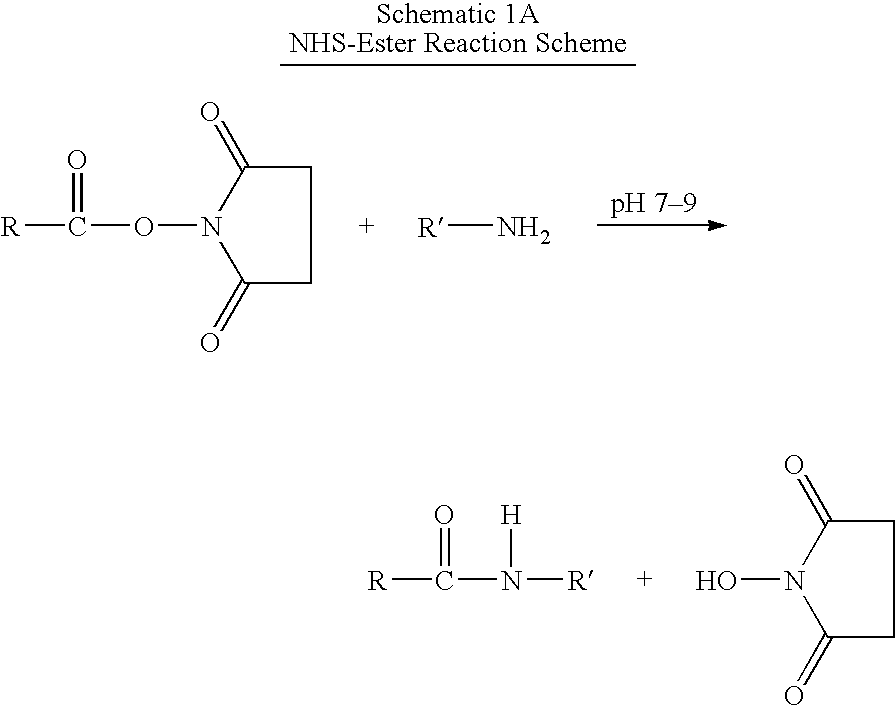
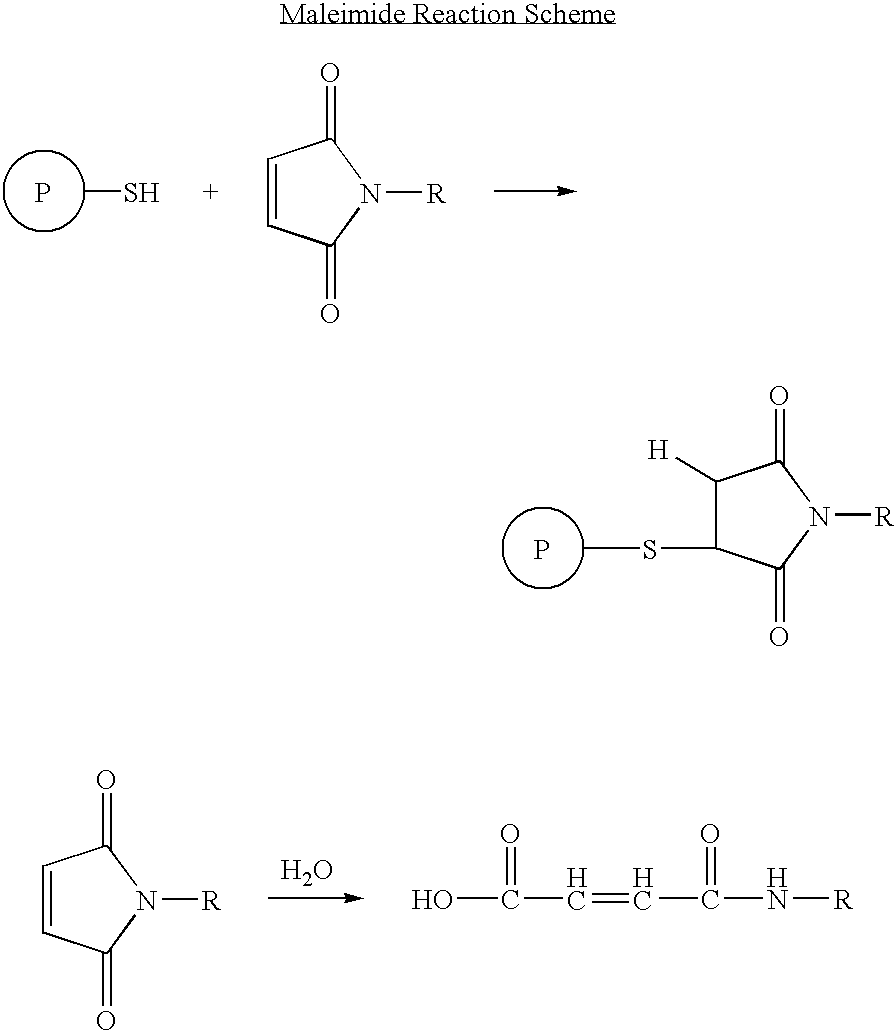
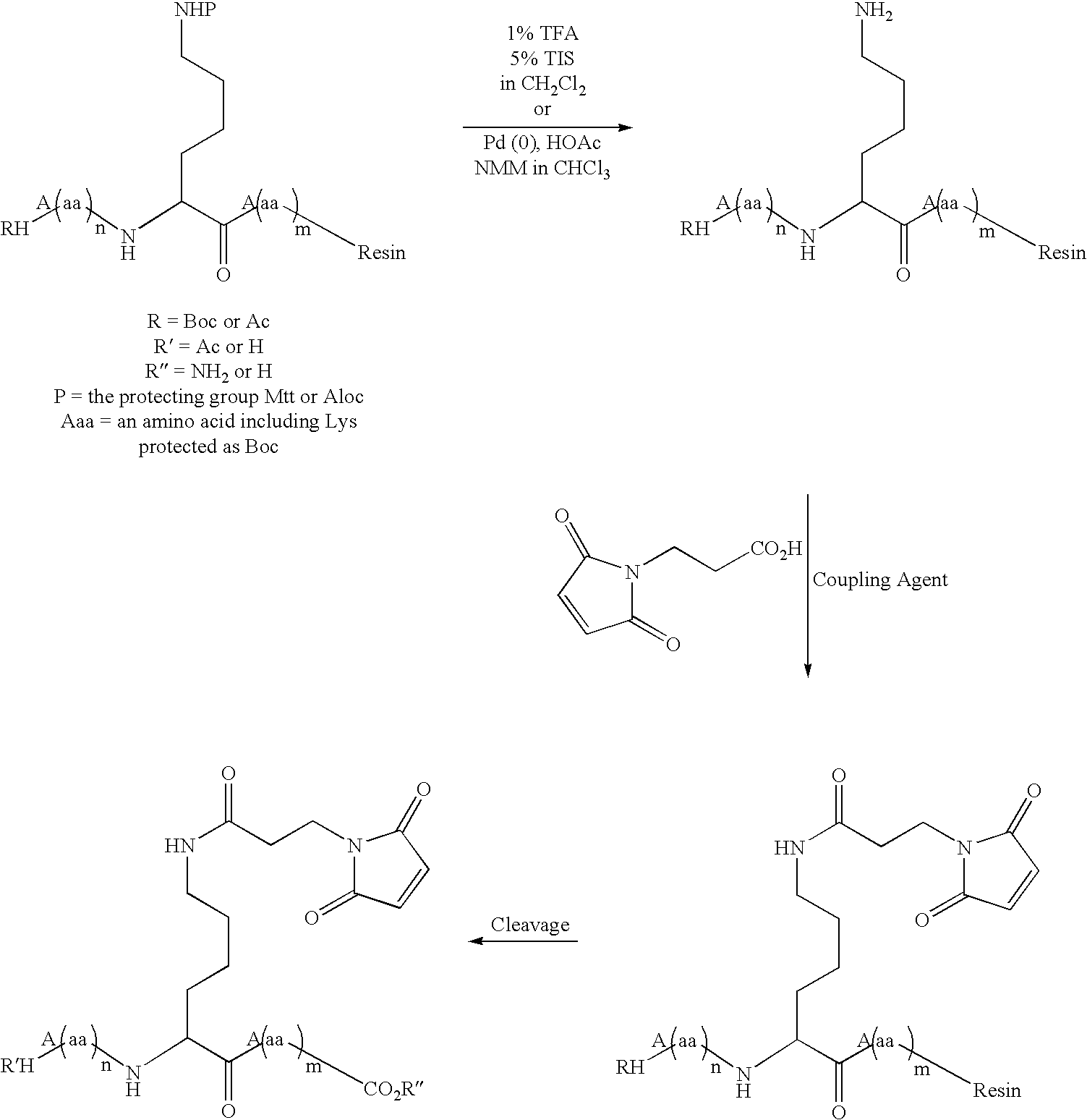
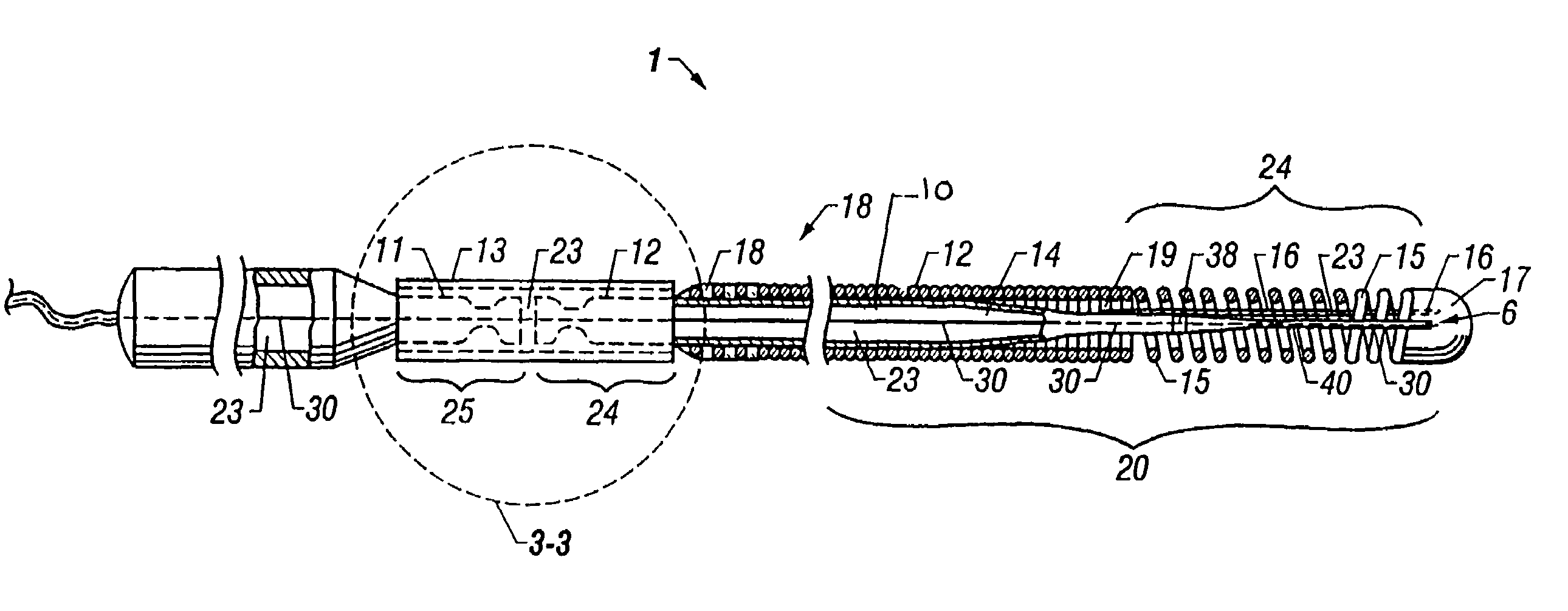
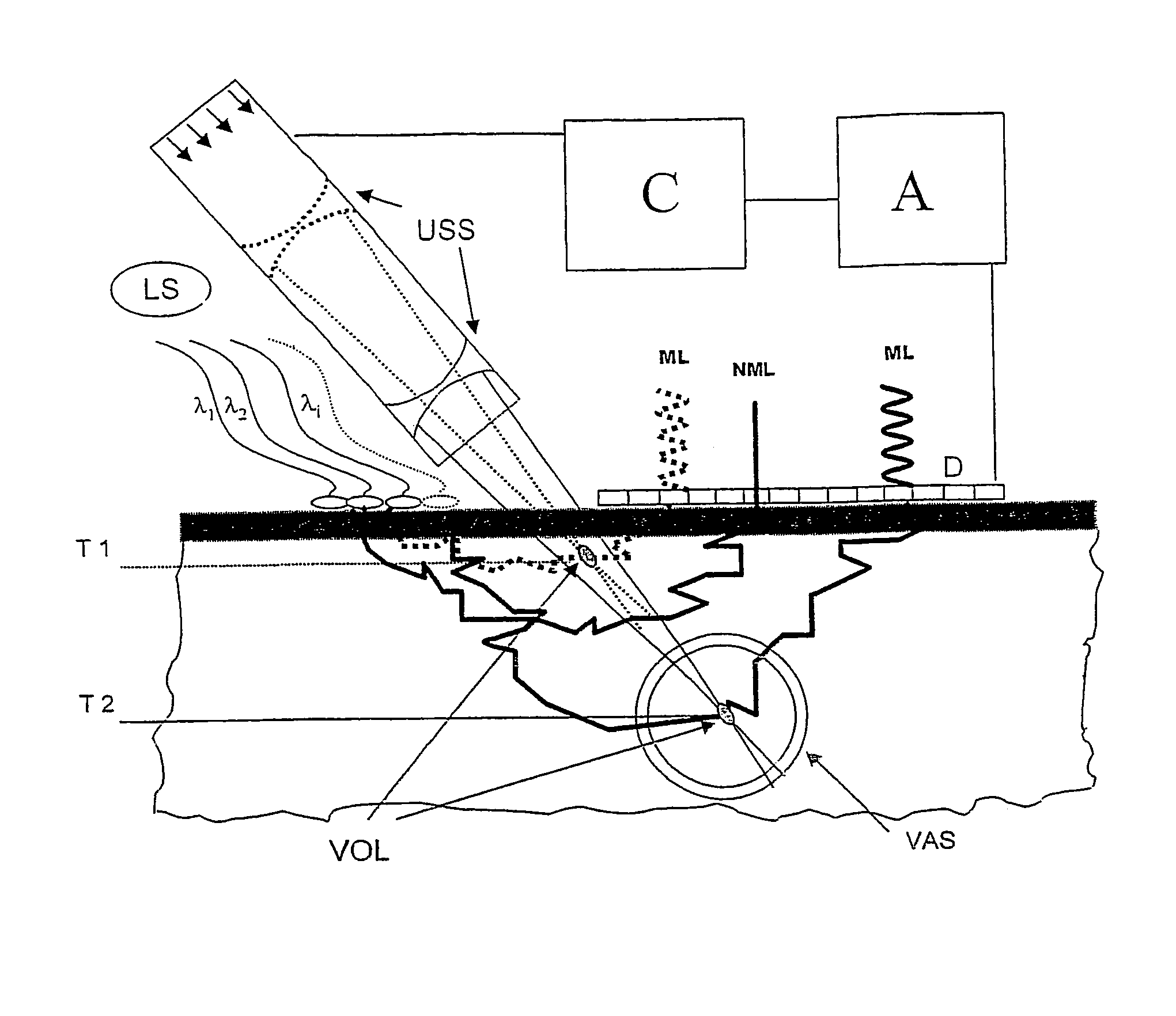
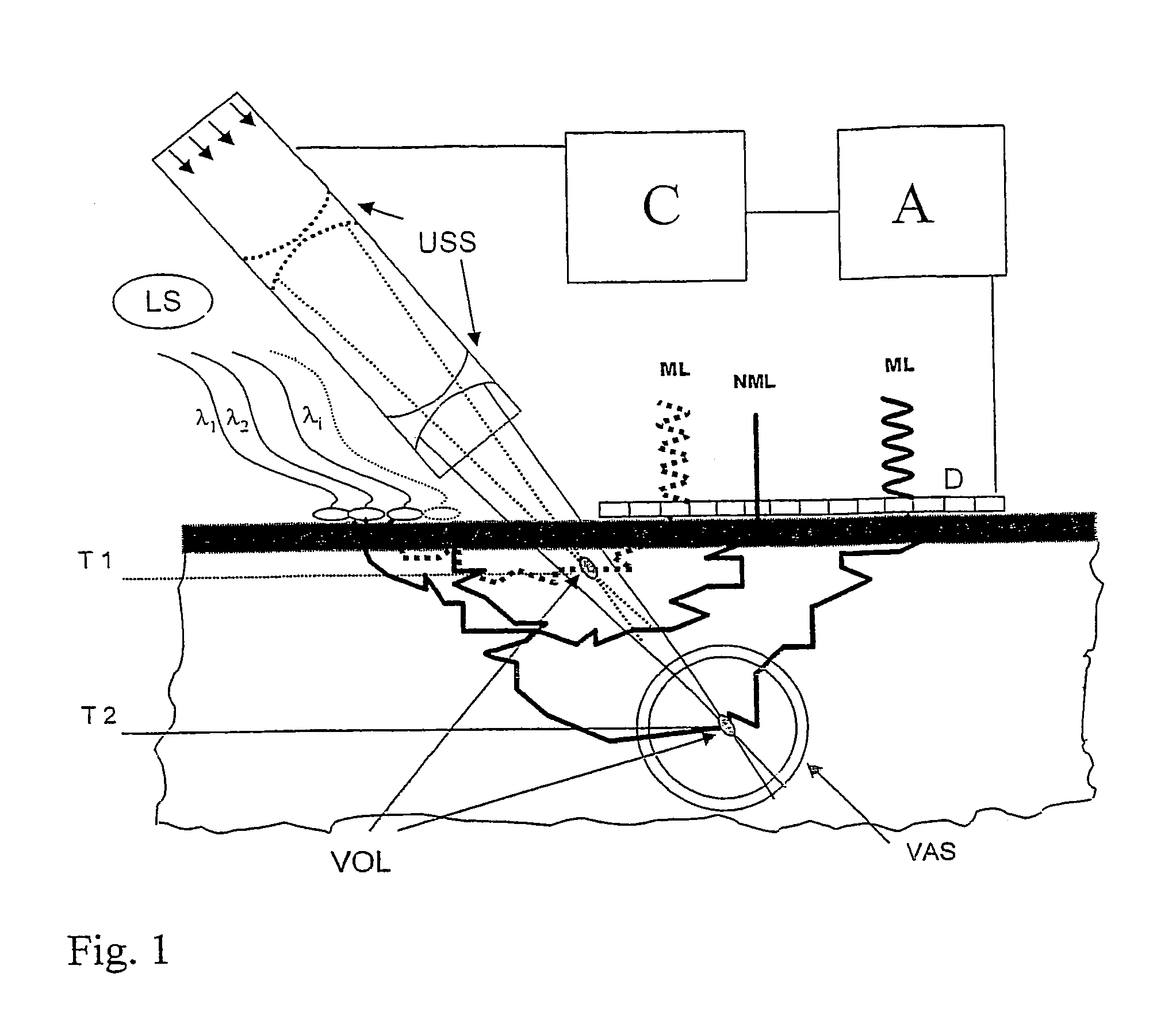
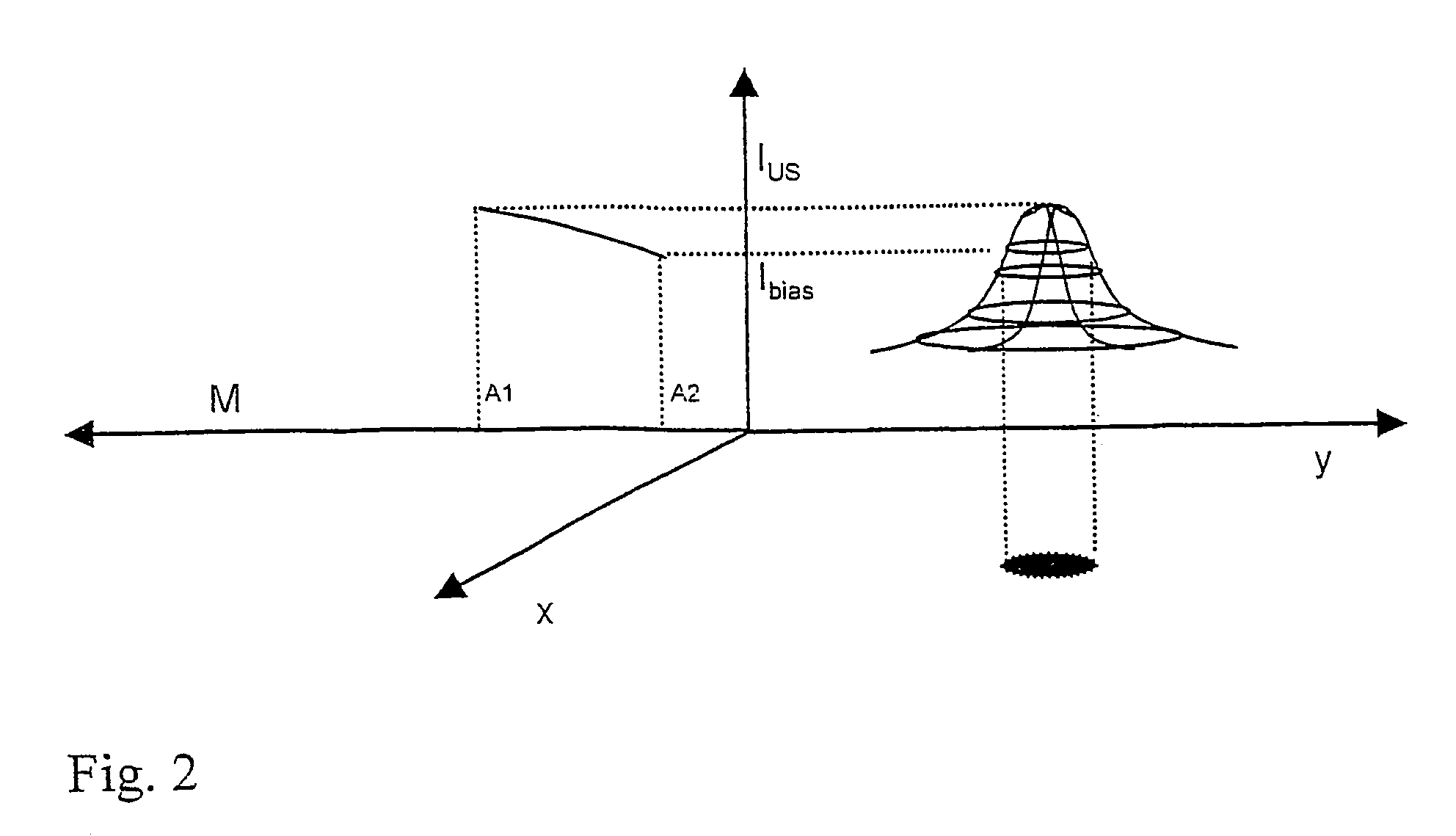
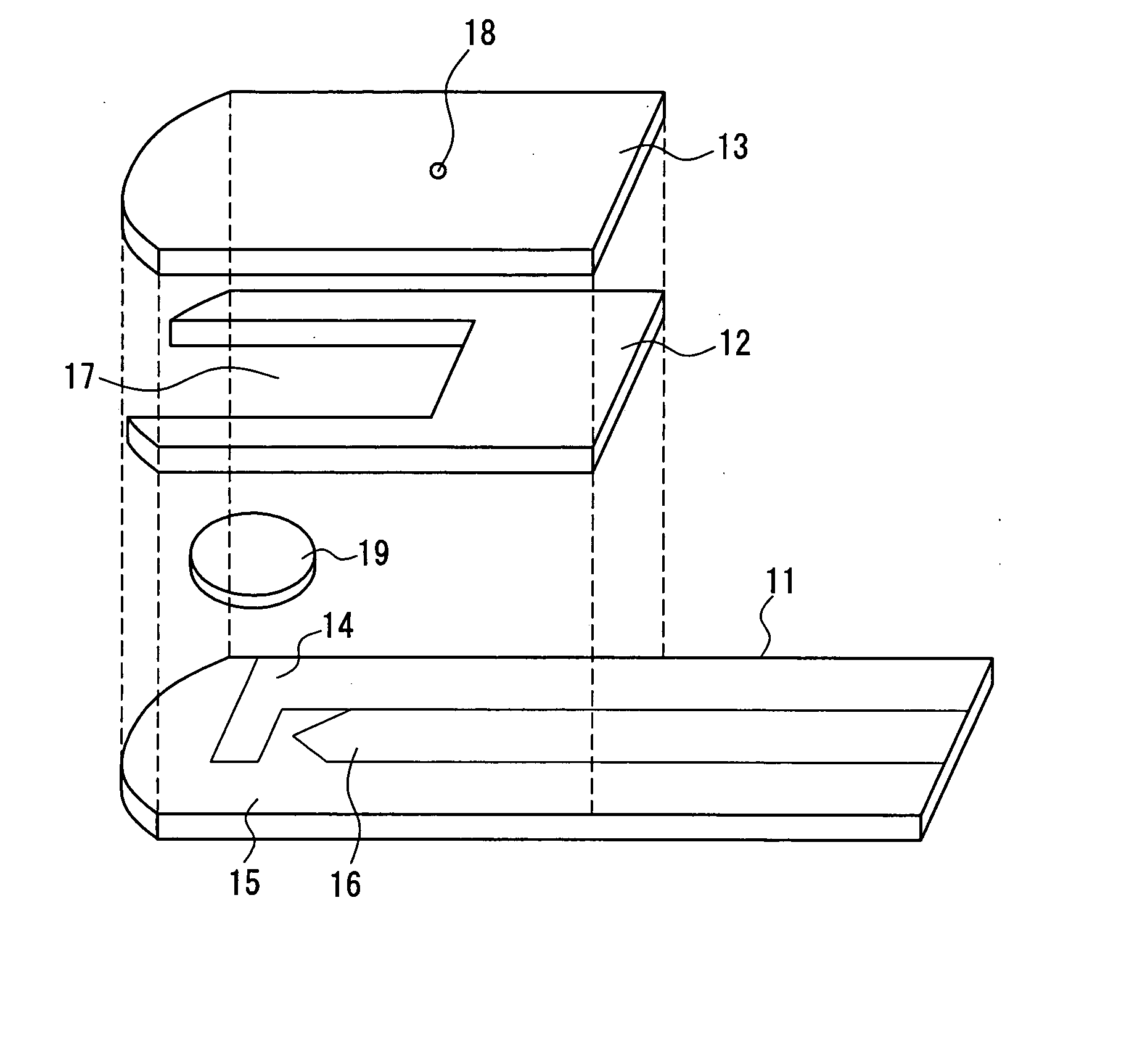
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
962 results about "Blood component" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human blood consists of about 22 percent solids and 78 percent water. The components of human blood are: Plasma, in which the blood cells are suspended, including: Red blood cells (erythrocytes) - carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
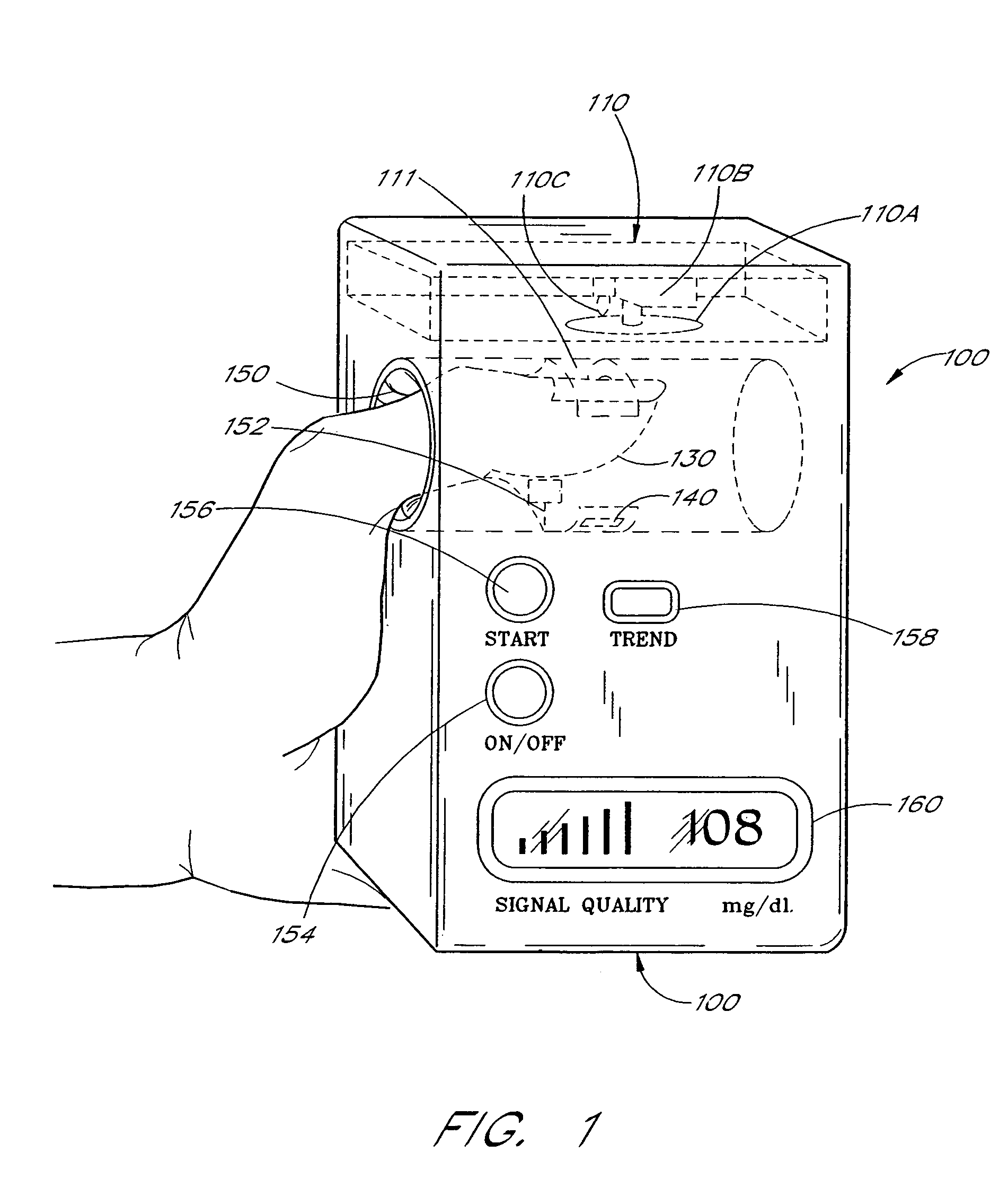
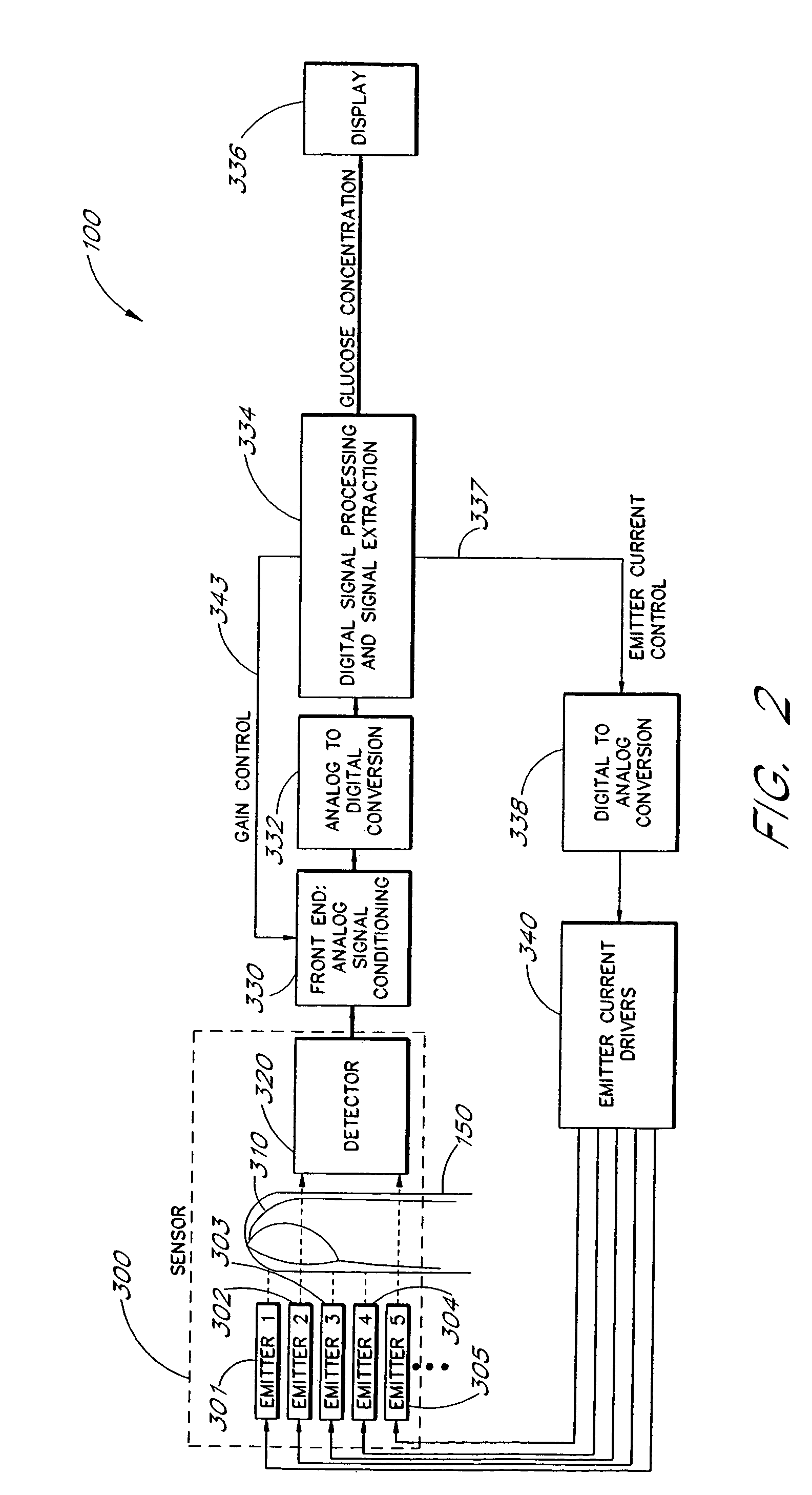
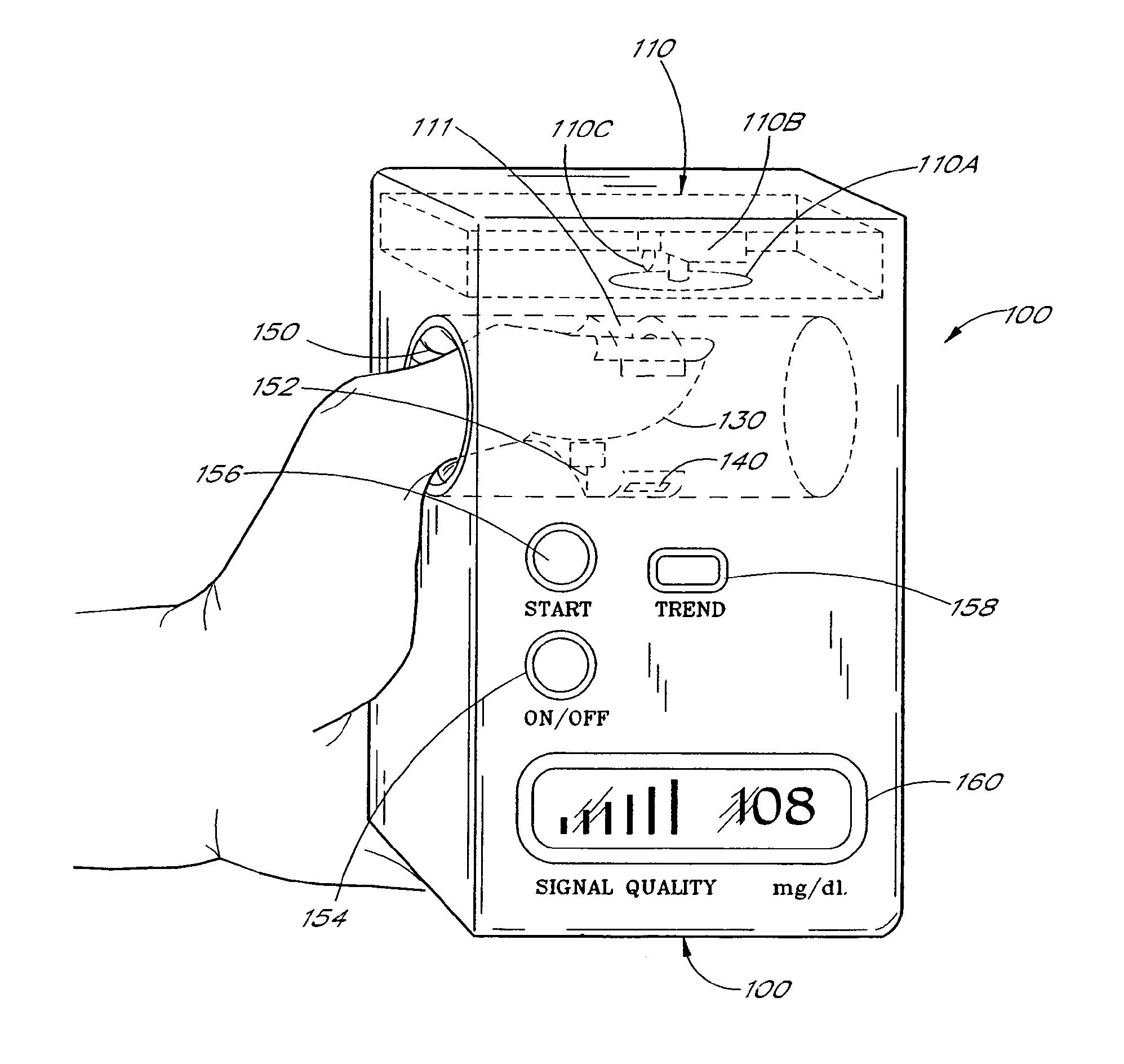
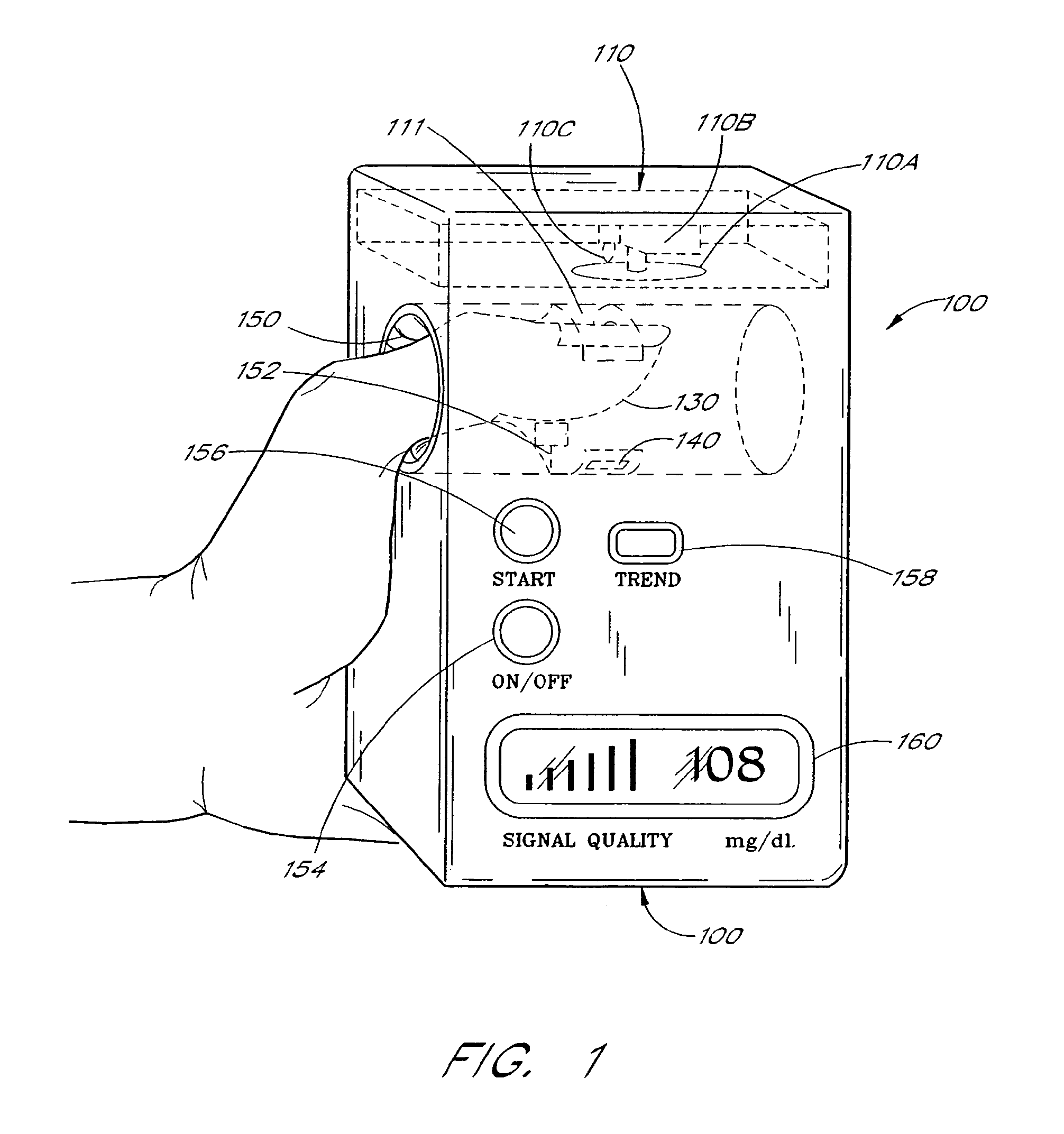
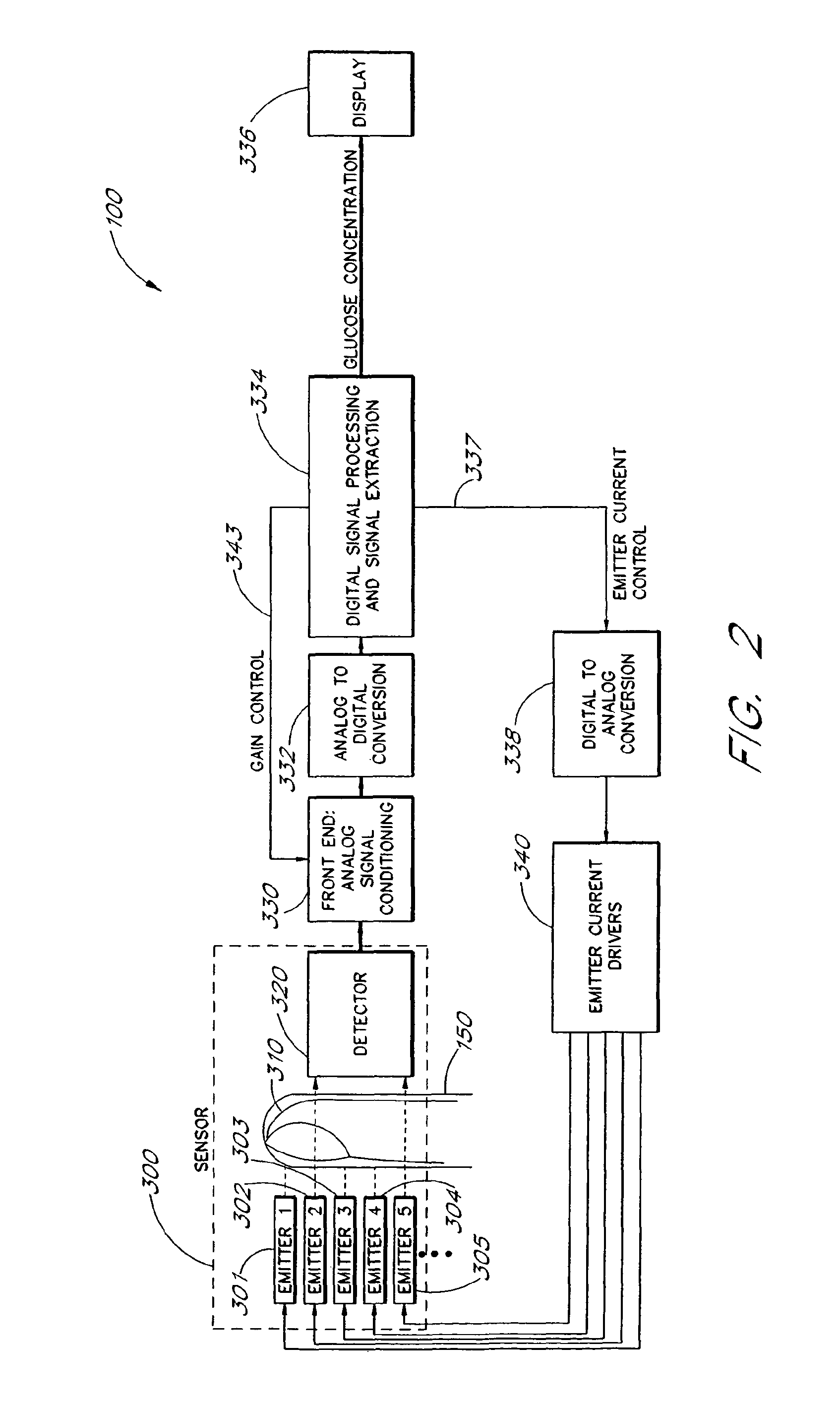
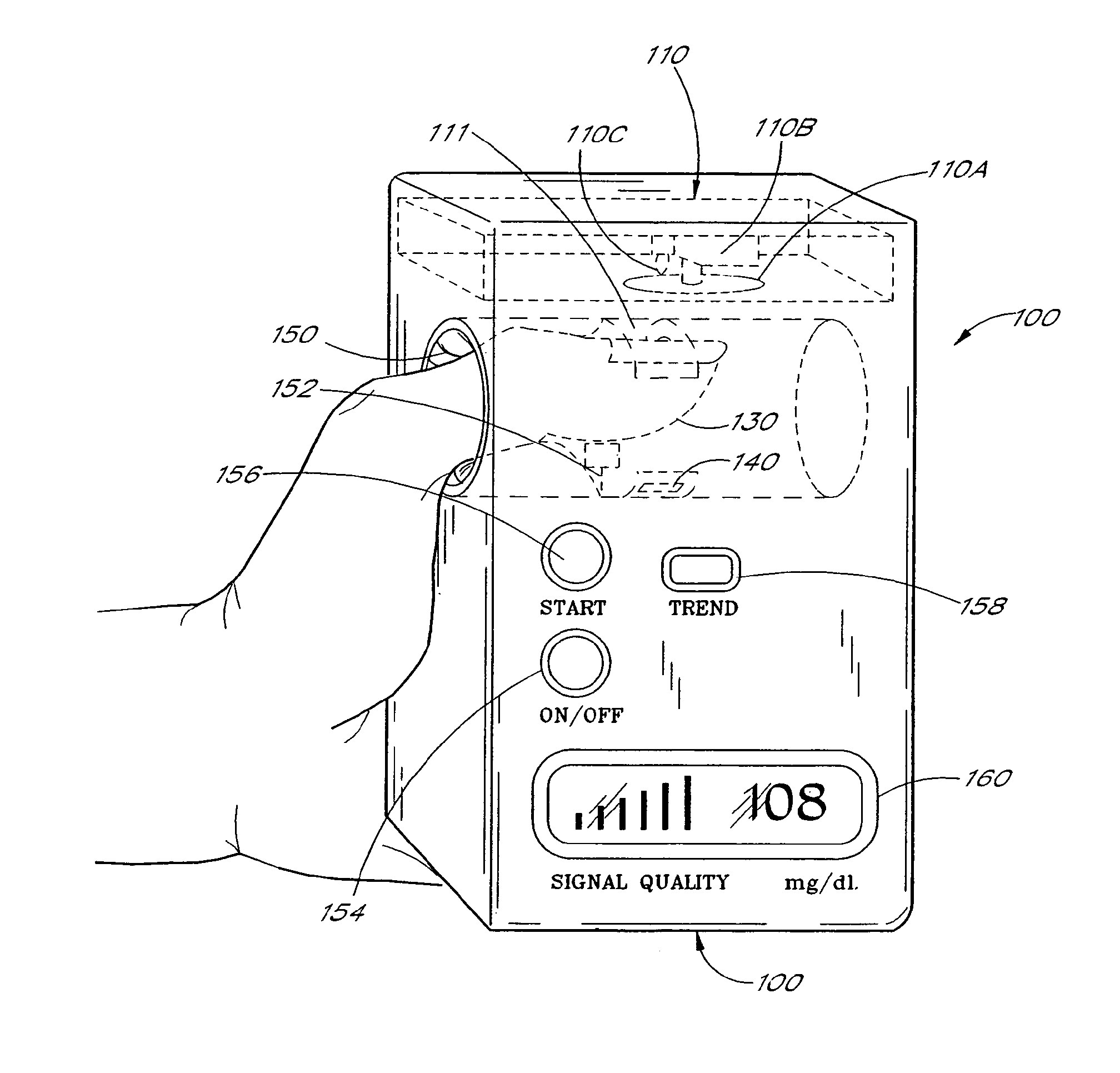
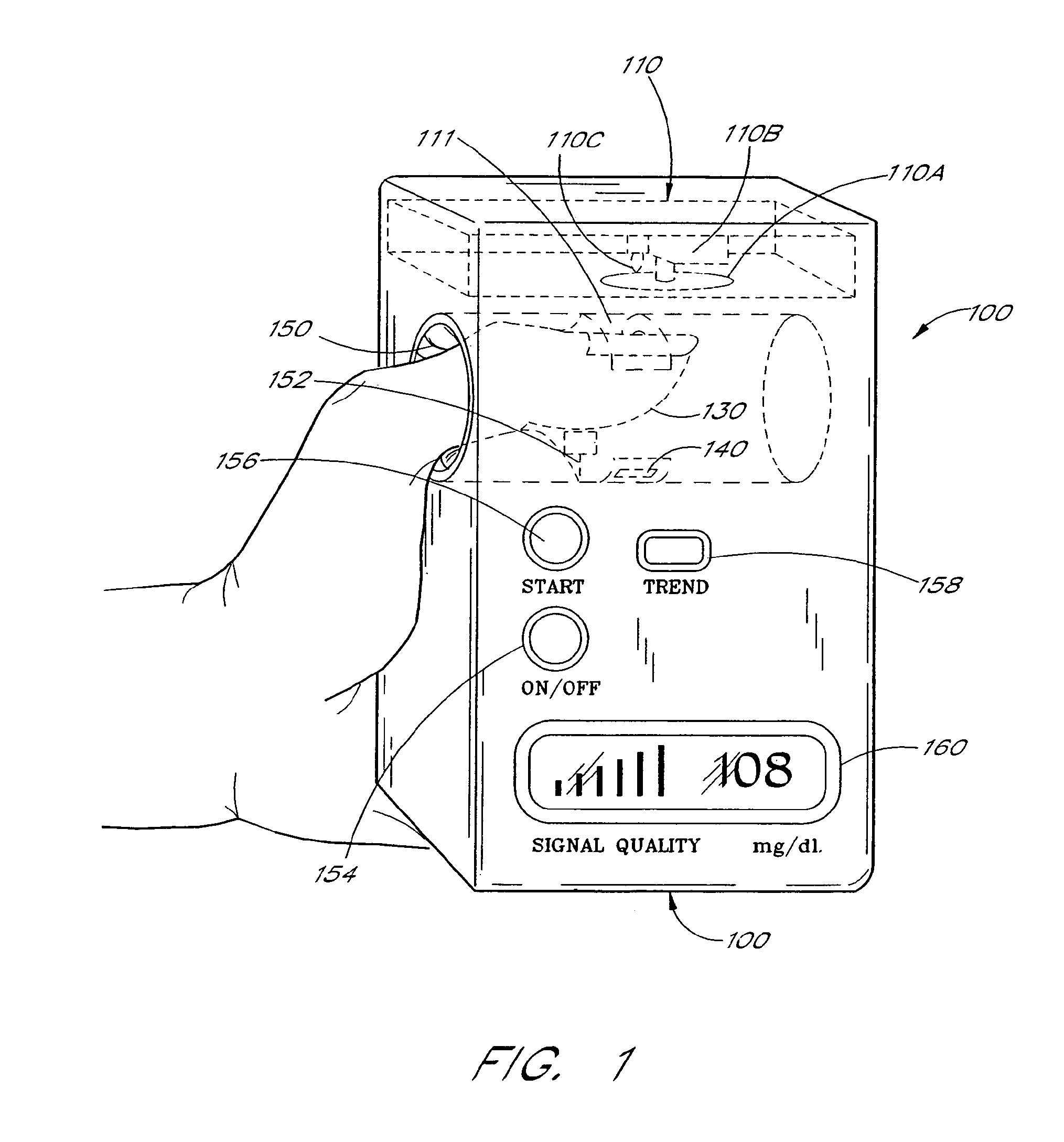
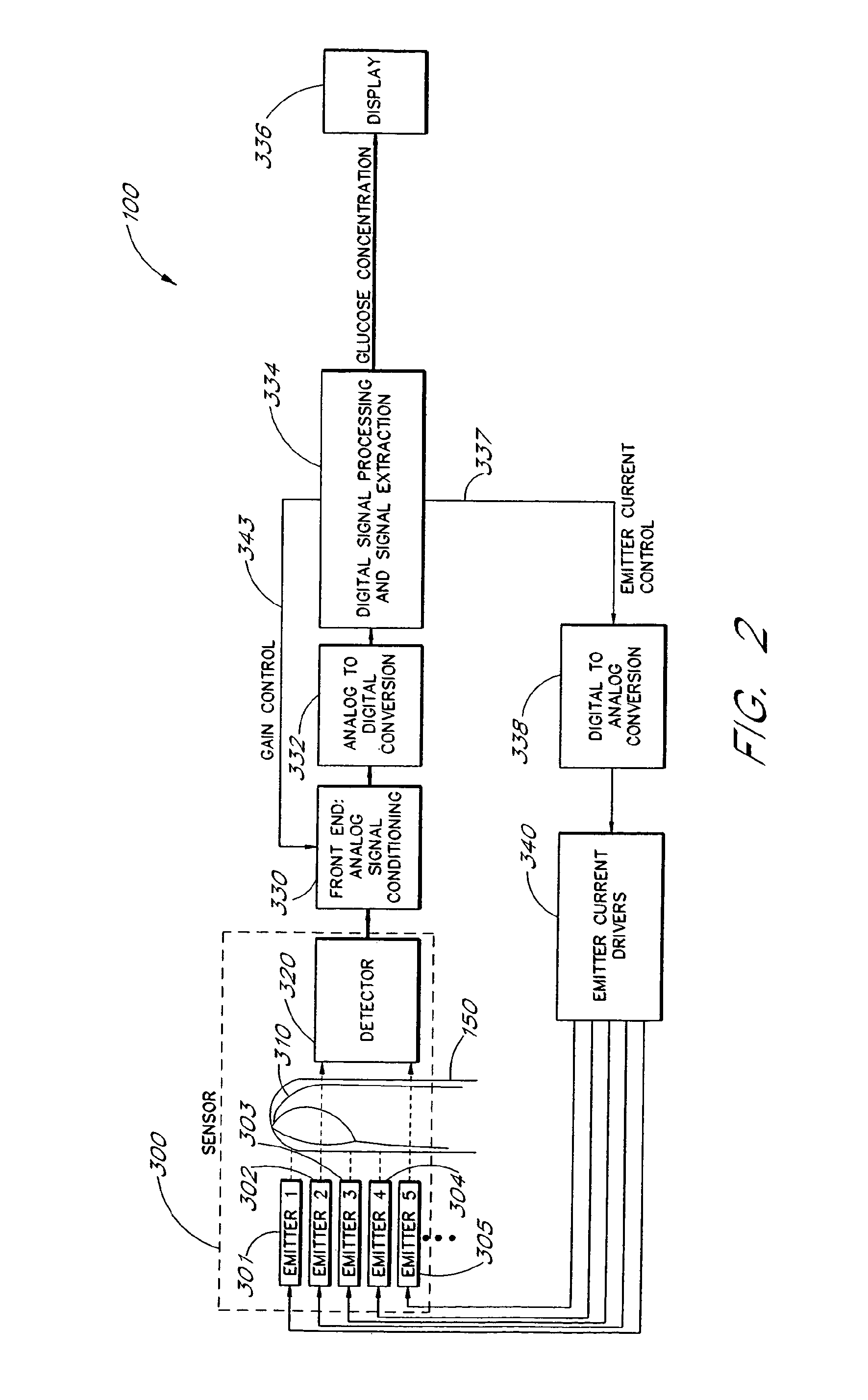
Active pulse blood constituent monitoring
InactiveUS6931268B1Ability to determinePreventing any perturbationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood volume pulseNon invasive
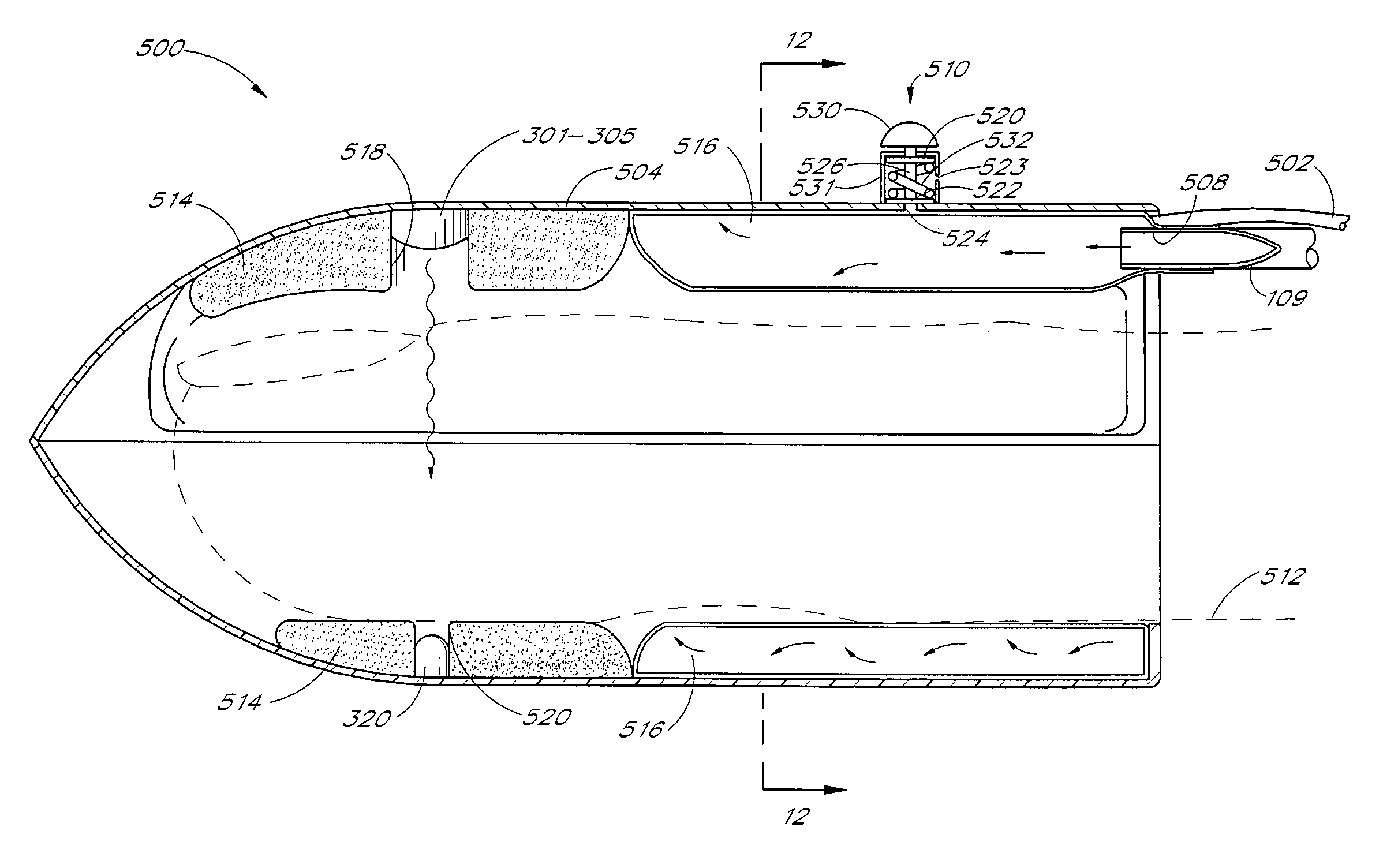
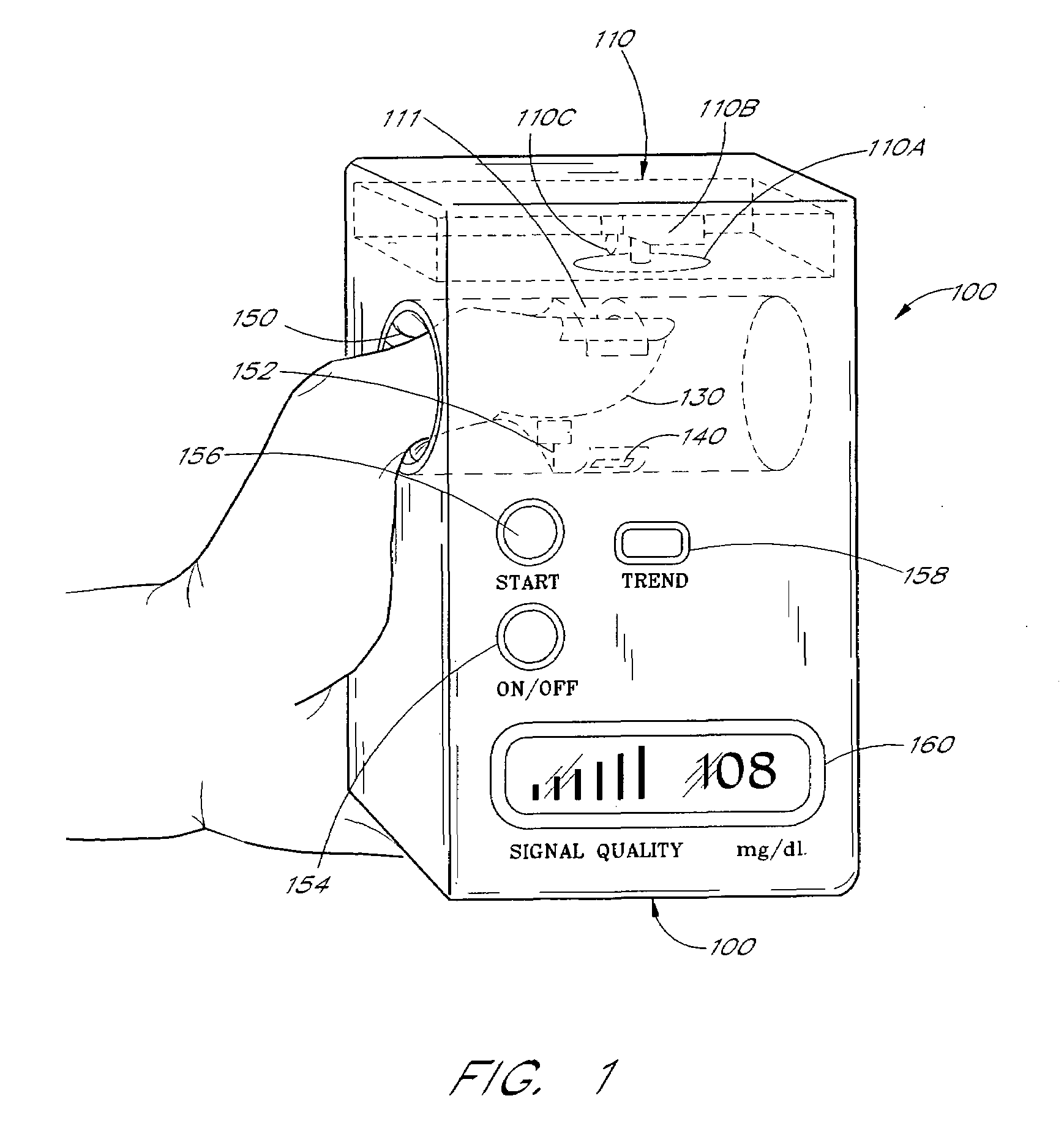
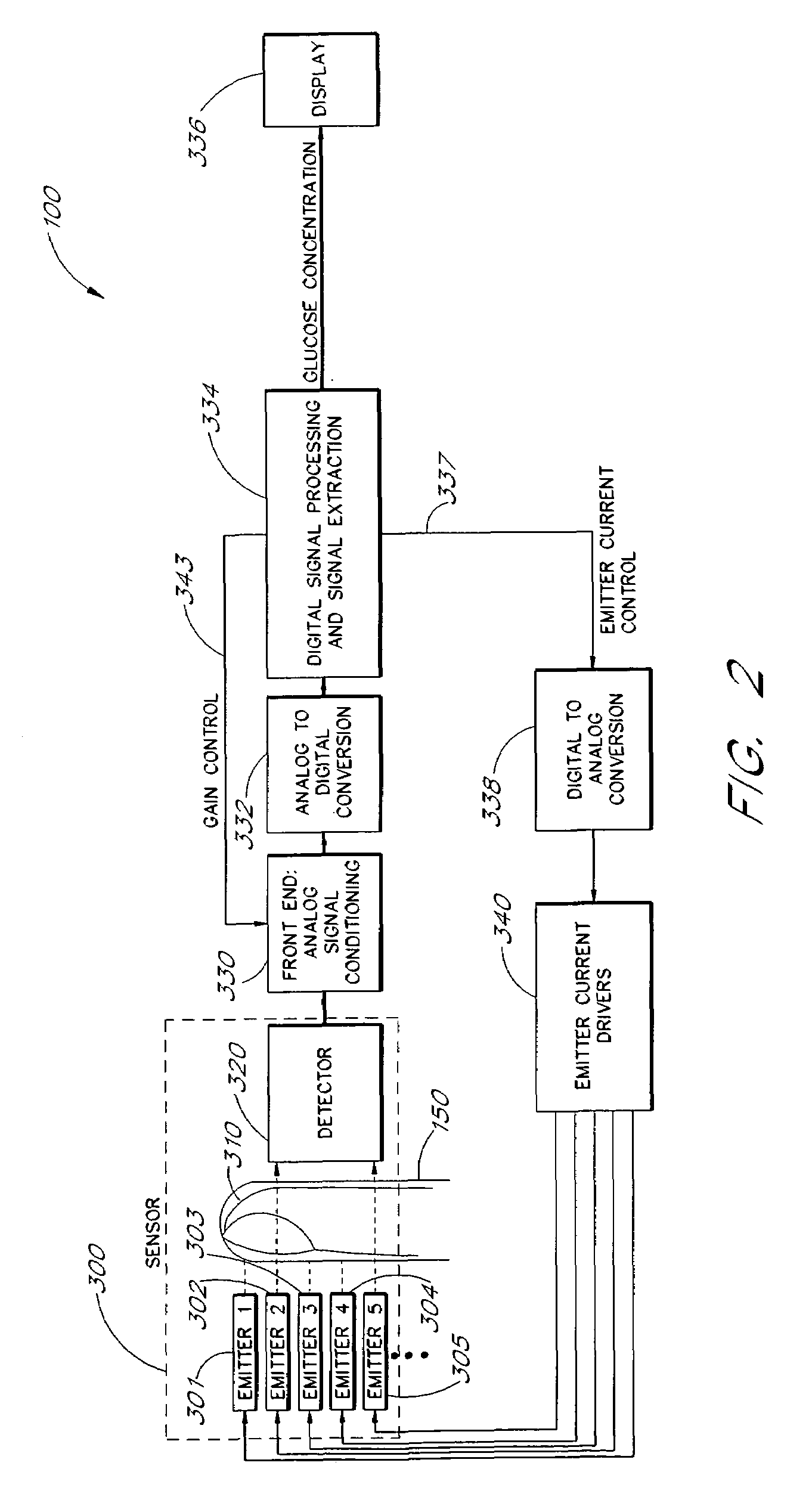
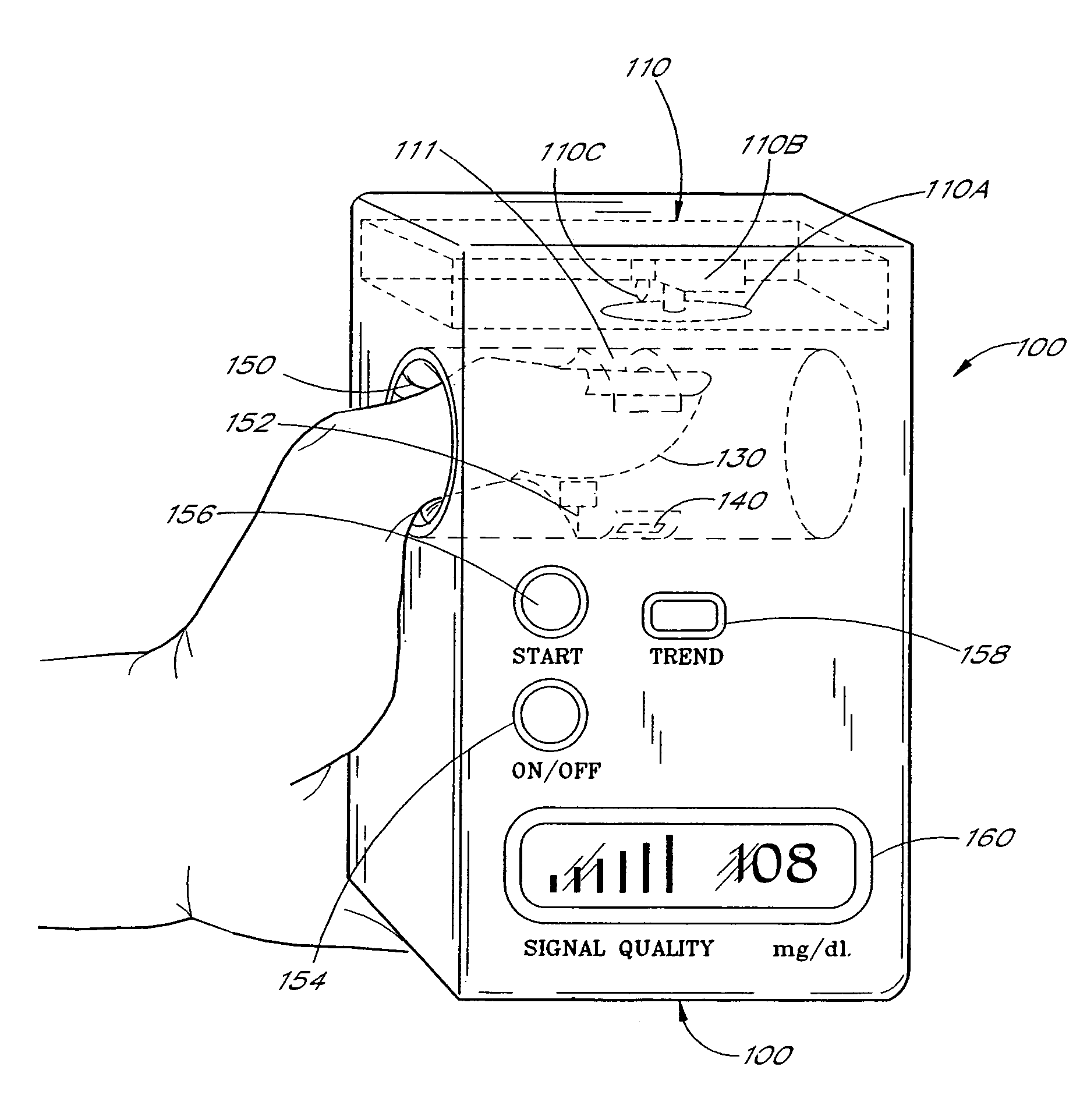
A blood glucose monitoring system is disclosed which provides for inducing an active pulse in the blood volume of a patient. The induction of an active pulse results in a cyclic, and periodic change in the flow of blood through a fleshy medium under test. By actively inducing a change of the blood volume, modulation of the volume of blood can be obtained to provide a greater signal to noise ratio. This allows for the detection of constituents in blood at concentration levels below those previously detectable in a non-invasive system. Radiation which passes through the fleshy medium is detected by a detector which generates a signal indicative of the intensity of the detected radiation. Signal processing is performed on the electrical signal to isolate those optical characteristics of the electrical signal due to the optical characteristics of the blood.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Active pulse blood constituent monitoring
