Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
723 results about "Atrial fibrillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A disease of the heart characterized by irregular and often faster heartbeat.
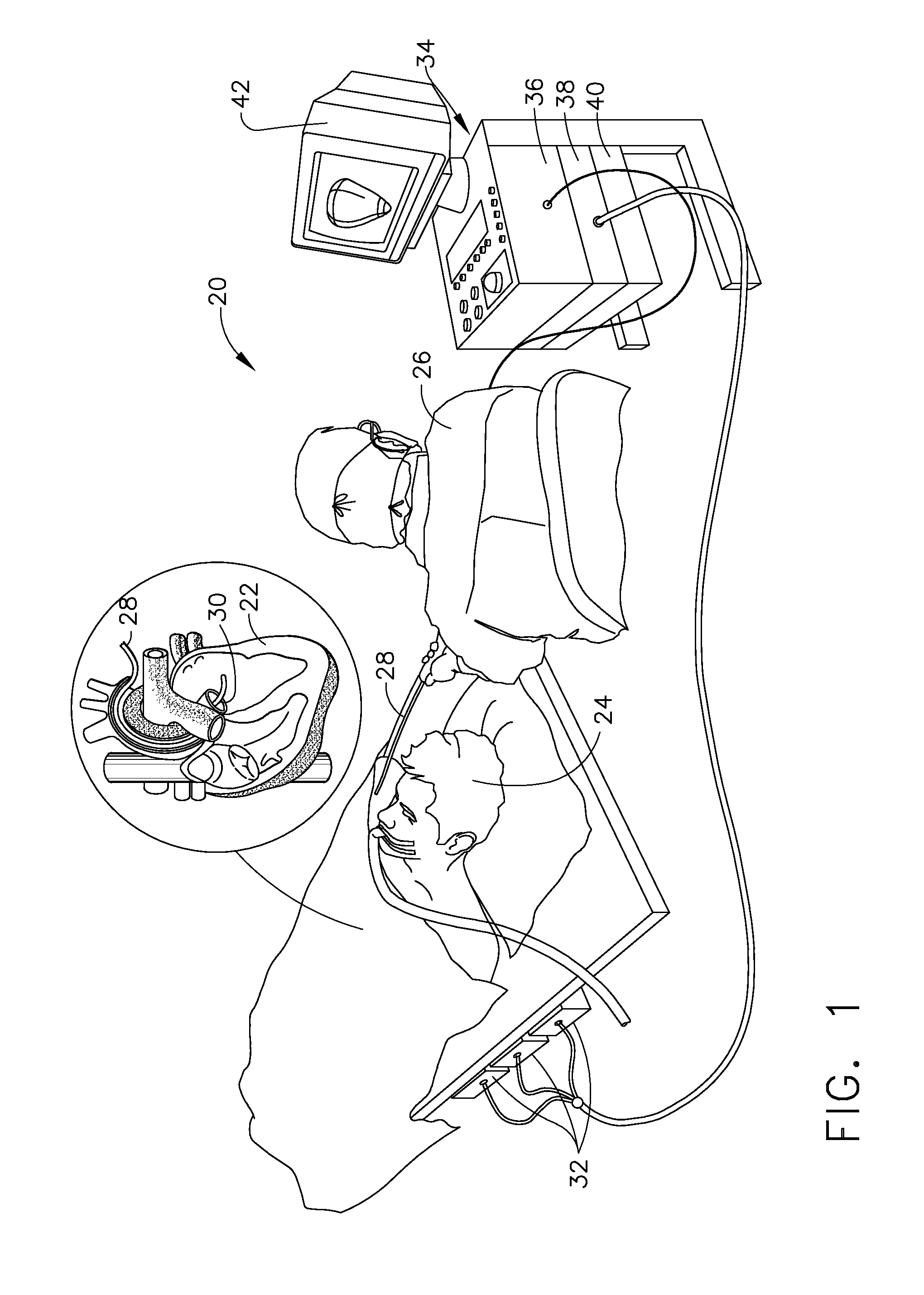
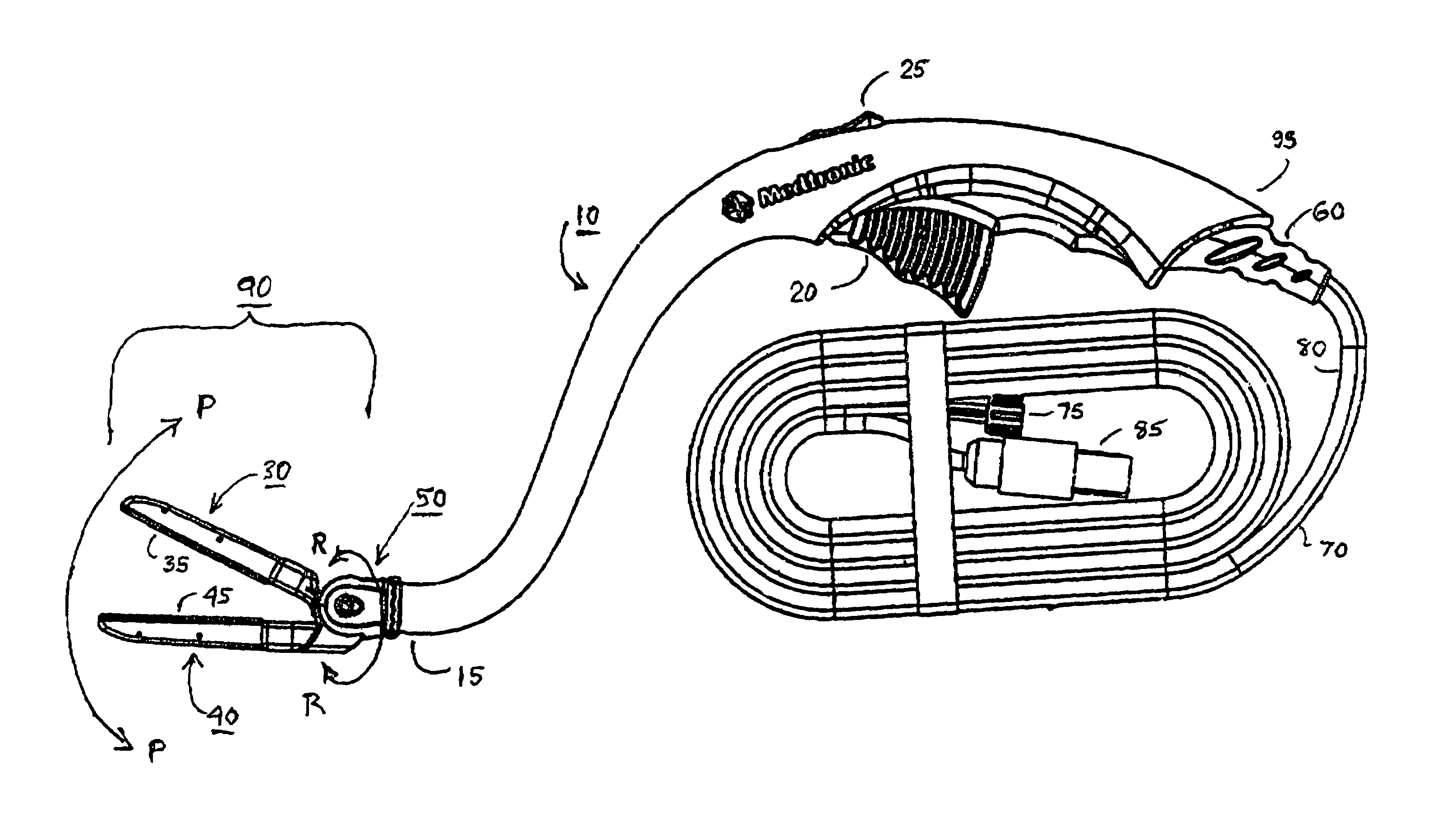
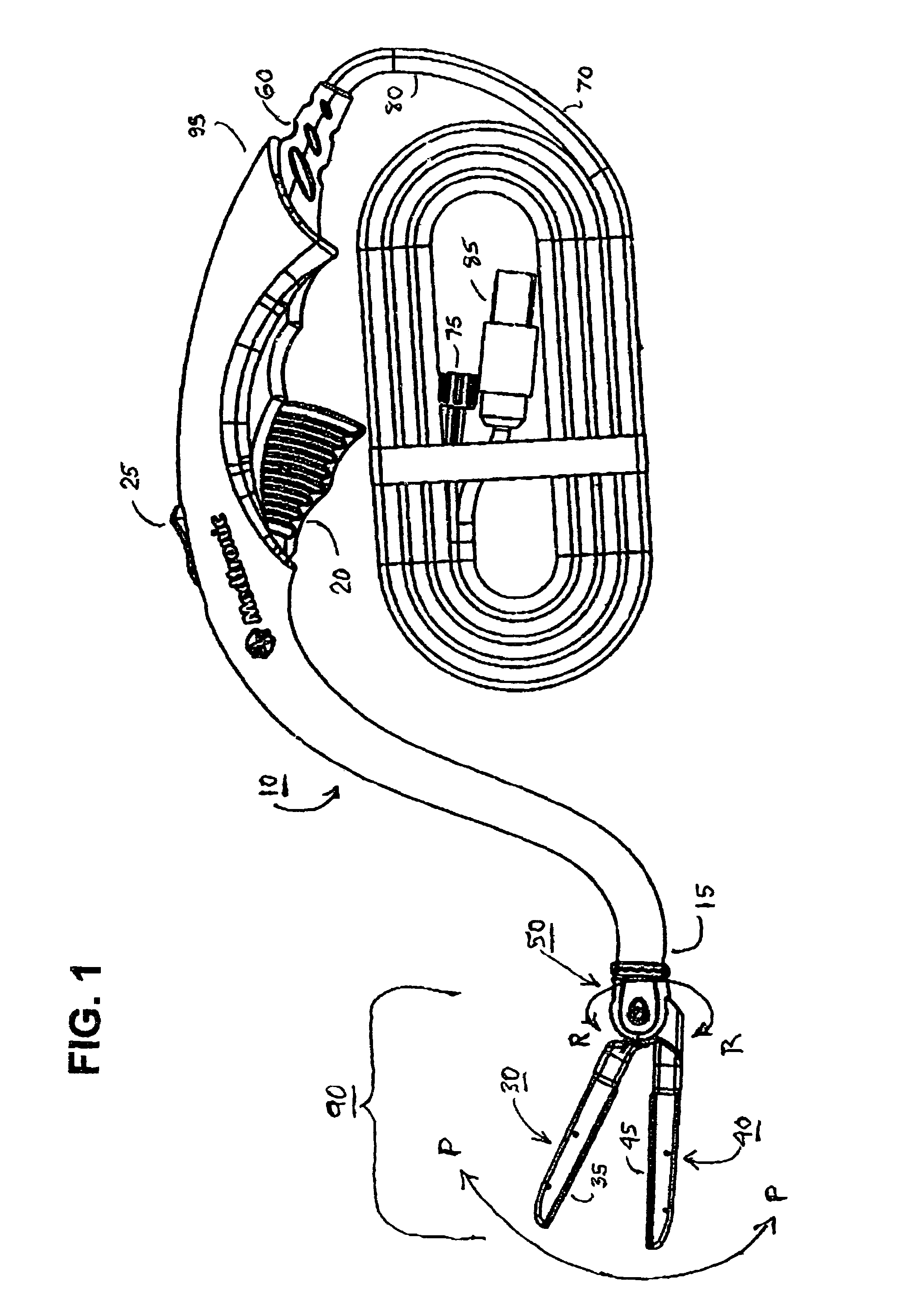
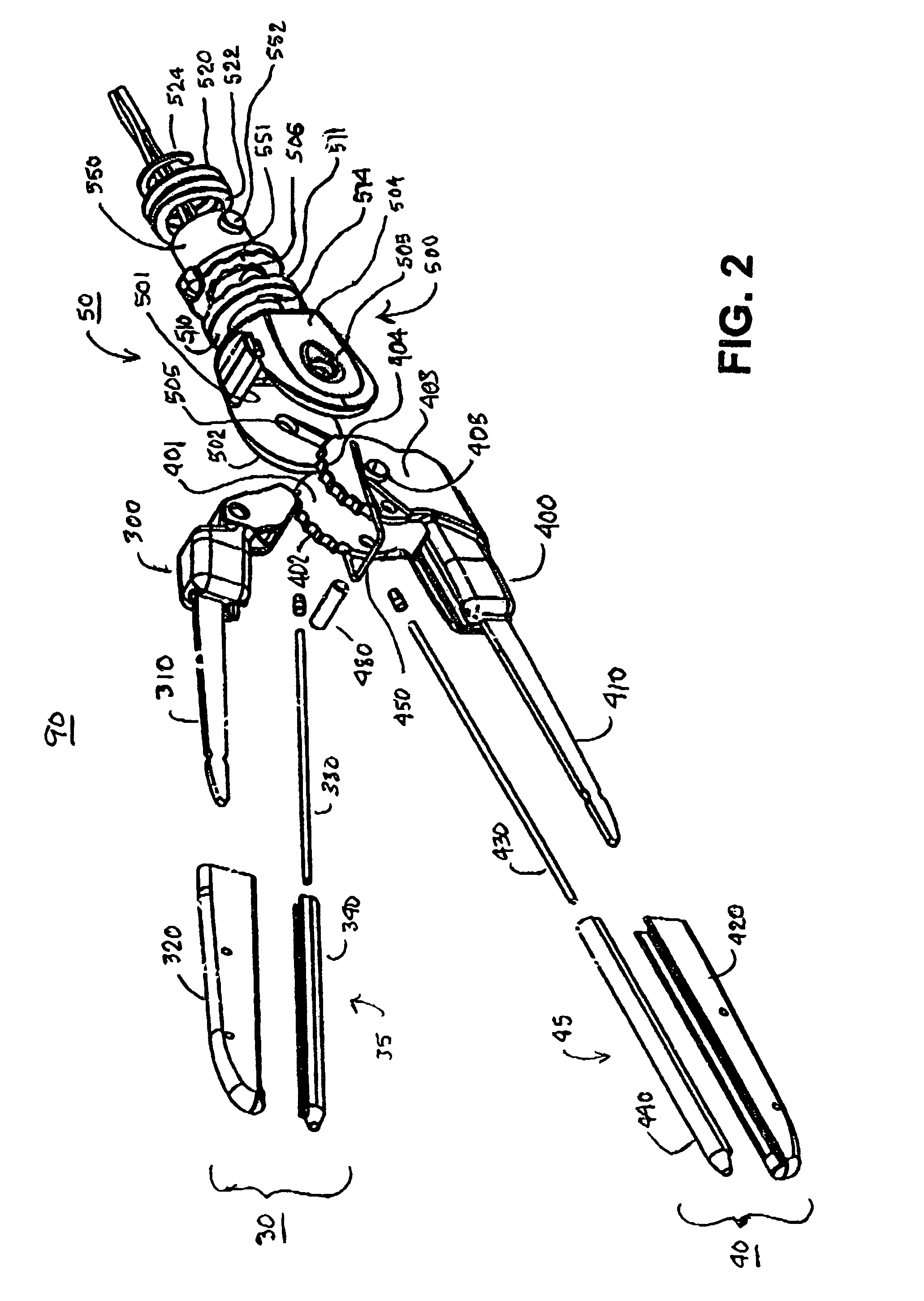
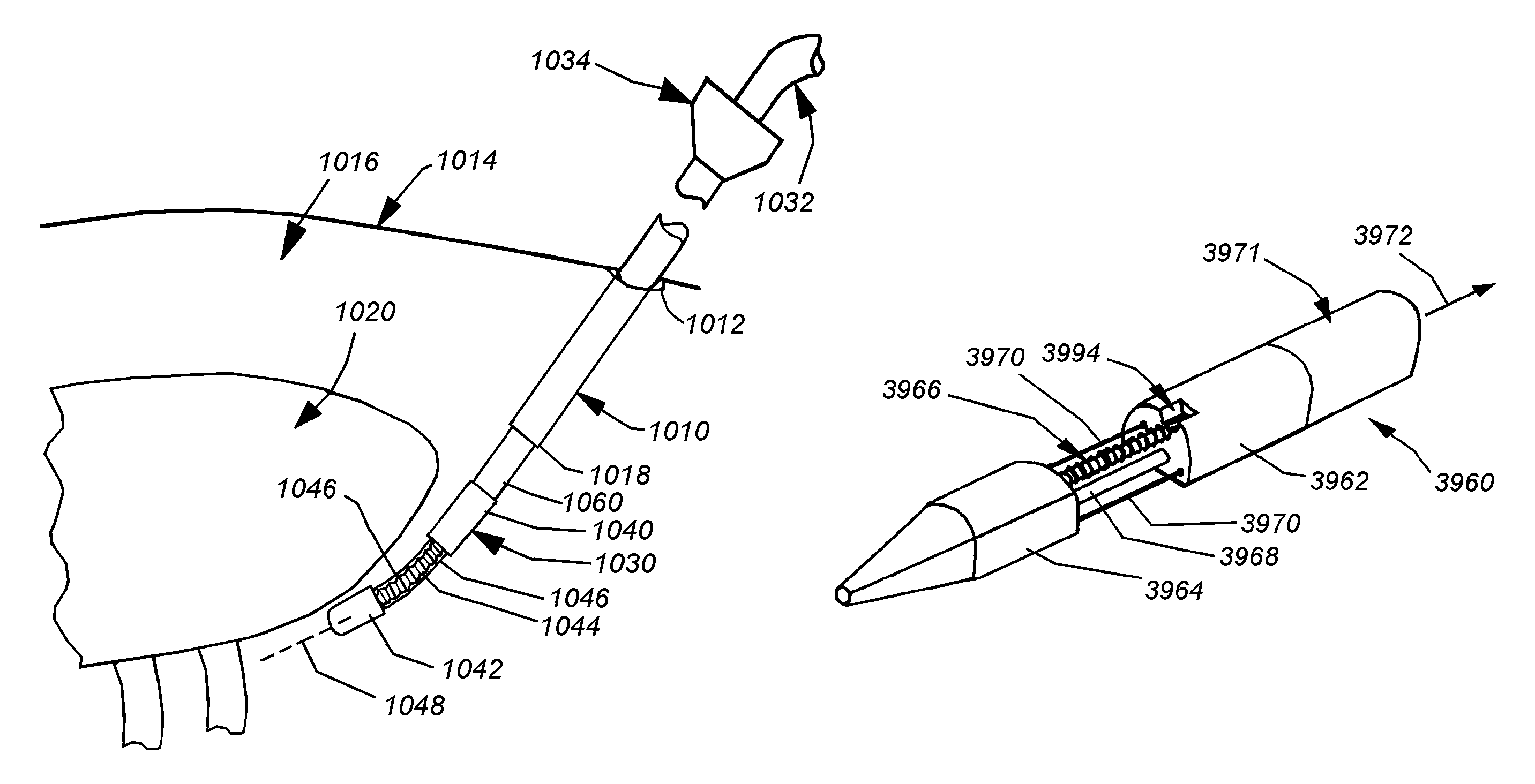
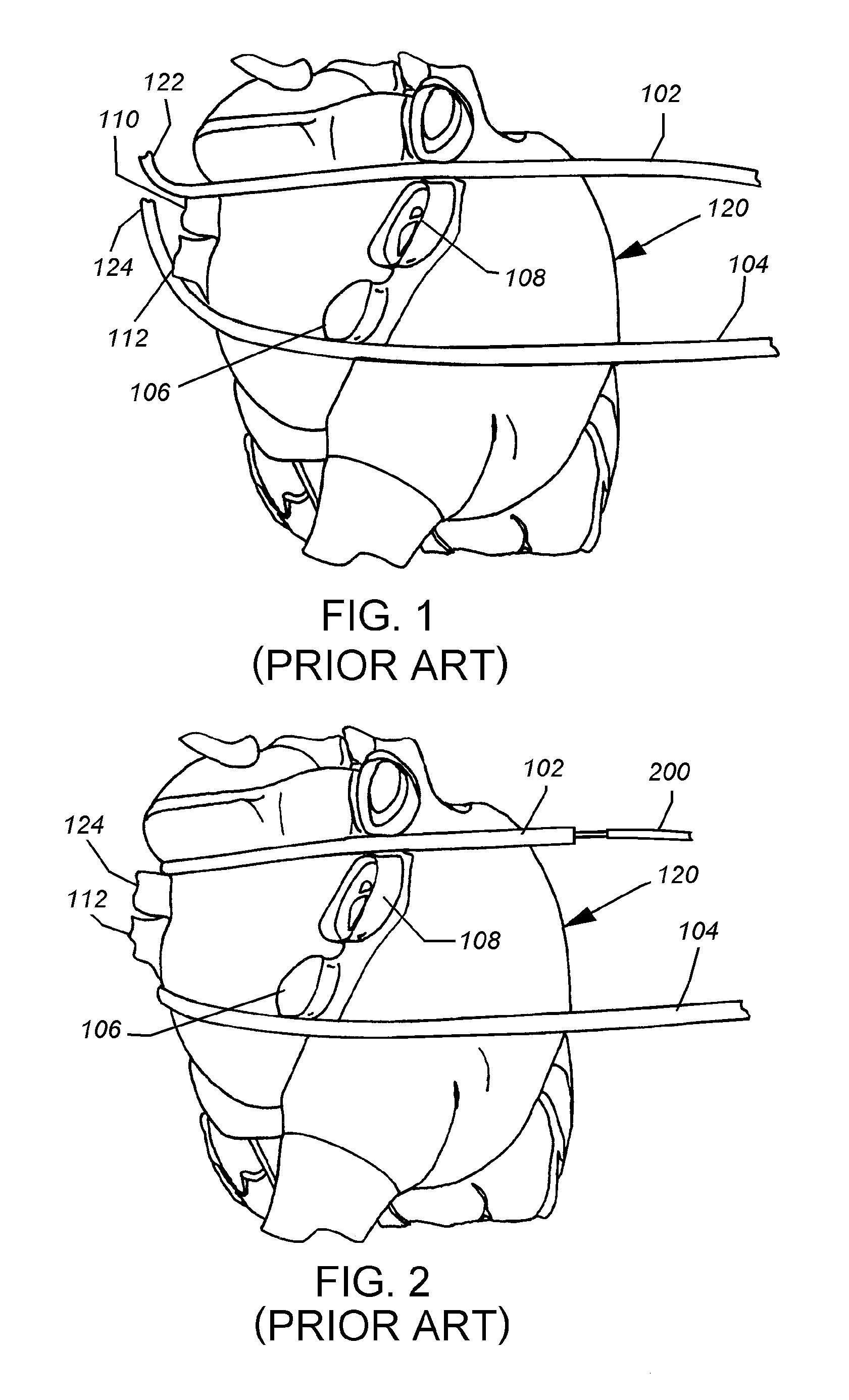
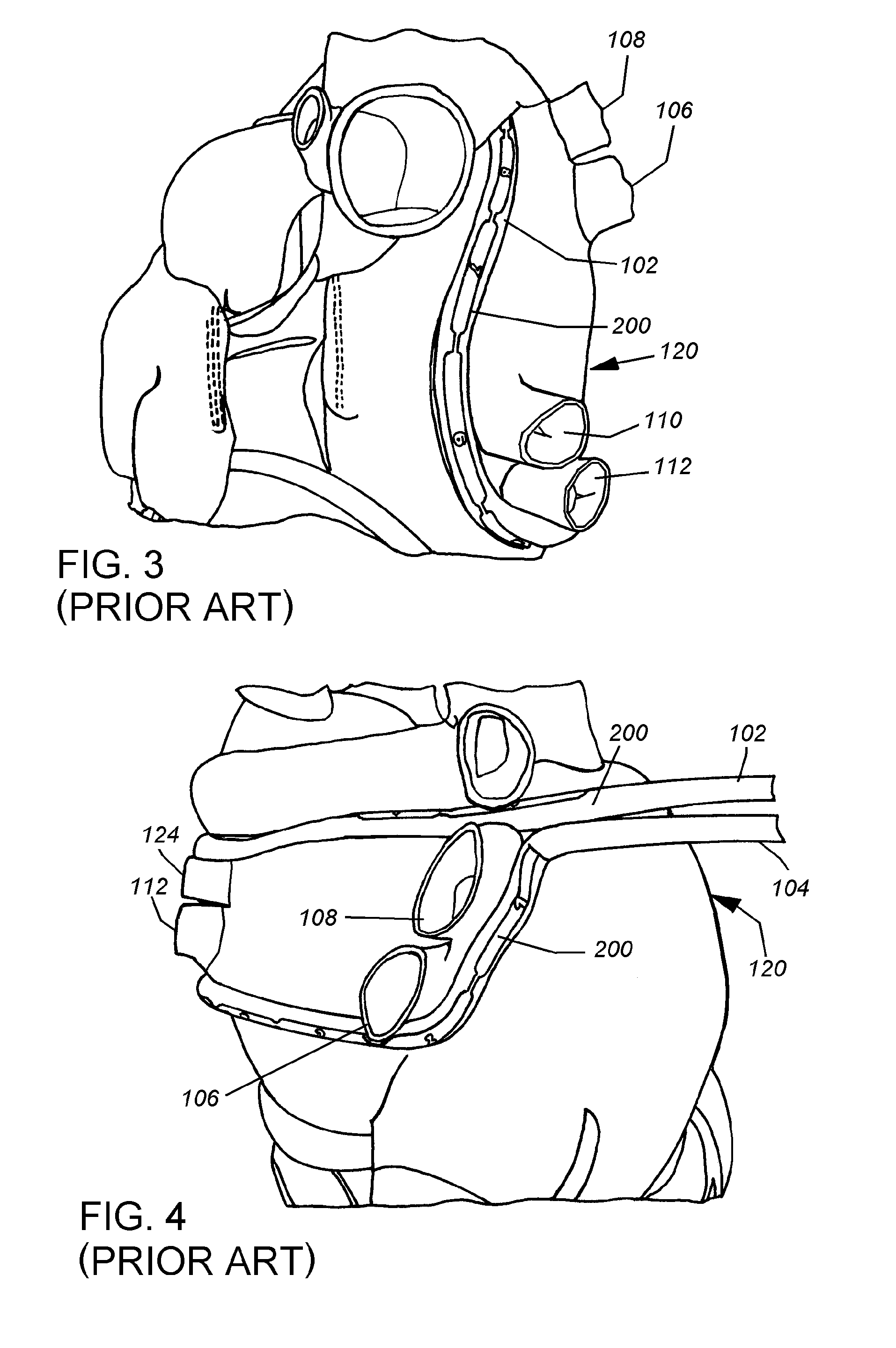
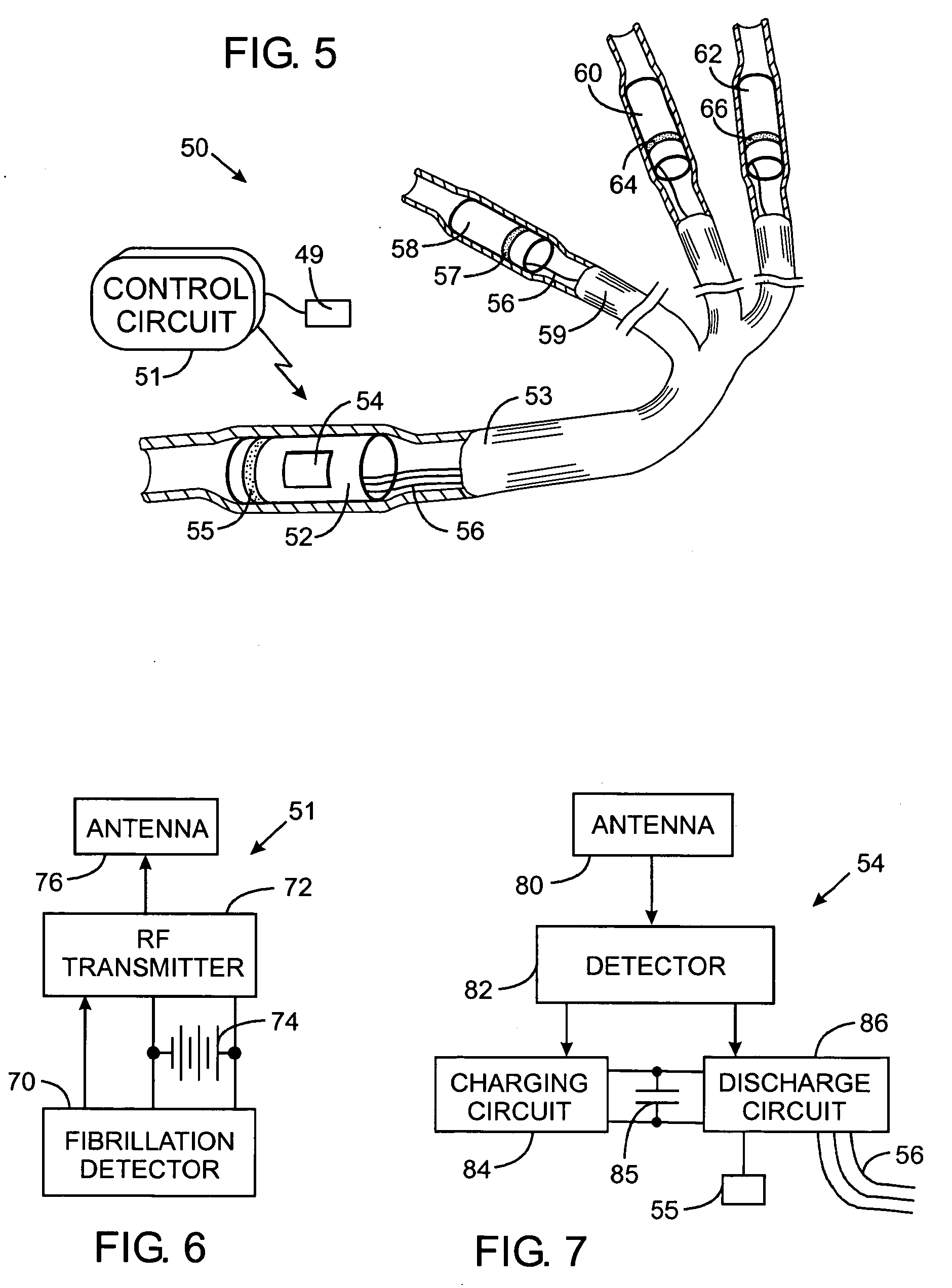
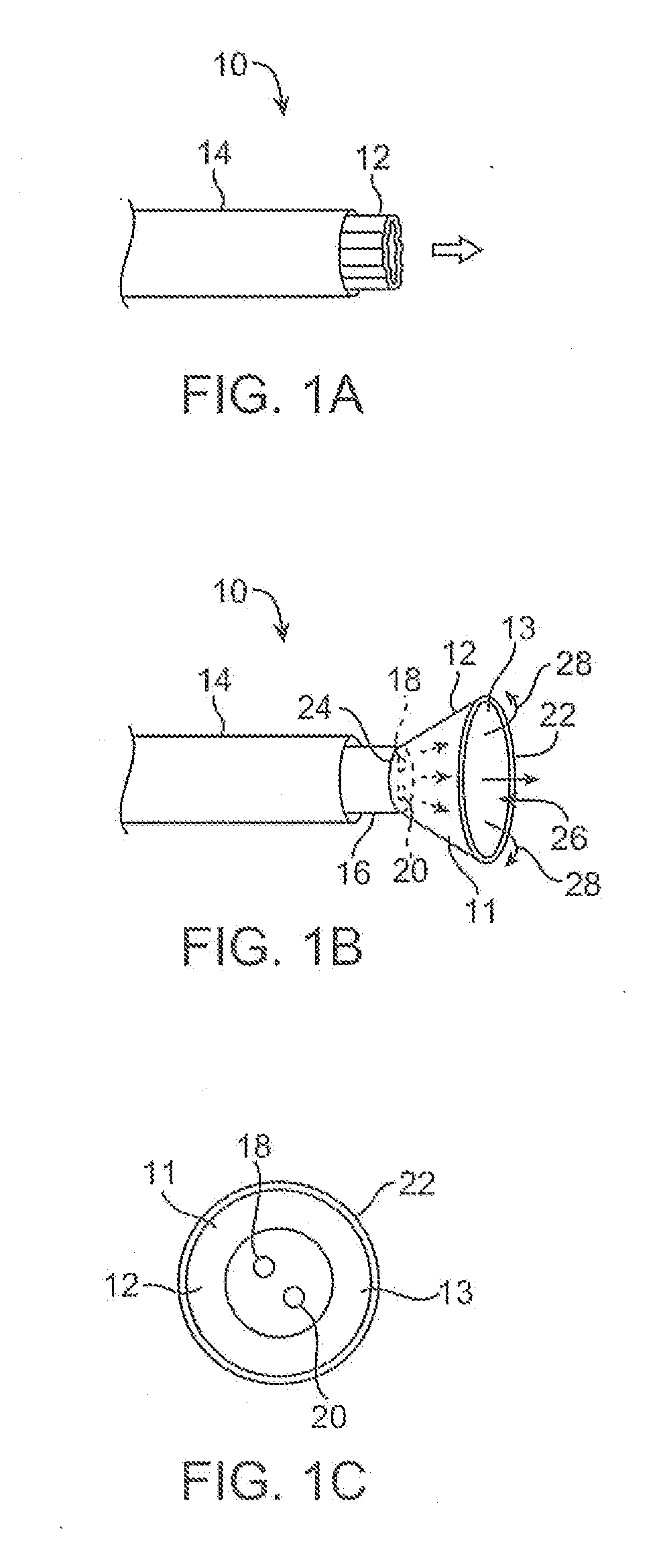
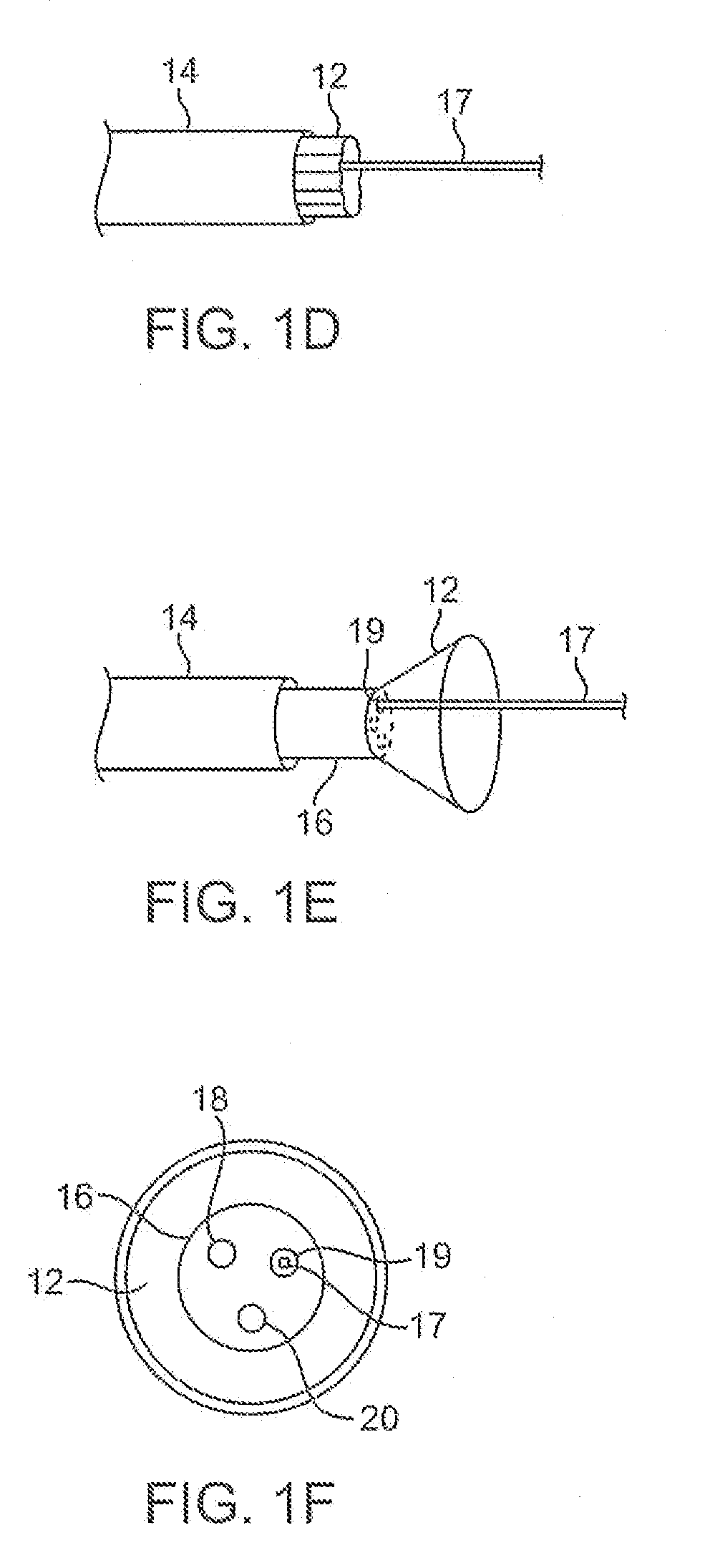
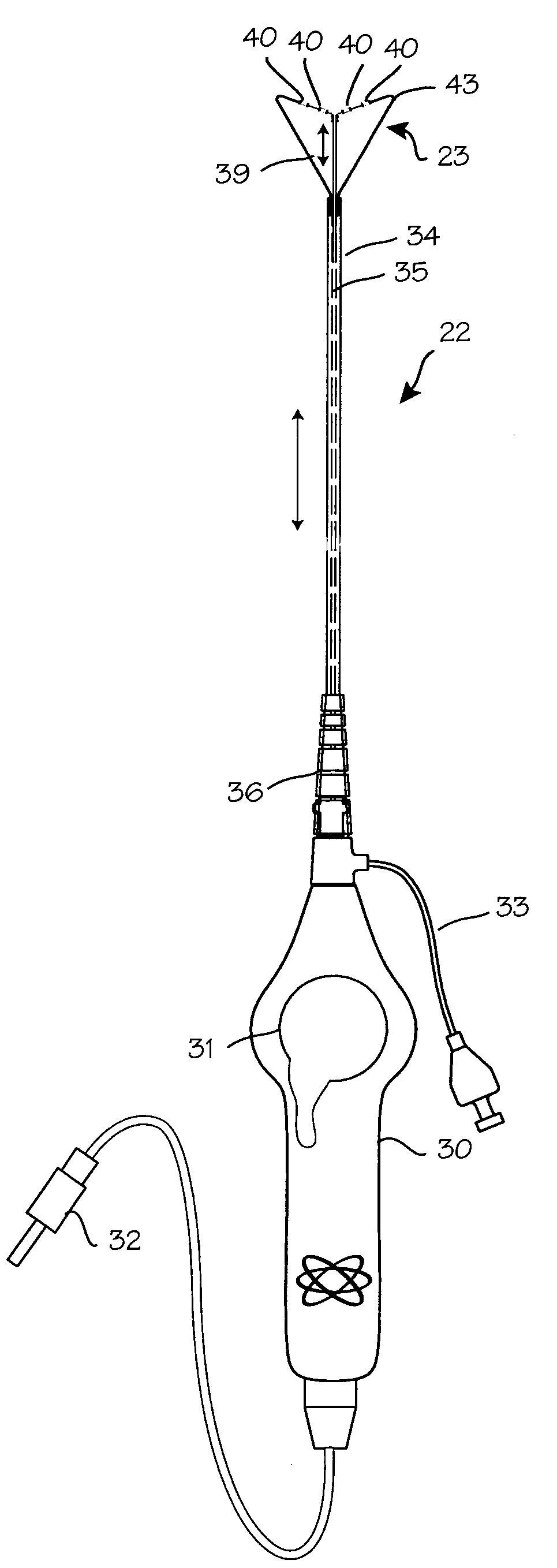
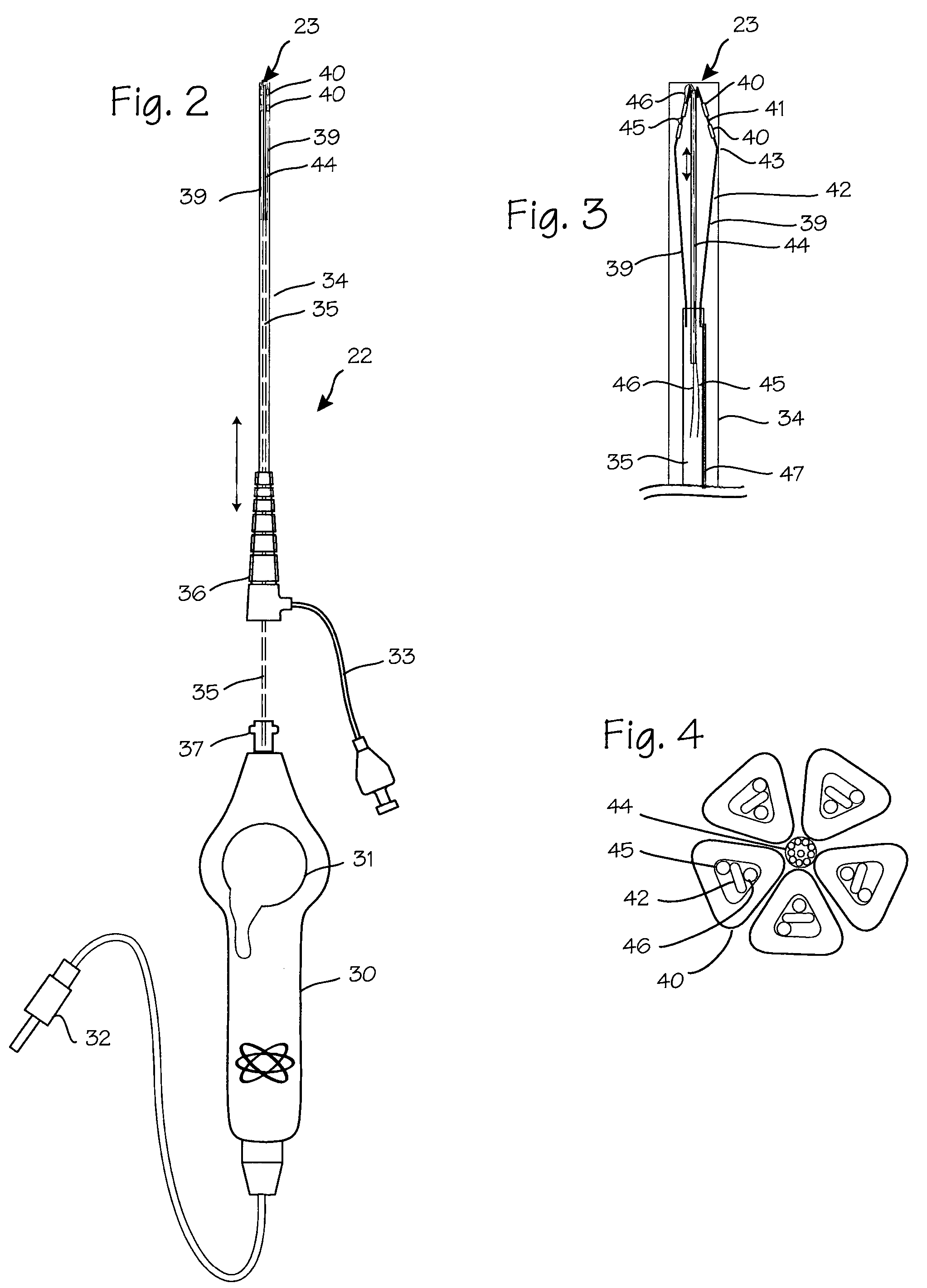
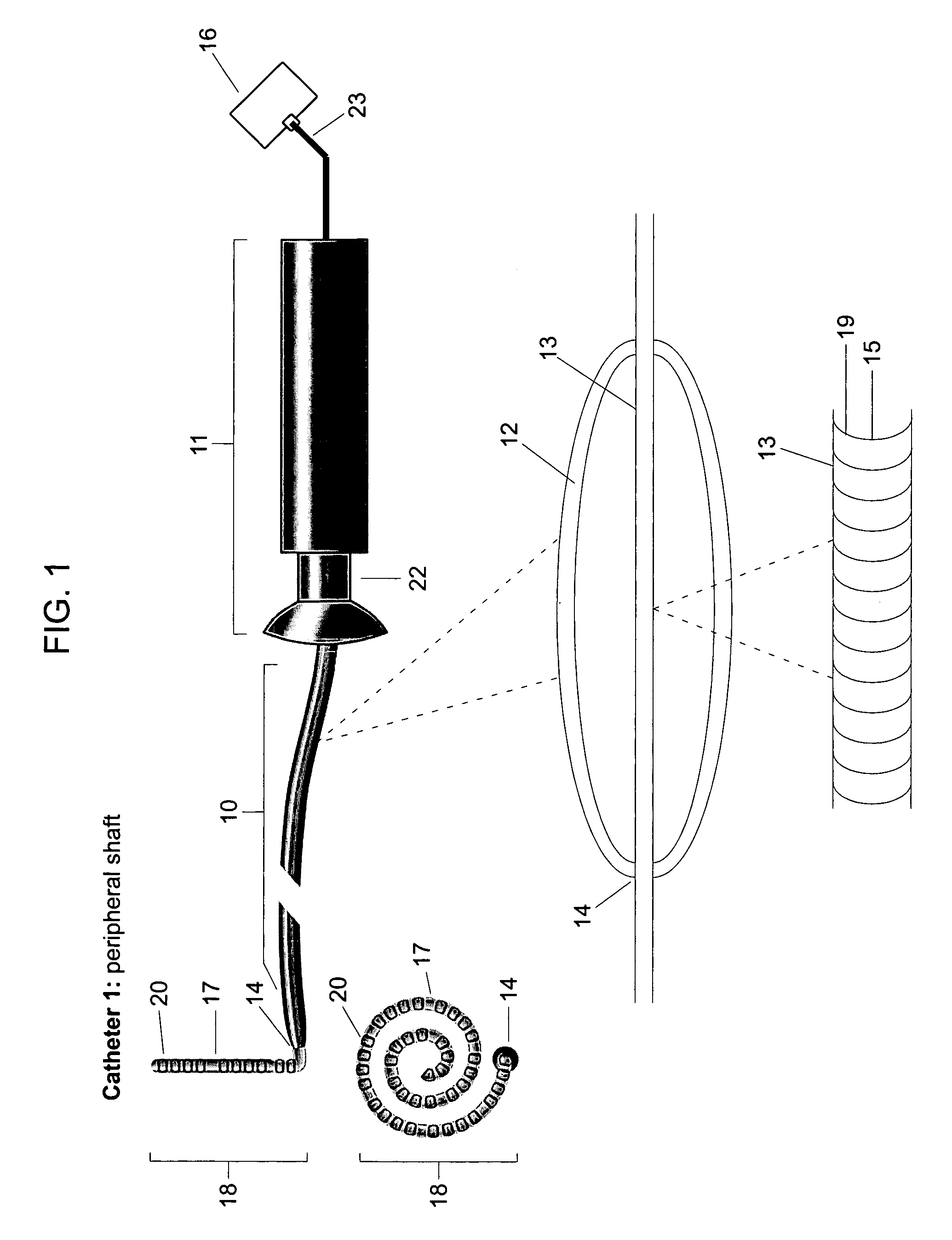
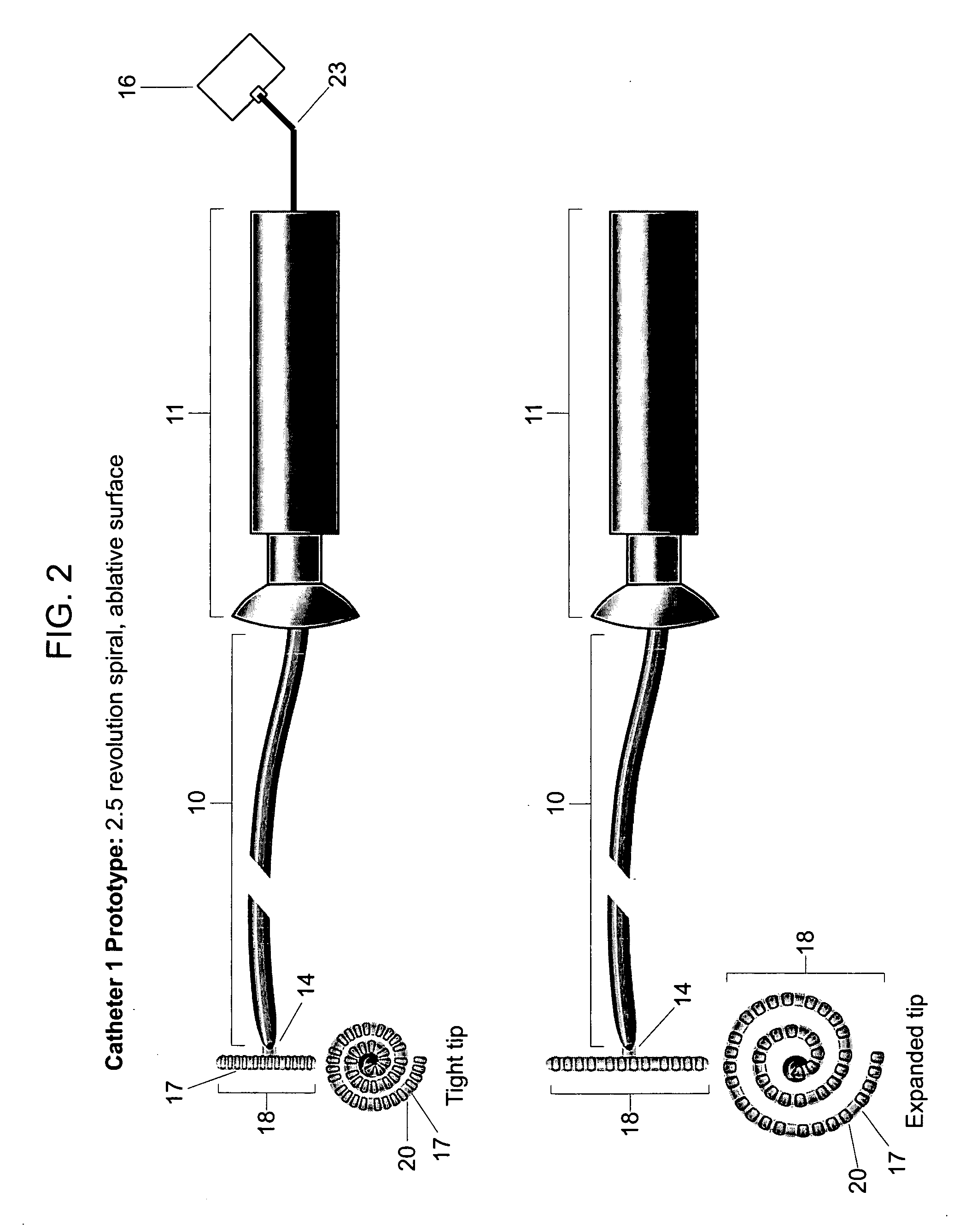
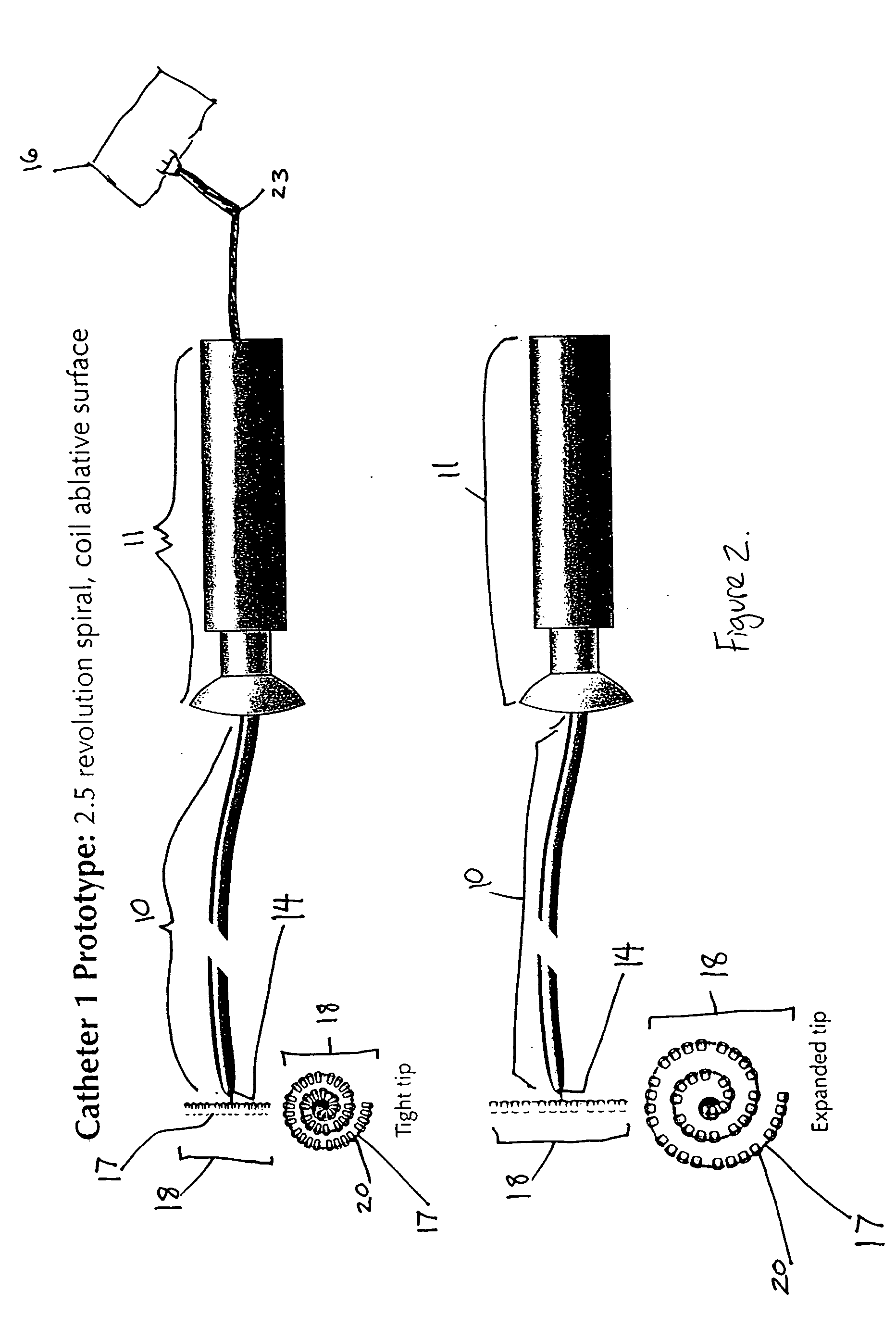
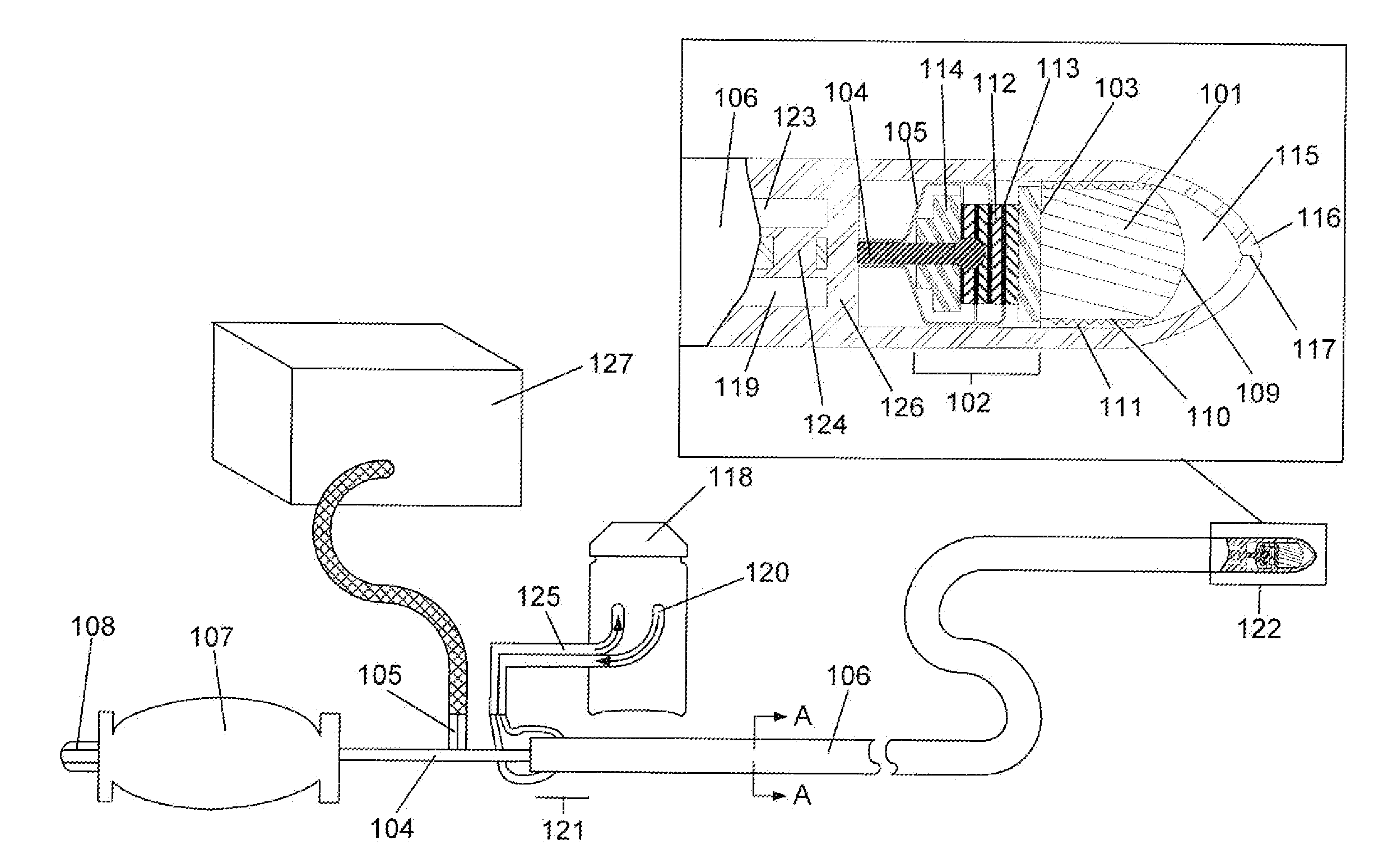
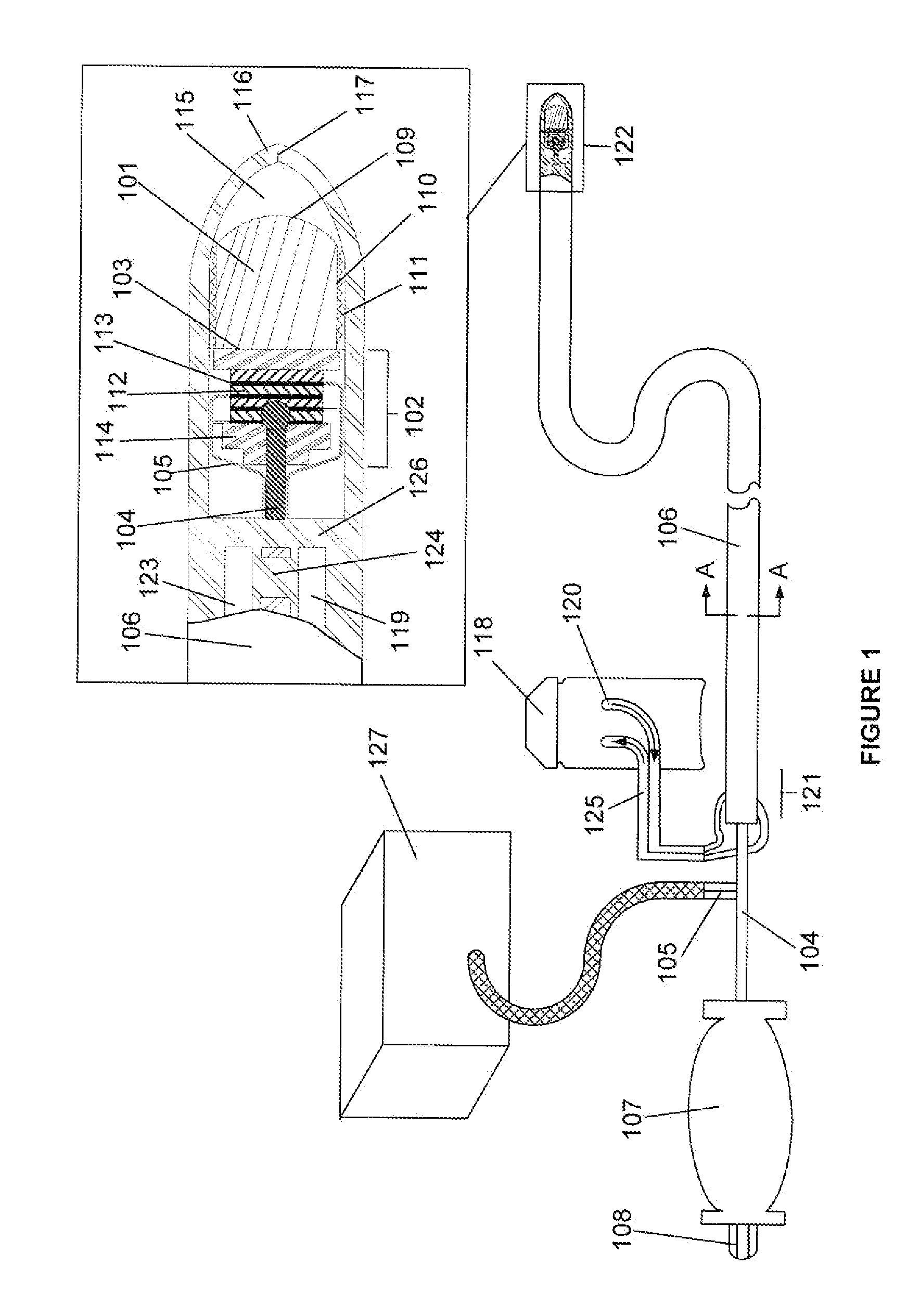
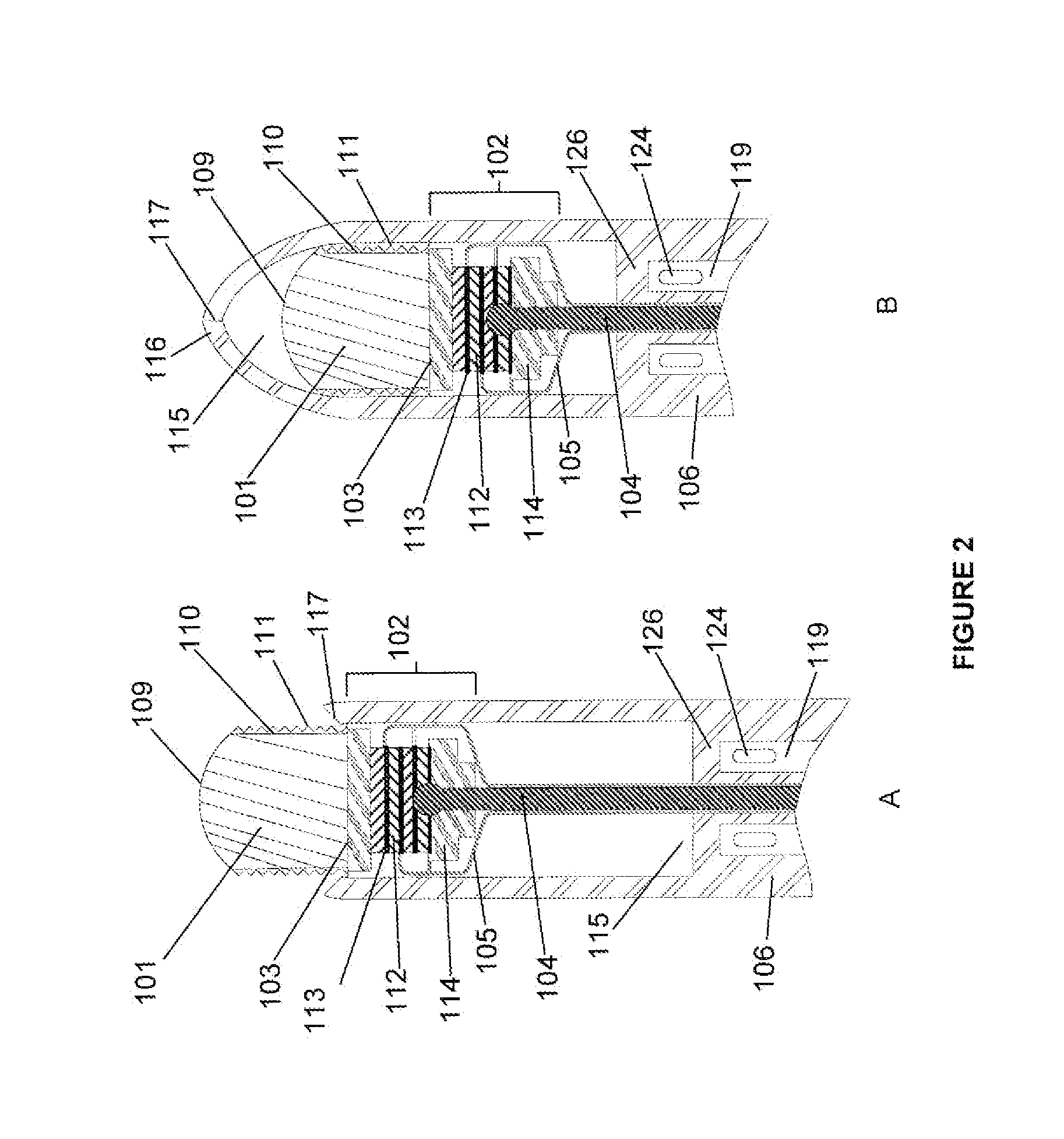
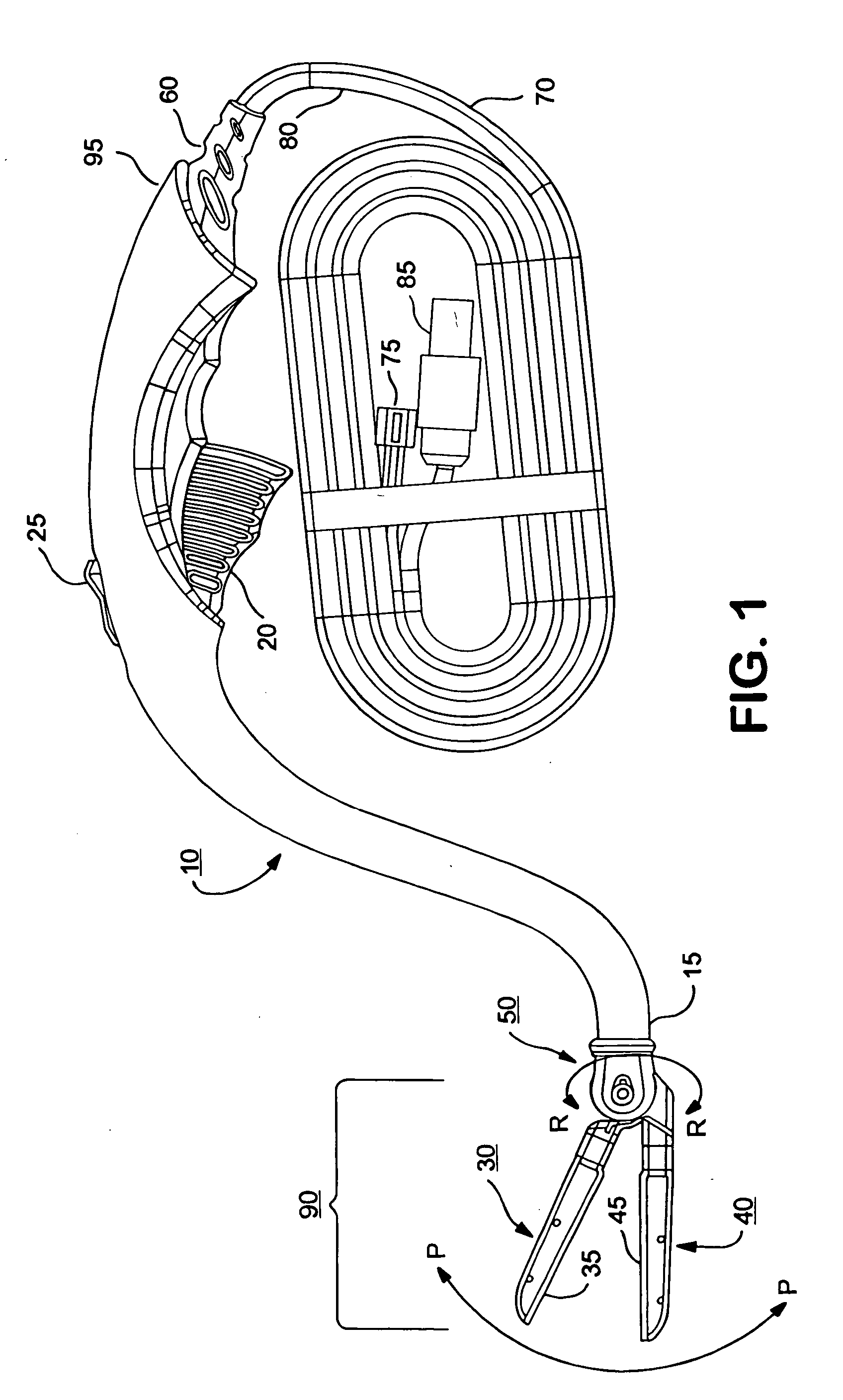
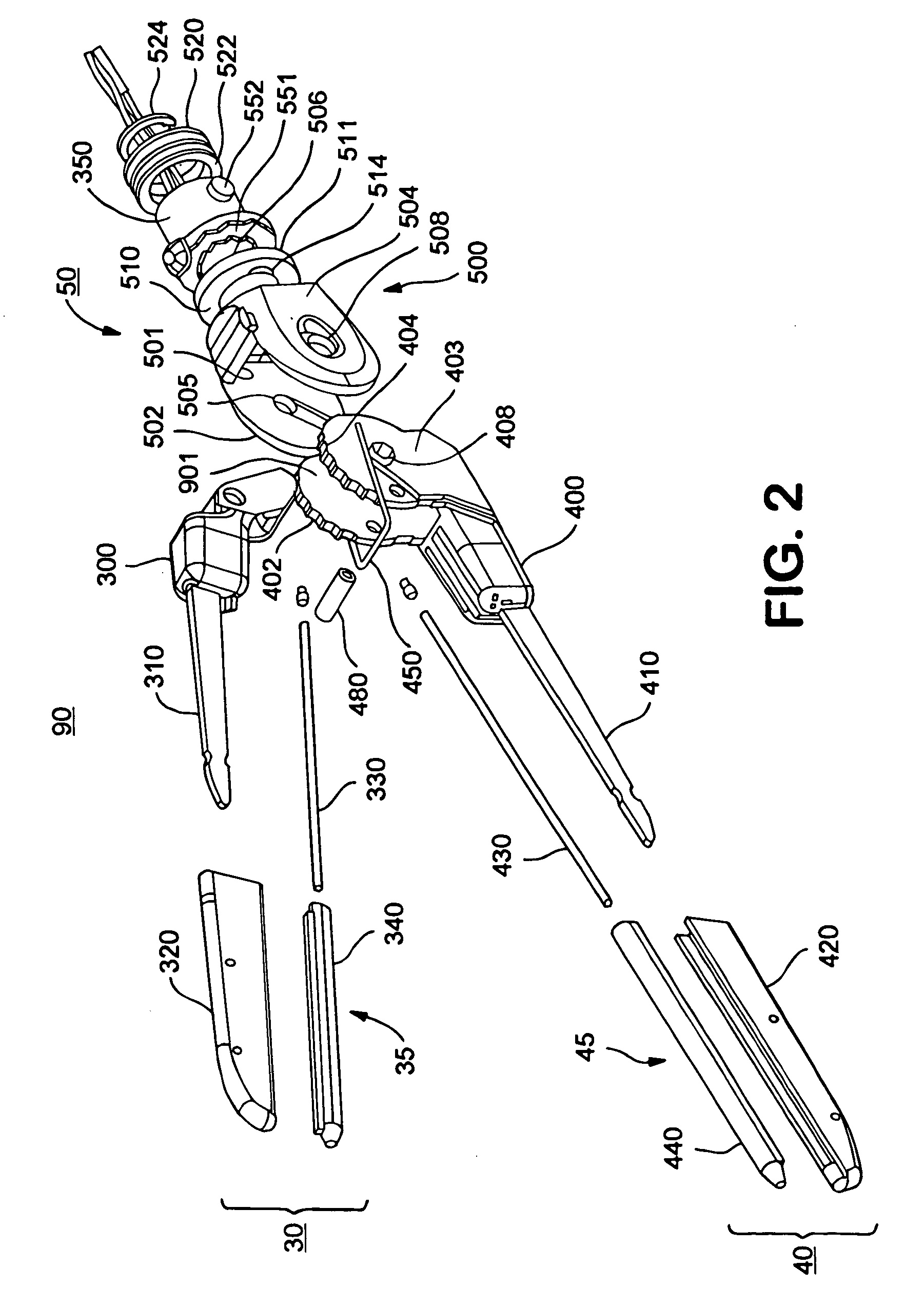
Electrosurgical hemostat
InactiveUS7083620B2Reduce usageImprove performanceCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingDetentEffective treatment
