Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
301results about "Respiratory device testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
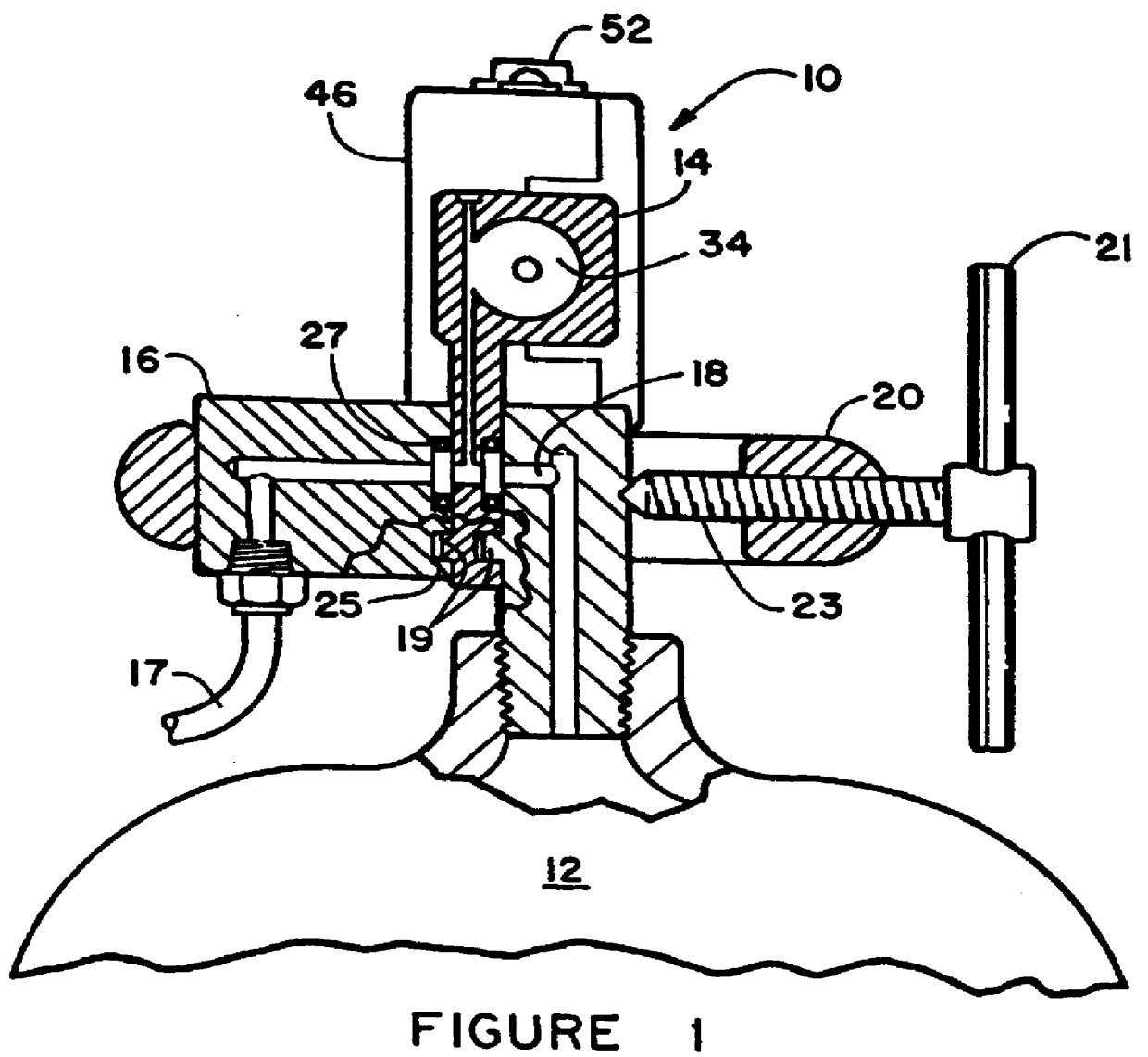
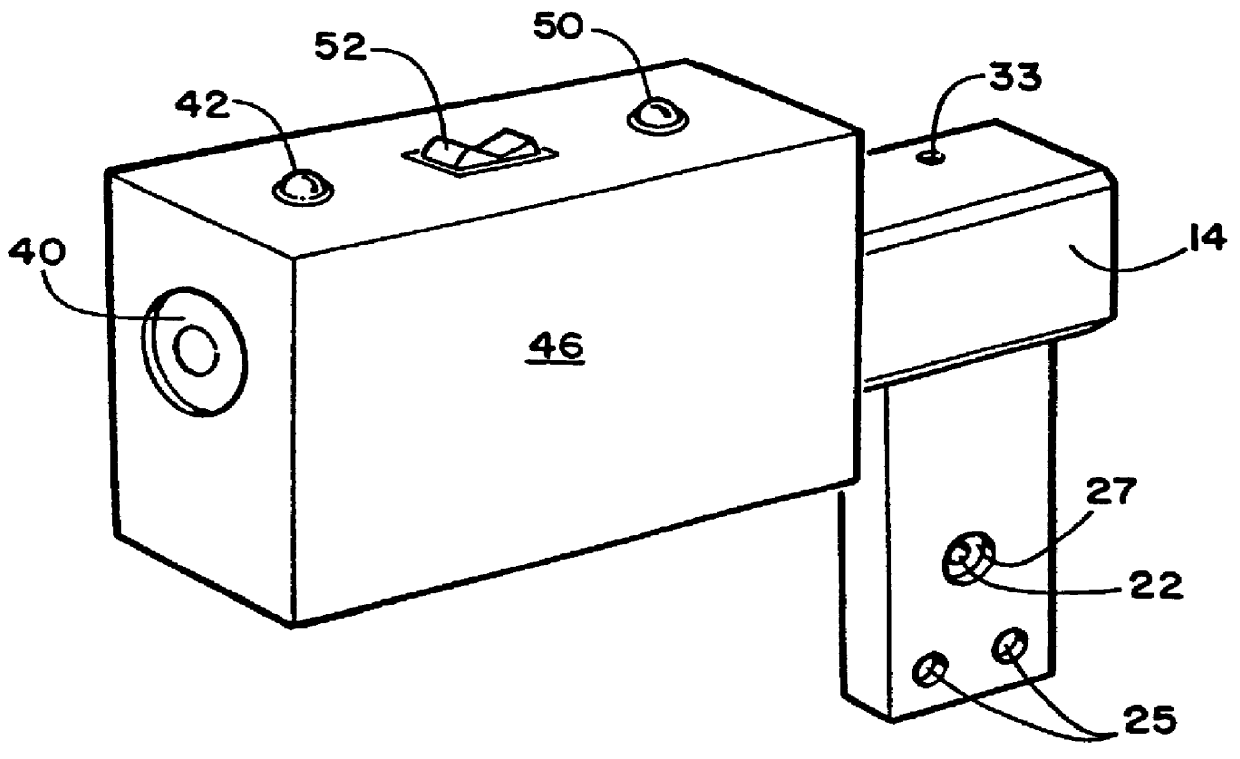
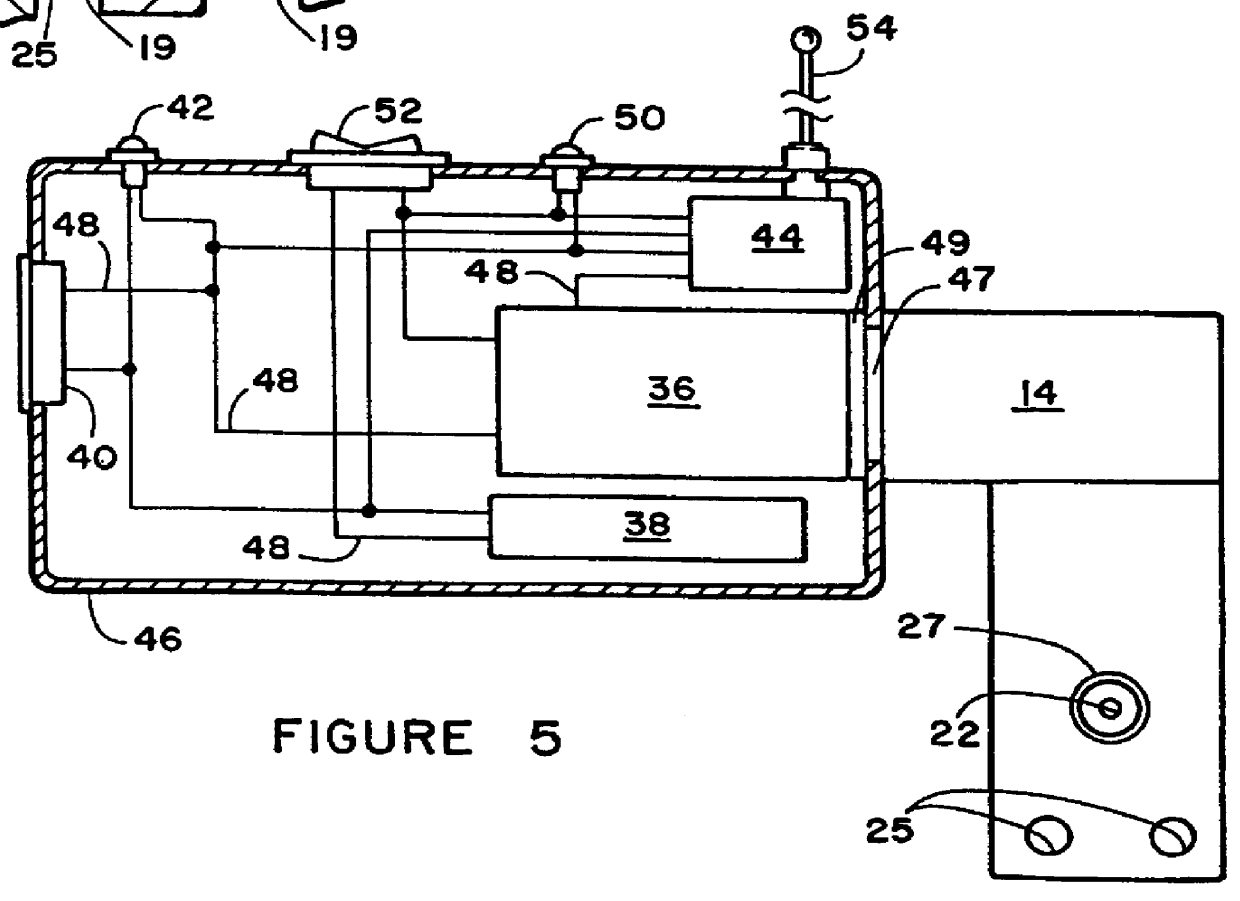
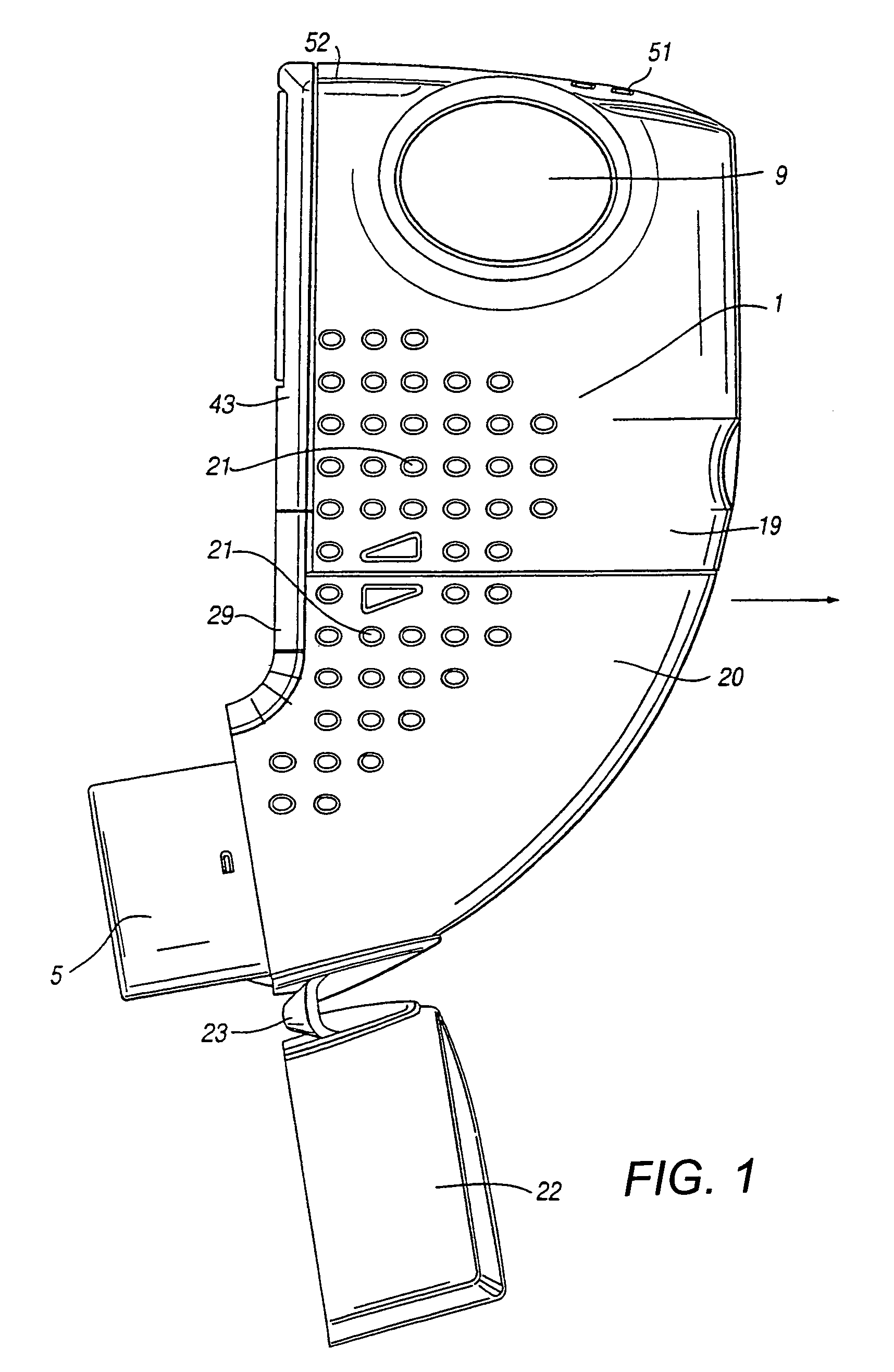
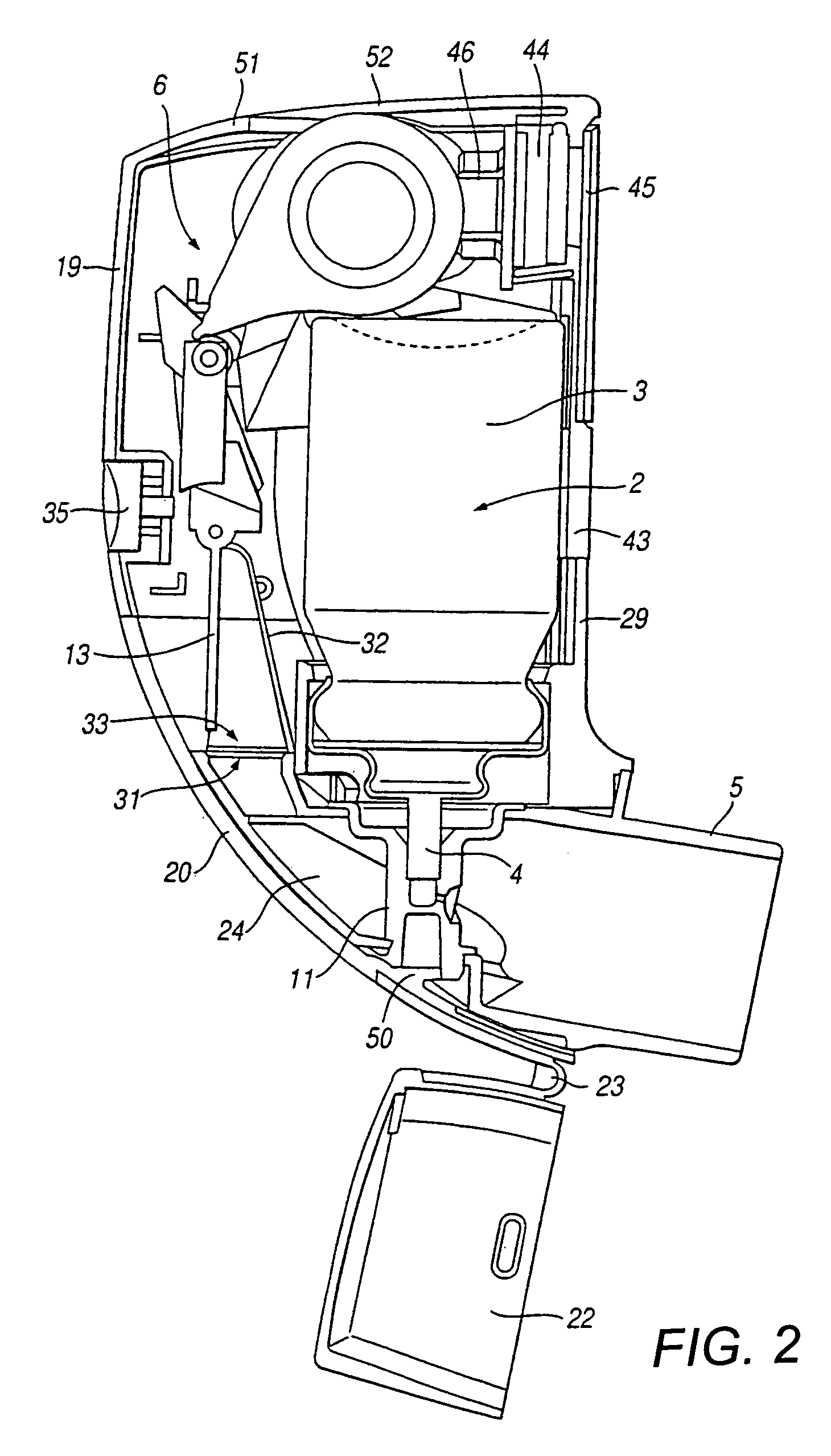
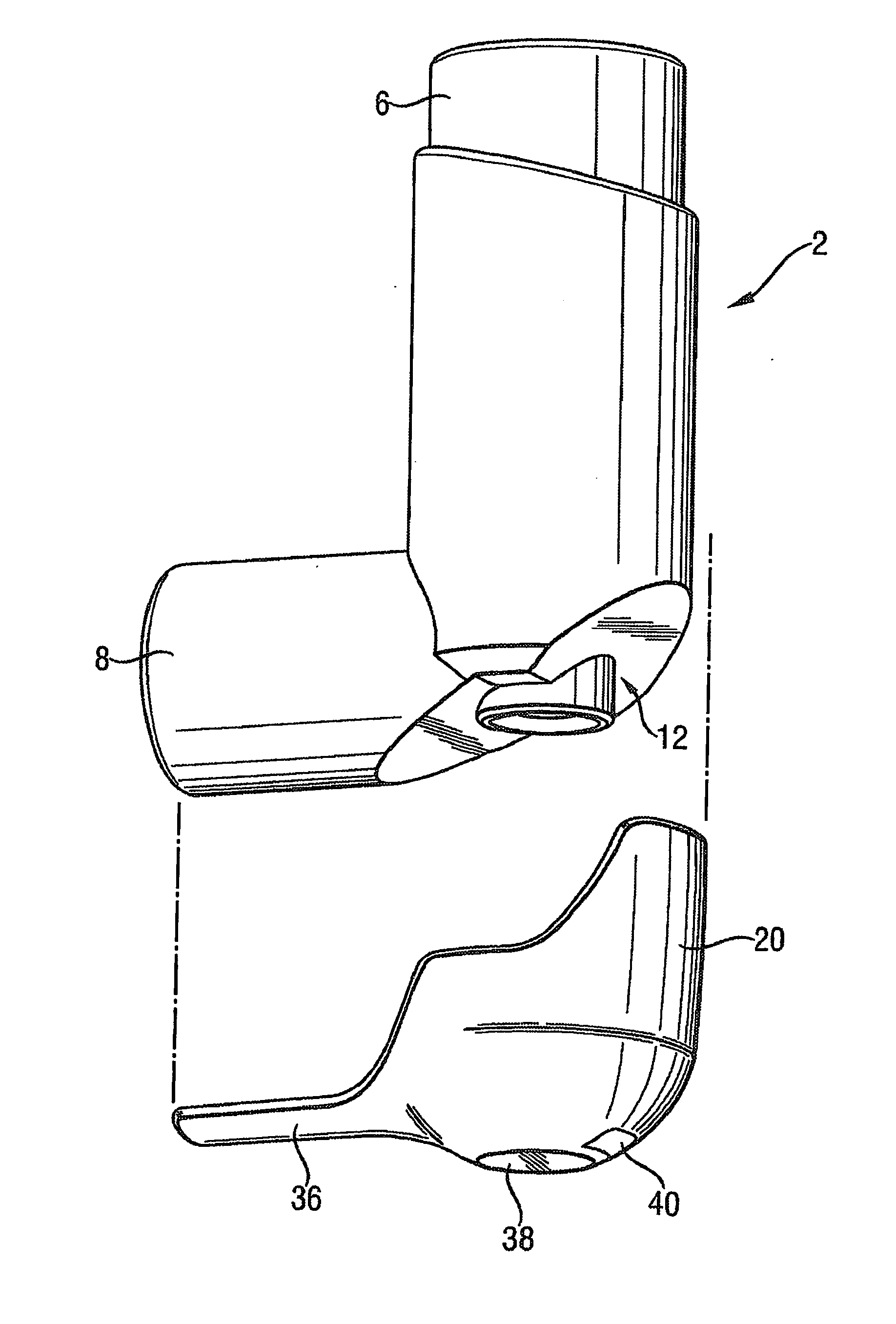
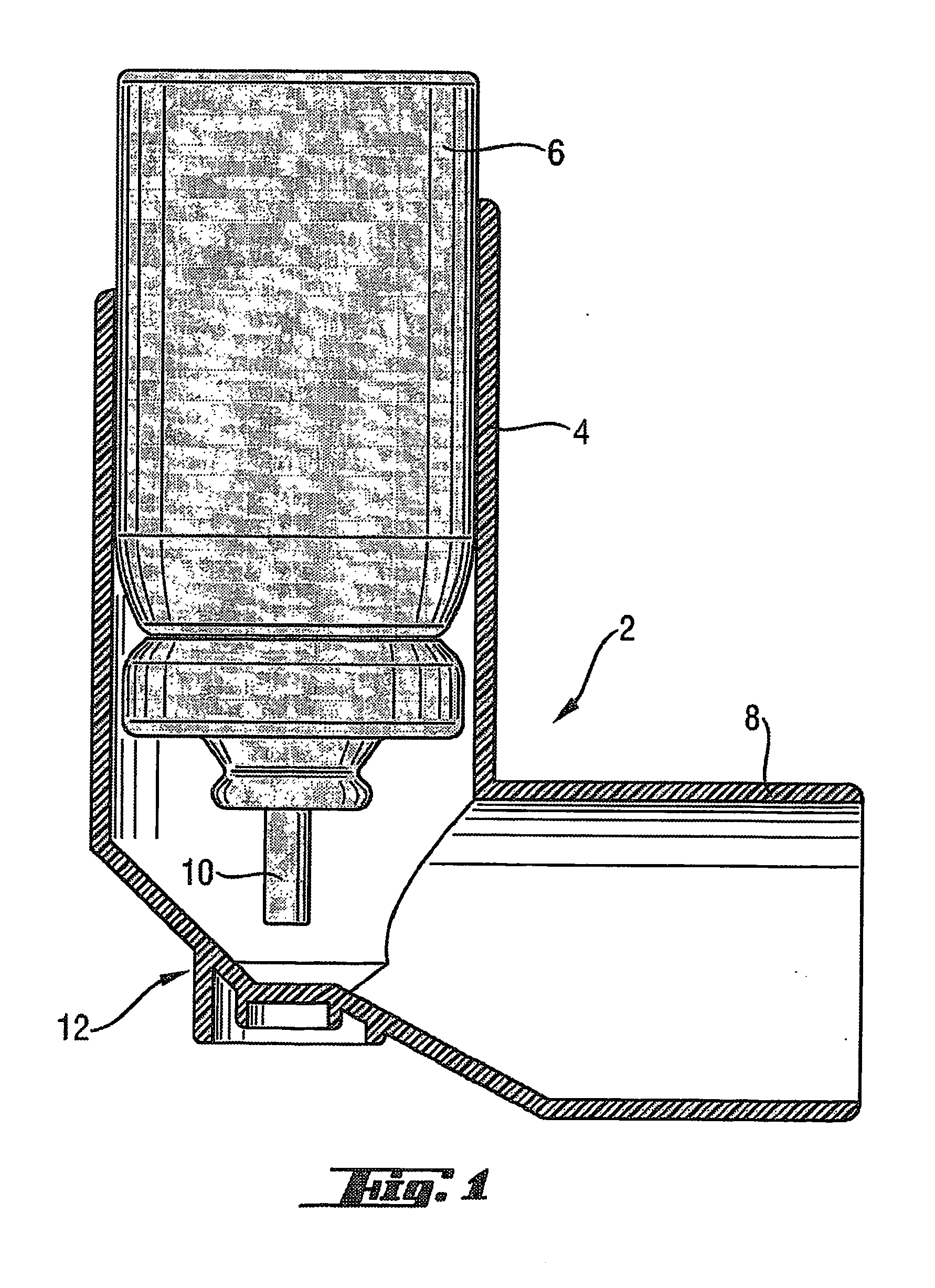
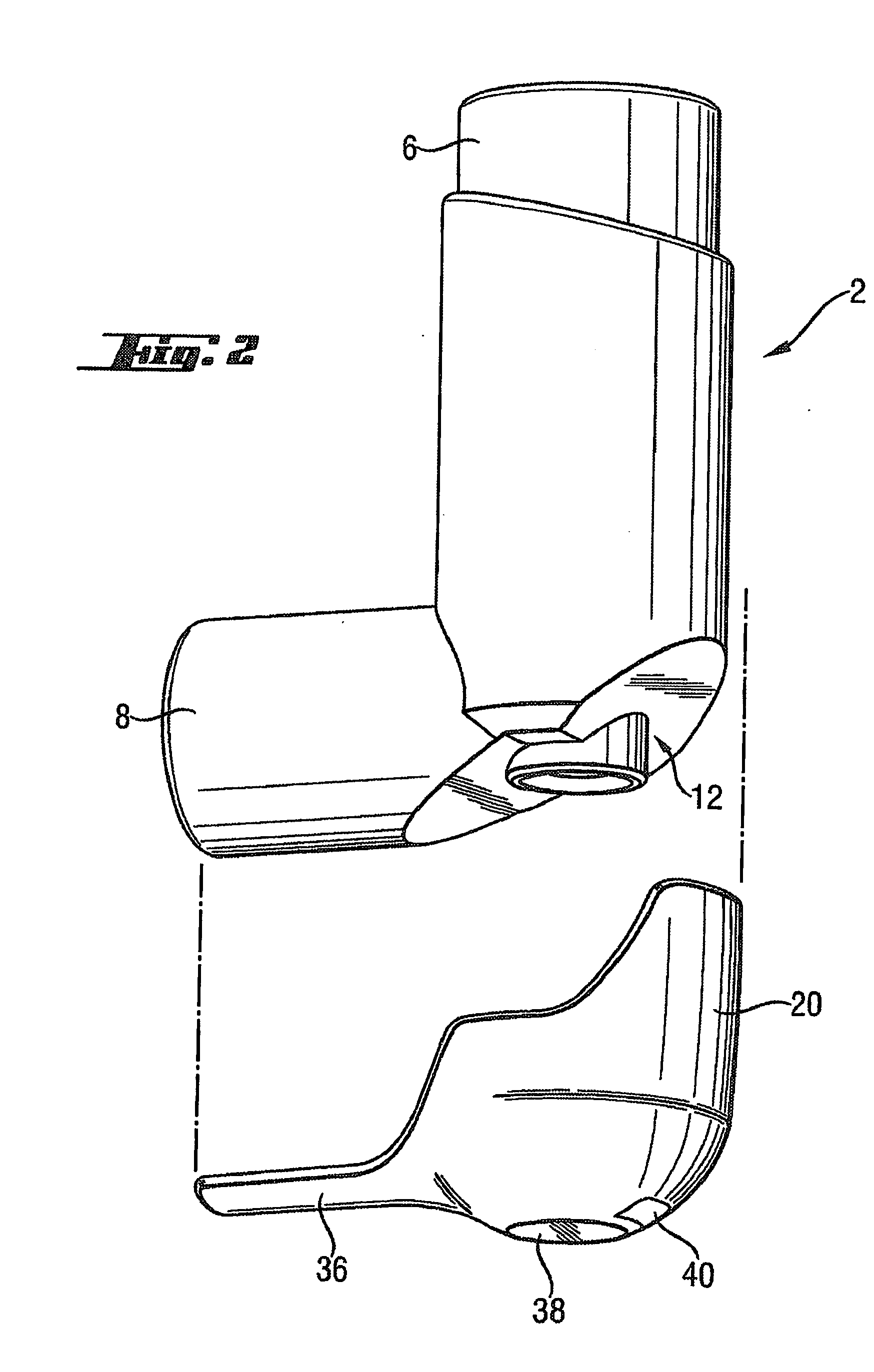
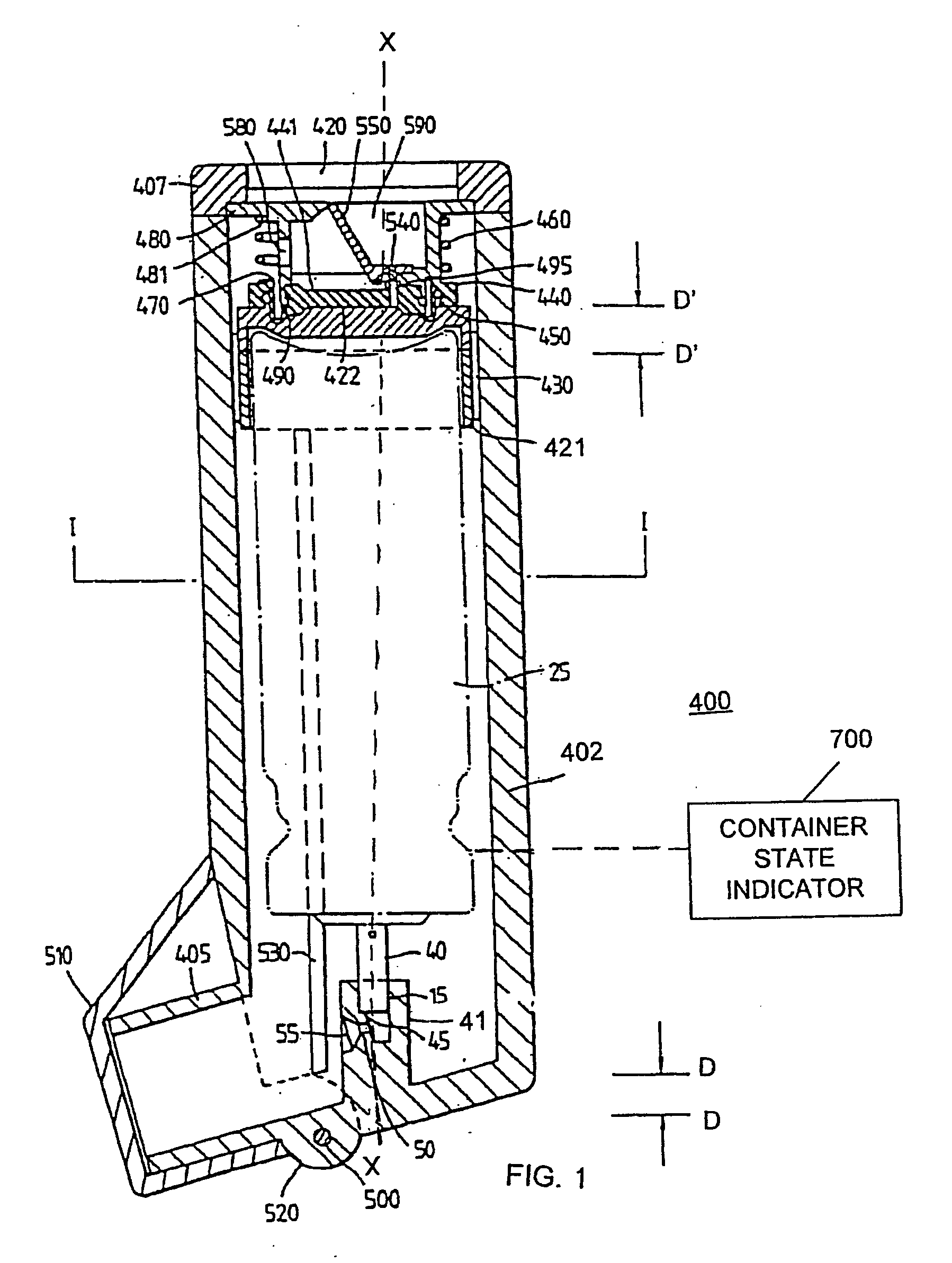
Medicament dispensing device with a display indicative of the state of an internal medicament reservoir
ActiveUS7331340B2Liquid surface applicatorsPowdered material dispensingDisplay deviceBiomedical engineering
A metered dose inhaler for use with a removable pressurized aerosol canister, or reservoir, having a display for indicating to a user the state of the canister. A memory device on the canister or a housing which houses the canister stores information indicative of doses dispensed from, or remaining in, the canister. That information is processed to provide and display information representative of the state of the canister.
