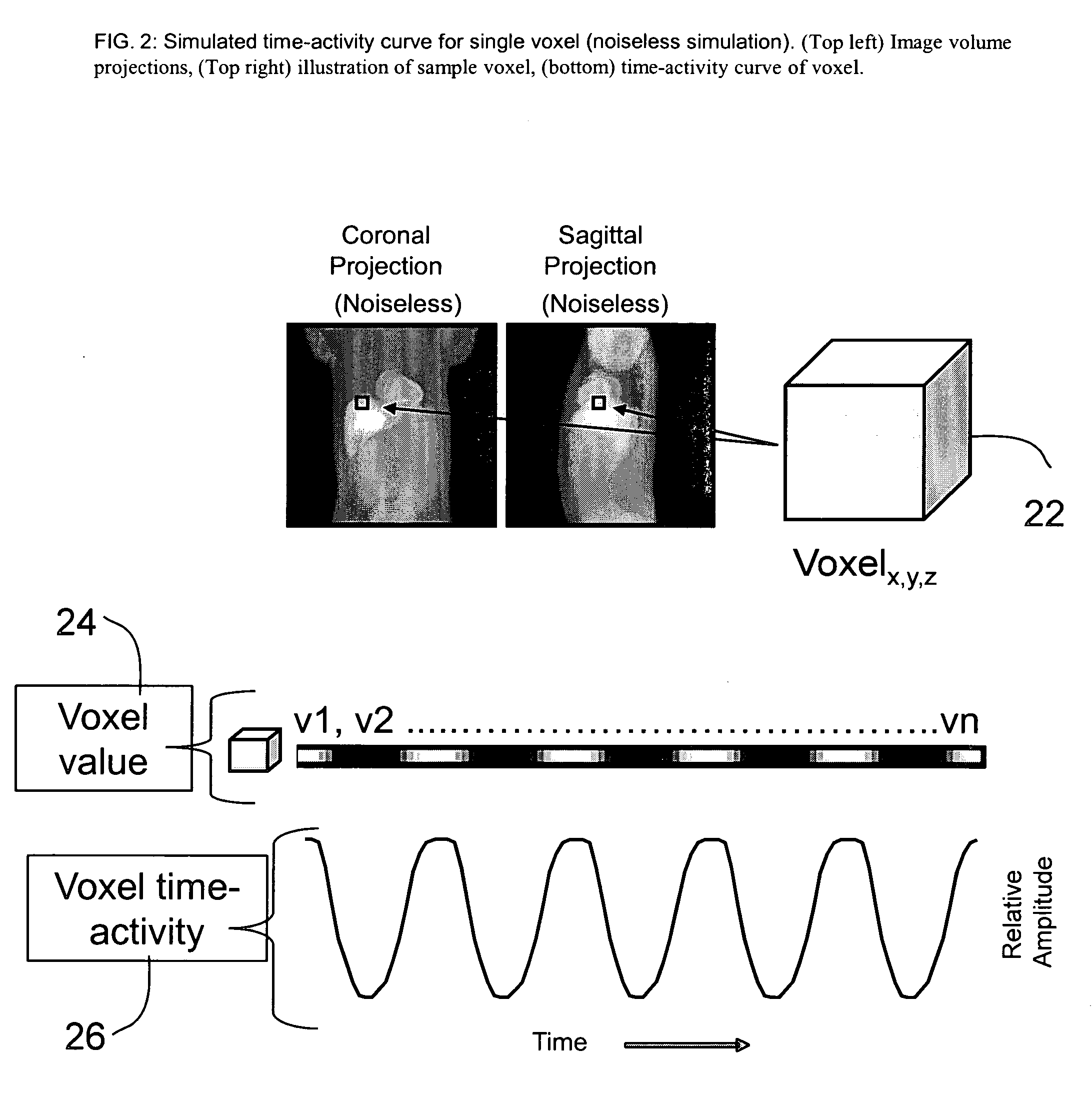
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Respiratory phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
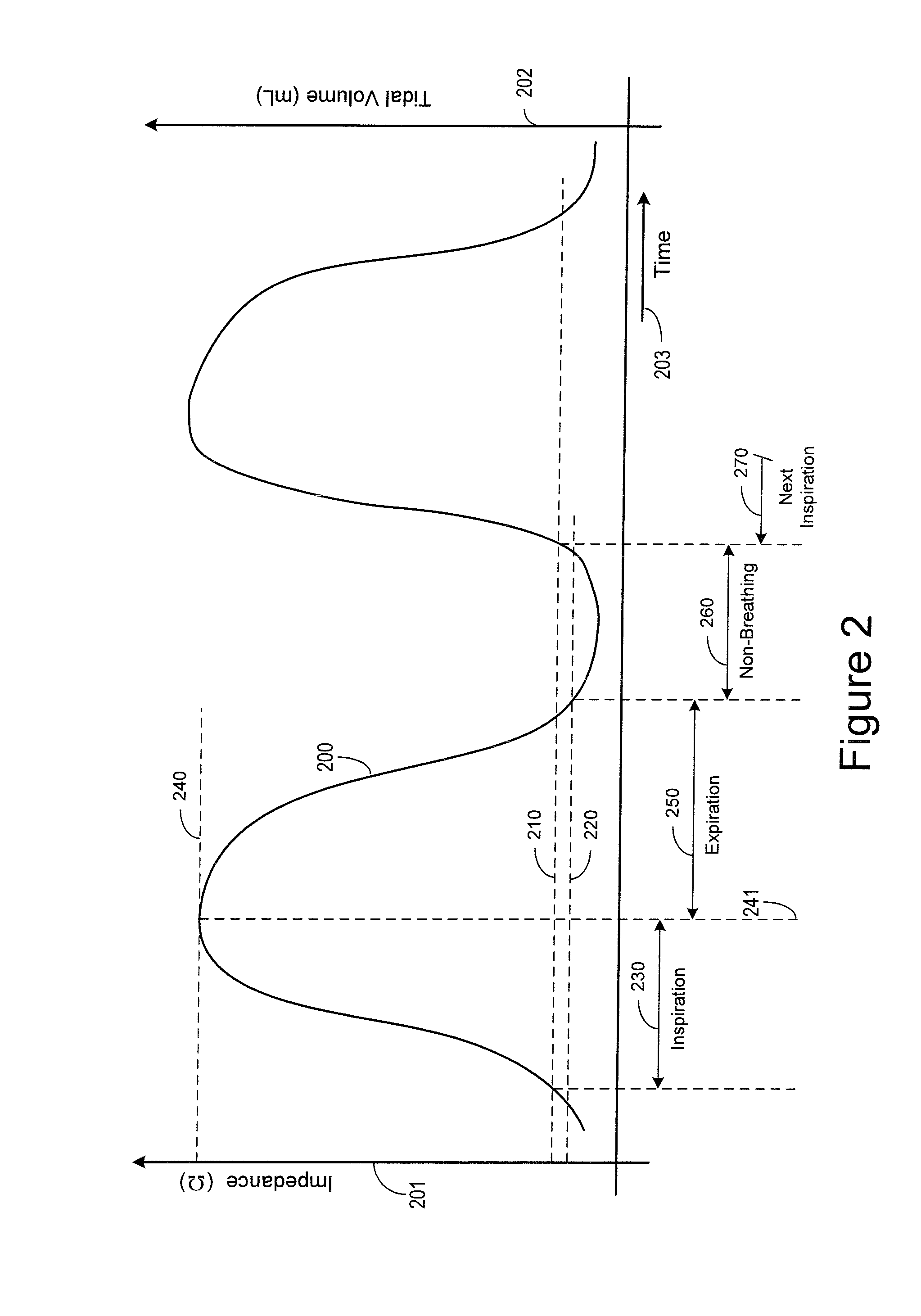
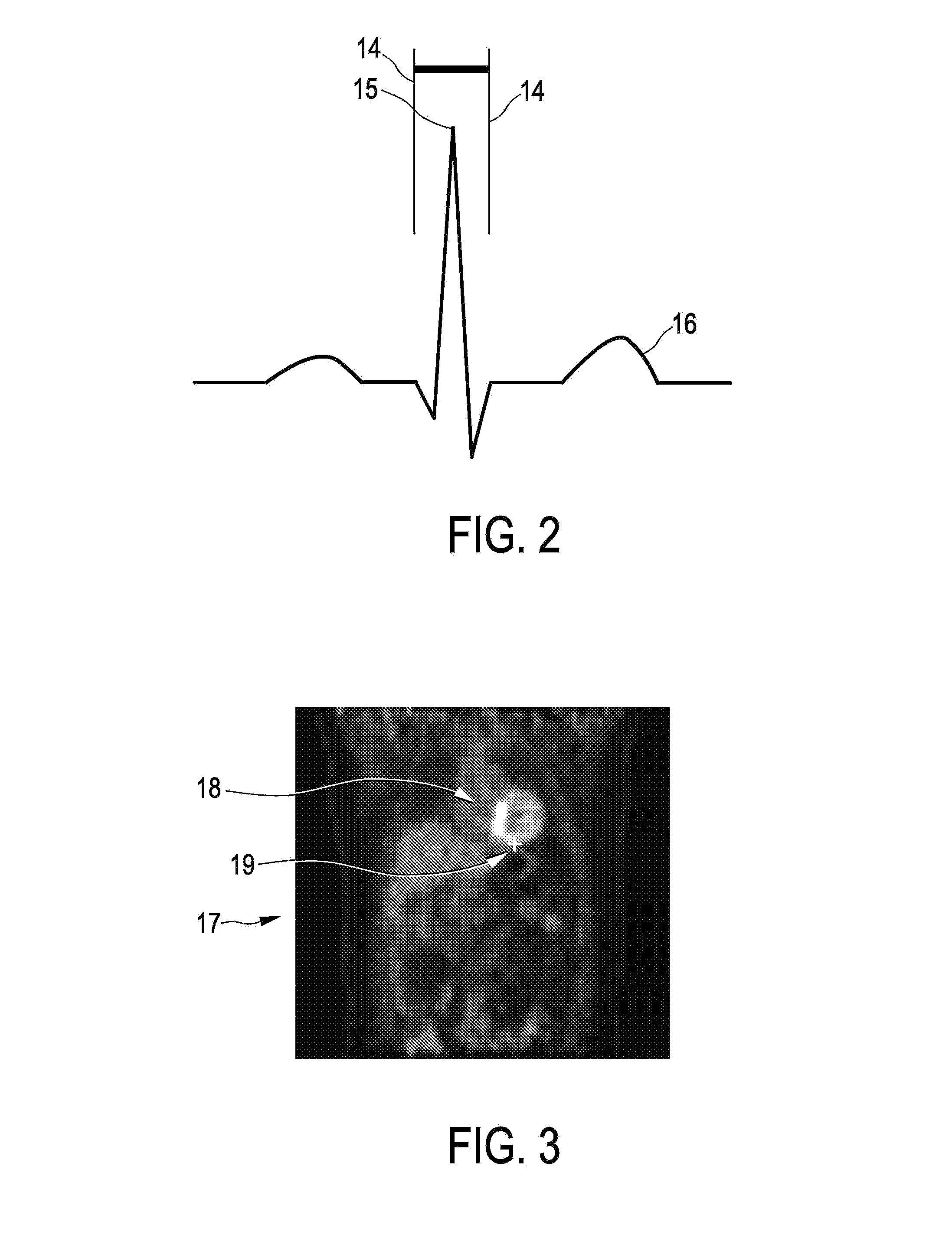
Expiratory phase. the portion of the respiratory cycle that involves exhalation, or moving air out of the lungs. In normal circumstances, it is passive.
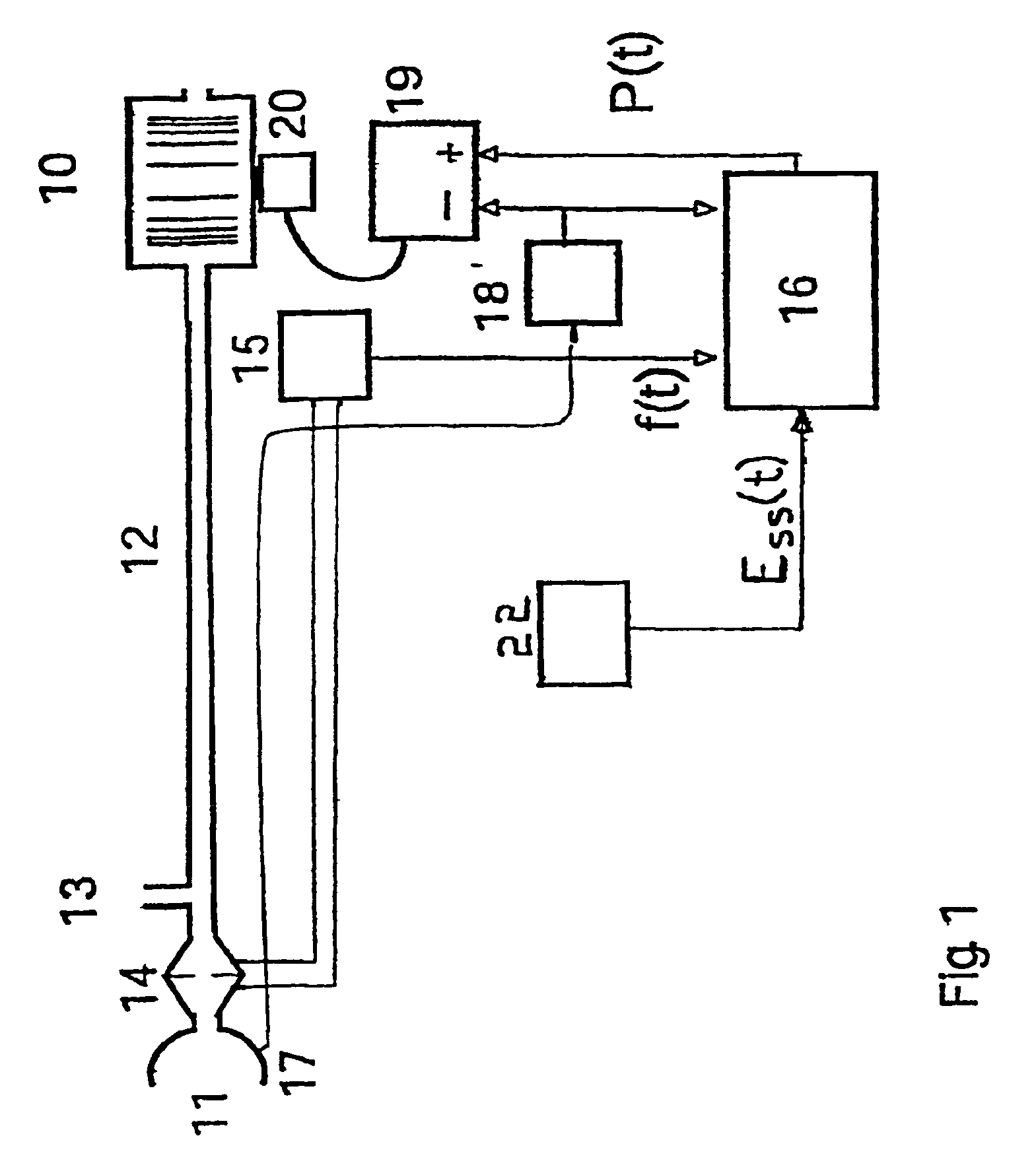
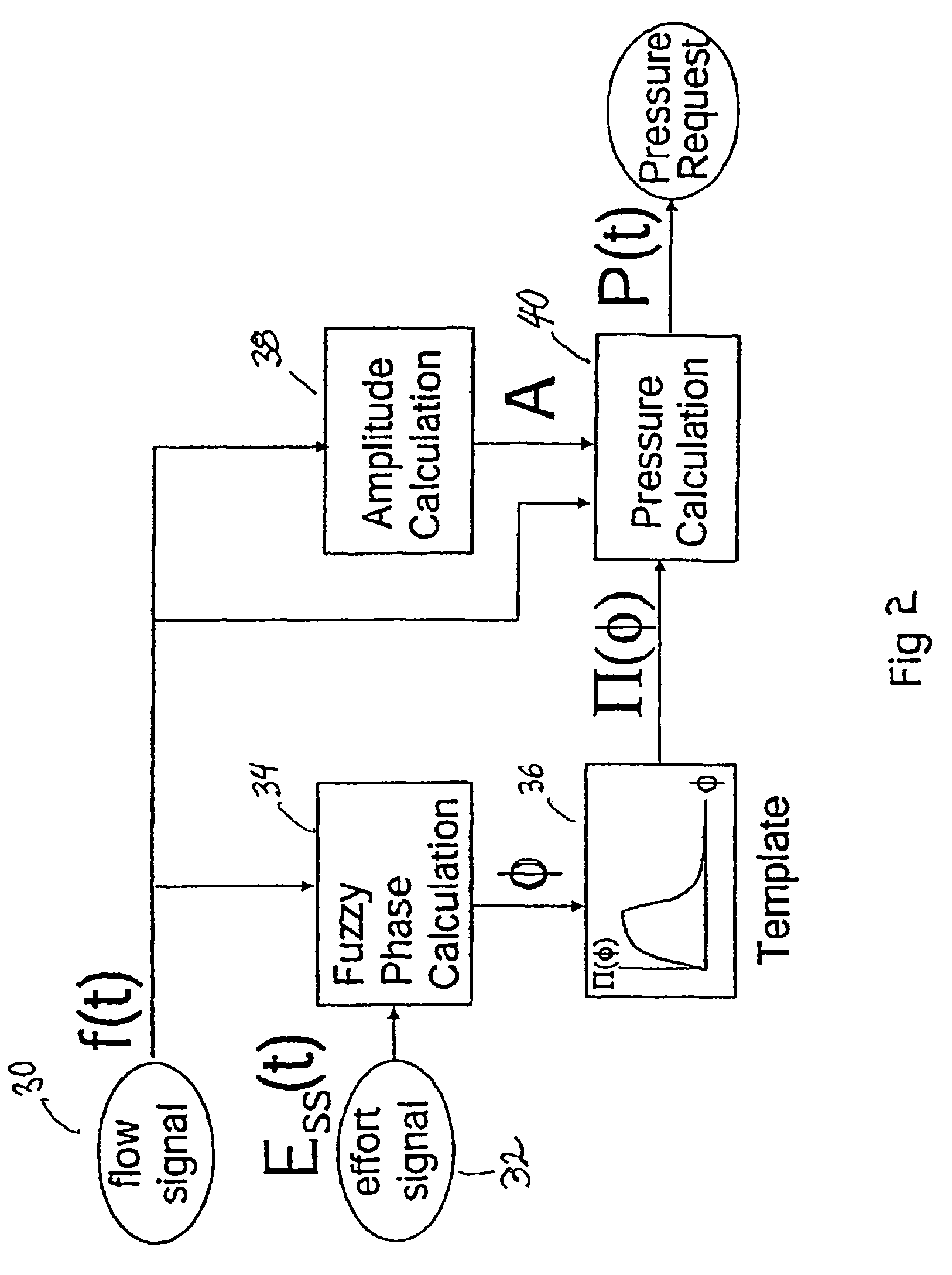
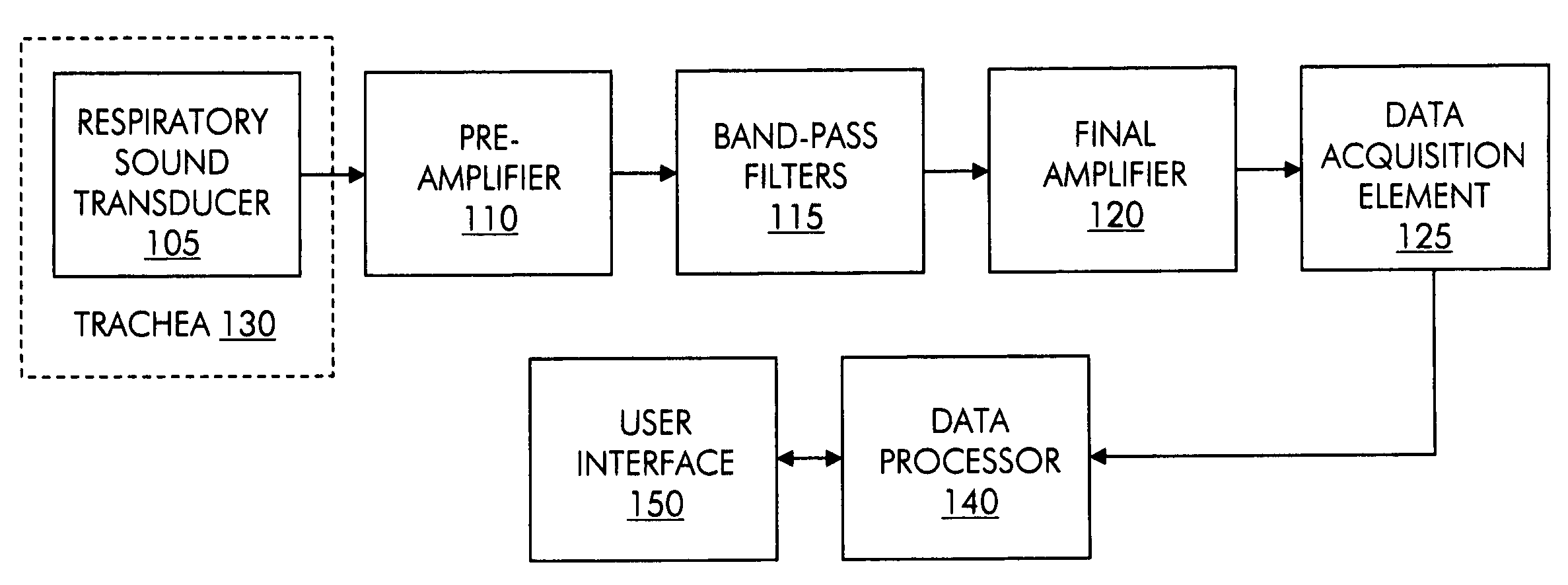
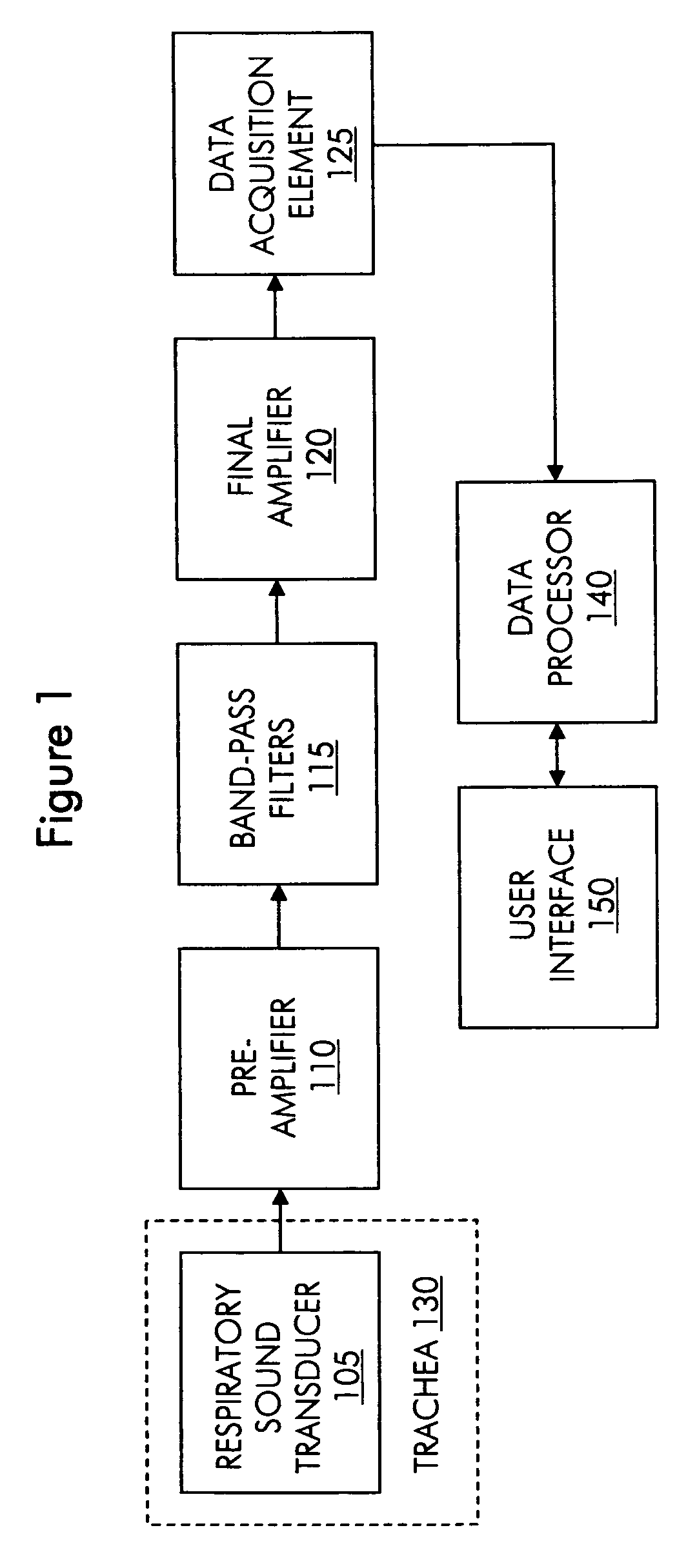
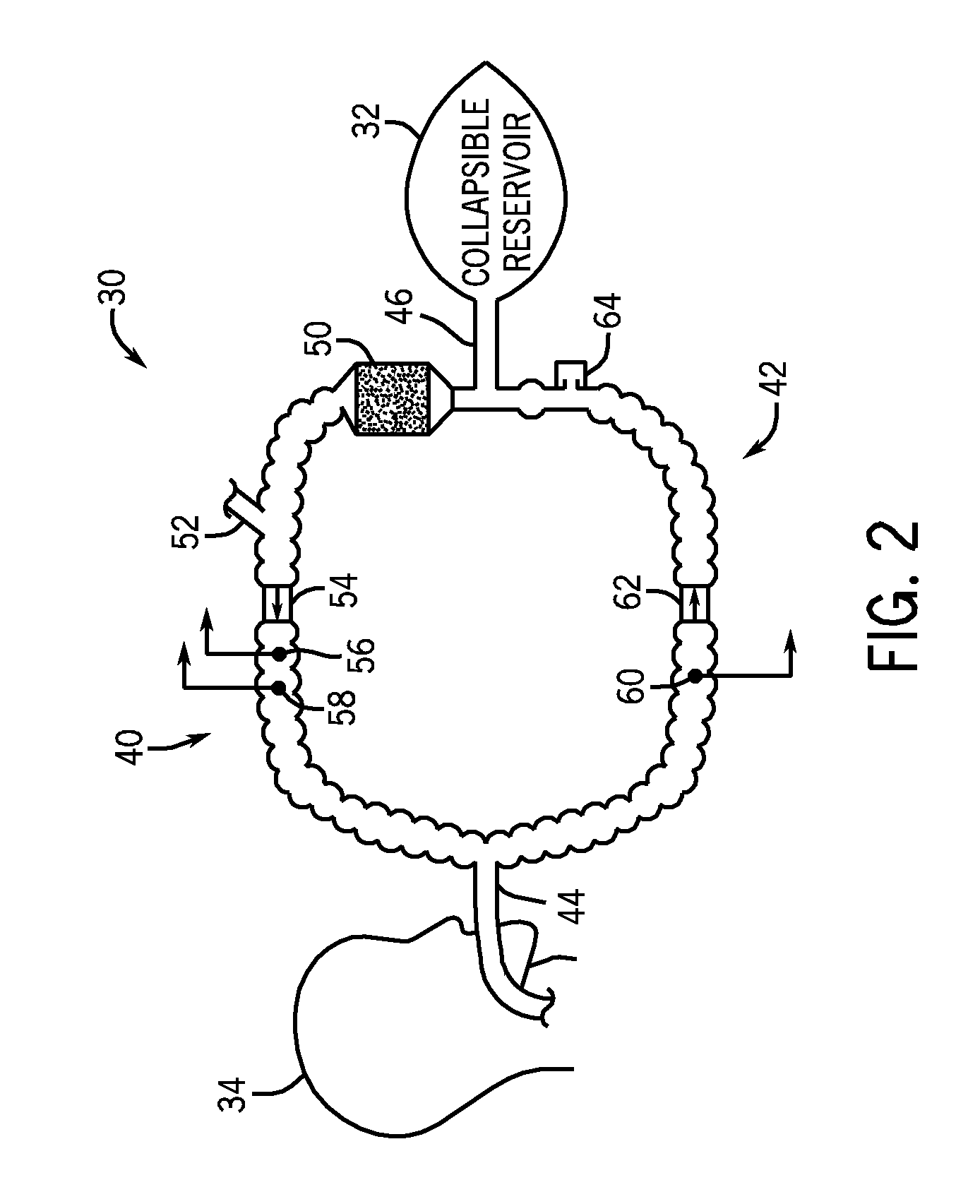
Patient-ventilator synchronization using dual phase sensors
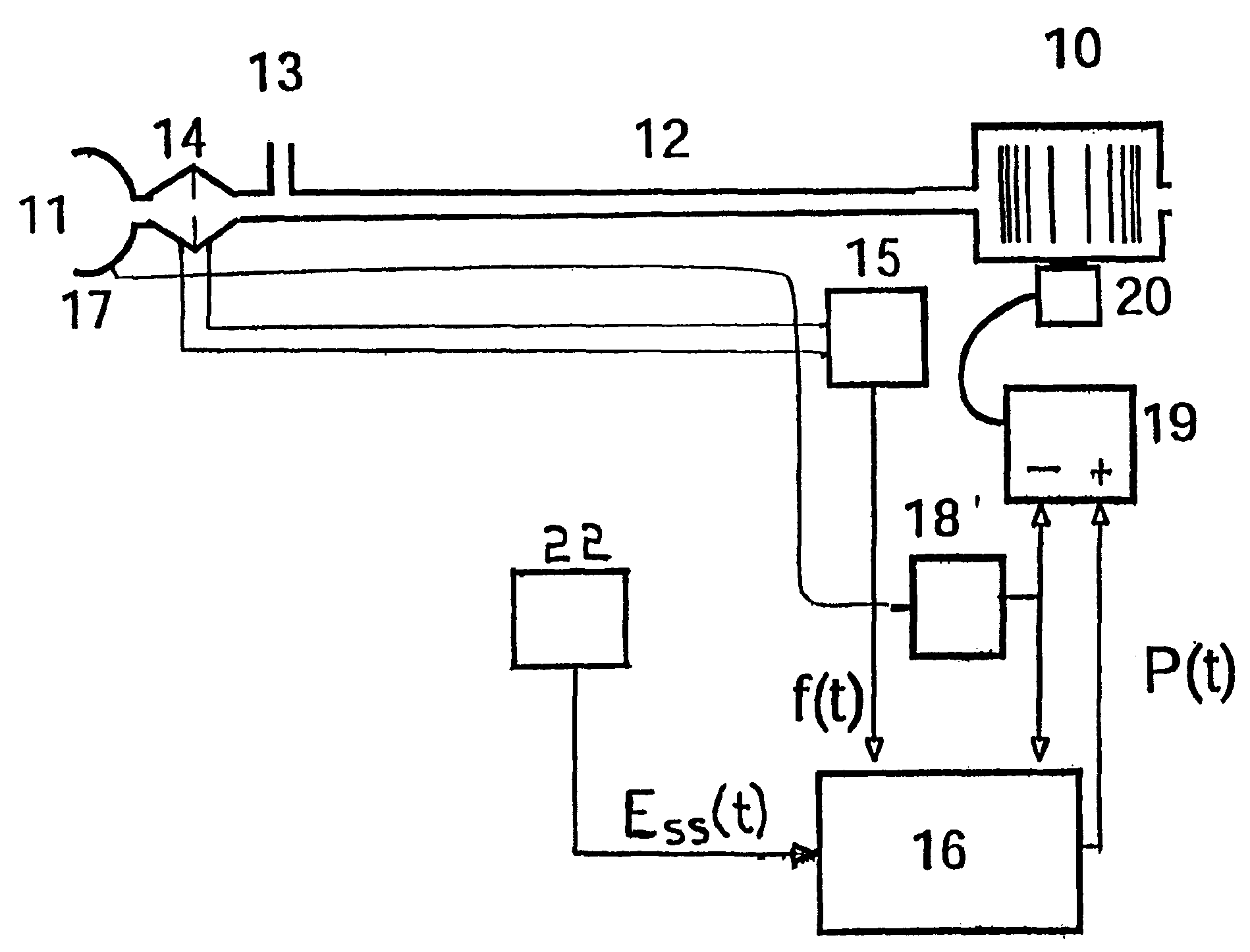
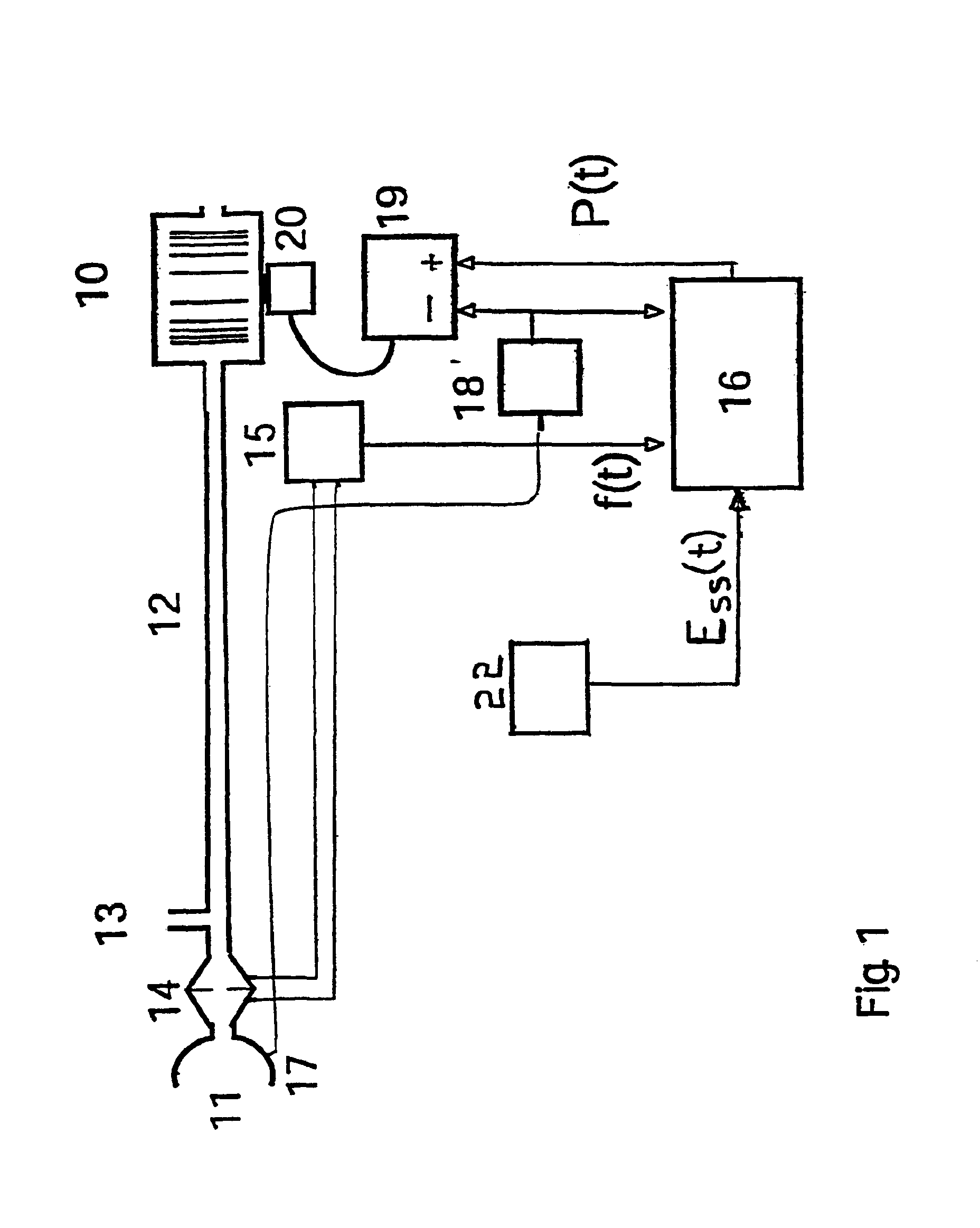
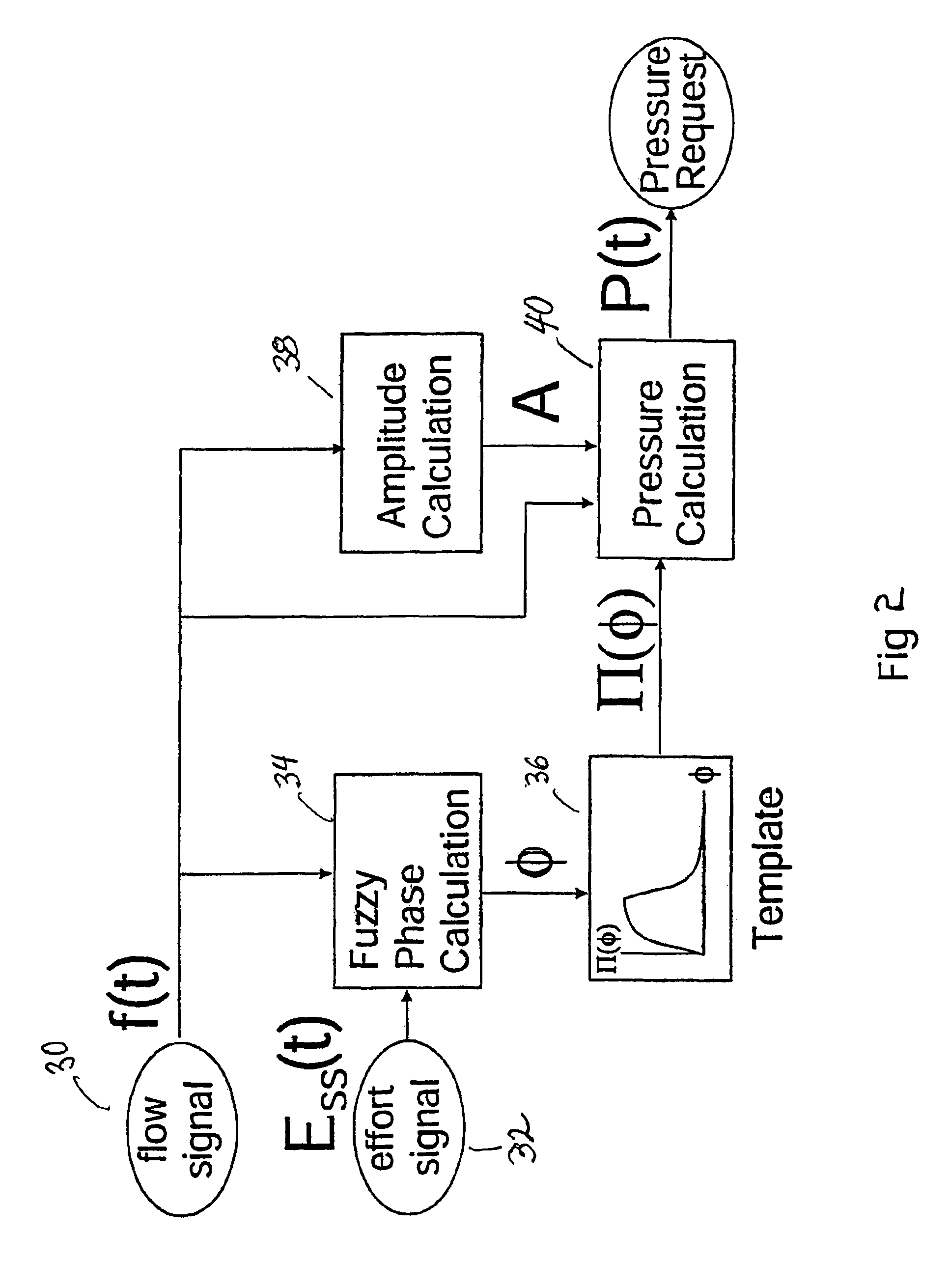
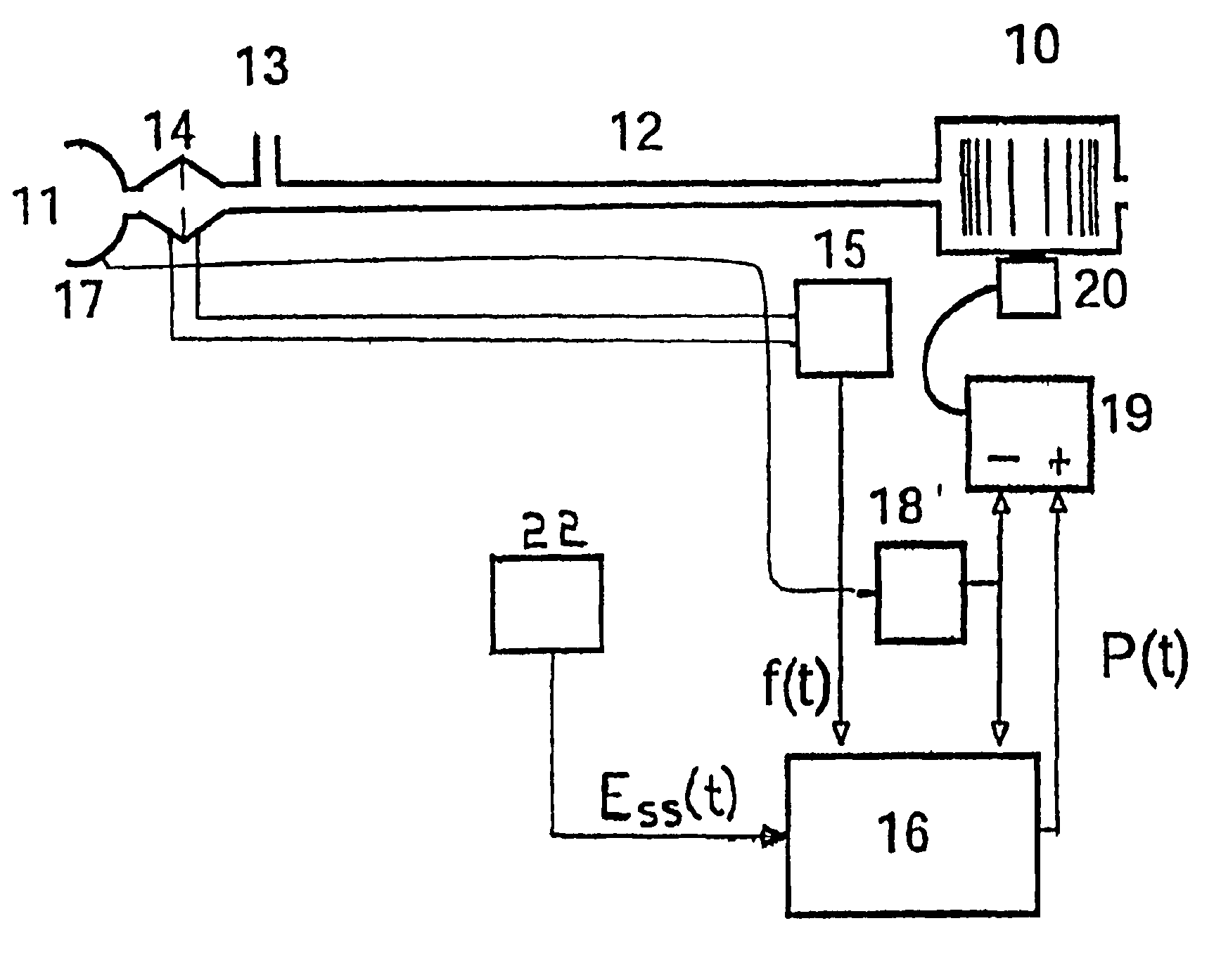
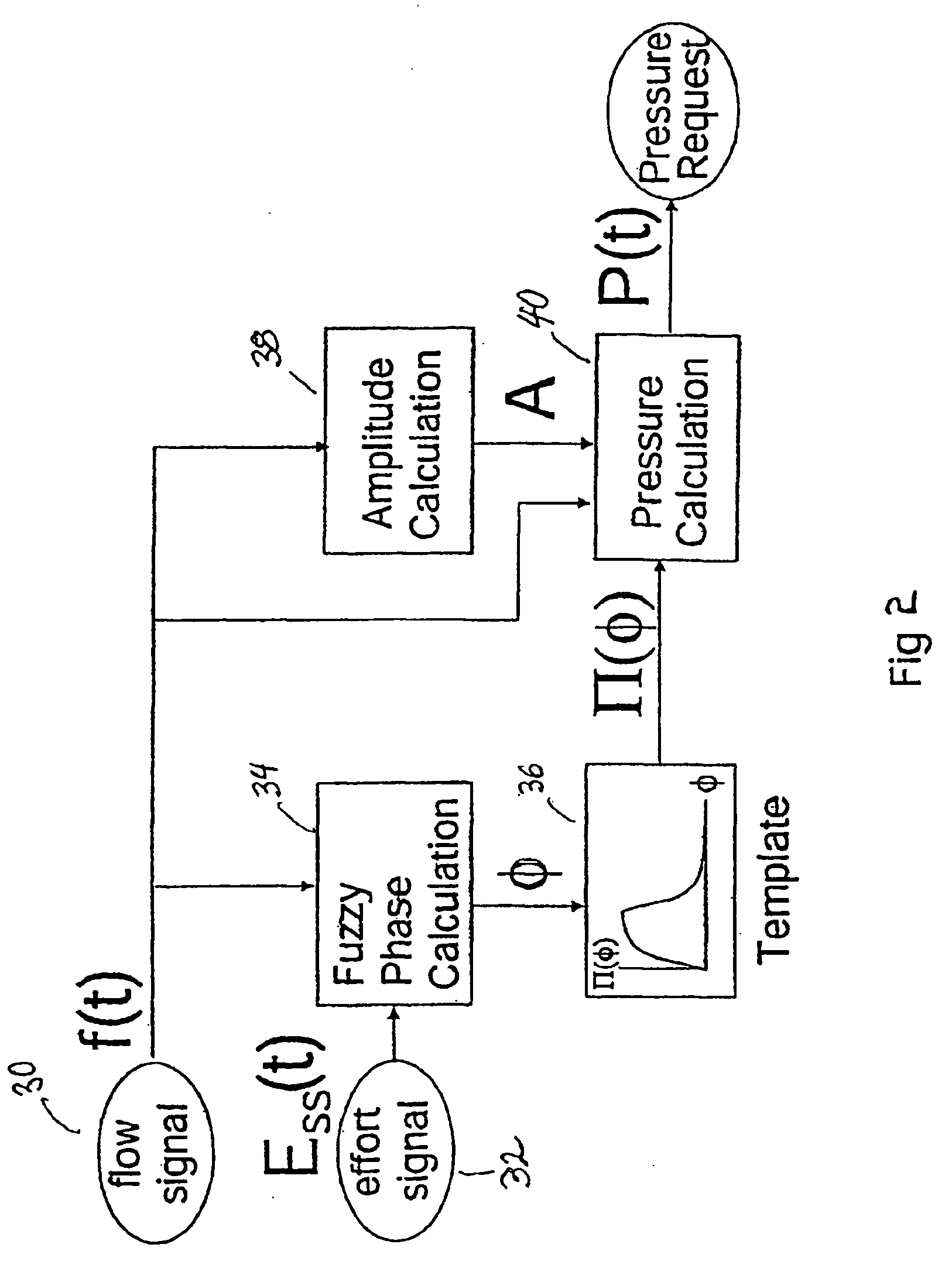
InactiveUS6910480B1Minimum ventilationImprove determinationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory phasePressure amplitude
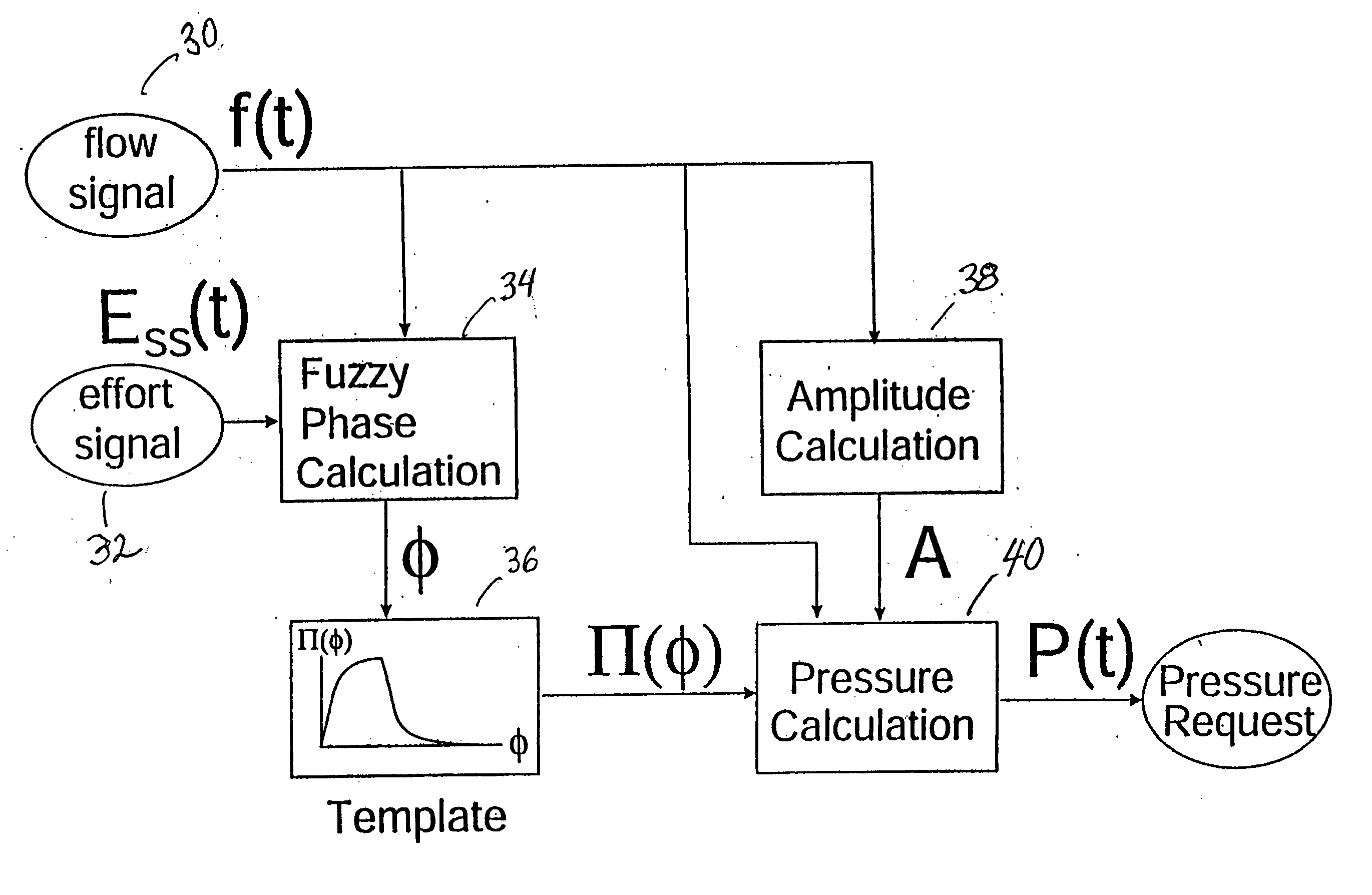
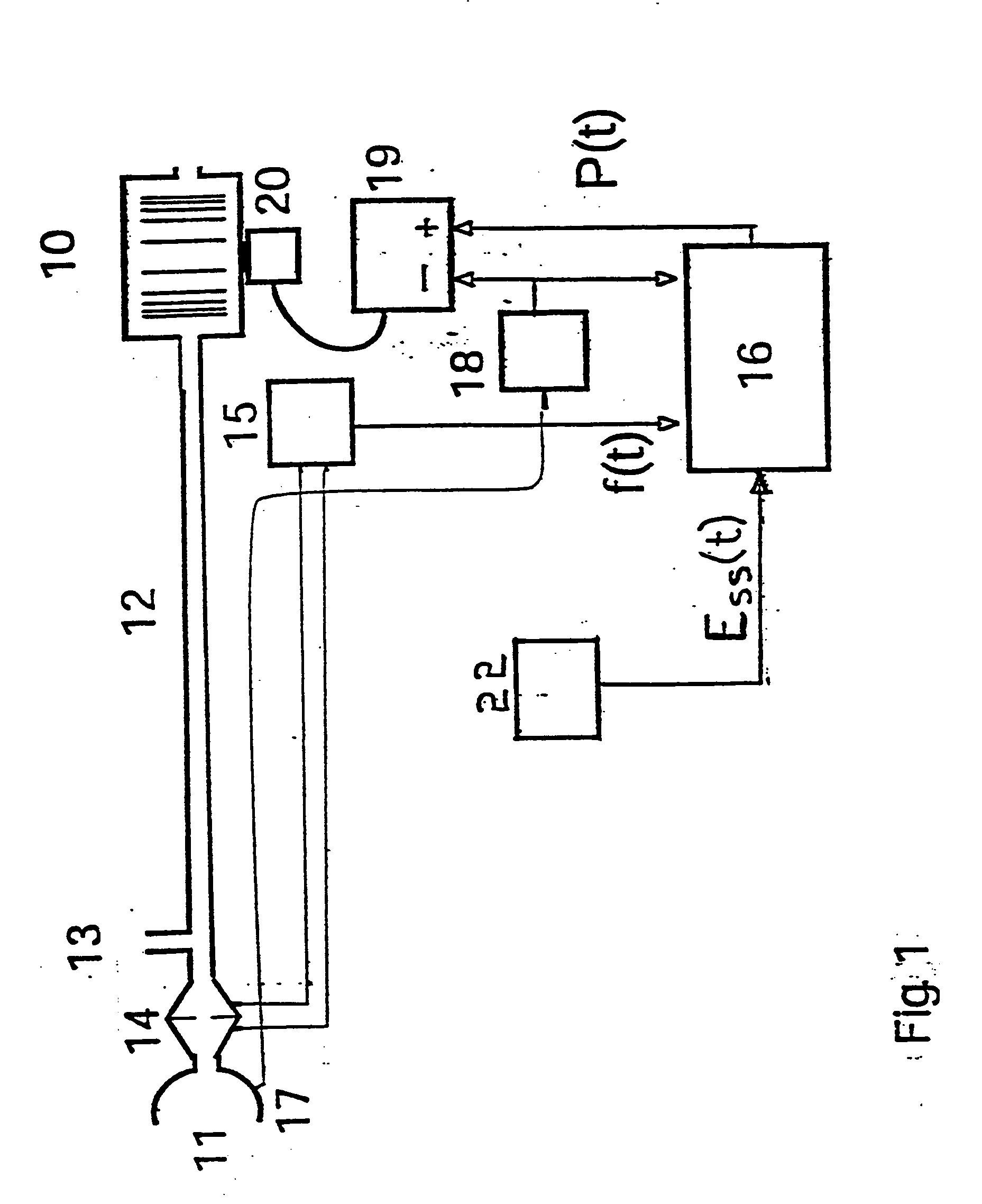
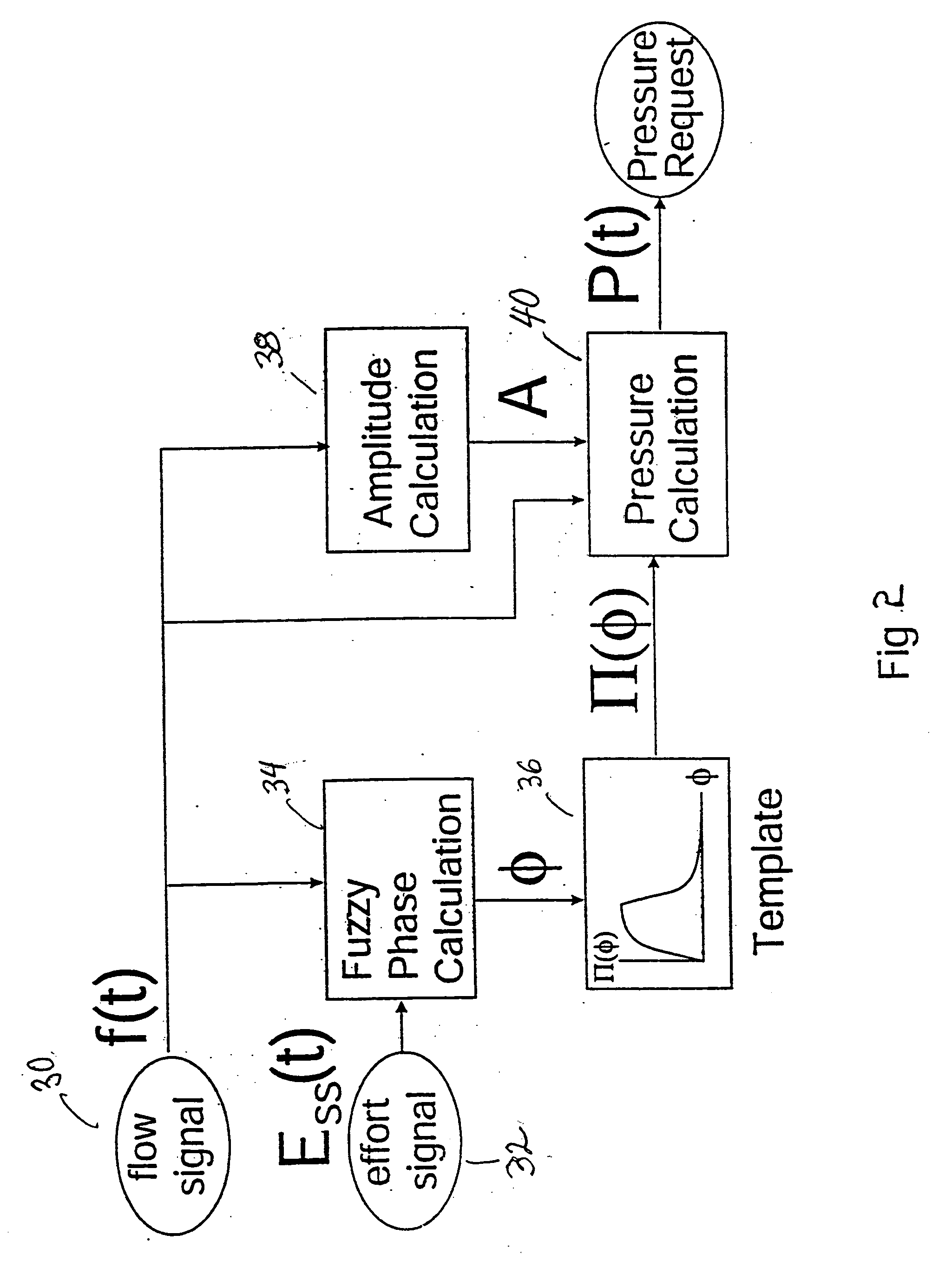
An improved ventilator which delivers ventilatory support that is synchronized with the phase of the patient's respiratory efforts and guarantees a targeted minimum ventilation. Improved synchronization is achieved through an instantaneous respiratory phase determination process based upon measured respiratory airflow as well as measured respiratory effort using an effort sensor accessory, preferably a suprasternal notch sensor. The ventilator processes a respiratory airflow signal, a respiratory effort signal and their respective rates of change to determine a phase using standard fuzzy logic methods. A calculated pressure amplitude is adjusted based upon the calculated phase and a smooth pressure waveform template to deliver synchronized ventilation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Patient-ventilator synchronization using dual phase sensors
InactiveUS7934499B2Minimum ventilationImprove determinationRespiratorsRespiratory device testingRespiratory phasePressure amplitude
An improved ventilator which delivers ventilatory support that is synchronized with the phase of the patients respiratory efforts and guarantees a targeted minimum ventilation. Improved synchronization is achieved through an instantaneous respiratory phase determination process based upon measured respiratory airflow as well as measured respiratory effort using an effort sensor accessory, preferably a suprasternal notch sensor. The ventilator processes a respiratory airflow signal, a respiratory effort signal and their respective rates of change to determine a phase using standard fuzzy logic methods. A calculated pressure amplitude is adjusted based upon the calculated phase and a smooth pressure waveform template to deliver synchronized ventilation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
