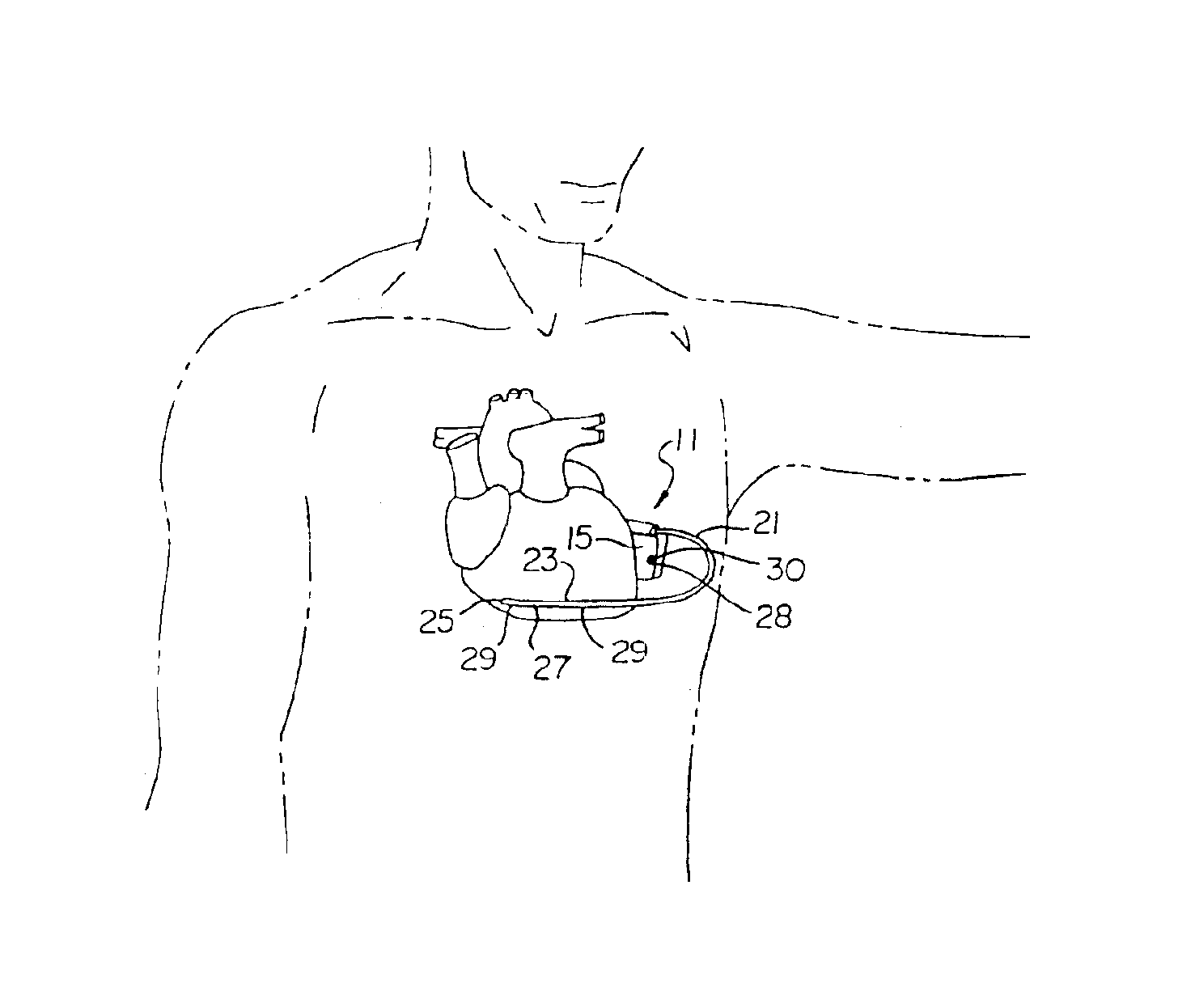
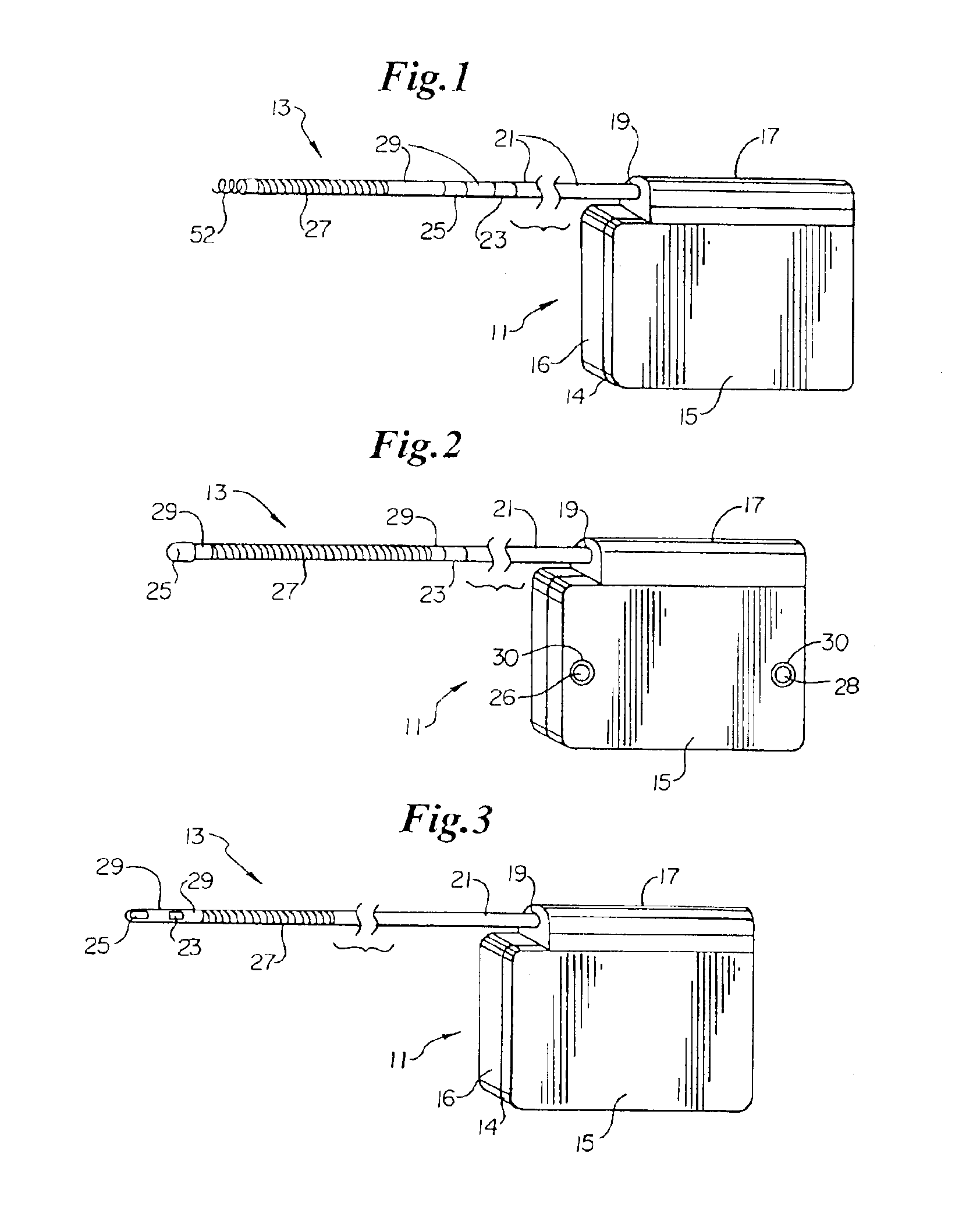
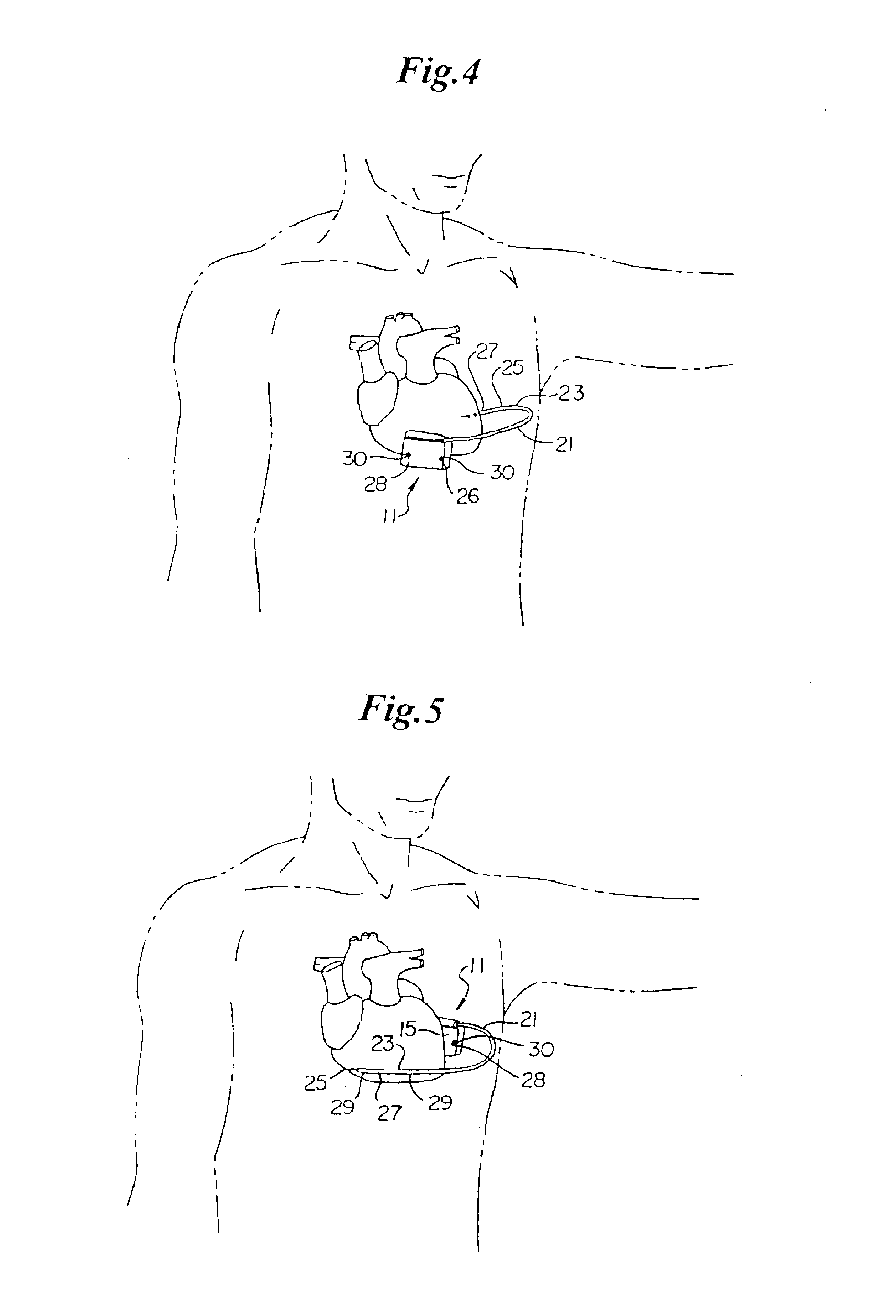
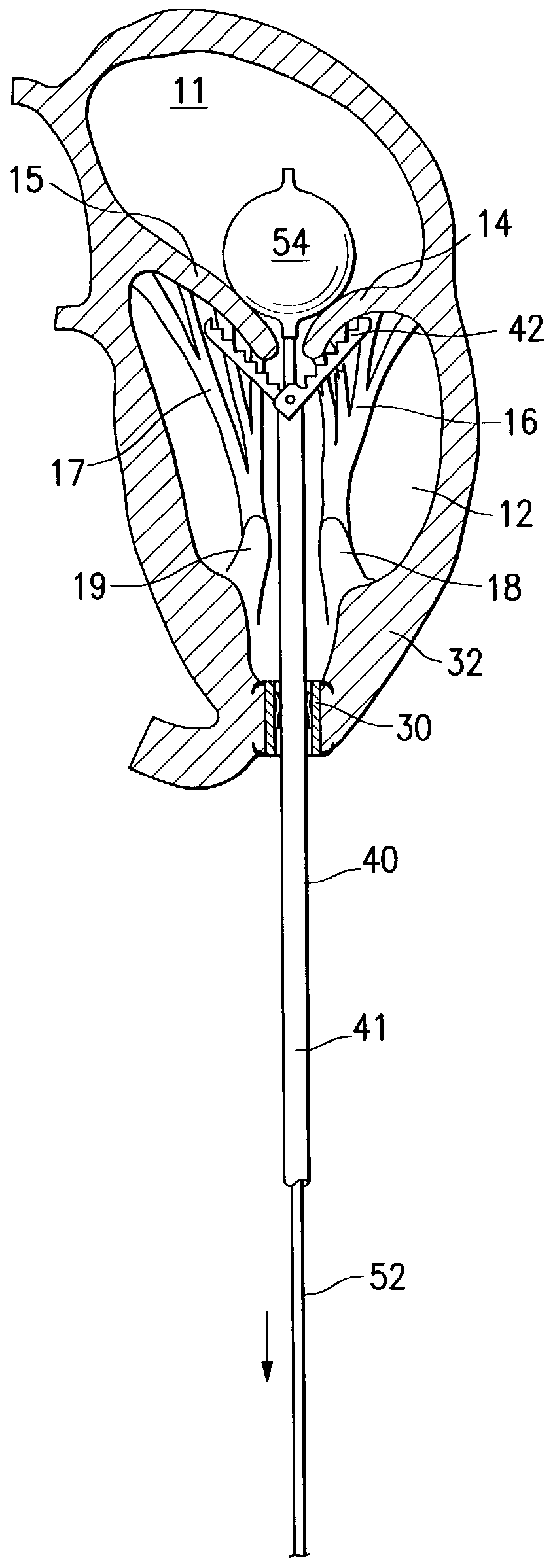
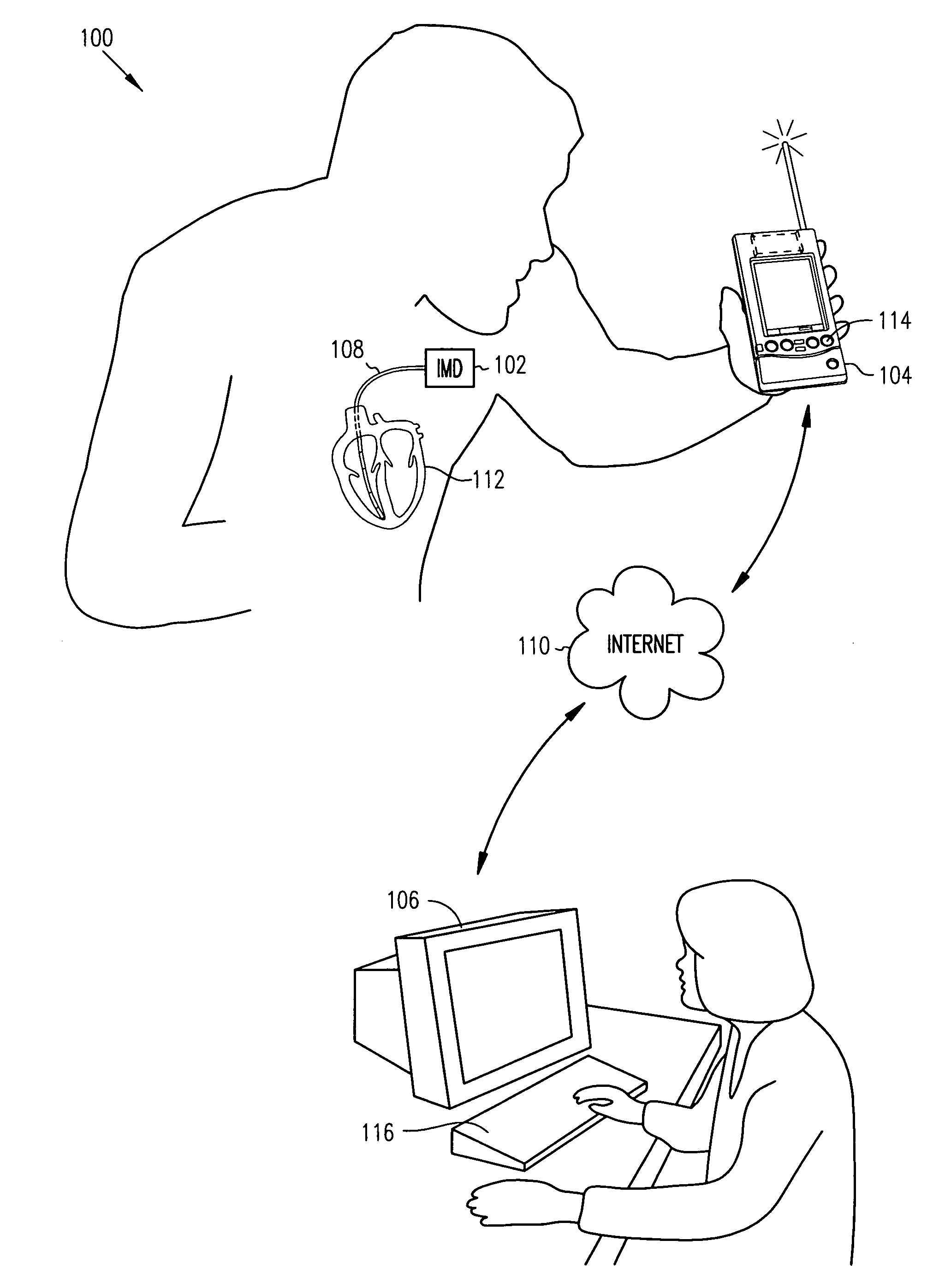
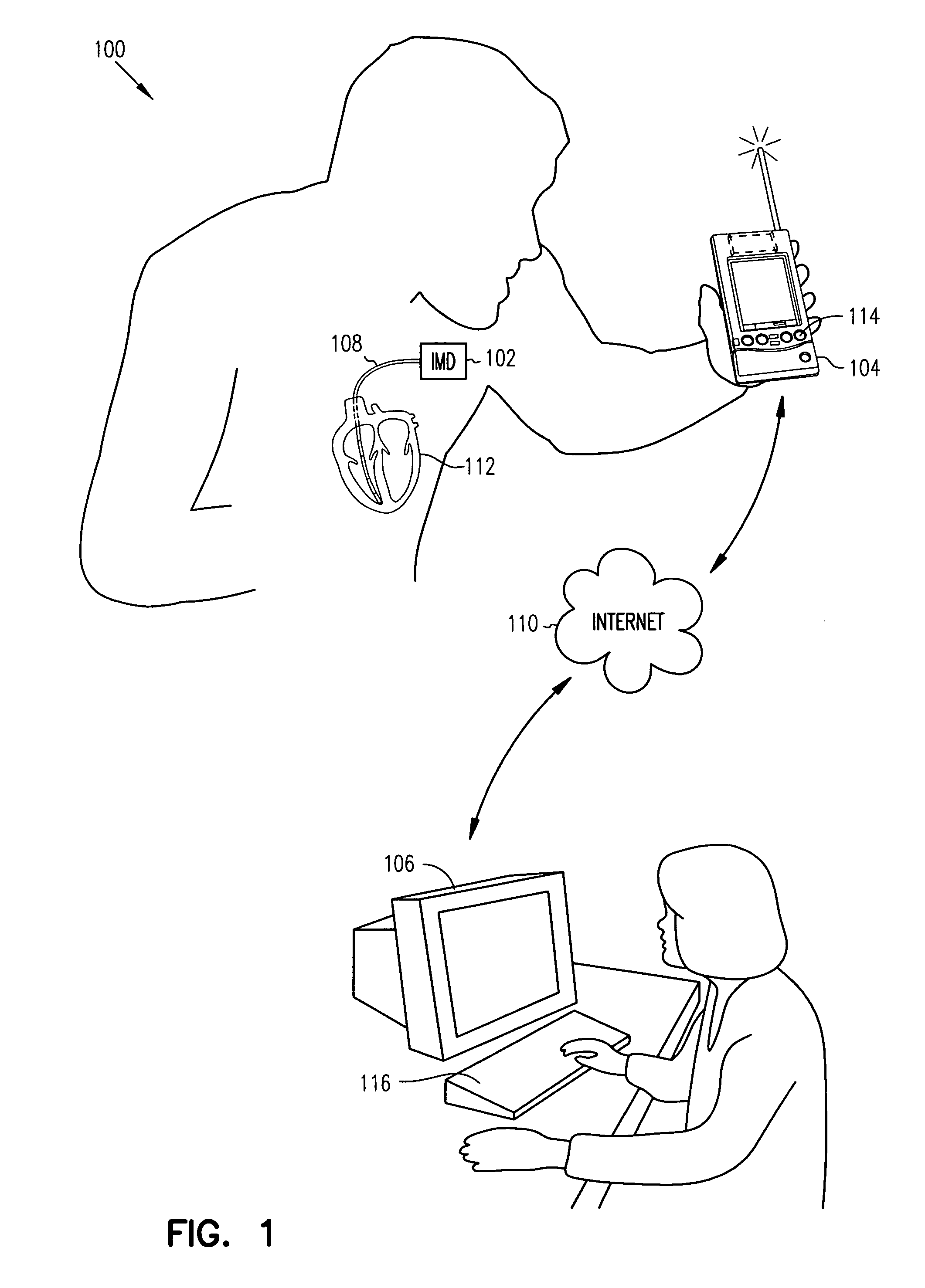
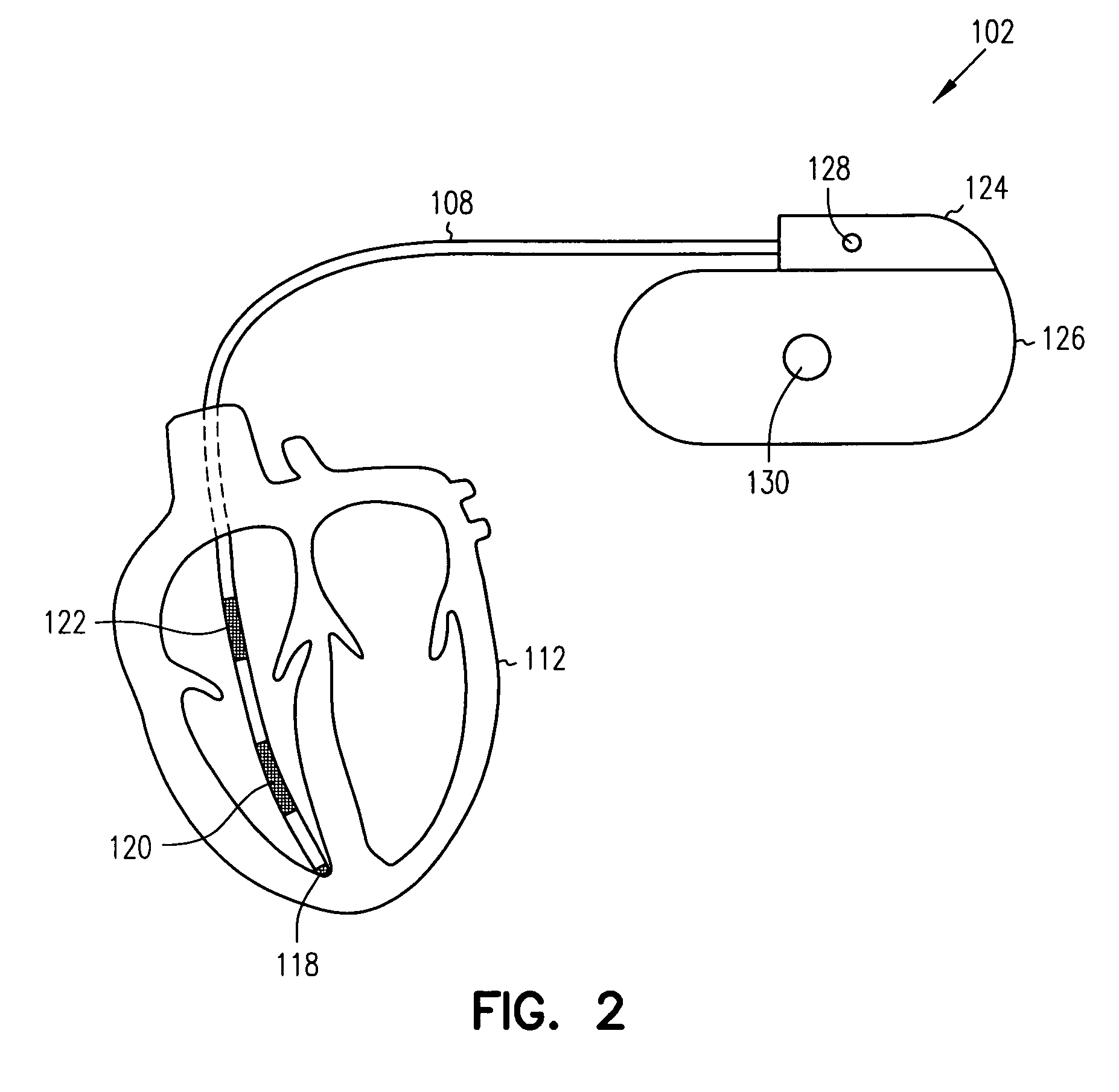
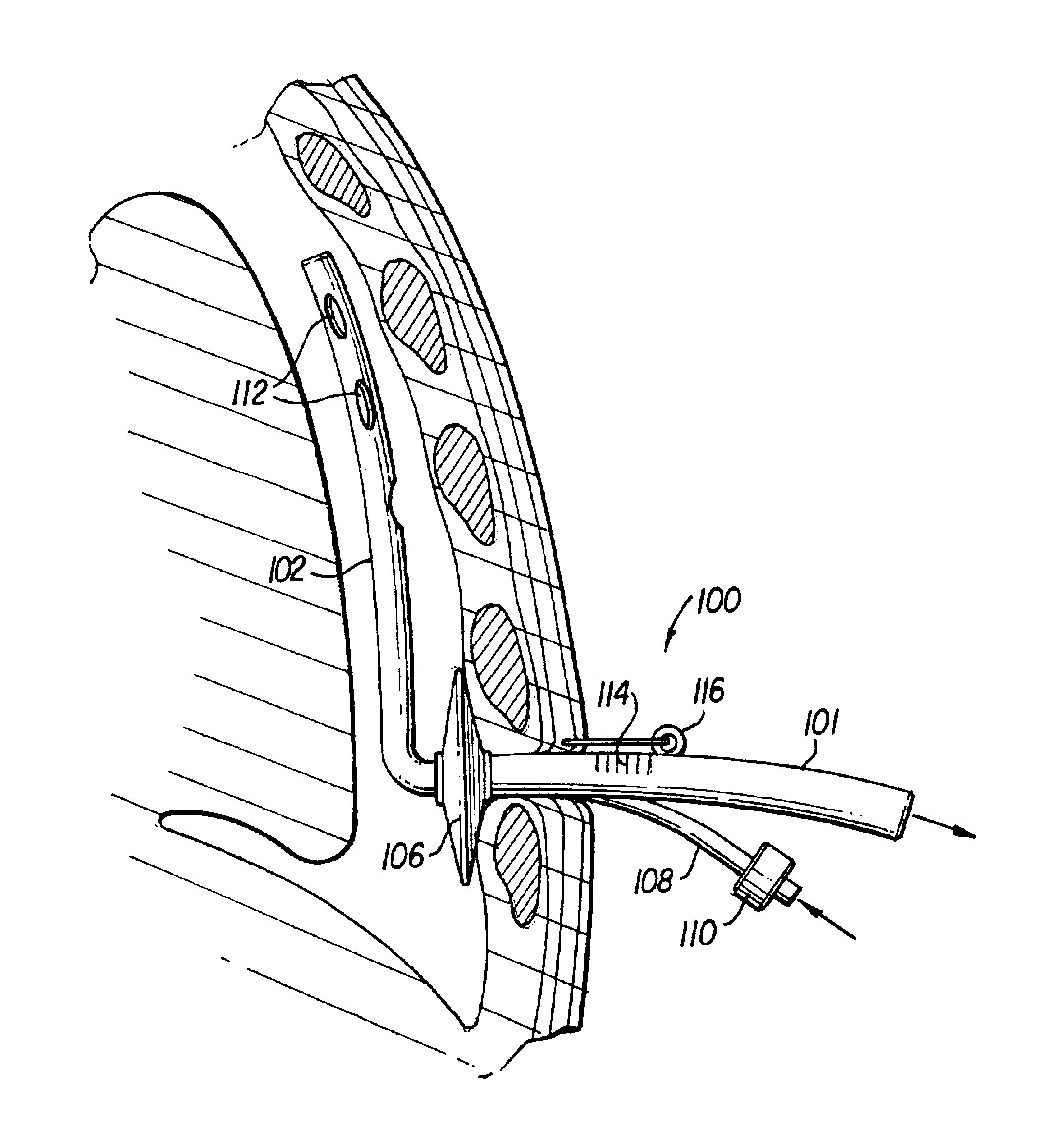
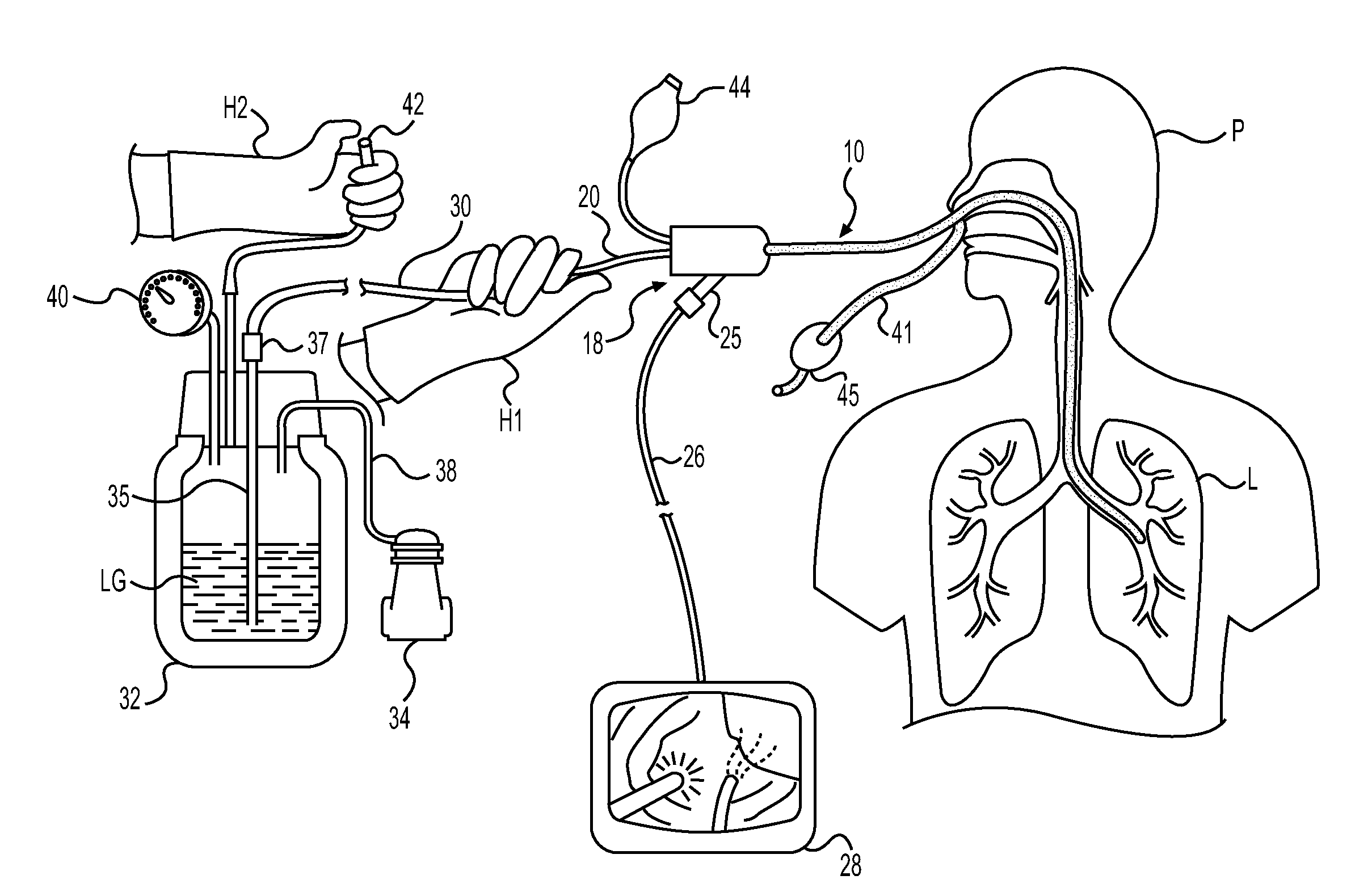
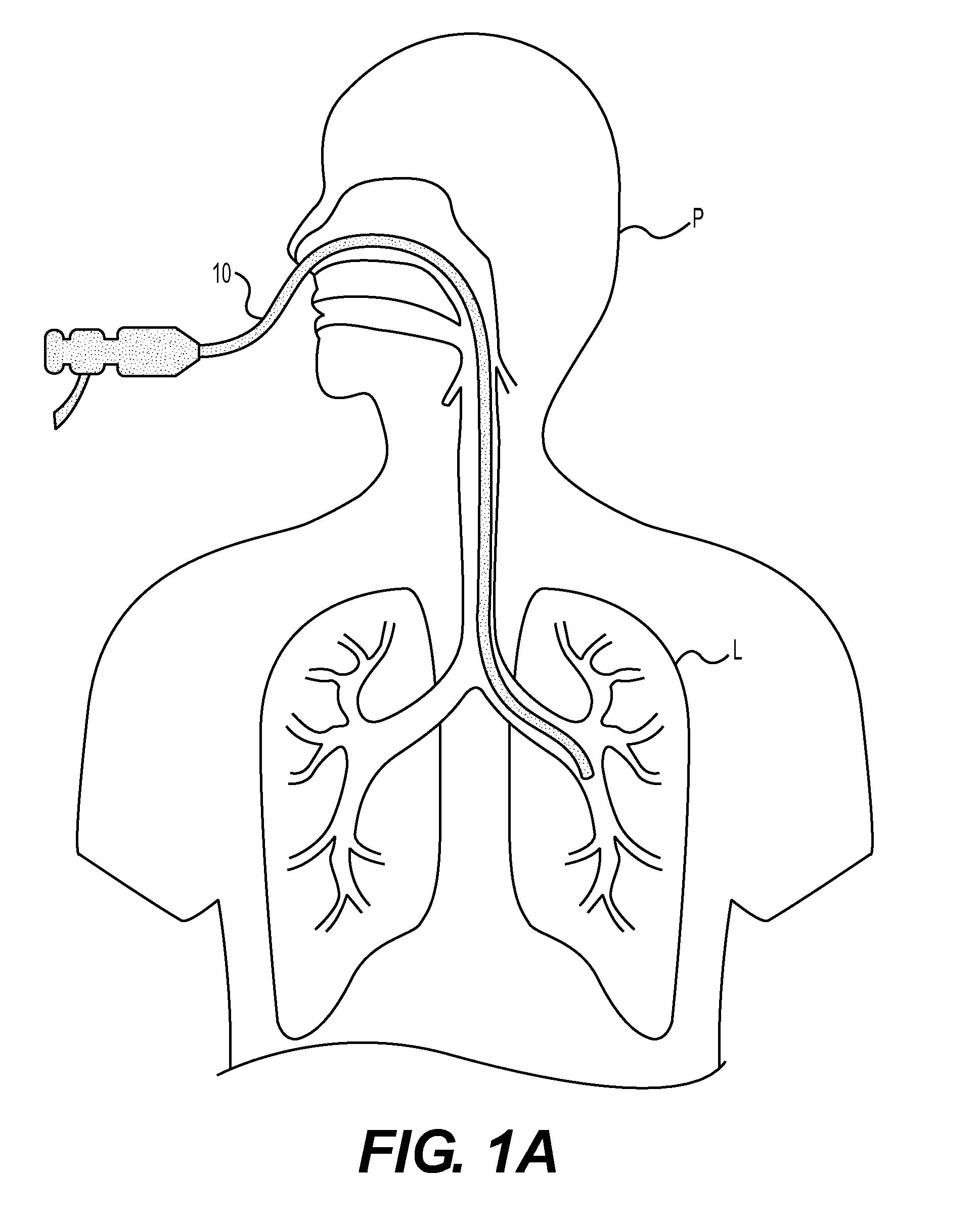
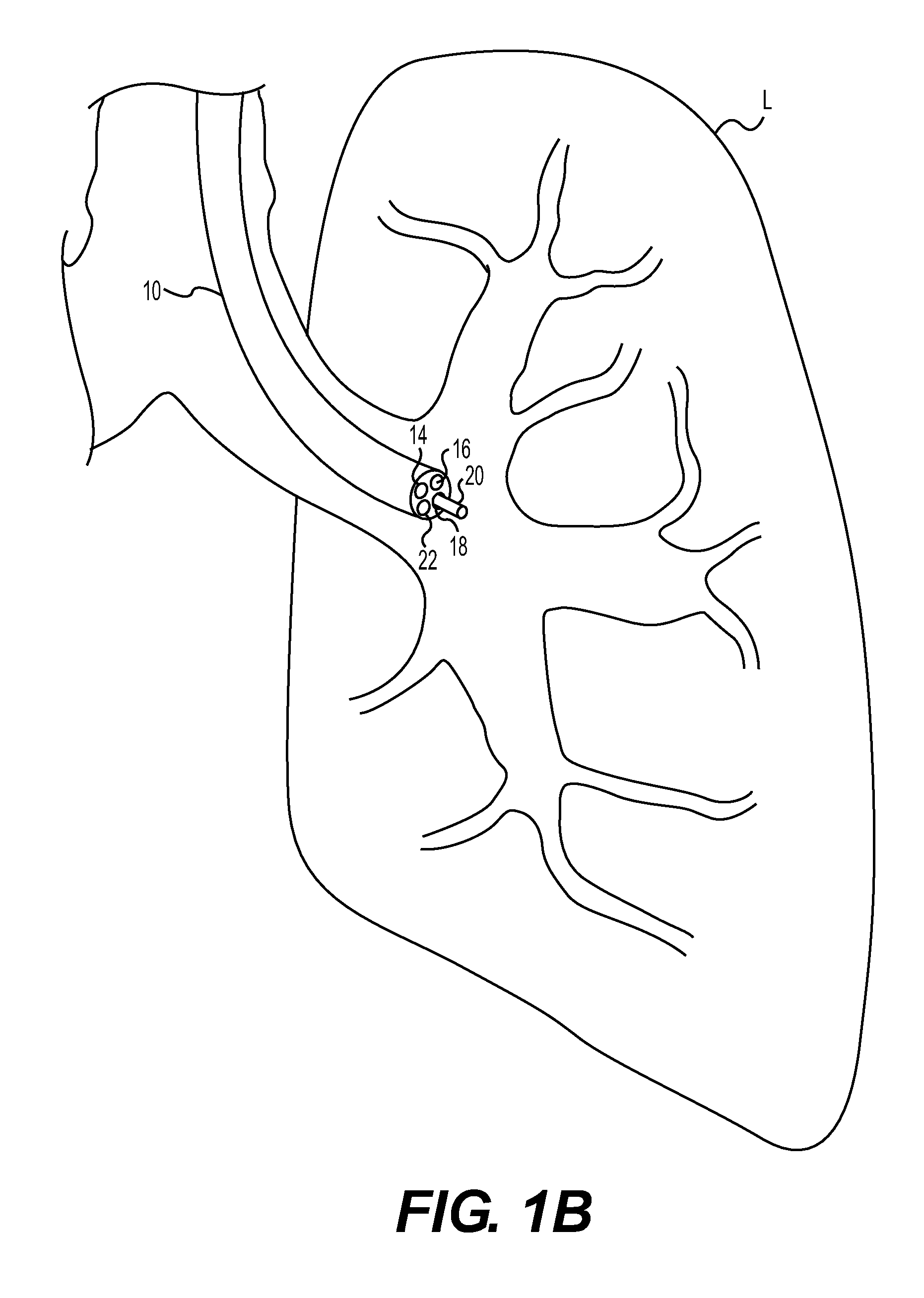
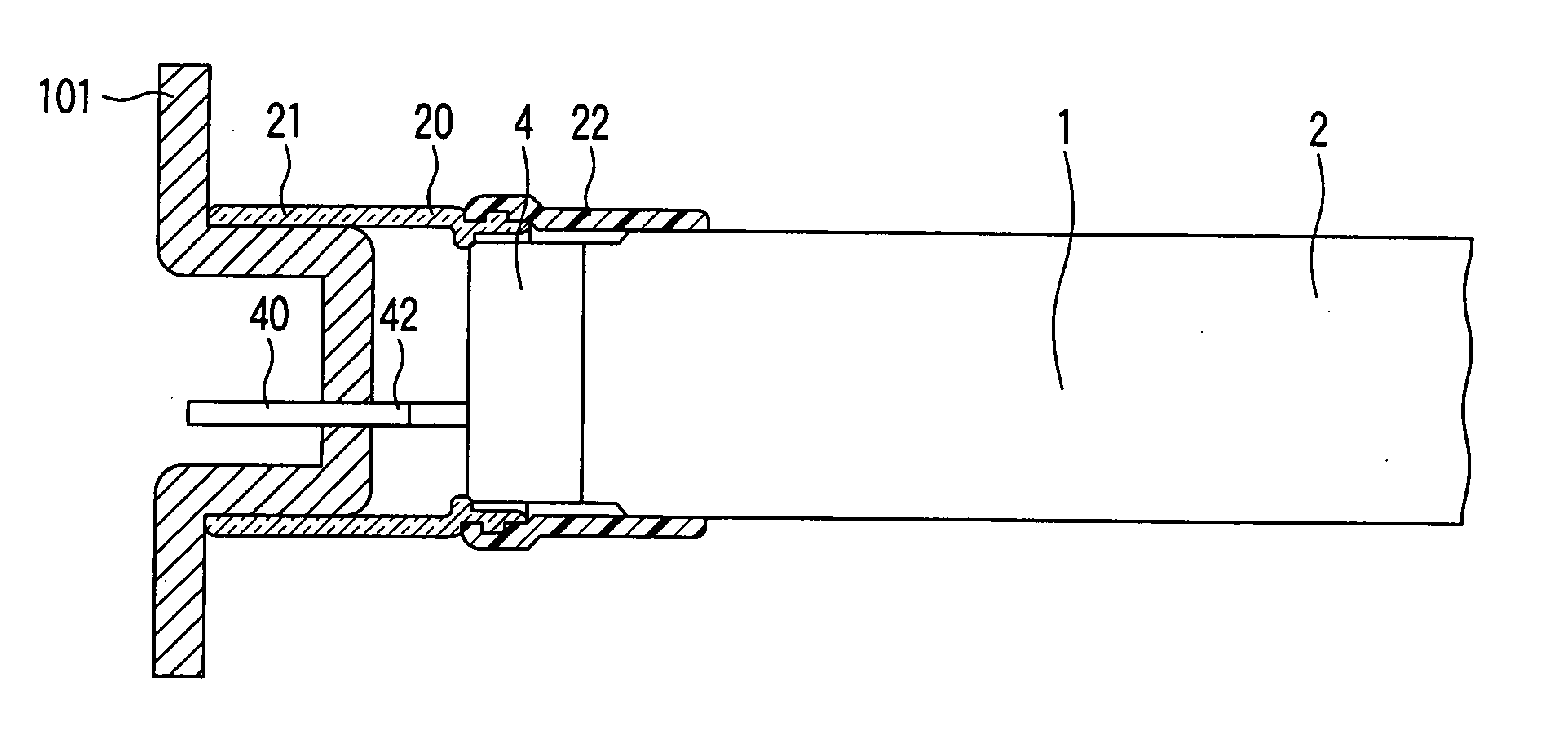
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1297 results about "Thoracic cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
