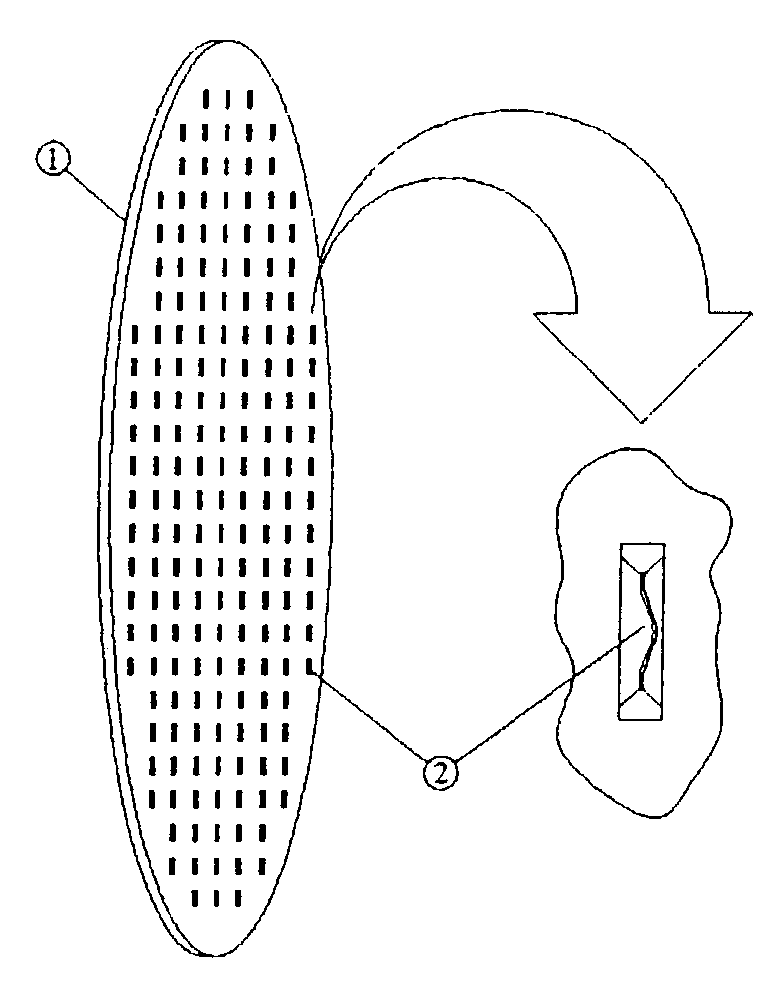
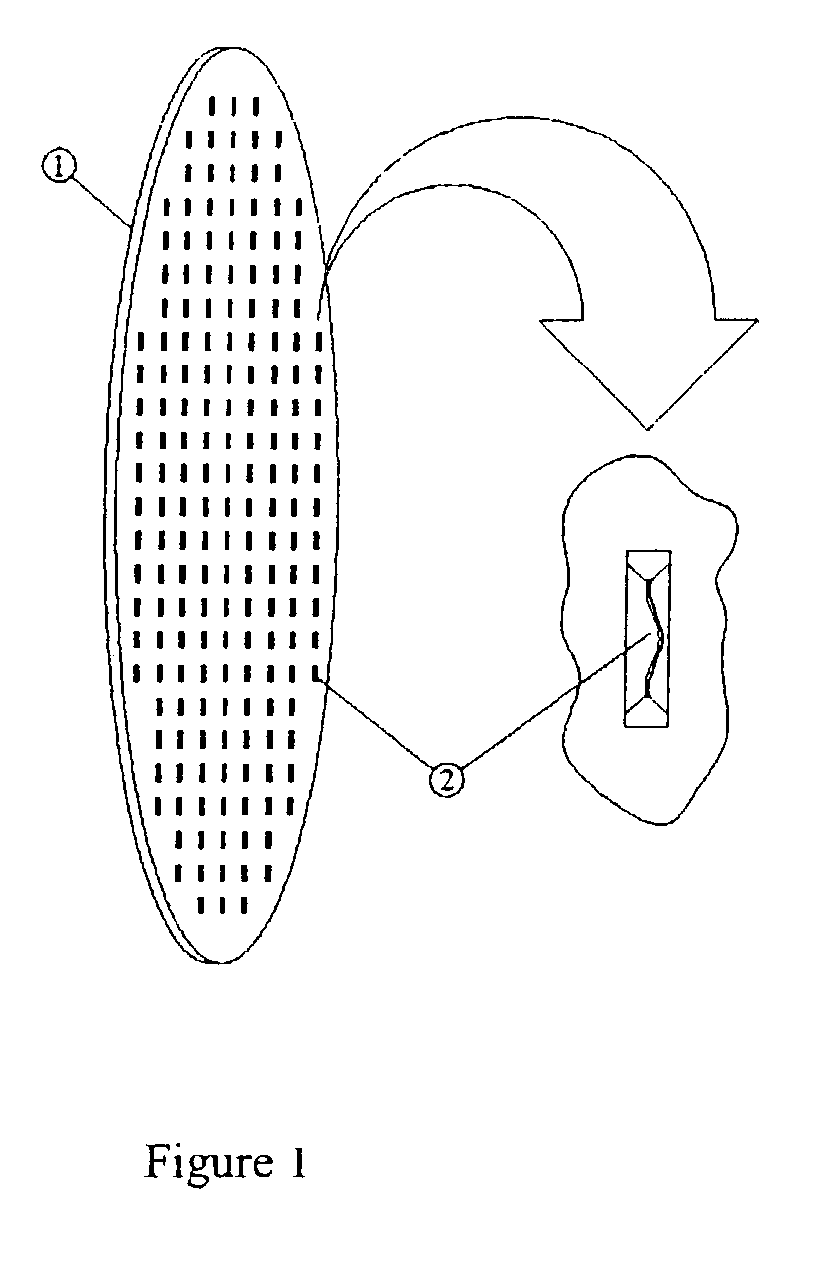
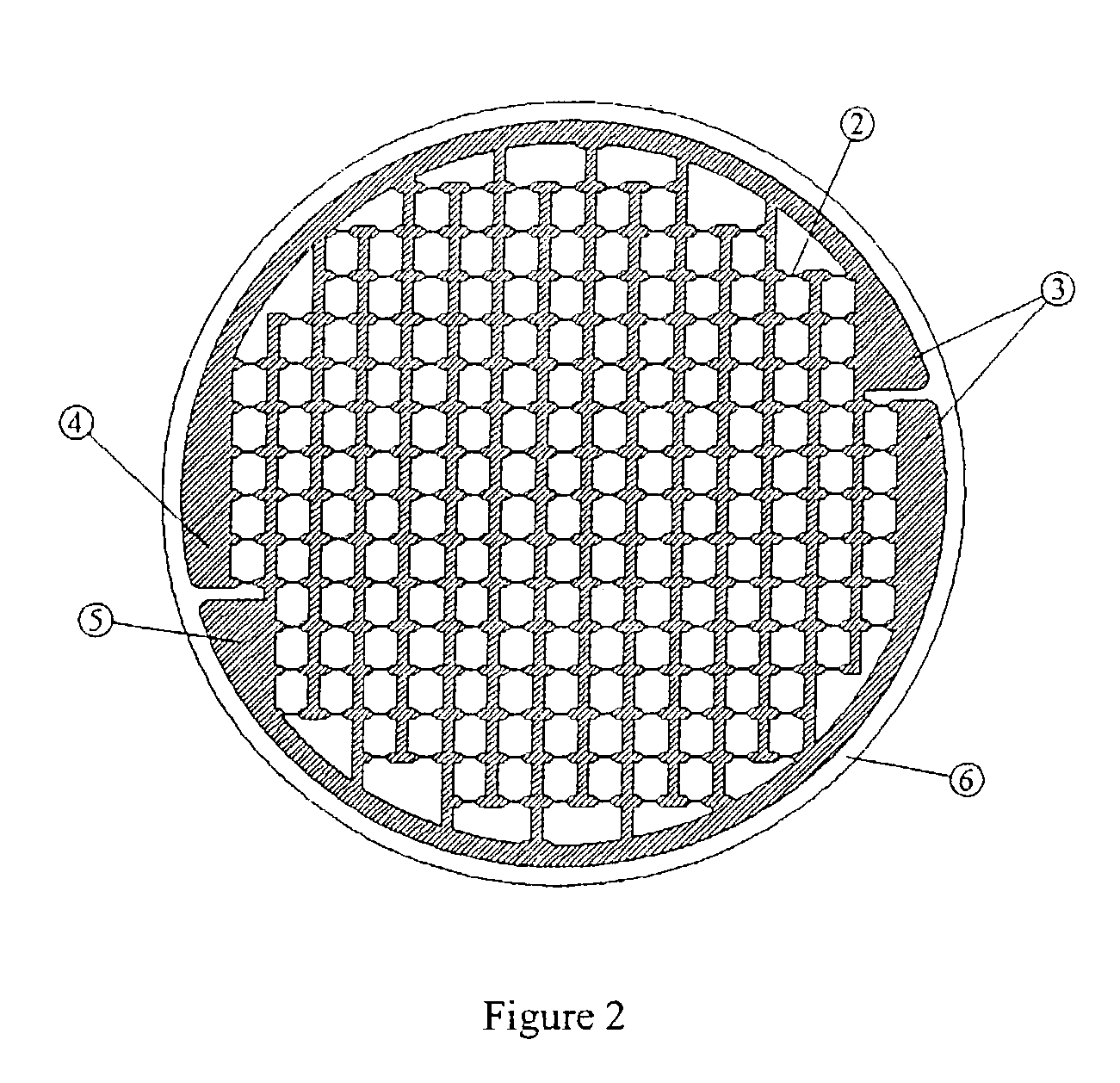
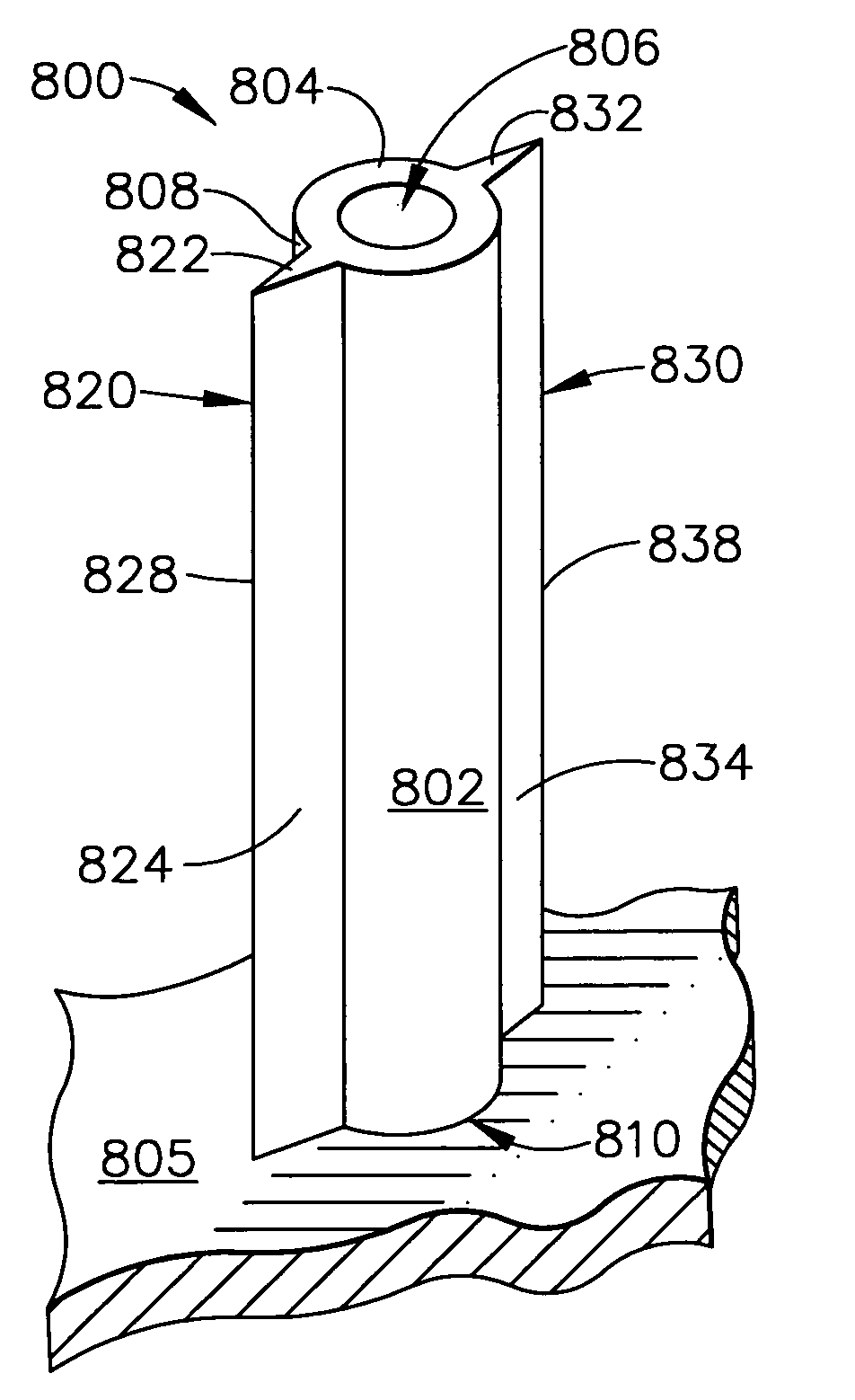
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2639results about "Microneedles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
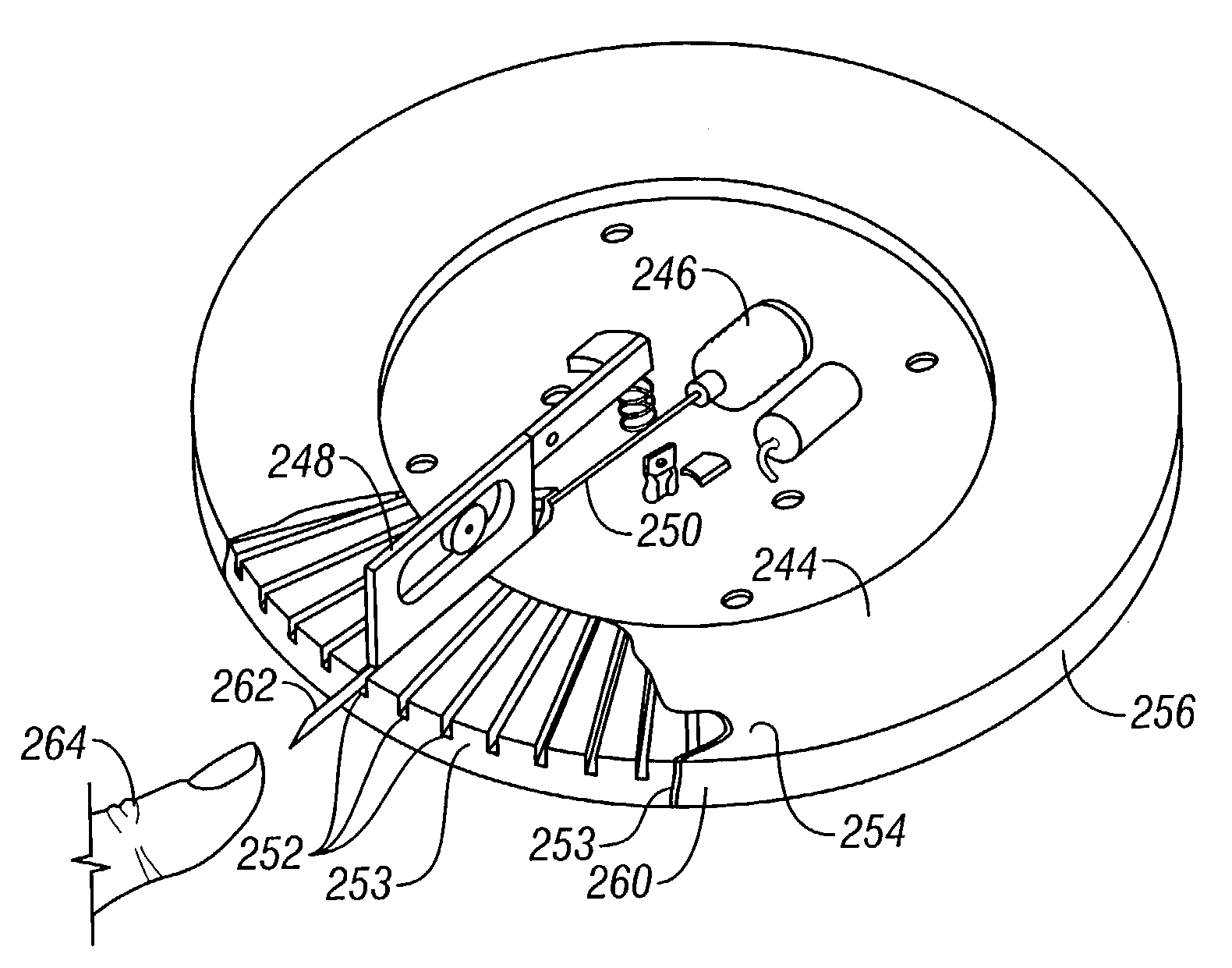
