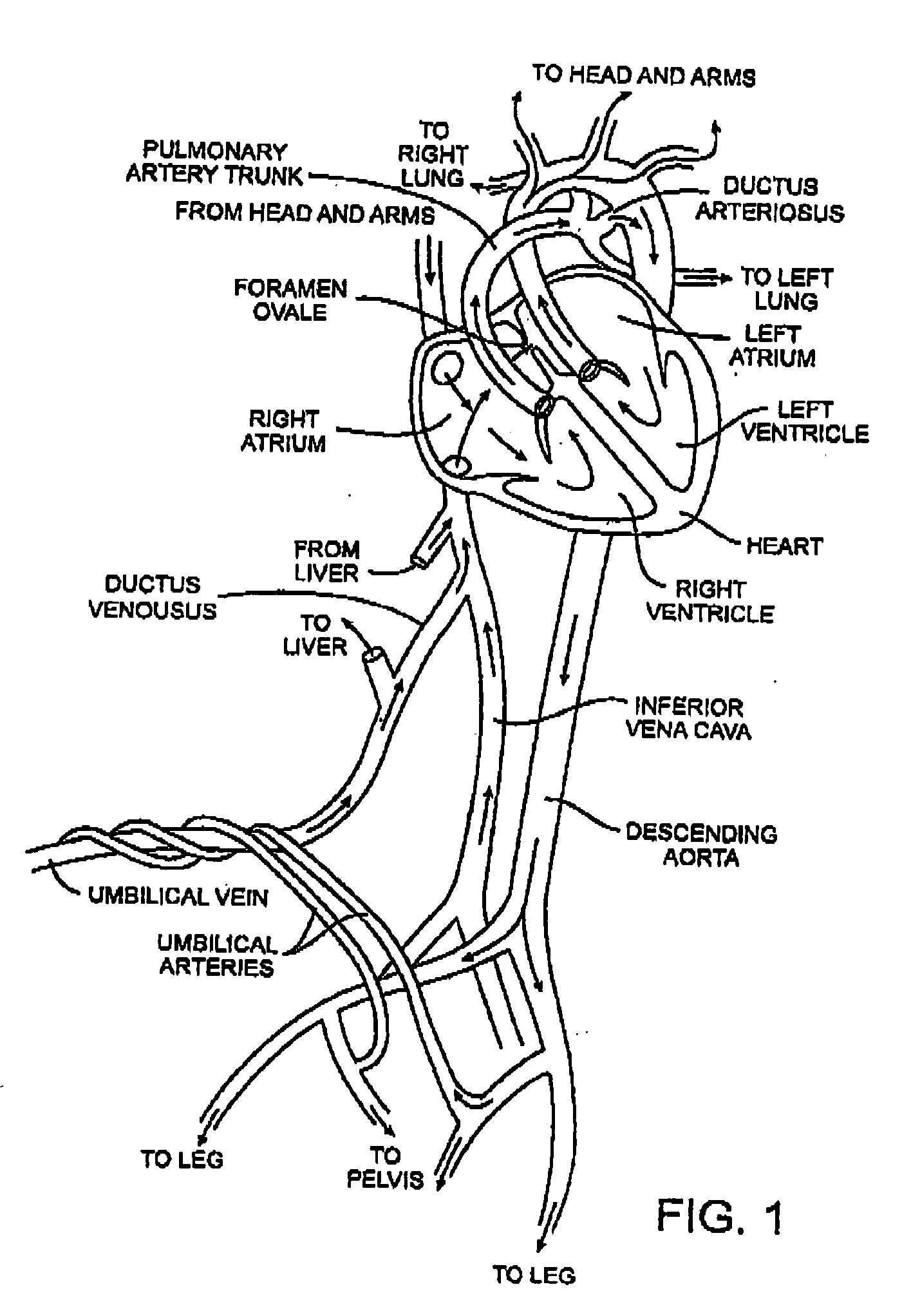
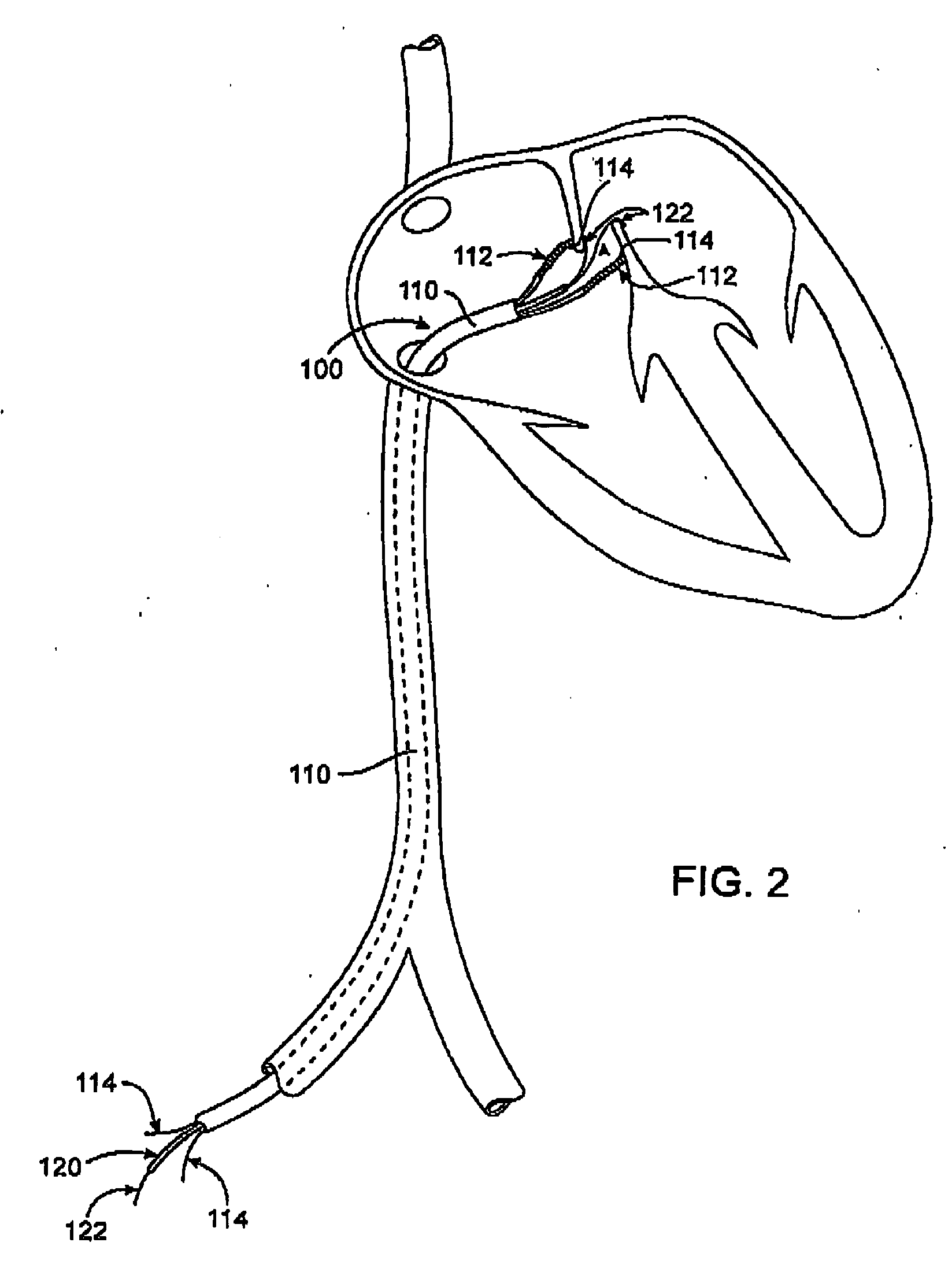
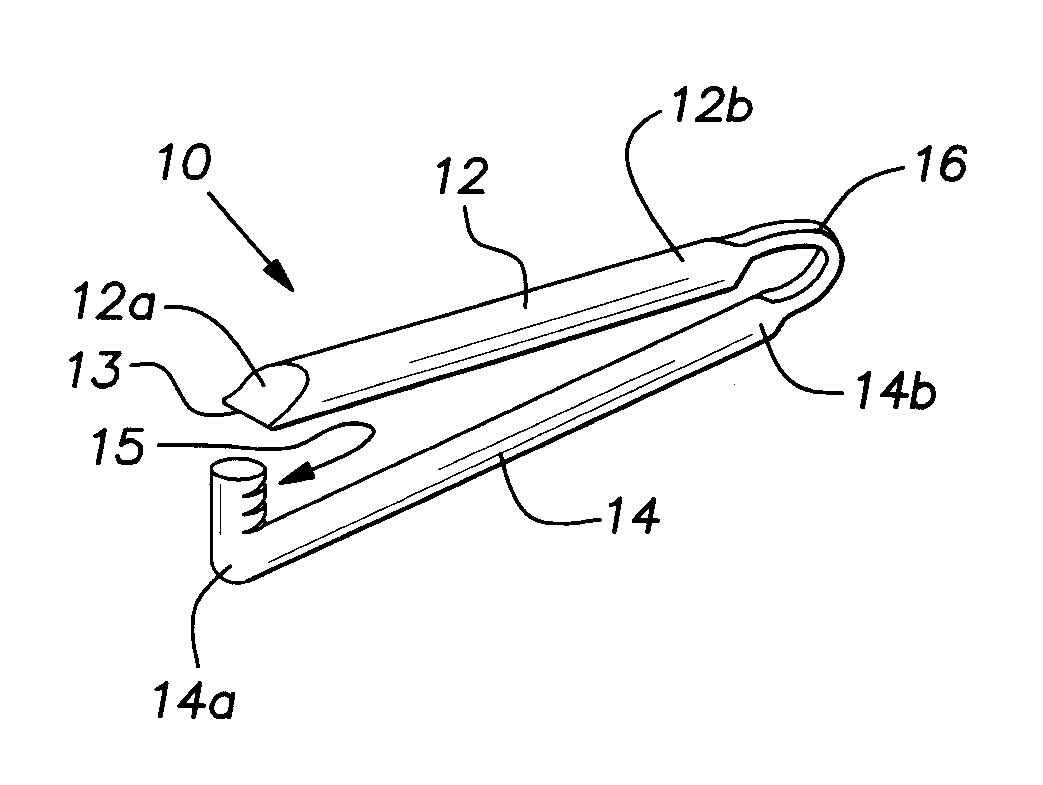
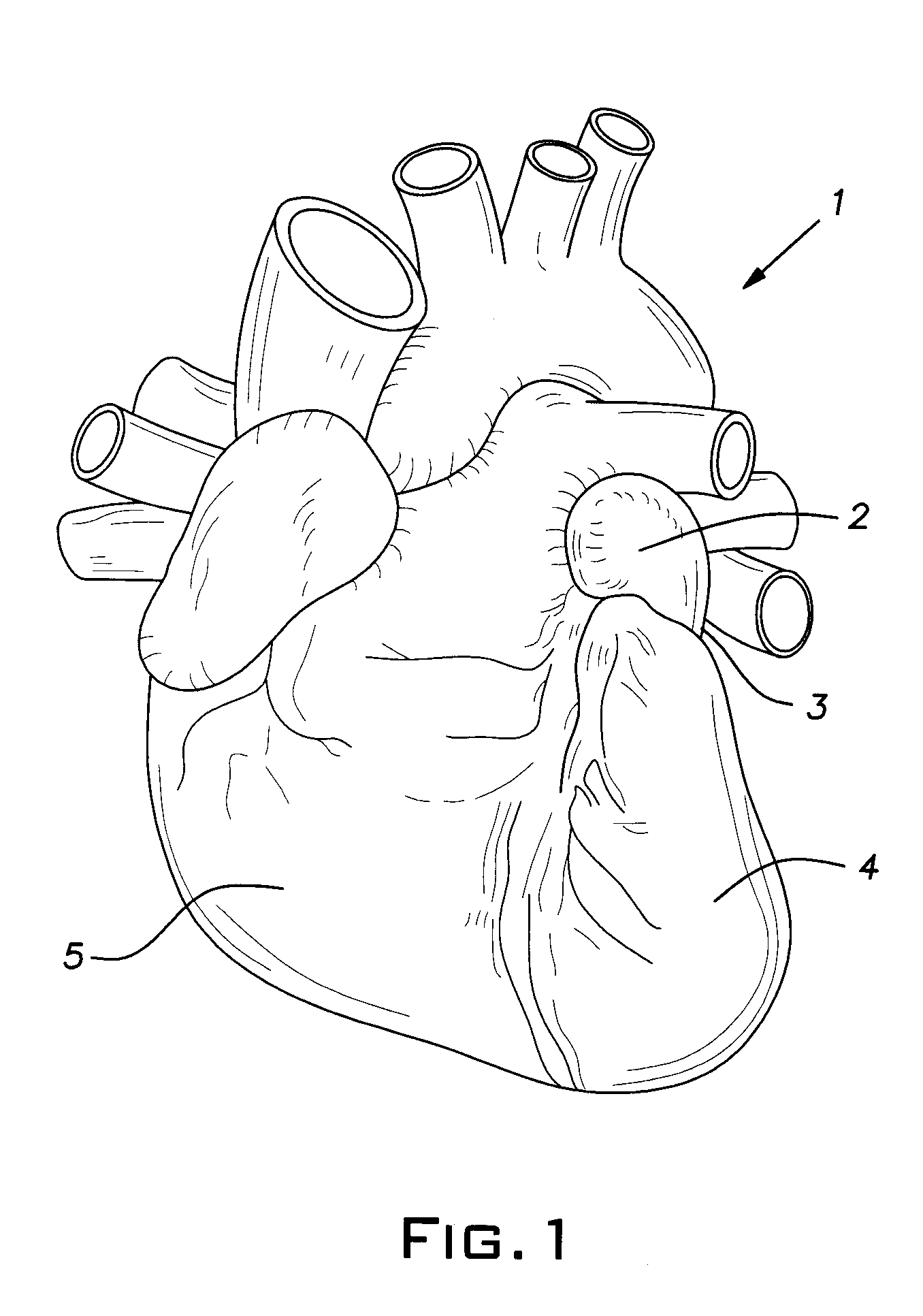
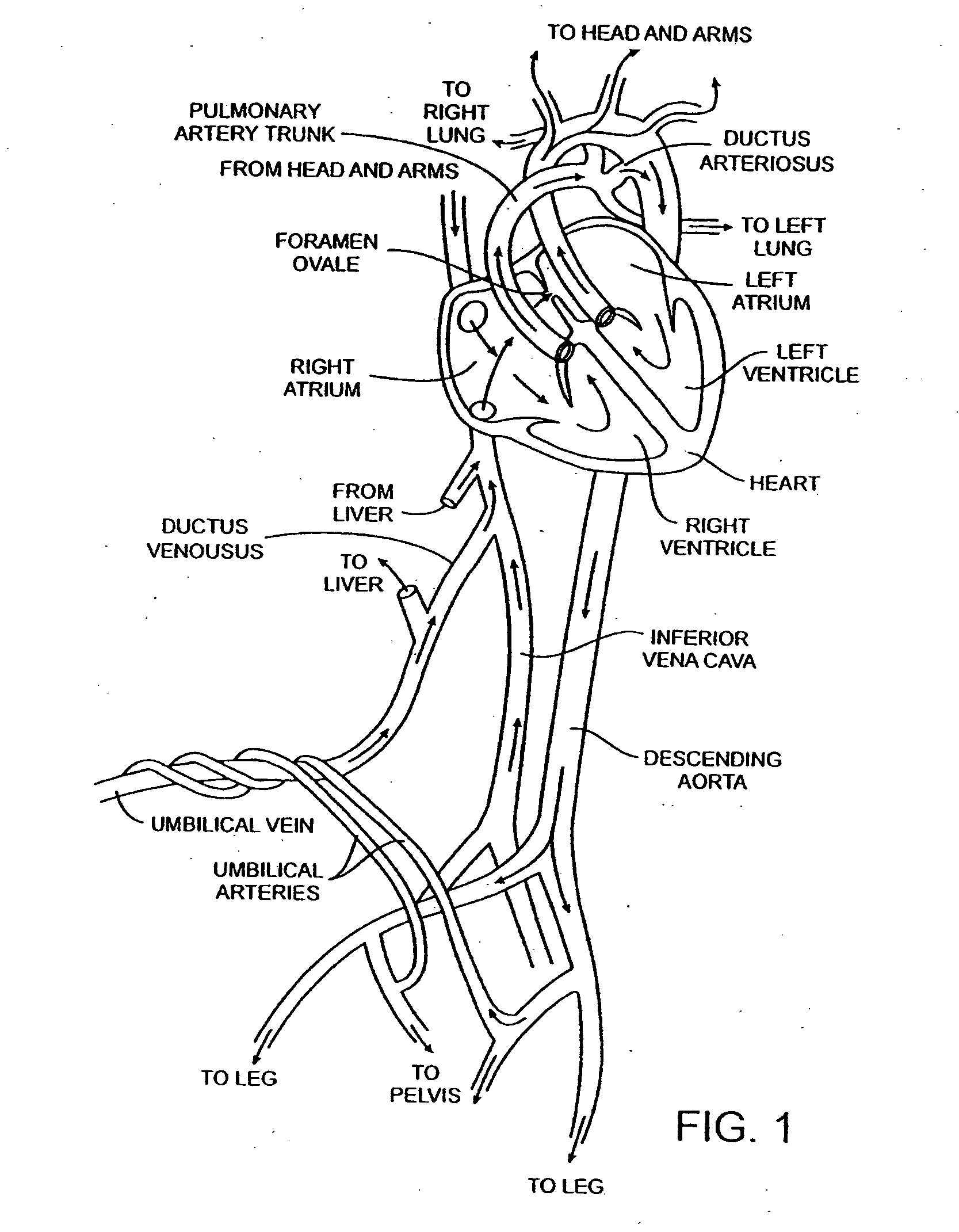
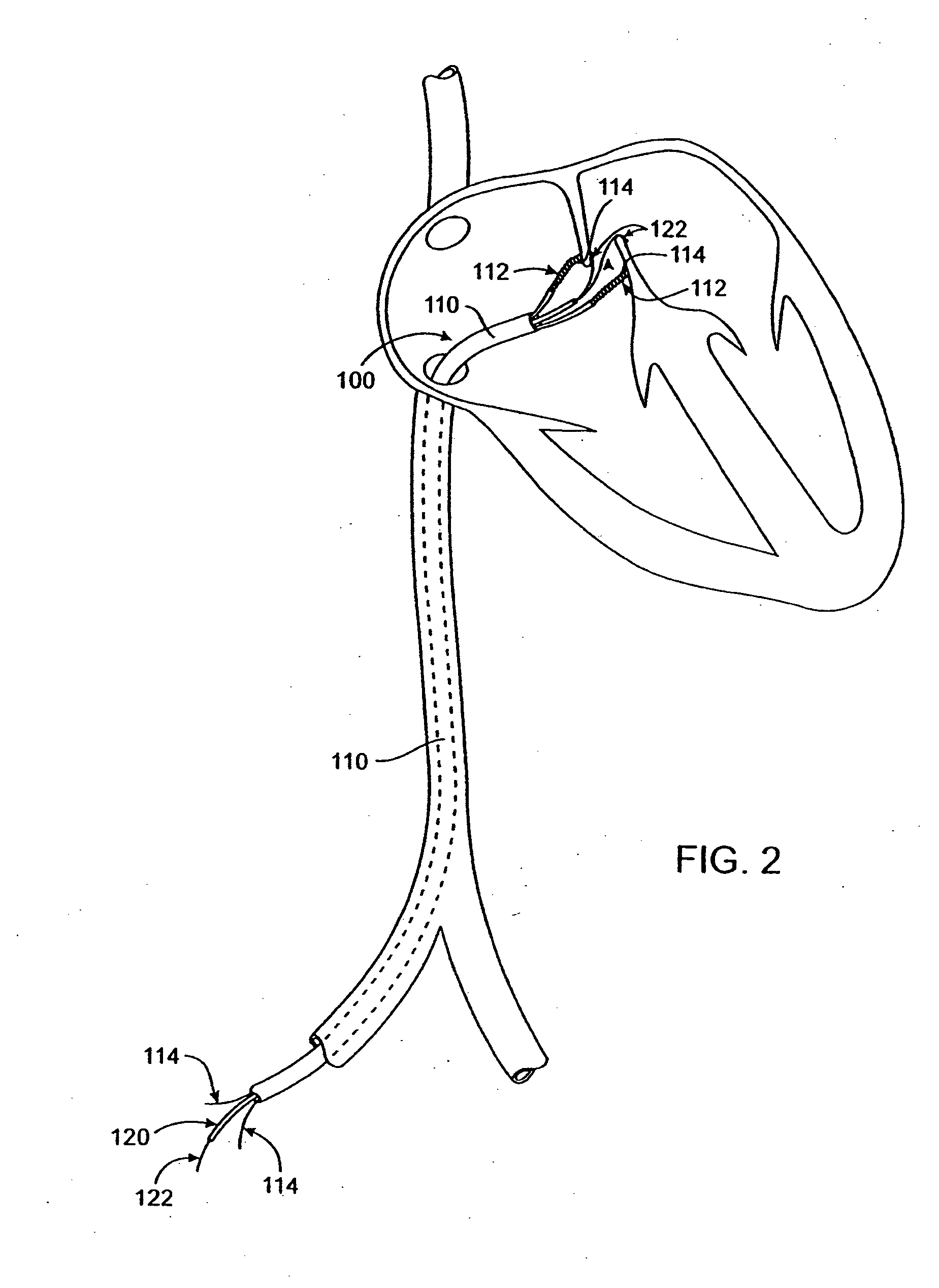
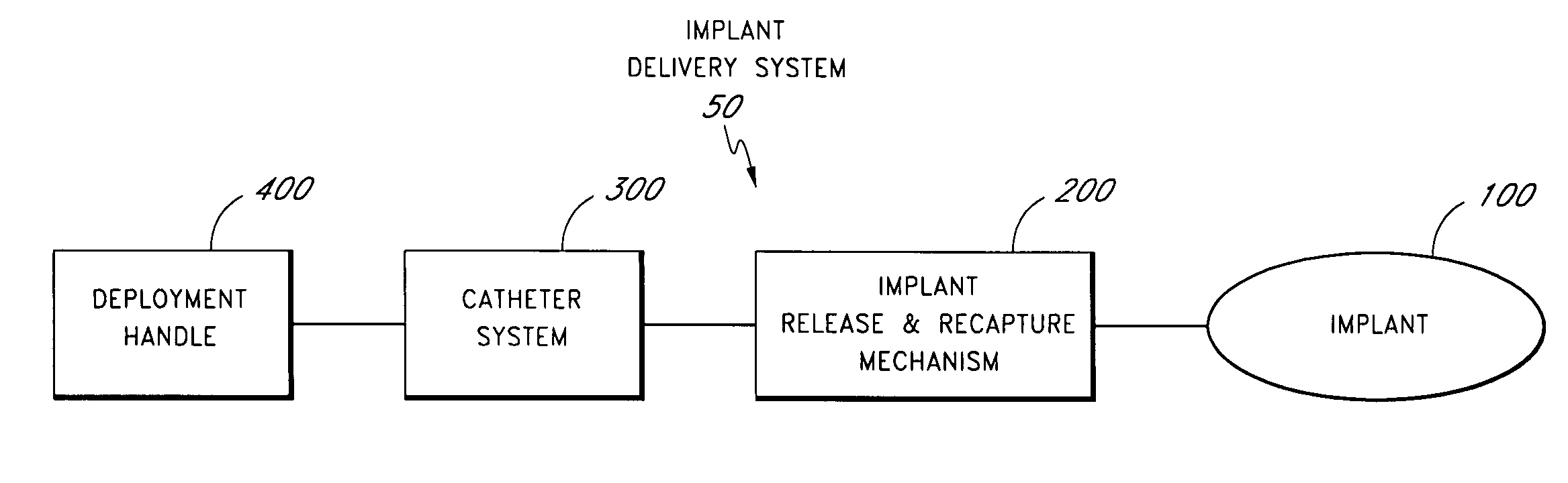
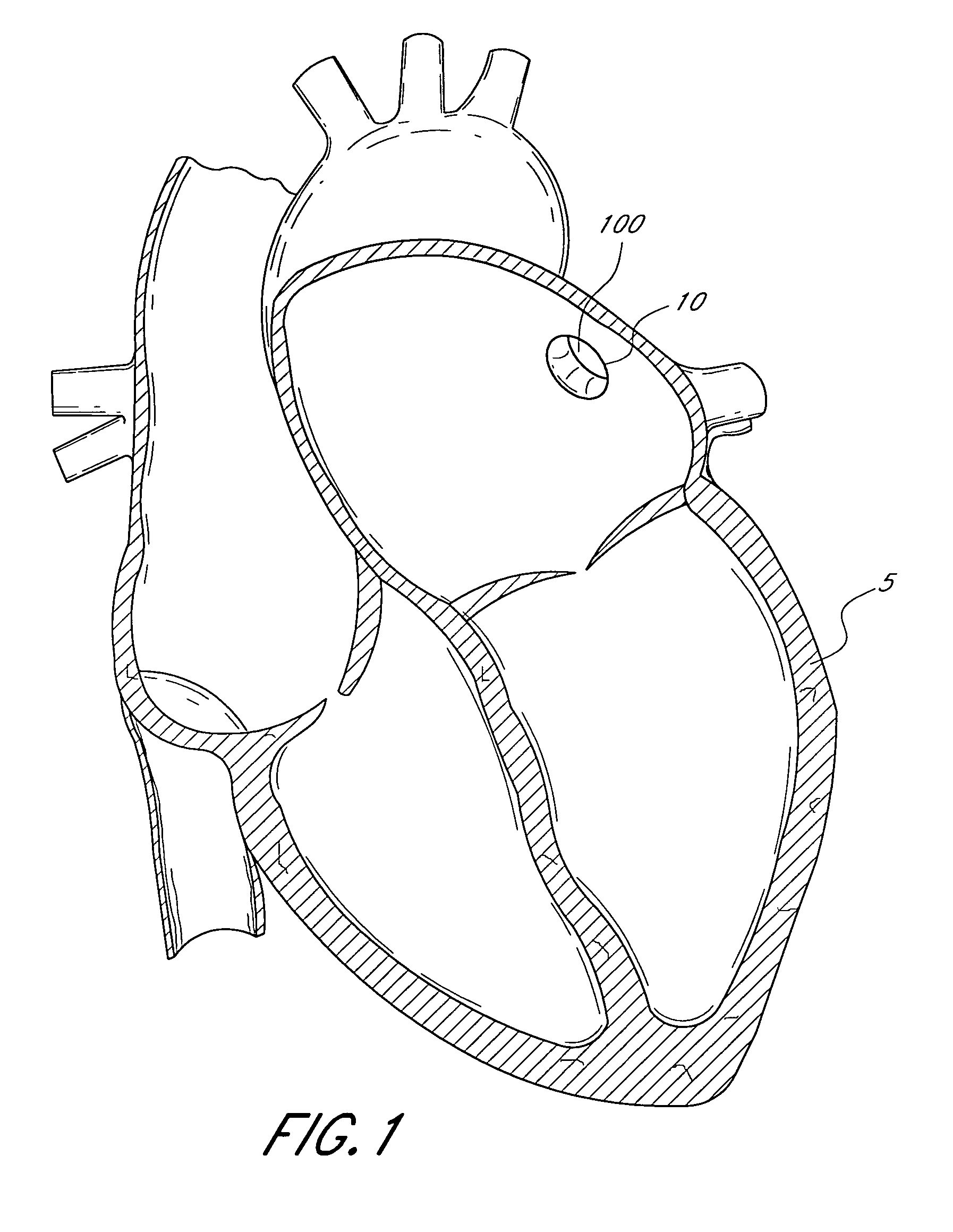
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
235 results about "Left atrial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
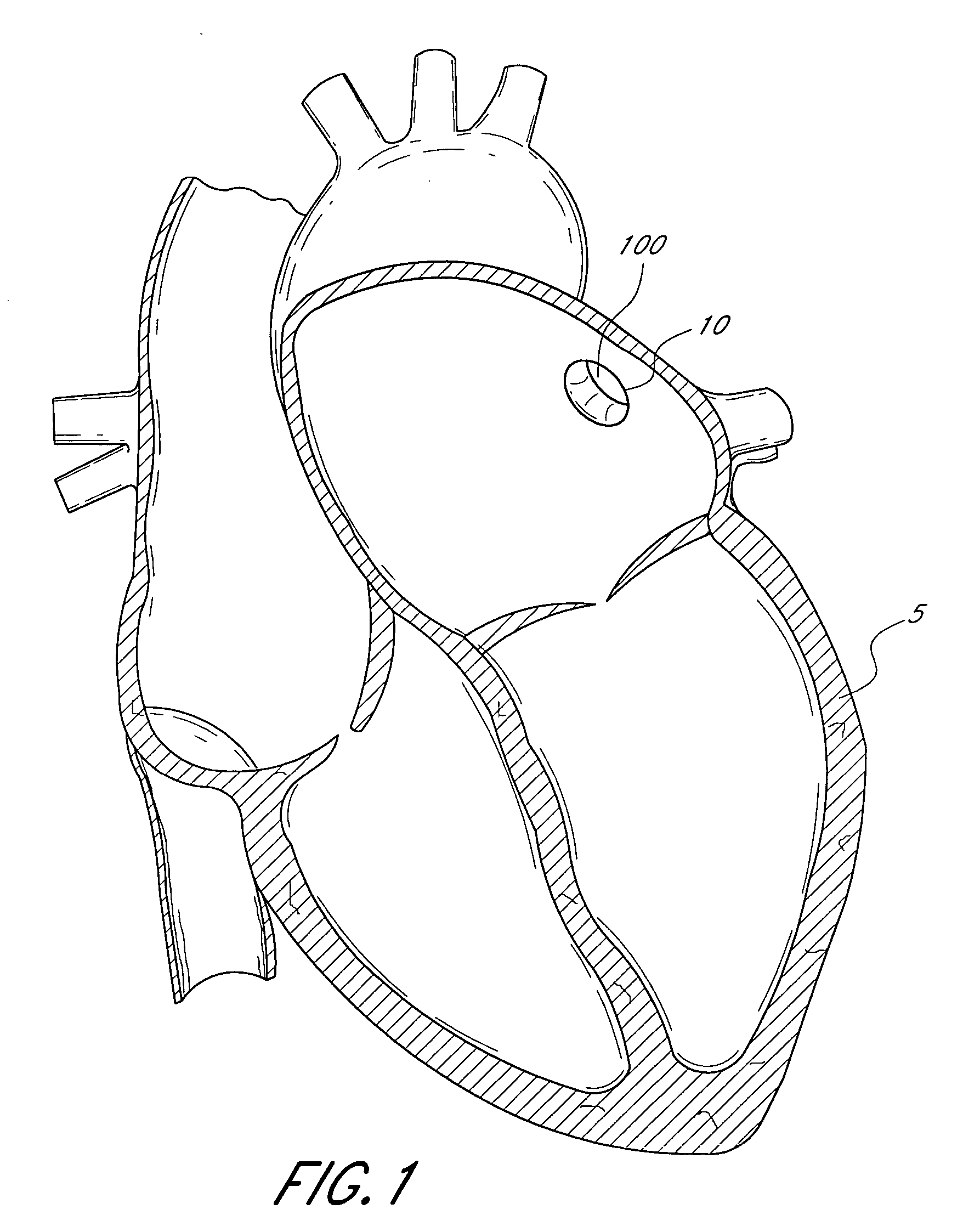
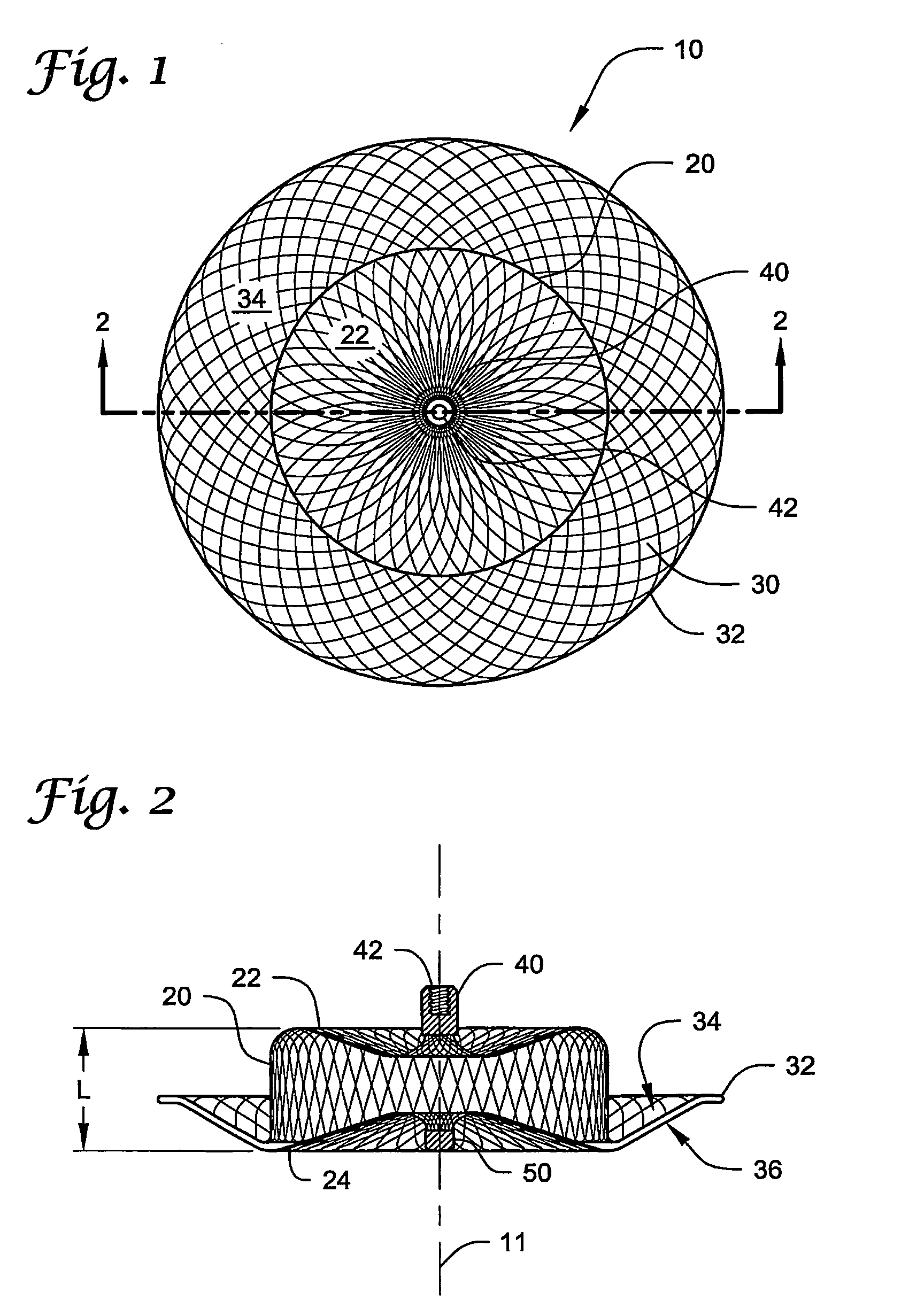
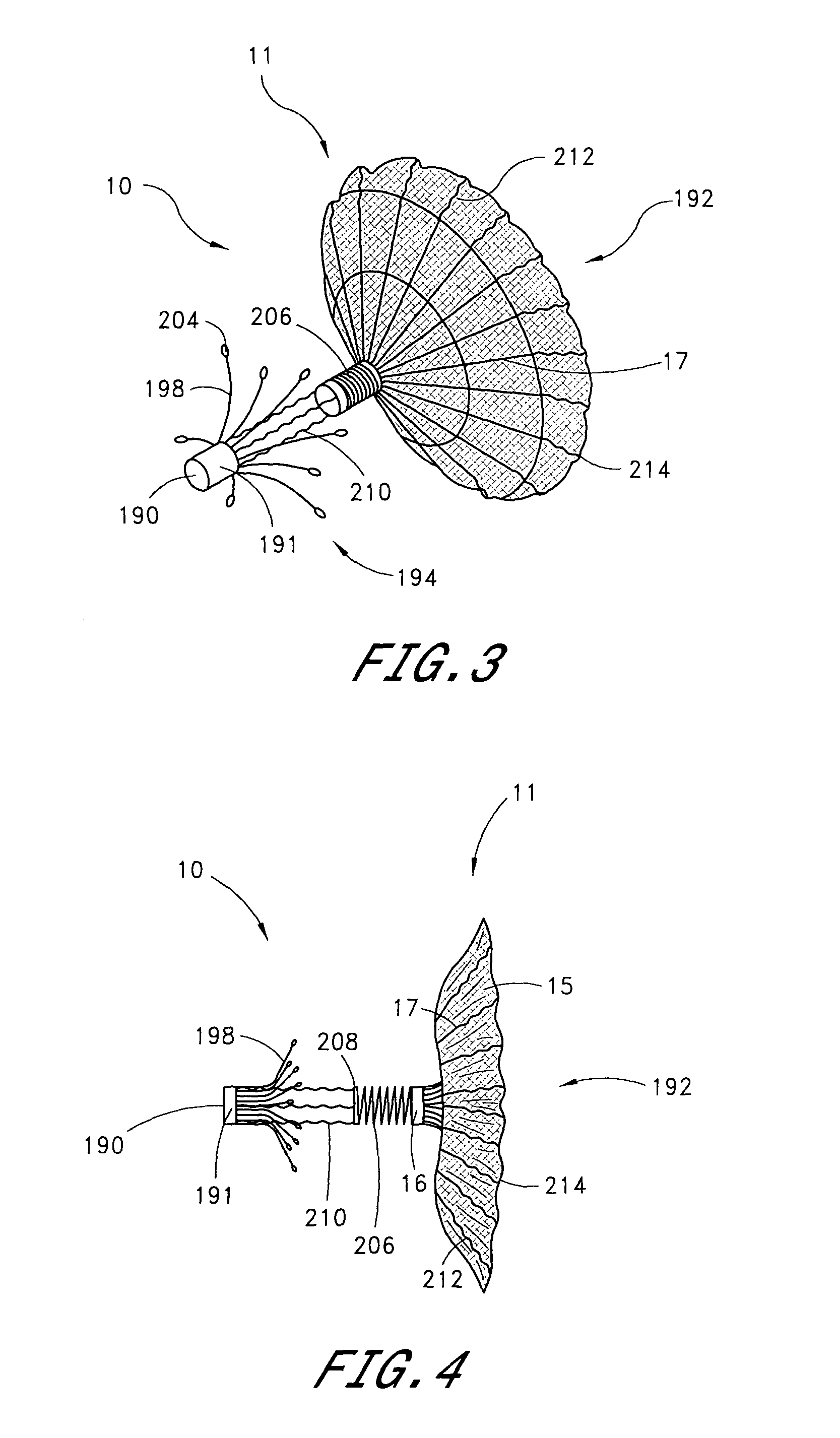
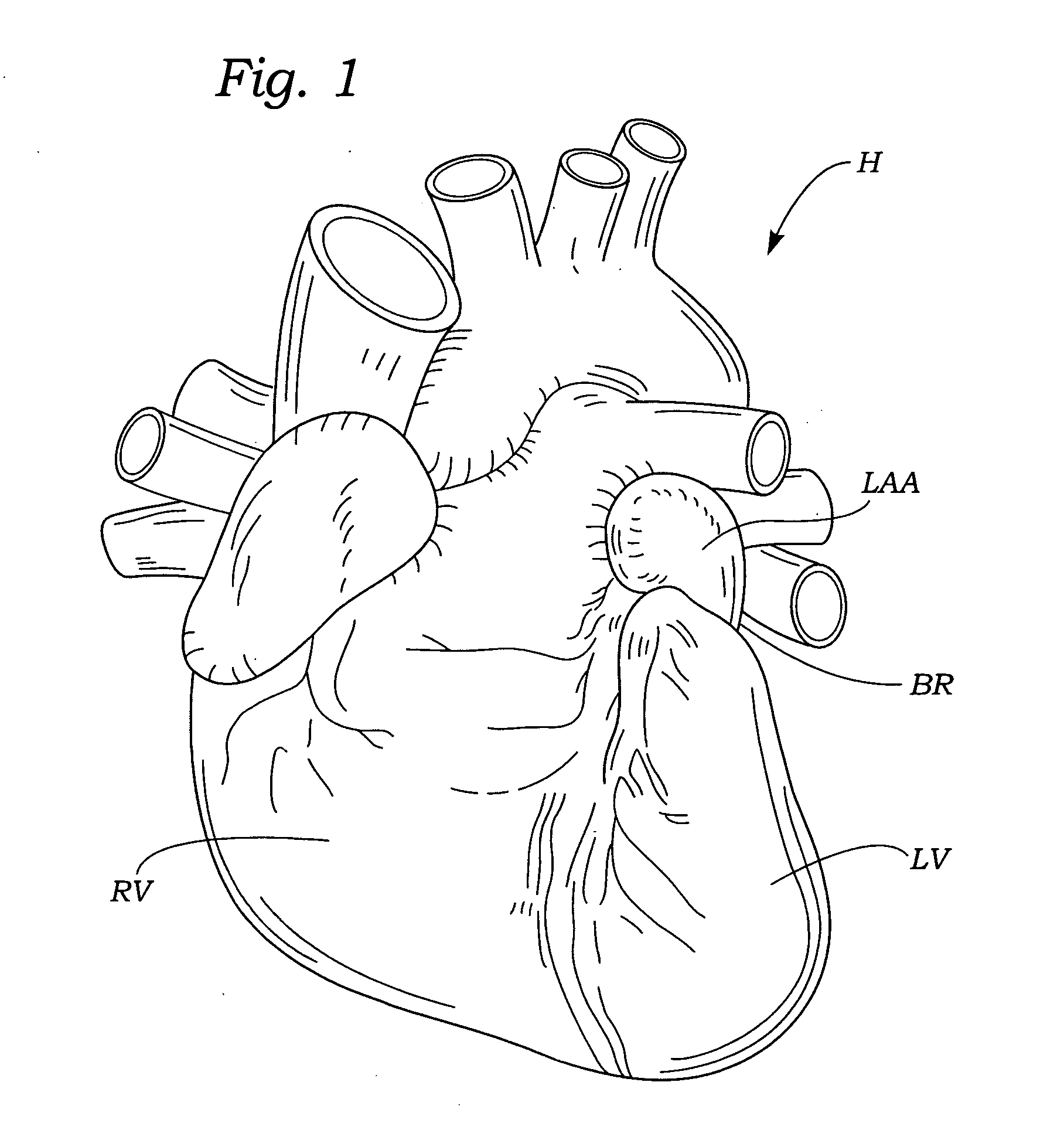
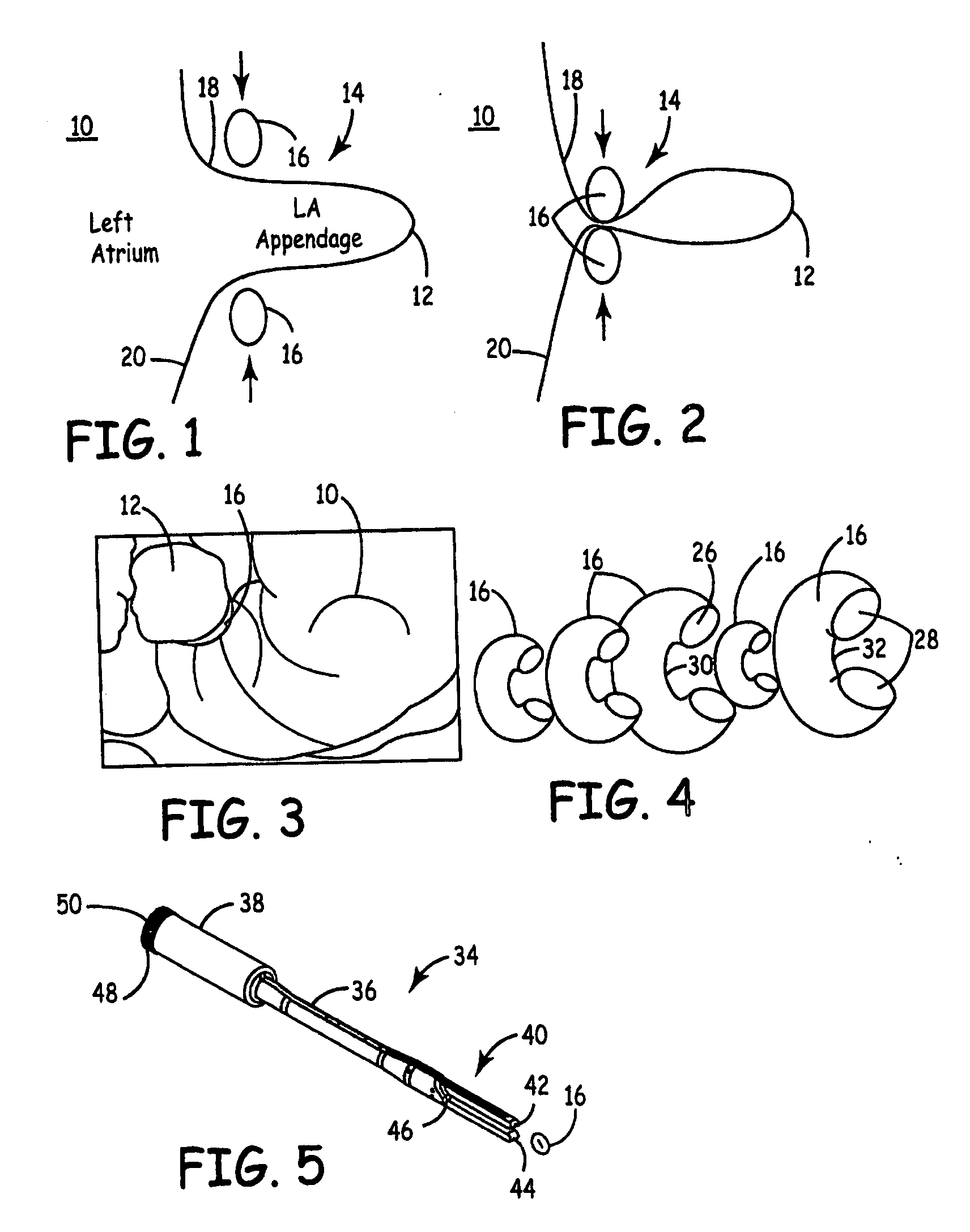
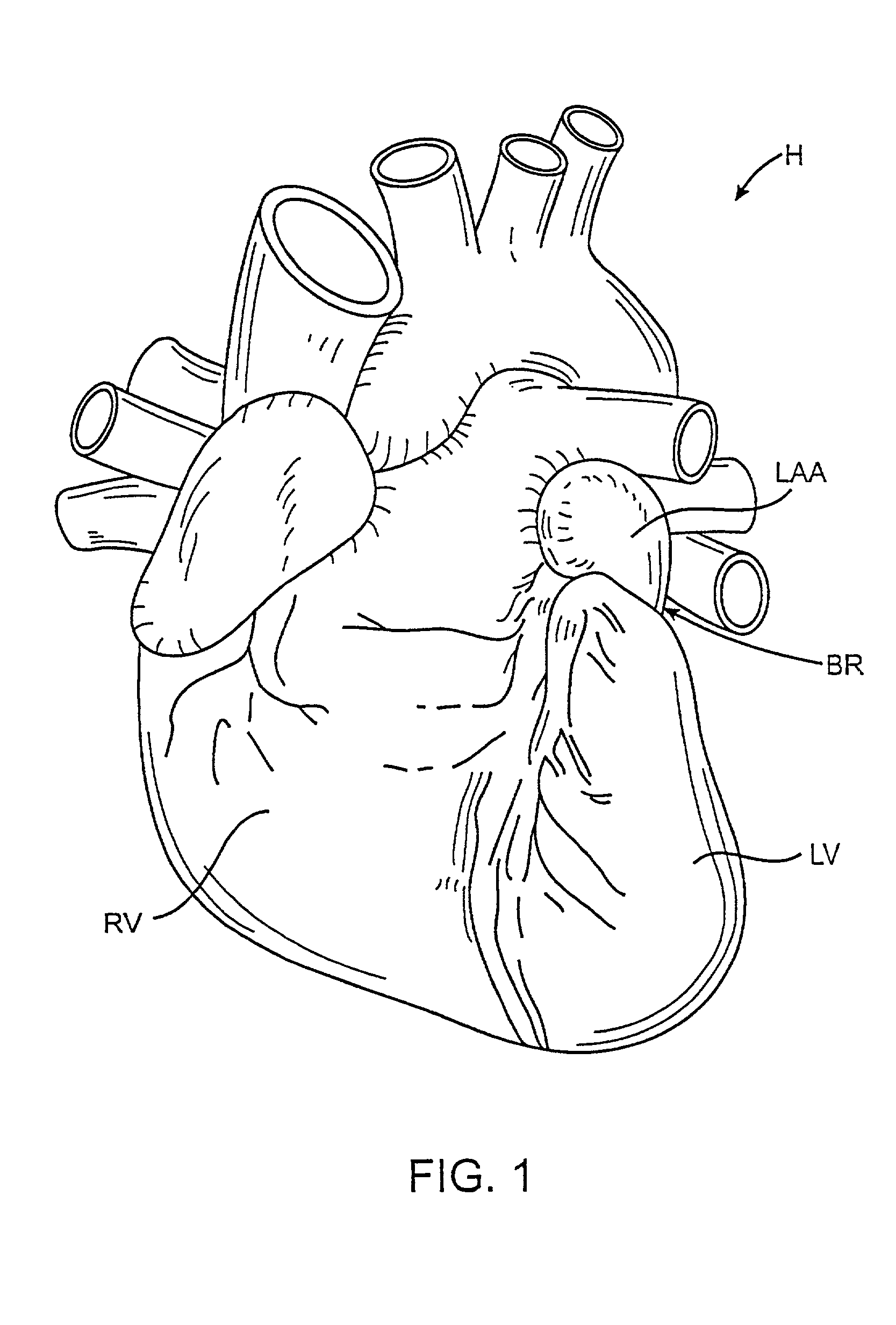