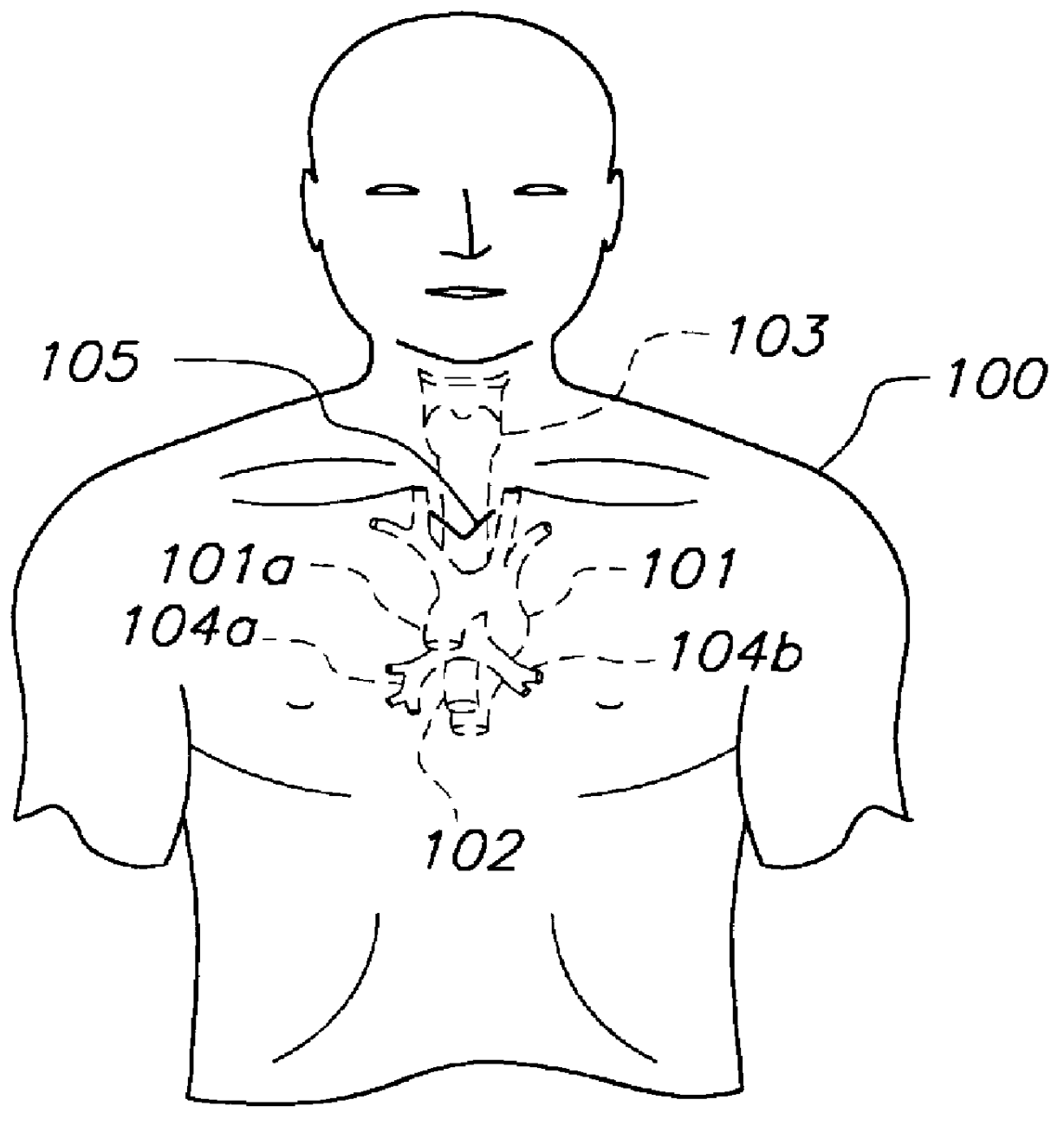
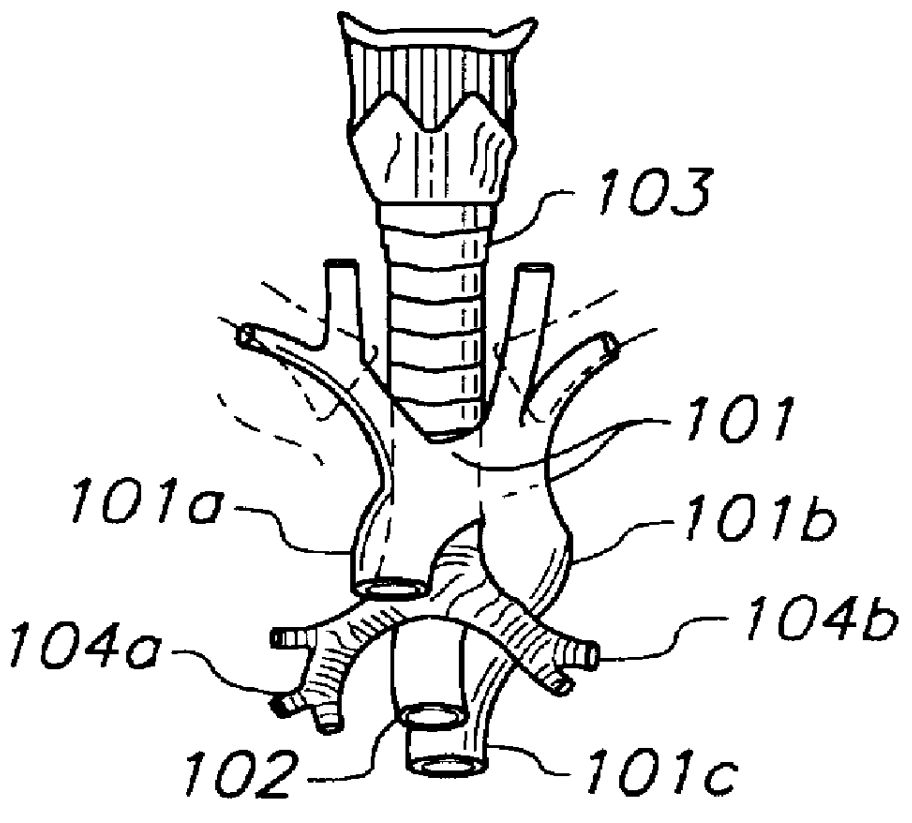
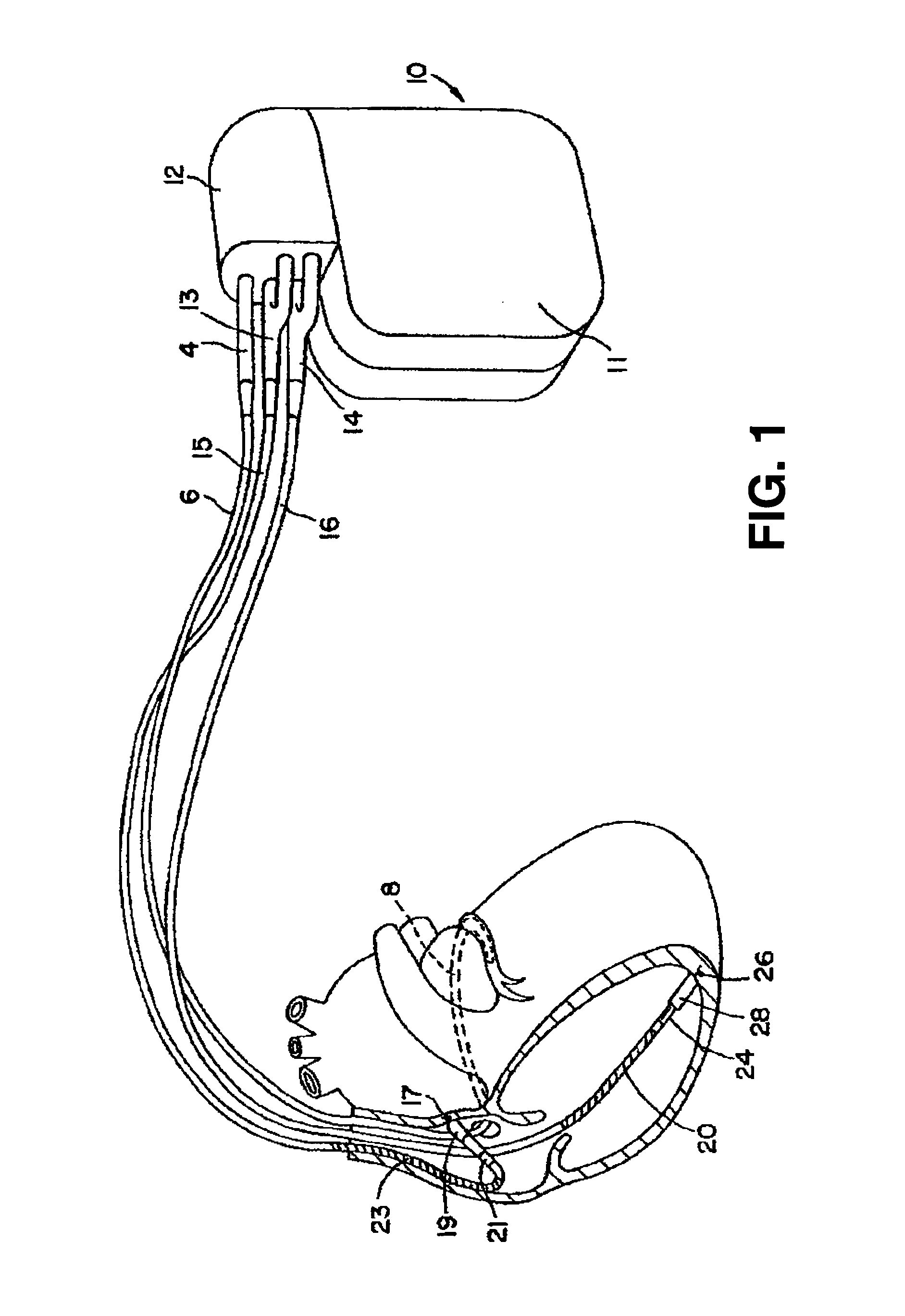
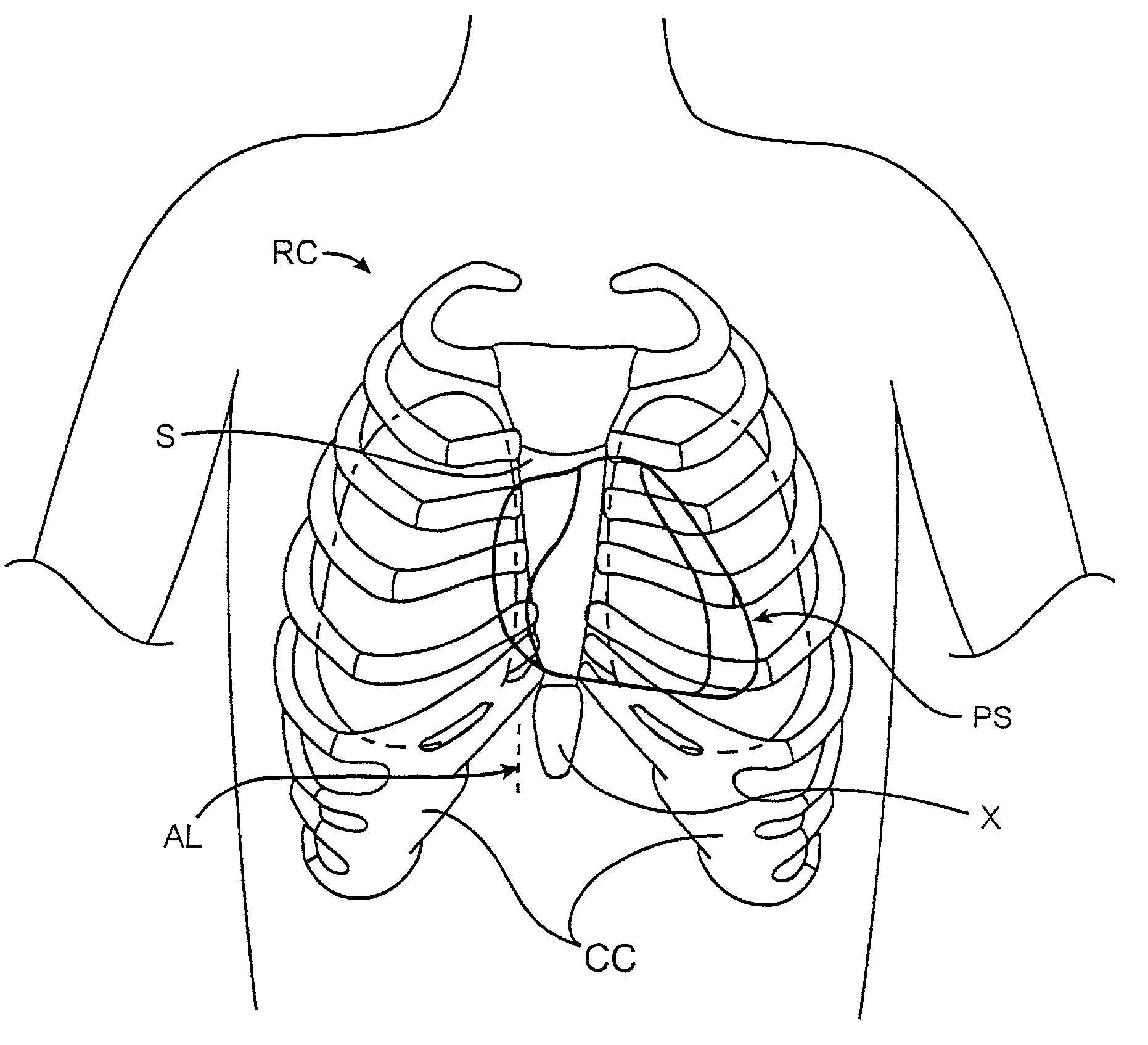
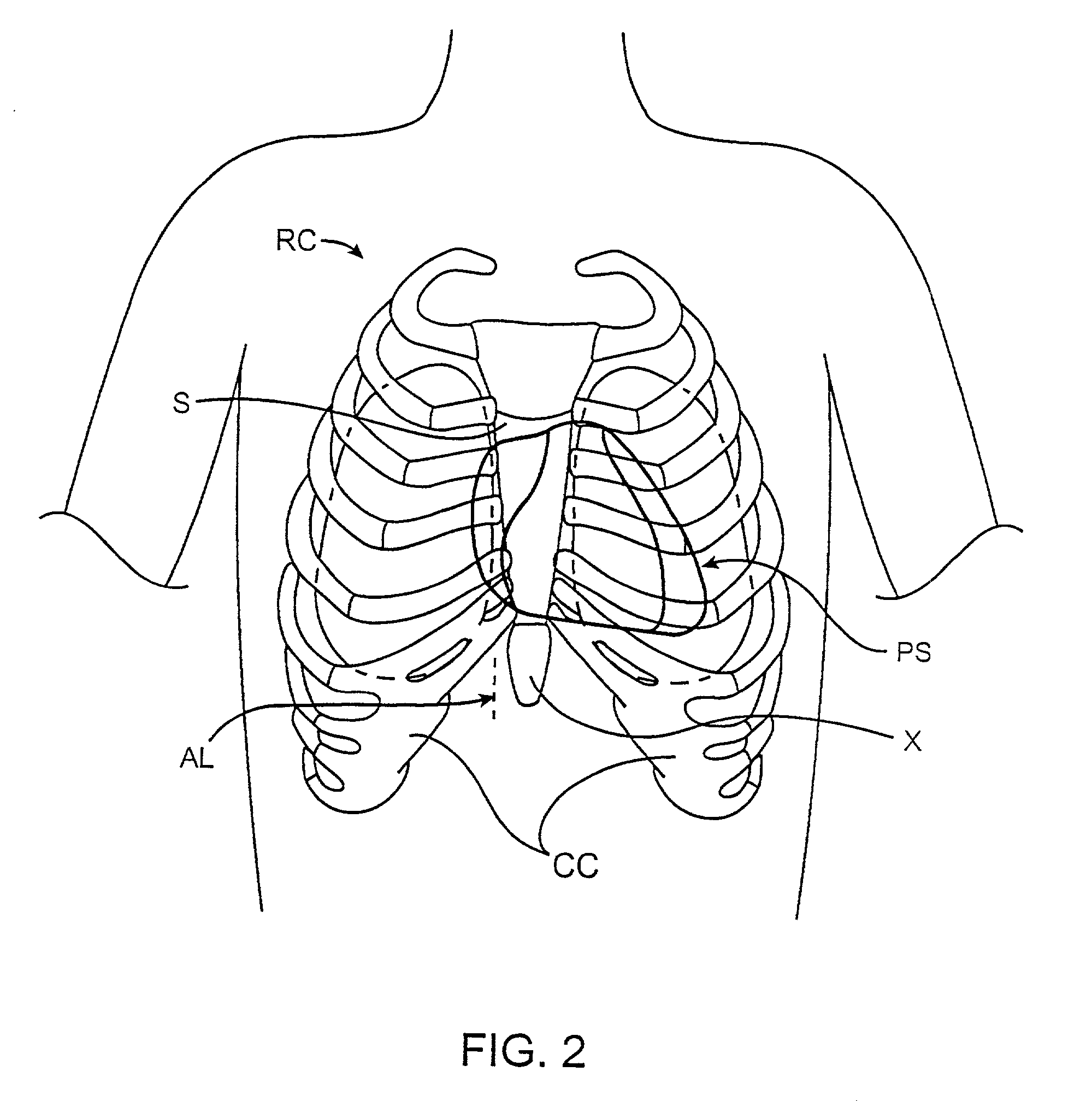
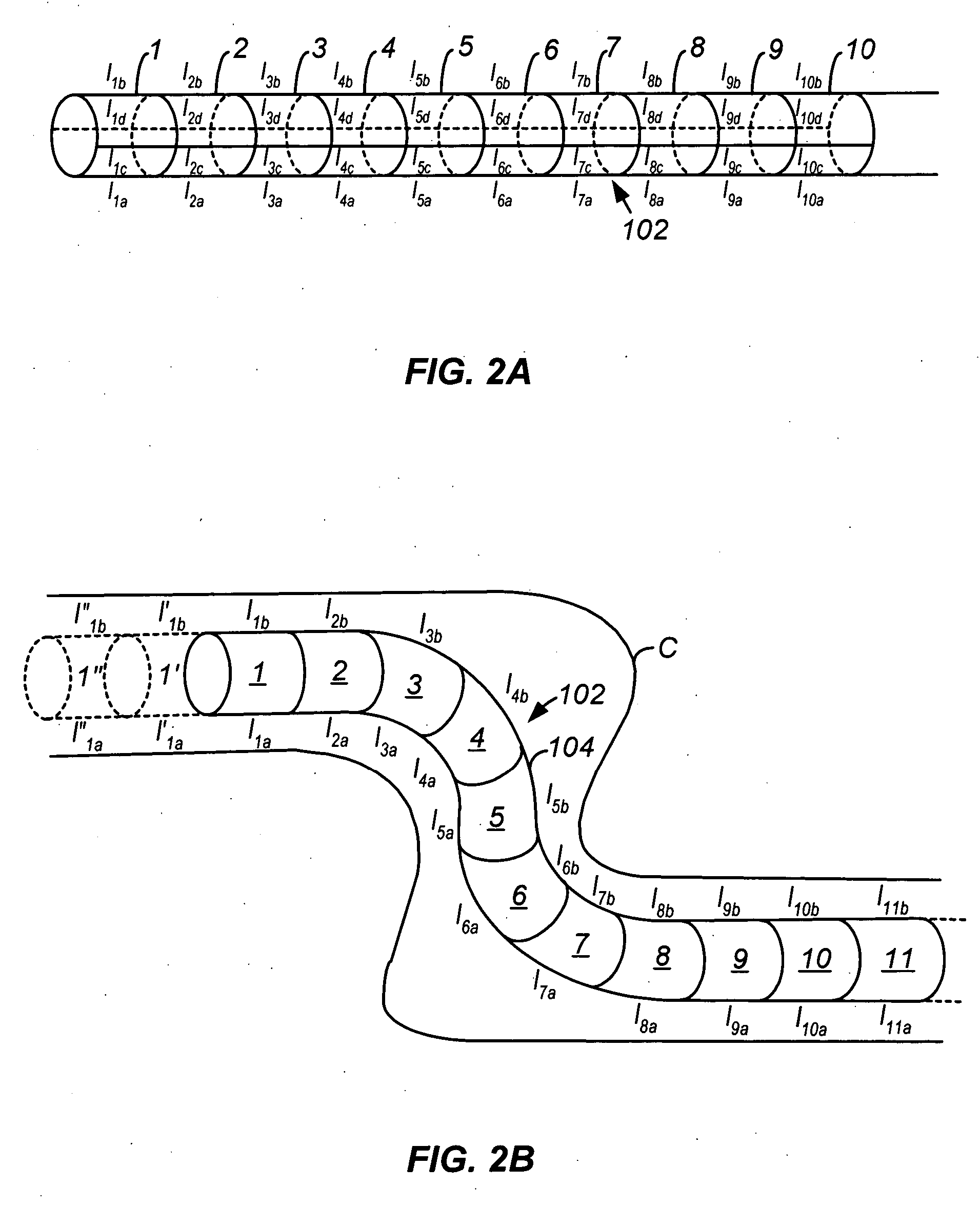
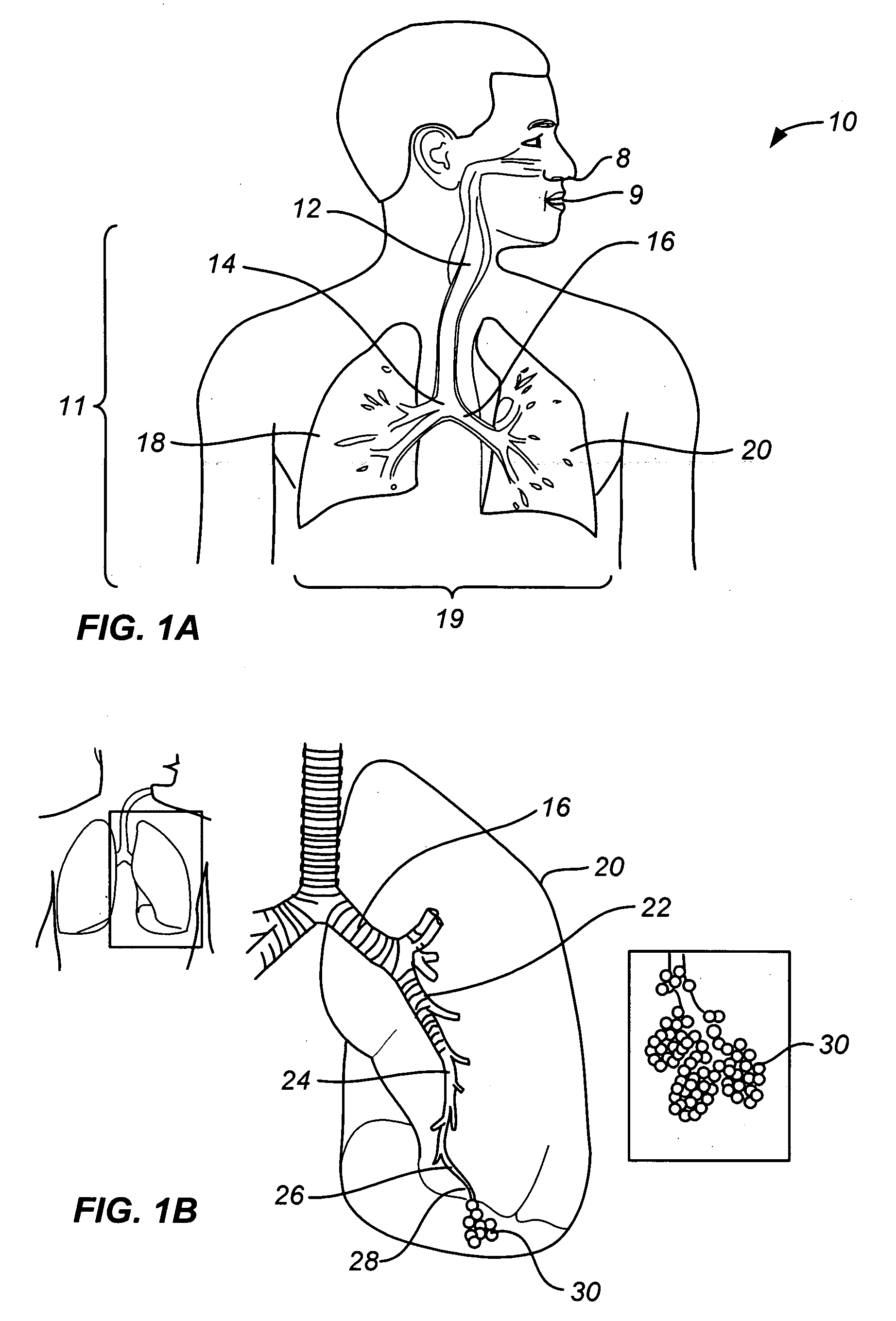
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There are two openings of the thoracic cavity, a superior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic inlet and a lower inferior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic outlet.
