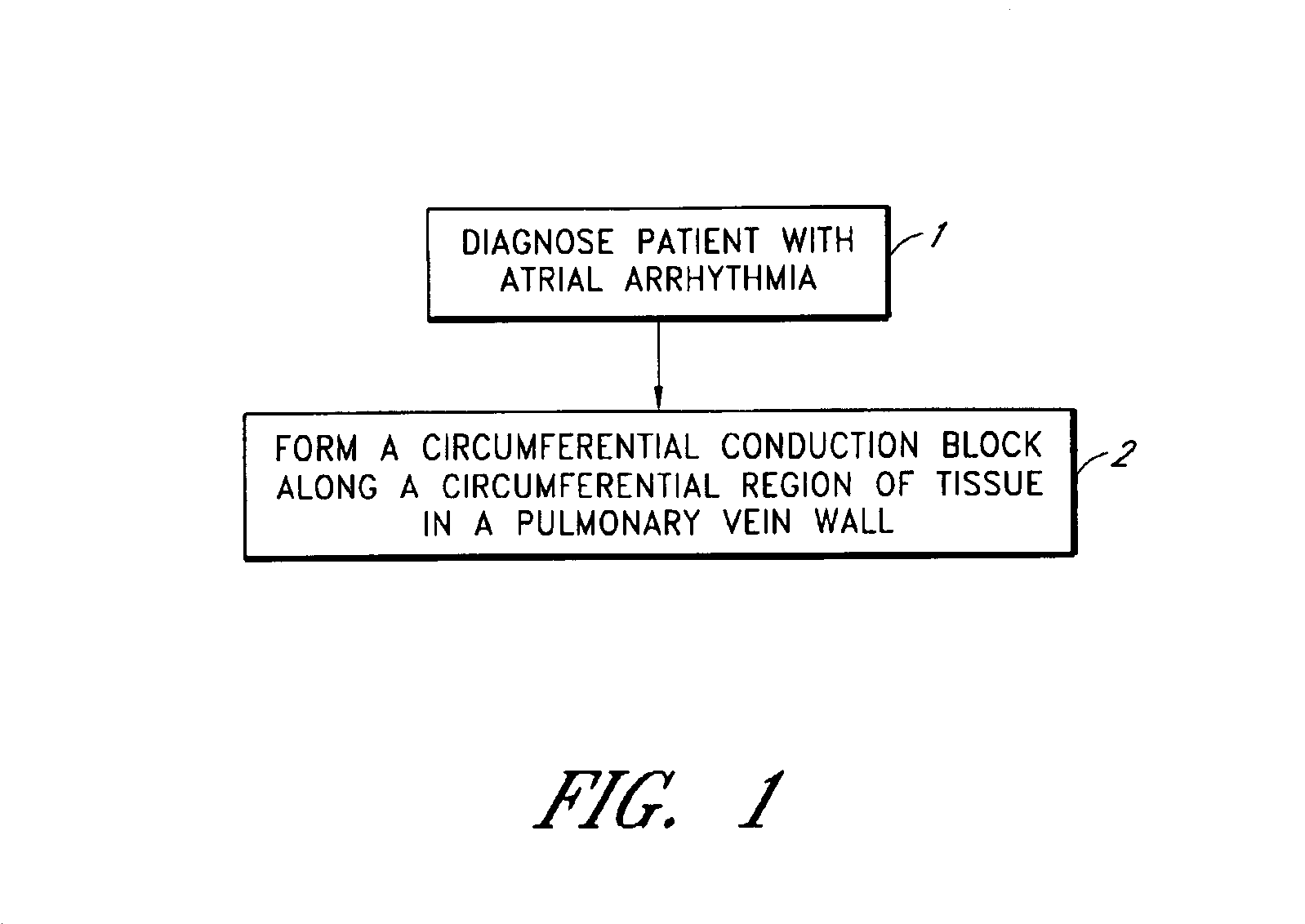
Patents
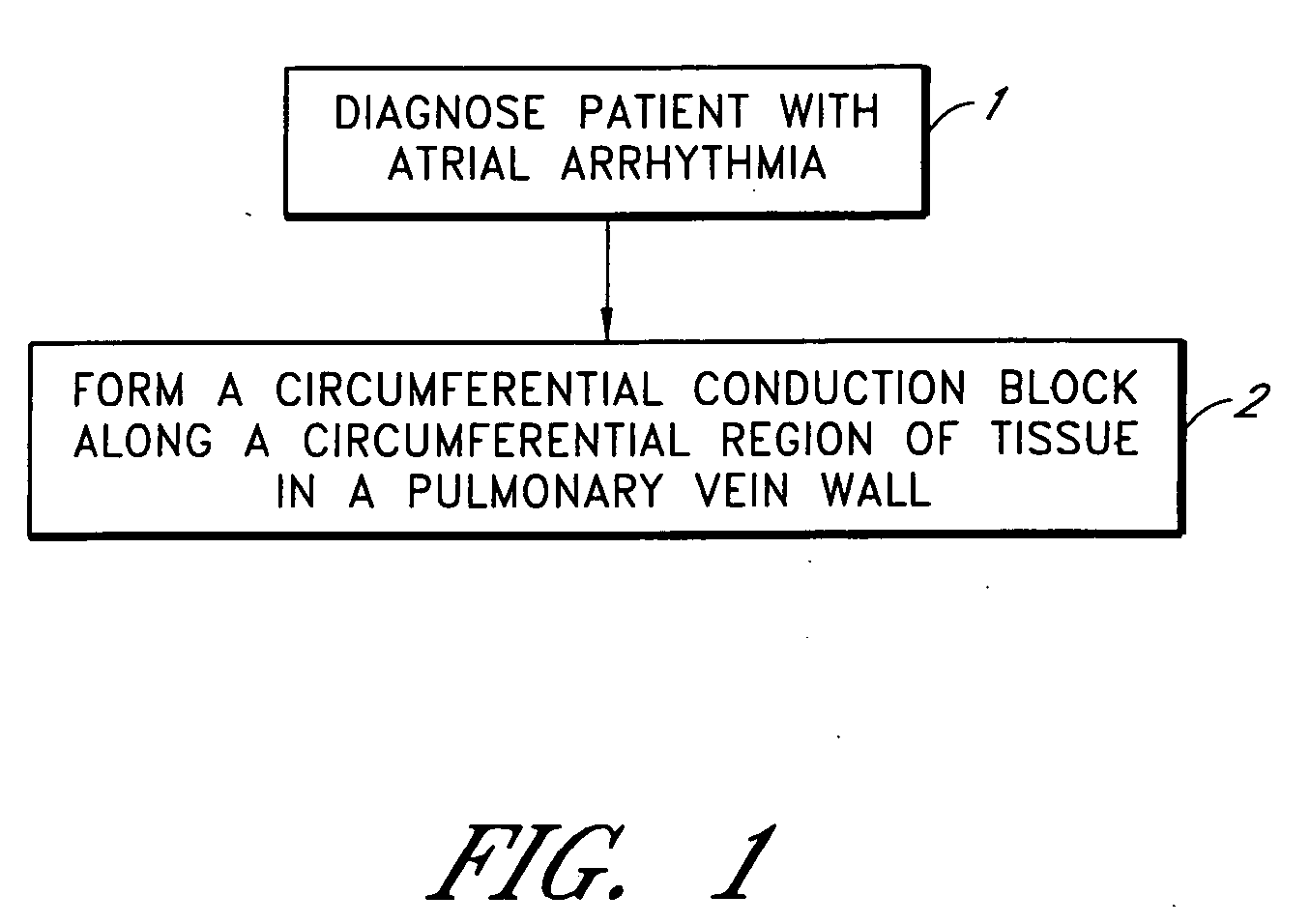
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
290 results about "Ostium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
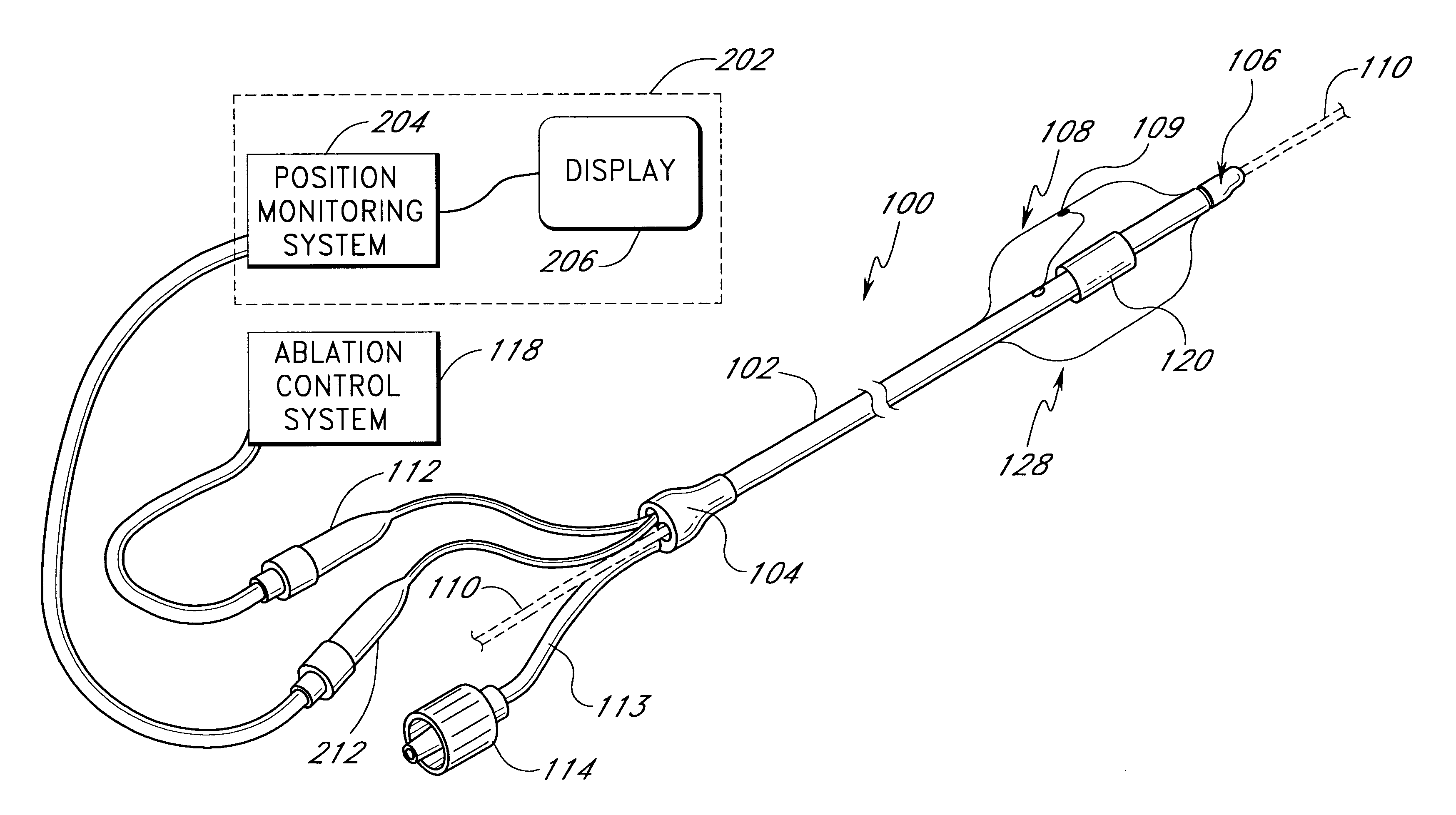
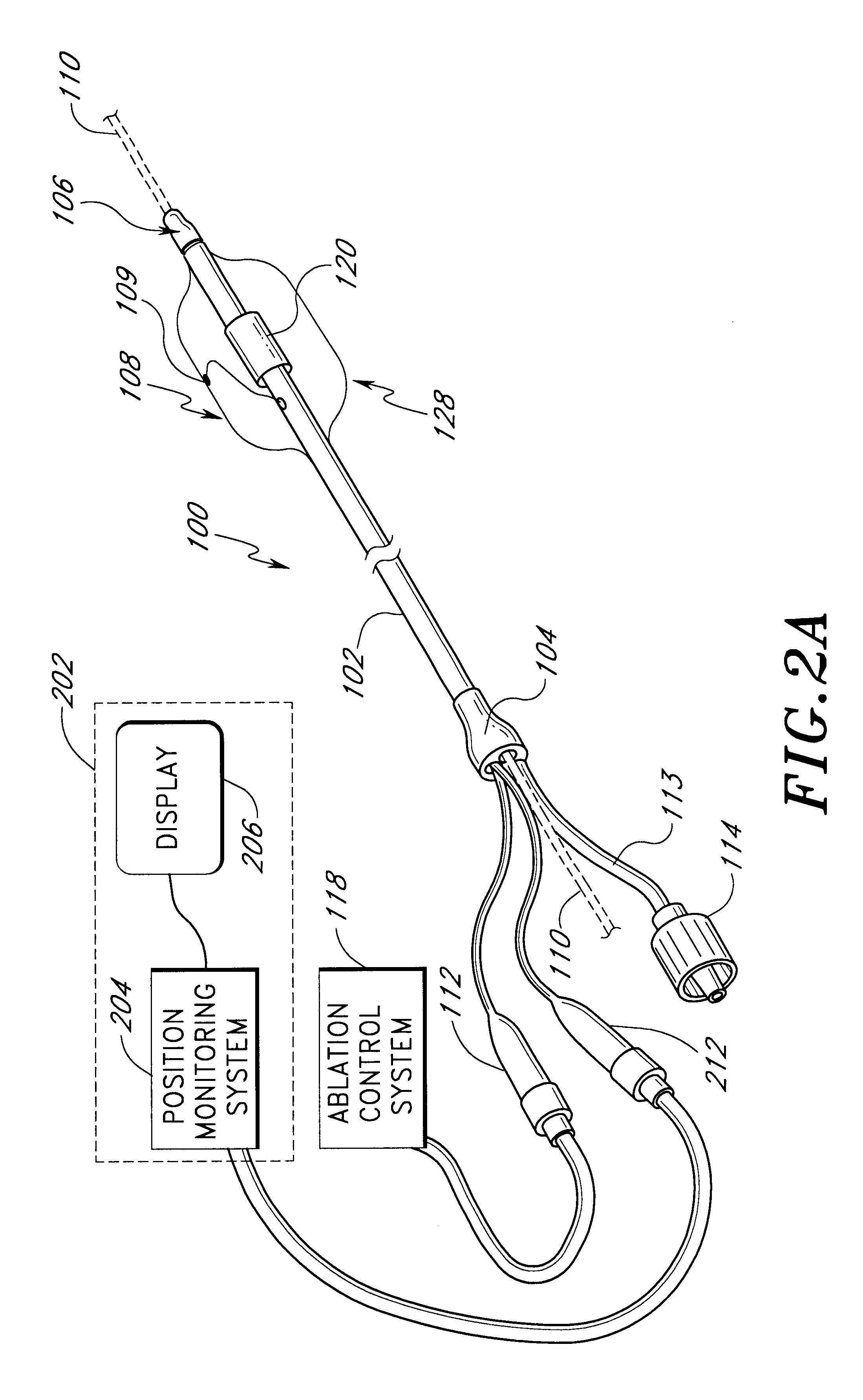
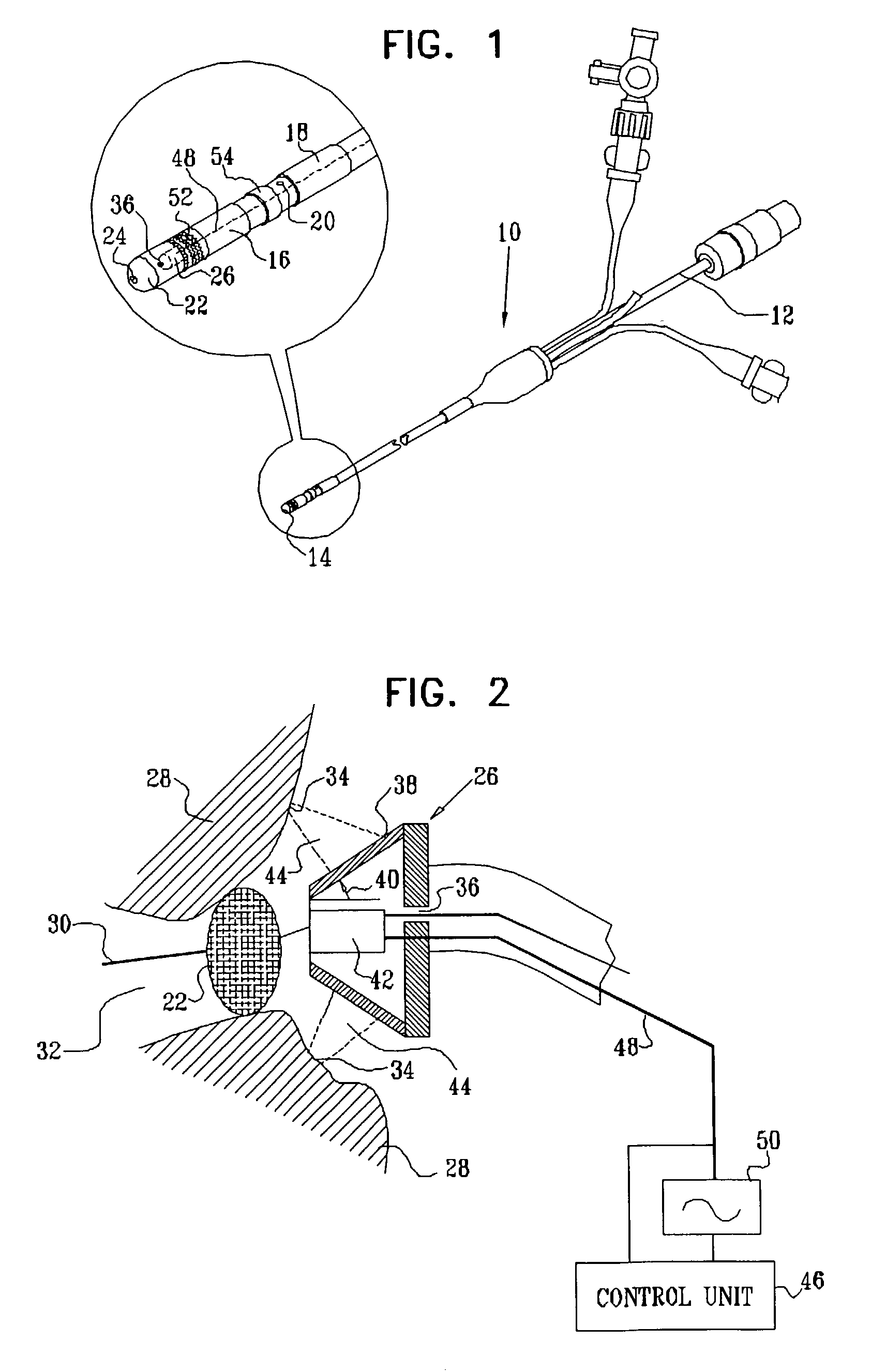
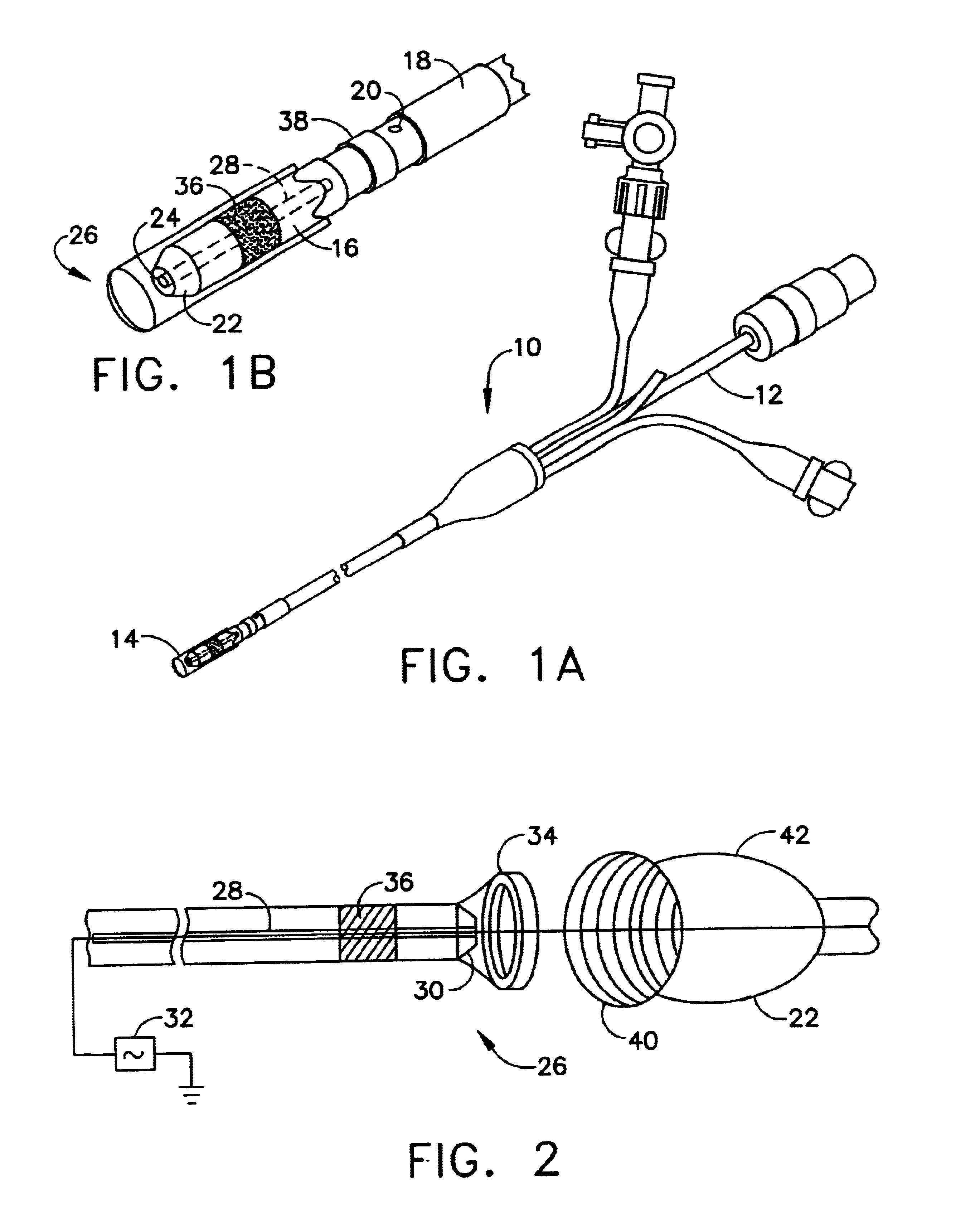
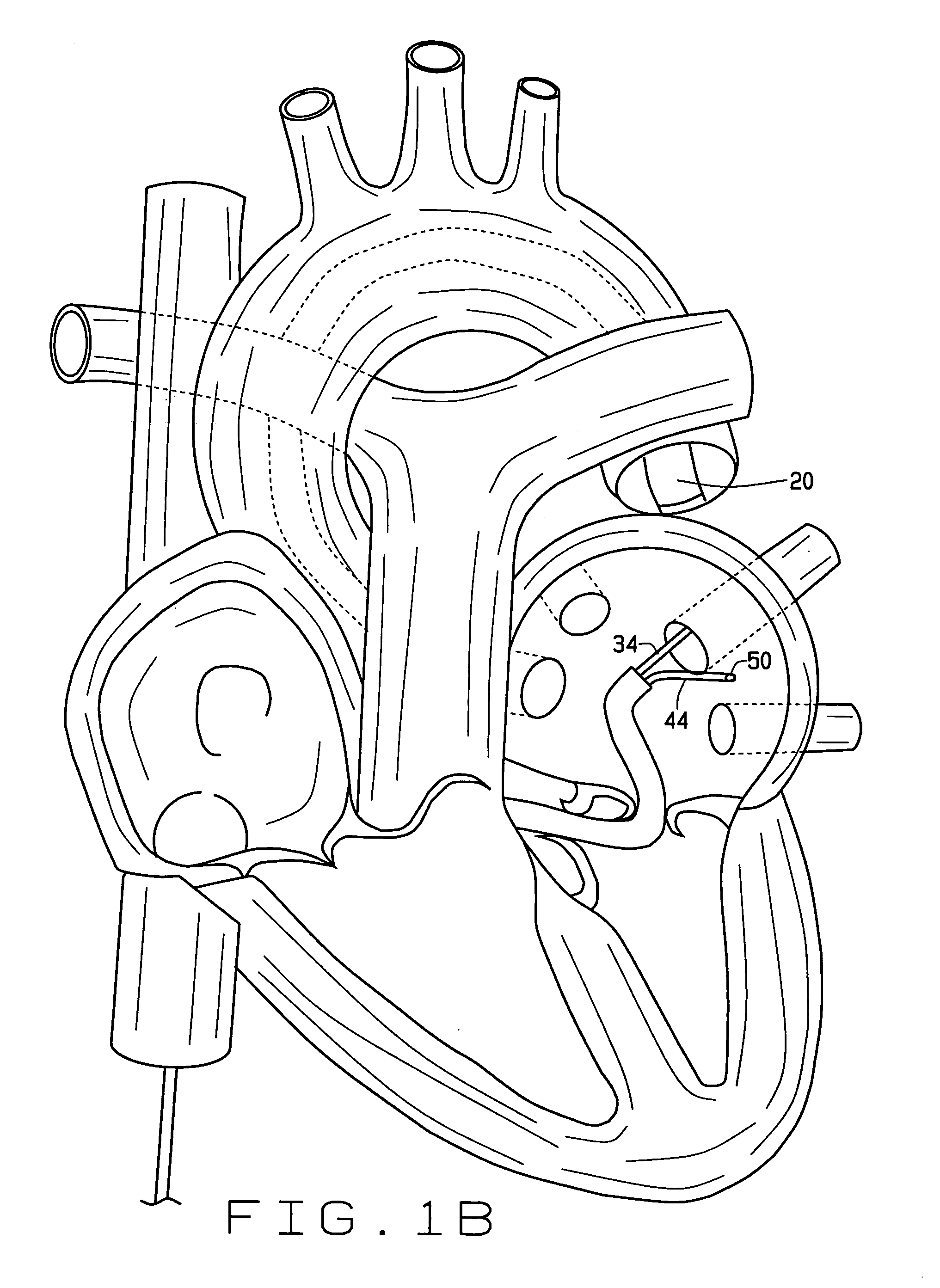
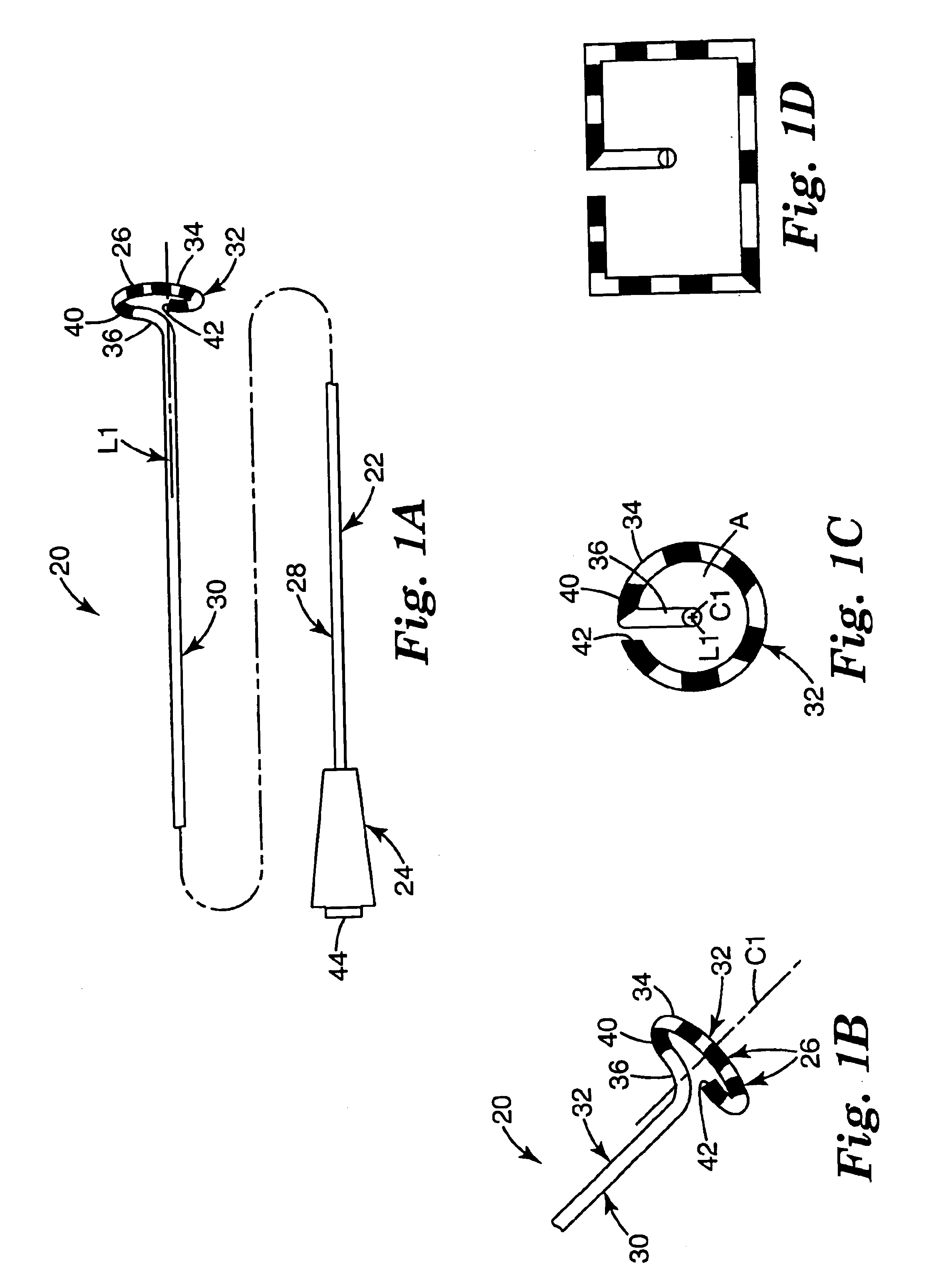
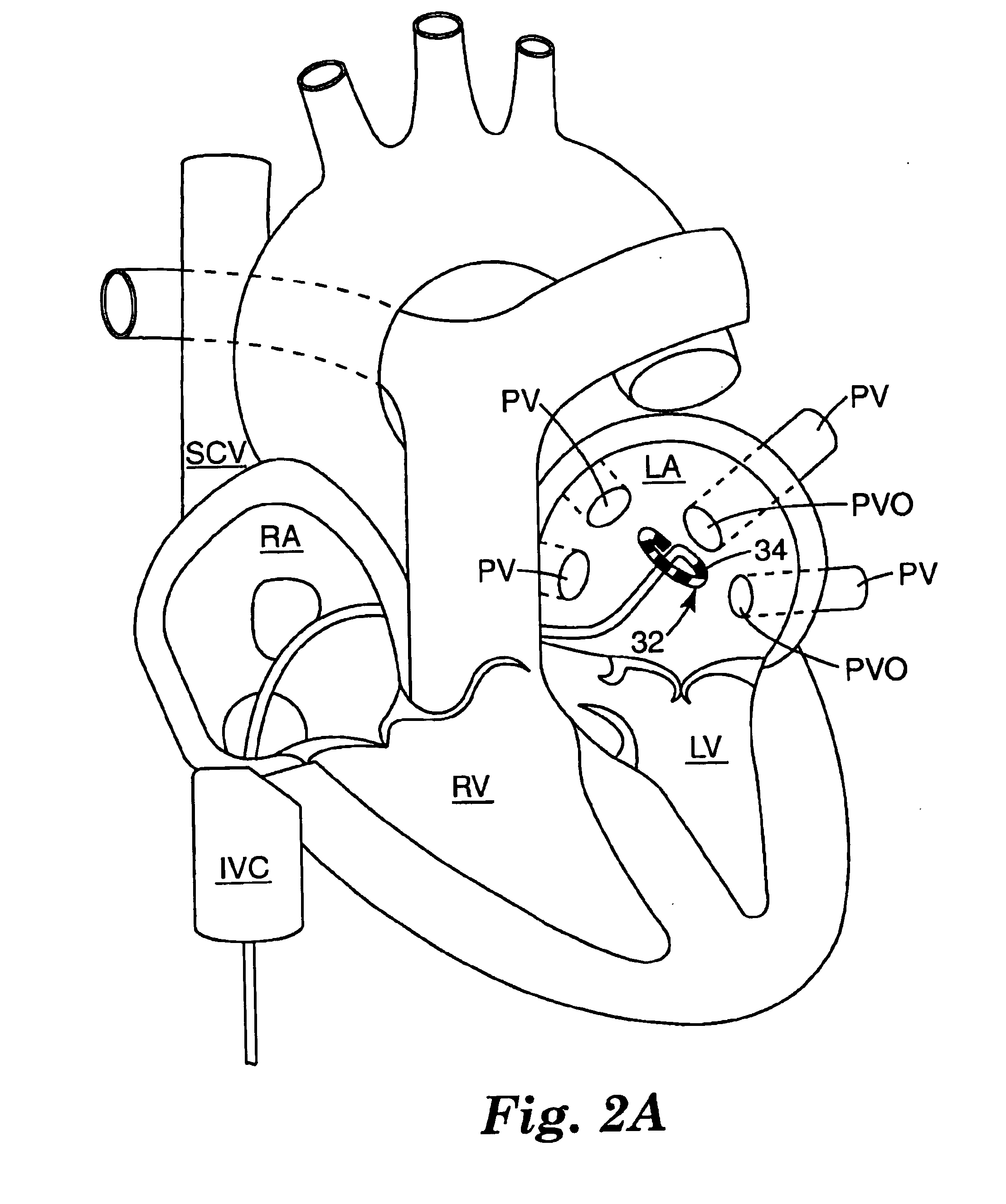
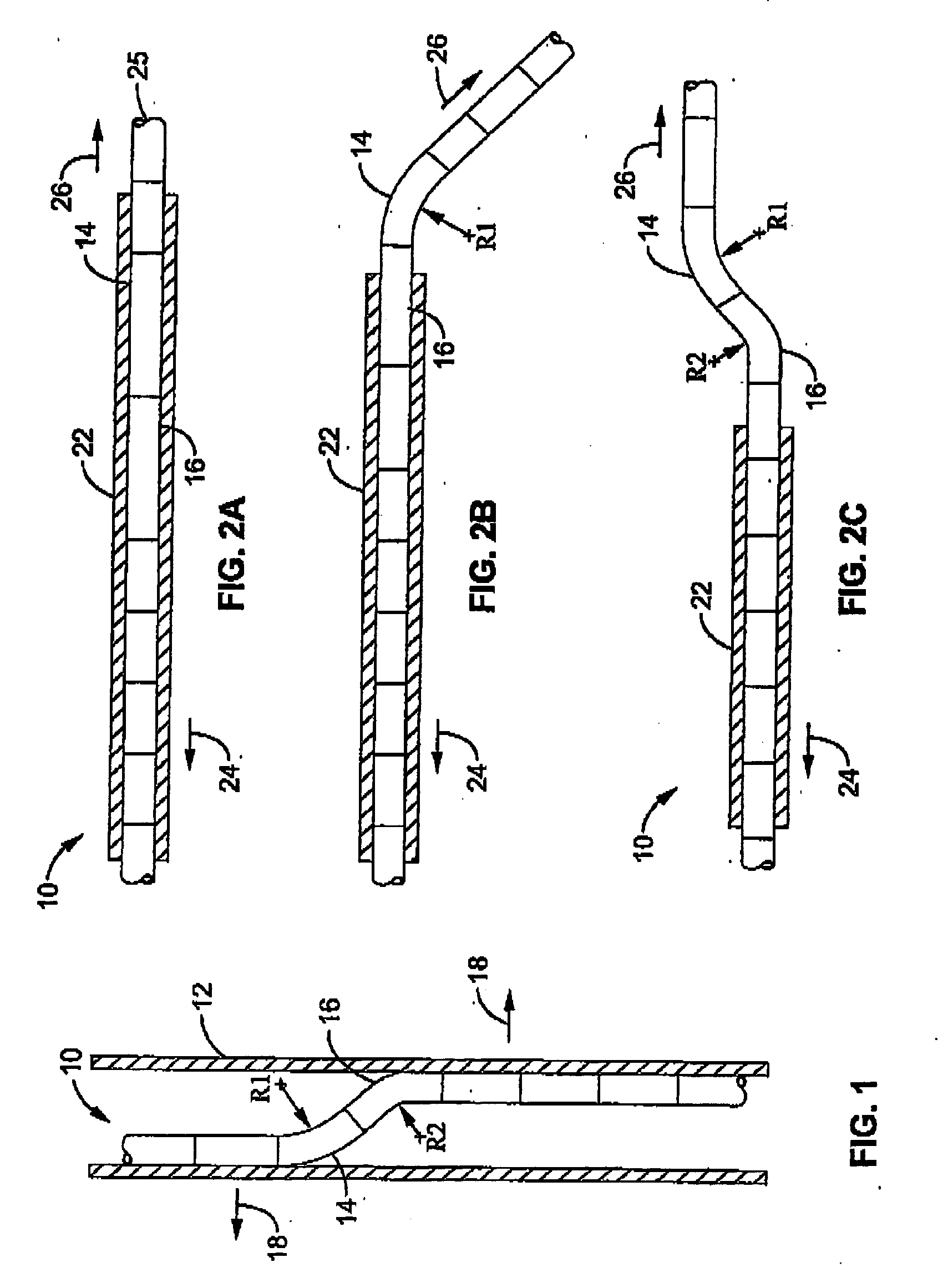
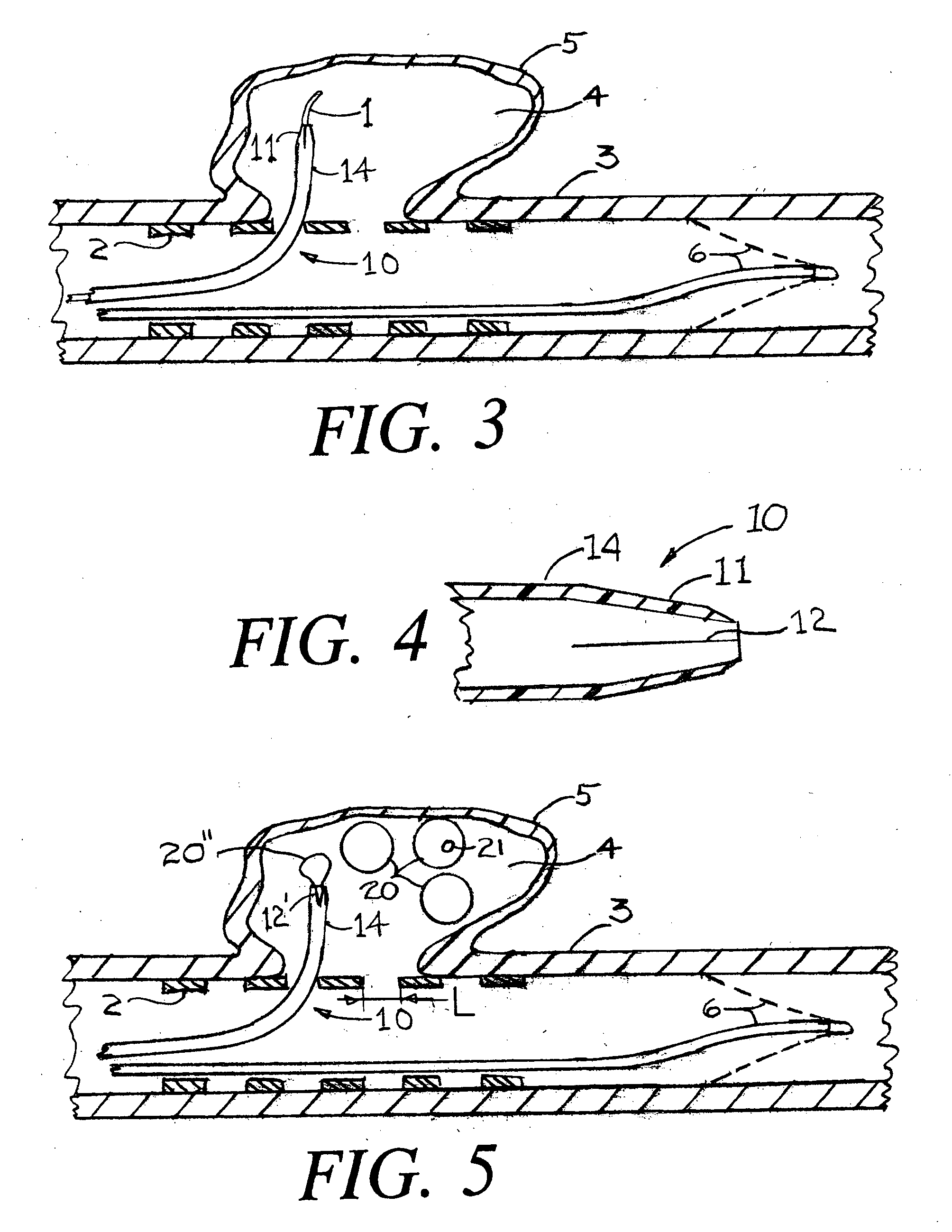
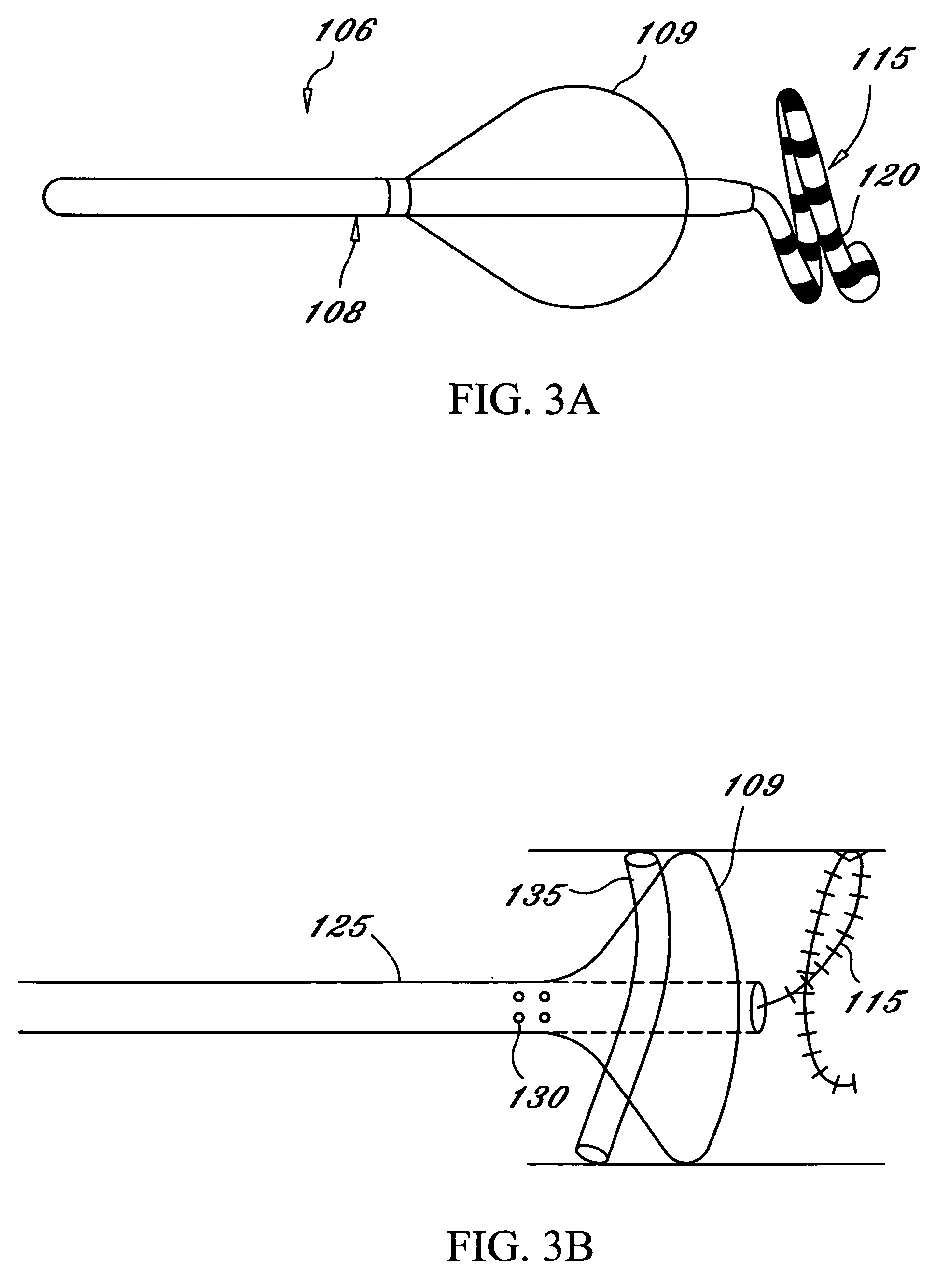
