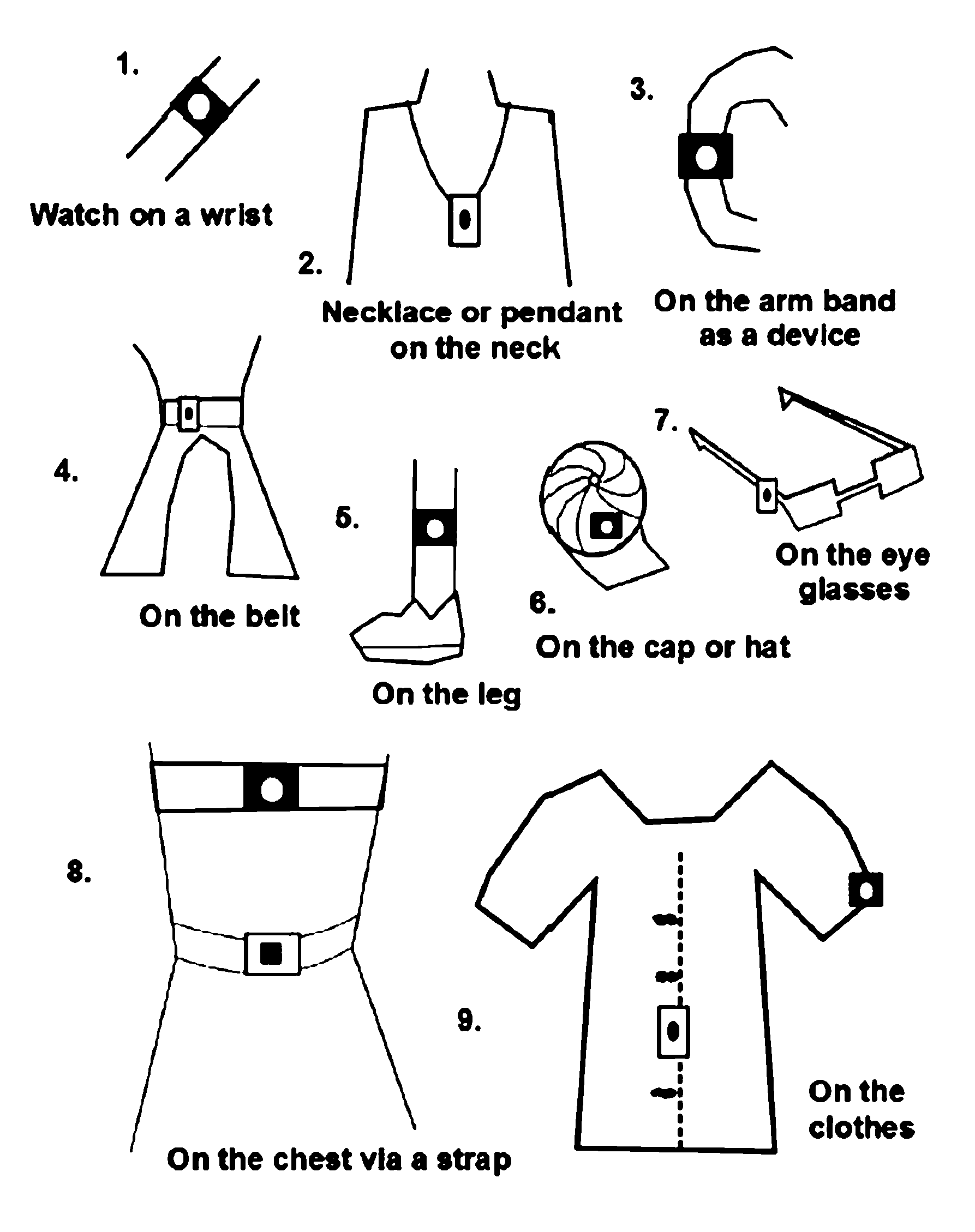
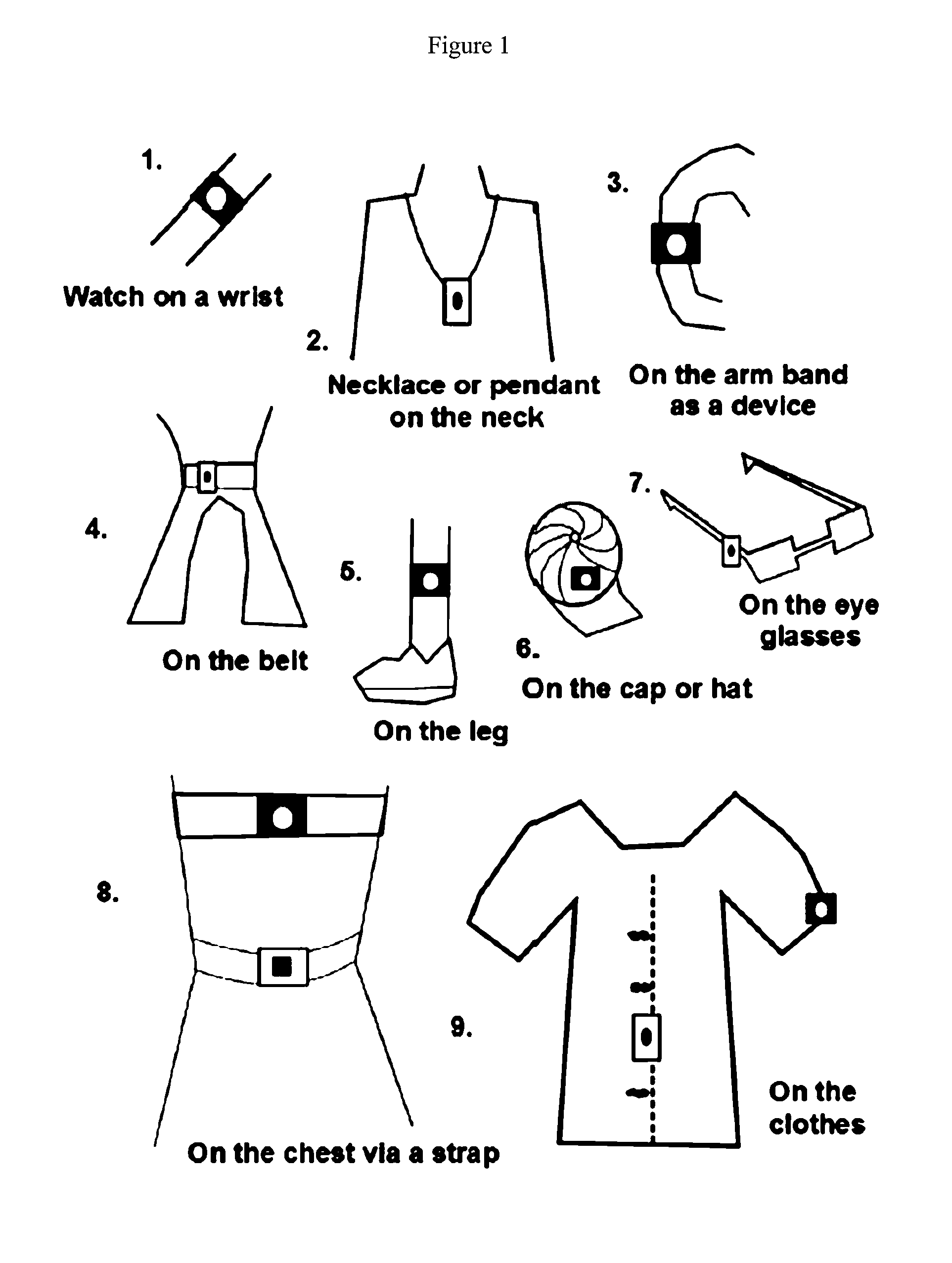
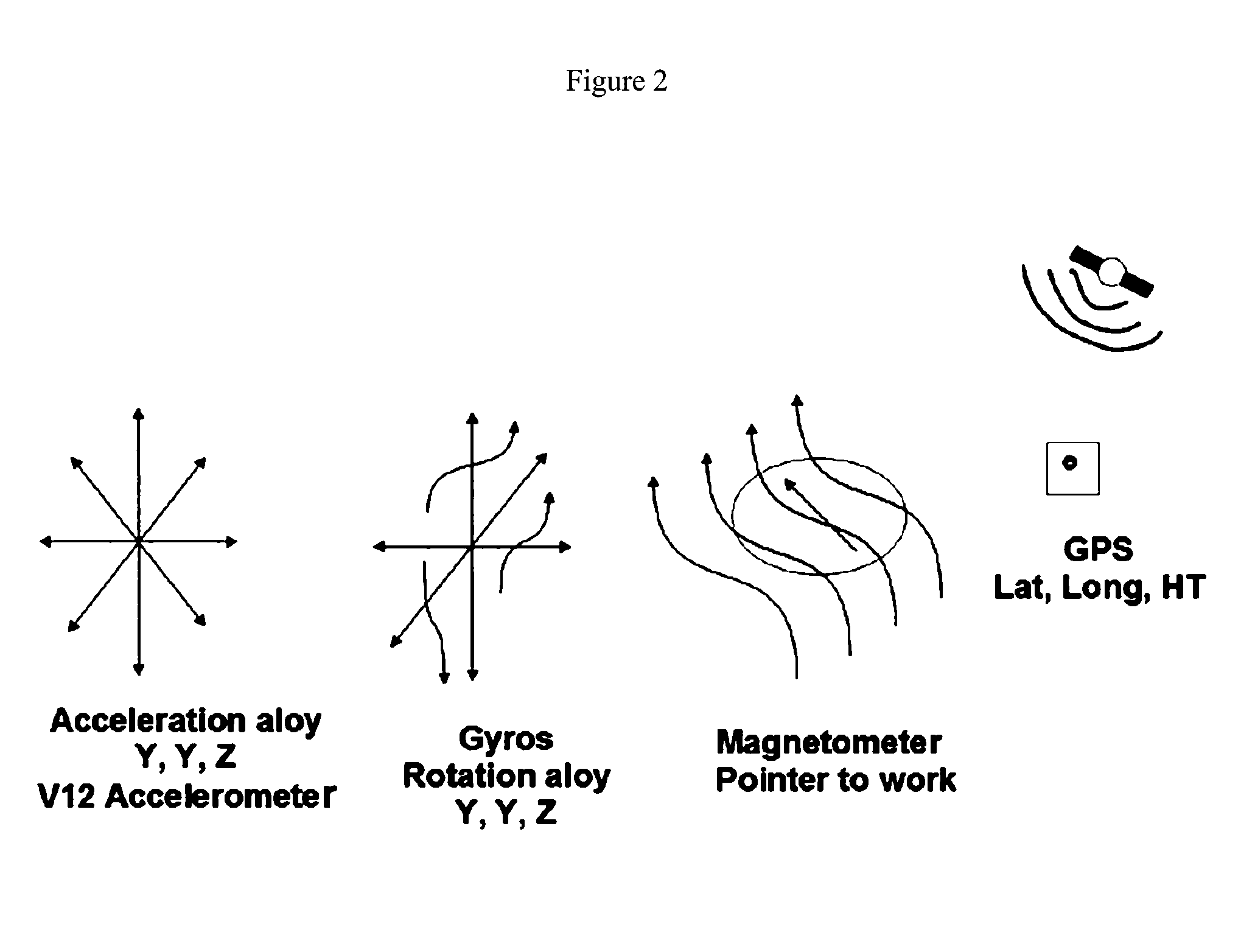
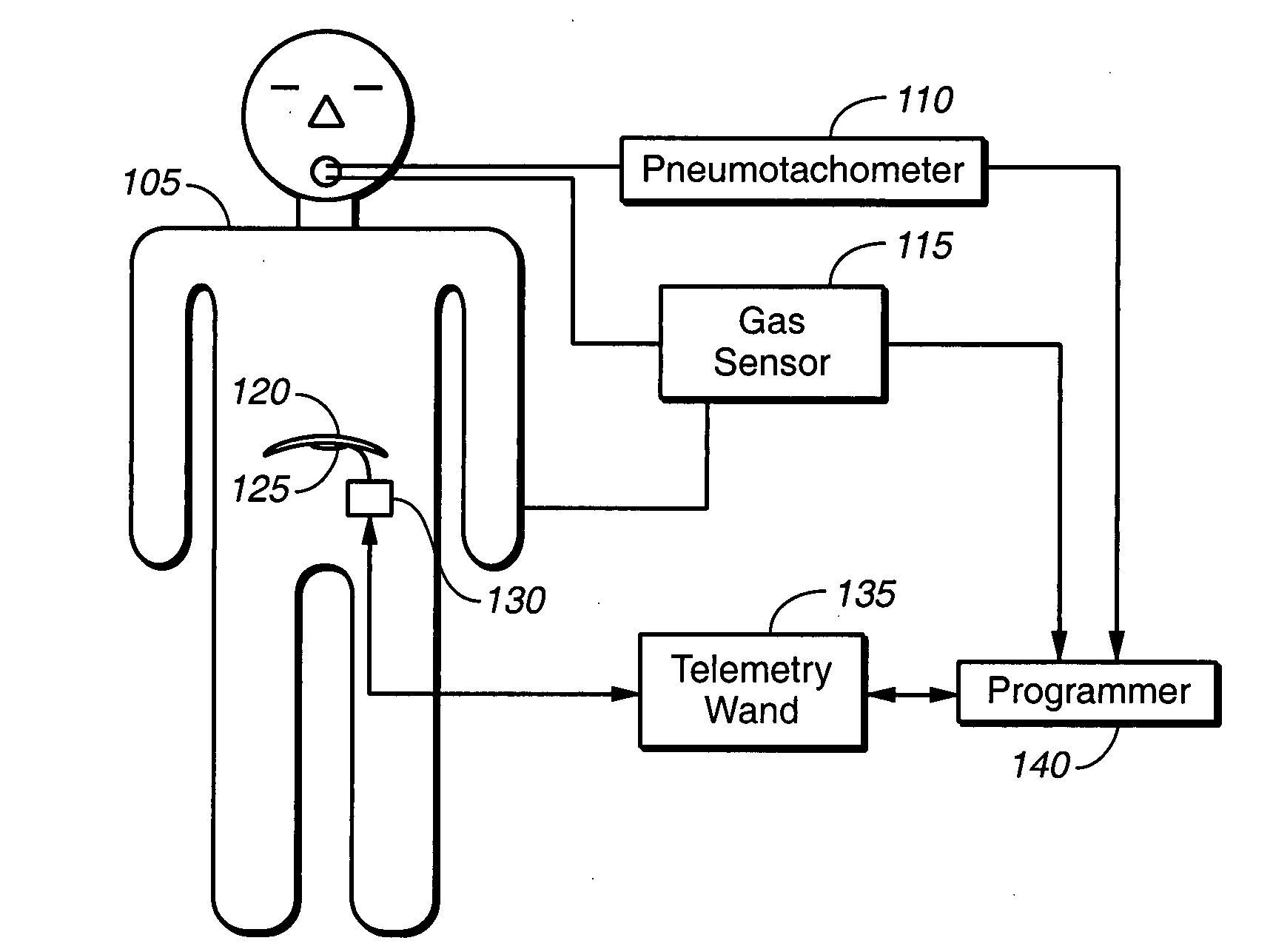
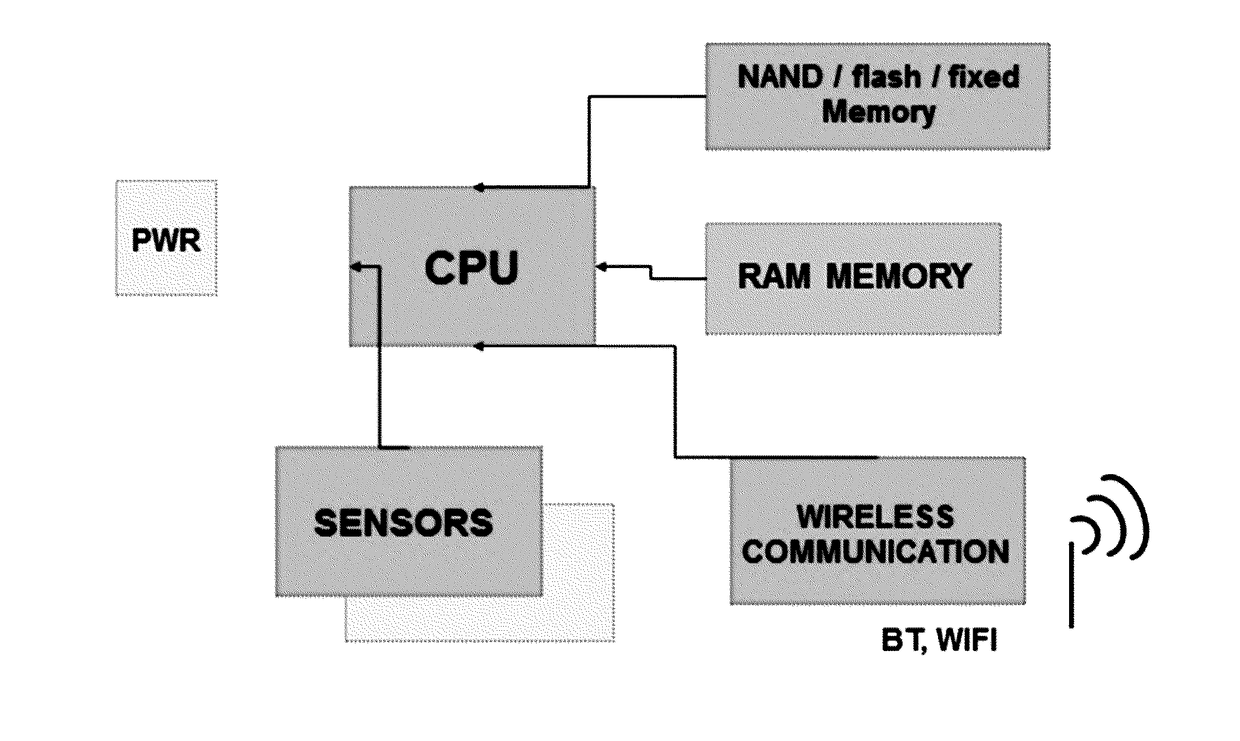
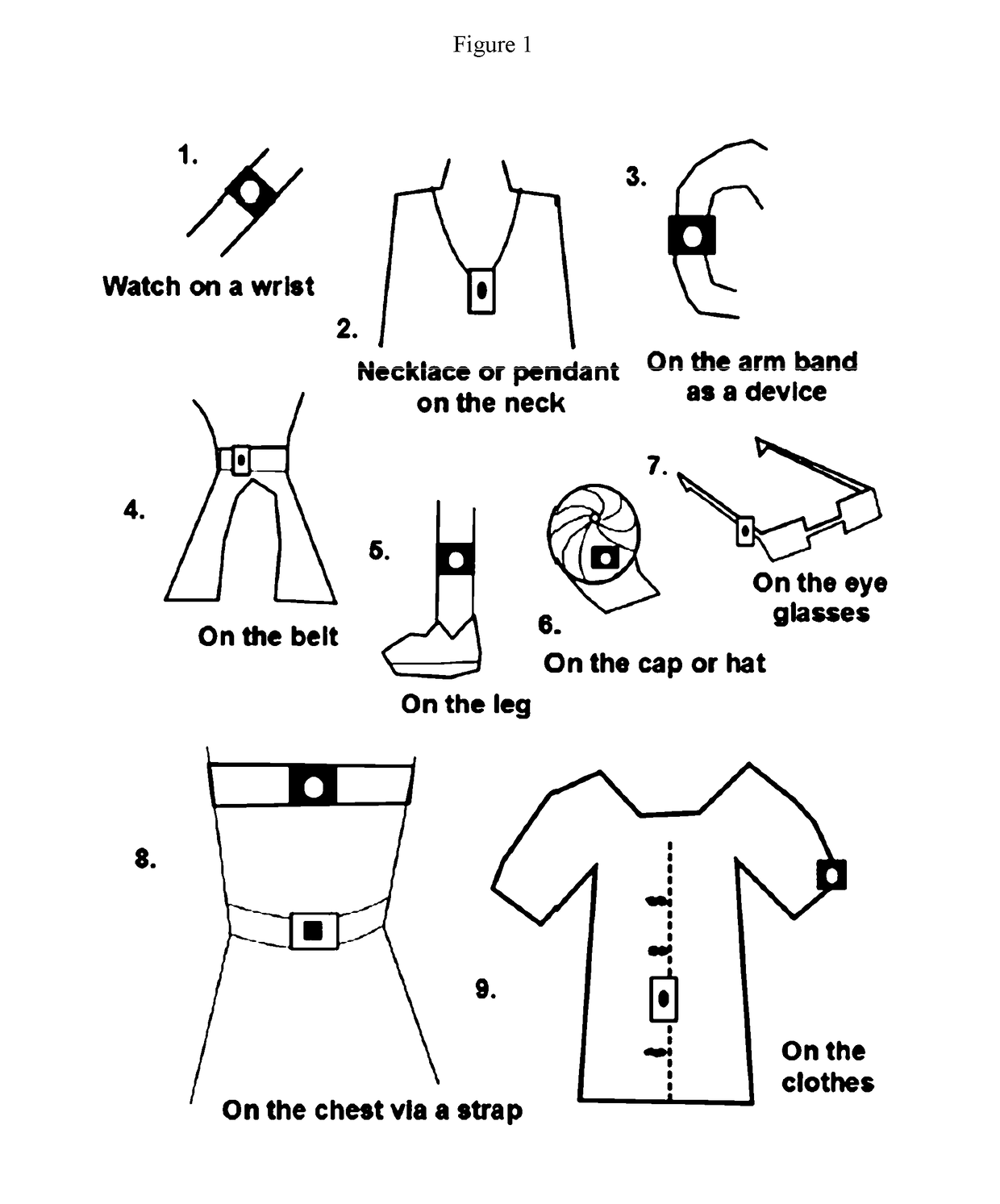
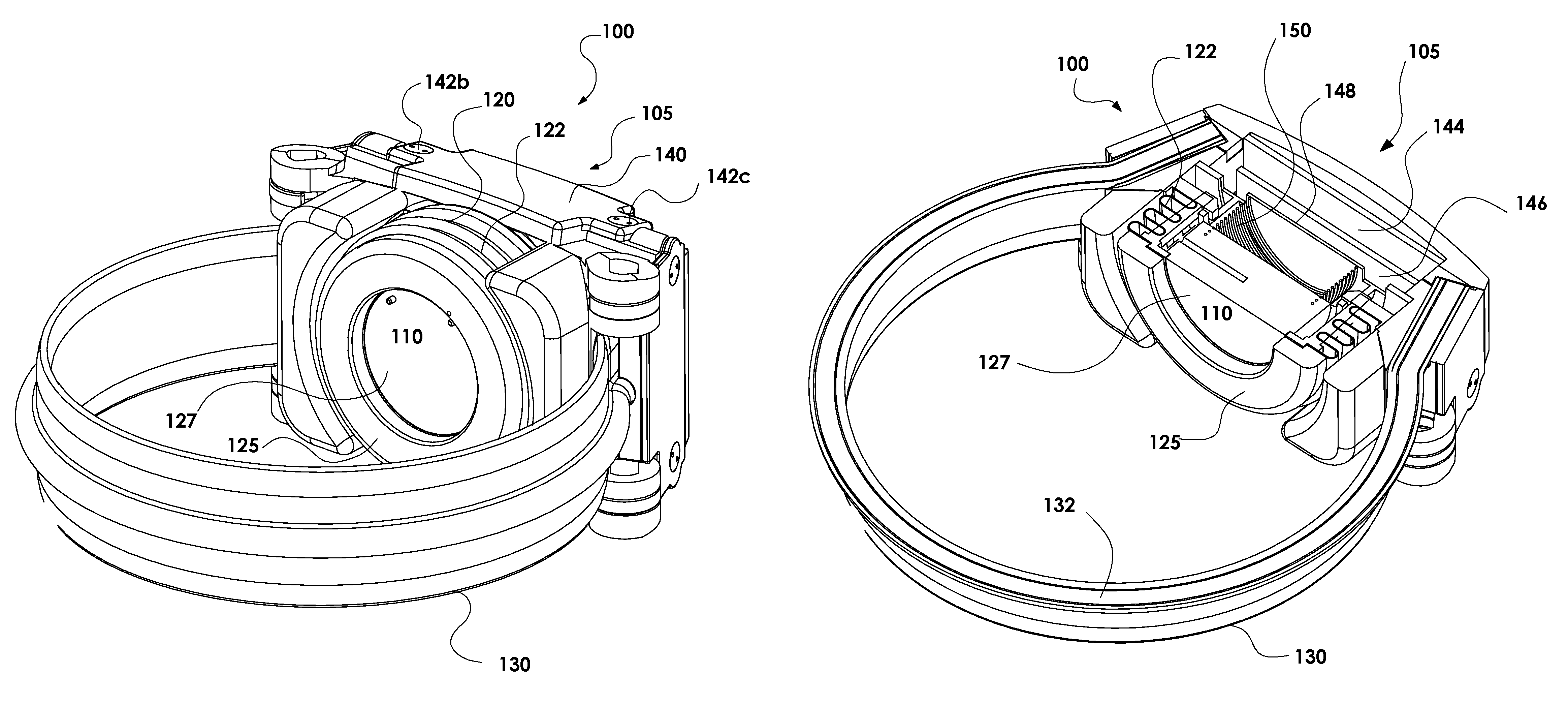
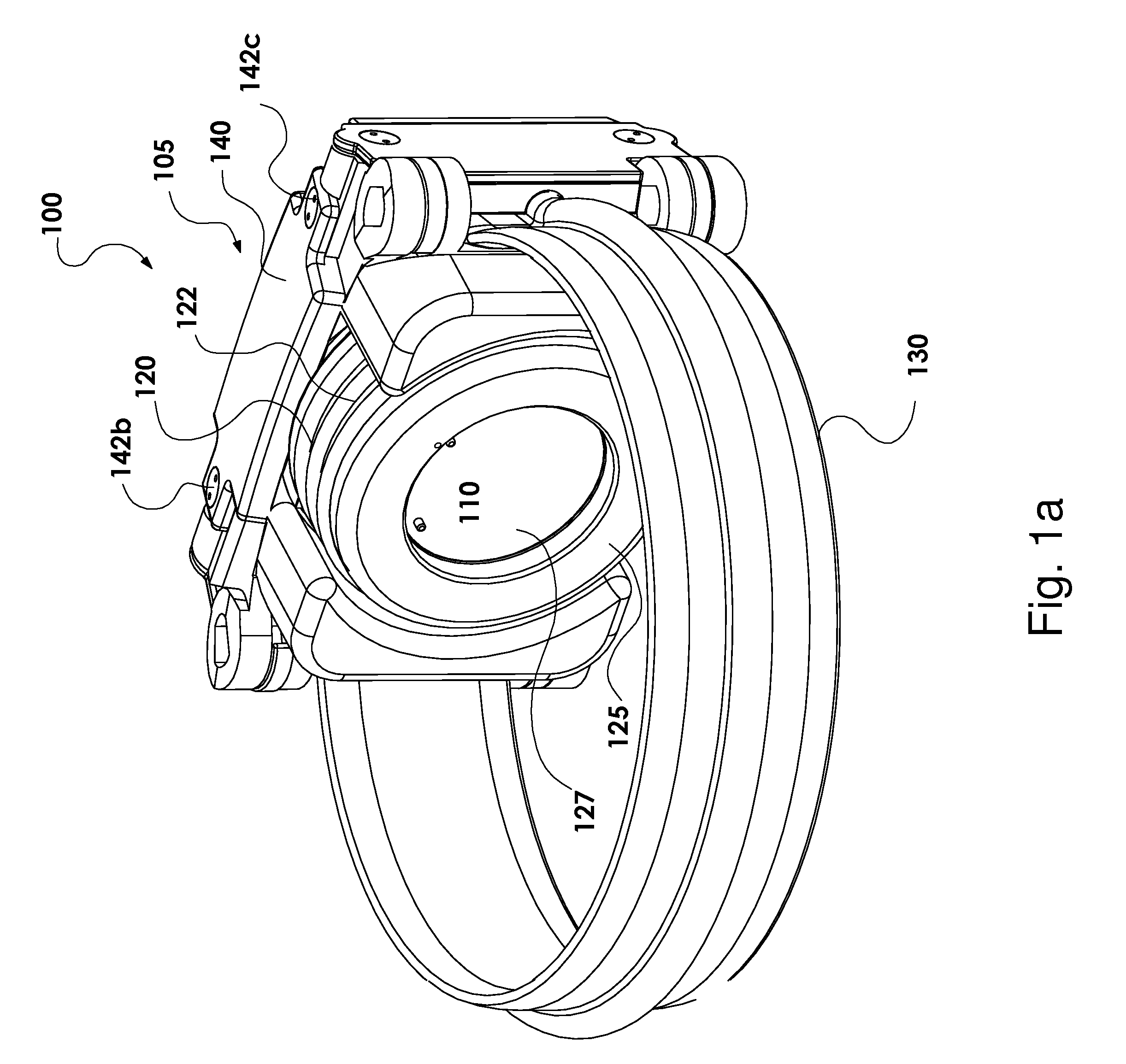
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
332 results about "Baseline values" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Baseline Value means the average of the Fair Market Value of one share of Common Stock over the 20 consecutive trading days immediately preceding the Initial Date of any Performance Period.