Owner:IVAX CORP
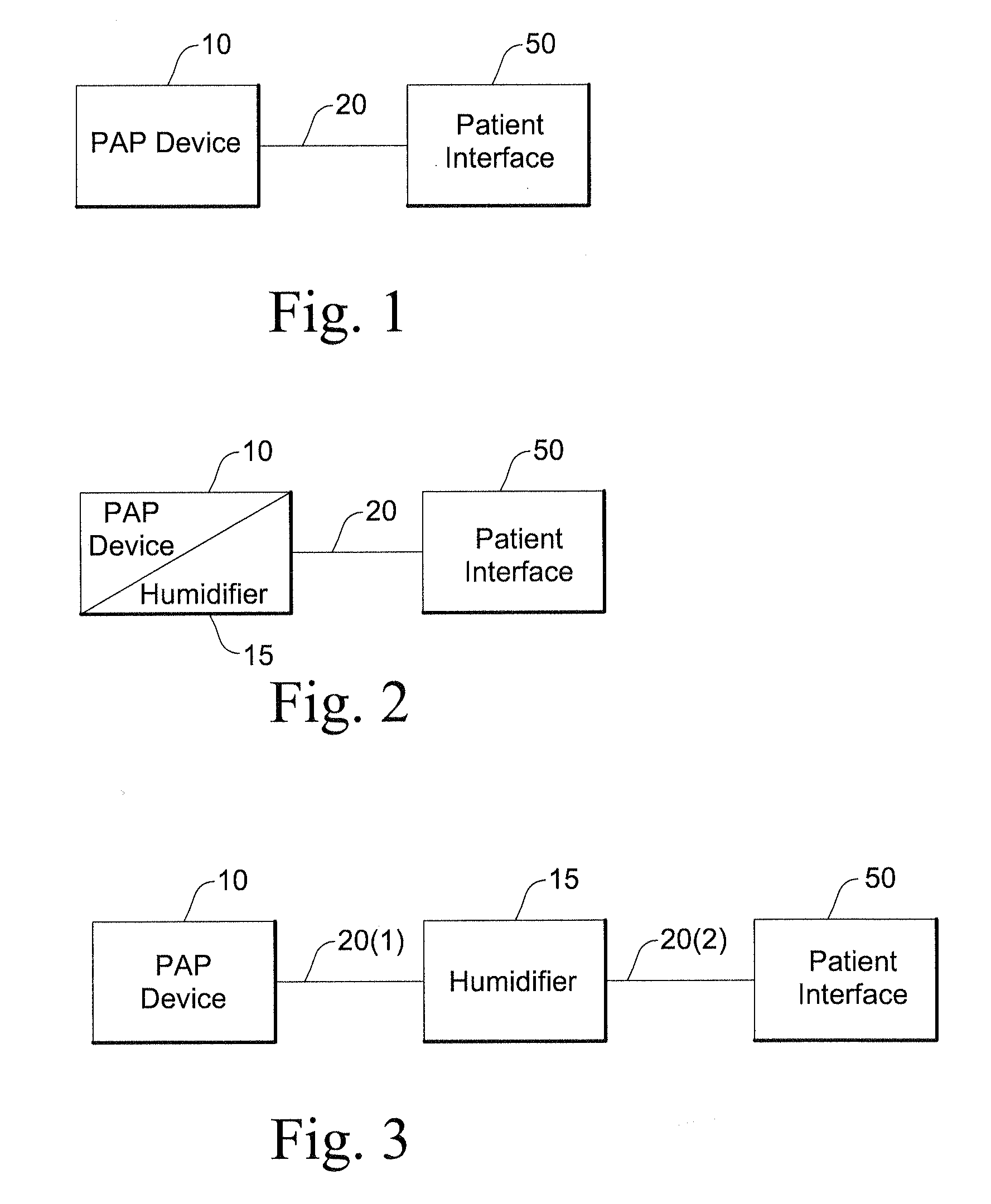
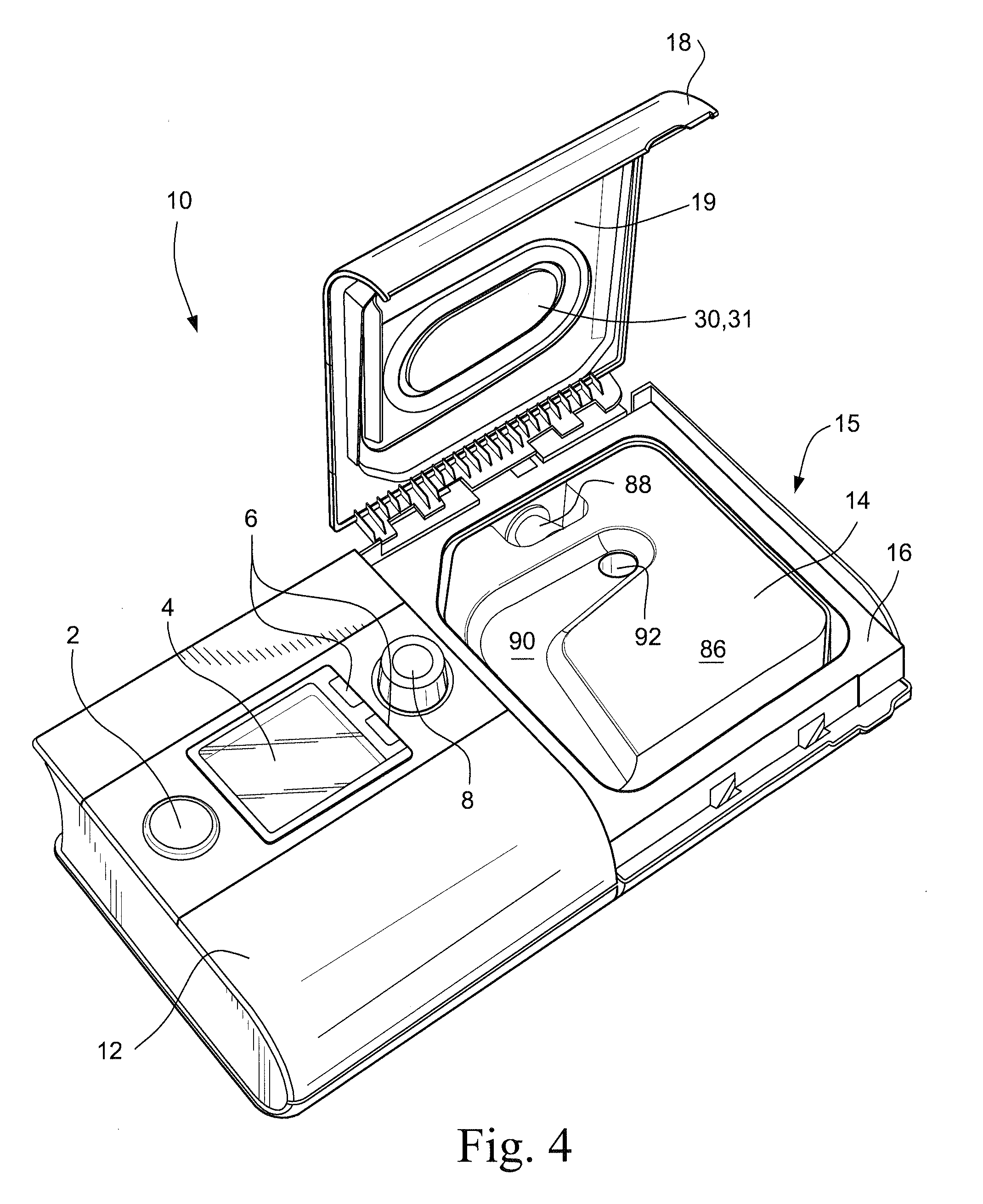
Wire heated tube with temperature control system, tube type detection, and active over temperature protection for humidifier for respiratory apparatus
ActiveUS20110023874A1Avoid overall overheatingReduce condensationRespiratory device testingOther heat production devicesTemperature controlWater vapor
A PAP system for delivering breathable gas to a patient includes a flow generator to generate a supply of breathable gas to be delivered to the patient; a humidifier including a heating plate to vaporize water and deliver water vapor to humidify the supply of breathable gas; a heated tube configured to heat and deliver the humidified supply of breathable gas to the patient; a power supply configured to supply power to the heating plate and the heated tube; and a controller configured to control the power supply to prevent overheating of the heating plate and the heated tube.
Owner:RESMED LTD
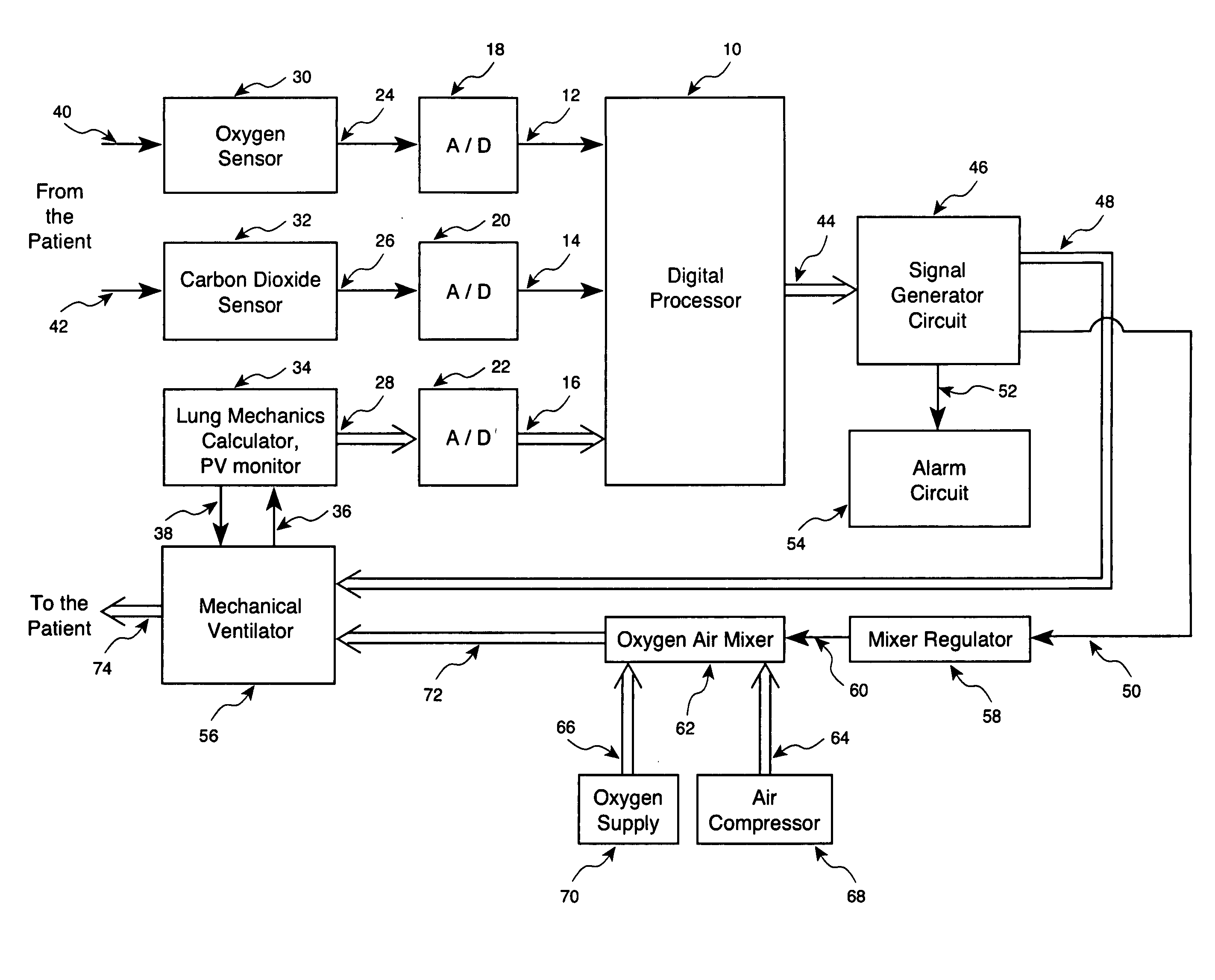
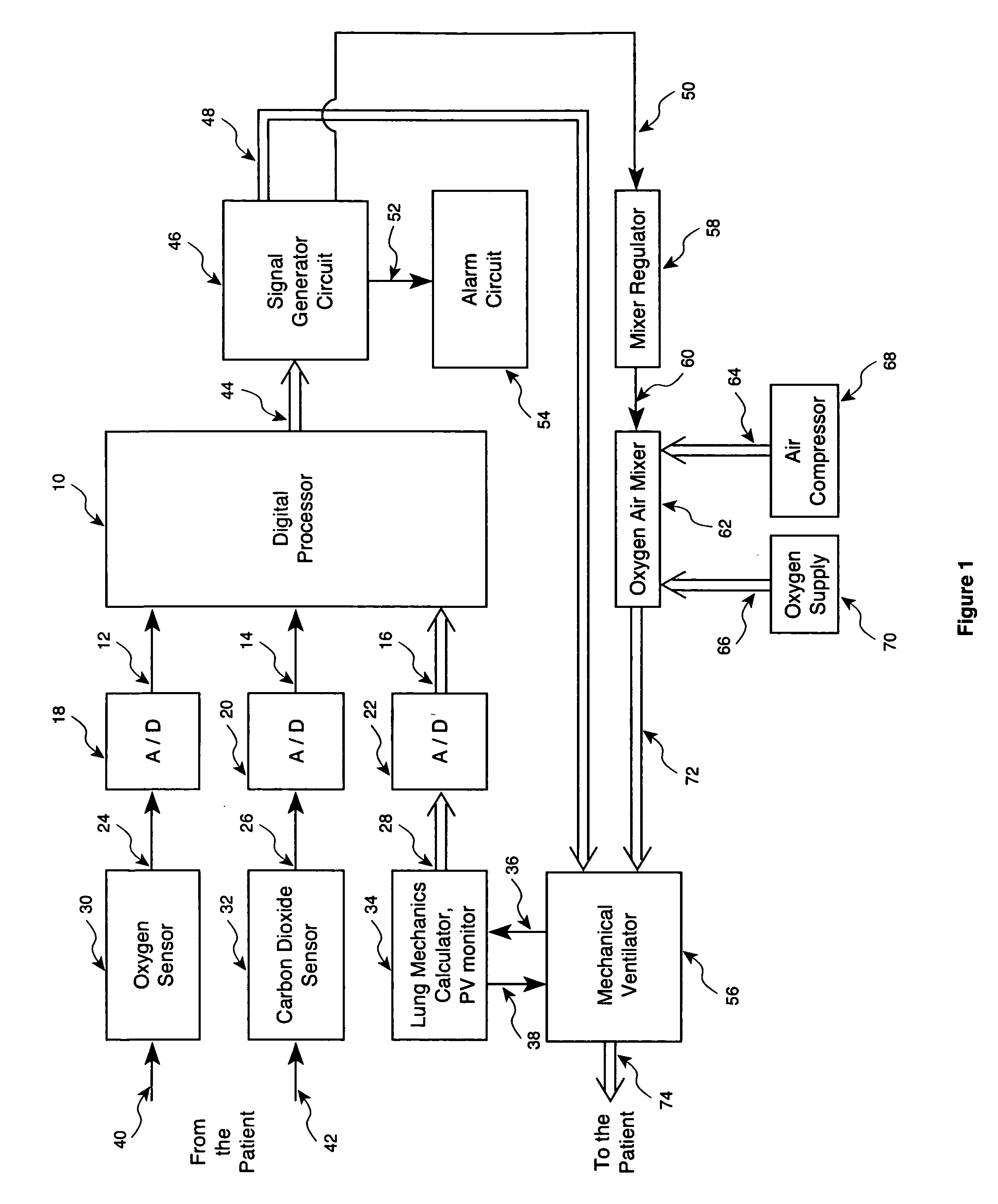
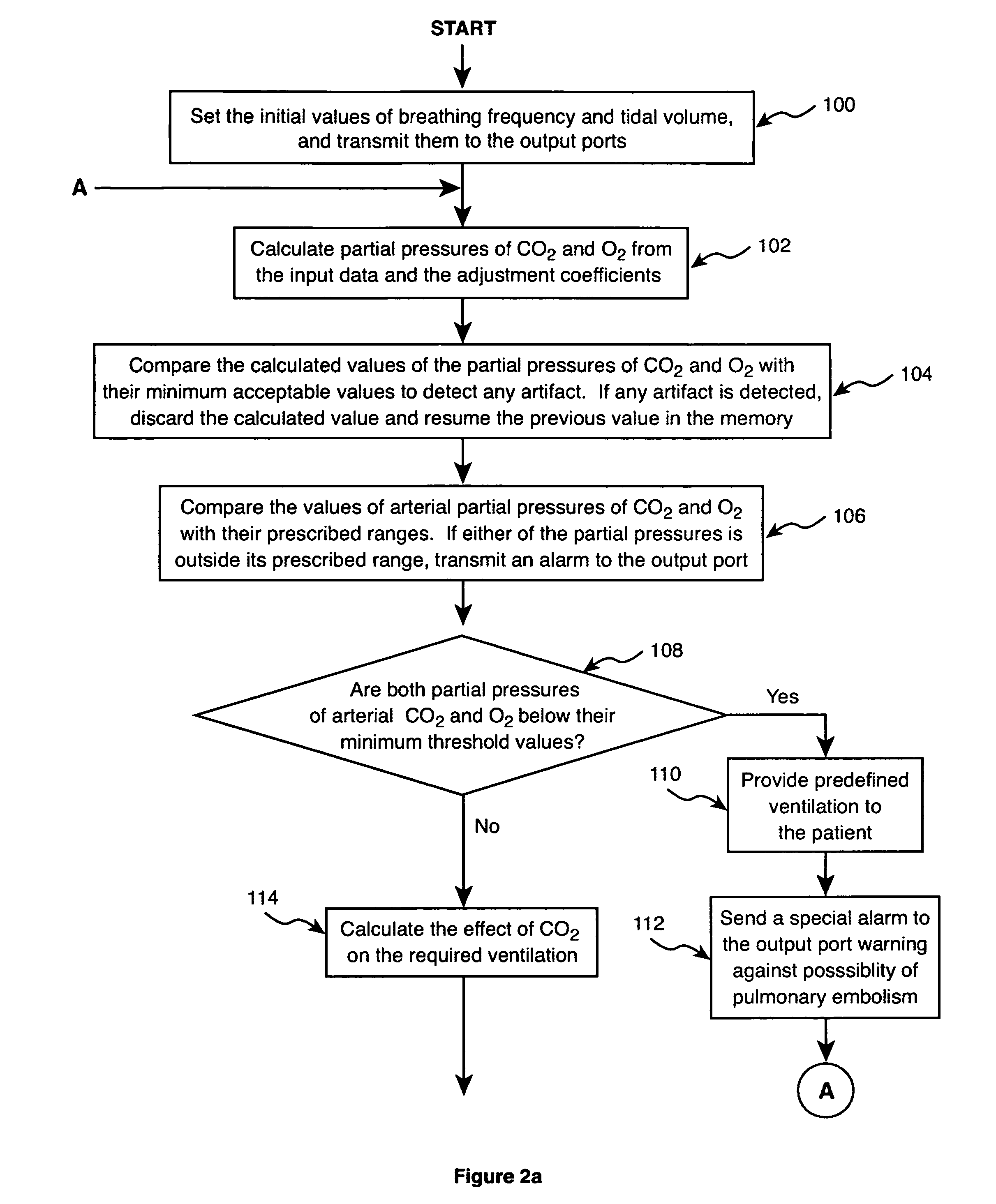
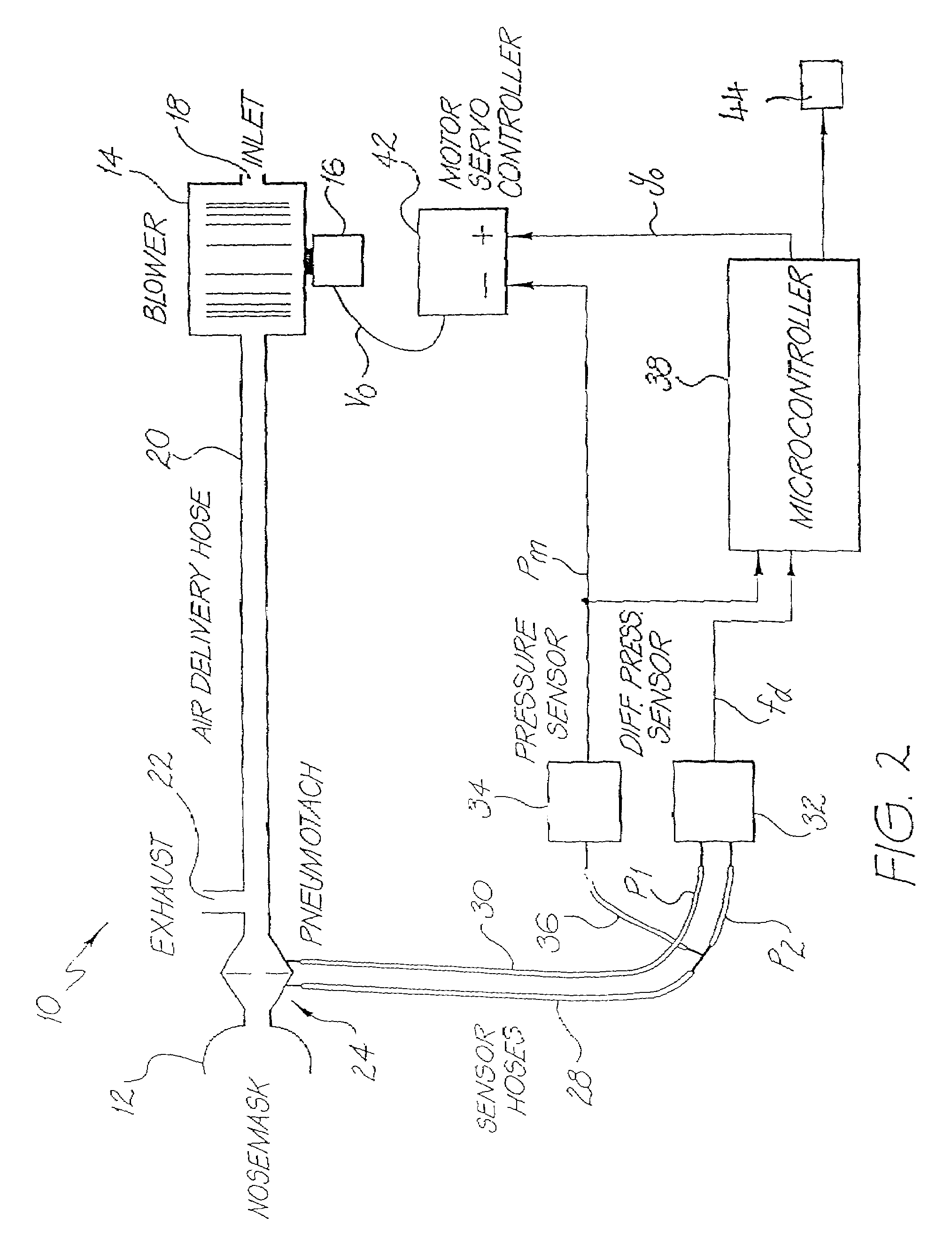
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator
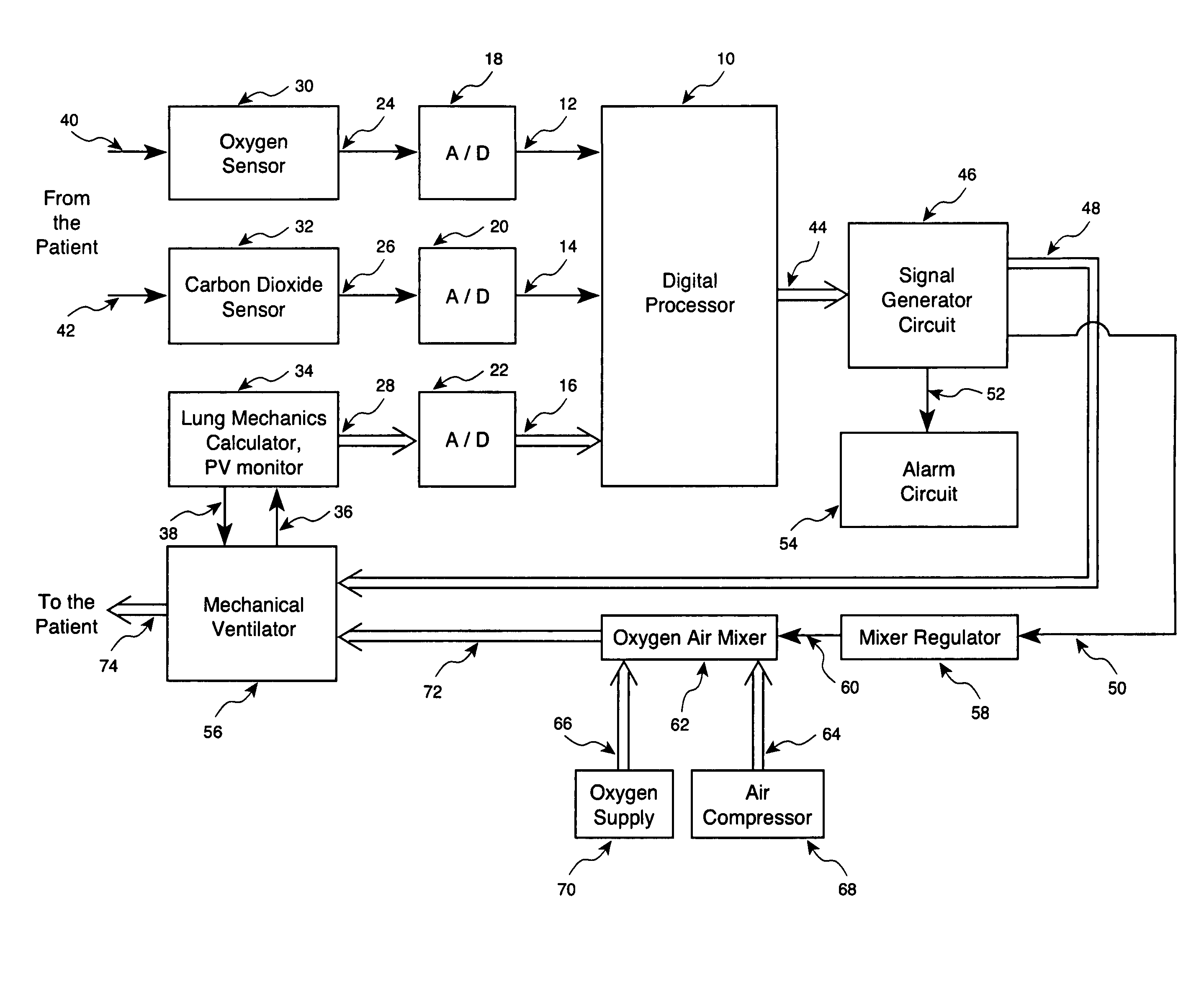
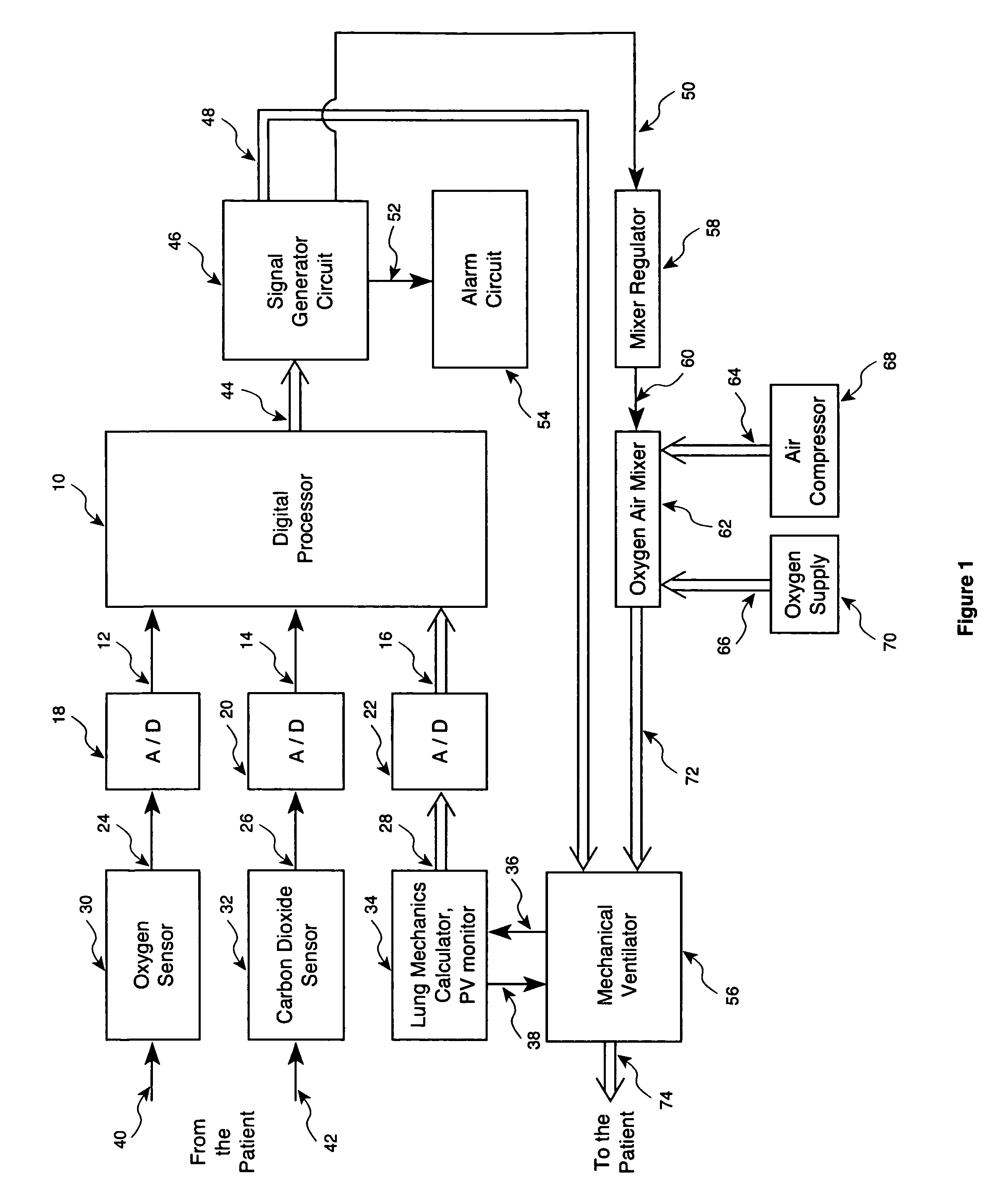
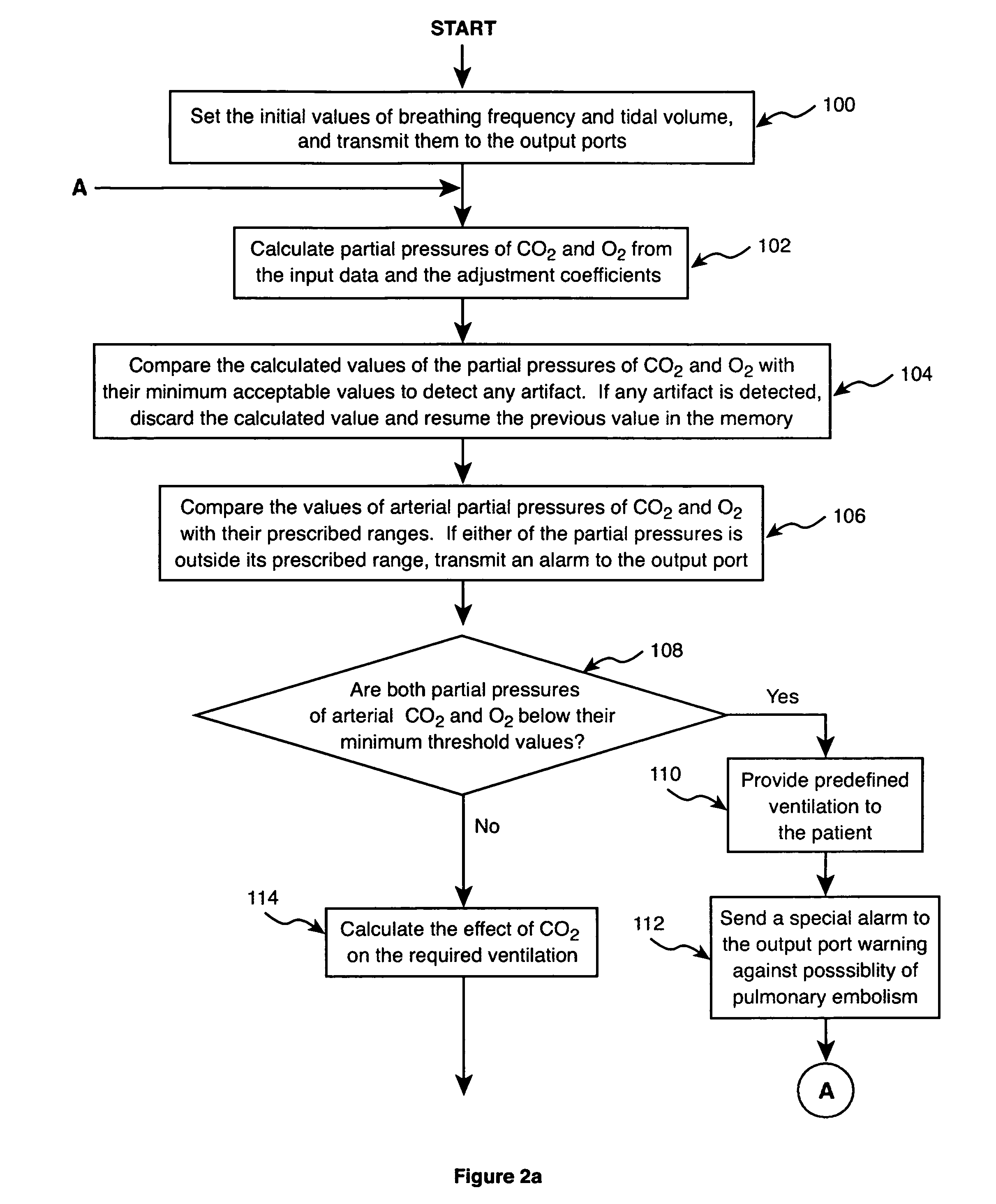
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator are described. The invention can be used to control mechanical ventilators as well as respiratory assist devices such as CPAP machines. The apparatus receives input data indicative of patient's oxygen level. A controller determines PEEP, or CPAP, and FIO2, on the basis of data indicative of the patient's oxygen level. In an alternative embodiment, the apparatus further receives input data indicative of patient's carbon dioxide levels, respiratory elastance and airway resistance, and barometric pressure. The controller further utilizes the said input data to determine the optimal values of tidal volume and breathing frequency for a next breath of the patient, and uses the respiratory elastance and airway resistance data to determine any necessary adjustments in the I:E ratio. The controller also applies safety rules, detects and corrects artifacts, and generates warning signals when needed.
Owner:TEHRANI FLEUR T
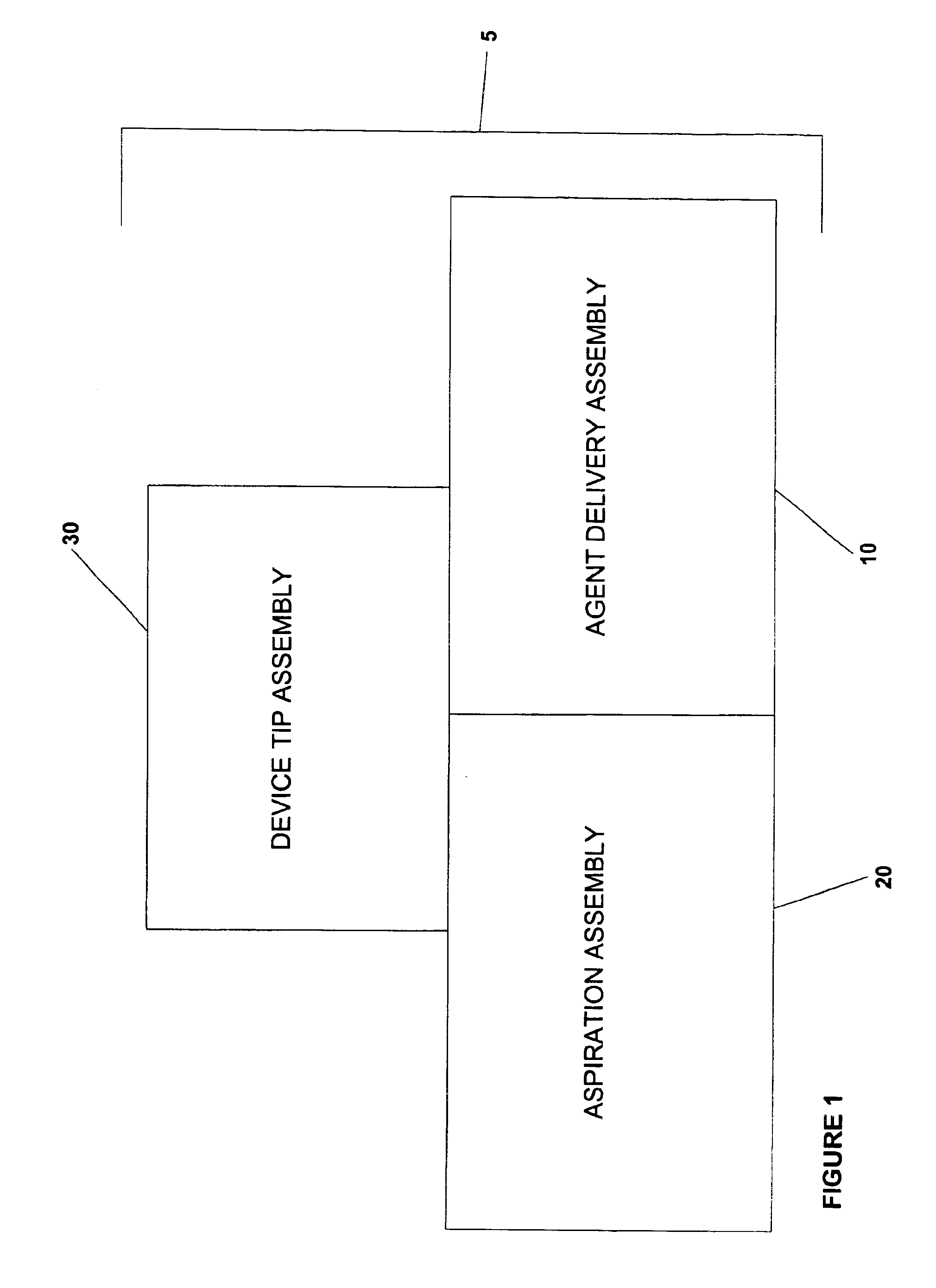
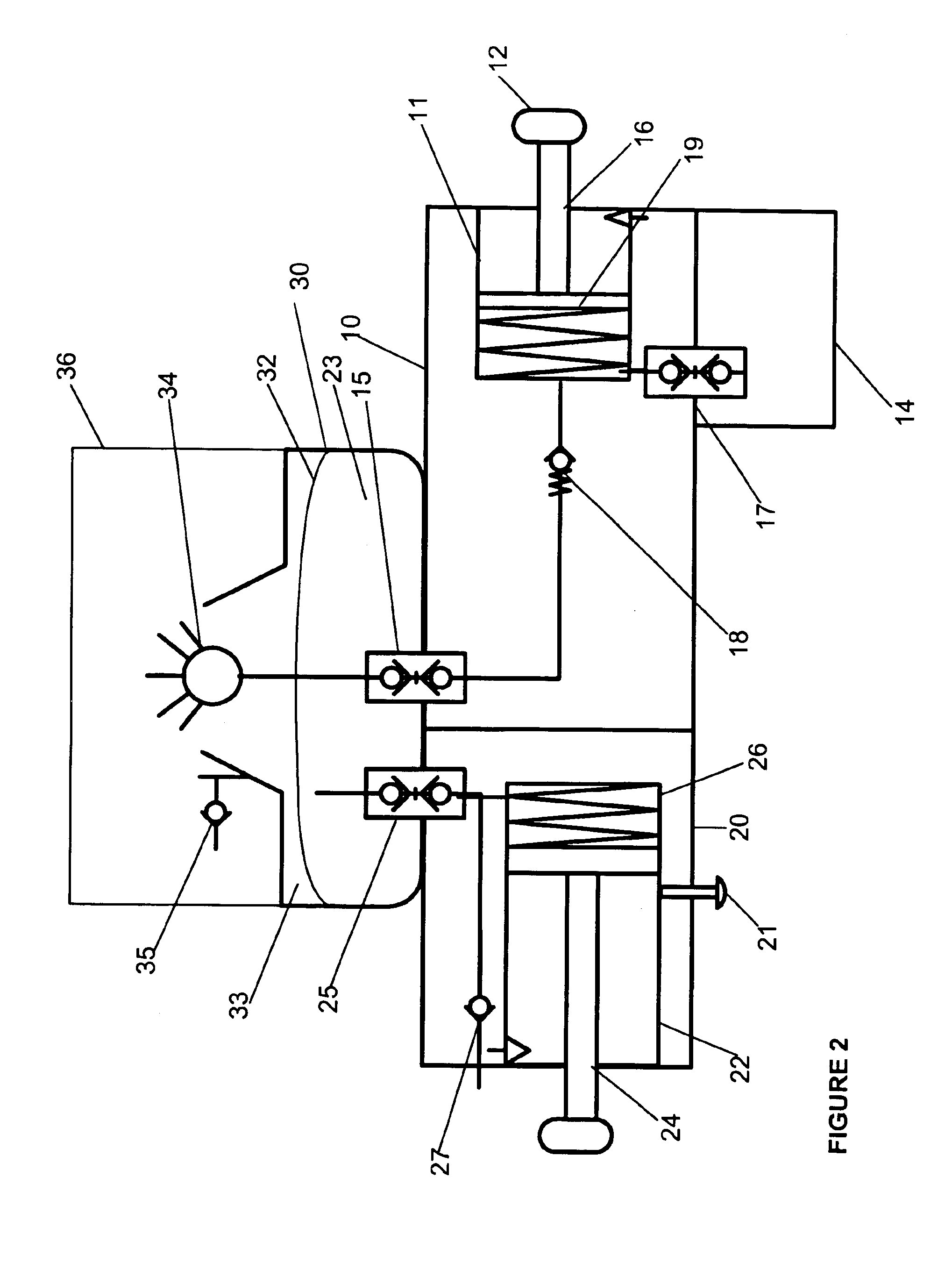
Agent delivery and aspiration device
The methods and devices disclosed provides for the delivery of agents to an orifice cavity and subsequent aspiration of the agent and orifice contents from the orifice cavity and related areas. In one form, the delivery and aspiration system comprises an agent delivery sub-assembly, an aspiration sub-assembly and a device tip sub-assembly. The subassemblies operate to first deliver an agent contained within the device to an orifice cavity and after an optional time delay, subsequently aspirate the delivered agent and orifice contents from the orifice cavity and related areas. In another form, a removable reservoir is provided whereby the aspirated agent and orifice contents from the orifice are assayed either independent of or within the device itself.
