Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
767 results about "Prosthetic valve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
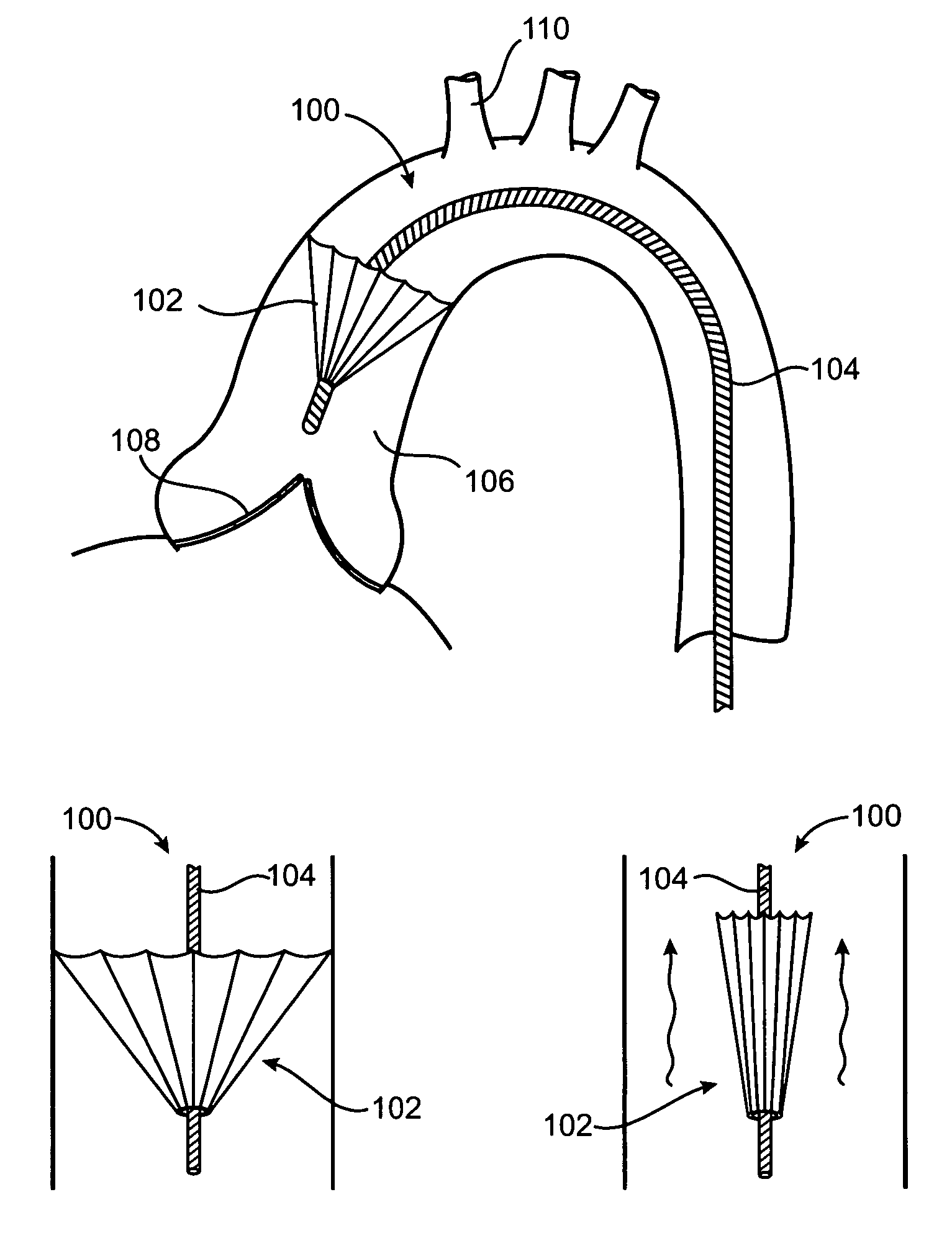
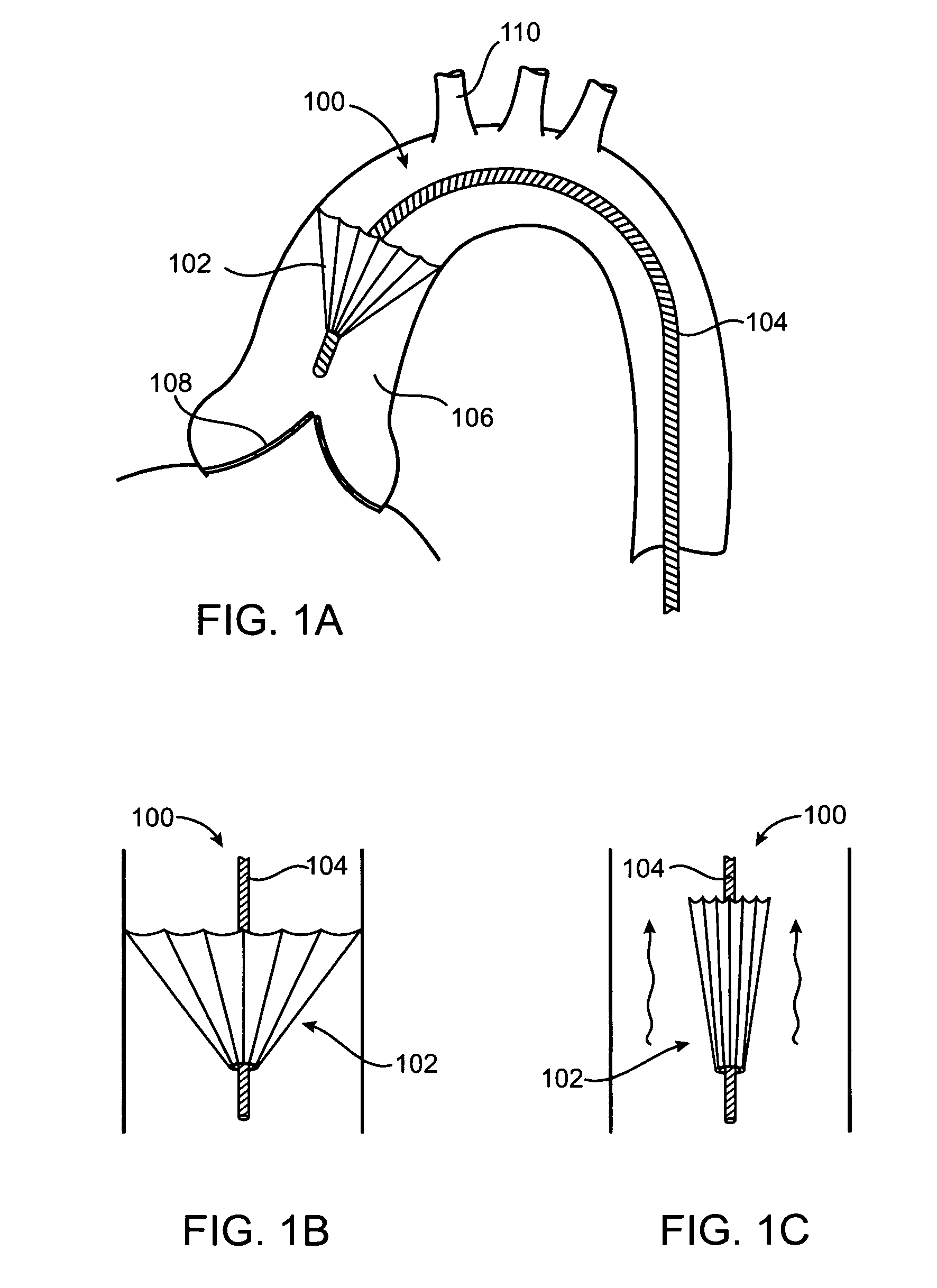
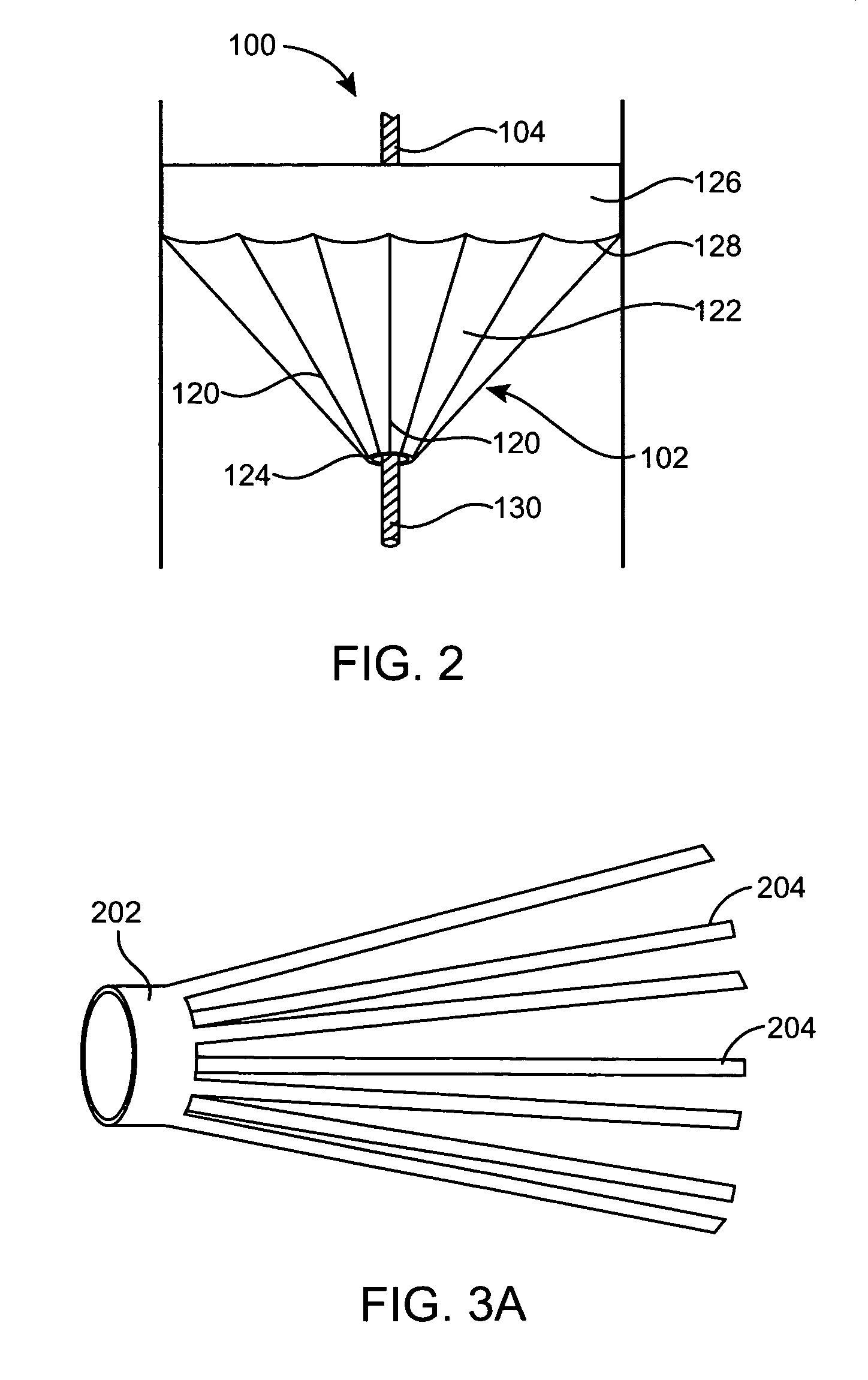
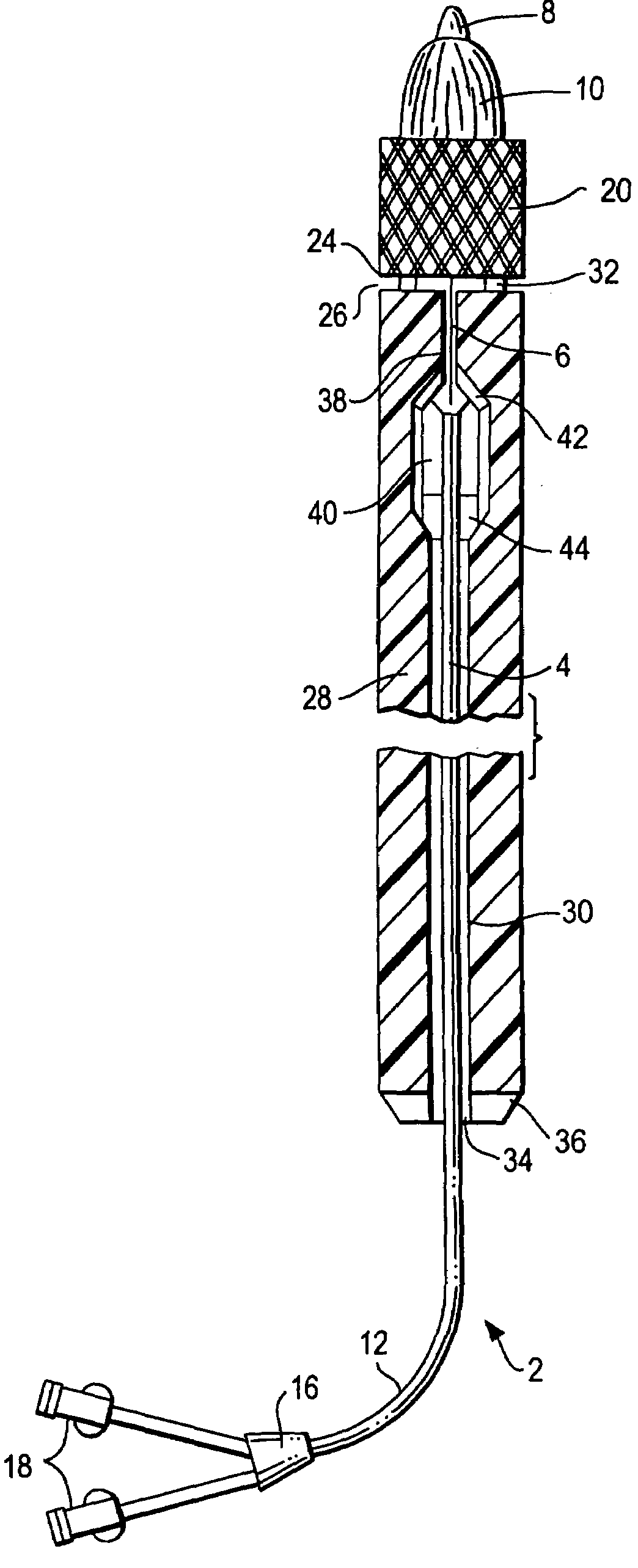
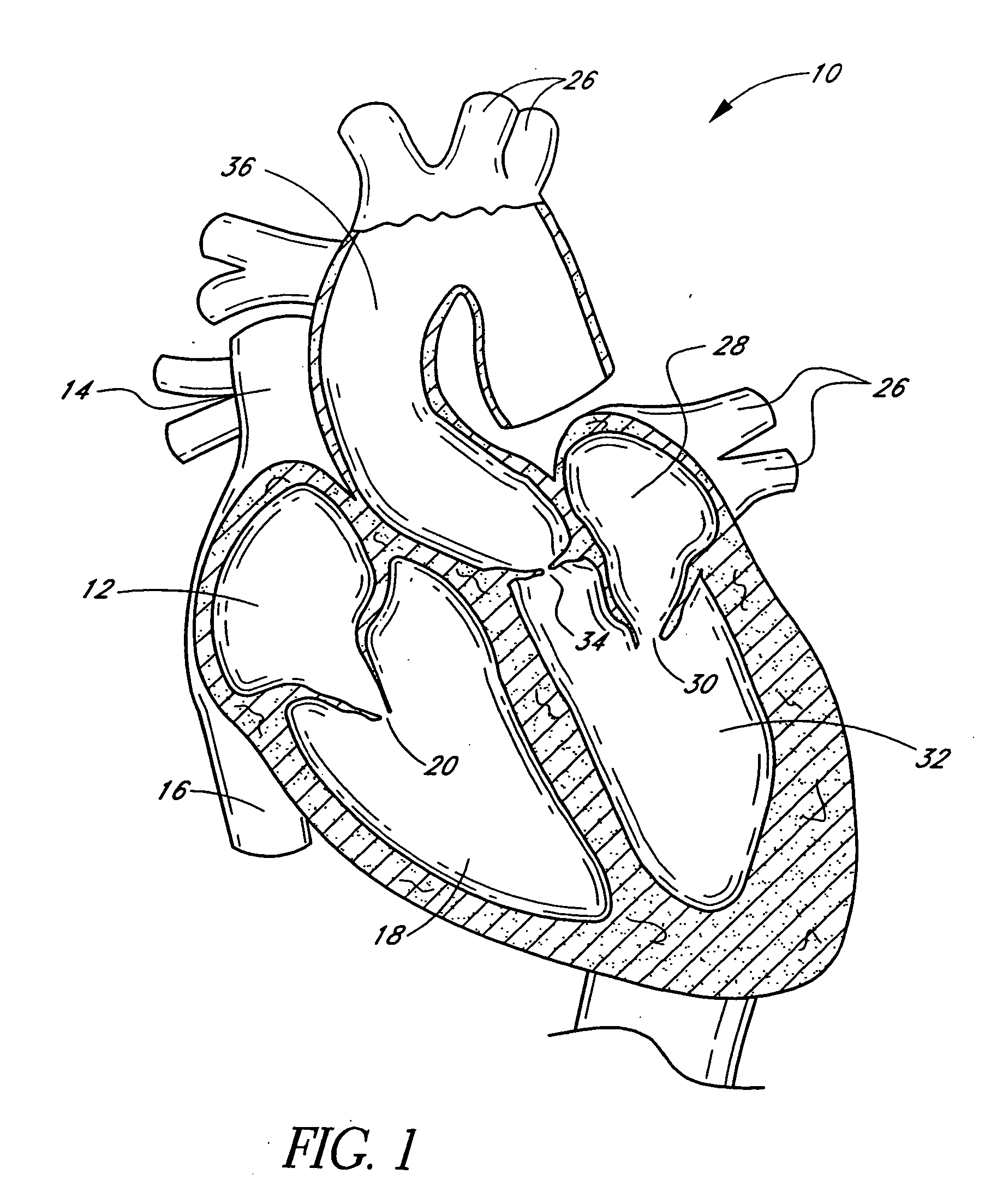
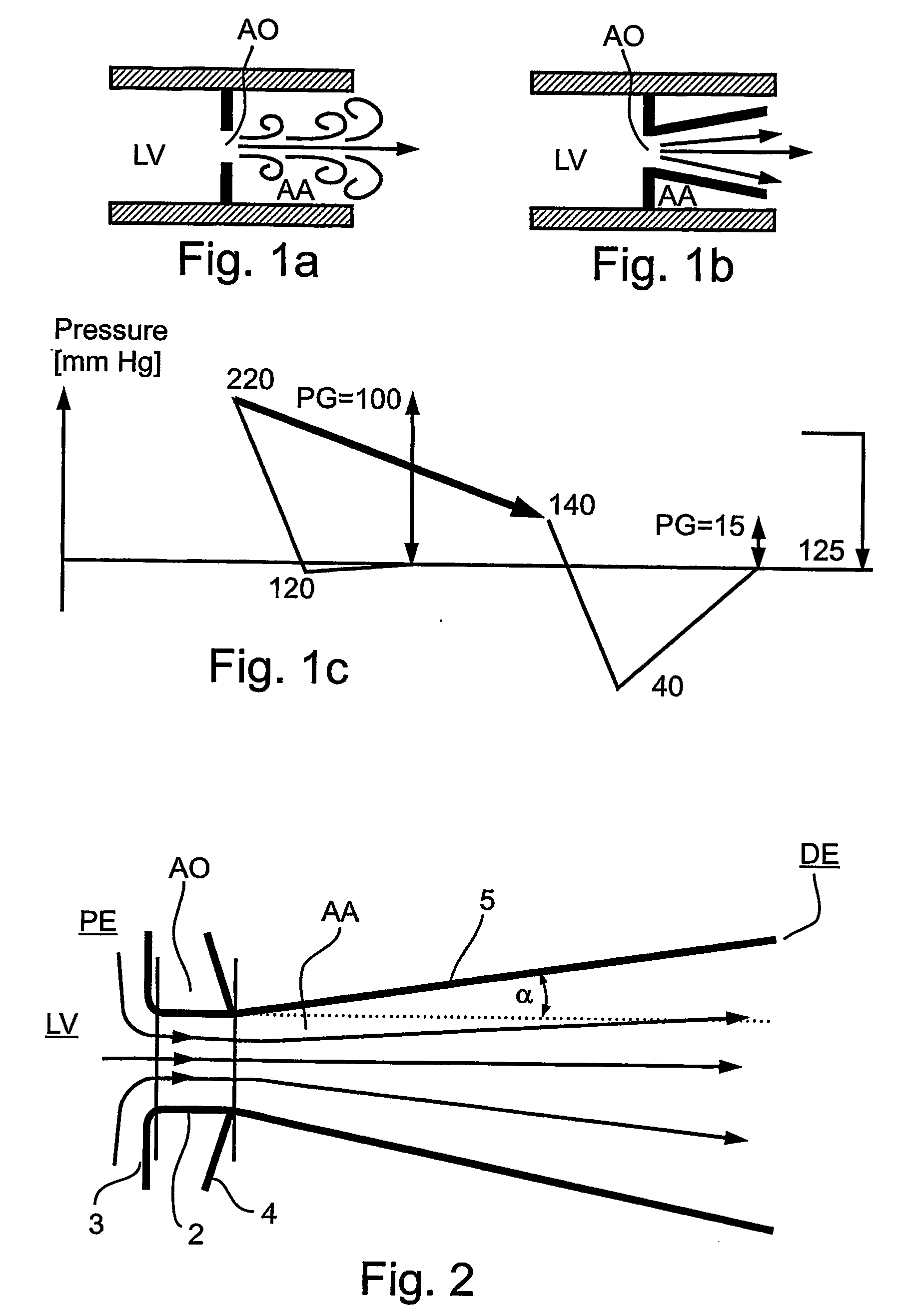
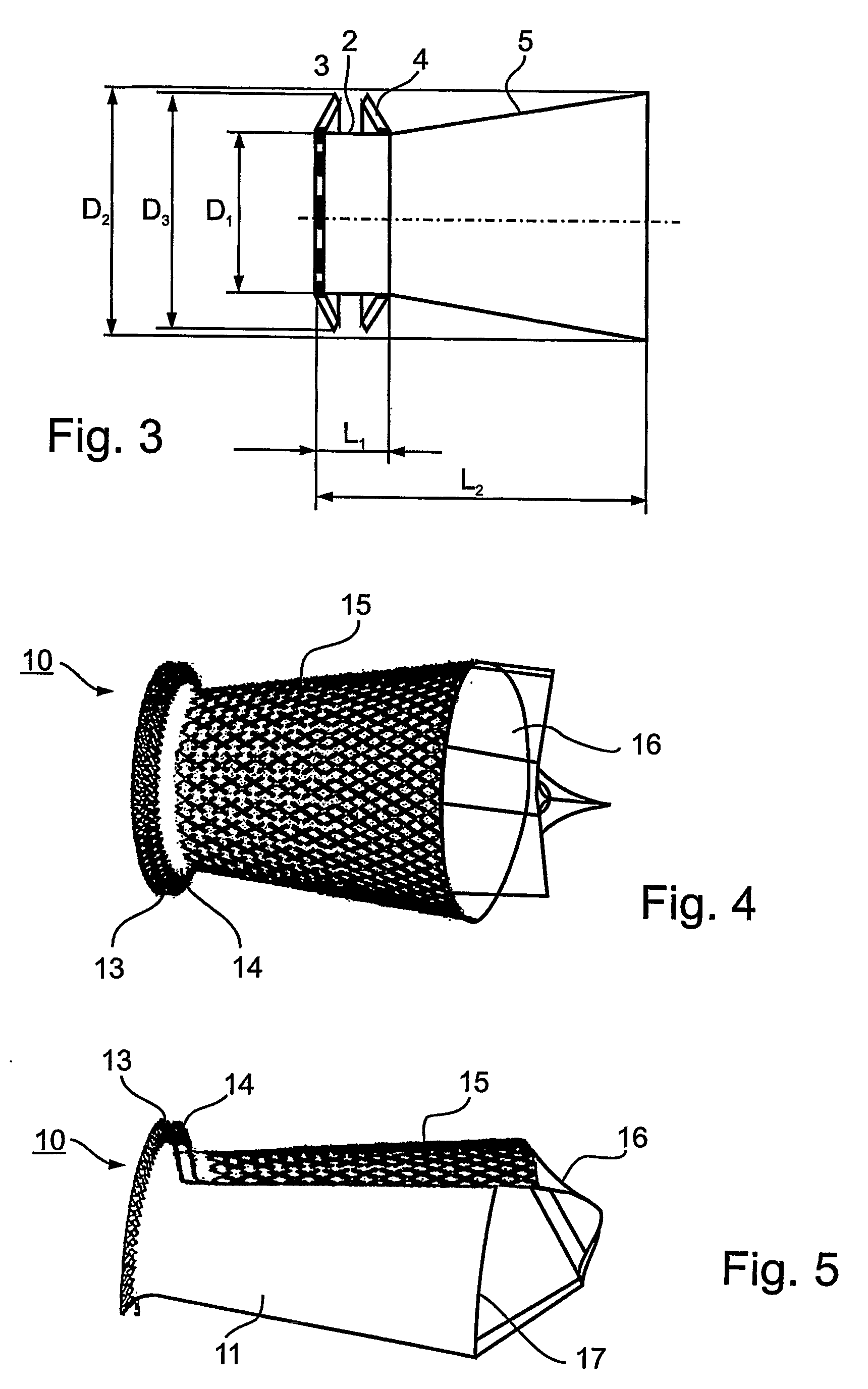
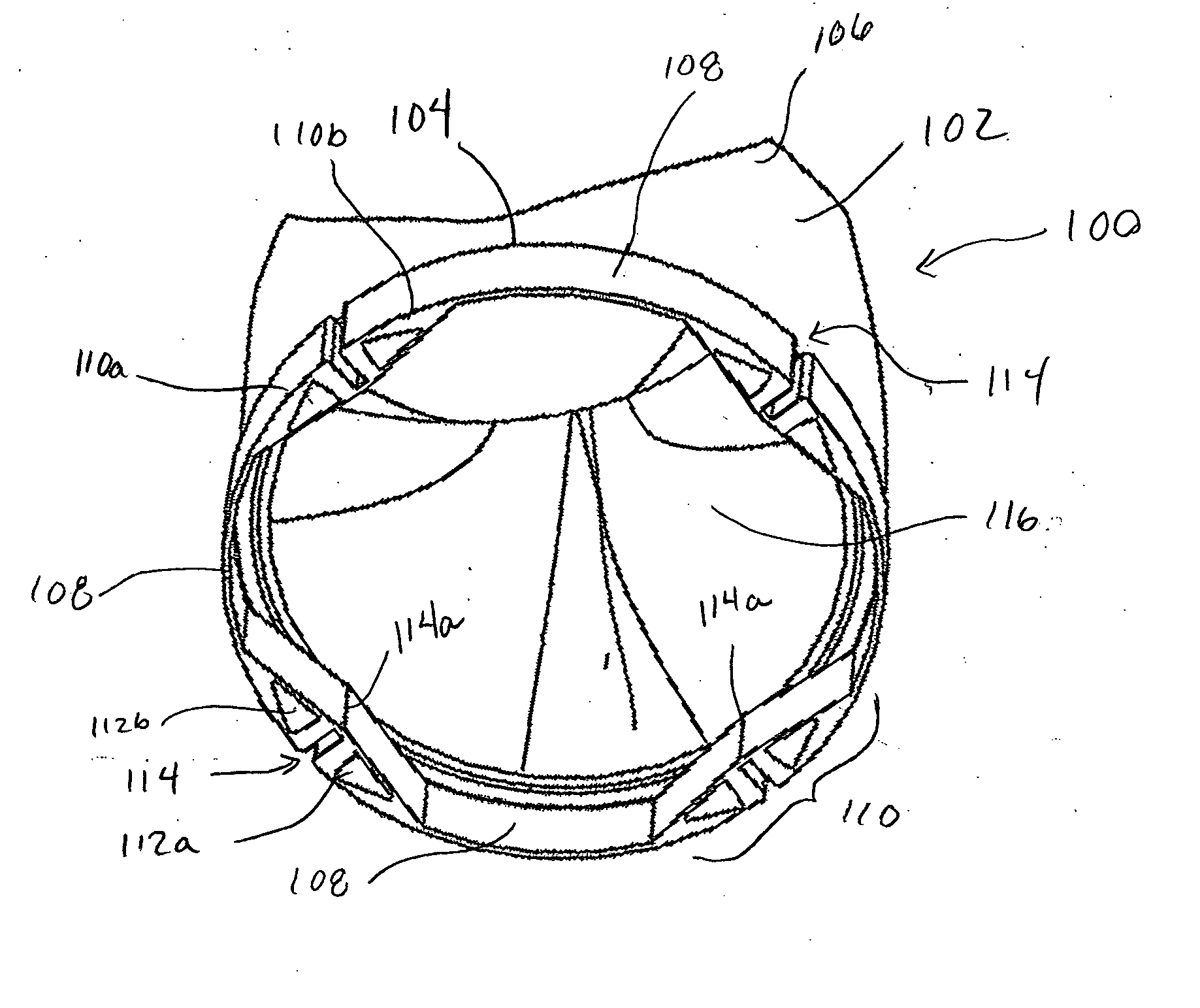
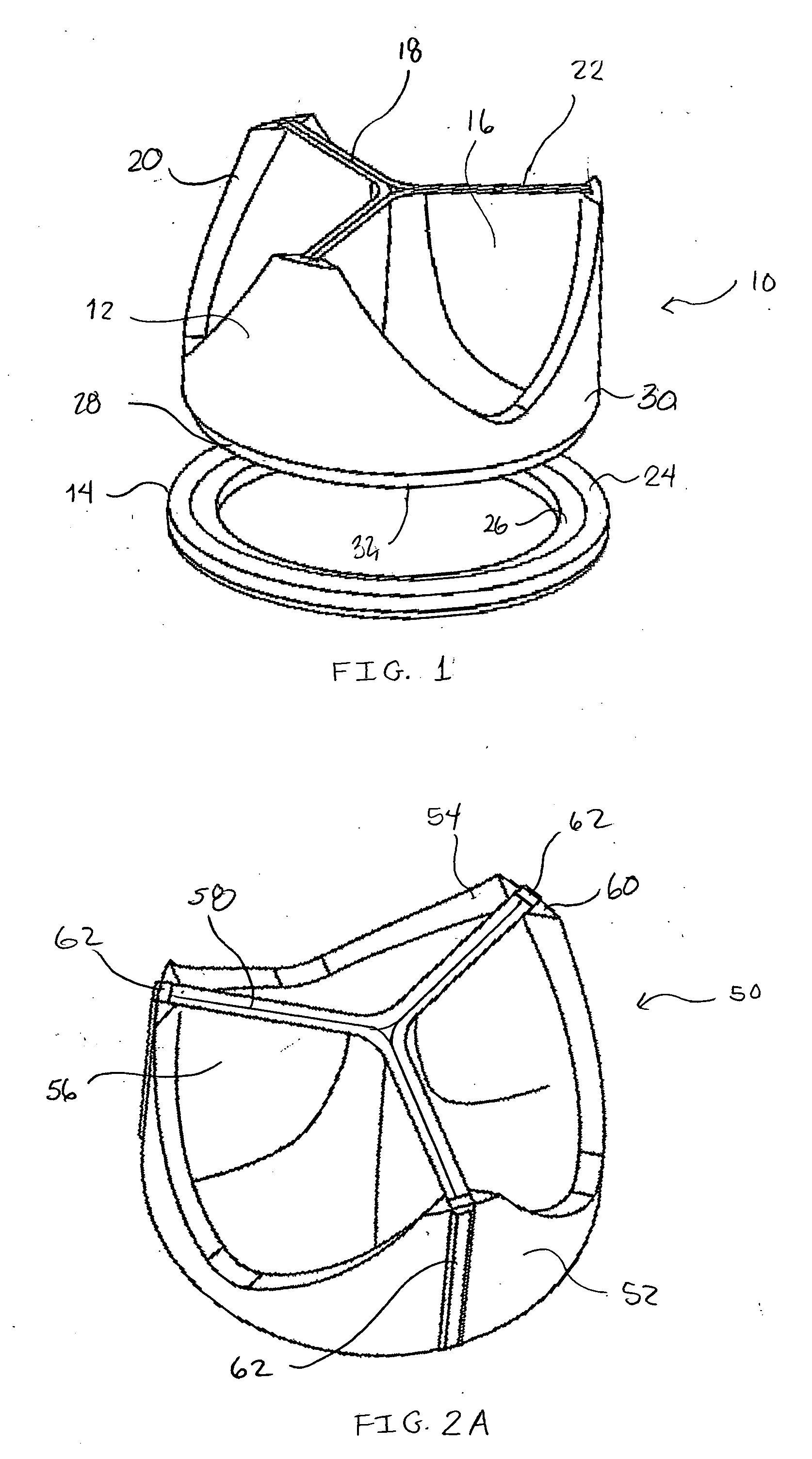
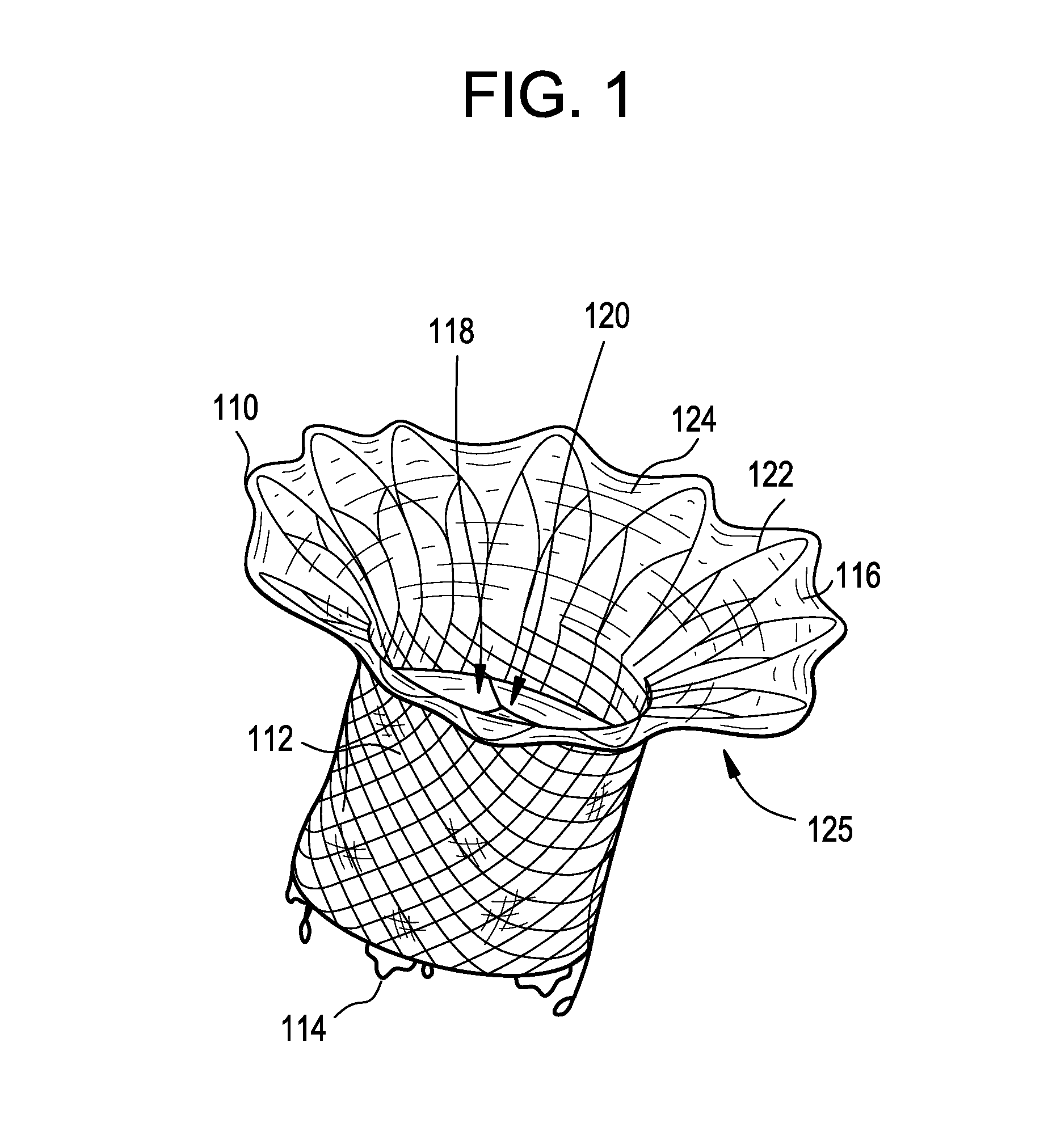
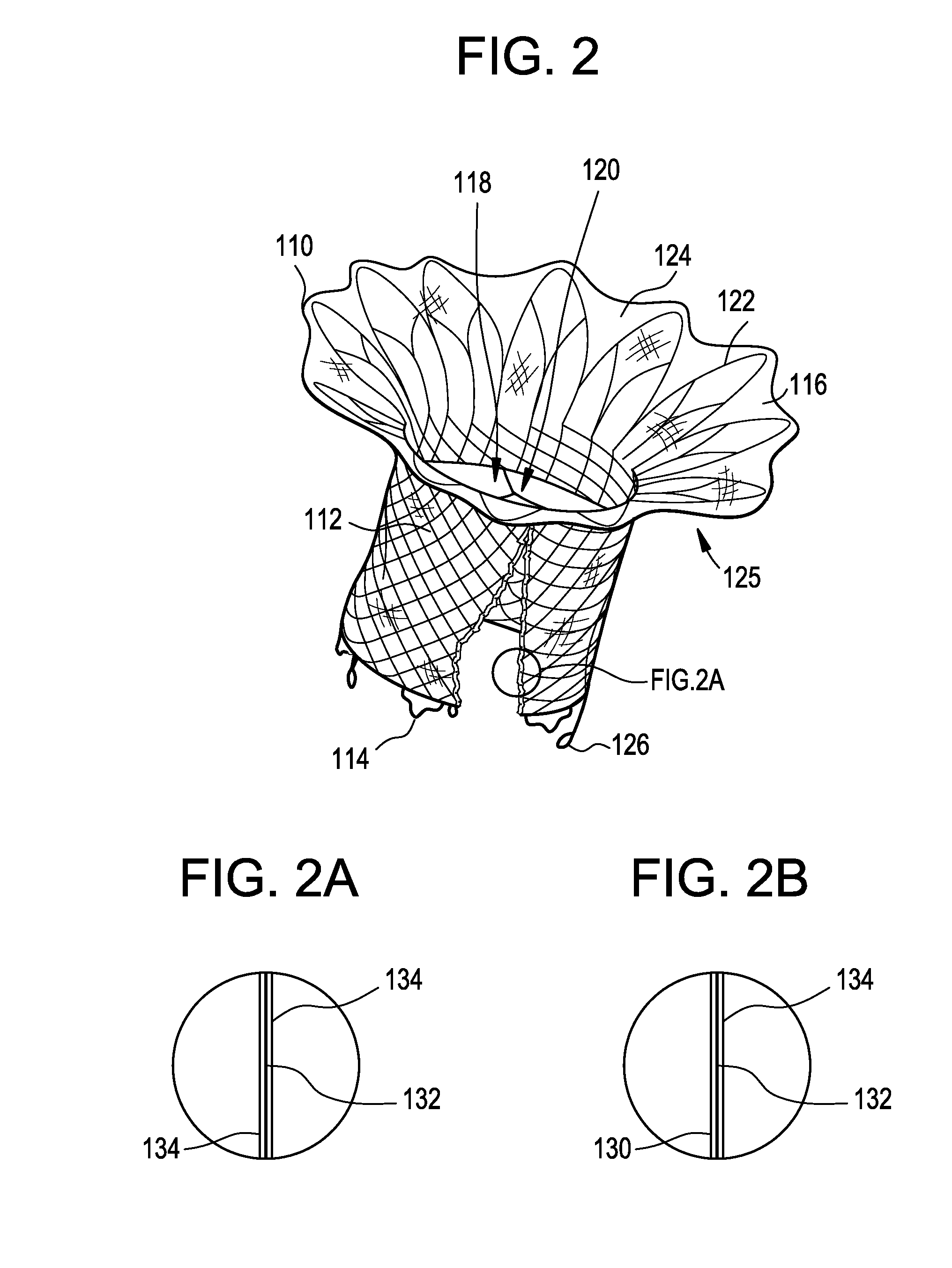
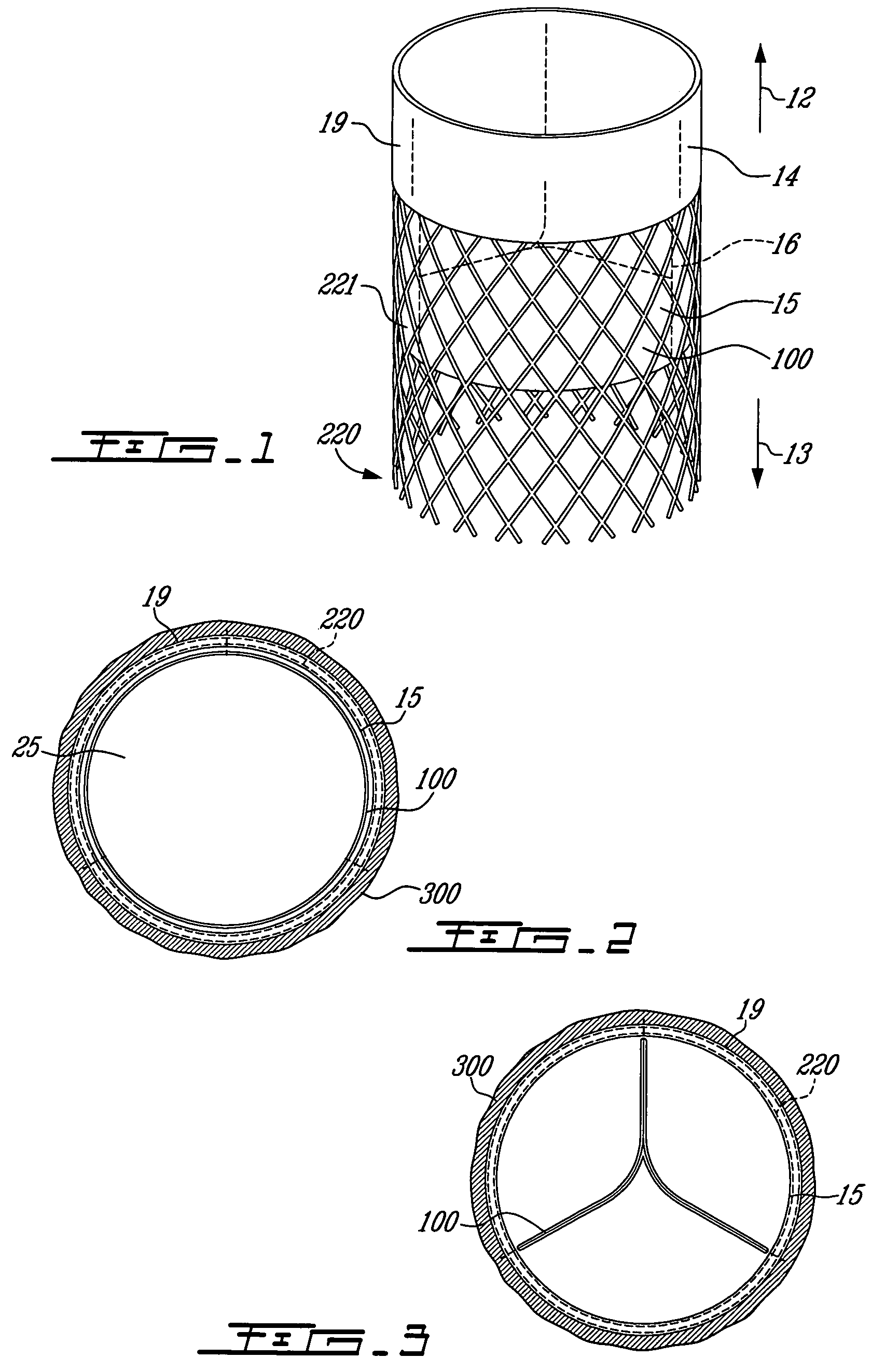
A prosthetic valve refers to a valve used in or right outside of the heart to replace an injured, damaged or missing heart valve. There are four places in the heart structure in which prosthetic valves may be used. These are the mitral and tricuspid valves, and the aortic valve (aorta) and pulmonary valve.
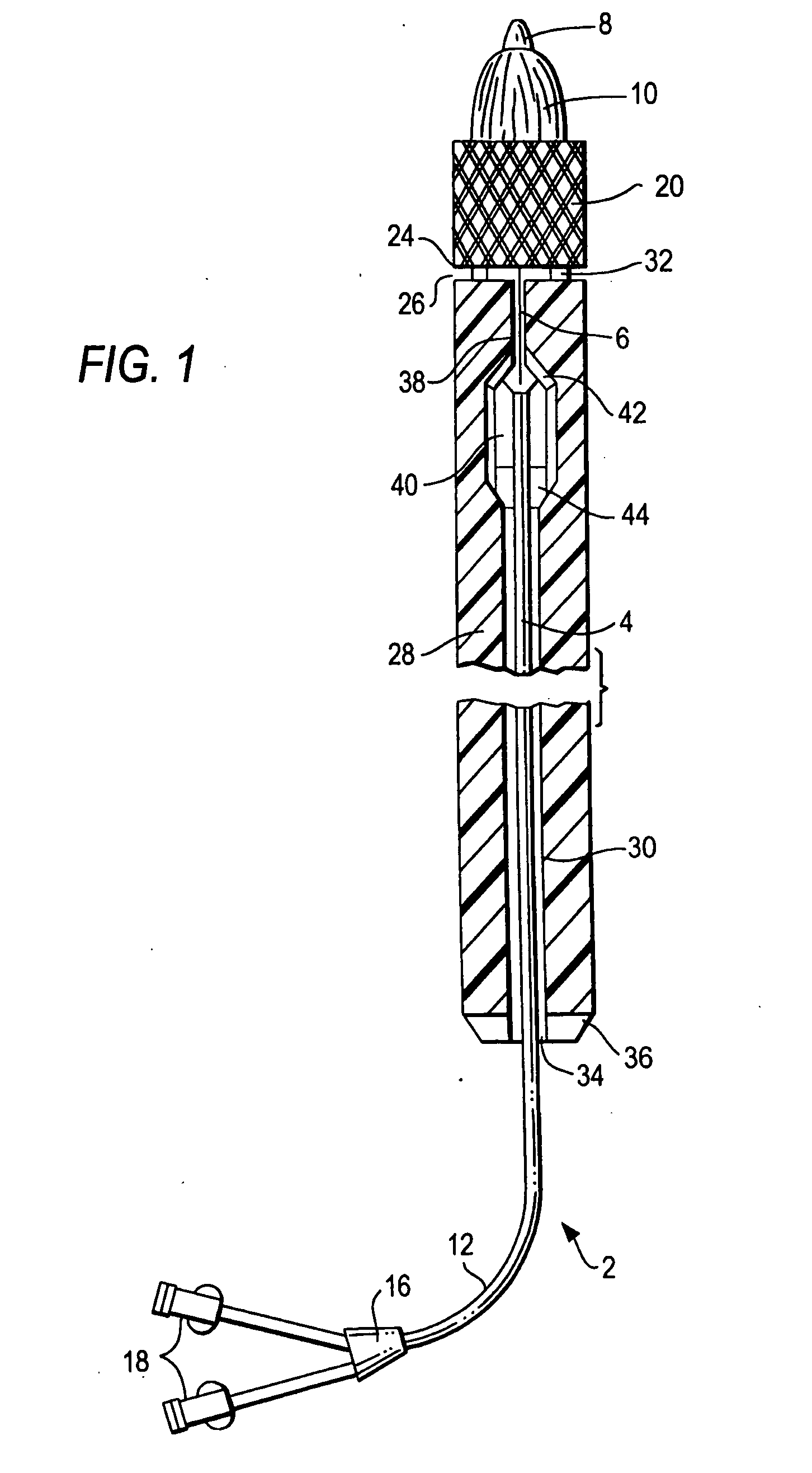
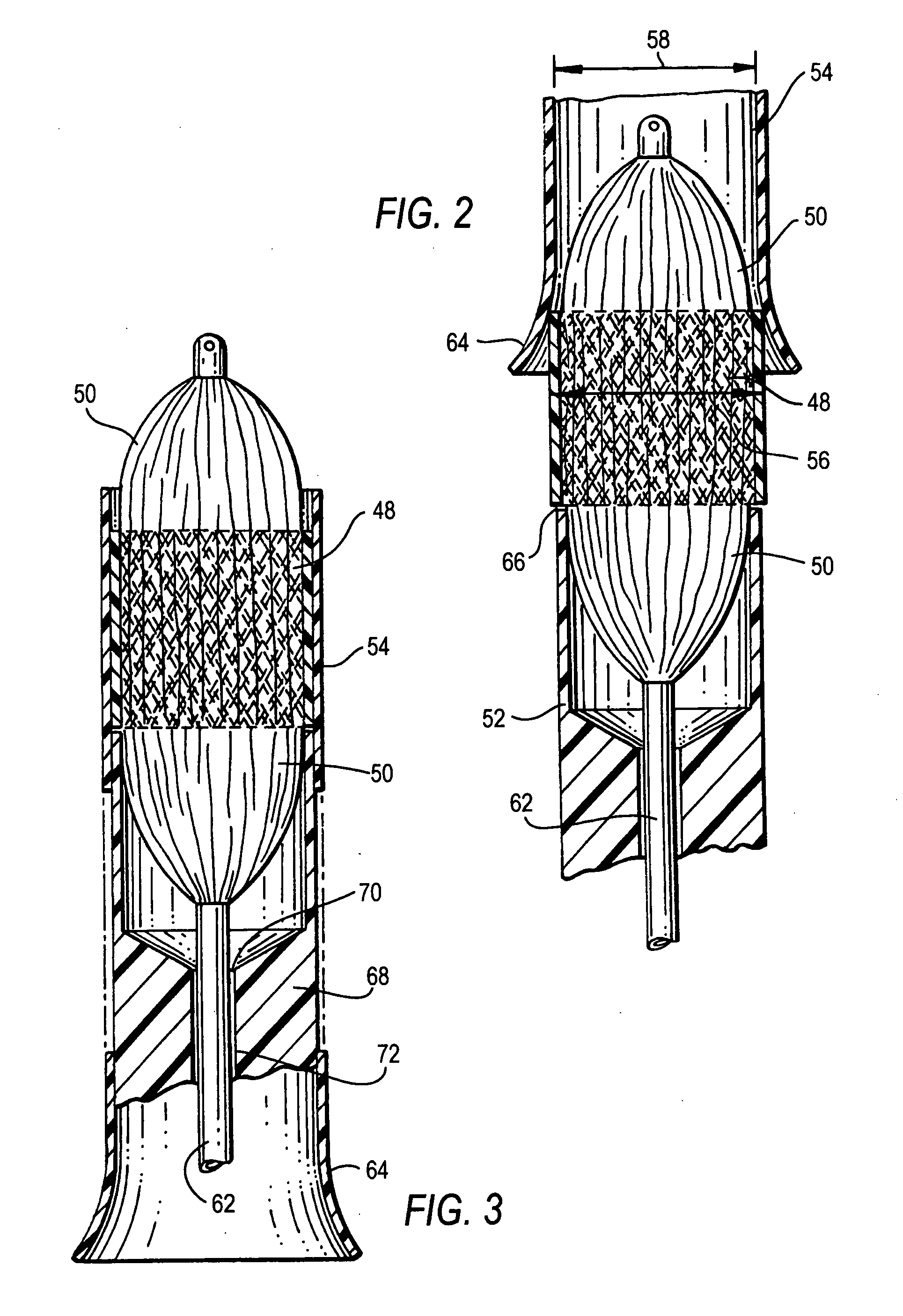
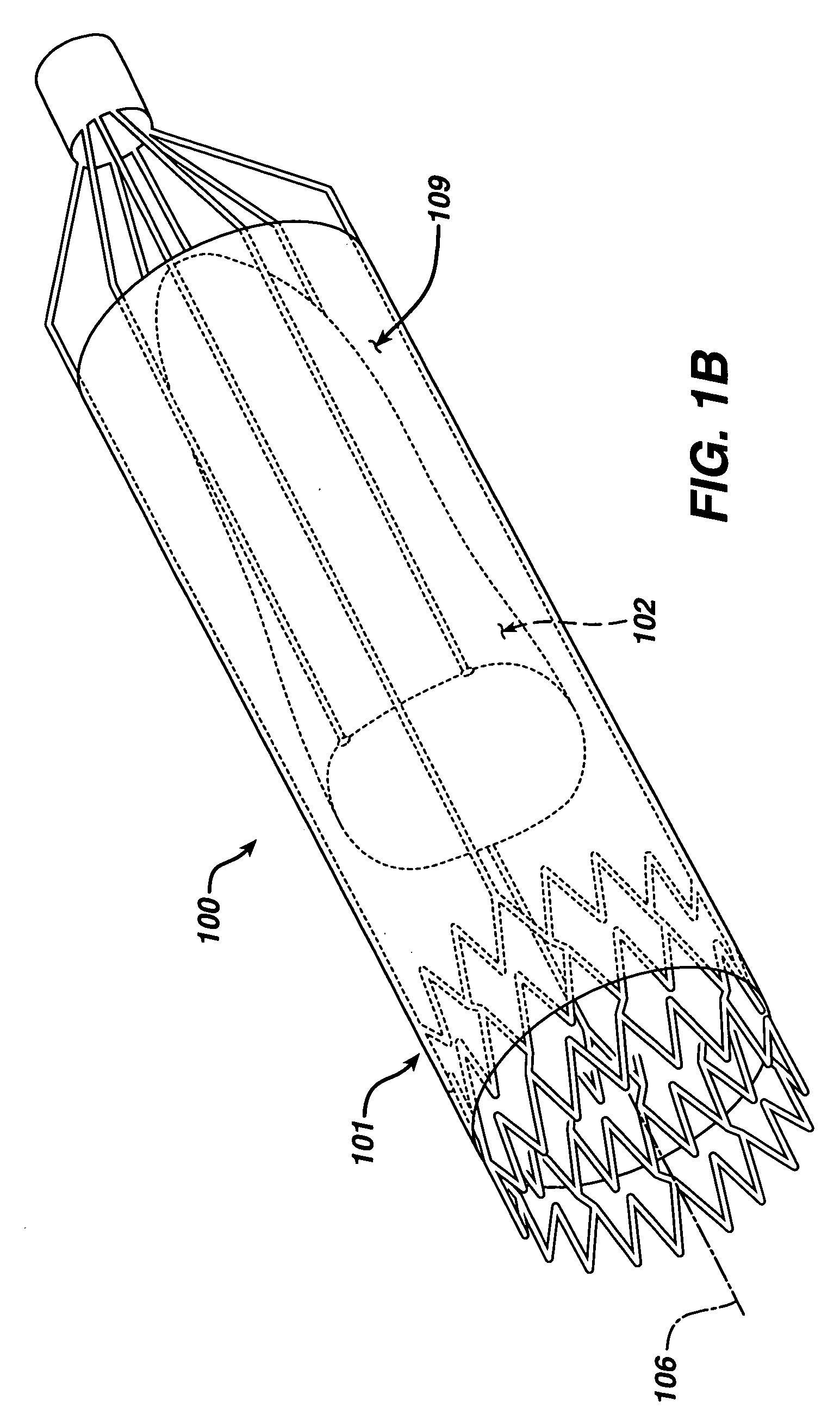
Low profile transcatheter heart valve
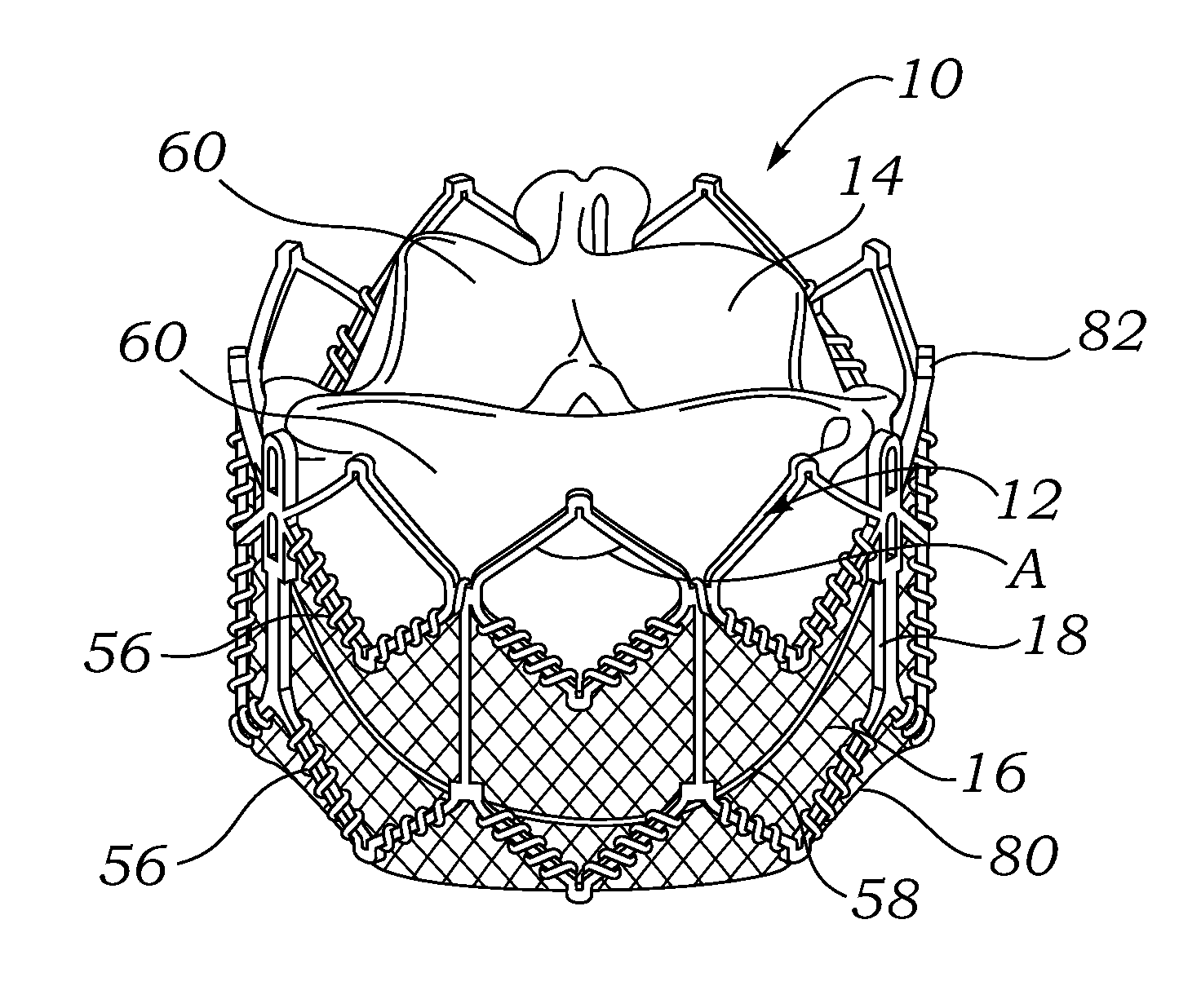
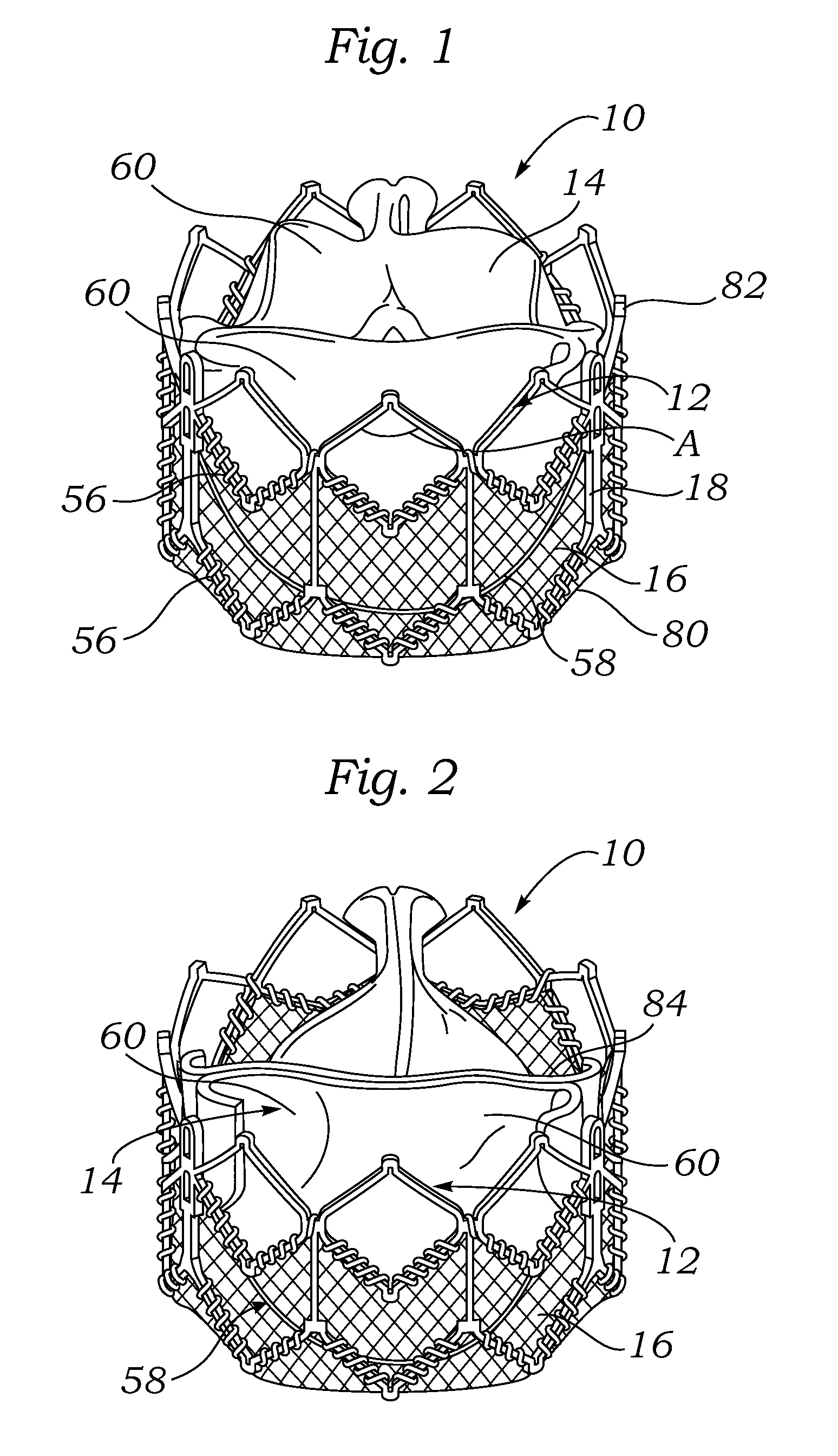
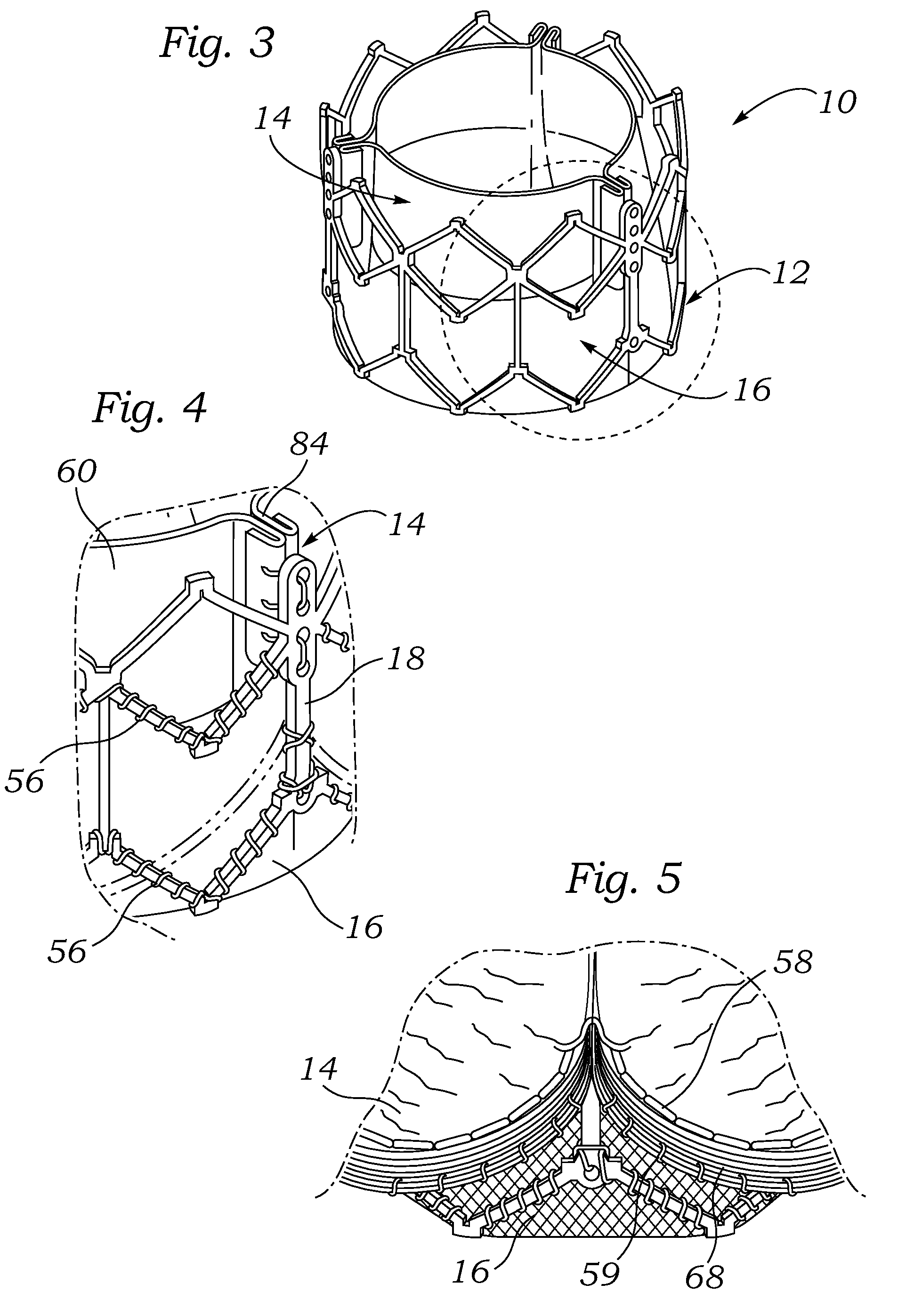
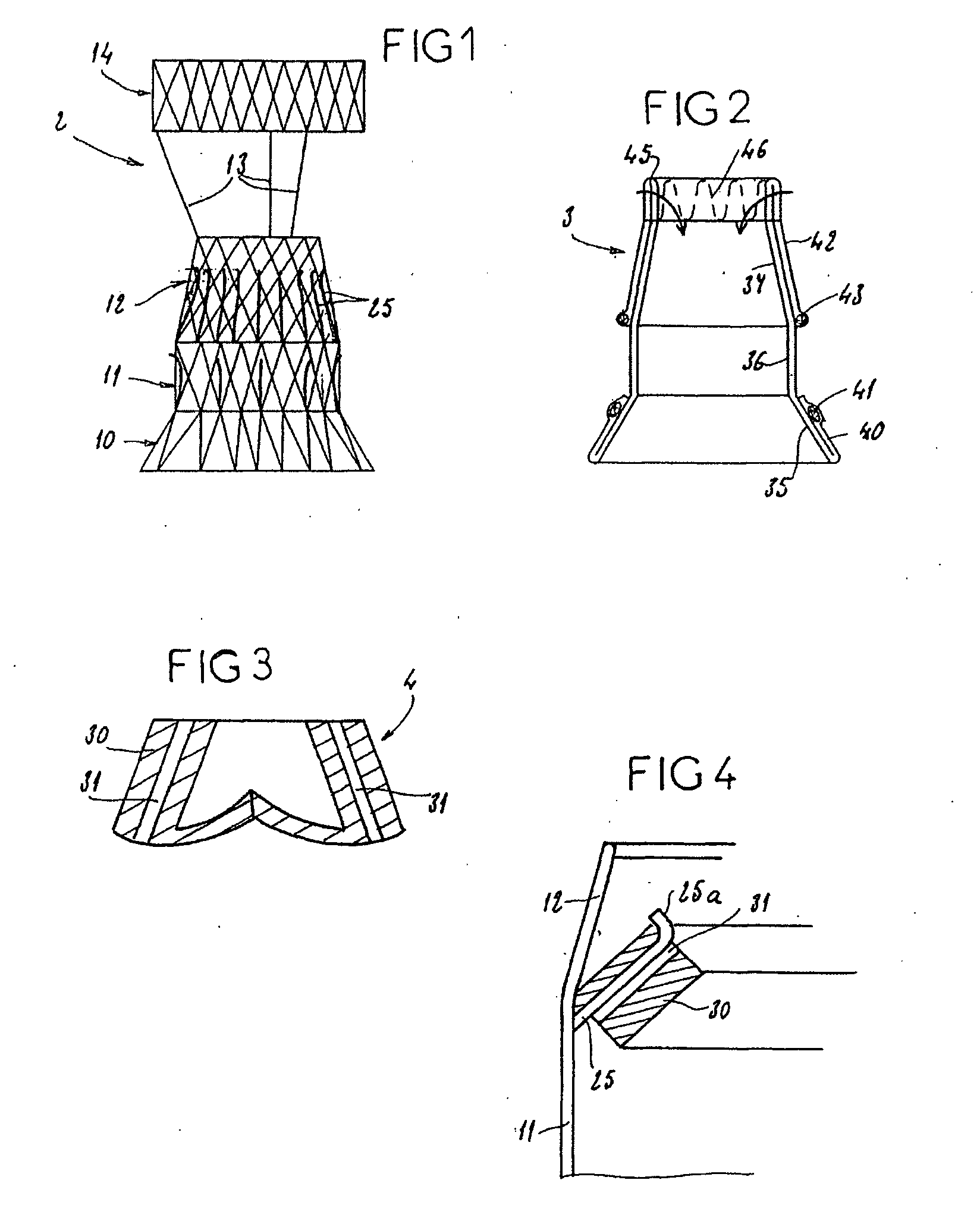
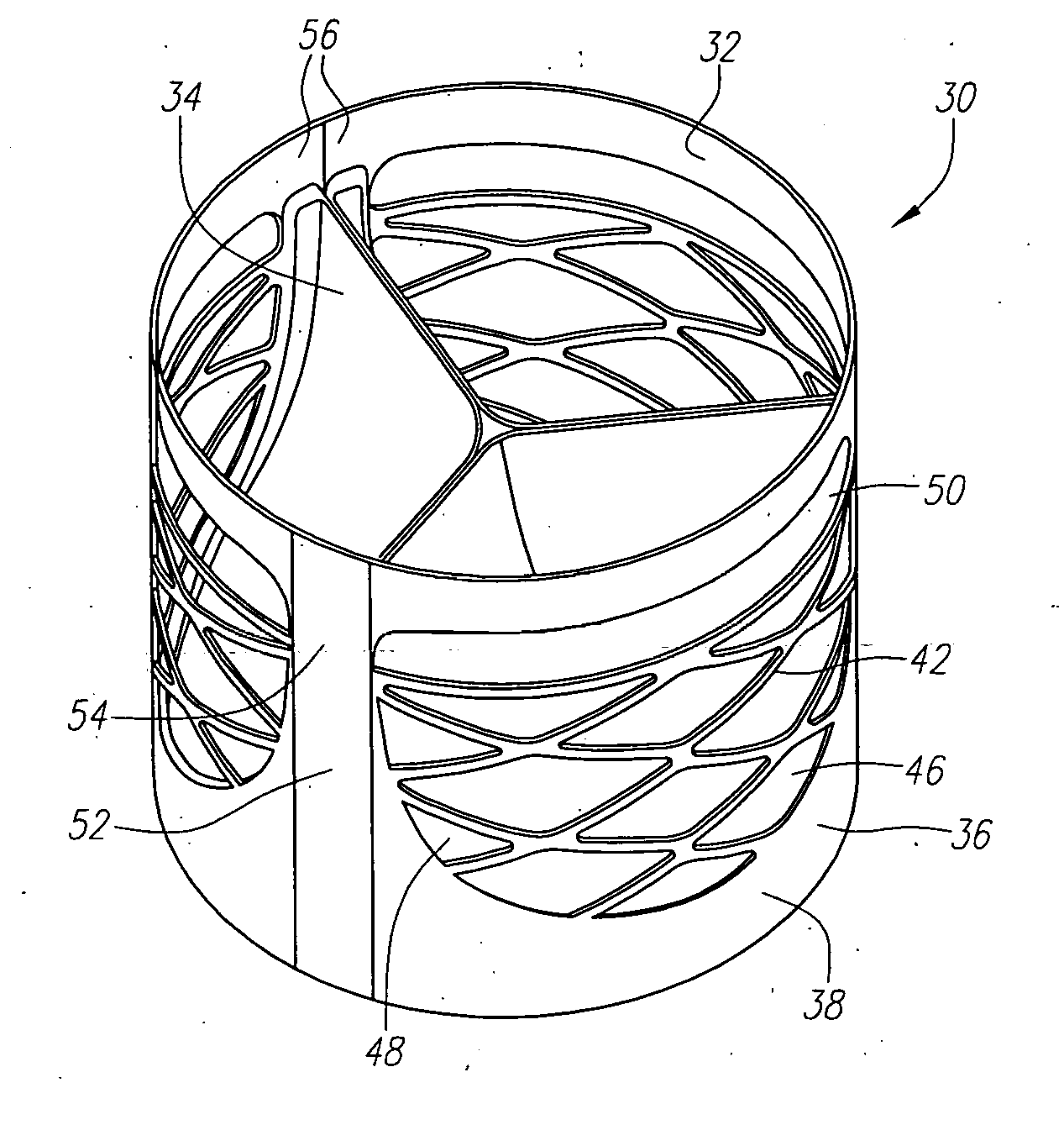
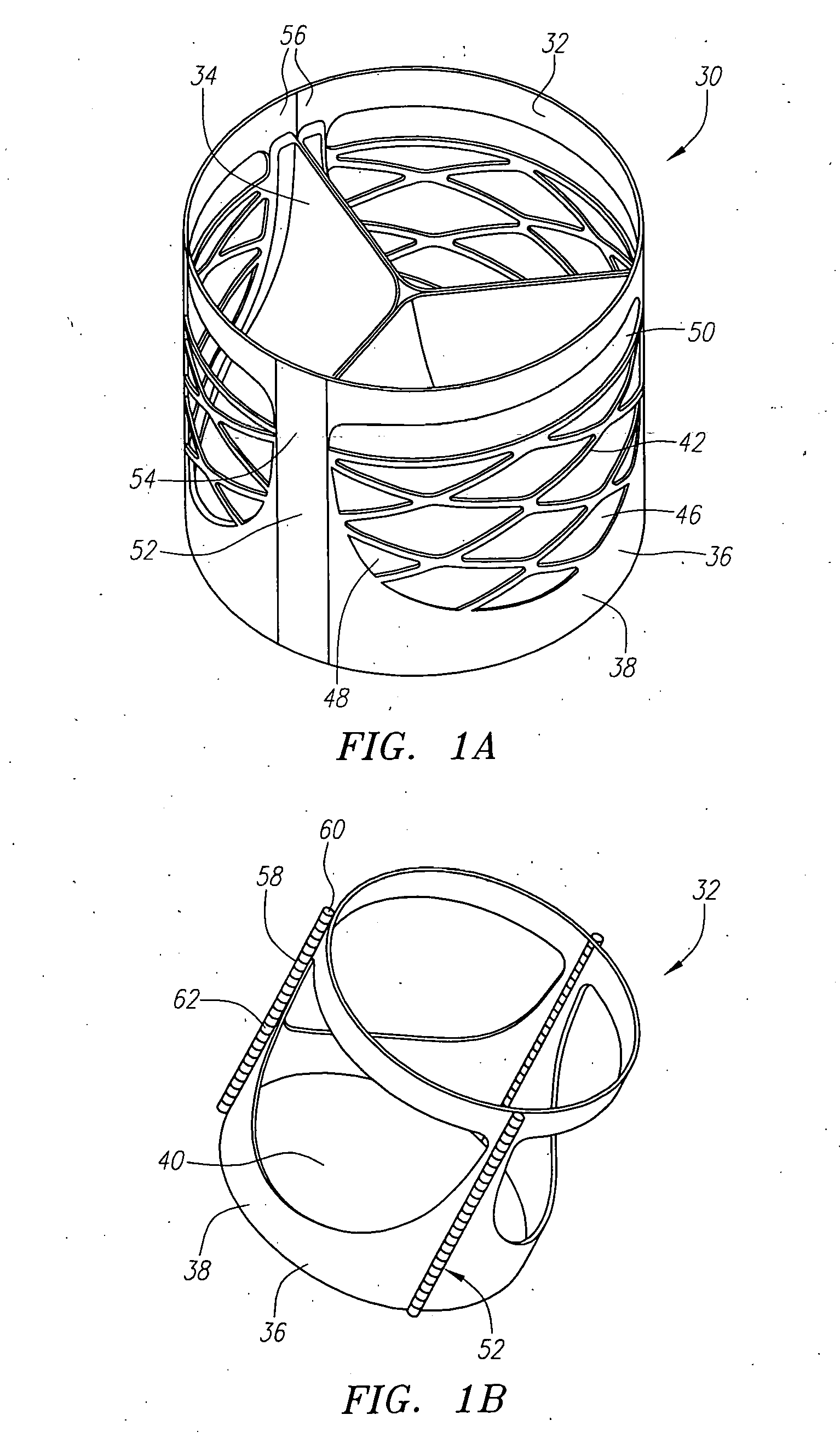
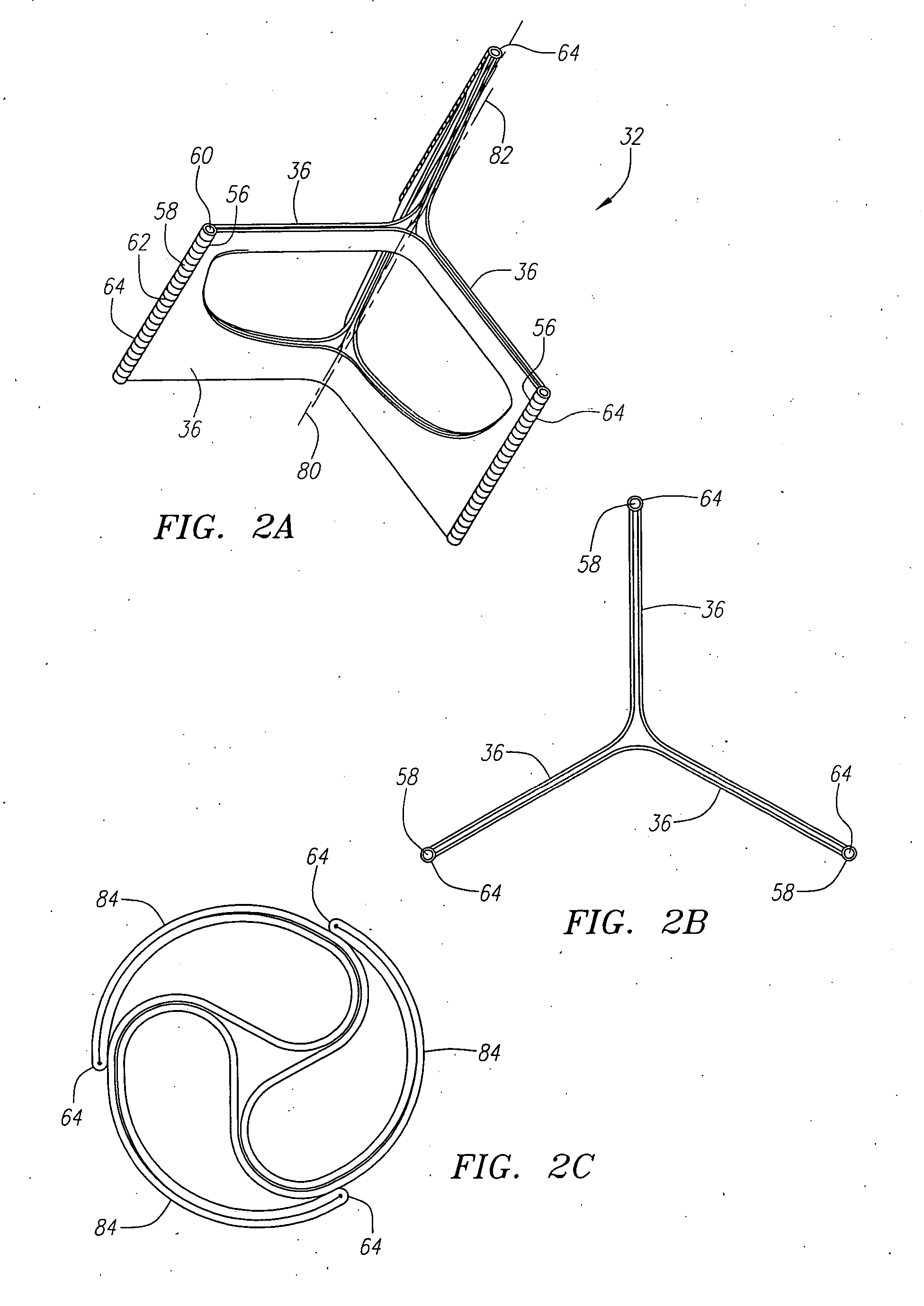
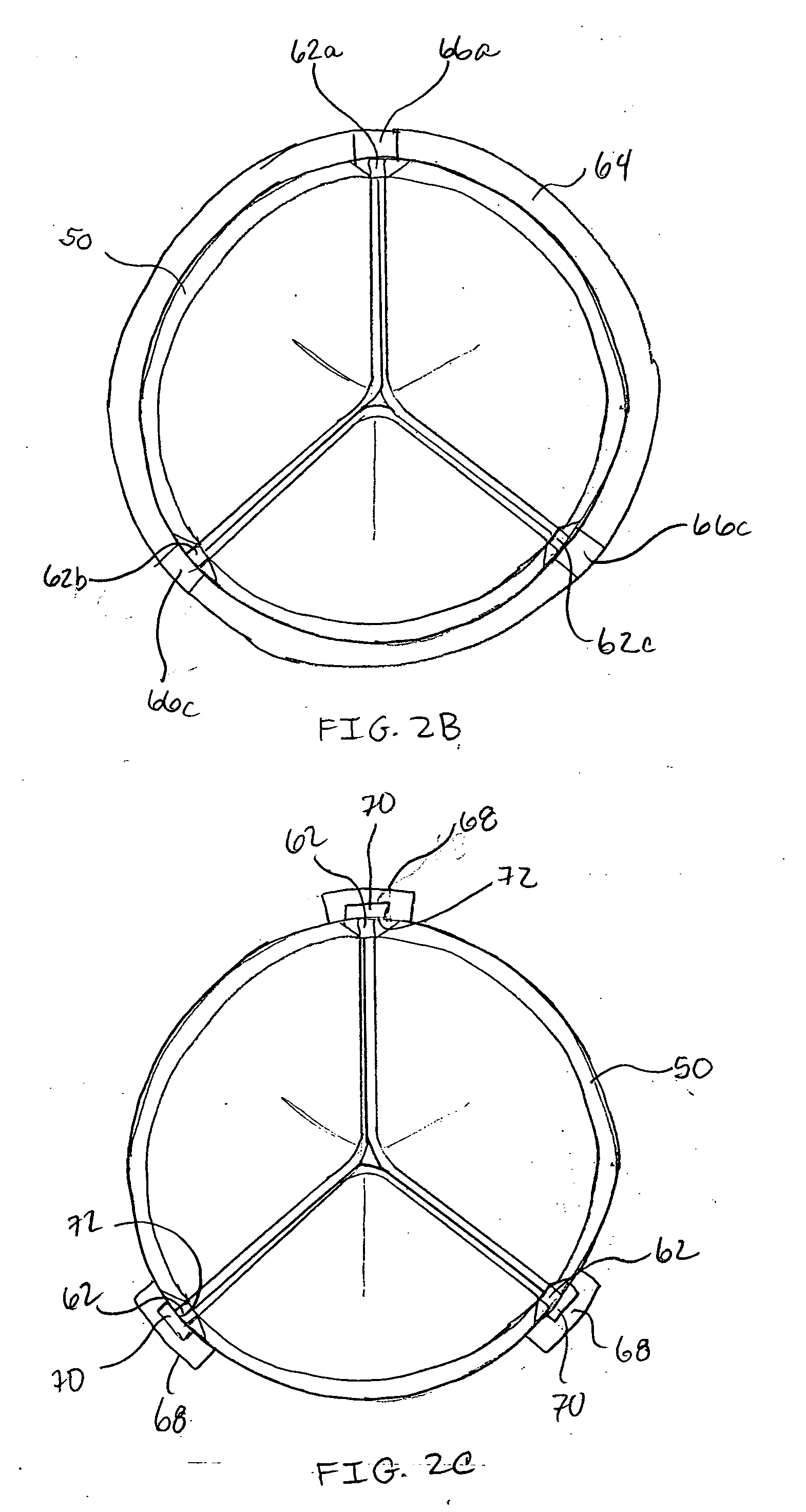
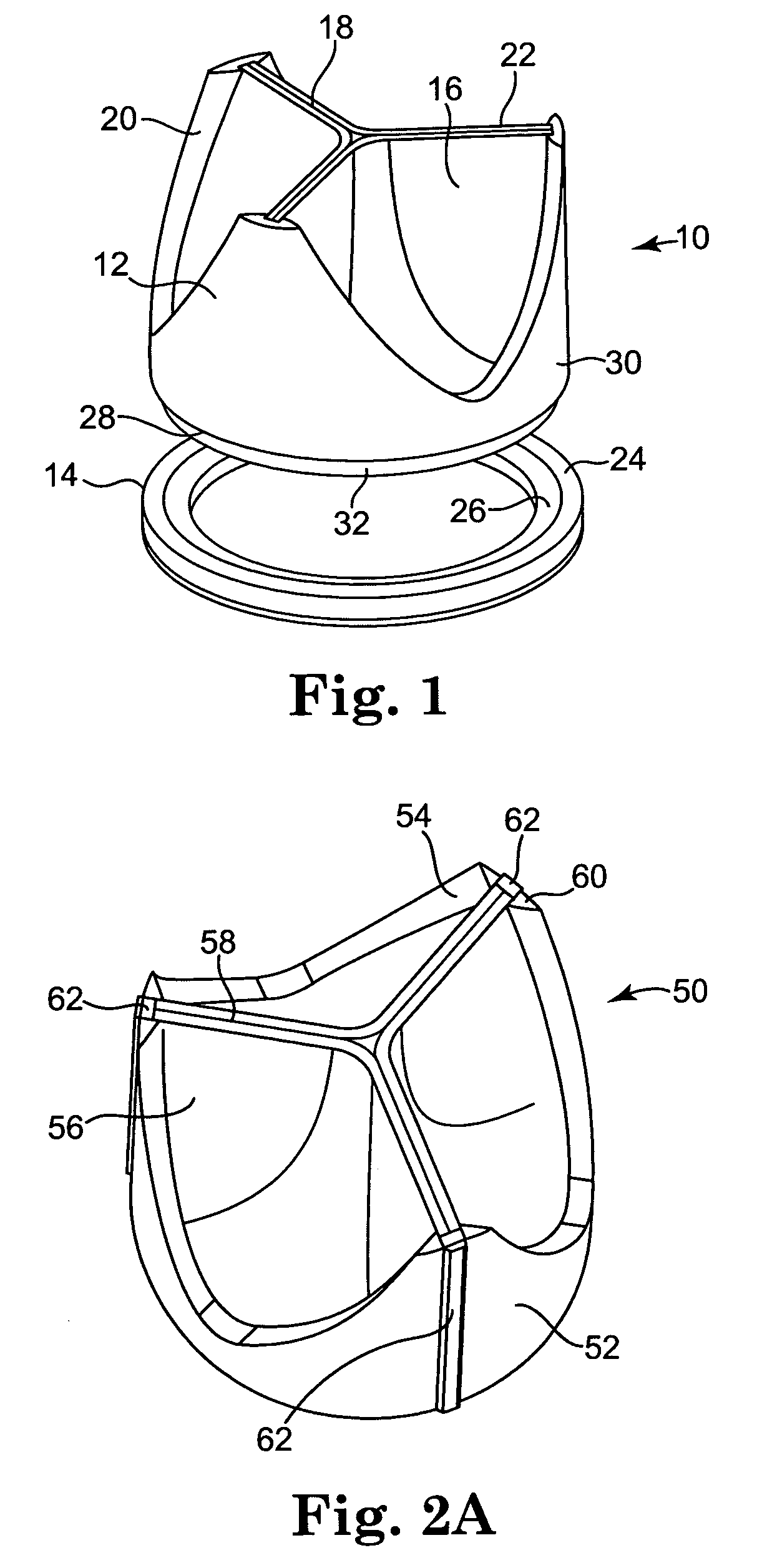
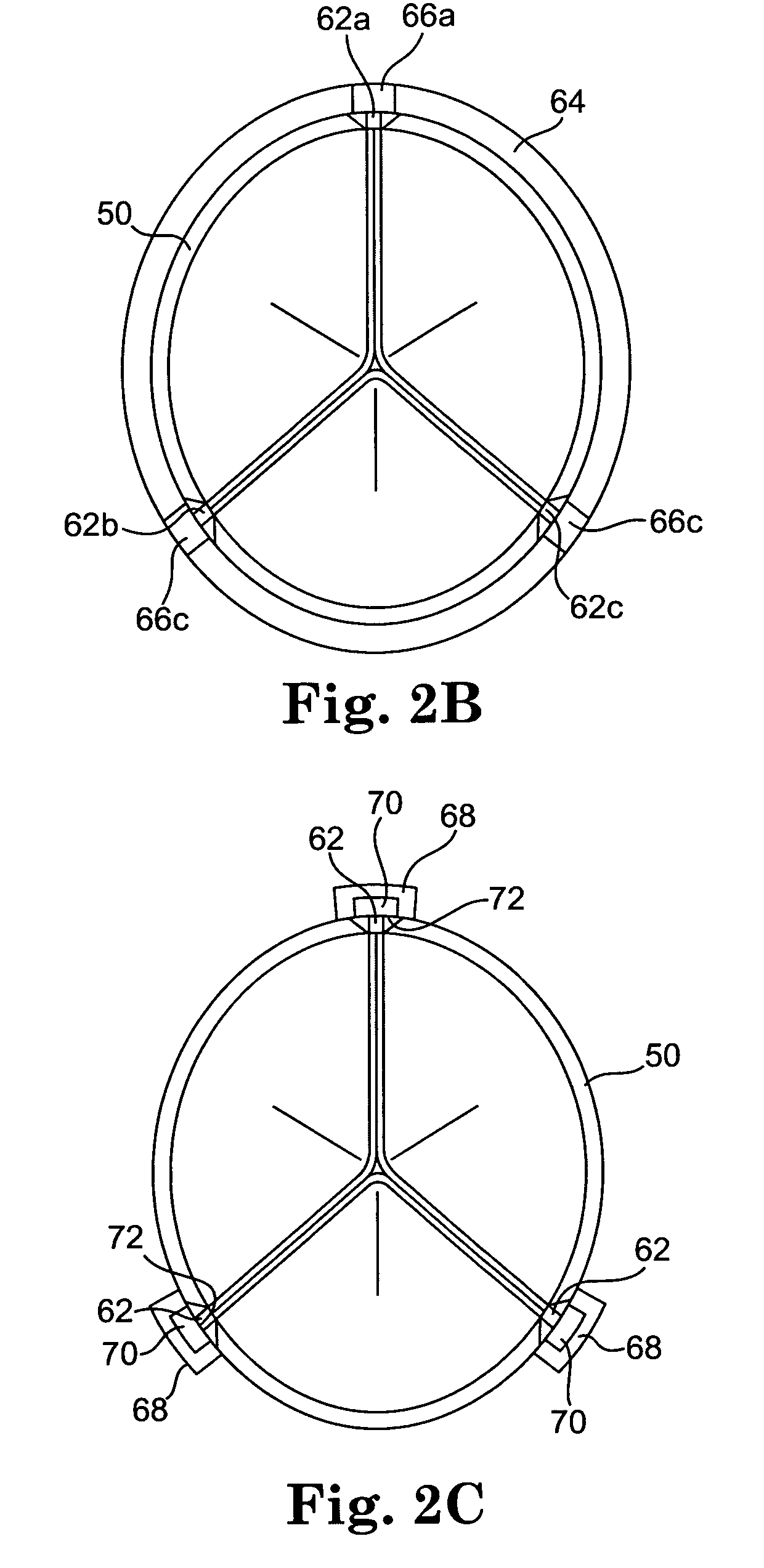
An implantable prosthetic valve, according to one embodiment, comprises a frame, a leaflet structure, and a skirt member. The frame can have a plurality of axial struts interconnected by a plurality of circumferential struts. The leaflet structure comprises a plurality of leaflets (e.g., three leaflets arrange to form a tricuspid valve). The leaflet structure has a scalloped lower edge portion secured to the frame. The skirt member can be disposed between the leaflet structure and the frame.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
