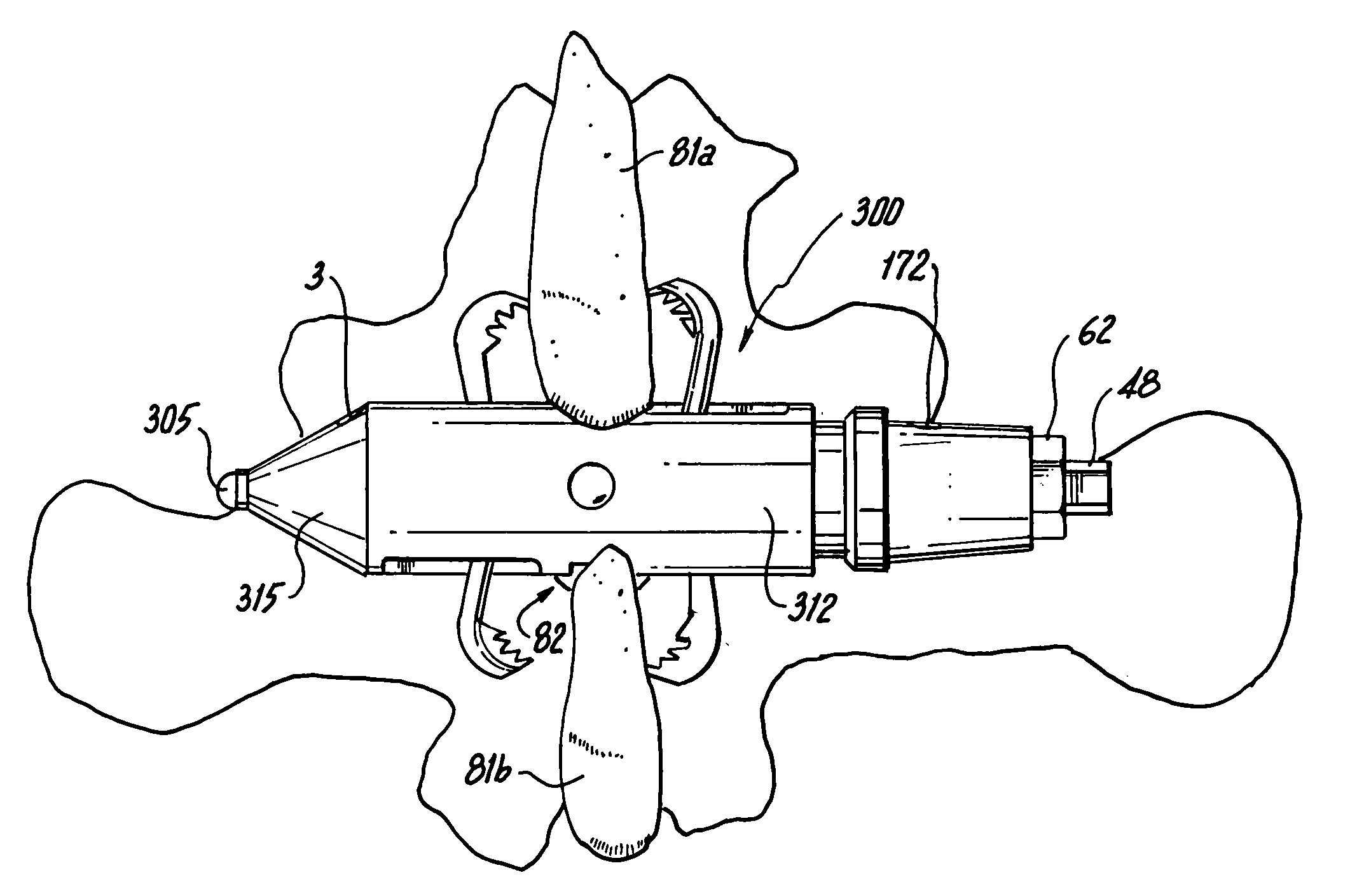
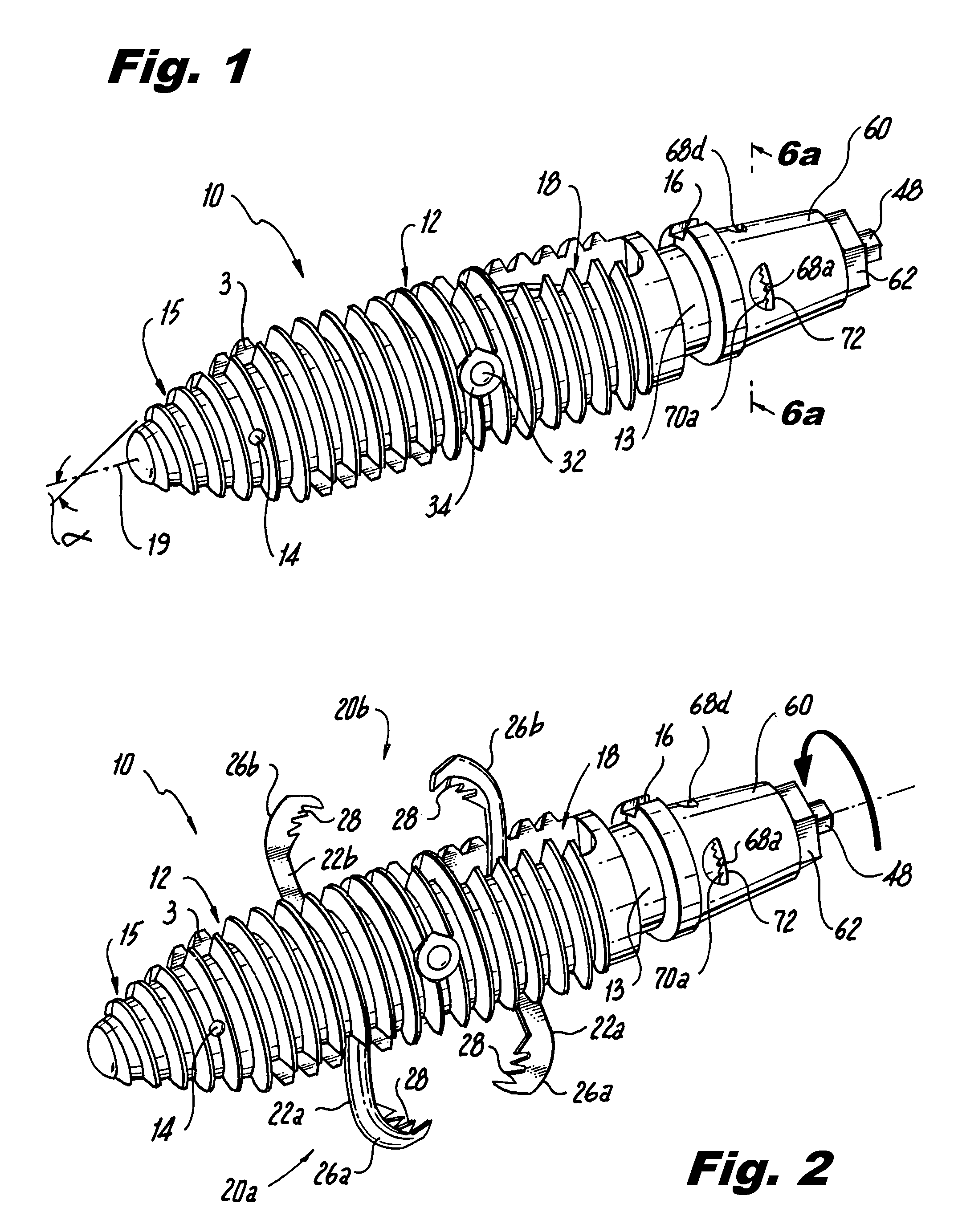
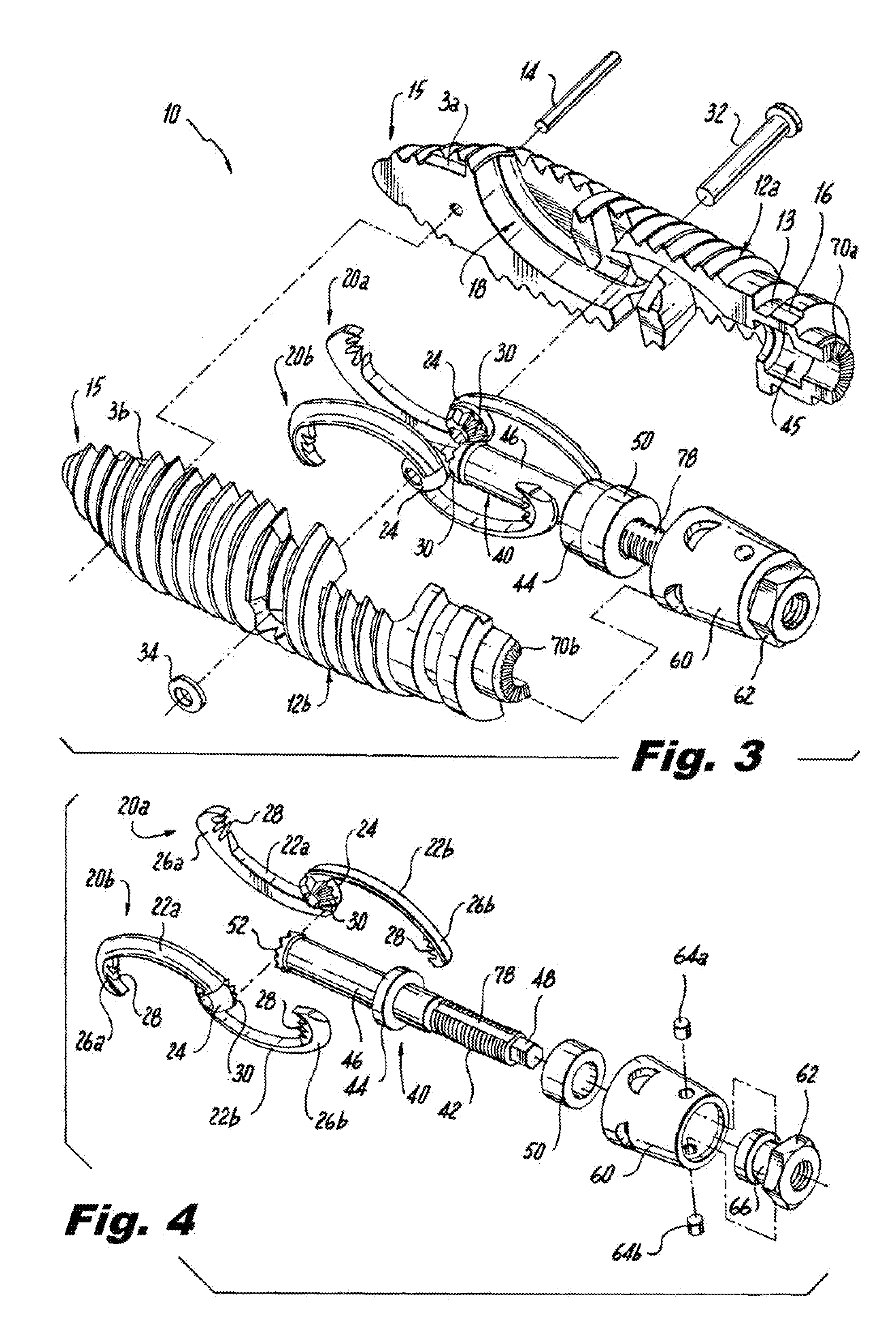
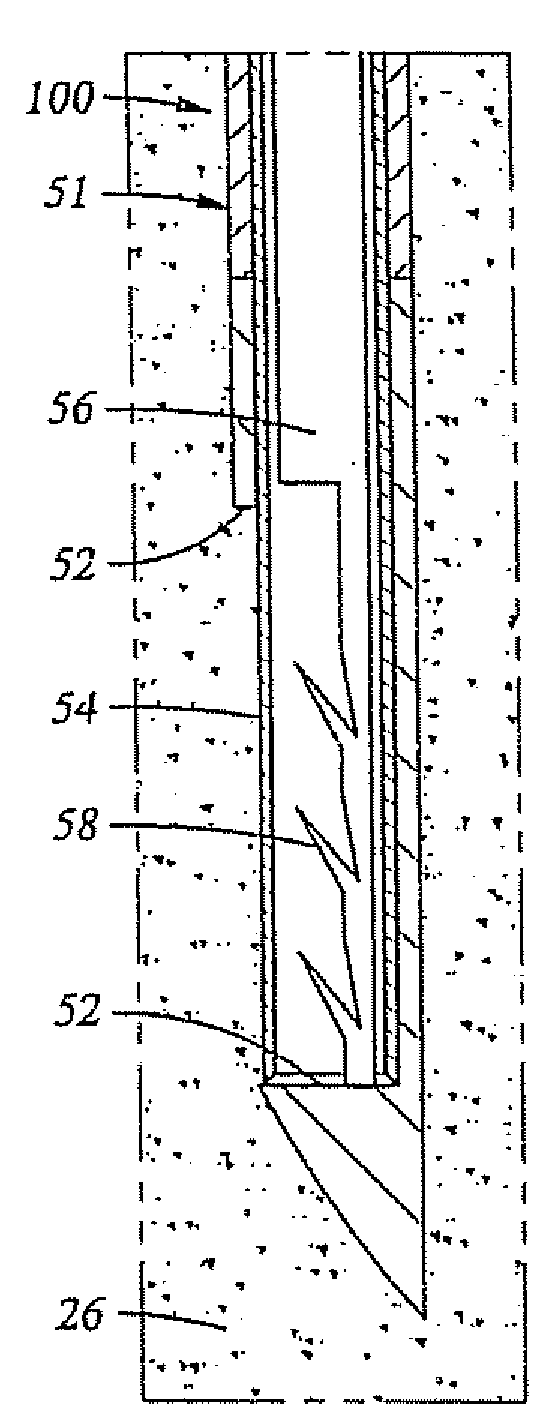
A tool set for implanting a rod in a human spine in conjunction with bone screws. The tool set includes a pair of end guide tools that receive opposite ends of the rod in channels and under manipulation by a surgeon facilitate transport of the rod toward the bone screws attached to the guide tools. Intermediate guide tools having guiding pass through slots are utilized to guide intermediate locations along the rod toward associated bone screws. An attachment structure operably connects the guide tools to the bone screws. The guide tools each include a lower guide and advancement structure to allow a closure top with mating structure to be rotated and driven downward against the rod and to cooperate with similar structure in the bone screw to seat and lock the rod therein. A method utilizing the tool set allows a surgeon to percutaneously implant the rod in the patient.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Laser ablation process and apparatus
InactiveUS20020045811A1Reduce Fresnel reflectionMaximize transmitted lightControlling energy of instrumentDiagnostics using spectroscopyFiberLaser light
A laser catheter is disclosed wherein optical fibers carrying laser light are mounted in a catheter for insertion into an artery to provide controlled delivery of a laser beam for percutaneous intravascular laser treatment of atherosclerotic disease. A transparent protective shield is provided at the distal end of the catheter for mechanically diplacing intravascular blood and protecting the fibers from the intravascular contents, as well as protecting the patient in the event of failure of the fiber optics. Multiple optical fibers allow the selection of tissue that is to be removed. A computer controlled system automatically aligns fibers with the laser and controls exposure time. Spectroscopic diagnostics determine what tissue is to be removed.