A blood constituent monitoring method for inducing an active pulse in the blood volume of a patient. The induction of an active pulse results in a cyclic, and periodic change in the flow of blood through a fleshy medium under test. By actively inducing a change of the blood volume, modulation of the volume of blood can be obtained to provide a greater signal to noise ratio. This allows for the detection of constituents in blood at concentration levels below those previously detectable in a non-invasive system. Radiation which passes through the fleshy medium is detected by a detector which generates a signal indicative of the intensity of the detected radiation. Signal processing is performed on the electrical signal to isolate those optical characteristics of the electrical signal due to the optical characteristics of the blood.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Active pulse blood constituent monitoring
A blood constituent monitoring method for inducing an active pulse in the blood volume of a patient. The induction of an active pulse results in a cyclic, and periodic change in the flow of blood through a fleshy medium under test. By actively inducing a change of the blood volume, modulation of the volume of blood can be obtained to provide a greater signal to noise ratio. This allows for the detection of constituents in blood at concentration levels below those previously detectable in a non-invasive system. Radiation which passes through the fleshy medium is detected by a detector which generates a signal indicative of the intensity of the detected radiation. Signal processing is performed on the electrical signal to isolate those optical characteristics of the electrical signal due to the optical characteristics of the blood.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Active pulse blood constituent monitoring
A blood constituent monitoring method for inducing an active pulse in the blood volume of a patient. The induction of an active pulse results in a cyclic, and periodic change in the flow of blood through a fleshy medium under test. By actively inducing a change of the blood volume, modulation of the volume of blood can be obtained to provide a greater signal to noise ratio. This allows for the detection of constituents in blood at concentration levels below those previously detectable in a non-invasive system. Radiation which passes through the fleshy medium is detected by a detector which generates a signal indicative of the intensity of the detected radiation. Signal processing is performed on the electrical signal to isolate those optical characteristics of the electrical signal due to the optical characteristics of the blood.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