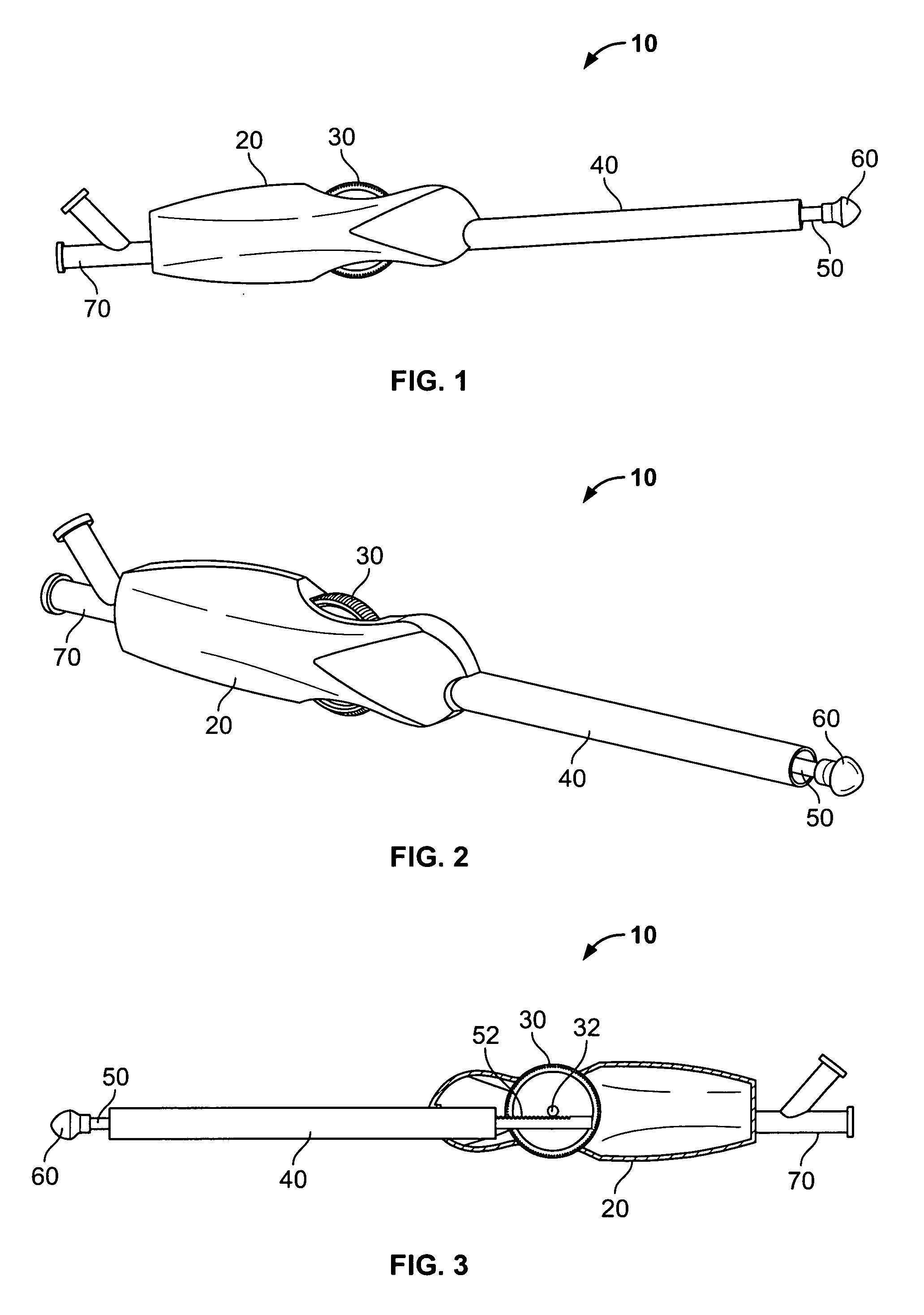
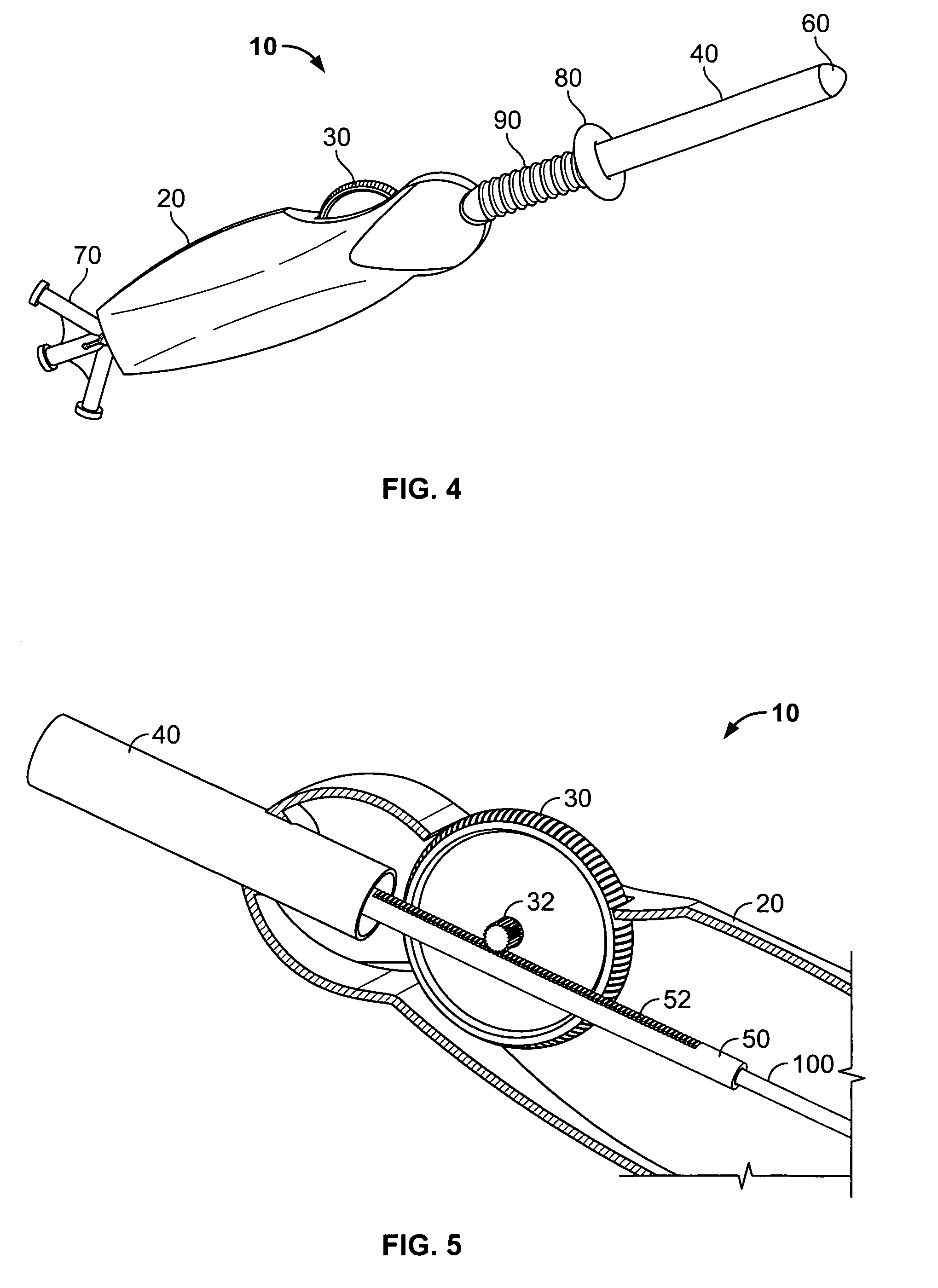
Kit enabling a prosthetic valve to be placed in a body enabling a prosthetic valve to be put into place in a duct in the body
InactiveUS20050043790A1Destruction damageRisk of destructionHeart valvesBlood vesselsProsthetic valveInsertion stent
The present invention is an assembly comprising a prosthetic valve to be implanted; a radially expandable stent comprising at least one zone intended to be expanded to allow the stent, in the expanded state, to bear against the wall of the body duct to be fitted with the valve, this bearing making it possible to immobilize this stent with respect to this wall; and means for mounting the valve with respect to the stent, making it possible to connect the valve to the stent in such a way that the placement of the stent allows the valve to be mounted in the body duct, and expansion means such as a balloon catheter being provided to trigger expansion of the stent at the implantation site. According to the invention, the valve and the stent are designed in such a way that, at the moment when the stent is expanded, the valve is situated outside the zone or zones of the stent that are subjected to said expansion means. The invention thus consists in separating the valve and said zone or zones to be expanded, so that the expansion of the stent can be effected with an expansion force suitable for perfect anchoring of this stent in the wall of the body duct to be fitted with the valve, and without any risk of destruction or damage of the valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
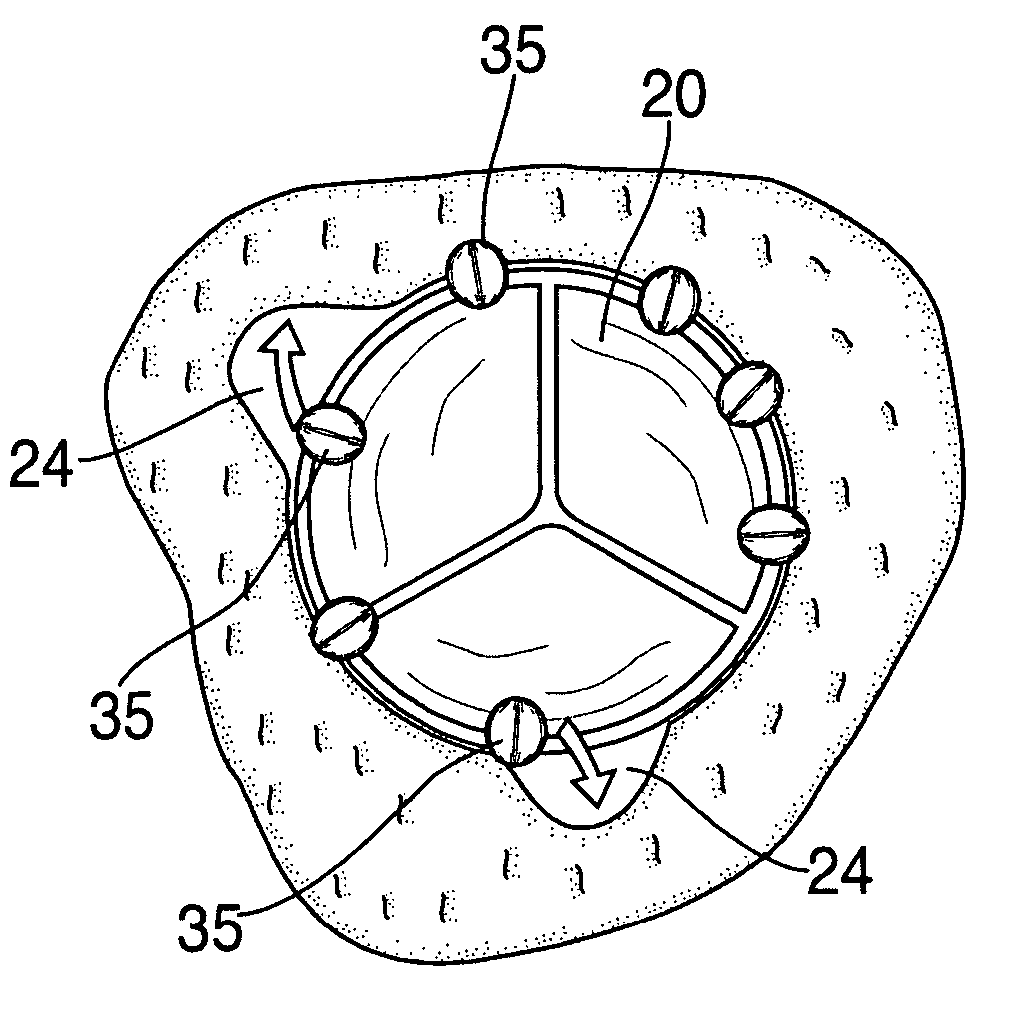