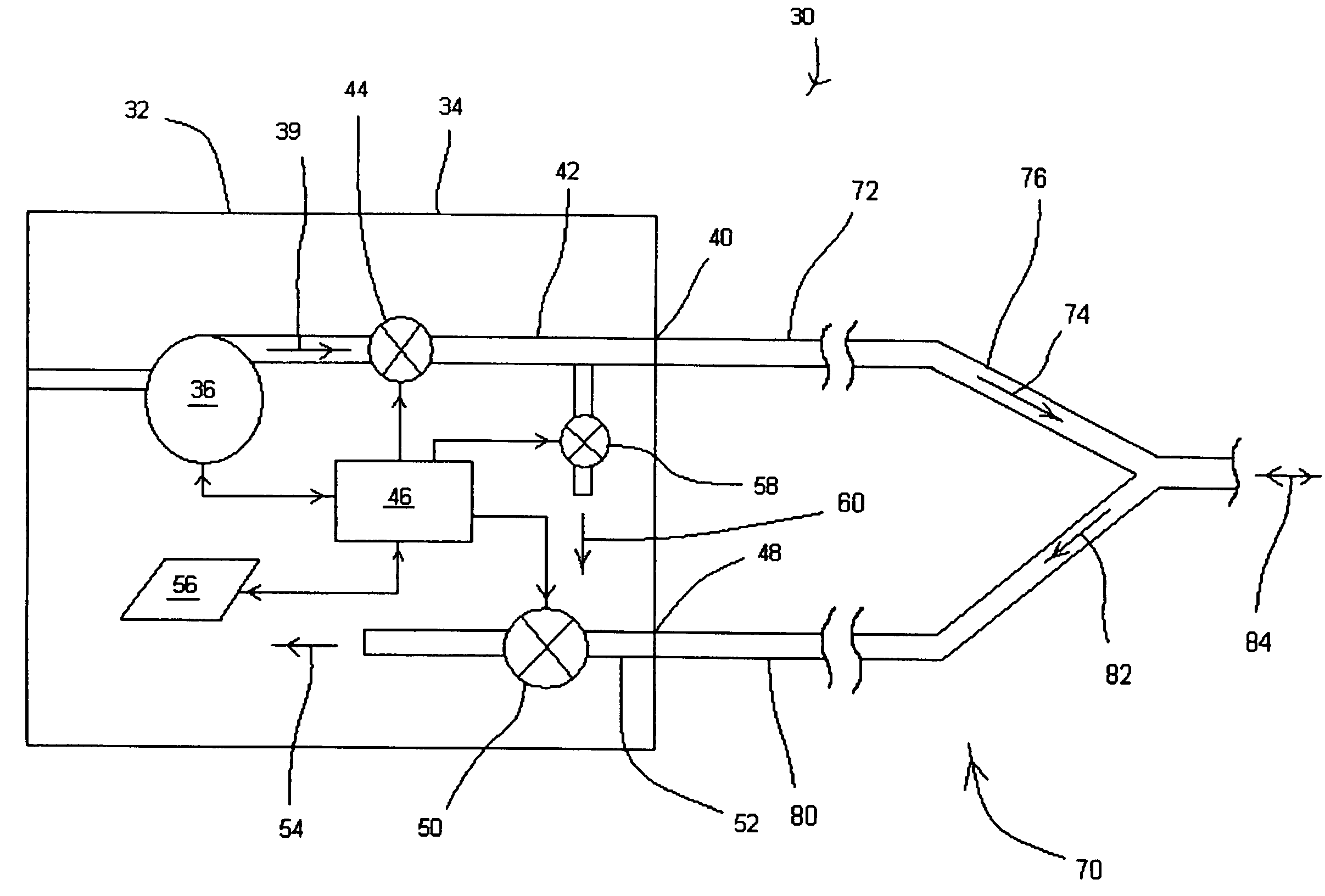
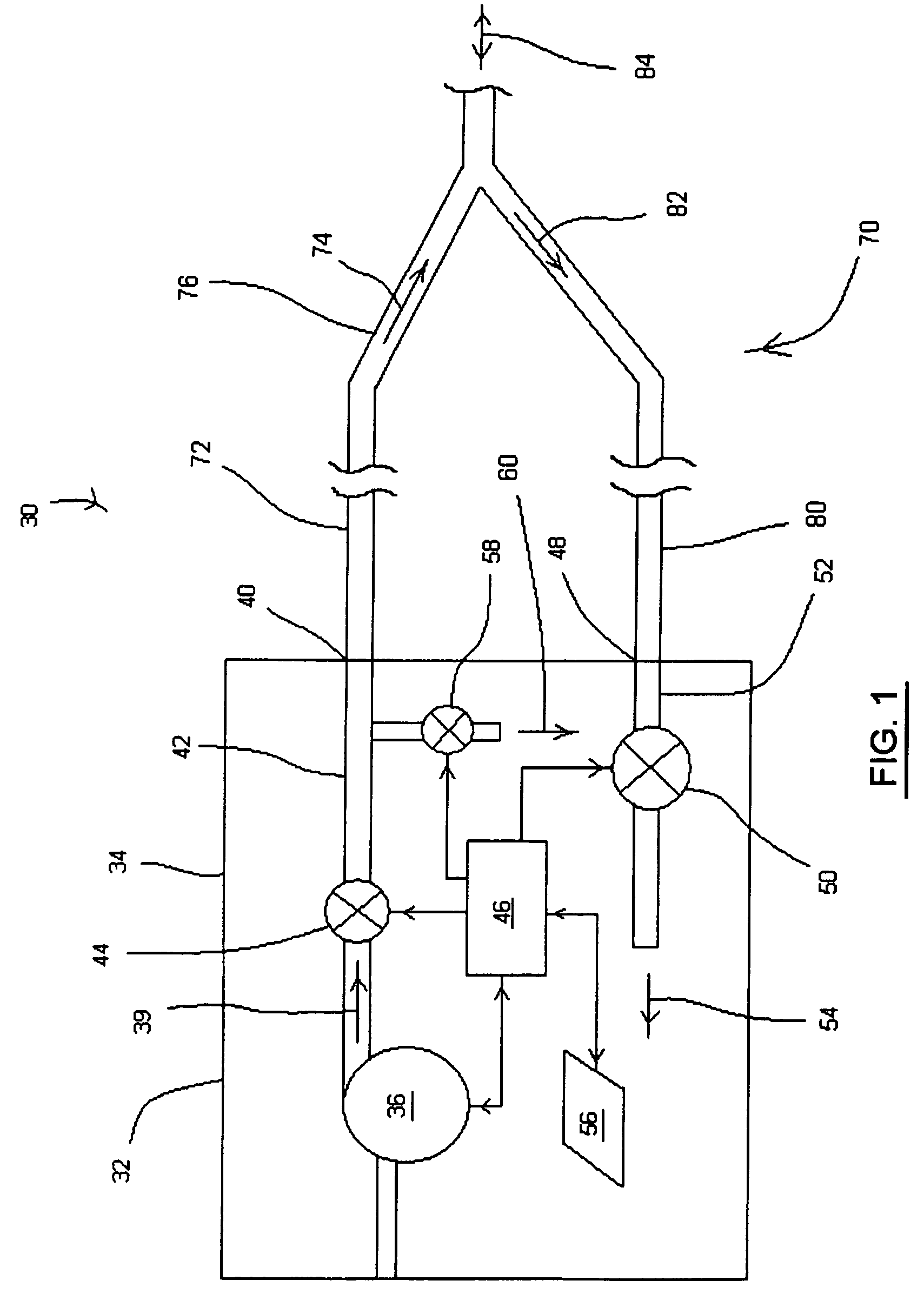
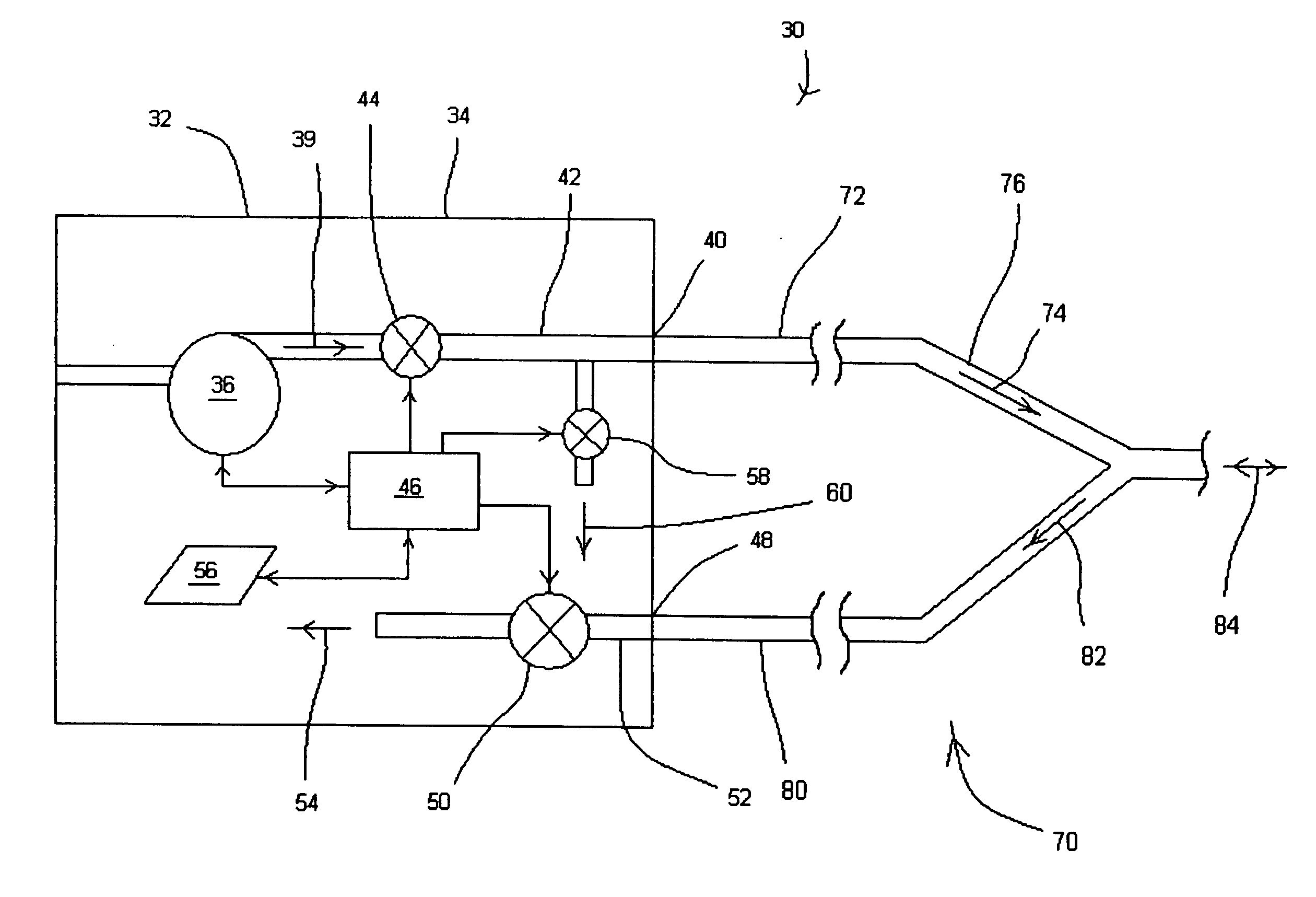
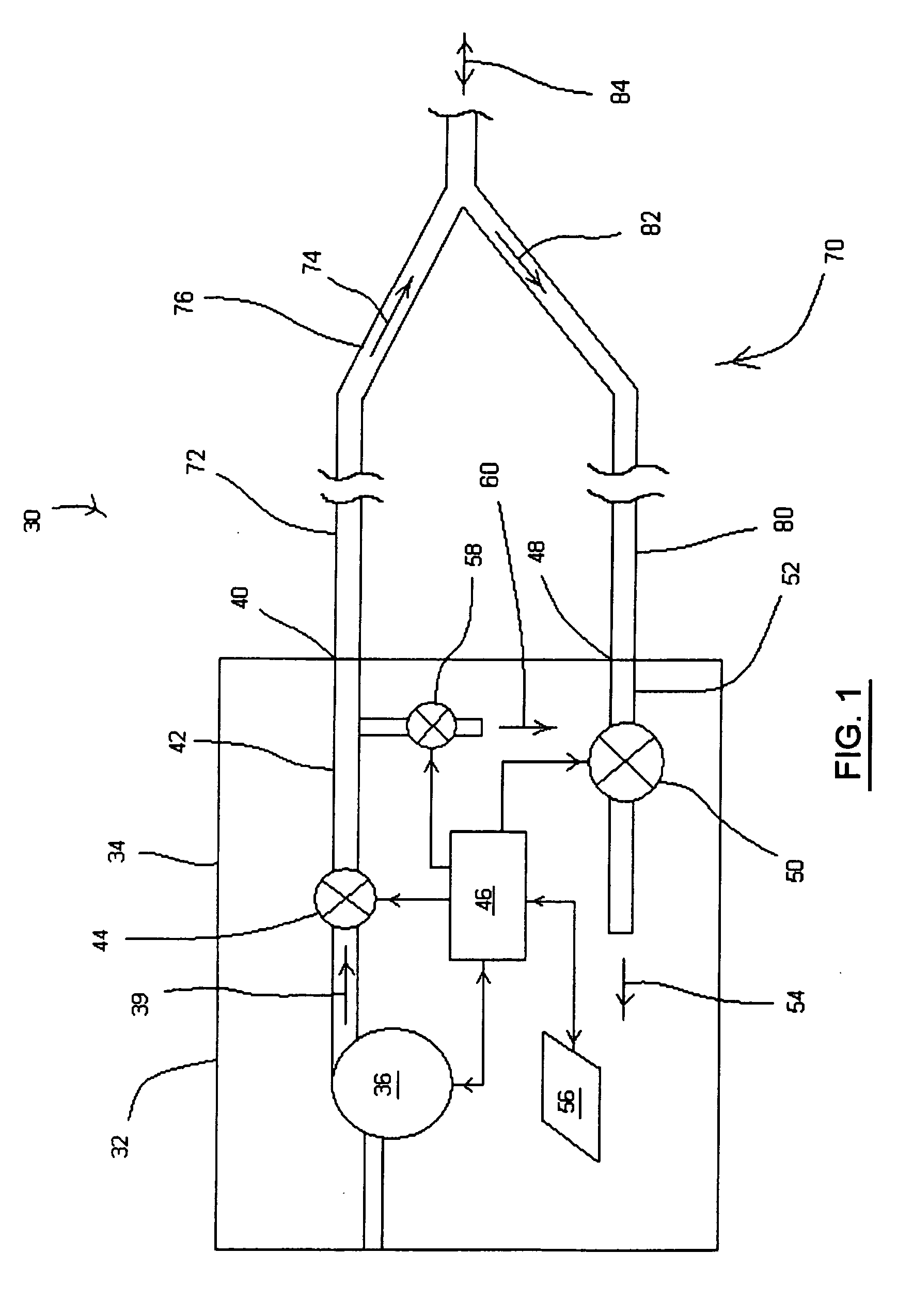
Ventilator adaptable for use with either a dual-limb circuit or a single-limb circuit
ActiveUS7617824B2Overcomes shortcomingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExhaust valveRespiratory phase
A ventilator of the present invention includes a housing, a gas flow generator disposed in the housing, a gas outlet port provided on an exterior surface of the housing, and a first conduit coupling the gas flow generator to the gas outlet port. A gas inlet port is also provided on an exterior surface of the housing. A second conduit couples the gas inlet port to a first exhaust valve in the housing that regulates a flow of exhaust gas from the second conduit. A second exhaust valve in the housing is coupled to the first conduit and regulates a flow of exhaust gas from the first conduit. A controller coupled to second exhaust valve causes the second exhaust valve to change a degree of flow restriction based on a respiratory phase of a patient coupled to the ventilator when the ventilator is operating in a single-limb ventilation configuration.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
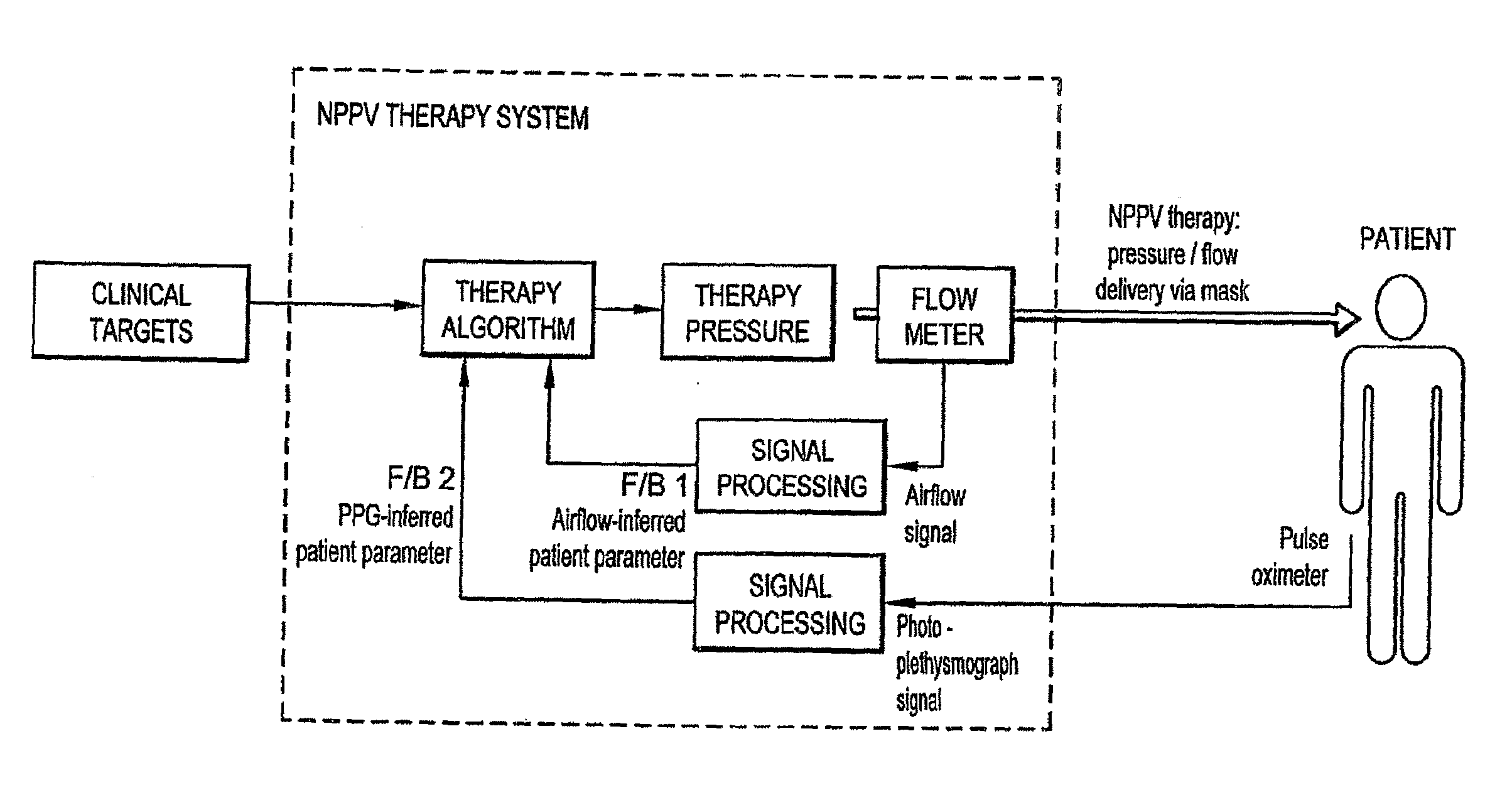
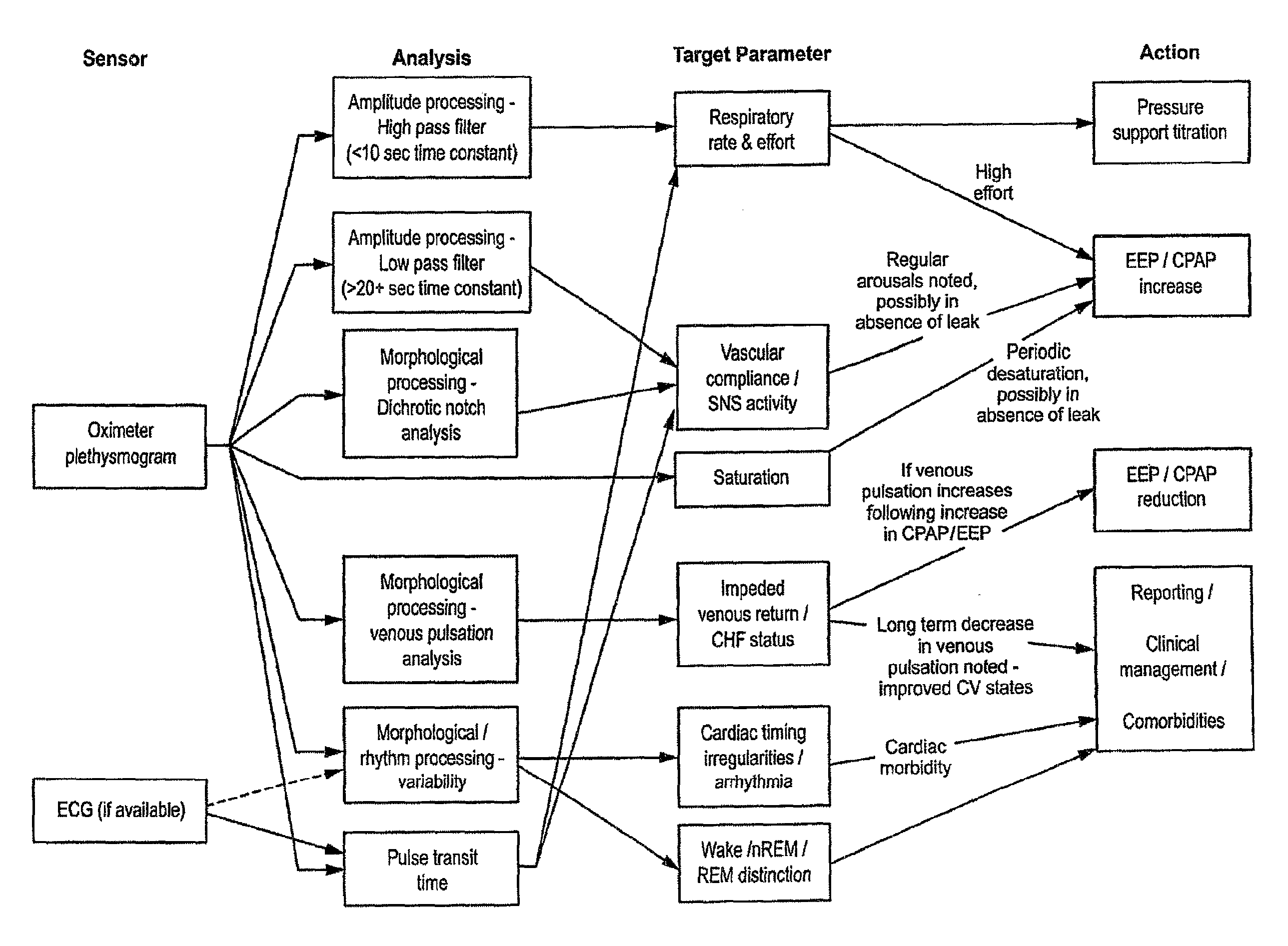
Systems, Methods, and/or Apparatuses for Non-Invasive Monitoring of Respiratory Parameters in Sleep Disordered Breathing
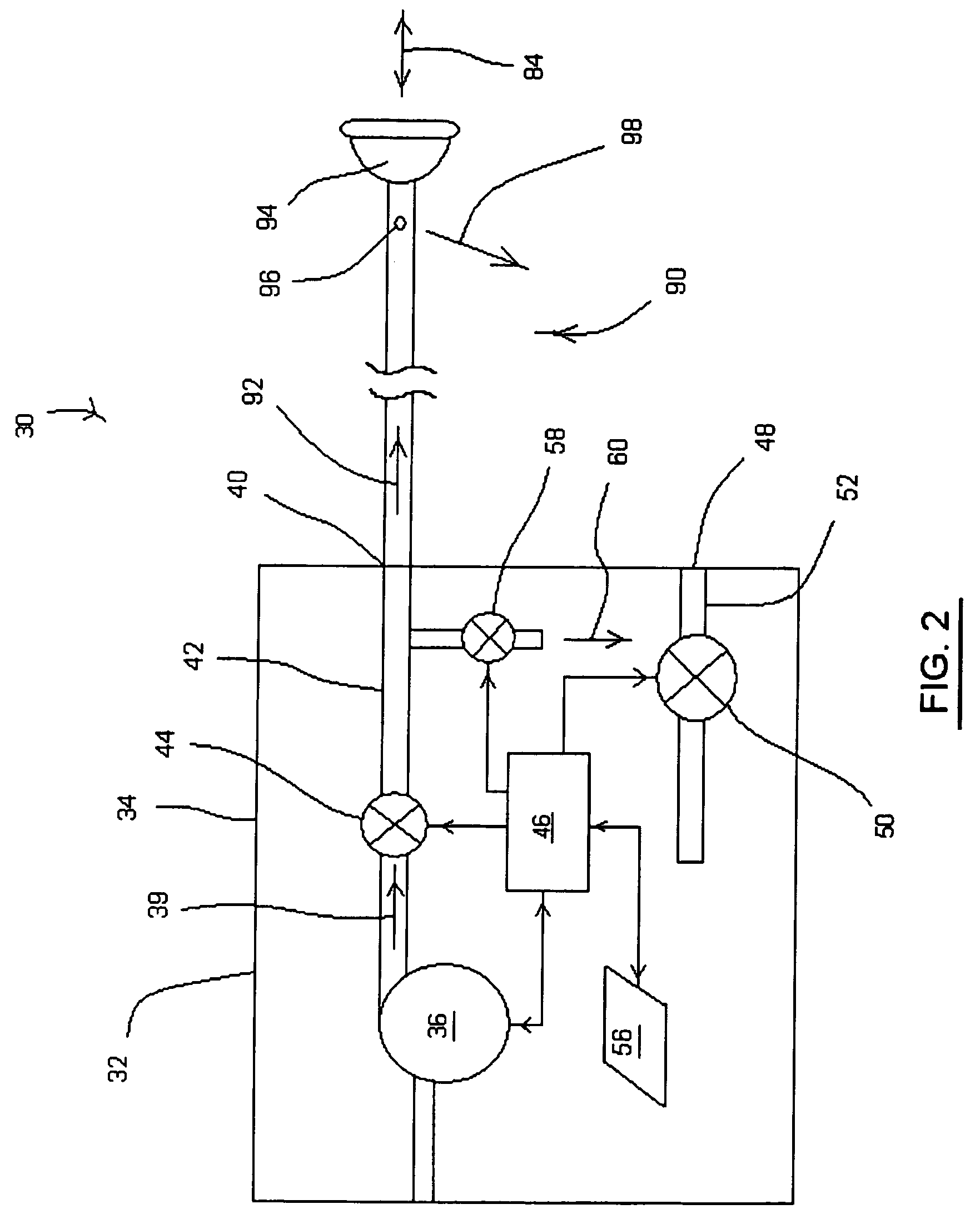
ActiveUS20100016694A1Eliminate side effectsIncrease pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPulse oximetersSleep disordered breathing
In certain example embodiments, an air delivery system includes a controllable flow generator operable to generate a supply of pressurized breathable gas to be provided to a patient for treatment and a pulse oximeter. In certain example embodiments, the pulse oximeter is configured to determine, for example, a measure of patient effort during a treatment period and provide a patient effort signal for input to control operation of the flow generator. Oximeter plethysmogram data may be used, for example, to determine estimated breath phase; sleep structure information; autonomic improvement in response to therapy; information relating to relative breathing effort, breathing frequency, and / or breathing phase; vasoconstrictive response, etc. Such data may be useful in diagnostic systems.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Methods, systems and devices for non-invasive open ventilation with gas delivery nozzles in free space
ActiveUS20100252039A1Work lessIncrease airway pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesNoseLung volumes