Owner:KITTRELL CARTER +2
Orthopedic implant rod reduction tool set and method
ActiveUS20050192570A1Good adhesionEasy to disengageInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsEngineeringBone staple
A tool set for implanting a rod in a human spine in conjunction with bone screws. The tool set includes a pair of end guide tools that receive opposite ends of the rod in channels and under manipulation by a surgeon facilitate transport of the rod toward the bone screws attached to the guide tools. Intermediate guide tools having guiding pass through slots are utilized to guide intermediate locations along the rod toward associated bone screws. An attachment structure operably connects the guide tools to the bone screws. The guide tools each include a lower guide and advancement structure to allow a closure top with mating structure to be rotated and driven downward against the rod and to cooperate with similar structure in the bone screw to seat and lock the rod therein. A method utilizing the tool set allows a surgeon to percutaneously implant the rod in the patient.
Owner:NUVASIVE
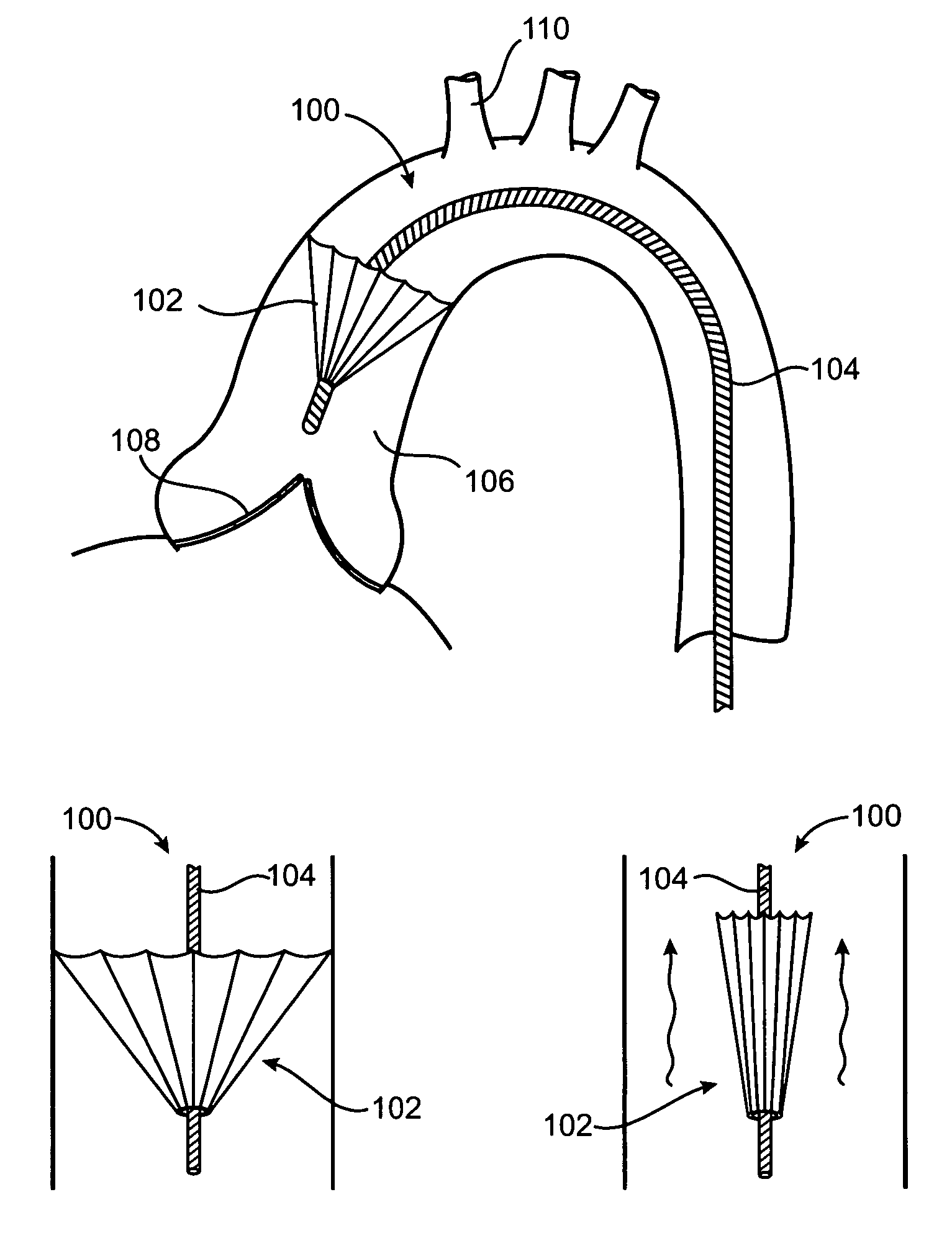
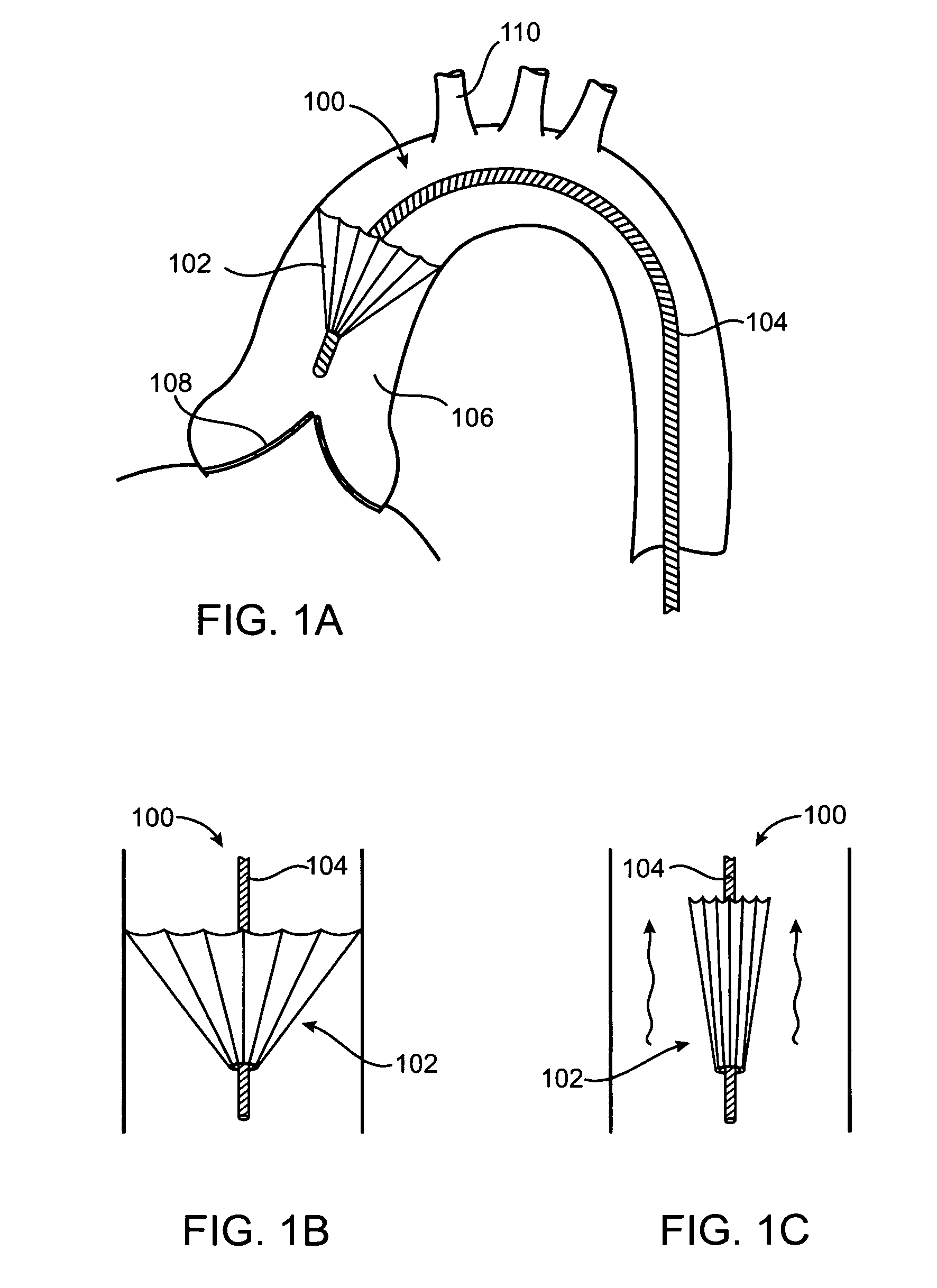
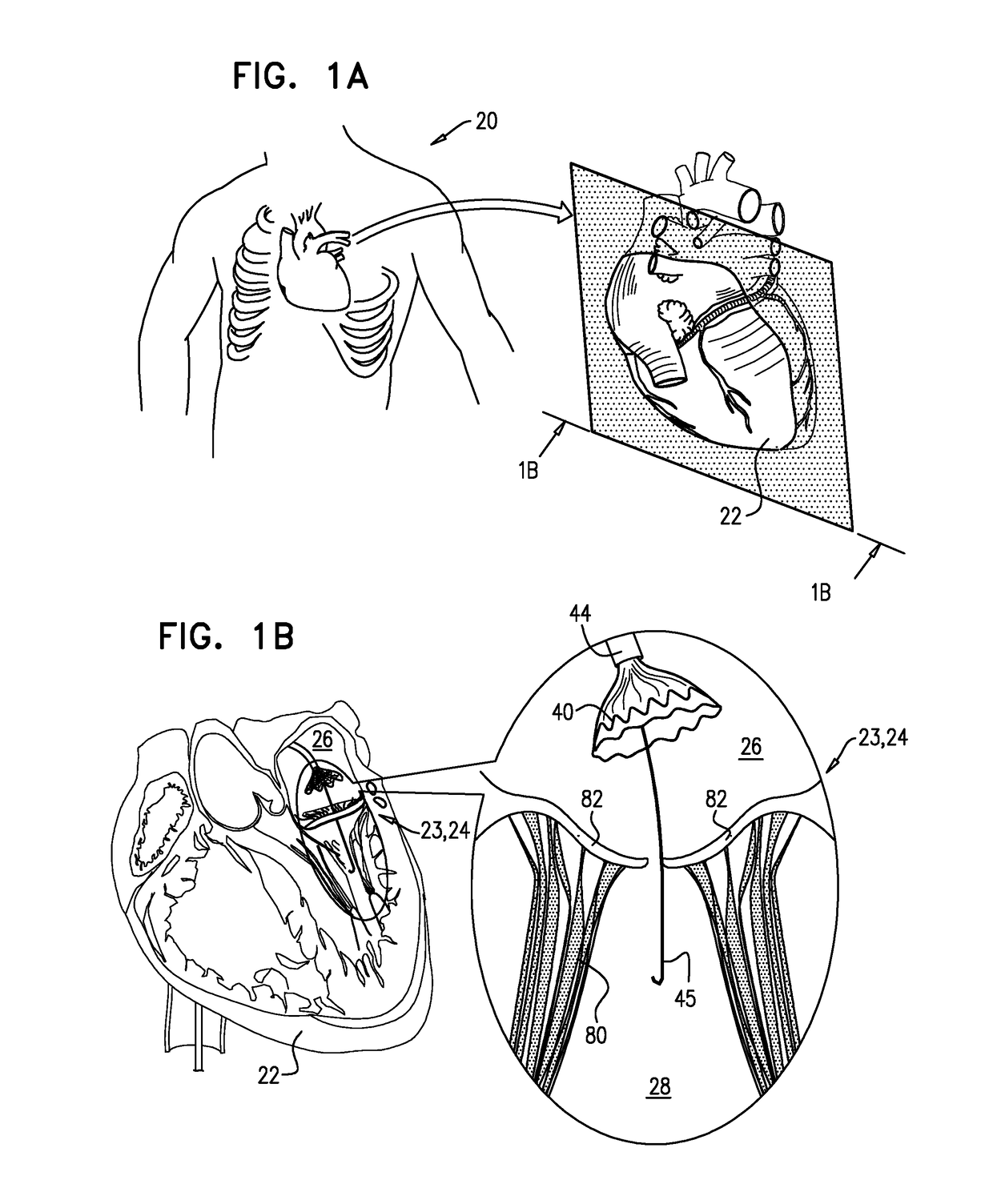
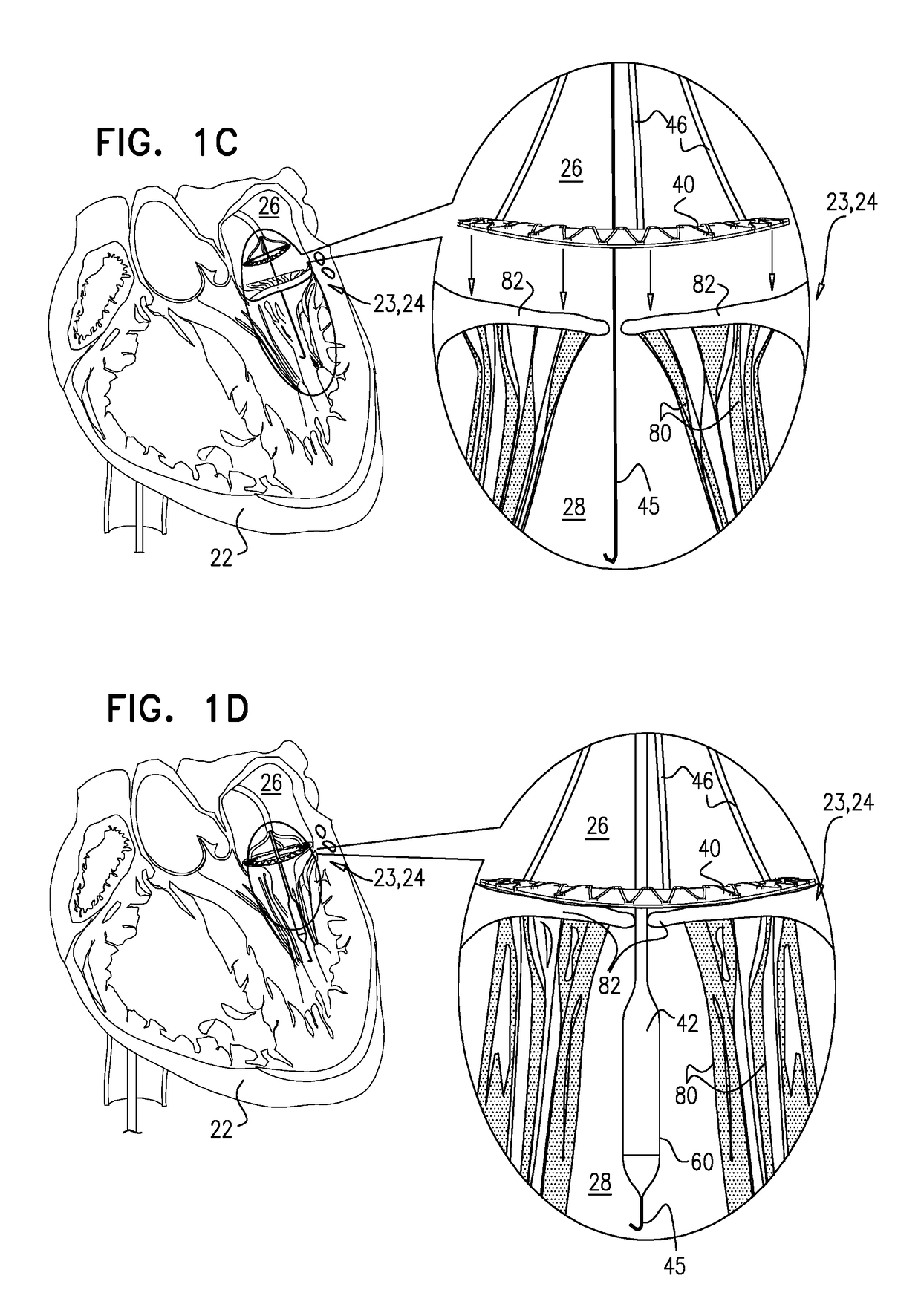
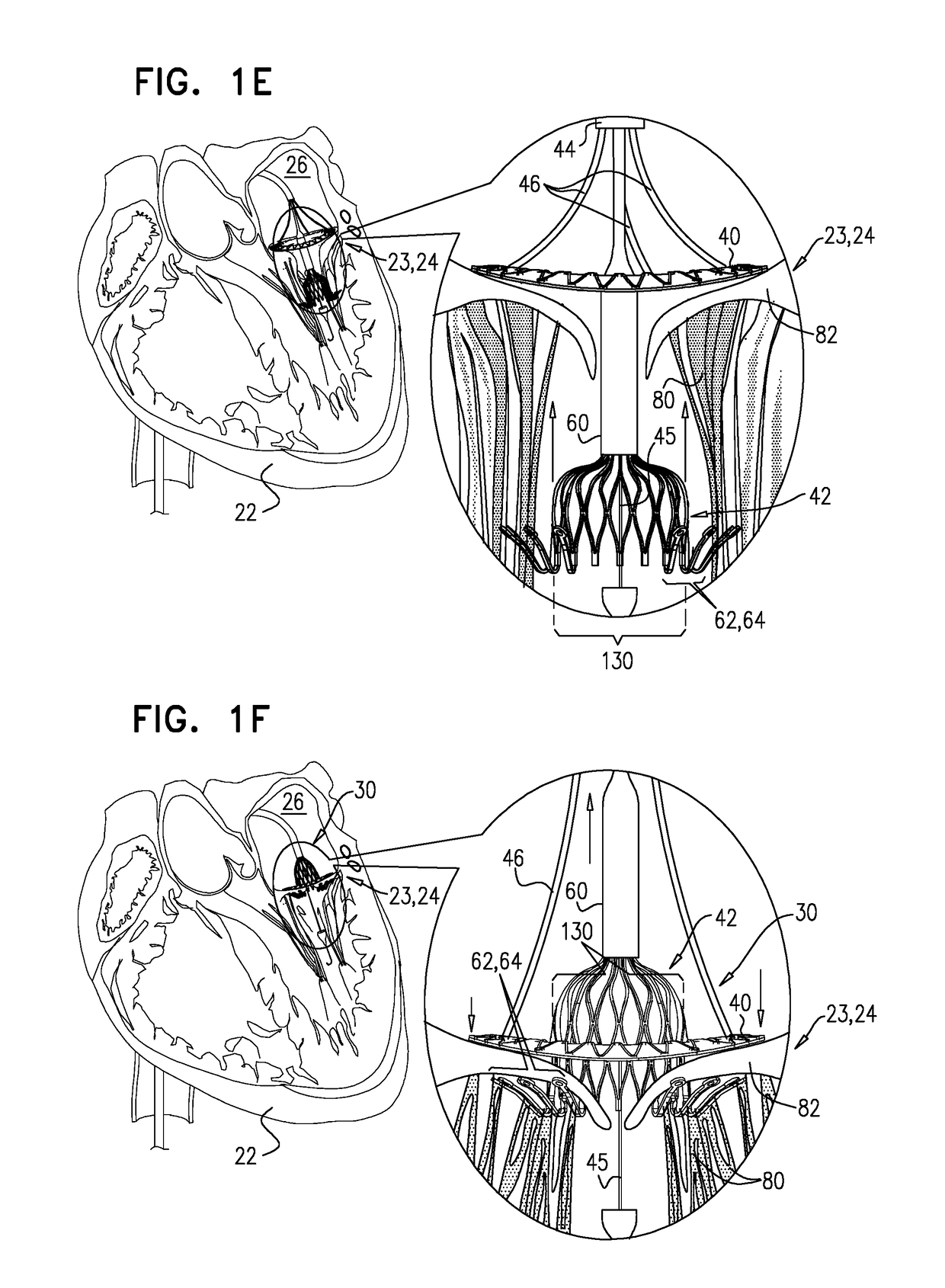
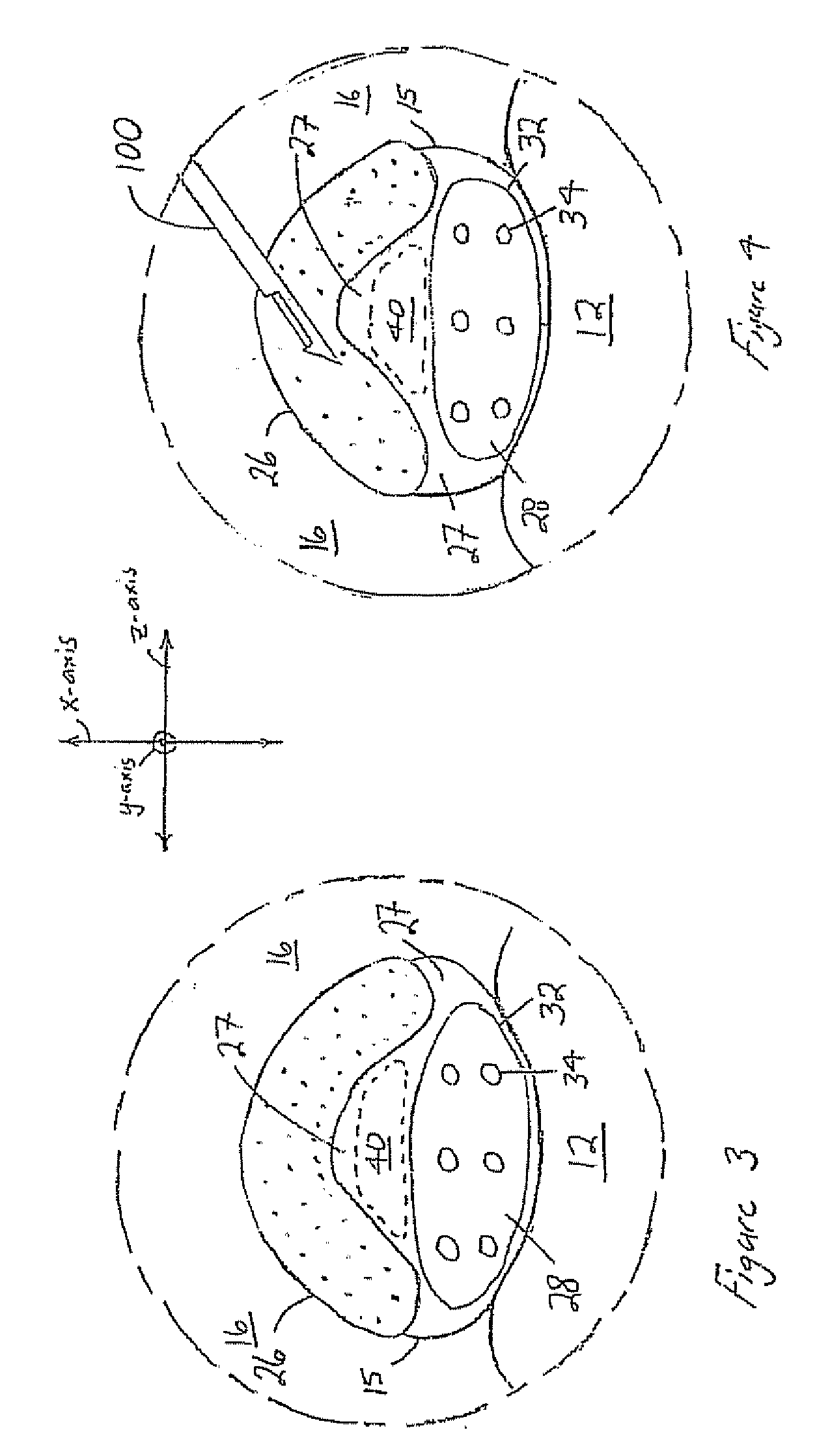
Techniques for percutaneous mitral valve replacement and sealing
Apparatus is described for use with a native heart valve of a subject, the apparatus including (1) a prosthetic valve support, comprising an upstream support portion, the upstream support portion having (a) a compressed configuration and an uncompressed configuration in which the upstream support portion has an inner perimeter that defines an opening; and (2) a prosthetic valve, advanceable into the opening defined by the upstream support portion, and intracorporeally couplable to the upstream support portion by being expanded within the opening defined by the upstream support portion, the apparatus being configured such that, when the prosthetic valve is expanded within the opening defined by the upstream support portion, the expansion of the prosthetic valve is restricted by the inner perimeter of the upstream support portion, without causing the prosthetic valve support to apply a radially-expansive force to the native annulus. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
