Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
281 results about "Systole" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
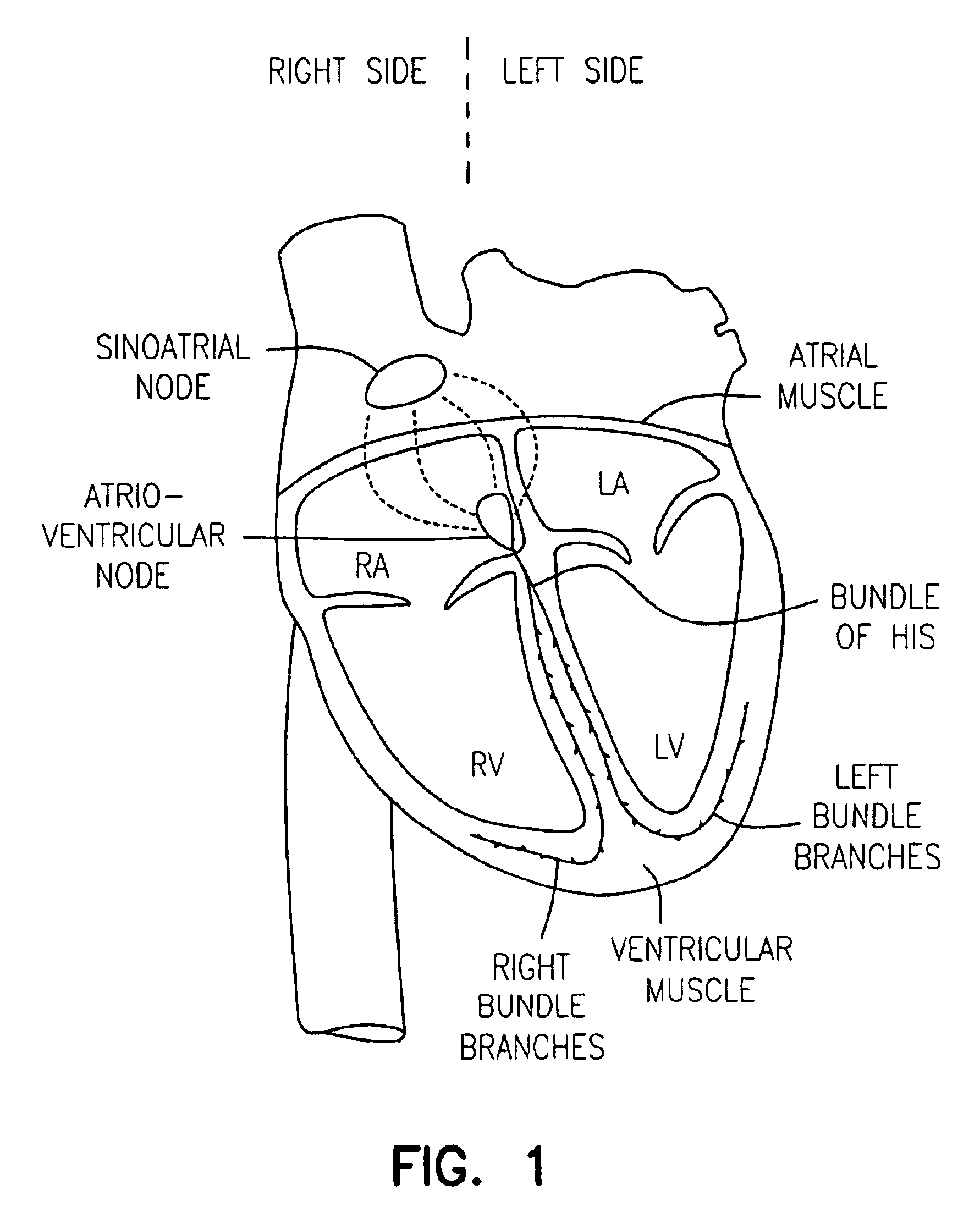
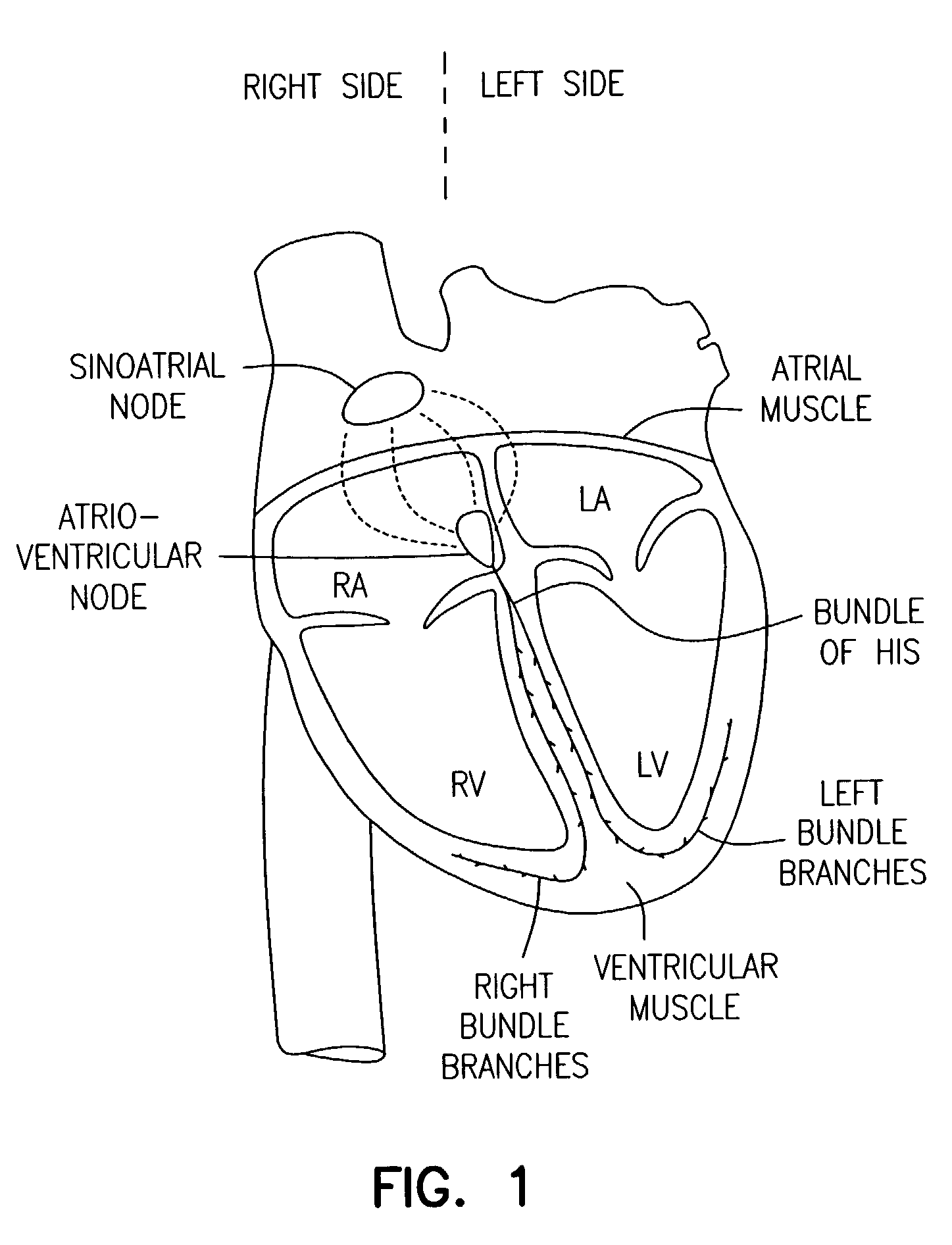
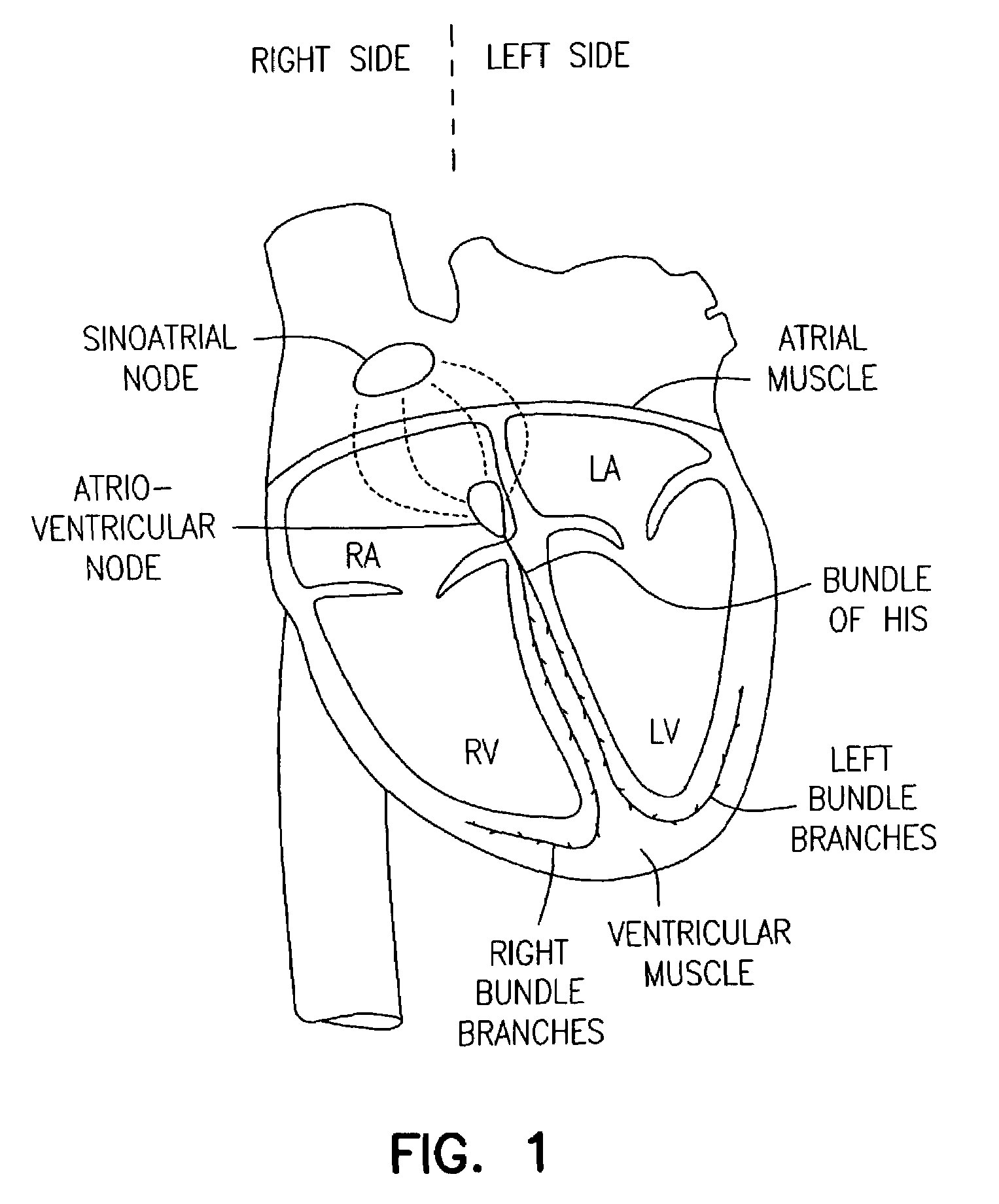
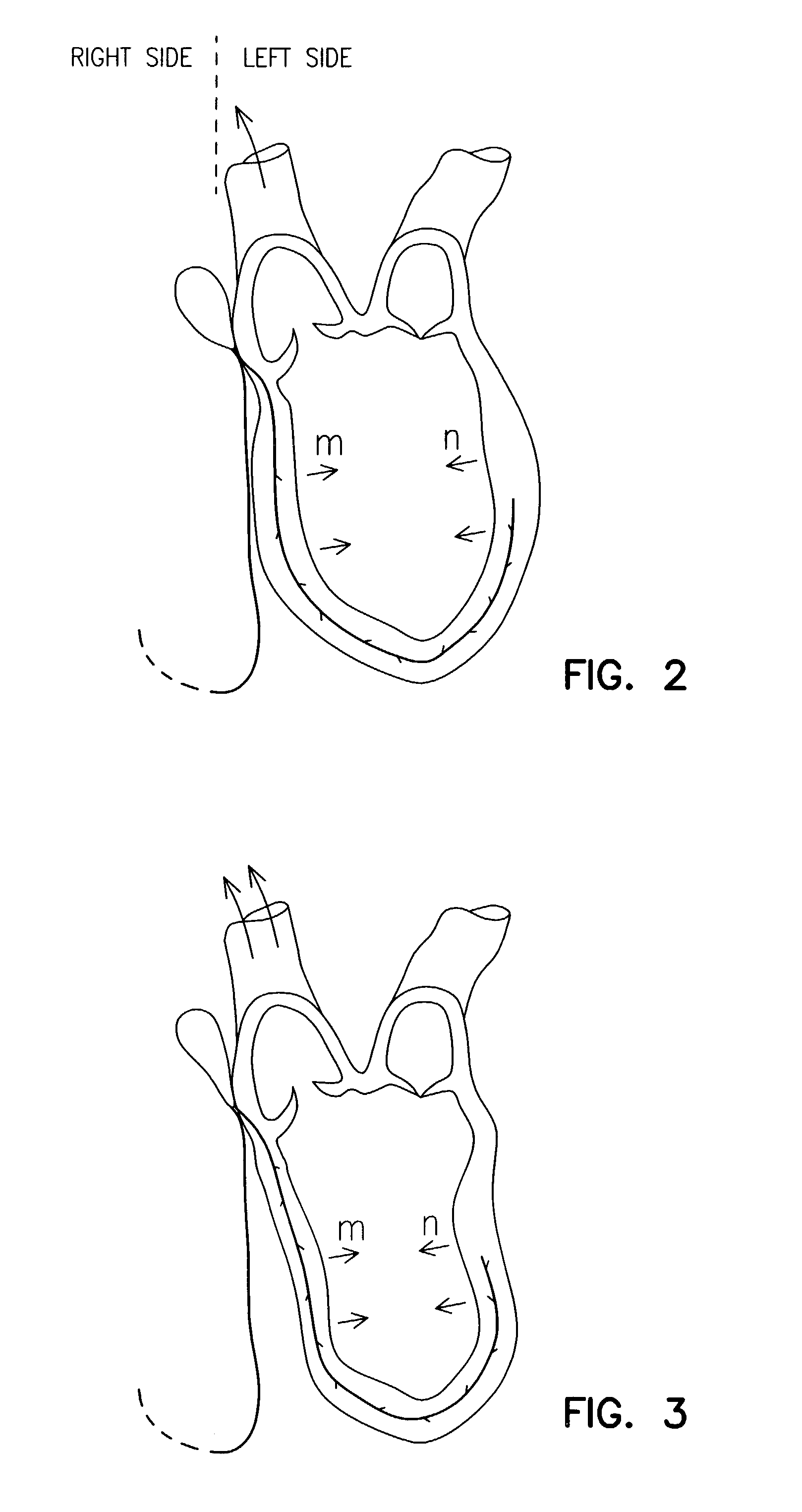
The systole /ˈsɪstəliː/ is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart muscle contract after refilling with blood. The term "systole" originates from New Latin via Ancient Greek συστολή (sustolē): from συστέλλειν (sustellein, "to contract") via [σύν (syn, "together") + στέλλειν (stellein, "send"). The use of systole, "to contract", is very similar to the use of the English term "to squeeze".