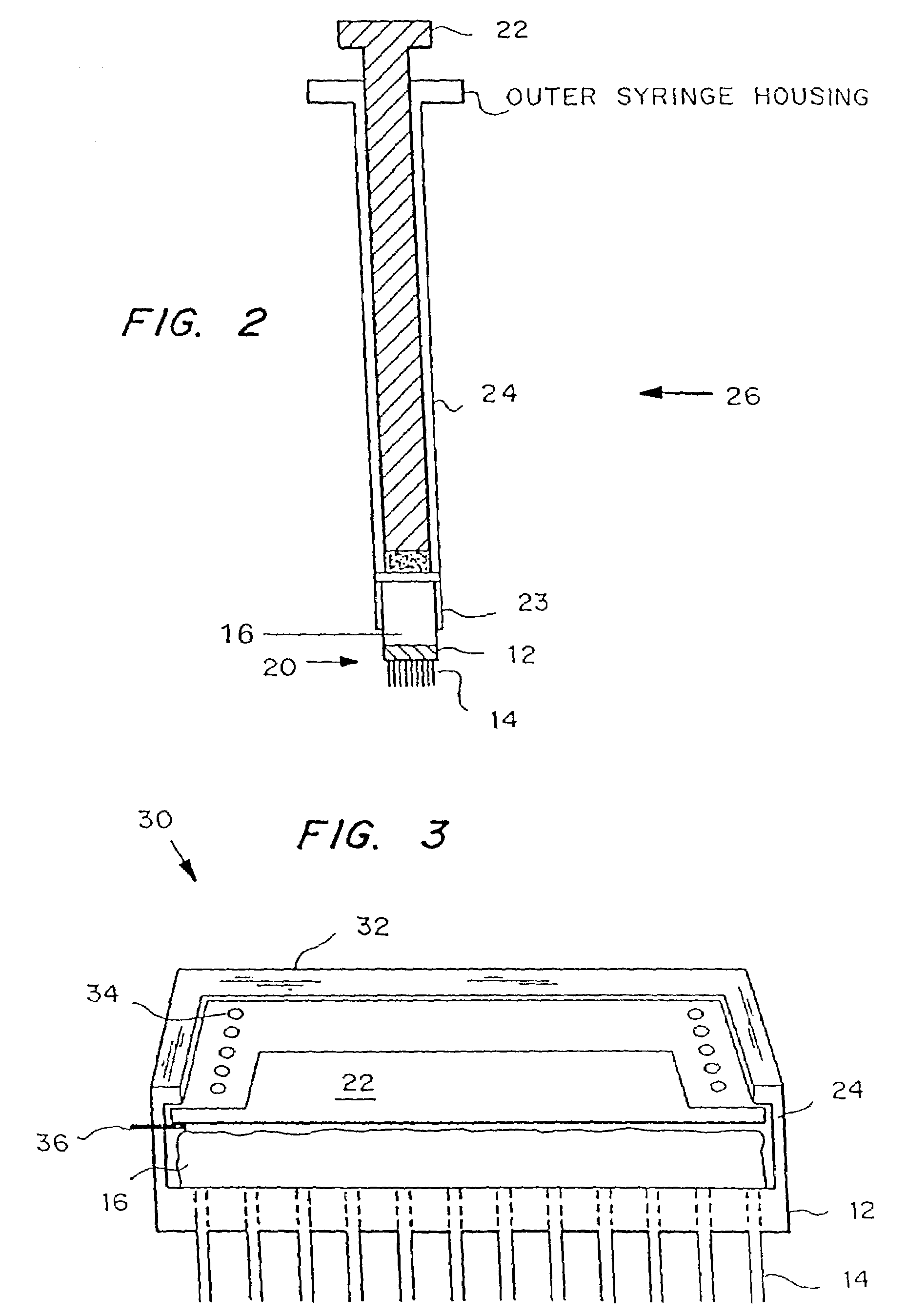
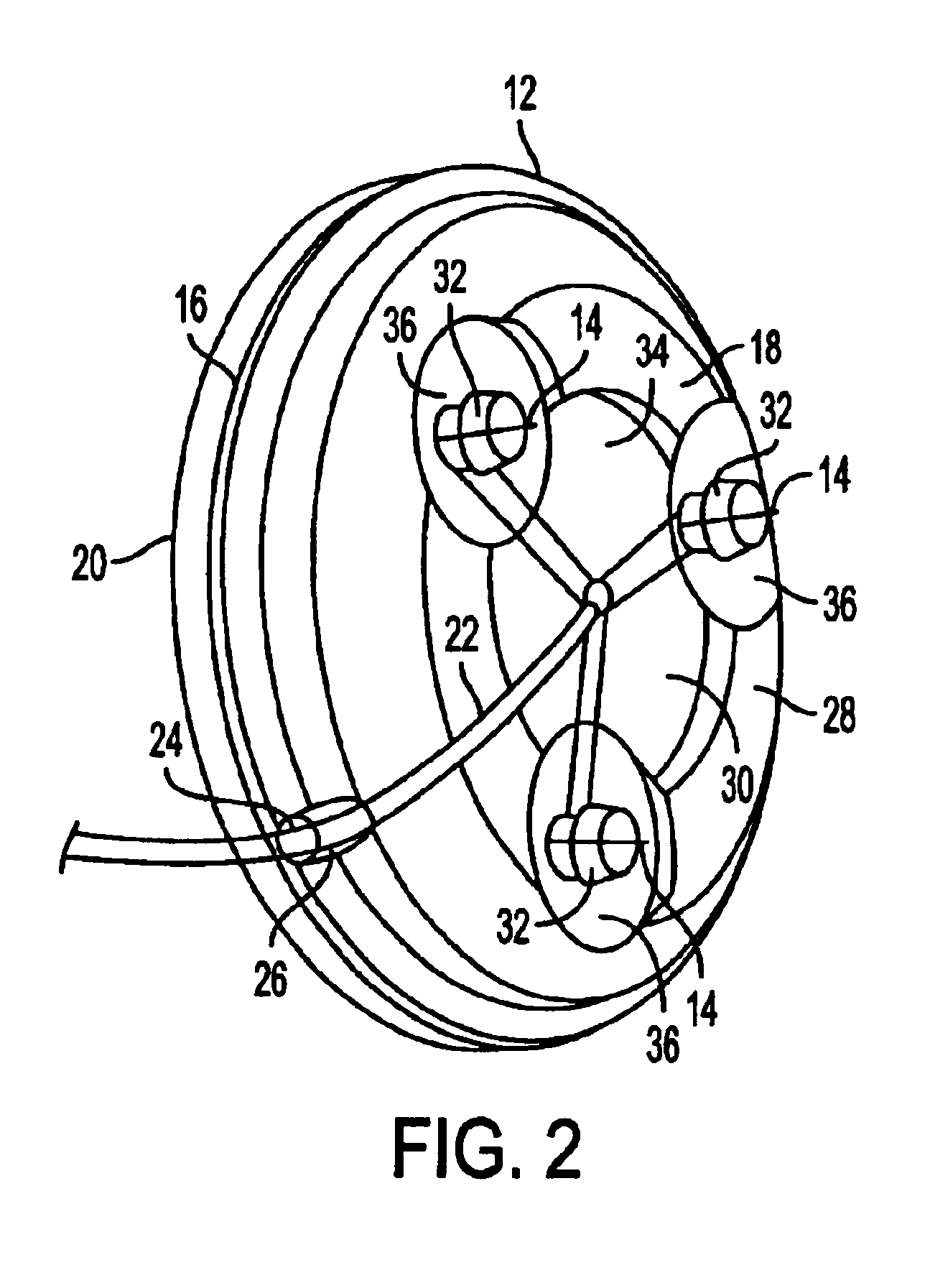
Method and apparatus for a multi-use body fluid sampling device with analyte sensing
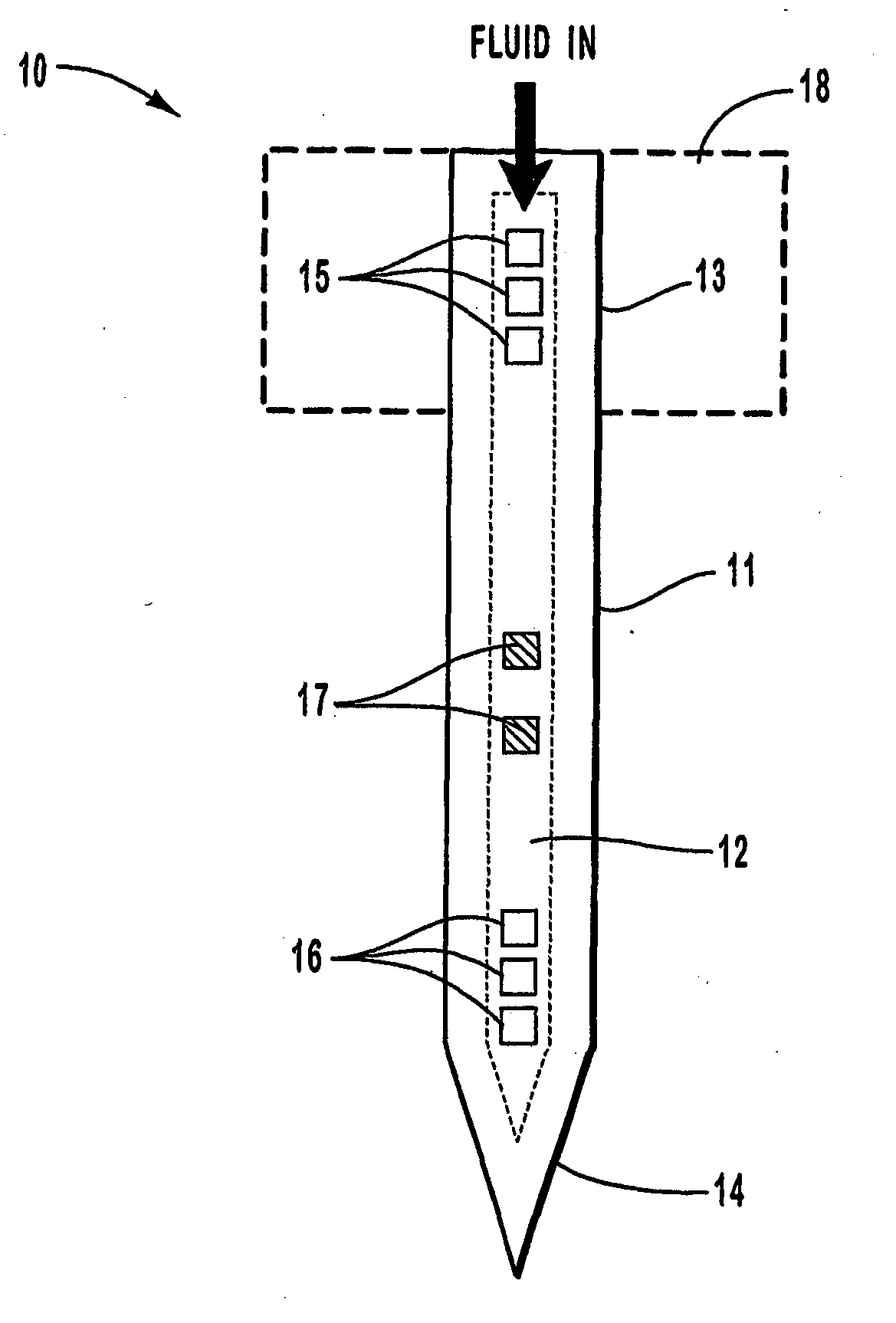
A device for use with a penetrating member driver to penetrate tissue is provided. A plurality of penetrating members are coupled to a single cartridge and are operatively