Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70 results about "Respiratory activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Physical activity augments the respiratory volume, and increases the volume of oxygen diffused in the cells. This increases the maximum amount of oxygen the body can use during a specified period, which is known as the aerobic capacity of the lungs.
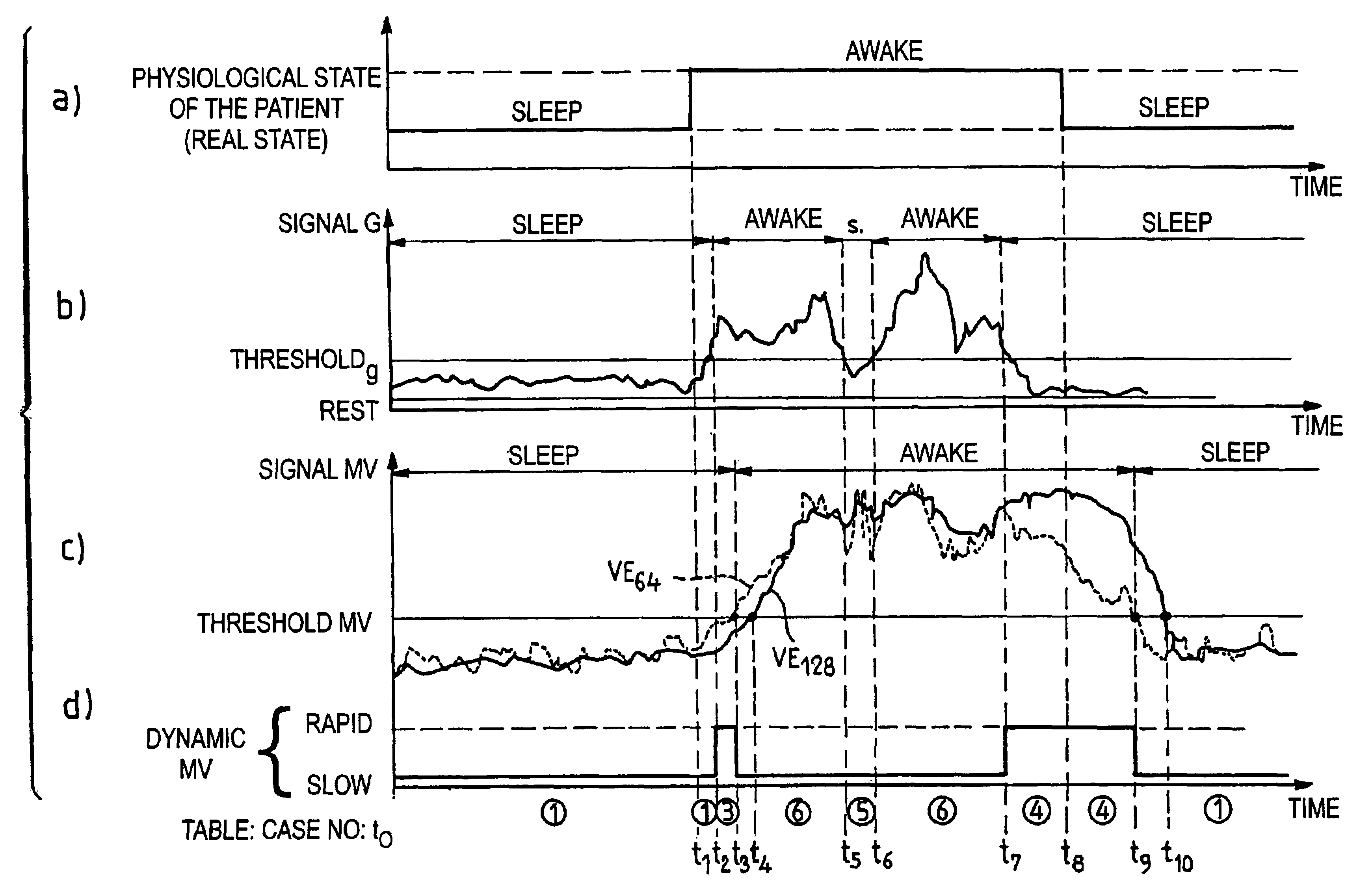
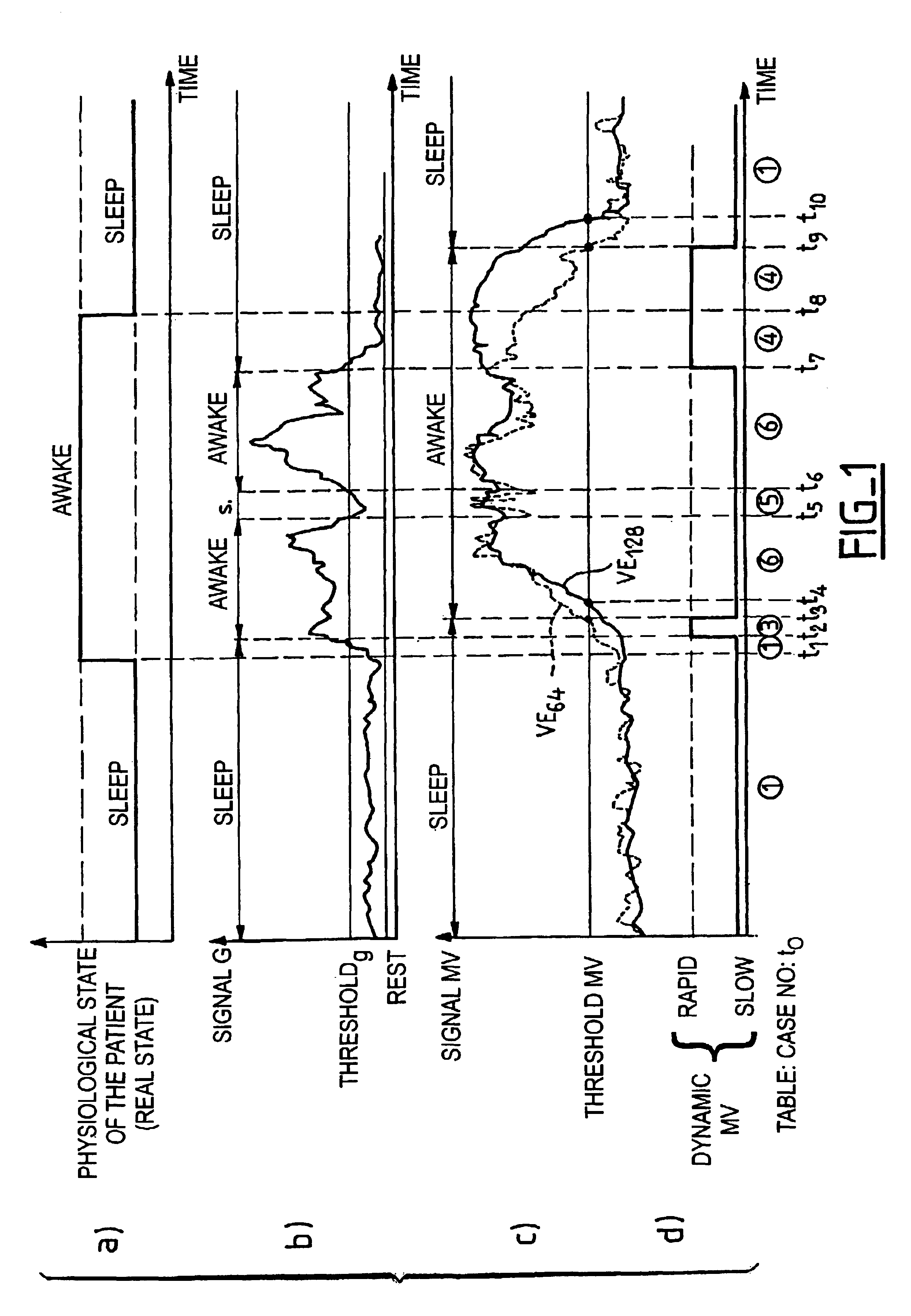
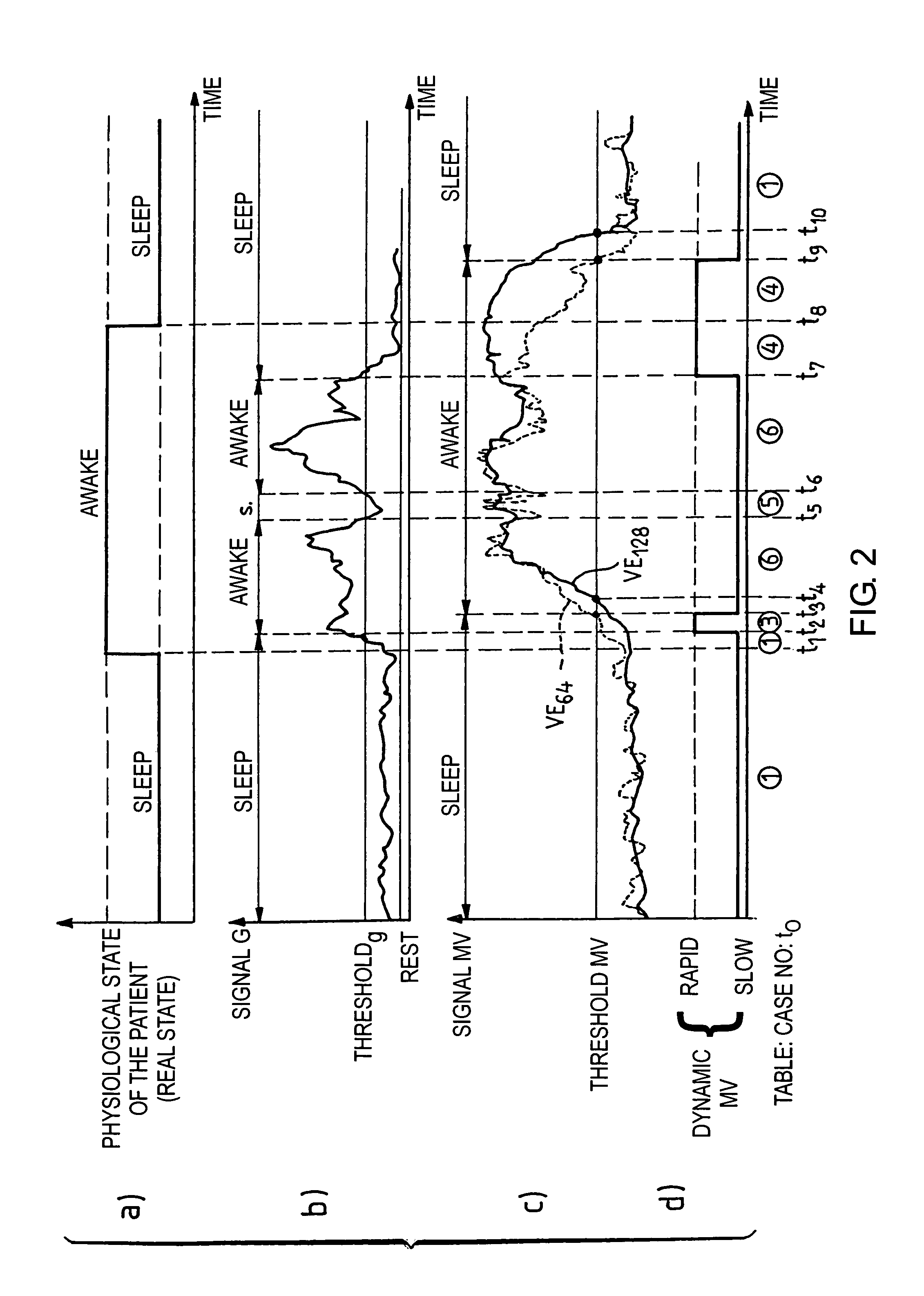
Active medical device for the diagnosis of the sleep apnea syndrome
InactiveUS6890306B2Risk minimizationElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationSleep stateMedical device
An active medical device have an improved diagnosis of a sleep apnea syndrome. This device measures the respiratory activity of the patient, determines a state of activity, this state being likely to take, according to satisfaction of predetermined criteria, a value representative of a state of sleep of the patient, and analyzes a detected signal corresponding to the respiratory activity to detect, when the aforementioned state is a state of sleep, the presence of respiratory pauses, and thereby to produce an indicating signal of sleep apnea in the event of the occurrence of a respiratory pause of duration longer than a first predetermined duration. The analysis also includes inhibiting the production of the aforesaid indicating signal, or a treatment to resolve an apnea, when the duration of the detected respiratory pause is longer than a second predetermined duration, typically of at least one minute.