Owner:NDT
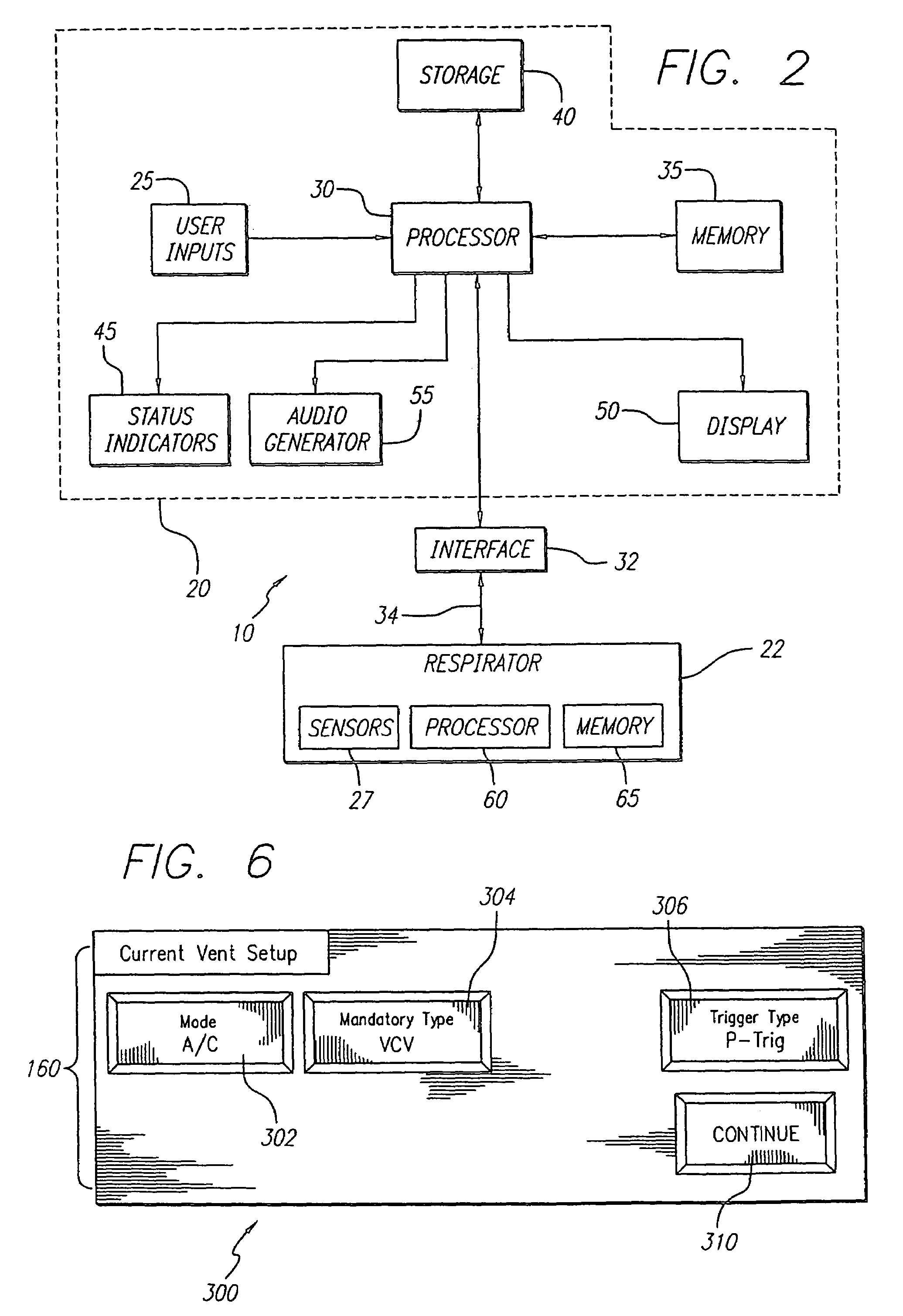
Ventilator breath display and graphic user interface
InactiveUS7036504B2Avoid harmIncrease speedRespiratory device testingMedical devicesGraphicsGraphical user interface
The invention is directed to a ventilation control system for controlling the ventilation of a patient. The ventilation control system utilizes a user-friendly user interface for the display of patient data and ventilator status. The user interface includes a graphic representation of a breath cycle that displays the breath cycle currently being ventilated, and is also responsive to changes in ventilation settings to assist the user in evaluation the effect of those changes on the ventilator strategy before the changes are implemented.
Owner:NELL COR PURITAN BENNETT INC (US)
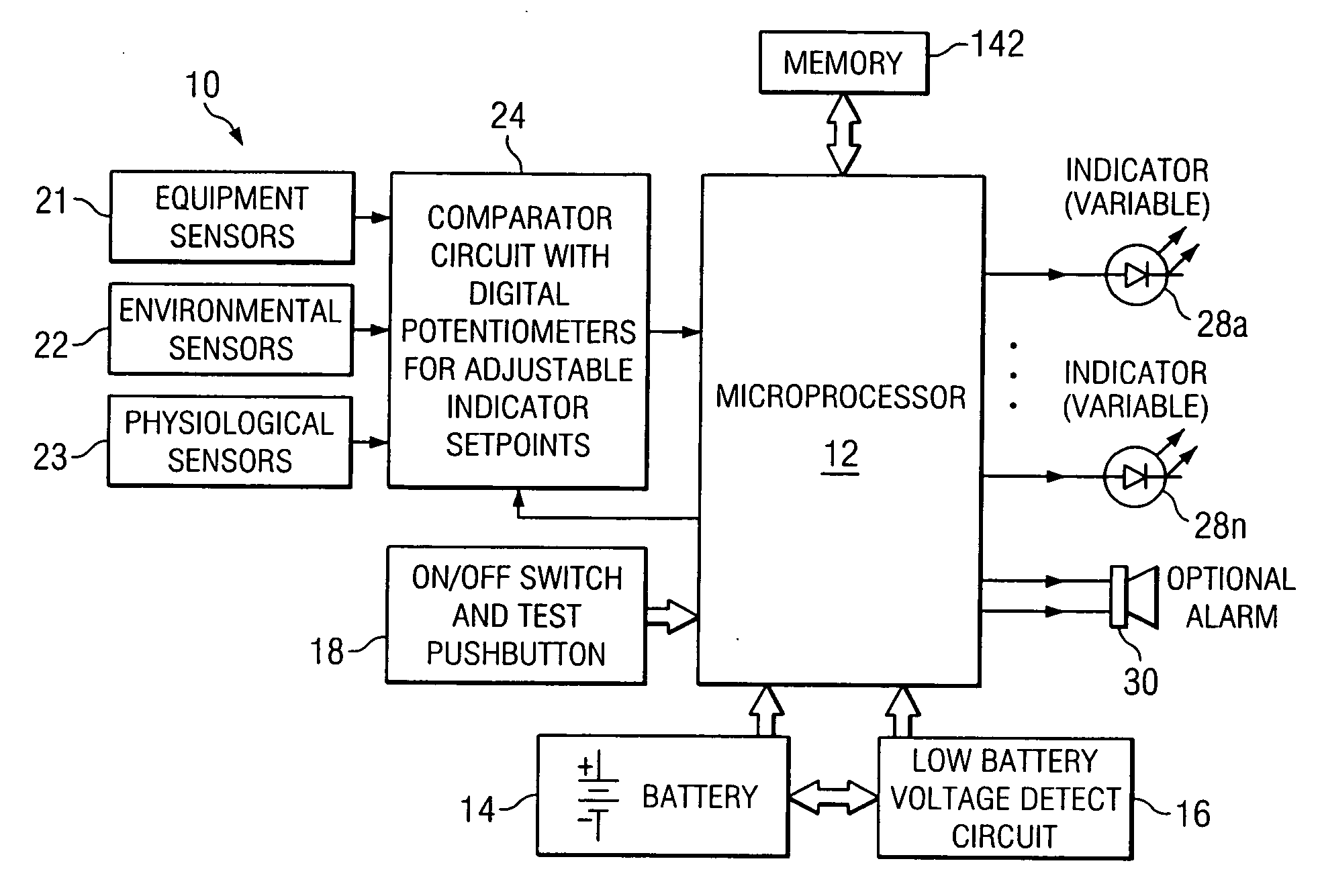
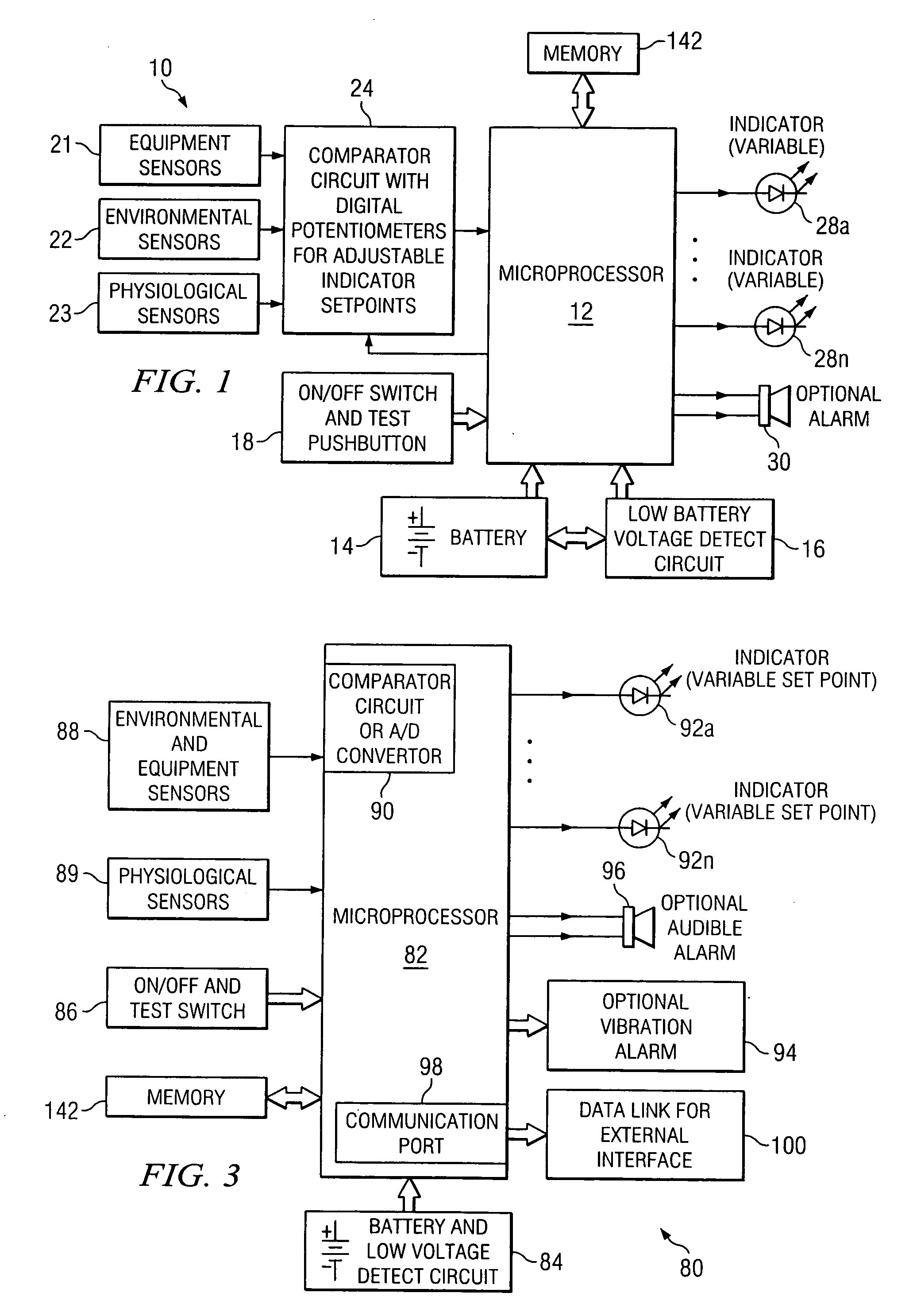
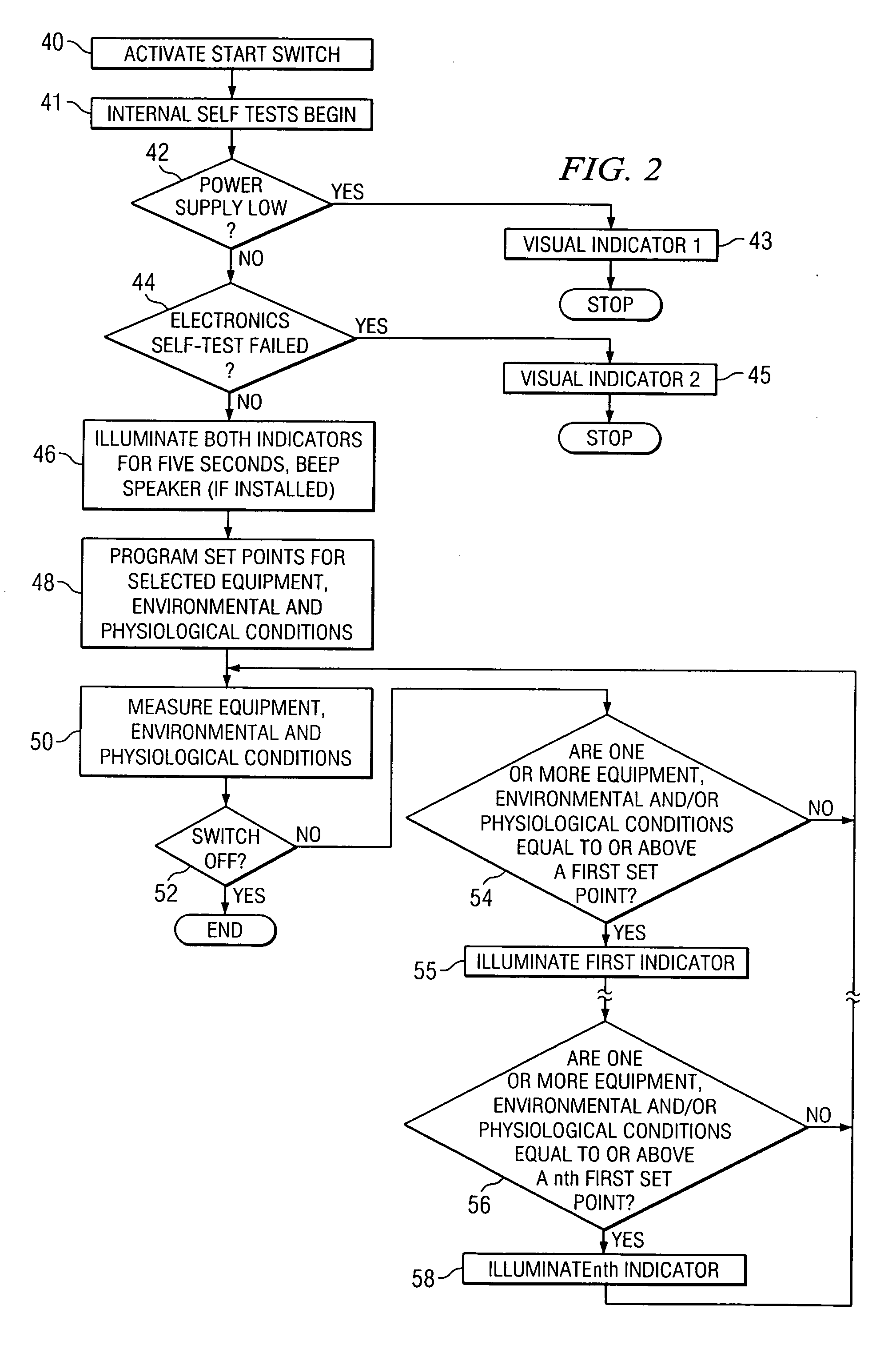
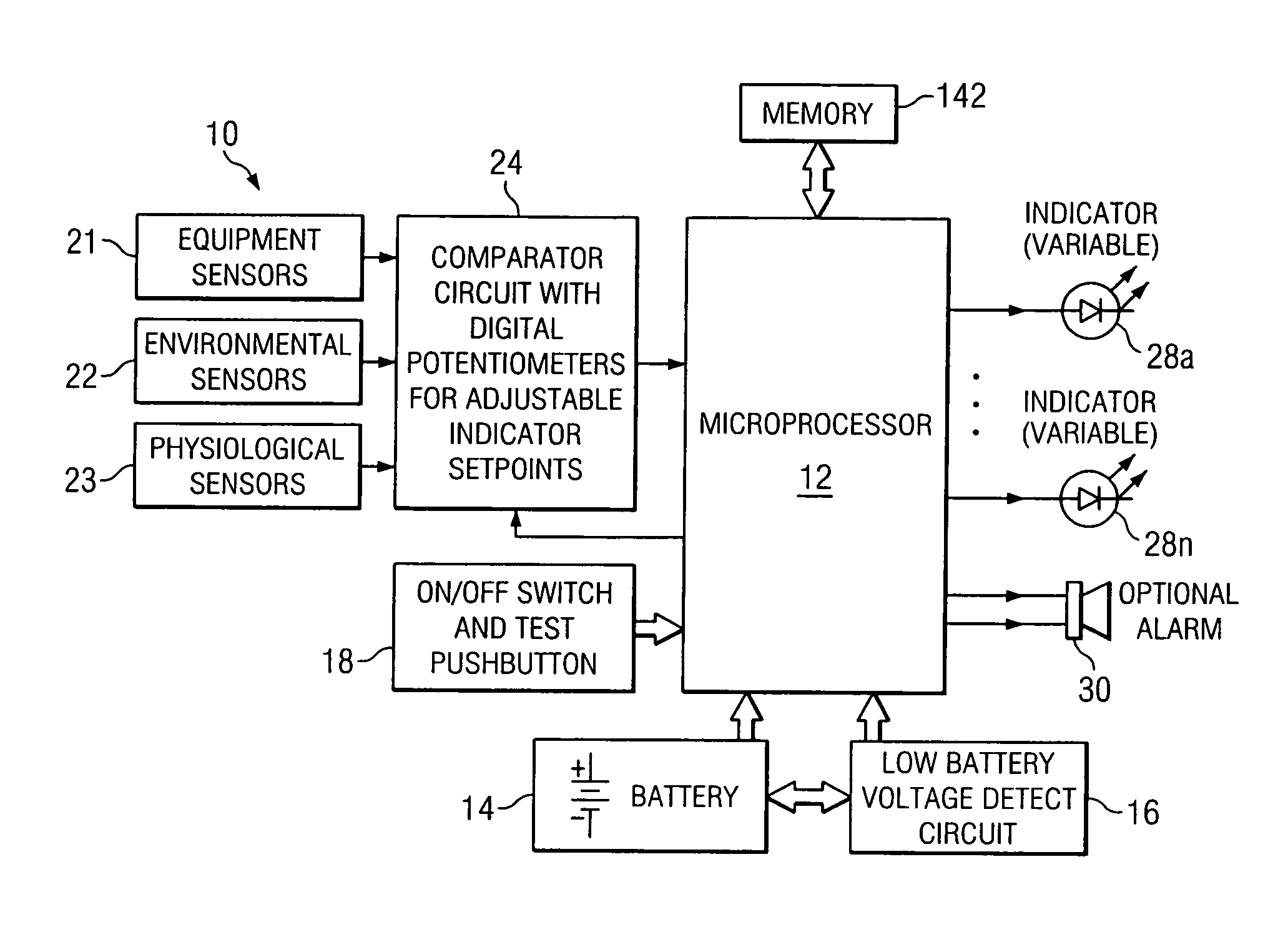
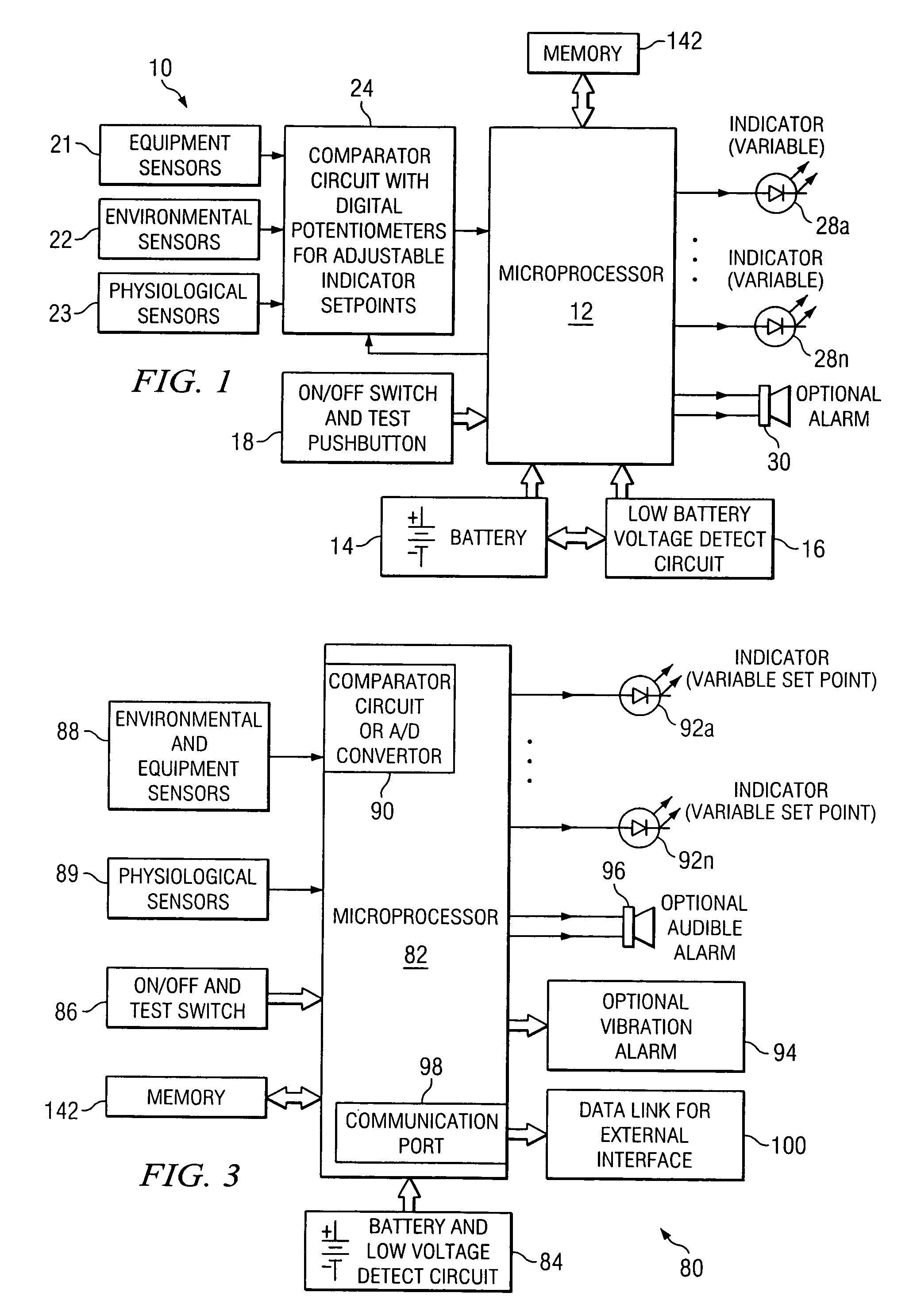
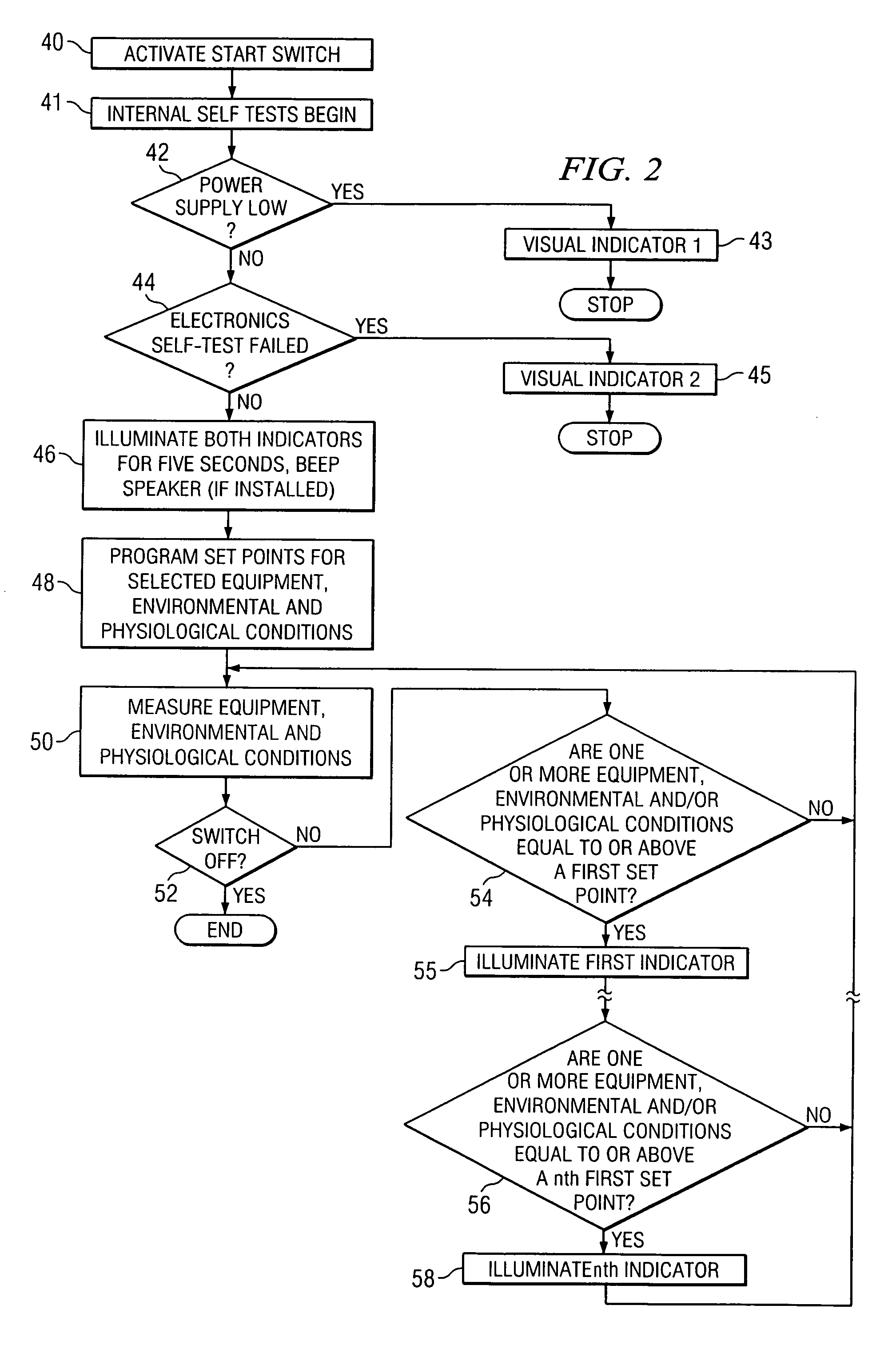
Equipment and method for identifying, monitoring and evaluating equipment, environmental and physiological conditions
InactiveUS20060125623A1Reduce in quantityChemical protectionHeat protectionEngineeringHazard potential
A system and method are disclosed for identifying monitoring and evaluating hazardous or potentially hazardous conditions. The system may be worn by safety personnel to detect equipment conditions such as low power supply, environmental conditions such as ambient temperature and / or physiological conditions such as heart rate of a wearer. The system may further include a control unit having electronics operable to communicate signals associated with equipment, environmental and physiological conditions.
