Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
111 results about "Vascular implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
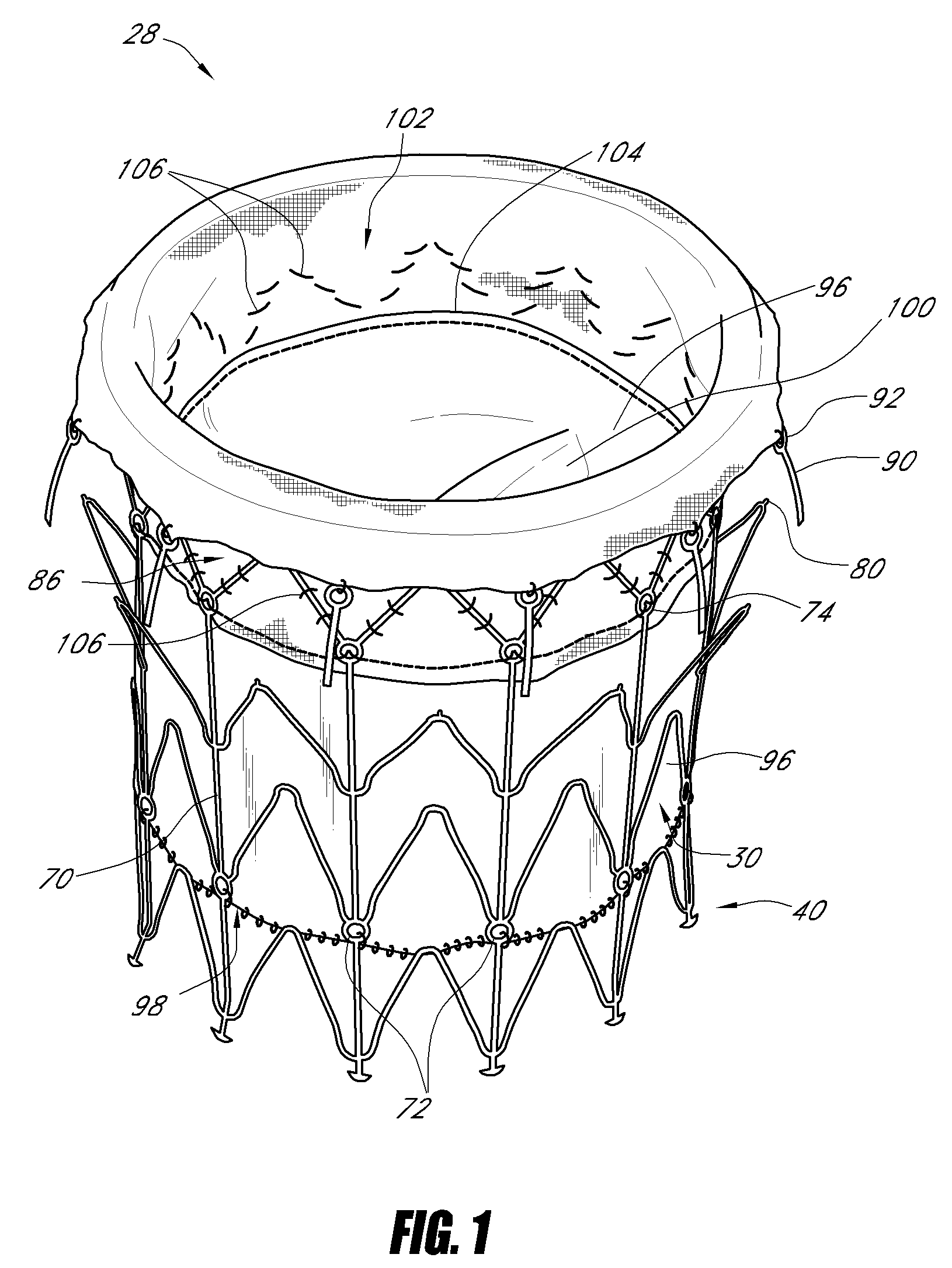
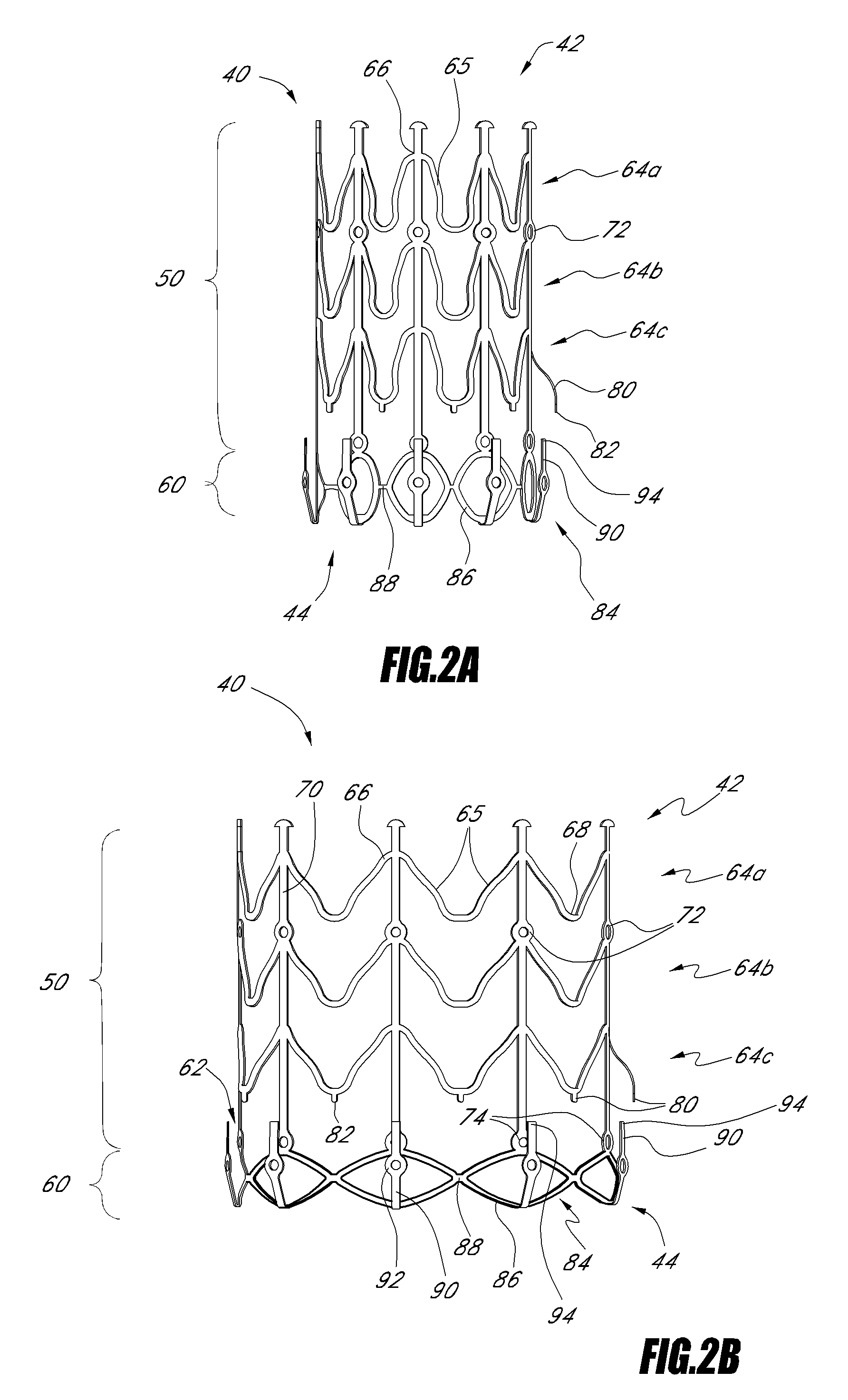
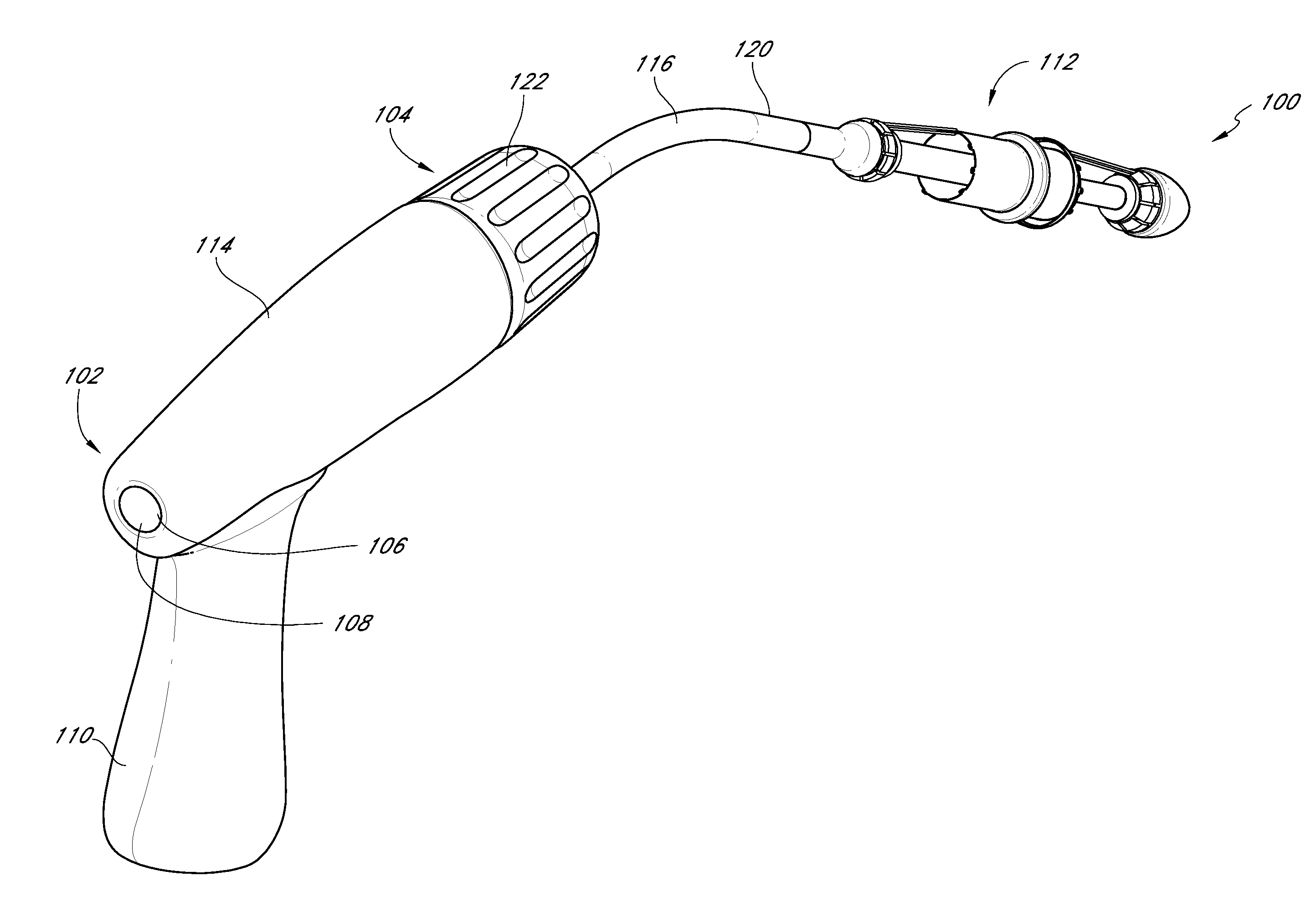
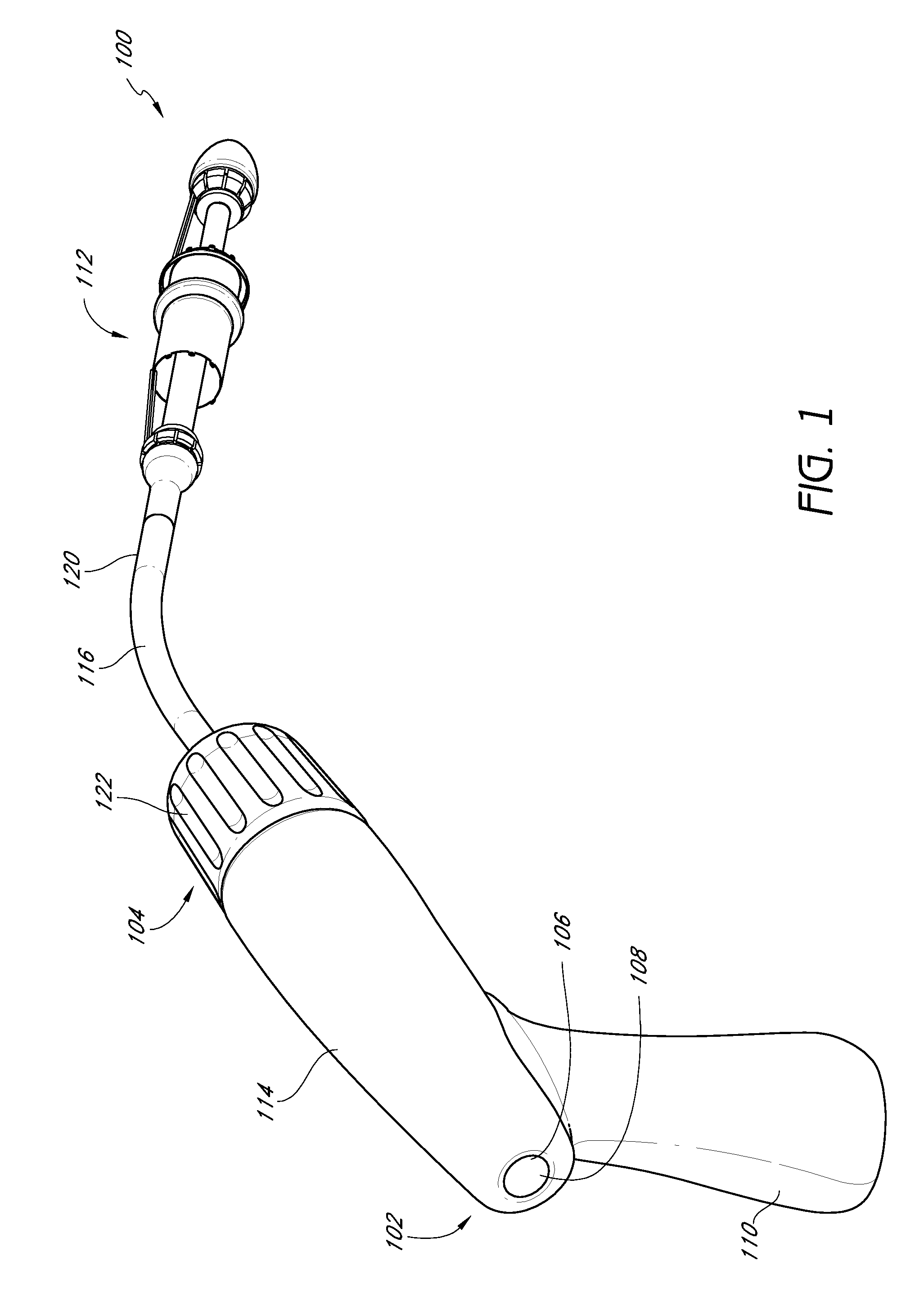
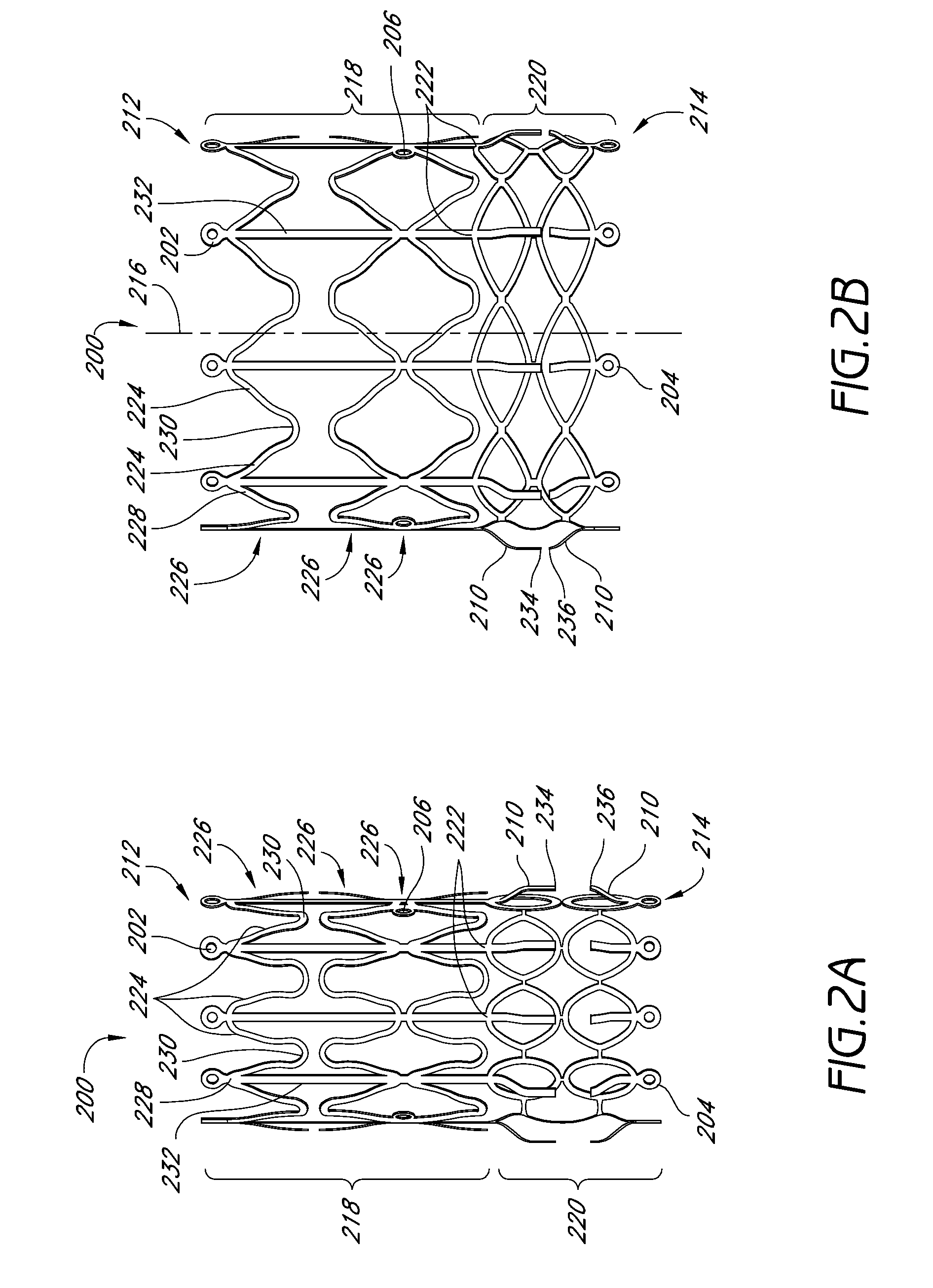
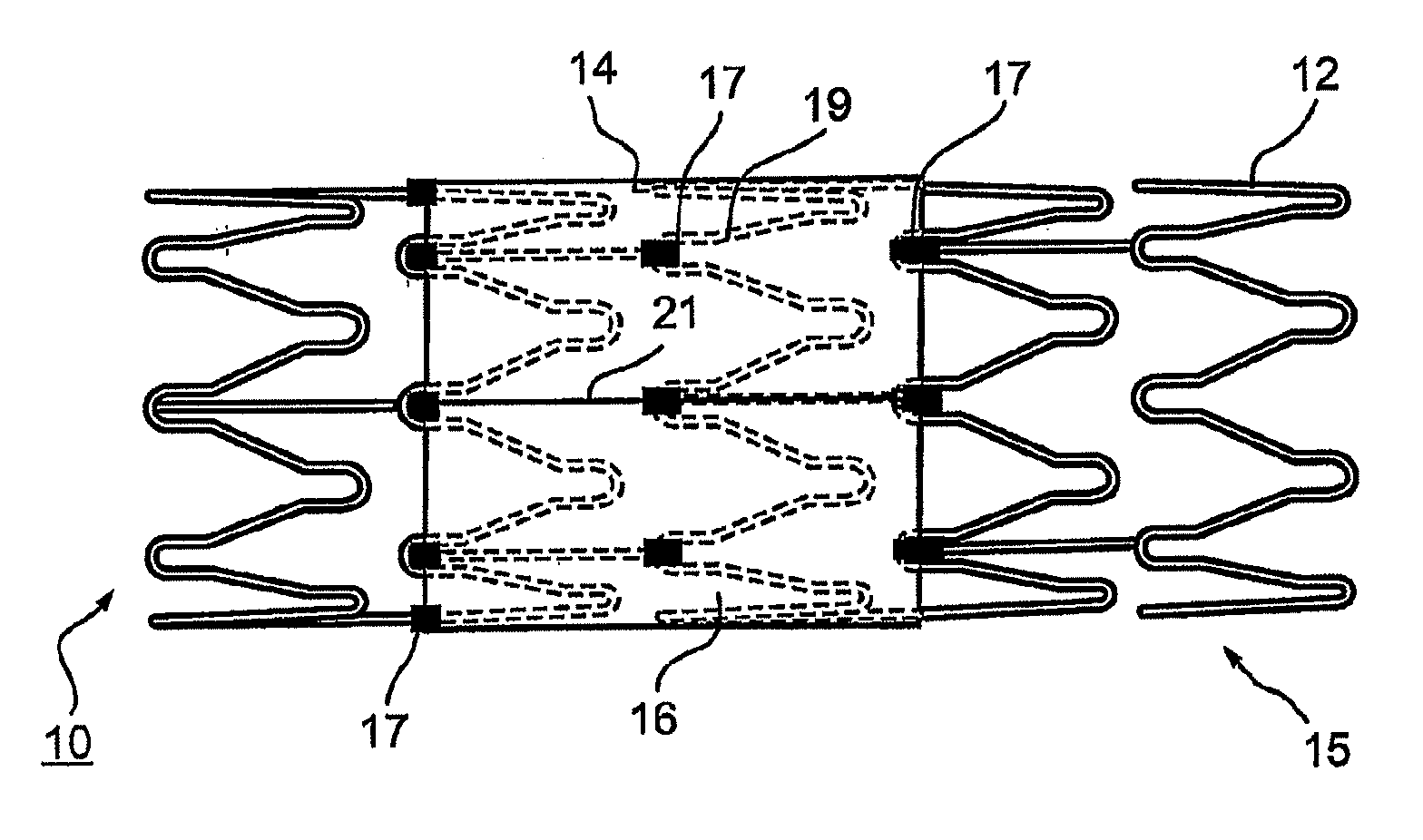
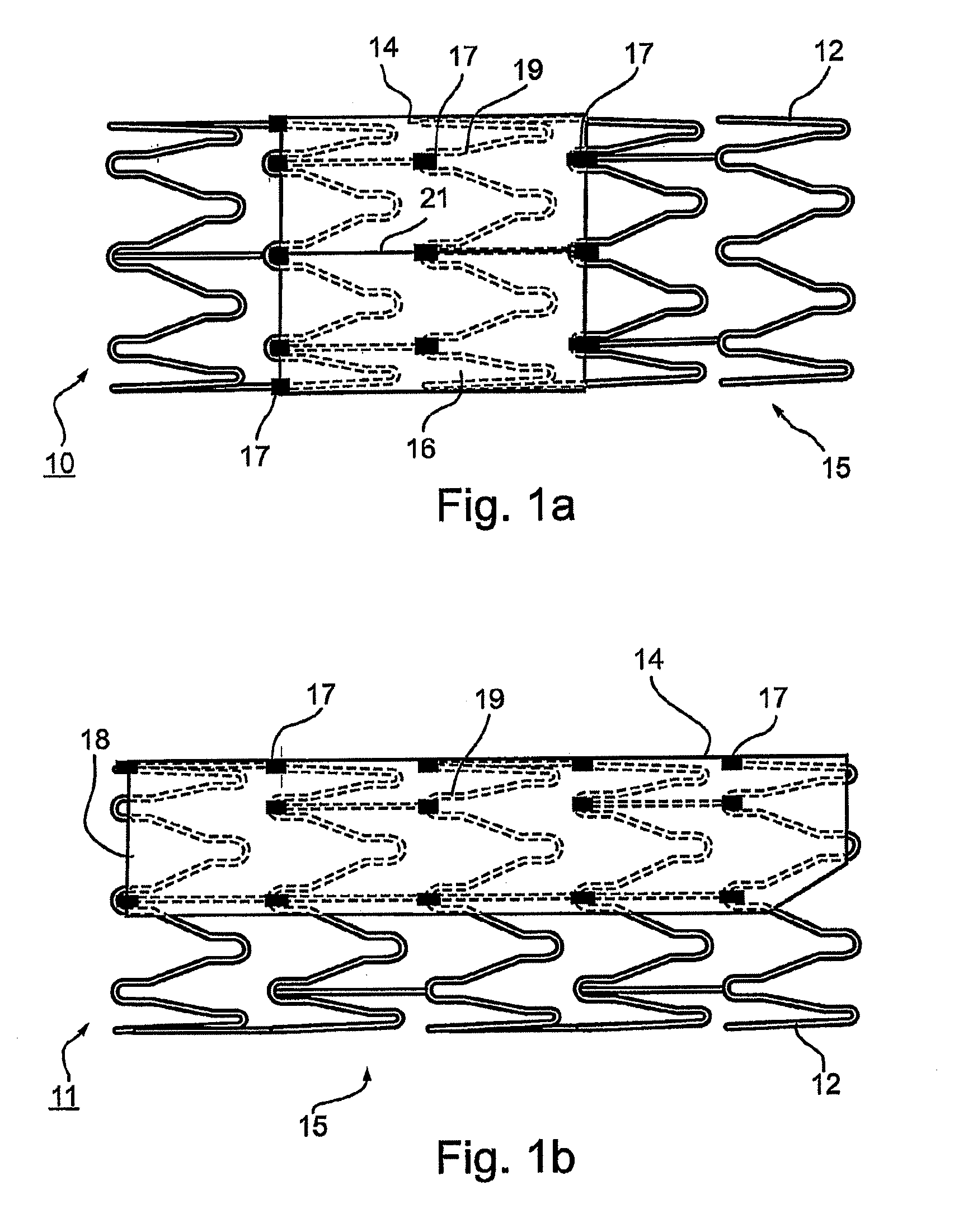
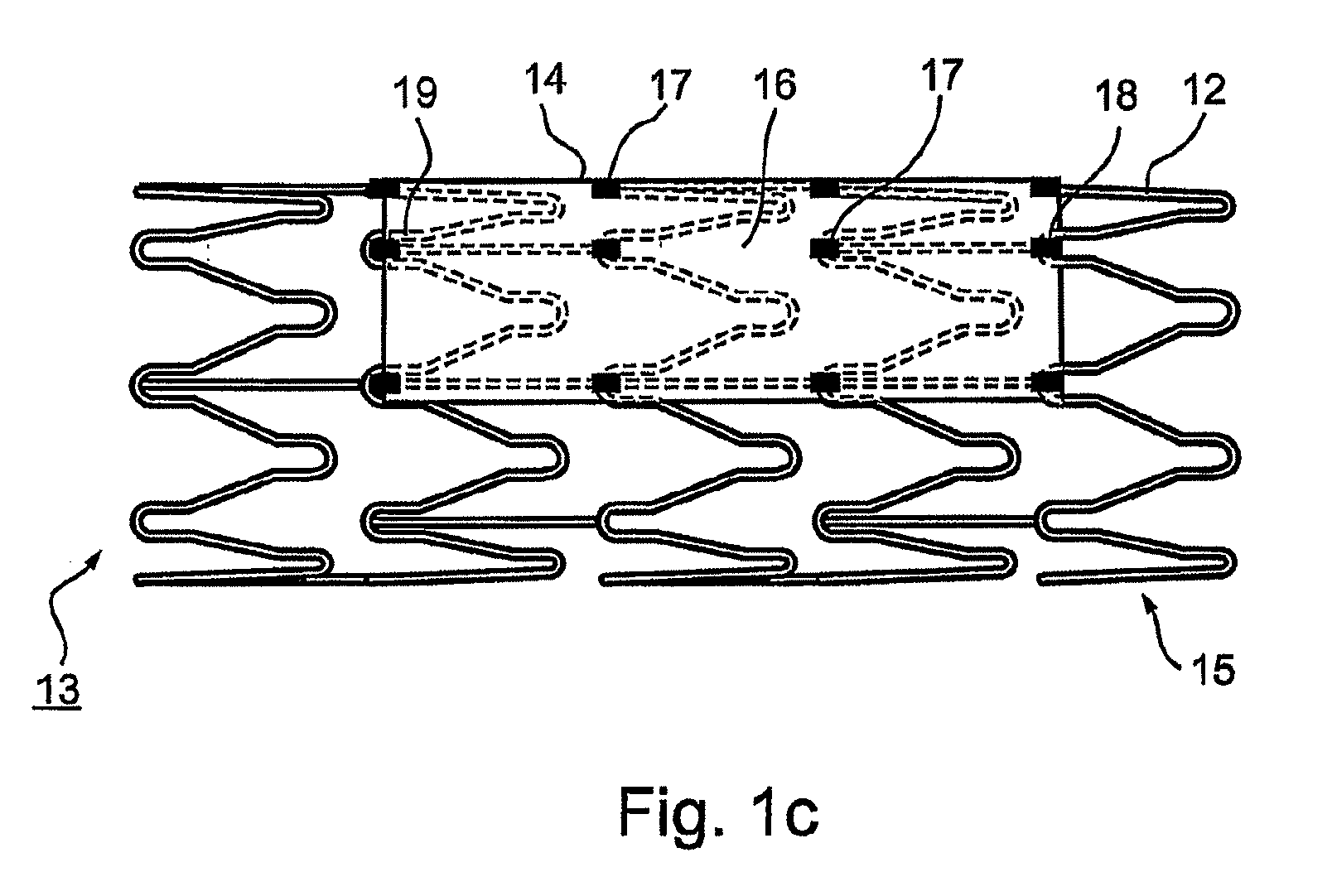
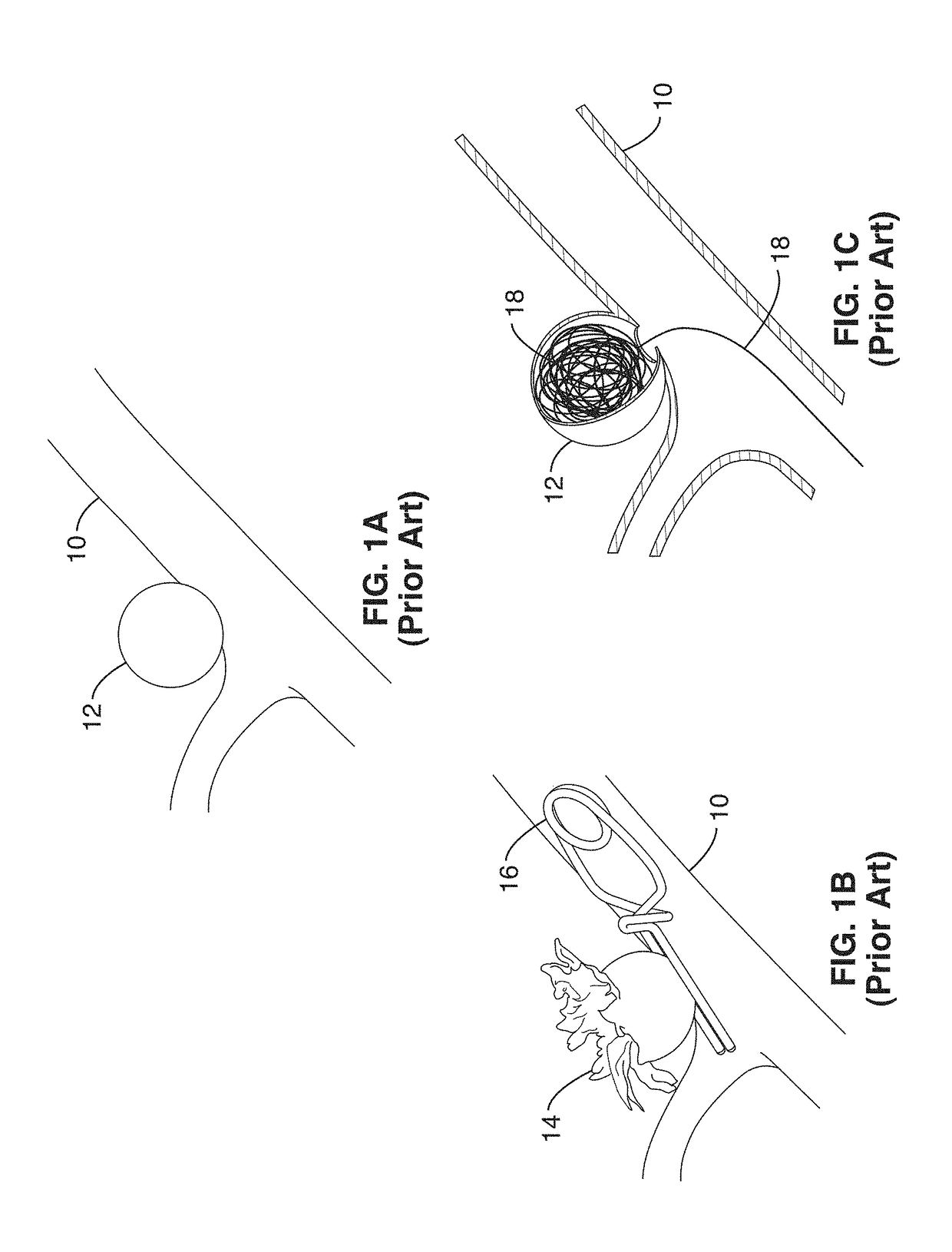
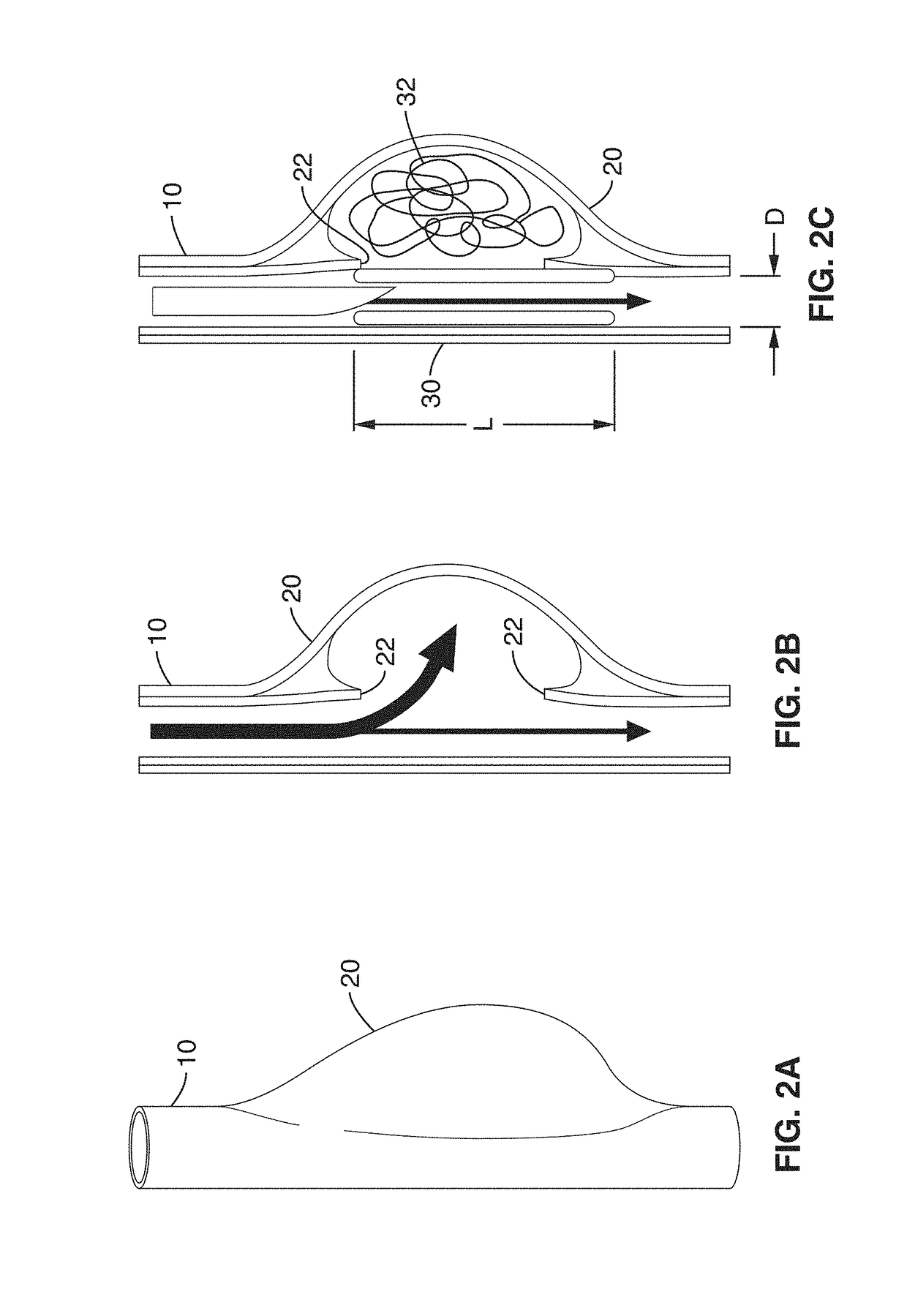
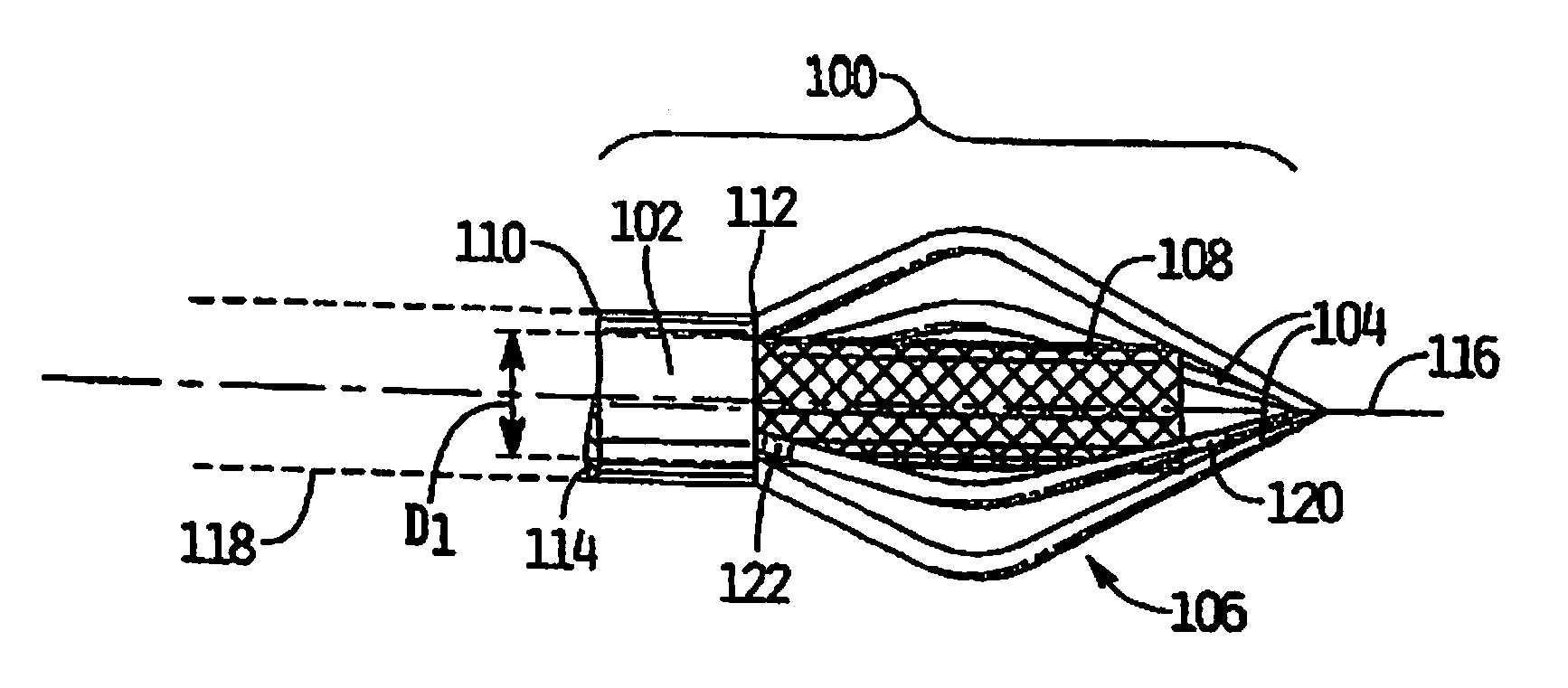
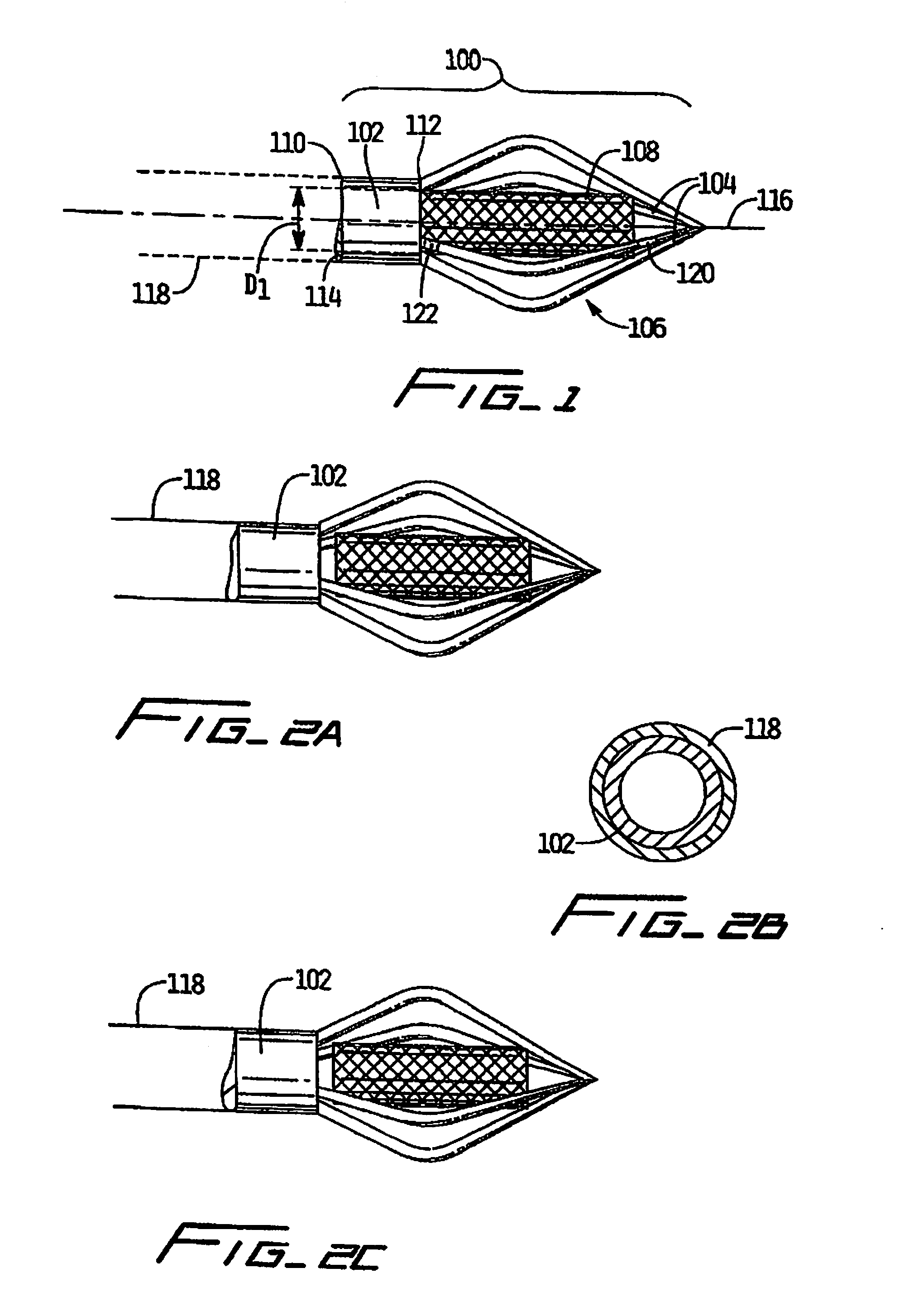
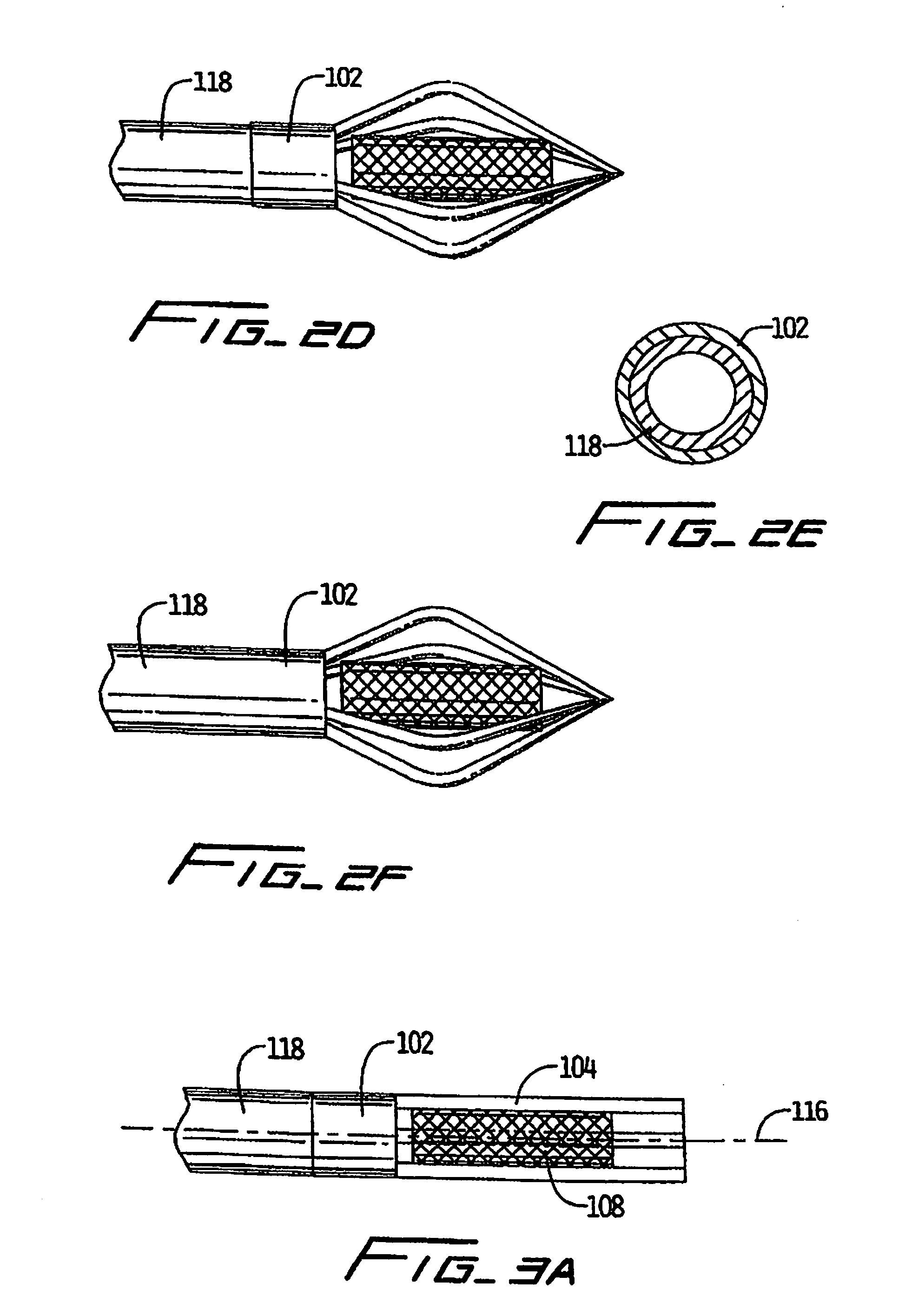
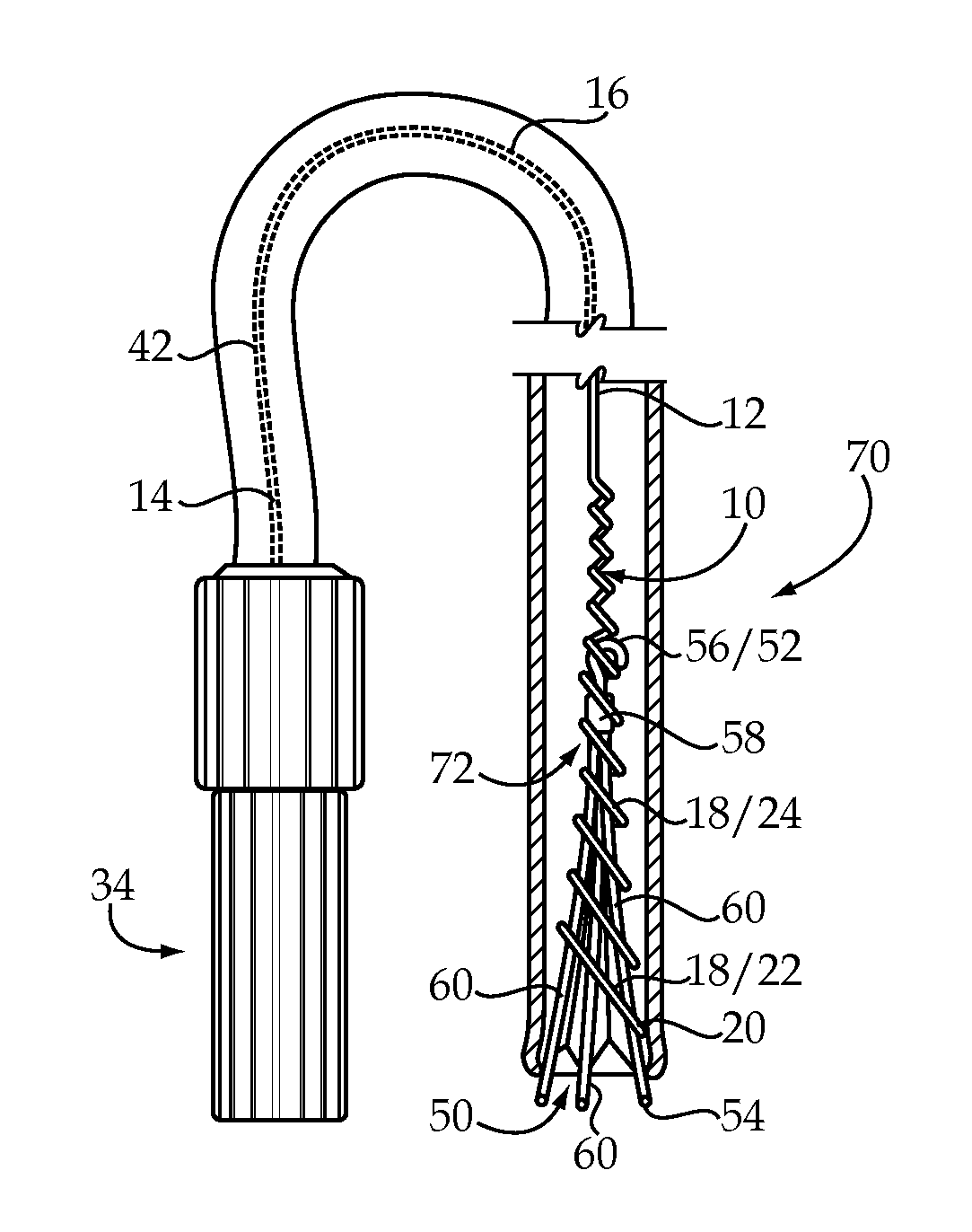
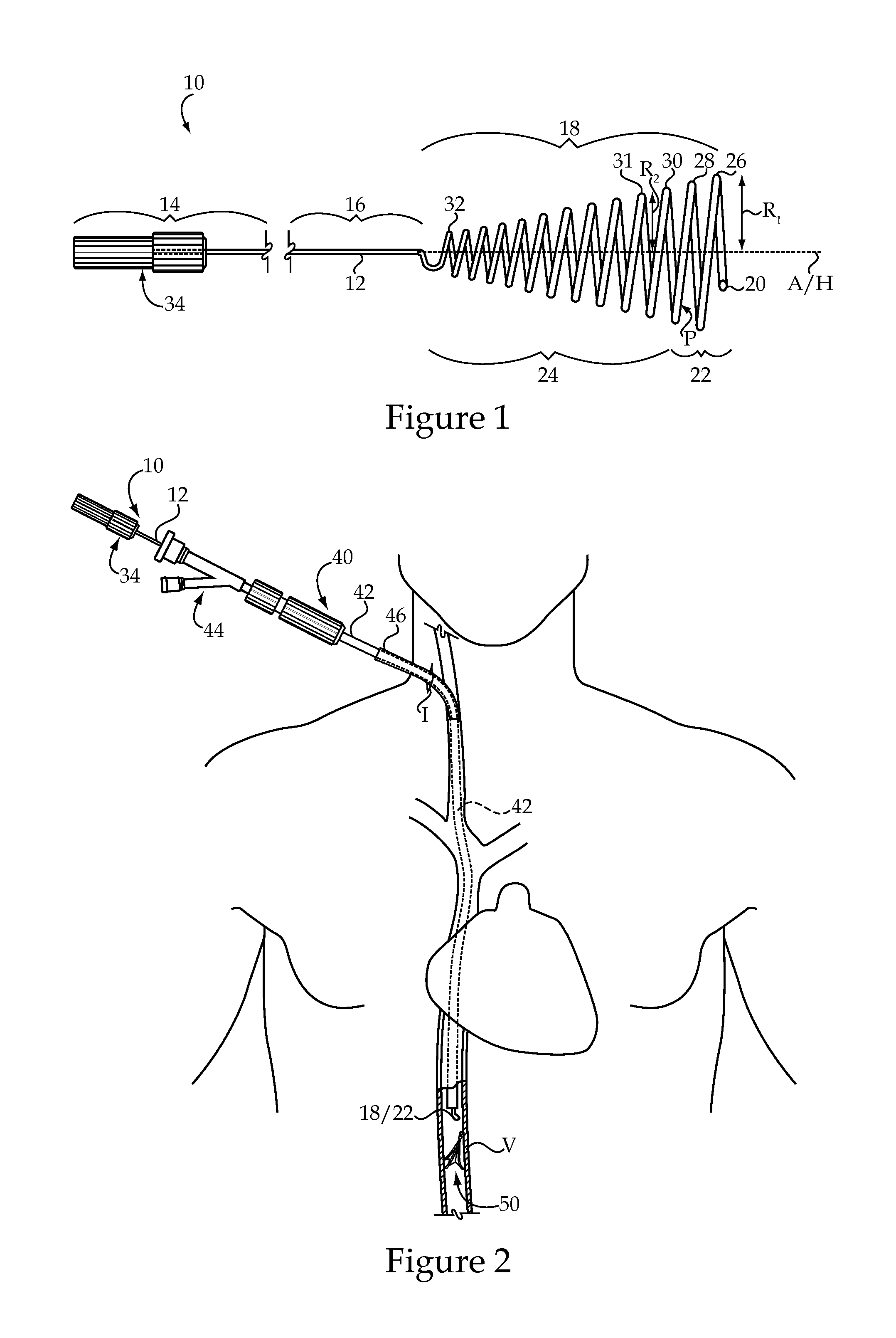
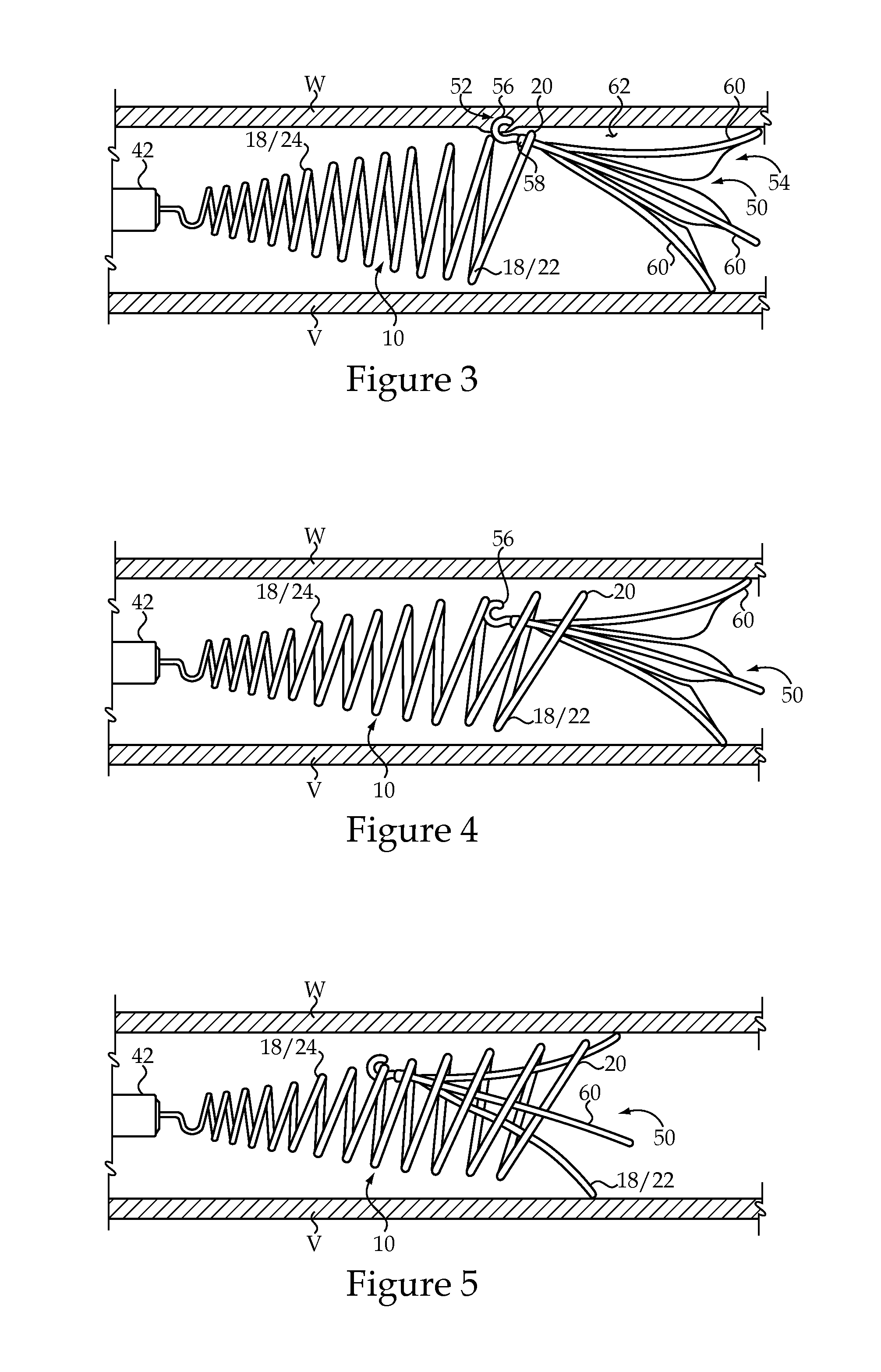
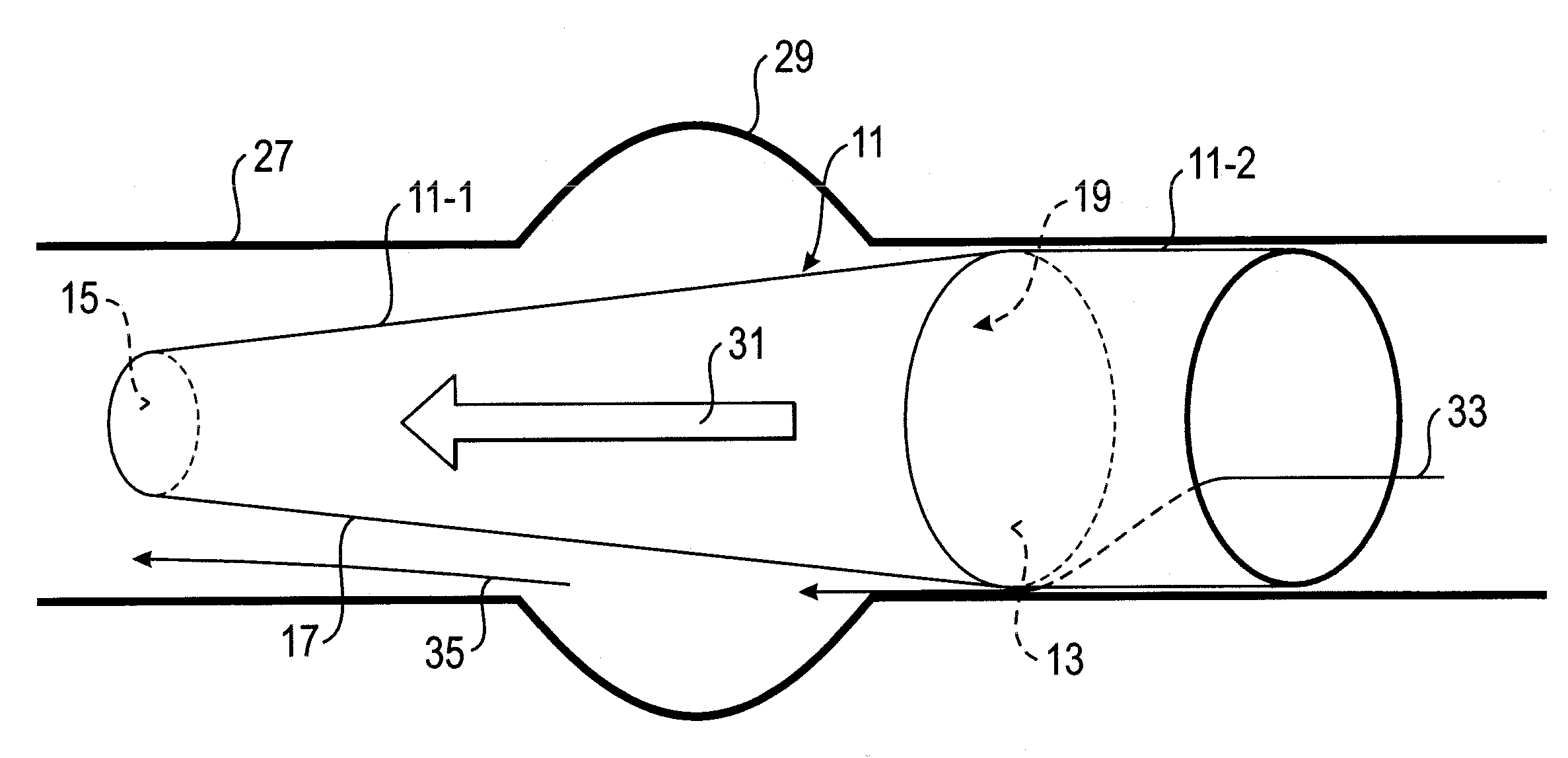
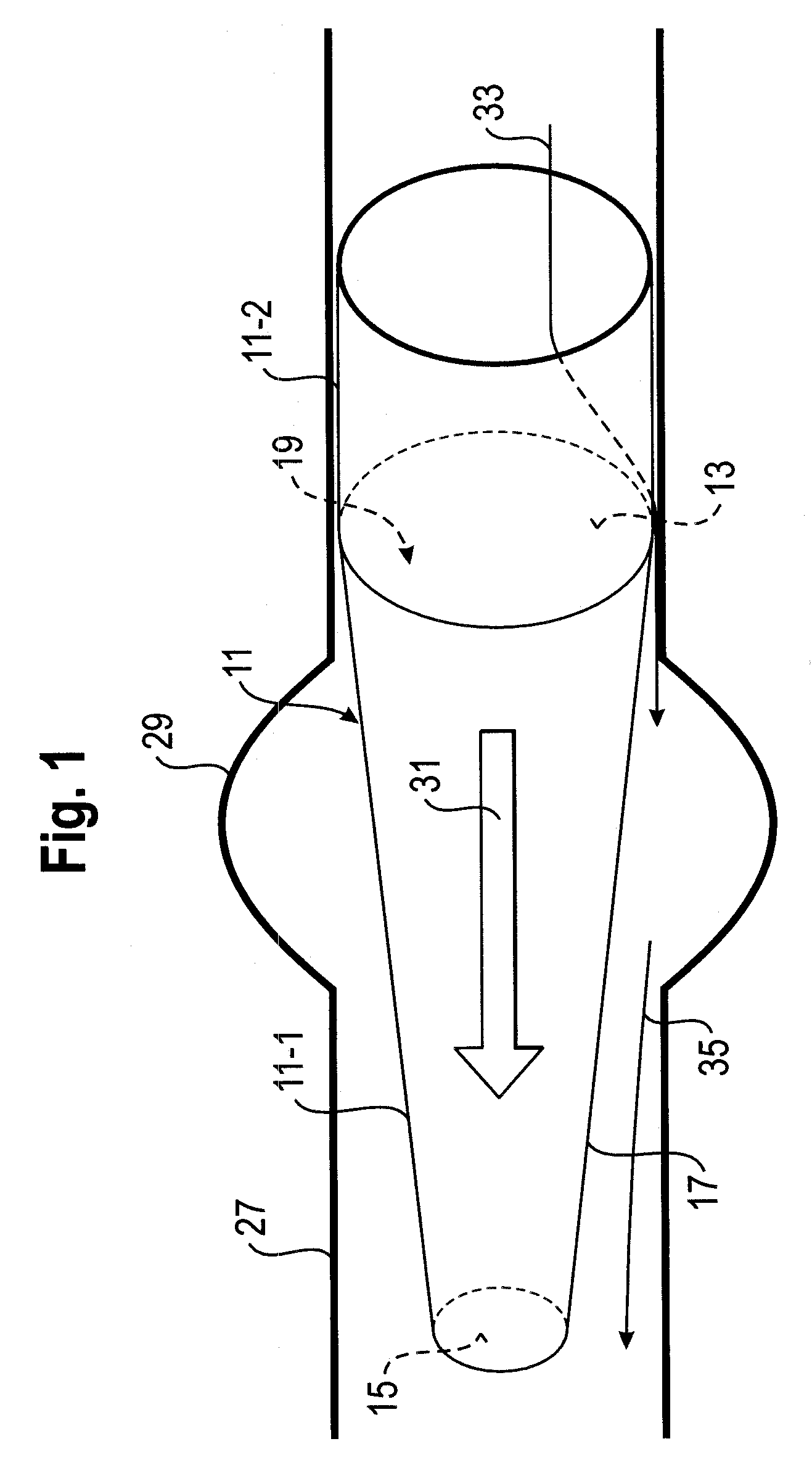
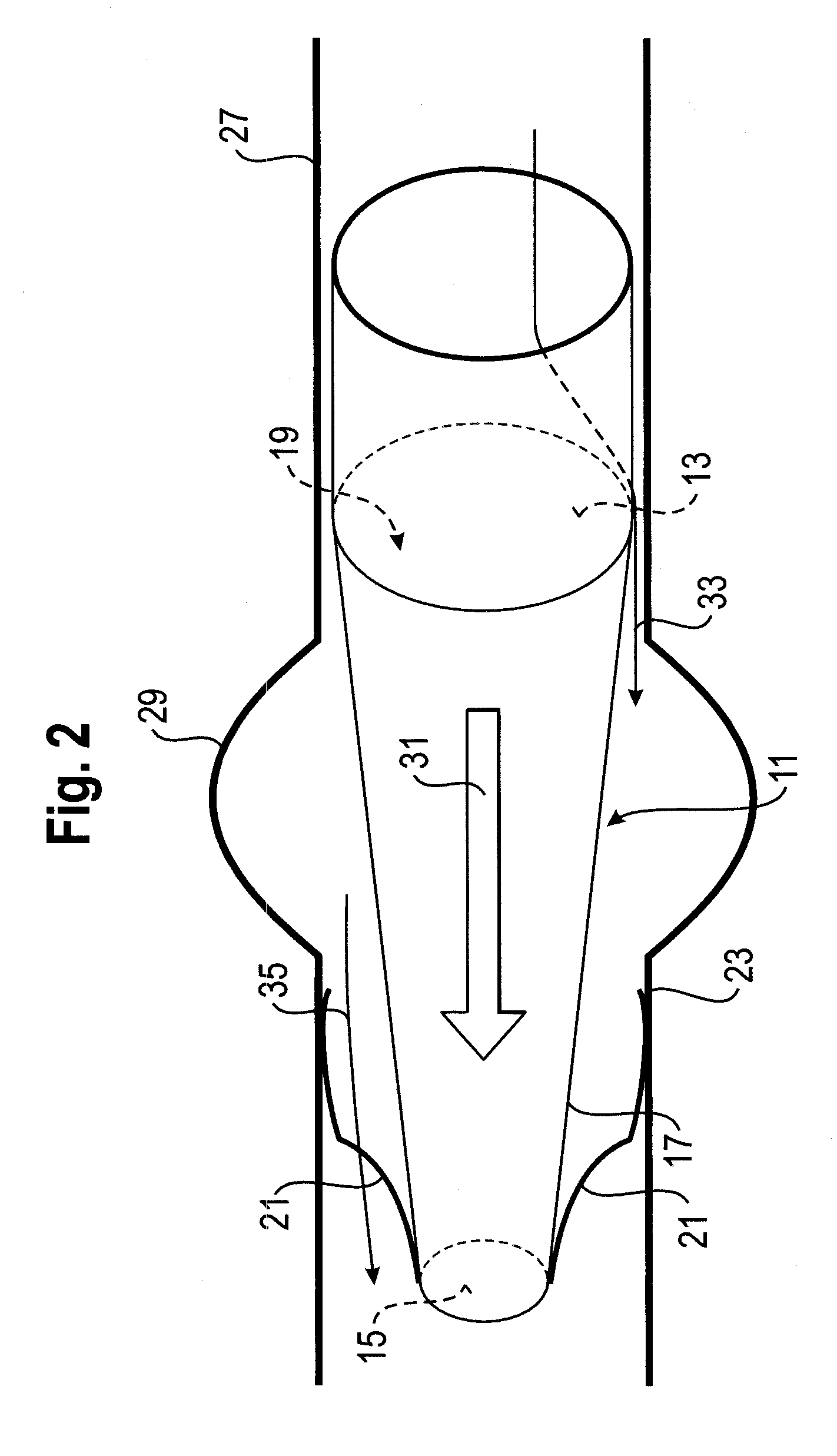
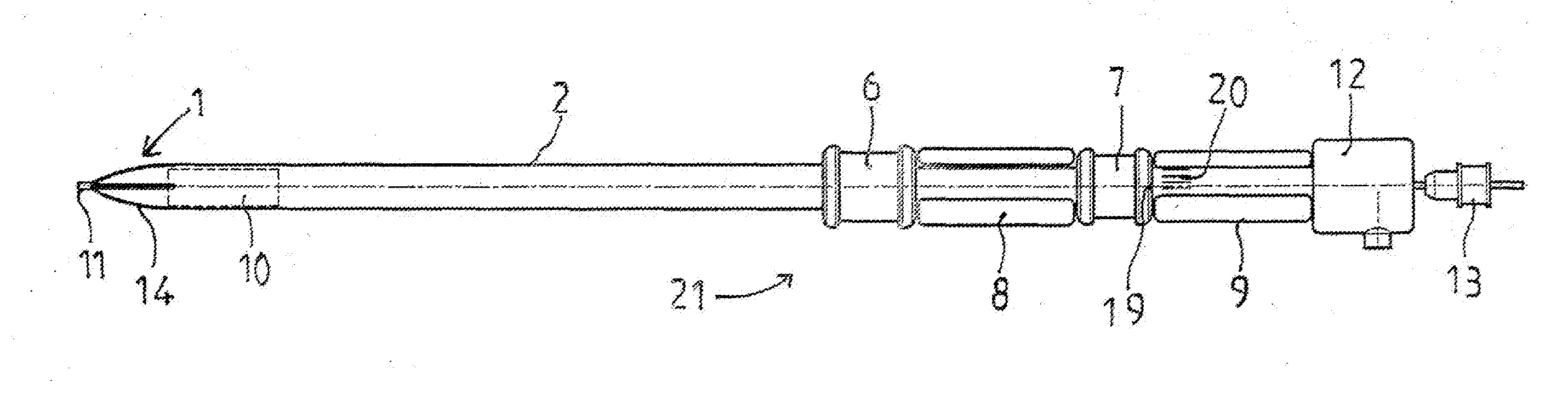
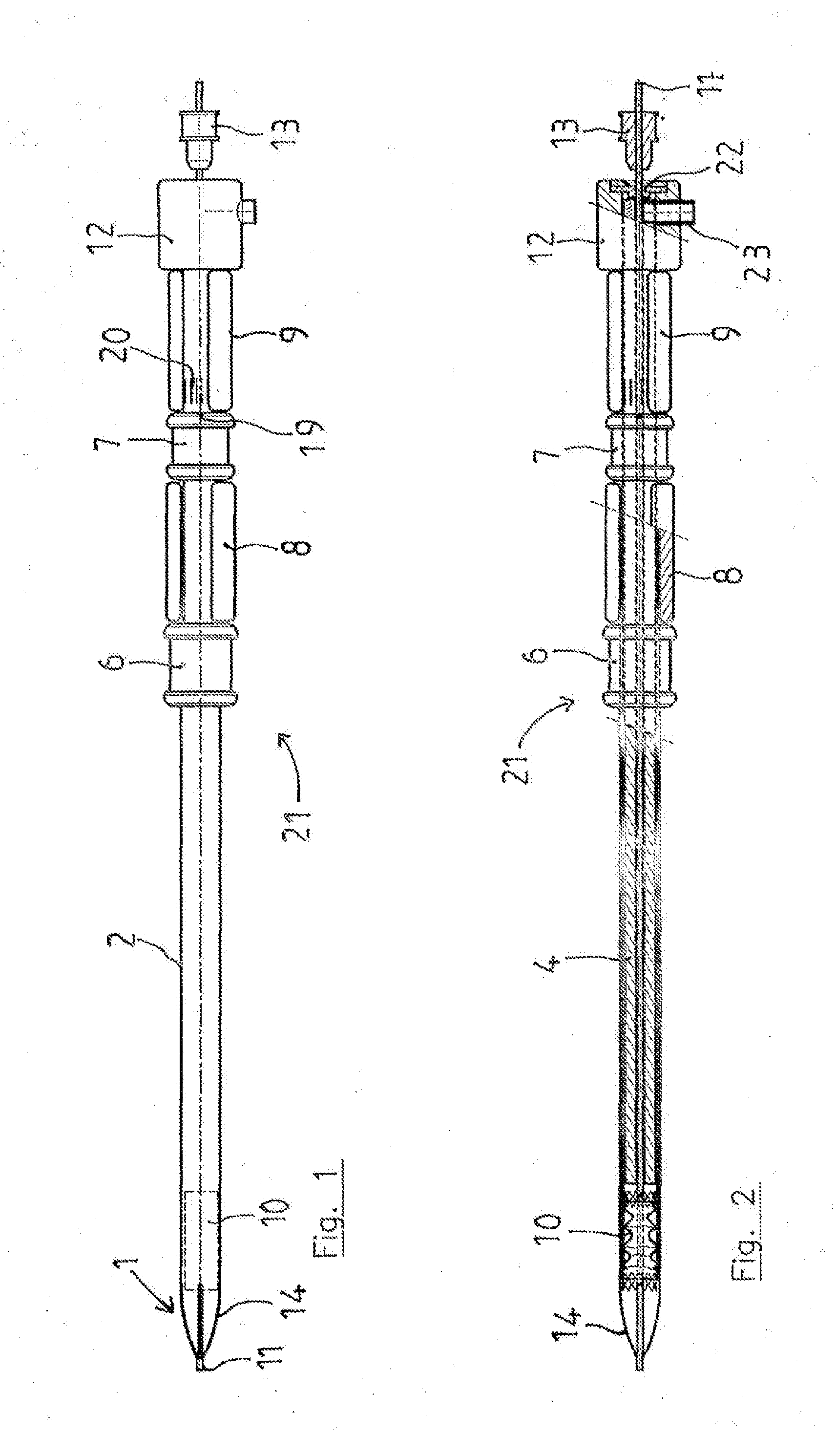
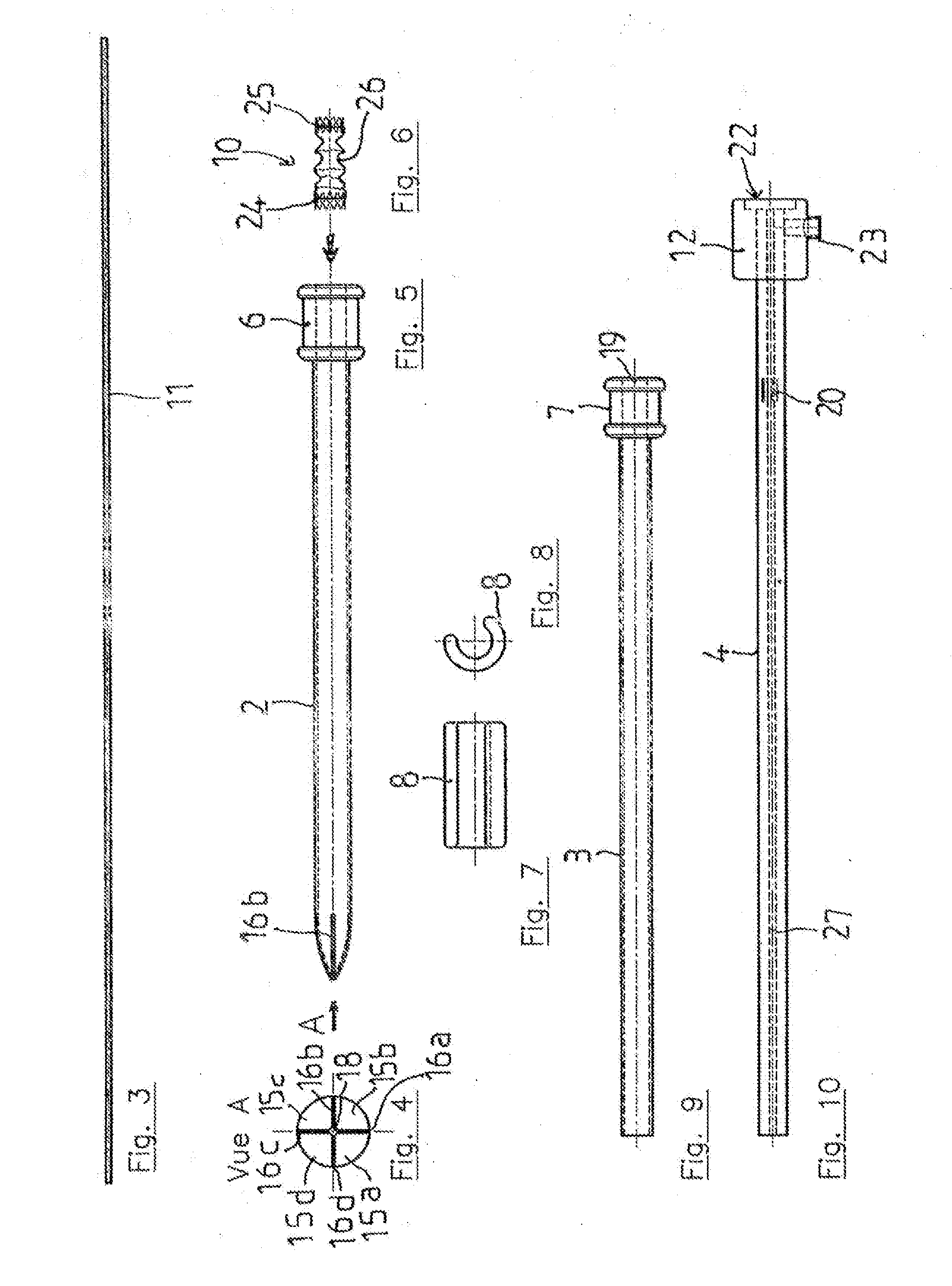
Vascular implant and delivery system
ActiveUS20100298931A1Reliable and controlled mannerStentsHeart valvesVascular implantInsertion stent
A vascular implant for replacing a native heart valve comprises a self expanding stent supporting a valve body having leaflets. The stent preferably comprises an anchoring structure configured to prevent the implant from passing through the valve annulus. For