Owner:SORIN CRM
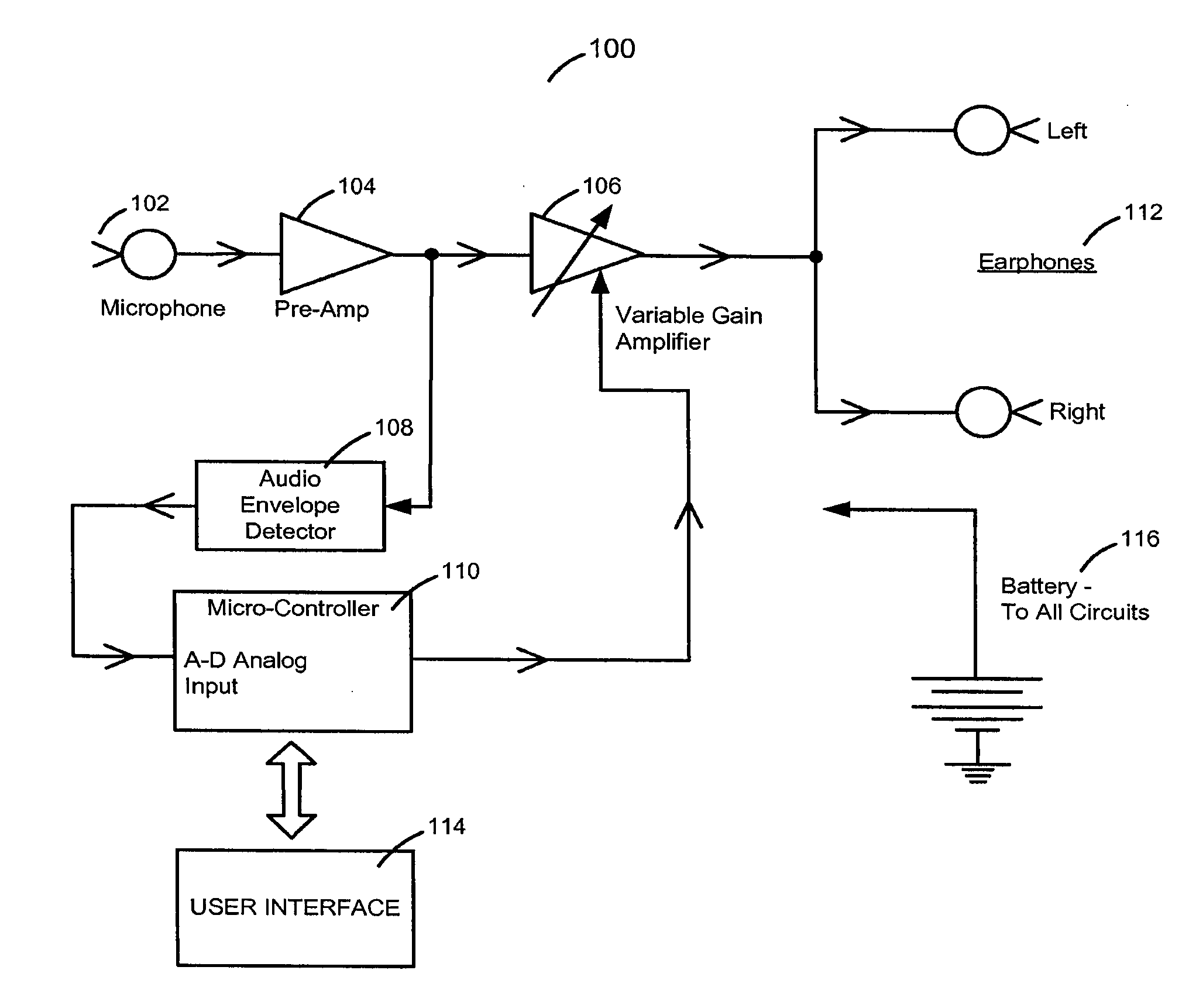
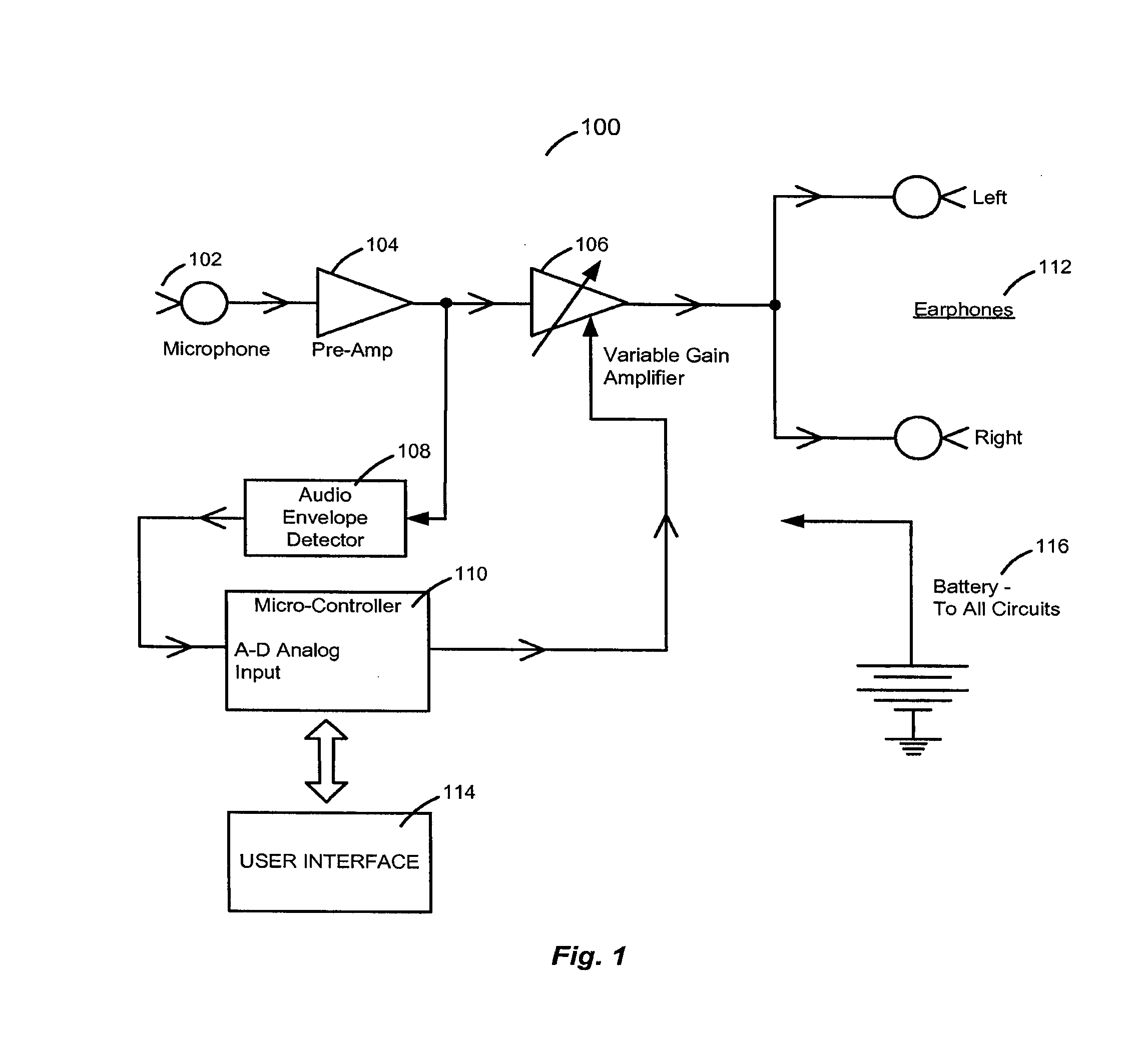
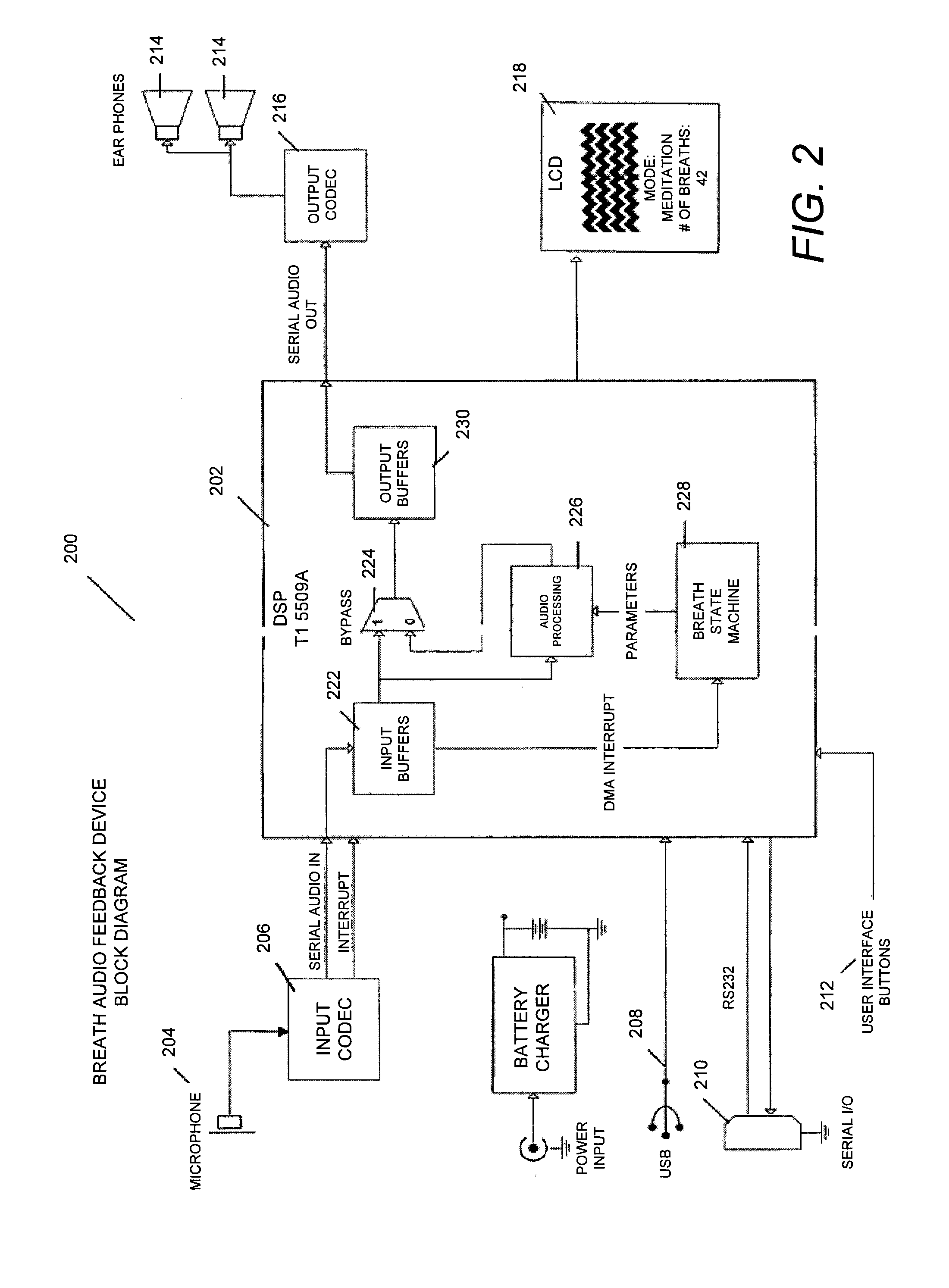
Respiratory biofeedback devices, systems, and methods
ActiveUS20100240945A1Improve respiratory activityImprove sleep qualityRespiratory organ evaluationAngiographyTime responseSound wave
Respiratory-based biofeedback devices, systems, and methods are provided. A respiratory biofeedback method includes producing a respiratory signal in response to a user's respiratory activity, generating an audio output signal that includes a modified version of the respiratory signal, and converting the audio output signal into sound waves output to the user to provide biofeedback. The sound waves can be output to the user in real time response to the user's respiratory activity. A microphone can be used to generate the respiratory signal. The generated audio output signal can includes the respiratory signal modified to increase a volume level of a portion of the respiratory signal where the volume level exceeds a specified volume level.
Owner:BREATH RES
Apparatus and method for monitoring pressure related changes in the extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system
ActiveUS20100222655A1Overcome disadvantagesEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterFrequency spectrumCardiac functioning