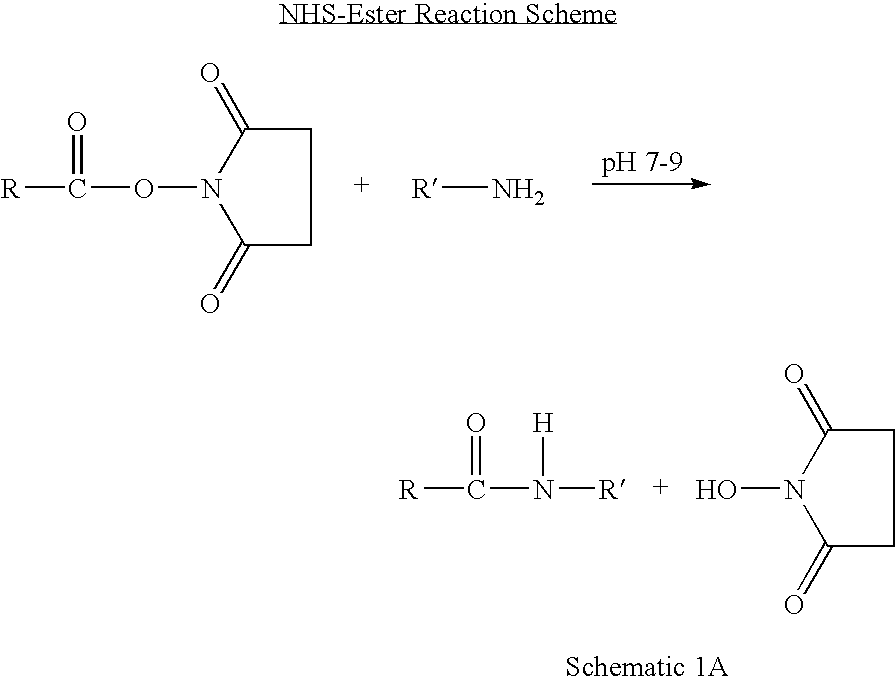
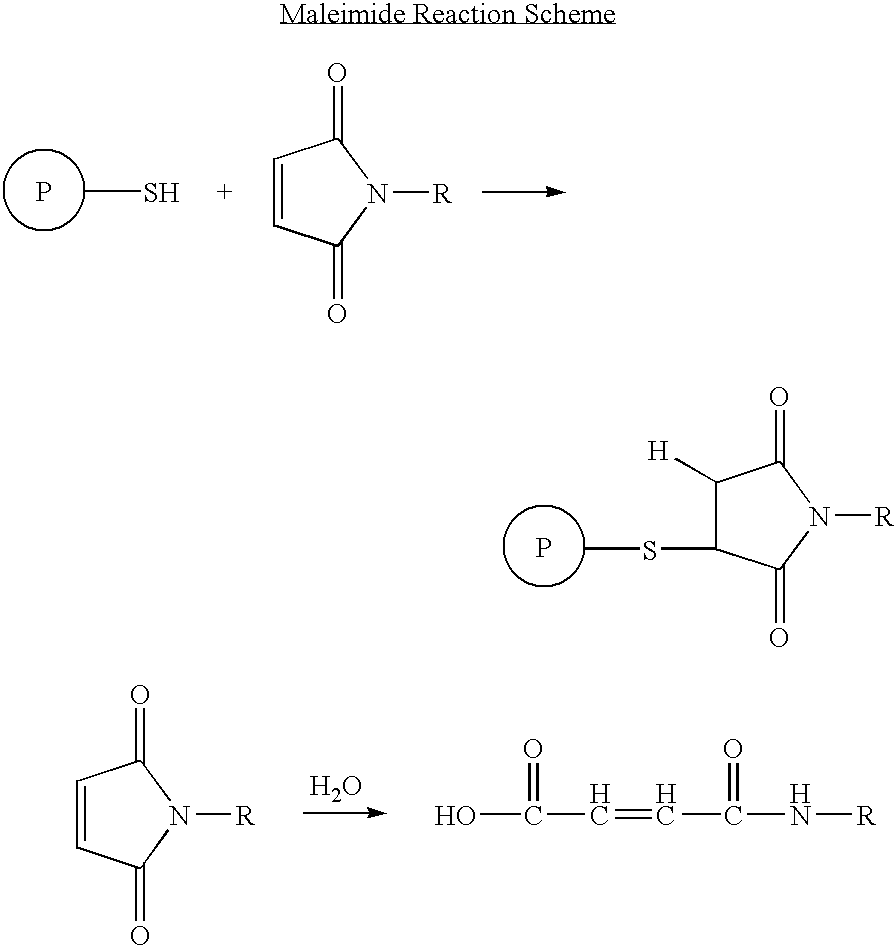
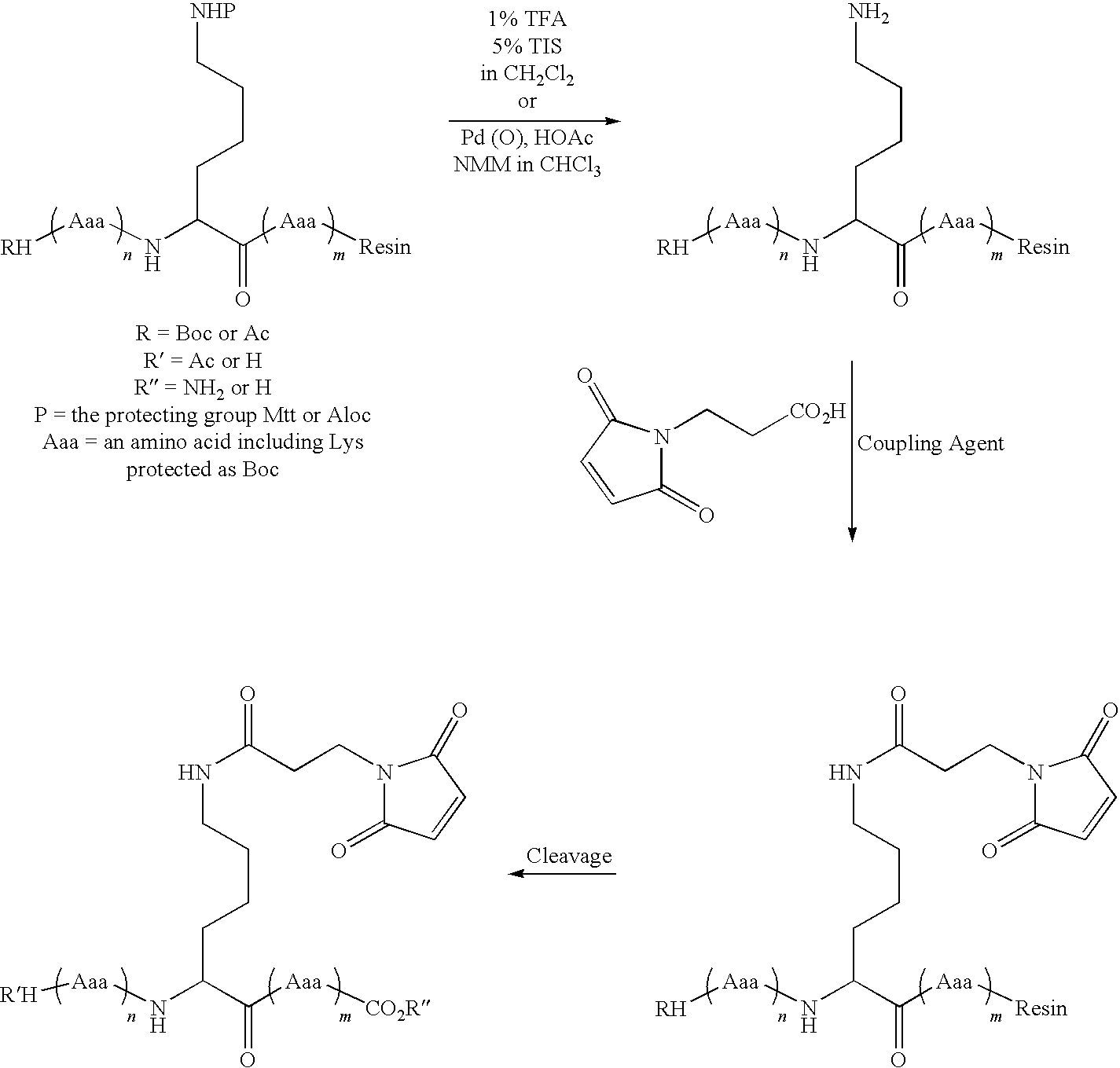
Protection of endogenous therapeutic peptides from peptidase activity through conjugation to blood components
InactiveUS6887470B1Easy to testPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBlood componentCombinatorial chemistry
A method for protecting a peptide from peptidase activity in vivo, the peptide being composed of between 2 and 50 amino acids and having a C-terminus and an N-terminus and a C-terminus amino acid and an N-terminus amino acid is described. In the first step of the method, the peptide is modified by attaching a reactive group to the C-terminus amino acid, to the N-terminus amino acid, or to an amino acid located between the N-terminus and the C-terminus, such that the modified peptide is capable of forming a covalent bond in vivo with a reactive functionality on a blood component. In the next step, a covalent bond is formed between the reactive group and a reactive functionality on a blood component to form a peptide-blood component conjugate, thereby protecting said peptide from peptidase activity. The final step of the method involves the analyzing of the stability of the peptide-blood component conjugate to assess the protection of the peptide from peptidase activity.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
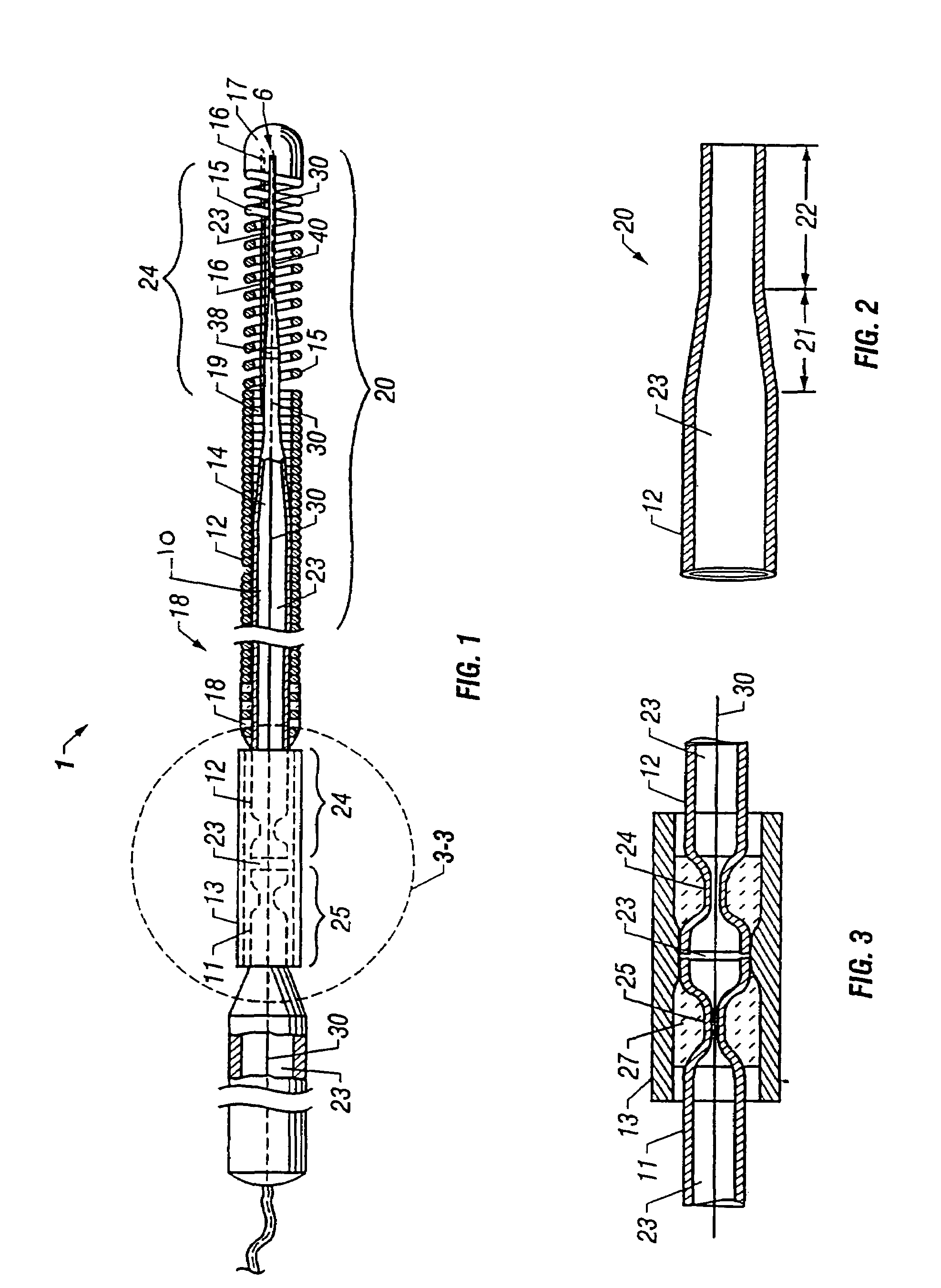
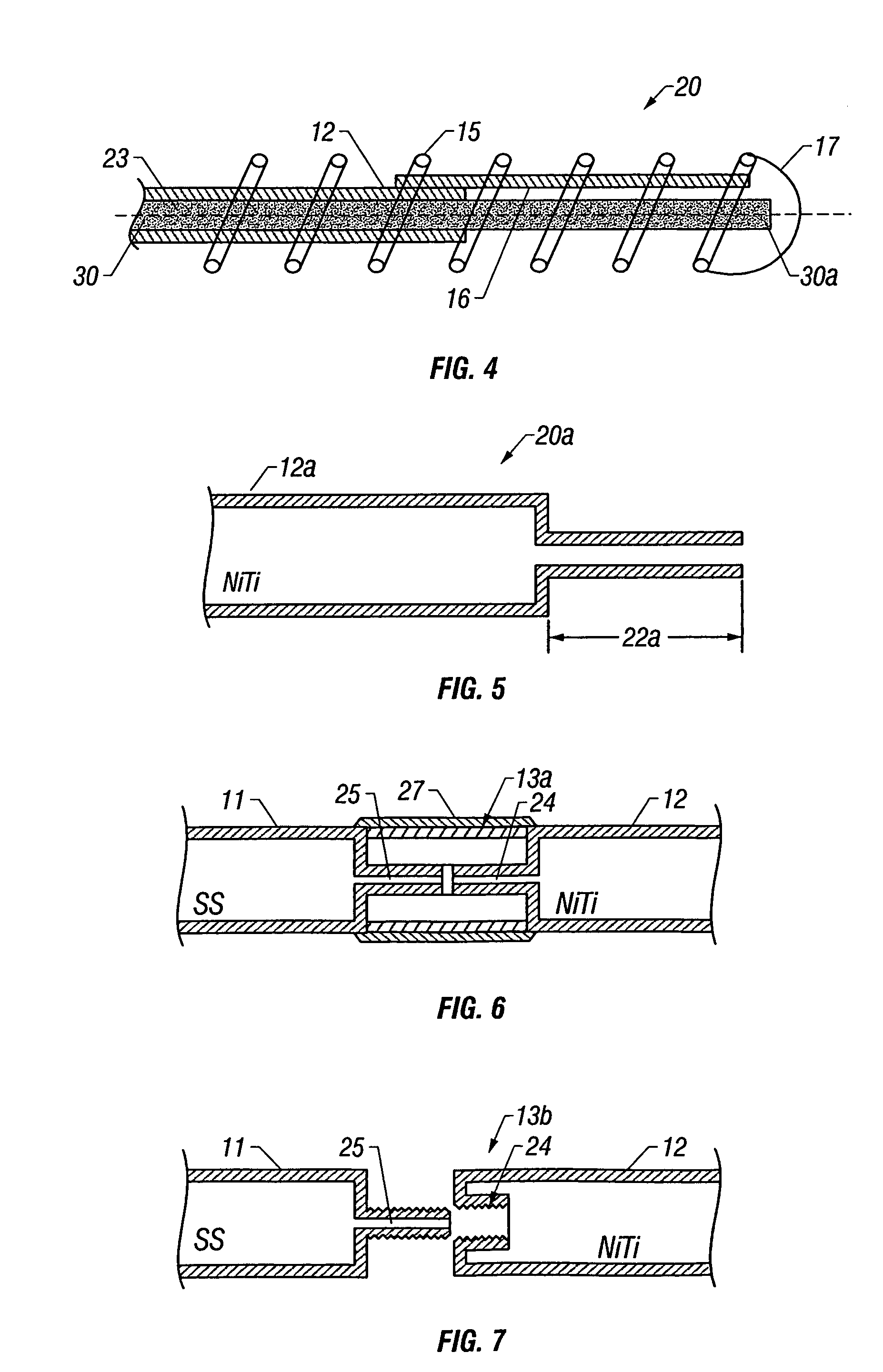
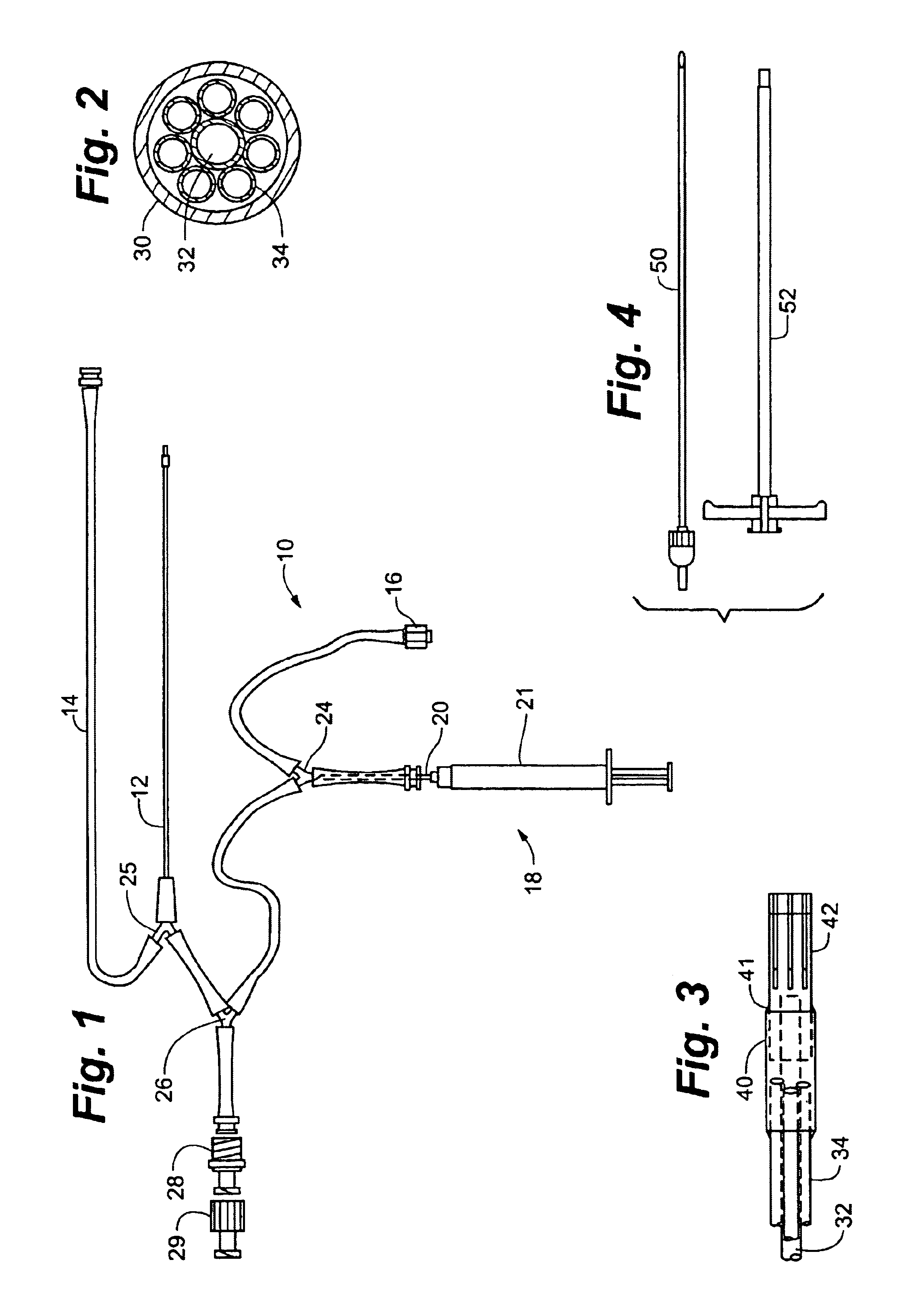
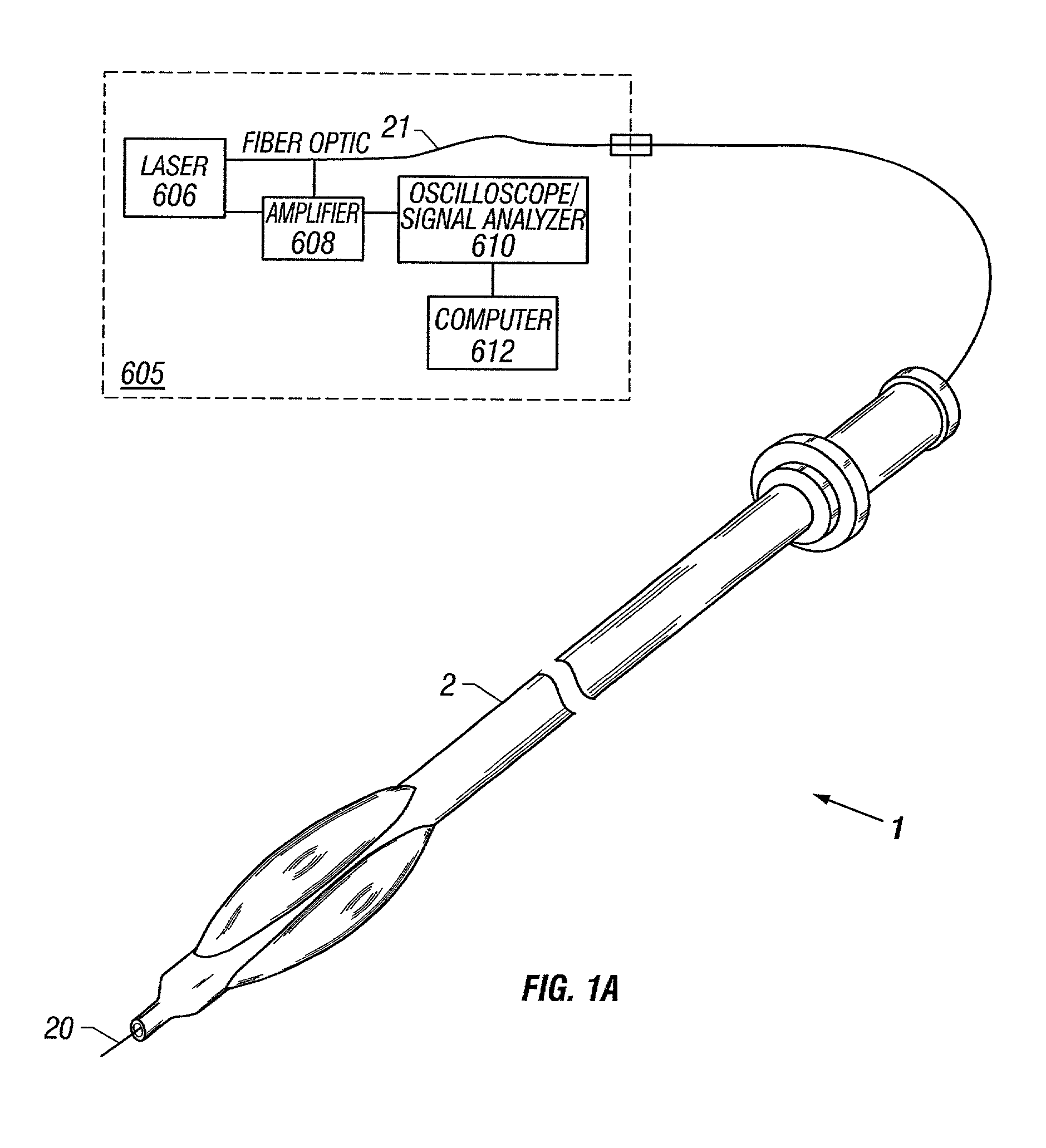
Guidewire with optical fiber
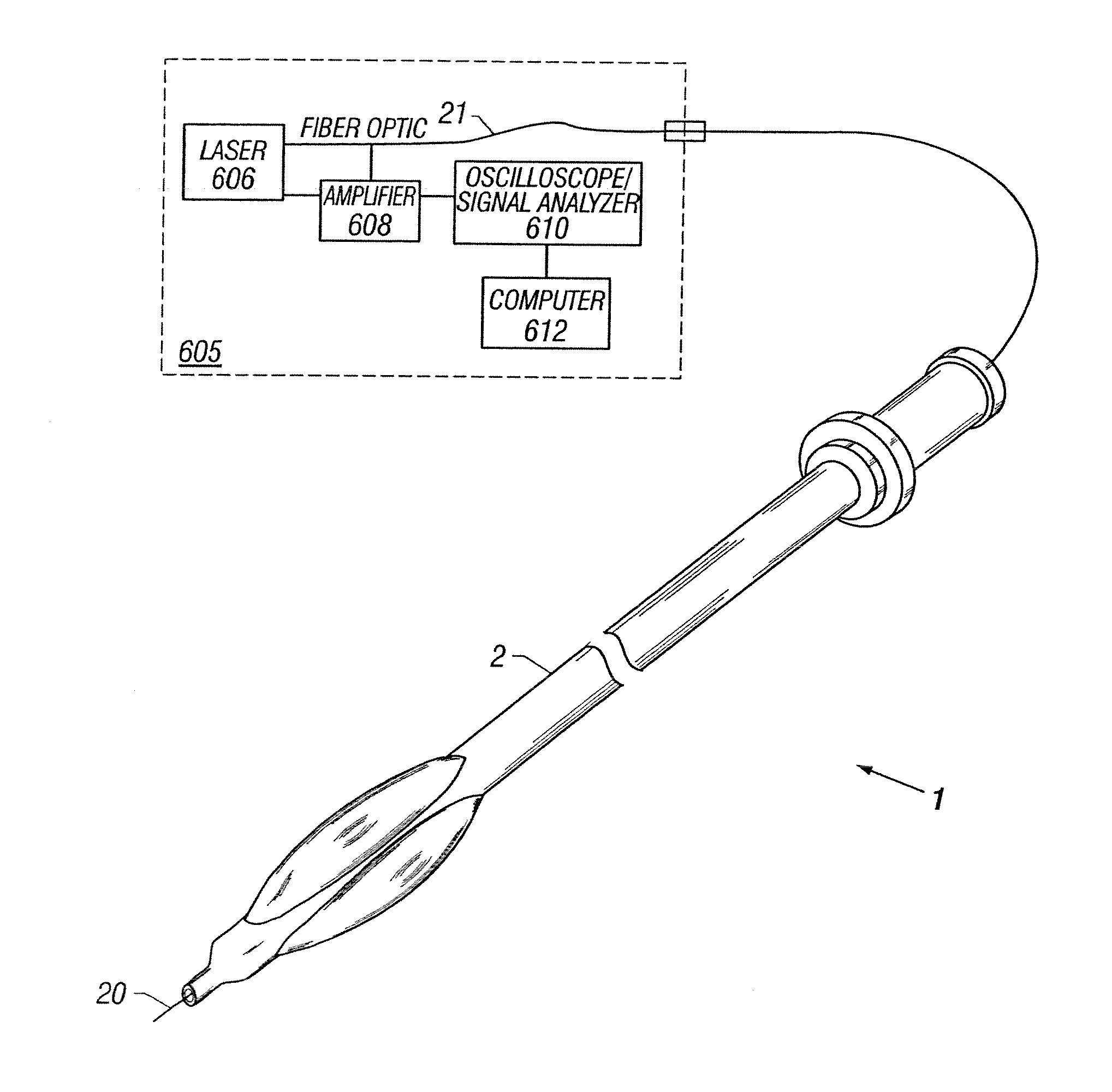
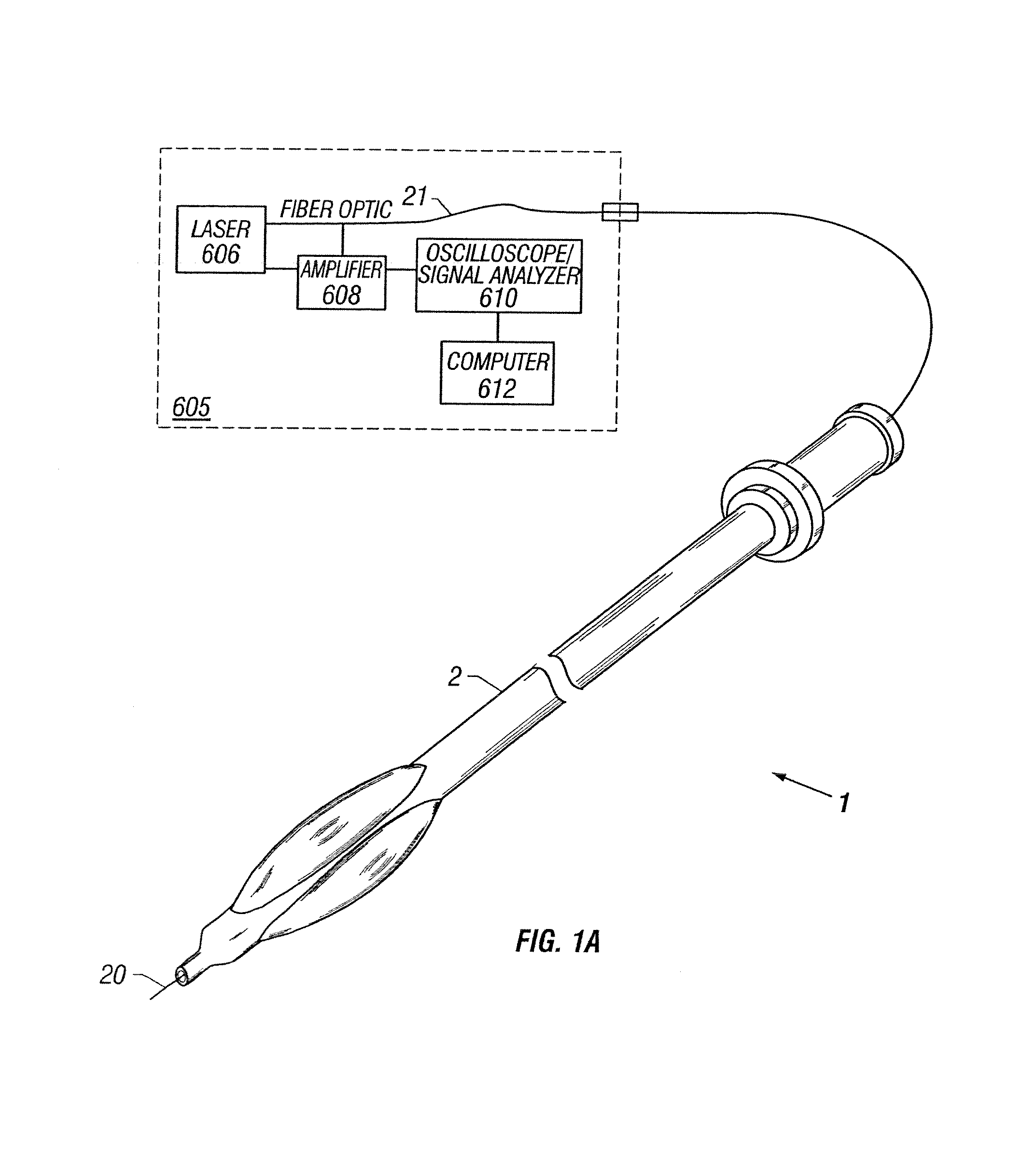
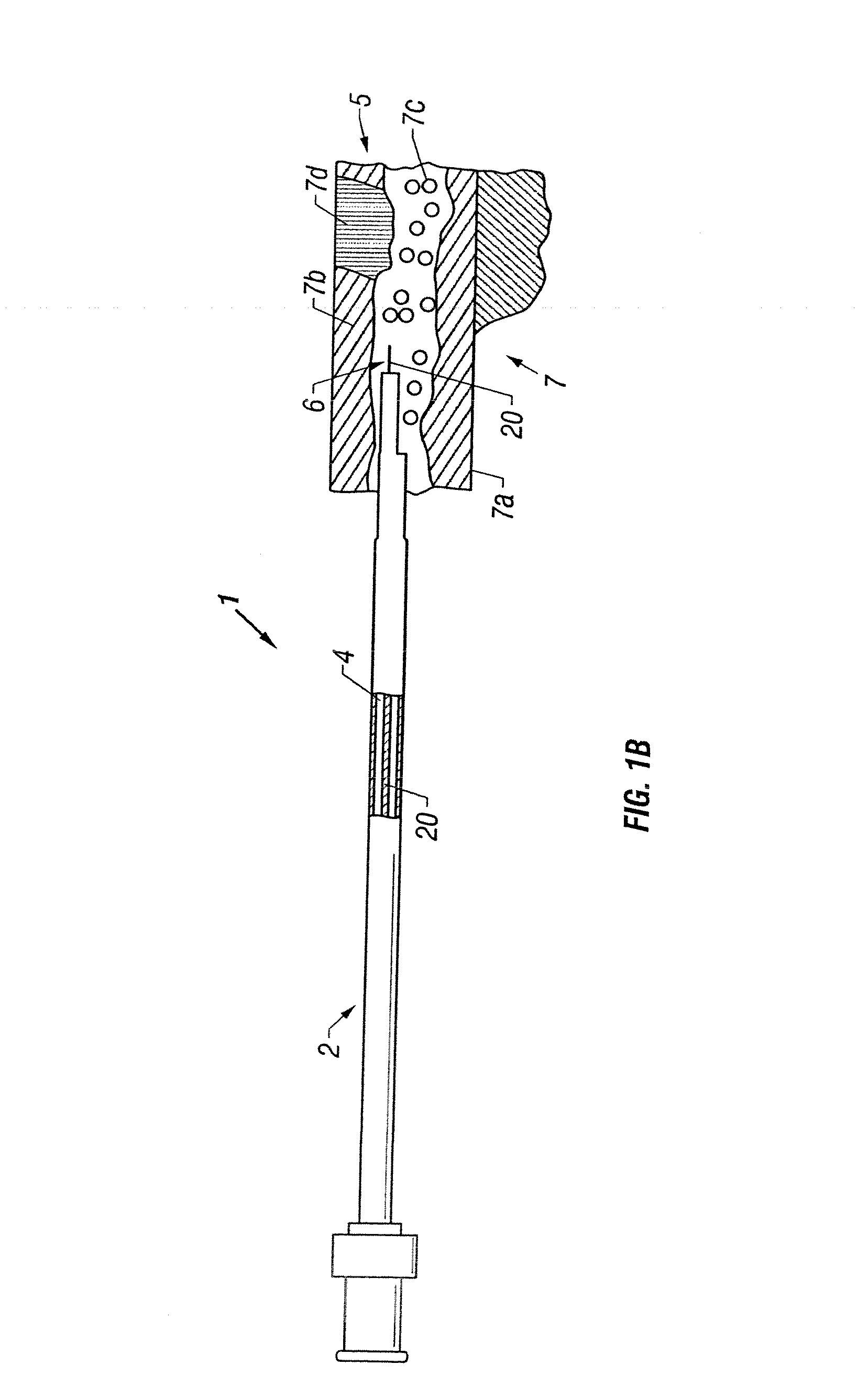
Apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment of this invention, the apparatus includes a therapeutic guidewire and at least one optical fiber disposed through the therapeutic guidewire, the optical fiber capable of providing diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
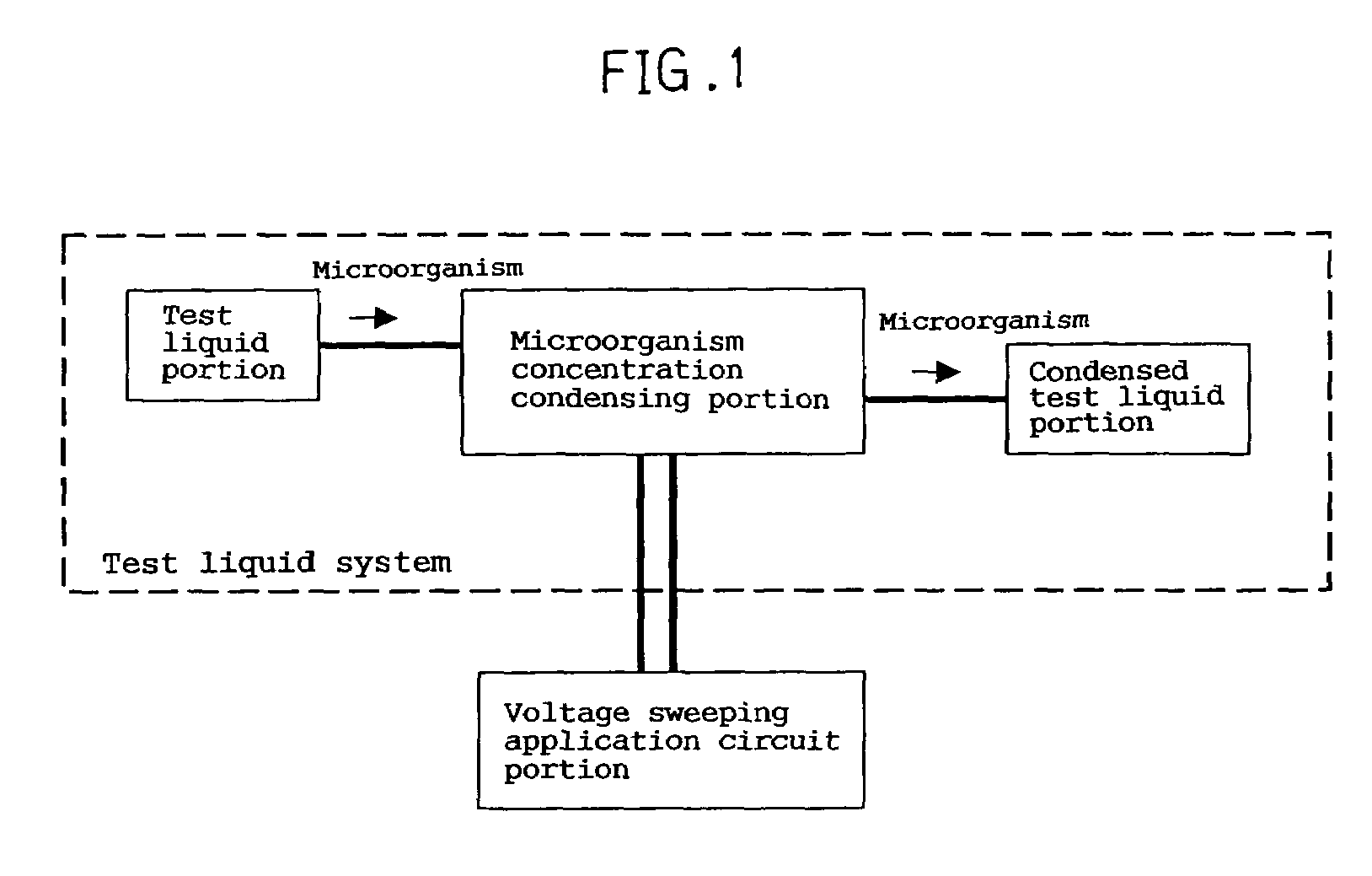
Electrochemical device for moving particles covered with protein
InactiveUS6972080B1Efficient disposalElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentBlood componentElectrolysis
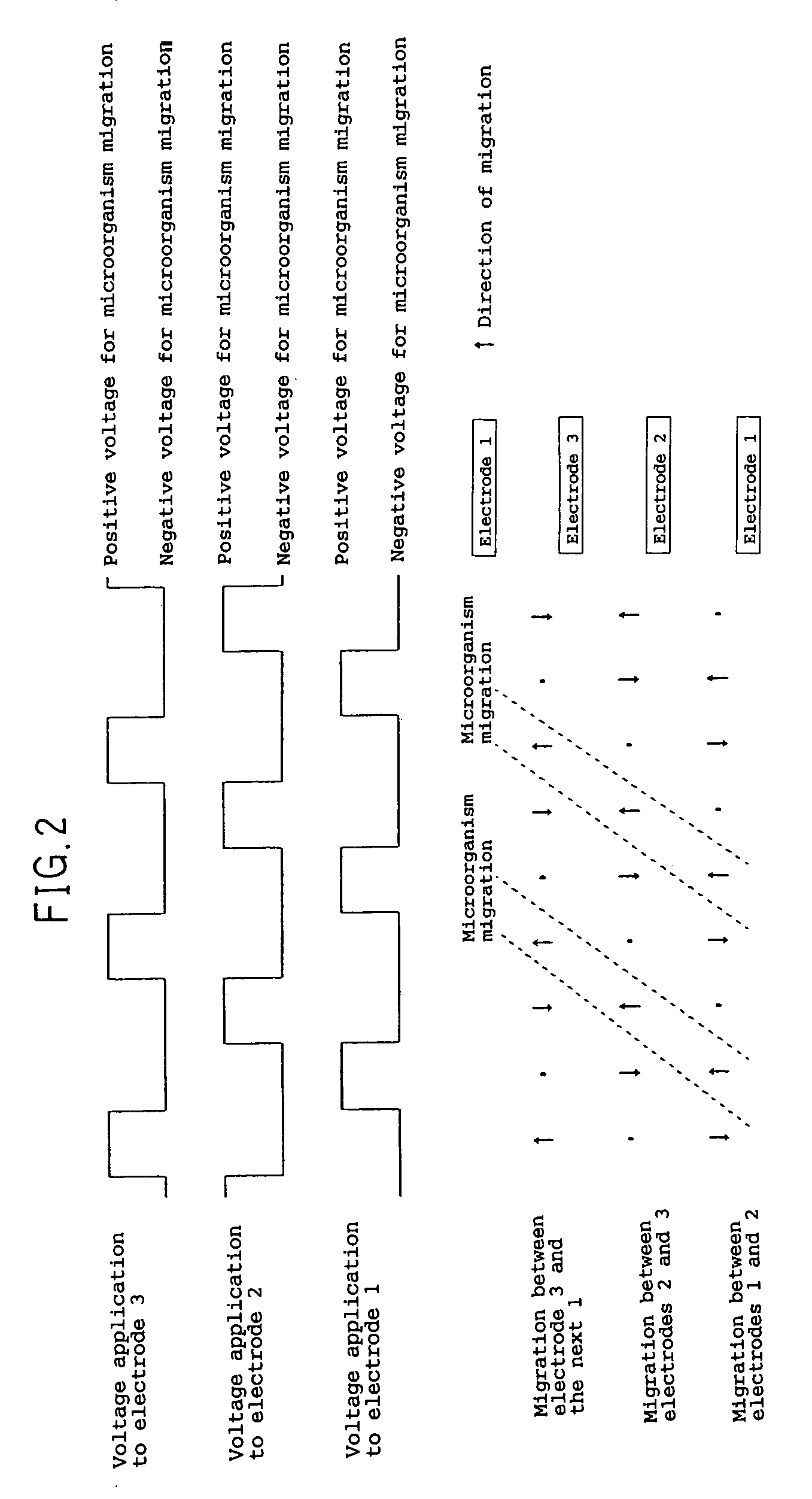