delivery, the implant is compacted within a delivery device and secured at one end. During delivery the implant is partially released from the delivery device, and positioning of the implant is verified prior to full release. The implant can be at least partially resheathed and repositioned if desired.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Vascular implant and delivery system
ActiveUS8414644B2Minimize axial movementPrevent radial movementStentsHeart valvesVascular implantLocking mechanism
A compacted vascular implant can be delivered to a target location within a delivery device. During delivery, the implant can be partially released from the delivery device before full deployment. The delivery device can include an elongated support tube, a locking mechanism, and a sheath. The locking mechanism can be provided on the support tube. The sheath can be configured to slide over the elongated support tube and can be configured to cover the locking mechanism and to restrain at least a portion of the implant.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Degradable implantable medical devices
InactiveUS20060229711A1Reduce probabilityLower resistanceStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantBlood vessel
Devices and methods are provided for an implantable medical device which is degradable over a clinically relevant period of time. The medical devices may have the form of implants, graft implants, vascular implants, non vascular implants, wound closure implants, sutures, drug delivery implants, biologic delivery implants, urinary tract implants, inter-uterine implants, organ implants, bone implants including bone plates, bone screws, dental implants, spinal disks, or the like. In preferred embodiments, the implantable medical device comprises an implantable luminal prosthesis, such as vascular and non-vascular stents and stents grafts.
Owner:ELIXIR MEDICAL CORP
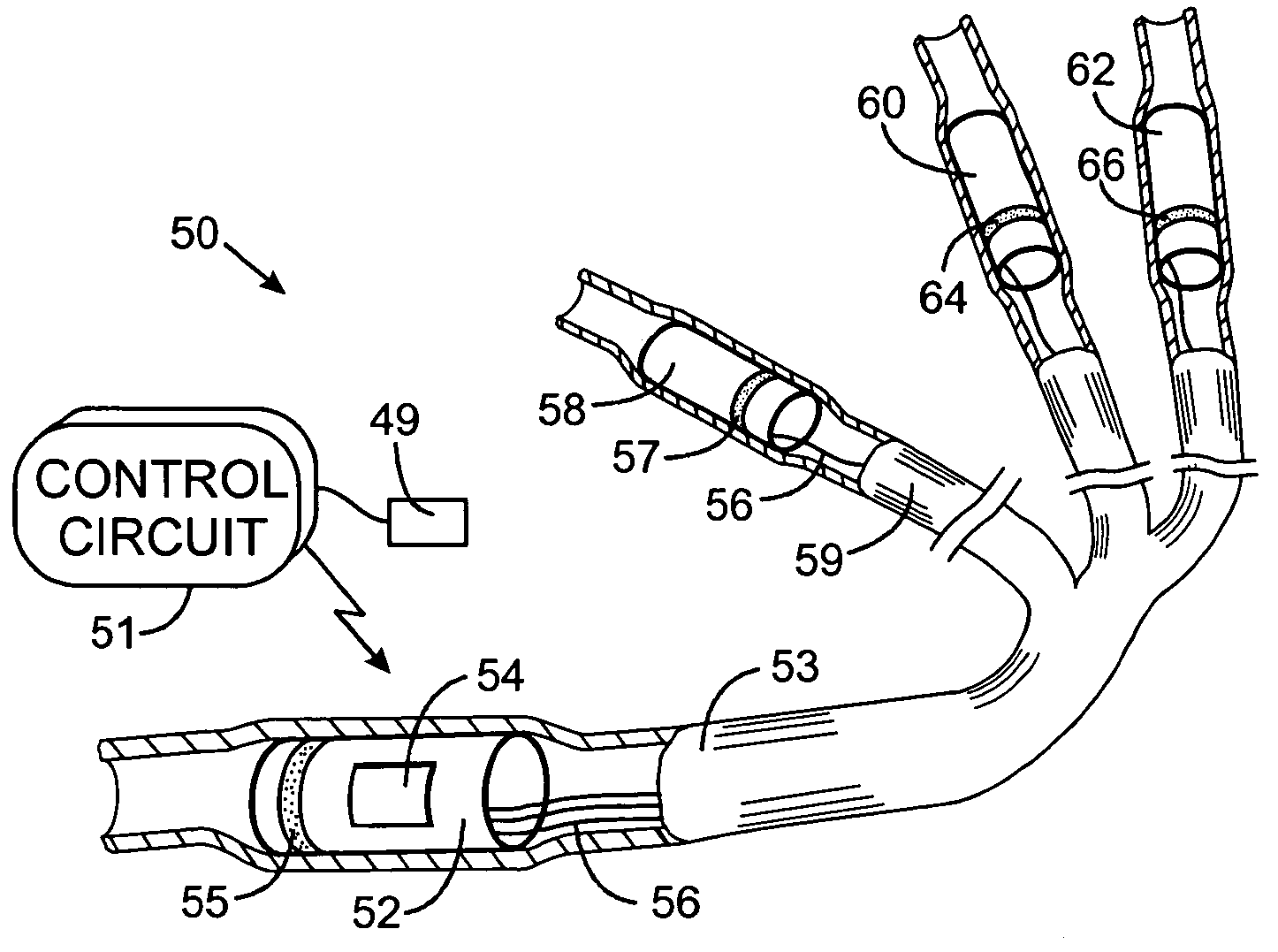
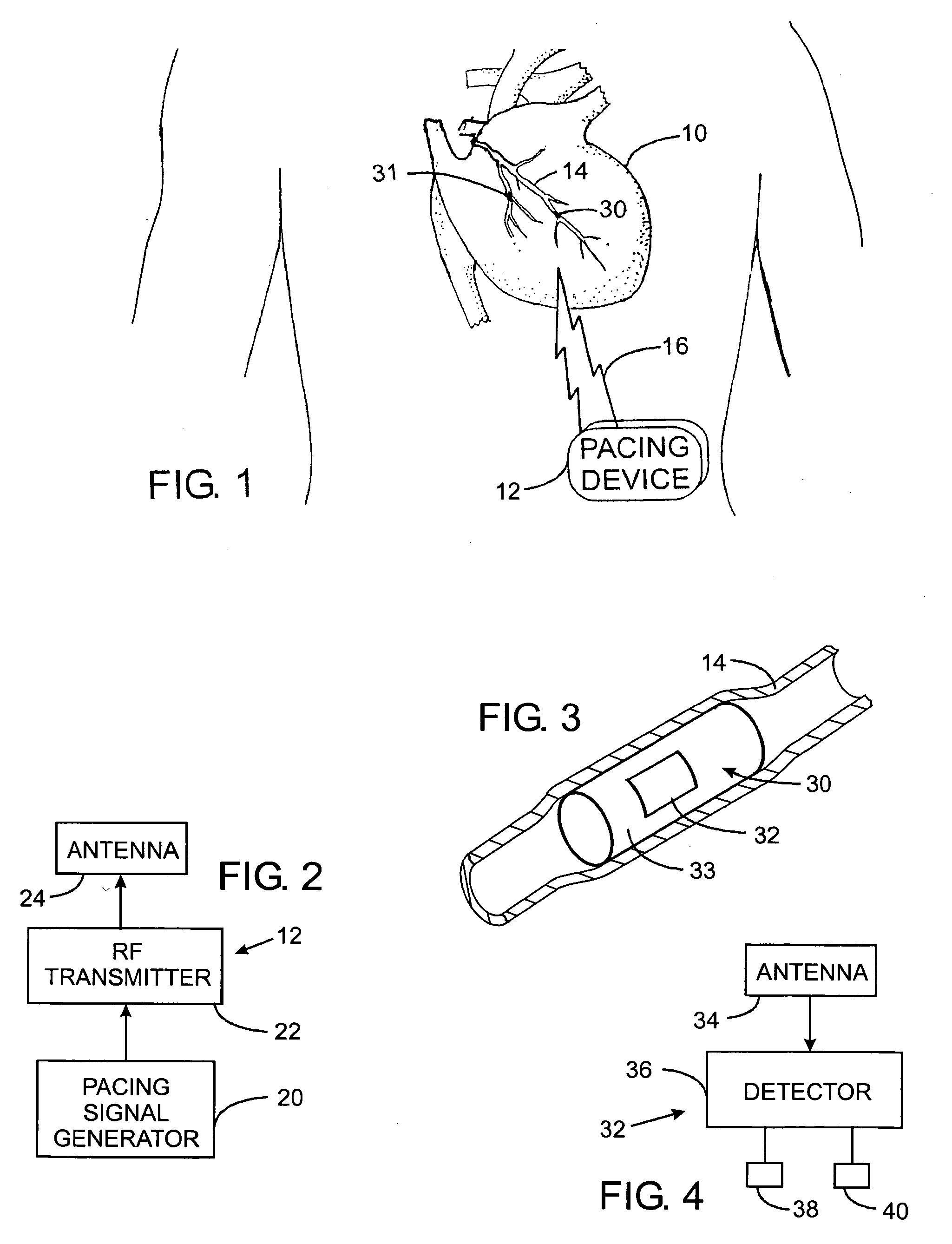
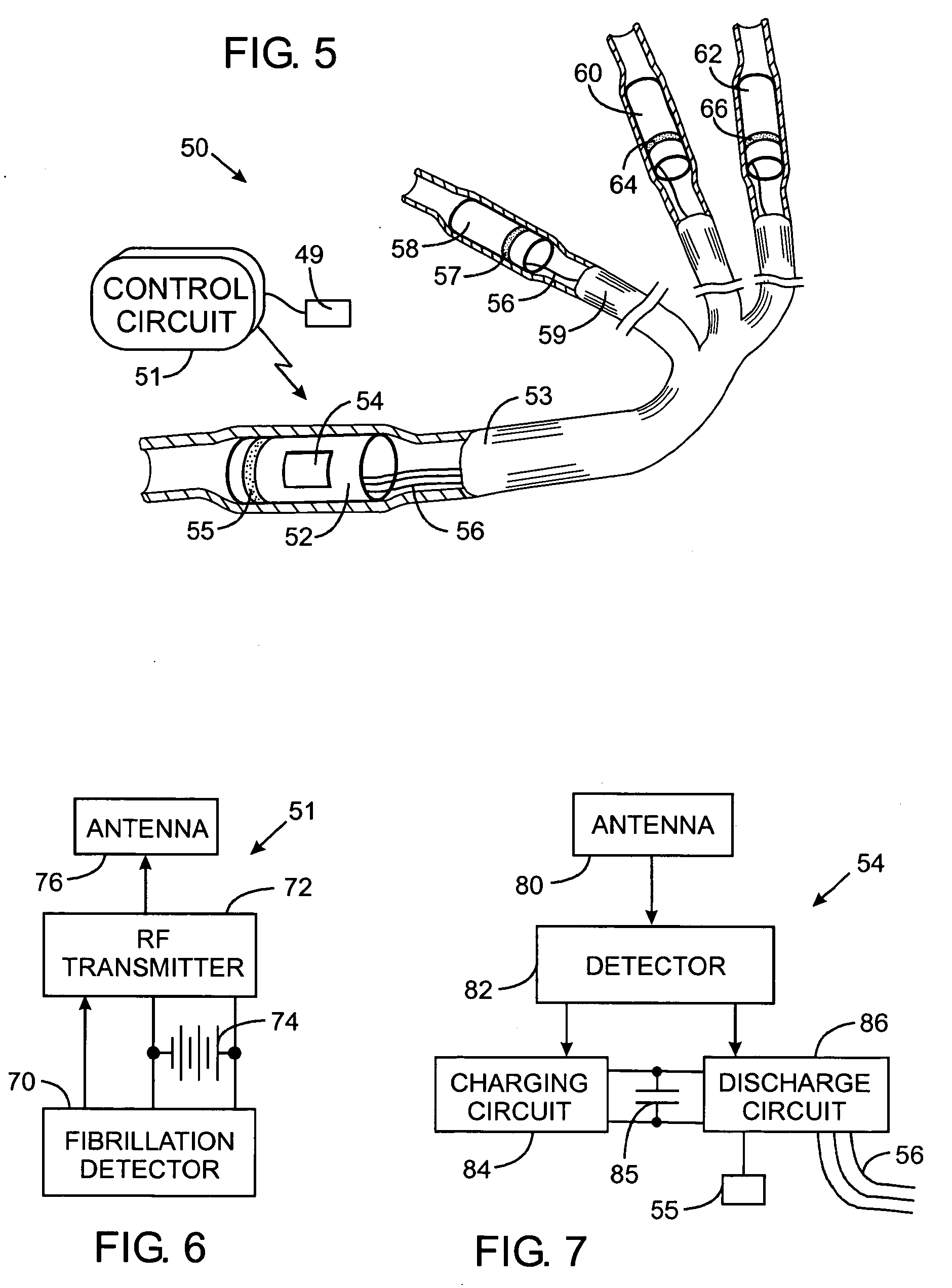
Vagal nerve stimulation using vascular implanted devices for treatment of atrial fibrillation
An abnormally rapid ventricular cardiac rate that results from atrial fibrillation can be reduced by stimulating a vagal nerve of the heart. An apparatus for such stimulation includes a power transmitter that emits a radio frequency signal. A stimulator, implanted in a blood vessel adjacent the vagal nerve, has a pair of electrodes and an electrical circuit thereon. The electrical circuit receives the radio frequency signal and derives an electrical voltage from the energy of that signal. The electrical voltage is applied in the form of pulses to the pair of electrodes, thereby stimulating the vagal nerve. The pattern of that stimulating pulses can be varied in response to characteristics of the atrial fibrillation or the ventricular contractions.