A non-invasive ventilation system may include an interface. The interface may include at least one gas delivery jet nozzle adapted to be positioned in free space and aligned to directly deliver ventilation gas into an entrance of a nose. The at least one gas delivery jet nozzle may be connected to a pressurized gas supply. The ventilation gas may entrain ambient air to elevate lung pressure, elevate lung volume, decrease the work of breathing or increase airway pressure, and wherein the ventilation gas is delivered in synchrony with phases of breathing. A support for the at least one gas delivery jet nozzle may be provided. A breath sensor may be in close proximity to the entrance of the nose. A patient may spontaneous breathe ambient air through the nose without being impeded by the interface.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Ventilator adaptable for use with either a dual-limb circuit or a single-limb circuit
ActiveUS20070144516A1Overcomes shortcomingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExhaust valveRespiratory phase
A ventilator of the present invention includes a housing, a gas flow generator disposed in the housing, a gas outlet port provided on an exterior surface of the housing, and a first conduit coupling the gas flow generator to the gas outlet port. A gas inlet port is also provided on an exterior surface of the housing. A second conduit couples the gas inlet port to a first exhaust valve in the housing that regulates a flow of exhaust gas from the second conduit. A second exhaust valve in the housing is coupled to the first conduit and regulates a flow of exhaust gas from the first conduit. A controller coupled to second exhaust valve causes the second exhaust valve to change a degree of flow restriction based on a respiratory phase of a patient coupled to the ventilator when the ventilator is operating in a single-limb ventilation configuration.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
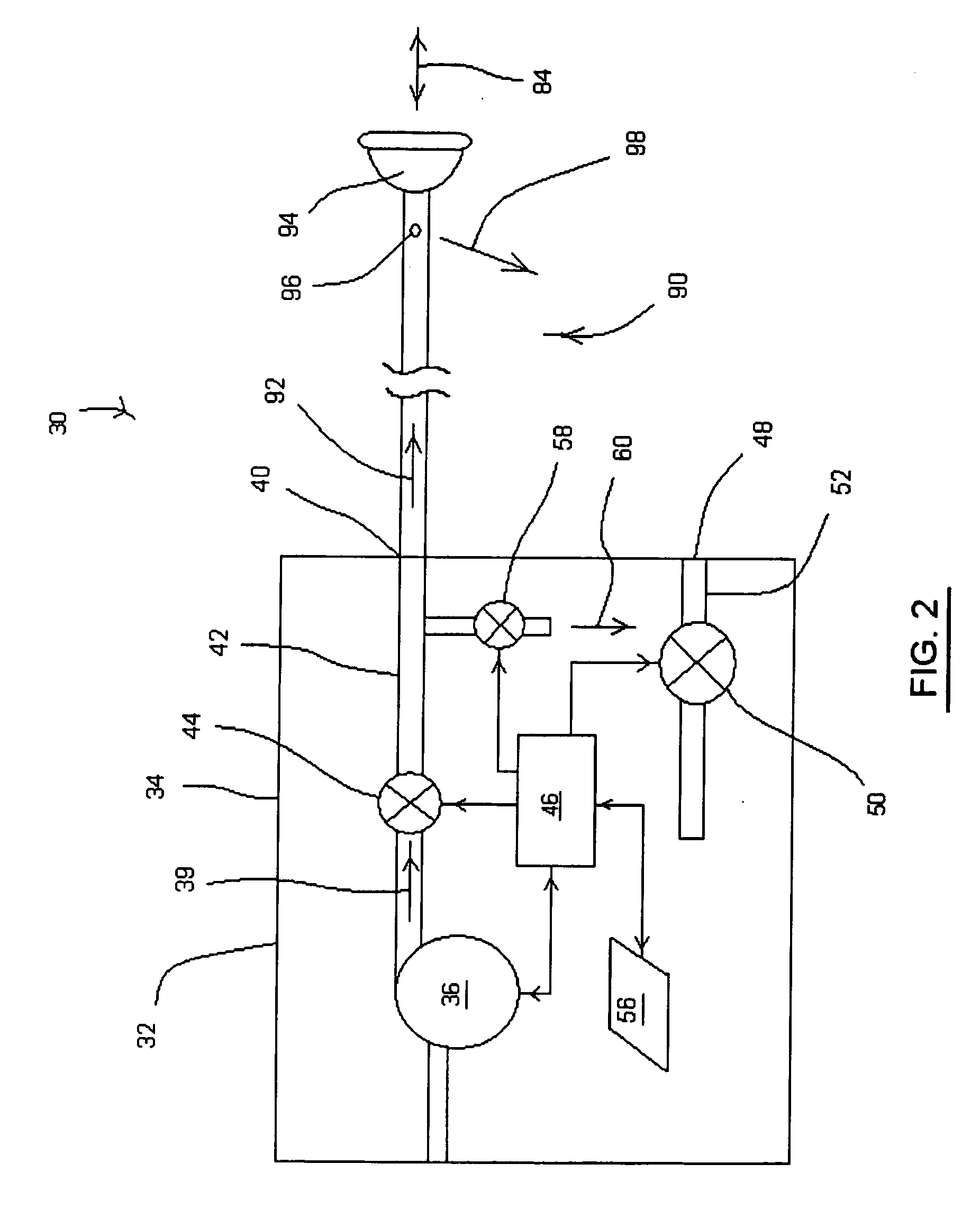
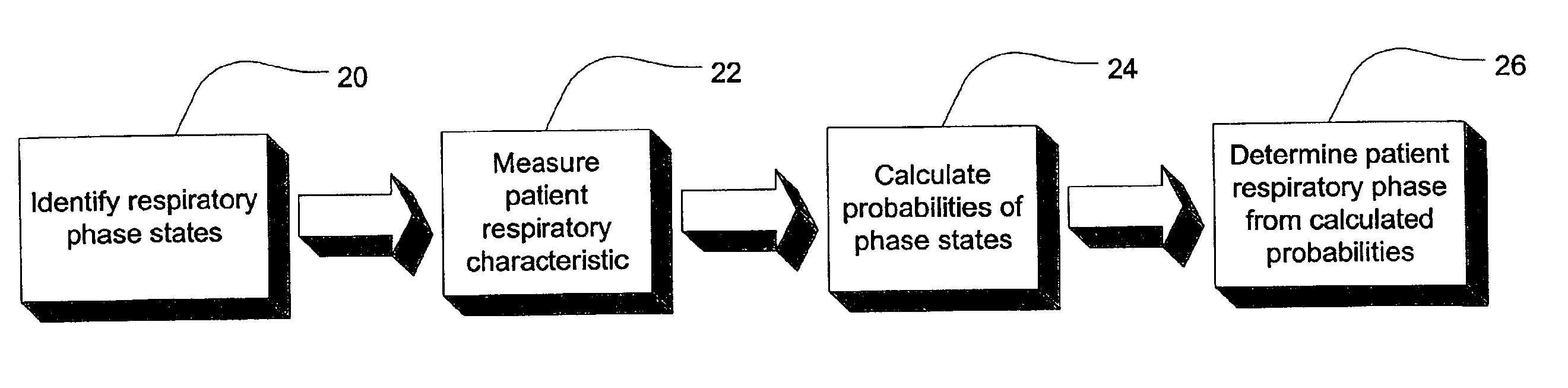
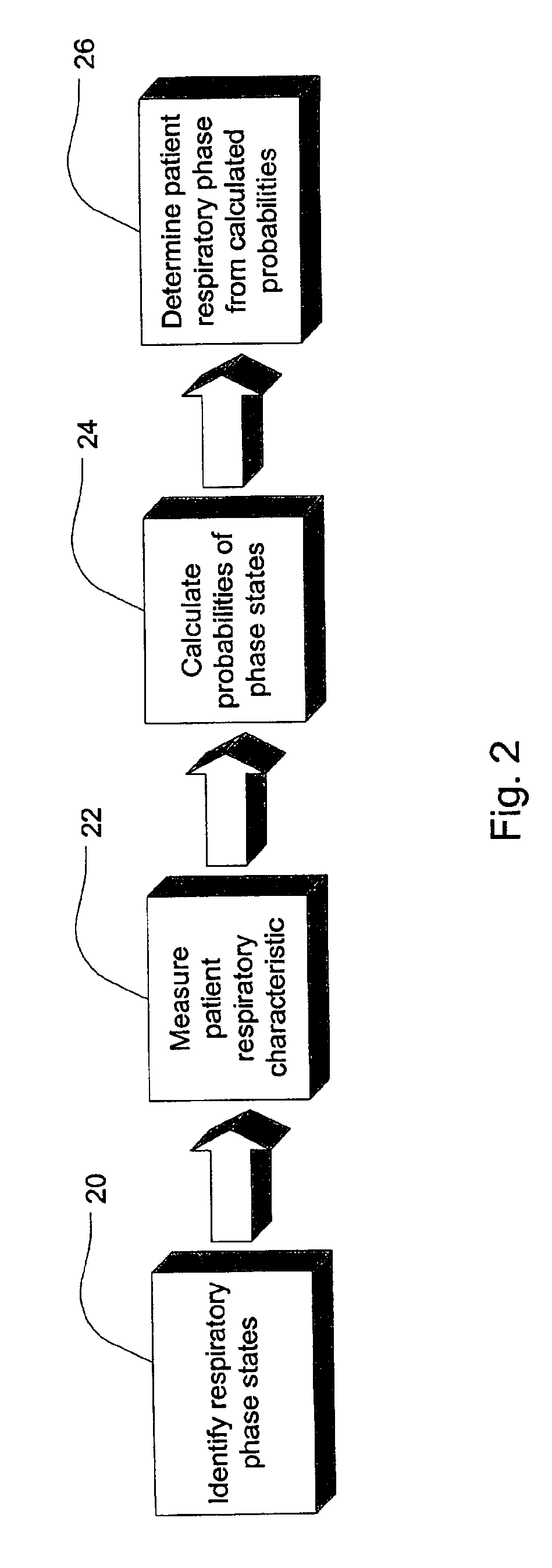
Ventilator patient synchronization
InactiveUS6860858B2Improve reliabilityImprove accuracyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory phasePhase state
A method and apparatus that provides an expert system for determining respiratory phase during ventilatory support of a subject. Discrete phase states are partitioned and prior probability functions and observed probability functions for each state are defined. The probability functions are based upon relative duration of each state as well as the flow characteristics of each state. These functions are combined to determine phase probabilities for each state using Bayes' theorem. The calculated probabilities for the states may then be compared to determine which state the subject is experiencing. A ventilator may then conform respiratory support in accordance with the most probable phase. To provide a learning feature, the probability functions may be adjusted during use to provide a more subject specific response that accounts for changing respiratory characteristics.