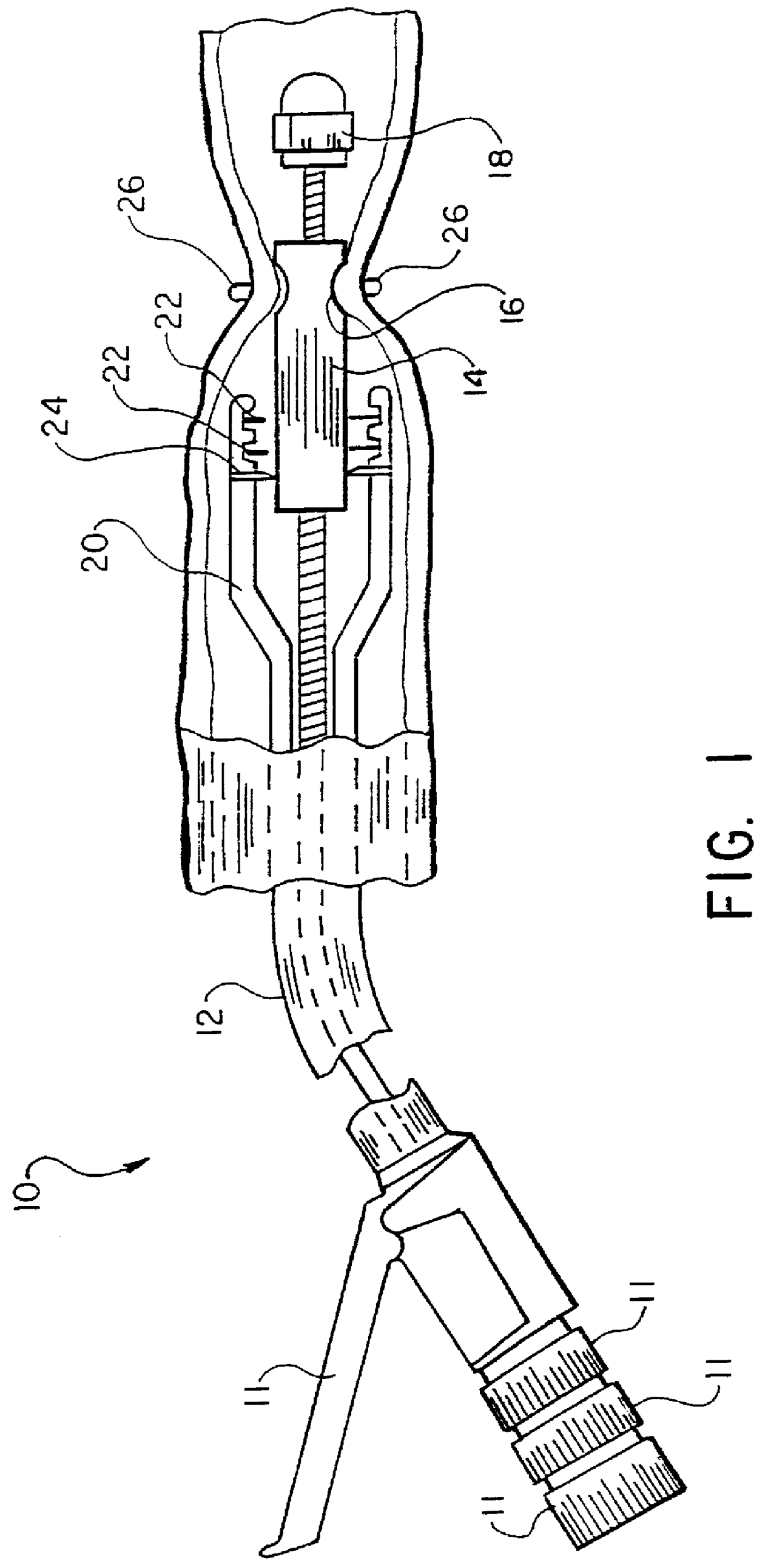
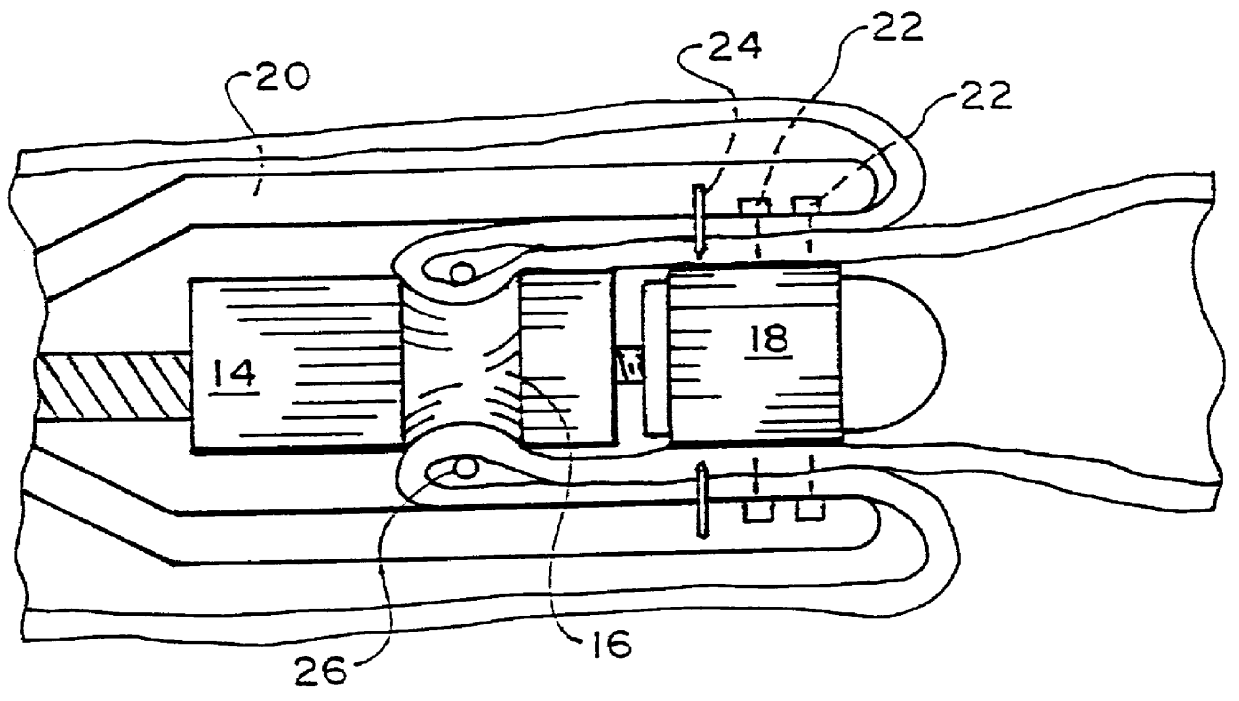
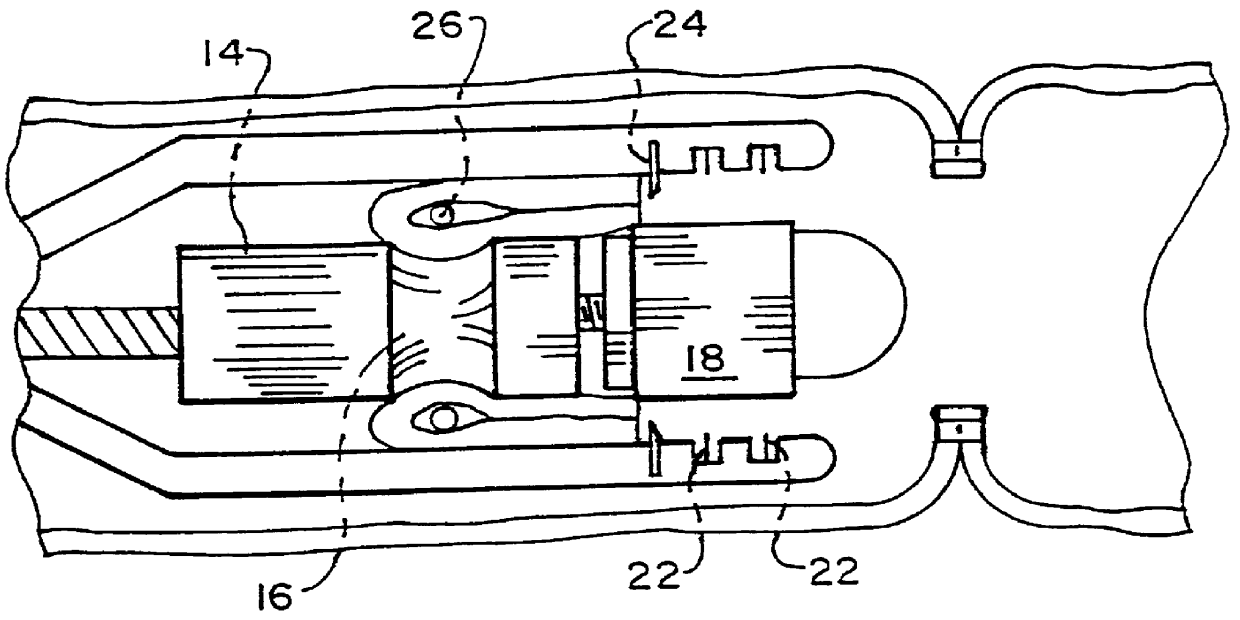
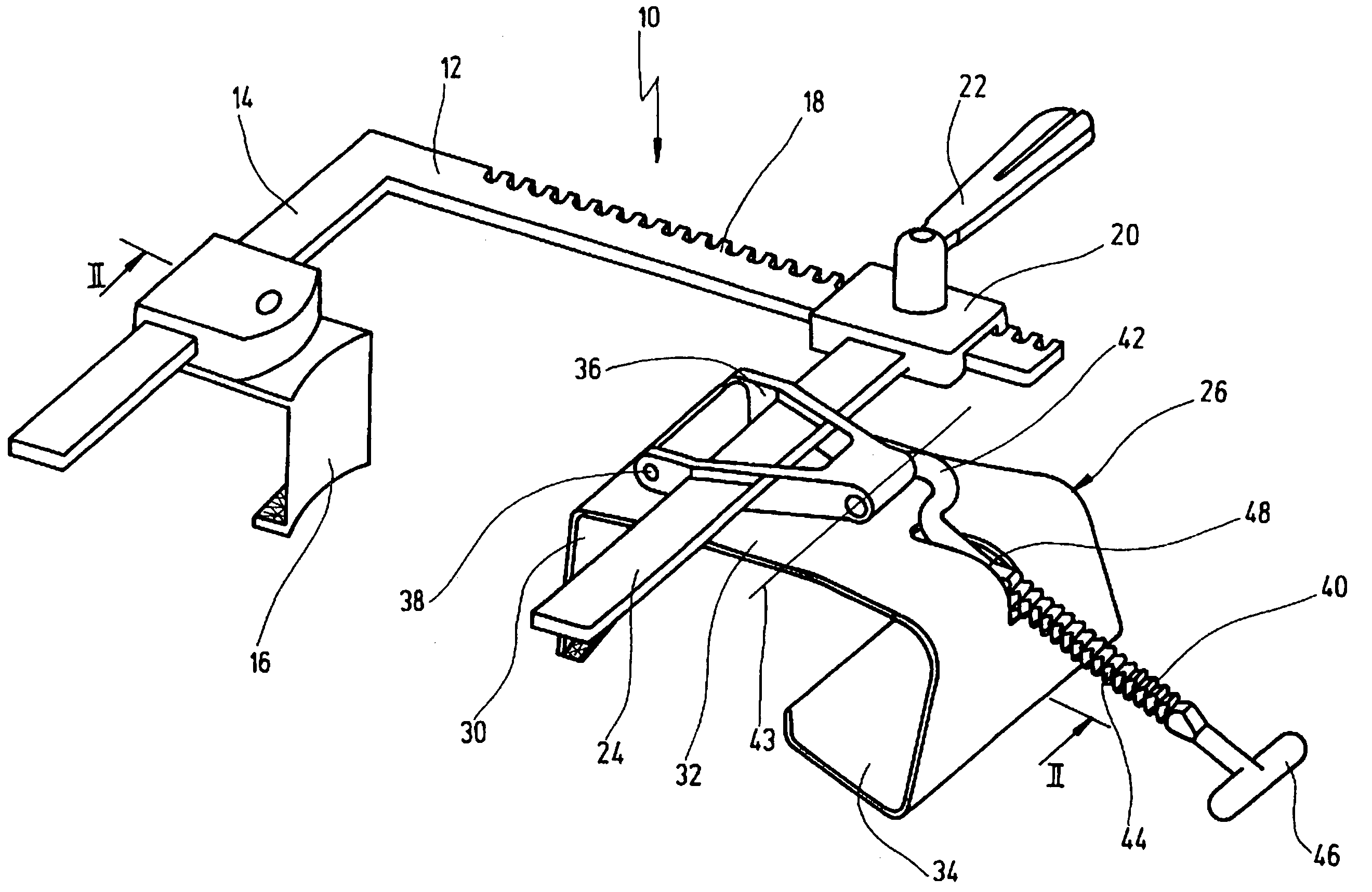
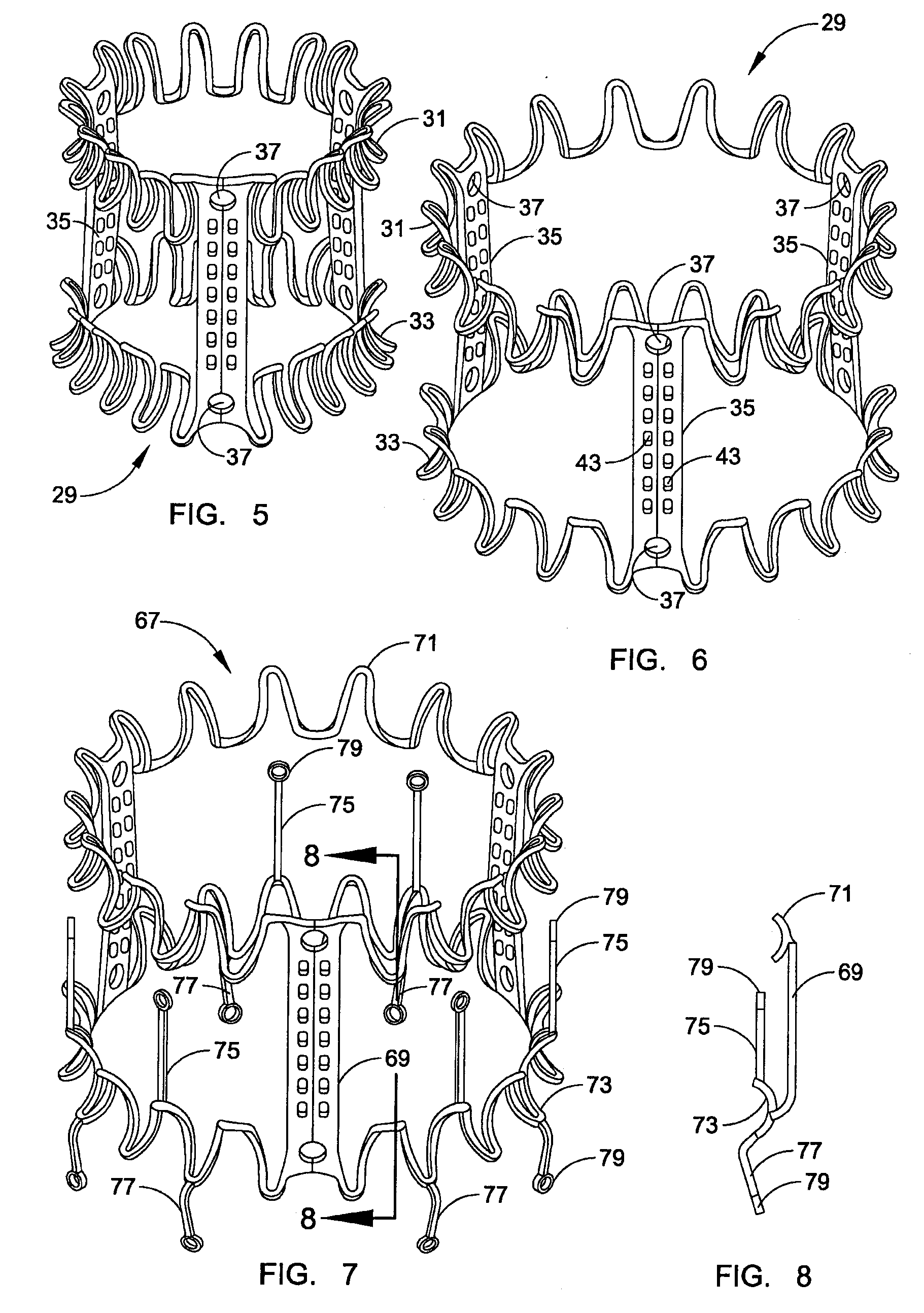
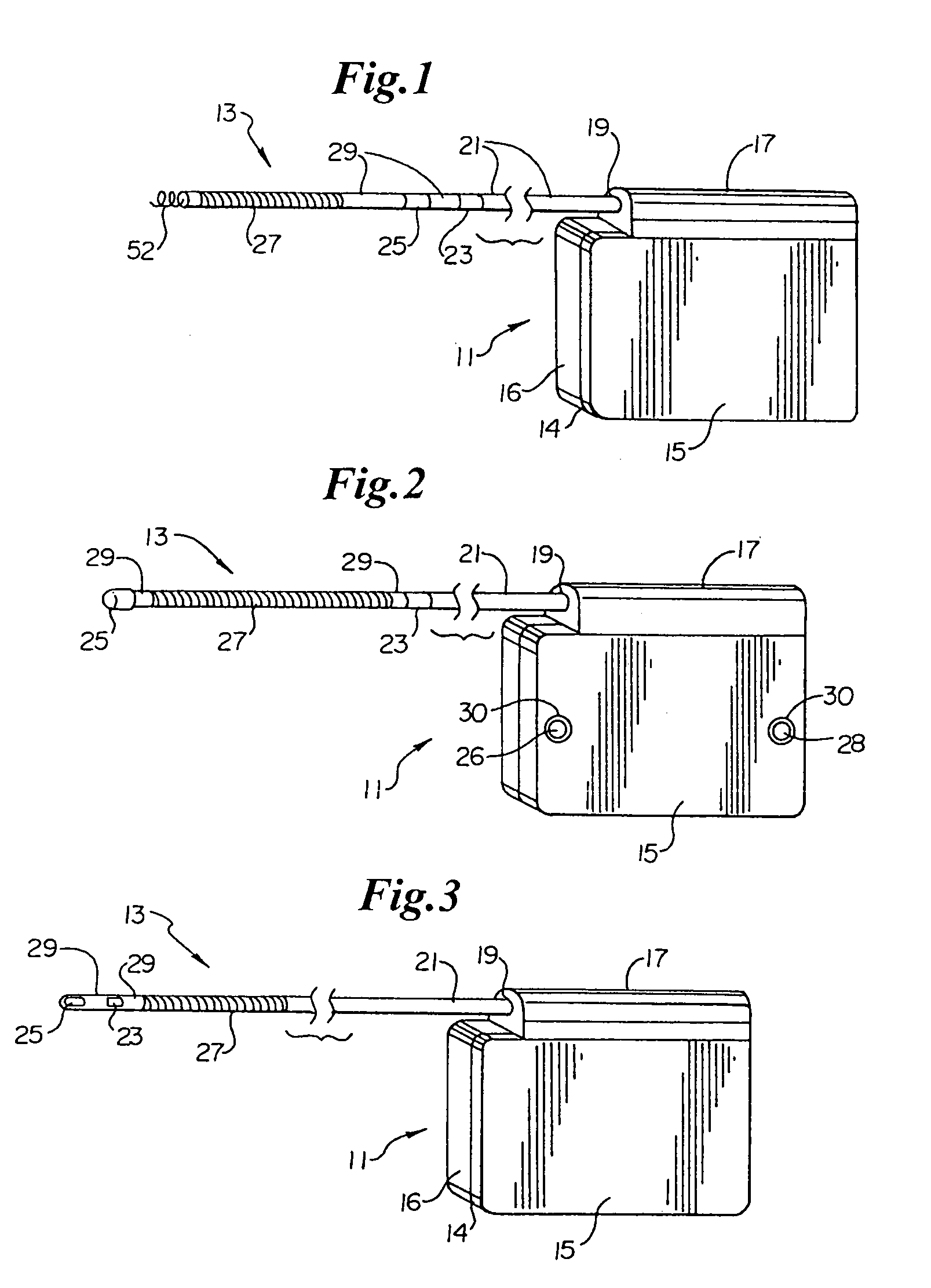
Intraluminal anastomotic device
InactiveUS6117148AEasy to disassembleSuture equipmentsStapling toolsThoracic structureAbdominal cavity
An intestinal intraluminal reconstruction and resection device includes a mechanism for intussusception of the bowel, a bowel anastomosis mechanism and a mechanism for severing the resected bowel. The surgical device allows the user to carry out intraluminally an anastomosis first, prior to resection of the intestine or any hollow viscus, therefore not exposing the dirty intraluminal content to the clean abdominal or thoracic cavities. The above is achieved by first intussuscepting the hollow viscus, then anastomosis and finally intraluminal resection.
Owner:RAVO BIAGIO +1
Retractor for performing heart and thorax surgeries
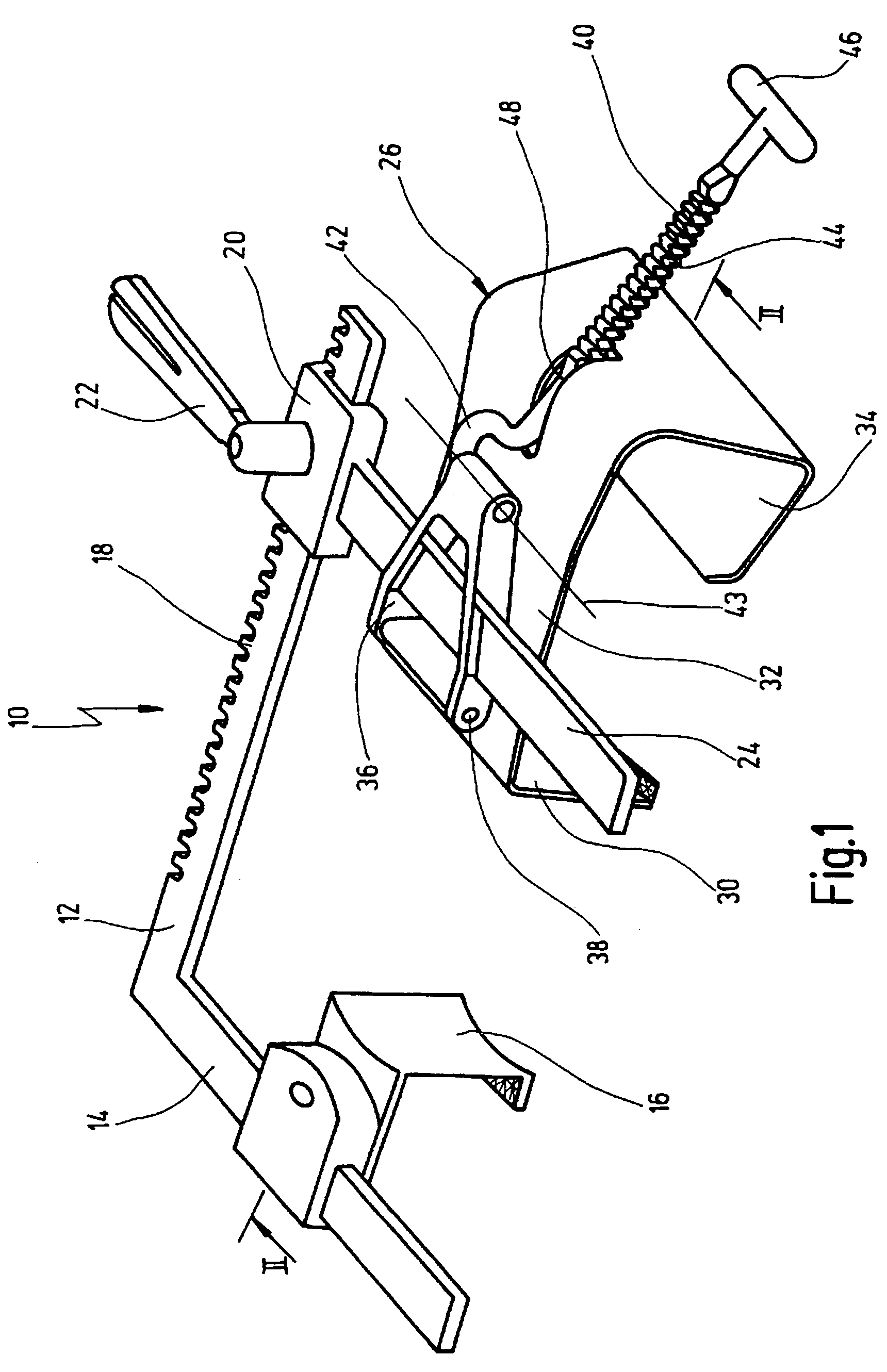
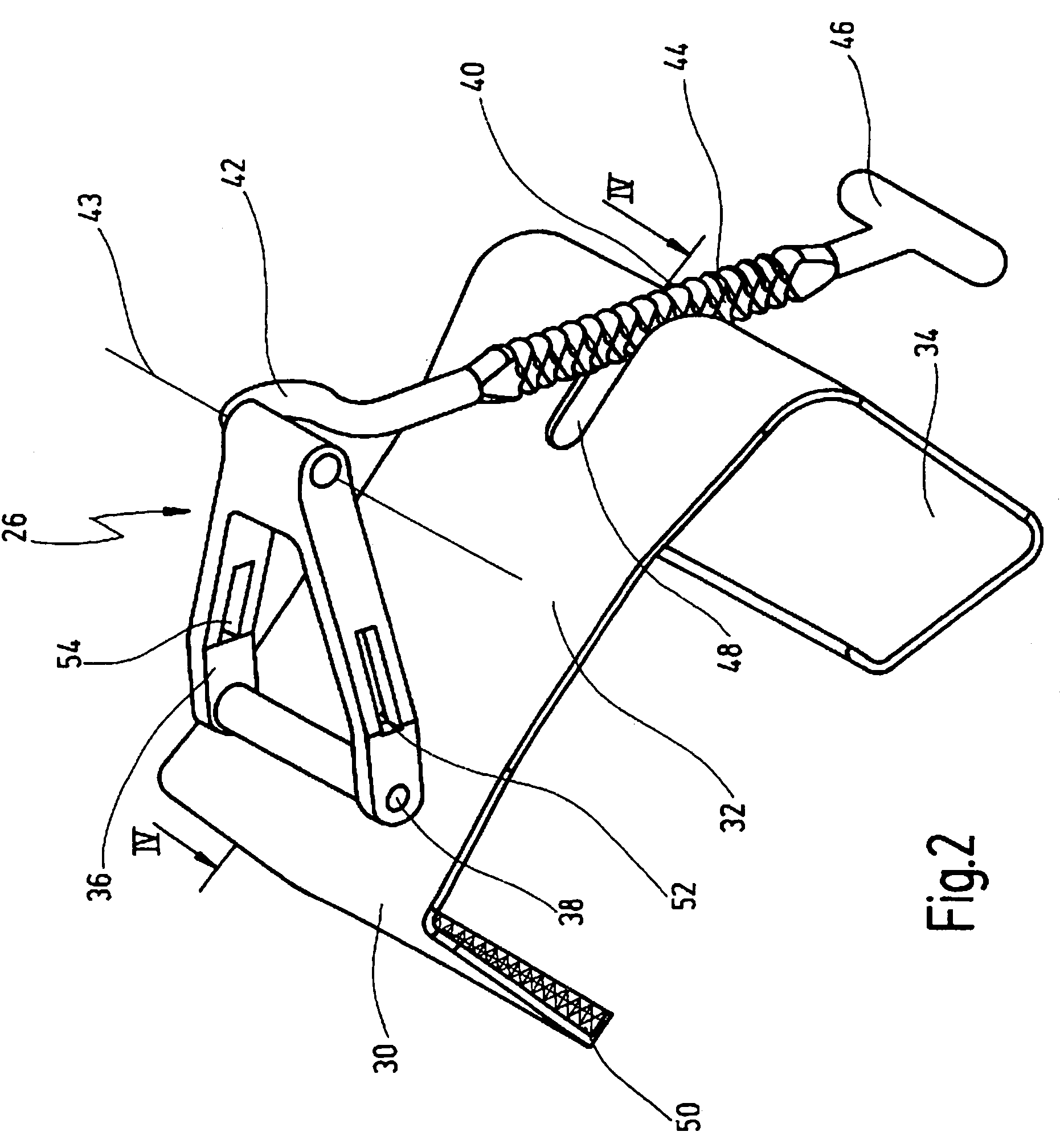
A retractor has a rail, a first holding arm protruding from this rail at an angle at a second holding arm extending approximately parallel to the first holding arm. A distance between the two arms being modifiable. At least one functional element is mounted on one of these holding arms, which functional element has a section extending transversely to the holding arms and a swivel bracket protruding from this transverse section. The functional element being pivotable about a pin extending roughly parallel to the arms via the swivel bracket, a swiveled position can be set by grasping the function element with a hand. A locking mechanism serves for locking the functional element in a swiveled position.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
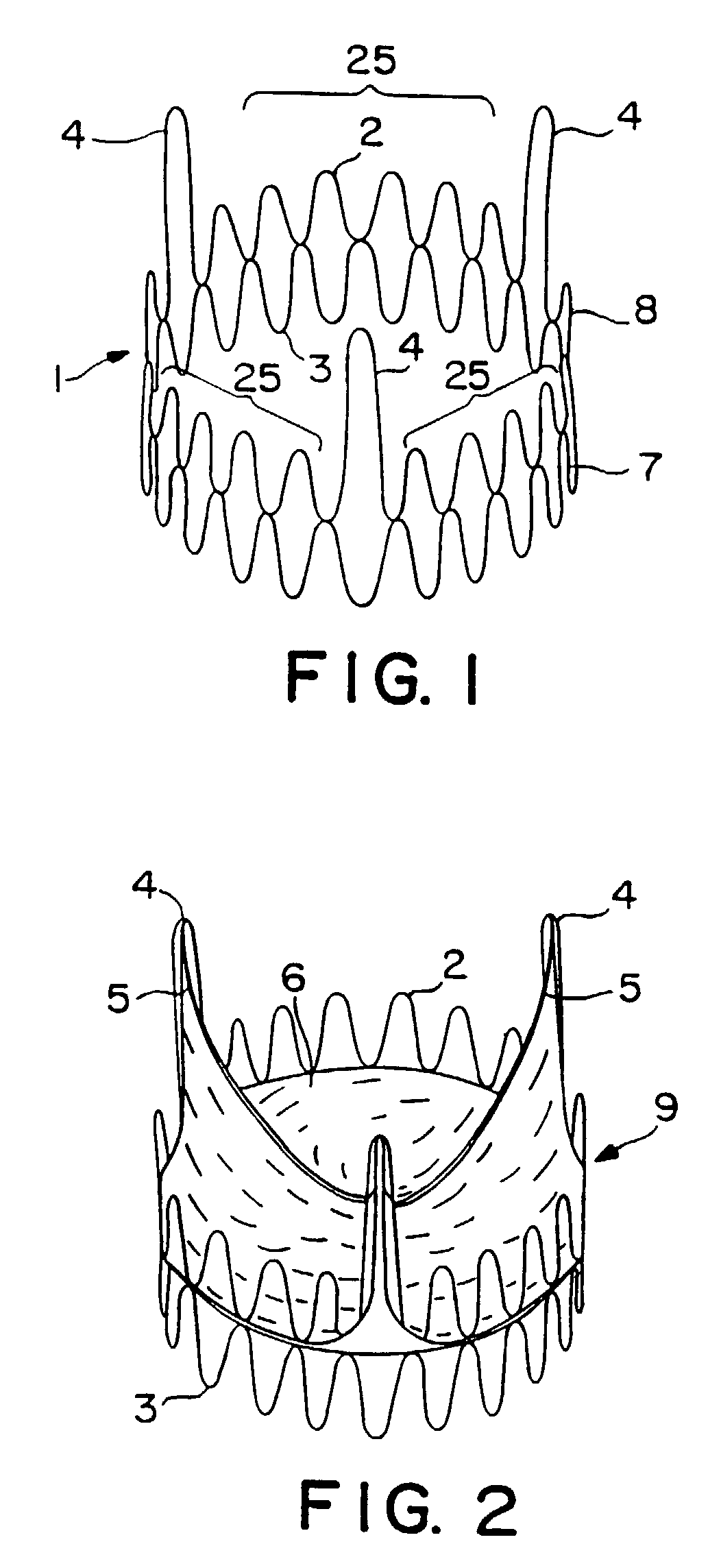
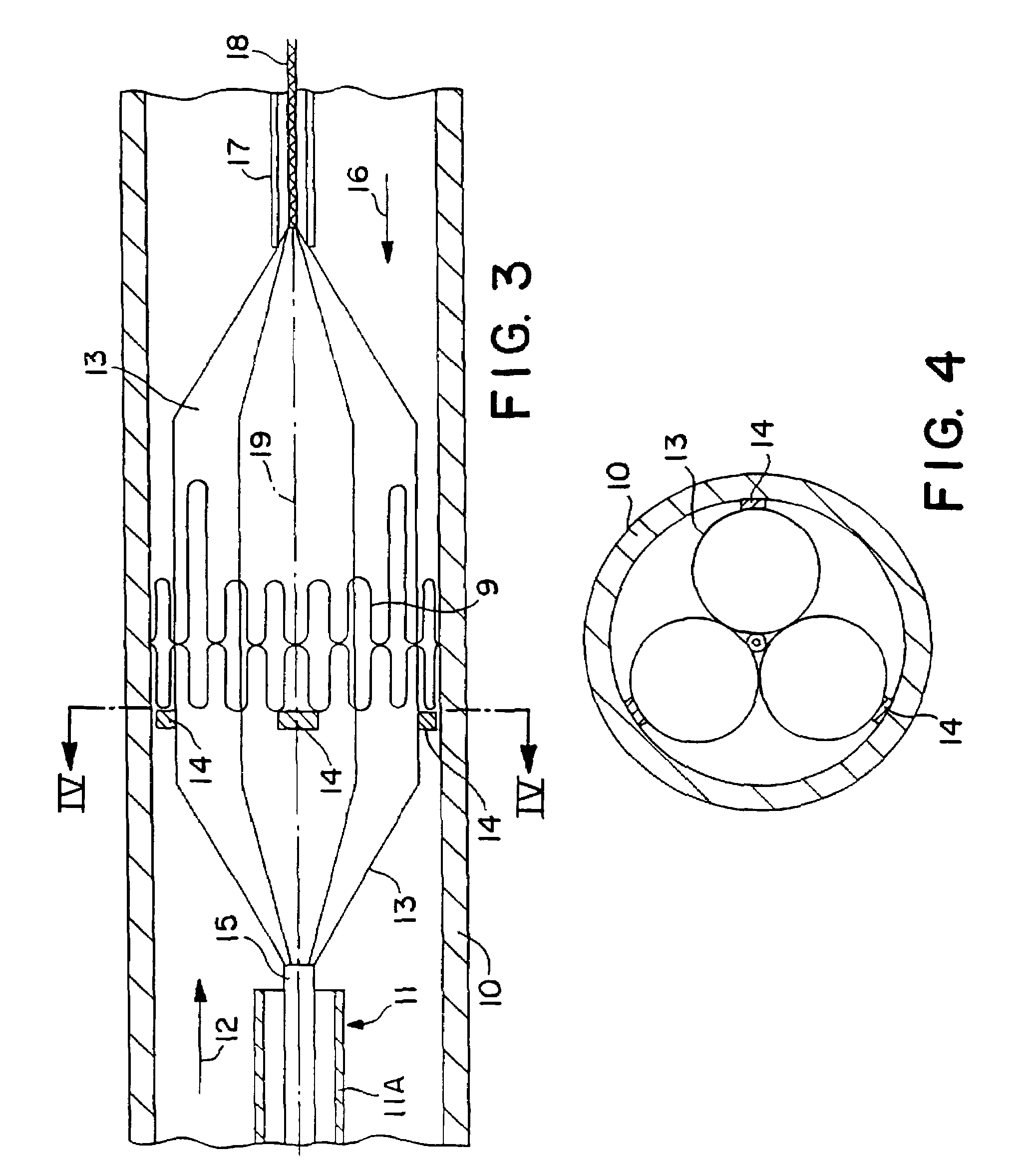
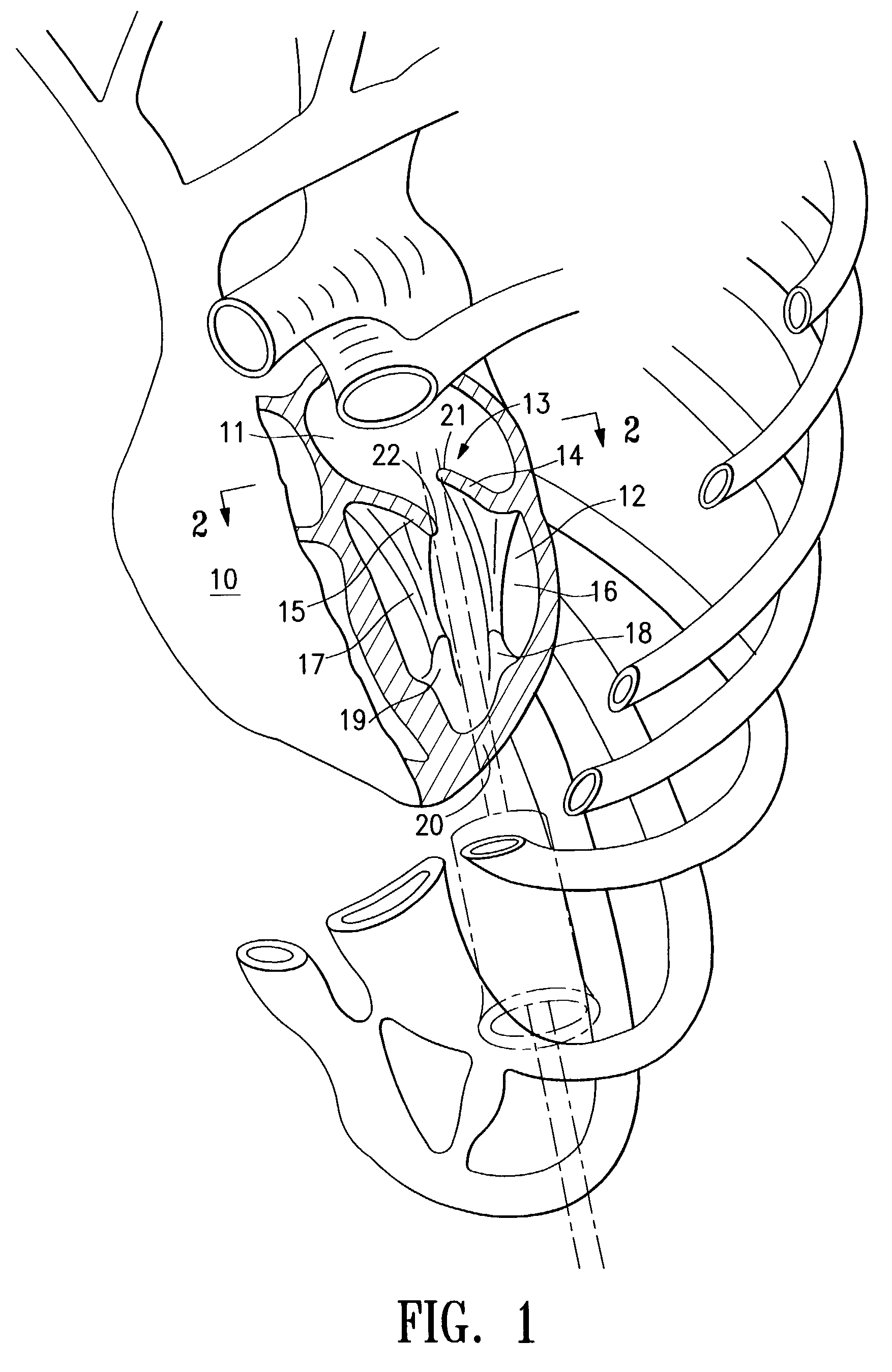
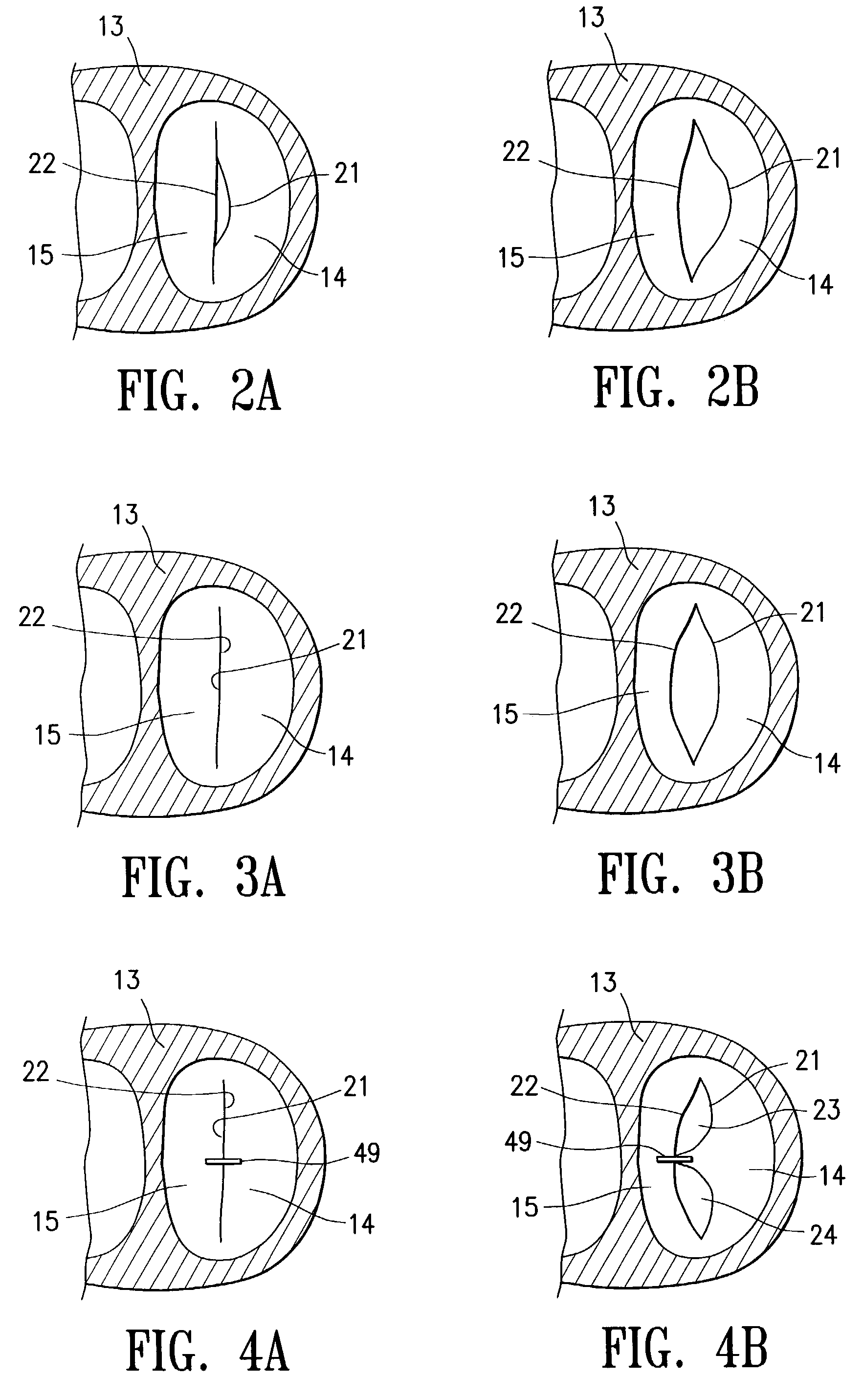
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement
ActiveUS20090005863A1Minimally invasiveSufficient flexibilityHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve replacementThoracic cavity
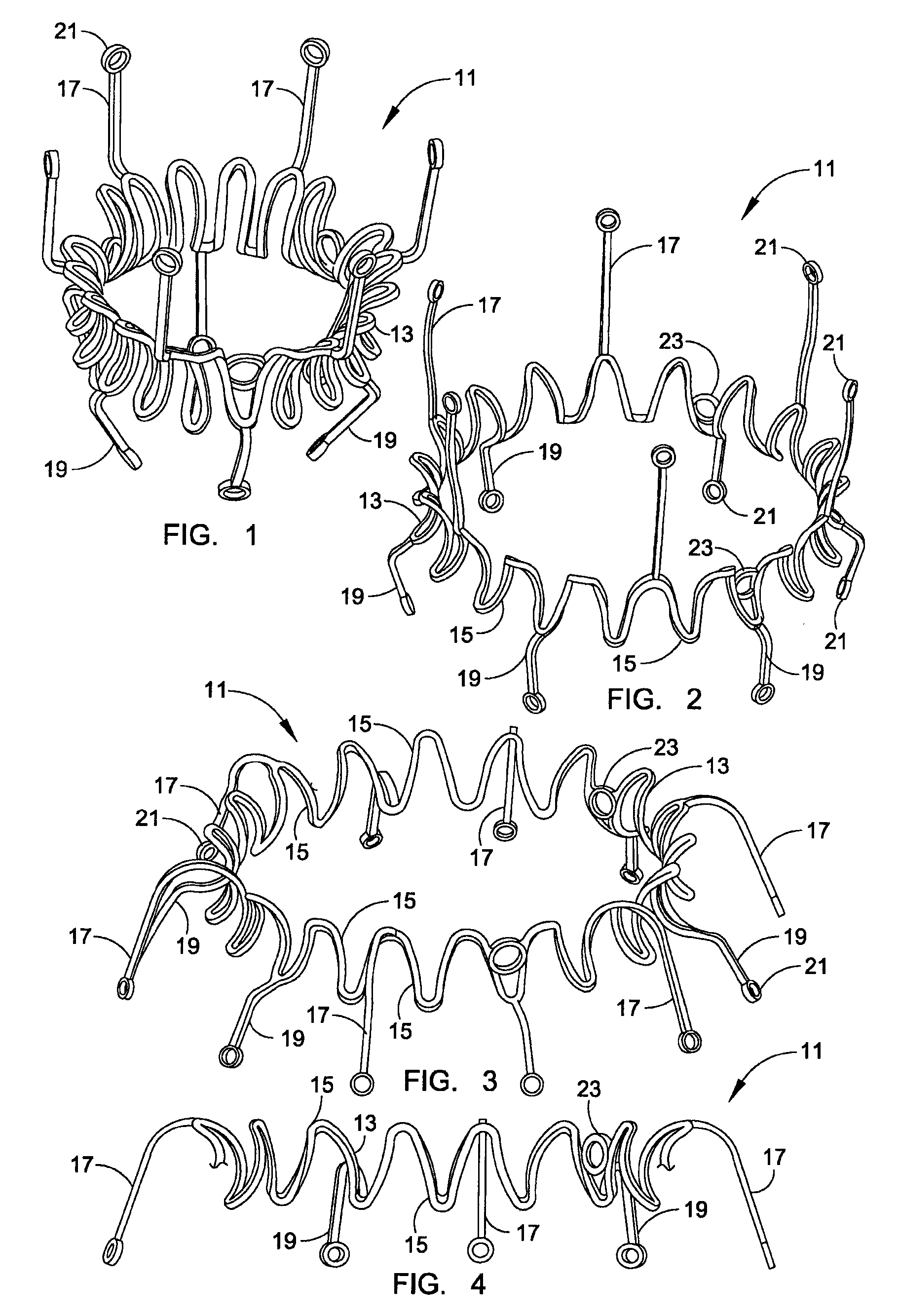
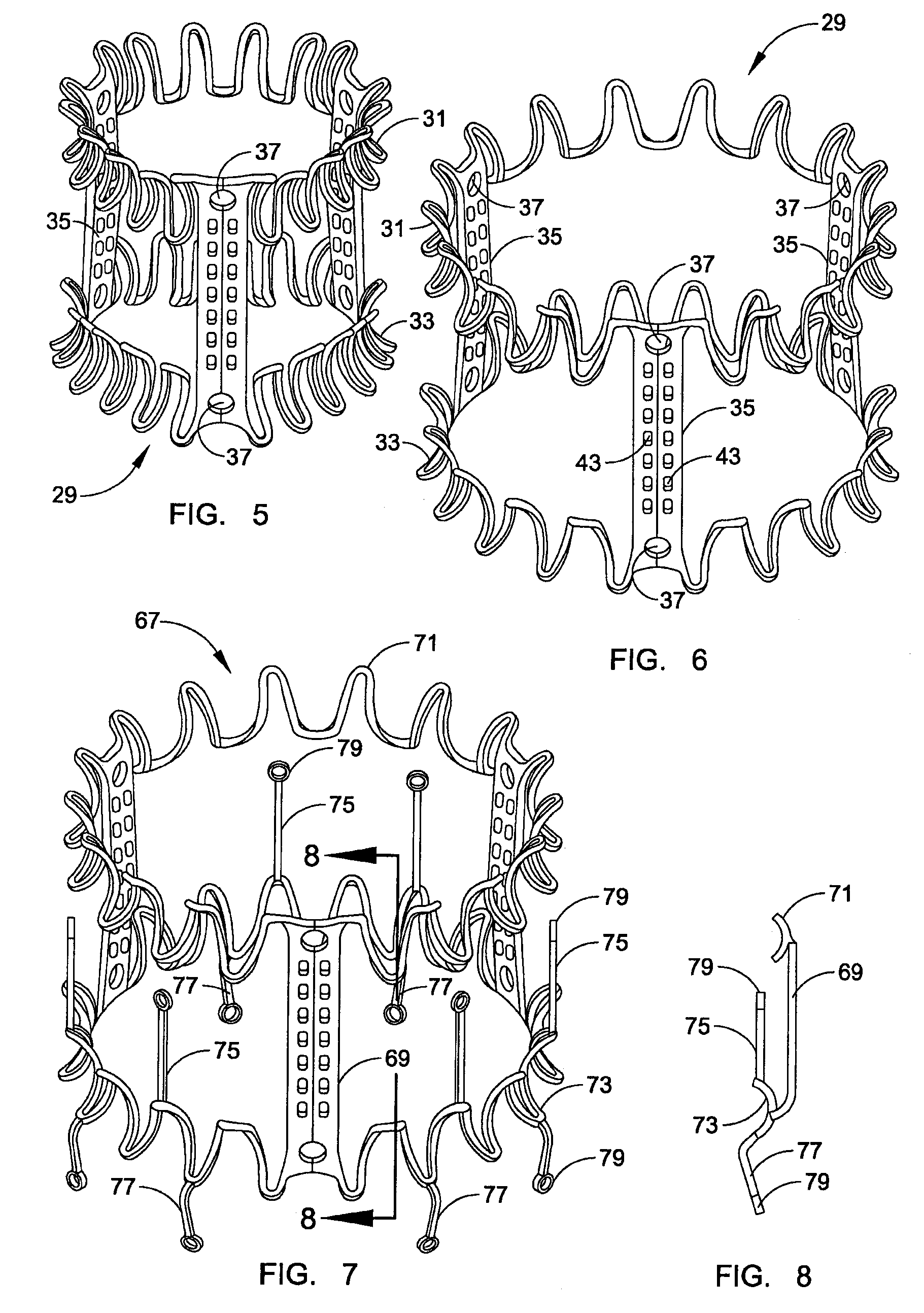
A replacement valve for implantation centrally within the orifice of a malfunctioning native heart valve. The valve is designed for minimally invasive entry through an intercostal opening in the chest of a patient and an opening in the apex of the human heart. The replacement valve includes either a separate anchor (11, 87, 111) or a combined anchor (67) that folds around the malfunctioning native valve leaflets, sandwiching them in a manner so as to securely anchor the replacement valve in a precise, desired location.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
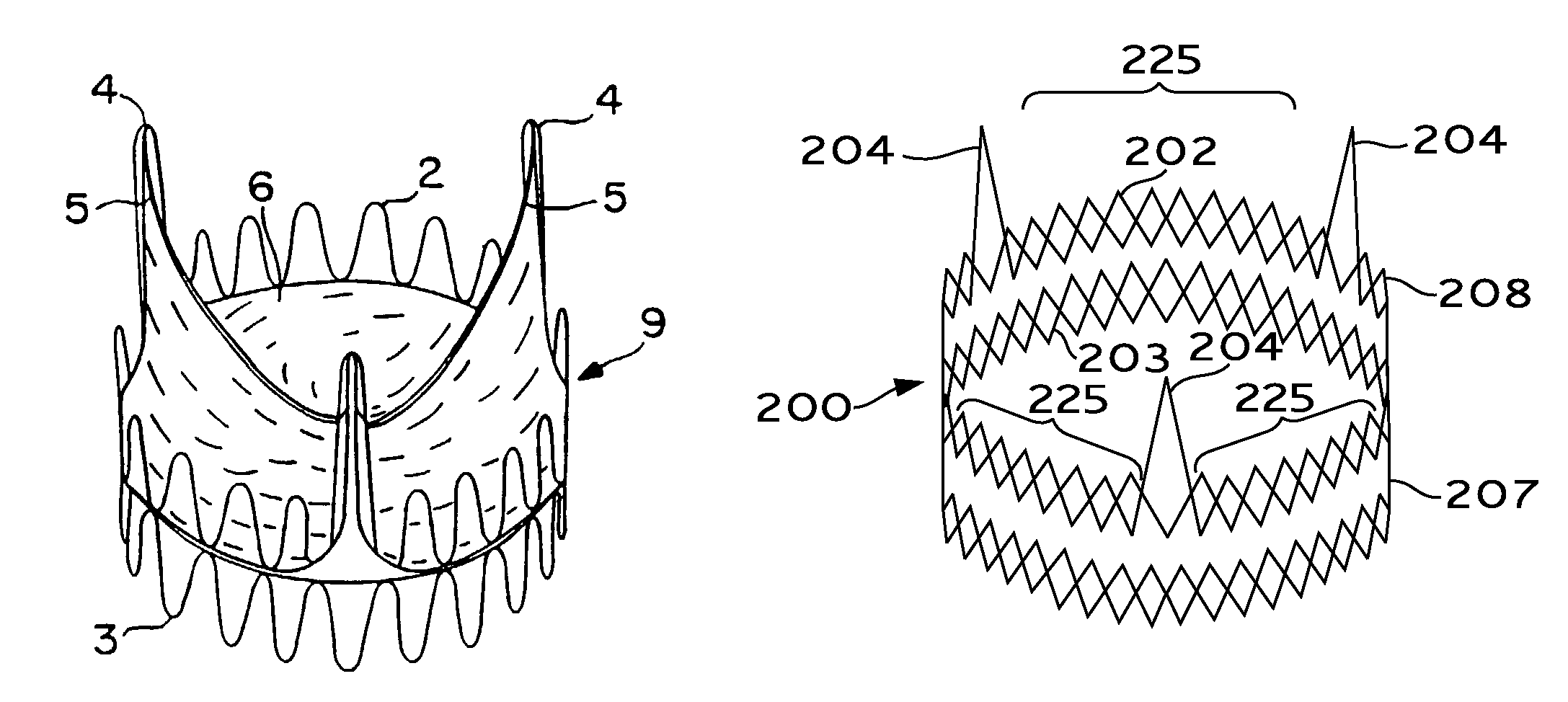
Valve prosthesis for implantation in the body and a catheter for implanting such valve prosthesis
InactiveUS7618446B2Inhibition of contractionEasy to shapeStentsBalloon catheterSurgical operationThoracic structure
A valve prosthesis for implantation in the body by use of a catheter includes a stent made from an expandable cylinder-shaped thread structure including several spaced apices. The elastically collapsible valve is mounted on the stent as the commissural points of the valve are secured to the projecting apices. The valve prosthesis can be compressed around balloons of the balloon catheter and inserted in a channel, for instance, in the aorta. When the valve prosthesis is placed correctly, the balloons are inflated to expand the stent and wedge it against the wall of the aorta. The balloons are provided with beads to ensure a steady fastening of the valve prosthesis on the balloons during insertion and expansion. The valve prosthesis and the balloon catheter make it possible to insert a cardiac valve prosthesis without a surgical operation involving opening the thoracic cavity.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Apparatus and methods of bioelectrical impedance analysis of blood flow
InactiveUS6095987AAccurately and non-invasively and continuously measuring cardiac outputCatheterSensorsBioelectrical impedance analysisCardiac pacemaker electrode
Apparatus and methods are provided for monitoring cardiac output using bioelectrical impedance techniques in which first and second electrodes are placed in the trachea and / or bronchus in the vicinity of the ascending aorta, while an excitation current is injected into the thorax via first and second current electrodes, so that bioelectrical impedance measurements based on the voltage drop sensed by the first and second electrodes reflect voltage changes induced primarily by blood flow dynamics, rather than respiratory or non-cardiac related physiological effects. Additional sense electrodes may be provided, either internally, or externally, for which bioelectrical impedance values may be obtained. Methods are provided for computing cardiac output from bioelectrical impedance values. Apparatus and methods are also provided so that the measured cardiac output may be used to control administration of intravenous fluids to an organism or to optimize a heart rate controlled by a pacemaker.