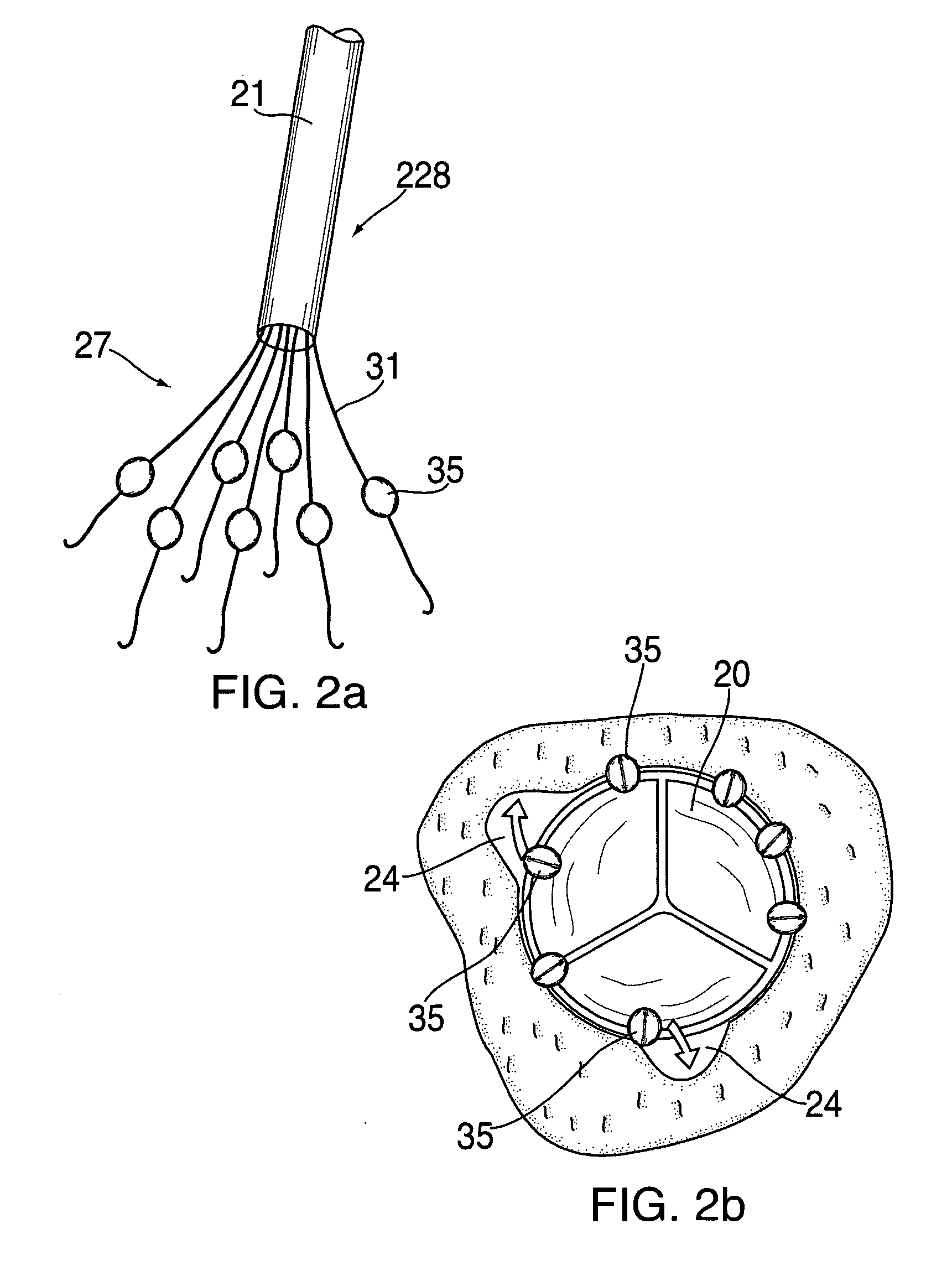
Apparatus and methods for valve repair
InactiveUS20050107871A1Dilation can be minimized and eliminatedAnnuloplasty ringsSurgical staplesAnterior leafletProsthetic valve
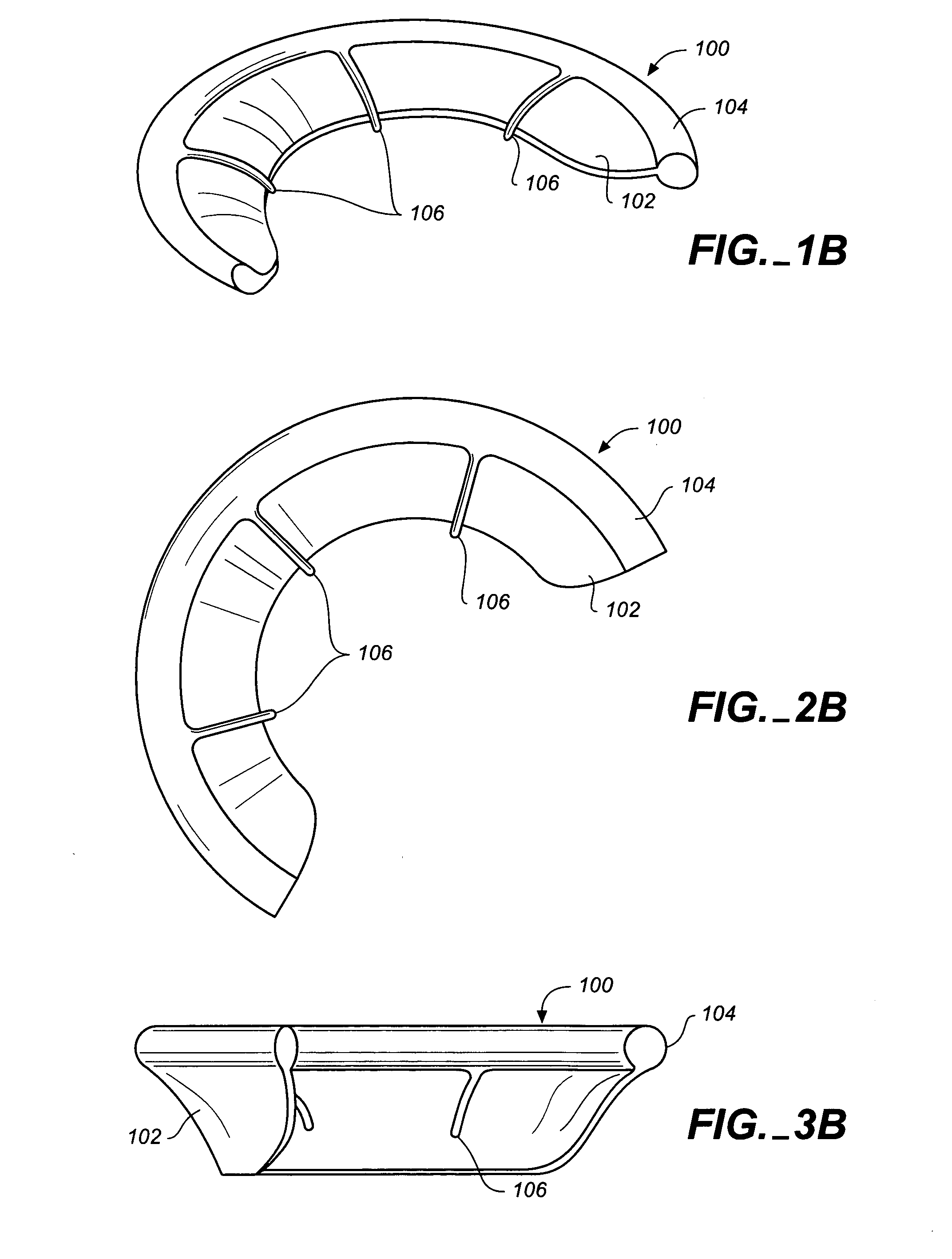
A valve implant or prosthesis includes a skirt or prosthetic valve leaflet configured to cover one of the leaflets of the valve to be repaired in a patient's heart. In one embodiment, a heart valve prosthesis includes a curved member and a skirt. The curved member can have first and second ends and be adapted to form a partial ring along a portion of one of the valve annulae in the patient's heart. Alternatively, the curved member can form a full ring that is adapted to extend along the entire valve annulus. The skirt extends along the curved member and depends therefrom. This prosthesis is especially useful in treating mitral valve insufficiency. In this case, the skirt can be configured so that when the prosthesis is secured to the mitral valve along the mitral valve annulus, the skirt covers the posterior leaflet and the opposed edges of the skirt and the anterior leaflet coapt. In addition, when the curved member is secured to the posterior portion of the mitral valve annulus, further annulus dilation can be minimized or eliminated. Implant delivery apparatus is provided for rapid implant delivery and securement to the valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
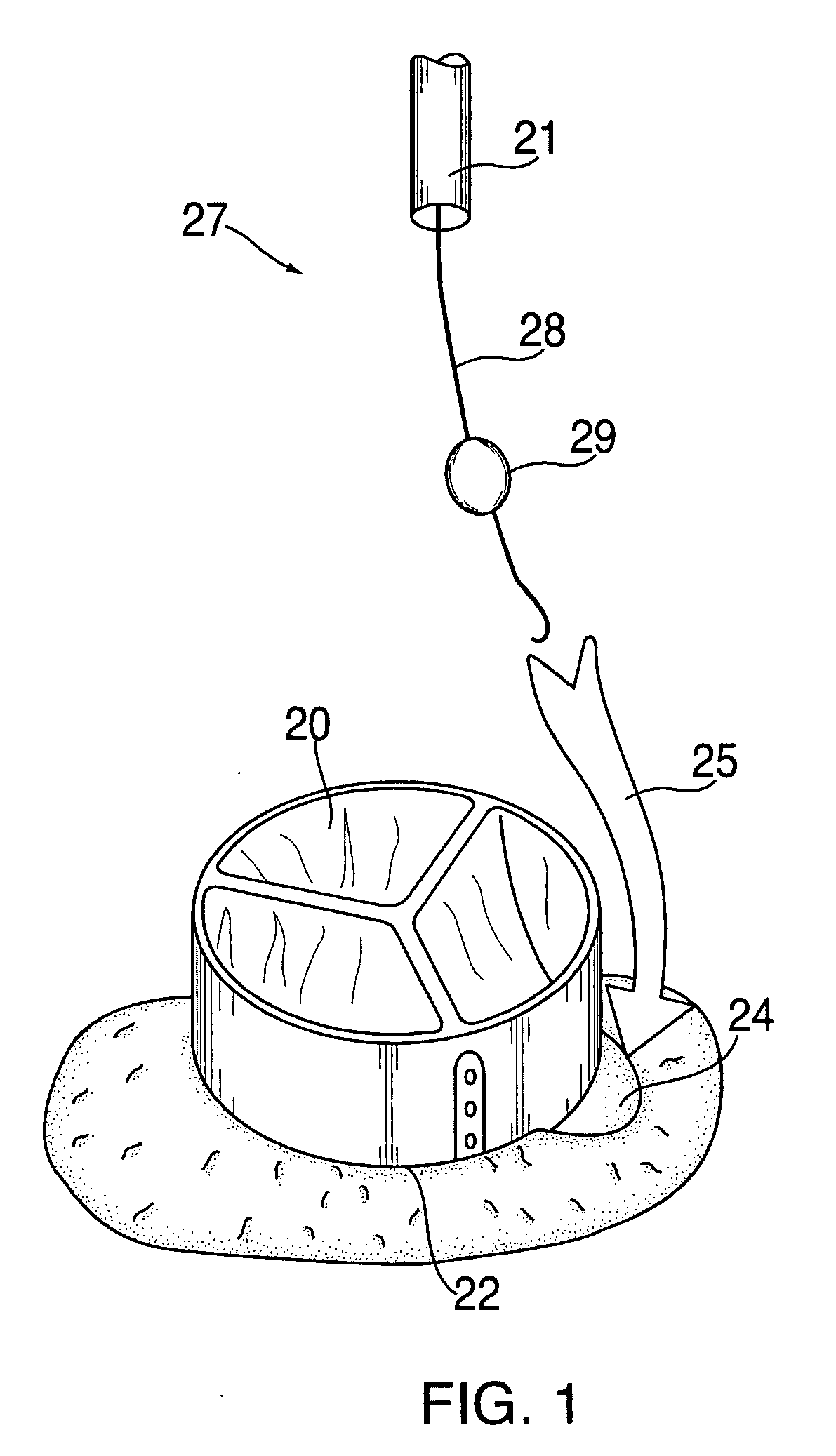
Method and system for cardiac valve delivery
The invention provides methods and systems for introducing a delivery device in the heart at or near the apex of the heart, wherein the delivery device includes a prosthesis, advancing the prosthesis to the target site, and disengaging the prosthesis from the delivery device at the target site for implantation. Specifically, the present invention