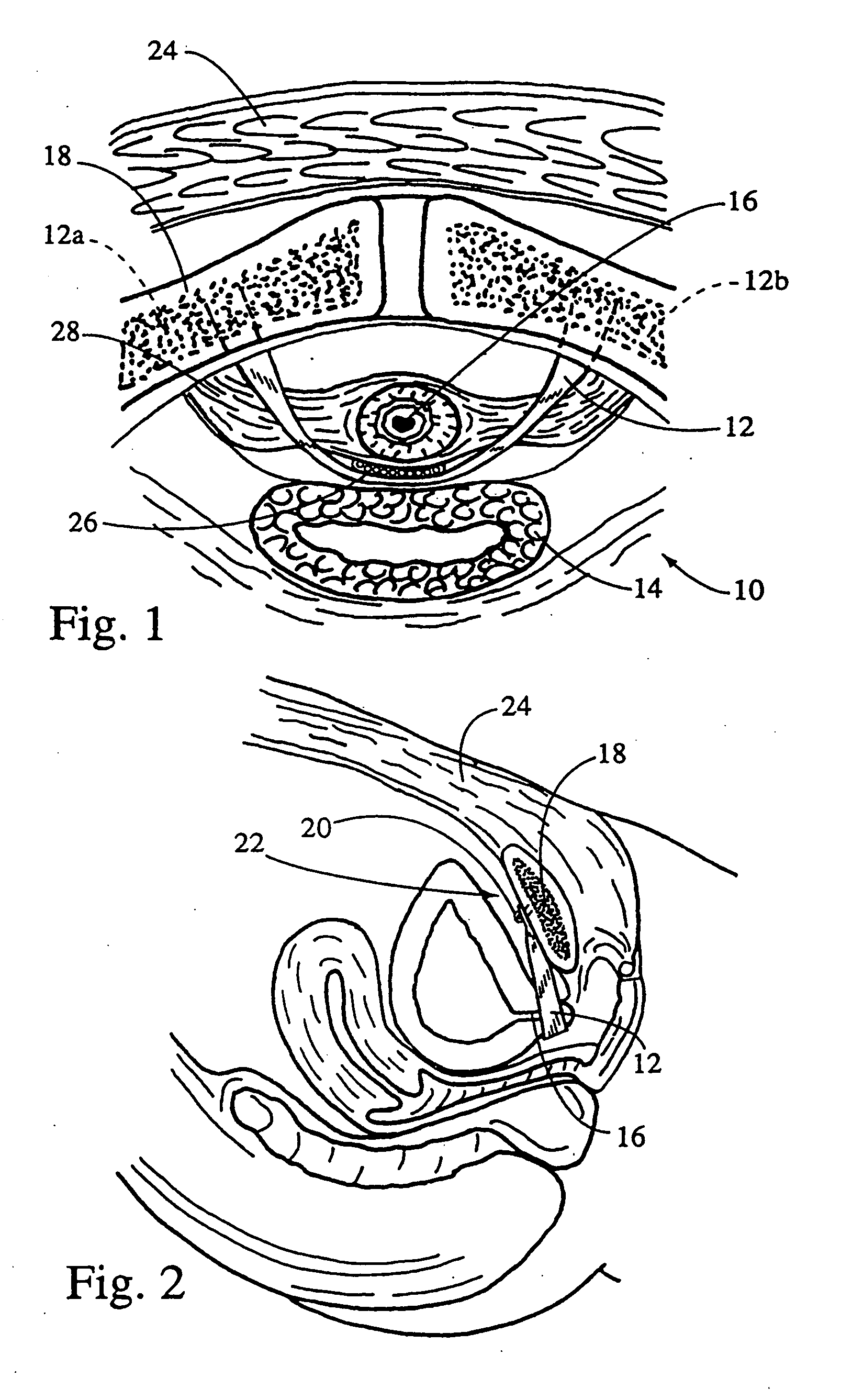
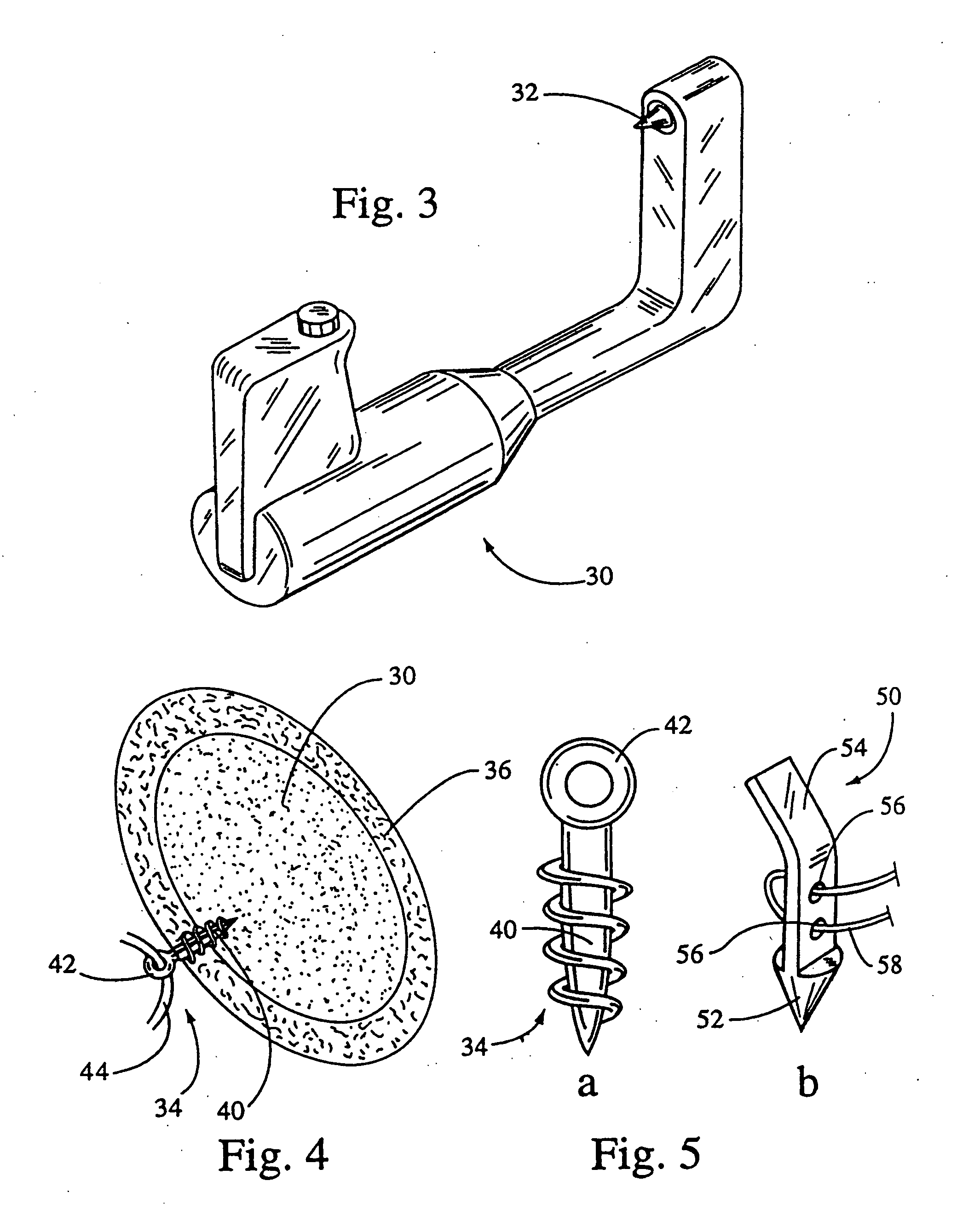
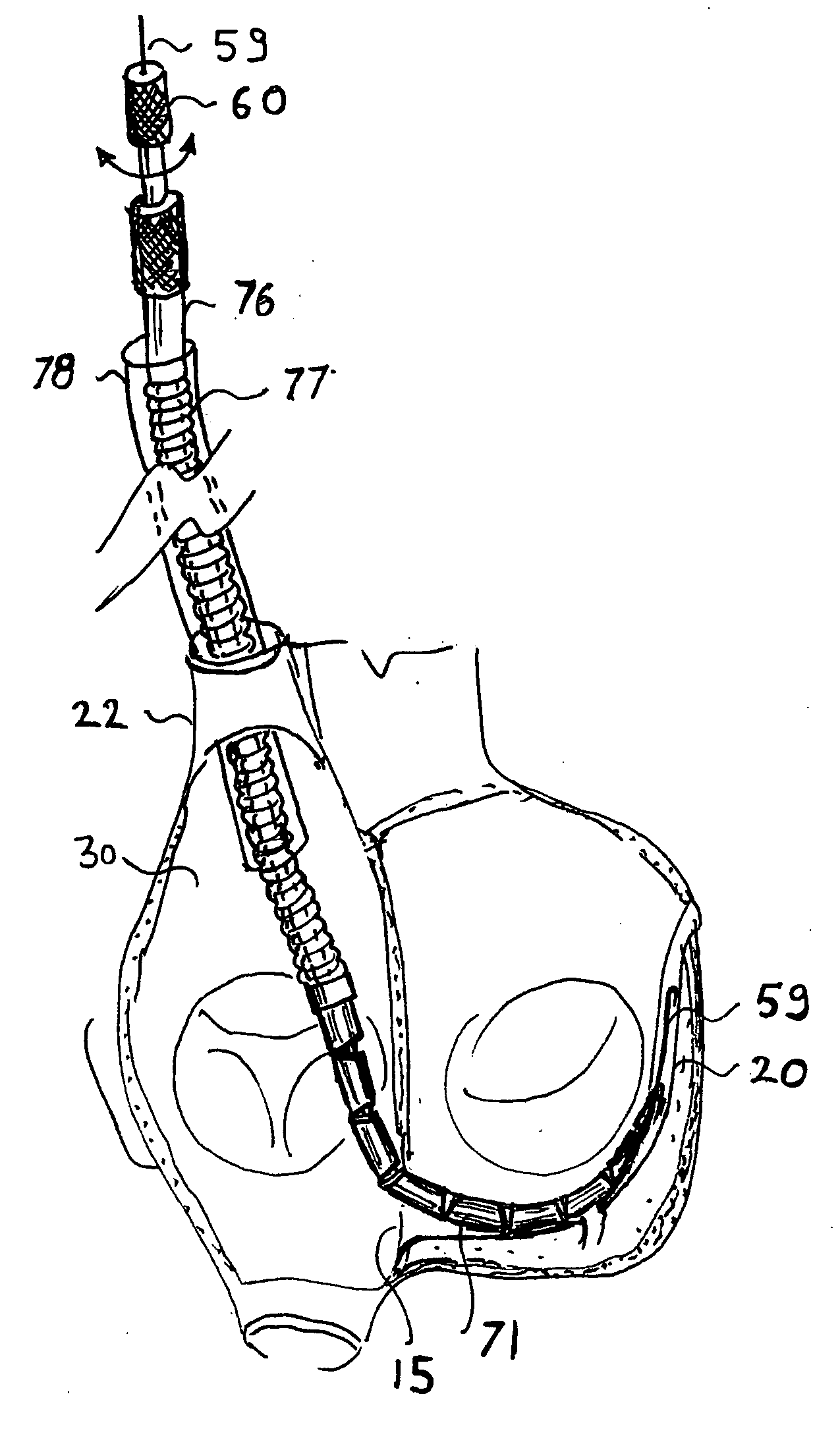
Intra dermal tissue fixation device
A device is disclosed for the securement of dermal tissues. The device provides approximation and eversion of the tissue as well as the placement of a fixation element that bridges a wound. The fixation element may be produced in several fixed or dynamic configurations that may or may not alter the ability to engage tissue in response to stresses placed upon the fixation member post-deployment. The delivery device inserts the fastener percutaneously through the epidermis into the sub-dermal position without entering the wound margins with any part of the approximation portion of the delivery device.
Owner:ETHICON INC
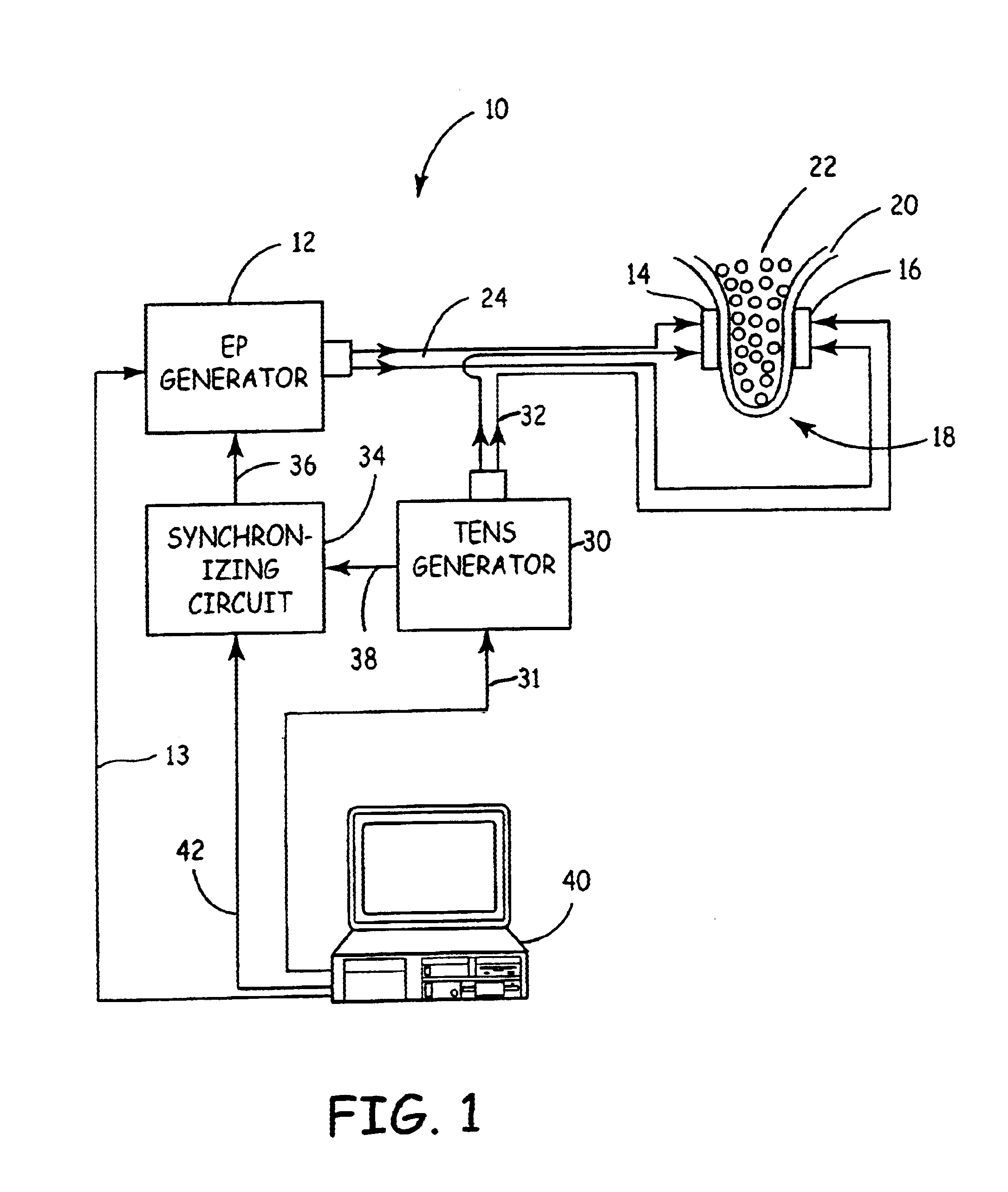
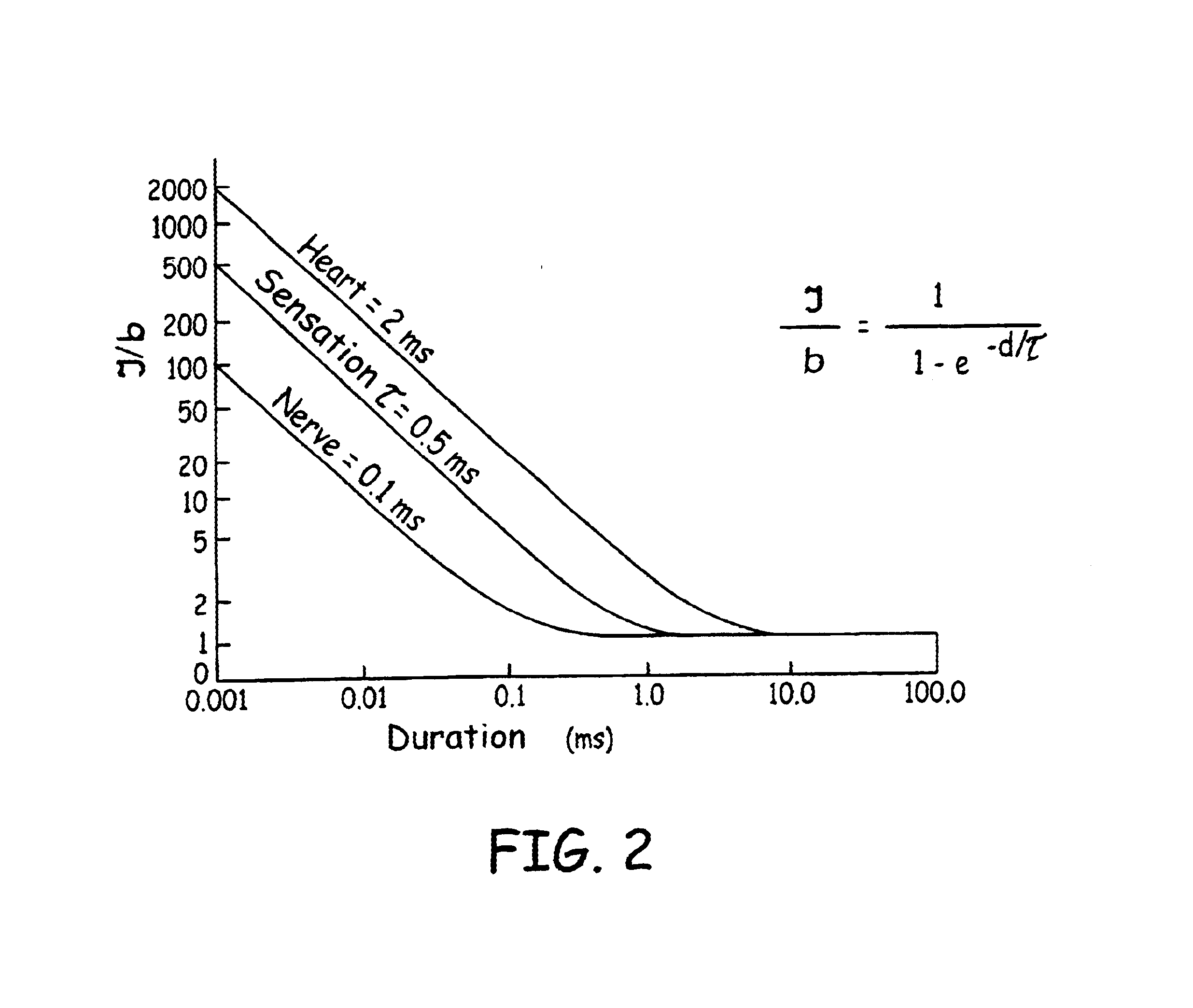
Apparatus and method for reducing subcutaneous fat deposits by electroporation with improved comfort of patients
InactiveUS6697670B2Improve comfortReducing subcutaneous fat depositsElectrotherapyElectricityReduced subcutaneous fat
An apparatus and method for non-invasive treatment in lieu of cosmetic surgery is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a combination of a high and low voltage pulse generators connected to two or more electrodes placed on a treatment site of the patient's body. High voltage pulses, delivered to the electrodes, create an electric field that kills subcutaneous fat cells. Low voltage pulses, delivered to the same or individual electrodes provide transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), blocking the signals of discomfort or pain that may arise from the high voltage pulsing.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Percutaneous valve prosthesis and system and method for implanting same
InactiveUS20090306768A1Minimizes gradientIncrease the areaHeart valvesBlood vesselsInsertion stentBalloon dilatation
A heart valve prosthesis includes a cylindrical valve cage stent constructed to be implanted percutaneously in the planar axis of a native valve annulus, an elastic and compressible, multi-leaflet valve insertable percutaneously into the body, and an attachment mechanism for attaching the valve to the superior rim of the valve cage stent. The valve can be of a bi-leaflet or a tri-leaflet type and includes a valve frame made from a memory metal and a tissue cover attached to the valve frame. The valve cage stent is self-expanding or balloon expandable, made respectively from memory metal or stainless steel but otherwise structurally the same.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