Owner:ECOM MED
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement
ActiveUS7837727B2Sufficient flexibilitySevere size constraintHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve replacementThoracic cavity
A replacement valve for implantation centrally within the orifice of a malfunctioning native heart valve. The valve is designed for minimally invasive entry through an intercostal opening in the chest of a patient and an opening in the apex of the human heart. The replacement valve includes either a separate anchor (11, 87, 111) or a combined anchor (67) that folds around the malfunctioning native valve leaflets, sandwiching them in a manner so as to securely anchor the replacement valve in a precise, desired location.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Locking mechanisms for fixation devices and methods of engaging tissue
InactiveUS20060020275A1Reduce frictional contactRestrict movementSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringThoracic cavity
Devices, systems and methods are provided for tissue approximation and repair at treatment sites. In particular, fixation devices are provided comprising a pair of elements each having a first end, a free end opposite the first end, and an engagement surface therebetween for engaging the tissue, the first ends being moveable between an open position wherein the free ends are spaced apart and a closed position wherein the free ends are closer together with the engagement surfaces generally facing each other. The fixation devices also include a locking mechanism coupled to the elements for locking the elements in place. The devices, systems and methods of the invention will find use in a variety of therapeutic procedures, including endovascular, minimally-invasive, and open surgical procedures, and can be used in various anatomical regions, including the abdomen, thorax, cardiovascular system, heart, intestinal tract, stomach, urinary tract, bladder, lung, and other organs, vessels, and tissues. The invention is particularly useful in those procedures requiring minimally-invasive or endovascular access to remote tissue locations, where the instruments utilized must negotiate long, narrow, and tortuous pathways to the treatment site.
Owner:EVALVE
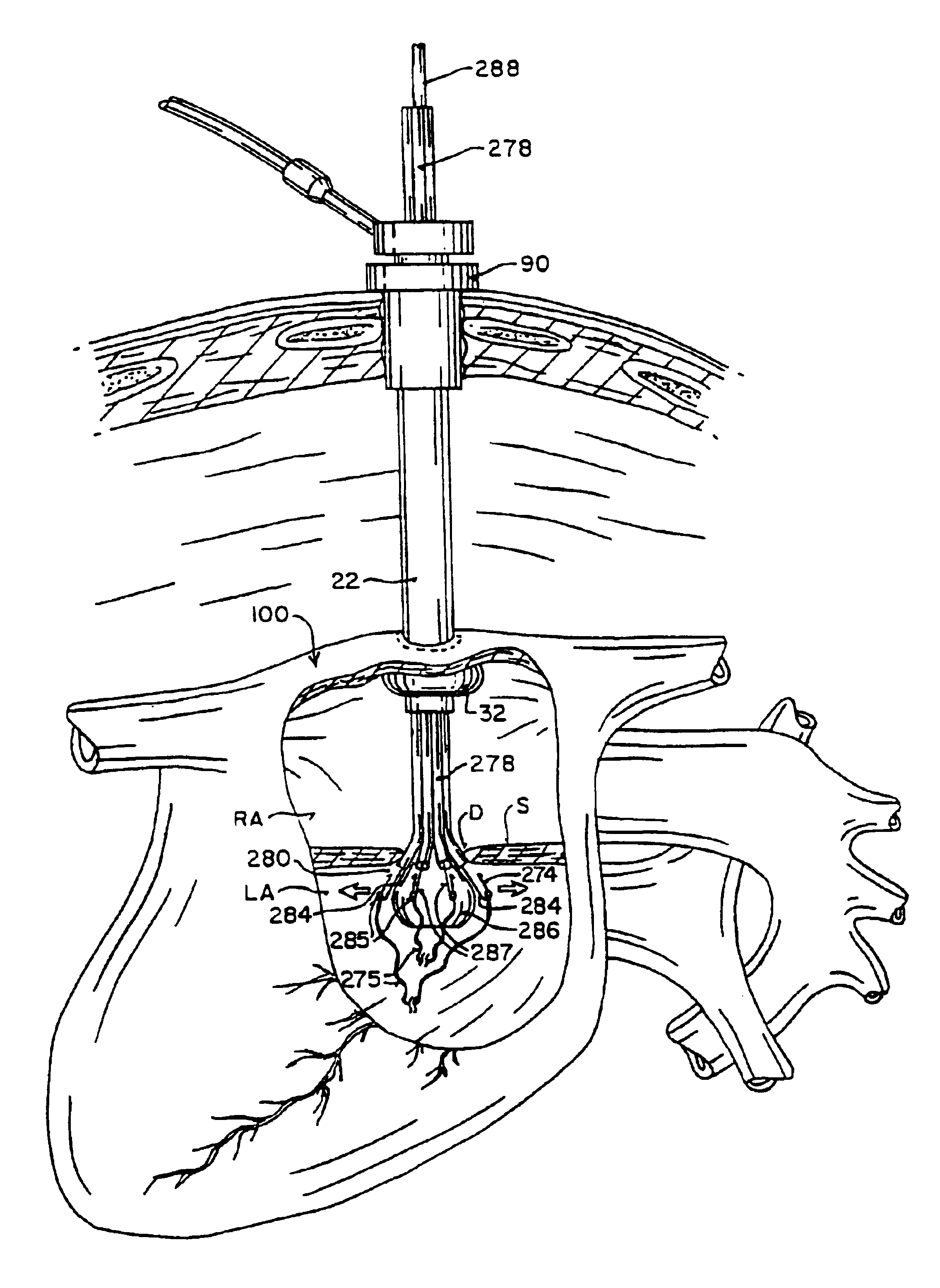
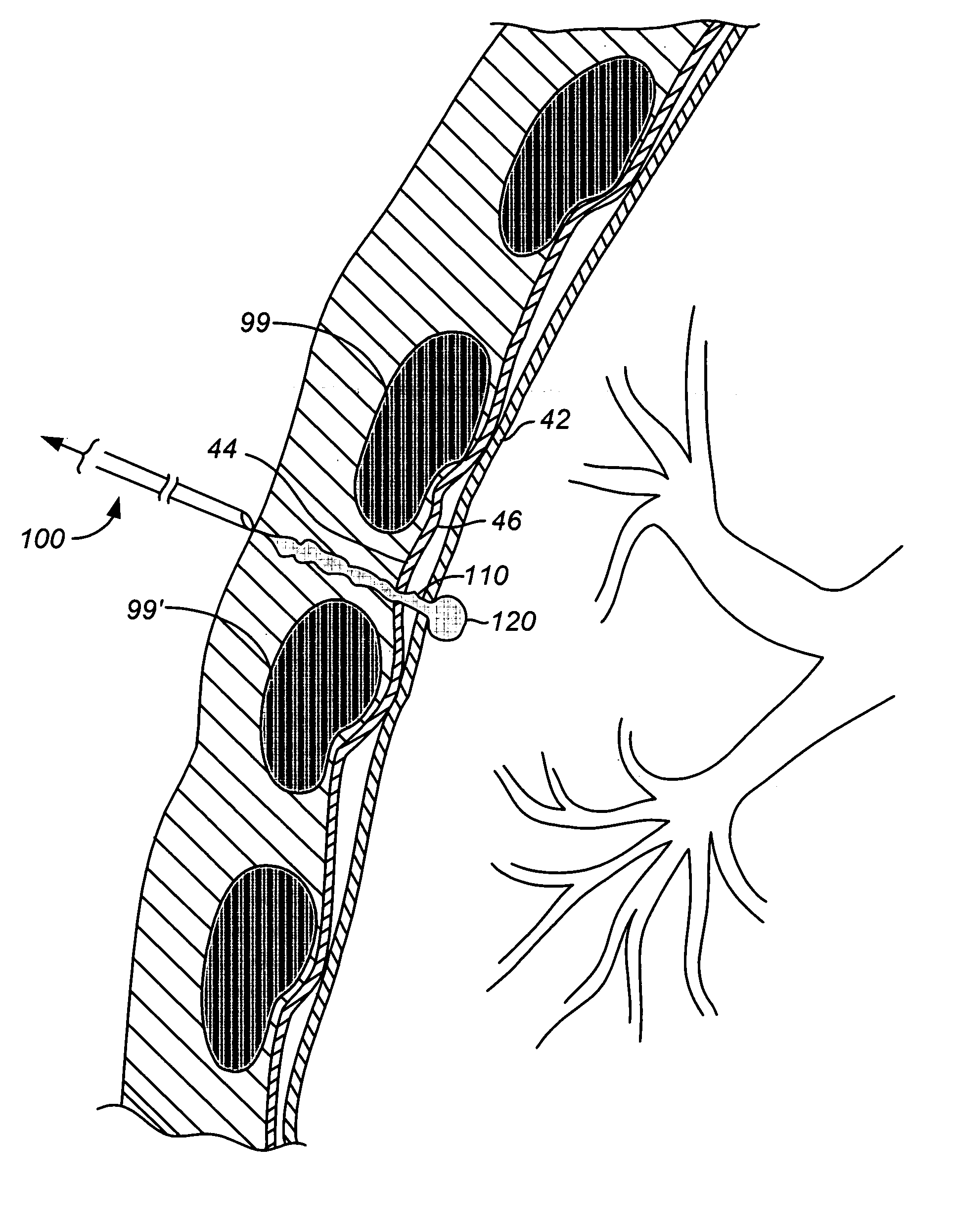
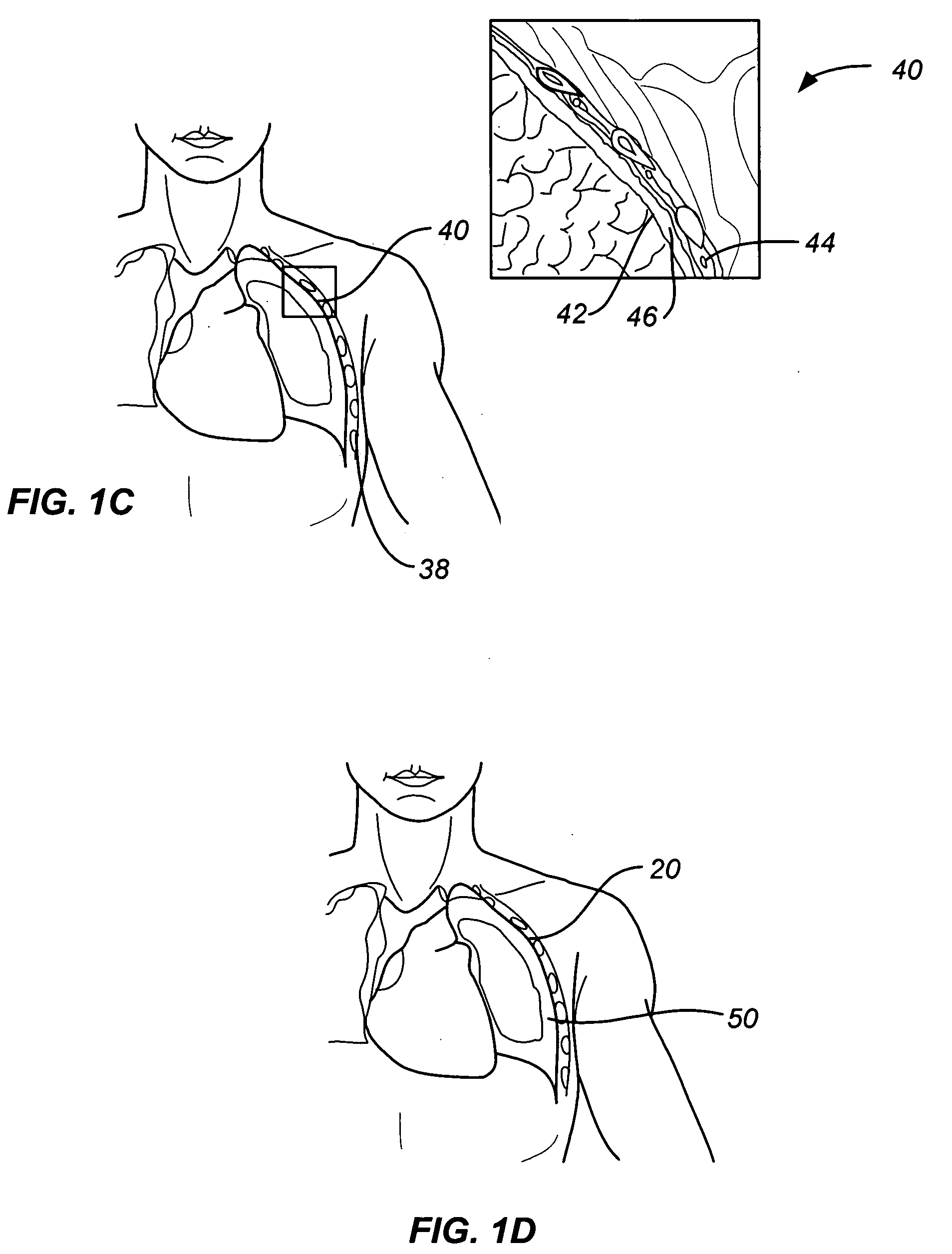
Method and apparatus for thoracoscopic intracardiac procedures
InactiveUS6955175B2Facilitate responsive and precise positionabilitySuture equipmentsElectrotherapyDefect repairThoracic cavity
Devices, systems, and methods are provided for accessing the interior of the heart and performing procedures therein while the heart is beating. In one embodiment, a tubular access device having an inner lumen is provided for positioning through a penetration in a muscular wall of the heart, the access device having a means for sealing within the penetration to inhibit leakage of blood through the penetration. The sealing means may comprise a balloon or flange on the access device, or a suture placed in the heart wall to gather the heart tissue against the access device. An obturator is removably positionable in the inner lumen of the access device, the obturator having a cutting means at its distal end for penetrating the muscular wall of the heart. The access device is preferably positioned through an intercostal space and through the muscular wall of the heart. Elongated instruments may be introduced through the tubular access device into an interior chamber of the heart to perform procedures such as septal defect repair and electrophysiological mapping and ablation. A method of septal defect repair includes positioning a tubular access device percutaneously through an intercostal space and through a penetration in a muscular wall of the heart, passing one or more instruments through an inner lumen of the tubular access device into an interior chamber of the heart, and using the instruments to close the septal defect. Devices and methods for closing the septal defect with either sutures or with patch-type devices are disclosed.
Owner:STEVENS JOHN H +4
Biphasic waveform for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathorasic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Treatment for patient with congestive heart failure
Owner:TRANSCARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
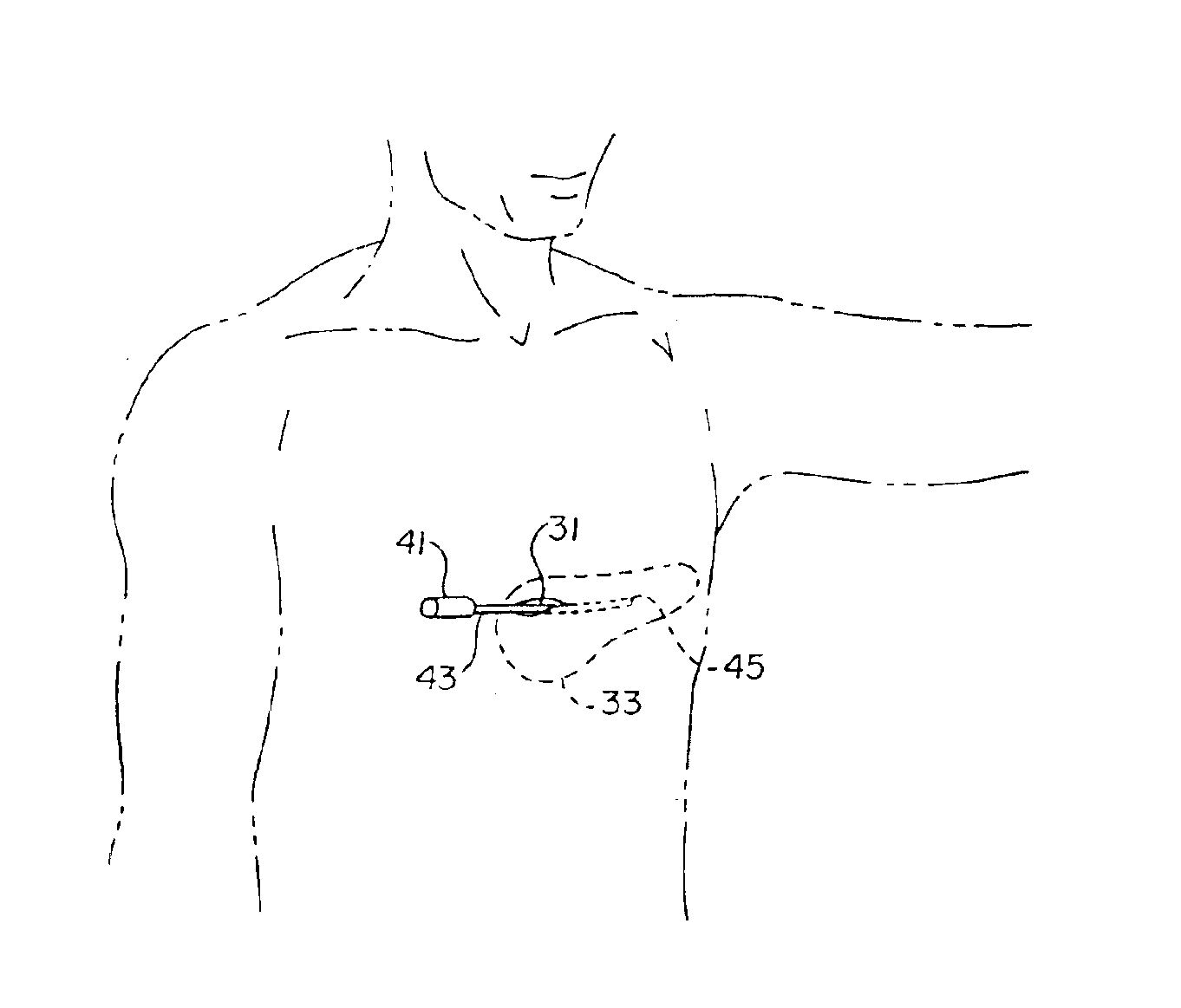
Method of insertion and implantation of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator canisters
InactiveUS6866044B2DiagnosticsHeart defibrillatorsThoracic cavityImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator
One embodiment of the present invention provides a method of inserting an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator within a patient, the method including the steps of providing a cardioverter-defibrillator canister having at least a portion of the cardioverter-defibrillator canister being non planar to maintain the cardioverter-defibrillator canister in a predetermined relationship with respect to a patient's heart, subcutaneously over a patient's ribcage; making a single incision into the patient; and advancing the cardioverter-defibrillator canister through the single incision and subcutaneously over the patient's ribcage.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Methods and systems for ultrasound imaging of the heart from the pericardium
InactiveUS20050203410A1Low costOptimize locationSurgeryHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesUltrasound imagingThoracic structure
A peritoneal ultrasound imager includes an elongated body less than about 20 inches in length that is adapted to be inserted through a cannula into or near the pericardium space, and an ultrasound transducer array at one end of the body that is suitable for ultrasound echocardiography. The cannula and ultrasound imager may be of a single piece construction. A method for imaging the heart includes introducing a cannula into the wall of a patient's chest, inserting the elongated body into the cannula, moving the inserted elongated body to a position near the heart, and imaging the heart with ultrasound echo.