Owner:KENERGY INC
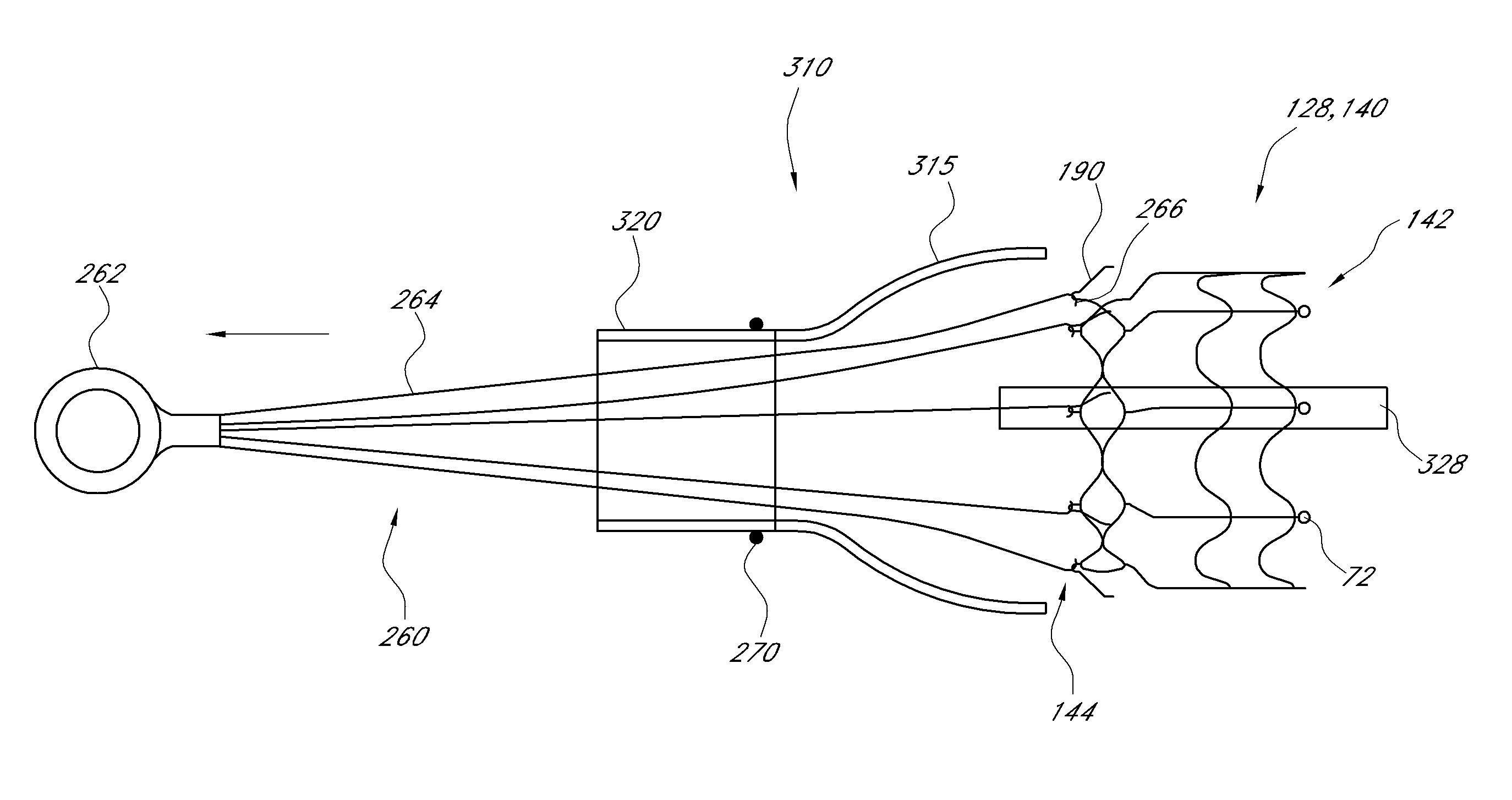
Delivery system for vascular implant
ActiveUS20100082089A1Precise positioningControl rateStentsHeart valvesVascular implantBiomedical engineering
A medical treatment system and method of treatment is described having an implant that can be positioned and deployed, then undeployed to allow repositioning of the implant. The system includes a self-expanding medical implant that longitudinally foreshortens upon radially expanding from a radially compacted state, a distal interface configured to attach the implant to a distal mount of a delivery device, and a proximal interface configured to attach the implant to a proximal mount of the delivery device. Moving the distal mount longitudinally away from the proximal mount applies a longitudinal tension to the implant causing the implant to expand longitudinally and contract radially, and moving the distal mount toward the proximal mount reduces a longitudinal tension in the implant allowing the implant to expand radially toward a fully expanded state.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Vascular embolization with an expansible implant
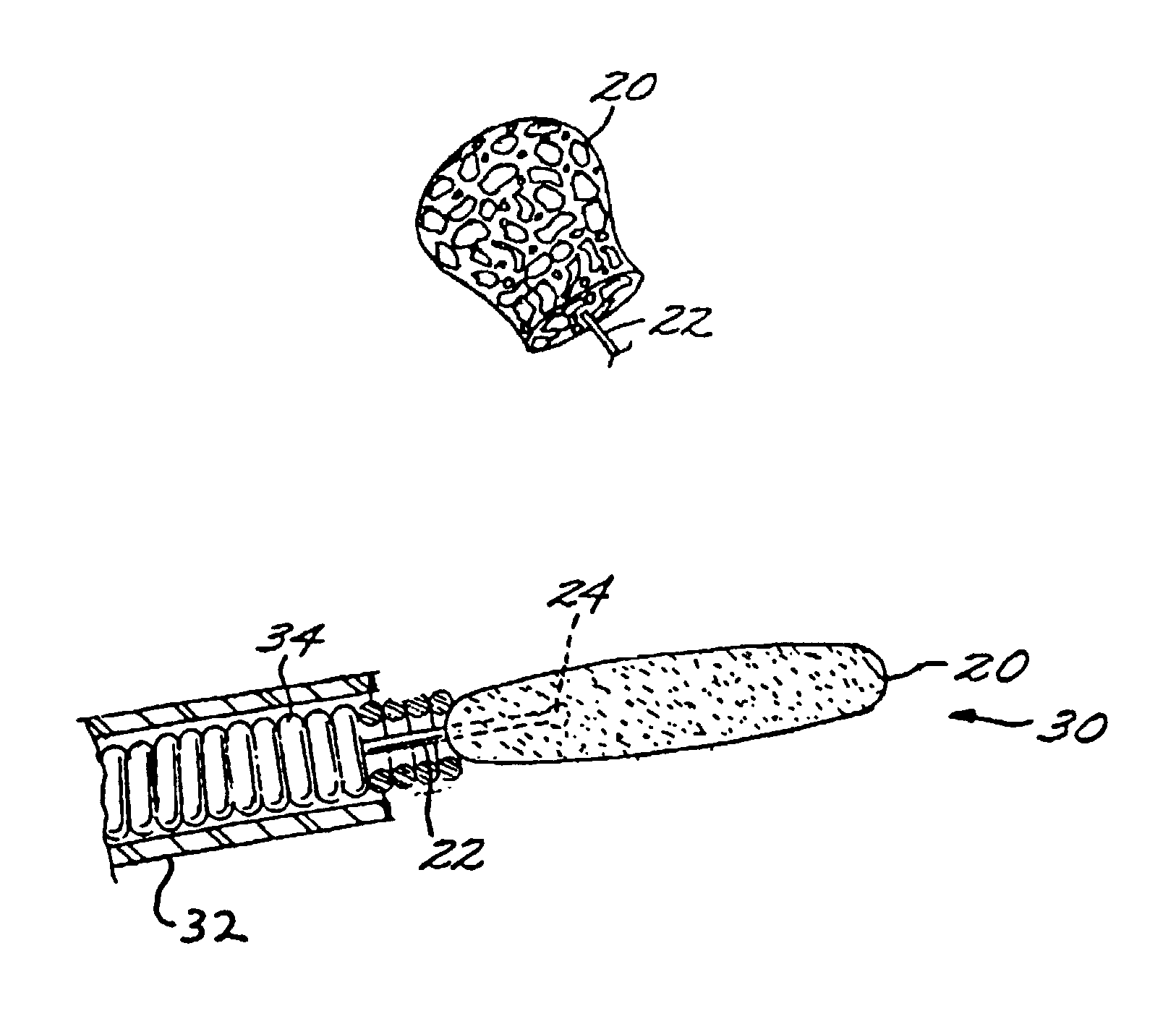
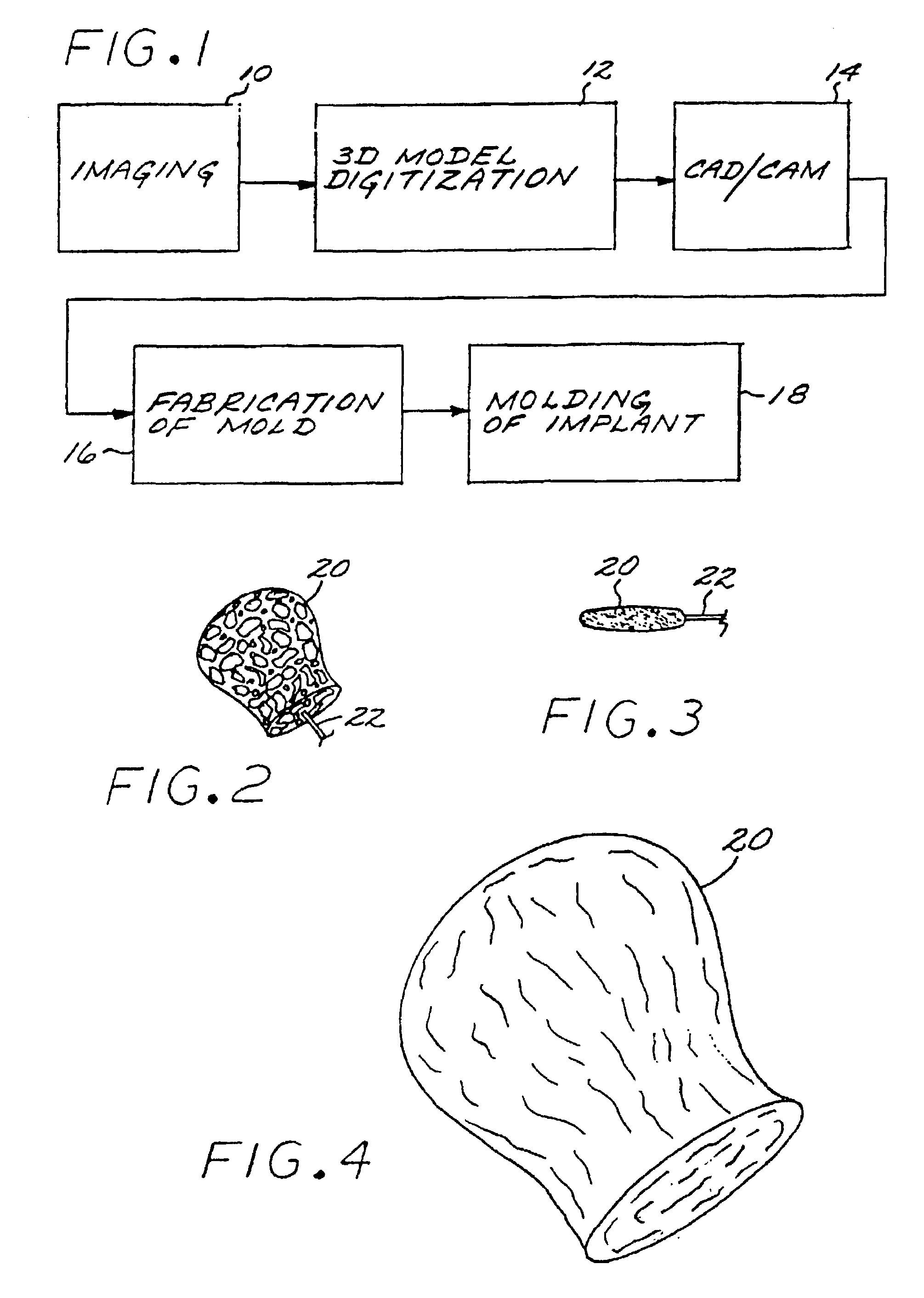
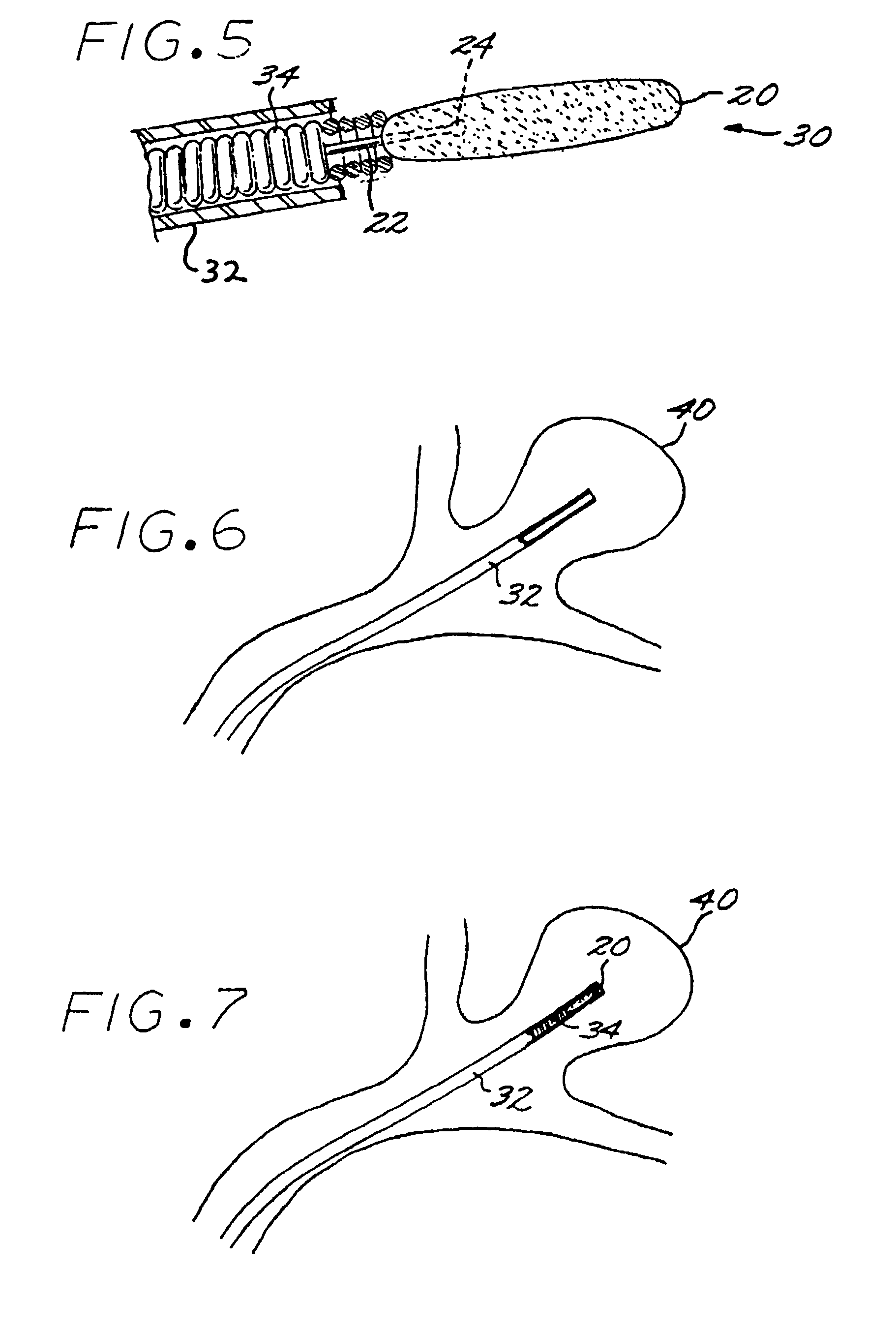
InactiveUS7029487B2EffectiveConvenient position controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusDiagnosticsVascular embolizationVascular implant
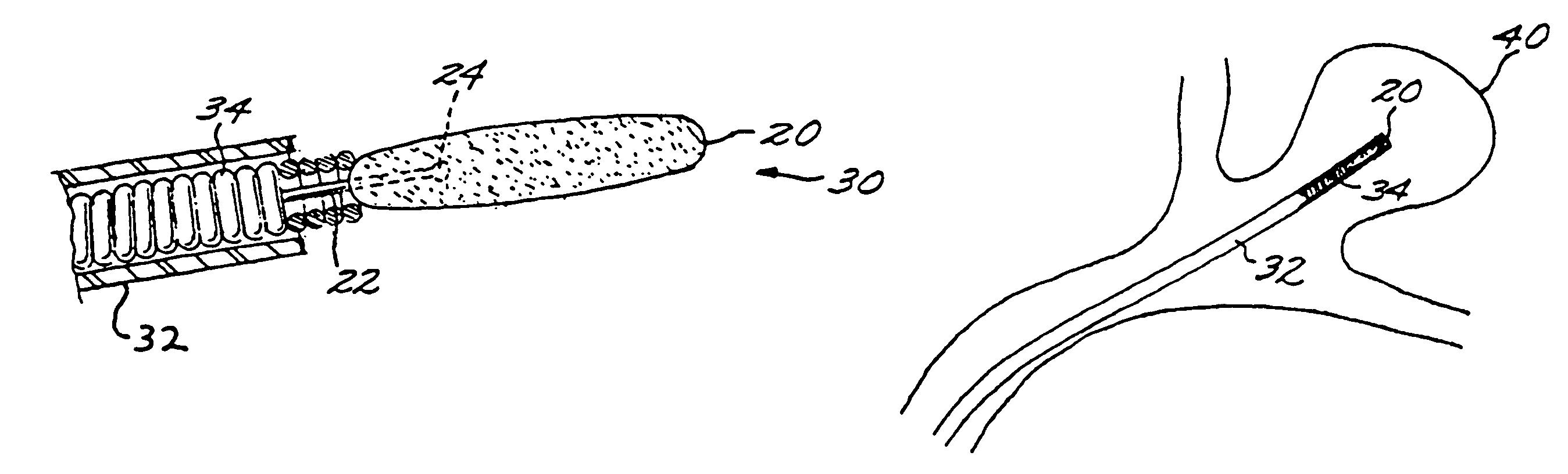
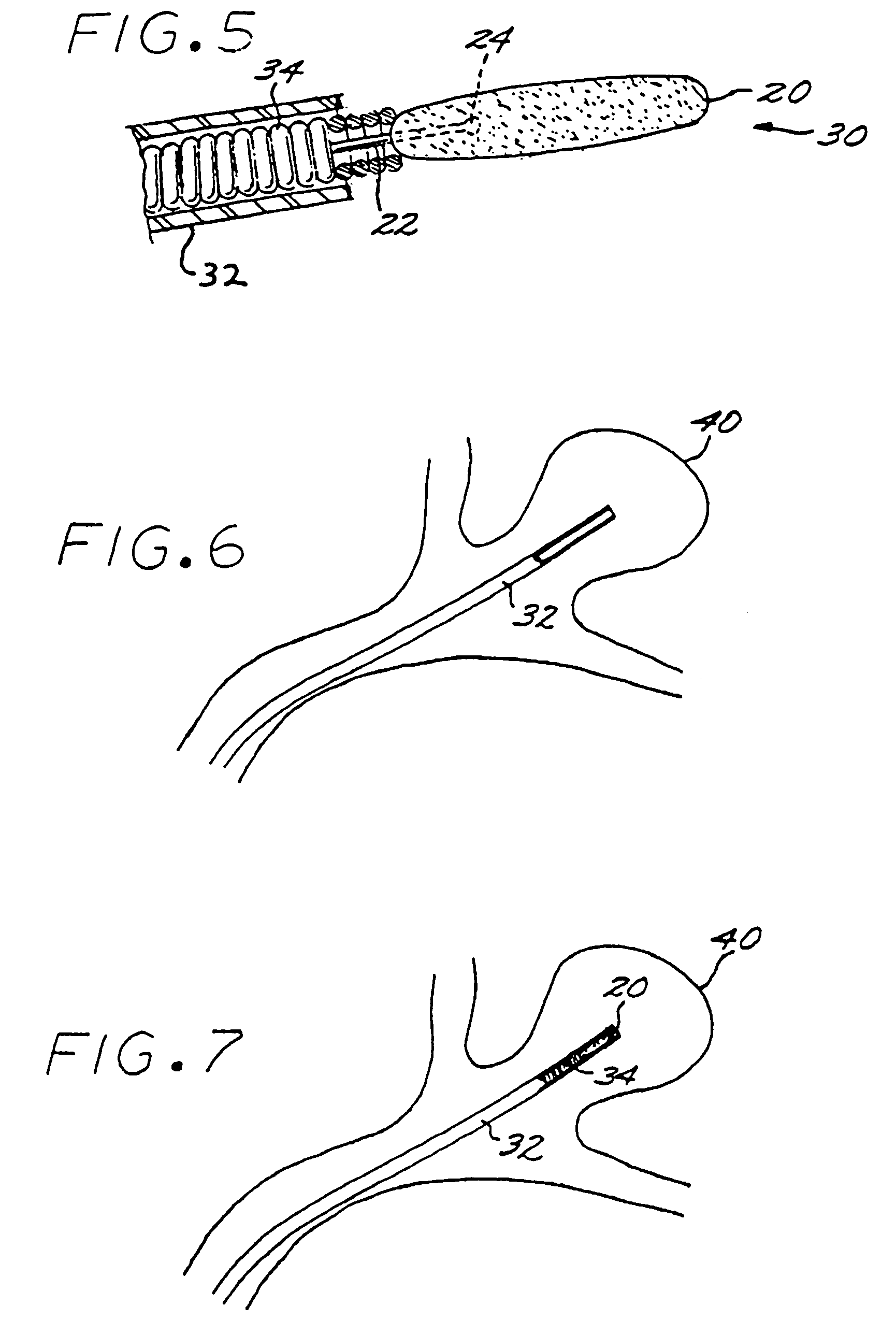
A vascular implant formed of a compressible foam material has a compressed configuration from which it is expansible into a configuration substantially conforming to the shape and size of a vascular site to be embolized. Preferably, the implant is formed of a hydrophilic, macroporous foam material, having an initial configuration of a scaled-down model of the vascular site, from which it is compressible into the compressed configuration. The implant is made by scanning the vascular site to create a digitized scan data set; using the scan data set to create a three-dimensional digitized virtual model of the vascular site; using the virtual model to create a scaled-down physical mold of the vascular site; and using the mold to create a vascular implant in the form of a scaled-down model of the vascular site. To embolize a vascular site, the implant is compressed and passed through a microcatheter, the distal end of which has been passed into a vascular site. Upon entering the vascular site, the implant expands in situ substantially to fill the vascular site. A retention element is contained within the microcatheter and has a distal end detachably connected to the implant. A flexible, tubular deployment element is used to pass the implant and the retention element through the microcatheter, and then to separate the implant from the retention element when the implant has been passed out of the microcatheter and into the vascular site.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Delivery system for vascular implant
ActiveUS8337541B2Precise positioningControl rateStentsHeart valvesVascular implantBiomedical engineering
A medical treatment system and method of treatment is described having an implant that can be positioned and deployed, then undeployed to allow repositioning of the implant. The system includes a self-expanding medical implant that longitudinally foreshortens upon radially expanding from a radially compacted state, a distal interface configured to attach the implant to a distal mount of a delivery device, and a proximal interface configured to attach the implant to a proximal mount of the delivery device. Moving the distal mount longitudinally away from the proximal mount applies a longitudinal tension to the implant causing the implant to expand longitudinally and contract radially, and moving the distal mount toward the proximal mount reduces a longitudinal tension in the implant allowing the implant to expand radially toward a fully expanded state.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Vascular implant and delivery system
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
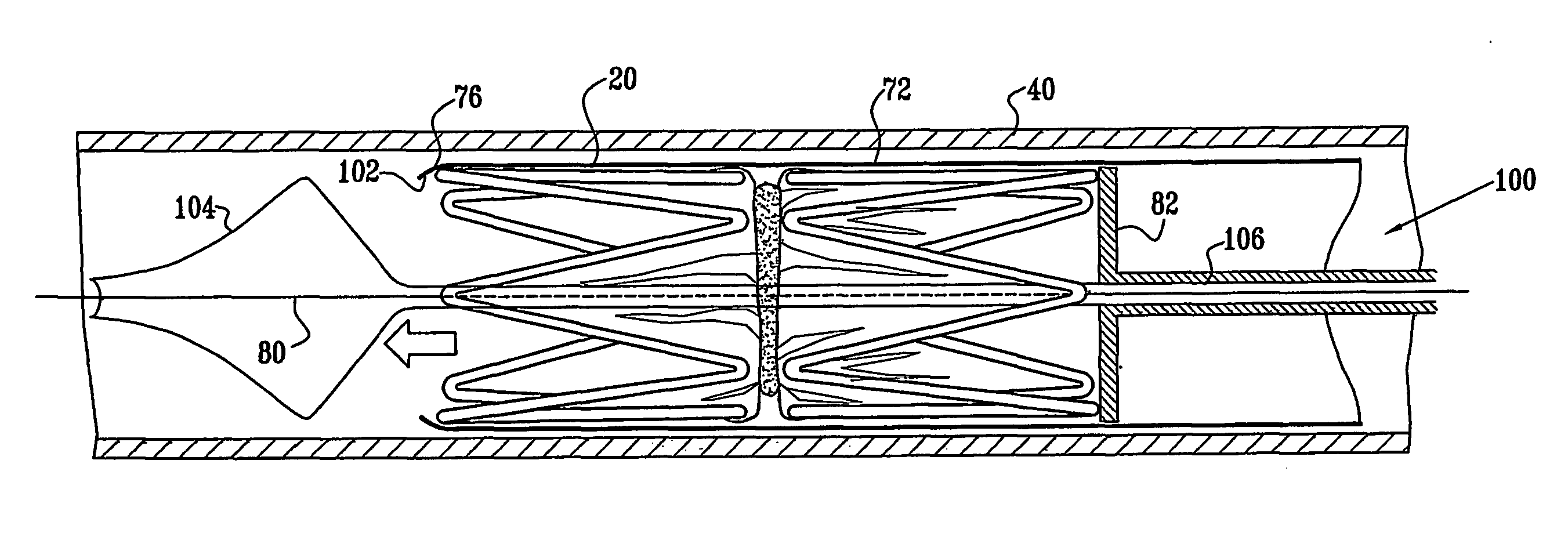
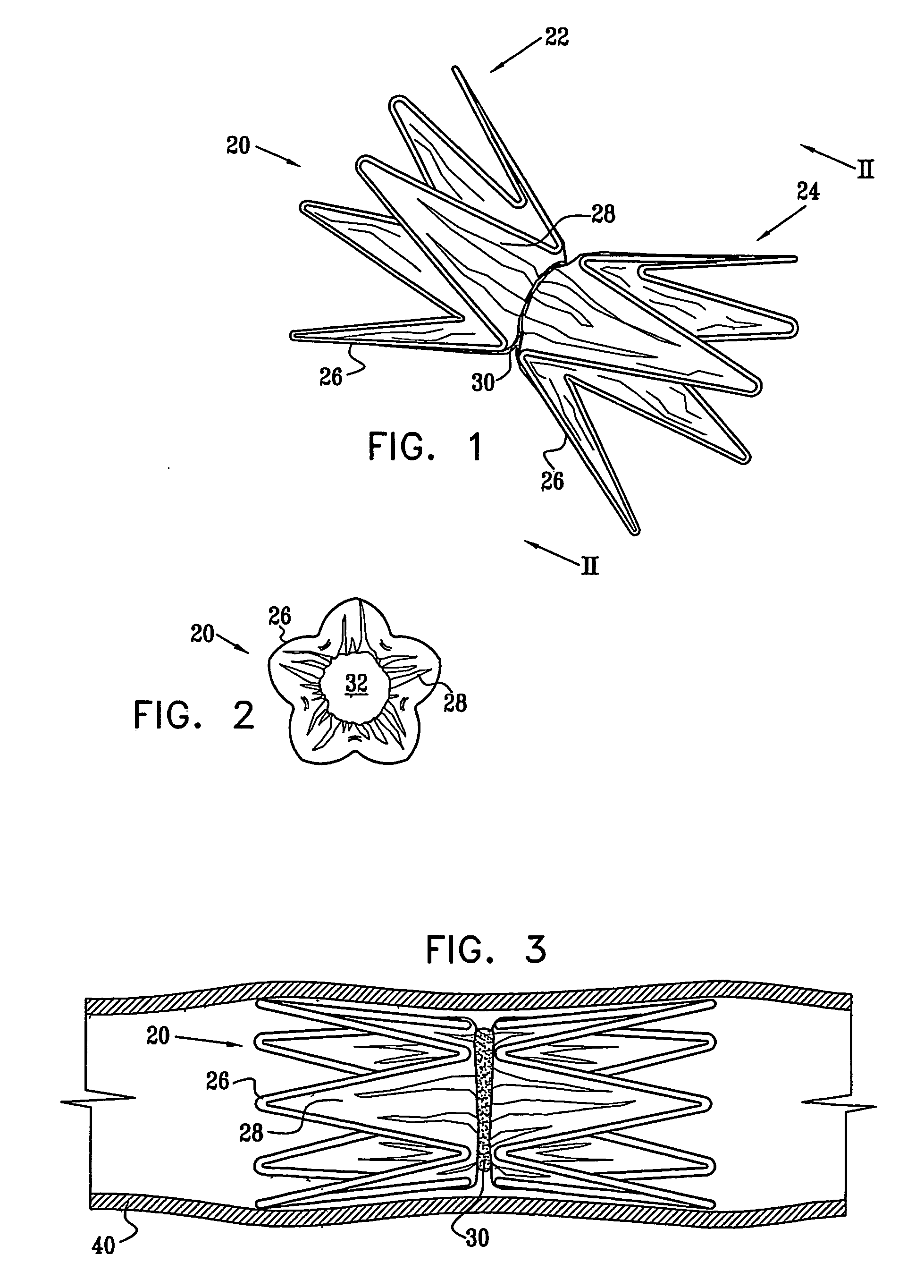
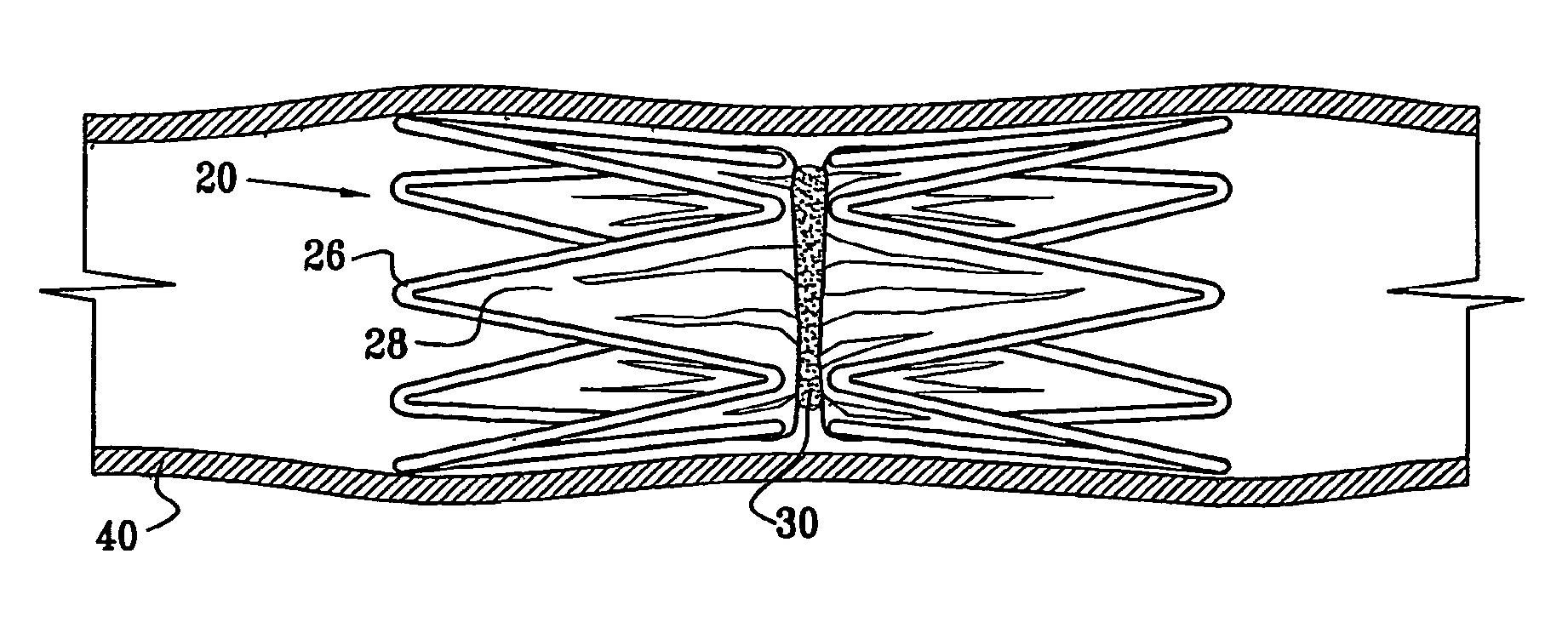