Owner:MINE SAFETY APPLIANCES CO
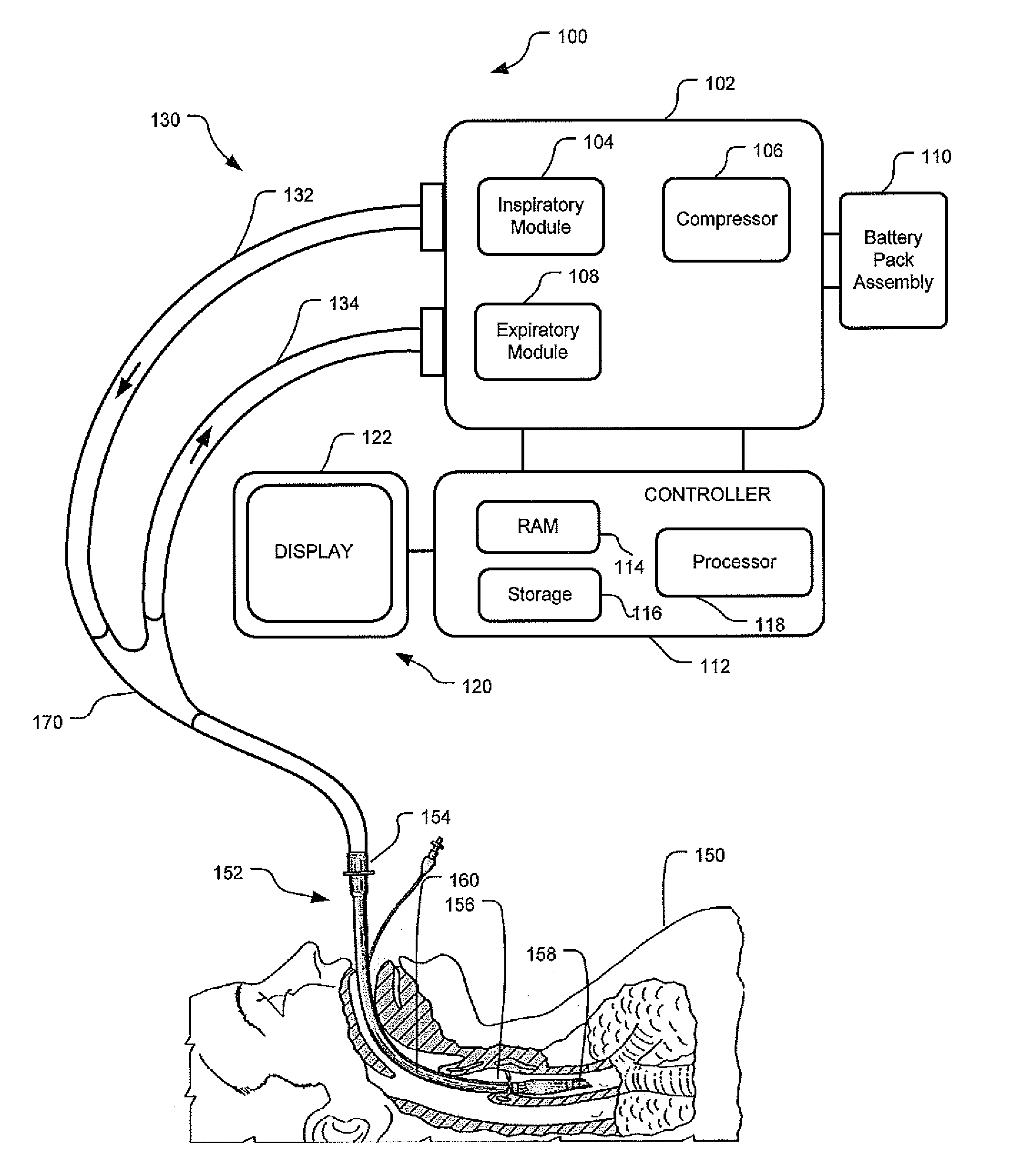
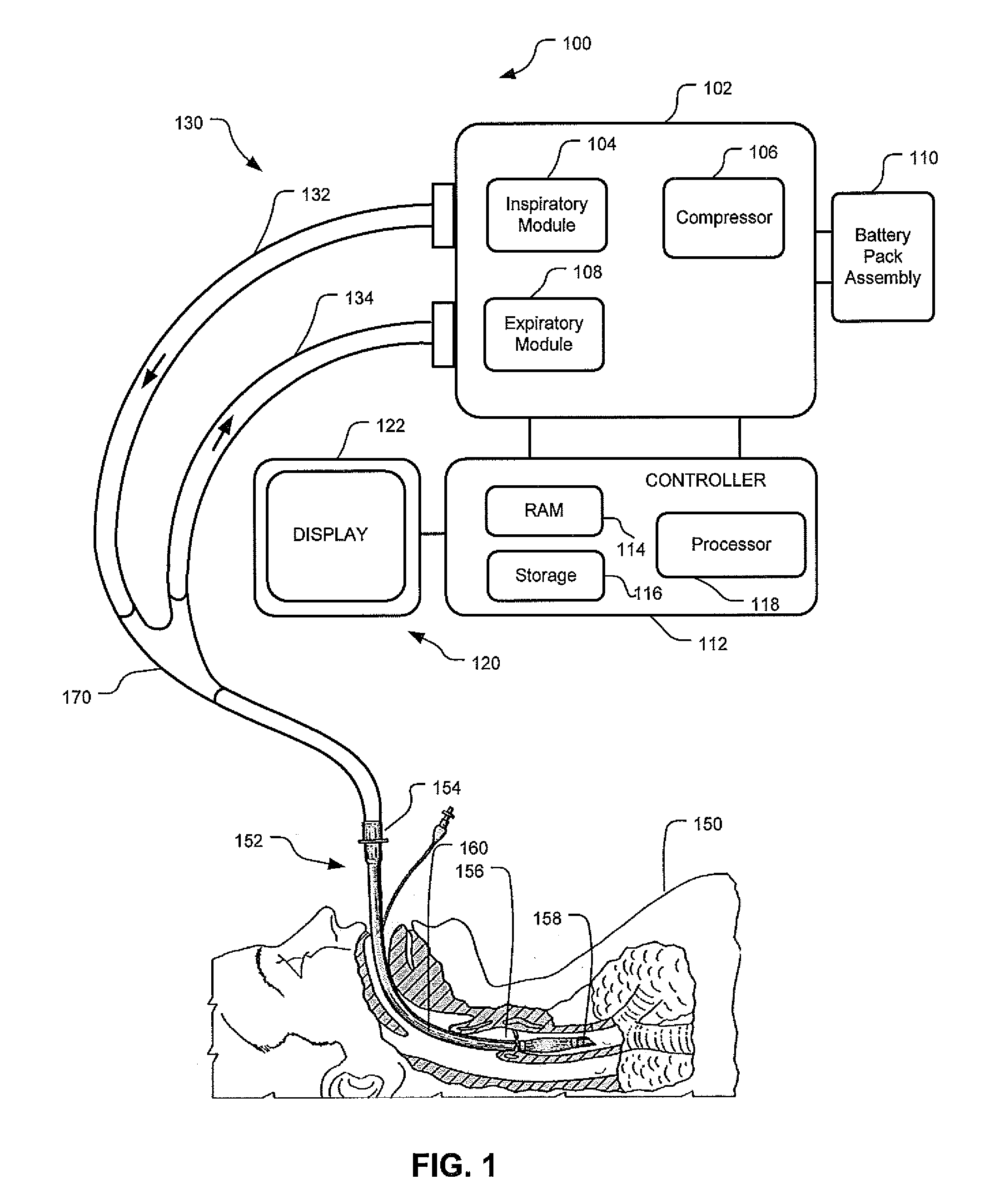
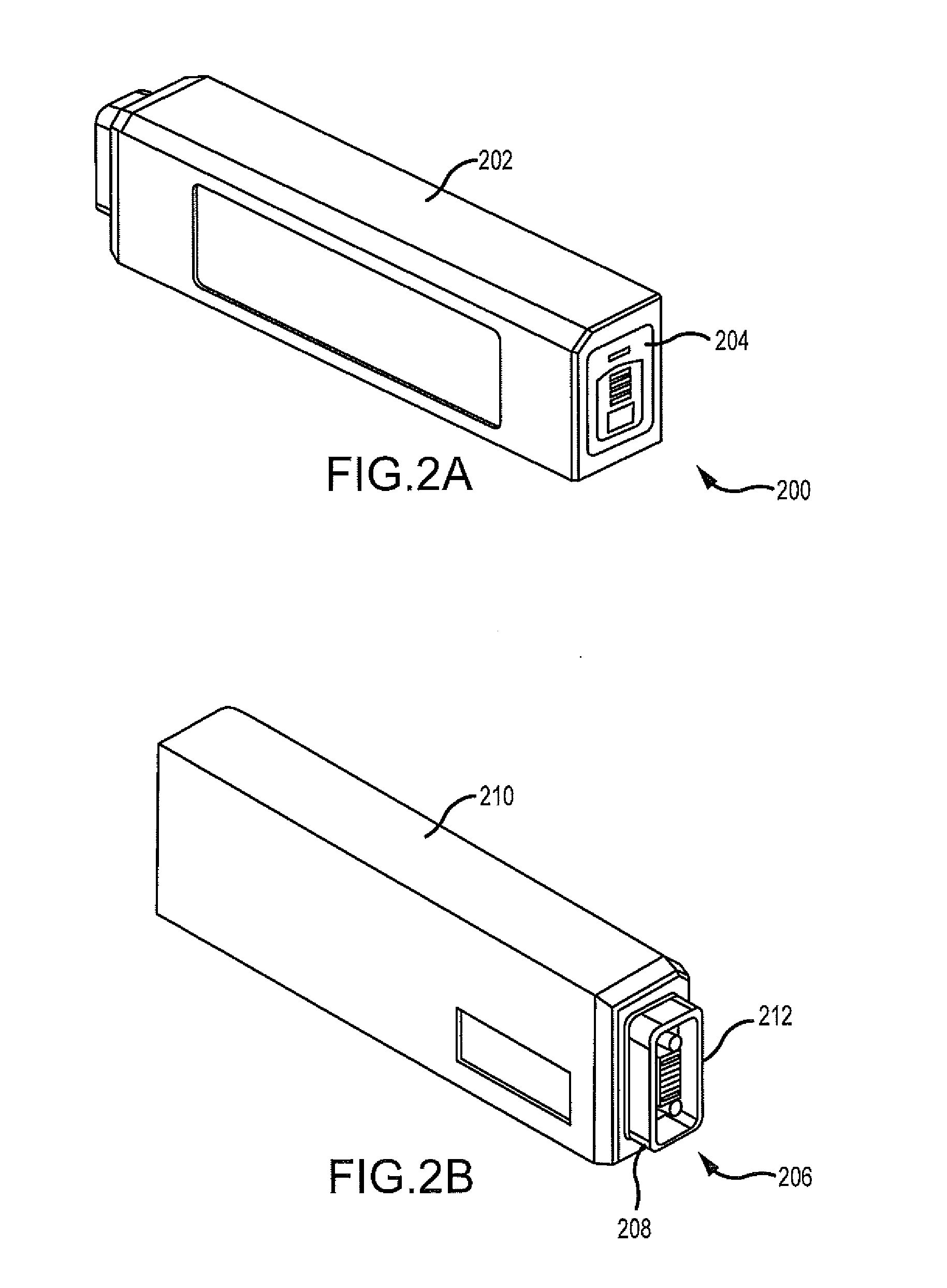
Apparatus And System For A Battery Pack Assembly Used During Mechanical Ventilation
This disclosure describes methods and apparatus for indicating battery cell status on a battery pack assembly used during mechanical ventilation. Embodiments described herein seek to provide methods for indicating battery cell status on the exposed exterior of a battery assembly pack both when the battery is in use and when the battery is not in use during mechanical ventilation. Embodiments utilize power from the ventilator as well as power from the battery pack itself to light the indicators during periods of battery use and non-use, respectively. Embodiments described herein further seek to provide an apparatus indicating battery cell status on the exposed exterior of the battery pack assembly during mechanical ventilation. Embodiments described herein further seek to provide an apparatus for a battery pack assembly used during mechanical ventilation. Embodiments described herein seek to provide a system for a ventilation system with an inserted battery pack assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
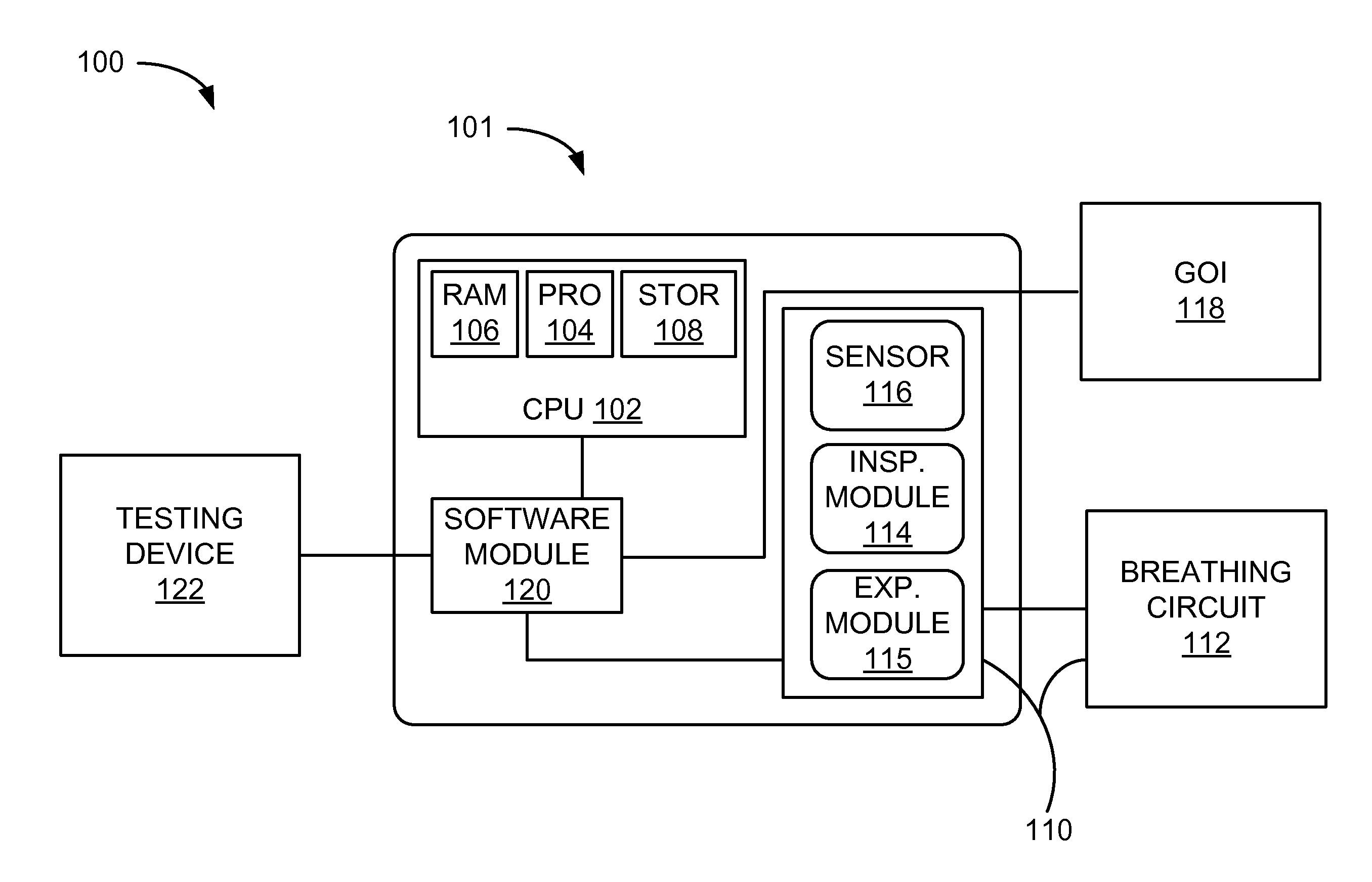
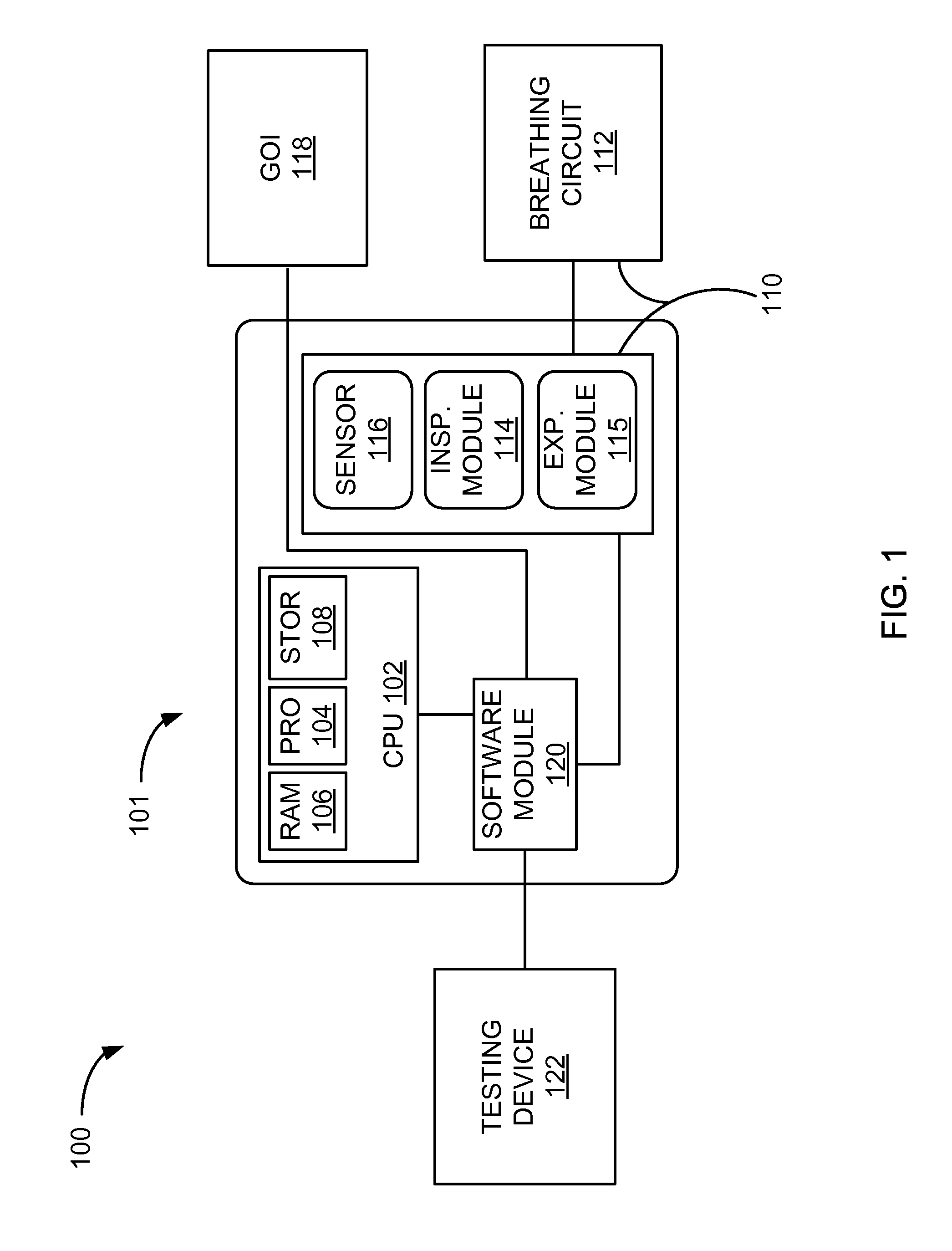
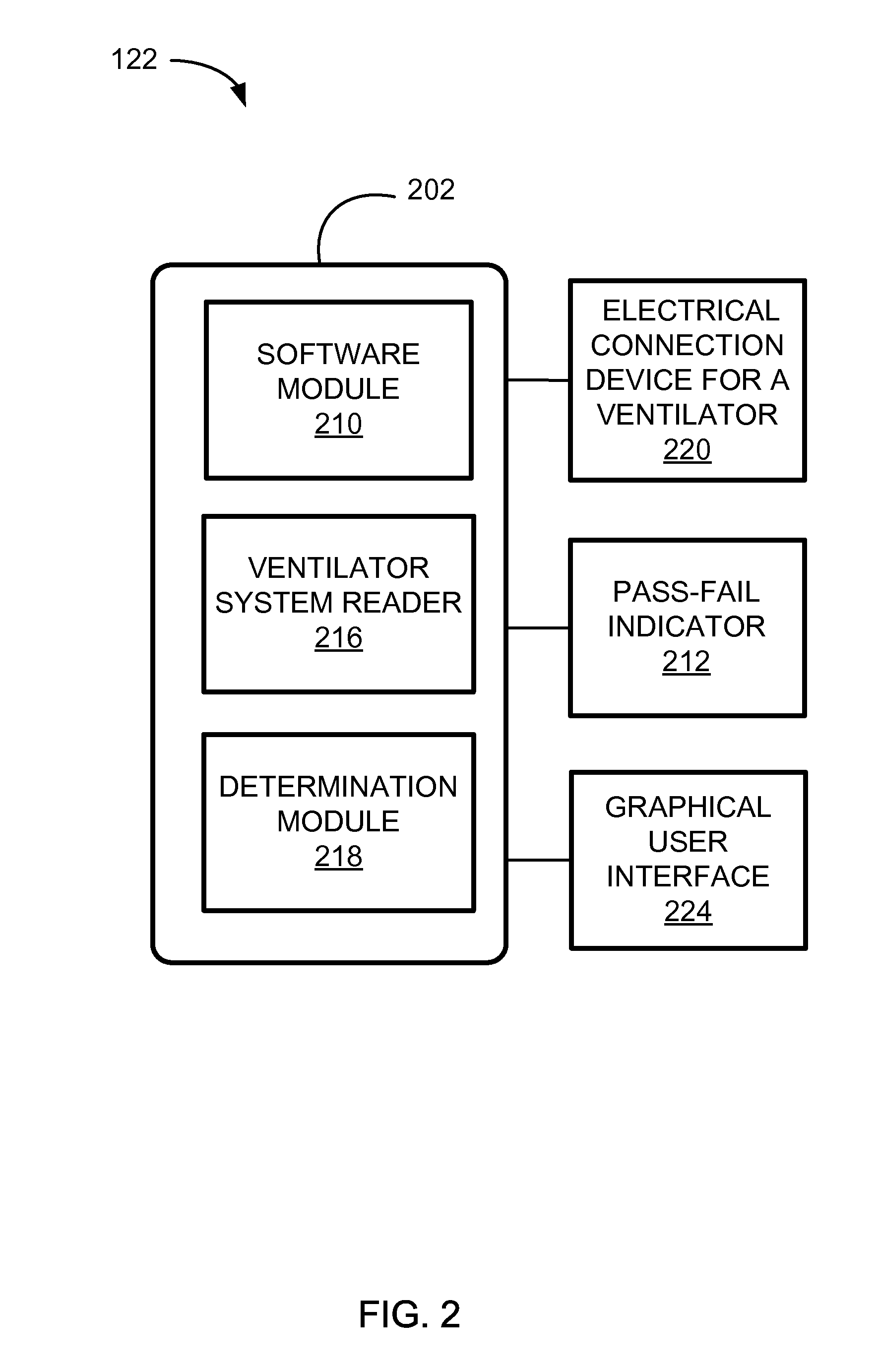
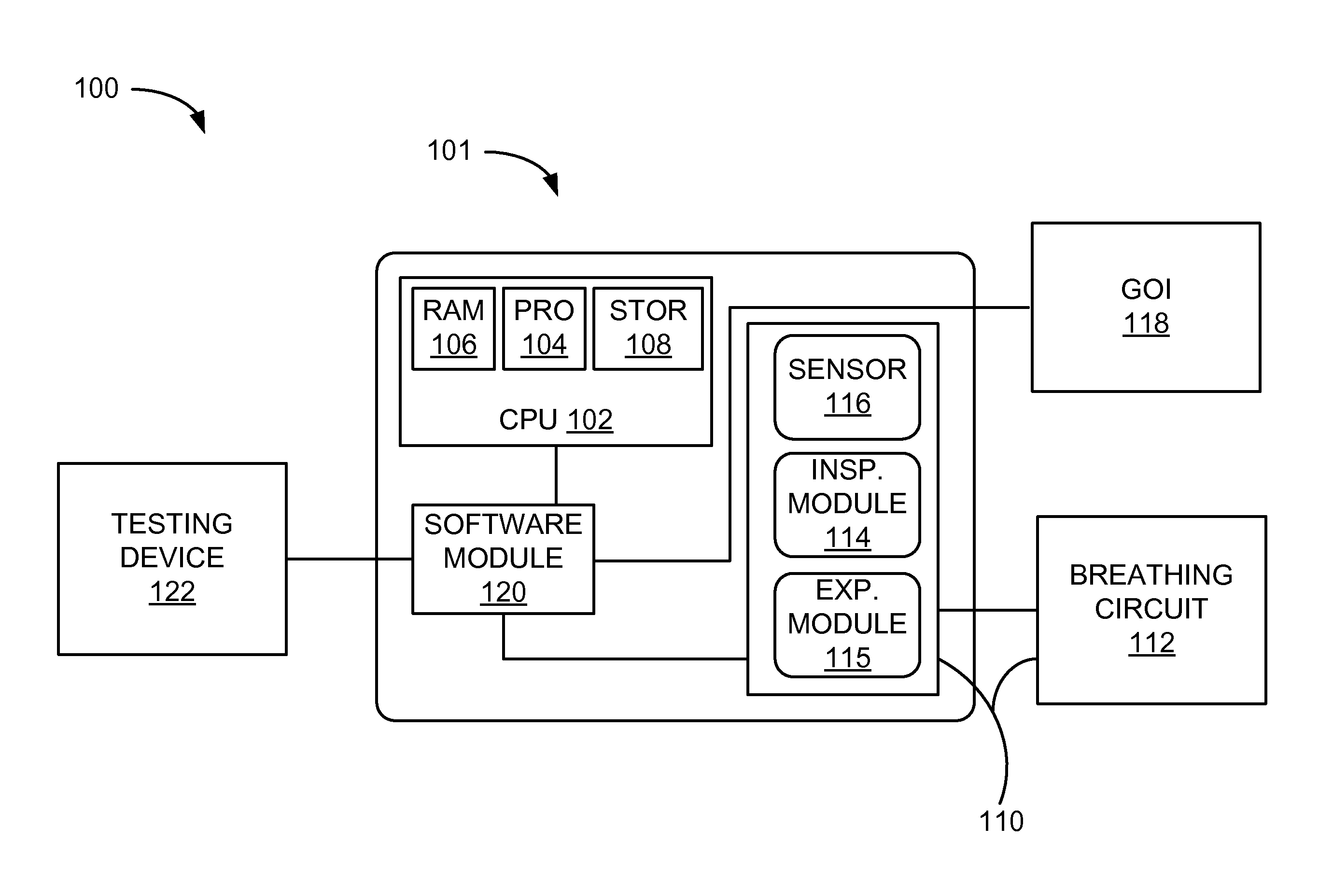
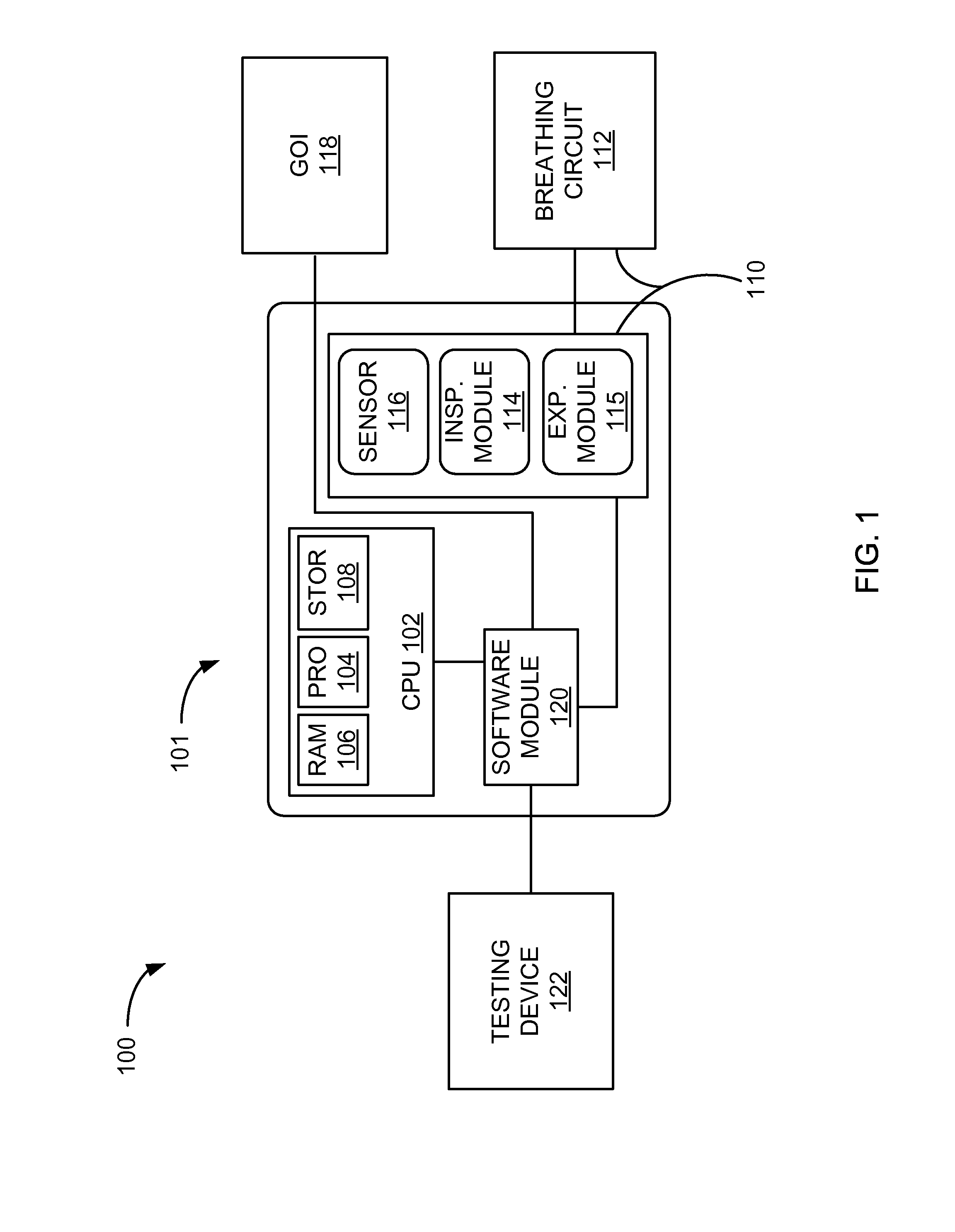
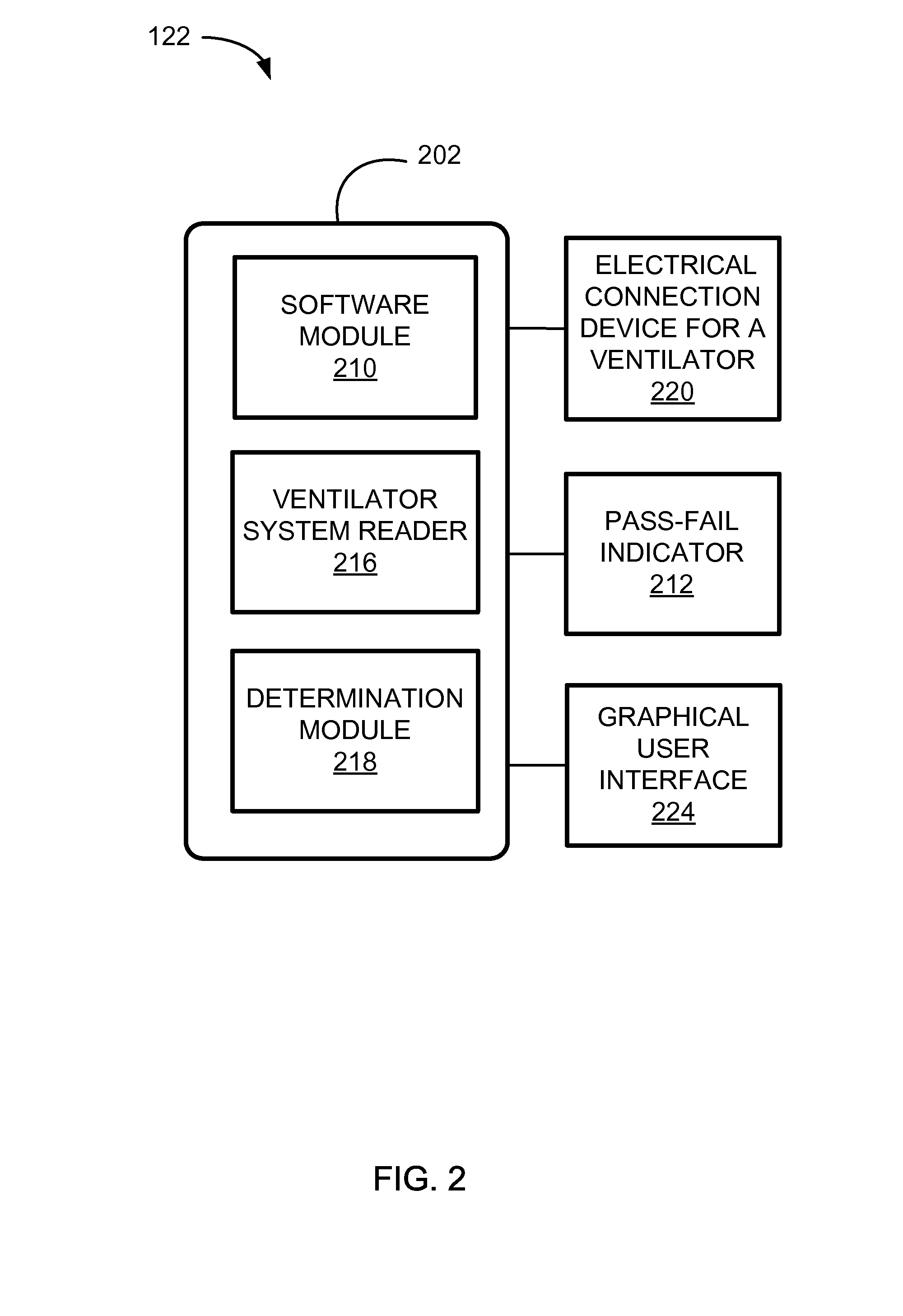
Systems And Methods For Medical Device Testing
ActiveUS20120197580A1Guaranteed functionVehicle testingRespiratory device testingMedicineMedical testing
This disclosure describes systems and methods for testing a medical device. The disclosure describes a novel approach determining if the ventilator system is functioning properly without having to connect the medical device to a patient.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
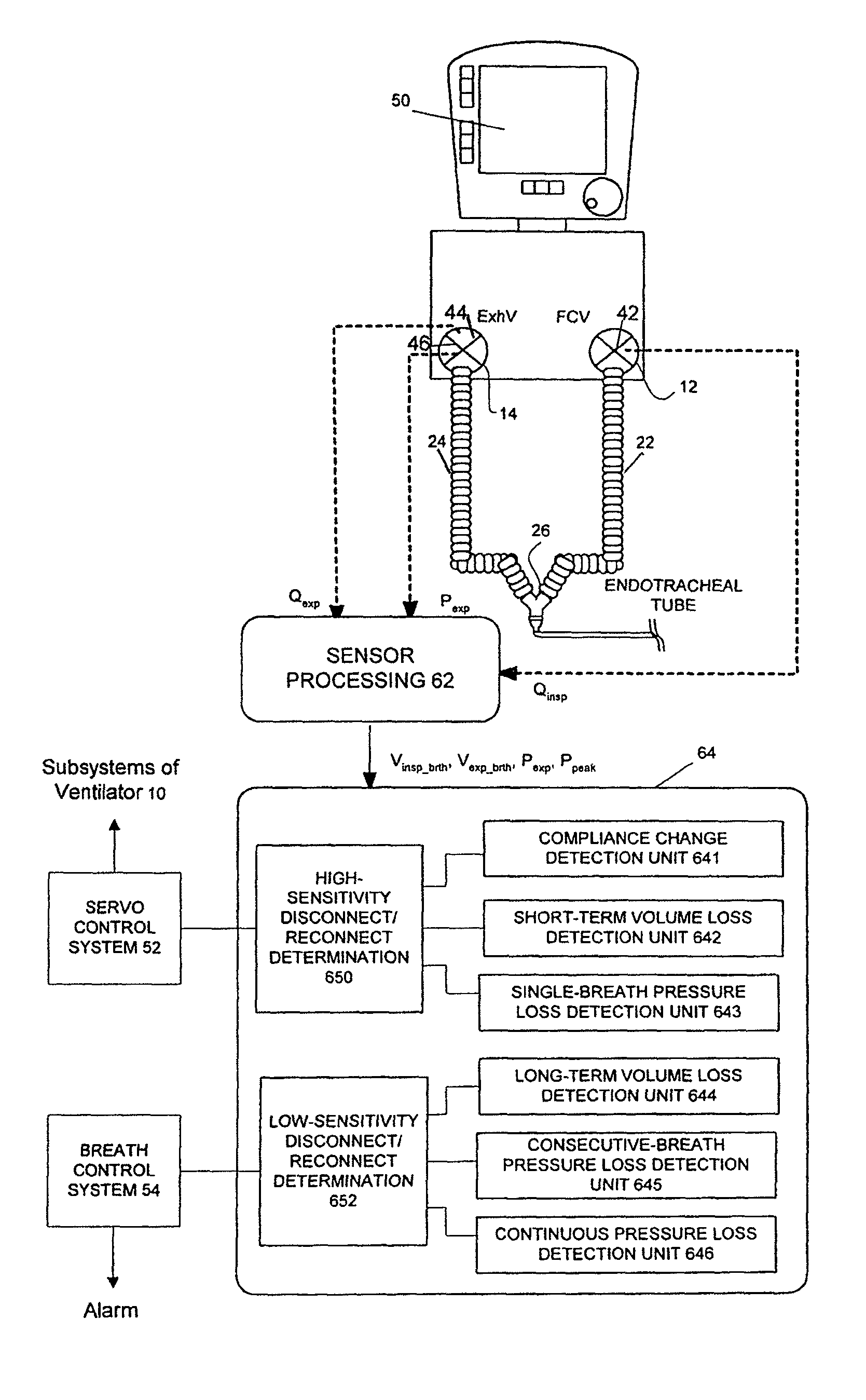
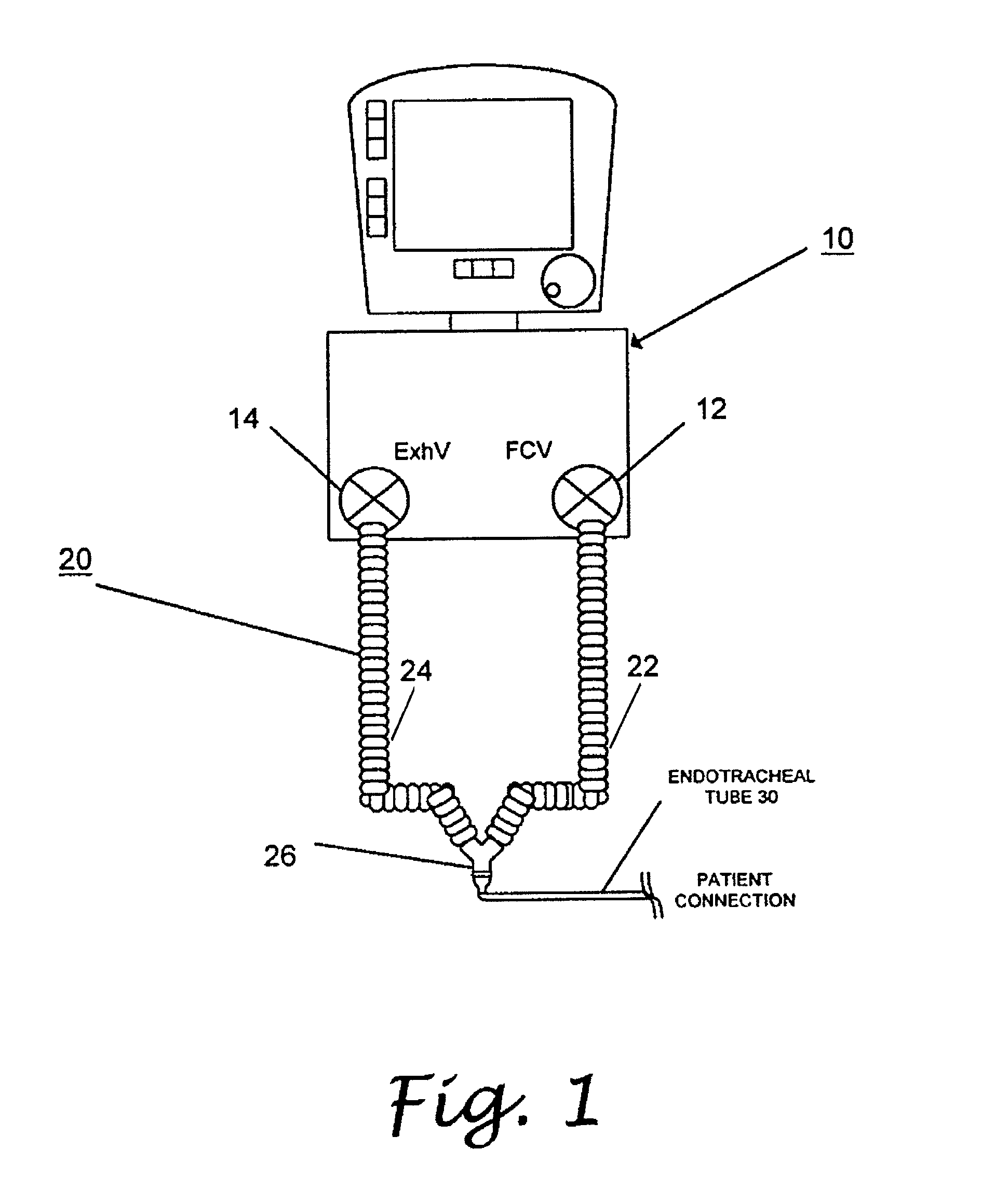
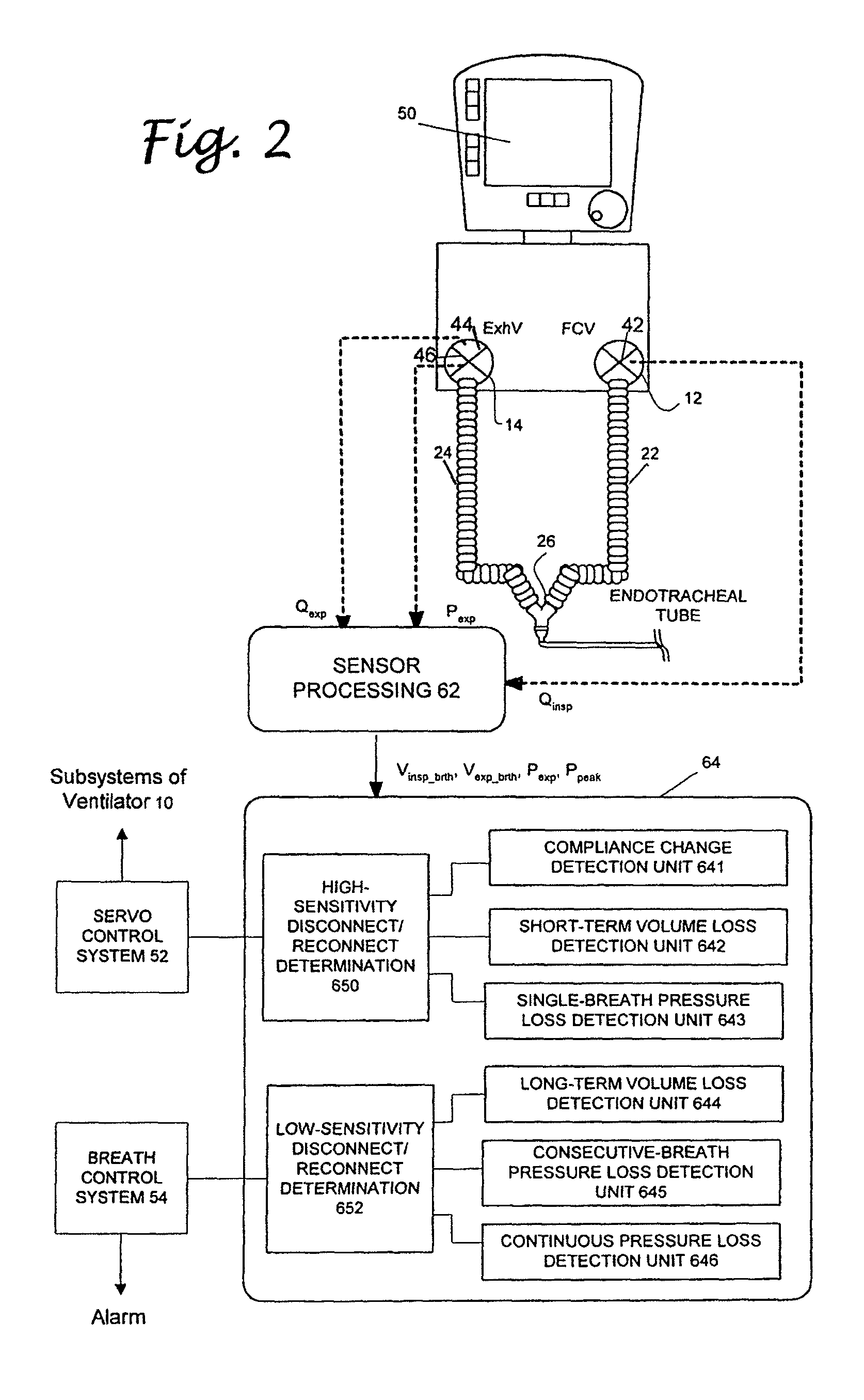
Patient circuit disconnect system for a ventilator and method of detecting patient circuit disconnect
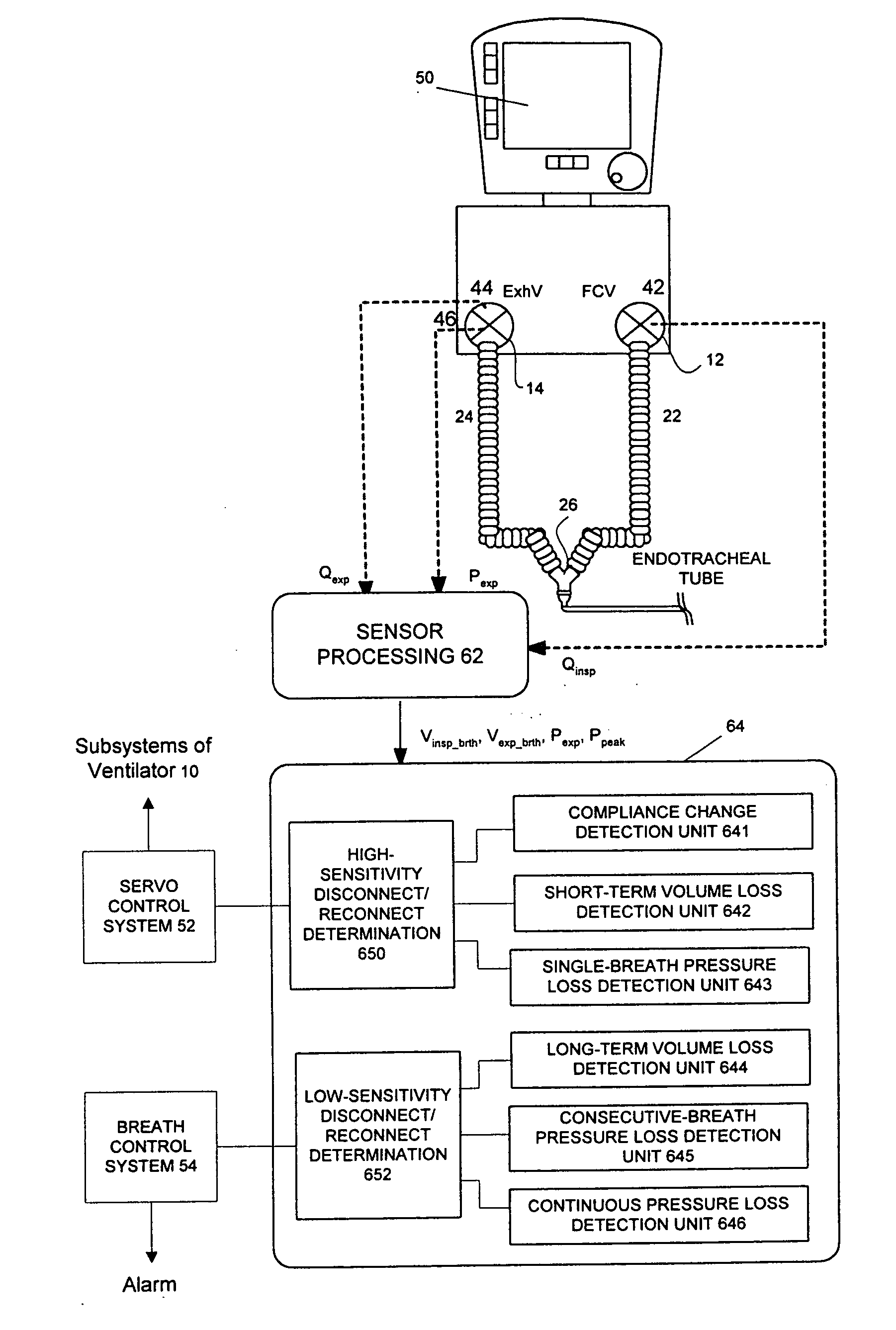
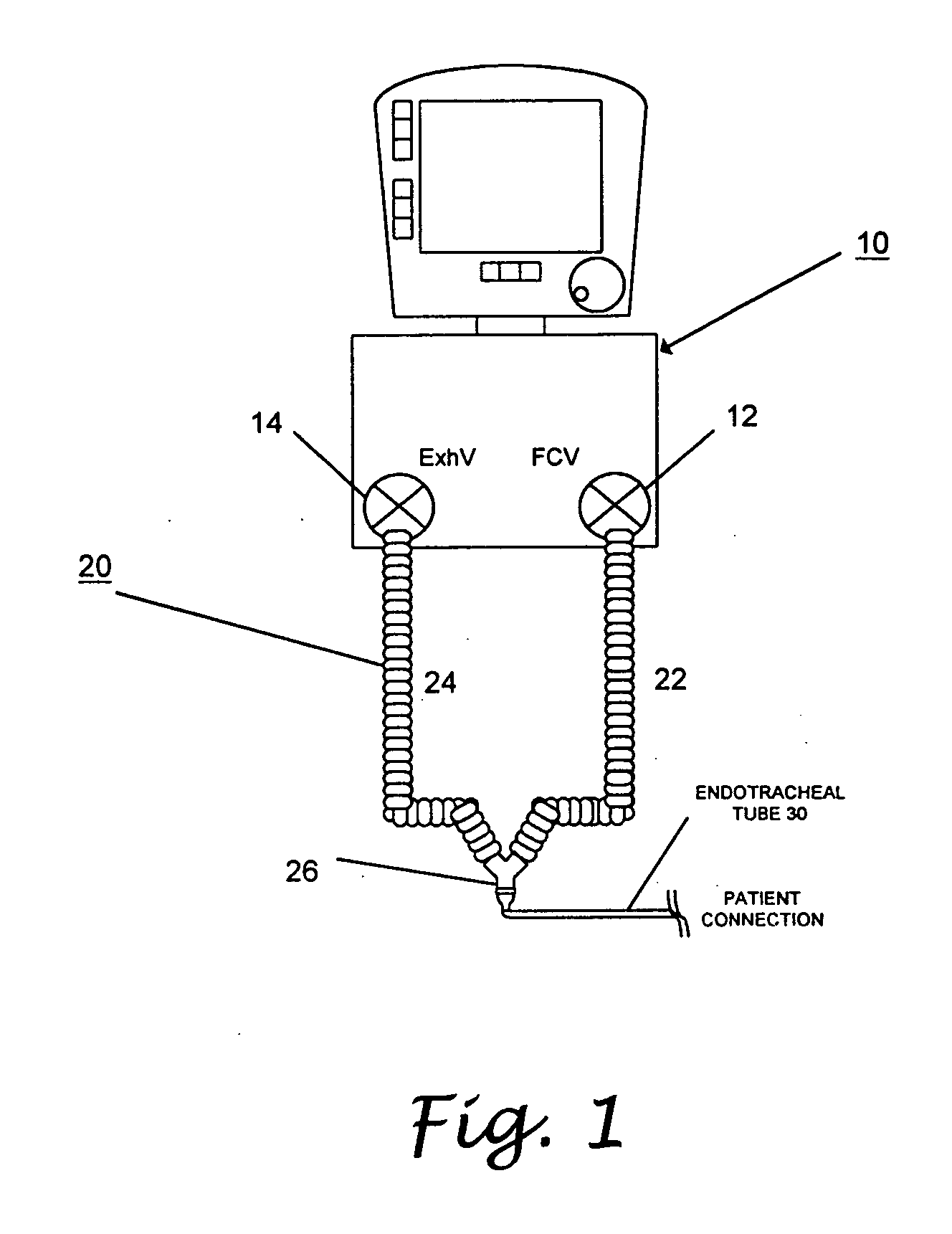
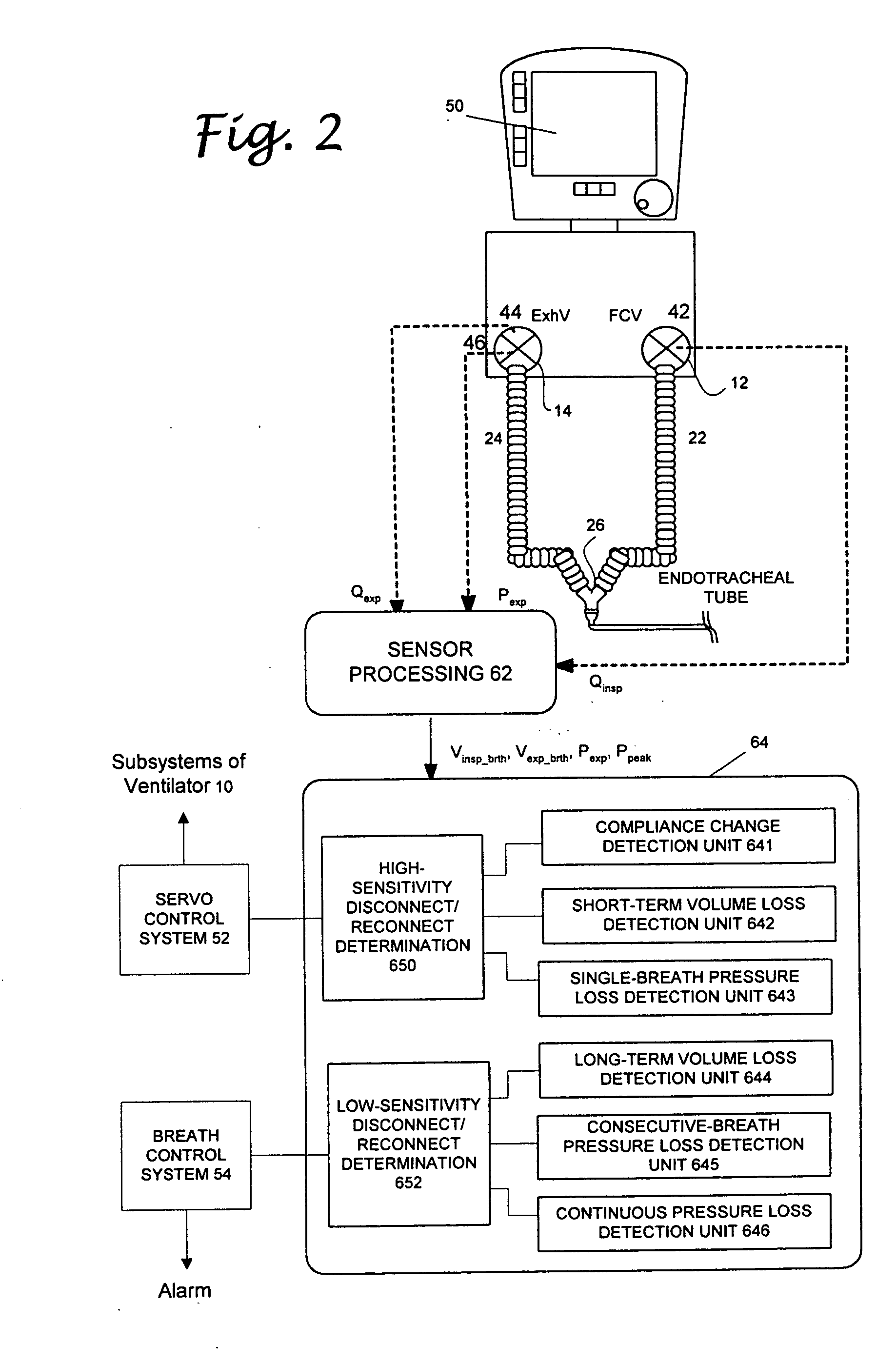
ActiveUS20060086357A1Easy to adjustRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMedicinePeak value
A method of detecting disconnect of a patient circuit of a ventilation system, wherein a circuit disconnect is detected with a first sensitivity and a second sensitivity. The circuit disconnect detected with the first sensitivity is performed by detecting a volume loss for a minimum period of time, detecting a peak pressure loss for at least two consecutive breathing cycles or a minimum period of time, and detecting a pressure loss continuing for a predetermined period of time. The circuit disconnect detected with the second sensitivity is performed by detecting a volume loss for a single breathing cycle, detecting a pressure loss for a single breathing cycle, and detecting an increase of compliance. The first sensitivity is lower than the second sensitivity. Preferably, an alarm is activated when the circuit disconnect is detected with the first sensitivity, and subsystems of the ventilation system is informed of the circuit disconnect that has been detected with the second sensitivity.
Owner:BIRD PRODS
Systems And Methods For Simulation And Software Testing
InactiveUS20120197578A1Guaranteed functionVehicle testingRespiratory device testingMedicineMedical device
This disclosure describes systems and methods for testing a medical device. The disclosure describes a novel approach determining if the ventilator system is functioning properly without having to connect the medical device to a patient.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