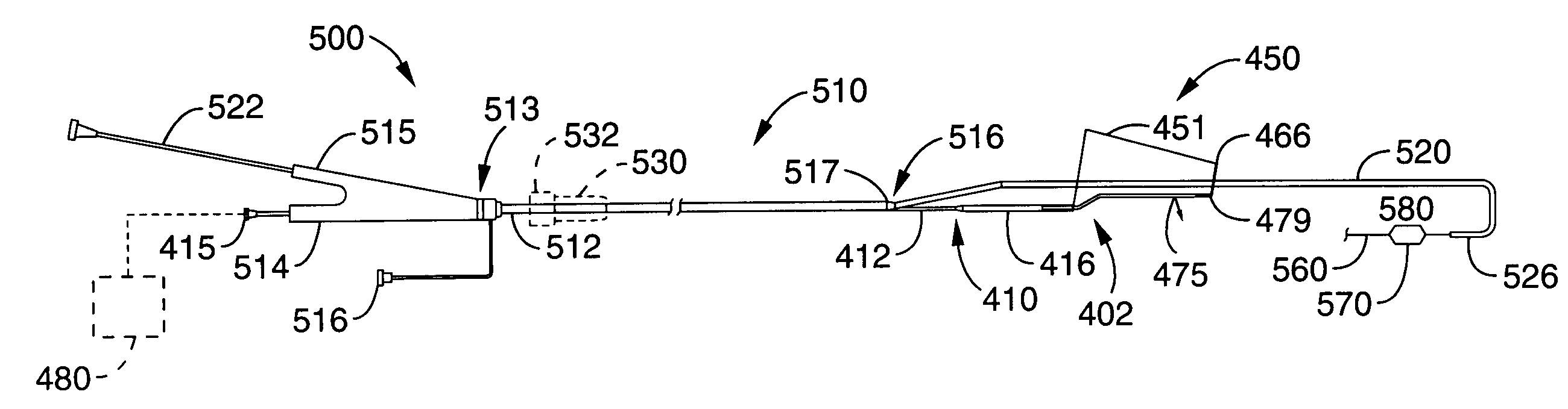
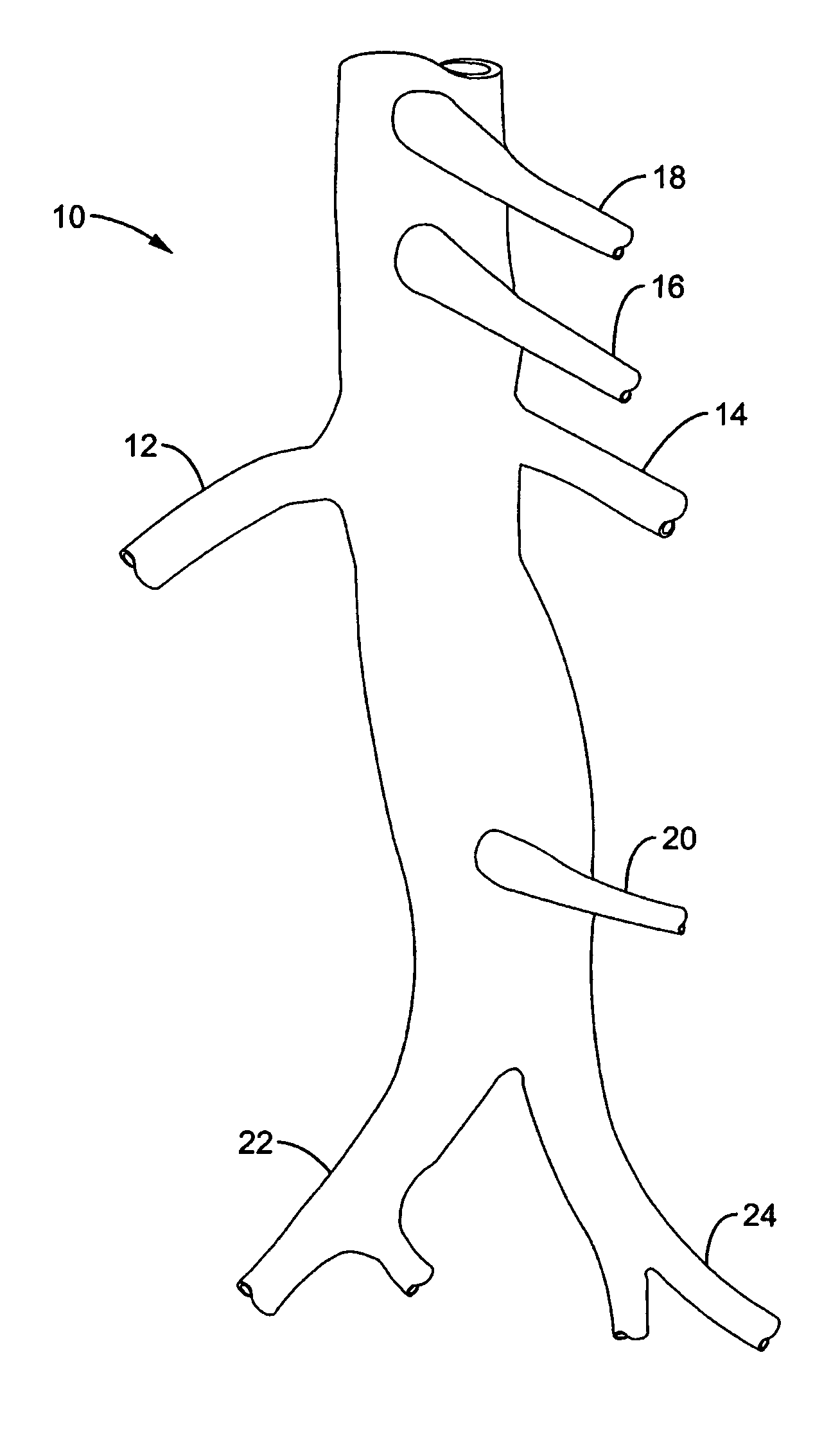
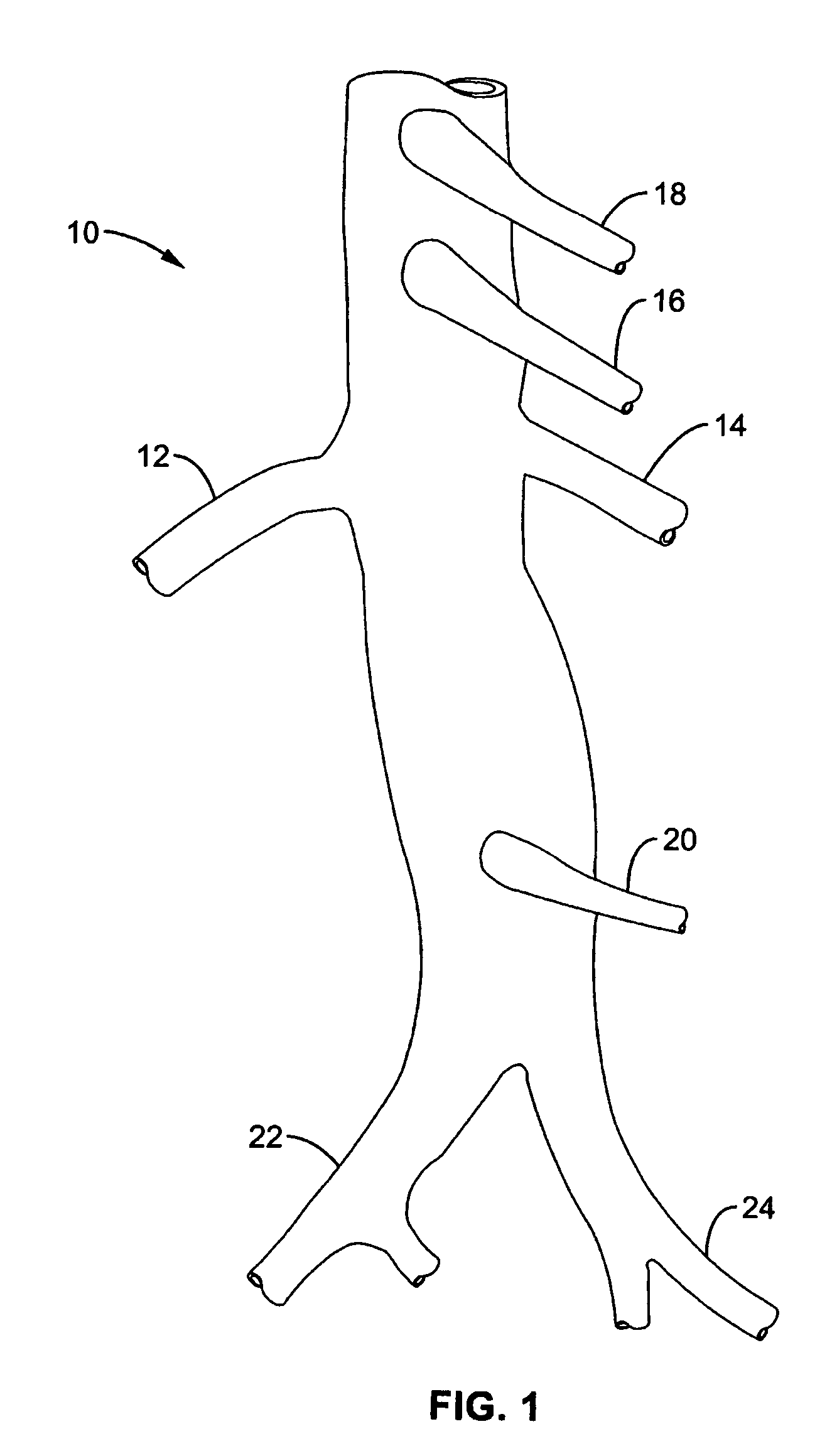
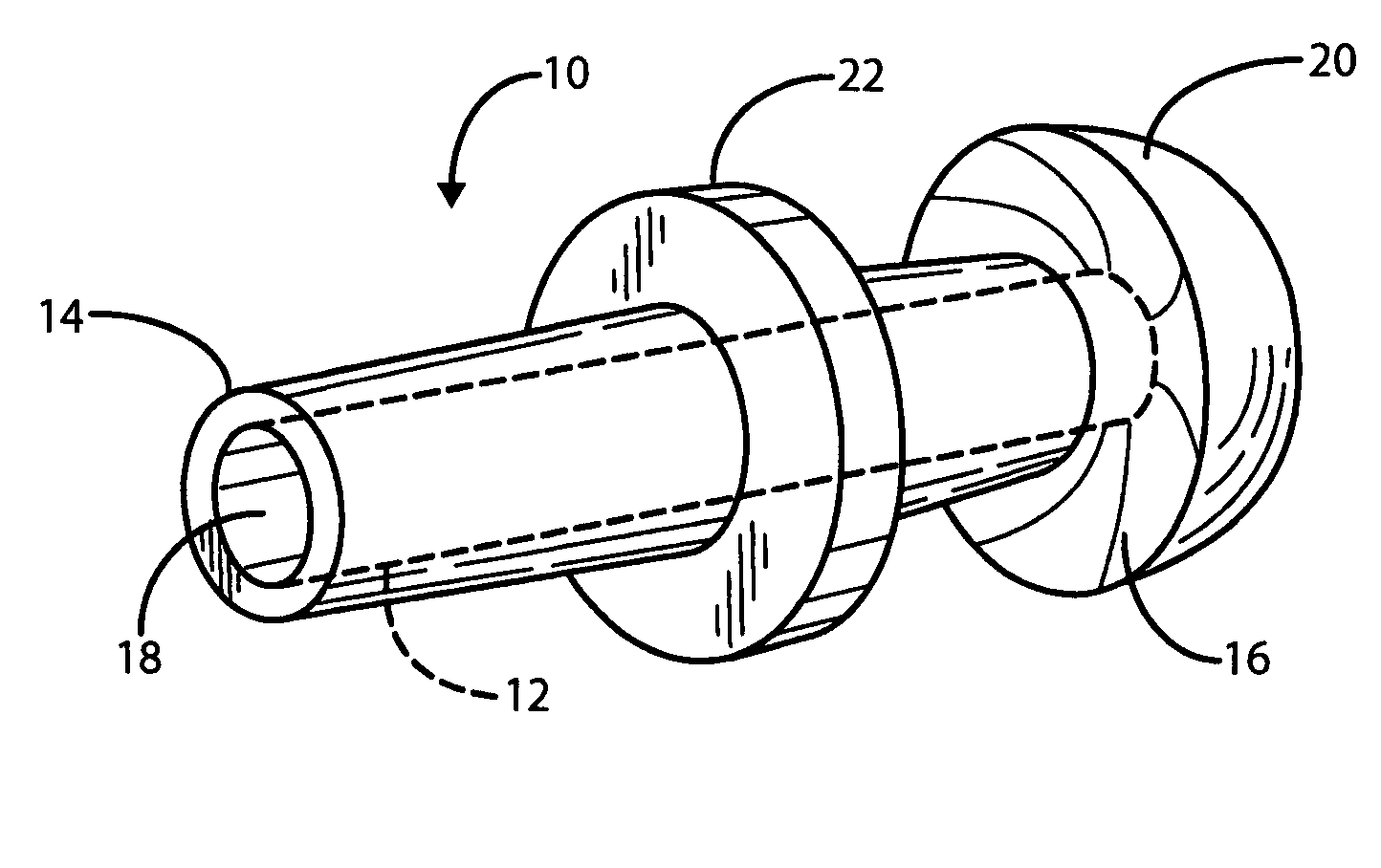
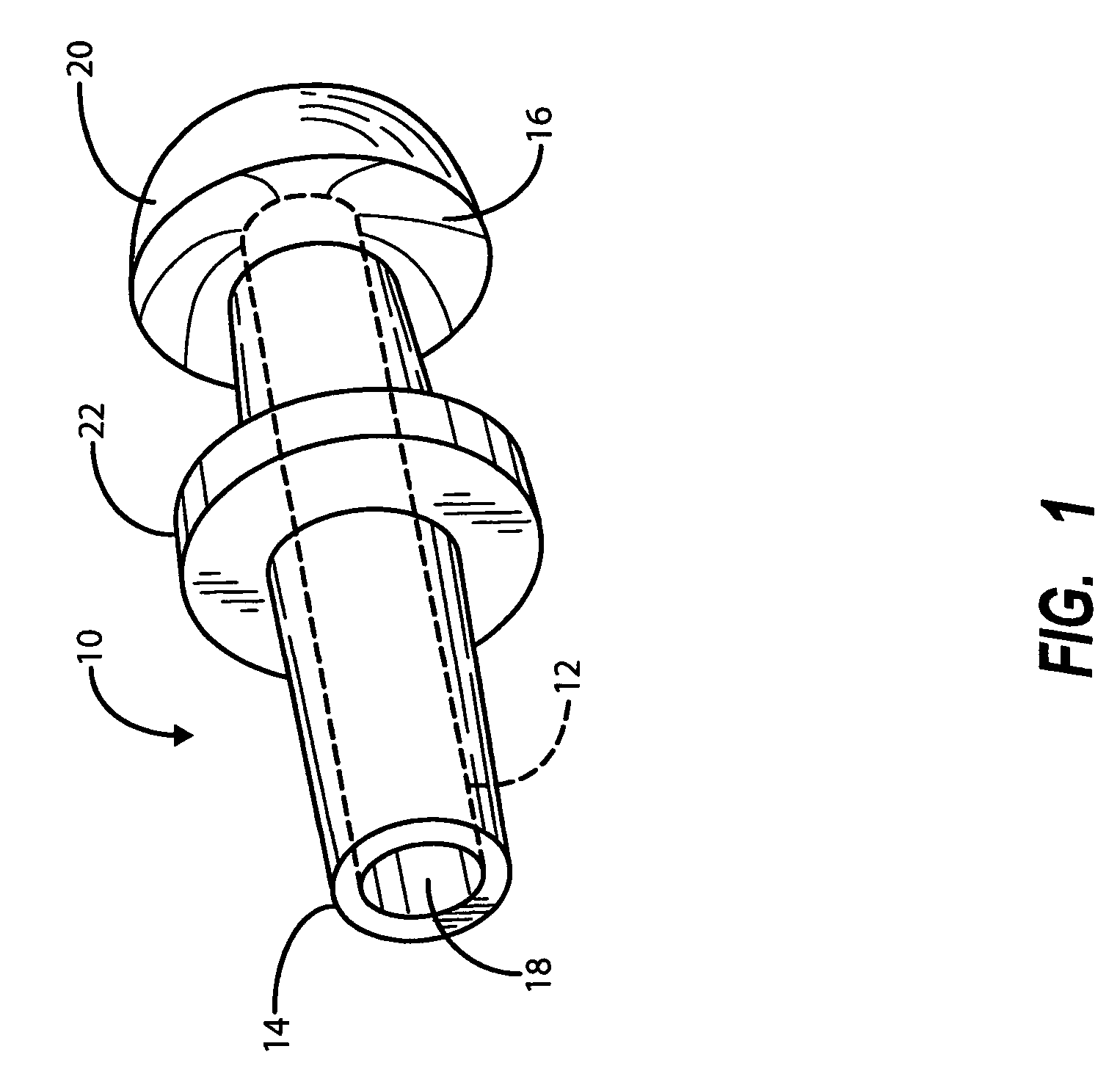
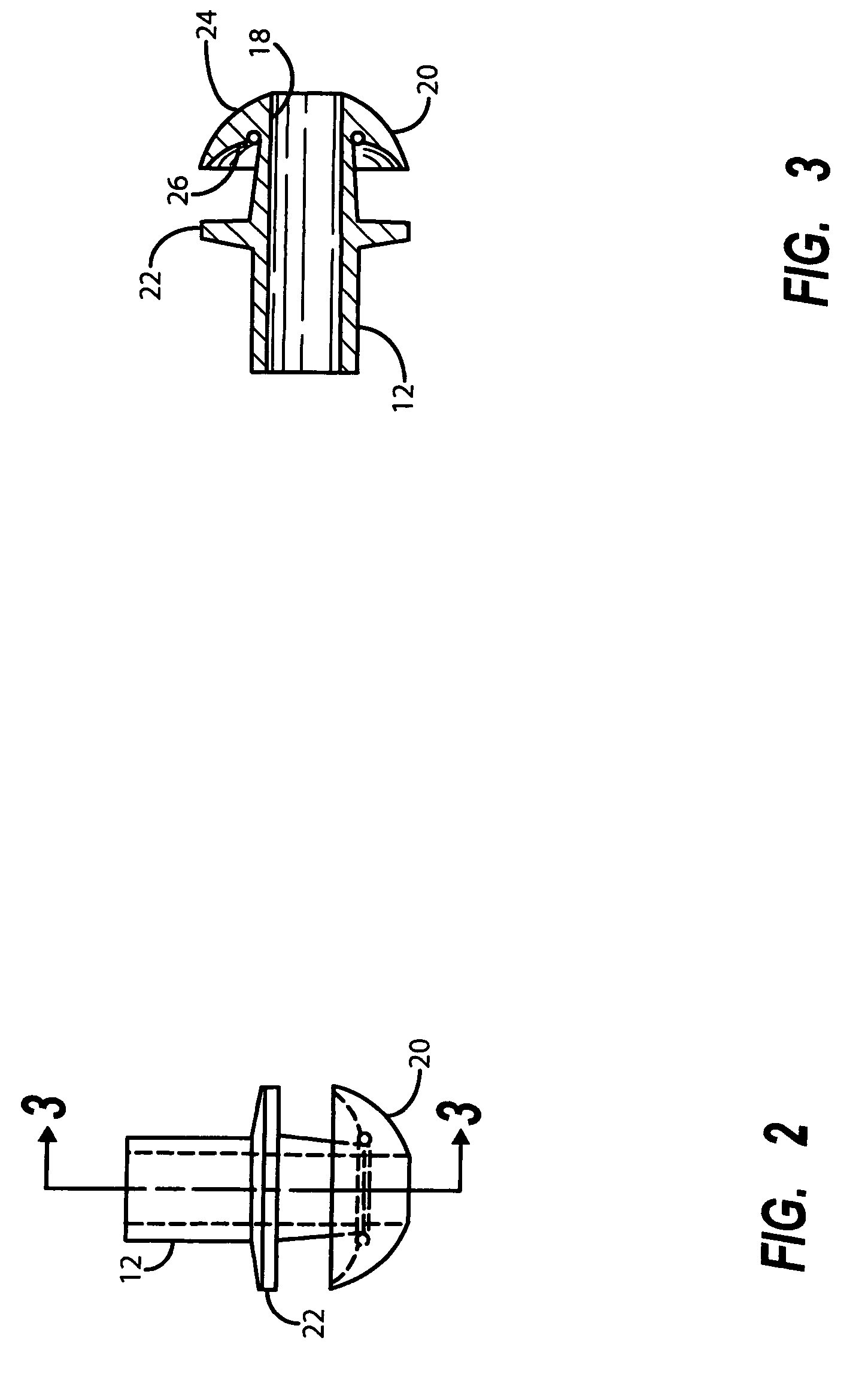
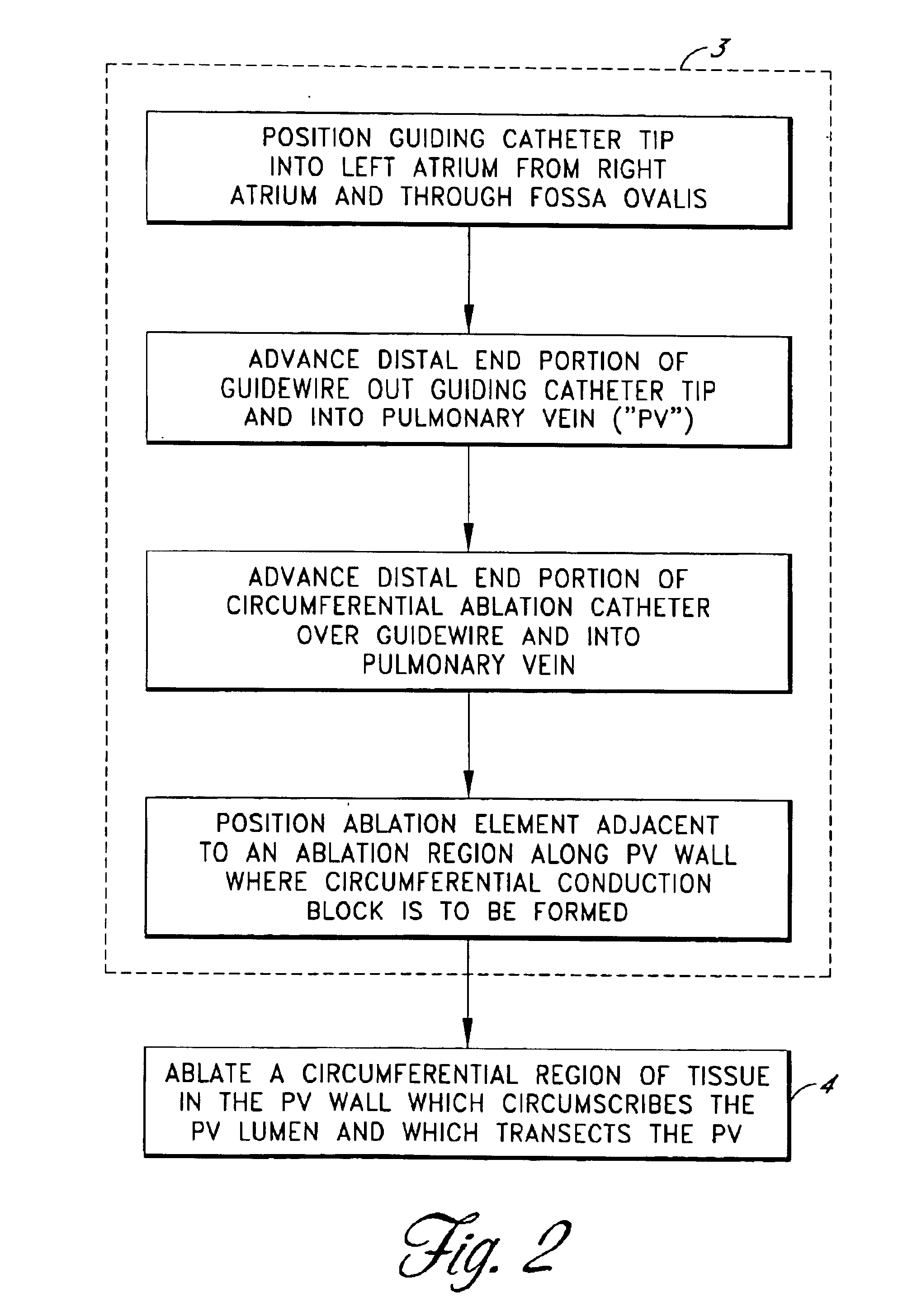
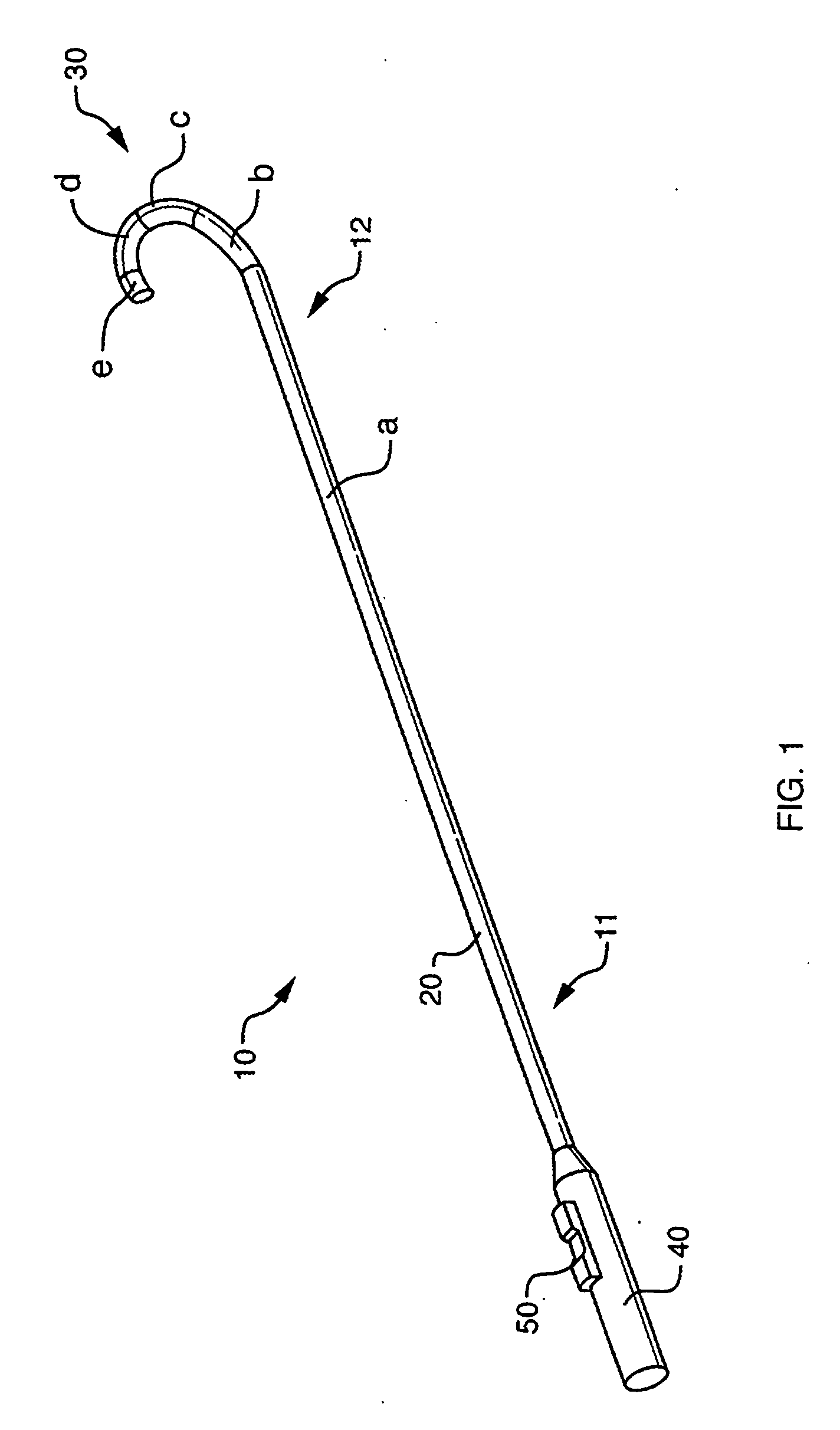
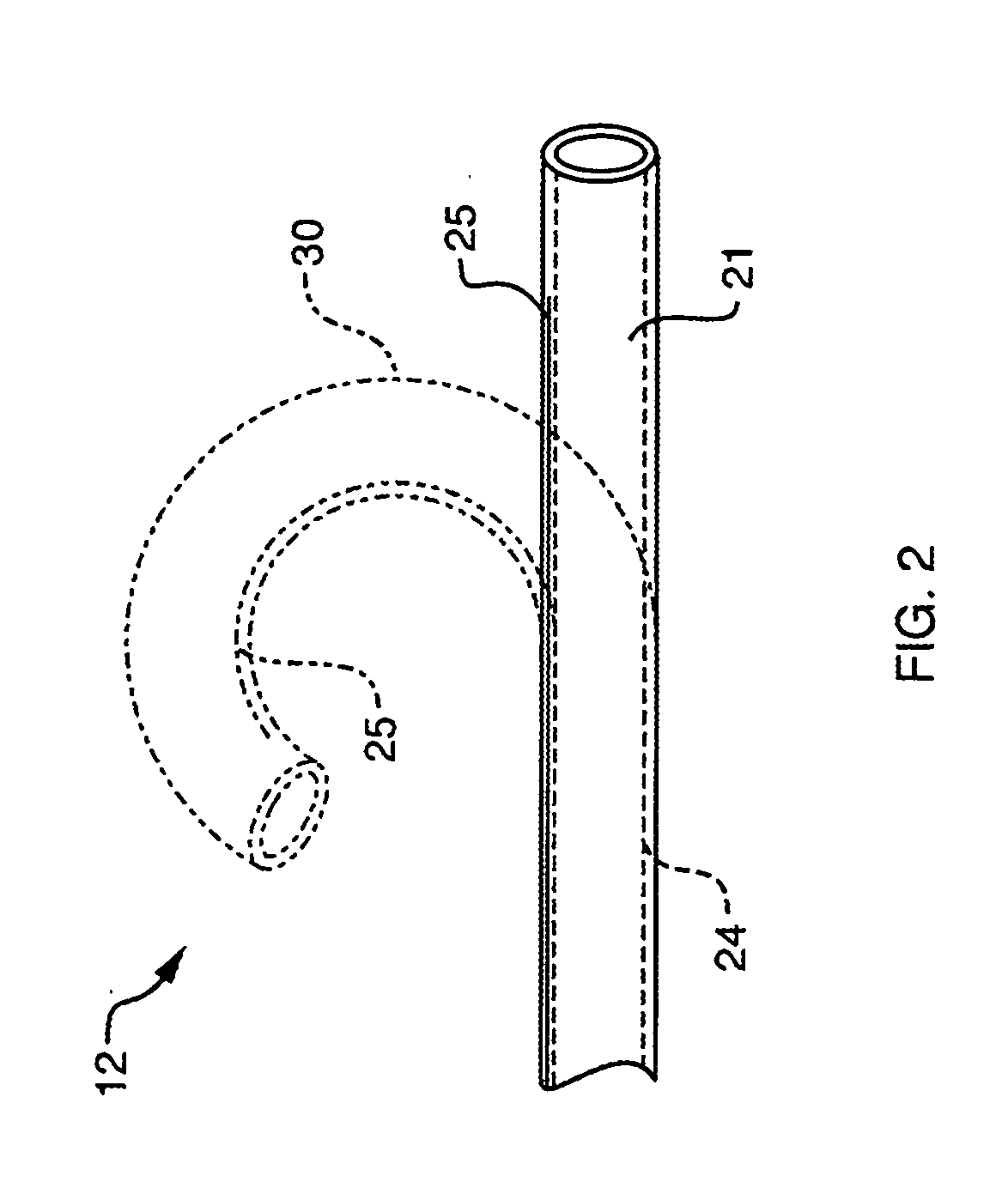
Positioning system and method for orienting an ablation element within a pulmonary vein ostium
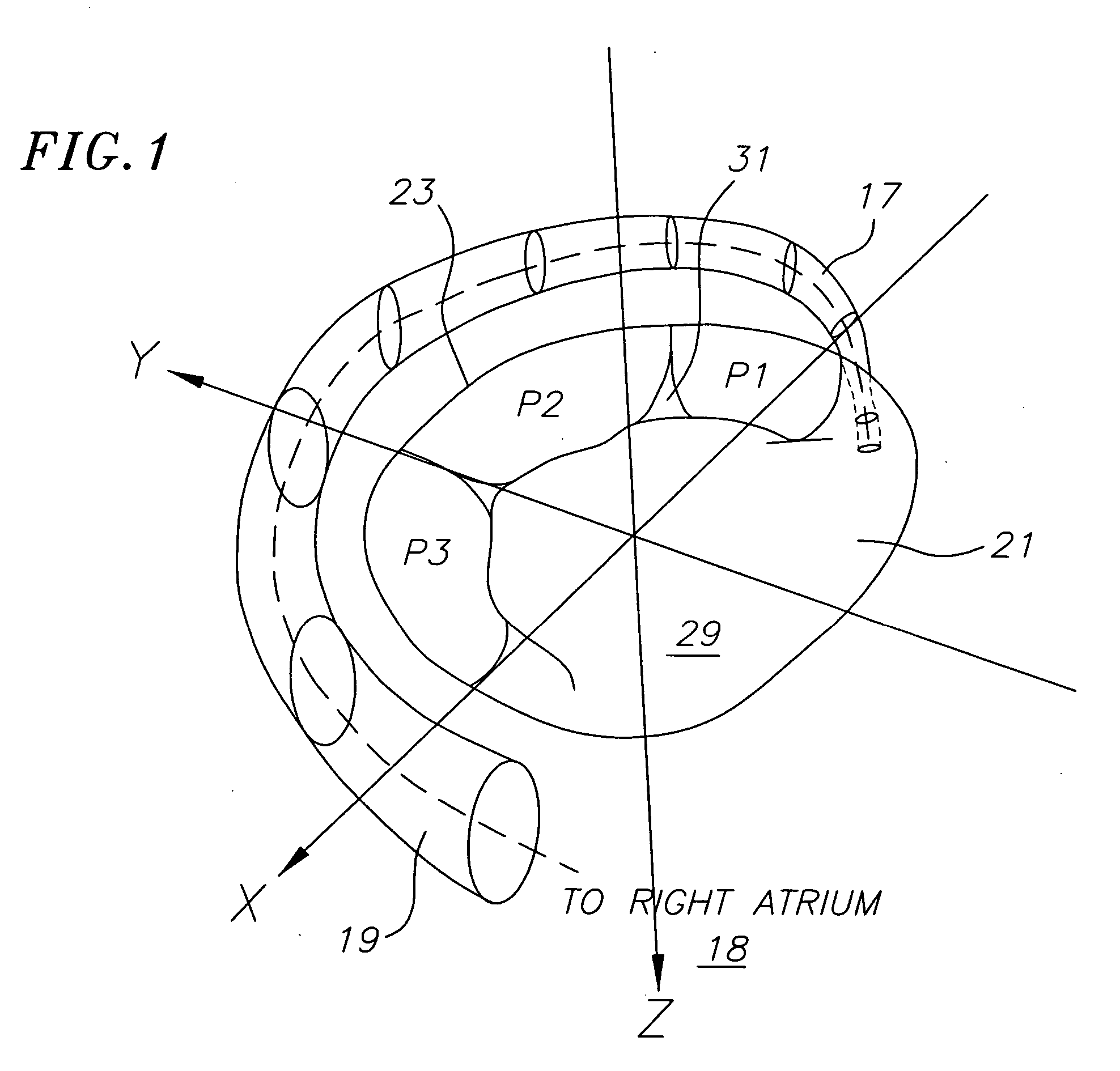
InactiveUS6514249B1Eliminates arrhythmogenic conductionPrevent atrial arrhythmiaUltrasound therapyElectrotherapySurgical operationVein
