Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
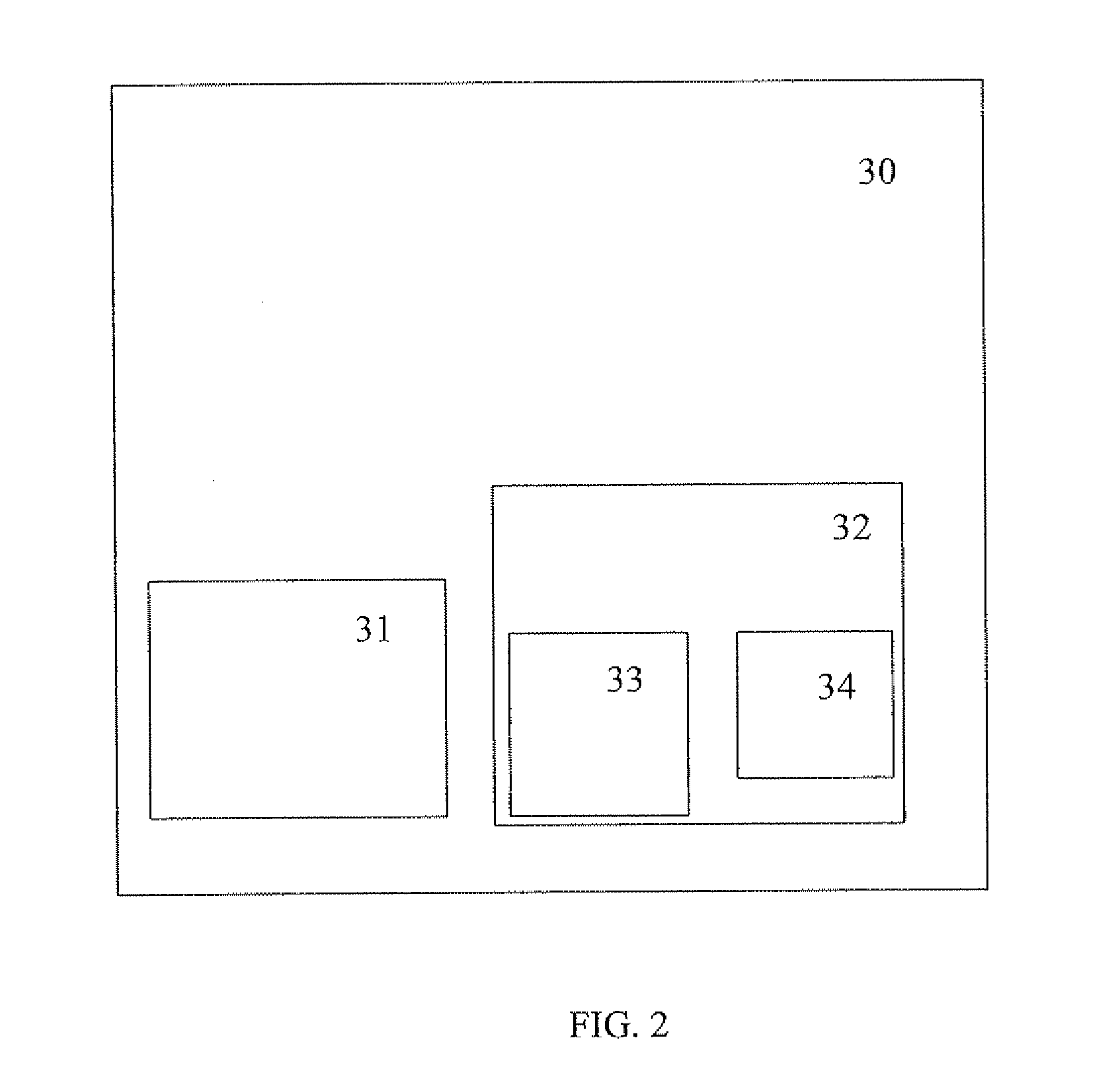
68 results about "Thoracic impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
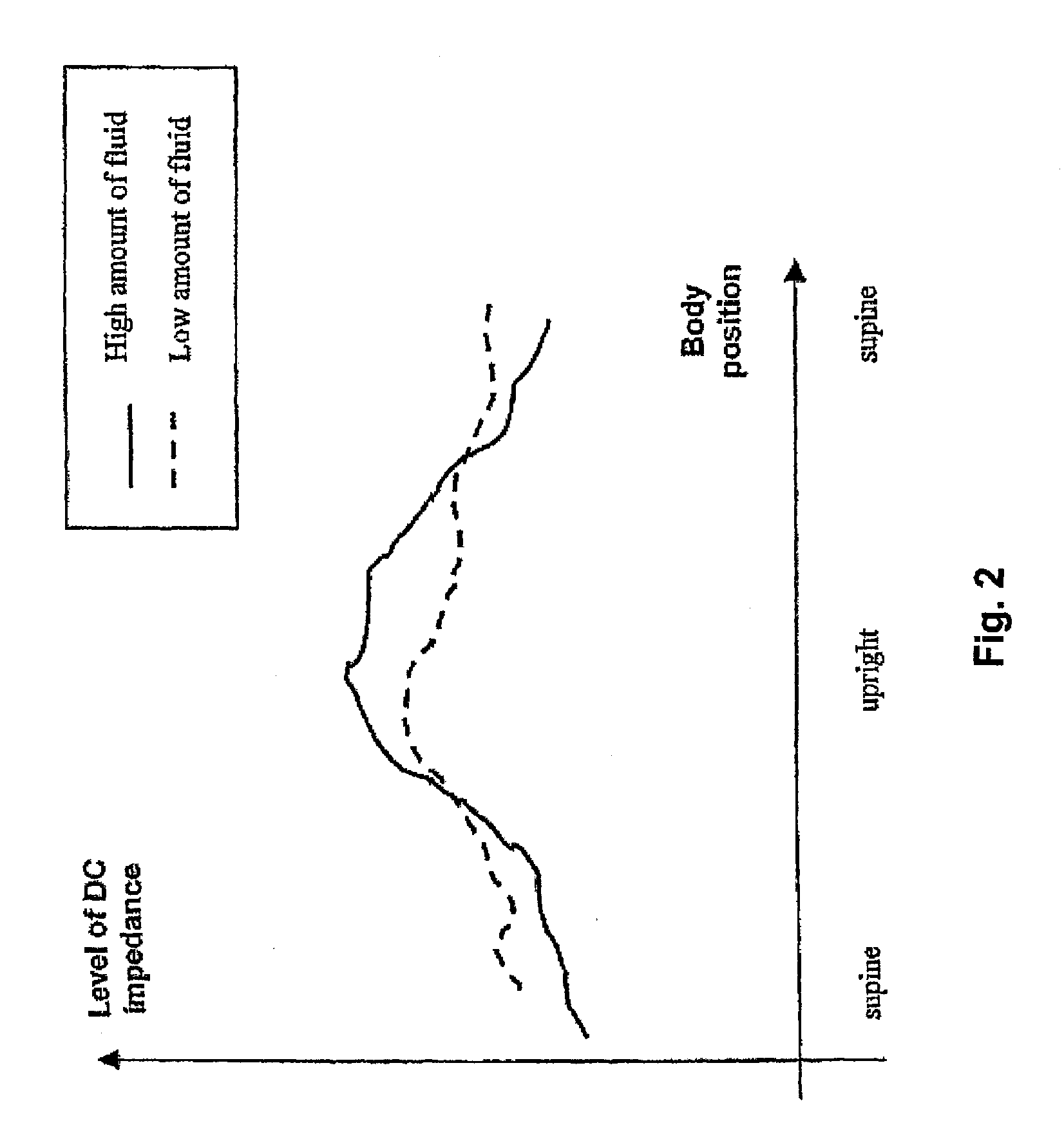
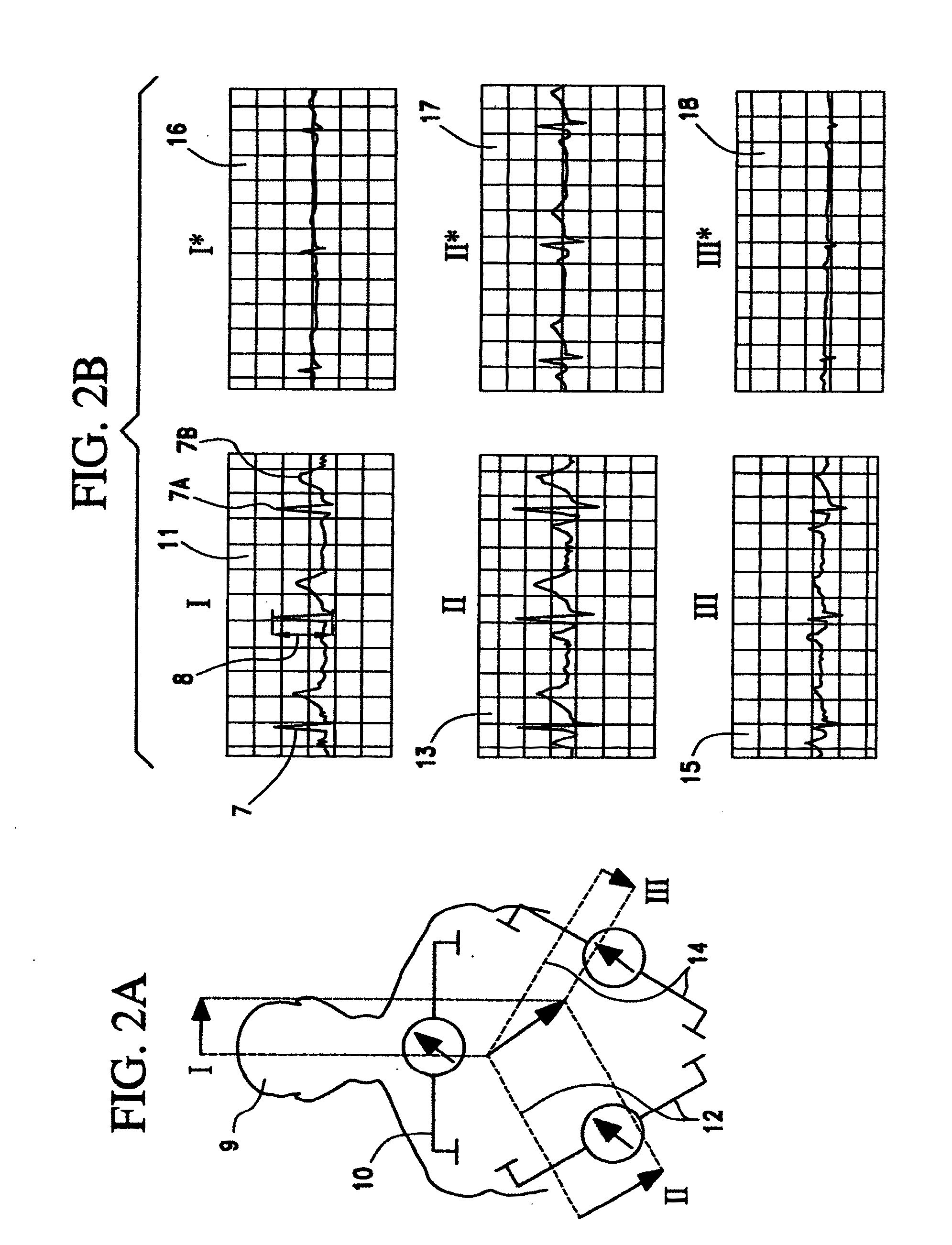
The primary aim of this study was to elucidate the potential of thoracic impedance to estimate SV and CO during the Wingate test, which is unknown, and to compare these responses to those obtained from graded exercise testing, which should elicit maximal values for these variables.
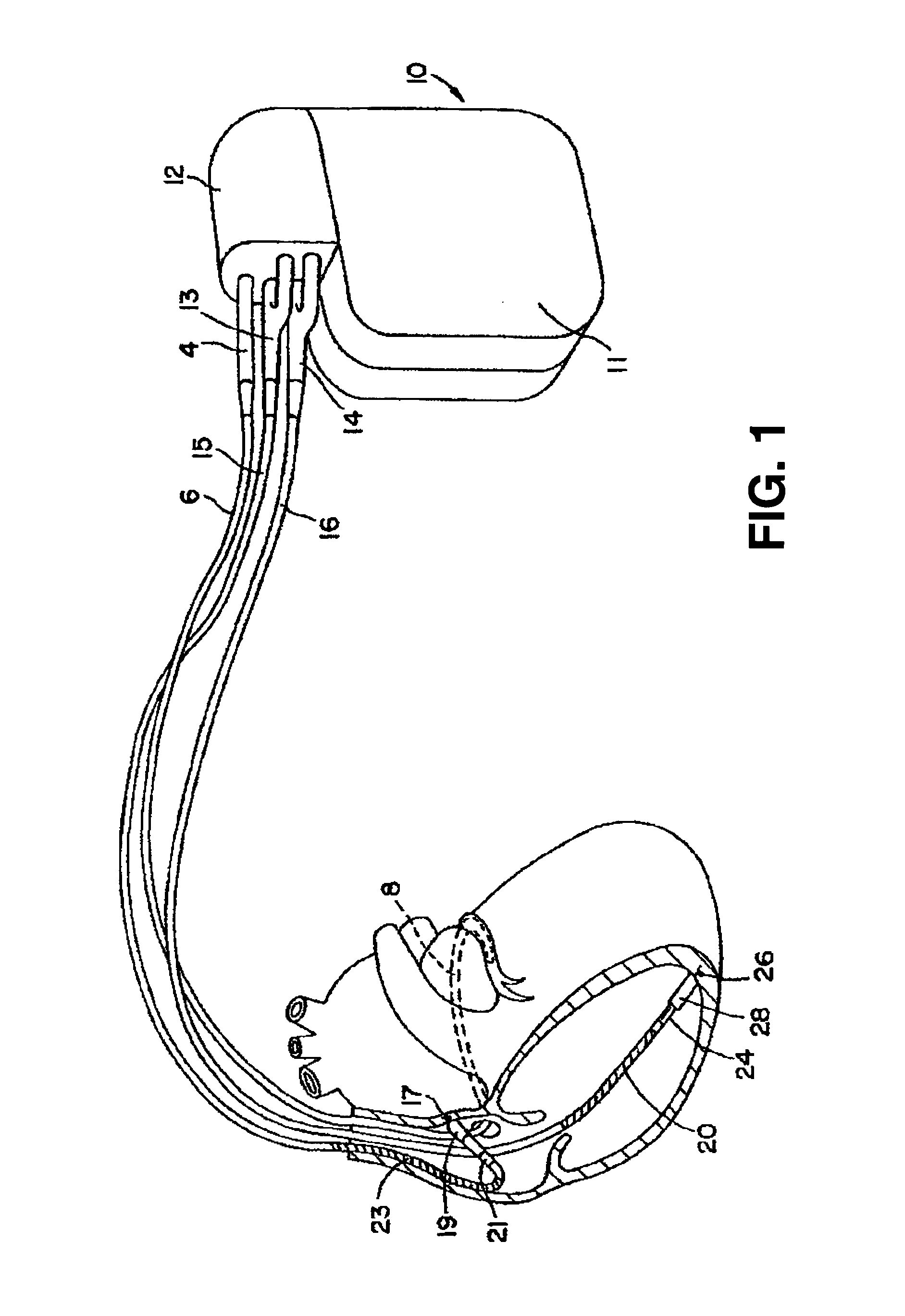
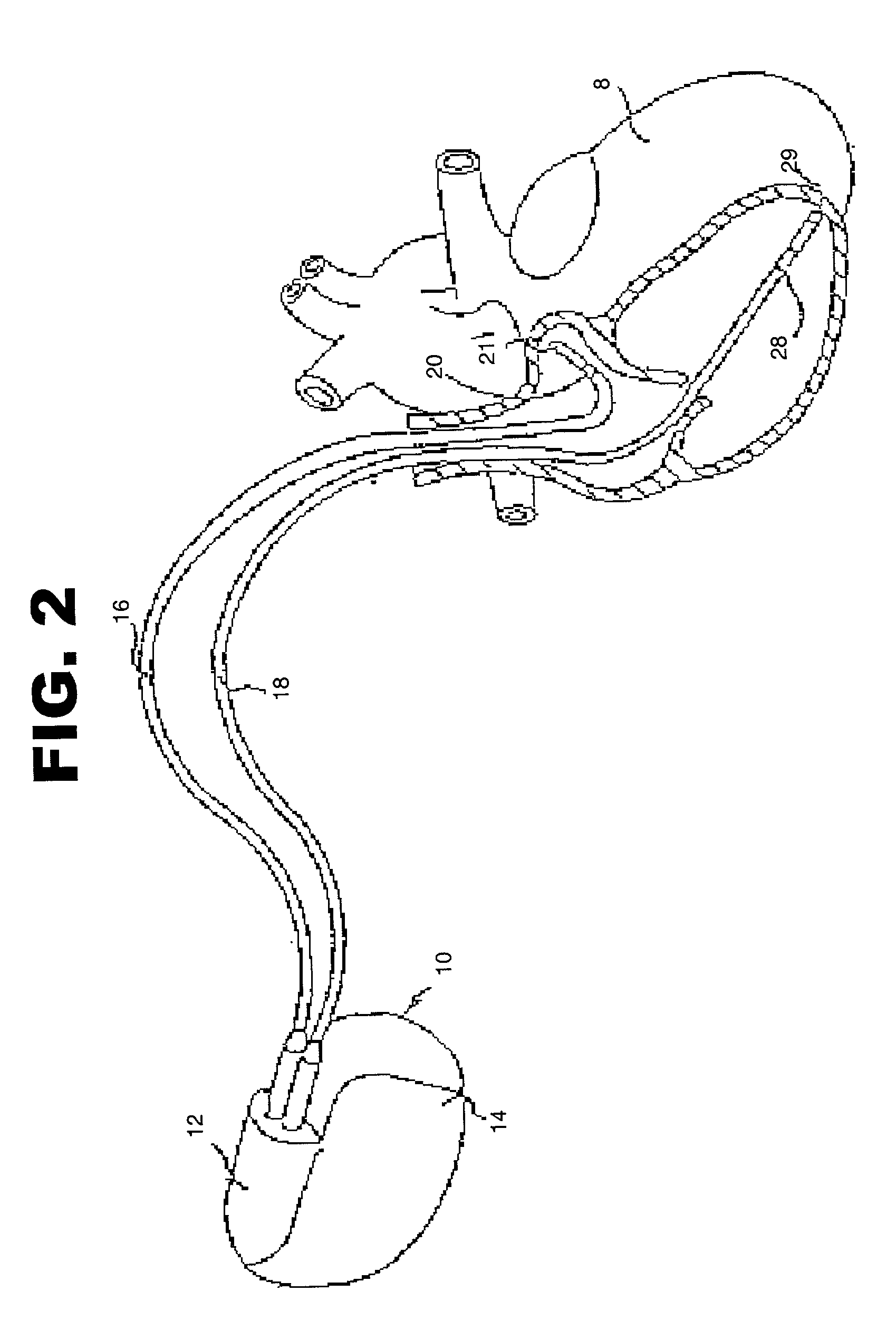
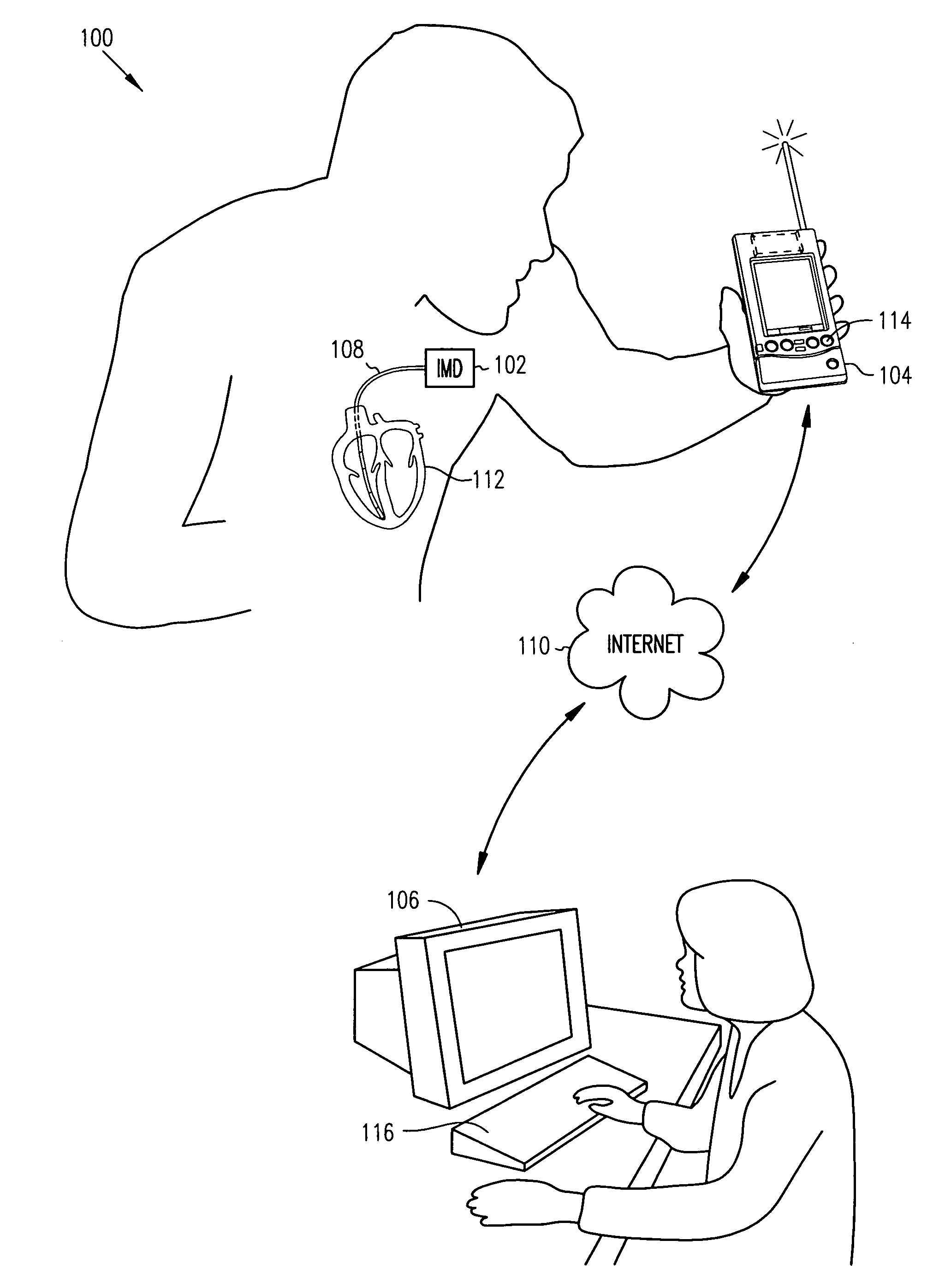
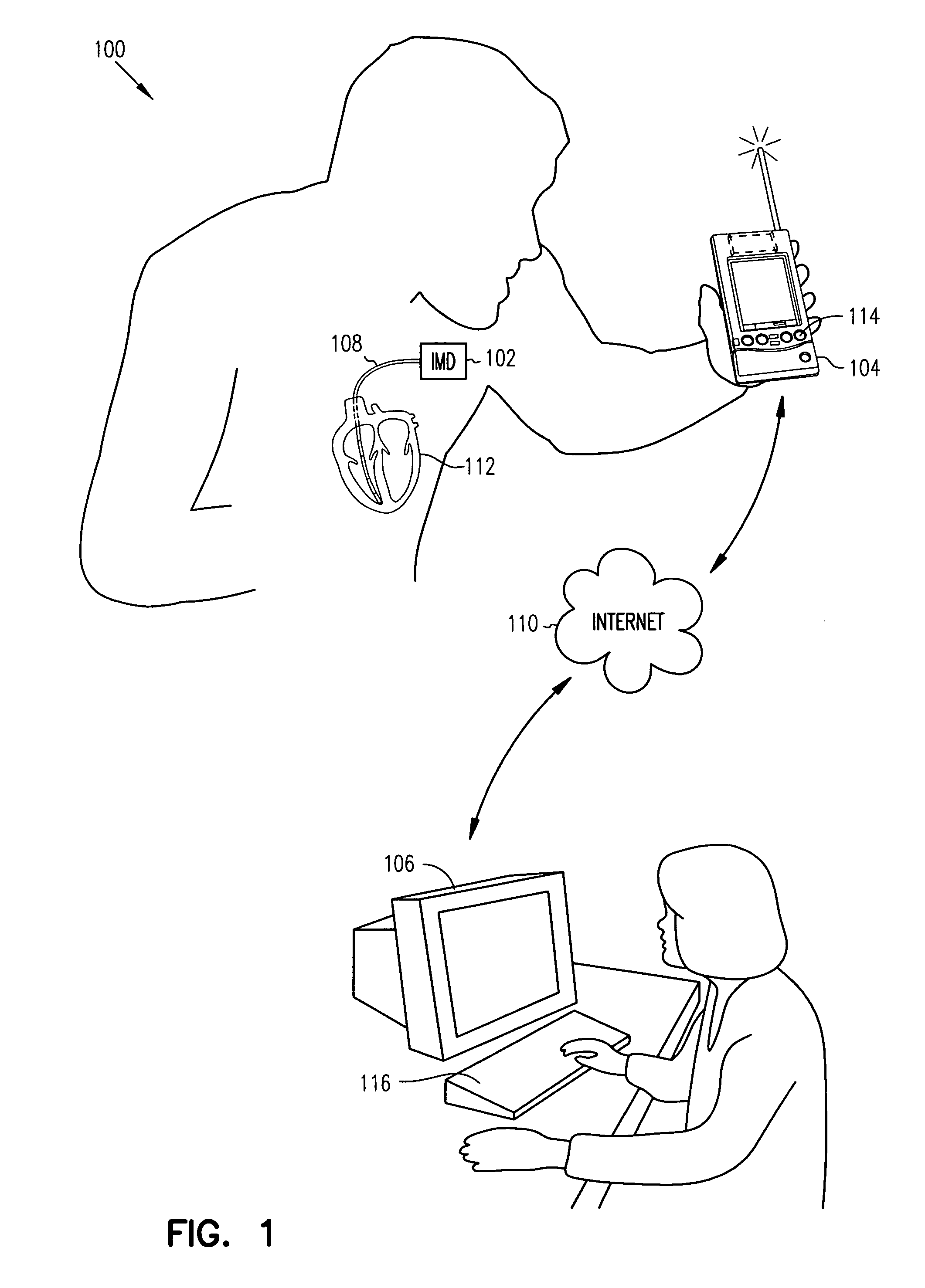
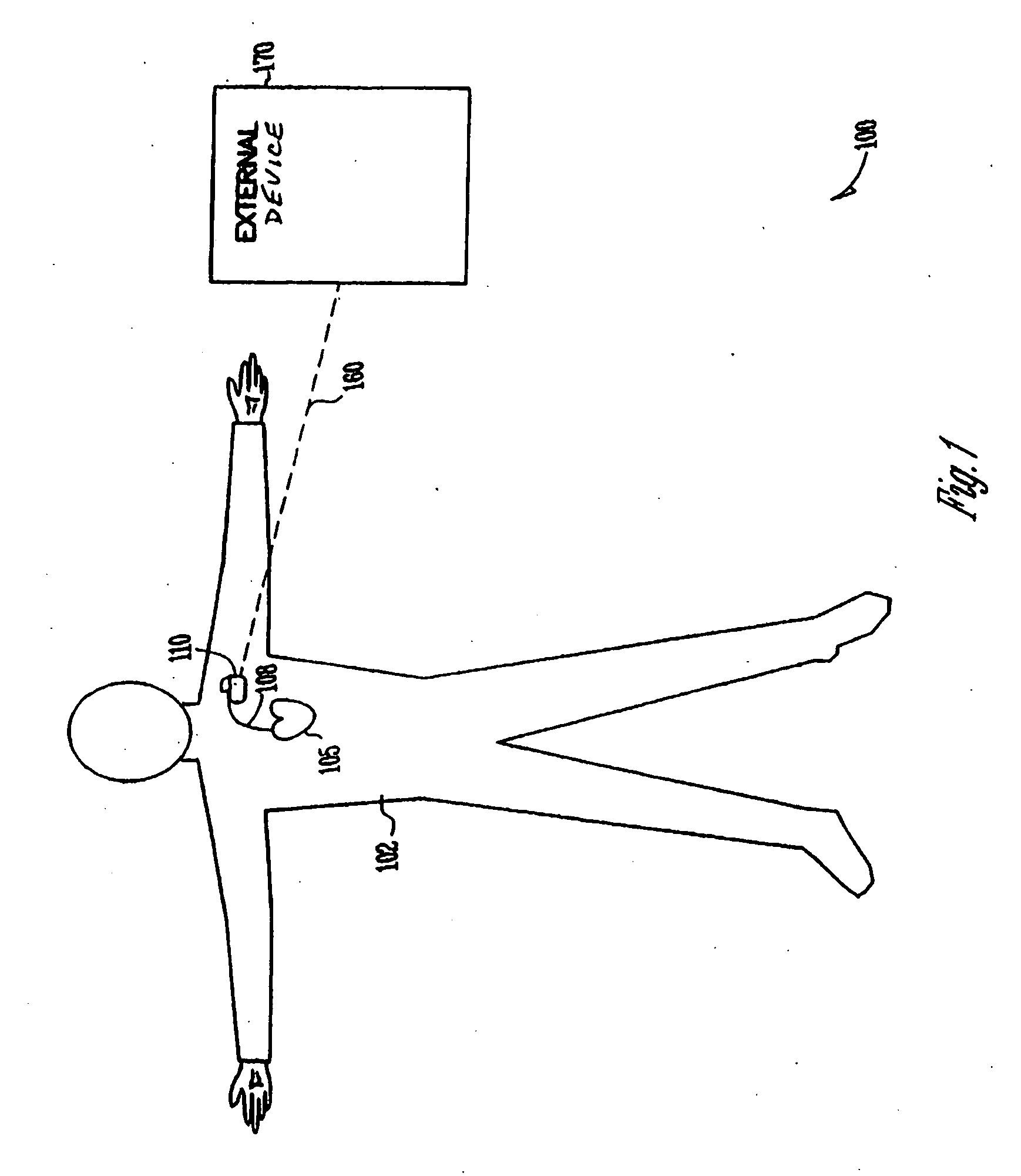
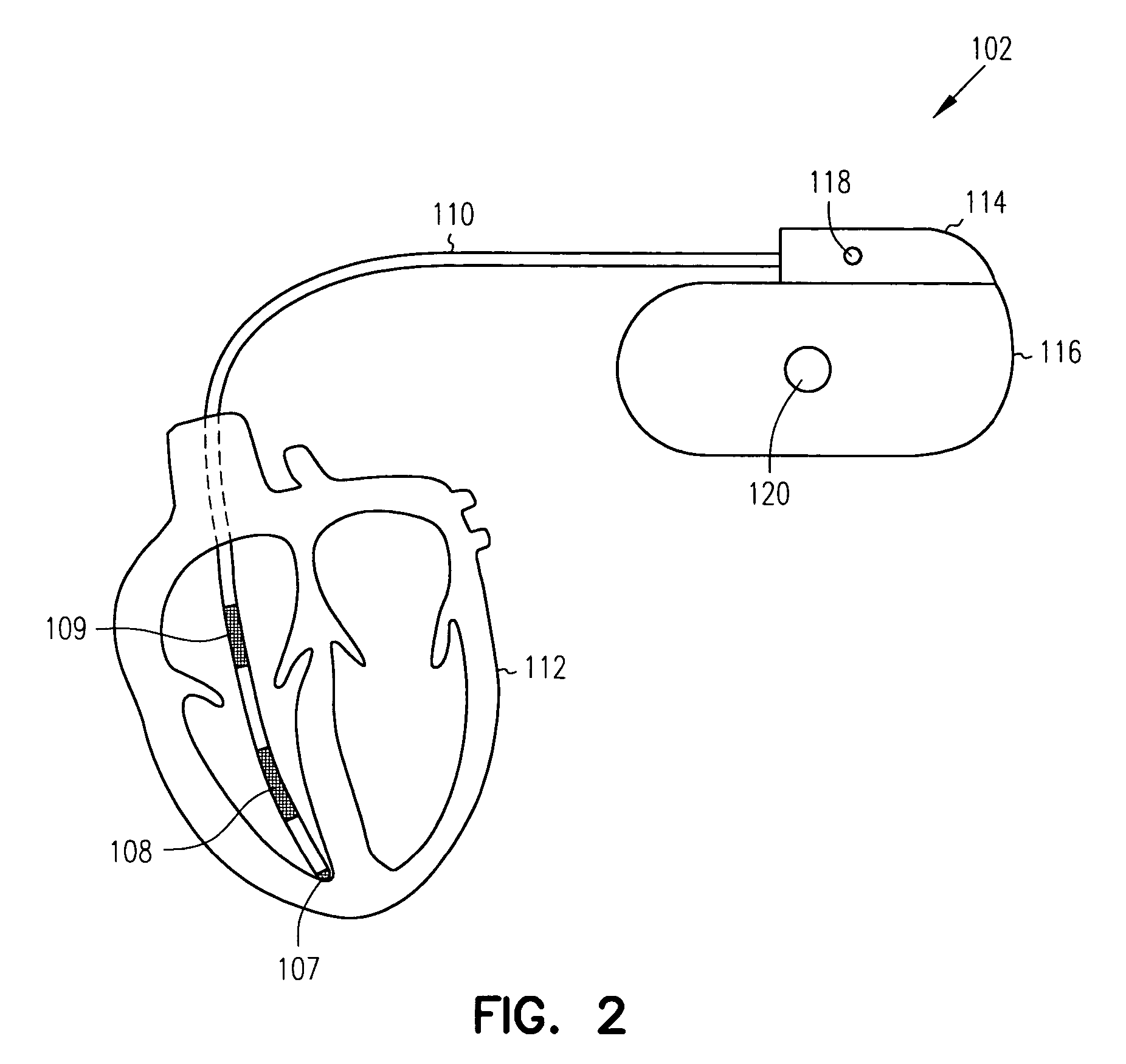
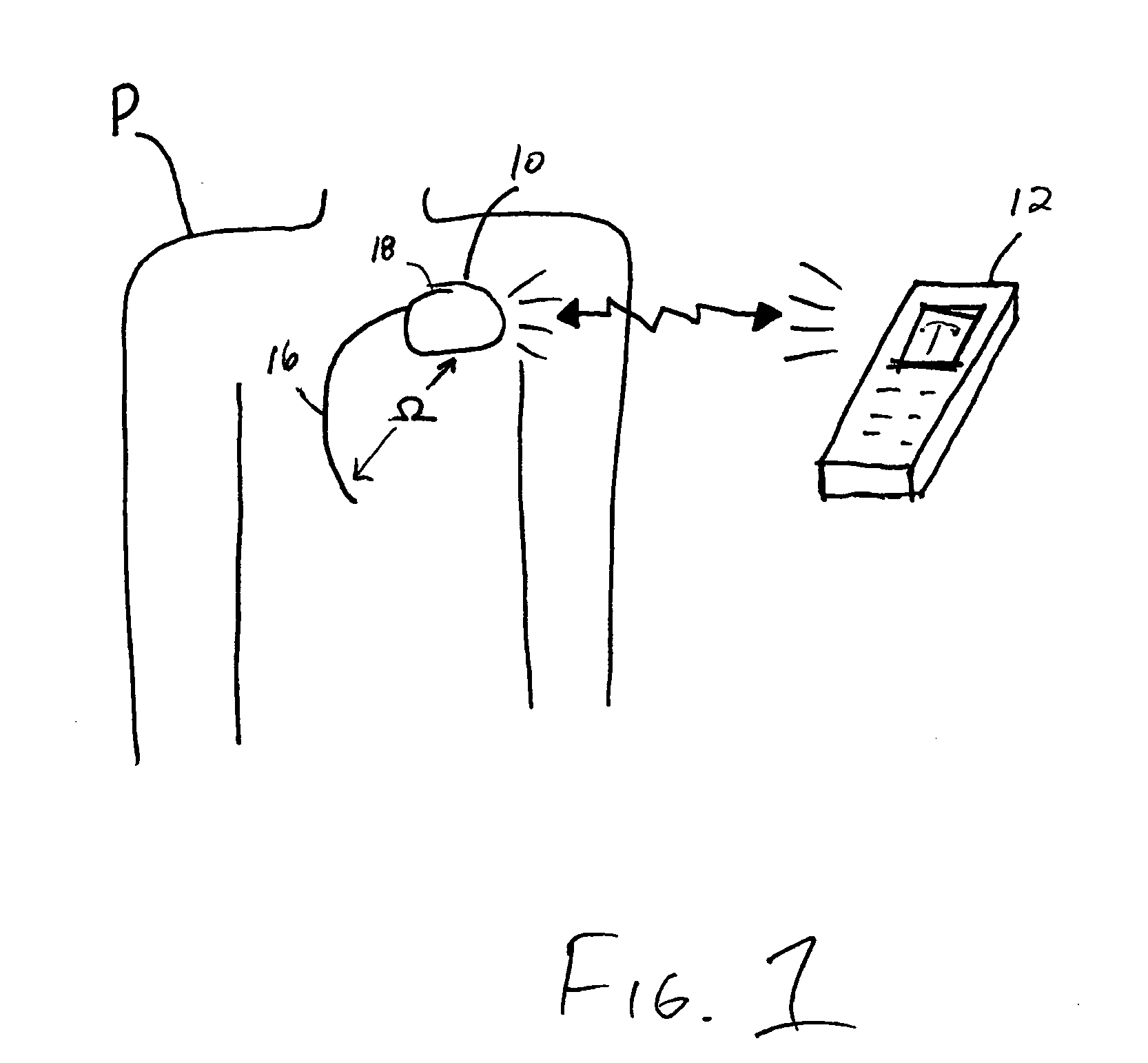
