Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
486 results about "Left atrium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
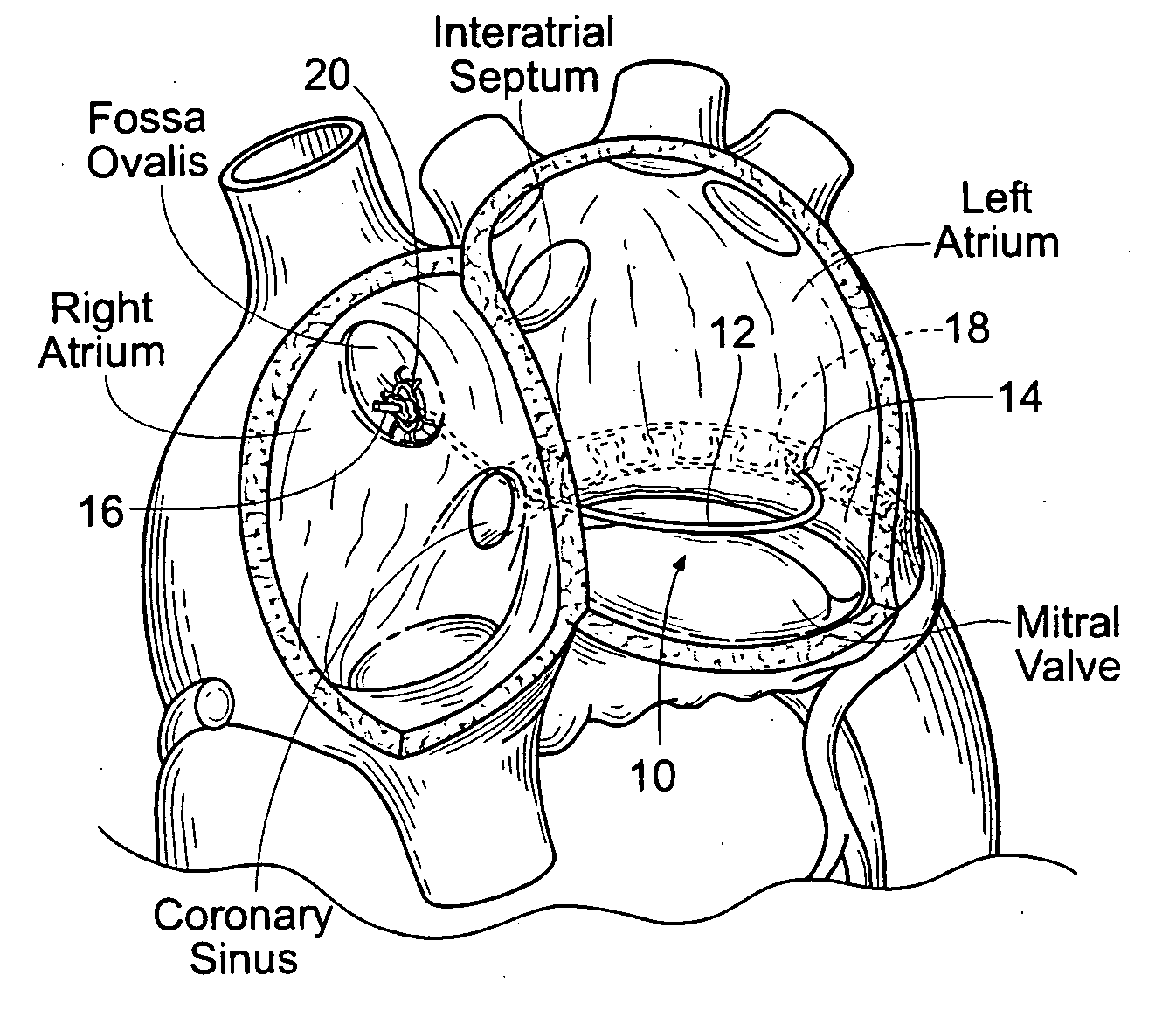
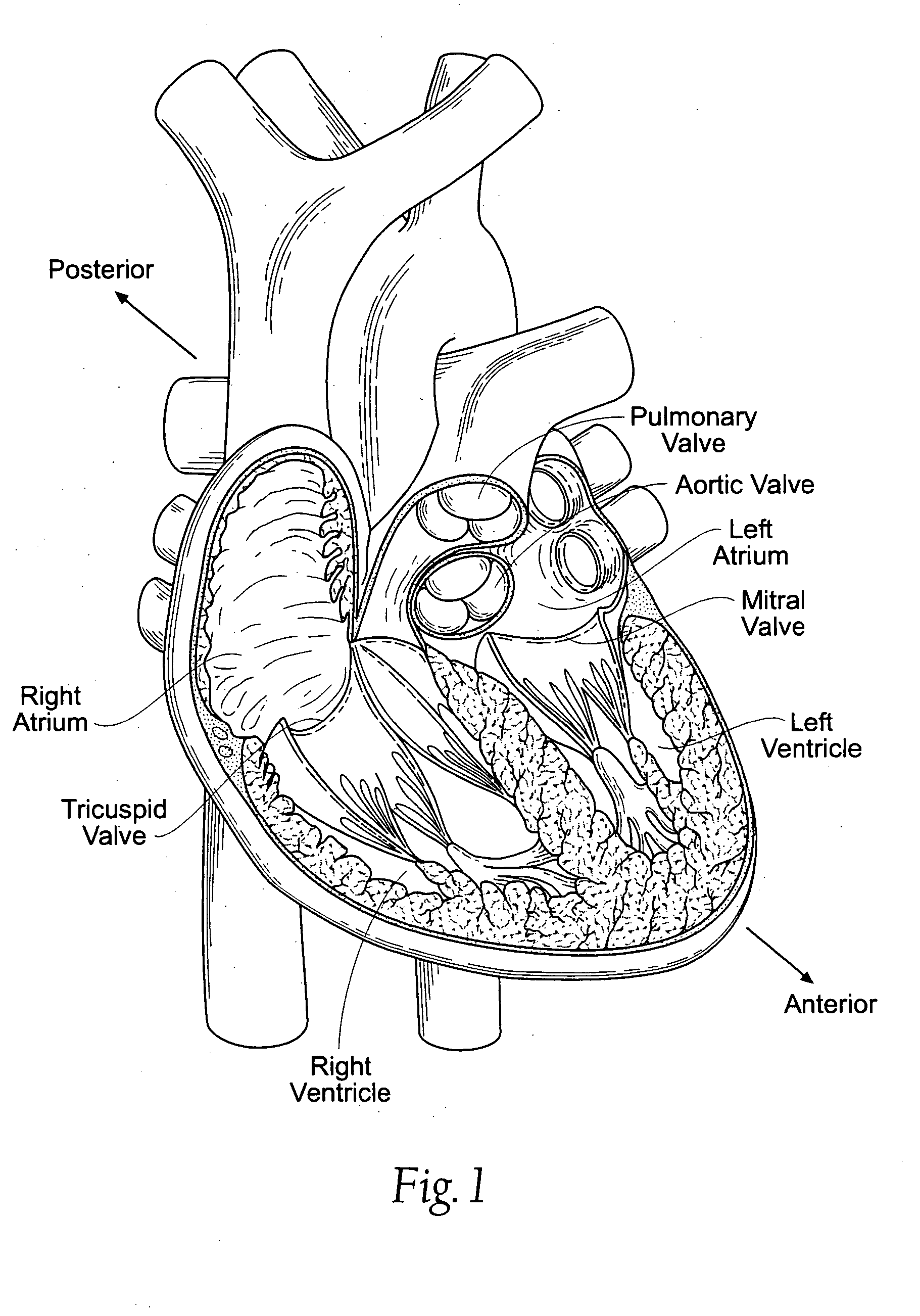
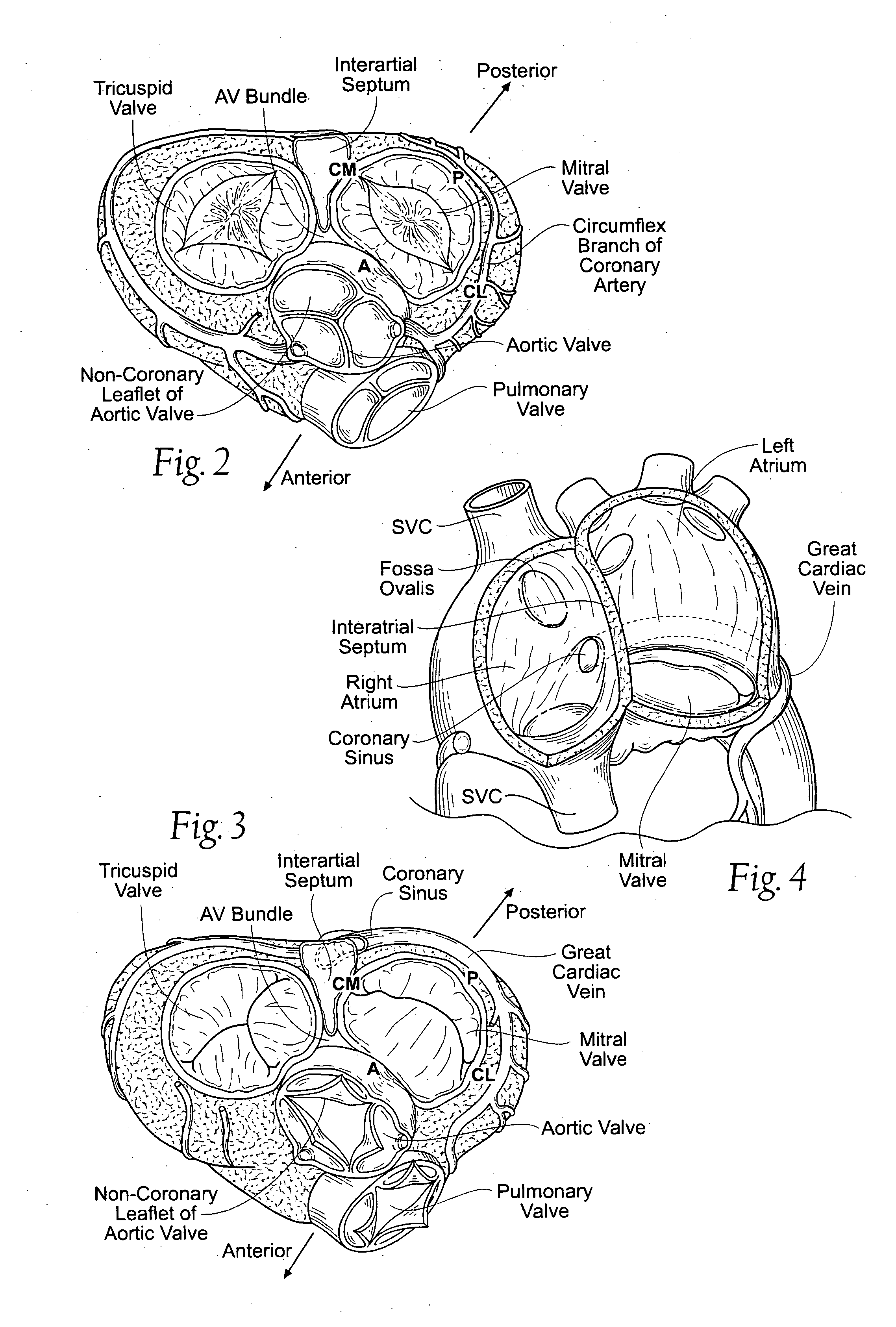
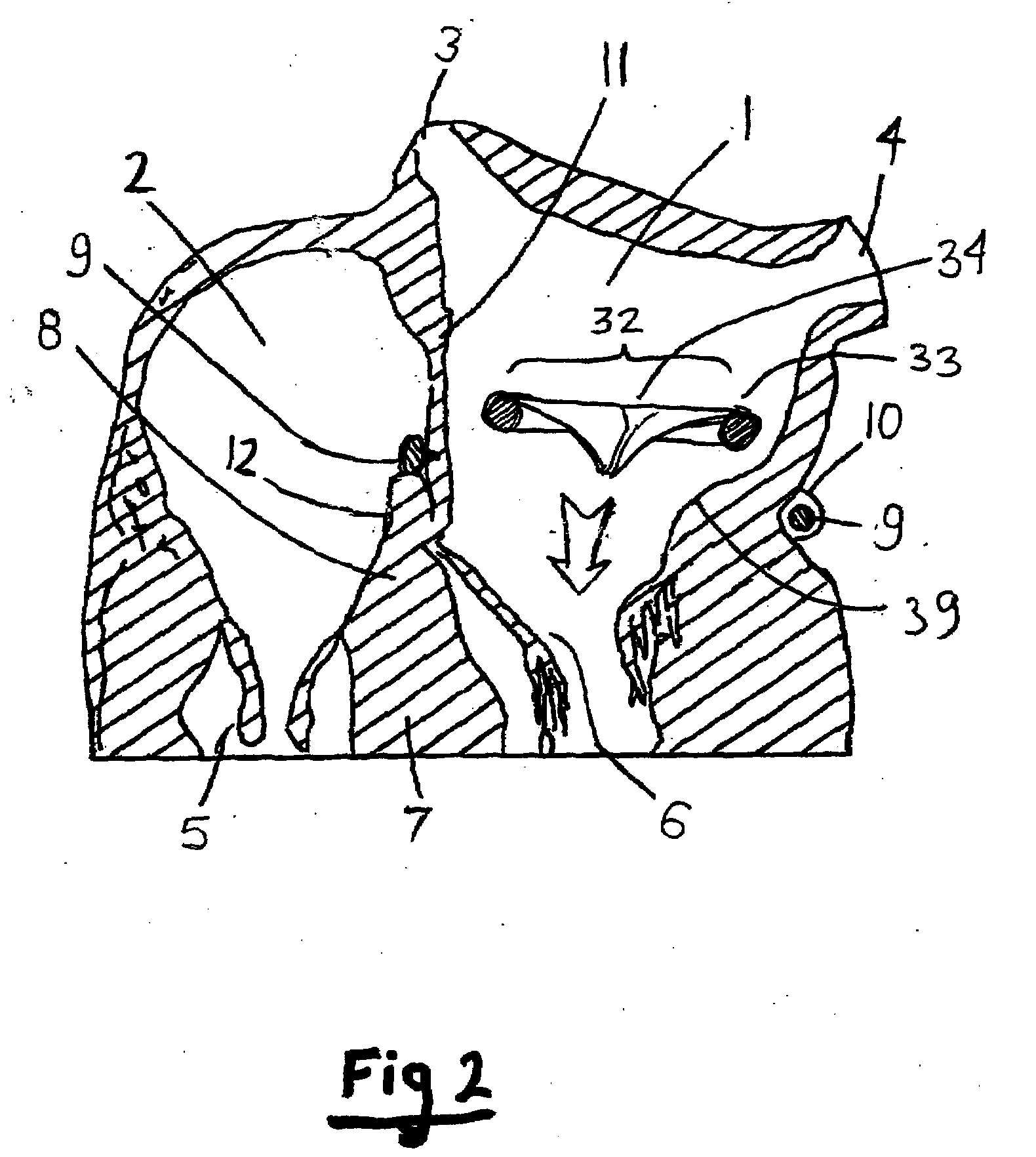
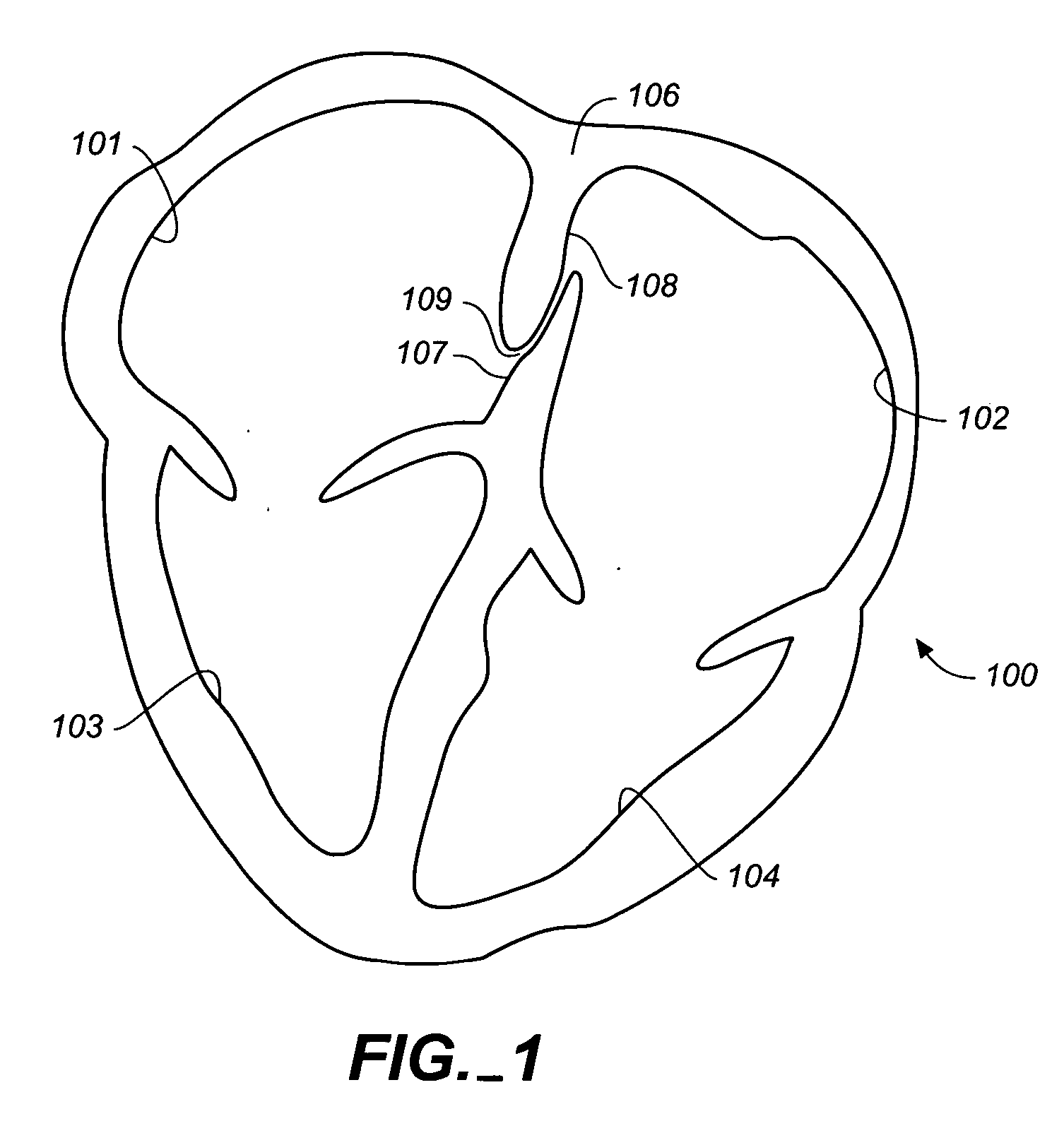
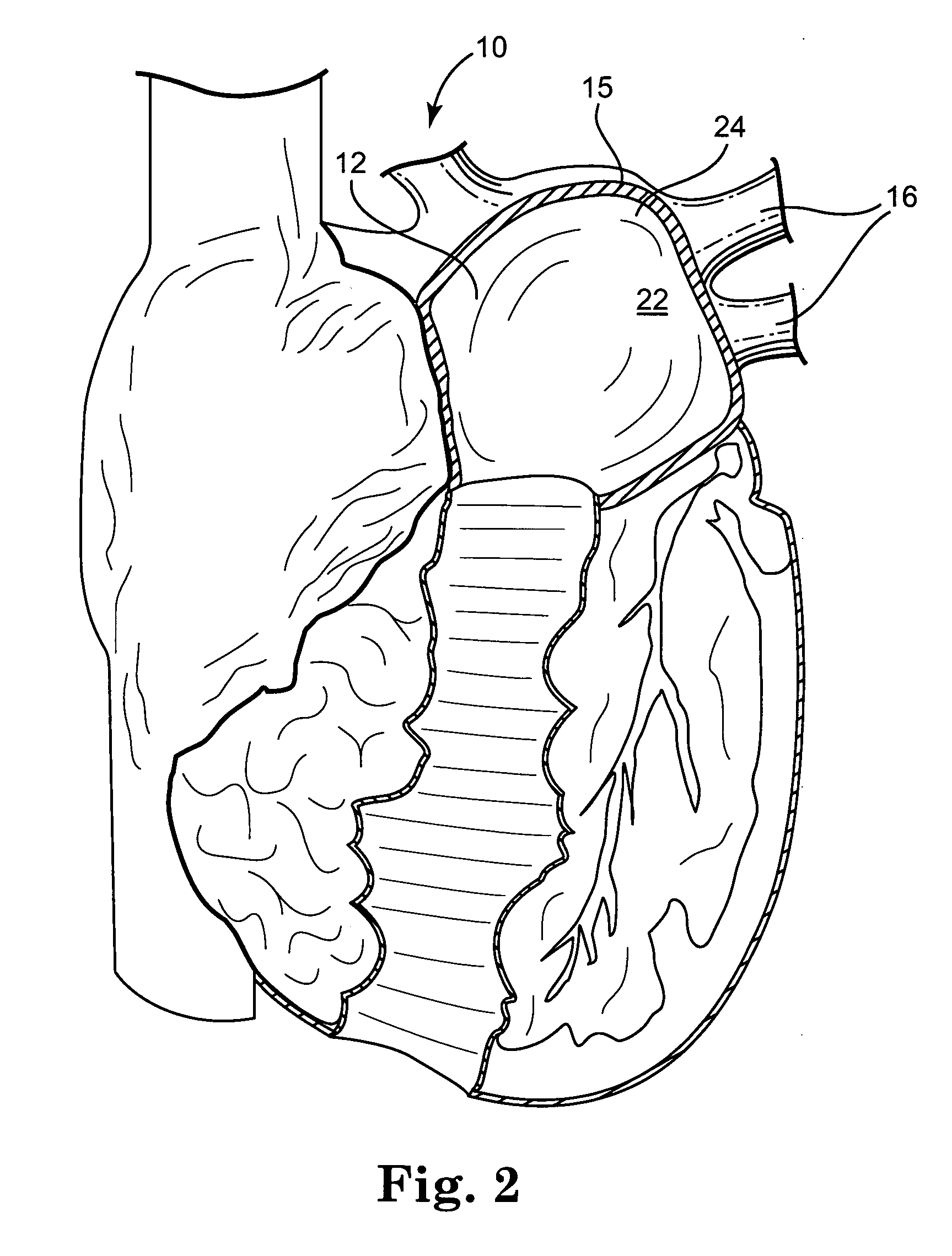
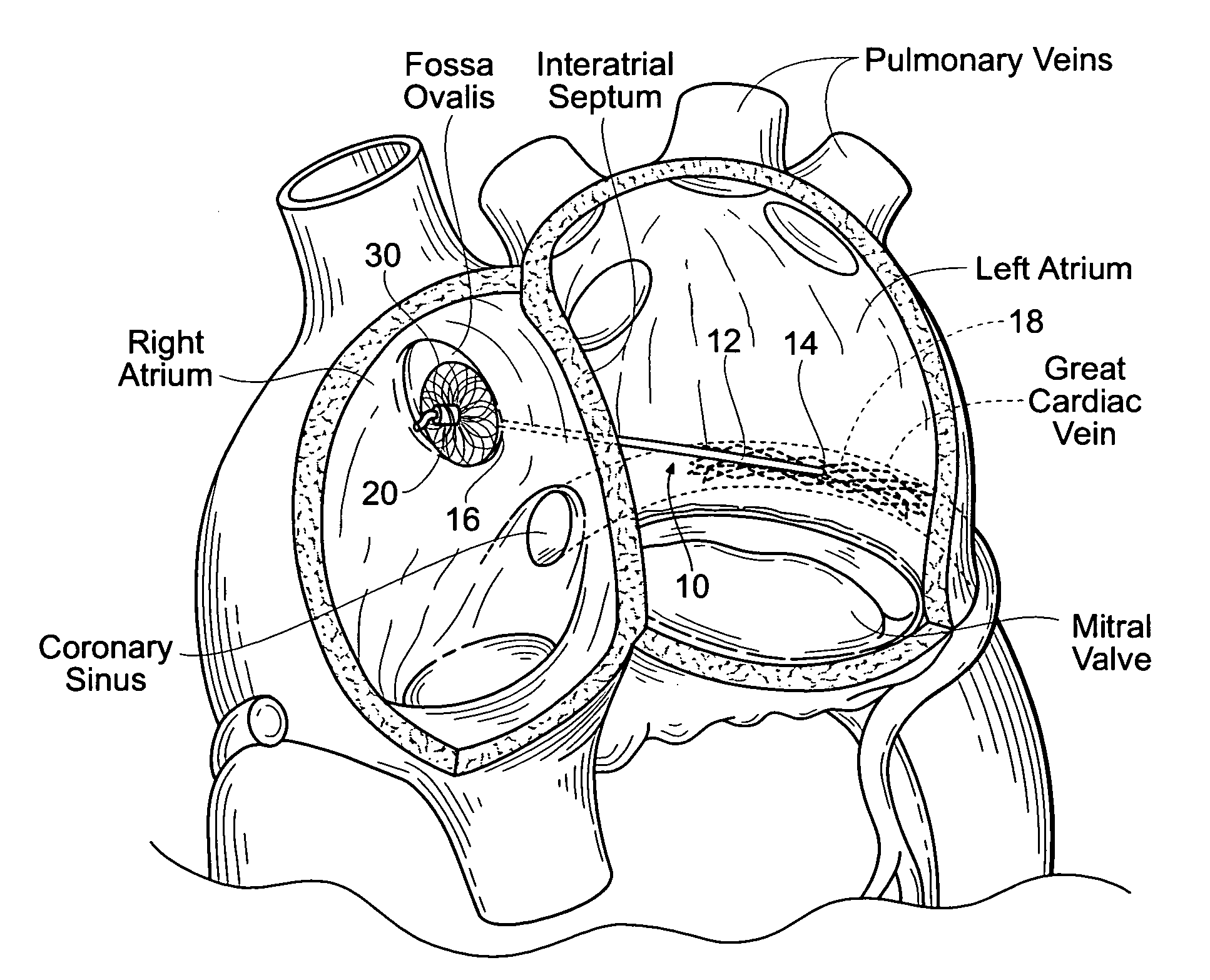
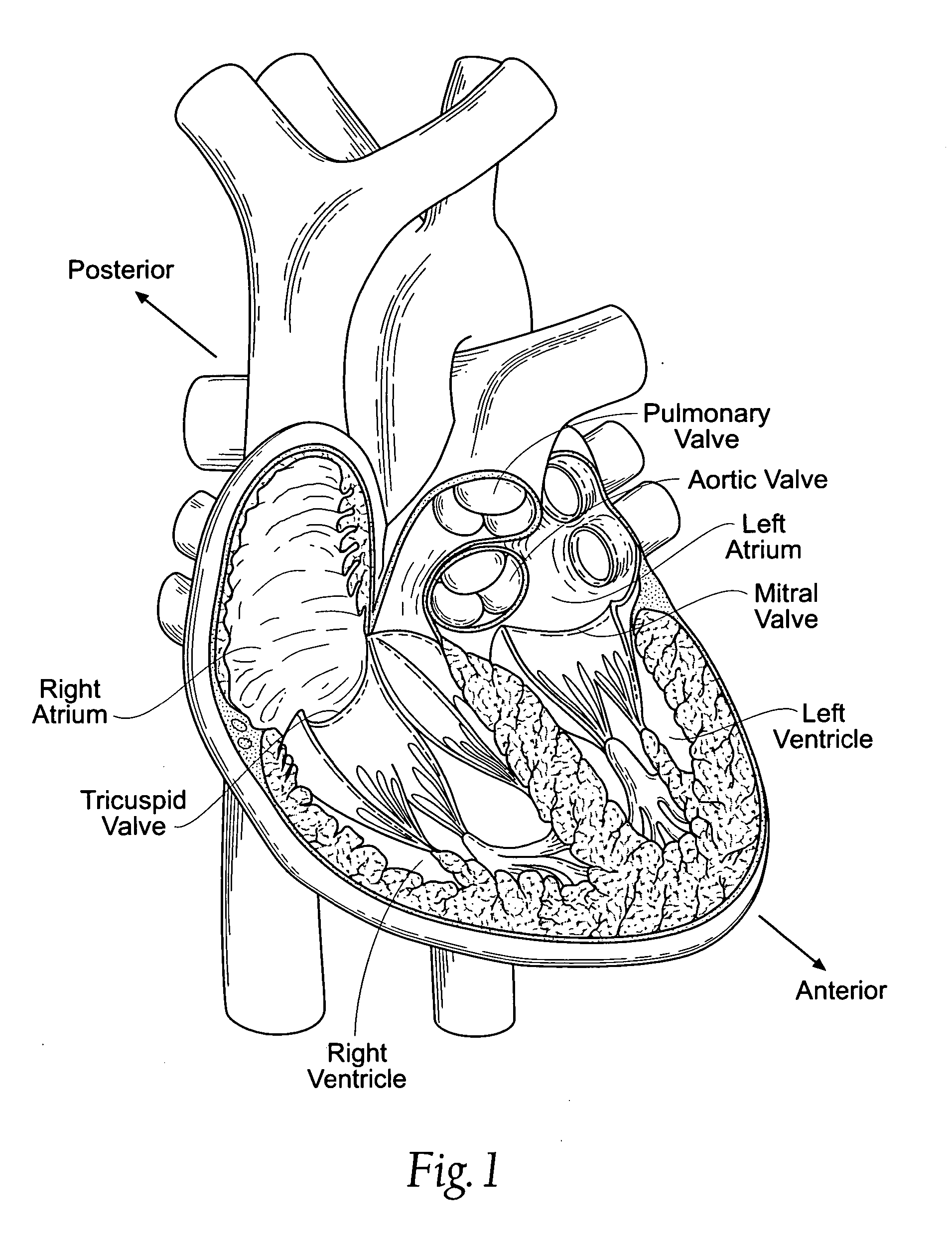
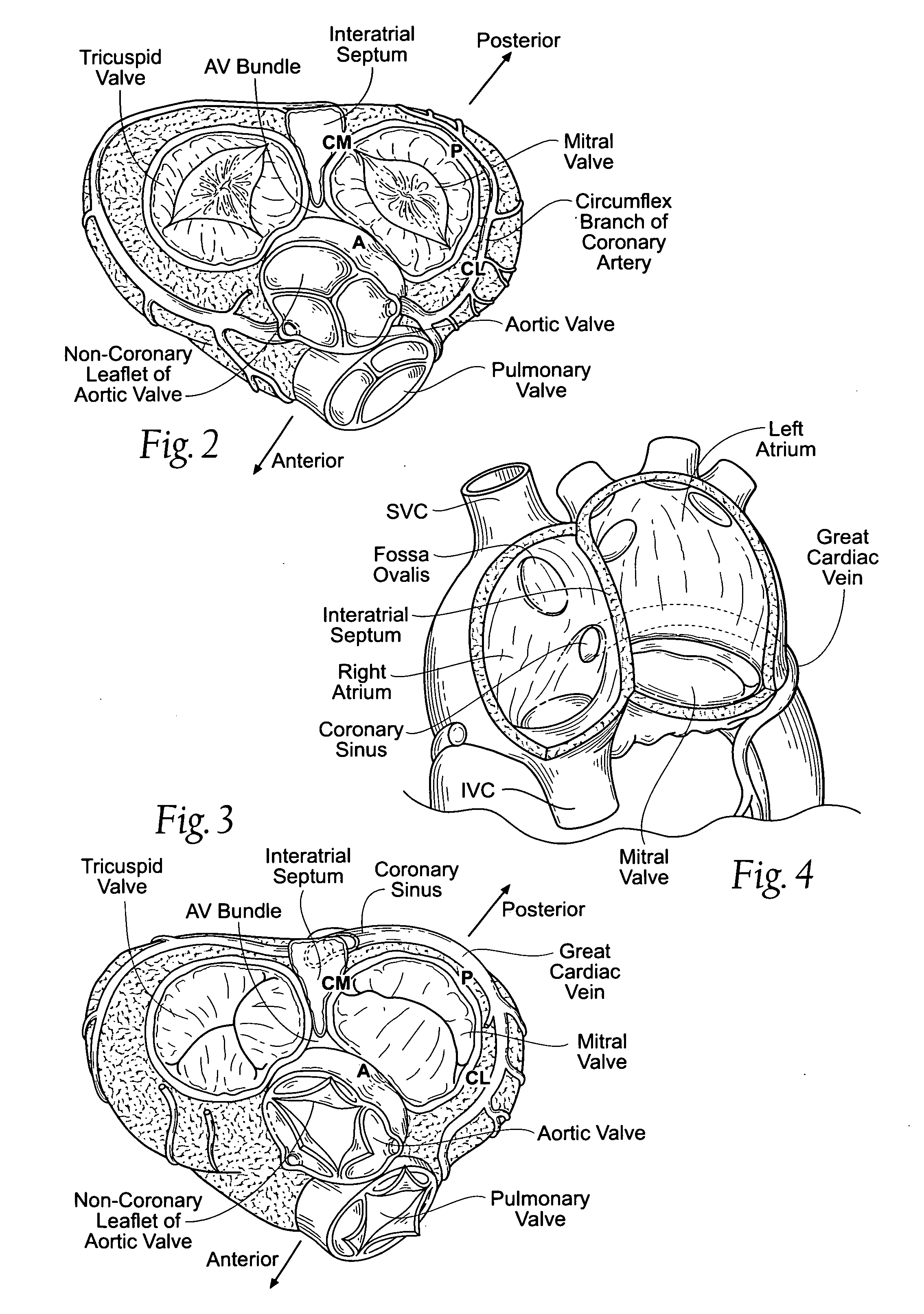