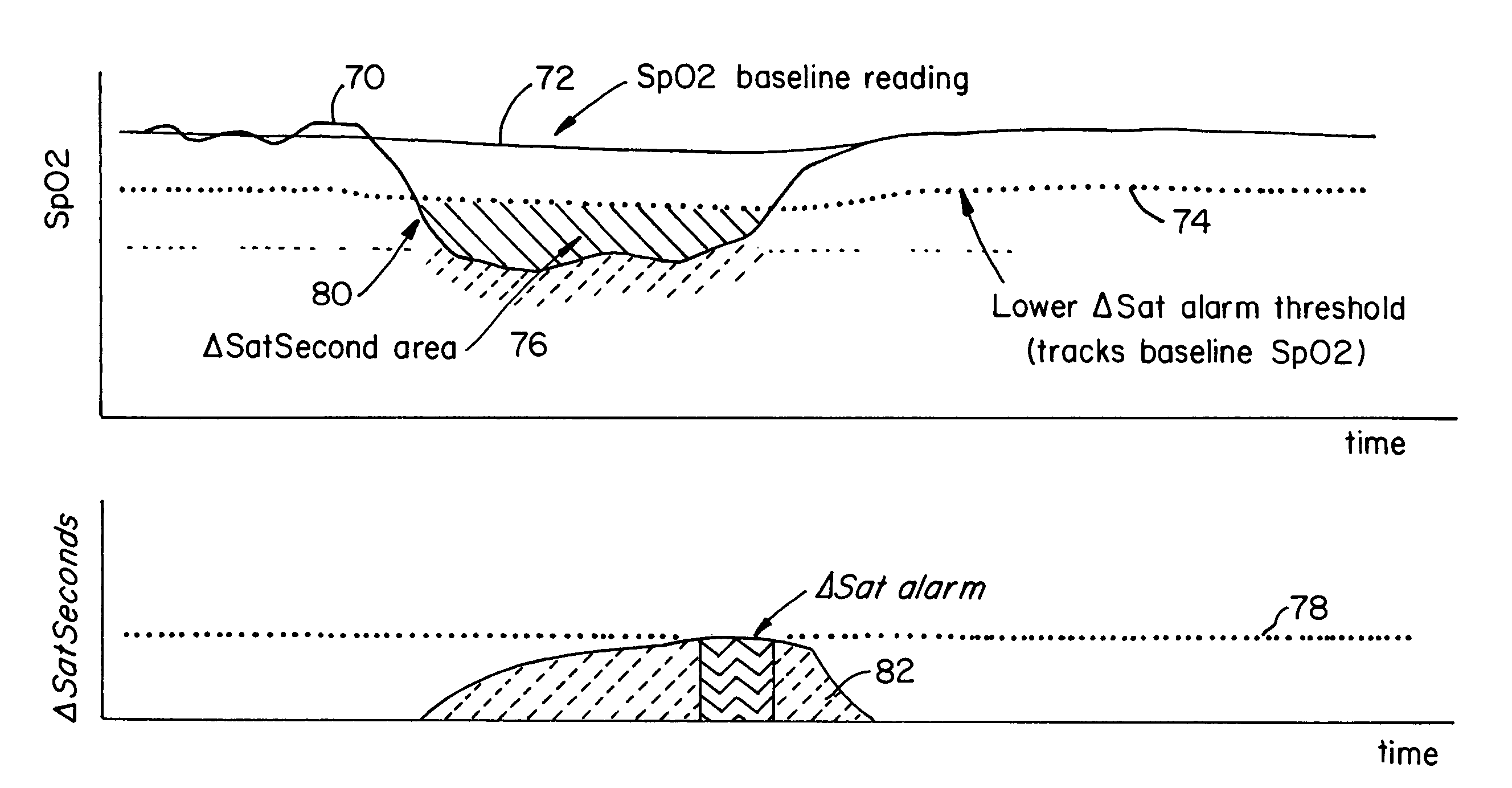
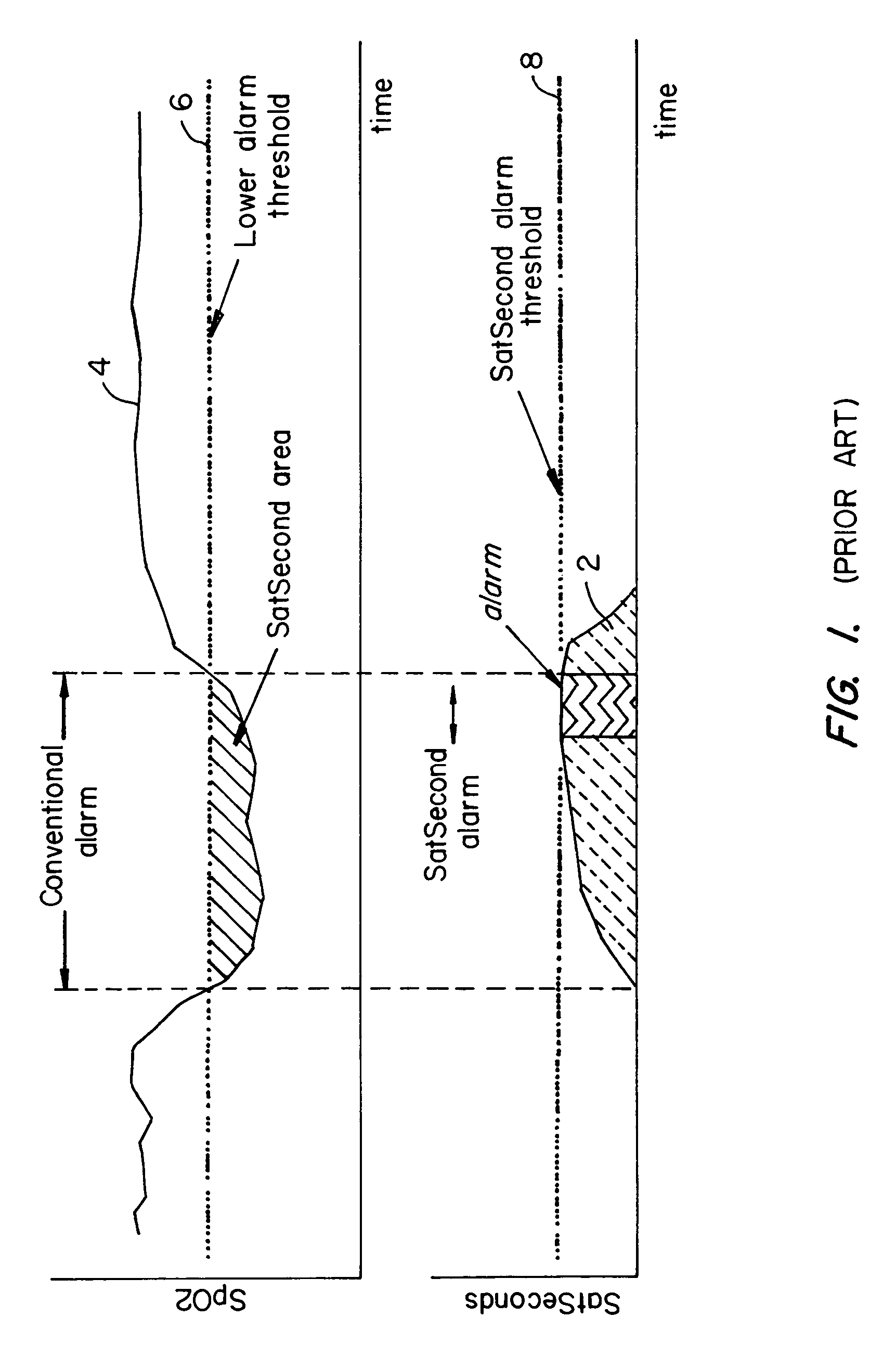
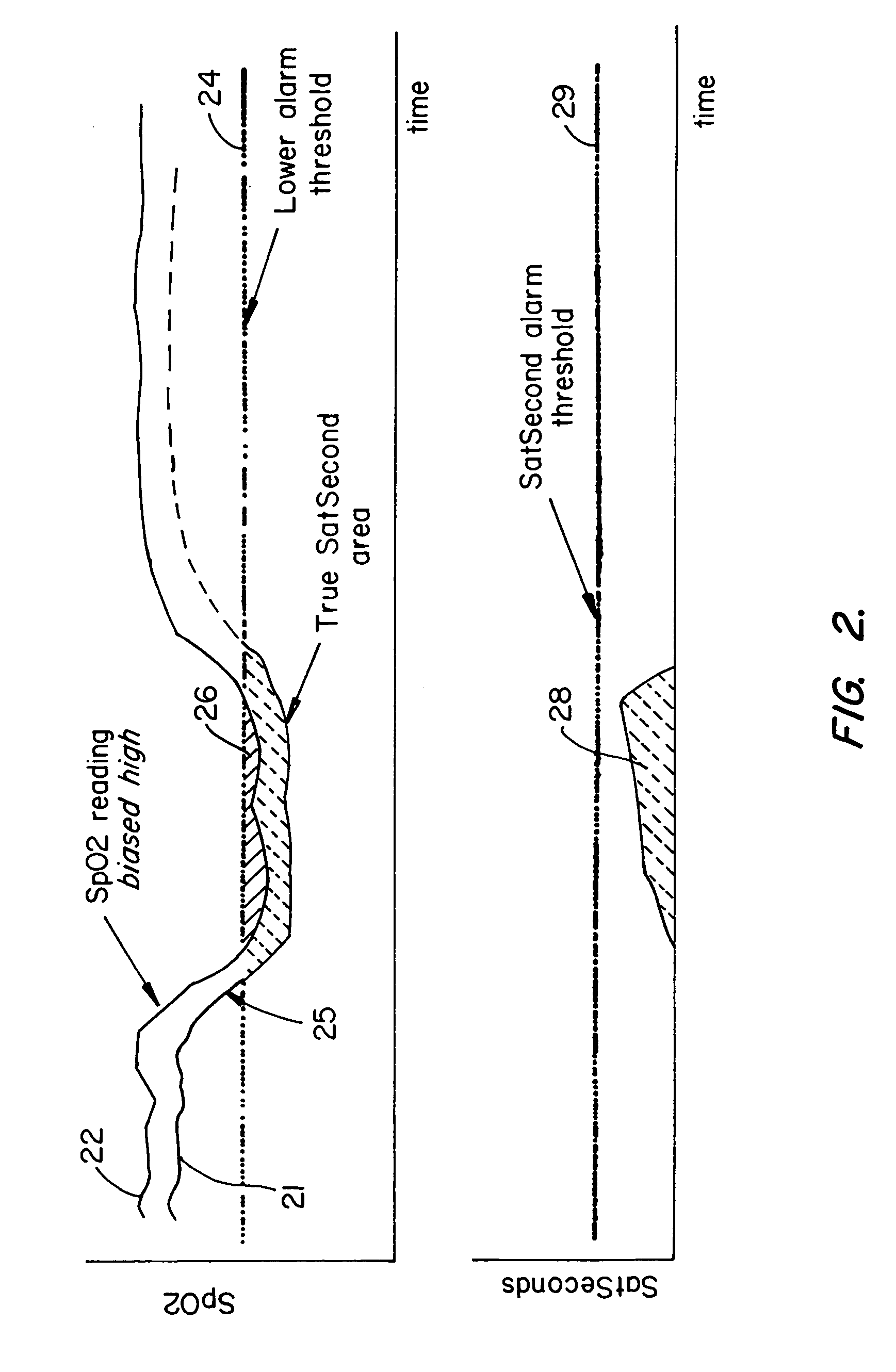
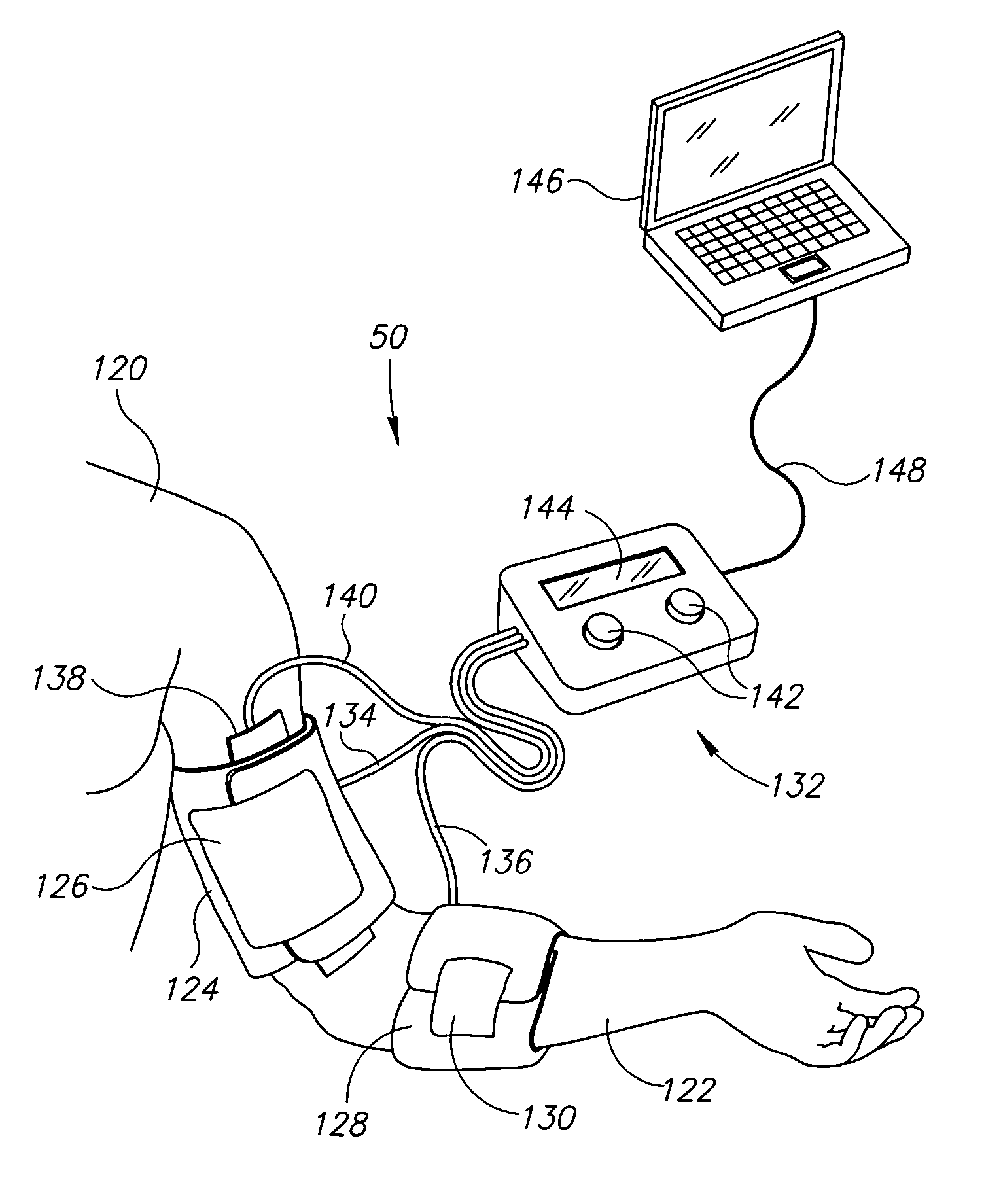
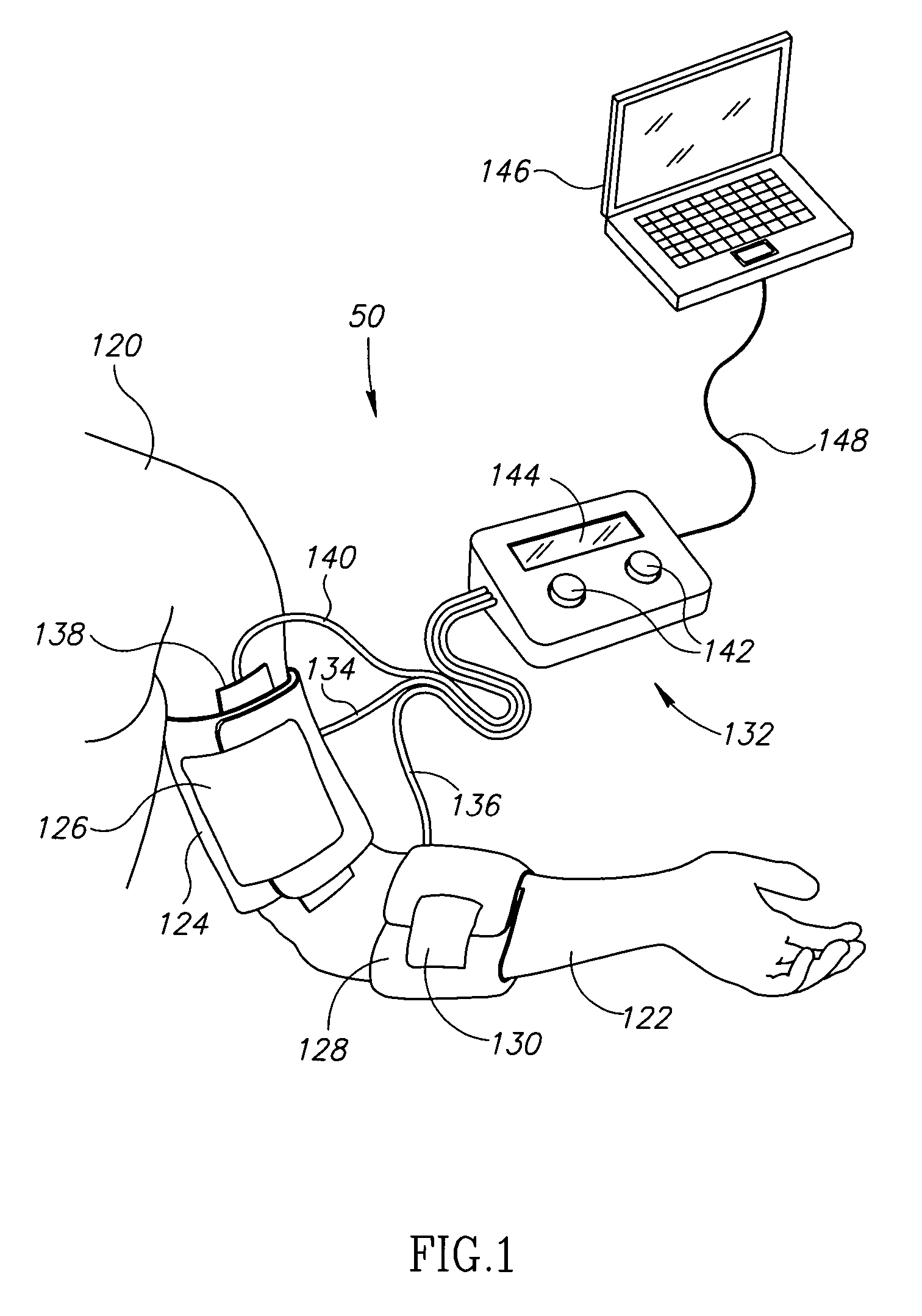
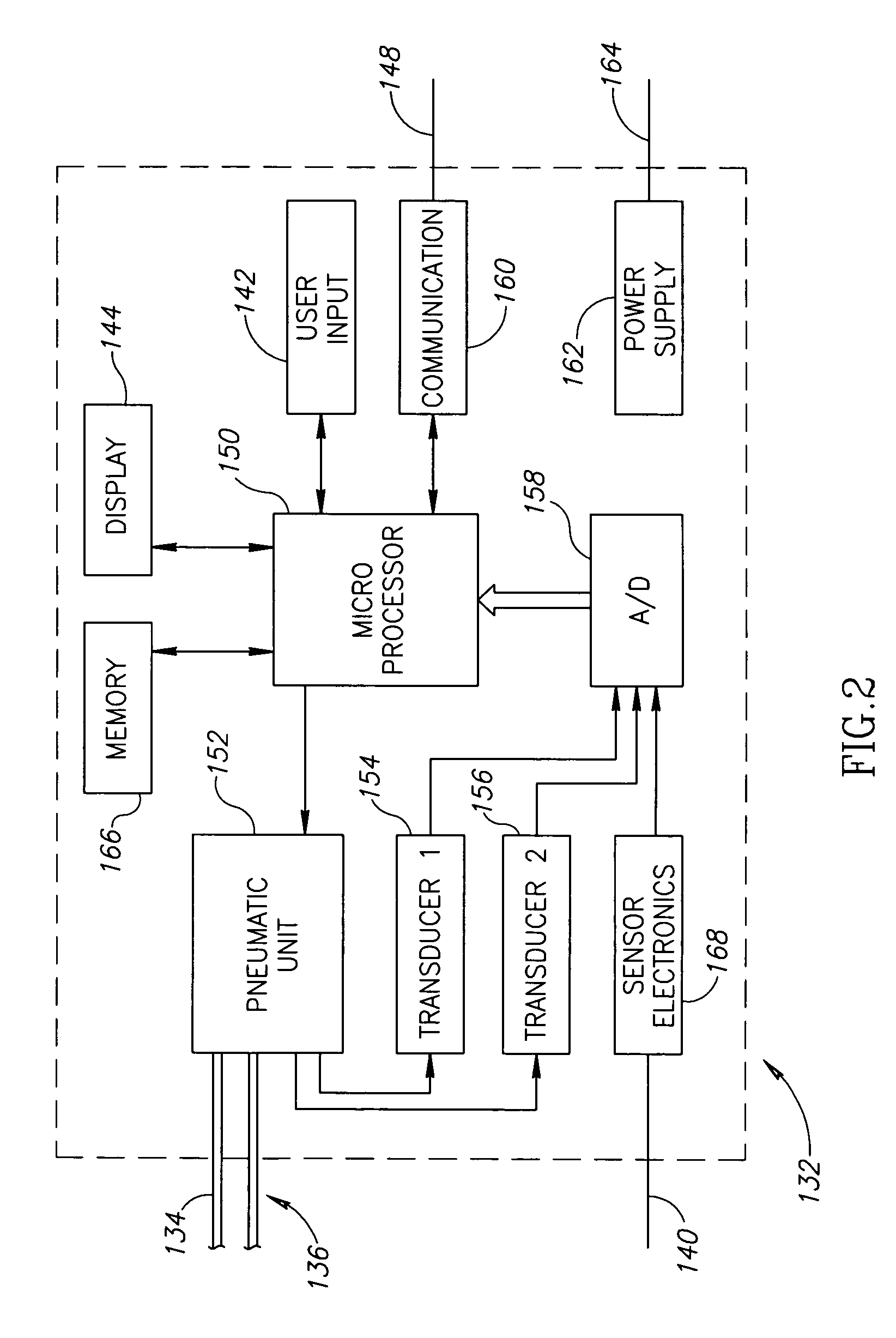
Nuisance alarm reductions in a physiological monitor
A method and apparatus for controlling alarms in a medical diagnostic apparatus where an alarm is generated when a measured value for a physiological parameter is outside a specified range. The method continuously calculates a baseline value, and establishes dynamic thresholds that are related to and continuously track the baseline value. The method determines the amount of time the measured value is past the dynamic threshold, and the amount by which the threshold is passed. Alarms are triggered based upon a combination of the amount of time and the amount by which the threshold is passed. Preferably, the combination is an integral or some function of an integral.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
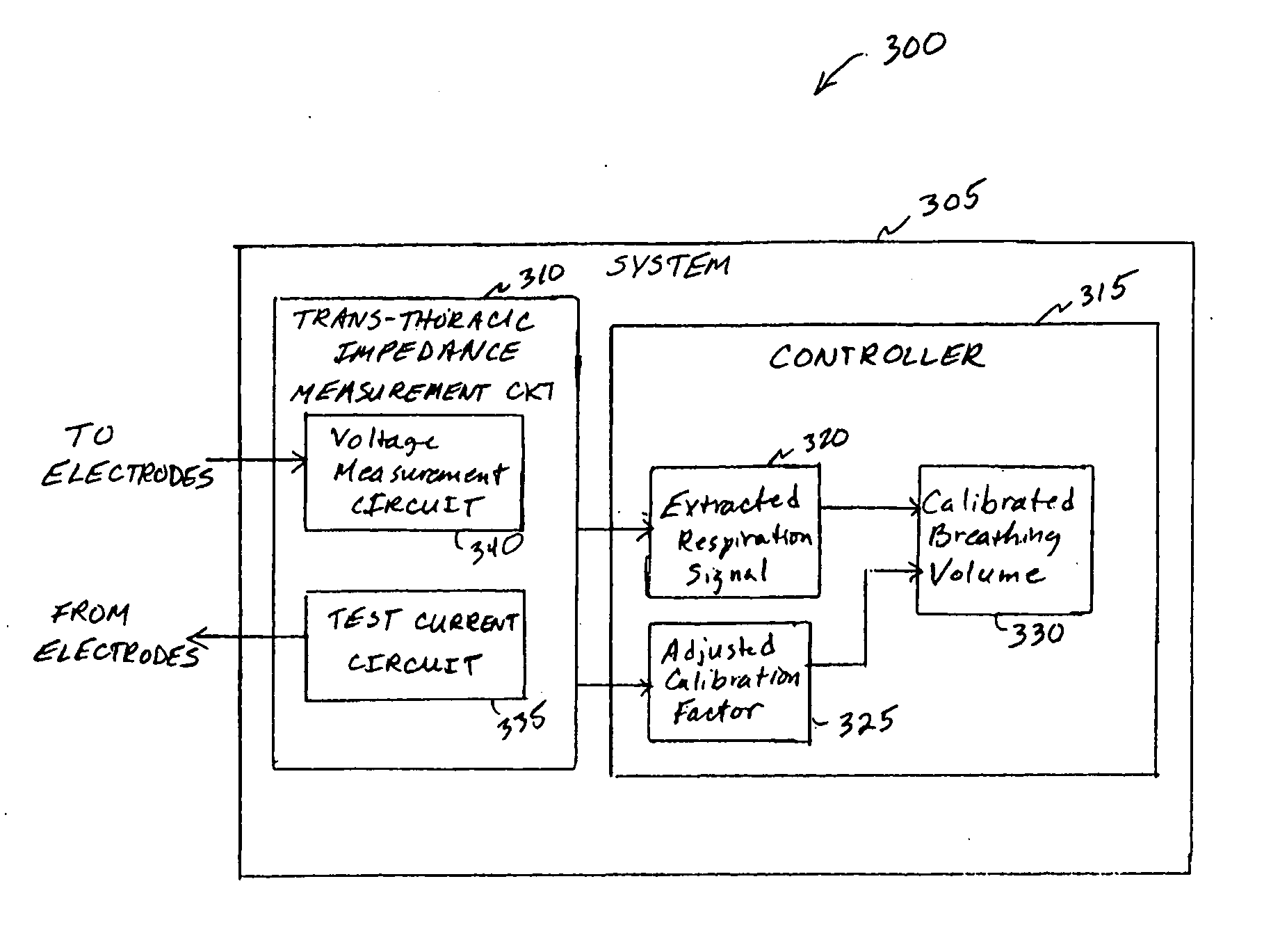
Calibration of impedance monitoring of respiratory volumes using thoracic D.C. impedance
InactiveUS20060241513A1Easy to monitorElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationRadiologyRespiratory capacity
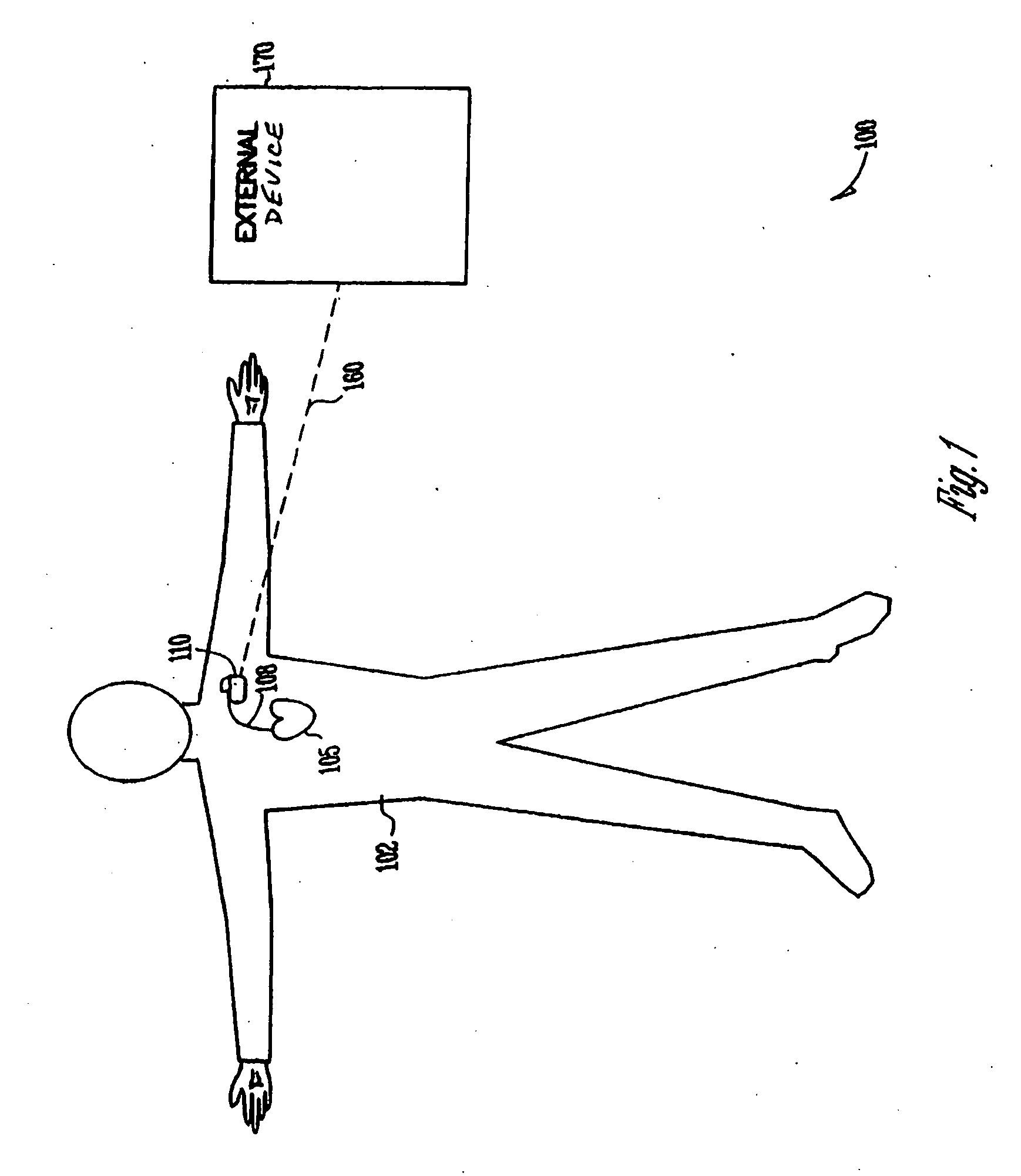
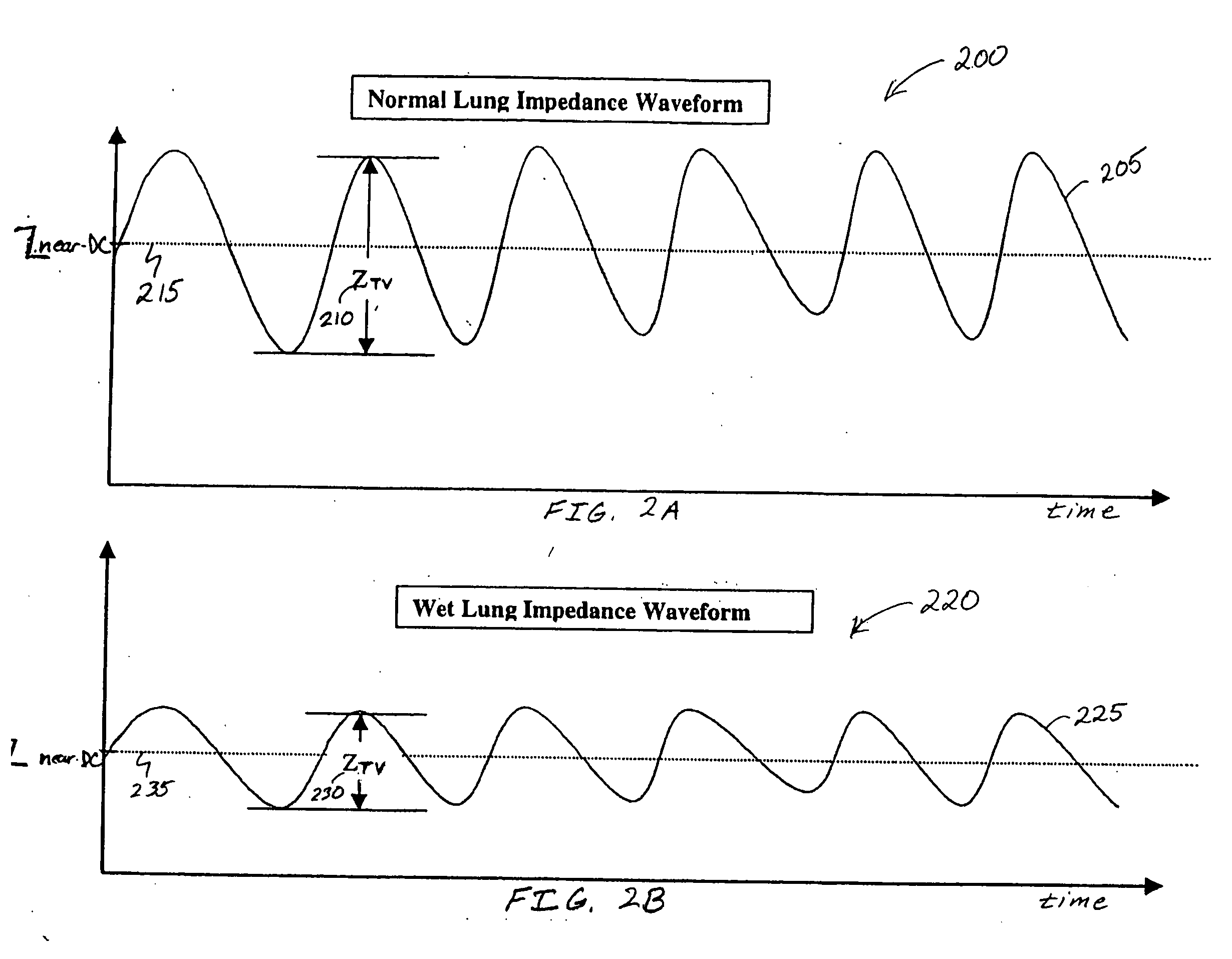
A system includes an implantable medical device that includes a trans-thoracic impedance measurement circuit providing a trans-thoracic impedance signal of a subject. A controller is coupled to the trans-thoracic impedance circuit. The controller extracts a respiration signal from the trans-thoracic impedance signal, measures a breathing volume of the subject using the amplitude of the respiration signal and a breathing volume calibration factor, computes an adjusted breathing volume calibration factor using a reference baseline value of the trans-thoracic impedance and a measured baseline value of the trans-thoracic impedance, and computes a calibrated breathing volume using the adjusted breathing volume calibration factor.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for detection of metal disturbance based on mutual inductance measurement
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
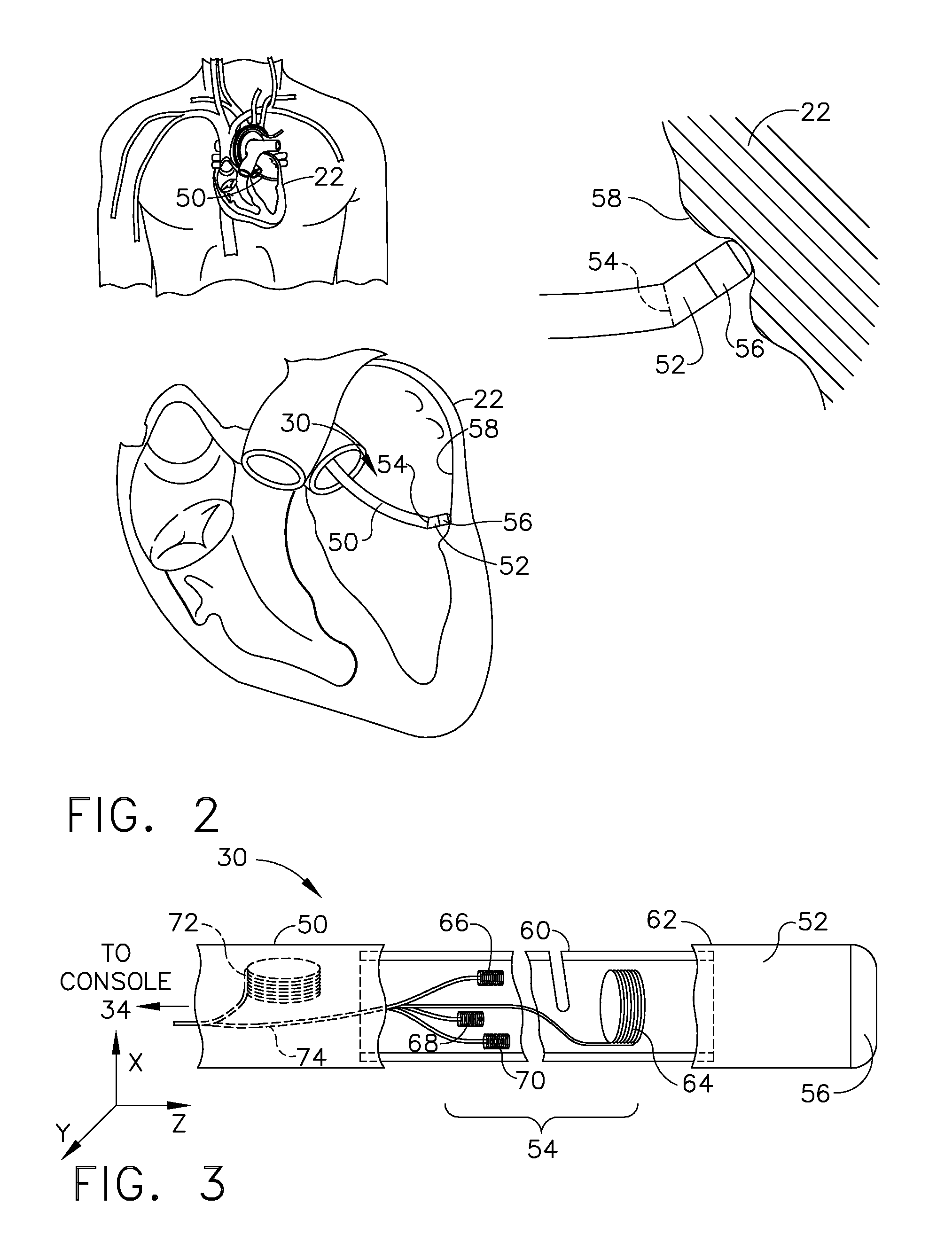
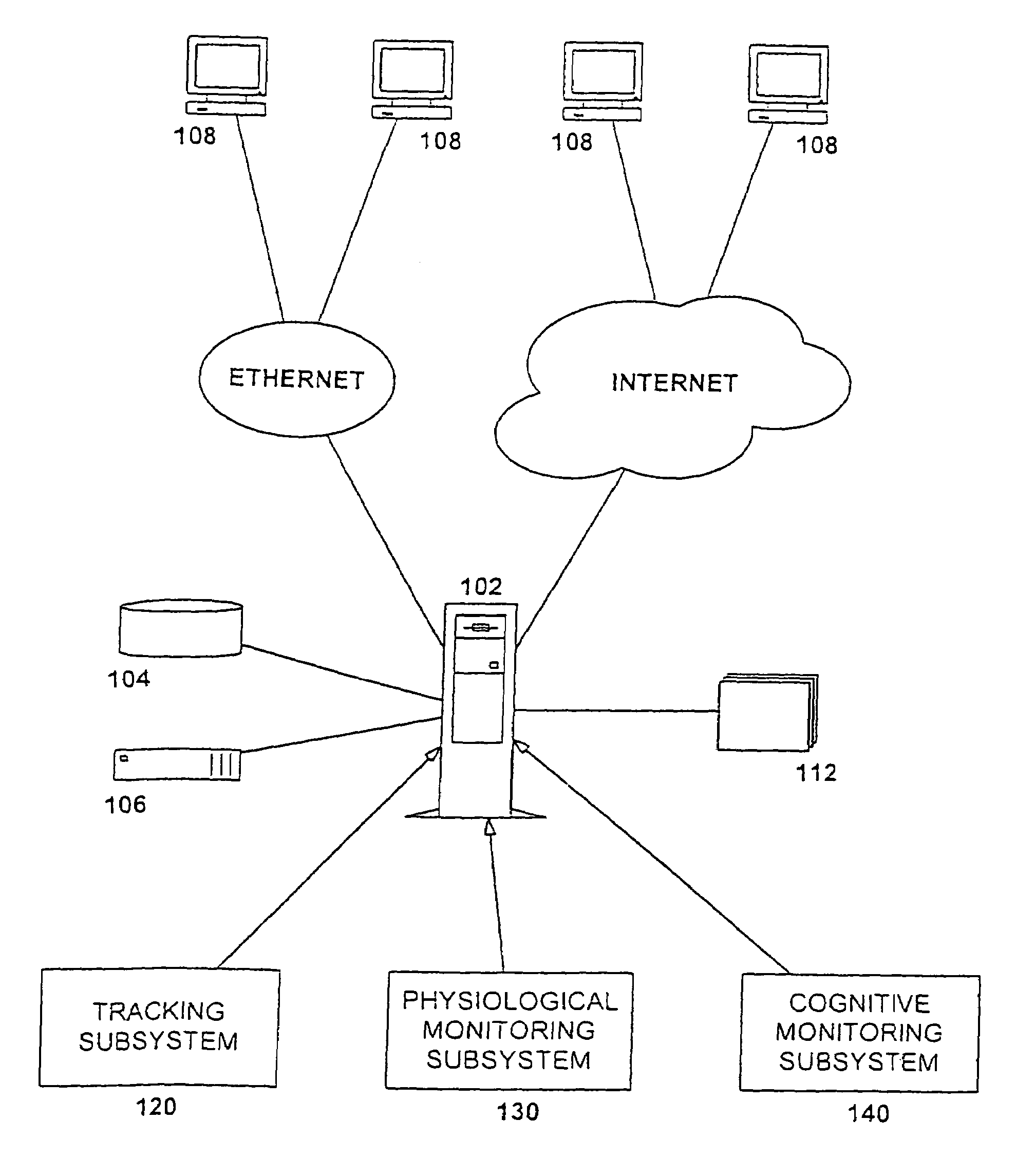
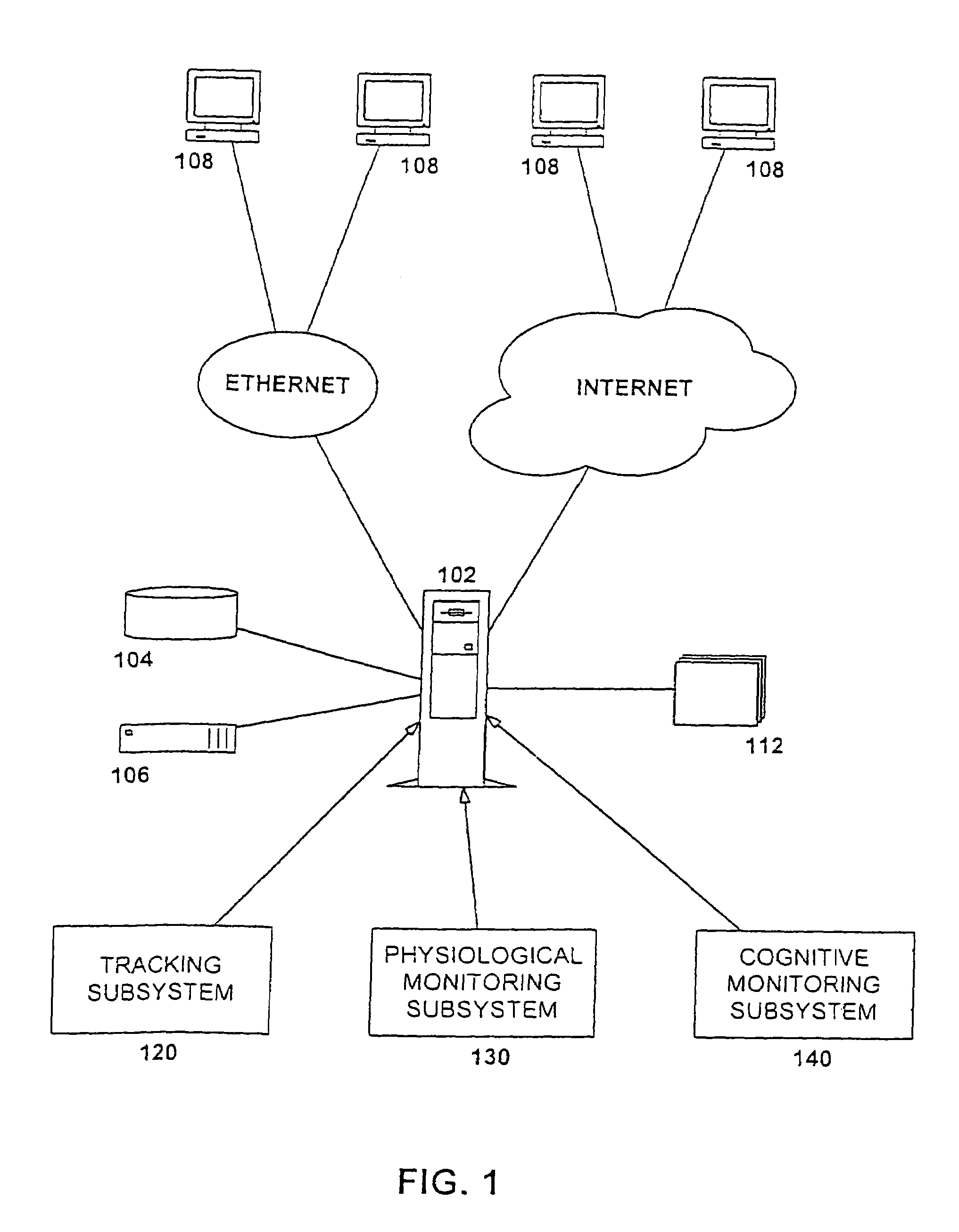
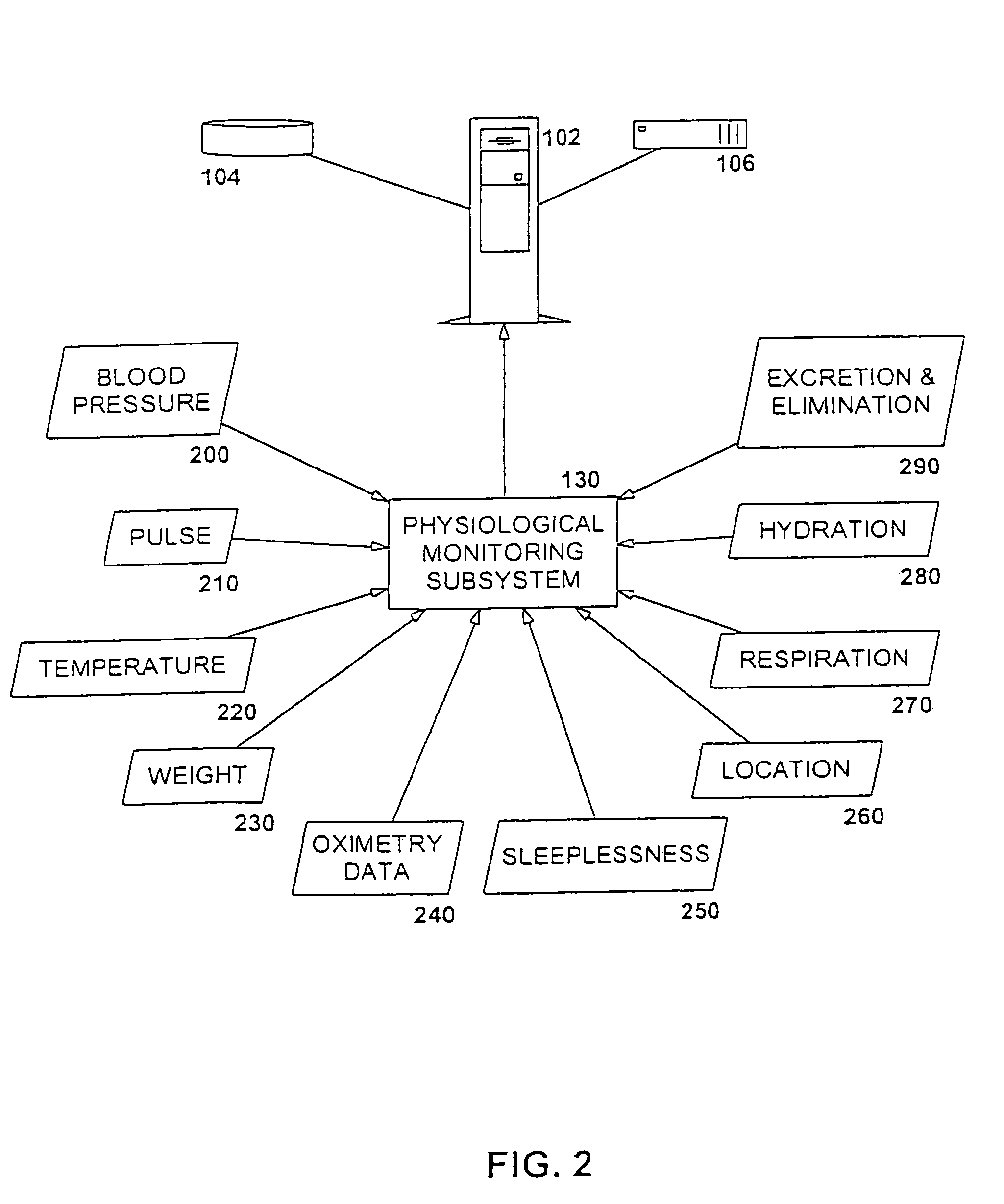
Apparatus for non-intrusively measuring health parameters of a subject and method of use thereof
InactiveUS7001334B2Facilitates measurement and collection and analysisSurgeryPerson identificationMedicineMonitoring system