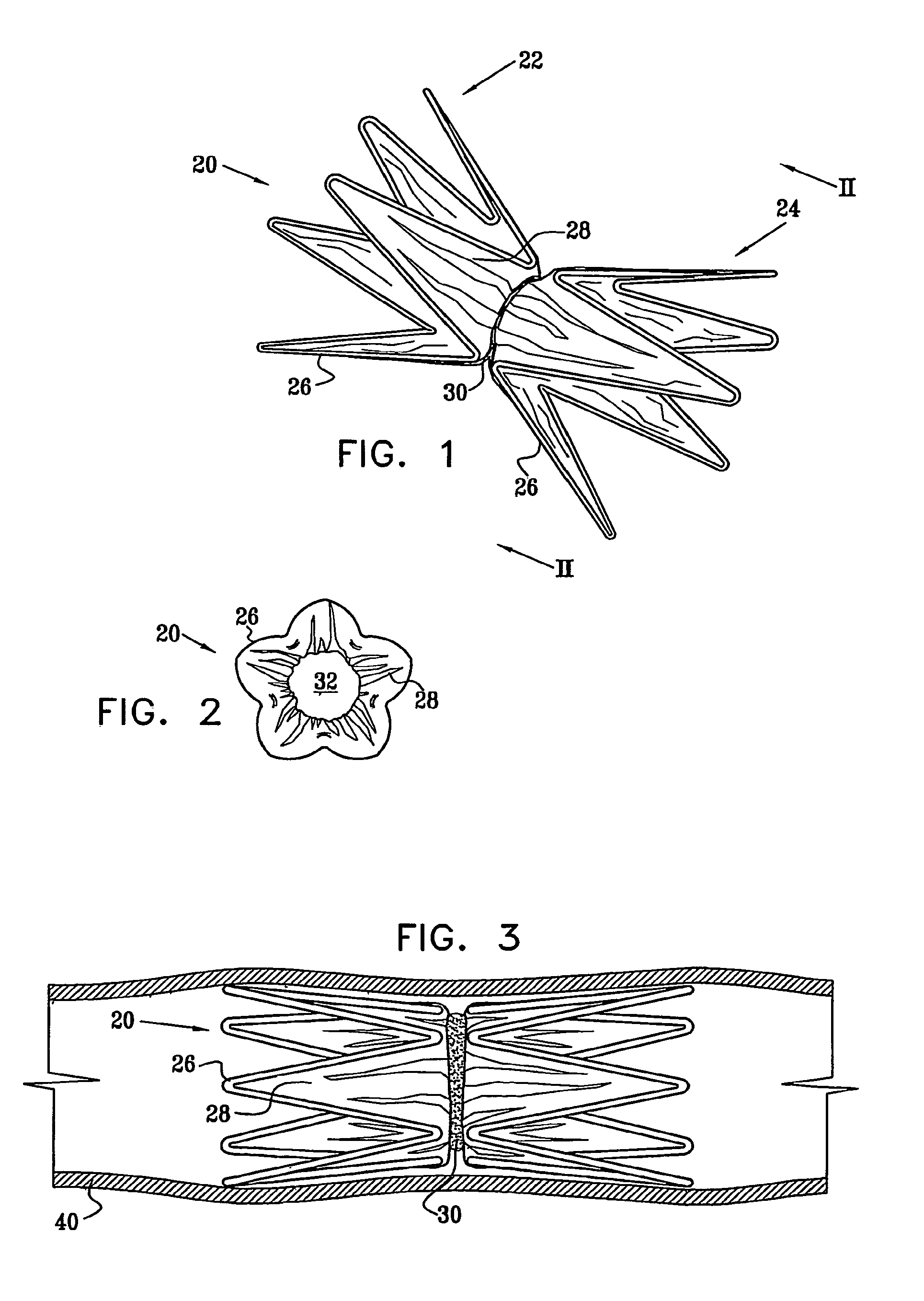
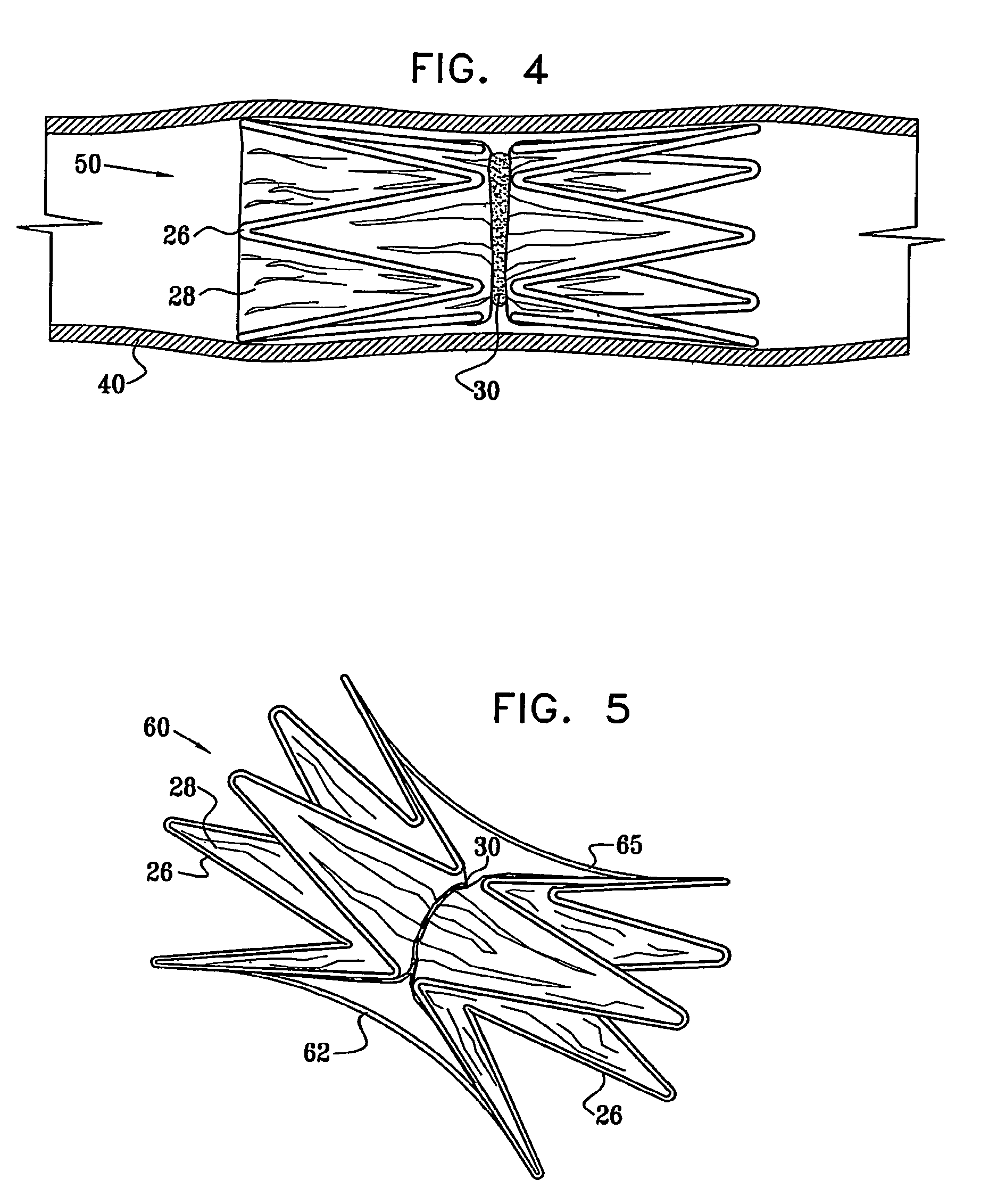
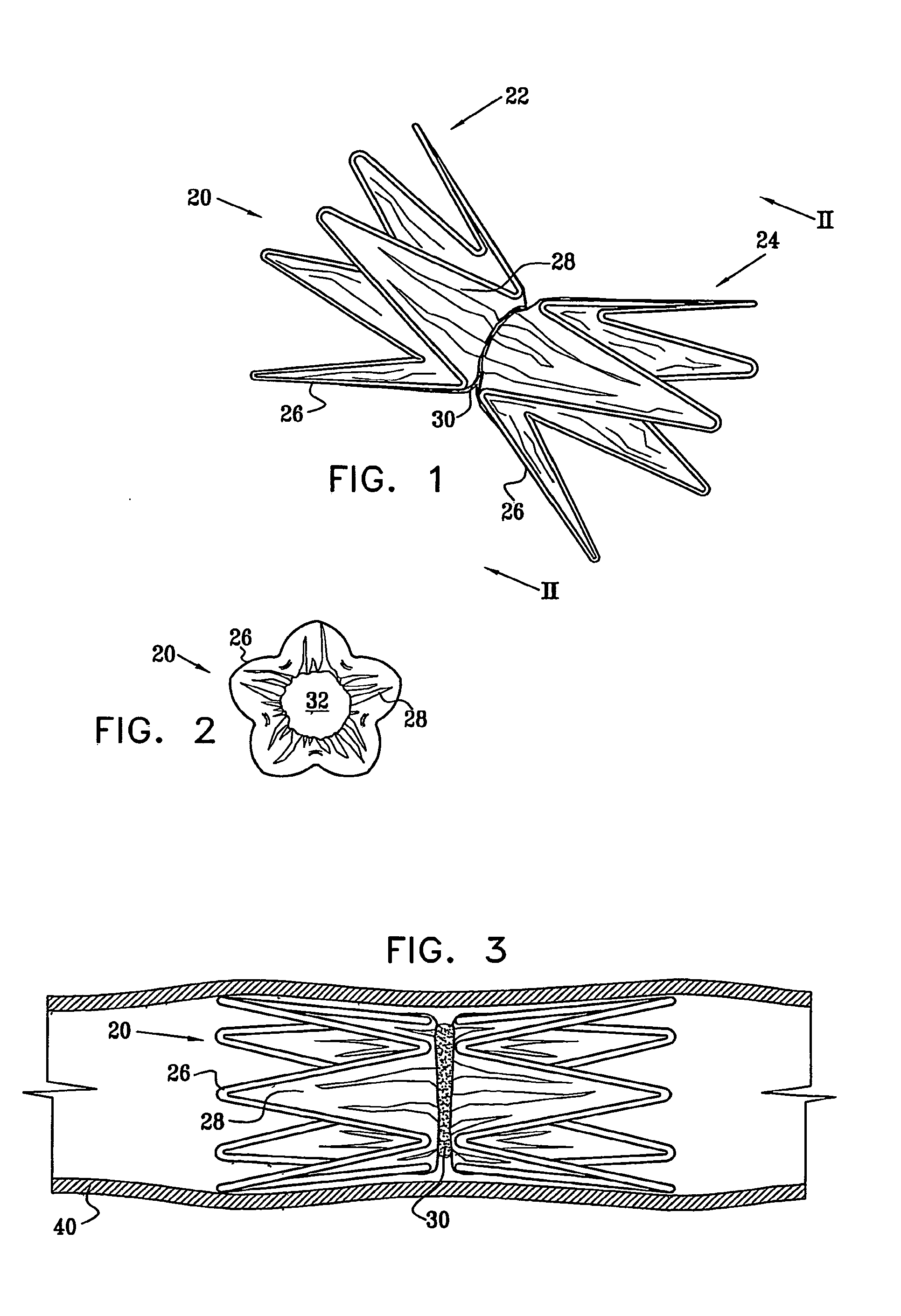
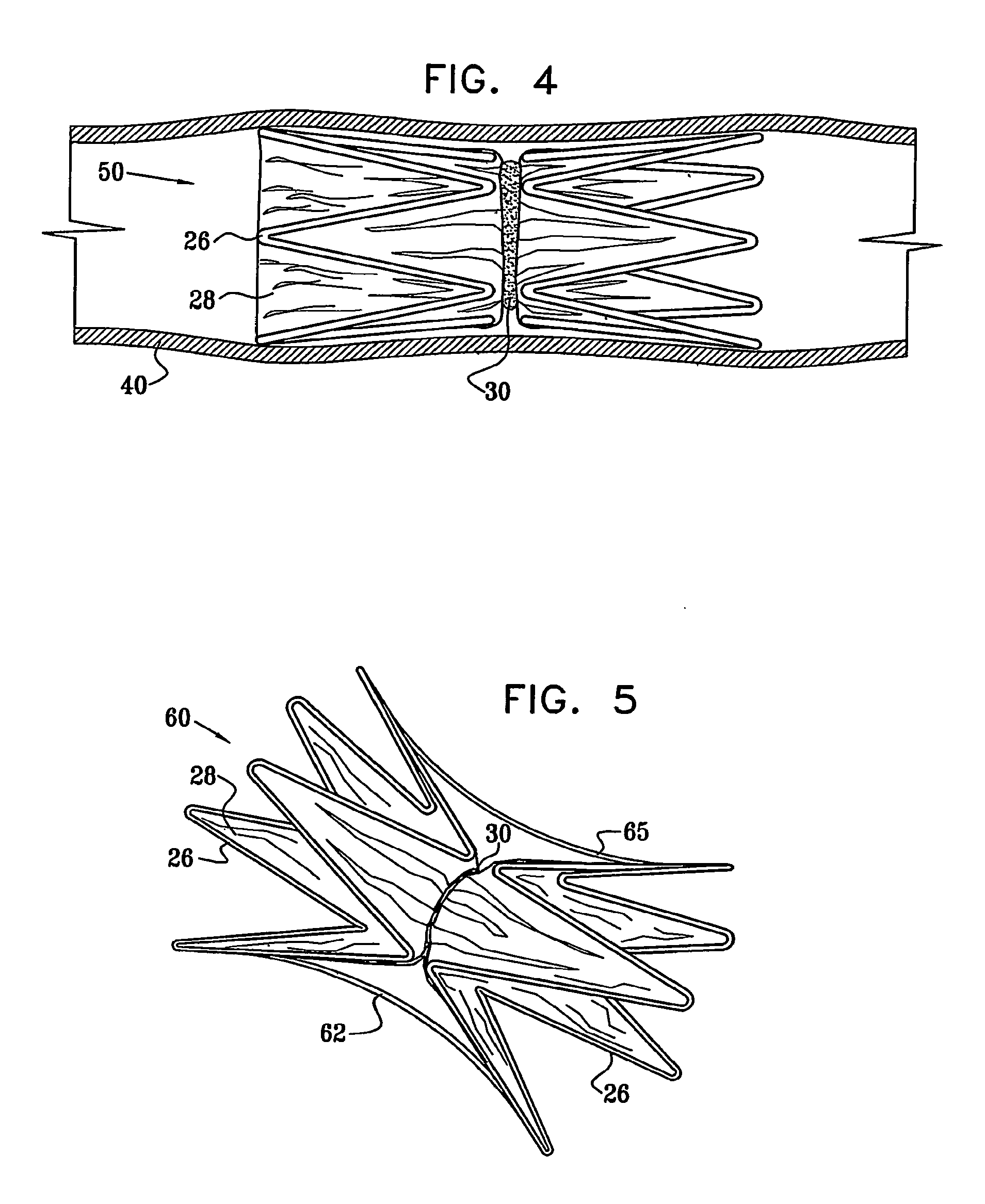
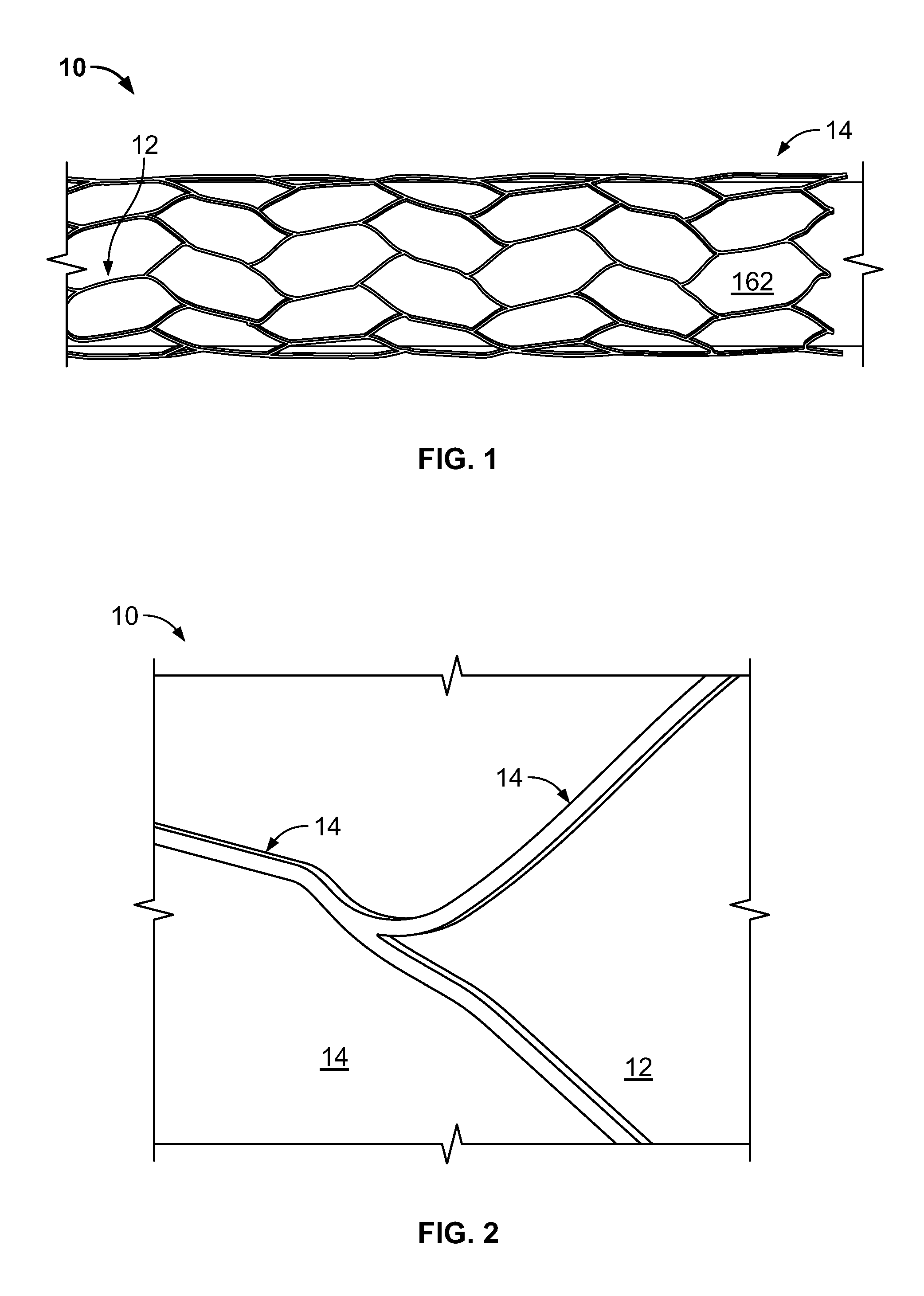
Vascular implant
InactiveUS20070027525A1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureReduce the overall diameterStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantEngineering
A medical implant (20) includes first and second ring members (22,24), each including a resilient framework (26) having a generally cylindrical form. A tubular sleeve (28) is fixed to the first and second ring members so as to hold the ring members in mutual longitudinal alignment, thereby defining a lumen (32) passing through the ring members. A constricting element (30) is fit around the sleeve at a location intermediate the first and second ring members so as to reduce a diameter of the lumen at the location.
Owner:NEOVASC MEDICAL LTD
Vascular implant
ActiveUS8911489B2Simple and inexpensive to manufactureReduce the overall diameterStentsEar treatmentVascular implantEngineering
A medical implant (20) includes first and second ring members (22, 24), each including a resilient framework (26) having a generally cylindrical form. A tubular sleeve (28) is fixed to the first and second ring members so as to hold the ring members in mutual longitudinal alignment, thereby defining a lumen (32) passing through the ring members. A constricting element (30) is fit around the sleeve at a location intermediate the first and second ring members so as to reduce a diameter of the lumen at the location.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
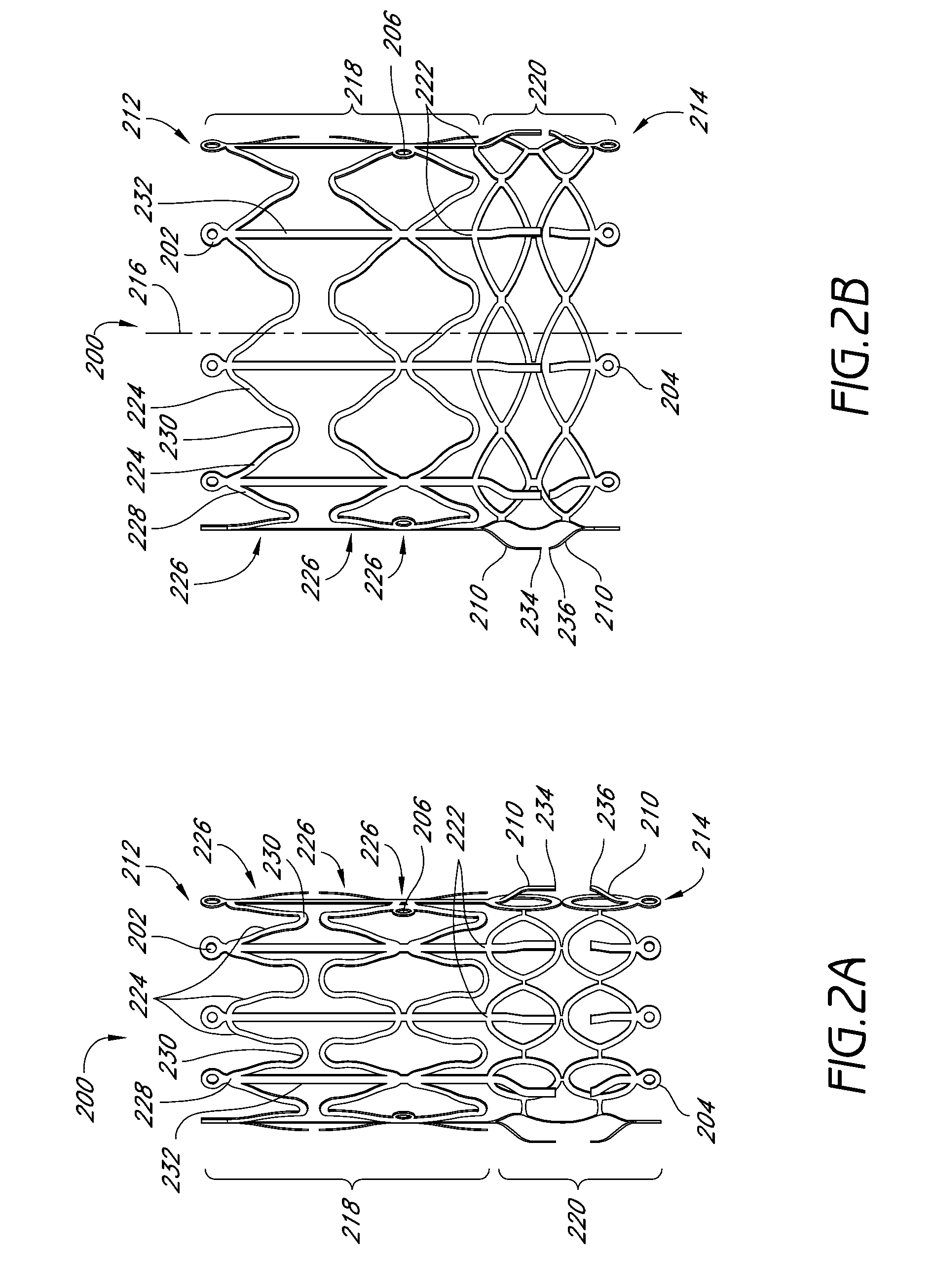
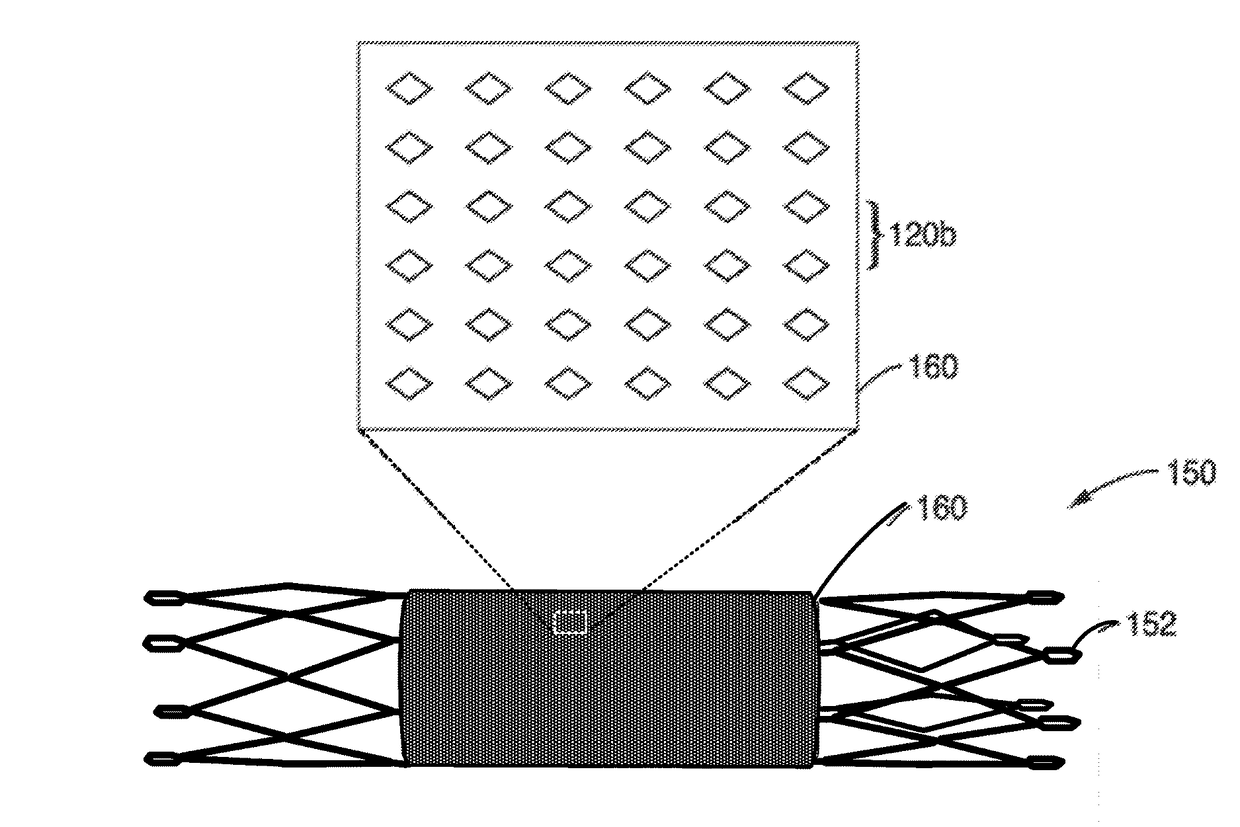
Vascular implants and methods of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070150051A1Facilitates cellular integration of deviceImproving and facilitating deliveryStentsHeart valvesCell-Extracellular MatrixVascular implant
The present invention is directed to vascular implants and methods for fabricating the same. The implantable devices include but are not limited to stents, grafts and stent grafts. The devices may include a biomaterial, such as an extracellular matrix, coated or attached to at least a portion of the device. The devices may be constructed of a single woven wire to form at least a main lumen having proximal and distal ends. In many embodiments, the devices include one or more side branch lumens interconnected with the main lumen.
Owner:TAHERI LADUCA
Thermally reversible implant and filler
The invention relates to the use of a thermal reversible gel, such as a copolymer composition, as a biological filler or implant. The gel has a semi-solid form at body temperature, but upon cooling to a temperature below a threshold level, the gel is liquefied and can be re-shaped, re-sized, manipulated or removed from the body. The gel may be used as a subcutaneous implant, a biological filler, joint or tissue spacer, for wrinkle filling or other cosmetic implants, as a soft-tissue replacement for reconstructive surgery, or as a barrier within the lumen of a biological structure, such as a blood vessel. The implant may be used to provide reversible birth control by providing, for example, a reversible barrier to the cervix or a reversible blockage of the lumen of the vas deferens.
Owner:CHENG YU LING +3
Vascular implant
ActiveUS20120022637A1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureReduce the overall diameterStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantEngineering
Owner:BIO IP VENTURES II LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
Implantable graft assembly and aneurysm treatment
InactiveUS20090069880A1Reduced flexibilityIncrease profile of implantStentsOcculdersVascular implantAneurysm treatment
Disclosed is an implantable graft assembly comprising a graft secured to a expandable tubular frame, the graft only partially covering the frame and the use of the graft assembly in treating an aneurysm, especially a cerebral aneurysm. Disclosed is also a method of treating an aneurysm by deploying an implantable graft assembly. Disclosed is also the use of serous tissue for the preparation of a cerebrovascular implant, especially as a graft, especially as a component of a cerebrovascular implantable graft assembly.