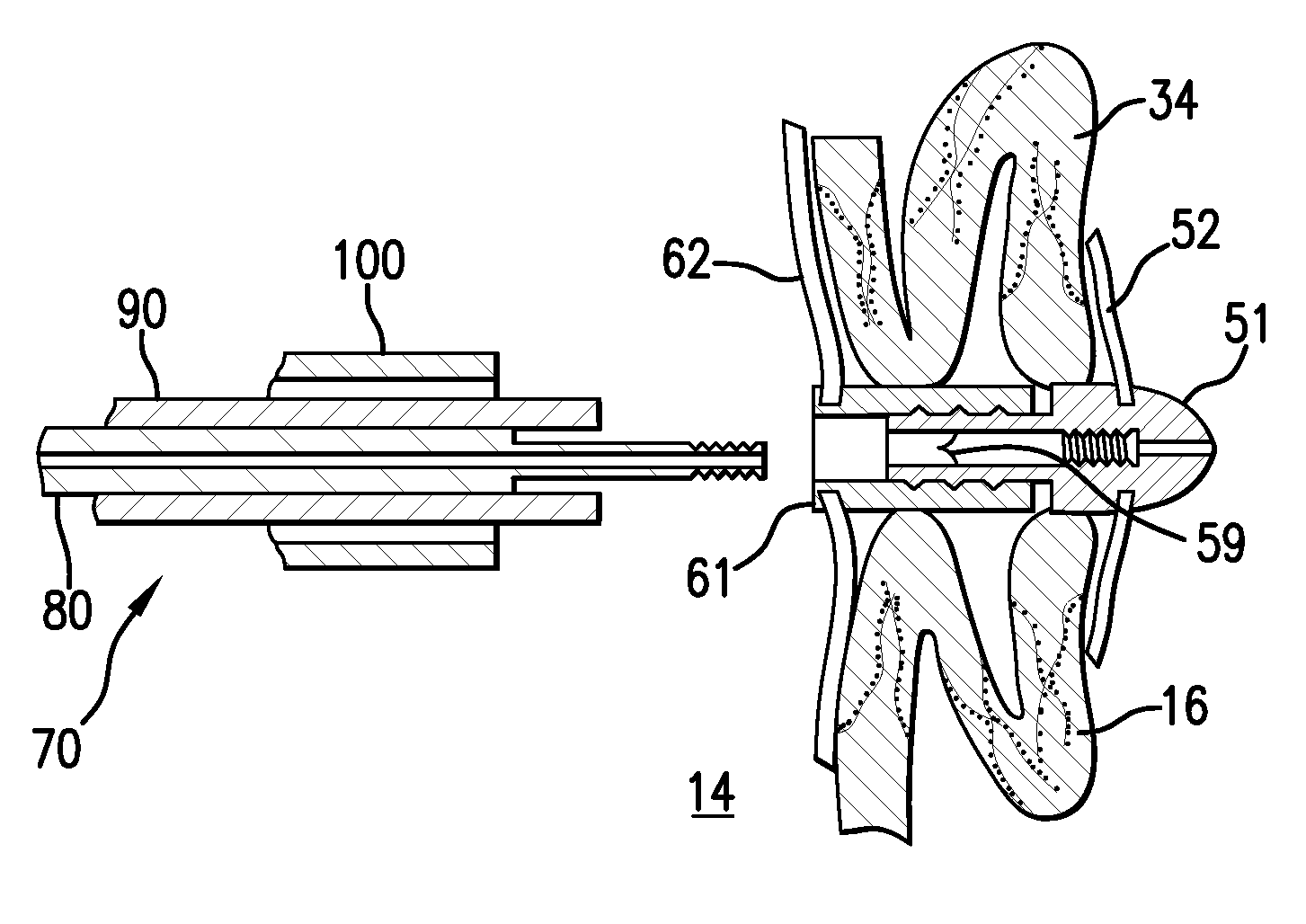
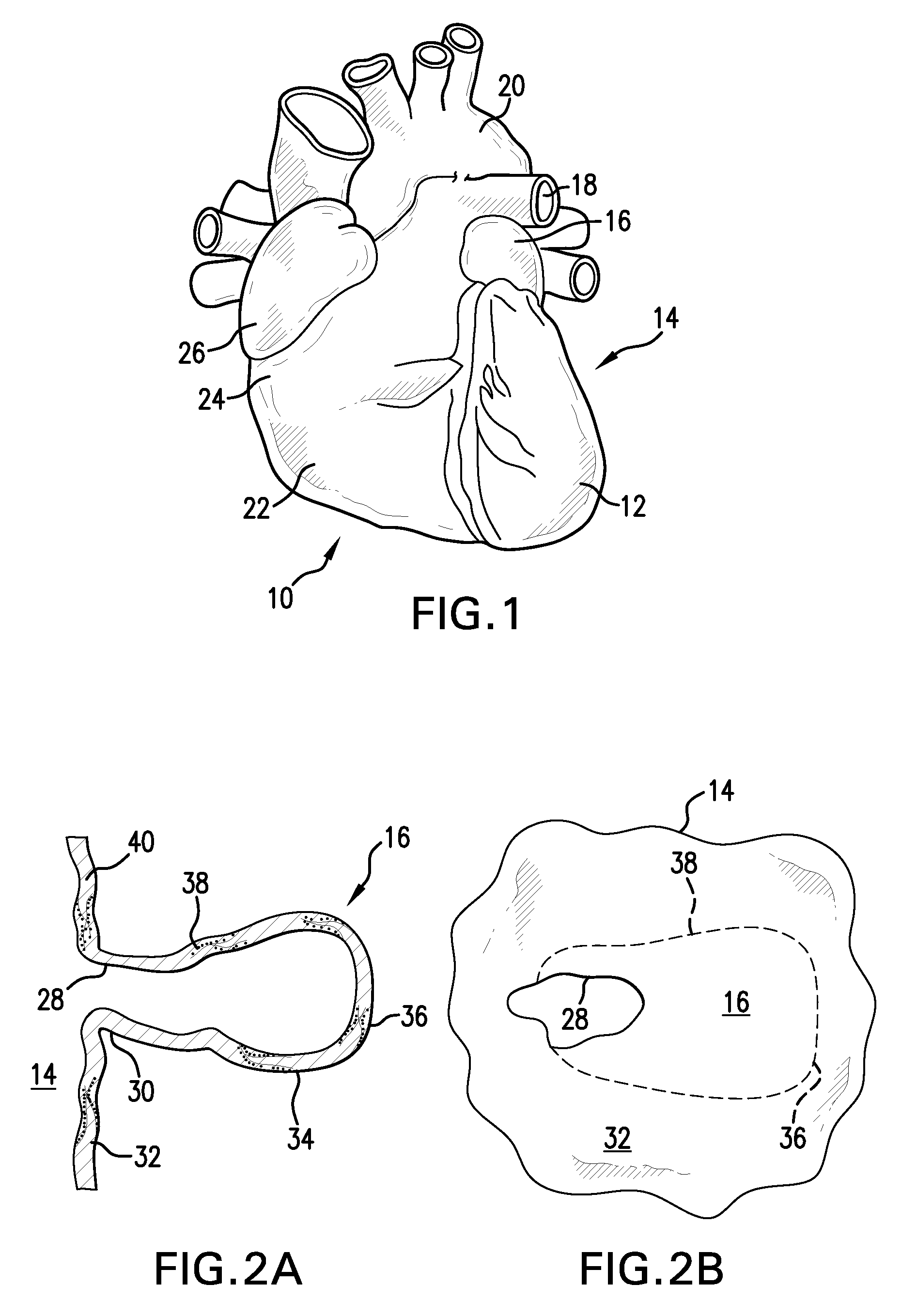
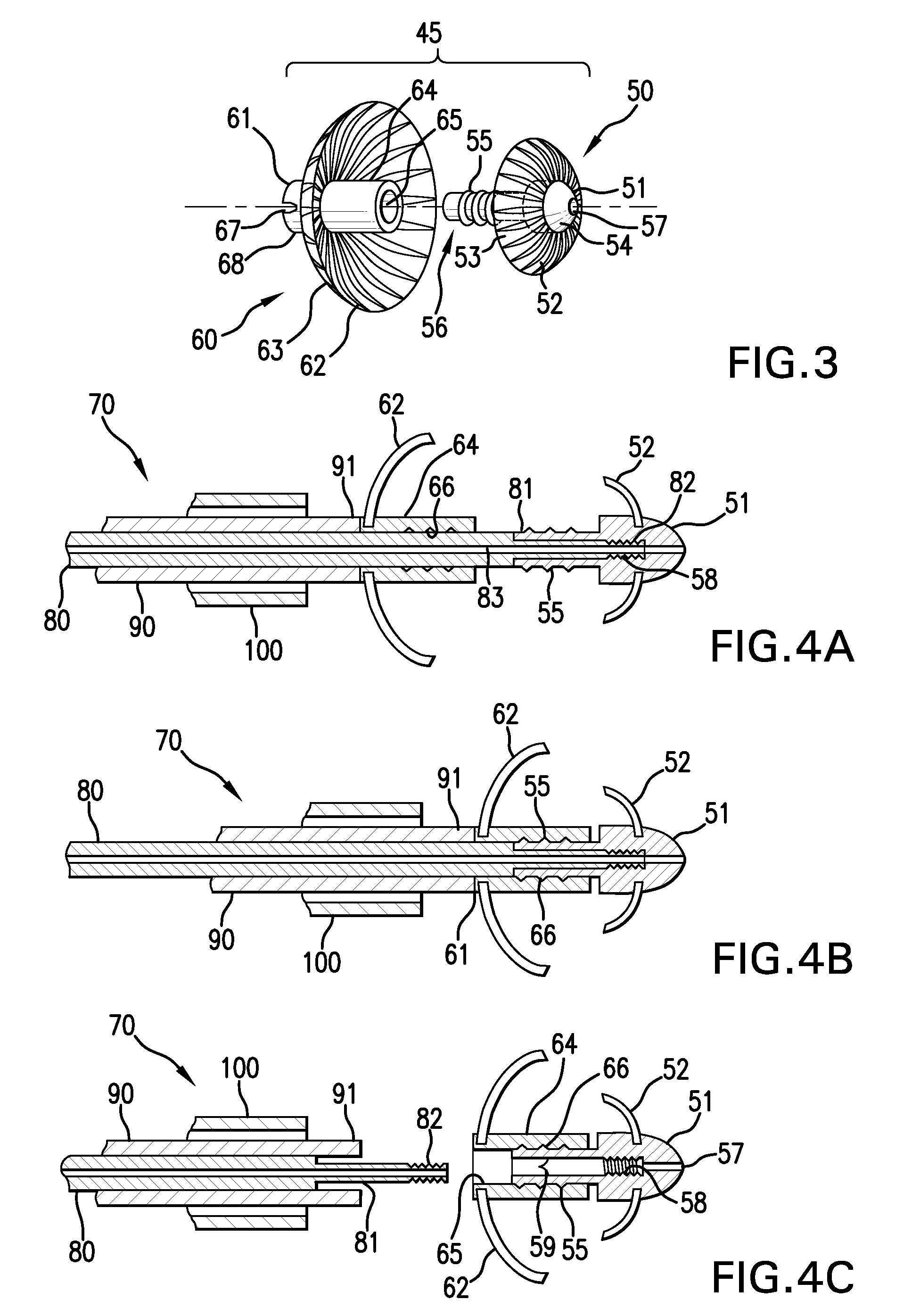
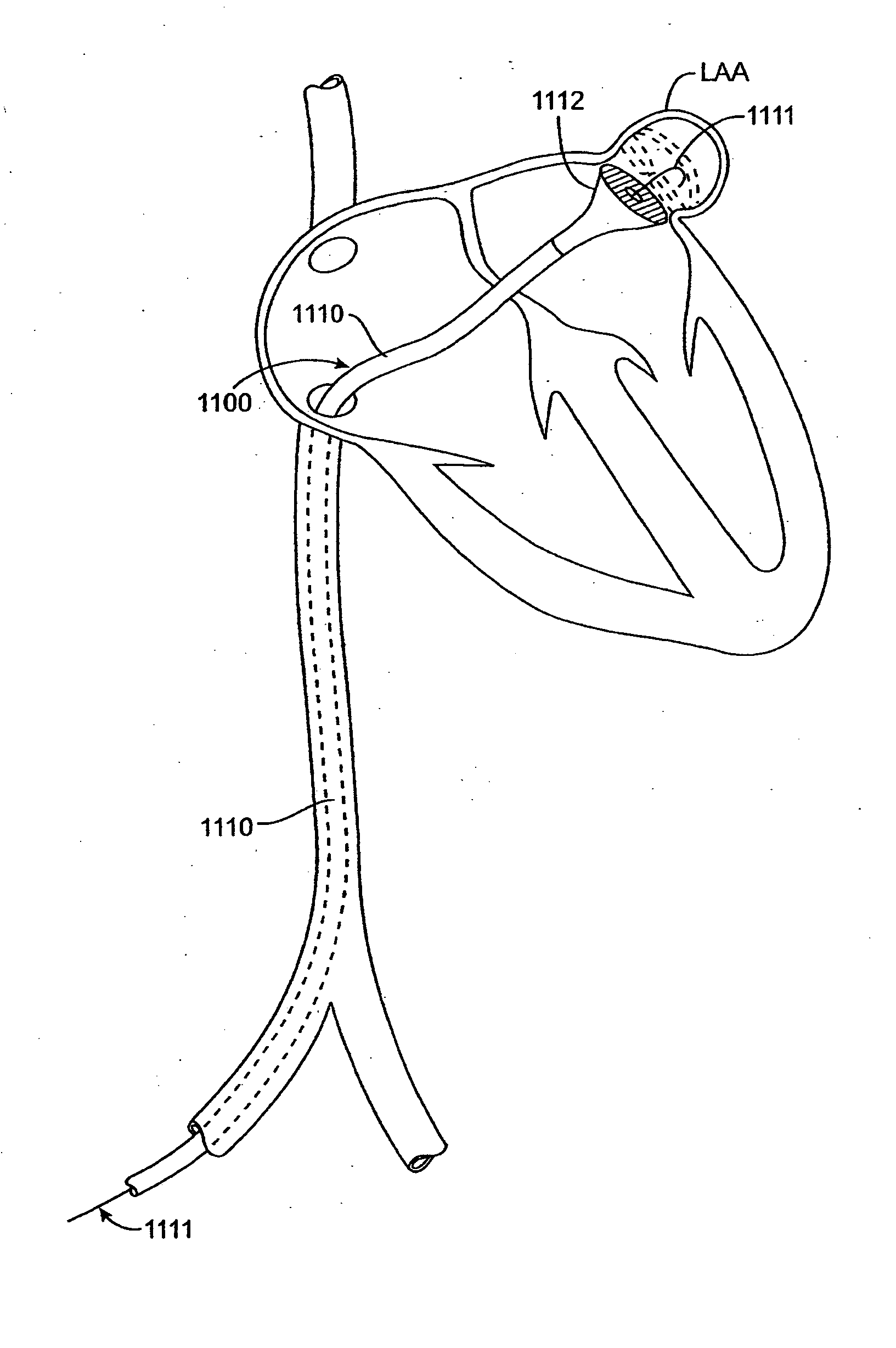
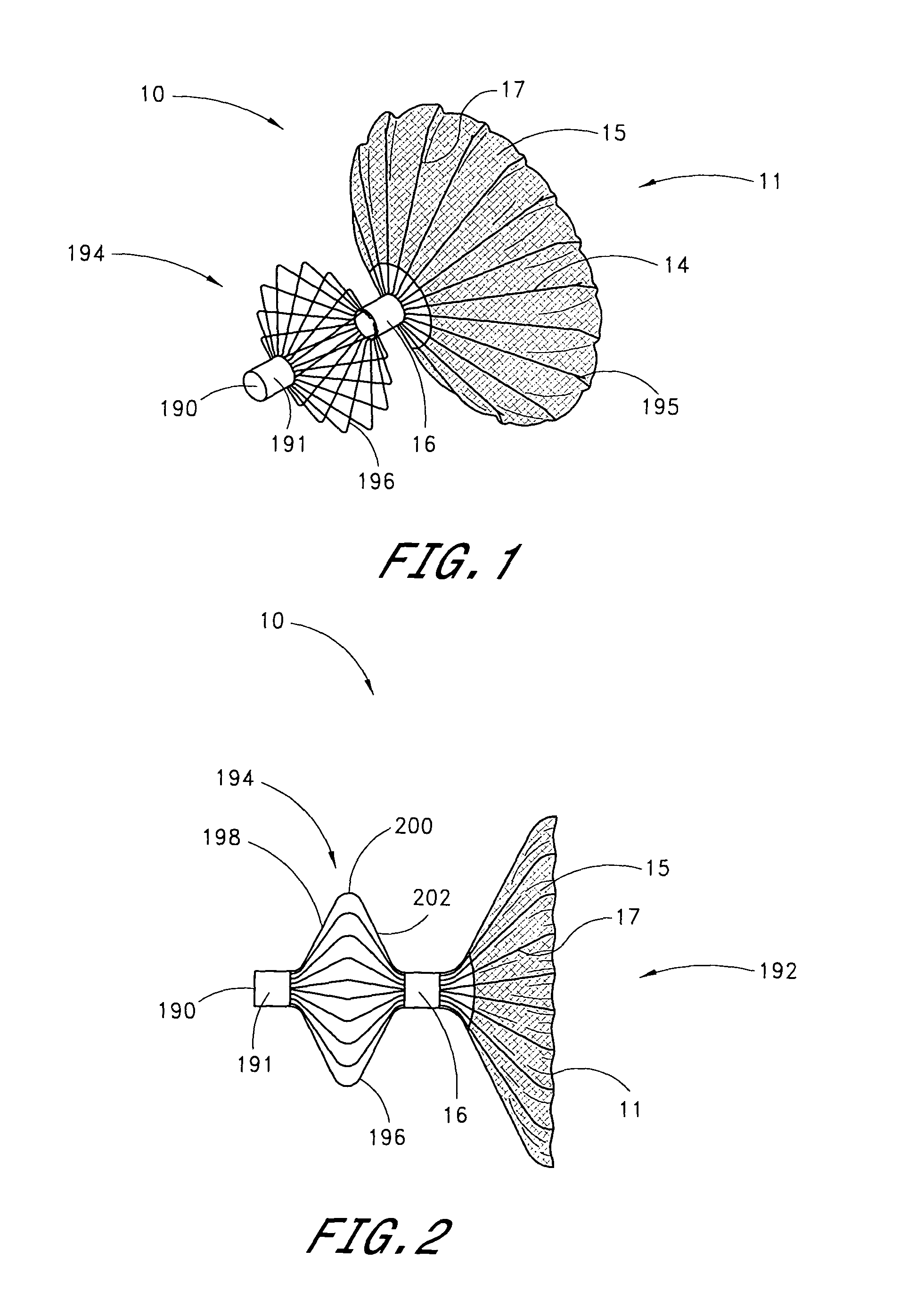
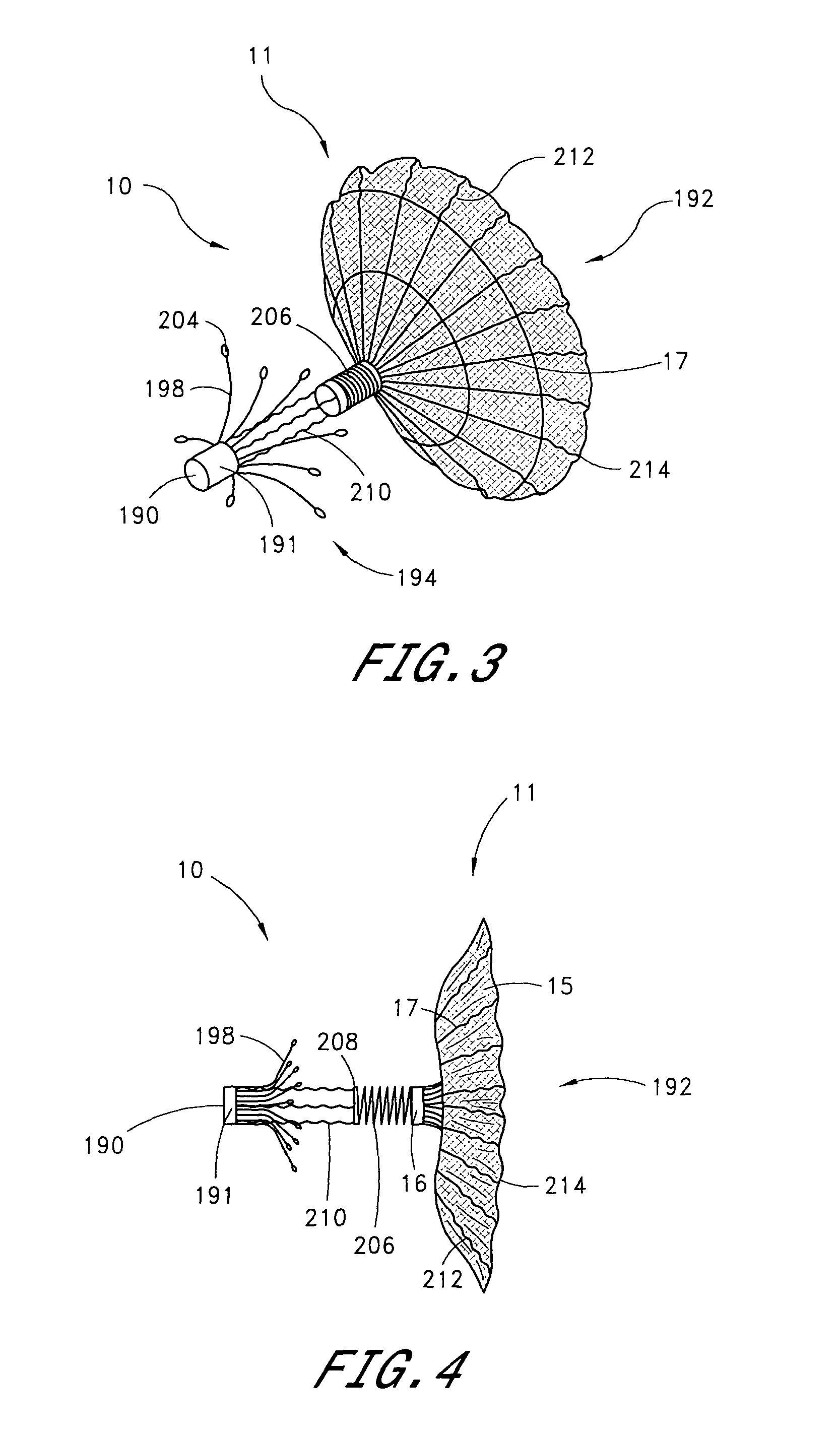
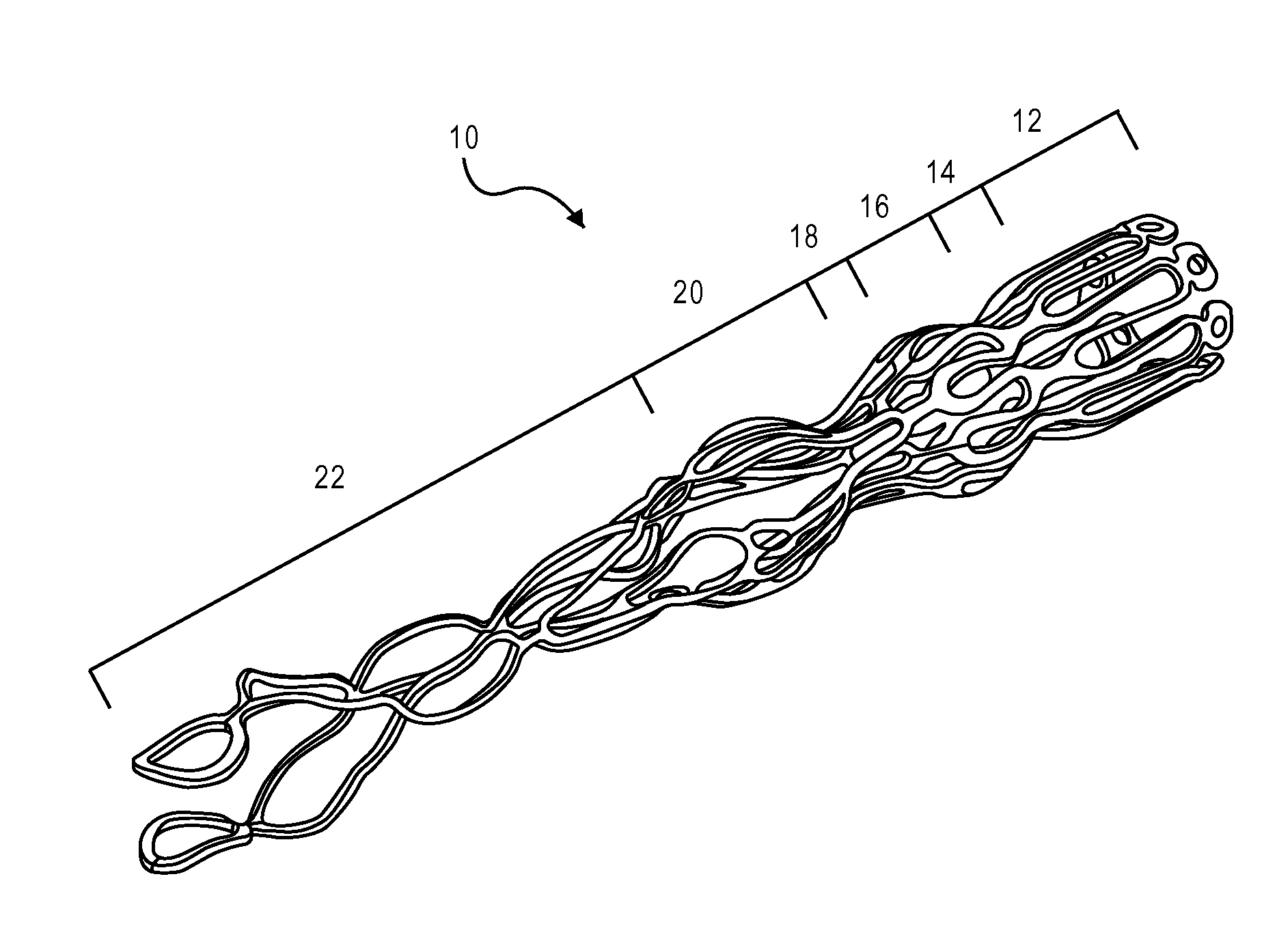
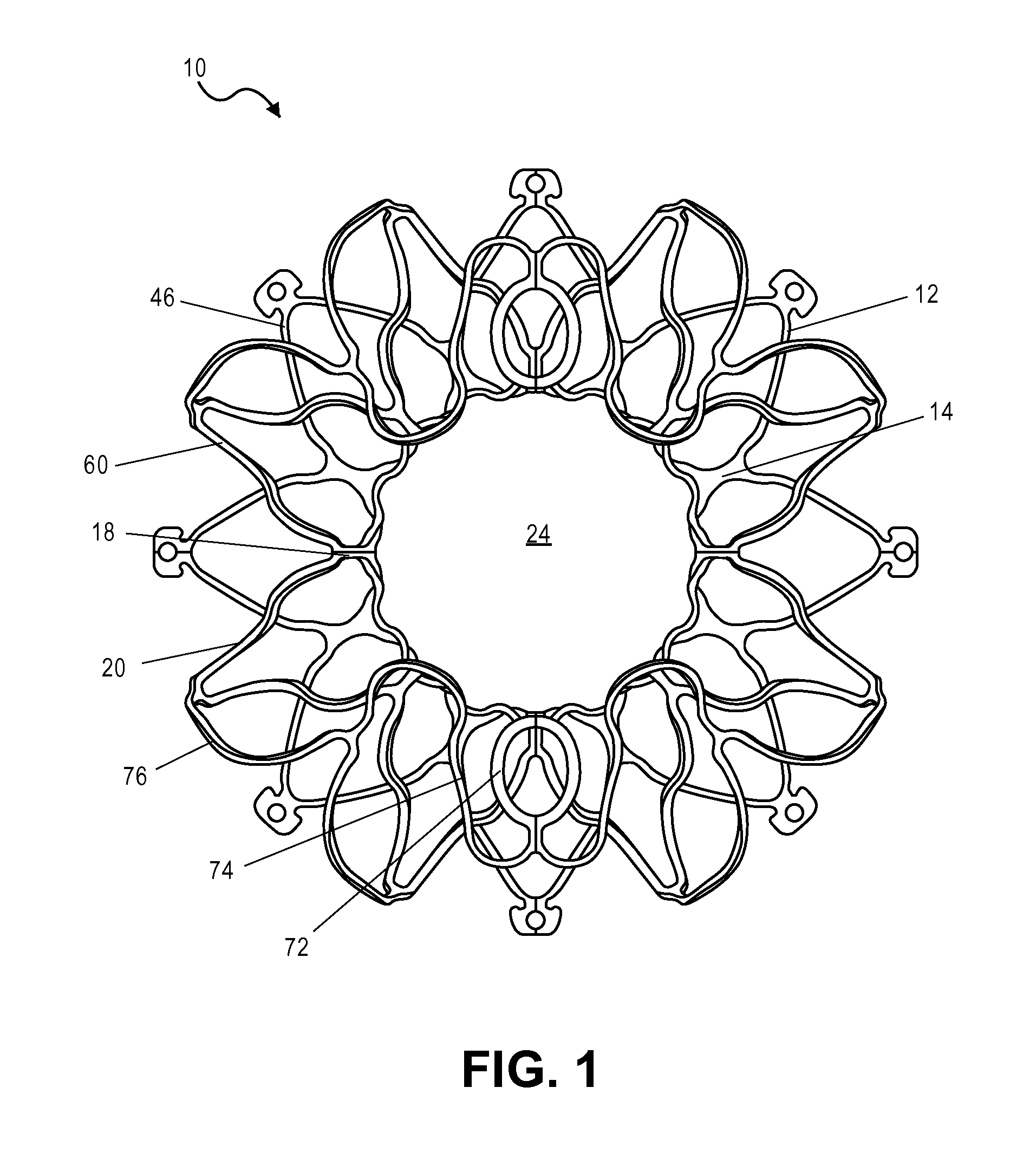
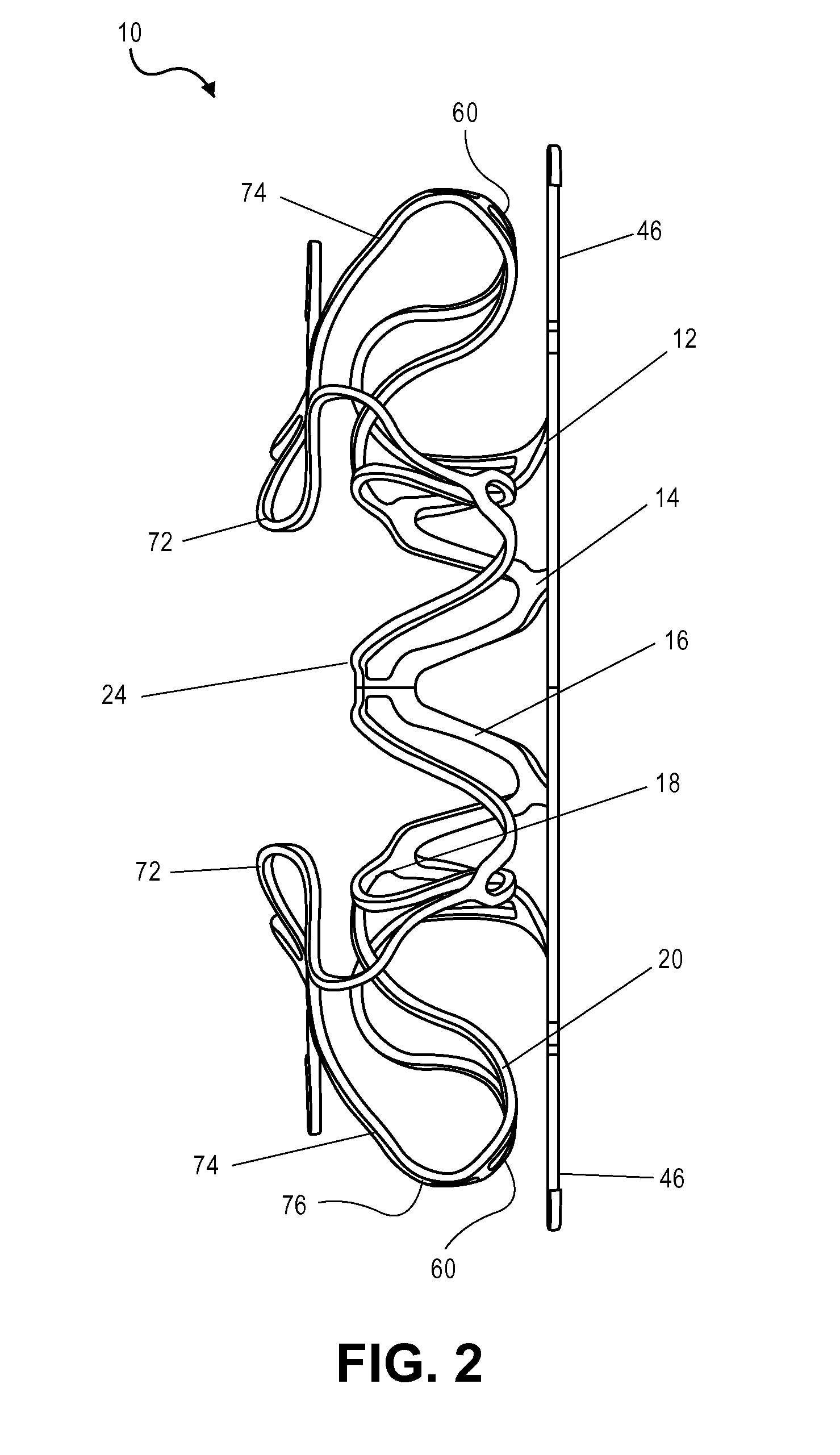
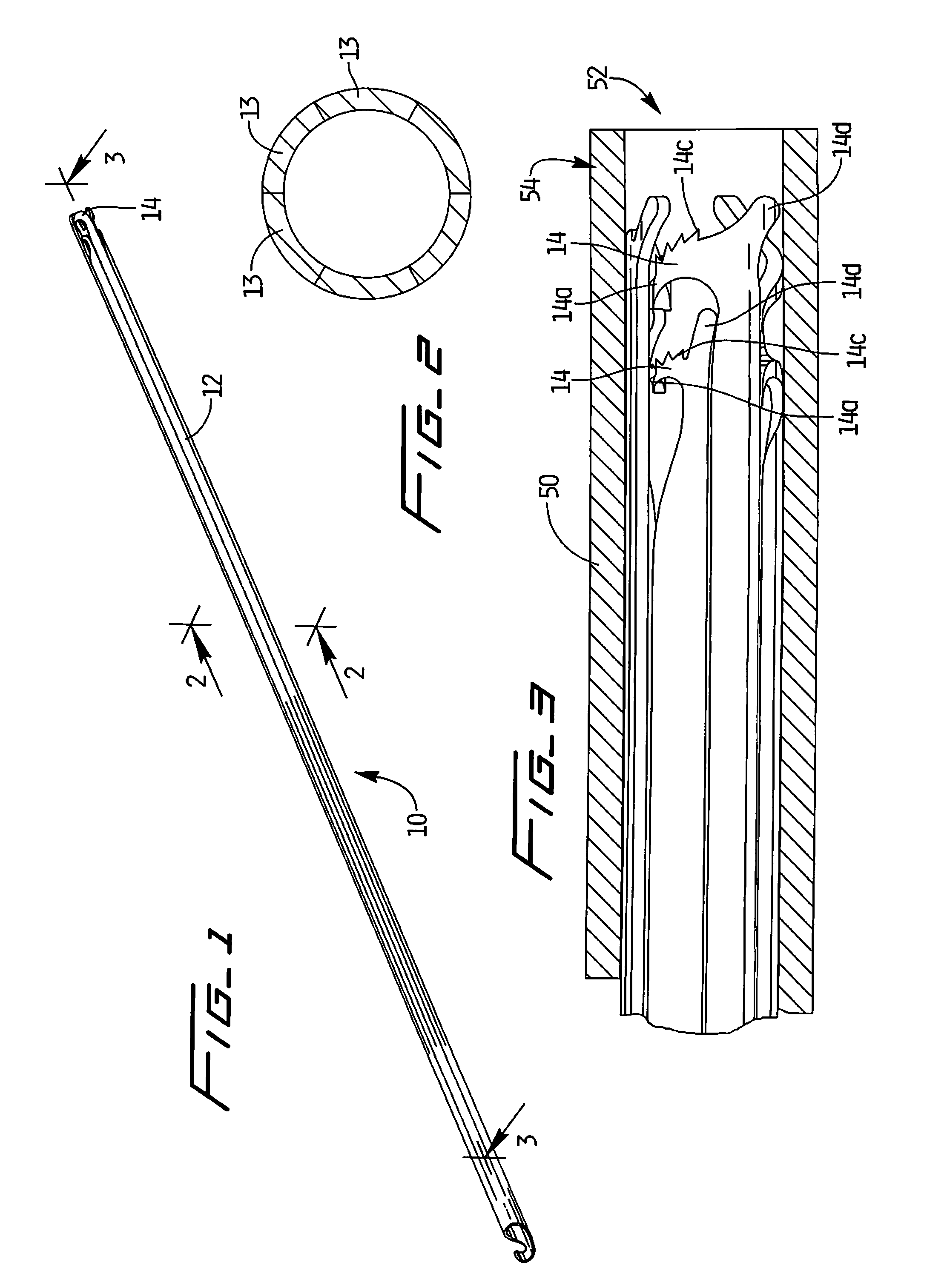
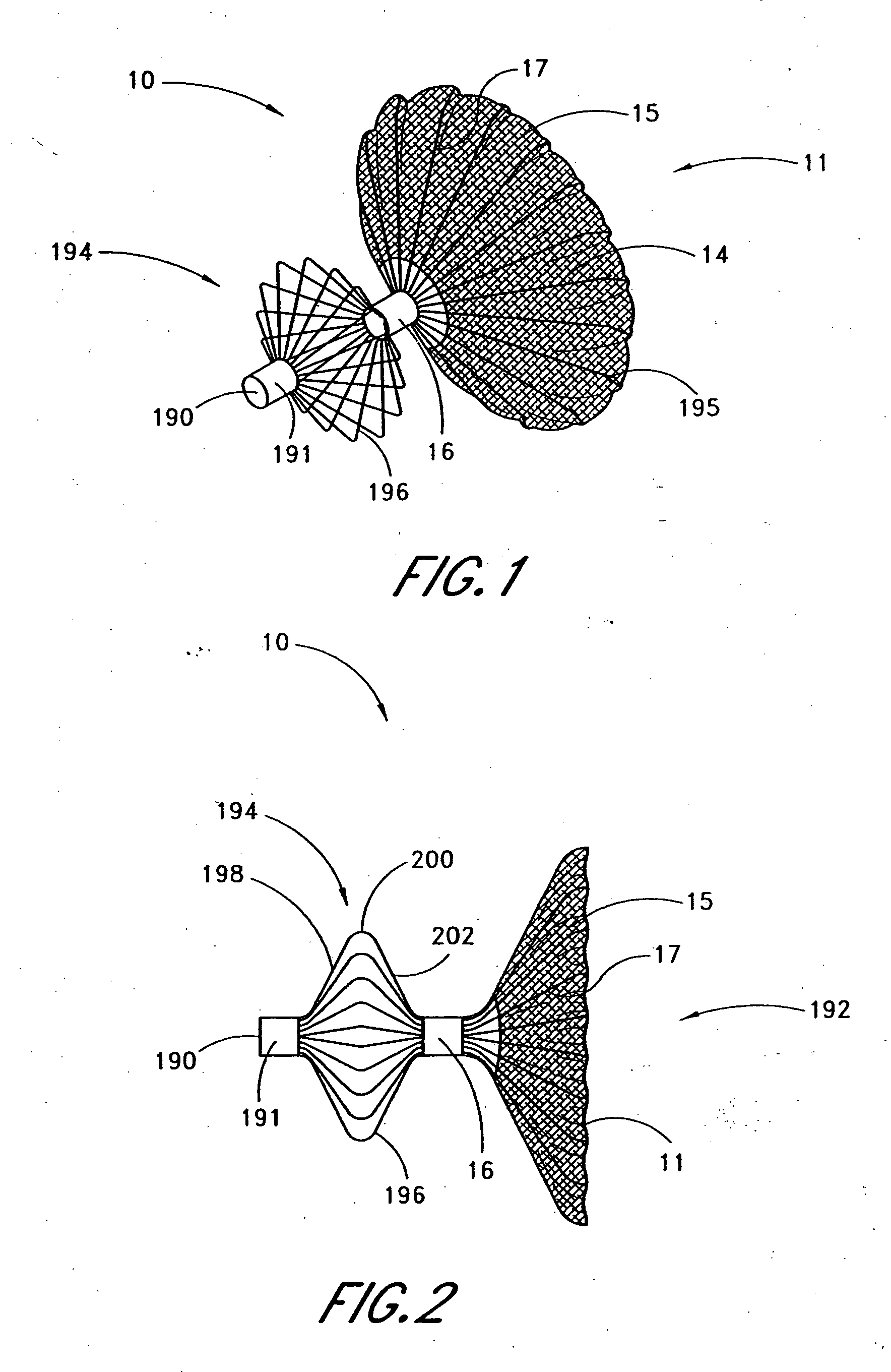
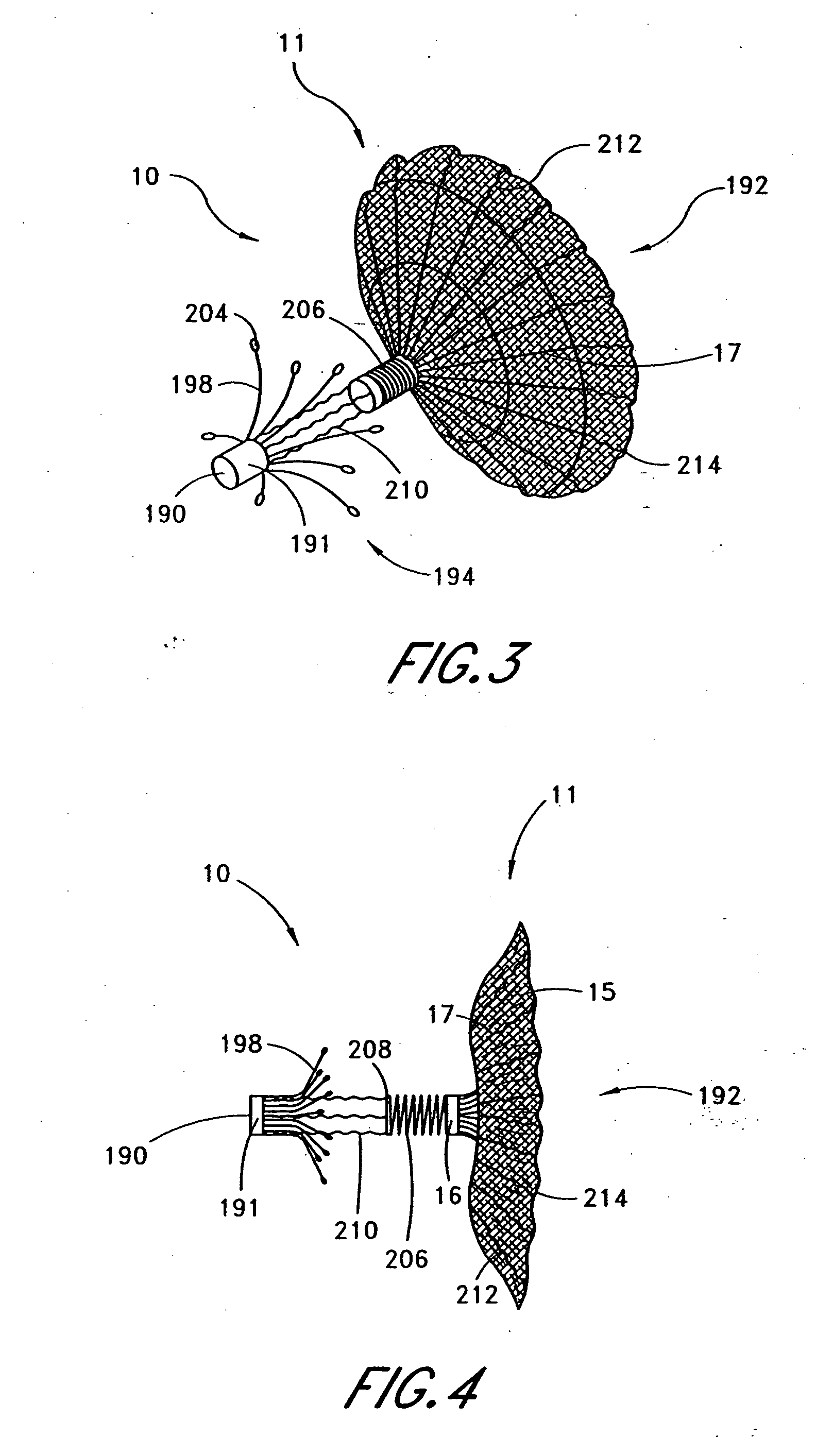
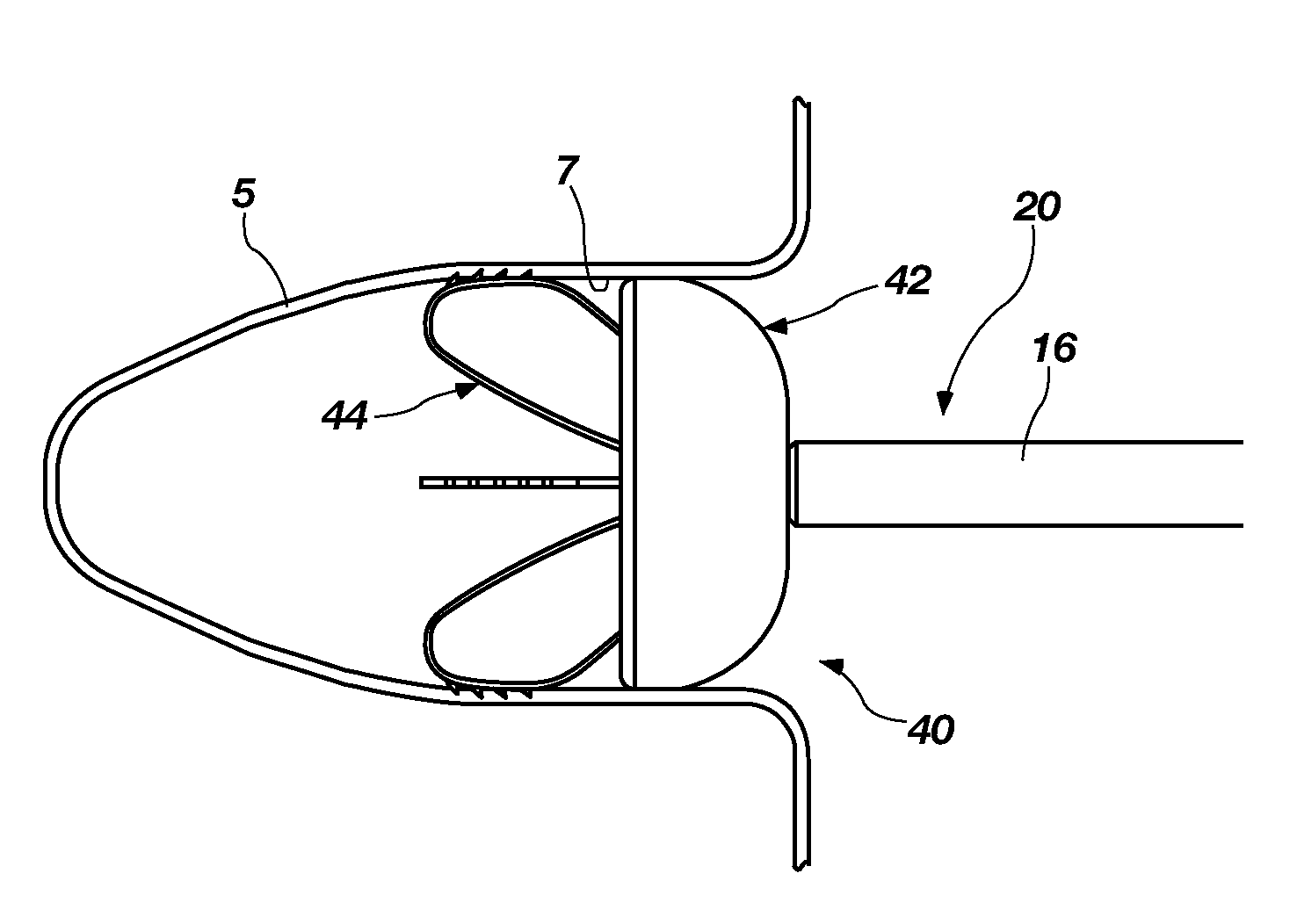
Device for occlusion of a left atrial appendage
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
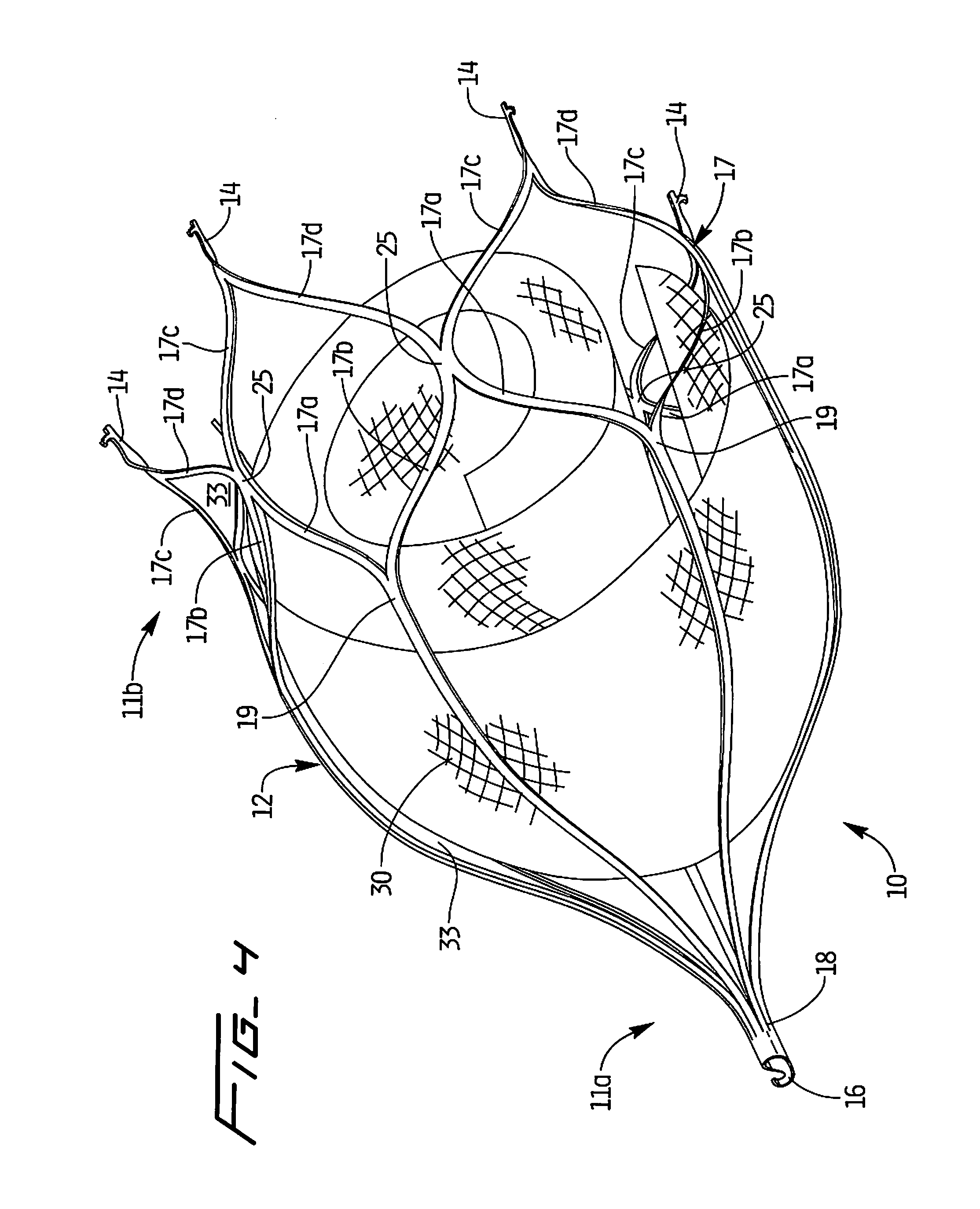
Left atrial appendage treatment systems and methods
ActiveUS8715302B2Safely cinchSimple and efficient and effectiveSuture equipmentsSurgical forcepsAnatomical structuresLeft atrial
Owner:ATRICURE +1
Left atrial appendage devices and methods
Devices and methods for clamping tissue and / or moving two tissue structures together by moving two plates or arm together. The pressure or force applied to the tissue may be used to bring the tissue together, to seal an opening or to cut through and remove a portion of the tissue. In one procedure disclosed, a clip applier may be used to apply one or more clips to the left atrial appendage of the heart to prevent clots from the left atrial appendage from embolizing and causing harm to the patient, such as a stroke.