An integrated subject monitoring system facilitates measurement, collection and analysis of data pertaining to the health status of a subject. The system includes a network-coupled computer and subsystems monitoring subject location within a defined space and the curtilage thereof and obtaining measurements of a subject's physiological or behavioral / cognitive parameters within the defined space. Parameter data is obtained primarily passively, without the cooperation or active participation of the subject. A method of monitoring the physiological and behavioral / cognitive health status of an ambulatory subject involves monitoring in a primarily passive fashion, irrespective of the active collaboration of the subject. Subject health indicia parameters are continuously monitored, sampled and recorded. Captured values are compared to initial baseline values established for each of the measured parameters as well as to the trend for the parameter of that subject. Readings falling outside the boundaries trigger a signal to be sent to an appropriate party.
Owner:BIP TECH
System and method of body motion analytics recognition and alerting
InactiveUS20150164377A1The result is morePerson identificationInertial sensorsAccelerometerTransceiver
Device, system and methods for using body worn sensors to analyze human body motion. The device, often configured to be worn on the user's wrist, arm, neck, belt or other location, comprises a processor, an output device (often a wireless transceiver), and at least one accelerometer, angle, location, direction, or physiological state sensor. The processor may be configured for various functions, such as analyzing habitual user activities, establishing normal baselines, classifying types of motion and reporting, and logging sensor readings or analysis results. Various algorithms may be used to determine when significant deviations from baseline values occur, and, depending on the type of deviation, the output device can transmit data and alerts. In some embodiments, the data and alerts may be further analyzed by other computerized devices such as mobile phones (smartphones), computers, internet servers, and the like.
Owner:NATHAN VAIDHI +1
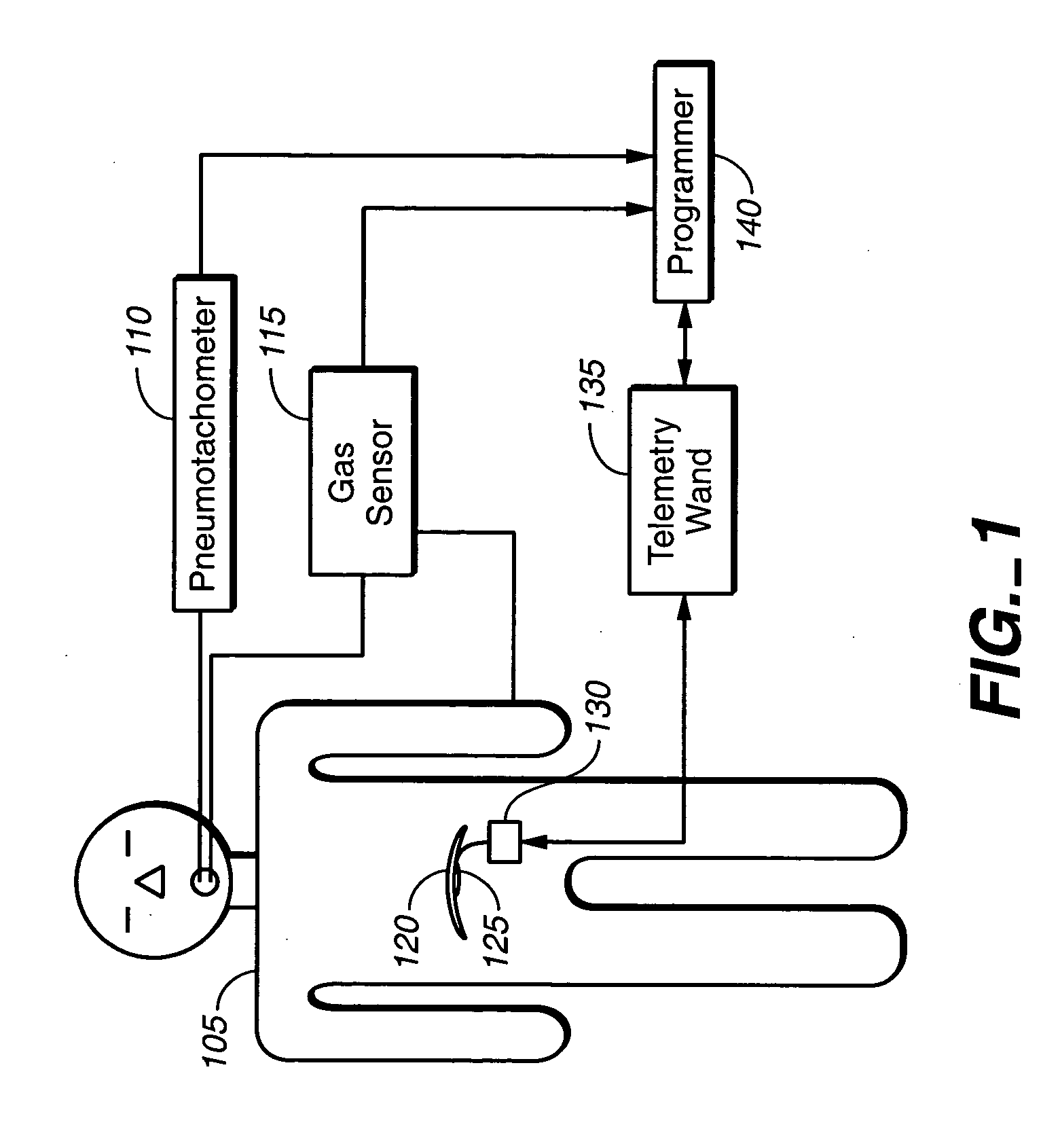
System and method for diaphragm stimulation
ActiveUS20050085867A1Enhanced negative intrapleural pressureNegative pressureRespiratorsElectrotherapyBlood gas testIntensive care medicine
A stimulation device is provided that stimulates breathing to manipulate blood gas concentrations such as SaO2 or PCO2 and thereby treat underlying causes of breathing disorders and heart failure progression. A programmable device is provided for setting diaphragm stimulation waveforms that adjust minute ventilation about a predetermined baseline value. Normal breathing of the subject is observed to establish a baseline reference minute ventilation, and the device is programmed to produce stimulation waveforms that may provide either a decrease or an increase in the patients minute ventilation. The minute ventilation of the subject may be decreased or increased from the baseline level by decreasing or increasing a parameter that changes minute ventilators.