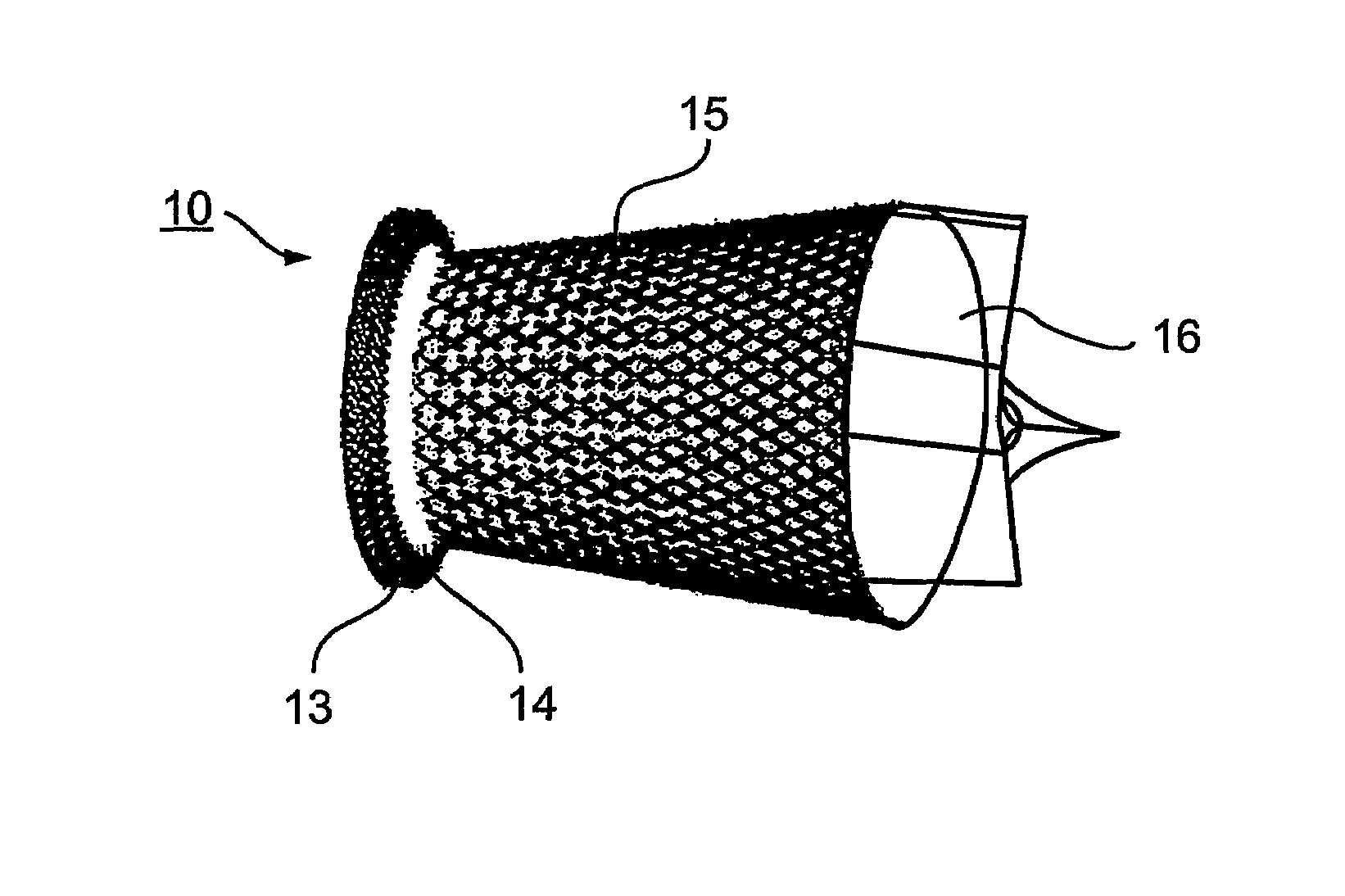
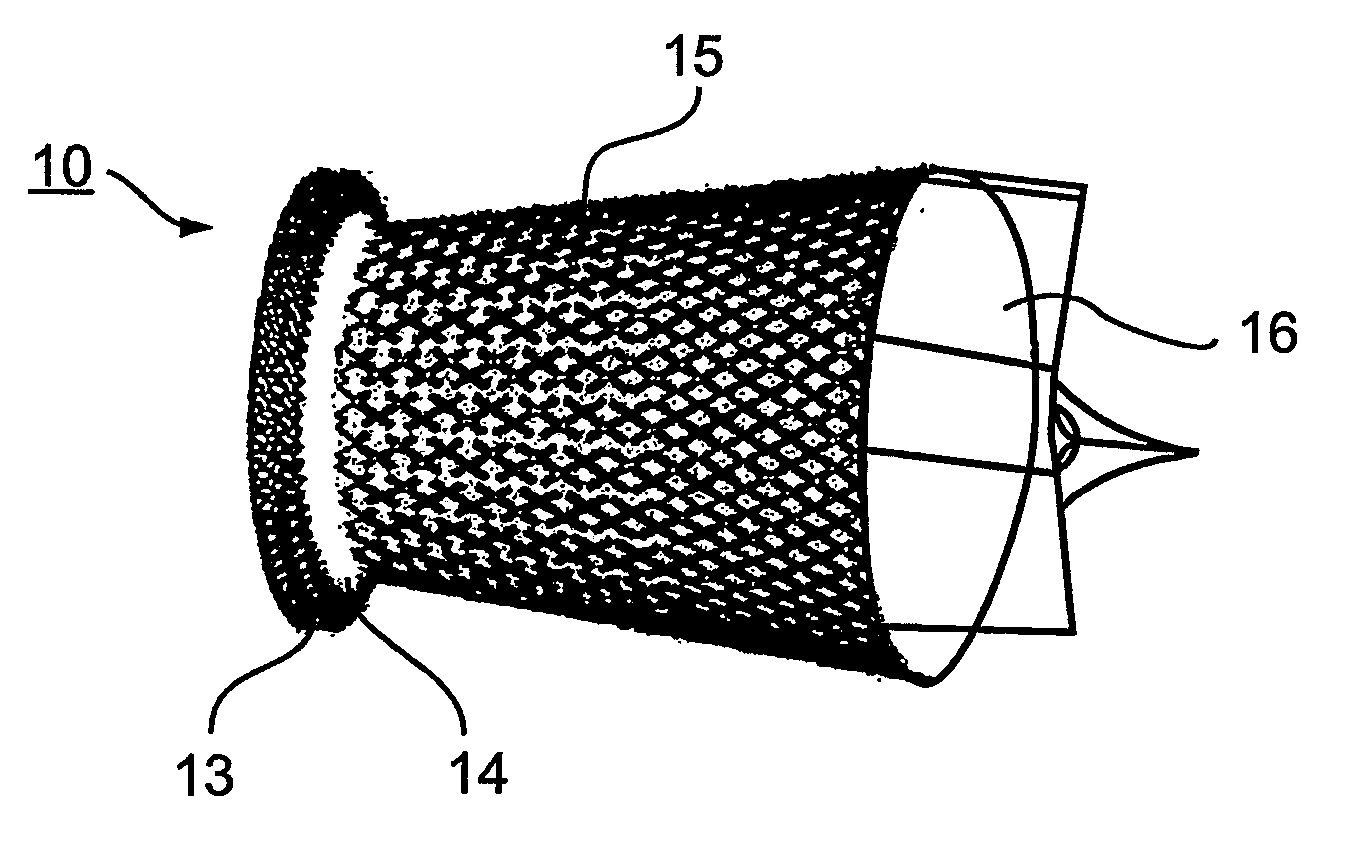
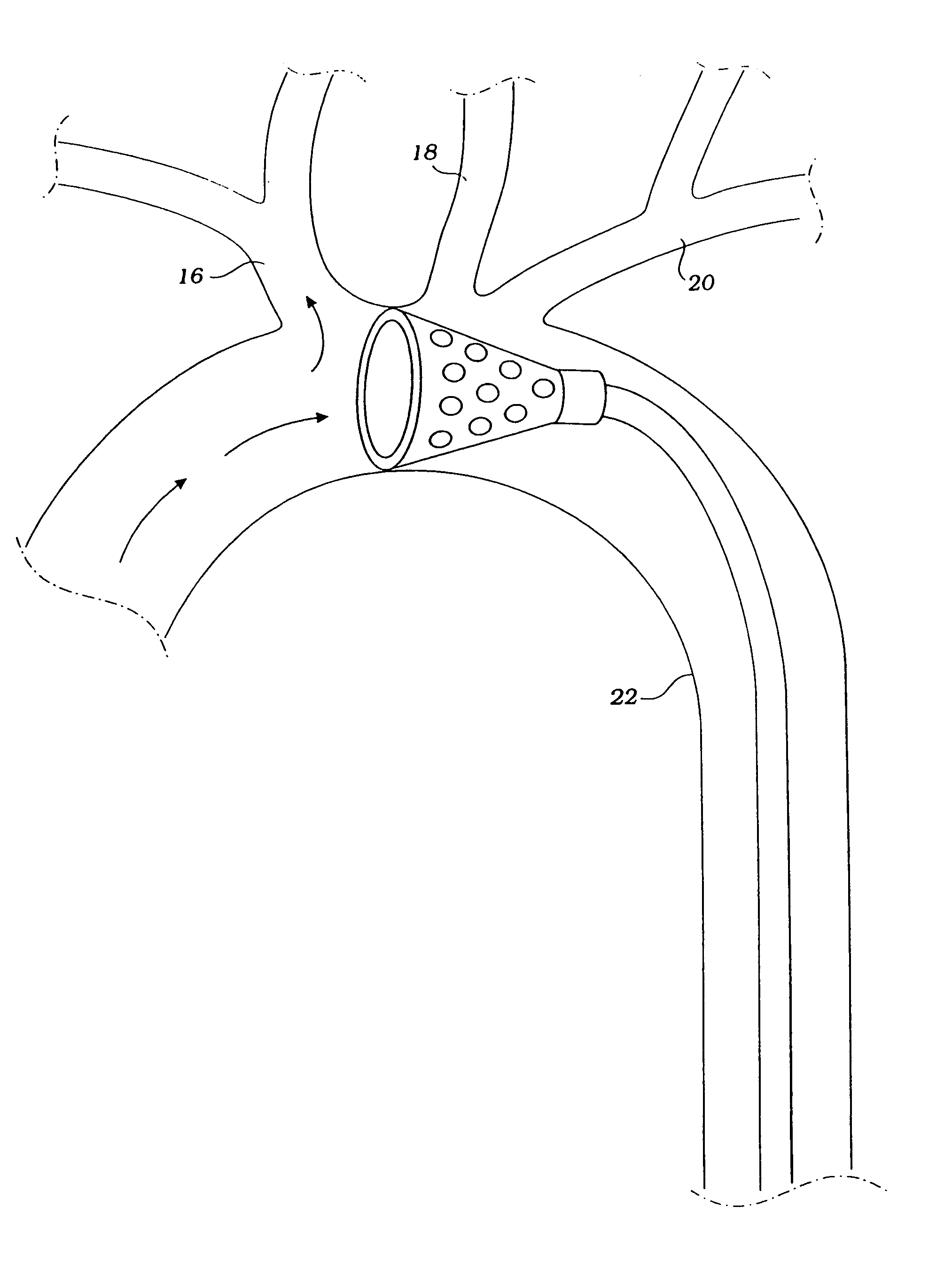
Aortic prosthetic devices
ActiveUS7429269B2Reduced permanent pressure lossReasonable hemodynamic profileStentsHeart valvesSystoleProsthesis
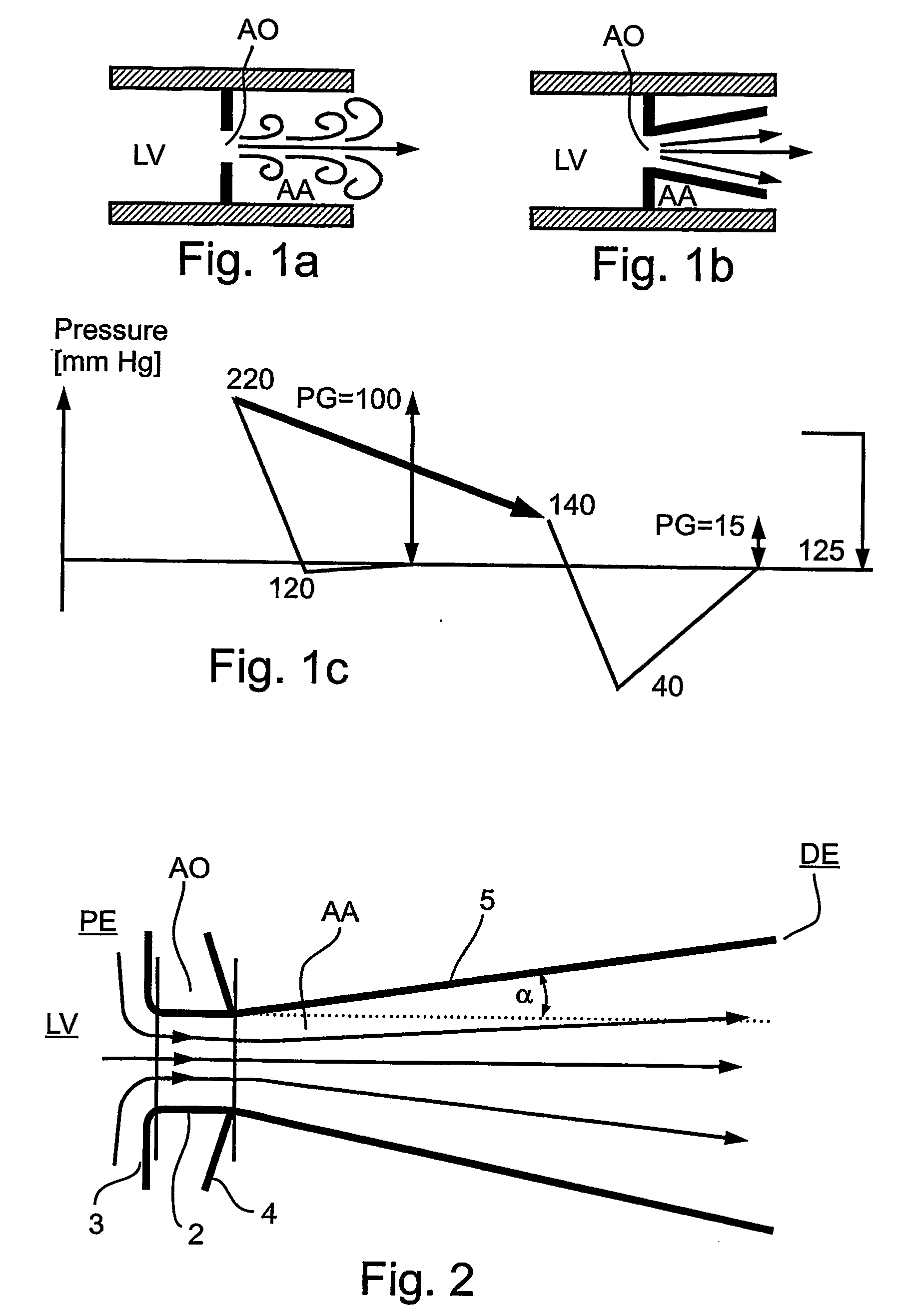
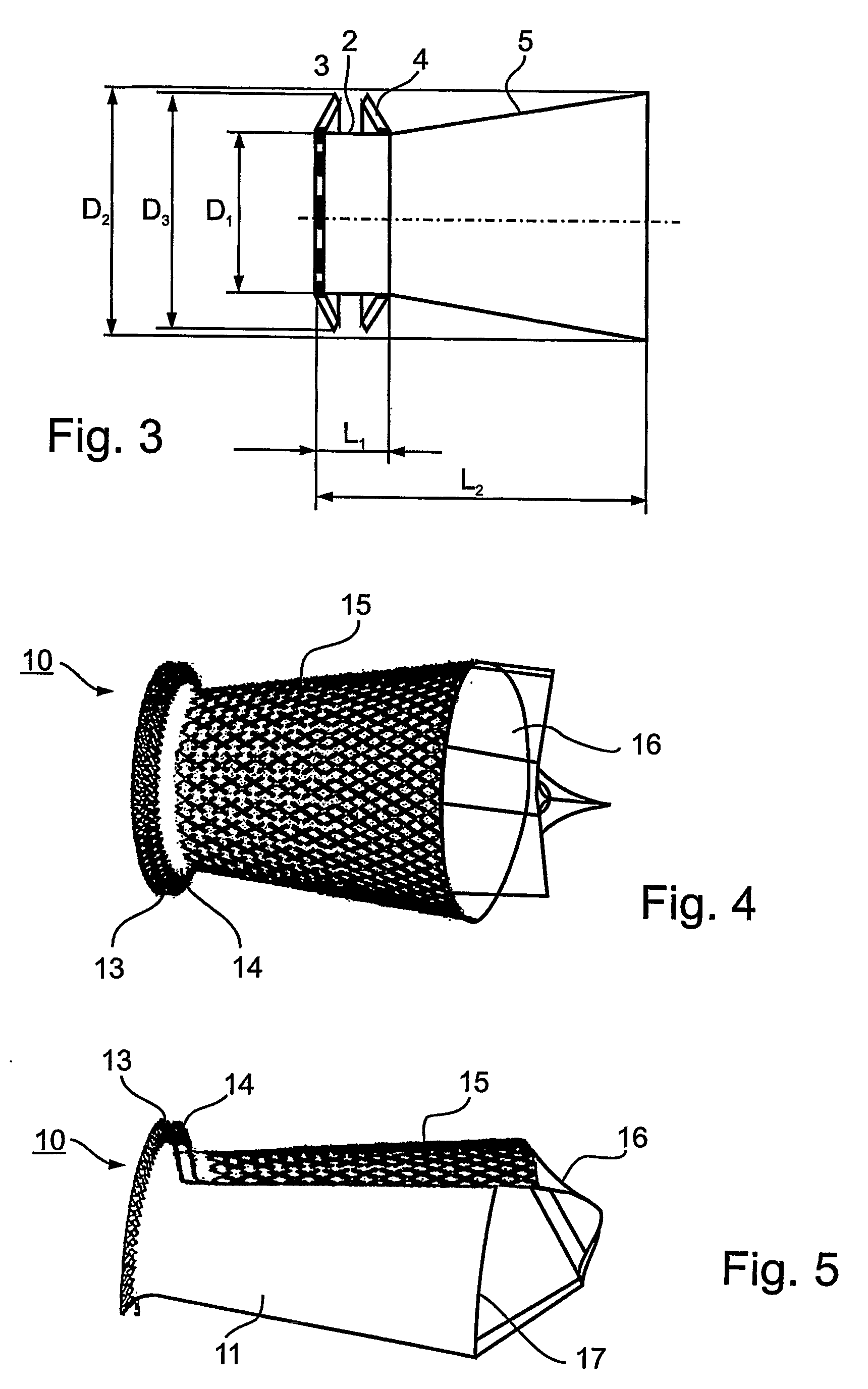
A prosthetic device is provided for treatment of an aortic valve, having a compressed state for transarterial delivery and being expandable to an expanded state for implantation. The device includes an expandable support implantable in the expanded state of the prosthetic device in an aortic annulus, and an inner envelope having an upstream portion that lines the inner surface of the support, and a downstream portion which, when the prosthetic device is in the expanded state, extends into an aorta and defines a diverging conical section having a diameter that gradually increases from an upstream end of the section to a downstream end of the section. The section is configured to produce, during systole, a non-turbulent blood flow into the aorta with pressure recovery at the downstream end of the section. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
Implantable prosthetic devices particularly for transarterial delivery in the treatment of aortic stenosis, and methods of implanting such devices
ActiveUS20060259134A1Reduce the possibilityReduced permanent pressure lossStentsHeart valvesSystoleProsthetic valve
Prosthetic devices as described for use in the treatment of aortic stenosis in the aortic valve of a patient's heart, the prosthetic device having a compressed state for transarterial delivery and being expandable to an expanded state for implantation. The prosthetic device includes an expandable metal base (10) constructed so as to be implantable in the expanded state of the prosthetic device in the aortic annulus of the aortic valve; and an inner envelope lining (11) tune inner surface of the metal base (10). The inner envelope, in the expanded state of the prosthetic device, extends into the aorta and is of a diverging conical configuration, in which its diameter gradually increases from its proximal end within the aortic annulus to its distal end extending into the aorta, such as to produce, during systole, a non-turbulent blood flow into the aorta with pressure recovery at the distal end of the inner envelope. Preferably, the distal end includes a prosthetic valve which is also concurrently implanted, but such a prosthetic valve may be implanted separately in the aorta Also described are preferred methods of implanting such prosthetic devices.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
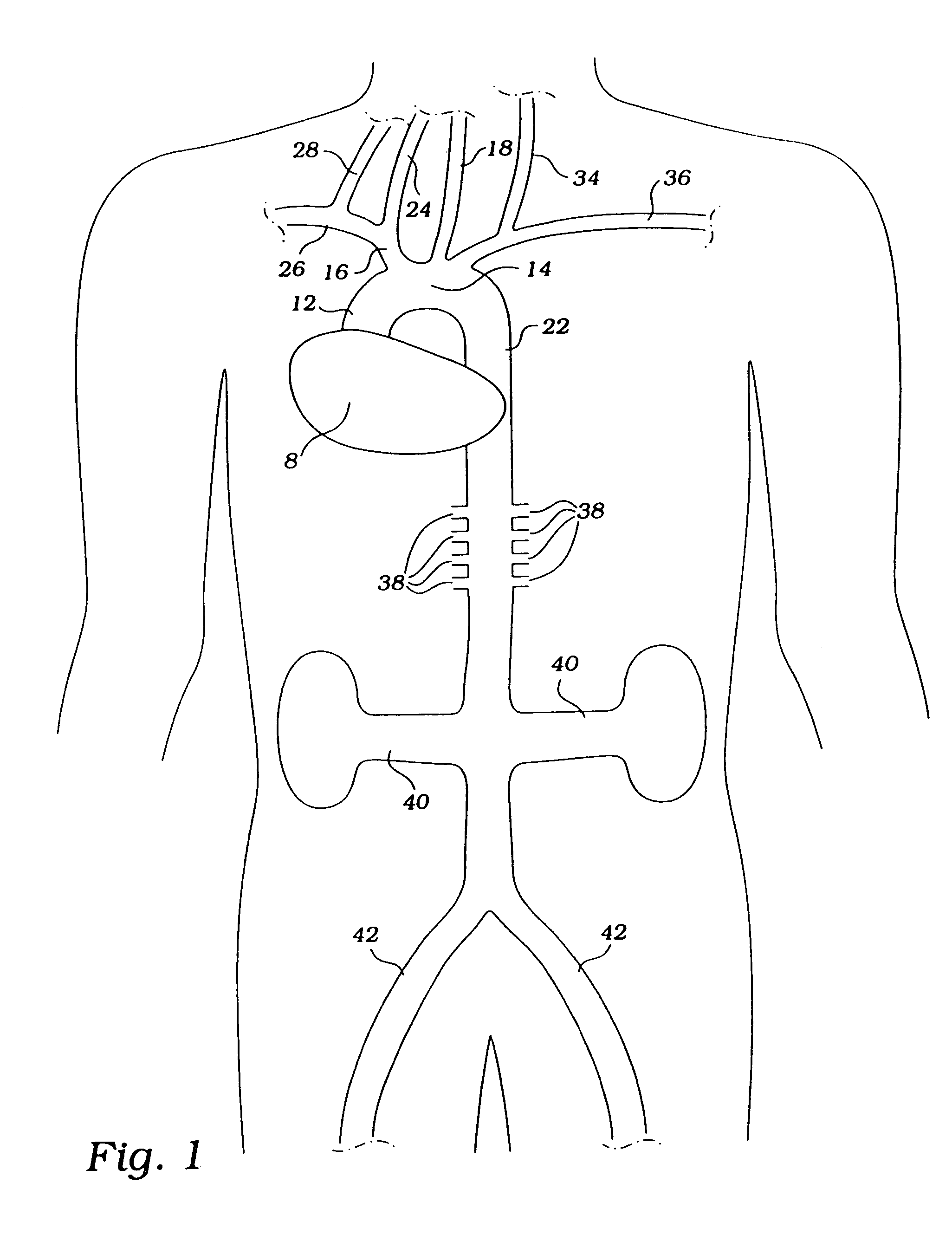
Cardiac disease treatment method
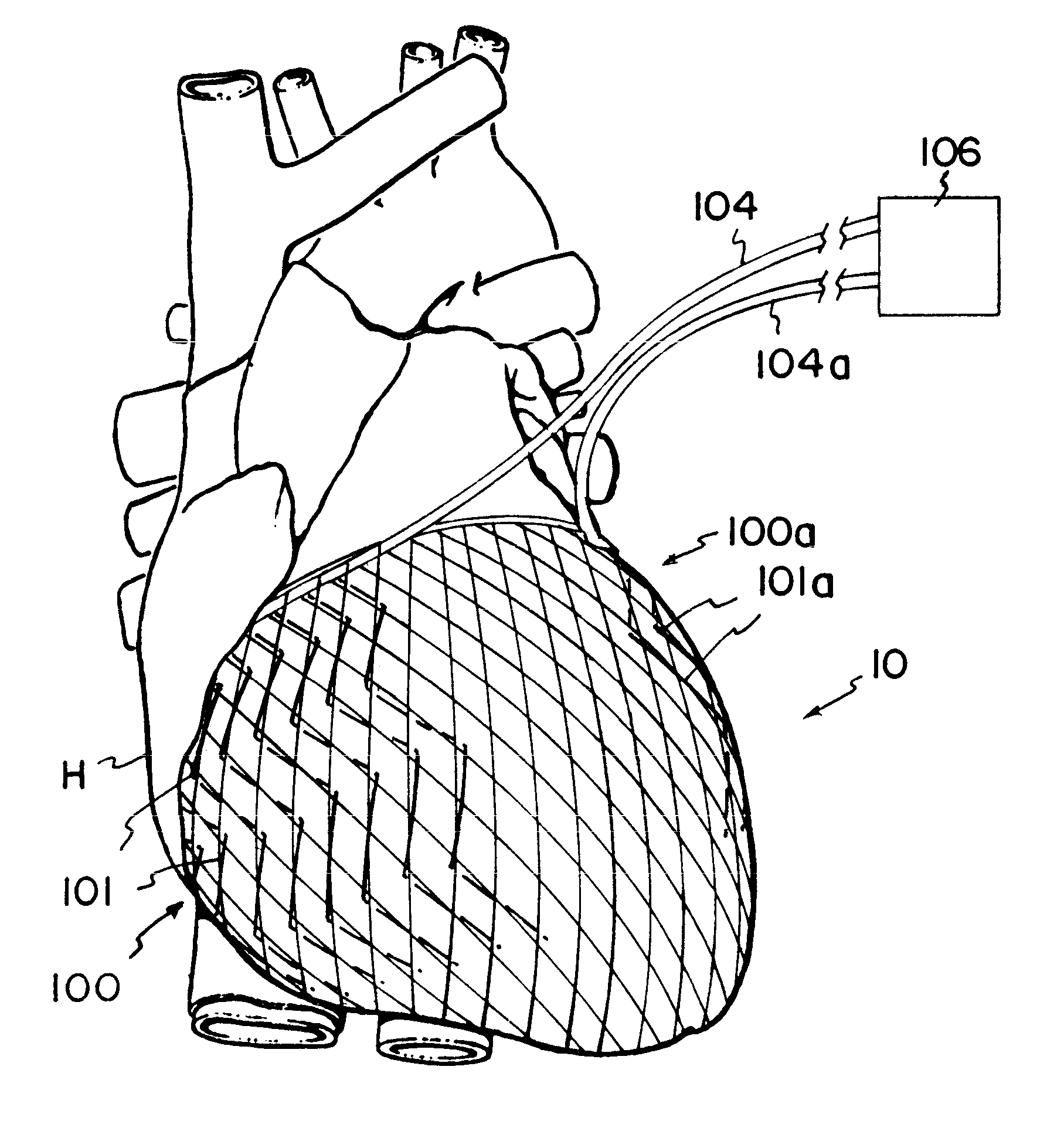
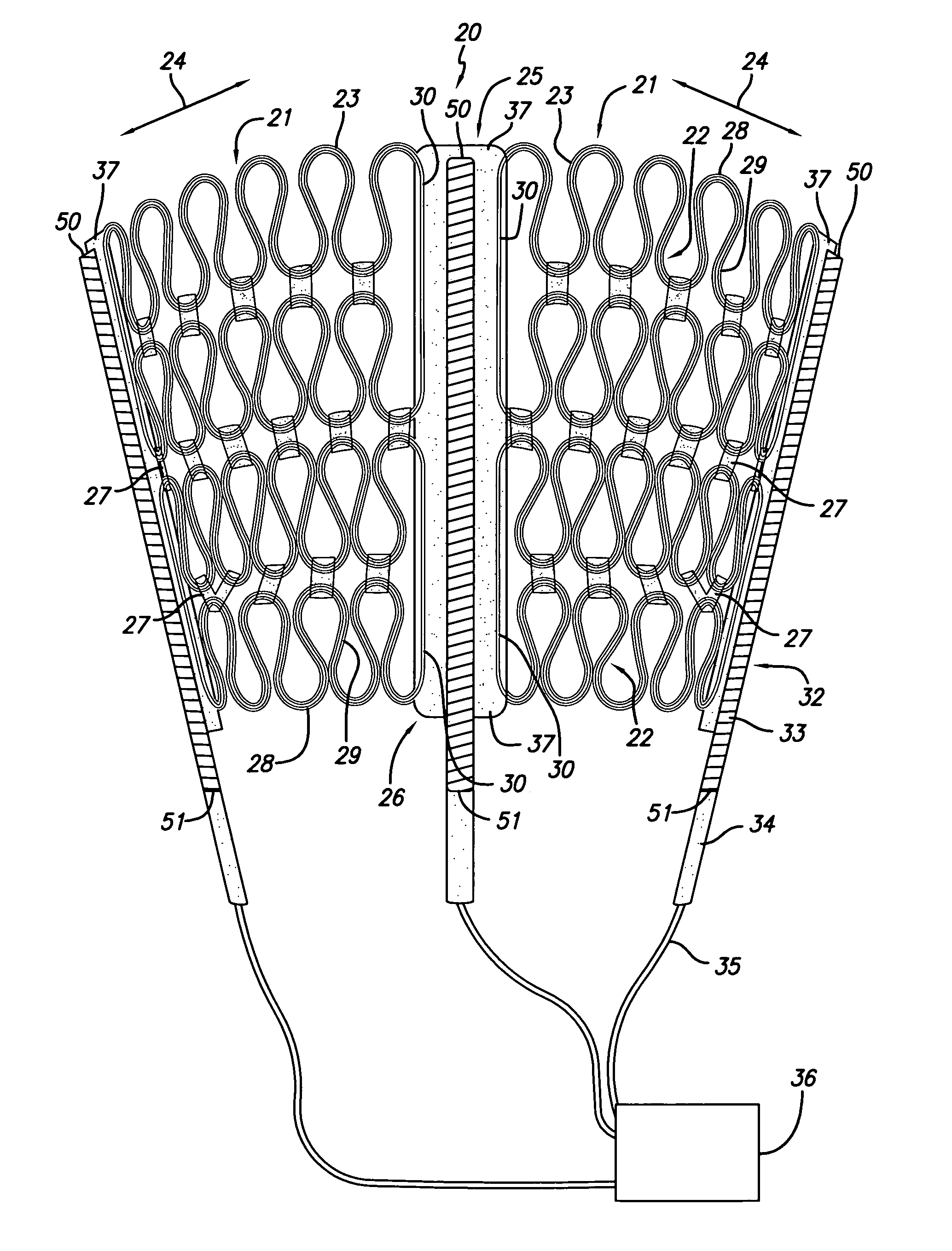
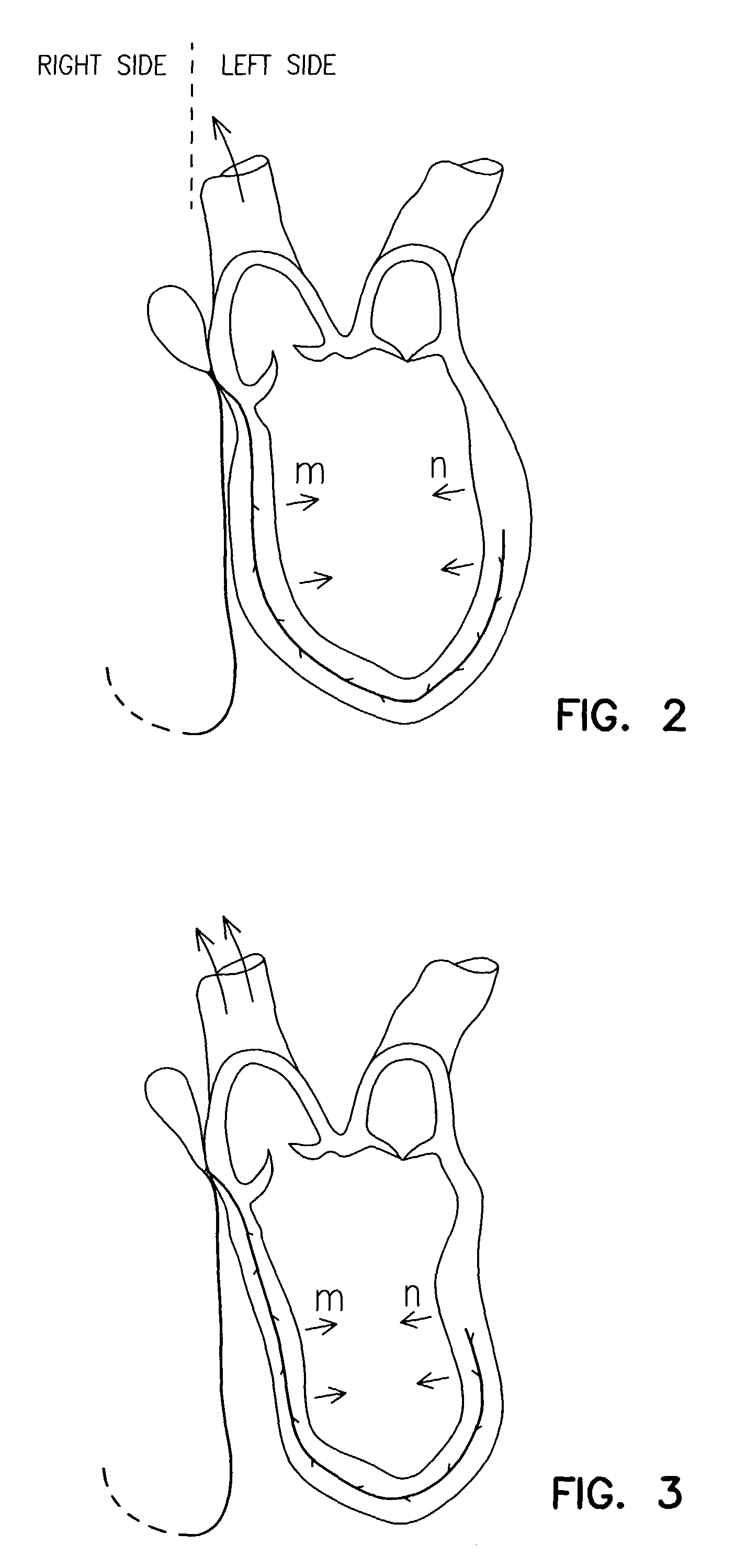
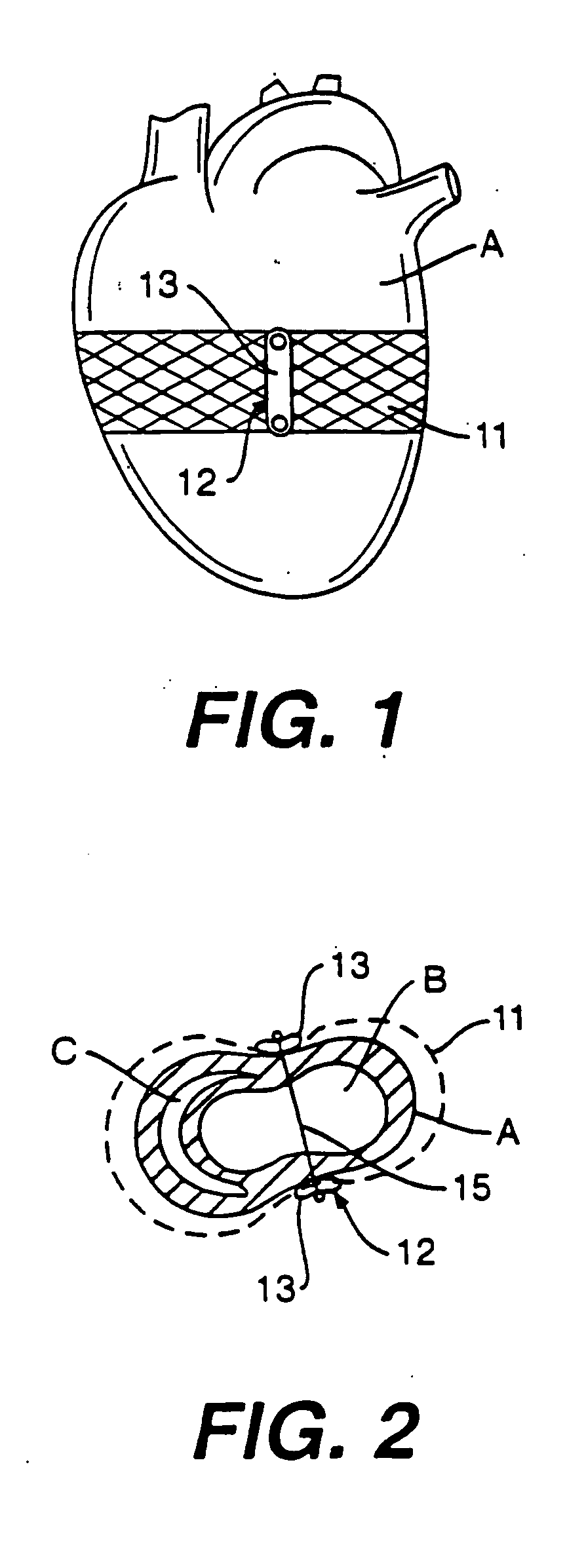
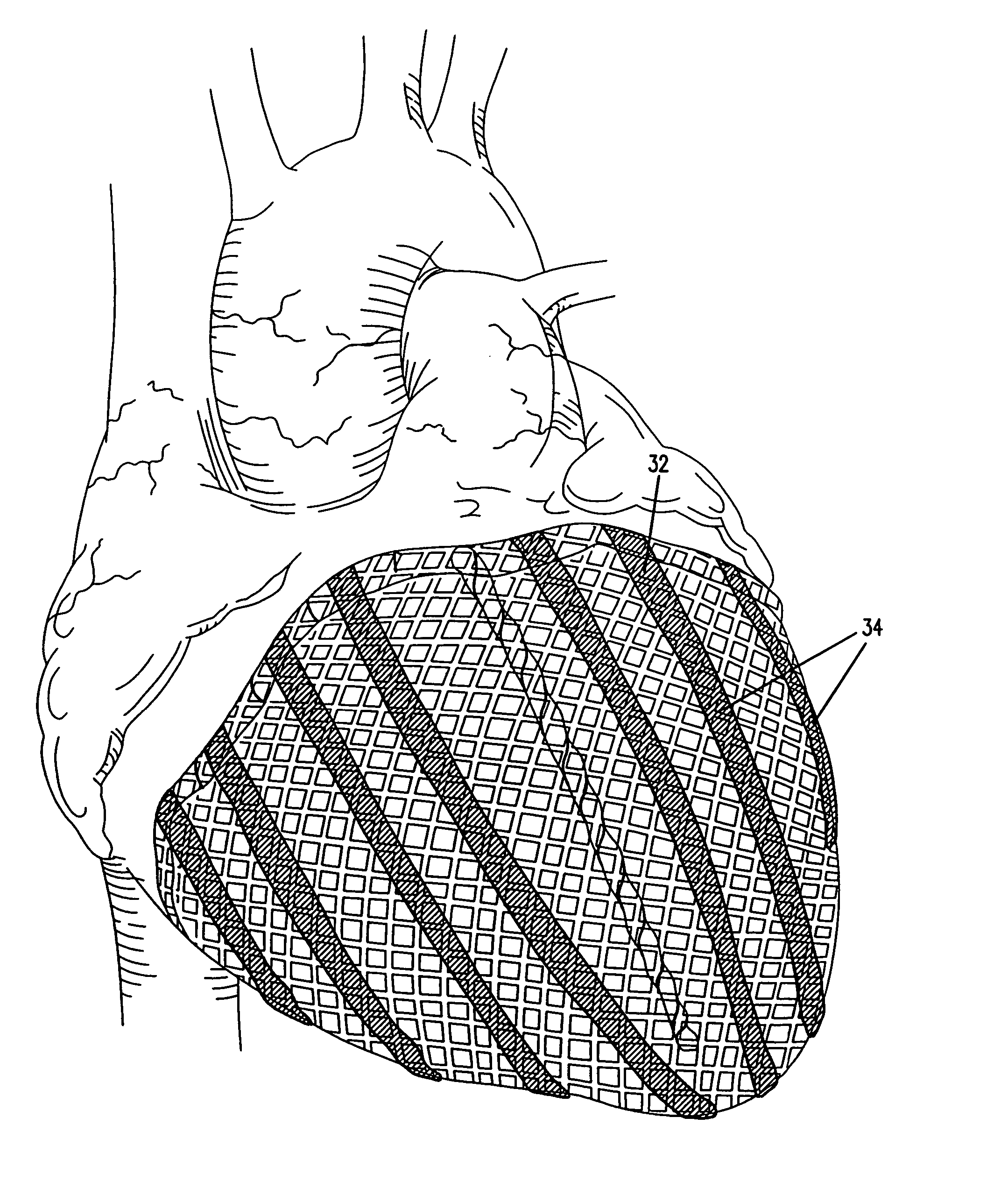
A jacket of biological compatible material has an internal volume dimensioned for an apex of the heart to be inserted into the volume and for the jacket to be slipped over the heart. The jacket has a longitudinal dimension between upper and lower ends sufficient for the jacket to surround a lower portion of the heart with the jacket surrounding a valvular annulus of the heart and further surrounding the lower portion to cover at least the ventricular lower extremities of the heart. The jacket is adapted to be secured to the heart with the jacket surrounding at least the valvular annulus and the ventricular lower extremities. The jacket is adjustable on the heart to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and assume a maximum adjusted volume for the jacket to constrain circumferential expansion of the heart beyond the maximum adjusted volume during diastole and to permit unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole.