couplable to the penetrating member driver. The penetrating members are movable to extend radially outward from the cartridge to penetrate tissue. A plurality of analyte sensors are coupled to the single cartridge and are positioned on the cartridge to receive body fluid from a wound in the tissue created by the penetrating member.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
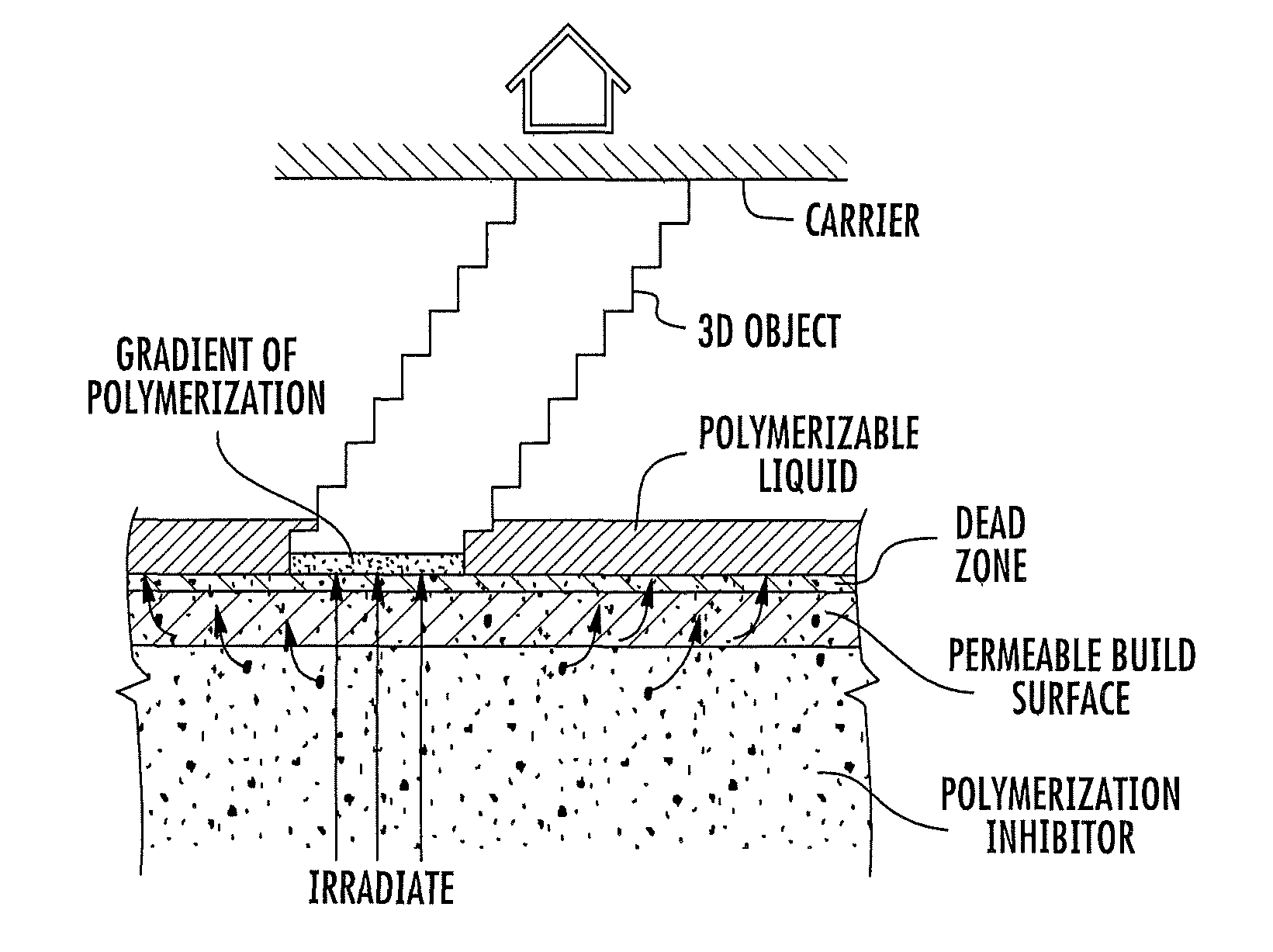
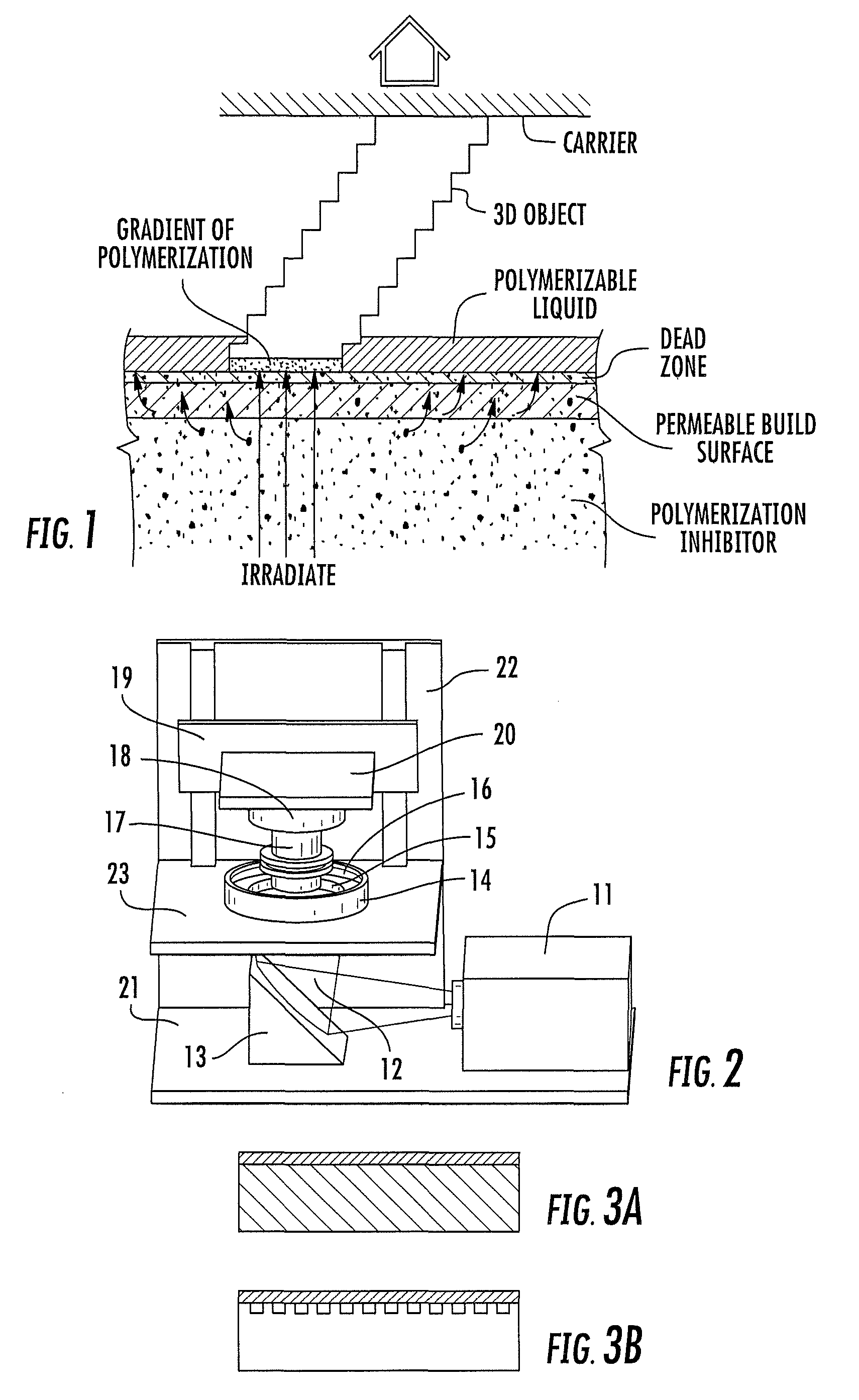
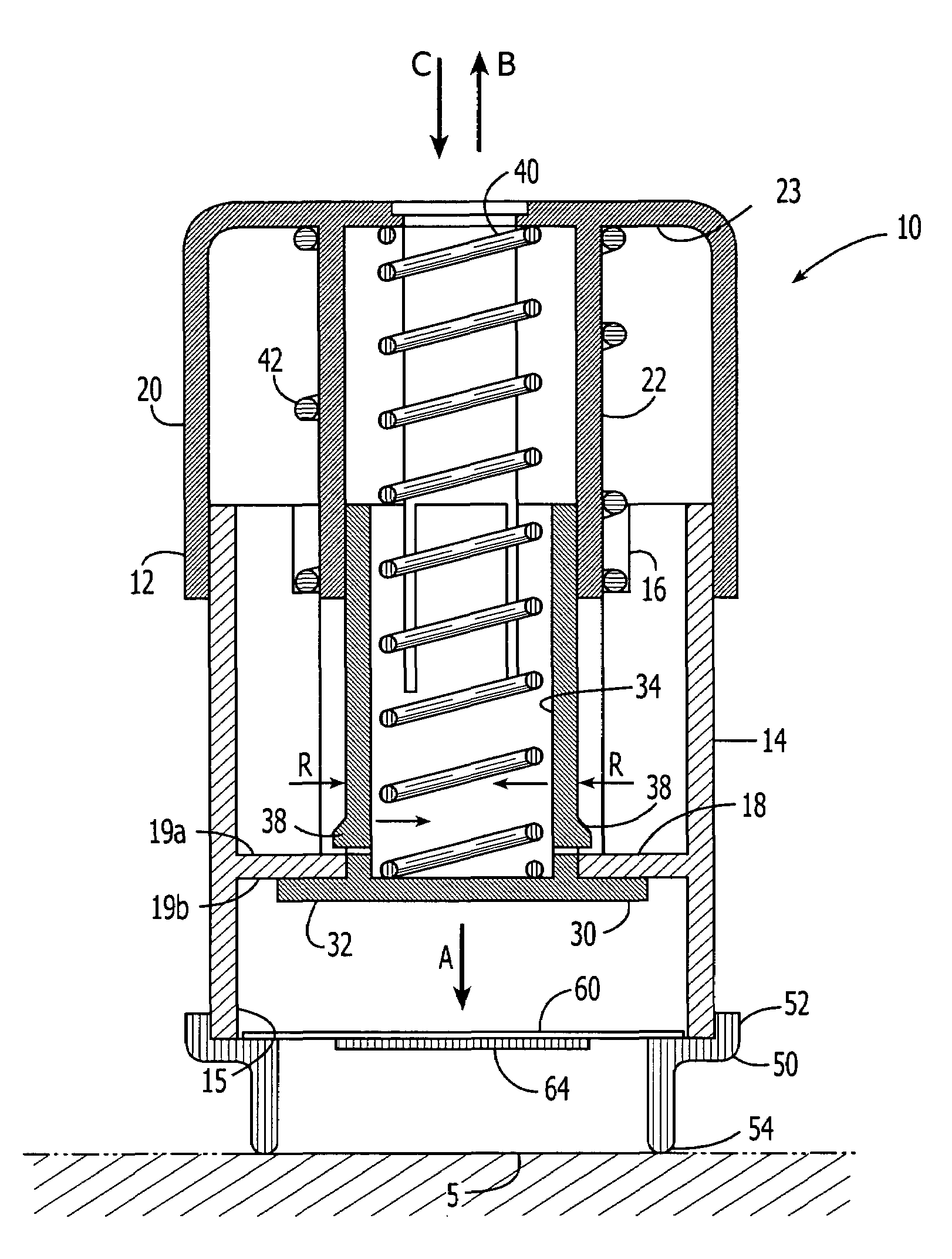
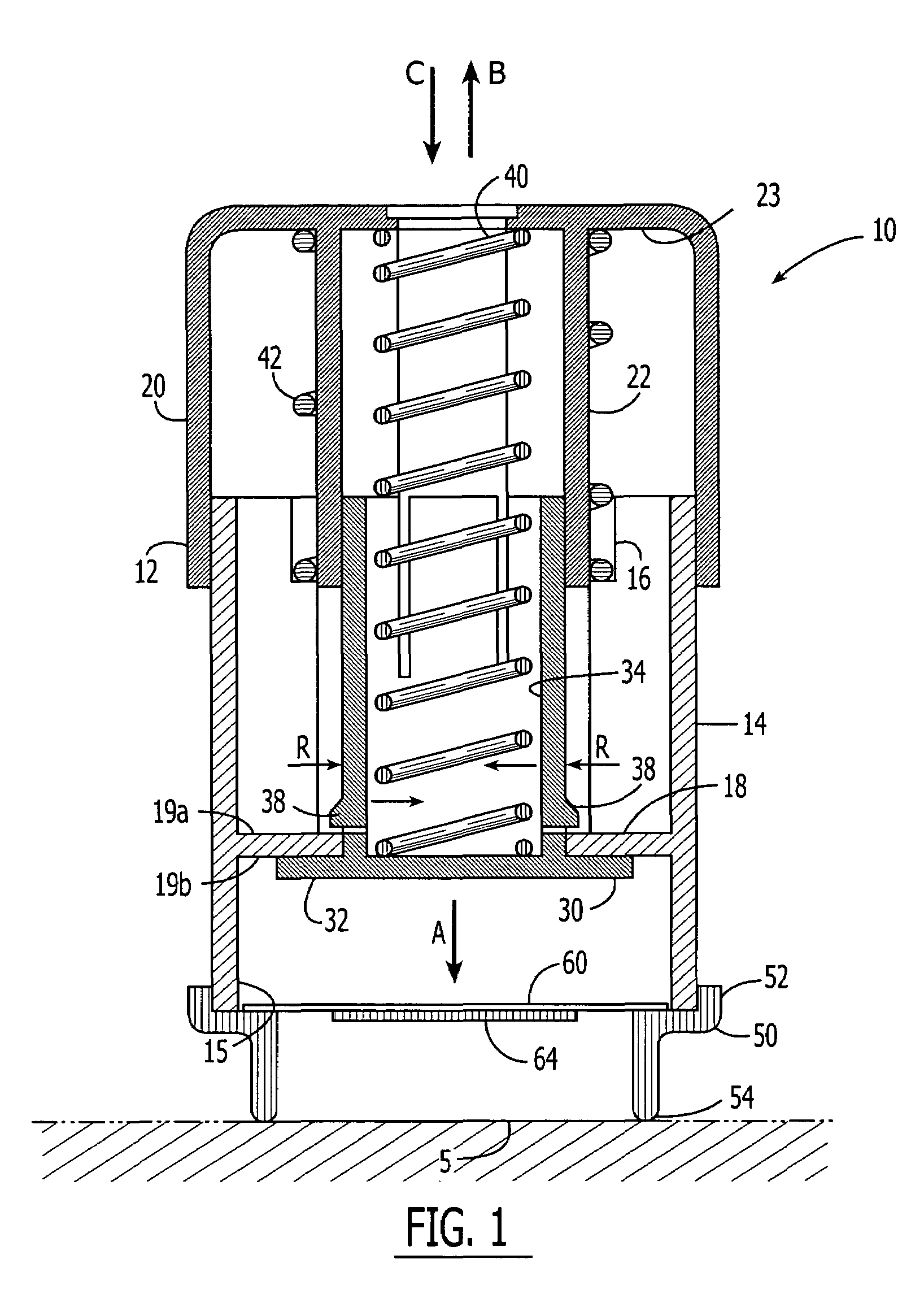
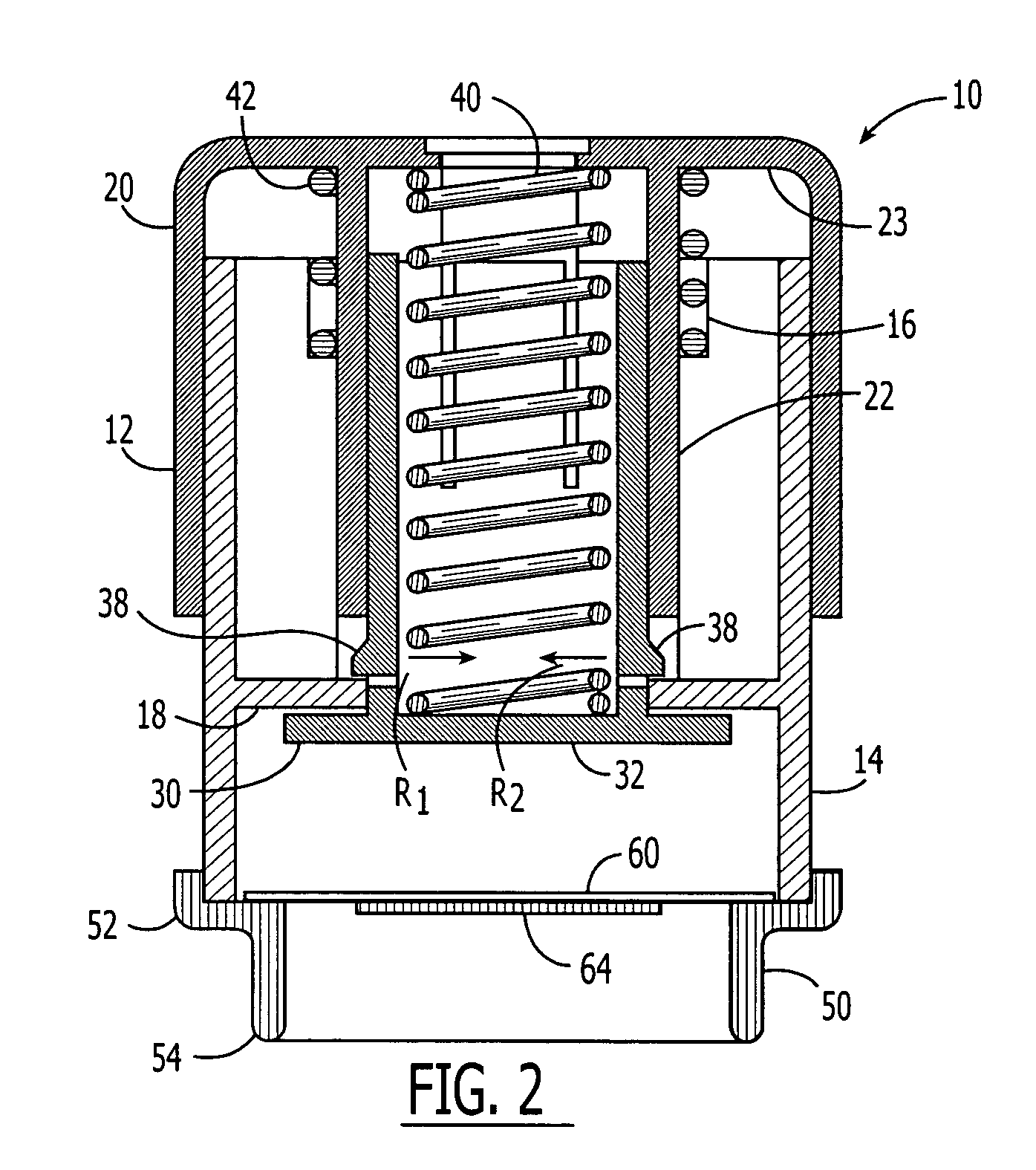
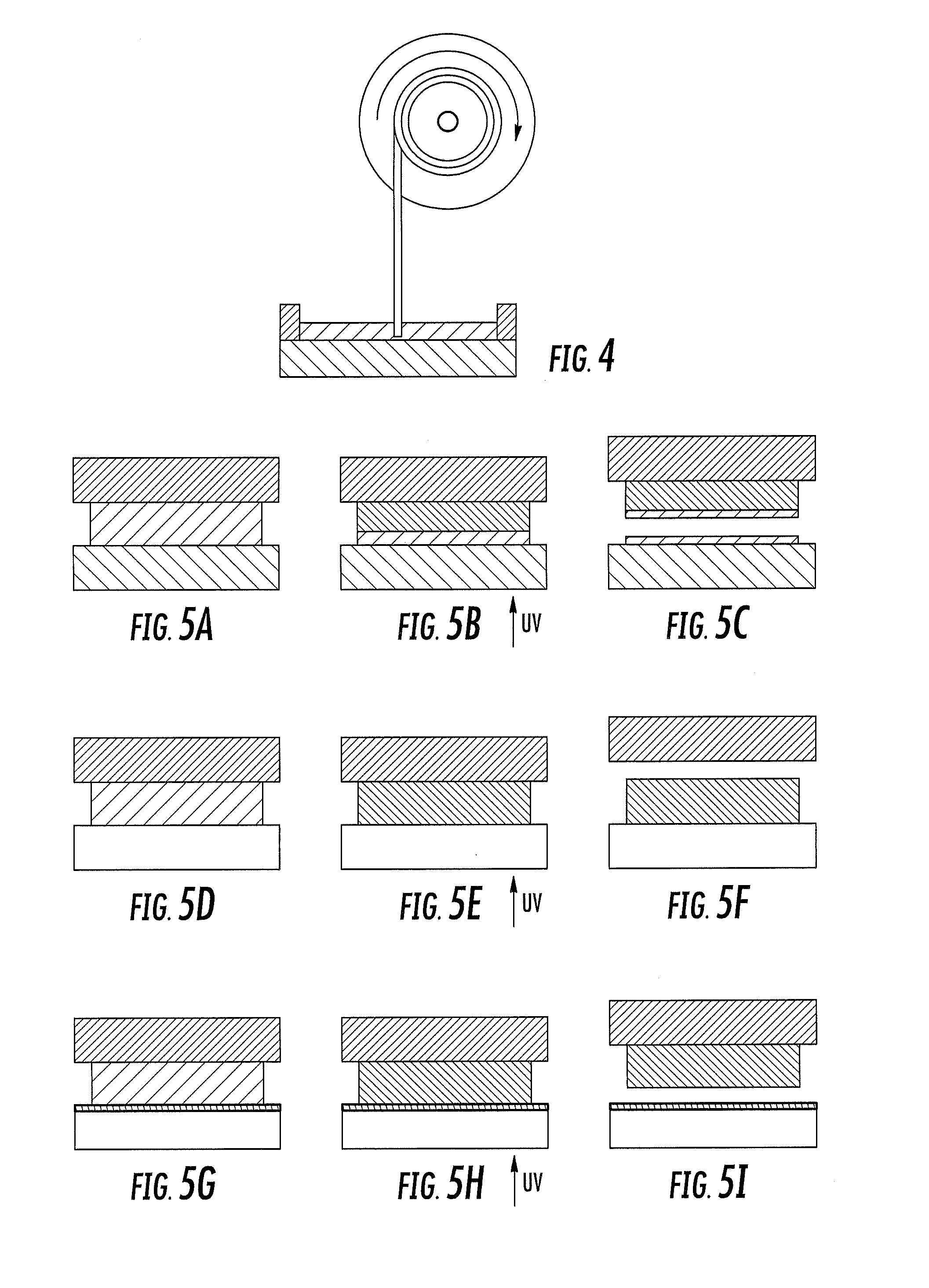
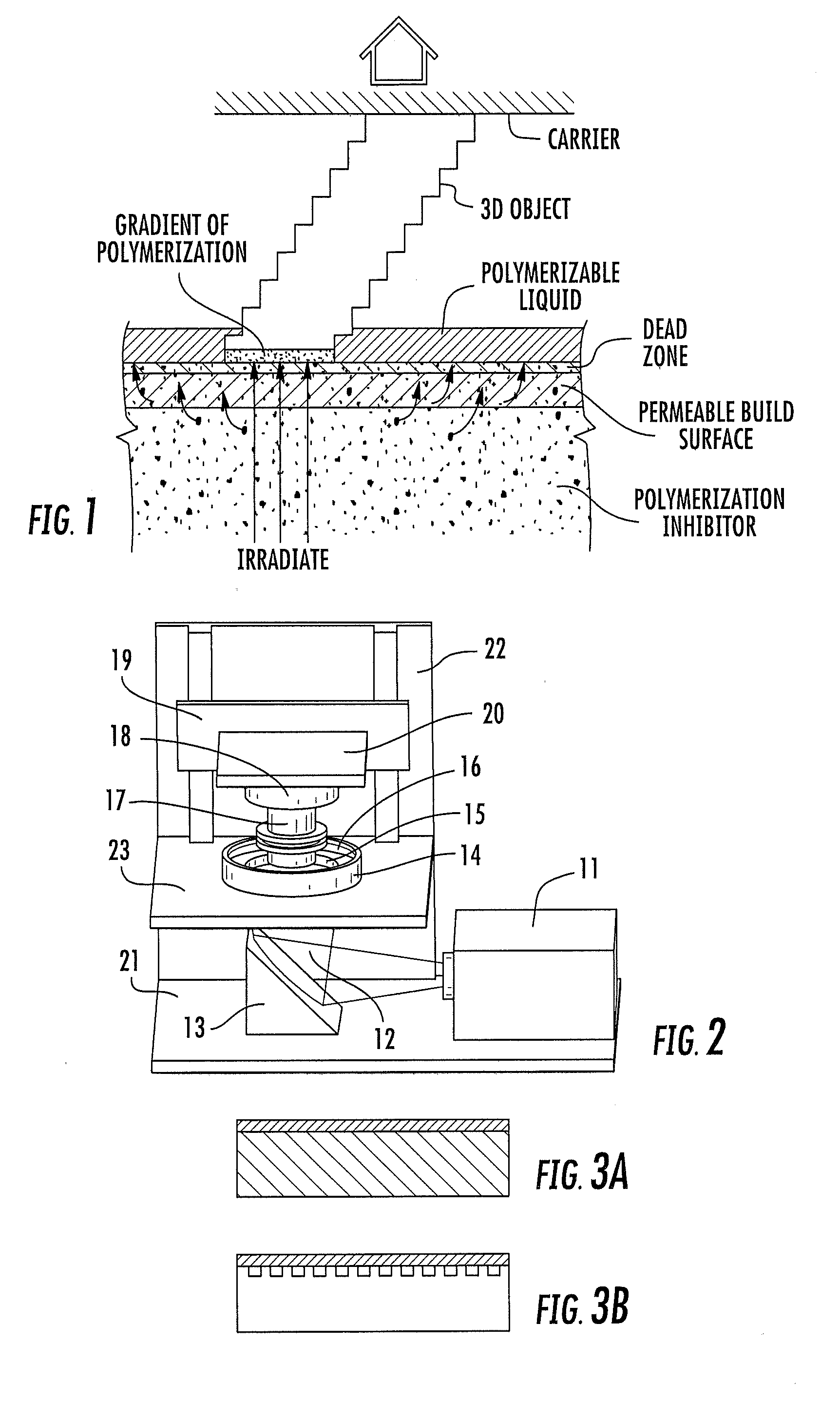
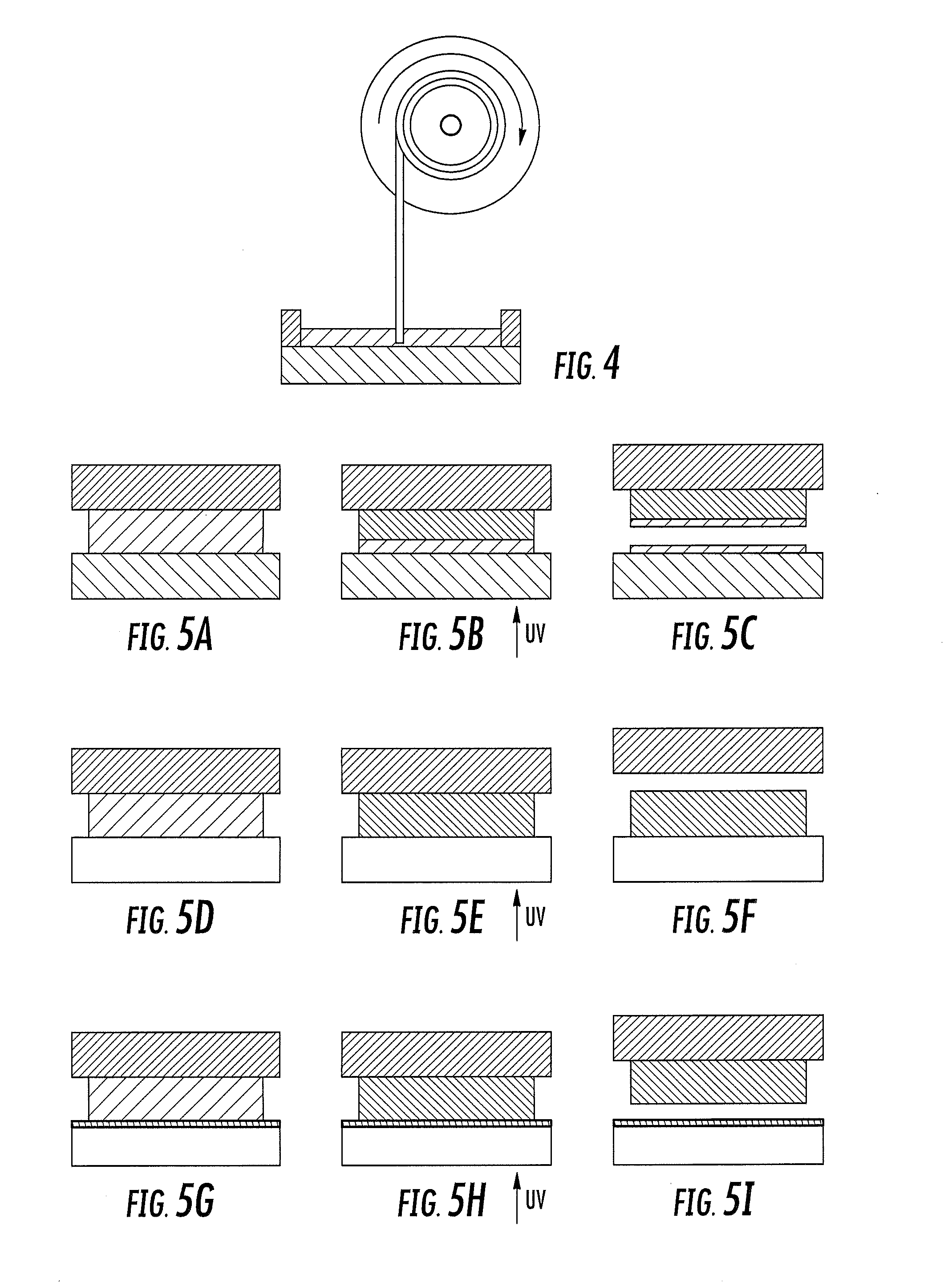