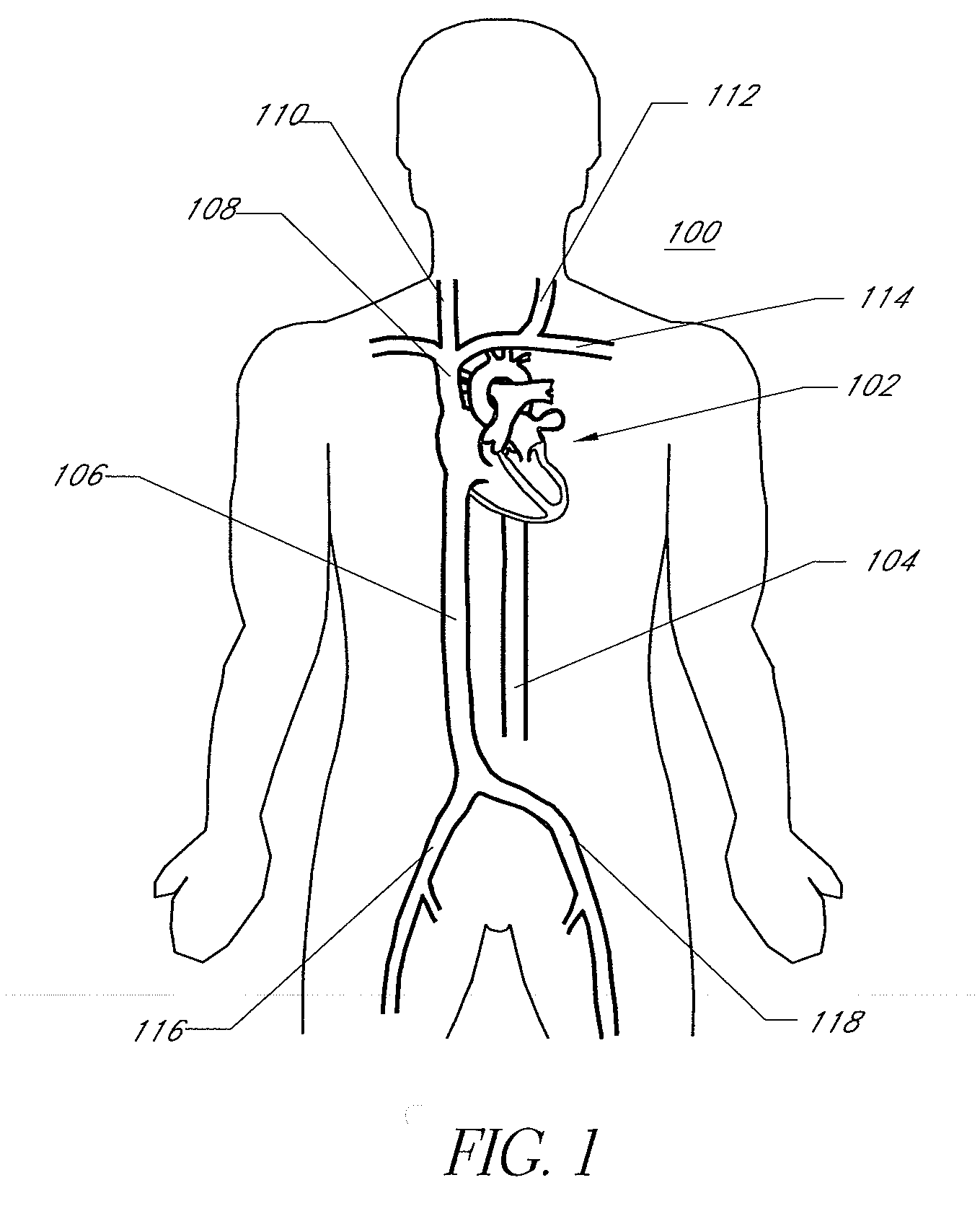
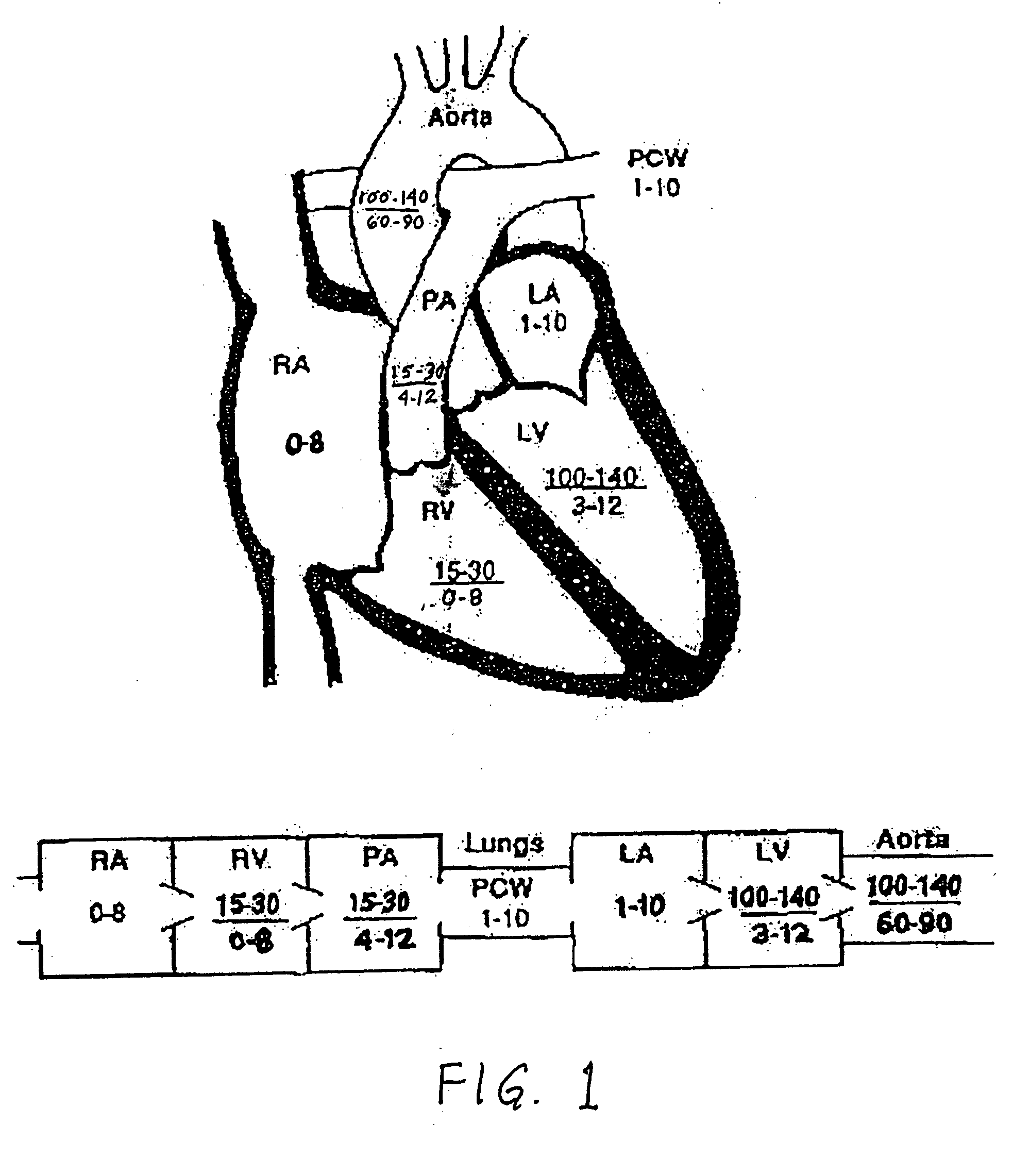
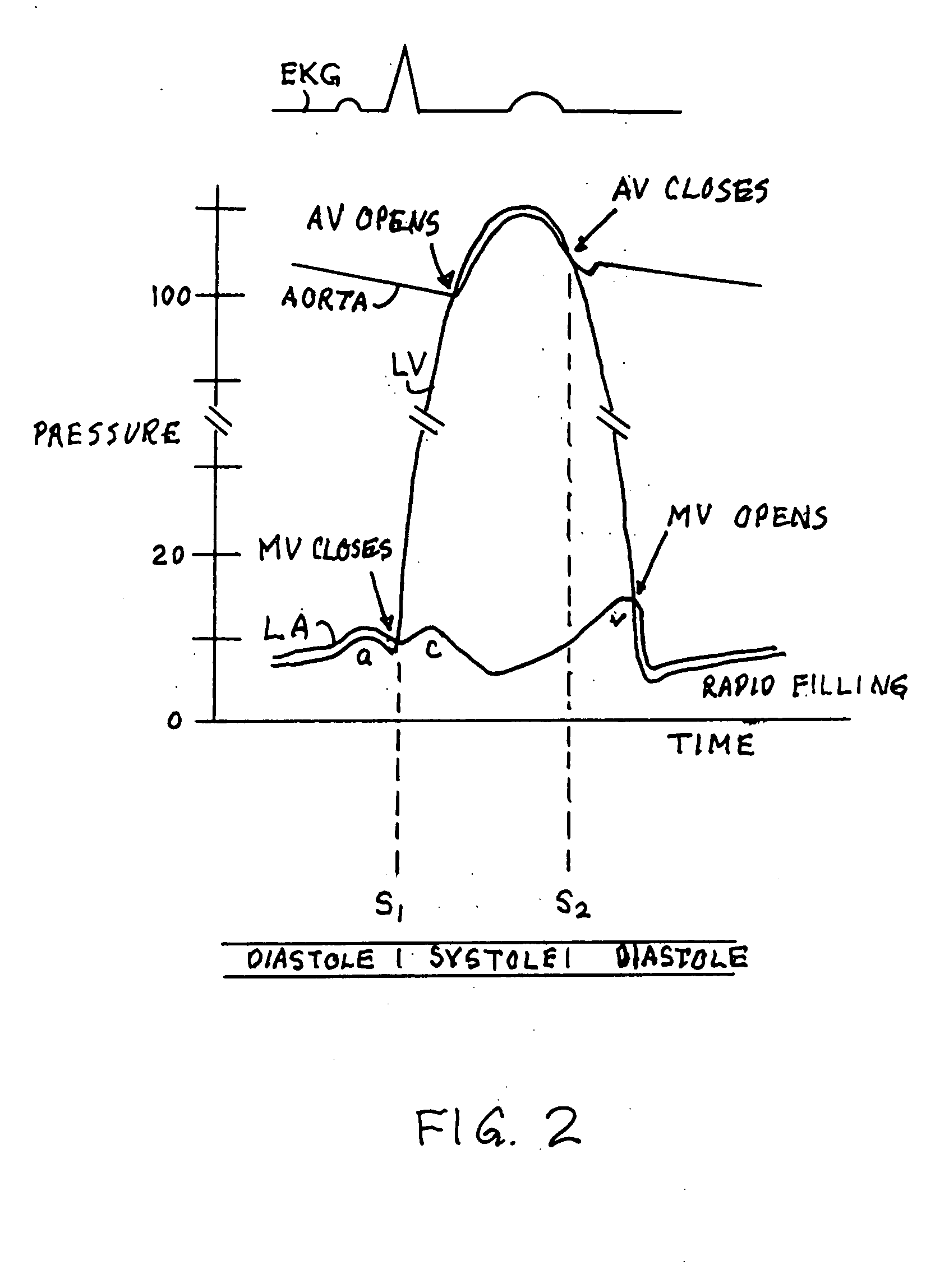
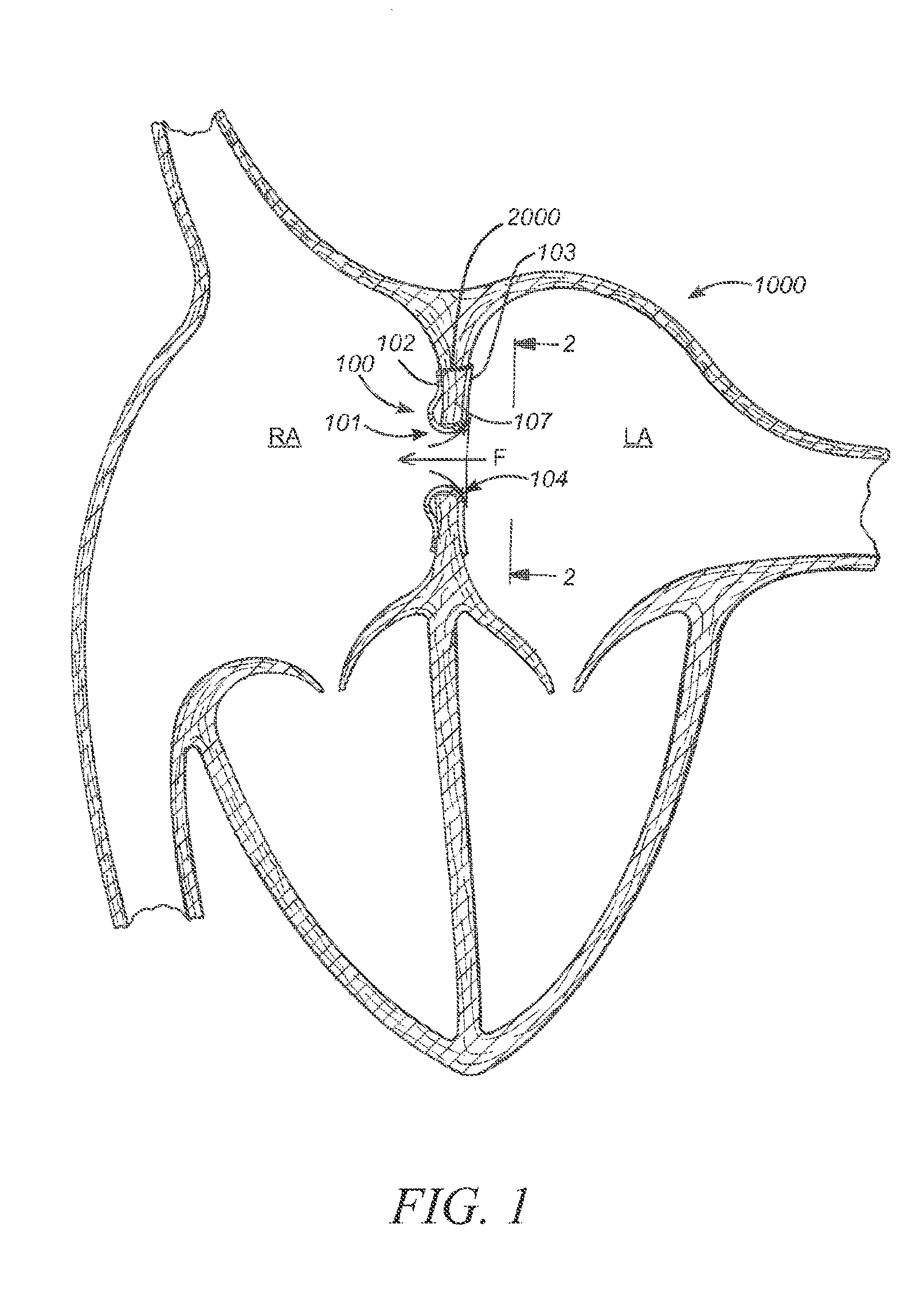
The left atrium is one of four chambers in the human heart. It receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins, and pumps it into the left ventricle, via the mitral valve. Atria facilitate circulation primarily by allowing uninterrupted venous flow to the heart, preventing the inertia of interrupted venous flow that would otherwise occur at each ventricular systole.