A method and apparatus for monitoring changes in the intra-thoracic pressure of a patient due to the patient's respiratory activity or volumetric changes in the extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system due to cardiac function based on the changes in pressure in the patient's extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system as measured by a plethysmography sensor, such as an photoplethysmograph. A frequency spectrum is generated for the plethysmograph signal and the frequencies of interest is isolated from the frequency spectrum by setting appropriate cutoff frequencies for the frequency spectrum. This isolated frequency is used to filter the plethysmograph signal to provide a signal indicative of the patient's respiratory activity or cardiac function.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
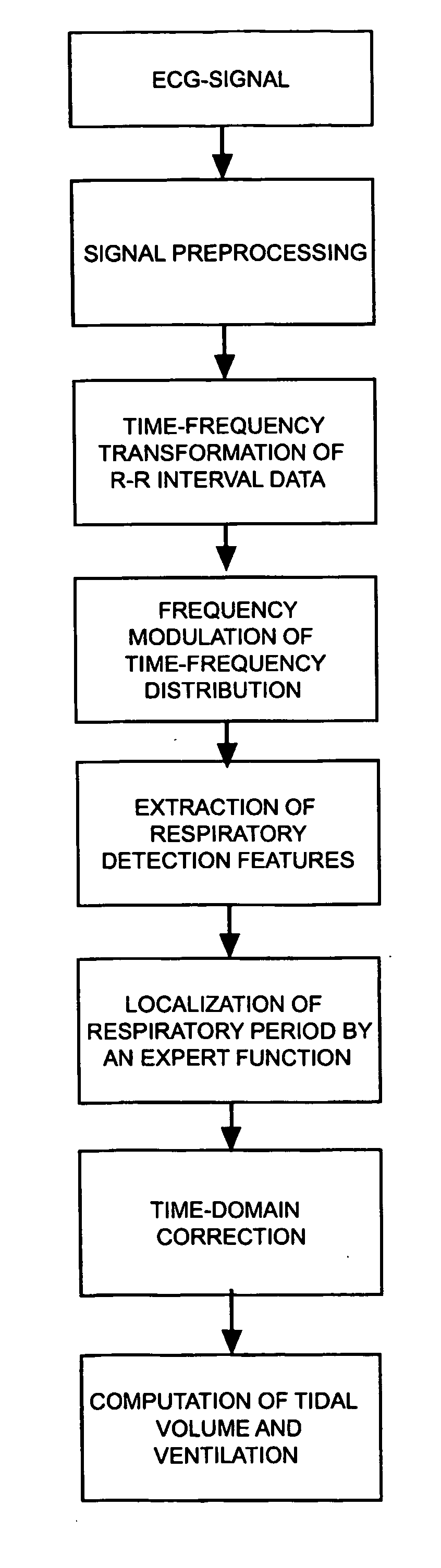
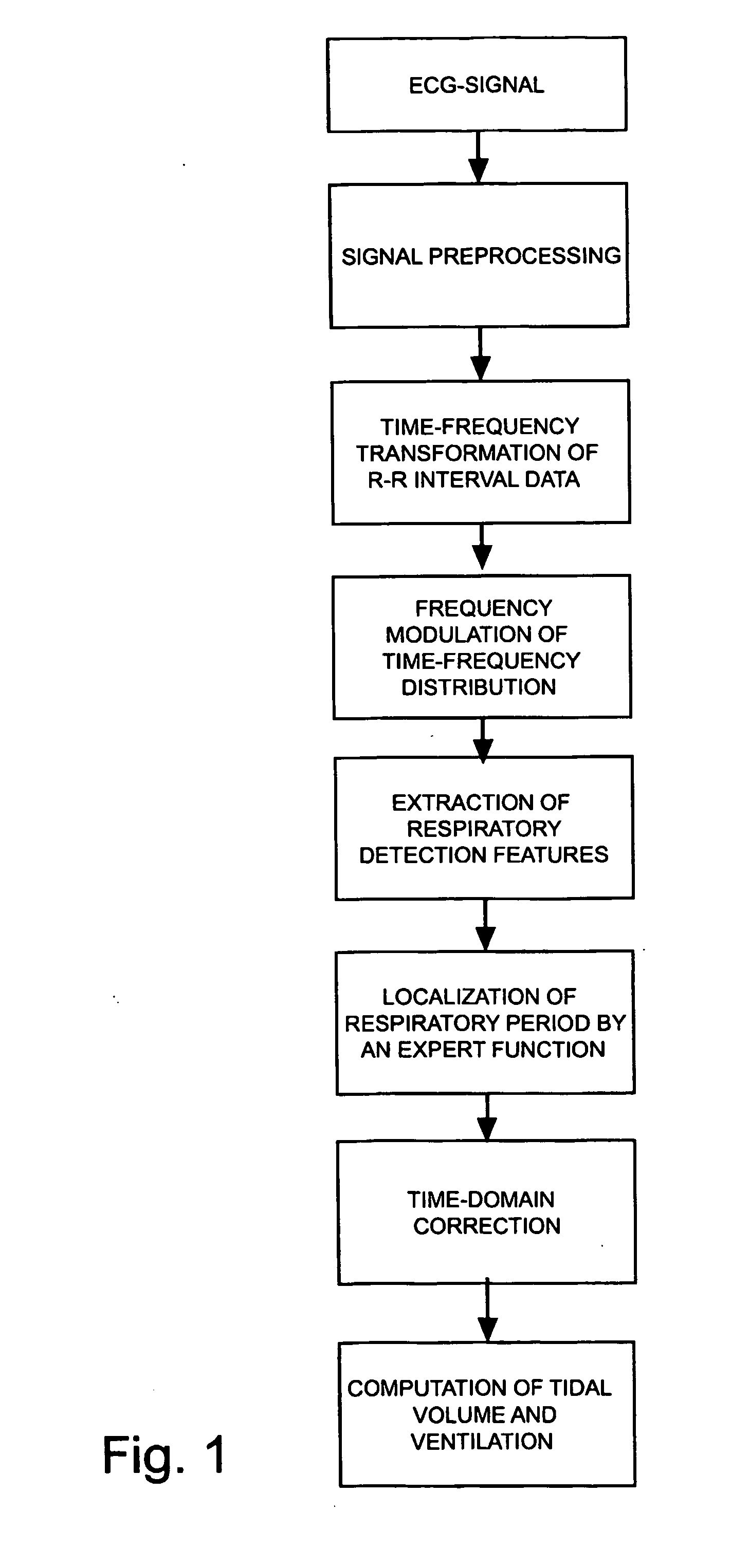
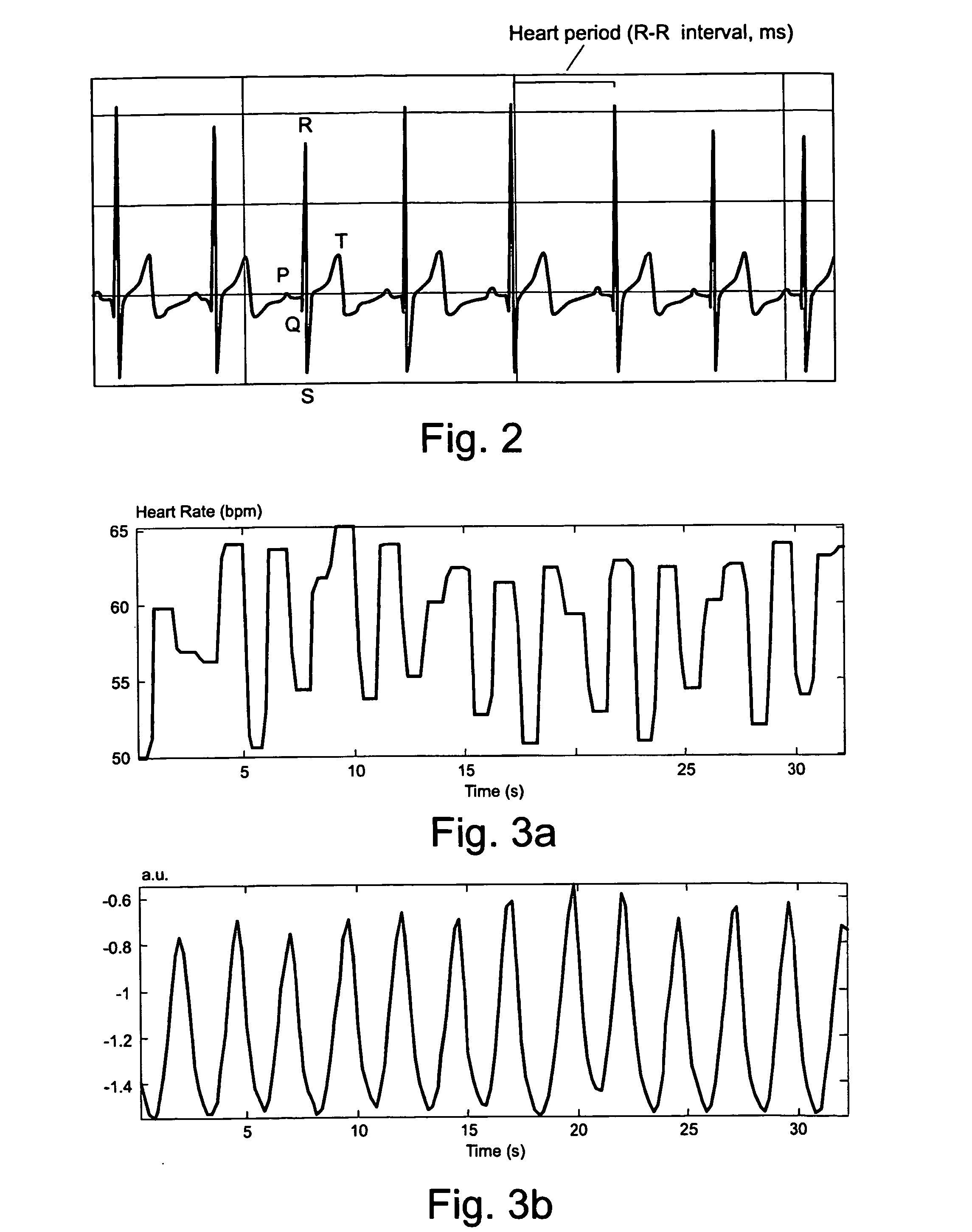
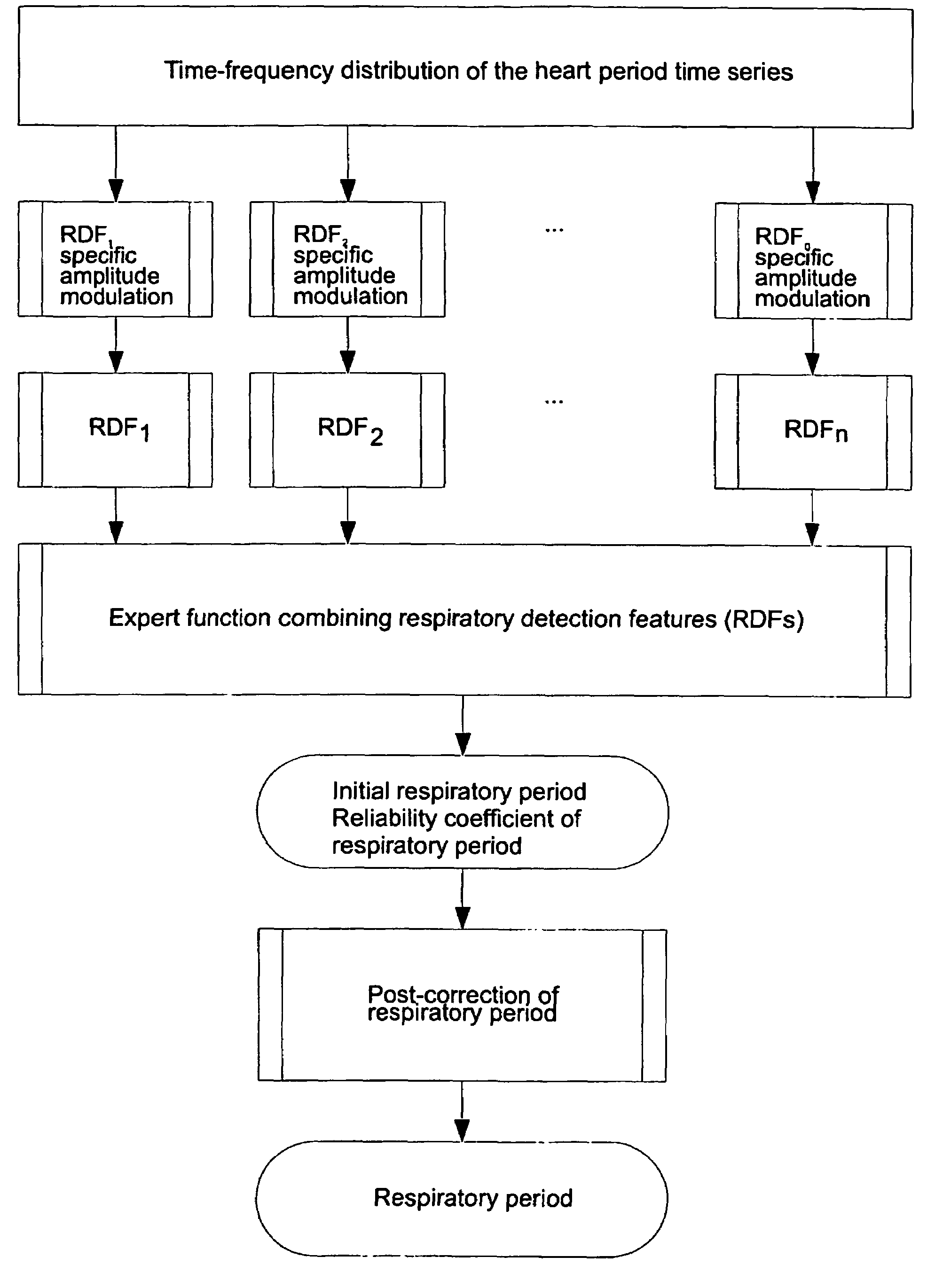
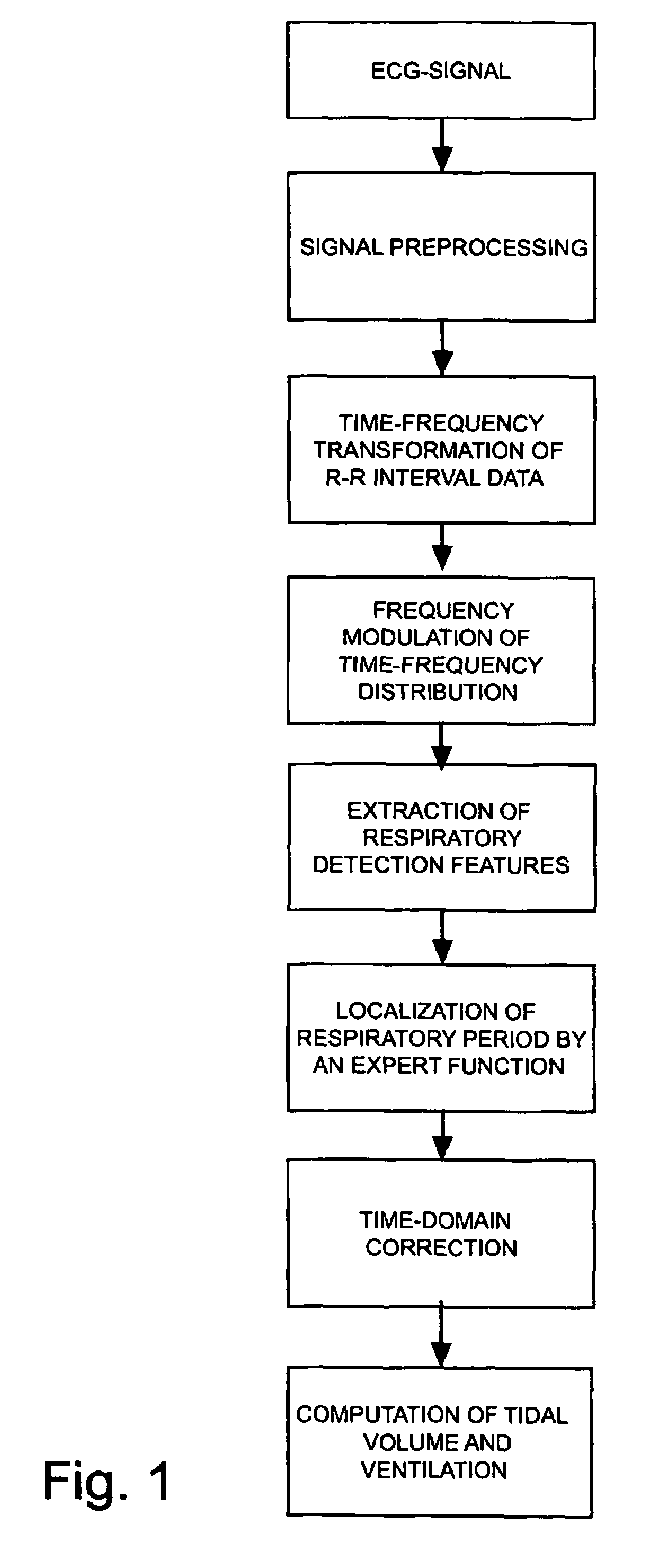
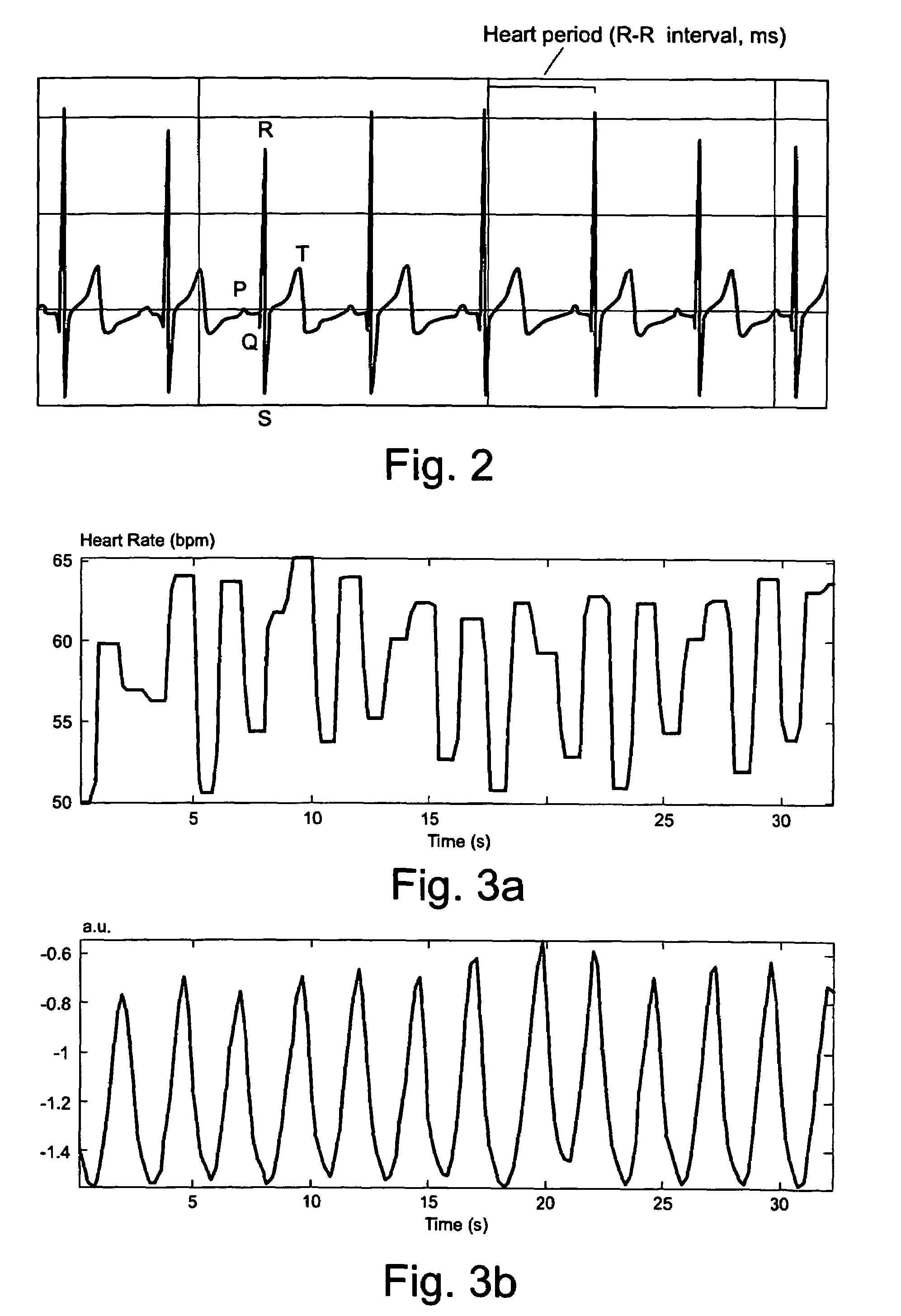
Procedure for deriving reliable information on respiratory activity from heart period measurement
The present invention describes a method of tracking minute ventilation from R-R intervals that are based on the acquisition of ECG signal. Sub-methods (RDF1), which are mainly based on heart rate variability, are used, wherein the respiratory frequency is determined from a pattern of rhythmic changes in heart beat data. The sub-methods (RDF1-n) are combined using an expert function, wherein each sub-method (RDF1-n) determines an estimate of the respiratory frequency.