Owner:EP MEDSYST
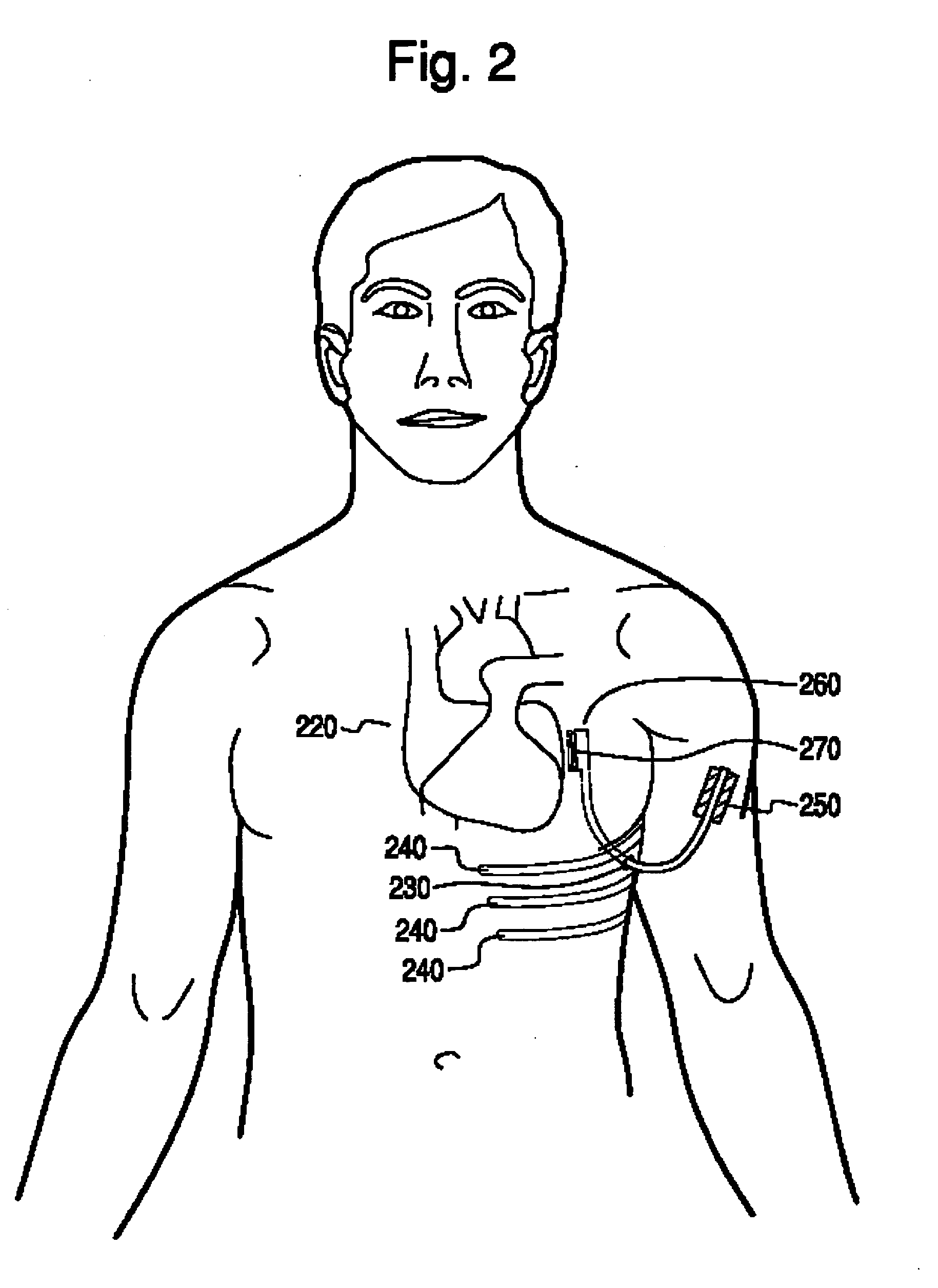
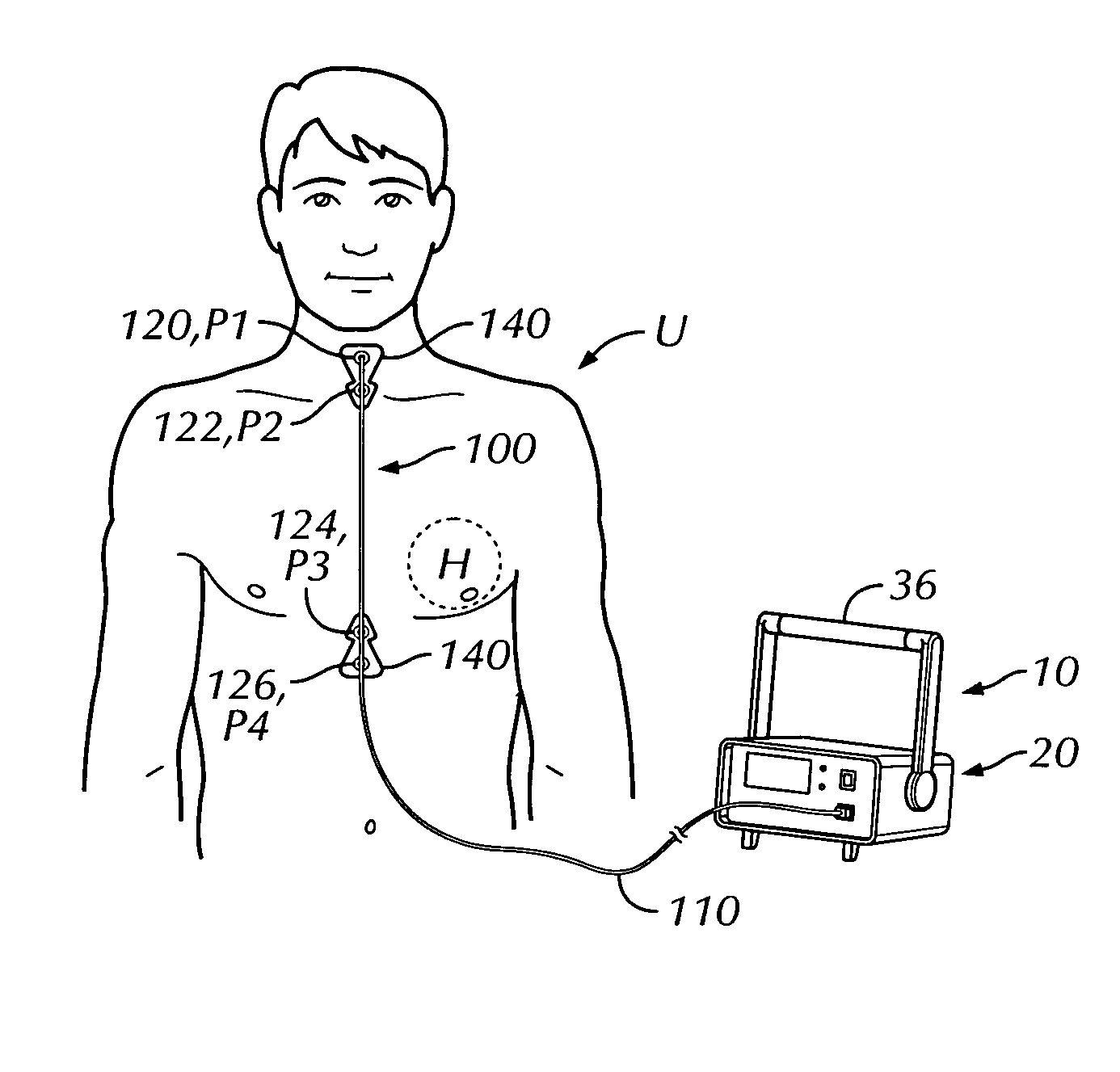
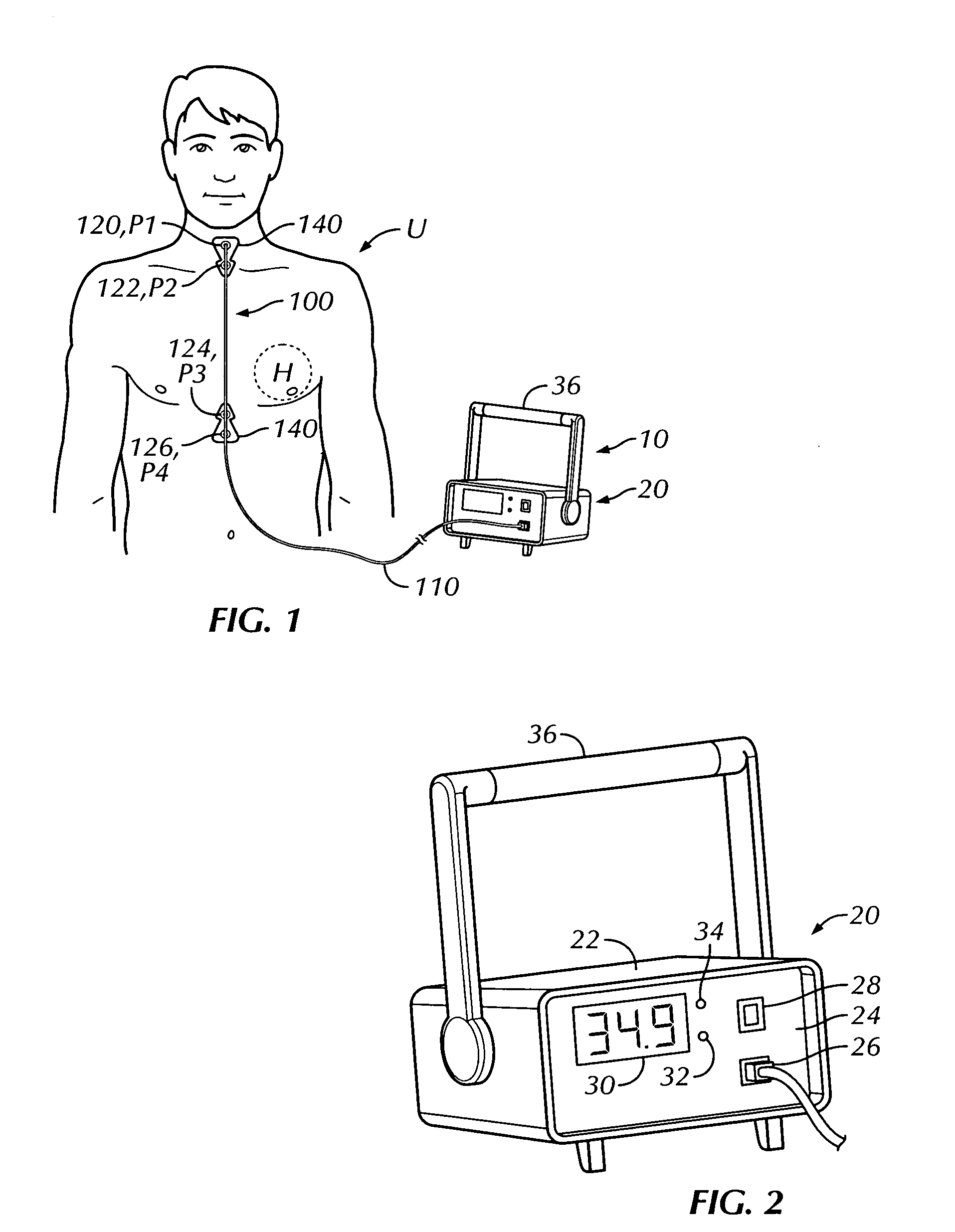
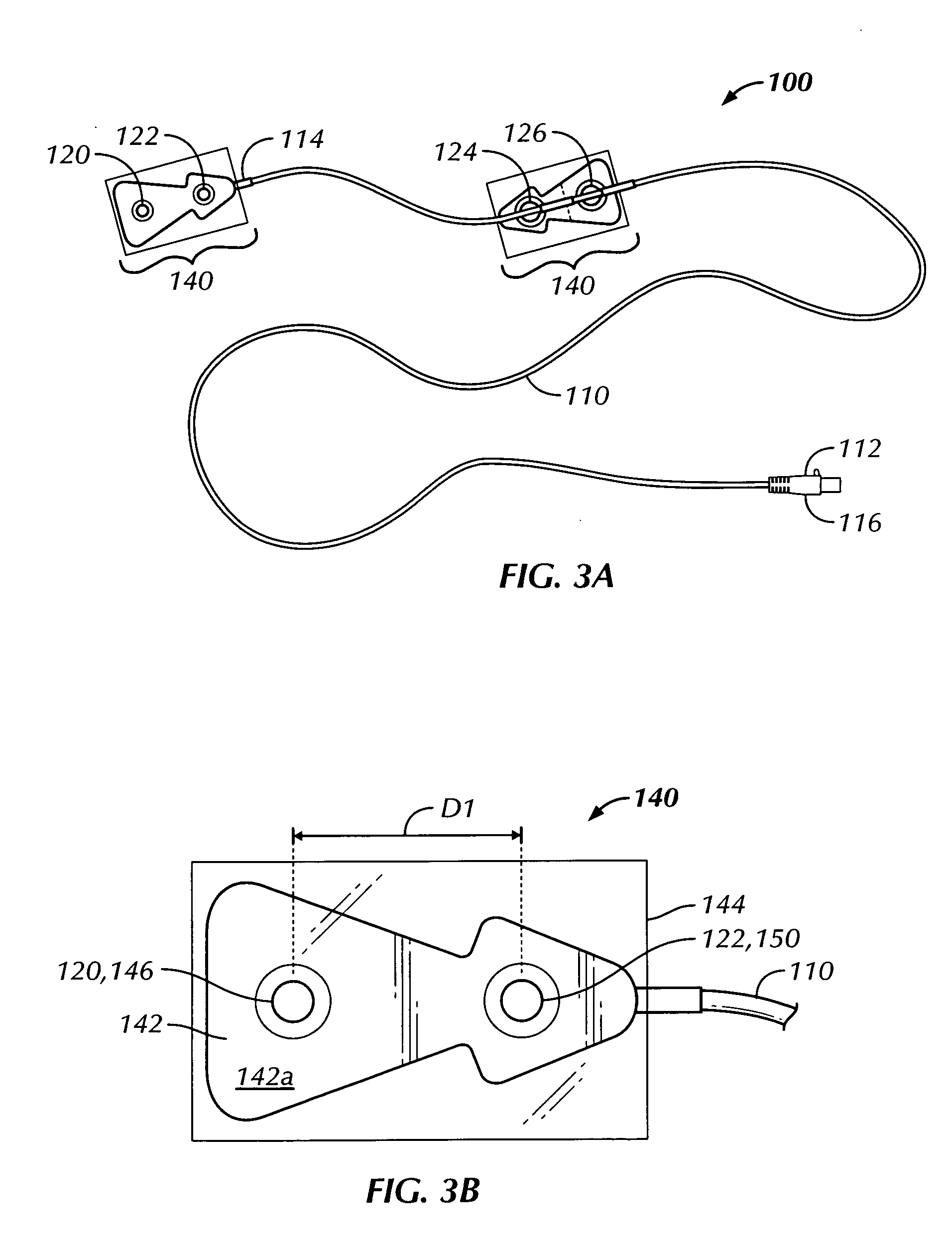
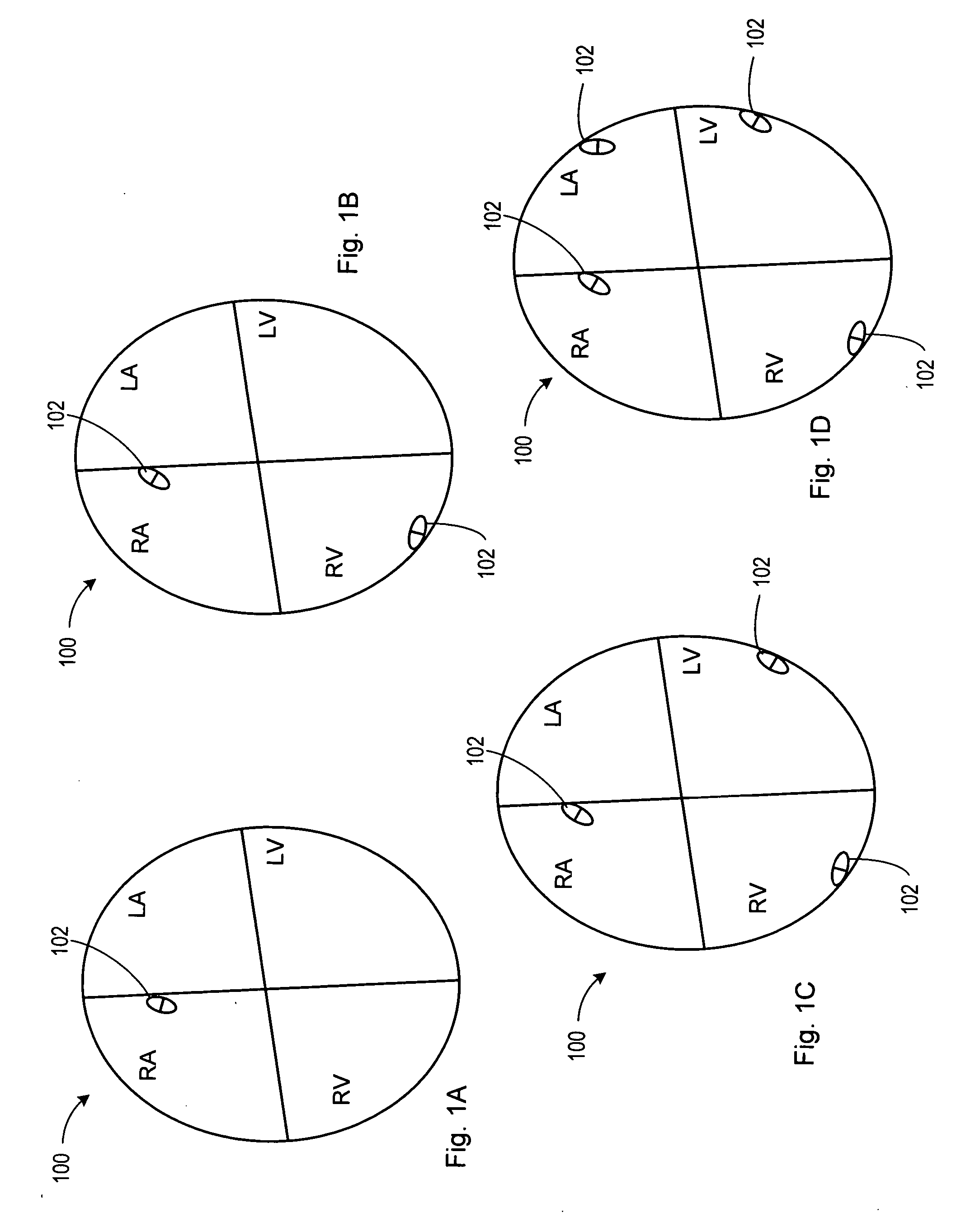
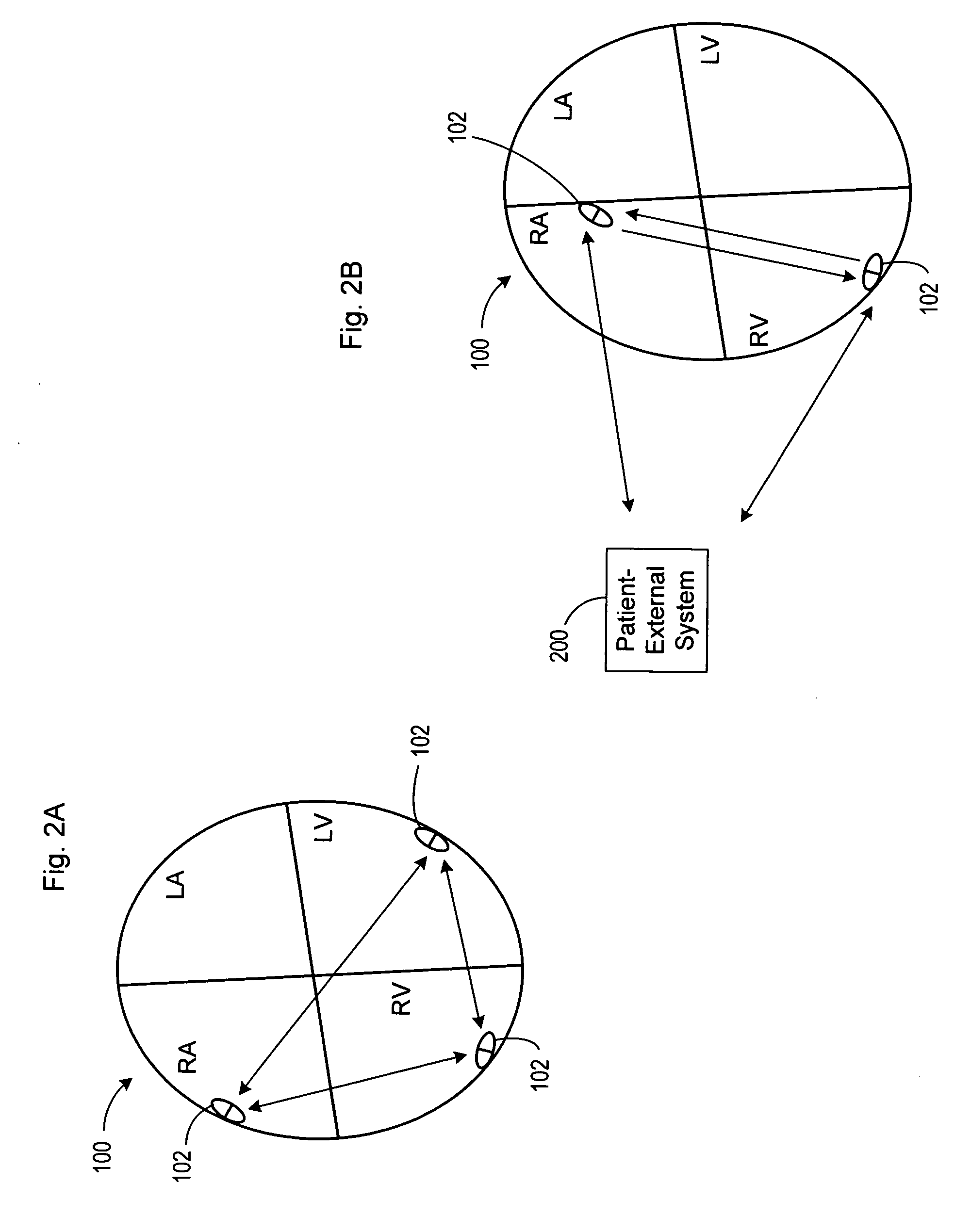
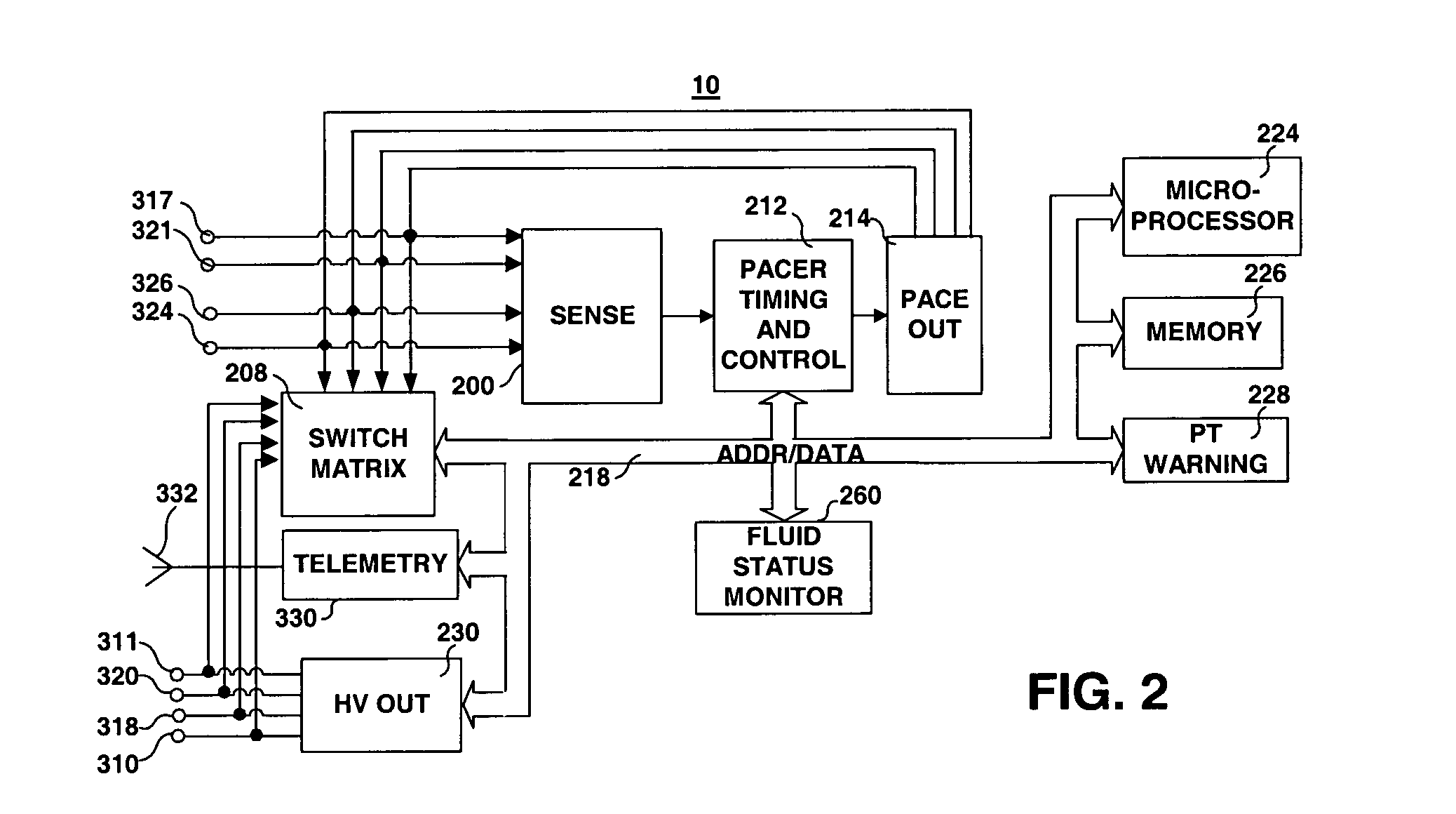
Thoracic impedance monitor and electrode array and method of use
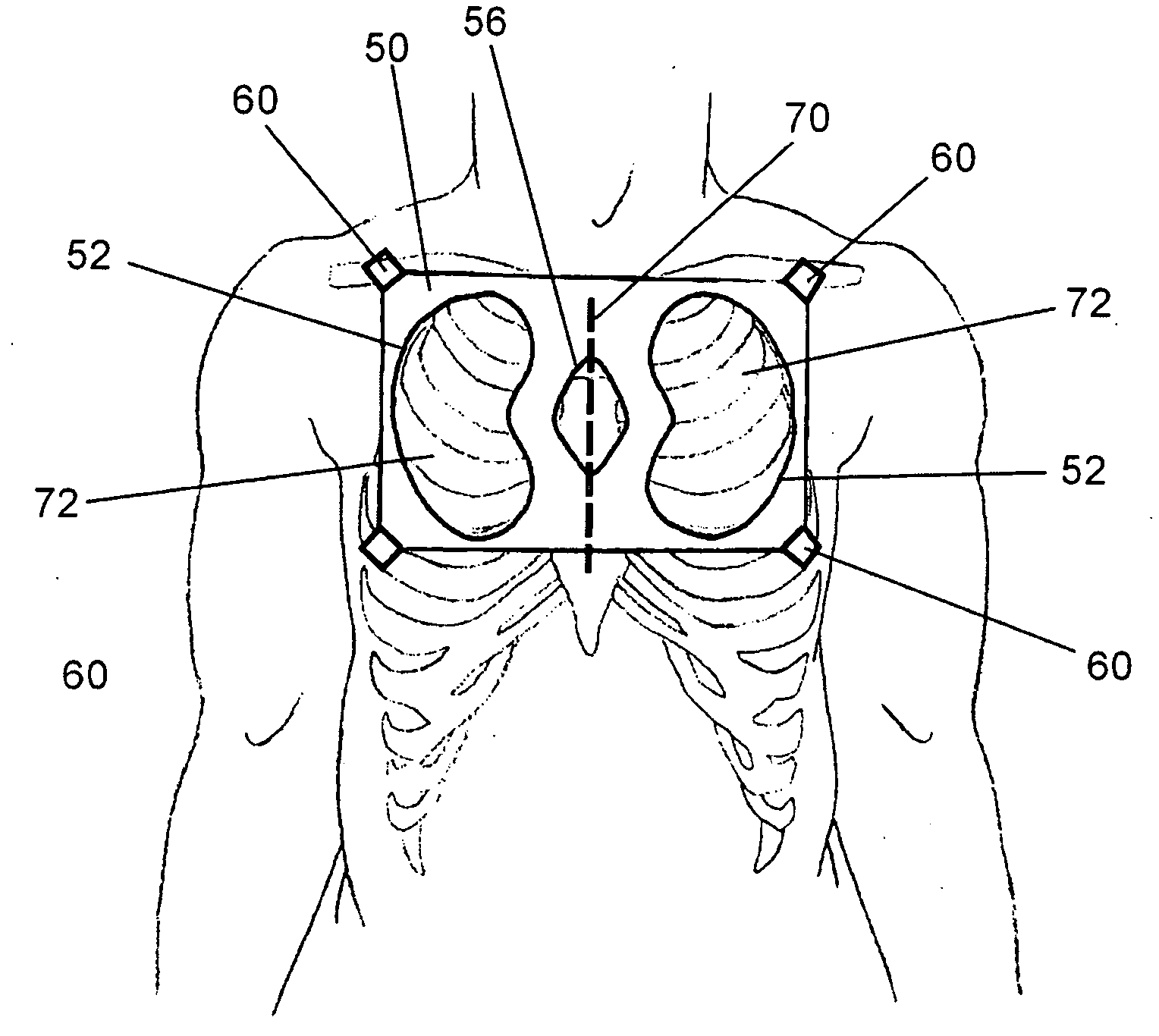
A portable thoracic impedance monitor for monitoring thoracic fluid levels, an electrode array assembly having a single linear electrode array lead with first, second, third, and fourth electrodes arranged sequentially and axially along the linear electrode array lead, and a method of use of the thoracic impedance monitor. A measurement of the user's thoracic impedance is obtained by connecting the second electrode to the user's body at the junction of the clavicles, superior to the sternum, the third electrode to the user's body at the xyphiod-sternal junction, and the first and fourth electrodes to the user's body substantially along a centerline of the user's sternum respectively at a first pre-determined distance above the second electrode and a second predetermined distance below the third electrode, followed by initiating operation of the monitor.
Owner:CALDWELL SIMPSON LLC
Leadless cardiac stimulation device employing distributed logic
ActiveUS20060135999A1Epicardial electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesCardiac activityThoracic cavity
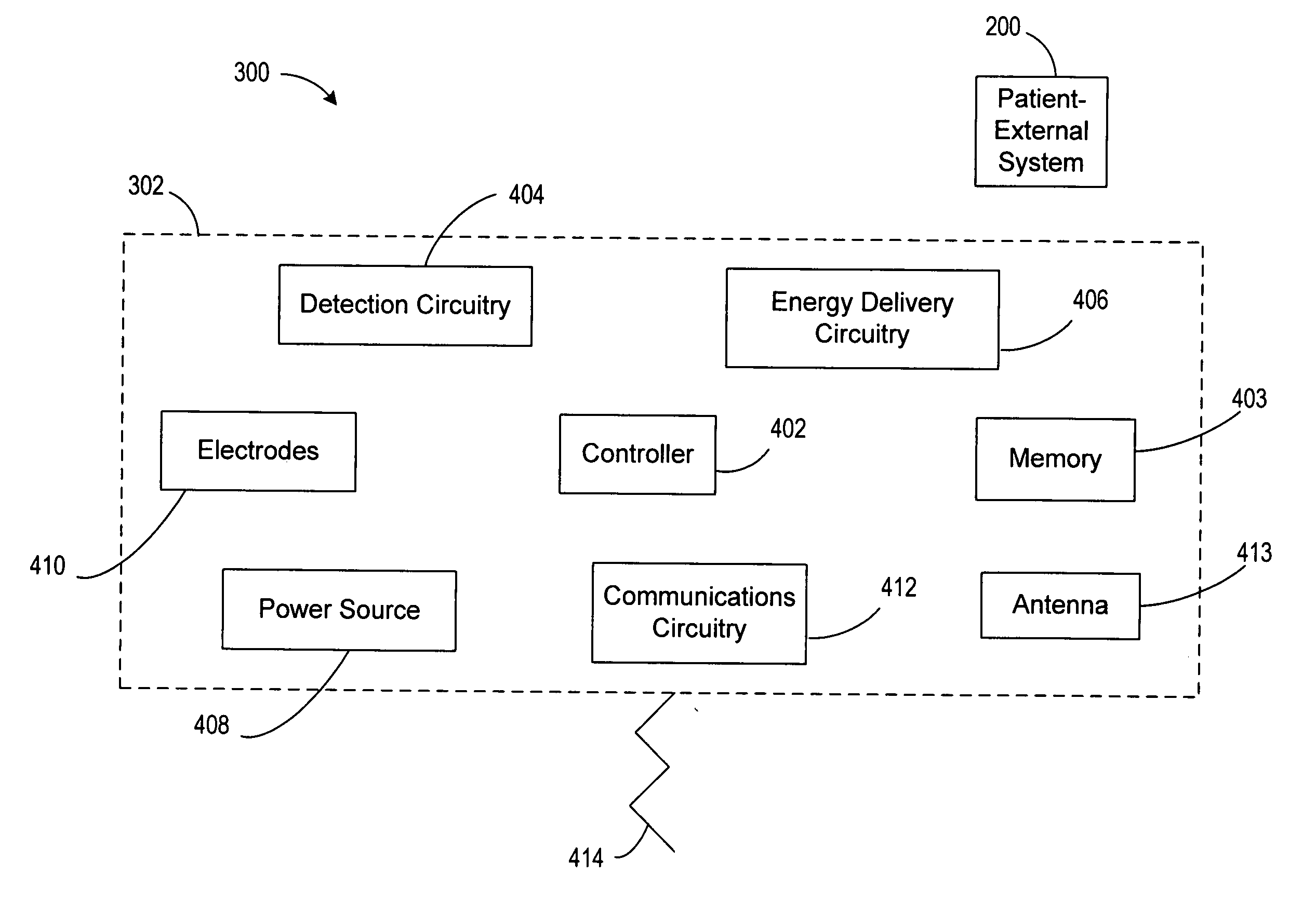
Systems and methods involve an intrathoracic cardiac stimulation device operable to provide autonomous cardiac sensing and energy delivery. The cardiac stimulation device includes a housing configured for intrathoracic placement relative to a patient's heart. A fixation arrangement of the housing is configured to affix the housing at an implant location within cardiac tissue or cardiac vasculature. An electrode arrangement supported by the housing is configured to sense cardiac activity and deliver stimulation energy to the cardiac tissue or cardiac vasculature. Energy delivery circuitry in the housing is coupled to the electrode arrangement. Detection circuitry is provided in the housing and coupled to the electrode arrangement. Communications circuitry may optionally be supported by the housing. A controller in the housing coordinates delivery of energy to the cardiac tissue or cardiac vasculature in accordance with an energy delivery protocol appropriate for the implant location.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
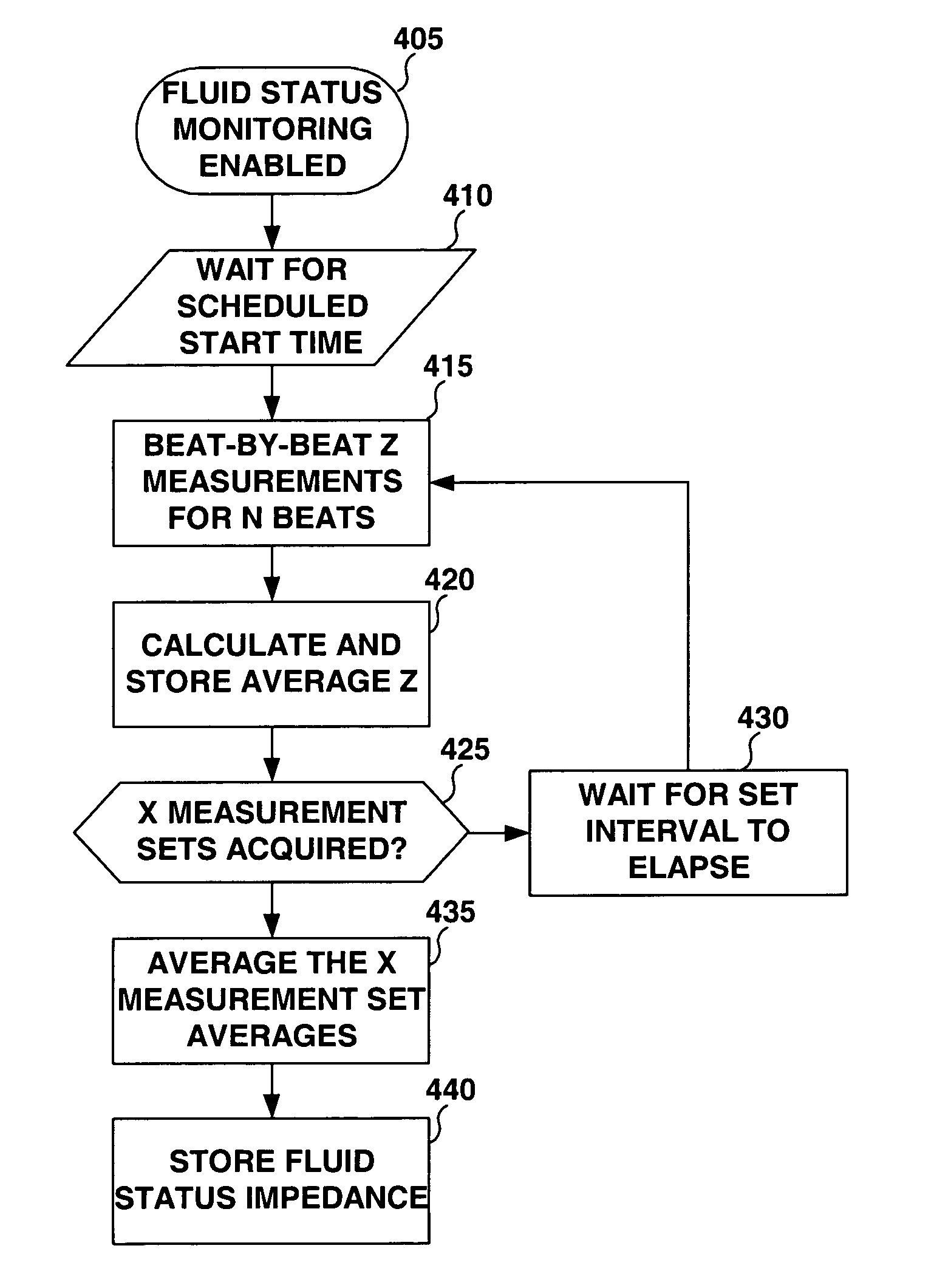
Method and apparatus for monitoring tissue fluid content for use in an implantable cardiac device
ActiveUS20050080460A1Easy to implementCancel noiseHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsThoracic FluidTissue fluid
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
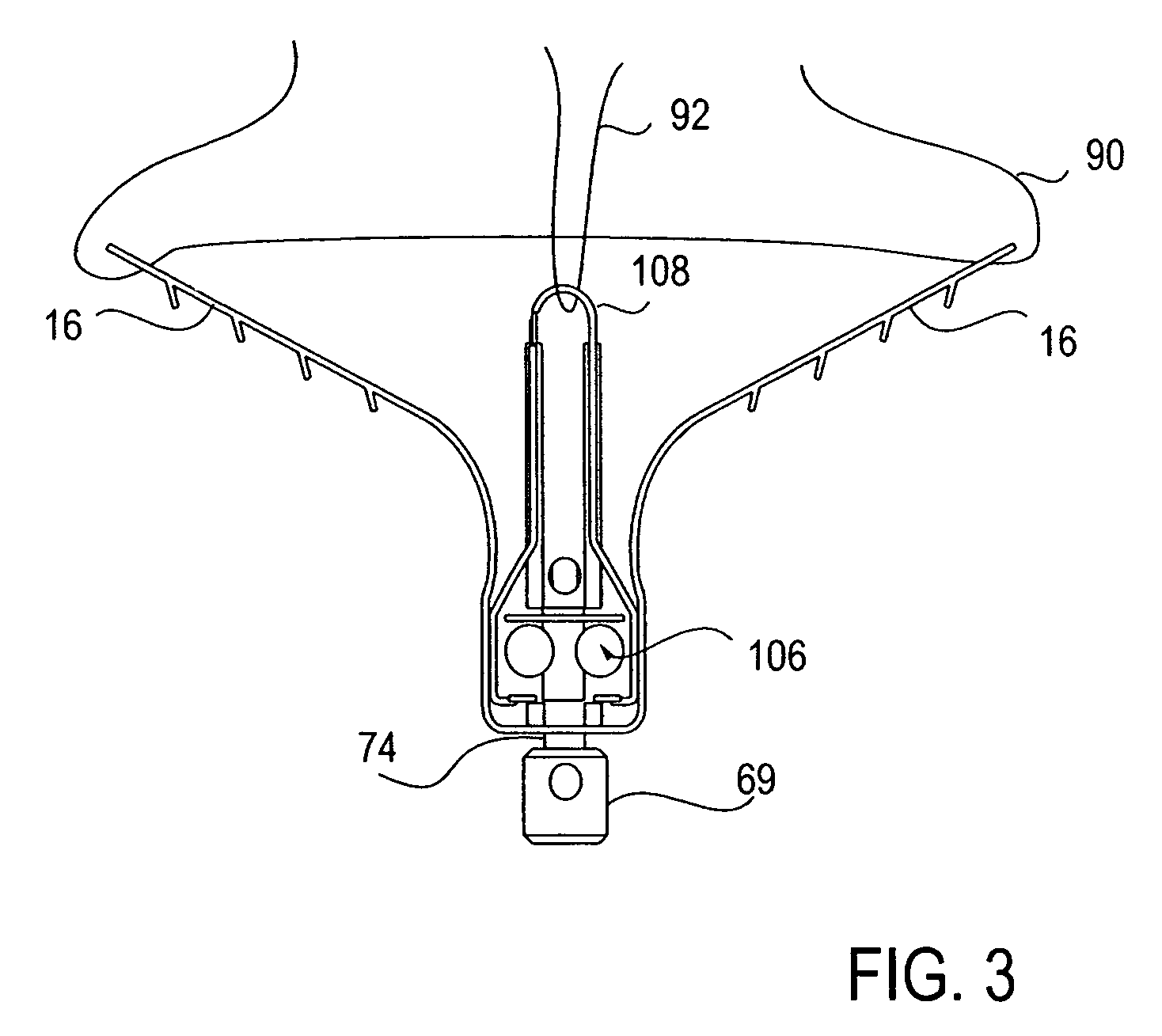
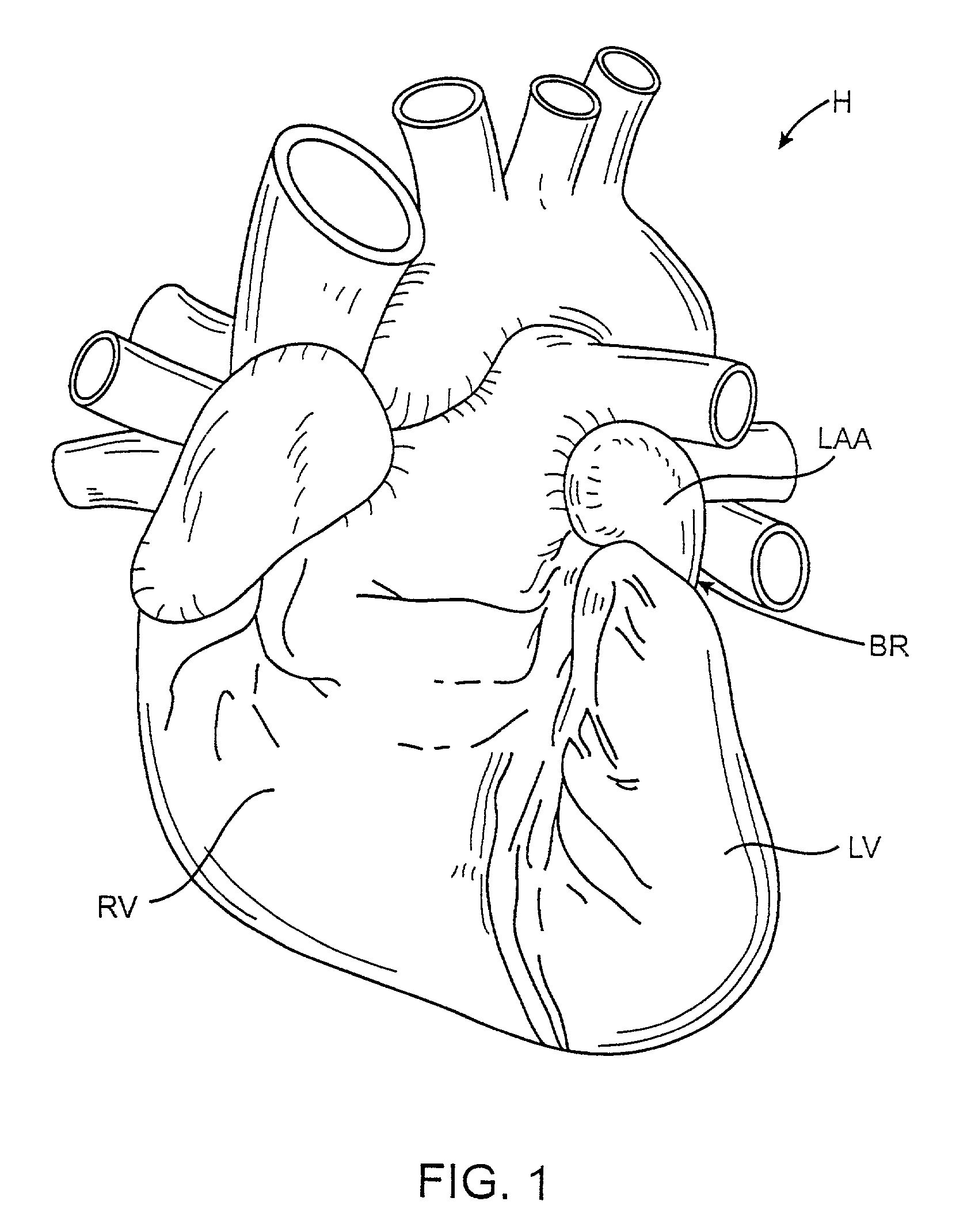
Methods and apparatus for transpericardial left atrial appendage closure
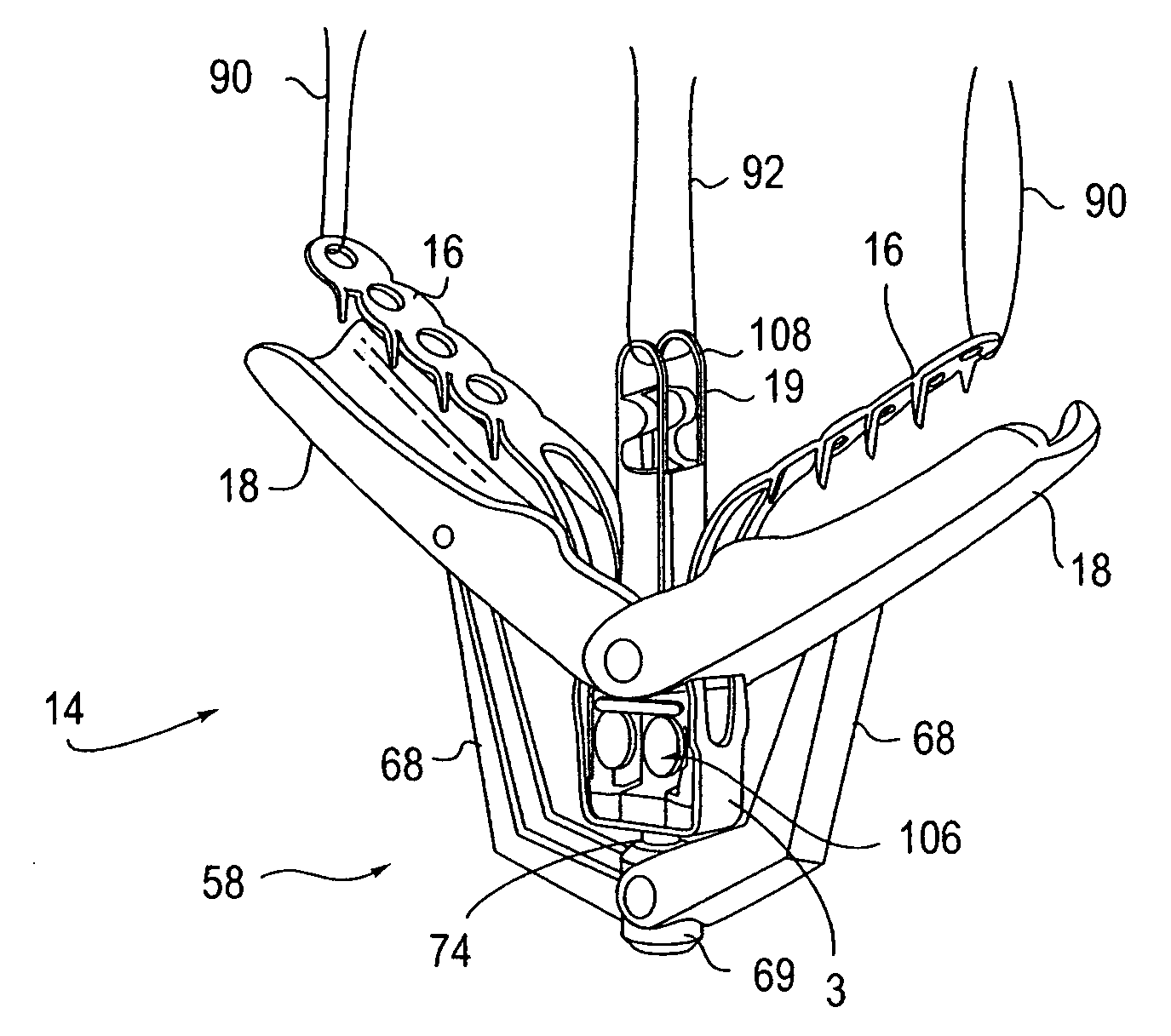
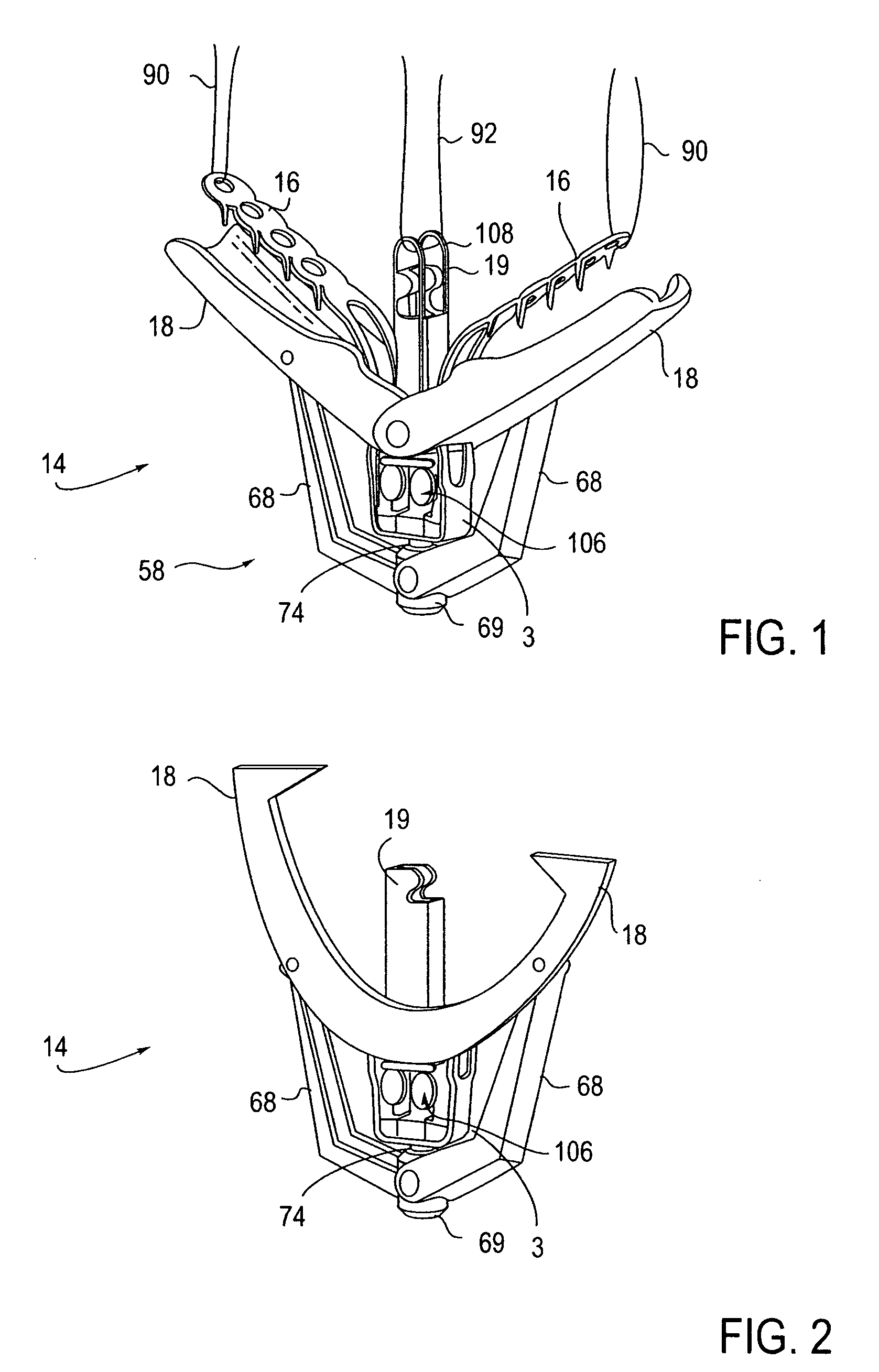
Methods and apparatus for closing a left atrial appendage are described. The methods rely on introducing a closure tool from a location beneath the rib cage, over an epicardial surface, and to the exterior of the left atrial appendage. The closure device may then be used to close the left atrial appendage, preferably at its base, by any one of a variety of techniques. A specific technique using graspers and a closing loop is illustrated.