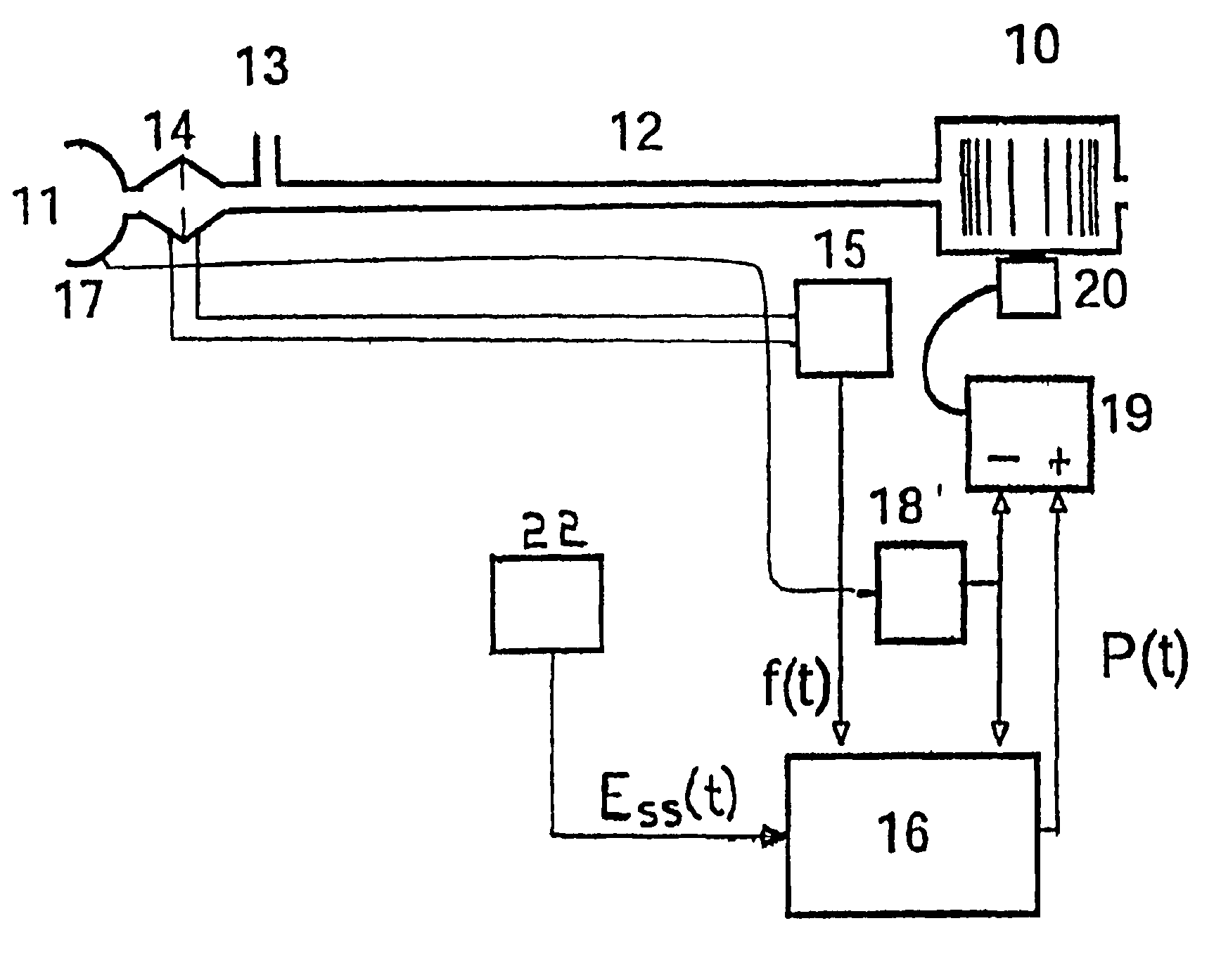
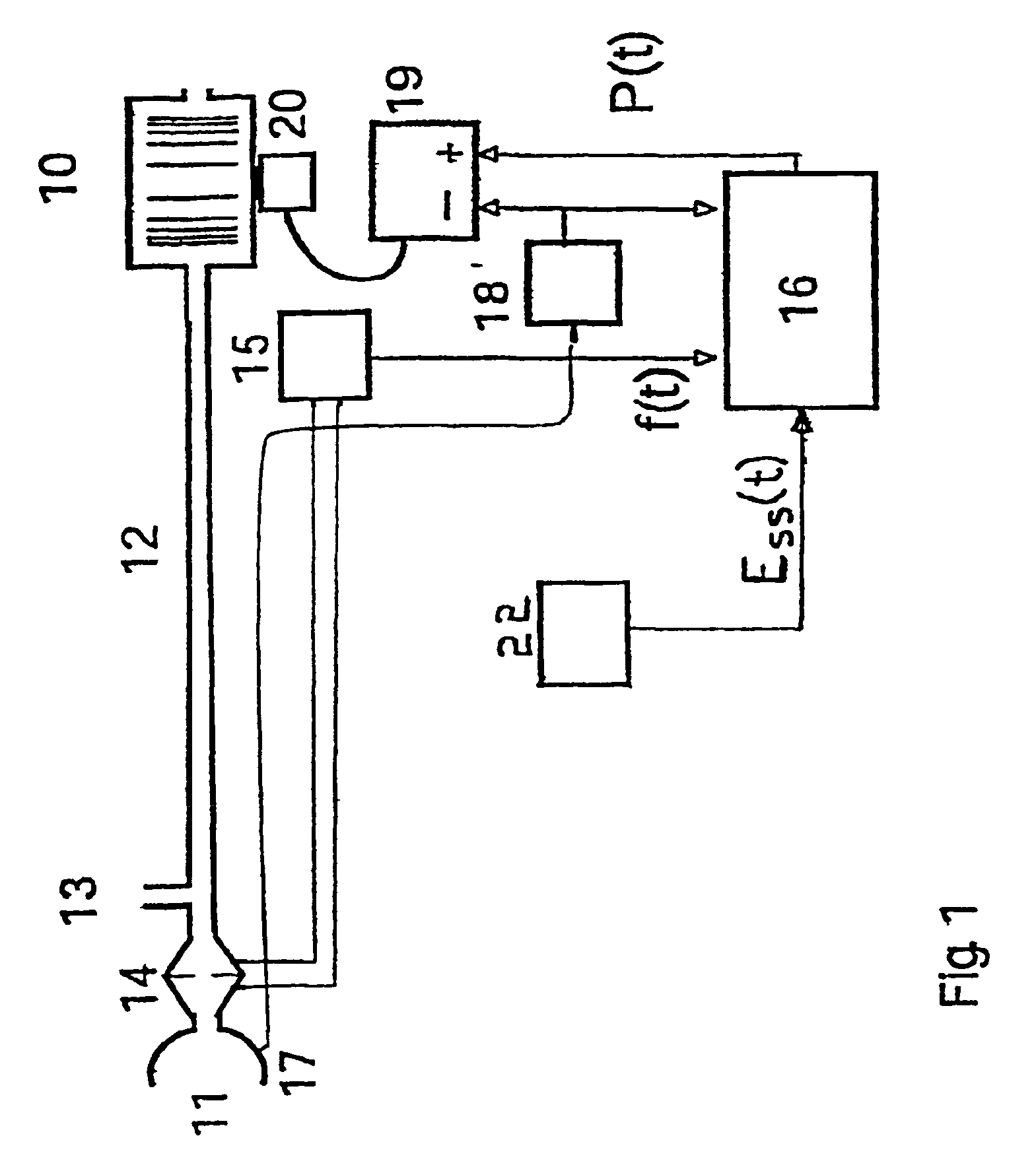
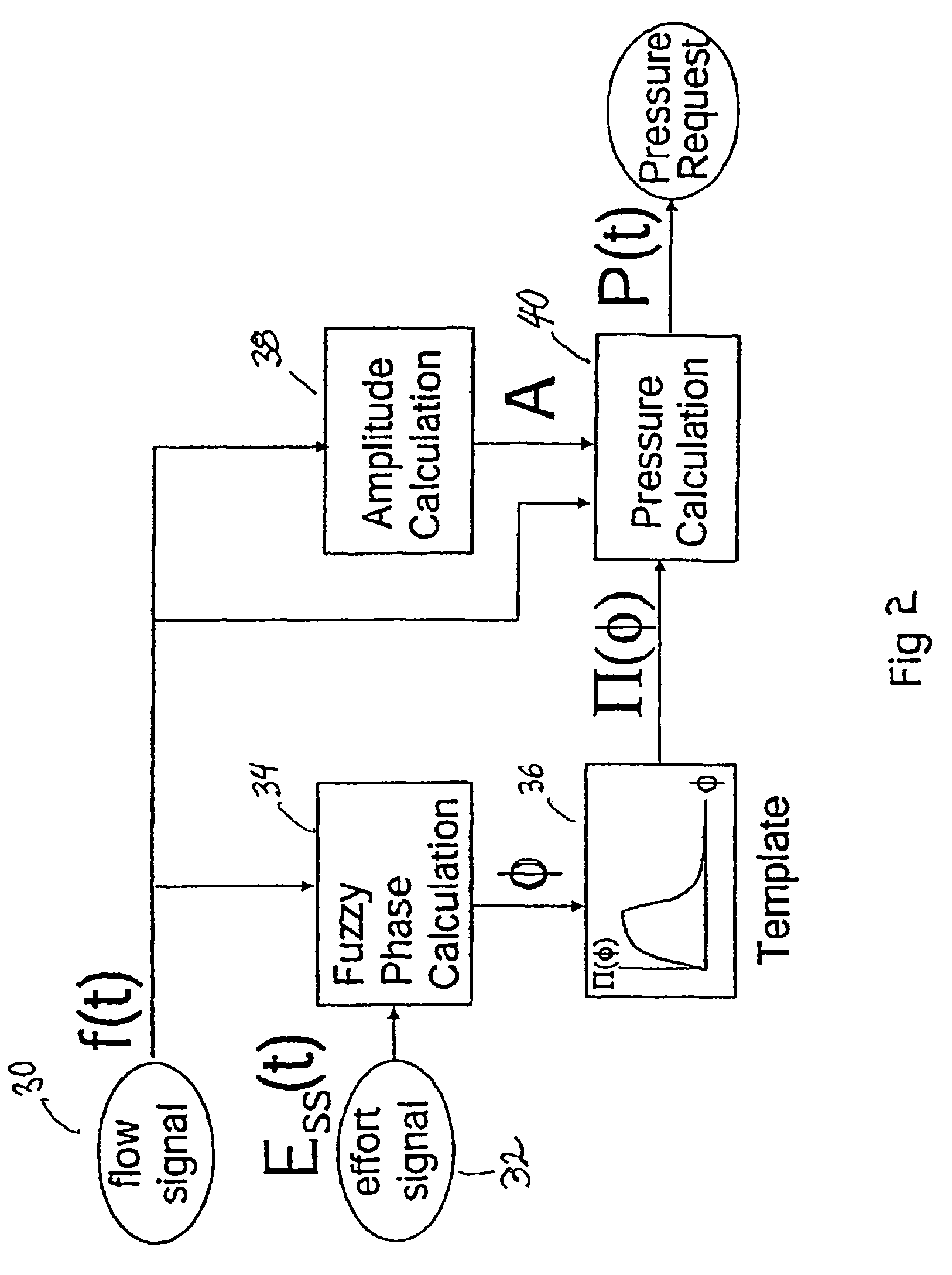
Patient-ventilator synchronization using dual phase sensors
InactiveUS7934499B2Minimum ventilationImprove determinationRespiratorsRespiratory device testingRespiratory phasePressure amplitude
An improved ventilator which delivers ventilatory support that is synchronized with the phase of the patients respiratory efforts and guarantees a targeted minimum ventilation. Improved synchronization is achieved through an instantaneous respiratory phase determination process based upon measured respiratory airflow as well as measured respiratory effort using an effort sensor accessory, preferably a suprasternal notch sensor. The ventilator processes a respiratory airflow signal, a respiratory effort signal and their respective rates of change to determine a phase using standard fuzzy logic methods. A calculated pressure amplitude is adjusted based upon the calculated phase and a smooth pressure waveform template to deliver synchronized ventilation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Pressure support compliance monitoring system
InactiveUS6910481B2Not easily fooledEasy to useRespiratorsRespiratory device testingSupporting systemCompliance Monitoring
A compliance monitoring system and method in which a modular compliance monitor is selectively disposed in-line in a patient circuit of a pressure support system. The monitor includes a housing having an inlet and an outlet, each of which is selectively connectable to the patient circuit so that the flow of gas in the patient circuit also passes through a passage is provided through the housing. A sensor operatively coupled to the passage detects a parameter indicative of patient breathing. A processor disposed in the housing and receives the output of the sensor and determines, from the output of the sensor, whether the patient is breathing into the patient circuit, and outputs compliance data based on this determination.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
Dose counting in metered dose inhaler
A counter for indicating the number of doses left in a canister that is suitable for use in a metered dose inhaler. The counter is affixed to the canister and includes a module for providing an indication of the number of doses left in the canister and a triggering mechanism for updating the indication in response to activation of the inhaler.
Owner:GENOVA PERRY +2
Methods and apparatus for safe application of an intubation device
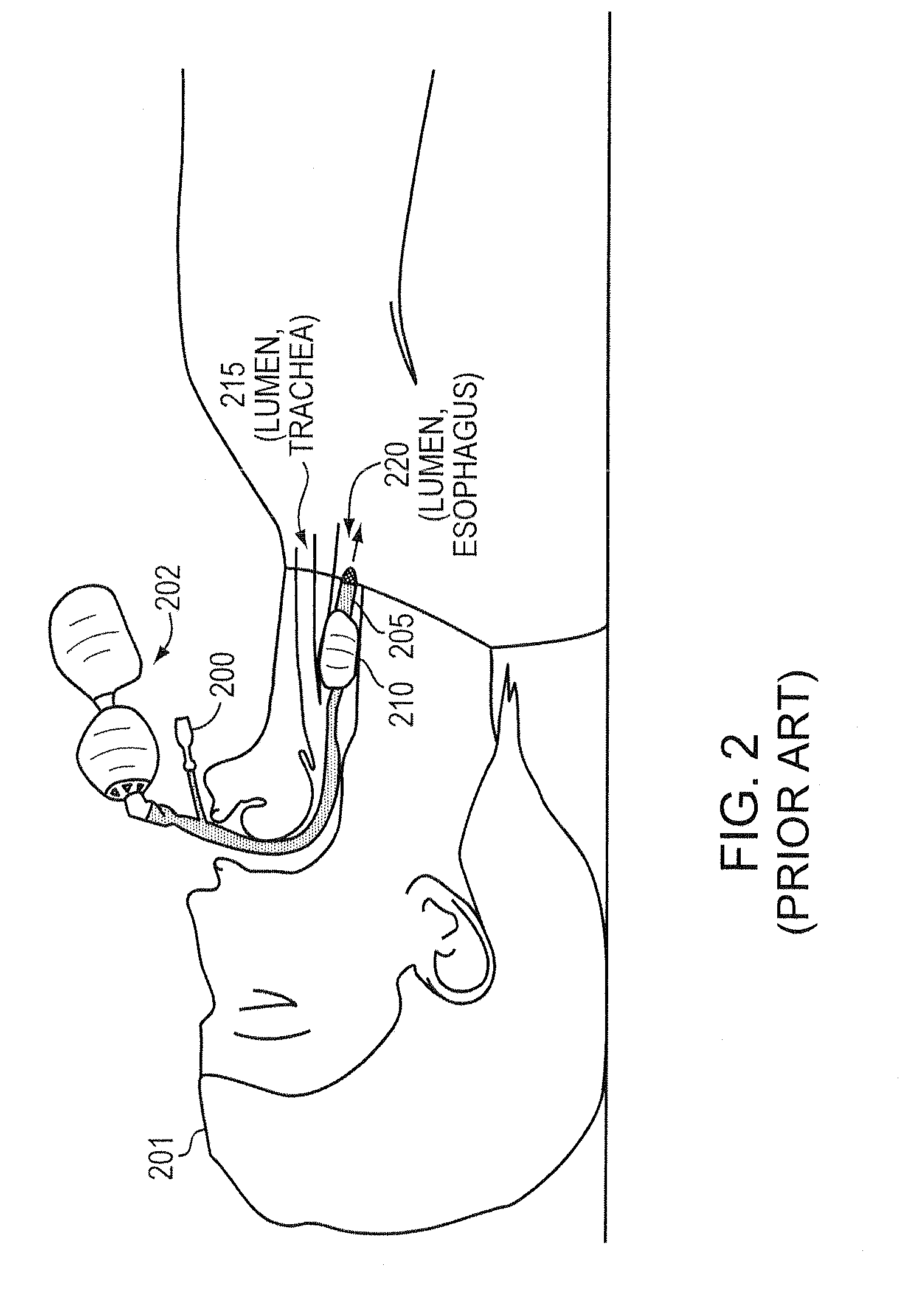
InactiveUS20100163023A1Accurately maintains pressureDirect contact guaranteeRespiratory device testingMedical devicesInternal bleedingCuff
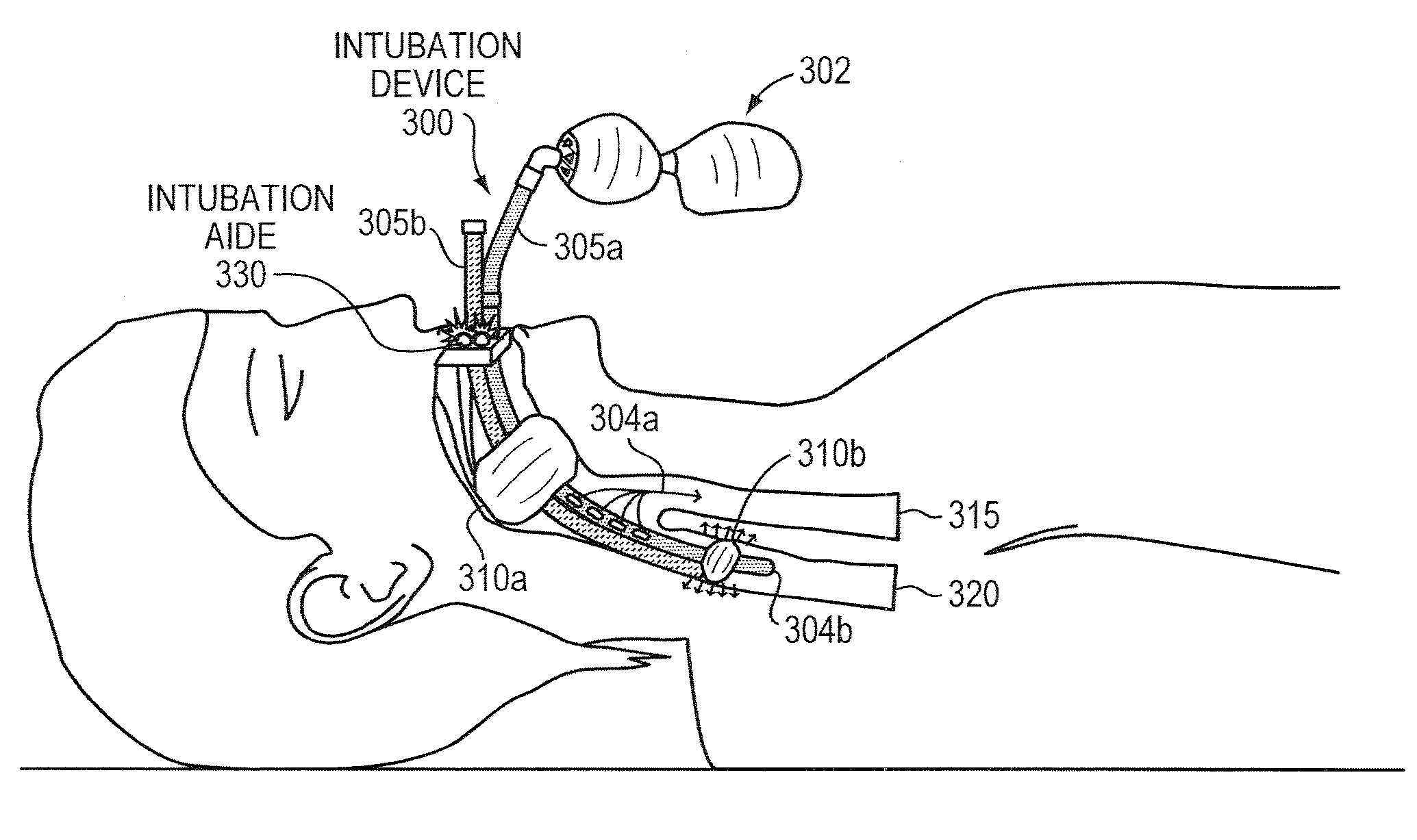
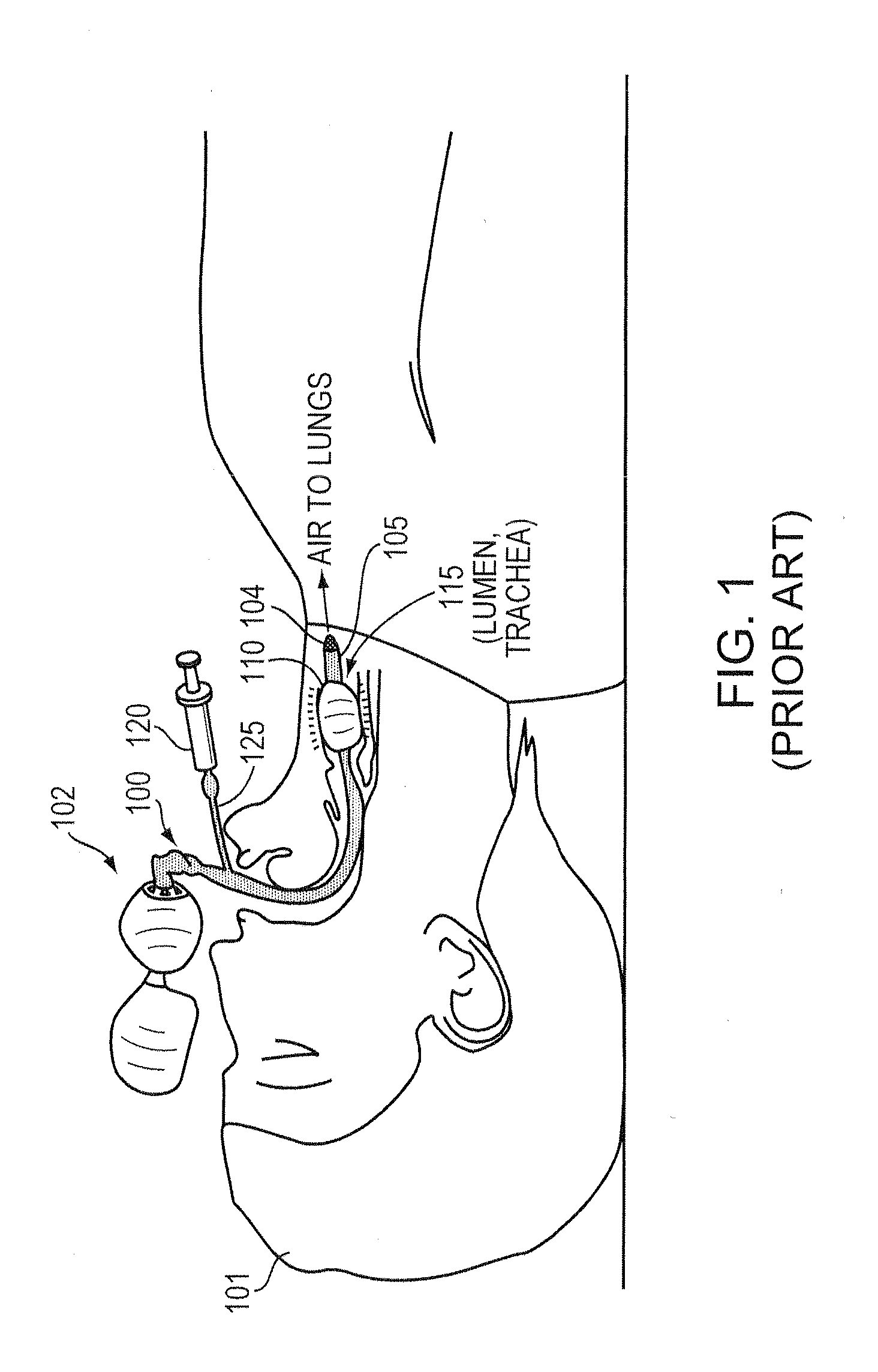
Intubation is a potentially dangerous invasive procedure with many plausible errors, such as over-inflation of a cuff and insertion of an intubation tube in the wrong lumen, potentially resulting in a patient's internal bleeding, suffocation, or even death. An intubation aide according to example embodiments of the present invention allows intubation of a patient, while eliminating potential injury to the patient, increasing accuracy and reliability of the placement of the intubation tube, and drastically decreasing procedural time. Within moments of insertion of the device into a patient, the medical caregiver knows, with complete certainty, the location of the intubation device without applying traditional time-consuming tasks. Embodiments also provide patient safety, if intubated for a prolonged periods, by regulating an inflation pressure of the cuff. The intubation aide can also be used for training purposes and is ideal for intubation in hospital and field settings.