Owner:ATRICURE
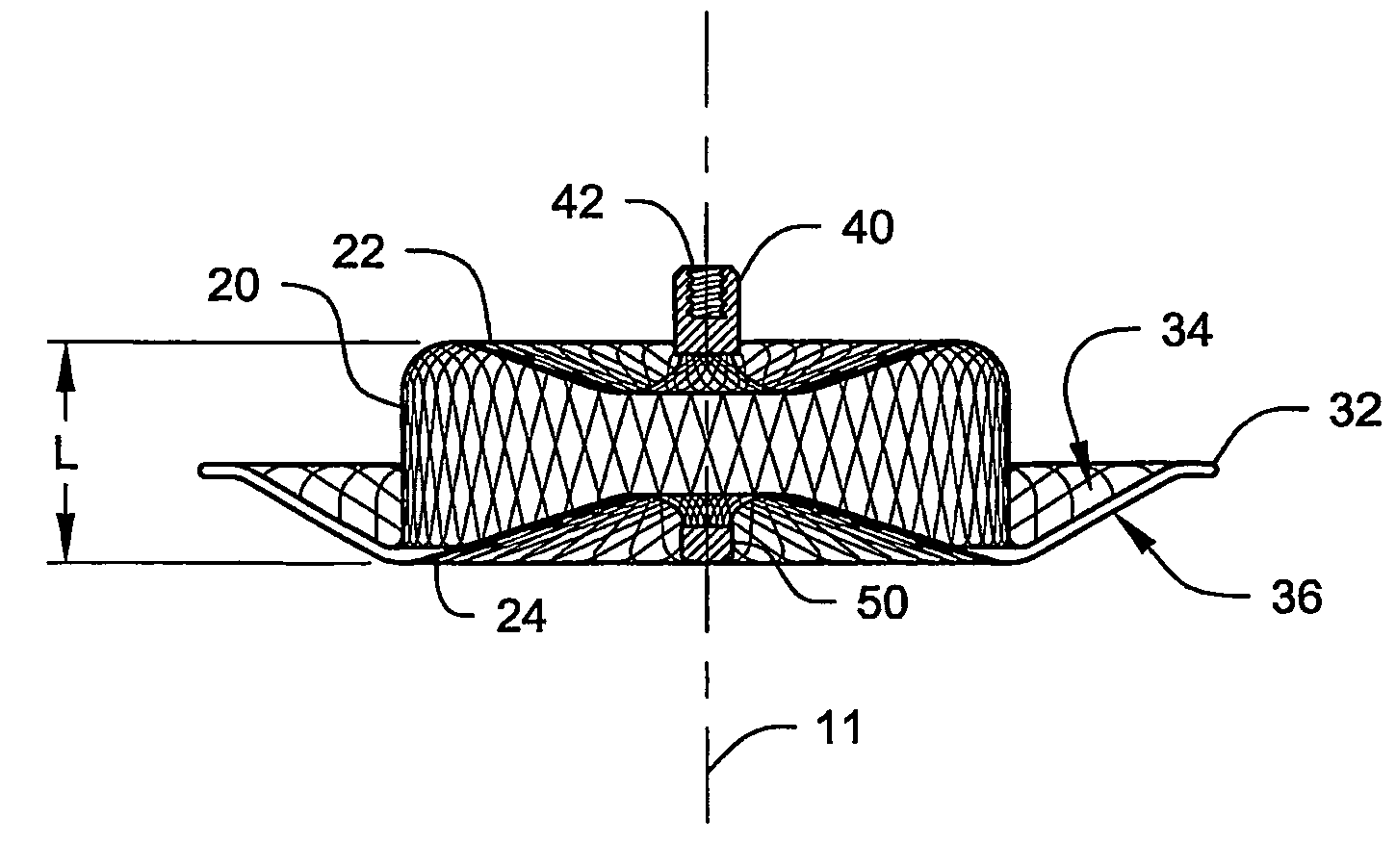
Device for containing embolic material in the LAA having a plurality of tissue retention structures
InactiveUS6994092B2Resisting compressionPreventing rotation and axial migrationStentsBalloon catheterLeft atrialAppendage
Disclosed is an occlusion device for use in a body lumen such as the left atrial appendage. The occlusion device includes an occlusion member and a plurality of tissue retention structures. The tissue retention structures inhibits movement of the device from the left atrial appendage. Methods are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
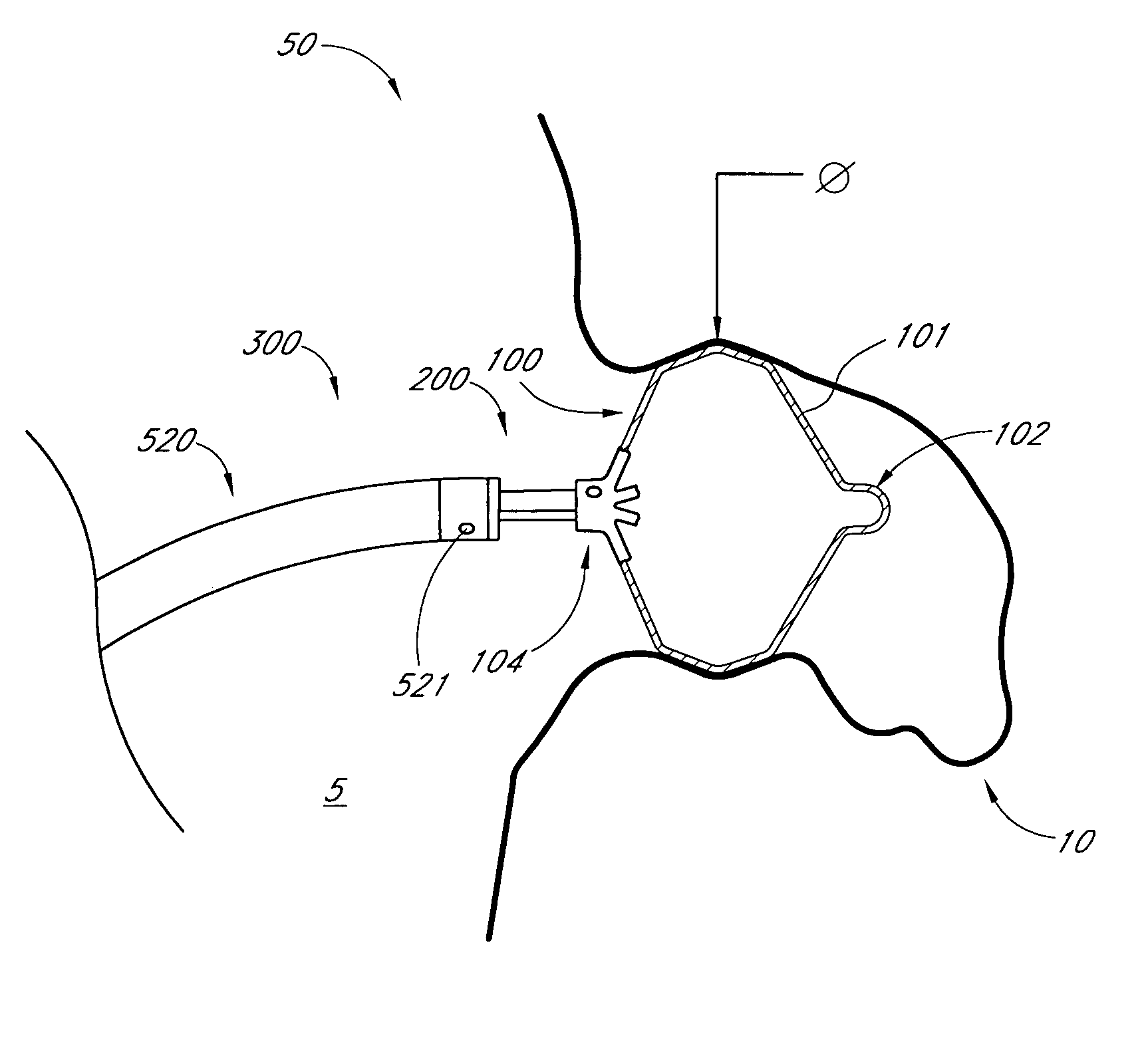
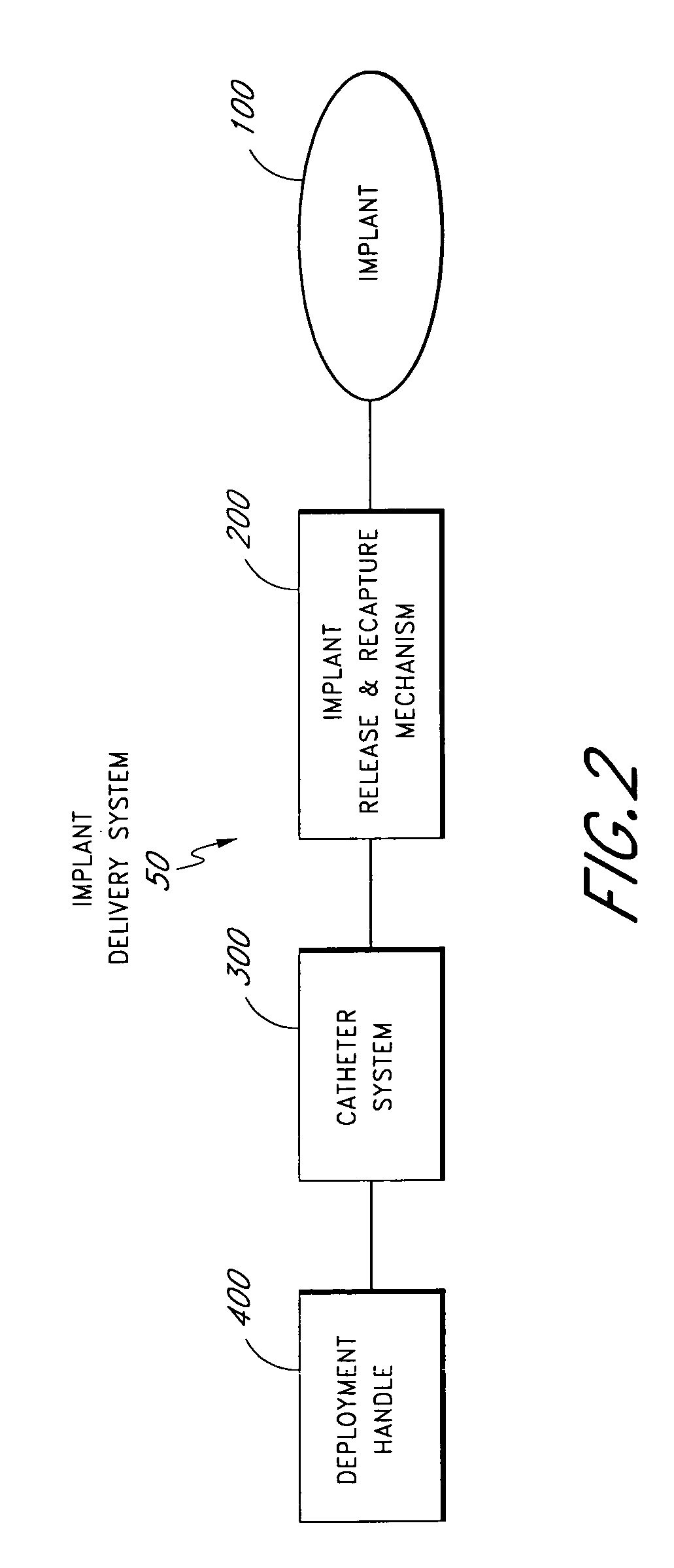
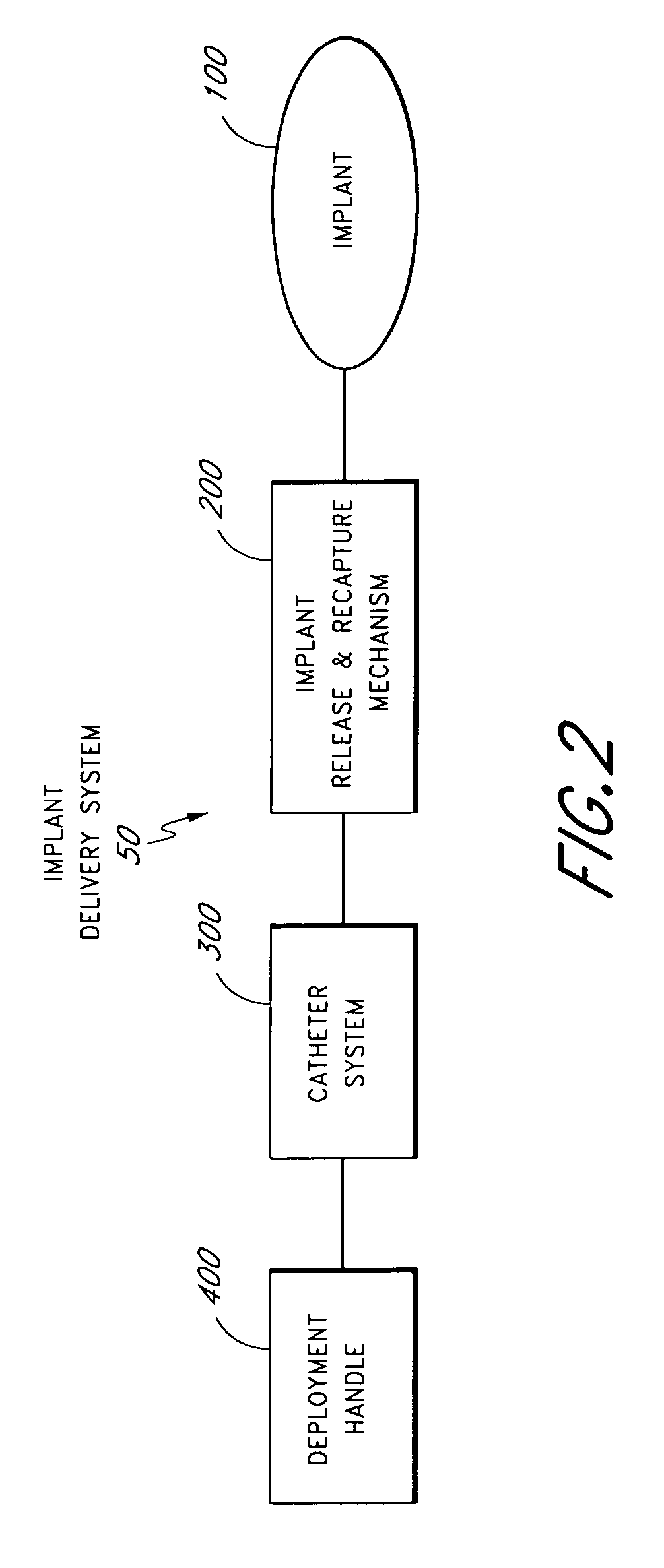
Method and apparatus for delivering an implant without bias to a left atrial appendage
InactiveUS20070135826A1Substantially eliminating,Eliminating implantation biasSuture equipmentsOcculdersImplanted deviceCatheter
A system and method for delivering an implant includes an implant, an actuation shaft, and a concentrically attachable disconnect mount. A distal guide tube is sometimes also provided. A proximal guide tube is also sometimes provided. The implantable device has a proximal, a distal end, and a plurality of supports. The implantable device is moveable between a collapsed and an expanded configuration. The distal guide tube, when provided, is at the distal end of the supports and extends toward the proximal end of the implantable device. The actuation shaft extends through the proximal end of the implantable device and is removeably engageable with the distal guide tube, or the distal end of the device when the distal guide tube is not provided. The disconnect mount is releasably engageable with the proximal end of the implantable device. The disconnect mount is concentrically attachable to the proximal end of the implantable device as well. The implantable device is self-expandable, and is collapsed by engaging the actuation shaft with the distal guide tube while applying a relatively proximal force to the proximal end of the implant with the disconnect mount.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Flanged occlusion devices and methods
Implantable occlusion devices that include one or more flanges extending from a tubular body are disclosed. The flange or flanges may assist in retention of the device within a vessel, cavity, appendage, etc. At least one flange on the occlusion device may include a concave surface proximate one end of a body. Because of the shape of the flange, e.g., its concavity, the occlusion device may resist dislocation due to e.g., the forces generated within the left atrial appendage during atrial filbrillation.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
System and method for delivering a left atrial appendage containment device
A device for containing emboli within a left atrial appendage of a patient includes a frame that is expandable from a reduced cross section to an enlarged cross section and a slider assembly. The frame extends between a proximal hub and a distal hub, and the slider assembly is coupled to the distal hub of the frame. The slider assembly includes a guide tube that has a channel extending proximally away from the distal hub, and a nut. The nut is longitudinally moveable within the channel of the guide tube over a predetermined distance relative to the guide tube. The nut is operable to be releasably coupled with an elongate core, and movement of the nut relative to the guide tube is at least partially limited by interference between a portion of the nut and a portion of the guide tube.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
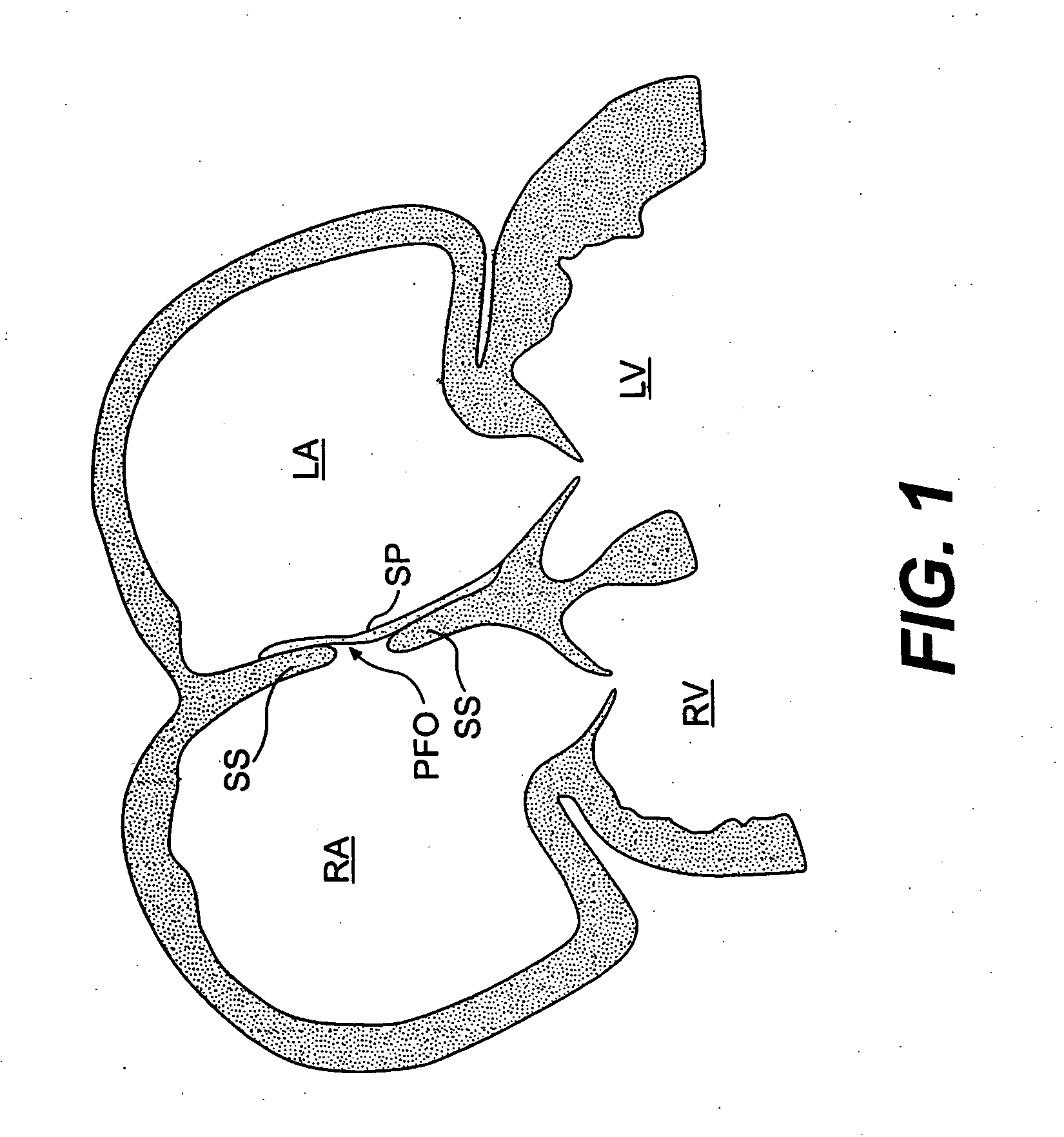
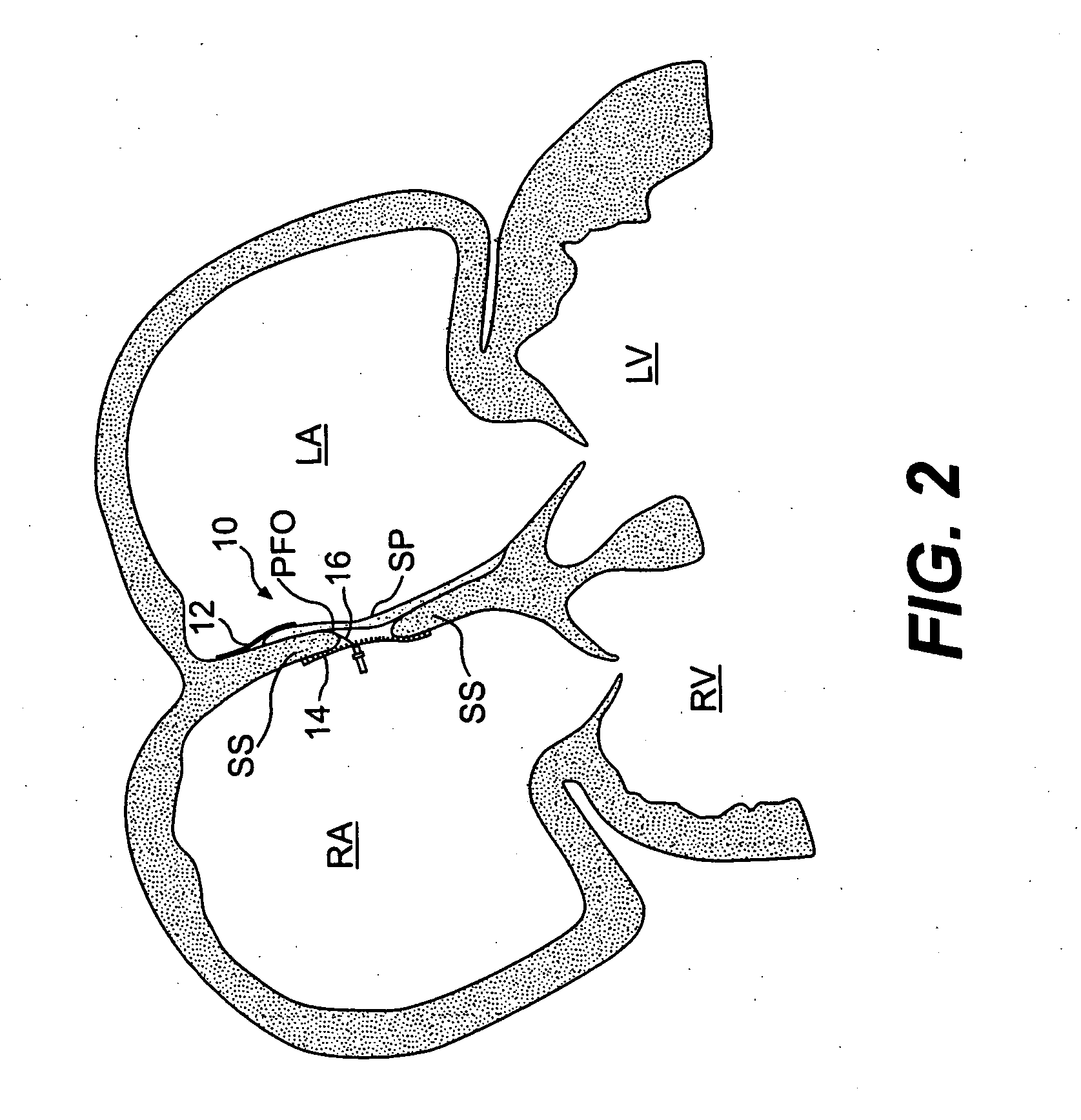
Closure devices, related delivery methods, and related methods of use
ActiveUS20060009800A1Prevent proximal movementPrevent movementDiagnostic markersSurgical veterinaryRight atriumLeft atrial