Owner:RESMED LTD
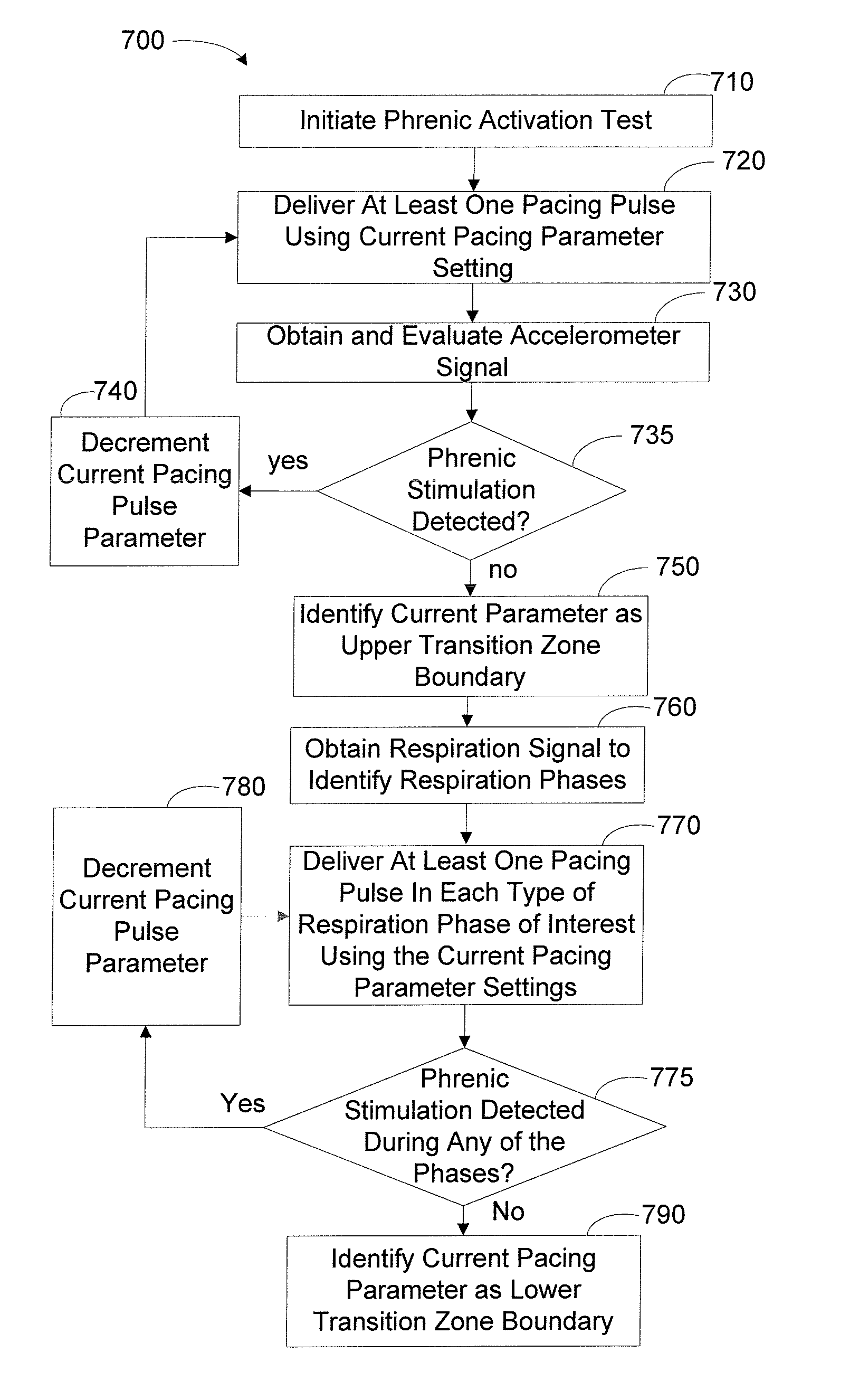
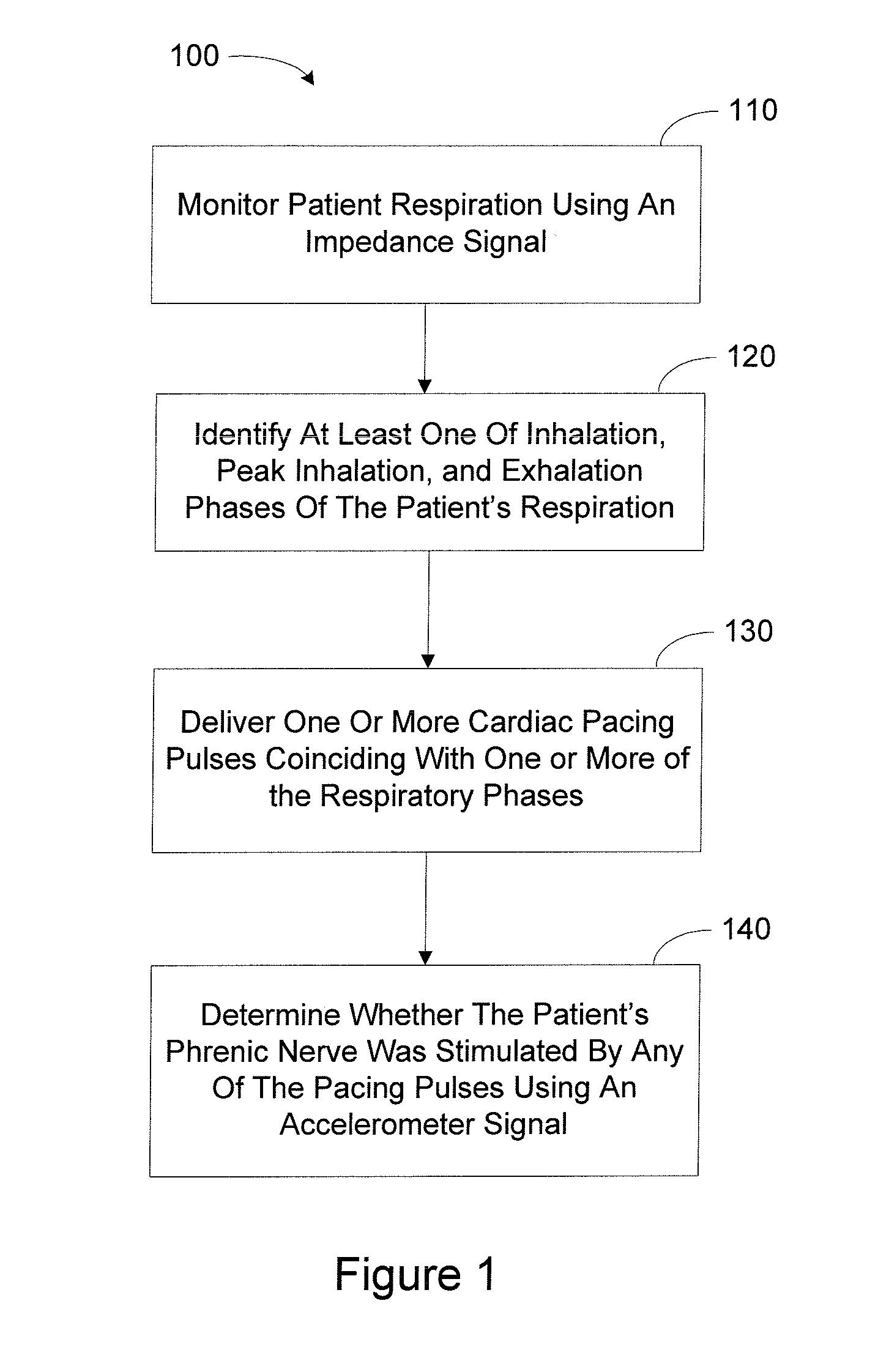
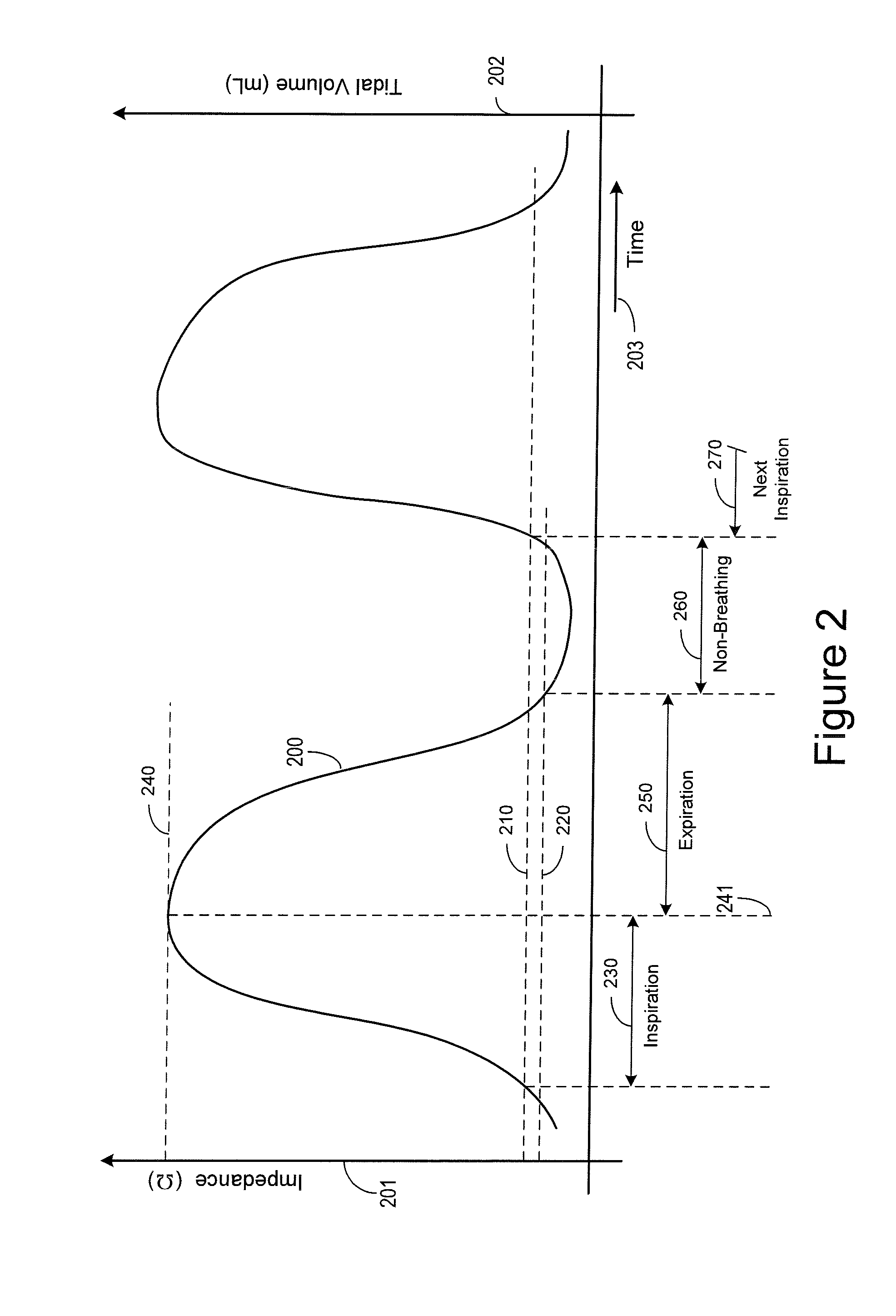
Method and Apparatus for Phrenic Nerve Activation Detection with Respiration Cross-Checking
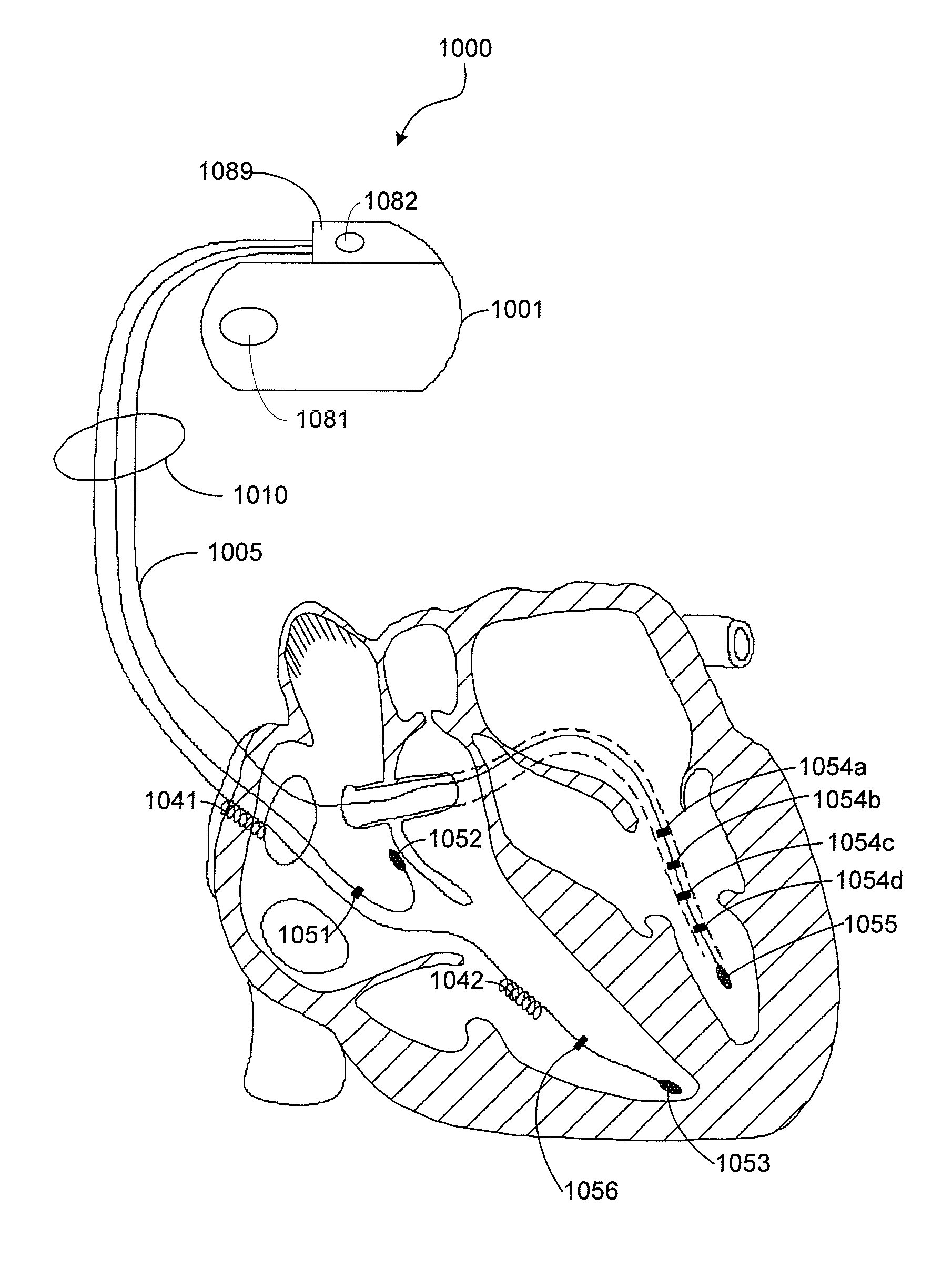
The present invention concerns phrenic nerve activation detection algorithms for characterization of phrenic nerve activation and phrenic nerve activation avoidance in cardiac pacing therapy.Various embodiments concern receiving a respiration signal indicative of respiratory activity of the patient, identifying respiratory phases based on the respiration signal, delivering cardiac pacing pulses within each of the identified respiratory phases, receiving a phrenic nerve activation signal indicative of activation of the patient's phrenic nerve, analyzing the phrenic nerve stimulation signal to determine if one or more of the pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient, and determining if at least one of the delivered pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient based on the phrenic nerve activation signal indicating activation of the patient's phrenic nerve associated with delivery of the at least one cardiac pacing pulse.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Patient-ventilator synchronization using dual phase sensors
InactiveUS20060102180A1Improve determinationMinimum ventilationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory phasePressure amplitude
An improved ventilator which delivers ventilatory support that is synchronized with the phase of the patients respiratory efforts and guarantees a targeted minimum ventilation. Improved synchronization is achieved through an instantaneous respiratory phase determination process based upon measured respiratory airflow as well as measured respiratory effort using an effort sensor accessory, preferably a suprasternal notch sensor. The ventilator processes a respiratory airflow signal, a respiratory effort signal and their respective rates of change to determine a phase using standard fuzzy logic methods. A calculated pressure amplitude is adjusted based upon the calculated phase and a smooth pressure waveform template to deliver synchronized ventilation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
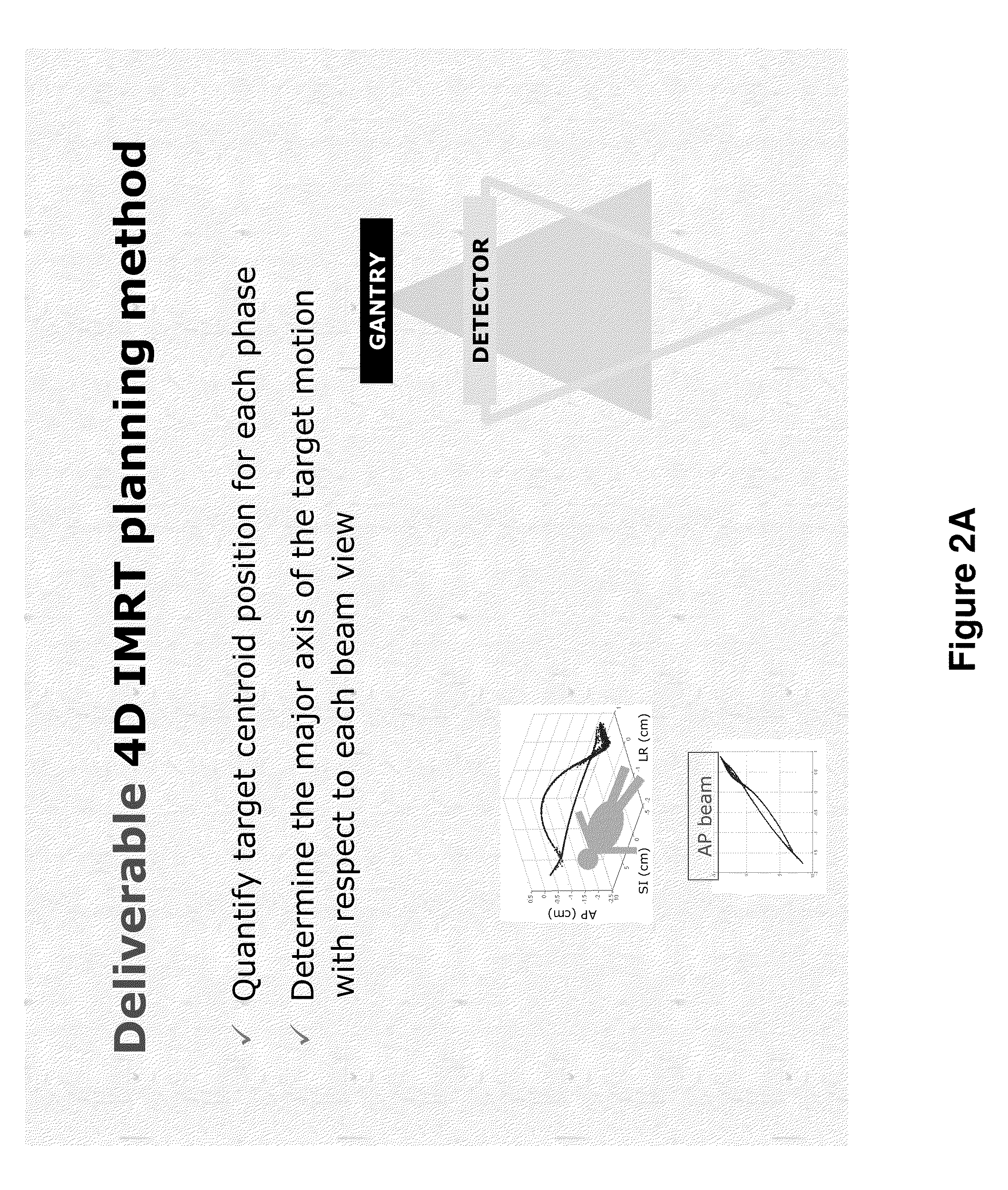
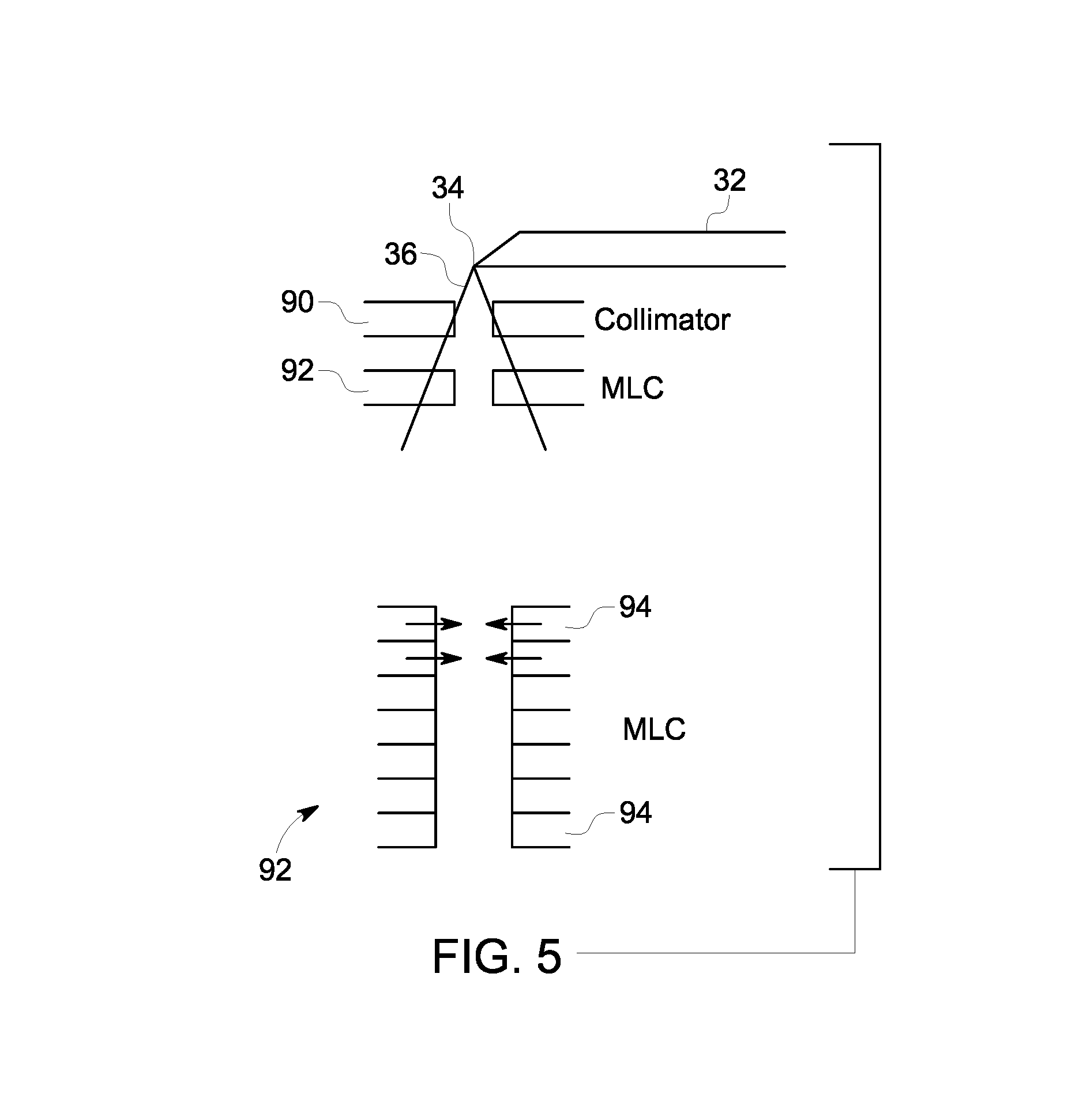
Method and system for four dimensional intensity modulated radiation therapy for motion compensated treatments
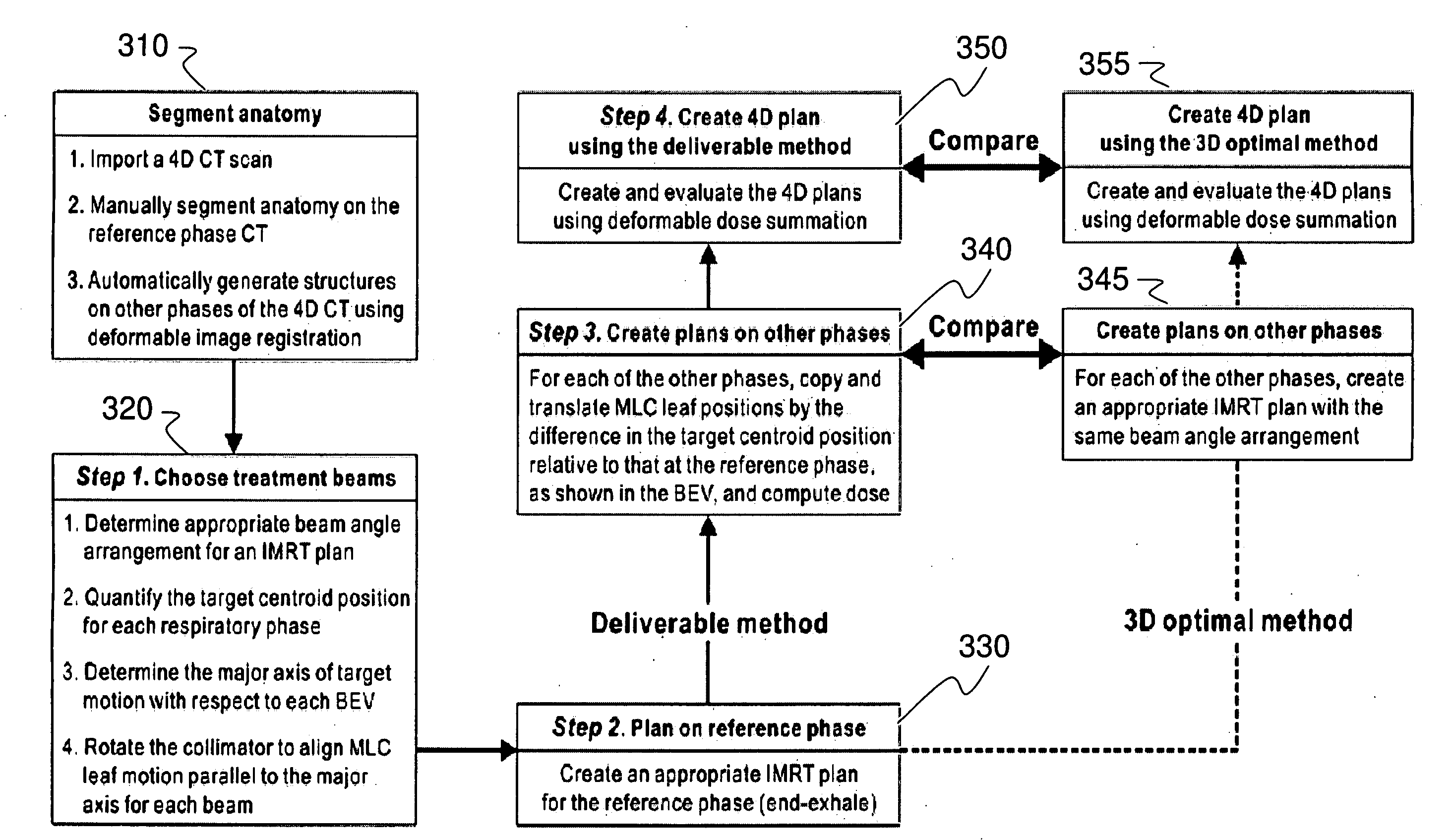
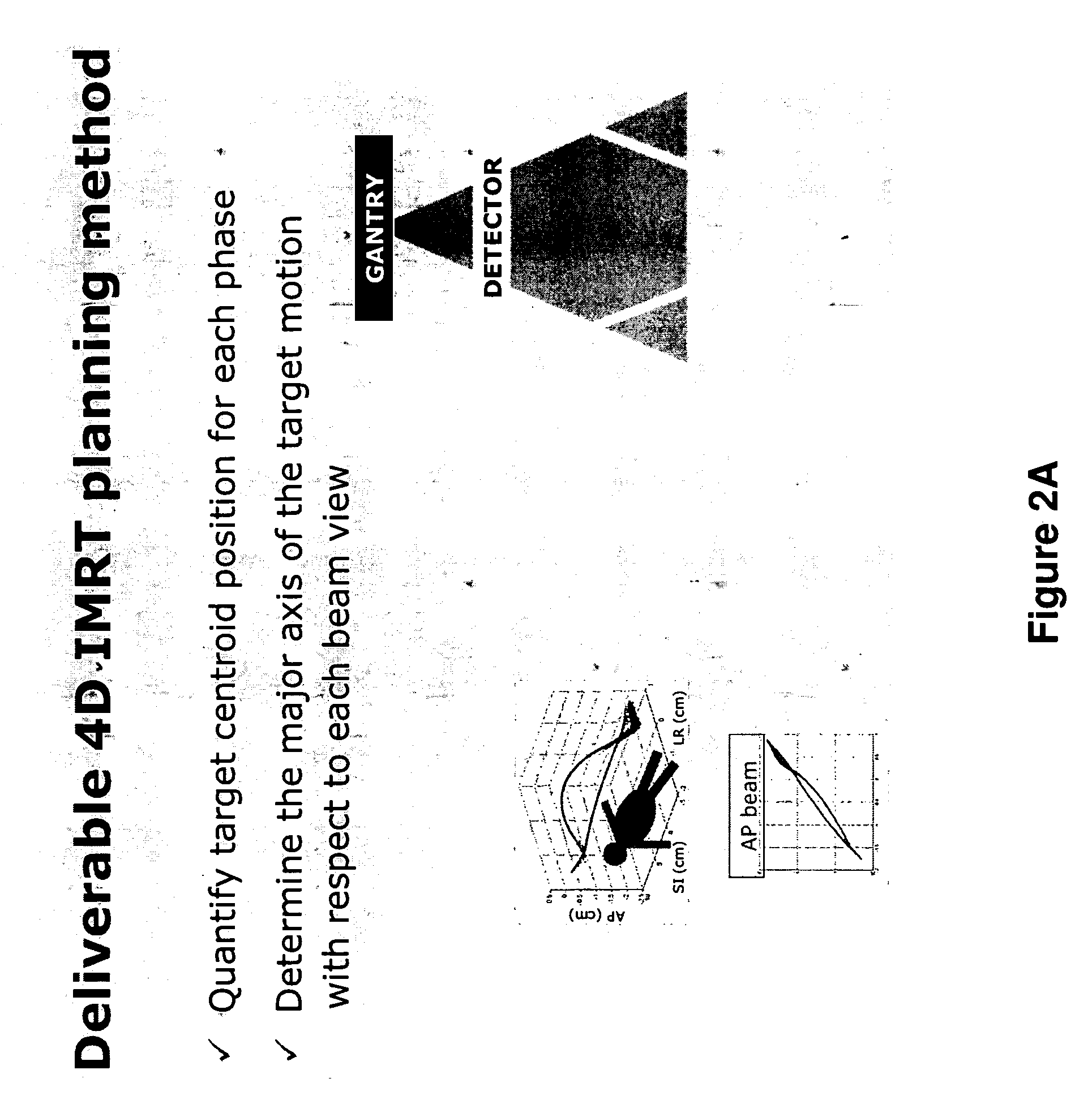
InactiveUS20090041188A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structuresTumour volume
A deliverable four dimensional (4D) intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) planning method is disclosed, for delivery using a linear accelerator with a dynamic multi-leaf collimator (DMLC). A 4D computed tomography (CT) scan is used for segmenting tumor anatomy on a reference phase of periodic motion of the tumor. Deformable registration of the 4D CT data is used to generate corresponding anatomical structures on other phases. Preferably, the collimator for each beam position is aligned using the gross tumor volume (GTV) centroid motion corresponding to the periodic motion of the tumor, as determined from the two dimensional (2D) projection of a given beam position. A deliverable IMRT plan is created on the 4D CT image set in which the MLC leaf positions and beam on / off status can vary as a function of respiratory phase by solving a four dimensional optimization problem. The mechanical constraints of the MLC leaves are included in the optimization.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for adaptive triggering of a breathing device, and breathing device with adaptive triggering
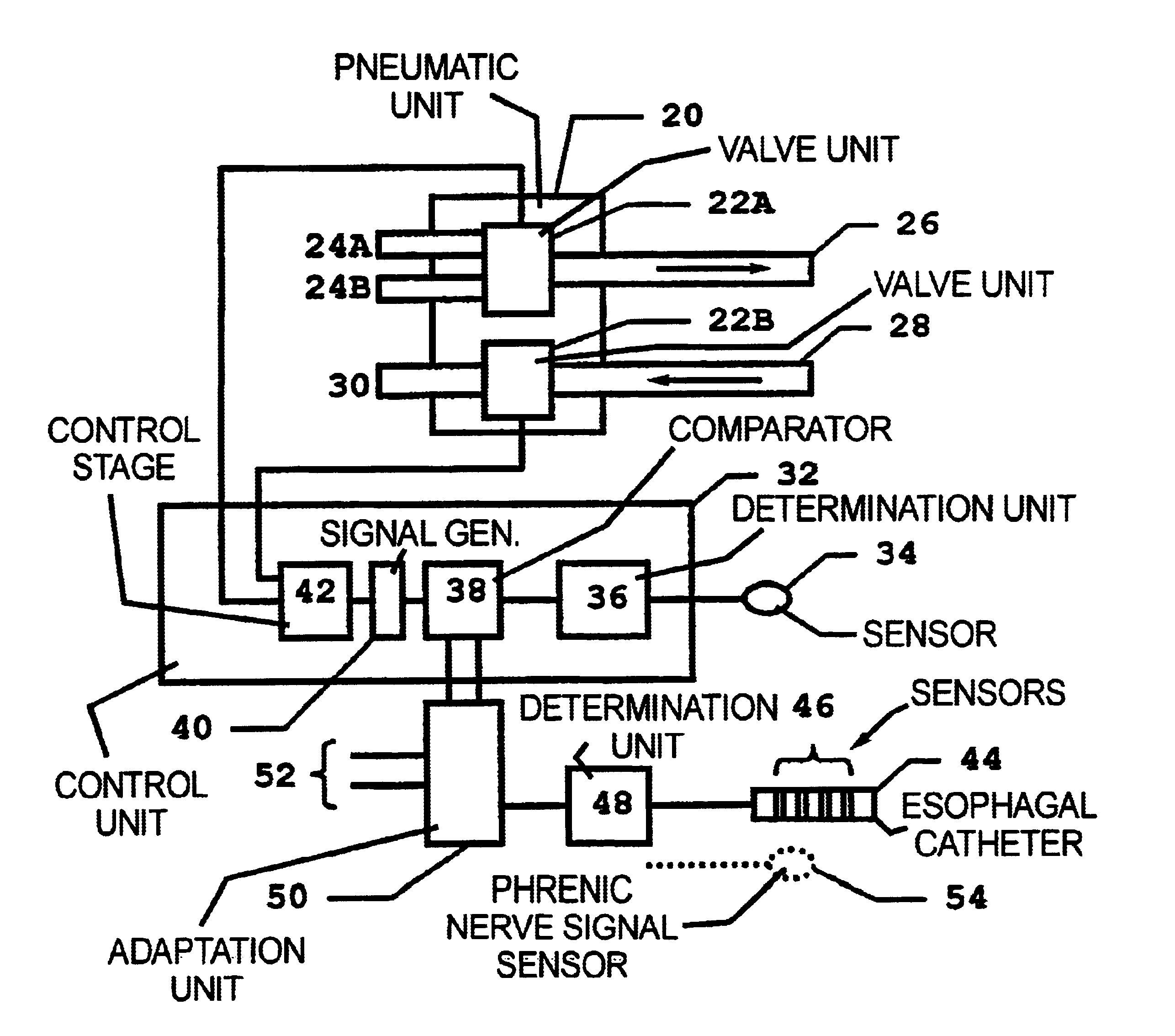
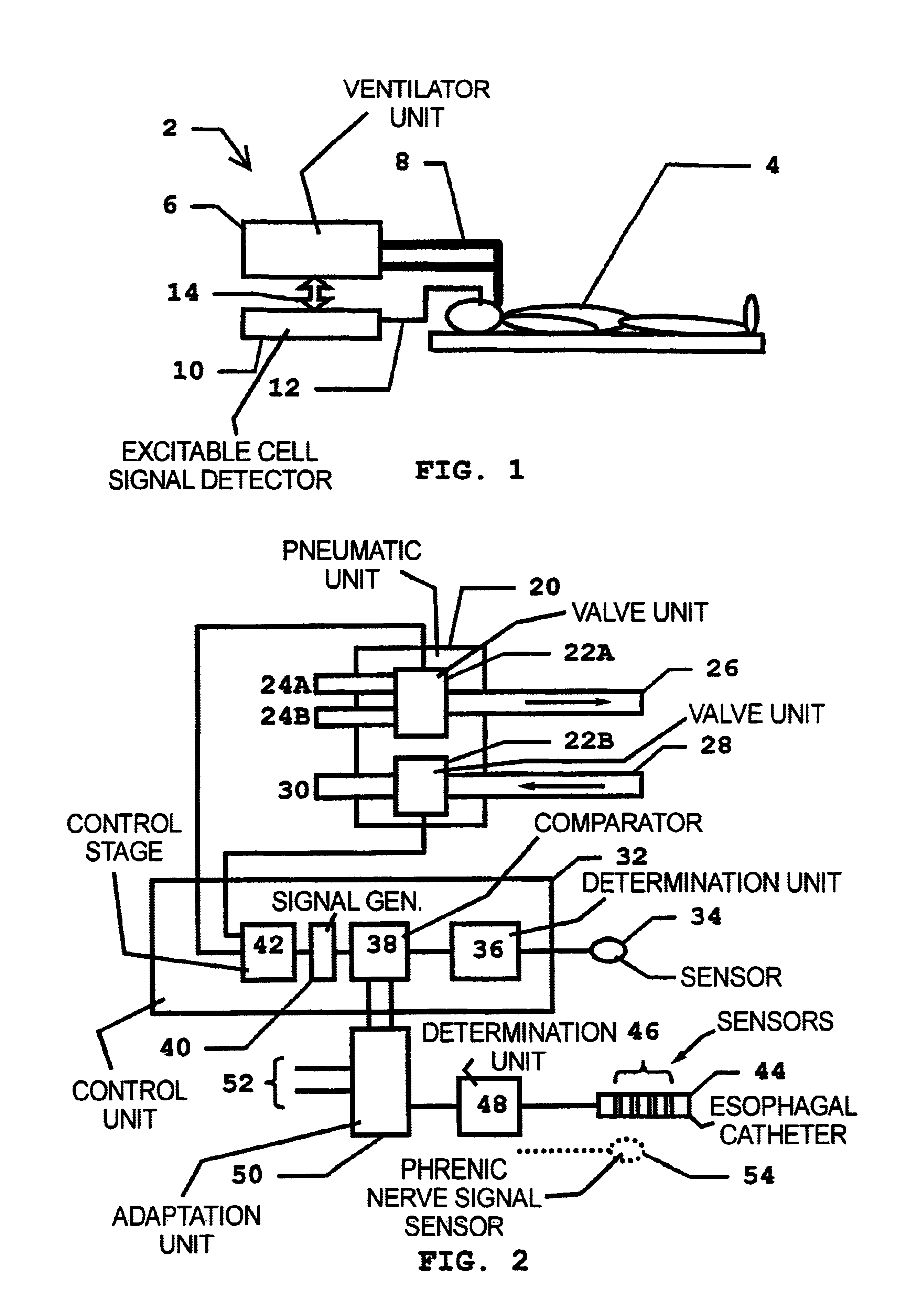
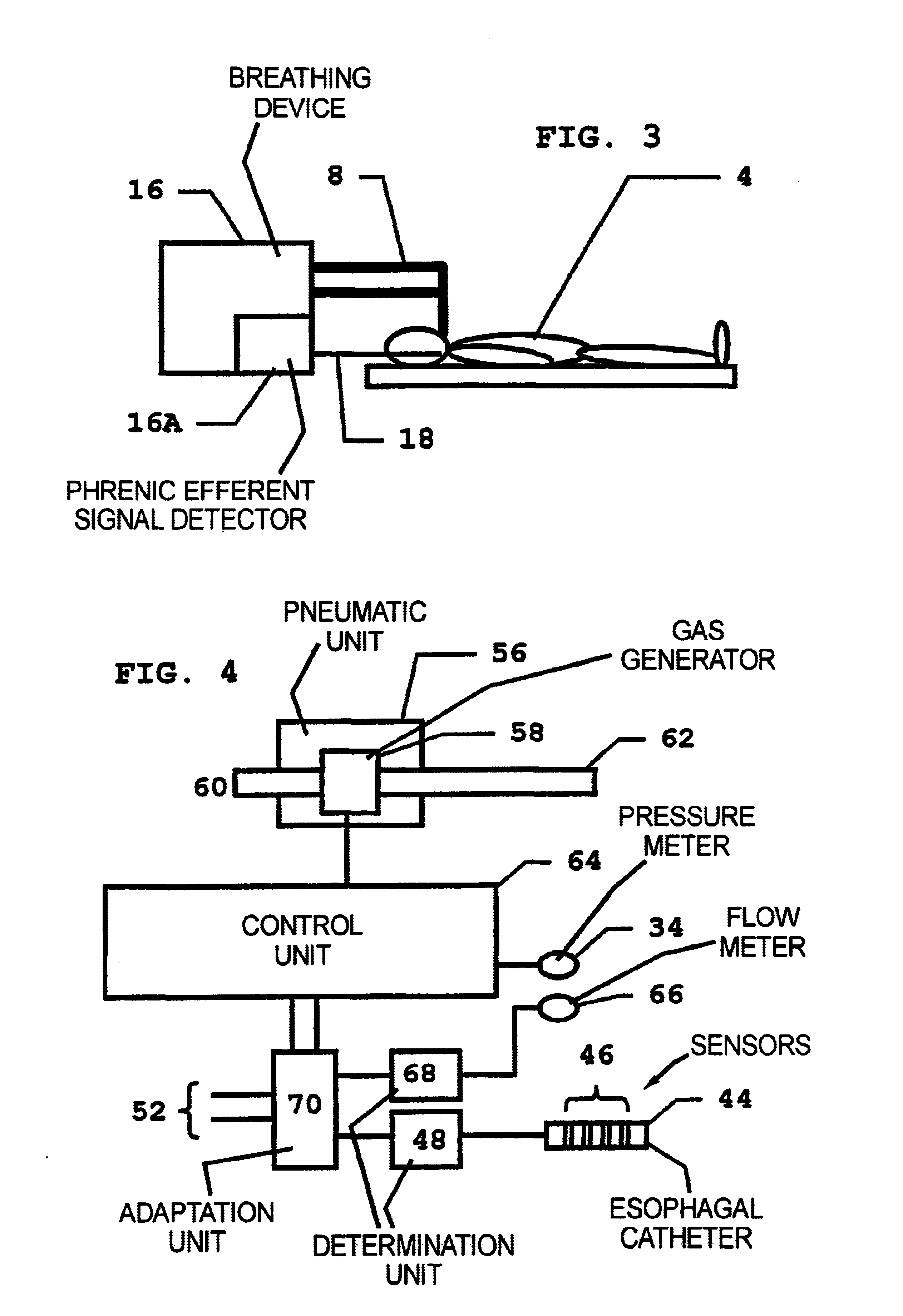
InactiveUS6837241B2Improves trigger methodRisk minimizationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory phaseExcitable cell
In a method for adaptive triggering of respiratory phases in a breathing device, and a breathing device operating according to the method, first respiration indicator signal is determined based on at least one of the parameters flow and pressure, the respiration indicator signal is compared with a trigger requirement and a trigger signal is generated when the respiration indicator signal fulfils the trigger requirement. In order to shorten response times to respiration changes without losing stability, an excitable cell signal related to respiration is measured, and a second respiration indicator signal is determined based on the measured excitable cell signal, and the trigger requirement is adapted in relation to the second respiration indicator signal.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
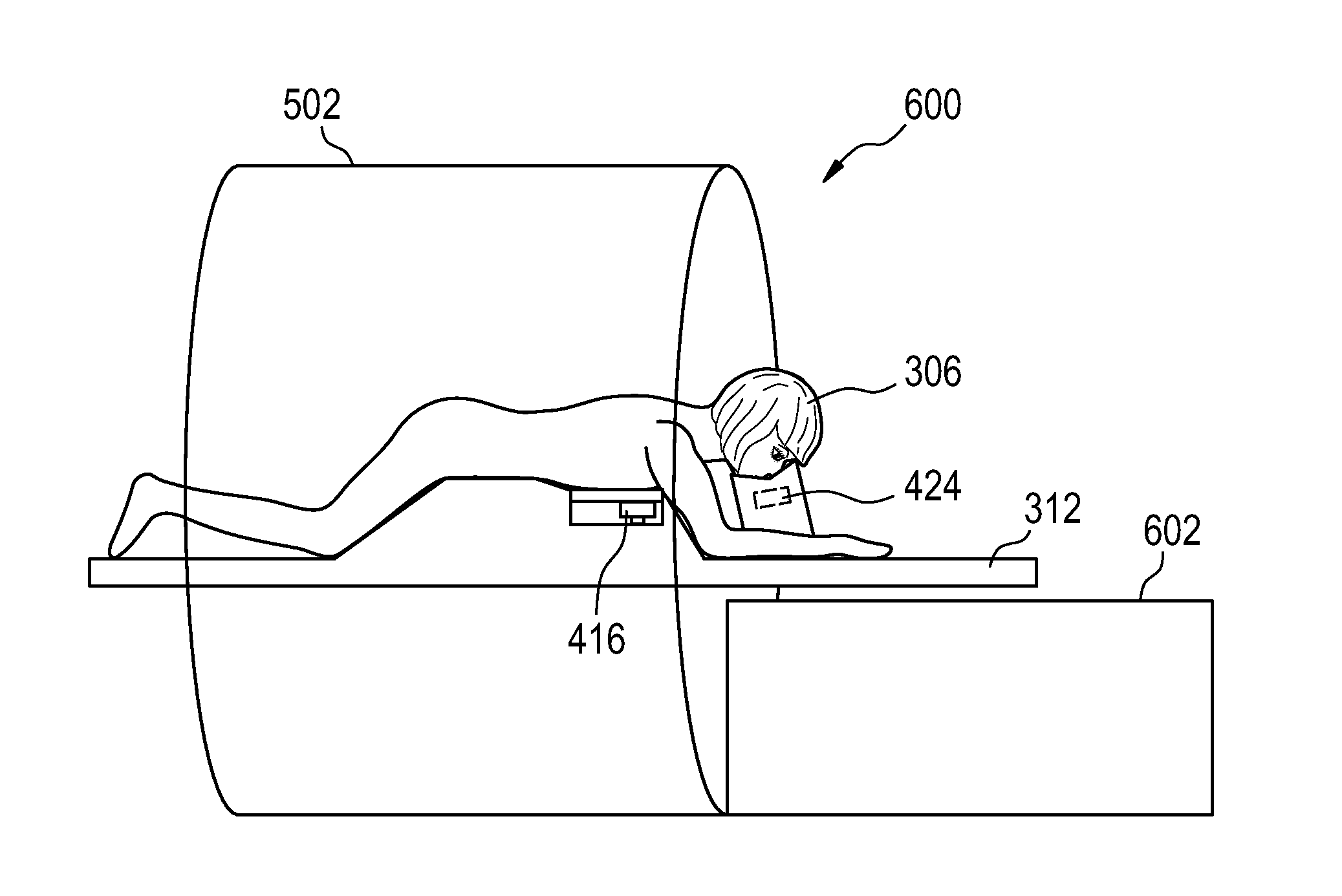
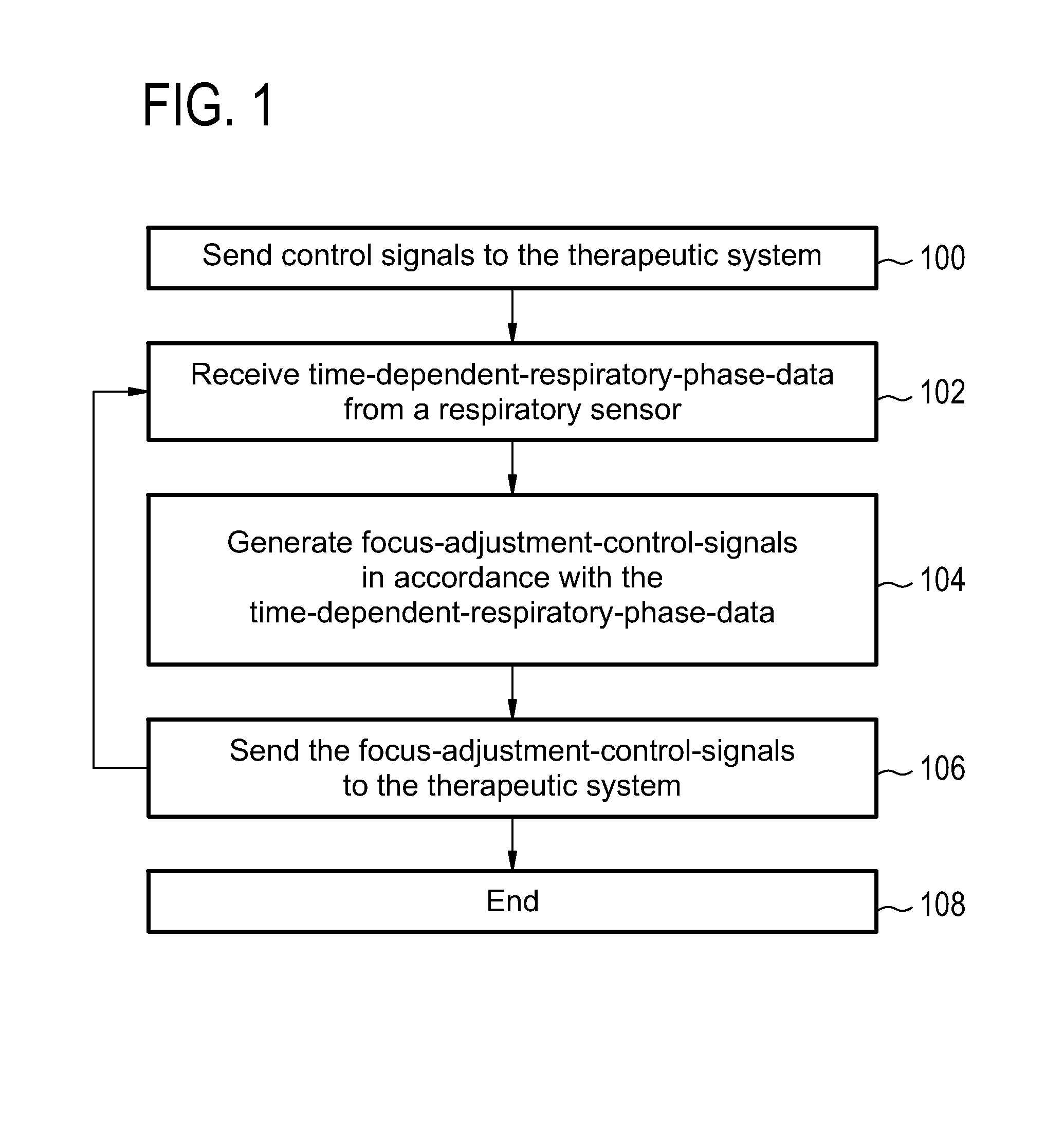
Therapeutic apparatus, computer-implemented method, and computer program product for controlling the focus of radiation into a moving target zone