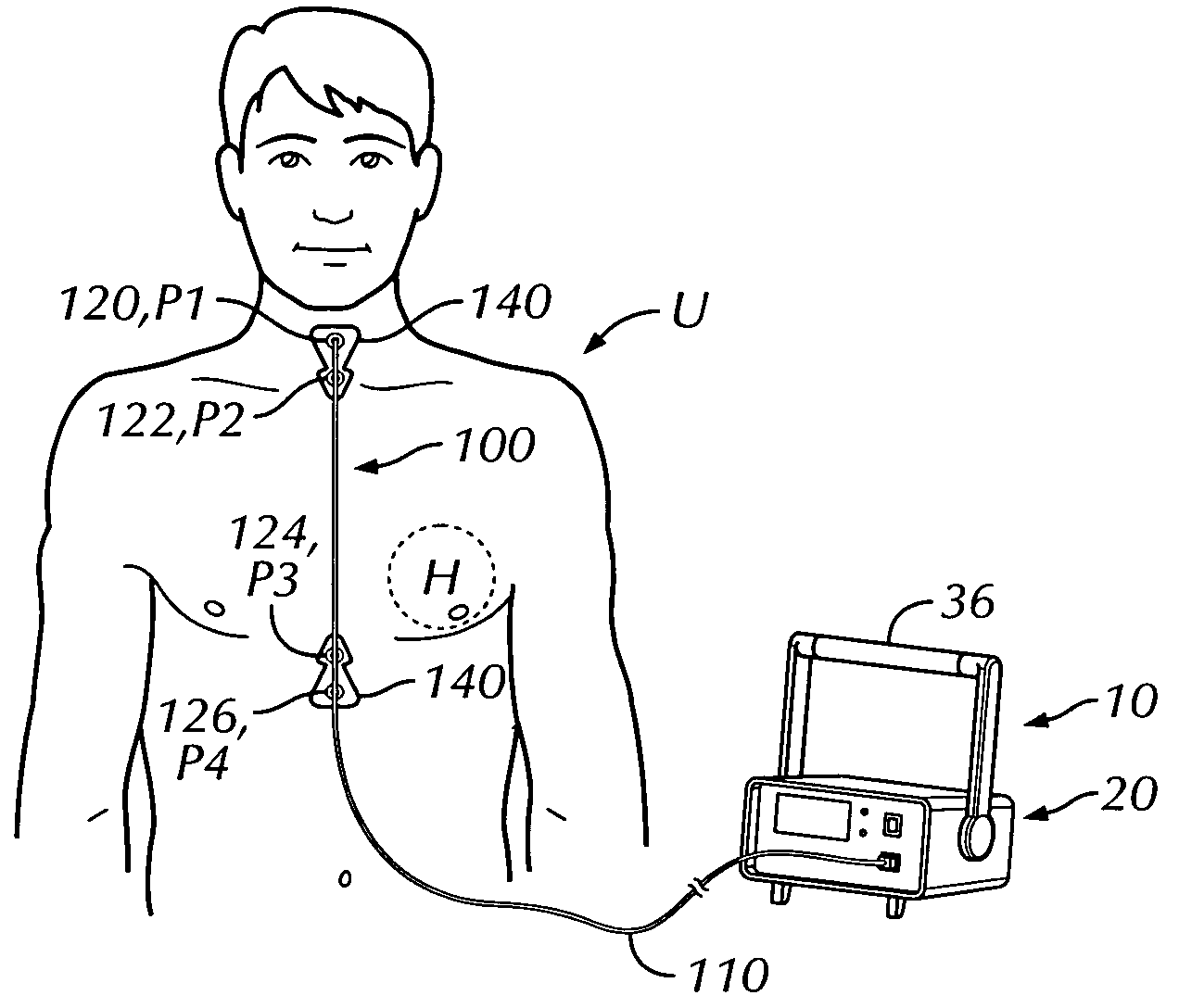
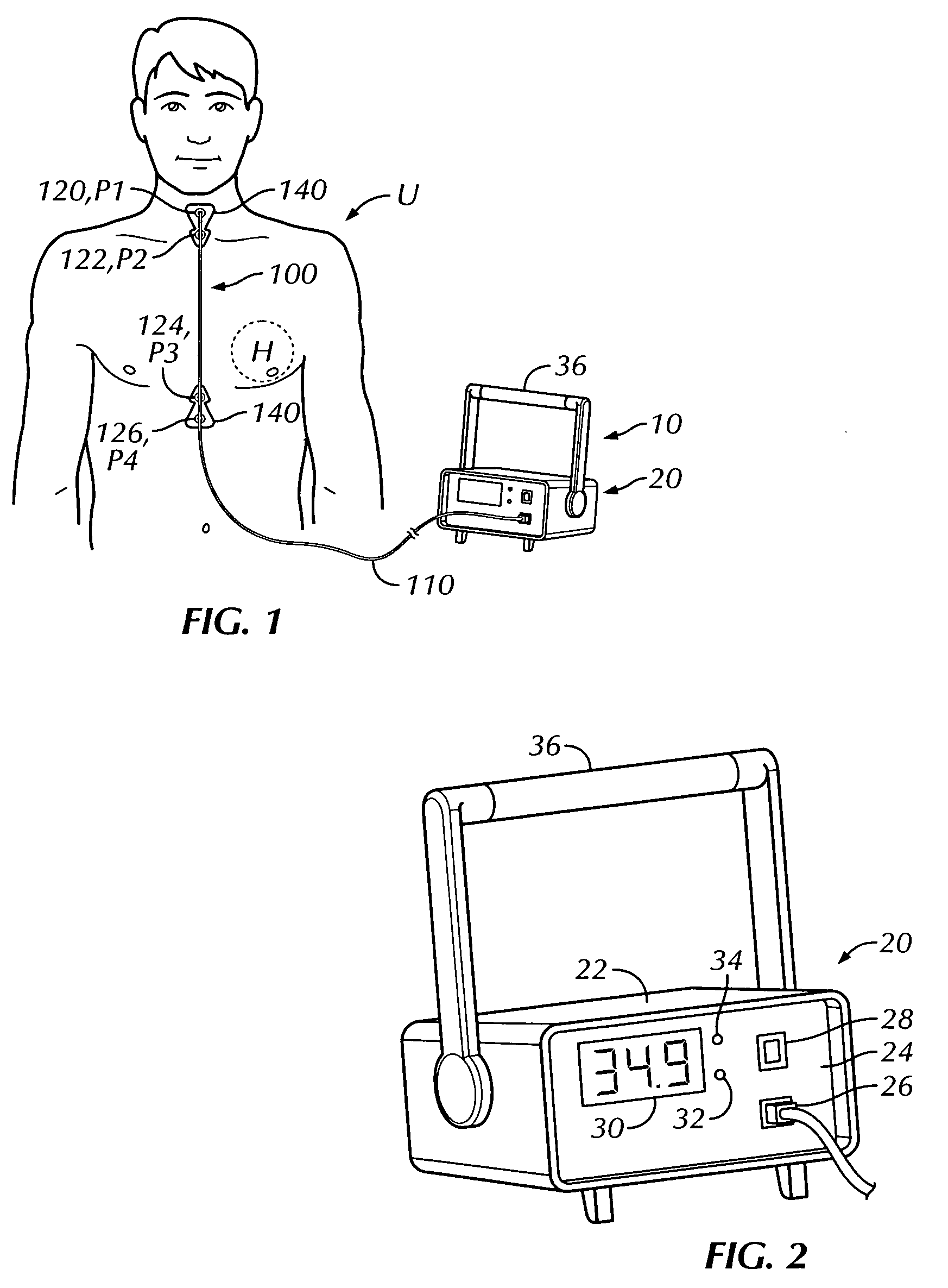
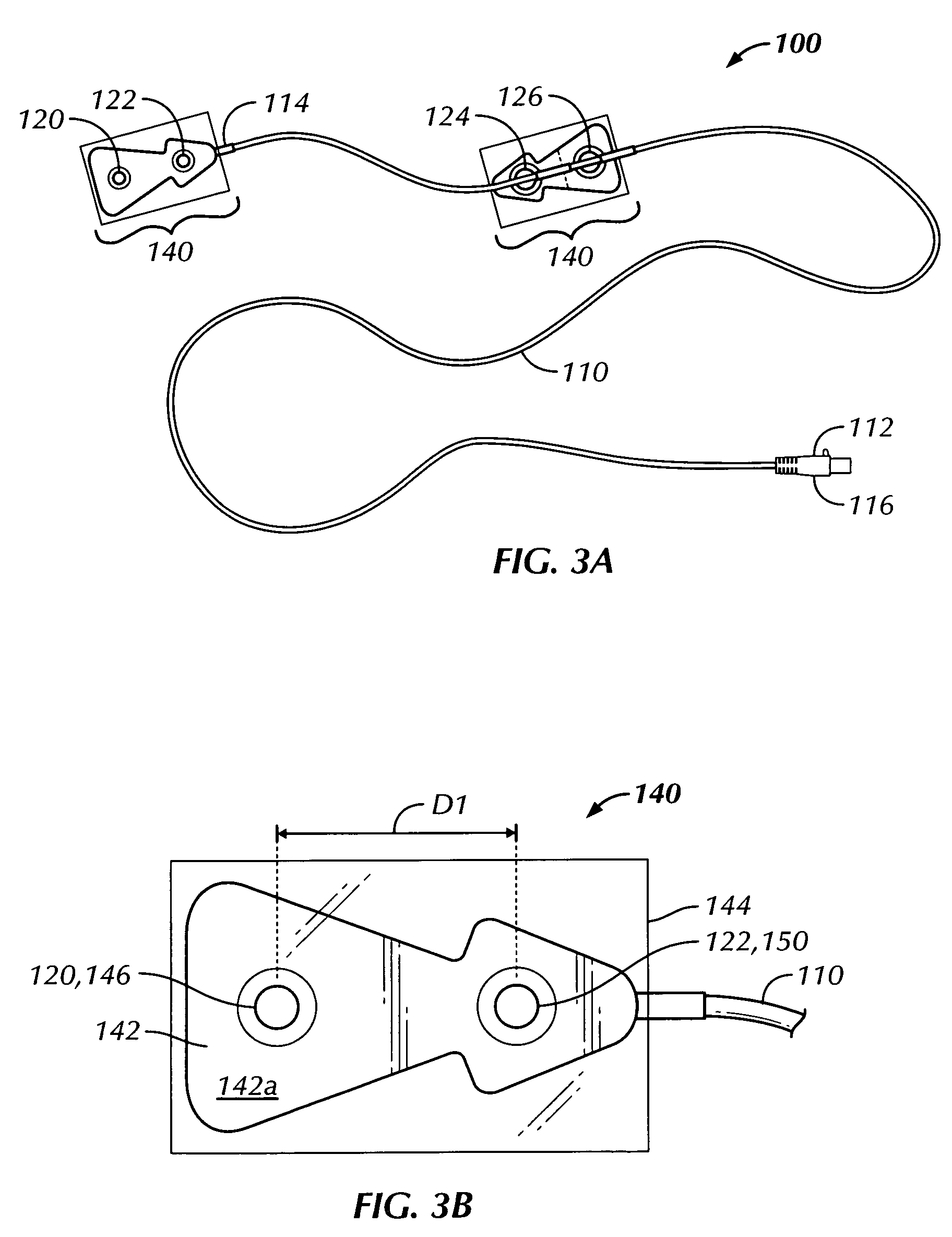
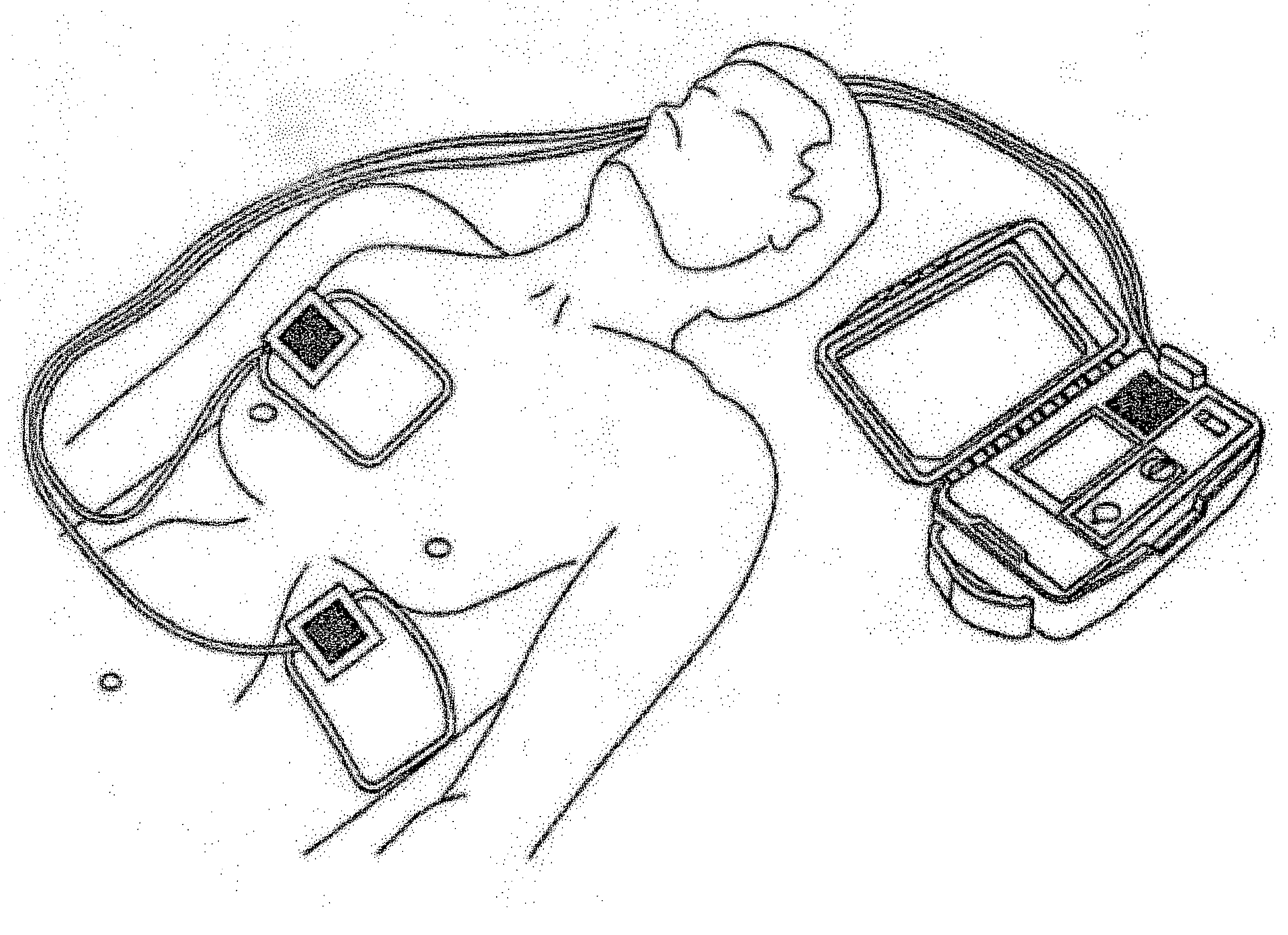
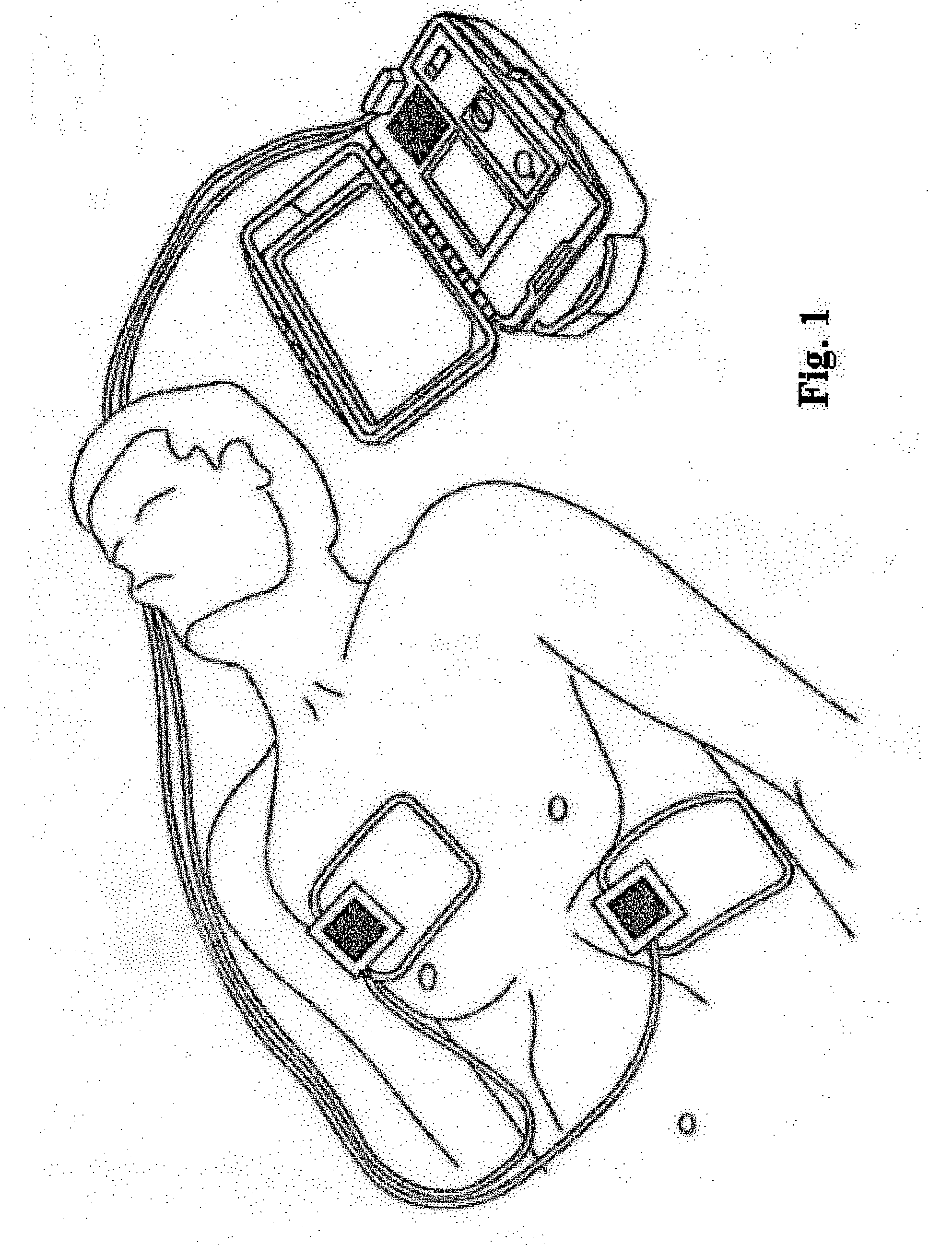
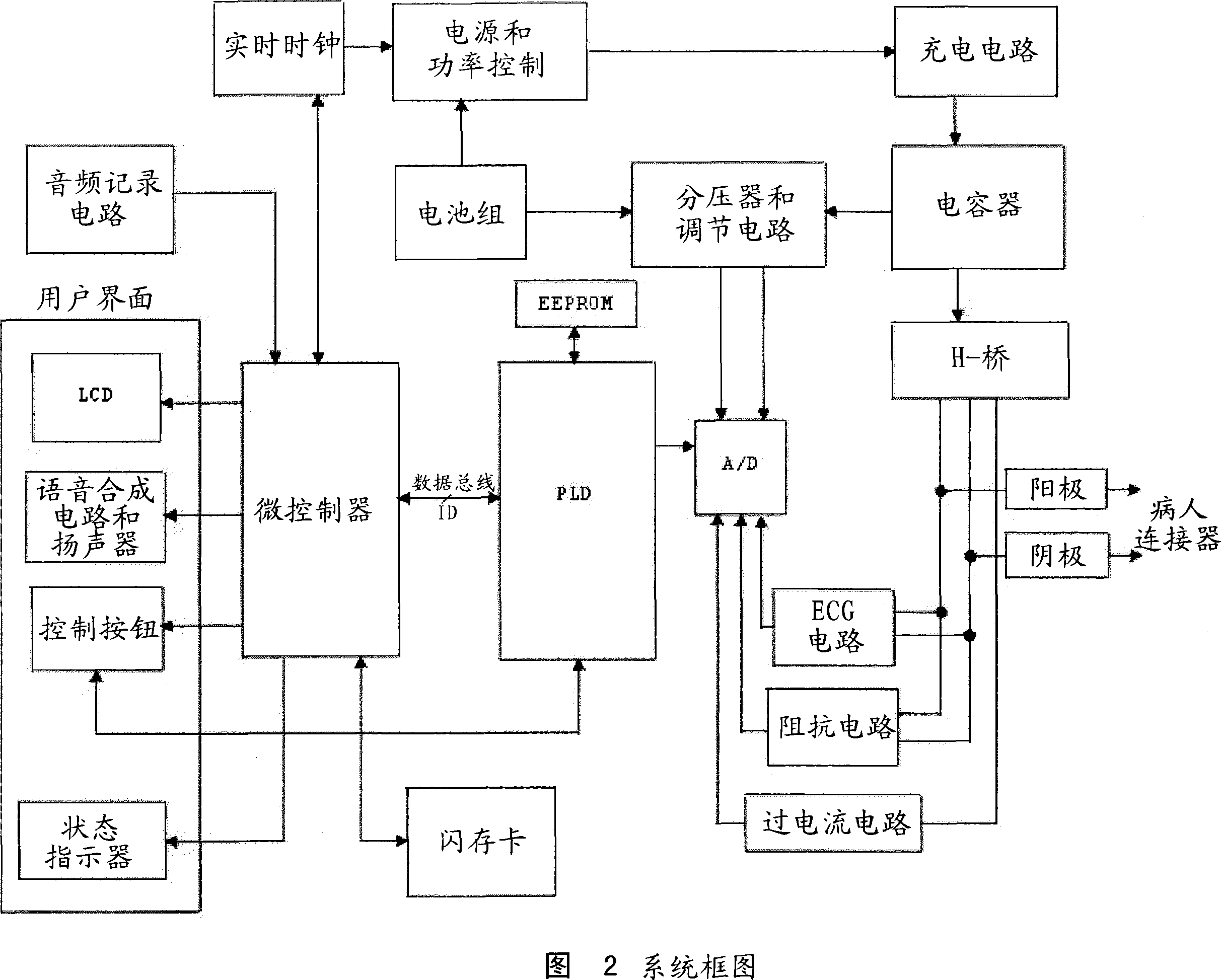
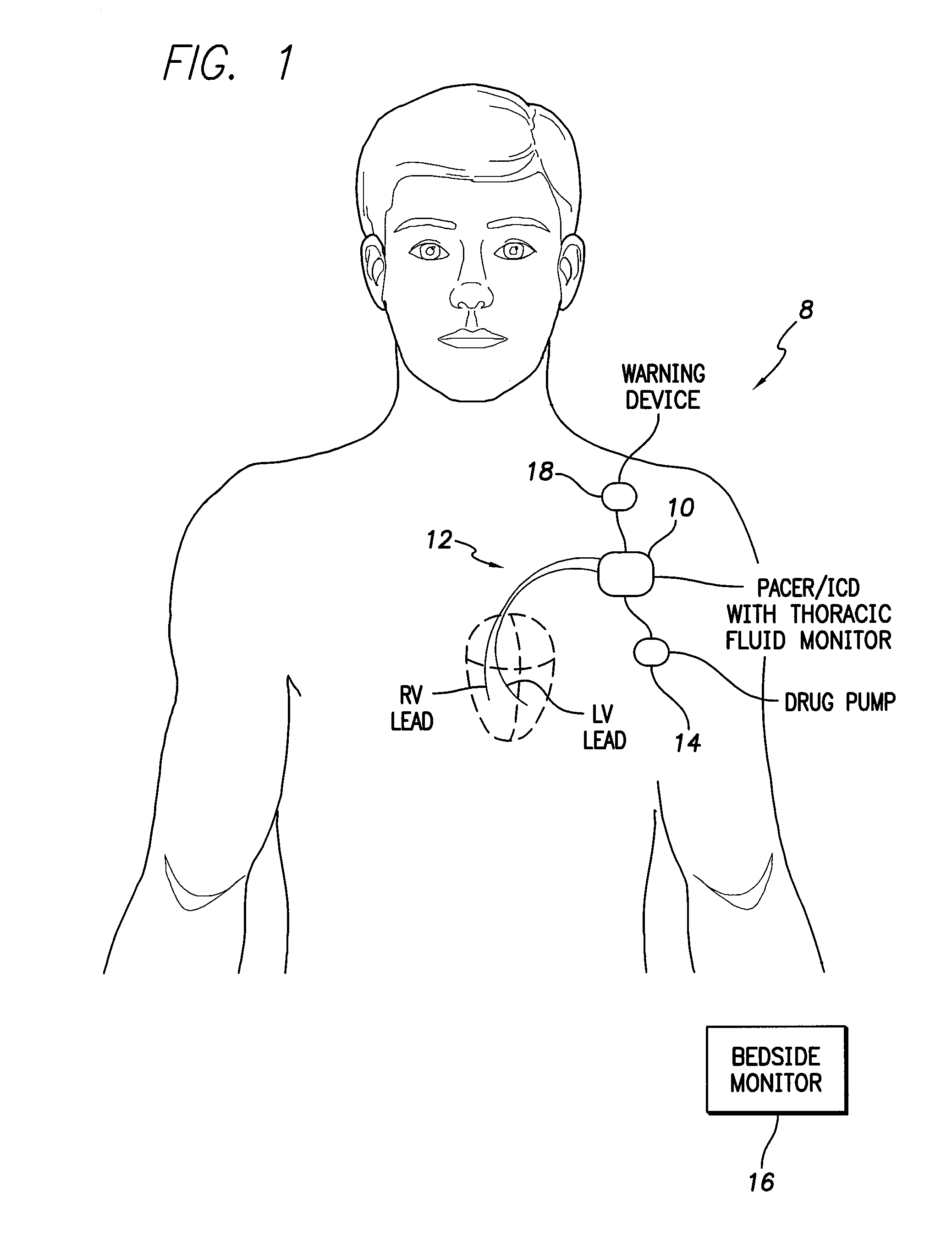
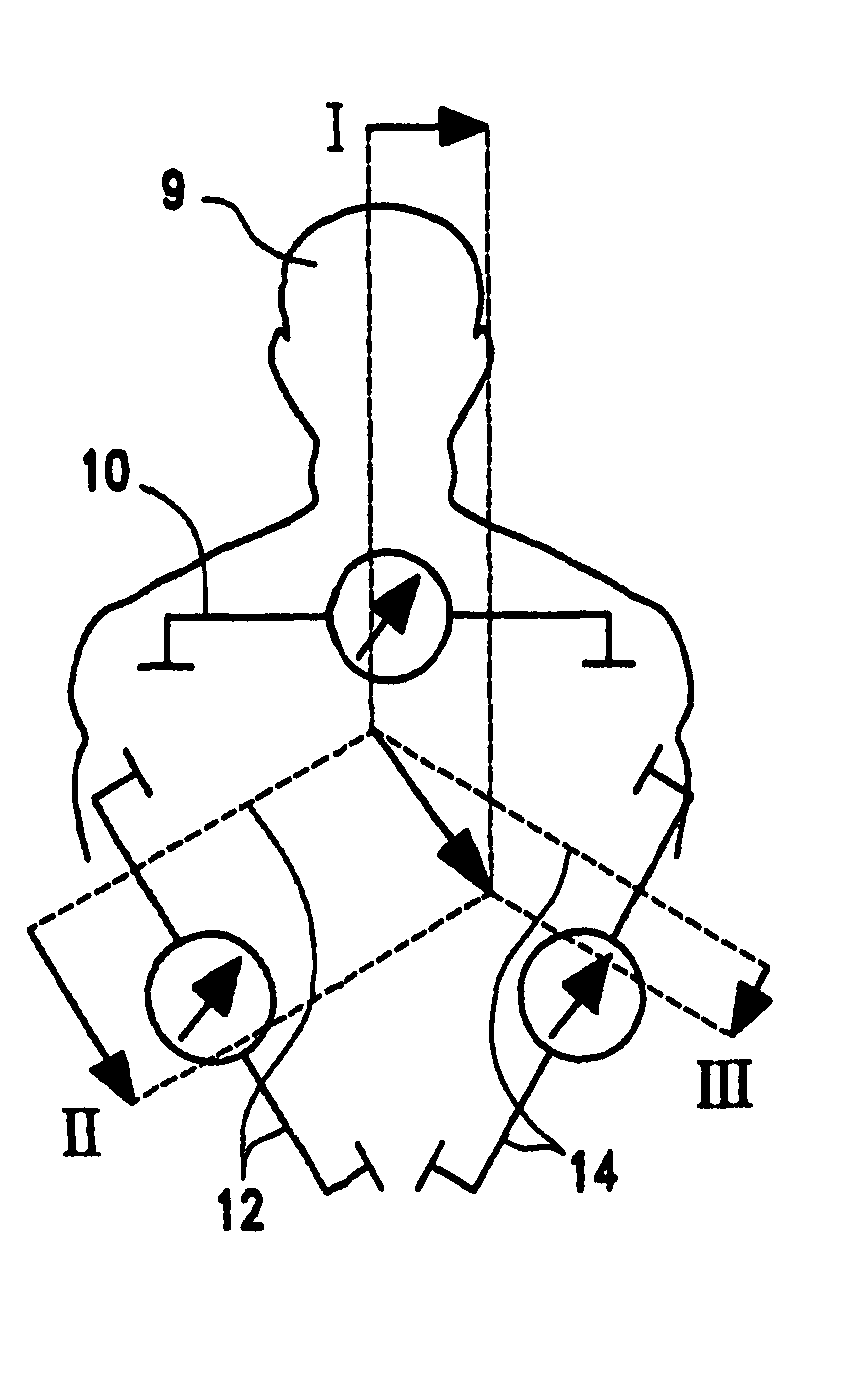
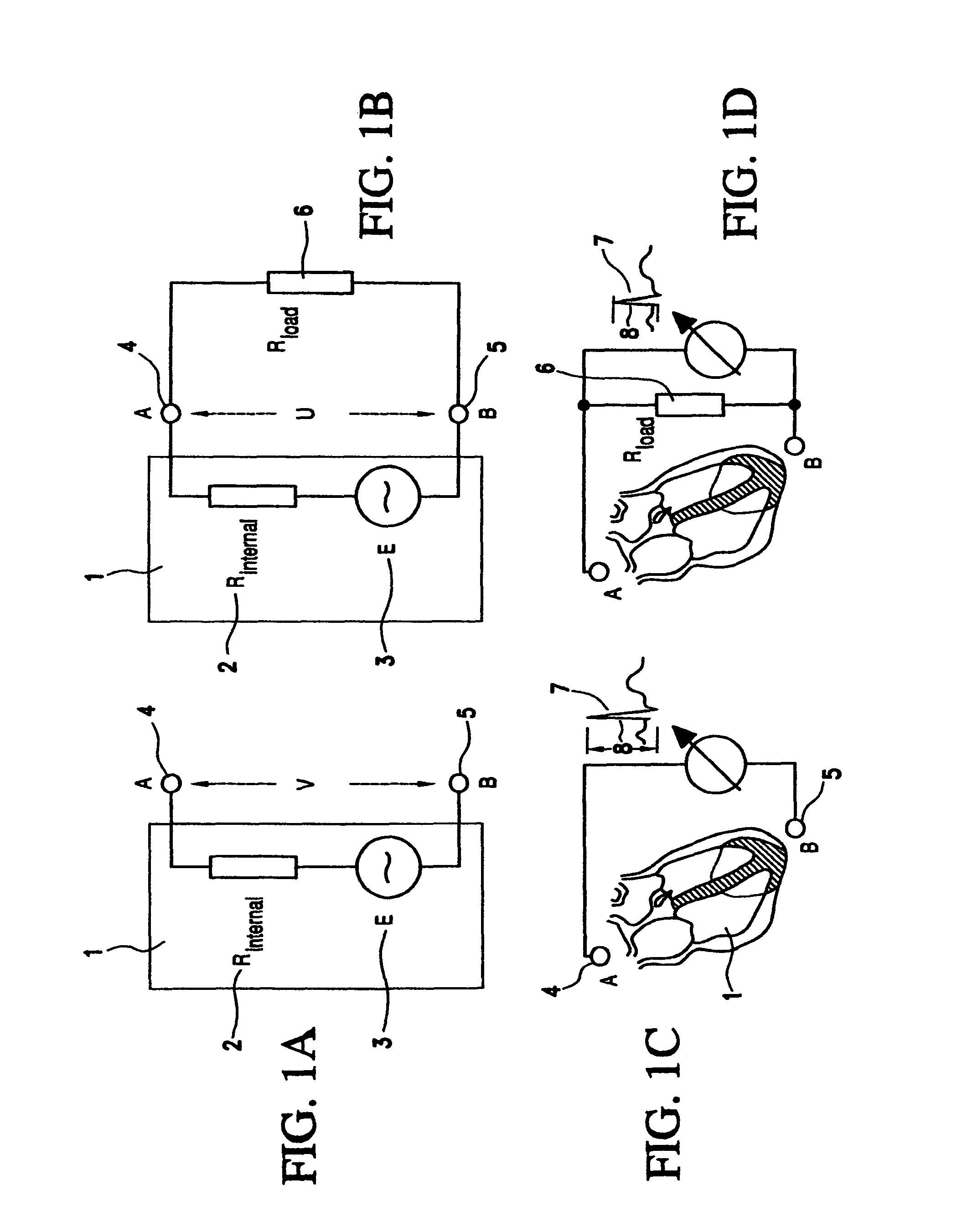
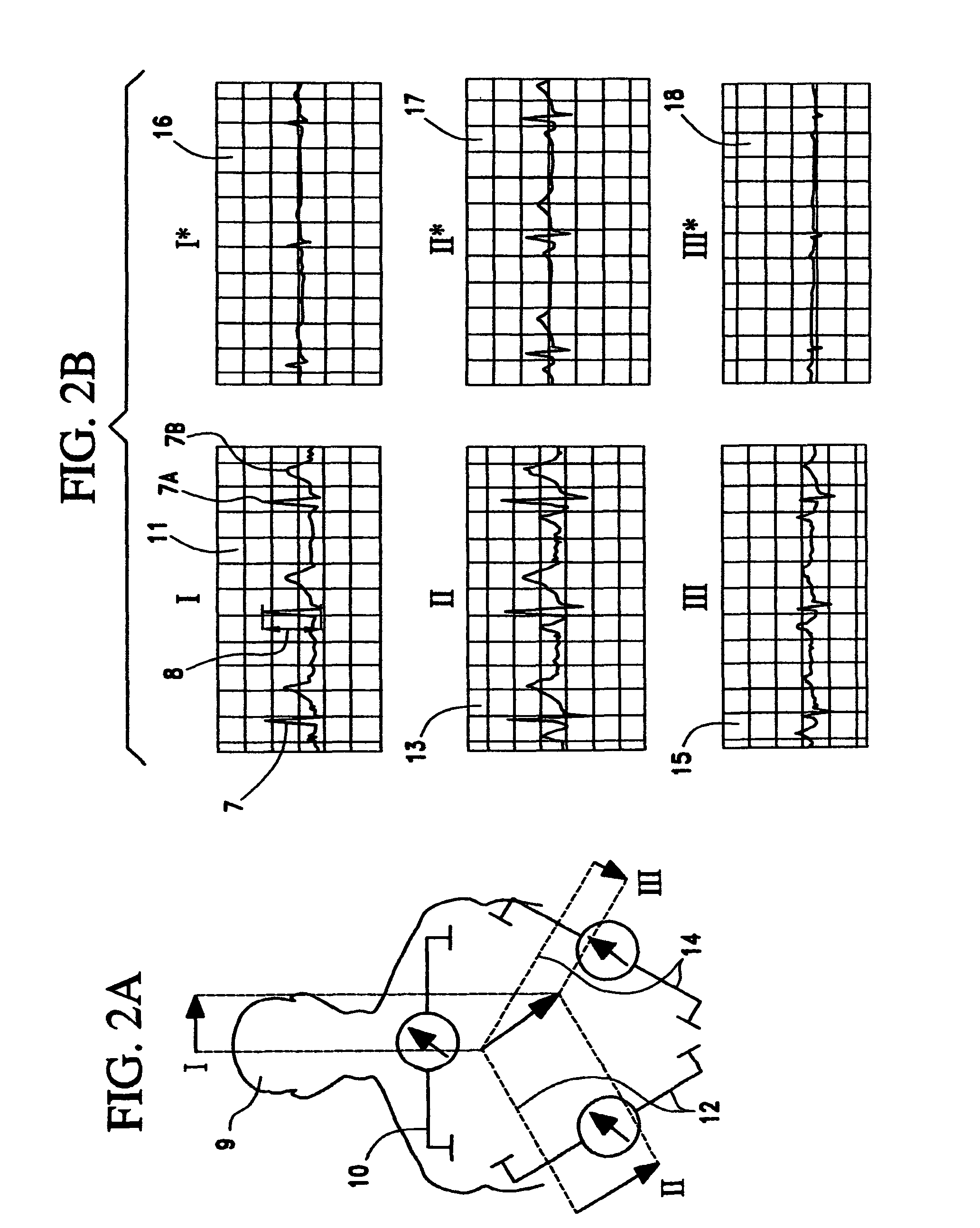
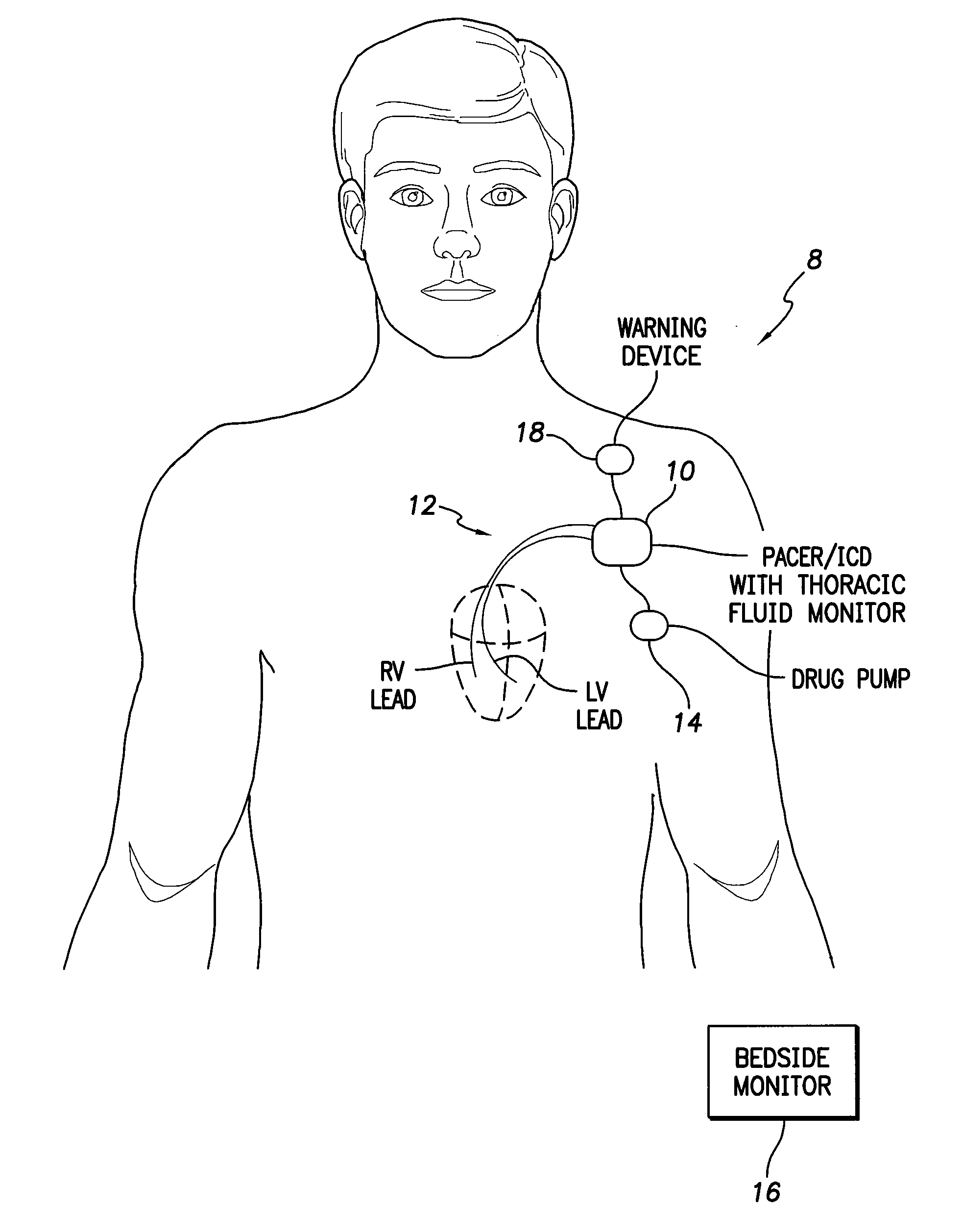
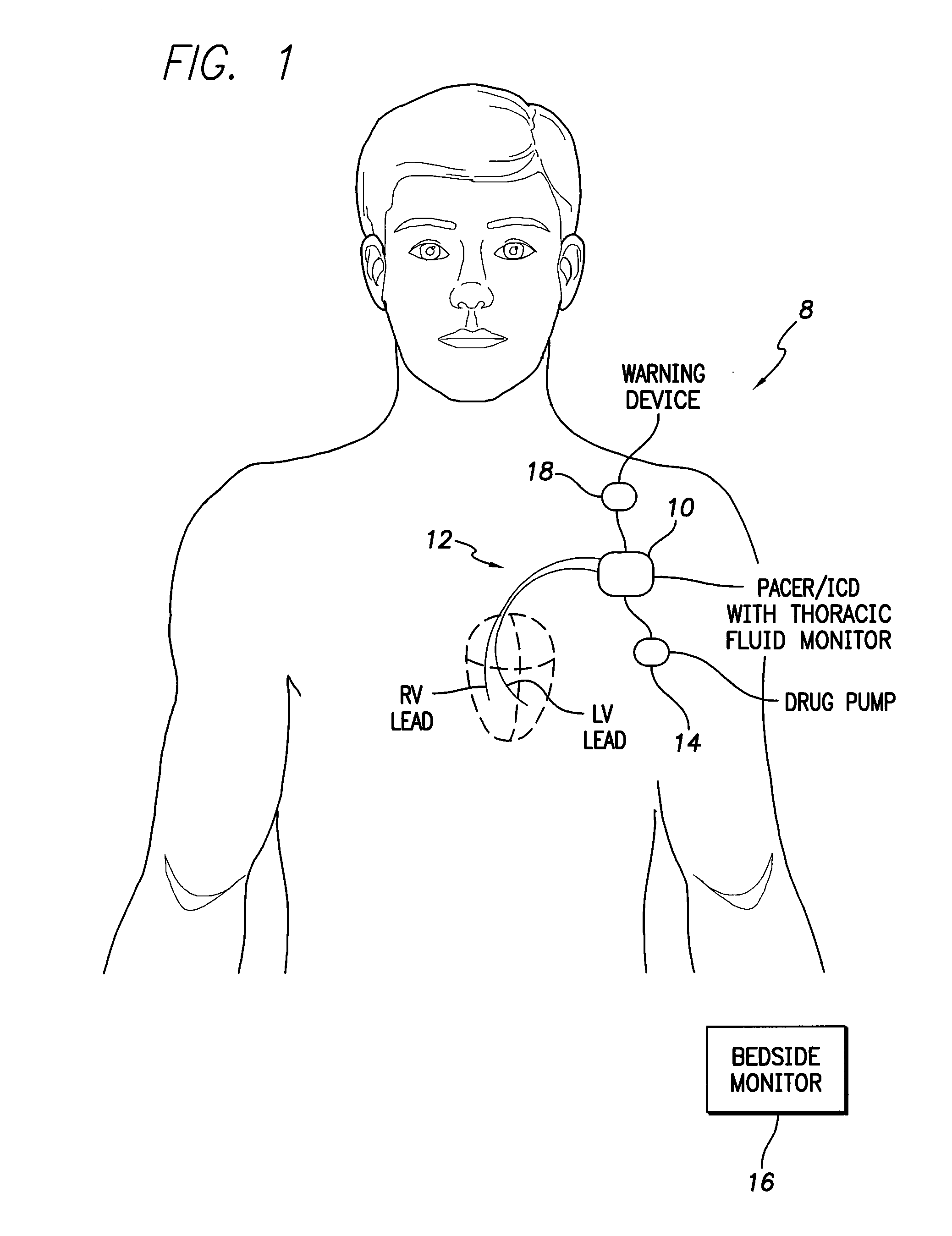
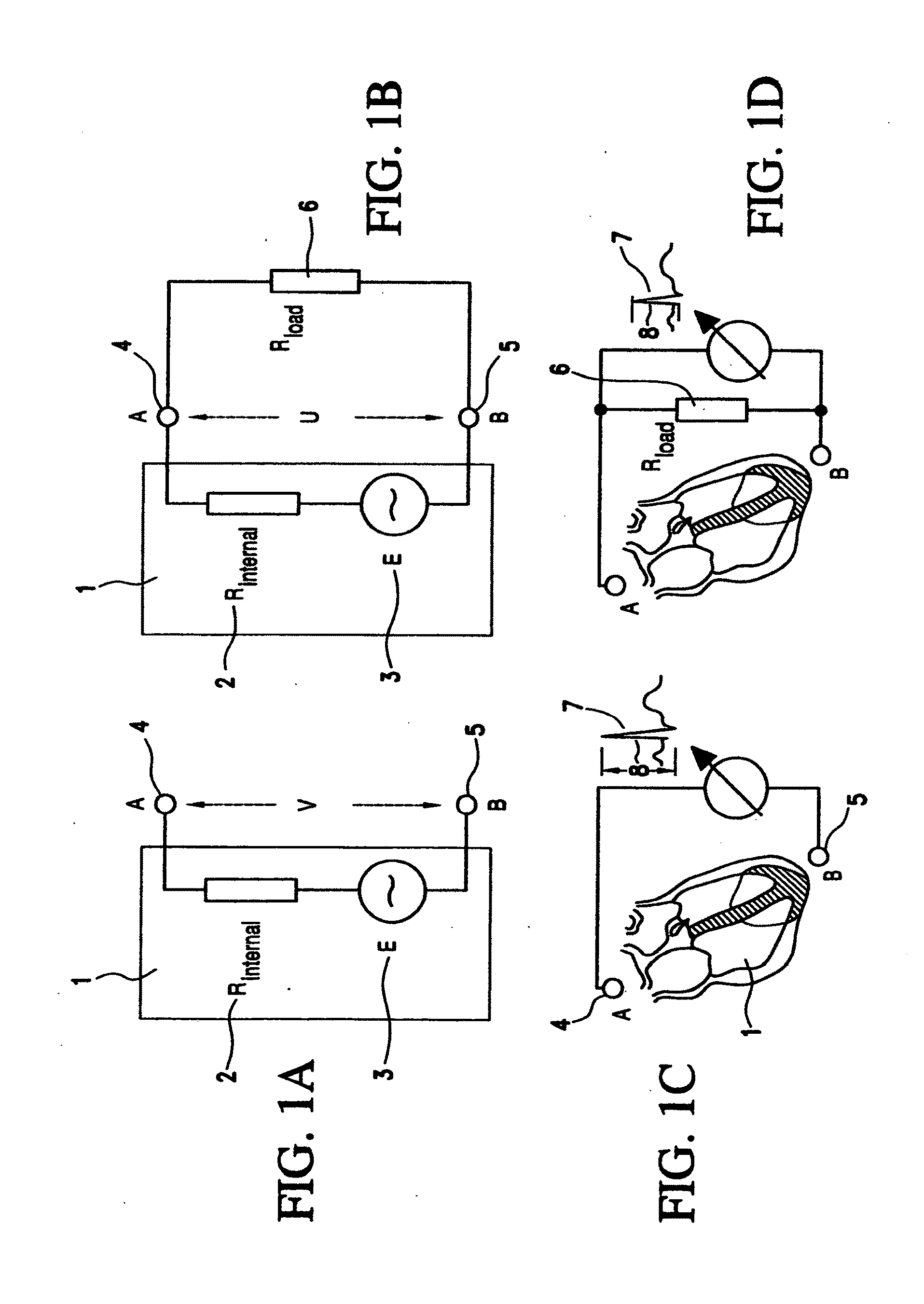
Thoracic impedance monitor and electrode array and method of use
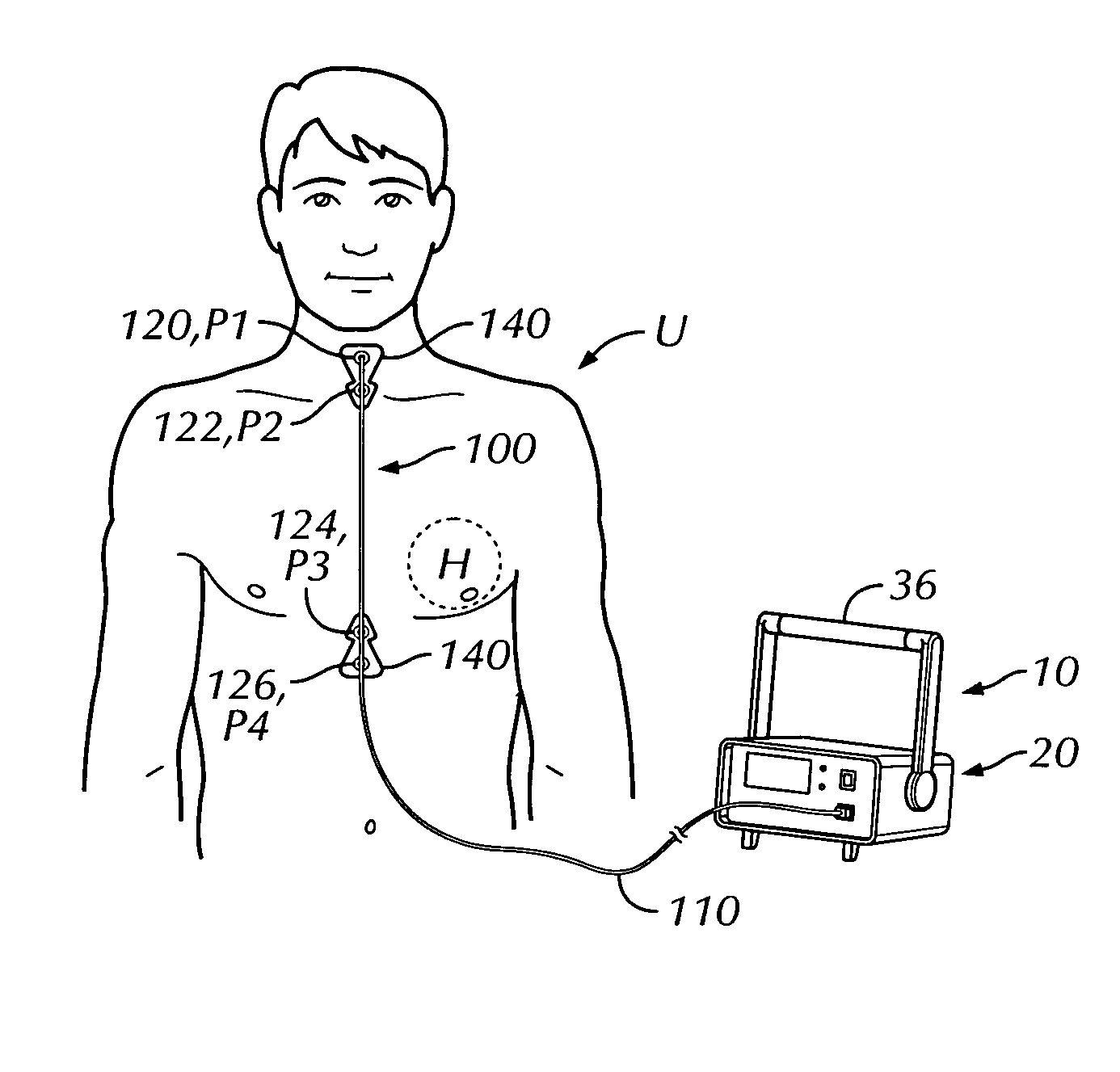
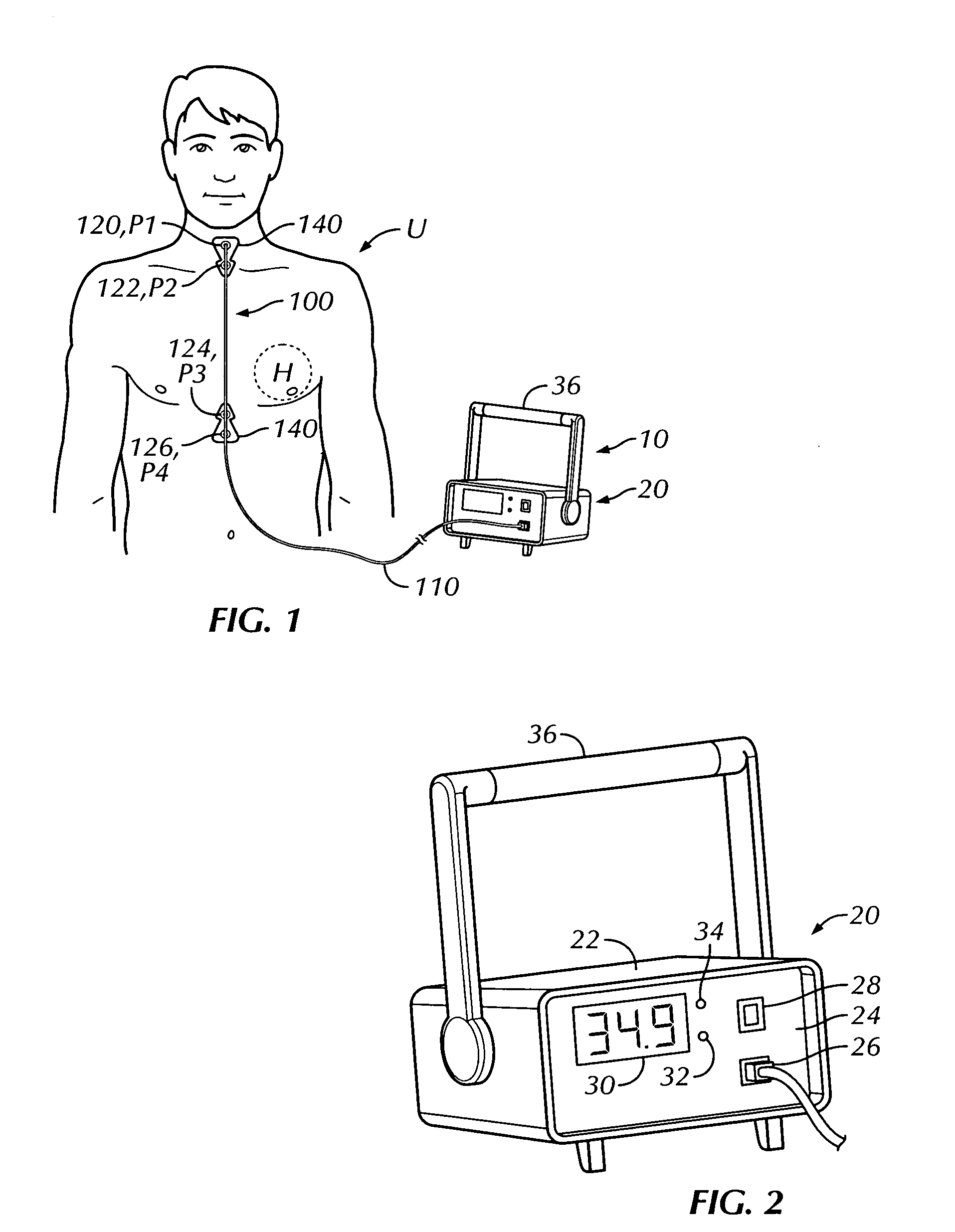
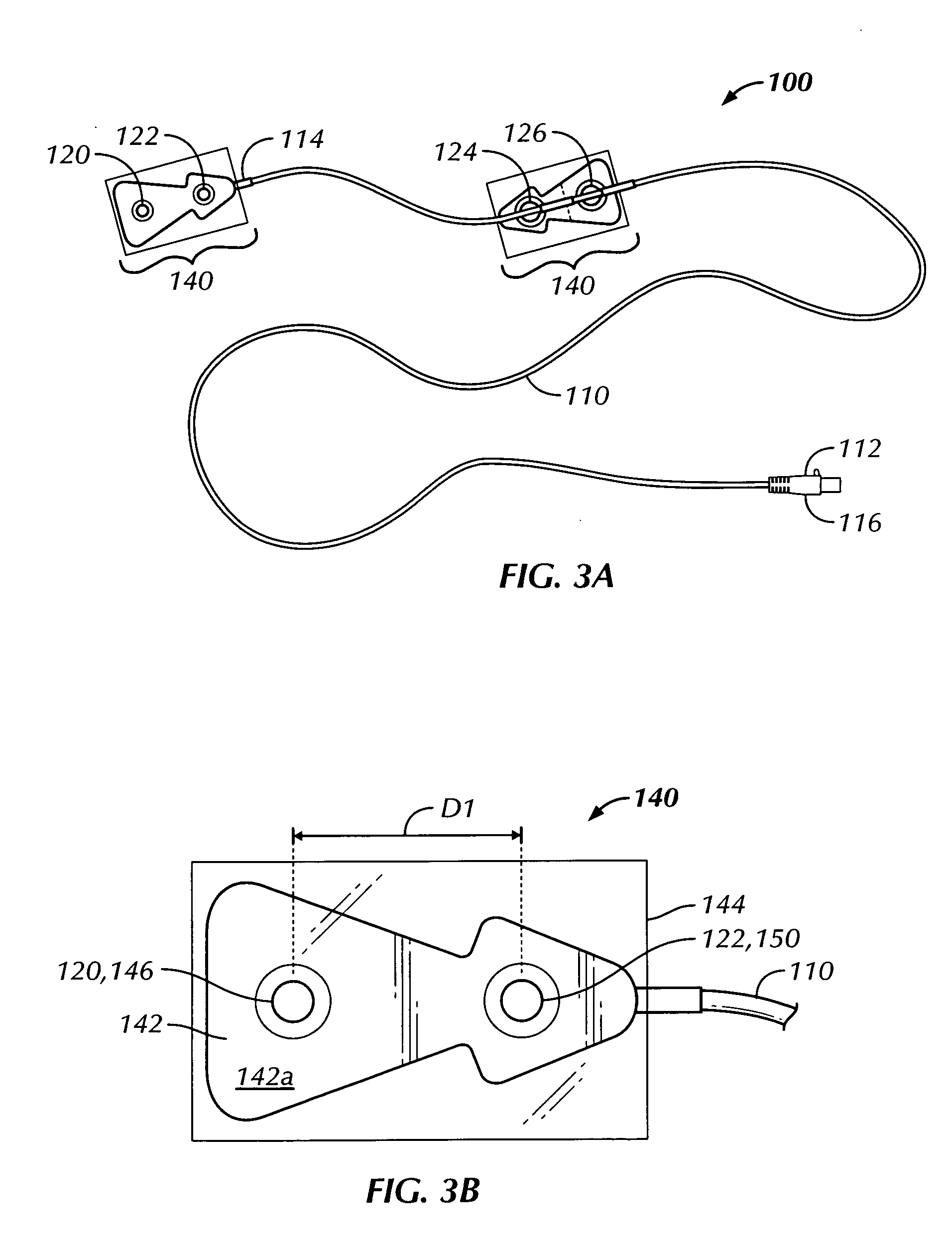
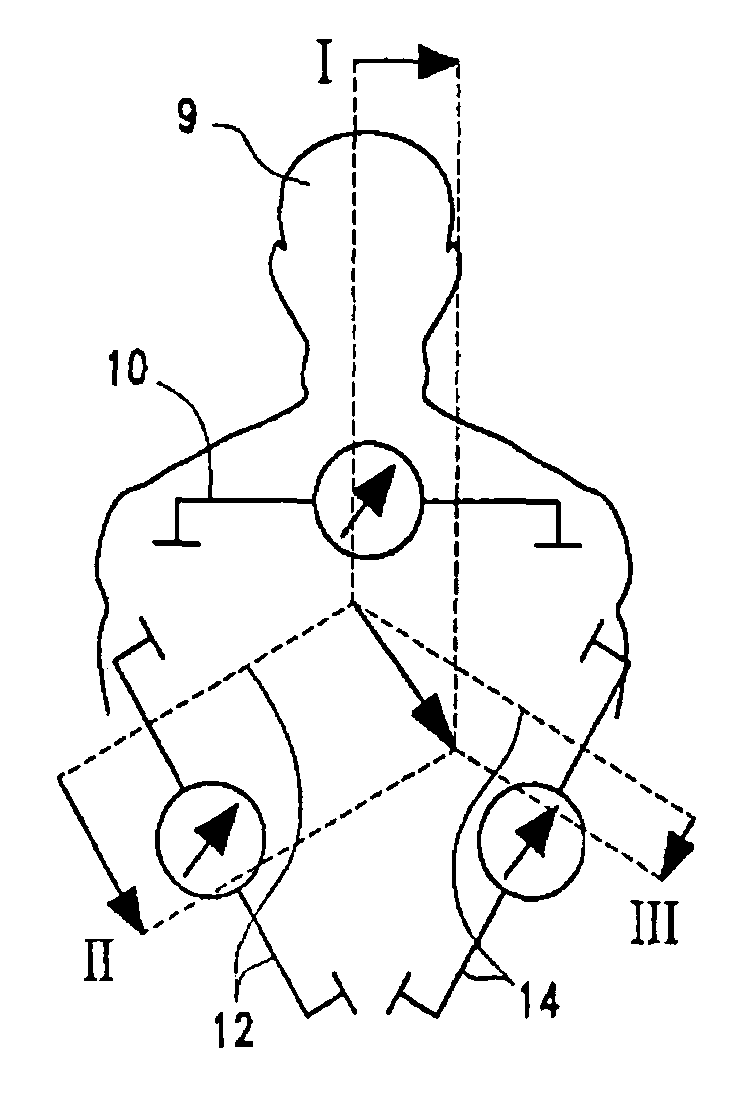
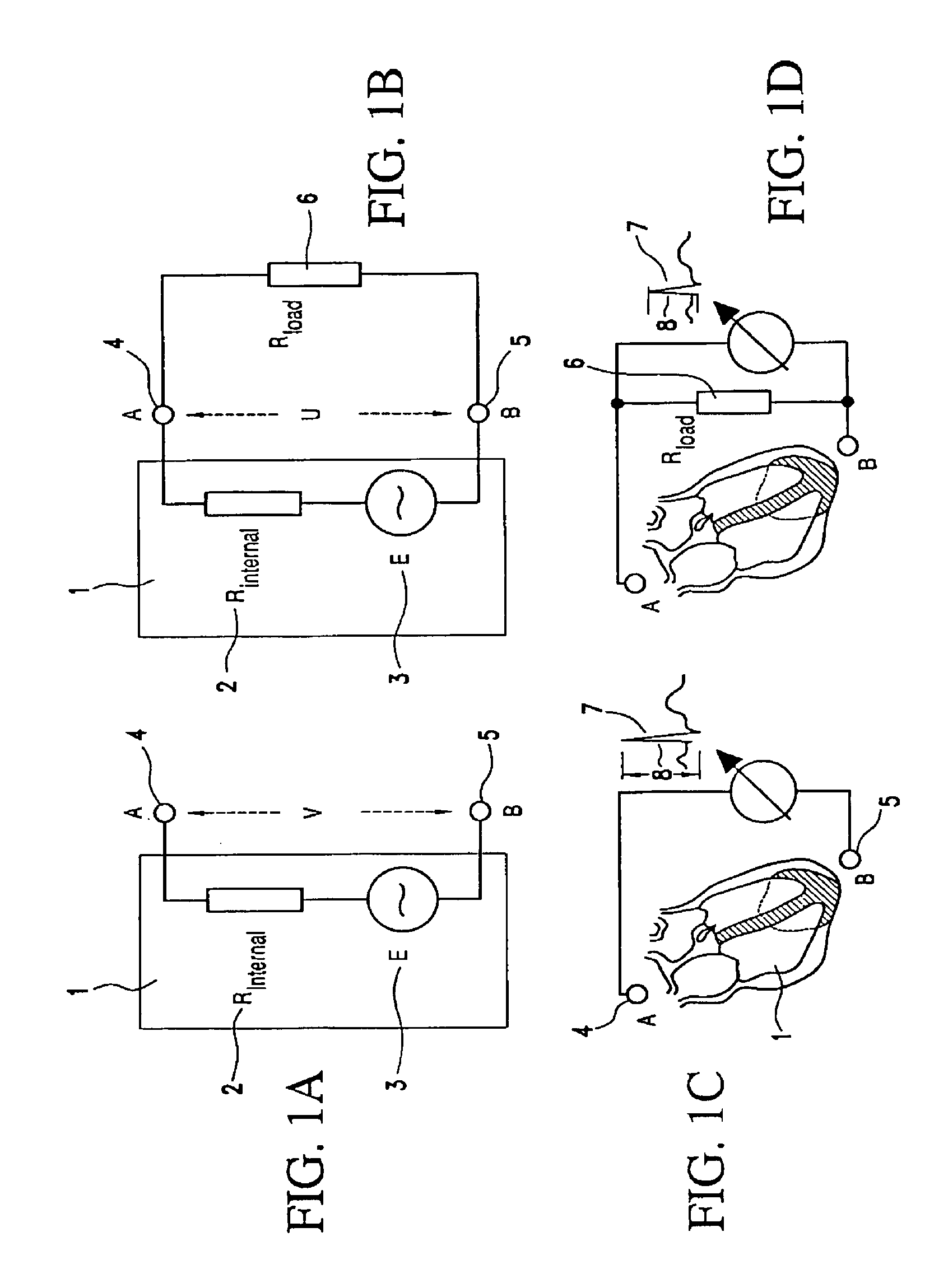
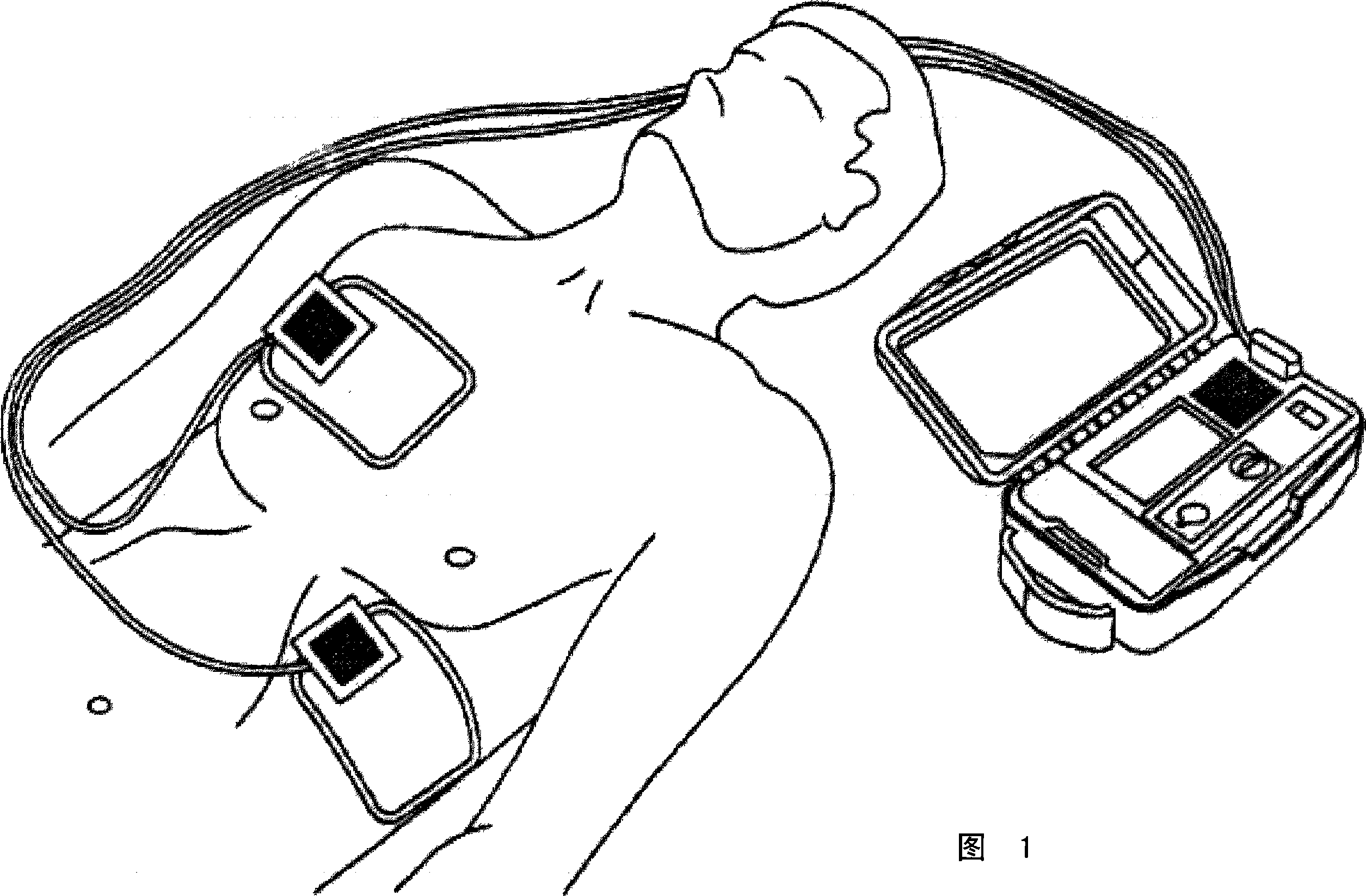
A portable thoracic impedance monitor for monitoring thoracic fluid levels, an electrode array assembly having a single linear electrode array lead with first, second, third, and fourth electrodes arranged sequentially and axially along the linear electrode array lead, and a method of use of the thoracic impedance monitor. A measurement of the user's thoracic impedance is obtained by connecting the second electrode to the user's body at the junction of the clavicles, superior to the sternum, the third electrode to the user's body at the xyphiod-sternal junction, and the first and fourth electrodes to the user's body substantially along a centerline of the user's sternum respectively at a first pre-determined distance above the second electrode and a second predetermined distance below the third electrode, followed by initiating operation of the monitor.