A device for sealing a patent foramen ovale (PFO) in the heart is provided. The device includes a left atrial anchor adapted to be placed in a left atrium of the heart, a right atrial anchor adapted to be placed in a right atrium of the heart, and an elongate member adapted to extend through the passageway and connect the left and right atrial anchors. A system for delivering the closure device includes side-by-side tubes. A device for retrieving a mis-deployed closure device includes a shaft portion and an expandable retrieval portion.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
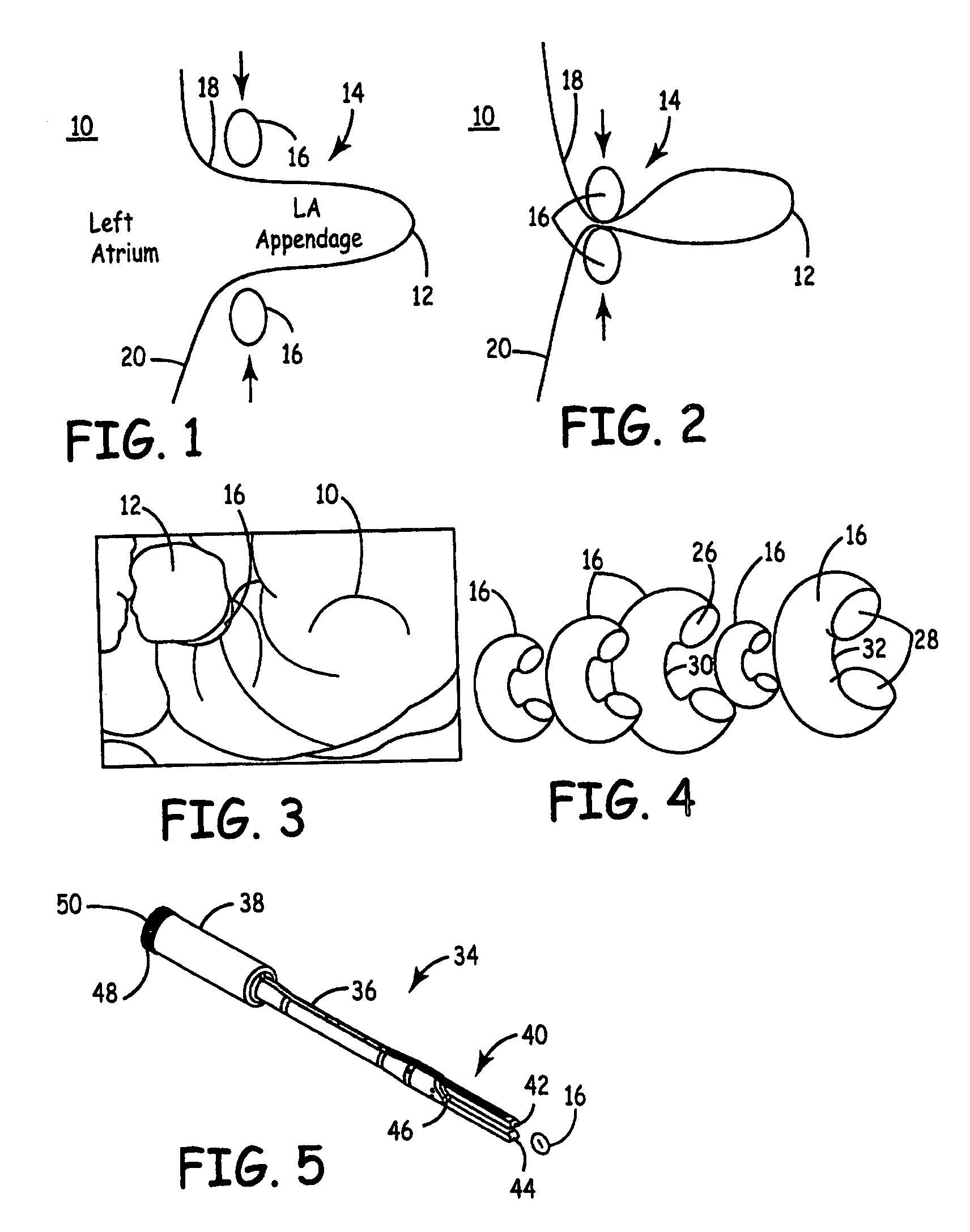
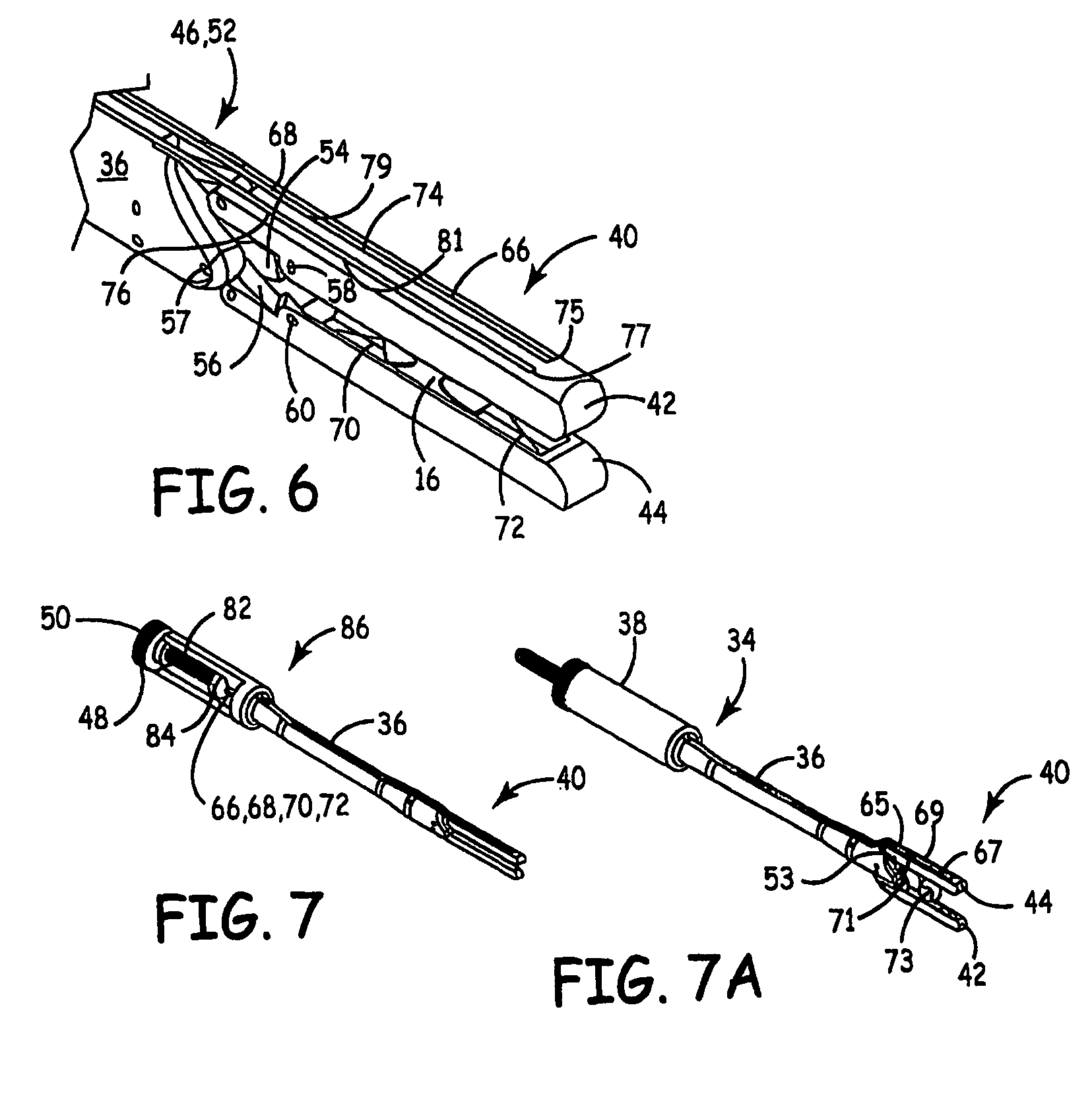
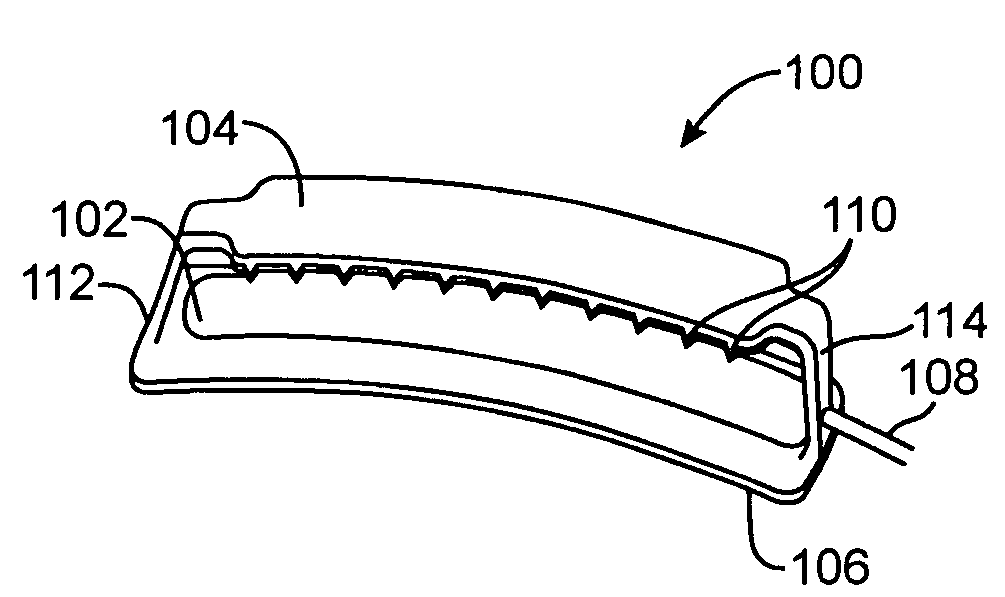
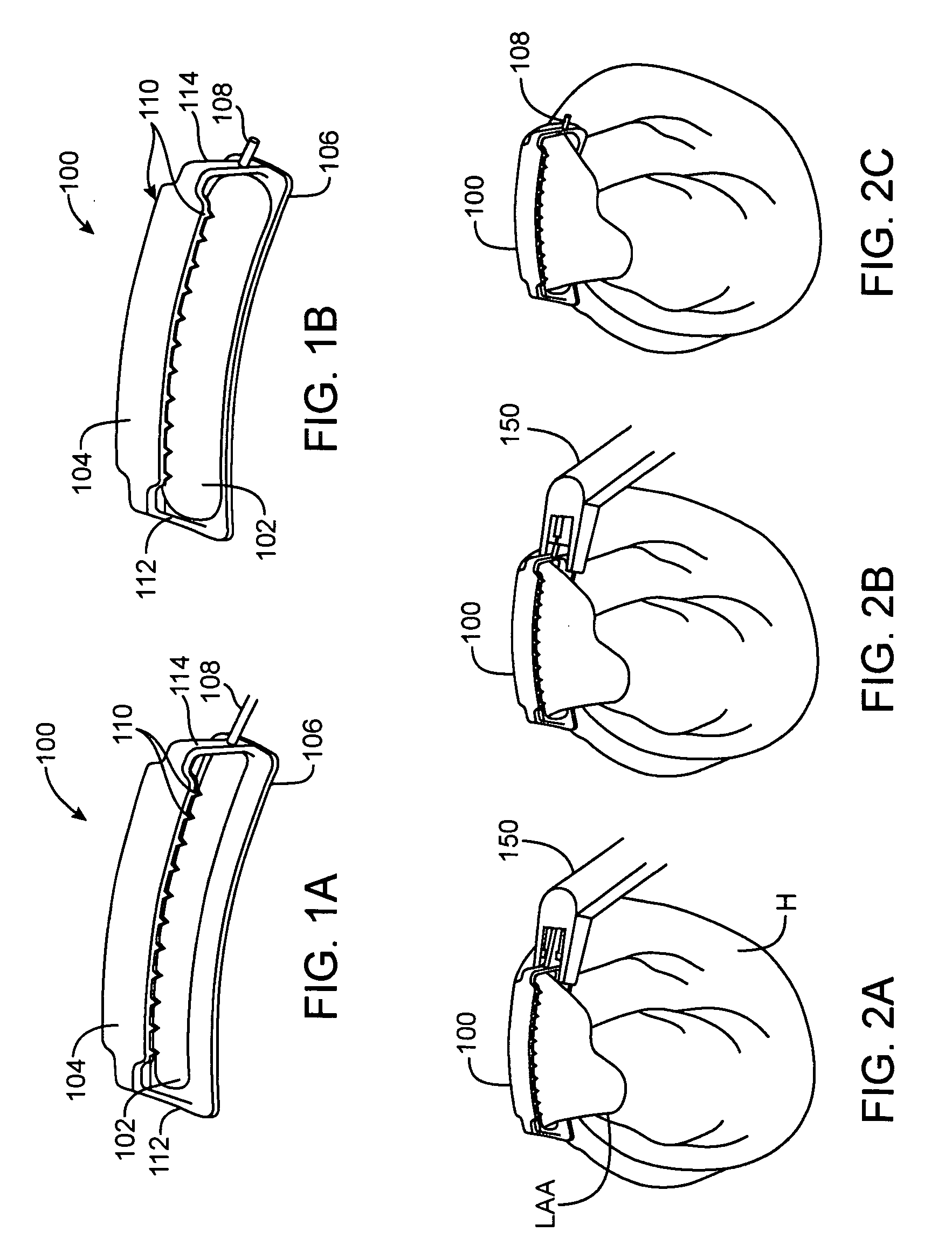
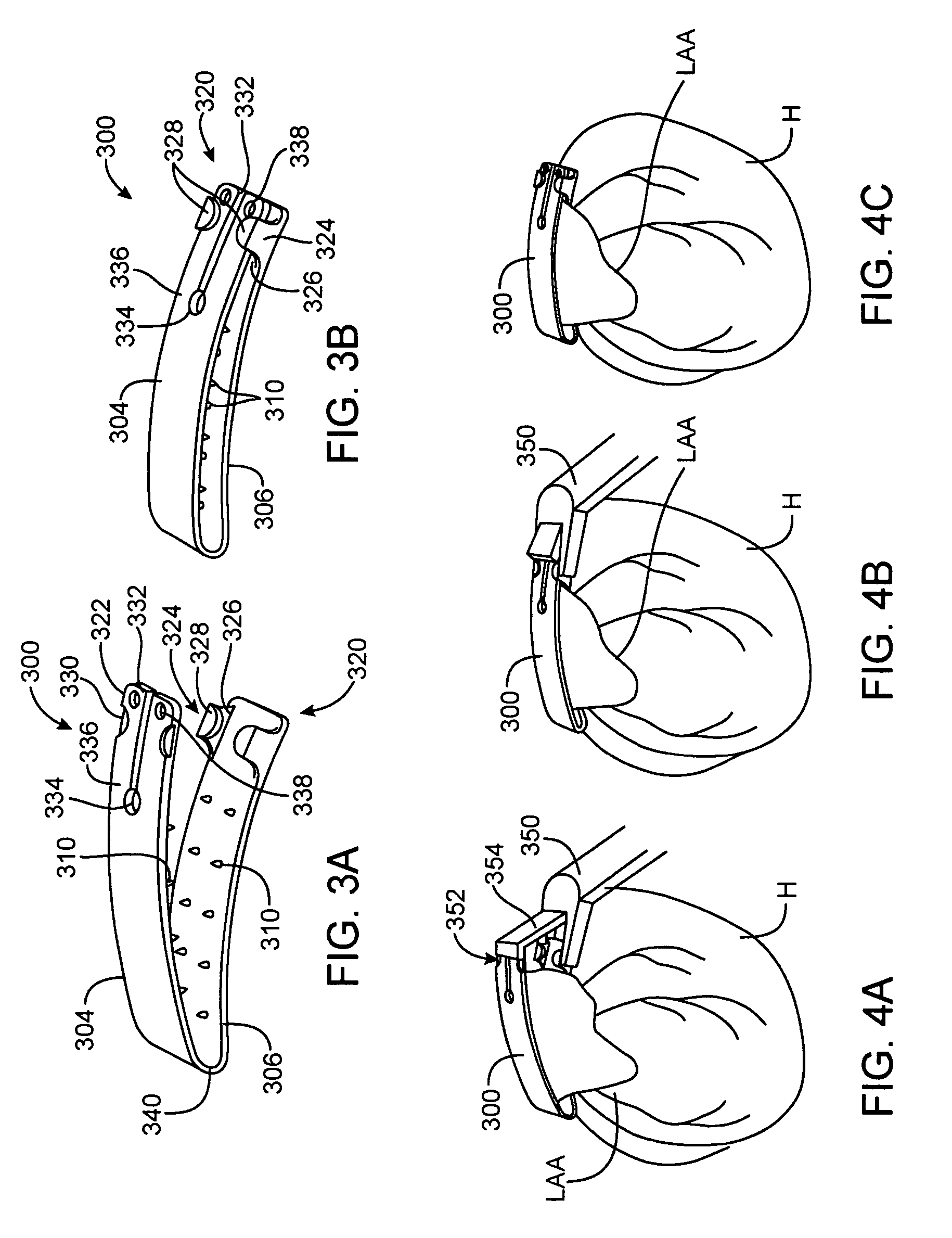
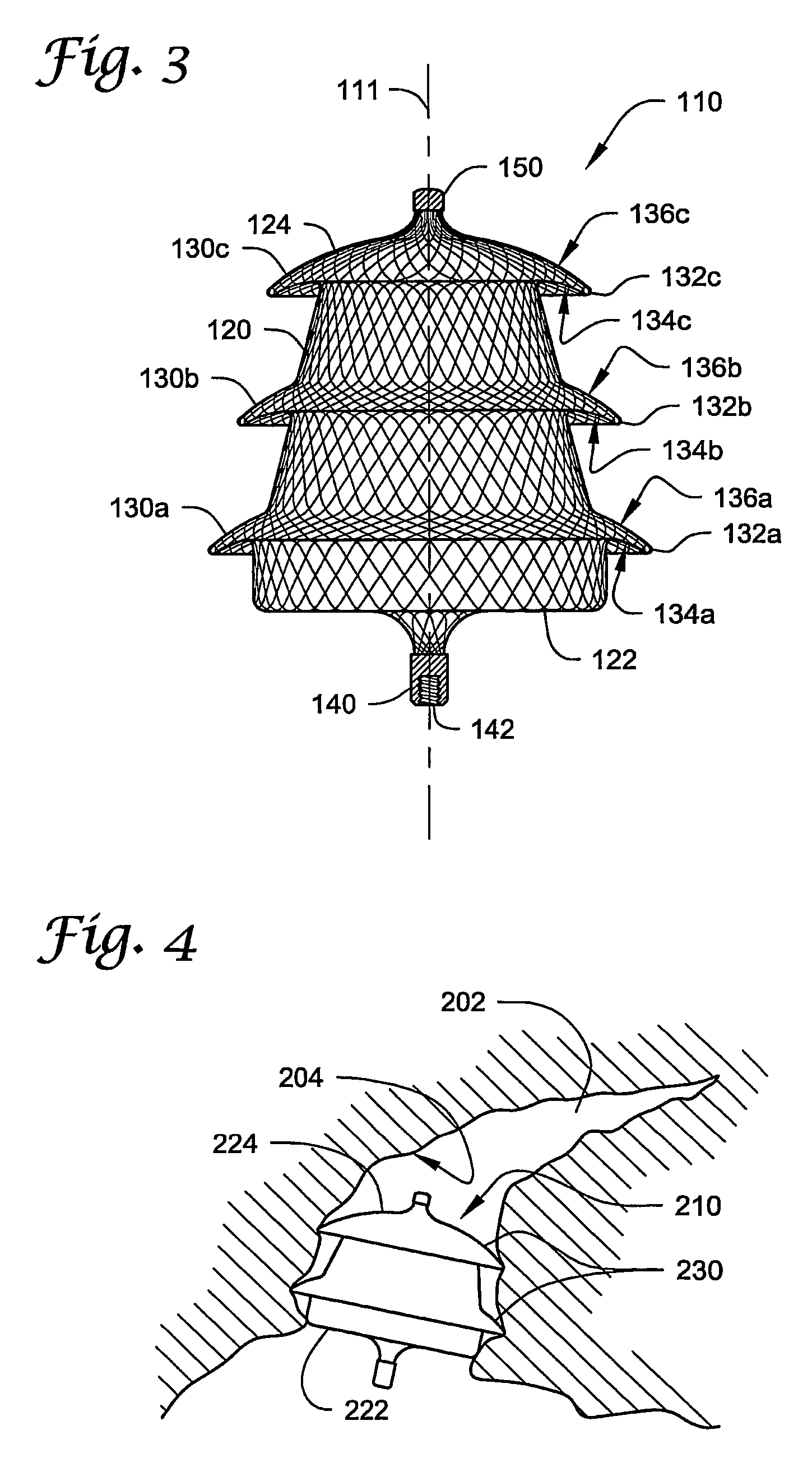
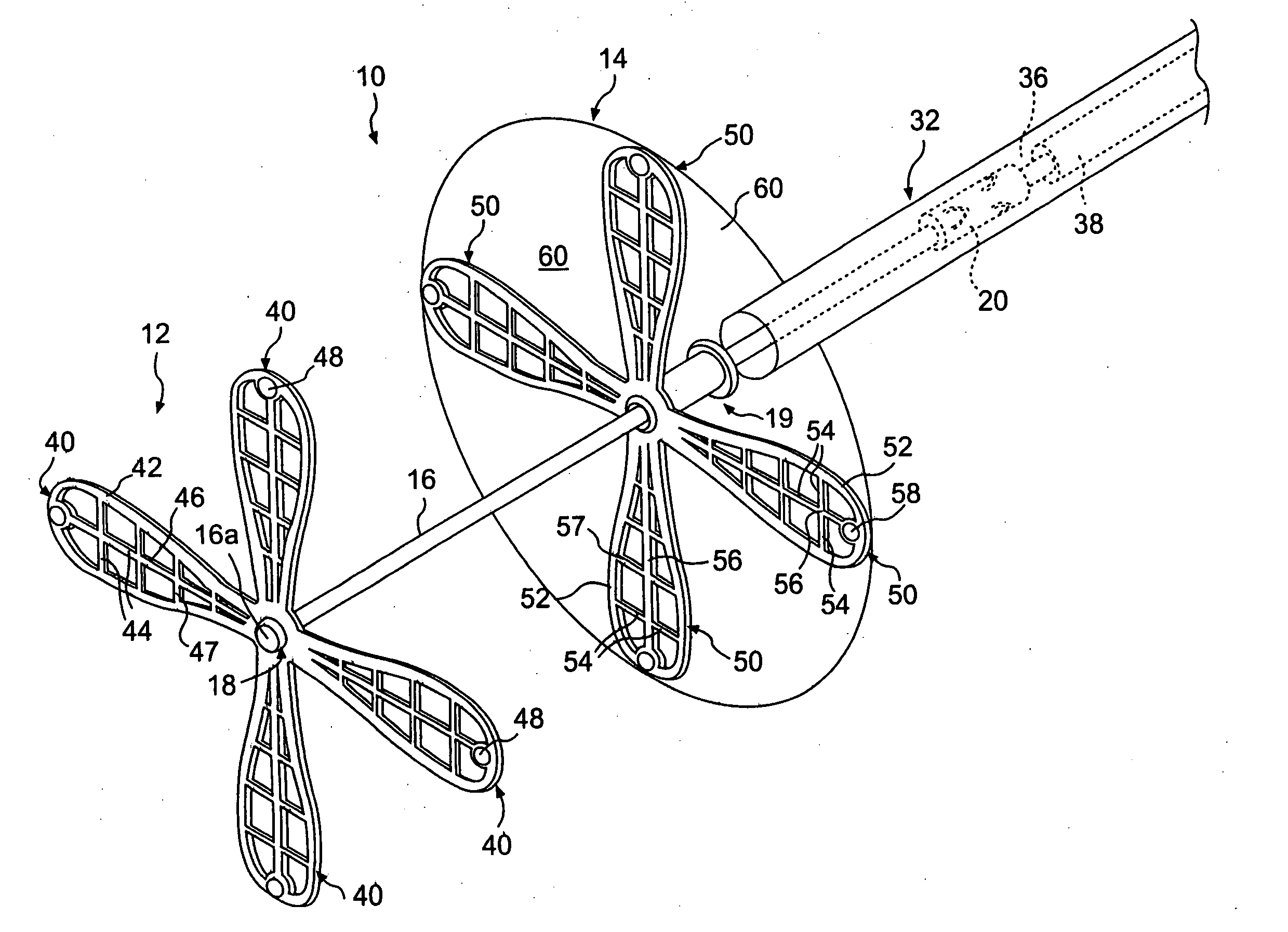
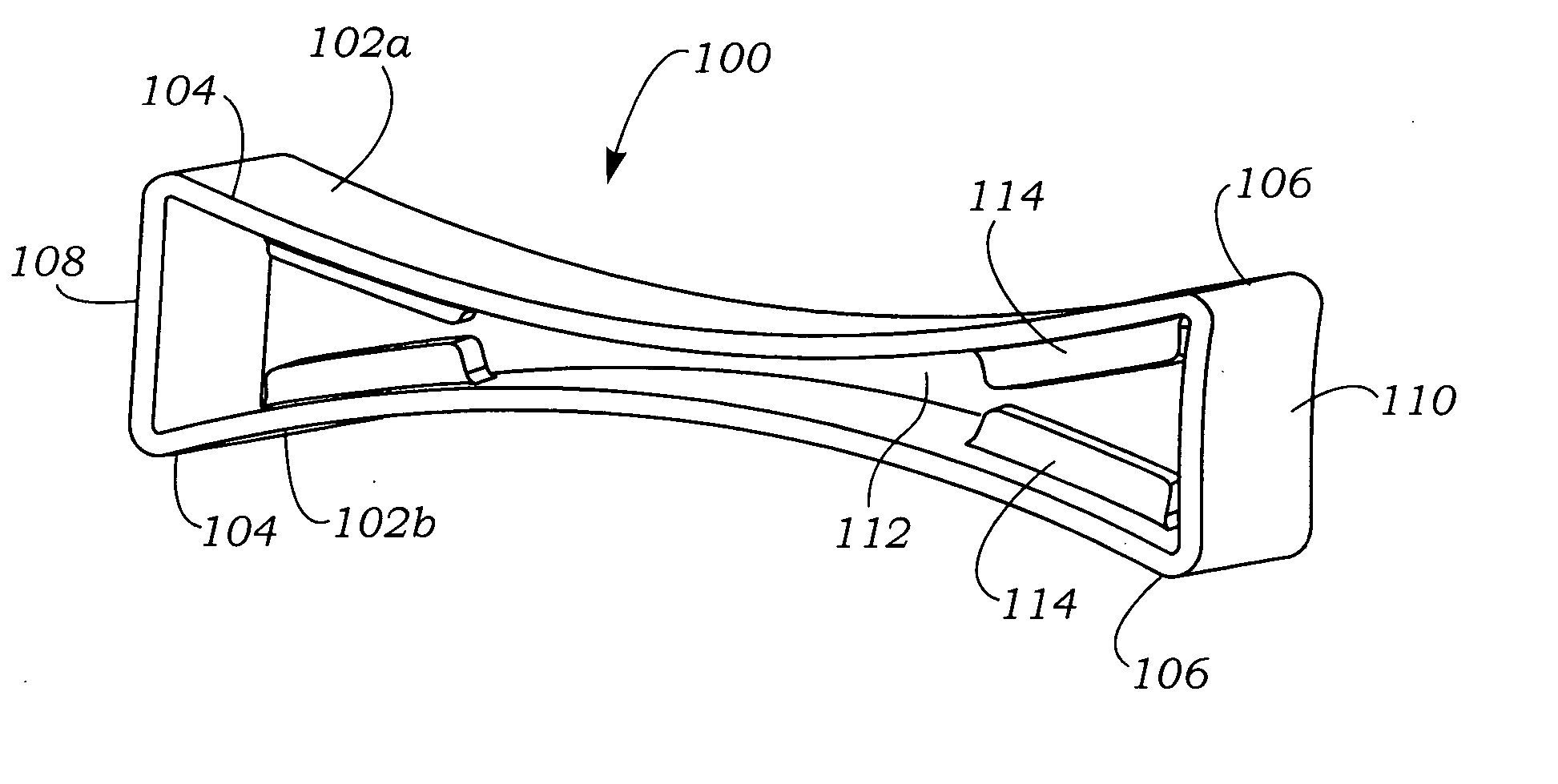
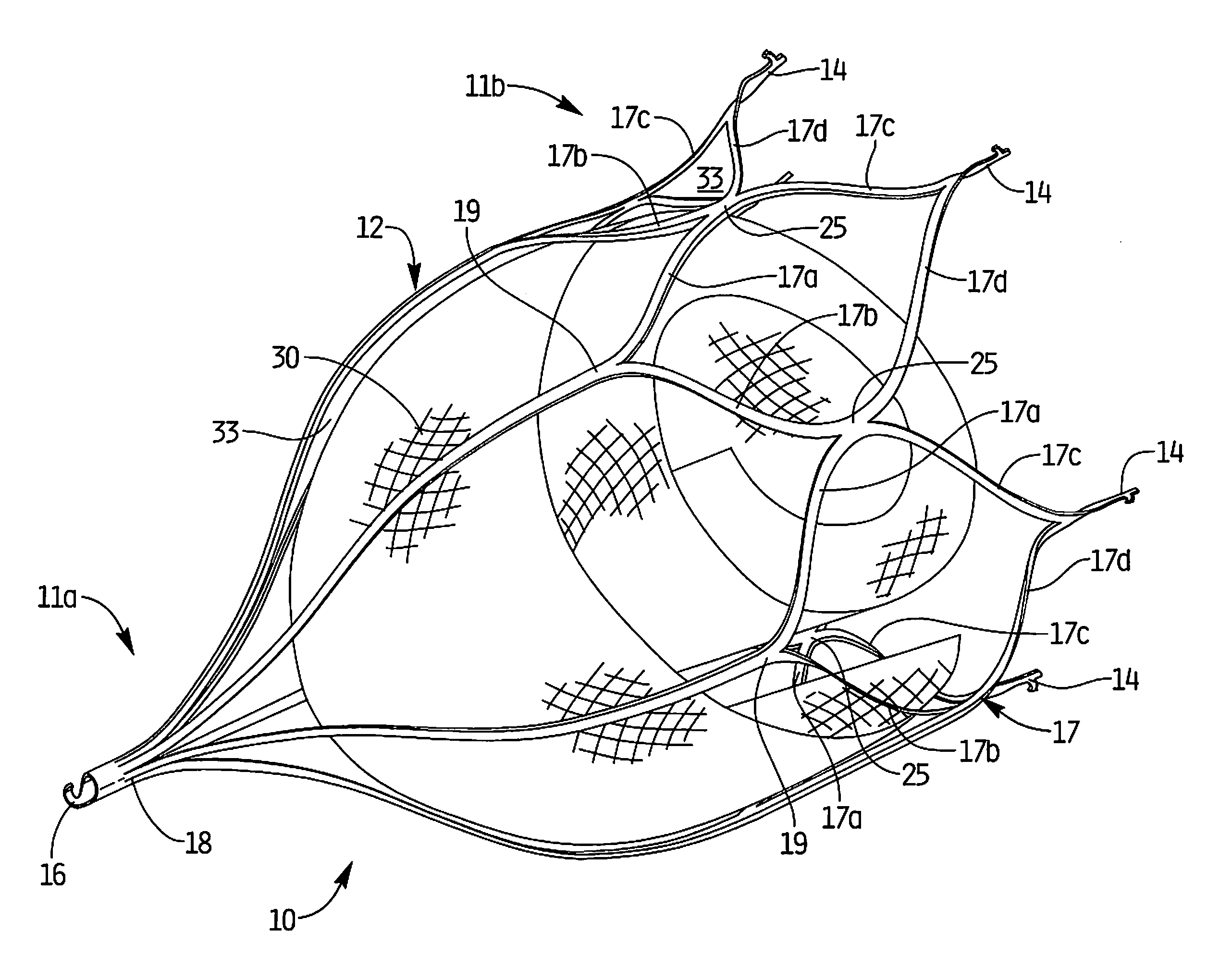
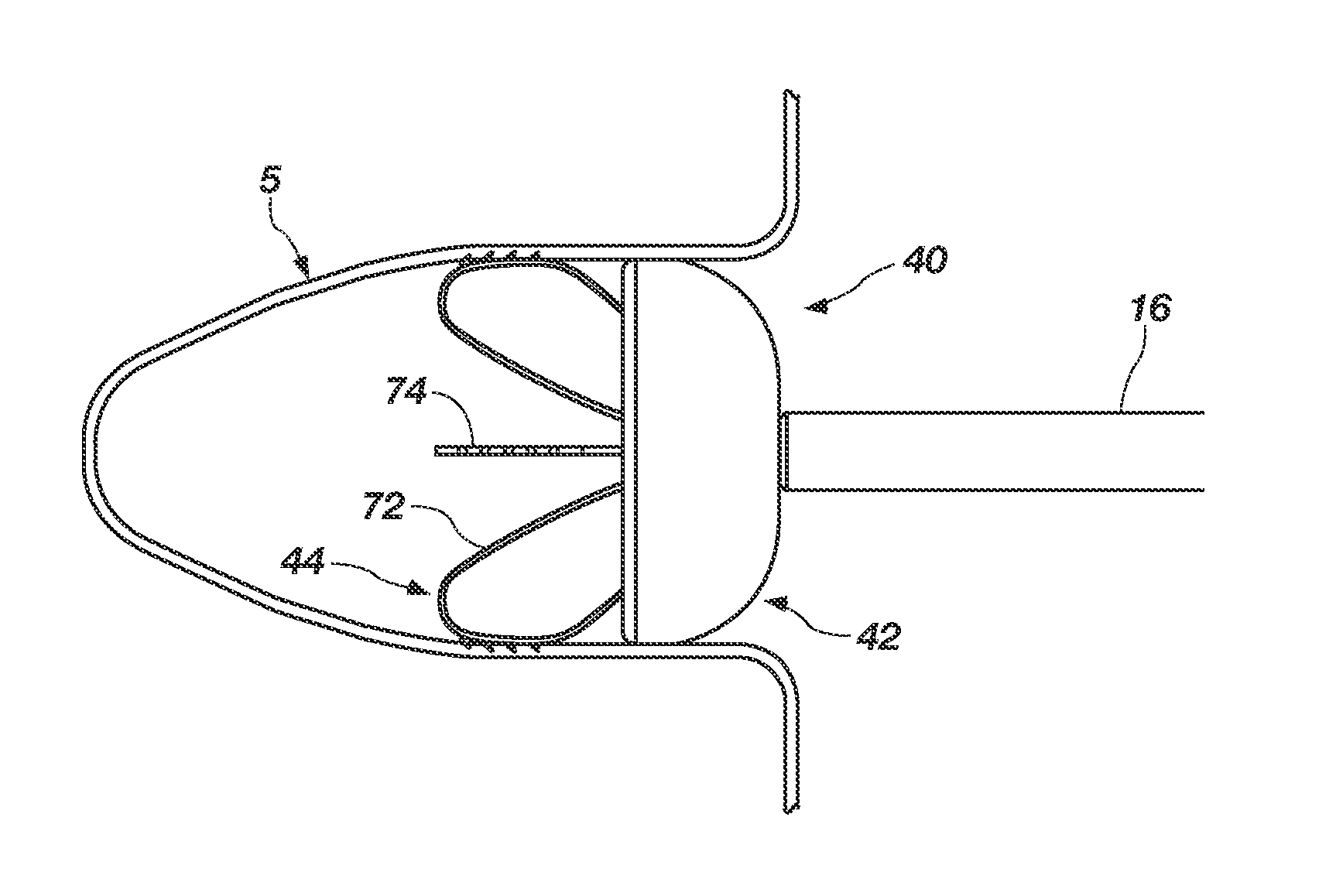
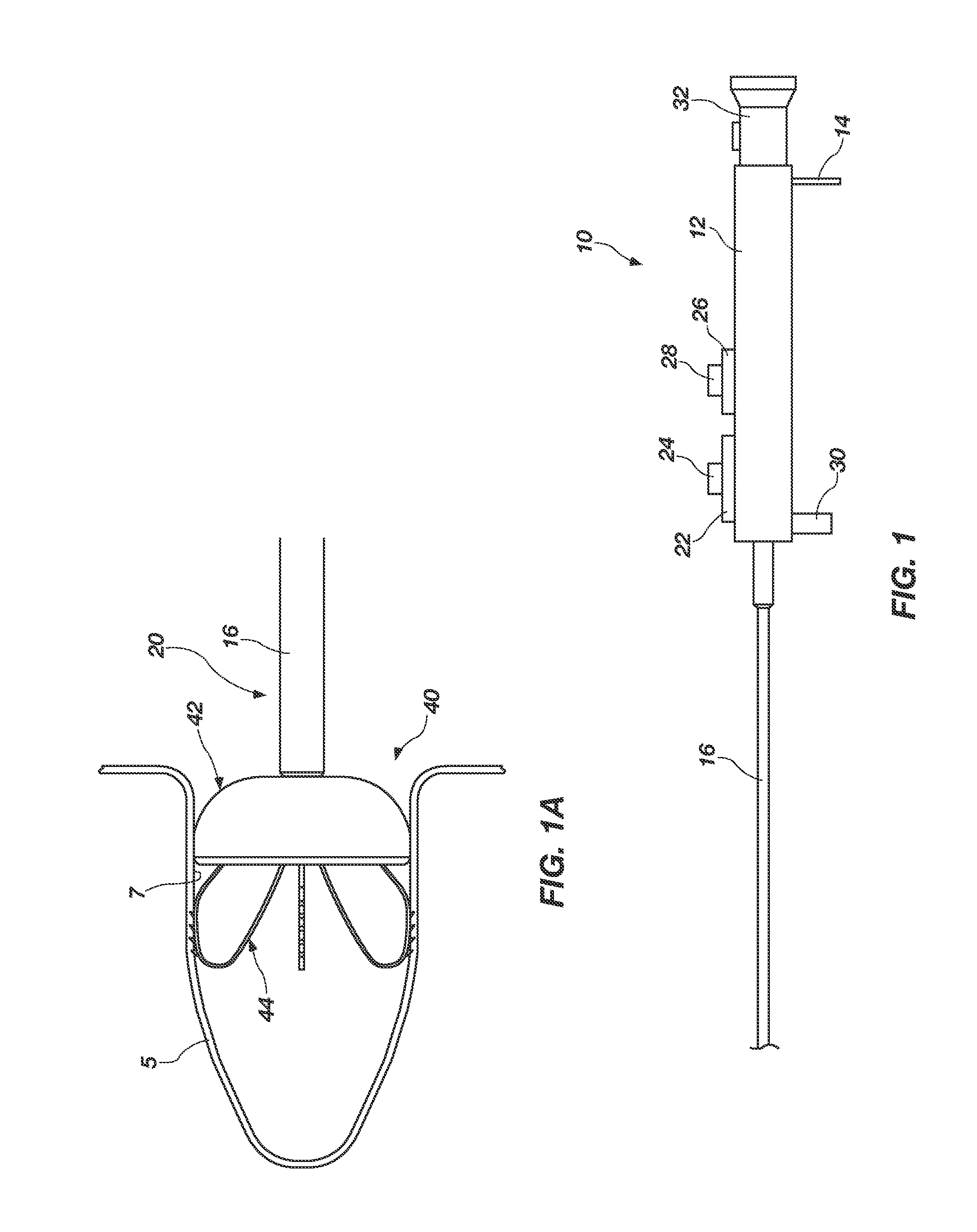
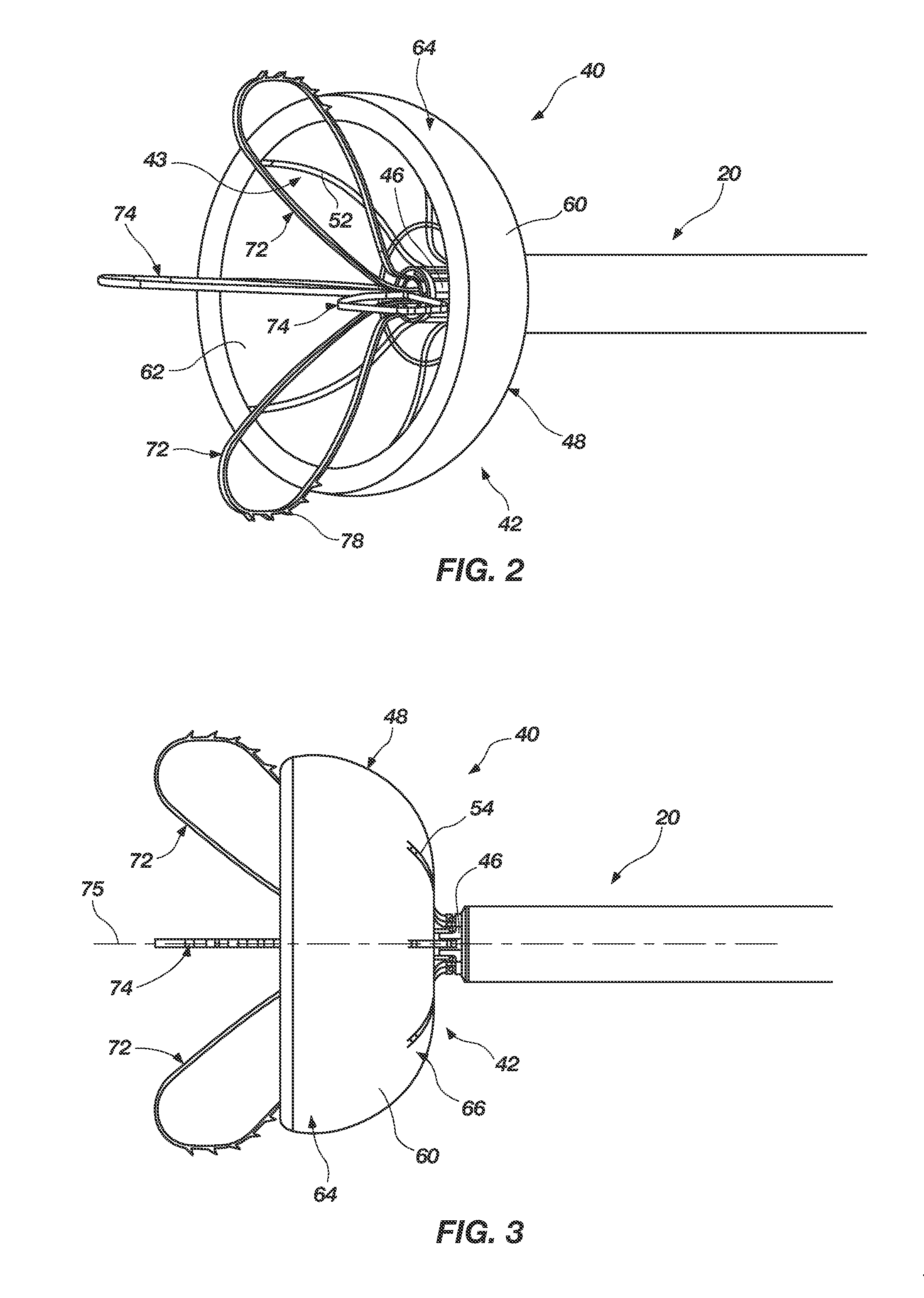
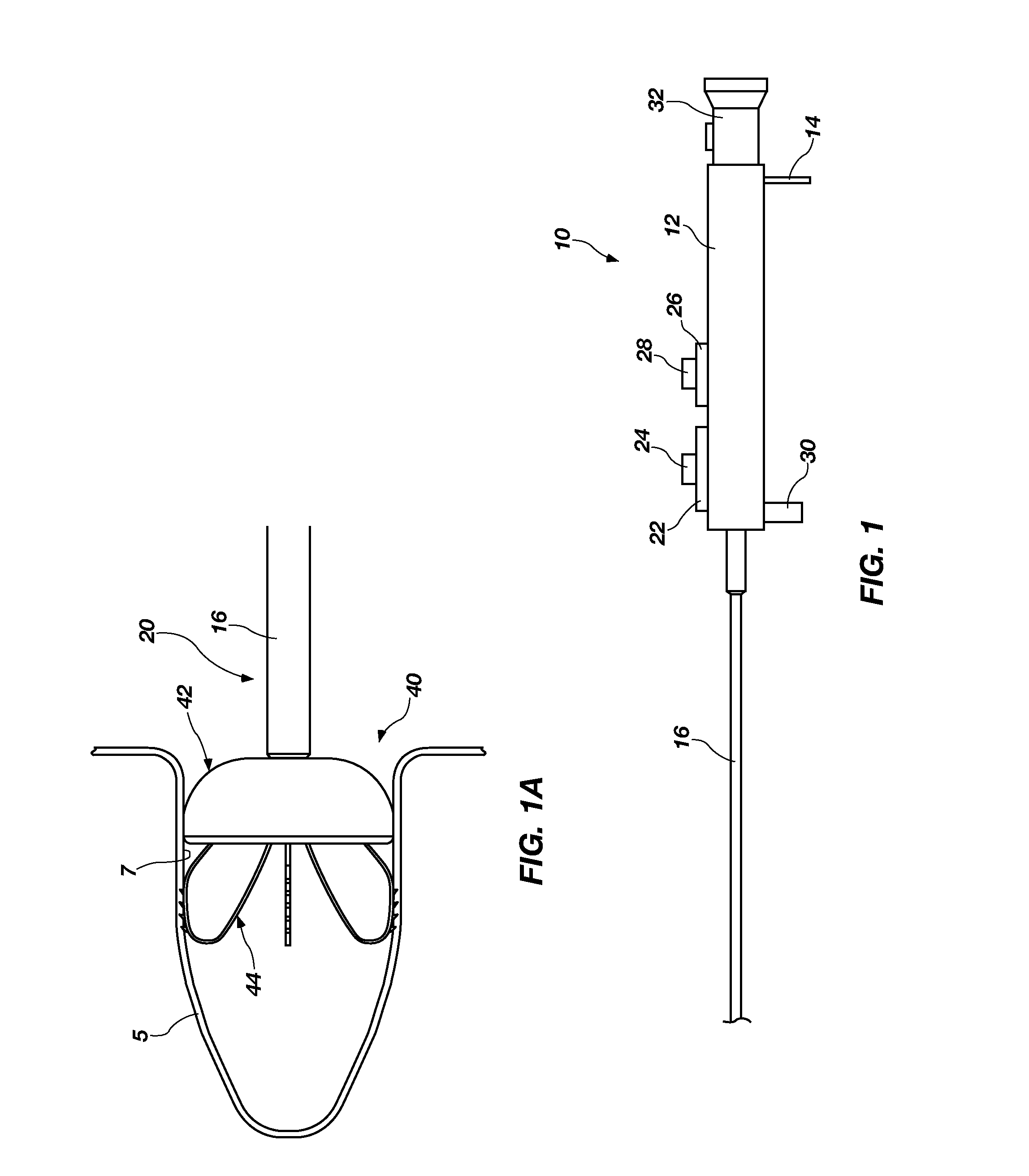
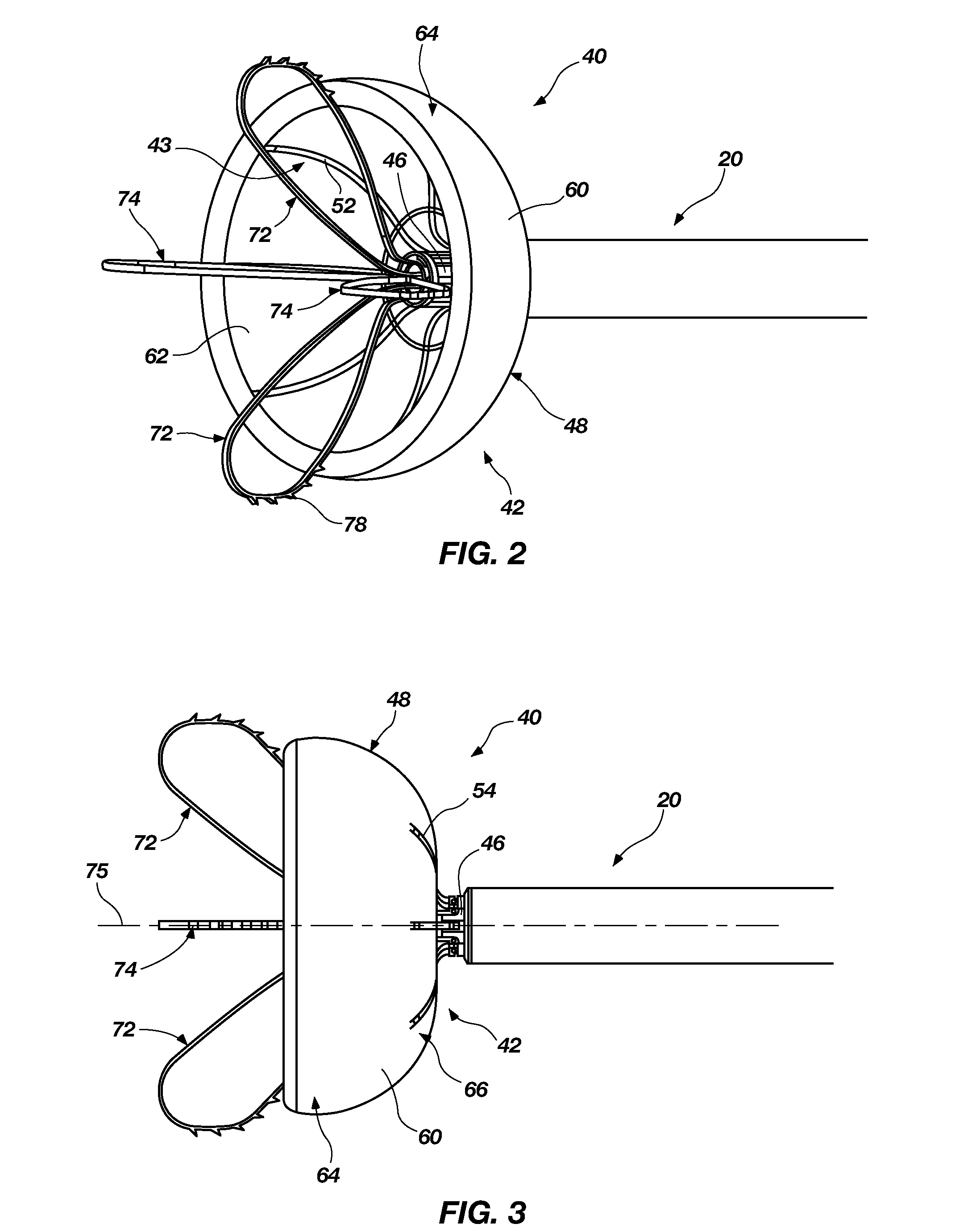
Left atrial appendage exclusion device
A device for excluding the inner cavity of the left internal appendage (LAA) from the interior of the left atrium LA may include a pair of compression members spaced apart and defining a closed periphery. The closed periphery has a variable-sized opening therein that can be enlarged to surround the LAA and then closed to compress and exclude the LAA. The closed periphery may be generally rectangular or lenticular, and may be a solid, contiguous periphery or separable at a closure. Inner protrusions or ribs may be provided on the compression members to help anchor the exclusion device in place. Needles may also be provided to pierce the LAA tissue and trap blood clots therein. The device may be non-linear in plan view so as to conform to the shape of the external left atrium. Deployment techniques or structures may be provided that squeeze the LAA in a direction starting adjacent the left atrium and then moving away from the left atrium. This squeezing motion helps prevent extrusion of any thrombus deposit within the LAA cavity into the left atrium.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Energy based devices and methods for treatment of anatomic tissue defects
Methods and apparatus for treatment of anatomic defects in human tissues, such as patent foramen ovale (PFO), atrial or ventricular septal defects, left atrial appendage, patent ductus arteriosis, blood vessel wall defects and certain electrophysiological defects, involve positioning a distal end of an elongate catheter device at the site of the anatomic defect, engaging tissues at the site of the anatomic defect to bring the tissues together, and applying energy to the tissues with the catheter device to substantially close the anatomic defect acutely. Apparatus generally includes an elongate catheter having a proximal end and a distal end, a vacuum application member coupled with the distal end for engaging tissues at the site of the anatomic defect and applying vacuum to the tissues to bring them together, and at least one energy transmission member coupled with the vacuum application member for applying energy to tissues at the site of the anatomic defect to substantially close the defect acutely.
Owner:TERUMO KK
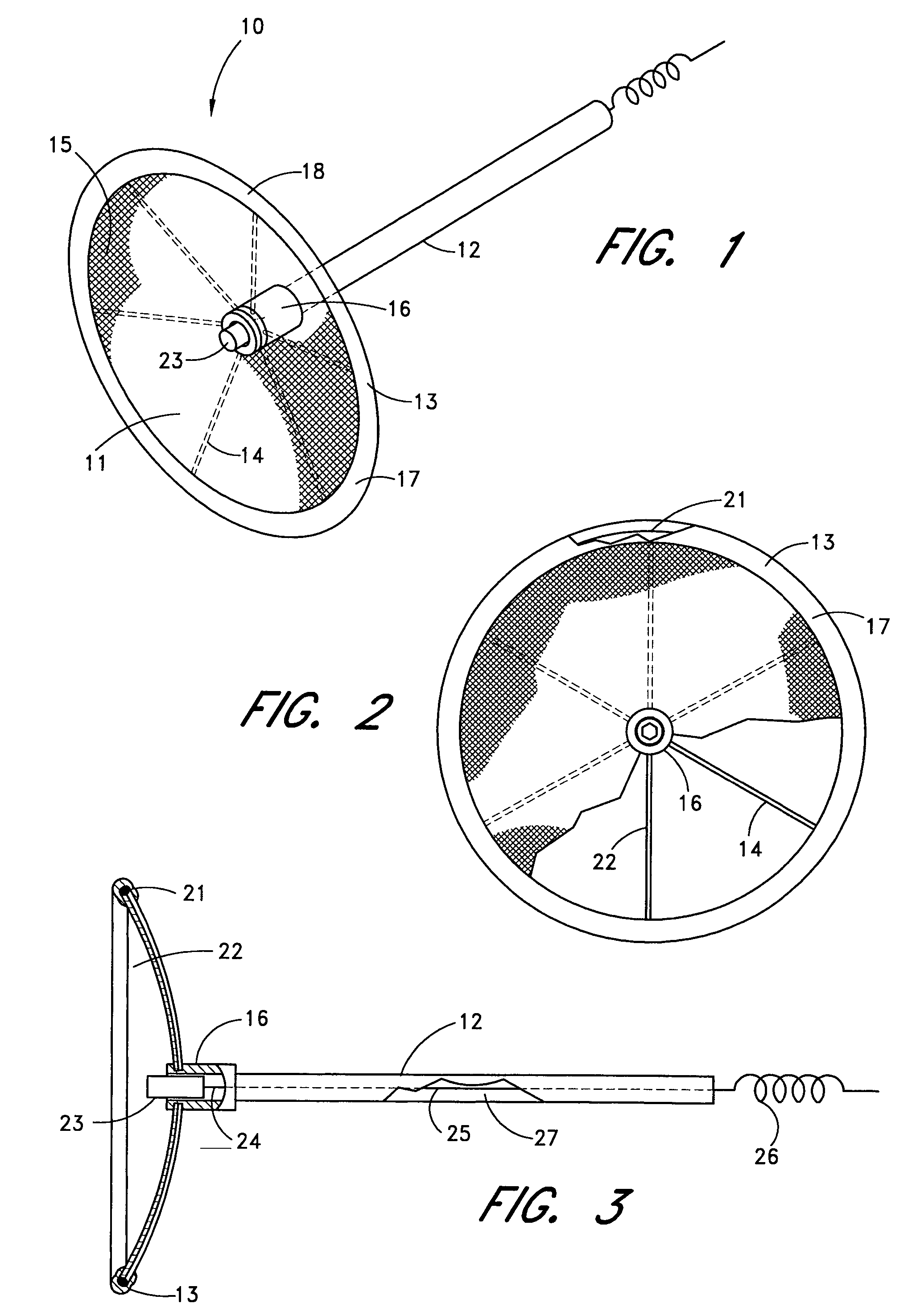
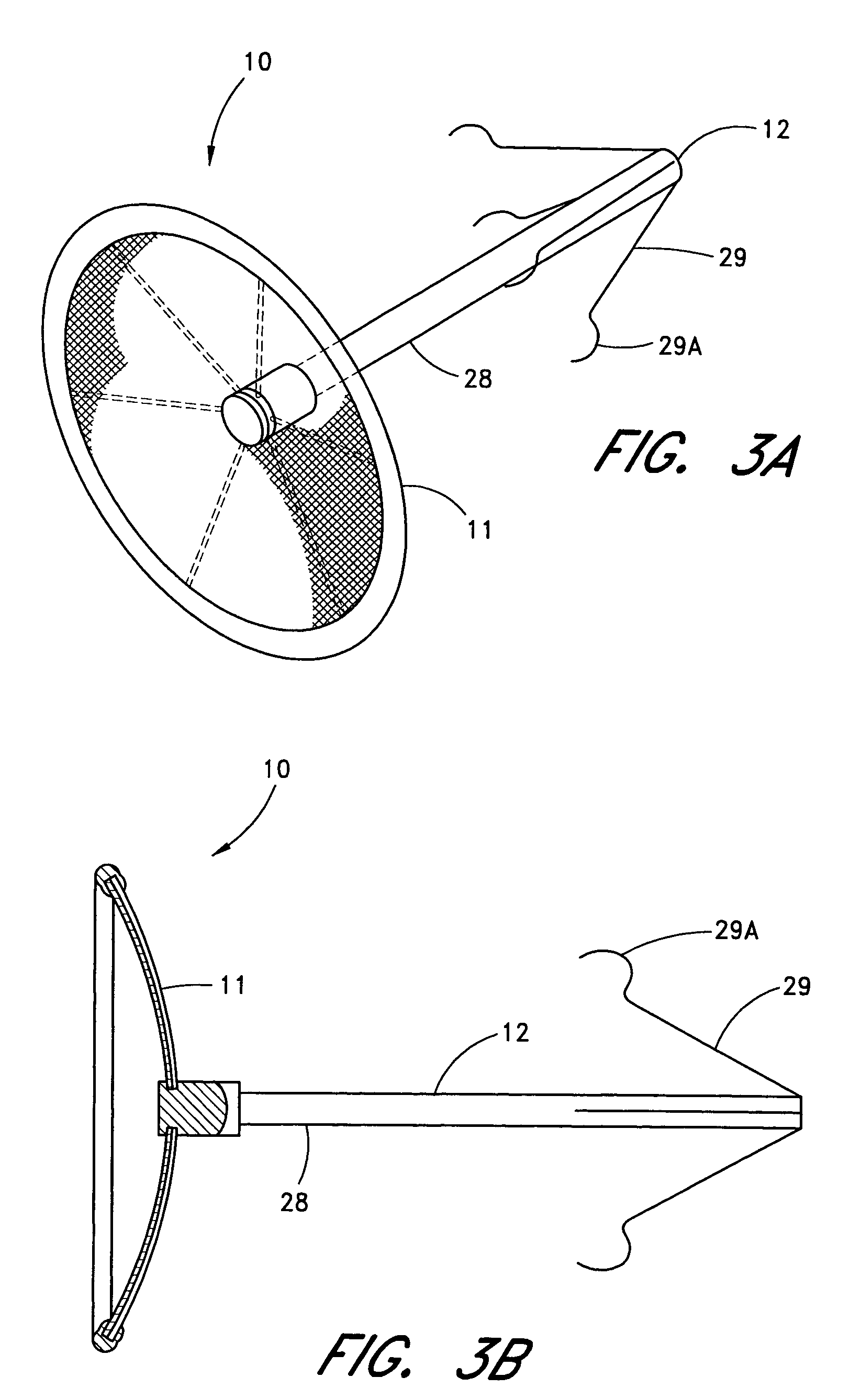
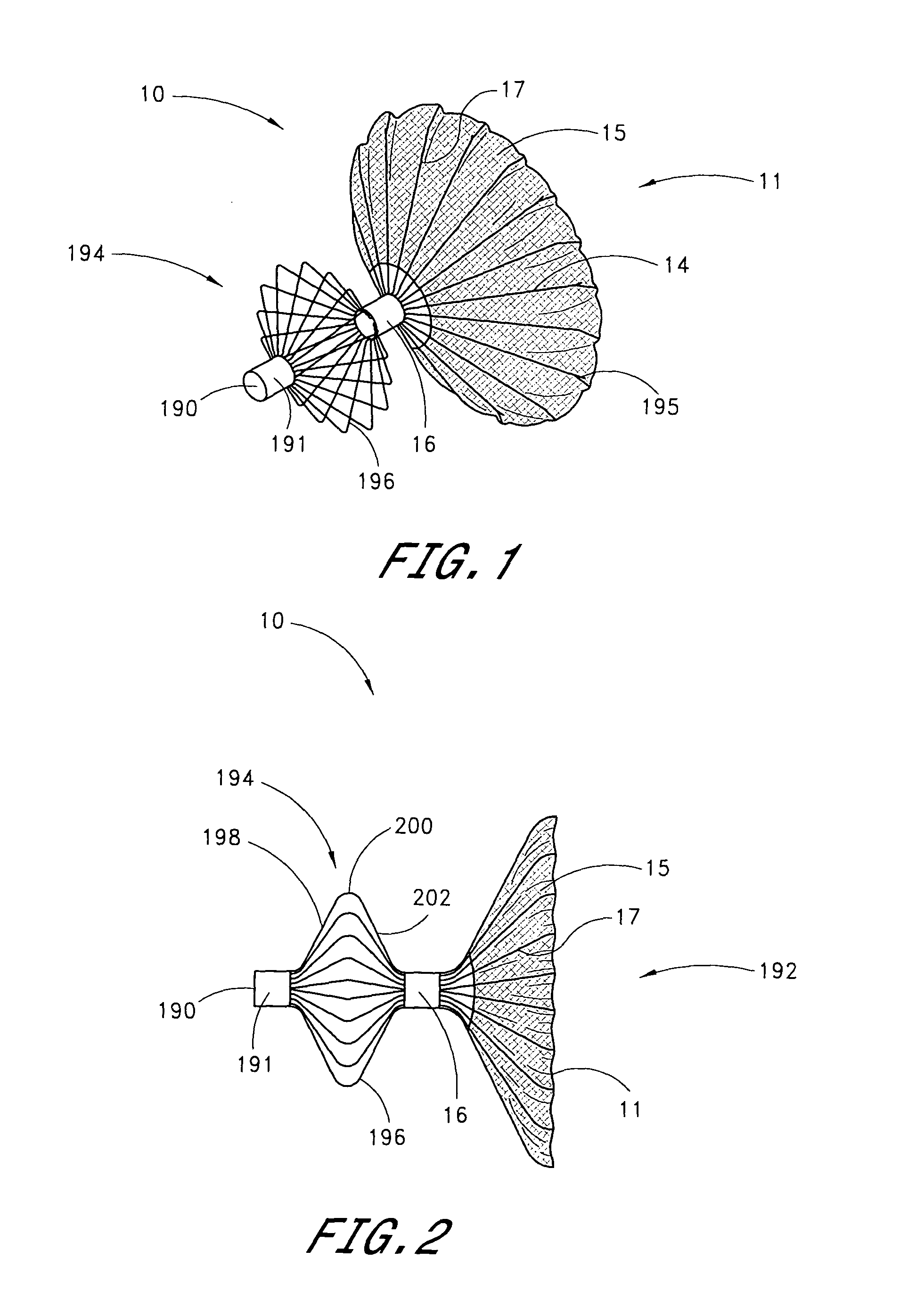
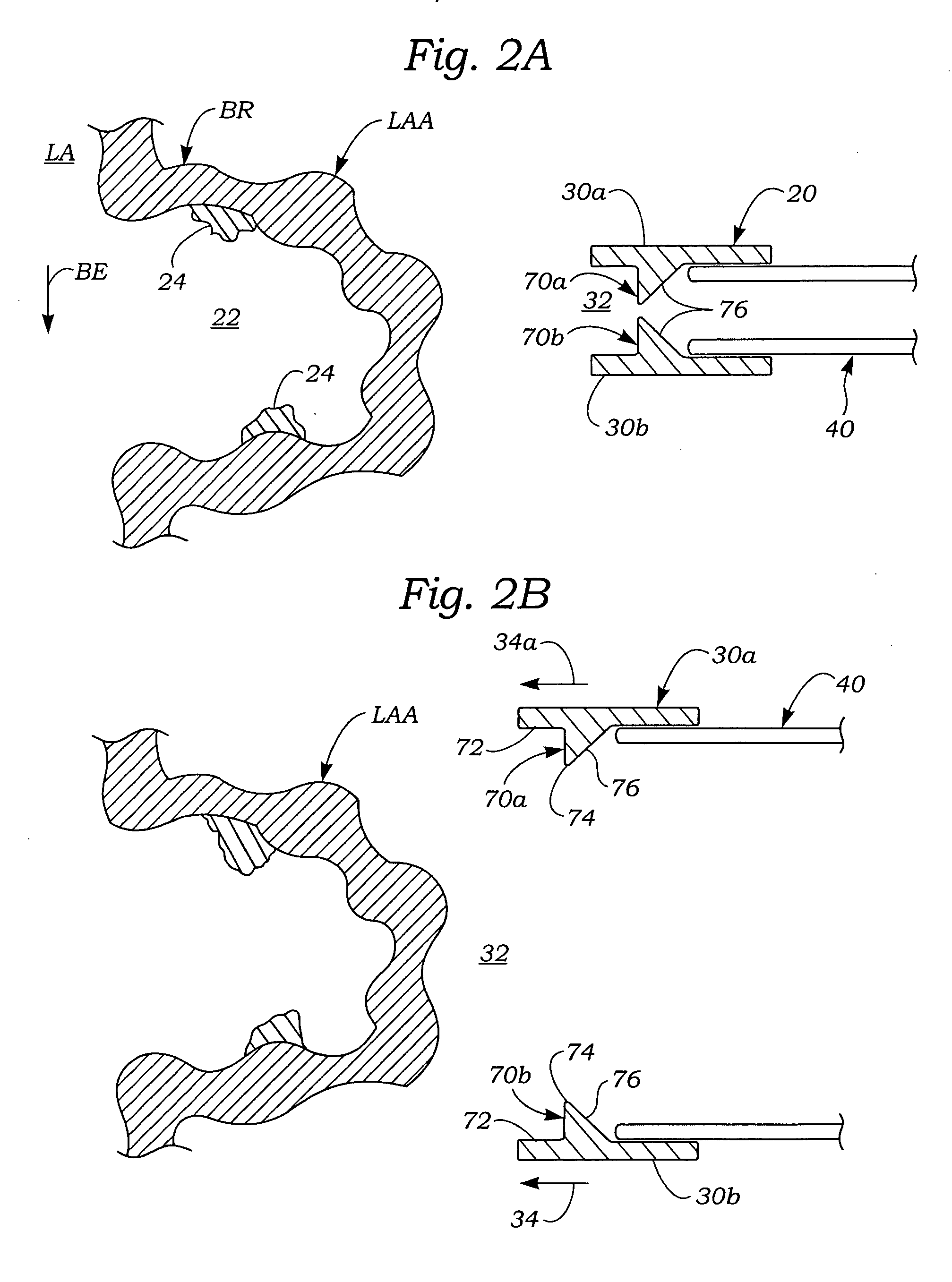
Exclusion of the left atrial appendage
A device for excluding the left atrial appendage (LAA) includes first and second members, each with first and second ends. The second ends are connected by a hinge. The first ends interlock to close the device about the LAA. The members are shaped such that they can exclude the LAA without causing the development of necrotic tissue. If desired, a flexible cover can be provided and the first and second members can be disposed within the cover. If such a cover is used, it will contact the LAA in order to cushion the contact between the members and the LAA and minimize the tendency of the LAA to bleed. The invention also includes methods for using the device to exclude the LAA.