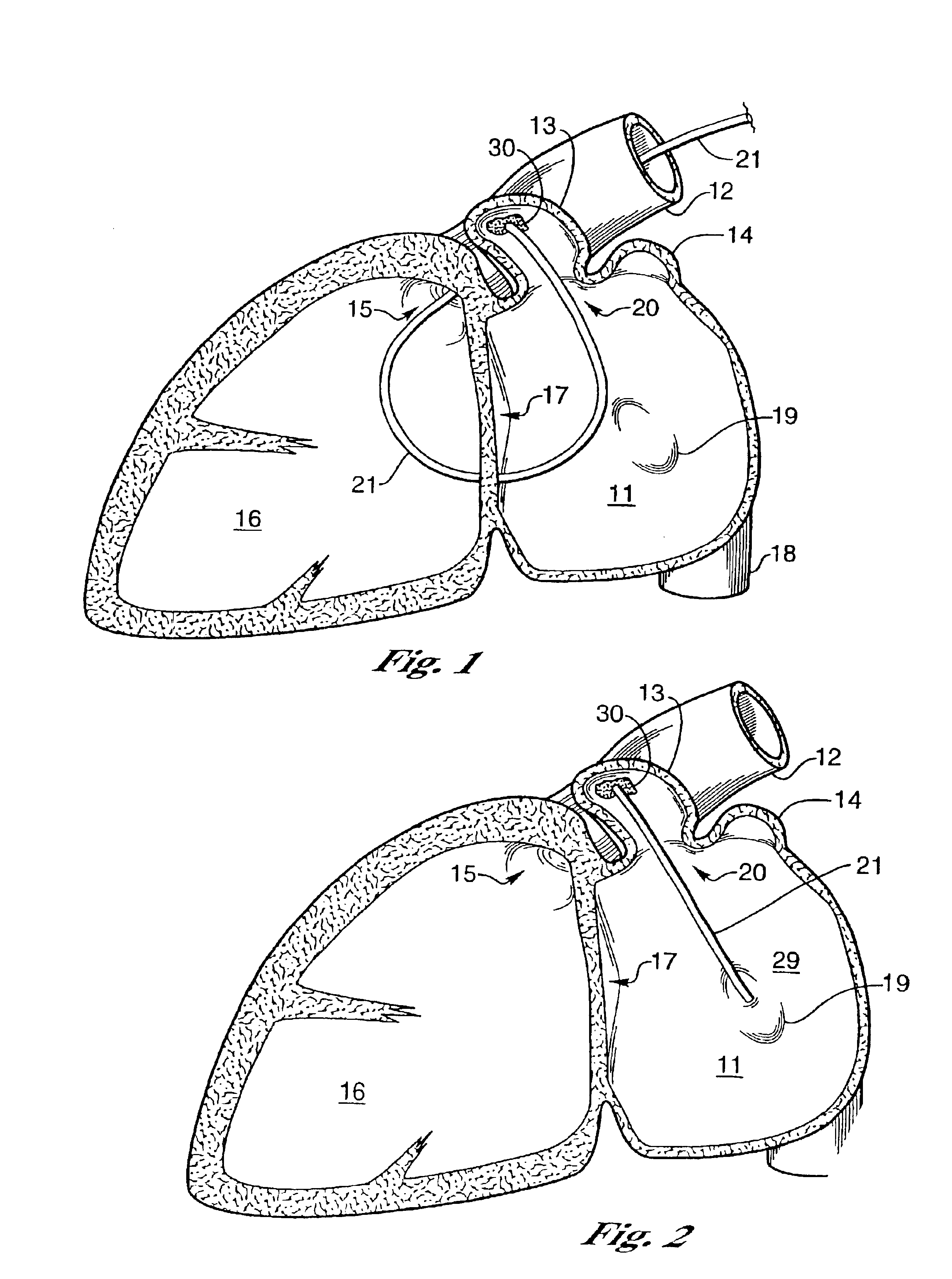
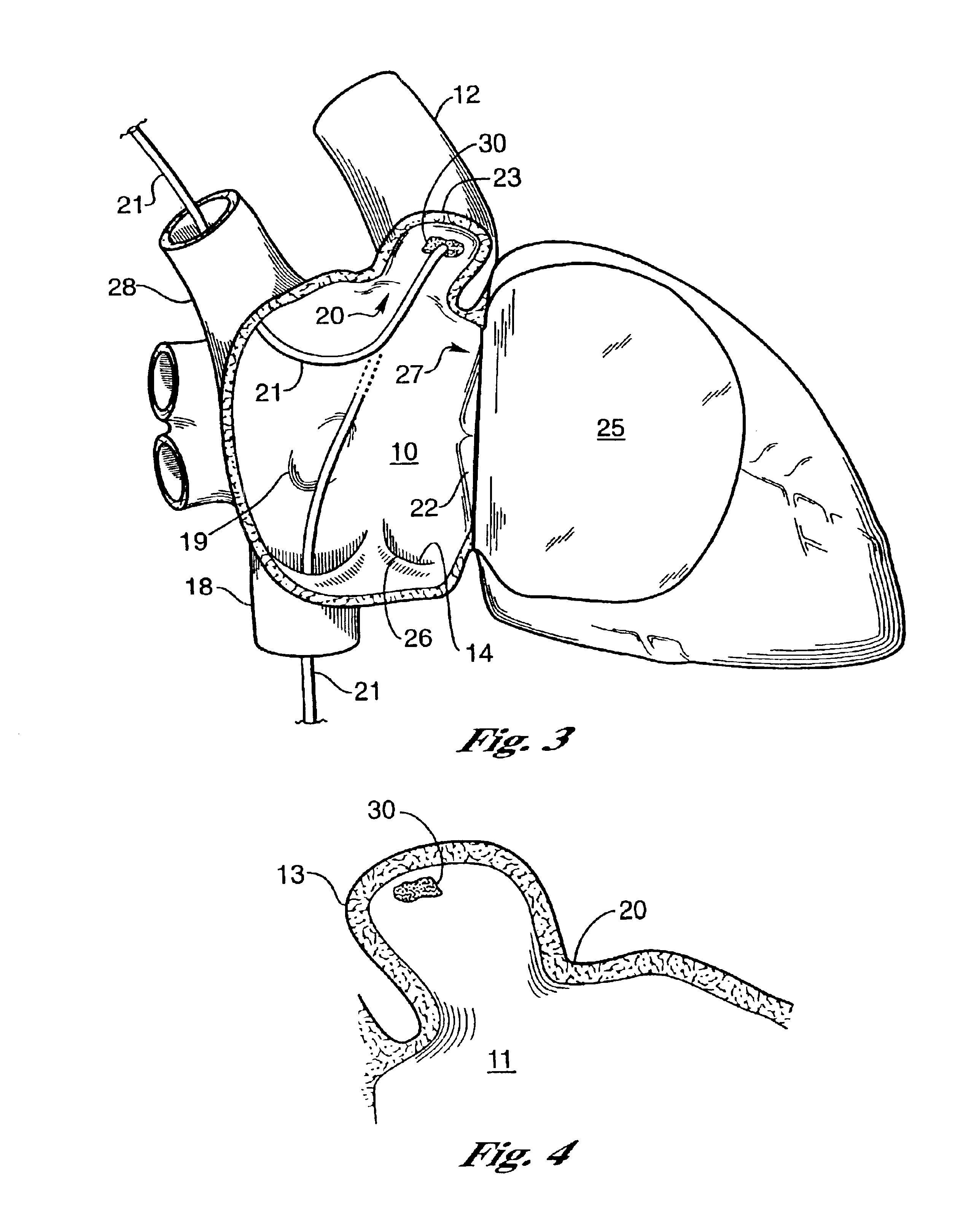
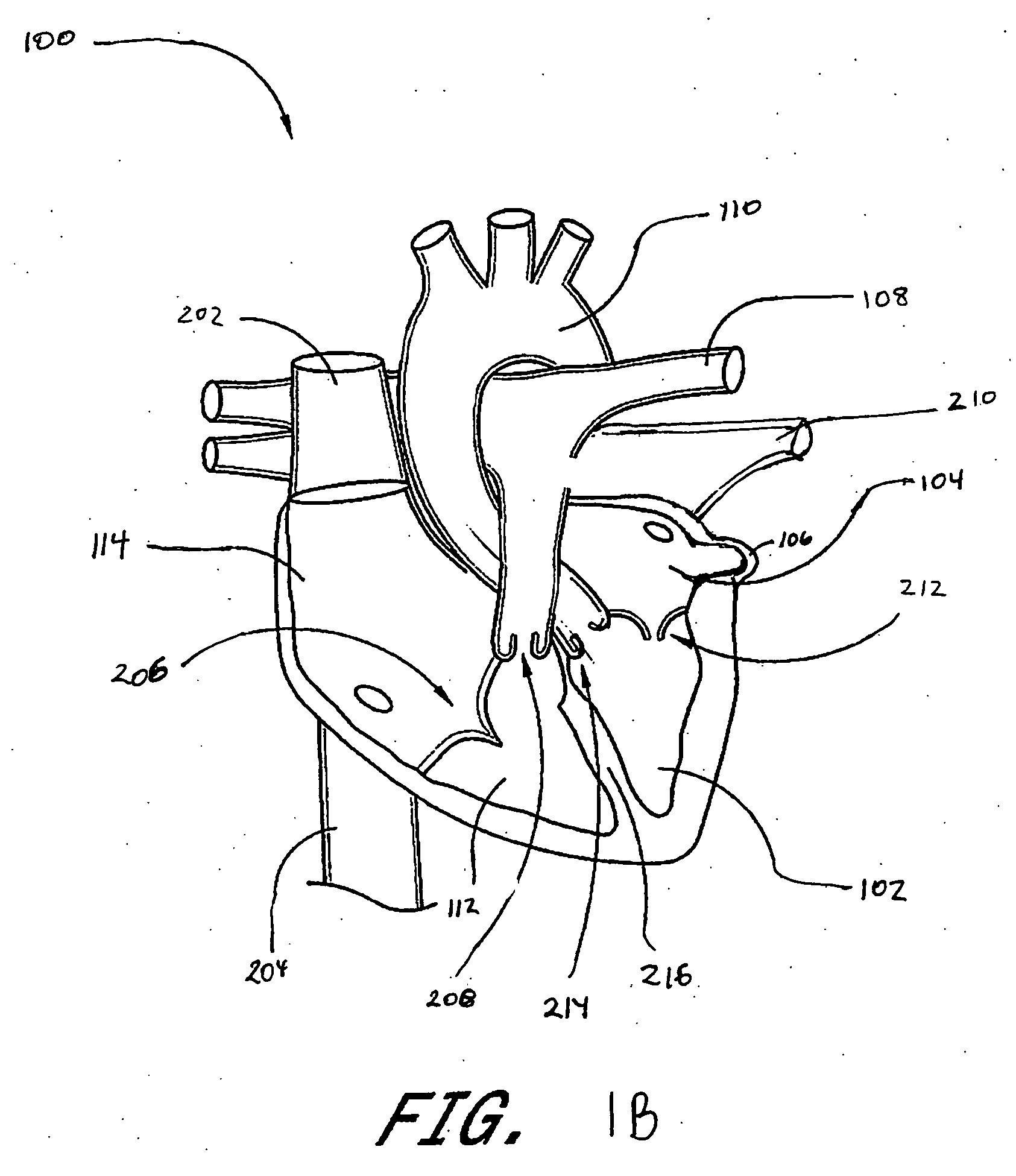
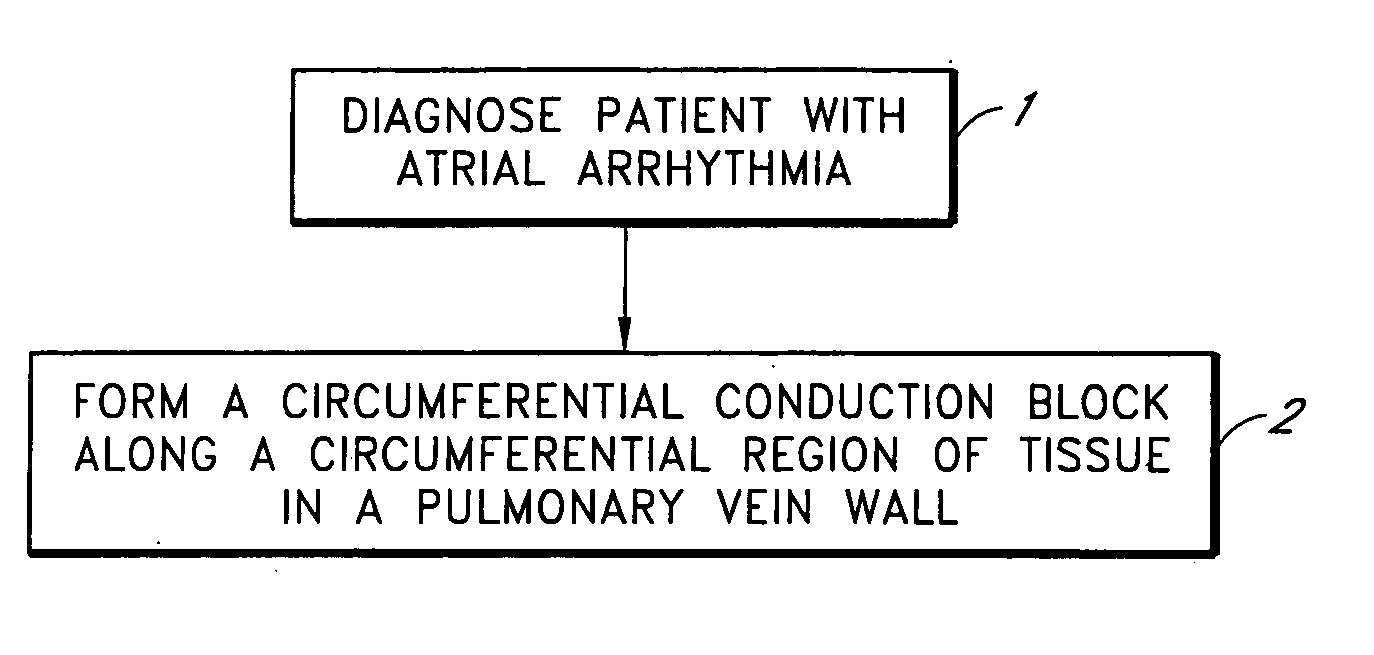
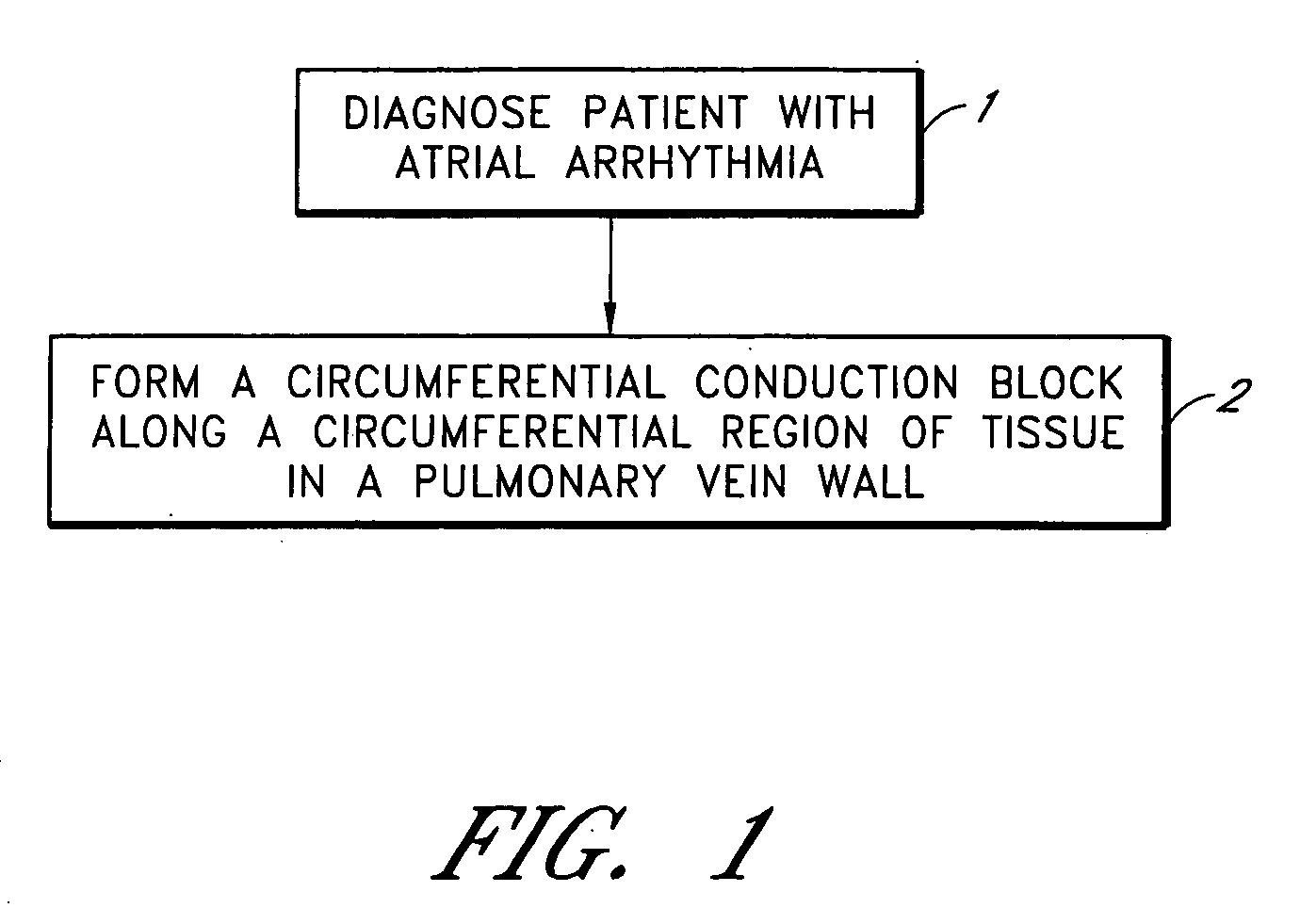
This invention relates to a surgical device and method. More particularly, it relates to a tissue ablation device assembly and method using a circumferential ablation member in combination with a position monitoring assembly in order to position the circumferential ablation member along a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from a left atrium.