Owner:CALDWELL SIMPSON LLC
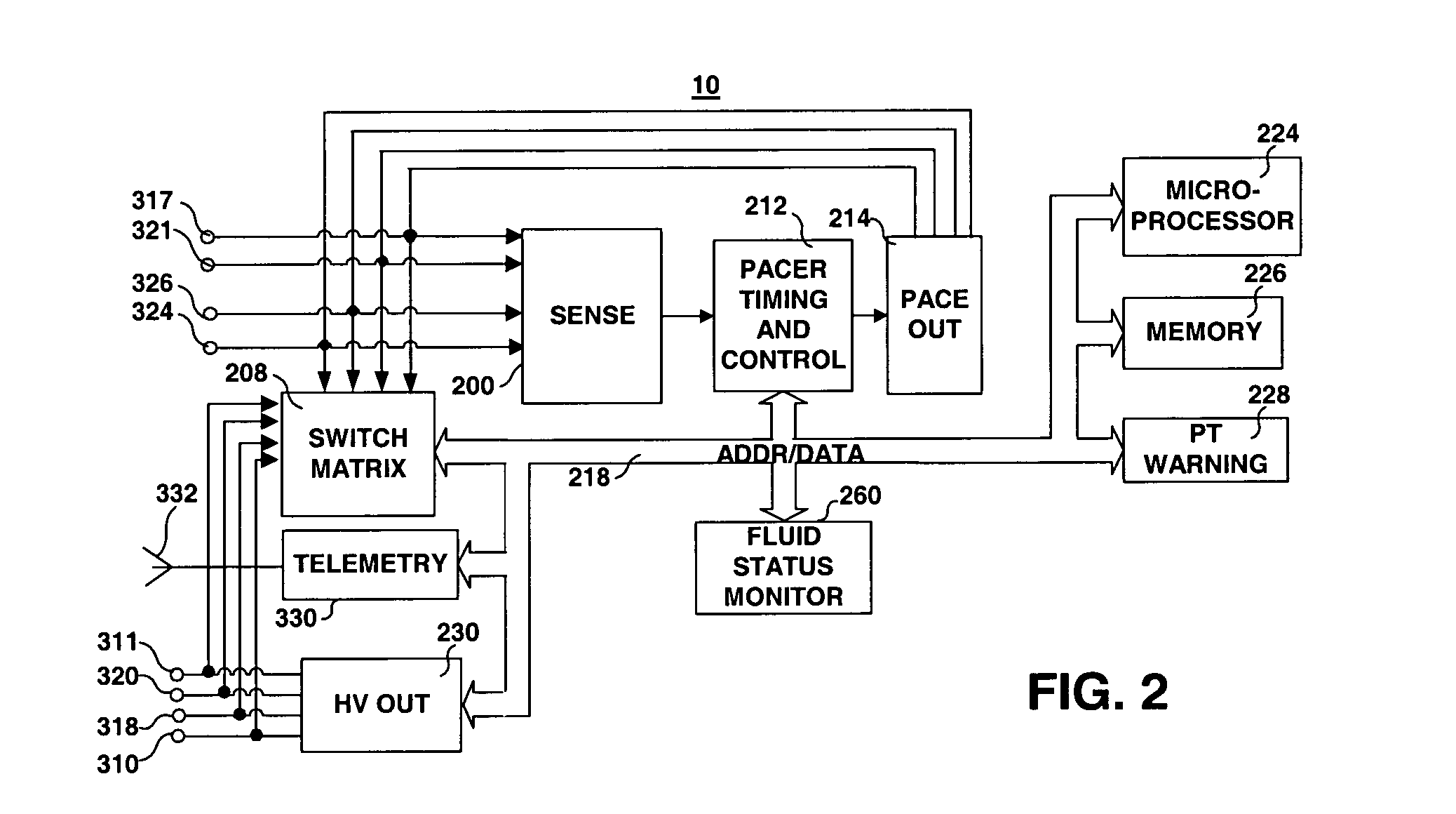
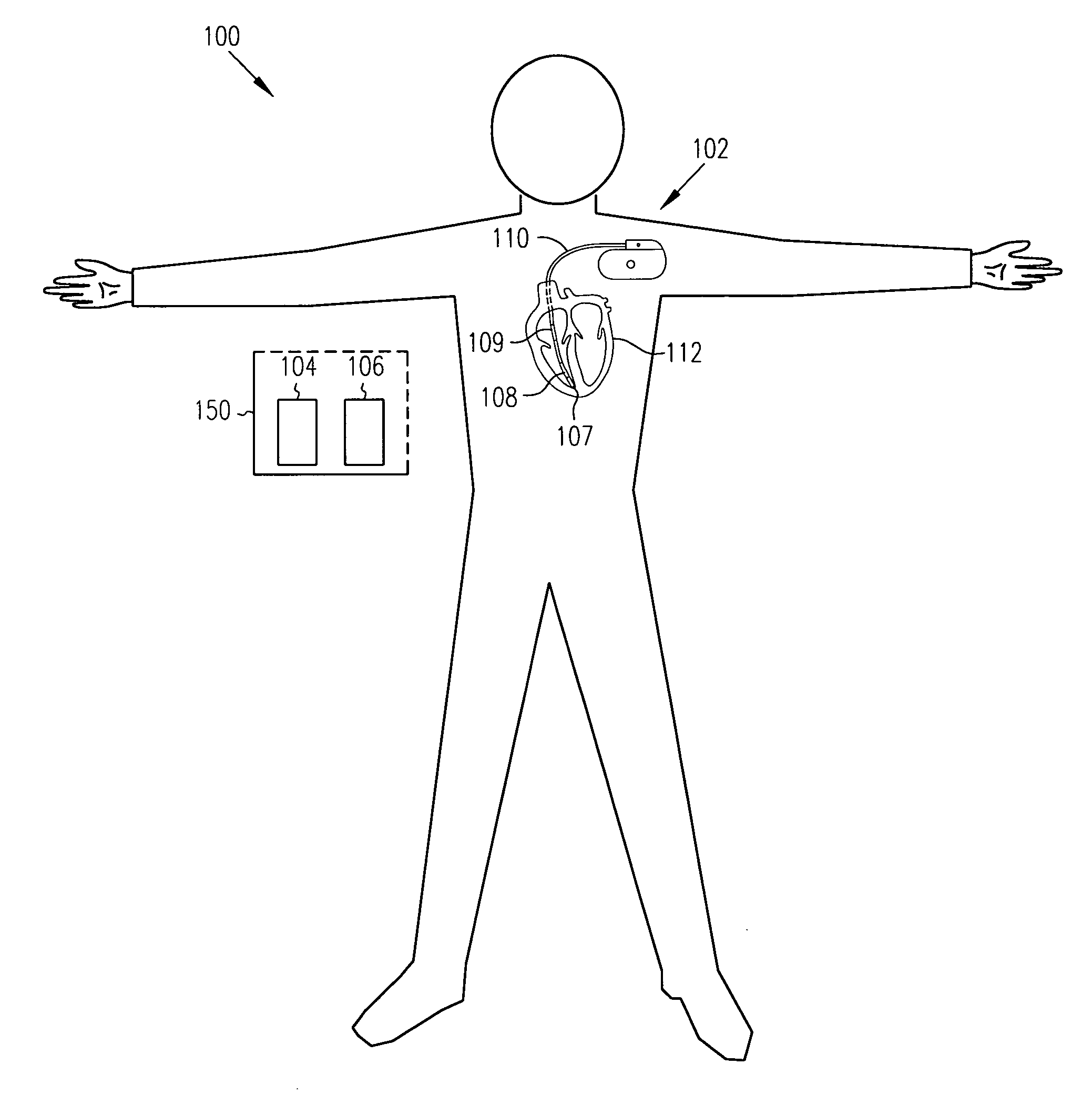
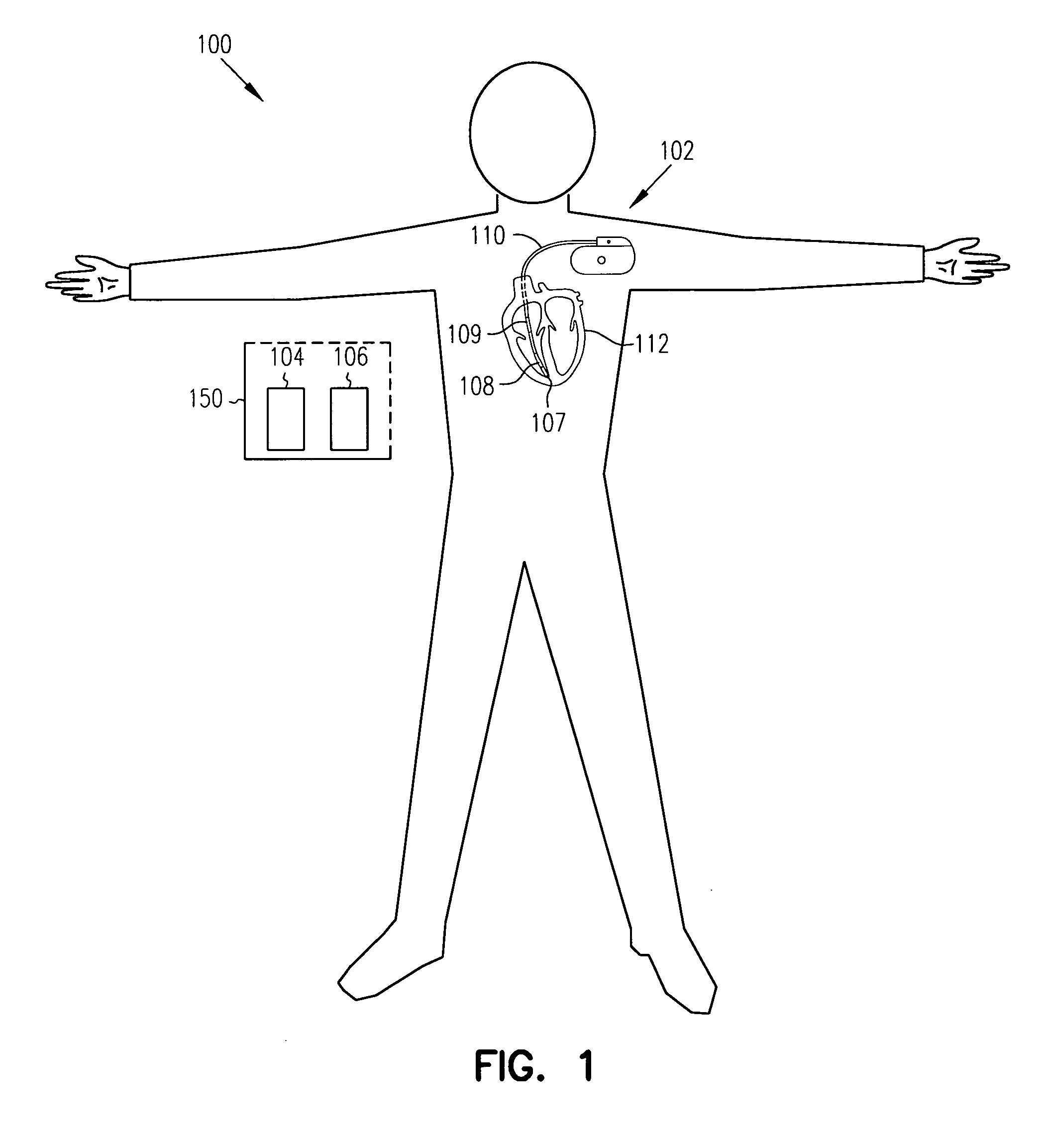
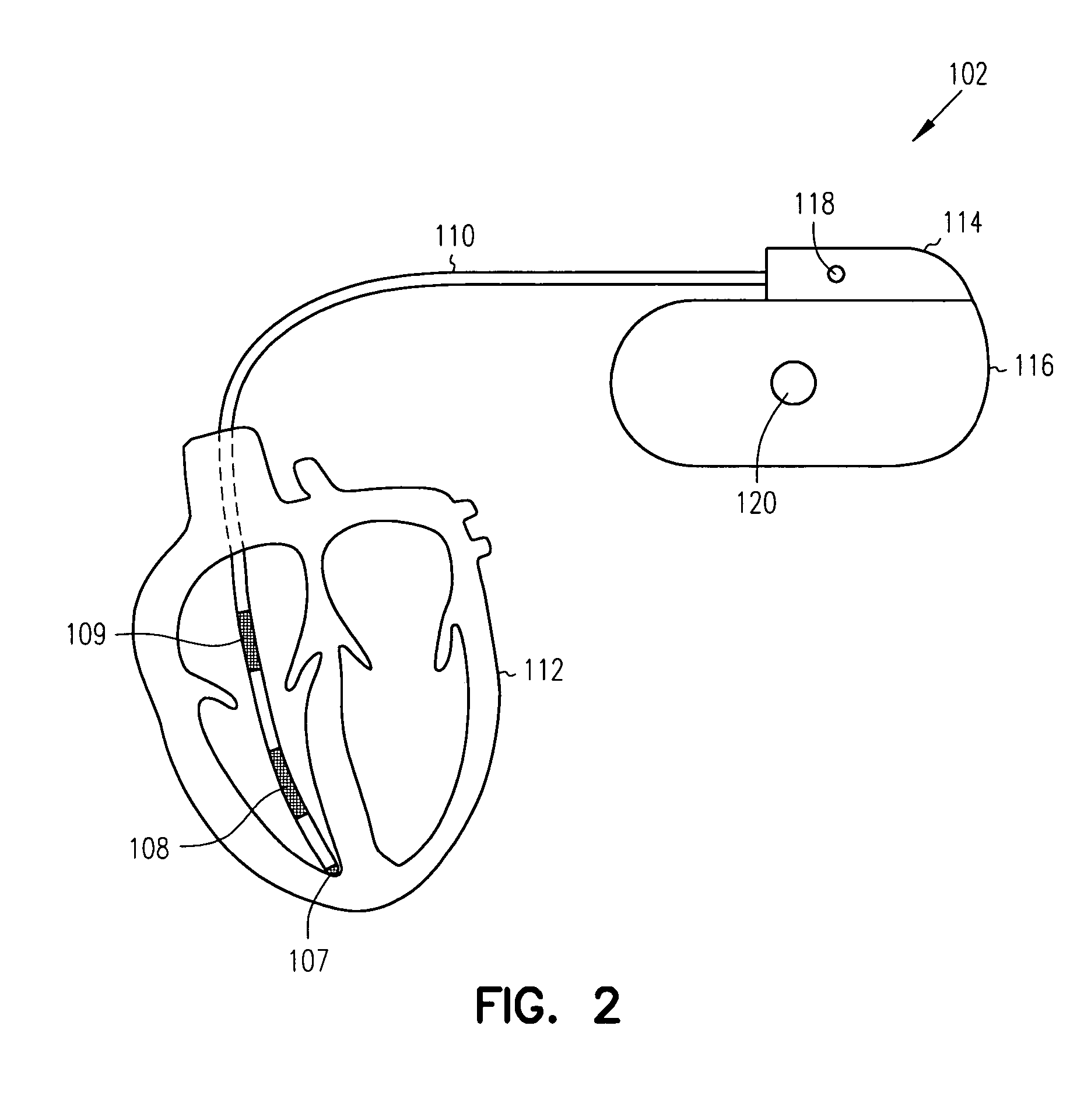
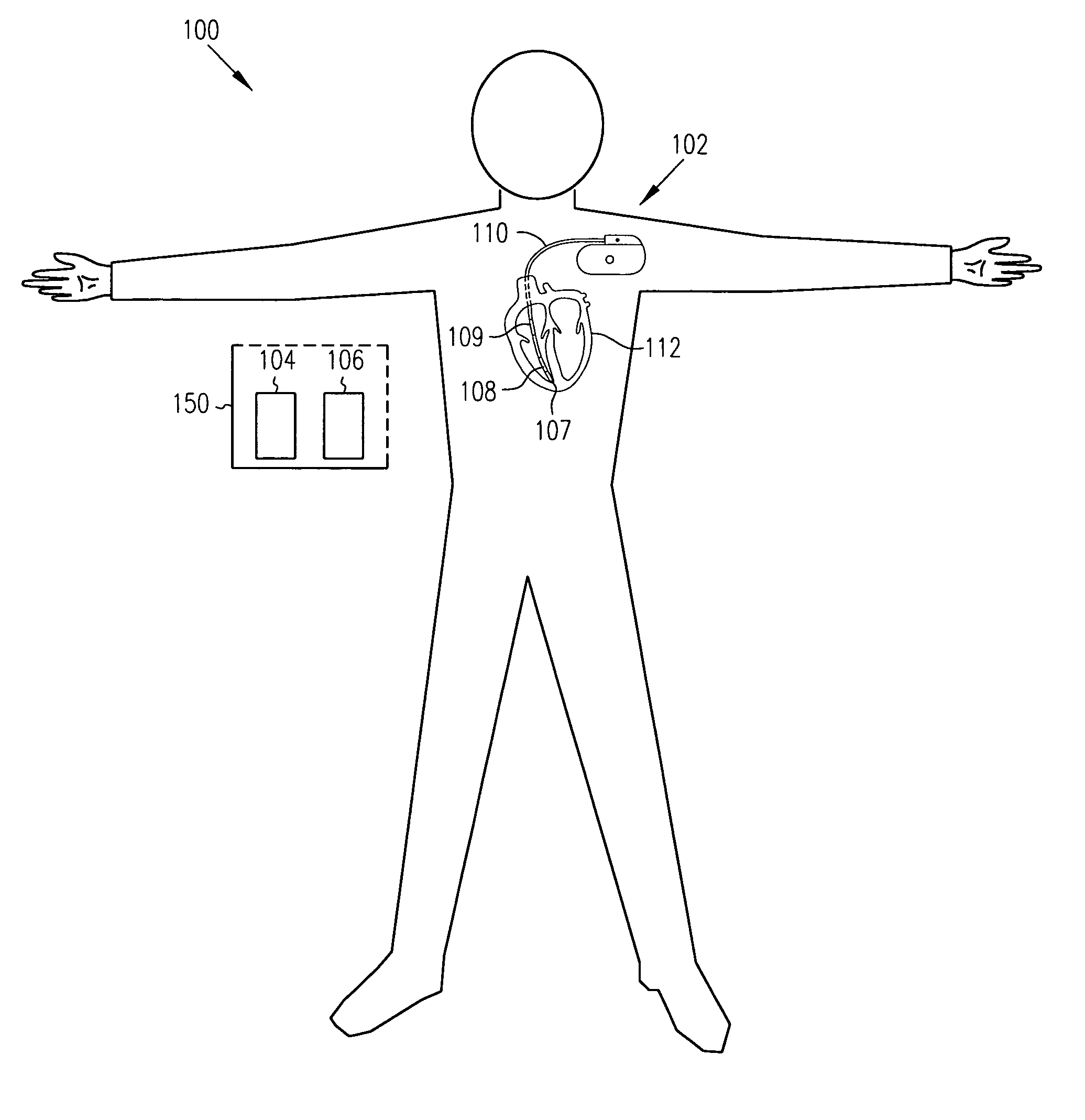
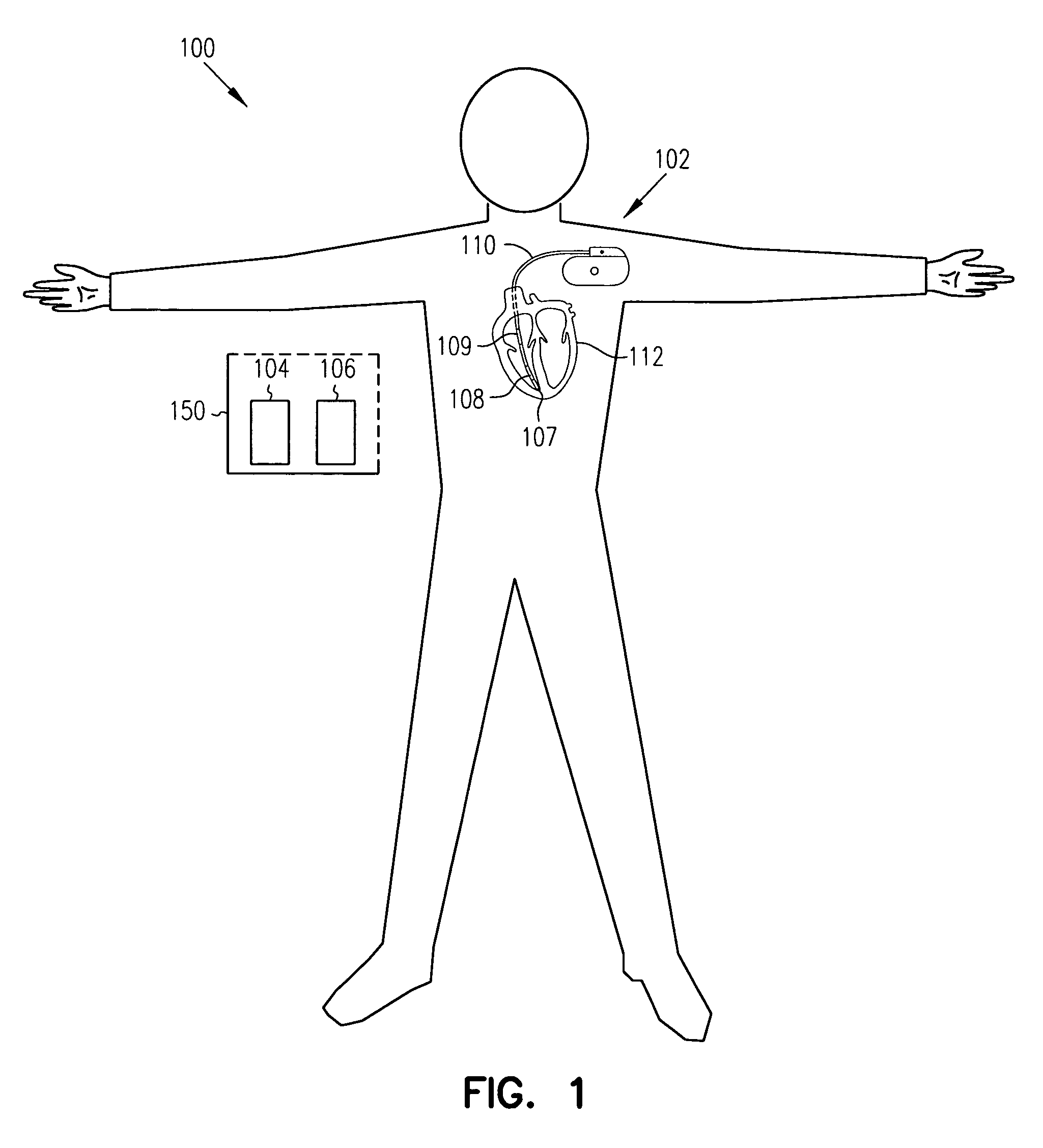
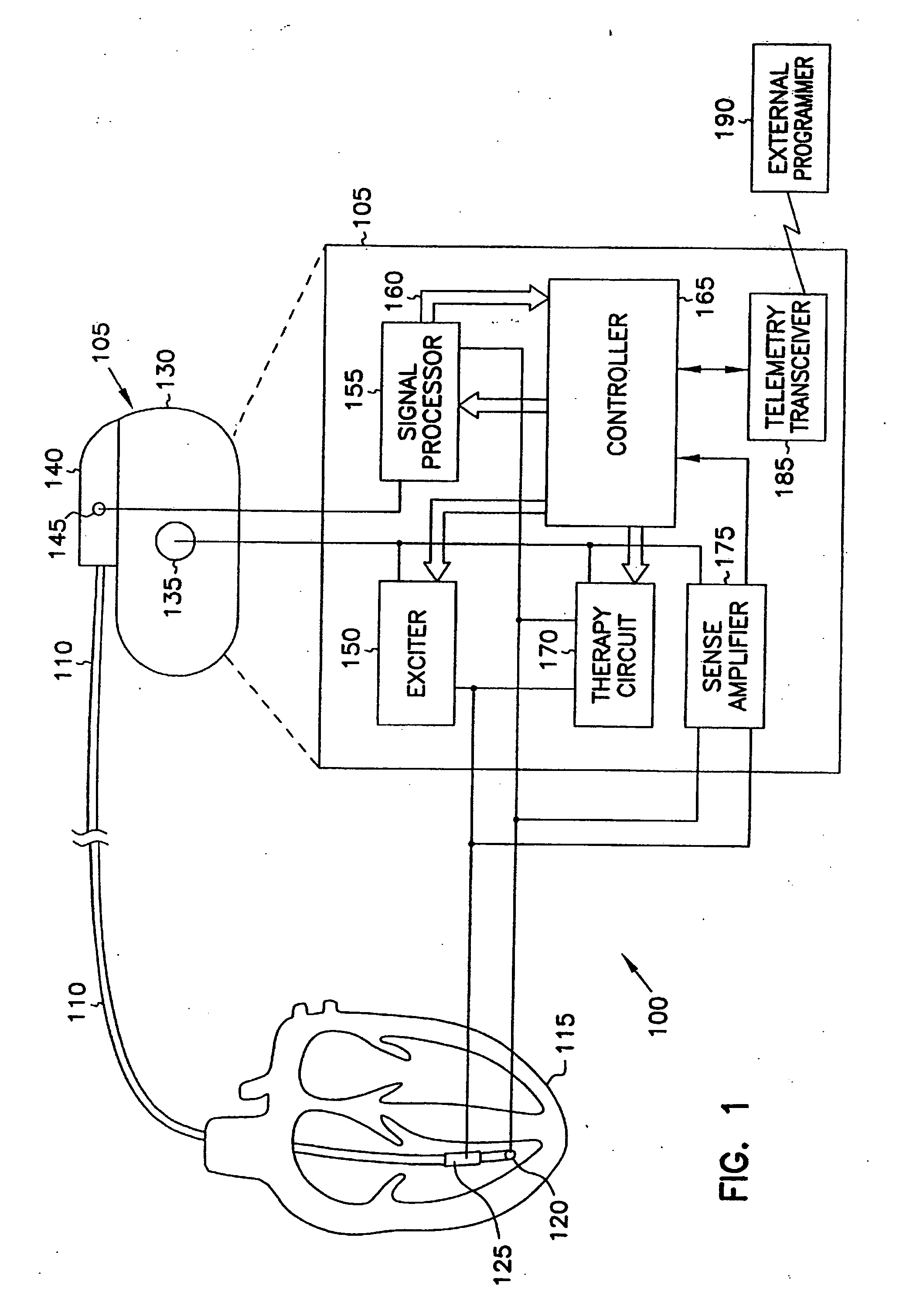
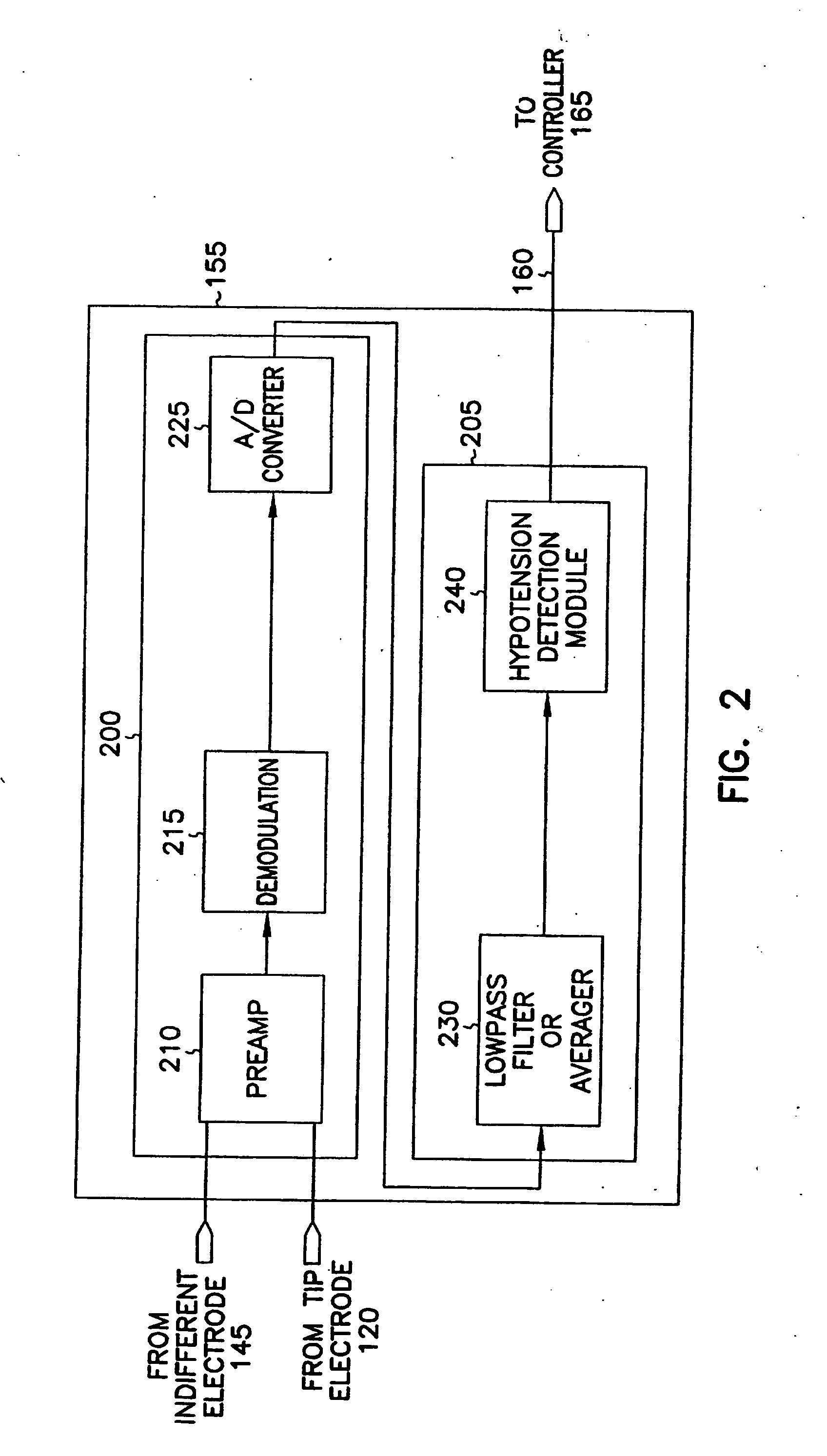
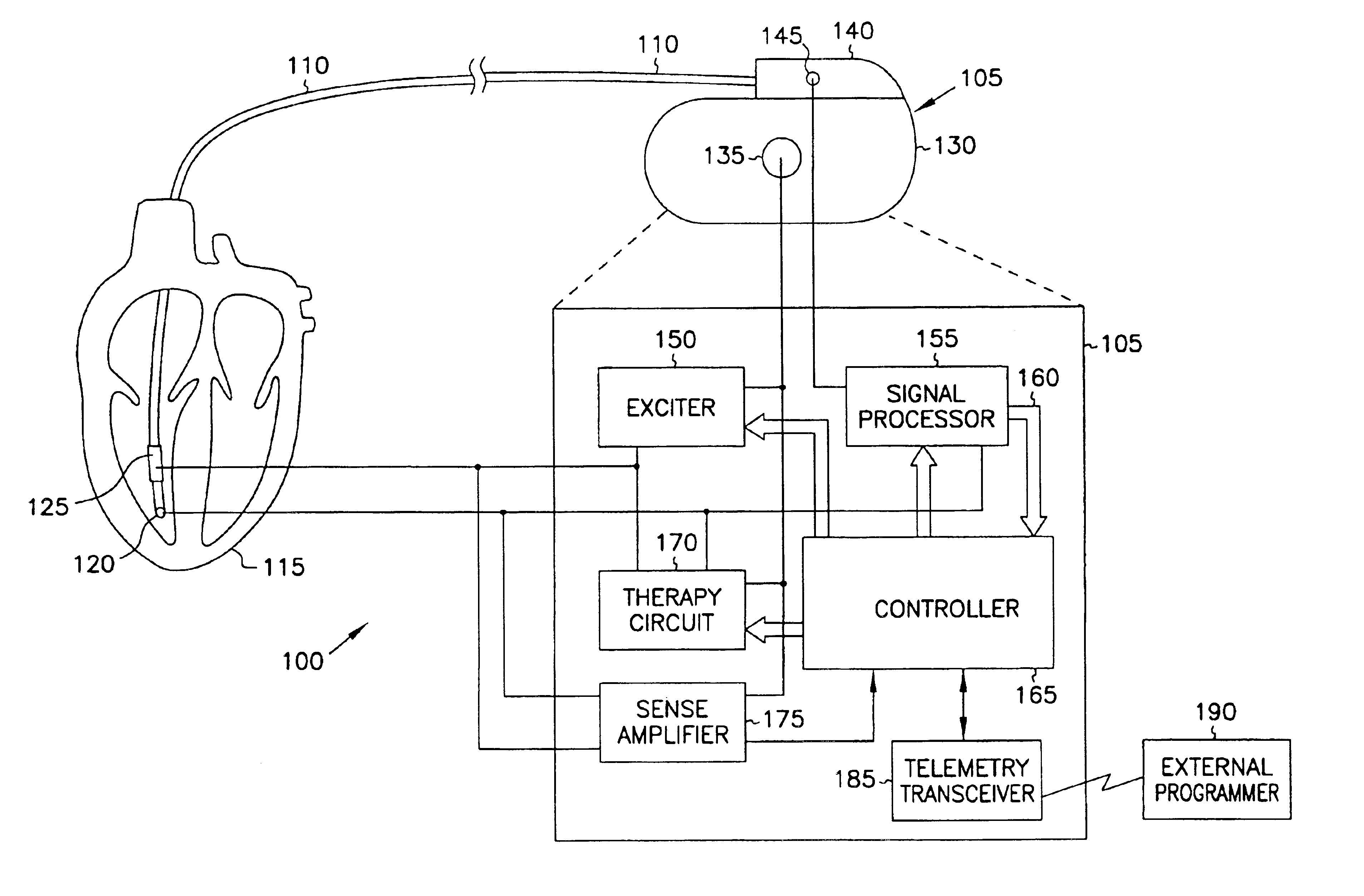
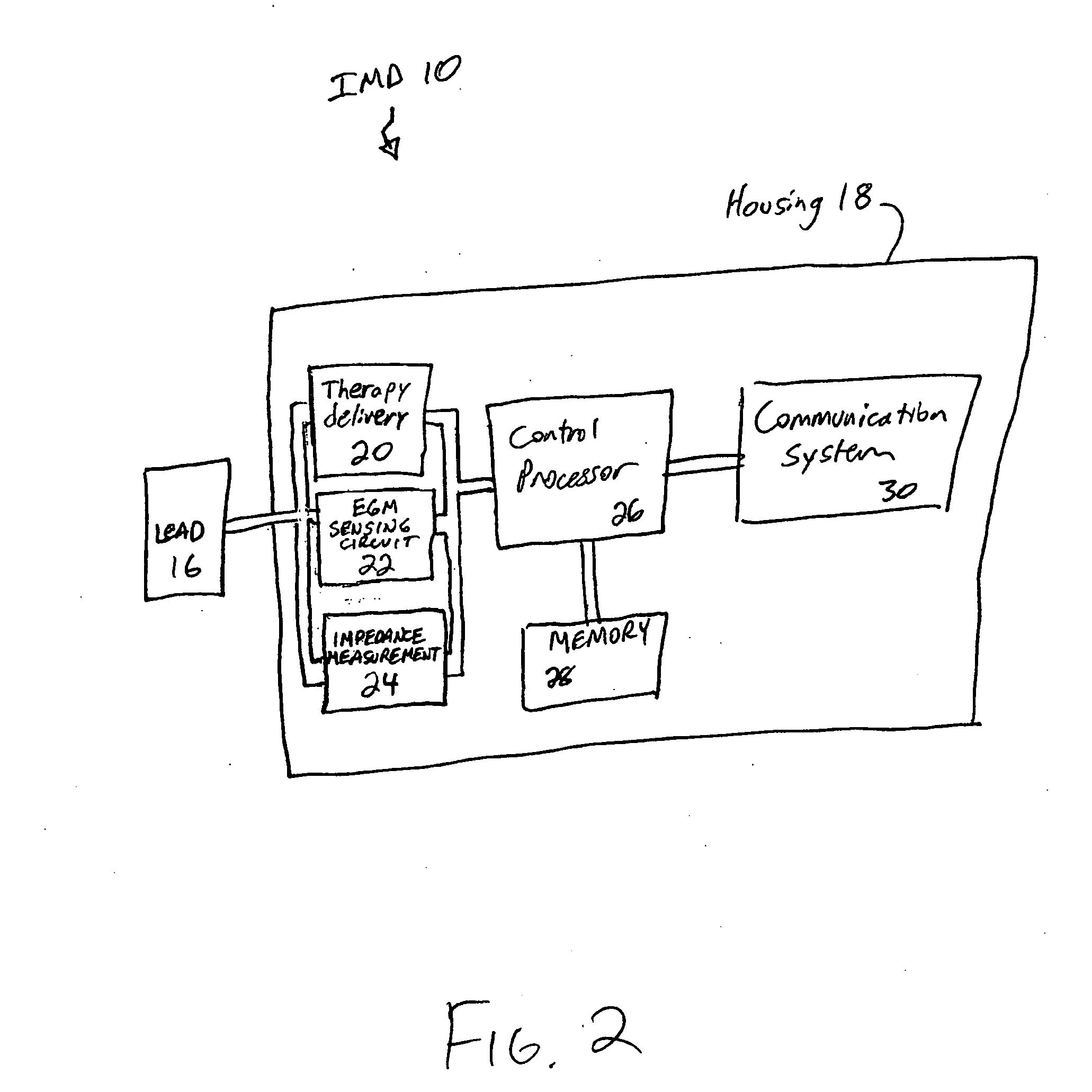
Method and apparatus for monitoring tissue fluid content for use in an implantable cardiac device
ActiveUS20050080460A1Easy to implementCancel noiseHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsThoracic FluidTissue fluid
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and system for diagnosing and administering therapy of pulmonary congestion
InactiveUS20030023184A1Accurate and efficient measurementMonitor pulmonary congestionElectrocardiographyCatheterPulse rateThoracic impedance
A method of diagnosing pulmonary congestion is provided. At least one decrease in a trans-thoracic impedance value from a baseline trans-thoracic impedance value is sensed. At least one increase in a heart rate value from a baseline heart rate value is also sensed. Pulmonary congestion is diagnosed if the decrease in the trans-thoracic impedance value corresponding to the increase in the heart rate does not increase after a predetermined interval. Systems and programs incorporating the method are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
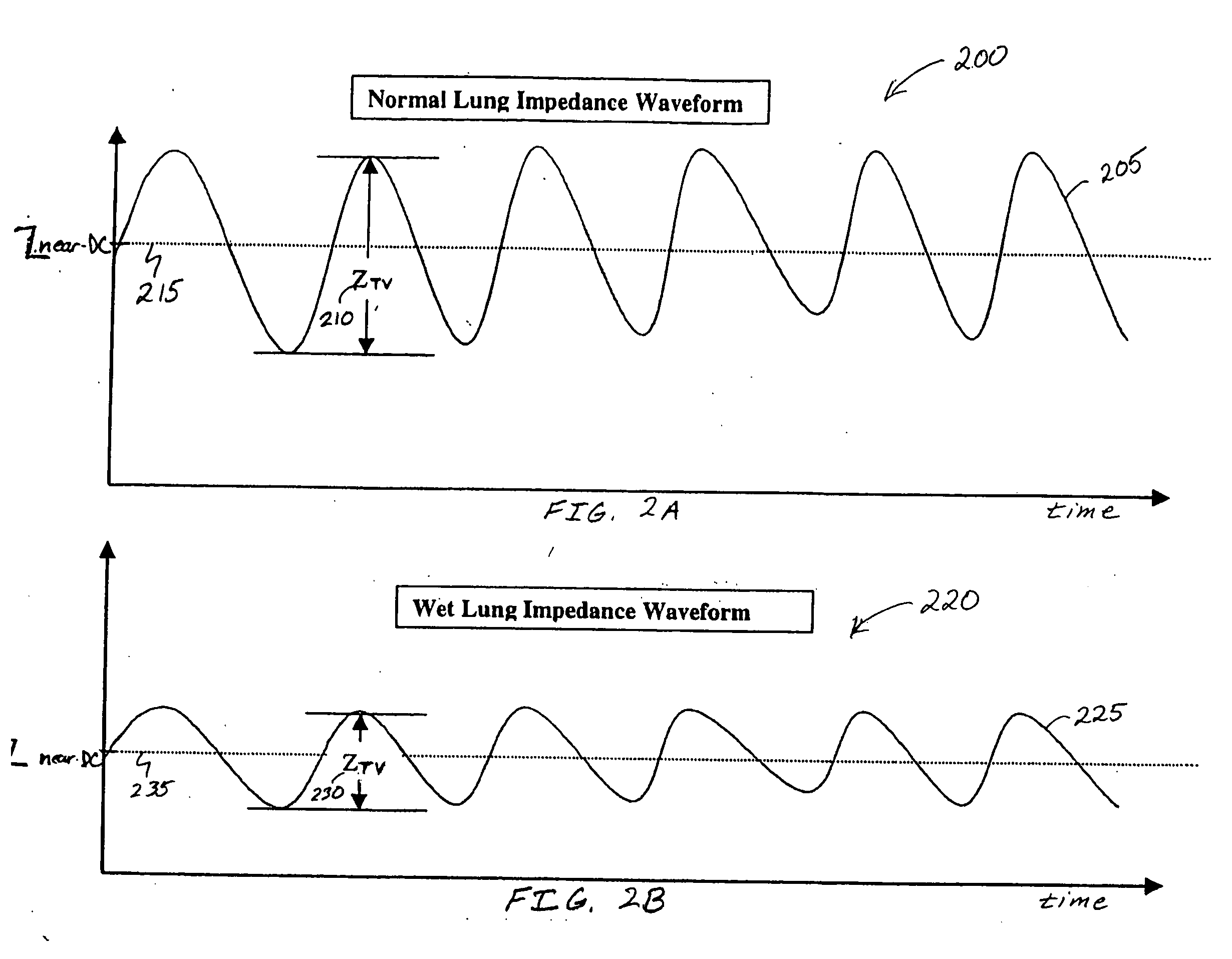
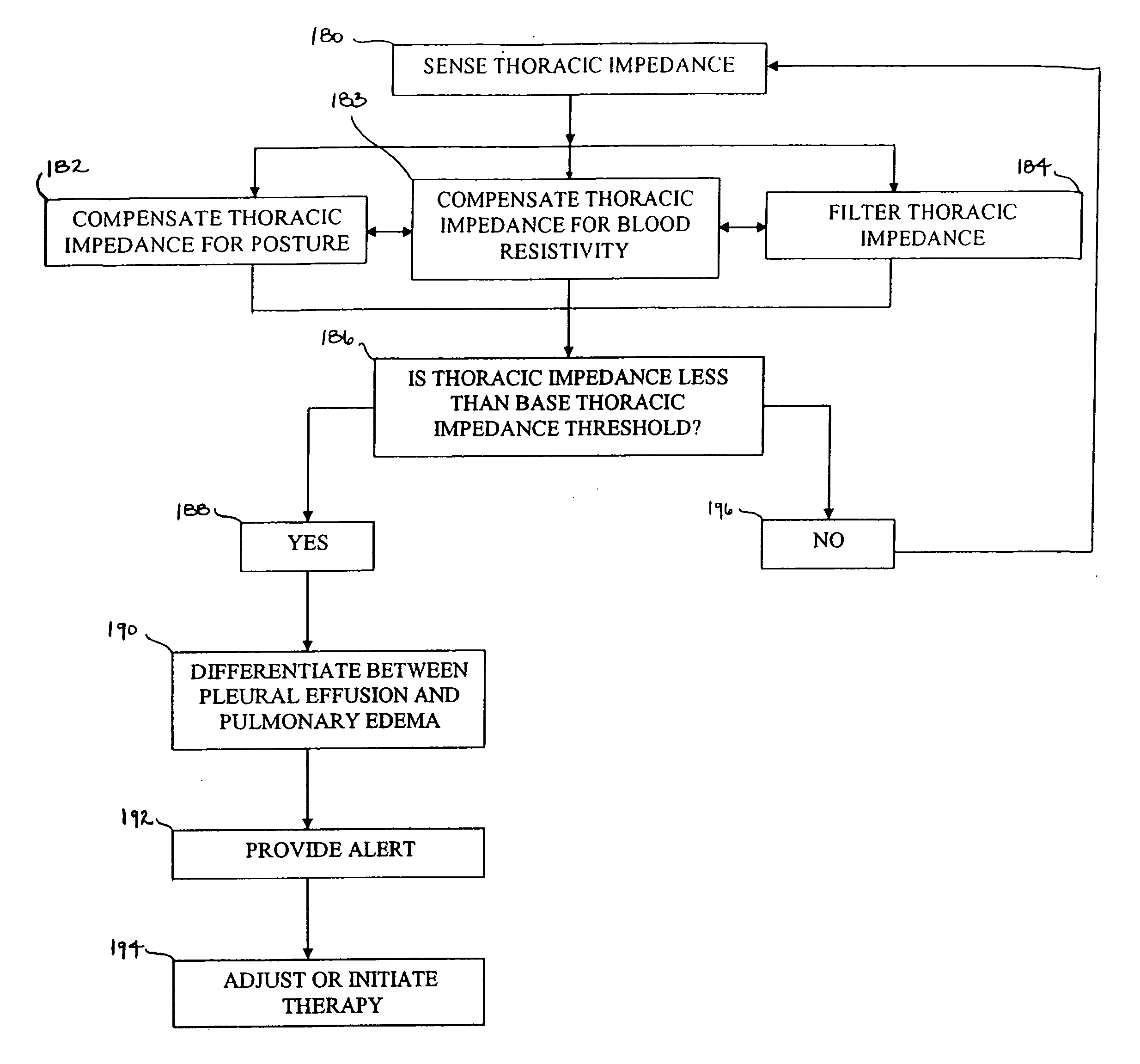
Sensitivity and specificity of pulmonary edema detection when using transthoracic impedance
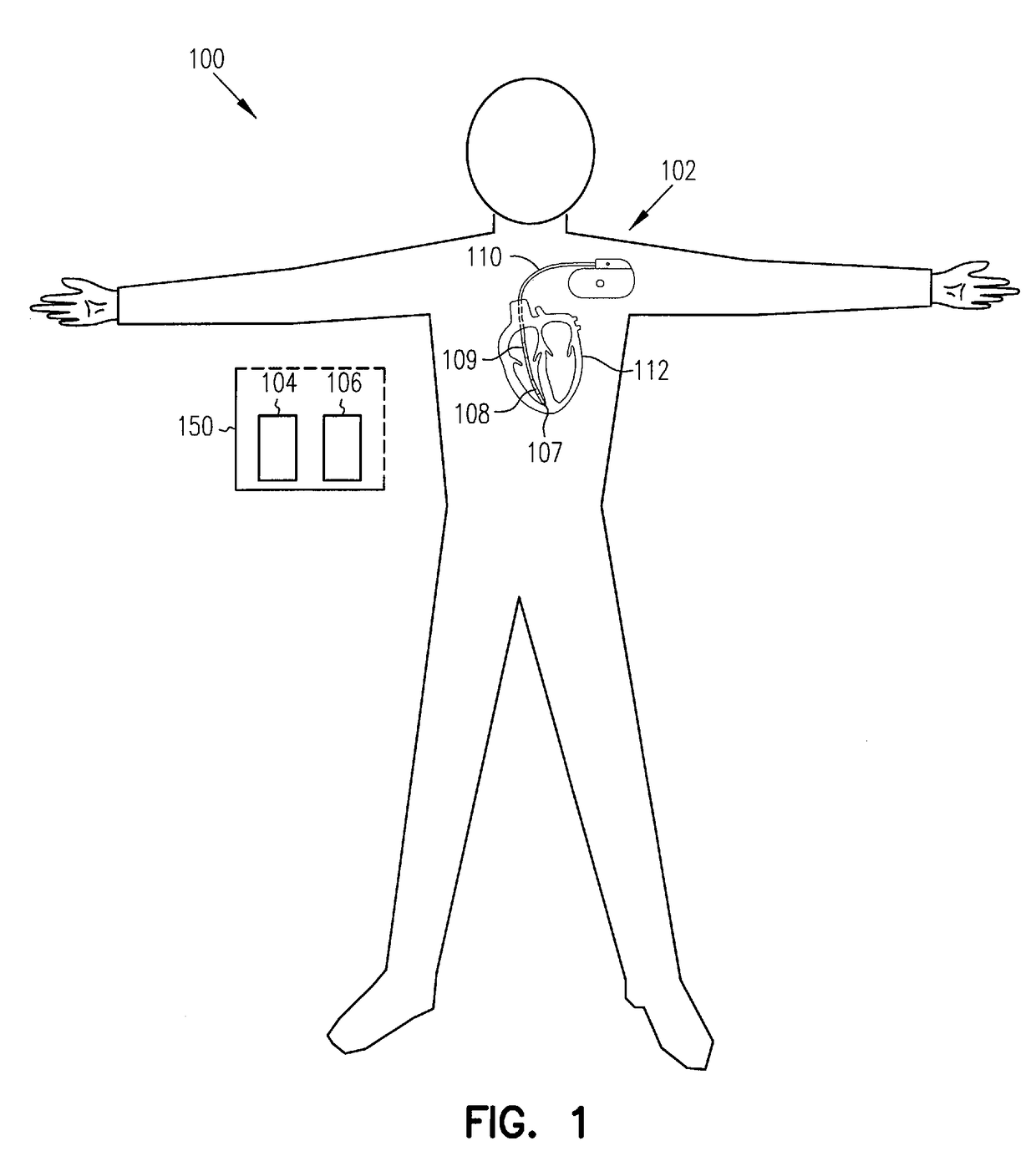
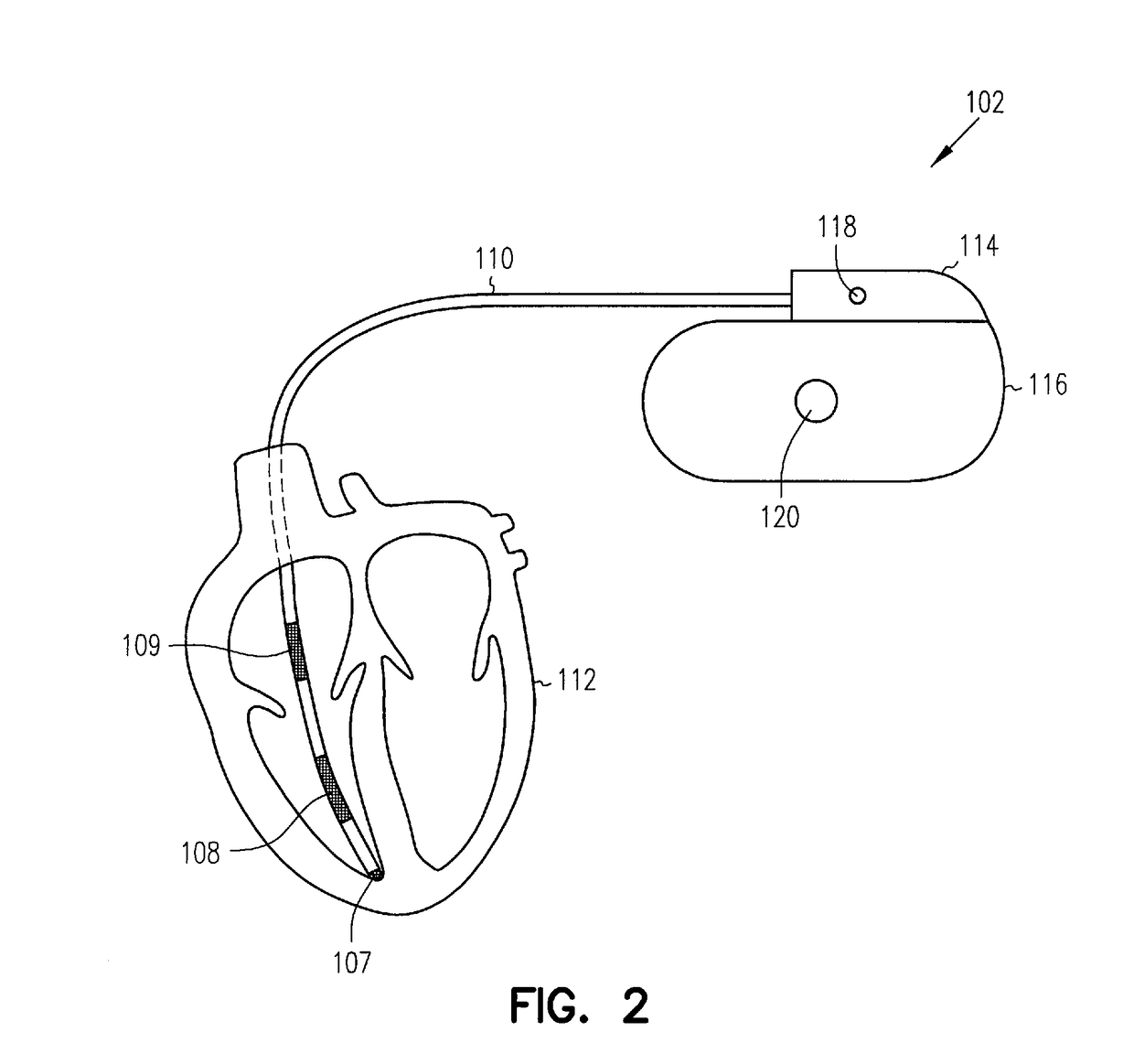
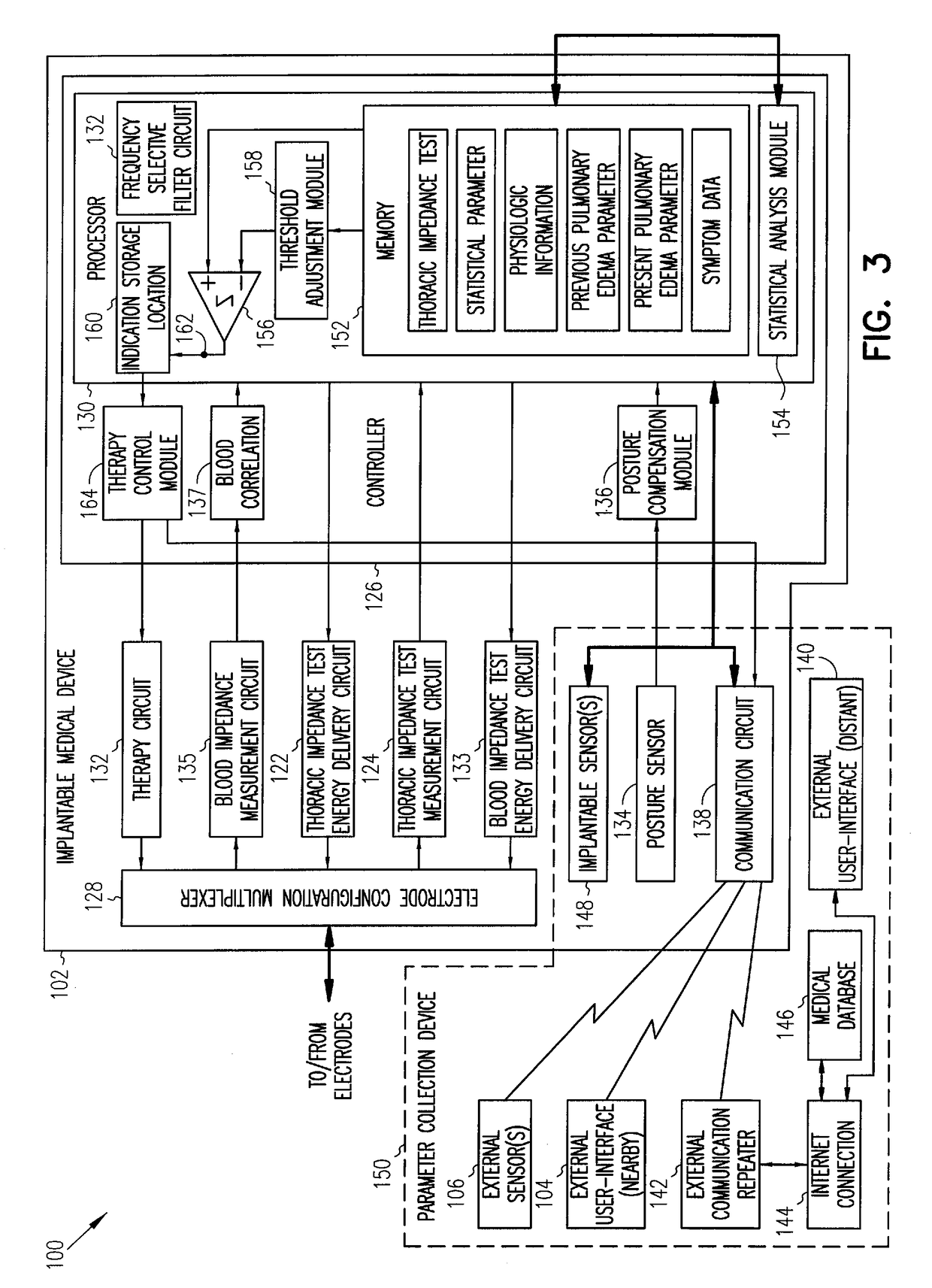
This patent document discusses, among other things, systems, devices, and methods for enhancing detection of pulmonary edema using, in addition to thoracic impedance, one or a combination of: physiologic information about a subject, at least one statistical parameter, a user-programmable detection level, at least one parameter associated with a previous pulmonary edema event, and patient symptom information about the subject. In one example, a (base) thoracic impedance threshold is modified to an adjusted thoracic impedance threshold. The adjusted thoracic impedance threshold provides an increased sensitivity of pulmonary edema detection as compared to the base thoracic impedance threshold. In another example, an alert is provided to a subject, a caregiver, or other user based on a pulmonary edema indication determined by the present systems, devices, and methods. In a further example, a therapy (provided to the subject) is adjusted or initiated in response to the pulmonary edema indication.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Detection of pleural effusion using transthoracic impedance
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
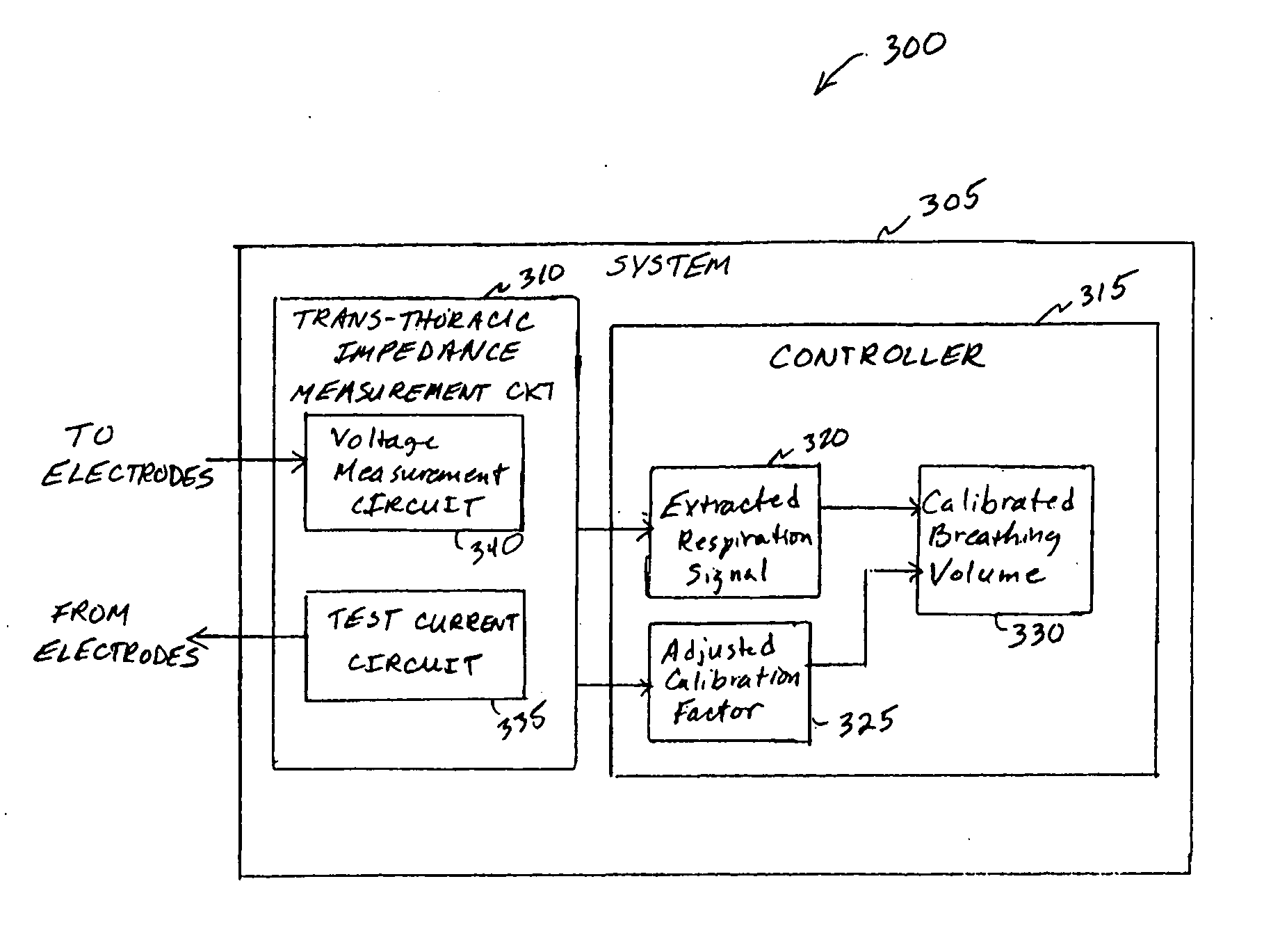
Calibration of impedance monitoring of respiratory volumes using thoracic D.C. impedance
InactiveUS20060241513A1Easy to monitorElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationRadiologyRespiratory capacity
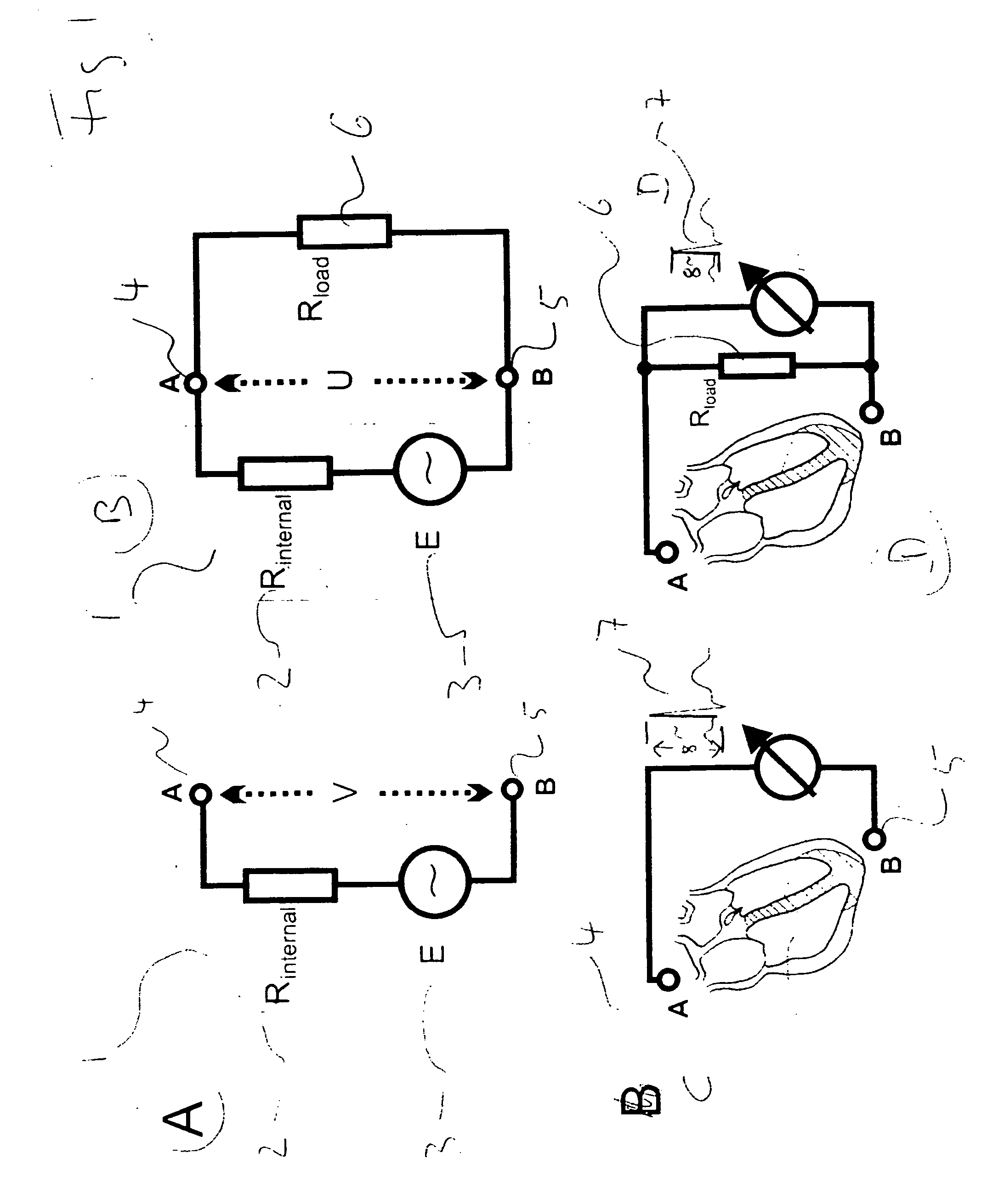
A system includes an implantable medical device that includes a trans-thoracic impedance measurement circuit providing a trans-thoracic impedance signal of a subject. A controller is coupled to the trans-thoracic impedance circuit. The controller extracts a respiration signal from the trans-thoracic impedance signal, measures a breathing volume of the subject using the amplitude of the respiration signal and a breathing volume calibration factor, computes an adjusted breathing volume calibration factor using a reference baseline value of the trans-thoracic impedance and a measured baseline value of the trans-thoracic impedance, and computes a calibrated breathing volume using the adjusted breathing volume calibration factor.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Enhancements to the detection of pulmonary edema when using transthoracic impedance