Owner:MARDIL
Methods and apparatus for mitral valve repair
InactiveUS20080039935A1Inhibiting and preventing prolapseSlide freelyAnnuloplasty ringsPosterior leafletSystole
Methods and apparatus for mitral valve repair are disclosed herein where the posterior mitral leaflet is supported or buttressed in a frozen or immobile position to facilitate the proper coaptation of the leaflets. An implantable apparatus may be advanced and positioned intravascularly beneath the posterior leaflet of the mitral valve. The apparatus may include one or more individual balloon members, each of which may be optionally configured with supporting integrated structures. A magnet chain catheter may be positioned within the coronary sinus and adjacent to the mitral valve to magnetically secure the apparatus in position beneath the posterior mitral leaflet. Alternatively, a split-ring device may be placed about the chordae tendineae supporting the mitral valve such that the ring slides along the chordae tendineae alternately against the mitral leaflet and towards the papillary muscles during systole and diastole.
Owner:BUCH WALLY +1
Cardiac disease treatment and device
InactiveUS6123662APermit contractionVolume adjustableHeart valvesPharmaceutical active ingredientsSystoleHeart disease
A jacket of biological compatible material has an internal volume dimensioned for an apex of the heart to be inserted into the volume and for the jacket to be slipped over the heart. The jacket has a longitudinal dimension between upper and lower ends sufficient for the jacket to surround a lower portion of the heart with the jacket surrounding a valvular annulus of the heart and further surrounding the lower portion to cover at least the ventricular lower extremities of the heart. The jacket is adapted to be secured to the heart with the jacket surrounding at least the valvular annulus and the ventricular lower extremities. The jacket is adjustable on the heart to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and assume a maximum adjusted volume for the jacket to constrain circumferential expansion of the heart beyond the maximum adjusted volume during diastole and to permit unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole.
Owner:MARDIL
Cerebral perfusion augmentation
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Cardiac disease treatment and device
A device for treating cardiac disease of a heart having an upper portion and a lower portion divided by an A–V groove, the device including a jacket adapted to be secured to the heart, and a delivery source for the delivery of one or more therapeutic agents to the surface of the heart. The jacket is fabricated from a flexible material defining a volume between an upper and a lower end, the jacket being adapted to be adjusted on the heart to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and assume a maximum adjusted volume for the jacket to constrain expansion of the heart beyond the maximum adjusted volume during diastole and permit substantially unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole. As a result of the flexible material, the jacket allows unimpeded diastolic filling of the heart. Also described is a method for treating cardiac disease including surgically accessing the heart, applying the treatment device of the invention, securing the treatment device to the heart, and surgically closing access to the heart while leaving the treatment device on the heart.