A hemostat-type device for ablative treatment of tissue, particularly for treatment of atrial fibrillation, is constructed with features that provide easy and effective treatment. A swiveling head assembly can allow the jaws to be adjusted in pitch and roll. Malleable jaws can permit curved lesion shapes. A locking detent can secure the jaws in a closed position during the procedure. An illuminated indicator provides confirmation that the device is operating. A fluid delivery system simplifies irrigated ablation procedures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
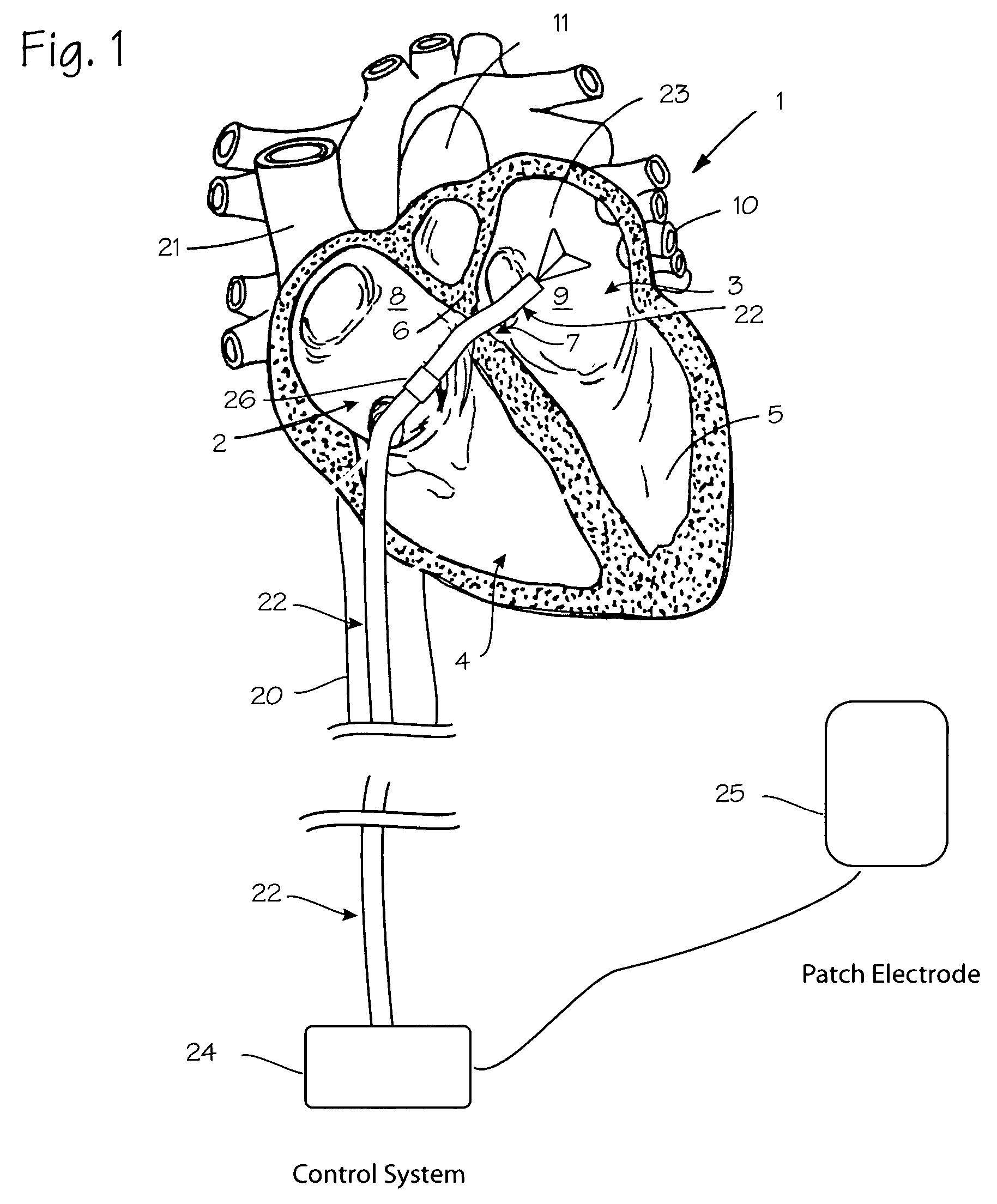
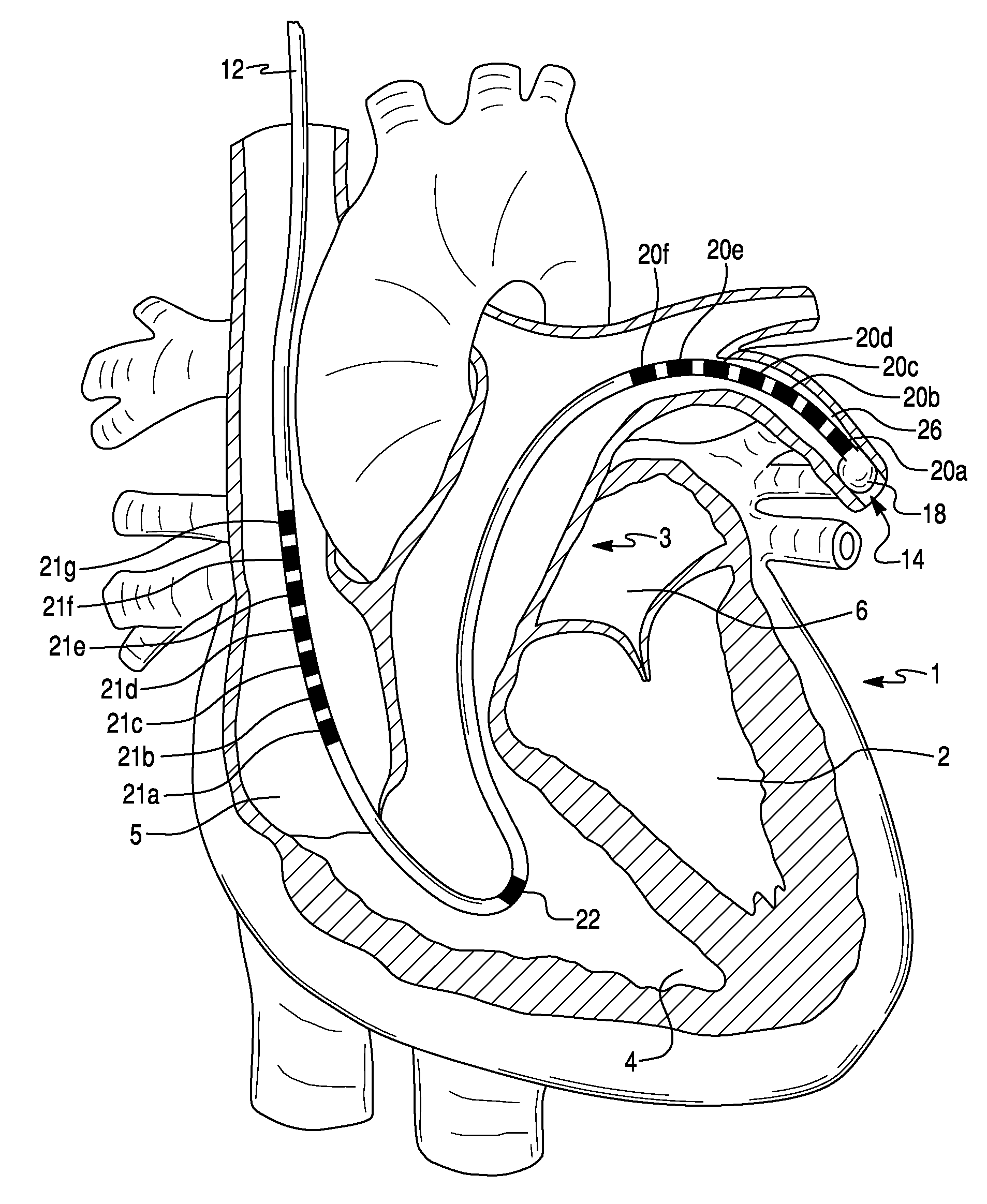
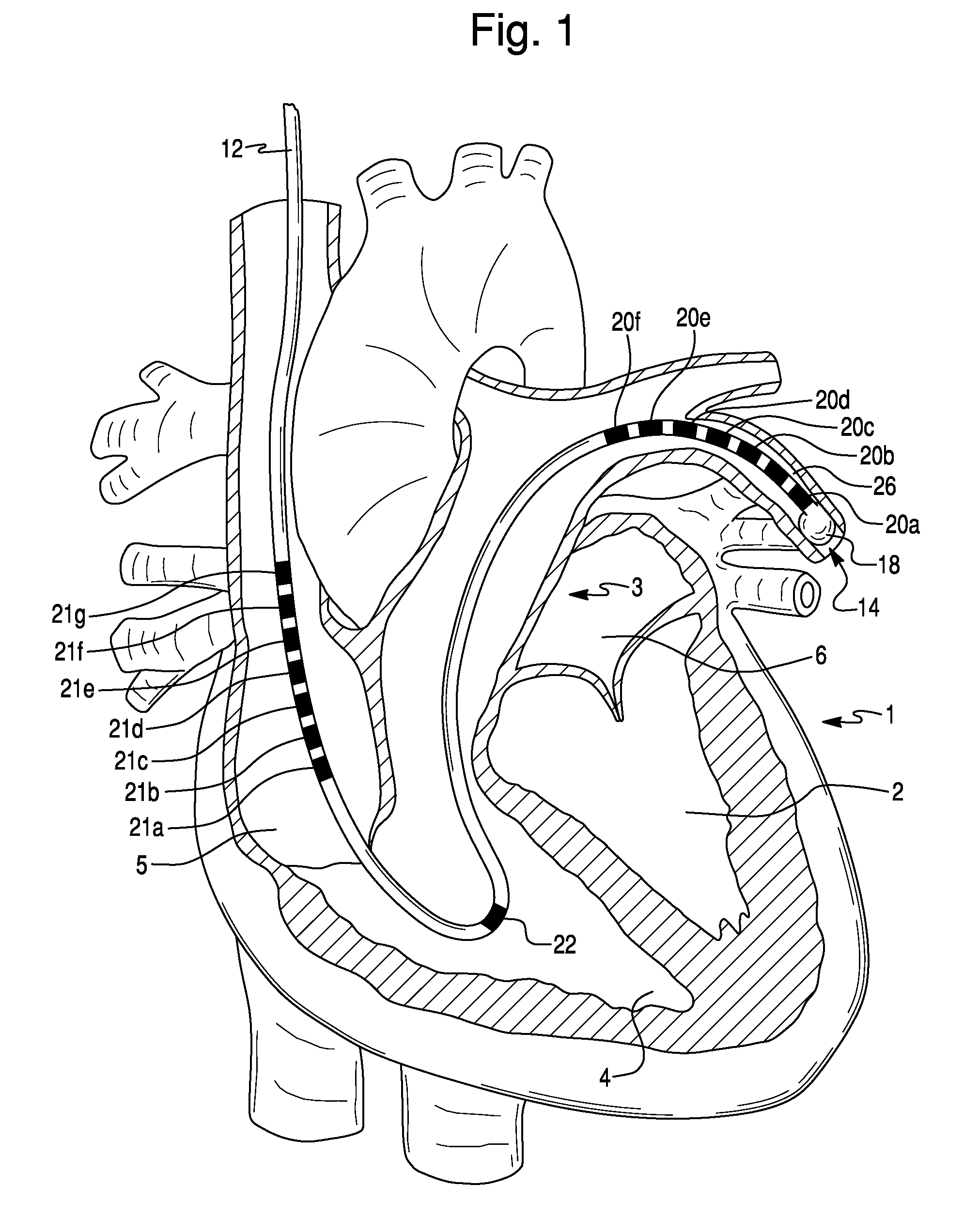
System and method for advancing, orienting, and immobilizing on internal body tissue a catheter or other therapeutic device
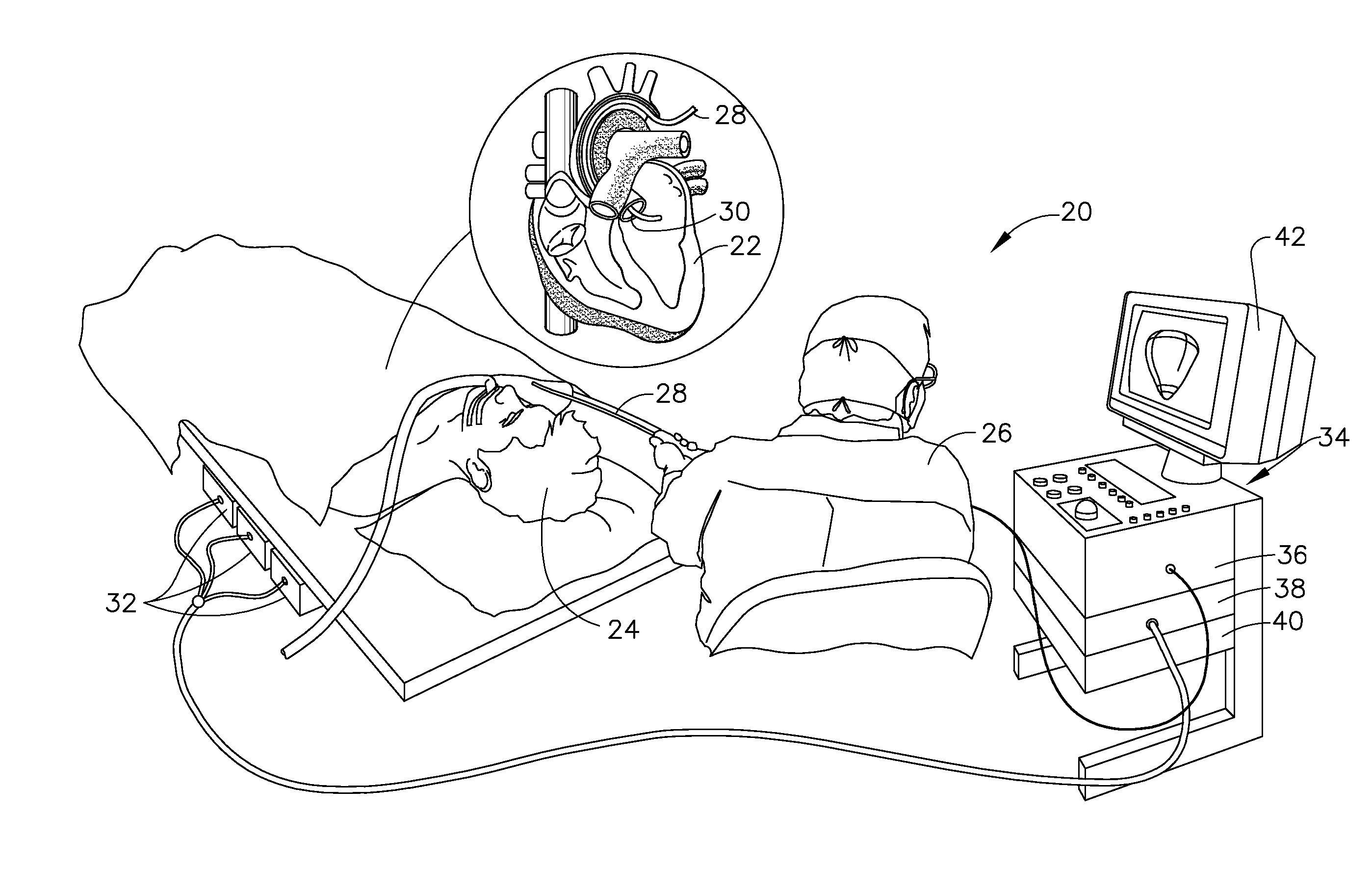
This invention provides a system and method that allows a therapeutic device, such as an atrial fibrillation microwave ablation catheter or ablation tip to be guided to a remote location within a body cavity and then accurately immobilized on the tissue, including that of a moving organ, such as the heart. In various embodiments, the system and method also enables accurate movement and steering along the tissue, while in engagement therewith. Such movement and engagement entails the use of vacuum or microneedle structures on at least two interconnected and articulated immobilizers that selectively engage to and release from the tissue to allow a crawling or traversing walking across the organ as the therapeutic catheter / tool tip applies treatment (AGE devices). In further embodiments that lack a movement capability (AID devices), the immobilizers allow a predetermined position for the introduced device to be maintained against the tissue while a treatment is applied to the location adjacent thereto. In the exemplary AID devices, variety of steering mechanisms and mechanisms for exposing and anchoring a catheter against the underlying tissue can be employed. In the exemplary AGE devices, a variety of articulation and steering mechanisms, including those based upon pneumatic / hydraulic bellows, lead screws and electromagnetic actuators can be employed.