This patent document discusses, among other things, systems, devices, and methods for enhancing detection of pulmonary edema using, in addition to thoracic impedance, one or a combination of: physiologic information about a subject, at least one statistical parameter, a user-programmable detection level, at least one parameter associated with a previous pulmonary edema event, and patient symptom information about the subject. In one example, a (base) thoracic impedance threshold is modified to an adjusted thoracic impedance threshold. The adjusted thoracic impedance threshold provides an increased sensitivity of pulmonary edema detection as compared to the base thoracic impedance threshold. In another example, an alert is provided to a subject, a caregiver, or other user based on a pulmonary edema indication determined by the present systems, devices, and methods. In a further example, a therapy (provided to the subject) is adjusted or initiated in response to the pulmonary edema indication.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Detection of pleural effusion using transthoracic impedance
This patent document discusses systems, devices, and methods for increasing a sensitivity or specificity of thoracic fluid detection in a subject and differentiating between pleural effusion and pulmonary edema. In one example, a thoracic impedance measurement circuit senses a thoracic impedance signal. In another example, a processor receives the thoracic impedance signal and determines whether such thoracic impedance signal is “significant.” A significant thoracic impedance signal indicates the presence of thoracic fluid and may be recognized by comparing the thoracic impedance signal (or variation thereof) to a thoracic impedance threshold. When a significant thoracic impedance signal is recognized, the processor is adapted to detect one or both of: a pleural effusion indication and a pulmonary edema indication using one or a combination of: physiologic information, patient symptom information, and posture information. In another example, the thoracic impedance threshold is adjusted using such physiologic, patient symptom, or posture information.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
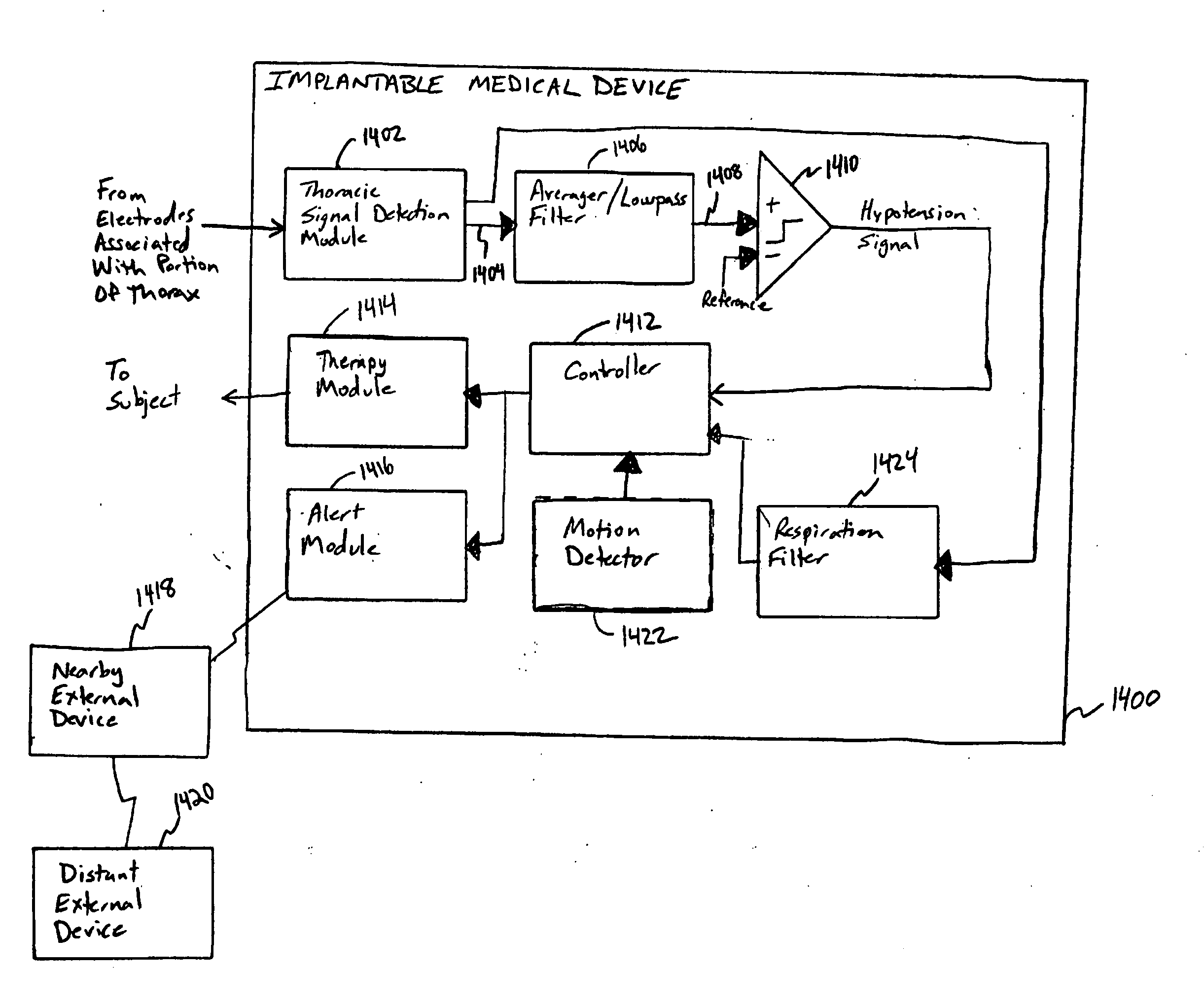
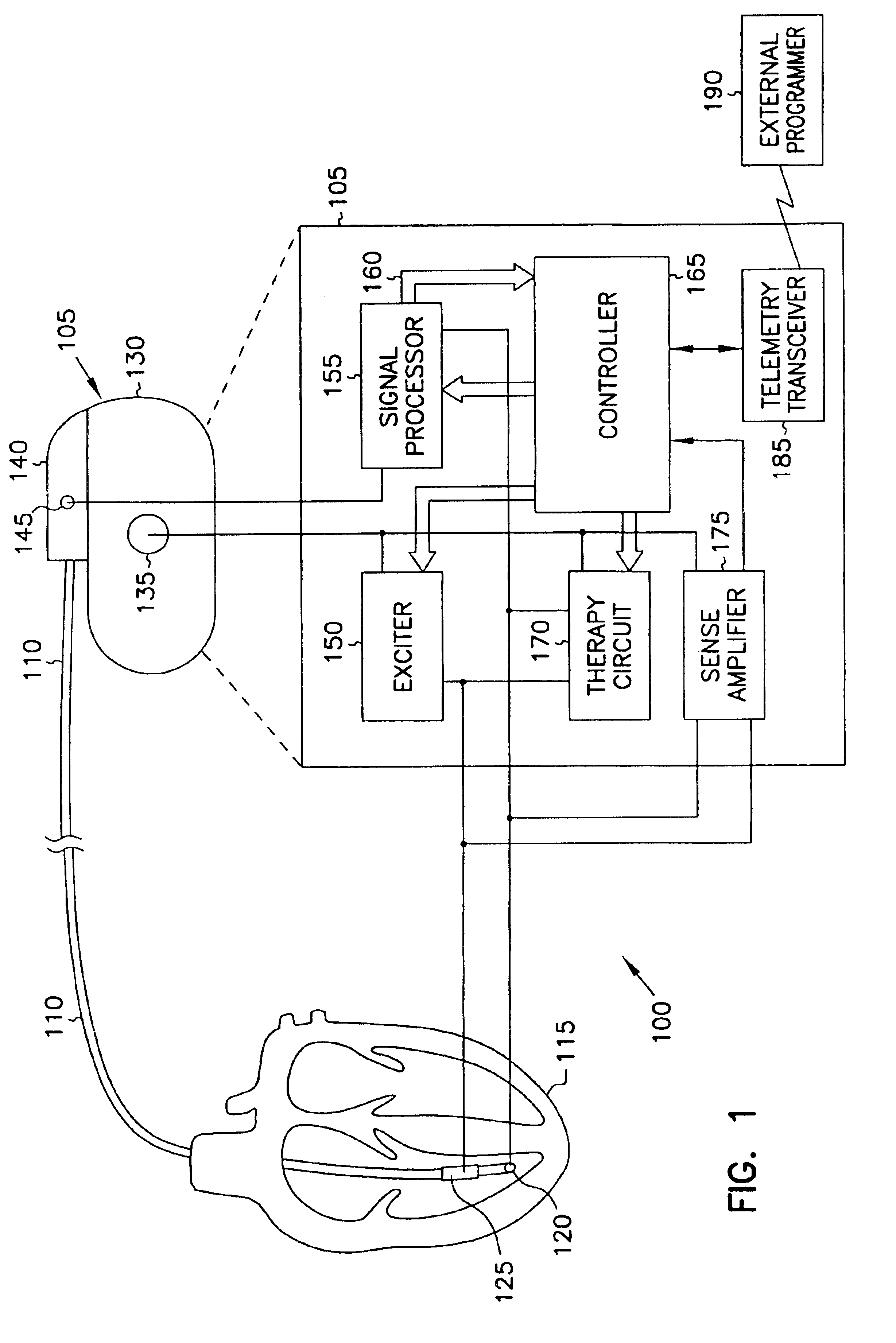
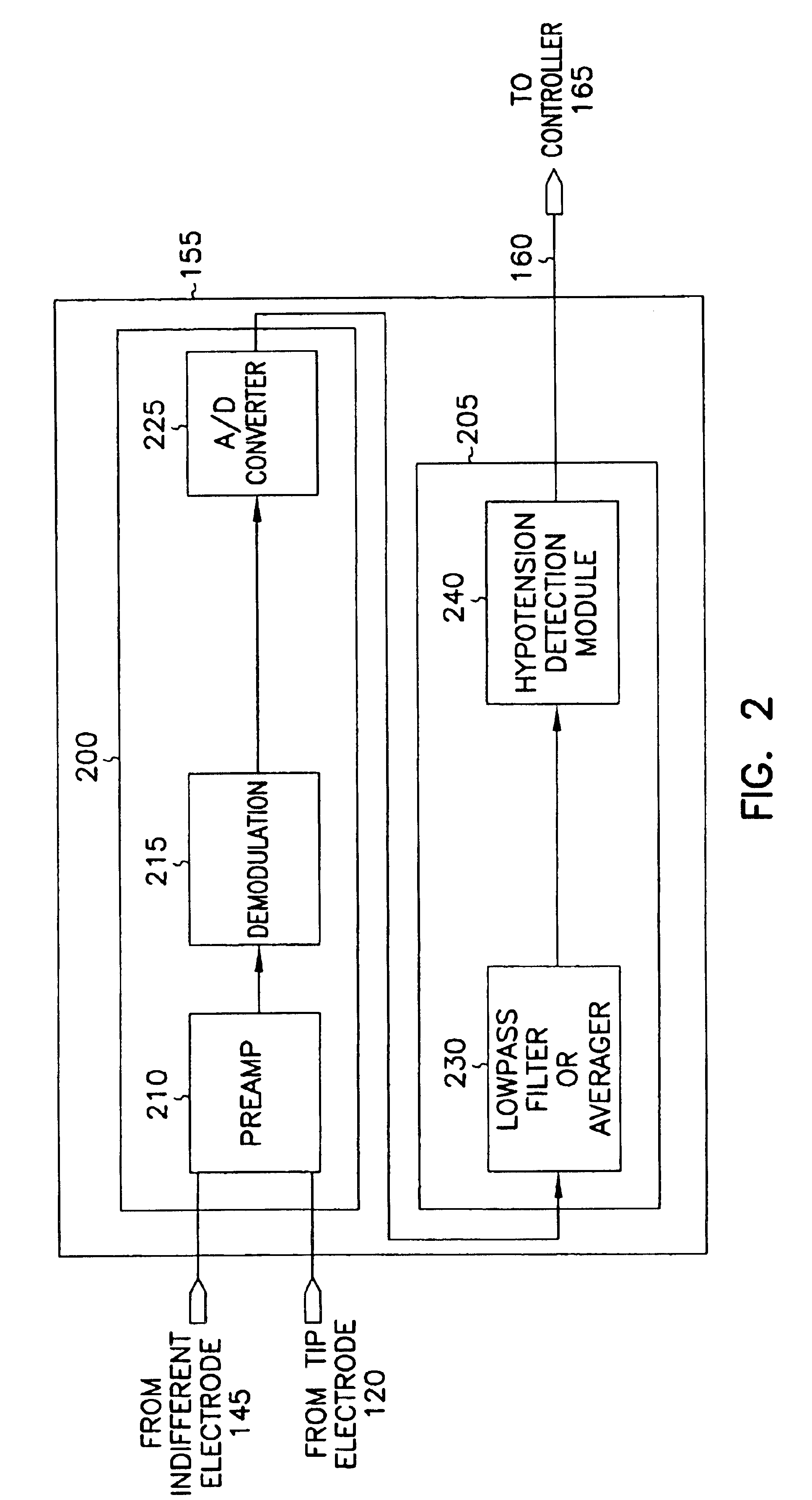
Systems and methods for hypotension
This document discusses, among other things, systems and methods that detect hypotension based on a measurement of thoracic impedance. It also provides an alert, a logging, or a therapy to treat the hypotension. Examples of anti-hypotension therapies include, among other things, pacing therapy, neural stimulation therapy, drug infusion therapy, or gene therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Cardiac rhythm management system for hypotension
A cardiac rhythm management system detects hypotension based on a measurement of thoracic impedance. It also provides therapy to treat the hypotension.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
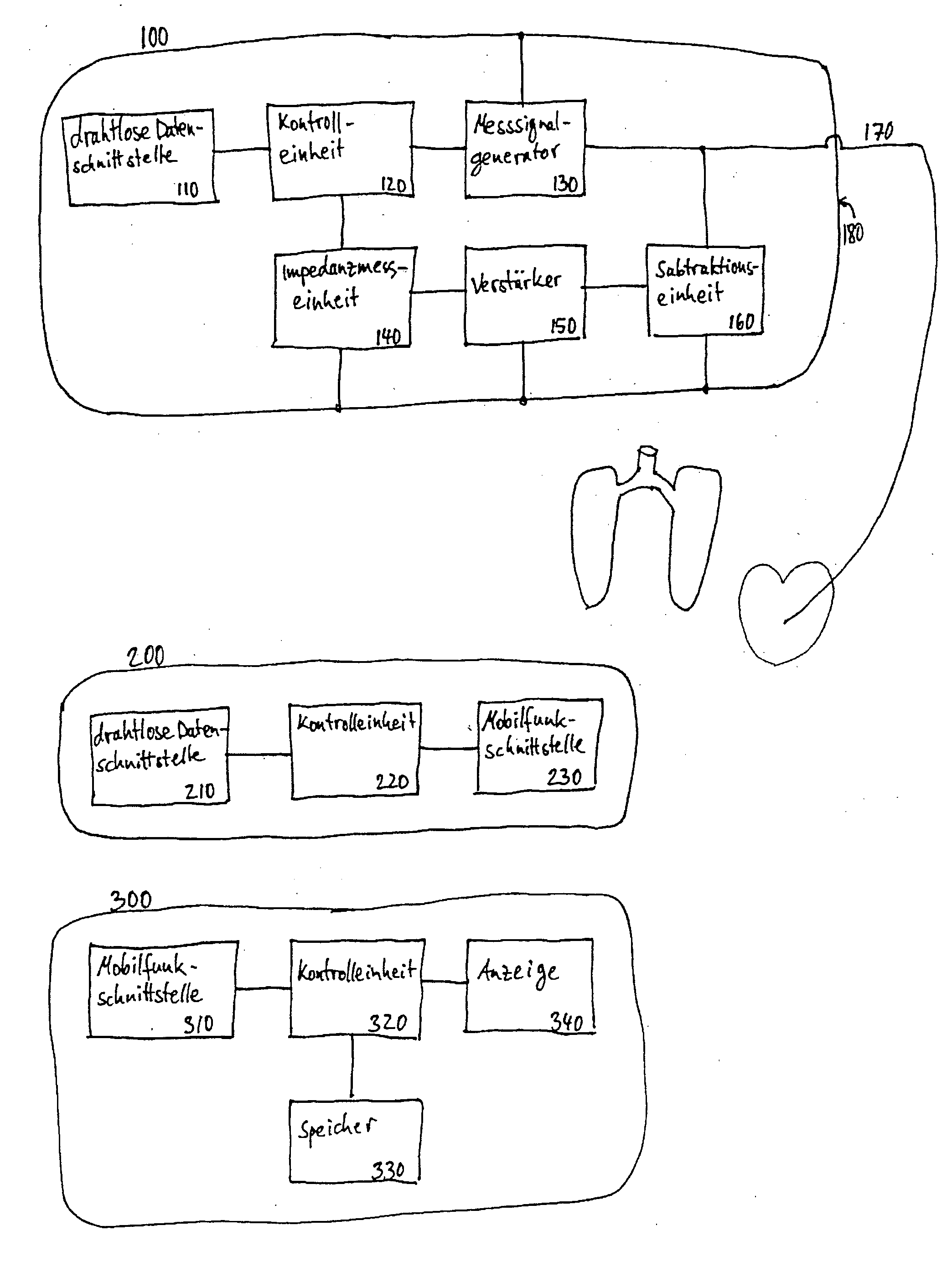
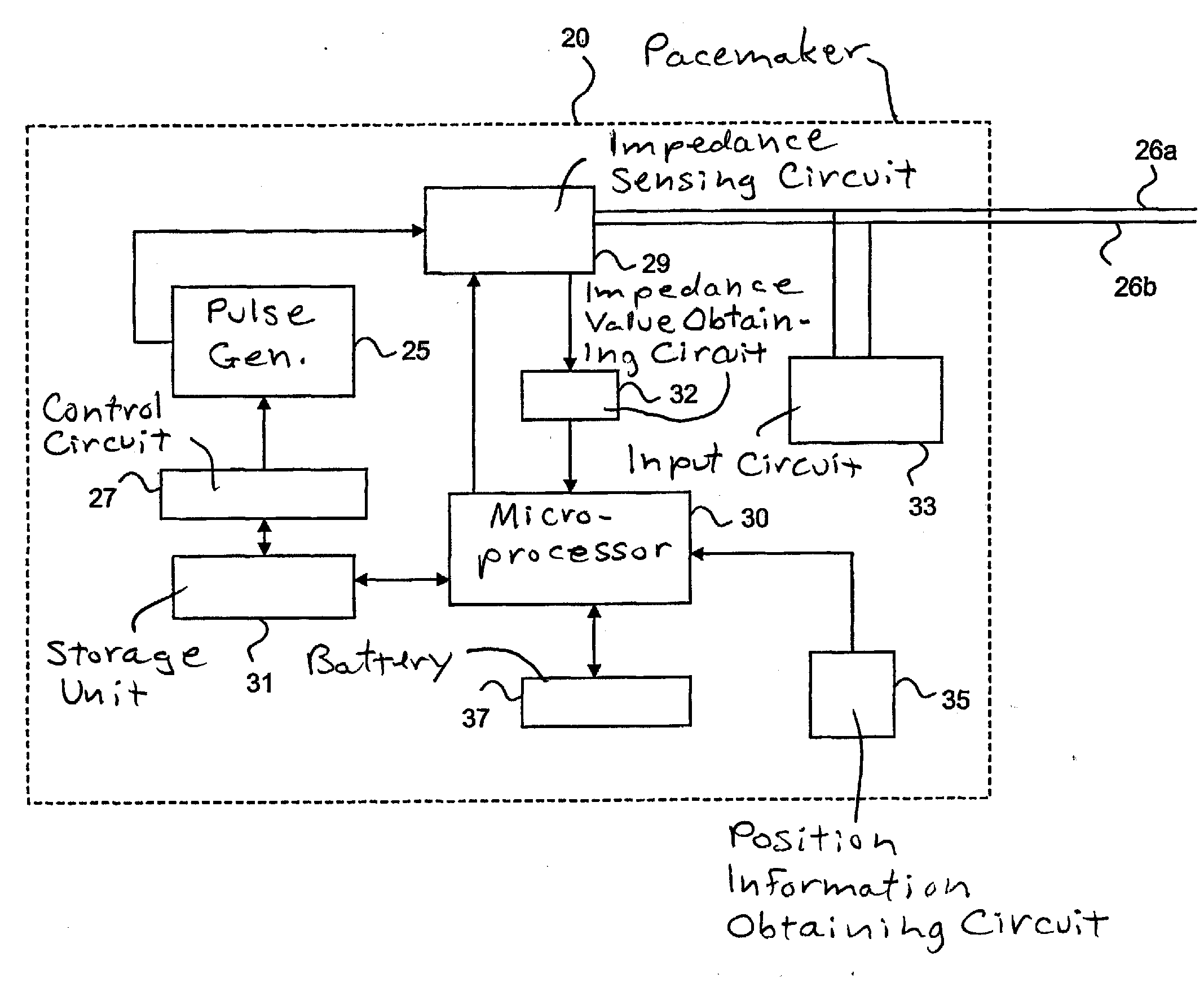
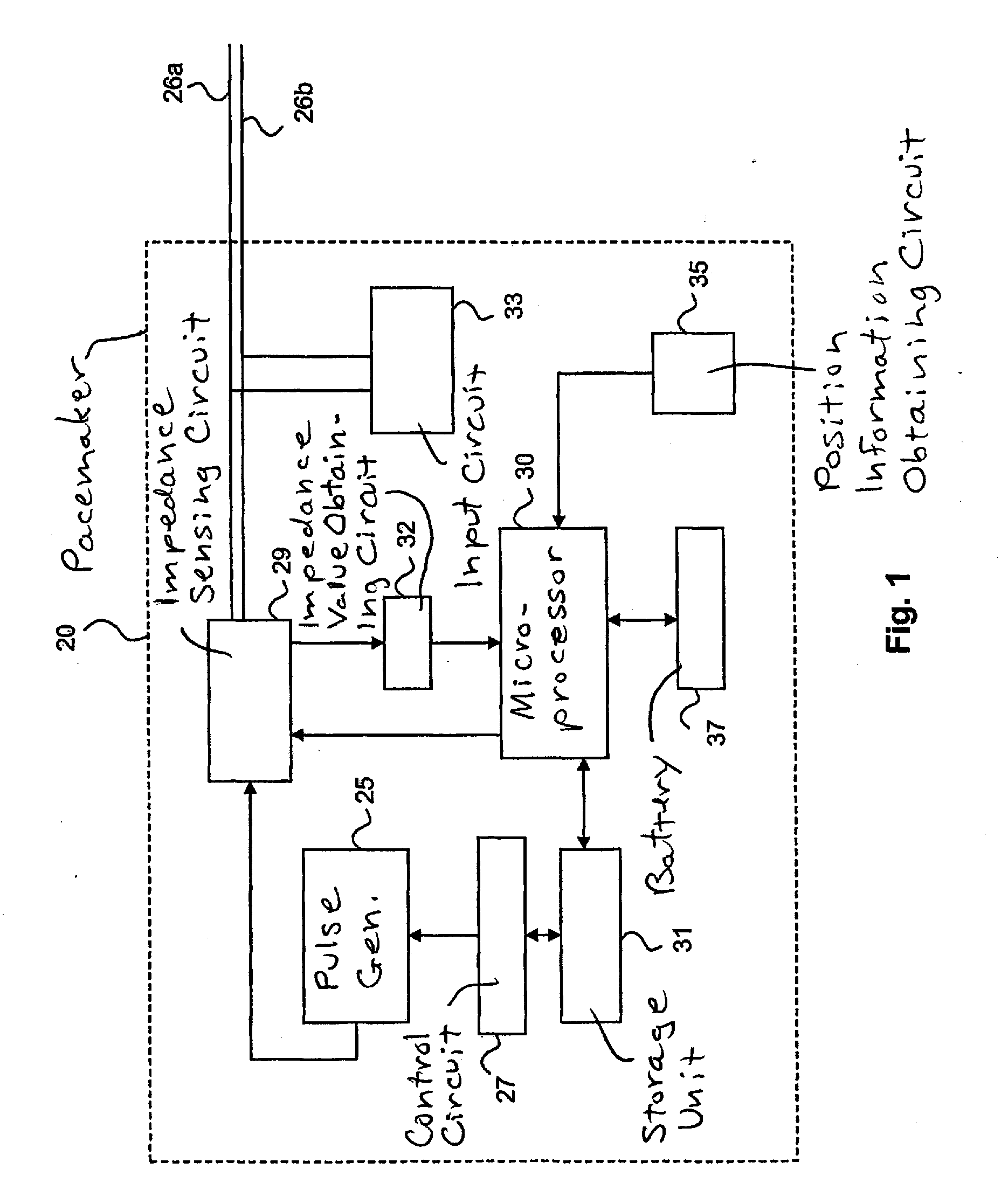
Device for determining thoracic impedance
ActiveUS20060135886A1Reliably determinedResistance/reactance/impedenceHeart stimulatorsPower flowSignal generator
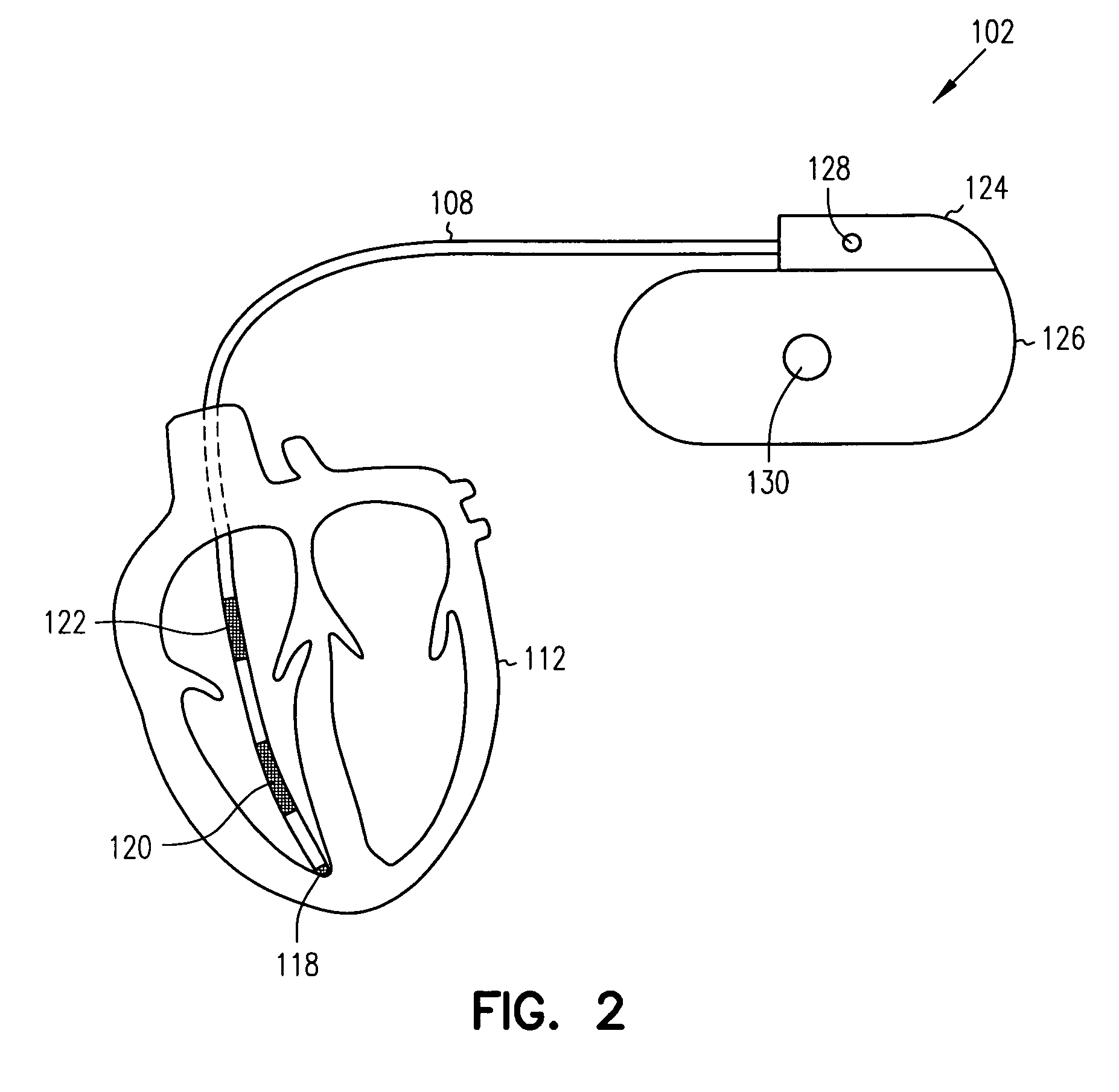