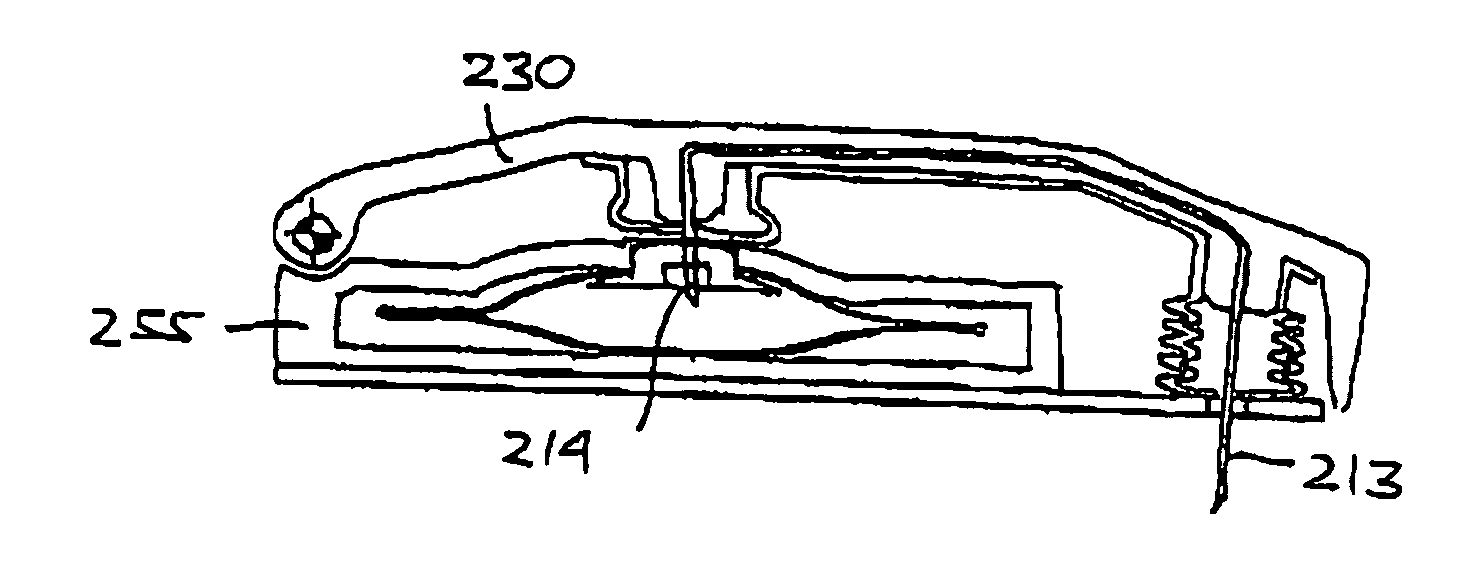
Retraction means for transcutaneous device
InactiveUS20070049865A1Easy to useRaise security concernsInfusion syringesMedical devicesIntermediate stateMedical device
The invention provides a transcutaneous medical device (502, 250, 150, 600) comprising a lower surface adapted for application towards the skin of a subjet, attaching means (571, 272, 161) for securing the lower surface relative to the skin, and a transcutaneous device (530, 182, 213, 651) adapted to penetrate the skin of the subject. The transcutaneous device is mounted for movement be-tween an extended position in which the transcutaneous device projects relative to the lower surface and a retracted position in which the transcutaneous device is retracted relative to the lower surface. The medical device further comprises release means (550, 275, 162) which can be oper-ated from a first state through an intermediate state to a second state, whereby operation of the release means from the first to the intermediate state causes the transcutaneous device to be moved from the extended position to the retracted position, and operation of the re-lease means from the intermediate to the second state causes release of the attaching means.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
System for securing sutures, grafts and soft tissue to bone and periosteum
InactiveUS20050004576A1Easy constructionEasy to useSuture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesEngineeringPeriosteum
Self-anchoring slings and deployment mechanisms for use therewith in selectively positioning a sling into position within the body. According to a preferred embodiment, the sling comprises an elongate sling portion having opposed ends. Formed upon each respective opposed end is an anchor member operative to be percutaneously advanced through soft tissue at a selected target site in a first direction but resist movement in an opposed direction. Such anchor members are operative to extend in opposed directions to thus enable a sling to be securely affixed into position and resist sag or otherwise lose its ability to support a given structure.