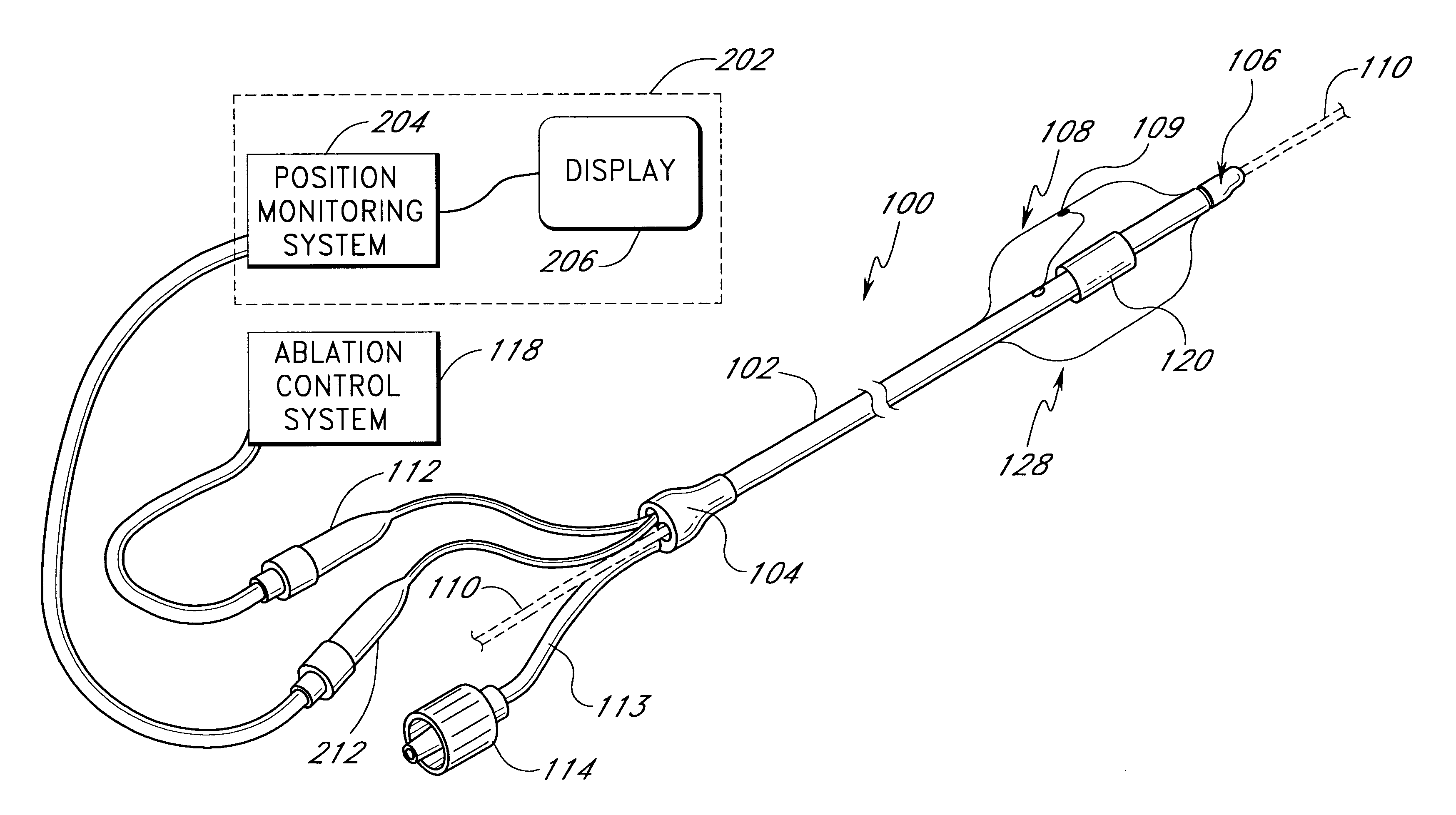
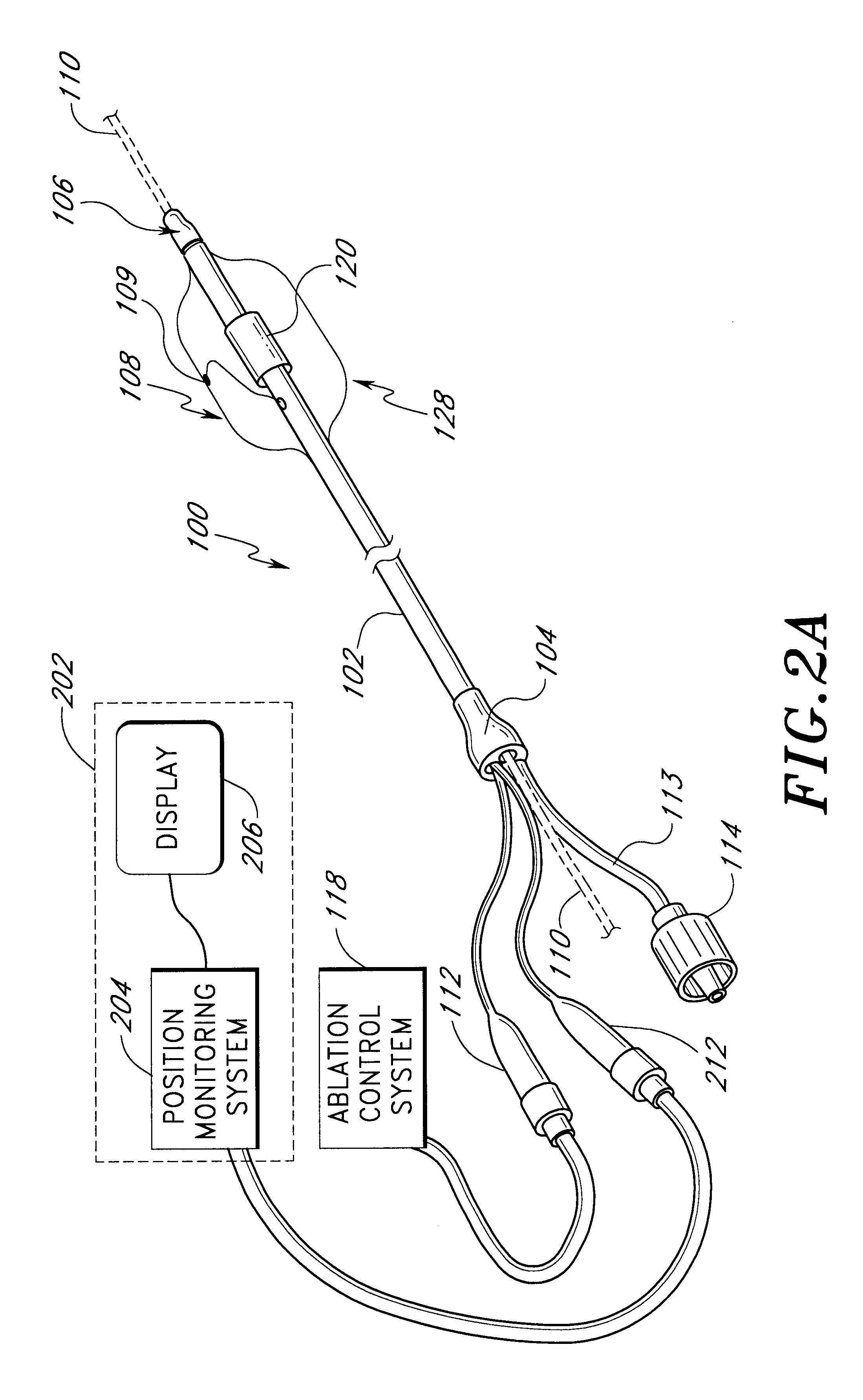
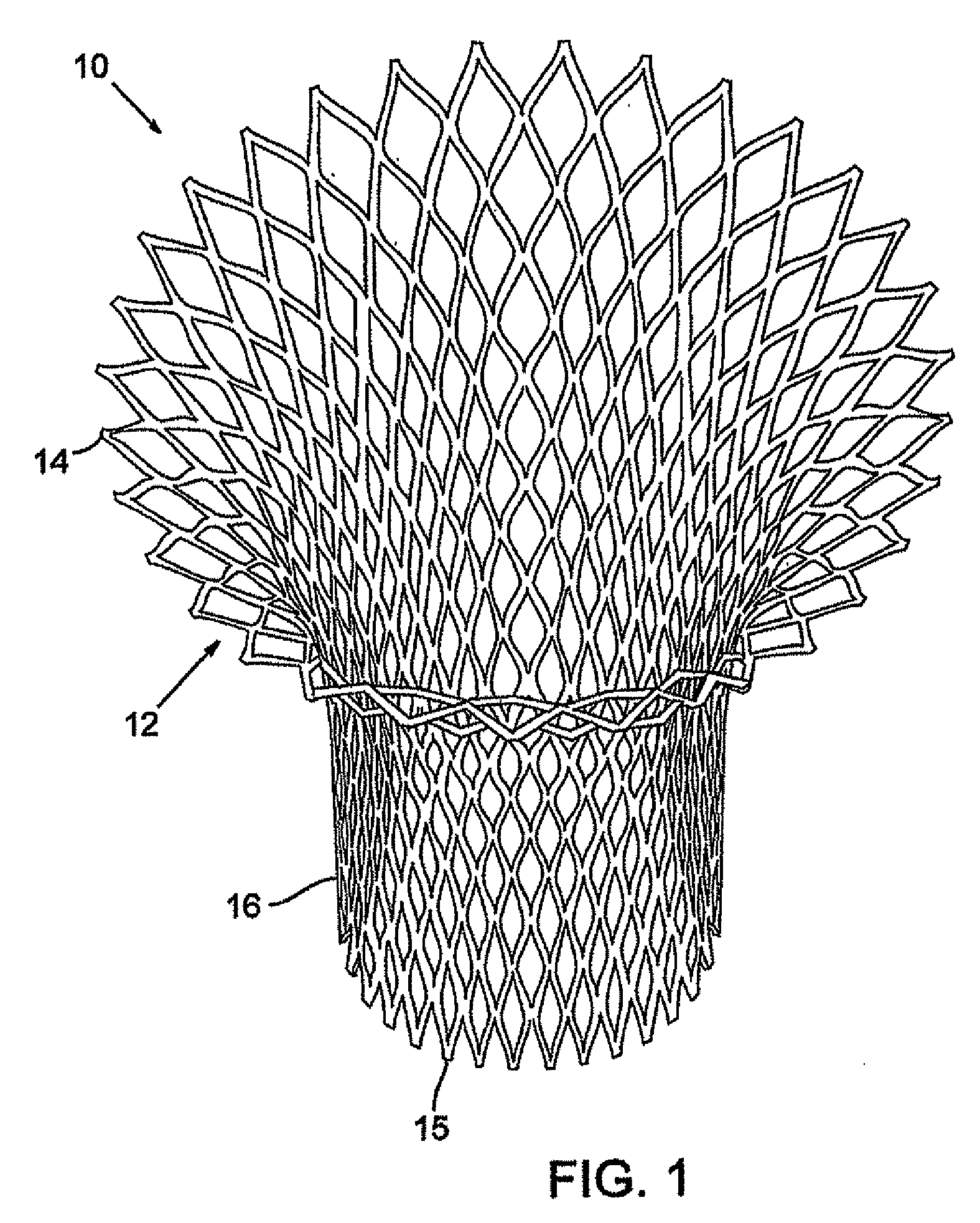
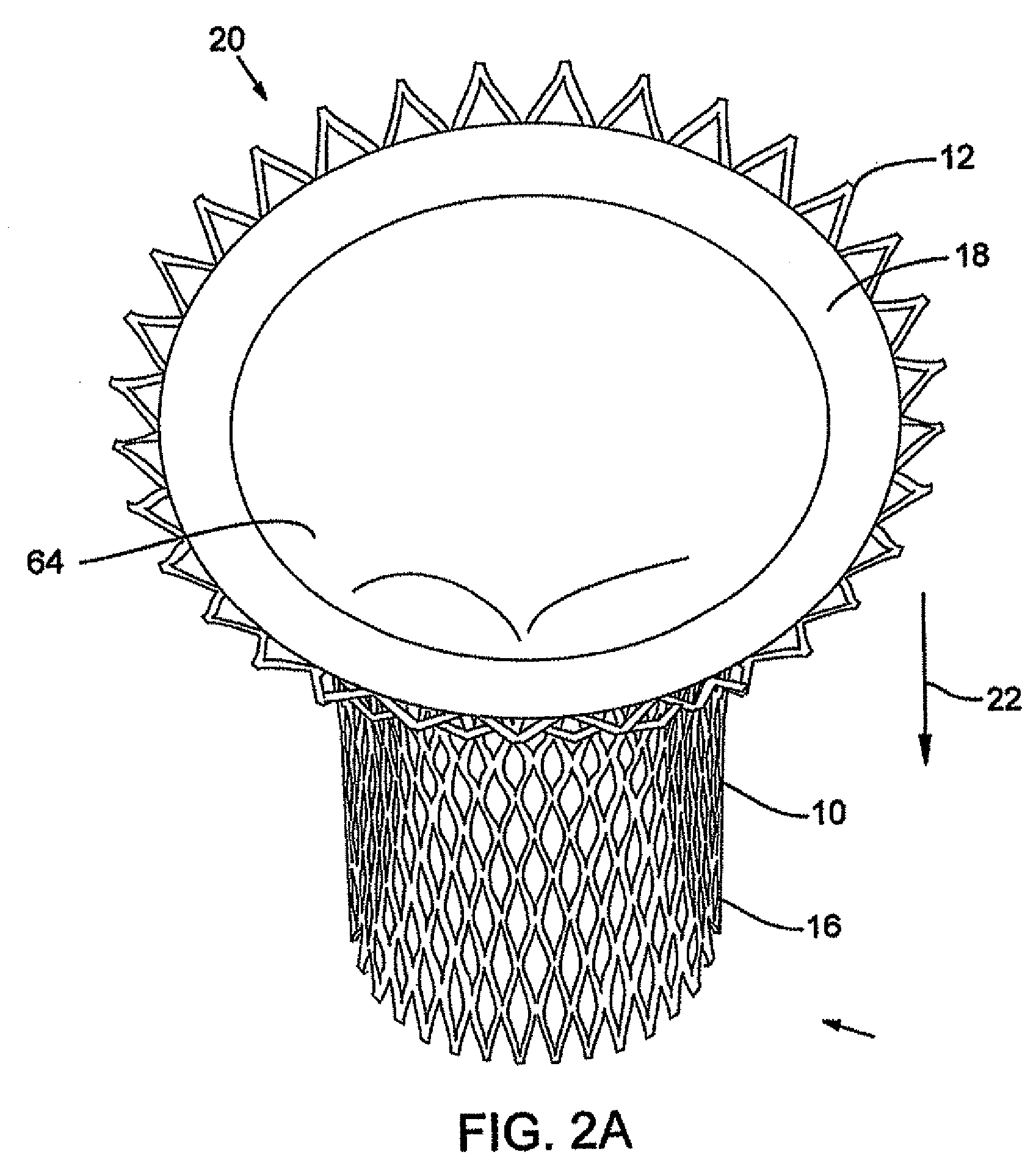
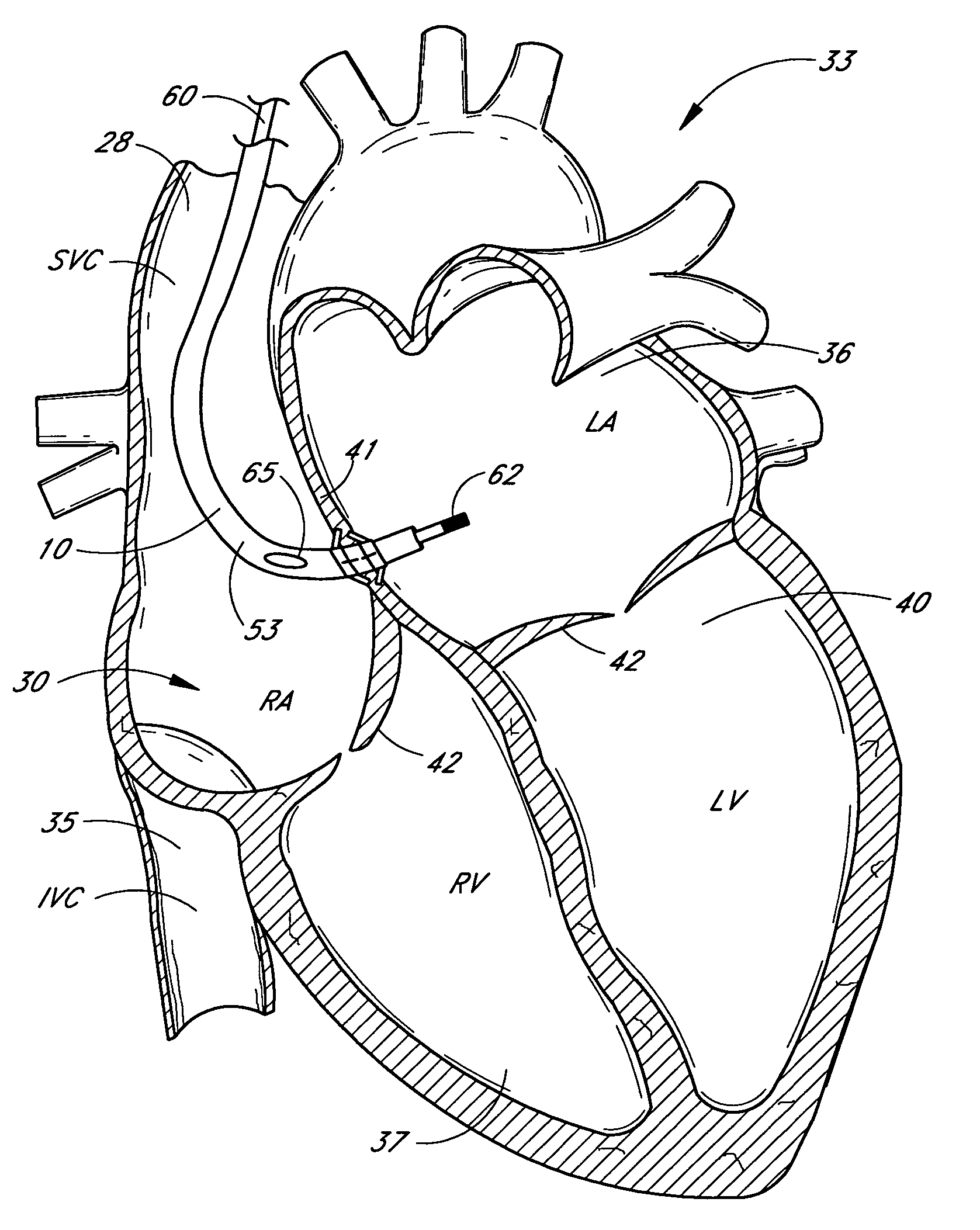
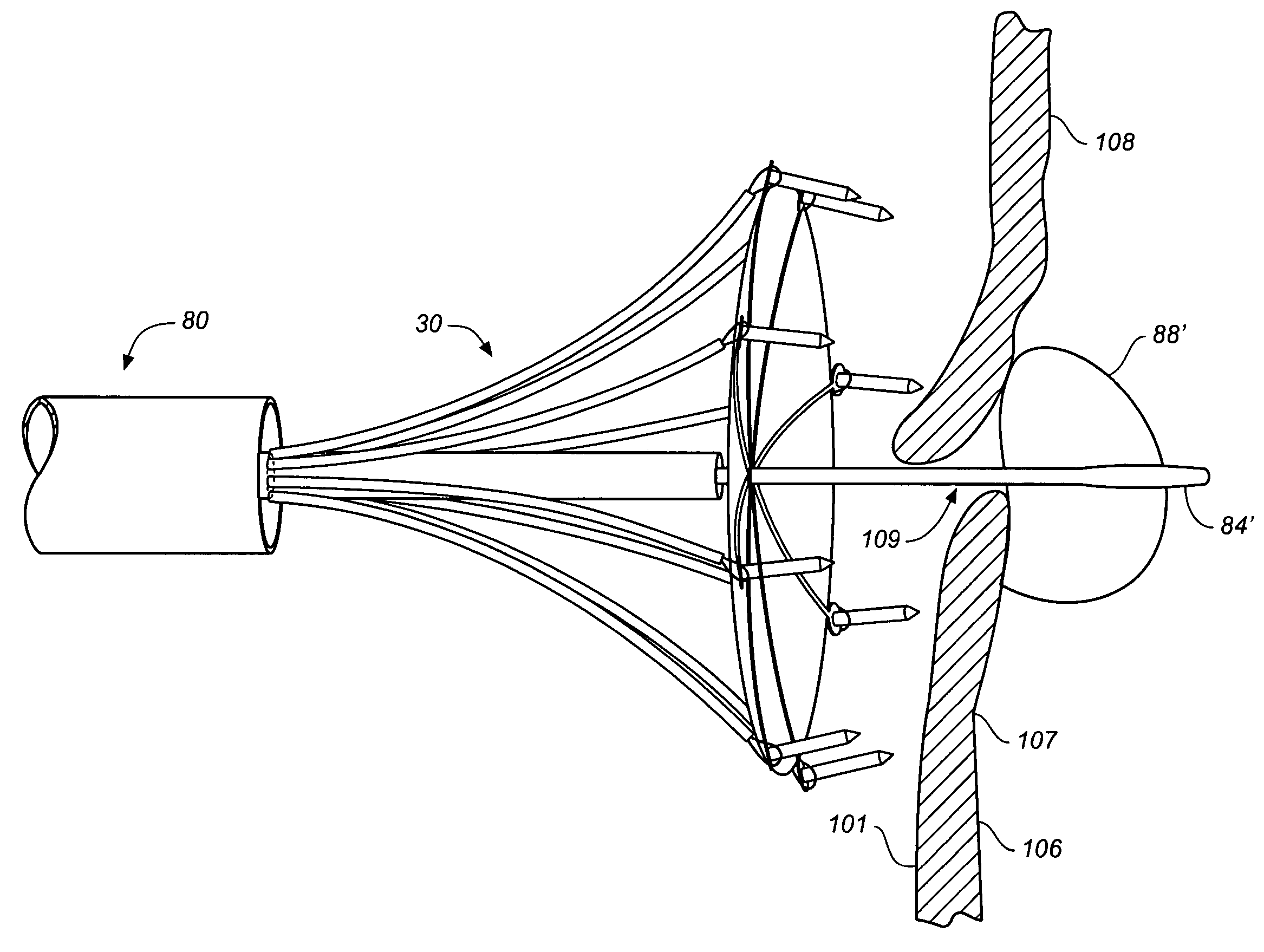
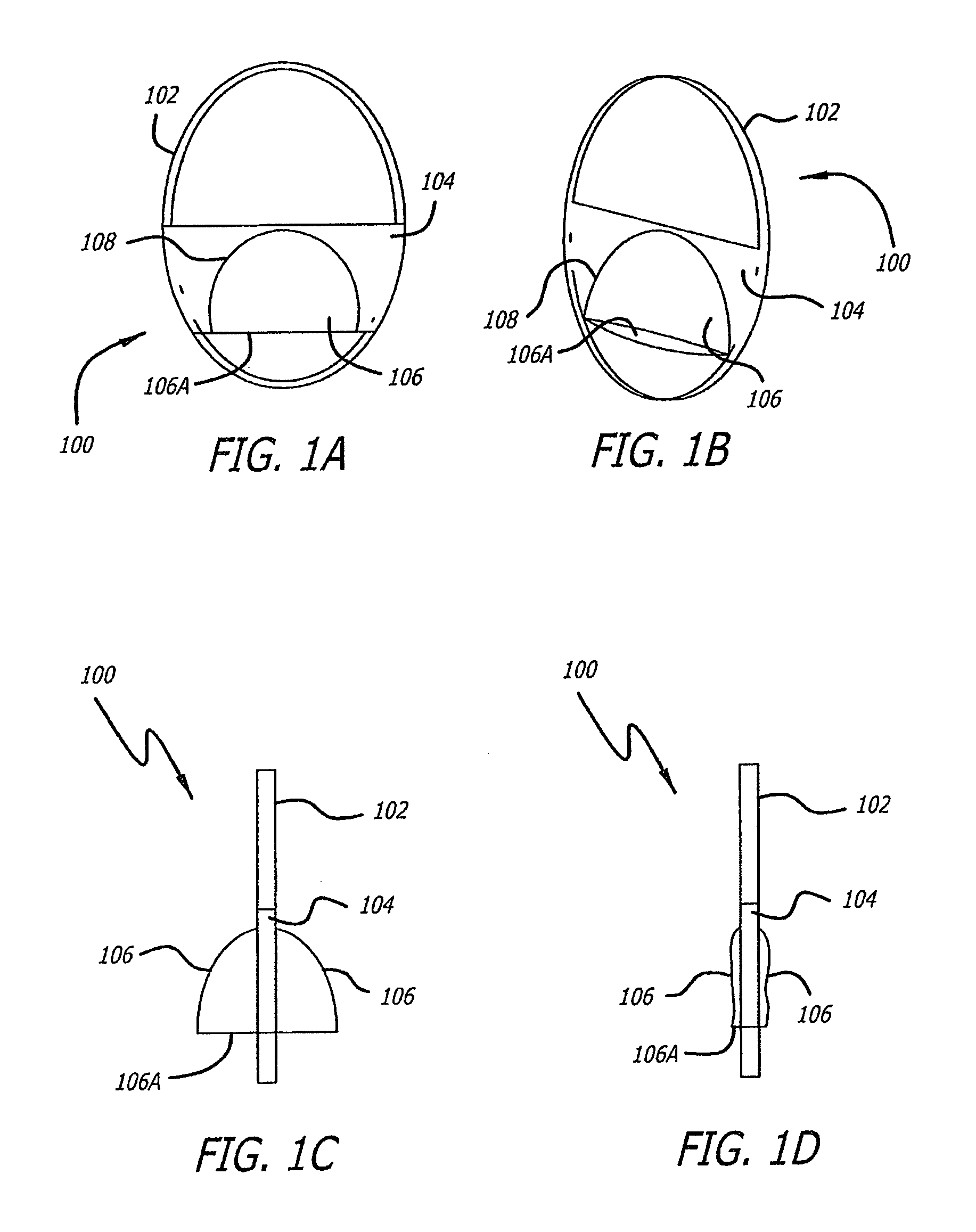
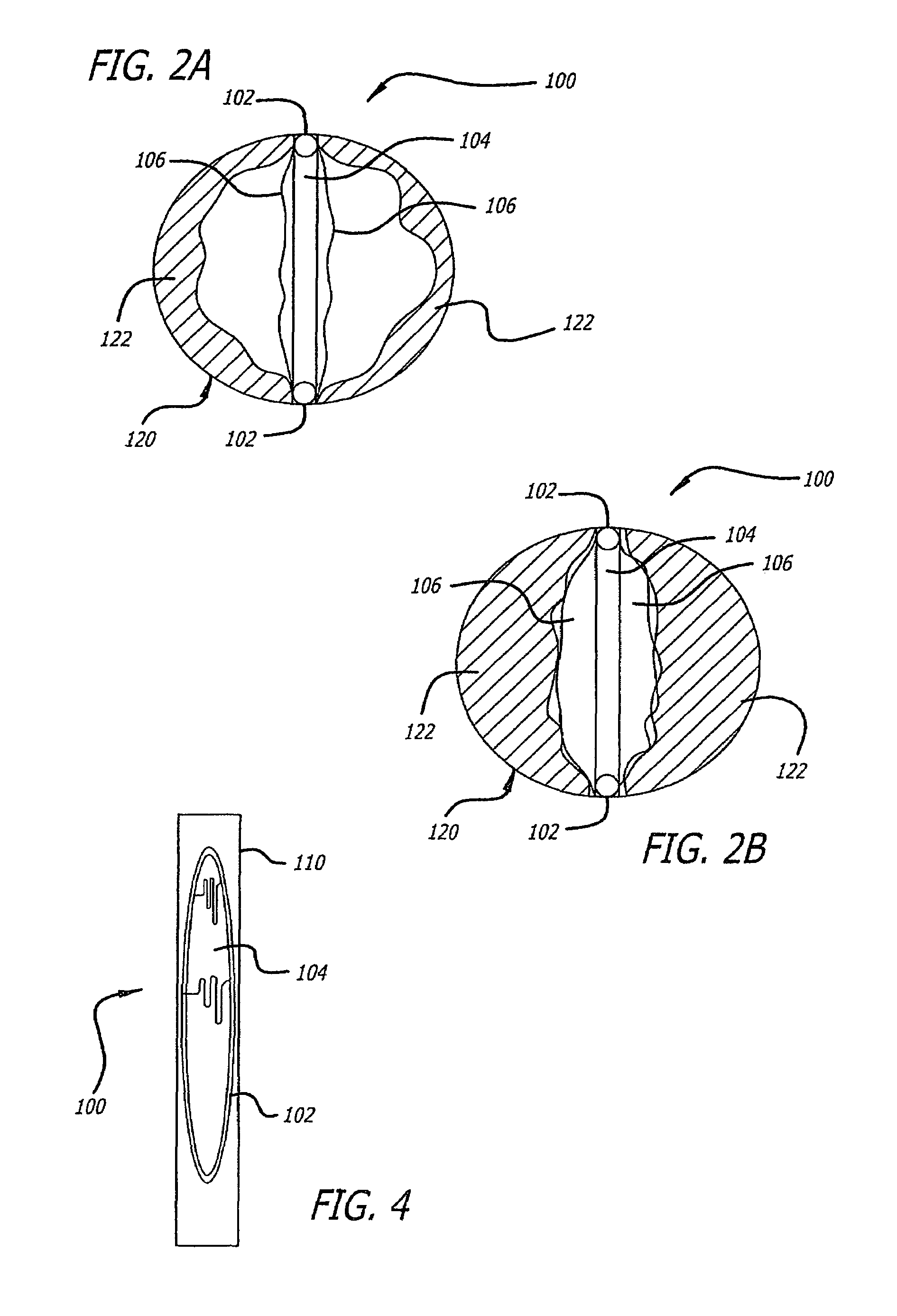
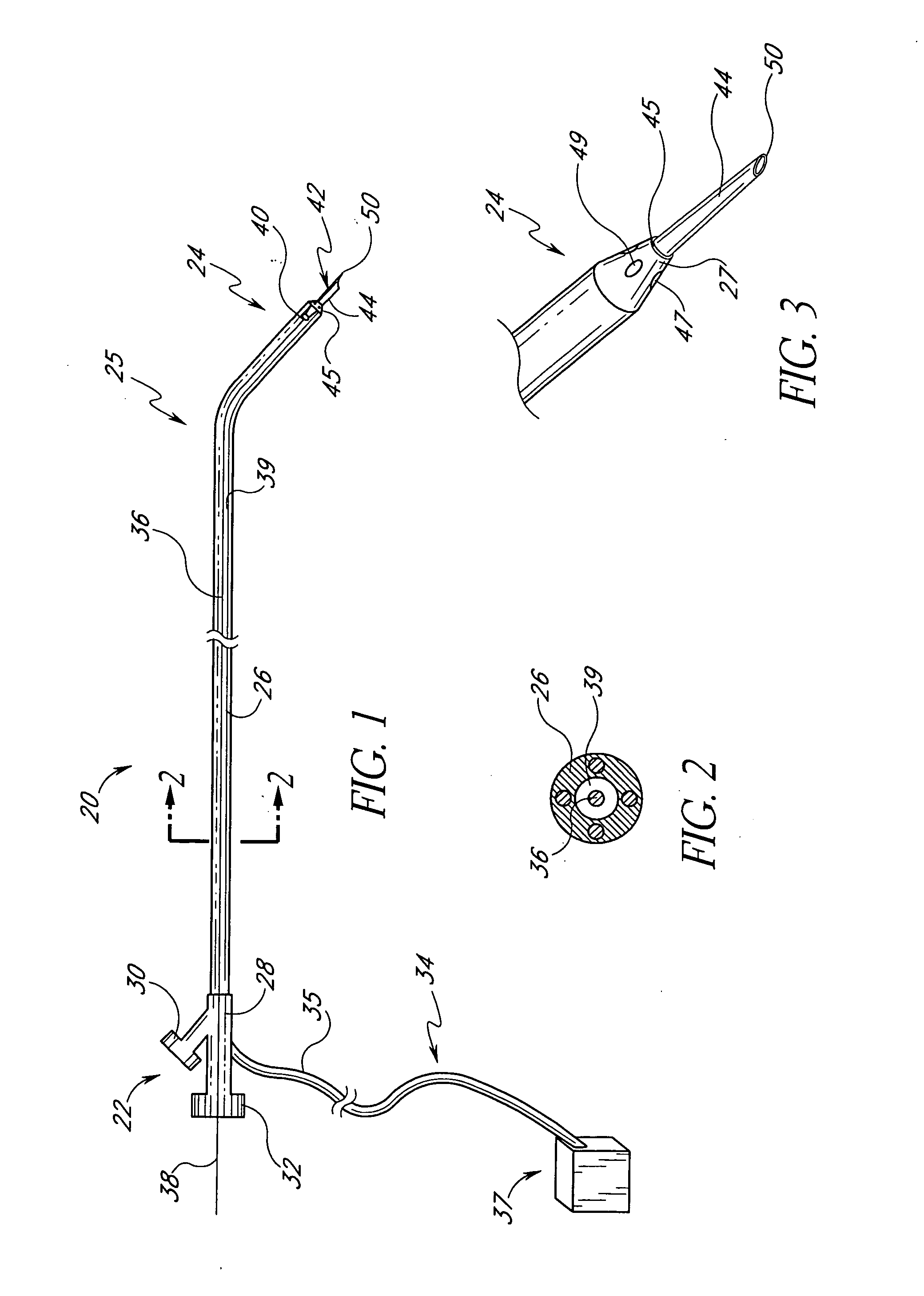
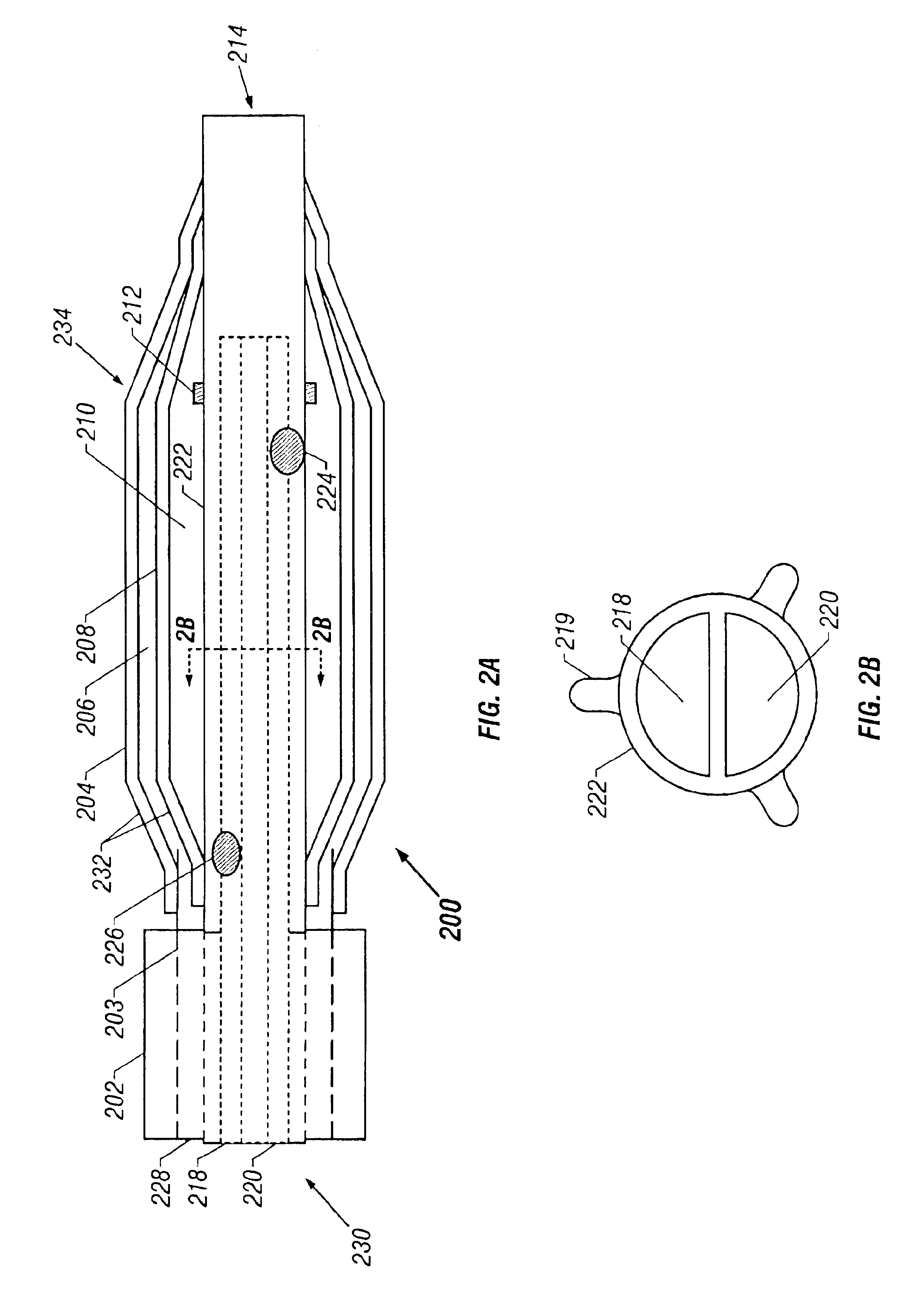
Positioning system and method for orienting an ablation element within a pulmonary vein ostium
InactiveUS6514249B1Eliminates arrhythmogenic conductionPrevent atrial arrhythmiaUltrasound therapyElectrotherapySurgical operationVein
This invention relates to a surgical device and method. More particularly, it relates to a tissue ablation device assembly and method using a circumferential ablation member in combination with a position monitoring assembly in order to position the circumferential ablation member along a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from a left atrium.
Owner:ATRIONIX
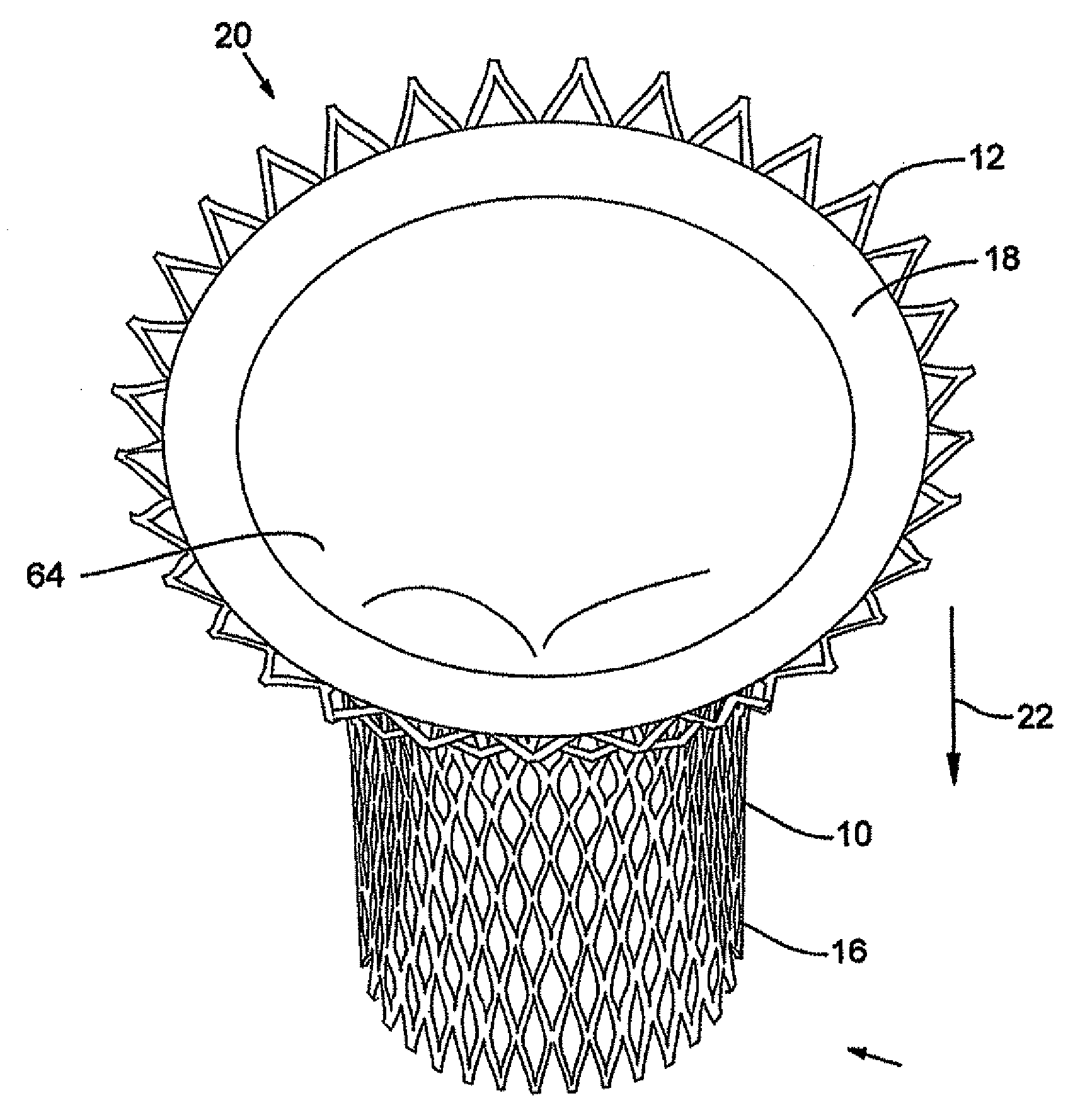
Device and method for replacing mitral valve
InactiveUS20090276040A1Prevent movementRelieve pressureSuture equipmentsStentsNative tissueProsthesis
A prosthetic mitral valve assembly and method of inserting the same is disclosed. In certain disclosed embodiments, the prosthetic mitral valve assembly has a flared upper end and a tapered portion to fit the contours of the native mitral valve. The prosthetic mitral valve assembly can include a stent or outer support frame with a valve mounted therein, The assembly can be adapted to expand radially outwardly and into contact with the native tissue to create a pressure fit. One embodiment of a method includes positioning the mitral valve assembly below the annulus such that the annulus itself can restrict the assembly from moving in an upward direction towards the left atrium. The mitral valve assembly is also positioned so that the leaflets of the mitral valve hold the assembly to prevent downward movement of the assembly towards the left ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for treatment of heart valve regurgitation
In one embodiment, the present invention provides a prosthesis that can be implanted within a heart to at least partially block gaps that may be present between the two mitral valve leaflets. In one preferred embodiment, the prosthesis includes an anchoring ring that expands within the left atrium to anchor the prosthesis and a pocket member fixed to the anchoring ring. The pocket member is positioned within the mitral valve, between the leaflets so that an open end of the pocket member is positioned within the left ventricle. When the mitral valve is open, blood flows past the pocket member, maintaining the pocket member in a collapsed state. When the mitral valve closes, the backpressure of the blood pushes into the pocket member, expanding the pocket member to an inflated shape. The mitral valve leaflets contact the expanded pocket member, allowing the prosthesis to block at least a portion of the openings between the leaflets, thereby minimizing regurgitated blood flow into the left atrium.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Laser pulmonary vein isolation