Owner:DESIGN & PERFORMANCE CYPRUS
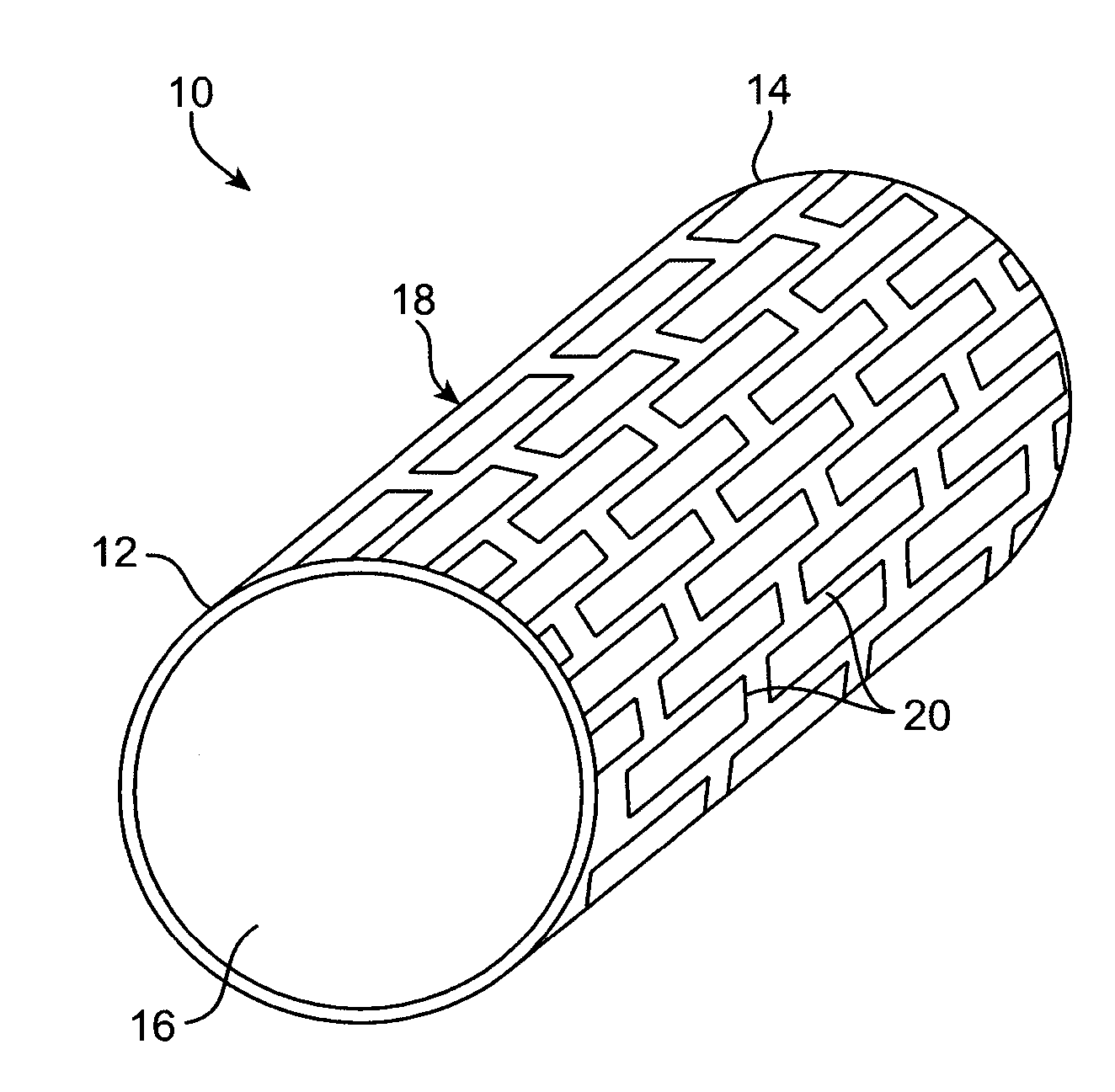
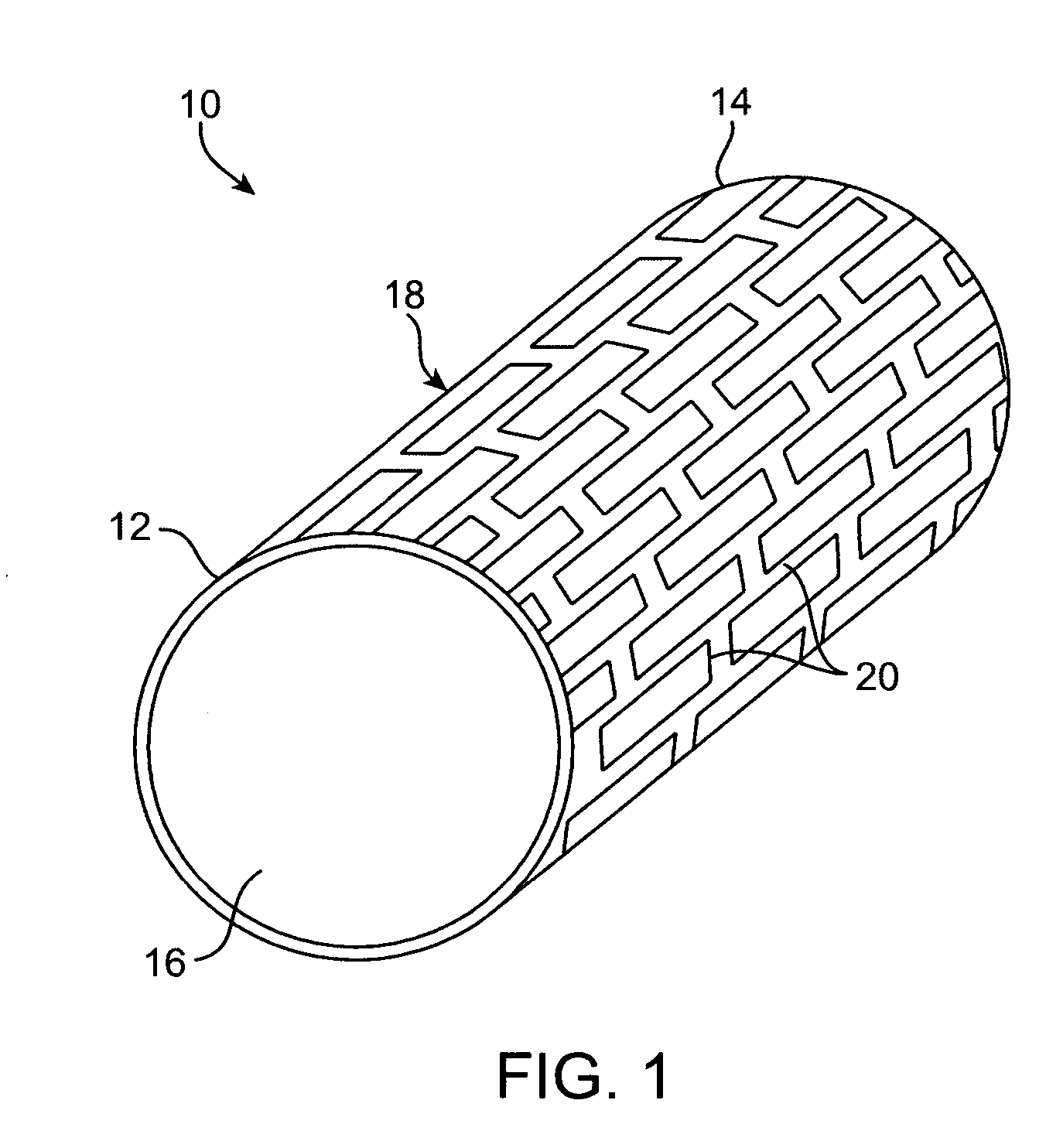
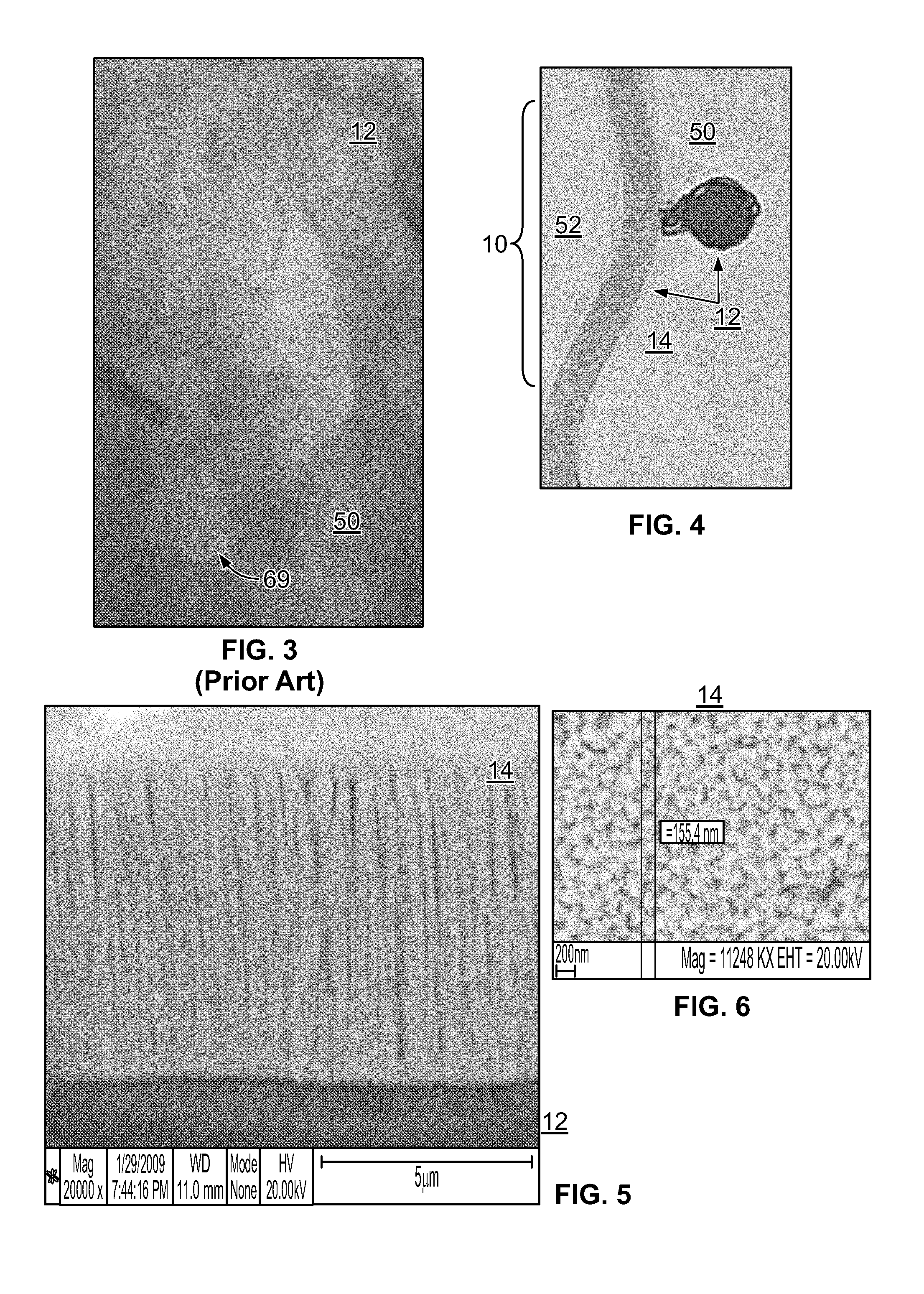
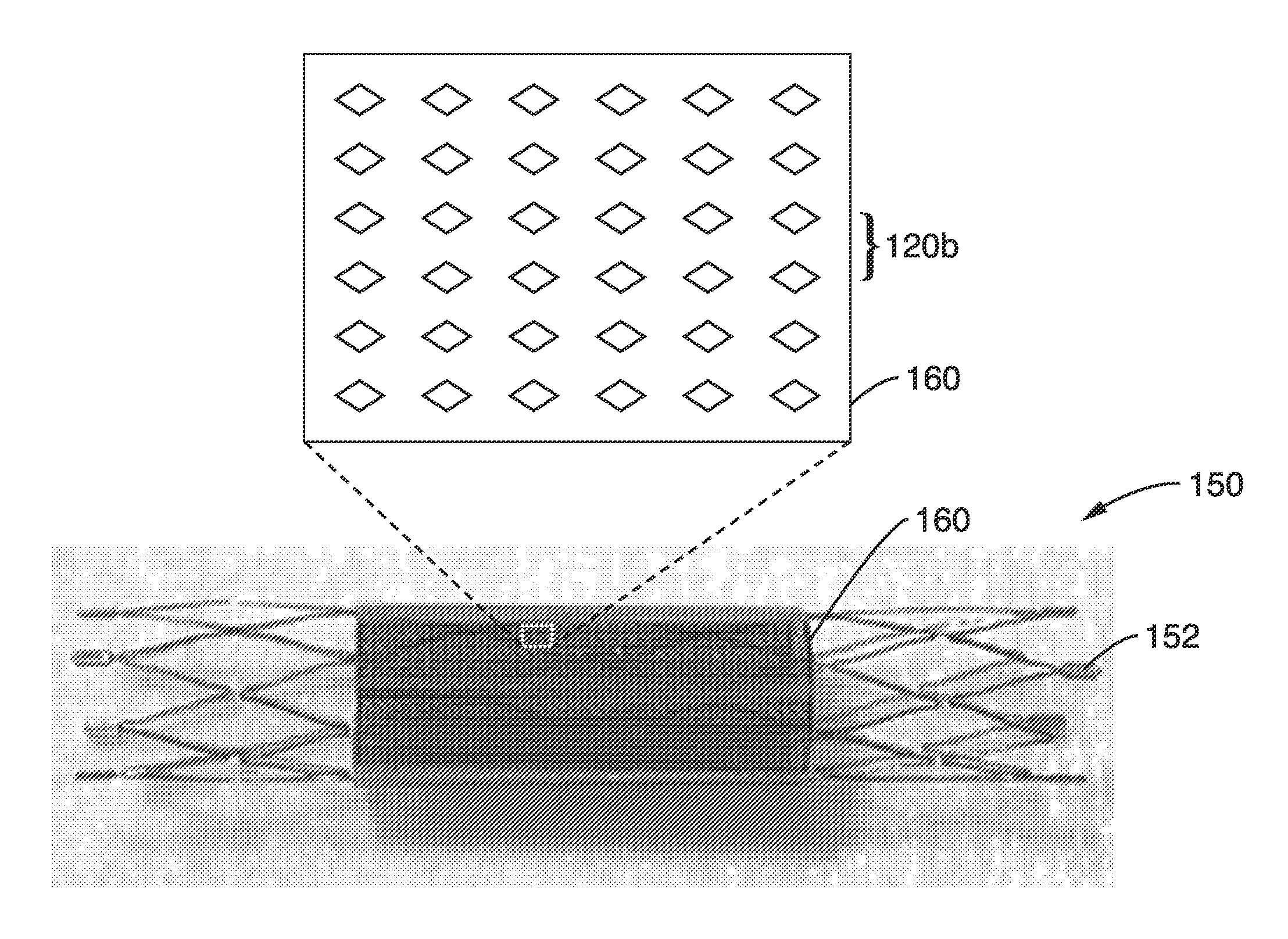
Thin film vascular stent and biocompatible surface treatment
A vascular implant, comprising a sheet comprising thin film nickel titanium (NiTi), wherein the sheet has at least one super-hydrophilic surface having a water contact angle of less than approximately 5 degrees. The sheet is configured to have a compacted form having a first internal diameter and a deployed form having a second internal diameter larger than the first internal diameter. The sheet may be delivered into a blood vessel in the compacted form and expanded to its deployed form at a treatment location within the blood vessel, wherein the stent is configured to expand onto an internal surface of the blood vessel and exert a radial force on said internal surface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Vascular embolization with an expansible implant
InactiveUS7201762B2Reduce riskFacilitates precise and highly controllable deploymentAdditive manufacturing apparatusDiagnosticsVascular embolizationVascular implant
A vascular implant formed of a compressible foam material has a compressed configuration from which it is expansible into a configuration substantially conforming to the shape and size of a vascular site to be embolized. Preferably, the implant is formed of a hydrophilic, macroporous foam material, having an initial configuration of a scaled-down model of the vascular site, from which it is compressible into the compressed configuration. The implant is made by scanning the vascular site to create a digitized scan data set; using the scan data set to create a three-dimensional digitized virtual model of the vascular site; using the virtual model to create a scaled-down physical mold of the vascular site; and using the mold to create a vascular implant in the form of a scaled-down model of the vascular site. To embolize a vascular site, the implant is compressed and passed through a microcatheter, the distal end of which has been passed into a vascular site. Upon entering the vascular site, the implant expands in situ substantially to fill the vascular site. A retention element is contained within the microcatheter and has a distal end detachably connected to the implant. A flexible, tubular deployment element is used to pass the implant and the retention element through the microcatheter, and then to separate the implant from the retention element when the implant has been passed out of the microcatheter and into the vascular site.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Method for high-resolution presentation of filigree vessel implants in angiographic images
ActiveUS20080267475A1Easy to demonstrateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular implantMedical imaging
The invention relates to a method for high-resolution display of vessel implants in angiographic images, featuring the steps: recording at least two images of an object-catheter combination including catheter markers with a medical imaging method; detection of an region of interest created in the form of an area between the balloon markers which completely contains the object to be registered for each recorded image; coarse registration of the region of interest images by registration of the respective pairs of balloon markers of all recorded images; fine registration of the region of interest image content / of the region of interest image by registration of the region of interest content; and arithmetic averaging across the fine-registered images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Nanostructure surface coated medical implants and methods of using the same
Compositions including a surface or film comprising nanofibers, nanotubes or microwells comprising a bioactive agent for elution to the surrounding tissue upon placement of the composition in a subject are disclosed The compositions are useful in medical implants and methods of treating a patient in need of an implant, including orthopedic implants, dental implants, cardiovascular implants, neurological implants, neurovascular implants, gastrointestinal implants, muscular implants, and ocular implants.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Method And Apparatus For Caged Stent Delivery
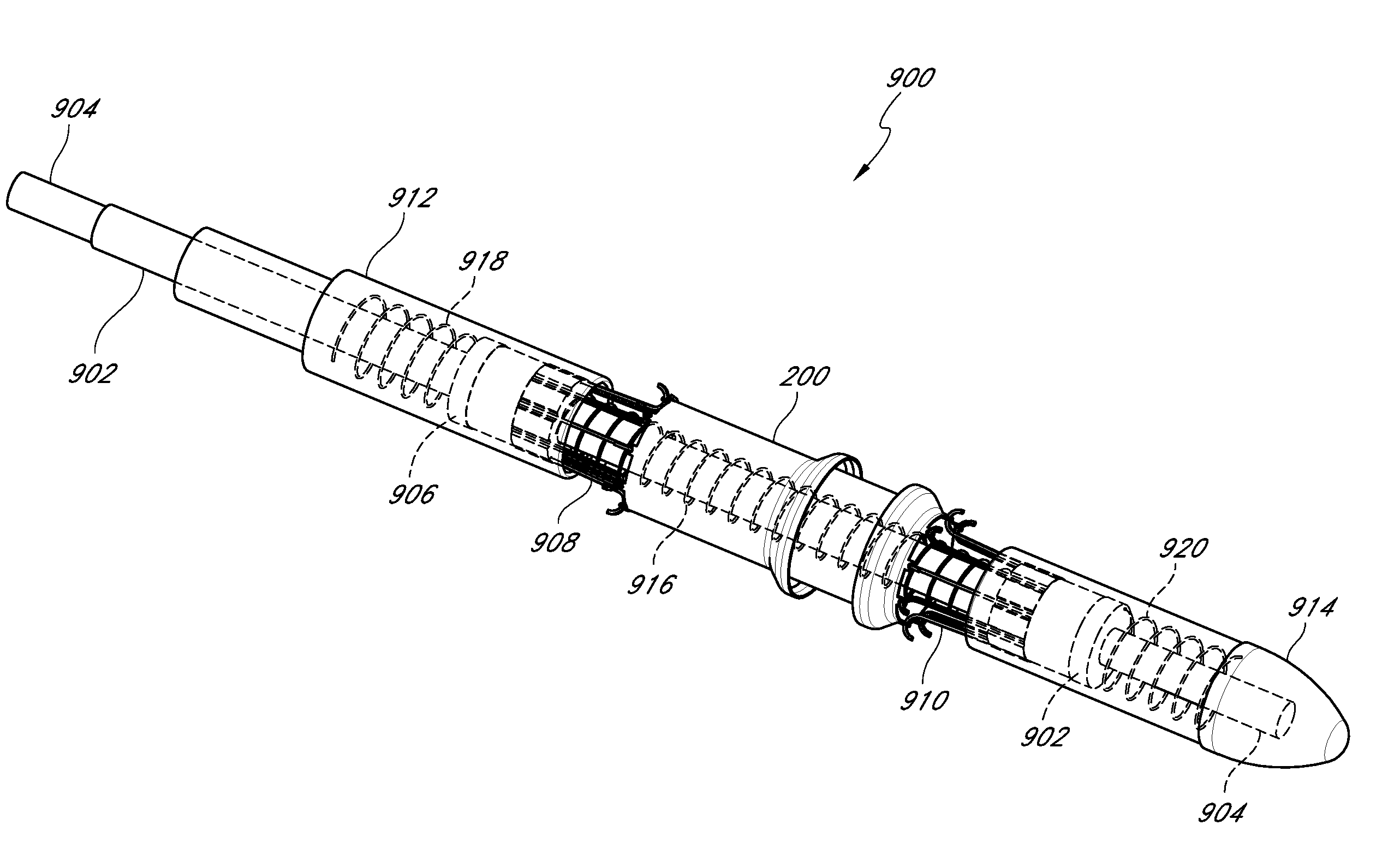
InactiveUS20110276121A1Shorten exchange timeReduce frictionStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantMedicine
In combination a device for delivering a stent within an intraluminal cavity and a stent including an elongated member configured to receive a stent thereon, a stent mounted on the elongated member and movable between a smaller diameter delivery position and an expanded placement position and a tubular portion attached to the elongated member. First and second stent engaging arms and a pusher arm extend distally of the tubular portion. The first and second engaging arms configured to constrain the stent in an area between the arms and the pusher arm configured to contact the proximal portion of the stent. The engaging arms are movable between a closed stent constraining position and an open stent release position. The delivery system can also be used to deliver other vascular implants.
Owner:LEVINE MARC ALAN
Method and apparatus for anchoring cardiovascular implants
InactiveUS20090030435A1Reduce risk of migrationReduce intrusionSuture equipmentsStentsVascular implantTherapeutic Devices
Methods, devices and systems facilitate retention of a variety of therapeutic devices. Devices generally include an anchoring element, which has been designed to promote fibrotic ingrowth, and an anchored device, which has been designed to firmly engage the complementary region of the anchoring element. The anchoring element may be placed in a minimally invasive procedure temporally separated from the deployment of the anchored device. Once enough time has passed to ensure appropriate fixation of the anchoring element by tissue and cellular ingrowth at the site of placement, the anchored device may then be deployed during which it firmly engages the complementary region of the anchoring element. In this manner, a firm attachment to the implantation site may be made with a minimum of required hardware. Some embodiments are delivered through a delivery tube or catheter and while some embodiments may require laparoscopy or open surgery for one or more of the placement procedures. Some embodiments anchor devices within the cardiovascular tree while others may anchor devices within the gastrointestinal, peritoneal, pleural, pulmonary, urogynecologic, nasopharyngeal or dermatologic regions of the body. An alternative embodiment provides for the placement of the anchoring element and anchored device simultaneously, but allows for their removal separately. This embodiment allows the device, which may be placed only temporarily and be designed to be removed, to experience significant fibrotic ingrowth, but then to be easily detached from the ingrowth-anchored region to allow for simple and quick device removal.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
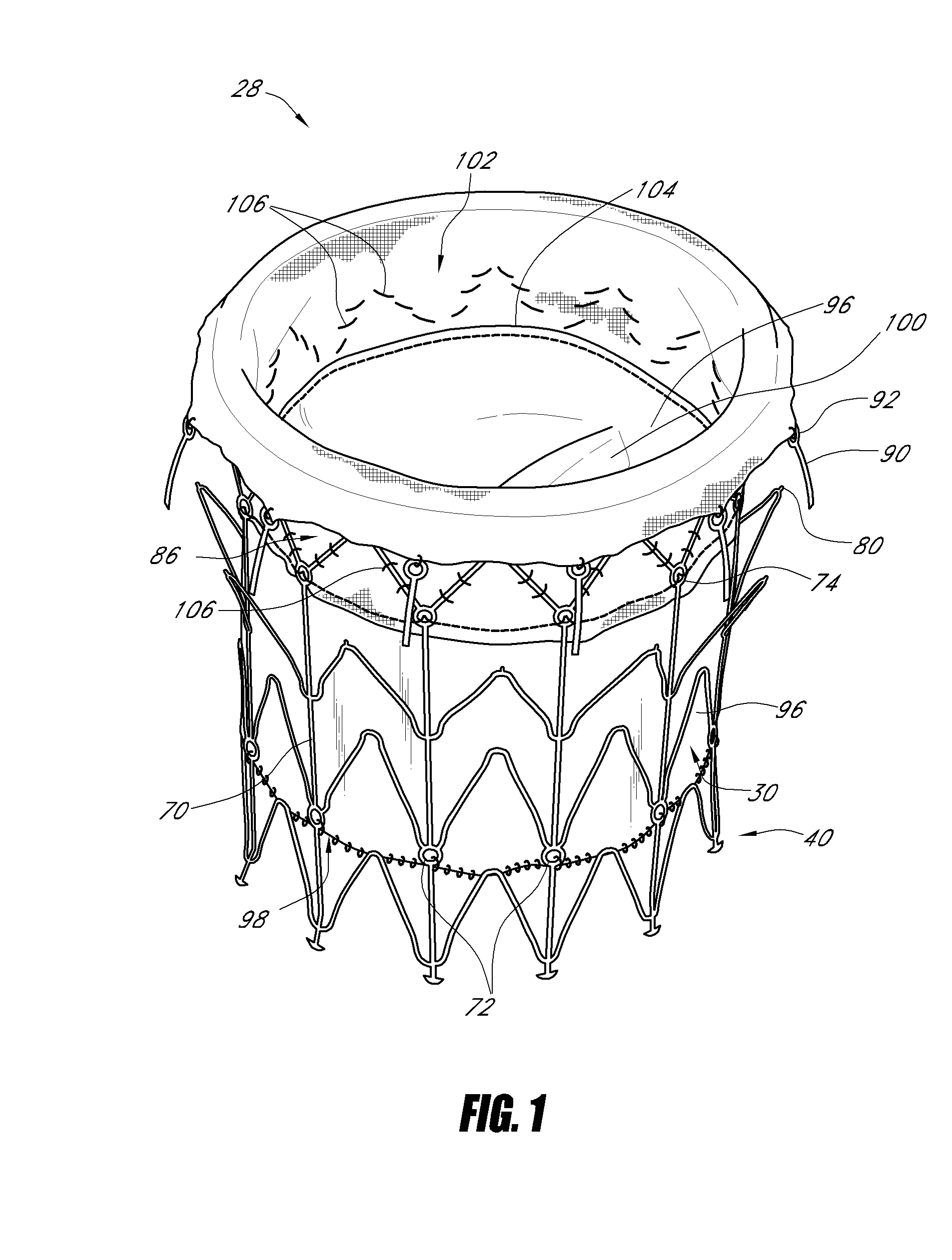
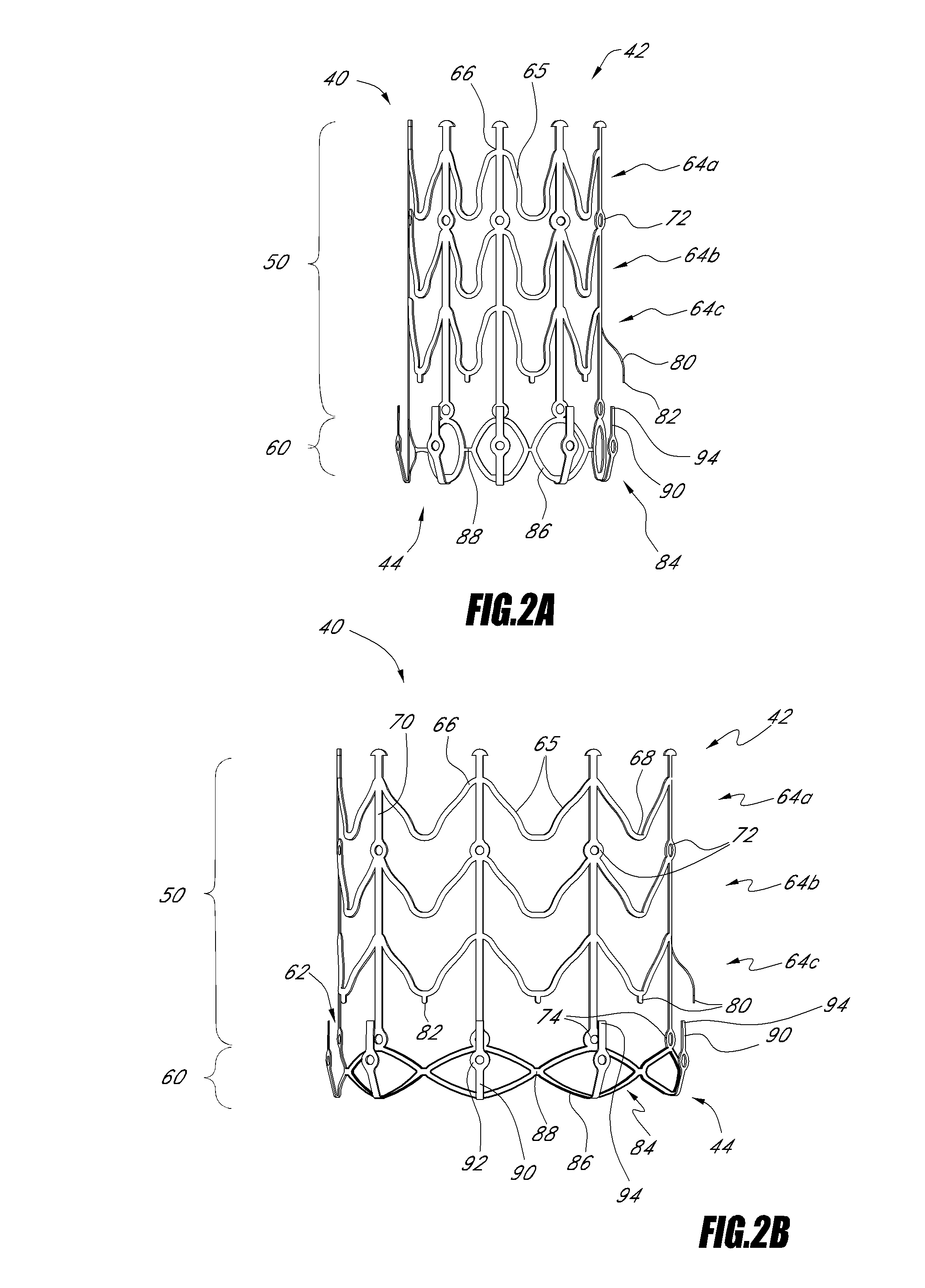
Endoluminal device and method
An endoluminal device can be configured for precise positioning during deployment within a vessel. The endoluminal device can be a tack, stent, vascular implant or other type of implant. The endoluminal device can have circumferential member with an undulating configuration having multiple inward and outward apexes and struts extending therebetween. Two of the struts can be used to establish a foot for the precise positioning of the device during deployment. A method of placing the endoluminal device can include withdrawing an outer sheath such that a portion of the endoluminal device is expanded prior to the rest of the endoluminal device.
Owner:INTACT VASCULAR
Endoluminal device and method
Owner:INTACT VASCULAR
Systems and devices for cerebral aneurysm repair
ActiveUS20140207180A1Good equipment stabilityImprove adhesionDiagnosticsGlovesVascular implantBlood component
An embolization device for treating ischemic stroke is disclosed, having a surface, wherein the body portion is configured to have a radiopaque and electropositive surface under physiological conditions when the device is emplaced, which ionically binds a blood component in an amount effective to promote stability of device in situ to bind to a tissue component in an amount effective to increase adhesion of the device as compared to a device without an electropositive surface. Embolic coils being so delivered are electrolytically detachable in under 10 seconds, according to the disclosed vascular implant systems.