Owner:MICHLER ROBERT E +1
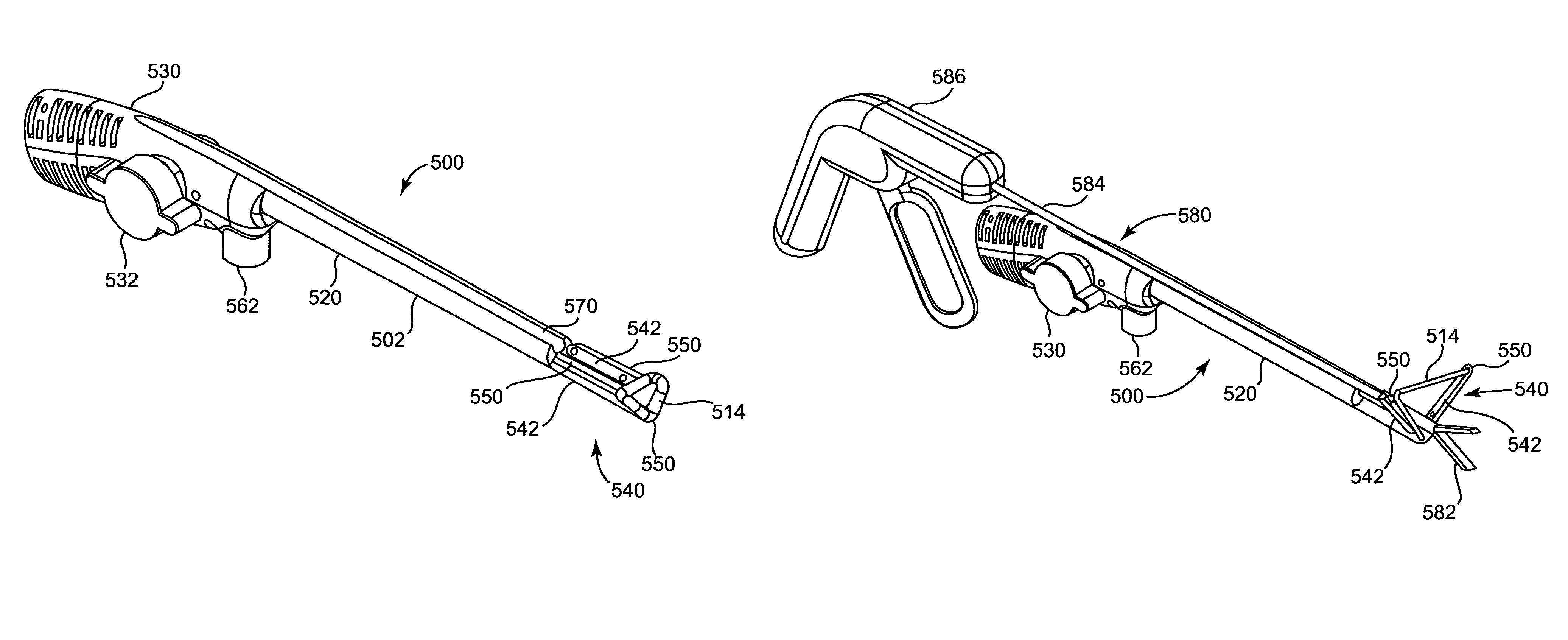
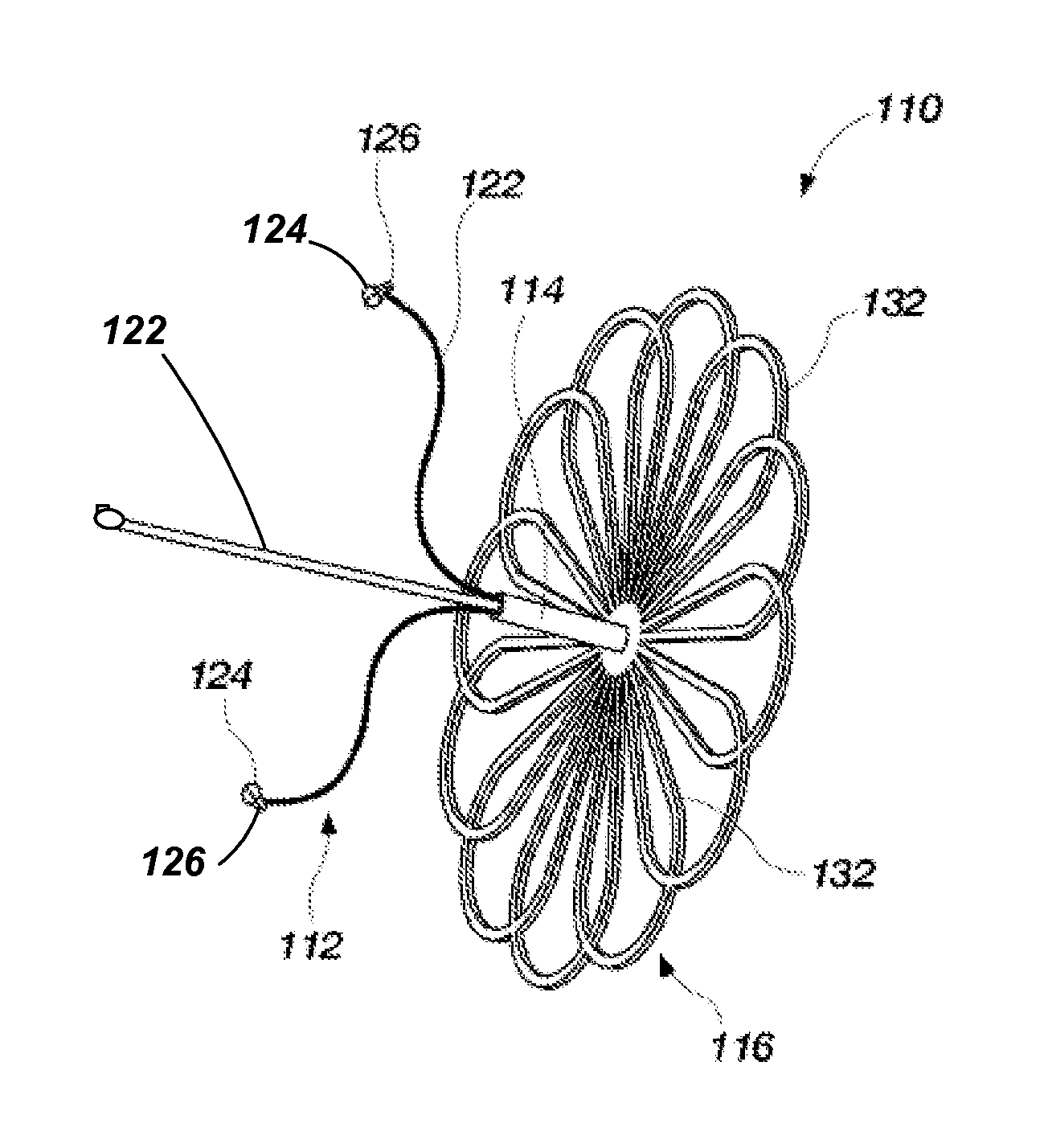
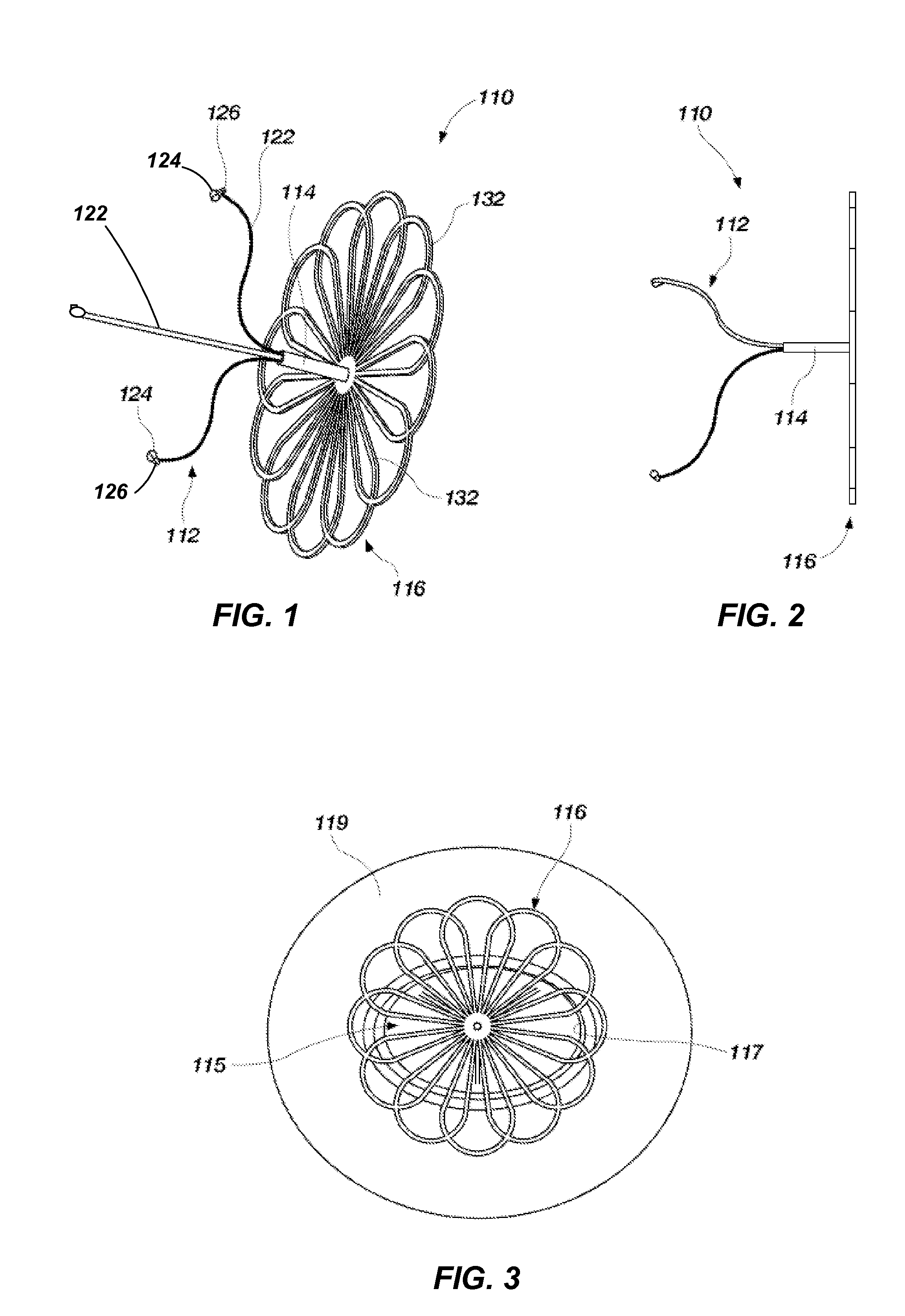
Methods and devices for occlusion of an atrial appendage
Some embodiments of the invention provide a system for occluding a left atrial appendage of a patient. Some embodiments of the system can include a ring occluder that can be positioned around the left atrial appendage and a ring applicator to position the ring occluder with respect to the left atrial appendage. One embodiment discloses a method of accessing endocardial surfaces of the heart through the atrial appendage. Additional embodiments of the invention provide a clip occluder that can be positioned around the left atrial appendage. A clip applicator can position the clip occluder with respect to the left atrial appendage.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
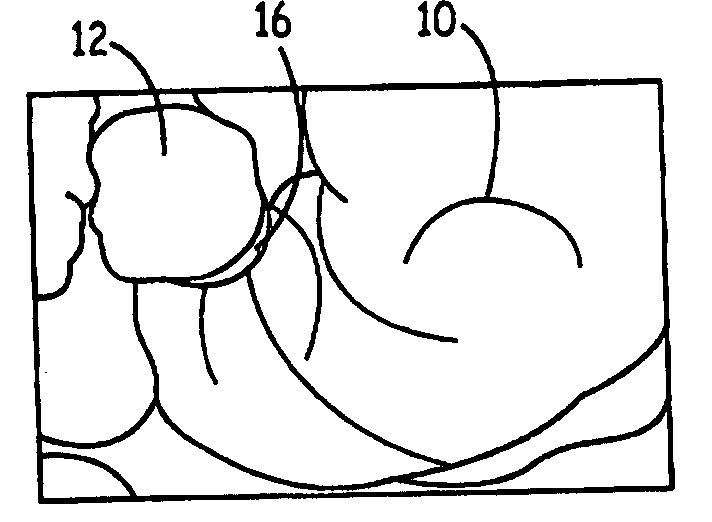
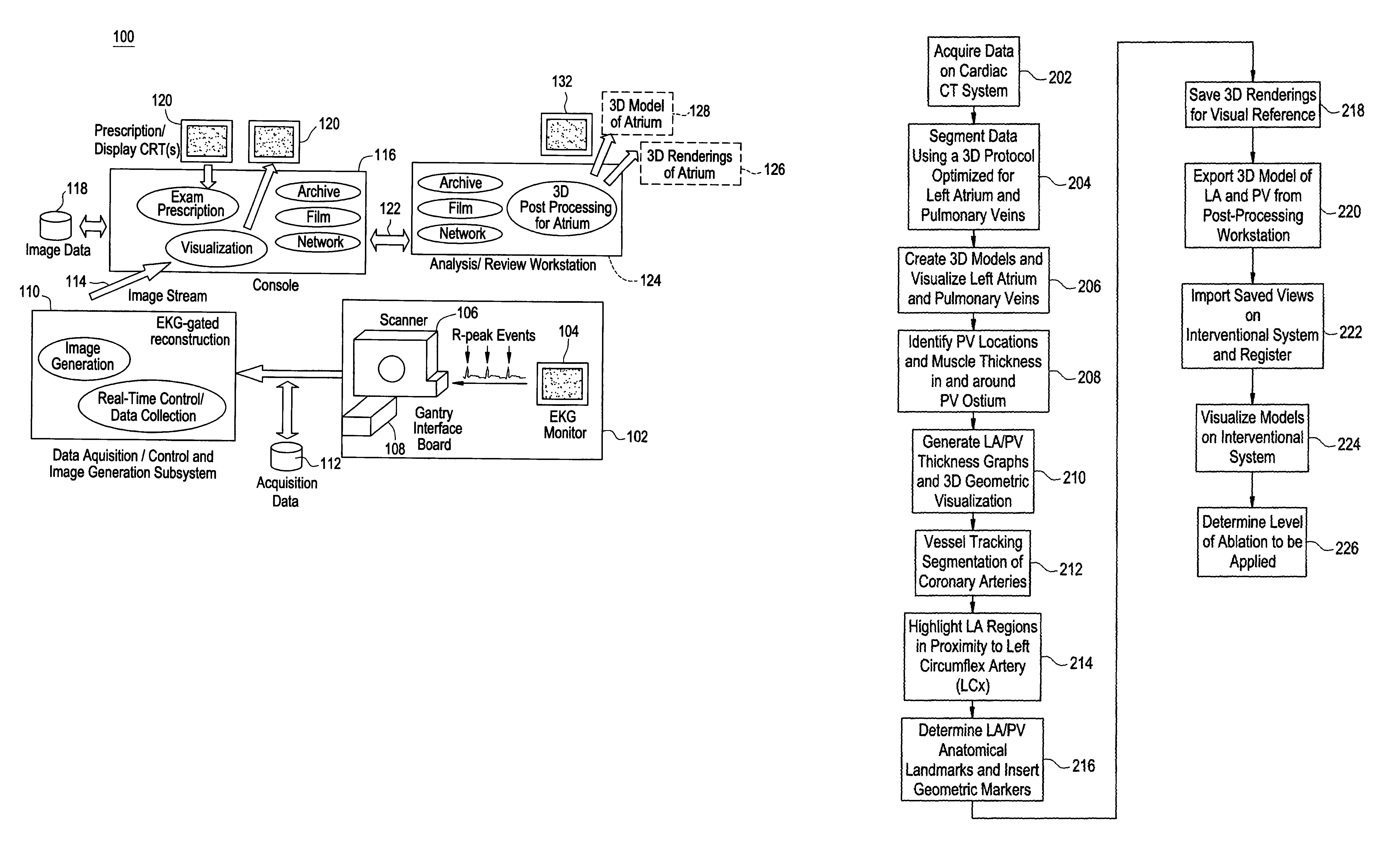
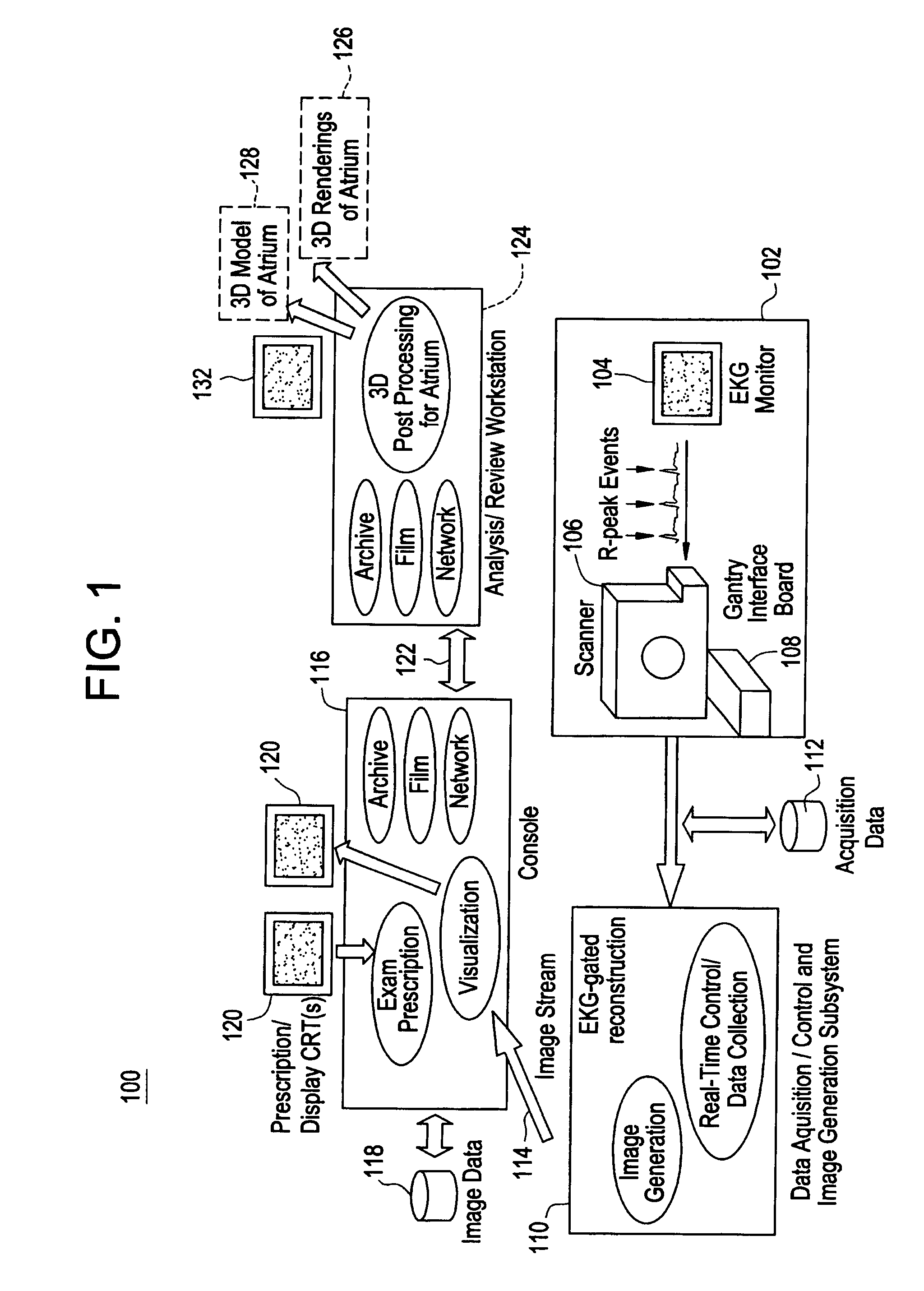
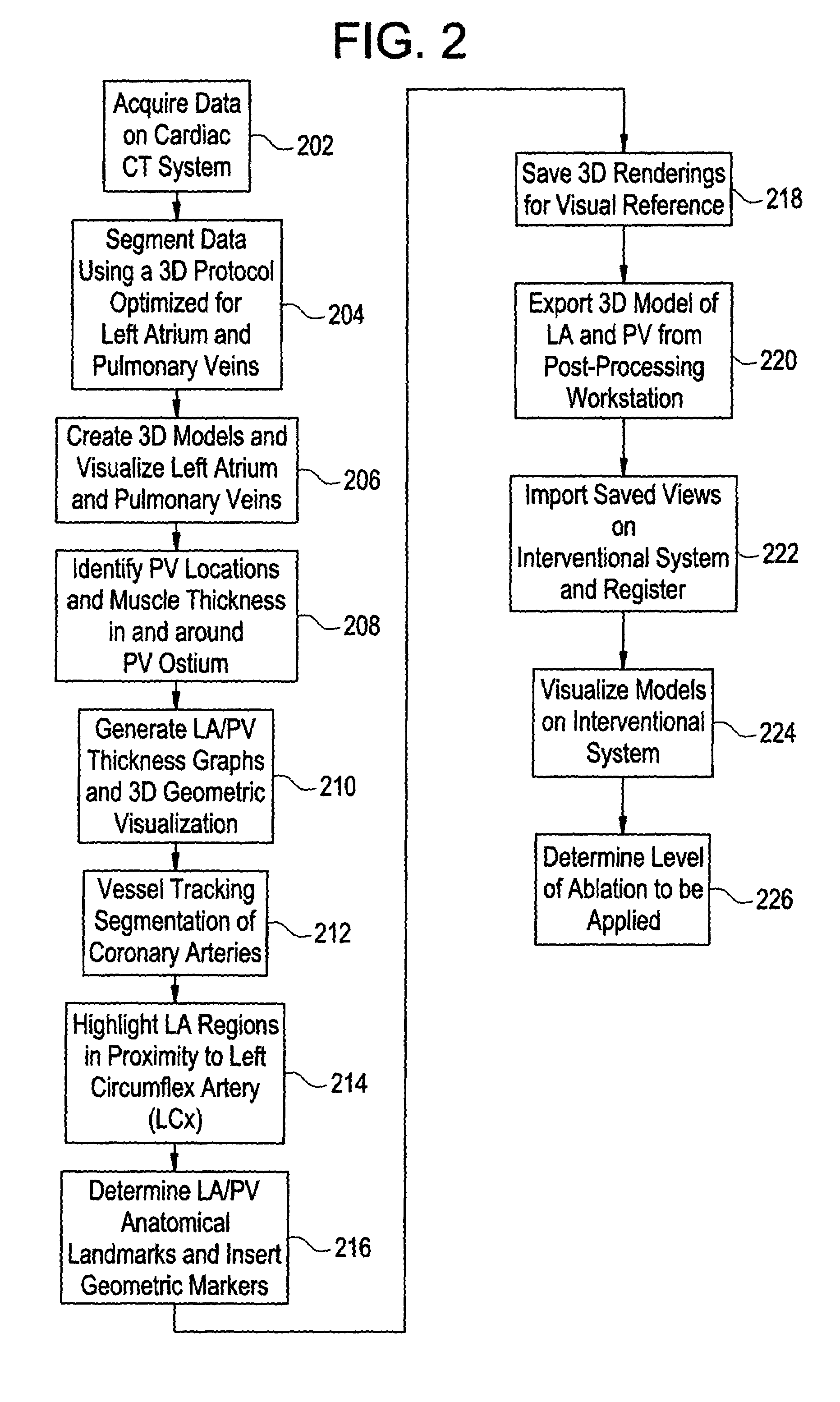
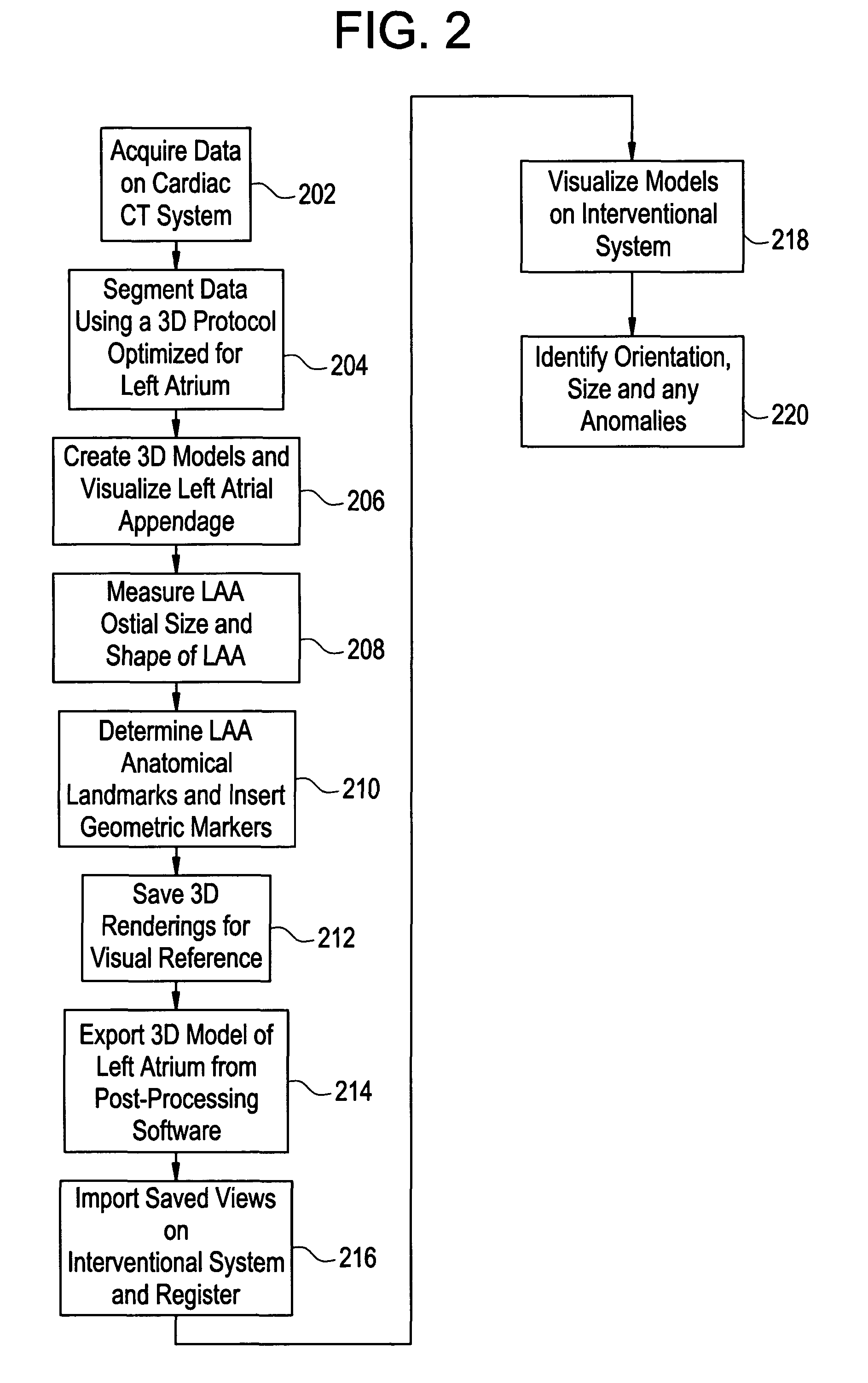
Cardiac CT system and method for planning atrial fibrillation intervention
A method for planning atrial fibrillation (AF) intervention for a patient includes obtaining acquisition data from a medical imaging system, and generating a 3D model of the left atrium and pulmonary veins of the patient. One or more left atrial anatomical landmarks are identified on the 3D model, and saved views of the 3D model are registered on an interventional system. One or more of the registered saved views are visualized with the interventional system.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC +1
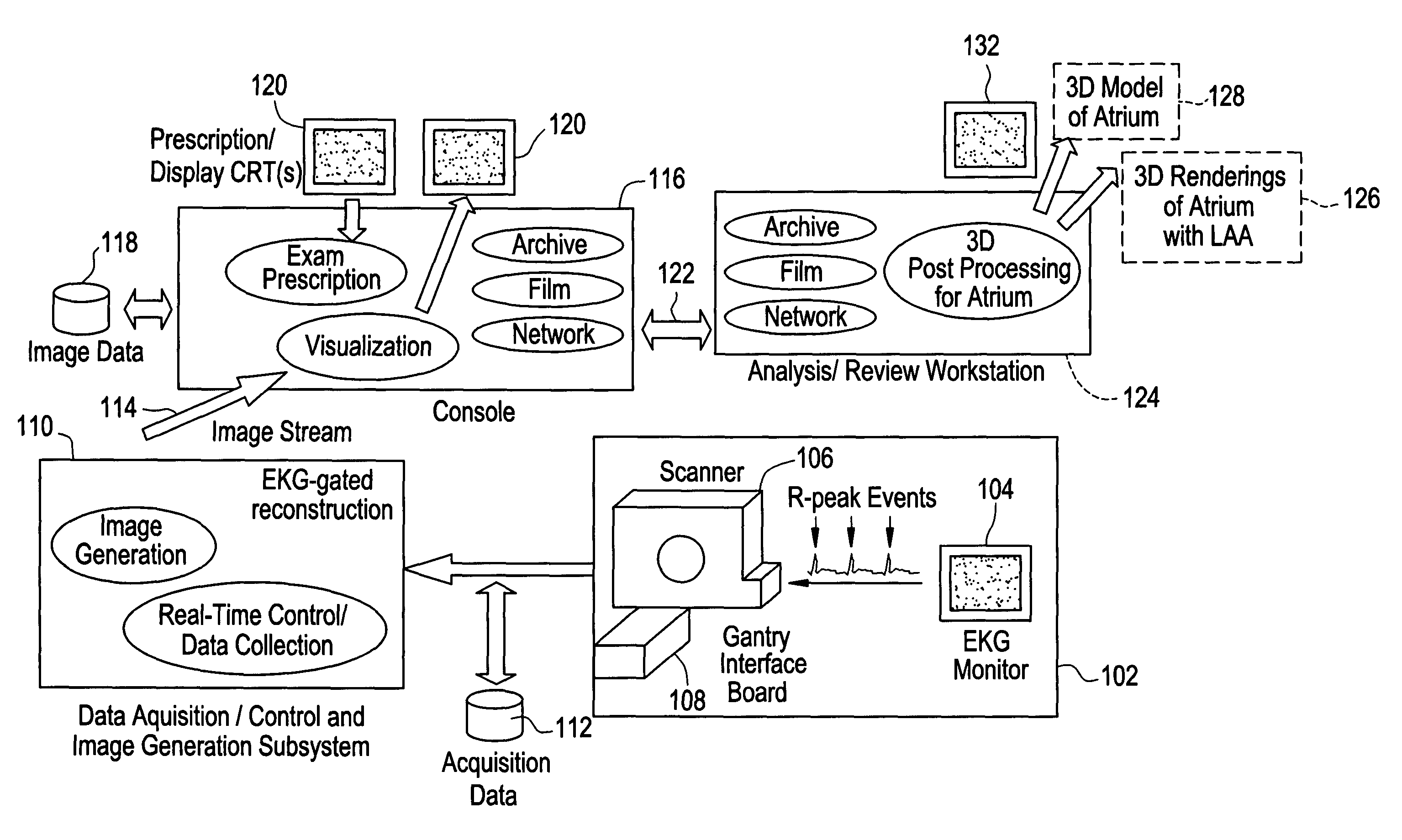
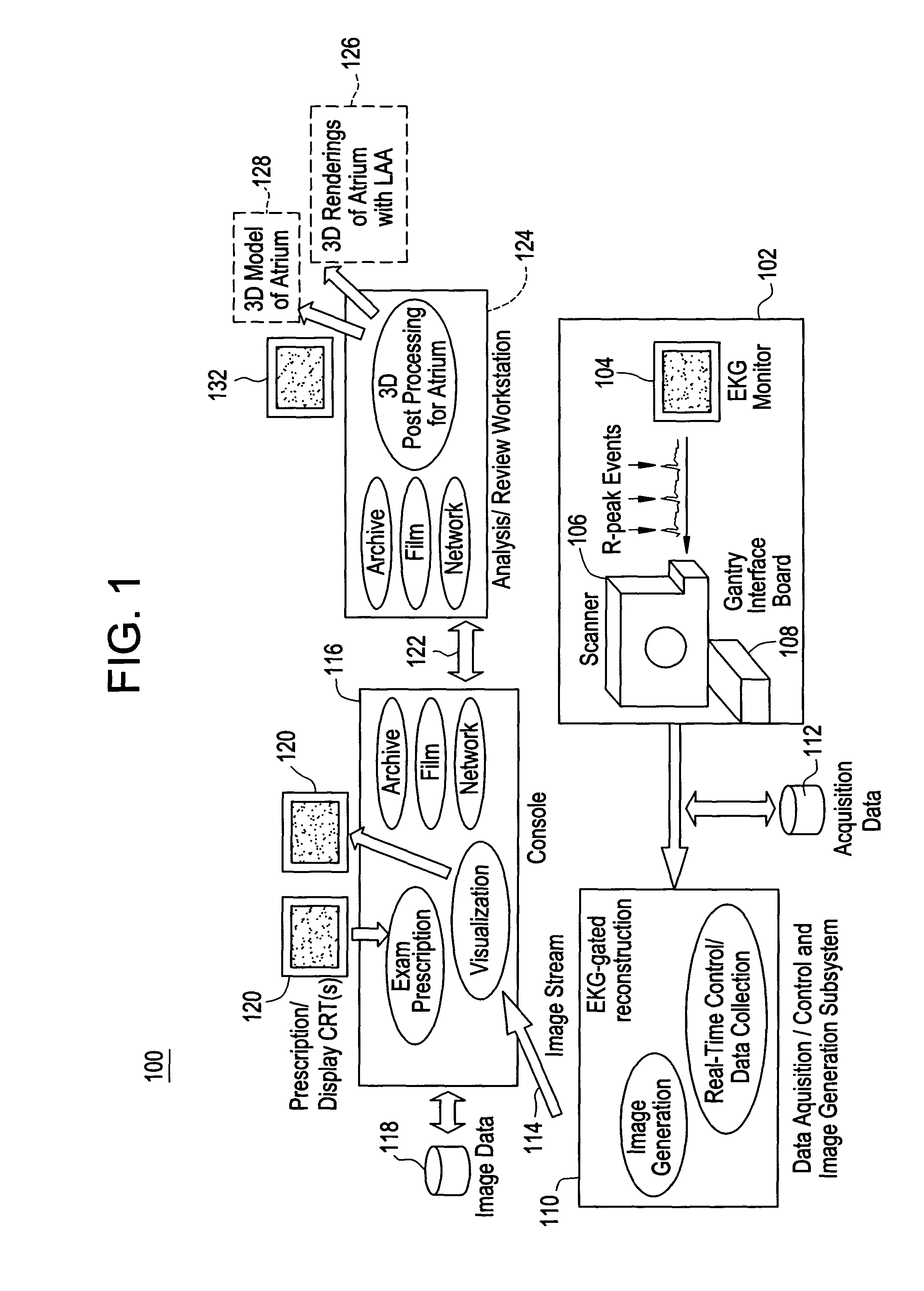
Cardiac CT system and method for planning left atrial appendage isolation
ActiveUS7747047B2Physical therapies and activitiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnatomical landmarkAtrial cavity
A method for planning left atrial appendage (LAA) occlusion for a patient includes obtaining acquisition data from a medical imaging system, and generating a 3D model of the left atrium of the patient. One or more left atrial anatomical landmarks are identified on the 3D model, and saved views of the 3D model are registered on an interventional system. One or more of the registered saved views are visualized with the interventional system.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC +1
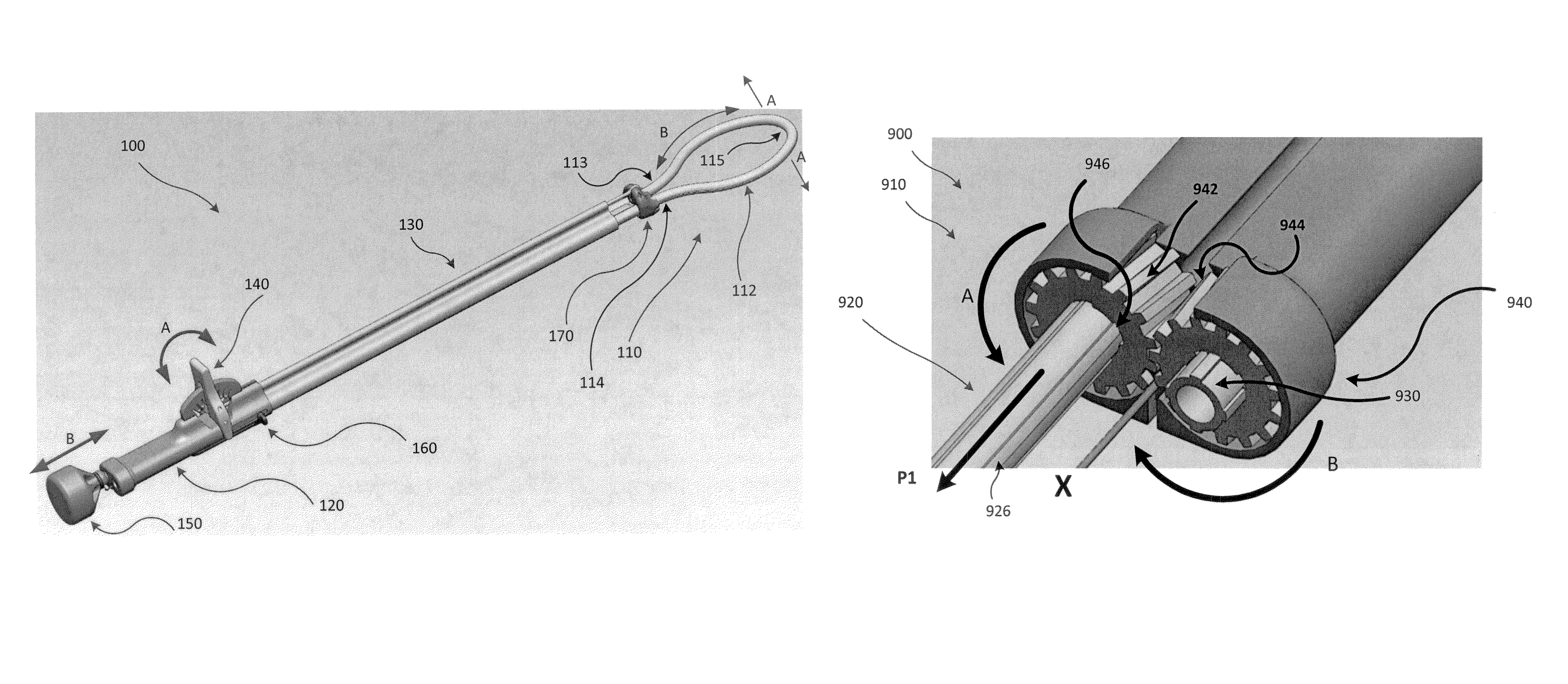
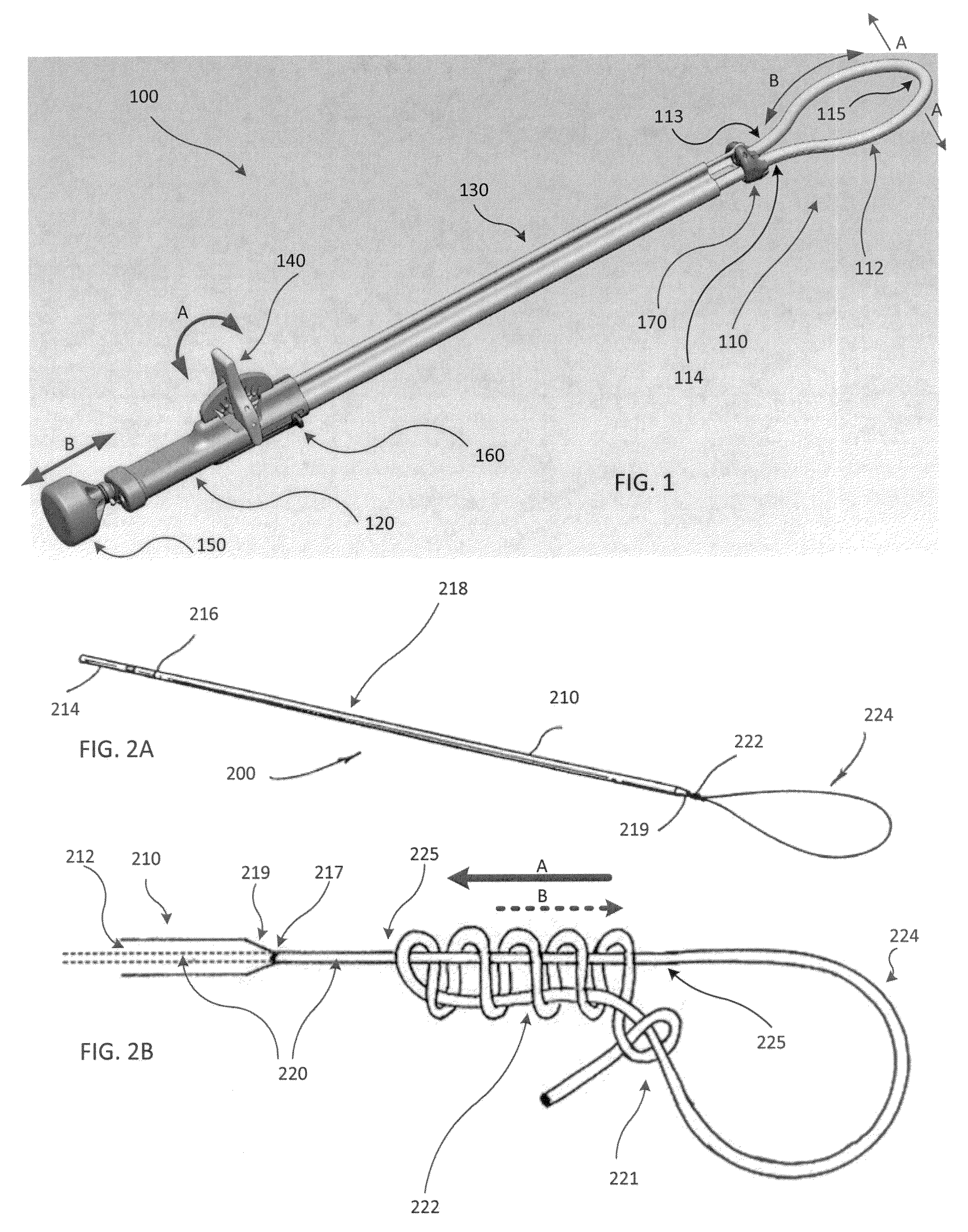
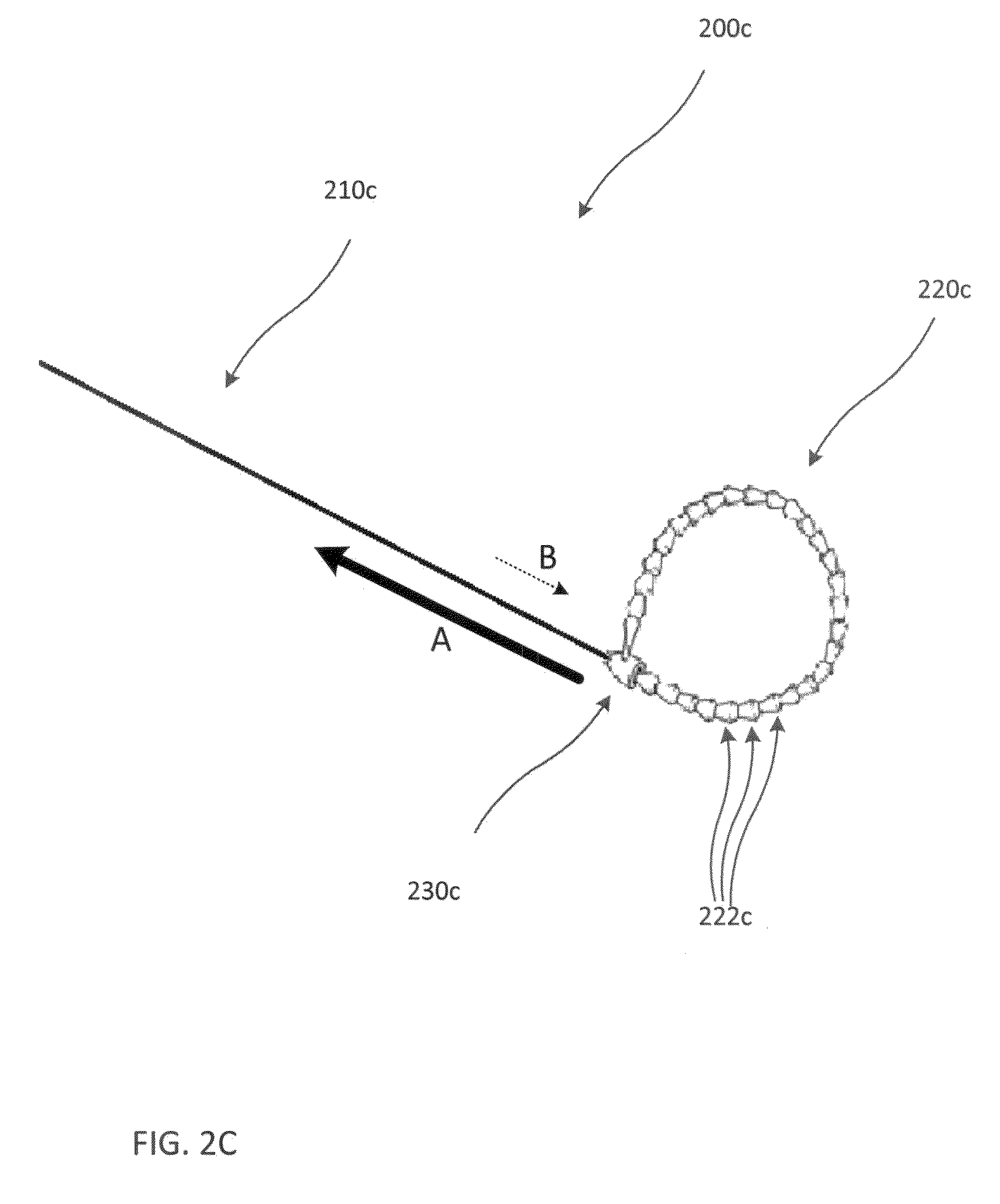
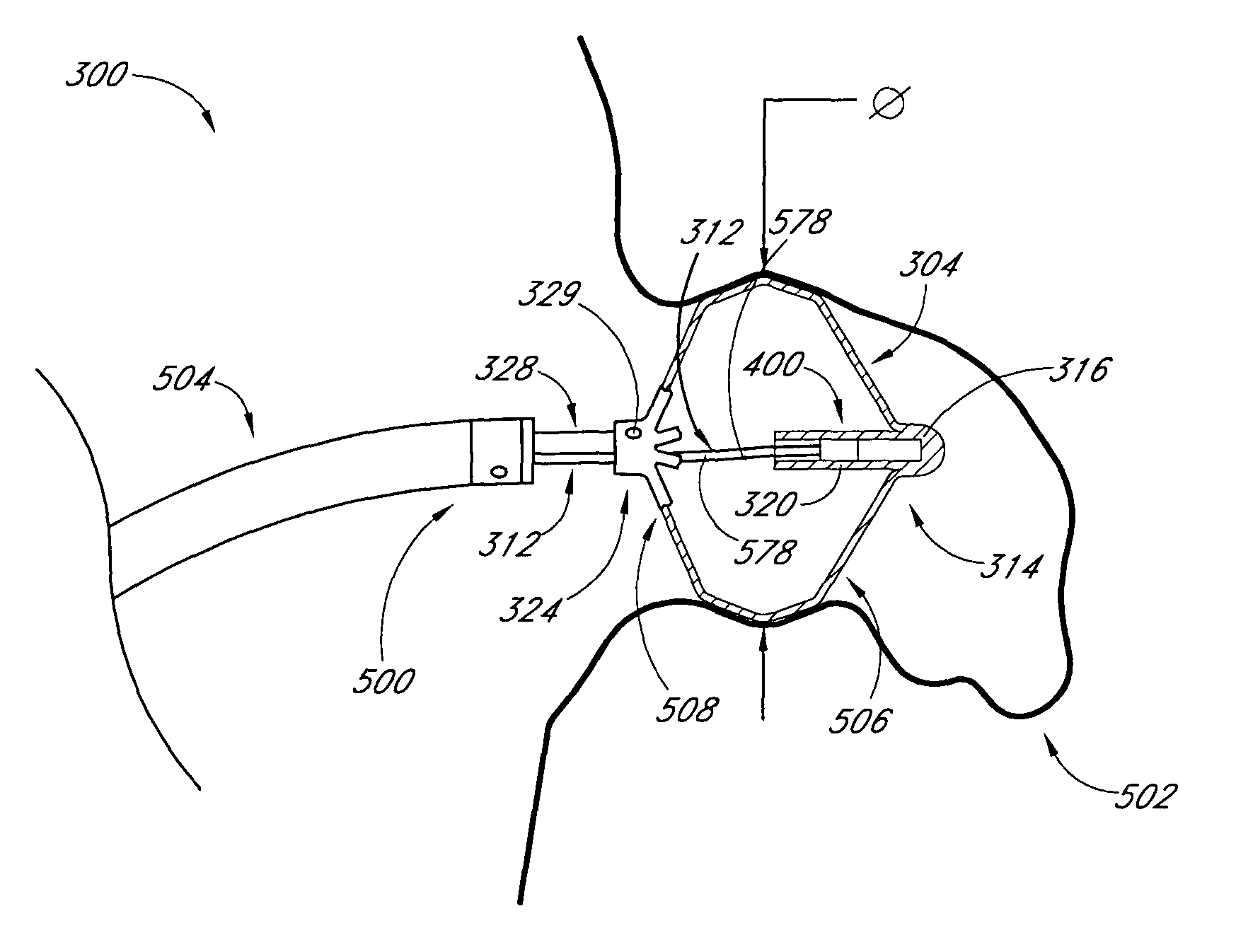
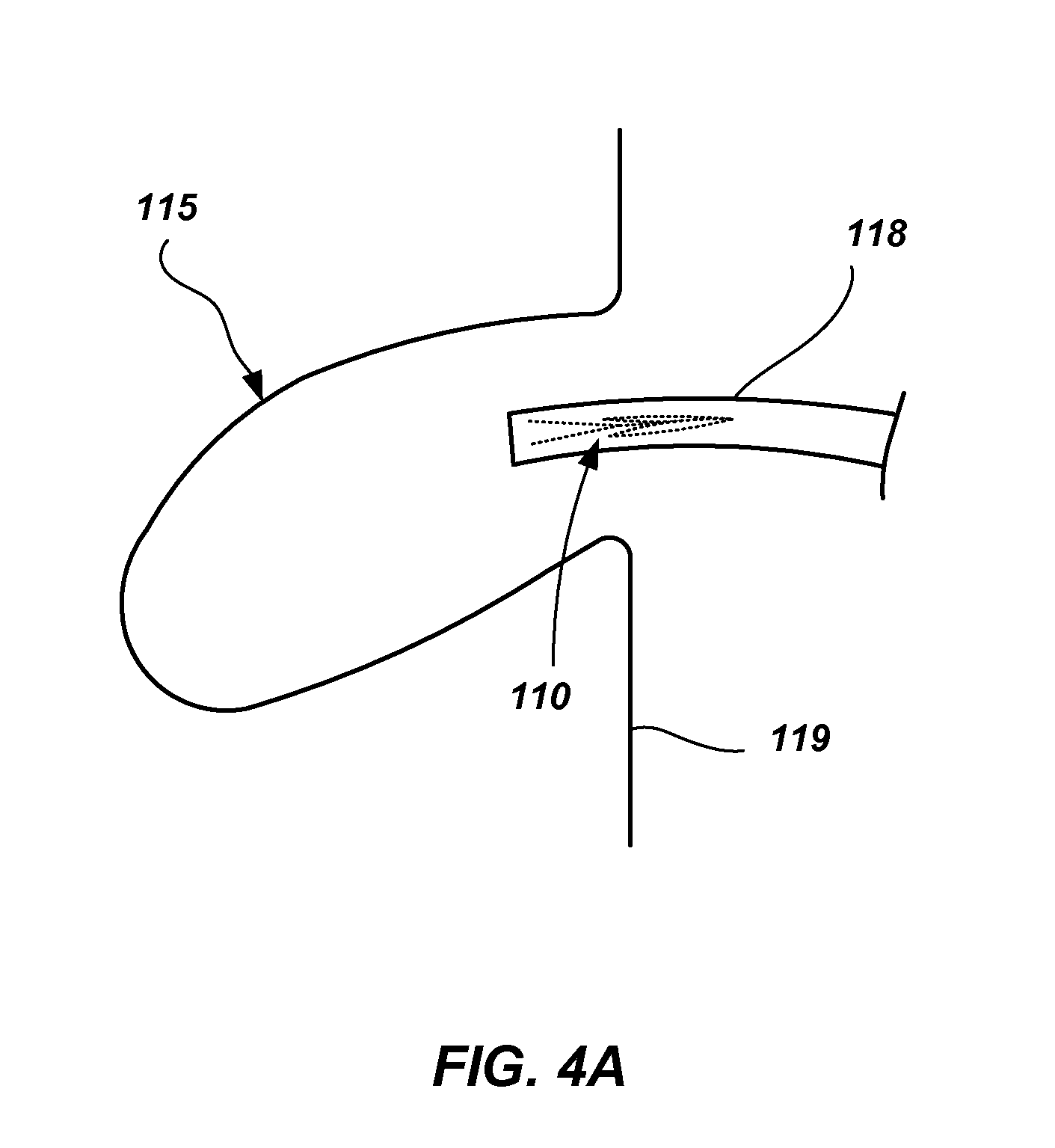
Methods and apparatus for transpericardial left atrial appendage closure
Methods and apparatus for closing a left atrial appendage are described. The methods rely on introducing a closure tool from a location beneath the rib cage, over an epicardial surface, and to the exterior of the left atrial appendage. The closure device may then be used to close the left atrial appendage, preferably at its base, by any one of a variety of techniques. A specific technique using graspers and a closing loop is illustrated.
Owner:SENTREHEART LLC
Apparatus And Methods For Excluding The Left Atrial Appendage
InactiveUS20110082495A1Lower the volumeReduce riskOcculdersSurgical veterinaryTunica intimaPericardium
Apparatus and methods are provided for excluding and reducing the volume of the left atrial appendage (“LAA”) by deploying a first tissue capture element in contact with the pericardium and a second tissue capture element in engagement with the endocardial surface adjacent to the ostium of the LAA, such that the LAA tissue is retained in a collapsed, reduced volume state therebetween. Methods of using the apparatus of the present invention to reduce or occlude the LAA also are provided.
Owner:RUIZ CARLOS E
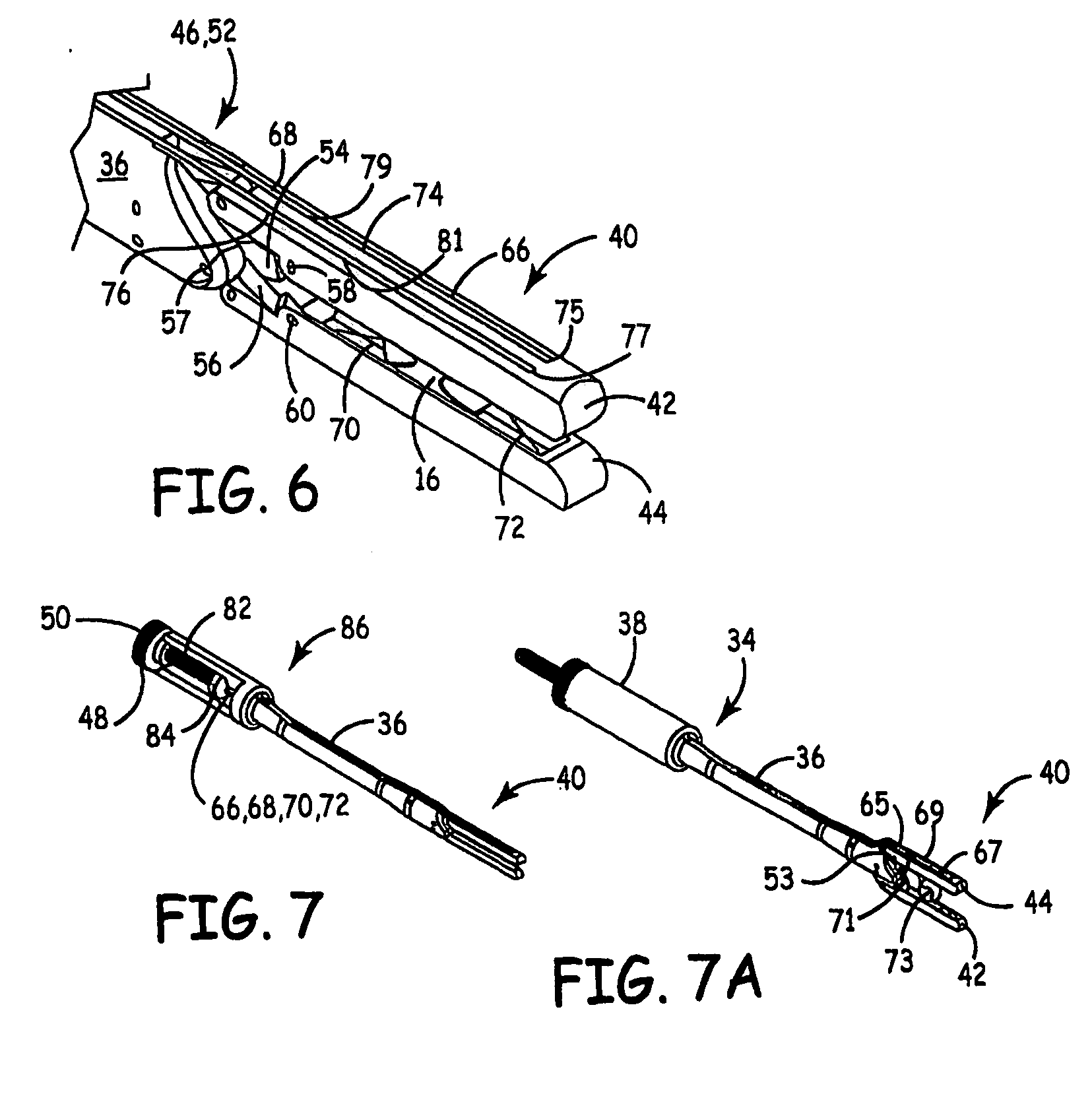
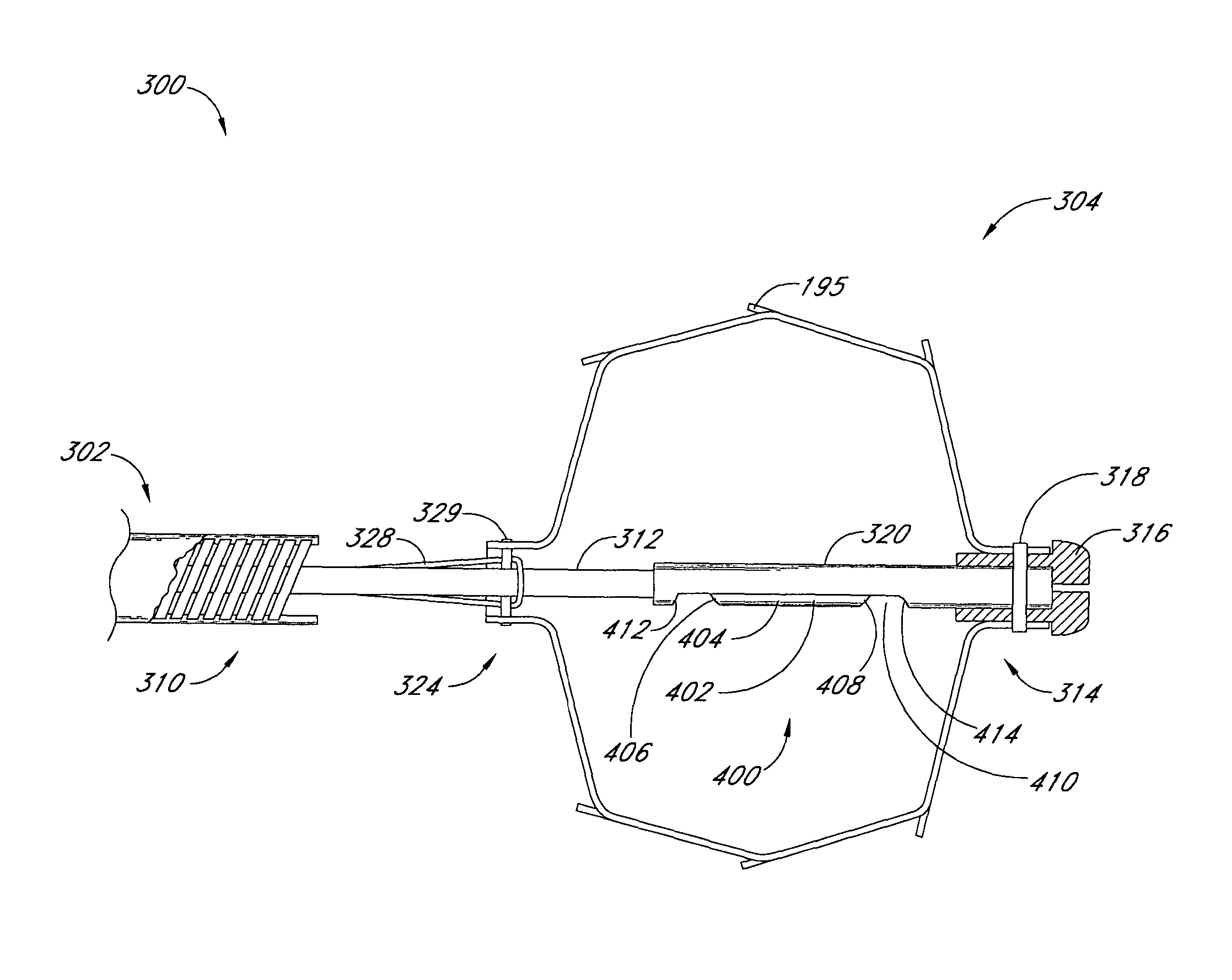
Method and apparatus for recapturing an implant from the left atrial appendage