Owner:RMX
Gesture cataloging and recognition
ActiveUS20090183193A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionScalar ValueCataloging
Methods and apparatus for cataloging and recognizing gestures are disclosed. A gesture may be detected using sample motion data. An energy value and a baseline value may be computed. The baseline value may be updated if the energy value is below a calm energy threshold. The sample motion data may be adjusted based on the updated baseline value. A local variance may be calculated over a predetermined number of samples. Sample motion data values may be recorded if the local variance exceeds a threshold. Sample motion data recording may stop if a local variance scalar value falls below a drop threshold. Input Gestures may be recognized by computing a total variance for sample values in an Input Gesture; calculating a figure of merit using sample values from the Input Gesture and one or more Catalog Gestures; and determining whether the Input Gesture matches a Catalog Gesture from the figure of merit.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTRTAINMENT LLC
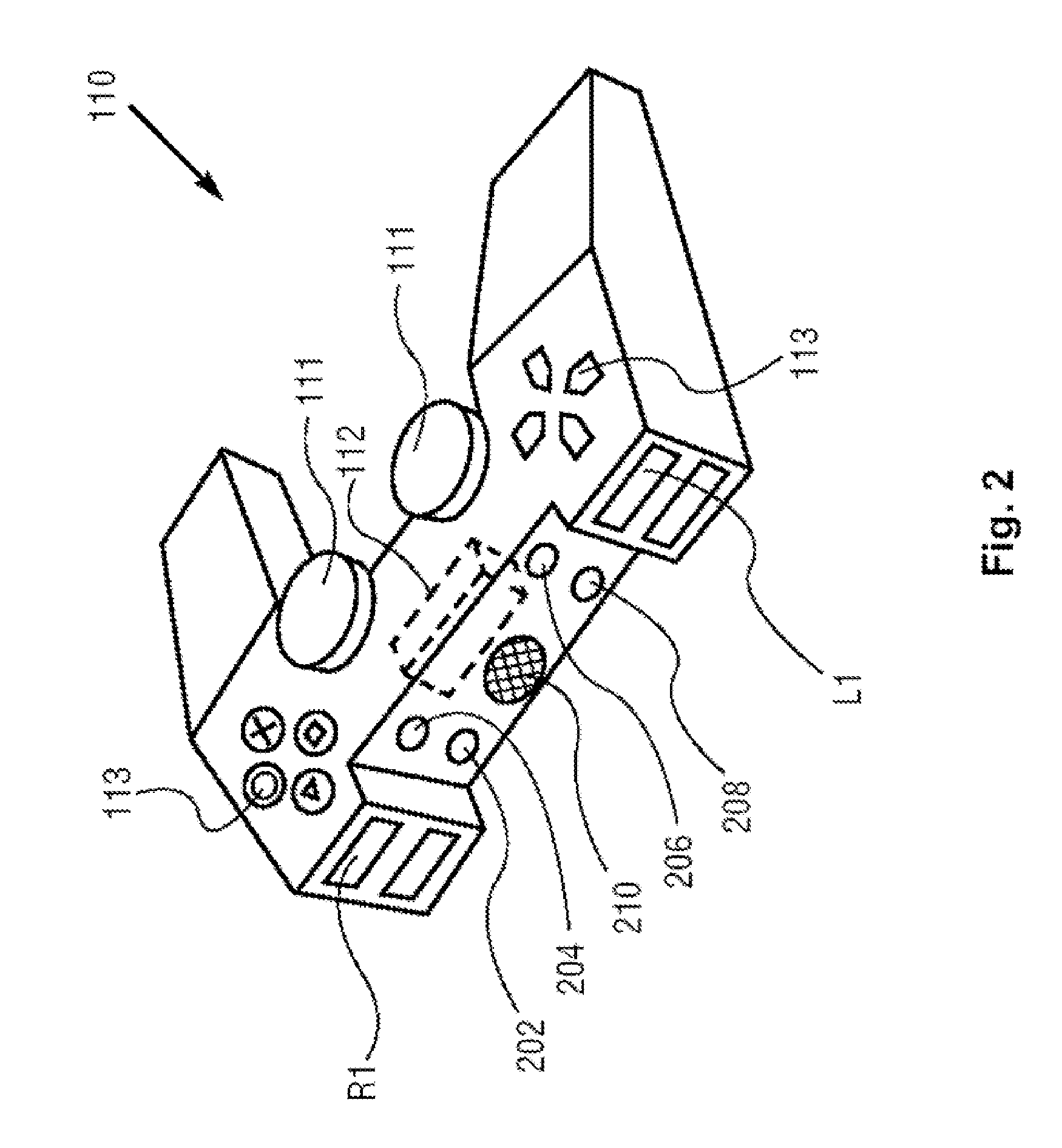
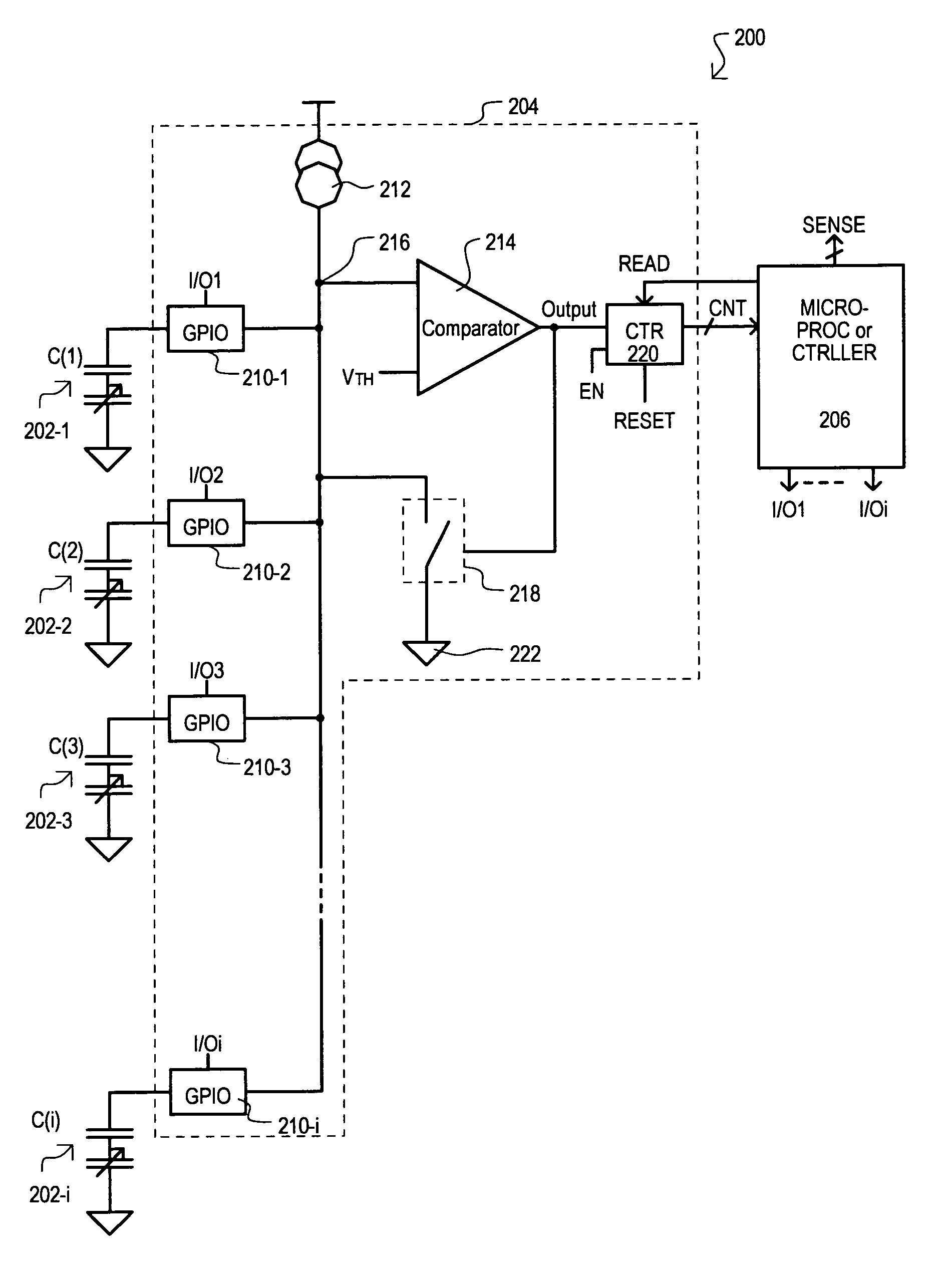
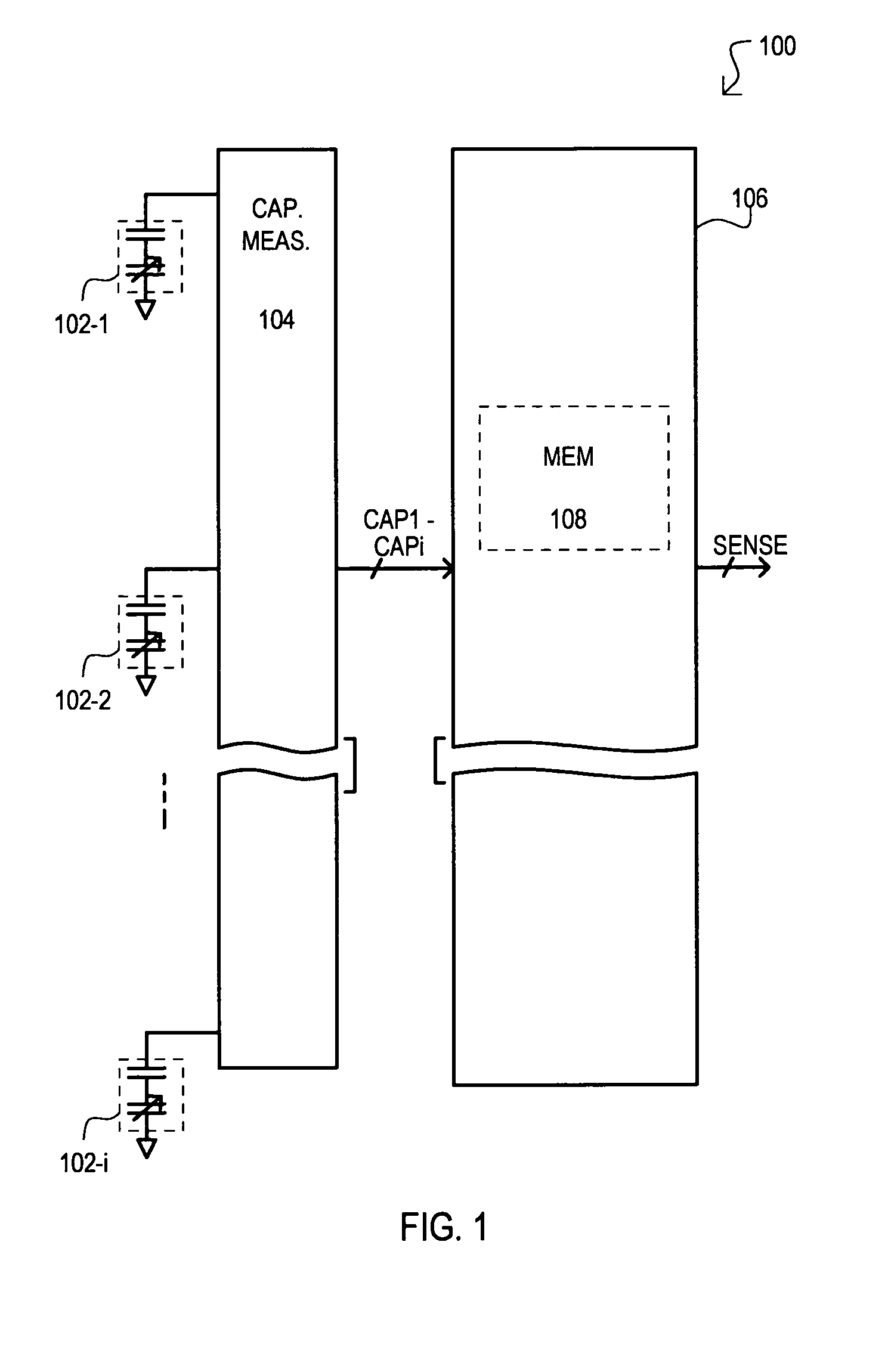
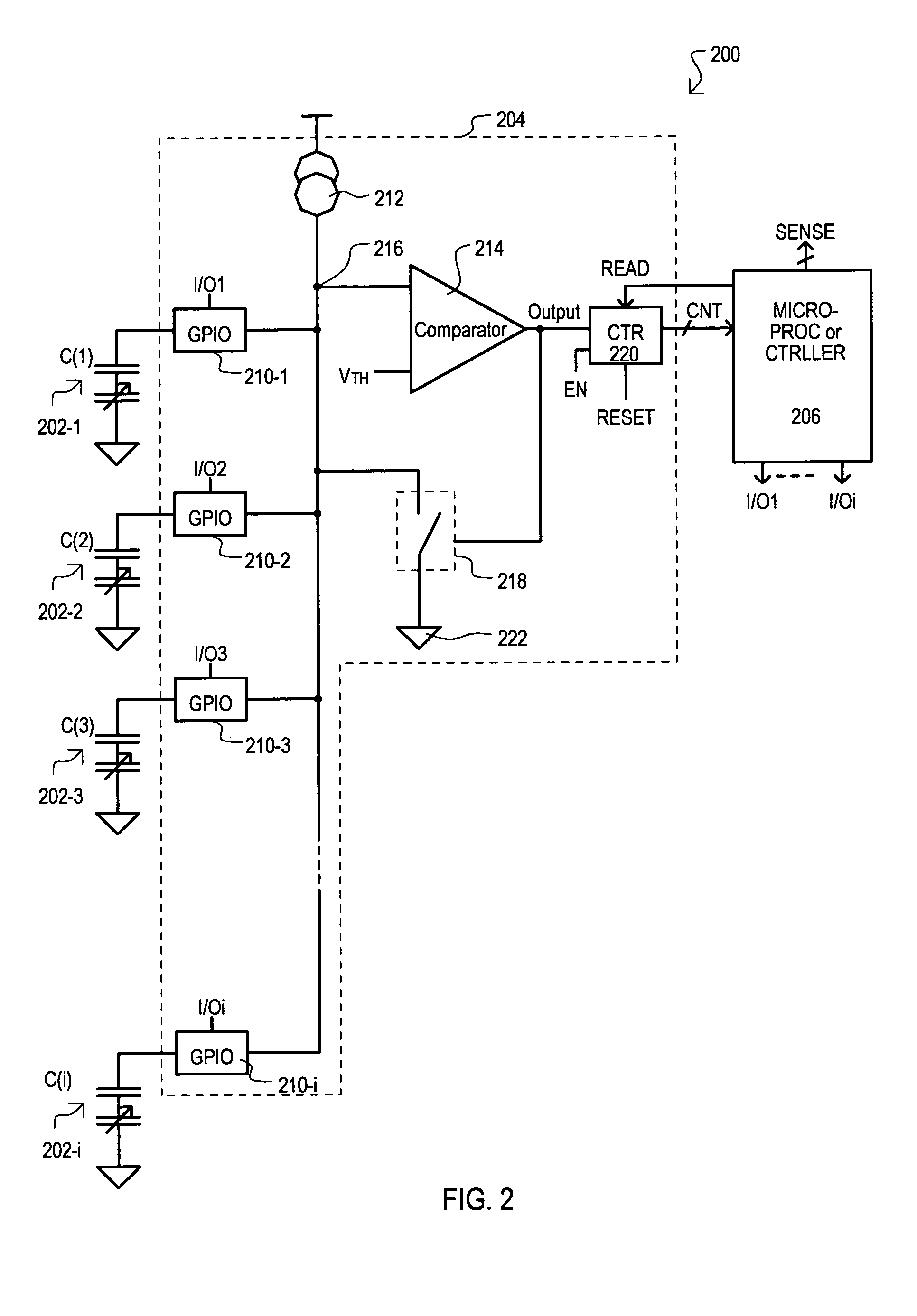
Automatically balanced sensing device and method for multiple capacitive sensors
Disclosed is method for compensating for variation in the capacitance between multiple capacitive sensors. Prior to sensing operations, baseline capacitance values can be acquired for all sensors. A correction factor can be calculated based on such baseline values. During sensing operations (run-time), variations in capacitance from baseline values can be modified by appropriate correction factors. Sensitivity between sensors can thus be made more uniform.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
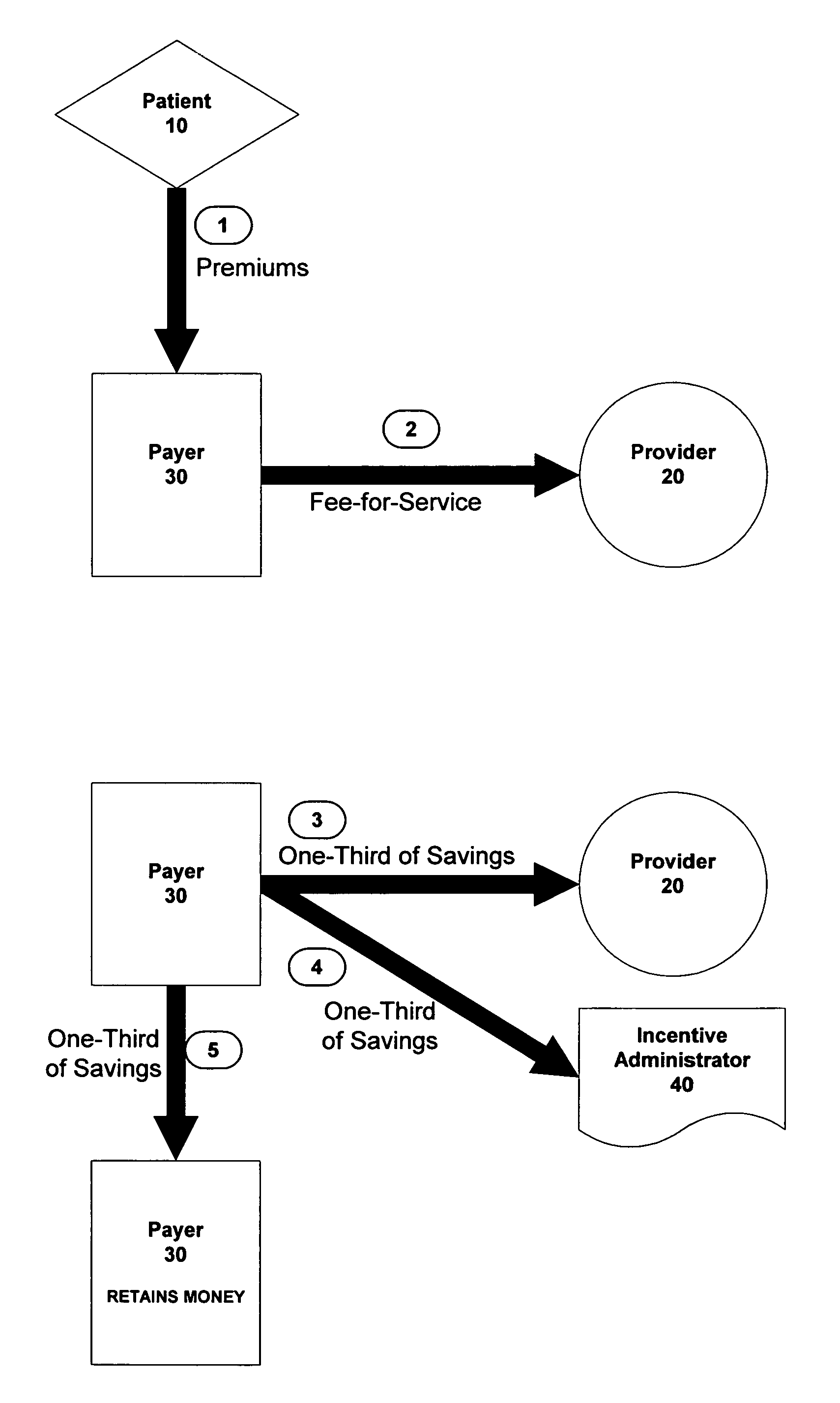
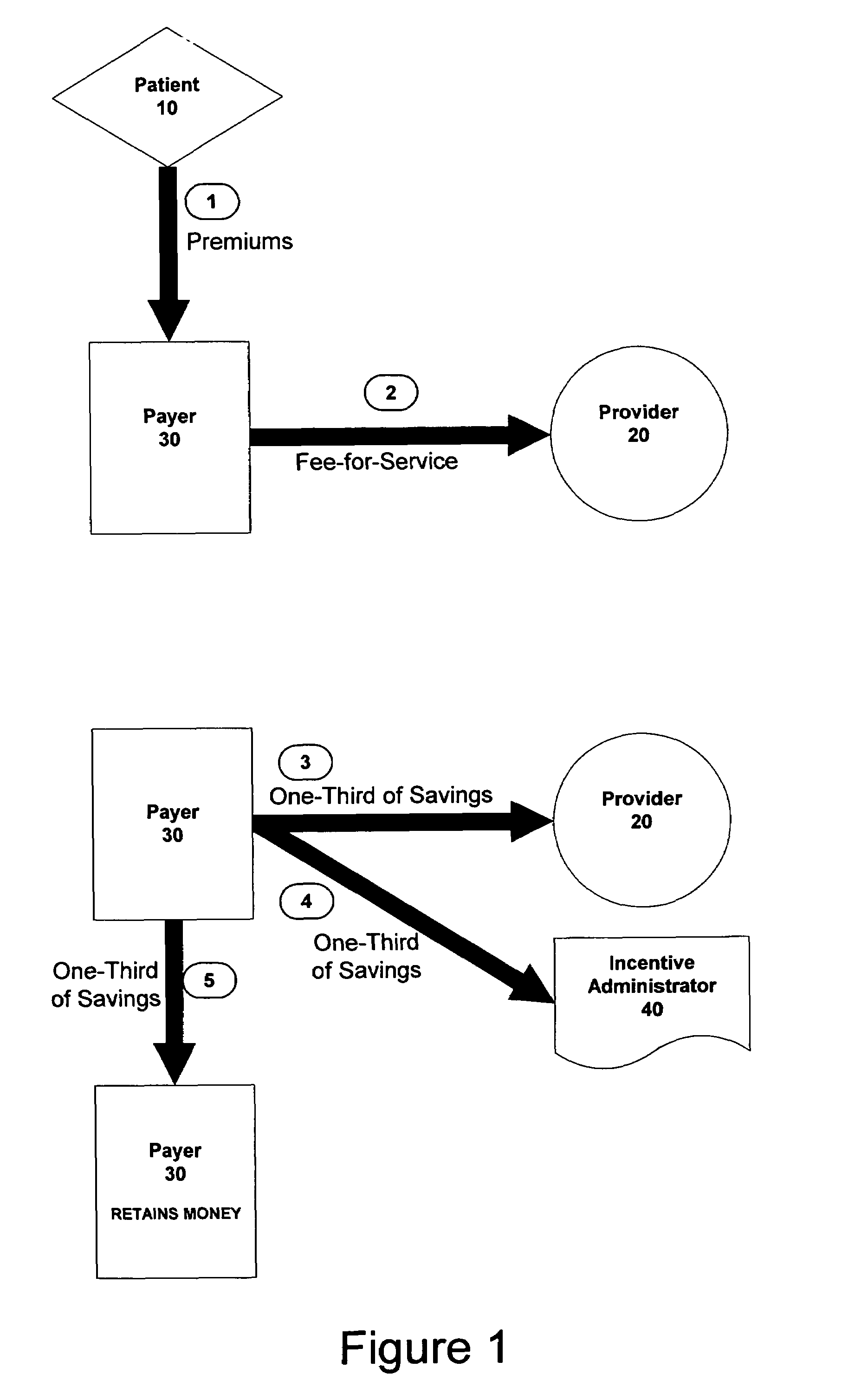
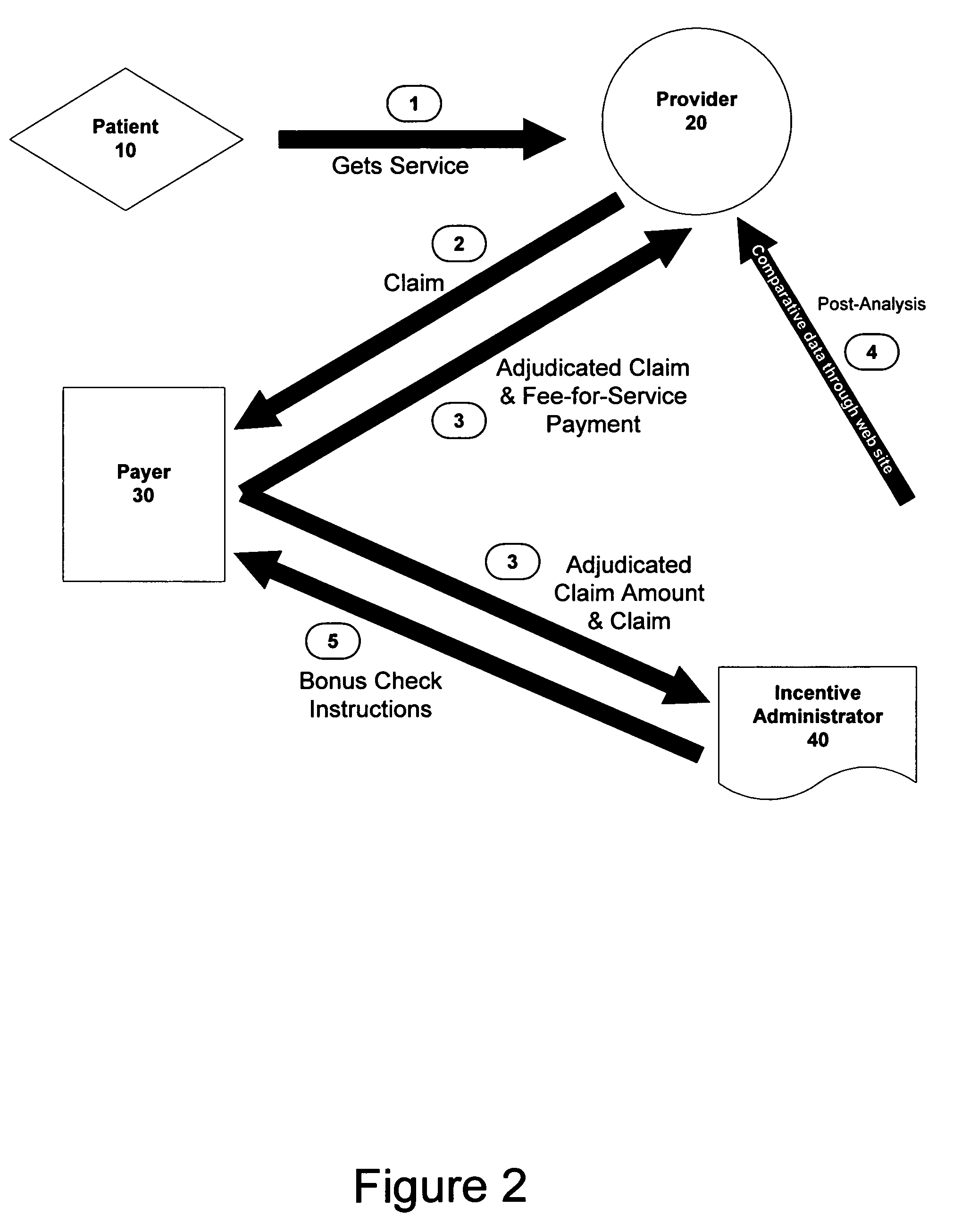
Method and apparatus for providing incentives to physicians
Owner:CLINTON B ASHFORD M D
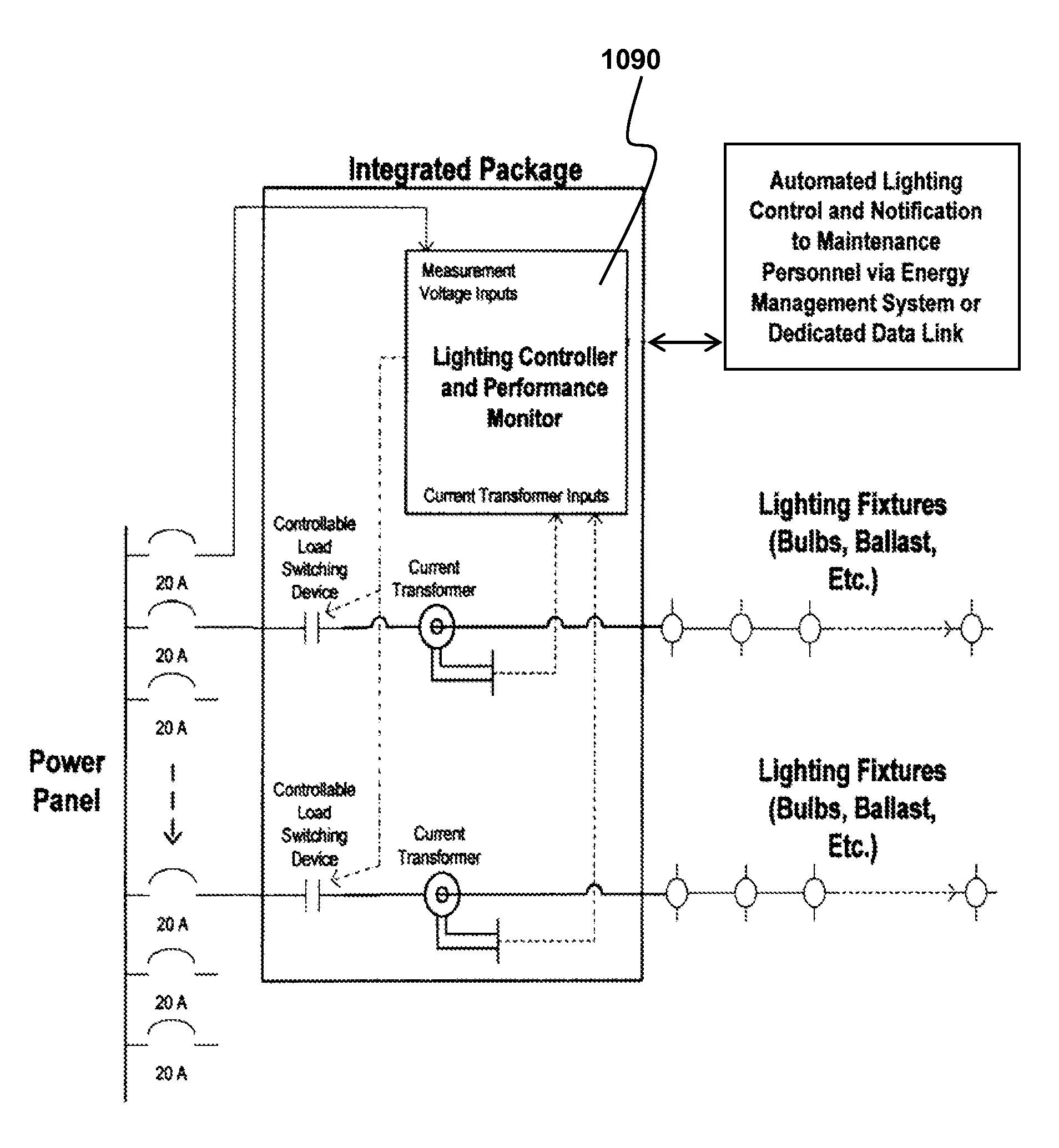
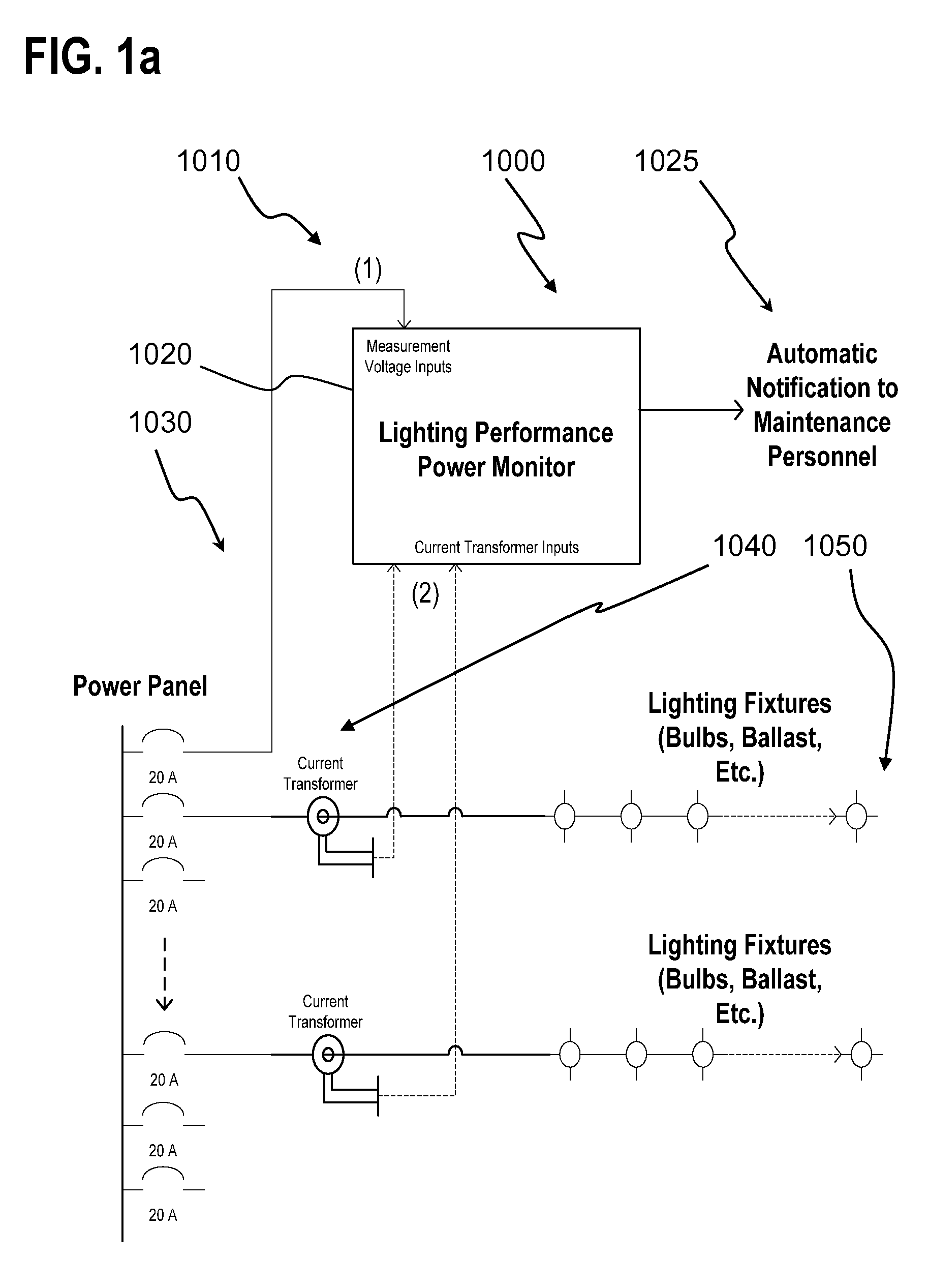
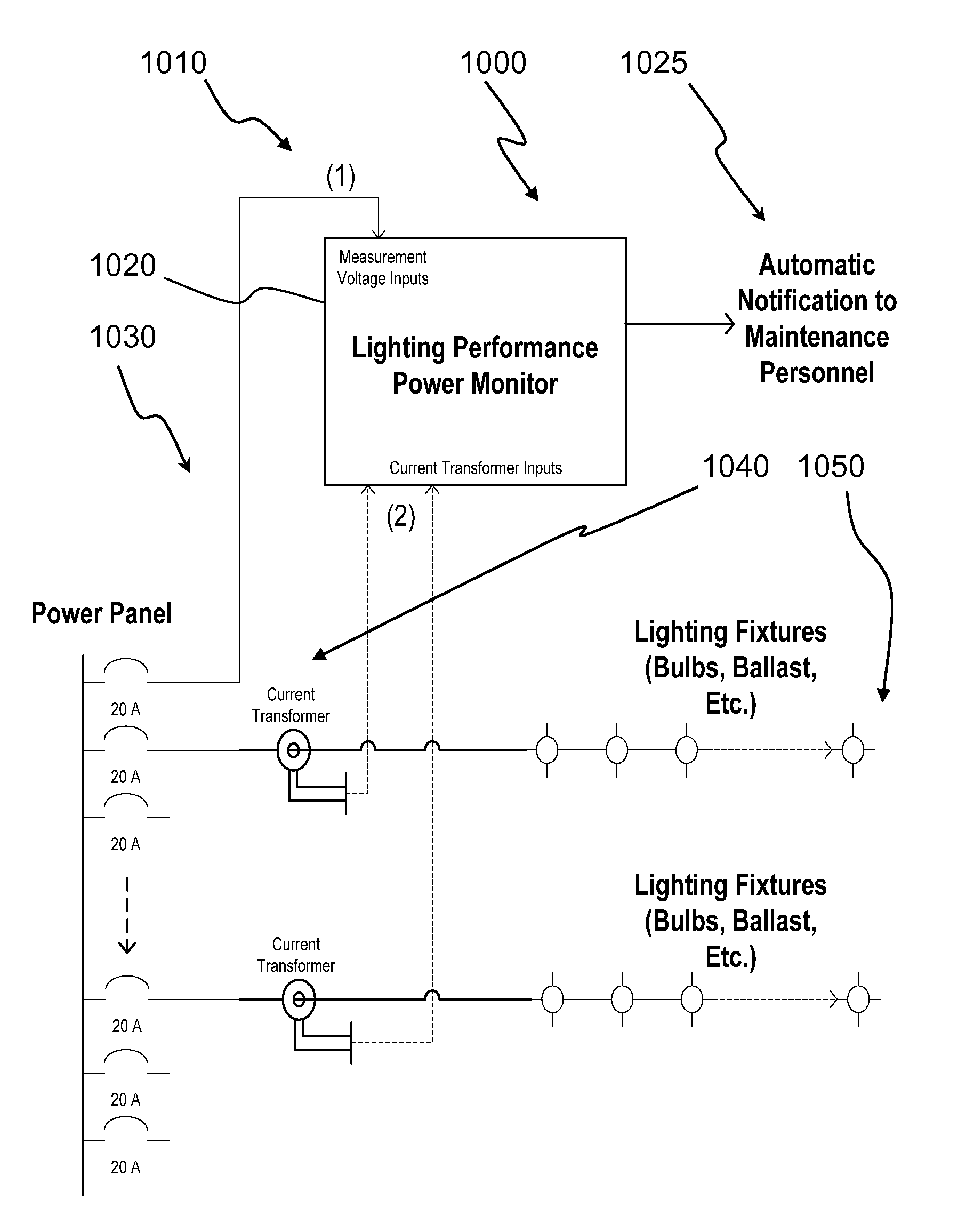
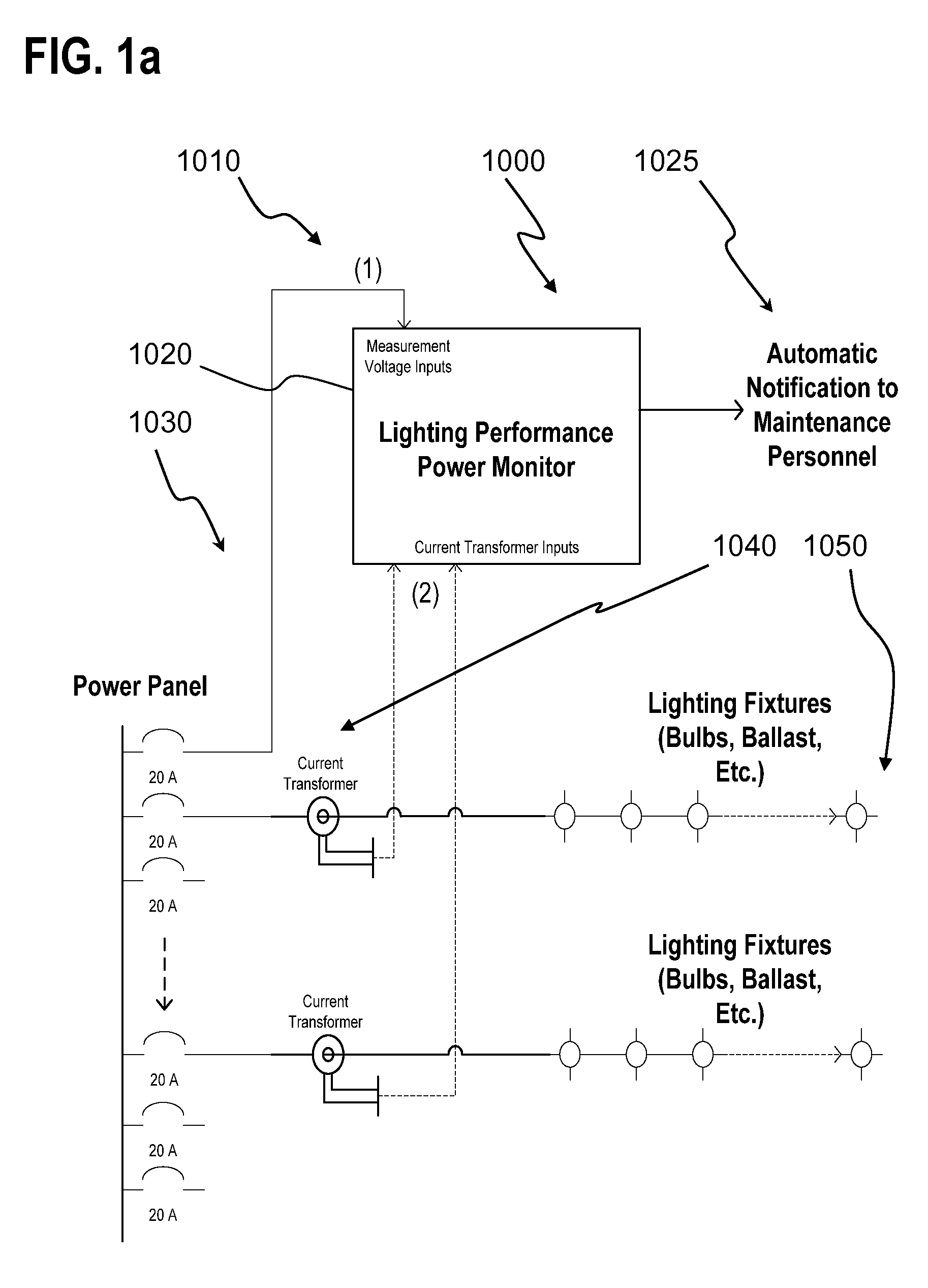
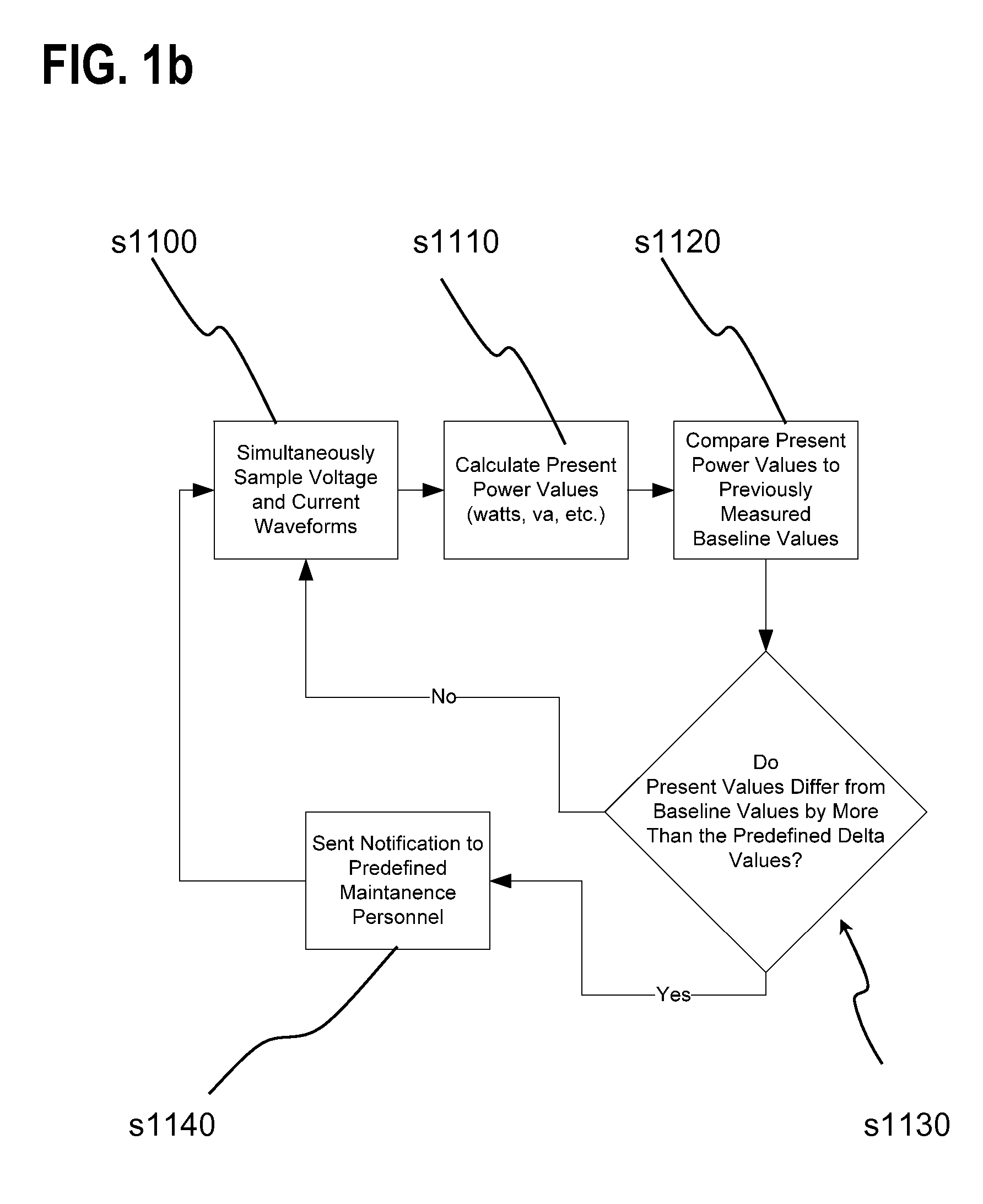
Lighting performance power monitoring system and method with optional integrated light control
ActiveUS7571063B2Save energyLow costLevel controlPower measurement by digital techniqueEngineeringBallast
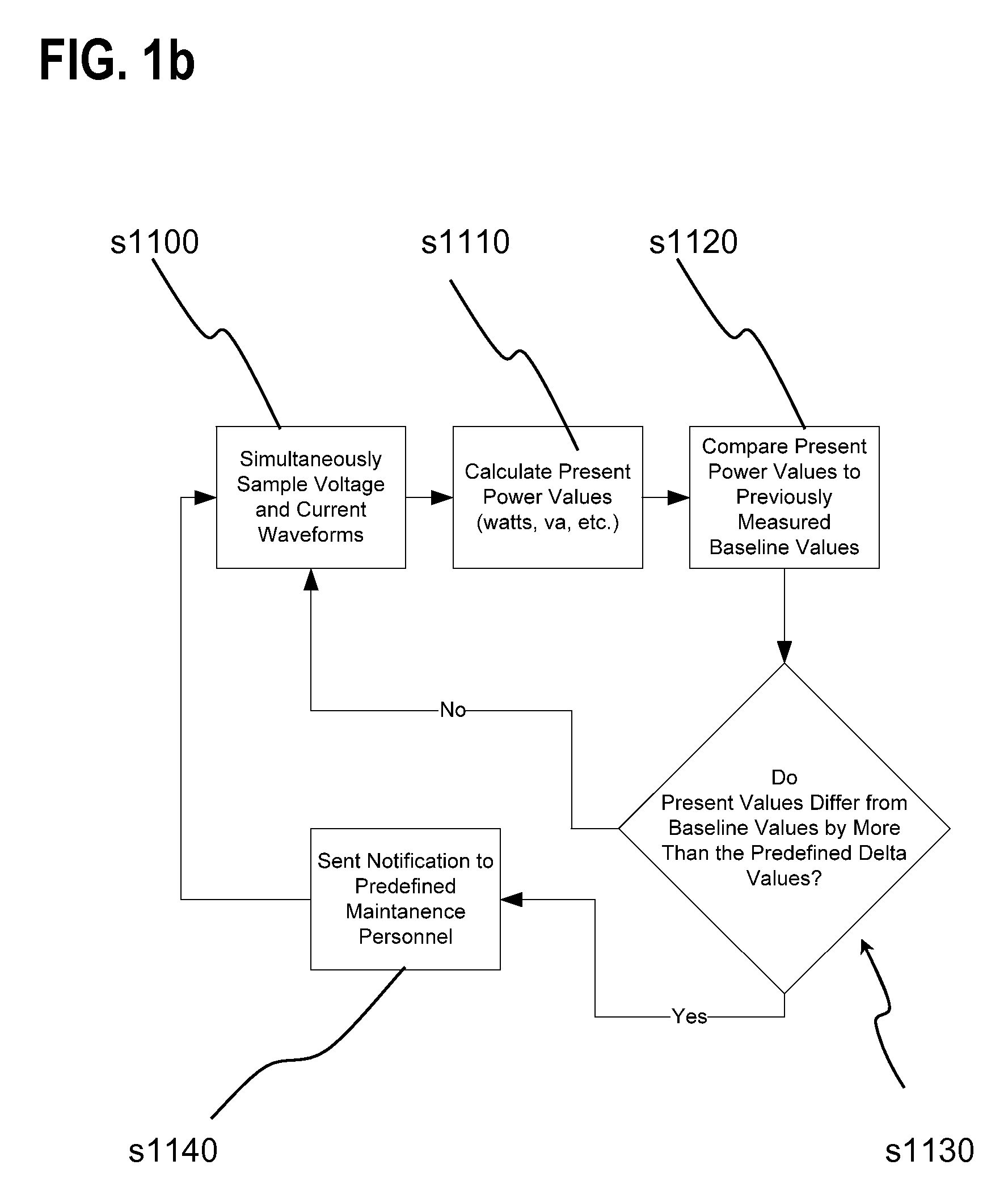
A light performance monitoring device and optionally integrated controller includes a monitor module that directly monitors energy usage of at least one energy load to generate at least one measurement of energy usage; a storage module stores a series of baseline values of energy usage of the energy load, a comparator module compares energy measurements made at predetermined intervals with the baseline values, and a notification module notifies a designated recipient that there is a deviation from the baseline values consistent with a burned out or non-operational light fixture, including but not limited to light bulbs or ballast devices. A control module optionally integrated with the light performance monitoring device can be operatively coupled to the monitor module to control energy usage by the at least one energy load via a data link in a pre-determined manner that is based on the at least one measurement of energy usage.