provides valve replacement systems for delivering a replacement heart valve to a target site in or near a heart. The valve replacement system comprises a trocar or other suitable device to penetrate the heart at or near the apex of the heart, a delivery member that is movably disposed within the trocar, and a replacement cardiac valve disposed on the delivery member. The delivery member may further comprise mechanical or inflatable expanding members to facilitate implantation of the prosthetic valve at the target site.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Prosthetic heart valves, scaffolding structures, and systems and methods for implantation of same
InactiveUS20050203617A1Improve radial strengthIncrease frictionBalloon catheterHeart valvesPercutaneous aortic valve replacementProsthetic valve
Prosthetic valves and their component parts are described, as are prosthetic valve delivery devices and methods for their use. The prosthetic valves are particularly adapted for use in percutaneous aortic valve replacement procedures. The delivery devices are particularly adapted for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:AORTX
System and method for implanting a two-part prosthetic heart valve
Expandable heart valves for minimally invasive valve replacement surgeries are disclosed. In a first embodiment, an expandable pre-assembled heart valve includes a plastically-expandable annular base having plurality of upstanding commissure posts. A tubular flexible member including a prosthetic section and a fabric section is provided, with the prosthetic section being connected to the commissure posts and defining leaflets therebetween, and the fabric section being attached to the annular base. In a second embodiment, an expandable heart valve includes an annular tissue-engaging base and a subassembly having an elastic wireform and a