A therapeutic apparatus (300, 400, 500, 600) comprising: a therapeutic system (302, 402) for treating a target zone (304) of a subject (306), wherein the therapeutic system has an adjustable focus for directing radiation (410) into the target zone; a respiration sensor (308, 310, 416, 424) for measuring a respiratory phase of the subject; a processor (322) for controlling the therapeutic apparatus; and a memory (326, 328) containing machine executable instructions (340, 342, 344, 346, 348, 350, 352) for execution by the processor, wherein execution of the instructions causes the processor to: send (100, 206) control signals to the therapeutic system that cause treatment of the target zone, receive (102, 208) time-dependant-respiratory-phase-data (330) from the respiration sensor, generate (104, 210) focus-adjustment-control-signals in accordance with the time-dependant-respiratory-phase-data, and send (106, 212) the focus-adjustment-control-signals to the therapeutic system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
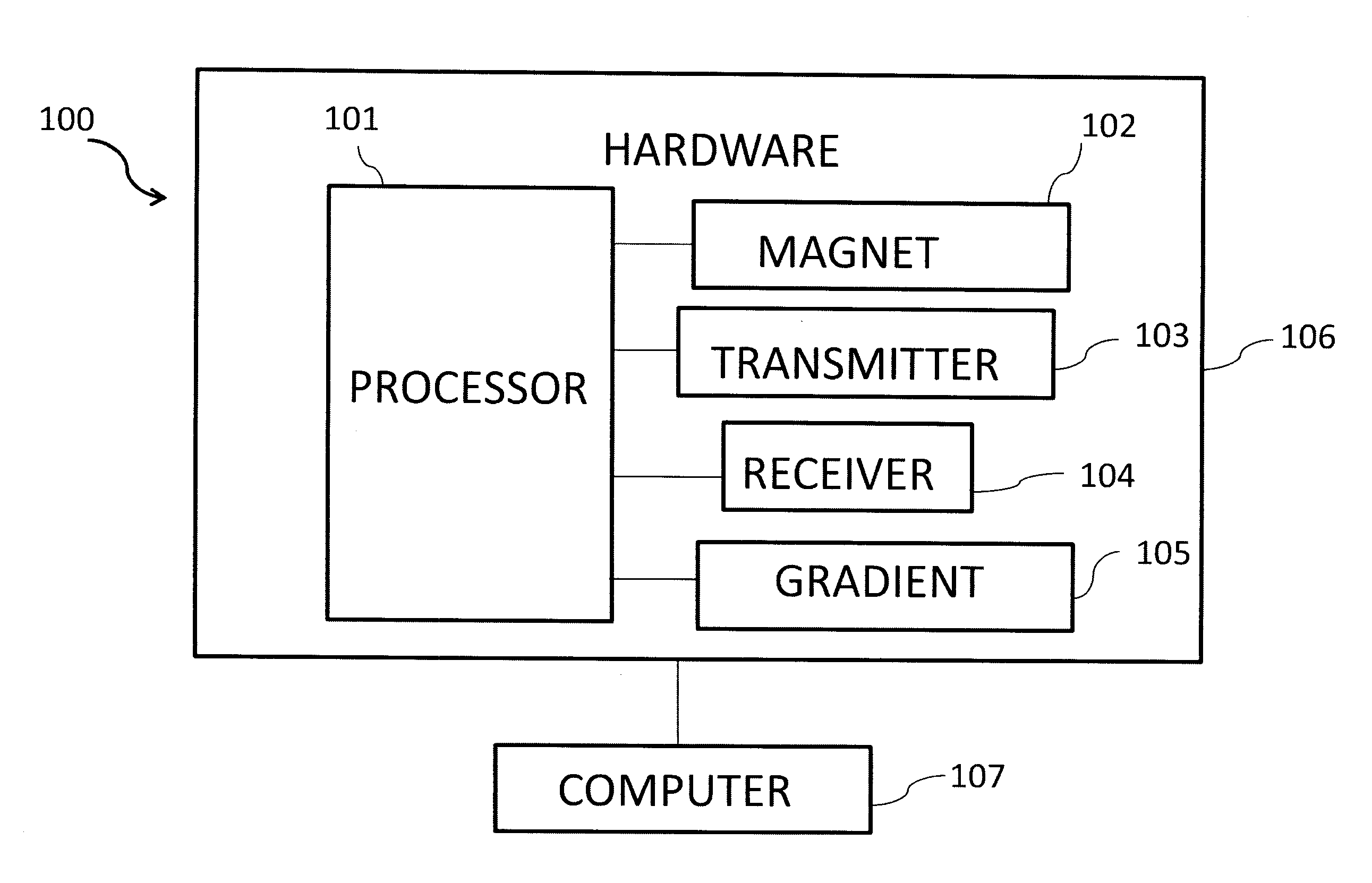
Characterization of respiratory motion in the abdomen using a 4d MRI technique with 3D radial sampling and respiratory self-gating
ActiveUS20160324500A1Magnetic measurementsOrgan movement/changes detectionRespiratory phaseAnesthesia
In some embodiments, the present application discloses utilizing a continuous spoiled gradient echo sequence with 3D radial trajectory and 1D self-gating for respiratory motion detection. In certain embodiments, data acquired are retrospectively sorted into different respiratory phases based on their temporal locations within a respiratory cycle, and each phase is reconstructed via a self-calibrating CG-SENSE program.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Method and apparatus for phrenic nerve activation detection with respiration cross-checking
The present invention concerns phrenic nerve activation detection algorithms for characterization of phrenic nerve activation and phrenic nerve activation avoidance in cardiac pacing therapy.Various embodiments concern receiving a respiration signal indicative of respiratory activity of the patient, identifying respiratory phases based on the respiration signal, delivering cardiac pacing pulses within each of the identified respiratory phases, receiving a phrenic nerve activation signal indicative of activation of the patient's phrenic nerve, analyzing the phrenic nerve stimulation signal to determine if one or more of the pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient, and determining if at least one of the delivered pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient based on the phrenic nerve activation signal indicating activation of the patient's phrenic nerve associated with delivery of the at least one cardiac pacing pulse.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
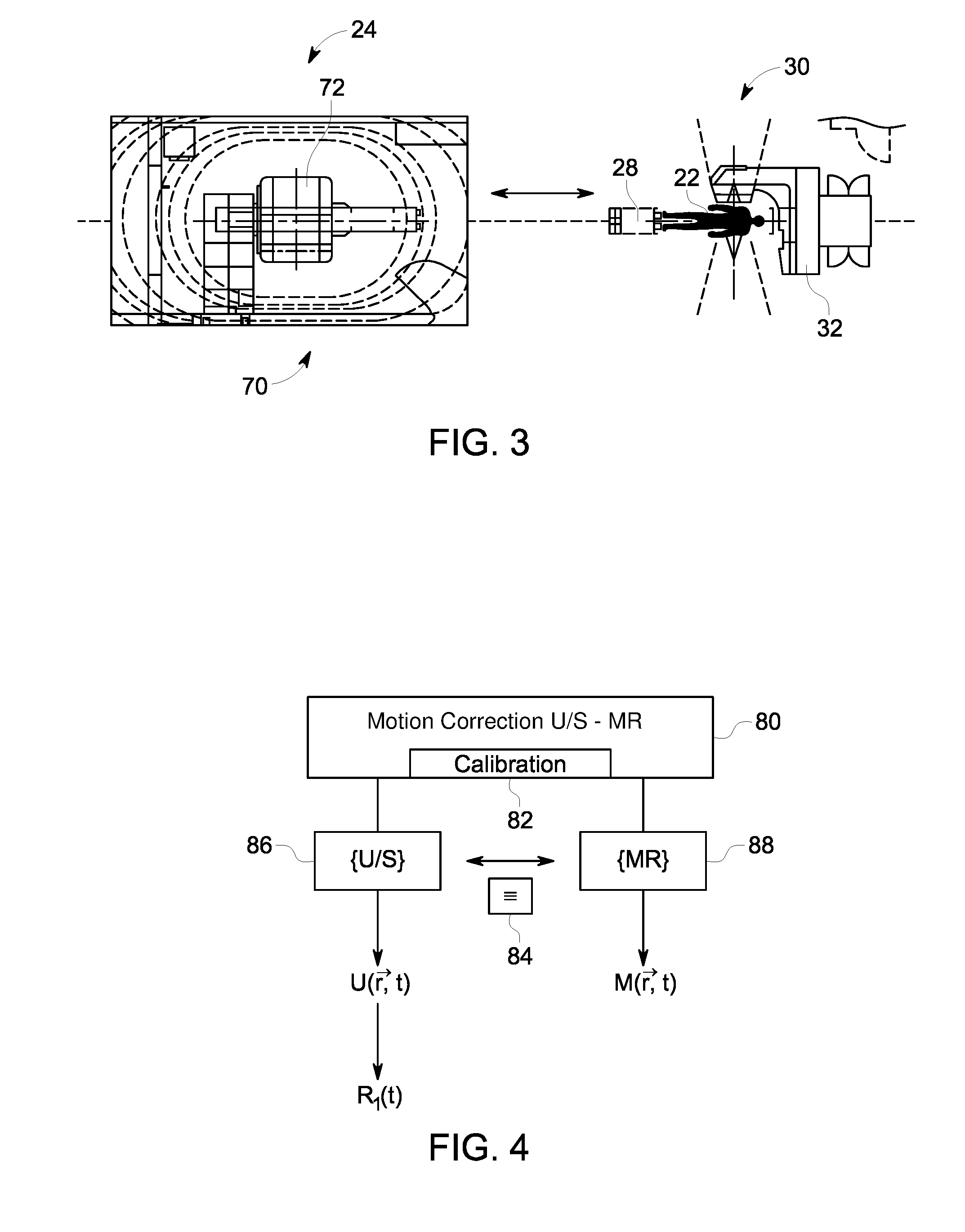
Respiratory motion determination apparatus
ActiveUS20140133717A1Improved respiratory motion compensationGood compensationImage enhancementMedical imagingRespiratory gatingIntermediate image
The invention relates to a respiratory motion determination apparatus for determining respiratory motion of a living being (3). A raw data providing unit (2) provides raw data assigned to different times, wherein the raw data are indicative of a structure like the apex of the heart muscle, which is influenced by cardiac motion and by respiratory motion, and a reconstruction unit (6) reconstructs intermediate images of the structure from the provided raw data. A structure detection unit (7) detects the structure in the reconstructed intermediate images, and a respiratory motion determination unit (10) determines the respiratory motion of the living being based on the structure detected in the reconstructed intermediate images. This allows determining respiratory motion with high accuracy, without relying on, for example, a stable correlation between a tracking signal of an external respiratory gating device and respiratory phases.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Systems, methods, and/or apparatuses for non-invasive monitoring of respiratory parameters in sleep disordered breathing
ActiveUS8646447B2Increase pressureEliminate side effectsRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPulse oximetersSleep disordered breathing
In certain example embodiments, an air delivery system includes a controllable flow generator operable to generate a supply of pressurized breathable gas to be provided to a patient for treatment and a pulse oximeter. In certain example embodiments, the pulse oximeter is configured to determine, for example, a measure of patient effort during a treatment period and provide a patient effort signal for input to control operation of the flow generator. Oximeter plethysmogram data may be used, for example, to determine estimated breath phase; sleep structure information; autonomic improvement in response to therapy; information relating to relative breathing effort, breathing frequency, and / or breathing phase; vasoconstrictive response, etc. Such data may be useful in diagnostic systems.