Owner:FIRSTBEAT ANALYTICS OY
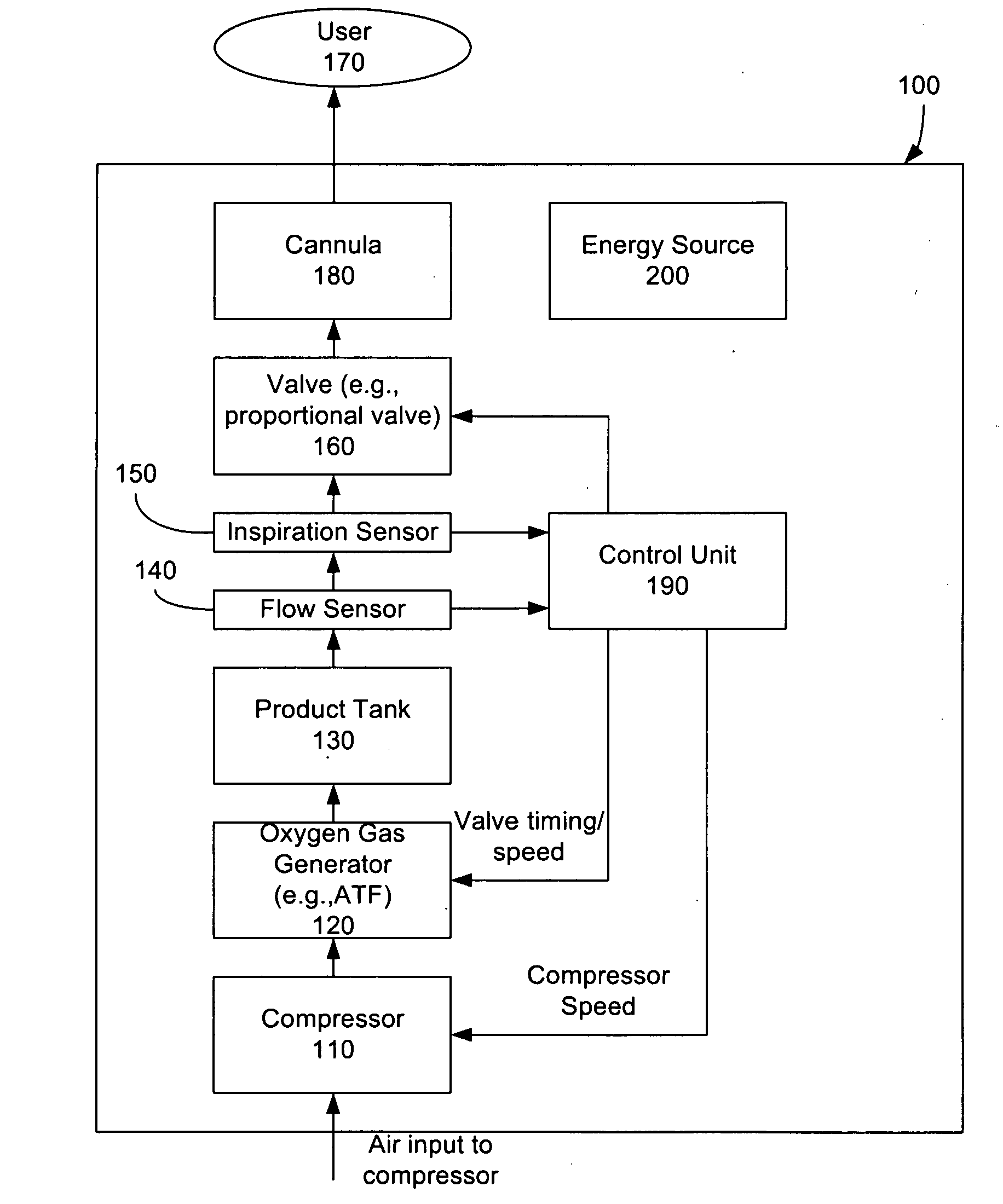
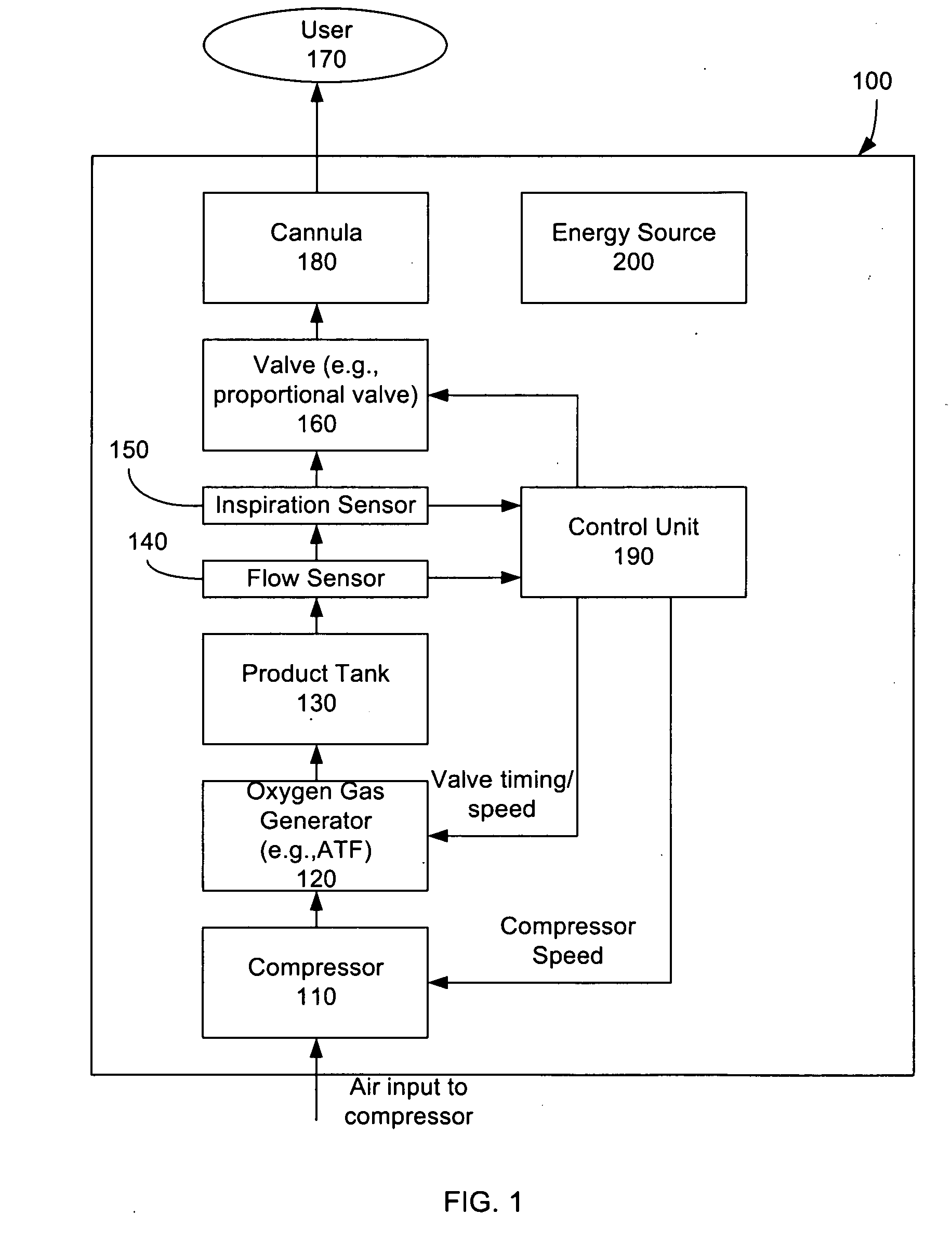
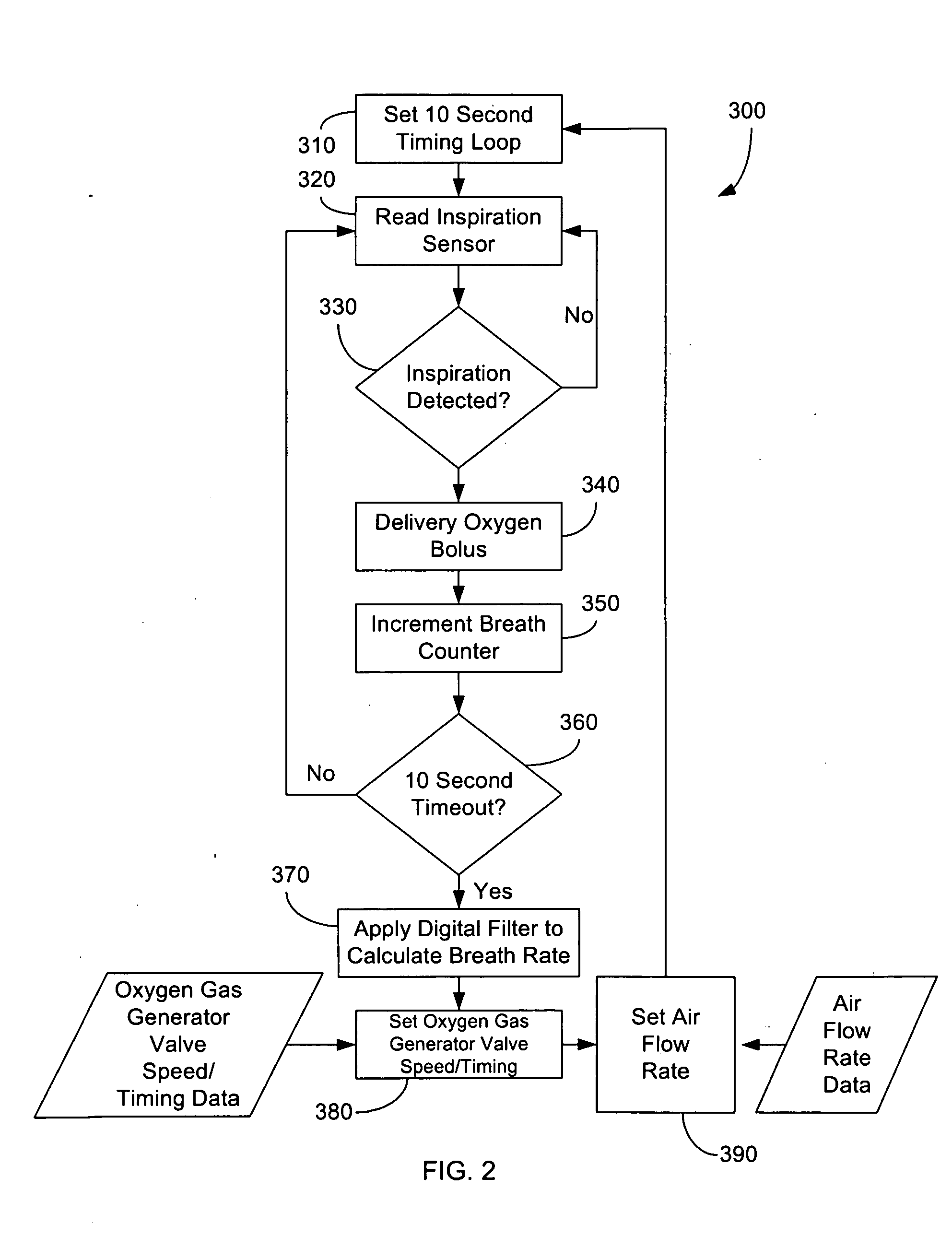
System and Method for Controlling Supply of Oxygen Based on Breathing Rate
A portable oxygen concentrator system weighing 4-20 pounds that is adapted to be readily transported by a user and deliver oxygen to the user includes a rechargeable energy source; a concentrator powered by said energy source and adapted to convert ambient air into concentrated oxygen gas for the user; an inspiration sensor that senses respiratory activity of the user, and produces a signal in response thereto; and a control unit that receives the signal in response to sensed respiratory activity, determines a breath rate based in part on the received signal in response to sensed respiratory activity and controls the portable oxygen concentrator system to deliver oxygen flow sufficient to meet oxygen demand of the user based at least in part on the determined breath rate.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Active implantable medical device equipped with means for the diagnosis of respiratory disorders, with sophisticated detection of respiratory cycles with artifacts
ActiveUS20050267380A1Easy to analyzeEliminate false positive falseRespiratory organ evaluationHeart stimulatorsDiseaseAutomatic control
An active implantable medical device comprising circuits for measuring trans-thoracic impedance and delivering an impedance signal varying with respiratory activity of a patient. A signal representative of the respiratory activity of the patient is delivered starting from the impedance signal, and circuits for diagnosing respiratory disorder analyze variations of the respiratory signal on a plurality of successive cycles to detect there a profile of predetermined variation in relation to a given respiratory disorder. The device also includes circuits for automatically controlling respiratory cycles with artifacts, able to identify in the impedance signal a jump of static impedance, and / or to identify in a respiratory cycle or in a sequence of respiratory cycles a predetermined singularity representative of a cycle with artifact.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Multi-lumen endotracheal tube
InactiveUS6918391B1Improve abilitiesEliminate requirementsTracheal tubesMale contraceptivesIntratracheal intubationEndotracheal tube
A multi lumen endotracheal tube having a balloon cuff to seal a patient's trachea during intubation. The ET tube having a main lumen for the exchange of respiratory and medicinal gases consequent to a medical procedure, a secondary lumen for inflation of the balloon cuff, and a tertiary lumen for transmission of sound waves via air medium contained therein, permitting ausculatory monitoring of a patient's breath sounds during intubation and subsequent monitoring of cardiac and respiratory activity after sealing of the ET tube. The ET tube is particularly a adapted for utilization by an anesthetist by including temperature sensor to permit remote monitoring of body core temperature and body cavity ausculation of cardiac and respiratory activity.