Owner:SPRINGBOARD MEDICAL VENTURES
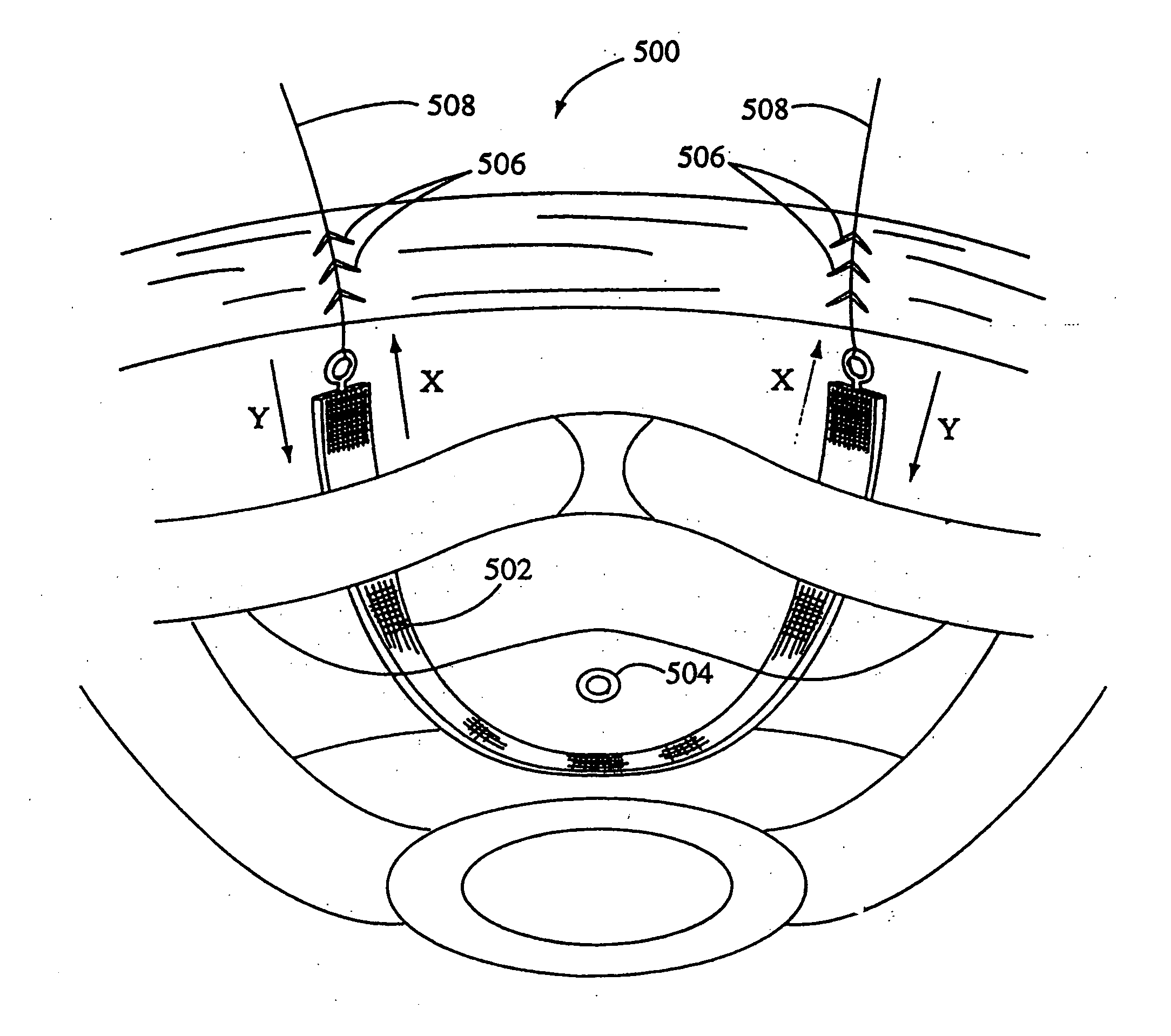
Method and apparatus for percutaneous reduction of anterior-posterior diameter of mitral valve
A method and apparatus for treating mitral regurgitation by approximating the septal and lateral (clinically referred to as anterior and posterior) annulus of the mitral valve. The distal end of the device is inserted into the coronary sinus of the heart and the proximal end of the device rests within the right atrium along the tendon of Todaro and extends to at least the membranous septum of the tricuspid valve. Because the coronary sinus approximates the lateral (posterior) annulus of the mitral valve and the tendon of Todaro approximates the septal (anterior) annulus of the mitral valve, the device encircles approximately one half of the mitral valve annulus. The apparatus is then adapted to deform the underlying structures i.e. the septal annulus and lateral annulus of the mitral valve in order to move the posterior leaflet anteriorly and the anterior leaflet posteriorly and thereby improve leaflet coaptation and eliminate mitral regurgitation.
Owner:KARDIUM
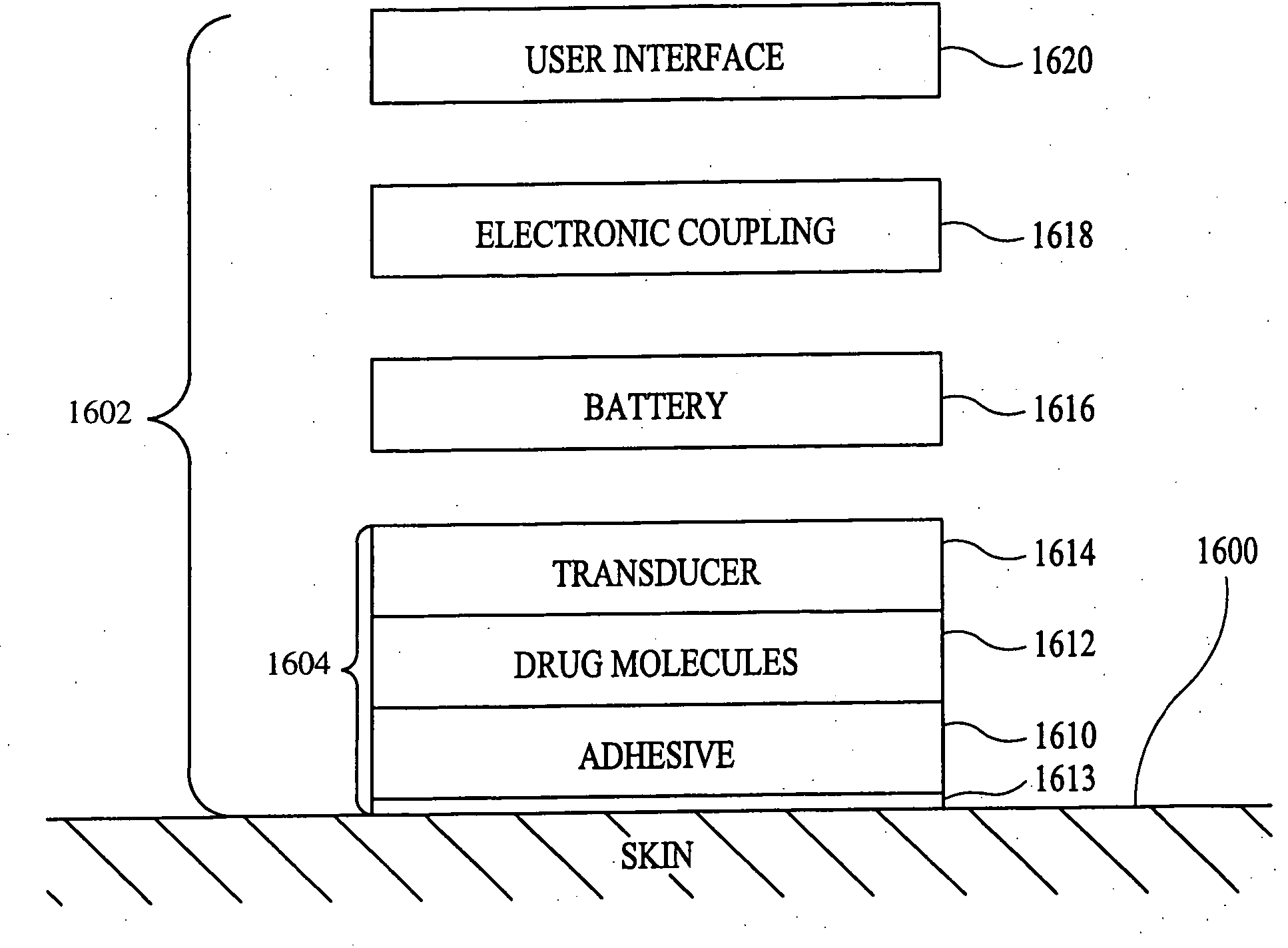
Method and apparatus for enhancement of transdermal transport
InactiveUS20040236268A1Effective to induce immune responseCompounds screening/testingElectrotherapyPharmaceutical drugTGE VACCINE
According to the present invention, a method for enhancing transdermal transport is disclosed. The method includes the steps of increasing a permeability of an area of a membrane with a permeabilizing device. The membrane may be, inter alia, biologic skin or synthetic skin. The permeabilizing device may be an ultrasound-producing device. A substance is transported into and through the area of the membrane. The substance may be a drug, a vaccine, or a component of interstitial fluid.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
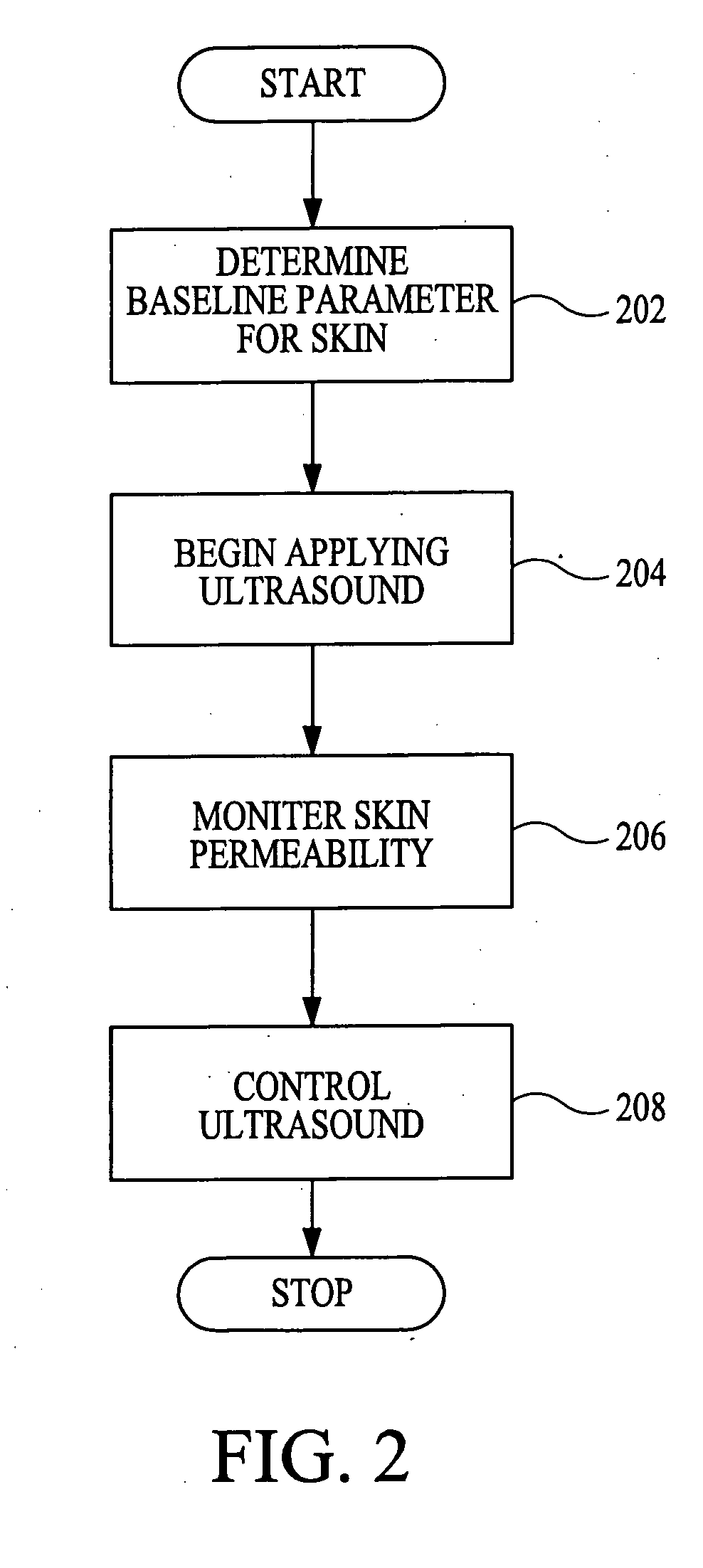
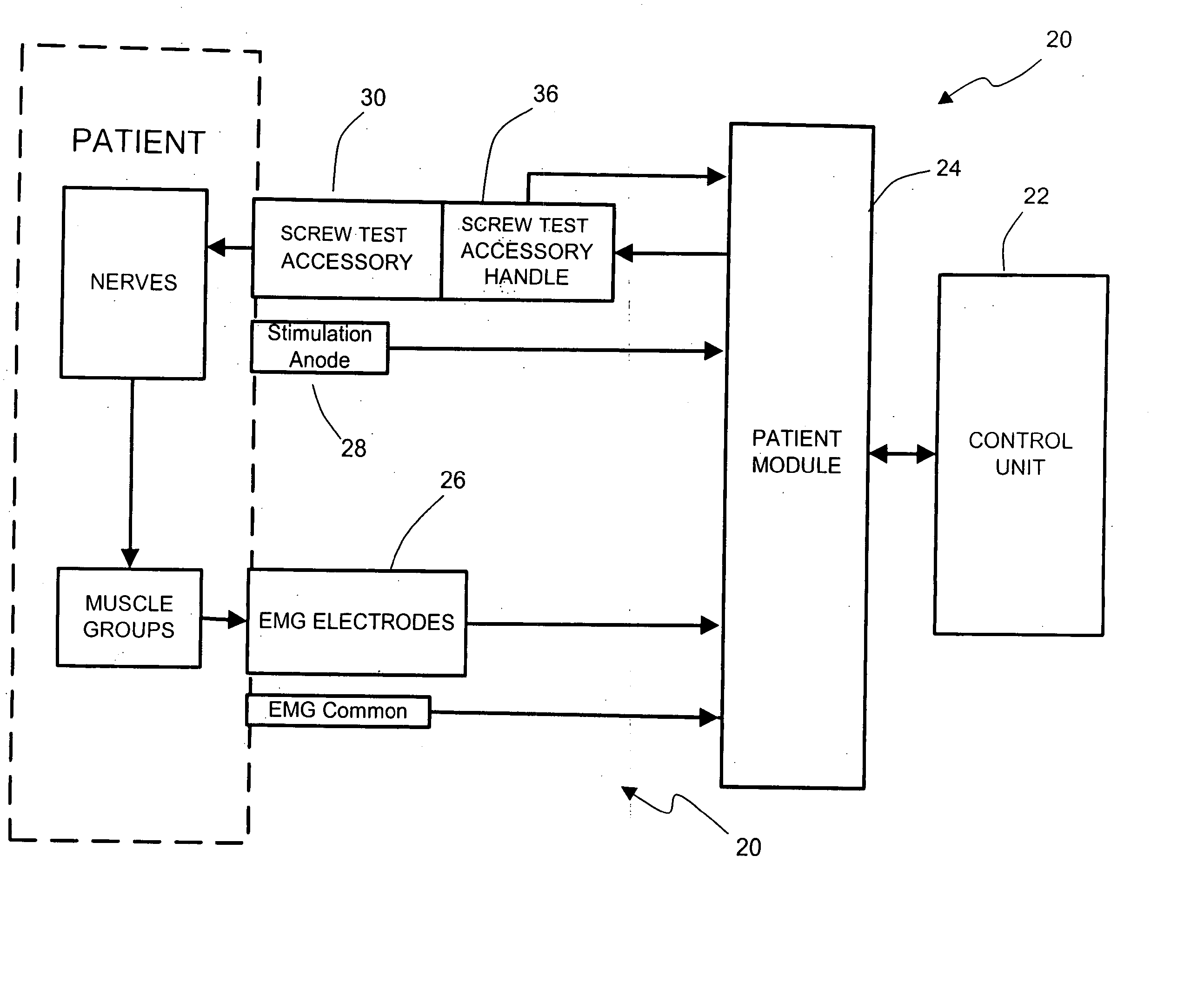
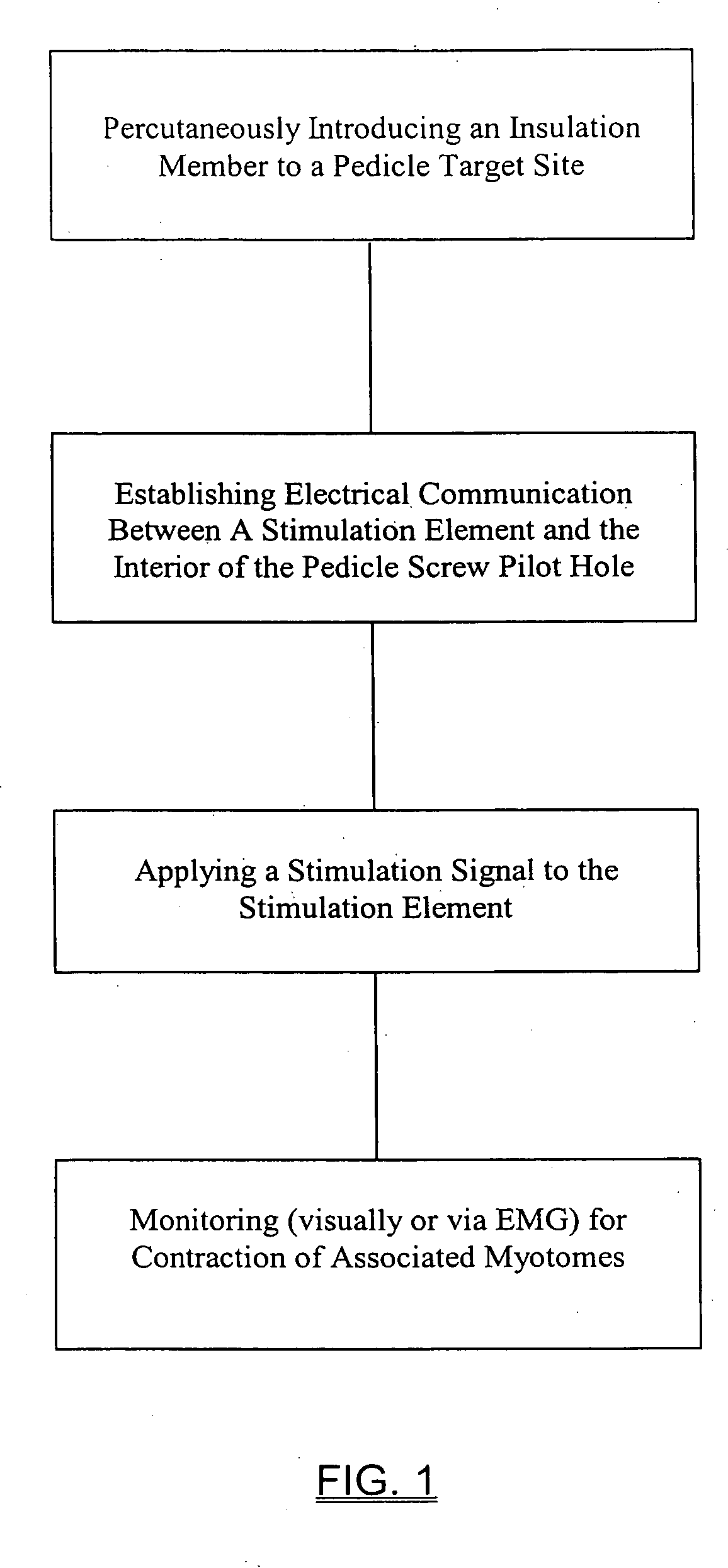
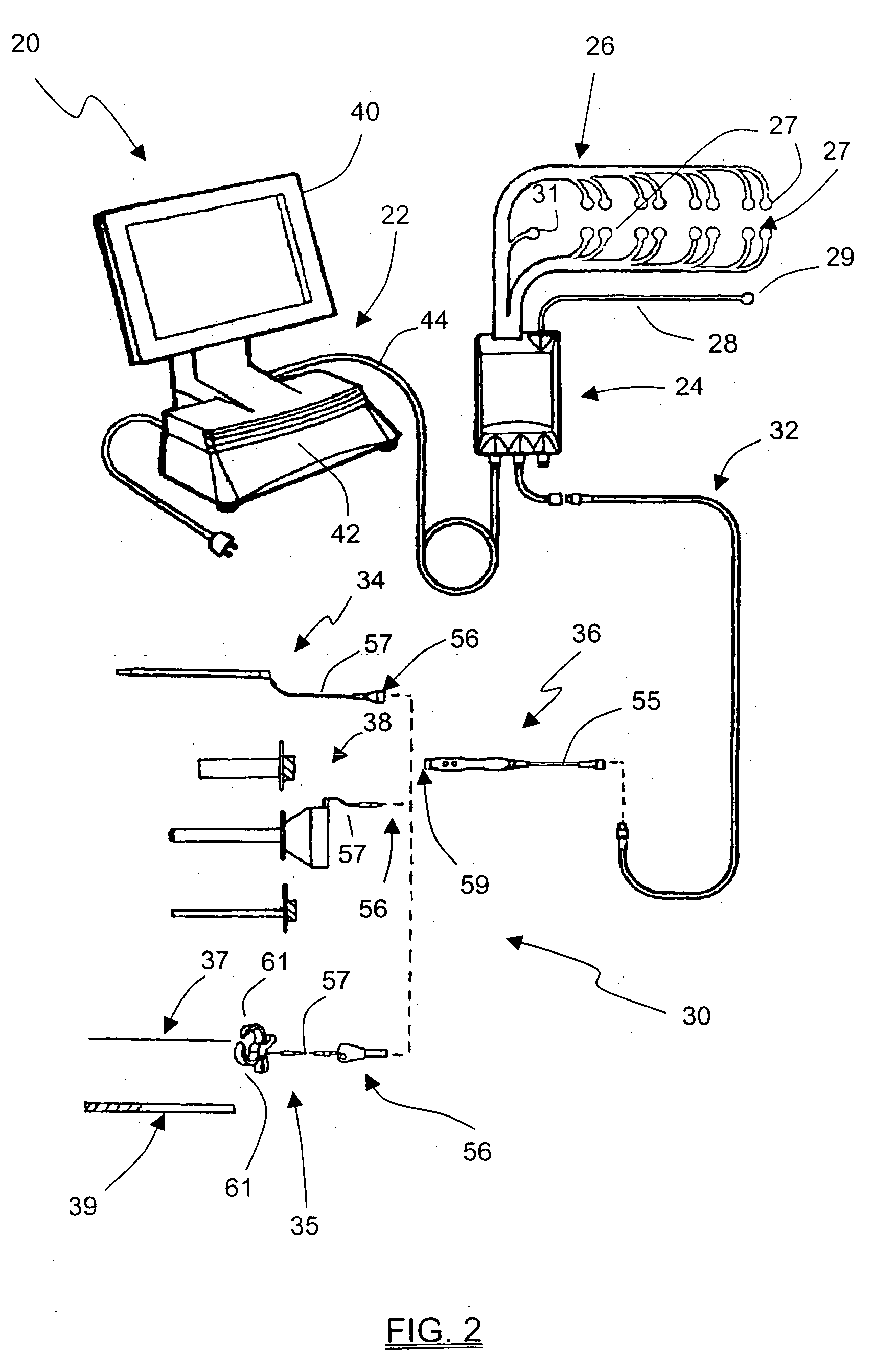
System and methods for performing percutaneous pedicle integrity assessments
The present invention involves systems and related methods for performing percutaneous pedicle integrity assessments involving the use of neurophysiology.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Laminated patient infusion device
InactiveUS20050021005A1Simplify designSimple design and manufactureSurgeryMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringBuilding construction
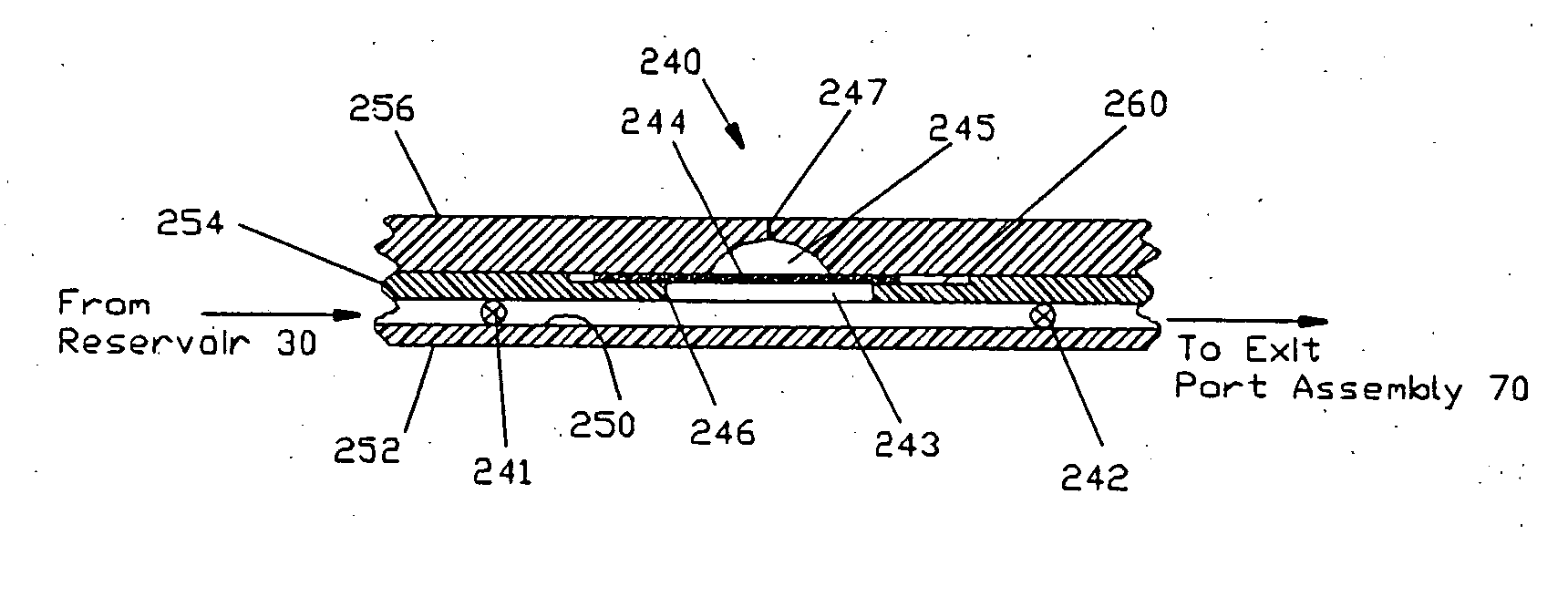
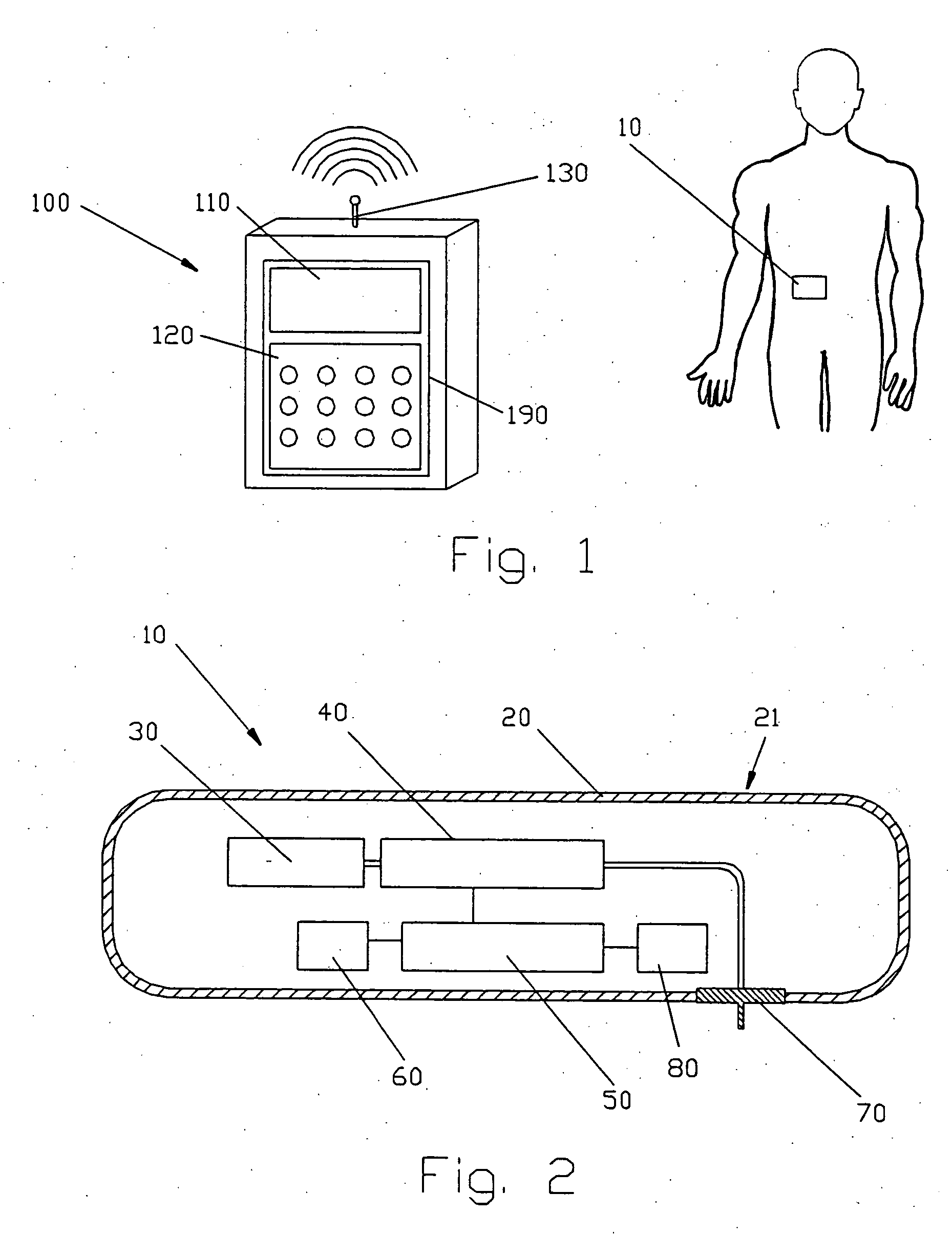
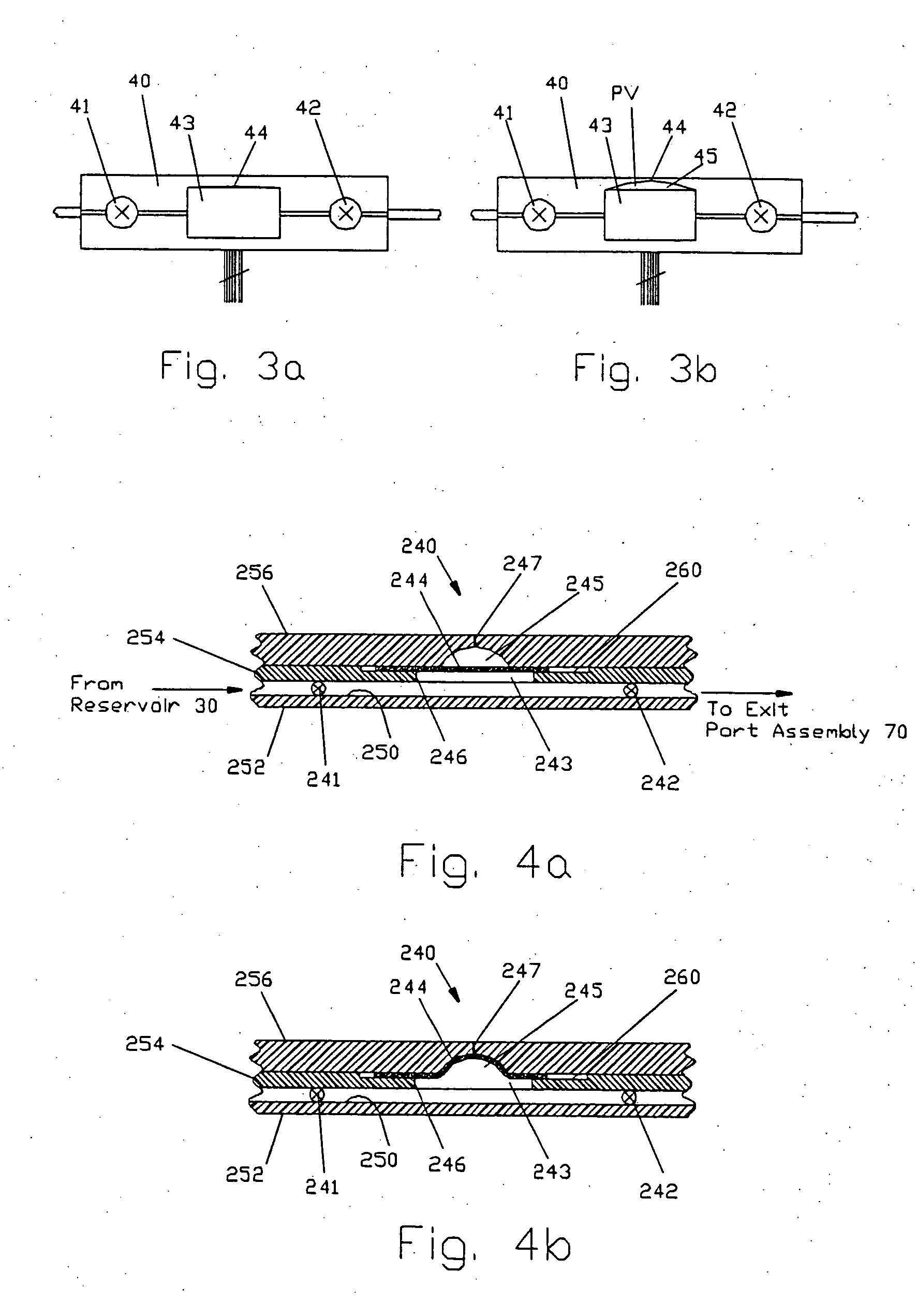
A device for delivering fluid to a patient including an exit port assembly adapted to connect to a transcutaneous patient access tool, and a dispenser including at least two laminated layers of material defining a passageway connected to the exit port assembly, and an expandable accumulator in fluid communication with the passageway for controlling fluid flow from a reservoir to the exit port assembly. The laminated construction provides many benefits including simplifying the design and manufacturing of the device, in order to further reduce the size, complexity and costs of the device so that the device lends itself to being small and disposable in nature.
Owner:INSULET CORP
Percutaneous heart valve prosthesis