Owner:GRIDPOINT
Method and system for monitoring containers to maintain the security thereof
A container and contents monitoring system includes a device, a reader, a server, and a software backbone. The device communicates with the reader in order to determine the security of the container to which the device is attached. The reader transmits the information from the device to the server. The sensor senses a distance or an angle value between a door of the container and a frame of the container and the sensed value is then transmitted to the device. The device obtains a baseline value that is related to a calculated mean value. The device also obtains a detection threshold. The device determines if a security condition has occurred based on the sensed value and the detection threshold.
Owner:COMMERCEGUARD
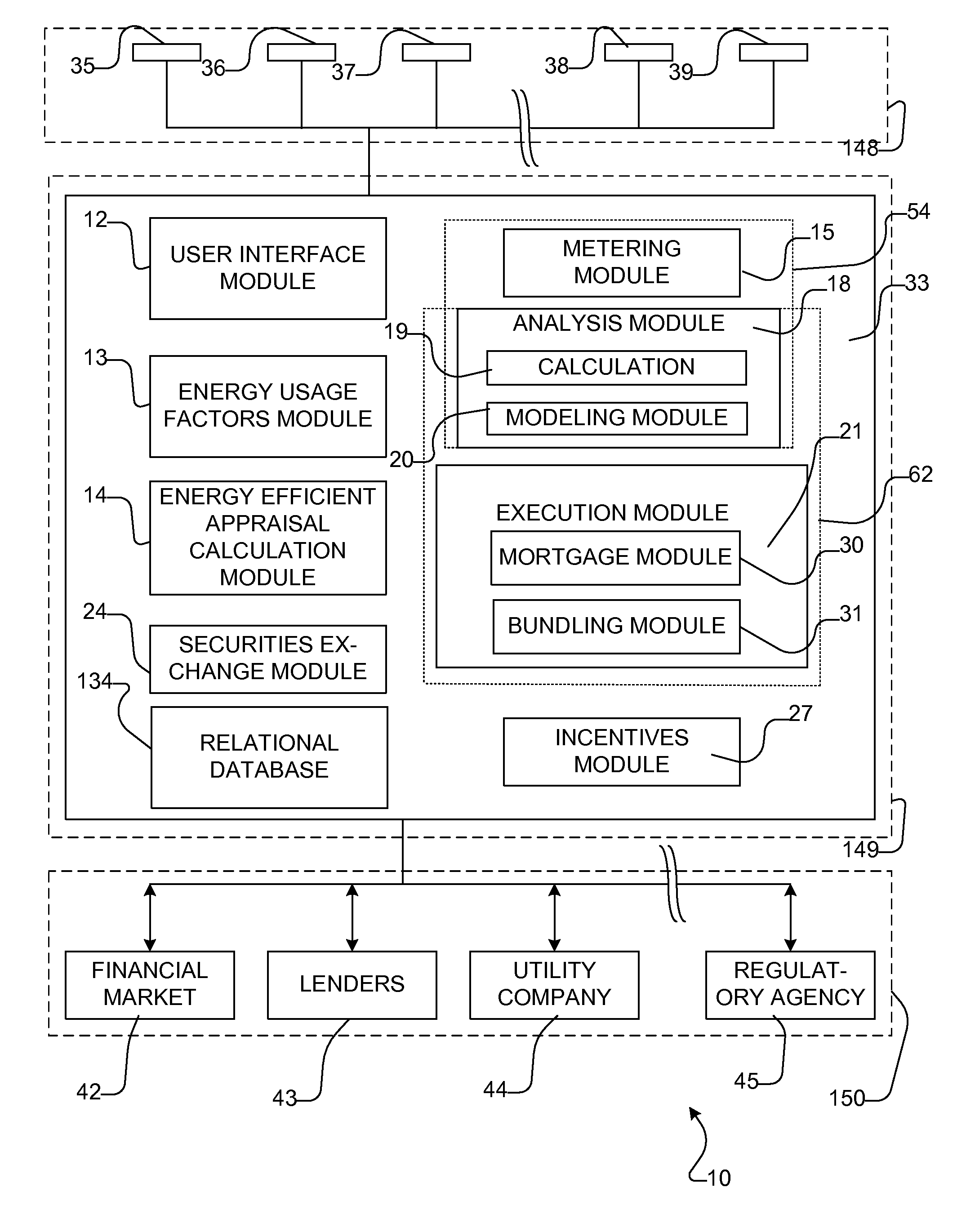
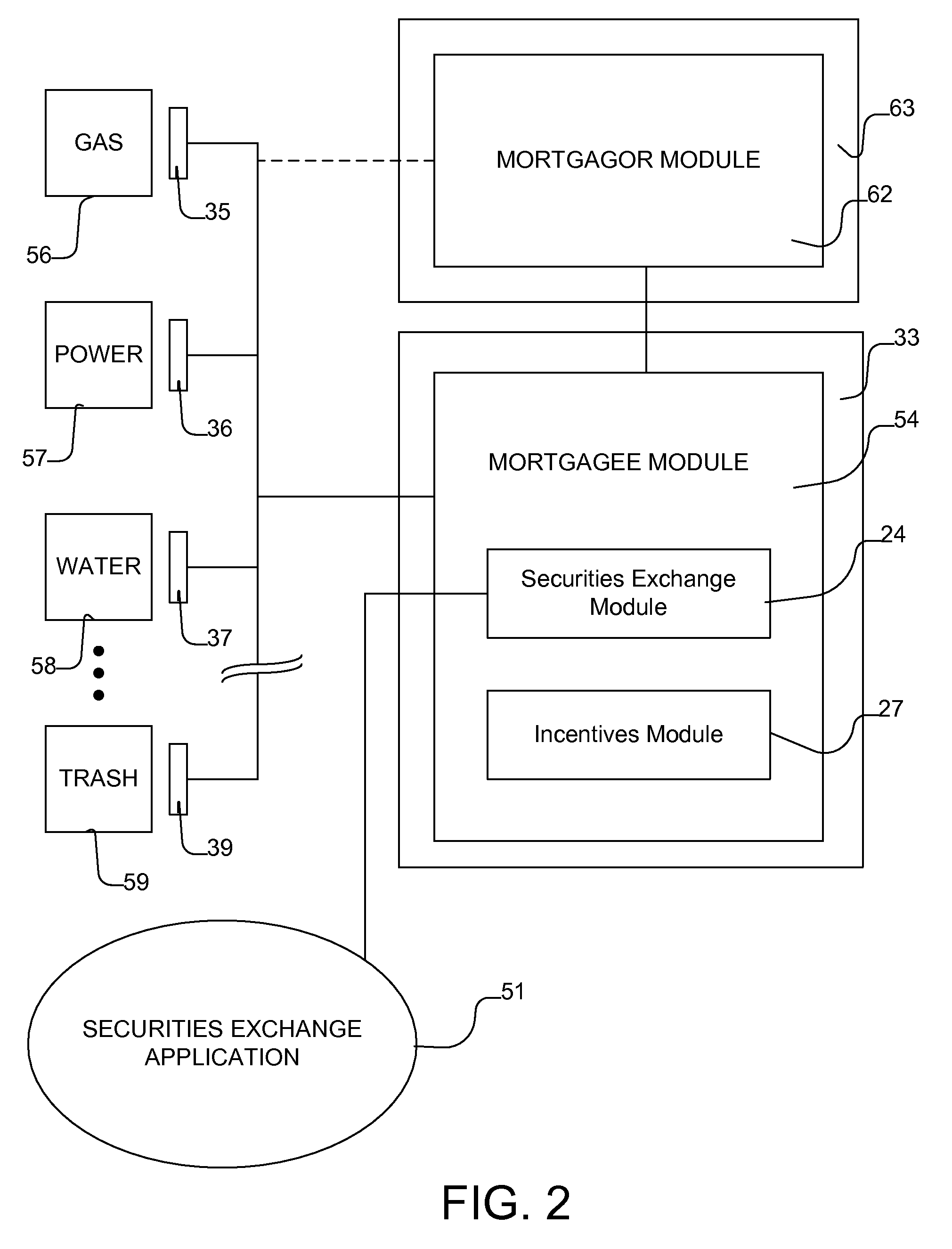
Apparatus, system, and method for quantifying energy usage and savings
InactiveUS8266076B2Facilitates capital fundingElectric devicesFinanceFinancial transactionComputer science
An apparatus, system, and method for quantifying energy usage and savings enables applying the savings to a financial transaction. Quantification includes estimating and / or monitoring usage of utilities by detectors, comparing the usage to a predetermined baseline value, and valuating an energy savings. Quantification relies on a comprehensive database to establish the baseline and to predict usage and savings. A portion of the savings may be applied to any of early repayment of a mortgage loan, investment in securities, and a request for a credit. The method and system standardizes values of energy units and / or monetary units, and quantifies savings. The method and system aids in qualifying the building project based on a concrete estimation of energy savings or a savings within a range. Thus, the method forms a bridge between green, other energy conserving, or sustainable technologies and the financial markets.
Owner:IIX
Assessment of vascular dilatation
A method and apparatus of assessment of relative changes in the cross sectional area of a limb artery. The method includes applying to the artery an external pressure, which causes the cross-sectional area of the artery to change between systole and diastole much more than if the pressure is not applied, determining, over one or more cardiac cycles, a baseline value for a parameter related to the cross-sectional area of the artery, while the pressure is applied, applying a stimulus to the artery, determining, over one or more cardiac cycles, a stimulus-affected value for the parameter related to the cross-sectional area of the artery, while the pressure is applied and while the artery is in a dilated state affected by the stimulus and evaluating the artery based on a comparison of the determined stimulus-affected and baseline values, the baseline value is determined while the artery is substantially not affected by the stimulus.