Owner:ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY FRONTIERS SPA
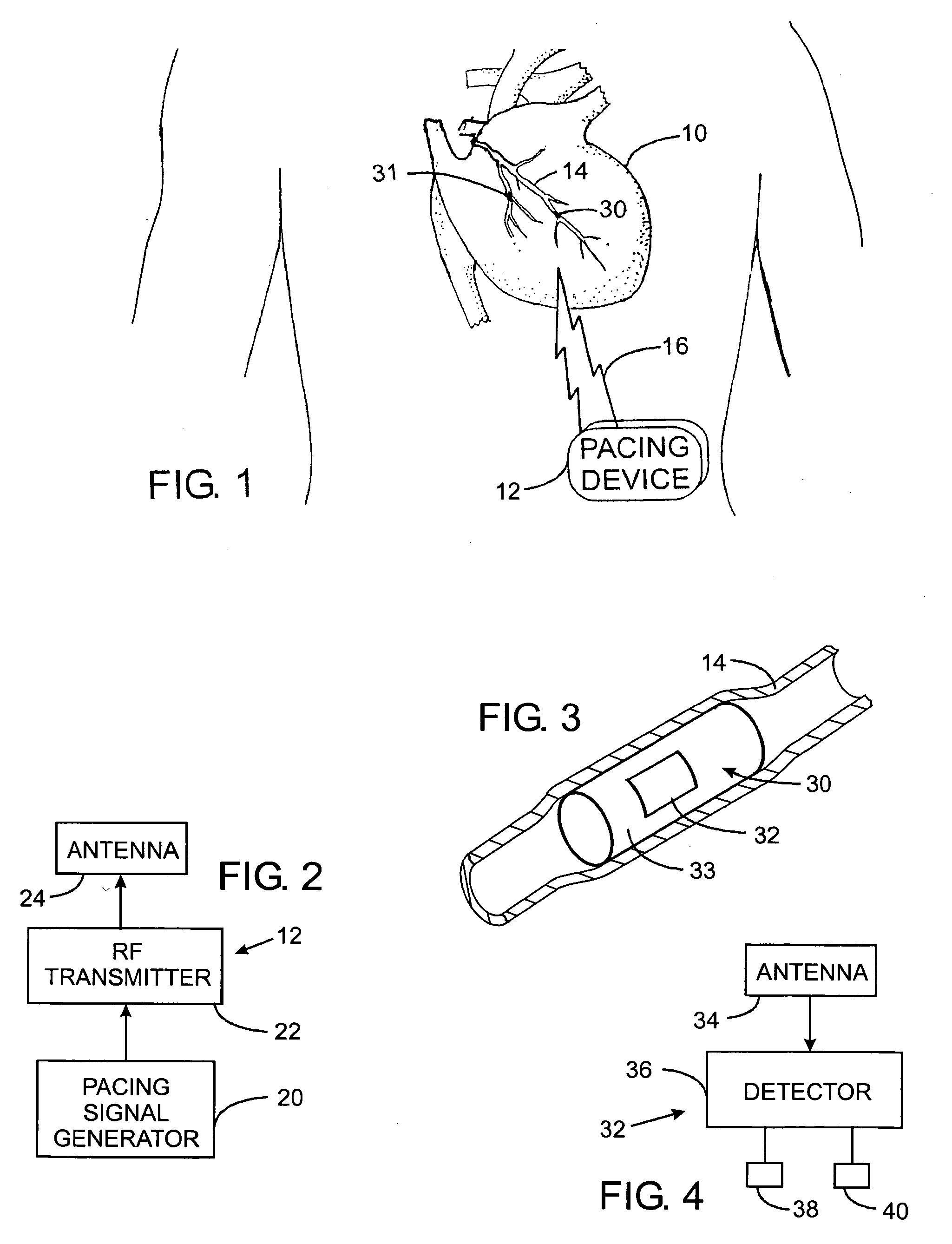
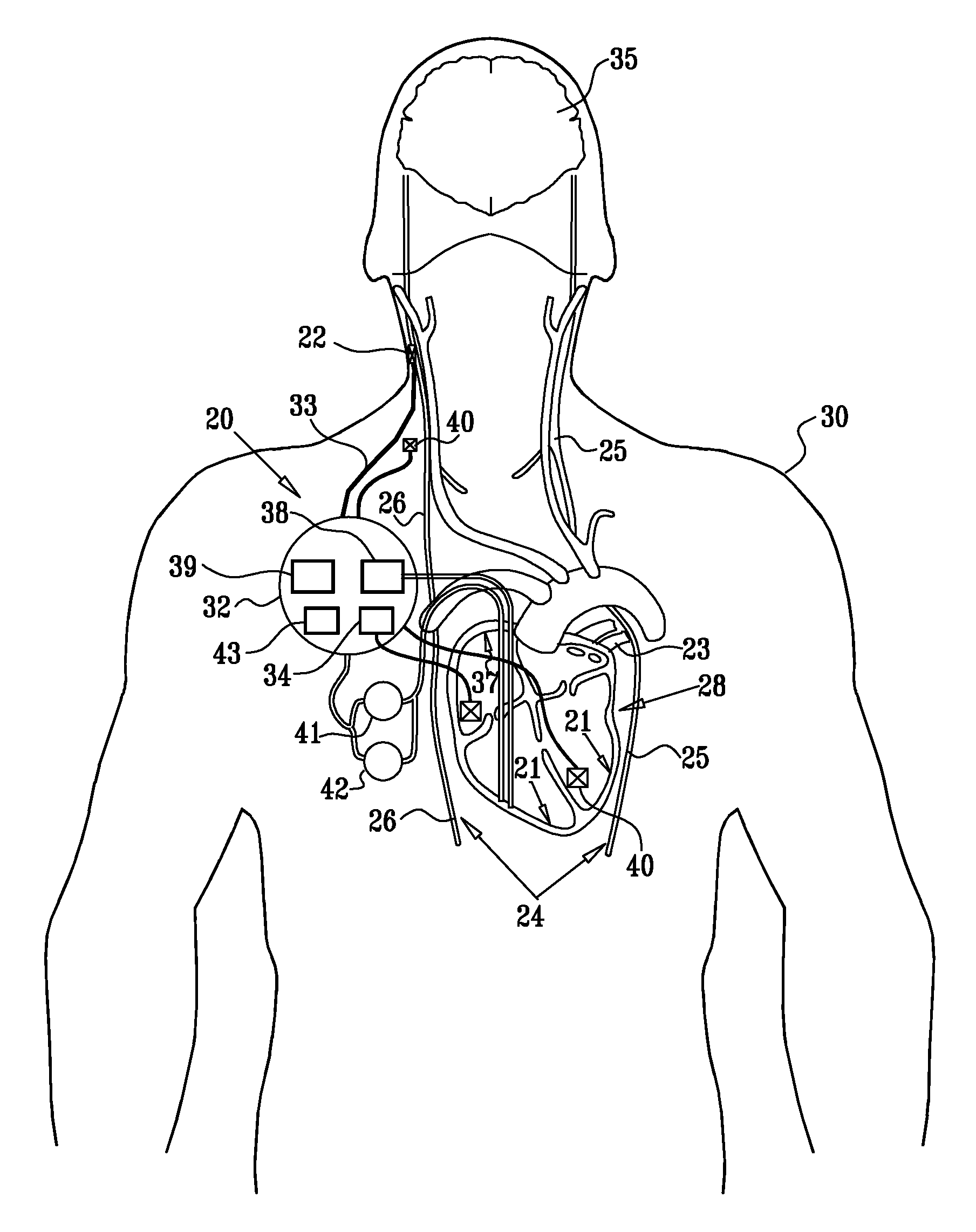
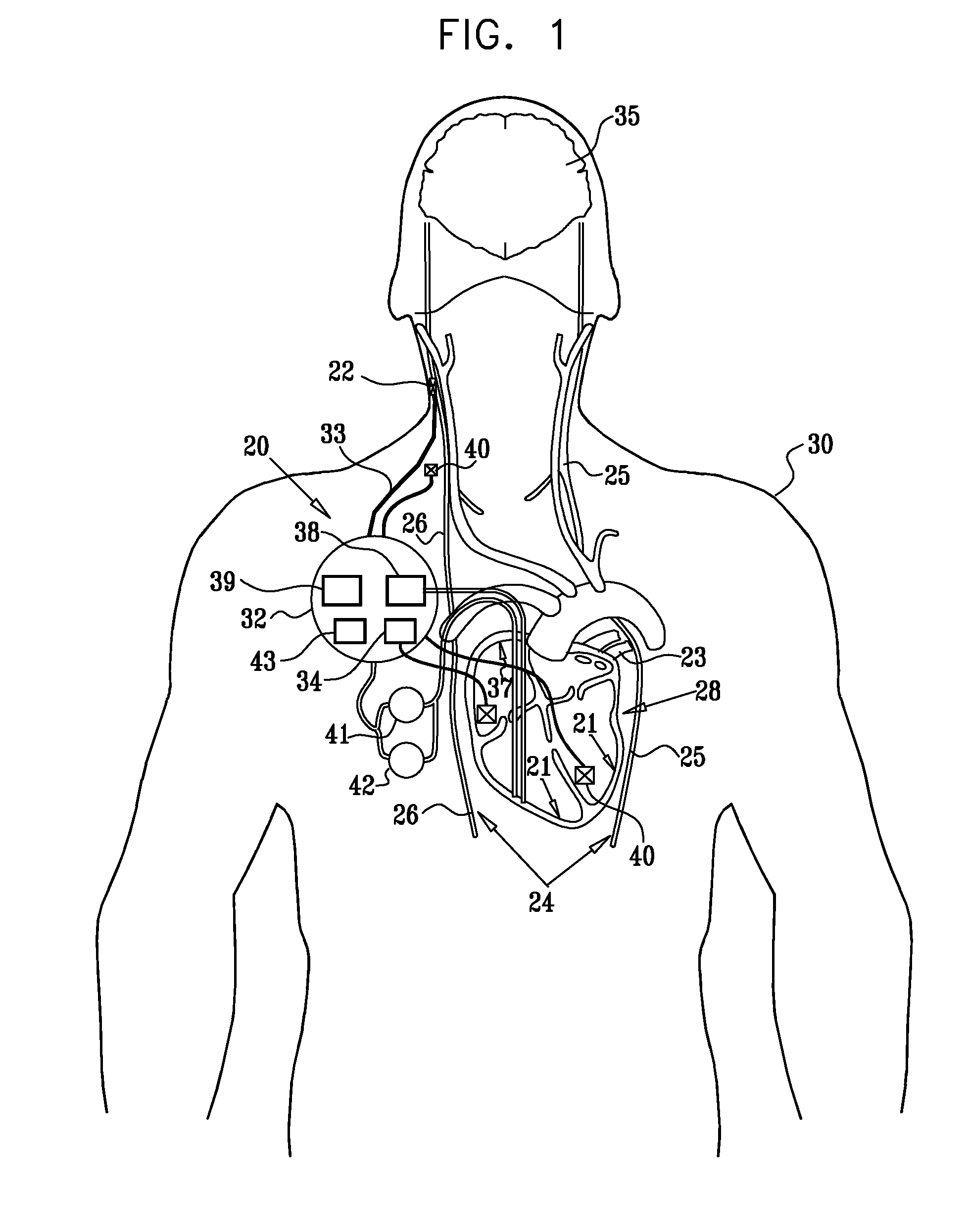
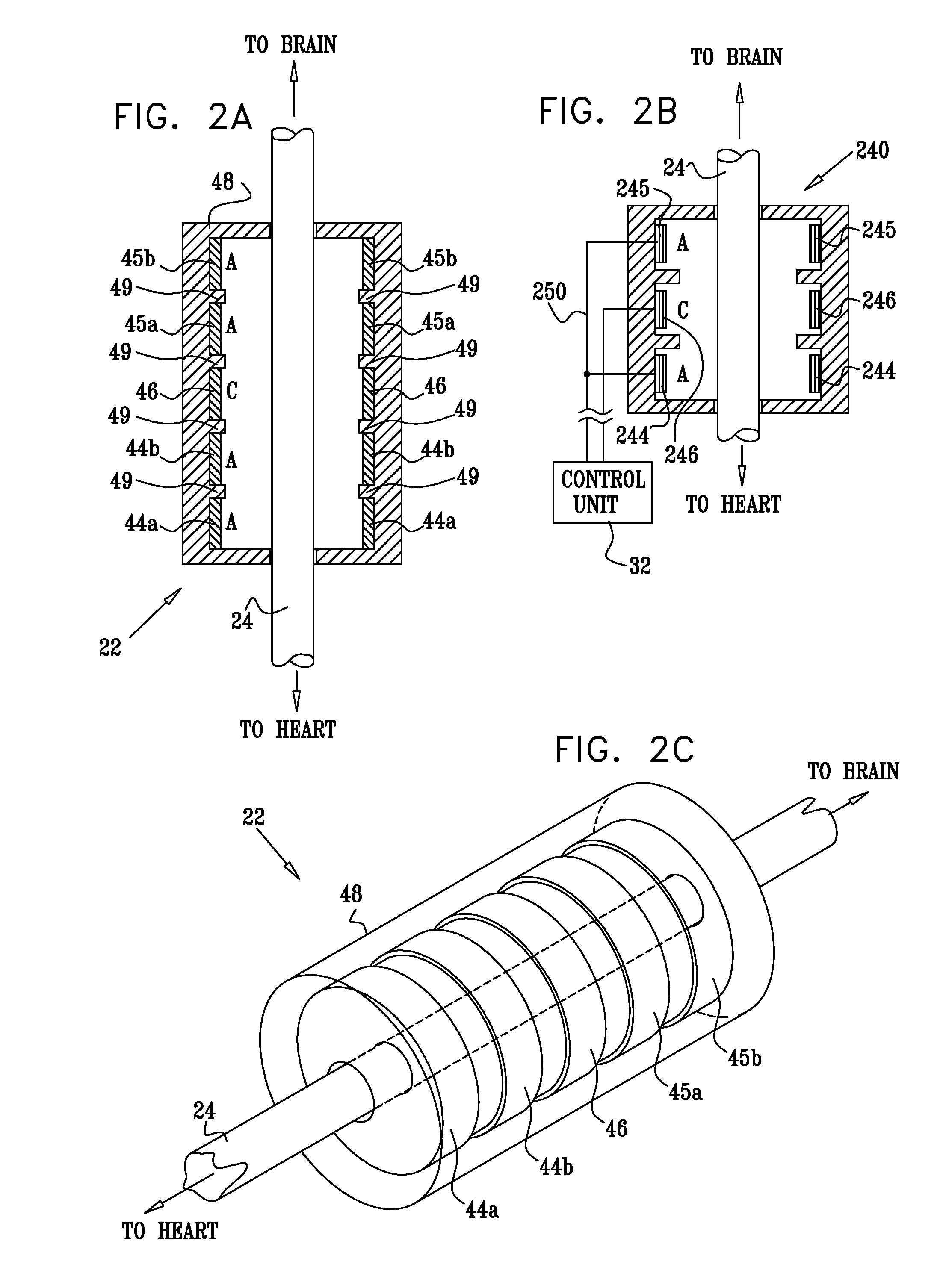
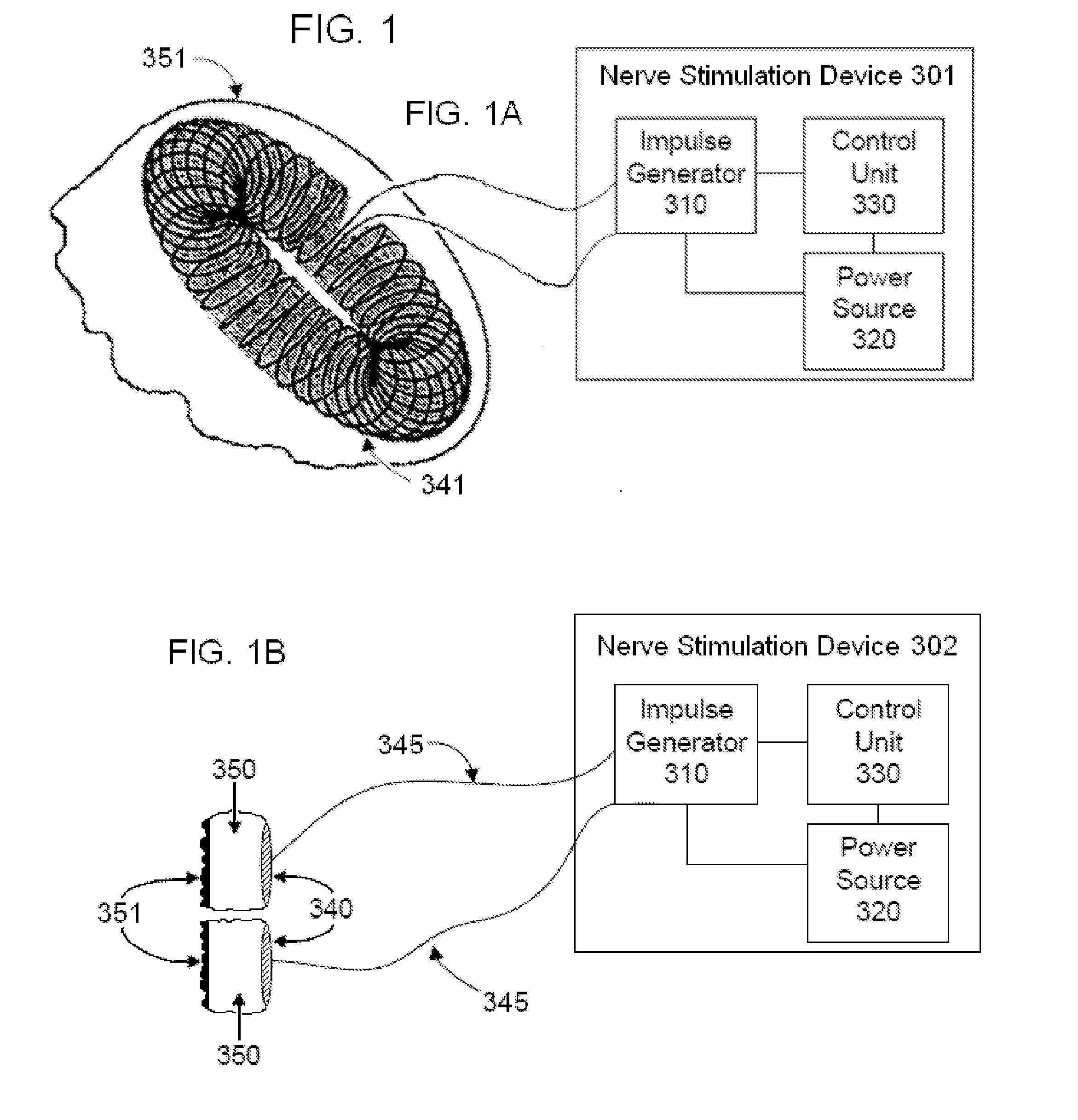
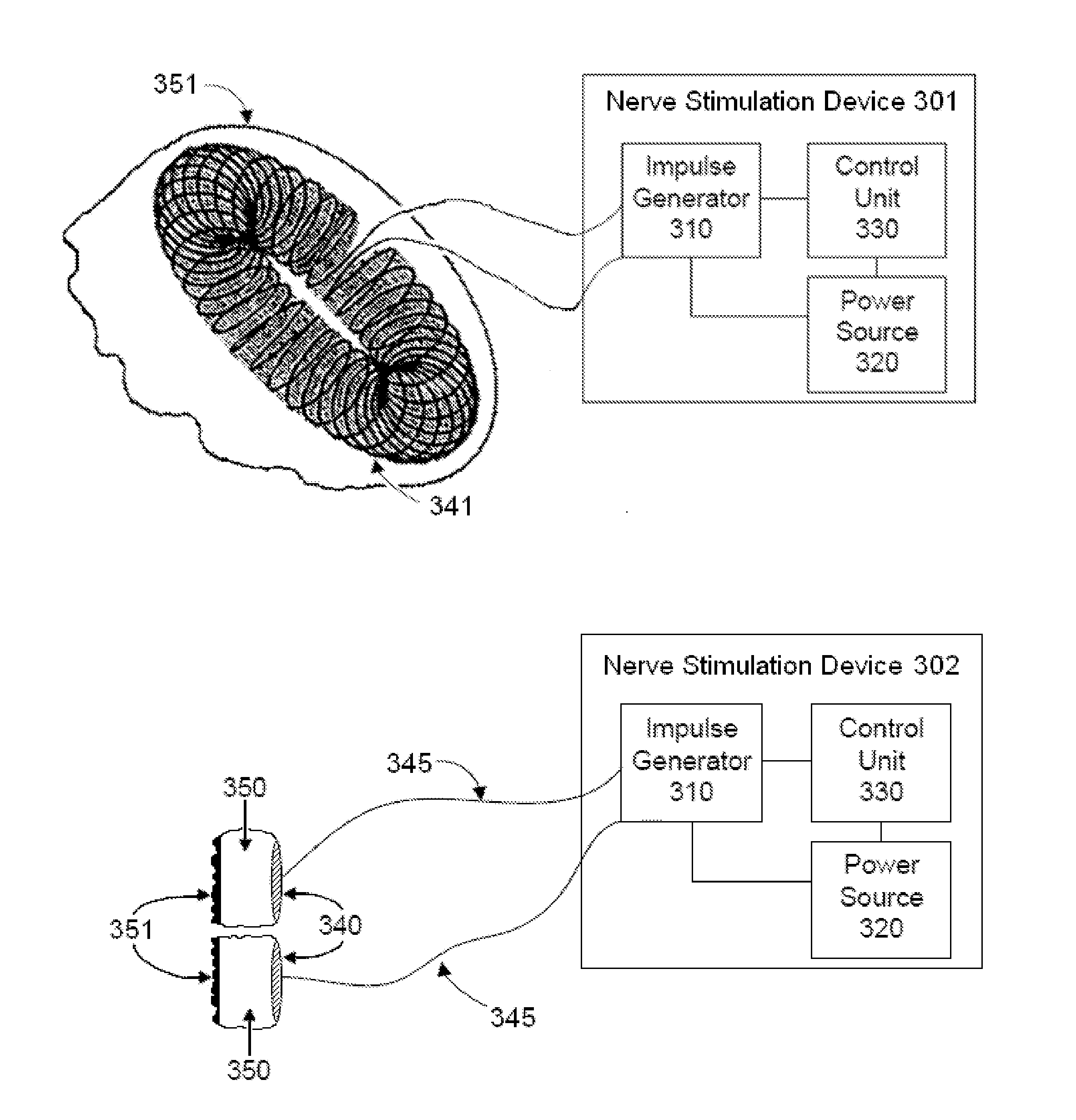
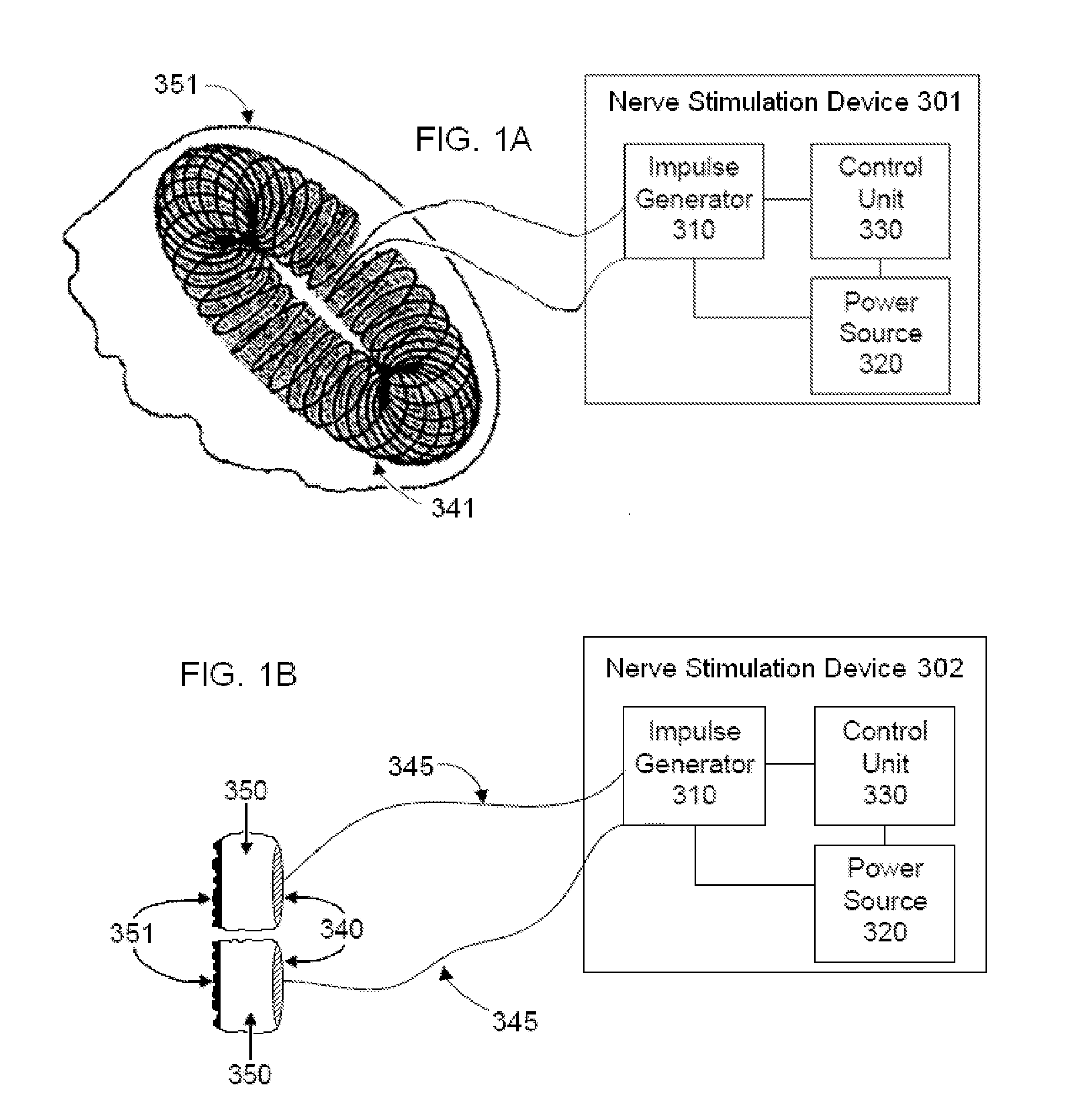
Vagal nerve stimulation using vascular implanted devices for treatment of atrial fibrillation
An abnormally rapid ventricular cardiac rate that results from atrial fibrillation can be reduced by stimulating a vagal nerve of the heart. An apparatus for such stimulation includes a power transmitter that emits a radio frequency signal. A stimulator, implanted in a blood vessel adjacent the vagal nerve, has a pair of electrodes and an electrical circuit thereon. The electrical circuit receives the radio frequency signal and derives an electrical voltage from the energy of that signal. The electrical voltage is applied in the form of pulses to the pair of electrodes, thereby stimulating the vagal nerve. The pattern of that stimulating pulses can be varied in response to characteristics of the atrial fibrillation or the ventricular contractions.
Owner:KENERGY INC
Vagal stimulation for atrial fibrillation therapy
InactiveUS7321793B2Reduce frequencyIncreased riskHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsPower flowThrombus
Apparatus for treating a subject suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a vagus nerve of the subject, and a control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply an electrical current to the vagus nerve, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Parasympathetic nerve stimulation
InactiveUS20120303080A1Optimal ventricular rateSlow heart rateSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsPower flowMedicine
A method is provided, including identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from atrial fibrillation (AF). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of an occurrence of an episode of the AF is reduced by coupling an electrode device to a site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue; driving, by a control unit, the electrode device to apply an electrical current to the site not responsively to any physiological parameters sensed by any device directly or indirectly coupled to the control unit; and configuring the current to stimulate autonomic nervous tissue in the site. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and apparatus for treatment of atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20080015569A1Early detectionEnabling detectionElectrotherapyEndoscopesBody fluidBiomedical engineering
Apparatus and methods for the treatment of atrial fibrillation are described herein where tissue to be ablated may be monitored under direct visualization. Such a system may include a deployment catheter and an attached imaging hood deployable into an expanded configuration. In use, the imaging hood is placed against or adjacent to the tissue to be imaged in a body lumen that is normally filled with an opaque bodily fluid such as blood. A translucent or transparent fluid can be pumped into the imaging hood until the fluid displaces any blood leaving a clear region of tissue to be imaged via an imaging element in the deployment catheter. An ablation probe may be advanced into the contained region where the tissue may be ablated and monitored for changes in color as well as appropriate positioning.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
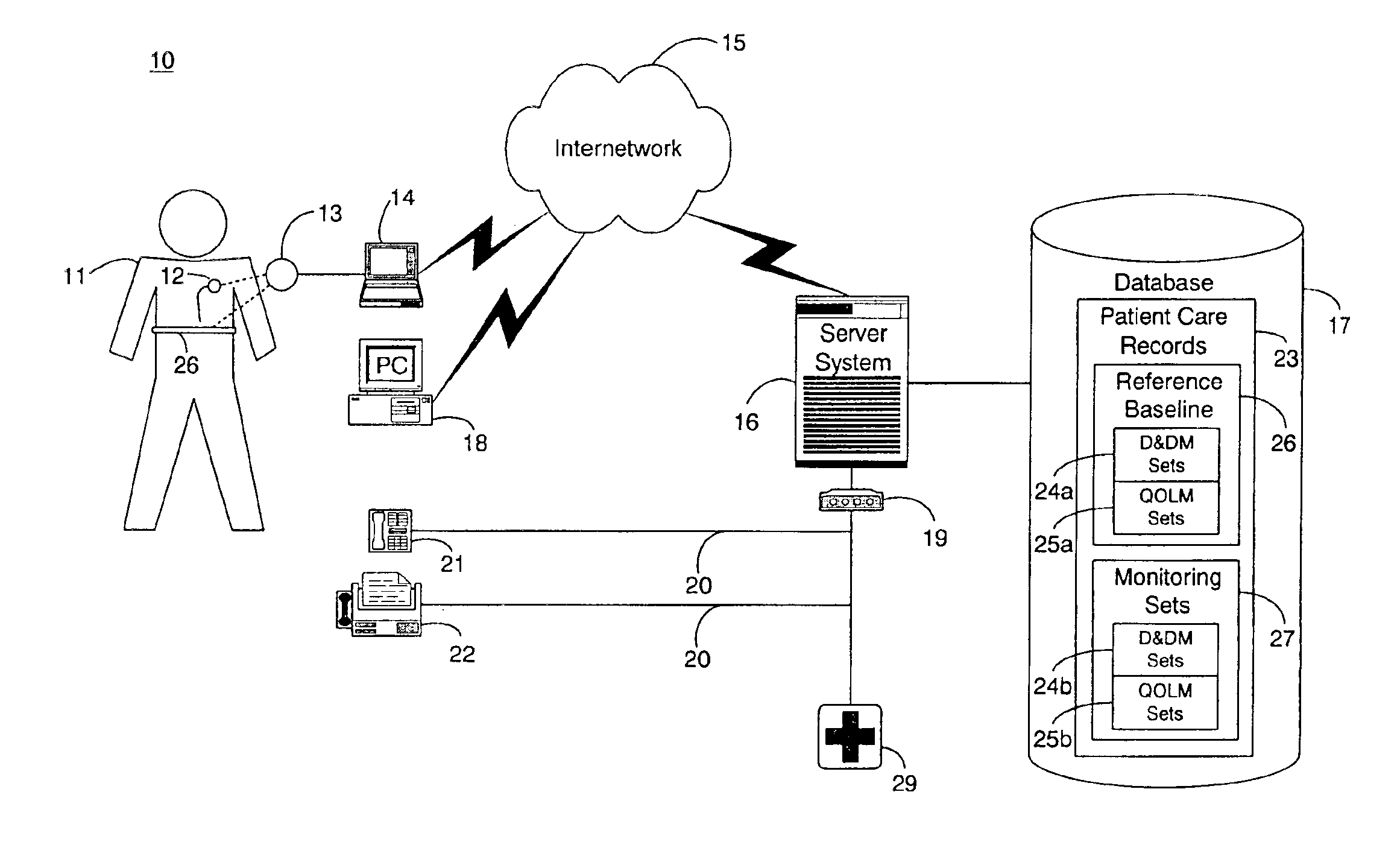
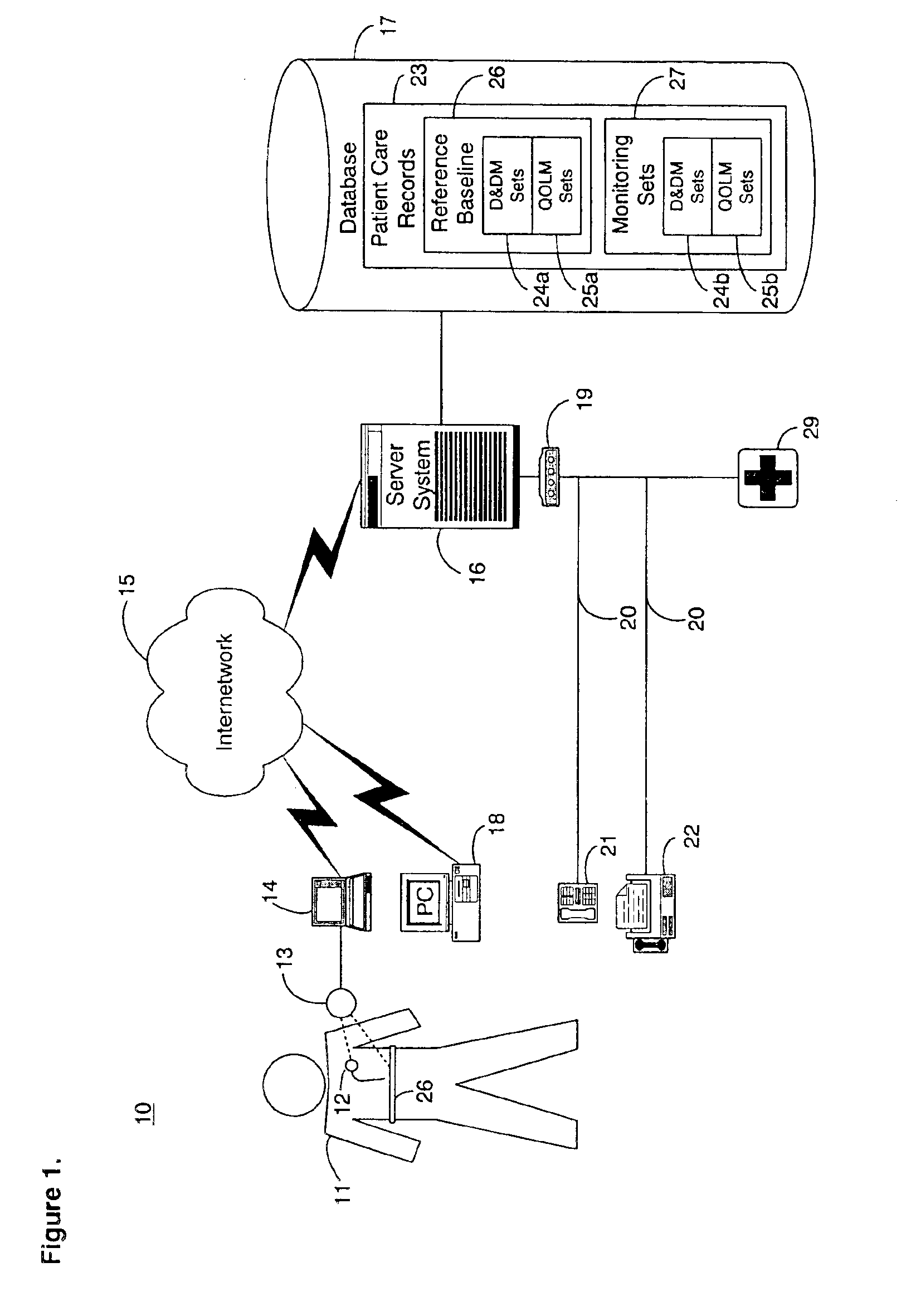
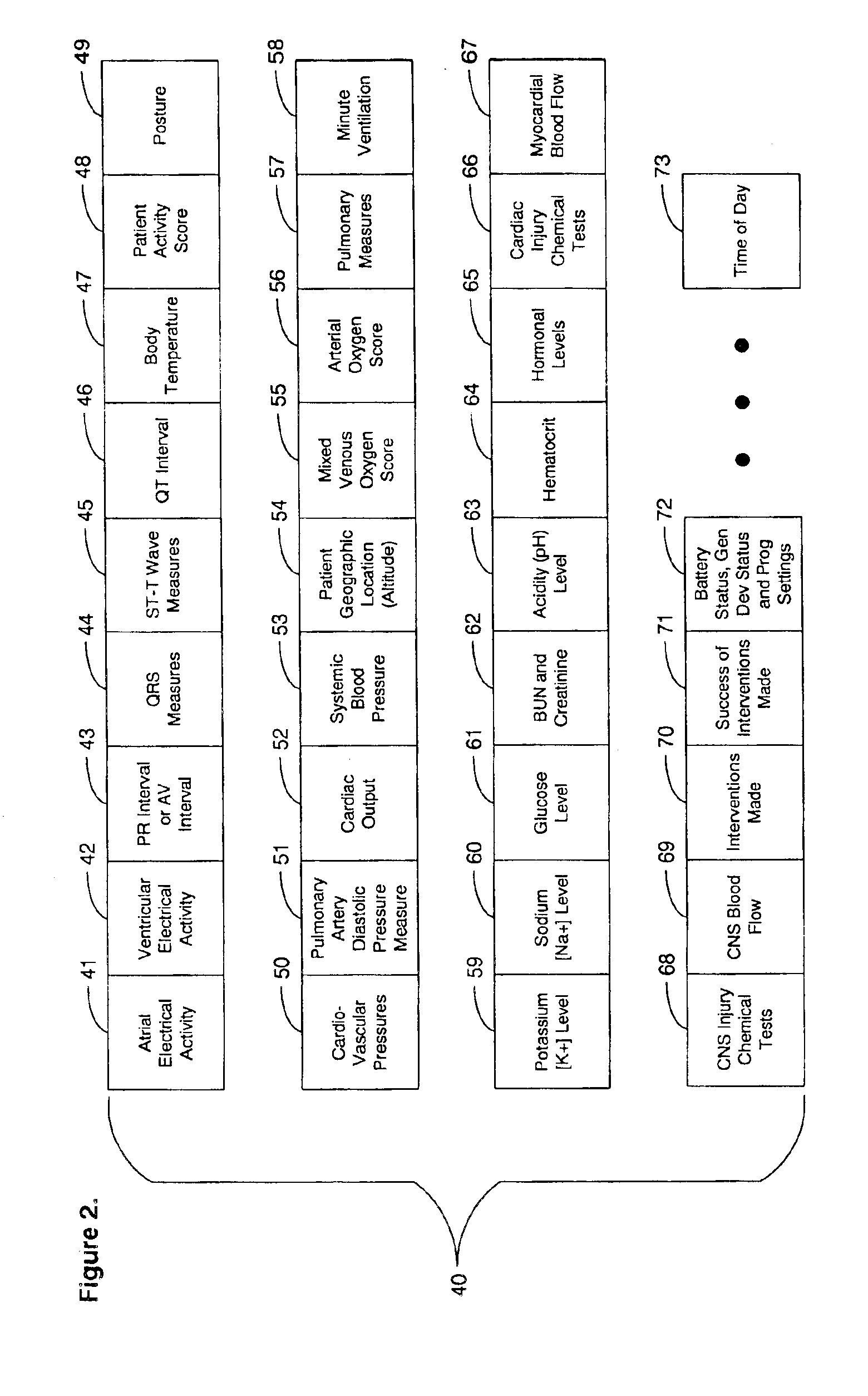
System and method for diagnosing and monitoring outcomes of atrial fibrillation for automated remote patient care
A system for diagnosing and monitoring outcomes of atrial fibrillation for remote patient care is presented. A database stores monitoring sets containing recorded measures relating to patient information recorded on a substantially continuous basis. A server retrieving and processing a plurality of the monitoring sets includes a comparison module receiving a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and determining patient status changes in response to the atrial fibrillation diagnosis by comparing periodically recorded measures from each of the monitoring sets to other recorded measures from another of the monitoring sets with both recorded measures relating to a same type of patient information; and an analysis module evaluating on a periodic basis each patient status change for an absence, an onset, a progression, a regression, and a status quo of atrial fibrillation against a predetermined indicator threshold corresponding to the same type of patient information as the recorded measures which were compared.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
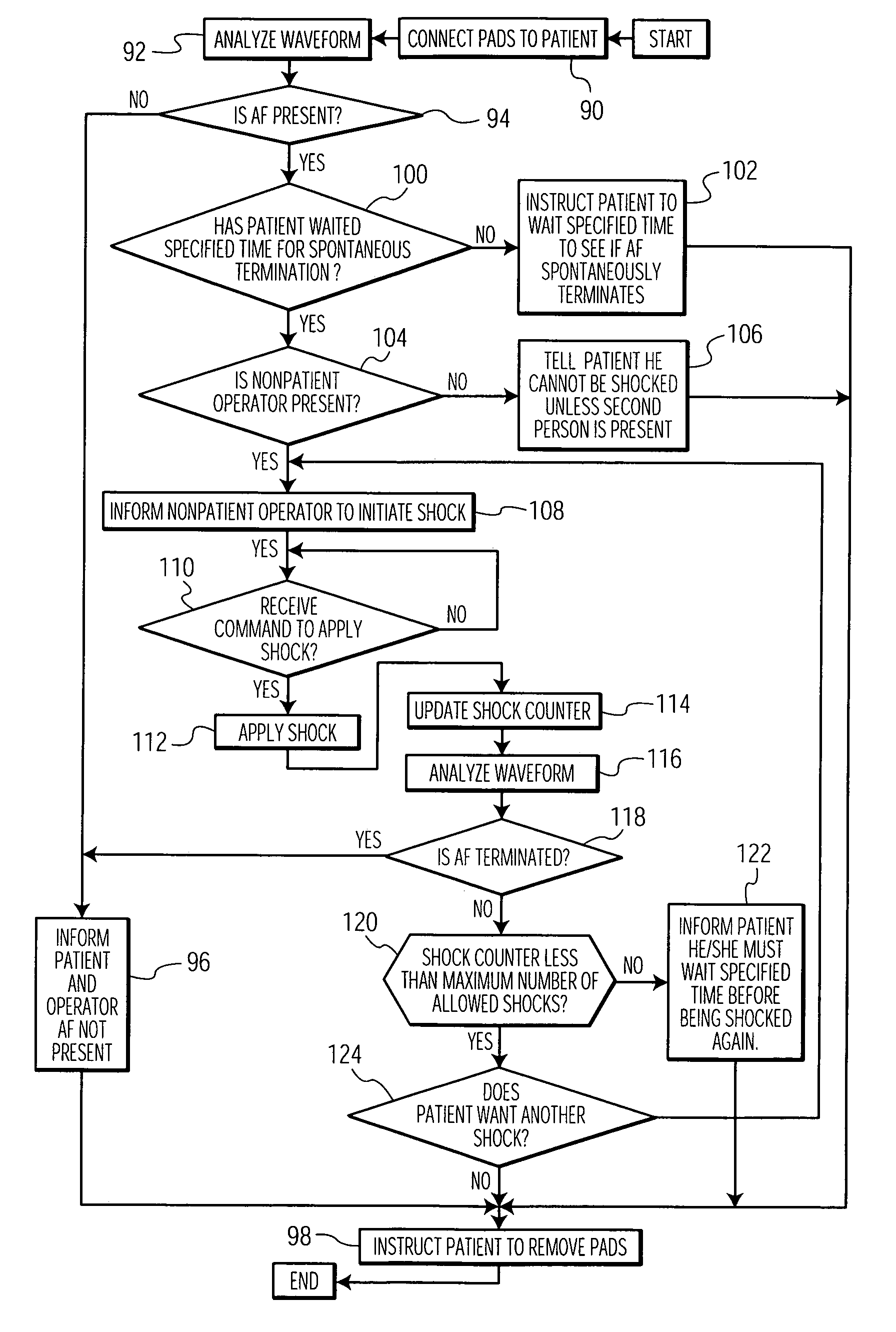
External atrial defibrillator and method for personal termination of atrial fibrillation