A catheter introduction apparatus provides an optical assembly for emission of laser light energy. In one application, the catheter and the optical assembly are introduced percutaneously, and transseptally advanced to the ostium of a pulmonary vein. An anchoring balloon is expanded to position a mirror near the ostium of the pulmonary vein, such that light energy is reflected and directed circumferentially around the ostium of the pulmonary vein when a laser light source is energized. A circumferential ablation lesion is thereby produced, which effectively blocks electrical propagation between the pulmonary vein and the left atrium.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Method for detecting, diagnosing, and treating cardiovascular disease
InactiveUS6970742B2Therapy is simpleGood informationPhysical therapies and activitiesLocal control/monitoringVascular diseaseTherapeutic treatment
A method of treating cardiovascular disease in a medical patient is provided. The method includes the steps of generating a sensor signal indicative of a fluid pressure within the left atrium of the patient's heart, and delivering an electrical stimulus to a location in the heart. The electrical stimulus is delivered based at least in part on the sensor signal. The method also includes the steps of generating a proccessor output indicative of a treatment to a signaling device. The processor output is based at least in part on the sensor signal. At least two treatment signals are provided to the medical patient. The treatment signals are distinguishable from one another by the patient, and are indicative of a therapeutic treatment. The treatment signals are based at least in part on the processor output.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
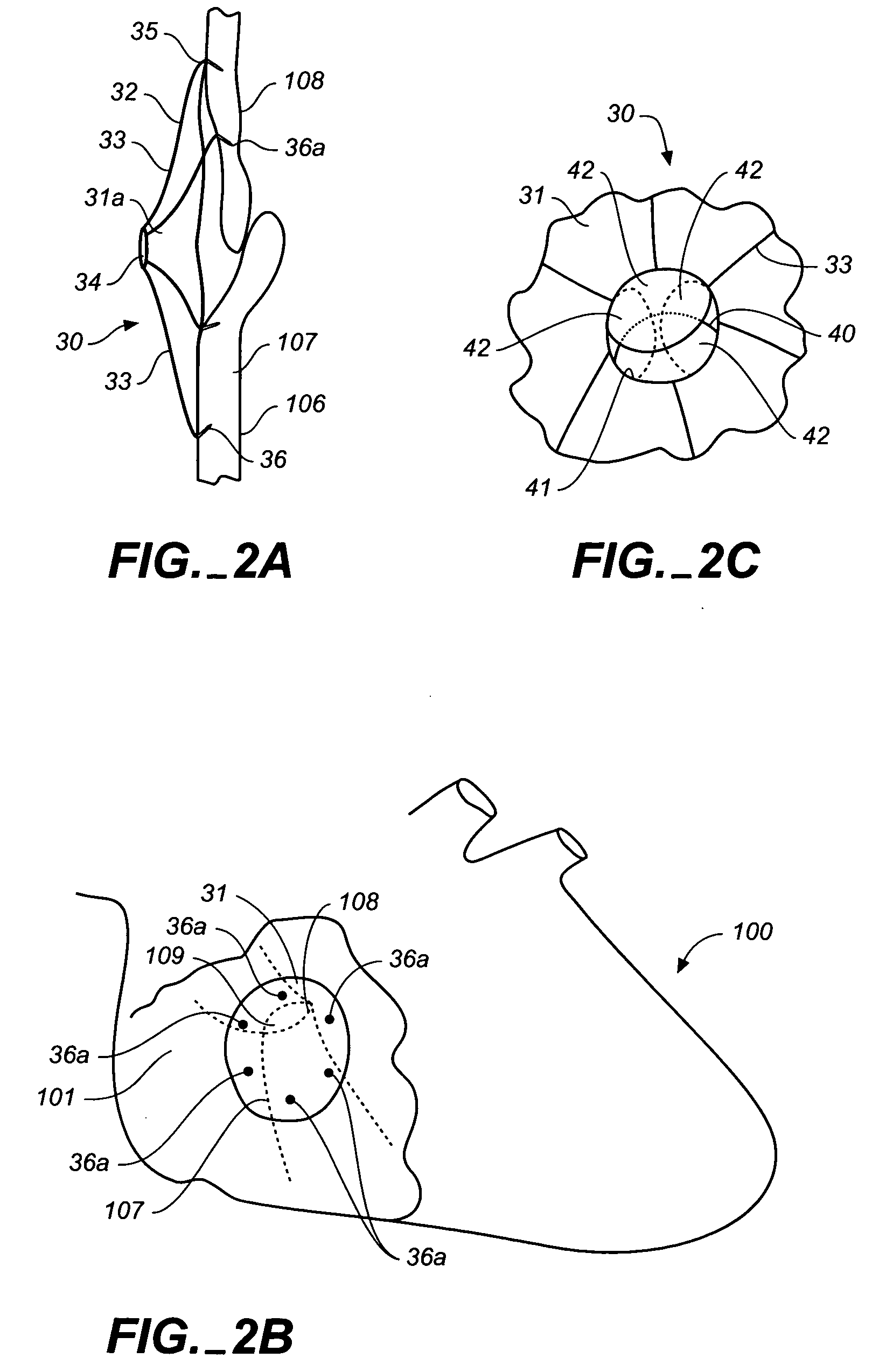
Devices, systems, and methods for reshaping a heart valve annulus
ActiveUS20050055089A1Improve septal-to-lateral dimensionImproved leaflet coaptionSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsMitral valve leafletLeft atrium
Implants or systems of implants apply a selected force vector or a selected combination of force vectors within or across the left atrium, which allow mitral valve leaflets to better coapt. The implants or systems of implants make possible rapid deployment, facile endovascular delivery, and full intra-atrial retrievability. The implants or systems of implants also make use of strong fluoroscopic landmarks.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
Method for anchoring a mitral valve
An artificial mitral valve is anchored in the left atrium by placing the valve between the annulus of the natural mitral valve and an artificial annulus. The artificial annulus is formed by inserting a tool into the coronary sinus, and adjusting the tool to force the wall of the left atrium to form an annulus above the artificial valve, this locking it in place and forming a hemostatic seal.