An electrochemical device for moving particles covered with a protein is provided. The device includes at least two electrodes that are in contact with a liquid containing the protein-covered particles and a circuit that generates a potential difference in a range that does not cause electrolysis of the liquid between the electrodes. The particles are moved by electrophoresis in the direction of the arrangement of the electrodes. The invention provided herein has numerous applications, including use in a microorganism concentration condensing device, a blood component induction device, and / or a blood component induction method, and / or an electric appliance that decreases the concentration of microorganisms present on the surface of a heat exchanger.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS7148209B2Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Noninvasive measurement of chemical substances
InactiveUS7041063B2High densityEarly diagnosisOrganic active ingredientsHeart defibrillatorsConjunctivaInfrared
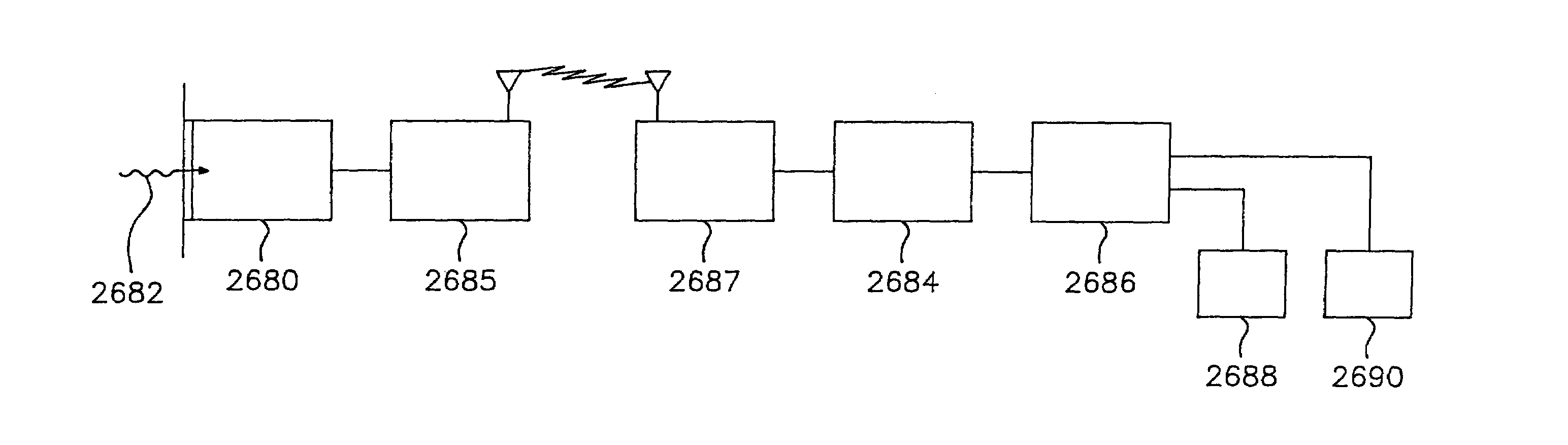
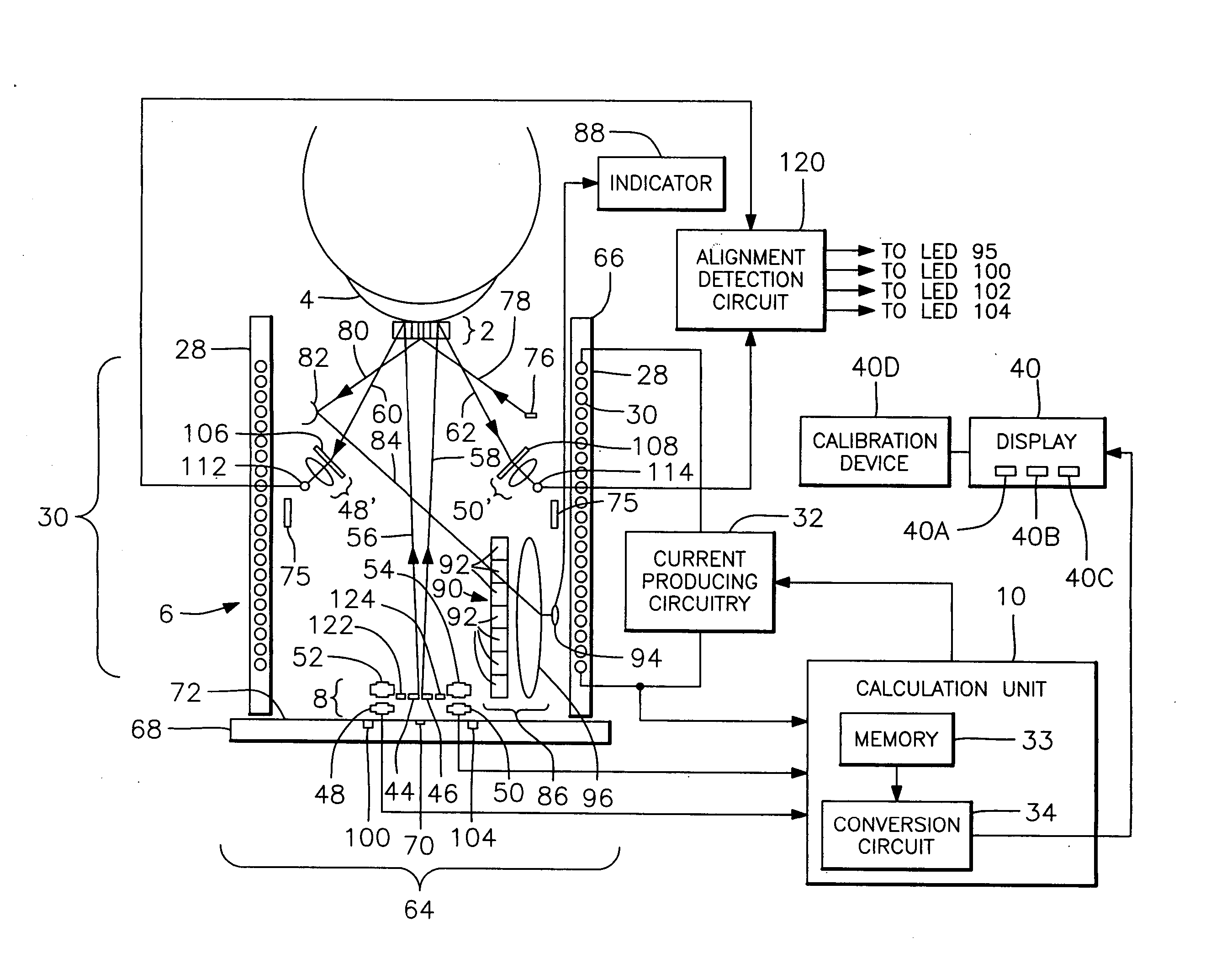
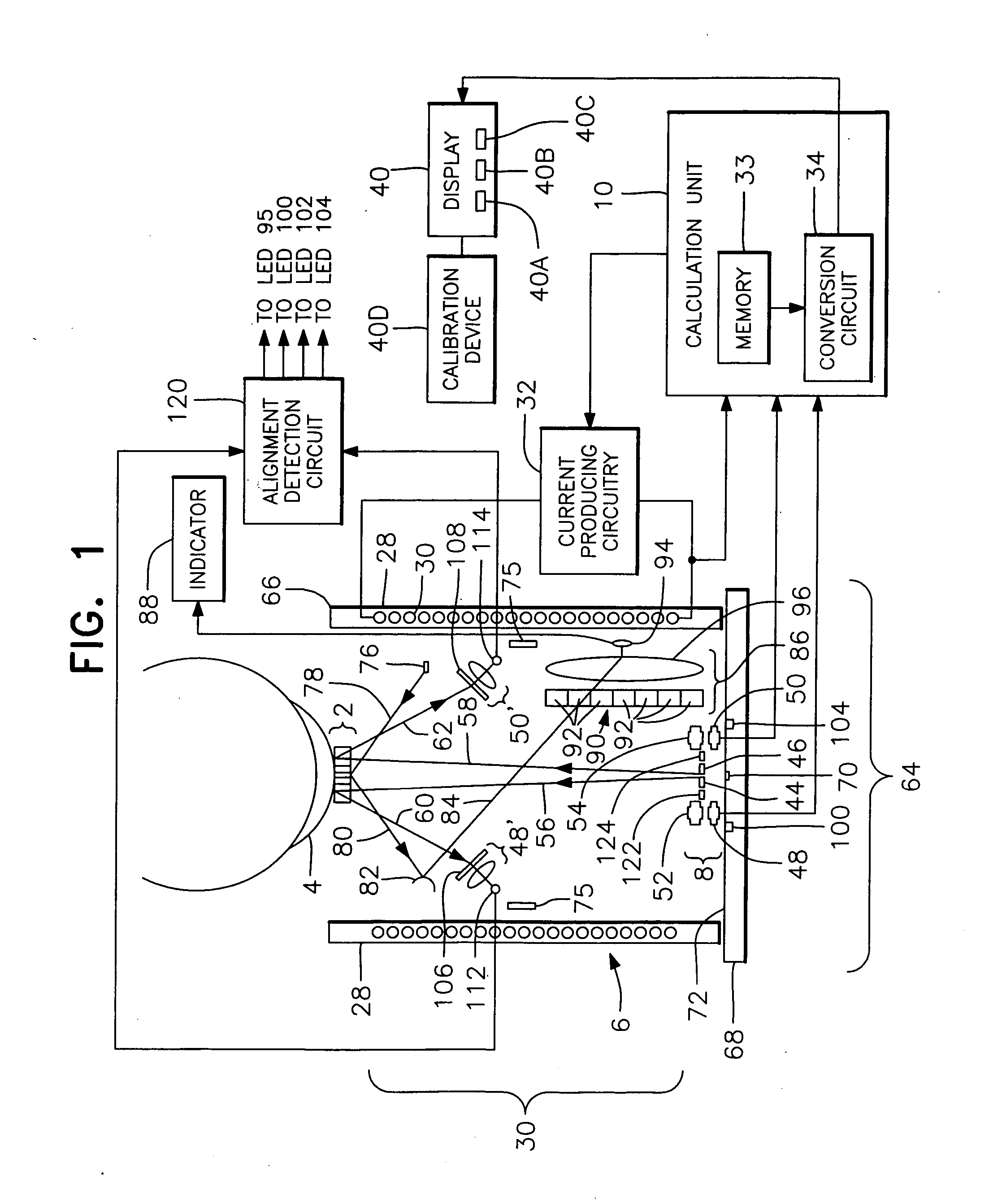
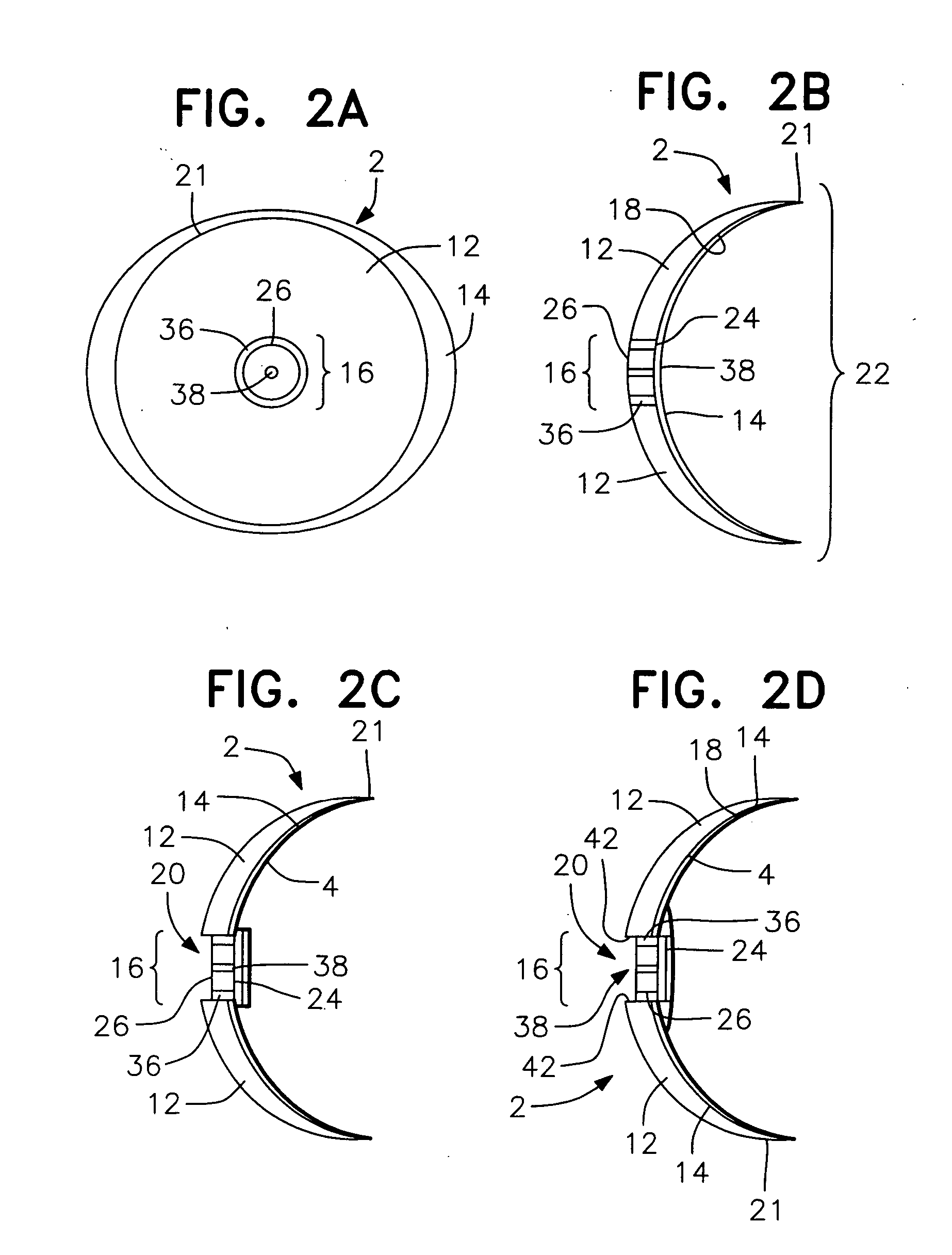
Utilization of a contact device placed on the eye in order to detect physical and chemical parameters of the body as well as the non-invasive delivery of compounds according to these physical and chemical parameters, with signals being transmitted continuously as electromagnetic waves, radio waves, infrared and the like. One of the parameters to be detected includes non-invasive blood analysis utilizing chemical changes and chemical products that are found in the conjunctiva and in the tear film. A transensor mounted in the contact device laying on the cornea or the surface of the eye is capable of evaluating and measuring physical and chemical parameters in the eye including non-invasive blood analysis. The system utilizes eye lid motion and / or closure of the eye lid to activate a microminiature radio frequency sensitive transensor mounted in the contact device. The signal can be communicated by wires or radio telemetered to an externally placed receiver. The signal can then be processed, analyzed and stored. Several parameters can be detected including a complete non-invasive analysis of blood components, measurement of systemic and ocular blood flow, measurement of heart rate and respiratory rate, tracking operations, detection of ovulation, detection of radiation and drug effects, diagnosis of ocular and systemic disorders and the like.