Continuous liquid interphase printing
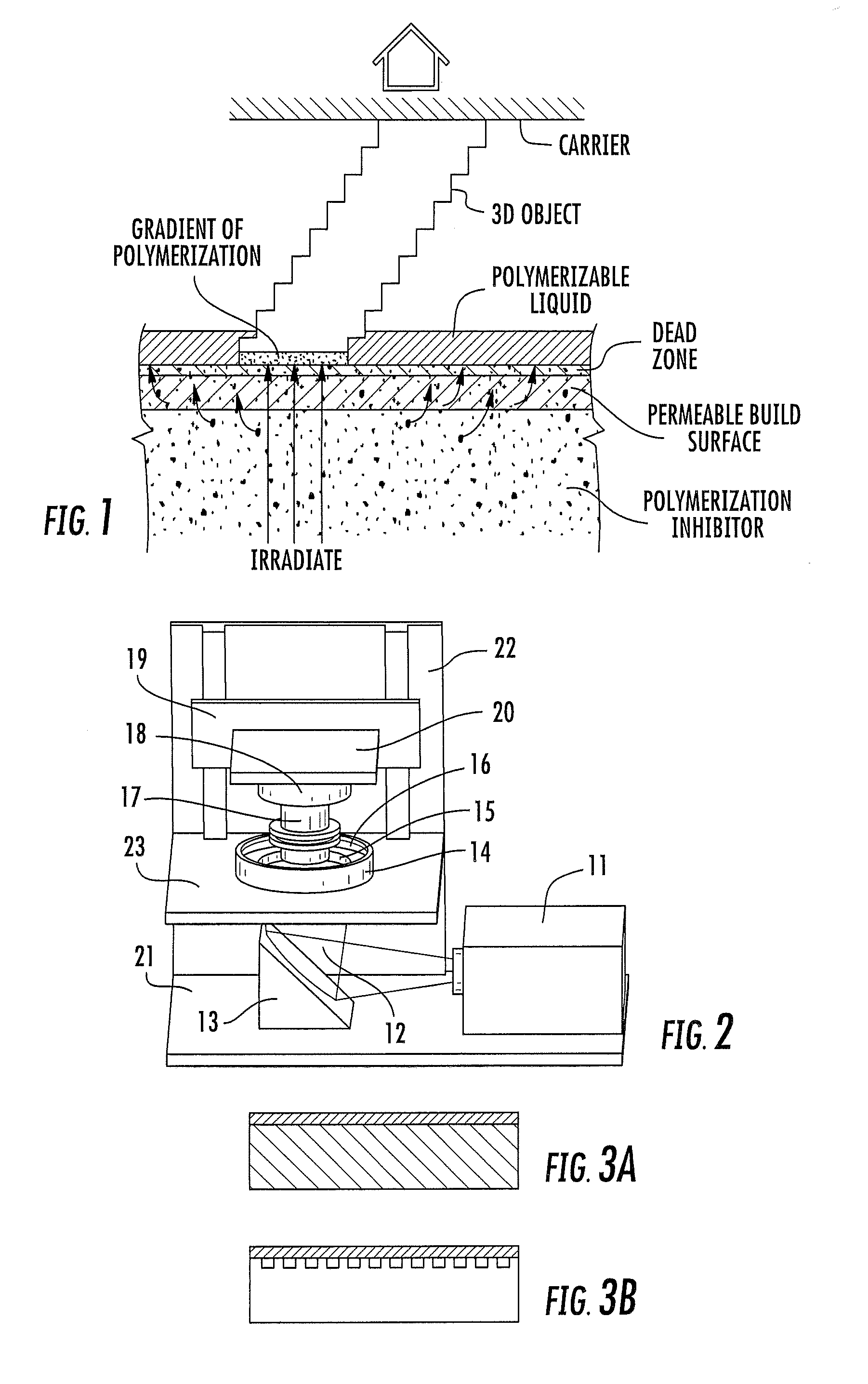
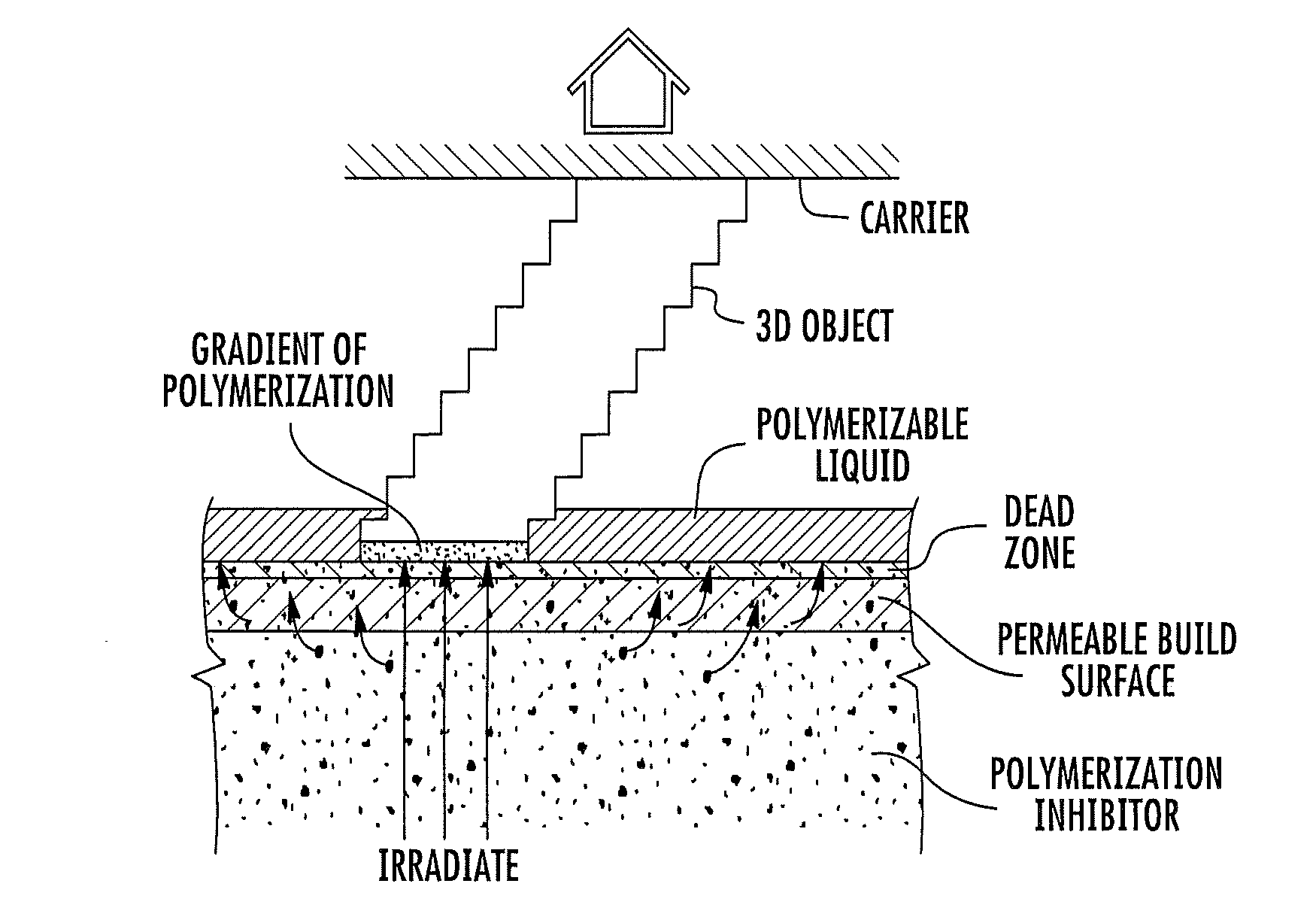
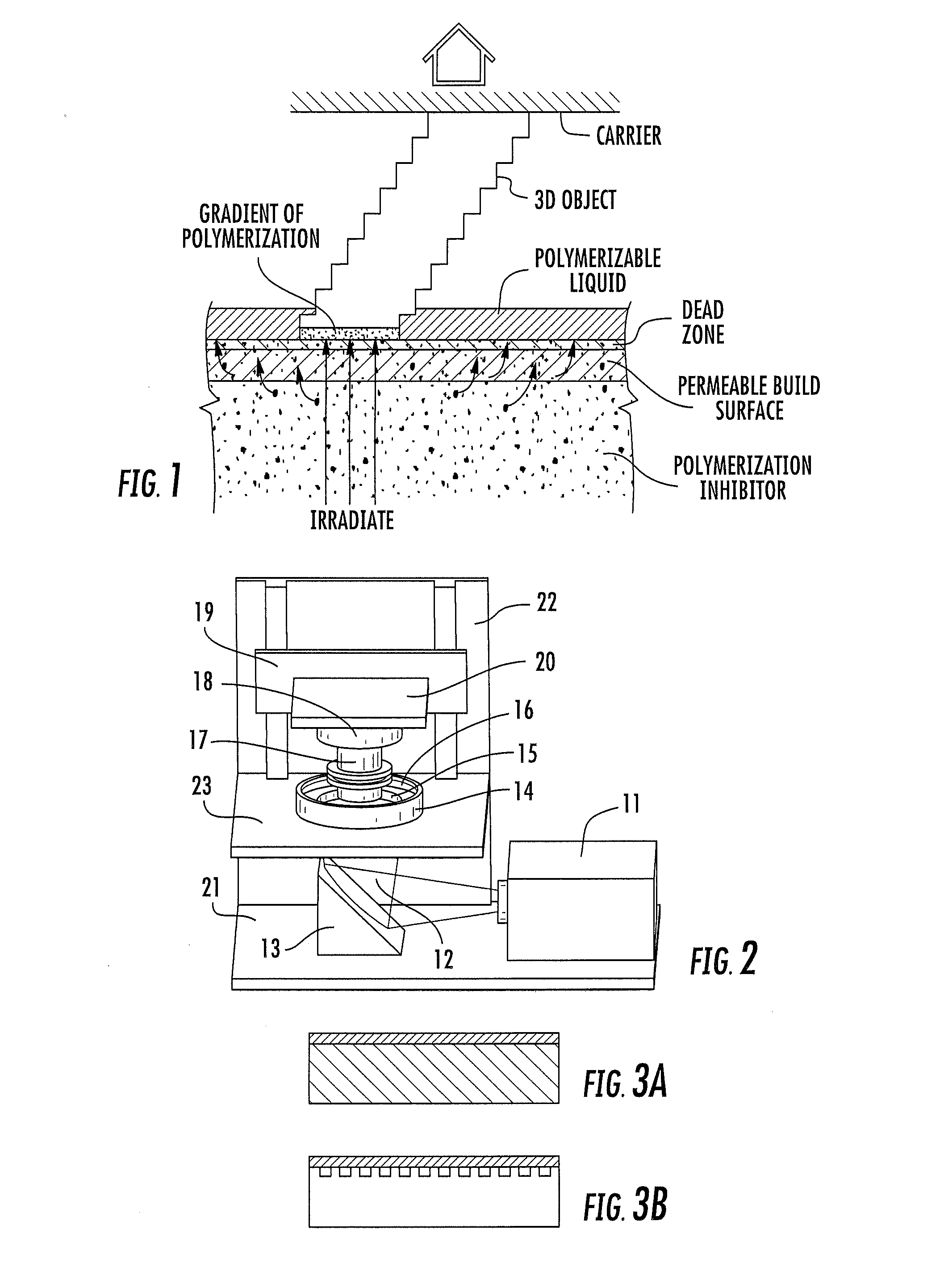
A method of forming a three-dimensional object, comprises providing a carrier and an optically transparent member having a build surface, the carrier and the build surface defining a build region therebetween; filling the build region with a polymerizable liquid; irradiating the build region through the optically transparent member to form a solid polymer from the polymerizable liquid while concurrently advancing the carrier away from the build surface to form the three-dimensional object from the solid polymer, while also concurrently: (i) continuously maintaining a dead zone of polymerizable liquid in contact with the build surface, and (ii) continuously maintaining a gradient of polymerization zone between the dead zone and the solid polymer and in contact with each thereof, the gradient of polymerization zone comprising the polymerizable liquid in partially cured form. Apparatus for carrying out the method is also described.