Owner:RESMED LTD
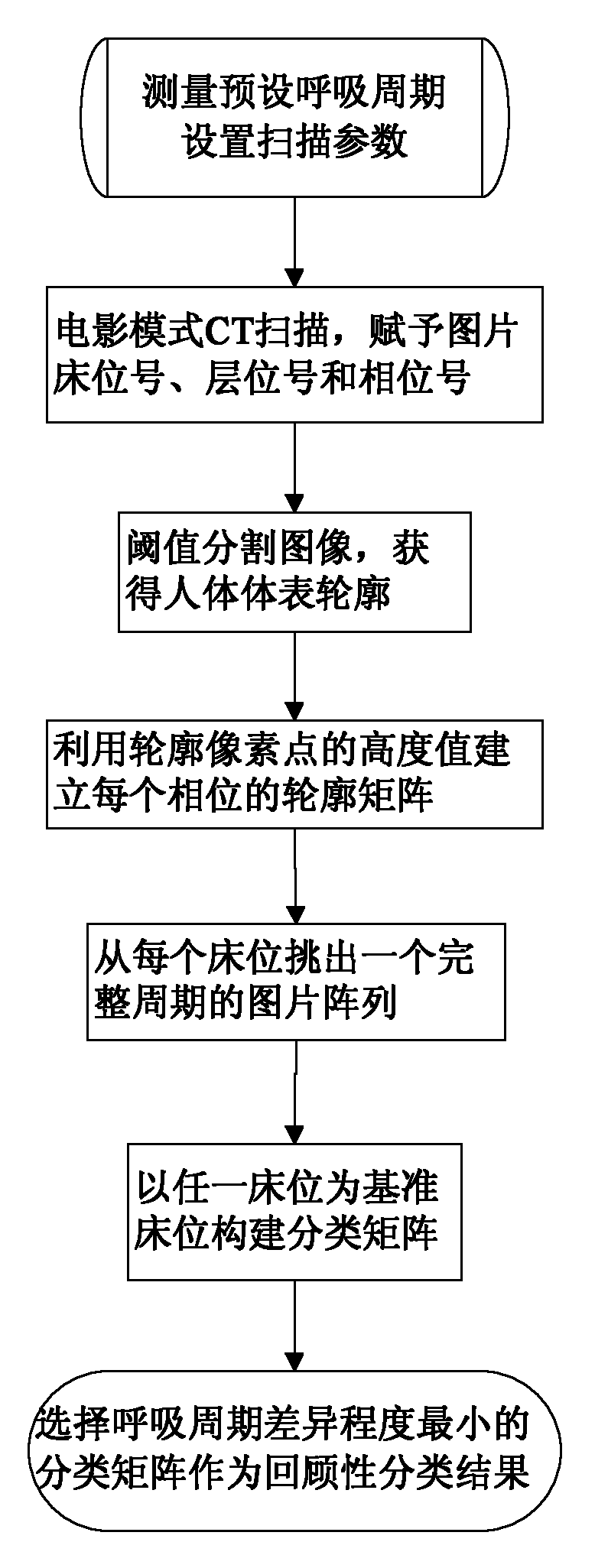
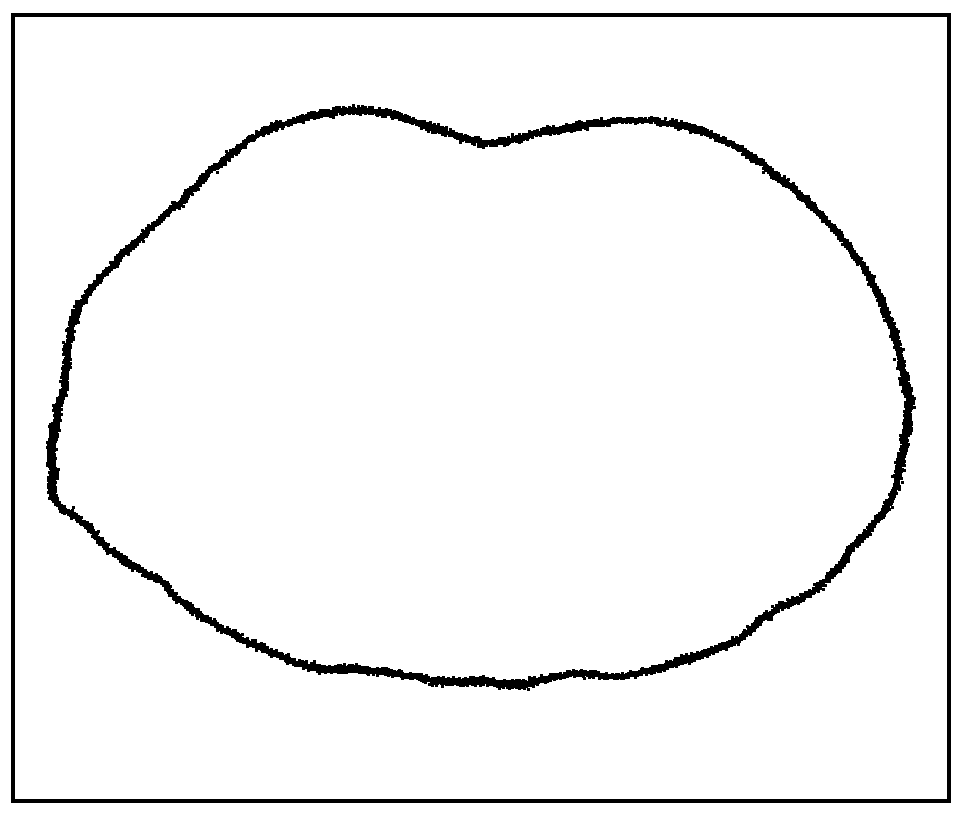
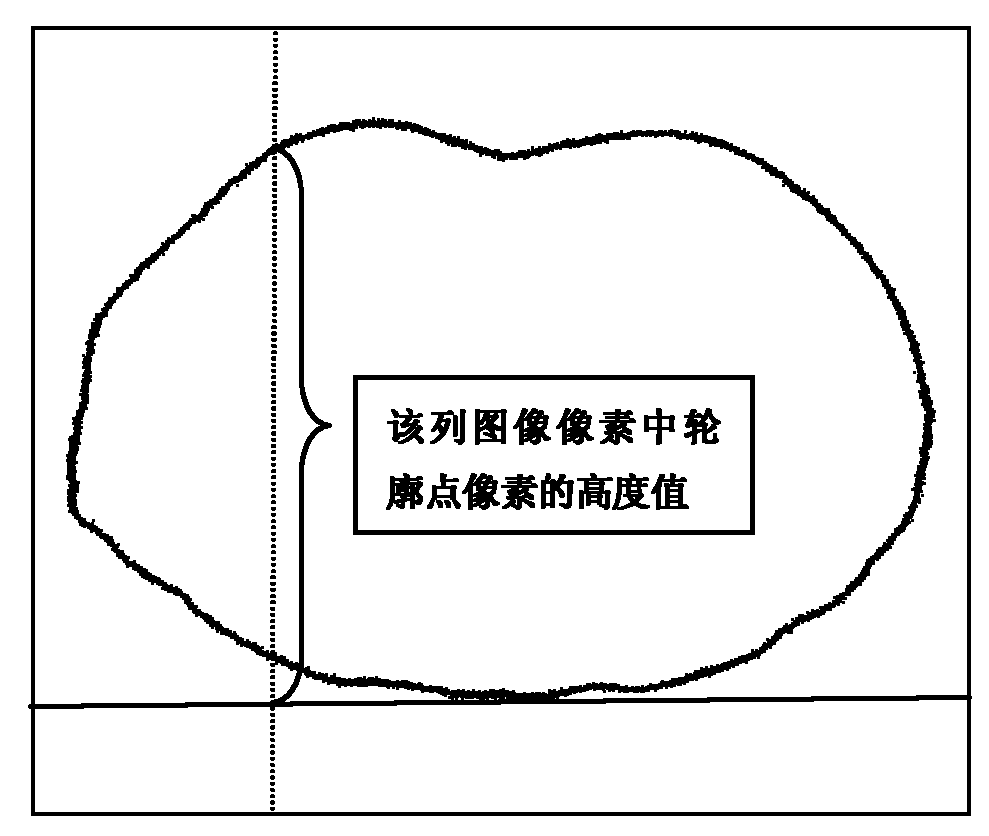
Method for retrospectively classifying chest or abdomen computed tomography (CT) images based on respiratory phase
InactiveCN102068271AImprove accuracyComputerised tomographsTomographyClassification methodsAbdomen computed tomography
The invention relates to a method for retrospectively classifying chest or abdomen computed tomography (CT) images based on a respiratory phase. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring a preset respiratory cycle and setting parameters of CT scanning; performing movie-mode CT scanning so as to obtain images and endowing each image with a bed number, a layer number and a phase number; performing threshold value segmentation on each image so as to obtain the surface profile of a human body; establishing a profile matrix of each phase by using the height values of pixel points of the surface profile of the human body; accumulating the height values of elements in the profile matrix of each phase and picking out a group of images which correspond to a maximum accumulated sum value from each bed, wherein the group of images serve as an image array of a complete cycle; performing cubic spline smooth fitting on each row of vectors of a profile matrix between two phases by taking any bed as a reference bed, calculating the distance sum of profile height difference between adjacent layers of two phases and picking out image sequence numbers with the minimum distance sum so as to establish a classification matrix; and selecting a classification matrix with the minimum retrospective cycle difference degree, wherein the classification matrix is taken as a retrospective classification result.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for four dimensional intensity modulated radiation therapy for motion compensated treatments
InactiveUS7835493B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersCharacter and pattern recognitionTumour volumeAnatomical structures
A deliverable four dimensional (4D) intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) planning method is disclosed, for delivery using a linear accelerator with a dynamic multi-leaf collimator (DMLC). A 4D computed tomography (CT) scan is used for segmenting tumor anatomy on a reference phase of periodic motion of the tumor. Deformable registration of the 4D CT data is used to generate corresponding anatomical structures on other phases. Preferably, the collimator for each beam position is aligned using the gross tumor volume (GTV) centroid motion corresponding to the periodic motion of the tumor, as determined from the two dimensional (2D) projection of a given beam position. A deliverable IMRT plan is created on the 4D CT image set in which the MLC leaf positions and beam on / off status can vary as a function of respiratory phase by solving a four dimensional optimization problem. The mechanical constraints of the MLC leaves are included in the optimization.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
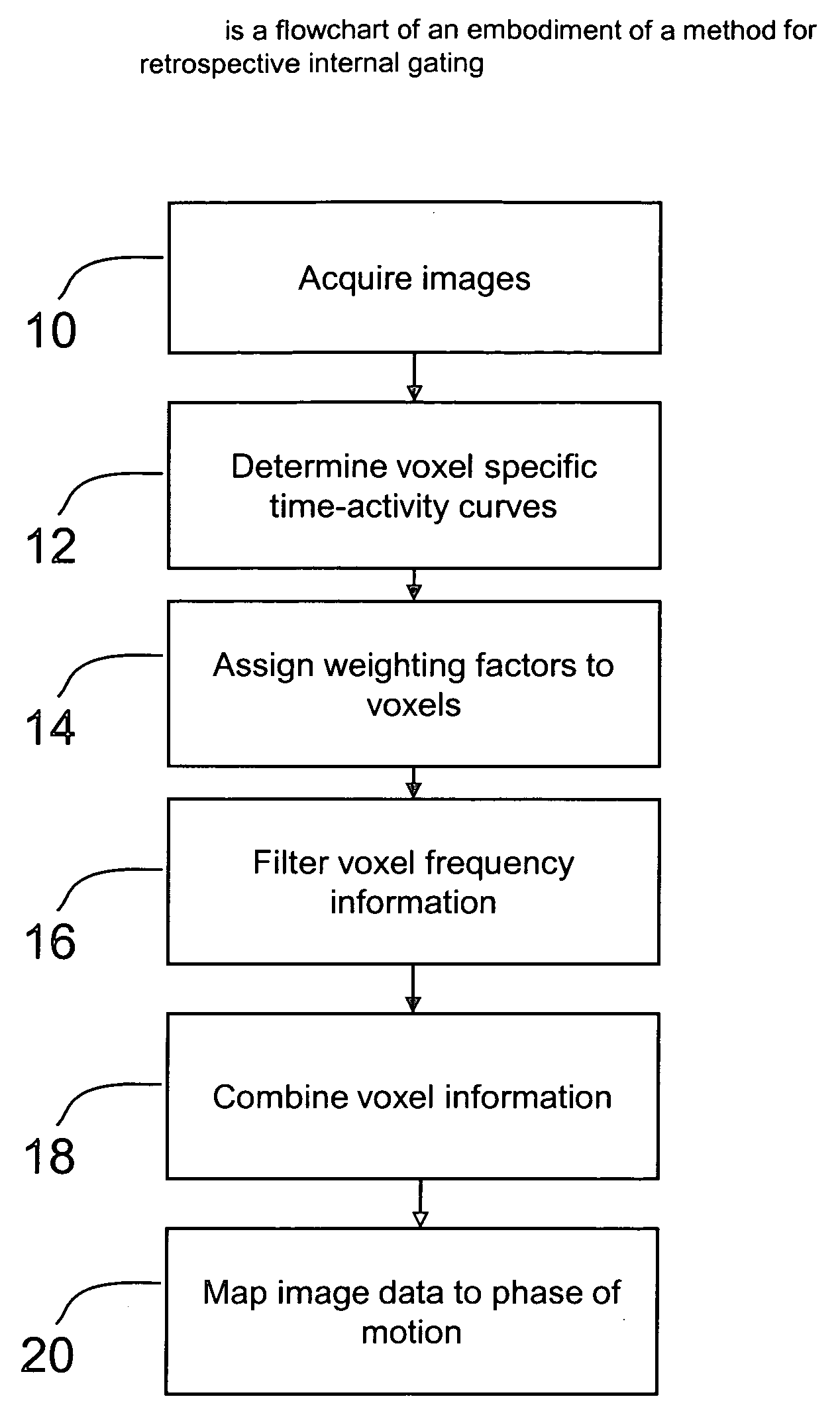
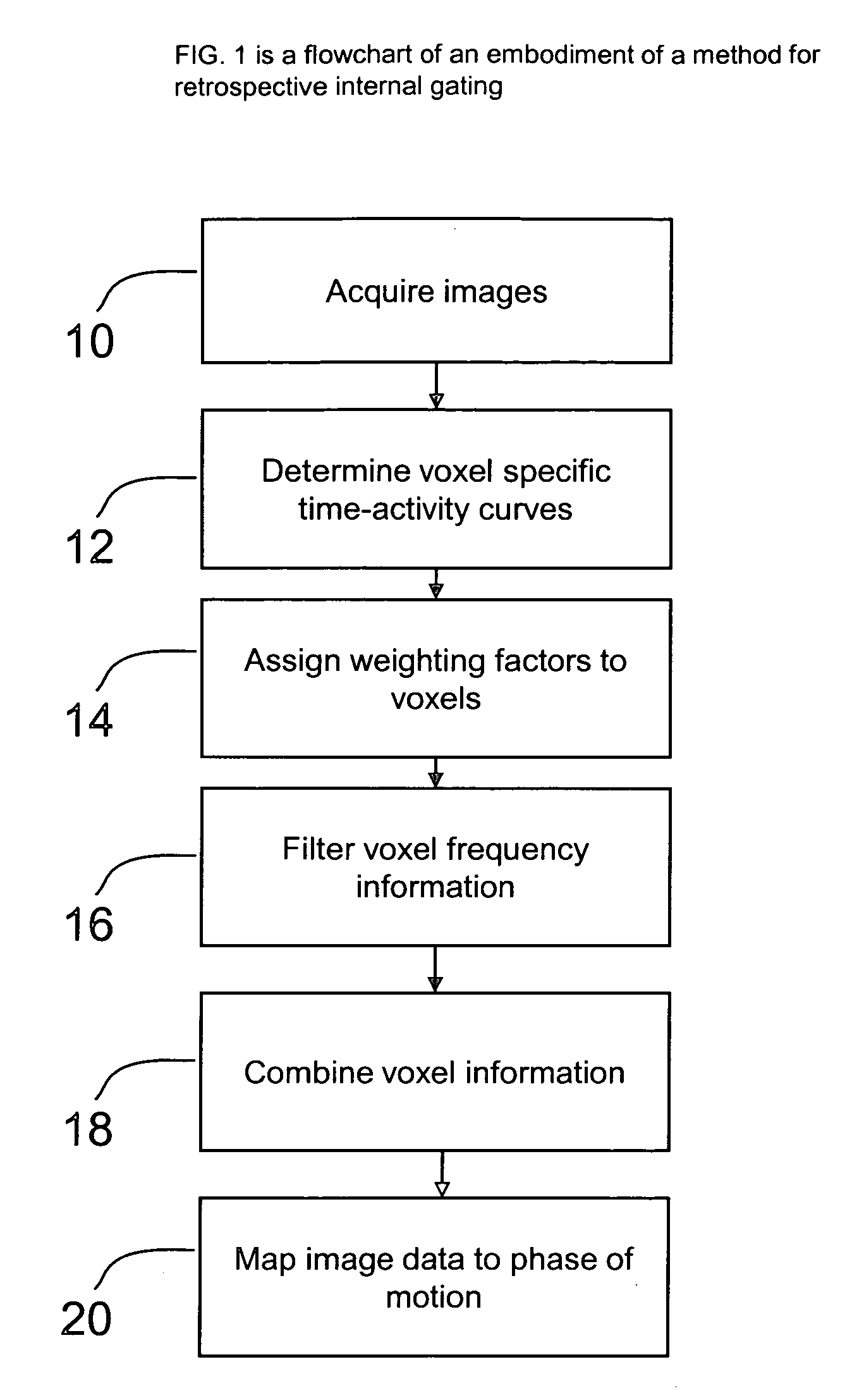
Methods and systems for retrospective internal gating
ActiveUS20080273785A1Character and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringVoxelRespiratory phase
The present invention, in one form, is a method for deriving respiratory gated PET image reconstruction from raw PET data. In reconstructing the respiratory gated images in accordance with the present invention, respiratory motion information derived from individual voxel signal fluctuations, is used in combination to create usable respiratory phase information. Employing this method allows the respiratory gated PET images to be reconstructed from PET data with out the use of external hardware, and in a fully automated manner.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
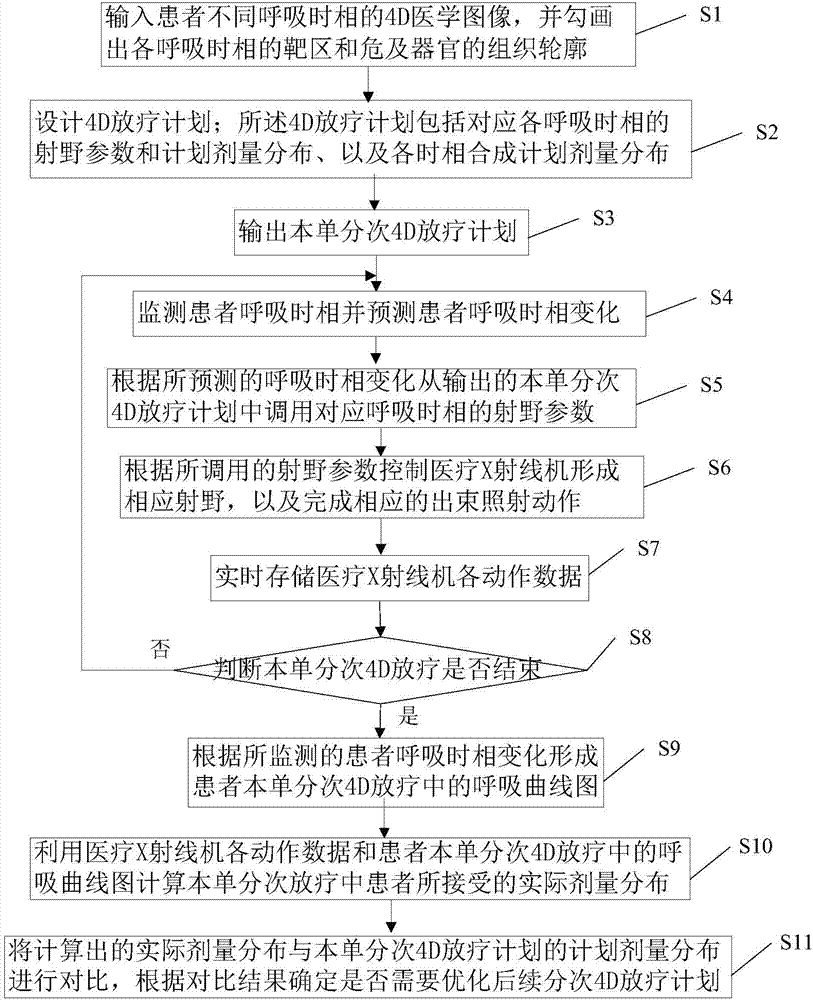
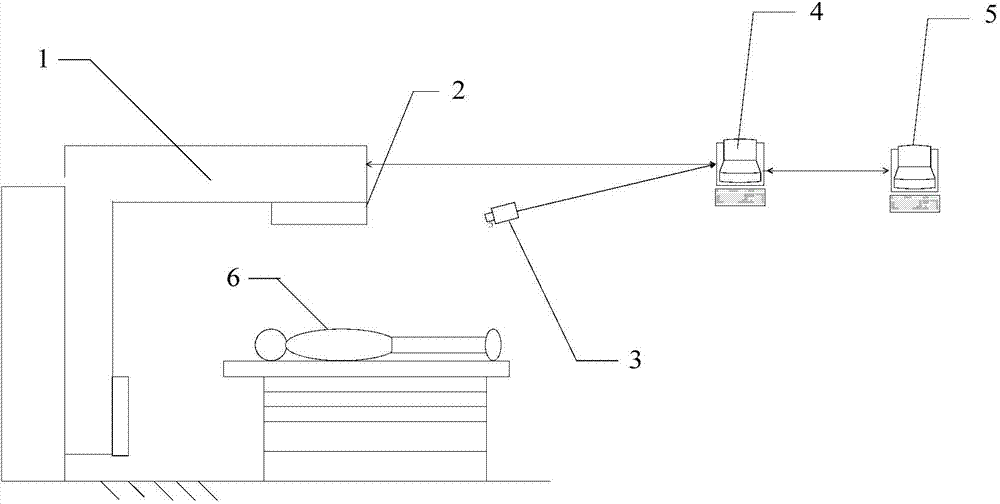
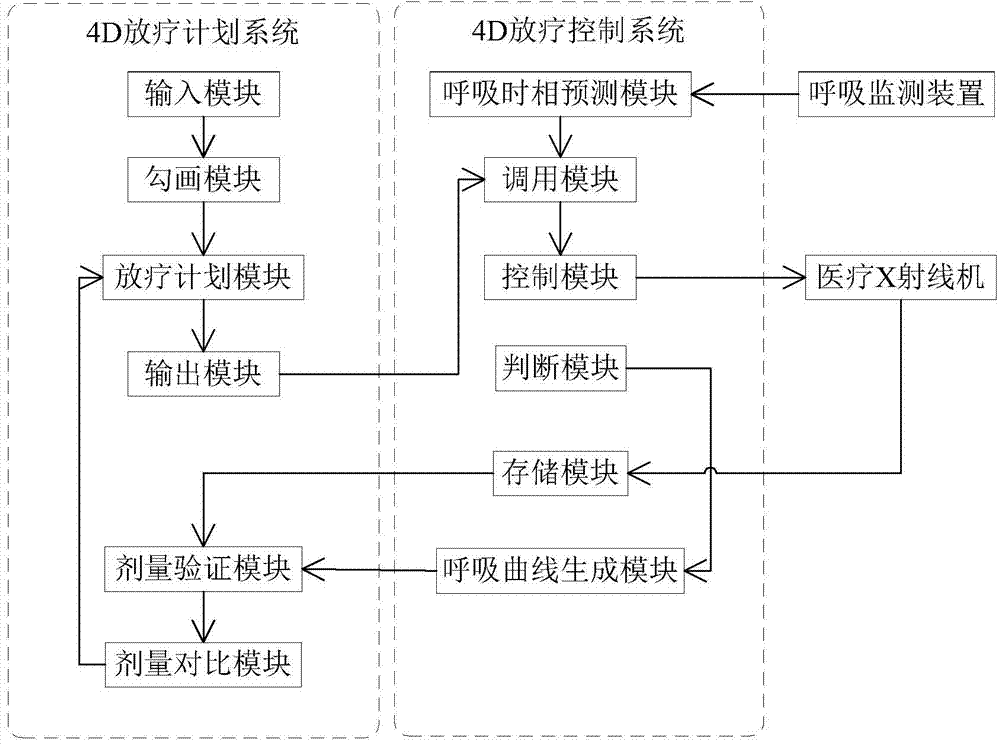
Implementation method and equipment for 4D radiotherapy plan with respiratory compensation
ActiveCN104225809AResolution timeSolution rangeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRespiratory compensationRespiratory phase
The invention discloses an implementation method and equipment for a 4D radiotherapy plan with respiratory compensation. The implementation method includes steps that inputting 4D medical images of different respiratory phases of a patient, and sketching a target region of each respiratory phase and a tissue outline of an organ at risk; designing the 4D radiotherapy plan; monitoring the respiratory phases of the patient and forecasting the respiratory phase change of the patient; dispatching field parameters corresponding to the respiratory phases; controlling a medical X-ray machine to form a corresponding field to finish the corresponding beam irradiation action; judging whether the 4D radiotherapy is ended, if so, forming a respiration curve diagram for the 4D radiotherapy of the patient; calculating the actual dosage distribution accepted by the patient in the radiotherapy; comparing the calculated actual dosage distribution with the planed dosage distribution of the 4D radiotherapy plane, and determining whether optimizing the subsequent 4D radiotherapy plan according to the comparative result. The implementation method and equipment for the 4D radiotherapy plan with the respiratory compensation is capable of accurately determining a four-dimensional radiotherapy target.
Owner:大连现代医疗设备科技有限公司
Radiation emission control method, apparatus and program
InactiveUS20060025672A1Minimize exposureConstant precisionRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsRespiratory phaseRadiation rays
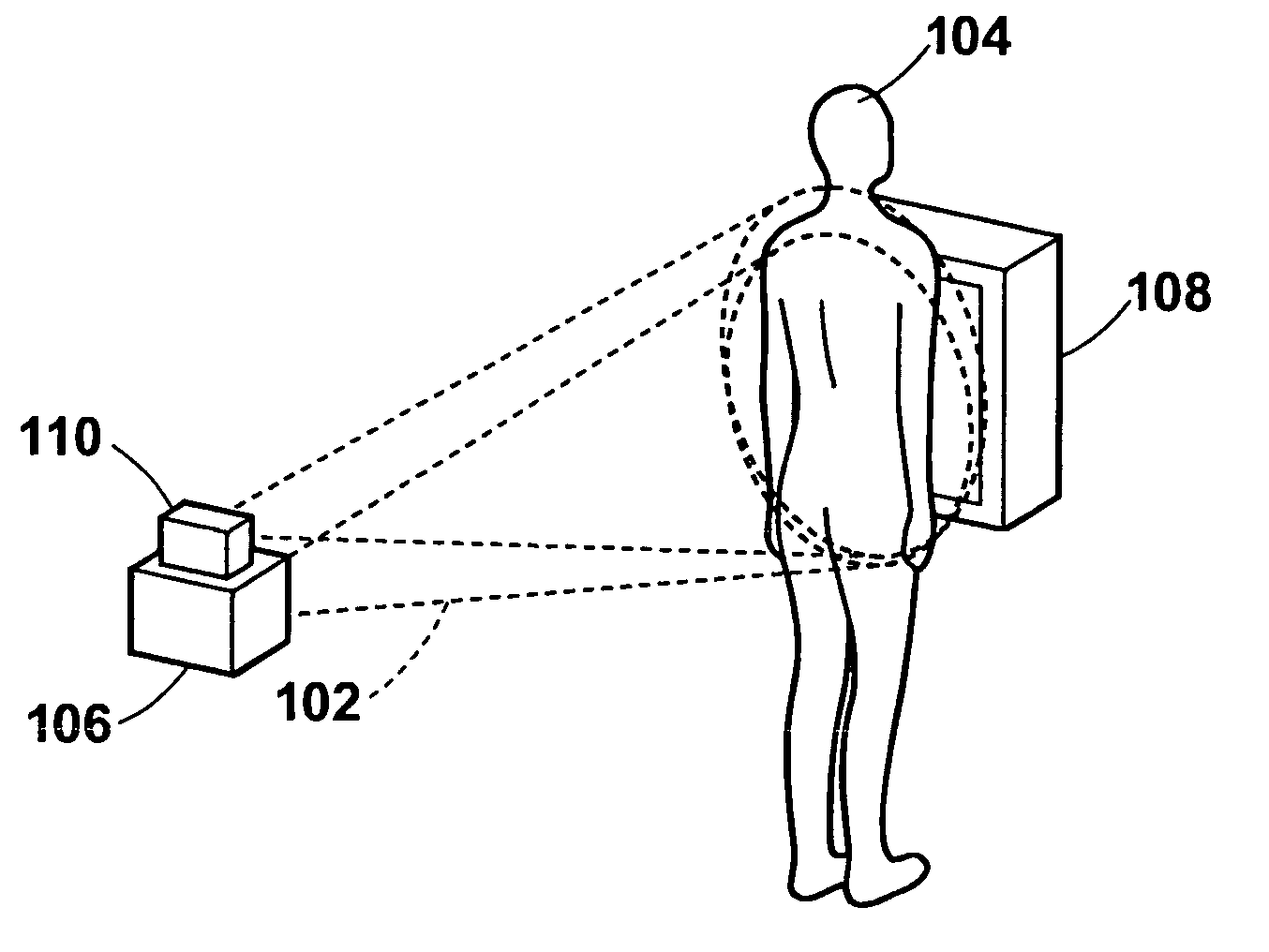