Owner:ATRIONIX
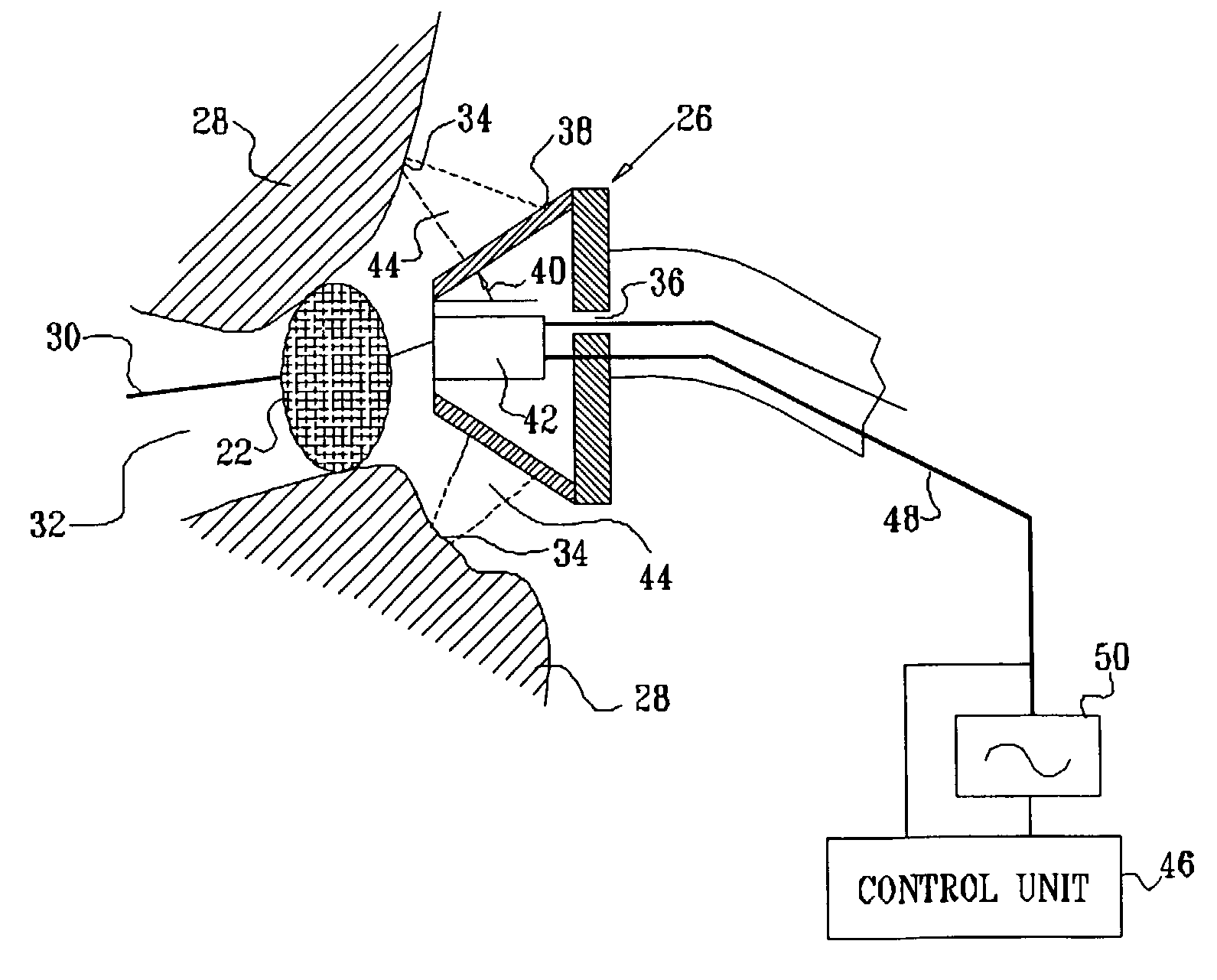
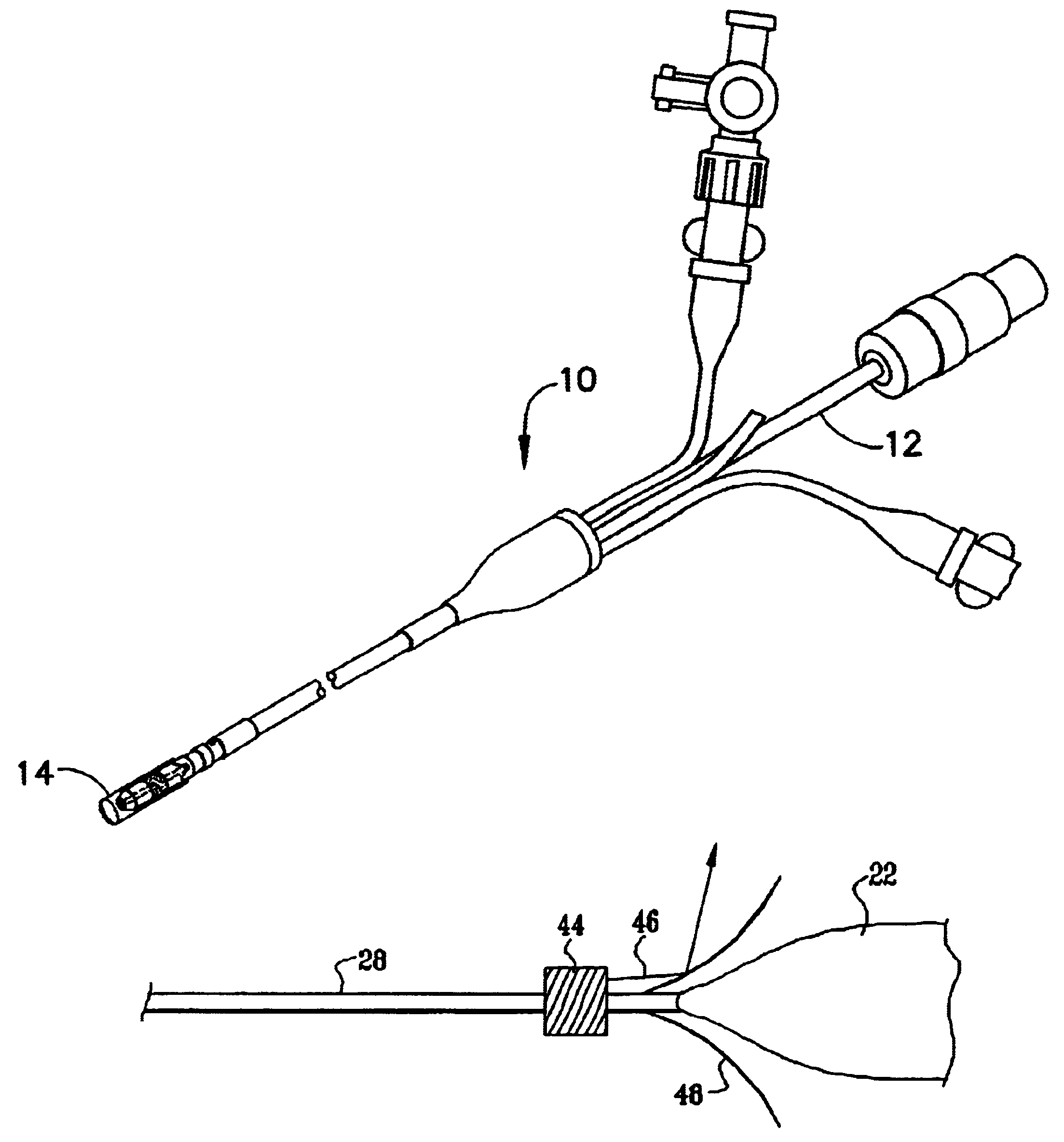
Ultrasound pulmonary vein isolation
A catheter introduction apparatus provides an ultrasound assembly for emission of ultrasound energy. In one application the catheter and the ultrasound assembly are introduced percutaneously, and transseptally advanced to the ostium of a pulmonary vein. An anchoring balloon is expanded to center an acoustic lens in the lumen of the pulmonary vein, such that energy is converged circumferentially onto the wall of the pulmonary vein when a transducer is energized. A circumferential ablation lesion is produced in the myocardial sleeve of the pulmonary vein, which effectively blocks electrical propagation between the pulmonary vein and the left atrium.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Laser pulmonary vein isolation
A catheter introduction apparatus provides an optical assembly for emission of laser light energy. In one application, the catheter and the optical assembly are introduced percutaneously, and transseptally advanced to the ostium of a pulmonary vein. An anchoring balloon is expanded to position a mirror near the ostium of the pulmonary vein, such that light energy is reflected and directed circumferentially around the ostium of the pulmonary vein when a laser light source is energized. A circumferential ablation lesion is thereby produced, which effectively blocks electrical propagation between the pulmonary vein and the left atrium.
Owner:BIOSENSE
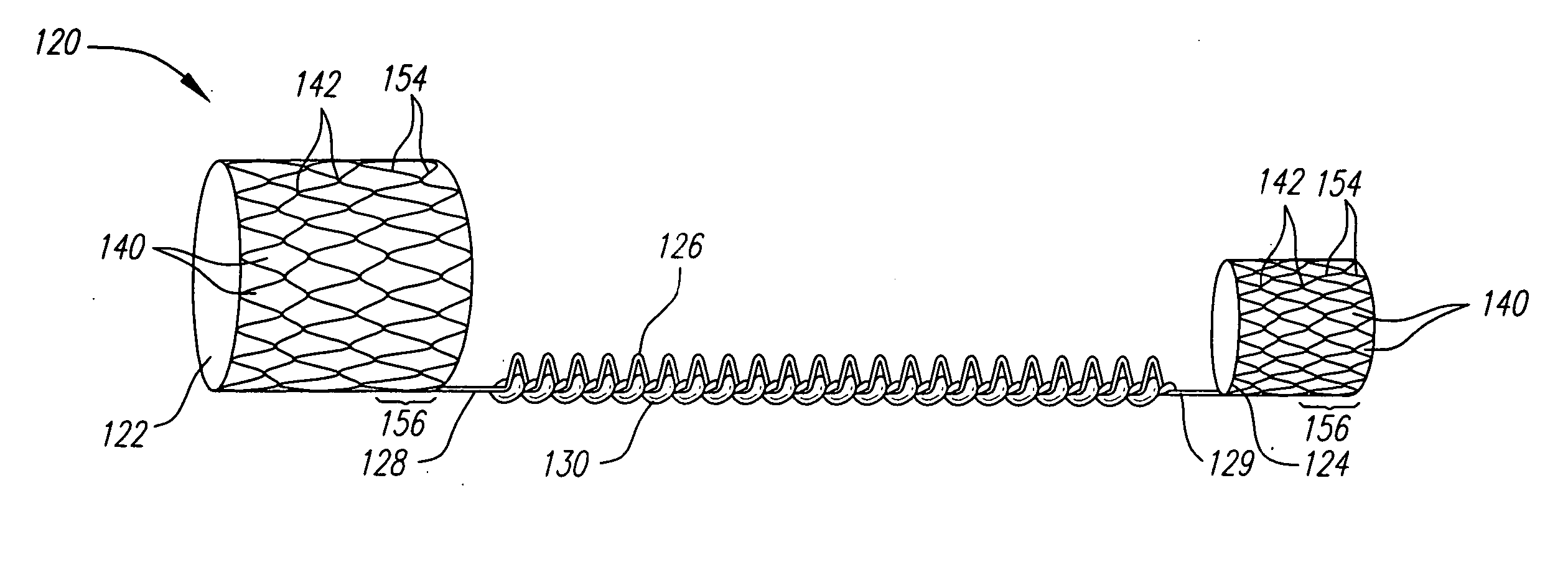
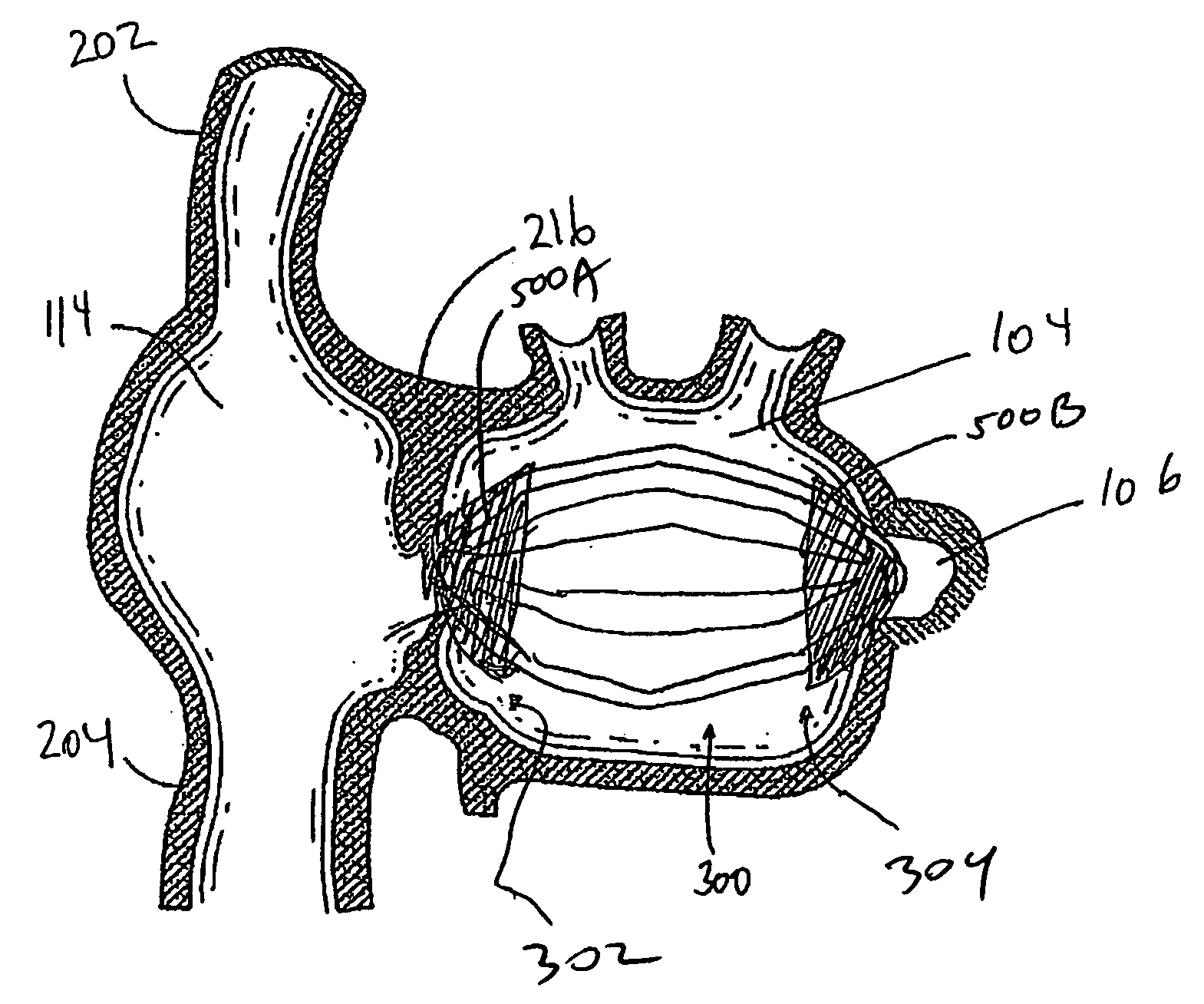
Axially compressible flared stents and apparatus and methods for delivering them
A stent includes a flaring portion and a main portion connected to the flaring portion. The main portion includes a plurality of bands of cells spaced apart axially from one another, adjacent bands of cells being intermittently connected to one another. During use, the stent is introduced into a main vessel in a contracted condition and positioned with the flaring portion adjacent an ostium. The flaring portion is flared, and the stent is advanced at least partially into the ostium. The stent is expanded further such that the main portion expands within the branch body lumen and / or the flaring portion expands adjacent the ostium. The main portion compresses axially during at least one of the steps when the stent is expanded, which may enhance conformance of the stent relative to the ostium and / or enhance reinforcement of the ostium.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
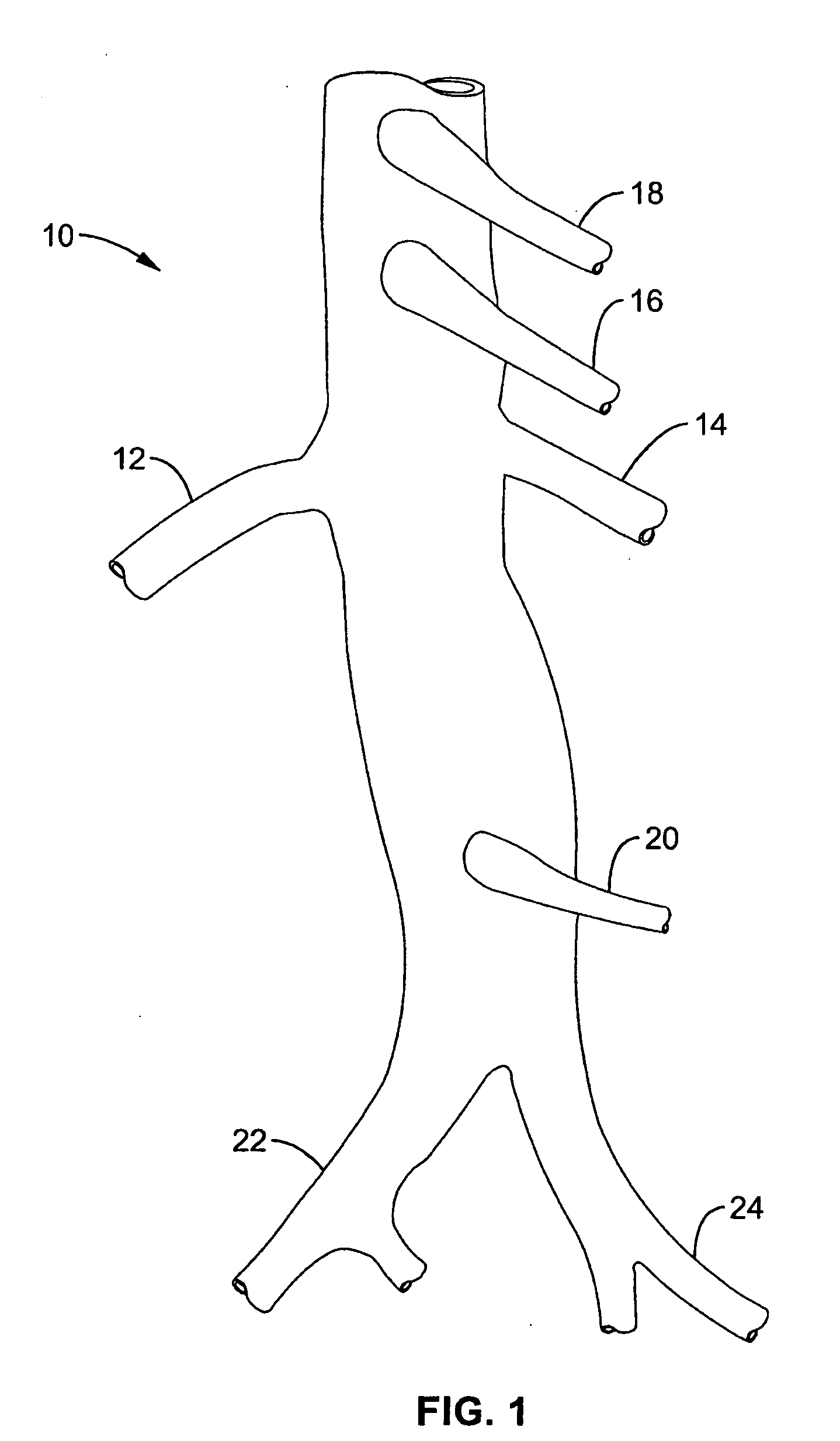
Intra-aortic renal delivery catheter
InactiveUS7063679B2Significant mixingIncreased taper pitchGuide needlesStentsPuncture WoundBoth kidneys
A renal flow system and method direct fluid into renal arteries from a location within the aorta. A renal flow assembly has a tapered tube that is adjustable between a radially collapsed condition for delivery to the location through a delivery sheath and a radially expanded condition that divides aortic flow into exterior and interior paths. The tube's wall is made from a sheet of flexible material, such as PTFE or ePTFE. Two, nickel-titanium rings radially support the tube's ends and are connected by a longitudinal spine support. A fluid delivery assembly injects drug to flow along the exterior flow path and the tubular wall directs the agent into the renal artery ostium. The tube's taper has localized shape for circumferential agent mixing to infuse both kidneys' renals. The flow assembly allows an interventional device, e.g. delivery catheter, to advance across the location while directing blood into the renals and perfusing downstream circulation. The renal flow assembly and distal device are used within a common guide sheath through a single puncture wound. Vasodilators, antioxidants, or diuretics are delivered to the kidneys to treat / prevent RCN, CHF, or ARF.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Apparatus and method for treatment of sinusitis
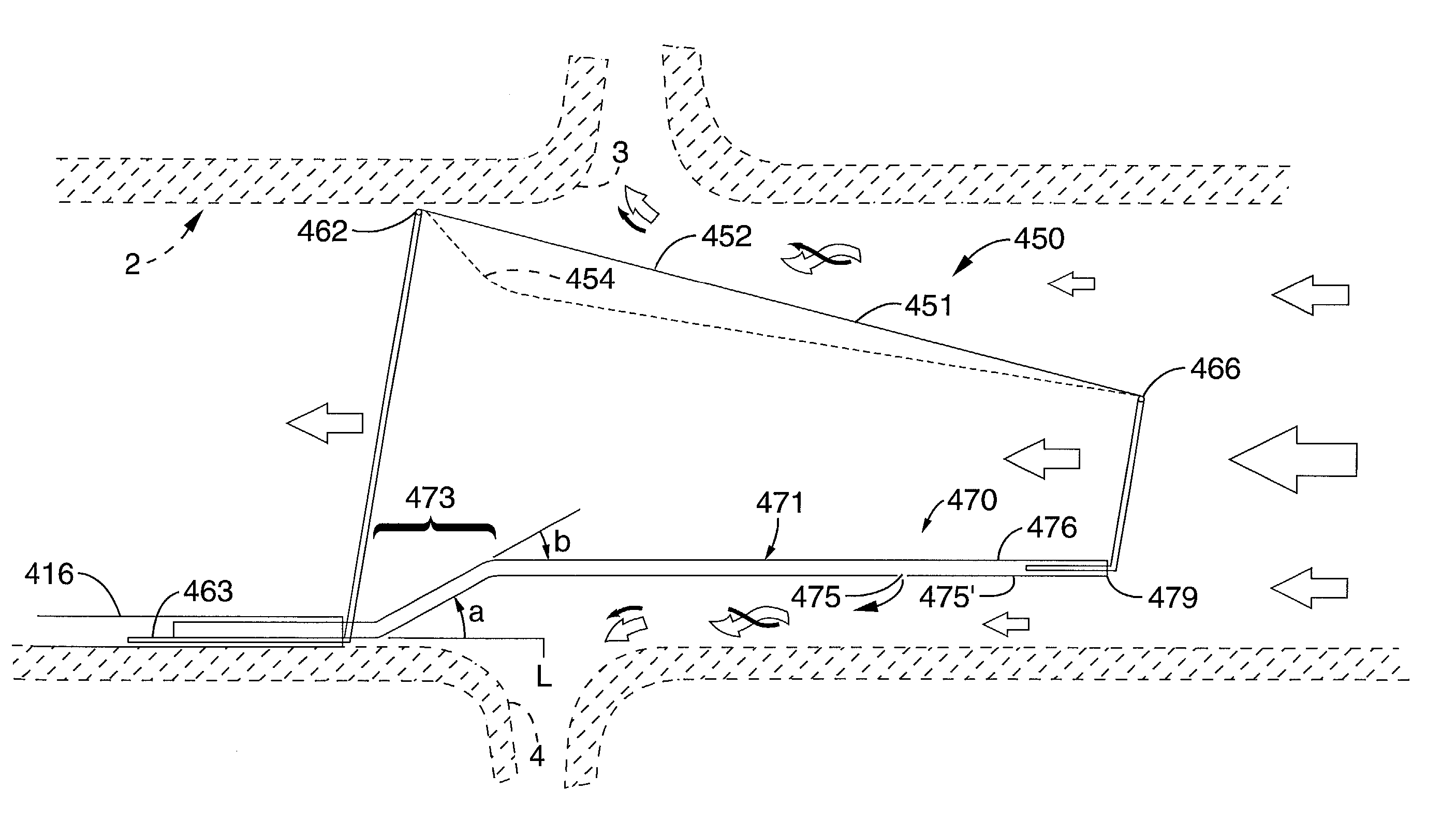
A method of treating a constricted sinus passageway of a patient includes traversing the canine fossa region of the patient so as to form a passageway in the sinus cavity. A cannula is positioned in the passageway. A visualization tool such as an endoscope is passed through a lumen or channel in the cannula to aid in visualization of the anatomical site of interest. A balloon dilation catheter is then deployed through or along the cannula so as to place the balloon within or across the constricted anatomical space (e.g., ostium). The balloon is then expanded so as to expand at least a portion of the constricted anatomical space. Alternative embodiments include the use of an optional guide wire and incorporating a endoscope lumen through the balloon dilation catheter.
Owner:ENTELLUS MEDICAL
Magnetically assisted pulmonary vein isolation
InactiveUS7008418B2Quickly and easily navigatedFacilitate fastElectrotherapyDiagnosticsVeinDistal portion
A method for forming an ablation pattern to electrically isolate a vessel having an ostium from a chamber formed within a patient for treatment of cardiac arrhythmia. The distal portion of a catheter is navigated to a chamber. An anchor member is deployed from the distal end of the catheter into the chamber, and the distal end is navigated into the ostium of the vessel, and temporarily secured in the vessel. An ablation member is deployed from the distal end of the catheter into the chamber and successively navigated into contact with tissue adjacent the ostium and ablating the tissue in contact with the ablation member to form a line of ablation. At least one of the navigating the distal portion of the catheter, navigating the anchor member and navigating the ablation member is performed by applying an external magnetic field to orient the device being navigated.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
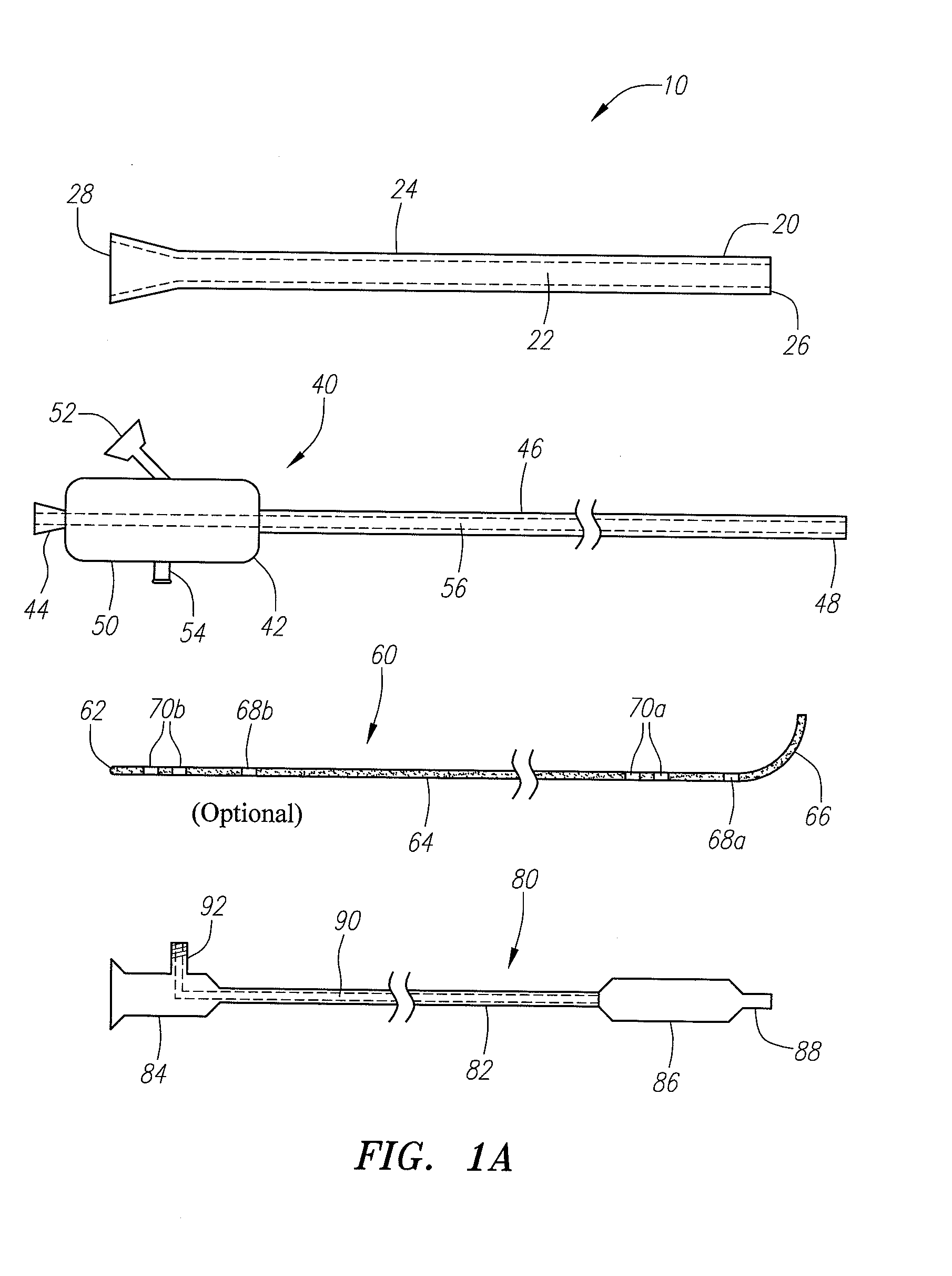
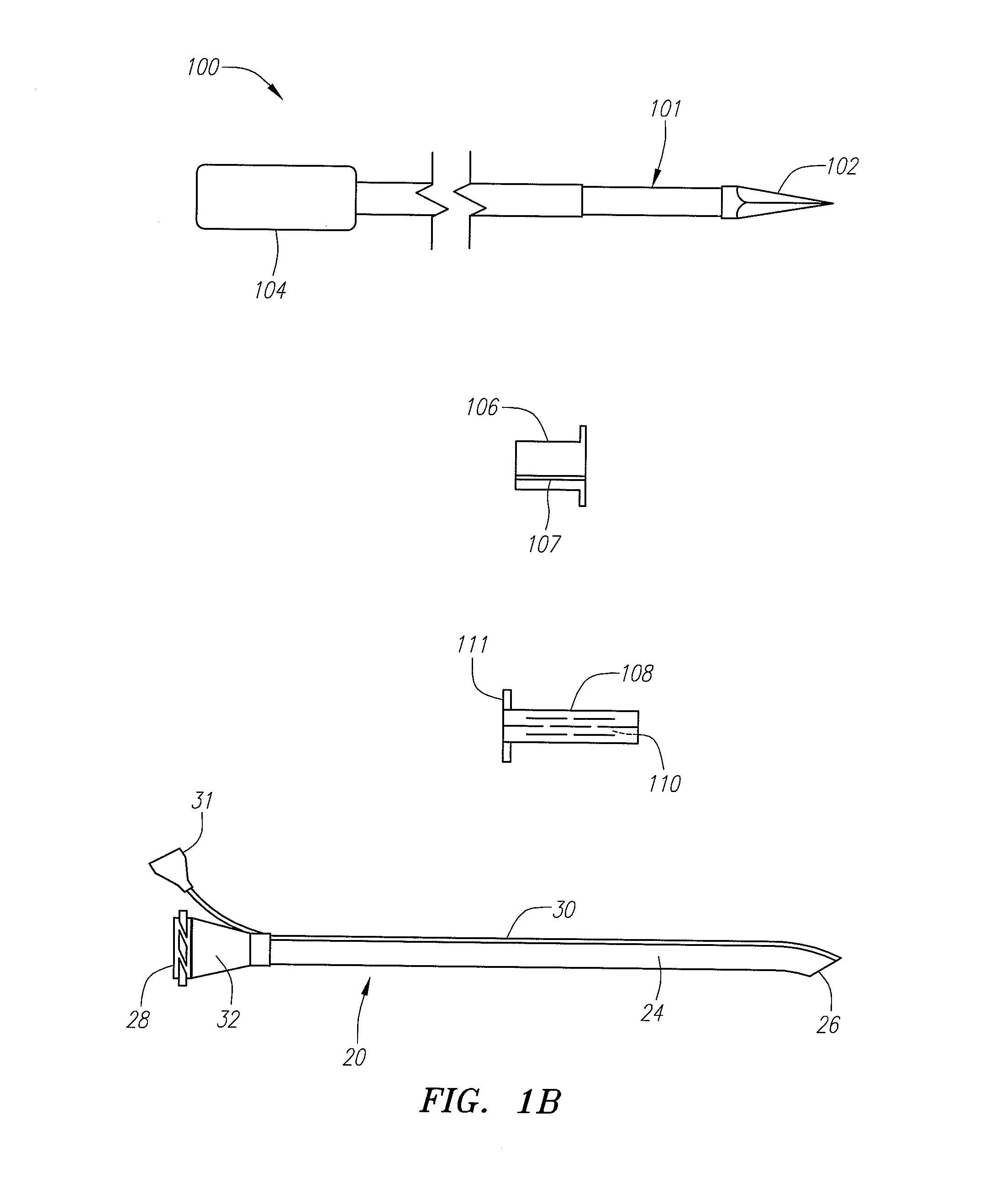
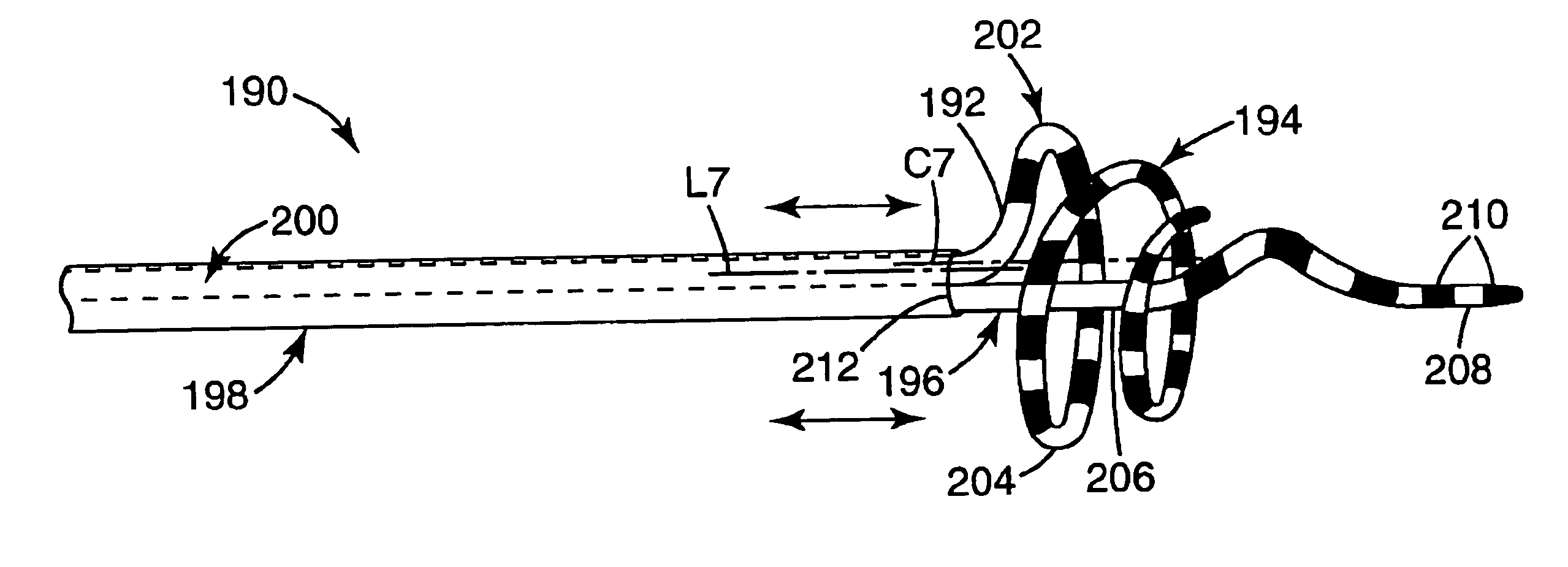
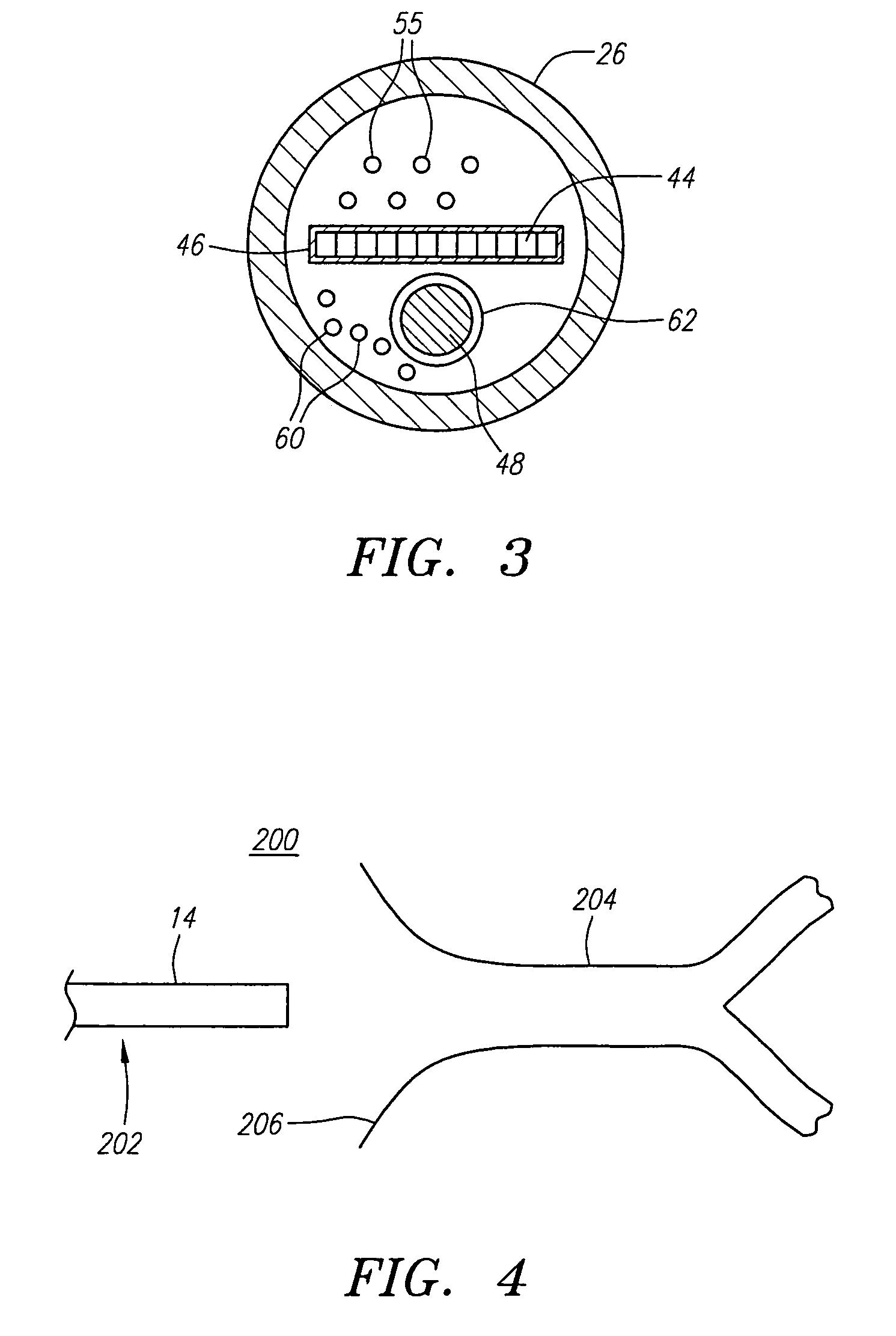
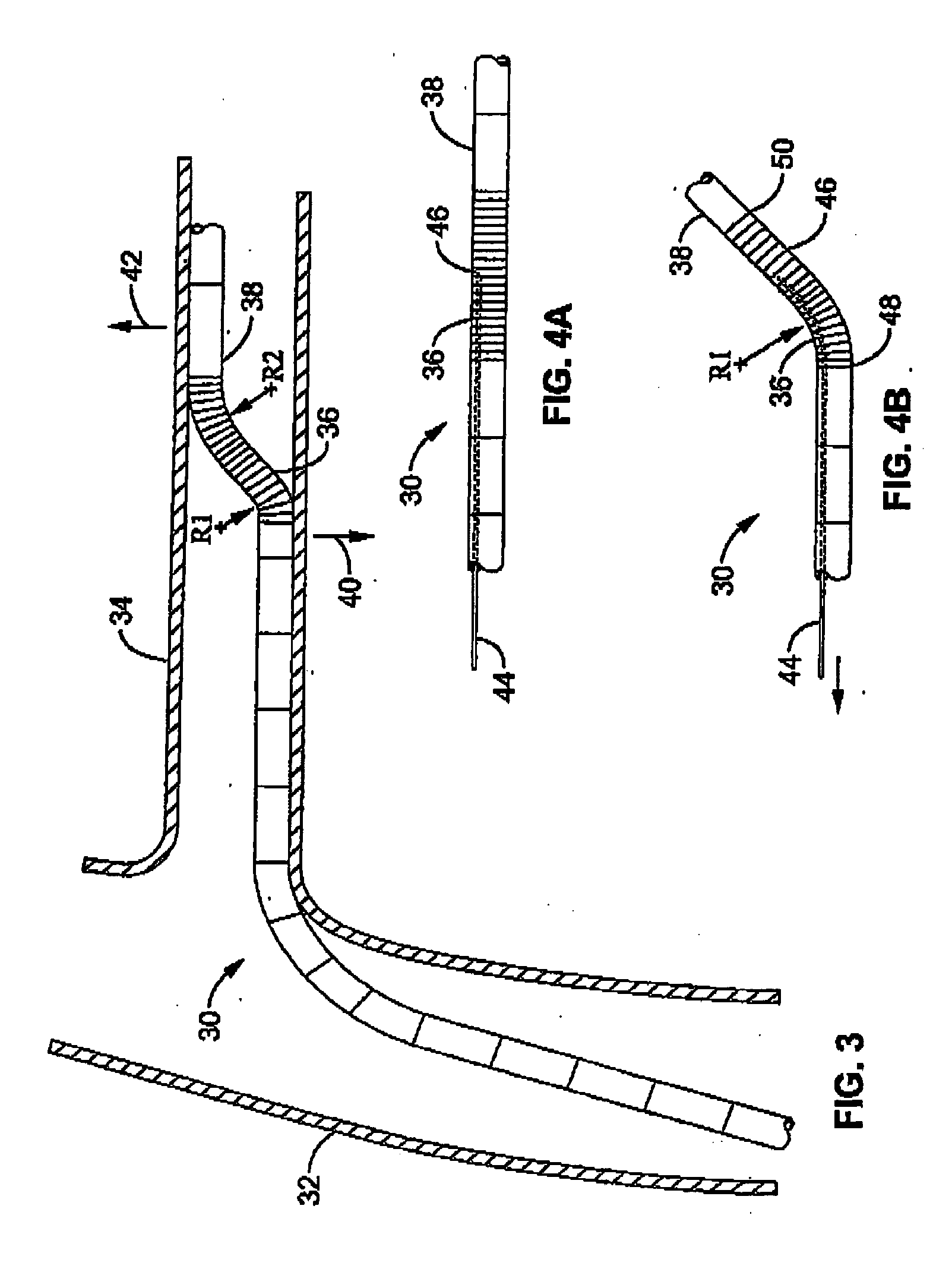
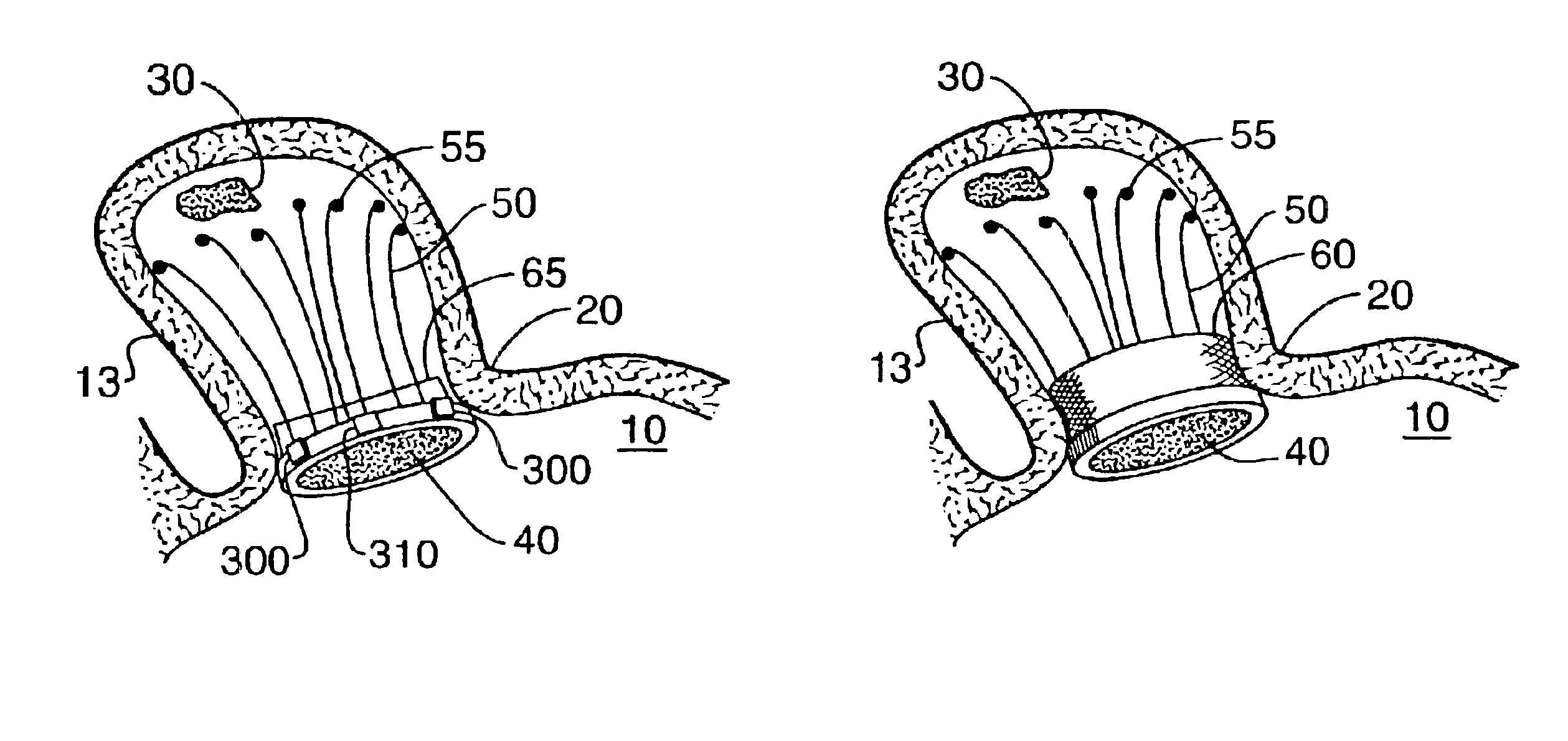
Tissue ablation device assembly and method for electrically isolating a pulmonary vein ostium from an atrial wall
This invention is related to a tissue ablation system and method that treats atrial arrhythmia by ablating a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium. The system includes a circumferential ablation member with an ablation element and also includes a delivery assembly for delivering the ablation member to the location. The circumferential ablation member is generally adjustable between different configurations to allow both the delivery through a delivery sheath into the atrium and the ablative coupling between the ablation element and the circumferential region of tissue.
Owner:ATRIONIX
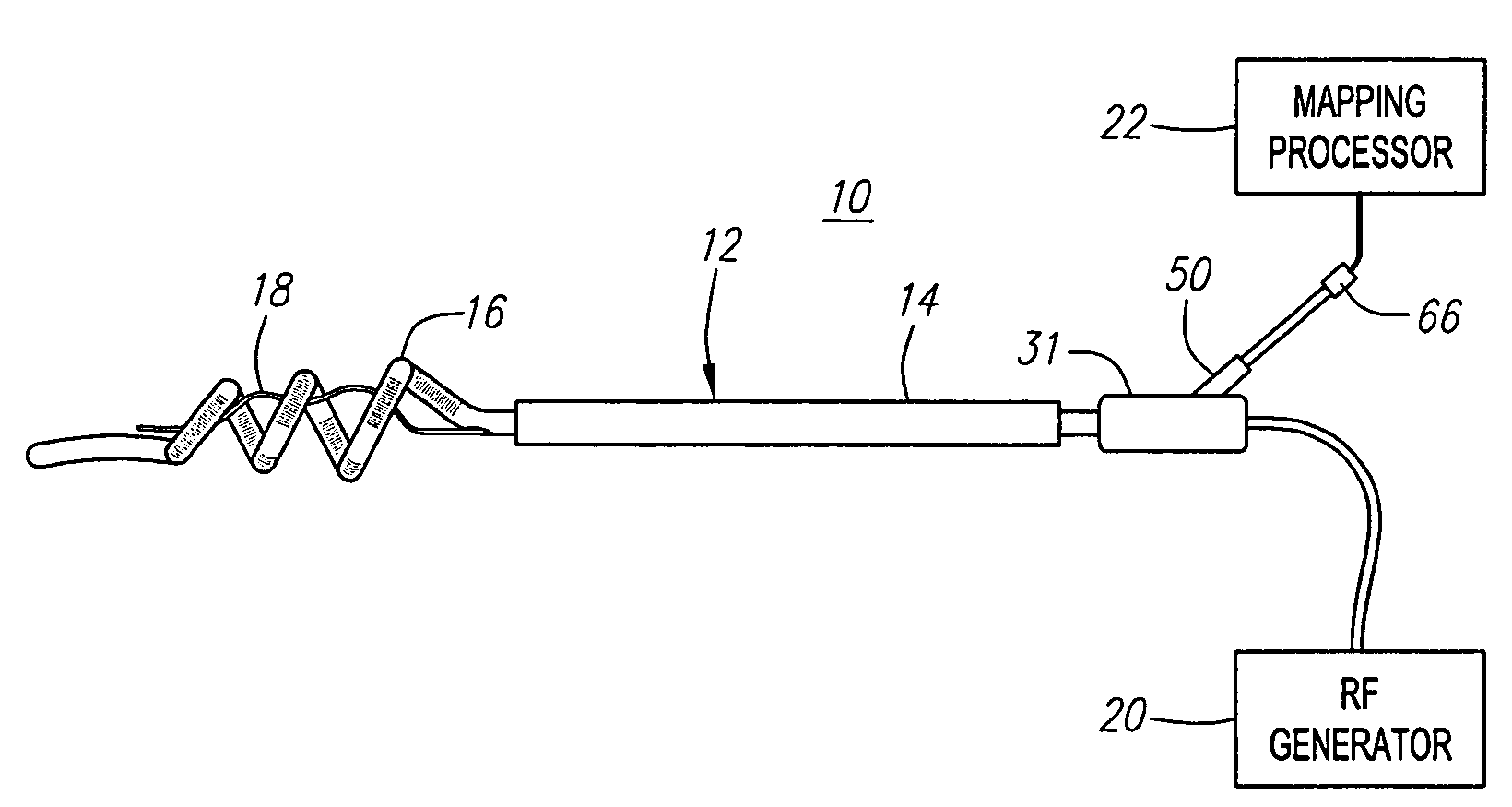
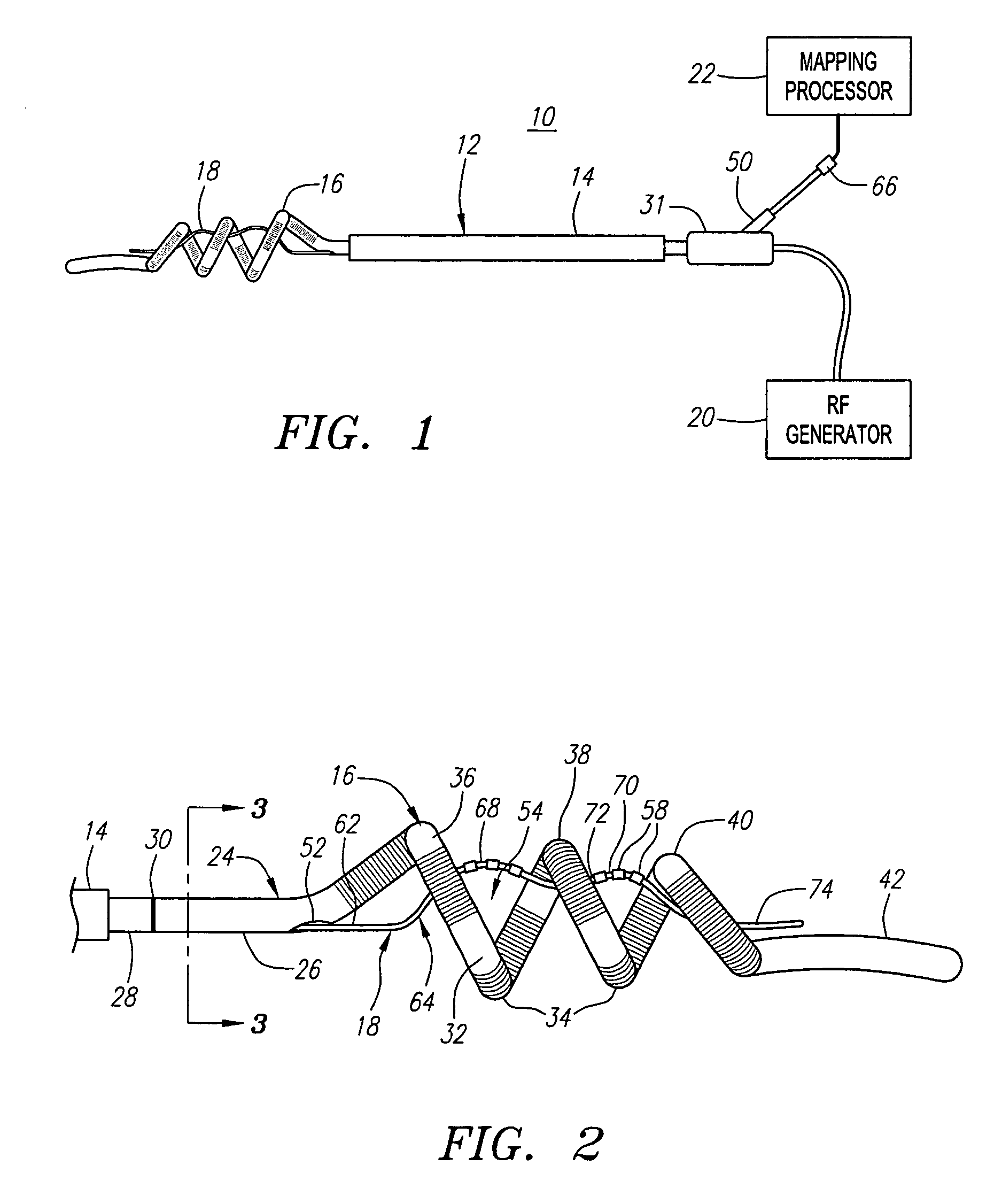
Ablation catheter and method for isolating a pulmonary vein