Owner:DAFNI EHUD
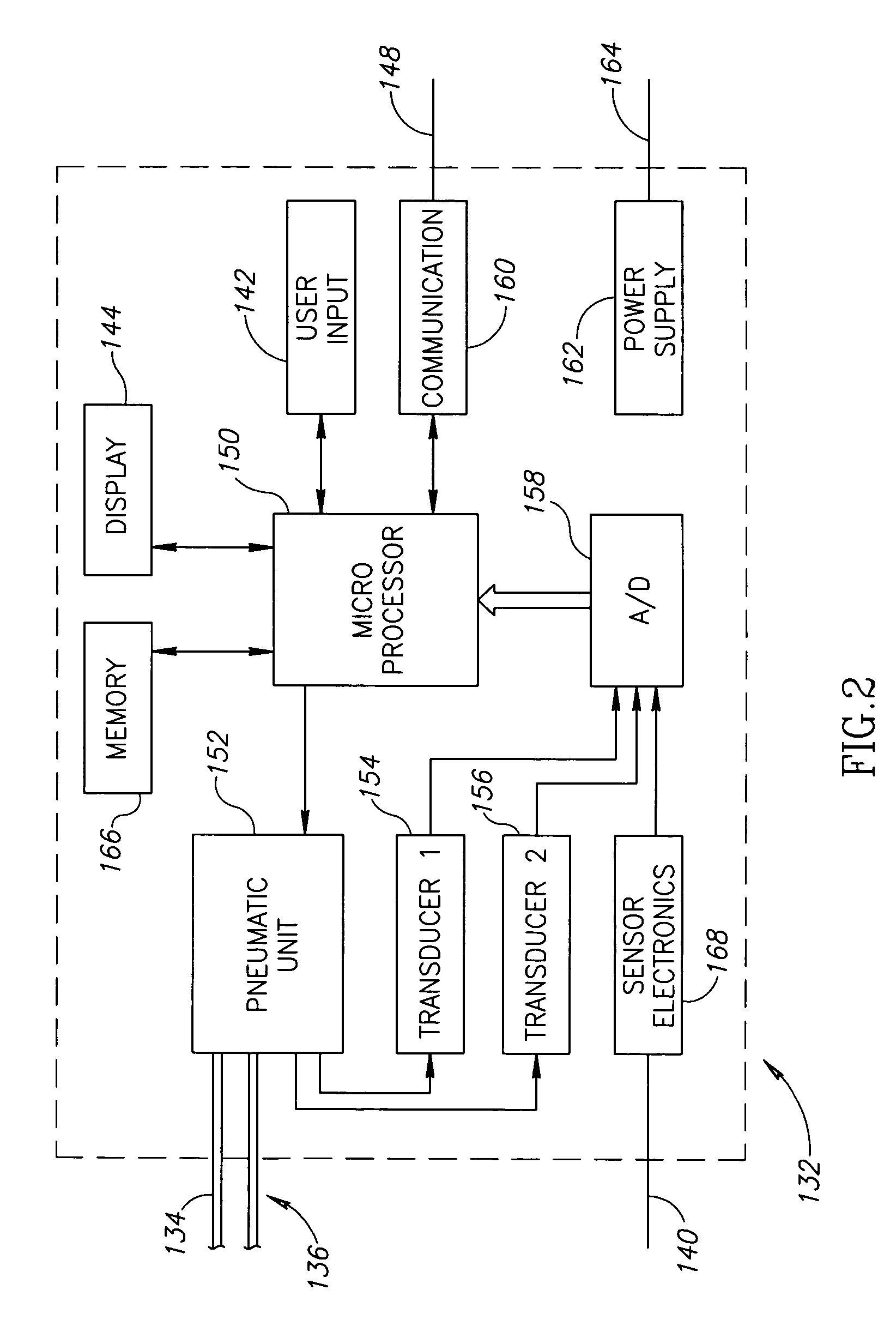
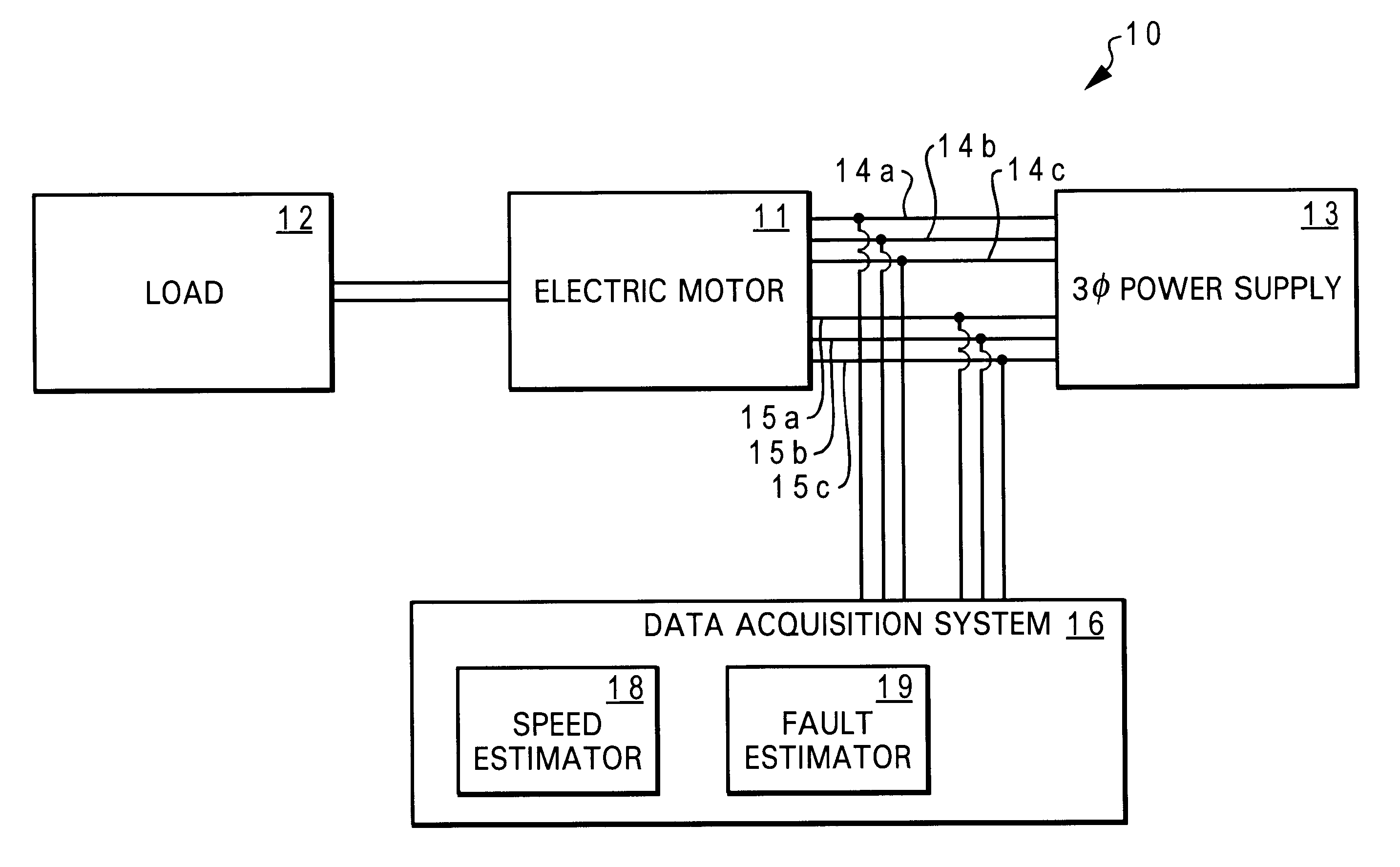
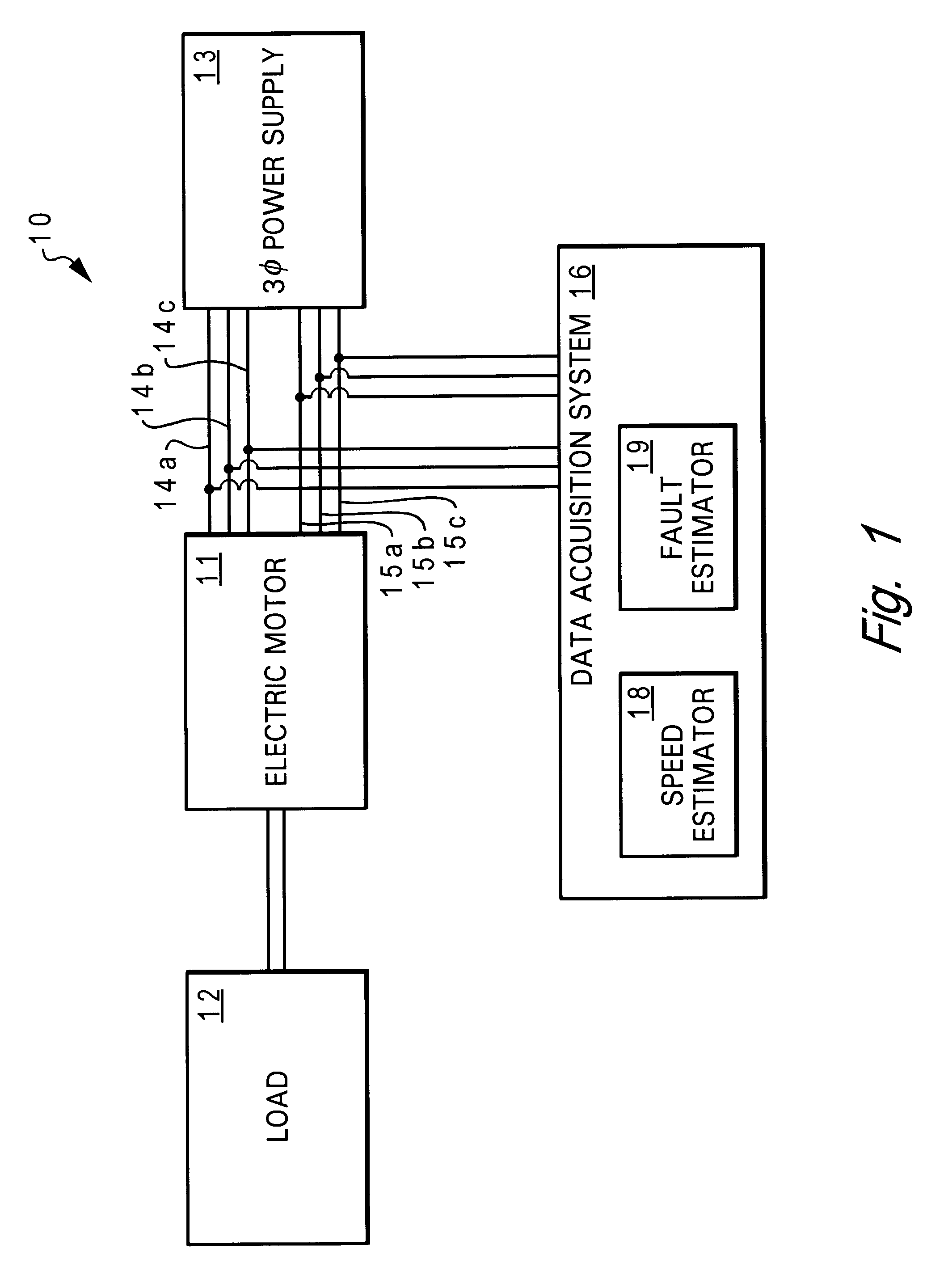
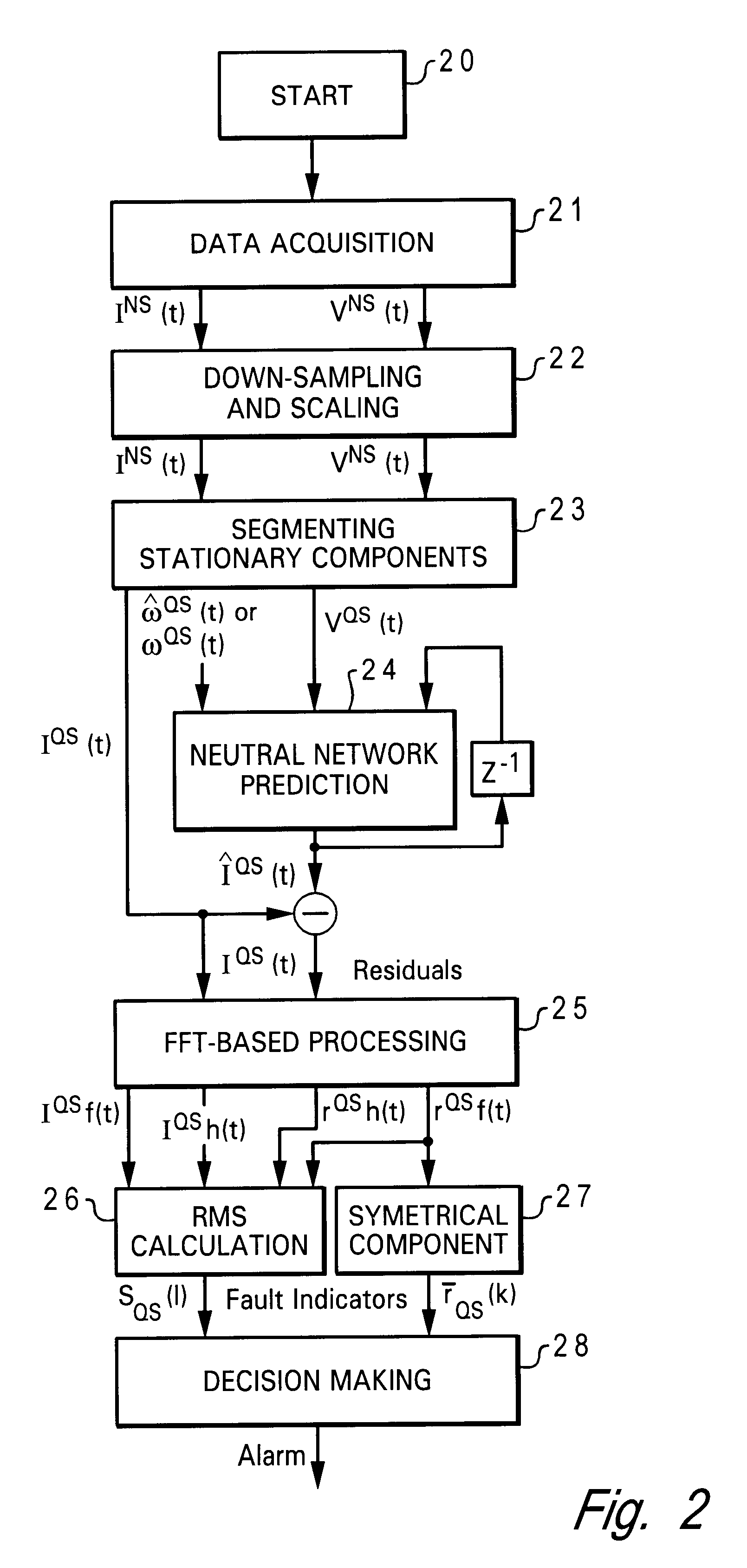
Method and system for early detection of incipient faults in electric motors
InactiveUS6590362B2Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersFault indicatorMotor speed
A method and system for early detection of incipient faults in an electric motor are disclosed. First, current and voltage values for one or more phases of the electric motor are measured during motor operations. A set of current predictions is then determined via a neural network-based current predictor based on the measured voltage values and an estimate of motor speed values of the electric motor. Next, a set of residuals is generated by combining the set of current predictions with the measured current values. A set of fault indicators is subsequently computed from the set of residuals and the measured current values. Finally, a determination is made as to whether or not there is an incipient electrical, mechanical, and / or electromechanical fault occurring based on the comparison result of the set of fault indicators and a set of predetermined baseline values.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Assessment of vascular dilatation
A method and apparatus of assessment of relative changes in the cross sectional area of a limb artery. The method includes applying to the artery an external pressure, which causes the cross-sectional area of the artery to change between systole and diastole much more than if the pressure is not applied, determining, over one or more cardiac cycles, a baseline value for a parameter related to the cross-sectional area of the artery, while the pressure is applied, applying a stimulus to the artery, determining, over one or more cardiac cycles, a stimulus-affected value for the parameter related to the cross-sectional area of the artery, while the pressure is applied and while the artery is in a dilated state affected by the stimulus and evaluating the artery based on a comparison of the determined stimulus-affected and baseline values, the baseline value is determined while the artery is substantially not affected by the stimulus.
Owner:DAFNI EHUD
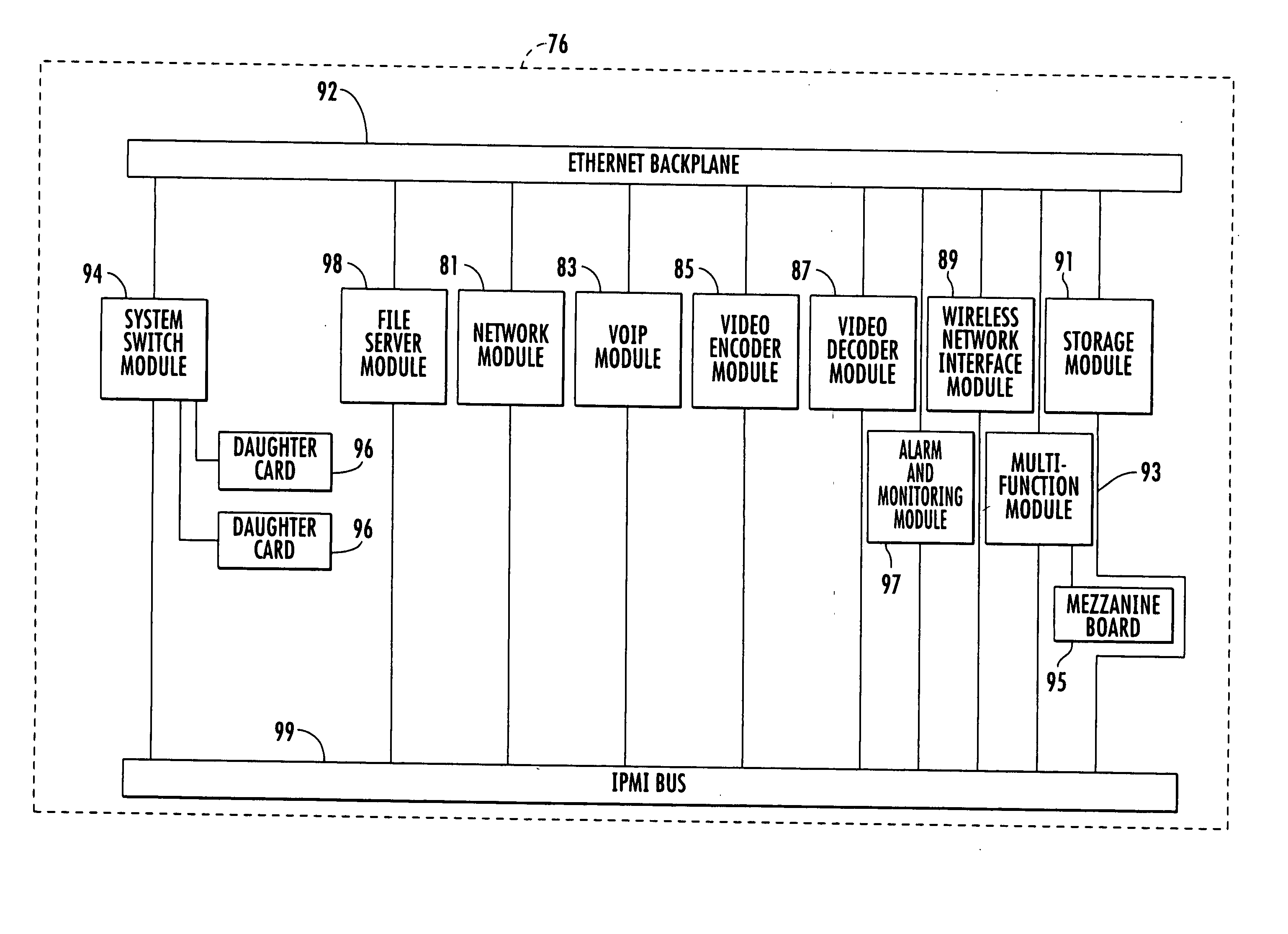
Telecommunications device and method
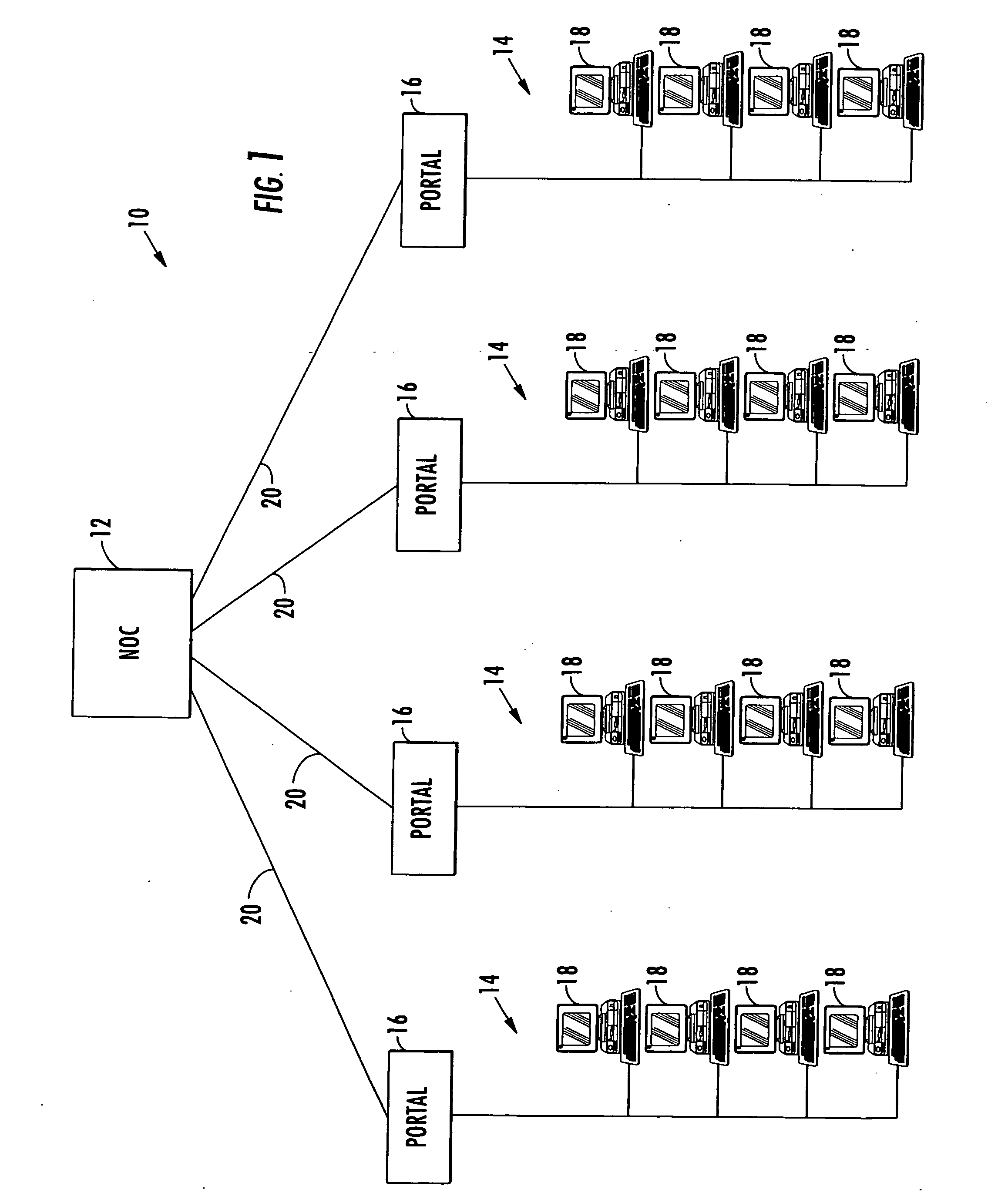
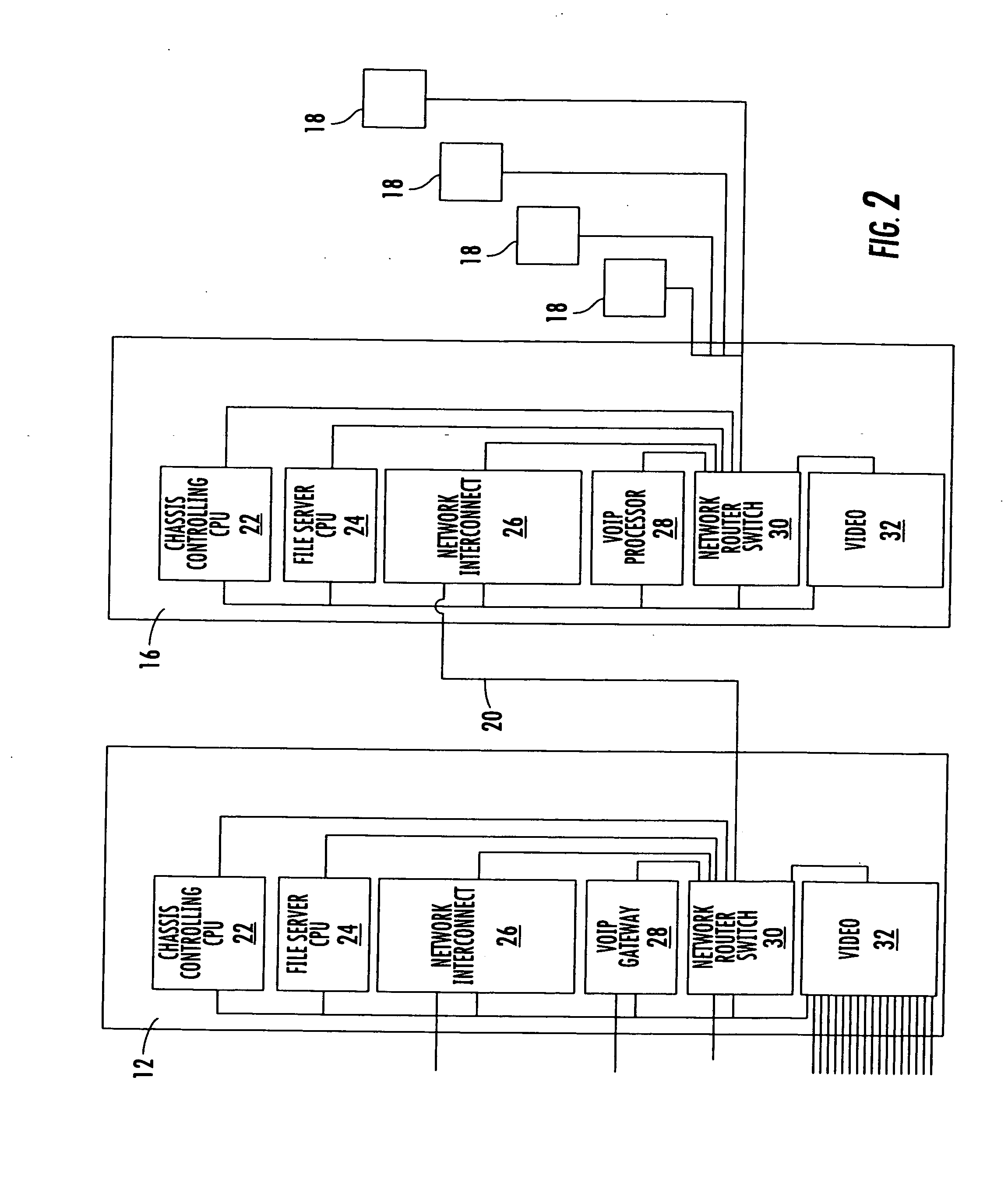
InactiveUS20050091304A1Easy to upgradePolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesMultiple digital computer combinationsControl systemModularity
A control system for a telecommunications portal includes a modular chassis including an Ethernet backplane and a platform management bus which houses at least one application module, at least one functional module, and a portal executive. The modules are connected to the backplane and the management bus. At least one sensor detects operational parameters of at least one of the modules and transmits sensor data representative of the operational parameters over the management bus. The portal executive includes receives the sensor data from the management bus, compares the sensor data to pre-established baseline values for the operational parameters, and performs a control action in response to a deviation of the sensor data from the baseline values.