Owner:MOORE JOHNNY V
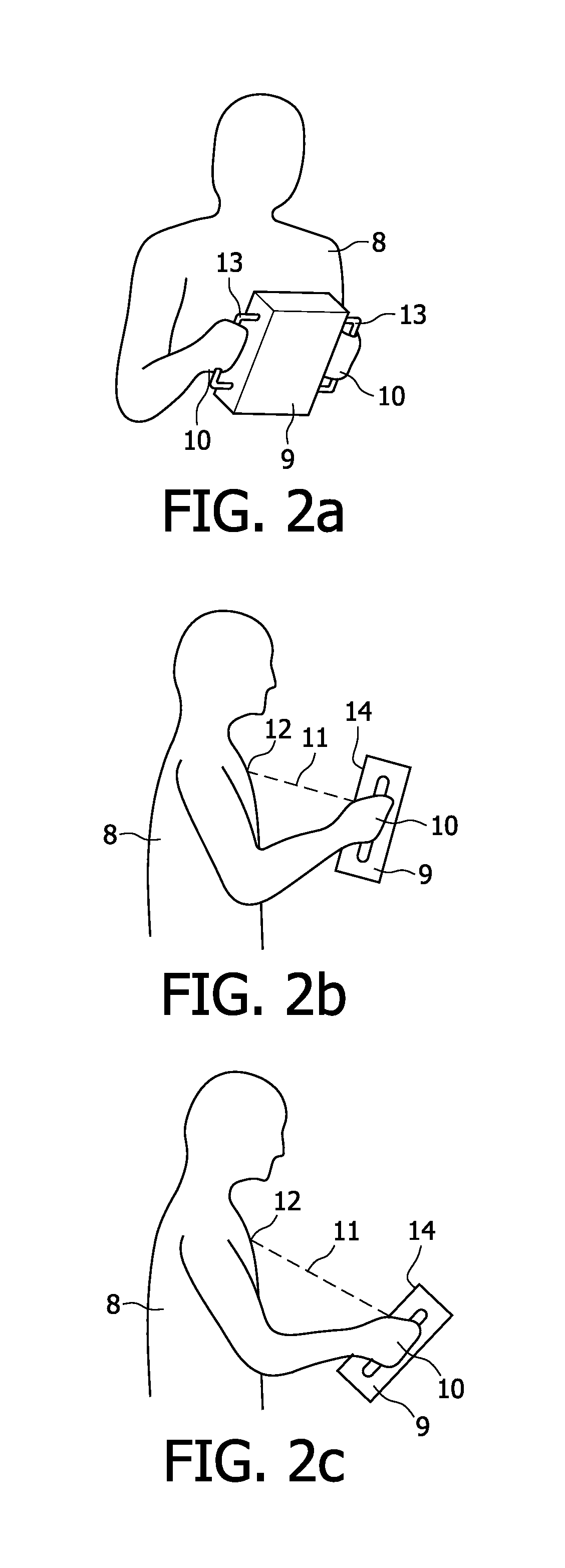
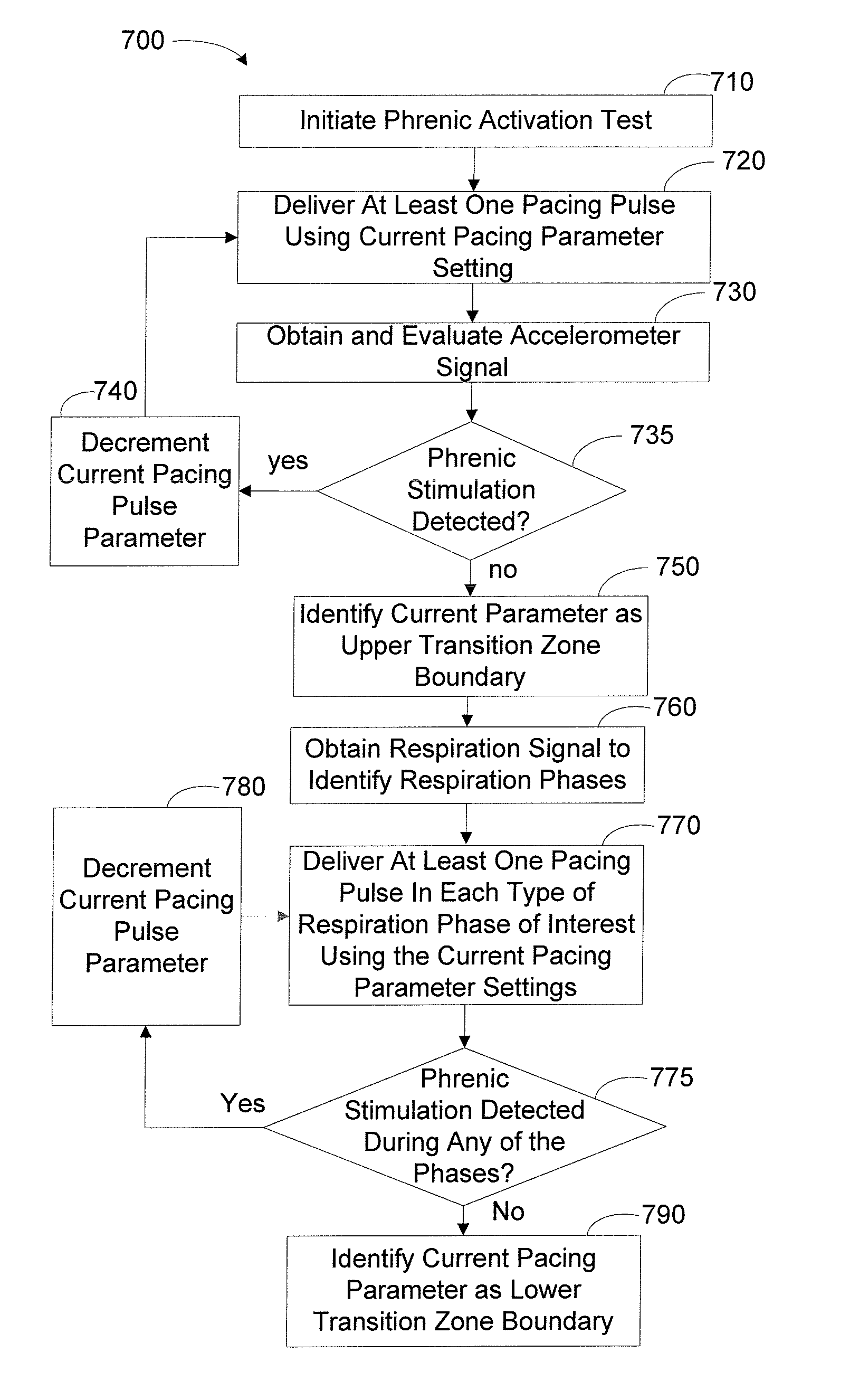
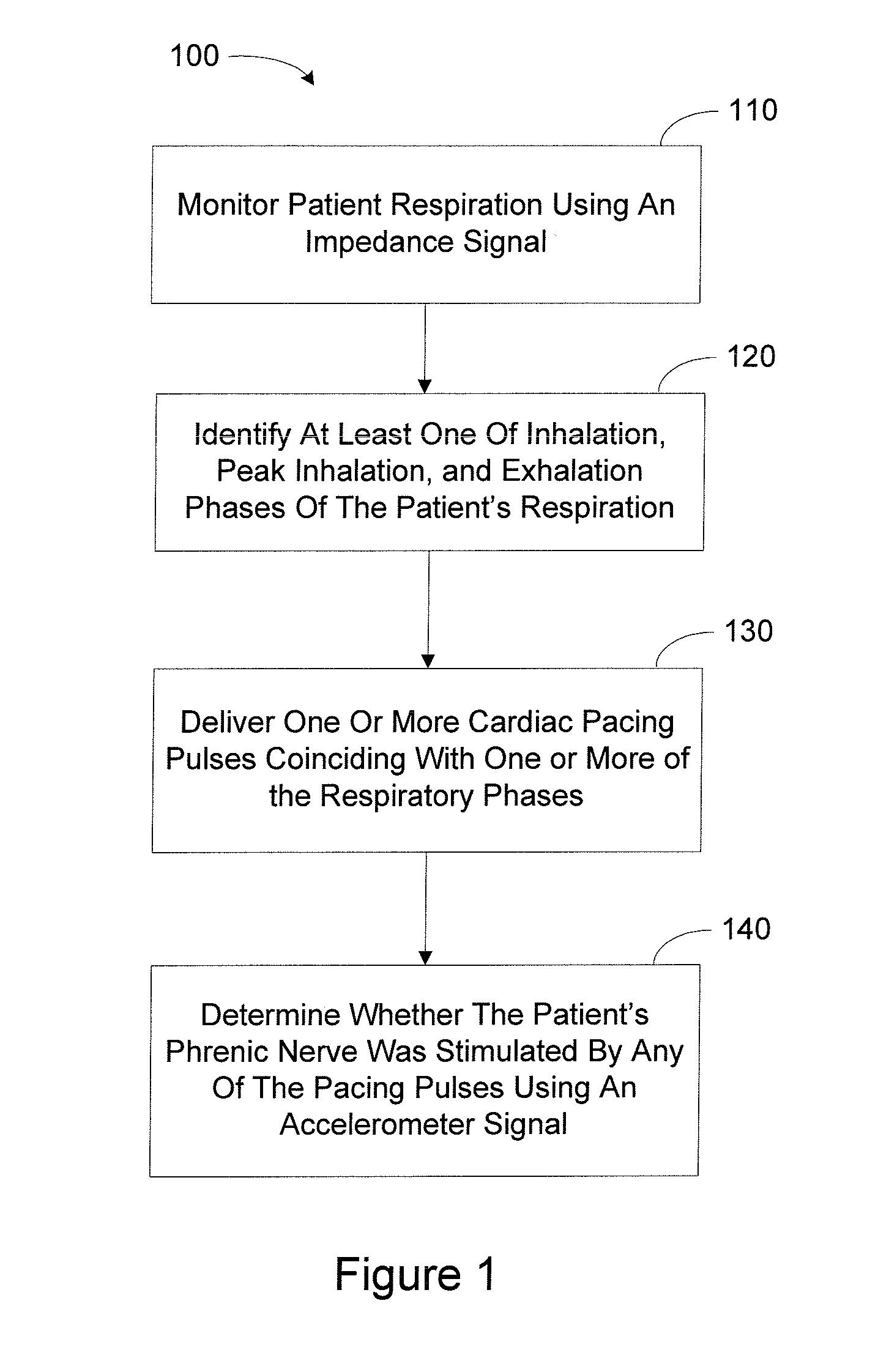
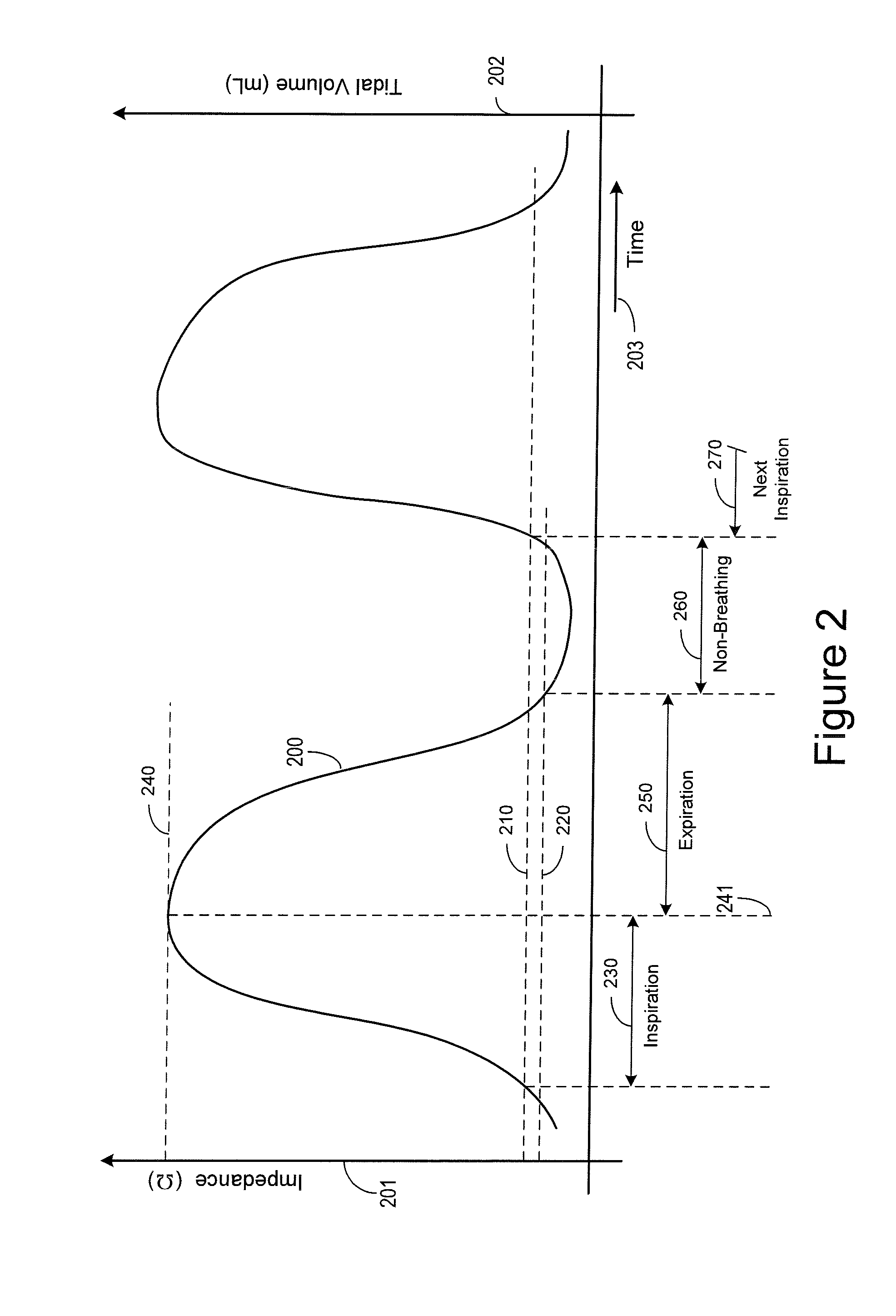
Method and Apparatus for Phrenic Nerve Activation Detection with Respiration Cross-Checking
The present invention concerns phrenic nerve activation detection algorithms for characterization of phrenic nerve activation and phrenic nerve activation avoidance in cardiac pacing therapy.Various embodiments concern receiving a respiration signal indicative of respiratory activity of the patient, identifying respiratory phases based on the respiration signal, delivering cardiac pacing pulses within each of the identified respiratory phases, receiving a phrenic nerve activation signal indicative of activation of the patient's phrenic nerve, analyzing the phrenic nerve stimulation signal to determine if one or more of the pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient, and determining if at least one of the delivered pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient based on the phrenic nerve activation signal indicating activation of the patient's phrenic nerve associated with delivery of the at least one cardiac pacing pulse.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Neck patch for tracheal cannulas or artificial noses having a speaking valve
ActiveUS20130213404A1Good respiratory activityImprove sealingTracheal tubesSurgical needlesIntratracheal intubationSurgery
There is provided a neck patch to be adhered on a tracheostoma, which is very light and has a good respiratory activity and an excellent sealing behavior when adhered on top of a tracheostoma in the neck of a patient. The neck patch is made of a thin, planar, flexible foil having a thickness of between 5 and 30 μm, which is adhesive on its proximal side only and has a centrically arranged hole on its distal side, and around which a hard, round plastic connector disk having a central recess is arranged, the neck patch further comprising a supporting frame that surrounds the outer edge of the film and is approximately five to ten times thicker than the film so that the neck patch can be positioned without being rolled together.
Owner:PRIMED HALBERSTADT MEDIZINTECHN
Portable water quality monitoring system
InactiveUS7666285B1Reliable and inexpensiveInexpensive and reliableImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsWater qualityEngineering
A disposable microsensor is designed, fabricated and tested for standard BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) measurements. A transparent Cyclic Olefin Copolymer (COC) substrate is used for sensor fabrication. Standard lithographic procedures in addition to techniques like screen printing and electroplating are used to fabricate the sensor. A microbial strain of Trichosporon Cutaneum is immobilized over one pair of sensor electrodes while the other is used as a reference. Depending on the respiratory activities of the microbial strain in different samples, the BOD values of the samples can be measured in terms of difference between the output signals. The sensor layer is attached to an injection-molded passive microfluidic channel on the top. Advantages of the BOD microsensor include, but are not limited to, fast BOD measurement, disposability because of its low cost, chemically inert polymer substrate, flow-through sample injection scheme and integration of on-chip optics.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Gas permeable membrane
InactiveUS20080034964A1Composition is limitedReduce concentrationCombination devicesSemi-permeable membranesAtmospheric airPolyamide
A gas permeable membrane comprising a thin polymeric coating on a microporous backing, said gas permeable membrane being permeable permitting for oxygen and carbon dioxide at different flow rates, wherein the gas permeable membrane is made from a copolymer of a polyether and a polyamide enables the achievement of a controlled atmosphere in a cargo region, wherein the membrane is able to obtain and hold low concentrations of carbon dioxide and of oxygen in the atmosphere in the cargo region and to produce an “ideal” or optimum storage atmosphere which will ensure a retardation of respiratory activity within the container.
Owner:MAERSK CONTAINER IND
Wearable respiratory inductance plethysmography device and method for respiratory activity analysis
InactiveUS20160150982A1Not hinder movementExcellent quality measurementEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterRespiratory inductance plethysmographyEngineering
It is described a system and a method for respiratory activity analysis comprising the use of Respiratory Inductance Plethysmography (RIP). In particular, a wearable system for extracting physiological parameters of a person by measuring at least one plethysmographic signal is disclosed. The system comprises: a wearable garment fitting a body part of the person; at least one wire supported by or embedded into the garment, each wire forming a loop around the body part when the person wears the garment for measuring a plethysmographic signal; and an electronic device supported by or fixed on the garment and including a Colpitts oscillator connected to each wire loop, wherein the Colpitts oscillator has an optimal frequency band from 1 MHz to 15 MHz for extracting the plethysmographic signal measured by each wire, the electronic device converting analog information measured by the Colpitts oscillator into digital analyzable information.