An atrial defibrillator includes a portable, non-implantable housing, a pair of defibrillator pads, a shock generator, and an analyzer. The pads are applied to the outside of a patient's body, and the shock generator delivers a shock to the patient via the pads. The analyzer receives a cardiac signal from the patient, determines from the signal whether the patient is experiencing atrial fibrillation, and enables the shock generator if the patient is experiencing atrial fibrillation. Unlike conventional external atrial defibrillators, such an atrial defibrillator can be used by a layperson in the comfort of a patient's own home. Furthermore, such a defibrillator does not cause the surgery-related problems associated with implantable atrial defibrillators. Moreover, because the patient can choose when to receive a shock, such a defibrillator is less likely to surprise and embarrass the patient than automatic implantable defibrillators are.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
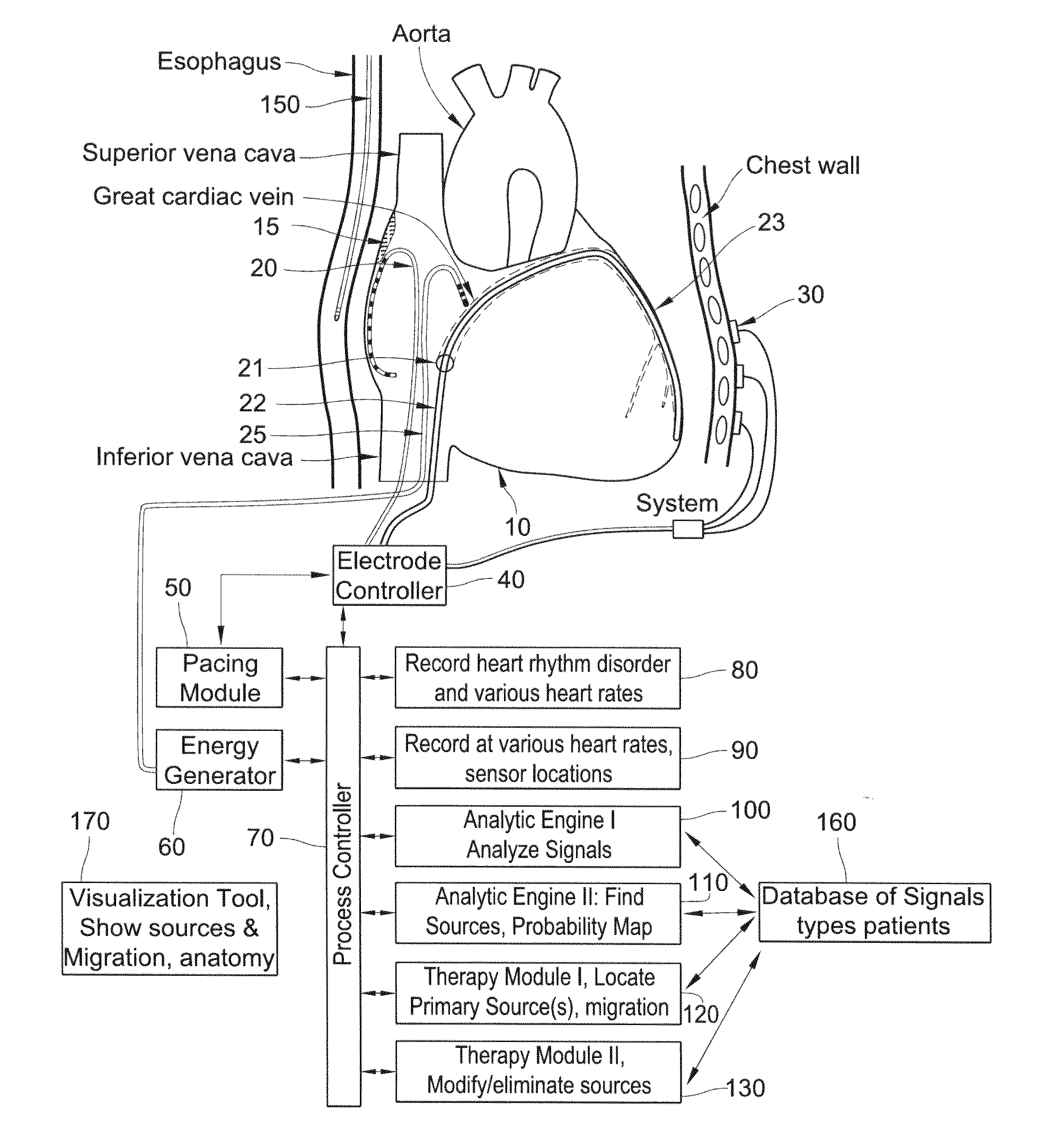
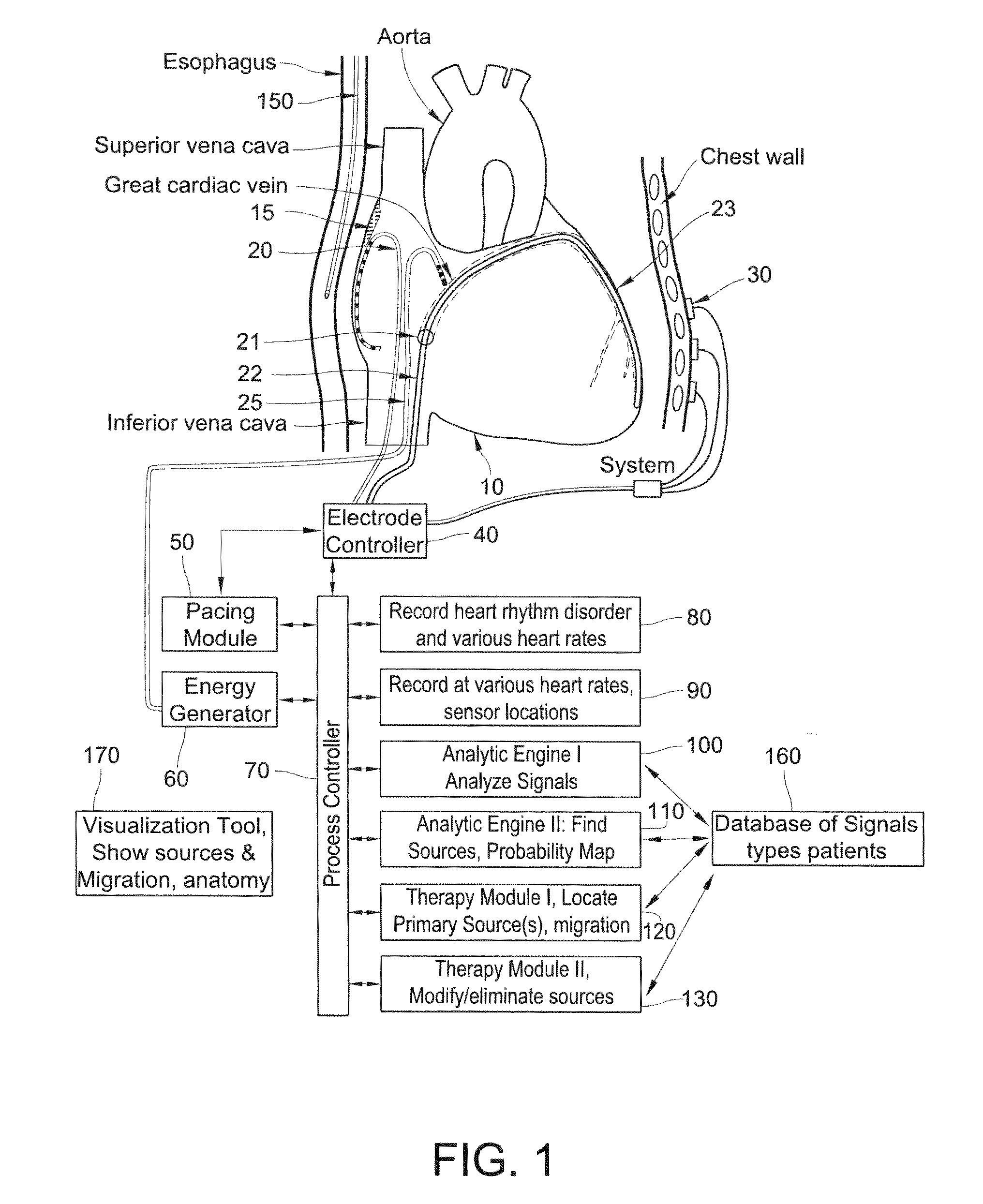
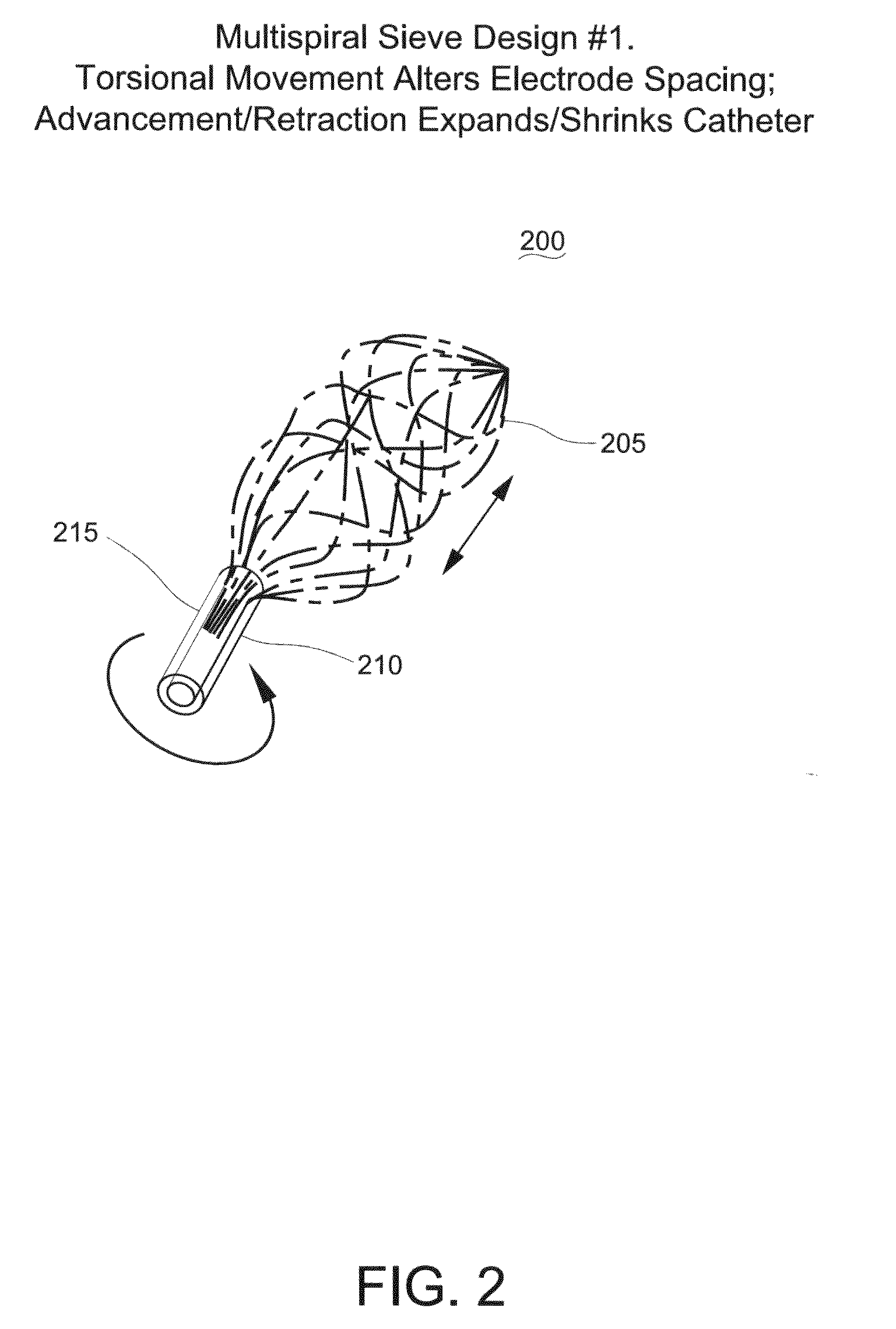
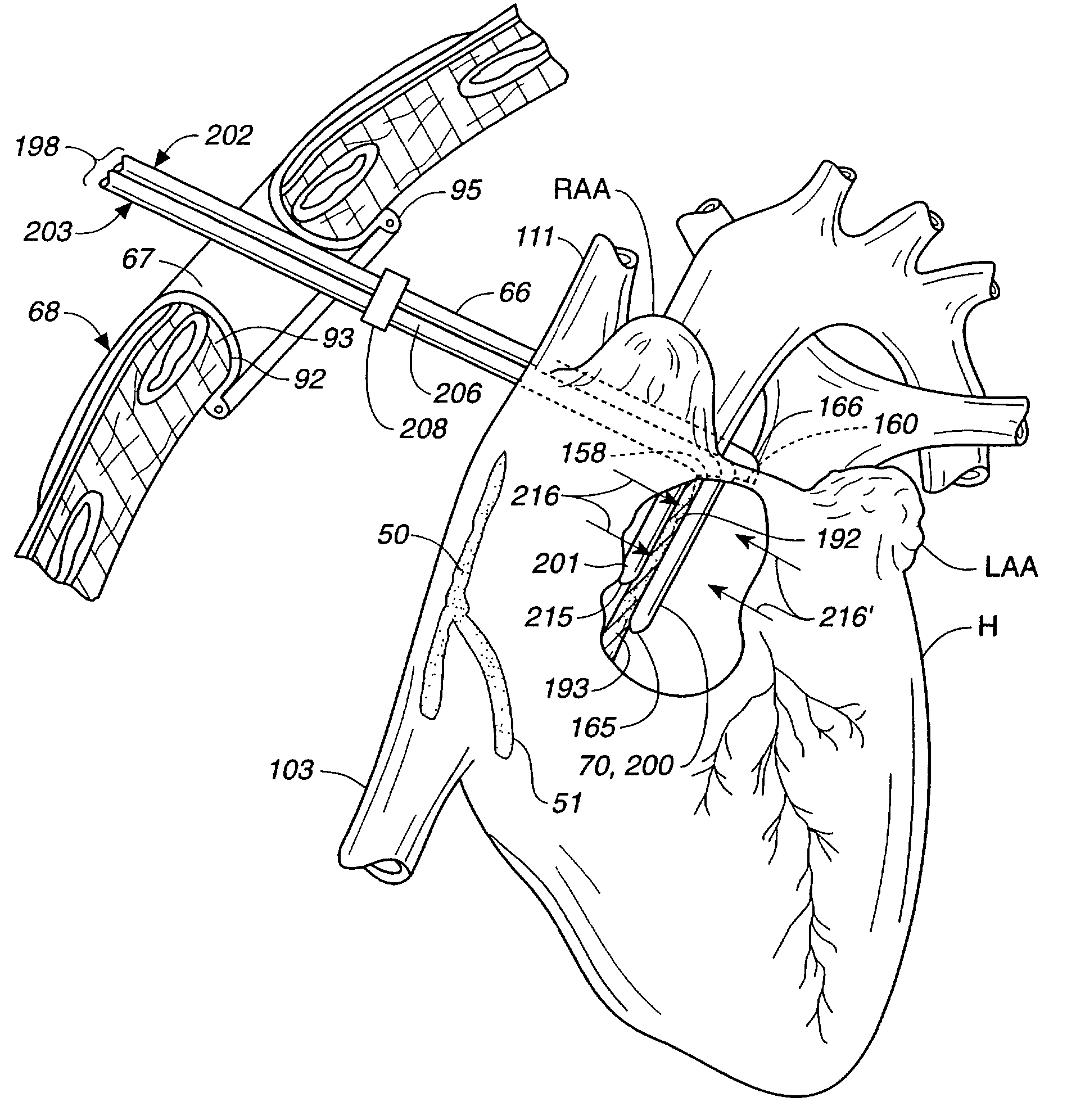
Methods, system and appartus for the detection, diagnosis and treatment of biological rhythm disorders
ActiveUS20100094274A1Improve abilitiesRemove obstaclesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyRhythmCardiac dysrhythmias
Method, system and apparatus to detect, diagnose and treat biological rhythm disorders. In preferred particularly desirable embodiment relating to the real-time detection of heart rhythm disorders, this invention identifies localized sources for complex rhythms including atrial fibrillation to guide the localized application of energy to modify the source and treat the rhythm disorder.
Owner:THE US REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS OFFICE OF THE GENERAL COUNSEL 024 +1
Surgical system and procedure for treatment of medically refractory atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS7387126B2Reduce complicationsShorten the timeSuture equipmentsCannulasMedicineBiomedical engineering
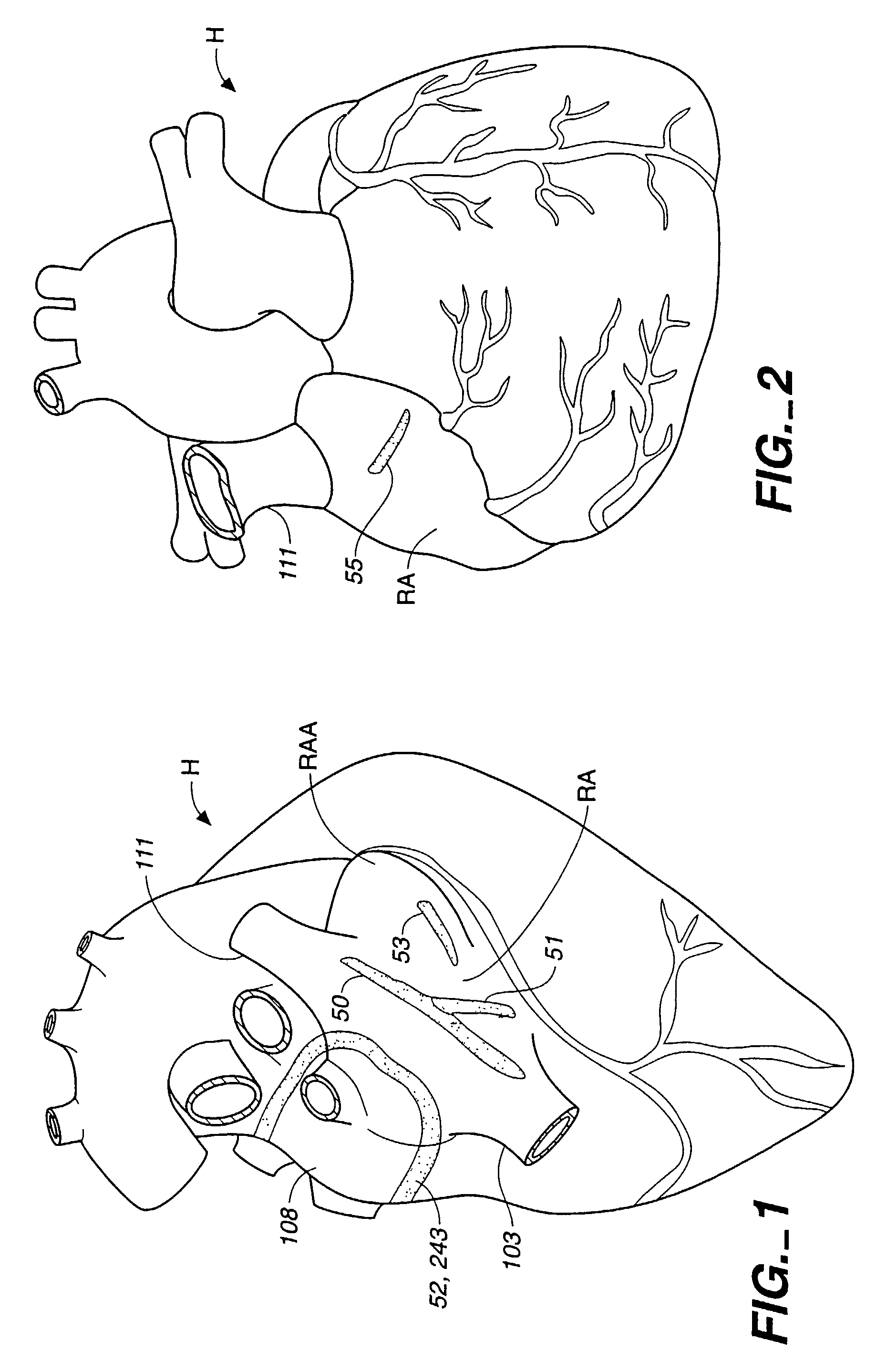
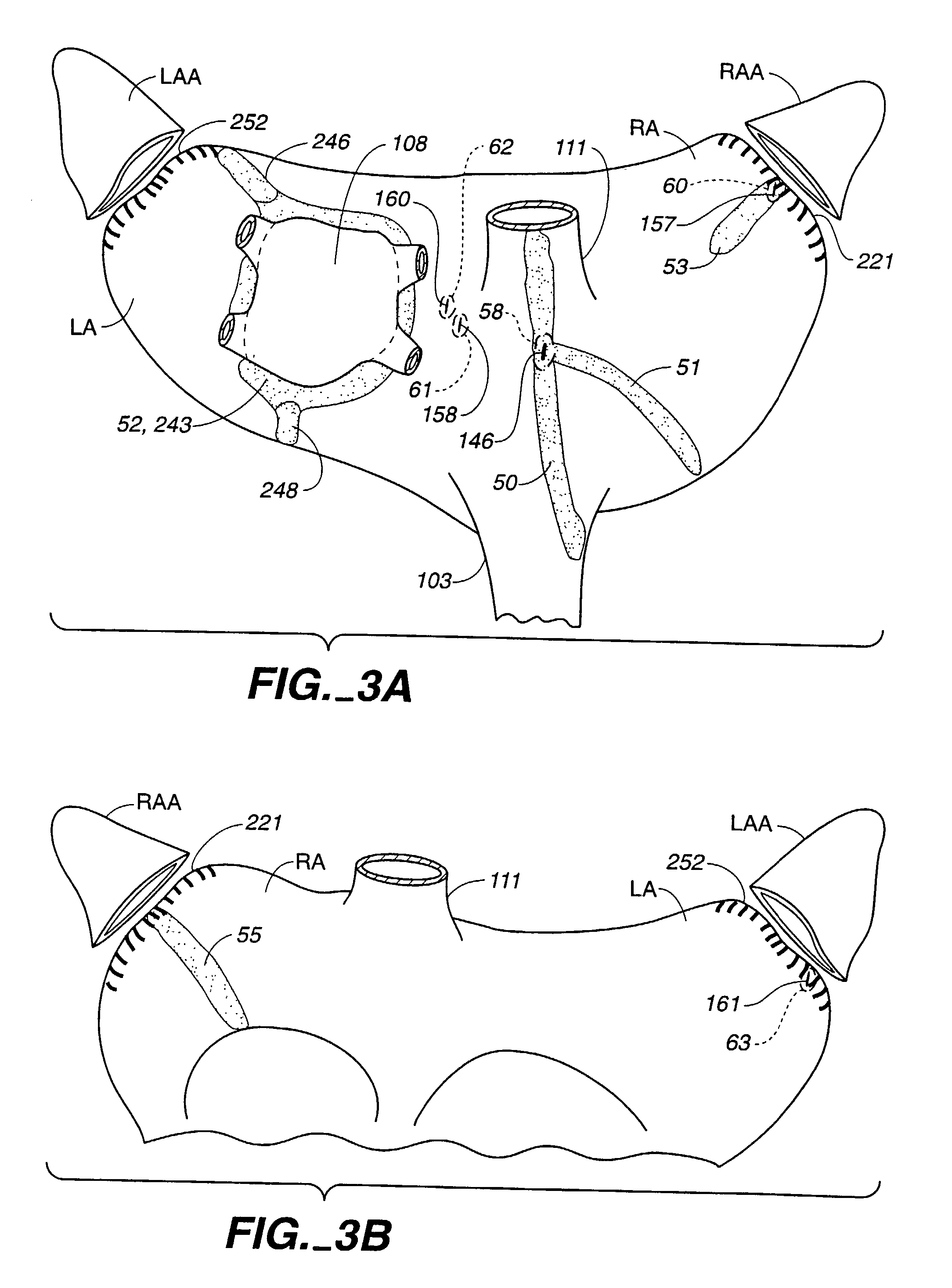
The invention provides surgical systems and methods for ablating heart tissue within the interior and / or exterior of the heart. A plurality of probes is provided with each probe configured for introduction into the chest for engaging the heart. Each probe includes an elongated shaft having an elongated ablating surface of a predetermined shape. The elongated shaft and the elongated ablating surface of each probe are configured to ablate a portion of the heart. A sealing device affixed to the heart tissue forms a hemostatic seal between the probe and the penetration in the heart to inhibit blood loss therethrough.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
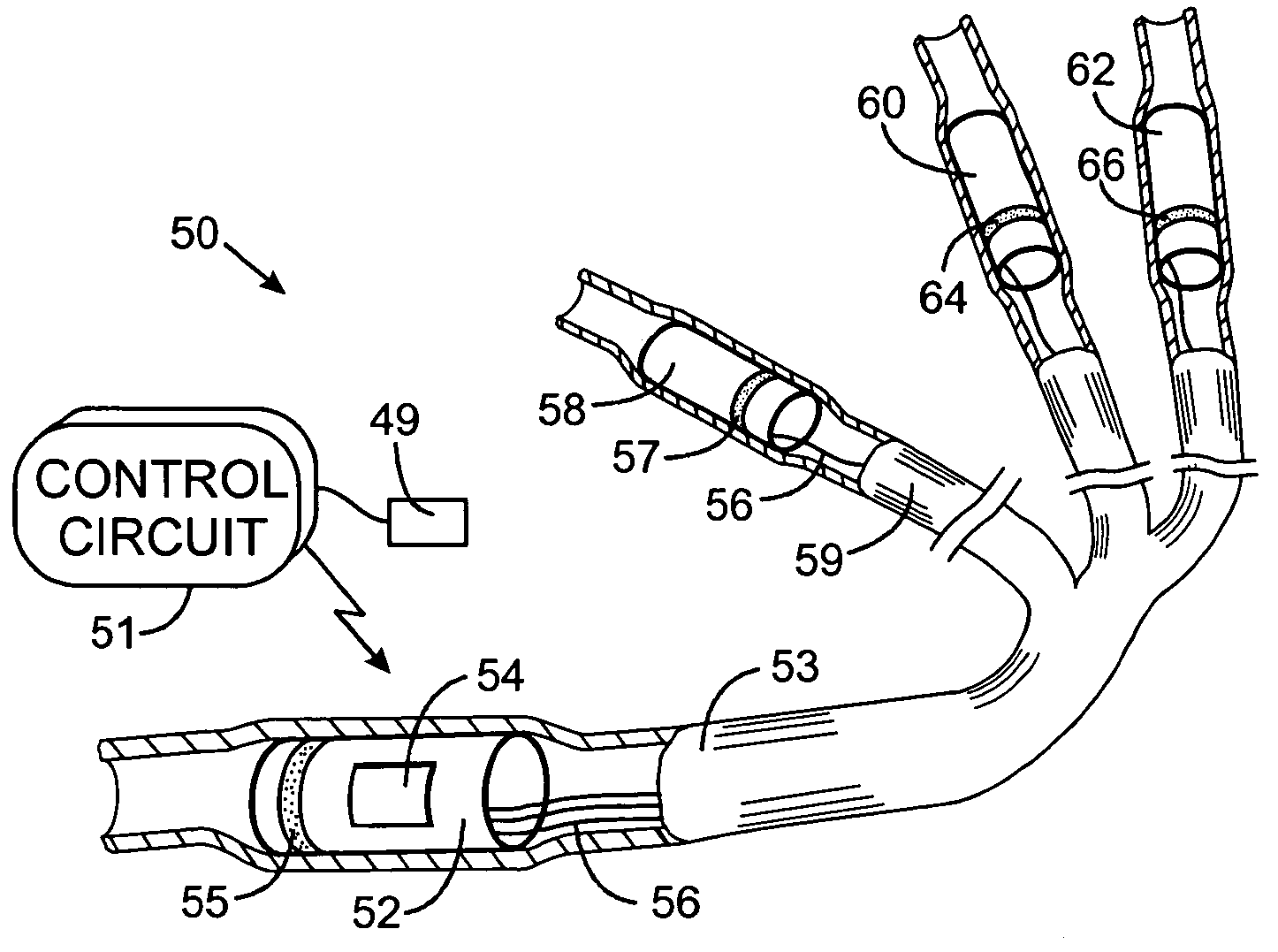
Treatment of atrial fibrillation using high-frequency pacing and ablation of renal nerves
ActiveUS20120143097A1Lower blood pressureReduce harmUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyAtrial cavityRenal nerve
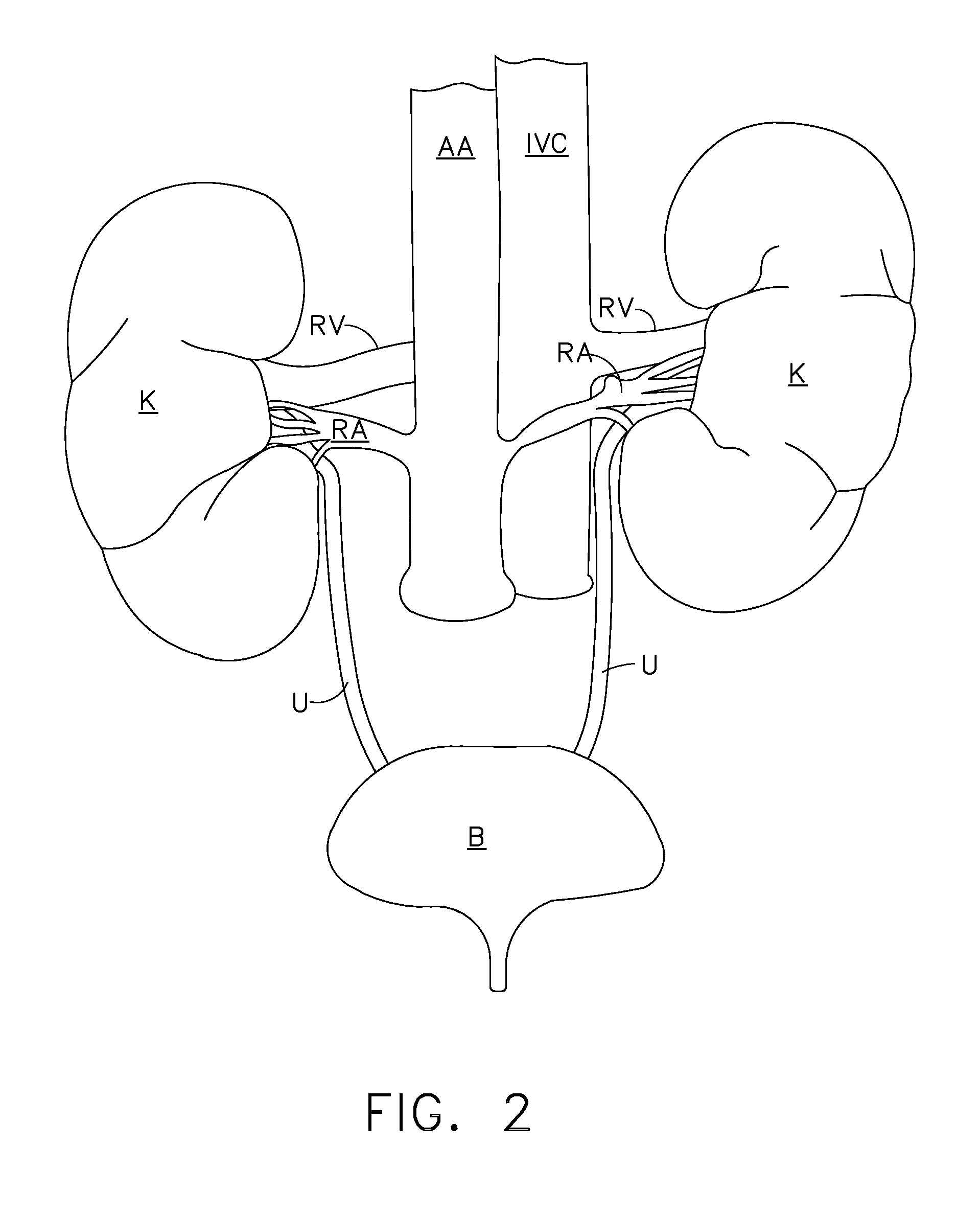
A method for the treatment of a patient for the purpose of lowering blood pressure and / or treating cardiac arrhythmias, particularly atrial fibrillation includes the insertion of an ablation catheter into the lumen of a renal artery. The ablation catheter is equipped with an electrode that can stimulate the wall tissue in the renal artery to help identify the location of a renal nerve. High-frequency stimulation of the renal nerve causes a decrease in the blood pressure of the patient thereby indicating that a renal nerve is nearby. The ablation catheter is used to ablate the renal nerve using radiofrequency, ultrasound, microwave energy or cryogenic cooling. An irrigated ablation catheter may be used to decrease damage to cells in the wall of the lumen of the renal artery other than the renal nerve, such as the endothelial cells.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Atrial ablation catheter and method of use
InactiveUS7429261B2Easy to deployEasy to retractElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsTunica intimaElectrode array
An atrial ablation catheter and methods for its use. The endocardial catheter includes an electrode array particularly adapted to locate and ablate foci of arrhythmia which are required for sustained atrial fibrillation is provided. The array is easily deployed and retracted from the catheter, and presents a distally oriented electrode array that can be pressed against the wall of the atrium.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Ablation catheters and methods for their use
InactiveUS20050033137A1Reduce riskGood electrical contactDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseCardiac disorders
The present invention relates generally to multifunctional catheters for performing ablation procedures, and more particularly to ablation catheters utilized in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and other cardiac disorders. The present invention eliminates many of the problems associated with previous ablation catheters by providing an ablation treatment not dependent upon continuous lesions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia utilizing ultrasound
InactiveUS20050080469A1Ultrasound therapyDiagnostic recording/measuringTreatment effectInvasive treatments
A noninvasive or minimally invasive treatment of cardiac arrhythmia such as supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias, specifically atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia, by treating the tissue with heat produced by ultrasound, (including High Intensity Focused Ultrasound or HIFU) intended to have a biological and / or therapeutic effect, so as to interrupt or remodel the electrical substrate in the tissue area that supports arrhythmia.