Owner:GEELUX HLDG LTD
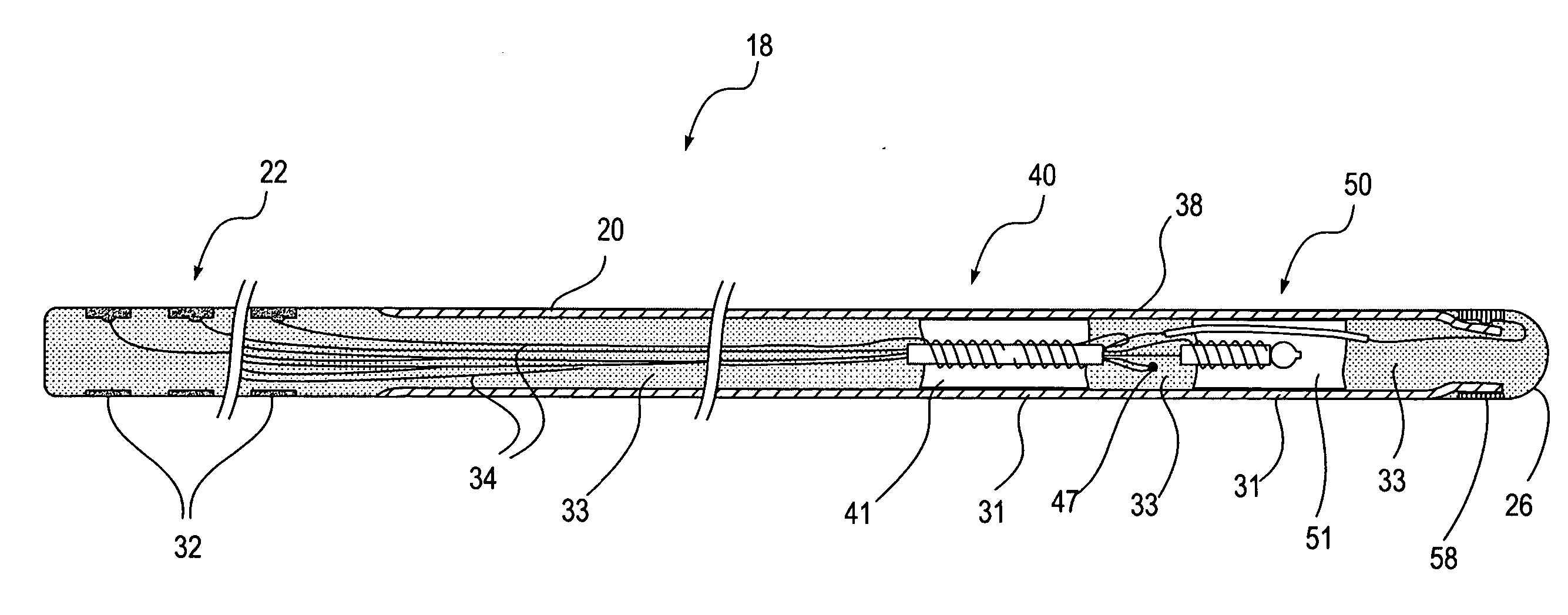
Autonomous, ambulatory analyte monitor or drug delivery device
ActiveUS20060094985A1Reduce frequencyEasy maintenanceAutomatic syringesMicroneedlesActuatorContinuous monitoring
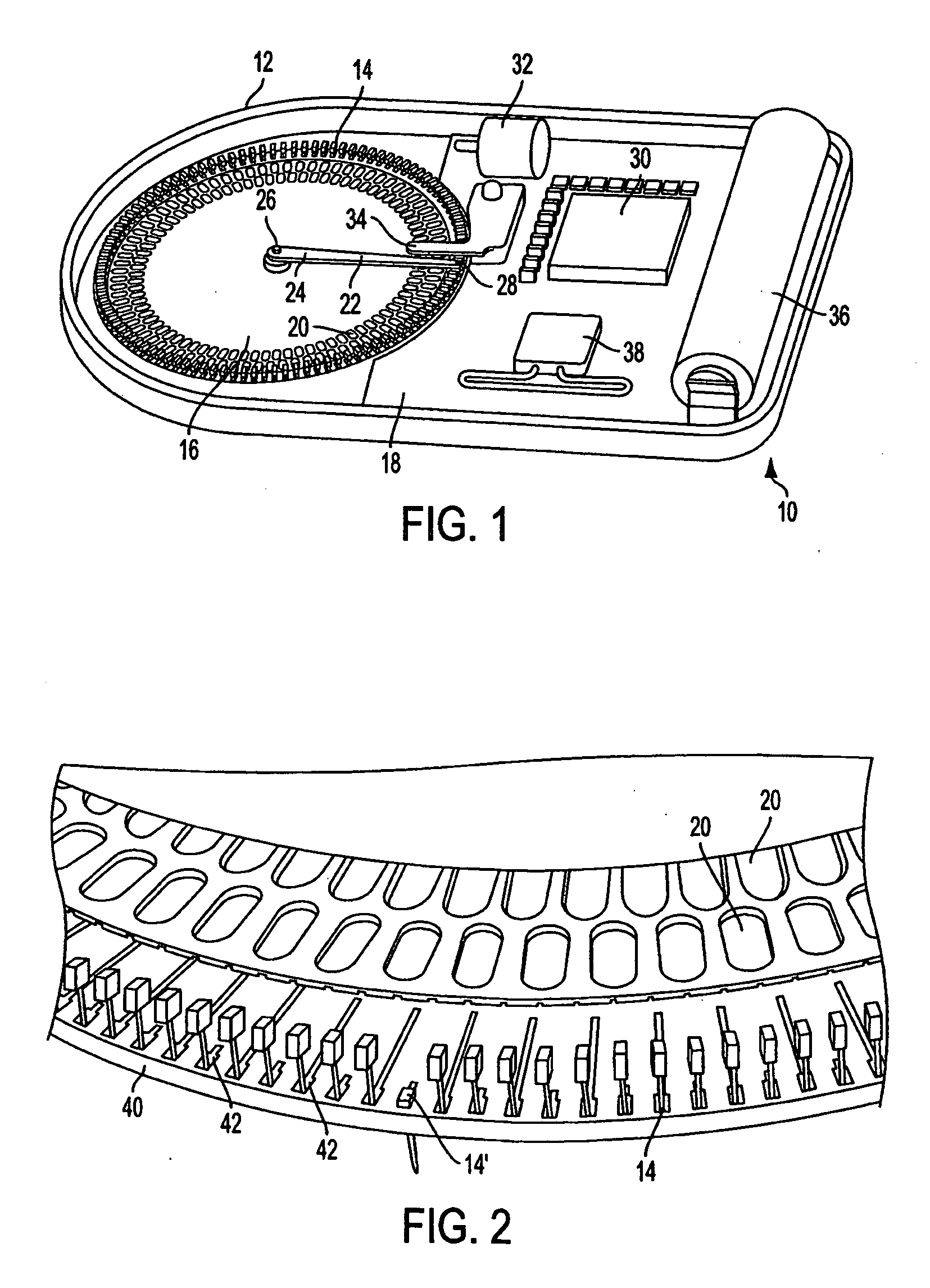
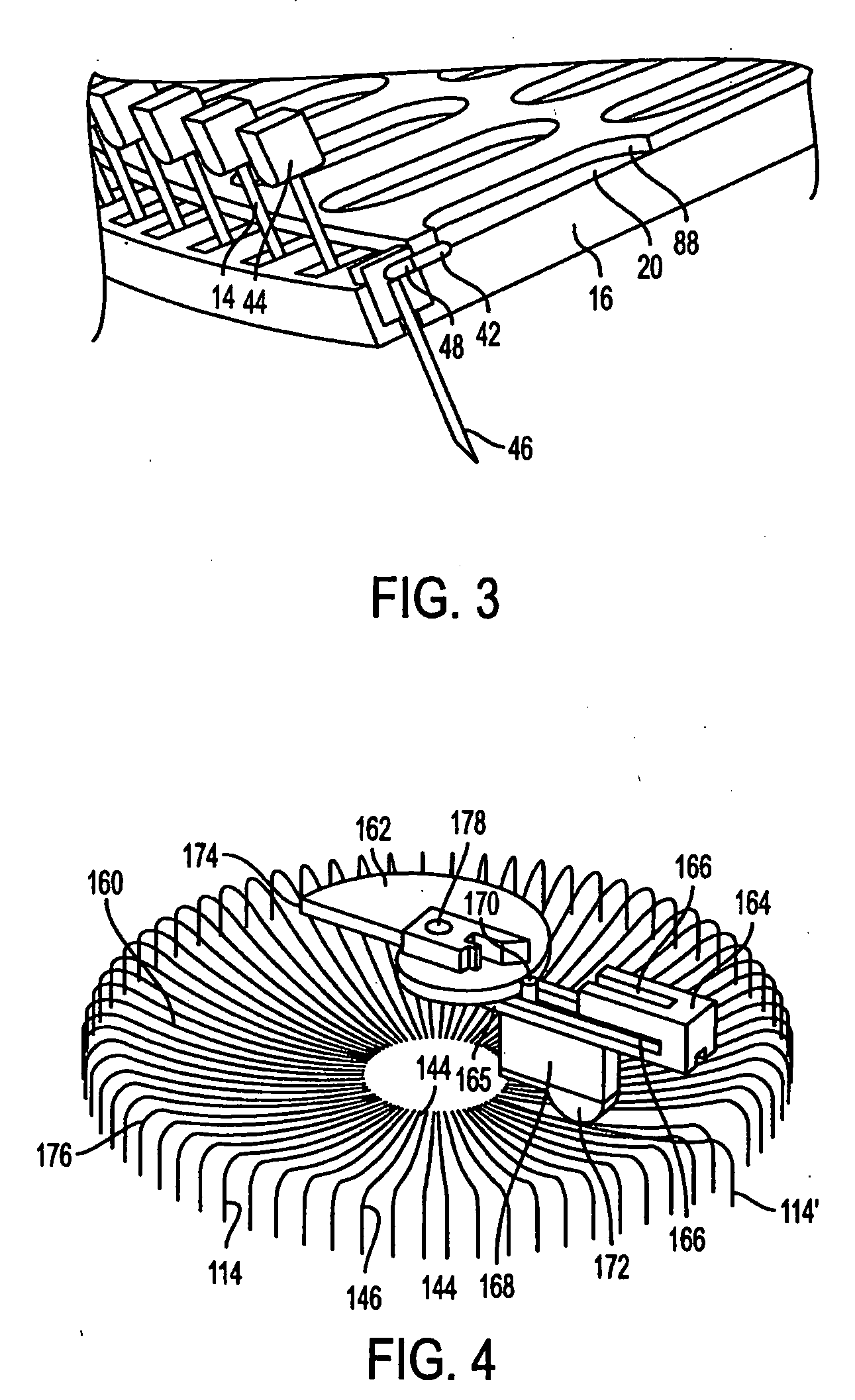
The invention relates to analyte monitoring / drug (pharmaceutical agent) delivery device. The invention is suited for monitoring various blood constituents such as glucose. The device has a housing that at least partially encloses a plurality of microneedles disposed on a carrier and an electronics portion. Each microneedle is in fluid communication with a corresponding microchannel. Each microneedle is individually addressable. That is, each microneedle can be extended and retracted individually via an actuator. The electronics portion includes a processor and associated circuitry (e.g., memory, supporting electronics and the like), a motor or the like, a sensor, a power supply (e.g., battery) and optionally an interface. In general, the processor controls the operation of the device and is data communication with the actuator, motor, sensor and interface. The invention provides for autonomous operation, that is, without intervention of the user. The invention can optionally provide for calibration without intervention of the user. The invention can also provide for semi-continuous monitoring for day and night time. The invention can provide for up to four, or more, weeks of operation. The invention can provide for a device that is relative small in size, and therefore unobtrusive. The invention can also provide for device with remote control and interactive electronics. The invention may be also used for the delivery of various pharmaceutical agents including high potency drugs to minimize patient intervention and minimize discomfort.
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Non-invasive blood component measurement system
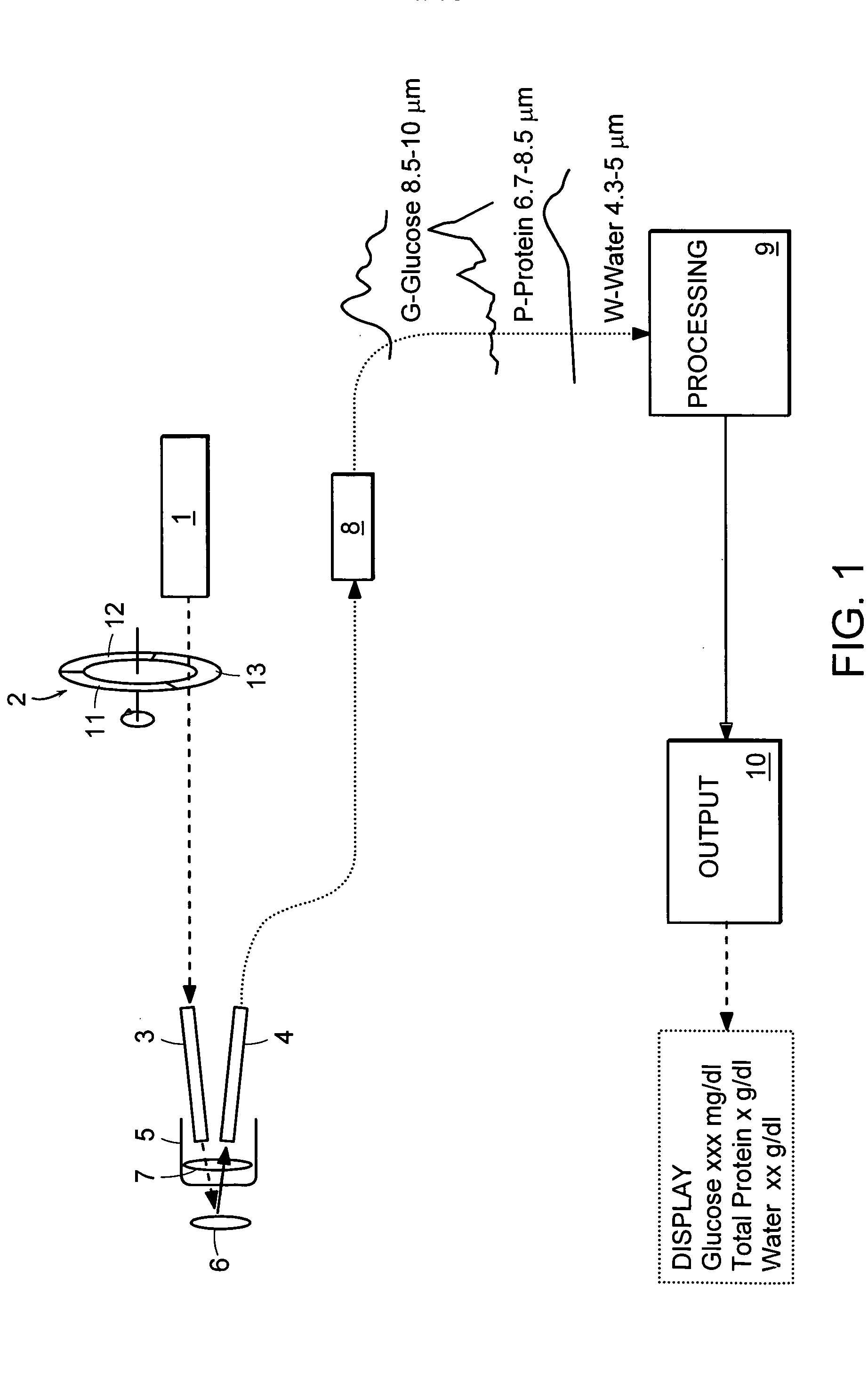
Non-invasive, optical apparatus and methods for the direct measurement of hemoglobin derivatives and other analyte concentration levels in blood using diffuse reflection and transmission spectroscopy in the wavelength region 400-1350 nm which includes the transparent tissue window from approximately 610 to 1311 nanometers and, using diffuse reflection spectroscopy, the mid-infrared region from 4.3-12 microns in wavelength. Large area light collection techniques are utilized to provide a much larger pulsate signal than can be obtain with current sensor technology. Sensors used in separate or simultaneous precision measurements of both diffuse reflection and transmission, either separately or simultaneously, from pulsate, blood-perfused tissue for the subsequent determination of the blood analytes concentrations such as arterial blood oxygen saturation (SaO2), carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), oxyhemoglobin (OHb), deoxyhemoglobin (dOHb), methemoglobin (metHb), water (H2O), hematocrit (HCT), glucose, cholesterol and proteins such as albumin and other analytes components.
Owner:3WAVE OPTICS
Long lasting synthetic glucagon-like peptide {GLP-1}
Modified insulinotropic peptides are disclosed. The modified insulinotropic peptides are capable of forming a peptidase stabilized insulinotropic peptide. The modified insulinotropic peptides are capable of forming covalent bonds with one or more blood components to form a conjugate. The conjugates may be formed in vivo or ex vivo. The modified peptides are administered to treat humans with diabetes and other related diseases.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
System for treating tissue swelling
InactiveUS6942634B2Easy to separateIncrease concentrationSemi-permeable membranesWound drainsUltrafiltrationBiology
Owner:TWIN STAR MEDICAL
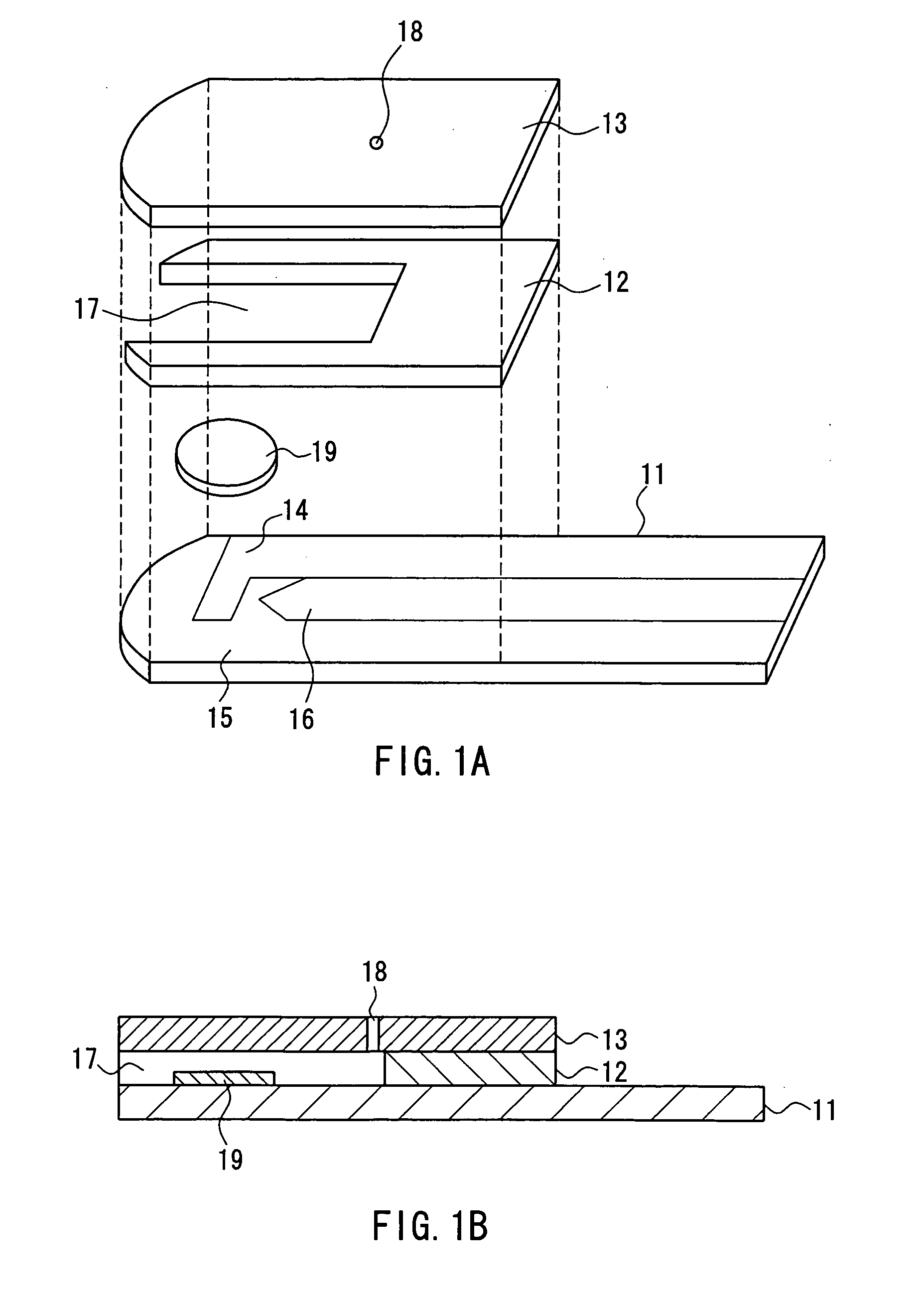
Method of measuring blood component, sensor used in the method, and measuring device
ActiveUS20070131565A1Easy to measureImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidoreductasePhysics
The present invention provides a method of measuring a component in blood, by which an amount of the component can be corrected accurately by measuring a hematocrit (Hct) value of the blood with high accuracy and high reliability and also provides a sensor used in the method. The sensor for measuring a component in blood has a first analysis portion and a second analysis portion. The first analysis portion has a first electrode system (11,12) and a reagent layer (14), and the reagent layer (14) has an oxidoreductase that acts on the component and a mediator. In the first analysis portion, the component in the blood is measured by causing a redox reaction of the component with the oxidoreductase in the presence of the mediator and detecting a redox current caused when a voltage is applied by the first electrode (11,12). The second analysis portion has a working electrode and a counter electrode, and a mediator is provided on the counter electrode but not on the working electrode. In the second analysis portion, a Hct value of the blood is measured by supplying the blood to the electrode system, applying a voltage to cause a current to flow, and detecting a value of the current. Using this Hct value, the amount of the component is corrected.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Endovascular device for entrapment of particulate matter and method for use