Owner:CARRE TECH
Body motion monitor
A system for monitoring the respiratory activity of a subject, which comprises one or more movement sensors, applied to the thorax of a subject, for generating first signals that are indicative of movement of the thorax of the subject; a receiver for receiving the first generated signals during breathing motion of the subject; and one or more computing devices in data communication with the receiver, for analyzing the breathing motion. The computing device is operable to generate a first breathing pattern from the first signals; divide each respiratory cycle experienced by the subject and defined by the first pattern into a plurality of portions, each of the portions delimited by two different time points and calculate, for each of the plurality of portions of a given respiratory cycle of the first pattern, a slope representing a thorax velocity; derive, from the given respiratory cycle of the first pattern, a pulmonary air flow rate of the subject during predetermined portions of the respiratory cycle; compare between corresponding portions of the first pattern and average flow rates during different phases of the breathing cycle, to calibrate a thorax velocities of the subject with pulmonary air flow rates; and determine respiratory characteristics of the subject for subsequent respiratory cycles experienced by the subject, based on a calculated thorax velocity and the calibration.
Owner:BREATHEVISION
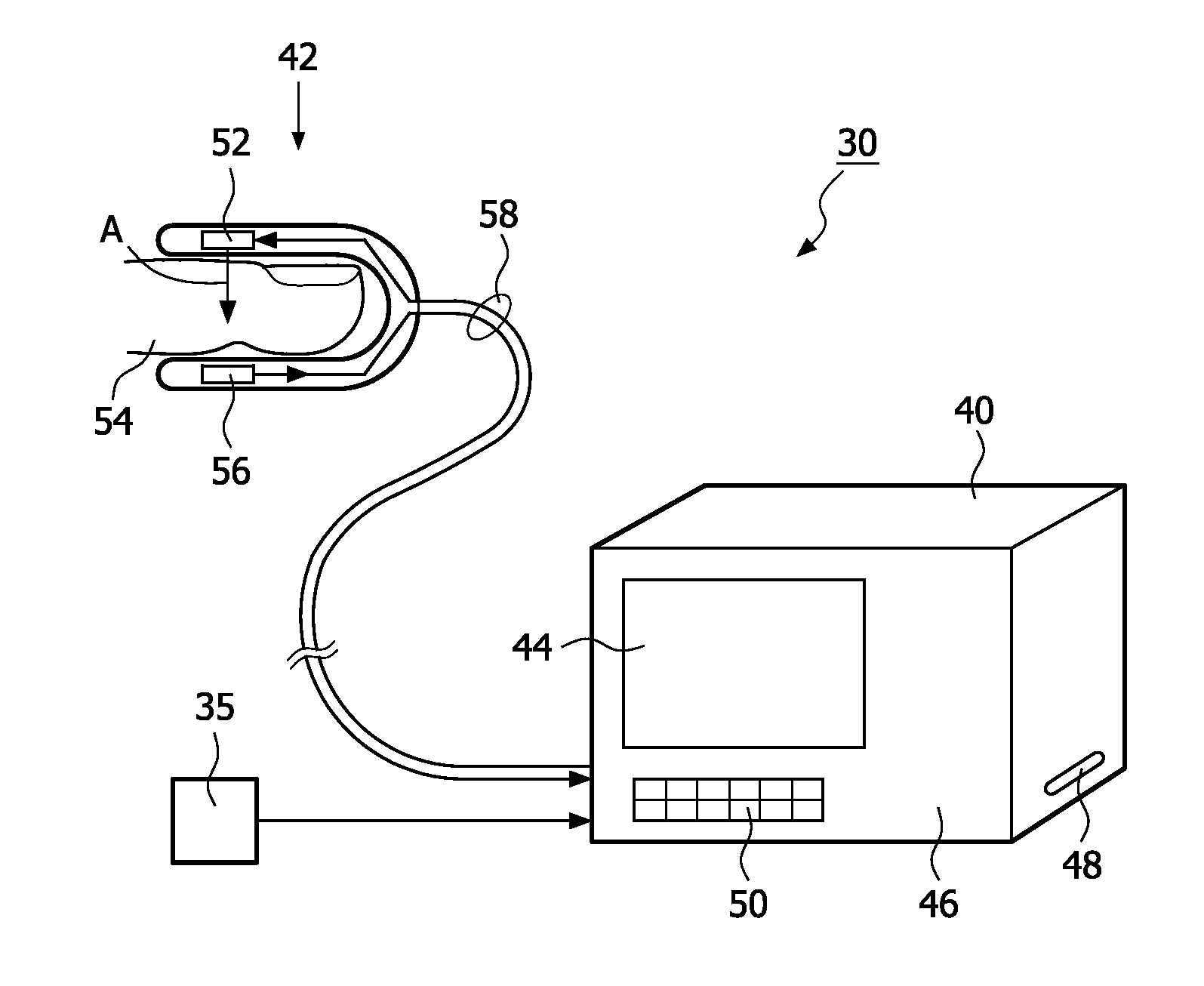
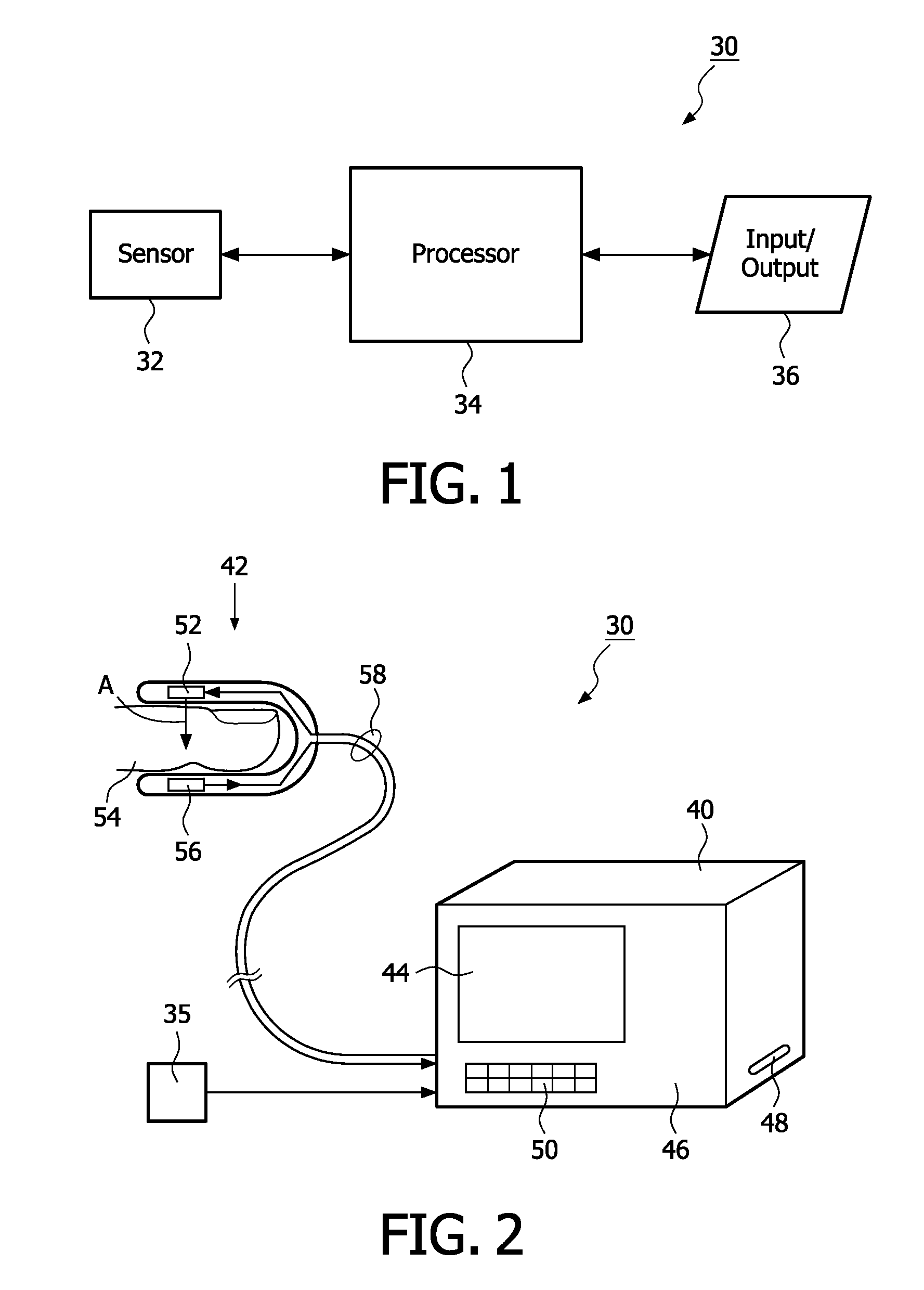
Contactless respiration monitoring of a patient and optical sensor for a photoplethysmography measurement
InactiveUS20110054277A1Reliable and fail-safe photoplethysmography measurementCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationRespiration monitoringHand held devices
The invention also relates to an optical sensor for a photoplethysmography measurement, comprising a light unit 1 with a light emitter 2 for emitting light into tissue of a patient 8 and / or a light detector 3 for detecting a part of the emitted light after interaction with the tissue, wherein the light unit is embedded in an elastic material 4. The invention further relates to a device for contactless respiration monitoring of a patient 8, comprising: a distance sensor for consecutively detecting the temporal distance variations relative to the patient's chest 12, preferably based on electromagnetic waves; and a calculating unit for determining the breathing activity based on the detected temporal distance variations. The invention is especially useful for providing a reliable and easy to use possibility for simultaneously monitoring respiration action, blood pressure and heart rate with a handheld device which can be used for spot-checking the vital parameters of patients in hospitals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for phrenic nerve activation detection with respiration cross-checking
The present invention concerns phrenic nerve activation detection algorithms for characterization of phrenic nerve activation and phrenic nerve activation avoidance in cardiac pacing therapy.Various embodiments concern receiving a respiration signal indicative of respiratory activity of the patient, identifying respiratory phases based on the respiration signal, delivering cardiac pacing pulses within each of the identified respiratory phases, receiving a phrenic nerve activation signal indicative of activation of the patient's phrenic nerve, analyzing the phrenic nerve stimulation signal to determine if one or more of the pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient, and determining if at least one of the delivered pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient based on the phrenic nerve activation signal indicating activation of the patient's phrenic nerve associated with delivery of the at least one cardiac pacing pulse.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Interconnecting Microfluidic Package, Fabrication Method and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20100175821A1Inexpensive and reliableElectrolysis componentsCircuit elementsEngineeringTrichosporon cutaneum
A disposable microsensor is designed, fabricated and tested for standard BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) measurements. A transparent Cyclic Olefin Copolymer (COC) substrate is used for sensor fabrication. Standard lithographic procedures in addition to techniques like screen printing and electroplating are used to fabricate the sensor. A microbial strain of Trichosporon Cutaneum is immobilized over one pair of sensor electrodes while the other is used as a reference. Depending on the respiratory activities of the microbial strain in different samples, the BOD values of the samples can be measured in terms of difference between the output signals. The sensor layer is attached to an injection-molded passive microfluidic channel on the top. Advantages of the BOD microsensor include, but are not limited to, fast BOD measurement, disposability because of its low cost, chemically inert polymer substrate, flow-through sample injection scheme and integration of on-chip optics.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Procedure for deriving reliable information on respiratory activity from heart period measurement
ActiveUS7460901B2Avoid the needReliable informationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalRR interval
The present invention describes a method of tracking minute ventilation from R-R intervals that are based on the acquisition of ECG signal. Sub-methods (RDF1), which are mainly based on heart rate variability, are used, wherein the respiratory frequency is determined from a pattern of rhythmic changes in heart beat data. The sub-methods (RDF1-n) are combined using an expert function, wherein each sub-method (RDF1-n) determines an estimate of the respiratory frequency.
Owner:FIRSTBEAT ANALYTICS OY
Gas permeable membrane
A gas permeable membrane comprising a thin polymeric coating on a microporous backing, said gas permeable membrane being permeable permitting for oxygen and carbon dioxide at different flow rates, wherein the gas permeable membrane is made from a copolymer of a polyether and a polyamide enables the achievement of a controlled atmosphere in a cargo region, wherein the membrane is able to obtain and hold low concentrations of carbon dioxide and of oxygen in the atmosphere in the cargo region and to produce an “ideal” or optimum storage atmosphere which will ensure a retardation of respiratory activity within the container.