Owner:SONORHYTHM
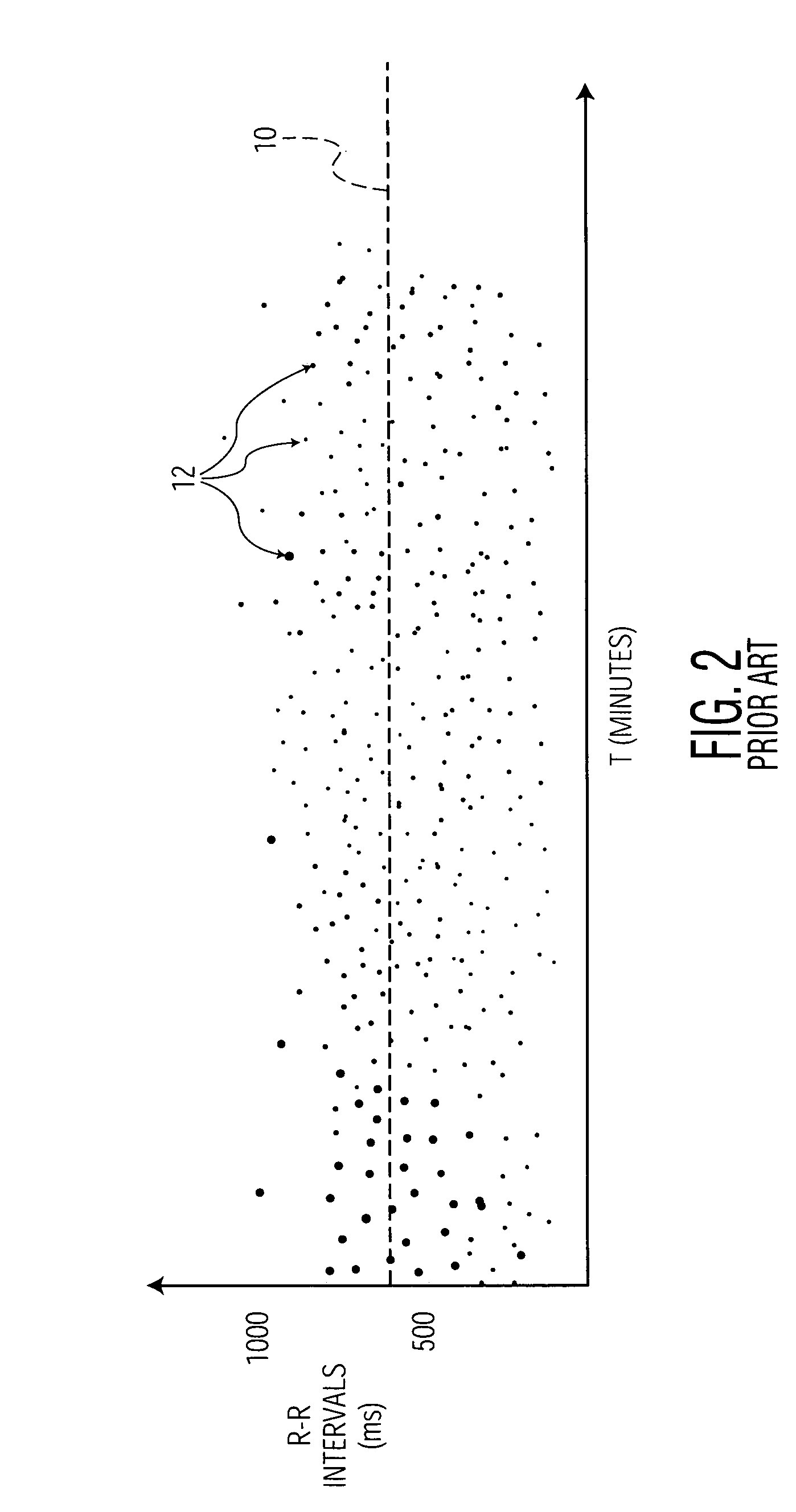
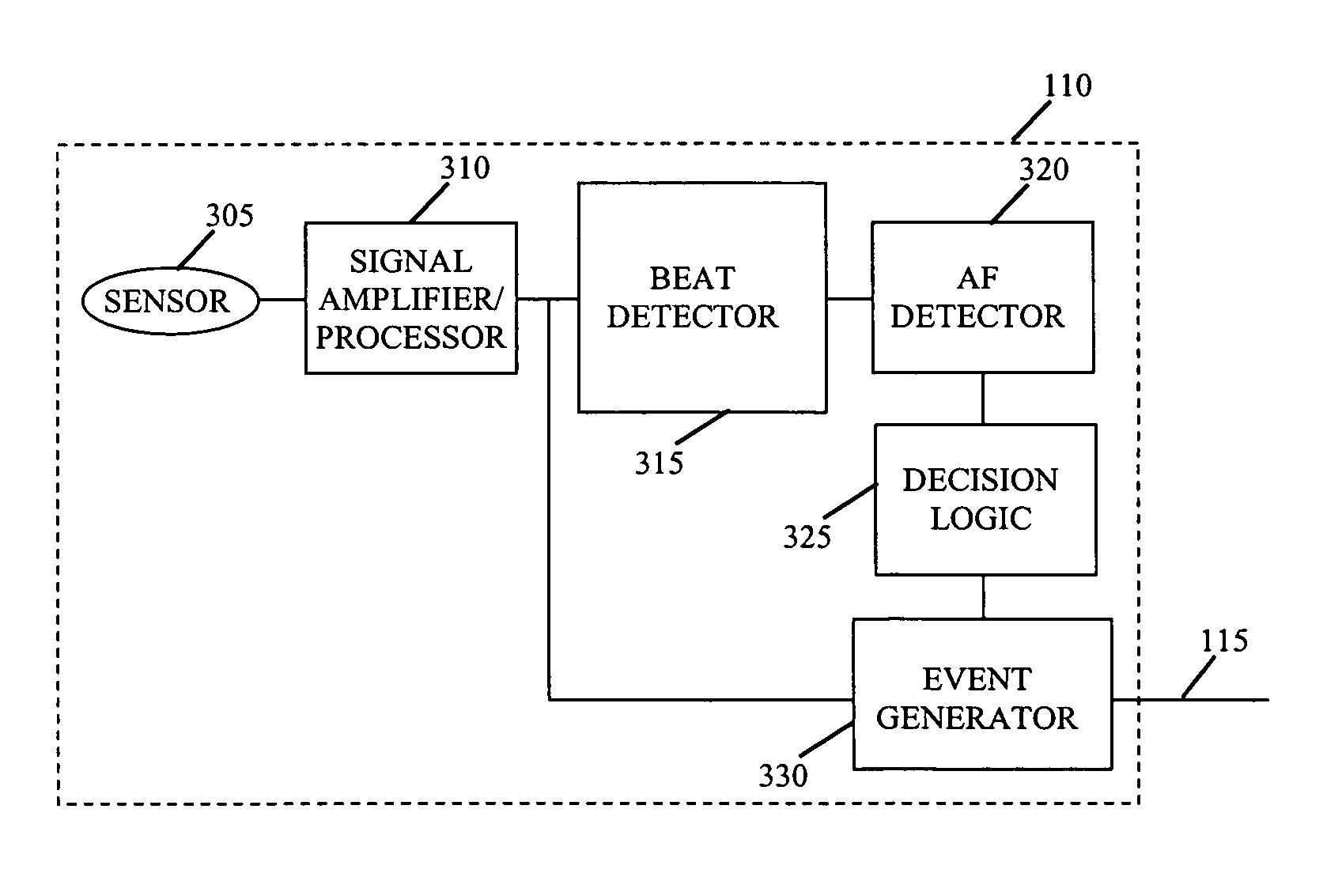
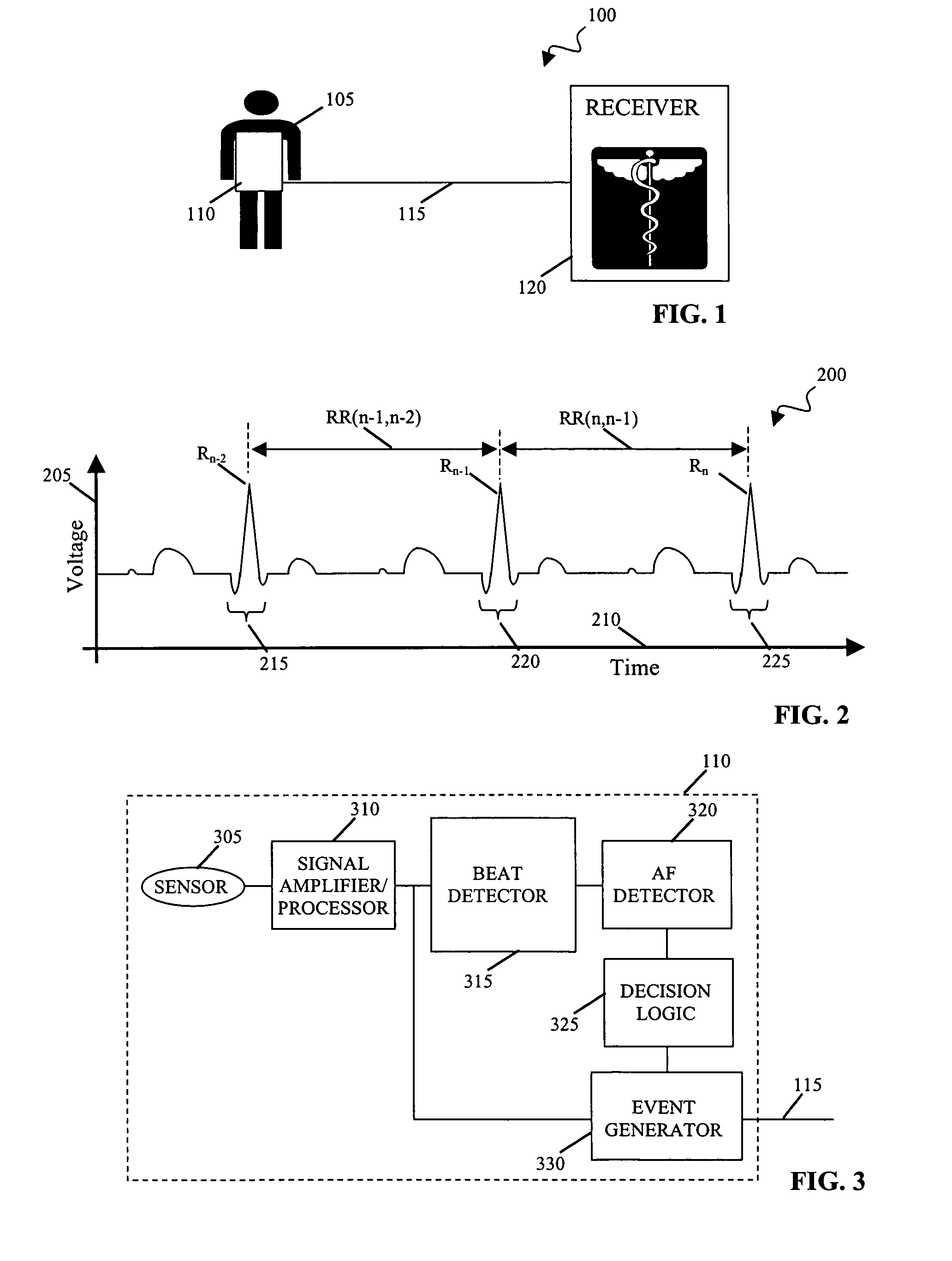
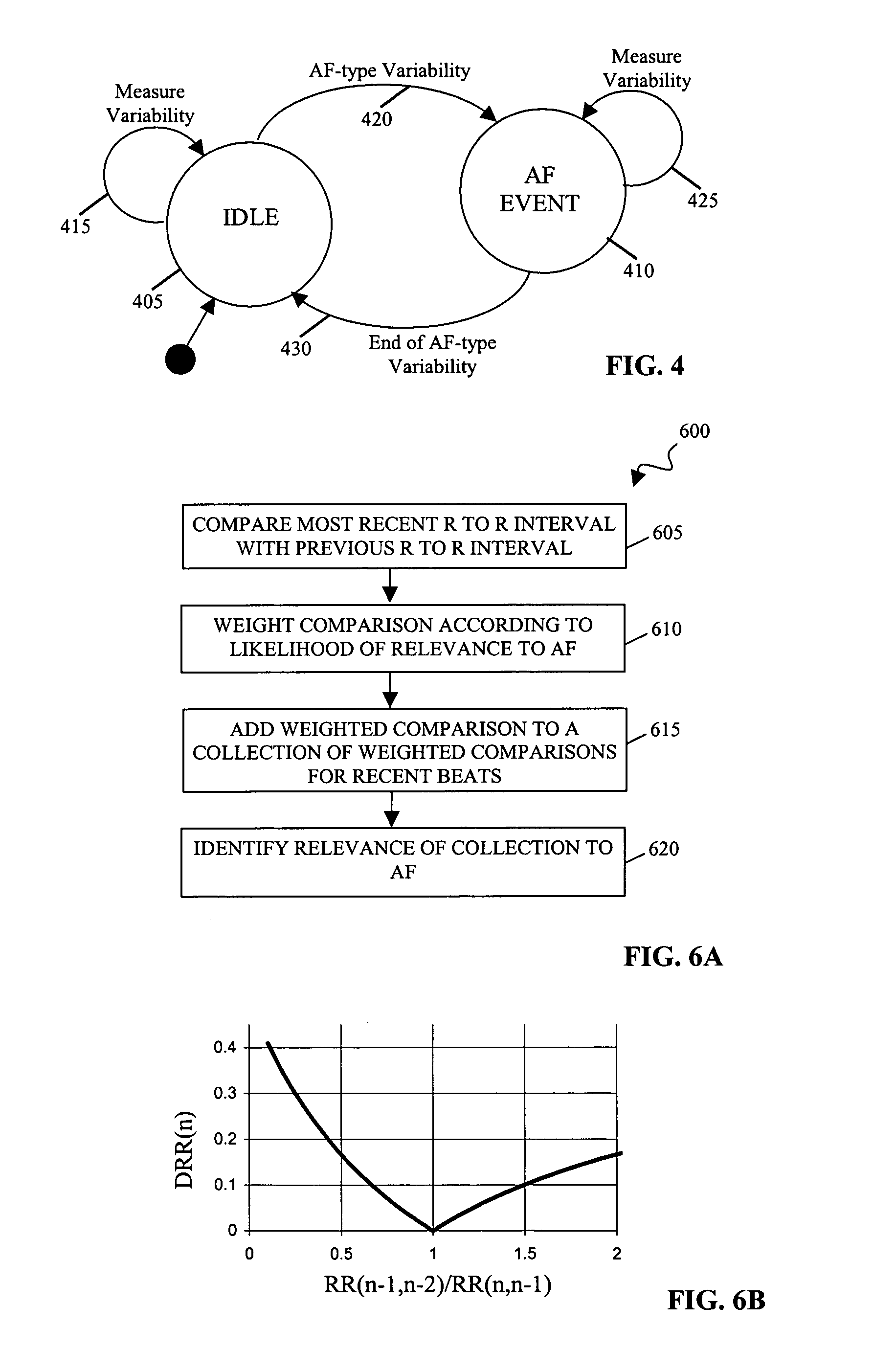
Long-term monitoring for detection of atrial fibrillation
A method and a system for detection of an arrhythmia, the method comprising determining a number of heart beat intervals; determining an instantaneous heart rate for each of the heart beat intervals; determining the variability of the instantaneous heart rates compared to a mean of the number of instantaneous heart rates; determining a non-linear value that represents the variability of the instantaneous heart rates; and detecting the arrhythmia by comparing the non-linear value with a predetermined threshold.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
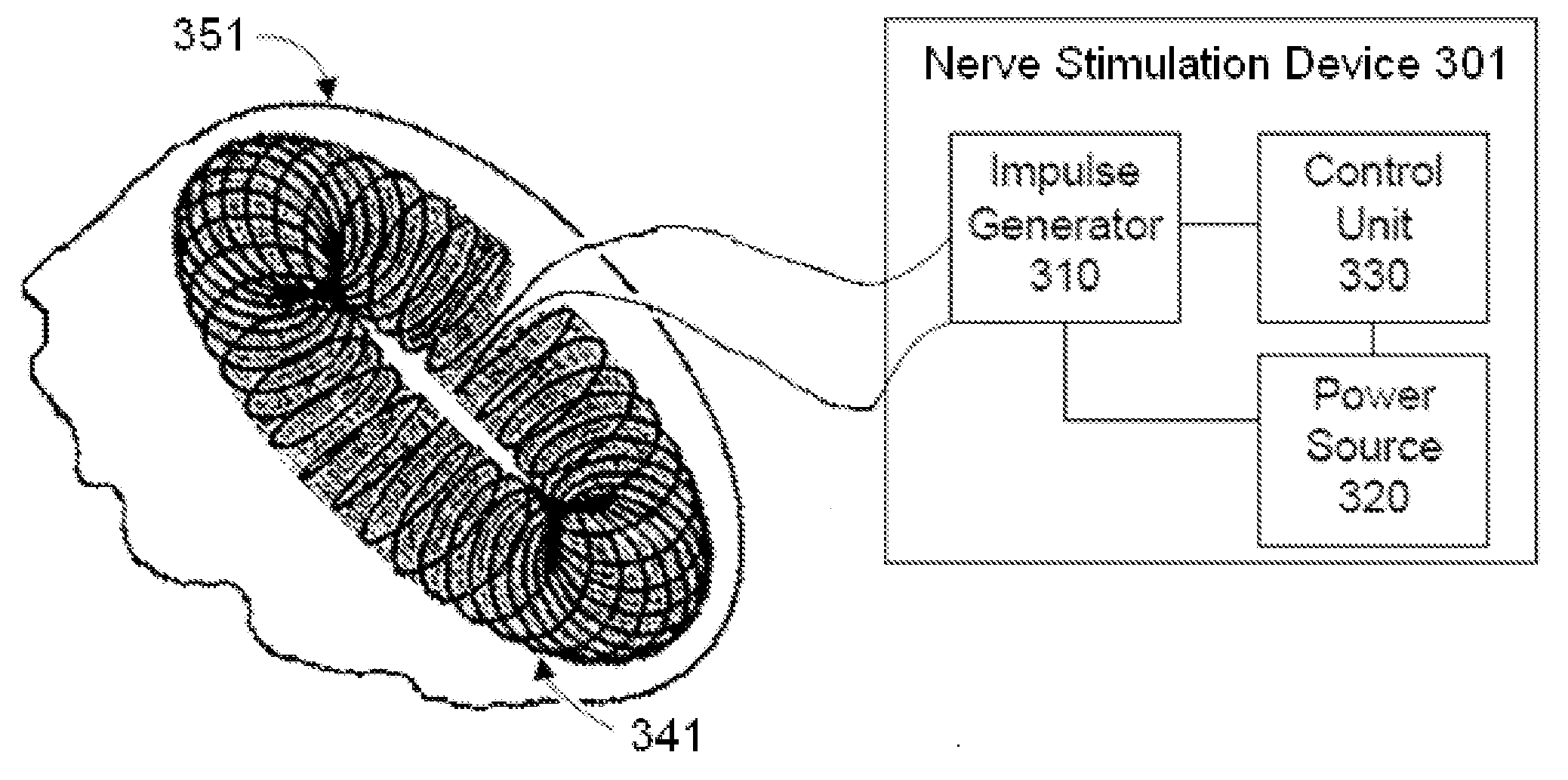
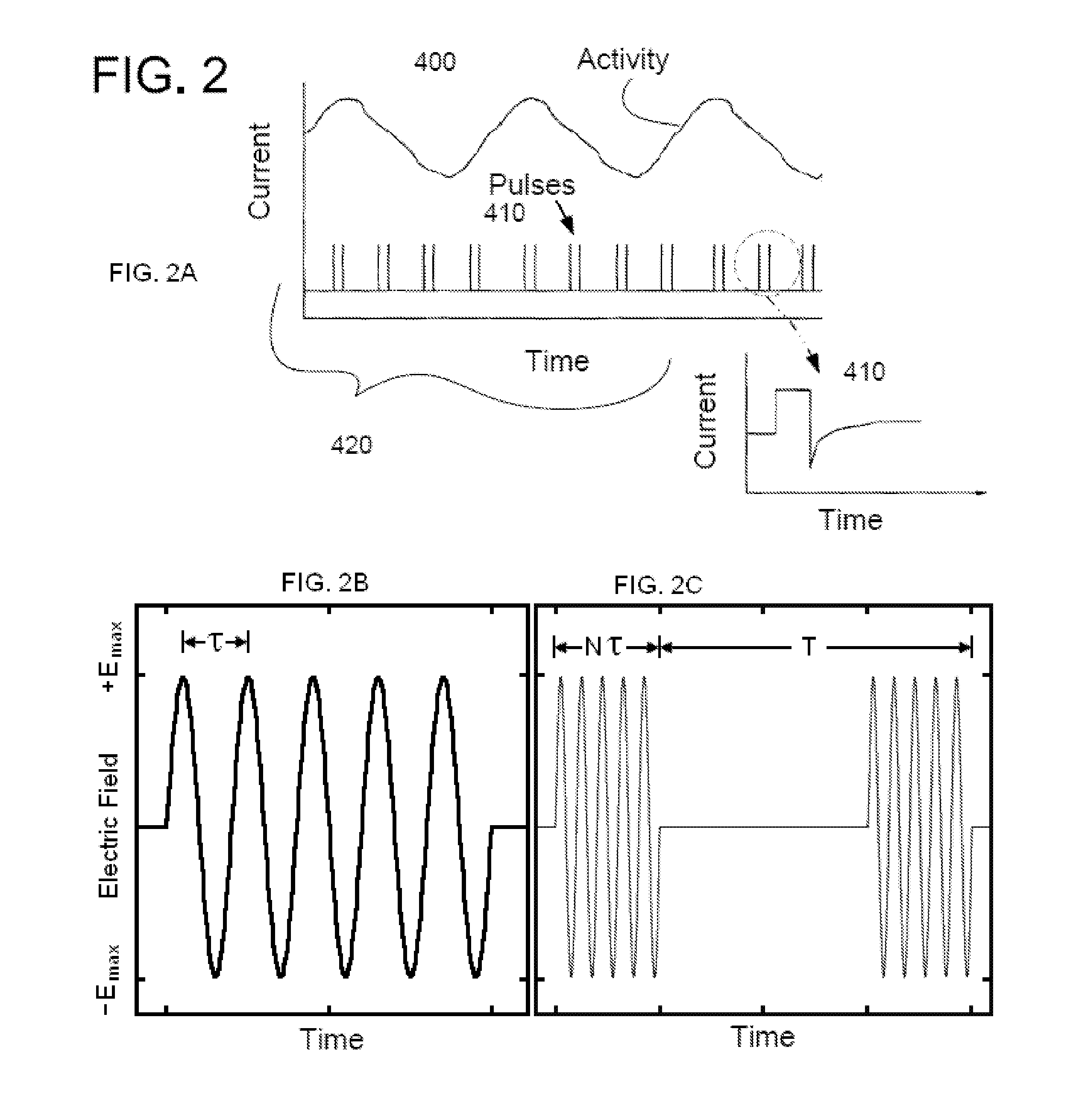
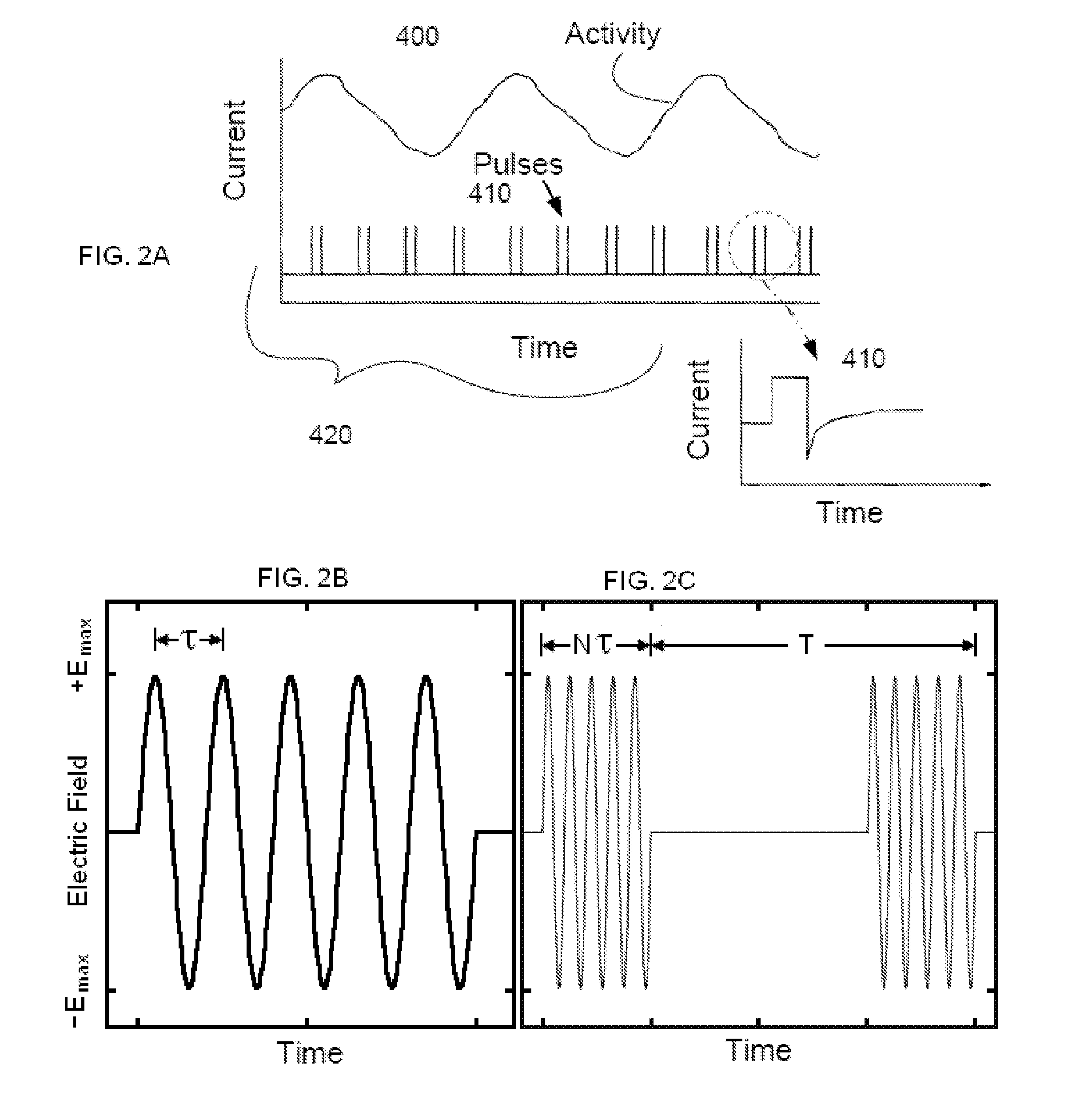
Nerve stimulation methods for averting imminent onset or episode of a disease
Transcutaneous electrical and magnetic nerve stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of averting imminent medical attacks using energy that is delivered noninvasively by the devices. The attacks comprise asthma attack, epileptic seizure, attacks of migraine headache, transient ischemic attack or stroke, onset of atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, onset of ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia, panic attack, and attacks of acute depression. The imminence of an attack is forecasted using grey-box or black-box models as used in control theory. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, a vagus nerve in the neck of a patient is stimulated noninvasively to avert the attack.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Ablation catheters
The present invention relates generally to multifunctional catheters for performing ablation procedures, and more particularly to ablation catheters utilized in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and other cardiac disorders. The present invention eliminates many of the problems associated with previous ablation catheters by providing an ablation treatment not dependent upon continuous lesions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Non-invasive method and apparatus for cardiac pacemaker pacing parameter optimization and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction
InactiveUS20050043767A1Uniform peak amplitudeEasy to detectHeart stimulatorsCardiac dysfunctionAmplitude response
A plethysmogram signal is sensed from a patient and provided to a programmer device for monitoring the condition of the patient and for optimizing pacing parameters of a cardiac device implanted in the patient. The programmer device analyzes the plethysmogram signal for cardiac performance associated with different pacing parameters. The cardiac performance is indicated by, for example, a pulse amplitude response, a degree of pulsus alternans, or irregularity in the pressure pulses detected in an atrial fibrillation patient. The pacing parameters resulting in the best cardiac performance are selected as the optimum pacing parameters. In one embodiment, the programmer device monitors a Valsalva maneuver performed by a patient. Optimum pacing parameters are derived by analysis of the plethysmogram signals obtained during performance of the Valsalva maneuver while the patient is paced using different pacing parameters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Ablative ultrasonic-cryogenic methods
InactiveUS20090221955A1Induced fastEasy to moveUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesCardiac muscleTransducer
An ablative apparatus and associated methods that can be used to treat atrial fibrillation and other cardiac arryhythmias by ablating cardiac tissue is disclosed. When the distal end of the apparatus reaches the tissue to be ablated, an ablation probe driven by a transducer is vibrated. Scratching the tissue with abrasive members, the vibrating ablation probe is capable of mechanically ablating tissues. This mechanical ablation may be utilized to penetrate epicardial fat, thereby exposing the underlying myocardium. The ablative apparatus may then be used subject the exposed myocardium to mechanical ablation, cryoablation, ultrasonic ablation, and / or any combination thereof.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