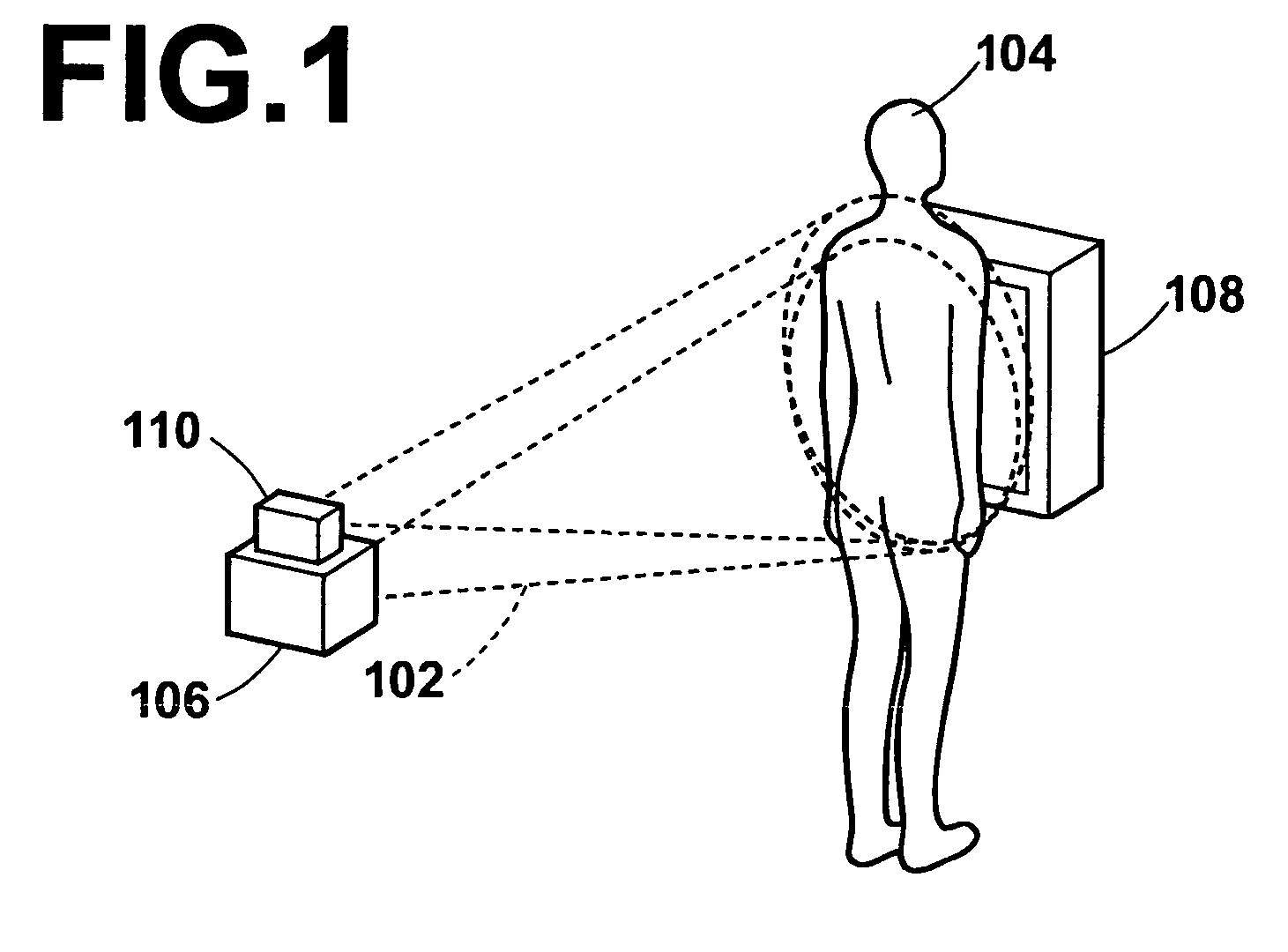
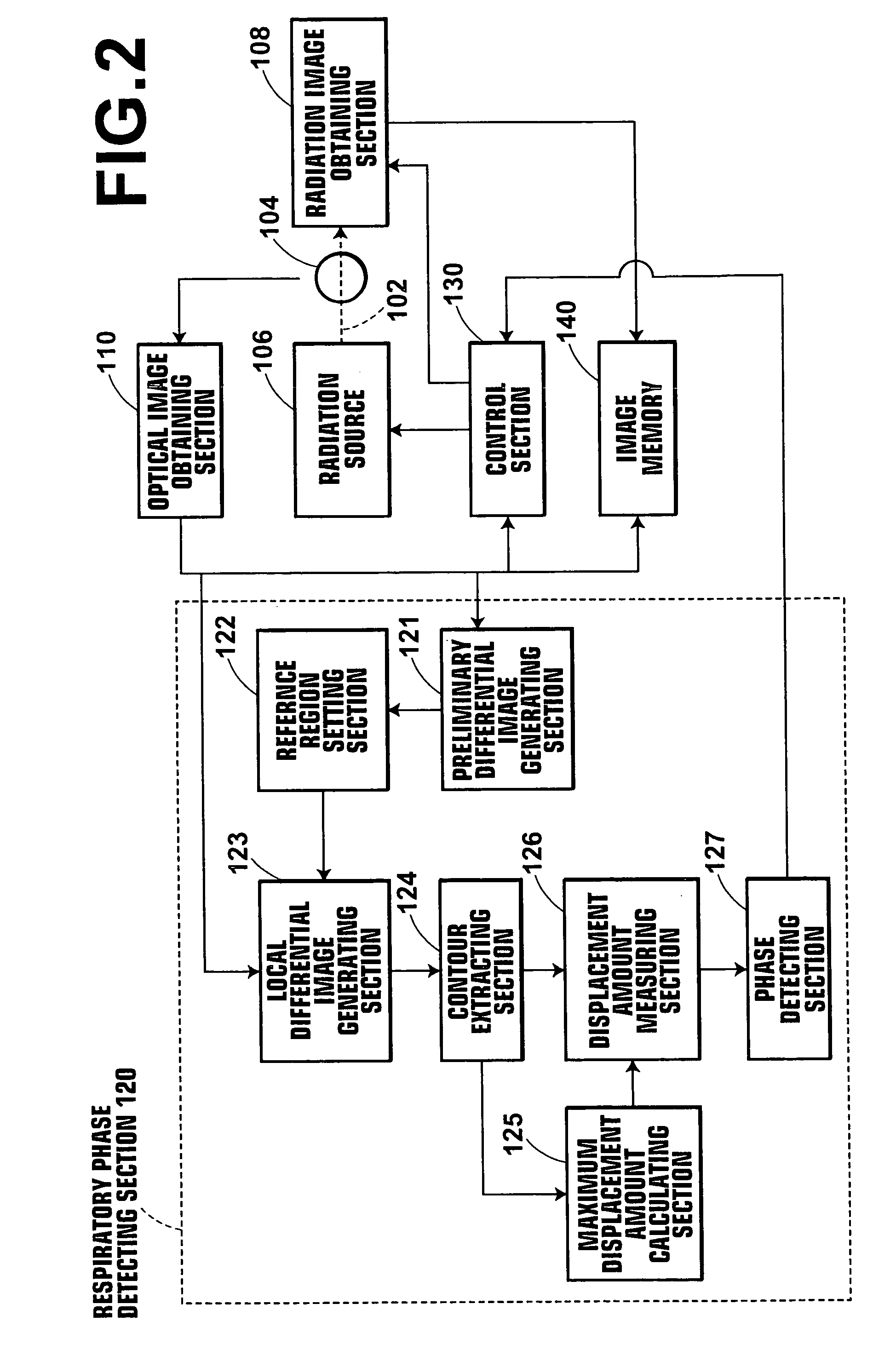
A radiation emission control method, apparatus and the program capable of detecting respiratory phases of a test subject with constant accuracy and emitting radiation rays to the test subject in synchronization with an intended respiratory phase, while minimizing the radiation exposure to the subject. A test subject having a contour that varies with the respiration is optically imaged continuously by the optical image obtaining section to sequentially obtain optical images of the subject, and respiratory phases of the subject are detected simultaneously with the optical imaging by the respiratory phase detecting section based on the contour of the subject on the optical images. During the optical imaging, a radiation source is controlled by the control section such that radiation rays are emitted to the test subject when the detected respiratory phase corresponds to an intended respiratory phase of the subject.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method for sorting ct image slices and method for constructing 3D ct image
ActiveUS20130195341A1Reduce and eliminate defectReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionRespiratory phase3d image
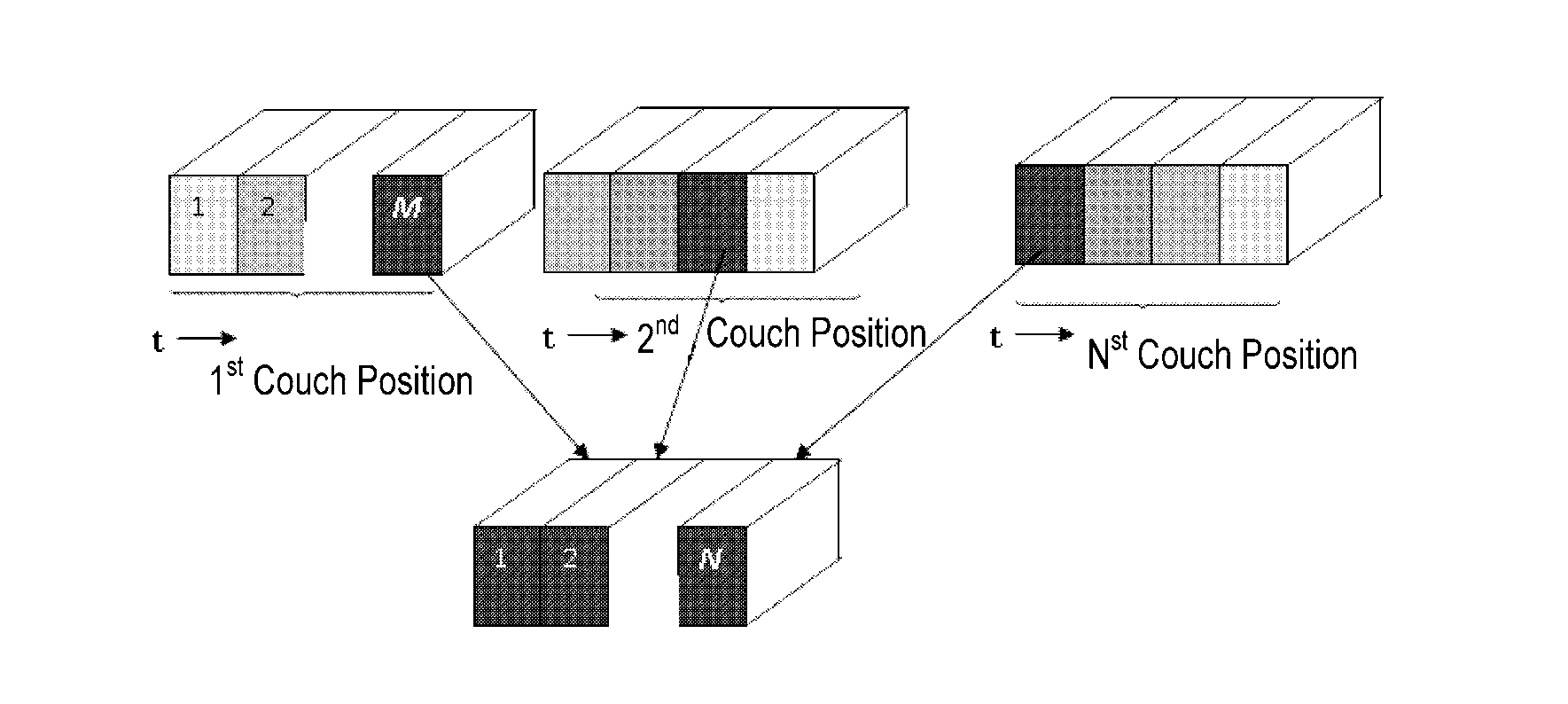
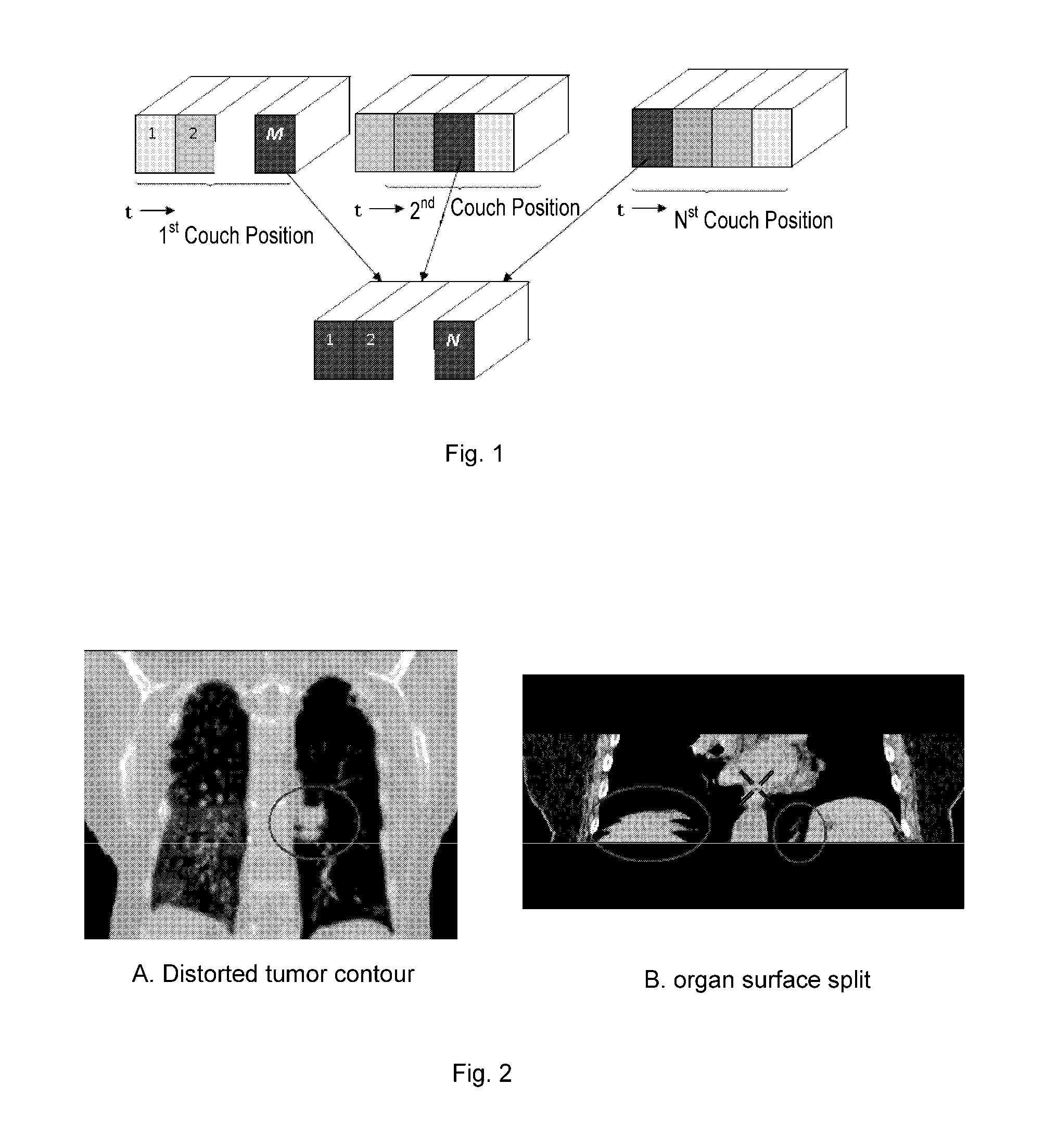
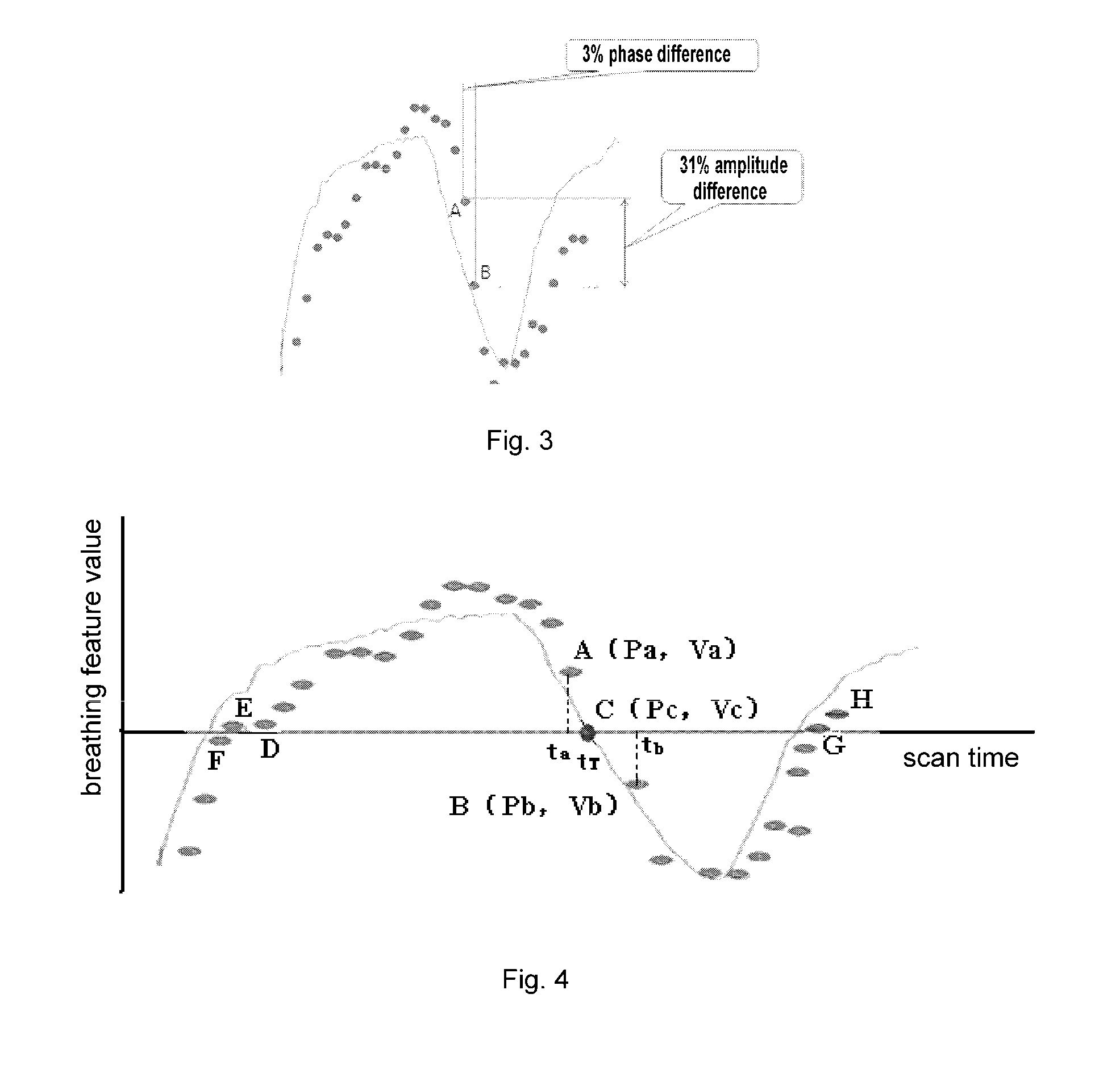
A method for sorting CT image slices comprising, if no image slice comprises a target respiratory phase at a couch position, determining a target breathing feature value corresponding to the target respiratory phase based on a respiratory motion curve of a scanned patient, searching from a plurality of image slices at the couch position for one or more image slices comprising a breathing feature value close to the target breathing feature value to serve as candidate image slices, and selecting, based on a breathing feature value difference between the breathing feature value of each of the candidate image slices and the target breathing feature value and / or an image difference between each of the candidate image slices and at least one reference image slice, a single image slice from the candidate image slices for constructing the 3D CT image for the target respiratory phase.
Owner:GE HANGWEI MEDICAL SYST
Ultrasound contrast perfusion parameter imaging method based on respiratory motion compensation
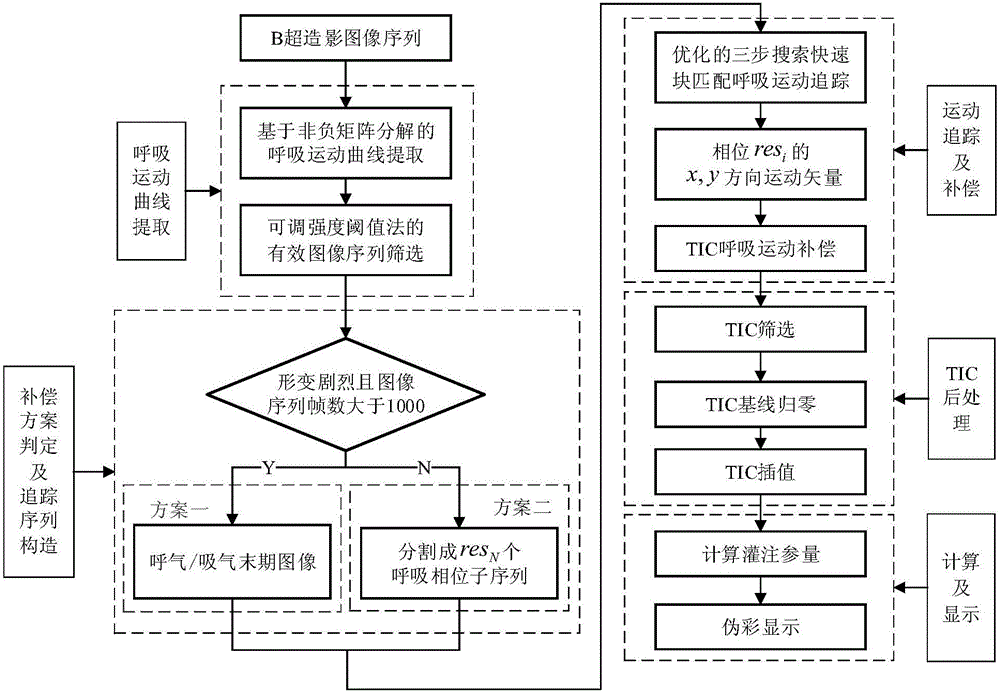
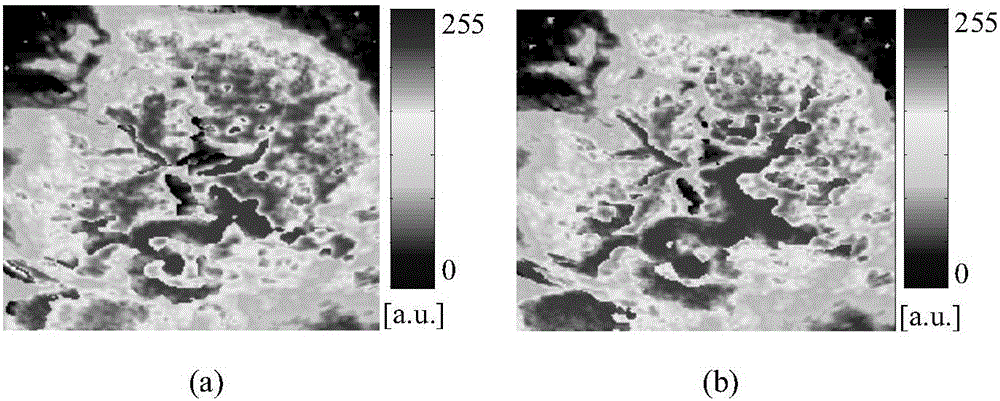
ActiveCN106056589AAvoid difficult choicesPhysically goodUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMatrix decompositionSonification
The invention provides an ultrasound contrast perfusion parameter imaging method based on respiratory motion compensation. Tracking sequences are built for respiratory phase subsequences at the last stages of exhalation and inhalation by combining a respiratory motion curve obtained through nonnegative matrix decomposition and two respiratory motion compensation schemes based on frame selection and respiratory phase segmentation, block matching respiratory motion displacement vector tracking calculation based on coarse-to-fine three-step search is performed, targeted characteristic compensation is performed on TIC of subsequence images corresponding to all respiratory phases, and finally, a perfusion parameter image after respiratory motion compensation is obtained. Compared with other perfusion parameter motion compensation methods, the method avoids complex manual frame selection and can well adapt to the organs in the abdomen, and the motion curve obtained through nonnegative matrix decomposition has good physiological significance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Method and system for respiratory phase classification using explicit labeling with label verification
InactiveUS20100262031A1Auscultation instrumentsMedical automated diagnosisRespiratory phaseAlgorithm
A method and system classify respiratory phases in a single channel acoustic signal as inspiratory and expiratory using explicit labeling with label verification. In the method and system, a subject explicitly indicates through a user input the start of a respiratory cycle (i.e. start of inspiration). The phase indication is applied to provisionally label several consecutive phases of a single channel acoustic signal as inspiratory and expiratory. A provisional phase rule set is then generated based on characteristic differences between the inspiratory and expiratory phases. The phase indication, provisional labeling and provisional rule set generation steps are then repeated. The two generated provisional rule sets are then compared for a match to verify the accuracy of the subject's phase indications and the ability to automatically recover phase in the event of signal loss.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
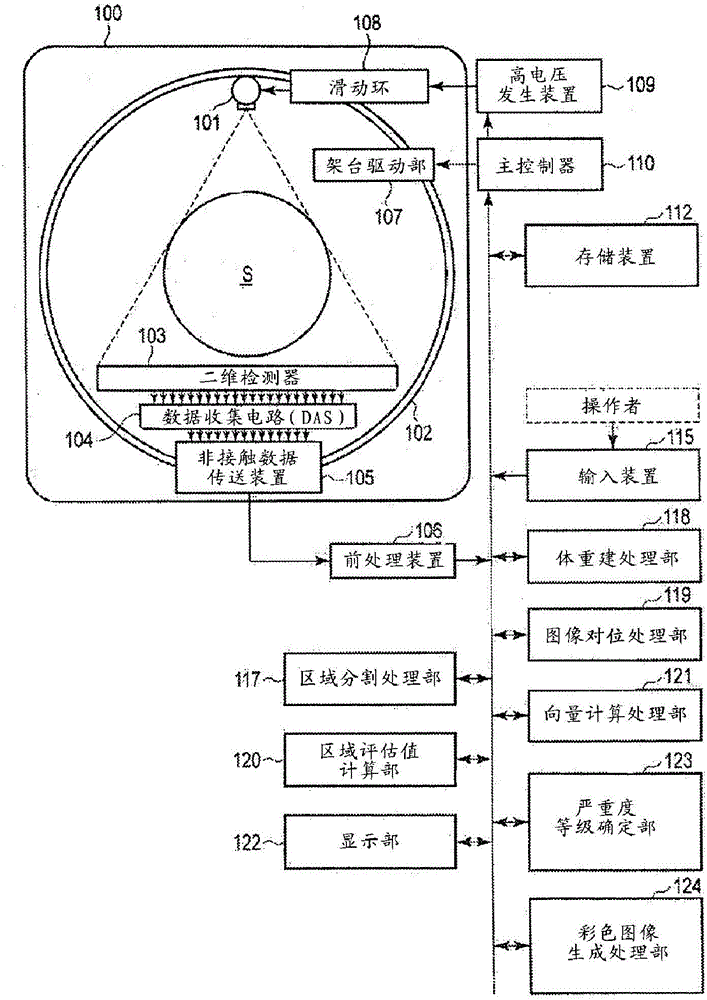
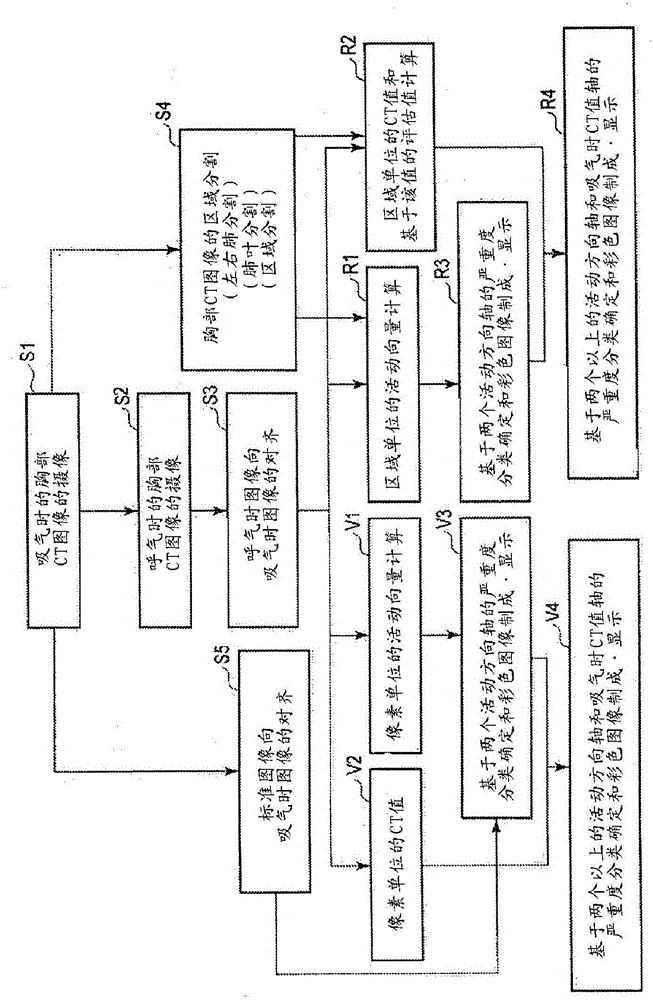
Medical image processing apparatus and medical image processing method
The present invention provides information that is an effective aid in diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease from thoracic volume images. The storage unit (112) of the medical image processing apparatus stores the data for multiple images of differing respiratory phases that represent the configuration of a subject's thoracic region. A vector-calculating unit (121) calculates the amount of movement of an area among the multiple images for each pixel or region. By combining at least two from among the amount of movement, a feature value determined from image pixel values and the rate of change in the size of a region, a level-determining unit (123) determines a level, which relates to the severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, for each pixel or region.