Owner:SENTREHEART
Detection of pleural effusion using transthoracic impedance
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
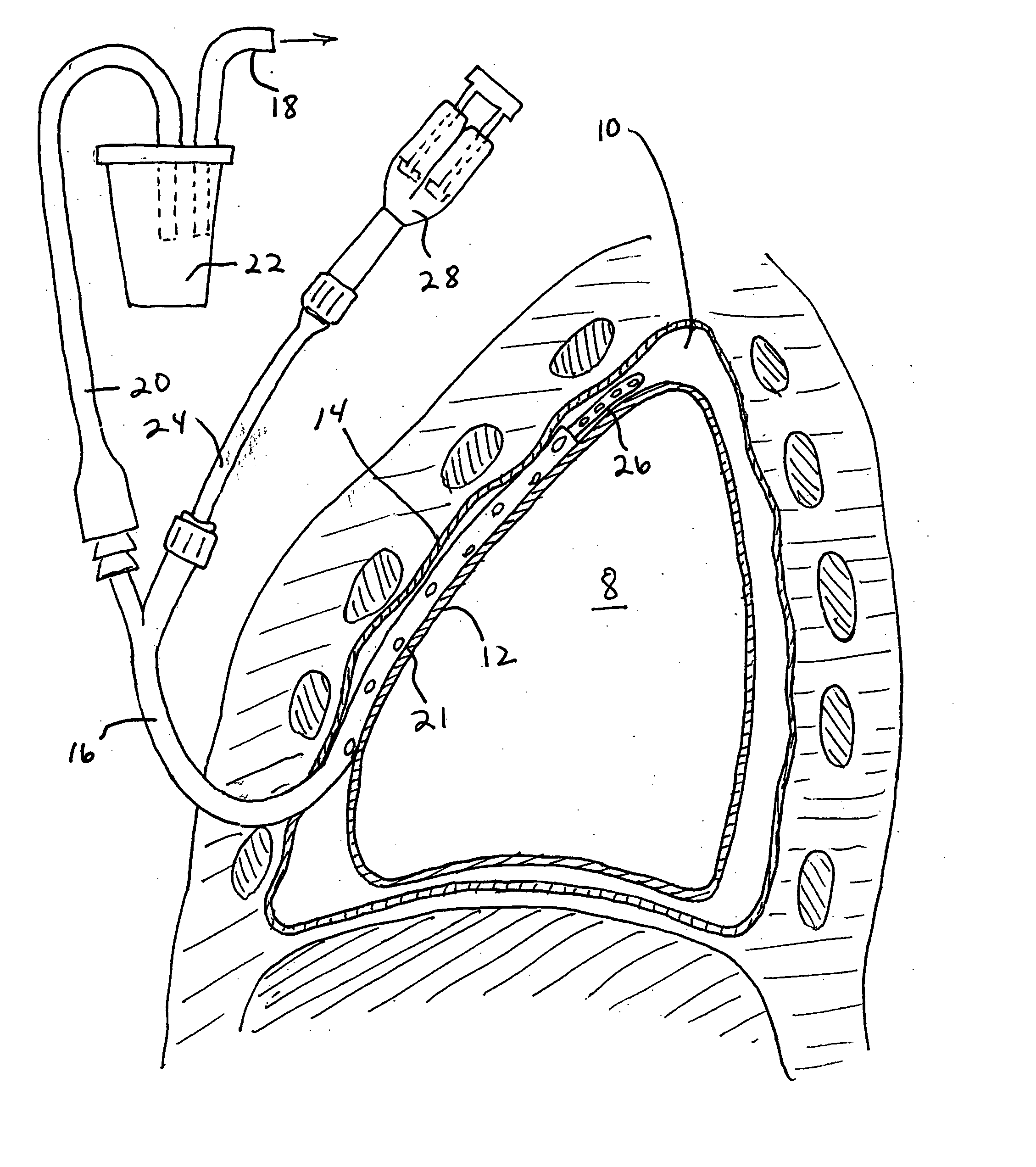
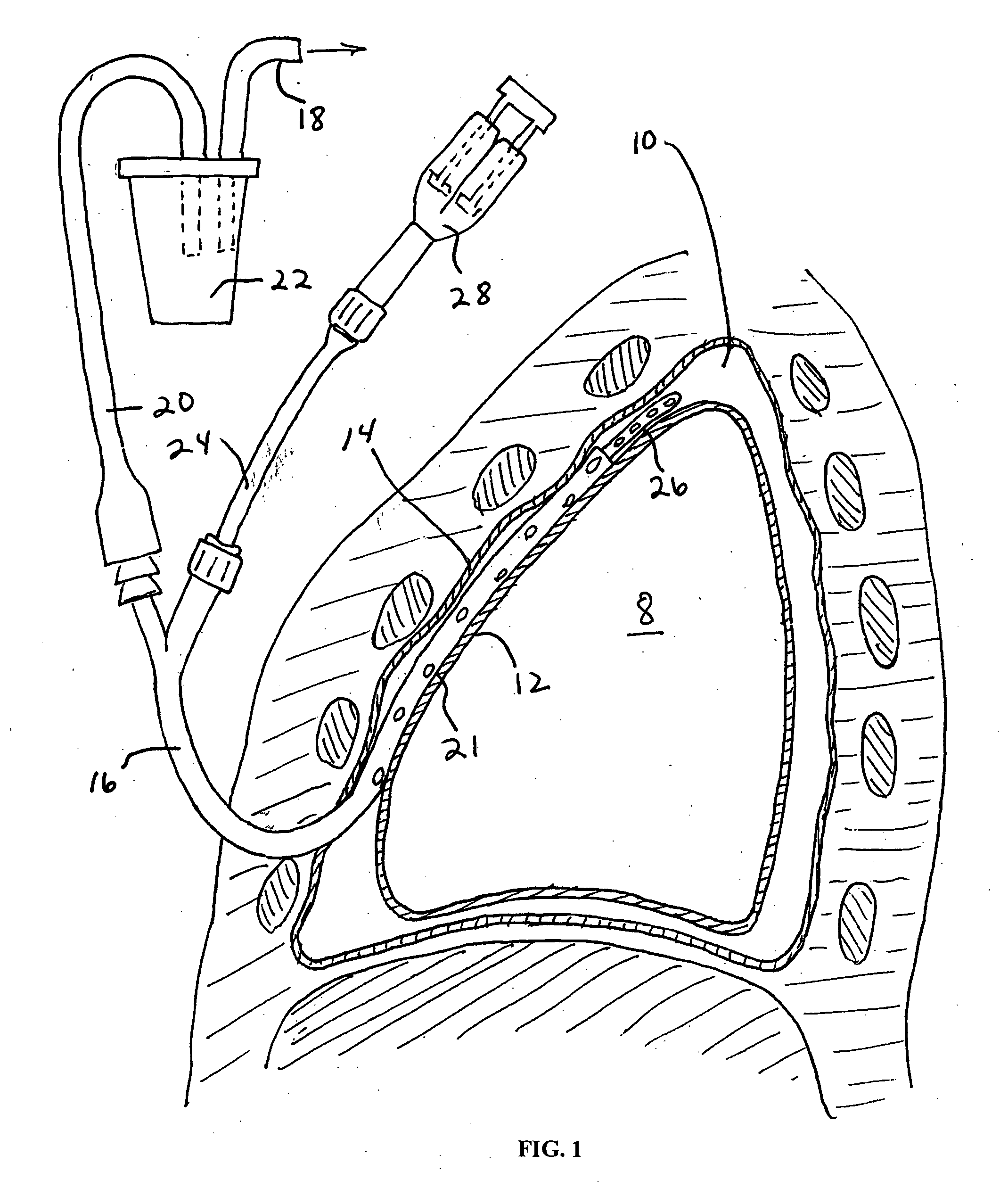
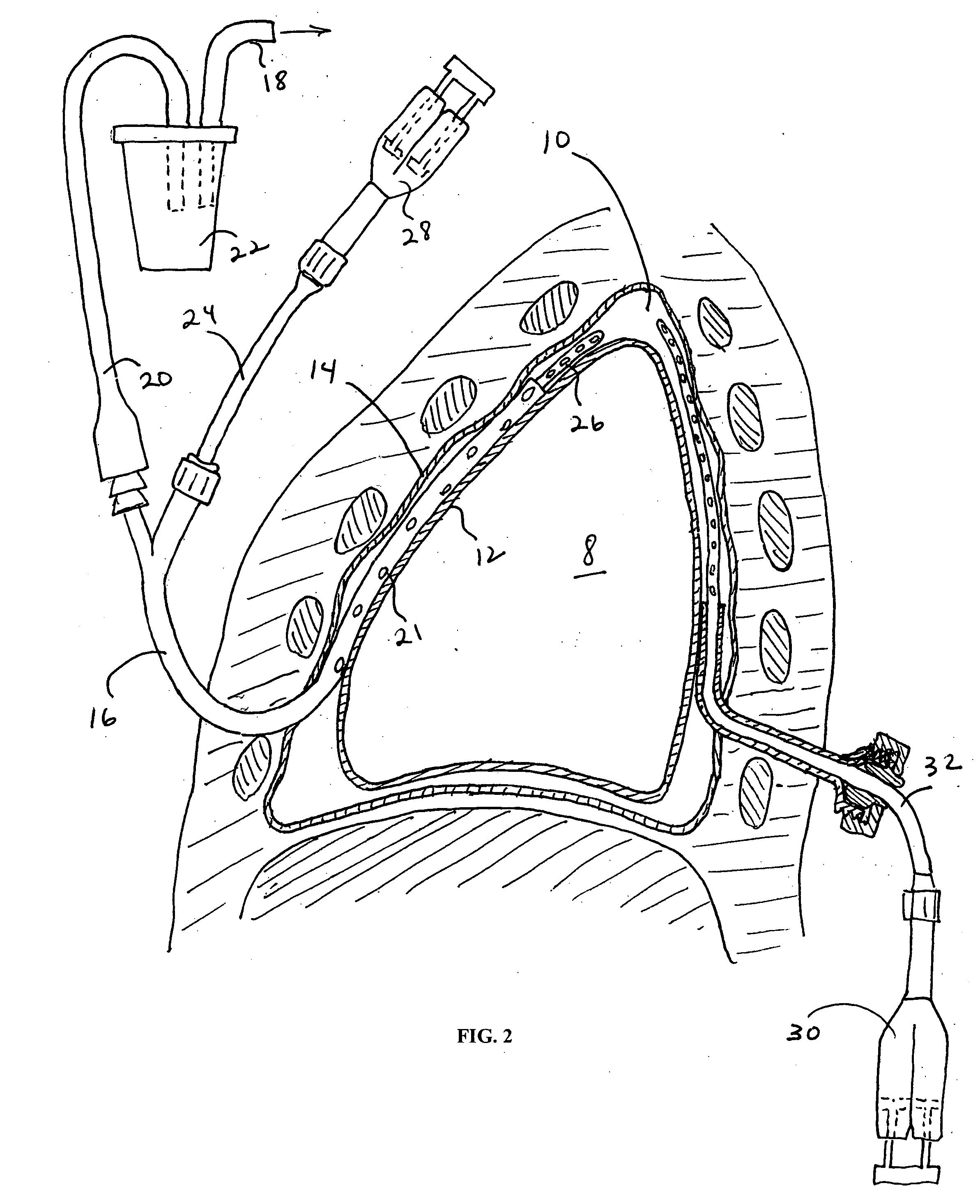
Method and apparatus for pleural drainage
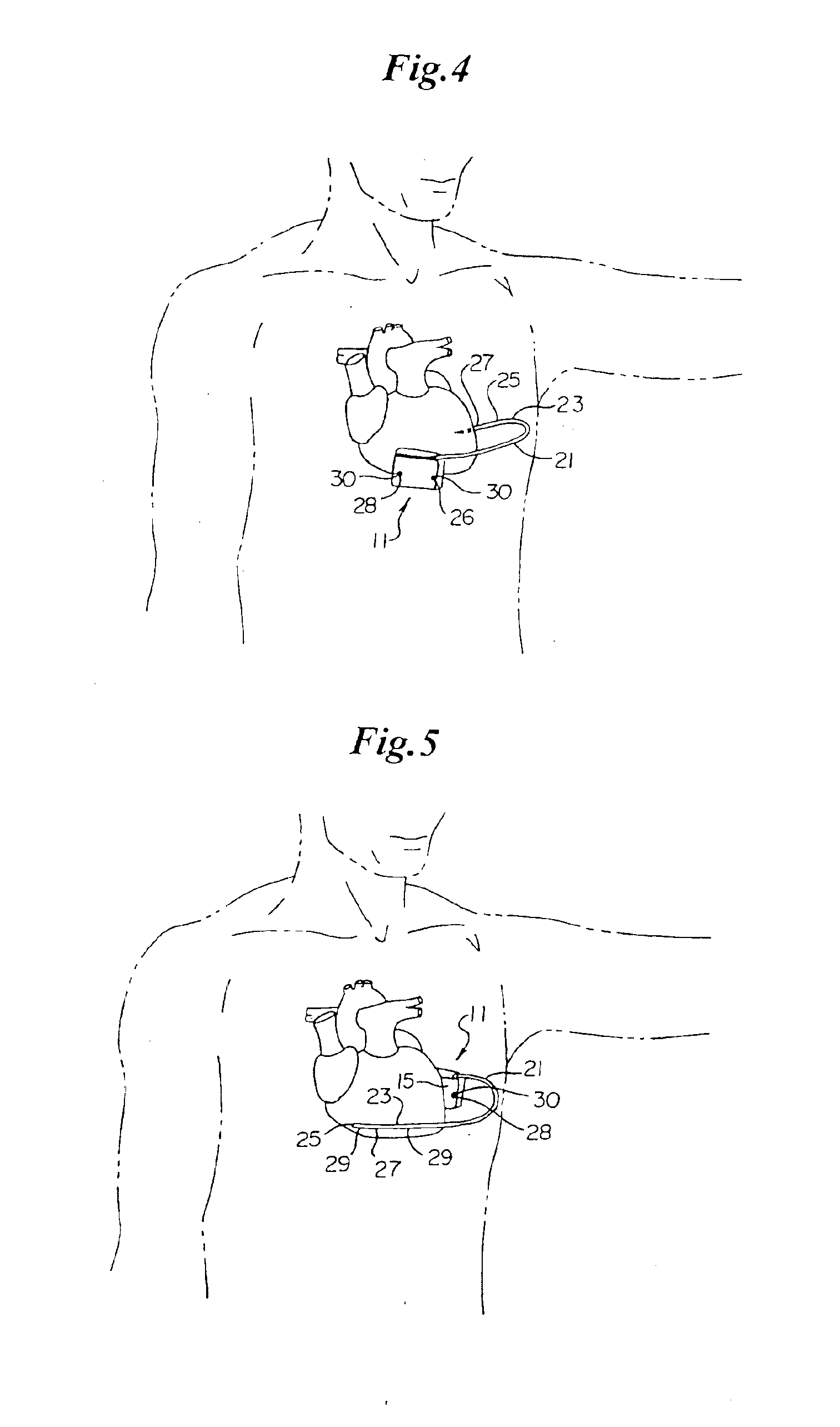
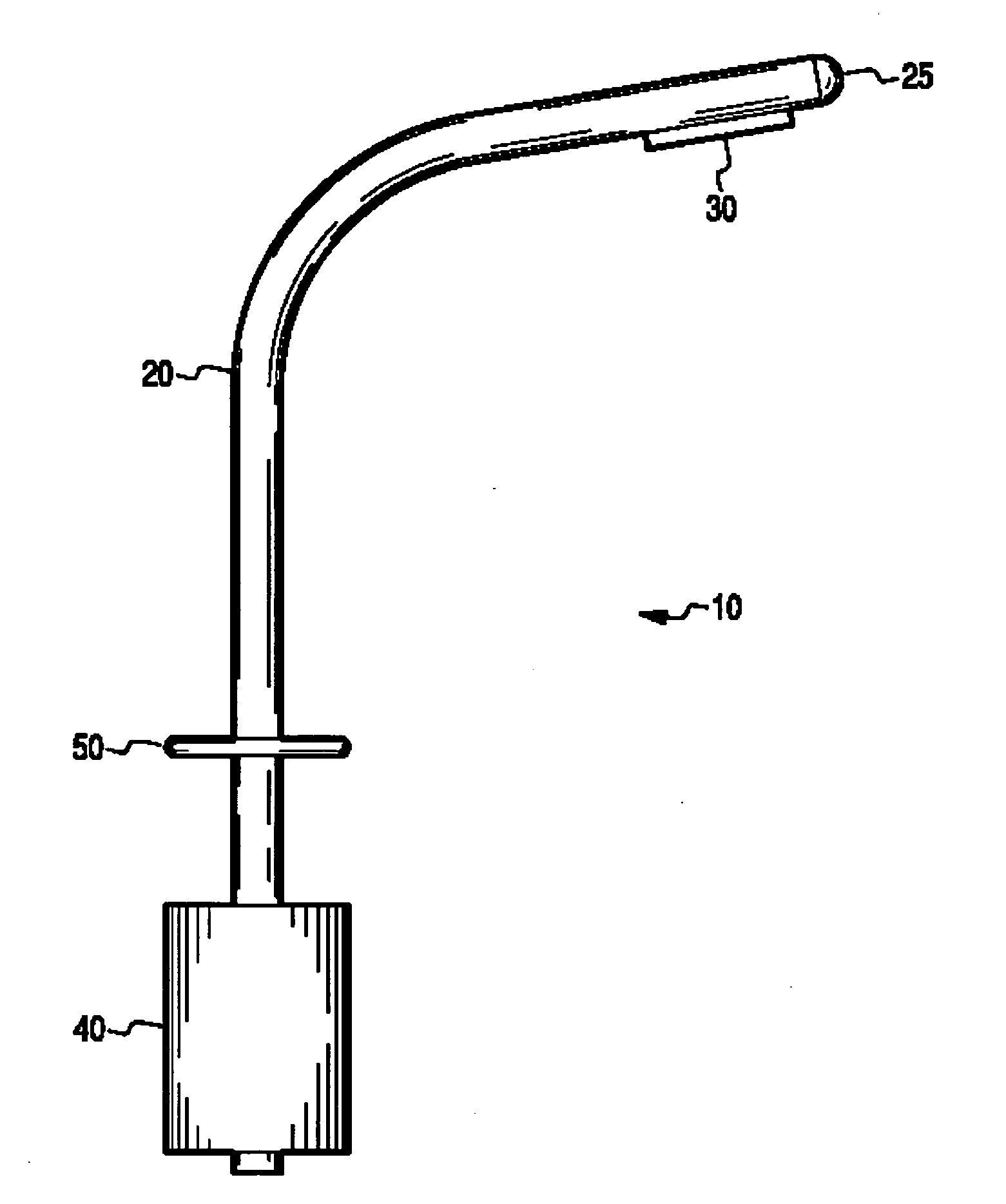
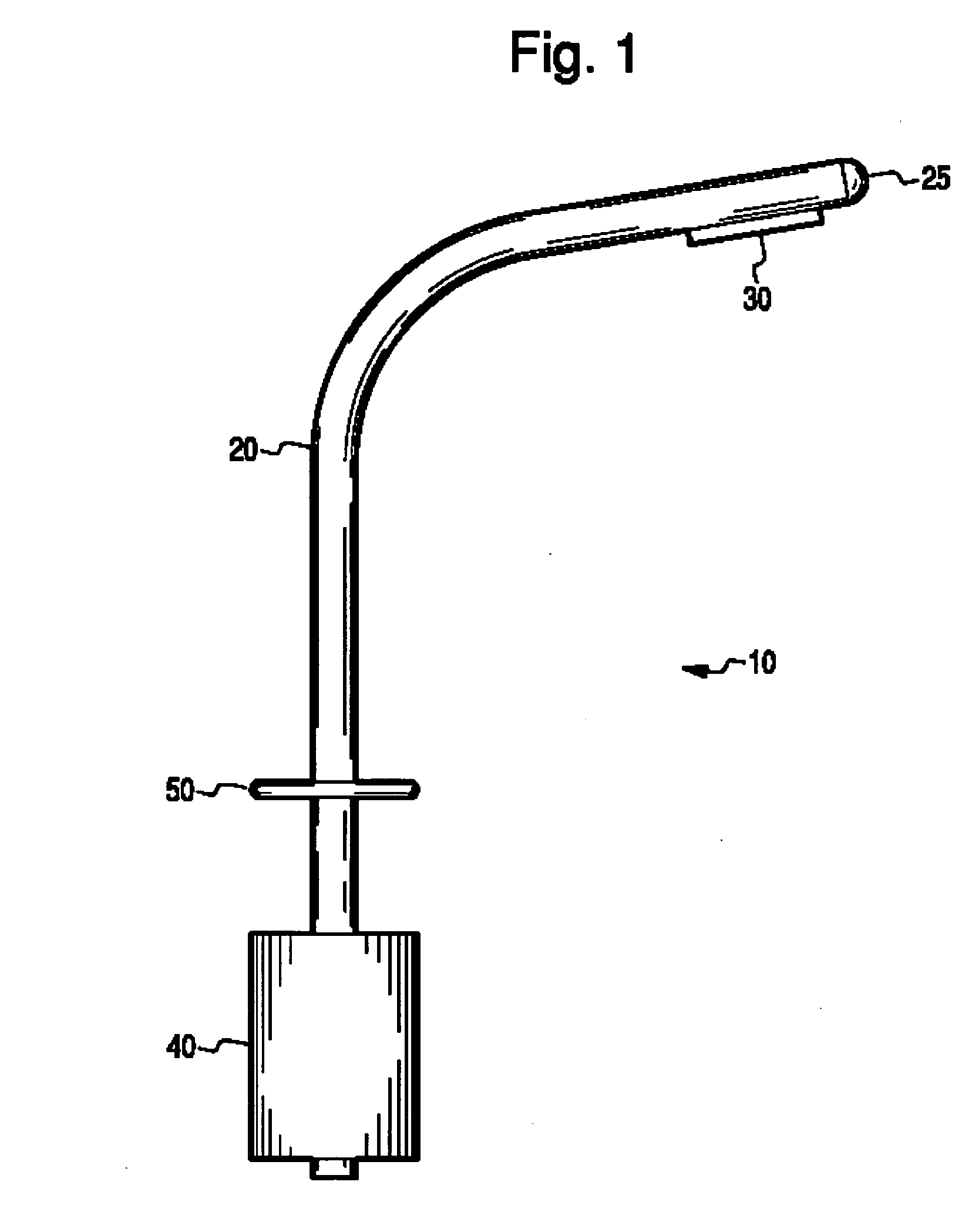
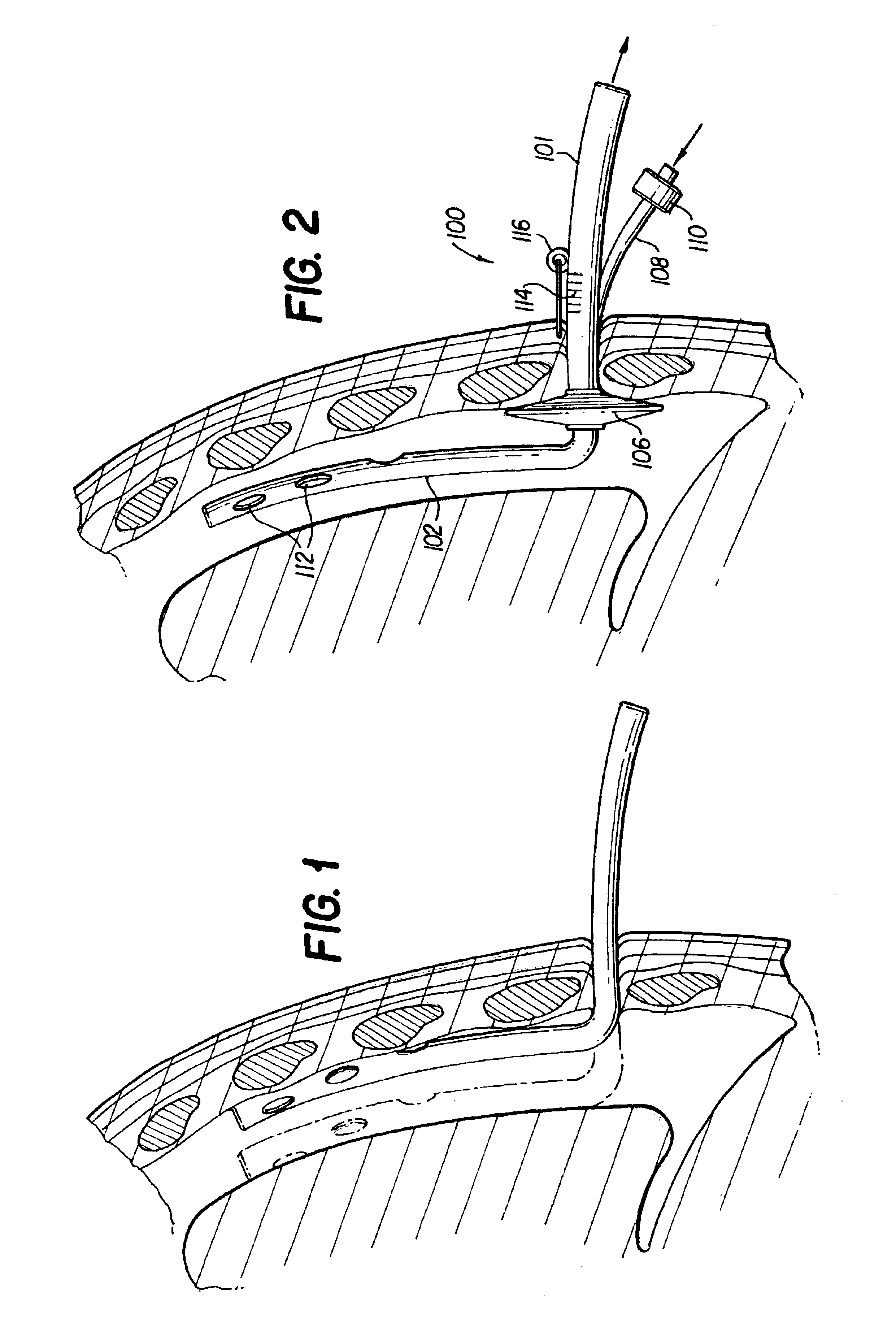
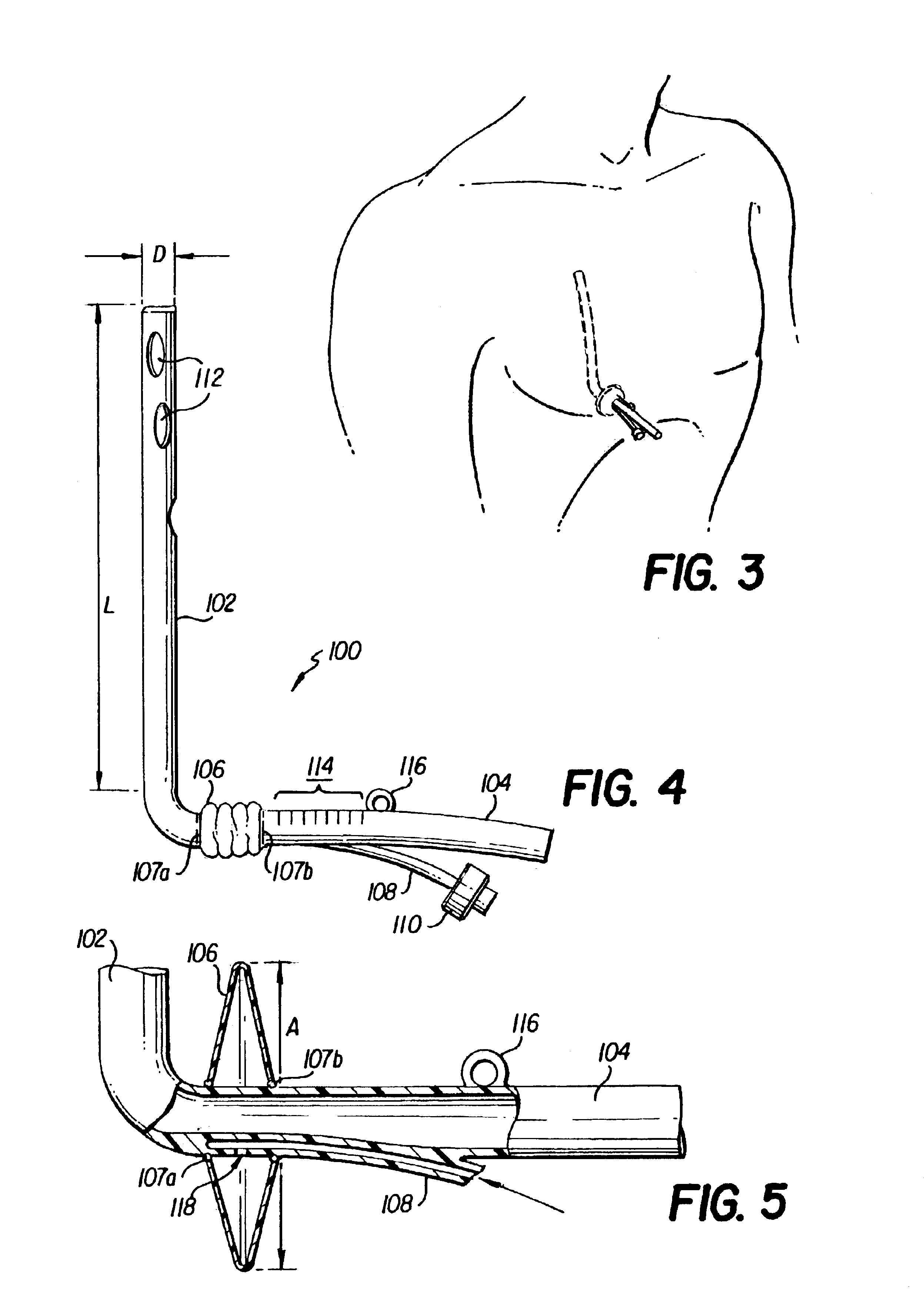
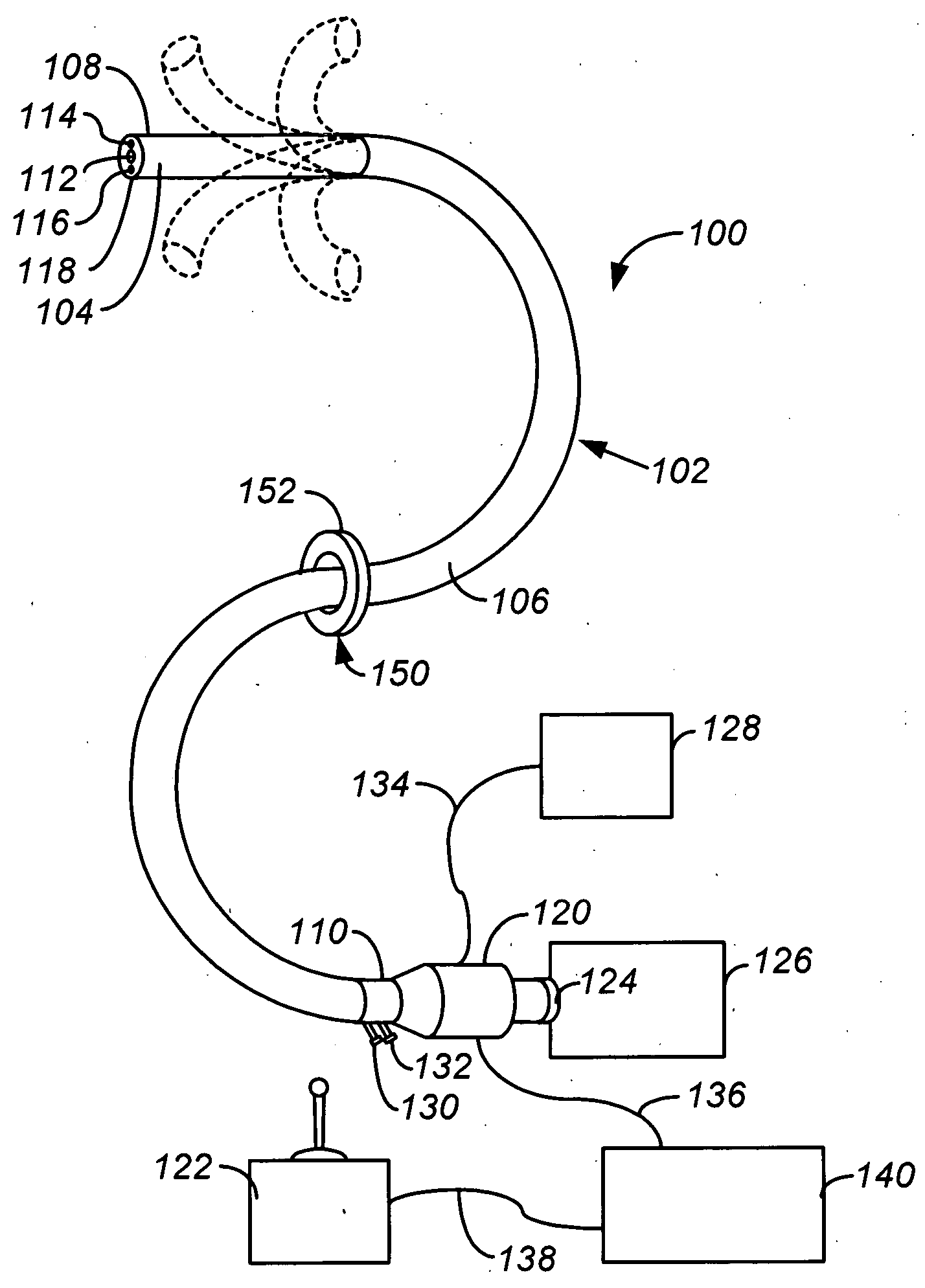
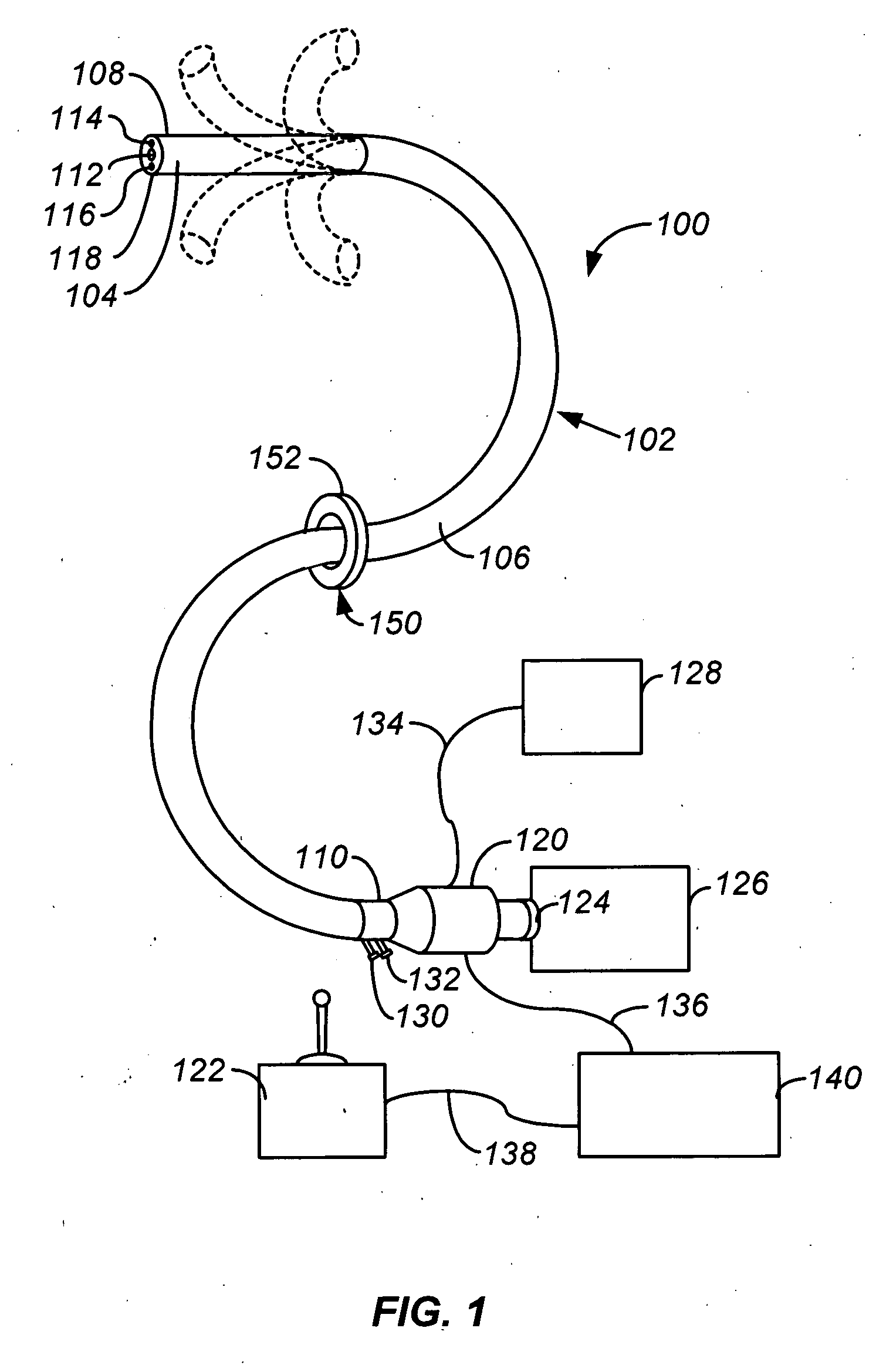
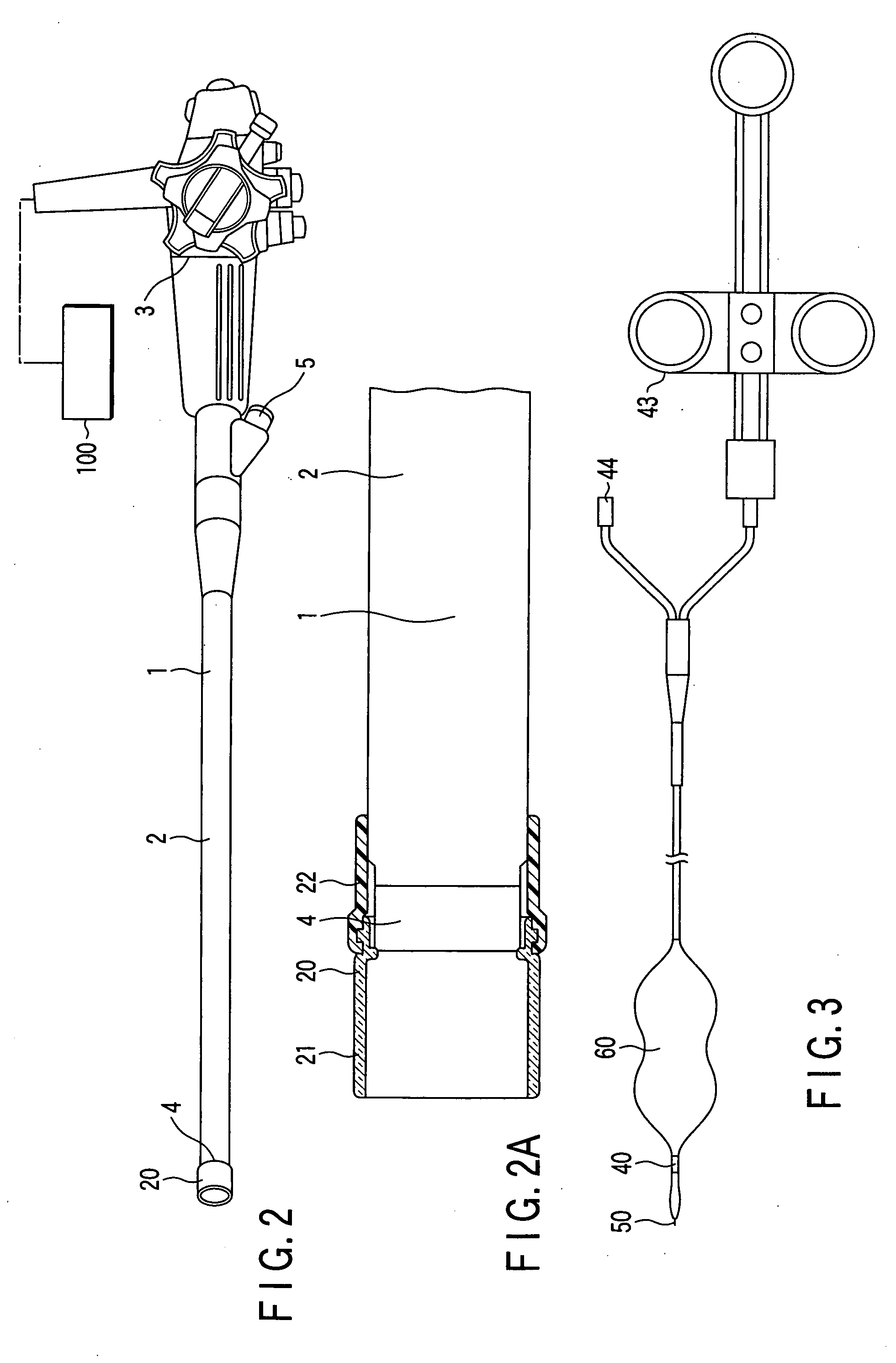
InactiveUS6849061B2Overcome disadvantagesAvoid obstructionWound drainsSurgeryPleural drainageThoracic cavity
Apparatus and method for evacuating material from a body cavity are disclosed. An elongated tubular member constructed and arranged to be inserted through an aperture in a patient's chest is provided. The tubular member is generally L-shaped and has a distal section and a proximal section. The distal section includes a plurality of openings for receiving air and liquids from within the patient's body. The proximal section receives and discharges air and liquids to a receiver. The proximal section includes an expandable cuff for positioning the tubular member in the patient's chest for preventing the plurality of openings from being obstructed in whole or in part.