Electrosurgical hemostat
InactiveUS20060041254A1Reduce usageImprove ease of useCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingMinimally invasive proceduresDetent
A hemostat-type device for ablative treatment of tissue, particularly for treatment of atrial fibrillation, is constructed with features that provide easy and effective treatment. The device may include a swiveling head assembly that allows the jaws to be adjusted in pitch and / or roll. The device may include a malleable or articulating handle shaft, as well as, malleable or curved rigid jaws that can permit curved lesion shapes. A locking detent can secure the jaws in a closed position during the procedure. The device may include one or more remote actuators making the hemostat-type device useful for minimally invasive procedures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method For Simultaneous Bi-Atrial Mapping Of Atrial Fibrillation
InactiveUS20070232949A1High resolutionFast informationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodeDisplay device
A method for diagnosing and mapping atrial fibrillation correlates recordings of electrical activity from intracardiac multielectrode catheters with the locations of electrodes within the heart to obtain a global mapping of cardiac electrical activity. Time delay and / or amplitude information in the recorded electrical activities is fused with electrode location information to generate a display on a 3-D anatomical template of the heart. Time delay and / or amplitude information is displayed using color code and / or lines of equal value, to aid diagnosis and localization of electrical activity irregularities. Mapping of atrial fibrillation enables physicians to treat arrhythmia by ablation, pacing, shock therapy and / or drugs at initiation or during an episode based on therapy delivery at critical mapped locations for arrhythmia onset or maintenance. Locations for placement of pacing leads and pacemaker timing parameters may also be obtained from the display.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Device and Method For Assisting Heat Ablation Treatment of the Heart
InactiveUS20080243112A1Simple designSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingThermal energyTemperature control
Owner:DE NEVE WERNER FRANCOIS
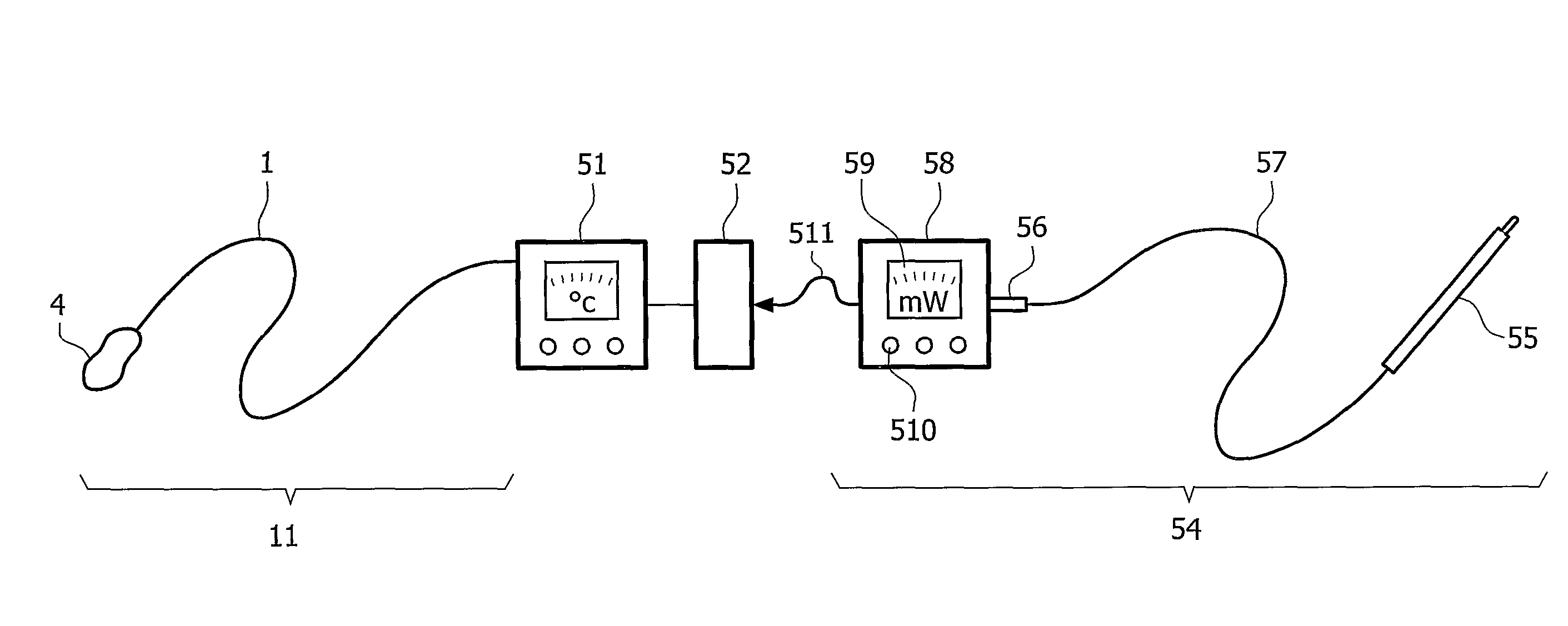
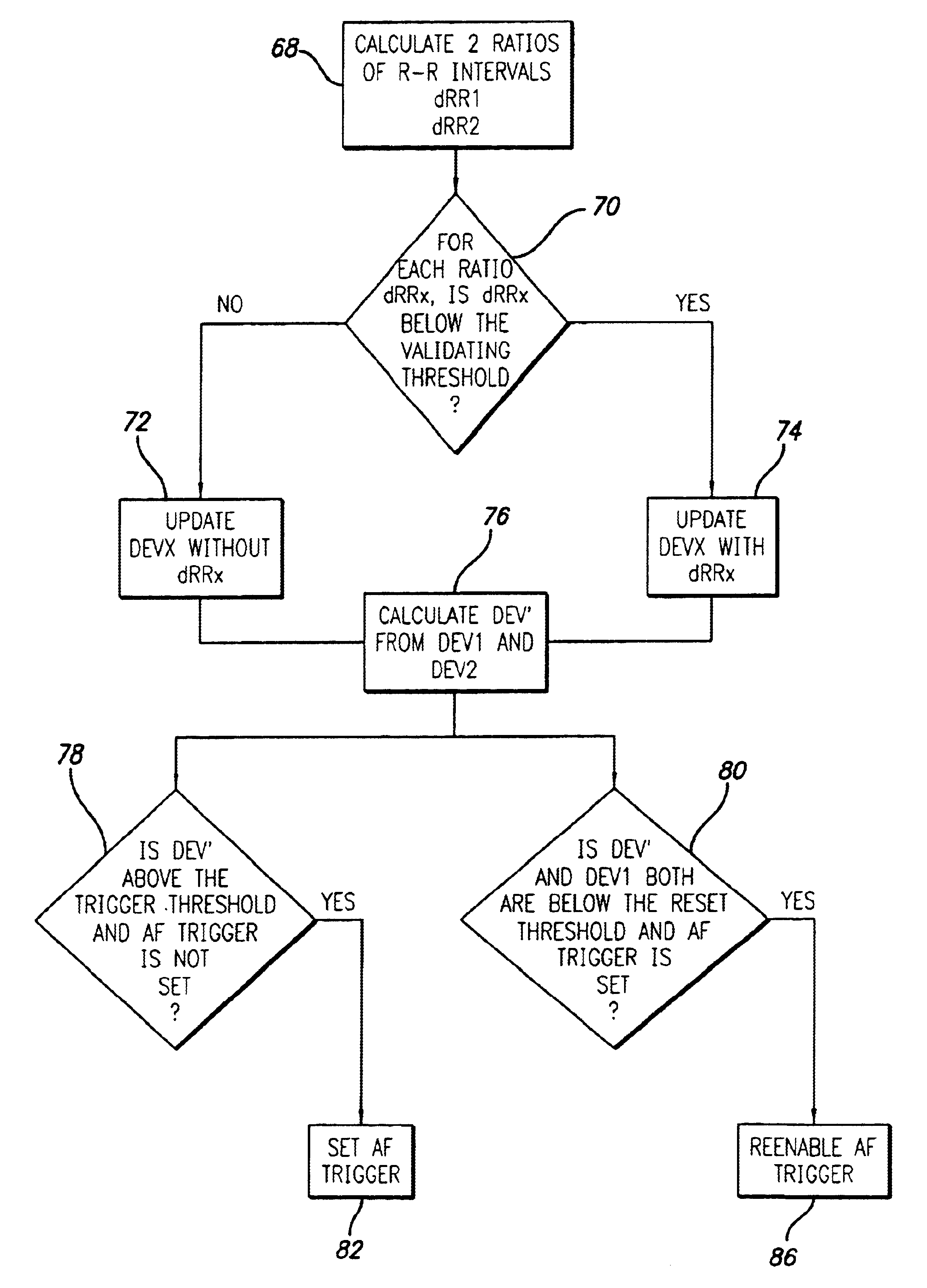
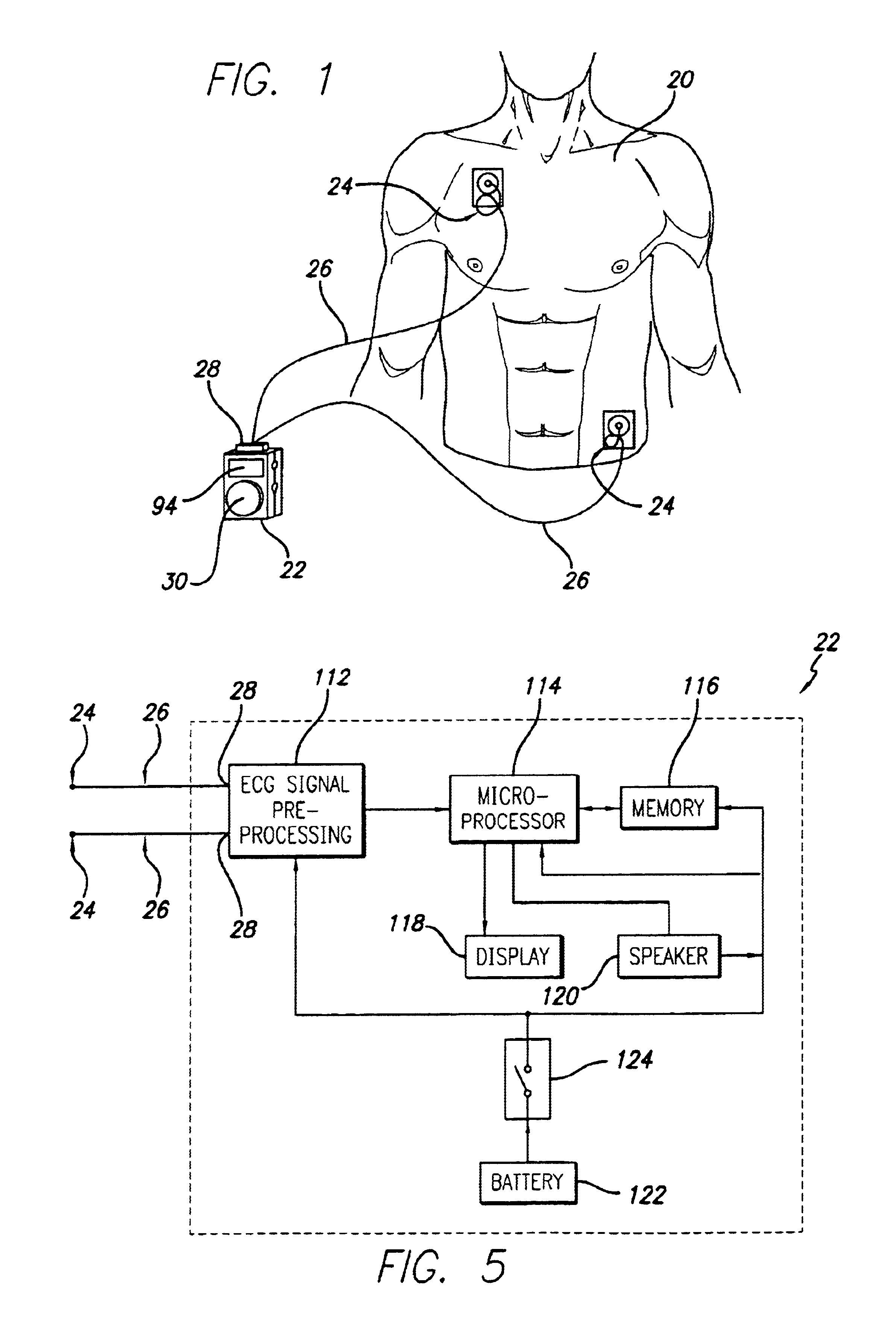
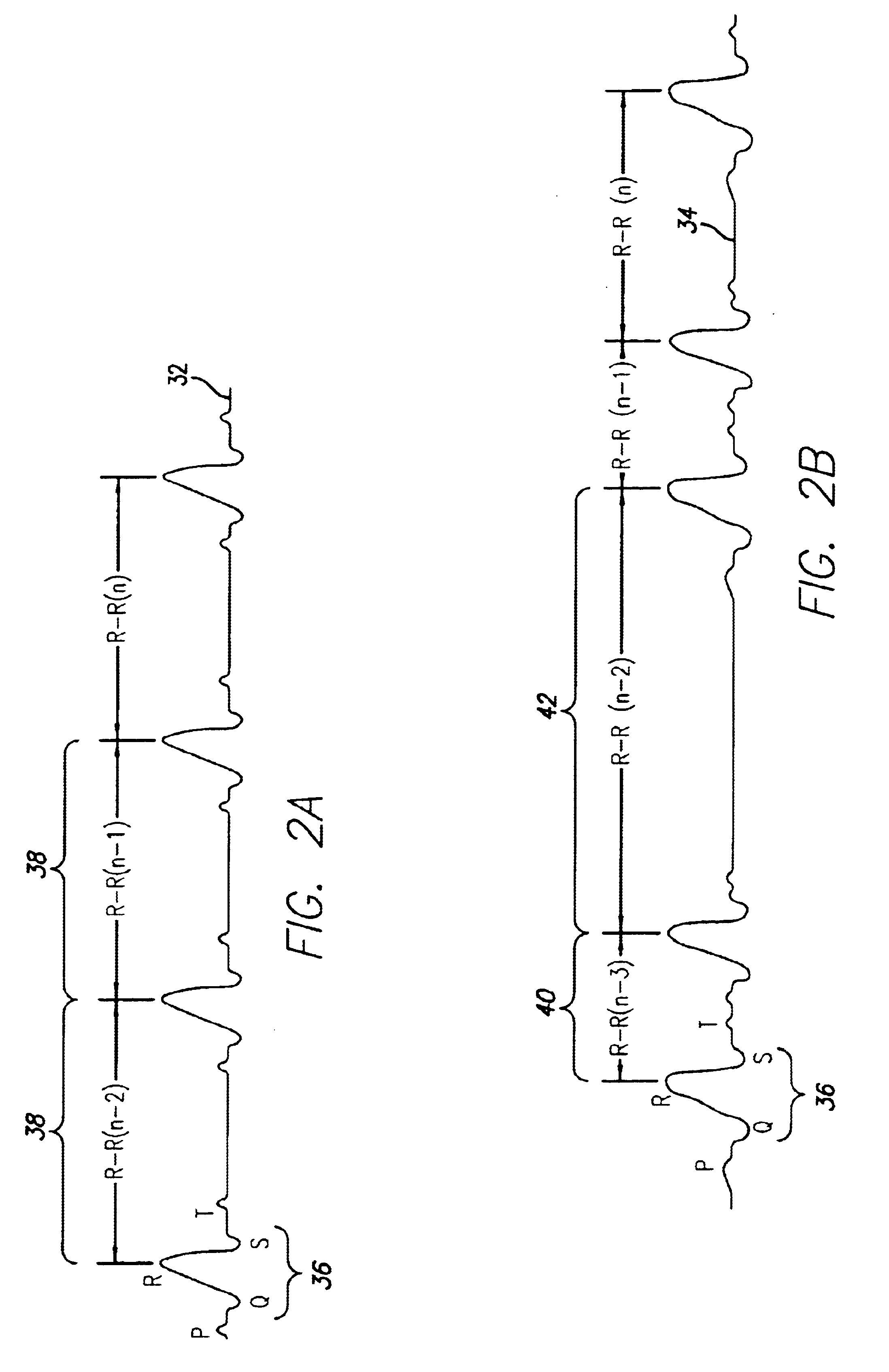
Portable ECG monitor and method for atrial fibrillation detection
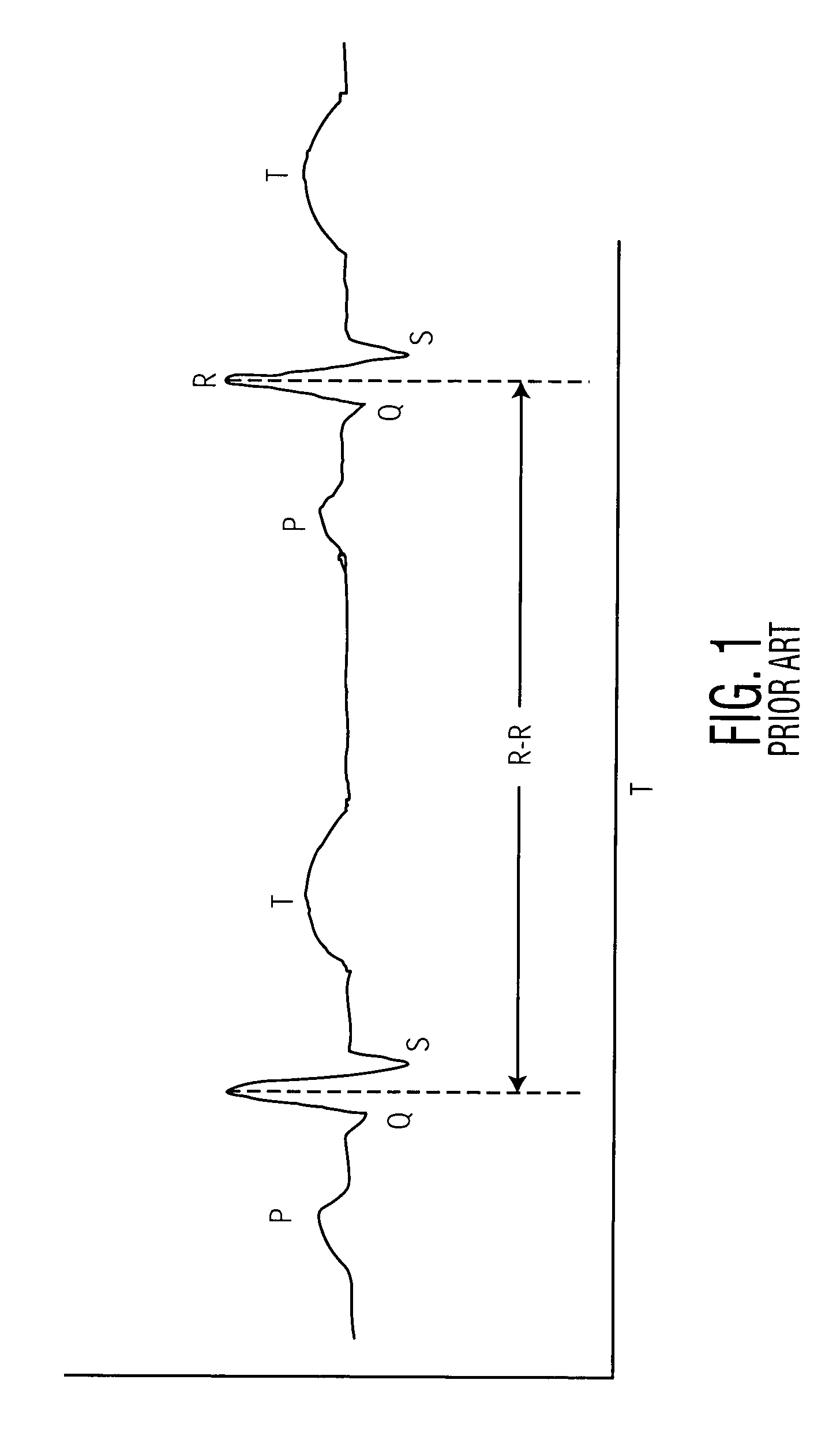
An apparatus and method for detecting an atrial fibrillation through monitoring the R—R intervals of a patient's QRS complexes. Ratios of the current R—R interval are made to previous R—R intervals. Multiple moving averages are taken of the ratio results. The ratios are compared to a validating threshold and if the particular ratio is within a selected range, a moving average is calculated with inclusion of the present R—R interval. If the ratio is outside the range, a moving average is calculated without inclusion of the current R—R interval. The moving averages are combined and this difference average is compared to a trigger threshold. If the difference average exceeds the threshold, an atrial fibrillation is determined to exist, a memory trigger is provided, and the QRS complex data within a selected period of time about the atrial fibrillation event are recorded and removed from overwrite status in the memory. A reset threshold, differing from the trigger threshold, is used and if the difference average falls below the reset threshold, the method and apparatus are re-enabled to record a new AFIB event.
Owner:LIFEWATCH SERVICES
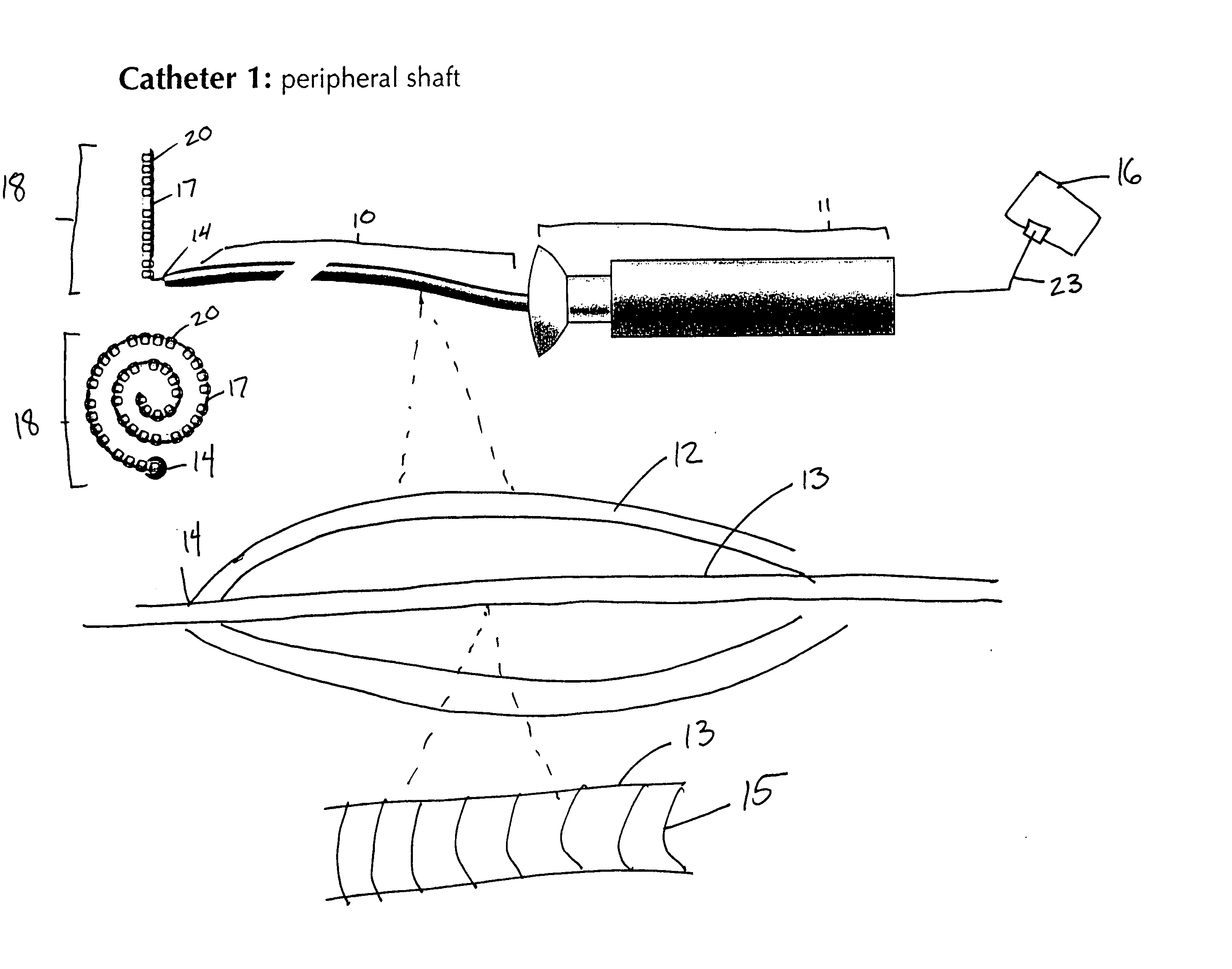
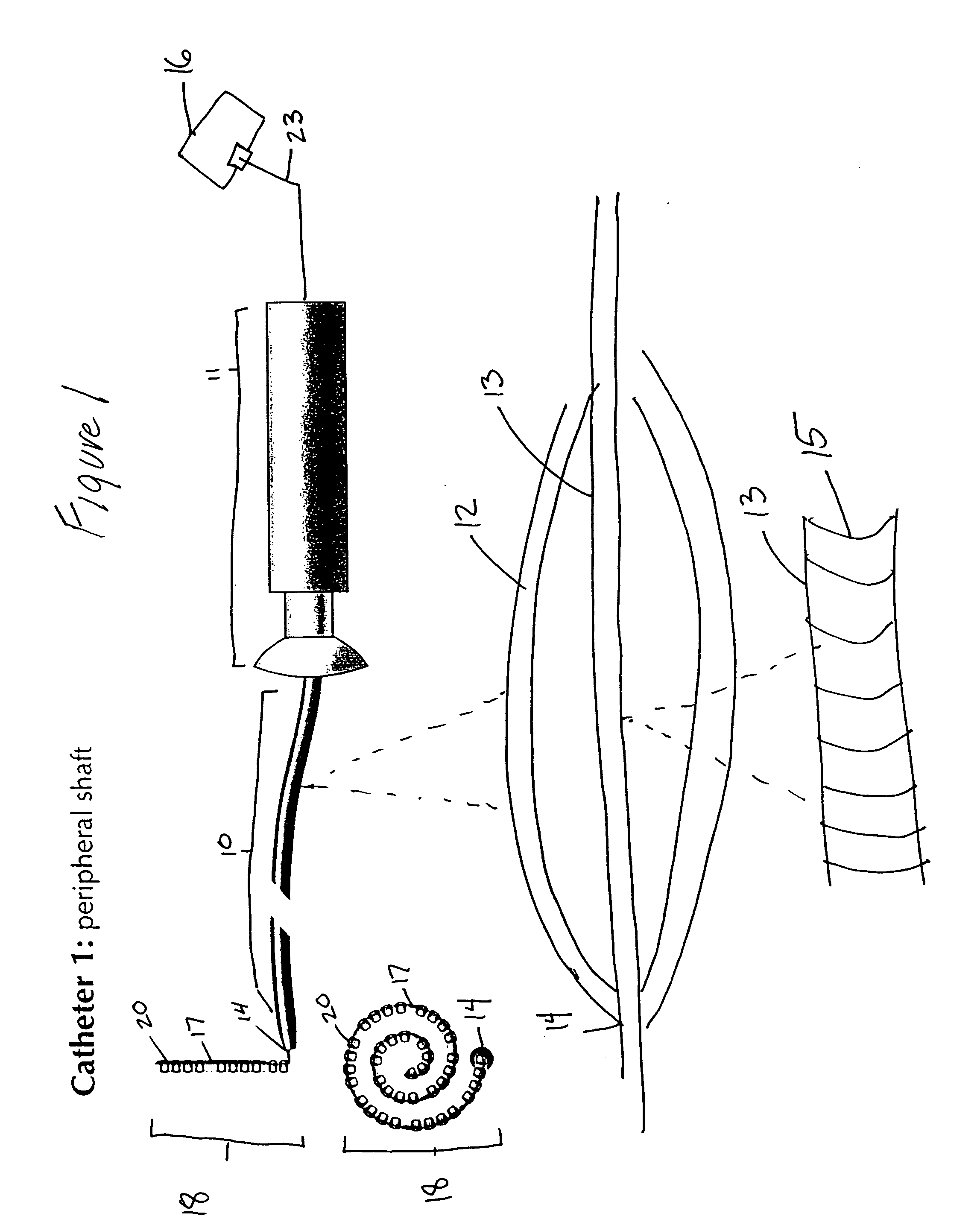
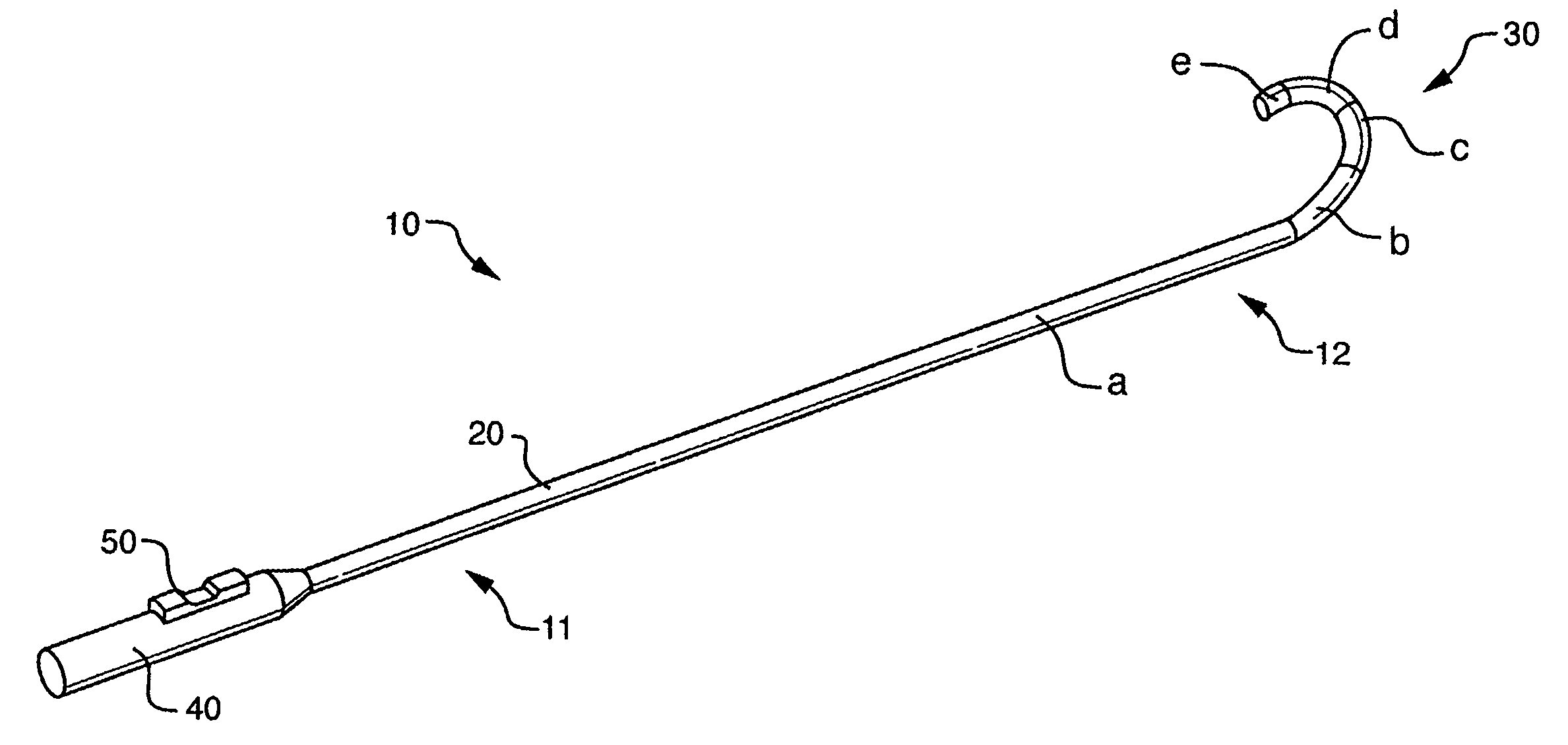
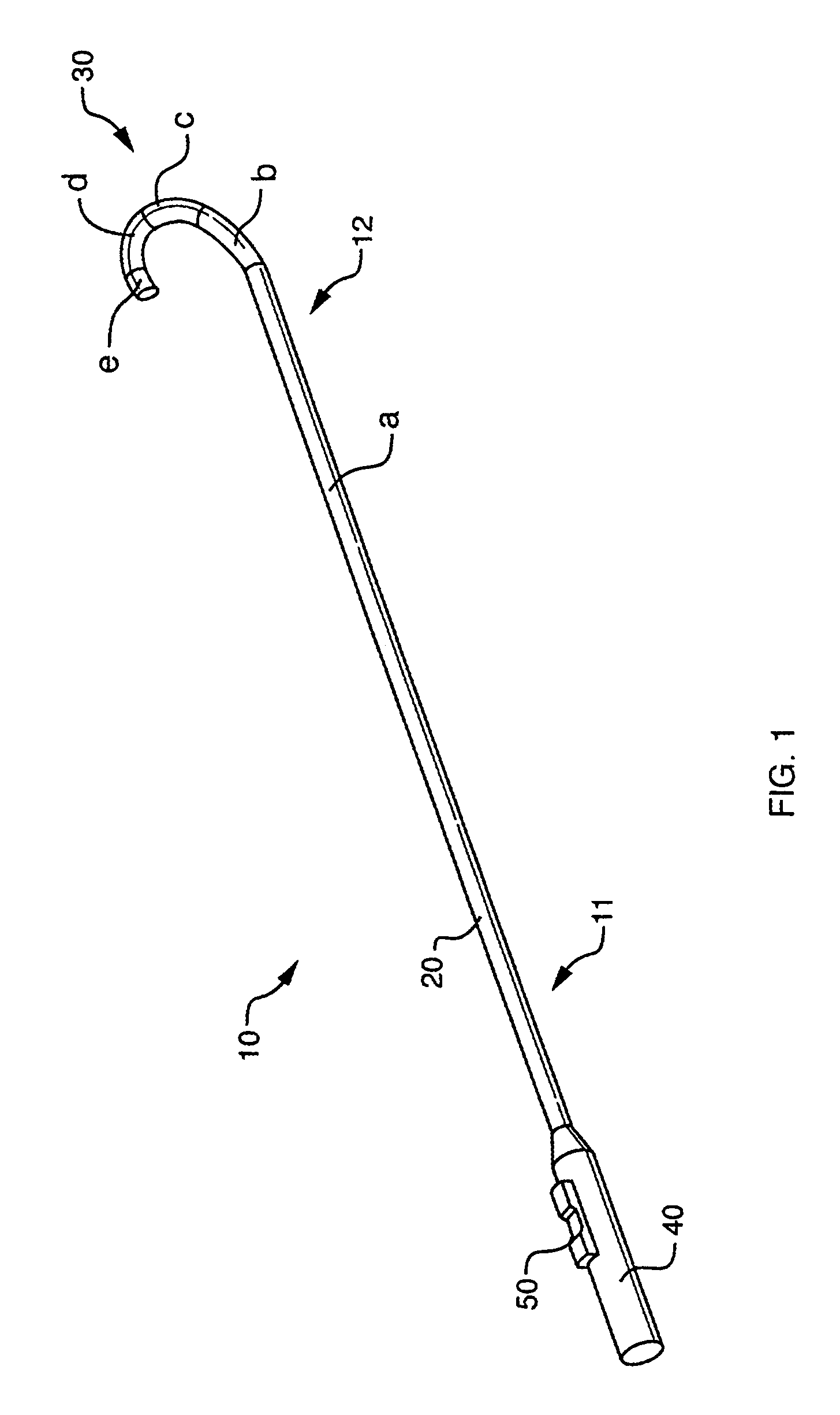
Deflectable sheath catheters
The present invention provides devices and methods for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. In one embodiment a deflectable sheath catheter includes an elongate catheter body having proximal and distal ends, the distal end having a distal tip region that includes a plurality of flexible segments with varying degrees of stiffness. A handle portion can be located at the proximal end of the catheter body to provide a steering mechanism that causes the distal tip region to deflect according to a compound curve.