plurality of leaflets connected thereto. The annular base and subassembly are separately stored and connected just prior to delivery to the host annulus. Preferably, the leaflet subassembly is stored in its relaxed configuration to avoid deformation of the leaflets. The expandable heart valves maybe implanted using a balloon catheter. Preferably, the leaflets of the heart valves are secured to the commissure regions of the expandable stents using a clamping arrangement to reduce stress.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
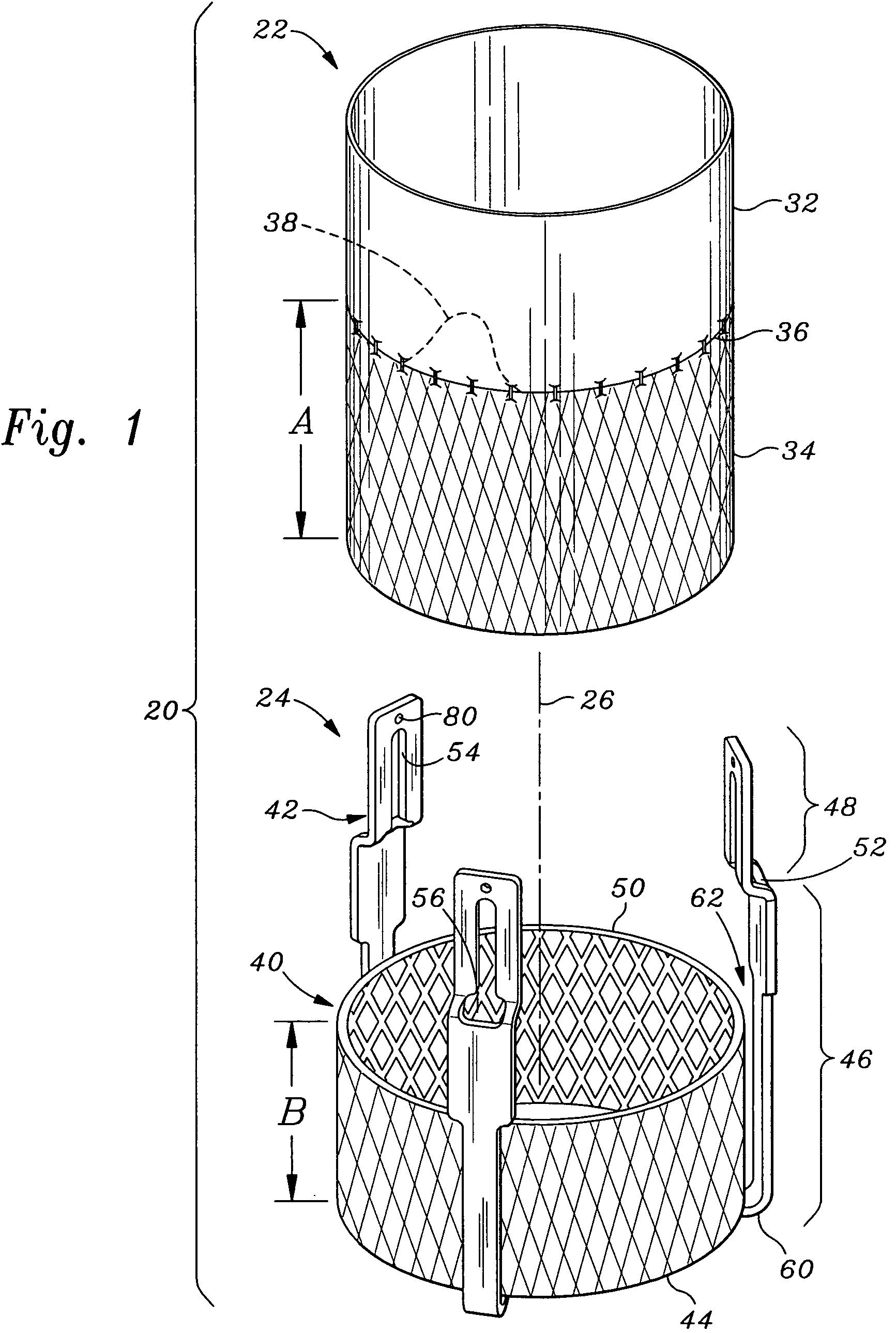
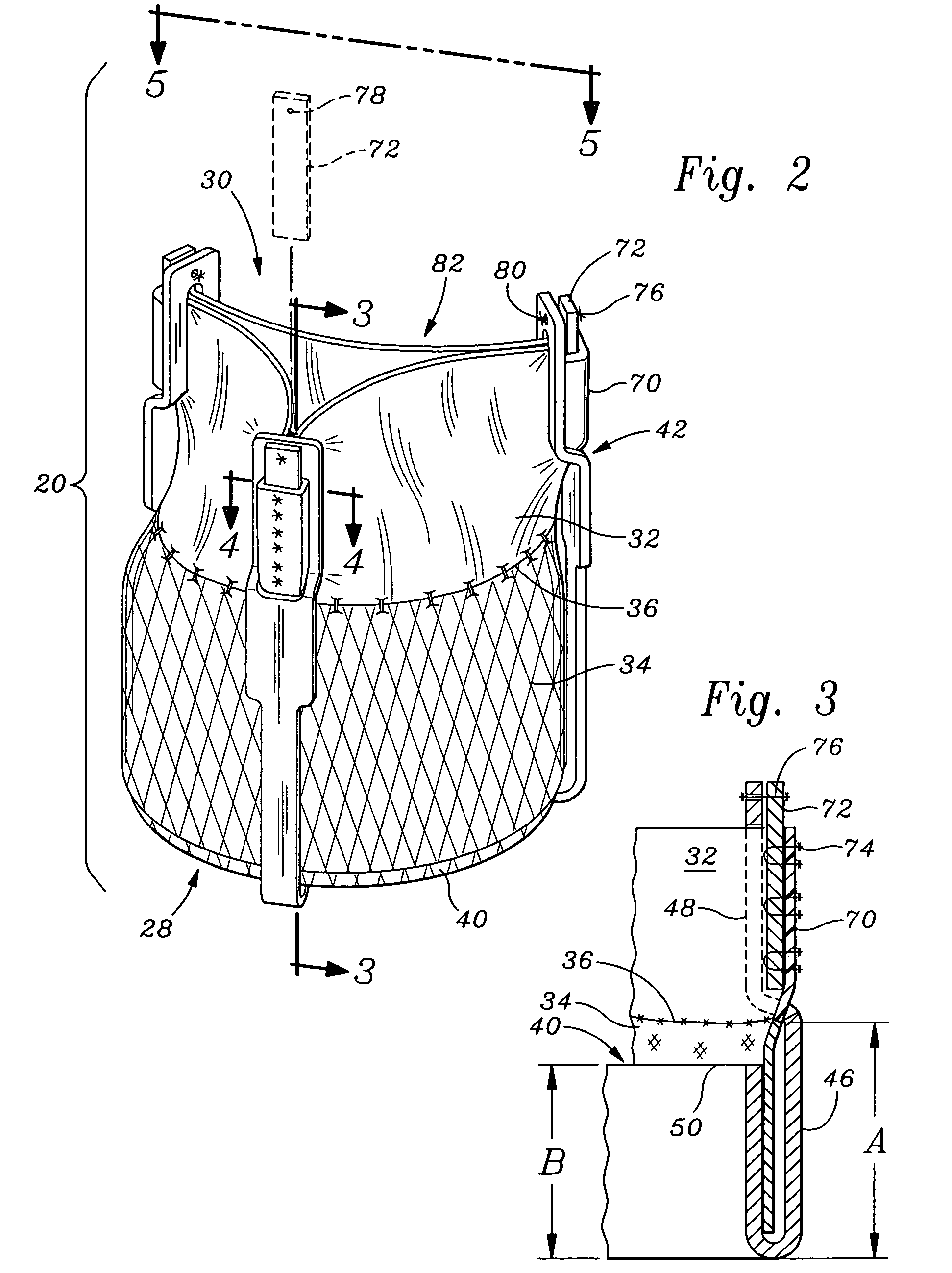
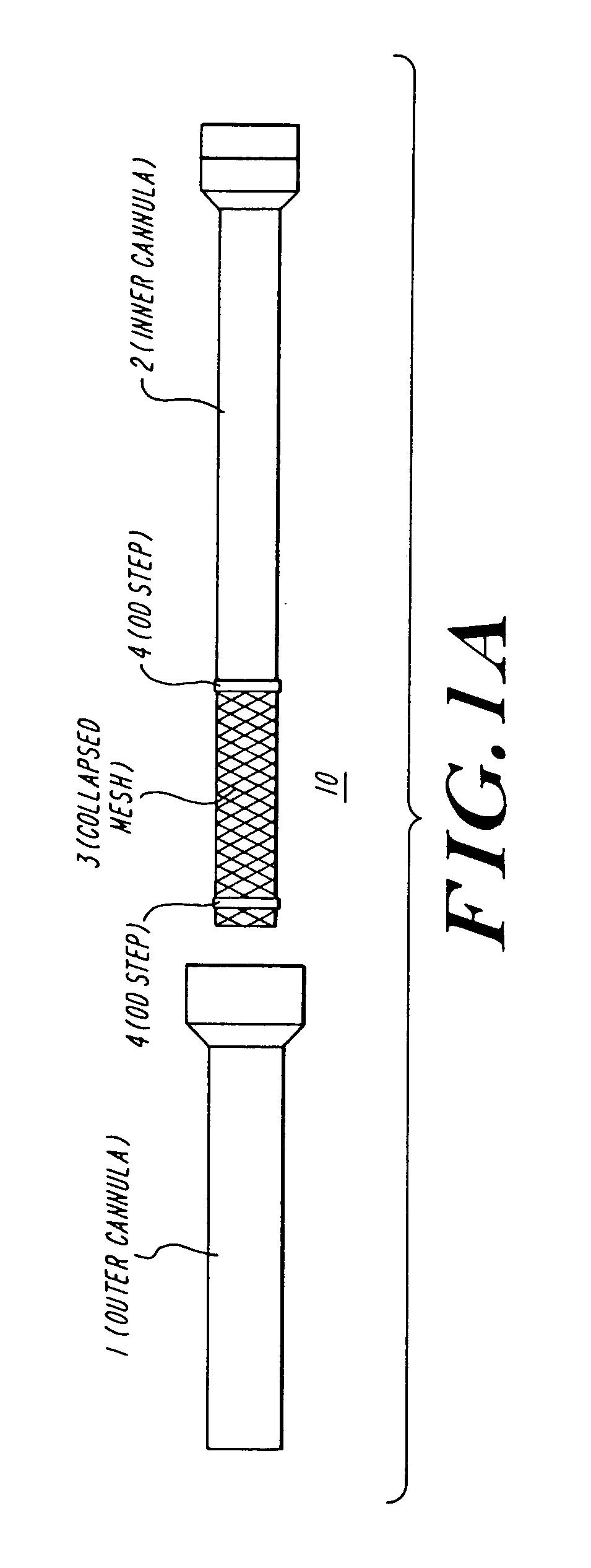
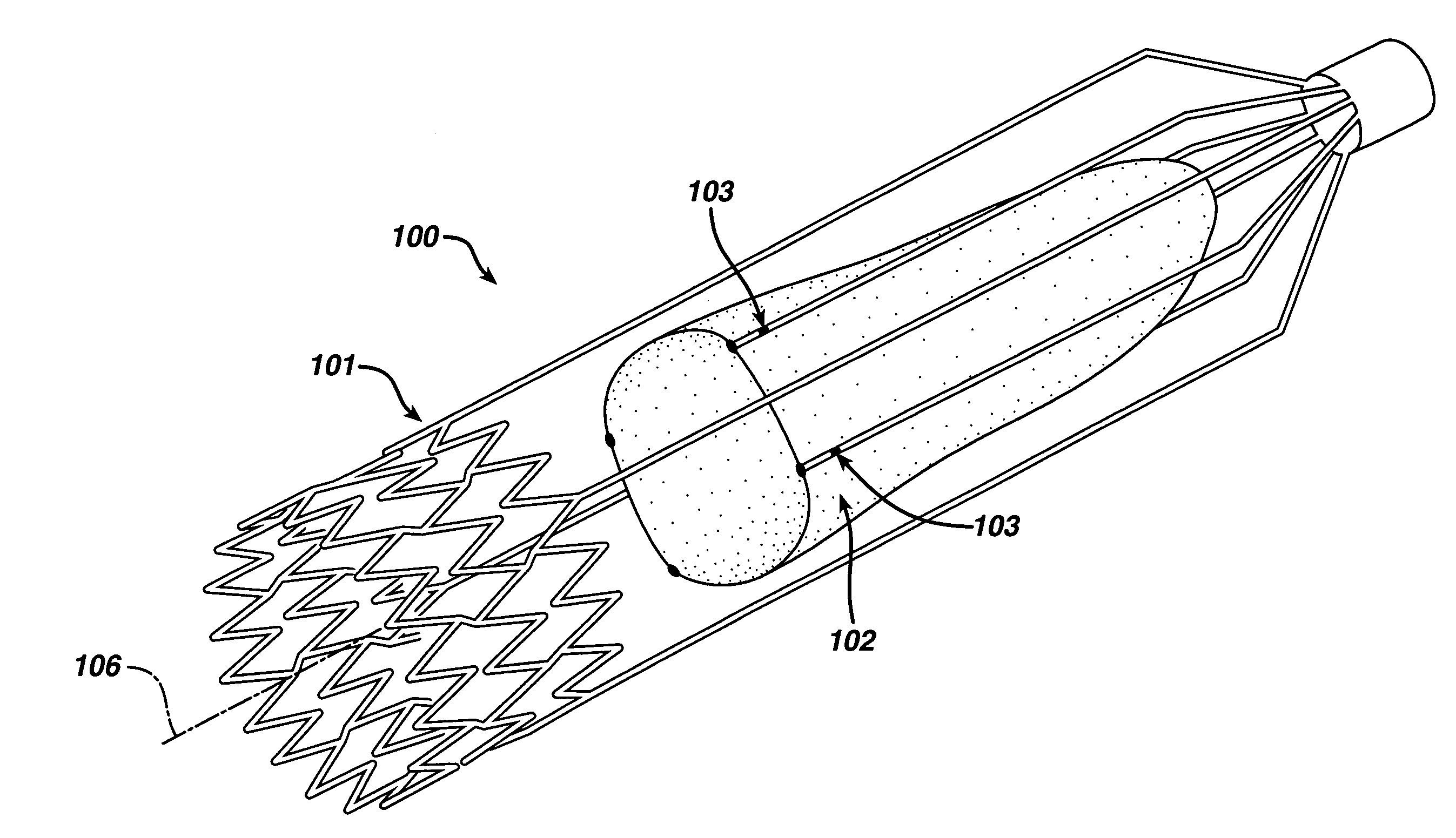
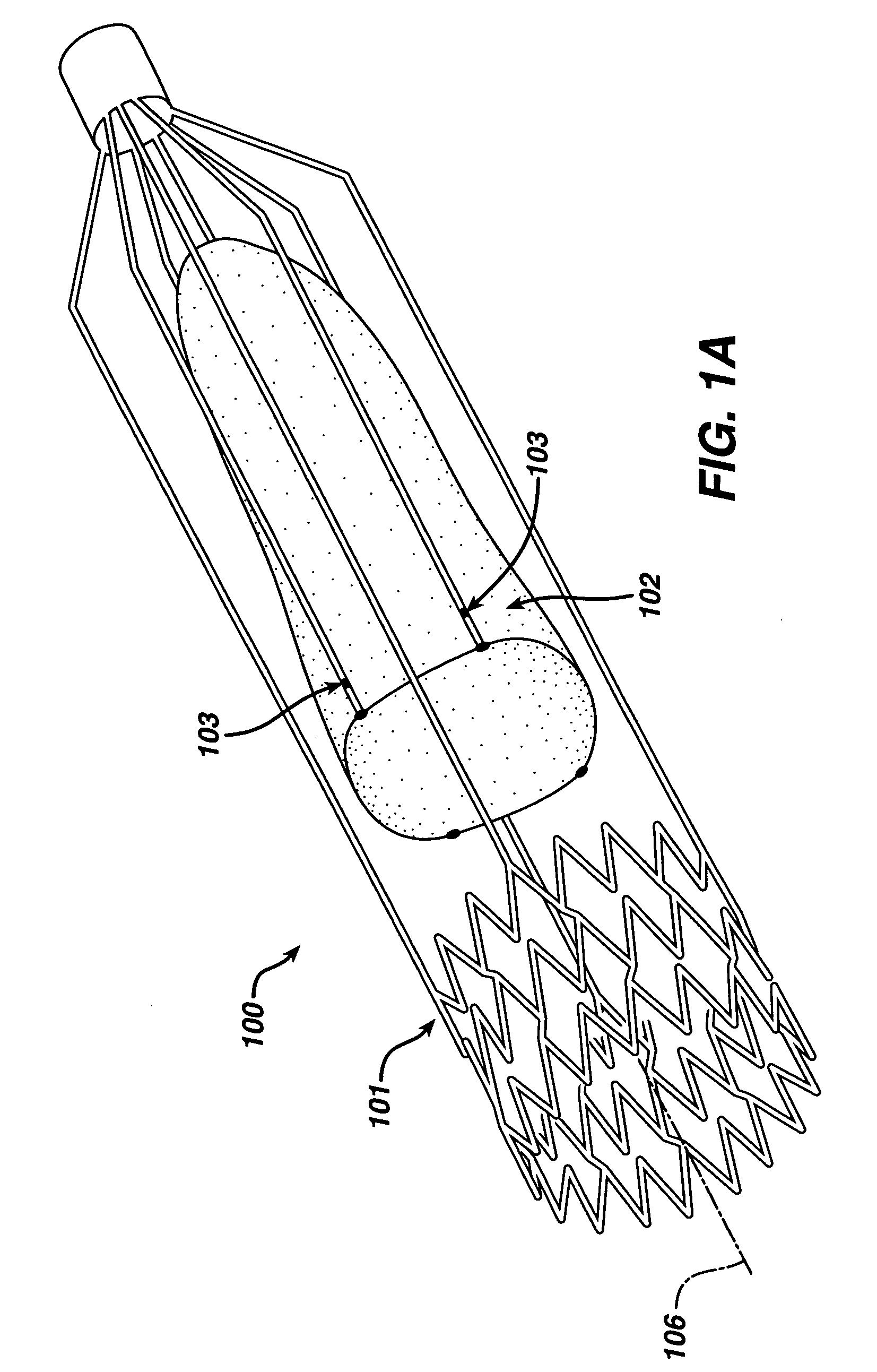
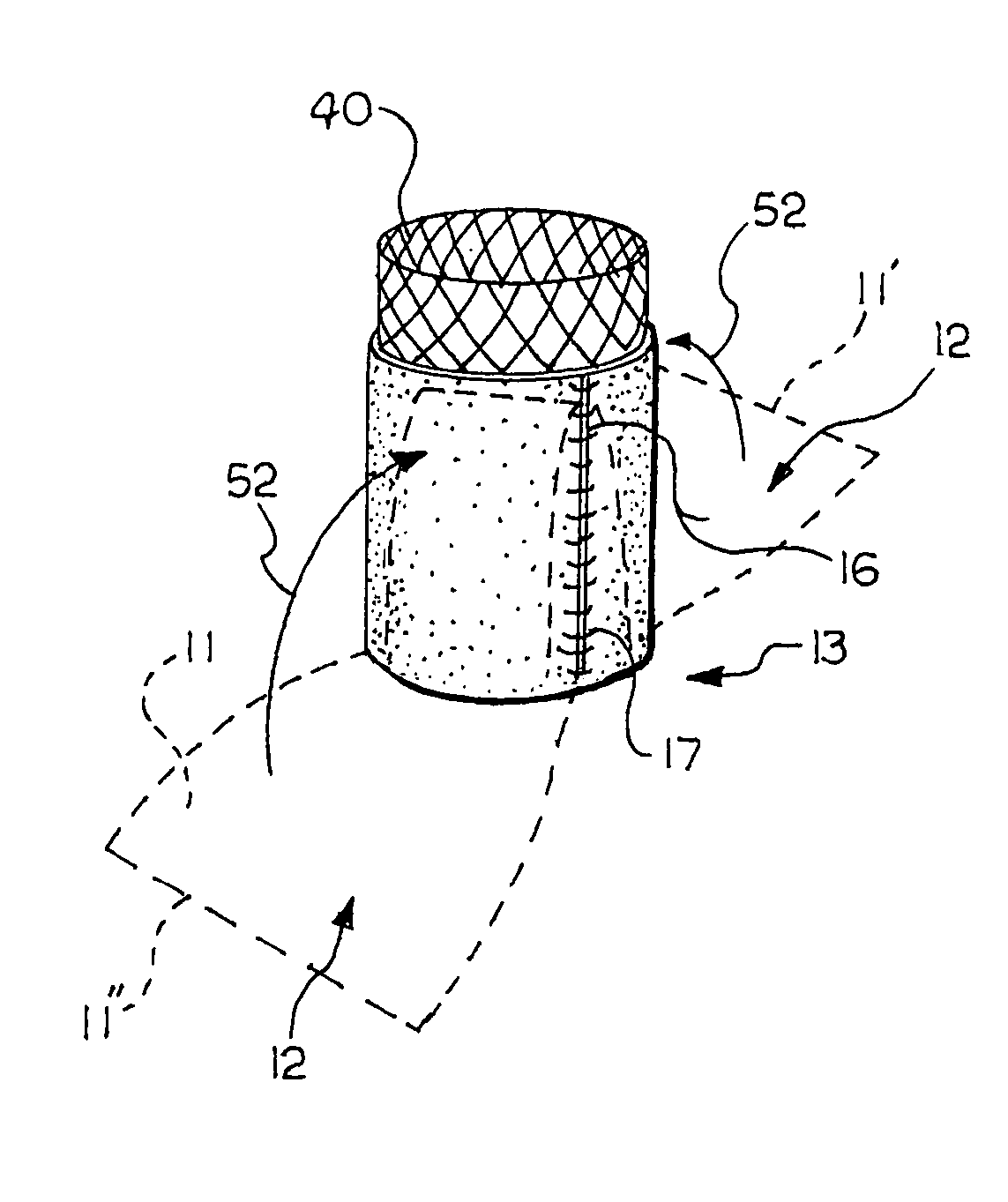
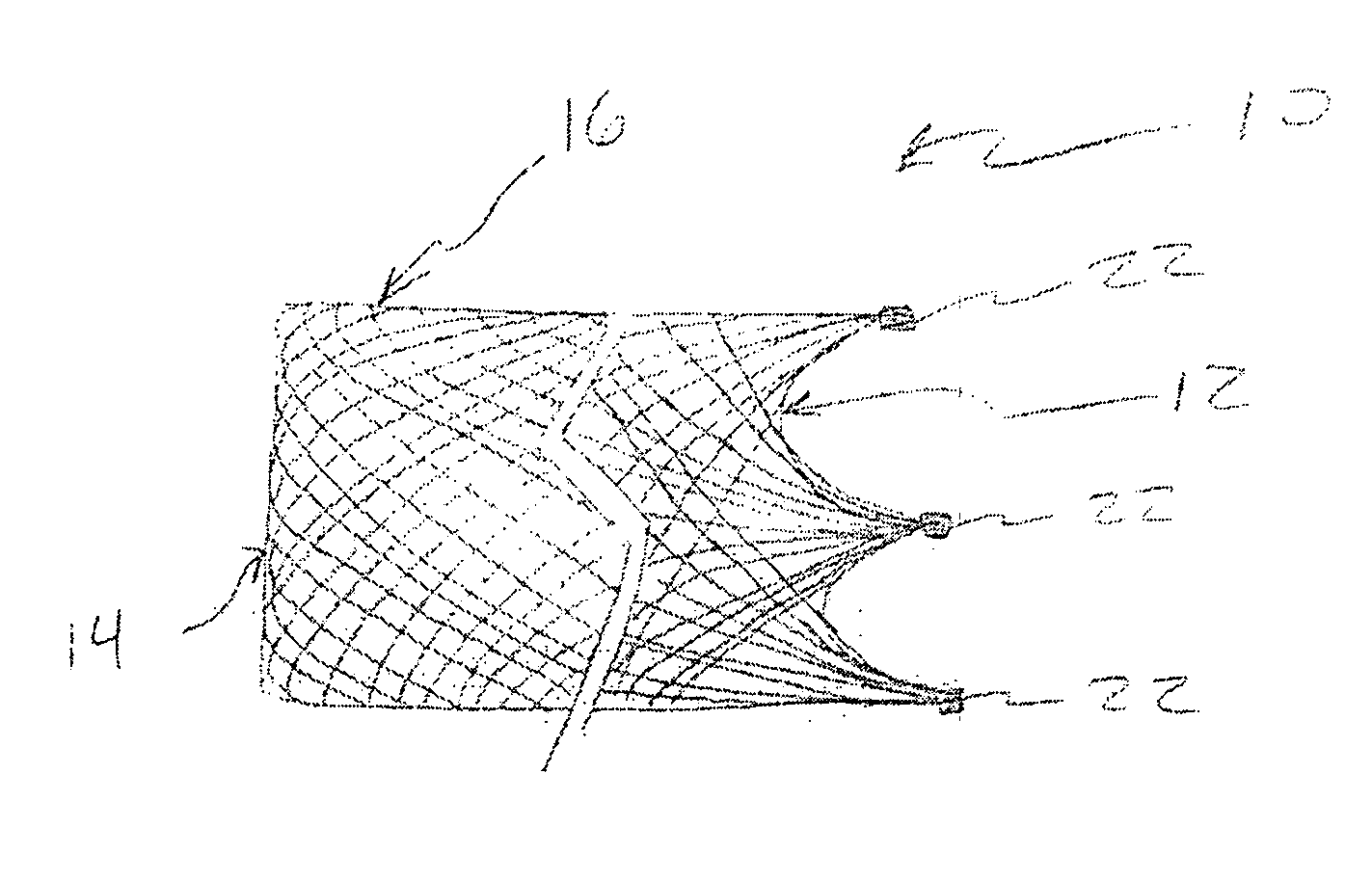
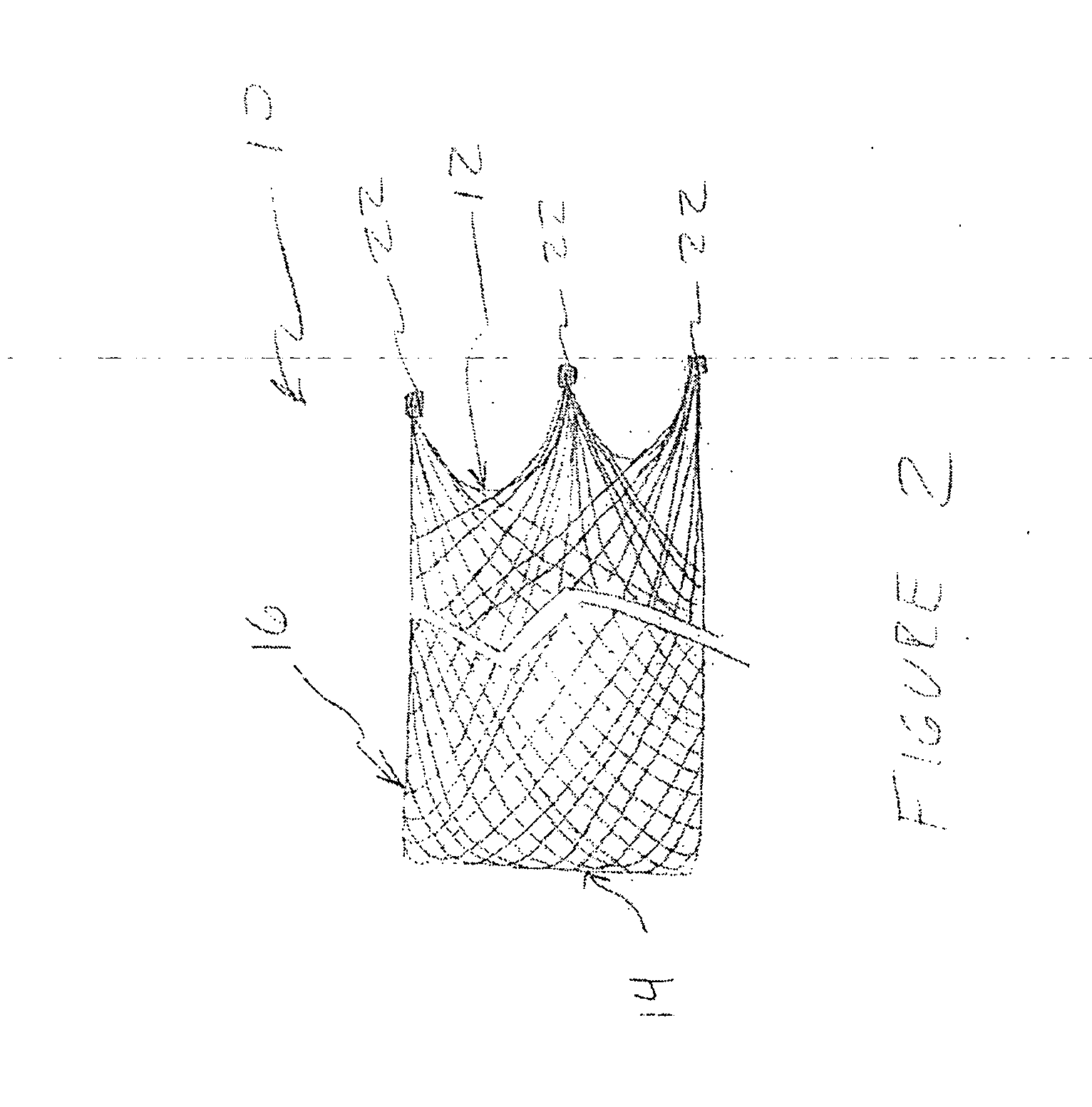
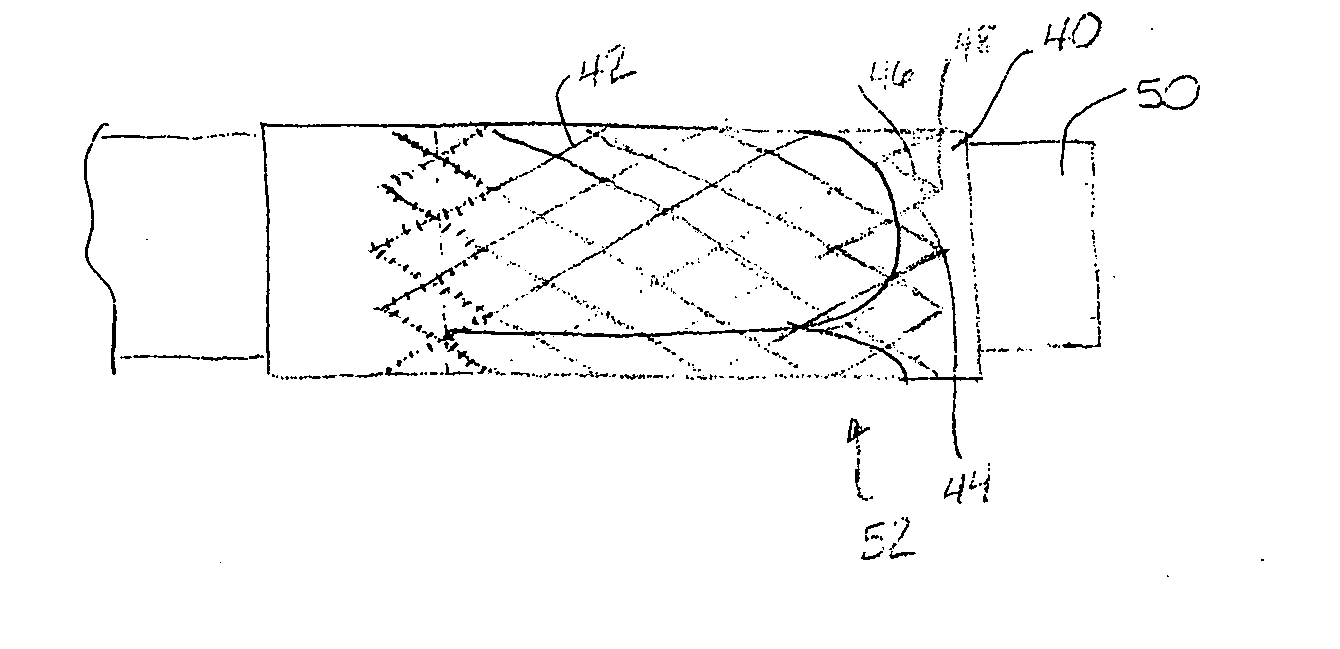
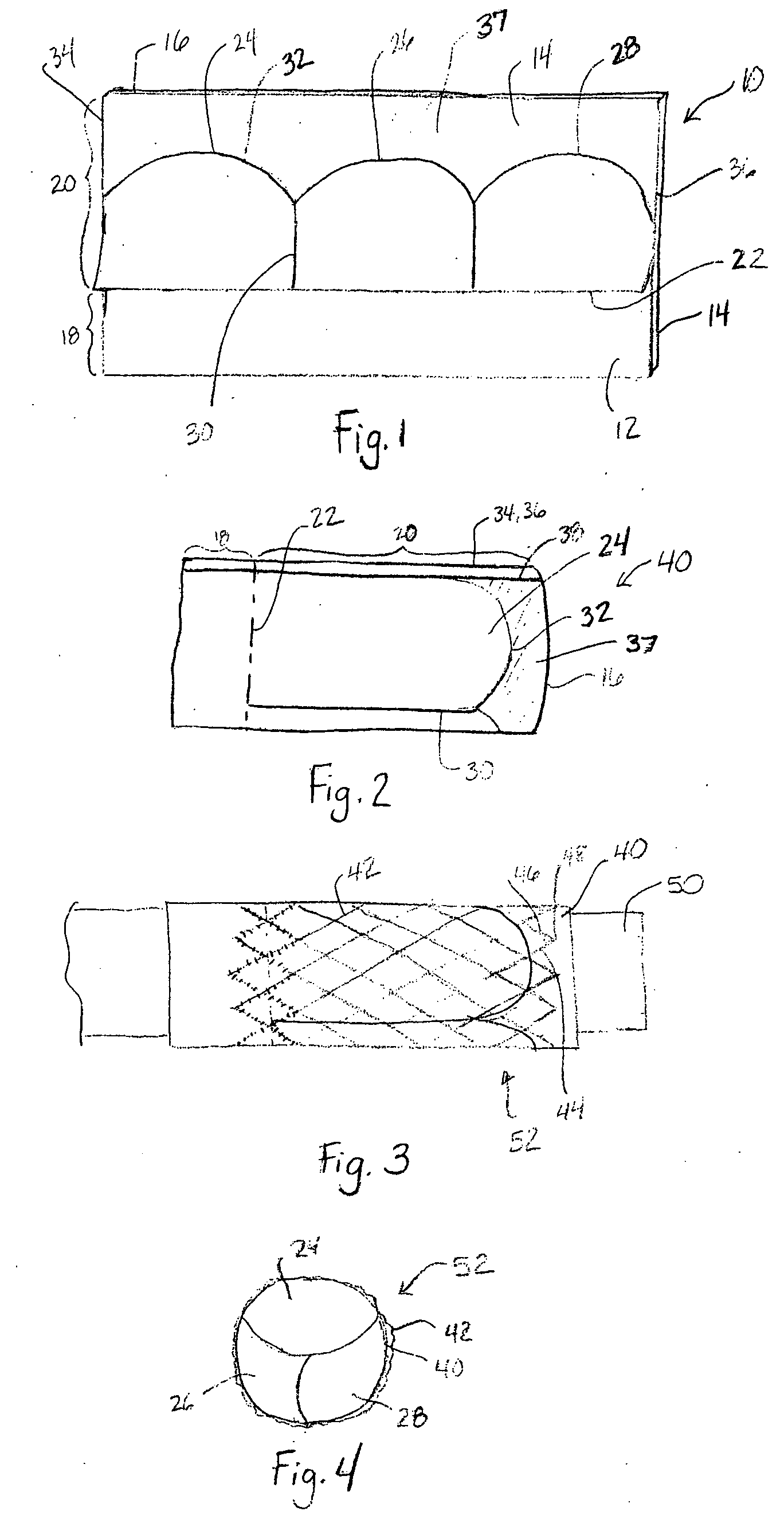
Stent mounted valve
ActiveUS20050137682A1Prevent backflowSmall amount of regurgitationHeart valvesBlood vesselsProsthetic valveInsertion stent
There is described a prosthetic valve to be inserted into a body lumen, the valve having leaflets that are spread apart during forward flow of fluid to create an orifice, and the leaflets coming into contact with each other during reverse flow of fluid, thereby impeding the reverse flow of fluid, the valve comprising: a hollow, cylindrical stent having an inner surface and an outer surface, and having a first and a second open end; and valve means formed from a single tubular membrane, the membrane mounted to the stent, the membrane having a graft portion internally folded and bonded to itself at a plurality of points to form pouches such that the leaflets extend from the pouches, and a sleeve portion on an outer surface of the stent to secure the membrane thereto.