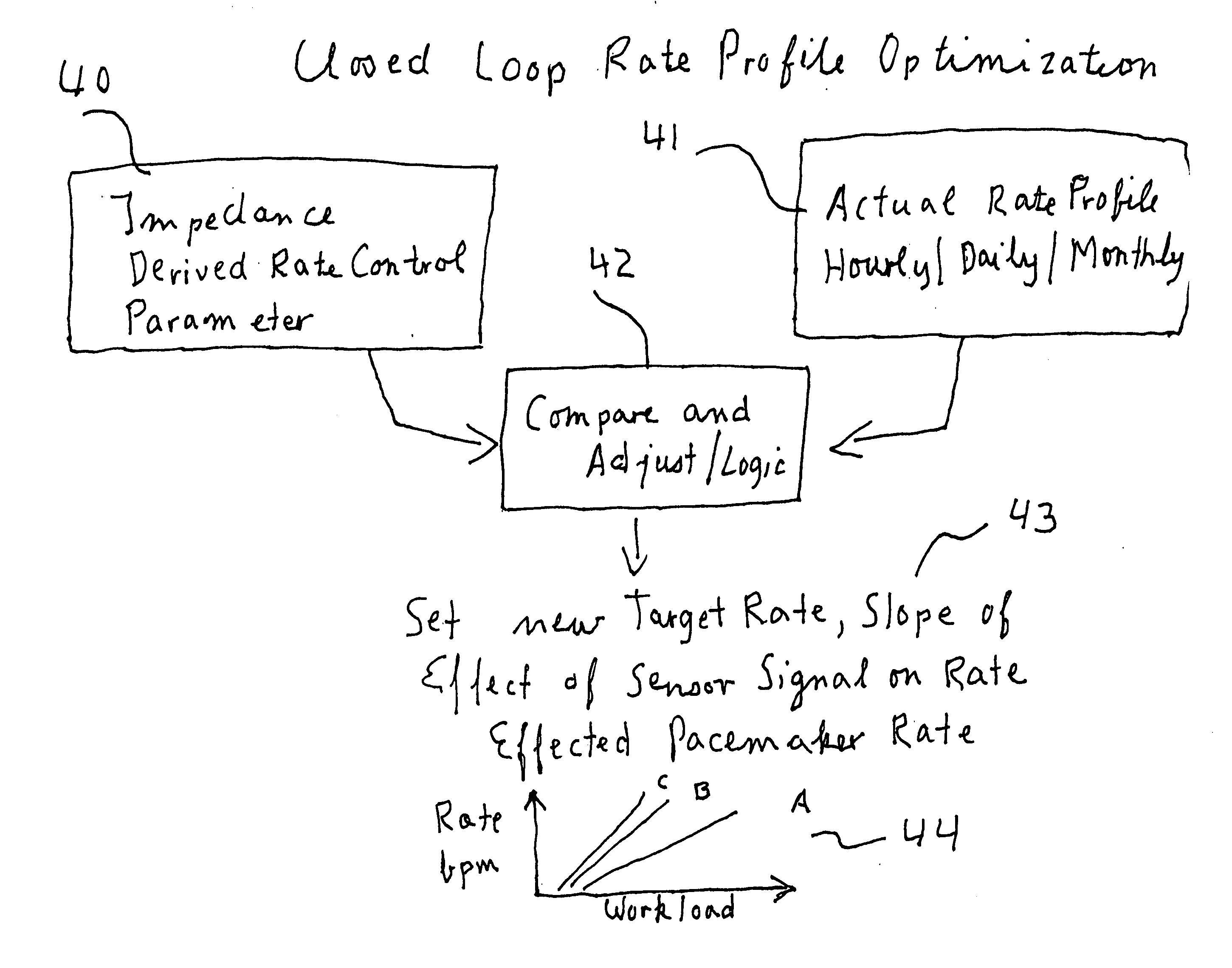
An electromedical implant includes a measuring signal generator, an impedance measuring unit to determine the impedance of human or animal tissue, a control unit which, for controlling the measuring signal generator and the impedance measuring unit, is at least indirectly connected to the measuring signal generator and to the impedance measuring unit, as well as an electrode arrangement comprising at least two electrodes which can be directly or indirectly connected or at least temporarily connected to the measuring signal generator and to the impedance measuring unit, or to a connection for such an electrode arrangement. The measuring signal generator is designed to generate and emit a current pulse or a series of current pulses, and the control unit is designed at a specific point in time to cause the measuring signal generator (to generate and emit a current pulse, and to cause the impedance measuring unit to measure the voltage that is present between the electrodes connected to the measuring signal generator and the impedance measuring unit after the passing of at least two time periods of different length that start with commencement of the current pulse being emitted and end before the end of emitting the current pulse, and to issue a voltage value which in each case represents the measured voltage.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
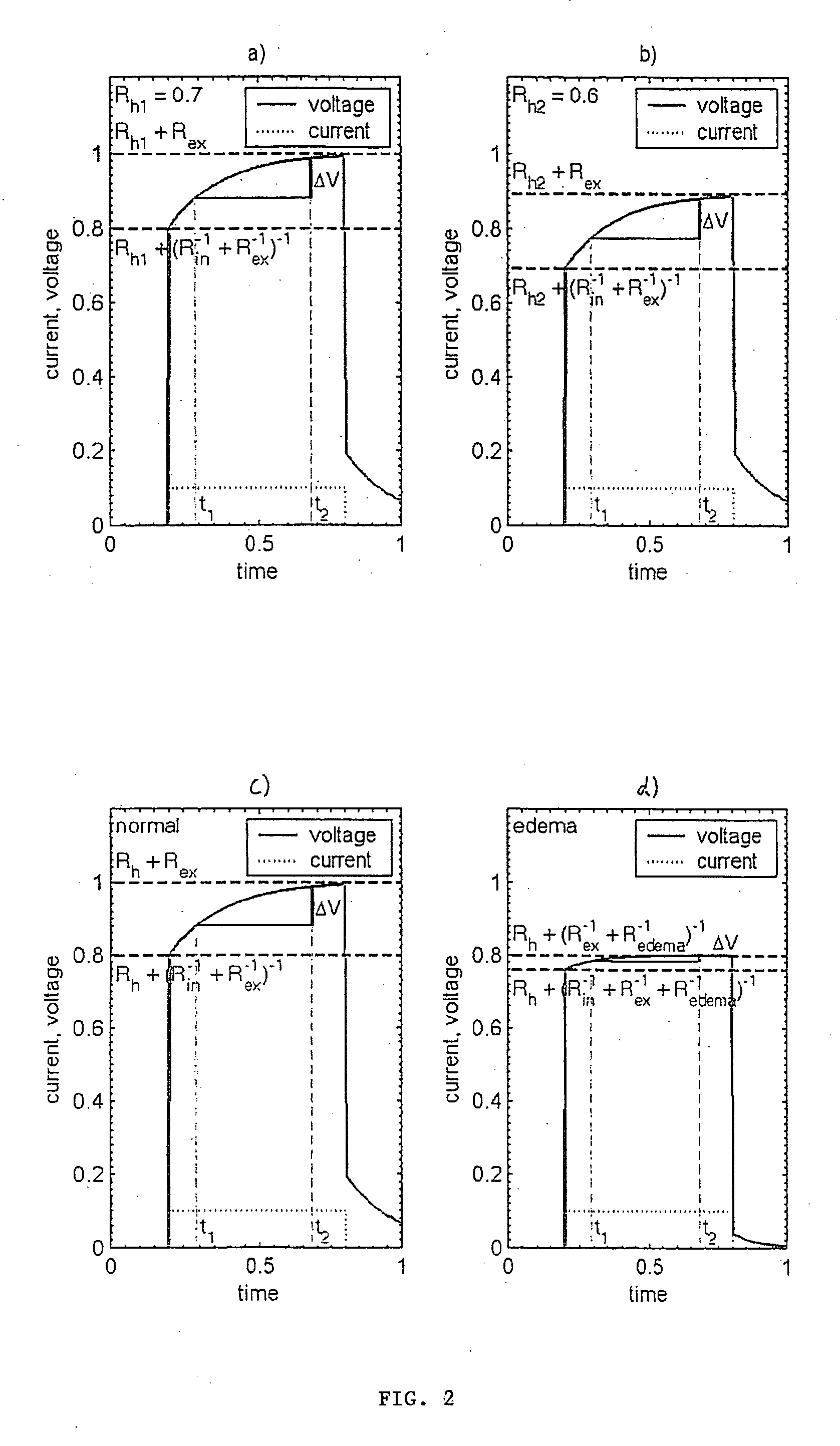
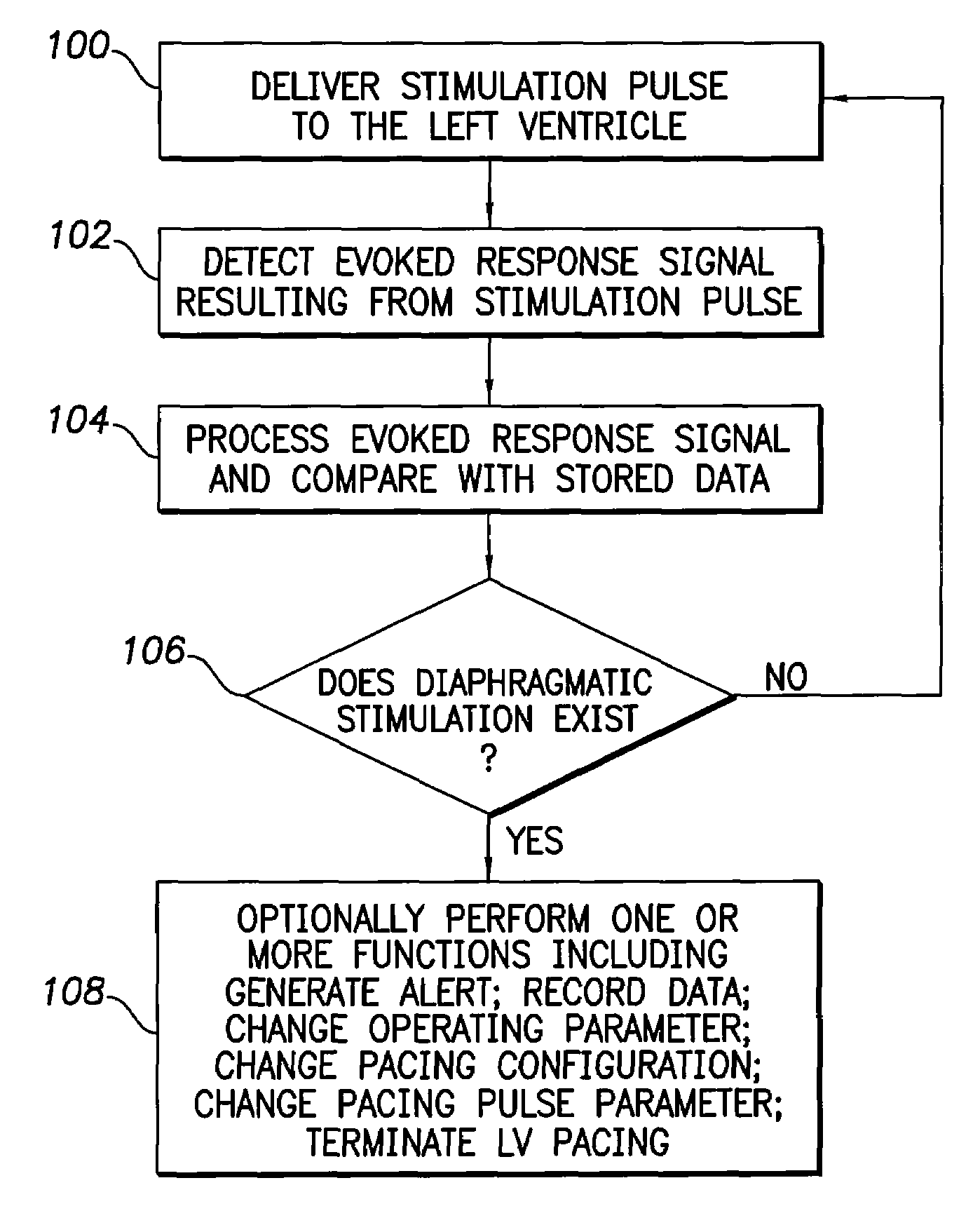
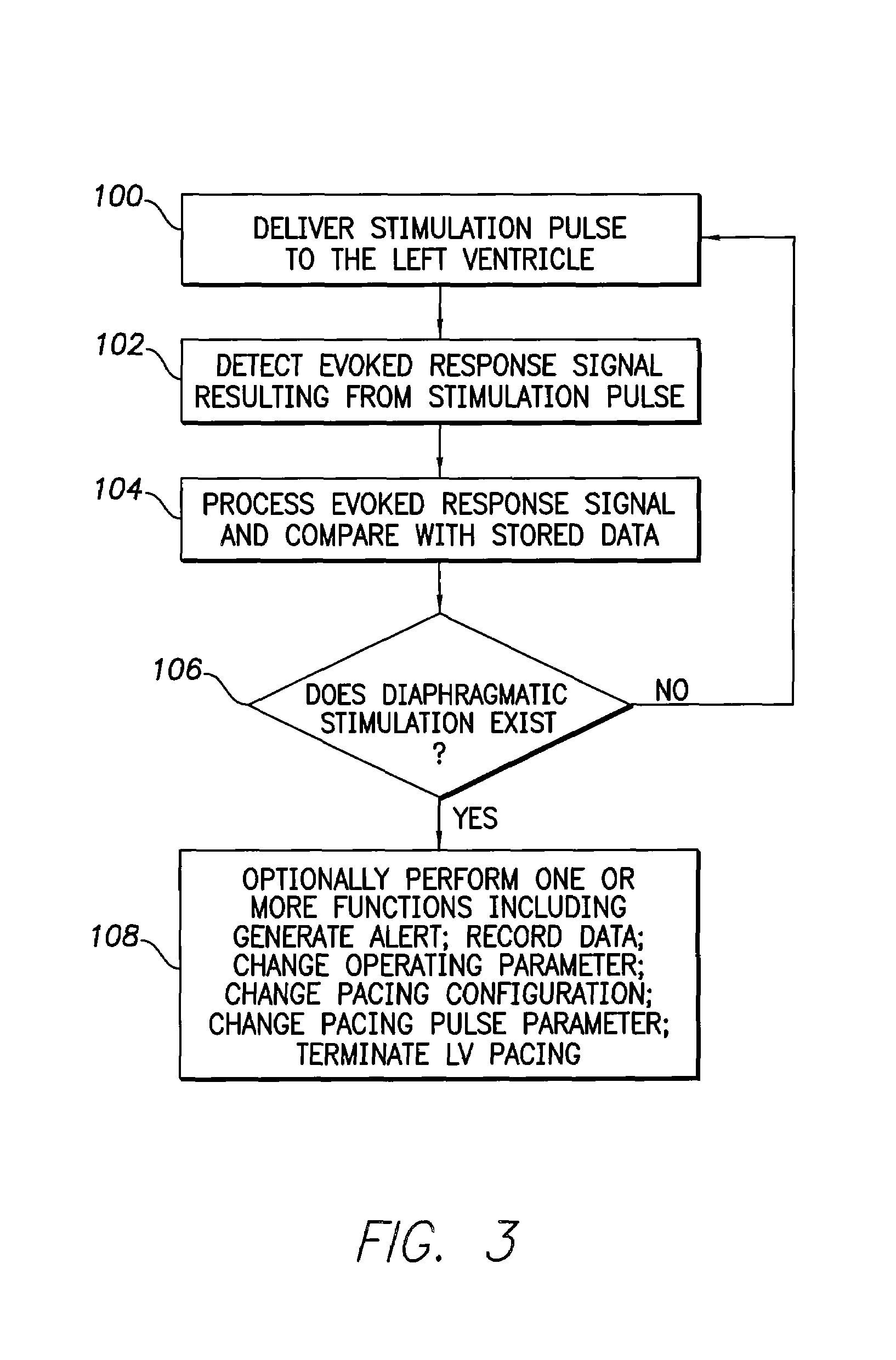
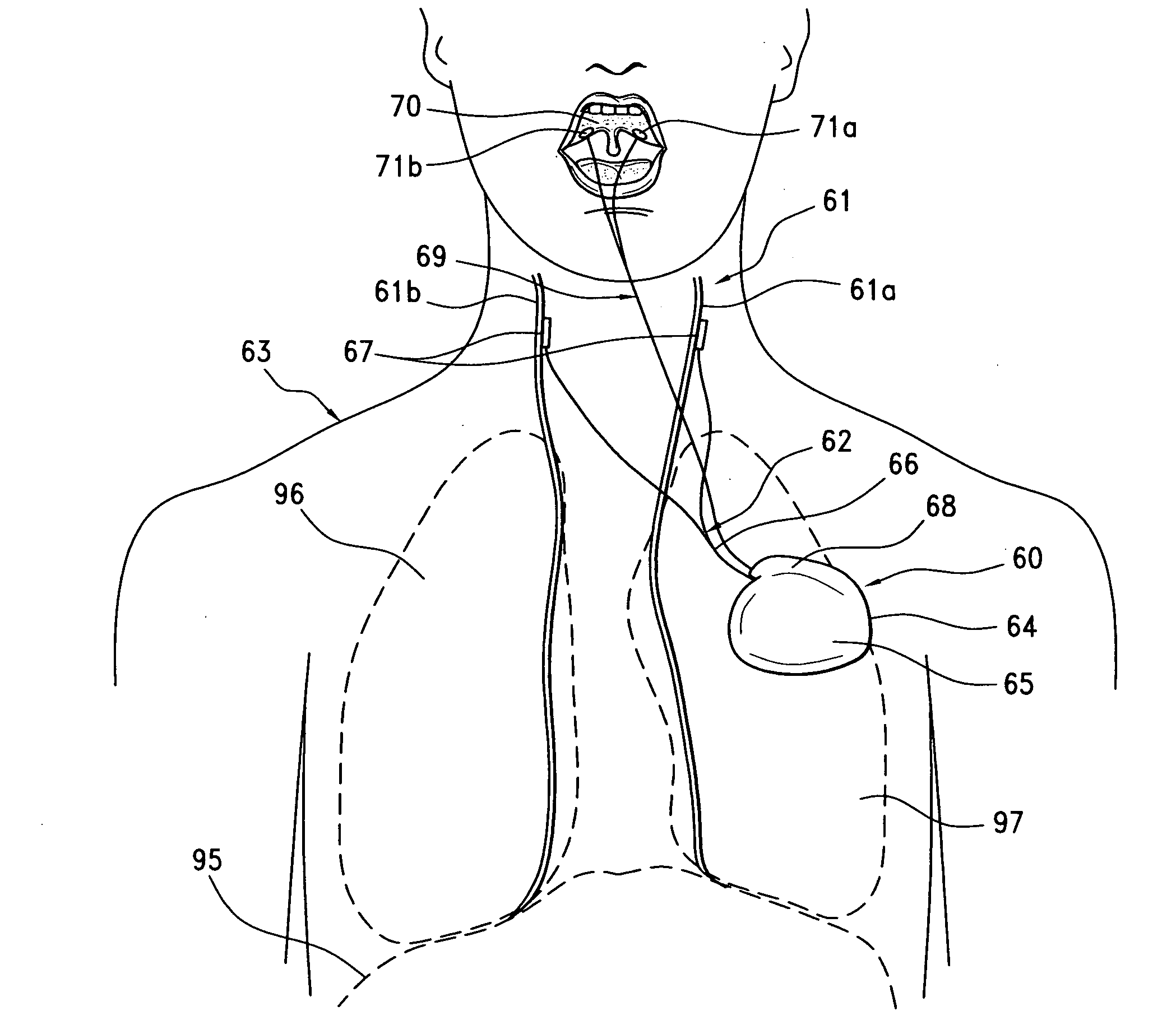
Evoked potential and impedance based determination of diaphragmatic stimulation
A system and method are described for automatically detecting diaphragmatic stimulation (DS) based on evoked response signals, electrogram data and / or thoracic impedance measurements. In addition, several optional modalities are described to circumvent this problem and alleviate symptoms related to DS while preserving LV pacing.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Edema monitoring system and method utilizing an implantable medical device
An edema monitoring system includes an implantable medical device (IMD) and a personal edema monitor. The IMD measures an intra-thoracic impedance and transmits intra-thoracic impedance data and other biological data to the personal edema monitor, which generates a user interface based on patient inputs relating to activities and health assessments, the measured intra-thoracic impedance data and the other biological data.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Active implantable medical device equipped with means for the diagnosis of respiratory disorders, with sophisticated detection of respiratory cycles with artifacts
ActiveUS20050267380A1Easy to analyzeEliminate false positive falseRespiratory organ evaluationHeart stimulatorsDiseaseAutomatic control
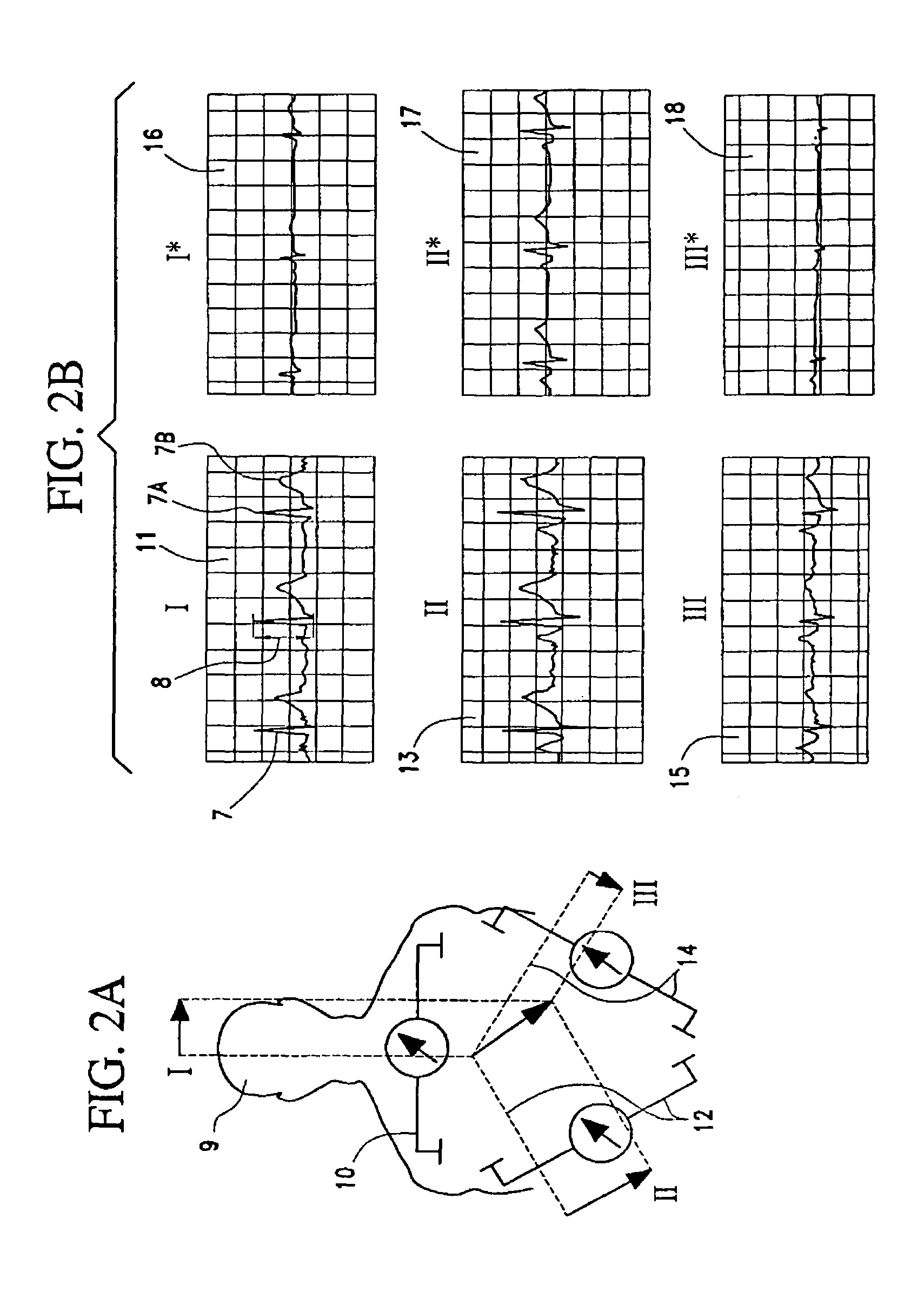
An active implantable medical device comprising circuits for measuring trans-thoracic impedance and delivering an impedance signal varying with respiratory activity of a patient. A signal representative of the respiratory activity of the patient is delivered starting from the impedance signal, and circuits for diagnosing respiratory disorder analyze variations of the respiratory signal on a plurality of successive cycles to detect there a profile of predetermined variation in relation to a given respiratory disorder. The device also includes circuits for automatically controlling respiratory cycles with artifacts, able to identify in the impedance signal a jump of static impedance, and / or to identify in a respiratory cycle or in a sequence of respiratory cycles a predetermined singularity representative of a cycle with artifact.