Owner:ADVANCED PREMISE TECH
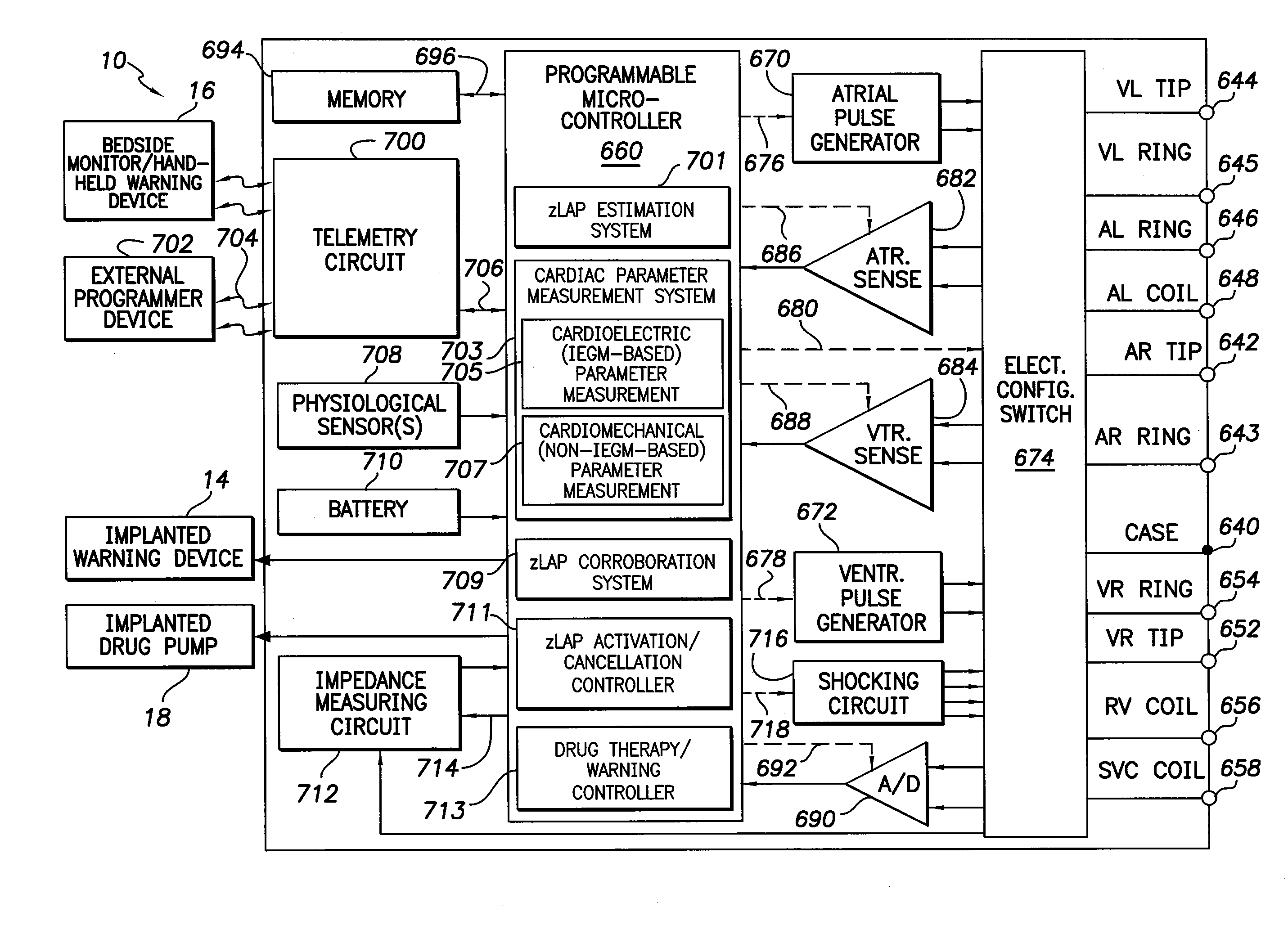
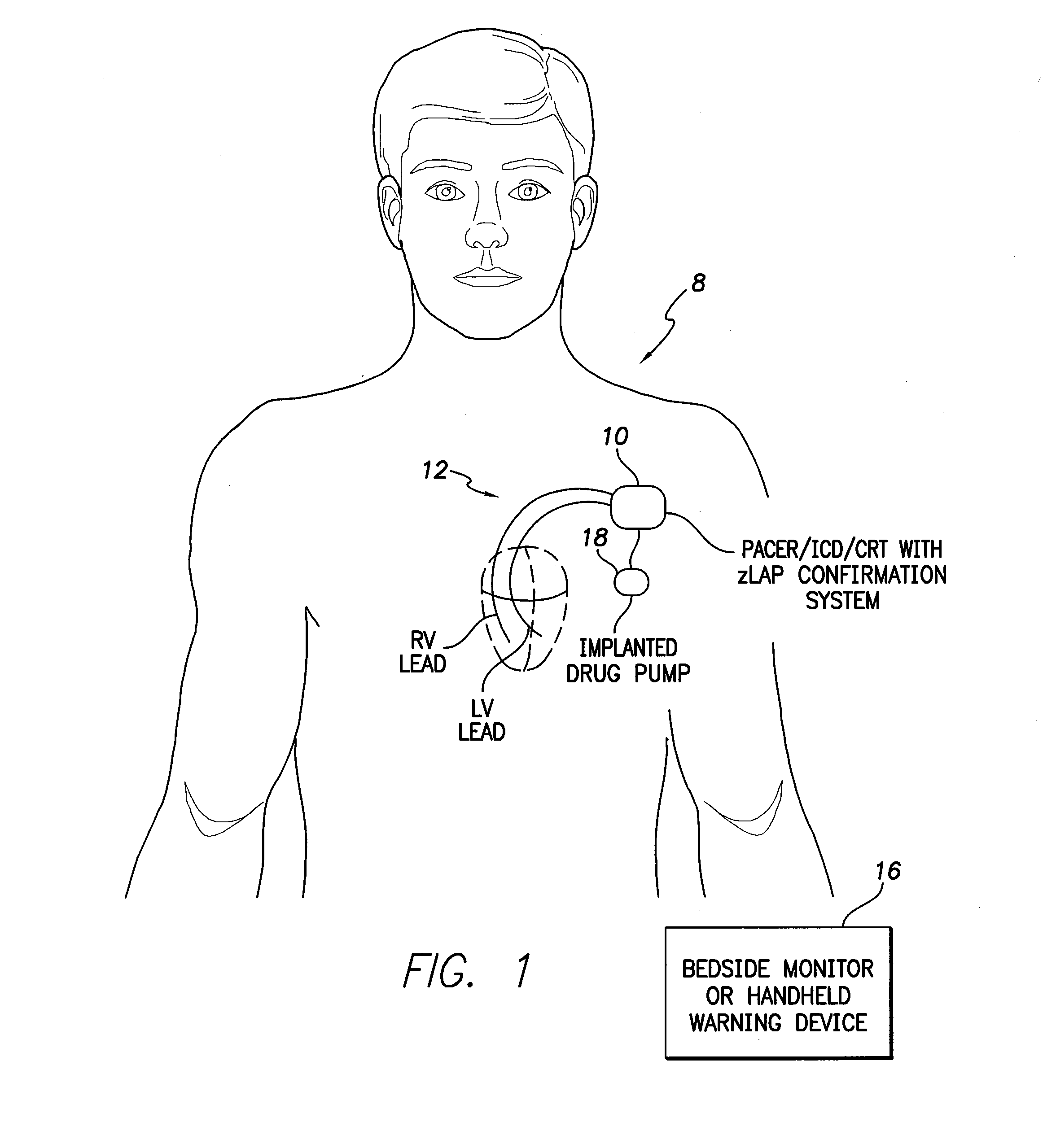
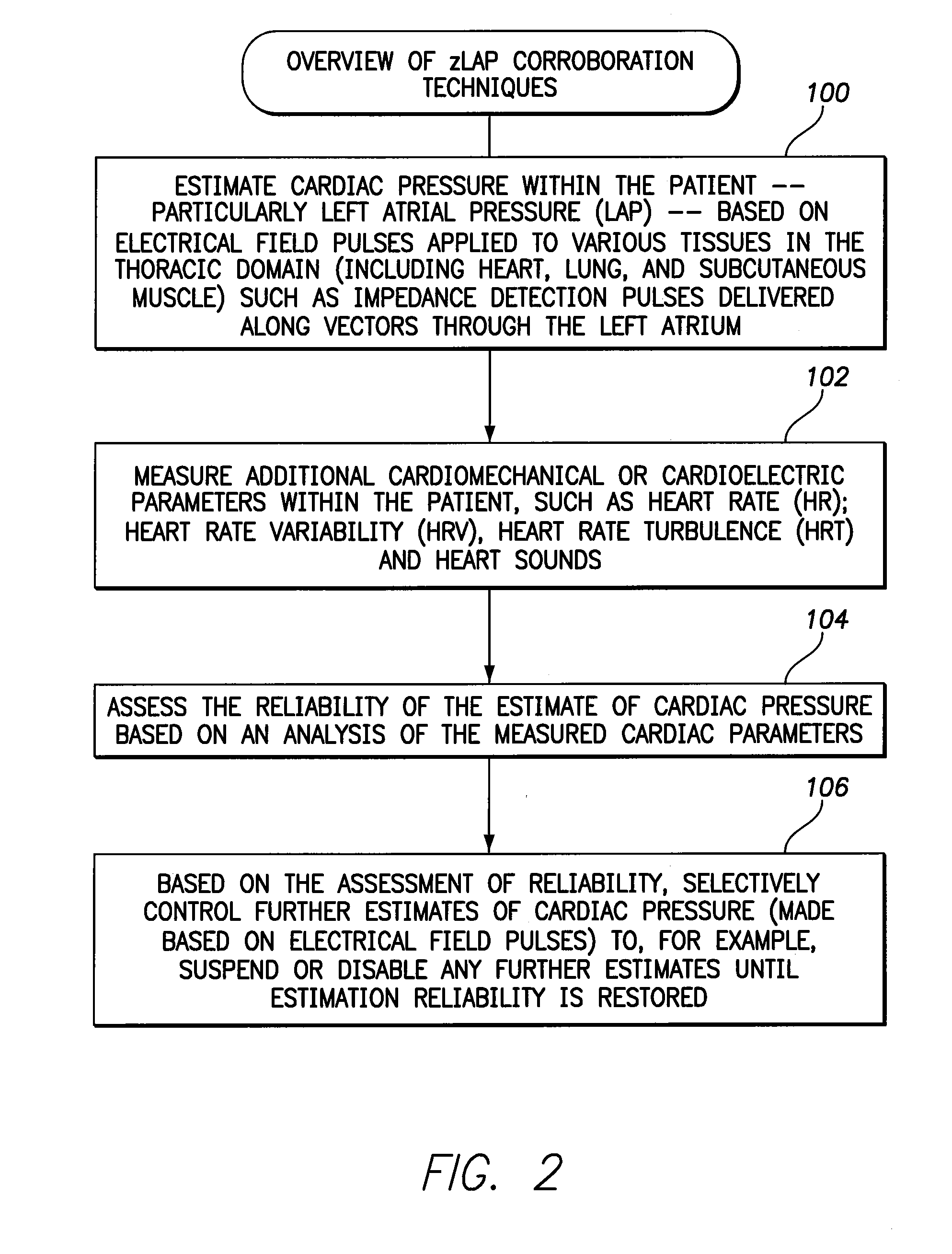
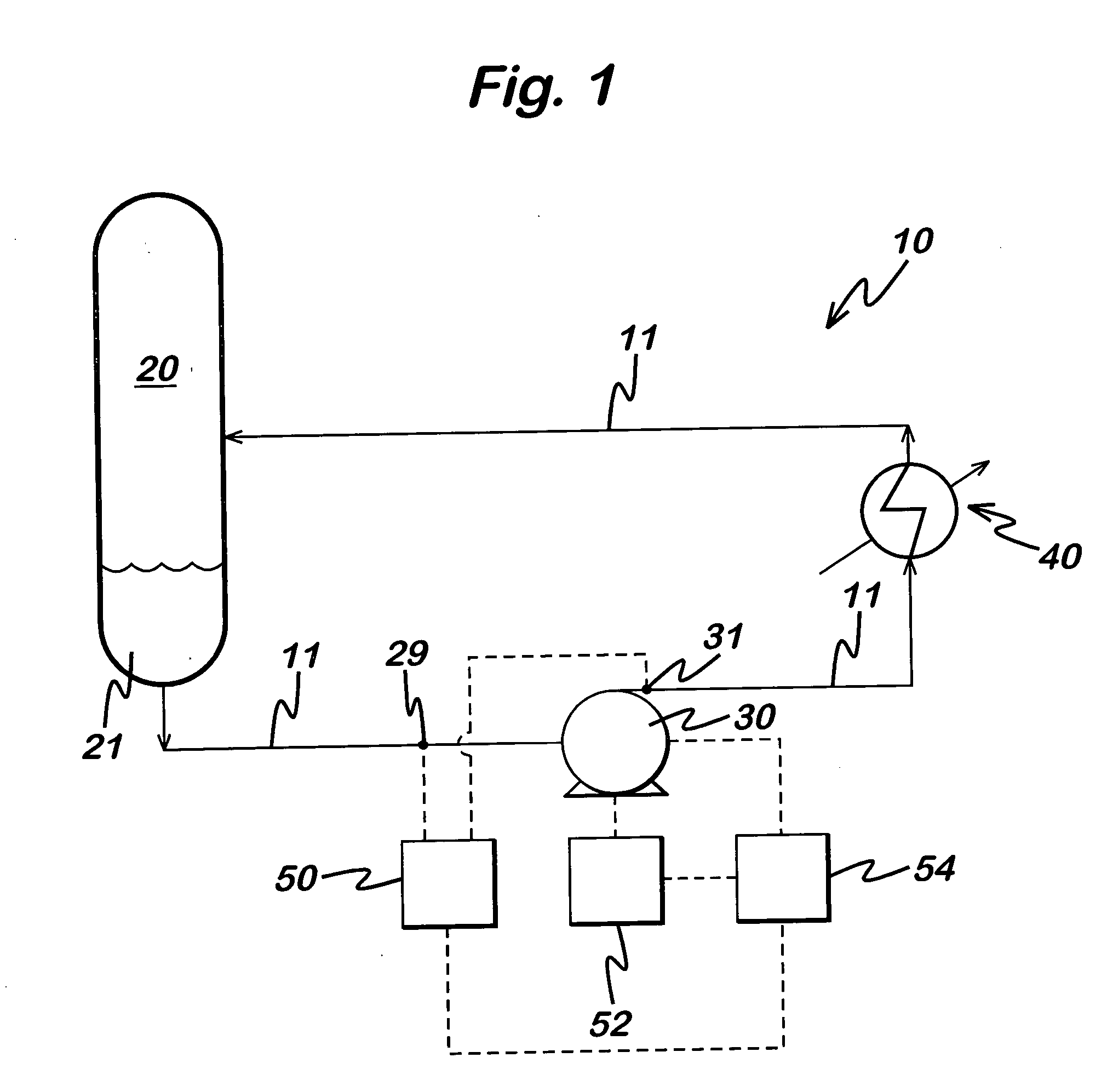
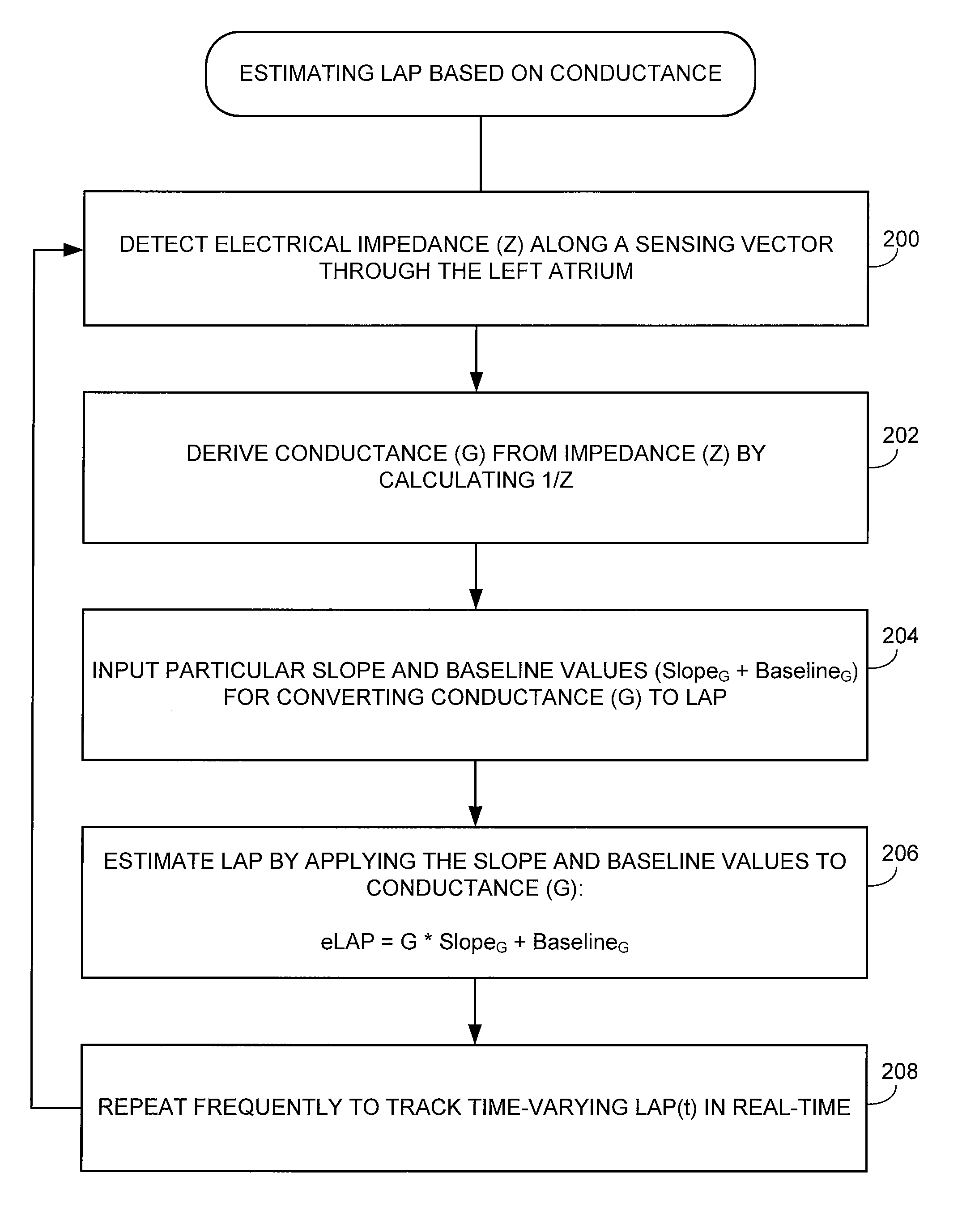
Systems and methods for corroborating impedance-based left atrial pressure (LAP) estimates for use by an implantable medical device
Various techniques are provided for assessing the reliability of left atrial pressure (LAP) estimates made by an implantable medical device based on impedance values or related electrical values. In one example, various cardioelectric and cardiomechanical parameters are used to corroborate LAP estimation in circumstances where the LAP estimates deviate from an acceptable, satisfactory or otherwise healthy range. The cardioelectric parameters include, e.g.: ST elevation; heart rate (HR); heart rate variability (HRV); T-wave alternans (TWA); QRS waveform parameters; P-wave duration; evoked response (ER) parameters; and intrinsic PV / AV / VV conduction delays. The cardiomechanical parameters include, e.g.: heart rate turbulence (HRT); cardiogenic impedance signals; heart sounds; and non-LAP blood pressure measurements, such as aortic pressure measurements. The device compares the cardioelectric and cardiomechanical parameters against corresponding baseline values to determine whether variations in the parameters corroborate the LAP estimates. If not, the LAP estimates are selectively cancelled or suspended, or the overall procedure is re-calibrated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
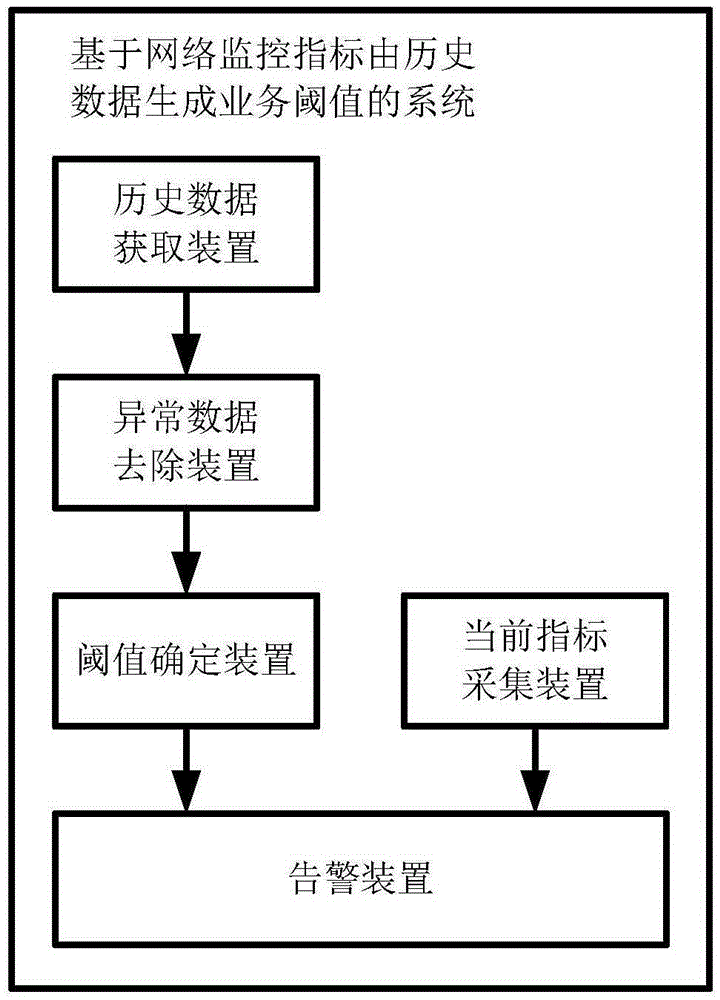
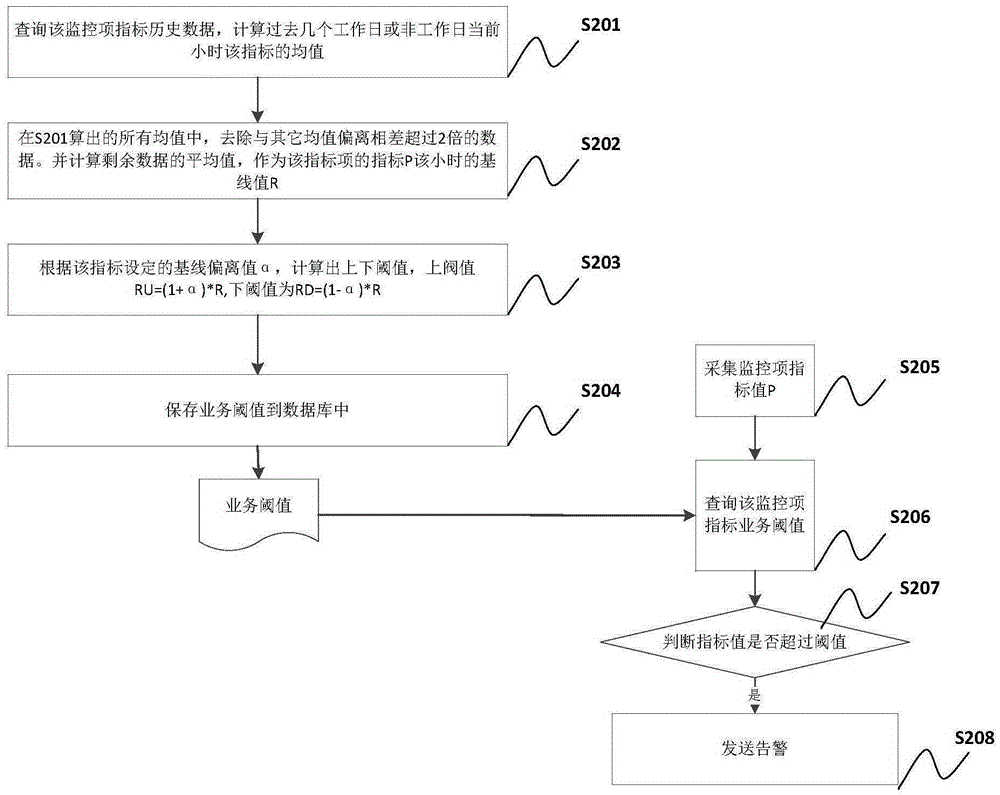
Method and system for generating service threshold by historical data based on network monitoring indexes
InactiveCN105406991AAvoid manual entryReduce operation and maintenance labor costsData switching networksNetwork monitoringBaselining
The invention provides a method and a system for generating a service threshold by historical data based on network monitoring indexes. The method comprises steps: S1, monitoring item index historical data during a time period for the current time in history corresponding to date attributes of the same day are acquired; S2, abnormal data in the monitoring item index historical data are removed, and the average value of the remaining data after the abnormal data in the monitoring item index historical data are removed serves as a baseline value R for the monitoring item index; and S3, according to the baseline value R, a threshold or a threshold interval corresponding to the baseline value R is obtained. Based on the index historical data, the service threshold is calculated and generated respectively according to the date attributes and the time, the abnormal data are removed, a different baseline deviation value can be set, the actual condition in the case of network monitoring application can be met, and the accuracy of monitoring warning is improved.
Owner:ECCOM NETWORK SYST CO LTD
Lighting performance power monitoring system and method with optional integrated light control
ActiveUS20070282547A1Save energyReduce materialLevel controlPower measurement by digital techniqueEngineeringElectric power
A light performance monitoring device and optionally integrated controller includes a monitor module that directly monitors energy usage of at least one energy load to generate at least one measurement of energy usage; a storage module stores a series of baseline values of energy usage of the energy load, a comparator module compares energy measurements made at predetermined intervals with the baseline values, and a notification module notifies a designated recipient that there is a deviation from the baseline values consistent with a burned out or non-operational light fixture, including but not limited to light bulbs or ballast devices. A control module optionally integrated with the light performance monitoring device can be operatively coupled to the monitor module to control energy usage by the at least one energy load via a data link in a pre-determined manner that is based on the at least one measurement of energy usage.