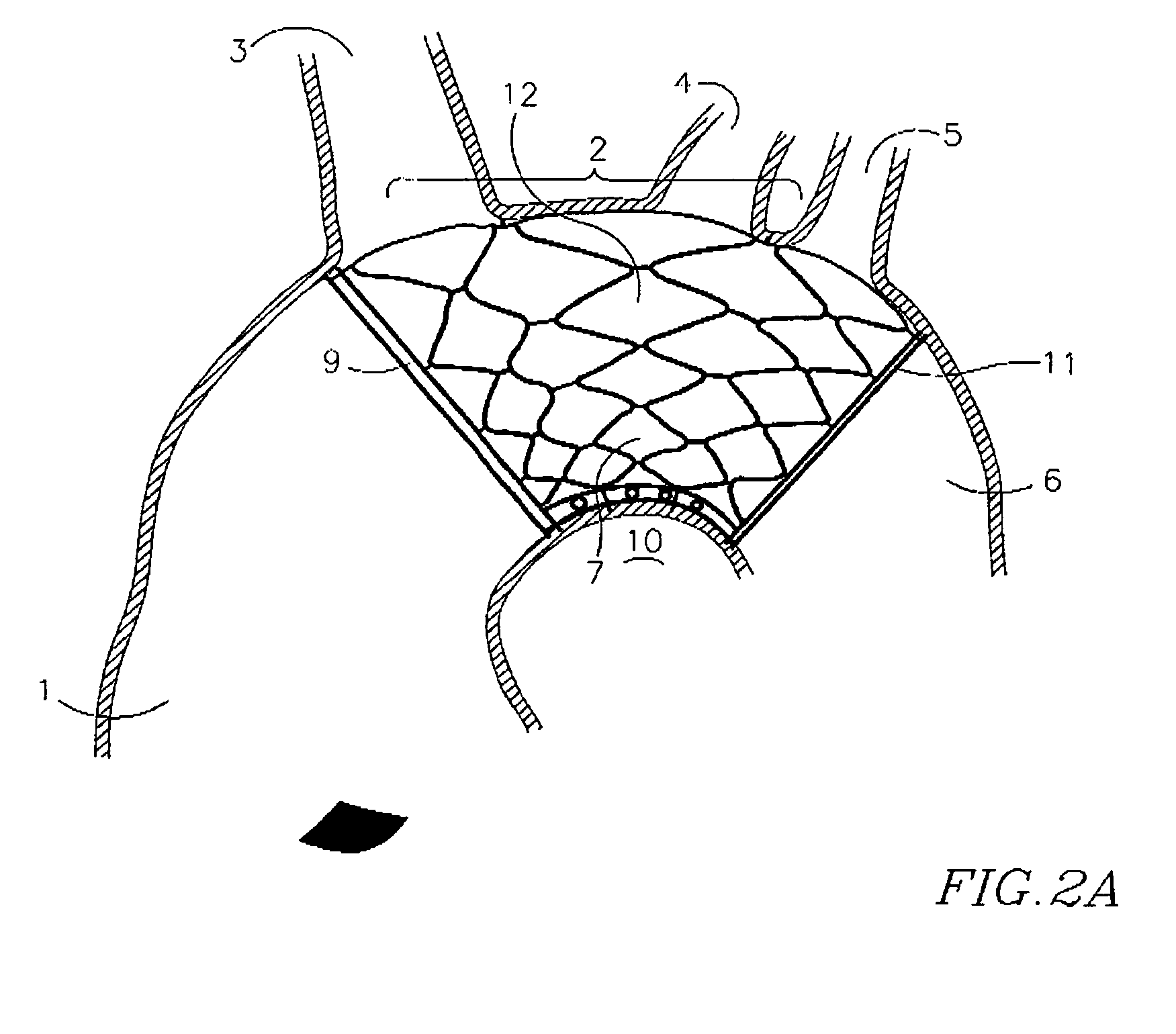
A device and method for protecting a blood vessel, and hence bodily tissues, against damage caused by particulate such as an embolus. The device may be a stent, for insertion in a large artery such as the ascending aorta, and may be combined with a filter. In one embodiment, the device includes an outer wire frame rather than a stent. The stent may be made of at least one layer of mesh, which is typically attached or mounted to the arterial wall. Typically only part of the stent is attached (for example at a reinforcing ring structure). Typically the size of the apertures of the mesh at the top portion of the stent is smaller than the bottom portion of the stent. The device and method are particularly useful in preventing blockages of flow to the brain, but have other uses as well. An electric charge may be placed on the device, for example, to prevent blood components from collecting.
Owner:KEYSTONE HEART
Contact lens for collecting tears and detecting analytes for determining health status, ovulation detection, and diabetes screening
InactiveUS20070016074A1Increase oxygenationIncreased riskOrganic active ingredientsHeart defibrillatorsConfocalChemical products
Owner:GEELUX HLDG LTD
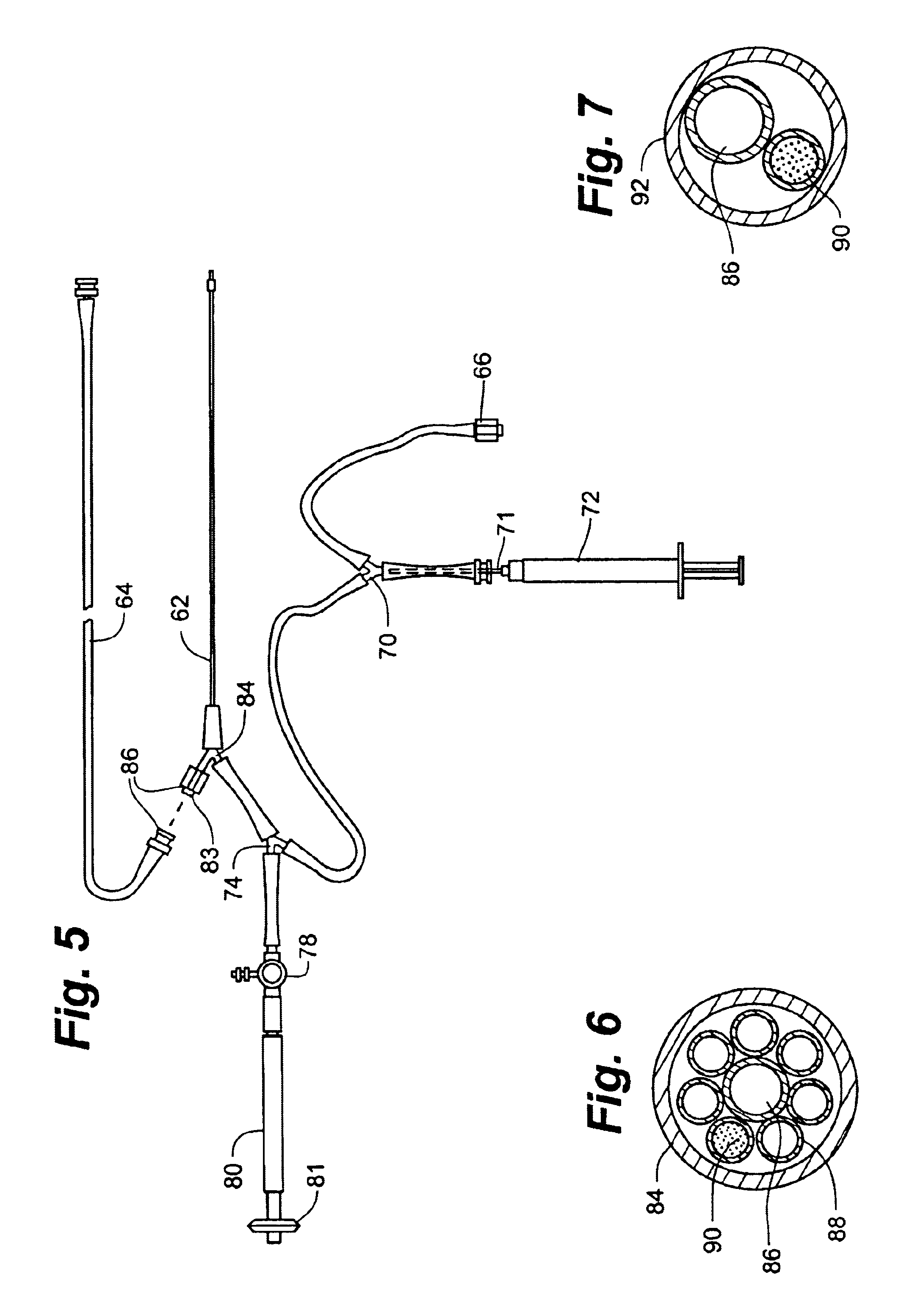
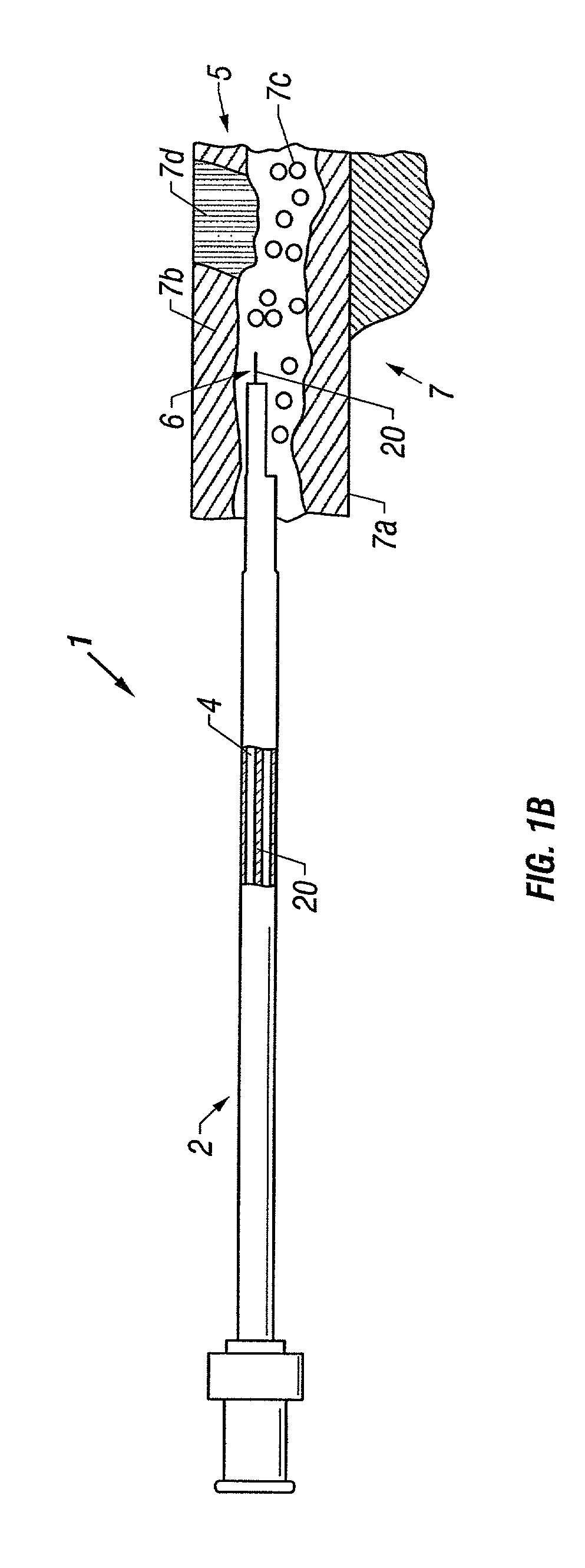
Catheter with optical fiber sensor
An apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes an intravascular device to perform a therapeutic treatment and at least one optical fiber disposed through the intravascular device. The optical fiber is configured to provide diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
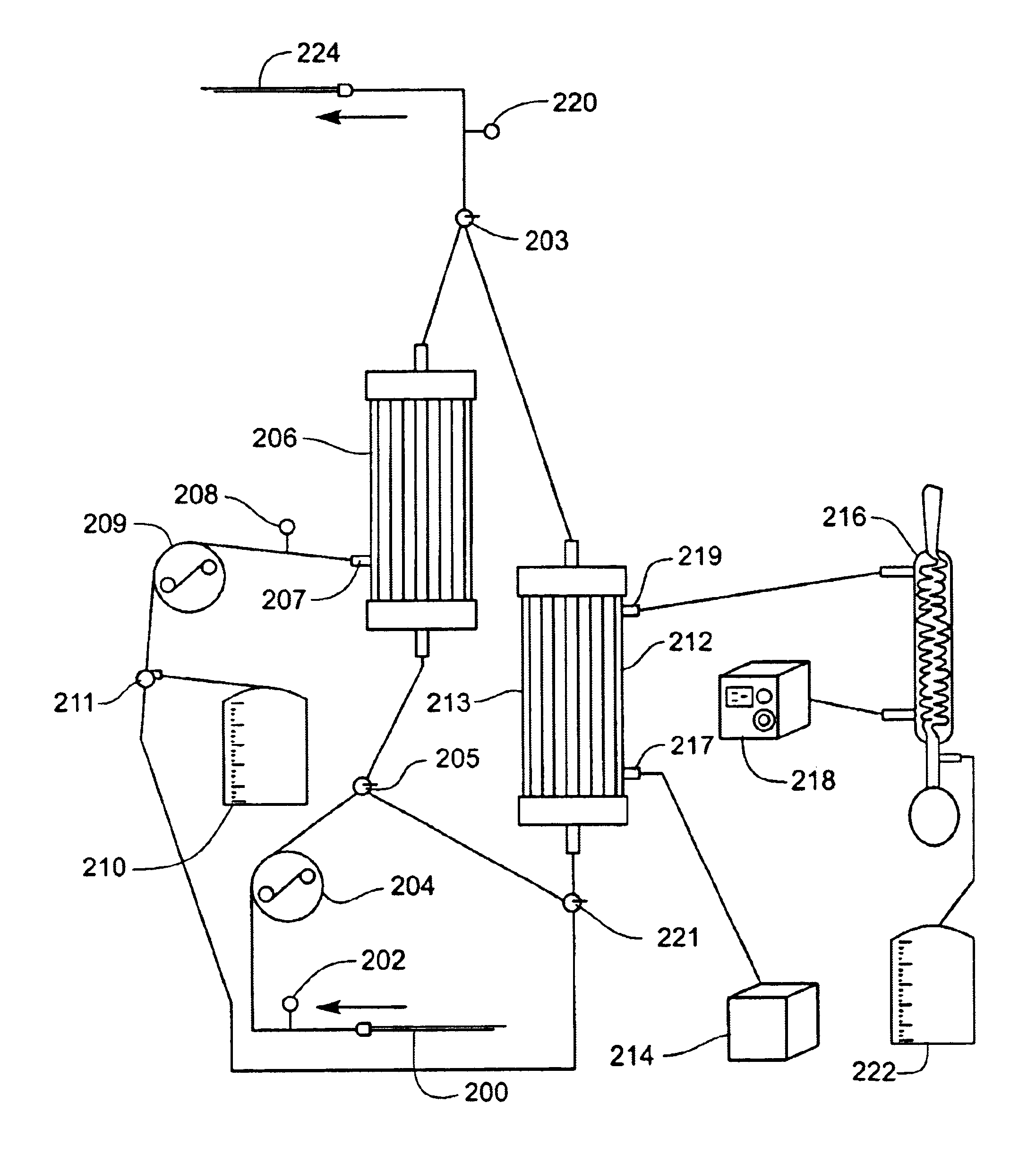
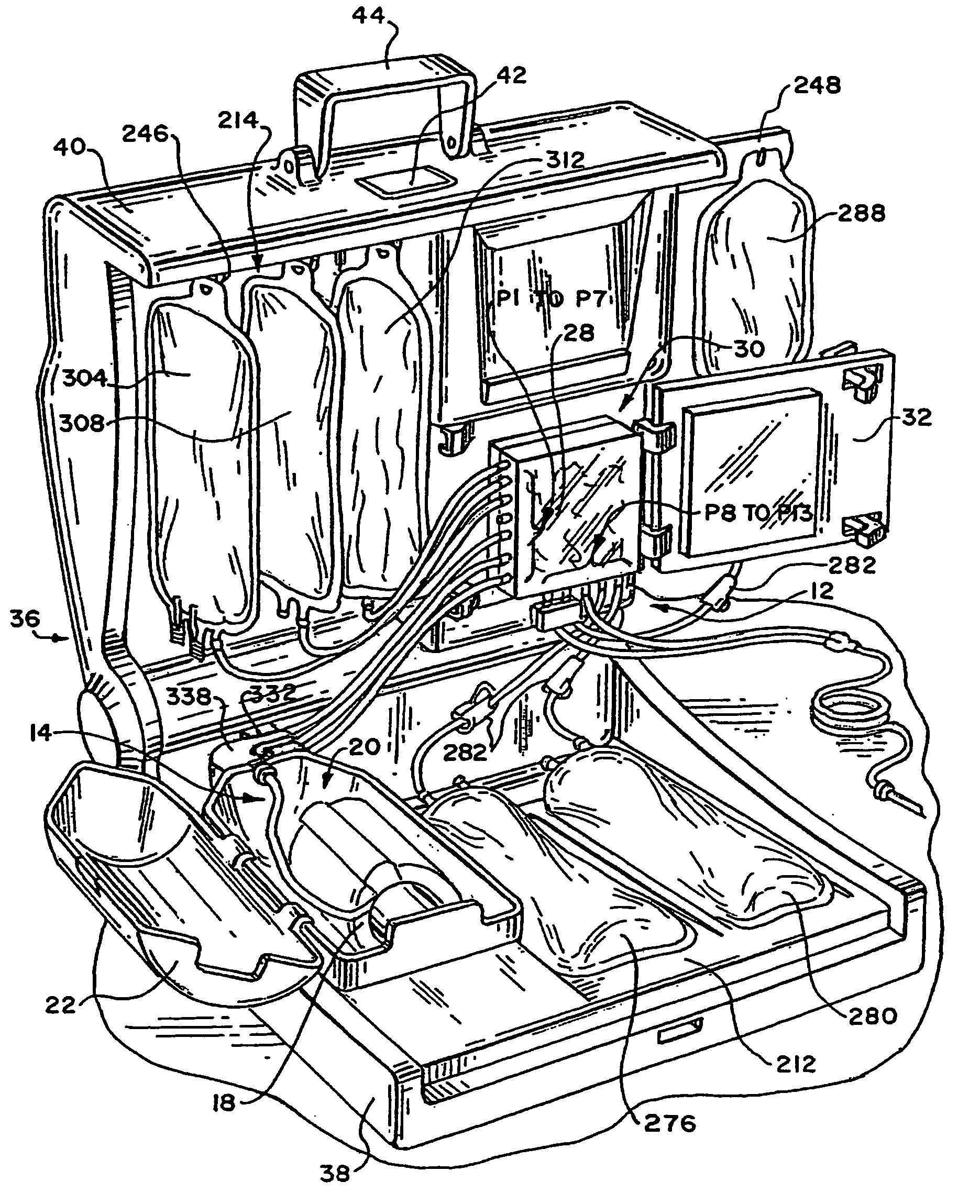
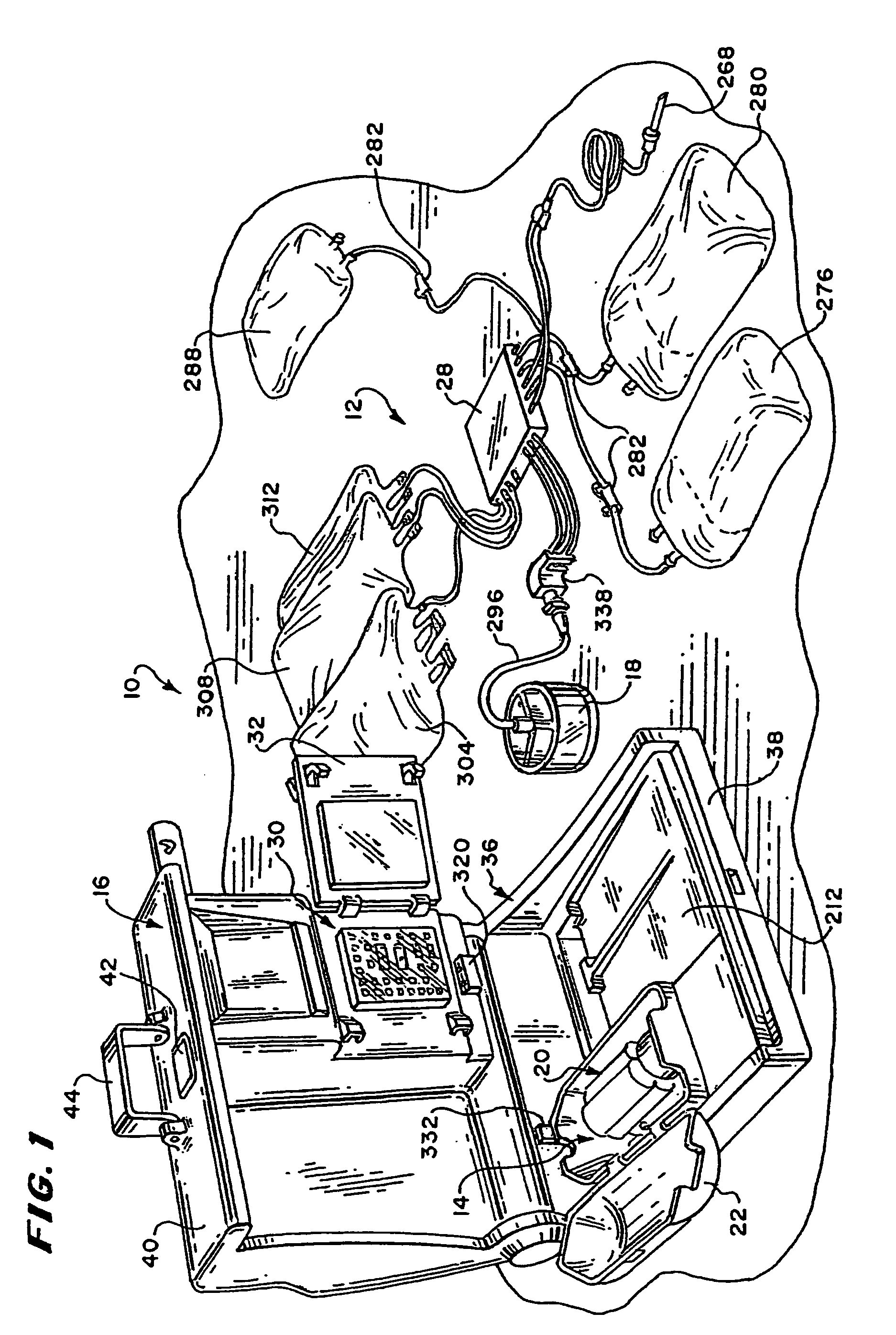
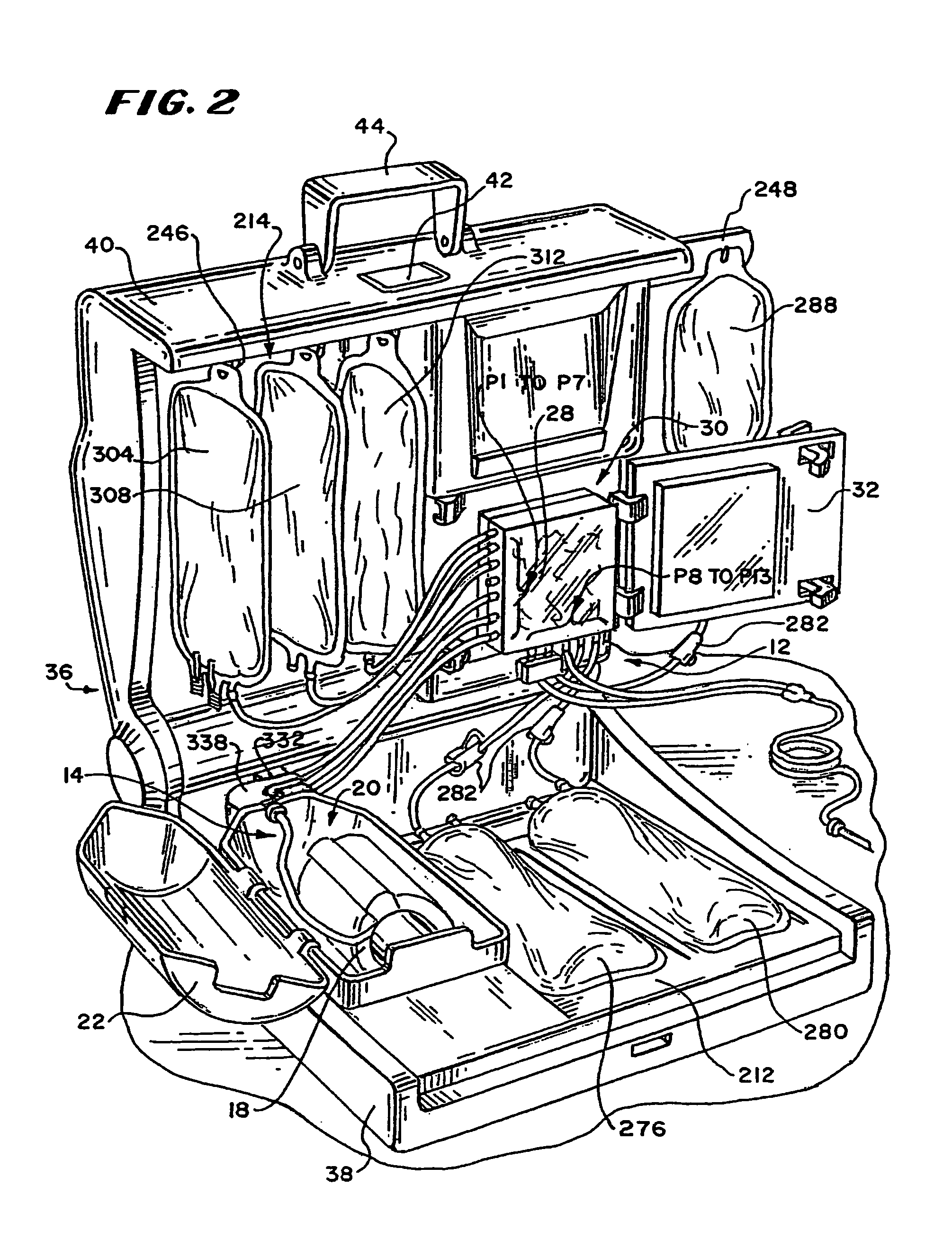
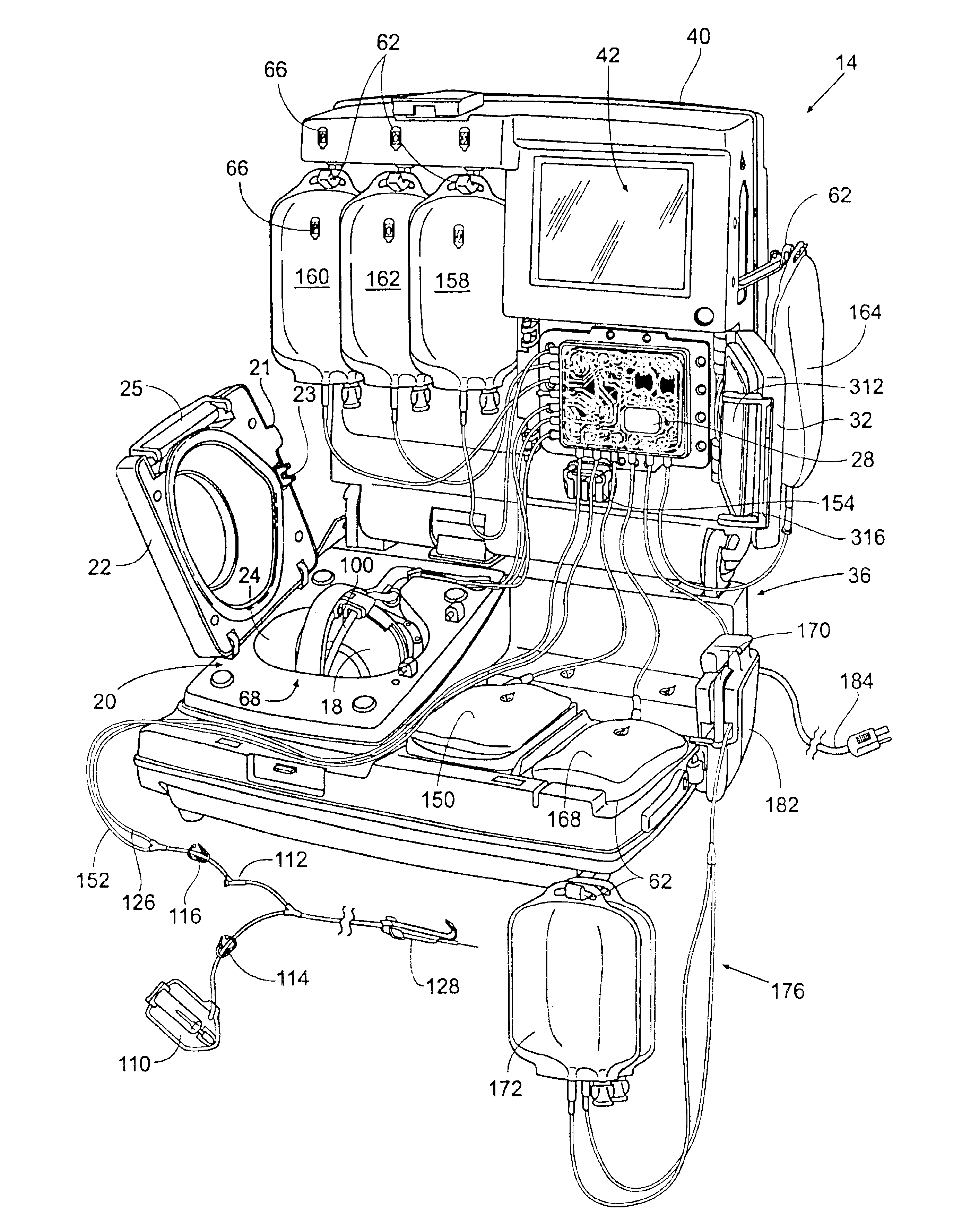
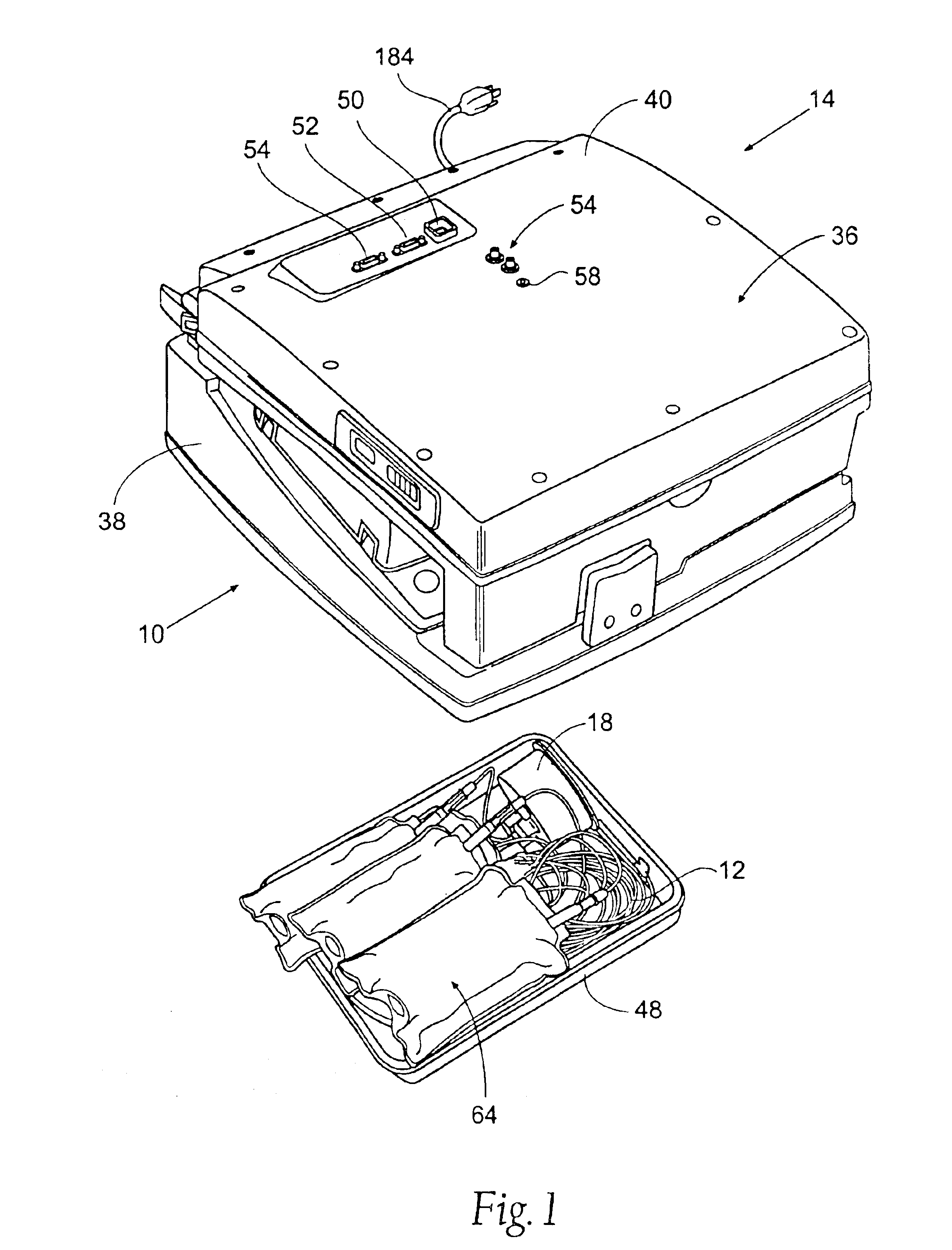
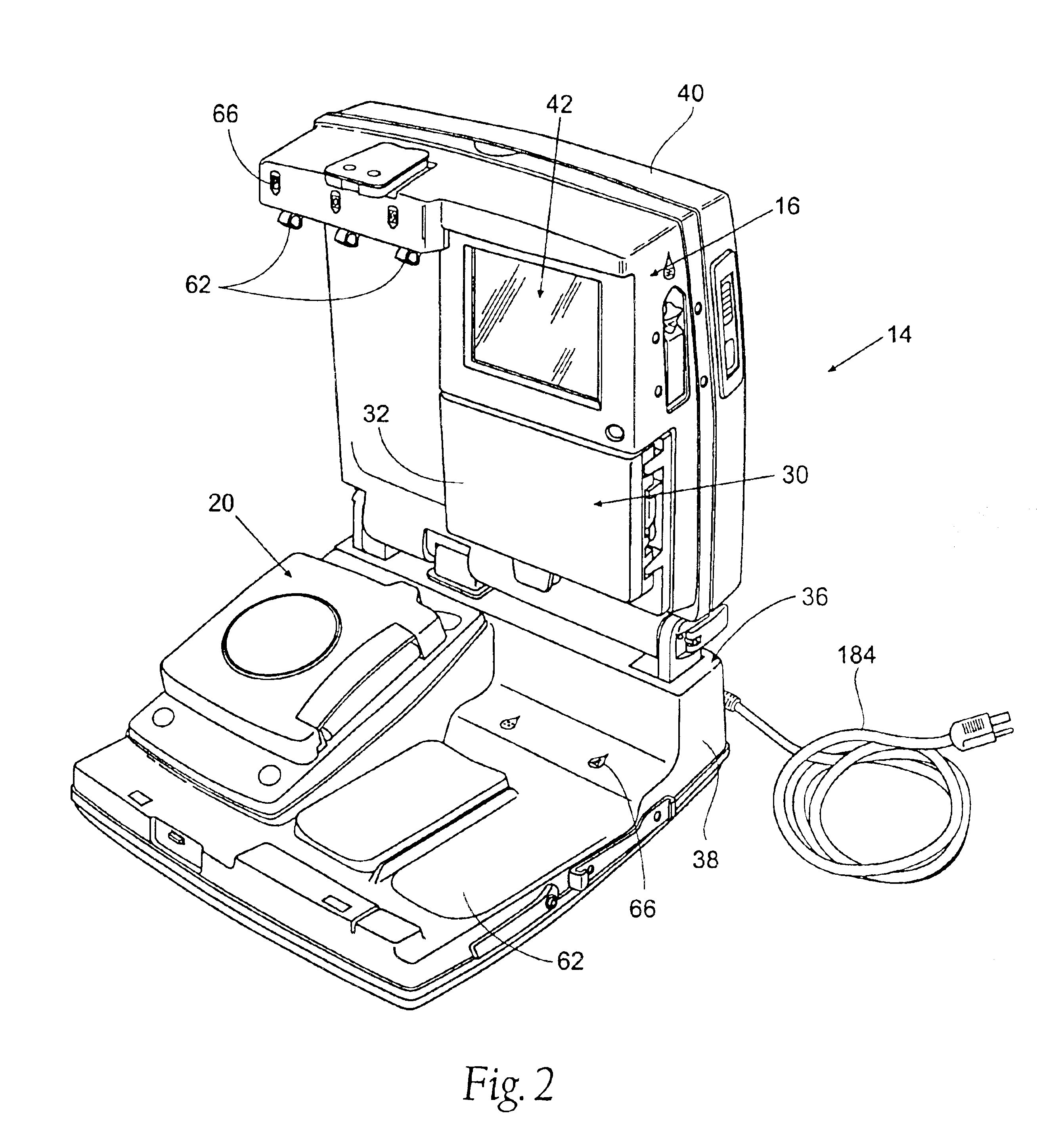
Blood separation systems and methods using a multiple function pump station to perform different on-line processing tasks
InactiveUS7041076B1Straightforward and accurate control functionReduce complexityOther blood circulation devicesRotary centrifugesBlood componentWhite blood cell
A multiple function pump station performs different on-line processing tasks. The pump station can be operated in one mode to draw blood from a donor can, in another mode, be operated to return blood to the donor. The pump station used to draw blood from a donor can also be used to perform subsequent blood processing tasks, such as mixing processing or additive fluids with the blood, or transfering a harvested blood component to a storage container, or finishing the processing of a harvested blood component, e.g., by passage through a filter to remove leukocytes.
Owner:FENWAL
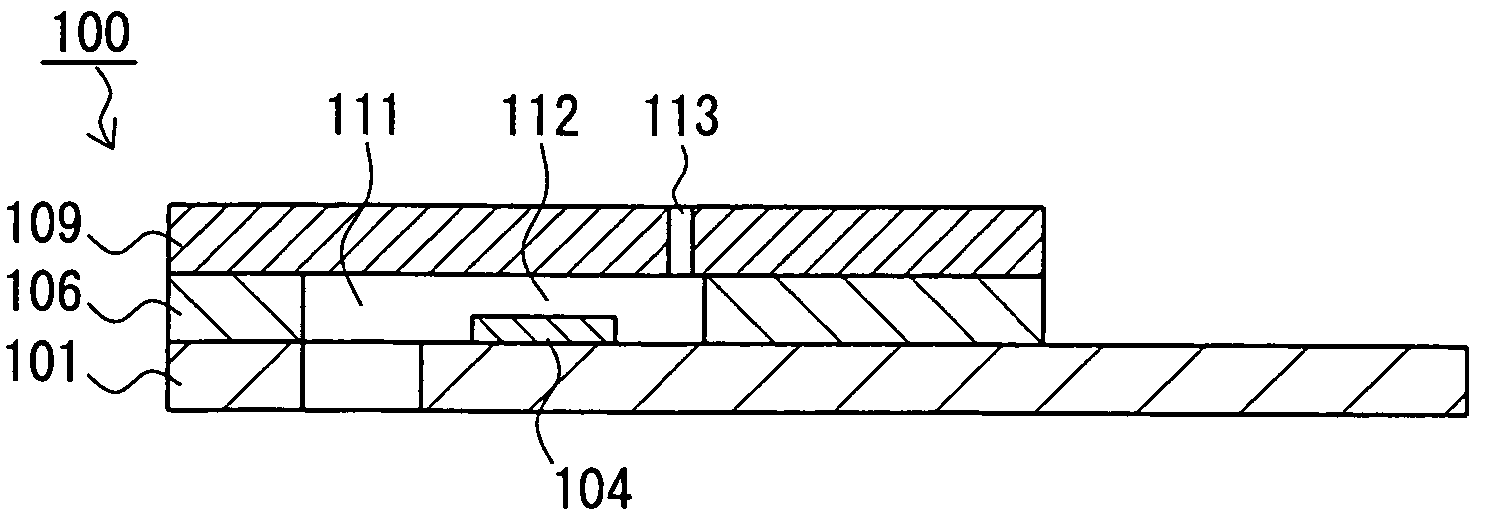
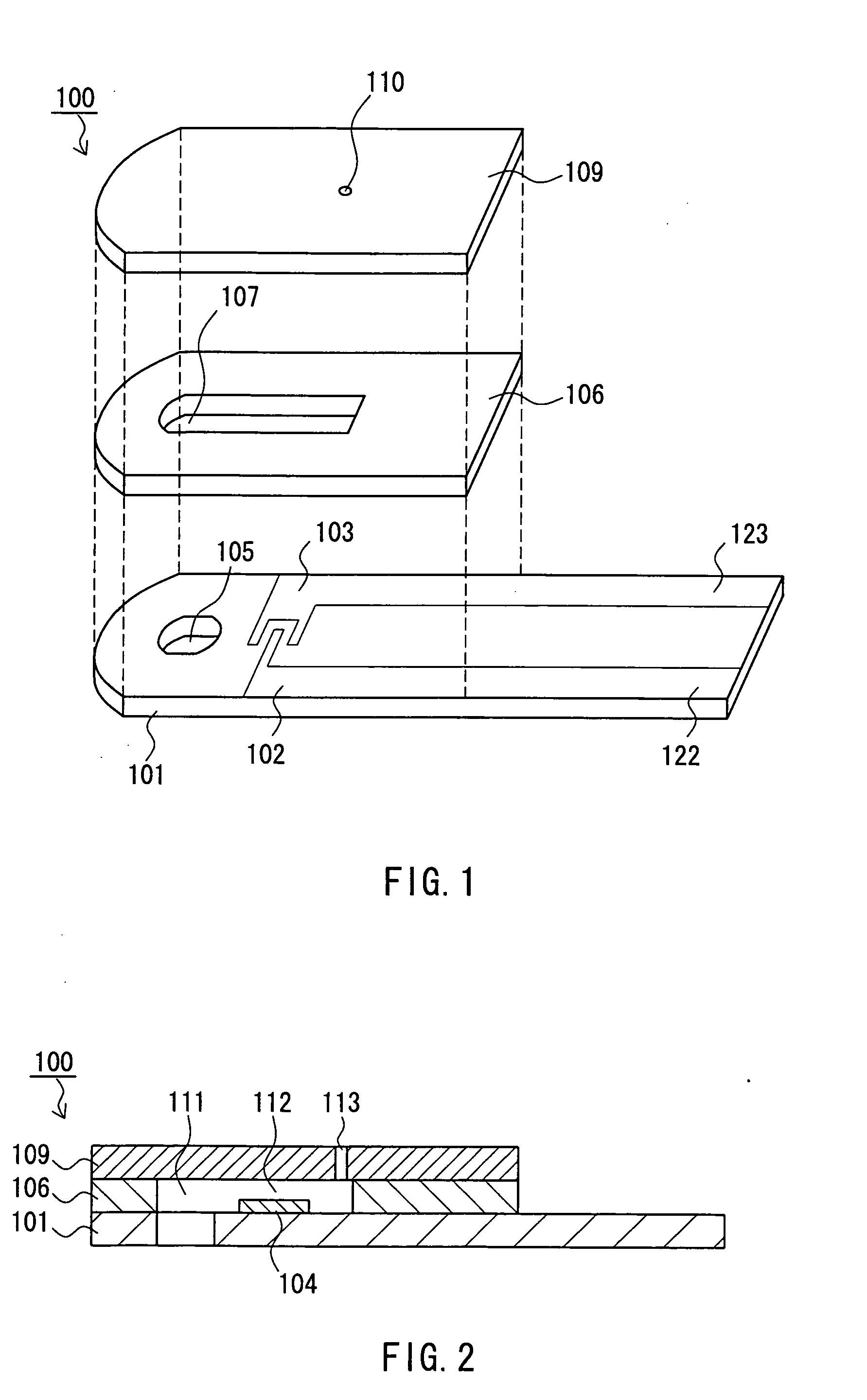
Sensor for blood component analysis
InactiveUS20050123443A1Reliable measurementLess painfulAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood collectionComing out
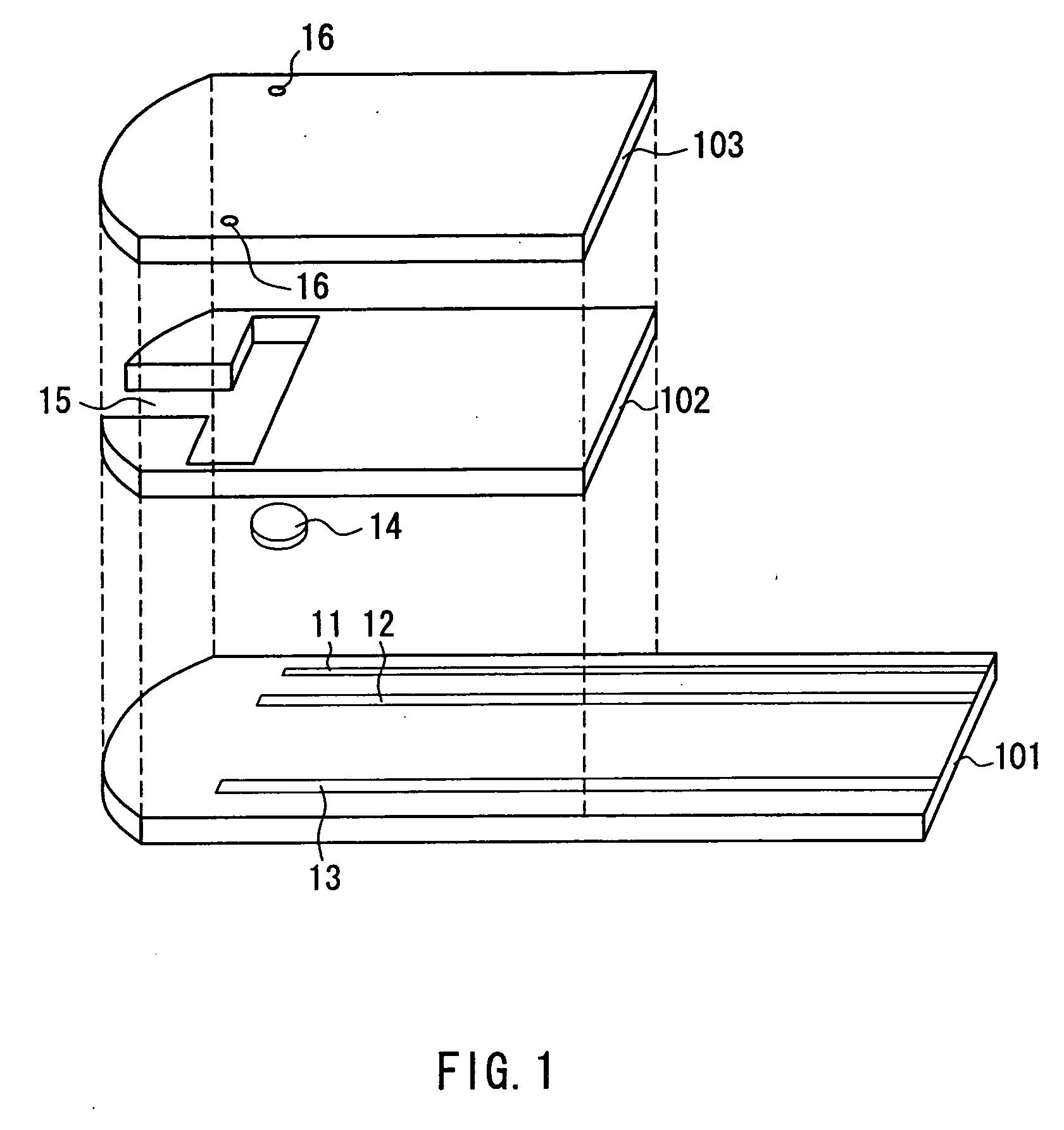
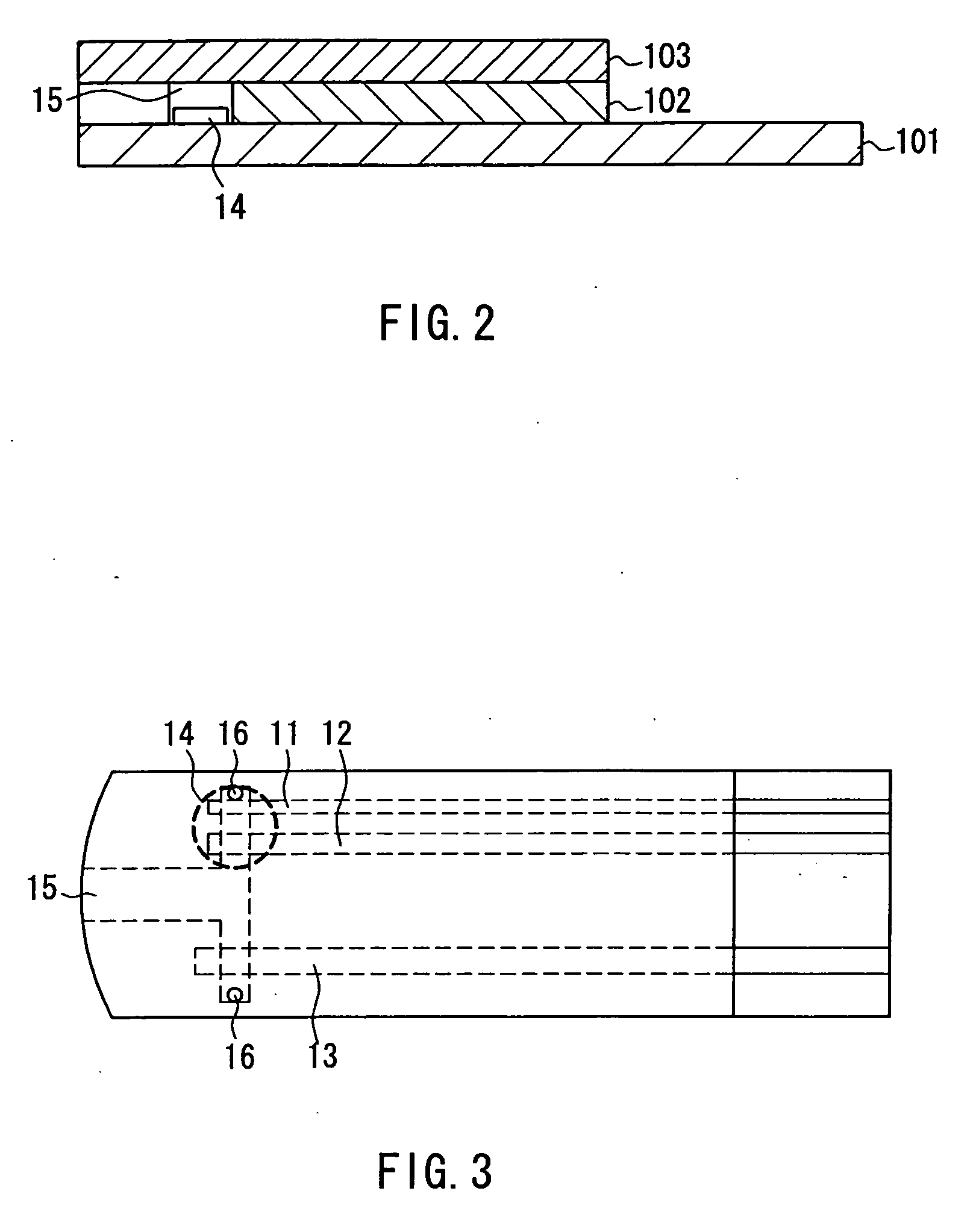
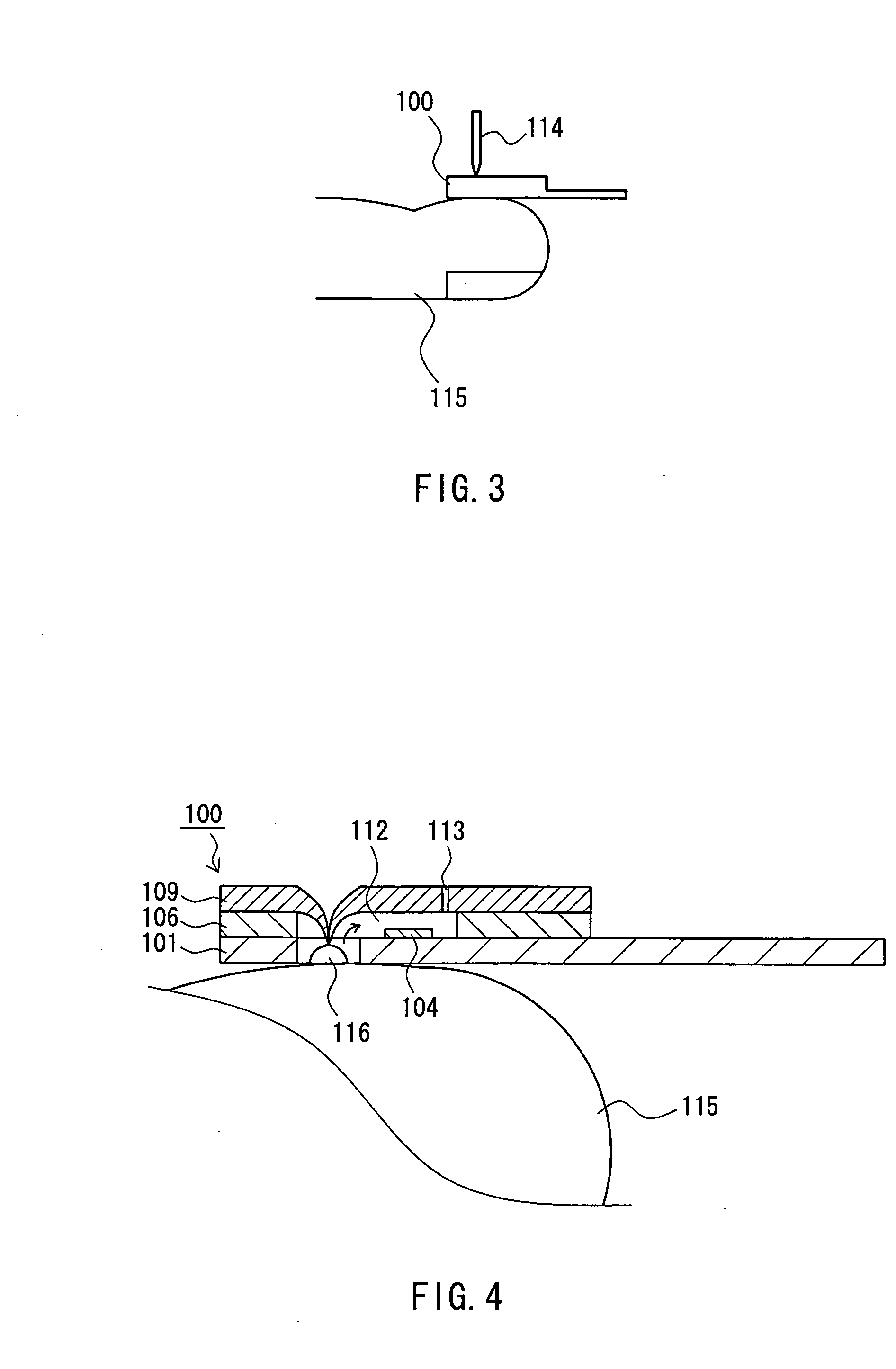
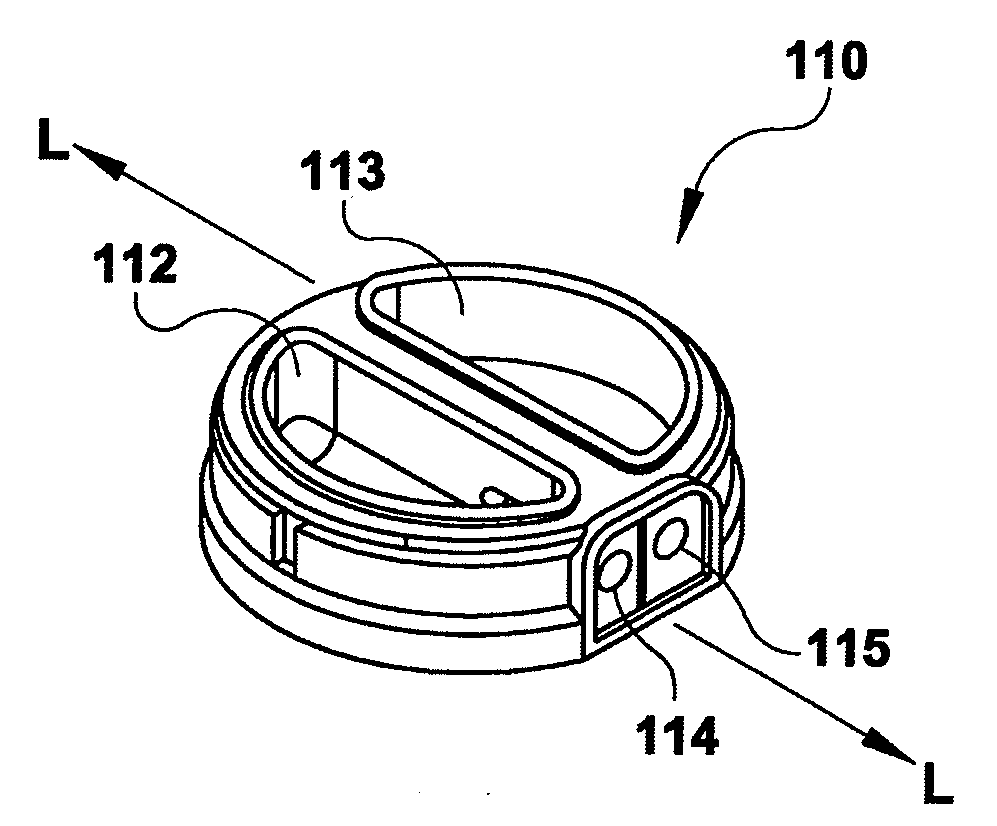
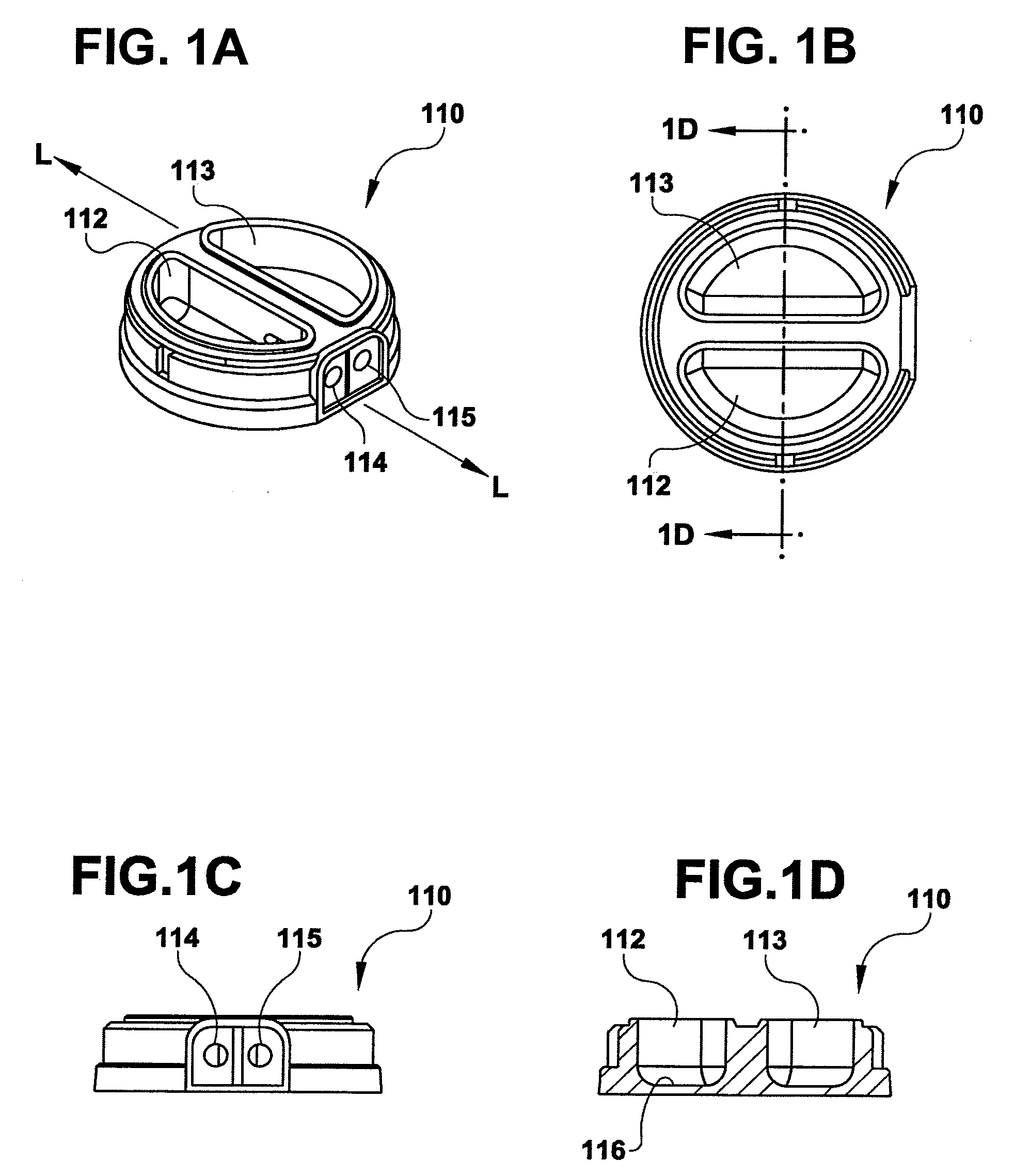
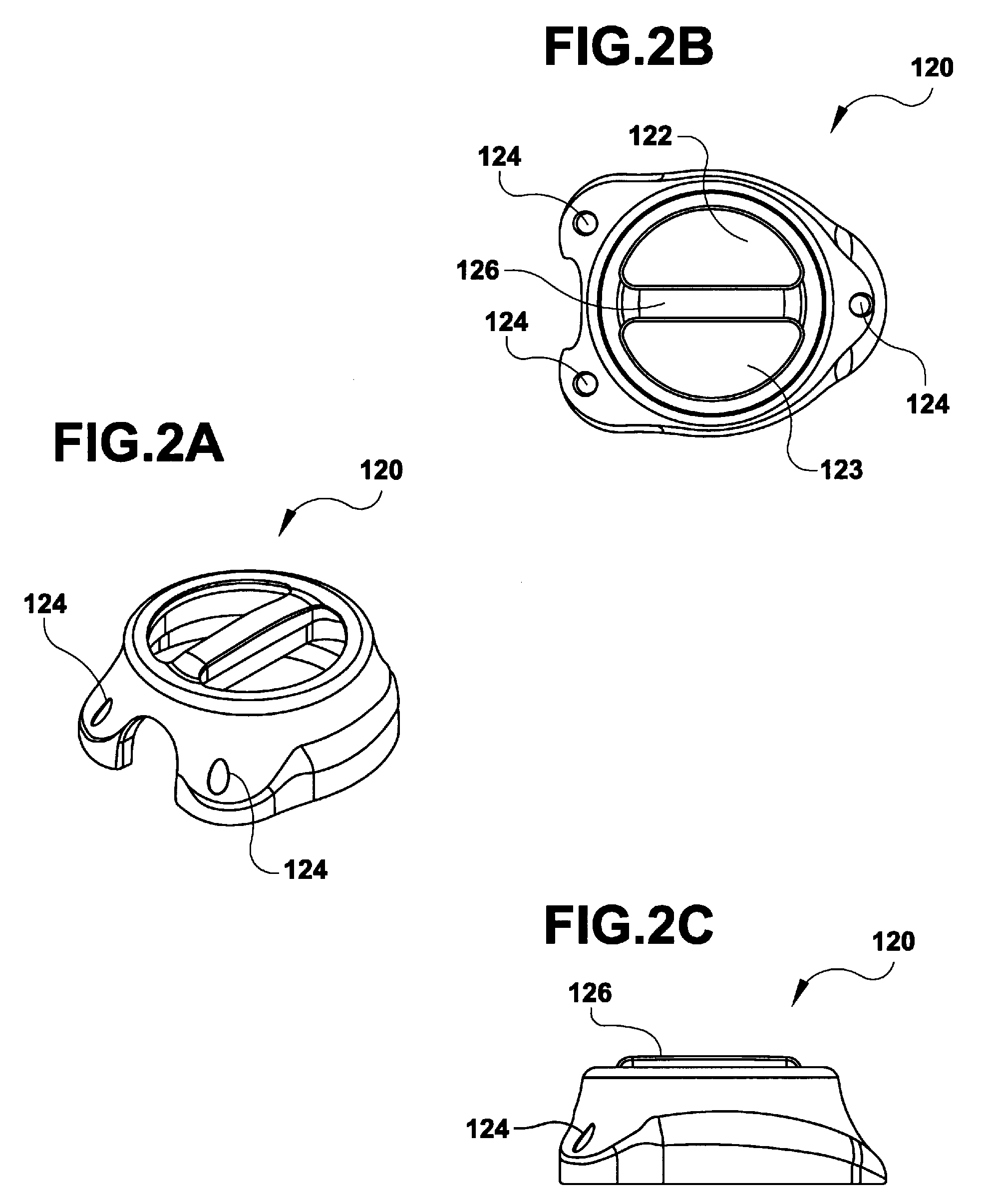
A sensor for blood component analysis, which allows even a trace amount of blood to be led to an analysis portion reliably. The sensor for blood component analysis includes a substrate, a spacer, and a cover. The cover is disposed on the substrate with the spacer intervening between the cover and the substrate, whereby a space that serves as an analysis portion and a channel for leading blood to the analysis portion is formed inside the sensor. Through holes are formed in the substrate and the spacer, respectively, so that a common through hole through which a needle of a lancet can pass is formed when the spacer is disposed on the substrate. The through hole of the spacer communicates with the channel and a top of the through hole of the spacer is covered with the cover, whereby a lancing portion is formed by the common through hole and a portion of the cover covering the top of the through hole of the spacer. In use, the sensor is placed at a position where blood collection is to be performed, the portion of the cover covering the lancing portion is broken through with the needle of the lancet so that the needle is allowed to pass through the common through hole to puncture the position, and blood that has come out is guided by a downwardly protruding burr formed when the cover is broken through so that the blood is led to the channel and flows through the channel to be led to the analysis portion.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Dual reservoir implantable access port
InactiveUS20090118683A1Small sizeReducing geometric footprintMedical devicesBlood componentGuide tube
An implantable access port for use in transferring fluid transdermally between an external fluid storage or dispensing device and a site within a patient is disclosed. The access port includes a body, at least two reservoirs defined within the access port body, and at least one septum secured to the body and enclosing the reservoirs within the body. The access port also includes reservoir outlets defined within the reservoirs. The access port also has body conduits defined within the body and in fluid communication with the reservoir outlets and external openings defined in the exterior of the body. An implantable access port and system for use in apheresis is also provided that includes an implantable access port, at least one needle, and a catheter that is fluidly connected to the access port.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Blood optode