Owner:KARDIUM
Mitral Prosthesis and Methods for Implantation
ActiveUS20120035722A1Minimizing peri-valvular leaksMaintain stabilityStentsHeart valvesMitral valve leafletLeft atrium
A mitral valve prosthesis and methods for implanting the prosthesis transapically (i.e., through the apex of the heart), transatrially (i.e., through the left atrium of the heart), and transseptally (i.e., through the septum of the heart). The prosthesis generally includes a self-expanding frame and two or more support arms. A valve prosthesis is sutured to the self-expanding frame. Each support arm corresponds to a native mitral valve leaflet. At least one support arm immobilizes the native leaflets, and holds the native leaflets close to the main frame.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
Cardiovascular defect patch device and method
The present invention provides a defect patch device and method that patches a defect in the heart or other cardiovascular tissue. One aspect provides a PFO closure device and method that patches a PFO in the right atrium without the device extending through the PFO into the left atrium. The patch device includes a patch and a heart tissue engaging member for attaching the device over the defect. A deployment device and method includes a device positioner to advance the device out of a catheter and to position the device over the defect to attach the device to the tissue around the defect. The positioner may include a device expander or opener that opens the device for deployment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Expandable trans-septal sheath
InactiveUS20060135962A1Inhibit bindingAvoid interferenceGuide needlesEar treatmentAccess routeDilator
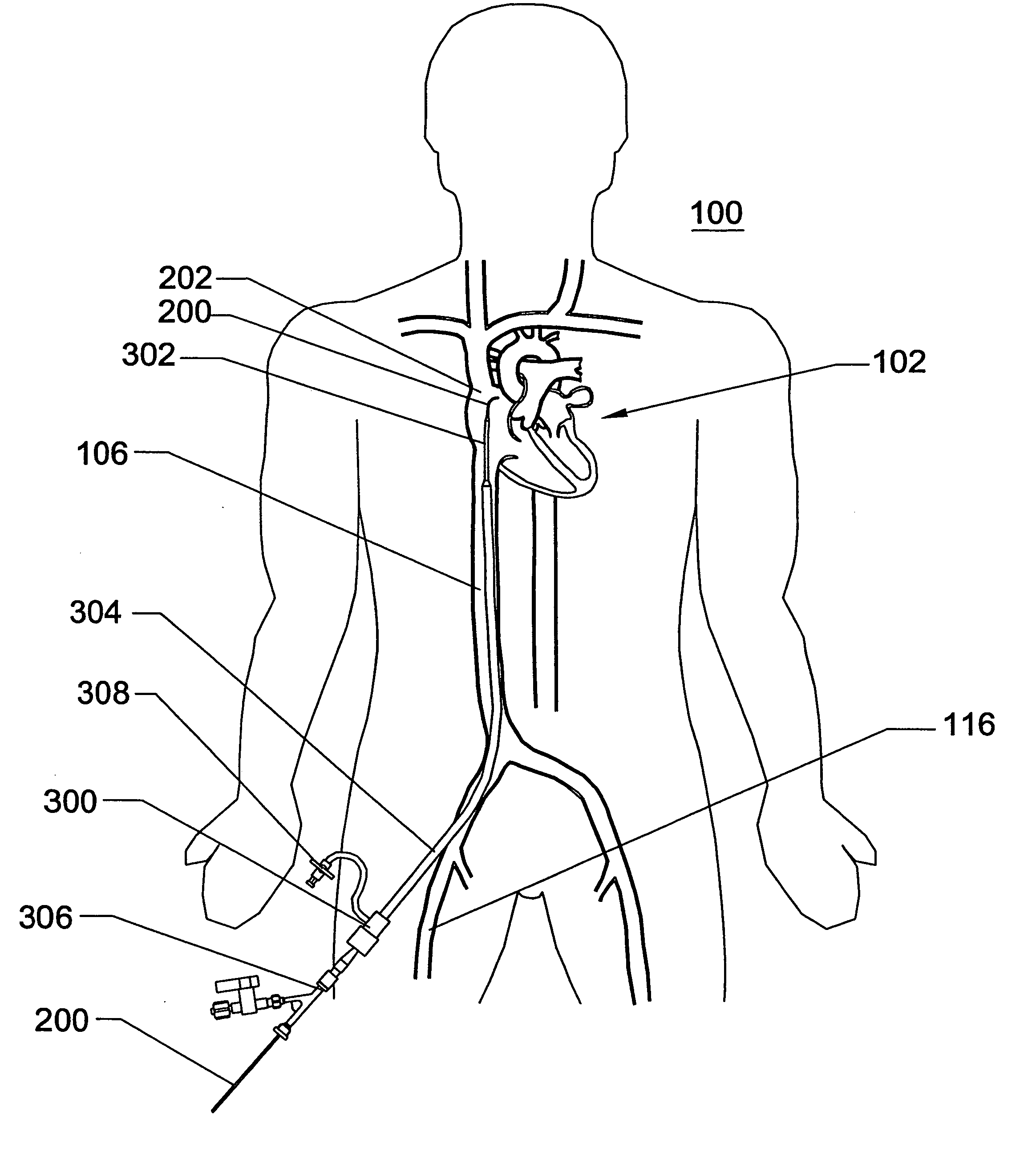
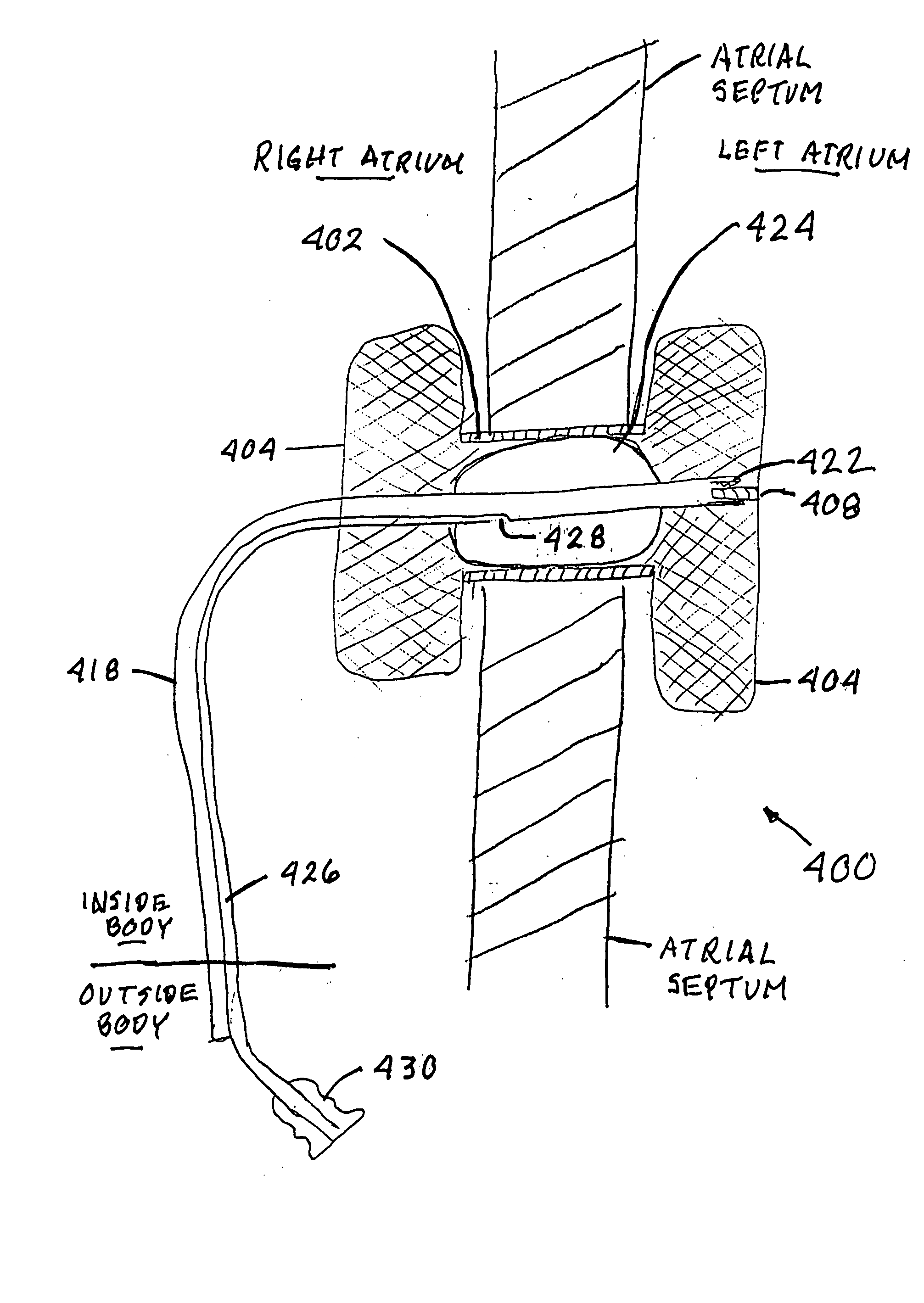
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is configured for use in the vascular system. The access route is through the inferior vena cava to the right atrium, where a trans-septal puncture, followed by advancement of the catheter is completed. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement through the atrial septum into the left atrium. The distal end of the sheath is expanded using a radial dilator. In one application, the sheath is utilized to provide access for a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure such as electrophysiological mapping of the heart, radio-frequency ablation of left atrial tissue, placement of atrial implants, valve repair, or the like.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Method and devices for treating atrial fibrillation by mass ablation
InactiveUS20060009756A1Reduce the total massUltrasound therapyInfusion devicesAtrial cavityChest cavity
Apparatus and method for ablating target tissue including a non-linear area of tissue in the left atrium of a patient. The method can include selecting an ablation apparatus having an ablator with a tissue engagement section, penetrating a chest cavity of the patient, and identifying the target tissue. The method can also include positioning the ablation apparatus adjacent to the target tissue so that the tissue engagement section can transfer ablation energy to the target tissue. The method can further include energizing the tissue engagement section with ablation energy in order to create a footprint on the non-linear area of tissue in the left atrium and to reduce an overall mass of excitable tissue in the left atrium.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for performing a procedure on a cardiac valve
InactiveUS20050055088A1Risk minimizationWithout riskHeart valvesBlood vesselsLeft atriumValvular prosthesis