Owner:SINGH MANU B
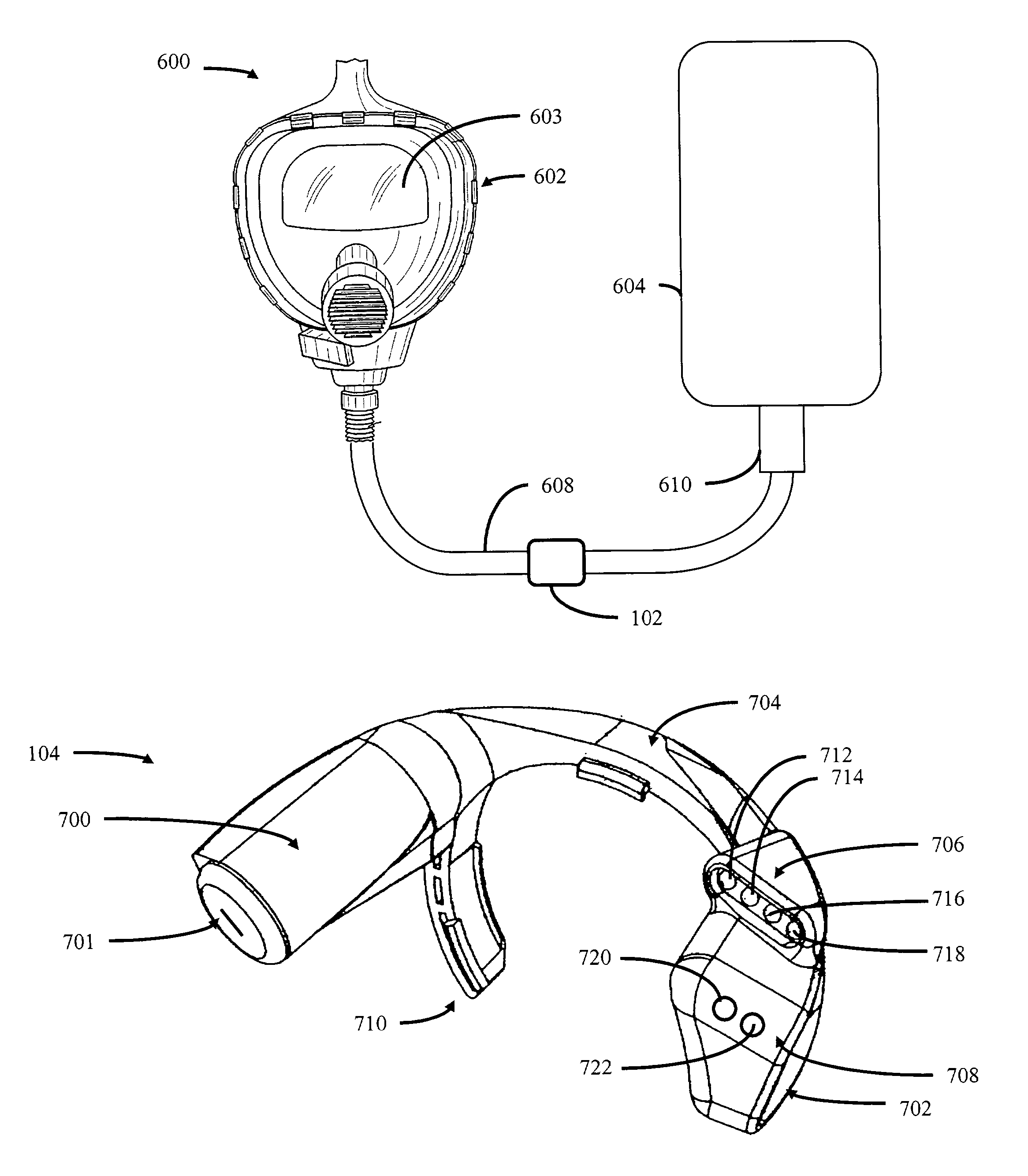
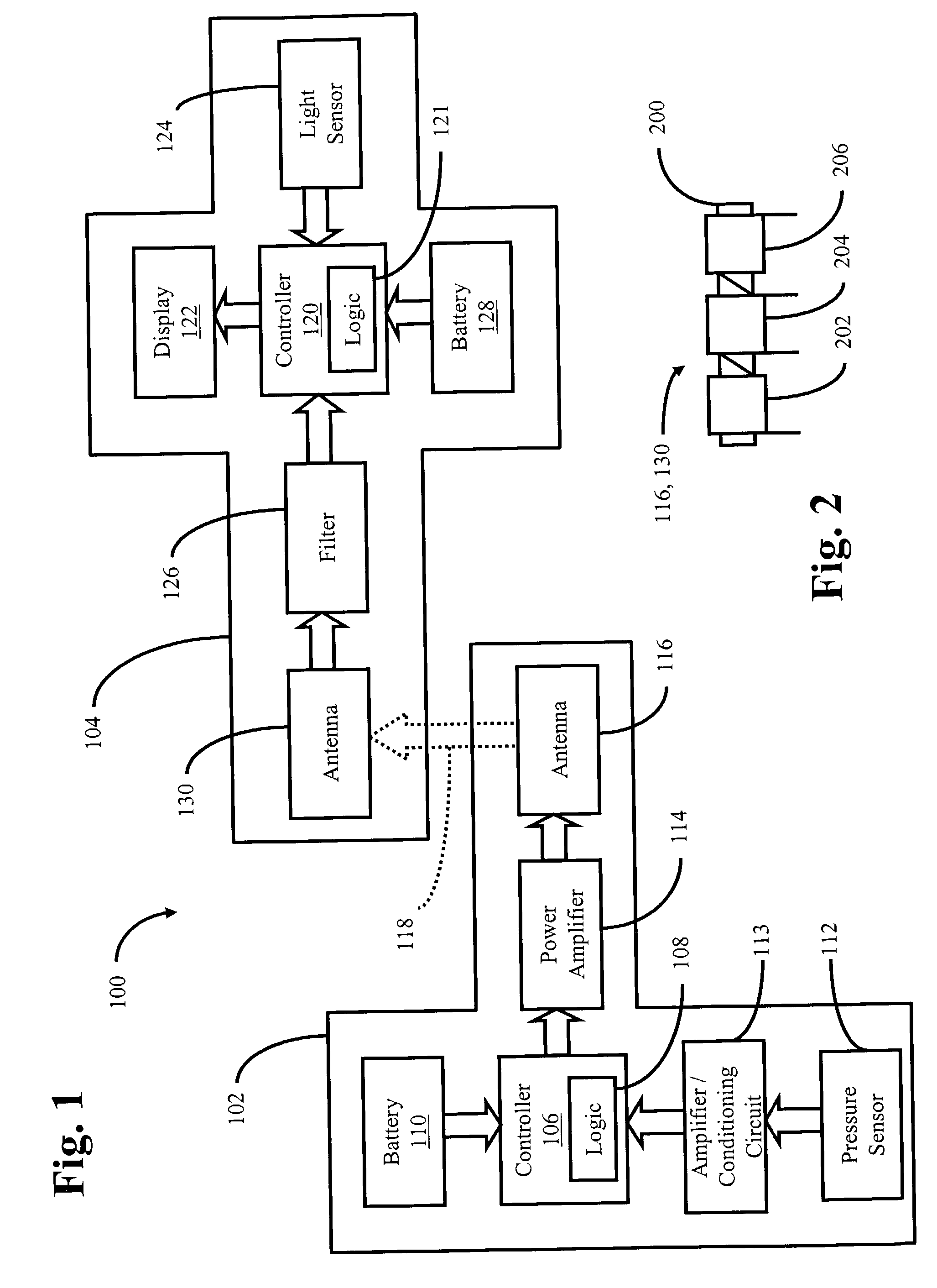
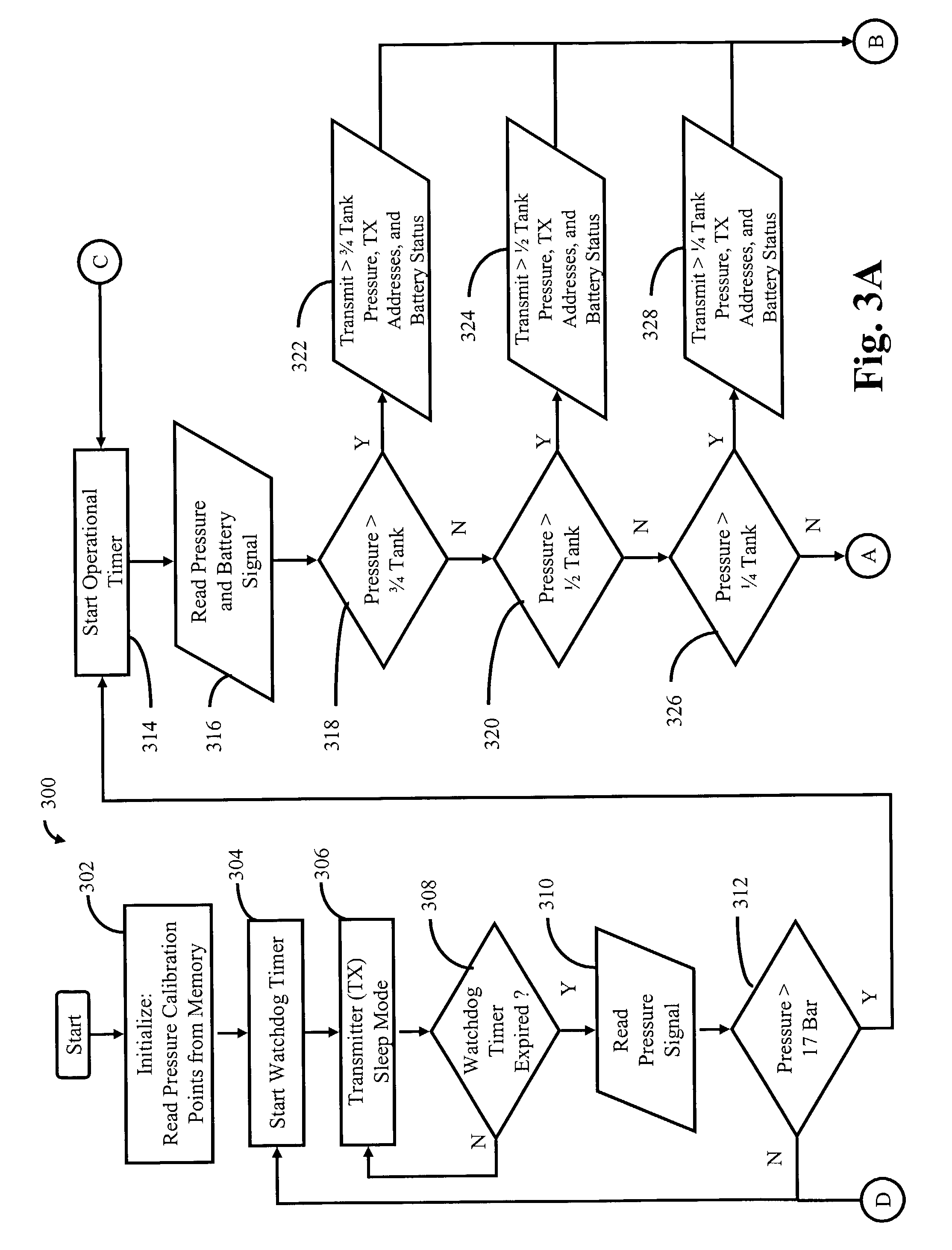
Wireless heads-up display for a self-contained breathing apparatus
A system and method of providing a wireless heads-up display for displaying the amount of breathing gas remaining in an associated breathing gas supply is provided. The system has a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter has a pressure sensor and a controller for interpreting the sensed pressure into levels indicative of the amount of breathing gas remaining in the breathing gas supply. These levels are transmitted via radio frequency to the receiver. The receiver, which can be mounted in a breathing mask, includes a display for displaying the amount of breathing gas remaining in the associated breathing gas supply.
Owner:UNDERSEA SENSOR SYST
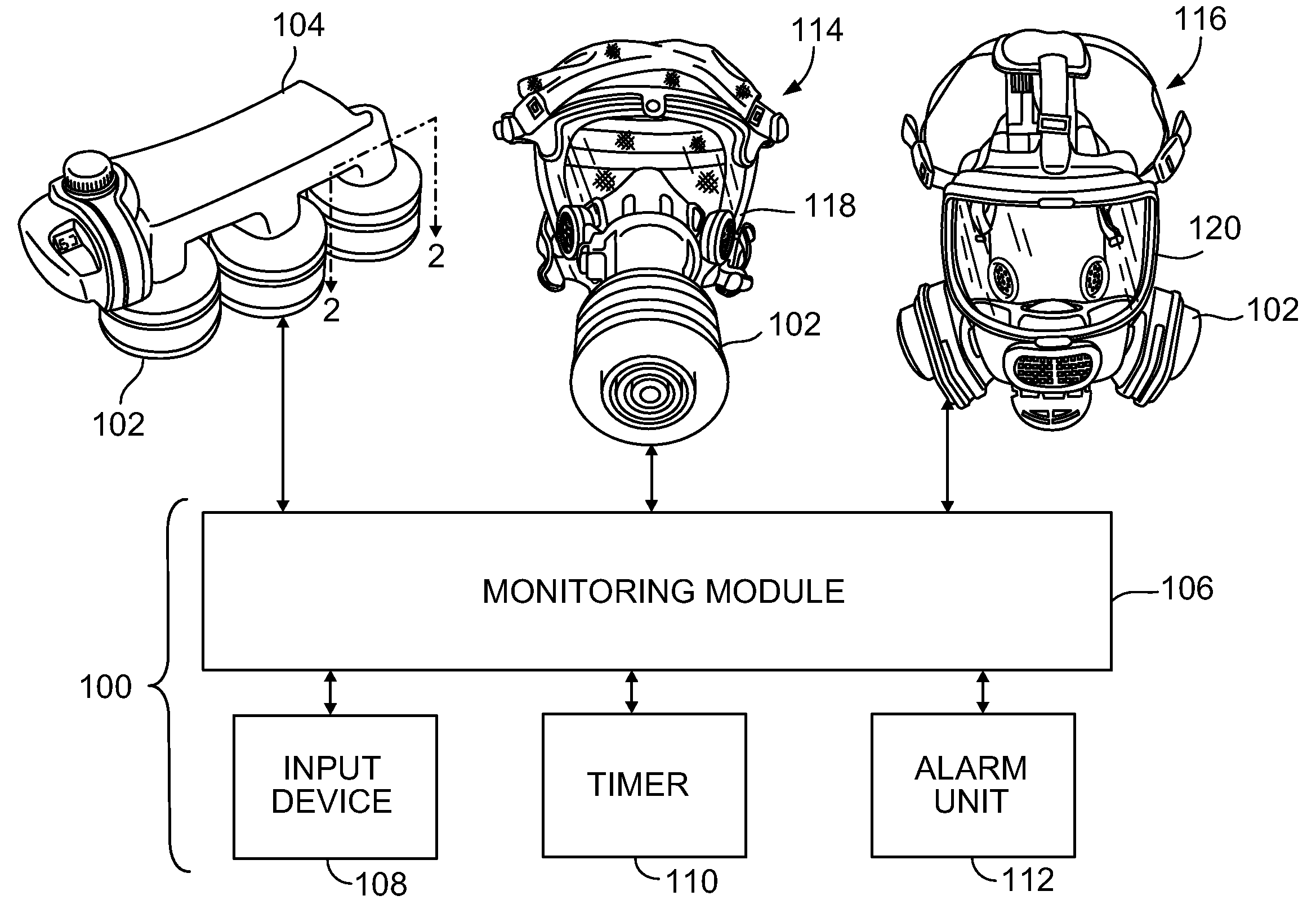
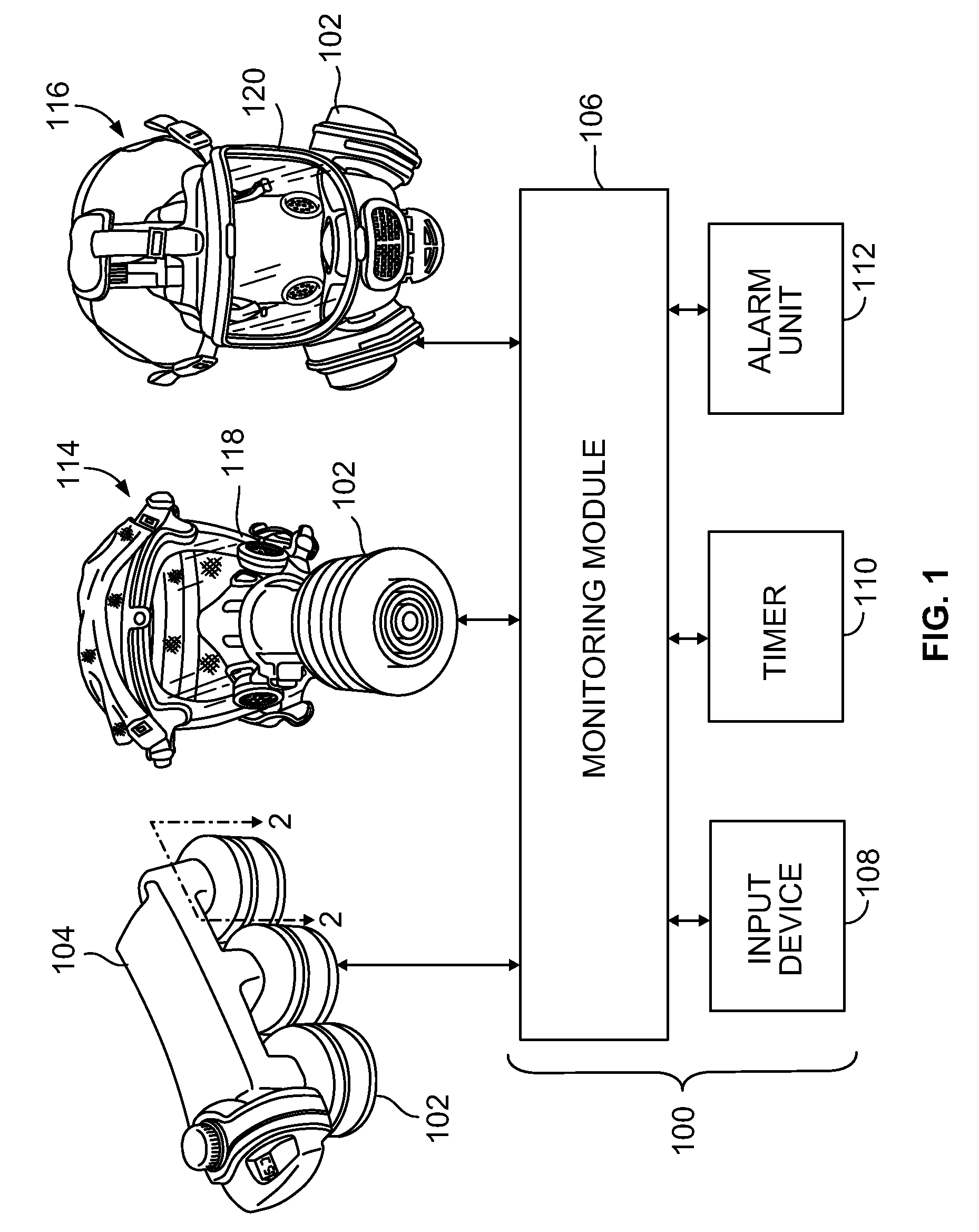
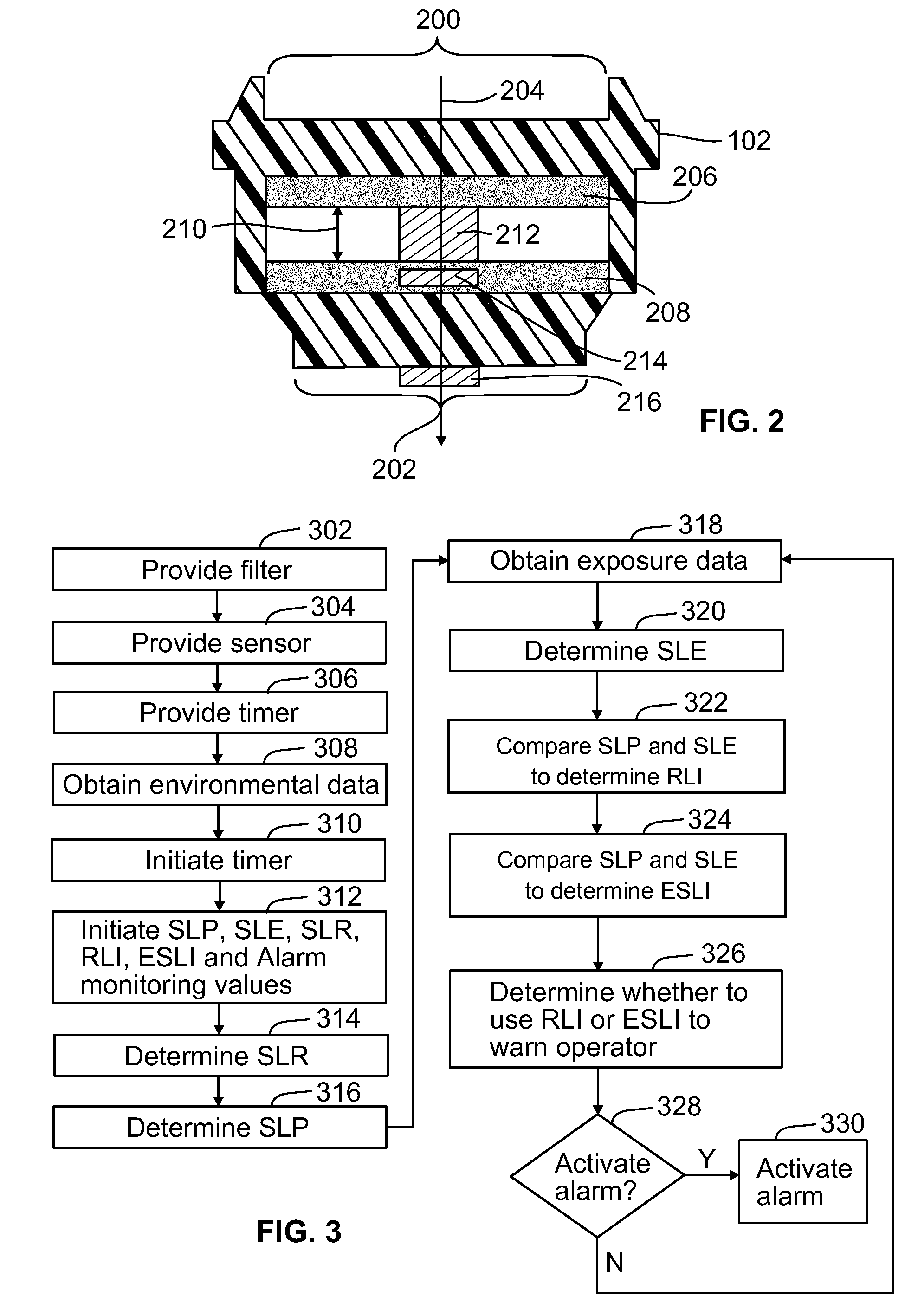
Systems and methods for determining filter service lives
A method for determining a service life for a filter includes measuring exposure data and calculating a service life estimate based on the exposure data. The service life estimate is representative of an estimated exposure time that the filter is exposed to ambient conditions represented by the exposure data before the contaminant passes through the filter at a breakthrough concentration. The method also includes obtaining environmental data and establishing a predicted service life based on the environmental data. The predicted service life is representative of a predicted exposure time that the filter is exposed to the ambient conditions represented by the environmental data before the contaminant passes through the filter at the breakthrough concentration. The method further includes determining the service life for the filter based on a comparison of the estimated and predicted service lives.