A catheter assembly and method for treatment of cardiac arrhythmia, for example, atrial fibrillation, by electrically isolating a vessel, such as a pulmonary vein, from a chamber, such as the left atrium. The catheter assembly includes a catheter body and at least one electrode. The catheter body includes a proximal portion, an intermediate portion and a distal portion. The intermediate portion extends from the proximal portion and defines a longitudinal axis. The distal portion extends from the intermediate portion and forms a substantially closed loop transverse to the longitudinal axis. The at least one electrode is disposed along the loop. With this configuration, the loop is axially directed into contact with the chamber wall about the vessel ostium. Upon energization, the electrode ablates a continuous lesion pattern about the vessel ostium, thereby electrically isolating the vessel from the chamber.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for delivering a mitral valve repair device
InactiveUS20070073391A1Promote progressIncrease the diameterHeart valvesBlood vesselsCoronary sinusMitral valve leaflet
A system and method is provided for treating a mitral valve. The method preferably includes advancing a guide catheter to an ostium of the coronary sinus and advancing a delivery catheter containing a medical implant through the guide catheter and into the coronary sinus. The delivery catheter has an inner member on which the medical implant is held and an outer sheath which is retractable for deploying and releasing the medical implant. In one embodiment, the medical implant has proximal and distal anchors and a bridge containing resorbable material. The inner member may have a flexible sleeve for gripping and holding a portion of the outer sheath, thereby providing a releasable attachment mechanism. In another embodiment, the inner member may include an inflatable balloon having a tapered distal region which extends from the outer sheath for providing an atraumatic tip. The inflatable balloon may also be used to expand the medical implant and to grip the outer sheath.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
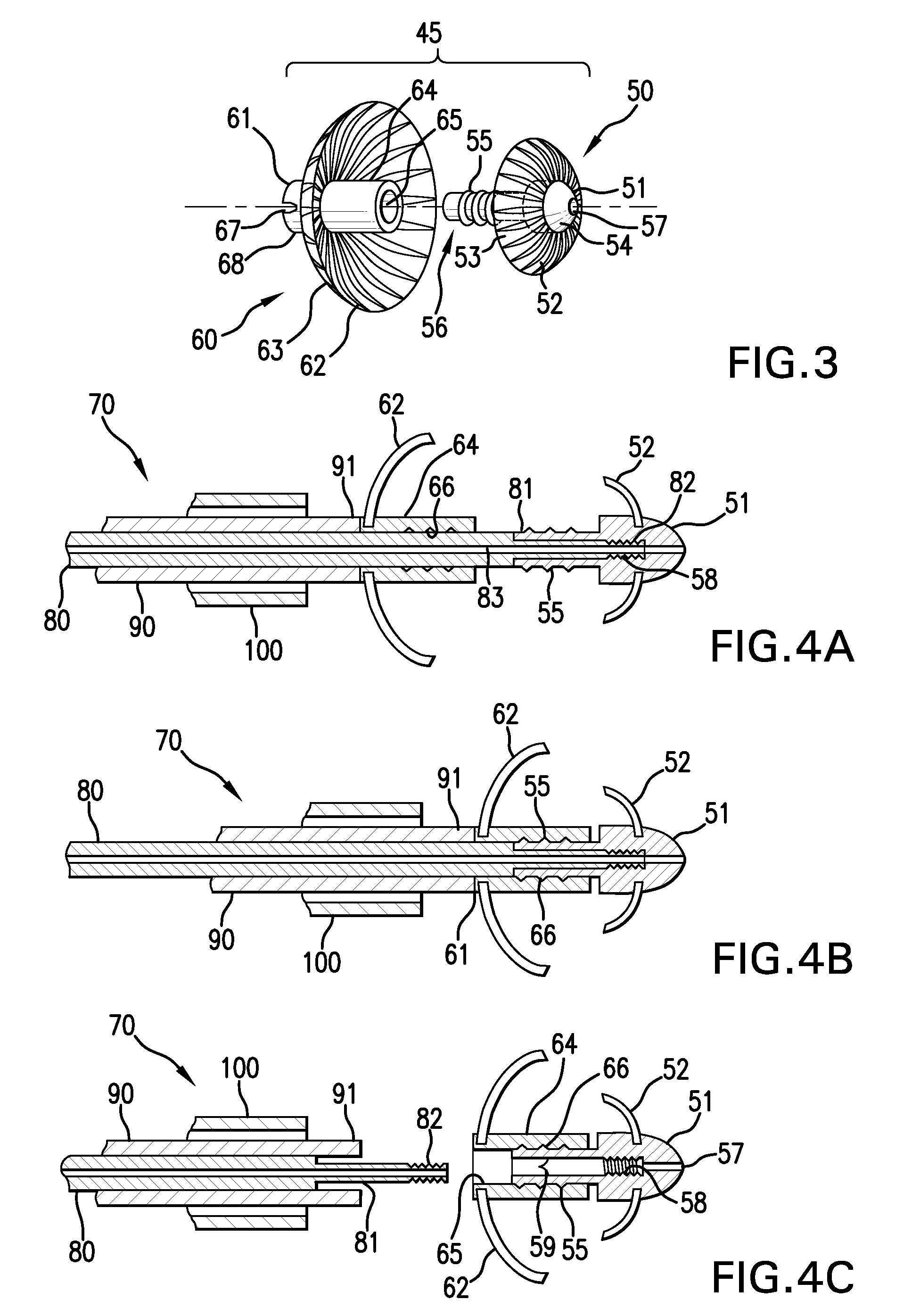
Medical probes for creating and diagnosing circumferential lesions within or around the ostium of a vessel
The present inventions provide assemblies, probes, and methods for creating circumferential lesions in tissue, e.g., the tissue within or around the ostium of a vessel. An ablation probe with an ablative structure can be placed in contact within or around the ostium of the vessel. A diagnostic probe can be introduced through a lumen within the ablation probe and inserted into the vessel. The energy can be provided to the ablative structure to create a circumferential lesion within or around the ostium of the vessel, and the diagnostic structure can be used to diagnose the tissue to determine whether the circumferential lesion can be properly created.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Tissue ablation device assembly and method of electrically isolating a pulmonary vein ostium from an atrial wall
This invention is related to a tissue ablation system and method that treats atrial arrhythmia by ablating a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium. The system includes a circumferential ablation member with an ablation element and also includes a delivery assembly for delivering the ablation member to the location. The circumferential ablation member is generally adjustable between different configurations to allow both the delivery through a delivery sheath into the atrium and the ablative coupling between the ablation element and the circumferential region of tissue.
Owner:ATRIONIX
Tissue ablation device assembly and method for electrically isolating a pulmonary vein ostium from an atrial wall
This invention is related to a tissue ablation system and method that treats atrial arrhythmia by ablating a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium. The system includes a circumferential ablation member with an ablation element and also includes a delivery assembly for delivering the ablation member to the location. The circumferential ablation member is generally adjustable between different configurations to allow both the delivery through a delivery sheath into the atrium and the ablative coupling between the ablation element and the circumferential region of tissue.
Owner:ATRIONIX
Method and apparatus for selective material delivery via an intra-renal catheter
Two renal delivery members have two distal ports that are adapted to be positioned within two renal arteries via their corresponding renal ostia at unique locations along an abdominal aortic wall. A proximal coupler assembly is outside the body and is coupled to deliver material to the two distal ports for bi-lateral renal therapy. One or both of the delivery members may be self-cannulating into the corresponding renal ostium, or may be controllably steered into the respective ostium. Non-occlusive anchors may be coupled with one or both of the delivery members at anchoring positions in the renal artery or abdominal aorta to secure the renal delivery member within the renal artery. Renal-active fluid agents are coupled to the bi-lateral delivery system. Another renal therapy system cannulates a renal vein from the vena cava and controls a retrograde delivery of agents to the respective kidney.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Means and method for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms
Disclosed is a system for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms using a stent and a aneurysm pocket fill structure delivery system. One embodiment of the present invention uses a highly radiopaque, drug eluting stent that is deployed with its sidewall over the ostium of the aneurysm pocket. A fill structure delivery catheter is then advanced through the patient's vascular system until the catheter's distal end is situated within the aneurysm pocket. Compressed aneurysm pocket filling structures are then pushed through the fill structure delivery catheter. As the aneurysm pocket filling structures emerge from an opening in the catheter's distal end, they promptly expand so that their minimum dimension is sufficiently large so that they cannot pass through the spaces between the struts of the stent that cover the ostium of the aneurysm pocket.
Owner:FISCHELL ROBERT E +1
Pulmonary vein valve implant
InactiveUS20050273160A1Reduced likelihoodReduce severityStentsBronchiPulmonary vasculatureAtrial cavity
The present invention involves placing a valve between the left atrium and the lung to prevent regurgitant flow from increasing the pulmonary pressures, which may lead to pulmonary edema and congestion. Mitral stenosis or poor synchronization of the mitral valve may add additional pressures to the left atrium thus raising the pulmonary pressures and leading to congestion in the lung vasculature. By blocking the additional pressures from the mitral regurgitant flow from reaching the pulmonary circulation, the left atrium may act as a sealed vessel to allow additional aortic output. The valve placement can be intralumenal or attached to the ostium of the atrium. The device can be placed via the vascular conduits or through a surgical procedure into the pulmonary circulation. One or more devices may be placed in each of the four pulmonary veins. Additionally only one, two, three or all four veins may be implanted with the valve as desired by the physician.