A system and method for retrieving an implantable device includes a delivery catheter, a recapture section, and a sheath. The delivery catheter has a proximal end and a distal end. The recapture section is axially extendable from the distal end of the delivery catheter. The sheath has a proximal end and a distal end and a lumen sized to receive the delivery catheter. A portion of the lumen of the sheath is actuatable from an enlarged inside diameter to a reduced inside diameter to apply an inwardly directed force to the recapture section. The delivery catheter can be actuated with respect to the sheath to extend or retract the recapture section with respect to the delivery catheter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
System and method for delivering a left atrial appendage containment device
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices and methods for treating heart failure
A device for implanting into an atrial septum of a patient. In some embodiments, the device has a core region to be disposed in an opening in the atrial septum; a distal retention region adapted to engage tissue on a left atrial side of the septal wall; a proximal retention region adapted to engage tissue on a right atrial side of the septal wall; and a retrieval region comprising a plurality of retrieval members, each retrieval member comprising a connector at a proximal end, the connector being adapted to connect to a delivery system. The device has a delivery configuration and a deployed configuration, the core region, distal retention region and proximal retention region each having a smaller diameter in the delivery configuration than in the deployed configuration, the retrieval member connectors being disposed proximal to and radially outward from the opening in the deployed configuration.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Device for preventing clot migration from left atrial appendage
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP +1
Medical device for modification of left atrial appendage and related systems and methods
Medical devices, systems and methods for modifying a left atrial appendage (“LAA”). In one embodiment, a medical device system includes a jailing member or structure positioned over the ostium of an LAA and at least one tissue growth member positioned within the LAA and retained within the LAA by the jailing member. In another embodiment, a medical device includes an atrial stent coupled with a patch that is configured to cover the ostium of an LAA. The patch may have a tissue growth member associated therewith. In another embodiment, the patch may include an open-cell frame which may be used as a jailing member or structure.
Owner:COHEREX MEDICAL
Medical device for modification of left atrial appendage and related systems and methods
Devices, methods and systems are provided for occluding an opening within the tissue of a body, such as a left atrial appendage. In one embodiment, a system for use in occluding an opening in the tissue of a body includes a handle, a catheter coupled with the handle and a medical device disposed within a lumen of the catheter. The medical device includes an anchor system having a plurality of anchor segments coupled with an anchor hub. The medical device further includes an occluder system having a plurality of occluder segments coupled with an occluder hub. A first actuator is configured to displace the occluder hub independent of, and relative to, the anchor hub to deploy the occluder system from a refracted state to an expanded state while the anchor system remains in a retracted state.
Owner:COHEREX MEDICAL
Medical device for modification of left atrial appendage and related systems and methods
A medical device, system and method for modifying a left atrial appendage (“LAA”). The medical device system includes a tether anchored within the LAA and one or more tissue growth members or occluders configured to be slid over the tether and lodged within the LAA. With this arrangement, a physician may close-off the LAA with a selective number of tissue growth members to meet the varying LAA sizes as determined from imaging information while conducting the procedure.