Owner:MAERSK CONTAINER IND
Method for measuring physiological stress
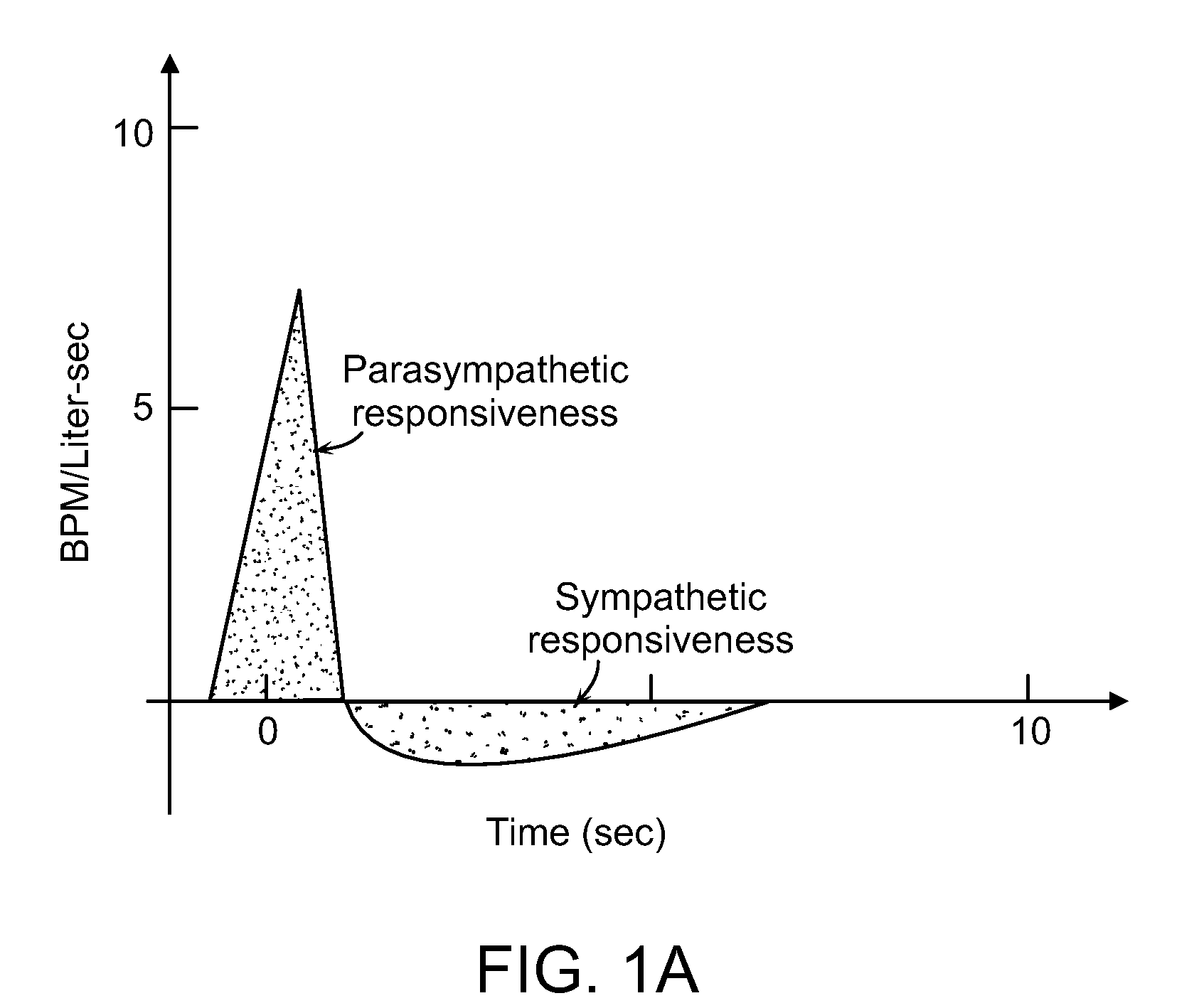
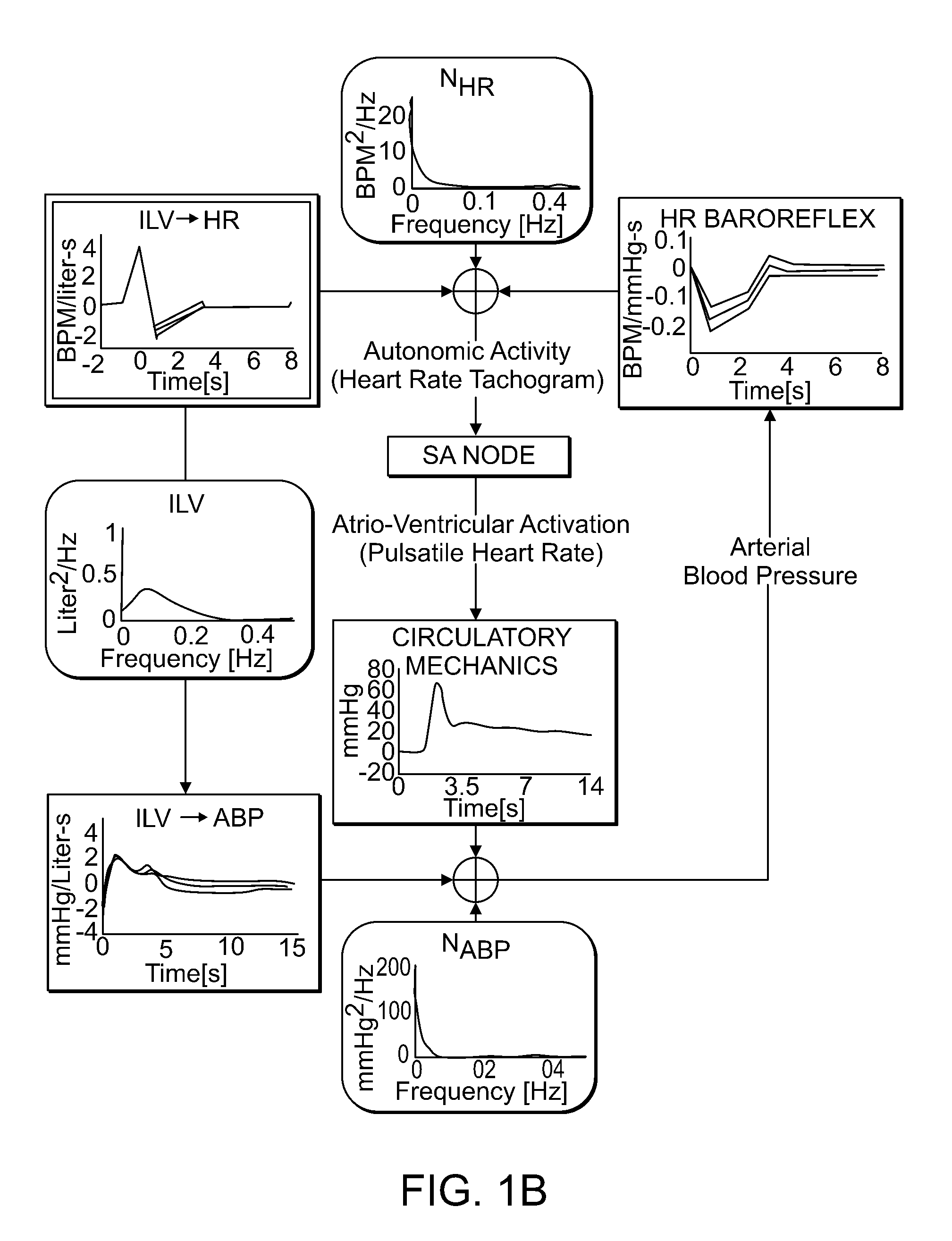
Method for determining physiological stress. One or more physiologic signals in a subject is detected. The one or more physiologic signals are processed to obtain one or more processed signals. The subject's stress level is estimated from the one or more processed signals. The one or more physiological signals may include the electrocardiogram, instantaneous lung volume or other signal reflecting respiratory activity, or the arterial blood pressure or other signal reflecting cardiovascular activity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Contactless respiration monitoring of a patient and optical sensor for a photoplethysmography measurement
InactiveCN102014737AEasy to useAccurate measurementRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEngineeringHand held devices
The invention also relates to an optical sensor for a photoplethysmography measurement, comprising a light unit (1) with a light emitter (2) for emitting light into tissue of a patient (8) and / or a light detector (3) for detecting a part of the emitted light after interaction with the tissue, wherein the light unit is embedded in an elastic material (4). The invention further relates to a device for contactless respiration monitoring of a patient (8), comprising: a distance sensor for consecutively detecting the temporal distance variations relative to the patient's chest (12), preferably based on electromagnetic waves; and a calculating unit for determining the breathing activity based on the detected temporal distance variations. The invention is especially useful for providing a reliable and easy to use possibility for simultaneously monitoring respiration action, blood pressure and heart rate with a handheld device which can be used for spot- checking the vital parameters of patients in hospitals.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Combination physiologic sensor
A multi sensor module especially designed for use in sleep-study applications includes a PVDF film piezoelectric transducer enclosed between an upper layer of a single-sided adhesive tape strip and a lower layer of a double-sided adhesive tape strip. Also adhesively affixed to the upper single-sided adhesive tape strip, but not overlaid by the lower double-sided adhesive tape strip are first and second conductive electrodes. The combination sensor module is adapted to be adhesively affixed to the chest area of a person and further included in an extension of the PVDF strip that is adapted to overlay the suprasternal notch of a person for producing signals responsive to respiratory activity of the person.
Owner:DYMEDIX
Portable kit, device and method for the execution of cardiopulmonary tests under strain, with the use of a normal bicycle
InactiveUS20080200308A1Reduced dimensionLow costRespiratory organ evaluationSpace saving gamesCardiopulmonary bypassEngineering
A device for the execution of cardiopulmonary tests under strain includes a device for measuring the respiratory activity of a user and physical exercise equipment to be used in combination with the measuring device. The physical exercise equipment is a portable training tool, to be used in combination with a normal bicycle in stationary position.
Owner:PEDRINI +1
Inhaler
ActiveUS20150053203A1Reliable indicationSimple and robust designMedical devicesMedical atomisersNostrilSurgery
This invention relates to an inhaler with a respiration indicator, whereby the inhaler has a chamber wall forming a chamber and a dispensing device for fluidic connection of the chamber to a bodily opening, preferably a nostril, whereby the respiration indicator has a wall section of the chamber wall or is formed in this way, whereby the wall section is designed to indicate a respiratory activity by deformation and / or movement.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
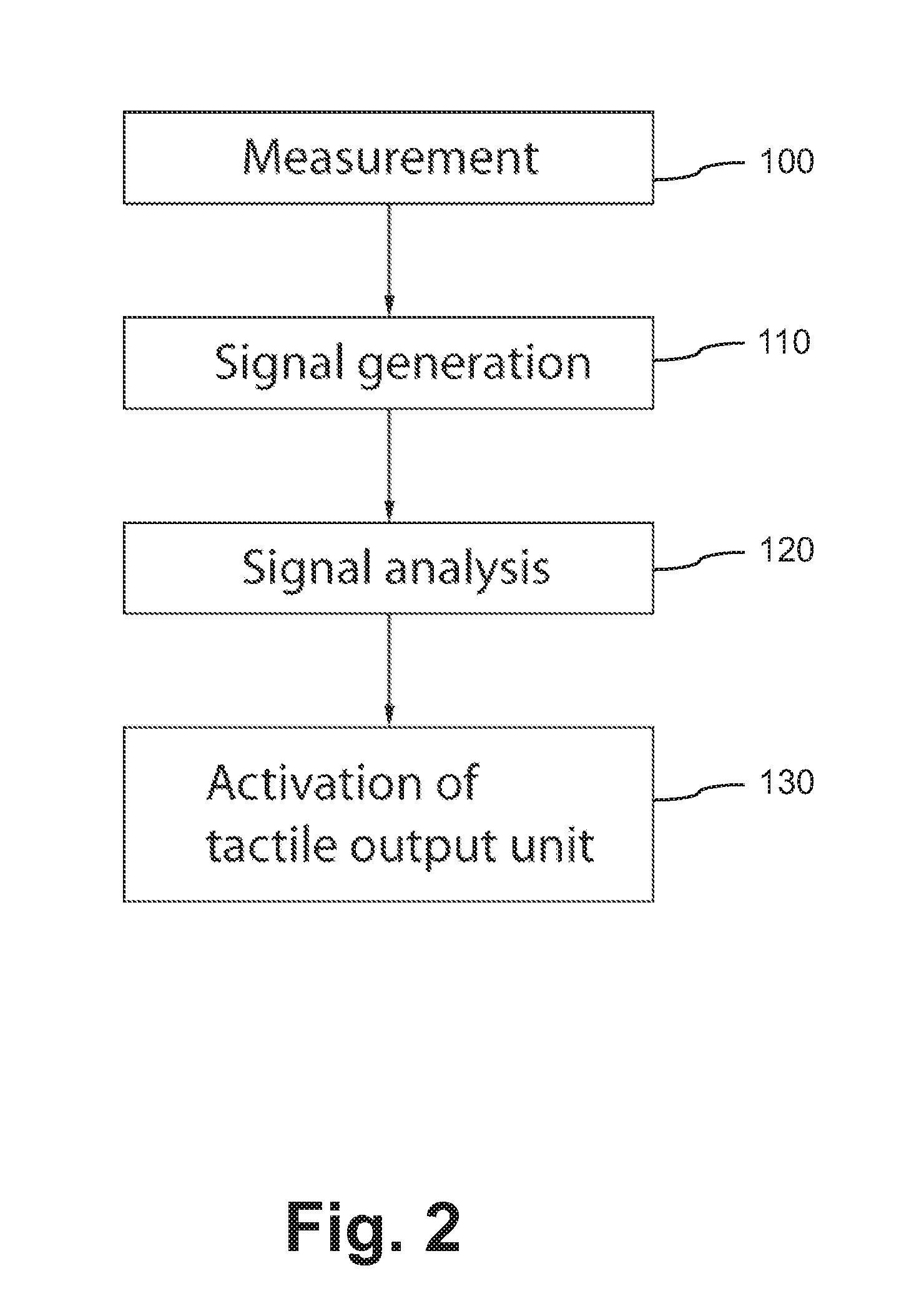
Method of automatically controlling a respiration system and a corresponding respirator
ActiveUS8109269B2Convenient for patientAccurate operationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory muscleAutomatic control
A method of automatically controlling a respiration system for proportional assist ventilation with a control device and with a ventilator. An electrical signal is recorded by electromyography with electrodes on the chest in order to obtain a signal uemg(t) representing the breathing activity. The respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is determined by calculating it in the control unit from measured values for the airway pressure and the volume flow Flow(t) as well as the patient's lung mechanical parameters. The breathing activity signal uemg(t) is transformed by means of a preset transformation rule into a pressure signal pemg(uemg)(t)) such that the mean deviation of the resulting transformed pressure signal pemg(t) from the respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is minimized. The respiratory effort pressure ppat(t) is determined as a weighted mean according to ppat(t)=a·pmus(t)+(1−a)·pemg(t), where a is a parameter selected under the boundary condition 0≦a≦1.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