Owner:JUSTINO HENRI
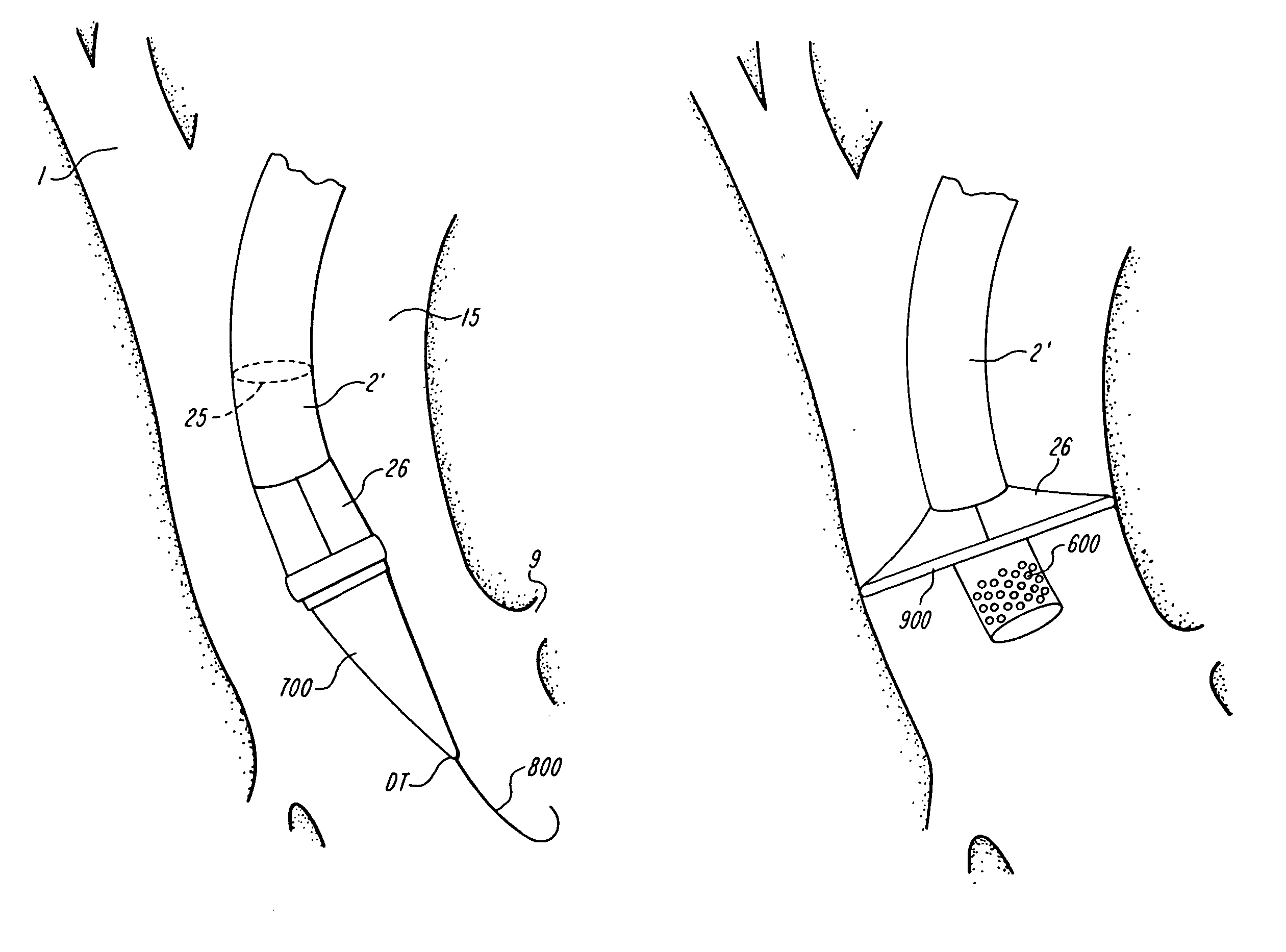
Paravalvular leak detection, sealing, and prevention
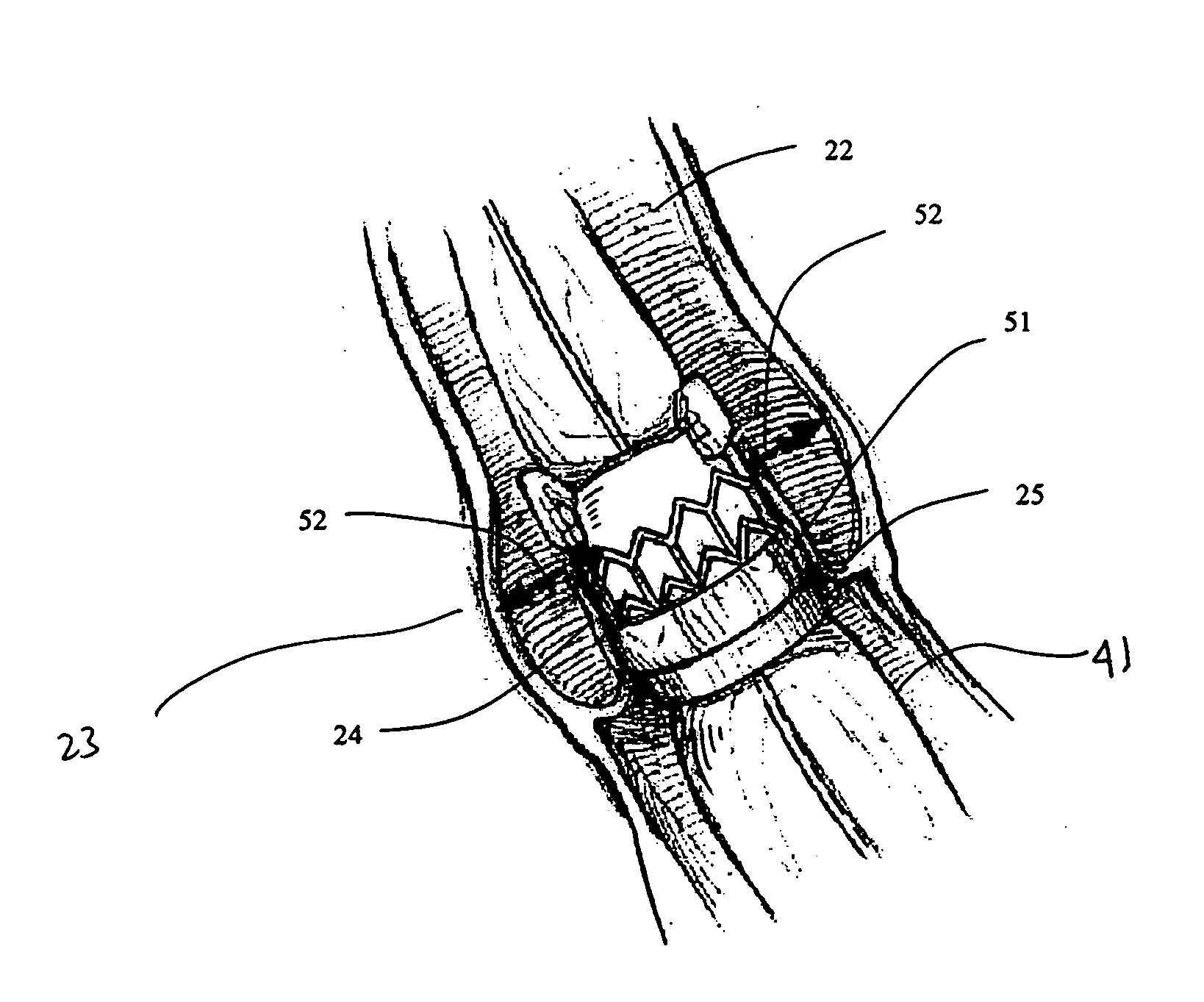
The present invention provides a series of new percutaneous concepts of paravalvular repairs including identifying the leak location, several repair techniques and finally built-in means for leak prevention, built on percutaneous valves. A catheter-delivered device locates cavities occurring between a prosthetic valve and the wall of the body vessel where the valve is implanted, the cavities producing paravalvular leaks during diastole, the device comprising at least one of a plurality of flexible wires, the wire having attached to it a balloon, wherein the balloon is pulled by the leak through the cavity and wherein the wire then serves to mark the cavity location.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
Paravalvular leak detection, sealing, and prevention
The present invention provides a series of new percutaneous concepts of paravalvular repairs including identifying the leak location, several repair techniques and finally built-in means for leak prevention, built on percutaneous valves. A catheter-delivered device locates cavities occurring between a prosthetic valve and the wall of the body vessel where the valve is implanted, the cavities producing paravalvular leaks during diastole, the device comprising at least one of a plurality of flexible wires, the wire having attached to it a balloon, wherein the balloon is pulled by the leak through the cavity and wherein the wire then serves to mark the cavity location.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
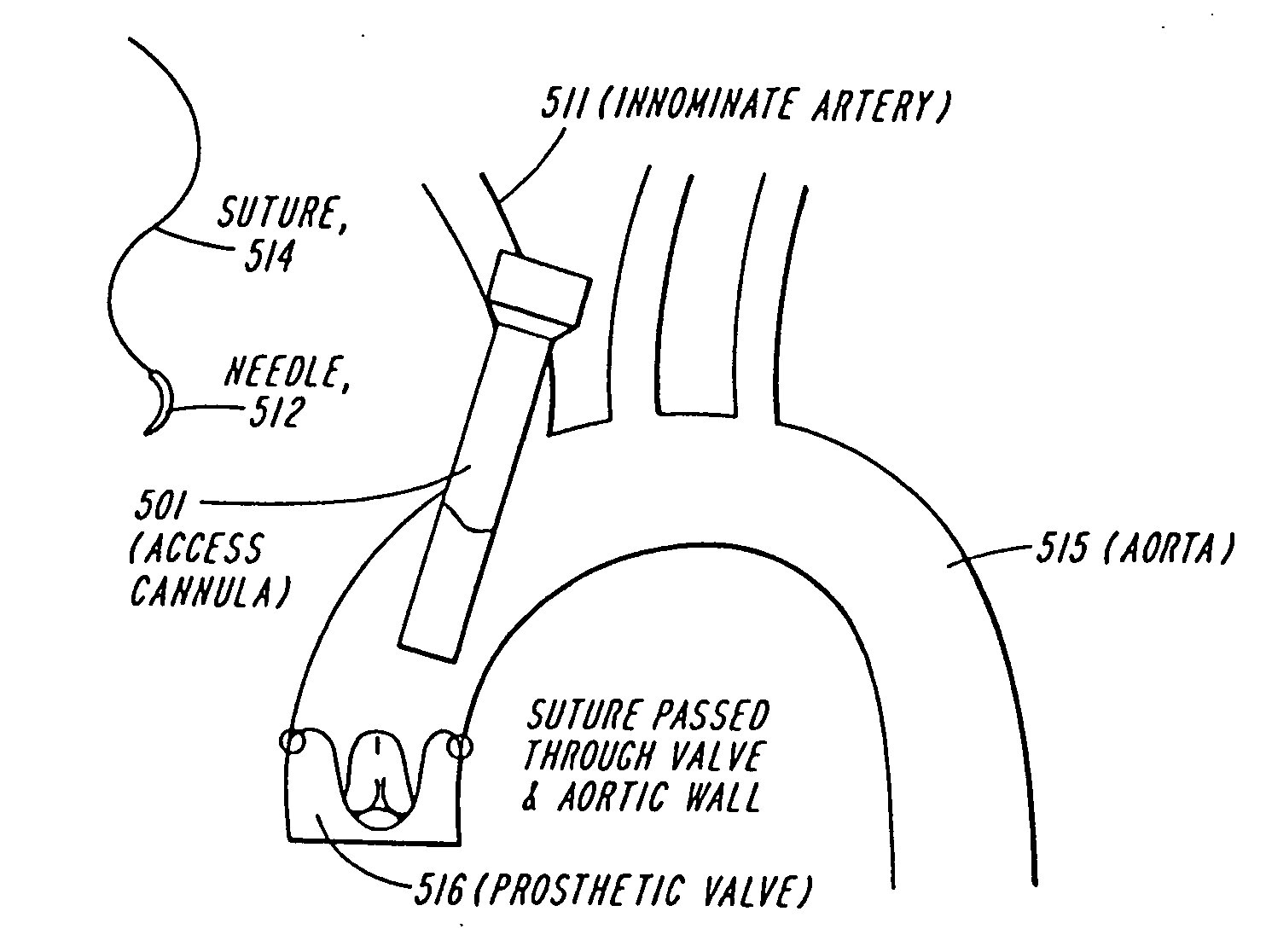
Device and method for assisting in the implantation of a prosthetic valve
ActiveUS20060004439A1Increase thrustReduce the overall diameterBalloon catheterHeart valvesBalloon dilatation catheterProsthetic valve
A system for percutaneously introducing a prosthetic valve into a patient's vasculature comprises a balloon dilatation catheter, a prosthetic valve mounted coaxial to the dilatation balloon, and a pusher member comprising a longitudinally extending tubular member encompassing the shaft of the catheter. The distal end of the pusher member preferably corresponds to the proximal end of the stent component of the prosthetic valve. The pusher member provides enhanced longitudinal pushability for facilitating advancement of the prosthetic valve to a treatment site. The system is well-suited for advancing a prosthetic valve or other medical device through an introducer sheath having a relatively small inner diameter. The introducer sheath may be formed with a tapered proximal end portion for receiving the prosthetic valve and for reducing a diameter of the prosthetic valve during advancement therethrough.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
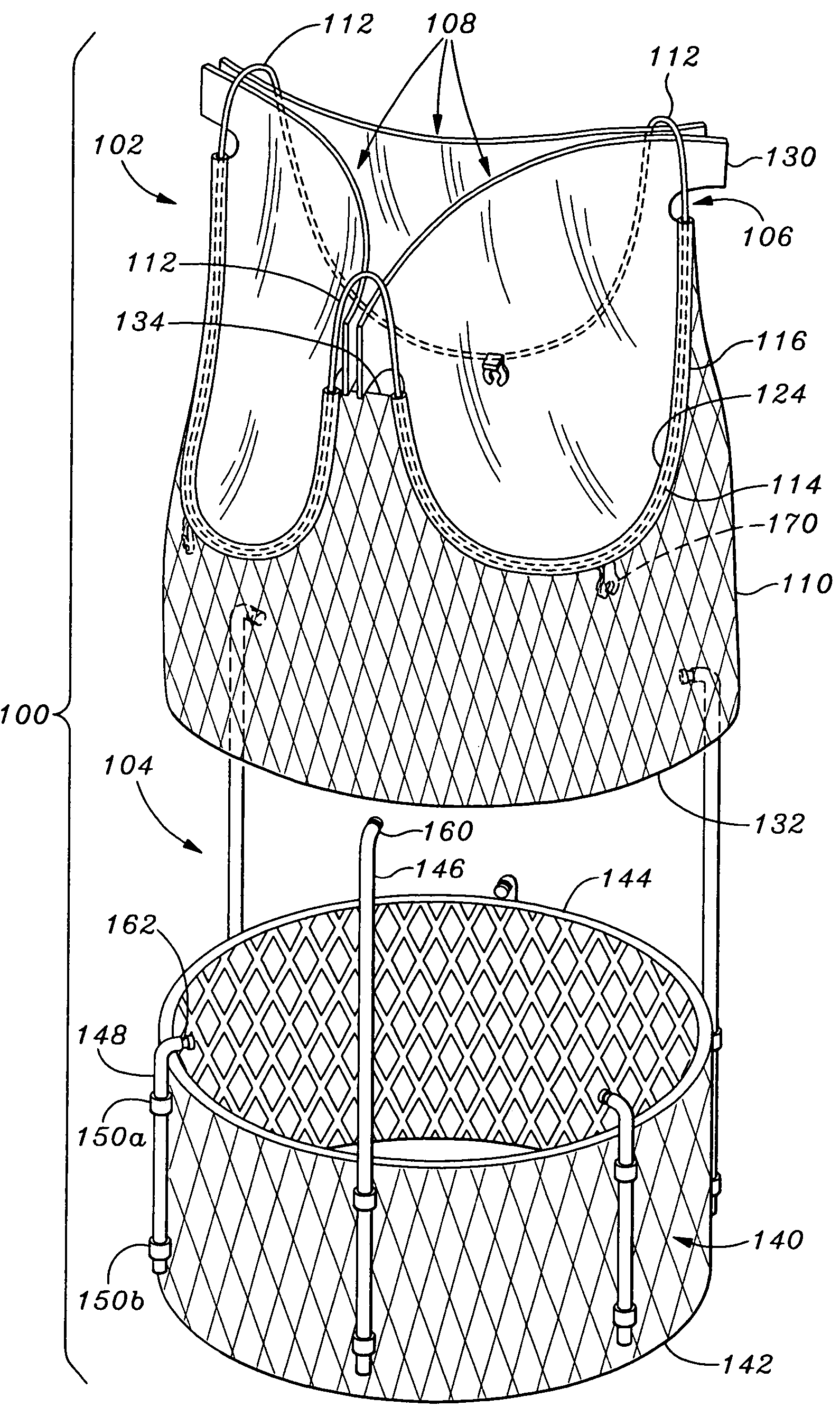
Cardiac valve procedure methods and devices
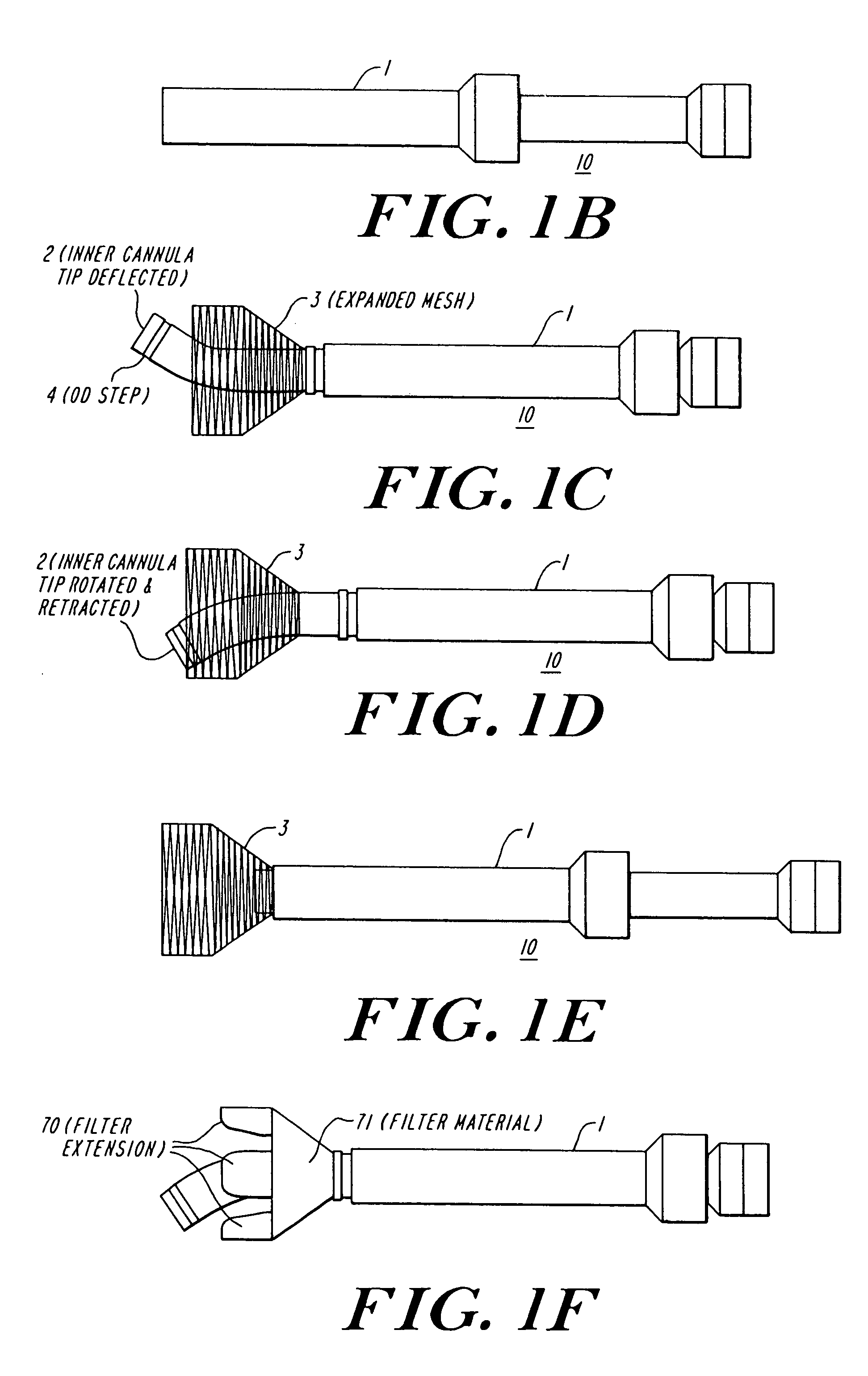
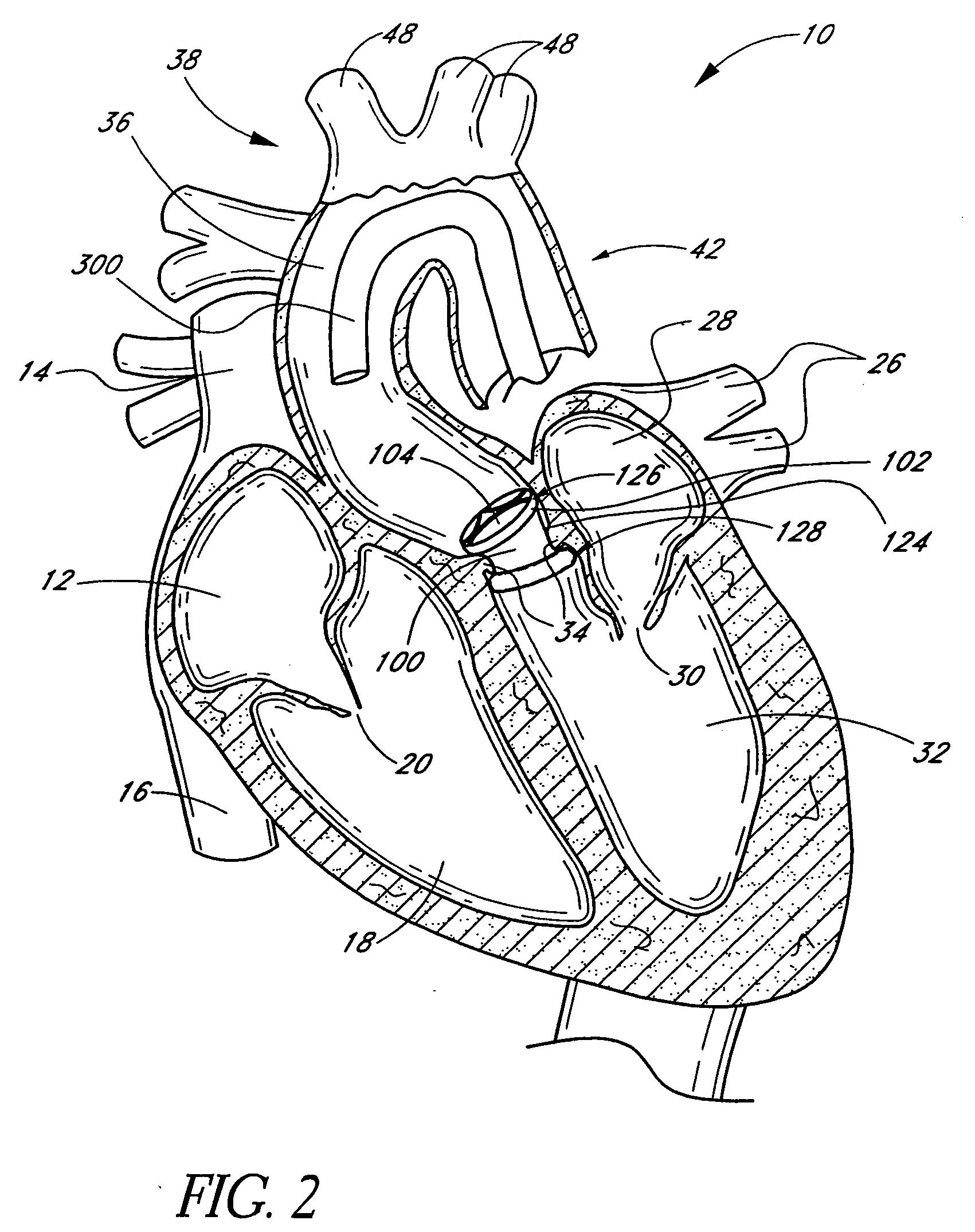
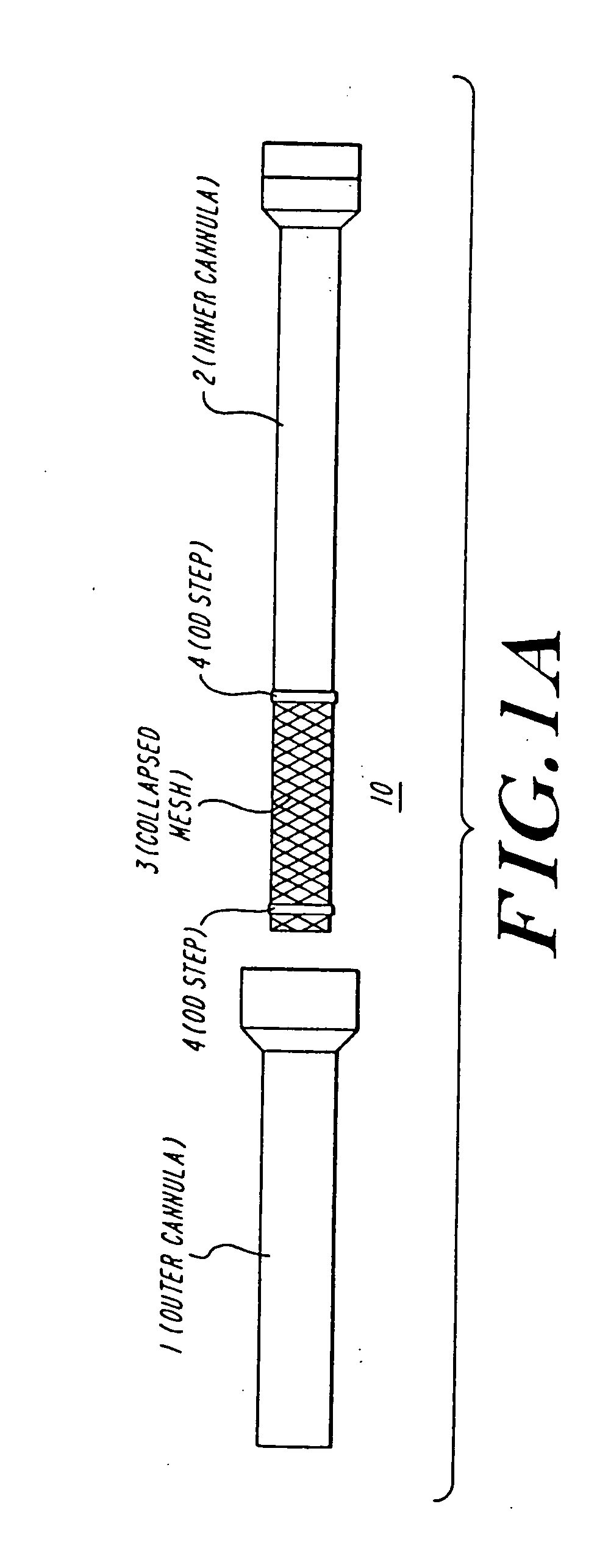
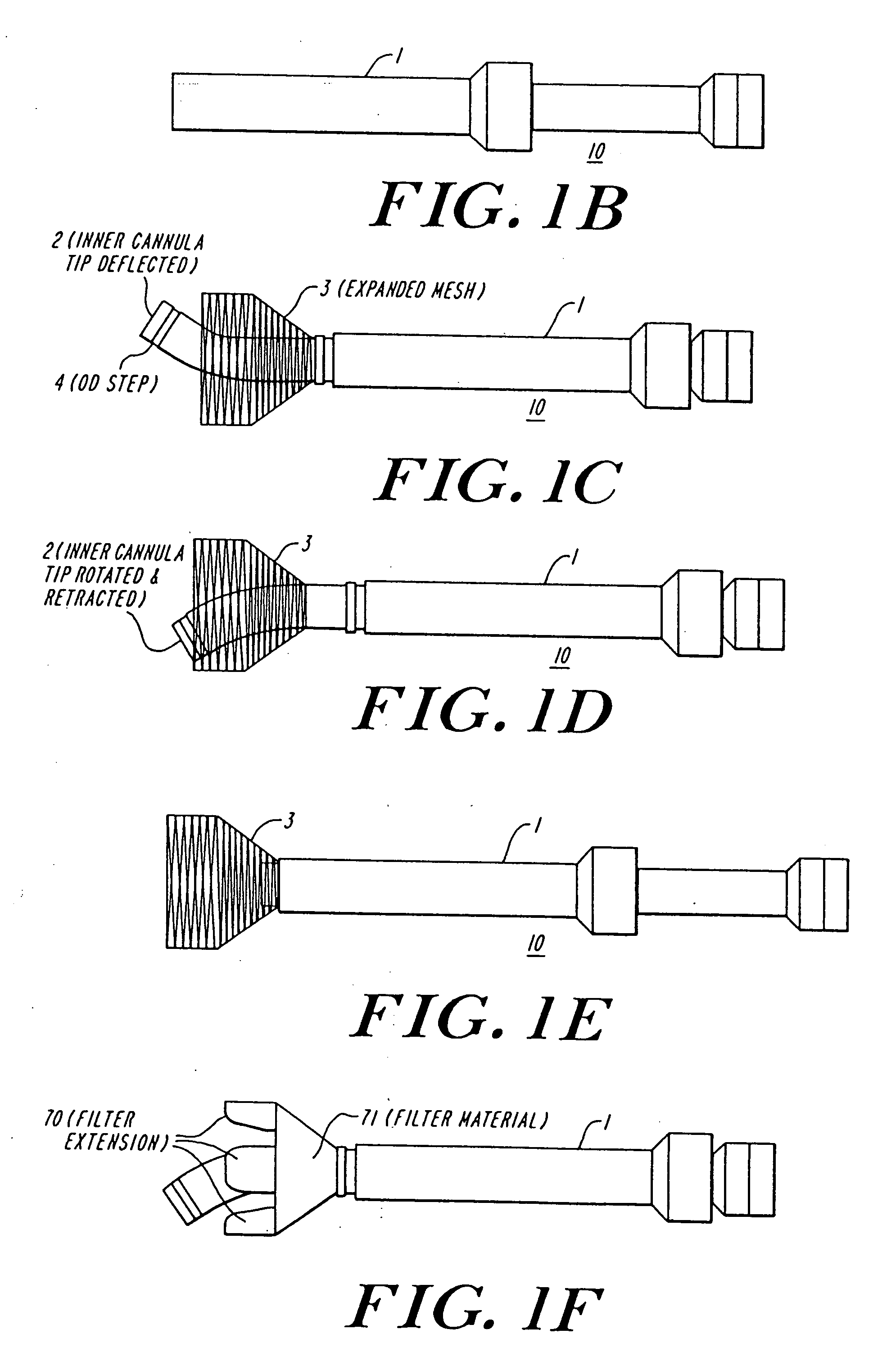
The present invention discloses devices and methods for performing intravascular procedures with out cardiac bypass. The devices include various embodiments of temporary filter devices, temporary valves, and prosthetic valves.The temporary filter devices have one or more cannulae which provide access for surgical tools for effecting repair of the cardiac valves. A cannula may have filters of various configurations encircling the distal region of the cannula, which prevent embolitic material from entering the coronary arteries and aorta.The temporary valve devices may also have one or more cannulae which guide the insertion of the valve into the aorta. The valve devices expand in the aorta to occupy the entire flow path of the vessel. In one embodiment, the temporary valve is a disc of flexible, porous, material that acts to filter blood passing therethrough. A set of valve leaflets extend peripherally from the disc. These leaflets can alternately collapse to prevent blood flow through the valve and extend to permit flow.The