Owner:BLOCKADE MEDICAL
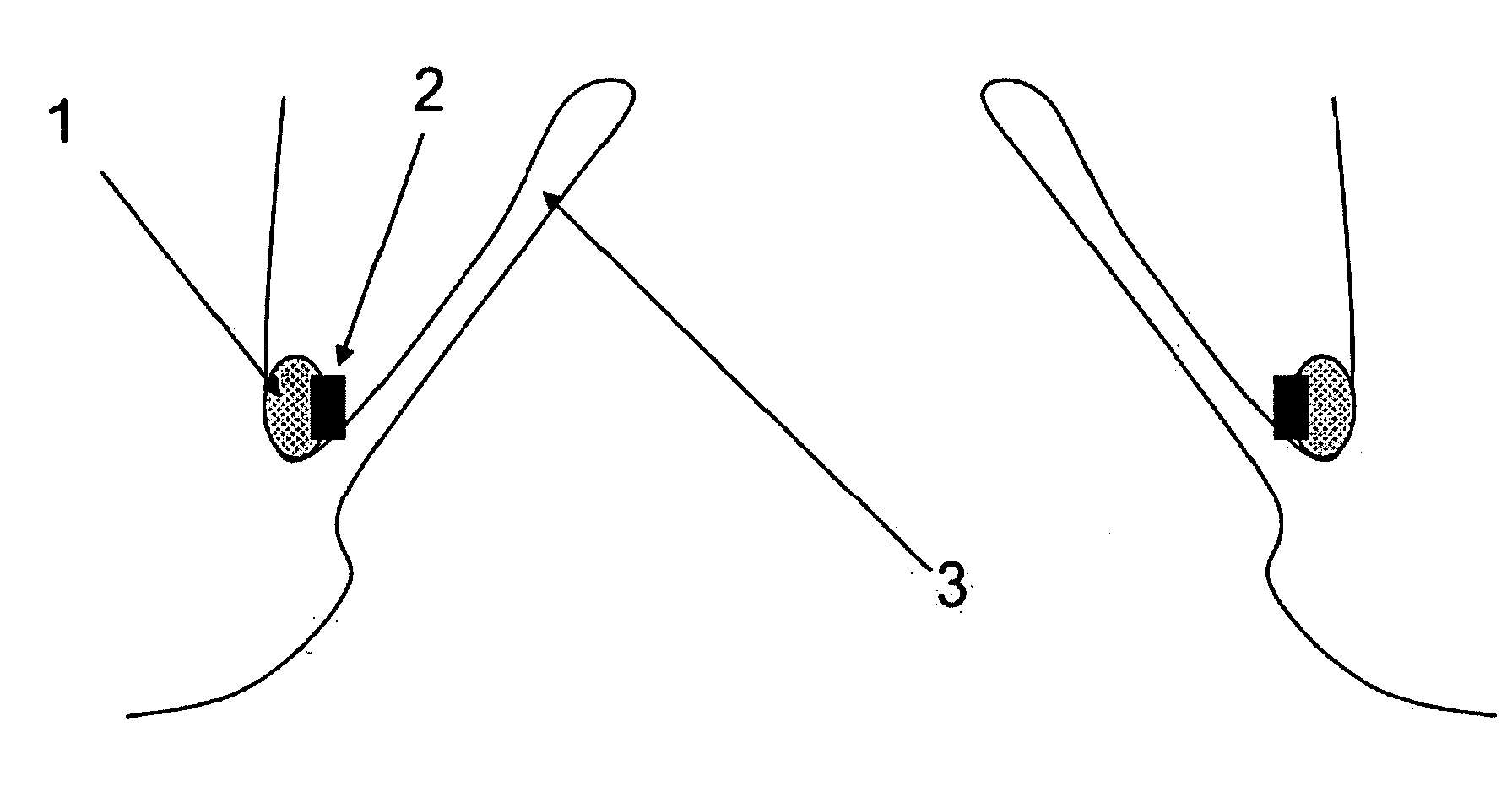
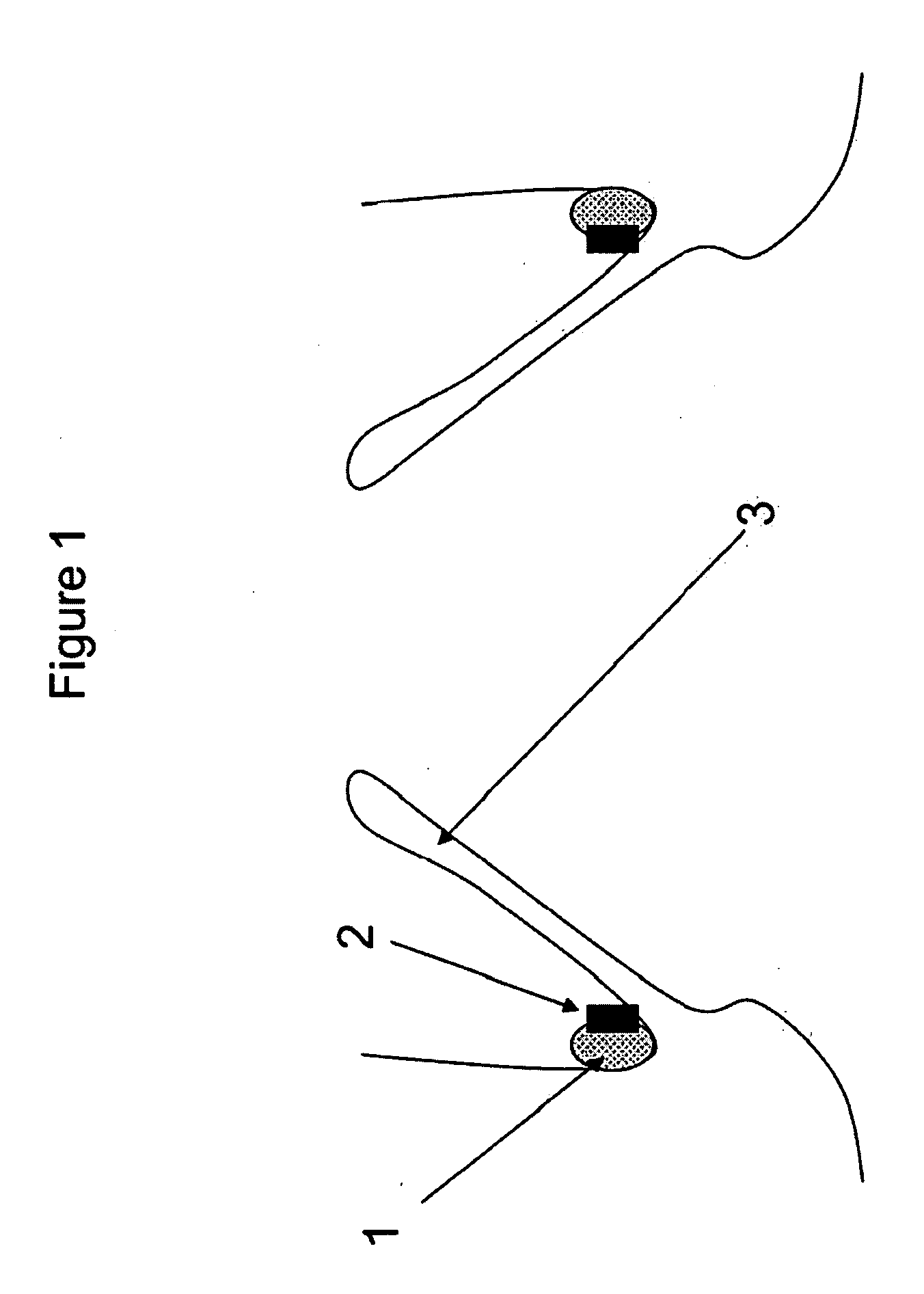
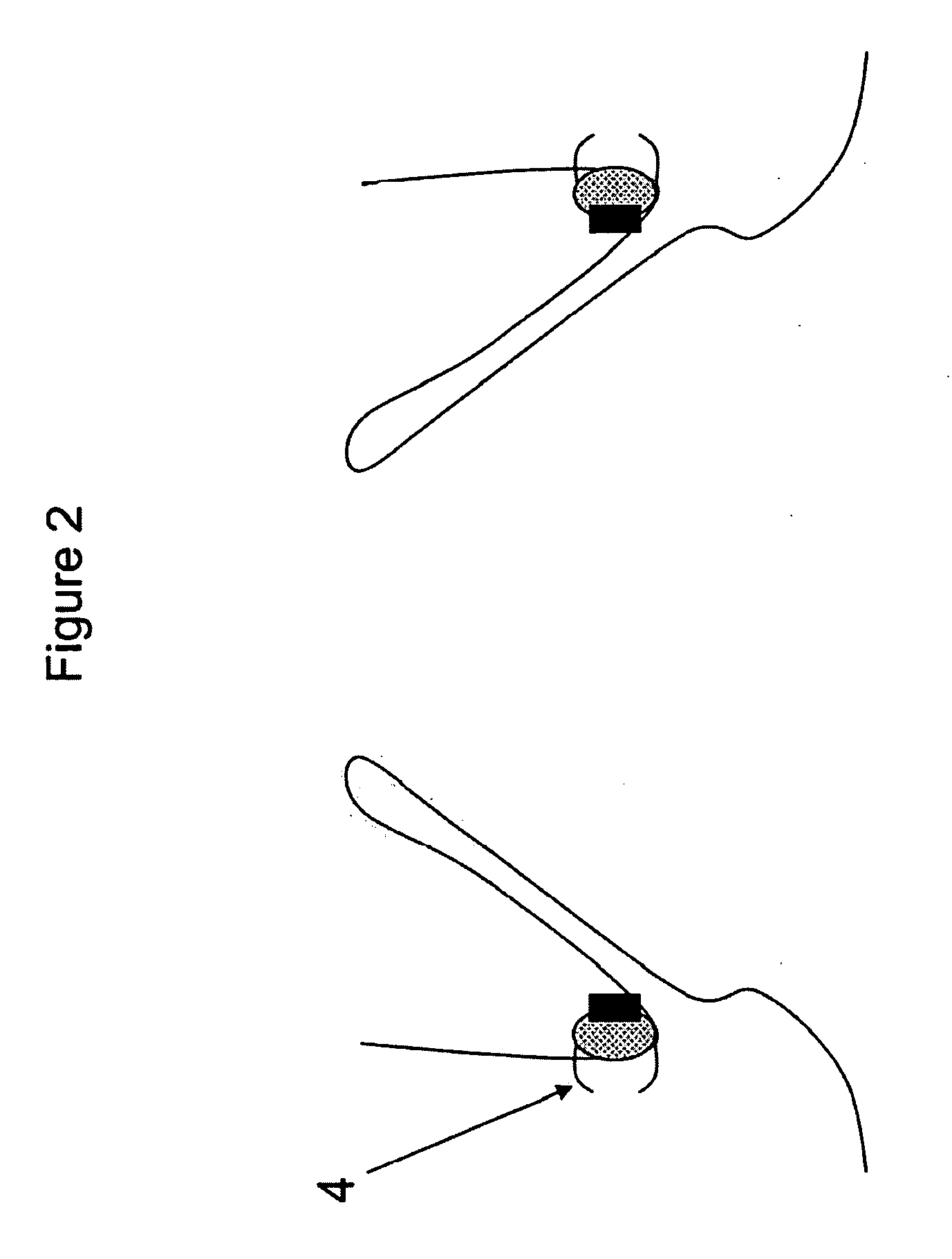
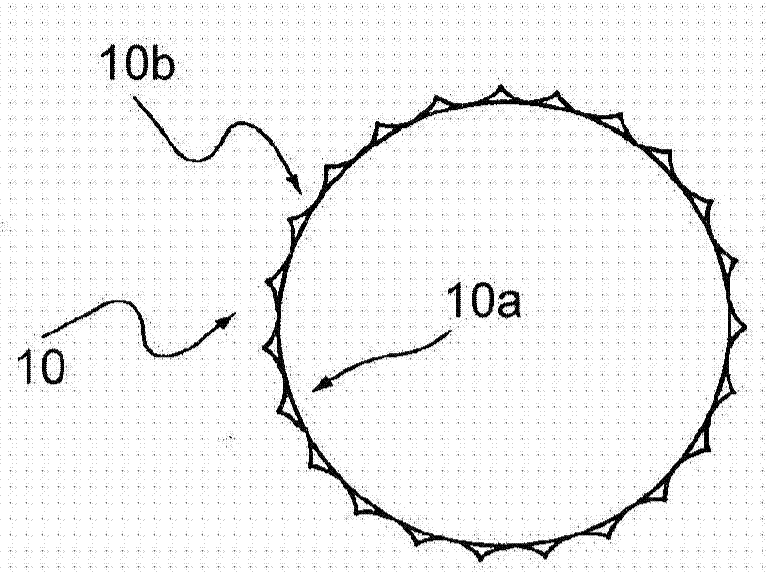
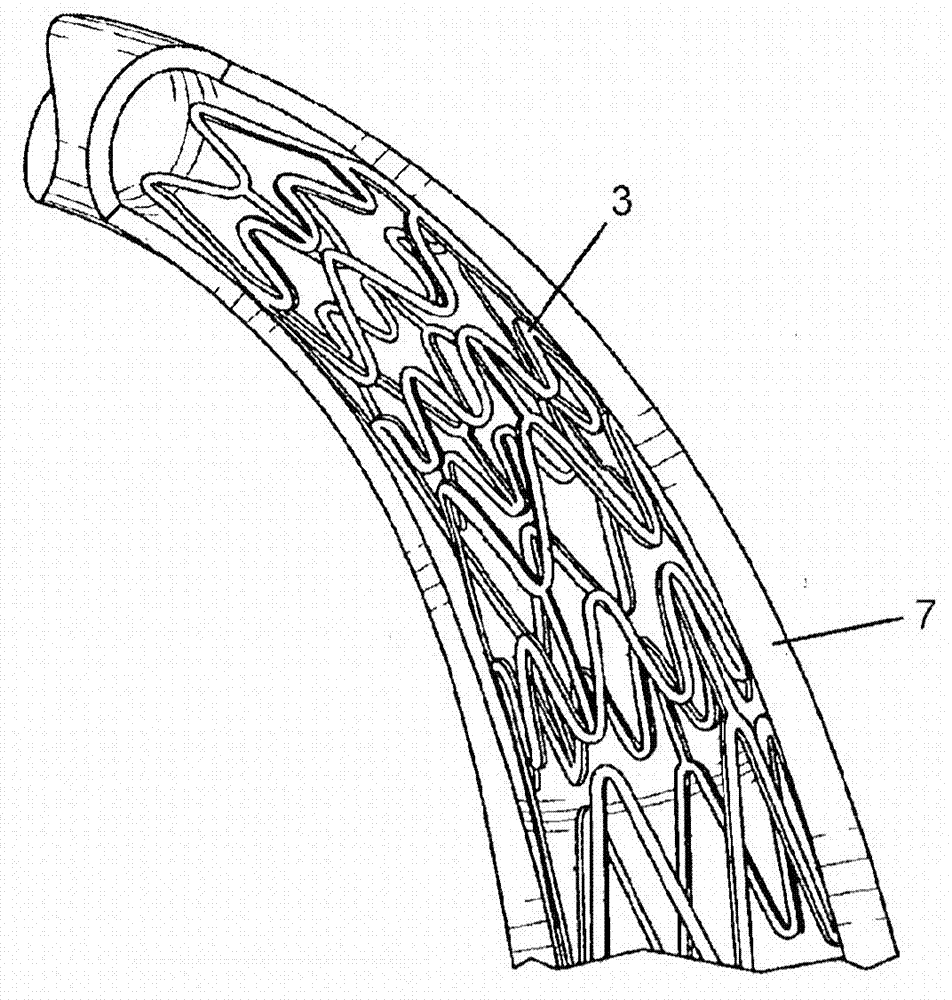
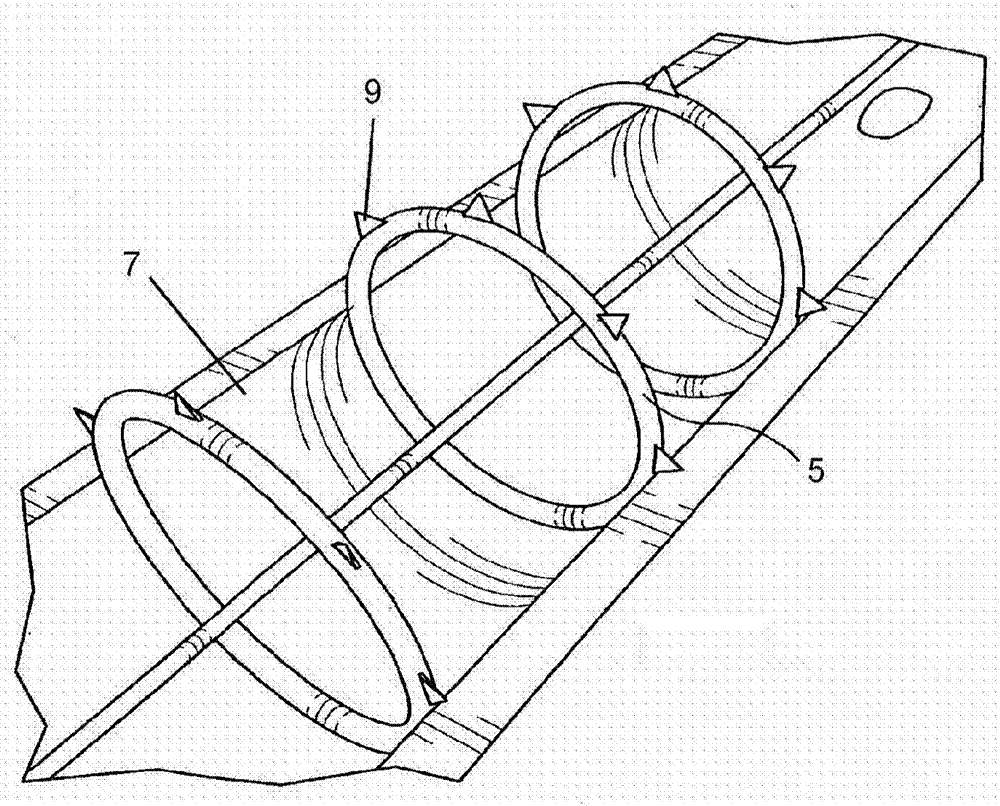
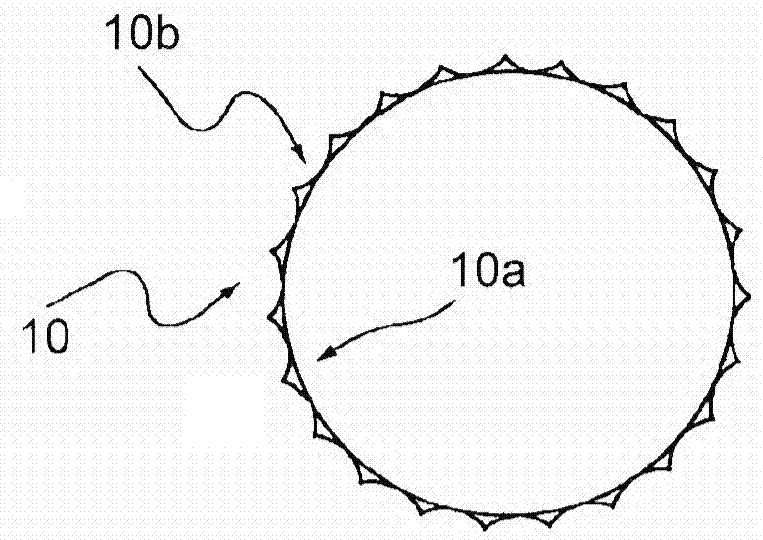
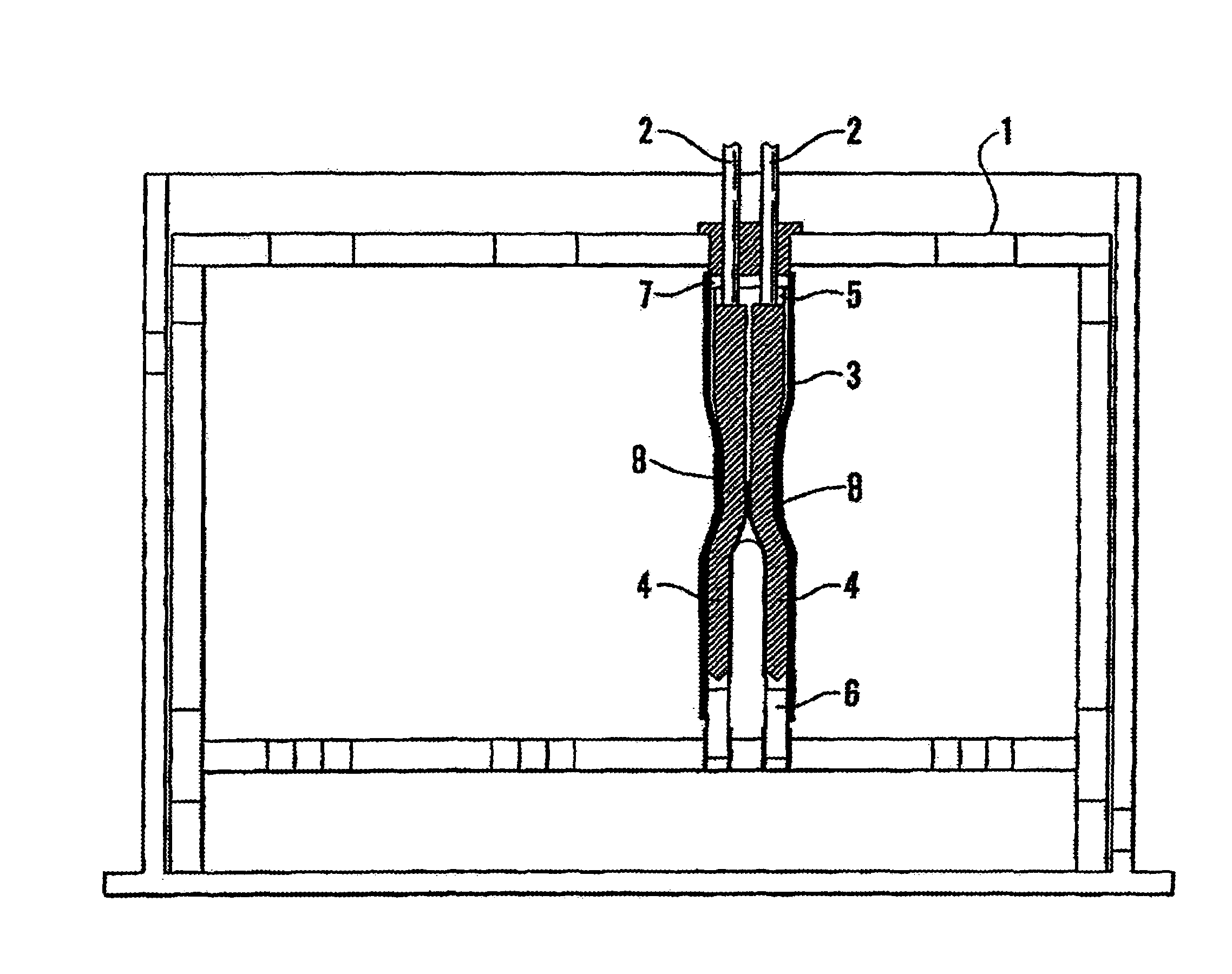
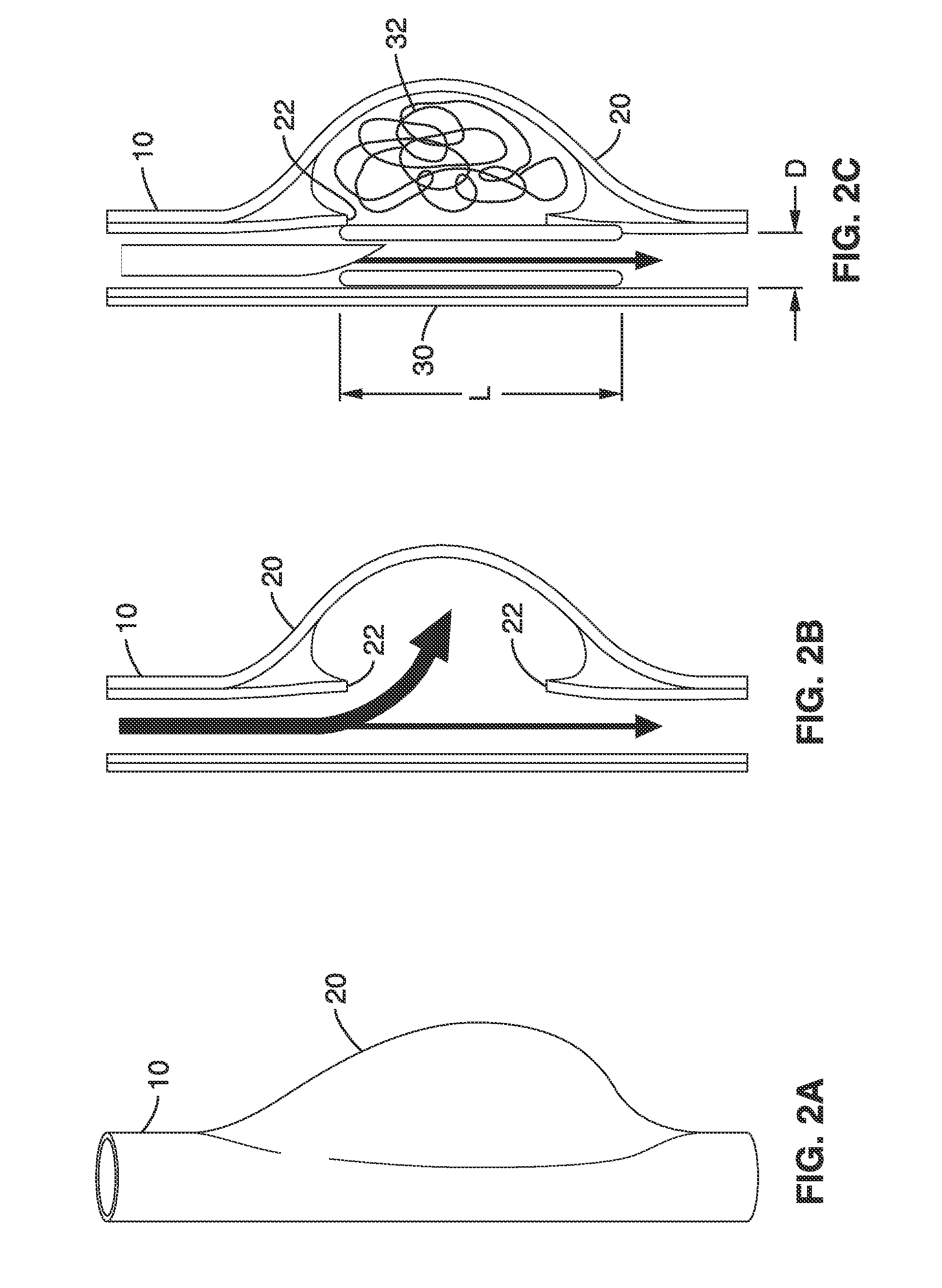
Method and apparatus for testing pulsatile endurance of a vascular implant
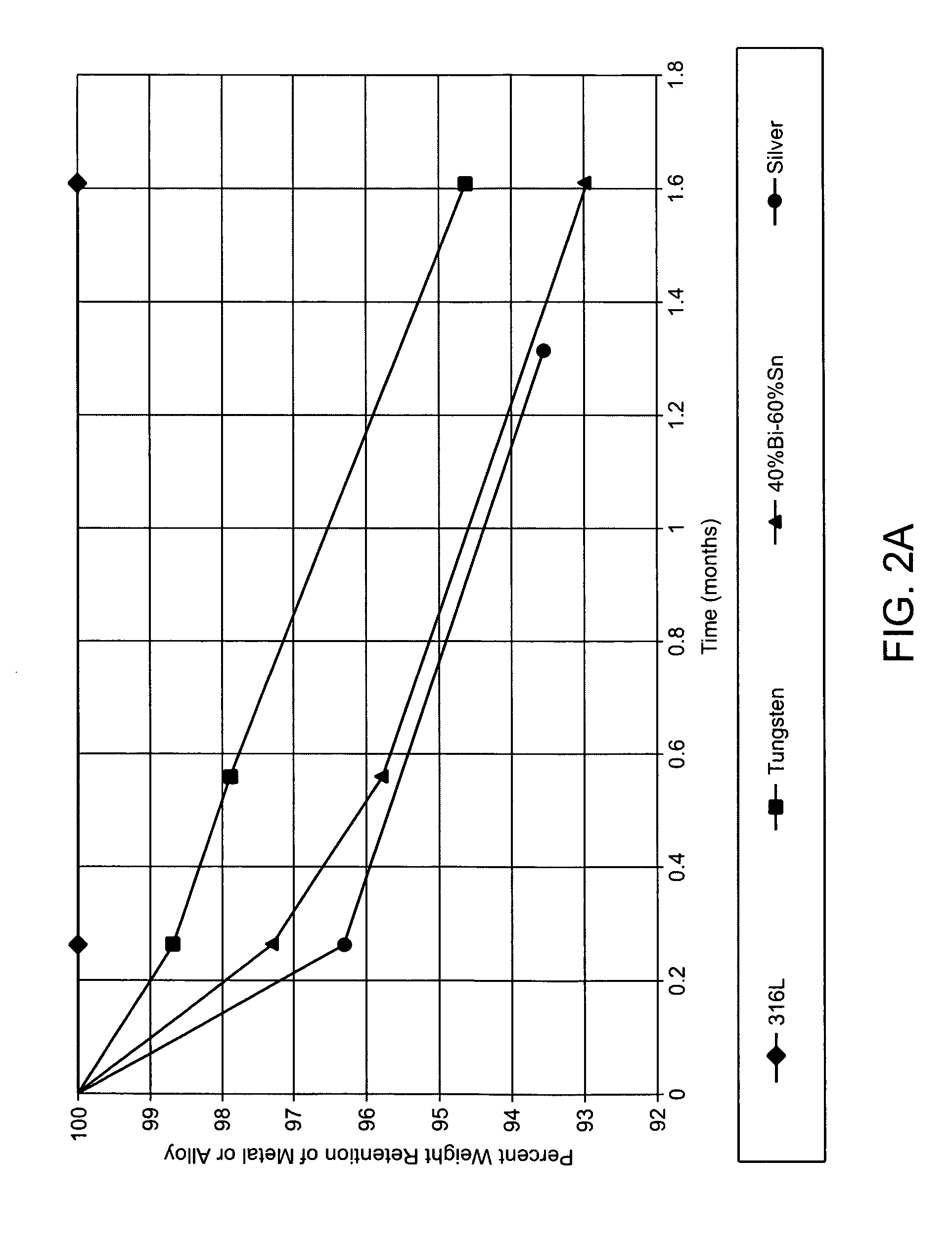
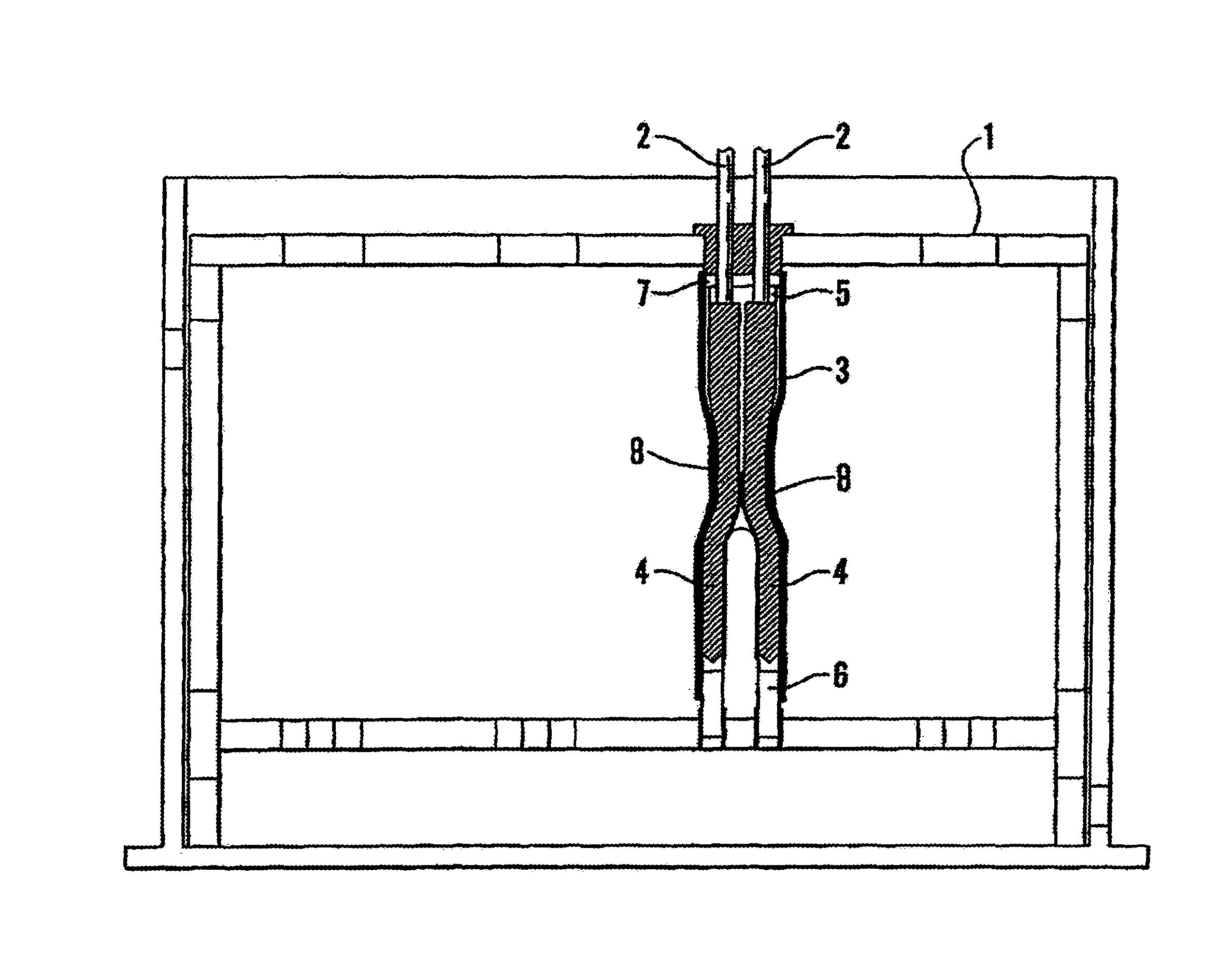
InactiveUS7254988B2Without risk of damageSmall attenuationWeather/light/corrosion resistanceHeart valvesVascular implantBlood vessel
A method for testing the pulsatile endurance of a vascular implant 3 comprises placing a resilient insert 4 into the implant and repeatedly expanding and contracting the insert, thereby expanding and contracting the implant. The insert preferably has a cavity therein and is repeatedly expanded and contracted by repeatedly increasing and decreasing the pressure in the cavity.