The present invention comprises a method for deploying an aortic valve prosthesis. This valve prosthesis may include any of the known aortic valves including, but not limited to, stented and unstented bioprosthetic valves, stented mechanical valves, and expandable or self-expanding valves, whether biological or artificial. The method involves the steps of: making a first opening leading to the left atrium; passing a valve prosthesis through the opening and into a cardiac chamber of the left side of the heart using a first manipulation instrument; making a second opening in the arterial system and advancing one end of a second manipulation instrument through the arterial opening and into the aforementioned cardiac chamber; securing the second manipulation instrument to the valve prosthesis; and using the second manipulation instrument to retract at least some portion of the valve prosthesis out of the aforementioned cardiac chamber.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for resecting and replacing an aortic valve
InactiveUS7544206B2Risk minimizationAccurate placementEar treatmentCannulasMitral valve leafletLeft atrium
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Supportless atrioventricular heart valve and minimally invasive delivery systems thereof
A supportless atrioventricular valve intended for attaching to a circumferential valve ring and papillary muscles of a patient comprising a singular flexible membrane of tissue or synthetic biomaterial, wherein a minimally invasive delivery system is provided through a percutaneous intercostal penetration and a penetration at the cardiac wall into a left atrium of the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Method for detecting, diagnosing, and treating cardiovascular disease
InactiveUS20040167580A1Physical therapies and activitiesLocal control/monitoringVascular diseaseTherapeutic treatment
A method of treating cardiovascular disease in a medical patient is provided. The method includes the steps of generating a sensor signal indicative of a fluid pressure within the left atrium of the patient's heart, and delivering an electrical stimulus to a location in the heart. The electrical stimulus is delivered based at least in part on the sensor signal. The method also includes the steps of generating a proccessor output indicative of a treatment to a signaling device. The processor output is based at least in part on the sensor signal. At least two treatment signals are provided to the medical patient. The treatment signals are distinguishable from one another by the patient, and are indicative of a therapeutic treatment. The treatment signals are based at least in part on the processor output.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
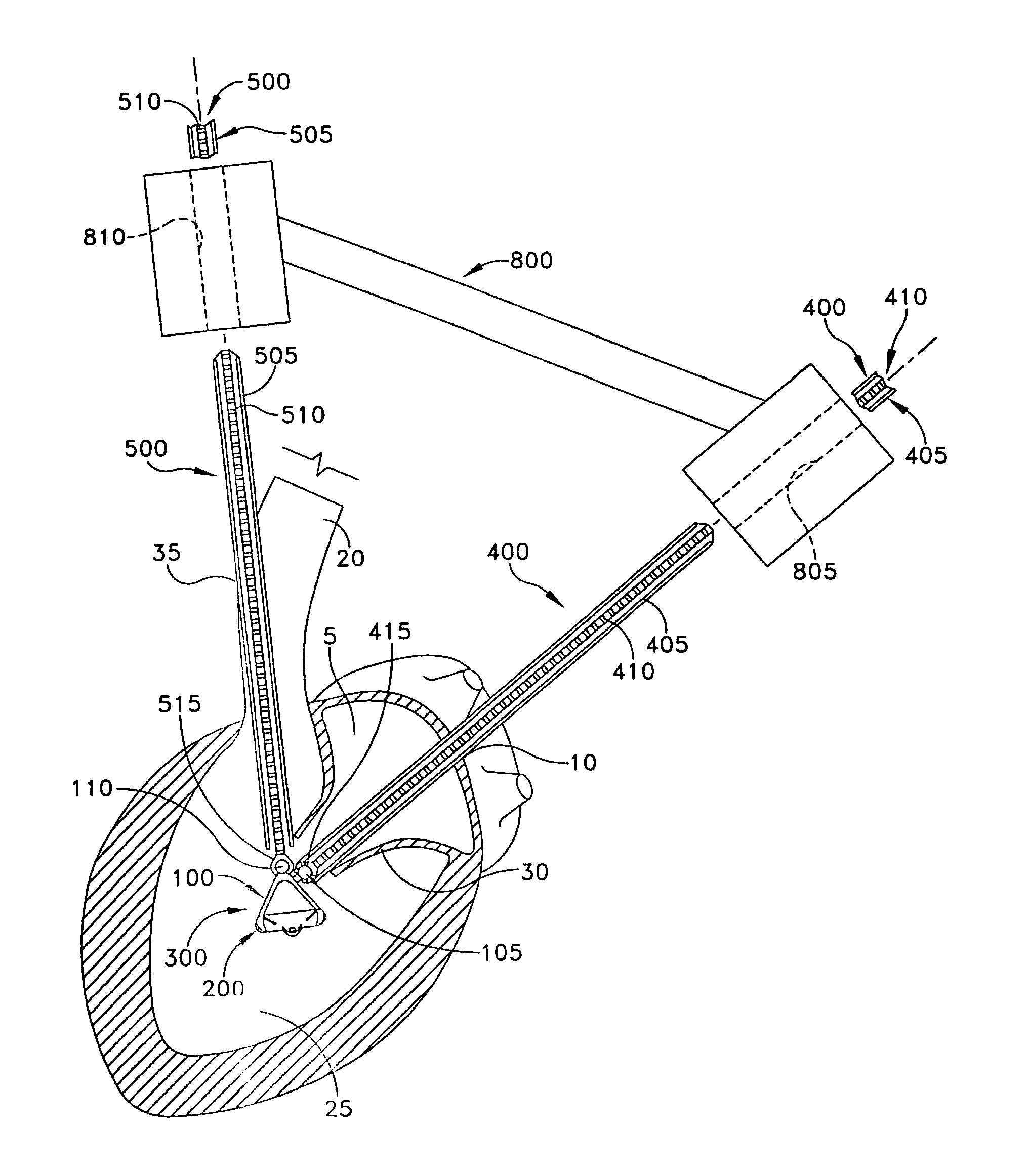
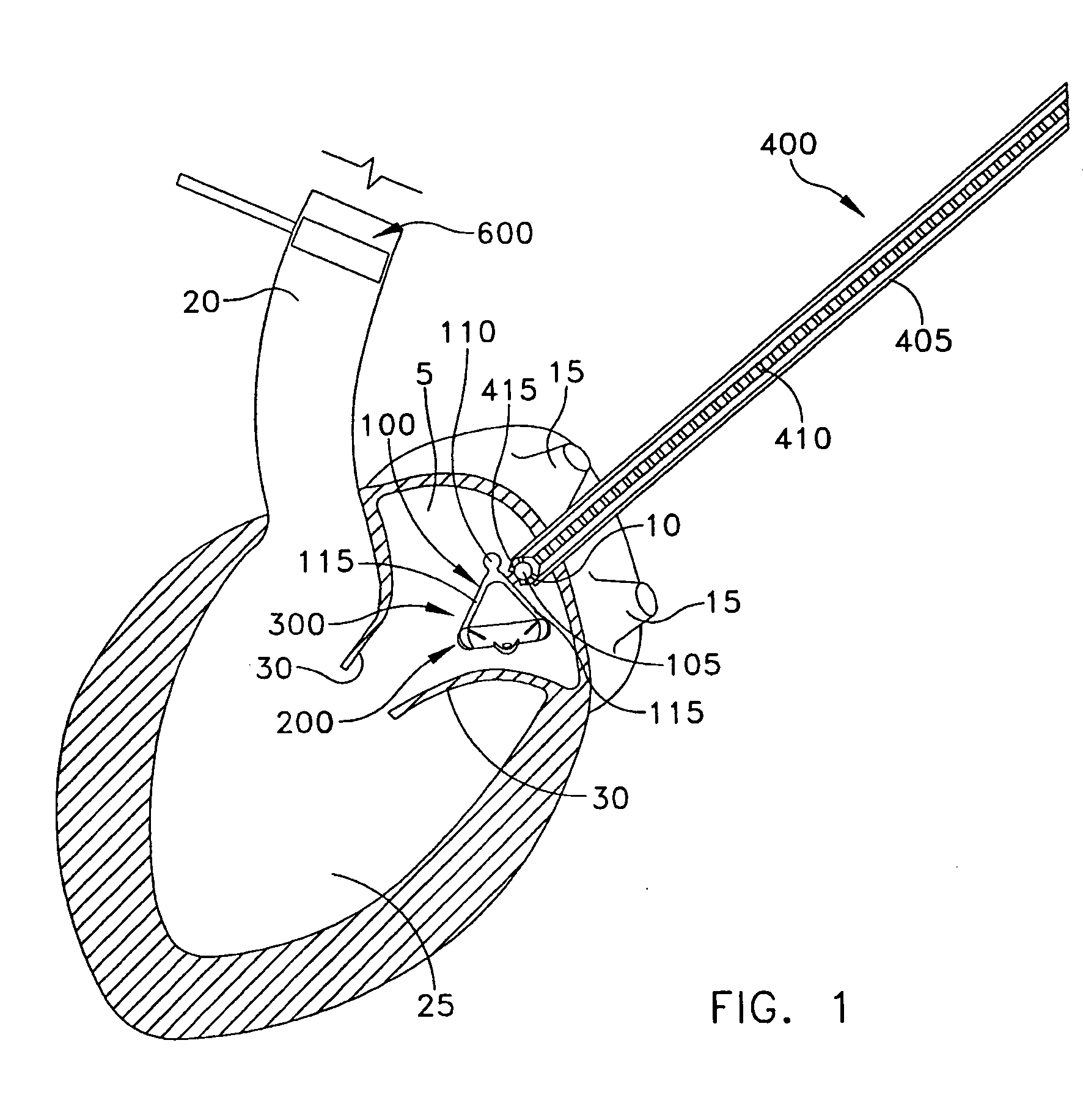
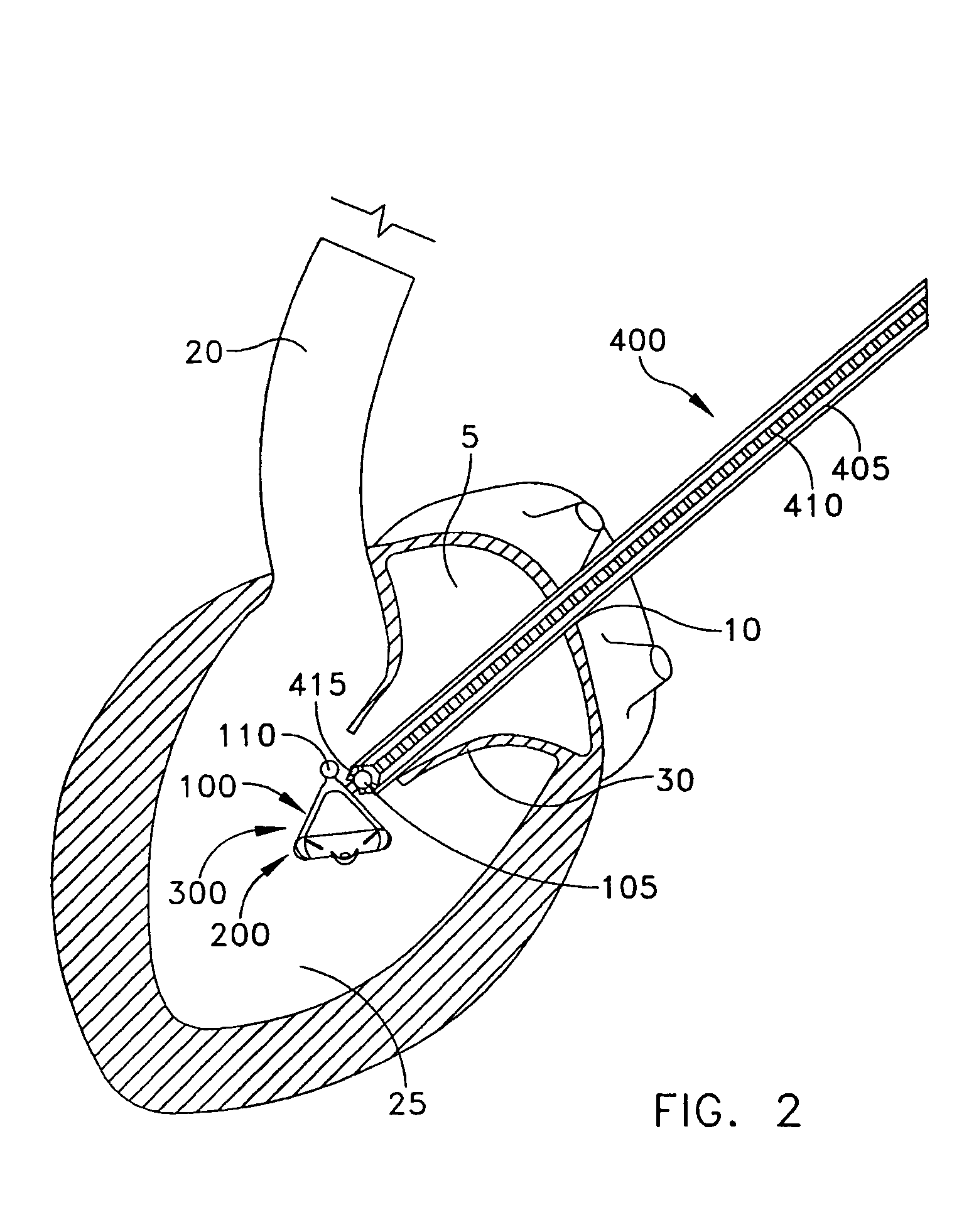
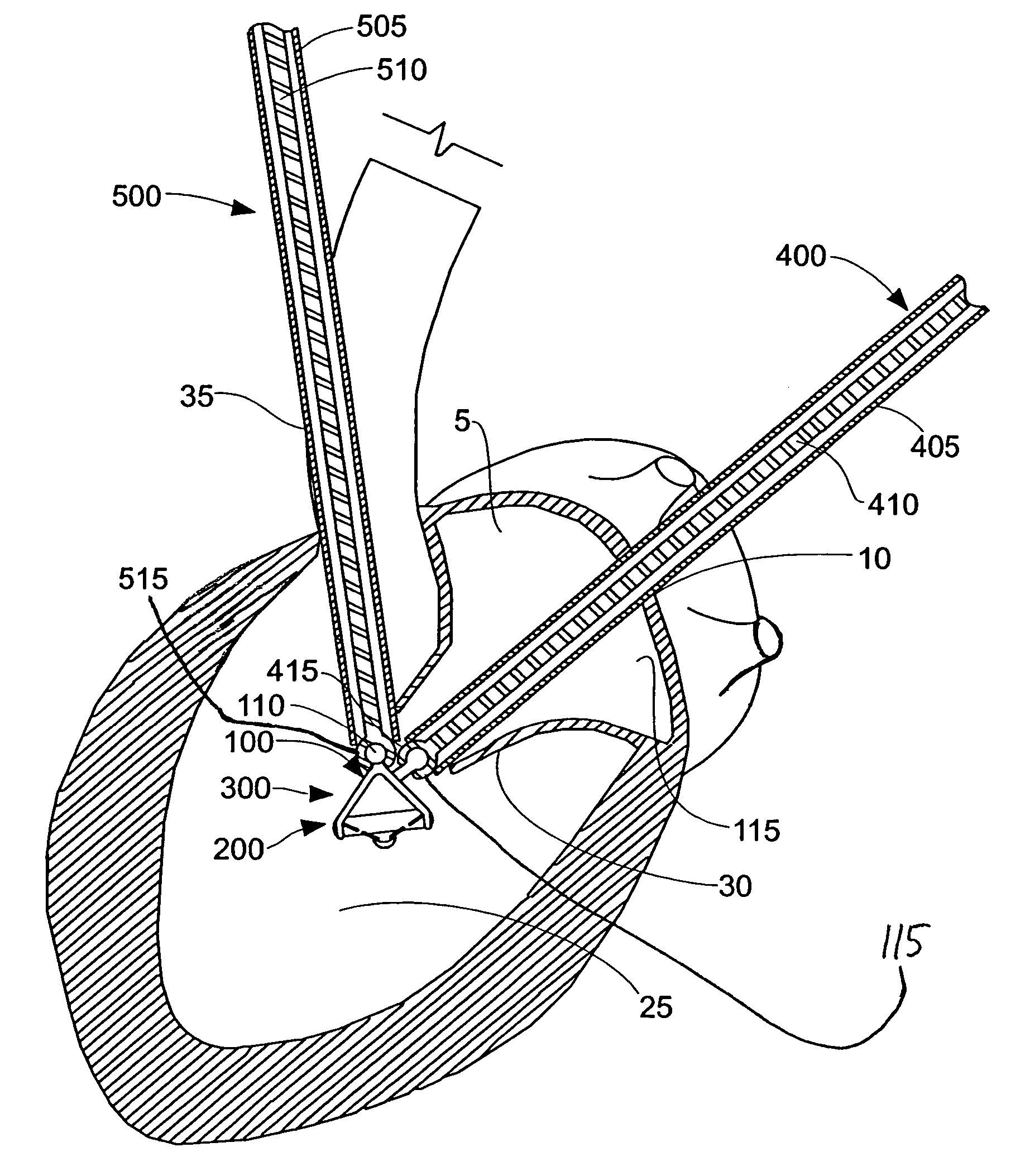
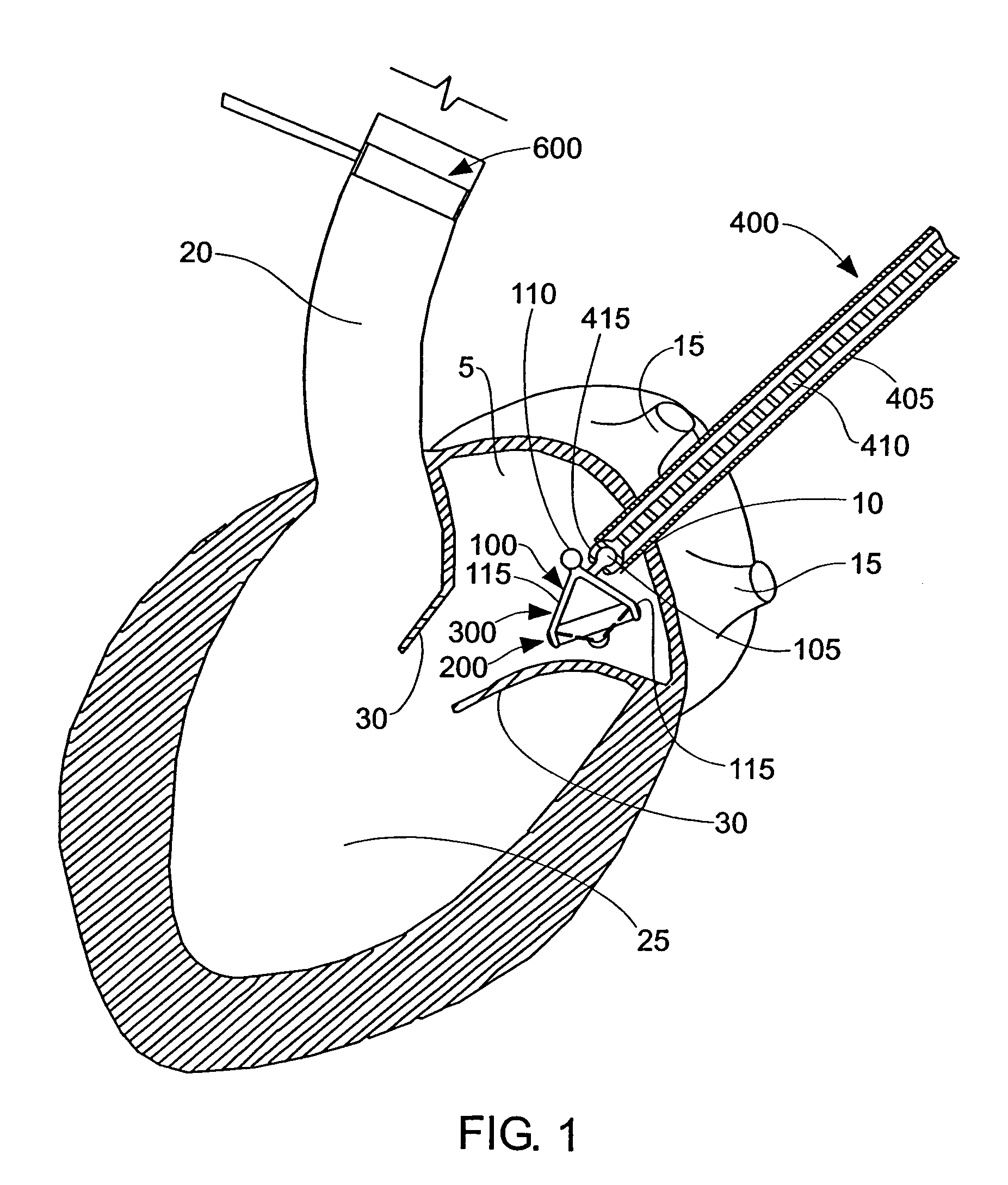
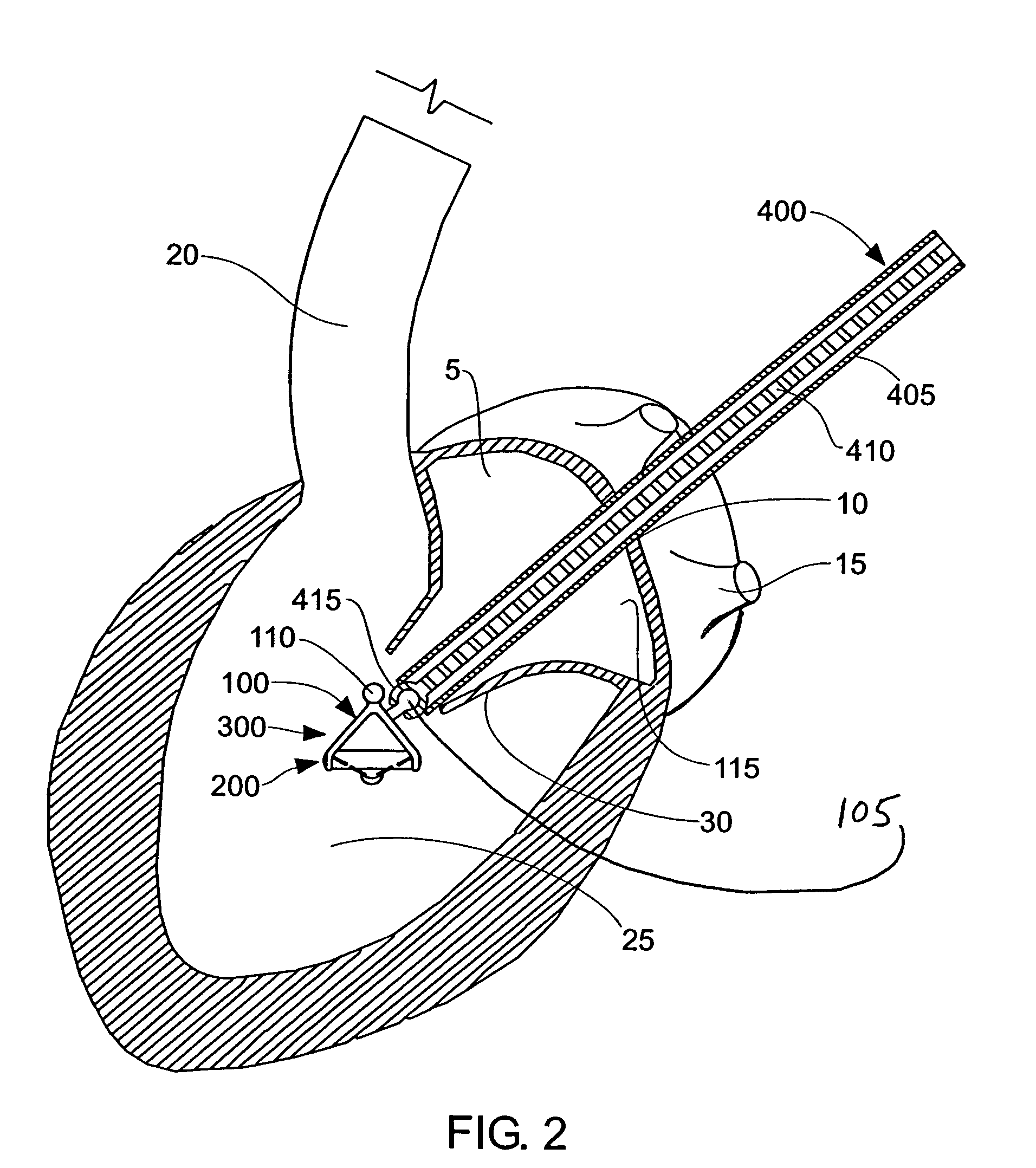
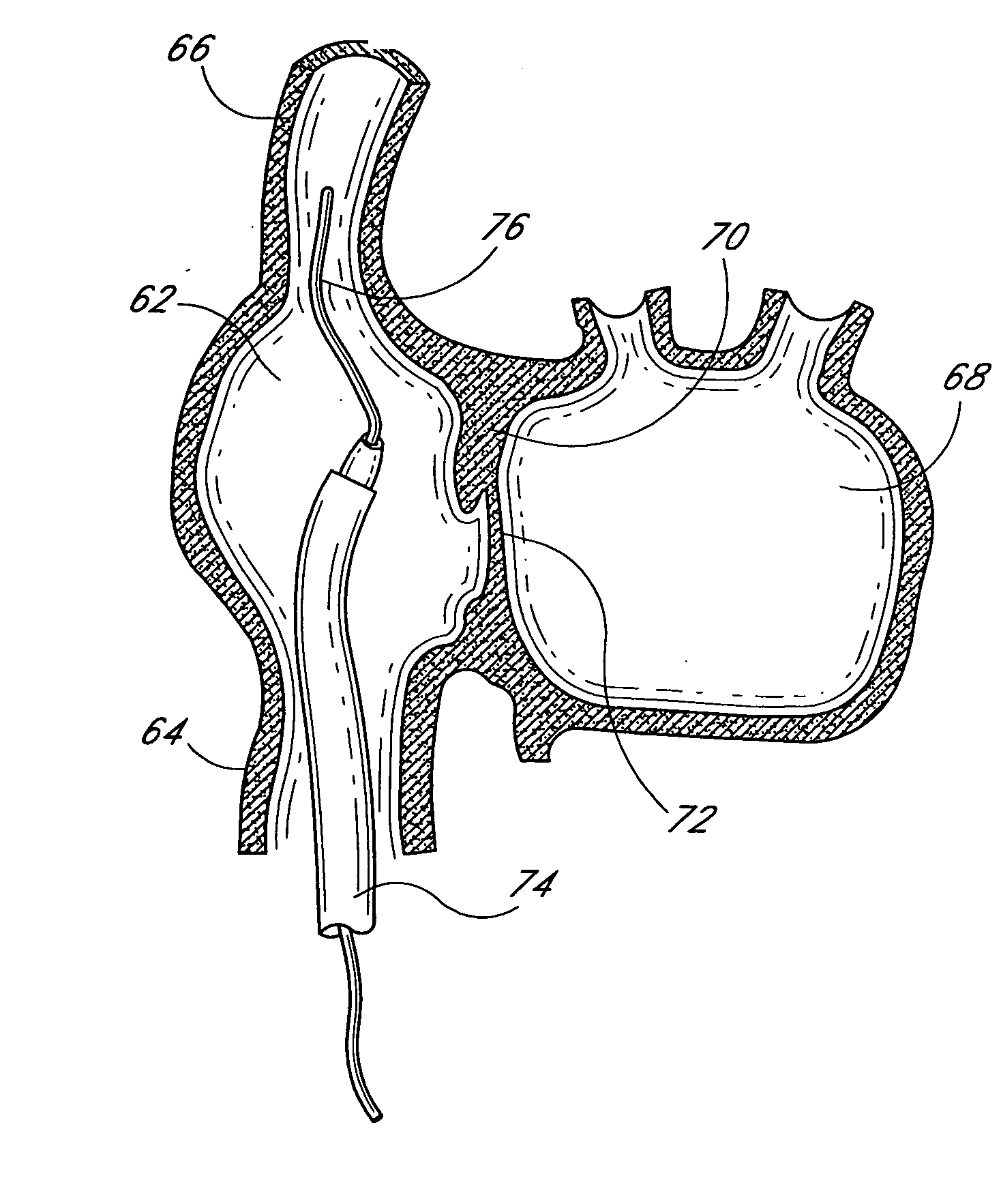
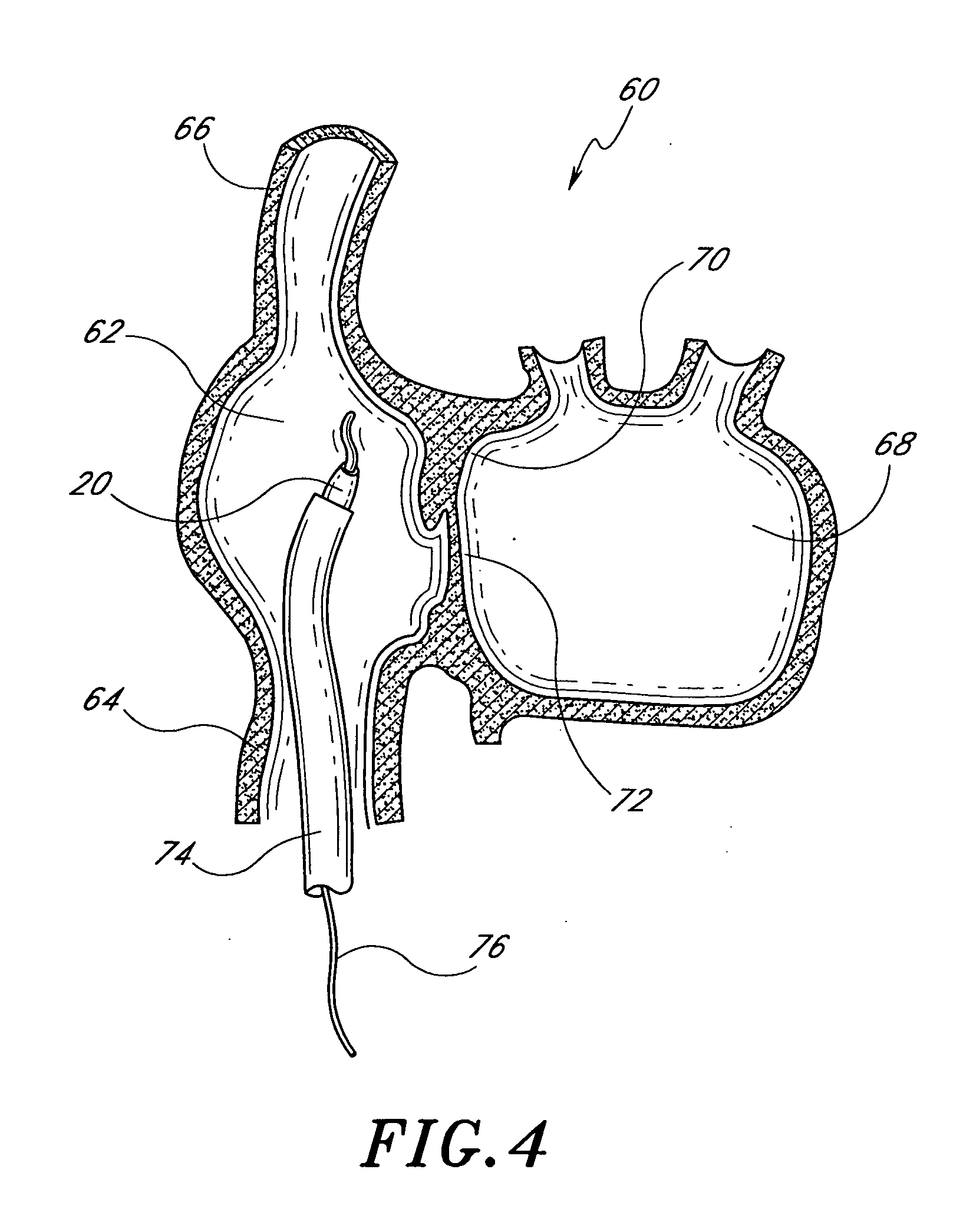
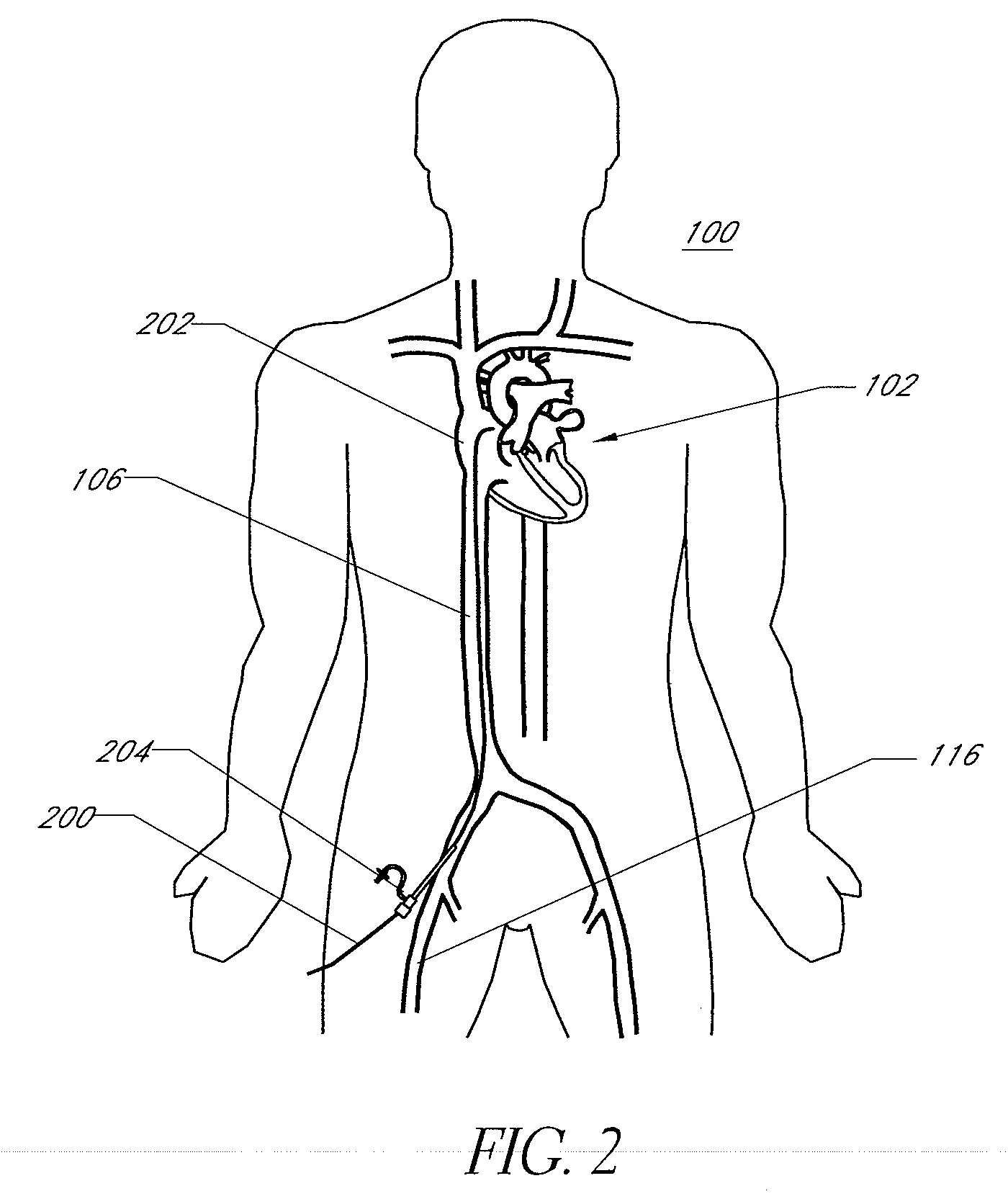
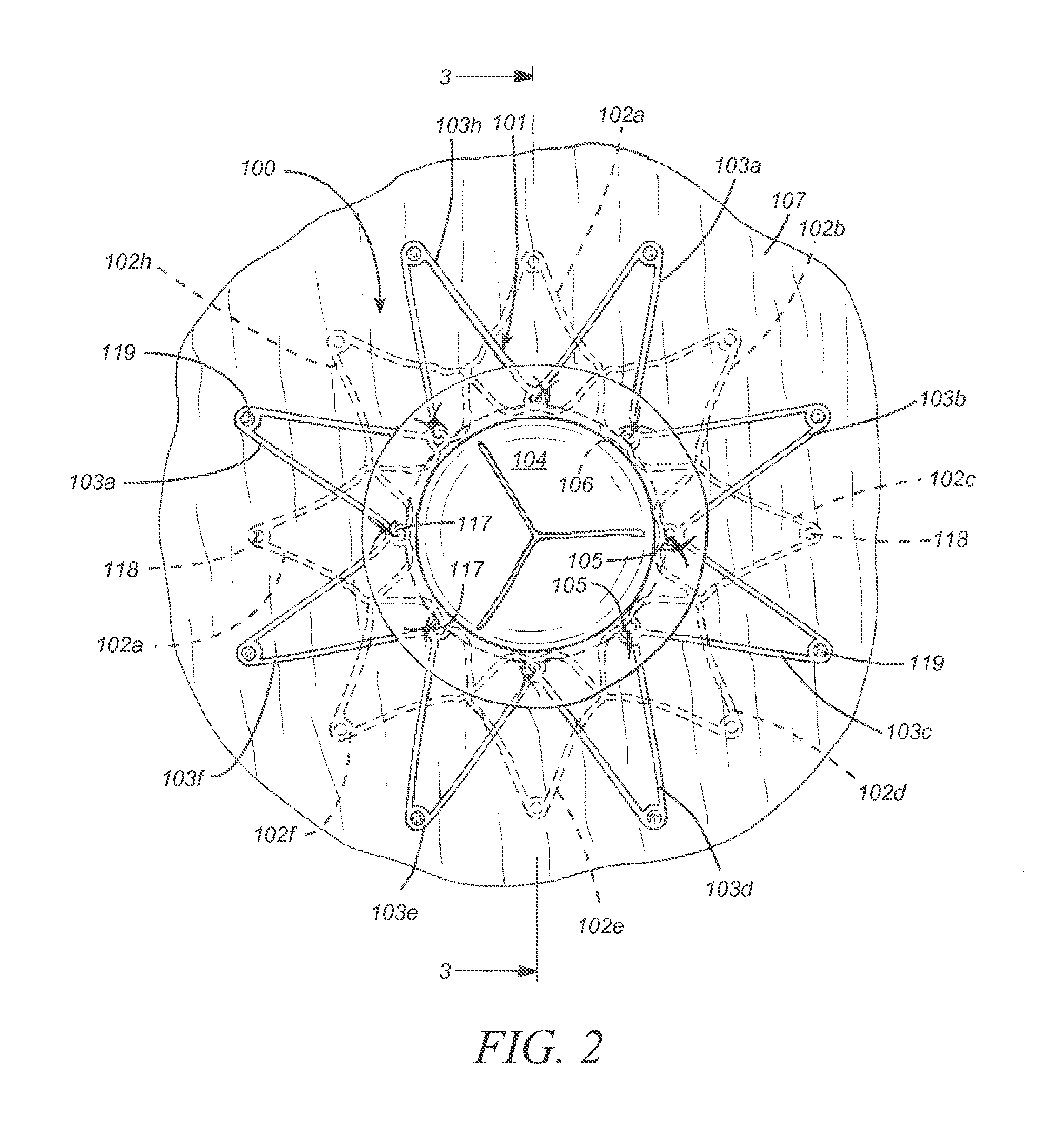
Method and apparatus for accessing the left atrial appendage
Disclosed is an apparatus for facilitating access to the left atrium, and specifically the left atrial appendage. The apparatus may comprise a sheath with first and second curved sections that facilitate location of the fossa ovalis and left atrial appendage. The apparatus may further comprise tissue piercing and dilating structures. Methods are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
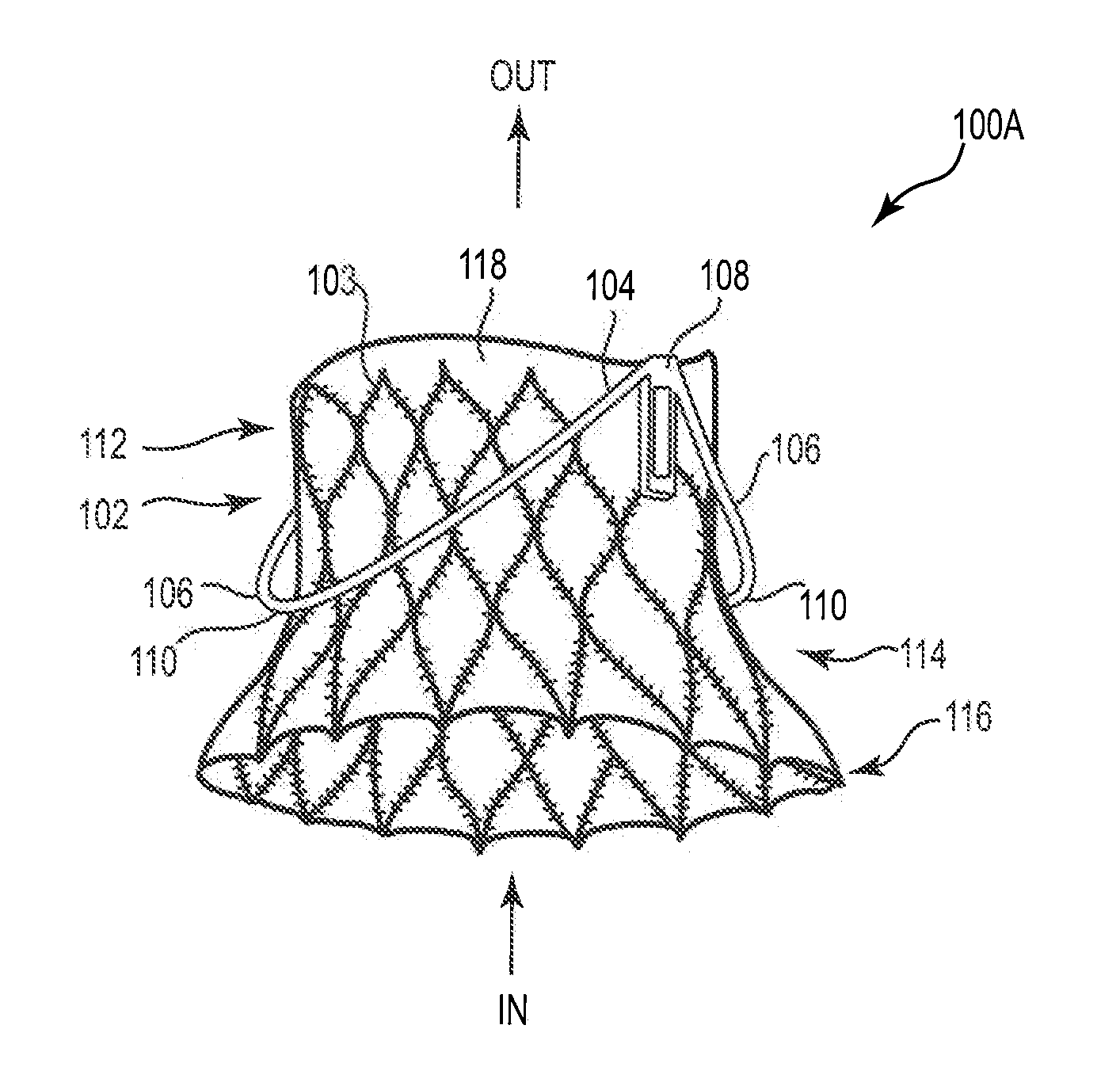
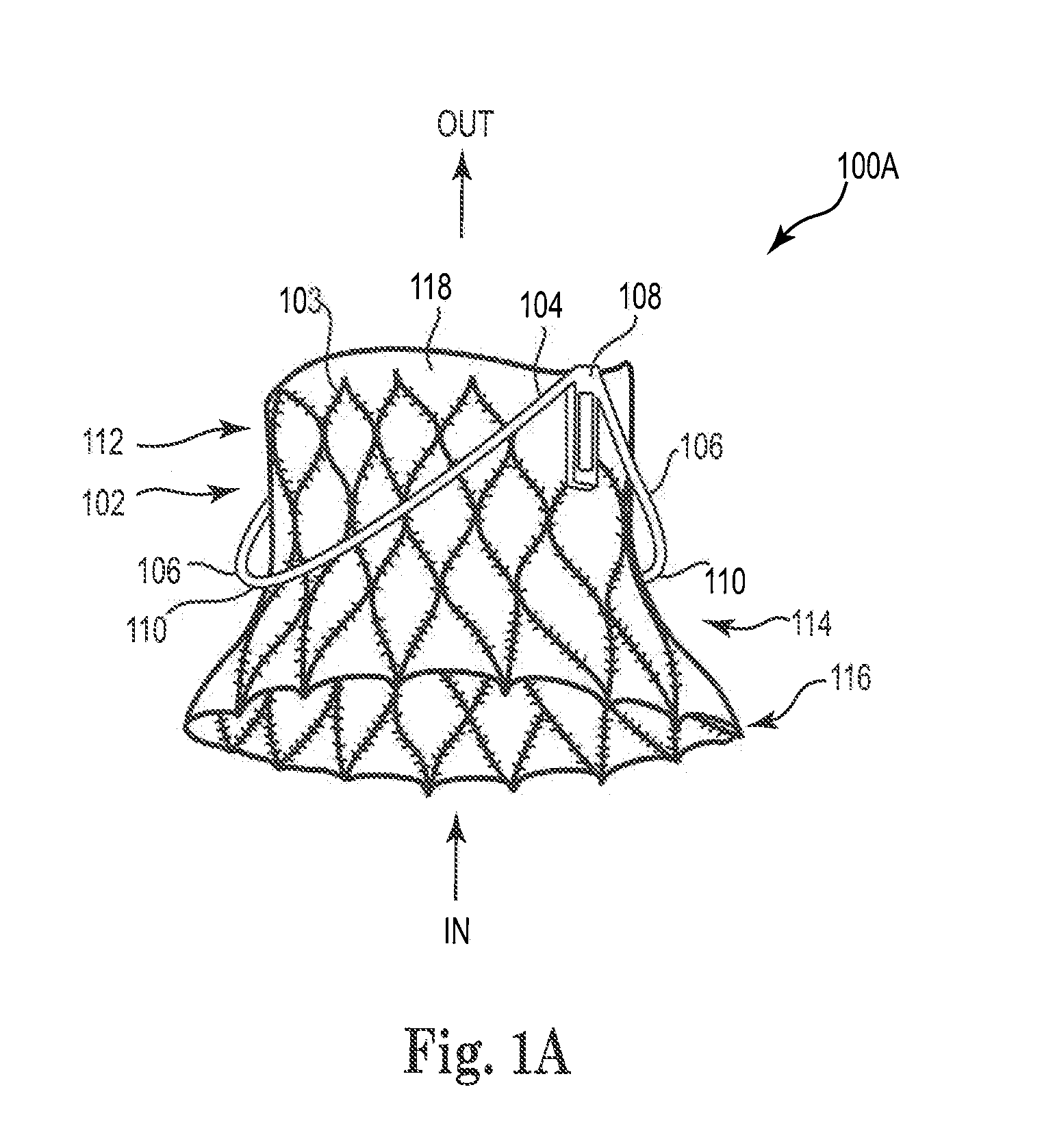
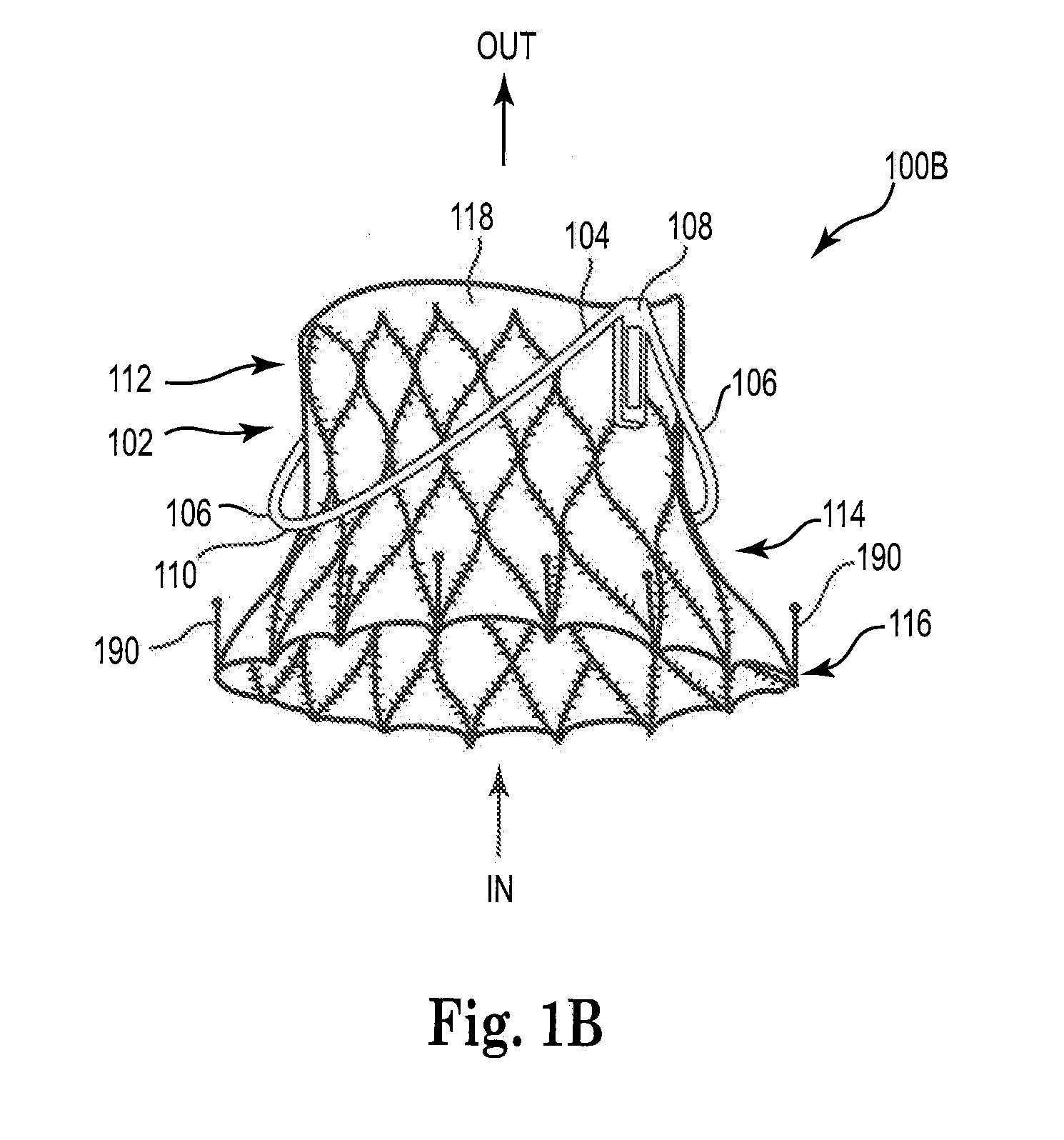
Adjustable endolumenal mitral valve ring
ActiveUS9180005B1Mitral regurgitation has been reduced and eliminatedStentsGuide needlesVentricular contractionMitral valve leaflet
Excessive dilation of the annulus of a mitral valve may lead to regurgitation of blood during ventricular contraction. This regurgitation may lead to a reduction in cardiac output. Disclosed are systems and methods relating to an implant configured for reshaping a mitral valve. The implant comprises a plurality of struts with anchors for tissue engagement. The implant is compressible to a first, reduced diameter for transluminal navigation and delivery to the left atrium of a heart. The implant may then expand to a second, enlarged diameter to embed its anchors to the tissue surrounding and / or including the mitral valve. The implant may then contract to a third, intermediate diameter, pulling the tissue radially inwardly, thereby reducing the mitral valve and lessening any of the associated symptoms including mitral regurgitation.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Device and method for treatment of heart valve regurgitation