A percutaneous heart valve prosthesis (1) has a valve body (2) with a passage (9) extending between the first and second ends (7, 8) of the valve body (2). The valve body (2) is collapsible about a longitudinal axis (10) of the passage (9) for delivery of the valve body (2) via a catheter (18). One or more flexible valve leaflets (3, 4) are secured to the valve body (2) and extend across the passage (9) for blocking bloodflow in one direction through the passage (9). An anchor device (5), which is also collapsible for delivery via catheter (18), is secured to the valve body (2) by way of an anchor line (6). A failed or failing mitral heart valve (101) is treated by percutaneously locating the valve body (2) in the mitral valve orifice (102) with the anchor device (5) located in the right atrium (107) and engaging the inter-atrial septum (103), such that the taught anchor line (6) acts to secure the valve body (2) within the mitral valve orifice (102).
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS CARDIOVASCULAR SOLUTIONS PTY LTD
Treating valve failure
A device (1) for treating valve failure in a patient is provided. The device has one or more engaging zones (3) for engaging the device with the annulus of the valve being treated. The device also has pre-disposition means for changing the geometry of the device to a predetermined configuration which is suitable for constricting the valve annulus. The device is compressible for percutaneous delivery to the valve. When in the predetermined configuration, the engaged device constricts the valve annulus facilitating substantial closure of leaflets of the valve.
Owner:KAYE DAVID +2
Percutaneous spinal implants and methods
Apparatuses and methods for performing minimally invasive medical procedures are disclosed herein. In one example, an apparatus includes a first body coupled to a second body. The first body and the second body collectively configured to be releasably coupled to an implant device configured to be disposed between adjacent spinous processes. A first engaging portion is coupled to the first body, and a second engaging portion is coupled to the second body. The first engaging portion and / or the second engaging portion is configured to be received within a first opening defined by the implant device. The first body configured to be moved relative to the second body such that a distance between the first engaging portion and the second engaging portion is moved between a first distance and a second distance and simultaneously a length of the implant device is moved between a first length and a second length.
Owner:MEDTRONIC EURO SARL
Sealing plug for an opening in a wall of a vessel or hollow organ
InactiveUS20060190036A1The way is simple and fastBleeding is stopped immediatelySurgical veterinaryProsthesisSurgical operationHuman body
The present invention relates to a sealing plug for an opening in a wall of a vessel or hollow organ of an animal or human body, in particular a blood vessel, to a device for placing such a sealing plug in such an opening, to a surgery kit for percutaneously sealing an opening in a wall of a vessel or hollow organ of an animal or human body, in particular a blood vessel, and to a method for percutaneously sealing of an opening in a wall of a vessel or hollow organ of an animal or human body.
Owner:UNIV TUBINGEN
Percutaneous mitral valve replacement and sealing
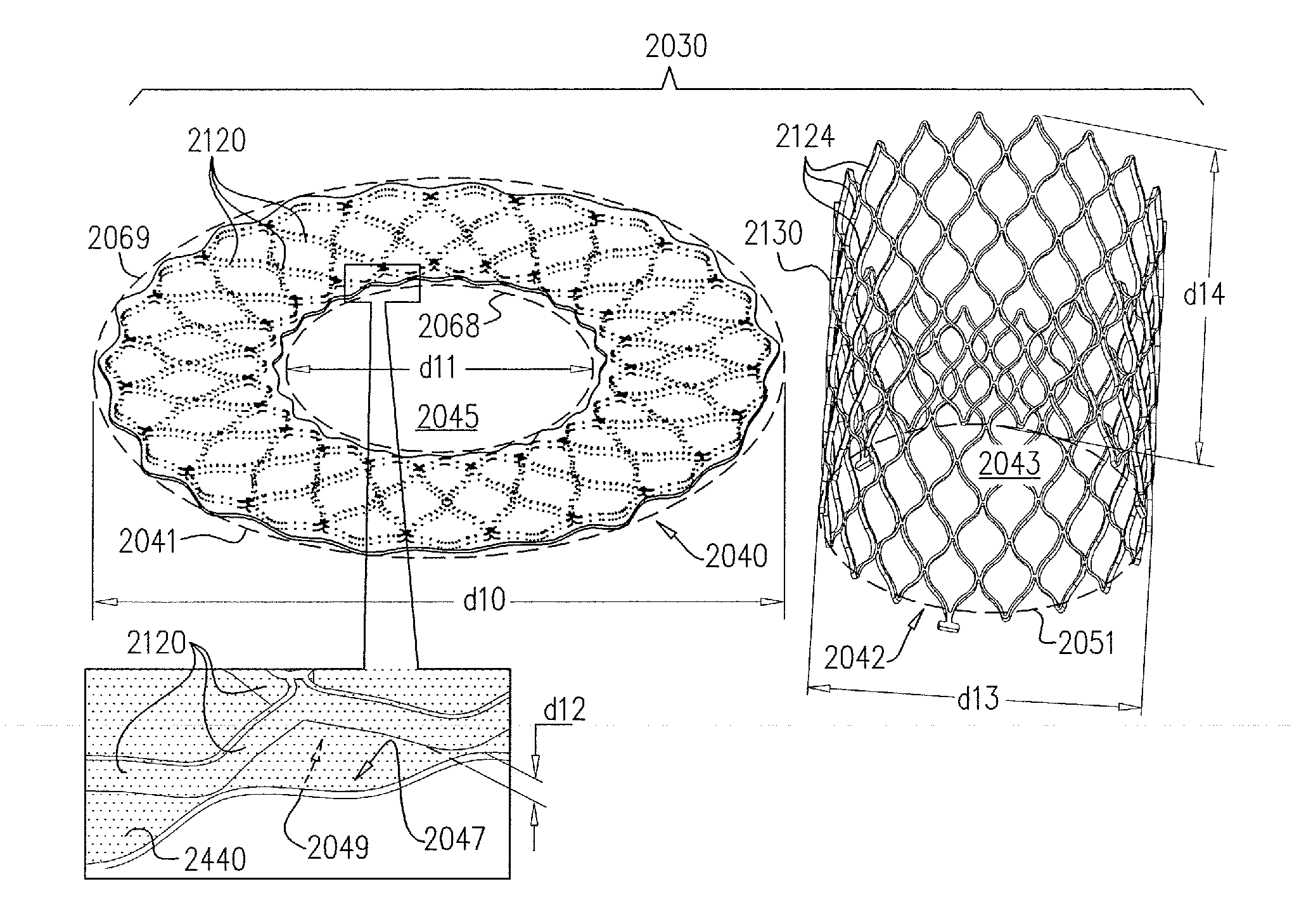
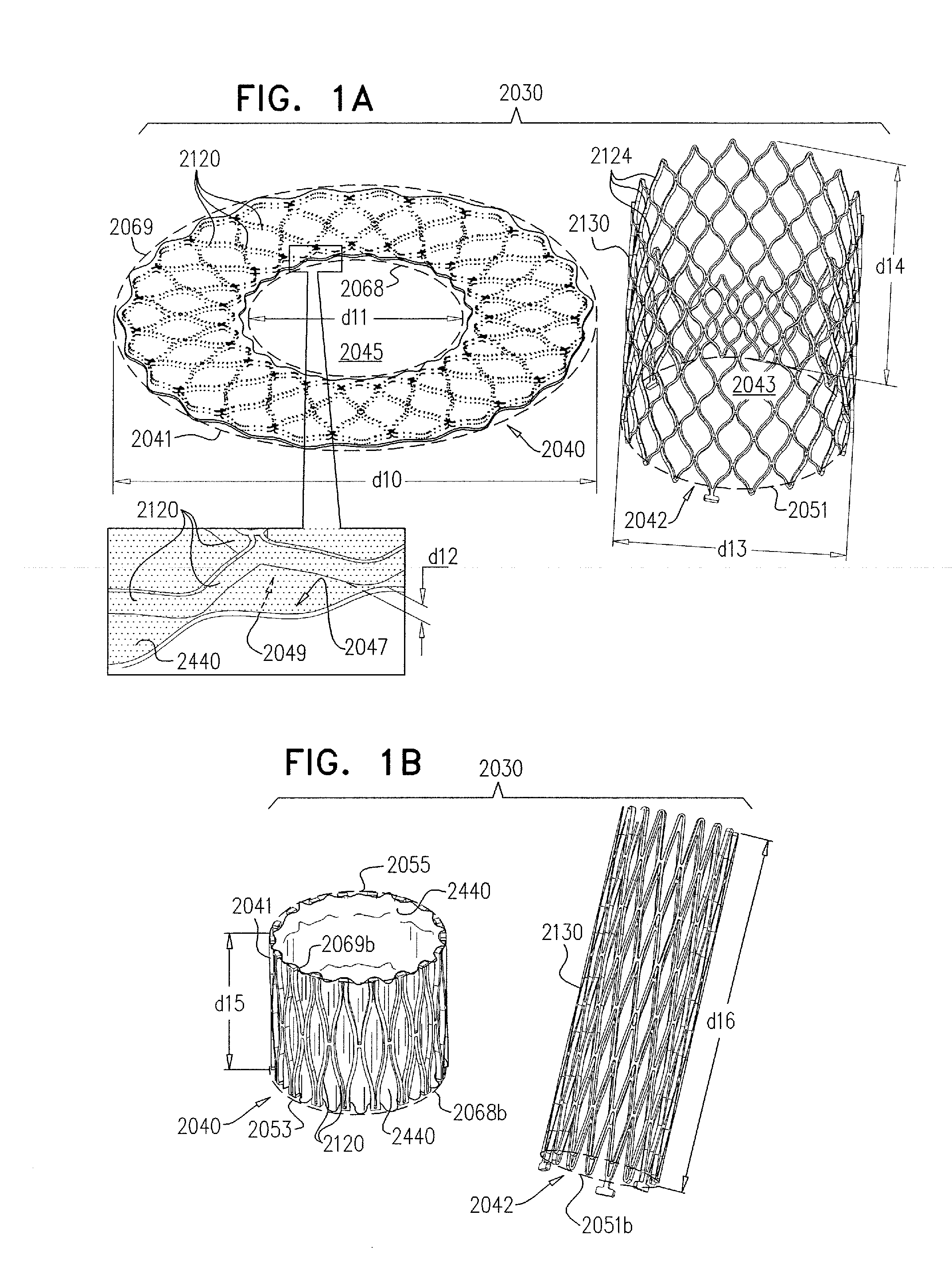
ActiveUS20140257475A1Enhanced couplingStentsAnnuloplasty ringsBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementBiomedical engineering
Apparatus is provided for use with a prosthetic valve for implantation at a native valve of a subject, the native valve including at least one native leaflet, the apparatus including (1) a prosthetic valve support, including (a) an upstream support portion, being configured to be placed against an upstream side of the native valve, and having an inner perimeter that defines an opening that is configured to receive the prosthetic valve, and (b) at least one clip (i) comprising at least two clip arms and a clip-controller interface, the clip-controller interface being coupled to at least one of the clip arms, and (ii) being configured to be coupled to a native leaflet of the native valve; and (2) at least one clip controller, reversibly couplable to the clip-controller interface, and configured to facilitate opening and closing of the clip. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Apparatus and method for inserting an intra-aorta catheter through a delivery sheath