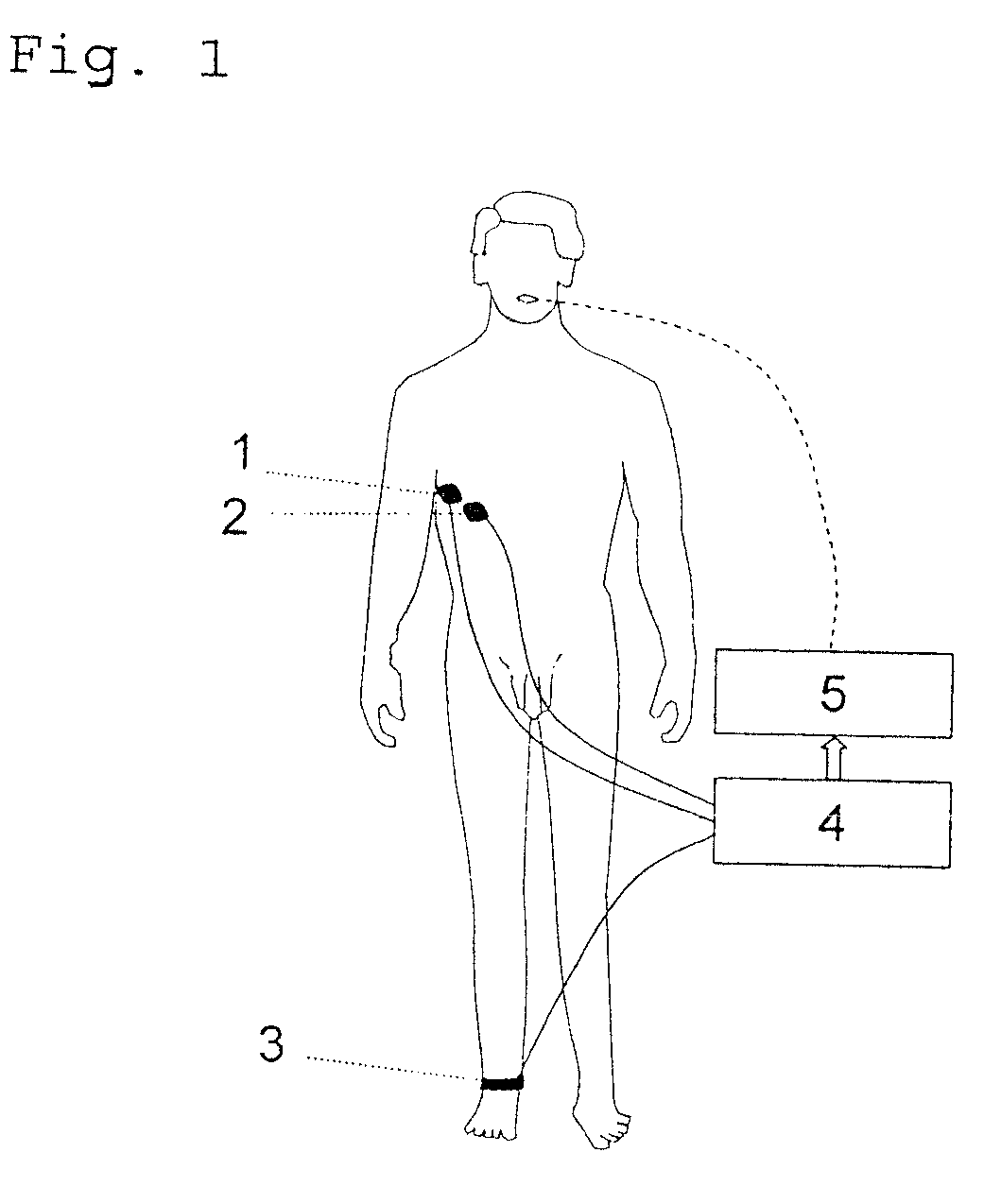
Breath pacing device and method for packing the respiratory activity of a subject
InactiveUS20130310636A1High acceptanceCompact designRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEngineeringRespiratory activity
The present invention is related to a breath pacing device (10) for pacing the respiratory activity of a subject, comprising an output unit (12) for outputting a sequence of output signals, a control unit (16) provided to control the output unit, and an input unit (14) connected to or integrated into the output unit for generating an input signal related to a respiration characteristic of a subject. The control unit is provided to control the length of the sequence at least based on characteristics of the input signal. The invention is further related to a corresponding method for pacing the respiratory activity of a subject.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
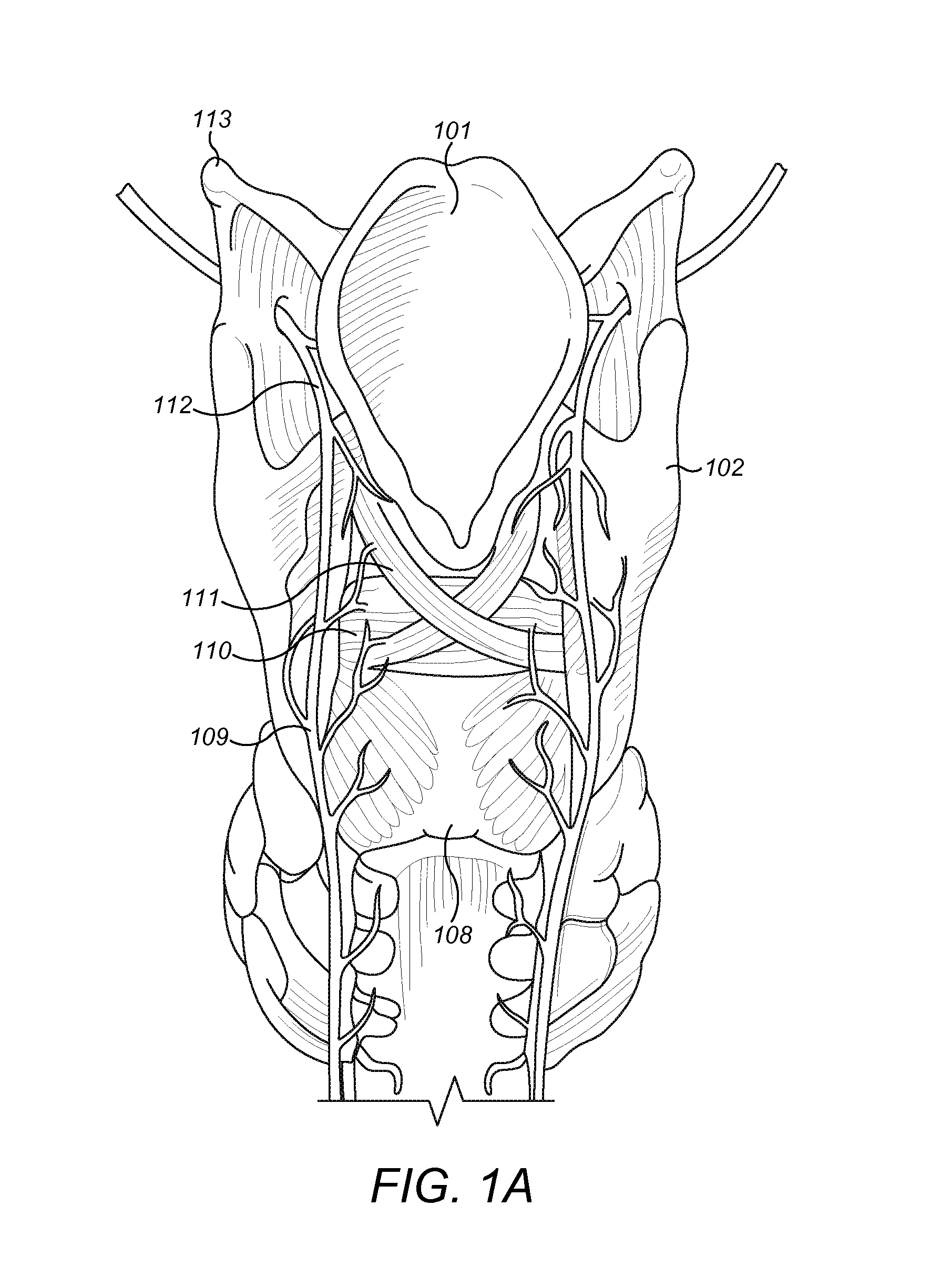
Acceleration Sensors For Recording Of Triggered Respiratory Signals In Neurostimulators
InactiveUS20150283381A1Easy to breatheElectrotherapyAuscultation instrumentsRadiologyRespiratory signal
A respiration implant system includes a pacing processor configured to receive a respiration signal and a movement signal to generate a respiration pacing signal that is synchronized with the detected respiration activity. The pacing processor is configured to optimize system power consumption over time by using multiple respiration sensing modes that reflect activity of the movement signal over time.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Flip Tray
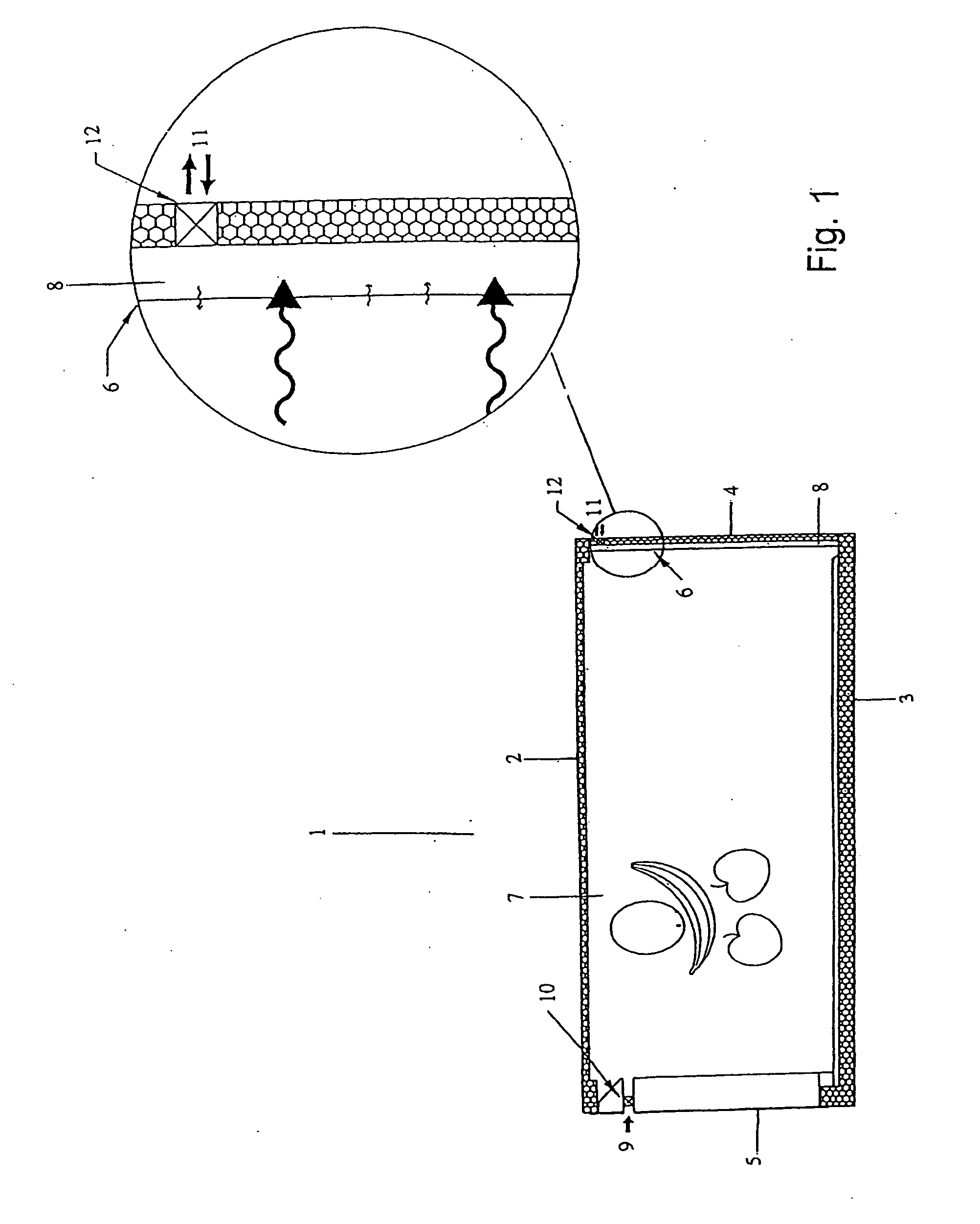
InactiveUS20090155435A1Extended shelf lifeEnsure air circulationClosuresInternal framesControl mannerEngineering
A flip tray is provided that includes a transparent, compartmentalized container body and a flexible sealing sheet sealed to partition walls and to the peripheral rim of the compartmentalized container body. Plant material with active respiratory activity such as fruits and vegetables are disposed in the compartments of the transparent container body. Each of the compartments exchanges respiratory gases through the micro-perforated sealing sheet individually in a controlled manner. A tray having a completely flat bottom is secured to the container body so as to underlie the flexible sealing sheet and includes peripheral vent conformations.
Owner:MANN PACKING
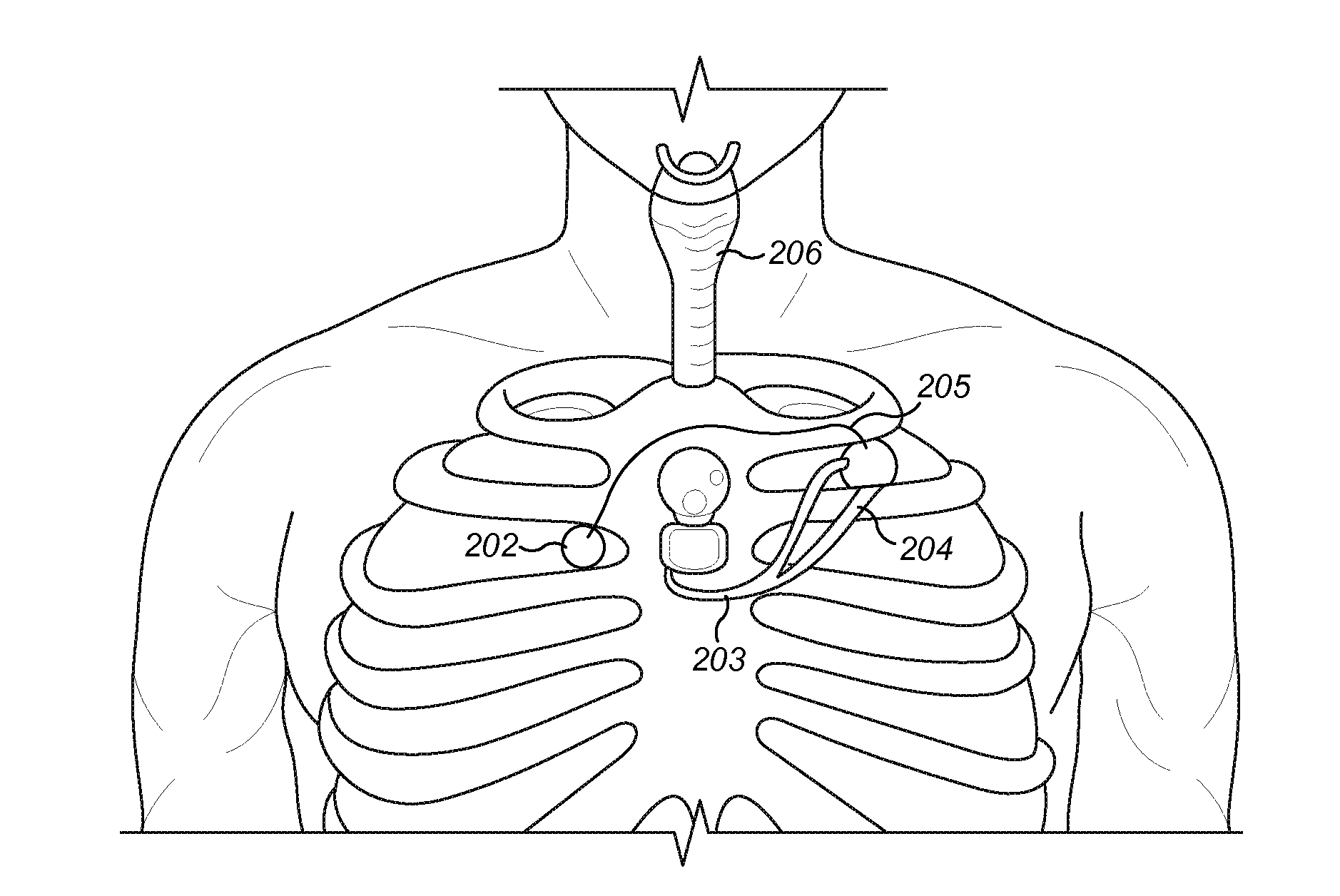
Detection and the treatment of ventilatory disorders during sleep for an active implantable medical device, in particular a pacemaker
InactiveUS7395115B2Inhibiting consequenceHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringHypopneaMedicine
An active medical device that is able to detect and treat ventiliatory activity disorders during sleep. This device measures the patient's respiratory activity, delivers a signal of the ventiliatory activity of the patient, analyzes the ventiliatory activity signal, and detects the occurrence of hypopneas. The analysis includes calculating at regular intervals a sliding average of the signal of ventiliatory activity, comparing the values of the successive sliding averages thus calculated, and detecting an occurrence of an hypopnea when, for two successive sliding averages, the difference between the averages crosses a predetermined threshold of comparison. When the device is one that also delivers cardiac stimulation pulses, it is advantageously envisaged to modify an operating parameter, in particular the stimulation rate based on the detected hypopnea, to treat the hypopnea.
Owner:ELA MEDICAL
Reusable airflow sensor
InactiveUS20050096560A1Wood working apparatusRespiratory organ evaluationPlastic materialsEngineering
A reusable airflow sensor for monitoring respiratory activity of patients in a sleep lab setting comprises a polyvinylidne fluoride (PVDF) film totally encased within a thermally conductive plastic material that is non-hydroscopic and therefore impervious to moisture which allows resterilization without comprising the electrical performance of the sensor.
Owner:GIFTCARDS LLC +1
Breath pacing system and method for pacing the respiratory activity of a subject
ActiveUS9392963B2Direct monitoringReduce frequencyRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsRespiratory activityBreathing process
To provide a breath pacing system and a corresponding method for pacing the respiratory activity of a subject that provide the possibility to adapt the output signal to the respiration characteristics of the subject automatically and effectively a breath pacing system (10) for pacing the respiratory activity of a subject and a respective method is proposed, comprising: an input unit (14) for generating or determining an input signal related to a respiration characteristic of a subject, a signal analyzing unit (16) provided to recognize a signal pattern within the input signal, and an output unit (12) for outputting output signals corresponding to a desired breathing sequence, wherein said output unit (12) is provided to be activated, upon a starting signal, to output a sequence of output signals comprising a signal pattern related to a previously recognized signal pattern.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com