Owner:WAGNER ROBERT B
Apparatus and methods for facilitating treatment of tissue via improved delivery of energy based and non-energy based modalities
InactiveUS20050020901A1Avoid excessive forceAccurately advancedEndoscopesCatheterThoracic structureAutomatic control
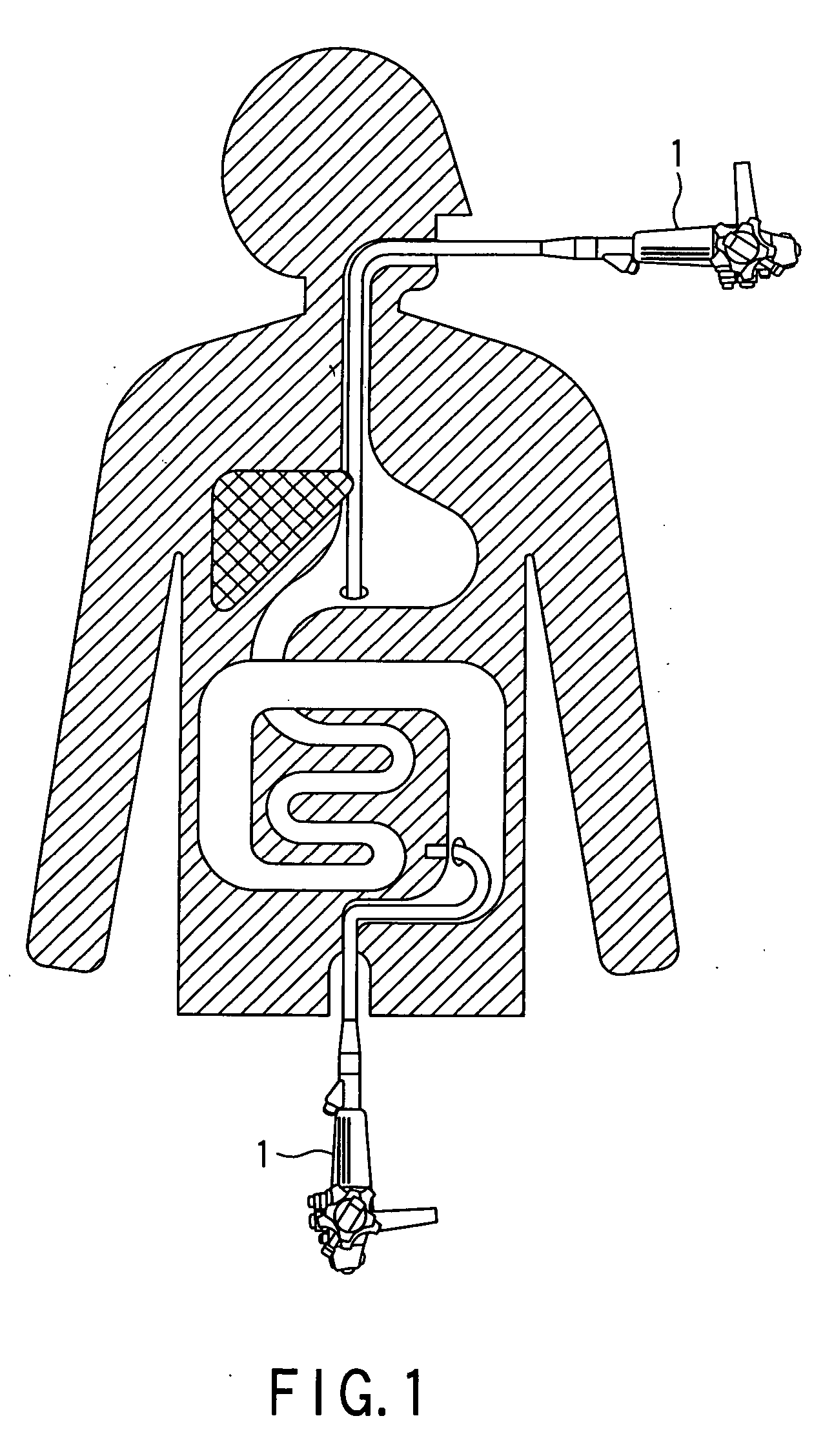
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating regions of the body are disclosed herein. Using an endoscopic device having an automatically controllable proximal portion and a selectively steerable distal portion, the device generally may be advanced into the body through an opening. The distal portion is selectively steered to assume a selected curve along a desired path within the body which avoids contact with tissue while the proximal portion is automatically controlled to assume the selected curve of the distal portion. The endoscopic device can then be used for accessing various regions of the body which are typically difficult to access and treat through conventional surgical techniques because the device is unconstrained by “straight-line” requirements. Various applications can include accessing regions of the brain, thoracic cavity, including regions within the heart, peritoneal cavity, etc., which are difficult to reach using conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Lung device with sealing features
InactiveUS20060025815A1Reduce air leakageMitigates pneumothorax and hemothoraxSurgical needlesMedical devicesThoracic structureThoracic cavity
This invention relates generally to a design of lung devices for safely performing a transthoracic procedure. In particular, the invention provides devices and methods of using these devices to access the thoracic cavity with minimal risk of causing pneumothorax or hemothorax. More specifically, the invention enables diagnostic and therapeutic access to a thoracic cavity using large bore instruments. This invention also provides a method for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures using a device capable of sealing the wound upon withdrawal of the device. The invention includes a device comprising an elongated body adapted to make contact with a tissue of a subject through an access hole, and a sealant delivery element. The invention also includes a method of performing tissue treatment or diagnosis in a subject.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Method for cryospray ablation
InactiveUS20090192505A1Increase load capacityAdequate doseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsThoracic structureDisease
The present invention relates to methods for treating tissue in the thoracic cavity of a subject by the application of a cryogen, or using the cryogen to create an isotherm in proximity to the tissue to be treated. A wide variety of conditions may be treated using the methods of the invention including asthma, neoplastic disease and a variety of conditions characterized by inflammation in lung and chest tissue.
Owner:RESET MEDICAL
Endoscopic system for treating inside of body cavity
InactiveUS20060025654A1Safe and reliableHelp positioningCannulasSurgical needlesThoracic structureHuman body
There is provided an endoscopic inserting system. The system includes an endoscope which is inserted into a lumen inside a body through a natural opening of a human body, an opening member which forms an opening for inserting the endoscope into a thoracic cavity or an abdominal cavity from the lumen inside the body at a wall portion of the lumen, and a retracting member which, when forming the opening, retracts the wall portion of the lumen.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
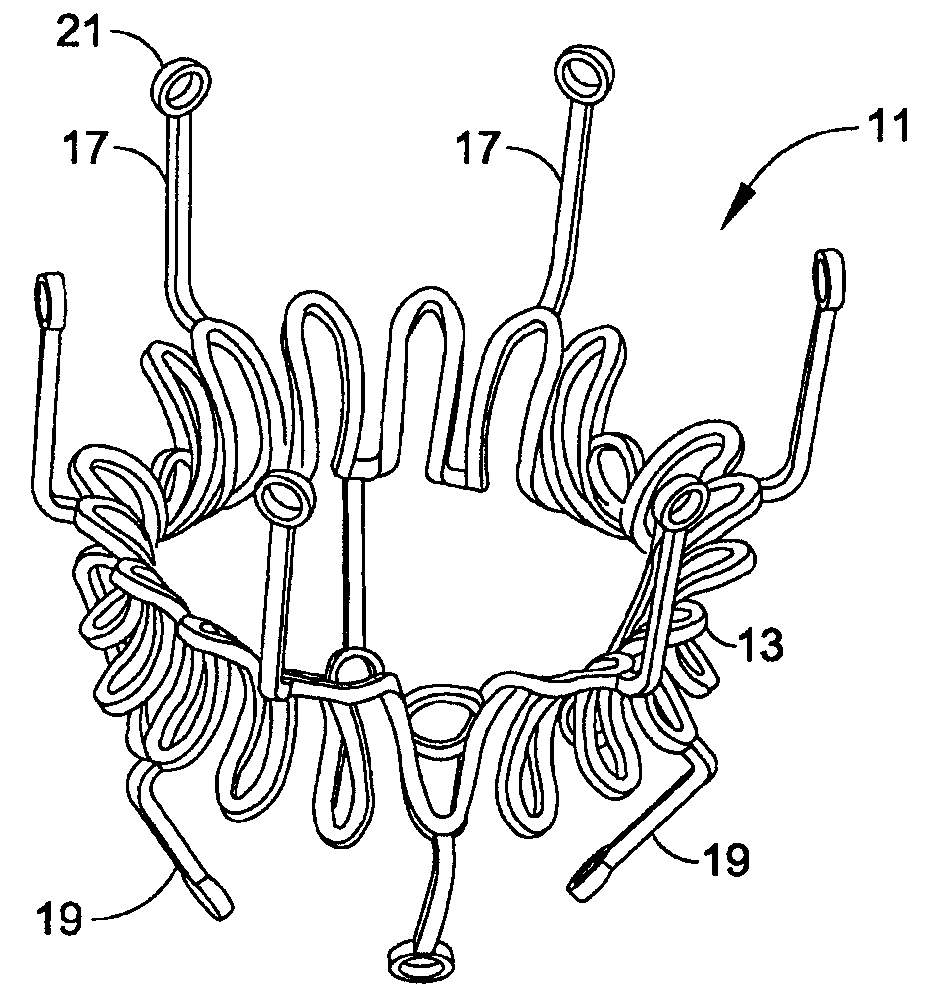
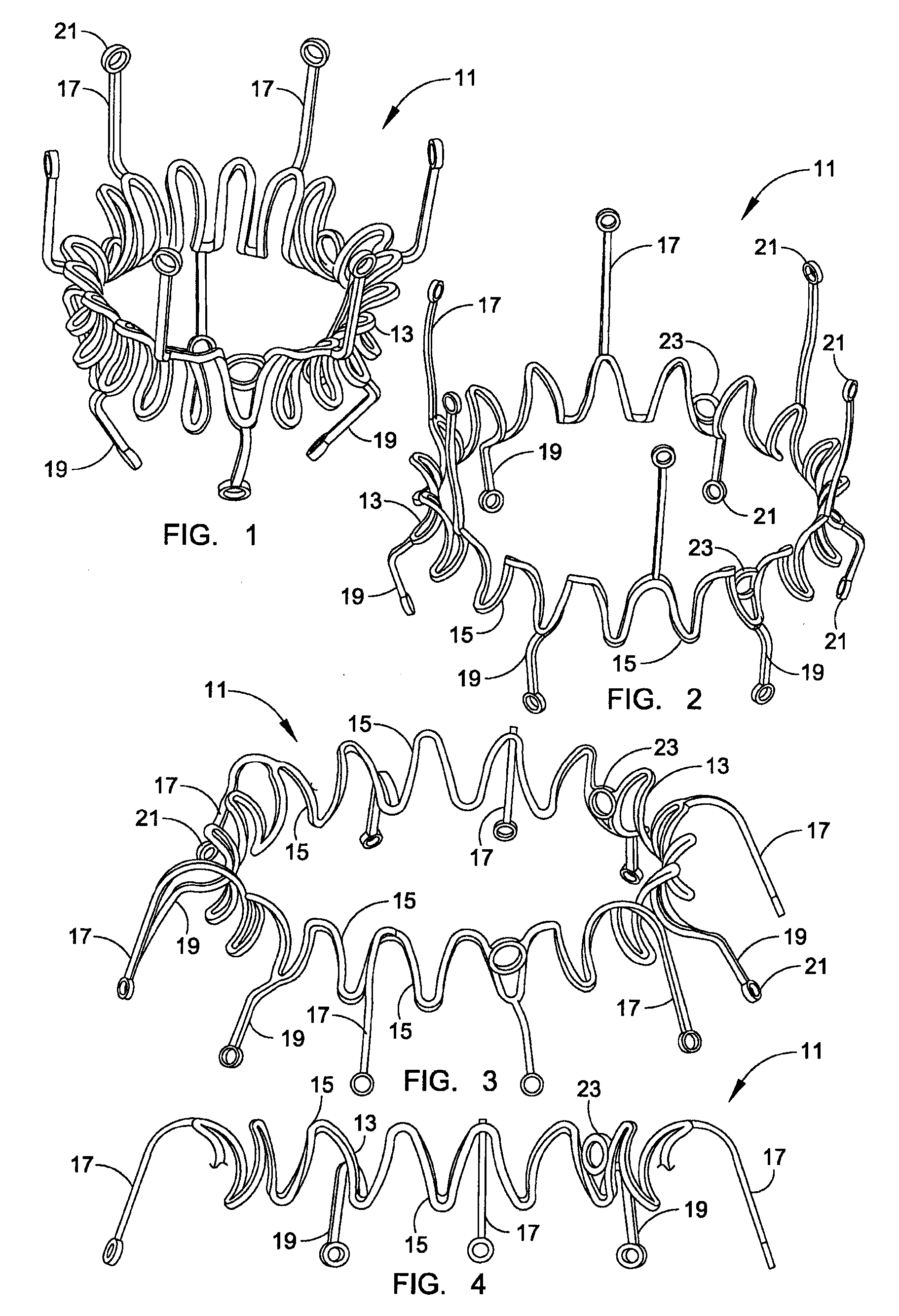
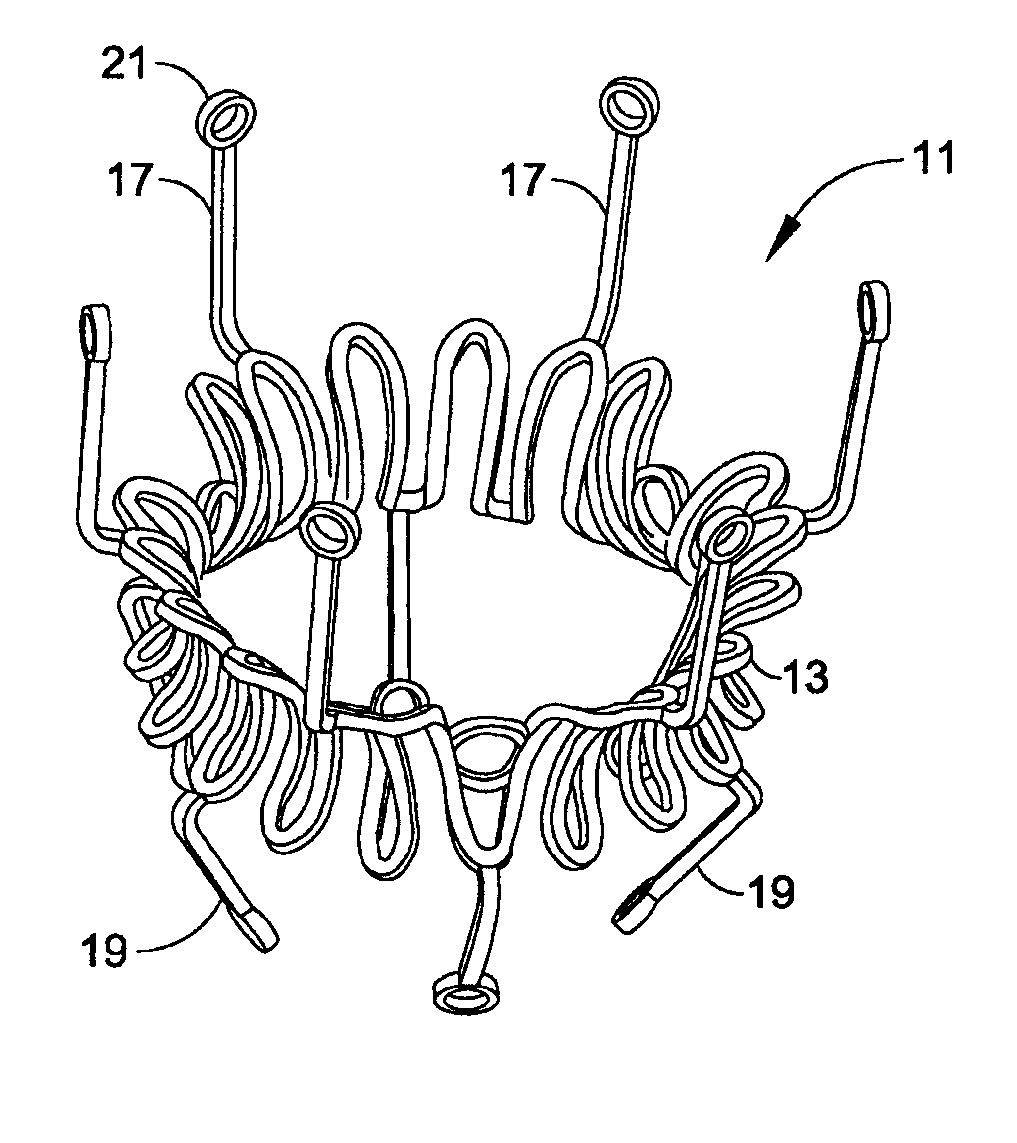
Sternotomy splinting assembly, kit and method for use
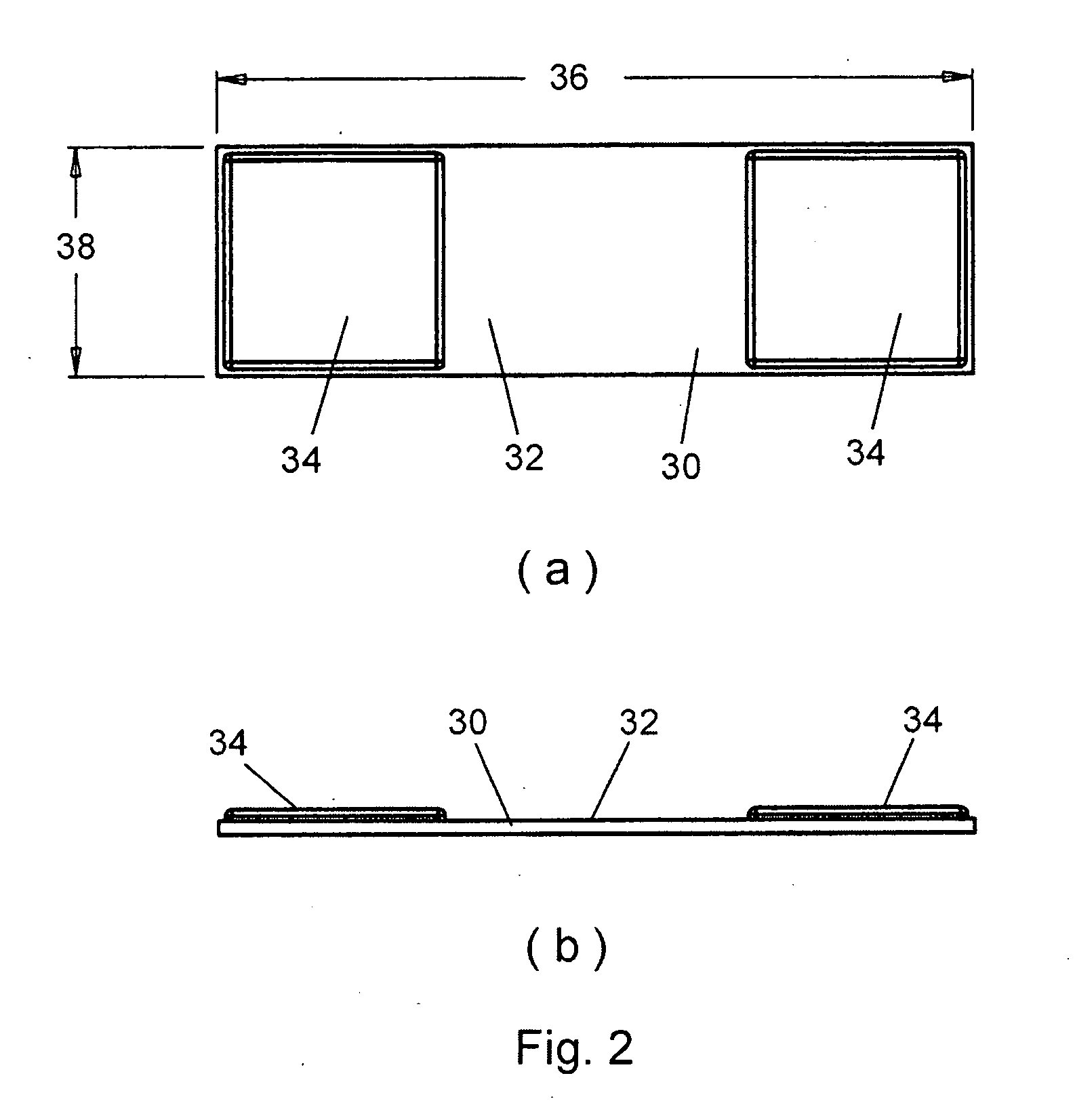
InactiveUS20090163949A1Promote healingRelieve painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisThoracic boneMedicine
Herein disclosed is a simple, passive splinting system for sternotomy patients designed to provide a continuous yet readily adjustable, compressive tangential stabilizing force to the ribcage so as to promote healing of a median sternotomy incision while minimizing patient pain.
Owner:ROLNICK MICHAEL A +2
Steerable epicardial pacing catheter system placed via the subxiphoid process
InactiveUS20100241185A1Free from damageEpicardial electrodesDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresThoracic cavity
The epicardial pacing system and related method includes an epicardial catheter configured to be disposed in the middle mediastinum of the thorax of a subject for use in electrical pacing of the heart at one or more locations on the epicardial surface. The epicardial pacing catheter may include at least one electrode whereby the electrode is insulated on at least one side to allow pacing of the heart without damage to adjacent anatomical structures.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Pleural effusion treatment device, method and material
The invention discloses a method of treating a patient for pleural effusion comprising percutaneously delivering an adhesive material to a pleural space of the patient. Suitable adhesive materials for performing any of the embodiments of the methods of the invention can be selected from the group consisting of hydrogels, collagen, poly(lactic acid), poly(glycolide), cyanoacrylates, glutaraldehyde, PEG, protein, and polysaccharide and derivatives thereof. The invention also discloses a pleural effusion treatment apparatus comprising an adhesive material adapted to adhere pleural membranes defining a pleural space and a pleural space access member adapted to deliver the adhesive material to the pleural space.
Owner:EKOS CORP
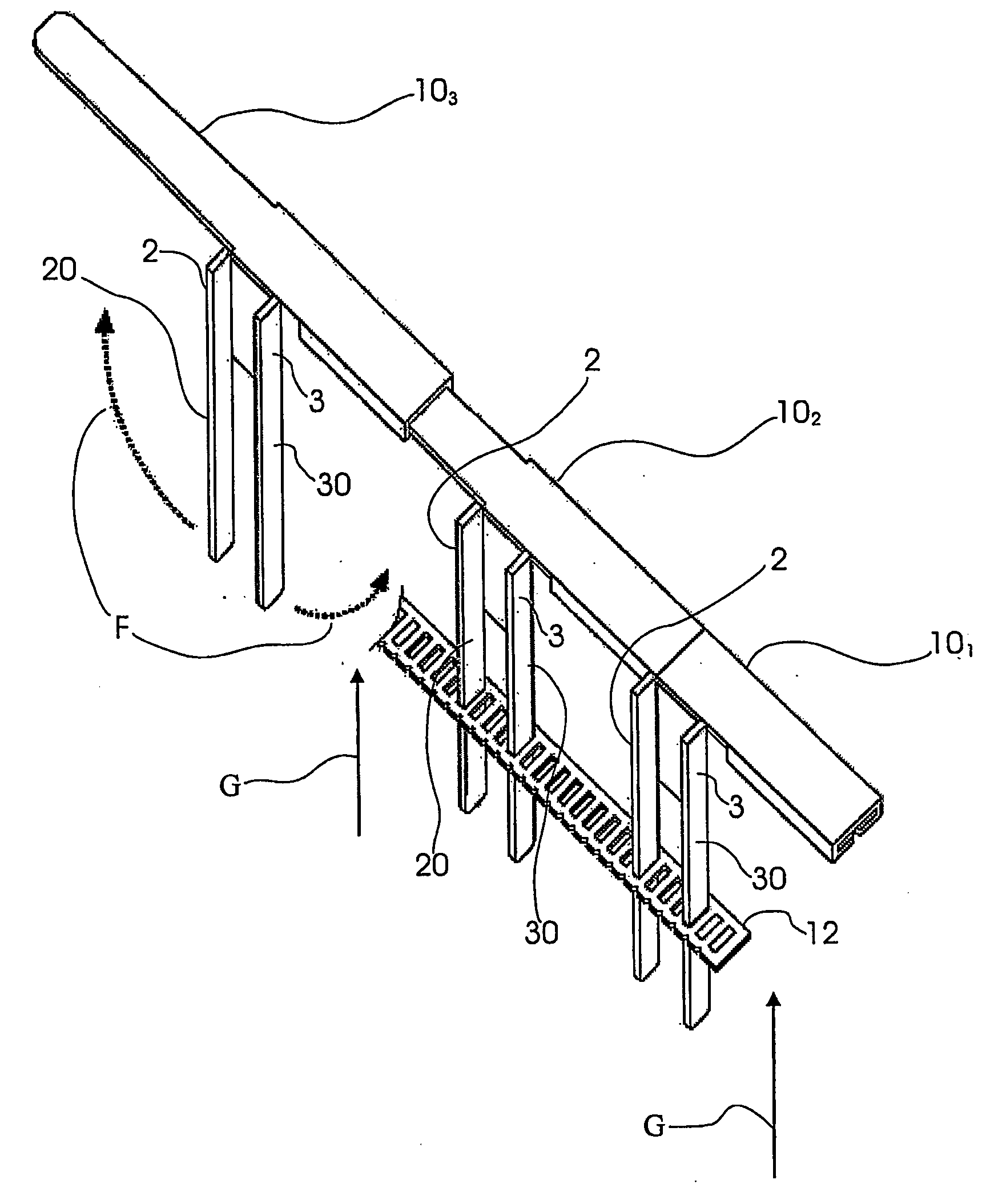
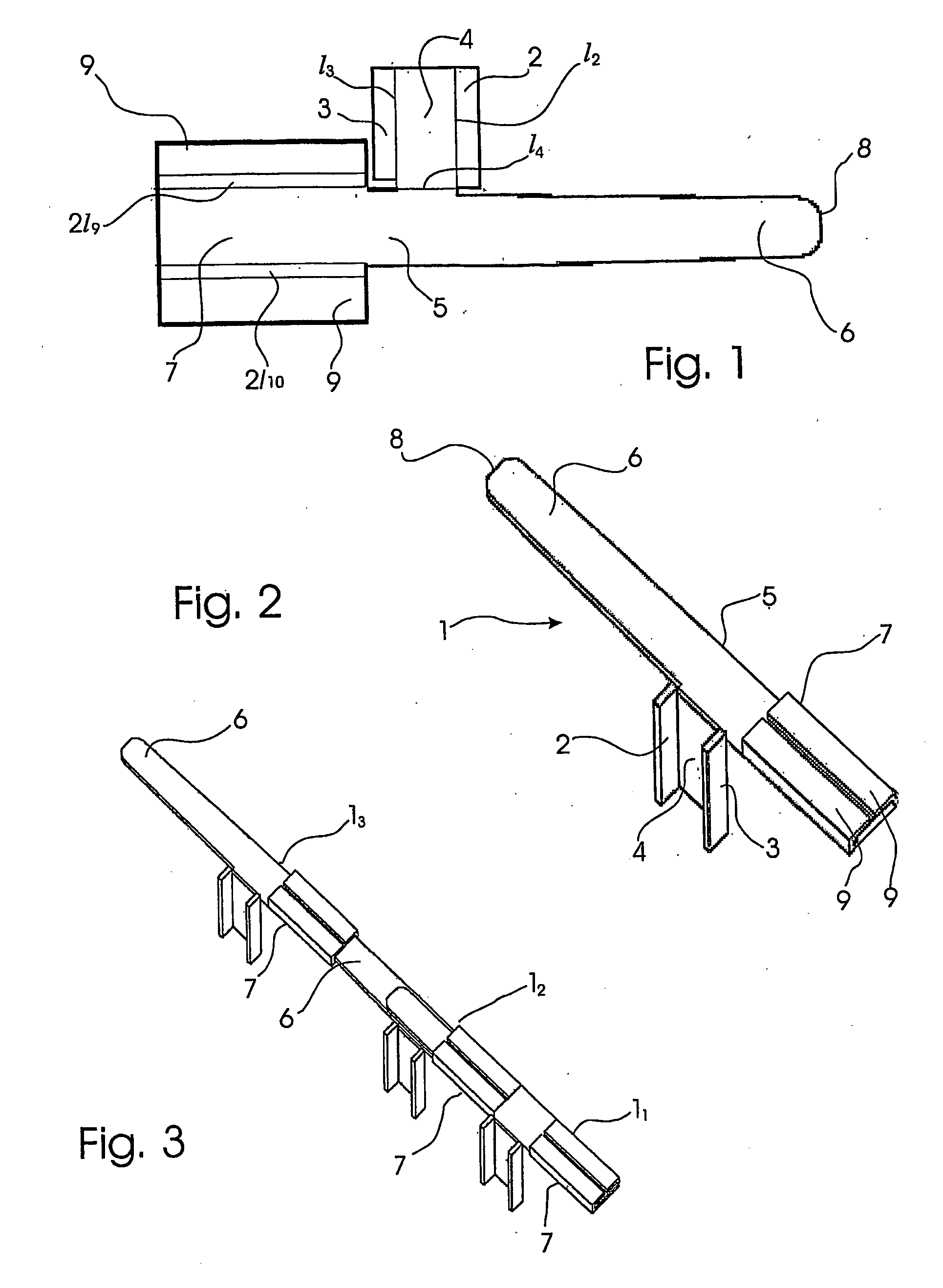
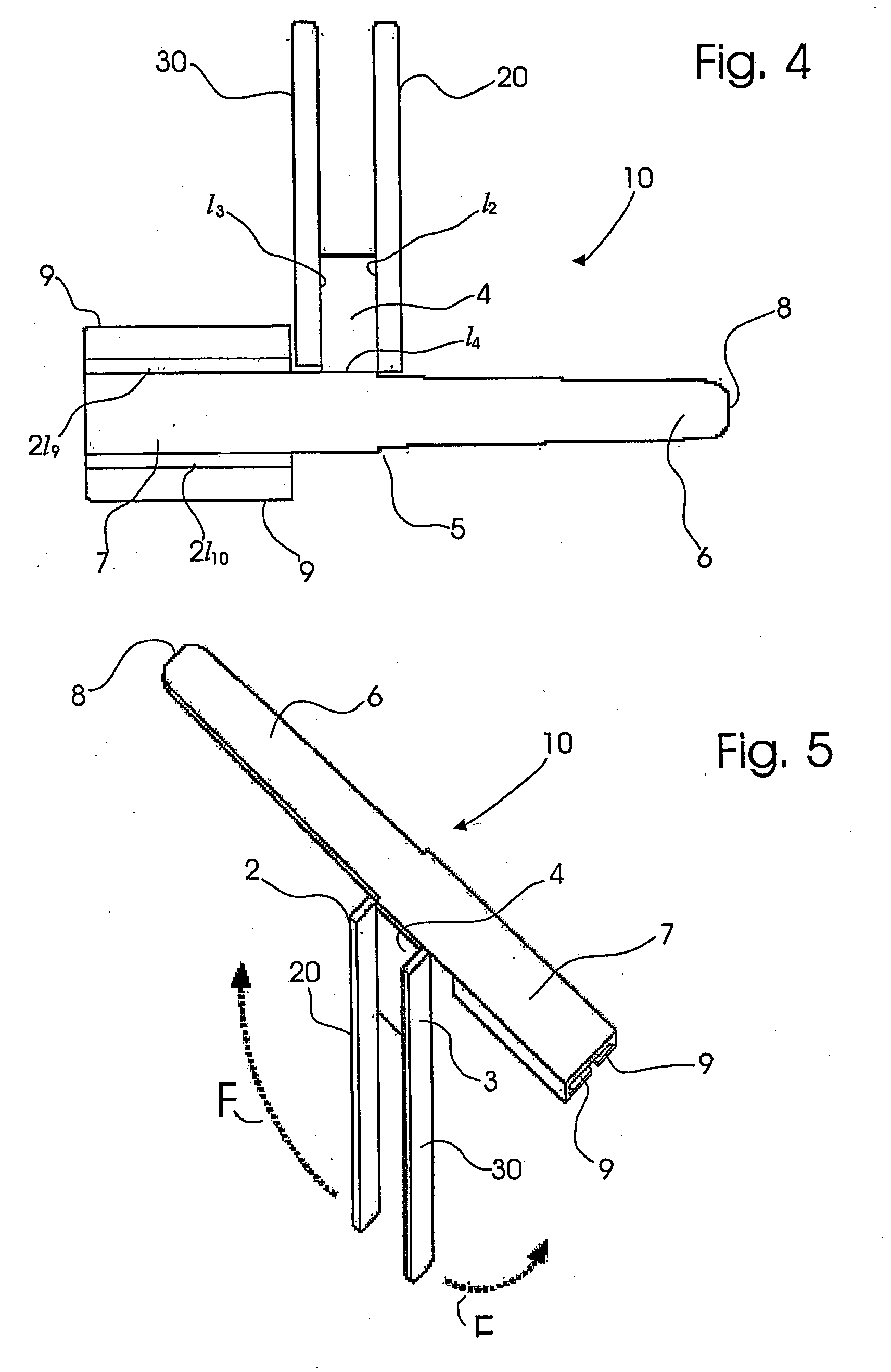
Sternum Reinforcing Device to be Used After a Sternotomy or a Sternal Fracture
ActiveUS20080221578A1High risk of damageInternal osteosythesisBone implantSternal fractureEngineering
A sternum reinforcing device to be used after a sternotomy or a sternal fracture, made of a biocompatible material, comprises an elongated modular member (10) with a pair of legs (20, 30), that are joined each other by a body portion (4), and a pair of arms (6, 7). The legs (20, 30) can be fitted in an intercostal space of the thorax of a patient, laterally to the sternum, and can be bent in a mutually opposite direction, on the internal side of the thorax, after being fitted therein. The arms (6, 7), extending from one side to the other of the body portion (4) and orthogonally to the pair of legs (20, 30), constitute a male part and a female part, respectively, of a prismatic type coupling for consecutive modular members.