ActiveUS7251518B2Diagnostics using lightScattering properties measurementsSonificationUltrasonic radiation
Owner:NIRLUS ENG
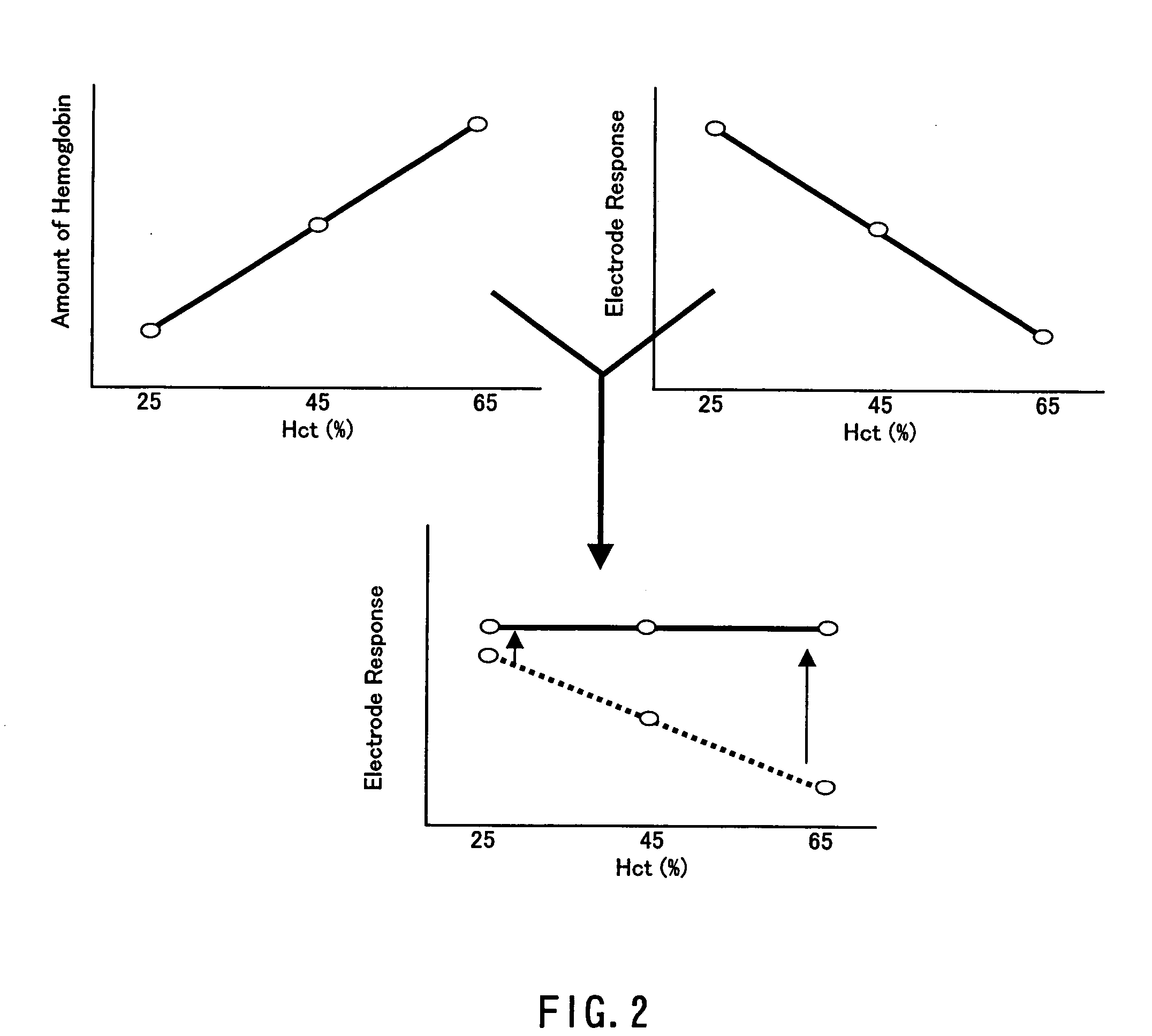
Method of measuring blood component and sensor used in the method
ActiveUS20050145490A1Great HctConvenient amountImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRed blood cellOxidoreductase
A sensor for blood component analysis that can correct the effect of a hematocrit easily is provided. The sensor includes an analysis portion including a working electrode, a counter electrode, and a reagent portion. The reagent portion includes an oxidoreductase that reacts with the blood component and a mediator, and the blood component is measured by causing a redox reaction between the blood component and the oxidoreductase in the presence of the mediator and detecting a redox current generated by the redox reaction by the working electrode and the counter electrode. In this sensor, the reagent portion further includes a hemolyzing agent (e.g., sodium cholate) for hemolyzing an erythrocyte, and when detecting the redox current, the erythrocyte is hemolyzed with the hemolyzing agent so as to cause hemoglobin released to an outside of the erythrocyte to react with the mediator and a current generated by this reaction also is detected to correct an effect of a hematocrit.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS20060029578A1Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
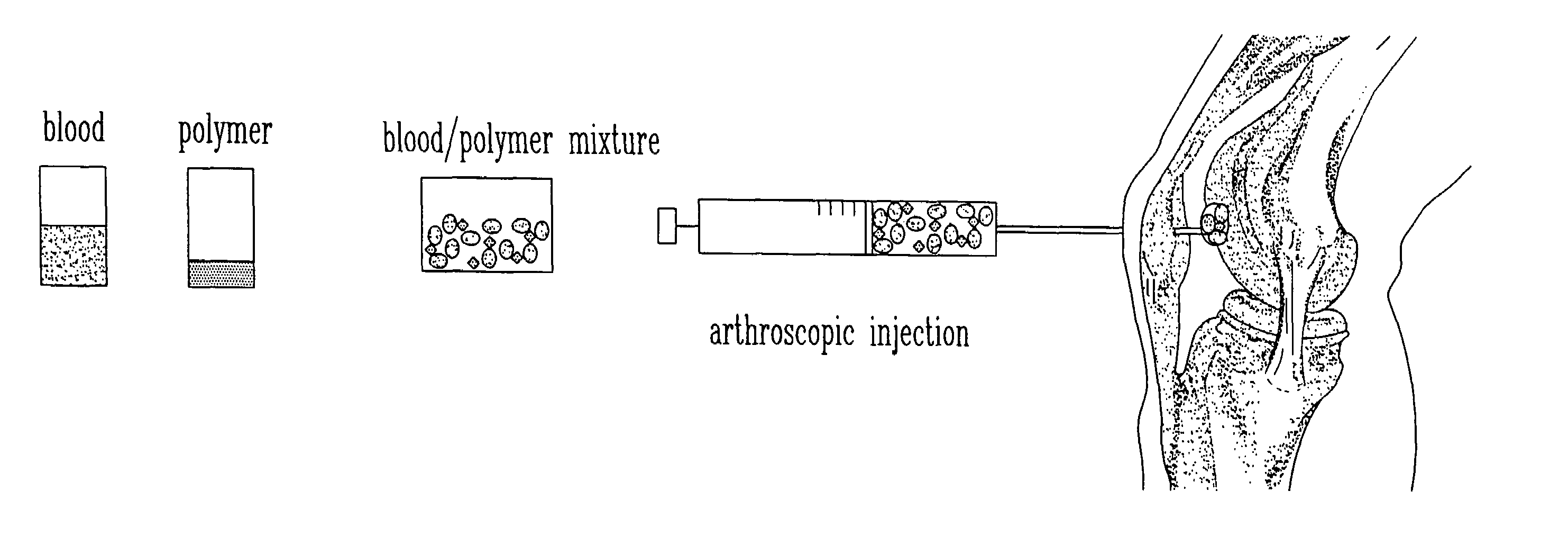
The present invention relates to a new method for repairing human or animal tissues such as cartilage, meniscus, ligament, tendon, bone, skin, cornea, periodontal tissues, abscesses, resected tumors, and ulcers. The method comprises the step of introducing into the tissue a temperature-dependent polymer gel composition such that the composition adhere to the tissue and promote support for cell proliferation for repairing the tissue. Other than a polymer, the composition preferably comprises a blood component such as whole blood, processed blood, venous blood, arterial blood, blood from bone, blood from bone-marrow, bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta blood, erythrocytes, leukocytes, monocytes, platelets, fibrinogen, thrombin and platelet rich plasma. The present invention also relates to a new composition to be used with the method of the present invention.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
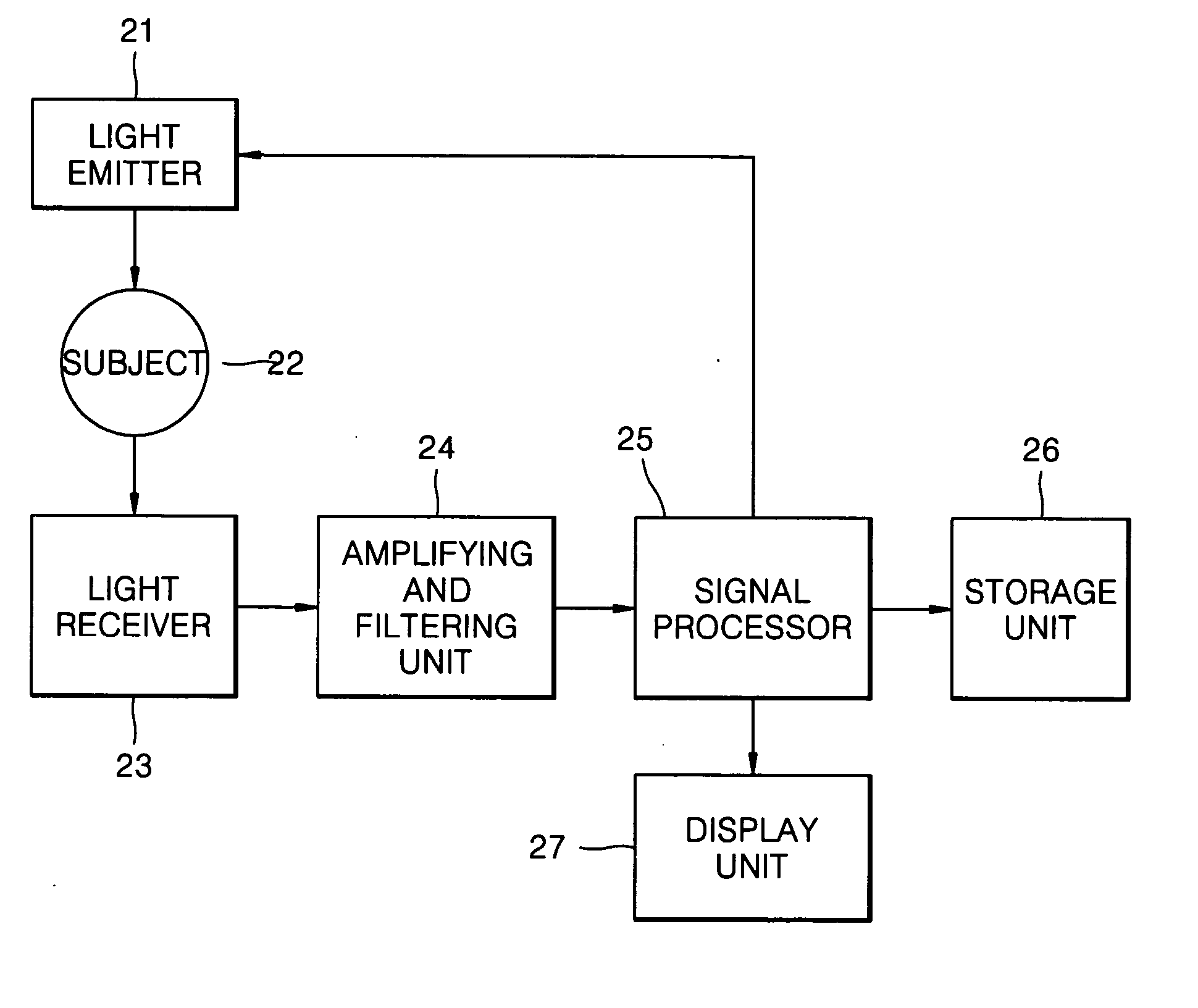
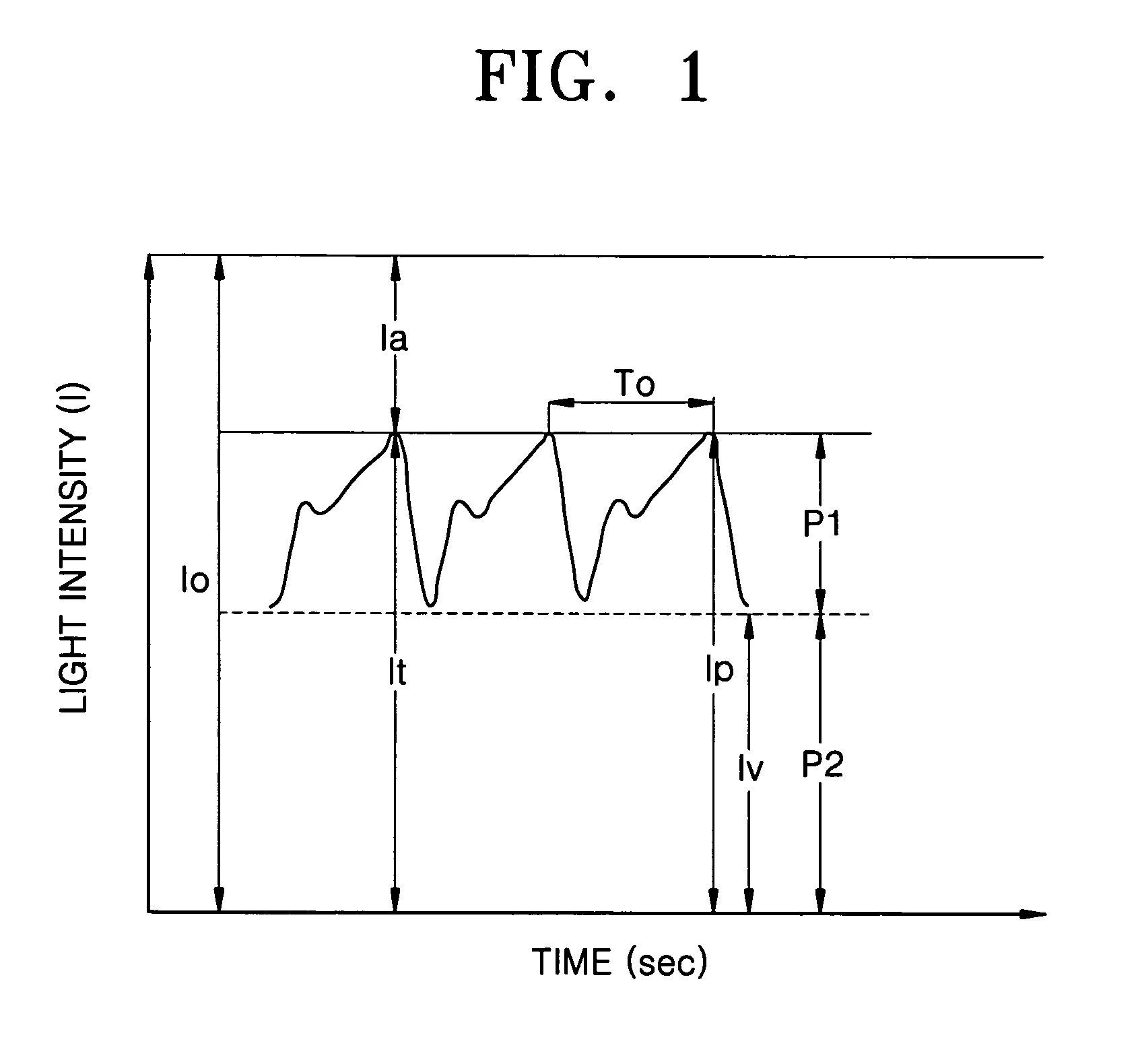
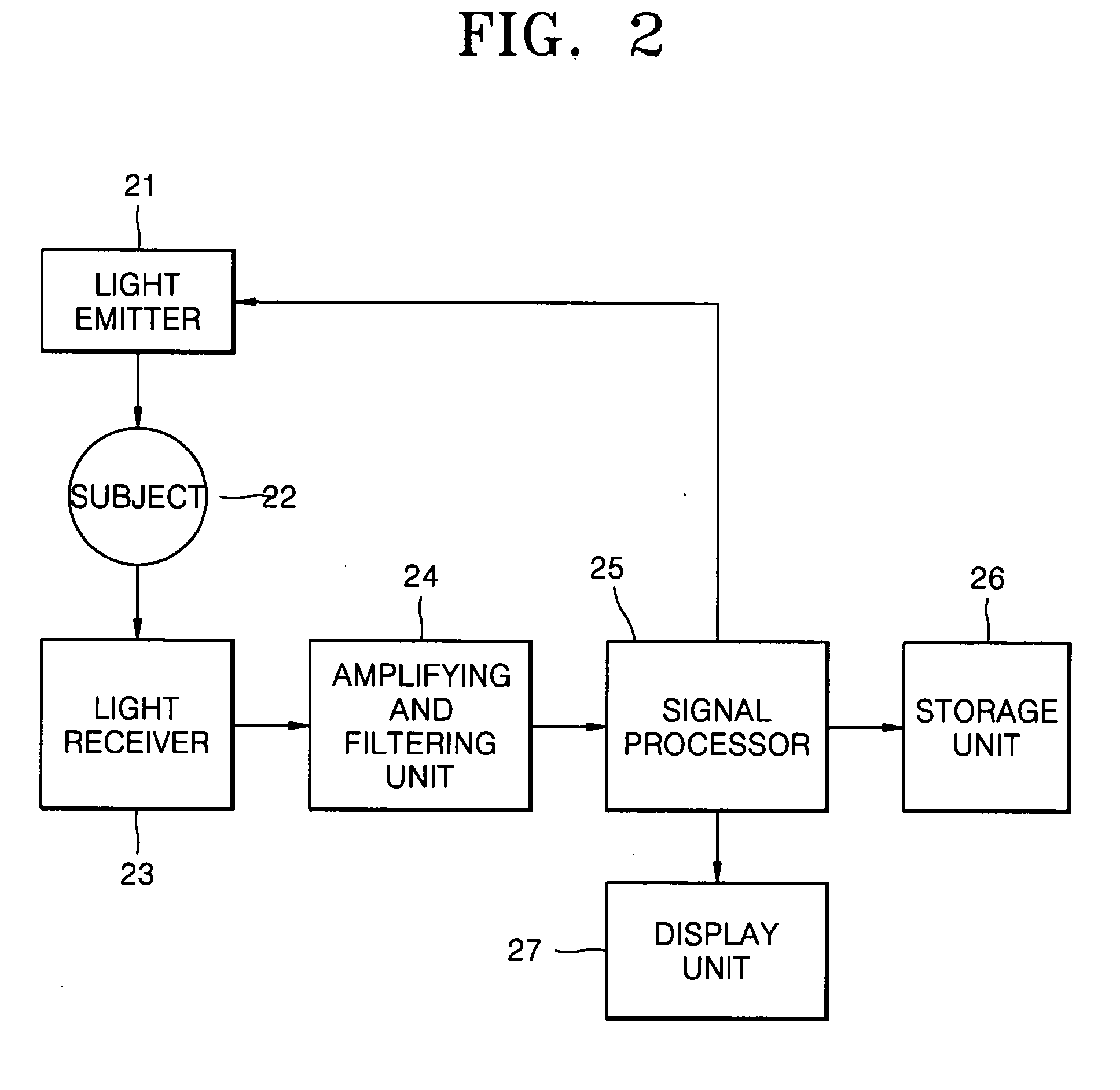
Method of removing abnormal data and blood component spectroscopy analysis system employing the same
InactiveUS20040204865A1Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionDigital variable/waveform displayOptical radiationBlood component
A method of removing abnormal data in a blood component analysis system using spectroscopy to estimate a concentration of a blood component by analyzing a photo-plethysmographic (PPG) signal obtained by radiating light of first and second wavelengths reacting to the blood component on a subject and detecting light corresponding to the first and second wavelengths output from the subject, includes collecting the PPG signal corresponding to the first and second wavelengths for a predetermined unit period of time, calculating "n" parameters, with respect to "n" pulse data included in the collected PPG signal, where n is a positive integer, calculating an average of the "n" parameters, and comparing a ratio of a number of parameters whose deviation from the average is greater than a predetermined standard deviation to the "n" parameters with a predetermined removal reference value to determine whether the "n" pulse data is valid.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiple laminar flow-based particle and cellular separation with laser steering
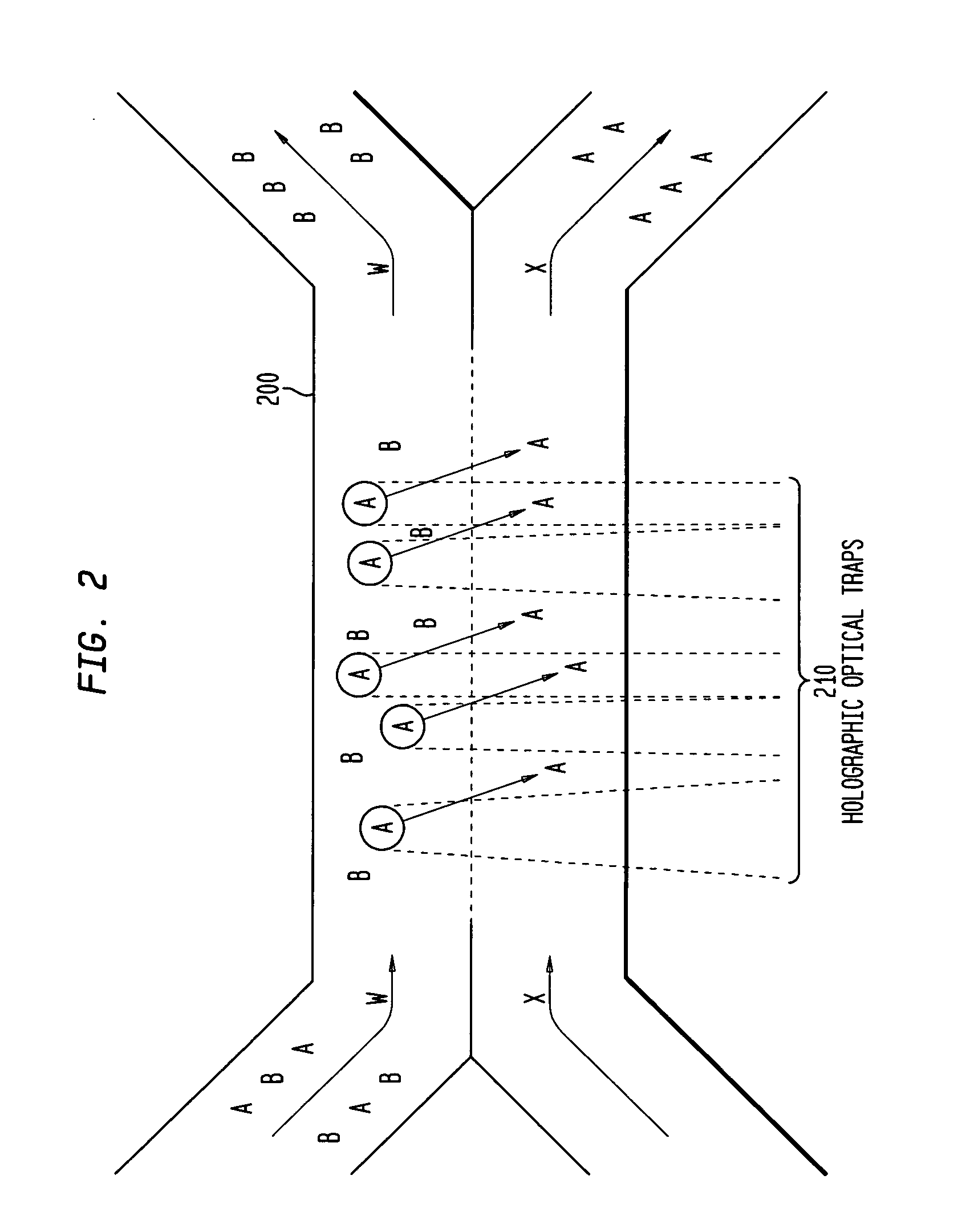
InactiveUS20050121604A1Save a lot of timeImprove throughputDielectrophoresisLaser detailsCellular componentBlood component
The invention provides a method, apparatus and system for separating blood and other types of cellular components, and can be combined with holographic optical trapping manipulation or other forms of optical tweezing. One of the exemplary methods includes providing a first flow having a plurality of blood components; providing a second flow; contacting the first flow with the second flow to provide a first separation region; and differentially sedimenting a first blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components into the second flow while concurrently maintaining a second blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components in the first flow. The second flow having the first blood cellular component is then differentially removed from the first flow having the second blood cellular component. Holographic optical traps may also be utilized in conjunction with the various flows to move selected components from one flow to another, as part of or in addition to a separation stage.