Owner:MARDIL
Heart support to prevent ventricular remodeling
InactiveUS6887192B1Reducing end-diastolic diameterRelieve stressHeart valvesControl devicesSystoleCardiac functioning
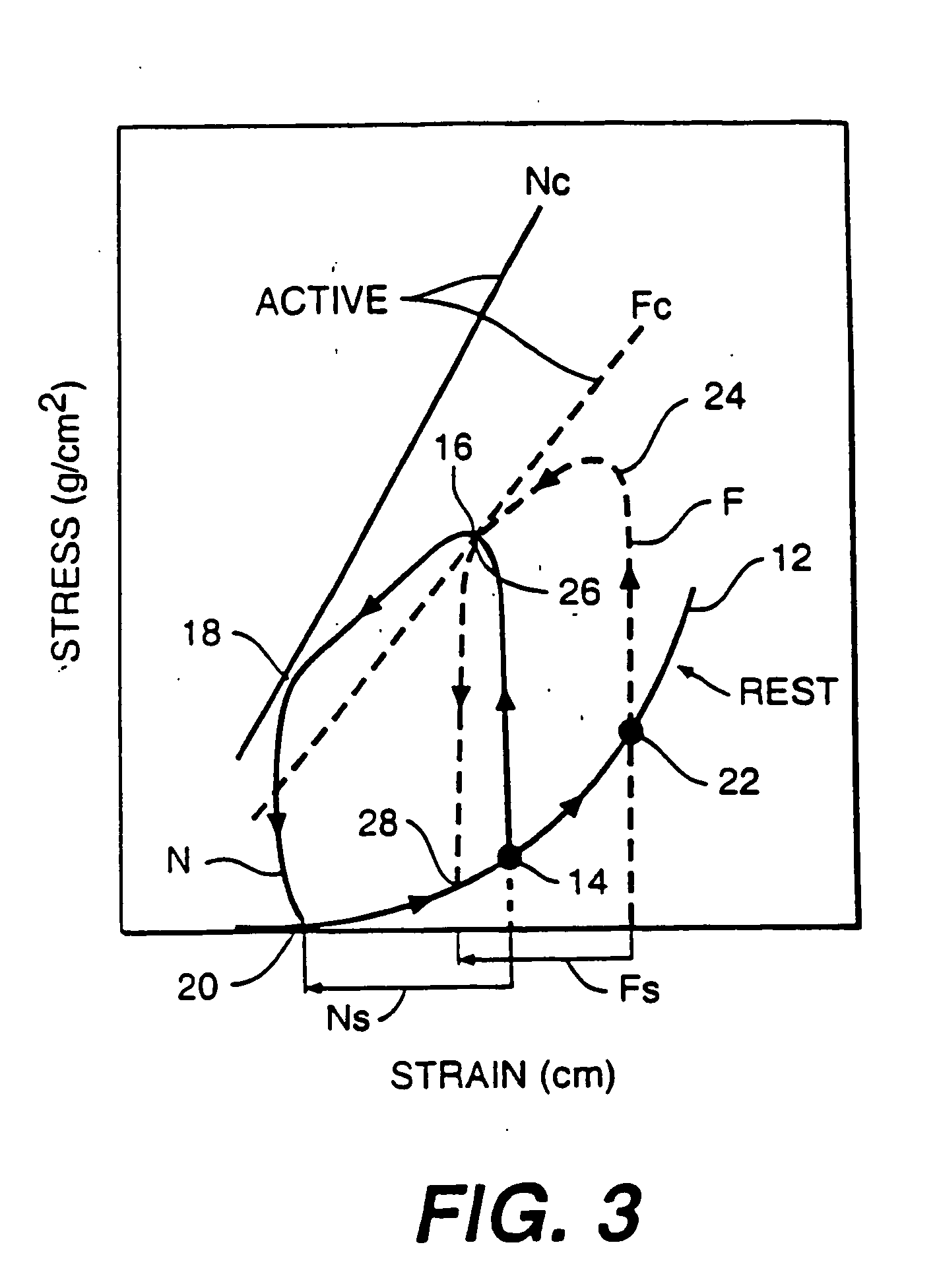
This is a support device that prevents, reduces, and delays remodeling of diseased cardiac tissue, and also decreases the impact of such remodeling on collateral tissue is disclosed. The invention further reinforces abnormal tissue regions to prevent over-expansion of the tissue due to increased afterload and excessive wall tension. As a result, the support device prevents phenomenon such as systolic stretch from occurring and propagating. The support structure maintains and restores diastolic compliance, wall motion, and ejection fraction to preserve heart functionality. As such, the support device prevents and treats cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure.
Owner:CONVERGE MEDICAL
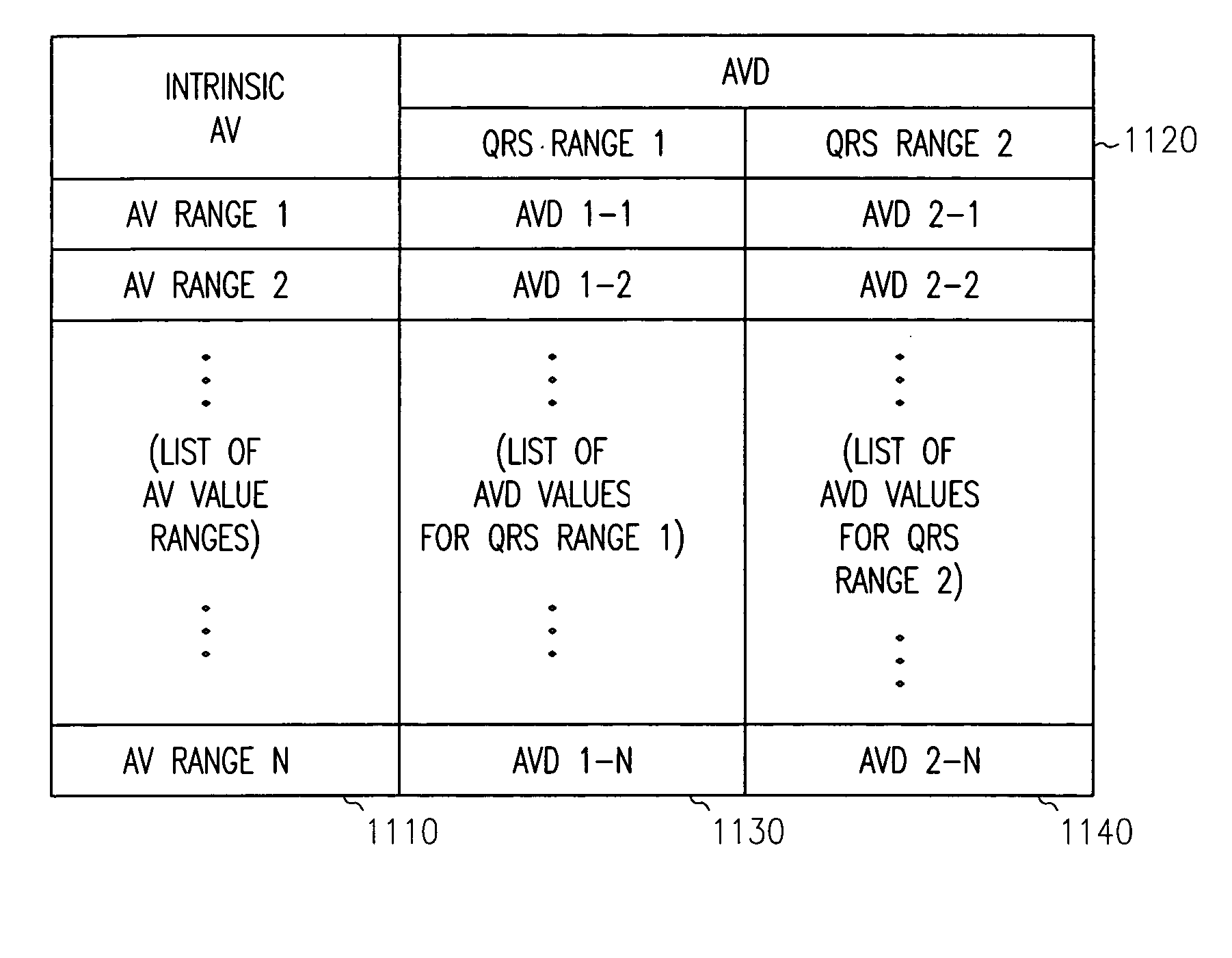
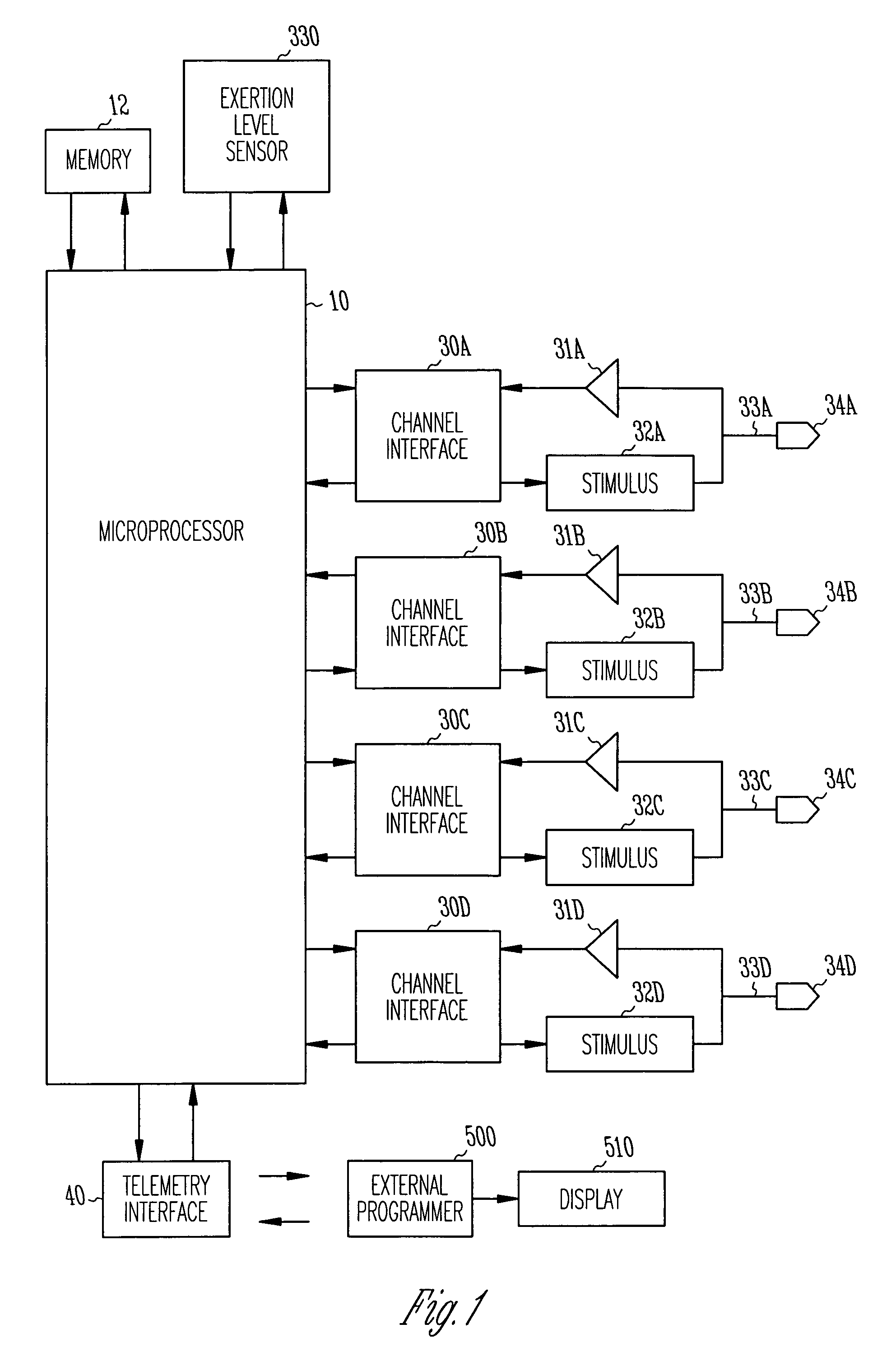
Method and apparatus for adjustable AVD programming using a table
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Defibrillating cardiac constraint
A device for treating cardiac disease of a heart includes a jacket of flexible material defining a volume between an open upper end and a lower end. The jacket is dimensioned for an apex of the heart to be inserted into the volume through the open upper end and for the jacket to be slipped over the heart. The jacket is adapted to be secured to the heart with the jacket having portions disposed on opposite sides of the heart. The jacket is adjustable to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and to constrain circumferential expansion of the heart during diastole and permit substantially unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole. A first and a second grid of electrodes are carried on the jacket. The grids are disposed to be in overlying relation to individual ones of the opposite sides of the heart when the jacket is secured to the heart. The first and second grids are connectable to a source of a defibrillating waveform.
Owner:MARDIL
Devices and methods for non-invasively improving blood circulation
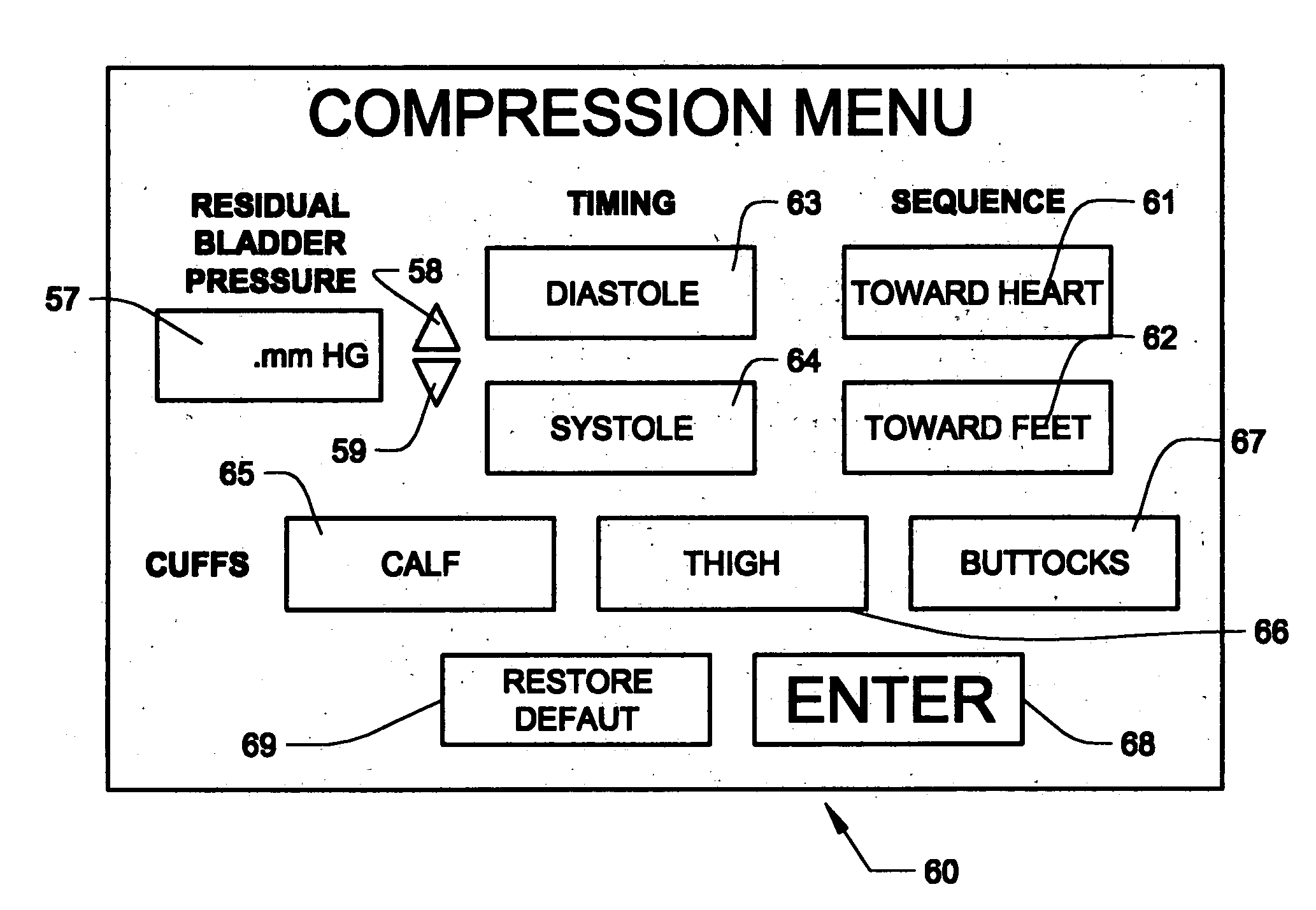
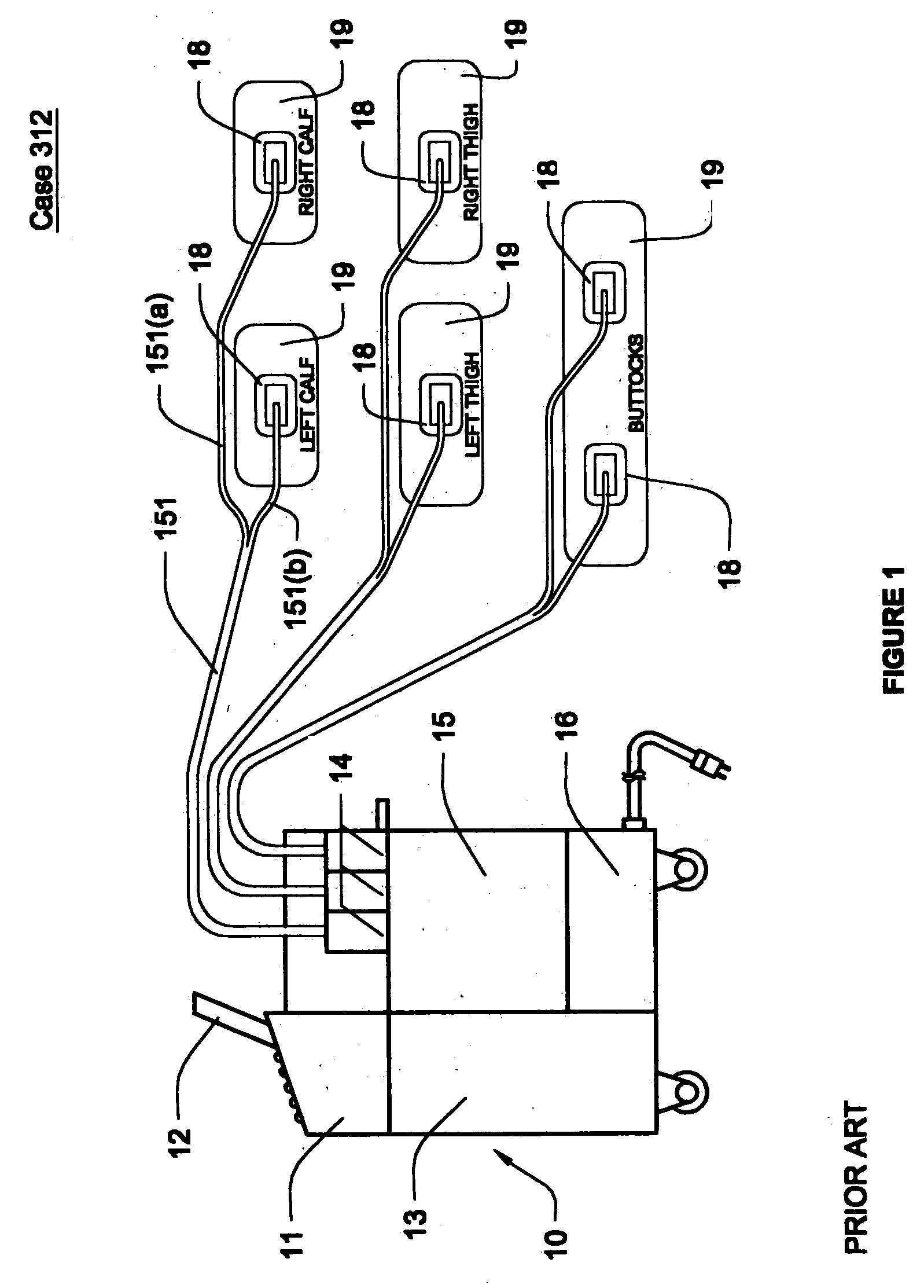
Circulatory assistance is provided in a non-invasive procedure safely and effectively using a microprocessor of an external counter pulsation device programmed to control the actuation of any or all of a plurality of valves, each of which is mounted on and in fluid communication with one of a plurality of individual inflatable bladders disposed in pockets within cuffs encasing the calves, thighs, buttocks, abdomen and / or chest of a person and an optional valve in fluid communication with the person's airway, in any desired sequence or order, toward the heart or toward the feet, either during diastole or systole, at desired inception times during the cardiac cycle, for selected durations and at chosen pressures, for treating a variety of cardiac, non-cardiac and circulatory conditions.