Owner:CARDIOFOCUS INC
Non-invasive method and apparatus for cardiac pacemaker pacing parameter optimization and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction
A plethysmogram signal is sensed from a patient and provided to a programmer device for monitoring the condition of the patient and for optimizing pacing parameters of a cardiac device implanted in the patient. The programmer device analyzes the plethysmogram signal for cardiac performance associated with different pacing parameters. The cardiac performance is indicated by, for example, a pulse amplitude response, a degree of pulsus alternans, or irregularity in the pressure pulses detected in an atrial fibrillation patient. The pacing parameters resulting in the best cardiac performance are selected as the optimum pacing parameters. In one embodiment, the programmer device monitors a Valsalva maneuver performed by a patient. Optimum pacing parameters are derived by analysis of the plethysmogram signals obtained during performance of the Valsalva maneuver while the patient is paced using different pacing parameters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Nerve stimulation methods for averting imminent onset or episode of a disease
Transcutaneous electrical and magnetic nerve stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of averting imminent medical attacks using energy that is delivered noninvasively by the devices. The attacks comprise asthma attack, epileptic seizure, attacks of migraine headache, transient ischemic attack or stroke, onset of atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, onset of ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia, panic attack, and attacks of acute depression. The imminence of an attack is forecasted using grey-box or black-box models as used in control theory. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, a vagus nerve in the neck of a patient is stimulated noninvasively to avert the attack.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Cardiac monitoring
ActiveUS7194300B2Improved positive predictabilityIncreased clinical significanceElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyPhysiological valuesCardiac monitoring
Systems and techniques for monitoring cardiac activity. In one aspect, a method includes collecting information describing the variability in heart rate over a series of beats, designating variability at a lower end of physiological values as being largely irrelevant to atrial fibrillation, designating variability in a midrange of physiological values as being indicative of atrial fibrillation, designating variability in an upper range of physiological values as being negatively indicative of atrial fibrillation, and determining a relevance of the variability described in the collection to atrial fibrillation.
Owner:BRAEMAR MFG
Ablation catheters
The present invention relates generally to multifunctional catheters for performing ablation procedures, and more particularly to ablation catheters utilized in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and other cardiac disorders. The present invention eliminates many of the problems associated with previous ablation catheters by providing an ablation treatment not dependent upon continuous lesions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
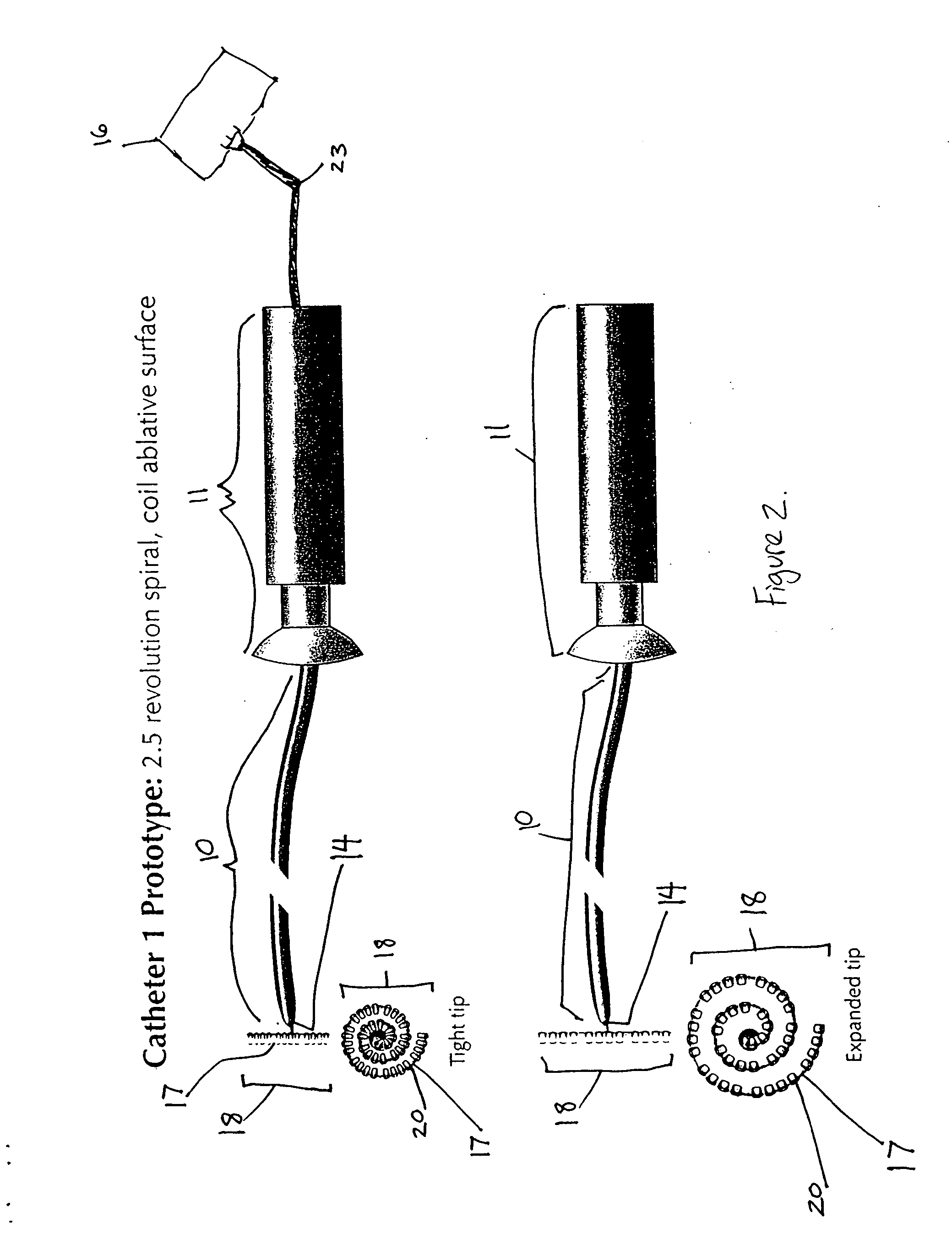
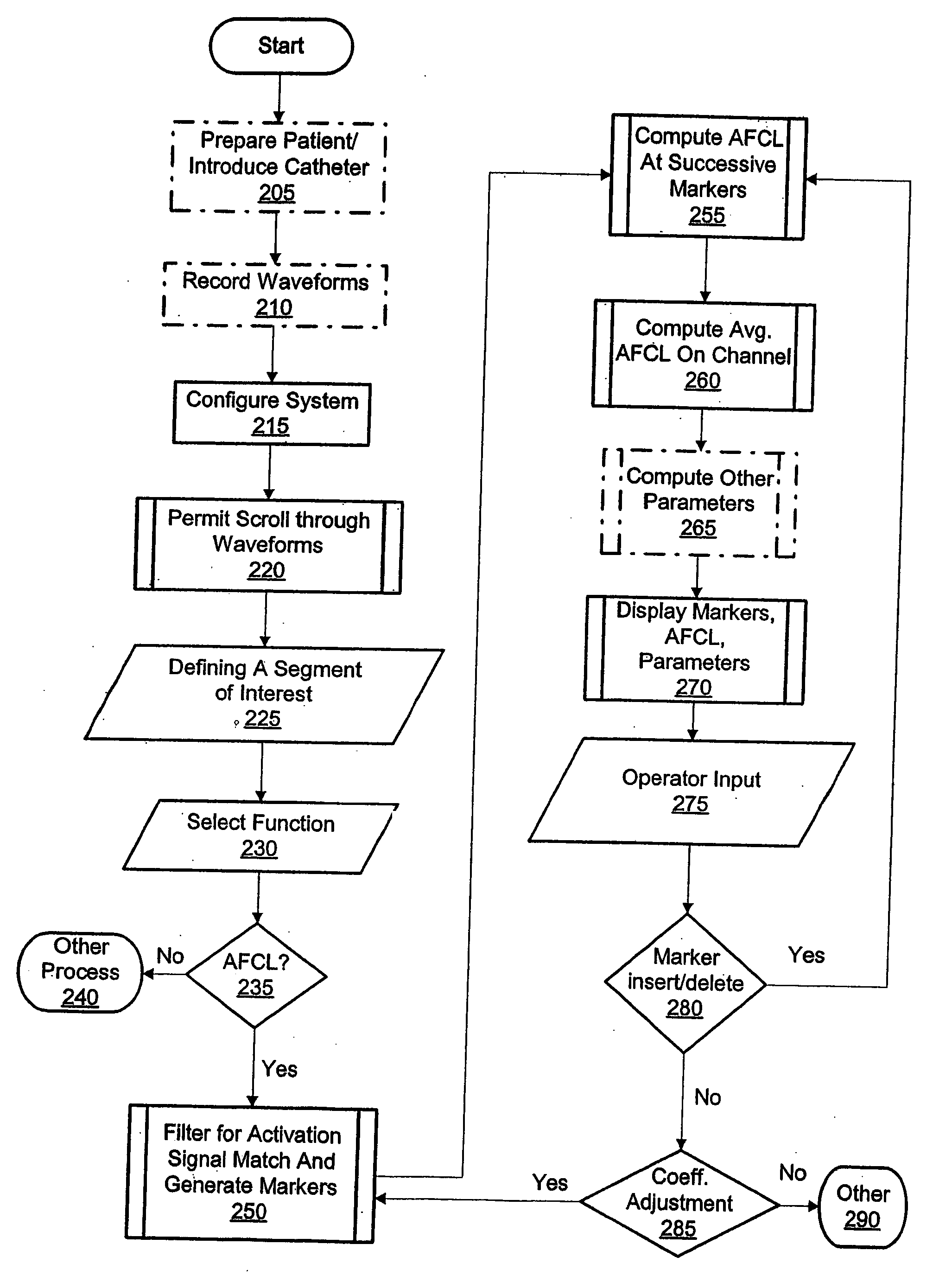
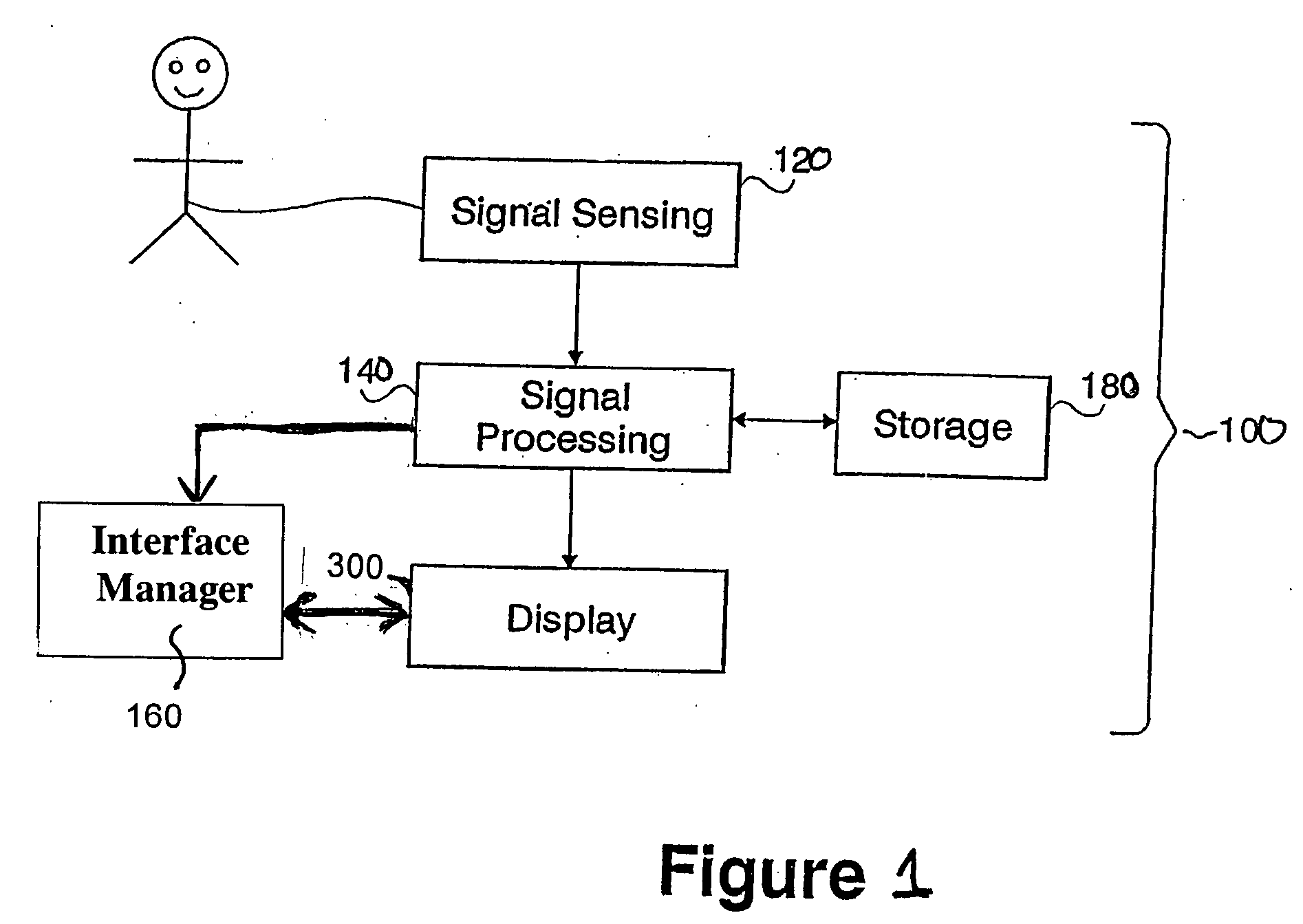
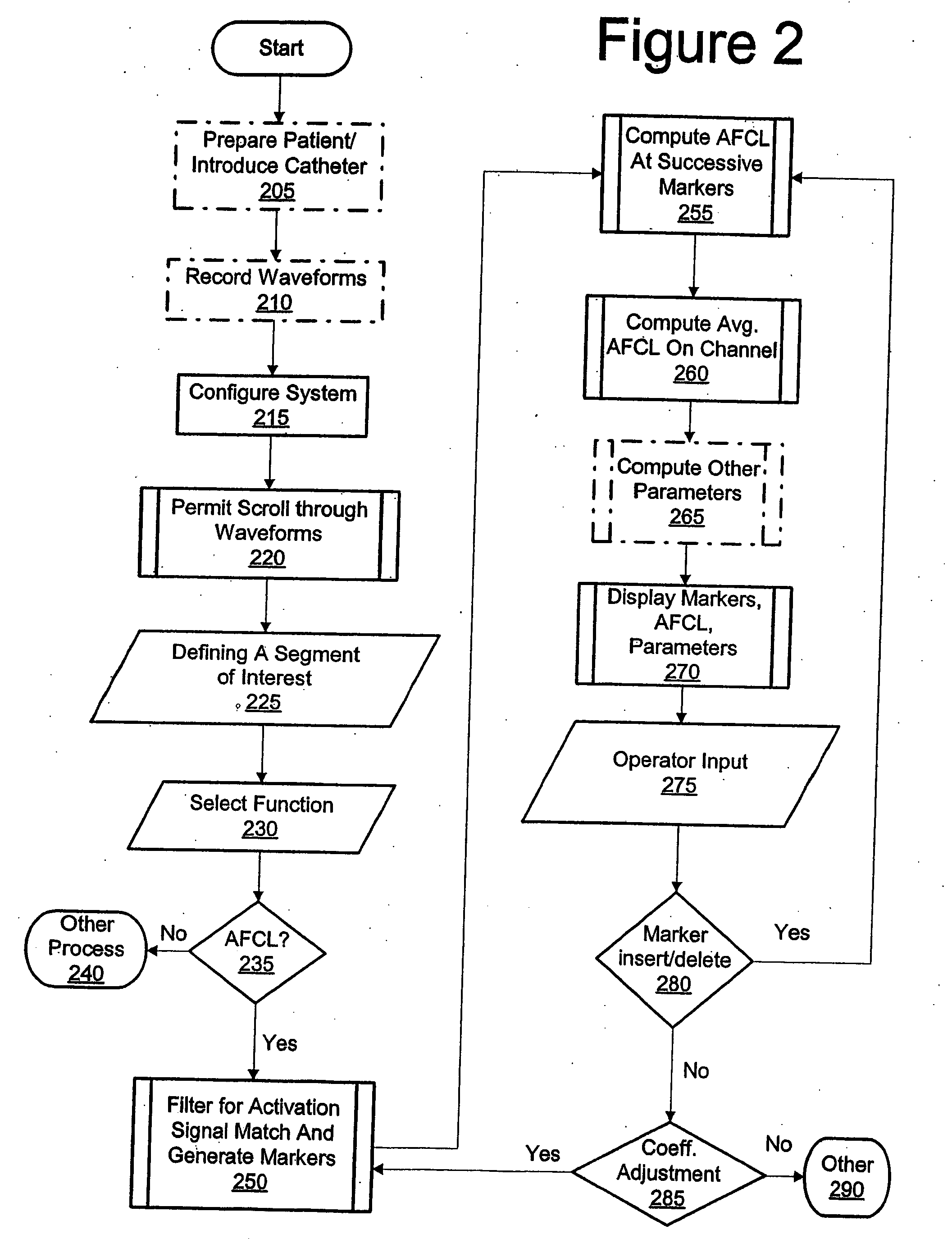
High density atrial fibrillation cycle length (AFCL) detection and mapping system
Systems and methods to assist in locating the focus of an atrial fibrillation include the association of atrial fibrillation cycle length values and statistics relating thereto with temporal locations on an electrogram of a given electrode, and / or the coordination of electrode locations with respective the spectral analyses of electrogram signals and further parameters and statistics relating thereto. Ablation therapy can proceed under guidance of such information.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Guided procedures for treating atrial fibrillation
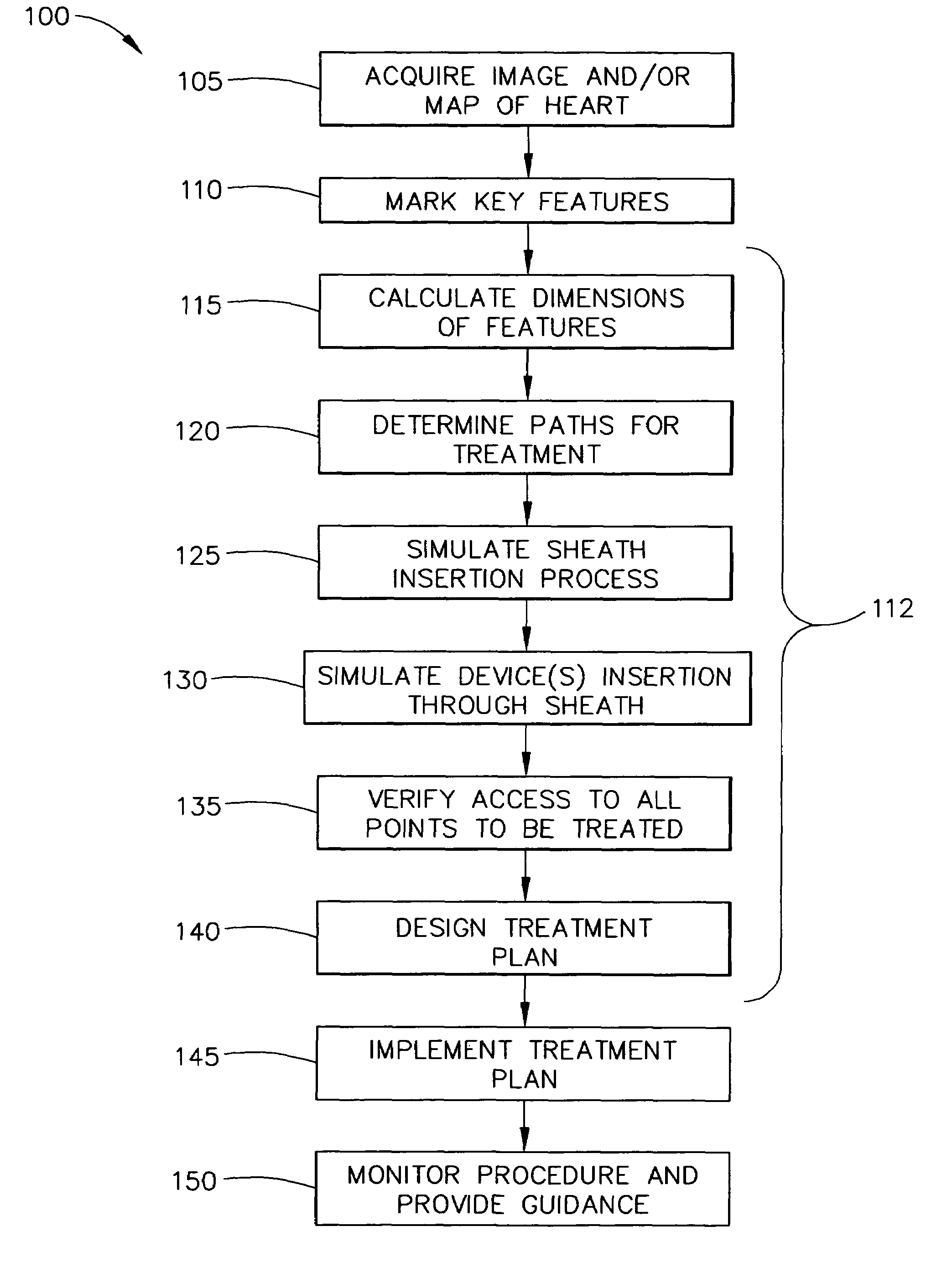
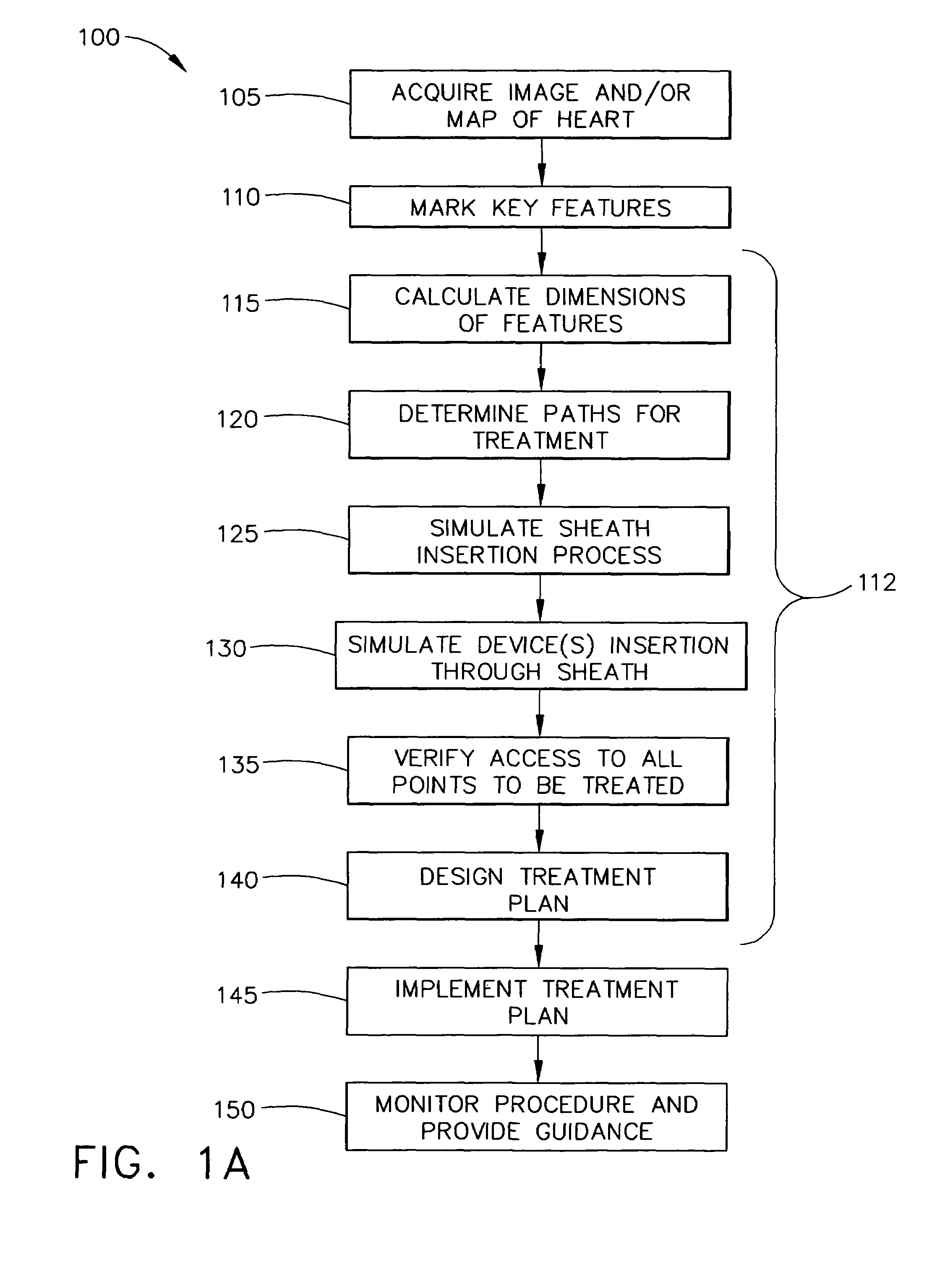
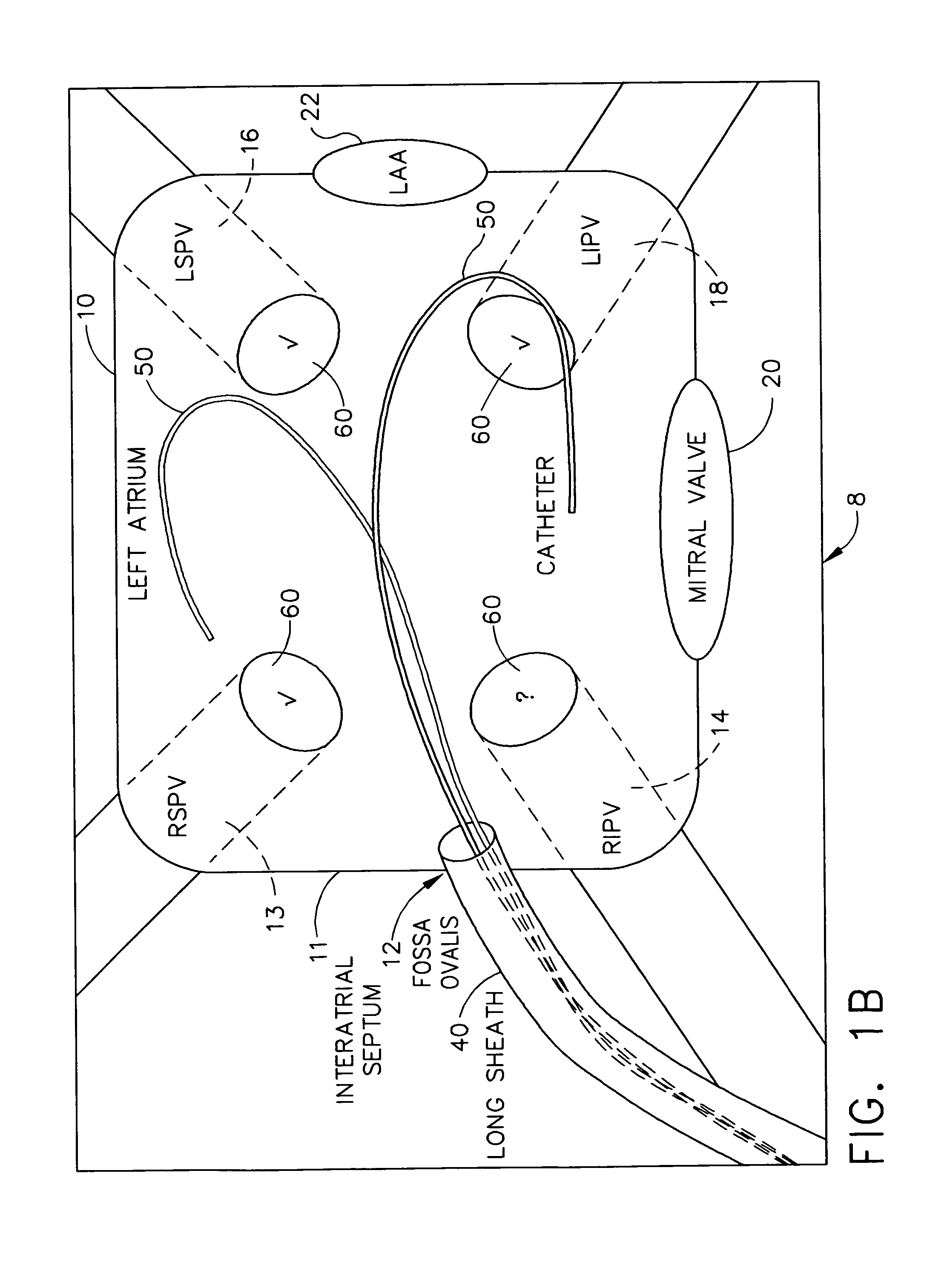
A method for treating atrial fibrillation in a heart of a patient includes placing an ultrasonic catheter in a first chamber of the heart; acquiring two-dimensional ultrasonic images of a second chamber of the heart and at least a portion of surrounding structures of the second chamber using the ultrasonic catheter placed in the first chamber; reconstructing a three-dimensional ultrasonic image based on the two-dimensional ultrasonic images; displaying the reconstructed three-dimensional ultrasonic image; identifying at least one key landmark on the reconstructed three-dimensional ultrasonic image; marking the least one key landmark on the reconstructed three-dimensional ultrasonic image; penetrating the septum for accessing the second chamber of the heart while using the marked at least one key landmark for guidance; positioning a sheath through the penetrated septum and within the second chamber of the heart; inserting an ablation catheter through the sheath and into the second chamber of the heart; and ablating a portion of the second chamber of the heart using the ablation catheter while under observation with the ultrasound catheter located in the first chamber of the heart.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com