In one embodiment, the present invention provides a prosthesis that can be implanted within a heart to at least partially block gaps that may be present between the two mitral valve leaflets. In one preferred embodiment, the prosthesis includes an anchoring ring that expands within the left atrium to anchor the prosthesis and a pocket member fixed to the anchoring ring. The pocket member is positioned within the mitral valve, between the leaflets so that an open end of the pocket member is positioned within the left ventricle. When the mitral valve is open, blood flows past the pocket member, maintaining the pocket member in a collapsed state. When the mitral valve closes, the backpressure of the blood pushes into the pocket member, expanding the pocket member to an inflated shape. The mitral valve leaflets contact the expanded pocket member, allowing the prosthesis to block at least a portion of the openings between the leaflets, thereby minimizing regurgitated blood flow into the left atrium.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
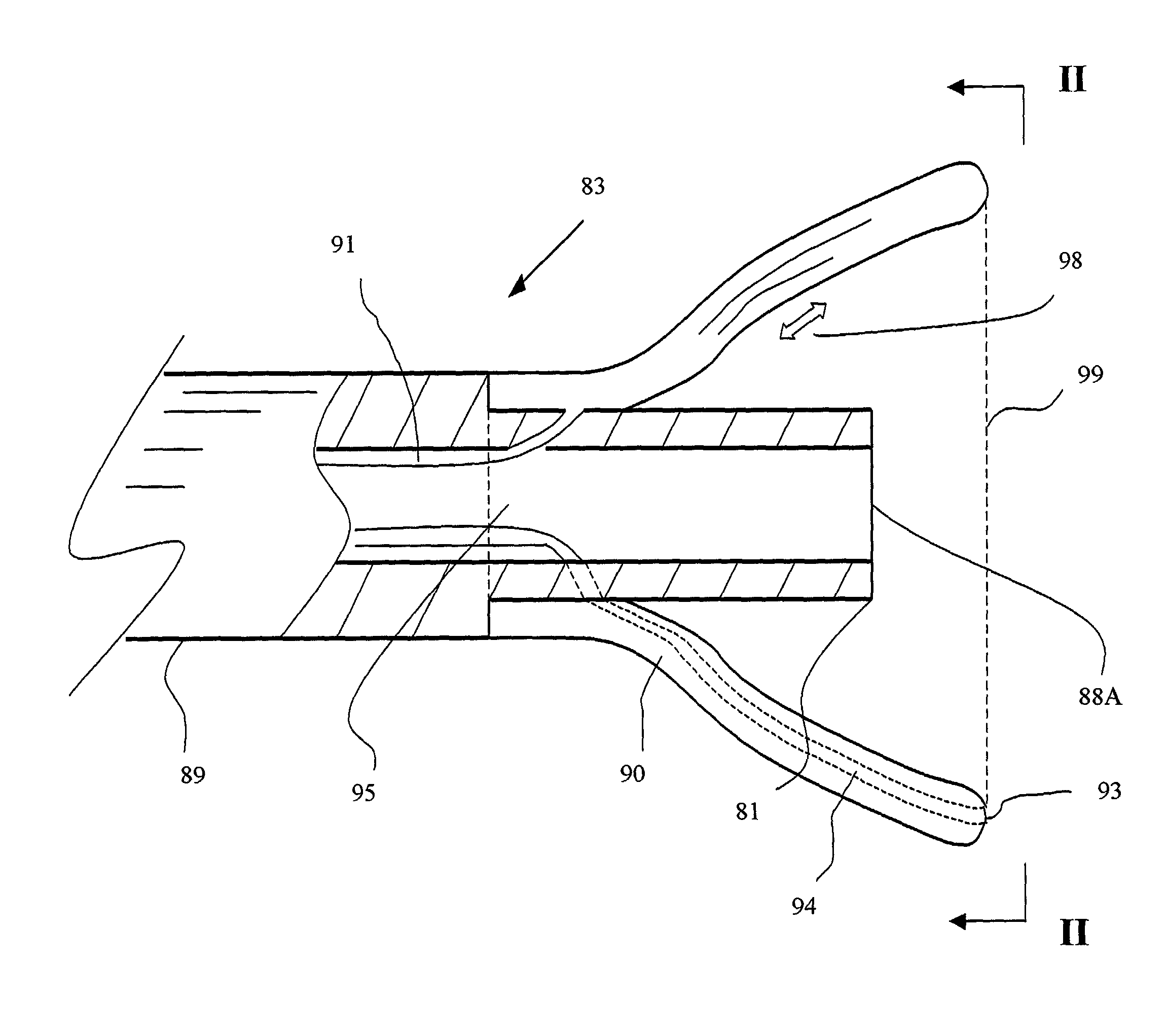
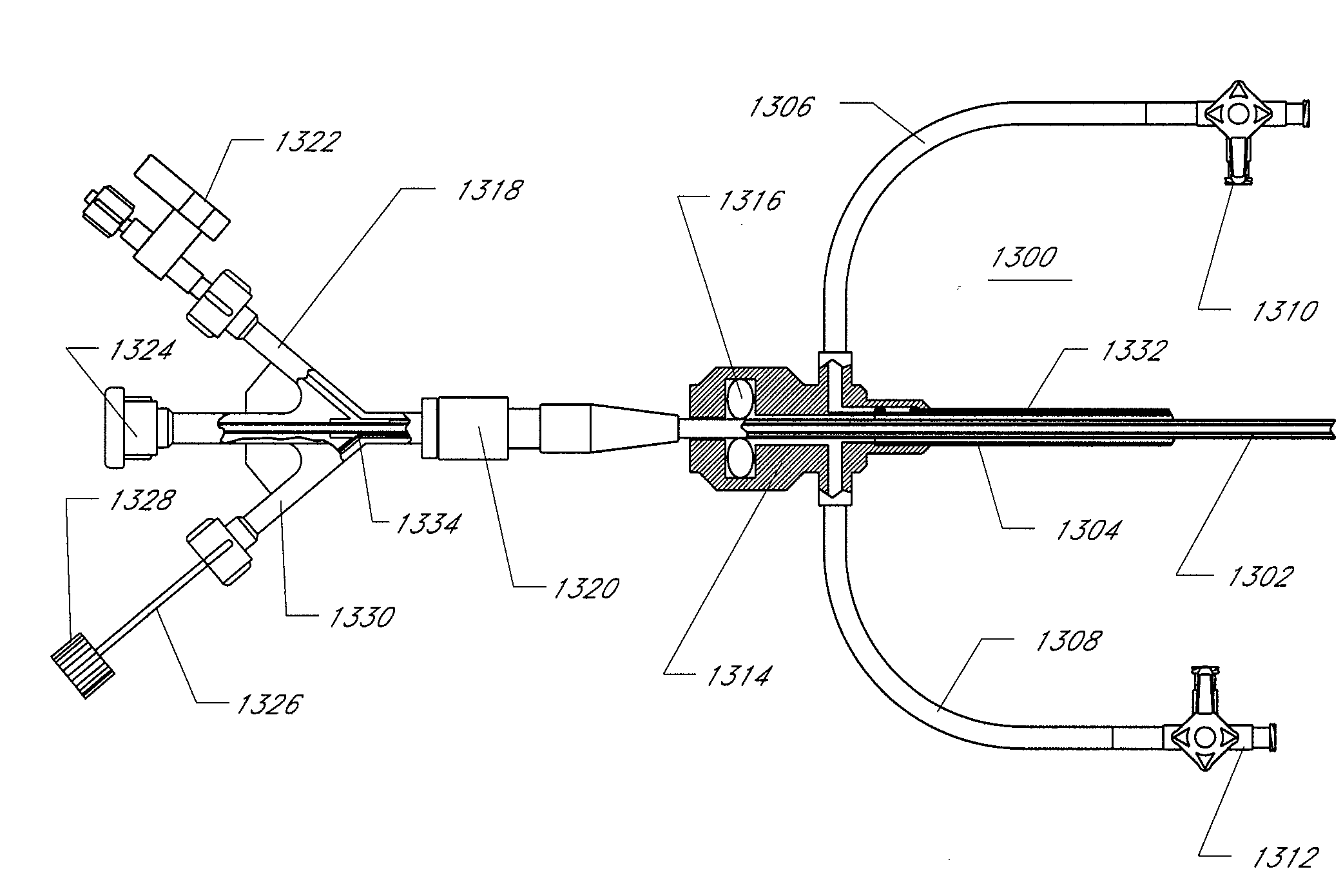
Ablation catheter and method for isolating a pulmonary vein
A catheter assembly and method for treatment of cardiac arrhythmia, for example, atrial fibrillation, by electrically isolating a vessel, such as a pulmonary vein, from a chamber, such as the left atrium. The catheter assembly includes a catheter body and at least one electrode. The catheter body includes a proximal portion, an intermediate portion and a distal portion. The intermediate portion extends from the proximal portion and defines a longitudinal axis. The distal portion extends from the intermediate portion and forms a substantially closed loop transverse to the longitudinal axis. The at least one electrode is disposed along the loop. With this configuration, the loop is axially directed into contact with the chamber wall about the vessel ostium. Upon energization, the electrode ablates a continuous lesion pattern about the vessel ostium, thereby electrically isolating the vessel from the chamber.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Ablation Therapy System and Method for Treating Continuous Atrial Fibrillation
InactiveUS20080281312A1Limited in amount of energyAvoid the needDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingVeinRf ablation
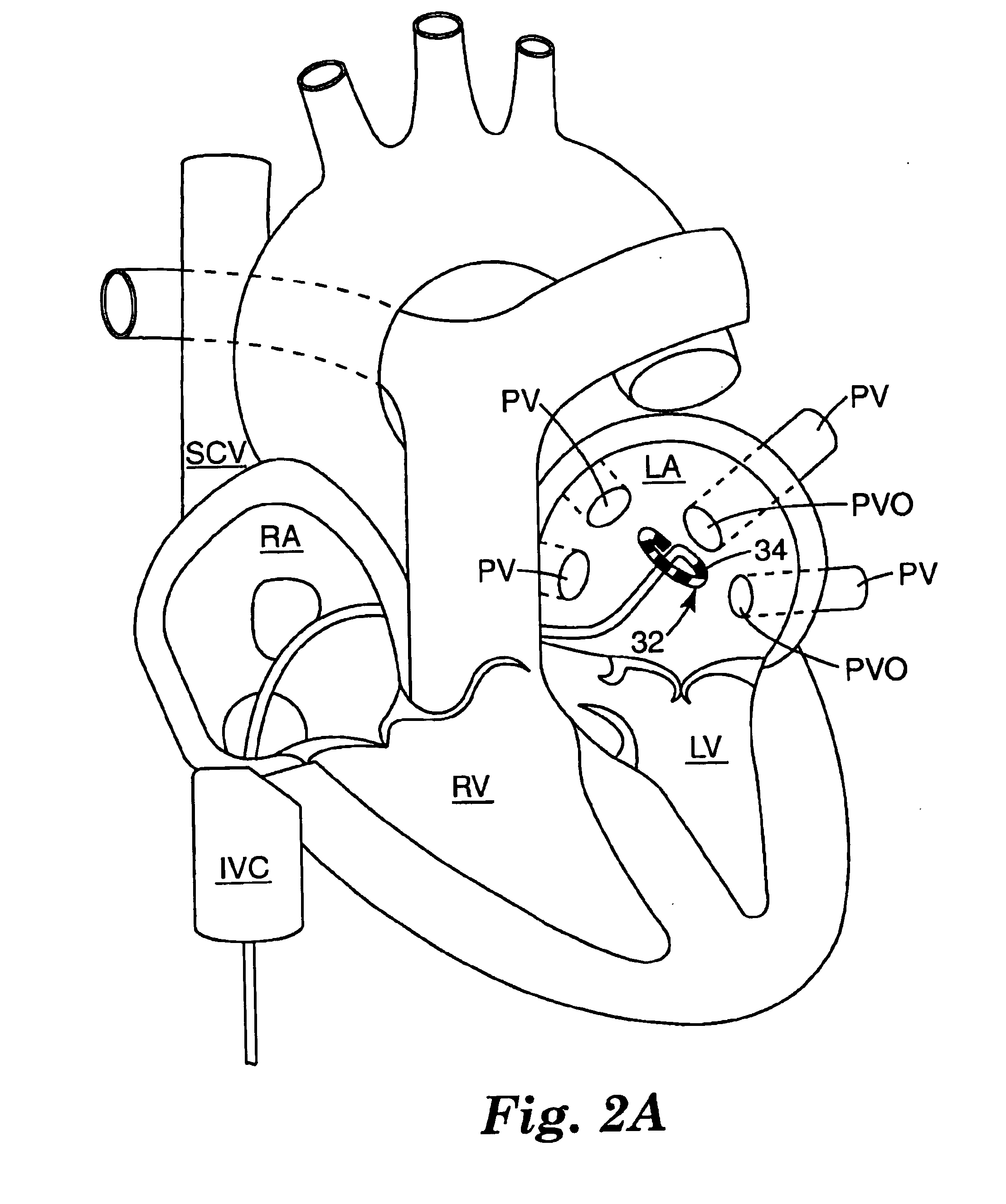
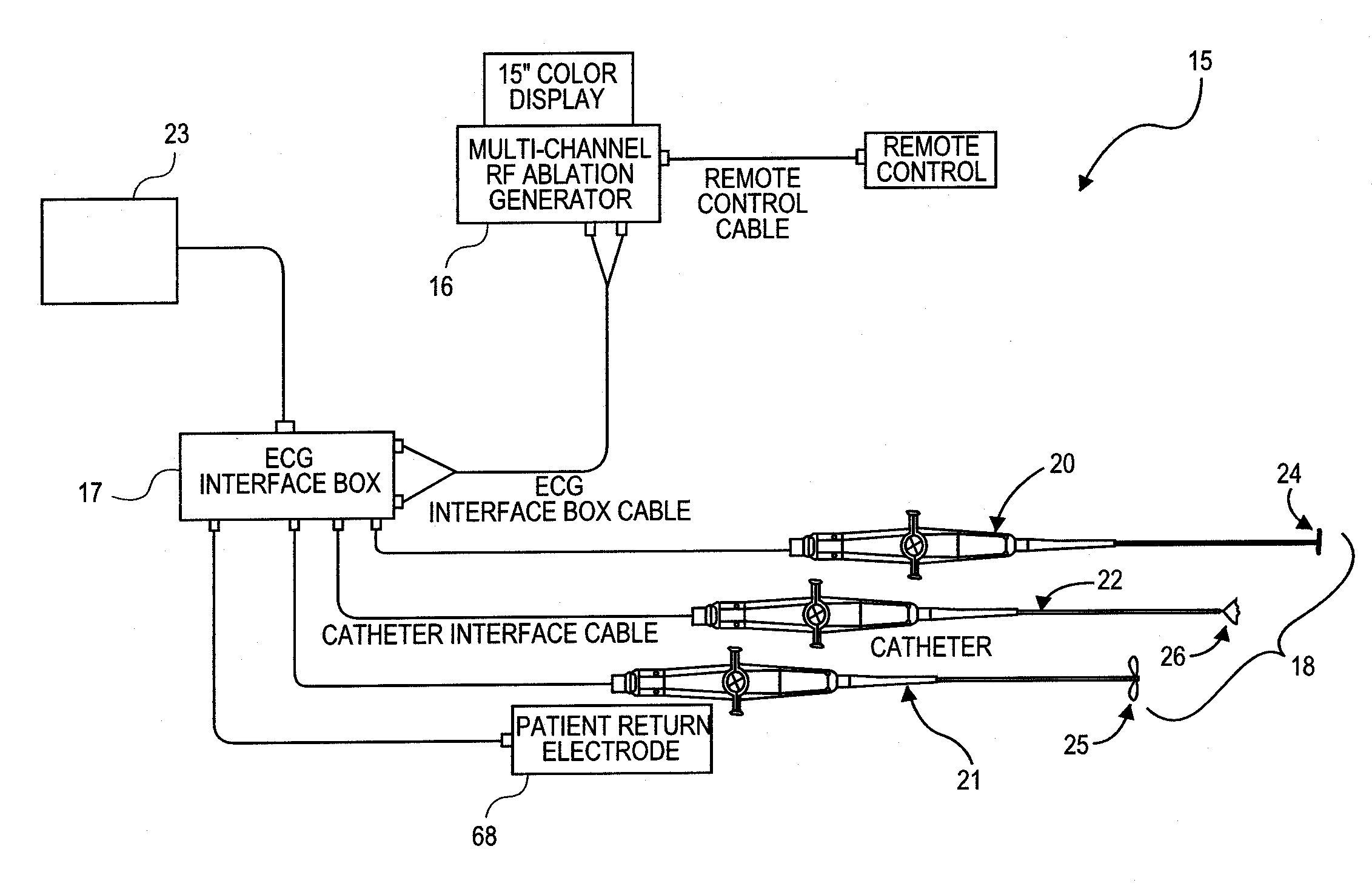
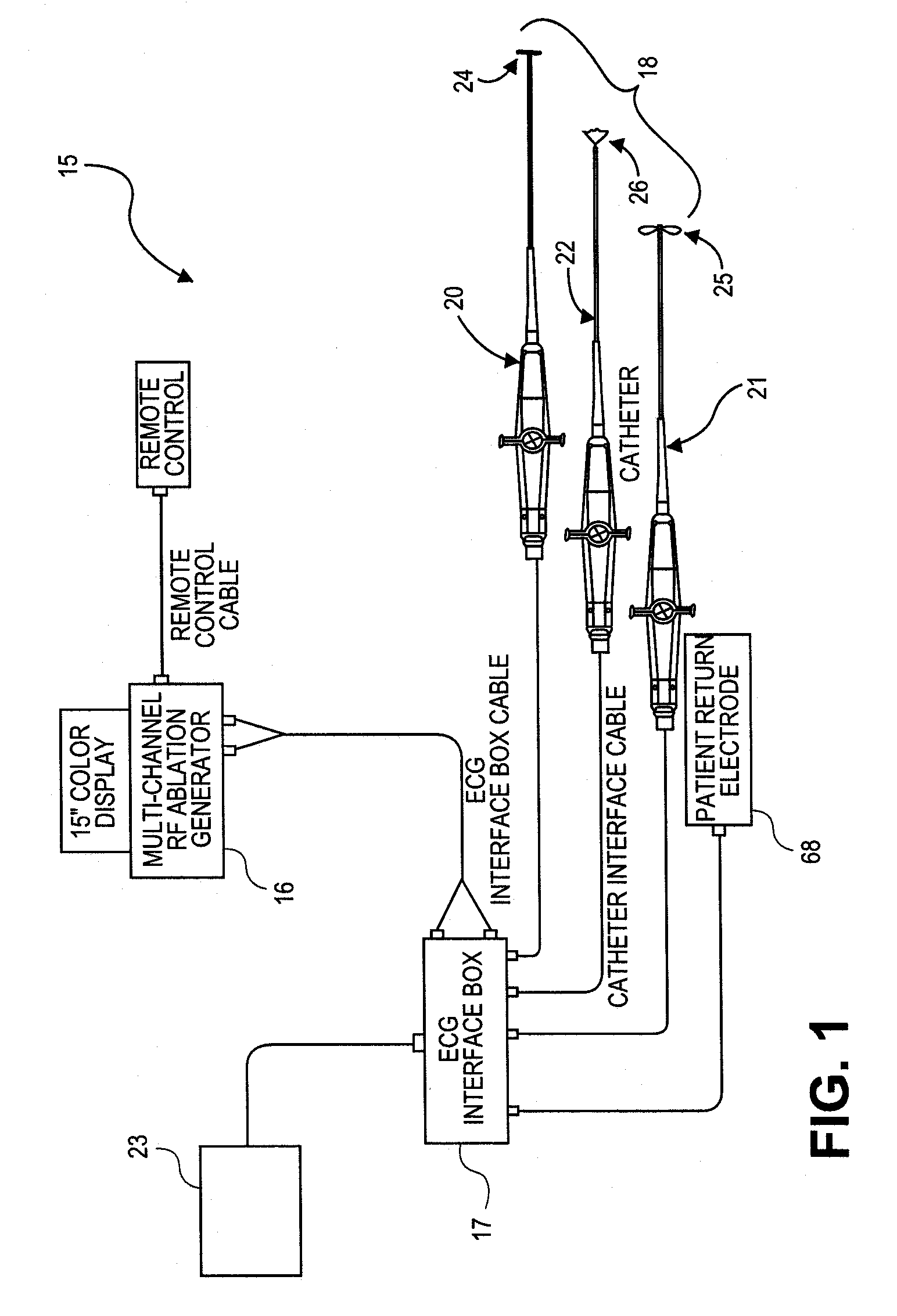
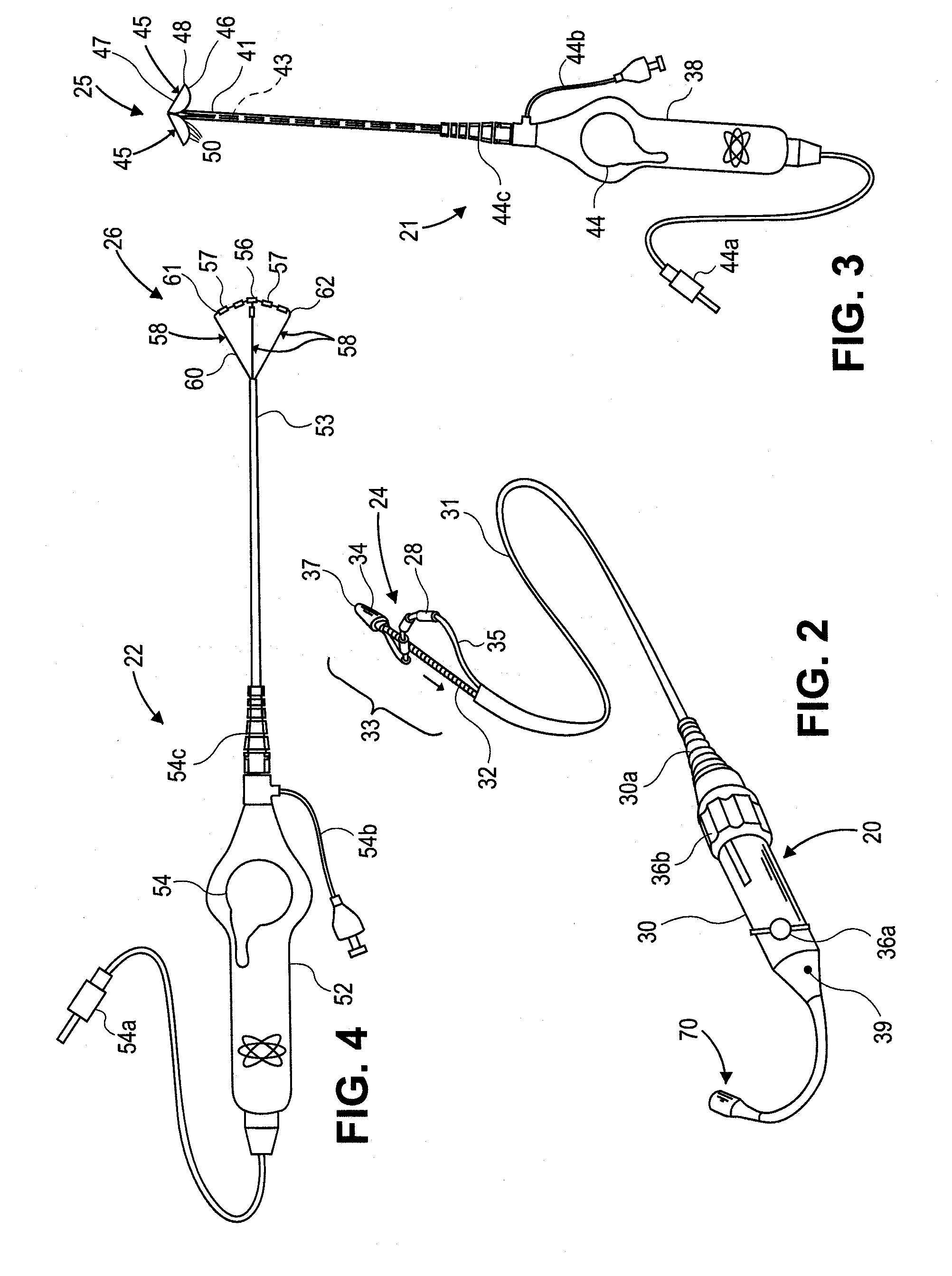
An ablation therapy system and systematic method is provided for treating continuous atrial fibrillation. The therapy system includes a Multi-Channel RF Ablation Generator, an ECG interface, an assembly of at least three ablation catheters, and an ECG interface operably coupling and interfacing the catheters to both an ECG unit and the RF Ablation Generator. The systematic method includes transseptally accessing the Left Atrium (LA) through the septum of the patient's heart, and performing an endocardial pulmonary vein ablation procedure on the pulmonary vein ostial tissue surrounding one or more pulmonary veins in a manner treating aberrant conductive pathways therethrough. After performing the pulmonary vein ablation, the method further includes performing an endocardial atrial septum ablation procedure on the septal tissue in a manner treating aberrant conductive pathways therethrough.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Method and apparatus for accessing the left atrial appendage
Disclosed is an apparatus for facilitating access to the left atrium, and specifically the left atrial appendage. The apparatus may comprise a sheath with first and second curved sections that facilitate location of the fossa ovalis and left atrial appendage. The apparatus may further comprise tissue piercing and dilating structures. Methods are also disclosed.