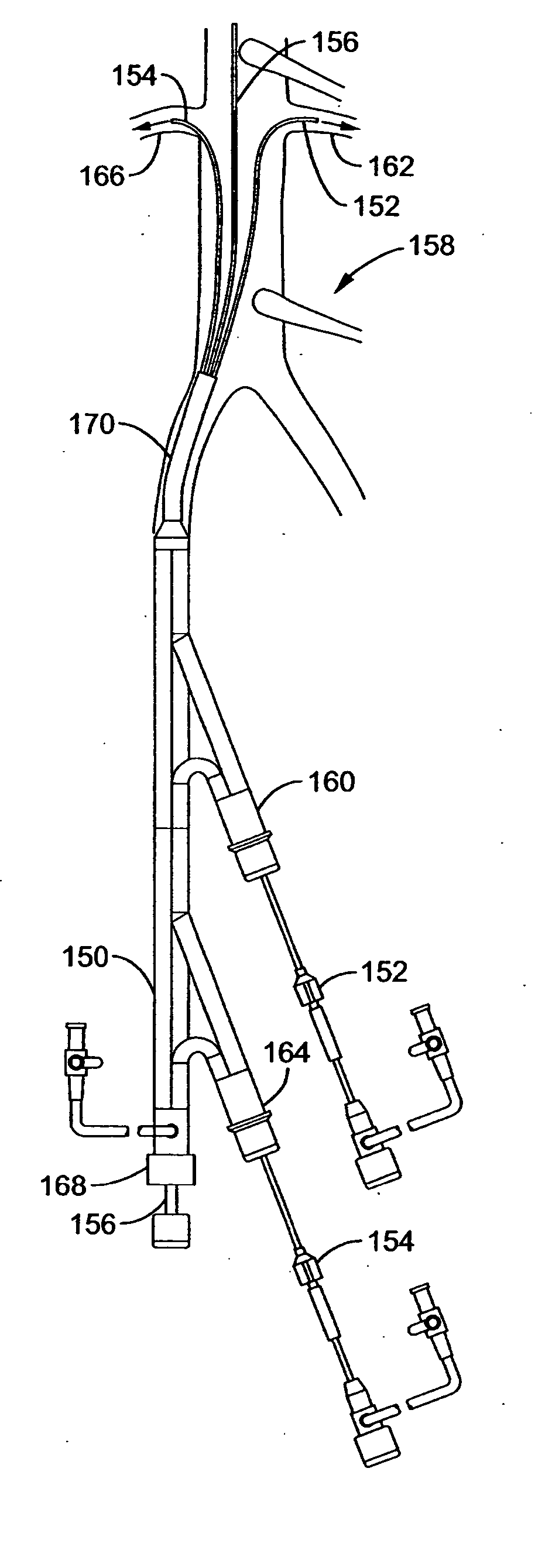
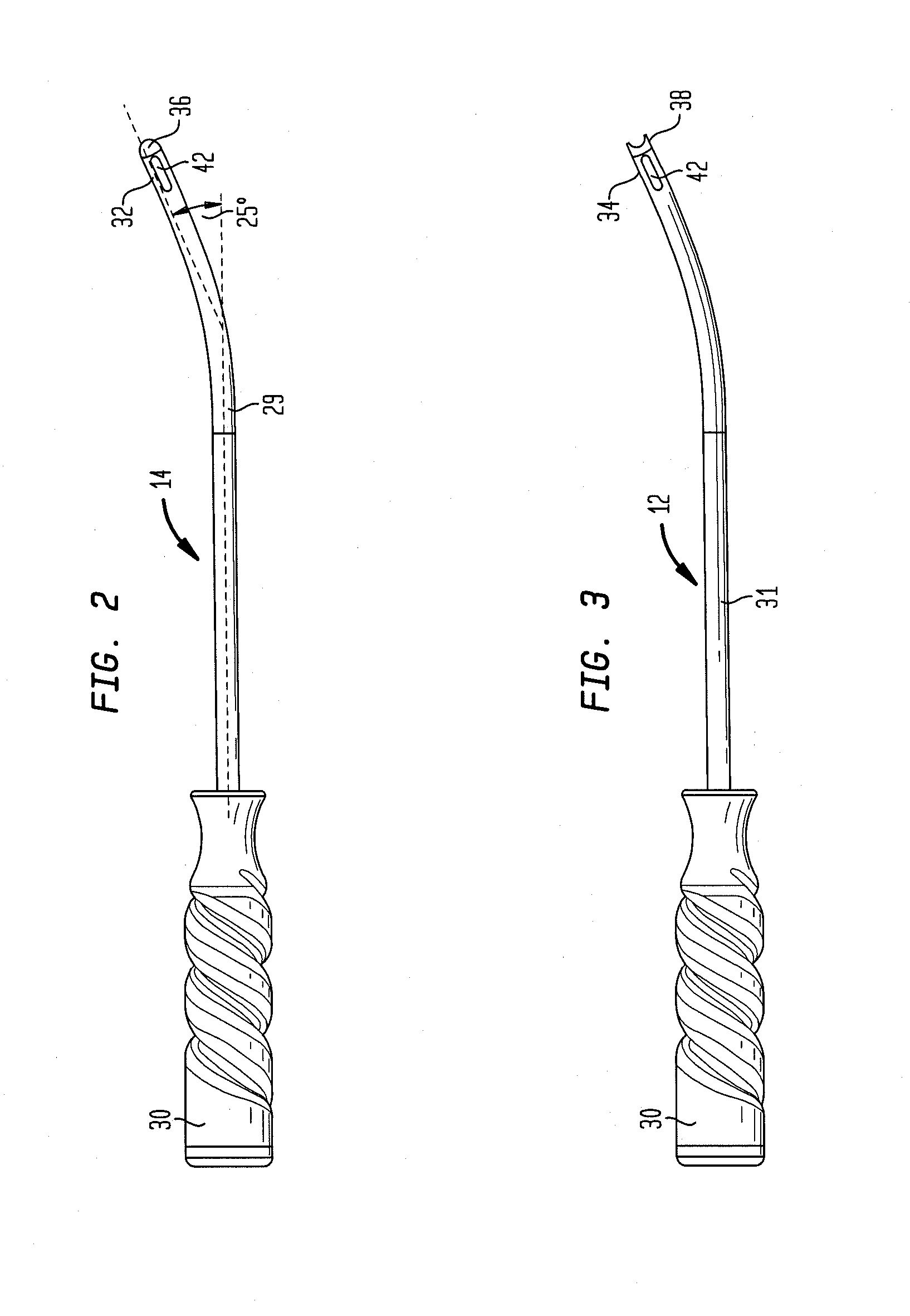
An introducer system delivers therapy locally to a renal system in a patient. A proximal coupler assembly is coupled to an introducer sheath that delivers multiple devices simultaneously into a location within an abdominal aorta associated with first and second renal artery ostia. The coupler assembly has a network of branch lumens arranged to allow for smooth slideable engagement of multiple coupled devices without substantial interference therebetween. A first branch lumen typically introduces a percutaneous translumenal interventional device such as an angiography or guiding catheter into the introducer sheath and is substantially aligned with a longitudinal axis of the sheath. One or more other branch lumen are off-axis from the longitudinal axis by about 30 degrees or less and introduce components of a bilateral renal delivery assembly into the introducer sheath in conjunction with the other device. Novel insertion devices are provided to coordinate the coupling of the multiple devices.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Sigmoid valve and method for its percutaneous implantation
Owner:THE INT HEART INST OF MONTANA FOUND
Medical Device with Transcutaneous Cannula Device
InactiveUS20080215006A1Avoid damagePrevent escapeMedical devicesPressure infusionCannula deviceMedical device
The present invention generally relates to the insertion of a transcutaneous device of the type comprising a cannula (651) and a therein moveably arranged insertion needle (661), as well as the connecting of such a transcutaneous device with a fluid supply. Thus, a device is provided comprising an insertion needle and a cannula disposed on and being axially moveable relative to the insertion needle, the insertion needle comprising a proximal fluid inlet, a seal (655) being provided between the cannula and the insertion needle allowing fluid to be transported from the fluid inlet to the distal fluid outlet, wherein the insertion needle after having been used to insert the cannula is arranged at a retracted position proximally of the initial position, thereby allowing the fluid inlet to be connected to a fluid supply when it is moved from its initial to its retracted position.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6027476AImprove isolationReduce complicationsSuture equipmentsCannulasThoracoscopeHeart operations
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Steerable introducer assembly for first percutaneously identifying target tissue and then defining a percutaneous path to the target tissue for an implantable medical device
An assembly for both targeting a location in a living being at which an implantable medical device is to be inserted and defining a percutaneous path to the target location. The assembly includes a guidewire with electrodes that is inserted percutaneously into the living being. Electrodes on the guidewire source and sink current to facilitate the identification of the target location. A dilator encased in a reinforced sleeve is disposed over the guidewire. Steering wires in the sleeve facilitate the advancement of the sleeve and the guidewire. Once the dilator and sleeve are advanced to the target location, the dilator is removed from the sleeve. The lumen in sleeve functions as the lumen in the living being through which the implantable device is delivered to the target location.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Techniques for percutaneous mitral valve replacement and sealing