prosthetic valves include valve fixation devices which secure the prosthetic valve to the wall of the vessel. In one embodiment, the prosthetic valves have at least one substantially rigid strut, at least two expandable fixation rings located about the circumference of the base of the apex of the valve, and one or more commissures and leaflets. The prosthetic valves are introduced into the vascular system a compressed state, advanced to the site of implantation, expanded and secured to the vessel wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Kit enabling a prosthetic valve to be placed in a body enabling a prosthetic valve to be put into place in a duct in the body
The present invention is an assembly comprising a prosthetic valve to be implanted; a radially expandable stent comprising at least one zone intended to be expanded to allow the stent, in the expanded state, to bear against the wall of the body duct to be fitted with the valve, this bearing making it possible to immobilize this stent with respect to this wall; and means for mounting the valve with respect to the stent, making it possible to connect the valve to the stent in such a way that the placement of the stent allows the valve to be mounted in the body duct, and expansion means such as a balloon catheter being provided to trigger expansion of the stent at the implantation site. According to the invention, the valve and the stent are designed in such a way that, at the moment when the stent is expanded, the valve is situated outside the zone or zones of the stent that are subjected to said expansion means. The invention thus consists in separating the valve and said zone or zones to be expanded, so that the expansion of the stent can be effected with an expansion force suitable for perfect anchoring of this stent in the wall of the body duct to be fitted with the valve, and without any risk of destruction or damage of the valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
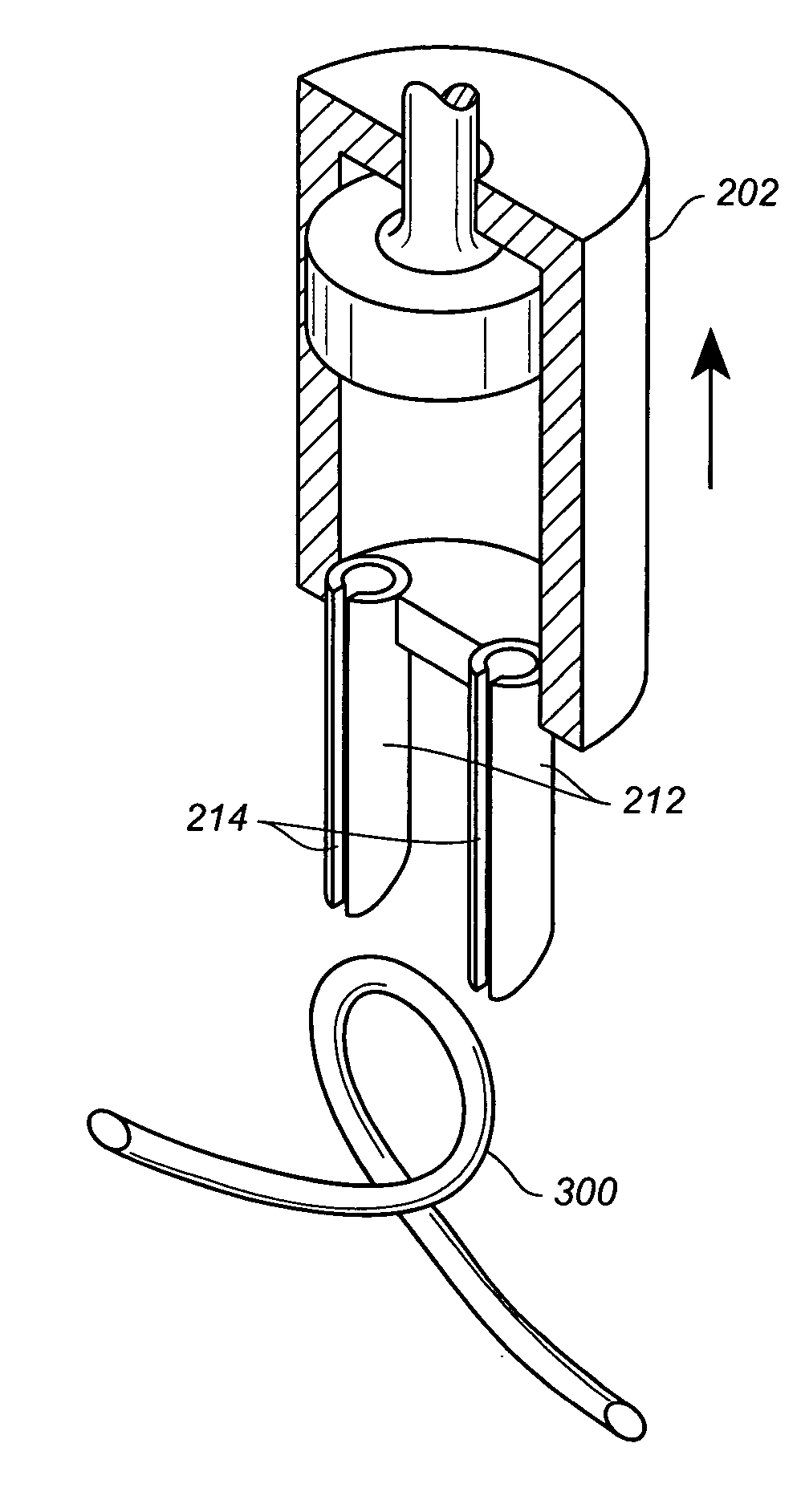
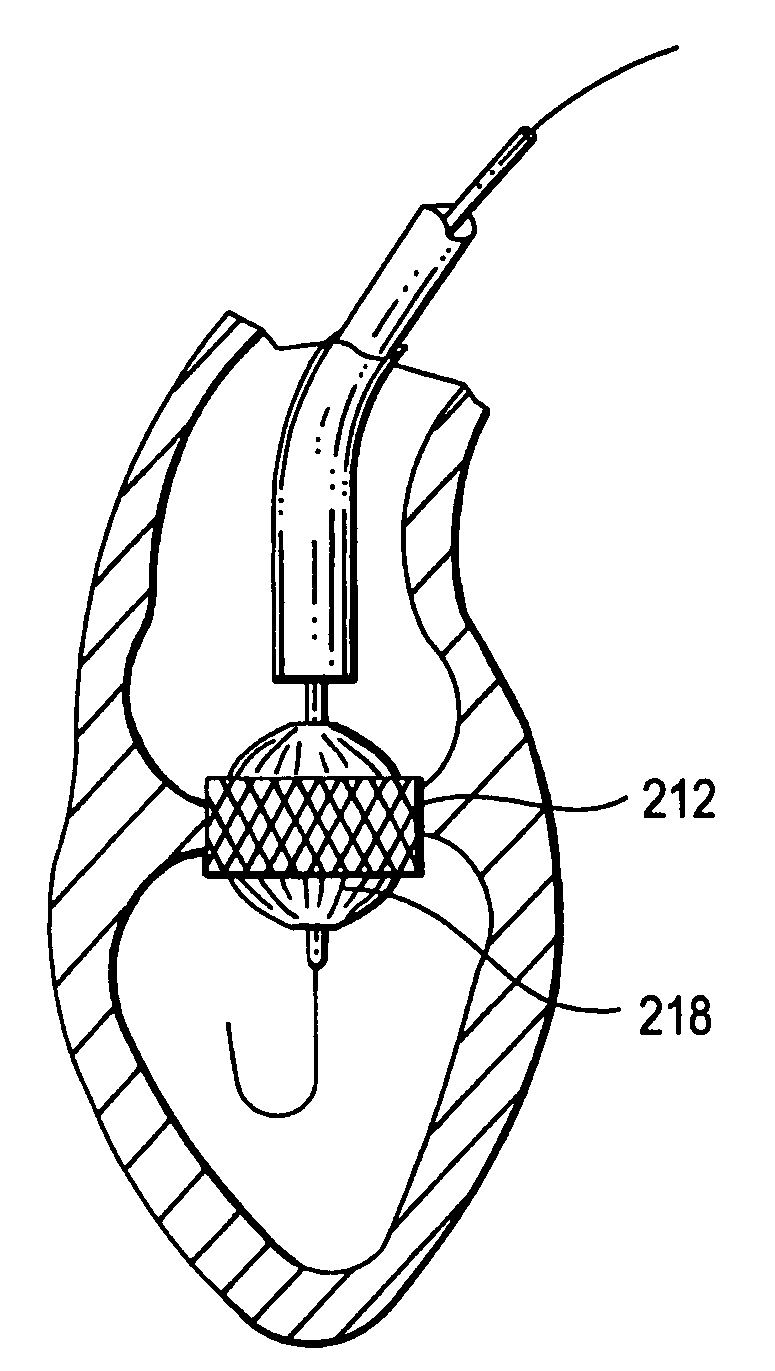
Percutaneously delivered temporary valve assembly
The percutaneously delivered temporary valve assembly of the present invention, and method of using the same, provides an elongate element and a temporary valve disposed on the elongate element. The temporary valve can comprise struts and a membrane attached to the struts. The elongate element can include at least one lumen. The percutaneously delivered temporary valve assembly can be used to replace an aortic valve by locating a temporary valve in a patient's ascending aorta; deploying the temporary valve; removing the native aortic valve past the temporary valve; implanting the prosthetic aortic valve past the temporary valve; collapsing the temporary valve; and removing the temporary valve from the patient. The temporary valve can be sized to the patient and can be left in place while the prosthetic aortic valve heals in.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Device and method for assisting in the implantation of a prosthetic valve
ActiveUS7462191B2Reduce the overall diameterReduce deliveryBalloon catheterHeart valvesBalloon dilatation catheterProsthetic valve
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
Nonstented heart valves with formed in situ support
InactiveUS20060020327A1Improve support rigidityMinimally invasive procedureSuture equipmentsHeart valvesProsthetic valveProsthesis
An implantable prosthetic valve having an in situ formable support structure and methods of deploying such a valve are disclosed. In one arrangement, the valve has a base and at least one flow occluder. A first flexible component which is incapable of retaining the valve at a functional site in the arterial vasculature extends proximally of the base of the valve. A second flexible component which is incapable of retaining the valve at a functional site in the arterial vasculature extends distally of the base of the valve. At least one rigidity component combines with at least one of the first and second flexible components to impart sufficient rigidity to the first or second components to retain the valve at the site.