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
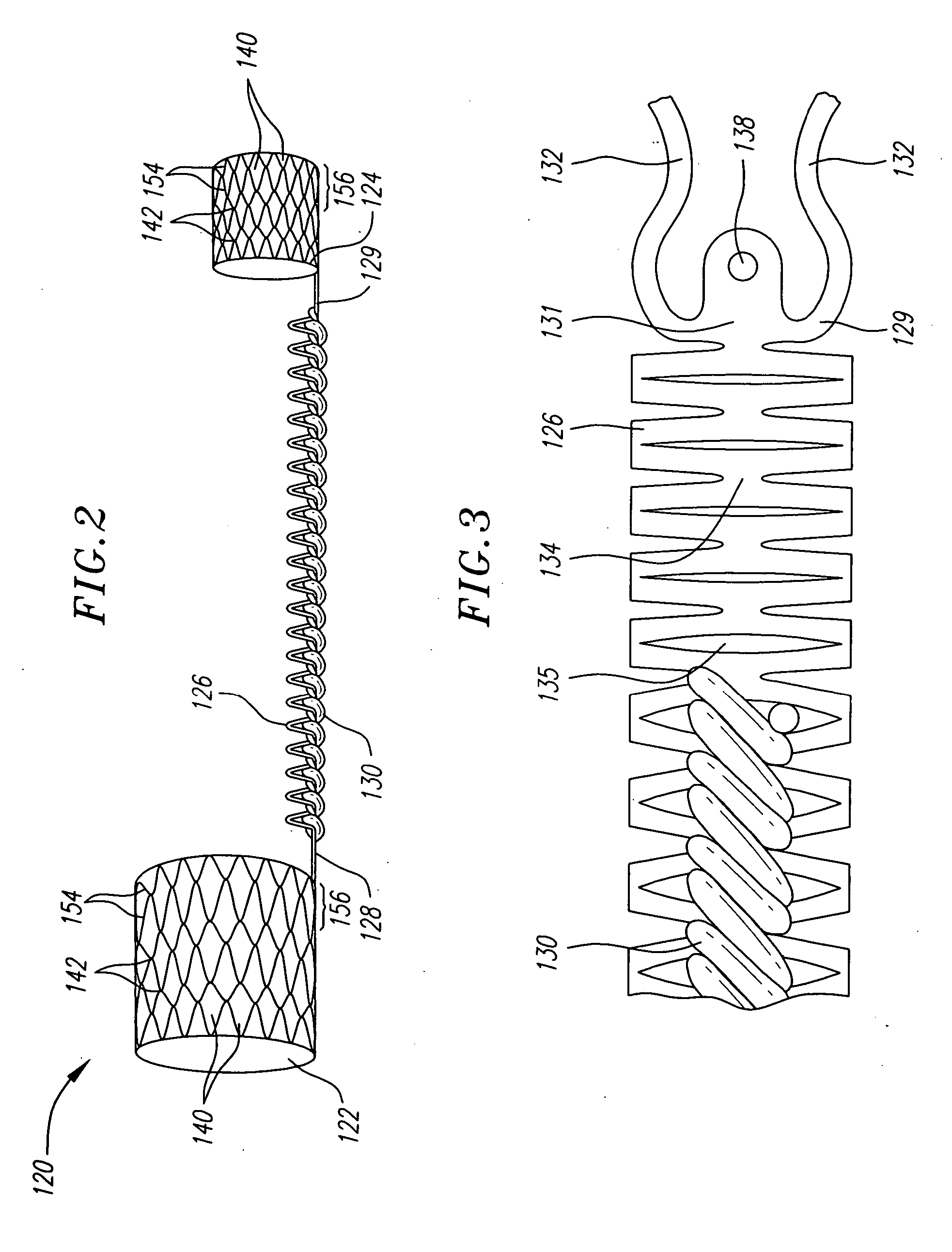
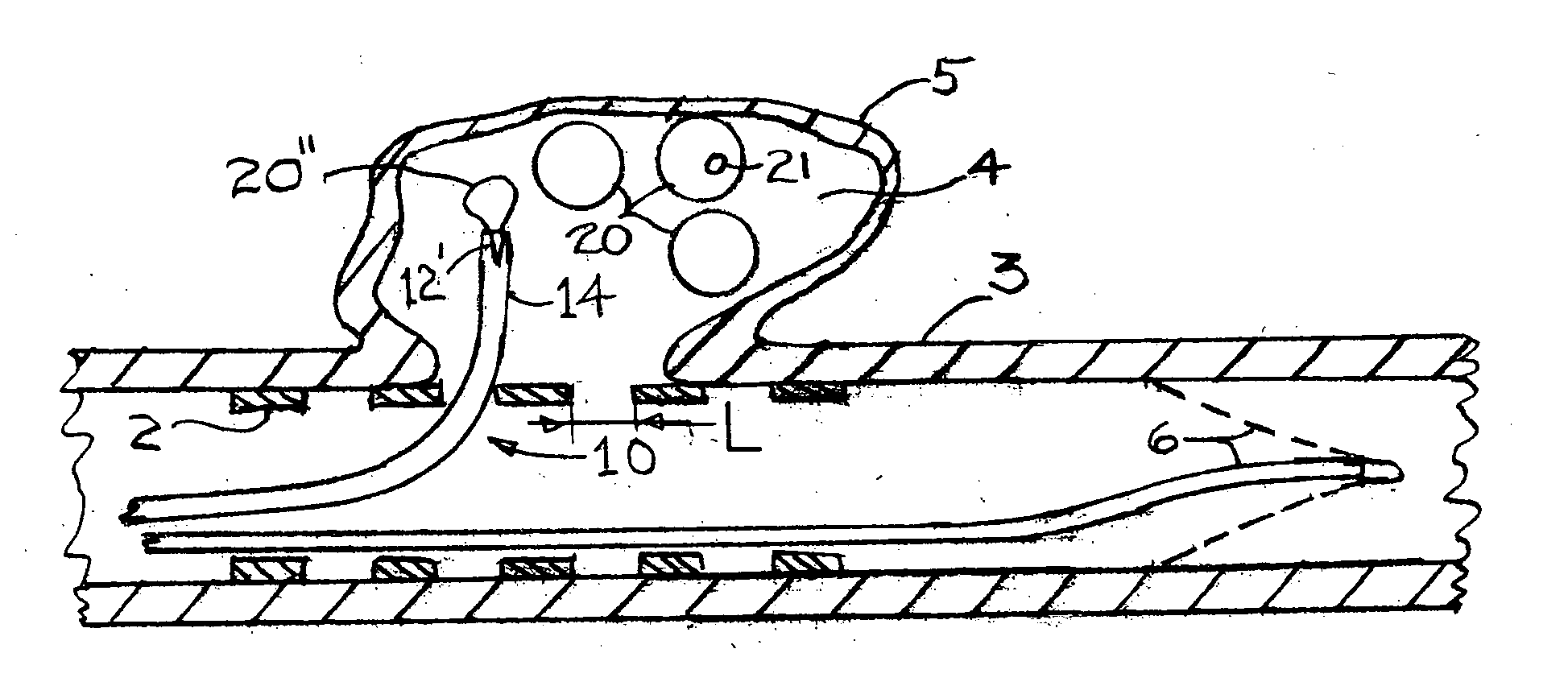
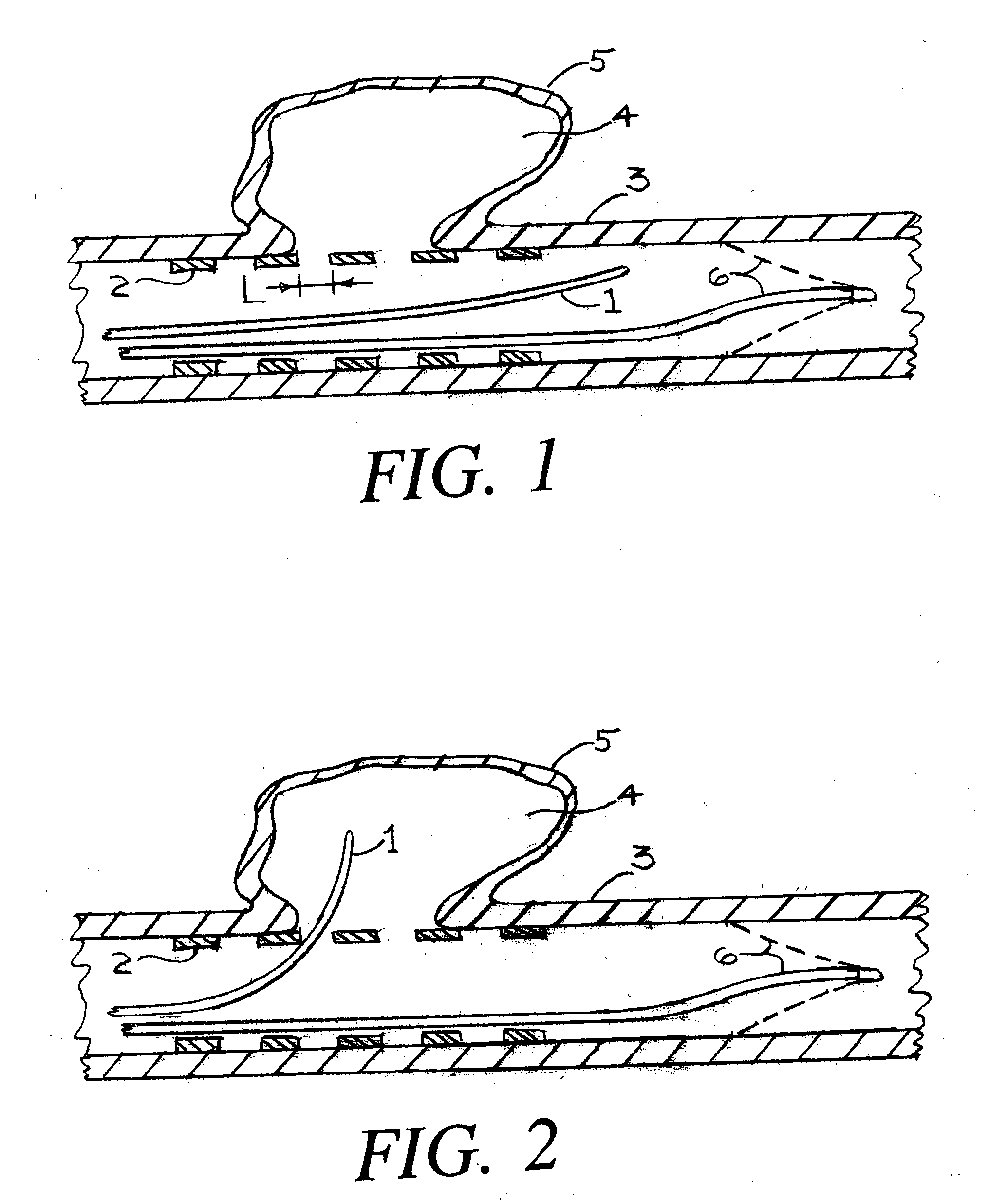
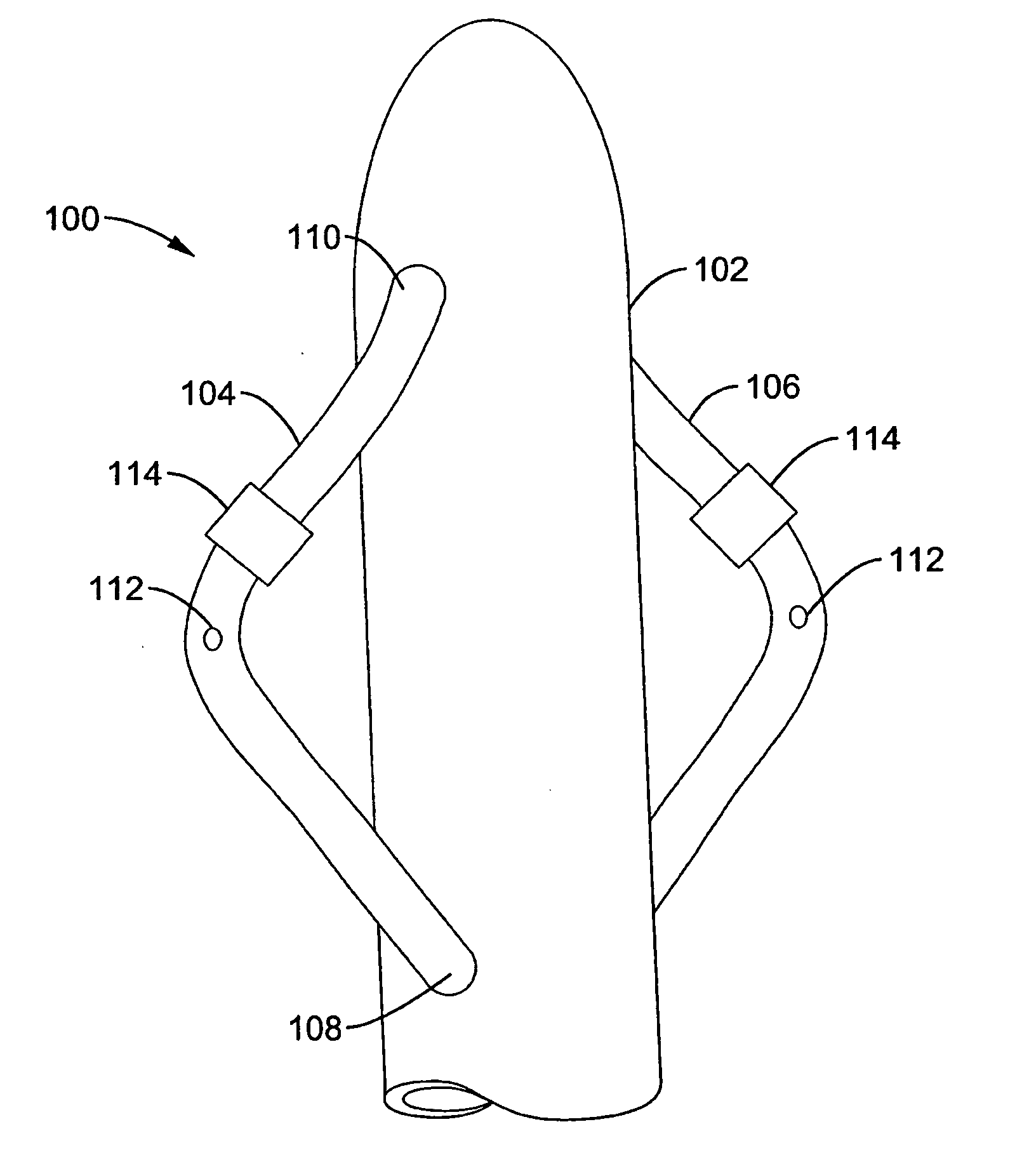
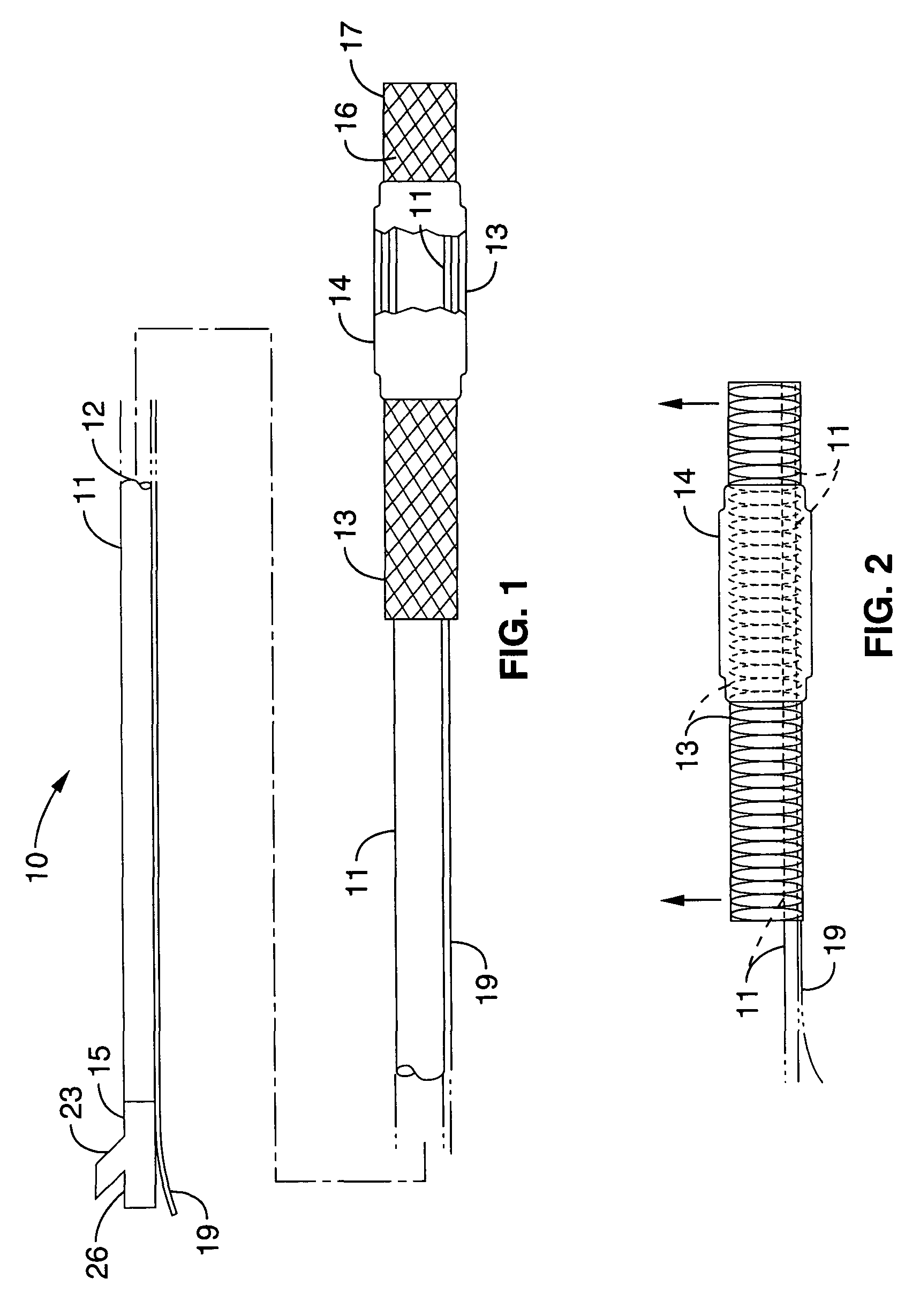
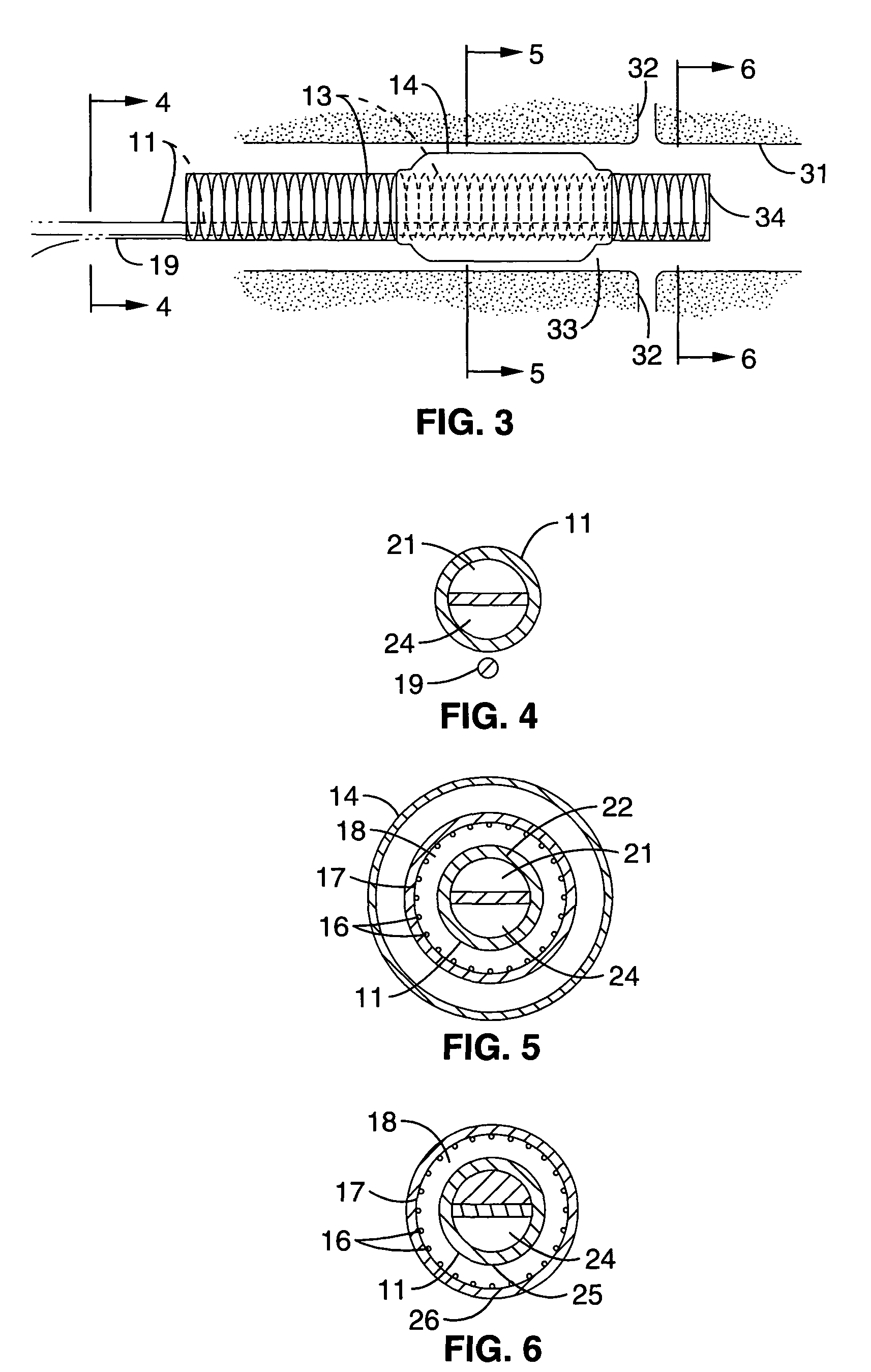
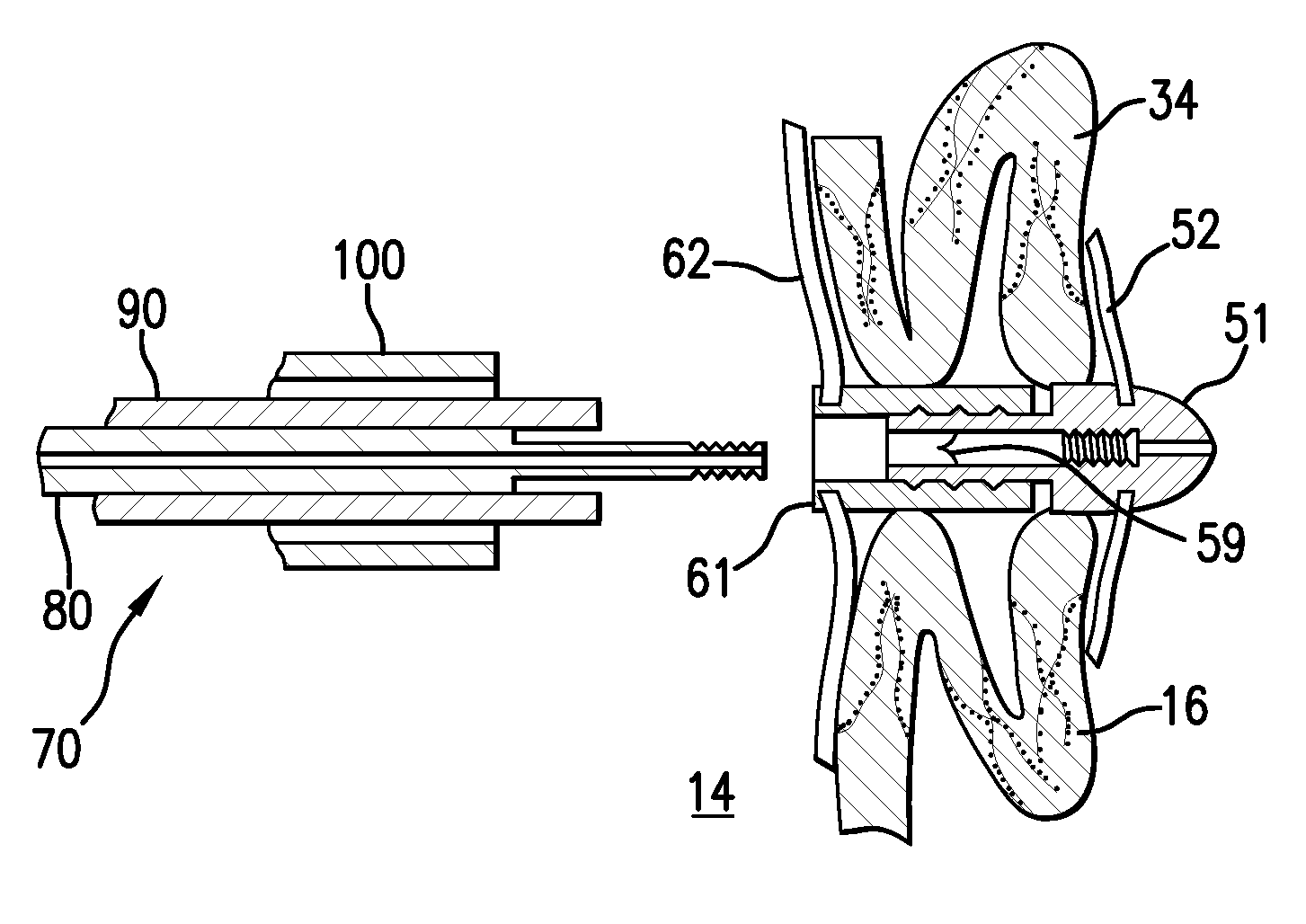
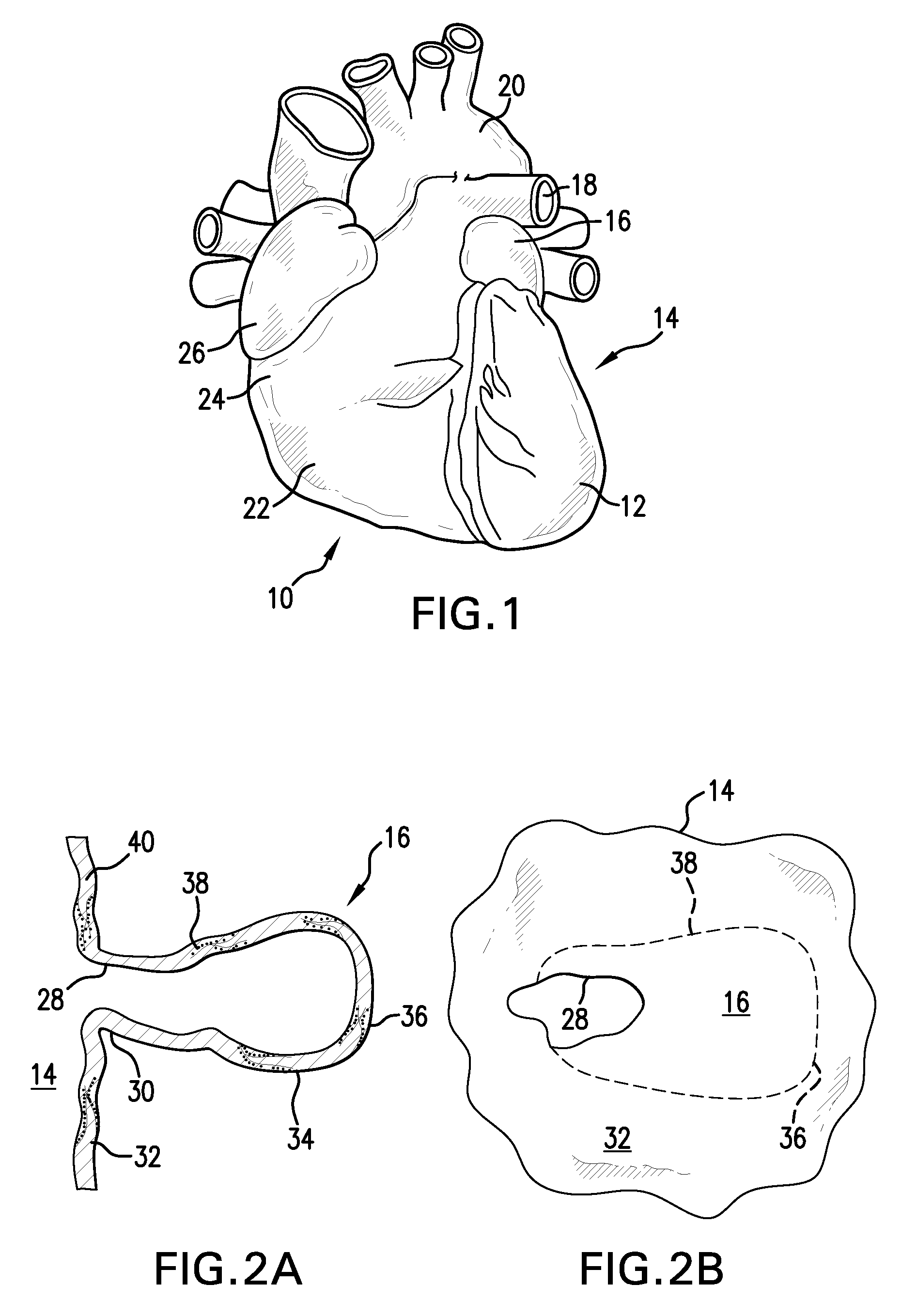
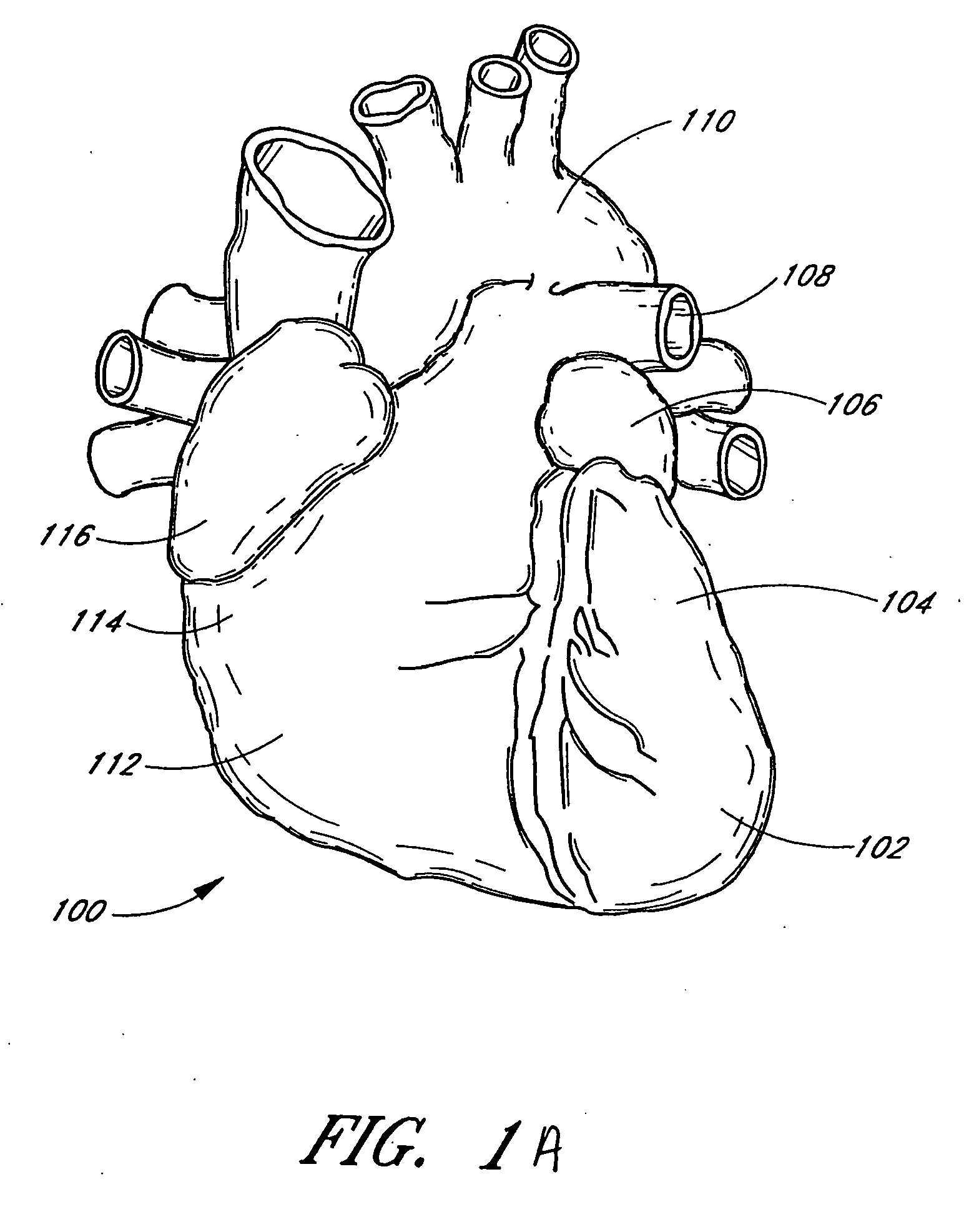
Barrier device for ostium of left atrial appendage
InactiveUS6949113B2Effective isolationPrevent escapeElectrocardiographyDilatorsBlood vessel occlusionThrombus
A membrane applied to the ostium of an atrial appendage for blocking blood from entering the atrial appendage which can form blood clots therein is disclosed. The membrane also prevents blood clots in the atrial appendage from escaping therefrom and entering the blood stream which can result in a blocked blood vessel, leading to strokes and heart attacks. The membranes are percutaneously installed in patients experiencing atrial fibrillations and other heart conditions where thrombosis may form in the atrial appendages. A variety of means for securing the membranes in place are disclosed. The membranes may be held in place over the ostium of the atrial appendage or fill the inside of the atrial appendage. The means for holding the membranes in place over the ostium of the atrial appendages include prongs, stents, anchors with tethers or springs, disks with tethers or springs, umbrellas, spiral springs filling the atrial appendages, and adhesives. After the membrane is in place a filler substance may be added inside the atrial appendage to reduce the volume, help seal the membrane against the ostium or clot the blood in the atrial appendage. The membranes may have anticoagulants to help prevent thrombosis. The membranes be porous such that endothelial cells cover the membrane presenting a living membrane wall to prevent thrombosis. The membranes may have means to center the membranes over the ostium. Sensors may be attached to the membrane to provide information about the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Cardiac ablation devices
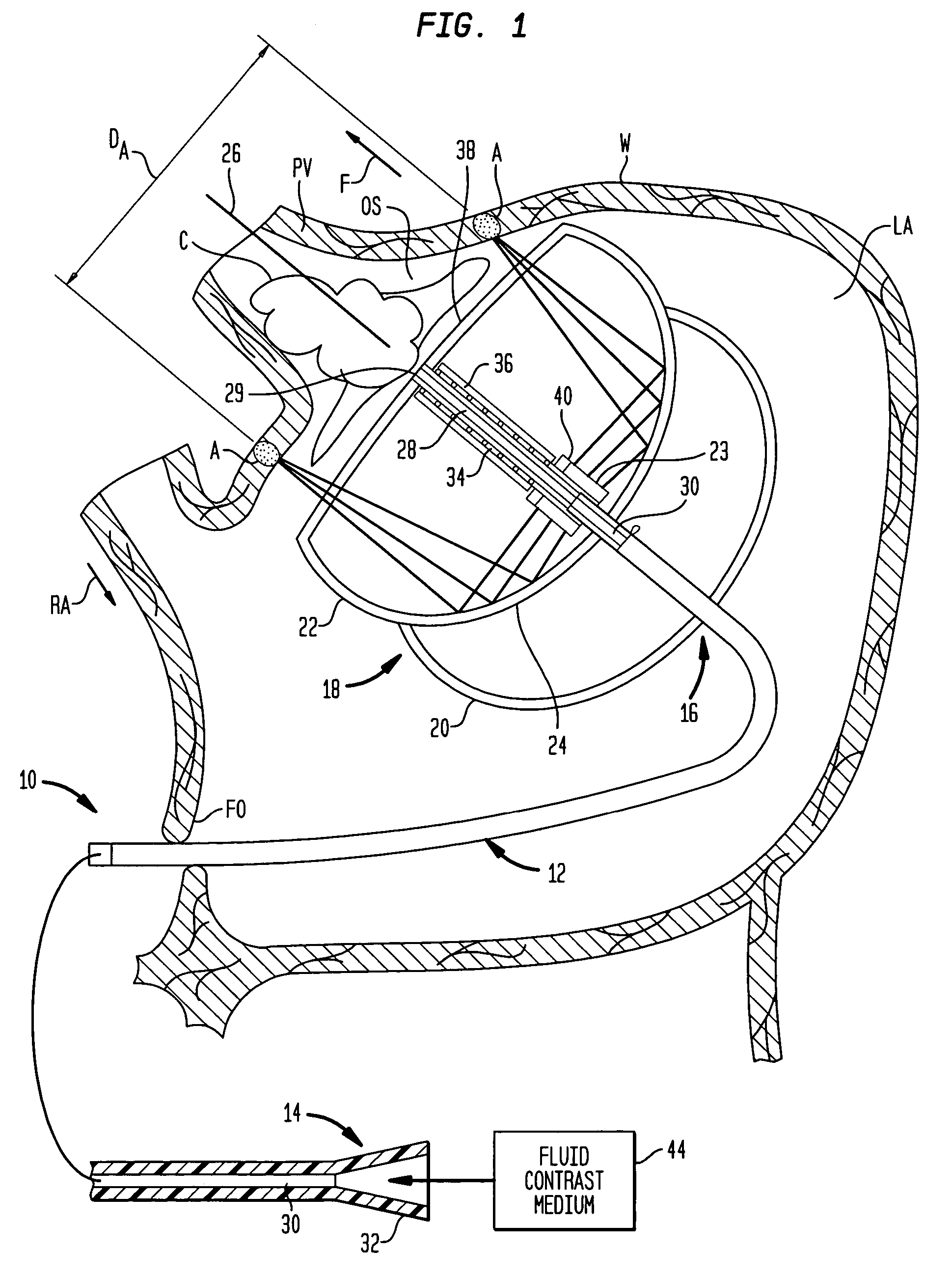
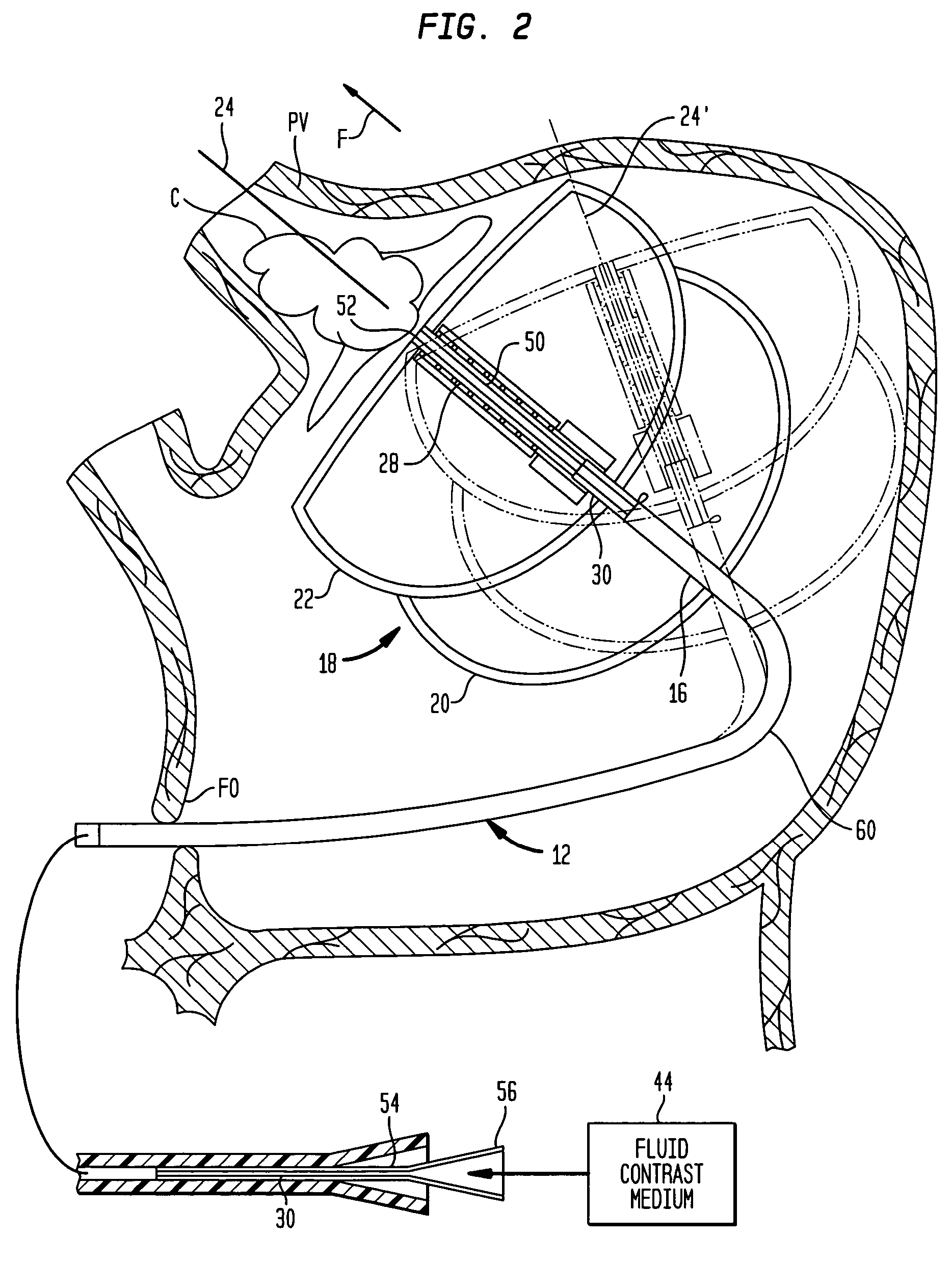
A cardiac ablation device treats atrial fibrillation by directing and focusing ultrasonic waves into a ring-like ablation region (A). The device desirably is steerable and can be moved between a normal disposition, in which the ablation region lies parallel to the wall of the heart for ablating a loop-like lesion, and a canted disposition, in which the ring-like focal region is tilted relative to the wall of the heart, to ablate only a short, substantially linear lesion. The ablation device desirably includes a balloon reflector structure (18, 1310) and an ultrasonic emitter assembly (23, 1326), and can be steered and positioned without reference to engagement between the device and the pulmonary vein or ostium. A contrast medium (C) can be injected through the ablation device to facilitate imaging, so that the device can be positioned based on observation of the images.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
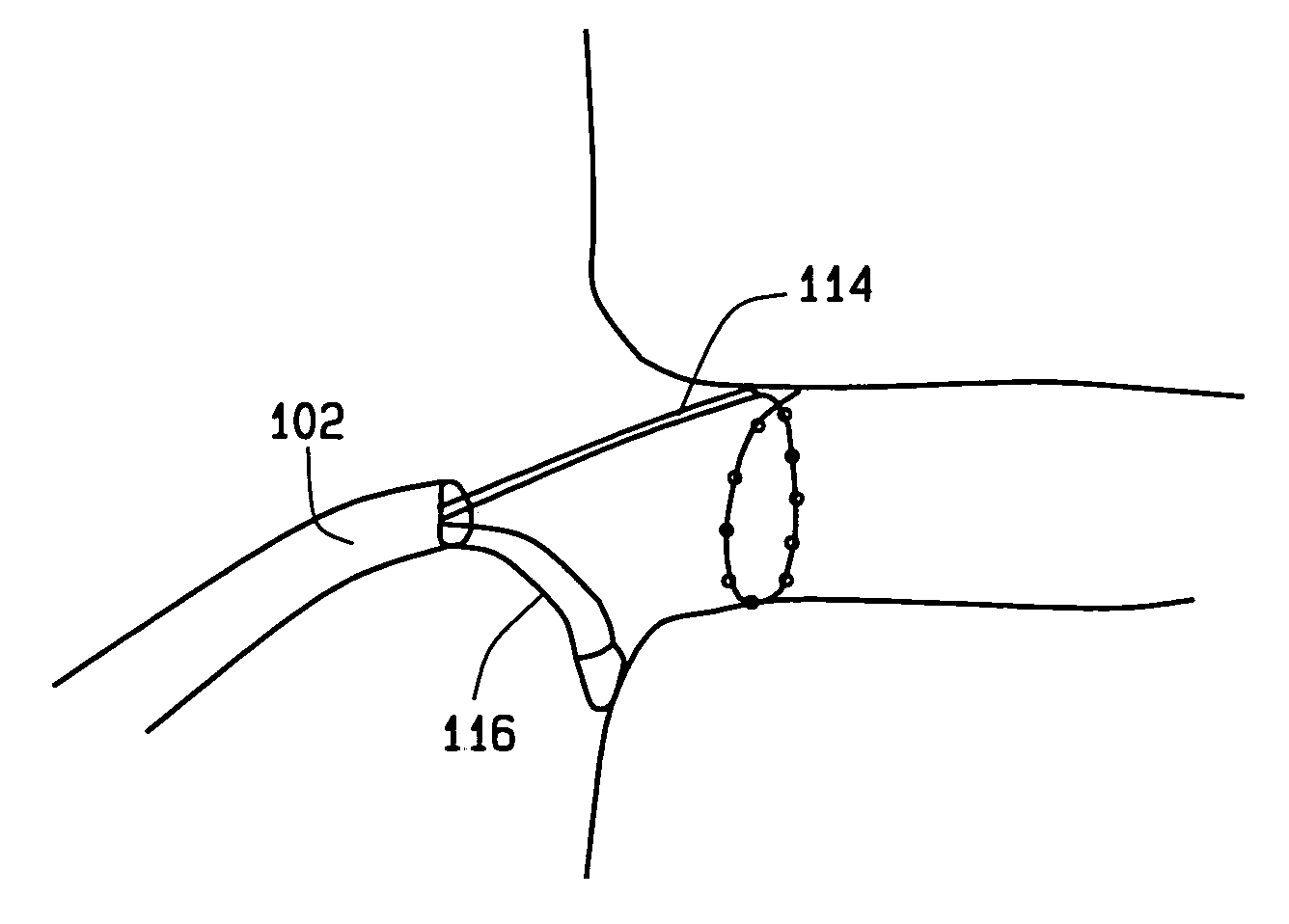
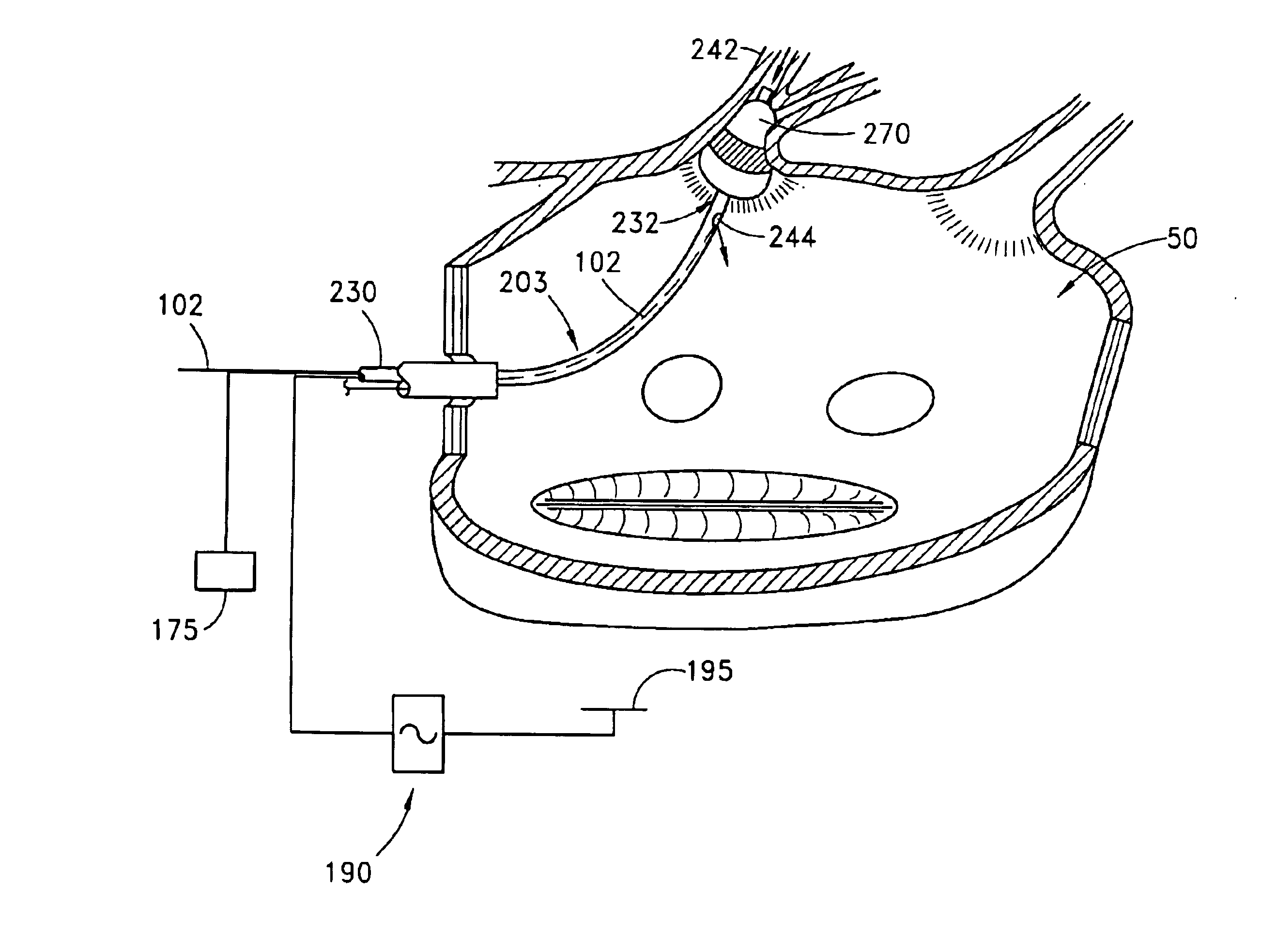
Tissue ablation system including guidewire with sensing element
A tissue ablation system for ablating human tissue wherein sensing and ablation procedures are performed and controlled independently. A sensing wire is positioned distally to the ablation region and is adapted to pass thorough the ablation device such that it may move with or independently of the ablation device without obstructing the surface tissue interface of the ablation energy. The ablation device can ablate a substantial portion of a circumferential region of tissue, for example at or near the location where the pulmonary vein extends from the atrium. The tissue ablation system comprises an ablation device comprised of an elongated catheter with a proximal region and a distal region and an ablation element located proximate the distal region of the catheter. A sensing device having an elongated body with a proximal portion and a distal portion is adapted to be positioned within a vessel at or near a vessel ostium, wherein the sensing device is adapted to be slidably received within a lumen of the ablation device. The sensing device, a guide wire for example, may be shaped in various configurations to allow sensing device such as electrodes disposed thereon to contact the vessel wall near the ablation region. In this fashion, the sensing and ablation procedures are de-coupled such that the sensing device does not interfere or obstruct the ablation member's interface with the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
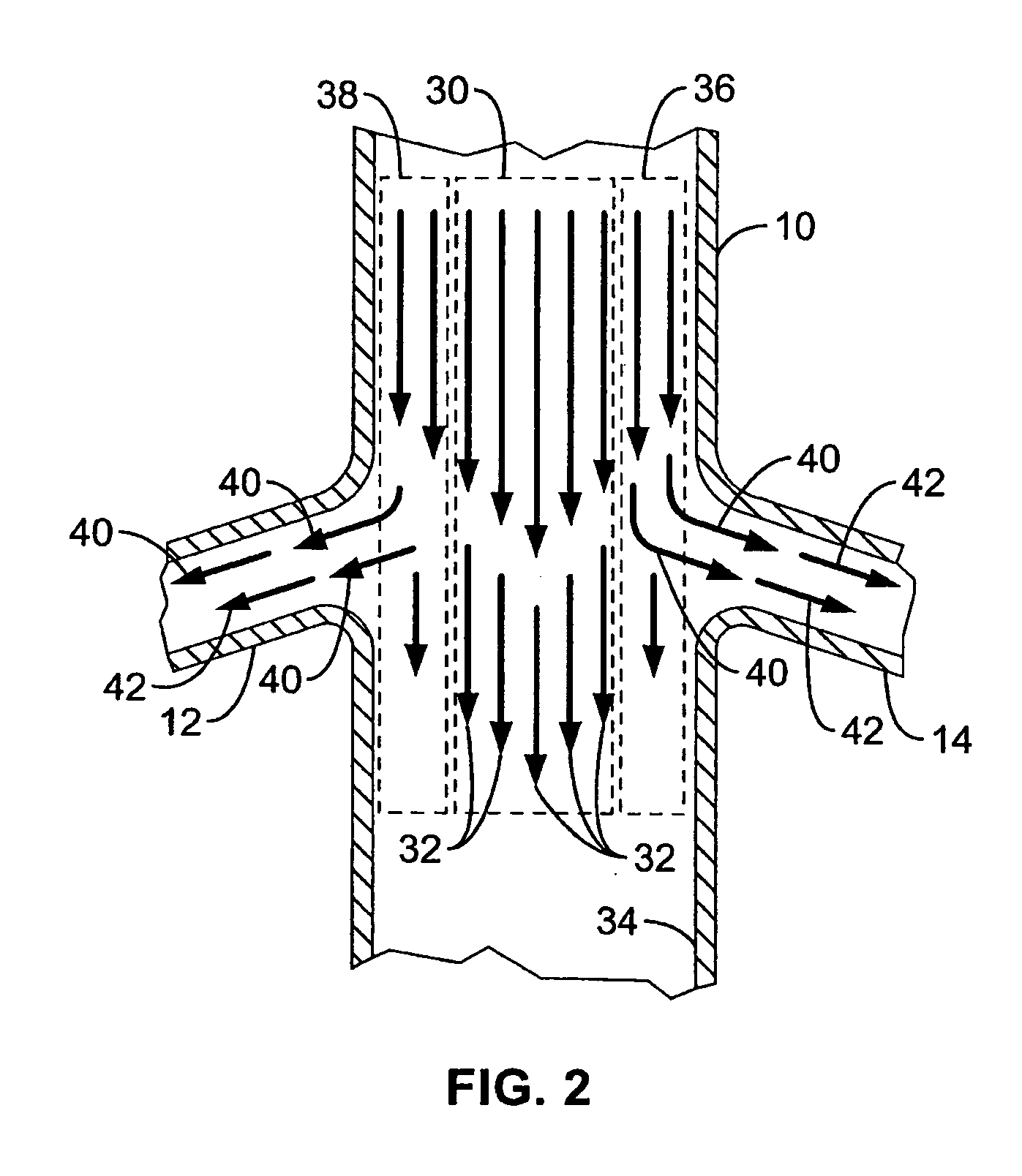
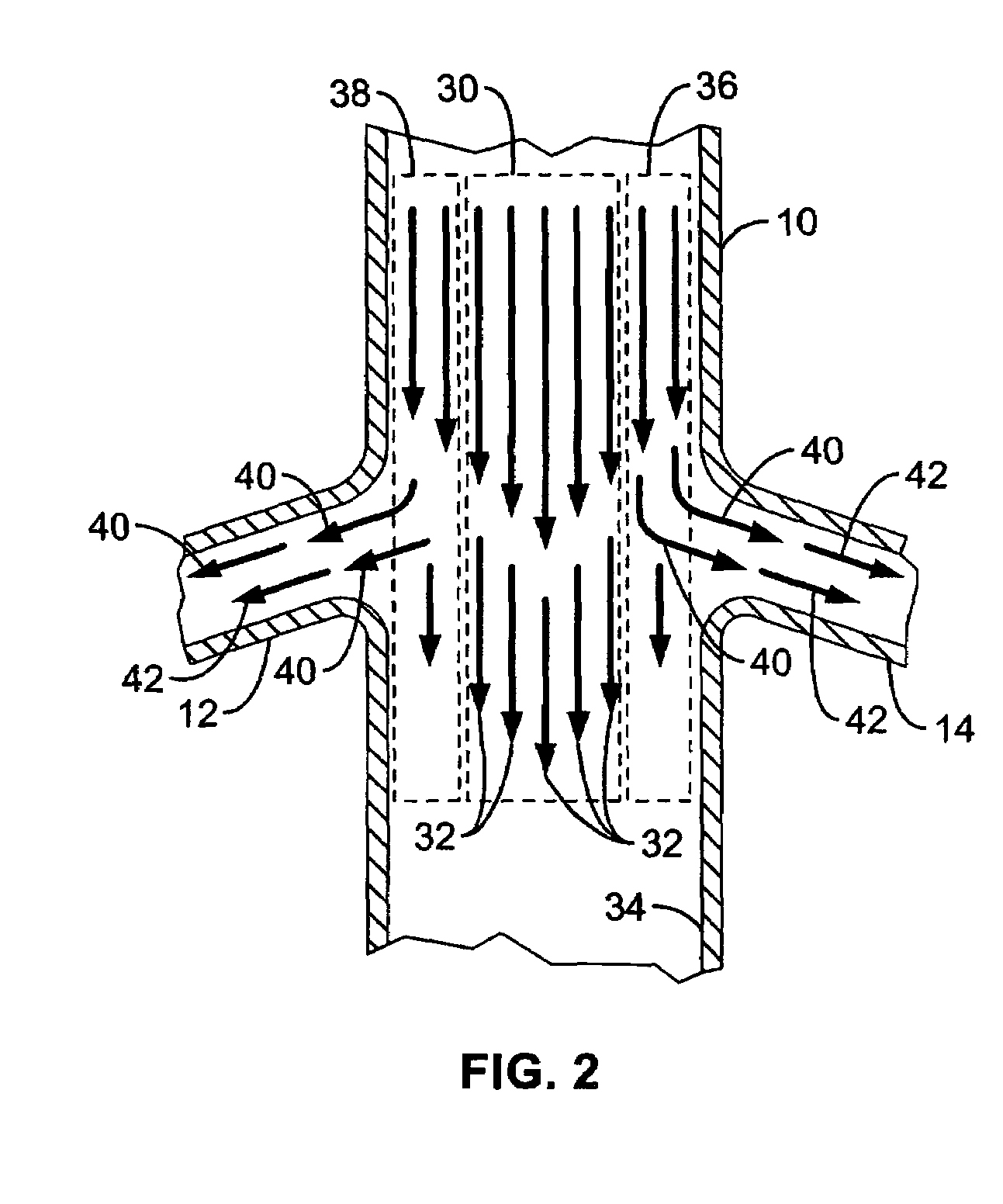
Method and apparatus for intra aortic substance delivery to a branch vessel
A renal flow system injects a volume of fluid agent into a location within an abdominal aorta in a manner that flows bilaterally into each of two renal arteries via their respectively spaced ostia along the abdominal aorta wall. A local injection assembly (100) includes two injection members (104, 106), each having an injection port (112) that couples to a source of fluid agent externally of the patient. The injection ports may be positioned within an outer region of blood flow along the abdominal aorta wall perfusing the two renal arteries.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Intra-aortic renal delivery catheter
A renal flow system and method direct fluid into renal arteries from a location within the aorta. A renal flow assembly has a tapered tube that is adjustable between a radially collapsed condition for delivery to the location through a delivery sheath and a radially expanded condition that divides aortic flow into exterior and interior paths. The tube's wall is made from a sheet of flexible material, such as PTFE or ePTFE. Two, nickel-titanium rings radially support the tube's ends and are connected by a longitudinal spine support. A fluid delivery assembly injects drug to flow along the exterior flow path and the tubular wall directs the agent into the renal artery ostium. The tube's taper has localized shape for circumferential agent mixing to infuse both kidneys' renals. The flow assembly allows an interventional device, e.g. delivery catheter, to advance across the location while directing blood into the renals and perfusing downstream circulation. The renal flow assembly and distal device are used within a common guide sheath through a single puncture wound. Vasodilators, antioxidants, or diuretics are delivered to the kidneys to treat / prevent RCN, CHF, or ARF.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Apparatus And Methods For Excluding The Left Atrial Appendage