Owner:CARDIOMEDICS +1
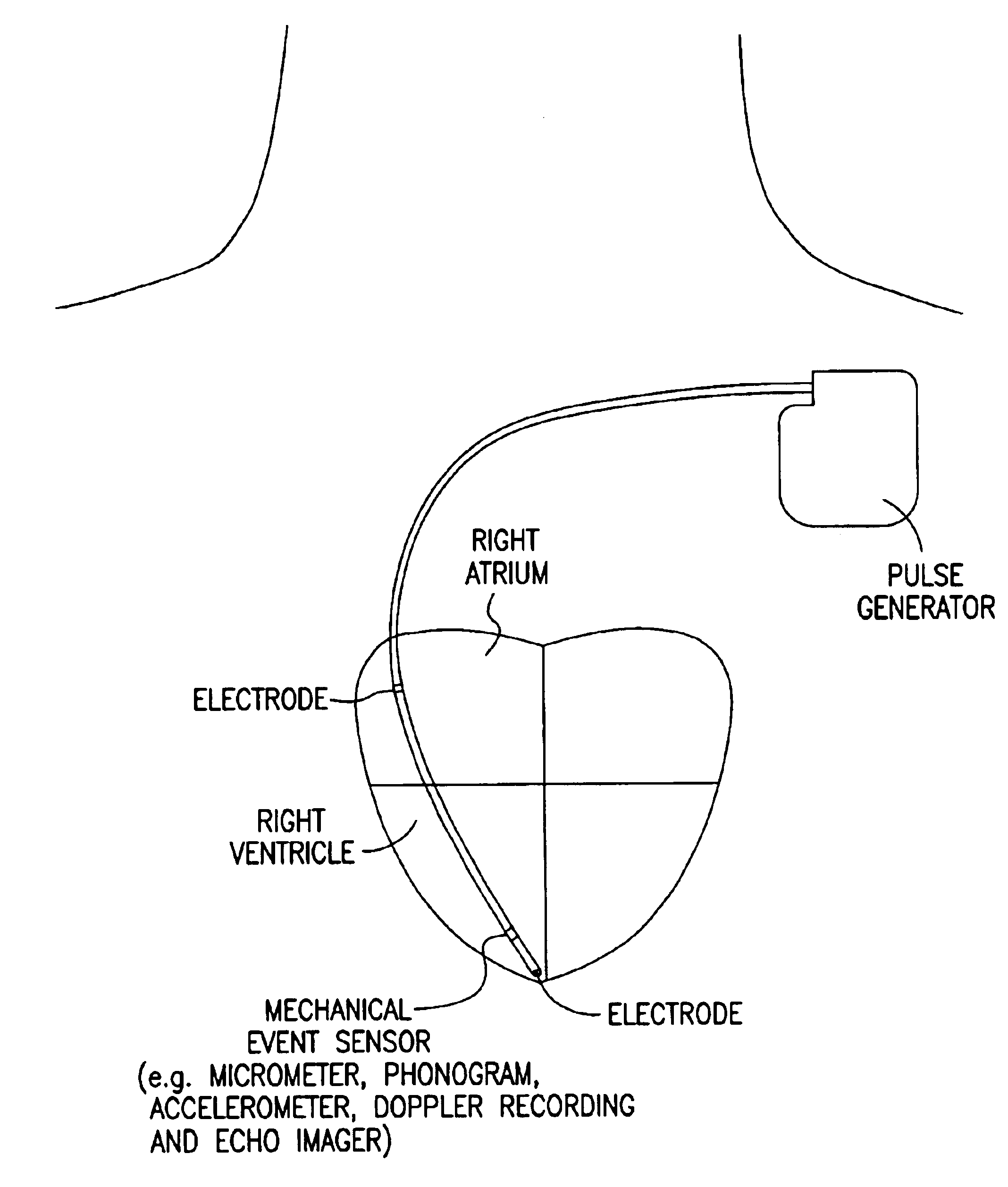
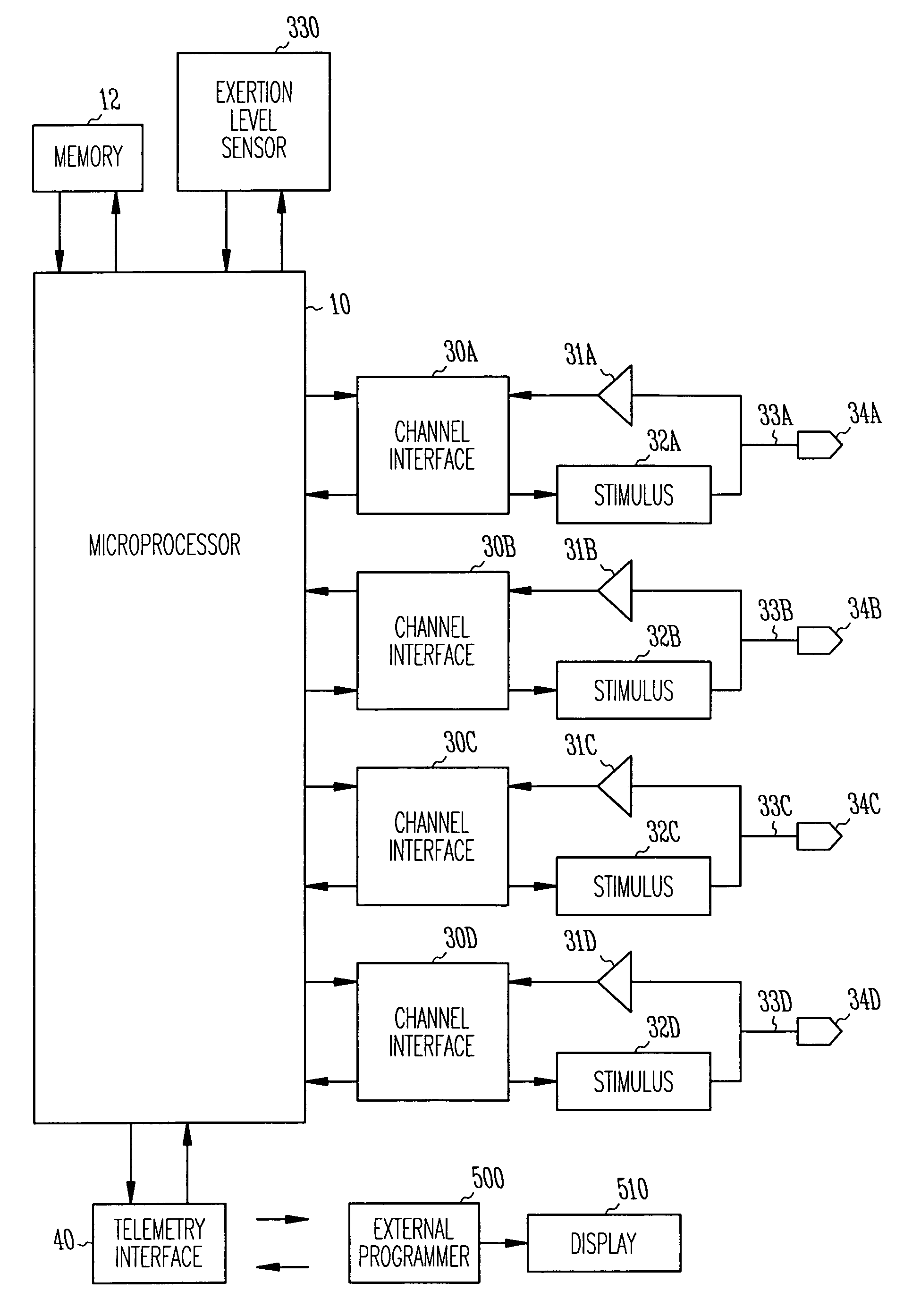
Cardiac pacing using adjustable atrio-ventricular delays
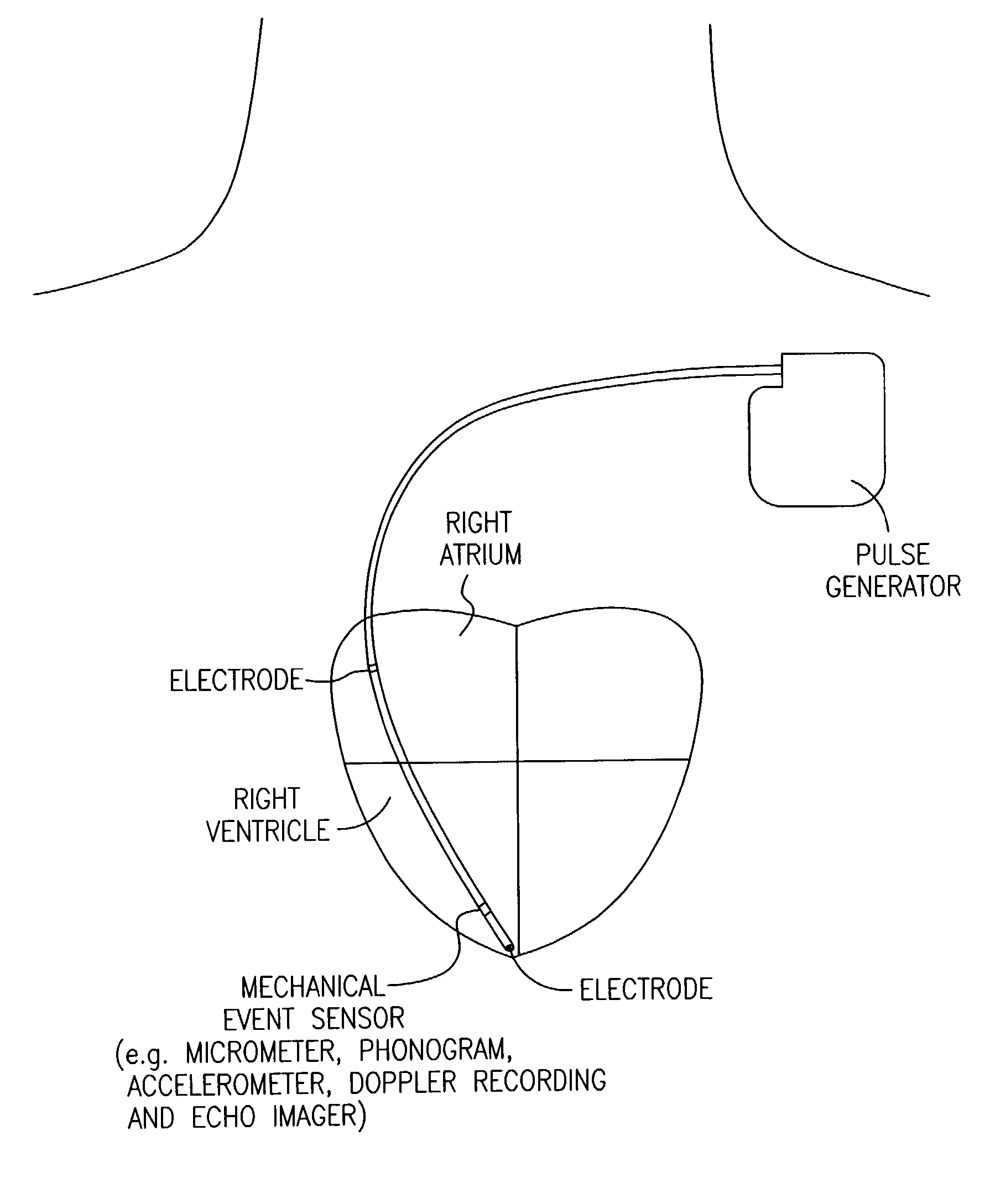
A pacing system for providing optimal hemodynamic cardiac function for parameters such as contractility (peak left ventricle pressure change during systole or LV+dp / dt), or stroke volume (aortic pulse pressure) using system for calculating atrio-ventricular delays for optimal timing of a ventricular pacing pulse. The system providing an option for near optimal pacing of multiple hemodynamic parameters. The system deriving the proper timing using electrical or mechanical events having a predictable relationship with an optimal ventricular pacing timing signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Cardiac harness for treating heart disease
InactiveUS7158839B2Limit cardiac functionFunction increaseEpicardial electrodesHeart valvesSystoleLead system
A system for treating the heart includes a cardiac harness associated with a cardiac rhythm management devise which does not have a lead system. The cardiac harness applies a compressive force on the heart during diastole and systole, and the cardiac rhythm management devise will deliver an electrical shock to the heart for defibrillation and / or can be used for pacing / sensing. The cardiac harness and cardiac rhythm management devise are both delivered and implanted by minimally invasive access.
Owner:PARACOR MEDICAL INC
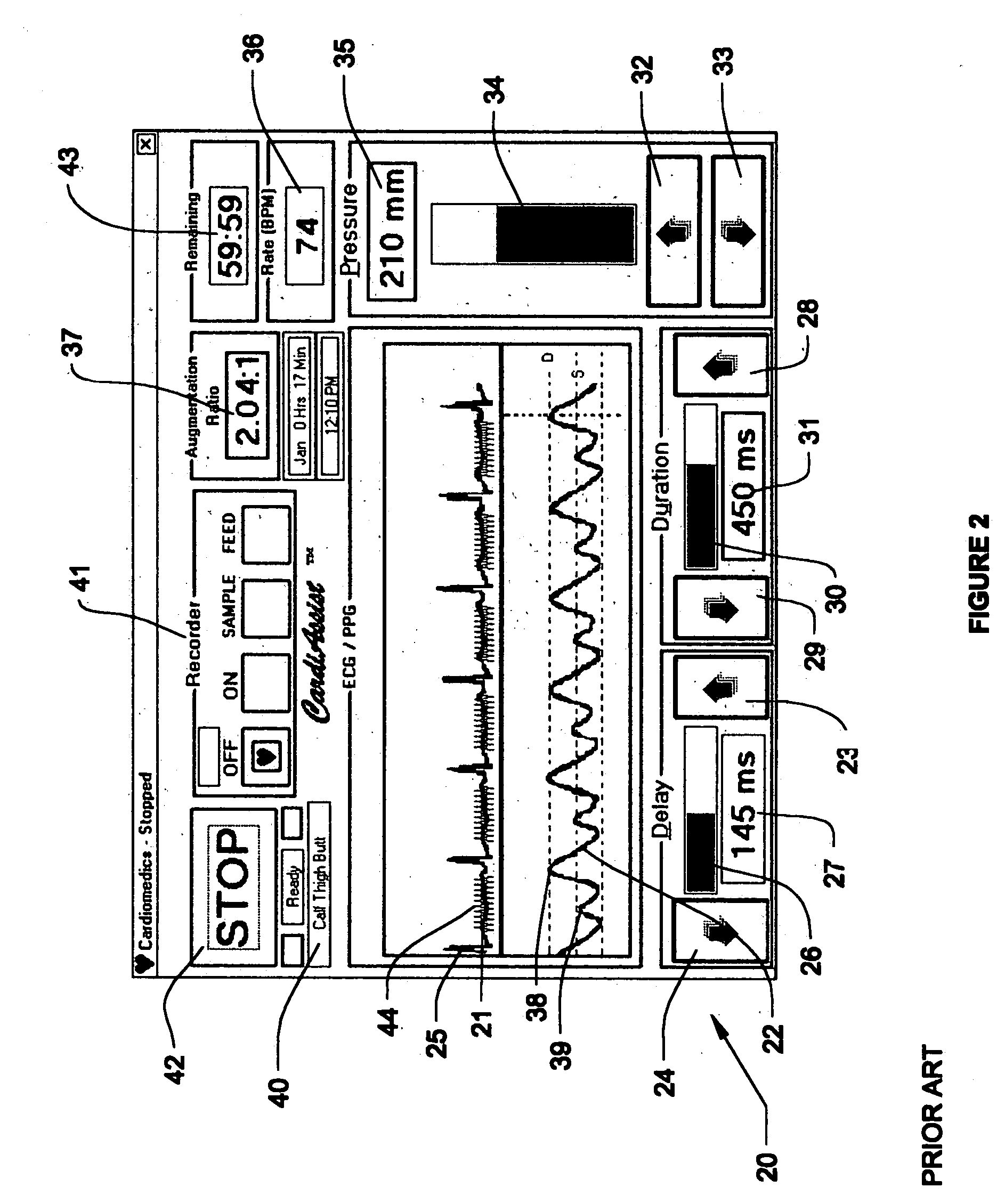
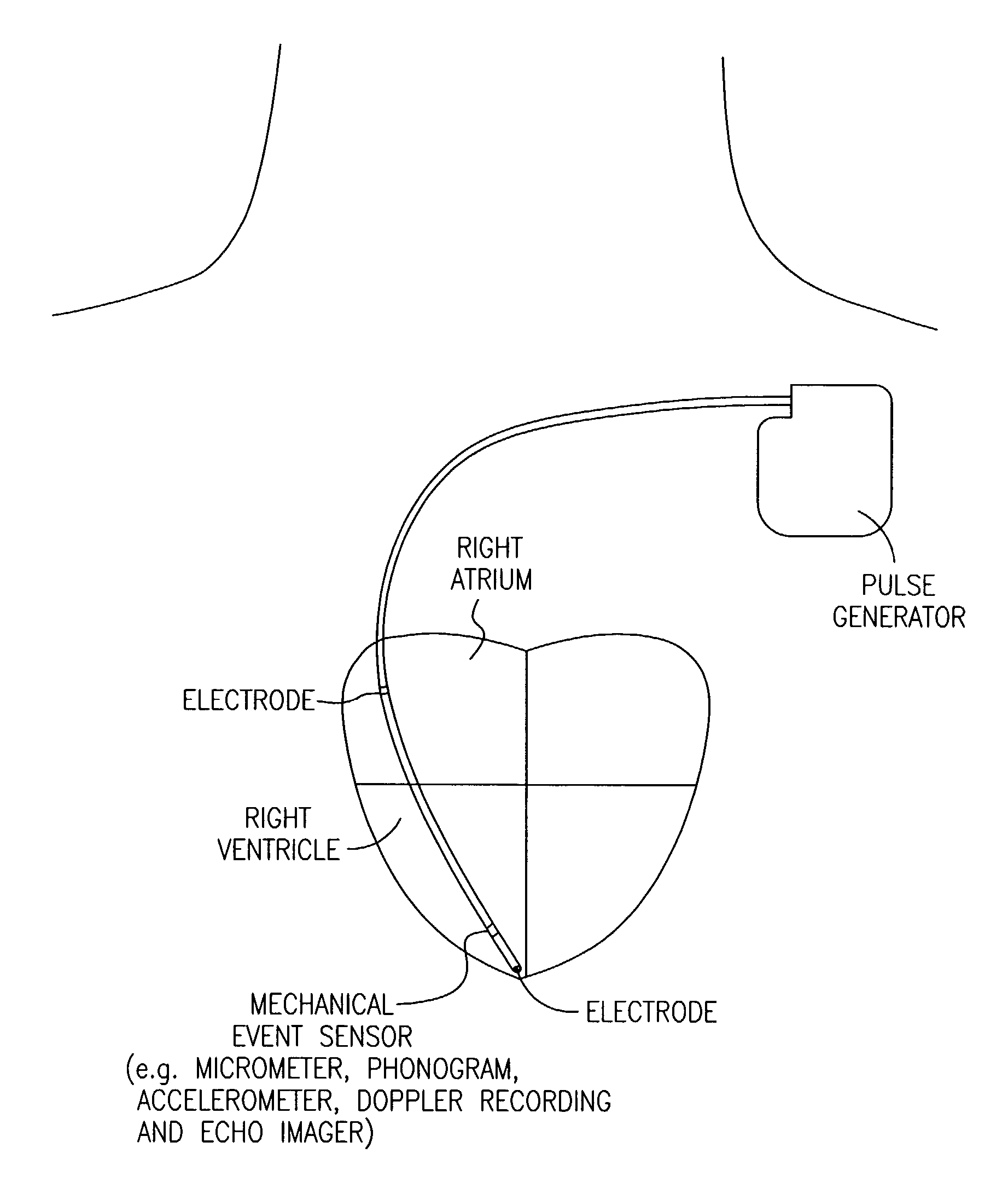
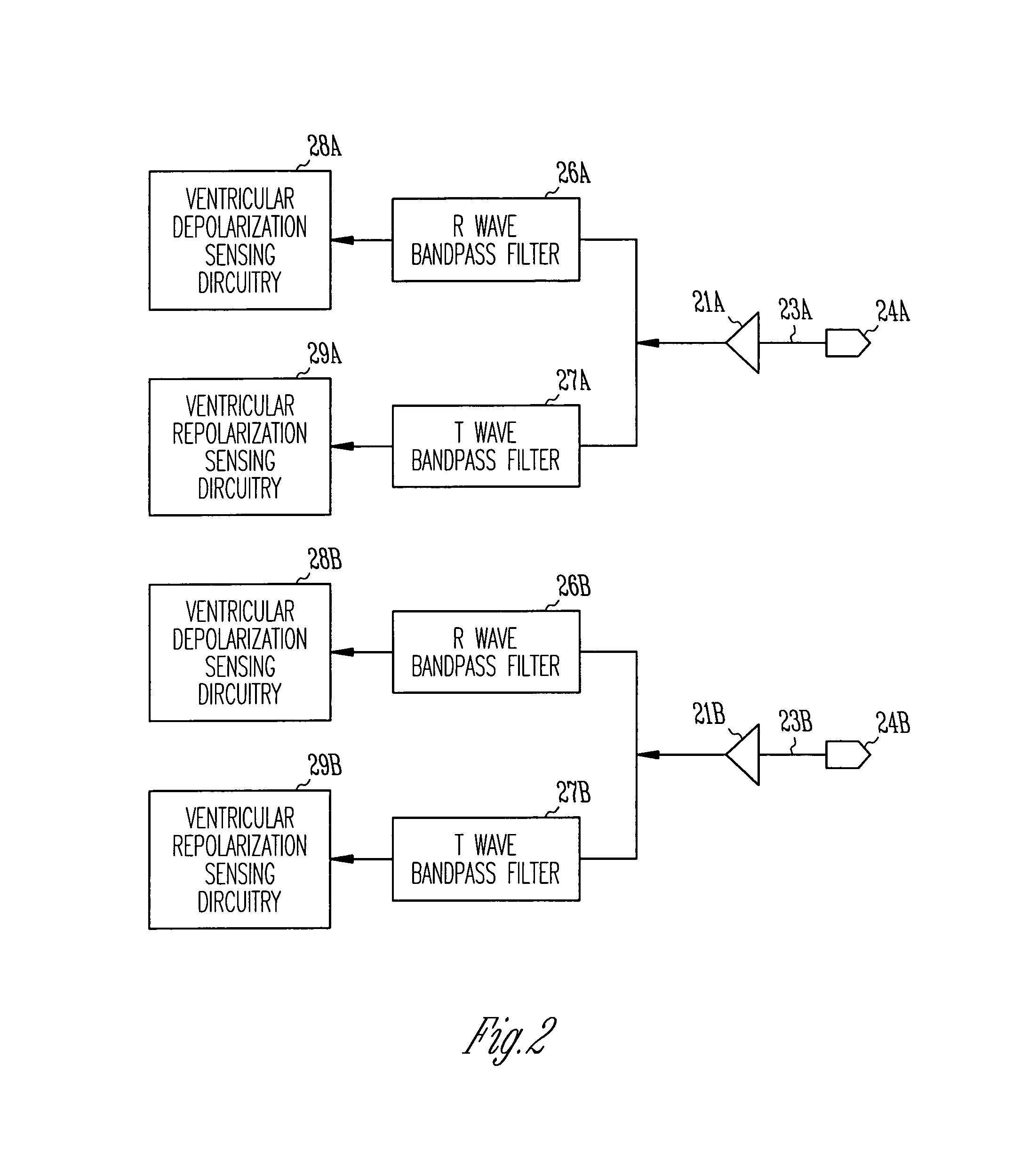
Method and apparatus for noninvasive determination of cardiac performance parameters
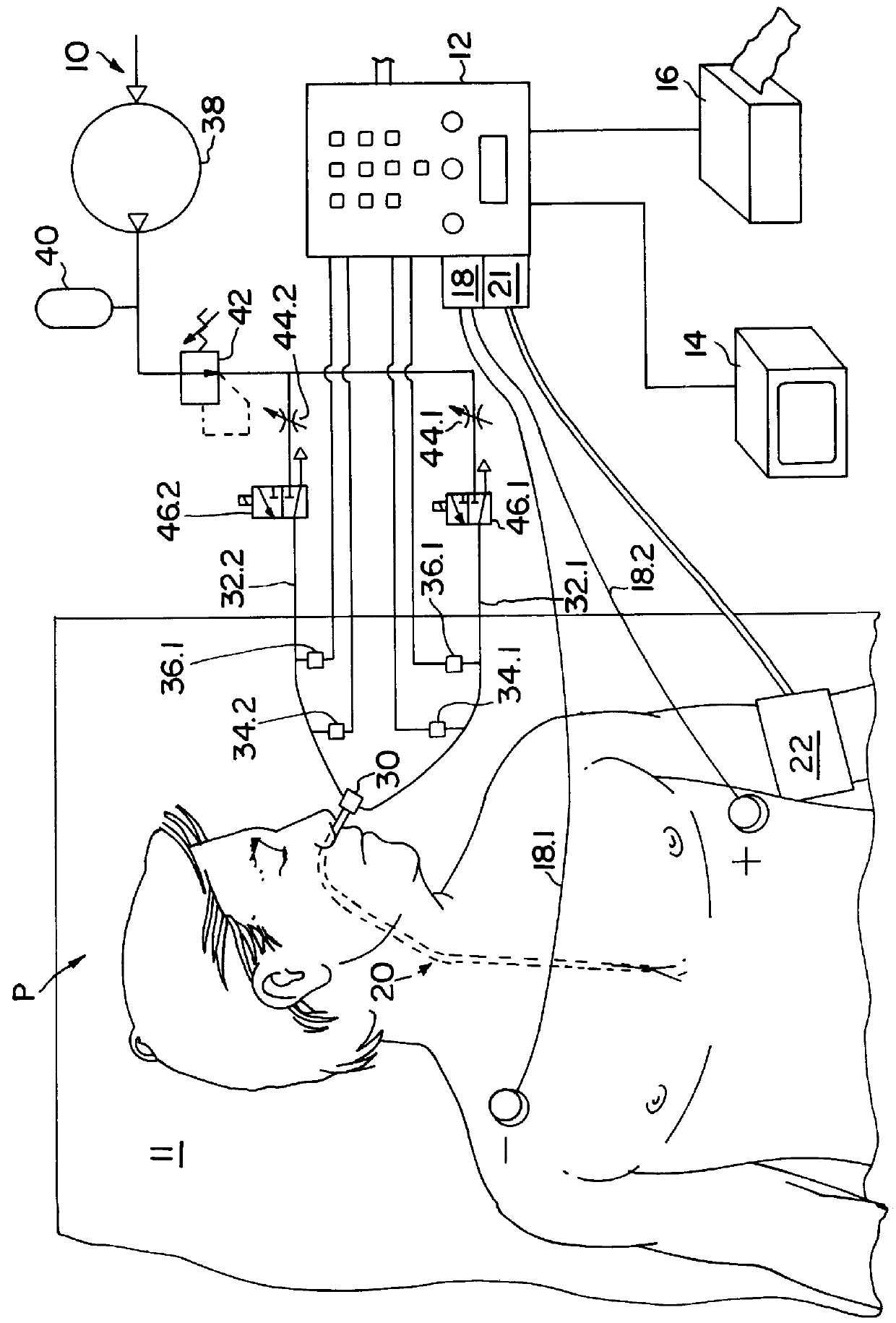
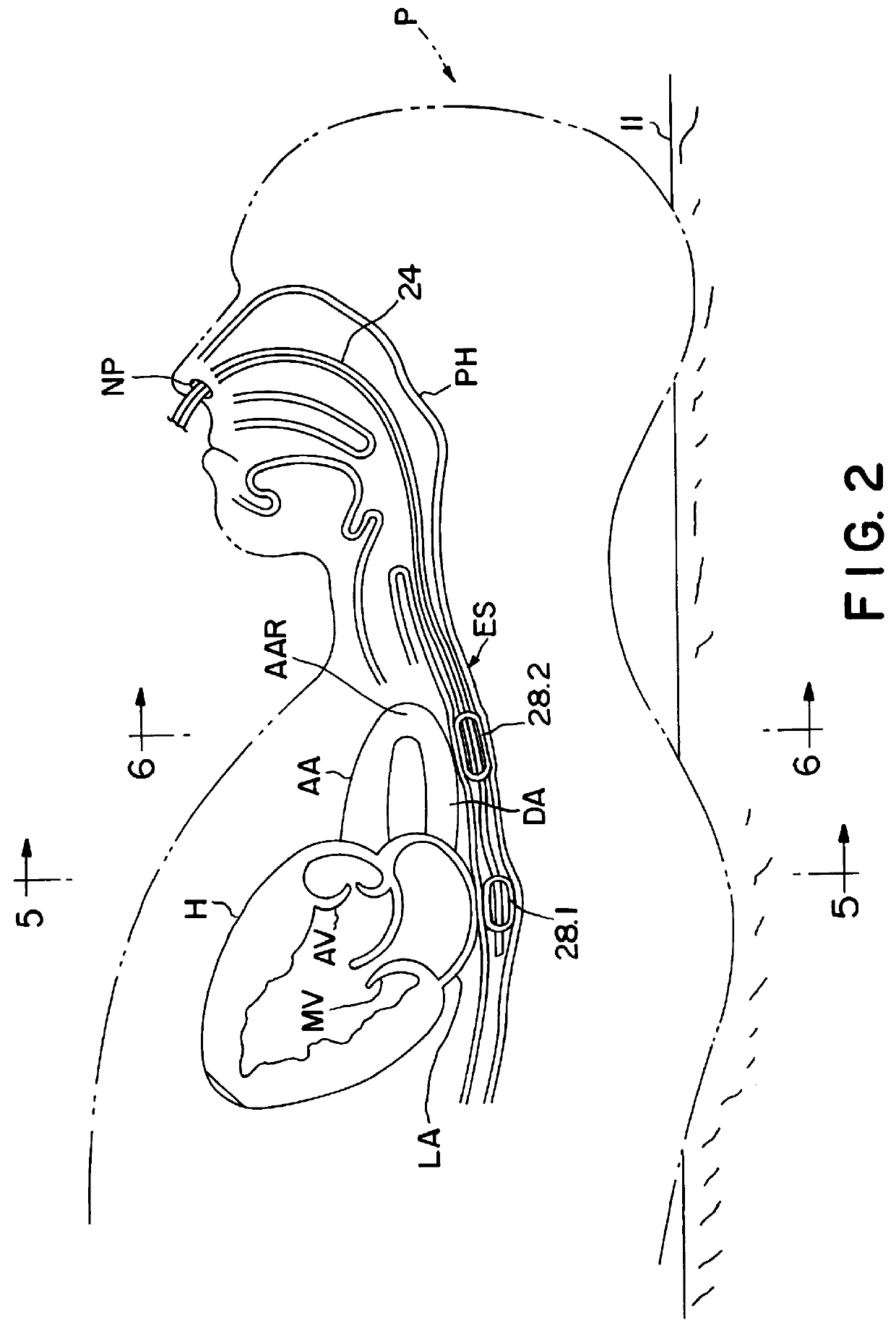
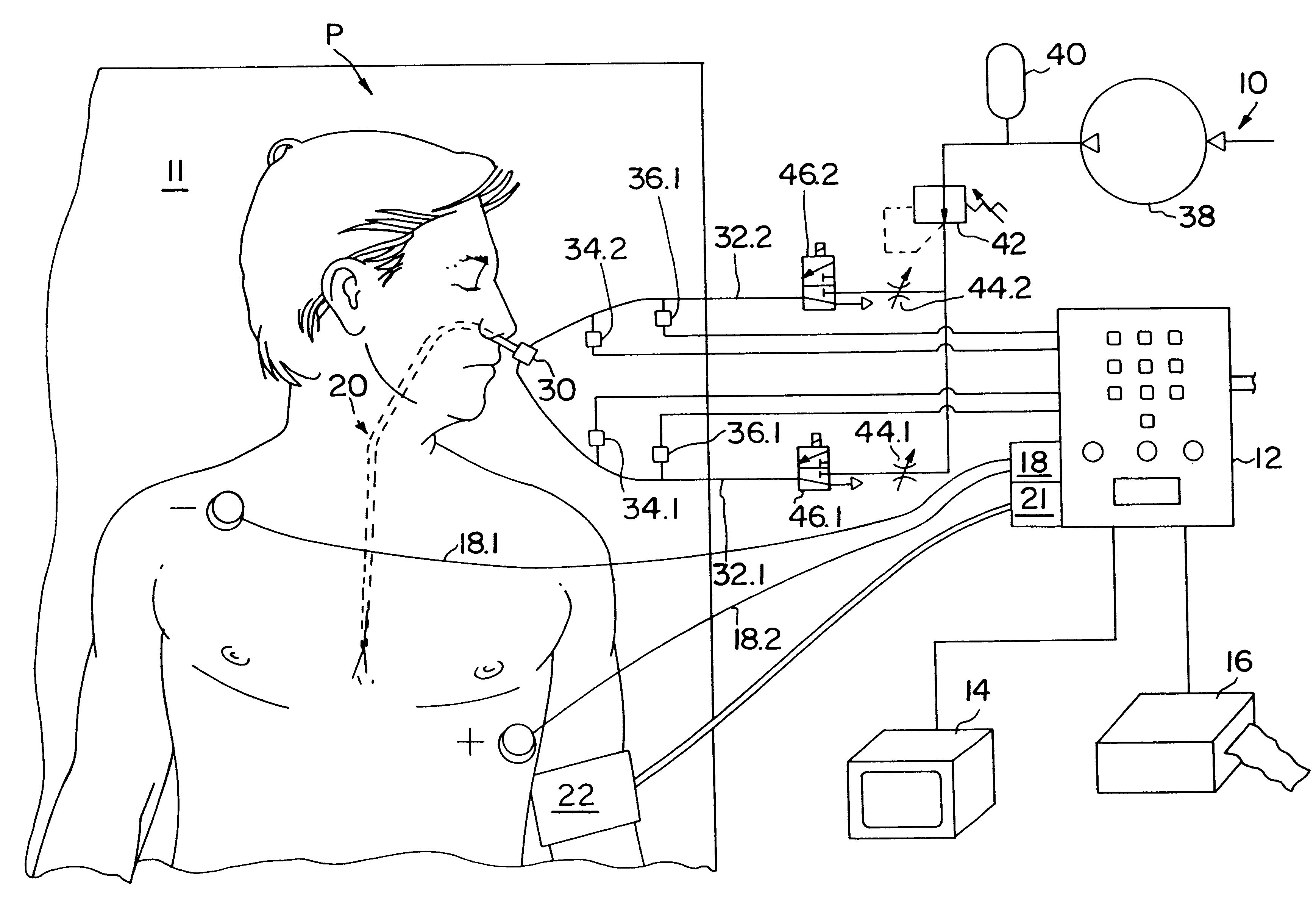
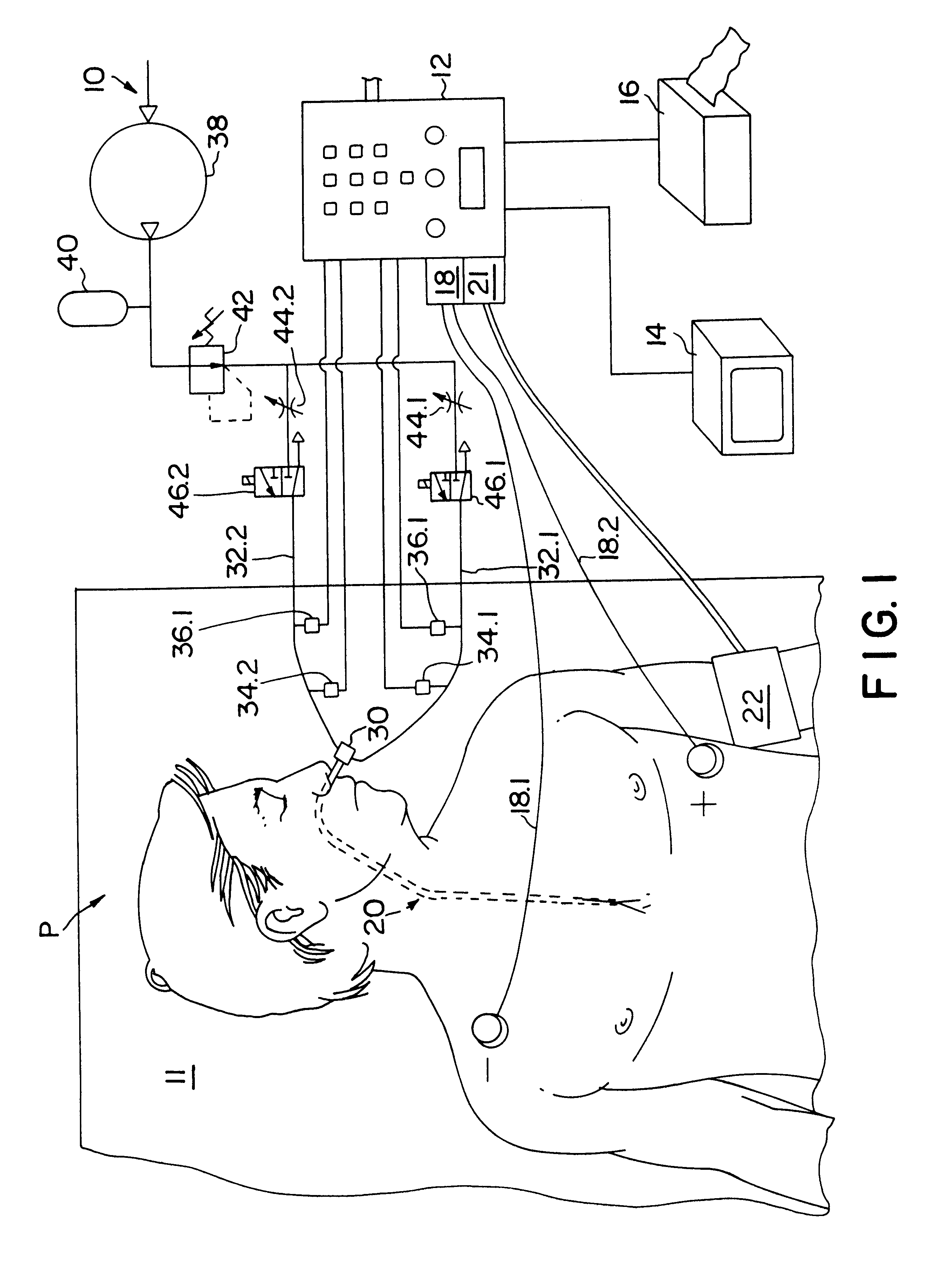
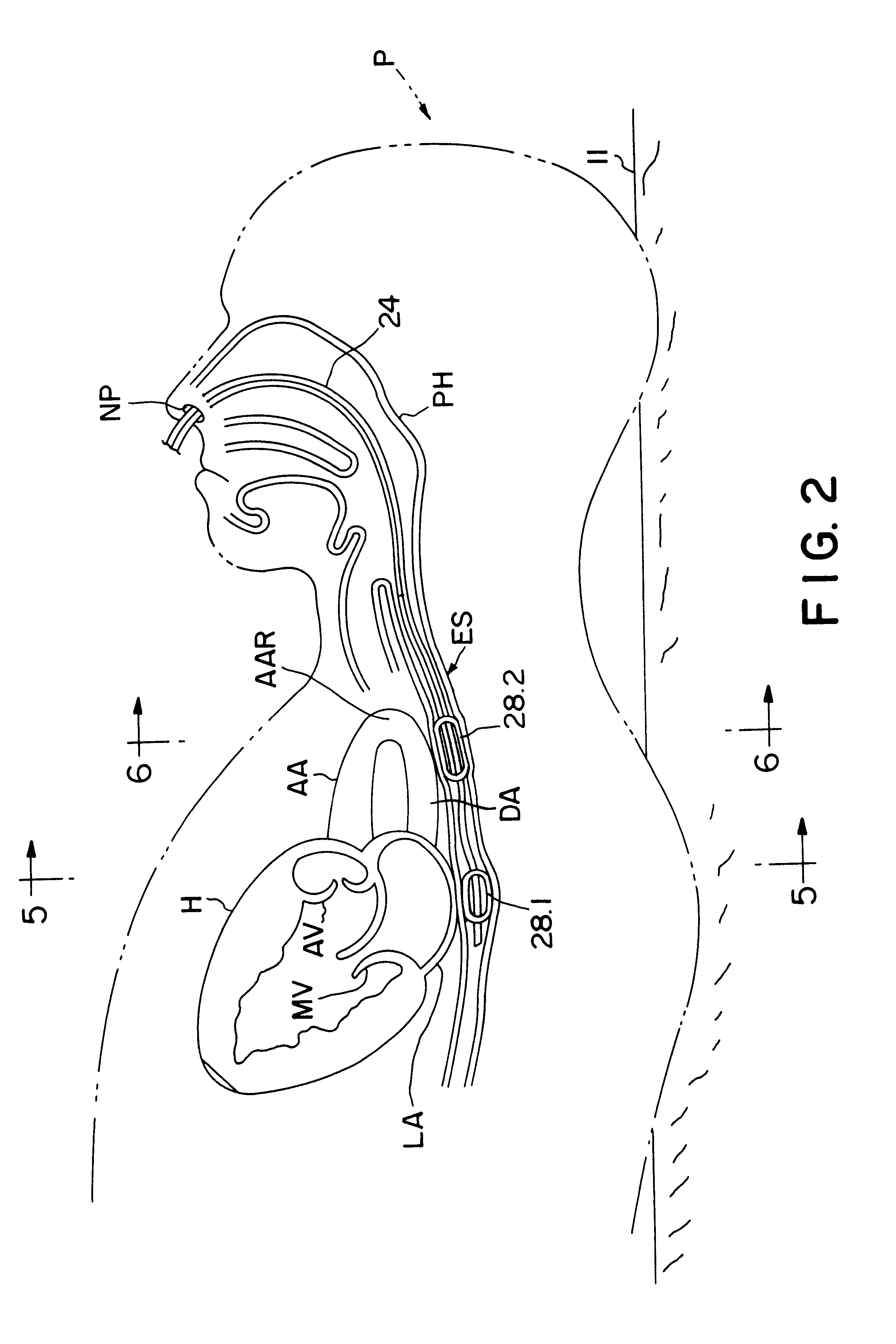
InactiveUS6120442AInexpensive and reliableEasy to usePerson identificationCatheterSystoleLeft atrial pressure
Apparatus and method for noninvasively determining cardiac performance parameters including 1) lengths of systolic time intervals, (2) contractility index, (3) pulse amplitude ratios while performing the Valsalva maneuver, (4) cardiac output index, and (5) a pulse wave velocity index. A catheter having at least one balloon is inserted into the esophagus and pressurized and positioned adjacent the aortic arch to sense aortic pressure. The effects of aortic pressure on the balloon are utilized to determine at least one of the cardiac performance parameters. The catheter may include a second balloon which is spaced from the aortic balloon a distance such that when the second balloon is in a position adjacent the left atrium to sense left atrial pressure the aortic balloon is in a position adjacent the aortic arch to sense aortic pressure, this distance being related to the distance between the left atrium and aortic arch in most adult persons.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and apparatus for optimizing stroke volume during DDD resynchronization therapy using adjustable atrio-ventricular delays
InactiveUS7158830B2Convenient timeMaximizes ventricular performanceHeart stimulatorsSystoleHemodynamics
A pacing system for providing optimal hemodynamic cardiac function for parameters such as ventricular synchorny or contractility (peak left ventricle pressure change during systole or LV+dp / dt), or stroke volume (aortic pulse pressure) using system for calculating atrio-ventricular delays for optimal timing of a ventricular pacing pulse. The system providing an option for near optimal pacing of multiple hemodynamic parameters. The system deriving the proper timing using electrical or mechanical events having a predictable relationship with an optimal ventricular pacing timing signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods and apparatus for reducing localized circulatory system pressure