Owner:SORIN CRM
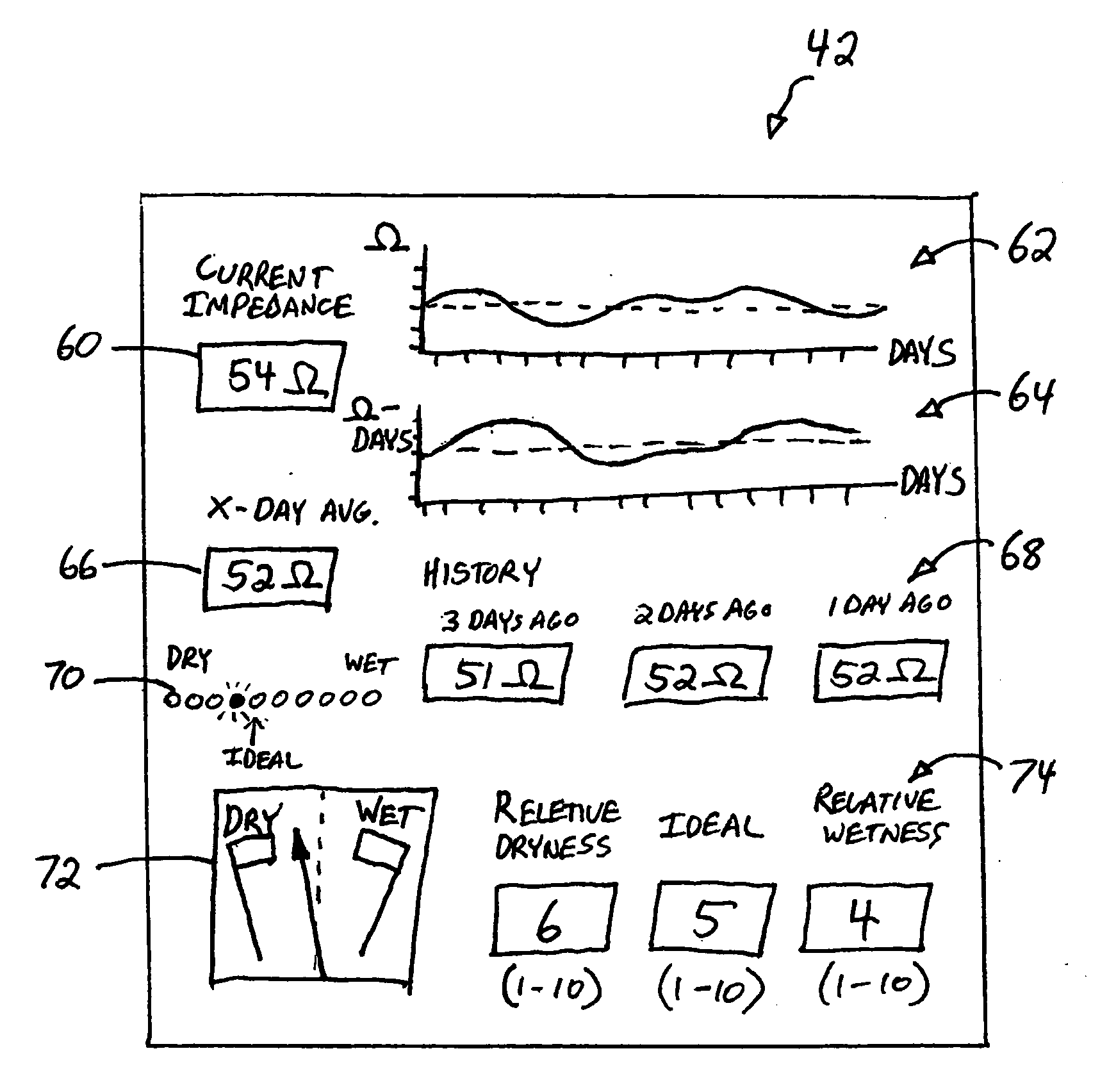
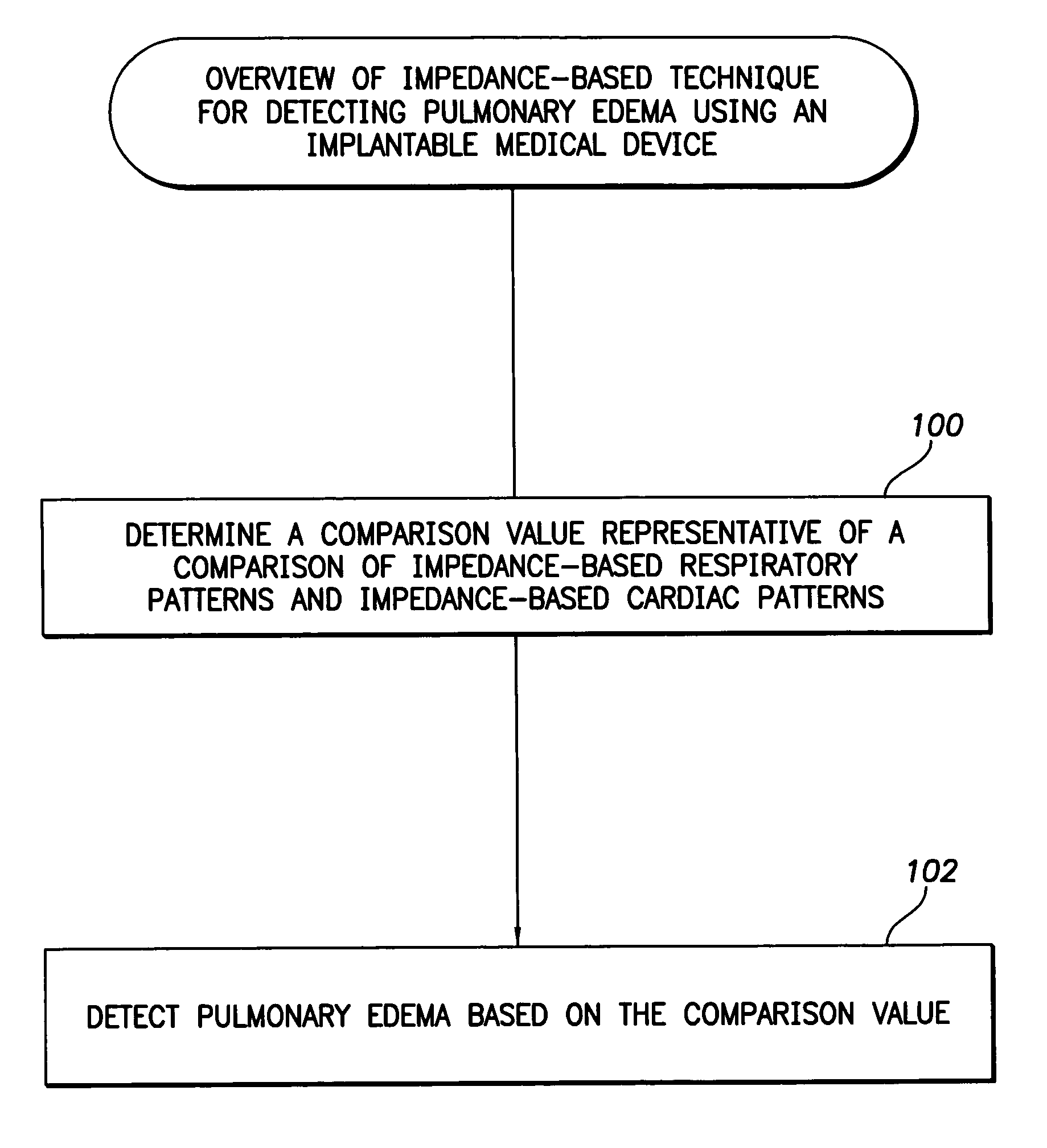
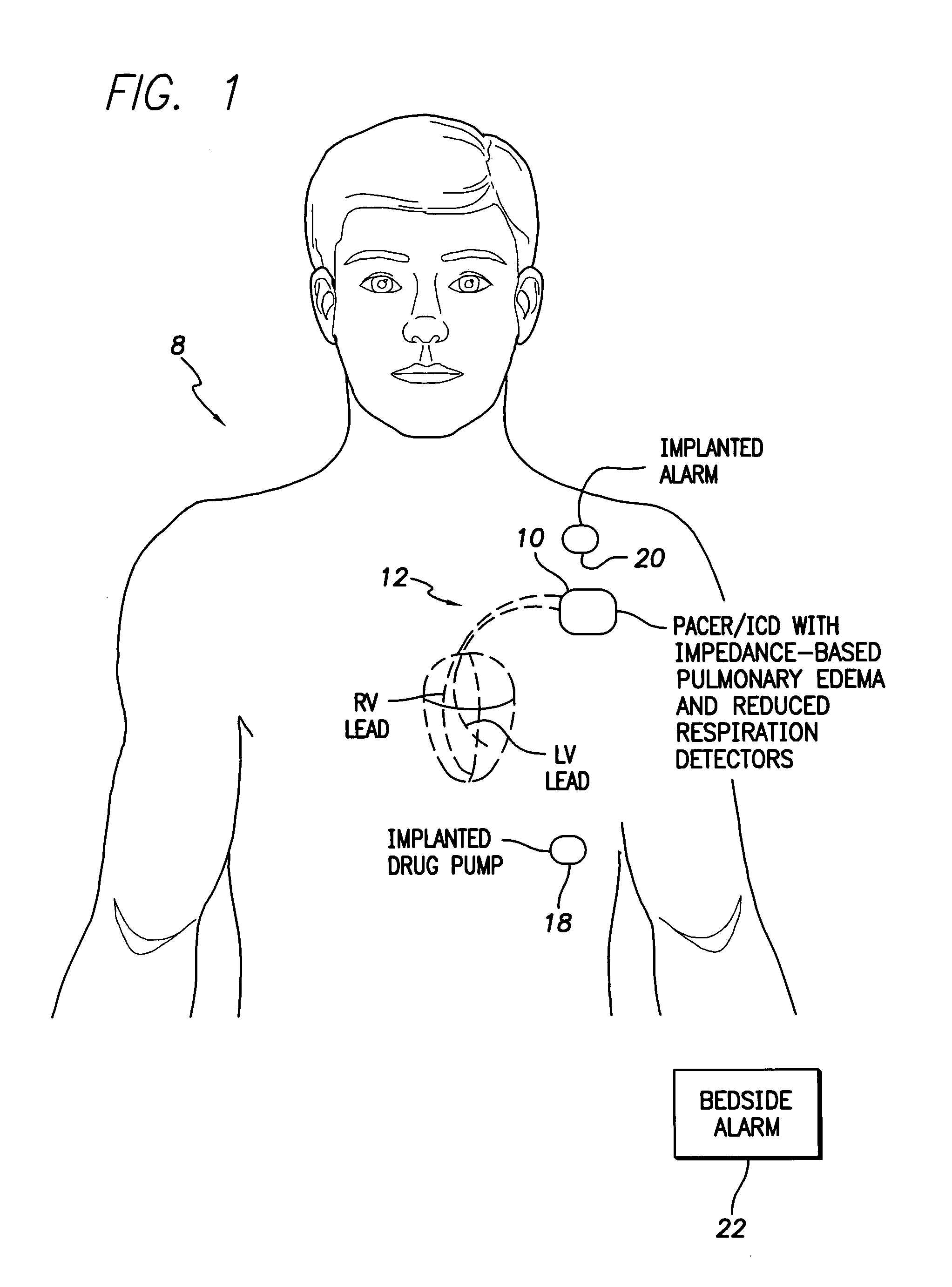
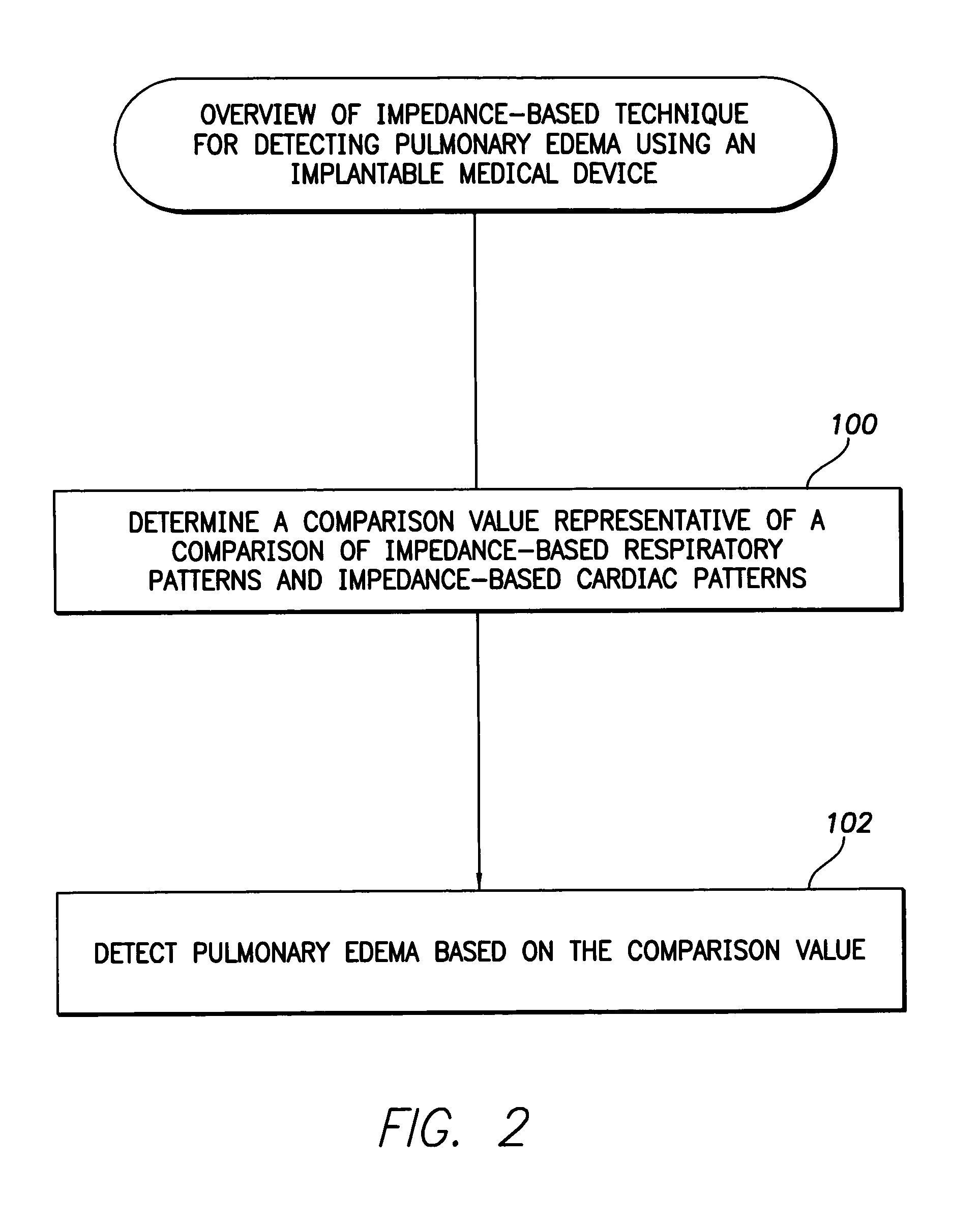
System and method for impedance-based detection of pulmonary edema and reduced respiration using an implantable medical system
Techniques are provided for detecting pulmonary edema based on a comparison of impedance-based respiratory patterns and impedance-based cardiac patterns, i.e. patterns derived from thoracic impedance signals. In one example, a numerical ratio is calculated between average peak-to-peak amplitudes of the respiratory patterns and average peak-to-peak amplitudes of the cardiac patterns. Pulmonary edema is detected if the amplitude ratio falls below a pulmonary edema detection threshold. Techniques are also provided for controlling operation of an impedance-based reduced respiration detector, i.e. a detector which seeks to detect apnea, hypopnea, or the like, based on analysis of respiratory patterns derived from a thoracic impedance signal. If the numerical ratio falls below a minimum reliability threshold, then the reduced respiration detector is deactivated because episodes of reduced respiration cannot then reliably be derived from an analysis of respiration patterns obtained from the thoracic impedance signals.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Thoracic impedance monitor and electrode array and method of use
A portable thoracic impedance monitor for monitoring thoracic fluid levels, an electrode array assembly having a single linear electrode array lead with first, second, third, and fourth electrodes arranged sequentially and axially along the linear electrode array lead, and a method of use of the thoracic impedance monitor. A measurement of the user's thoracic impedance is obtained by connecting the second electrode to the user's body at the junction of the clavicles, superior to the sternum, the third electrode to the user's body at the xiphoid-sternal junction, and the first and fourth electrodes to the user's body substantially along a centerline of the user's sternum respectively at a first pre-determined distance above the second electrode and a second predetermined distance below the third electrode, followed by initiating operation of the monitor.
Owner:CALDWELL SIMPSON LLC
Method and device for using impedance measurements based on electrical energy of the heart
InactiveUS20050288726A1Function increaseInertial sensorsRespiratory organ evaluationThoracic impedanceElectric energy
A method and a device are disclosed for evaluating the cardio-circulatory and pulmonary condition of a patient, including determining the patient's thoracic impedance based on information solely derived from the electrical energy generated by the patient's own heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
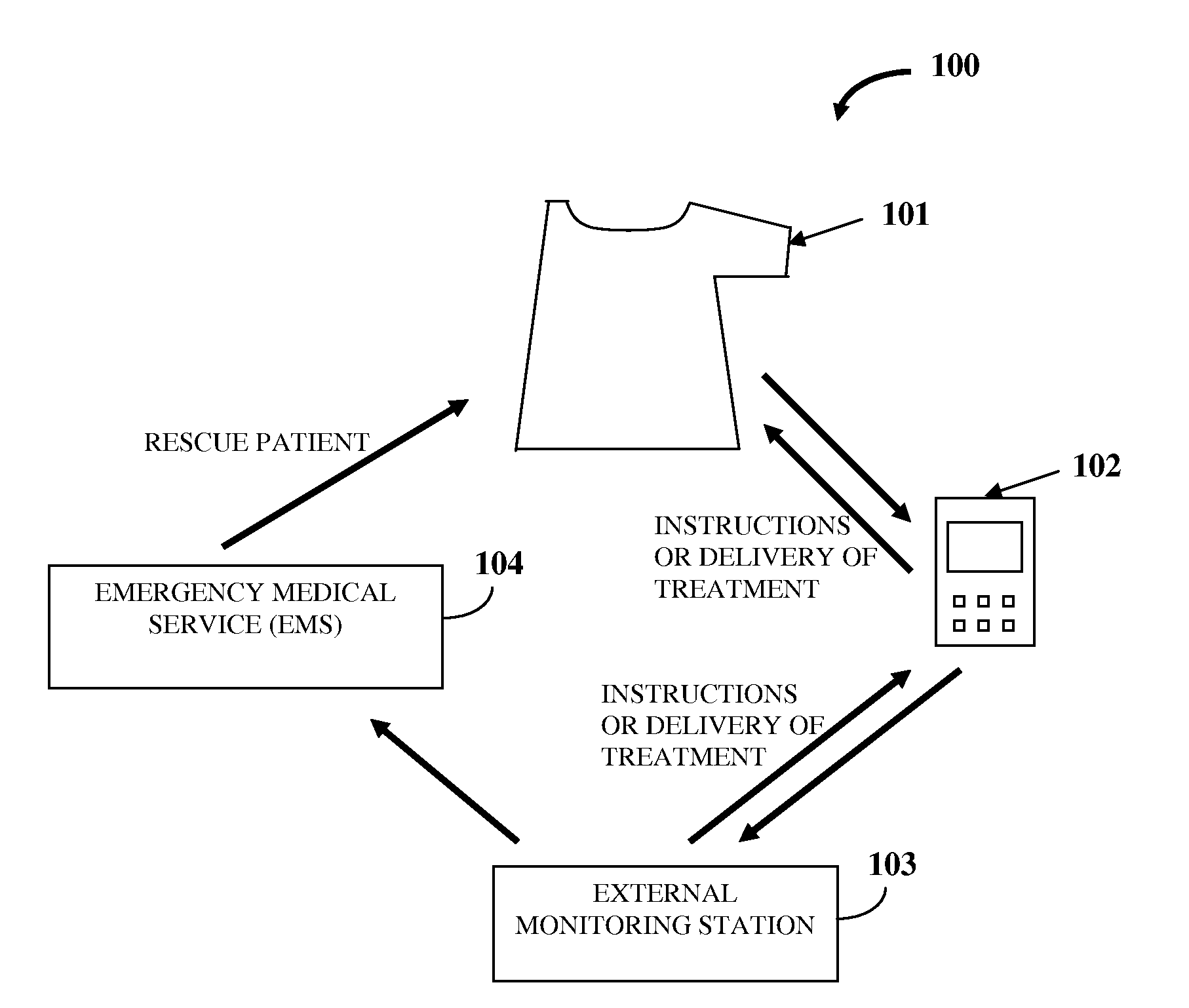
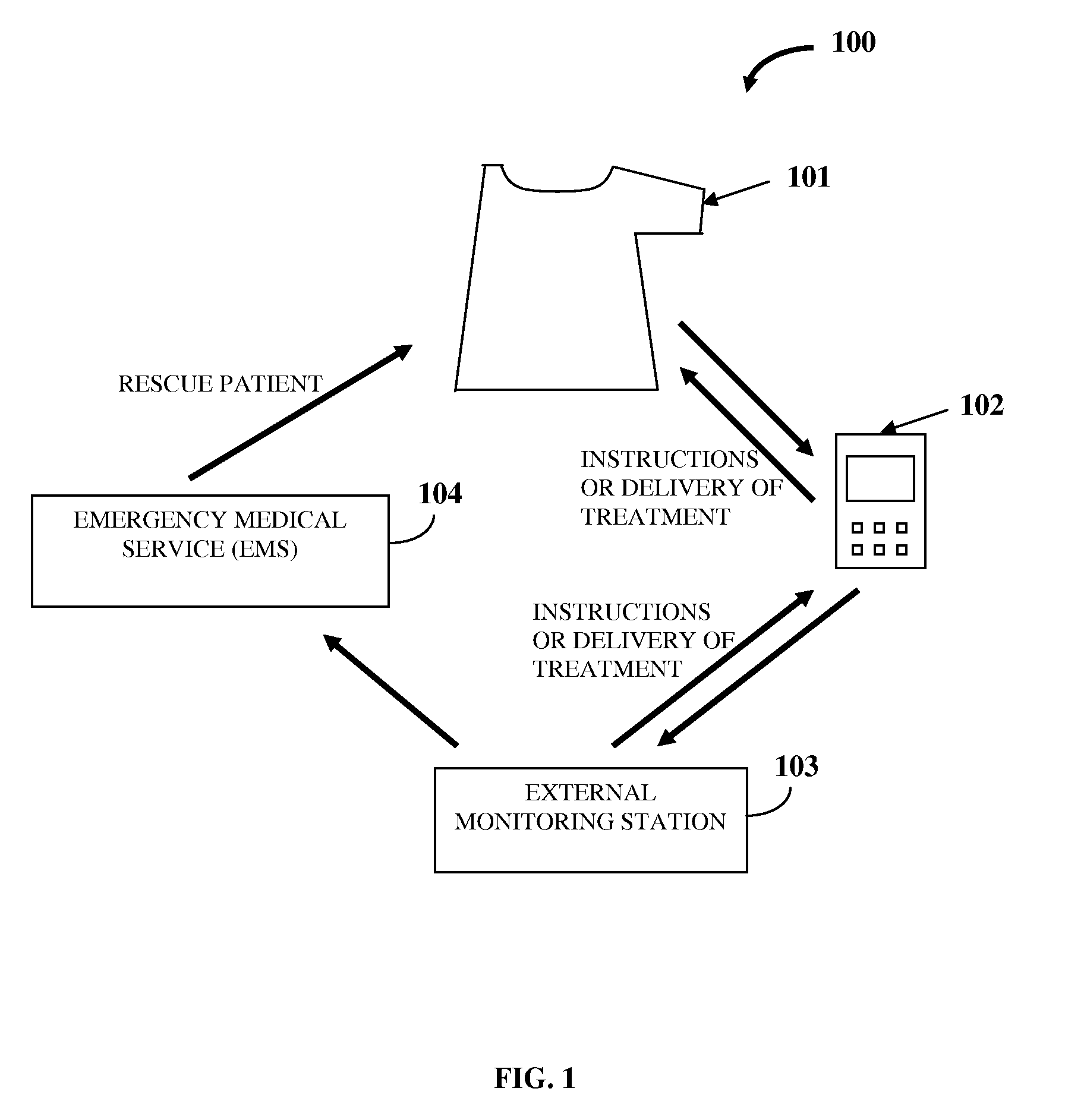
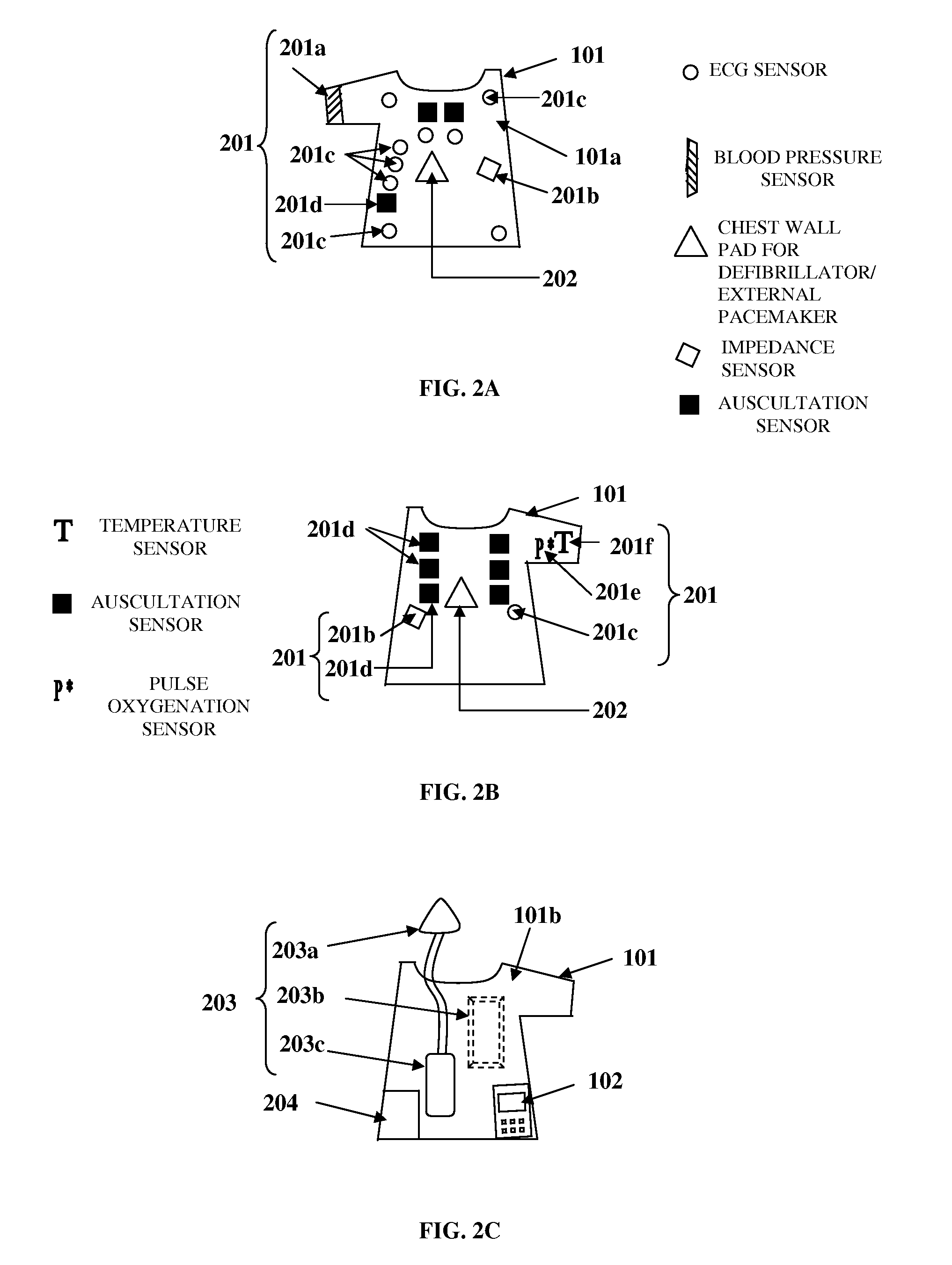
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Chest Casing
A system and method is provided for detection, forewarning, and rapid therapeutic treatment of a patient's ischemic and arrhythmic heart condition, congestive heart failure, respiratory failure, etc. The system comprises a chest casing of a form fitting material. The inner surface of the chest casing comprises electrocardiogram sensor electrodes, auscultation sensors, impedance sensor electrodes, etc. The electrocardiogram sensor electrodes detect abnormal electrocardiogram signals. The auscultation sensors record internal sounds at predefined cardiac and respiratory auscultation sensor points. The impedance sensor electrodes measure thoracic impedance across two or more points on the chest wall. A control unit is connected to the sensors for collecting and processing patient information. The control unit transmits the processed patient information to an external monitoring station. The chest casing comprises therapeutic delivery points for delivering therapeutic electrical dosages and different therapies, for example, cooling therapy, to the patient via therapeutic devices connected on the chest casing.
Owner:AZIZ KUSAI SAADELDIN
Method and device for using impedance measurements based on electrical energy of the heart
InactiveUS7778709B2Function increaseInertial sensorsRespiratory organ evaluationThoracic impedanceElectric energy
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
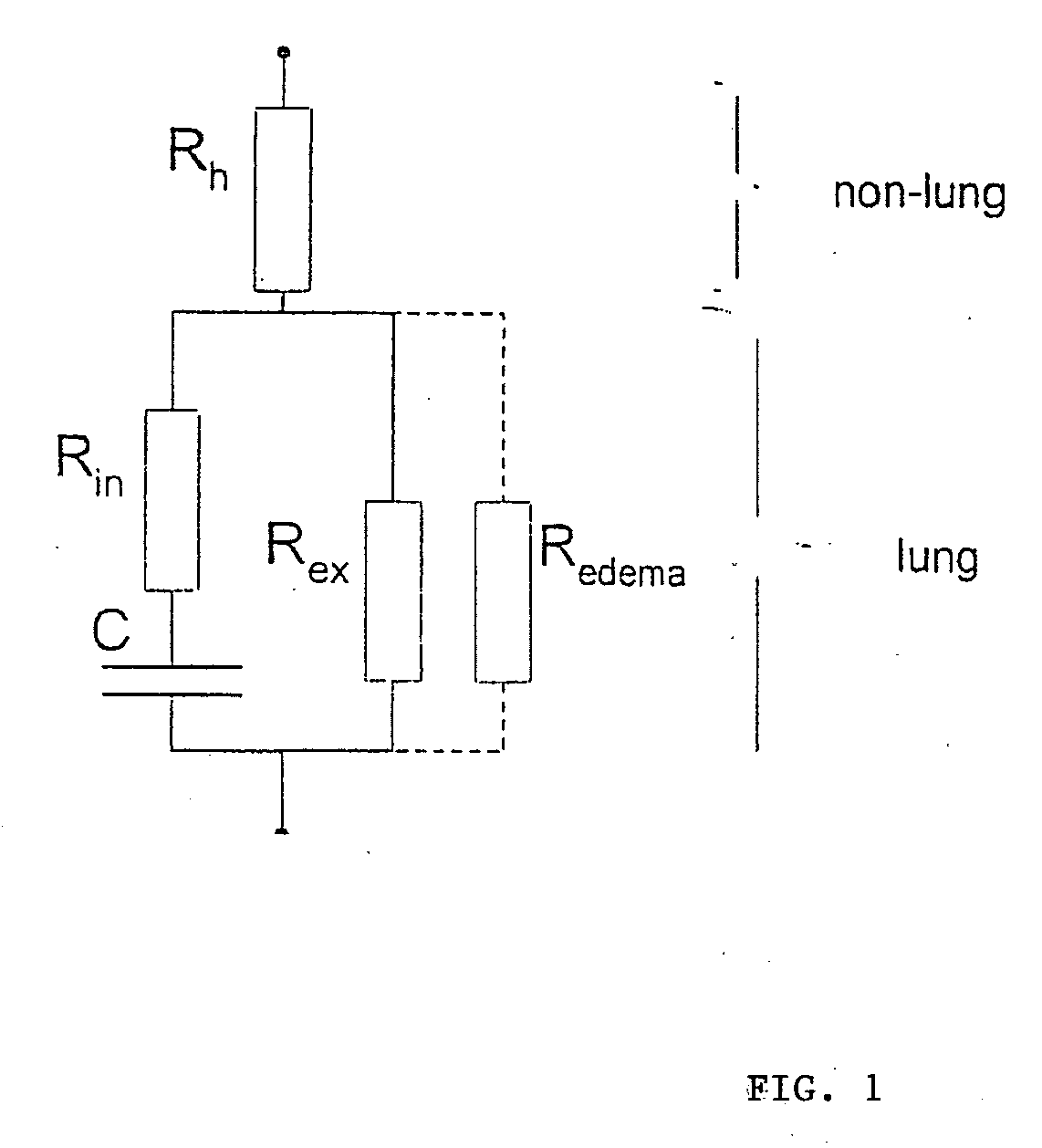
Device and method for predicting and preventing pulmonary edema and management of treatment thereof
InactiveUS20100106046A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProphylactic treatmentTherapy management
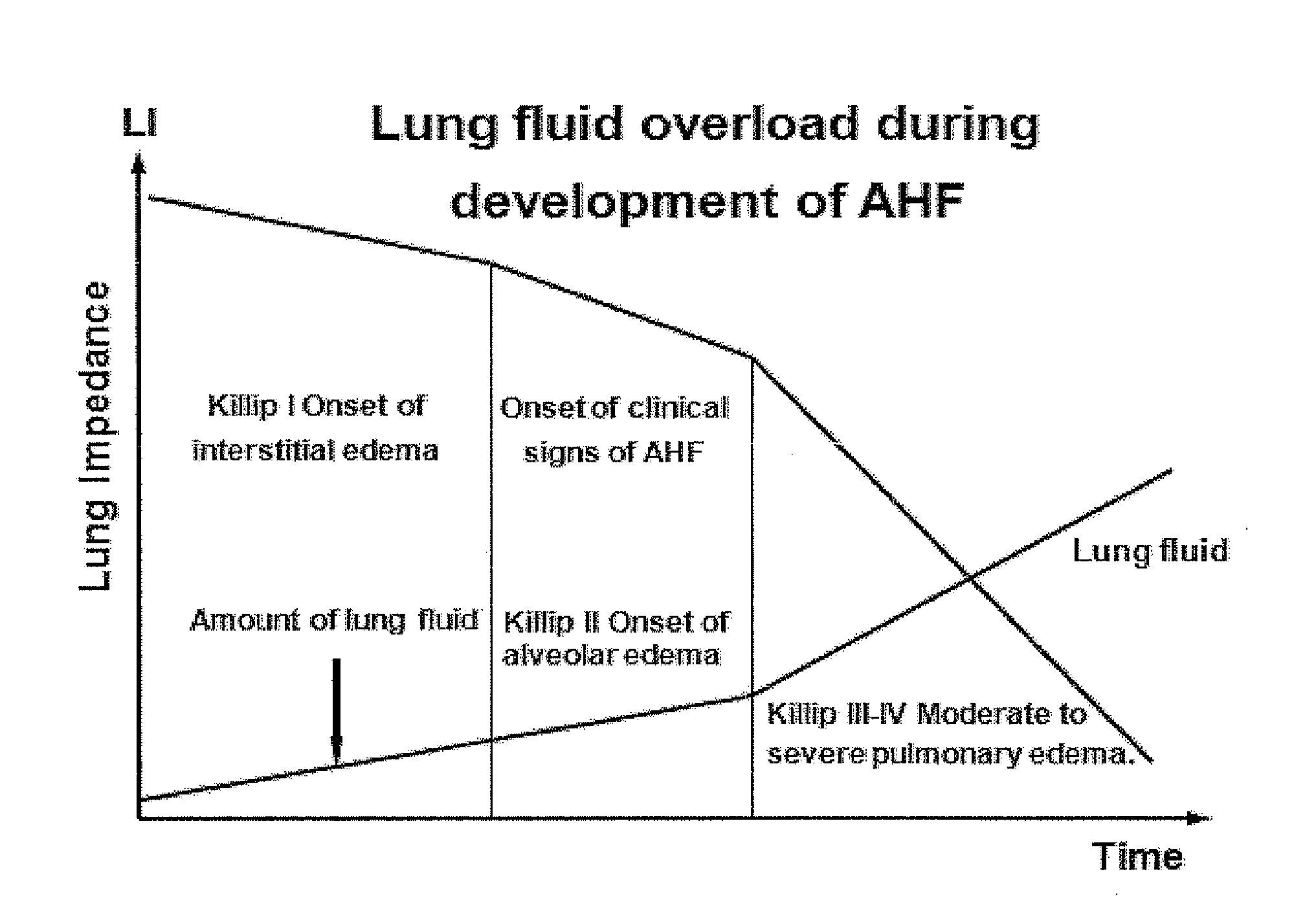
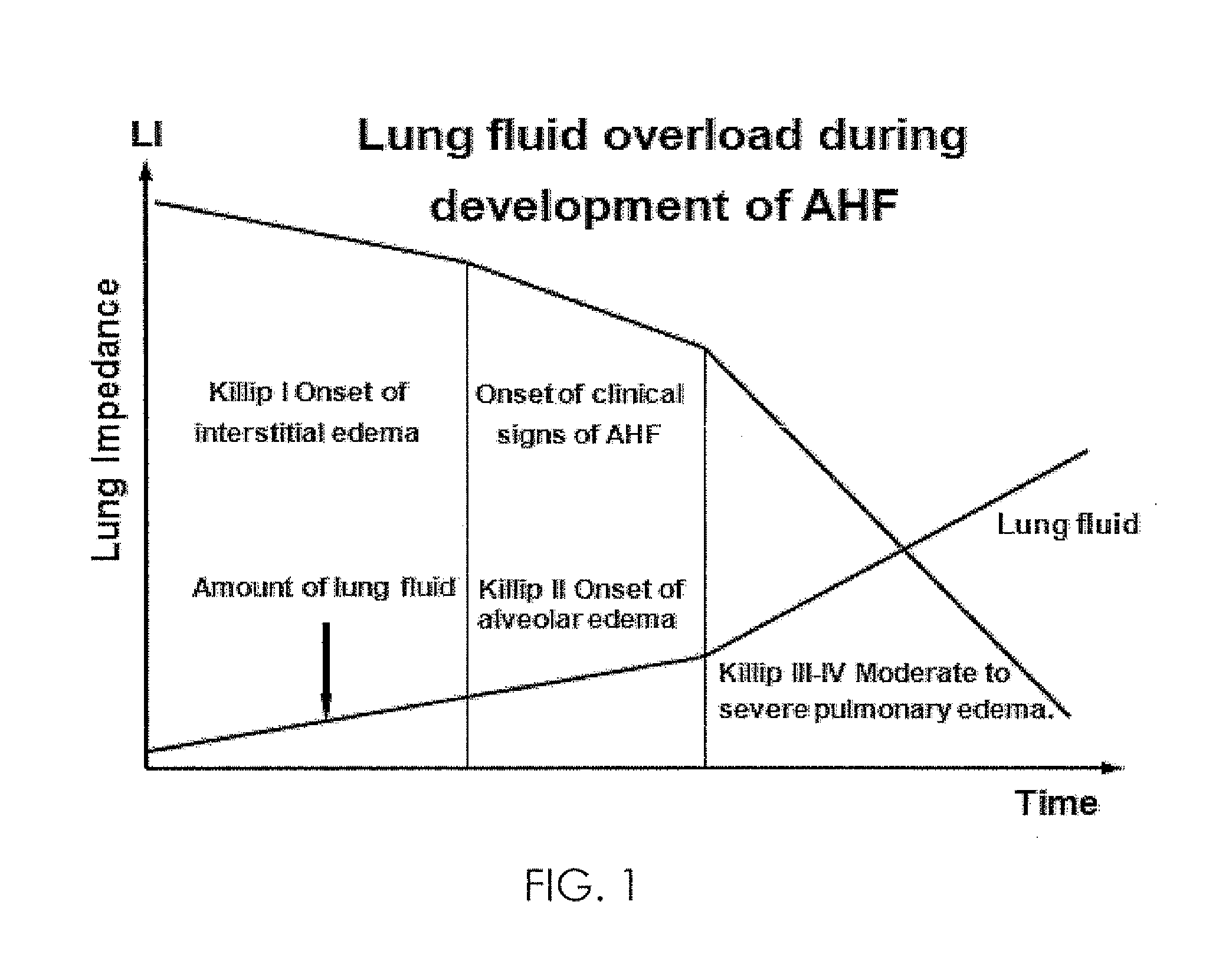
A device and a method for preventive treatment of evolving pulmonary edema in patients which are at risk of complication associated with pulmonary edema which is based on the monitoring of internal thoracic impedance of the patient. The device extracts the internal thoracic impedance from measured trans-thoracic impedance and is relatively immune to variations in skin / electrode interface impedance. The method includes identification of a stage of interstitial edema development before the appearance of a clinical indication and the beginning of an appropriate medicinal treatment in accordance to variations of the monitored internal thoracic impedance. The method also indicates the appropriate moment for terminating the medicinal treatment and can be applied when the patient and his treating physician are positioned at remote locations.
Owner:SHOCHAT MICHAEL +1
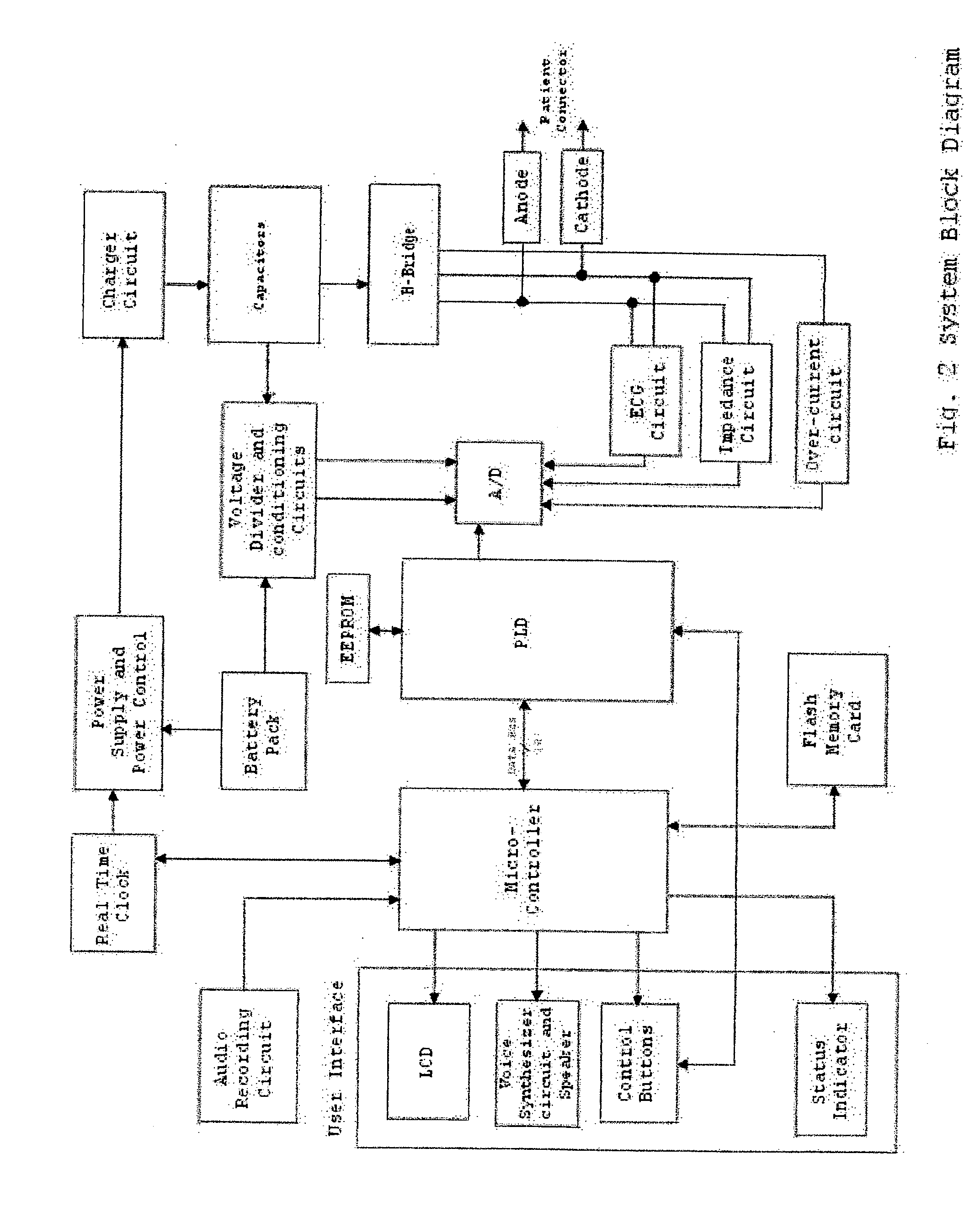
Automated external defibrillator (AED) with discrete sensing pulse for use in configuring a therapeutic biphasic waveform
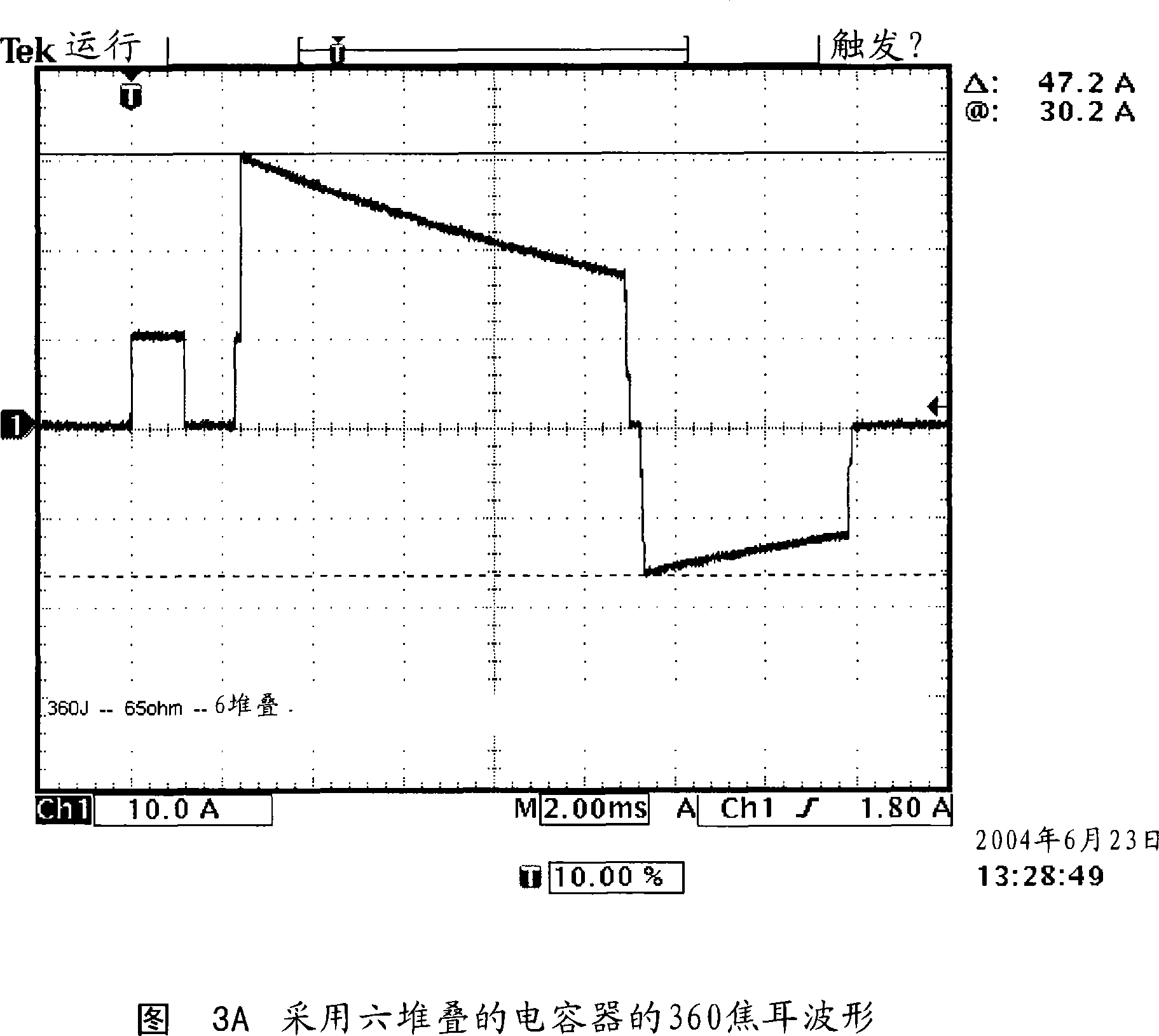
InactiveUS20060111750A1Current is limitedHeart defibrillatorsAutomatic external defibrillatorAutomated external defibrillator
An automatic external defibrillator (AED) with a discrete sensing pulse for use in configuring a therapeutic biphasic waveform. The sensing pulse is used to determine a patient-specific parameter (e.g., thoracic impedance) prior to delivery of the therapy waveform. The defibrillator adjusts the therapy waveform, based on the patient-specific parameter, prior to delivery to the patient.