Owner:COHEREX MEDICAL
Method of implanting an adjustable occlusion device
Disclosed is an adjustable occlusion device for use in a body lumen such as the left atrial appendage. The occlusion device is removably carried by a deployment catheter. The device may be enlarged or reduced to facilitate optimal placement or removal. Methods are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
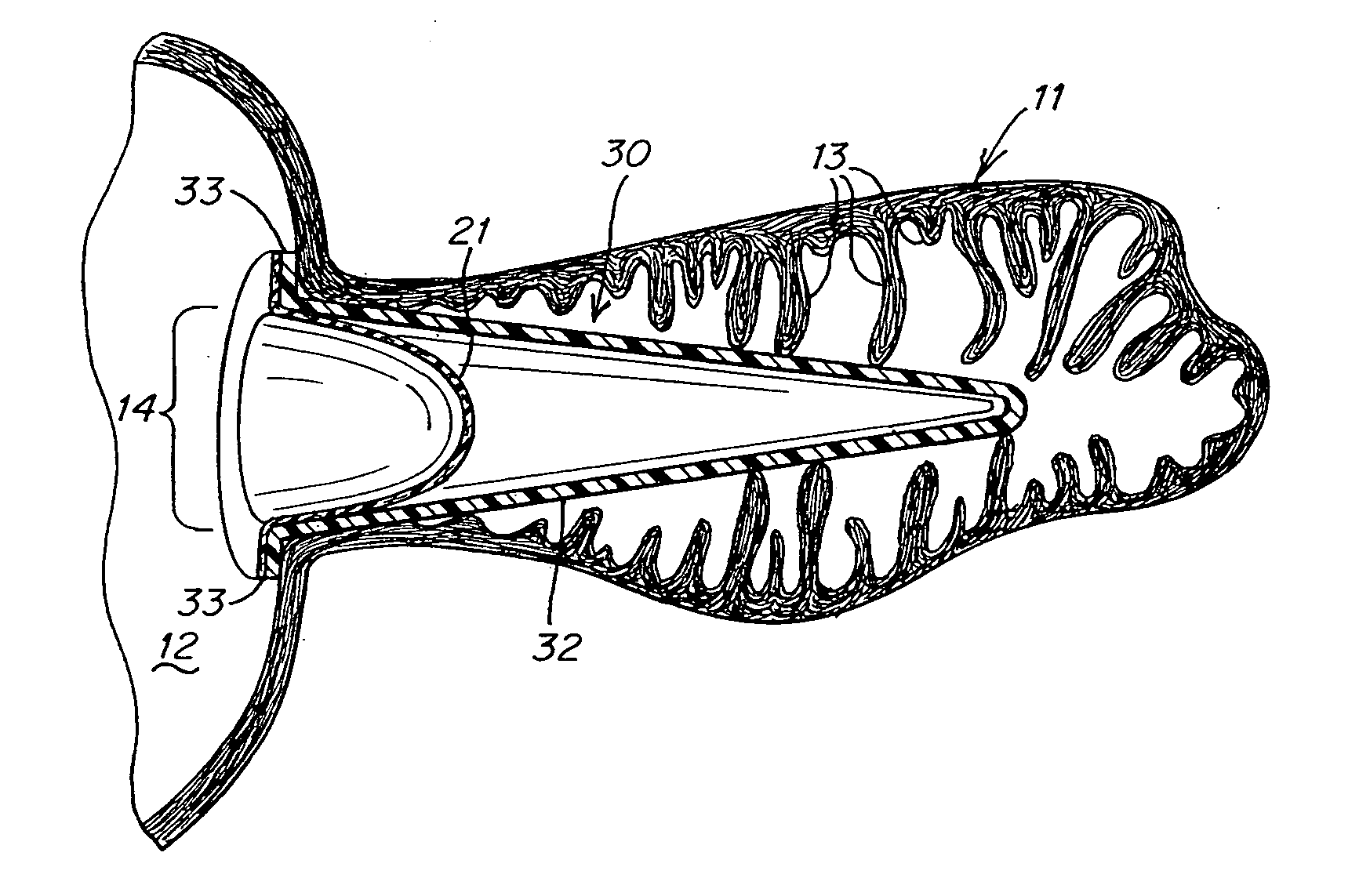
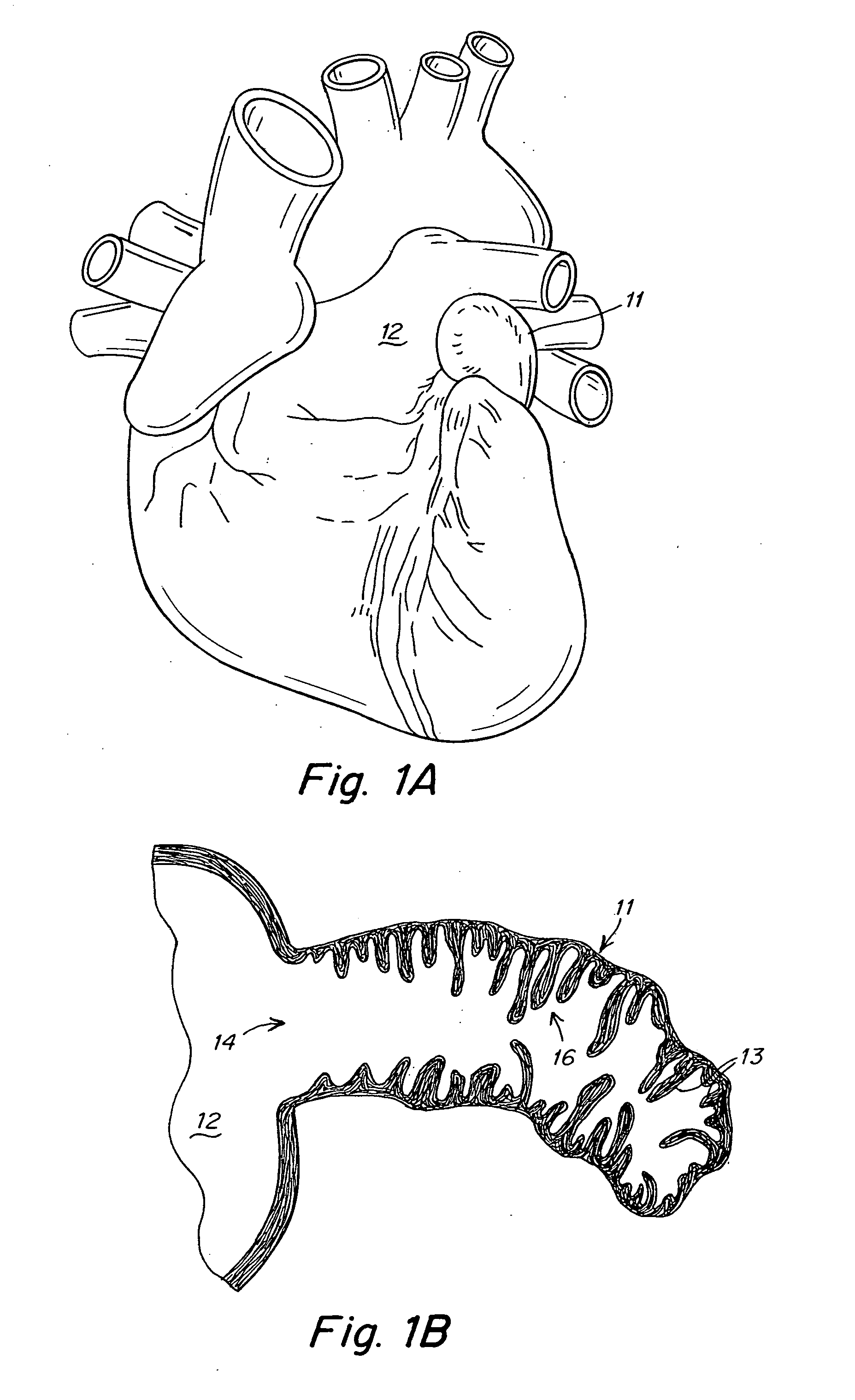
Device and methods for preventing formation of thrombi in the left atrial appendage
ActiveUS20050070952A1Reduce the possibilityPrevents dislodgement and migrationDilatorsOcculdersBlood flowThrombus
The embodiments of the present invention provide a device that modifies the left atrial appendage (LAA) to reduce the likelihood of thrombus formation therein. The device includes a liner that reduces the volume of the LAA and remodels the interior geometry and surfaces of the LAA thereby minimizing the crenellations in the LAA that impede blood flow. According to some embodiments, the device further includes an anchor component. The anchor component helps to expand the liner upon deployment of the device in-vivo and further prevents dislodgement and migration of the device, by ensuring the device is properly seated and completely sealed against the walls and ostium of the LAA.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC +1
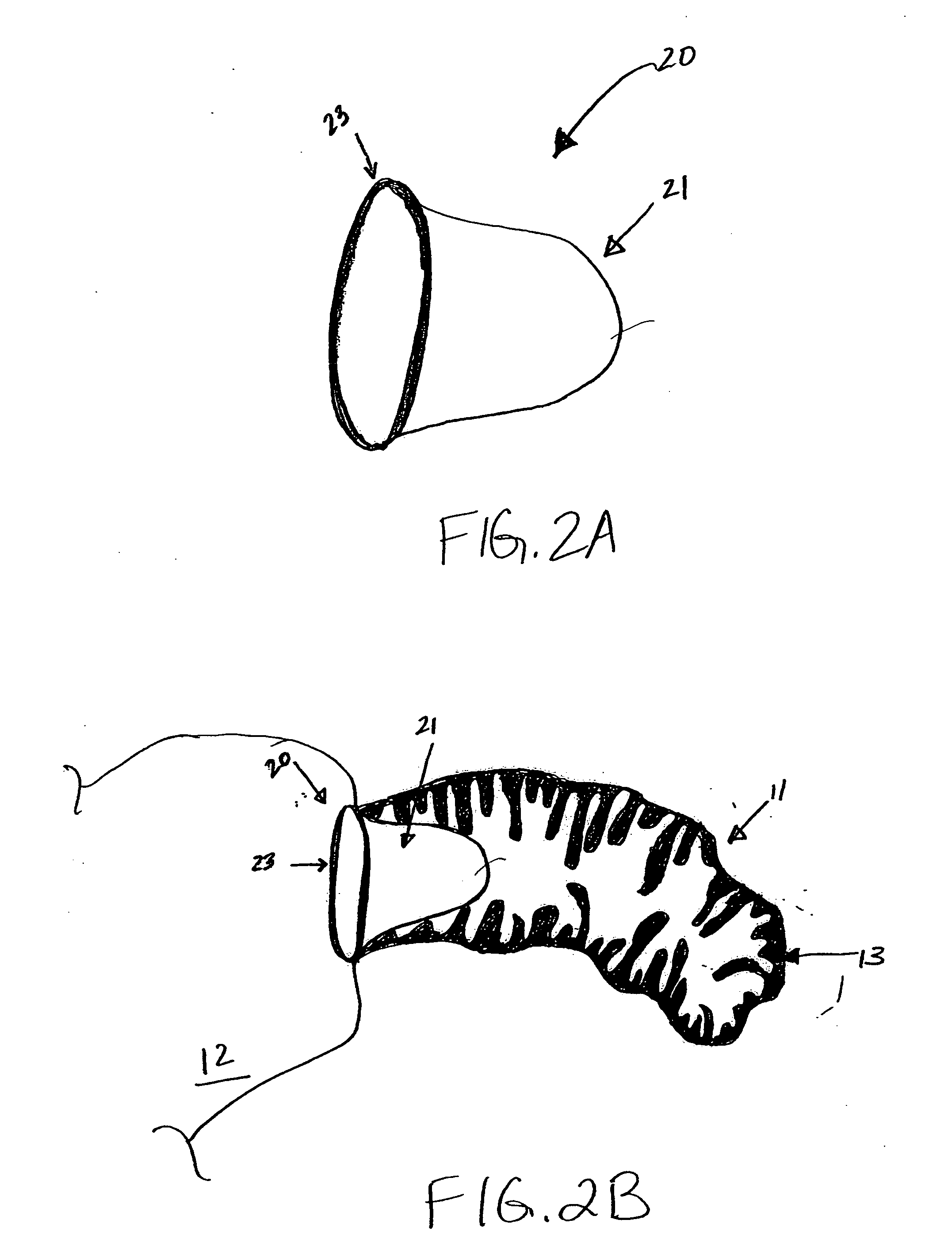
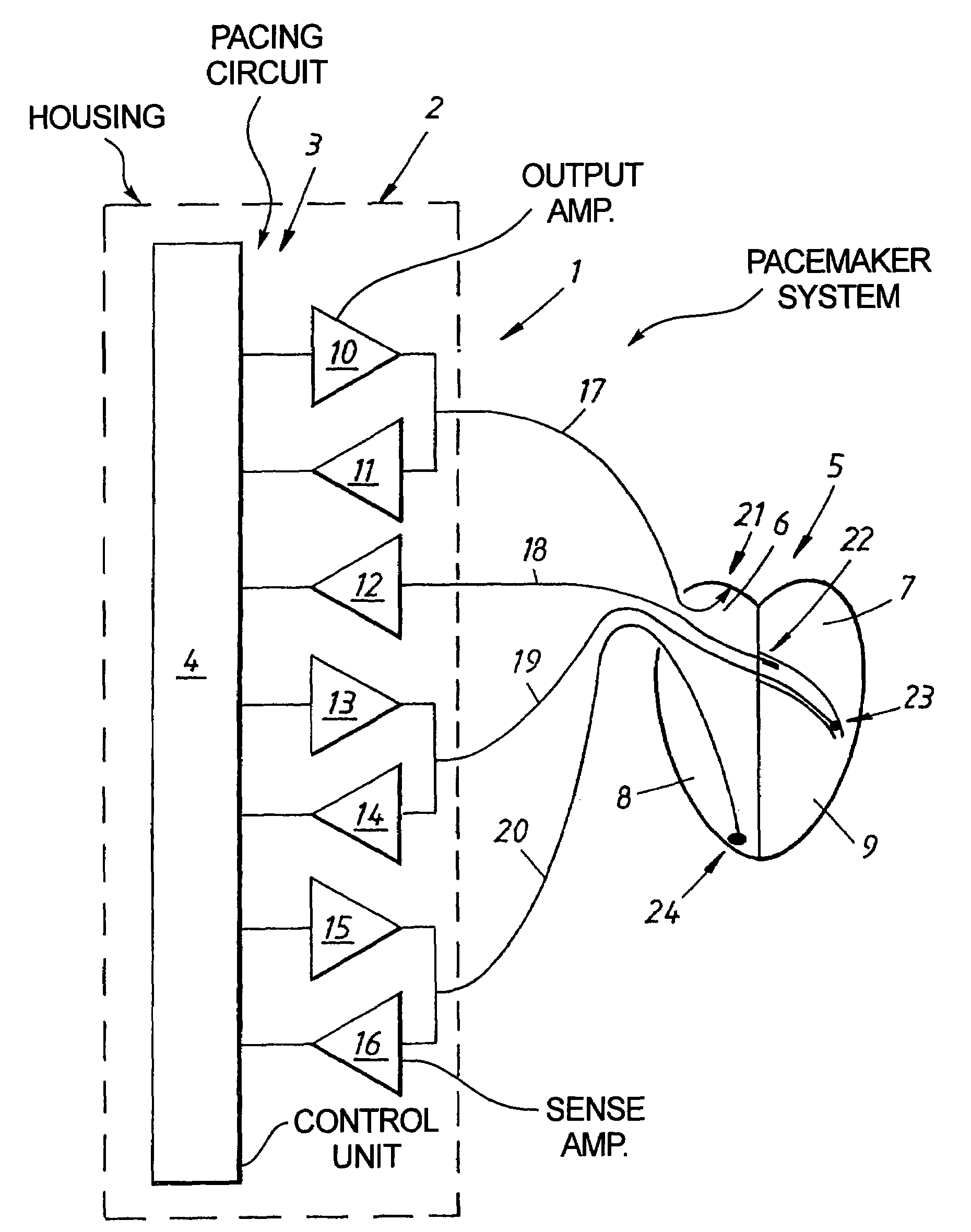
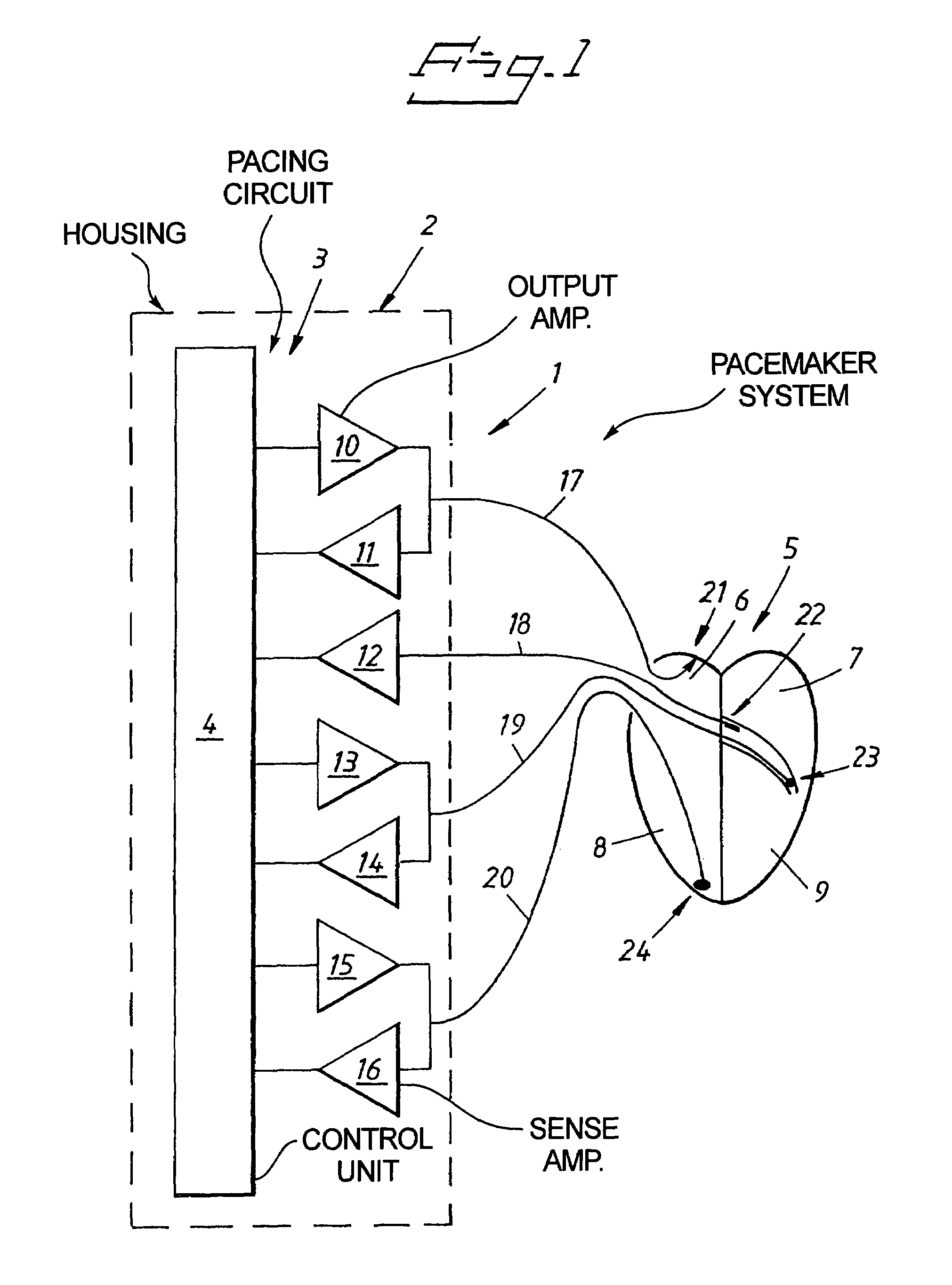
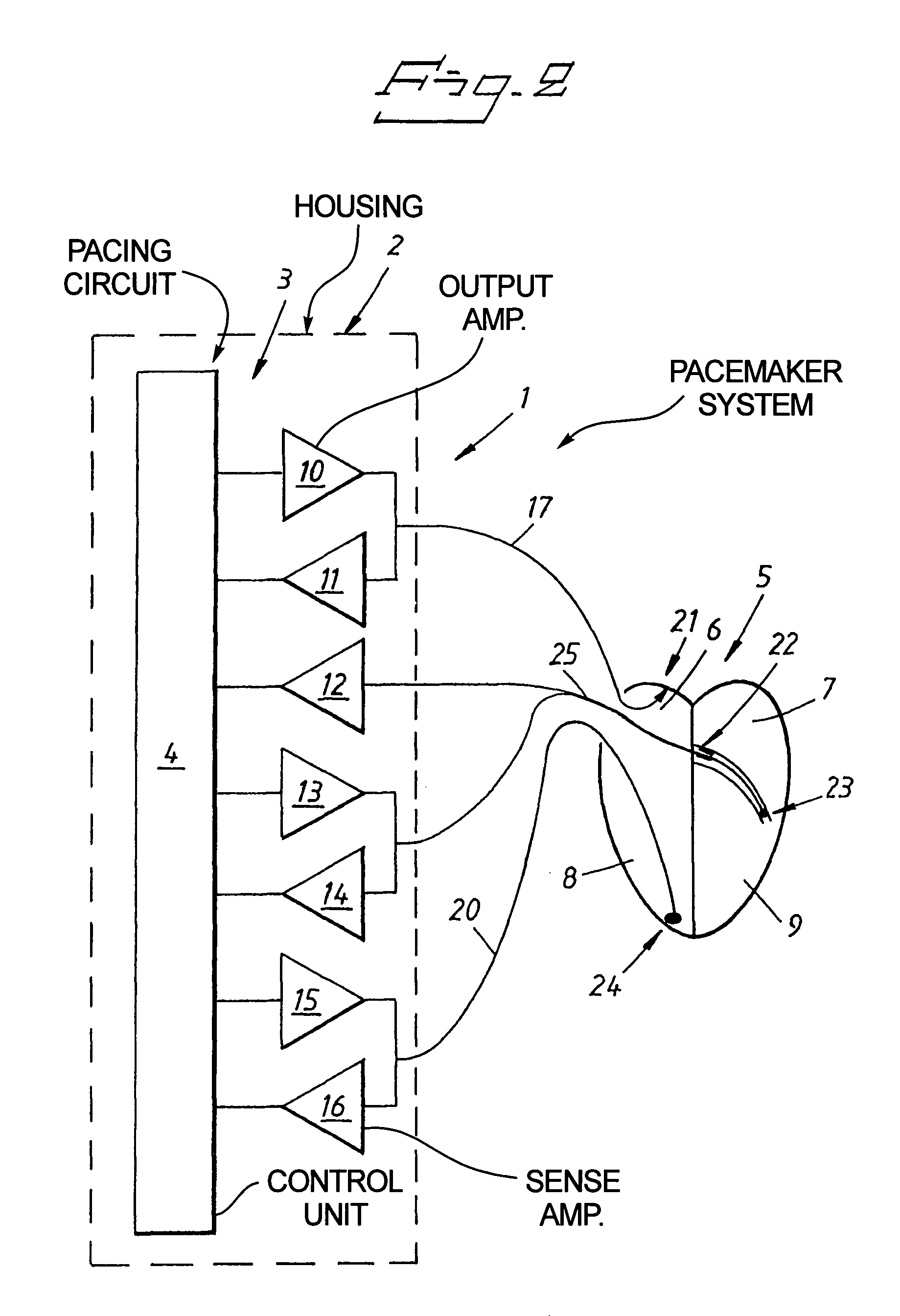
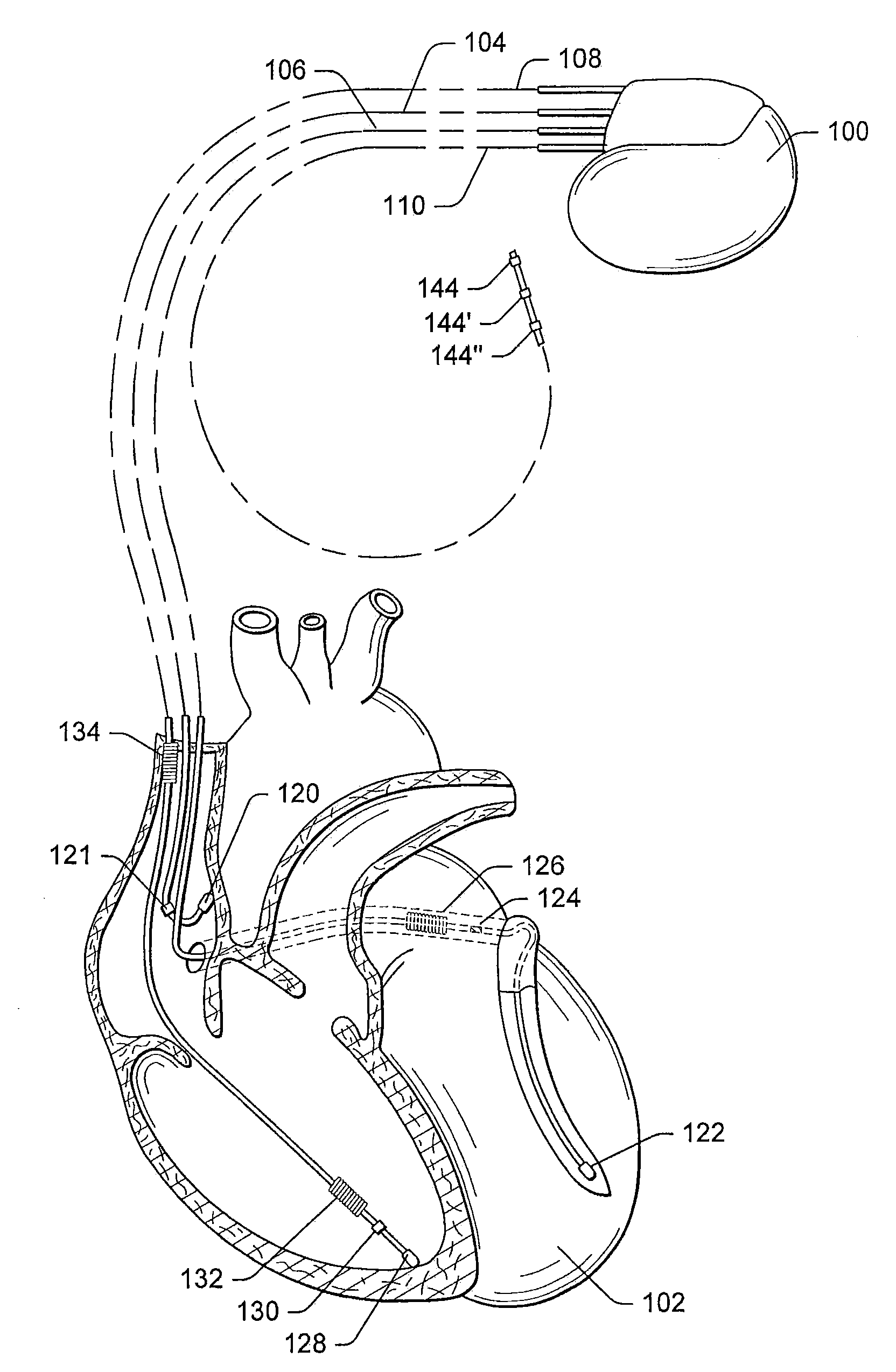
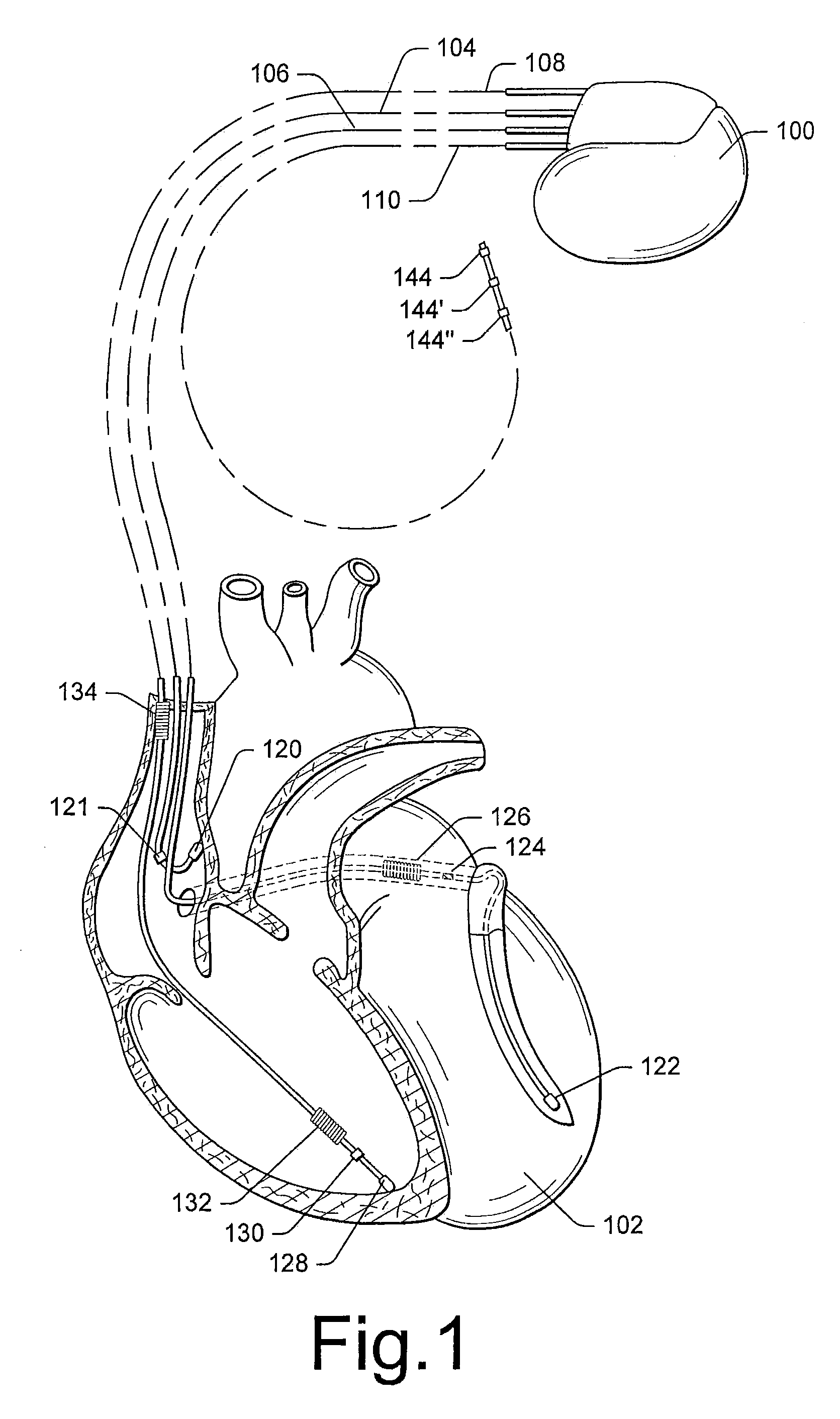
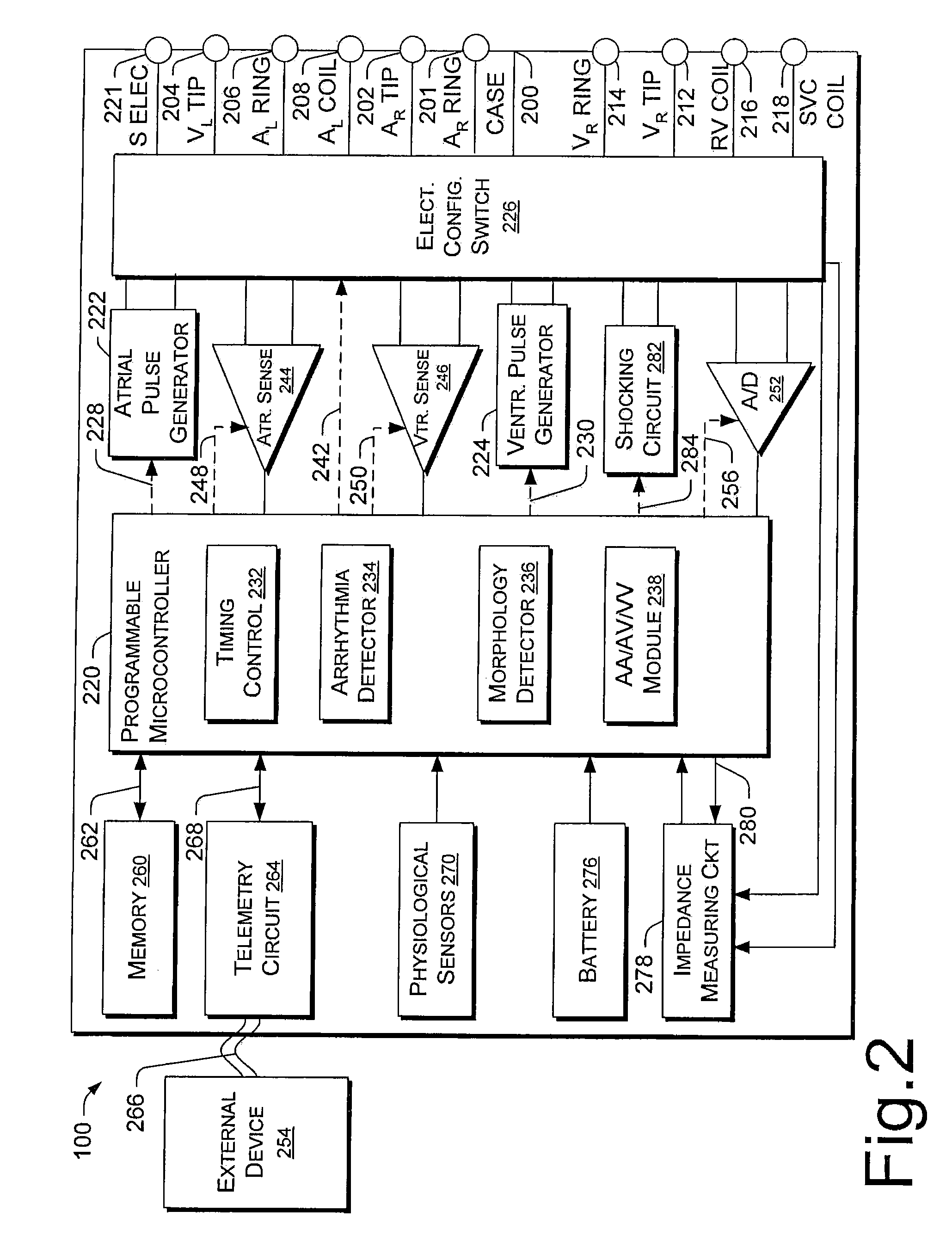
Cardiac stimulating device
An implantable cardiac stimulating device has a pacing circuit connected via an electrode lead system to a first electrode which stimulates and detects activity in the left ventricle, a second electrode to stimulate and detect activity in the right atrium, and to a third electrode to detect activity in the left atrium. Upon the occurrence of a paced or sensed depolarization of the right atrium, a first AV-delay is started. When the subsequent left atrial depolarization is detected, a new AV-interval is started that is optimized for the left side of the heart. Either the left ventricle only, or both ventricles, is paced at the optimized left side AV-interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Systems and methods for determining inter-atrial conduction delays using multi-pole left ventricular pacing/sensing leads
Techniques are provided for use by a pacemaker or other implantable medical device for estimating optimal atrio-ventricular pacing delays within a patient. The inter-atrial conduction delays (IACDs) are determined based, at least in part, on atrial far-field (AFF) signals sensed using a multi-pole left ventricular (LV) lead, such as an LV lead implanted via the coronary sinus (CS) with a plurality of electrodes. In one example, for intrinsic atrial events, the IACD is equal to the interval from the beginning of a P-wave detected via a right atrial lead and the end (or peak) of an AFF event detected via a left atrial ring electrode of a CS / LV lead. For paced atrial events, the IACD is instead equal to the interval from the A-pulse to the end (or peak) of the AFF event detected via the CS / LV lead. AV / PV pacing delays are then calculated based on the IACD adjusted by an offset.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Medical Device and Delivery System for Modification of Left Atrial Appendage and Methods Thereof
Devices, methods and systems are provided for occluding an opening within the tissue of a body, such as a left atrial appendage. In one embodiment, a delivery system for use in occluding an opening in the tissue of a body includes an actuation assembly operatively coupled to a medical device including an anchor portion and an occluder portion. The actuation assembly is configured to move the anchor portion between a deployed state and retracted state while the occluder portion maintains a deployed state. With this arrangement, the deployed occluder portion can be visualized via imaging at a preferred position prior to deploying the anchor portion of the medical device.
Owner:COHEREX MEDICAL
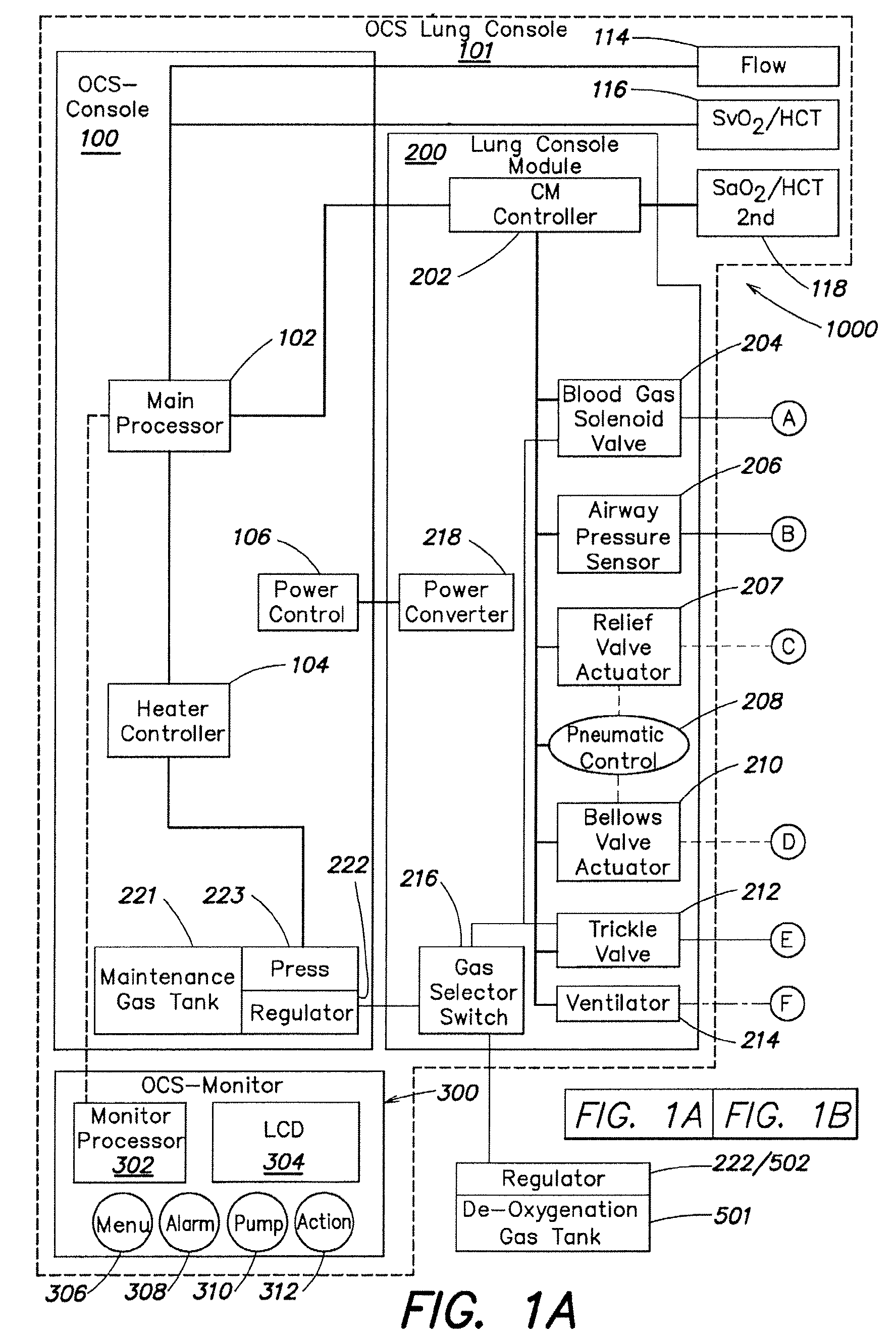
Systems and methods for ex vivo lung care
Methods and systems of maintaining, evaluating, and providing therapy to a lung ex vivo. The methods and systems involve positioning the lung in an ex vivo perfusion circuit; circulating a perfusion fluid through the lung, the fluid entering the lung through a pulmonary artery interface and leaving the lung through a left atrial interface; and ventilating the lung by flowing a ventilation gas through a tracheal interface. Maintaining the lung for extended periods involves causing the lung to rebreath a captive volume of air, and reaching an equilibrium state between the perfusion fluid and the ventilation gas. Evaluating the gas exchange capability of the lung involves deoxygenating the perfusion fluid and measuring a time taken to reoxygenate the perfusion fluid by ventilating the lung with an oxygenation gas.
Owner:TRANSMEDICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com