InactiveUS8091556B2Preventing further deteriorationIncrease pressureDiagnosticsHeart valvesSystoleLeft ventricular size
Methods and apparatus for decreasing cardiac pressure in a patient by implanting a shunt communicating with an area outside a first portion, whereby a volume of blood sufficient to reduce pressure in a first portion is released. Preferably, the end diastolic pressure in the left ventricle is reduced, which is accomplished by having the shunt communicate with the left ventricle so a small volume of blood is released from the left ventricle. Most preferably, the shunt selectively permits flow when a pressure differential between the left ventricle and another chamber of a heart above a threshold pressure, so that shunting is prevented during left ventricular systole, or, alternatively, selectively permits flow when a pressure differential between the left ventricle and another chamber of a heart is between a lower threshold and a higher threshold. In certain embodiments a semi-passive check-valve is controlled and actuated by an external signal.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
Stress reduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050143620A1Relieve pressureRelieve muscle stressSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac cycleStress reduction
The device and method for reducing heart wall stress. The device can be one which reduces wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle or only a portion of the cardiac cycle. The device can be configured to begin to engage, to reduce wall stress during diastolic filling, or begin to engage to reduce wall stress during systolic contraction. Furthermore, the device can be configured to include at least two elements, one of which engages full cycle and the other which engages only during a portion of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Method and apparatus for creation of drug delivery and/or stimulation pockets in myocardium
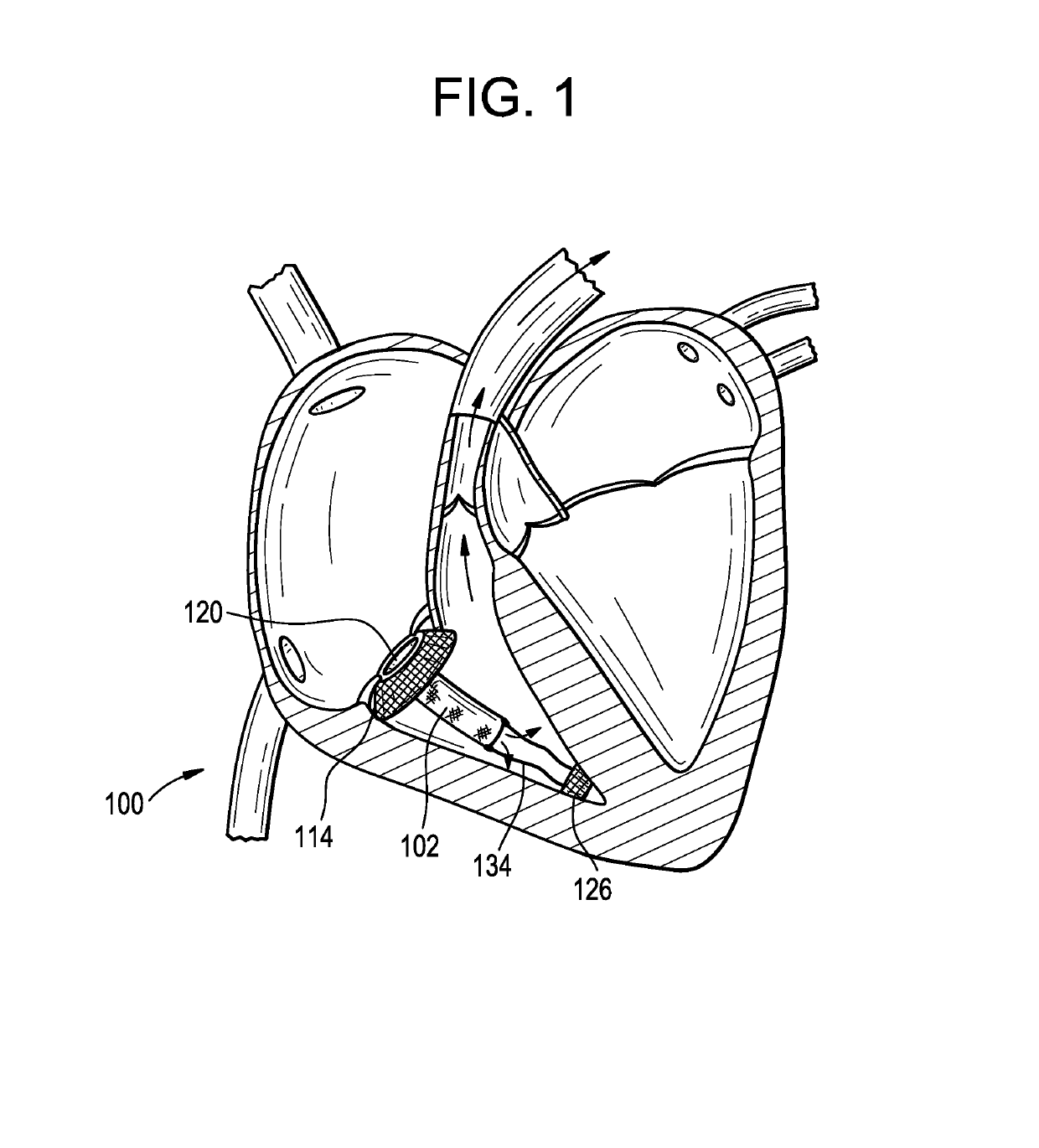
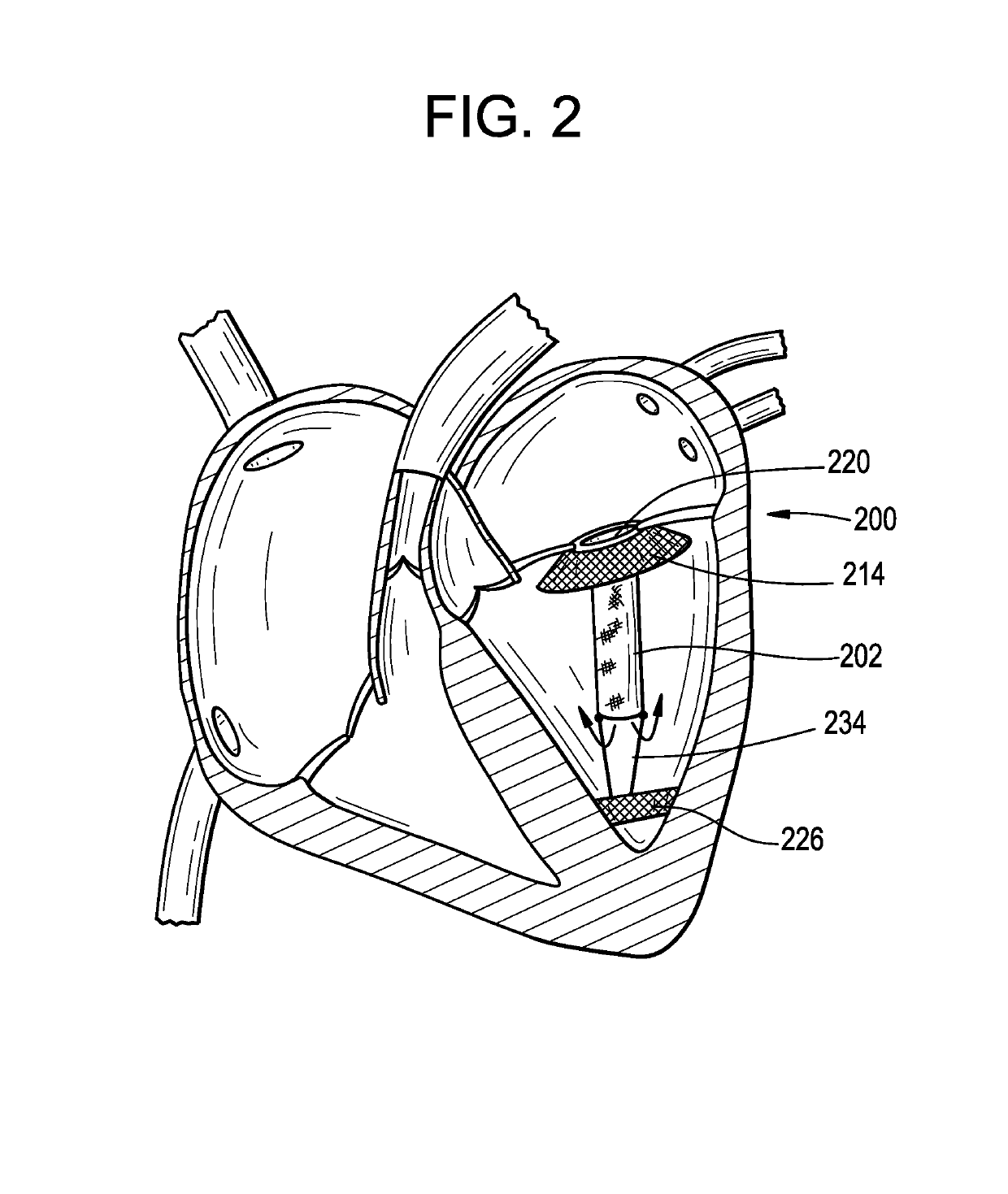
An apparatus and method for creating drug-filled pockets within muscle tissue, such as myocardium of the heart for increasing angiogenesis. More particularly, the apparatus has an excising assembly with a dilator tip for penetrating and advancing through the surface and body of a muscle or organ, such as the heart. Preferably, the dilator tip has a low level laser optical fiber emission to ease the passage of the excising assembly and provide thermal damage which also stimulates angiogenesis. More preferably, the dilator tip also disperses a pharmacologically active substance as the apparatus is passed through the tissue and / or creates pockets. The excising assembly is connected to a hand-held control device from which the operator pushes a switch to activate a punching mechanism within the excising assembly. The punching mechanism cuts a discrete piece of muscle tissue and traps it within the excising assembly leaving a pocket in the remaining muscle tissue. The excising assembly may also optionally release a bolus of the pharmacologically active substance into the pocket so created. Most preferably, there is a timing mechanism to measure the contraction of the heart, and the timing mechanism is synchronized with the operator's switch on the hand-held device to ensure that the punching occurs at maximum contraction of systole. A measurement guide determines how much excised tissue is trapped in the reservoir of the excising assembly. At a threshold level of filling, the surgeon will remove the excising assembly from the hand-held control device and open the punching mechanism for release of tissue. More preferably, the threshold level of filling will automatically turn off the switch to the punching mechanism to indicate to the surgeon the need to empty the excising assembly of tissue.