Owner:PREMIUM GENETICS UK
Modified therapeutic peptides with extended half-lives in vivo
A method for protecting a peptide from peptidase activity in vivo, the peptide being composed of between 2 and 50 amino acids and having a C-terminus and an N-terminus and a C-terminus amino acid and an N-terminus amino acid is described. In the first step of the method, the peptide is modified by attaching a reactive group to the C-terminus amino acid, to the N-terminus amino acid, or to an amino acid located between the N-terminus and the C-terminus, such that the modified peptide is capable of forming a covalent bond in vivo with a reactive functionality on a blood component. In the next step, a covalent bond is formed between the reactive group and a reactive functionality on a blood component to form a peptide-blood component conjugate, thereby protecting said peptide from peptidase activity. The final step of the method involves the analyzing of the stability of the peptide-blood component conjugate to assess the protection of the peptide from peptidase activity.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
Blood component processing systems and methods using fluid-actuated pumping elements that are integrity tested prior to use
Blood component processing systems and methods are coupled to a blood component processing device. The systems and methods include a fluid circuit that comprises at least one fluid pressure actuated pump station, at least one fluid flow path communicating with the pump station, and at least one valve in the fluid flow path. A control module is sized and configured to interact with the fluid circuit. The control module includes an actuator to selectively apply fluid pressure to the pump station in concert with operation of the valve to pump fluid through the fluid flow path in response to a control program. A controller coupled to the control module includes the control program and a fluid circuit integrity test function. The fluid circuit integrity test function commands the control module to selectively apply fluid pressure to the pump station in concert with operation of the valve to introduce a fluid within a region of the fluid circuit and to confine the fluid within the region while applying fluid pressure to the pump chamber. The fluid circuit integrity test function generates an integrity output in response to sensing leakage of fluid from the region.
Owner:FENWAL
Catheter with optical fiber sensor
An apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes an intravascular device to perform a therapeutic treatment and at least one optical fiber disposed through the intravascular device. The optical fiber is configured to provide diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
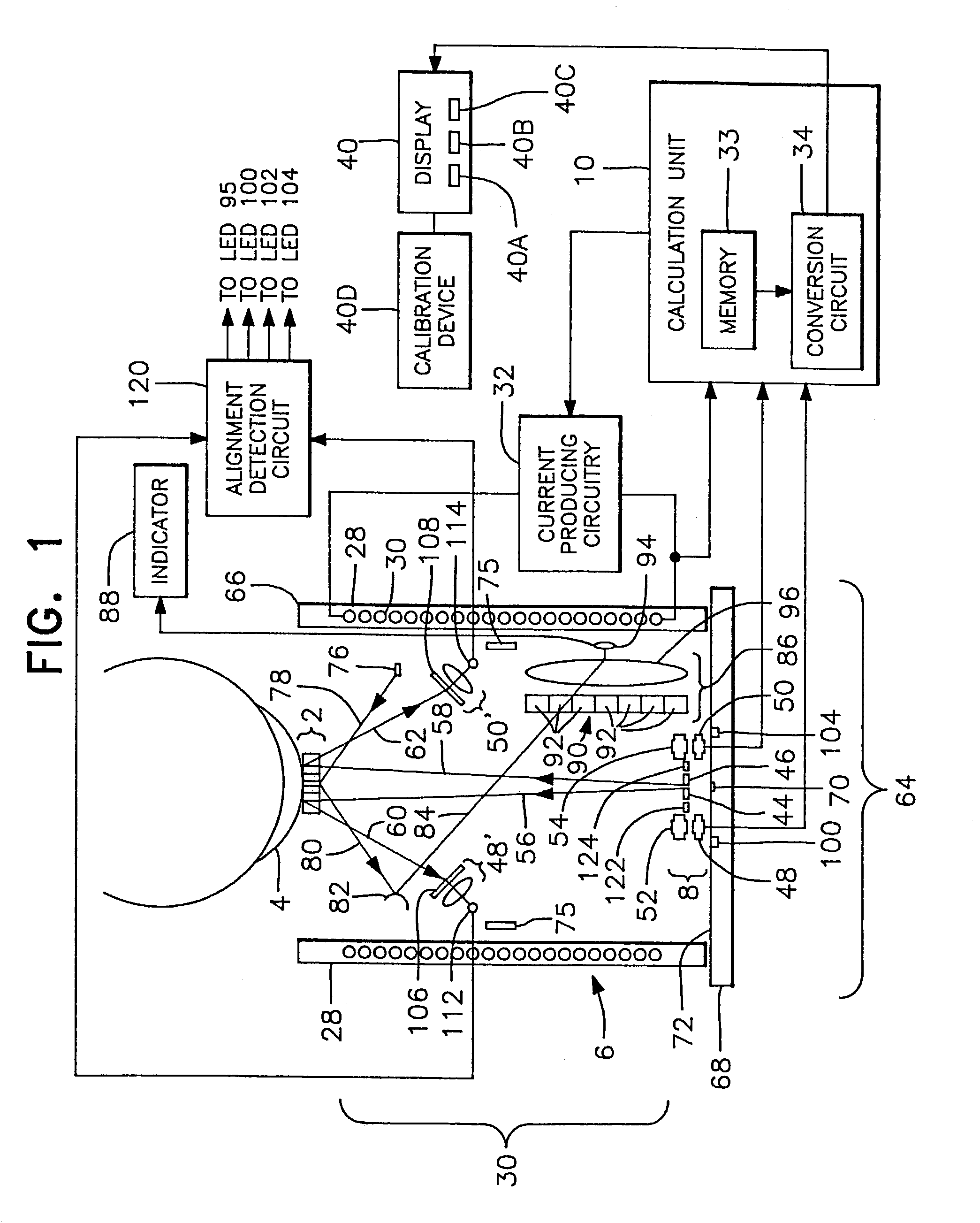
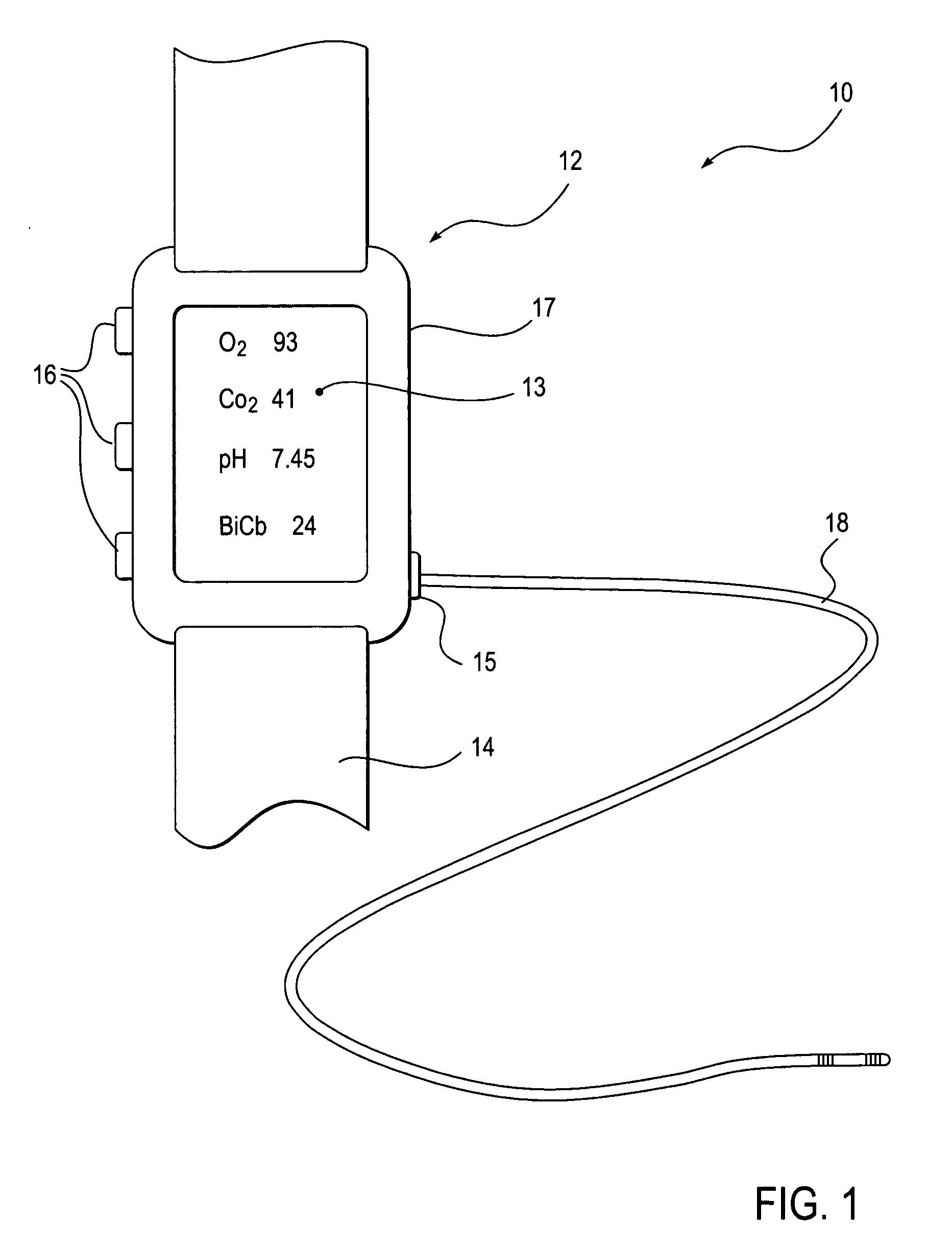
Apparatus for ascertaining blood characteristics and probe for use therewith
InactiveUS20050054905A1Heightened risk of mechanical and therapeutic misadventureImprove the lubrication effectCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringBlood componentAntithrombogenic surface
An apparatus for use with a patient having a vessel carrying blood to ascertain characteristics of the blood. The apparatus includes a display module and a probe having a distal extremity adapted to be inserted into the vessel of the patient and having a proximal extremity coupled to the display module. The probe includes a sensor in the distal extremity for providing an electrical signal to the display module when the probe is disposed in the blood. The probe can have an antithrombogenic surface treatment for inhibiting the adhesion of blood components to the probe when disposed in the blood.
Owner:KEIMAR INC
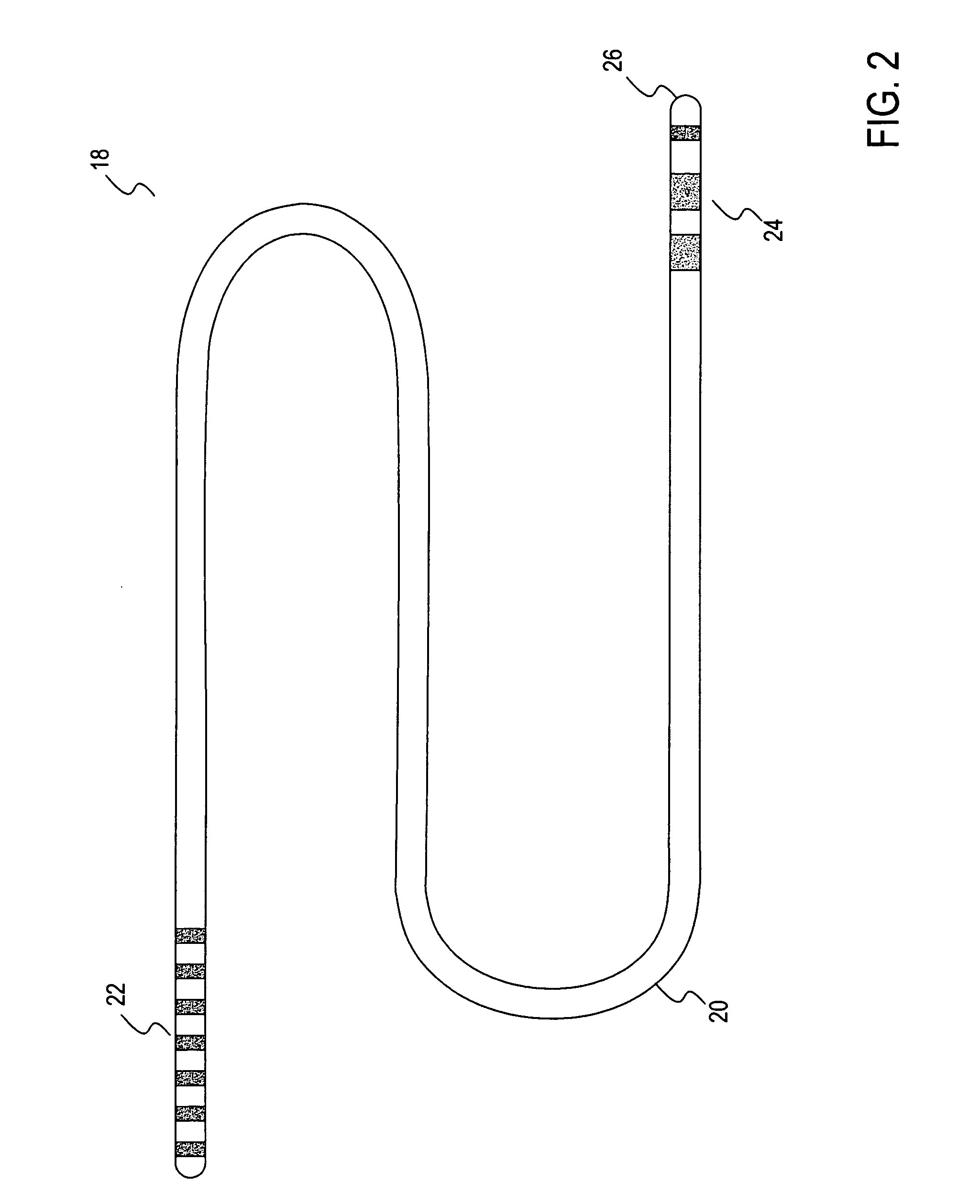
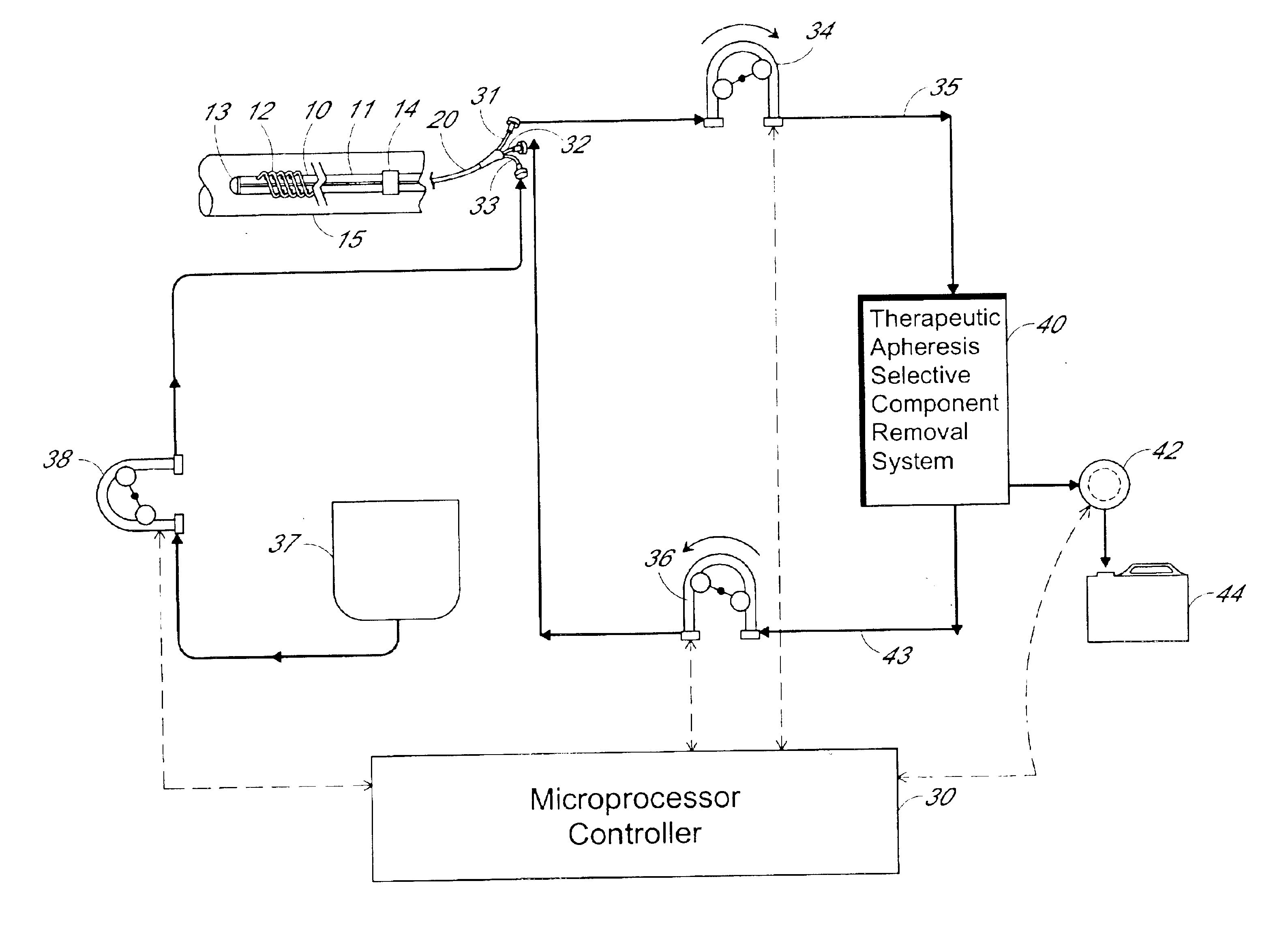
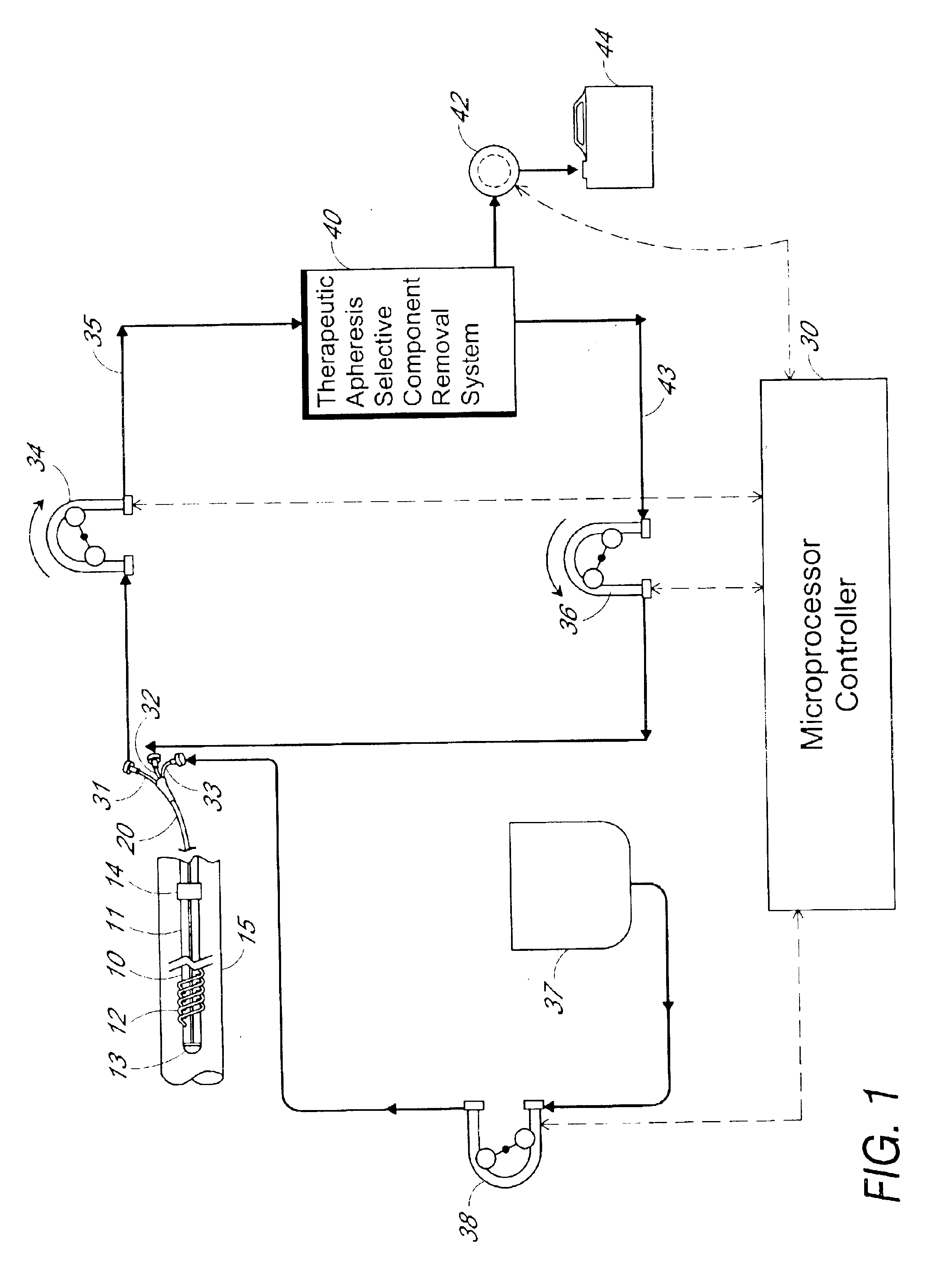
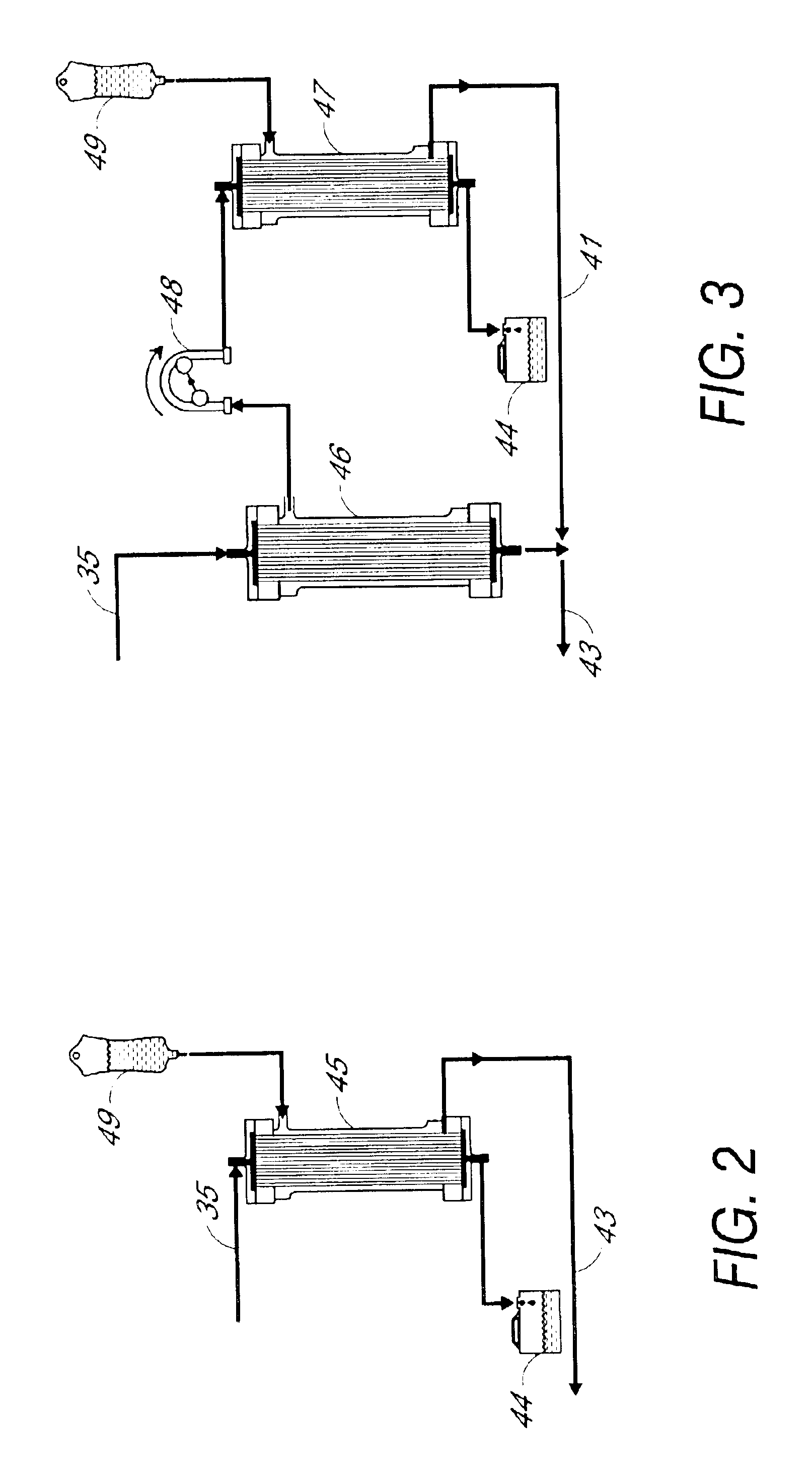
Method and apparatus for therapeutic apheresis
InactiveUS6849183B2Low mass densityIncrease mass densitySemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionDiseaseBlood plasma
A method for carrying out therapeutic apheresis comprises separating plasma from whole blood in-vivo and removing selected disease-related components from the separated plasma. Apparatus for carrying out therapeutic apheresis includes a filter device for being implanted in a blood vessel for carrying out in-vivo plasma separation having one or more elongated hollow tubes and a plurality of elongated hollow microporous fibers capable of separating plasma from whole blood at pressure and blood flow within a patient's vein, a multiple lumen catheter secured to the proximal end of the filter device having one or more lumens in fluid communication with the interior of said one or more hollow tubes and a plasma return lumen, and therapeutic apheresis apparatus for removing and / or separating selected disease-related components from the separated plasma and means for directing plasma between said catheter and the selective component removal apparatus.
Owner:TRANSVIVO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com