Owner:SIC BREVETTI SRL
Subcutaneous electrode with improved contact shape for transthorasic conduction
One embodiment of the present invention provides a lead electrode assembly for use with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator subcutaneously implanted outside the ribcage between the third and twelfth ribs comprising the electrode.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
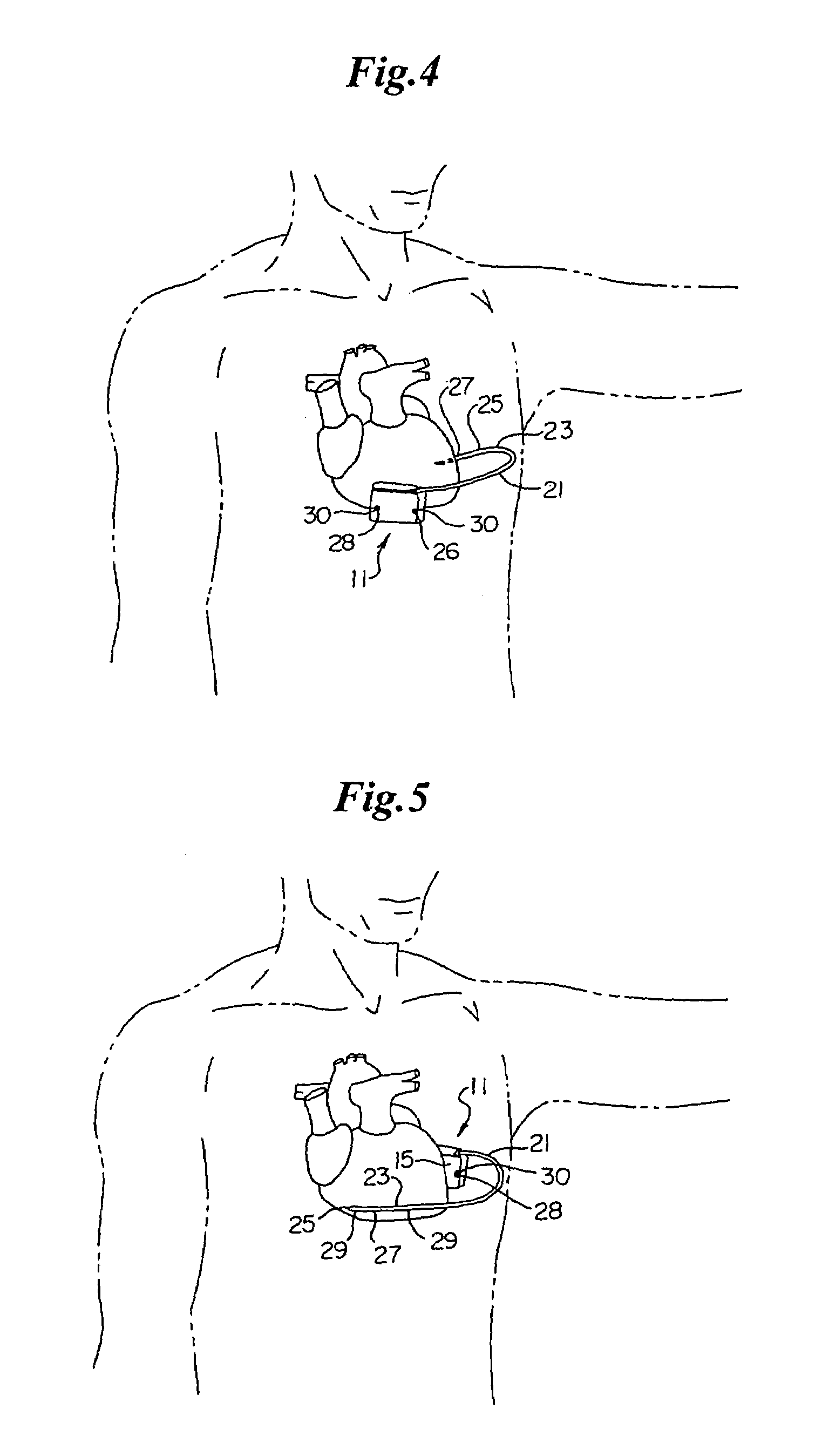
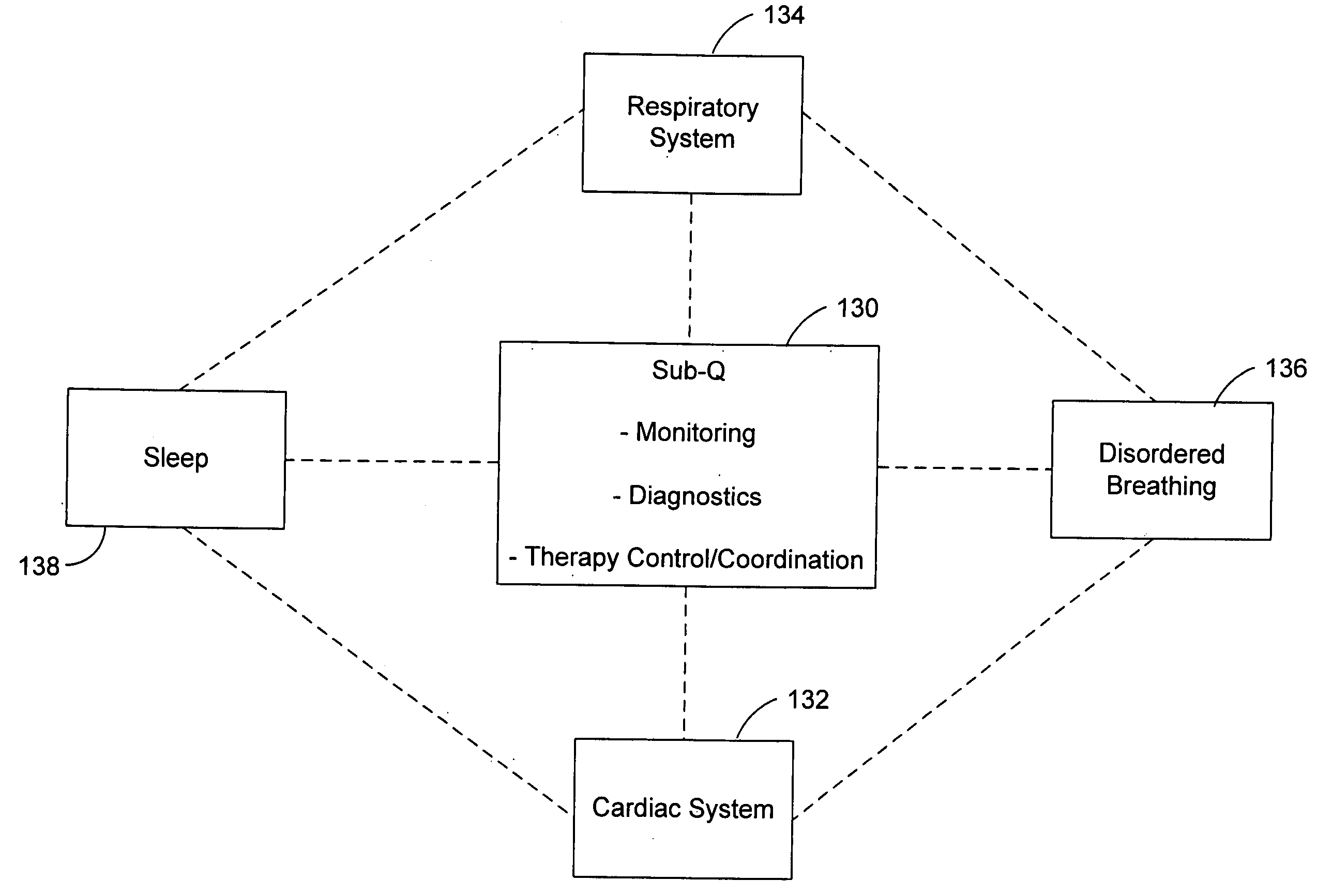
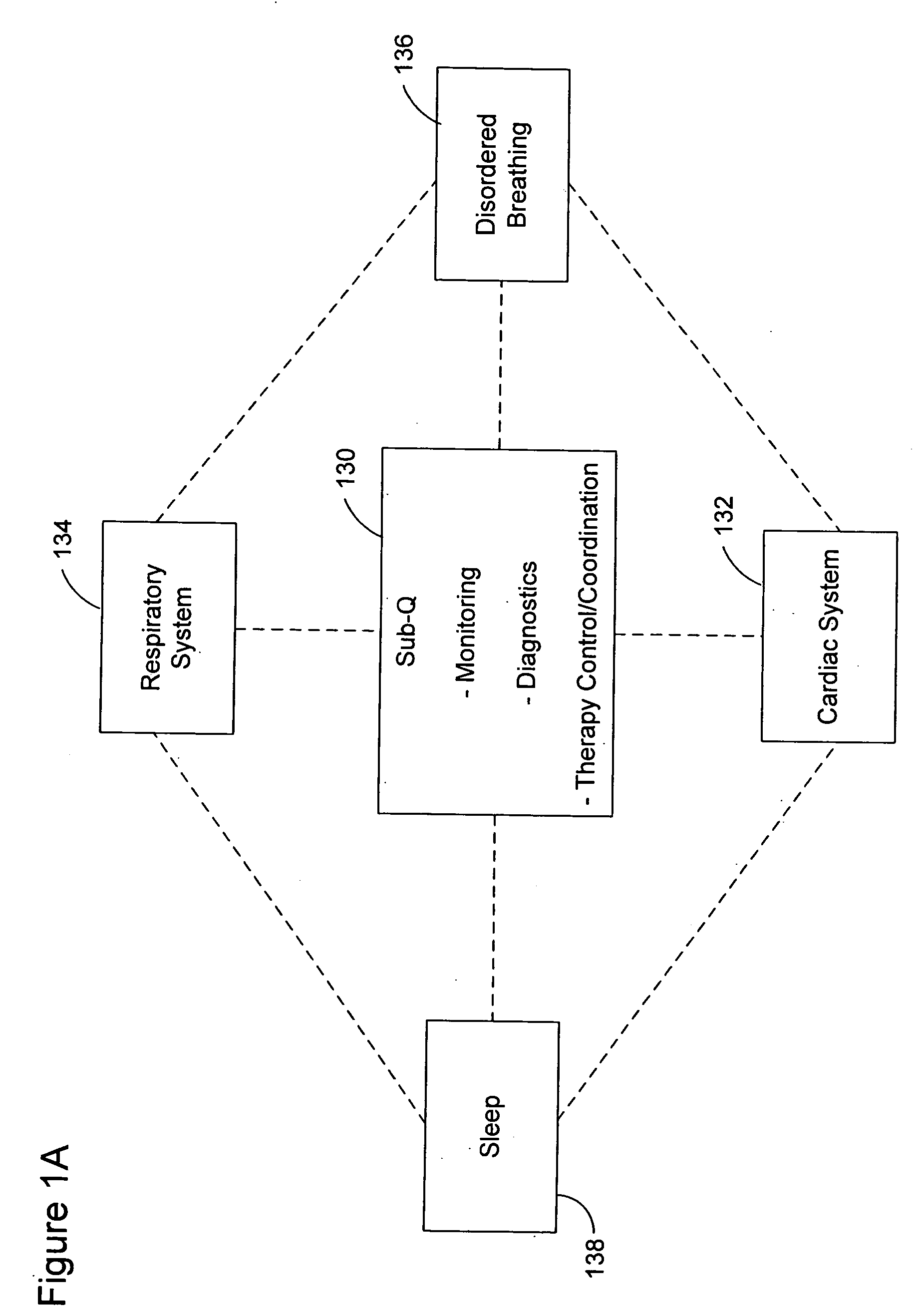
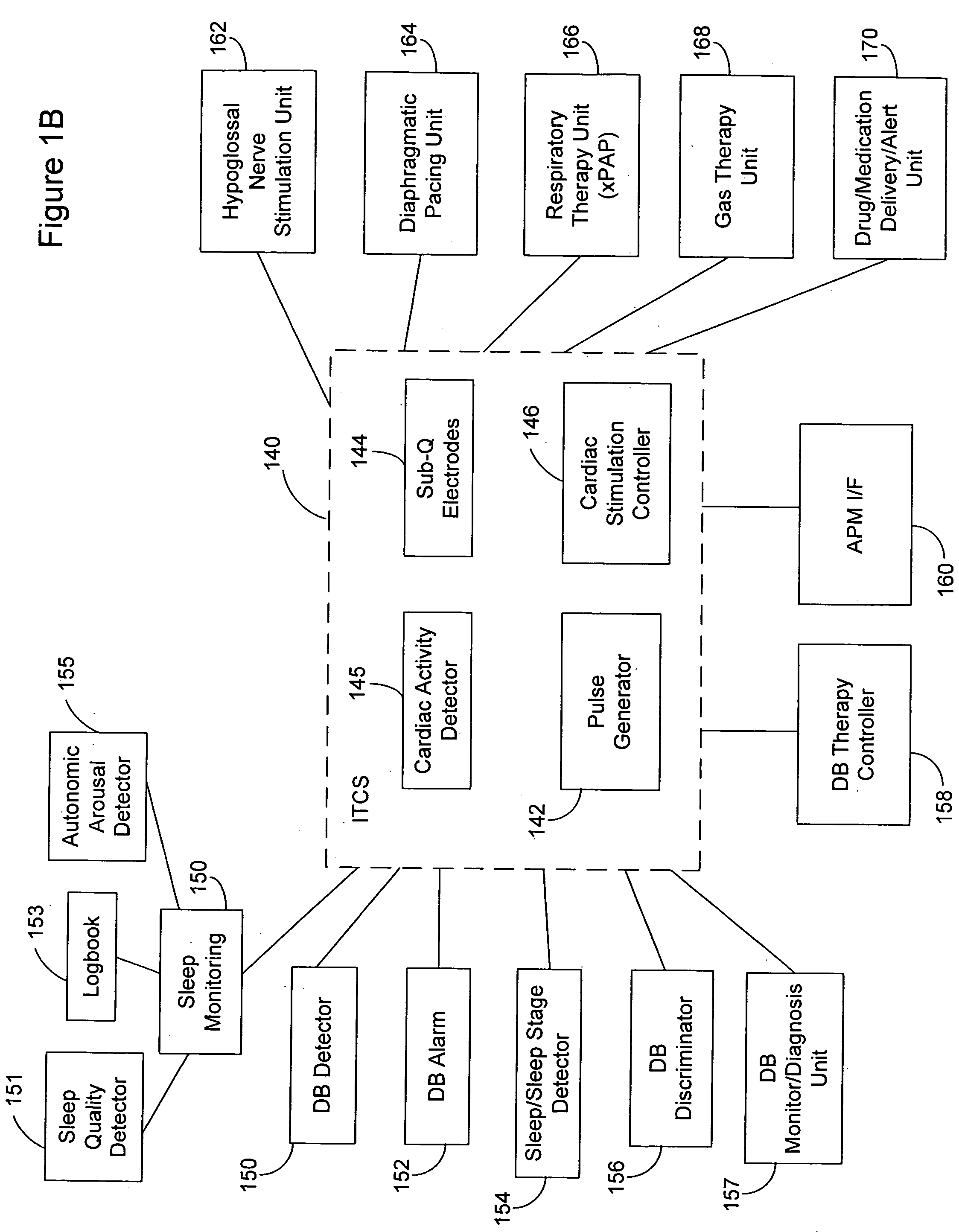
Subcutaneous cardiac rhythm management with disordered breathing detection and treatment
InactiveUS20050107838A1Heart defibrillatorsInertial sensorsPositive airway pressure deviceCardiac activity
A lead system, coupled to an implantable device, is configured for subcutaneous, non-intrathoracic placement relative to a patient's heart. Cardiac activity detection circuitry is coupled to the lead system and configured to detect cardiac rhythms. Disordered breathing detection circuitry is coupled to the lead system and configured to detect disordered breathing. One or both of cardiac therapy circuitry and disordered breathing therapy circuitry may be coupled to the lead system and configured to delivery therapies to treat disordered breathing. Such therapies include cardiac pacing, diaphragmatic pacing, and hypoglossal nerve stimulation therapies. A patient-external respiratory device, such as a positive airway pressure device, may be configured to deliver a disordered breathing therapy. One or more of a patient-internal drug delivery device, a patient-external drug delivery device, or a gas therapy device may be employed to treat disordered breathing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
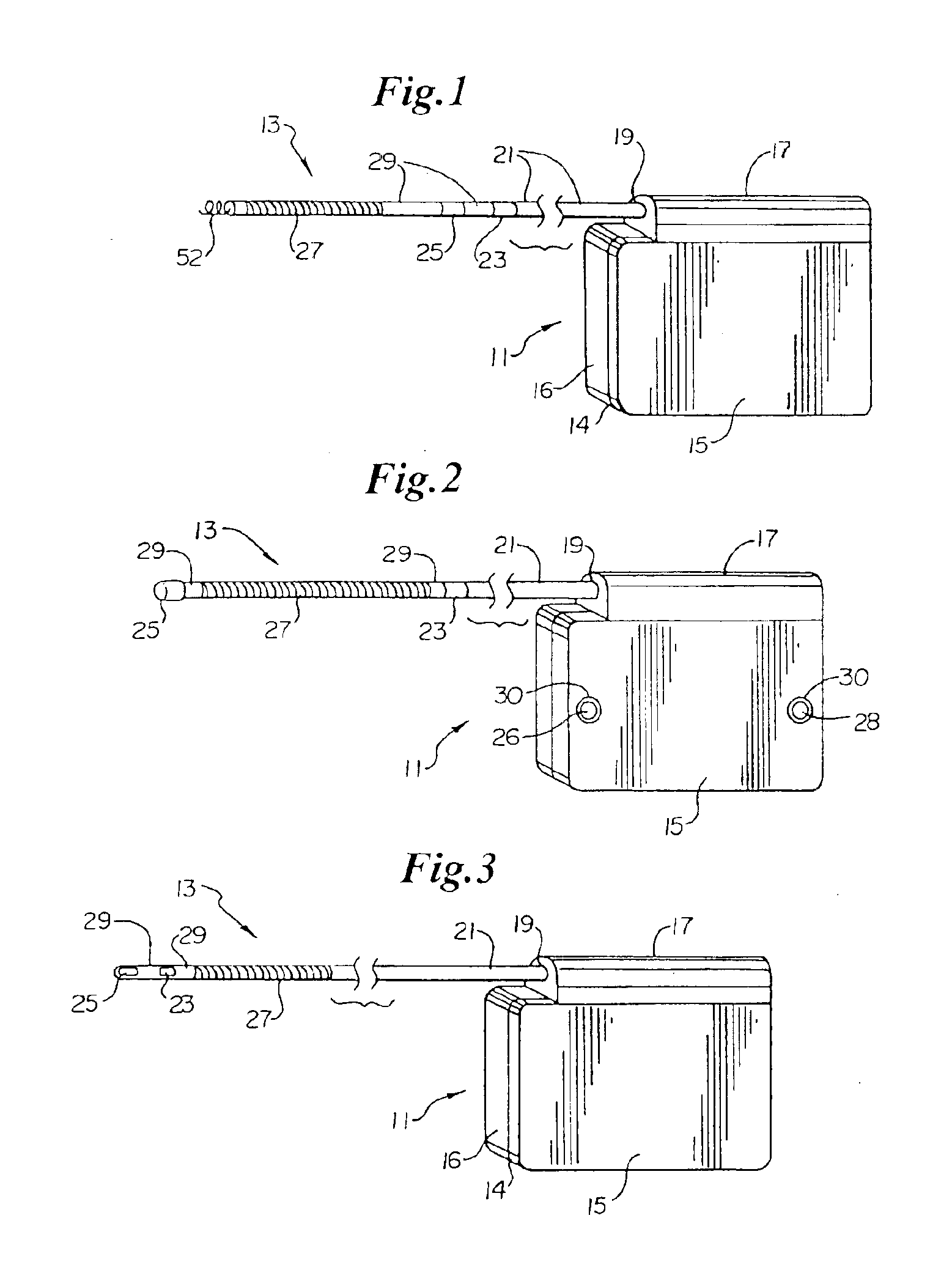
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator having two spaced apart shocking electrodes on housing
InactiveUS6988003B2Heart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsThoracic cavityImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator
One embodiment of the present invention provides an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning over a patient's ribcage, the implantable cardioverter-defibrillator includes a housing having a first end and a second end; a first electrode disposed upon the first end of the housing; a second electrode disposed upon the second end of the housing; an electrical circuit located within the housing, wherein the electrical circuit is electrically coupled to the first electrode and the second electrode; and a lead electrode electrically coupled to the electrical circuit located within the housing.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
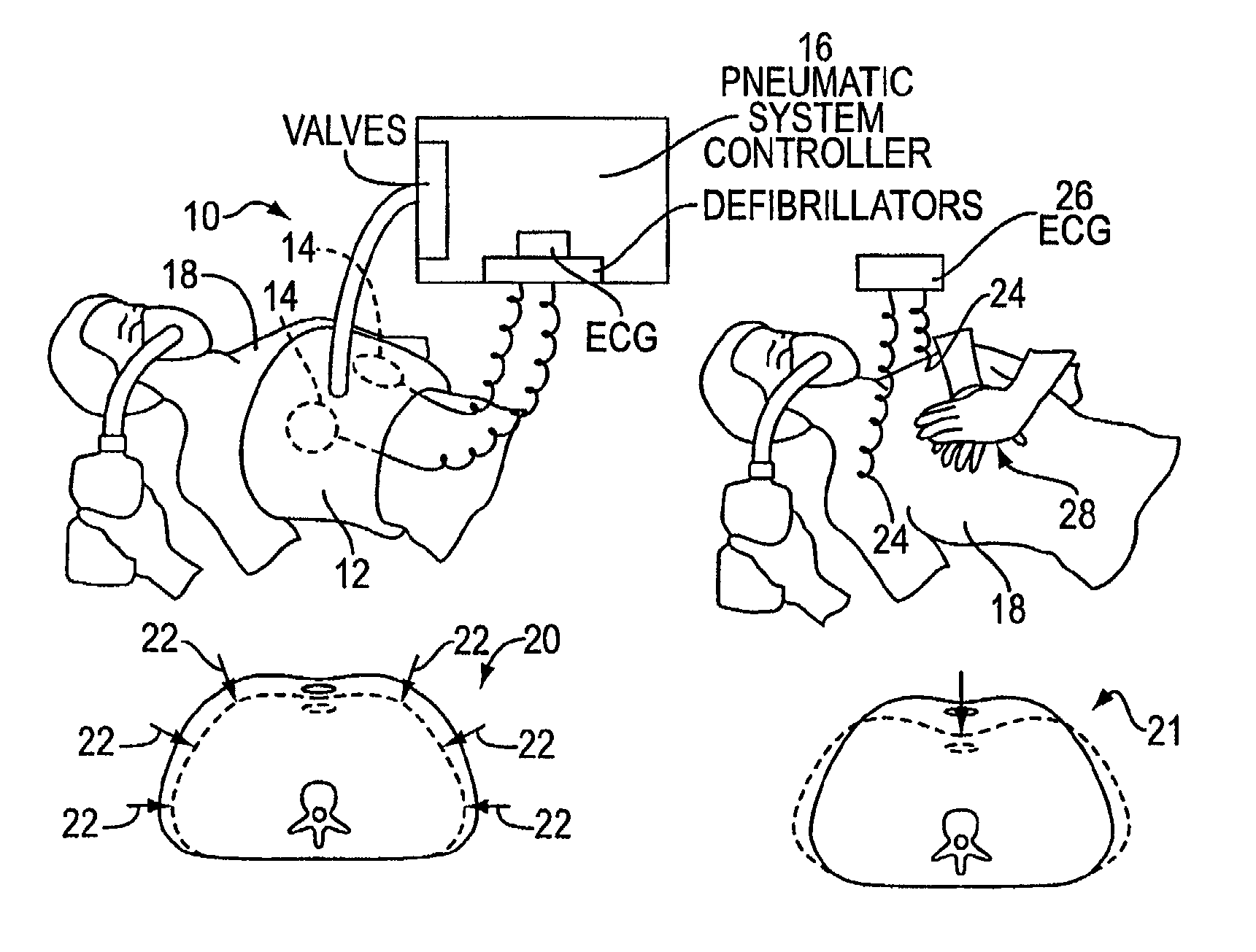
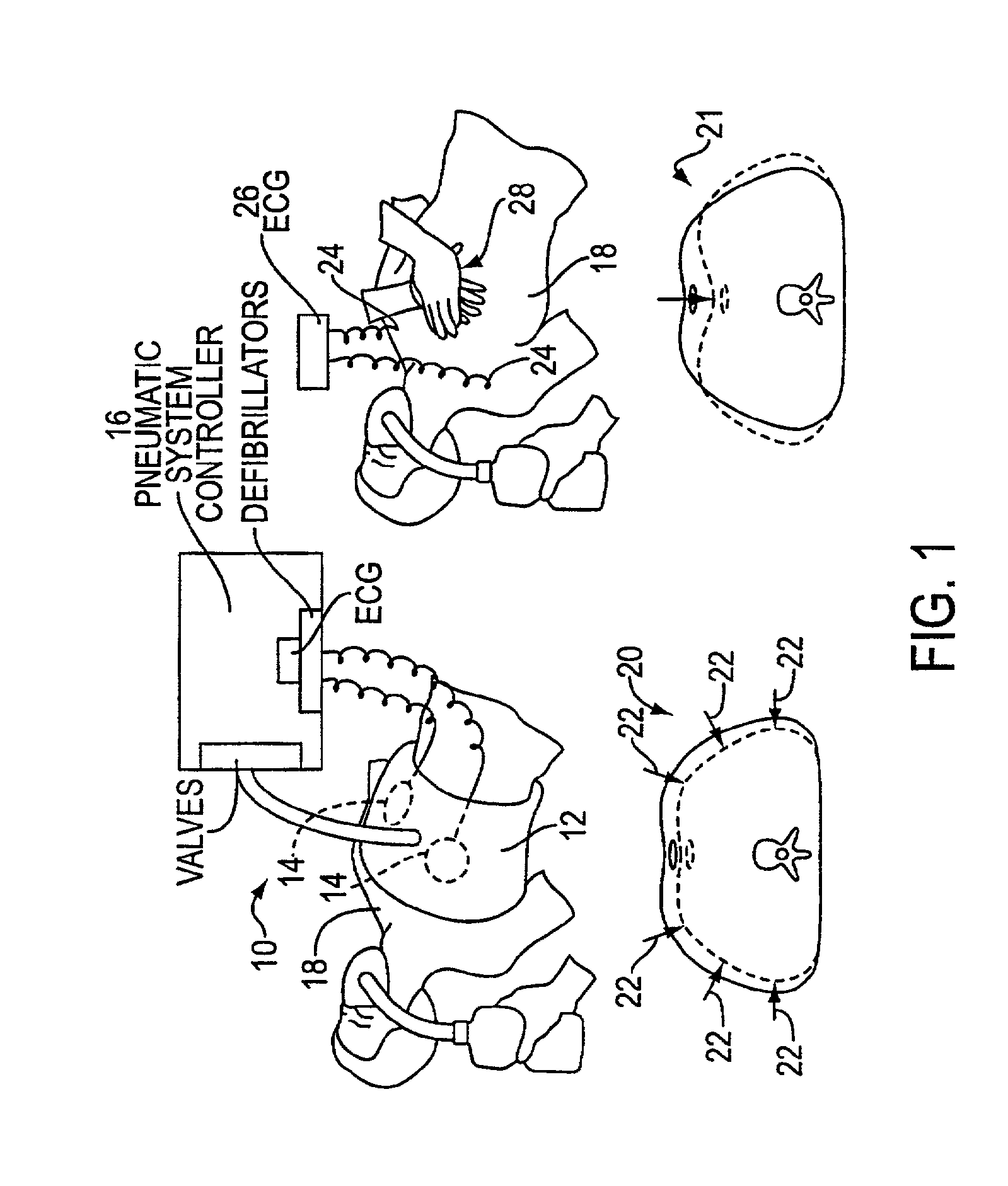
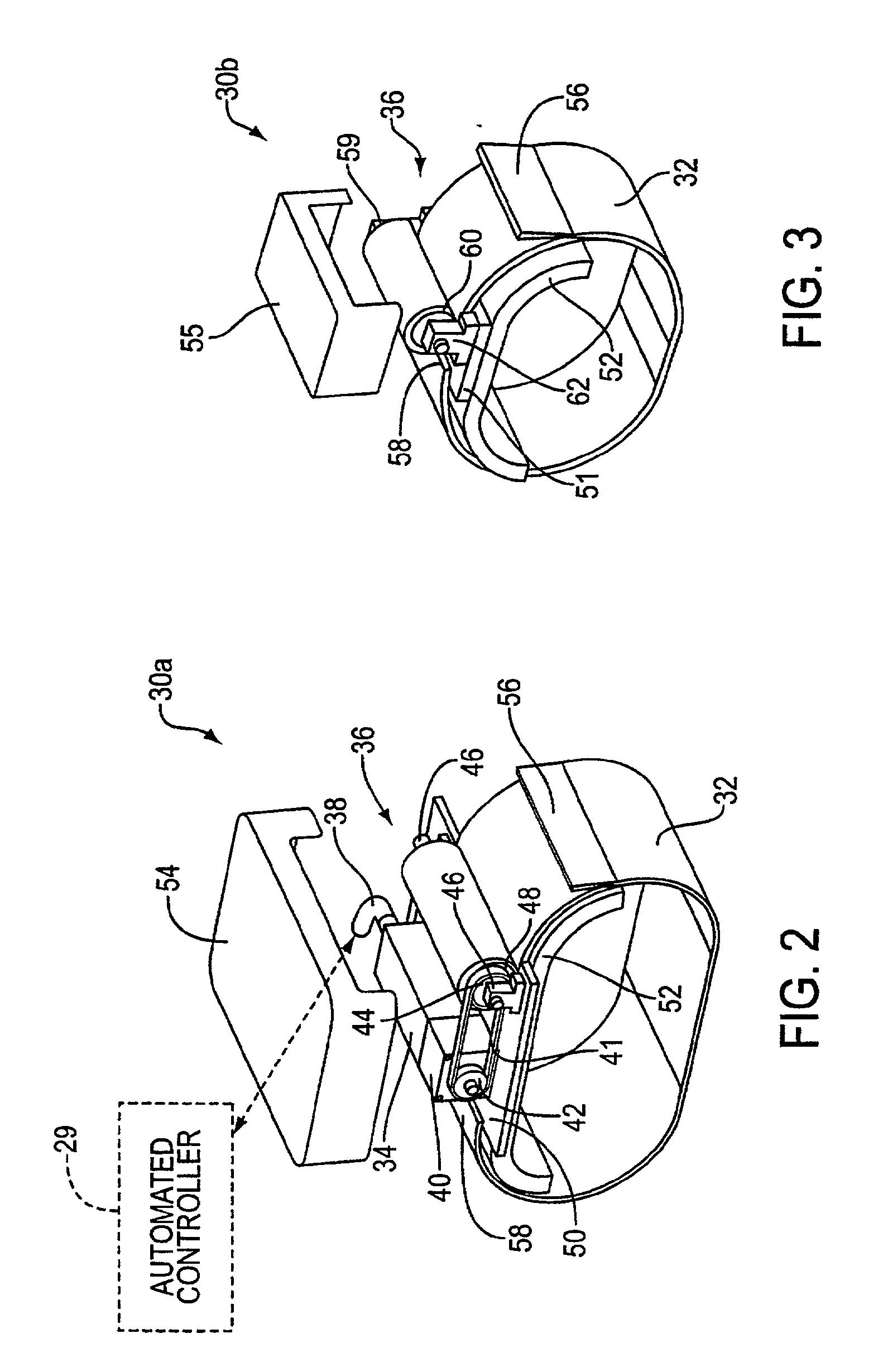
Automated chest compression apparatus
A system applies cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to a recipient. An automated controller is provided together with a compression device which periodically applies a force to a recipient's thorax under control of the automated controller. A band is adapted to be placed around a portion of the torso of the recipient corresponding to the recipient's thorax. A driver mechanism shortens and lengthens the circumference of the band. By shortening the circumference of the band, radial forces are created acting on at least lateral and anterior portions of the thorax. A translating mechanism may be. provided for translating the radial forces to increase the concentration of anterior radial forces acting on the anterior portion of the thorax. The driver mechanism may comprise a tension device for applying a circumference tensile force to the band. The driver mechanism may comprise an electric motor, a pneumatic linear actuator, or a contracting mechanism defining certain portions of the circumference of the band. The contracting mechanism may comprise plural fluid-receiving cells linked together along the circumference of the band. The width of each of the fluid-receiving cells becomes smaller as each cell is filled with a fluid. This causes the contraction of the band and a resulting shortening of the circumference of the band.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com