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
Cardiac valve procedure methods and devices
The present invention discloses devices and methods for performing intravascular procedures with out: cardiac bypass. The devices include various embodiments of temporary filter devices, temporary valves, and prosthetic valves. The temporary filter devices have one or more cannulae which provide access for surgical tools for effecting repair of the cardiac valves. A cannula may have filters of various configurations encircling the distal region of the cannula, which prevent embolitic material from entering the coronary arteries and aorta. The temporary valve devices may also have one or more cannulae which guide the insertion of the valve into the aorta. The valve devices expand in the aorta to occupy the entire flow path of the vessel. In one embodiment, the temporary valve is a disc of flexible, porous, material that acts to filter blood passing therethrough. A set of valve leaflets extend peripherally from the disc. These leaflets can alternately collapse to prevent blood flow through the valve and extend to permit flow. The prosthetic valves include valve fixation devices which secure the prosthetic valve to the wall of the vessel. In one embodiment, the prosthetic valves have at least one substantially rigid strut, at least two expandable fixation rings located about the circumference of the base of the apex of the valve, and one or more commissures and leaflets. The prosthetic valves are introduced into the vascular system a compressed state, advanced to the site of implantation, expanded and secured to the vessel wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
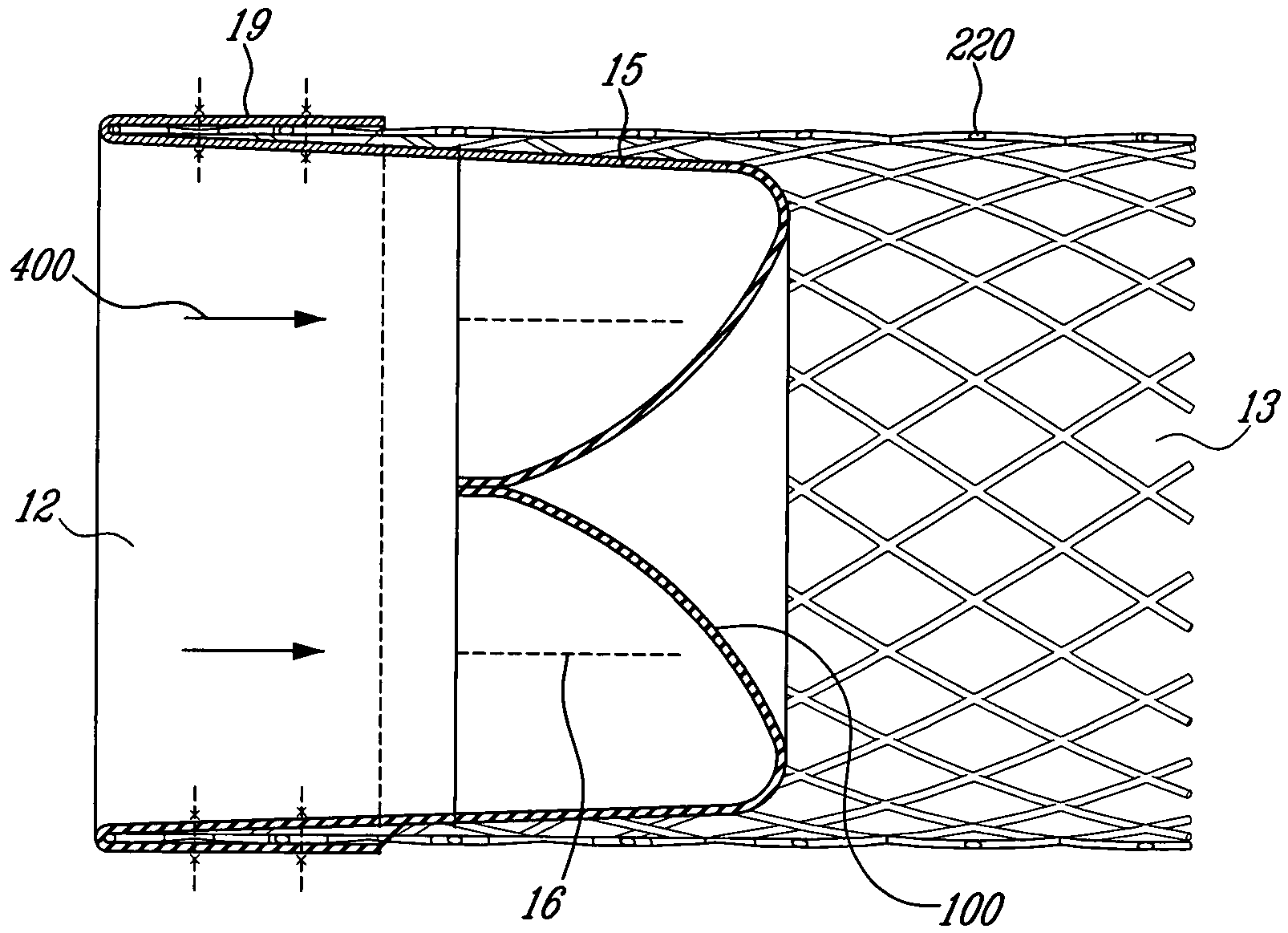
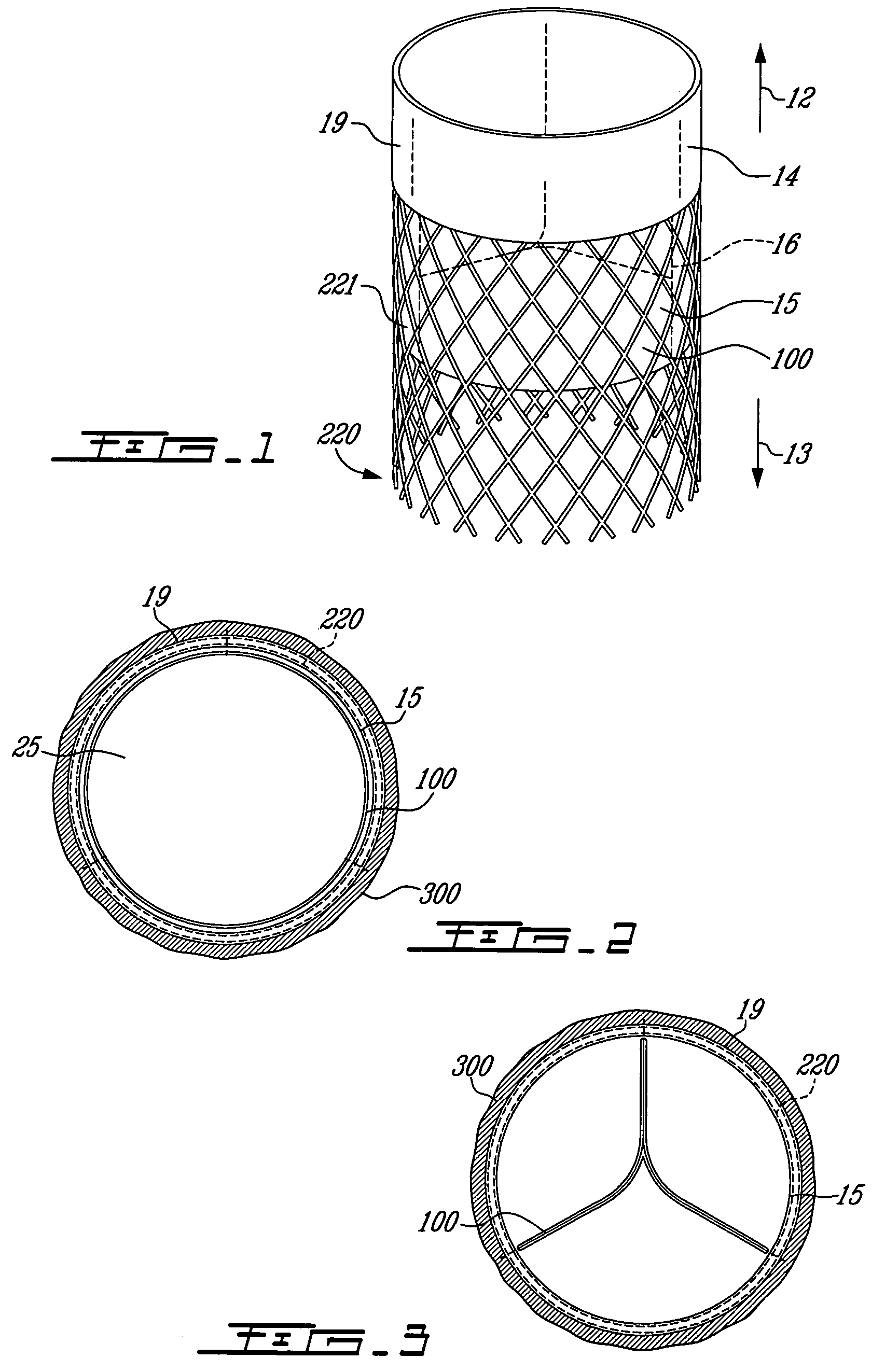
Endoluminal cardiac and venous valve prostheses and methods of manufacture and delivery thereof
This invention relates to prosthetic cardiac and venous valves and a single catheter device and minimally invasive techniques for percutaneous and transluminal valvuloplasty and prosthetic valve implantation.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Apparatus and method for implanting collapsible/expandable prosthetic heart valves
Apparatus for delivering a prosthetic heart valve into a patient by means that are less invasive than conventional open-chest, open-heart surgery. The prosthetic valve may be collapsed while in a delivery device. When the valve reaches the desired implant site in the patient, the valve can be released from the delivery device, which allows the valve to re-expand to the configuration in which it can function as a heart valve. For example, the delivery device may be constructed to facilitate delivery of the prosthetic valve into the patient via the apex of the patient's heart.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Implantable valvular prosthesis
The present invention relates to a medical device, and in particular, to a stent-based valve. The valve includes a radially expandable structural frame including an anchor structure having a first and a second open end, a connecting member having a first and a second end, and a cantilever valve strut having a first and a second end. The first end of the connecting member is attached to the second end of the anchor structure. The first end of the cantilever valve strut is cooperatively associated with the second end of the connecting member. The prosthetic valve further includes a biocompatible membrane assembly having a substantially tubular configuration about the longitudinal axis, with a first open and a second closed end. The first end of the membrane assembly is attached to the structural frame along the second end of the cantilever valve strut.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Prosthetic valve devices and methods of making such devices
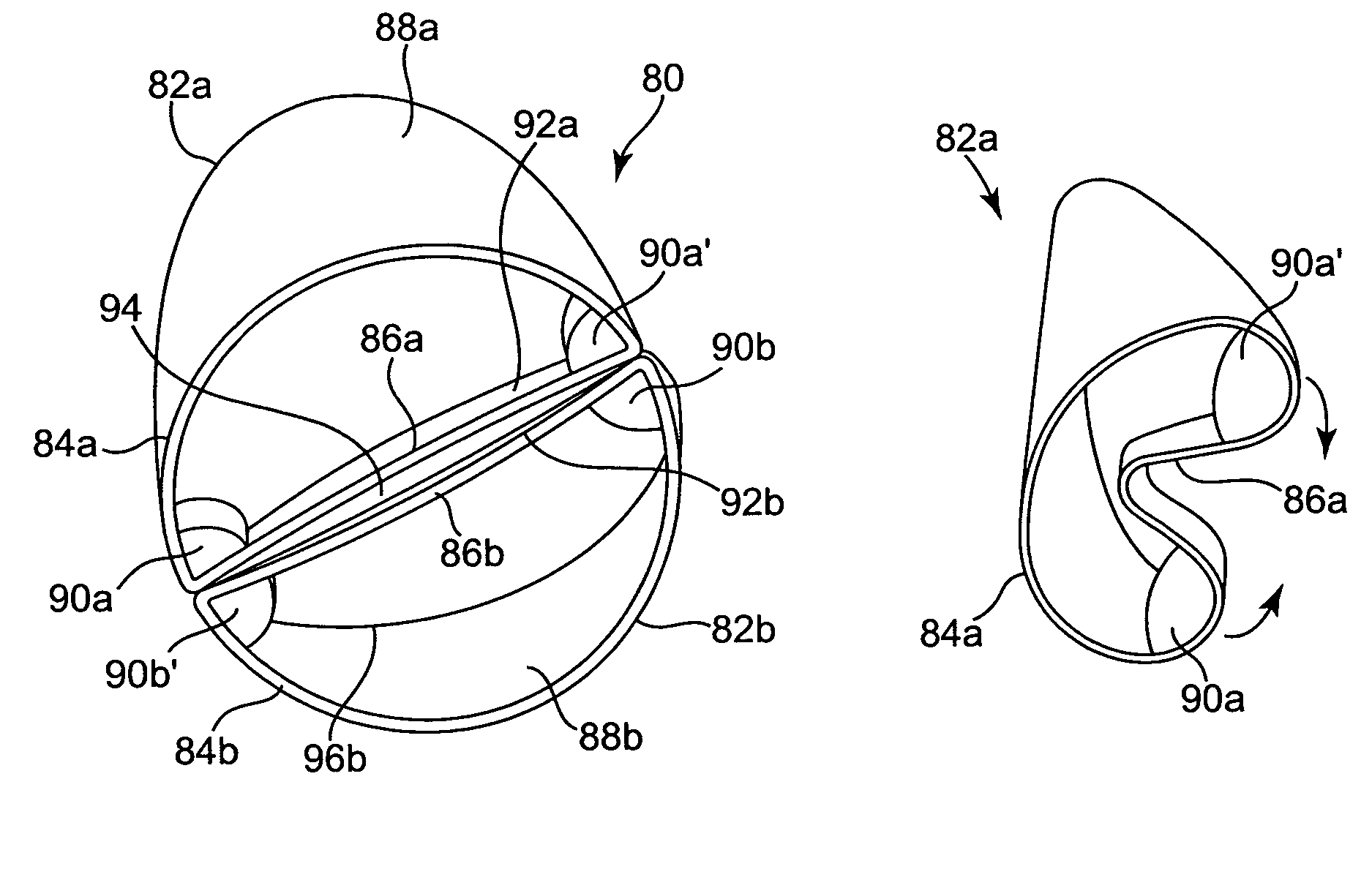
Prosthetic valve devices for implantation in body vessels, and methods of making same, are provided. The device has a main body with first and second ends and defining a lumen, with the second end being inverted into the lumen. A valve is disposed at the second end. In multiple valve devices, valves are disposed at the first and second ends, and individually may be inverted into the lumen. The prosthetic valve devices may further include a support structure such as a stent. Methods of making a prosthetic valve device include providing a main body having first and second ends and defining a lumen, forming a valve at the second end, and inverting the second end into the lumen. Methods may further comprise forming multiple valves and may also include attaching a support structure.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
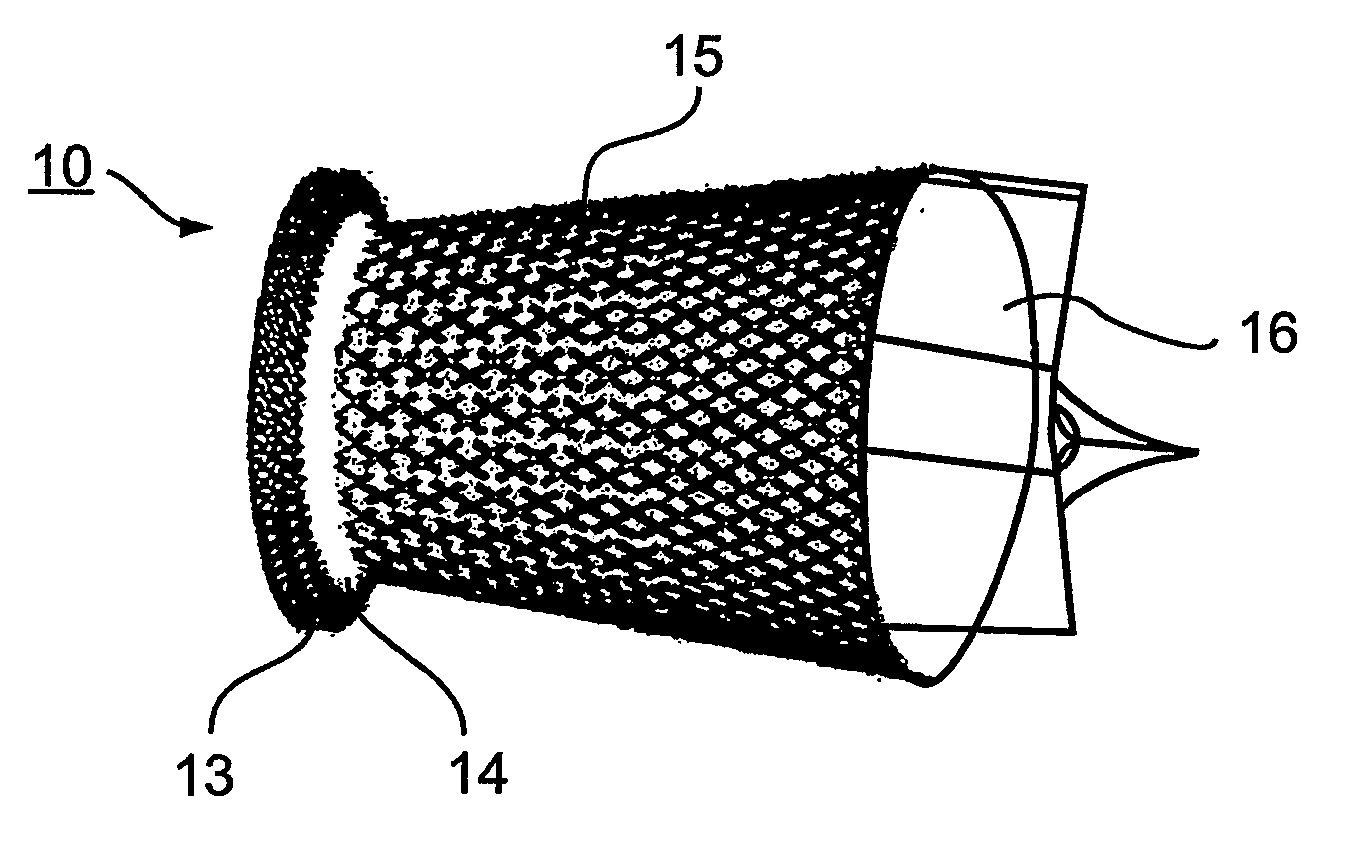
Stentless support structure
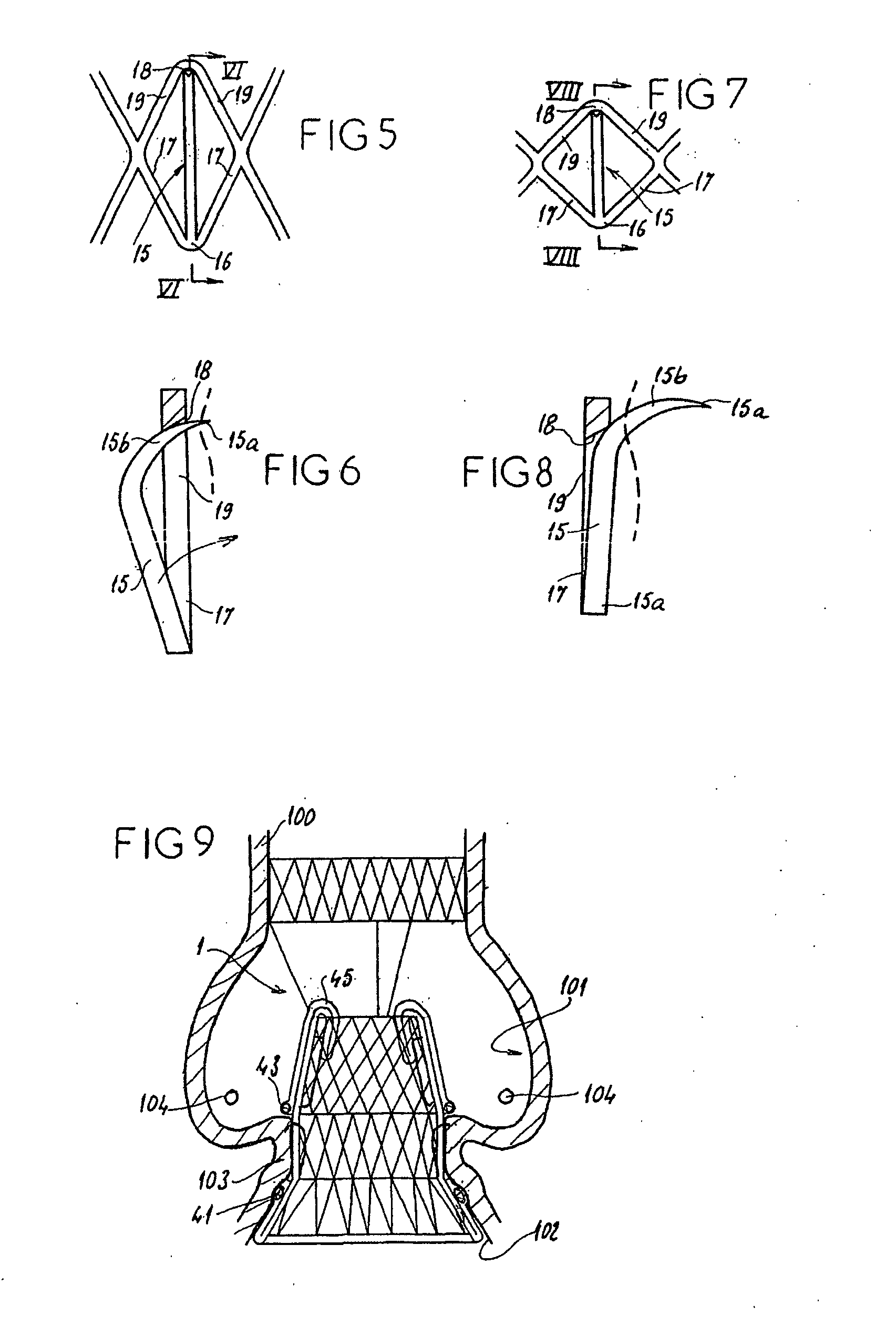
ActiveUS20060271166A1Avoid damageSmall diameterStentsHeart valvesProsthetic valveUltimate tensile strength
A stentless support structure capable of being at least partly assembled in situ. The support structure comprises a braided tube that is very flexible and, when elongated, becomes very long and very small in diameter, thereby being capable of placement within a small diameter catheter. The support structure is preferably constructed of one or more thin strands of a super-elastic or shape memory material such as Nitinol. When released from the catheter, the support structure folds itself into a longitudinally compact configuration. The support structure thus gains significant strength as the number of folds increase. This radial strength obviates the need for a support stent. The support structure may include attachment points for a prosthetic valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Prosthetic cardiac valve formed from pericardium material and methods of making same
ActiveUS20070233228A1Barrier to undesired abrasionPrevent and minimize valve leakageHeart valvesFinal product manufactureProsthetic valveProsthesis
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Adjustable prosthetic valve implant
A prosthetic implant for treating a diseased aortic valve is described. The prosthetic implant includes a substantially tubular body configured to be positioned in an aorta of a patient, at or near the patient's aortic valve. The body includes a lumen extending through the body from a proximal end to a distal end of the body; and an adjustable frame surrounding the lumen. The prosthetic implant further includes at least one adjustable element located in or on the body and extending at least partially around a circumference of the lumen. The at least one adjustable element includes a shape memory material and is transformable, in response to application of an activation energy, from a first configuration to a second configuration, wherein the first configuration and second configuration differ in a size of at least one dimension of the at least one adjustable element. The at least one adjustable element may engage at least one of a root of the aorta, an annulus of the aortic valve, and the patient's left ventricle, when the at least one adjustable element is in the second configuration.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Translumenally implantable heart valve with multiple chamber formed in place support
InactiveUS20060025855A1Minimally invasive procedurePrevent disengagementSuture equipmentsHeart valvesProsthetic valveEngineering
A cardiovascular prosthetic valve comprises an inflatable body that has at least a first inflatable chamber and a second inflatable chamber that is not in fluid communication with the first inflatable chamber. The inflatable body is configured to form, at least in part, a generally annular ring. A valve is coupled to the inflatable body. The valve is configured to permit flow in a first axial direction and to inhibit flow in a second axial direction opposite to the first axial direction. A first inflation port is in communication with the first inflatable chamber. A second inflation port in communication with the second inflatable chamber.
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
Implantable prosthetic devices particularly for transarterial delivery in the treatment of aortic stenosis, and methods of implanting such devices
ActiveUS20060259134A1Reduce the possibilityReduced permanent pressure lossStentsHeart valvesSystoleProsthetic valve
Prosthetic devices as described for use in the treatment of aortic stenosis in the aortic valve of a patient's heart, the prosthetic device having a compressed state for transarterial delivery and being expandable to an expanded state for implantation. The prosthetic device includes an expandable metal base (10) constructed so as to be implantable in the expanded state of the prosthetic device in the aortic annulus of the aortic valve; and an inner envelope lining (11) tune inner surface of the metal base (10). The inner envelope, in the expanded state of the prosthetic device, extends into the aorta and is of a diverging conical configuration, in which its diameter gradually increases from its proximal end within the aortic annulus to its distal end extending into the aorta, such as to produce, during systole, a non-turbulent blood flow into the aorta with pressure recovery at the distal end of the inner envelope. Preferably, the distal end includes a prosthetic valve which is also concurrently implanted, but such a prosthetic valve may be implanted separately in the aorta Also described are preferred methods of implanting such prosthetic devices.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
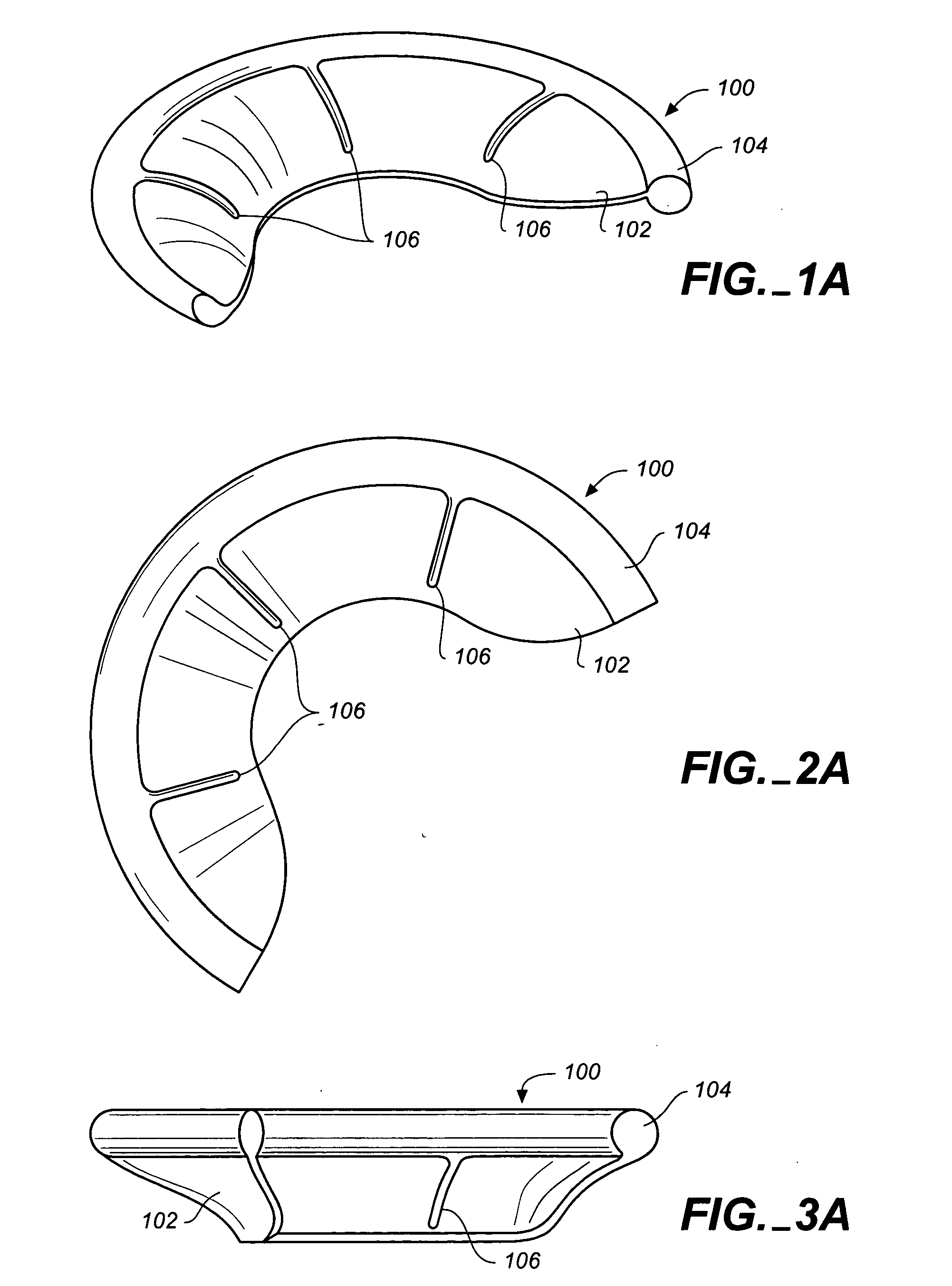
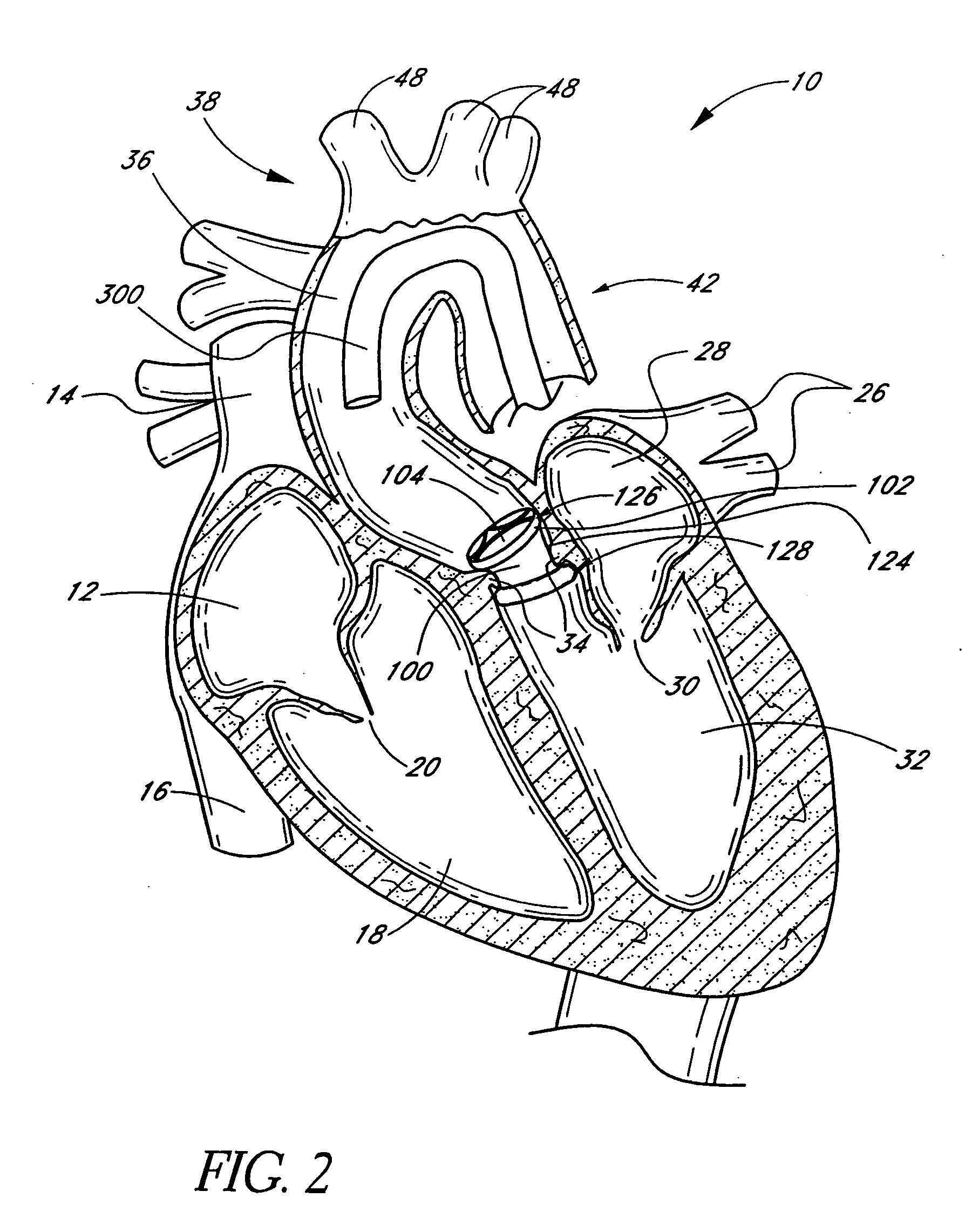
Prosthetic cardiac valves and systems and methods for implanting thereof
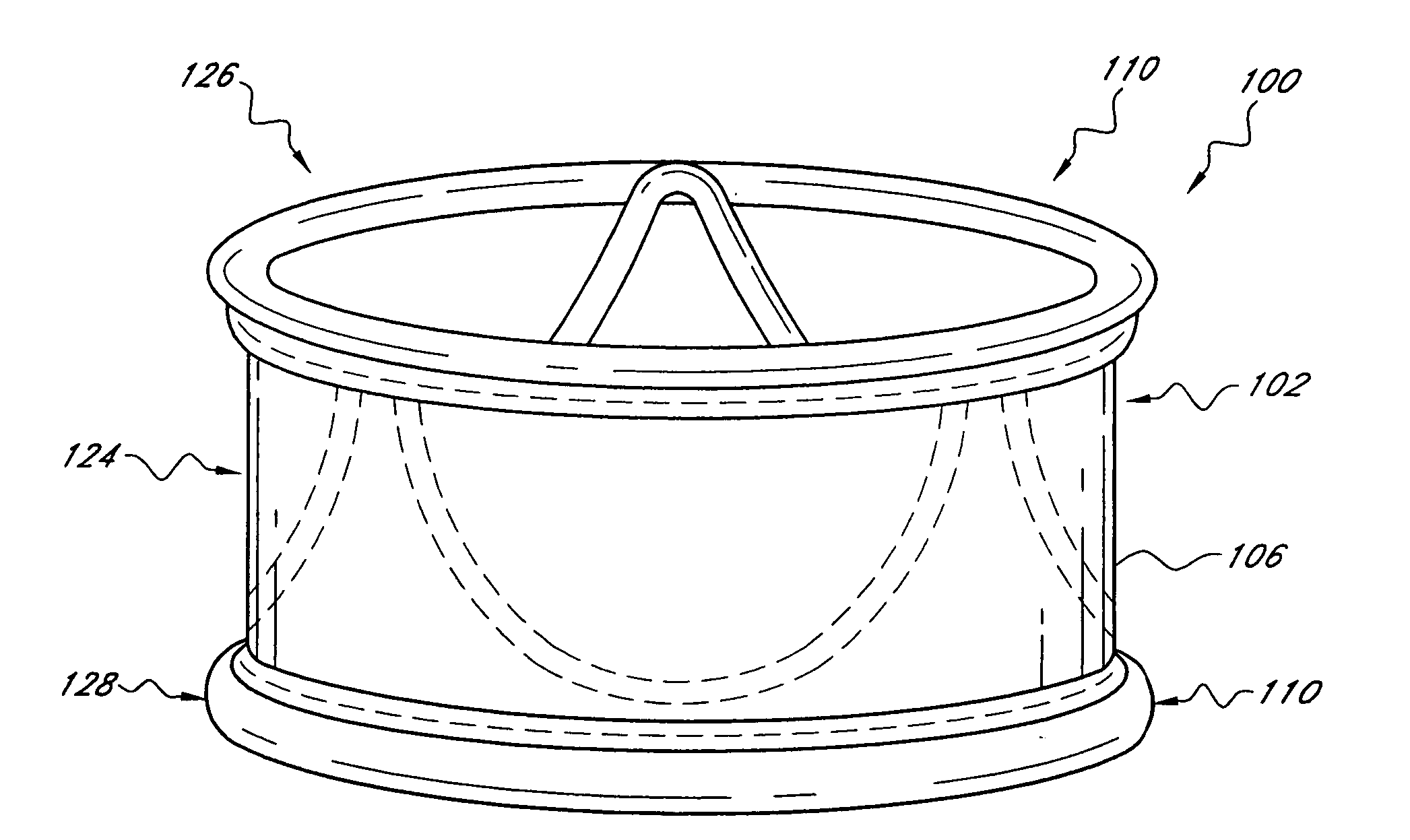
Implantable prosthetic valve systems and methods for implanting them are provided. Magnets are employed within one or more components of the valve systems to facilitate anchoring of the prosthetic valve at a target implant site, delivery of the prosthetic valve to the target implant site or both.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Prosthetic cardiac valves and systems and methods for implanting thereof
ActiveUS7186265B2Easy to anchorFacilitate delivery and deploymentHeart valvesProsthetic valveProsthesis
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Stented Valve Having Dull Struts
A system for replacing a pulmonary valve includes a conduit having a lumen, a delivery catheter and a replacement valve device disposed on the delivery catheter. The replacement valve device includes a prosthetic valve connected to a valve support region of an expandable support structure. The valve support region includes a plurality of protective struts disposed between a first stent region and a second stent region. A method for replacing a pulmonary valve includes implanting a conduit and delivering a replacement valve device to the conduit. The replacement valve device includes a valve connected to a valve support region that includes a plurality of protective struts. The method also includes deploying the prosthetic valve device from a delivery catheter into the lumen, positioning the prosthetic valve device within the conduit lumen and expanding the prosthetic valve device into contact with the inner wall of the conduit.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Prosthetic valves and related inventions
ActiveUS20140214159A1Low height to width profilePrevent perivalvular leakSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis, collared or uncollared, which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Stent mounted valve
ActiveUS7261732B2Prevent backflowSmall amount of regurgitationHeart valvesBlood vesselsProsthetic valveProsthesis
There is described a prosthetic valve to be inserted into a body lumen, the valve having leaflets that are spread apart during forward flow of fluid to create an orifice, and the leaflets coming into contact with each other during reverse flow of fluid, thereby impeding the reverse flow of fluid, the valve comprising: a hollow, cylindrical stent having an inner surface and an outer surface, and having a first and a second open end; and valve means formed from a single tubular membrane, the membrane mounted to the stent, the membrane having a graft portion internally folded and bonded to itself at a plurality of points to form pouches such that the leaflets extend from the pouches, and a sleeve portion on an outer surface of the stent to secure the membrane thereto.
Owner:JUSTINO HENRI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com