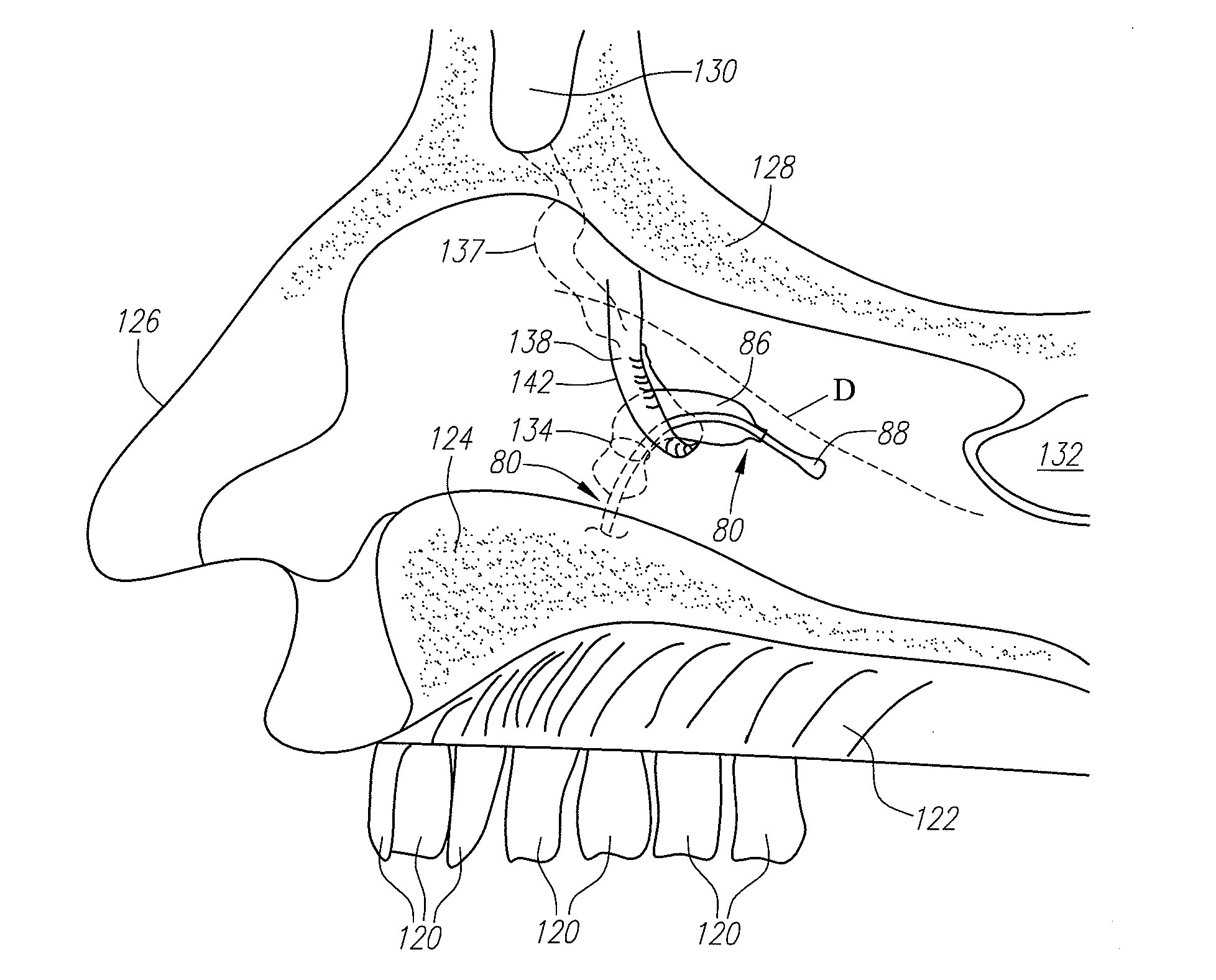
InactiveUS20110082495A1Lower the volumeReduce riskOcculdersSurgical veterinaryTunica intimaPericardium
Apparatus and methods are provided for excluding and reducing the volume of the left atrial appendage (“LAA”) by deploying a first tissue capture element in contact with the pericardium and a second tissue capture element in engagement with the endocardial surface adjacent to the ostium of the LAA, such that the LAA tissue is retained in a collapsed, reduced volume state therebetween. Methods of using the apparatus of the present invention to reduce or occlude the LAA also are provided.
Owner:RUIZ CARLOS E
Intracardiac cage and method of delivering same
InactiveUS20070066993A1Prevent materialObstruct passageHeart valvesDilatorsExpandable cageRight atrium
A method of preventing ingress of material into the left atrium of a heart includes providing a delivery sheath, advancing the sheath distal end through an opening between the right atrium and the left atrium of the heart, providing an expandable cage, delivering the expandable cage to the left atrium, and expanding the expandable cage within the left atrium. The expandable cage includes a proximal end, a distal end, and a plurality of supports extending therebetween. The expandable cage also includes a first membrane provided at its proximal end and a second membrane provided at its distal end. The expandable cage has a collapsed configuration so that it can be received within the lumen of the delivery sheath, and an expanded configuration for deployment within the heart. When expanded, the first membrane is positioned at an opening between the left and right atria of the heart, and the second membrane is positioned at the ostium of the left atrial appendage. The first membrane substantially prevents passage of blood between the atria and the second membrane prevents passage of embolic material from the left atrial appendage into the left atrium of the heart.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Tissue ablation device assembly and method for electrically isolating a pulmonary vein ostium from an atrial wall
This invention is related to a tissue ablation system and method that treats atrial arrhythmia by ablating a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium. The system includes a circumferential ablation member with an ablation element and also includes a delivery assembly for delivering the ablation member to the location. The circumferential ablation member is generally adjustable between different configurations to allow both the delivery through a delivery sheath into the atrium and the ablative coupling between the ablation element and the circumferential region of tissue.
Owner:ATRIONIX
Method and apparatus for intra-aortic substance delivery to a branch vessel
A renal flow system injects a volume of fluid agent into a location within an abdominal aorta in a manner that flows bi-laterally into each of two renal arteries via their respectively spaced ostia along the abdominal aorta wall. A local injection assembly includes two injection members, each having an injection port that couples to a source of fluid agent externally of the patient. The injection ports may be positioned with an outer region of blood flow along the abdominal aorta wall perfusing the two renal arteries. A flow isolation assembly may isolate flow of the injected agent within the outer region and into the renals. The injection members are delivered to the location in a first radially collapsed condition, and bifurcate across the aorta to inject into the spaced renal ostia. A delivery catheter for upstream interventions is used as a chassis to deliver a bilateral local renal injection assembly to the location within the abdominal aorta.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Sphenoid sinus stent
A stent specifically designed for use in treating chronic sphenoid sinusitis comprises a soft compressible plastic tube of a predetermined diameter having a proximal end, a distal end and a lumen extending therebetween. The stent has a generally hemispherical hollow dome integrally molded to its distal end. The diameter of the dome is greater than the predetermined diameter of the plastic tube. The stent further includes an integrally molded annular flange located a short predetermined distance proximal to the hemispherical dome. The device is designed to be fitted through a surgically enlarged ostium of the sphenoid sinus such that the dome resides within the sinus cavity and the flange abuts the bony wall surrounding the ostium. The stent maintains the ostium patent and permits irrigation / suctioning via the stent's lumen.
Owner:MICROMEDICS
Method and apparatus for intra-aortic substance delivery to a branch vessel
A renal flow system injects a volume of fluid agent into a location within an abdominal aorta in a manner that flows bi-laterally into each of two renal arteries via their respectively spaced ostia along the abdominal aorta wall. A local injection assembly includes two injection members, each having an injection port that couples to a source of fluid agent externally of the patient. The injection ports may be positioned with an outer region of blood flow along the abdominal aorta wall perfusing the two renal arteries. A flow isolation assembly may isolate flow of the injected agent within the outer region and into the renals. The injection members are delivered to the location in a first radially collapsed condition, and bifurcate across the aorta to inject into the spaced renal ostia. A delivery catheter for upstream interventions is used as a chassis to deliver a bilateral local renal injection assembly to the location within the abdominal aorta.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Catheter system for the treatment of atrial fibrillation
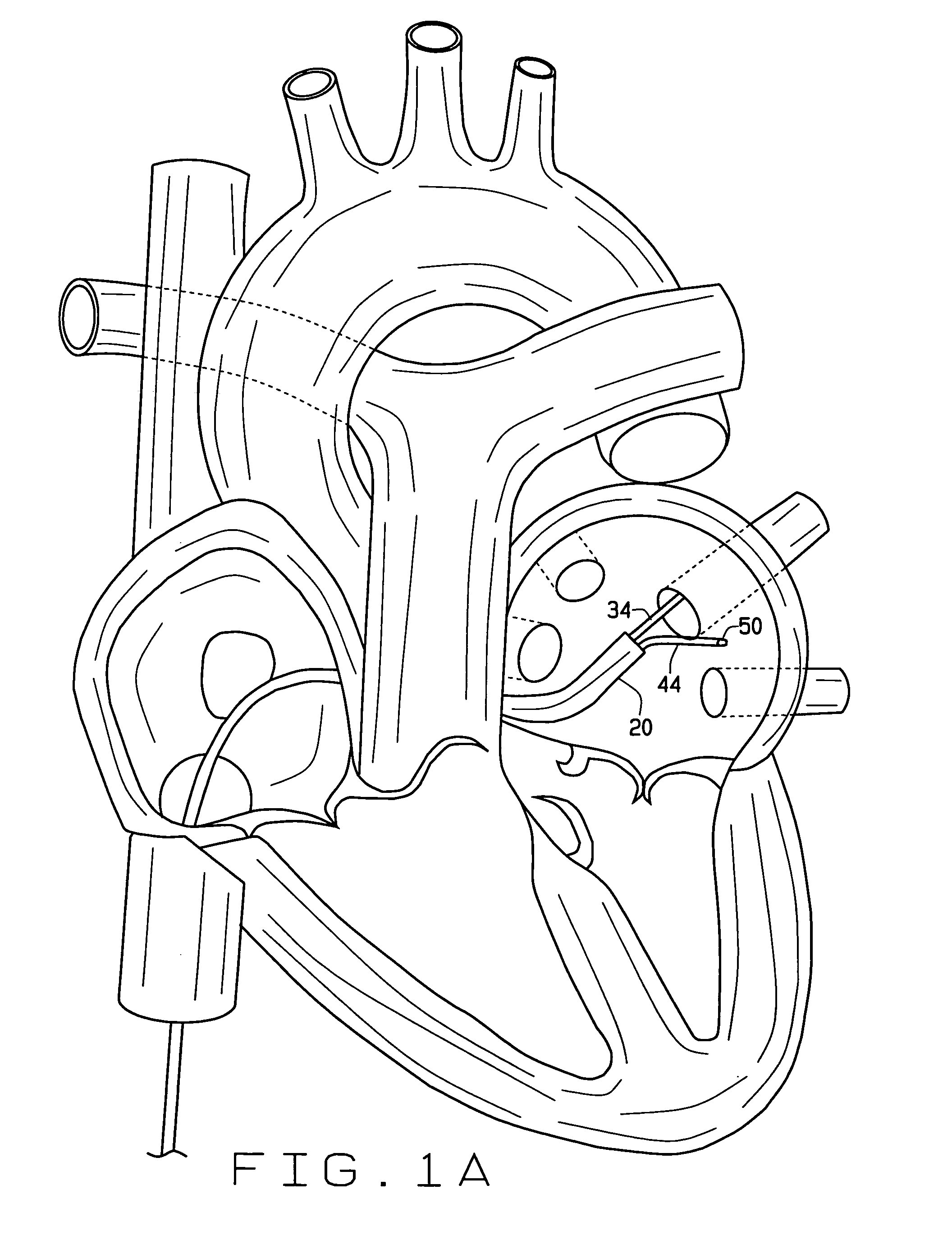
InactiveUS20060224153A1Accurate and fast positioningReduce riskCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingVeinCatheter
Disclosed are a means and method for rapidly and accurately positioning a toroidal balloon with its distal surface placed tightly against the endocardial surface of the left atrium at a location that is close to the ostium of a pulmonary vein. On the exterior surface of the toroidal balloon can be an electrically conducting wire that is capable of causing rf energy to be placed into the tissue of the left atrium so as to ablate that tissue to alter the conduction of aberrant electrical signals of the heart that are associated with atrial fibrillation. The toroidal balloon is wrapped circumferentially around a tapered balloon that is placed into the pulmonary vein. This system can be applied successively to at least one or as many as all four of the pulmonary veins that enter the left atrium to treat the patient's atrial fibrillation.