ActiveUS20180344457A1Promote expansionFacilitate compressionStentsBalloon catheterEngineeringBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
Apparatus is provided for use with a native valve of a heart of a subject. The apparatus includes: (1) an annular upstream support portion, comprising an expandable first frame, the upstream support portion configured to be placed against an upstream surface of the native valve; (2) a flexible polyester connector; and (3) an anchoring element, flexibly coupled to the upstream support portion by the connector, and configured to anchor the upstream support portion to the native valve by engaging tissue of the native valve.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Interspinous process implants having deployable engagement arms
ActiveUS20090292316A1Good torque transmissionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionSpinal implant
Spinal implants include an elongated body portion dimensioned and configured for percutaneous introduction into a target interspinous process space, at which interspinous distraction and / or spinal fusion are desired. The body portion can include a threaded outer surface, or alternatively a smooth surface. The body portion can include one or more interior cavities, and can include deployable engagement members adapted and configured to move in tandem between a stowed position retracted within the interior cavity of the body portion and a deployed position extended from the interior cavity of the body for engaging adjacent spinous processes. An internal drive assembly for selectively moving the engagement members from the stowed position to the deployed position can be provided, as can a elements for locking the engagement members in a deployed position.
Owner:SPINAL SIMPLICITY
Tools for Percutaneous Spinal Ligament Decompression and Device for Supporting Same
InactiveUS20070055263A1Reduce stenosisVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsExcision instrumentsSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
A device for providing percutaneous access to a surgical site. In an embodiment, the device comprises a handle. In addition, the device comprises a bone-cutting member extending from the handle, wherein the bone-cutting member includes a handle end fixed to the handle and a cutting end. Further, the device comprises a portal including a first end, a second end, and a through bore extending therebetween, wherein the bone-cutting member is disposed within the through bore and concentric with the portal Still further, the portal has a first position with the second end releasably coupled to the handle and a second position with the second end released from the handle and the bone-cutting member.
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
Suture anchor implantation instrumentation system
ActiveUS20110015675A1Easy to implementLarge range of motionSuture equipmentsBaby-comfortersEngineeringDrill bit
A system for implanting an anchor into bone, the system comprising a curved cannulated guide for percautaneous insertion, having a proximal end and a distal end; a flexible drill insertable through the curved guide from the proximal end to the distal end, the flexible drill having a shaft having a flexible portion; and a flexible inserter for inserting a suture anchor into a bore at the anatomical site formed by the flexible drill, the flexible inserter having a shaft having a flexible portion, wherein the flexible portions of both the flexible drill and flexible inserter include a series of discrete, interlocking segments.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com