Owner:SCOTT TECH INC
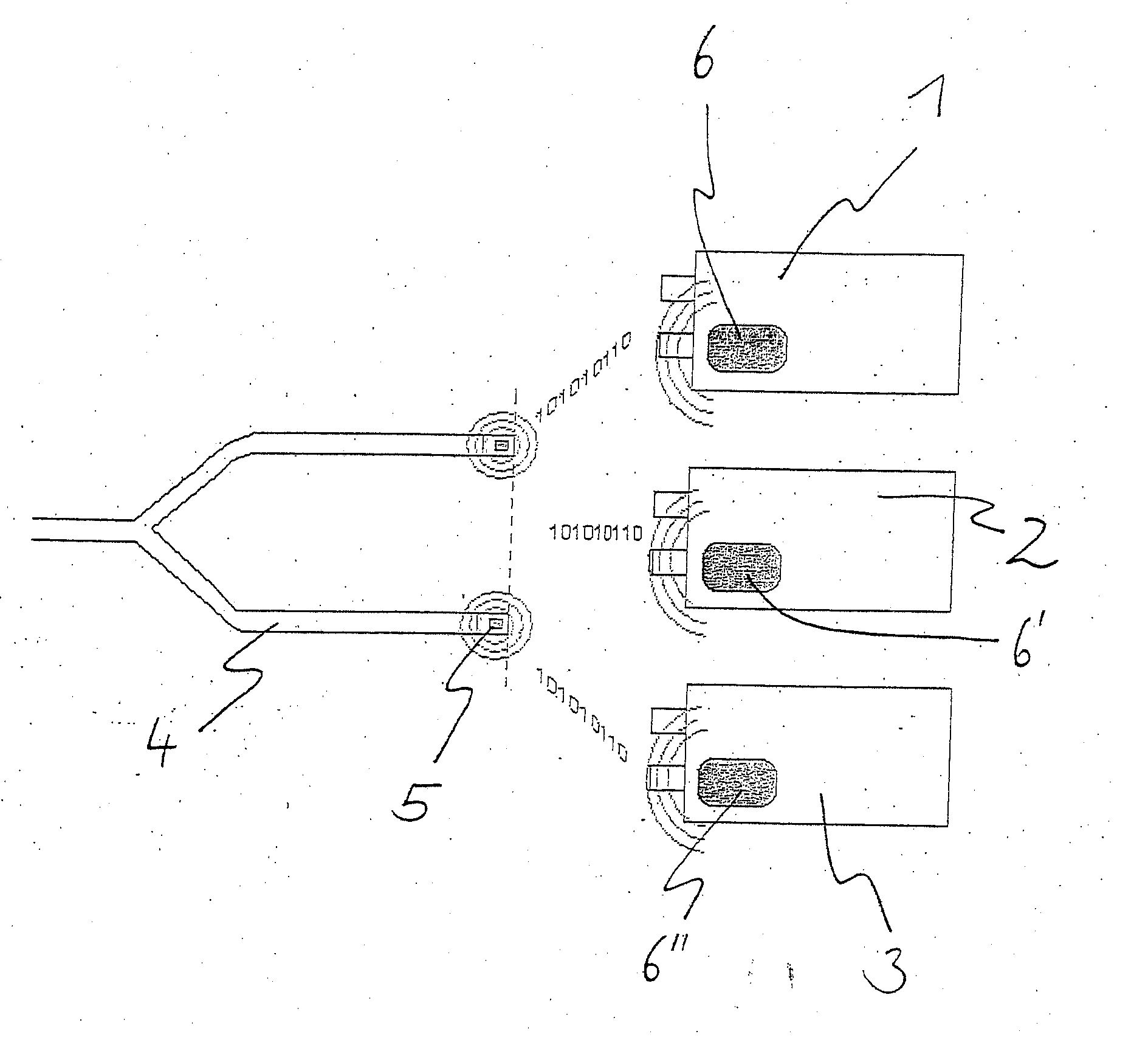
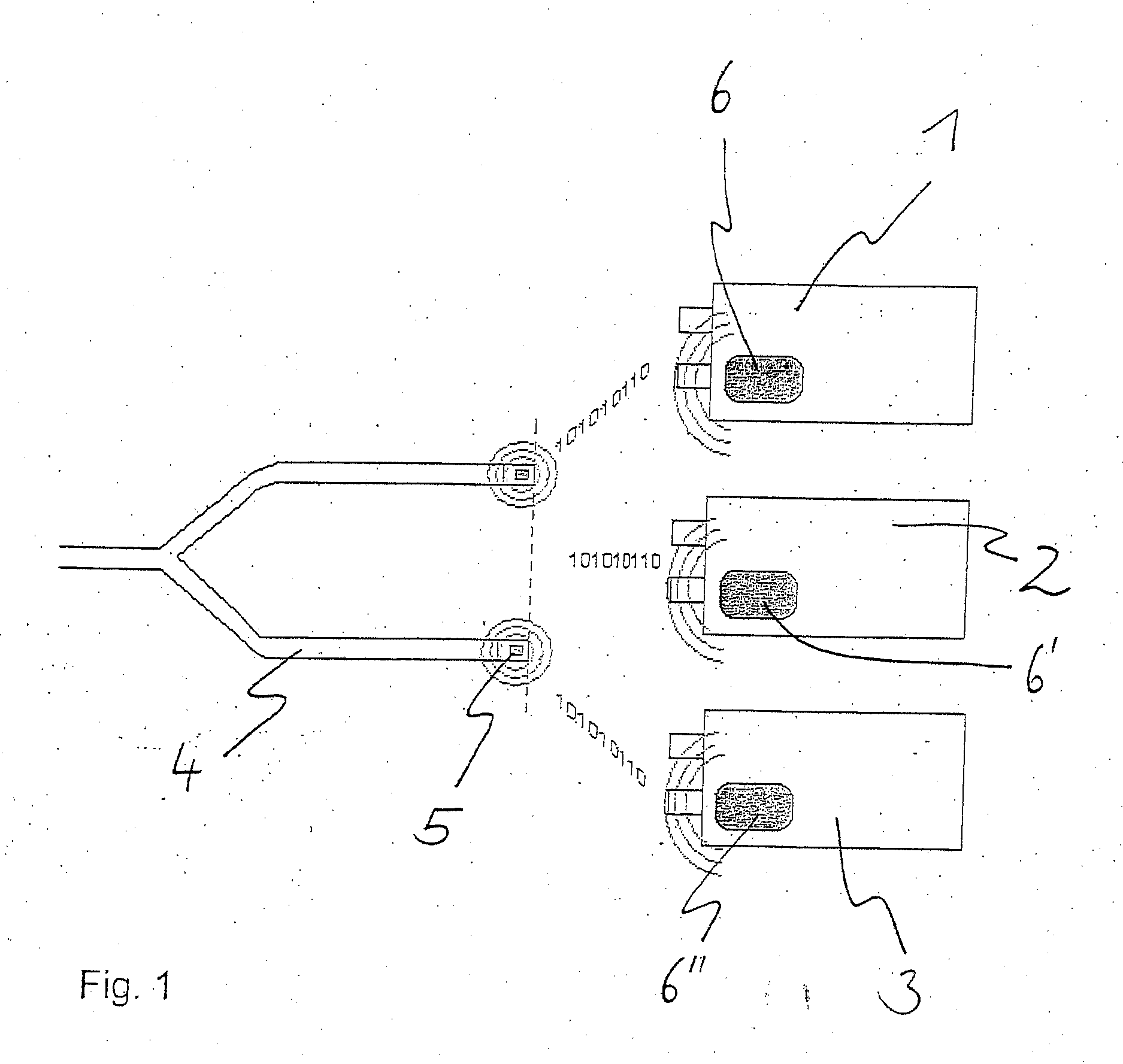
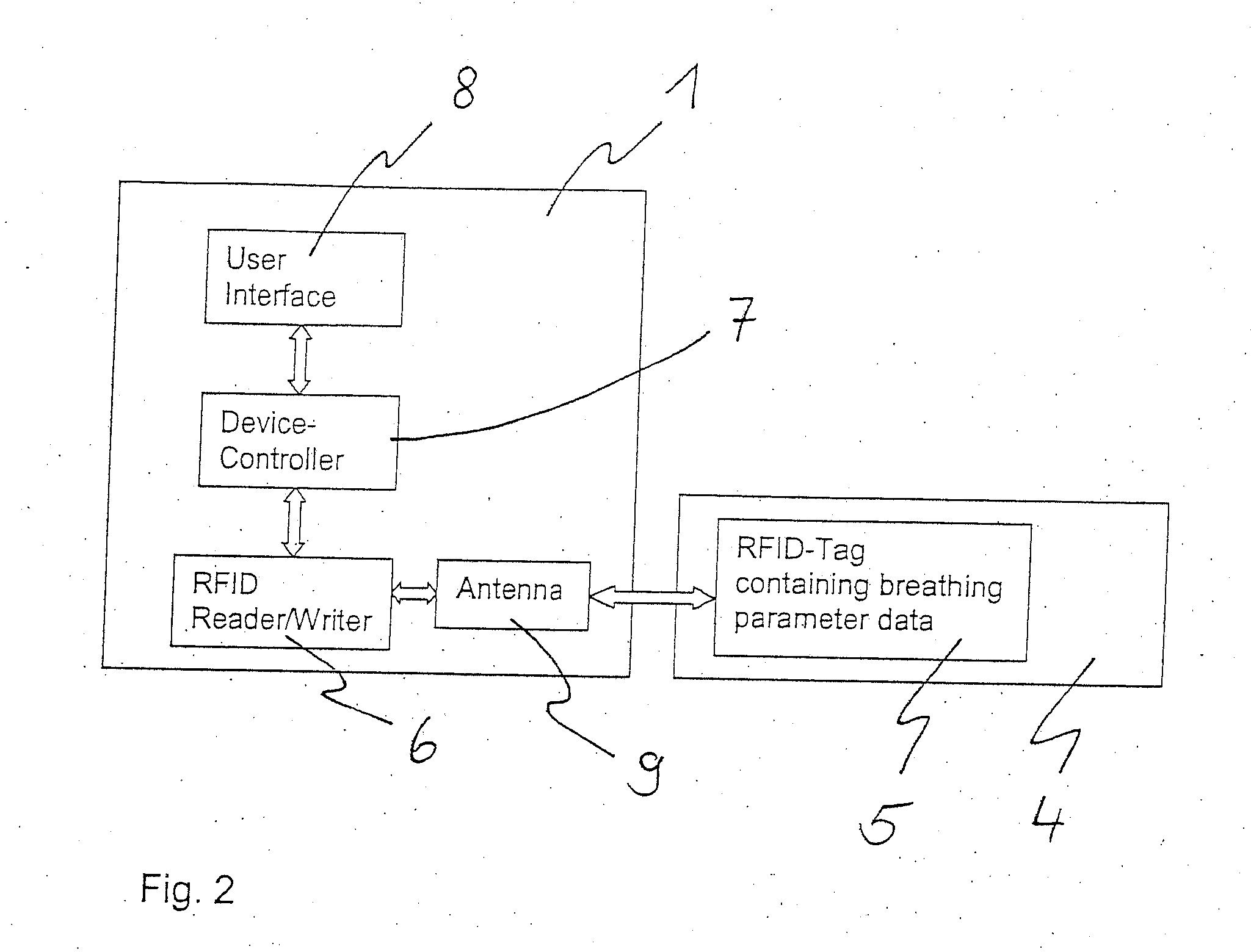
Process and device for the automatic identification of breathing tubes
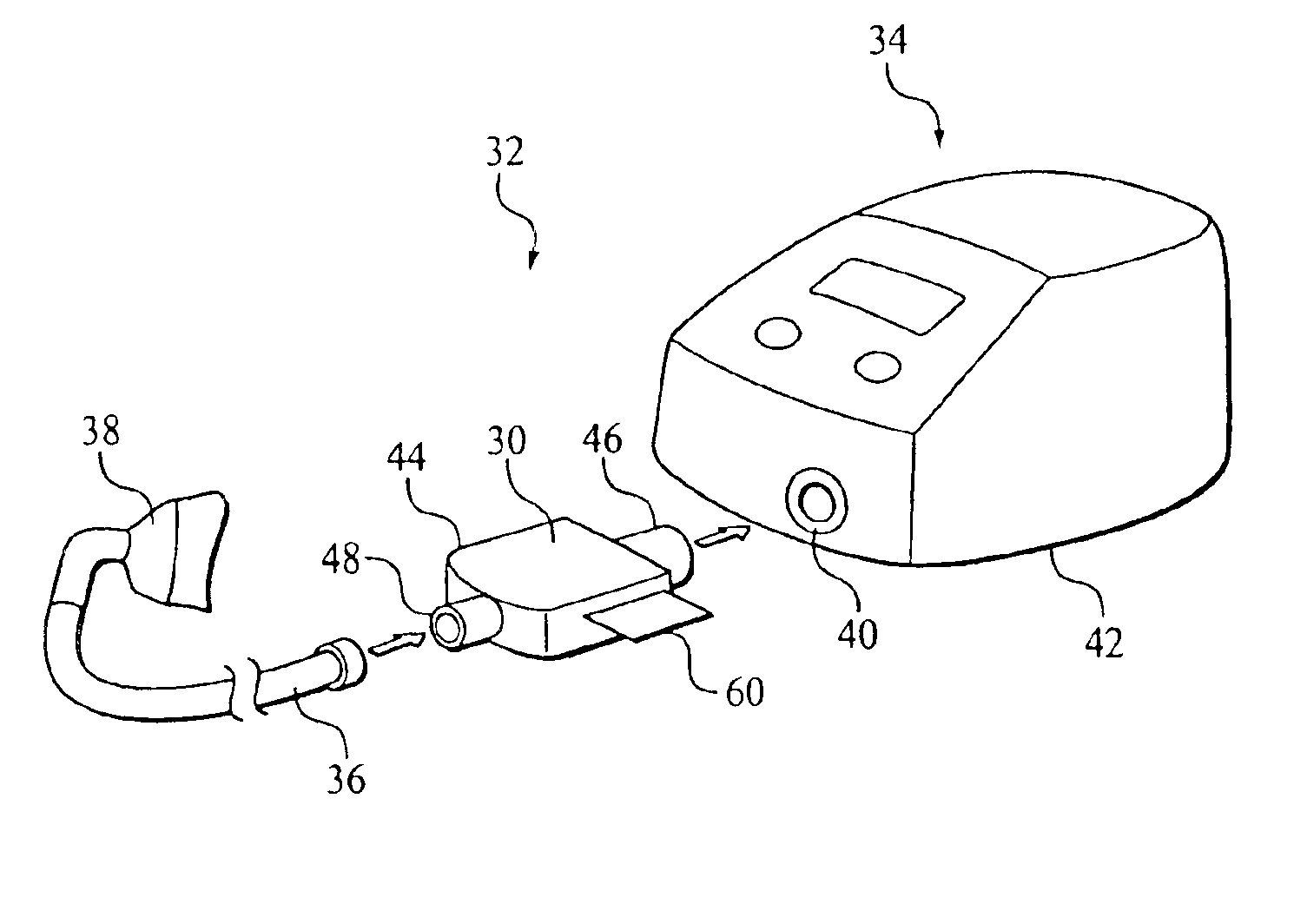
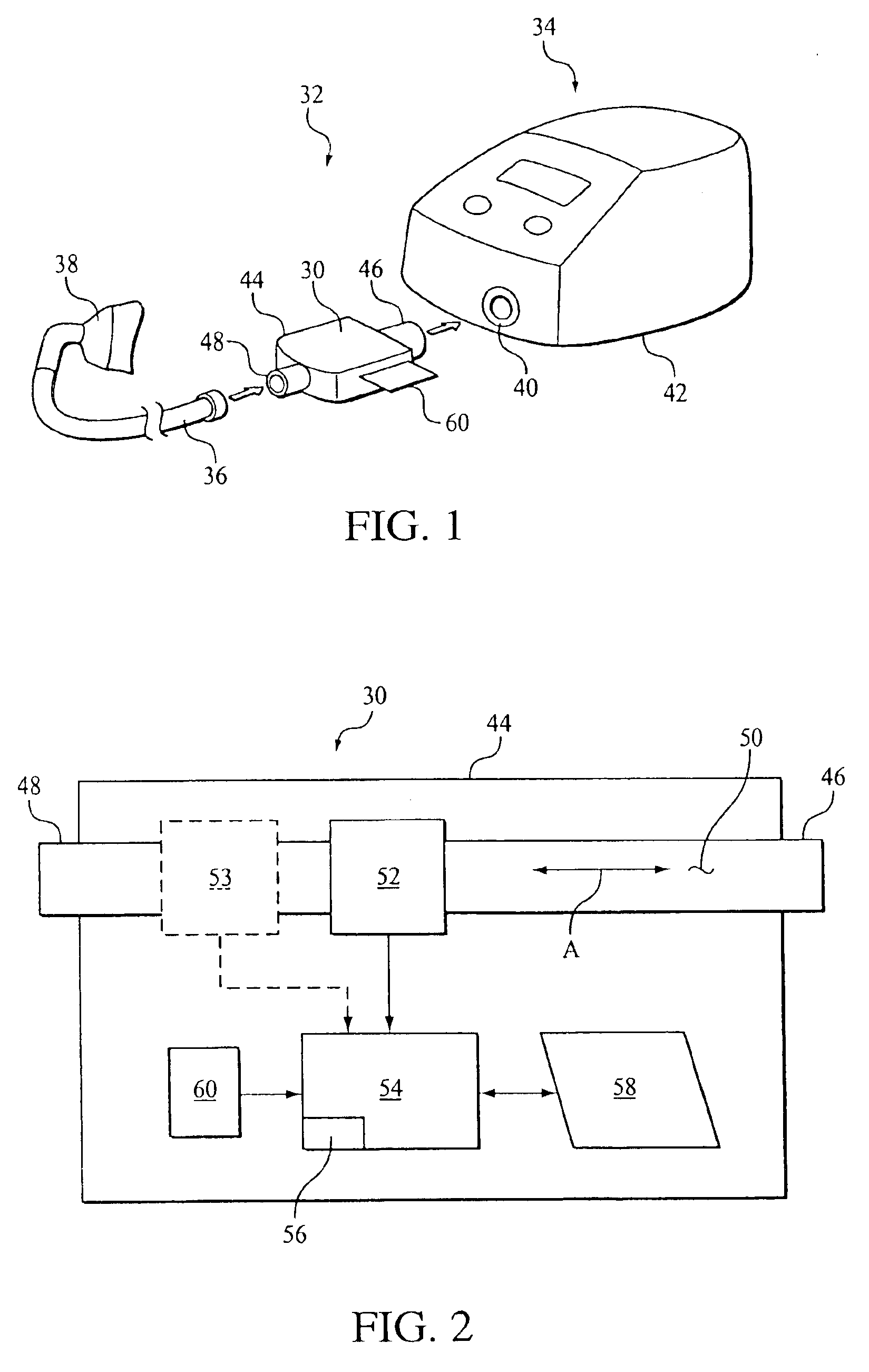
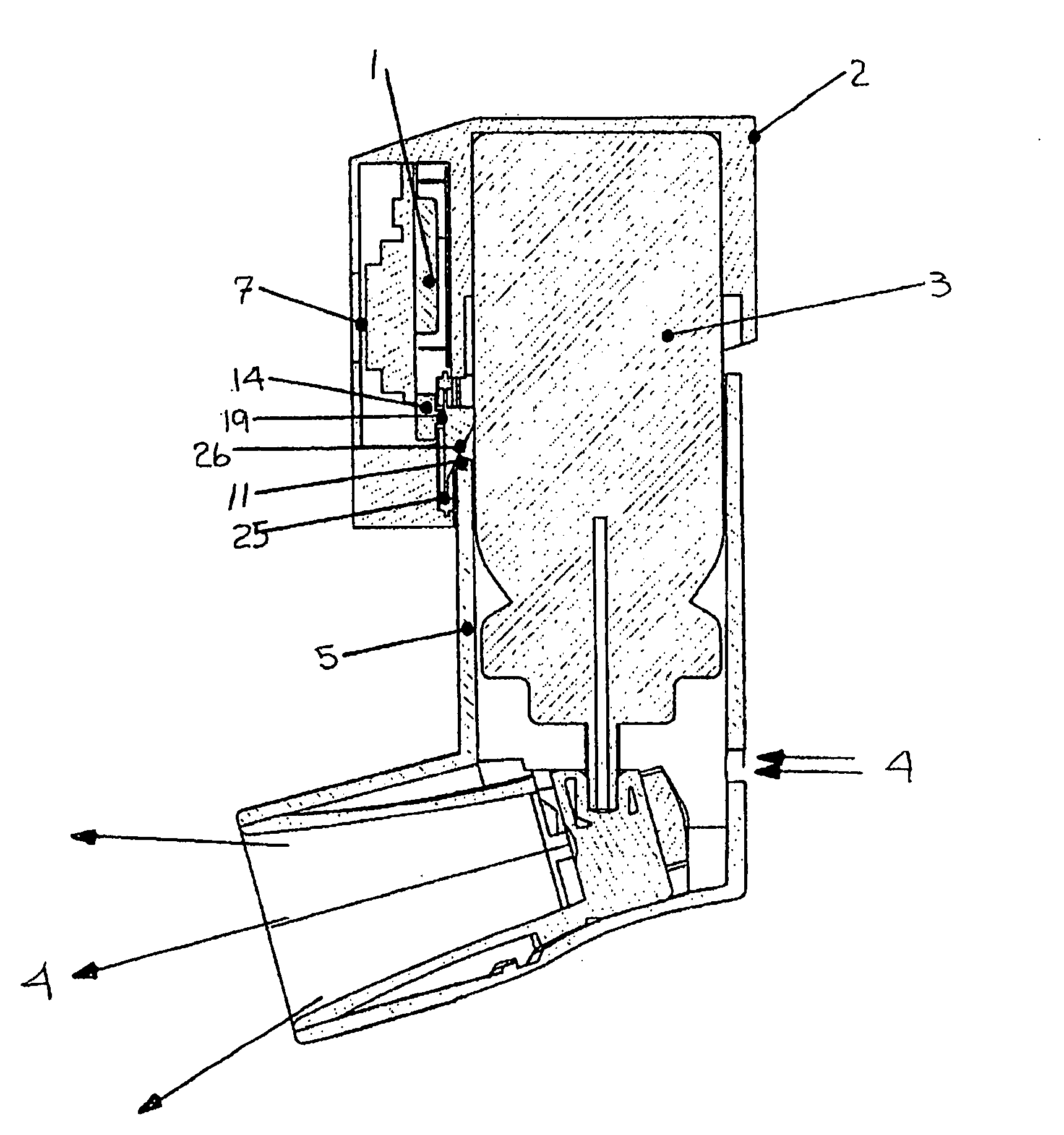
ActiveUS20060278221A1Frequent replacementAvoid long connectionsRespiratorsRespiratory device testingRespiratorBiomedical engineering
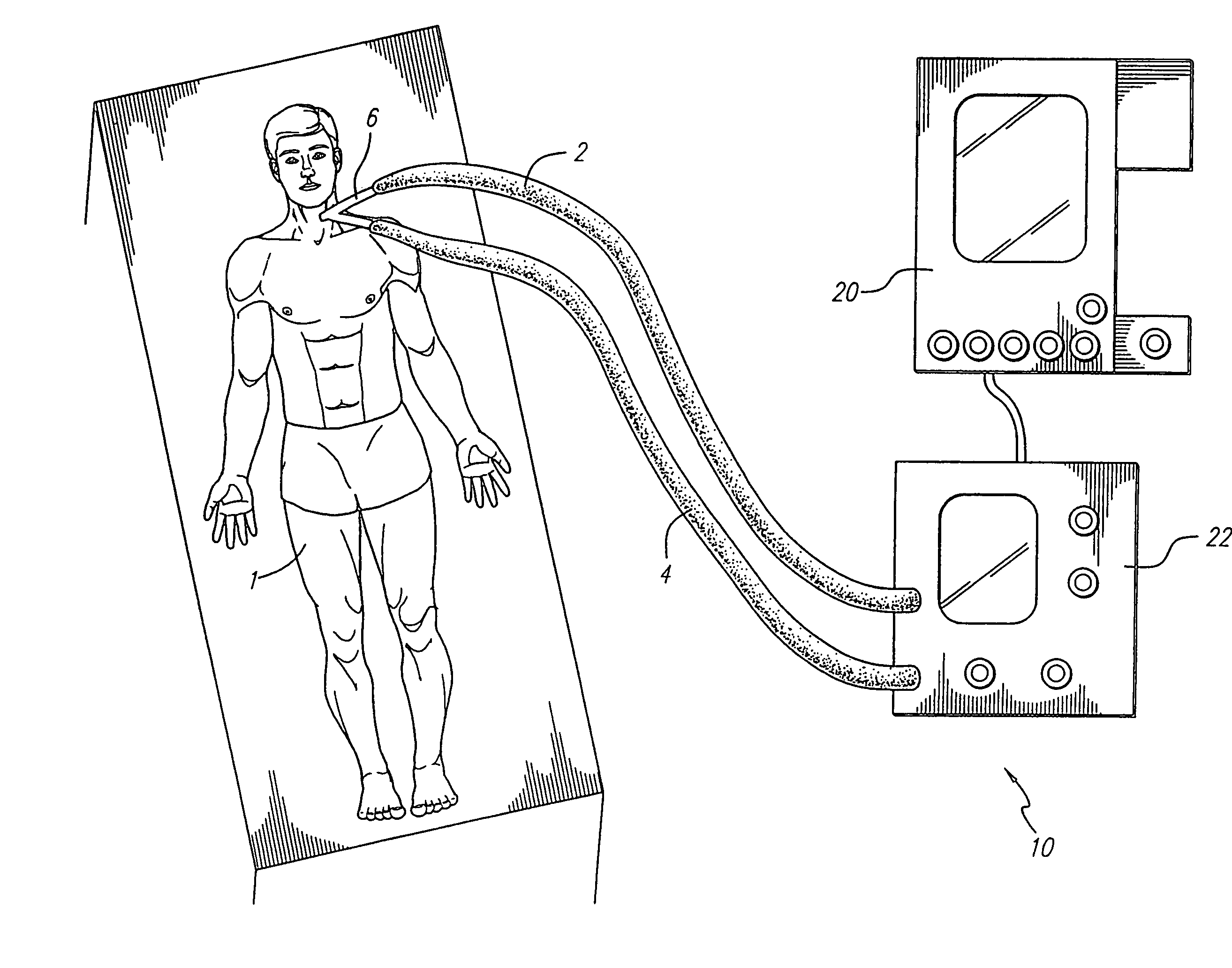
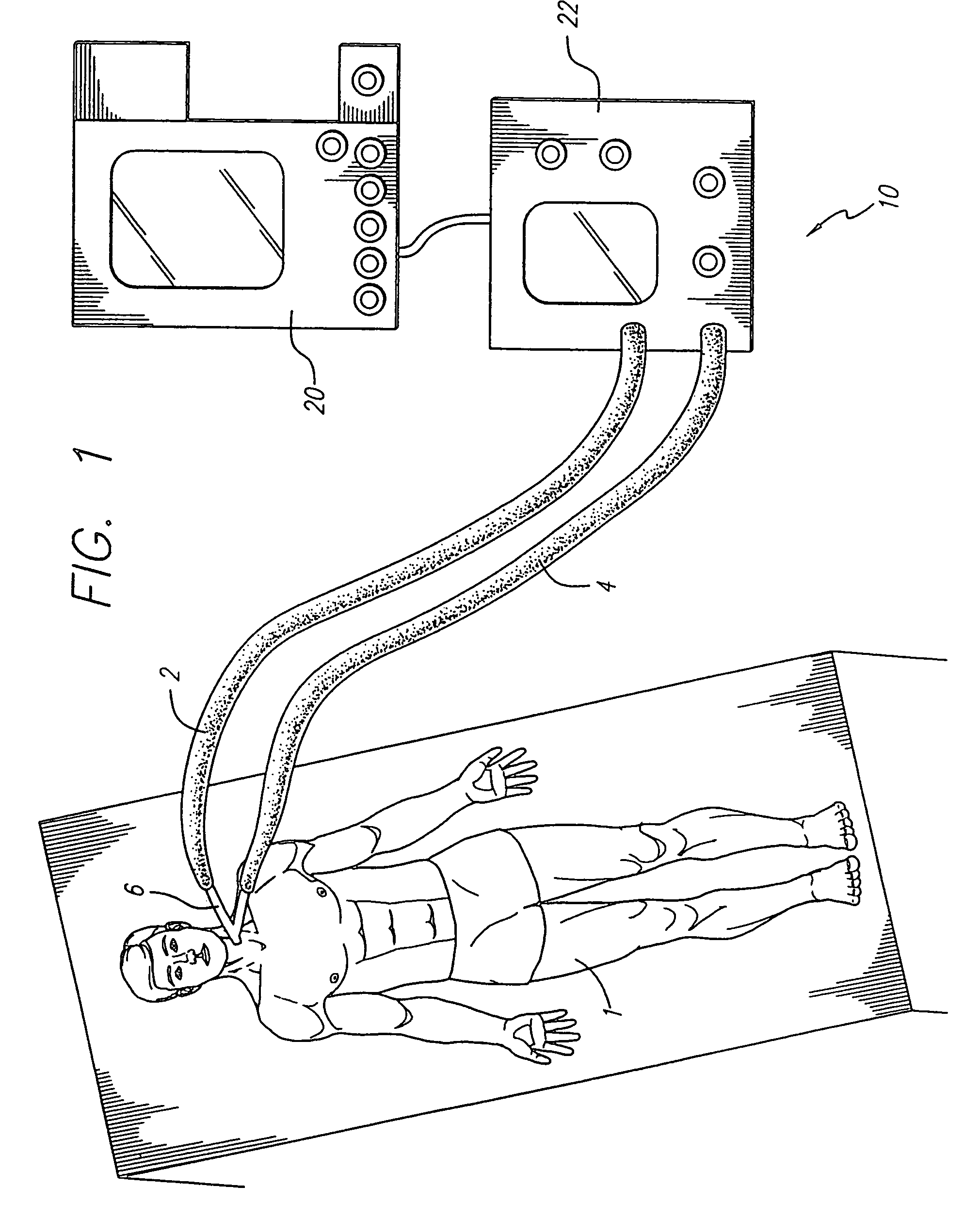
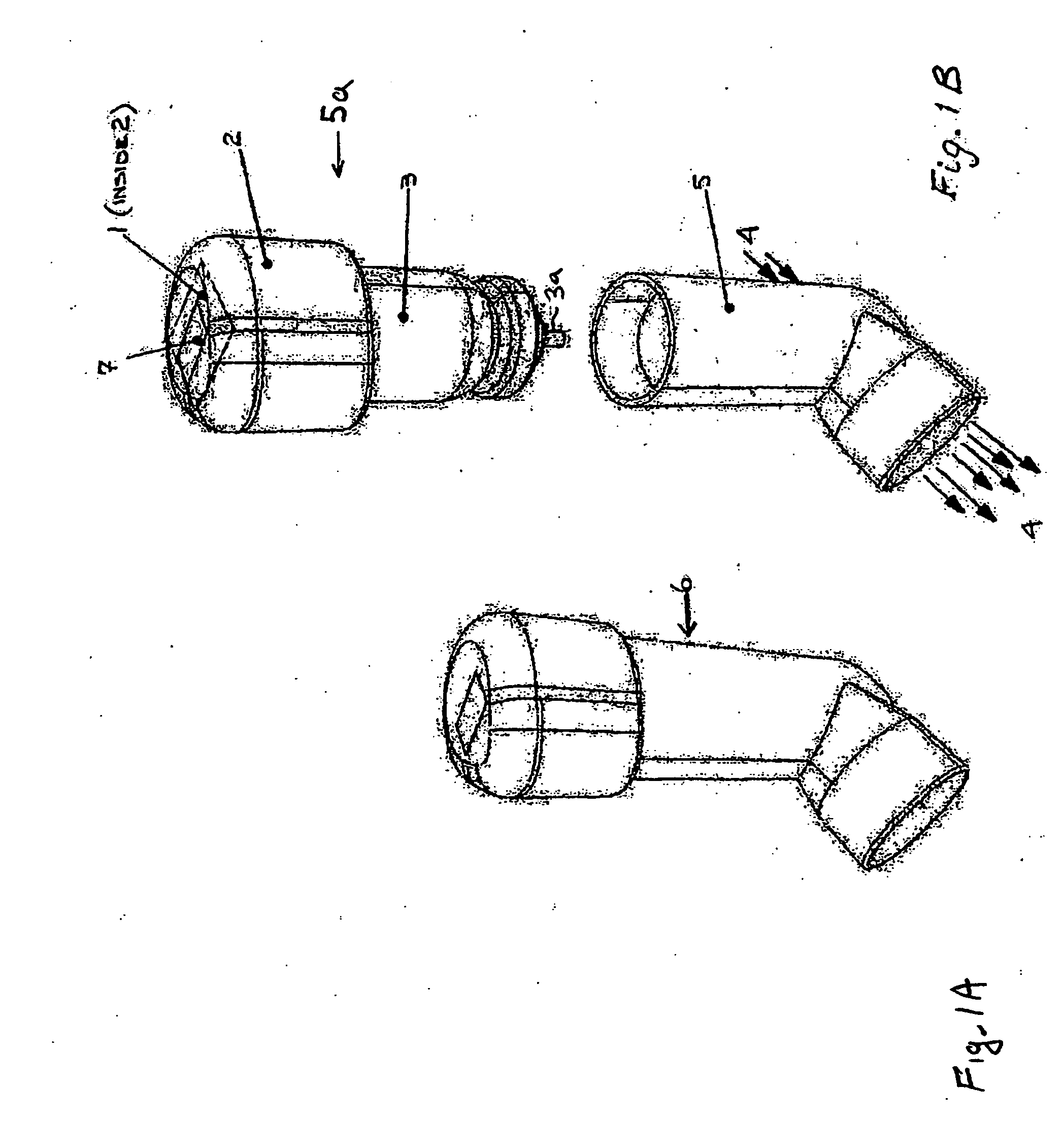
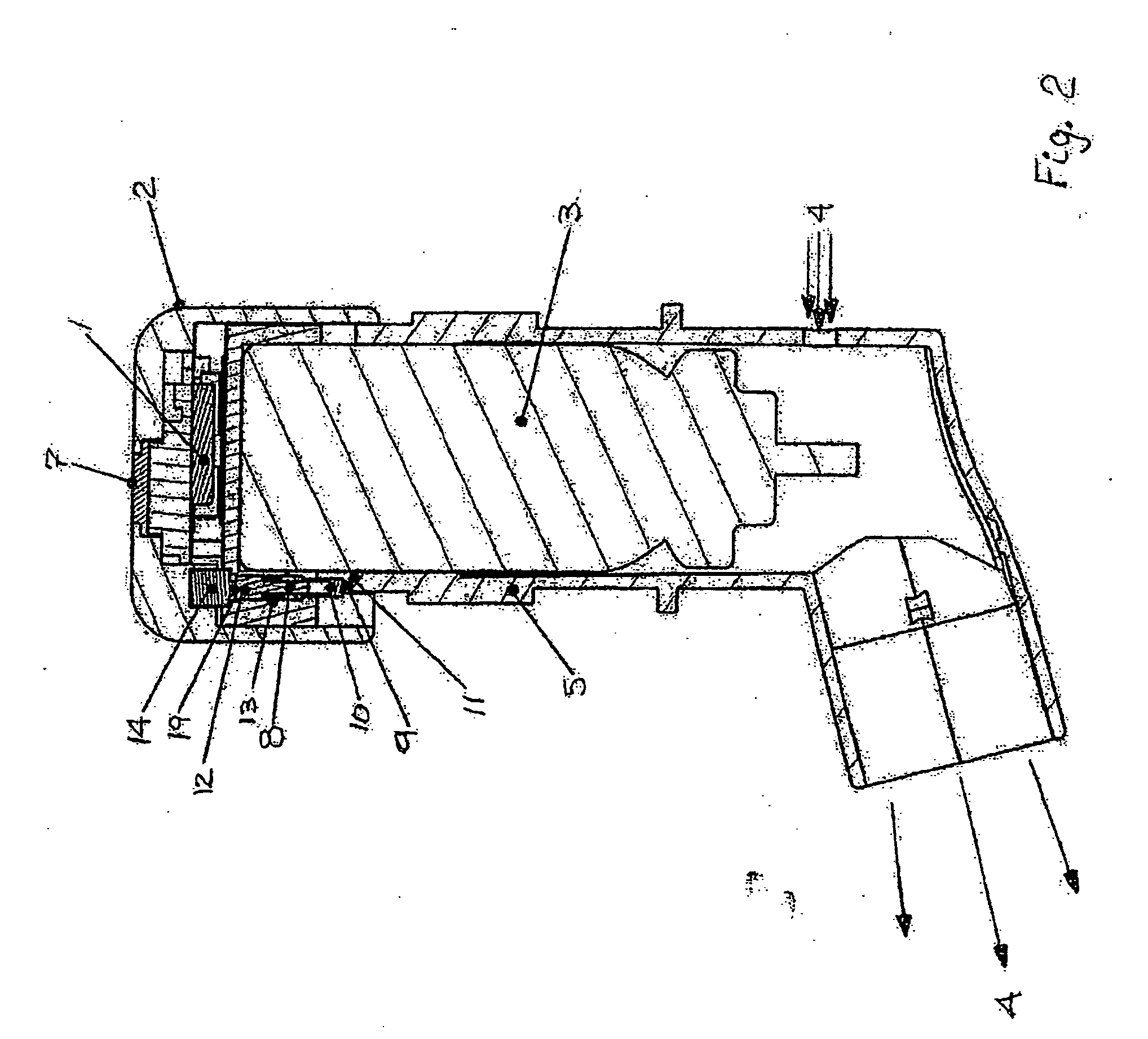
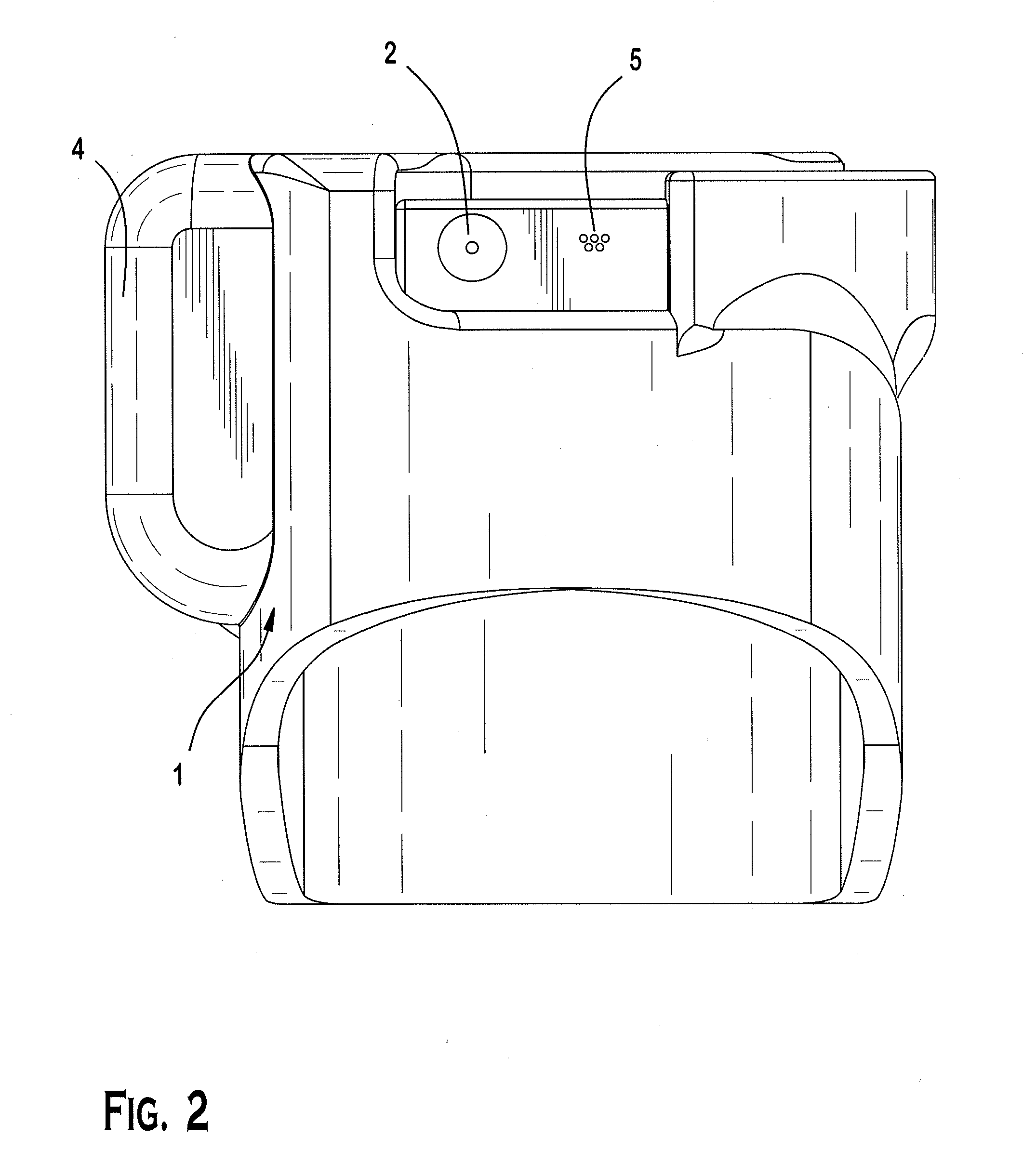
A process and a device / system are provided for the automatic identification of the type of a breathing tube. A memory element (5) is connected to the breathing tube (4). The memory element carries stored data identifying the breathing tube (4). The data are read by a reading unit (6), which is part of a respirator (1). The data may be read when the breathing tube (4) is brought into the vicinity ofthe respirator (1) or connected thereto.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Method and apparatus to measure, aid and correct the use of inhalers
ActiveUS20160144141A1Improve responseImprove to medicationLiquid surface applicatorsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesEngineeringElectronic component
A detachable cap for measuring usage of an inhaler includes a hollow receiving portion adapted to removably receive the inhaler. A vent is formed in a roof portion of the cap to allow airflow through the cap to the inhaler. An extension portion is provided for containing electronic components, including an electronic circuit provided in the extension portion, the electronic circuit including a controller coupled to a storage device and a power source. A pressure sensor is provided adjacent to the vent, the pressure sensor communicatively coupled to the controller and adapted to detect an air pressure within the cap. The controller is programmed to calculate an air flow rate through the cap based on the detected air pressure and to store the calculated air flow rate in the storage device.
Owner:COGNITA LABS LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator are described. The invention can be used to control mechanical ventilators as well as respiratory assist devices such as CPAP machines. The apparatus receives input data indicative of patient's oxygen level. A controller determines PEEP, or CPAP, and FIO2, on the basis of data indicative of the patient's oxygen level. In an alternative embodiment, the apparatus further receives input data indicative of patient's carbon dioxide levels, respiratory elastance and airway resistance, and barometric pressure. The controller further utilizes the said input data to determine the optimal values of tidal volume and breathing frequency for a next breath of the patient, and uses the respiratory elastance and airway resistance data to determine any necessary adjustments in the I:E ratio. The controller also applies safety rules, detects and corrects artifacts, and generates warning signals when needed.