Owner:FISCHELL ROBERT E +1
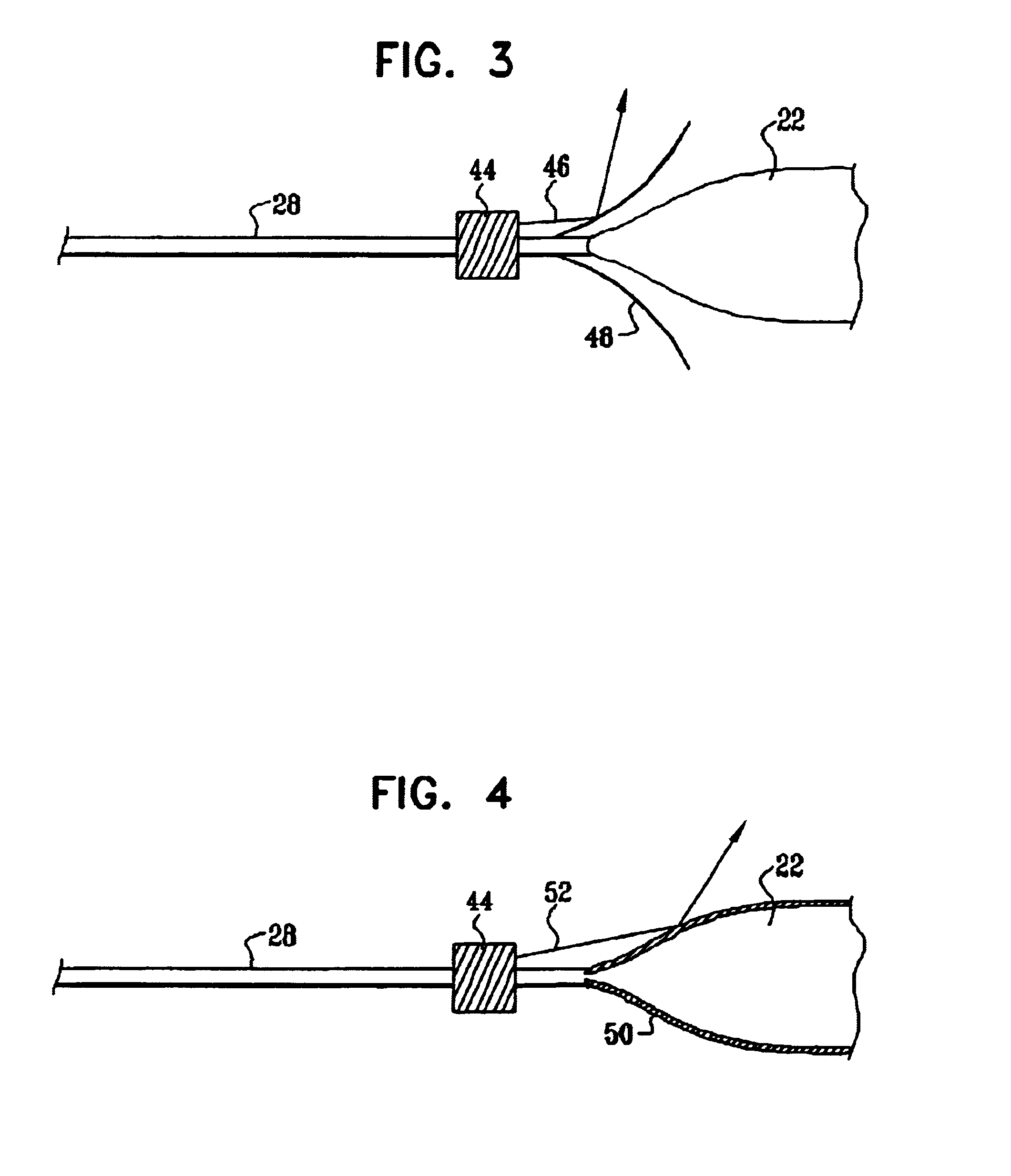
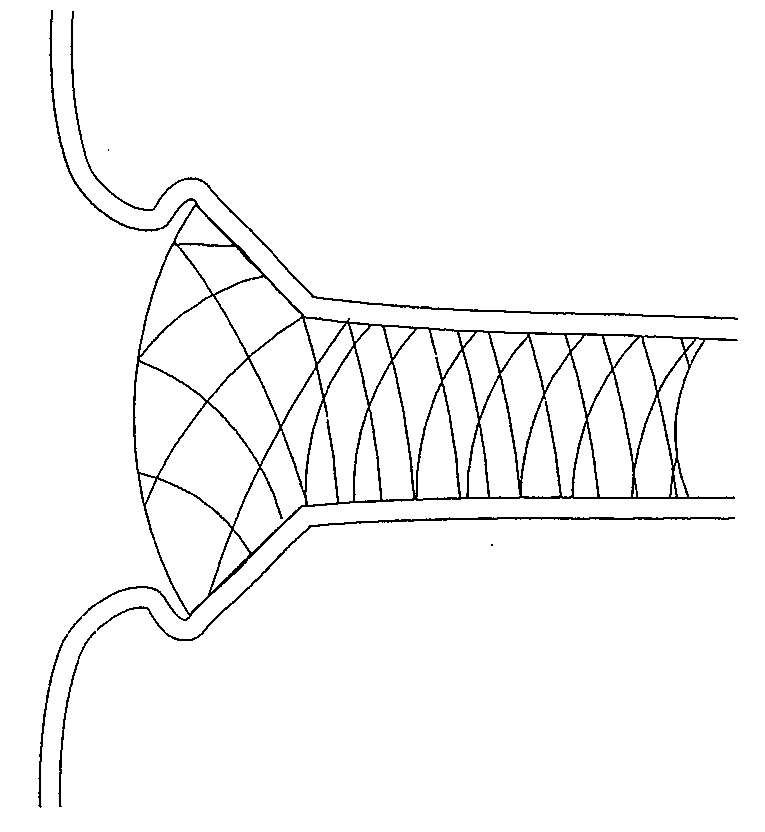
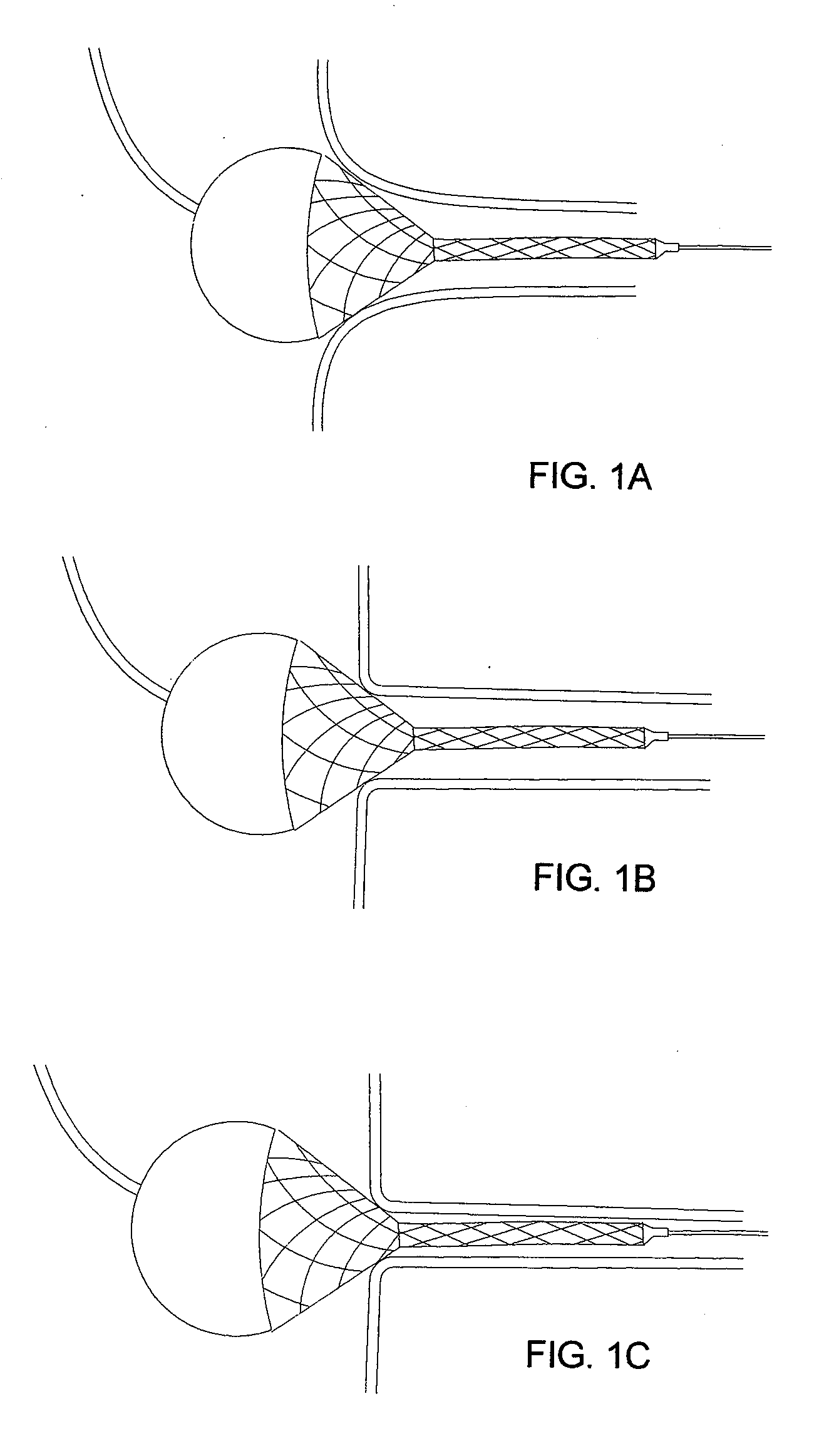
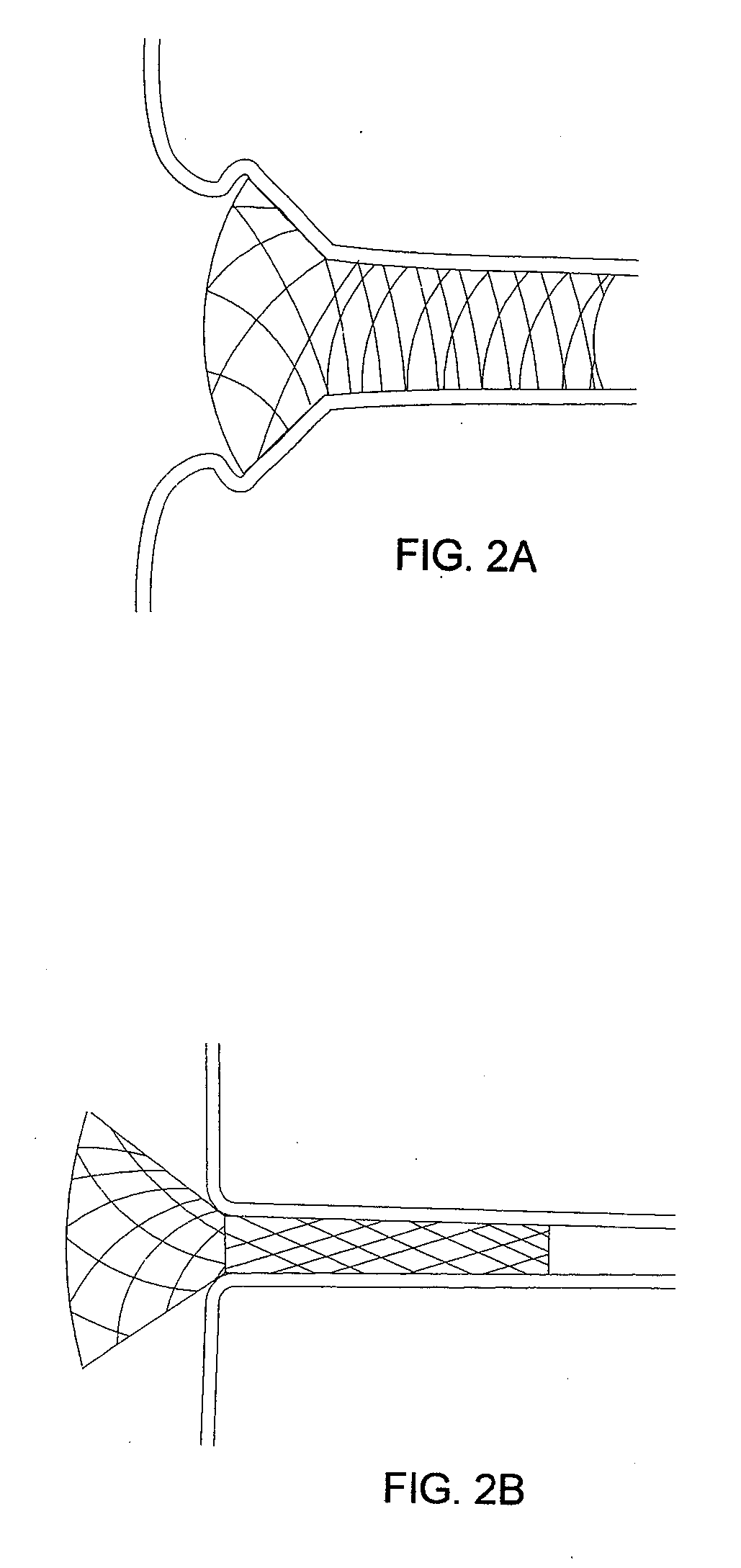
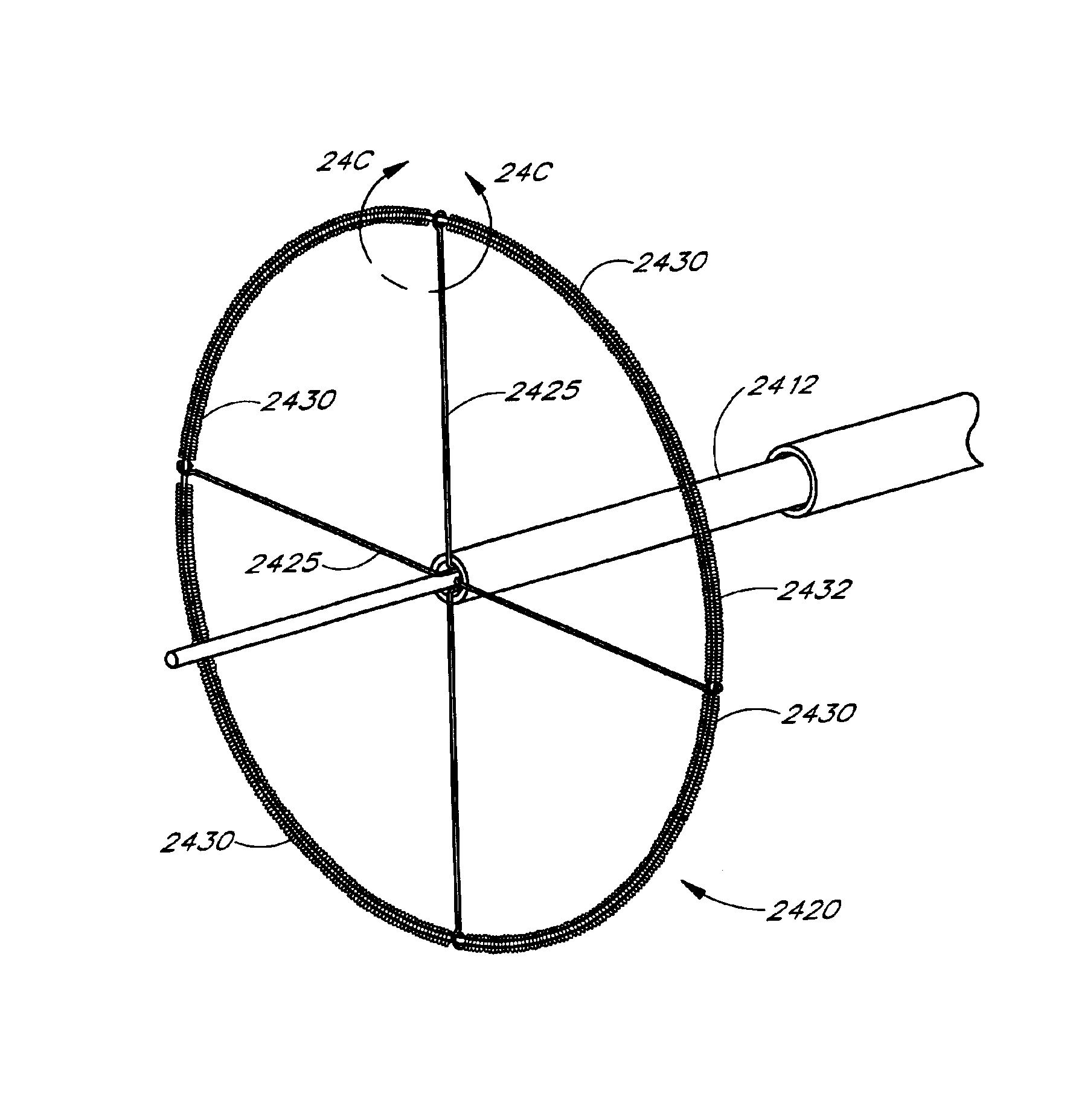
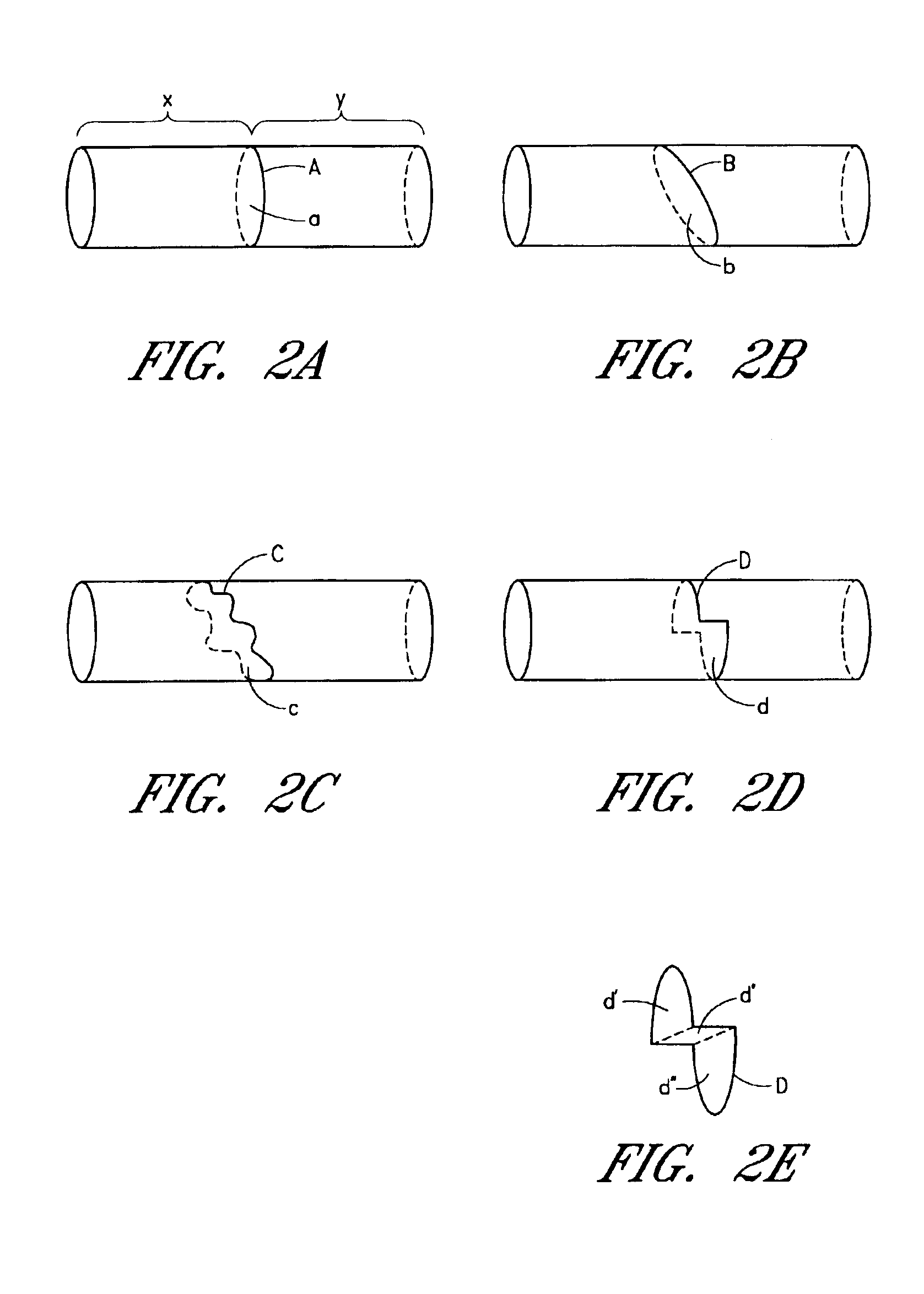
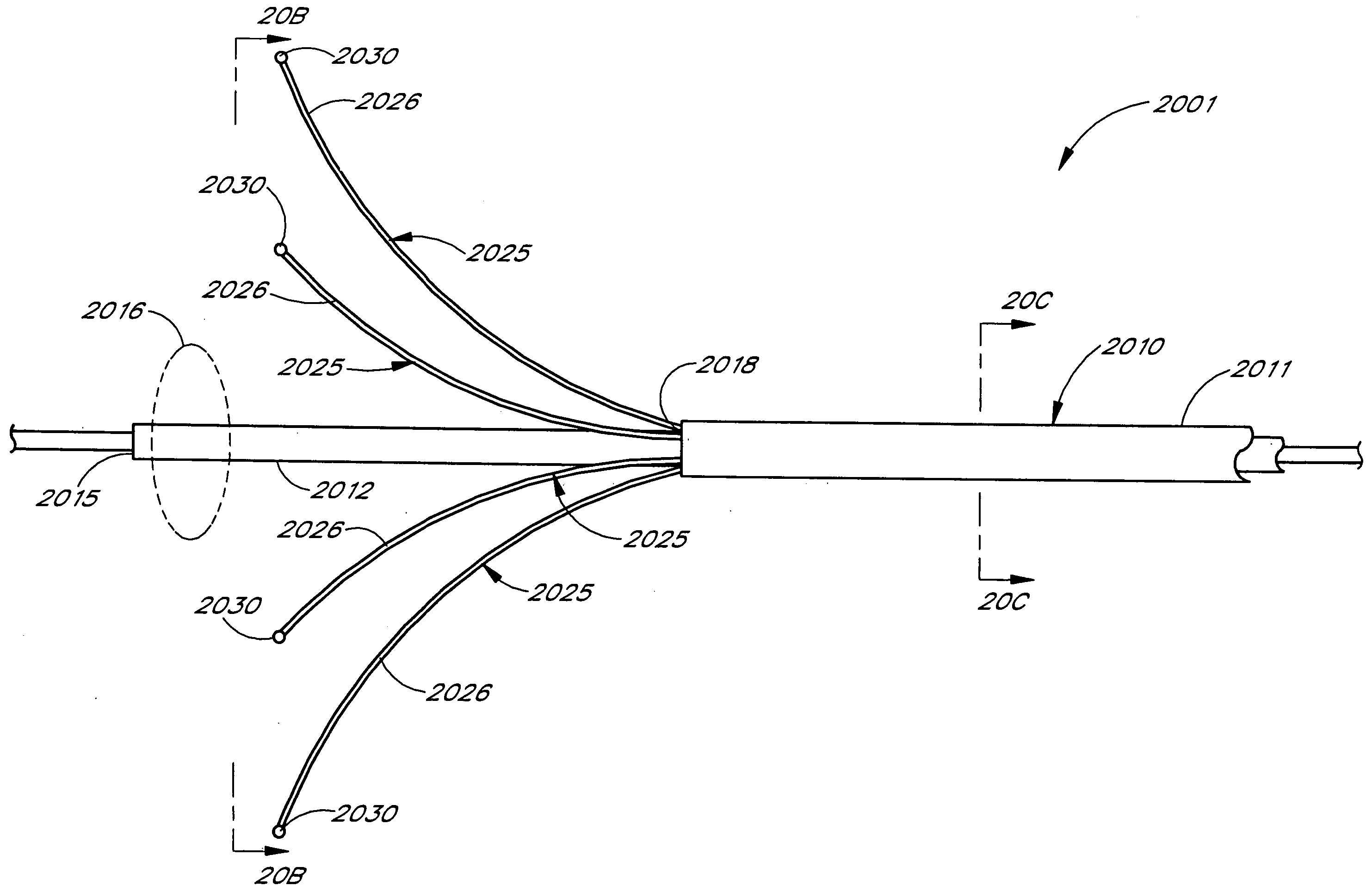
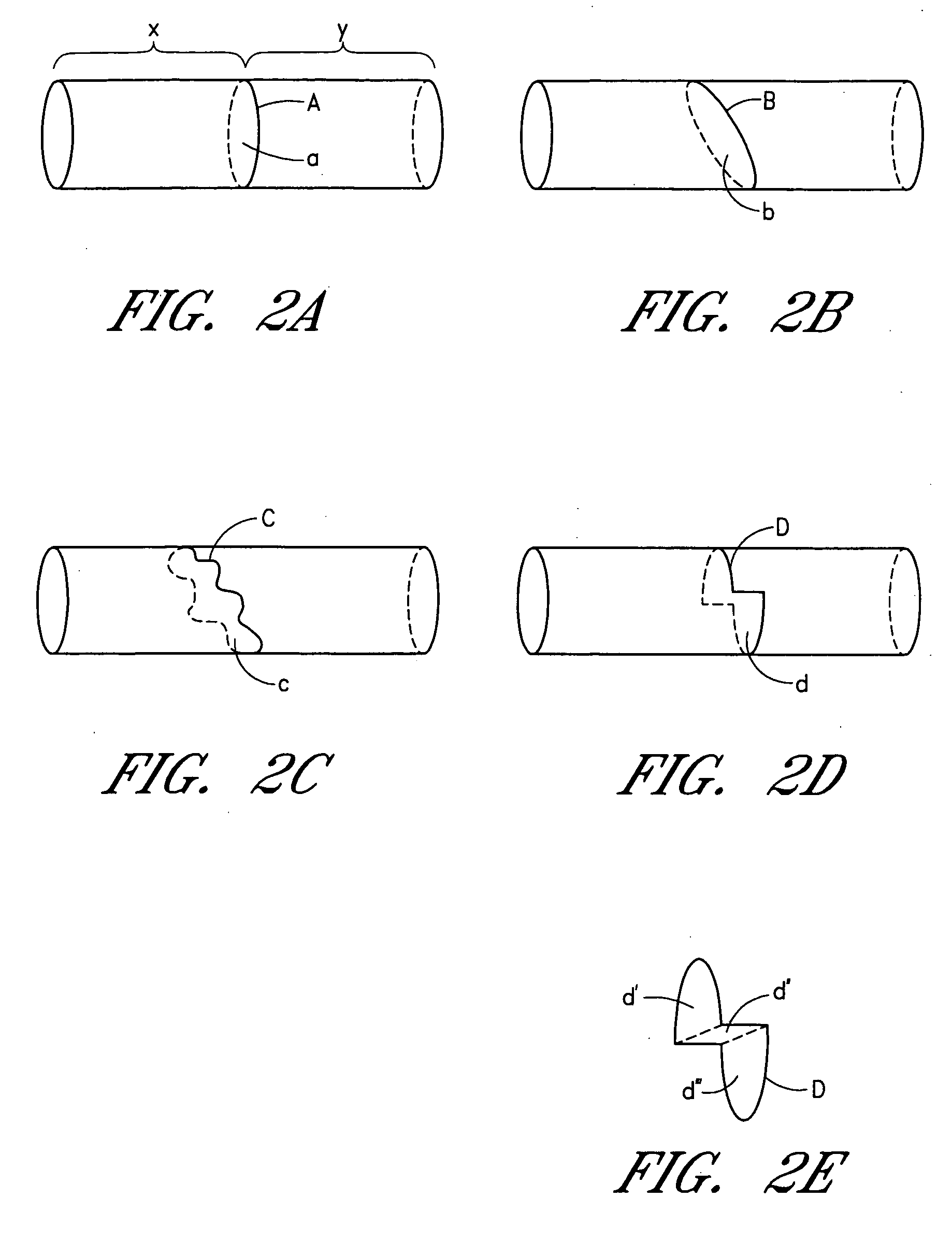
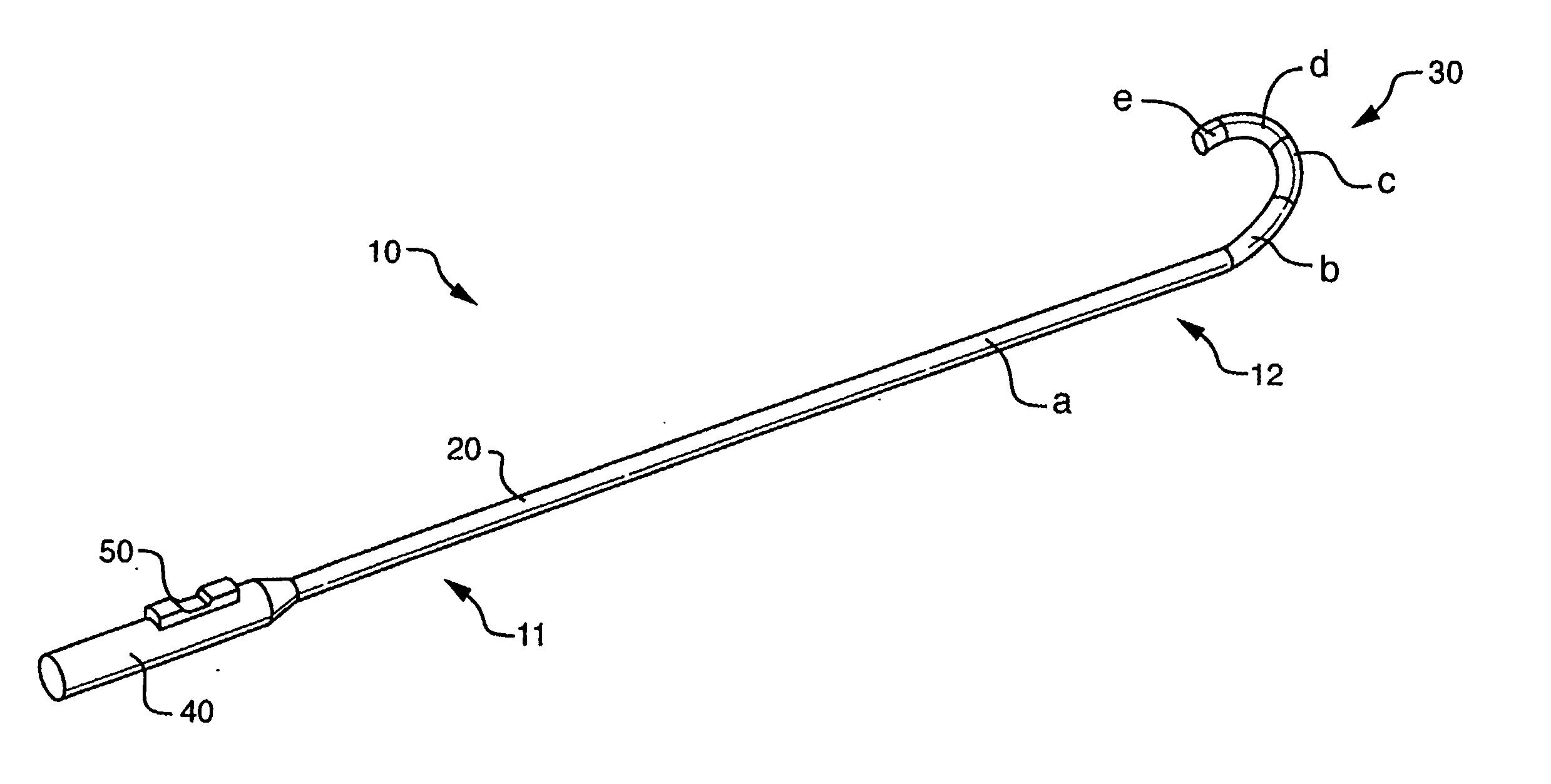
Circumferential ablation device assembly
This invention is a circumferential ablation device assembly which is adapted to forming a circumferential conduction block in a pulmonary vein. The assembly includes a circumferential ablation element which is adapted to ablate a circumferential region of tissue along a pulmonary vein wall which circumscribes the pulmonary vein lumen, thereby transecting the electrical conductivity of the pulmonary vein against conduction along its longitudinal axis and into the left atrium. The circumferential ablation element includes an expandable member with a working length that is adjustable from a radially collapsed position to a radially expanded position. An equatorial band circumscribes the outer surface of the working length and is adapted to ablate tissue adjacent thereto when actuated by an ablation actuator. The equatorial band has a length relative to the longitudinal axis of the expandable member that is narrow relative to the working length, and is also substantially shorter than its circumference when the working length is in the radially expanded position. A pattern of insulators may be included over an ablation element which otherwise spans the working length in order to form the equatorial band described. The expandable member is also adapted to conform to the pulmonary vein in the region of its ostium, such as by providing a great deal of radial compliance or by providing a taper along the working length which has a distally reducing outer diameter. A linear ablation element is provided adjacent to the circumferential ablation element in a combination assembly which is adapted for use in a less-invasive “maze”-type procedure in the region of the pulmonary vein ostia in the left ventricle.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of cardiac ablation in the vicinity of the right inferior pulmonary vein
The present invention provides devices and methods for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. In one embodiment a method for ablating tissue about an ostium of a right inferior vein of a heart includes positioning a sheath catheter having a deflectable distal end segment with a bent tip element in the left atrium of a heart, causing the distal end segment to deflect in a compound curve as the catheter is advanced towards an ostium of a right inferior vein, orienting said sheath catheter such that an ablation instrument can be delivered through the sheath catheter to a position proximal to the right inferior vein, and activating the ablation instrument to form at least one lesion about the right inferior vein.
Owner:CARDIOFOCUS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com