Owner:GRIDPOINT
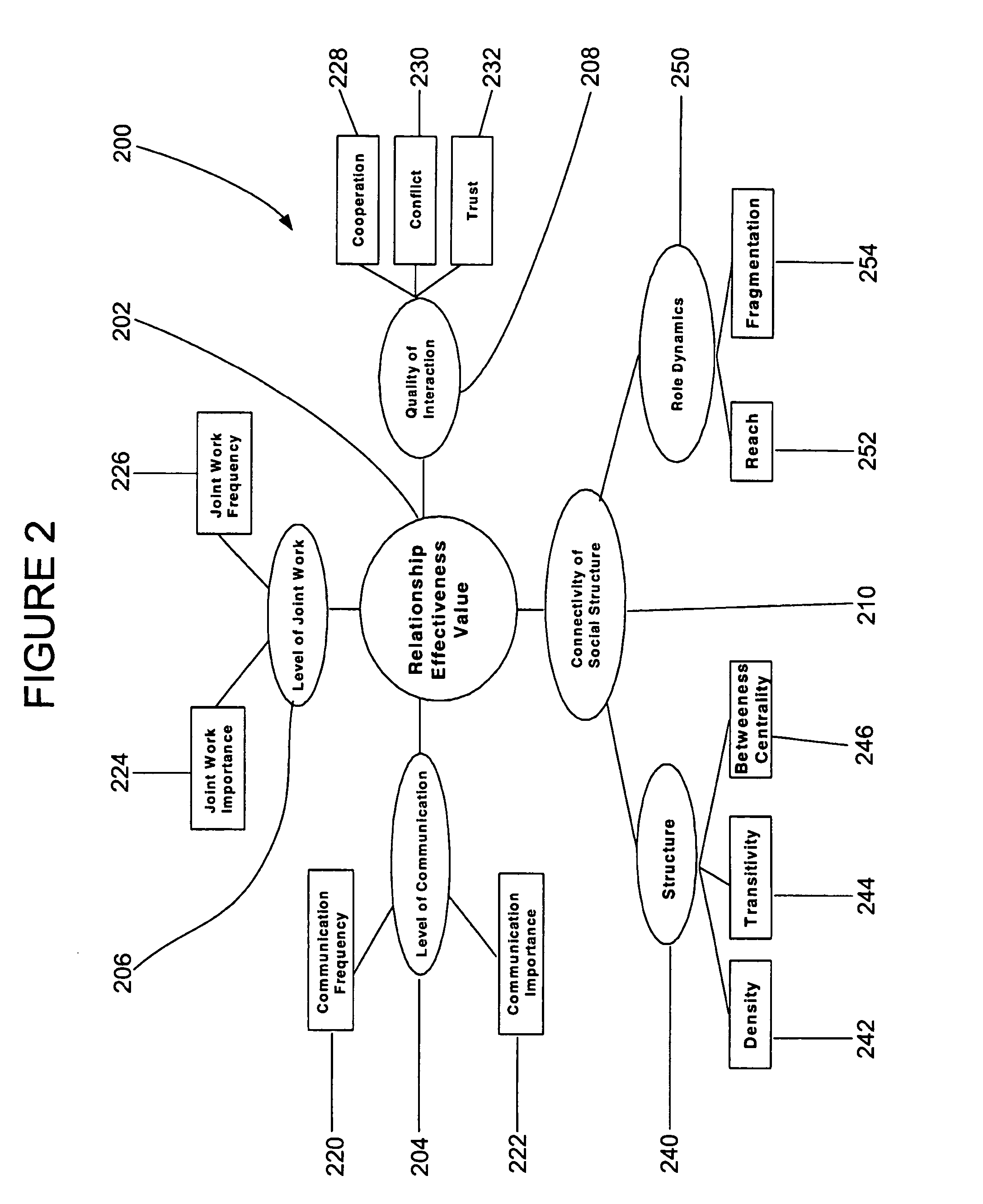
System and model for performance value based collaborative relationships
InactiveUS20050080655A1Office automationSpecial data processing applicationsAnalytic relationModel dynamics
The present invention provides a model for assessing performance of a dynamic collaborative relationship. The present invention provides a method of modeling dynamic relationships by inputting data related to the collaborative relationship into a model, which comprises a plurality of components key to the collaborative relationship. Each of these components is interrelated with the model, and the model generates a value indicative of a condition or performance of the relationship. The relationship value can be analyzed by comparison with baseline values correlated to exemplary collaborative relationships. The present invention further provides methods of developing a model capable of assessing dynamic collaborative relationships.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and Method for Detecting Sheathing and Unsheathing of Localization Elements
ActiveUS20140257071A1Reduce the burden onMeasurement less-reliableElectrocardiographyCatheterElectrophysiology studyRadiology
A method of detecting whether a localization element is within or outside of an introducer sheath generally includes obtaining a localization signal from the localization element and detecting the state of the localization element relative to the sheath based upon the quadrature component of the localization signal. A baseline quadrature component is typically established with the localization element outside of the sheath. When the quadrature component deviates from this baseline value, it is indicative of the localization element being within the sheath. Conversely, when the quadrature component remains relatively close to the baseline value, it is indicative of the localization element being outside of the sheath. In an electrophysiology study, the state information can be used to take corrective action with respect to the data being collected.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
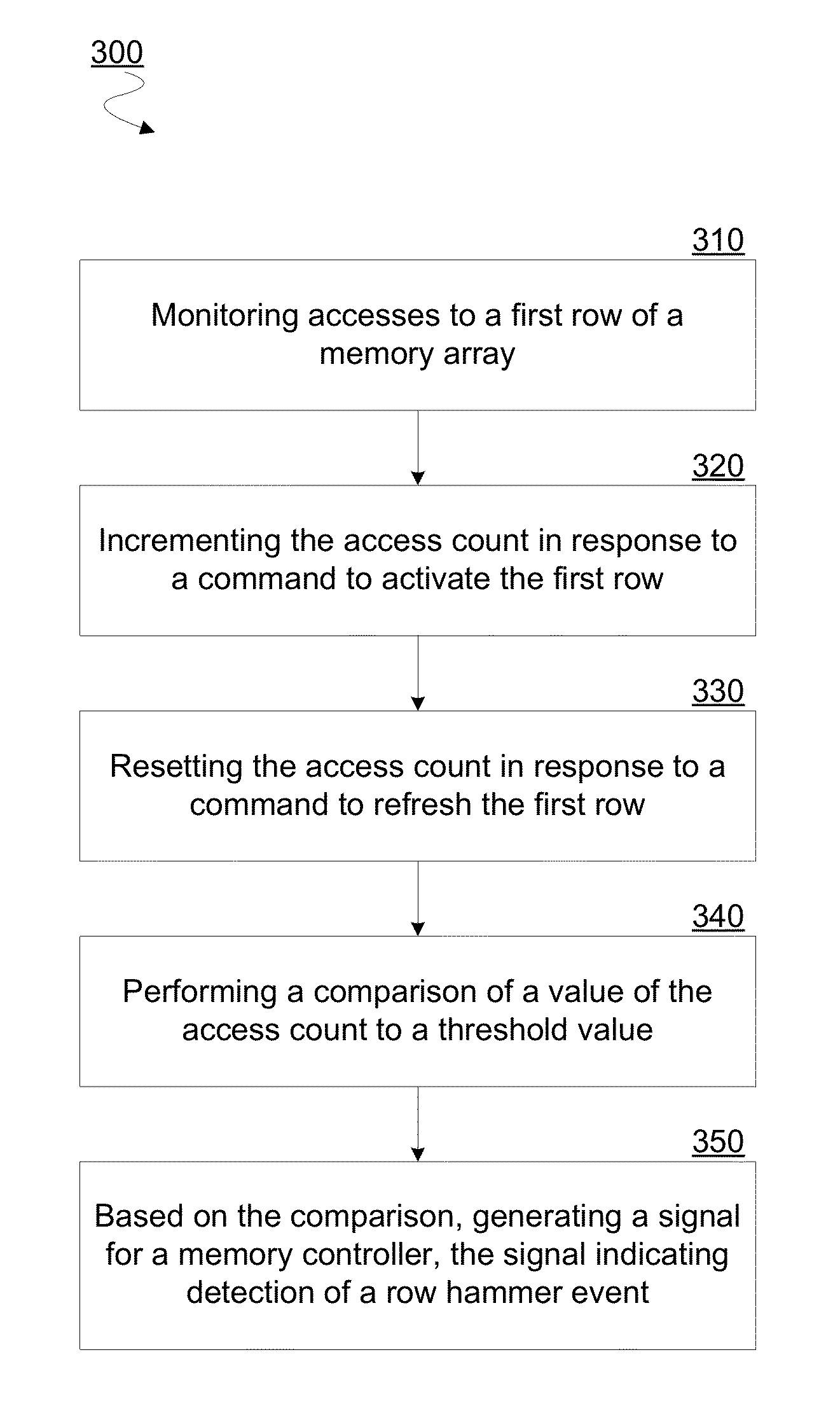
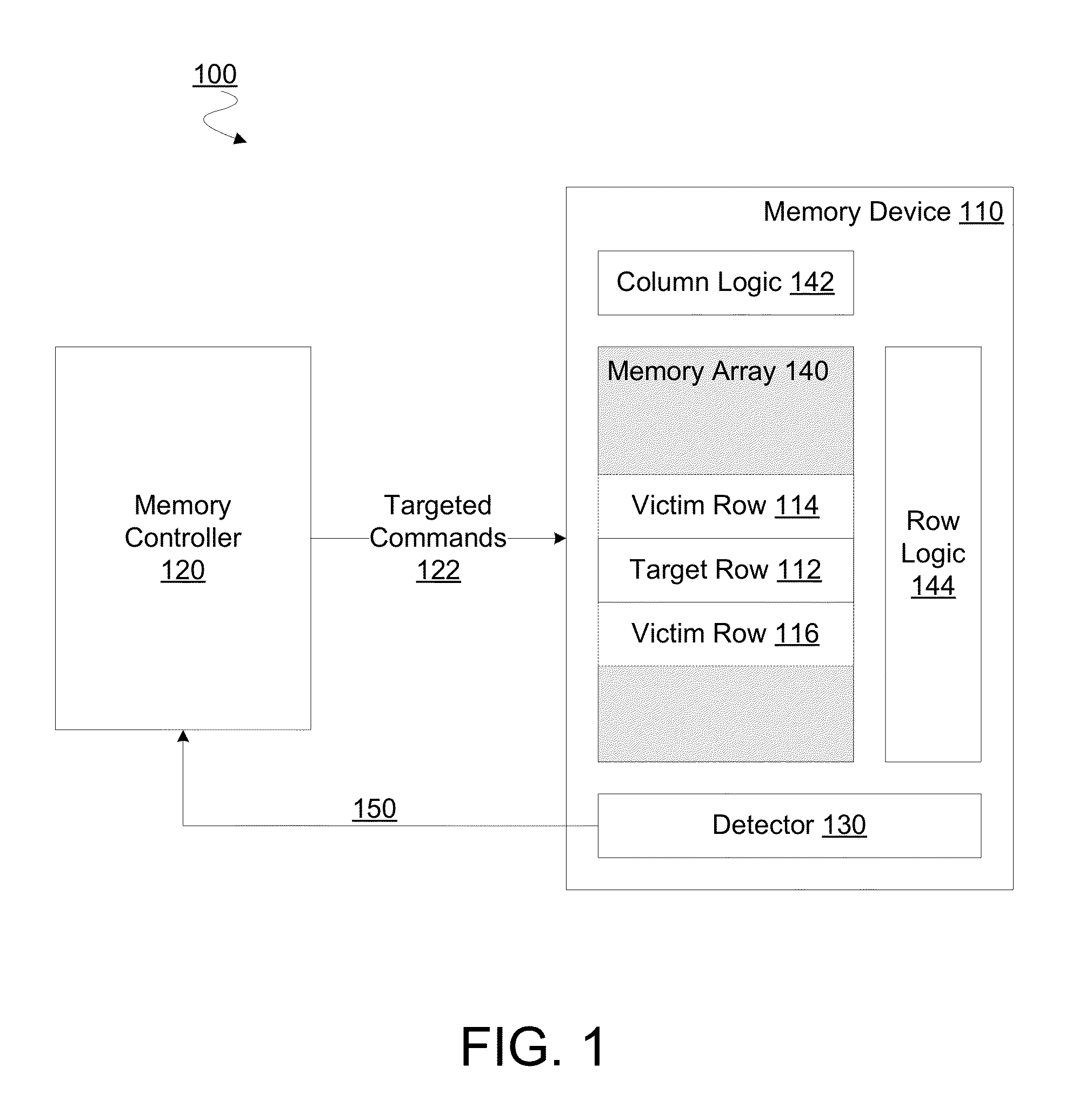
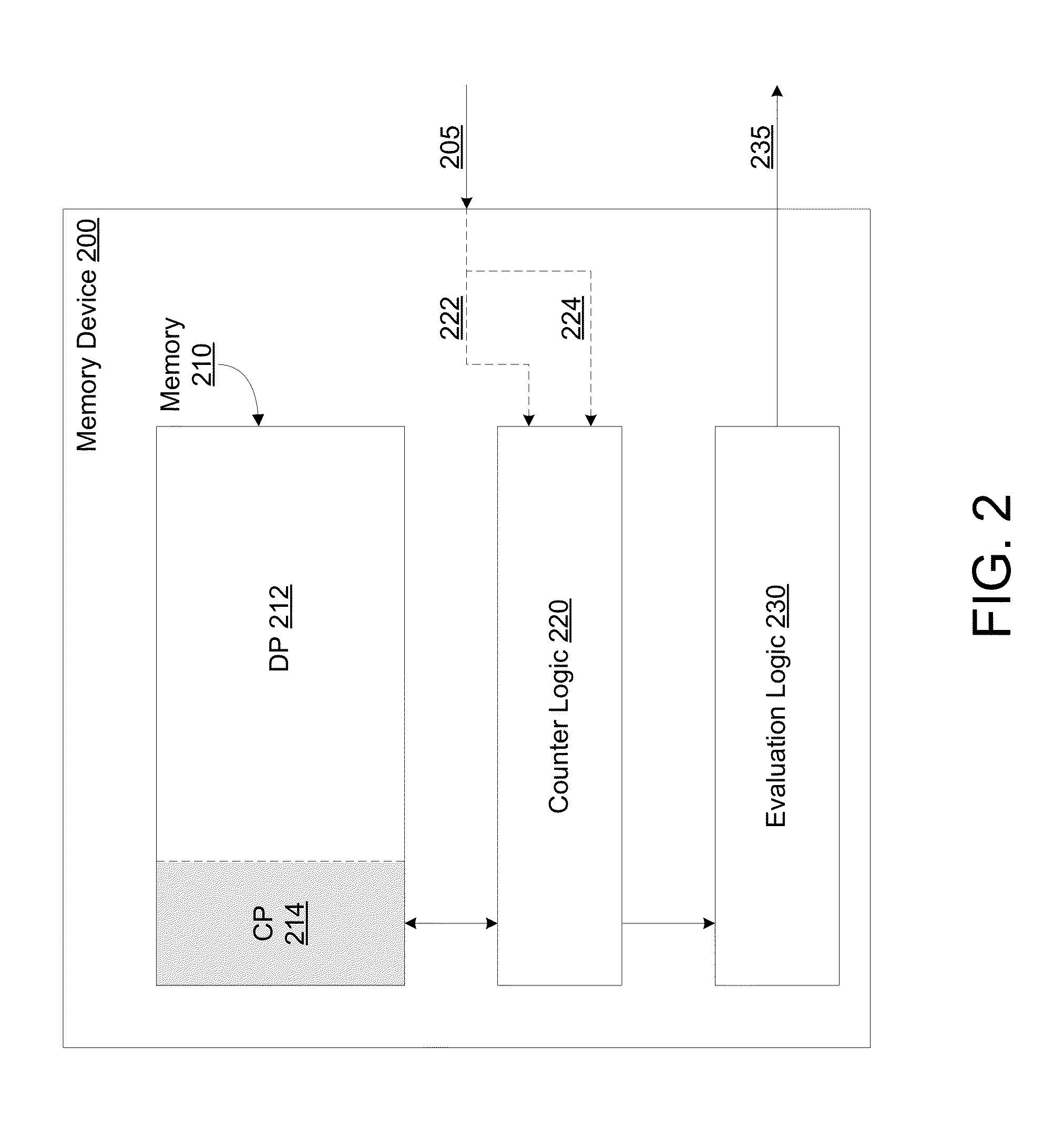
Method, apparatus and system for determining a count of accesses to a row of memory
Techniques and mechanisms for determining a count of accesses to a row of a memory device. In an embodiment, the memory device includes a counter comprising circuitry to increment a value of the count in response to detecting a command to activate the row. Circuitry of counter may further set a value of the count to a baseline value in response to detecting a command to refresh the row. In another embodiment, the memory device includes evaluation logic to compare a value of the count to a threshold value. A signal is generated based on the comparison to indicate whether a row hammer event for the row is indicated.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Process flow control circuit
InactiveUS20050191184A1Fluid parameterPump controlControl circuitElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:VINSON JAMES WOODROW JR
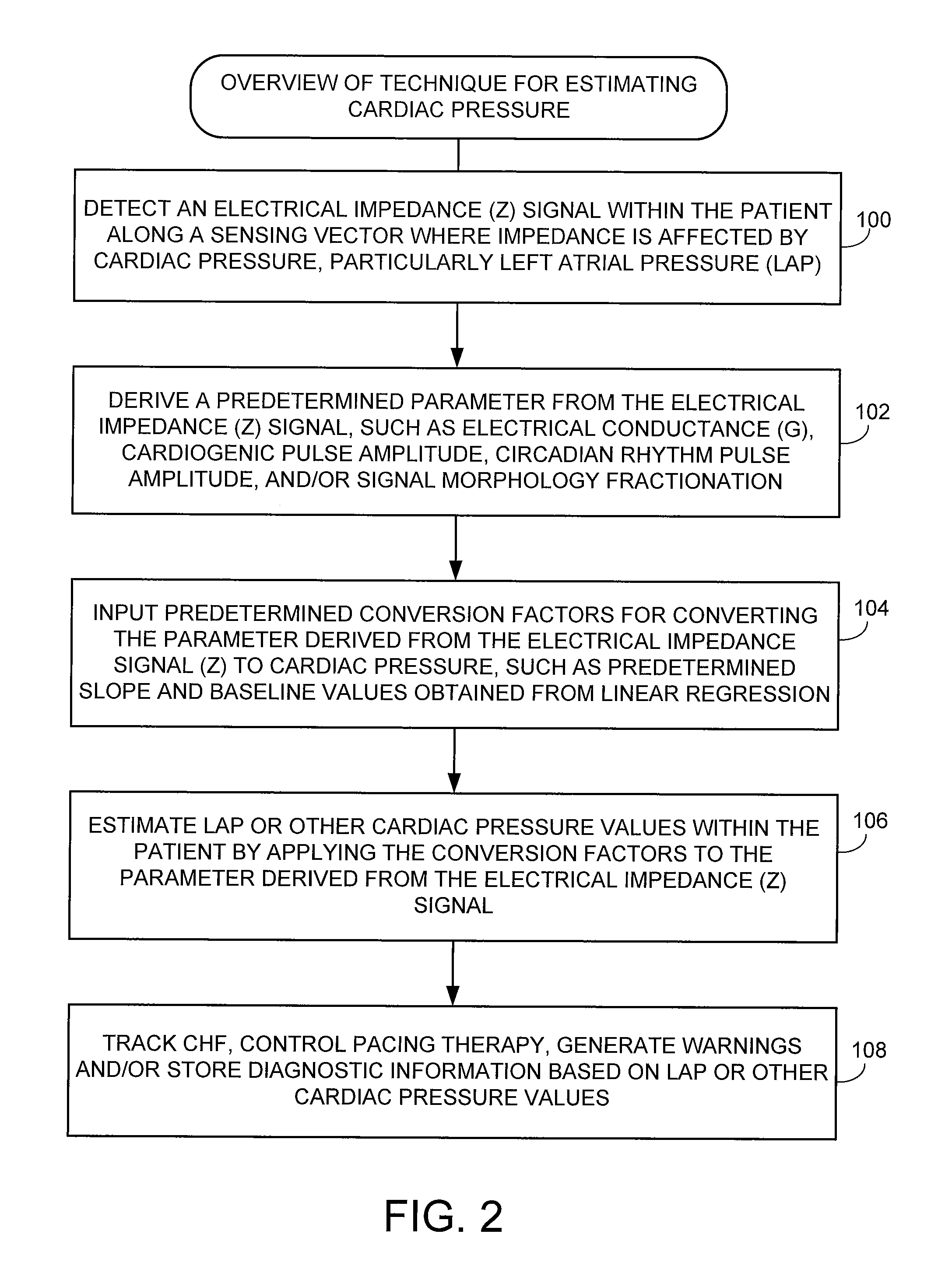
System and method for estimating cardiac pressure using parameters derived from impedance signals detected by an implantable medical device
Techniques are provided for estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) or other cardiac pressure parameters based on various parameters derived from impedance signals. In particular, effective LAP is estimated based on one or more of: electrical conductance values, cardiogenic pulse amplitudes, circadian rhythm pulse amplitudes, or signal morphology fractionation values, each derived from the impedance signals detected by the implantable device. Predetermined conversion factors stored within the device are used to convert the various parameters derived from the electrical impedance signal into LAP values or other appropriate cardiac pressure values. The conversion factors may be, for example, slope and baseline values derived during an initial calibration procedure performed by an external system, such as an external programmer. In some examples, the slope and baseline values may be periodically re-calibrated by the implantable device itself.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method of body motion analytics recognition and alerting
PendingUS20170188895A1The result is moreInertial sensorsTelemetric patient monitoringTransceiverAccelerometer
Device, system and methods for using body worn sensors to analyze human body motion. The device, often configured to be worn on the user's wrist, arm, neck, belt or other location, comprises a processor, an output device (often a wireless transceiver), and at least one accelerometer, angle, location, direction, or physiological state sensor. The processor may be configured for various functions, such as analyzing habitual user activities, establishing normal baselines, classifying types of motion and reporting, and logging sensor readings or analysis results. Various algorithms may be used to determine when significant deviations from baseline values occur, and, depending on the type of deviation, the output device can transmit data and alerts. In some embodiments, the data and alerts may be further analyzed by other computerized devices such as mobile phones (smartphones), computers, internet servers, and the like.
Owner:SMART MONITOR
Systems and methods for transdermal secretion detection
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for detecting chemicals. As an example, a system is disclosed that includes a chemical sensor, a processor, and a computer readable medium. The computer readable medium includes instructions executable by the processor to: receive a plurality of outputs from the chemical sensor; calculate a baseline value using the plurality of outputs from the chemical sensor; and report an event when the baseline value is exceeded.
Owner:BI
Methods and apparatus for click detection on a force pad using dynamic thresholds
ActiveUS20150084874A1Improve usabilityFunction increaseInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingObject basedEngineering
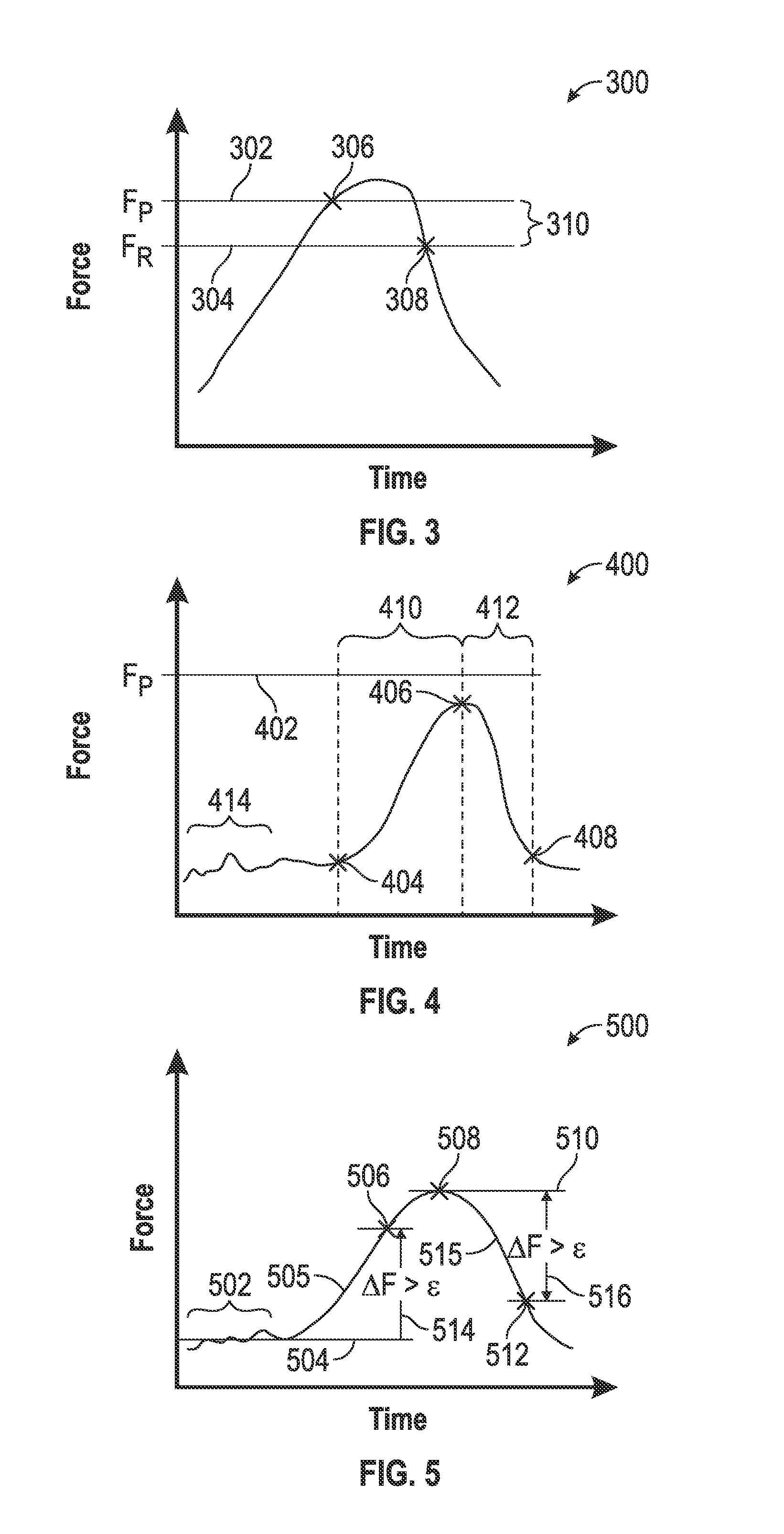
A method and device are provided for measuring force on a force enabled input device having a touch surface. The method includes detecting force information associated with an input object contacting the touch surface, and determining a push event if the force information is either greater than a predetermined static push threshold value, or a substantially monotonic increase of at least a dynamic push threshold value above a low baseline value. The method thereafter determines a release event if the force information either decreases below a predetermined static release threshold value, or decreases from a maximum baseline value by an amount greater than a dynamic release threshold value. The method initiates a first type of user interface action associated with the input object based on a determination of the push event and the release event, wherein the first type of user interface action may comprise determining a virtual button click.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Device and methods for modifying keratinous surfaces
InactiveUS20100224205A1Less compositionPrecise applicationCosmetic preparationsHair removalEmbedded systemBaseline values
An apparatus for modifying a keratinous surface having an applicator, a first modification agent; a sensor; and a CPU. The sensor reads the properties of a small portion of the keratinous surface, the readings are transmitted to the CPU, and the CPU compares the readings to a predetermined baseline value. The CPU then calculates the variance between the reading and the baseline value. When that variance exceeds a predetermined threshold the CPU sends a signal to the applicator which is activated to apply a portion of the first modification composition to the same portion of the keratinous surface that had the reading with a variance above the threshold value.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Anti-entrapment and anti-dead head function
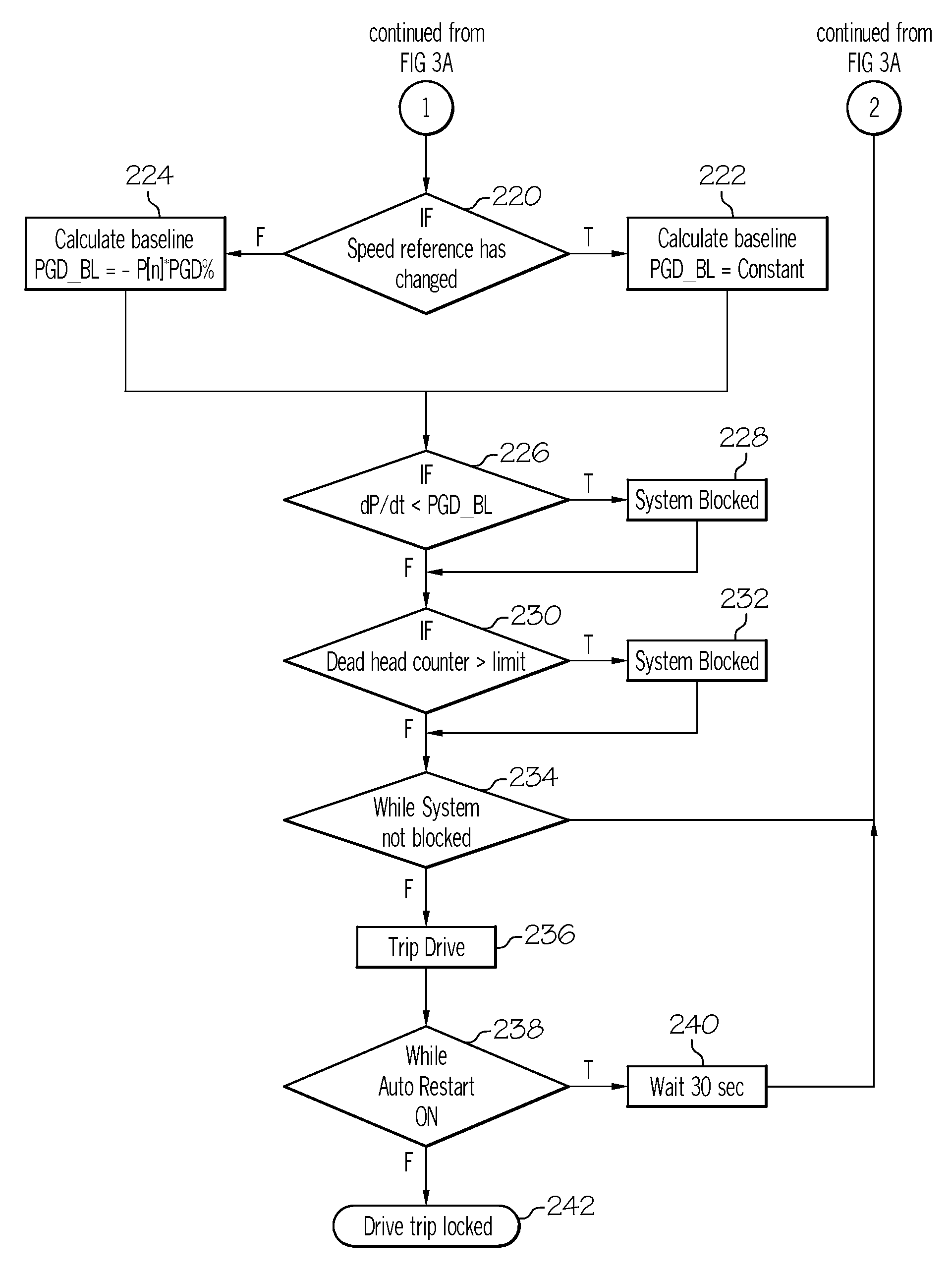
Embodiments of the invention provide a system including a pump, a motor, and a controller. The controller establishes a baseline value of power consumption during a deadhead condition, increases a counter when a current value decreases below the baseline value, and determines a deadhead condition when the counter exceeds a limit. The controller also compares a current value to an immediately previous power consumption value to determine an entrapment condition indicated by a sudden decrease in power consumption.
Owner:DANFOSS POWER ELECTRONICS AS +1
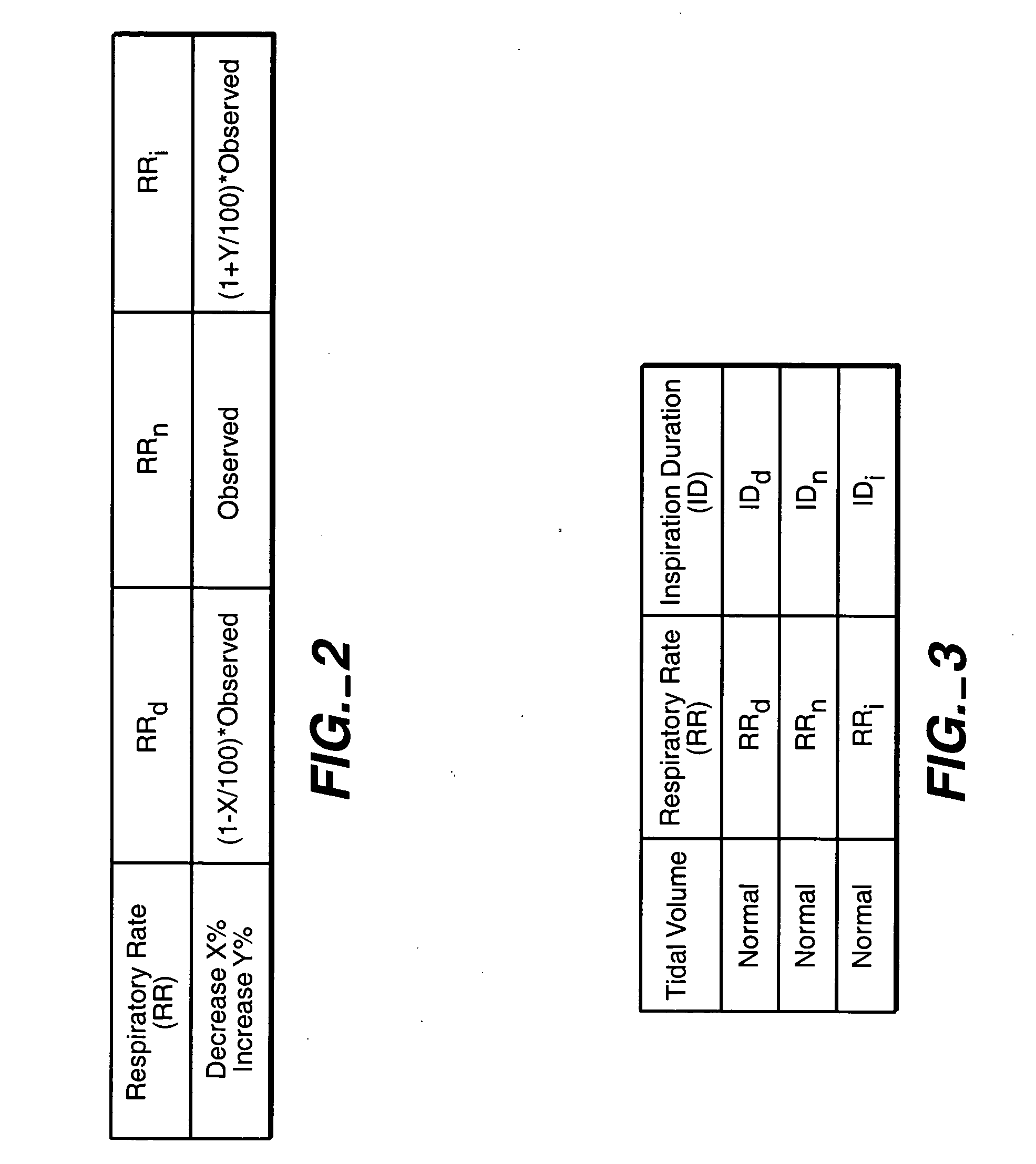
Cough/sneeze analyzer and method
ActiveUS7104962B2Improve analysis accuracyImprove accuracyAuscultation instrumentsRespiratory organ evaluationAir compressionMedicine
A cough event is differentiated from a sneeze event of a test subject enclosed within a plethysmograph test chamber by measuring air pressure changes during the event, and comparing the pressure changes against criteria indicative of a cough to determine the likelihood that the event is a cough. Air pressure changes are recorded as pressure and / or sound values. A graphical record of a waveform of changes in the air pressure during an event relative to a baseline value is recorded, and a value is calculated that is indicative of the likelihood that the event is a cough based on the sizes of areas between the waveform and baseline during the event, said areas including a first area indicative of the change in air pressure during air inspiration, a second area indicative of the change in air pressure during air compression, and a third area indicative of the change in air pressure during expiration.
Owner:DATA SCI INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com