Owner:ANSON MEDICAL LTD
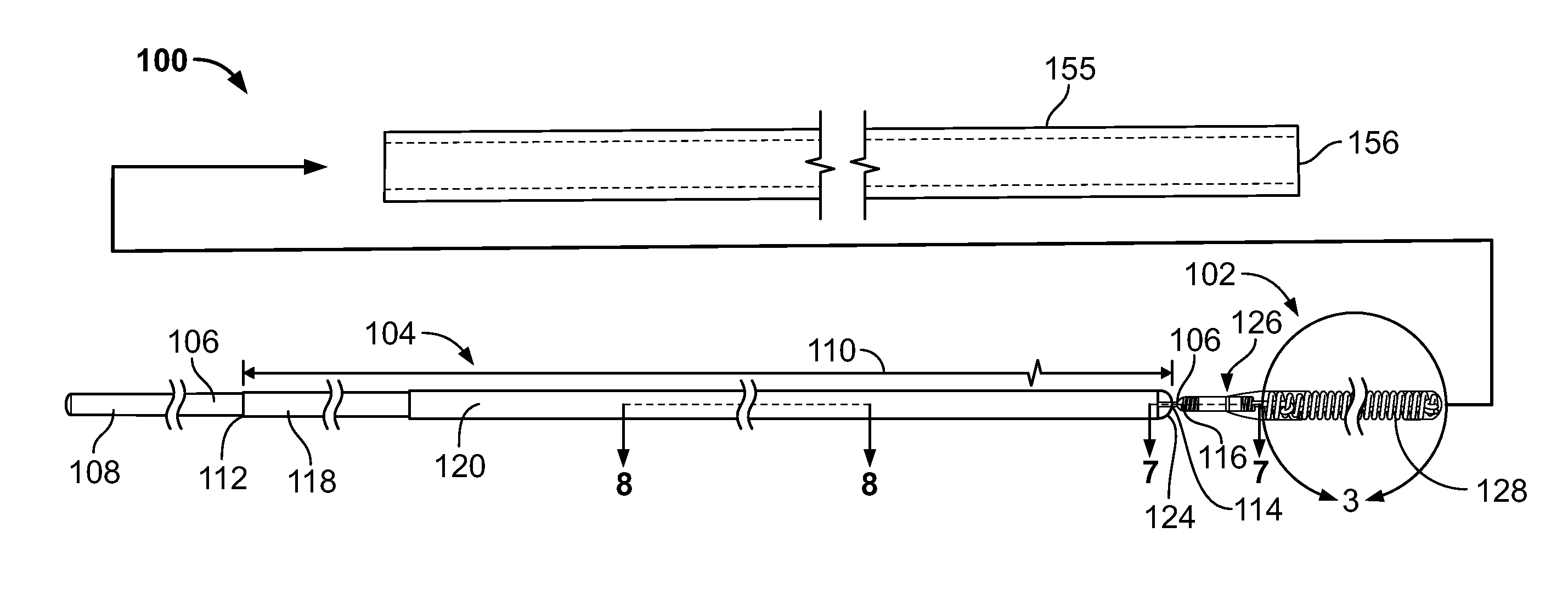
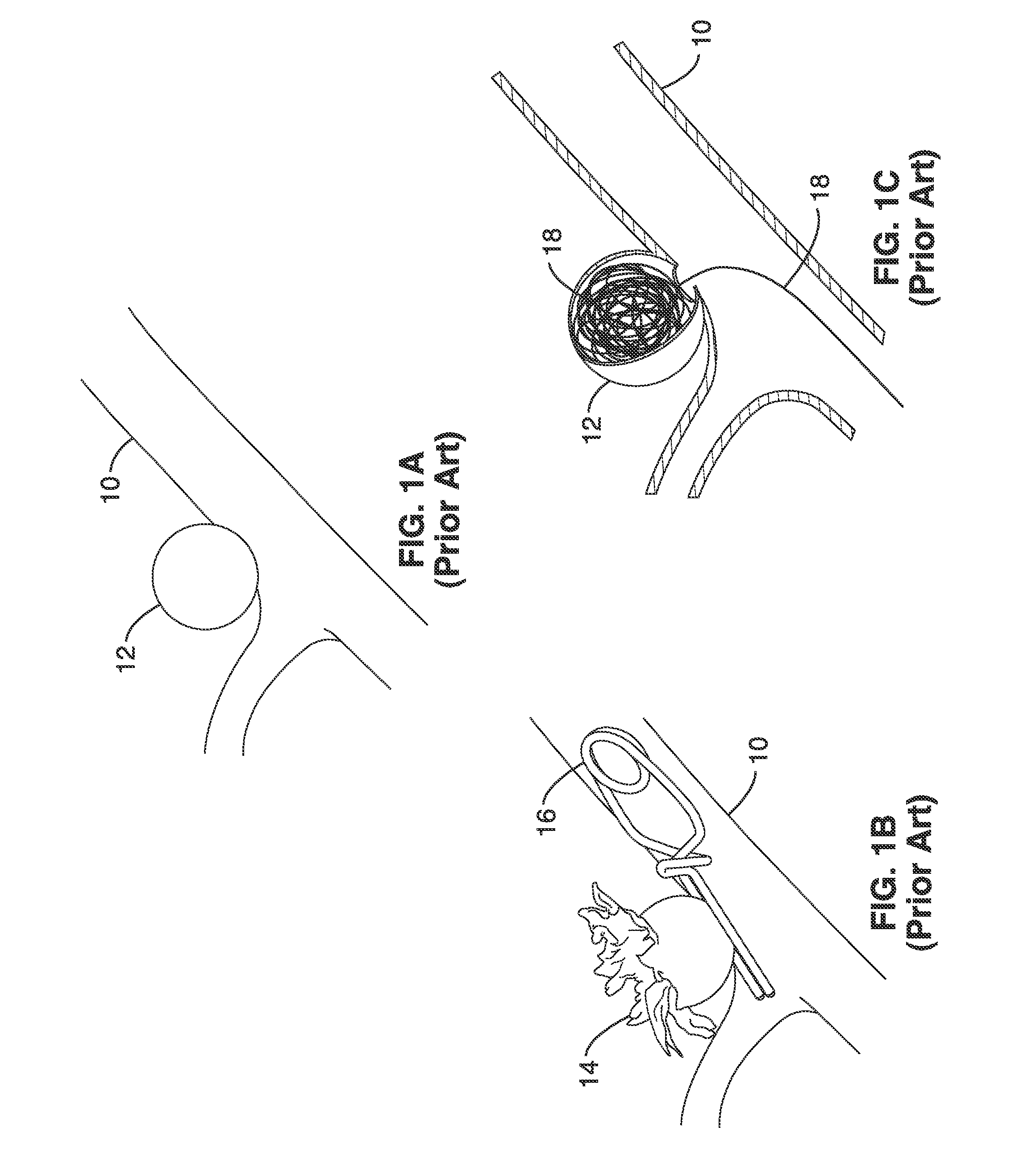
Vascular Implant Retrieval Method, Retrieval Assembly And Tool For Same
A method of retrieving a vascular implant from a patient includes winding a distal segment of a retrieval tool about a vascular implant, at least in part by rotating a proximal segment of the retrieval tool, coupling the retrieval tool with the vascular implant and removing the vascular implant and the retrieval tool from the patient. The retrieval tool may include a wire having proximal, middle and distal segments. The distal segment may include a guide segment and a coupling segment, a tip and at least two turns about a longitudinal axis defined by the middle segment. The wire may further have an increasing stiffness profile in a proximal direction from the tip. A vascular implant retrieval assembly includes a vascular implant, such as a vascular filter, a retrieval tool have a distal segment wound about the vascular implant and a sheath surrounding a middle segment of the retrieval tool.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Vessel implant for the treatment of an aneurysm
The invention relates to a vessel implant for the treatment of an aneurysm, i.e. a dilatation of the cross-sectional area of a blood vessel, comprising an elongate body which has an inlet opening, an outlet opening and a passage connecting the inlet opening to the outlet opening for blood flowing through the blood vessel, with the passage being bounded in the peripheral direction by a blood-impermeable wall, and with the inlet opening having a larger cross-sectional area than the outlet opening.
Owner:STENGEL MAX
Varying diameter vascular implant and balloon
Owner:NEOVASC MEDICAL LTD
Thin film vascular stent and biocompatible surface treatment
A vascular implant, comprising a sheet comprising thin film nickel titanium (NiTi), wherein the sheet has at least one super-hydrophilic surface having a water contact angle of less than approximately 5 degrees. The sheet is configured to have a compacted form having a first internal diameter and a deployed form having a second internal diameter larger than the first internal diameter. The sheet may be delivered into a blood vessel in the compacted form and expanded to its deployed form at a treatment location within the blood vessel, wherein the stent is configured to expand onto an internal surface of the blood vessel and exert a radial force on said internal surface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Device for placing a vascular implant
Provided is an implant placement device that includes an envelope that contains an implant with a first auto-expandable element expandable in a radial direction, a nose at a distal end of the envelope, a sheath that confines a portion of the implant therein and restricts expansion of a second auto-expandable element of the implant, and a plunger. The sheath moves within the envelope in a longitudinal direction perpendicular to the radial direction and the plunger moves in the longitudinal direction within the sheath with the implant positioned between an end of the plunger and the nose, to discharge the implant from the device at a desired position. The sheath slides in the longitudinal direction towards the nose to bring the first auto-expandable element in contact with an interior of the plurality of slots, thereby opening the nose.
Owner:MIALHE CLAUDE
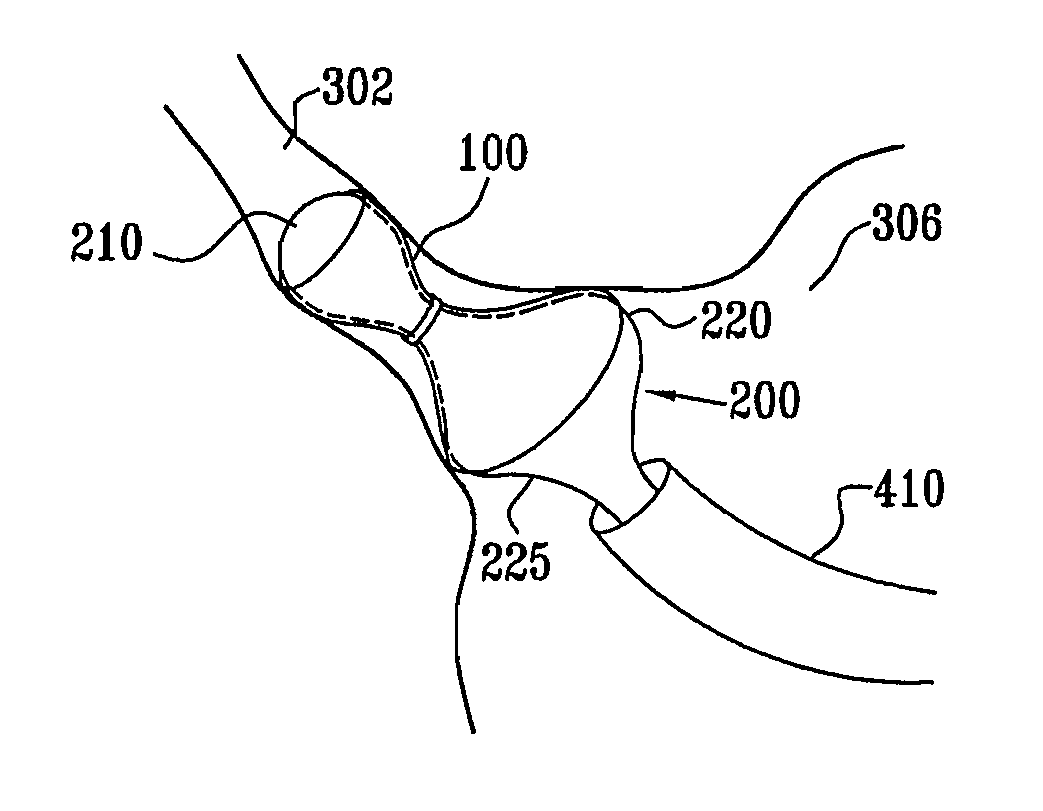
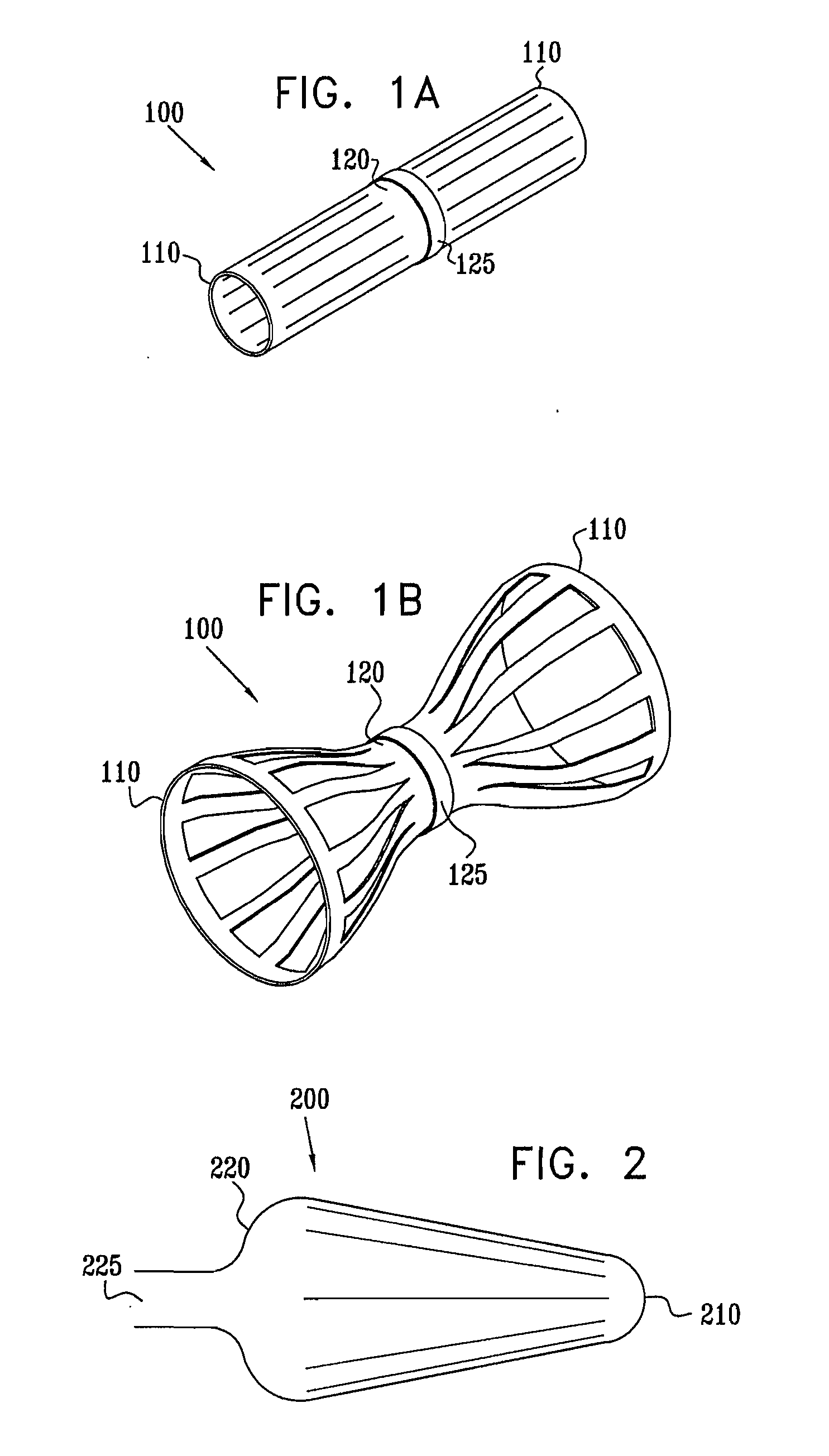
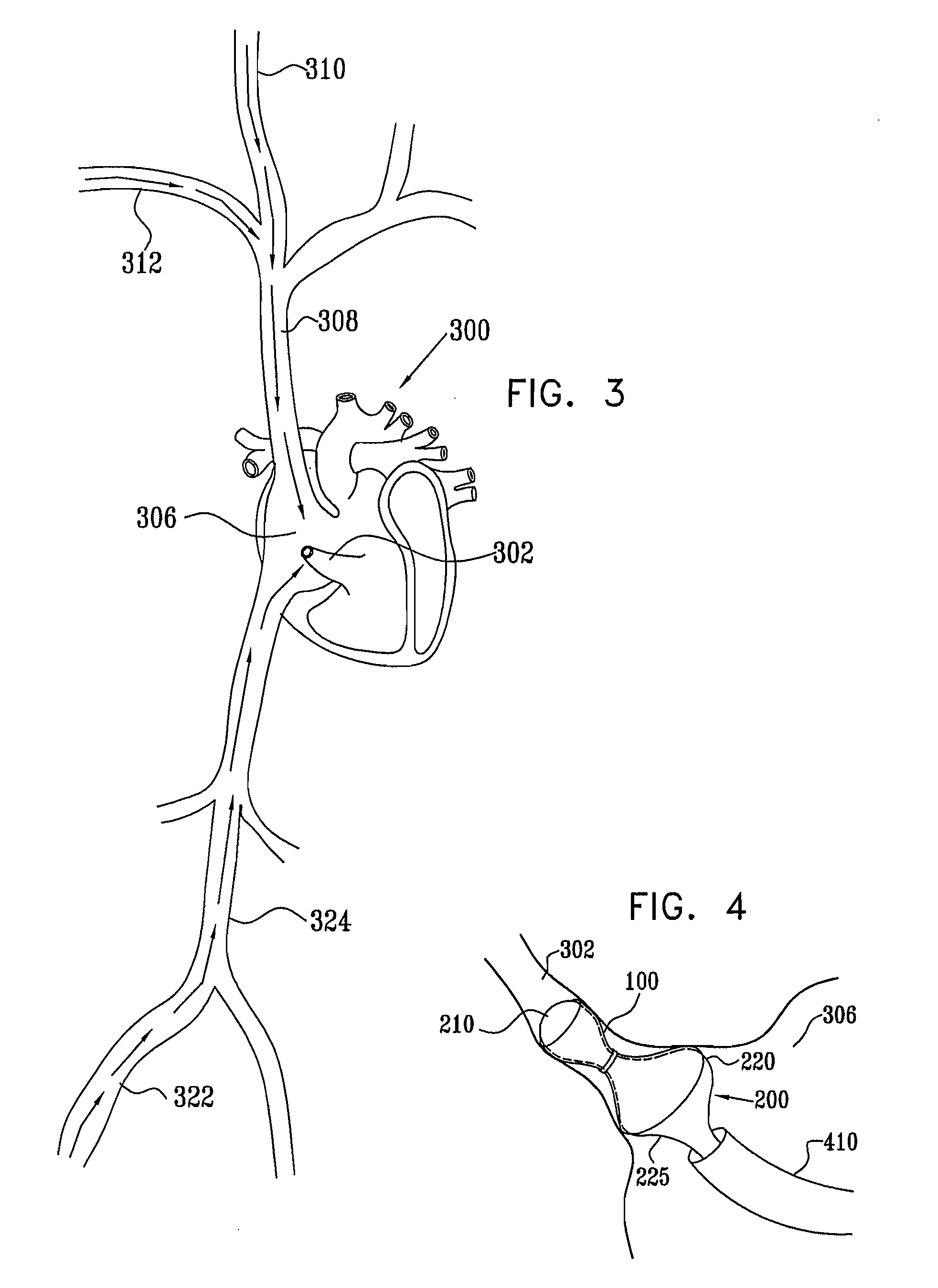
Varying-diameter vascular implant and balloon
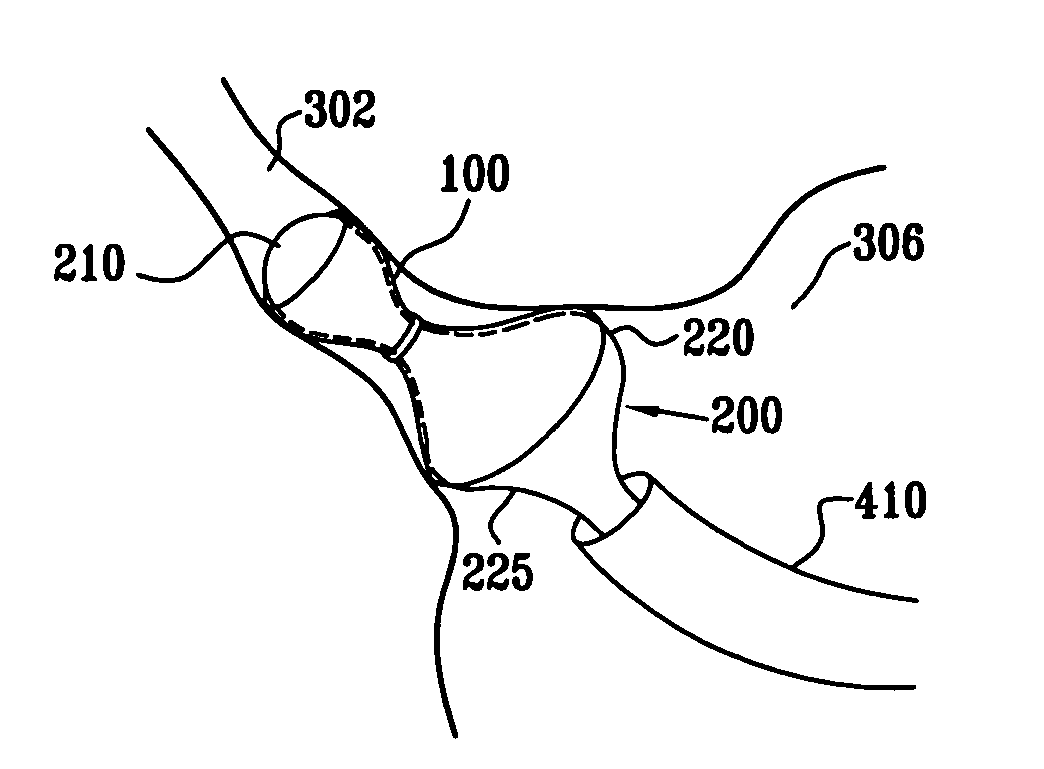
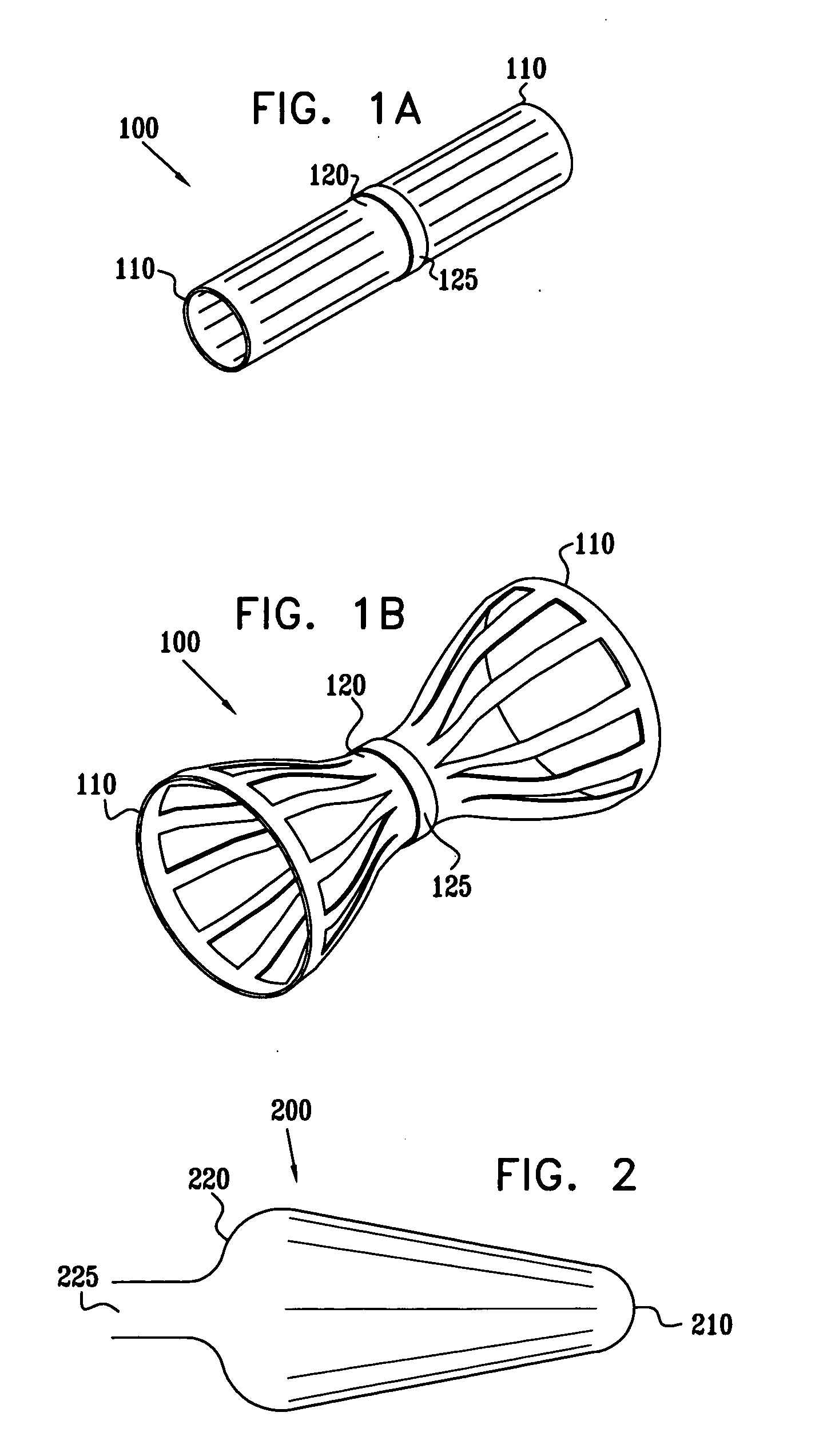
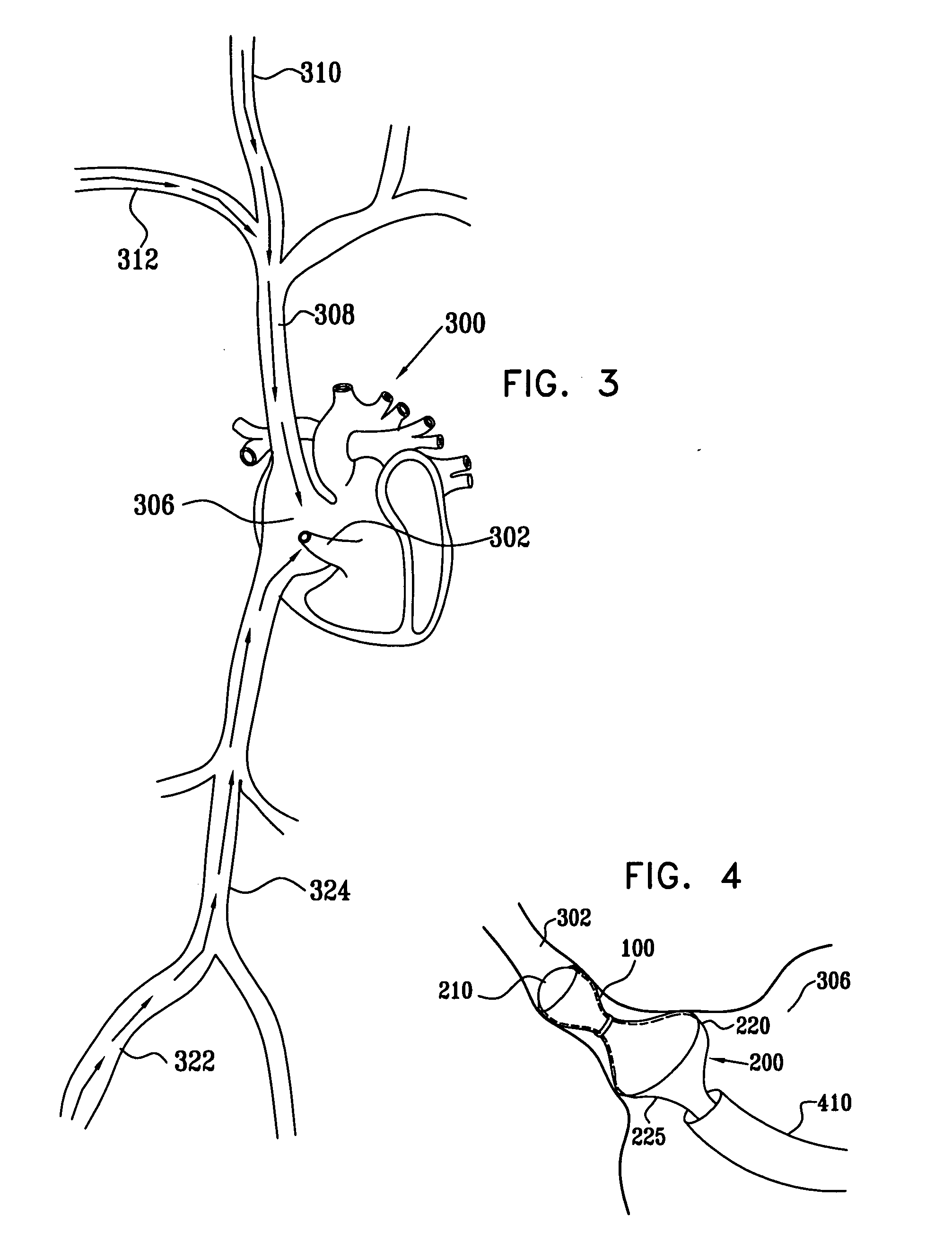
A method for deploying an expandable implant (100) in a body passage (302) of varying diameter includes selecting a balloon (200) having a radial dimension that varies, when the balloon is inflated, in accordance with the varying diameter of the body passage. The balloon is inserted, in a deflated state, into the body passage, with the expandable implant fitted radially around the balloon. The balloon is inflated so as to cause the implant to open, responsively to the varying radial dimension of the balloon, into an expanded shape that approximately matches the varying diameter of the body passage, thus anchoring the implant in the body passage.
Owner:NEOVASC MEDICAL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com