Owner:ECLIPSE SURGICAL TECH
Cardiac disease treatment and device
A jacket of biological compatible material has an internal volume dimensioned for an apex of the heart to be inserted into the volume and for the jacket to be slipped over the heart. The jacket has a longitudinal dimension between upper and lower ends sufficient for the jacket to surround a lower portion of the heart with the jacket surrounding a valvular annulus of the heart and further surrounding the lower portion to cover at least the ventricular lower extremities of the heart. The jacket is adapted to be secured to the heart with the jacket surrounding at least the valvular annulus and the ventricular lower extremities. The jacket is adjustable on the heart to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and assume a maximum adjusted volume for the jacket to constrain circumferential expansion of the heart beyond the maximum adjusted volume during diastole and to permit unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole.
Owner:MARDIL
Cardiac disease treatment and device
A cardiac constraint device comprising a jacket of biological compatible material and an adjustment member. The jacket is adapted to be secured to the heart to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and assume a maximum adjusted volume to constrain circumferential expansion of the heart beyond the maximum adjusted volume during diastole and to permit unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole. The adjustment mechanism is configured to alter the internal volume defined by the jacket after the jacket is secured to the heart. The invention also provides a method for treating cardiac disease.
Owner:MARDIL
Method and apparatus for optimizing ventricular synchrony during DDD resynchronization therapy using adjustable atrio-ventricular delays
InactiveUS7110817B2Convenient timeMaximizes ventricular performanceTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsSystoleCardiac functioning
A pacing system for providing optimal hemodynamic cardiac function for parameters such as ventricular synchorny or contractility (peak left ventricle pressure change during systole or LV+dp / dt), or stroke volume (aortic pulse pressure) using system for calculating atrio-ventricular delays for optimal timing of a ventricular pacing pulse. The system providing an option for near optimal pacing of multiple hemodynamic parameters. The system deriving the proper timing using electrical or mechanical events having a predictable relationship with an optimal ventricular pacing timing signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
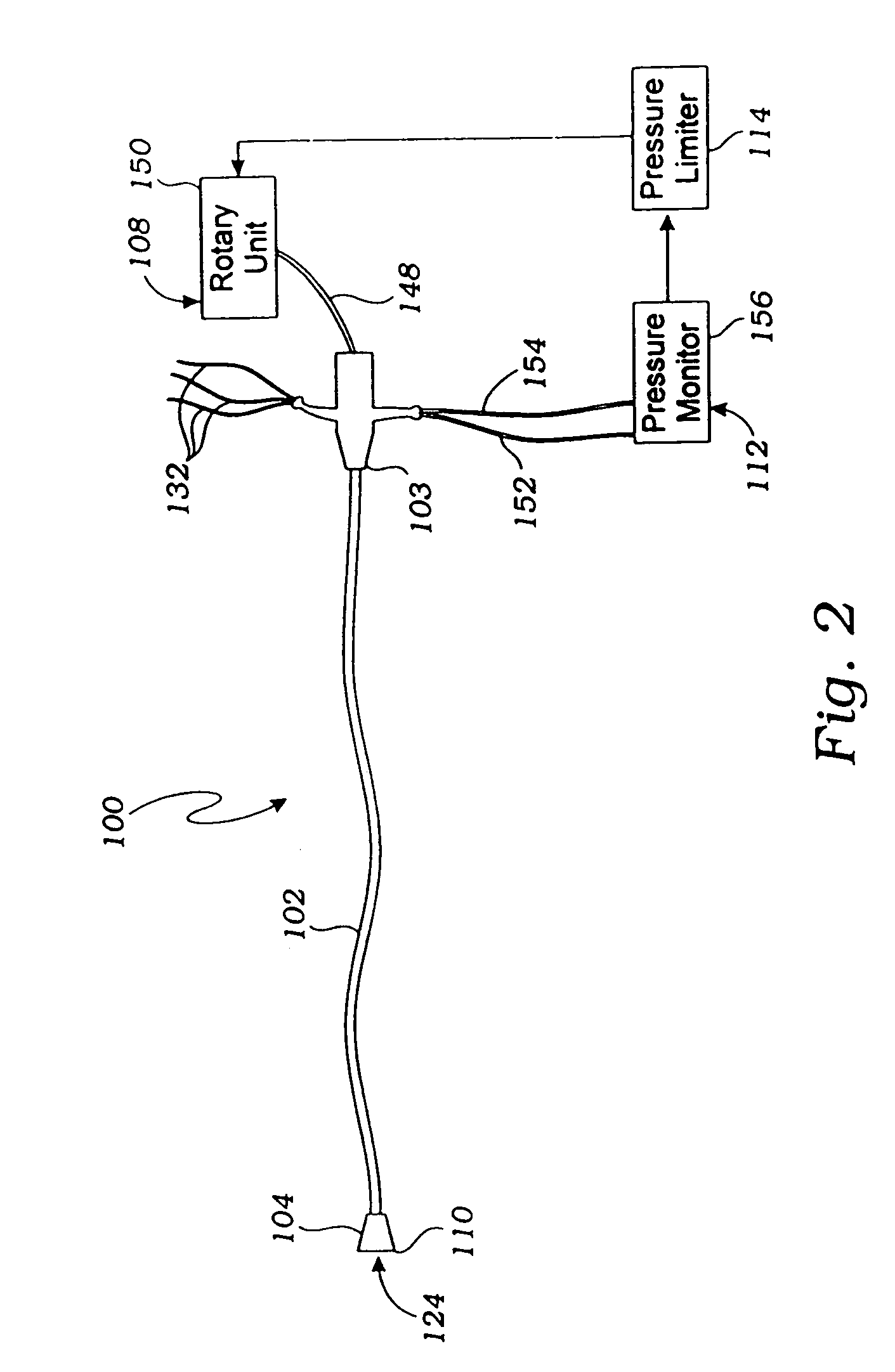
Pressure differential actuated prosthetic medical device
The invention relates to a medical prosthesis, and in particular a heart valve substitute comprising a pliant tubular conduit mounted on a resilient annular frame and tethered to a non-perforating anchor within the right or left ventricle of the heart, wherein the pliant tubular conduit is a reciprocating mechanical member that is compressed by pressurized working fluid within the ventricle during systole.