Owner:CANON MEDICAL SYST COPRPORATION +1
Method and system for using computed tomography to test pulmonary function
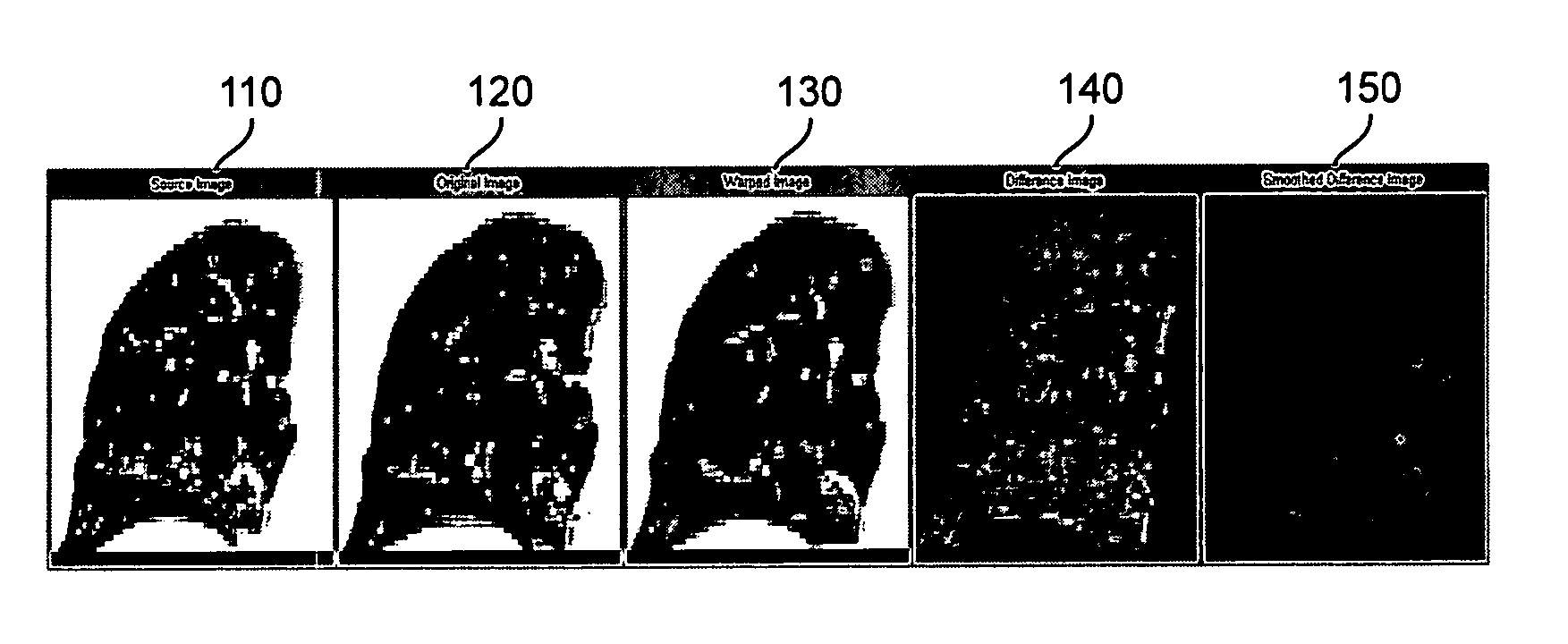
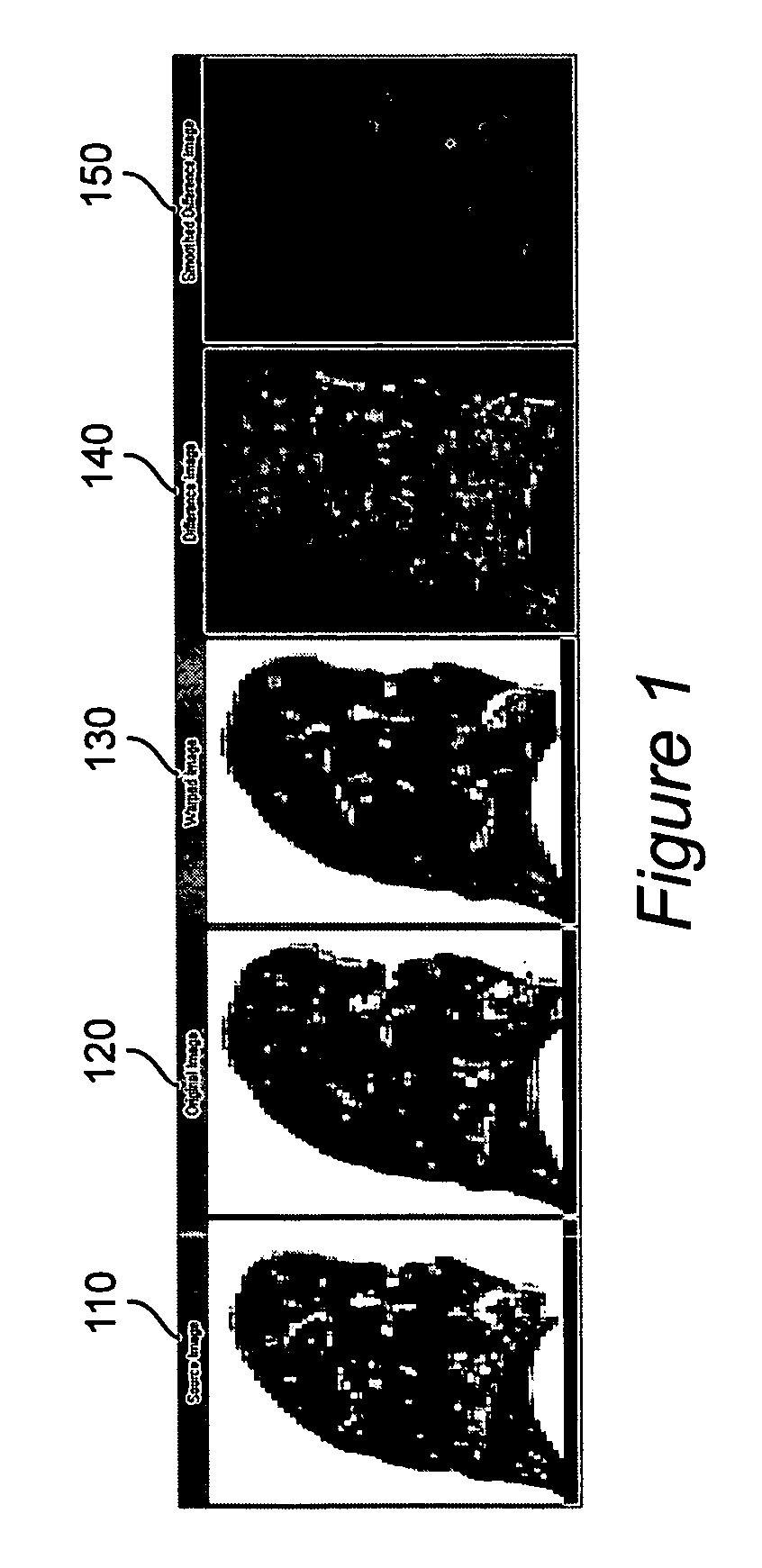
ActiveUS20070086636A1Image analysisRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsRespiratory phaseImage warping
Computed axial tomography images of different respiratory phases of lungs are obtained, where the intensity of the image measures lung density. One image is deformed to the coordinate space of the other image, and the differences between the intensity values of the other image as compared to the mapped image are evaluated as measures of ventilation.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
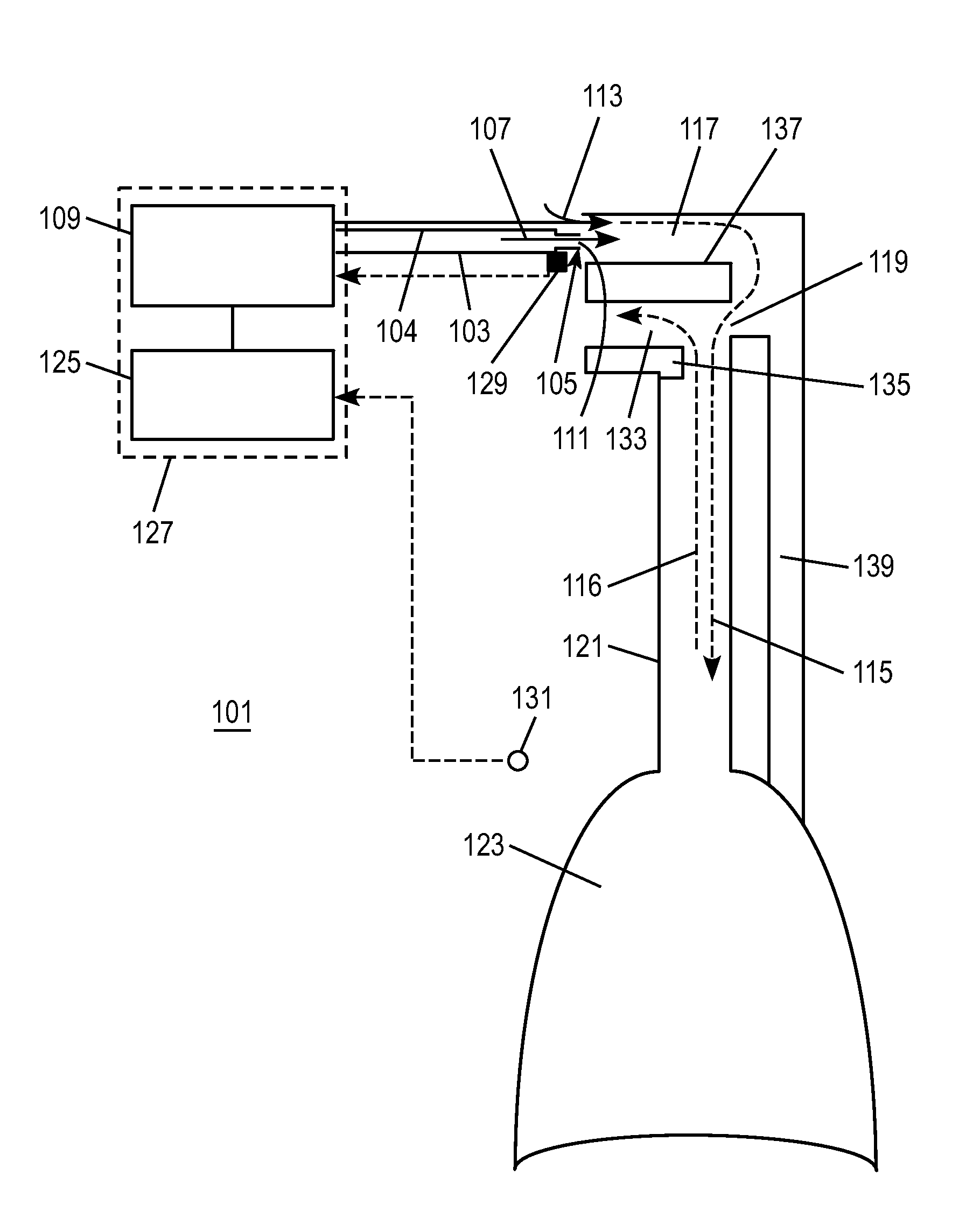
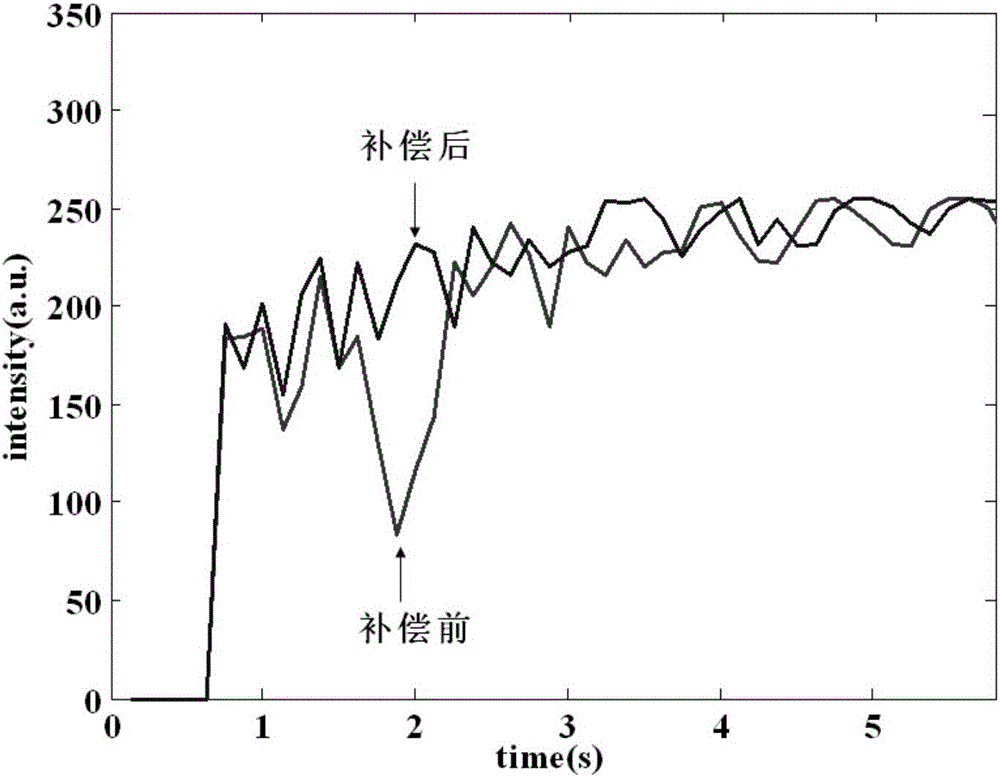
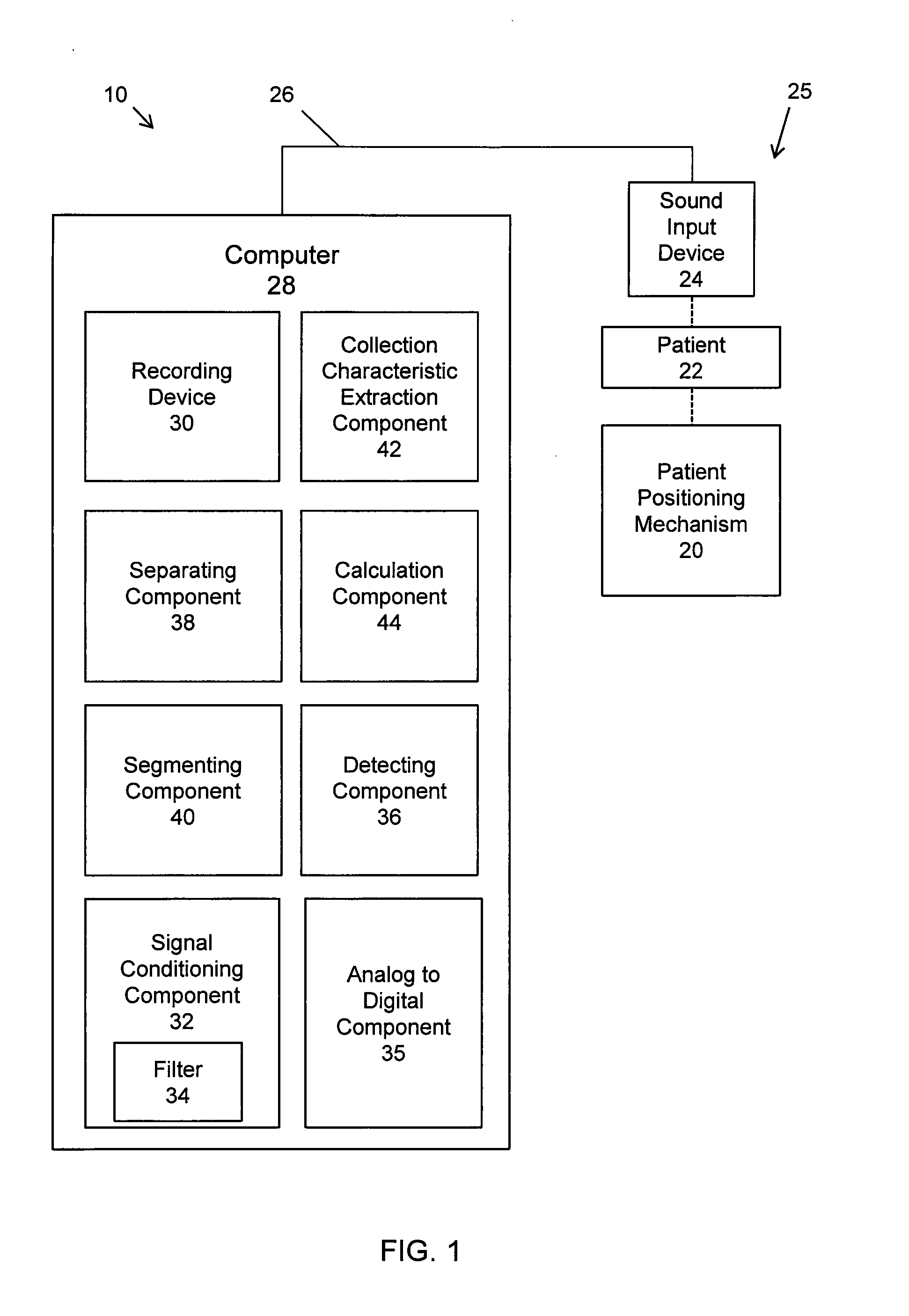
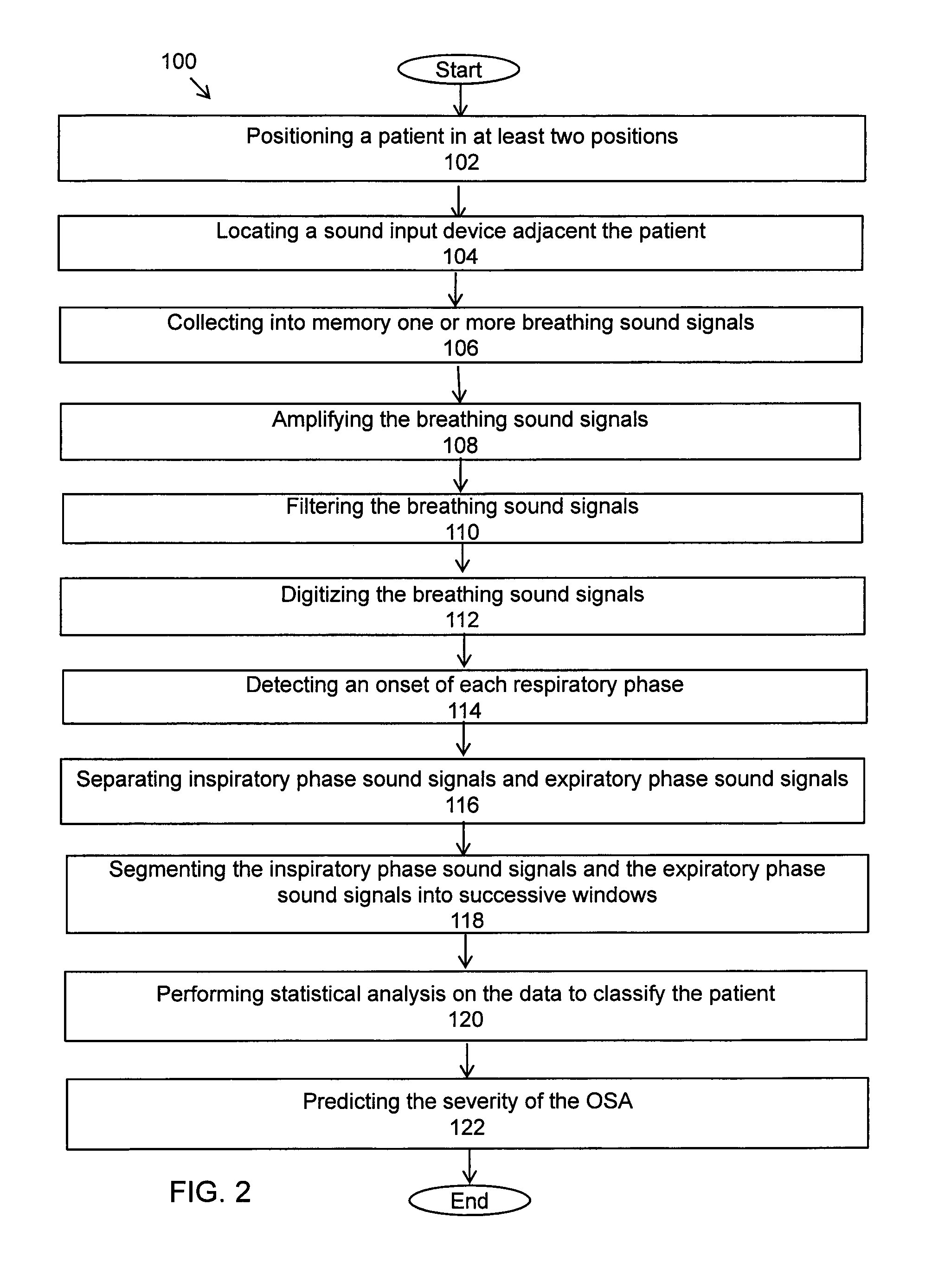
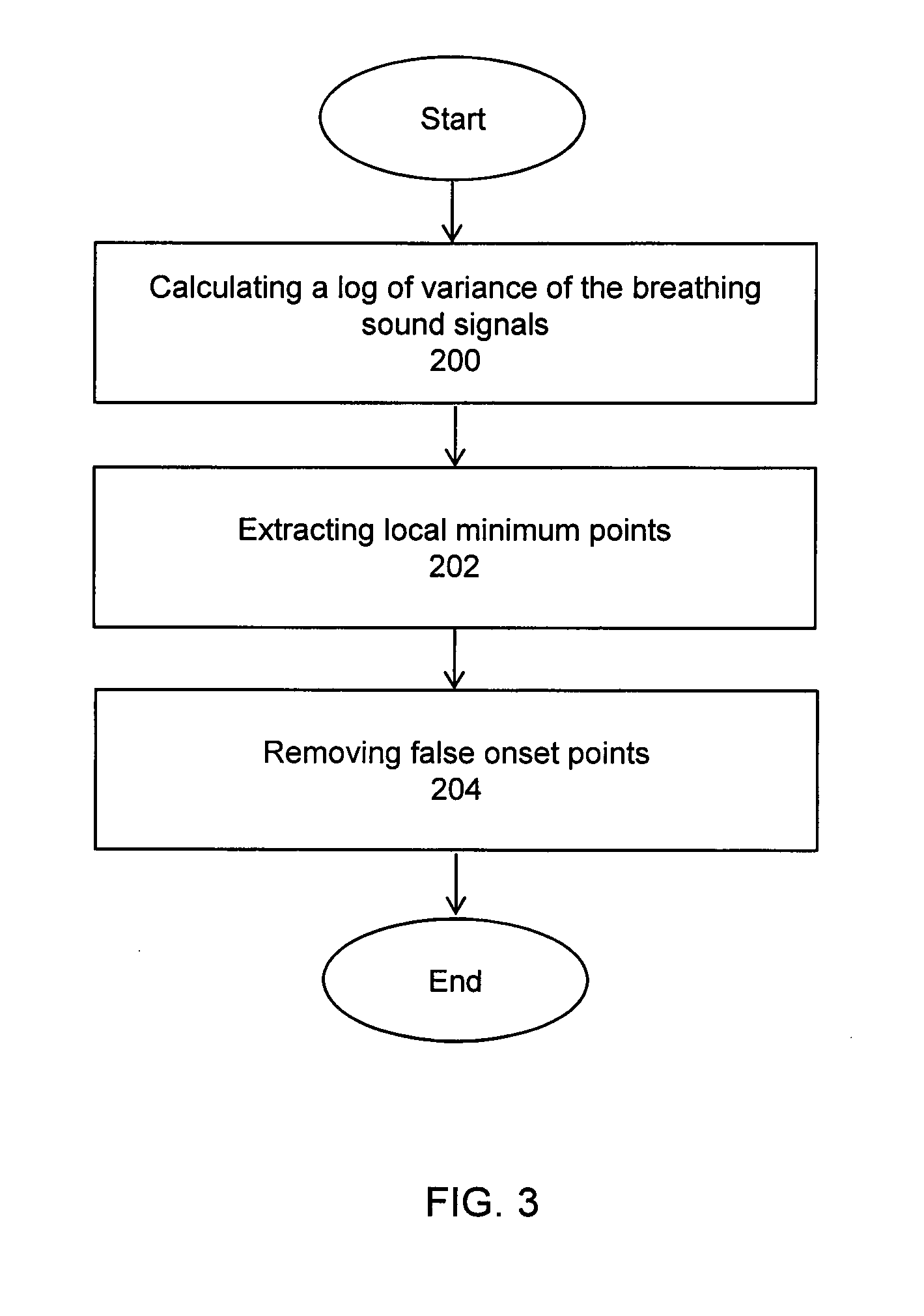
System and methods of acoustical screening for obstructive sleep apnea during wakefulness
ActiveUS20130253357A1Non invasiveComparable accuracyStethoscopeAcoustic sensorsRespiratory phaseFeature extraction
A system and methods using tracheal sound intensity variations to screen patients suspected of obstructive sleep apnea during wakefulness. The system includes a mechanism positioning the patient and a sound input device attached to a recording device to receive breathing sound signals. A signal conditioning component amplifies and filters the breathing sound signals, and an analog to digital component digitizes the signals. A detecting component detects onsets of respiratory phases, and a separating component separates inspiratory sound signals and expiratory sound signals from the breathing sound signals. A segmenting component segments the inspiratory and expiratory phase signals into a short duration of overlapping windows, and a collection characteristic extraction component obtains characteristics from each window. A calculation component performs statistical analysis to reduce the number of significant characteristics and classify the patient as OSA or non-OSA and predicts severity of the OSA as one of mild, moderate and severe.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
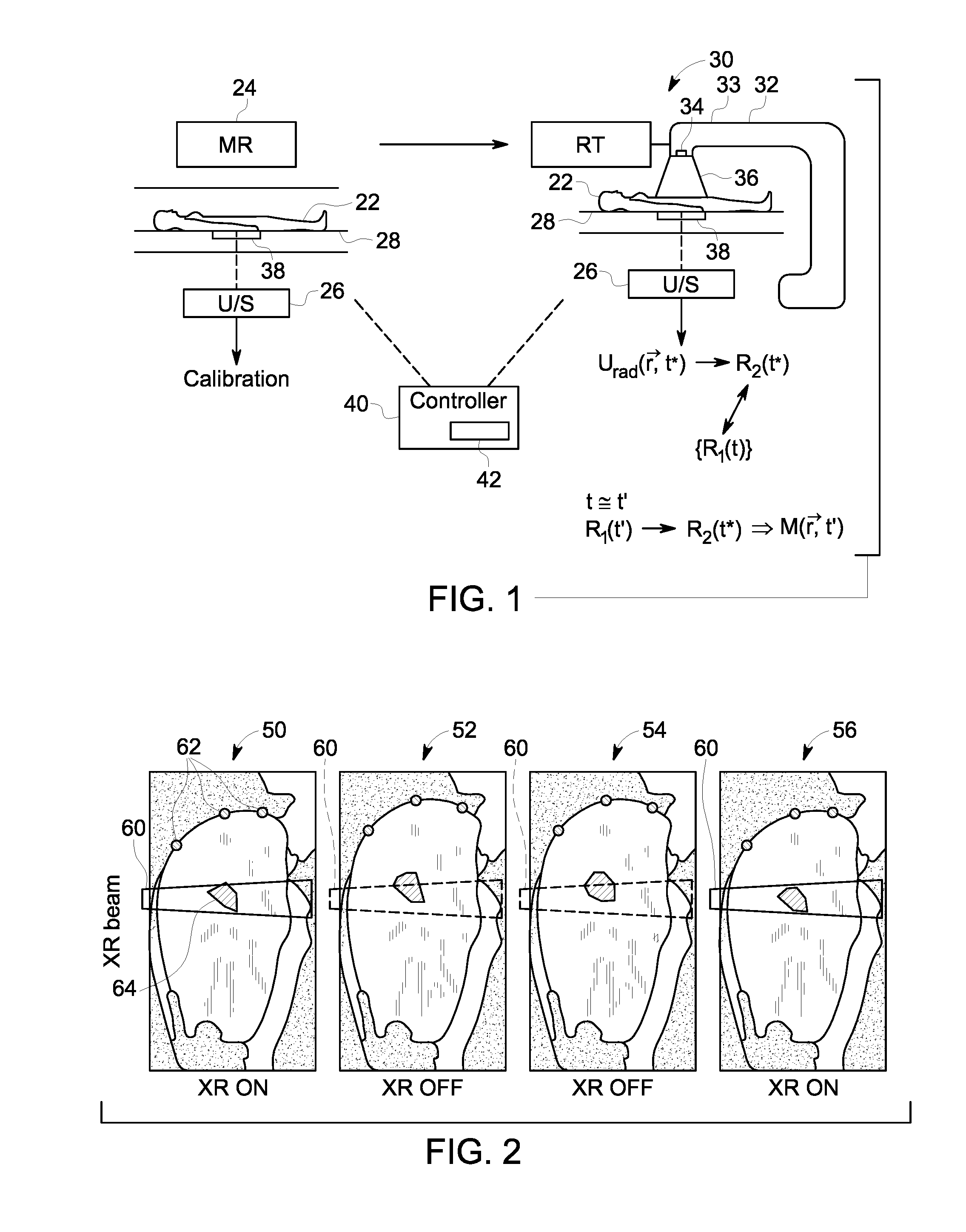
Methods and systems to determine respiratory phase and motion state during guided radiation therapy
ActiveUS20170014645A1Organ movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiation therapyIntensity modulation
Methods and systems using magnetic resonance and ultrasound for tracking anatomical targets for radiation therapy guidance are provided. One system includes a patient transport configured to move a patient between and into a magnetic resonance (MR) system and a radiation therapy (RT) system. An ultrasound transducer is also provided that is hands-free and electronically steerable, securely attached to the patient, such that the ultrasound transducer is configured to acquire four-dimensional (4D) ultrasound images concurrently with one of an MR acquisition or an RT radiation therapy session. The system also includes a controller having a processor configured to use the 4D ultrasound images and MR images from the MR system to control at least one of a photon beam spatial distribution or intensity modulation generated by the RT system. The system determines the previously-acquired correct MR images that represent a specific motion state at some time, t, by a plurality of transformations that allow the representation of the position of fiducial markers in the corresponding ultrasound images to match that of a prior ultrasound acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
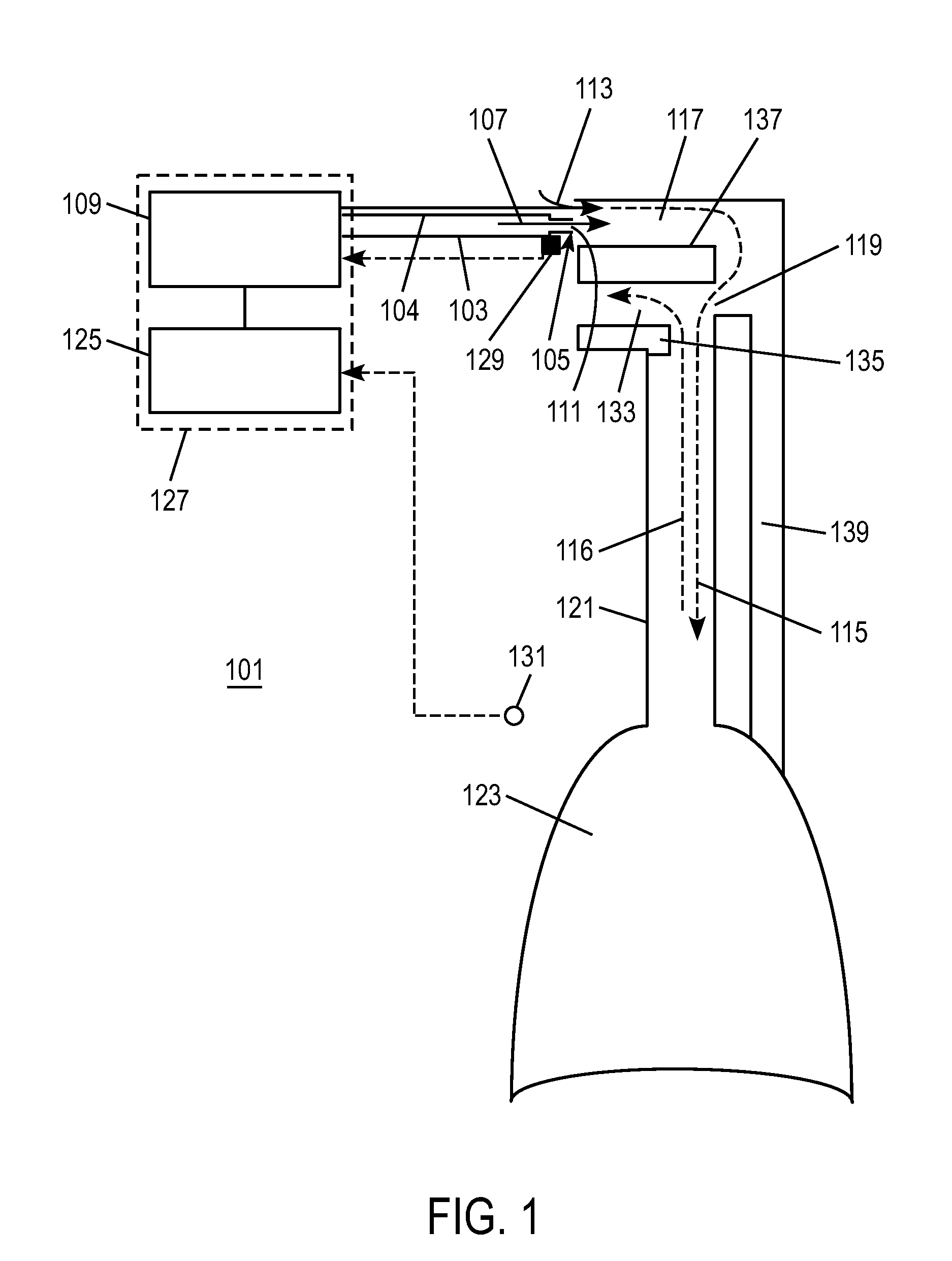
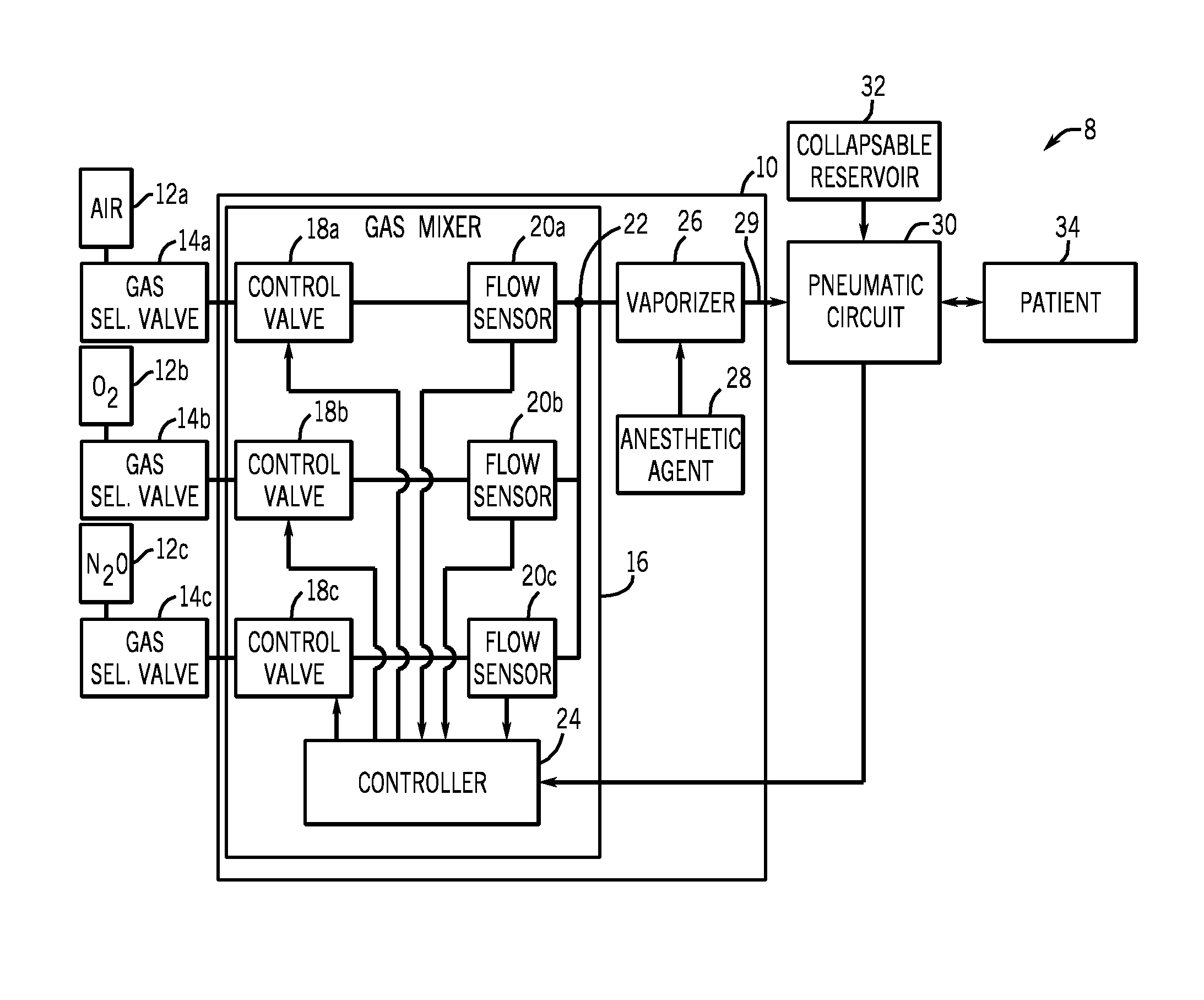
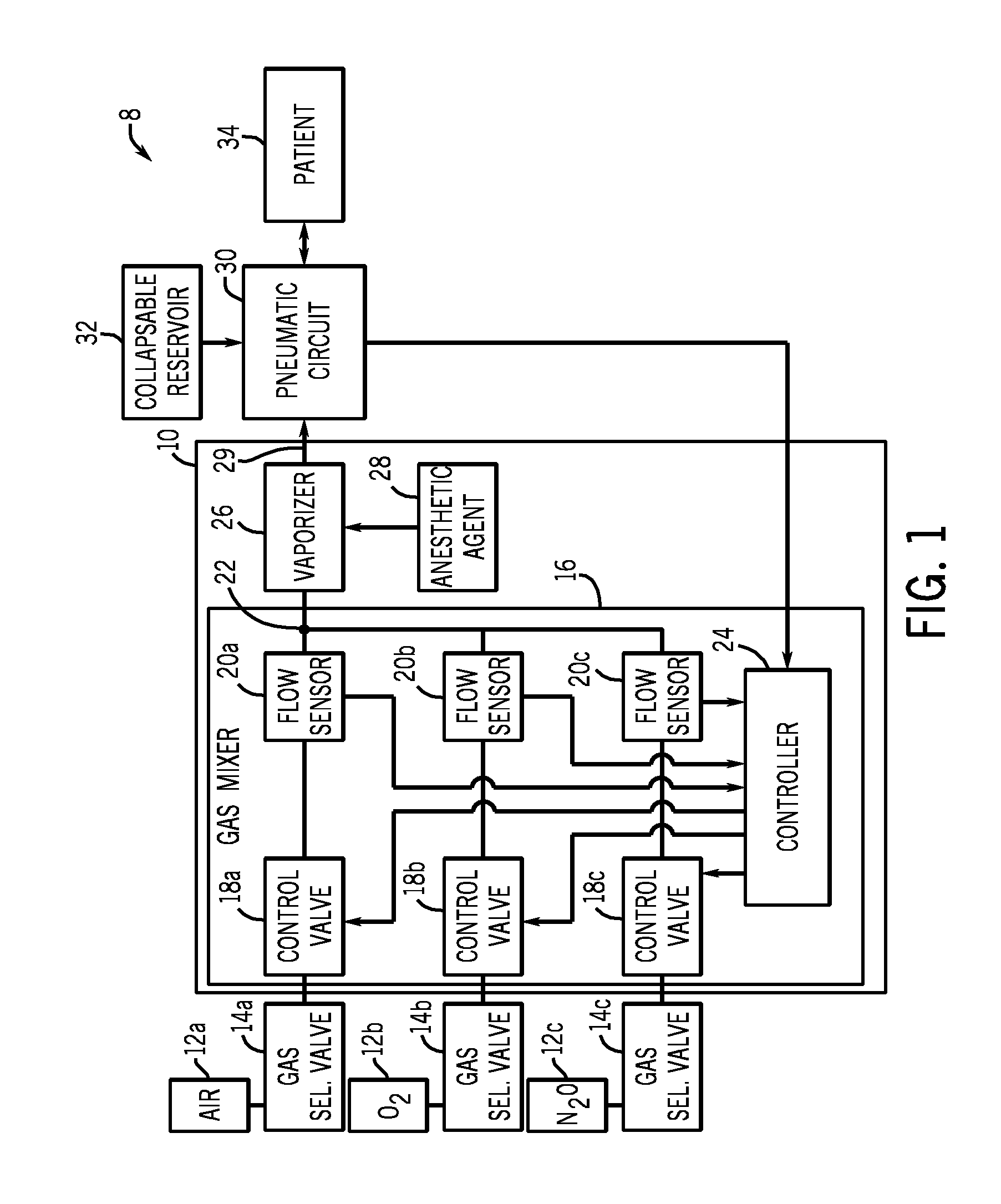
Automatic fresh gas control system
An anesthesia system is disclosed herein. The anesthesia system includes a pneumatic circuit comprising an inspiratory limb, an expiratory limb, and a sensor. The anesthesia system also includes an anesthesia machine comprising a controller. The controller is operatively connected to the sensor, and is configured to identify a respiratory phase of the patient based on feedback from the sensor. The controller is further configured to regulate the flow rate of a fresh gas in response to the identified respiratory phase.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Patient-ventilator synchronization using dual phase sensors
InactiveUS20050081855A1Minimum ventilationImprove determinationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure amplitudeRespiratory phase
An improved ventilator which delivers ventilatory support that is synchronized with the phase of the patent's respiratory efforts and guarantees a targeted minimum ventilation. Improved synchronization is achieved through an instantaneous respiratory phase determination process based upon measured respiratory airflow as well as measured respiratory effort using an effort sensor accessory, preferably a suprastemal notch sensor. The ventilator processes a respiratory airflow signal, a respiratory effort signal and their respective rates. of change to determine a phase using standard fuzzy logic methods. A calculated pressure amplitude is adjusted based upon the calculated phase and a smooth pressure waveform template to deliver synchronized ventilation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com