Owner:TEHRANI FLEUR T
Pressure monitor and alarm for compression mounting with compressed gas storage tank
InactiveUS6137417AImprove securityReduce tank pressureValve arrangementsMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateGas cylinderEngineering
A warning device configured for removable mounting in combination with a high pressure gas cylinder and a regulator used to regulate the high pressure gas supplied by the cylinder. The device compression mounts between the regulator and tank outlet on conventional portable oxygen and gas supply systems using a specially configured manifold. The device features one or a combination of alarms, from a group including audio, visual, electronic, and remotely transmitted alarms. These alarms are activated by a pressure switch monitoring the remaining supply in the gas cylinder through a conduit the manifold. The alarm signal from the device alerts the user, or a third party monitoring the user, of current tank pressure or will sound an alarm when remaining high pressure gas inside the gas cylinder drops below a predetermined level.
Owner:INGEN TECH
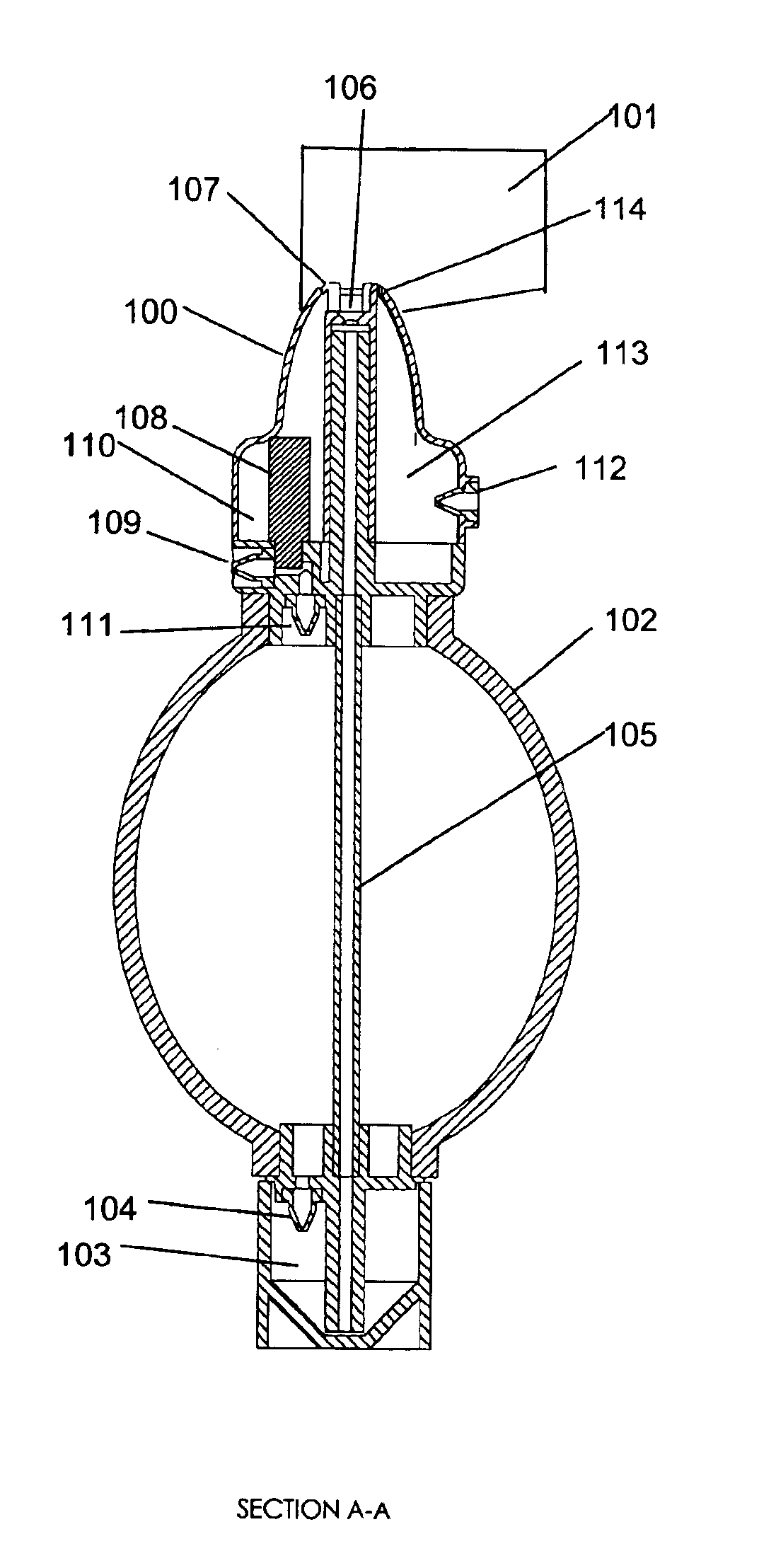
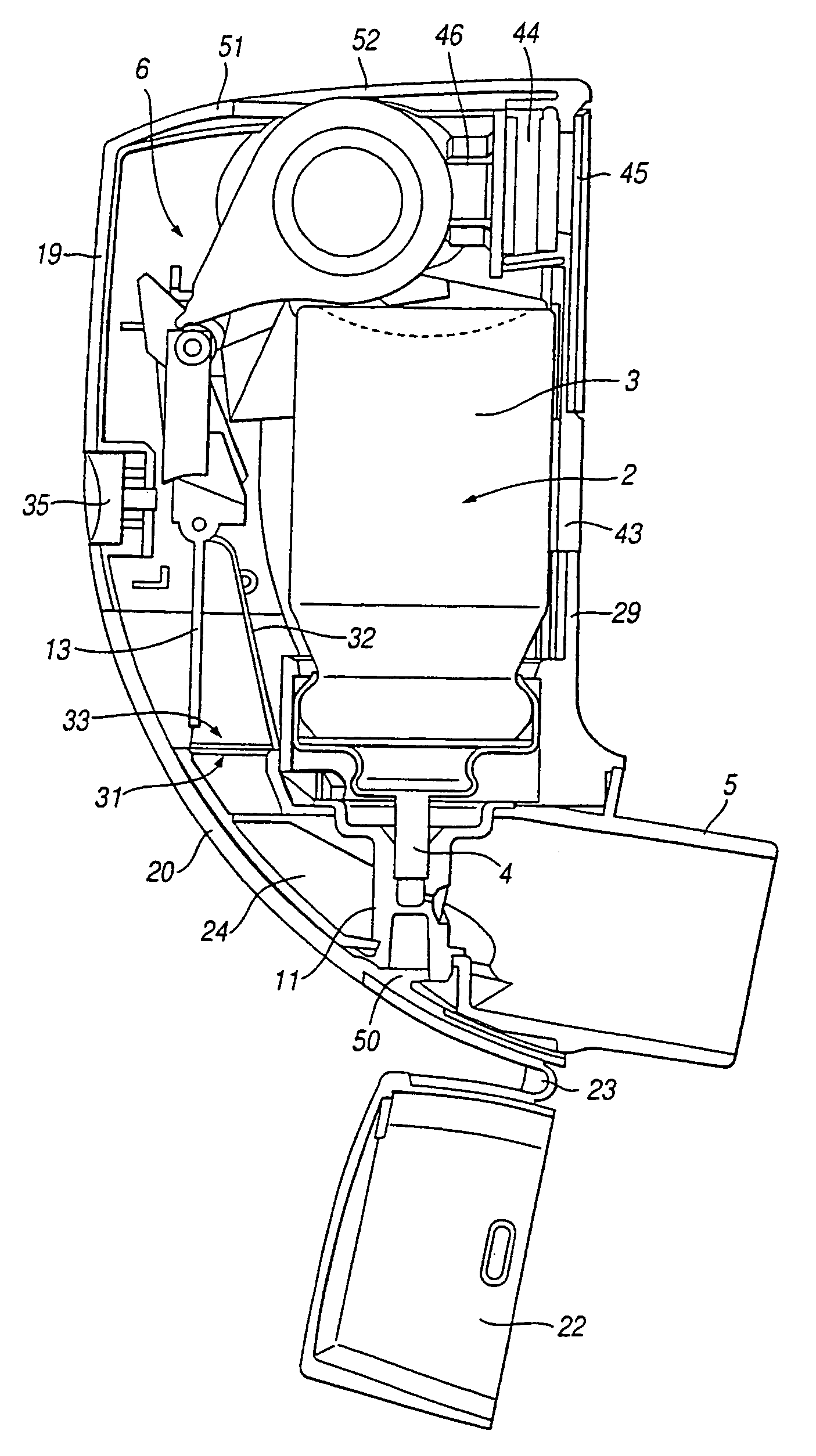
Inhaler
An inhaler for holding a canister (2) of medicament. The canister (2) has a mount (26) secured thereto mounting an indication member (41) movable slidably from a first state to a second state. A ratchet arrangement (41a, 42) is provided between the mount (26) and the indication member (41) to make the movement irreversible. The inhaler has a catch (49) for moving the indication member from the first state to the second state on removal of the canister (2) from the inhaler. An electrical switch contact (48) detects the state of the indication member (41), thereby providing an indication of whether the canister (2) has been used before. An LCD display is controlled in response to the detection.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Method and arrangement for detecting a leak in anesthesia system
A method and arrangement for detecting a leak in an anesthesia system. The method includes controlling respiratory movements by means of ventilator gas flows and measuring the ventilator gas flow added for an inspiration and removed for an expiration. The method also includes supplying a fresh gas flow for a respiration and measuring the fresh gas flow added for the respiration. The method further includes receiving information indicative of the measured gas flows, determining based on said received information both the gas volume added and the gas volume removed and comparing these determined gas volumes to each other. The method also includes determining based on comparing the anesthesia system leakage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pressure support compliance monitoring system
A compliance monitoring system and method in which a modular compliance monitor is selectively disposed in-line in a patient circuit of a pressure support system. The monitor includes a housing having an inlet and an outlet, each of which is selectively connectable to the patient circuit so that the flow of gas in the patient circuit also passes through a passage is provided through the housing. A sensor operatively coupled to the passage detects a parameter indicative of patient breathing. A processor disposed in the housing and receives the output of the sensor and determines, from the output of the sensor, whether the patient is breathing into the patient circuit, and outputs compliance data based on this determination.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
Determination of mask fitting pressure and correct mask fit
InactiveUS7100608B2Respiratory device testingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringFit test
Owner:RESMED LTD
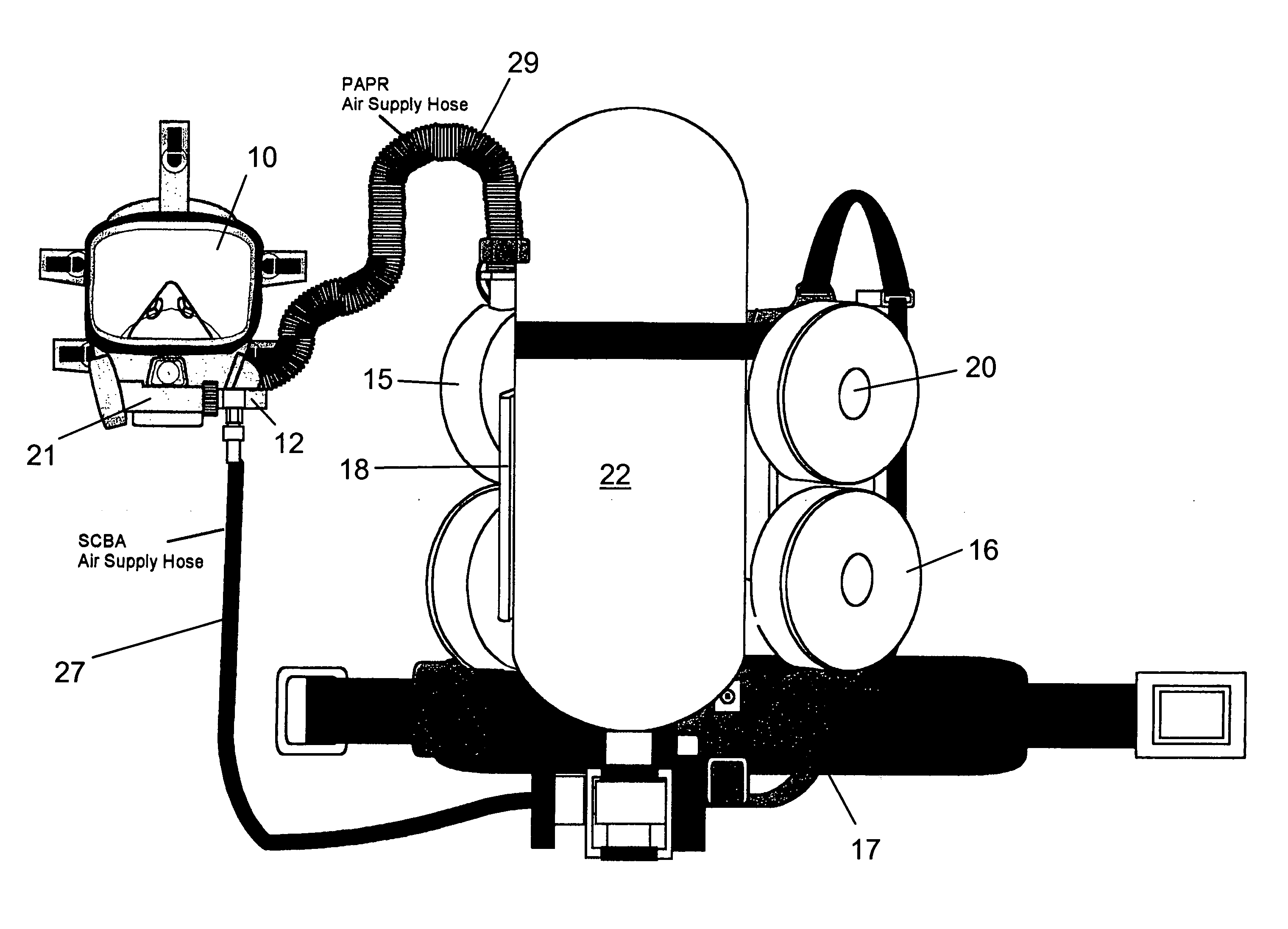
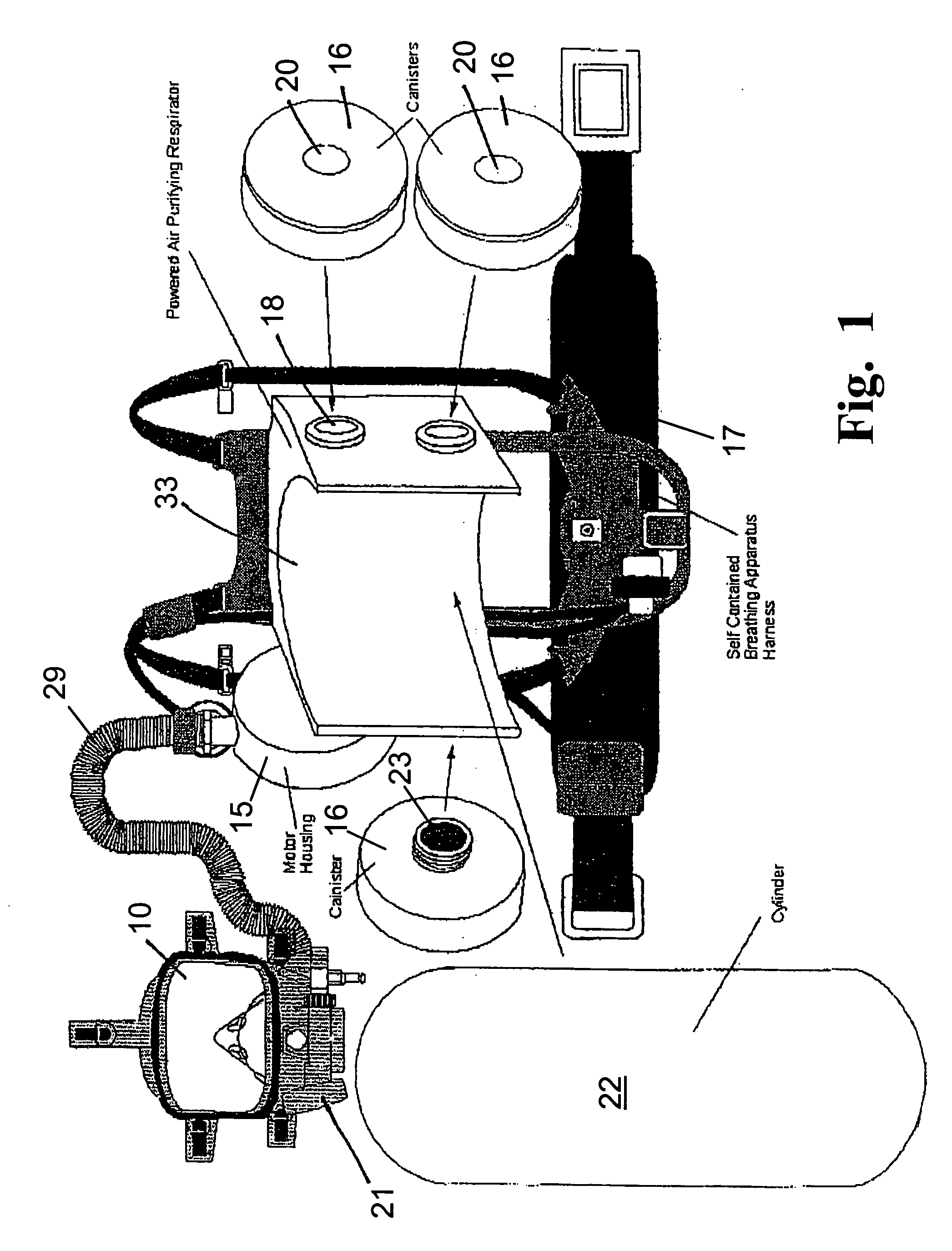
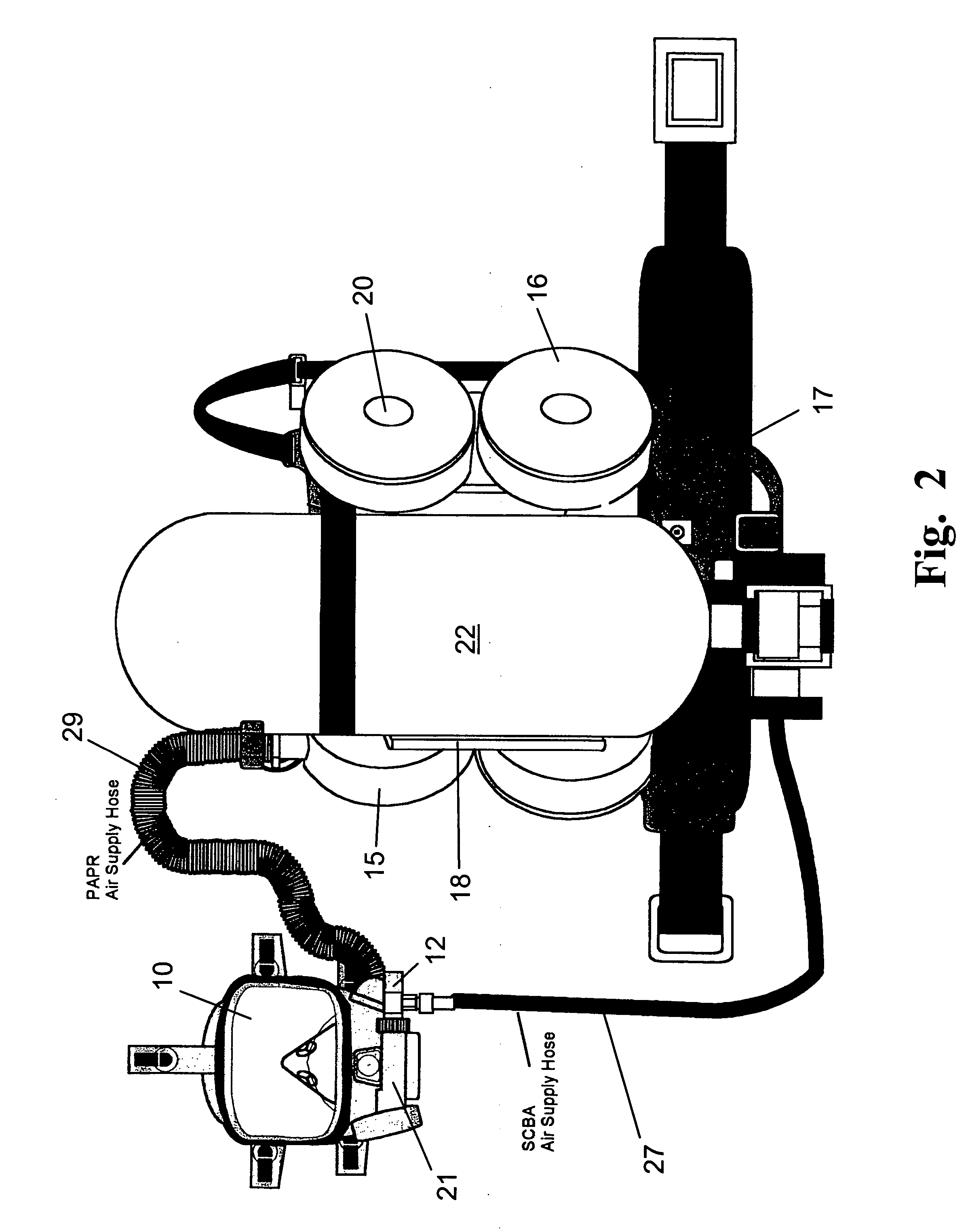
Breathing apparatus
An improvement to a combination of an SCBA system for providing bottled air to a user and a PAPR system for purifying ambient air for use by a user wherein a sensor is included to determine the oxygen content of the breathing gas and the presence of contaminations in the atmosphere to control operation of the two systems depending on the contaminated condition of the ambient air and the oxygen content of the ambient air.
Owner:IMMEDIATE RESPONSE TECH +1
Compliance monitor and method
ActiveUS20070023034A1Easily, or automatically, actuatedRespiratorsRespiratory device testingBiomedical engineeringDrug delivery
A compliance monitor (20) is attachable to or forms part of a drug delivery device, such as an inhaler (2). The monitor comprises a flexible portion (38) to enable a switch which is actuated by a user when delivering a dose of medicament. The monitor further comprises a sensor for sensing whether the device is properly positioned in contact with or relative to the user's body for administration of the medicament. For example, where the device is an inhaler and the sensor a temperature sensor, temperature variations caused by insertion of an inhaler mouthpiece into the user's mouth indicate whether the dose has been delivered into the patient's mouth. A memory in the compliance monitor stores a compliance record indicating whether or not the device was properly positioned each time a dose was delivered.
Owner:COVIS PHARM GMBH
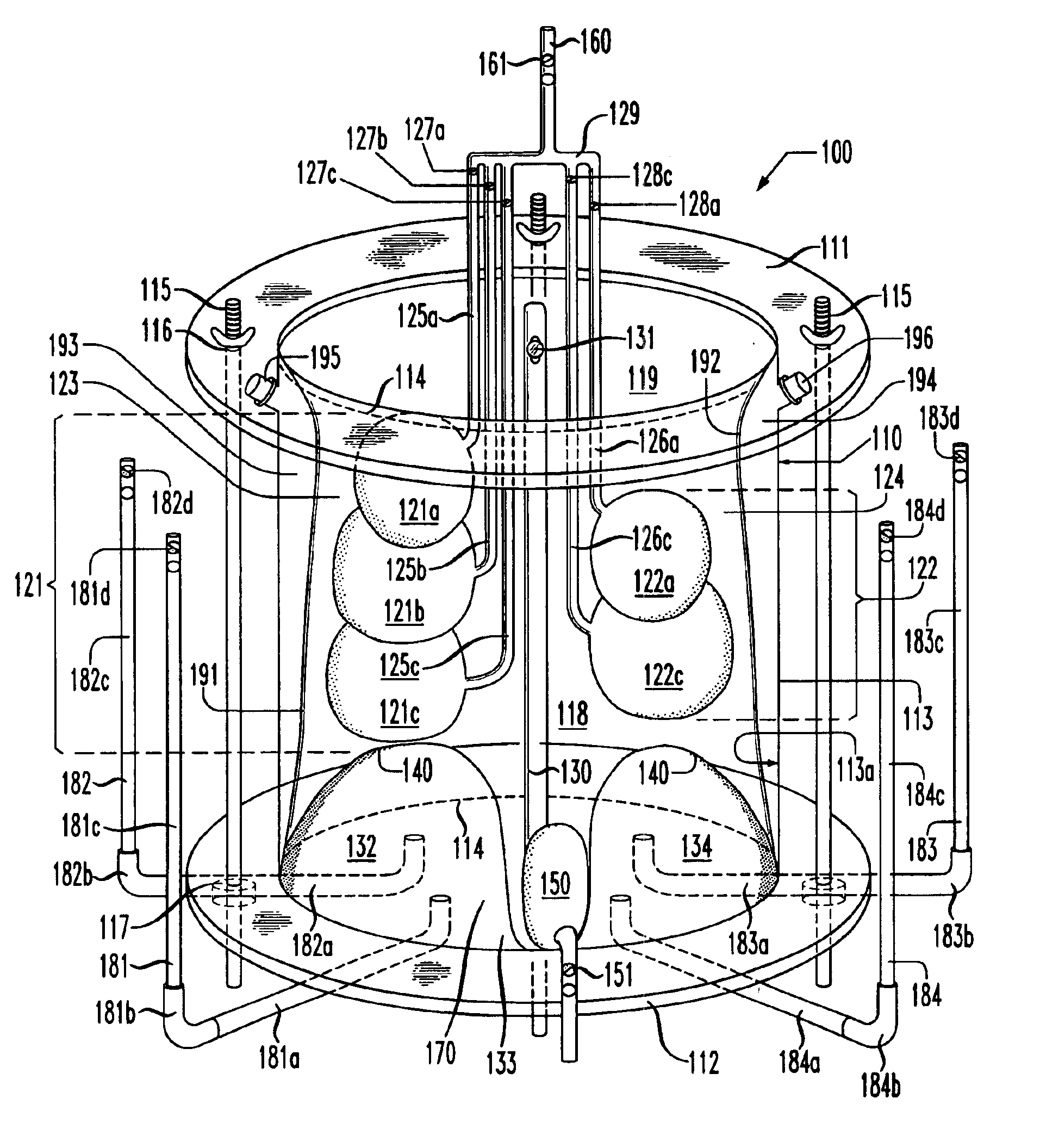
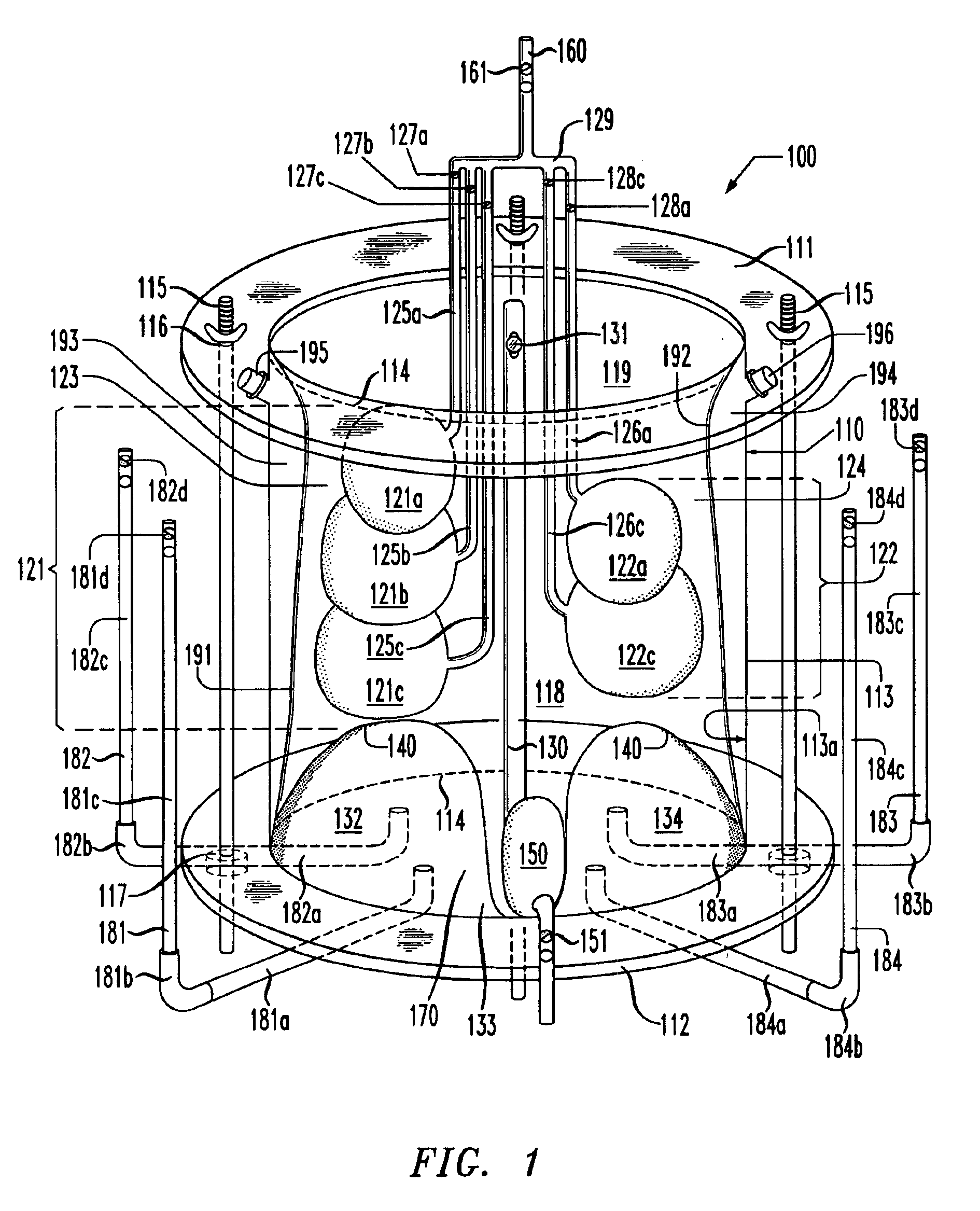
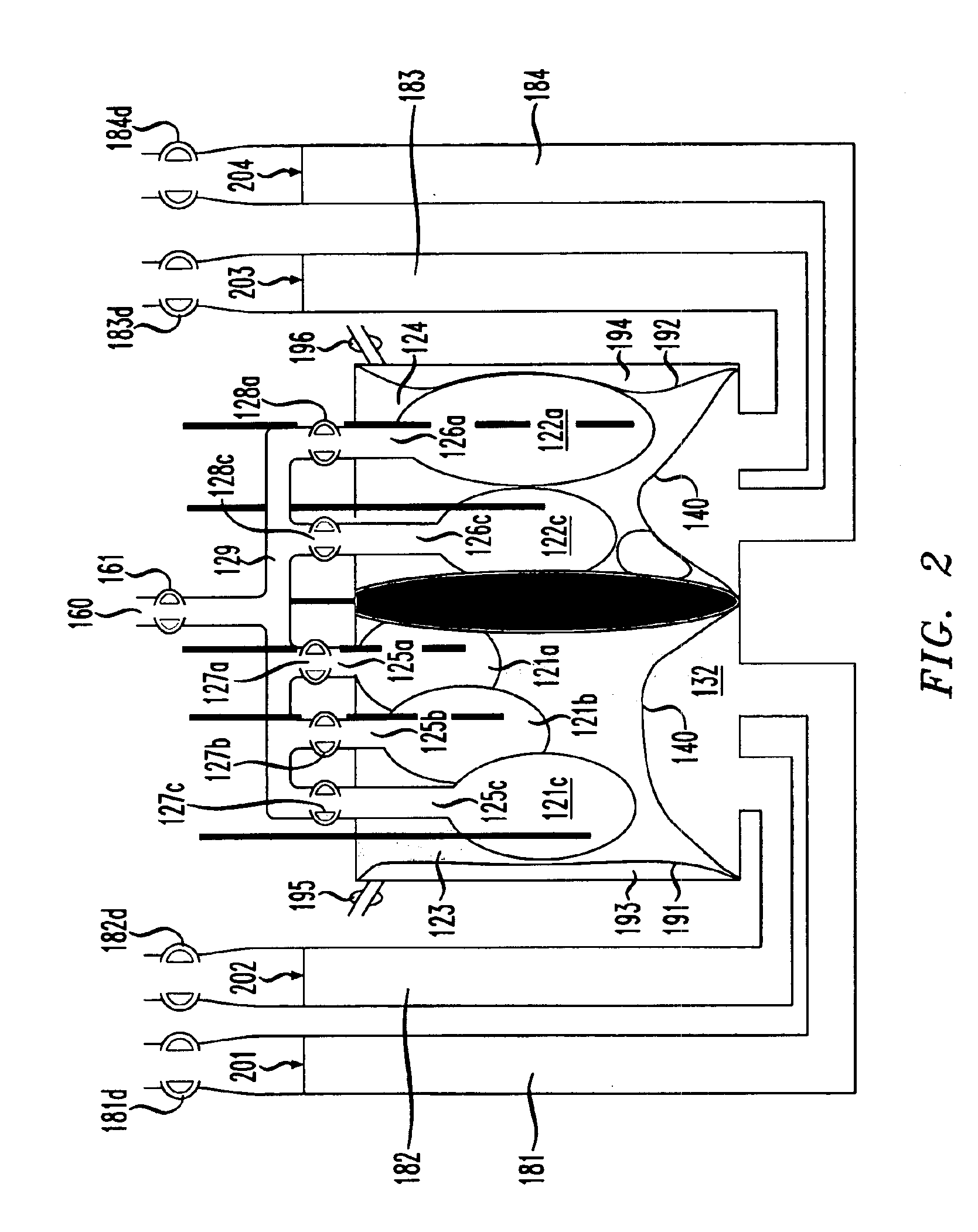
Lung simulator
The present invention provides a lung simulator comprising a substantially-rigid, fluid-tight, translucent housing simulating a human thoracic cavity and at least one flexible air-tight bag simulating a lung having a plurality of simulated lung lobes, and a corresponding plurality of valves, each of the plurality of valves coupled to a one of the plurality of simulated lung lobes and configured to simulate varying degrees of fluid flow resistance. In a preferred embodiment, the substantially-rigid, fluid-tight, transparent housing has isolated simulated left and right thoracic cavities therein and the at least one flexible air-tight bag is located within one of the simulated thoracic cavities. The present invention further provides a method of manufacturing a lung simulator.
Owner:ESTETTER ROBERT H +2
Equipment and method for identifying, monitoring and evaluating equipment, environmental and physiological conditions
A system and method are disclosed for identifying monitoring and evaluating hazardous or potentially hazardous conditions. The system may be worn by safety personnel to detect equipment conditions such as low power supply, environmental conditions such as ambient temperature and / or physiological conditions such as heart rate of a wearer. The system may further include a control unit having electronics operable to communicate signals associated with equipment, environmental and physiological conditions.
Owner:MINE SAFETY APPLIANCES CO
Medicament dispensing device with a display indicative of the state of an internal medicament reservoir
ActiveUS20050081846A1Save battery powerLiquid surface applicatorsRespiratory device testingDisplay deviceBiomedical engineering
A metered dose inhaler for use with a removable pressurized aerosol canister, or reservoir, having a display for indicating to a user the state of the canister. A memory device on the canister or a housing which houses the canister stores information indicative of doses dispensed from, or remaining in, the canister. That information is processed to provide and display information representative of the state of the canister.
Owner:IVAX CORP
Patient circuit disconnect system for a ventilator and method of detecting patient circuit disconnect
ActiveUS7984712B2Easy to adjustRespiratorsRespiratory device testingType ventilatorIntensive care medicine
A method of detecting disconnect of a patient circuit of a ventilation system, wherein a circuit disconnect is detected with a first sensitivity and a second sensitivity. The circuit disconnect detected with the first sensitivity is performed by detecting a volume loss for a minimum period of time, detecting a peak pressure loss for at least two consecutive breathing cycles or a minimum period of time, and detecting a pressure loss continuing for a predetermined period of time. The circuit disconnect detected with the second sensitivity is performed by detecting a volume loss for a single breathing cycle, detecting a pressure loss for a single breathing cycle, and detecting an increase of compliance. The first sensitivity is lower than the second sensitivity. Preferably, an alarm is activated when the circuit disconnect is detected with the first sensitivity, and subsystems of the ventilation system is informed of the circuit disconnect that has been detected with the second sensitivity.
Owner:BIRD PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com