Owner:VDYNE INC
Assessment of vascular dilatation
A method and apparatus of assessment of relative changes in the cross sectional area of a limb artery. The method includes applying to the artery an external pressure, which causes the cross-sectional area of the artery to change between systole and diastole much more than if the pressure is not applied, determining, over one or more cardiac cycles, a baseline value for a parameter related to the cross-sectional area of the artery, while the pressure is applied, applying a stimulus to the artery, determining, over one or more cardiac cycles, a stimulus-affected value for the parameter related to the cross-sectional area of the artery, while the pressure is applied and while the artery is in a dilated state affected by the stimulus and evaluating the artery based on a comparison of the determined stimulus-affected and baseline values, the baseline value is determined while the artery is substantially not affected by the stimulus.
Owner:DAFNI EHUD
Method and apparatus for noninvasive determination of cardiac performance parameters
InactiveUS6238349B1Inexpensive and reliableEasy to usePerson identificationCatheterSystoleLeft atrial pressure
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and apparatus for assessing and treating myocardial wall stress
InactiveUS6965797B2Prevent and reverse myocardial remodelingHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringSystoleElectric stimulation therapy
An apparatus and method for assessing myocardial wall stress is disclosed. The method may be used in conjunction with electro-stimulatory therapy for preventing or reversing ventricular remodeling. In such therapy, one or more stimulatory pulses are delivered to the heart such that a stressed region of the myocardium is pre-excited relative to other regions, thereby subjecting the stressed region to a lessened preload and afterload during systole. The unloading of the stressed myocardium over time effects reversal of undesirable ventricular remodeling.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
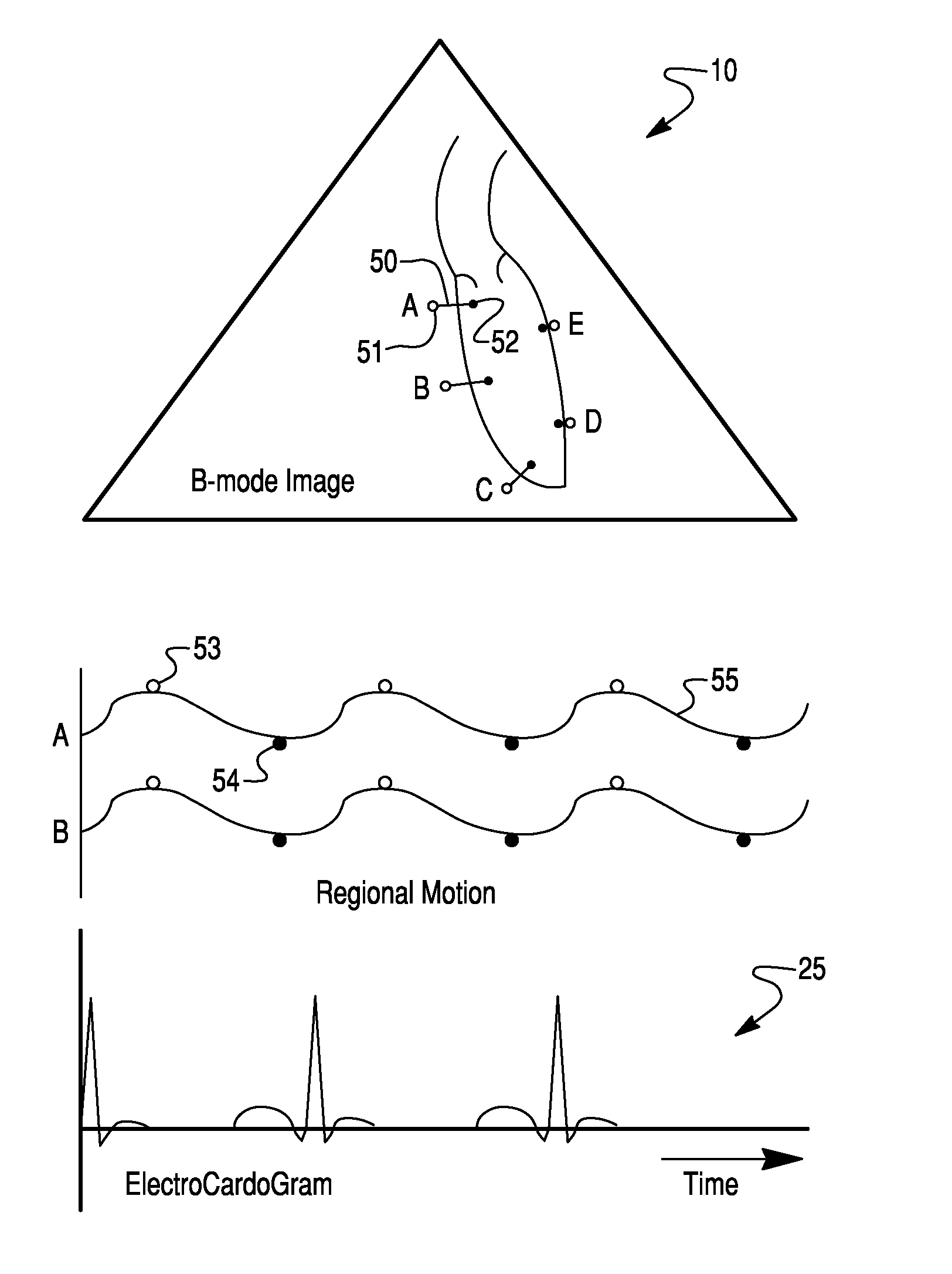
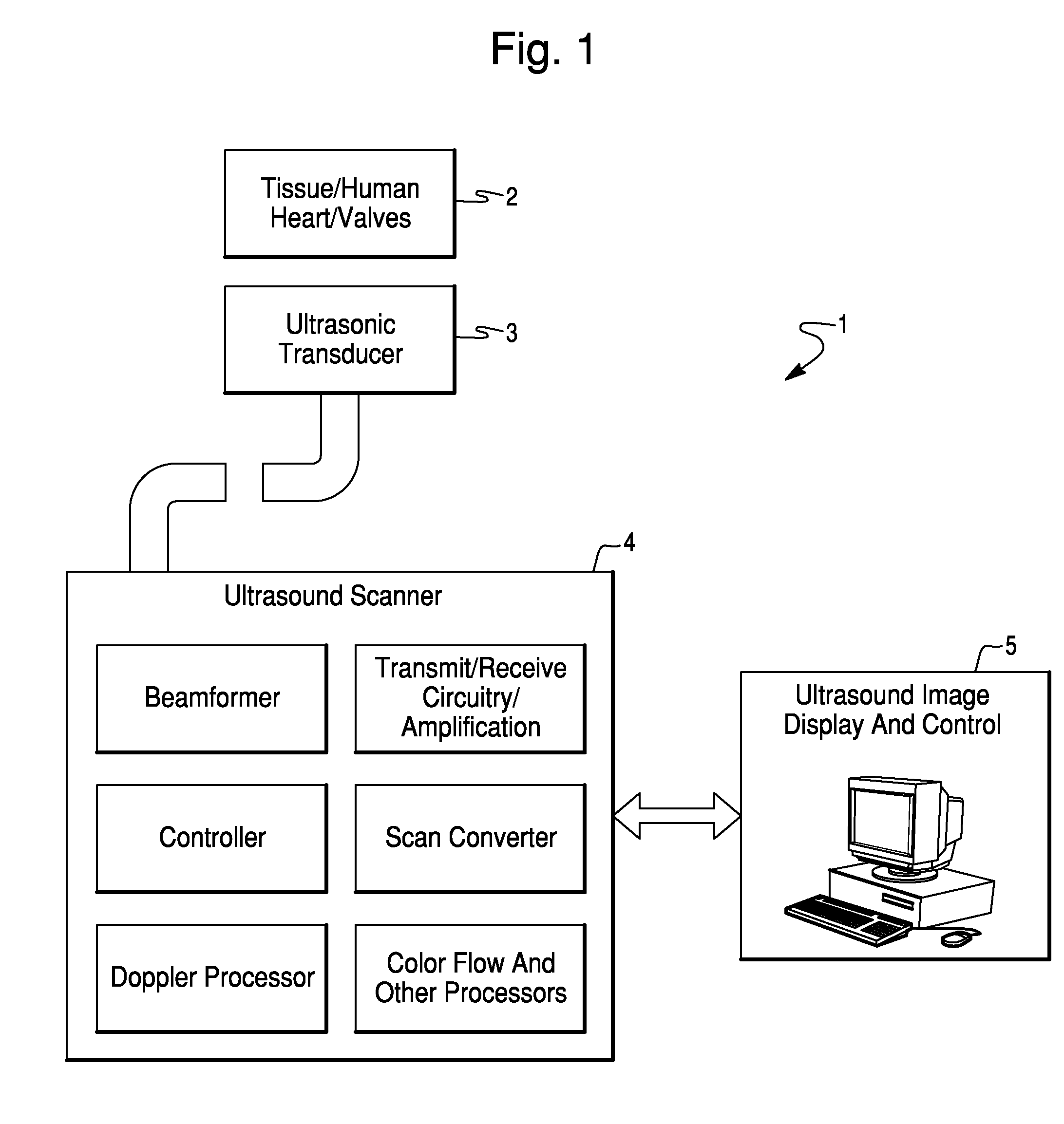
Method and System For Estimating Cardiac Ejection Volume And Placing Pacemaker Electrodes Using Speckle Tracking
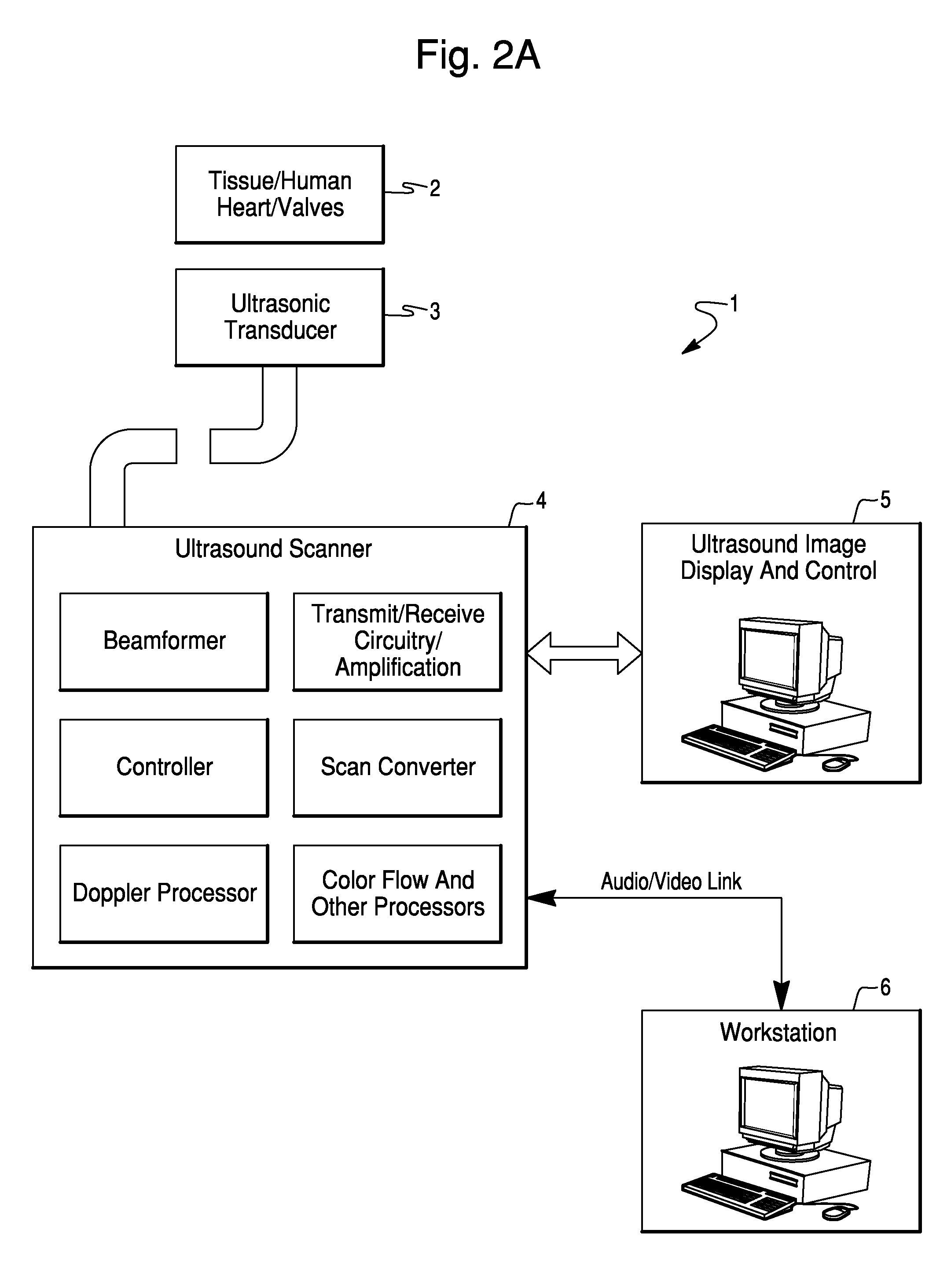
InactiveUS20070167809A1Eliminate error of inputReduce duplicationBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsEcg signalSystole
A method and system for estimating the volume of blood ejected from a cardiac ventricle or atrium uses ultrasound to track speckle patterns in the heart. The process utilizes the M-mode to estimate volume differences in a view of the ventricle or atrium over time using speckle pattern motion to estimate volume differences between systole and diastole. Alternatively, the ultrasound speckle tracking method may be used in combination with Doppler processing techniques or to obtain temporal flow profiles across flow cross-sectional areas, from which the flow volume is computed. The method can also measure the phase delay of motion of sites on the cardiac wall relative to each other or relative to an ECG signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Cardiac disease treatment and device
A device for treating cardiac disease of a heart having an upper portion and a lower portion divided by an A-V groove, the device including a jacket adapted to be secured to the heart, and a non-adherent material in association with the jacket. The jacket is fabricated from a flexible material defining a volume between an upper and a lower end, the jacket being adapted to be adjusted on the heart to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and assume a maximum adjusted volume for the jacket to constrain expansion of the heart beyond the maximum adjusted volume during diastole and permit substantially unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole. As a result of the flexible material, the jacket allows unimpeded diastolic filling of the heart. Also described is a method for treating cardiac disease including surgically accessing the heart, applying the treatment device of the invention, securing the treatment device to the heart, and surgically closing access to the heart while leaving the treatment device on the heart.
Owner:MARDIL
Septomarginal trabecula attachment for heart valve repair
The invention relates to a medical prosthesis, and in particular a tether platform for attaching to or mounting on the septomarginal trabecula of the right ventricle for securing and positioning heart valve repair devices, and in particular for securing a heart valve substitute comprising a pliant tubular conduit mounted on a resilient annular frame and tethered to a non-perforating anchor within the right ventricle of the heart, wherein the pliant tubular conduit is a reciprocating mechanical member that is compressed by pressurized working fluid within the ventricle during systole.
Owner:VDYNE LLC
Assessment of vascular dilatation
A method and apparatus of assessment of relative changes in the cross sectional area of a limb artery. The method includes applying to the artery an external pressure, which causes the cross-sectional area of the artery to change between systole and diastole much more than if the pressure is not applied, determining, over one or more cardiac cycles, a baseline value for a parameter related to the cross-sectional area of the artery, while the pressure is applied, applying a stimulus to the artery, determining, over one or more cardiac cycles, a stimulus-affected value for the parameter related to the cross-sectional area of the artery, while the pressure is applied and while the artery is in a dilated state affected by the stimulus and evaluating the artery based on a comparison of the determined stimulus-affected and baseline values, the baseline value is determined while the artery is substantially not affected by the stimulus.
Owner:DAFNI EHUD
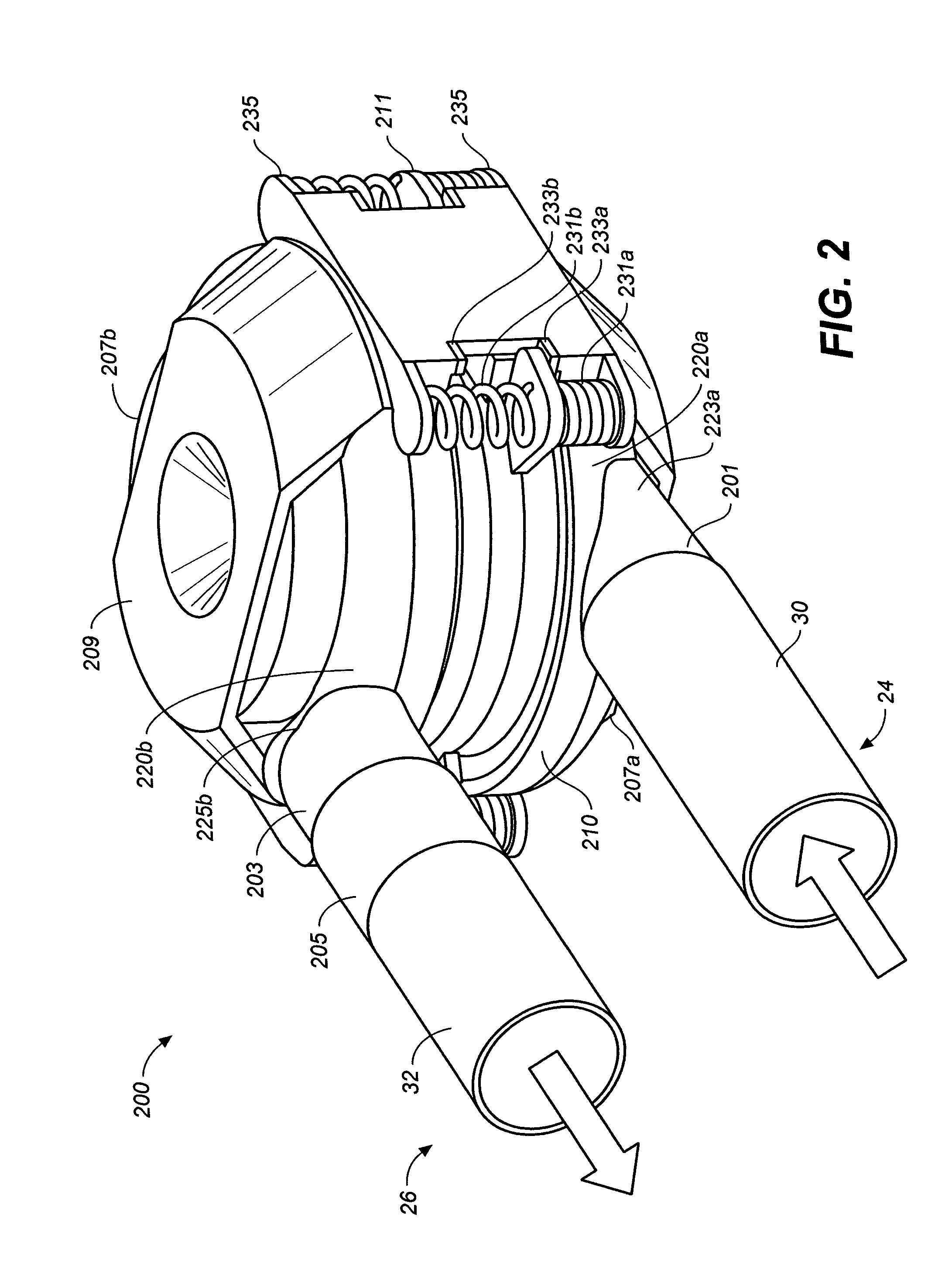
Miniature, pulsatile implantable ventricular assist devices and methods of controlling ventricular assist devices
ActiveUS6969345B2Small sizeSmall and efficient and atraumatic and fully implantableControl devicesBlood pumpsSystoleEngineering
A pumping system for assisting either or both ventricles of the heart. In one embodiment, separate devices are provided for each ventricle. In another embodiment, one device provides both right and left pumping. The pumping system is small, efficient, atraumatic, and fully implantable. In addition, the pumping system can provide pulsatile flow during systole. The ventricular assist device includes an actuator plate between a pair of serially connected pumping chambers that operate in a two-stroke mode, specifically a power stroke and a transfer stroke. The ventricular assist device also includes an electromagnetic drive system that provides adjustment to the pump pressure according to the current through an electromagnet. For the pumping system, springs provide a “spring force” on the actuator plate that is towards the high-pressure pump chamber. The bias force allows the springs to store and deliver energy from the electromagnetic drive system to provide better utilization of the pump components, and to reduce the pump size and consumption of electricity.
Owner:WORLD HEART
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com