Owner:ATRITECH INC
Devices, systems, and methods for reshaping a heart valve annulus
Implants or systems of implants and methods apply a selected force vector or a selected combination of force vectors within or across the left atrium, which allow mitral valve leaflets to better coapt. The implants or systems of implants and methods make possible rapid deployment, facile endovascular delivery, and full intra-atrial retrievability. The implants or systems of implants and methods also make use of strong fluoroscopic landmarks. The implants or systems of implants and methods make use of an adjustable implant and a fixed length implant. The implants or systems of implants and methods may also utilize a bridge stop to secure the implant, and the methods of implantation employ various tools.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
Method and device for performing cooling or cryo-therapies, for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS7001378B2Minimize and inhibit bio-chemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Expandable trans-septal sheath
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Method and apparatus for treating heart failure
InactiveUS20050165344A1Prevent cryptogenic strokeReduce stroke occurrenceHeart valvesWound drainsThrombusCatheter
An apparatus for treating heart failure, including a conduit positioned in a hole in the atrial septum of the heart, to allow flow from the left atrium into the right atrium. The conduit is fitted with one or more emboli barriers or one-way valve members, to prevent thrombi or emboli from crossing into the left side circulation.
Owner:BUILDING ADDRESS
Pulmonary vein valve implant
InactiveUS20050273160A1Reduced likelihoodReduce severityStentsBronchiPulmonary vasculatureAtrial cavity
The present invention involves placing a valve between the left atrium and the lung to prevent regurgitant flow from increasing the pulmonary pressures, which may lead to pulmonary edema and congestion. Mitral stenosis or poor synchronization of the mitral valve may add additional pressures to the left atrium thus raising the pulmonary pressures and leading to congestion in the lung vasculature. By blocking the additional pressures from the mitral regurgitant flow from reaching the pulmonary circulation, the left atrium may act as a sealed vessel to allow additional aortic output. The valve placement can be intralumenal or attached to the ostium of the atrium. The device can be placed via the vascular conduits or through a surgical procedure into the pulmonary circulation. One or more devices may be placed in each of the four pulmonary veins. Additionally only one, two, three or all four veins may be implanted with the valve as desired by the physician.
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
Left and right side heart support
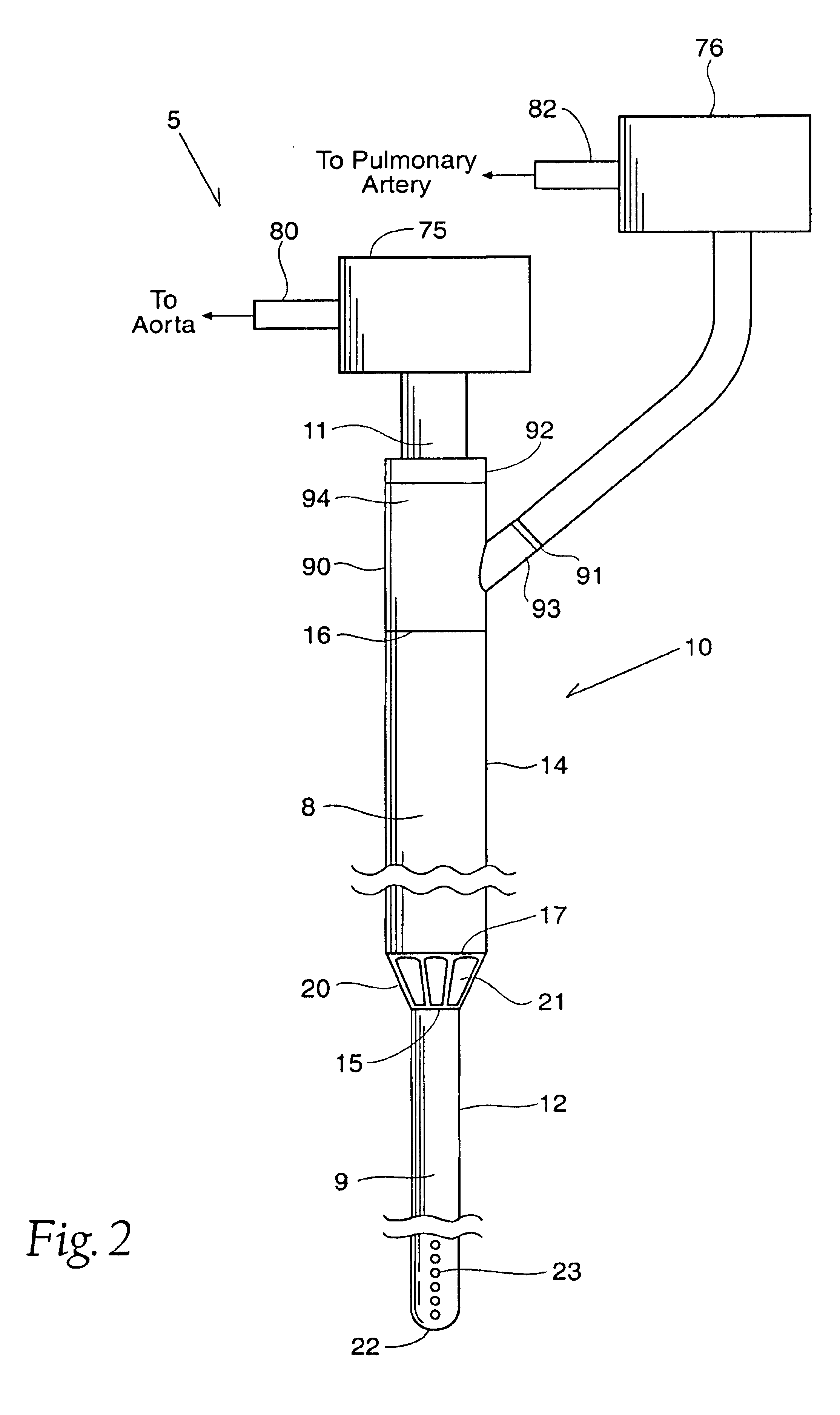
InactiveUS6926662B1Lower the volumeReduce the amount requiredOther blood circulation devicesBlood pumpsOuter CannulaRight atrium
A cannulation system for cardiac support uses an inner cannula disposed within an outer cannula. The outer cannula includes a fluid inlet for placement within the right atrium of a heart. The inner cannula includes a fluid inlet extending through the fluid inlet of the outer cannula and the atrial septum for placement within at least one of the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. The cannulation system also employs a pumping assembly coupled to the inner and outer cannulas to withdraw blood from the right atrium for delivery to the pulmonary artery to provide right heart support, or to withdraw blood from at least one of the left atrium and left ventricle for delivery into the aorta to provide left heart support, or both.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Devices and methods for coronary sinus pressure relief
A method and devices for relieving pressure in the left atrium of a patient's heart is disclosed. The method includes using an ablative catheter in a minimally invasive procedure to prepare an opening from the coronary sinus into a left atrium of the patient's heart. Once the opening is prepared, the opening may be enlarged by a technique such as expanding a balloon within the opening. A stent is then placed within the coronary sinus of the patient, with a transverse portion expanding within the opening, allowing blood to flow from the left atrium to the coronary sinus and then to the right atrium. Pressure within the left atrium is thus relieved.
Owner:DC DEVICES
Method and device for performing cooling- or cryo-therapies for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS6905494B2Minimize and inhibit biochemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
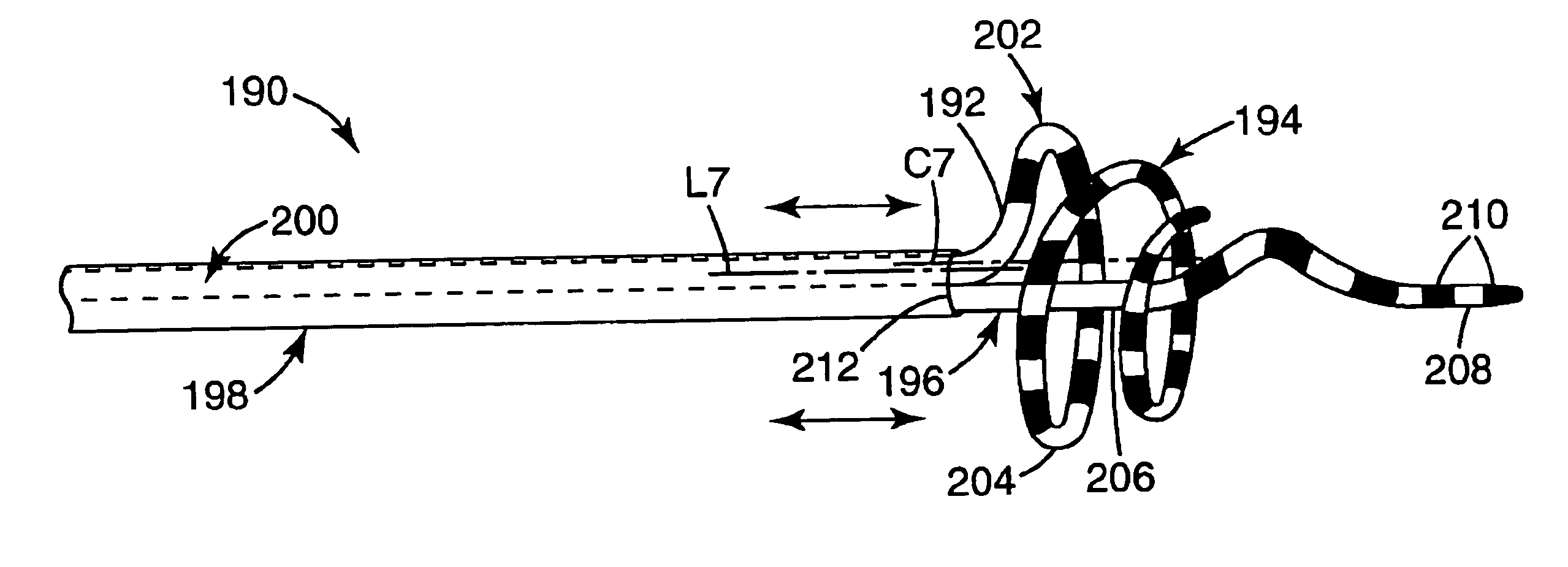
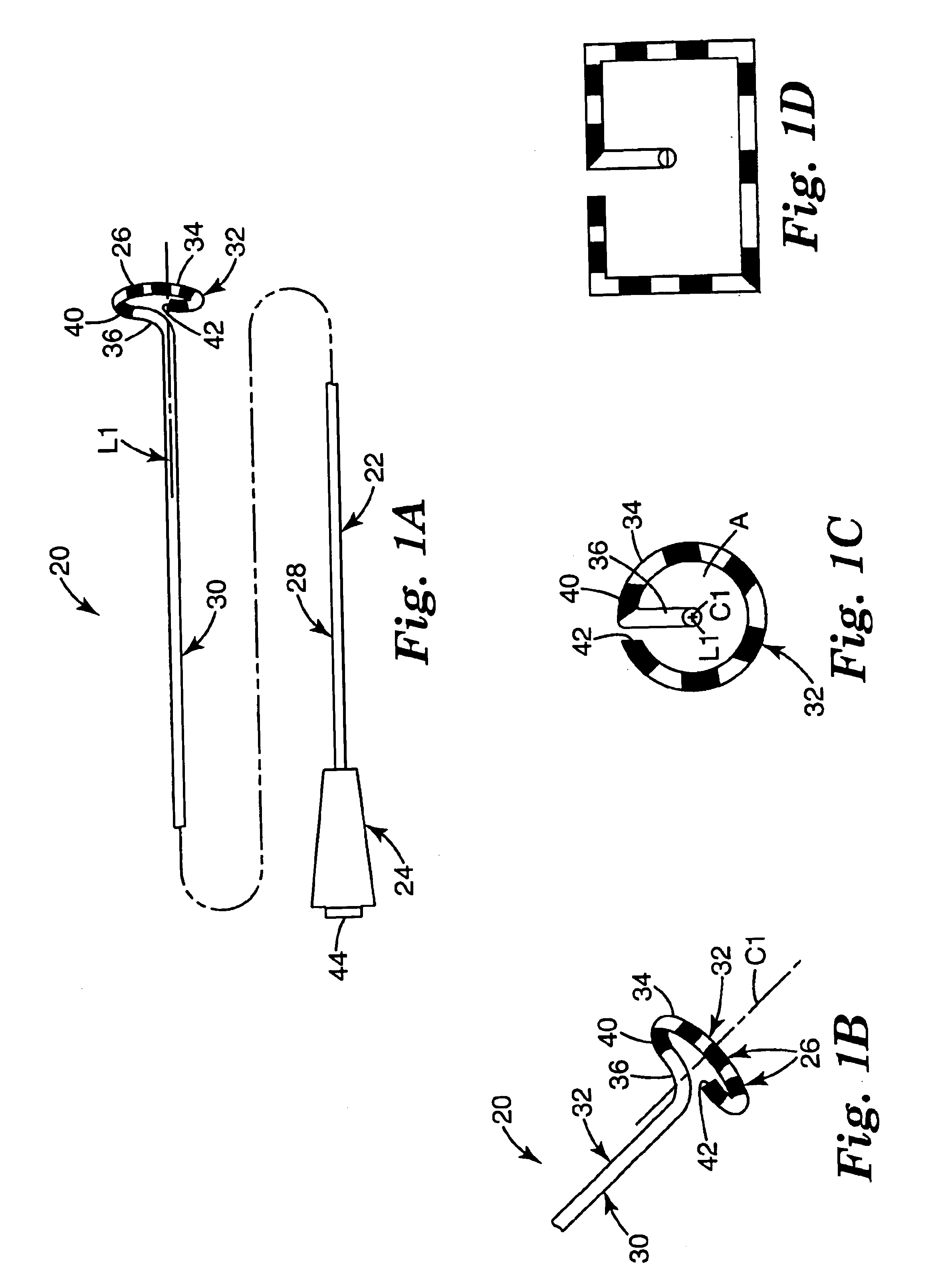
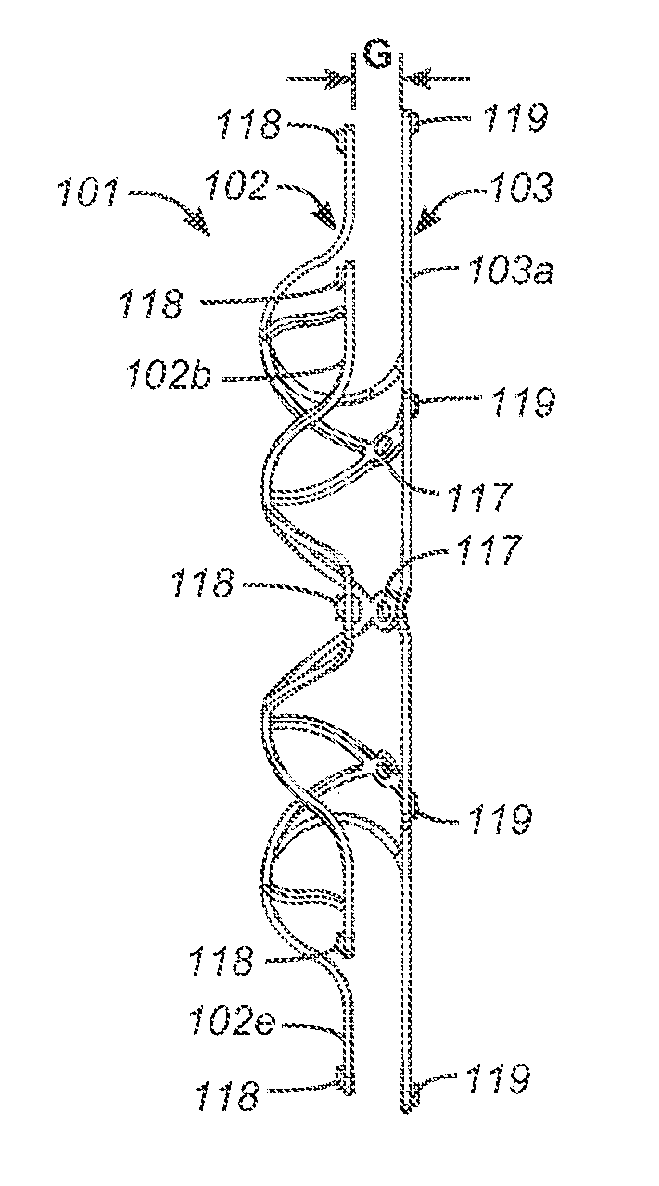
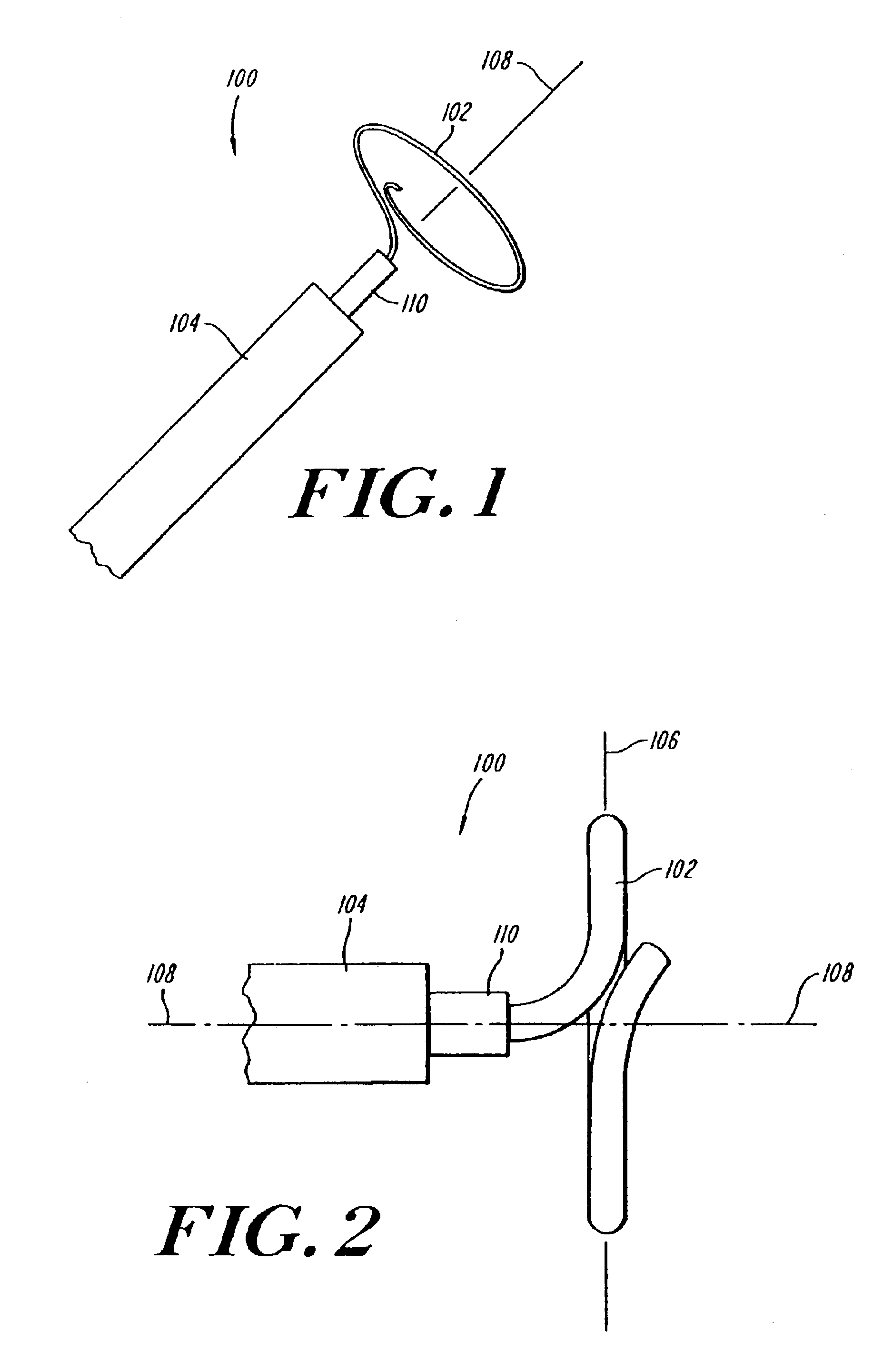
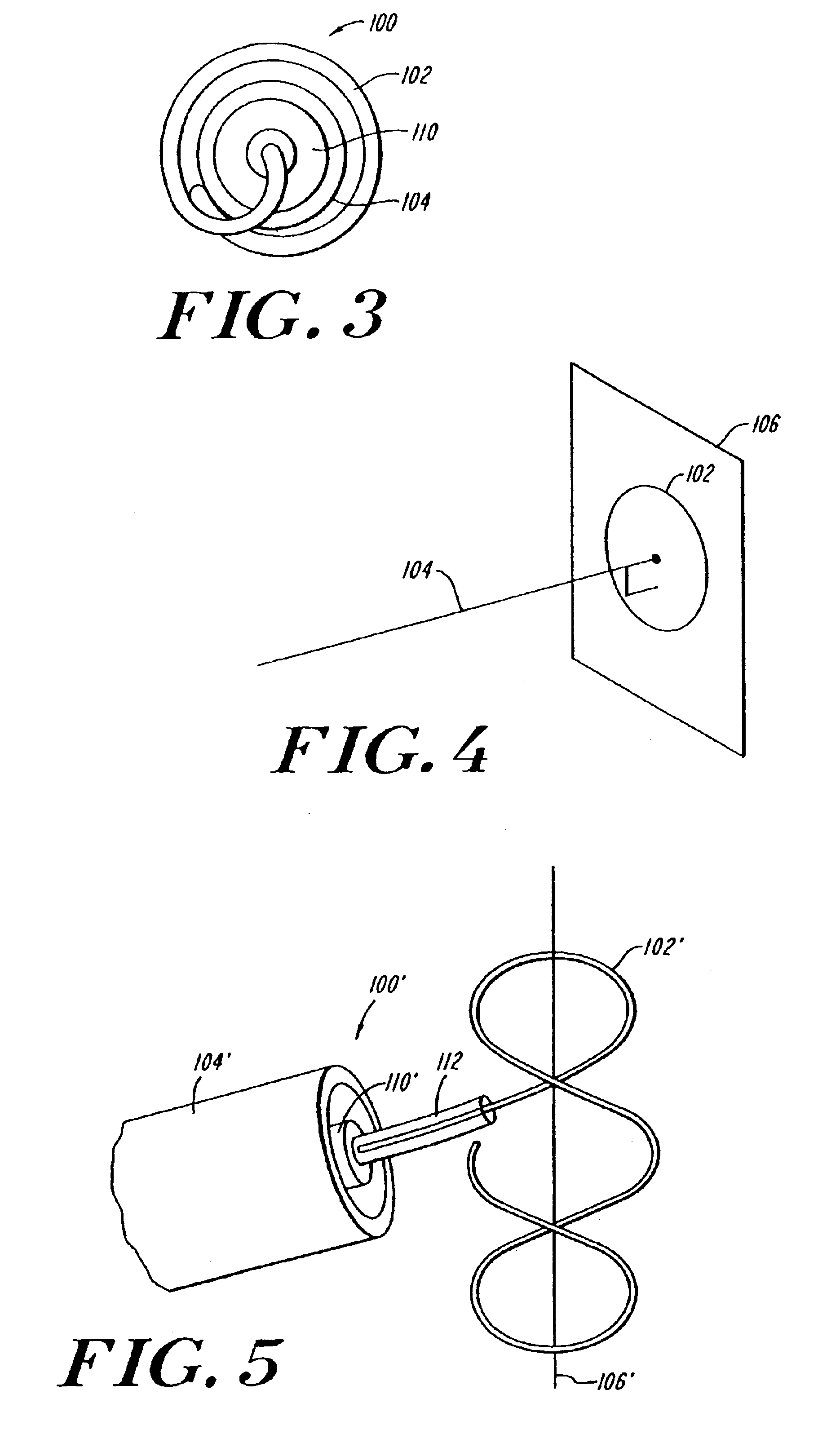
Coiled ablation catheter system
InactiveUS6960206B2Facilitate formation of lesionPromote formationStentsSurgical instruments for heatingVeinCardiac Ablation
A cardiac ablation catheter includes a coil-like ablating element that is deployable from an elongate, flexible sheath. The ablating element, while in the deployed position, has a shape with at least one revolution oriented in a plane that is orthogonal to a longitudinal axis of the sheath. The catheter system is well-suited to ablate a circumferential region of tissue about a pulmonary vein or the posterior wall of the left atrium proximate the pulmonary vein os. The treated tissue region electrically isolates the atria from the pulmonary vein.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com