Owner:ACCESS CARDIOSYST
Enhancements to the detection of pulmonary edema when using transthoracic impedance
This patent document discusses, among other things, systems, devices, and methods for enhancing detection of pulmonary edema using, in addition to thoracic impedance, one or a combination of: physiologic information about a subject, at least one statistical parameter, a user-programmable detection level, at least one parameter associated with a previous pulmonary edema event, and patient symptom information about the subject. In one example, a (base) thoracic impedance threshold is modified to an adjusted thoracic impedance threshold. The adjusted thoracic impedance threshold provides an increased sensitivity of pulmonary edema detection as compared to the base thoracic impedance threshold. In another example, an alert is provided to a subject, a caregiver, or other user based on a pulmonary edema indication determined by the present systems, devices, and methods. In a further example, a therapy (provided to the subject) is adjusted or initiated in response to the pulmonary edema indication.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Automated external defibrillator (aed) with discrete sensing pulse for use in configuring a therapeutic biphasic waveform
InactiveCN101115525AHeart defibrillatorsAutomatic external defibrillatorAutomated external defibrillator
An automatic external defibrillator (AED) with a discrete sensing pulse for use in configuring a therapeutic biphasic waveform. The sensing pulse is used to determine a patient-specific parameter (e.g., thoracic impedance) prior to delivery of the therapy waveform. The defibrillator adjusts the therapy waveform, based on the patient-specific parameter, prior to delivery to the patient.
Owner:ACCESS CARDIOSYST
High-performance lung function detecting system and method based on thoracic impedance measurement
InactiveCN109567805AProtection securityGuaranteed no distortionRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsMicrocontrollerSignal conditioning
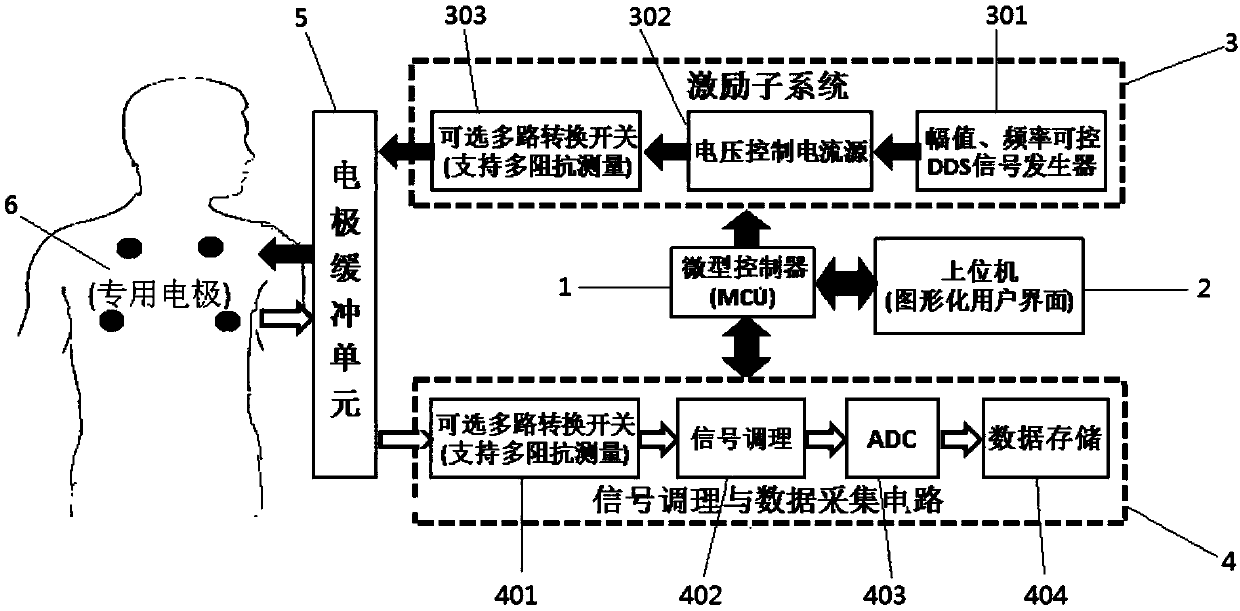
The invention relates to a high-performance lung function detecting system and method based on thoracic impedance measurement. The high-performance lung function detecting system comprises a microcontroller, an upper computer, an exciting circuit, a signal conditioning and data collection circuit, an electrode buffer unit and a special electrode array, wherein the exciting circuit generates an exciting current under control of the microcontroller, and the exciting current is obtained by converting a differential voltage signal and acts on the special electrode array through the electrode buffer unit; the signal conditioning and data collection circuit collects an exciting current signal and a response voltage signal through the electrode buffer unit; the microcontroller demodulates the exciting current signal and the response voltage signal, calculates the amplitude and phase of thoracic impedance and uploads the amplitude and phase of the thoracic impedance to the upper computer; andthe upper computer obtains the assessment result of lung functions of a detected object according to the amplitude and phase of the thoracic impedance. Compared with the prior art, the high-performance lung function detecting system and method have the advantages of easy implementation, low system cost, high detection sensitivity, fast and convenient measurement and the like, and the detecting experience of a doctor and a patient can be effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
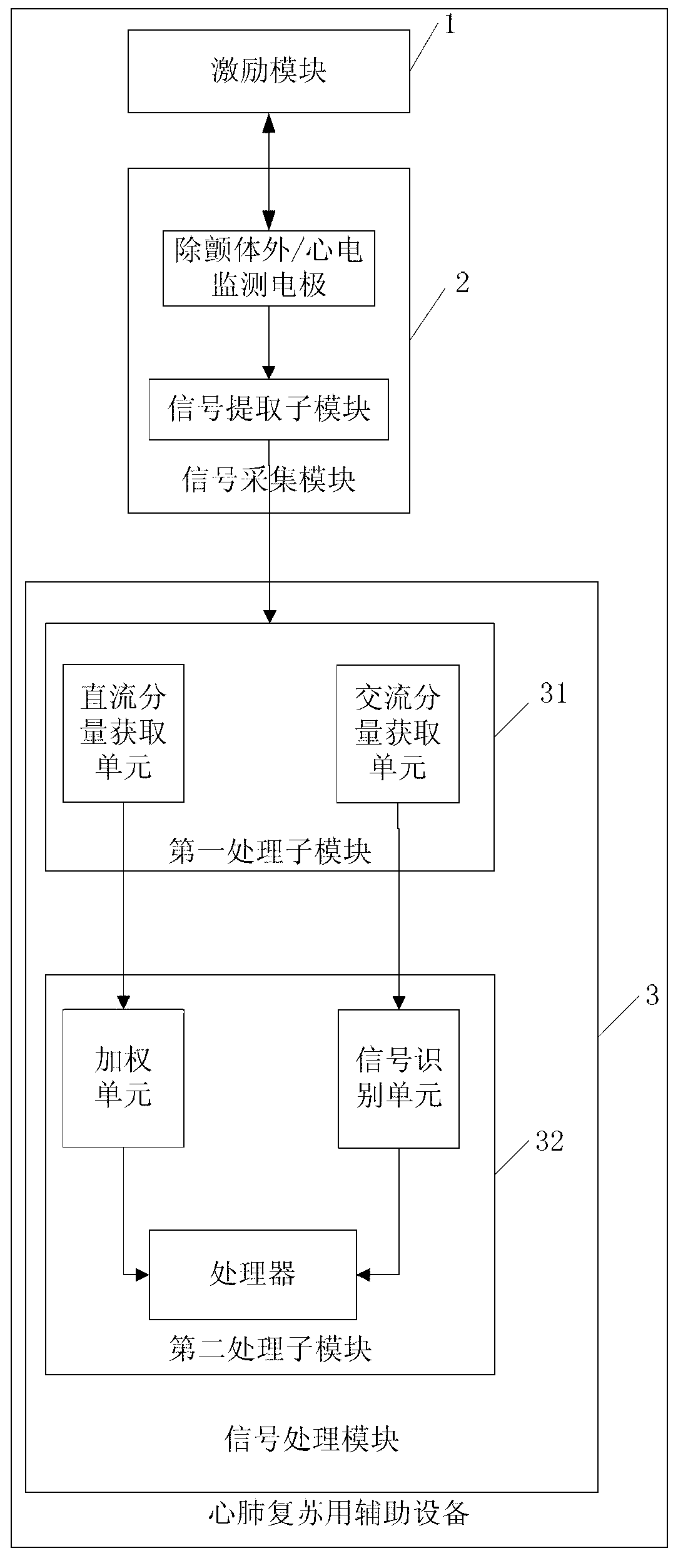
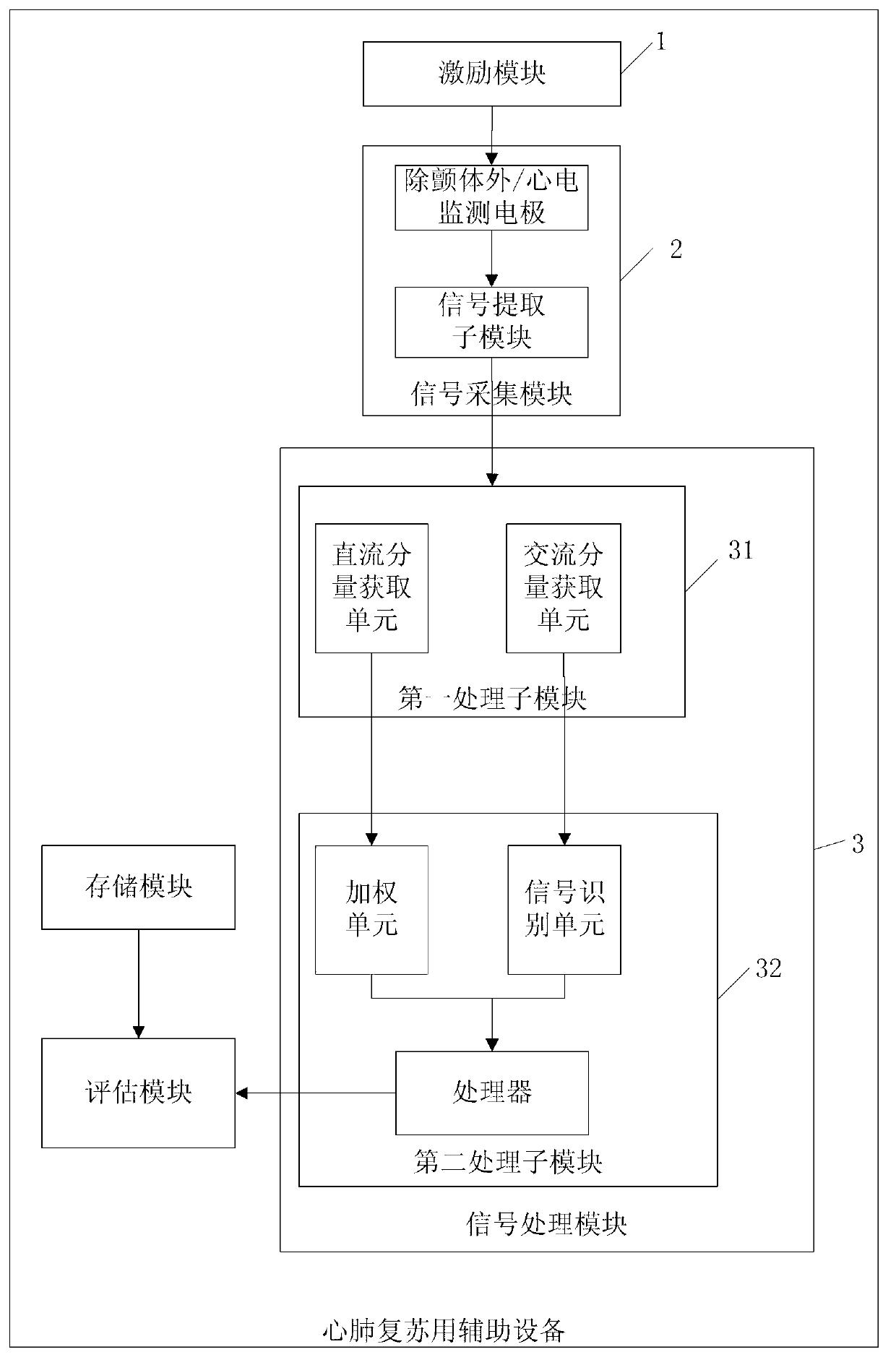
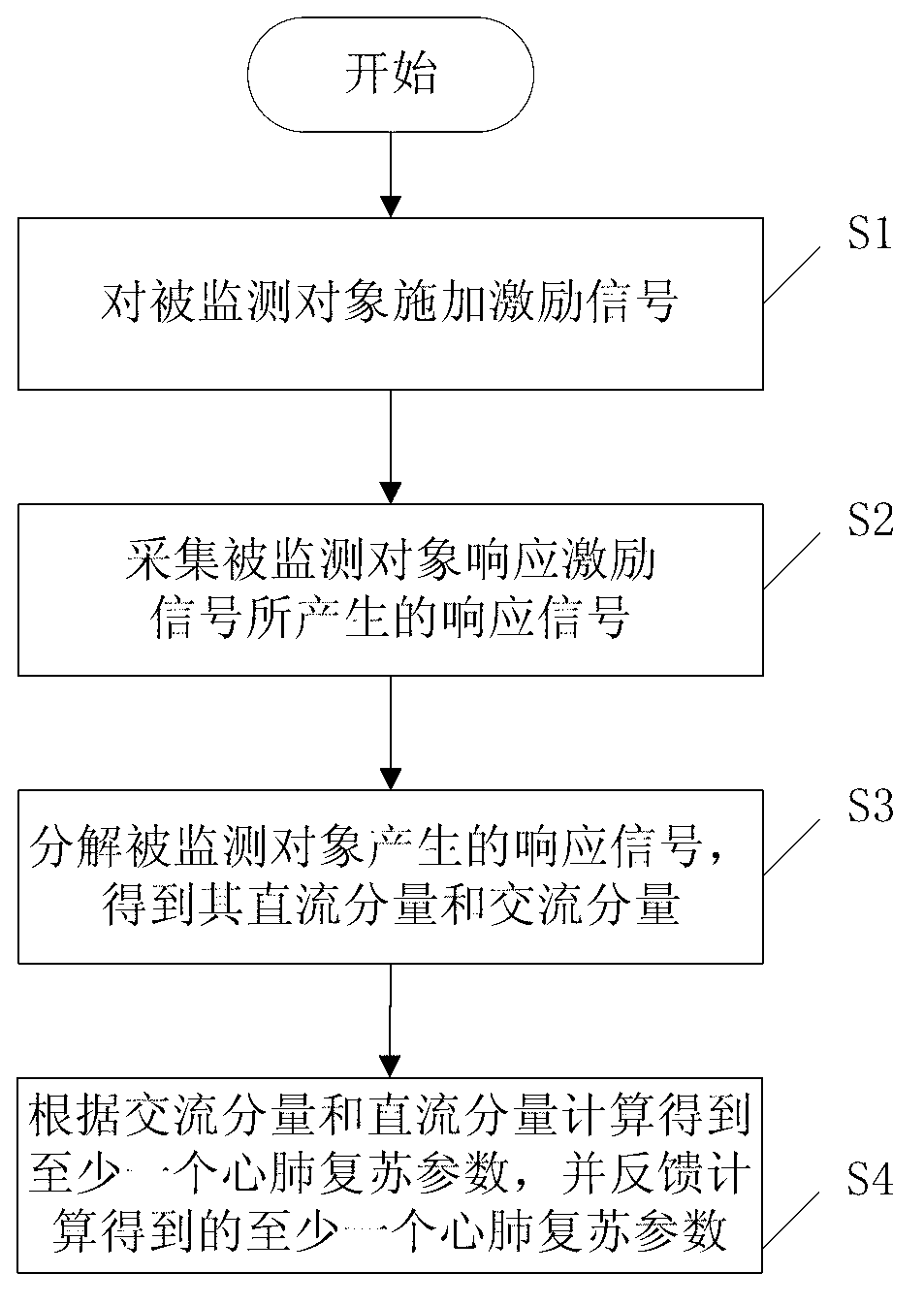
Method and auxiliary device of determining cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality parameters during process of cardiopulmonary resuscitation
ActiveCN102973402AIncrease success rateGood cardiopulmonary resuscitationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSignal onComputer science
The invention discloses a method and an auxiliary device of determining cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality parameters during the process of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The auxiliary device comprises an incentive module, a signal collection module and a signal processing module. The incentive module is used for exerting an incentive signal on a target object. The signal collection module is used for collecting a responding signal produced by the target object to the incentive signal. The signal processing module is used for analyzing and collecting the responding signal to obtain a direct current component and an alternating current component of the signal processing module, and is used for analyzing and calculating the cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality parameters of the target object according to the direct current component and the alternating current component. According to the method and the device of determining the cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality parameters during the process of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, the incentive signal is exerted on the target object, the responding signal produced by the target object thoracic impedance when responding to the incentive signal is detected, analysis and calculation are carried out according to the responding signal, so that the parameters related to the cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality is obtained. Therefore, the whole quality of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation can be known in real time and cardiopulmonary resuscitation measure can be adjusted in time according to the parameters to achieve the perfect cardiopulmonary resuscitation effect.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
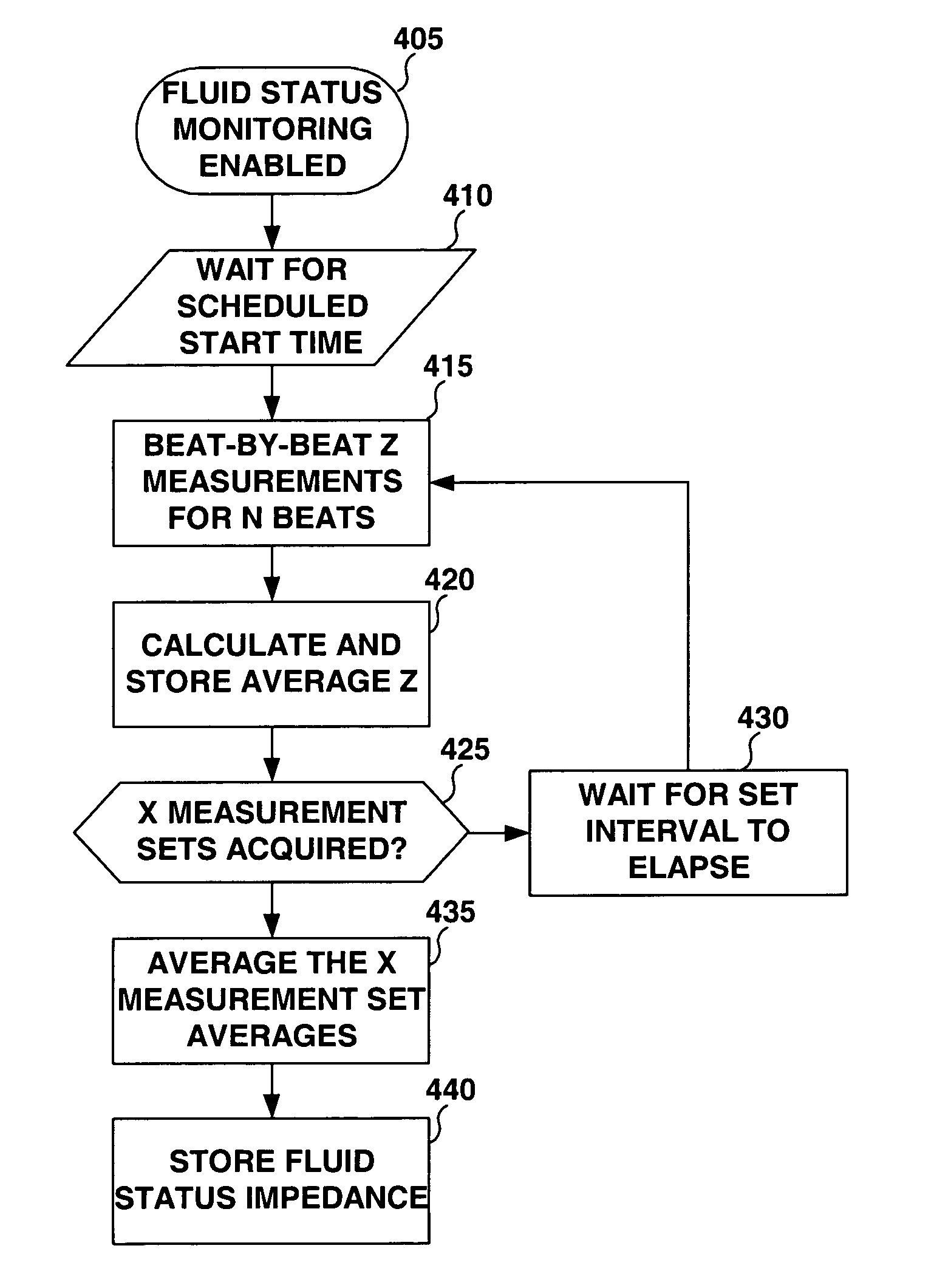
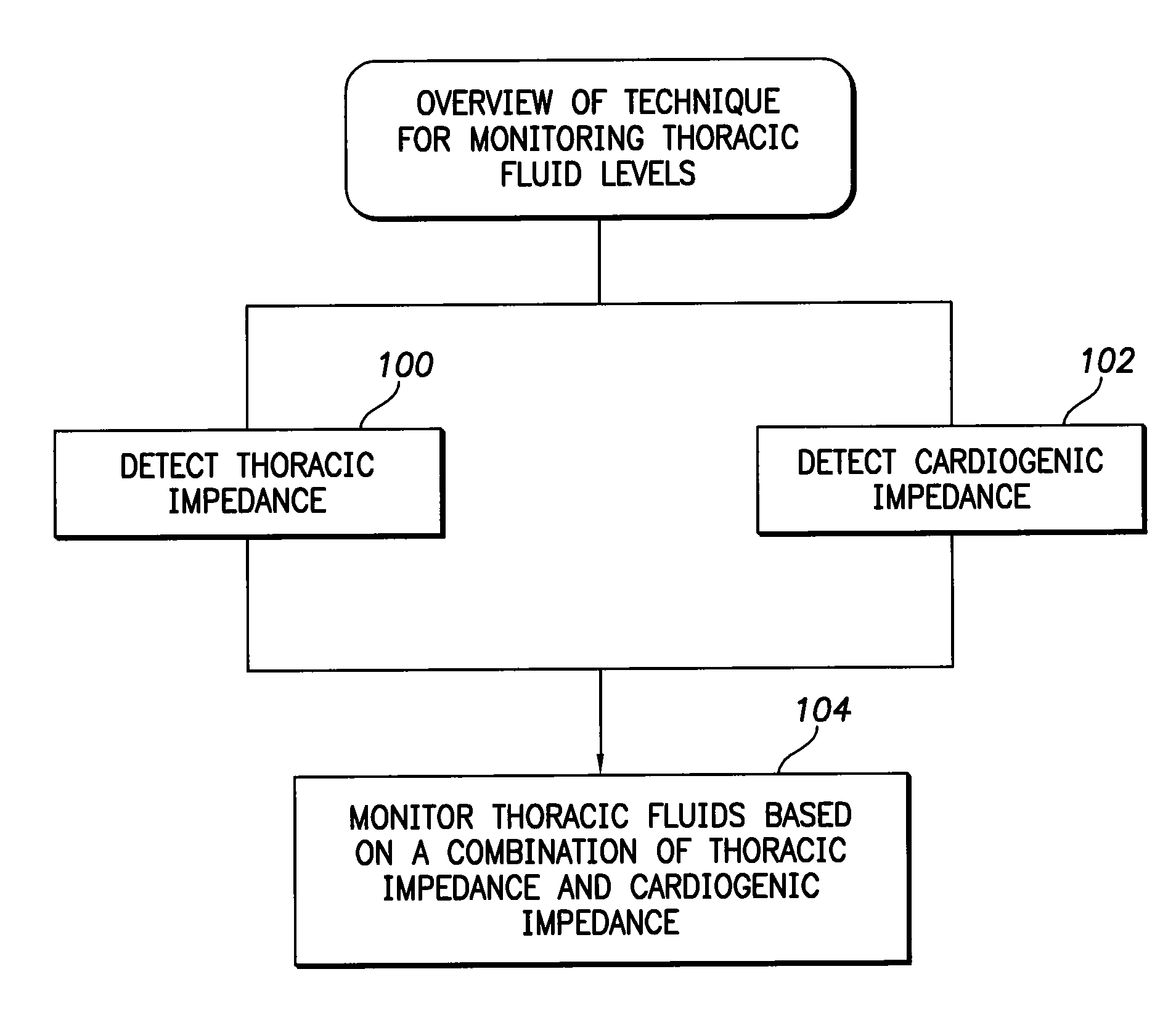
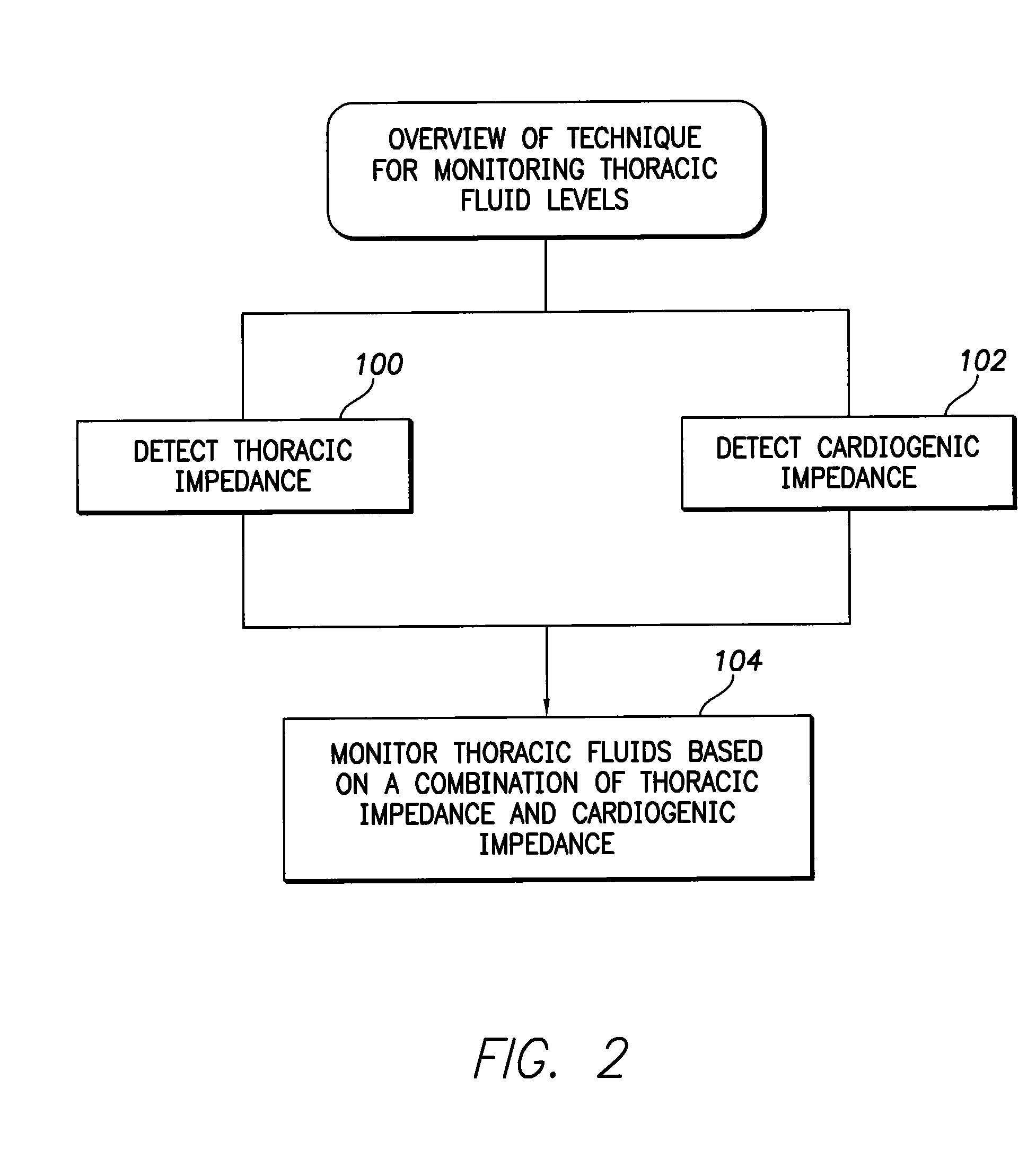
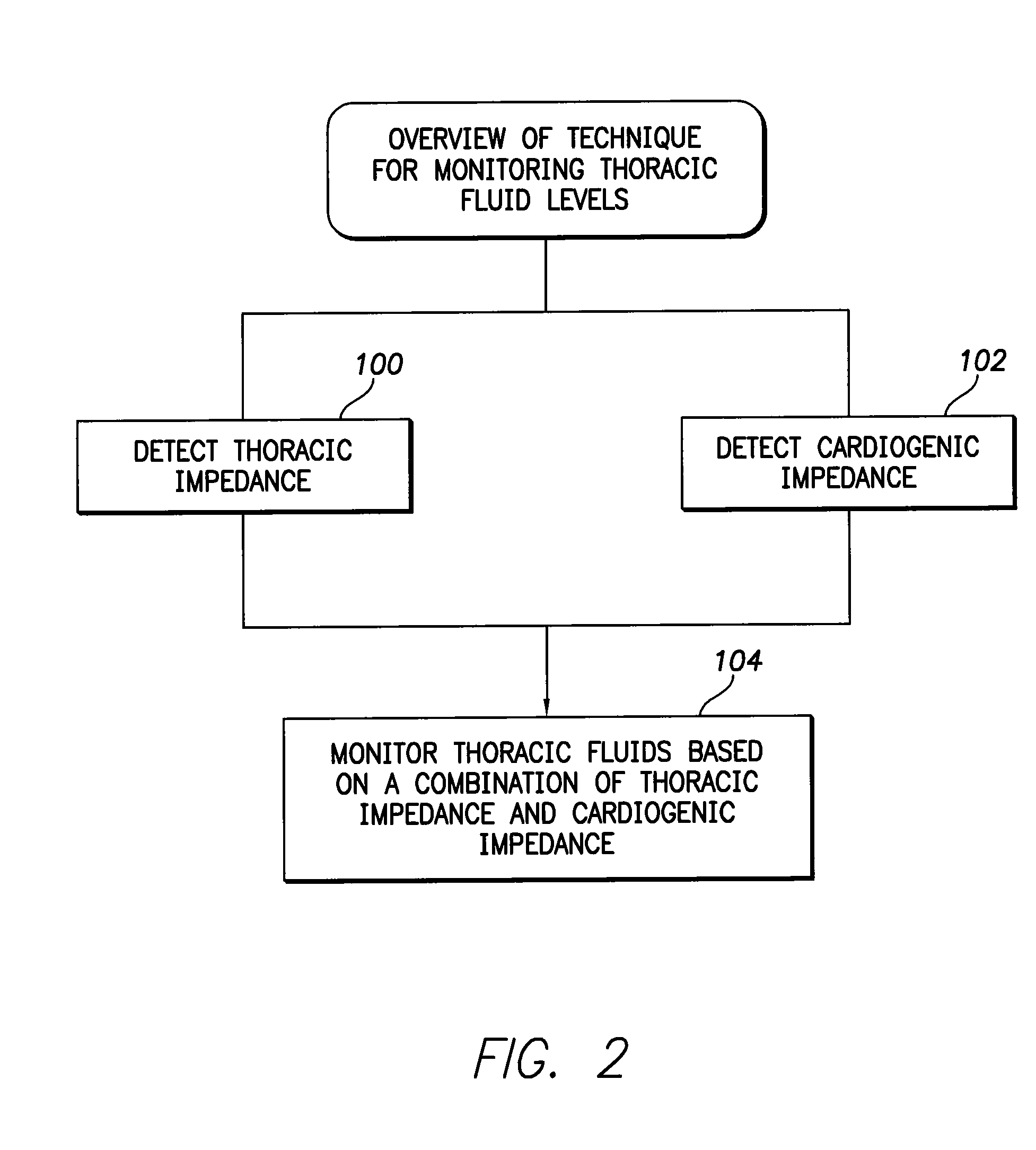
System and method for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on impedance using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS8032212B2Monitored more effectivelyEffective monitoringElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on thoracic impedance (ZT) and cardiogenic impedance (ZC). In one example, the implantable device tracks the maximum time rate of change in cardiogenic impedance (i.e. max(dZC / dt)) to detect trends toward hypervolemic or hypovolemic states within the patient based on changes in heart contractility. The detection of these trends in combination with trends in thoracic impedance allows for a determination of whether the thoracic cavity of the patient is generally “too wet” or “too dry,” and thus allows for the titration of diuretics to avoid such extremes. In particular, a decrease in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too wet” (i.e. a fluid overload). Conversely, an increase in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too dry” (i.e. a fluid underload).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and implantable medical device for assessing a degree of pulmonary edema of a patient
ActiveUS20090099475A1Reduce startImprove accuracyElectrotherapyPerson identificationPulmonary edemaMedical device
In a method and an implantable medical device for assessing a degree of pulmonary edema of a patient, at least two specific body patients of the patent are detected and at least one impedance sensing session is initiated to sense trans-thoracic impedance signals from the patient when the patient is in one of the at least two specific positions. Impedance values are obtained from the impedance signals, and a relation between respective impedance values at the at least two positions is determined. This relation is then used as a metric of pulmonary edema to assess the degree of pulmonary edema, and is provided as an output.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Method of vagal stimulation to treat patients suffering from congestive heart failure
InactiveUS8457743B2Shorten the progressReduce failureElectrotherapyInertial sensorsCardiac cycleClosed loop
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on impedance using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20100069778A1Avoid problemsExcellent stateElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on thoracic impedance (ZT) and cardiogenic impedance (ZC). In one example, the implantable device tracks the maximum time rate of change in cardiogenic impedance (i.e. max(dZC / dt)) to detect trends toward hypervolemic or hypovolemic states within the patient based on changes in heart contractility. The detection of these trends in combination with trends in thoracic impedance allows for a determination of whether the thoracic cavity of the patient is generally “too wet” or “too dry,” and thus allows for the titration of diuretics to avoid such extremes. In particular, a decrease in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too wet” (i.e. a fluid overload). Conversely, an increase in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too dry” (i.e. a fluid underload).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method of detecting sleep apnea and treatment thereof
InactiveUS20110190642A1Simple methodDrain can be reducedElectrotherapyElectrocardiographySignal processing circuitsProper treatment
A method is presented for evaluating whether an episode of sleep apnea is occurring in a patient suffering from chronic sleep apnea disorder, for delivery of appropriate therapy. The method, performed by an implantable device, includes sensing the patient's EKG signal and using electrical energy generated by the heart to power subsequent signal processing. This signal is applied as the sole input to a differential signal processing circuit for passage through both a high impedance path and a substantially lower impedance path and amplification of the difference in magnitude between the resulting two signals, to determine changes in the patient's thoracic impedance. Based on such changes, the presence or absence of patient ventilation is detected, to enable an assessment of whether an episode of sleep apnea is occurring. An actual episode of sleep apnea is deemed to have occurred if lack of ventilation exceeds a predetermined interval of time between otherwise regular respiratory cycles. If sleep apnea is indicated, the appropriate therapy is delivered by the device to induce ventilation and halt the apnea episode.
Owner:ALT ECKHARD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com