Owner:CARBON INC
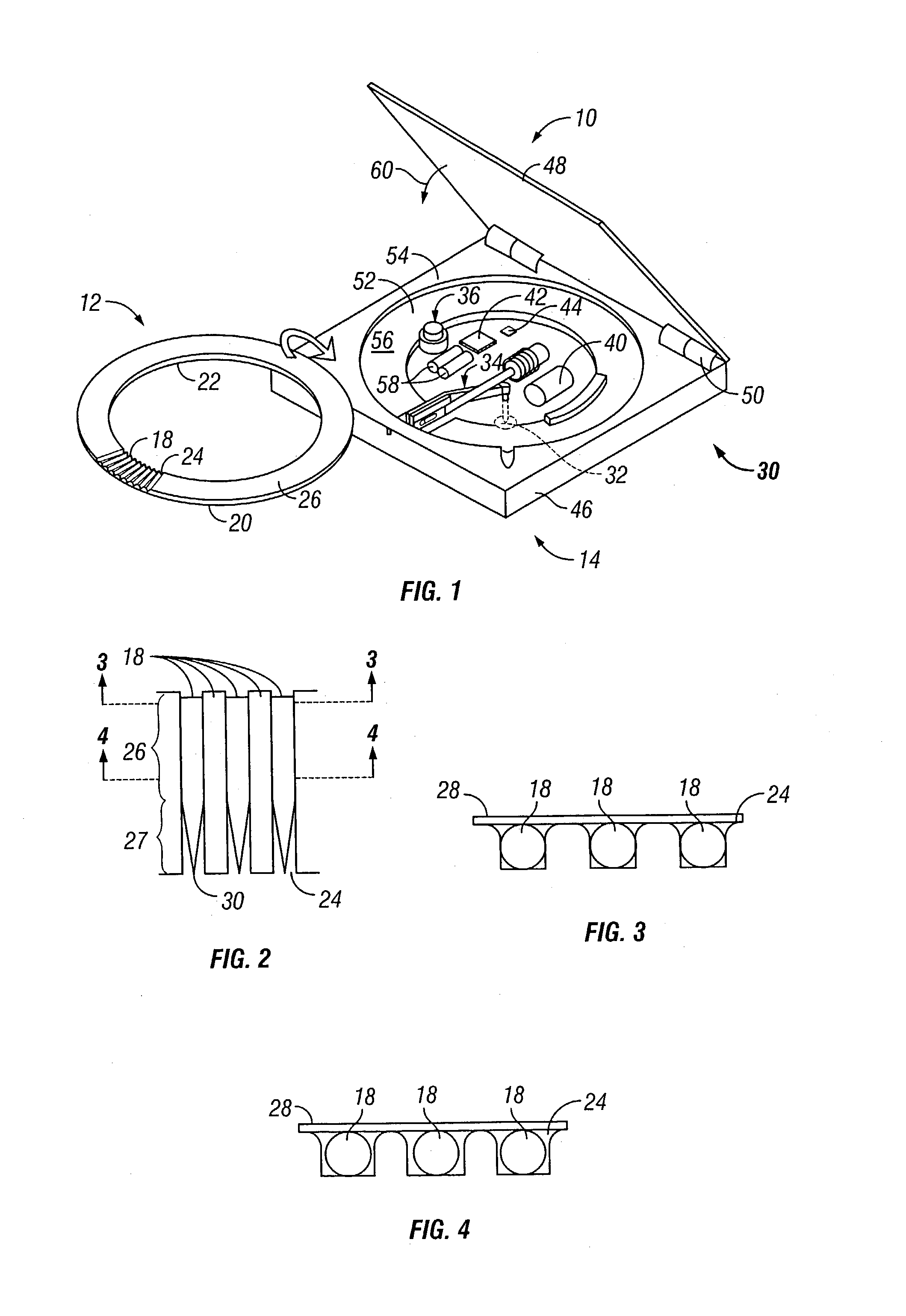
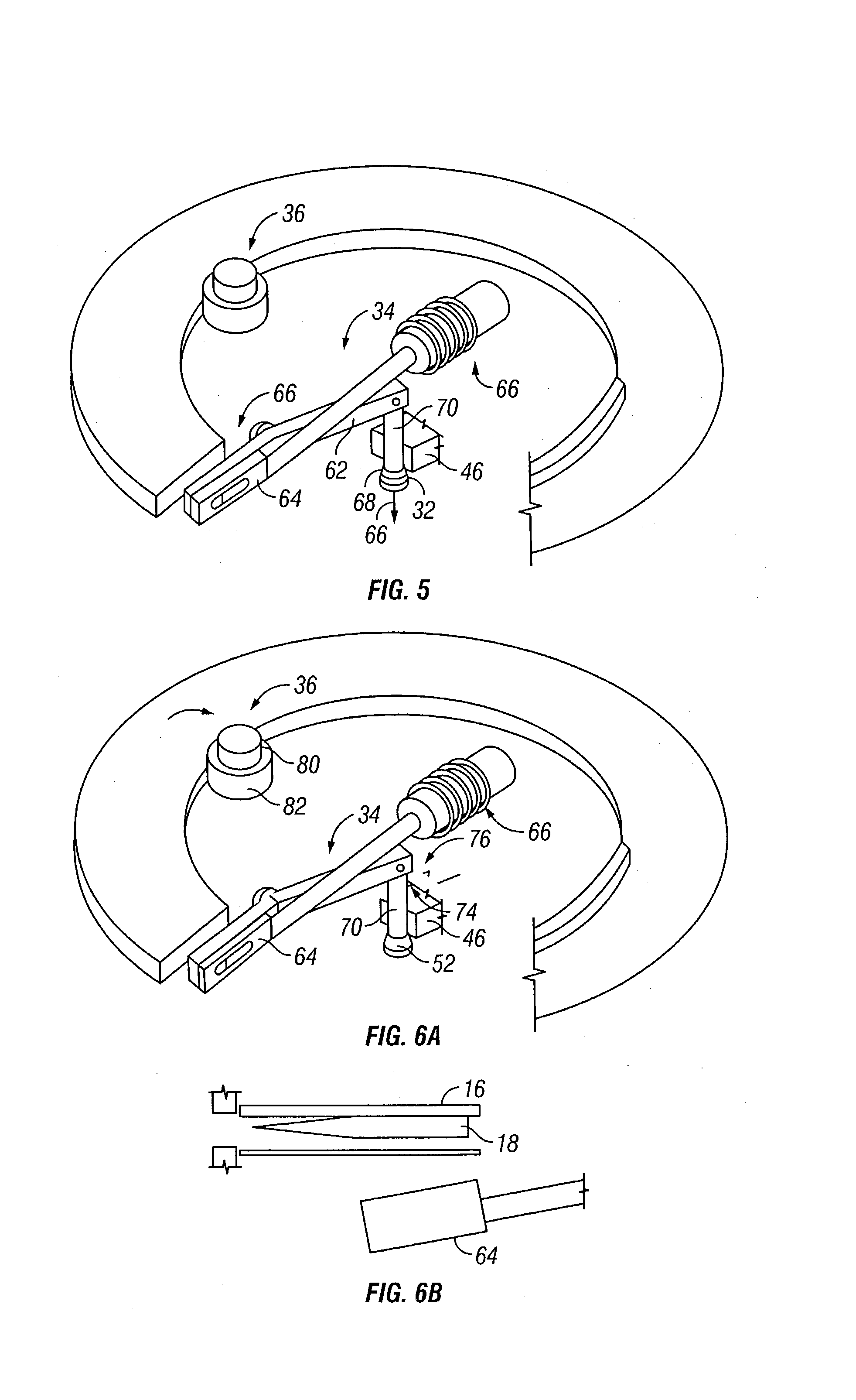
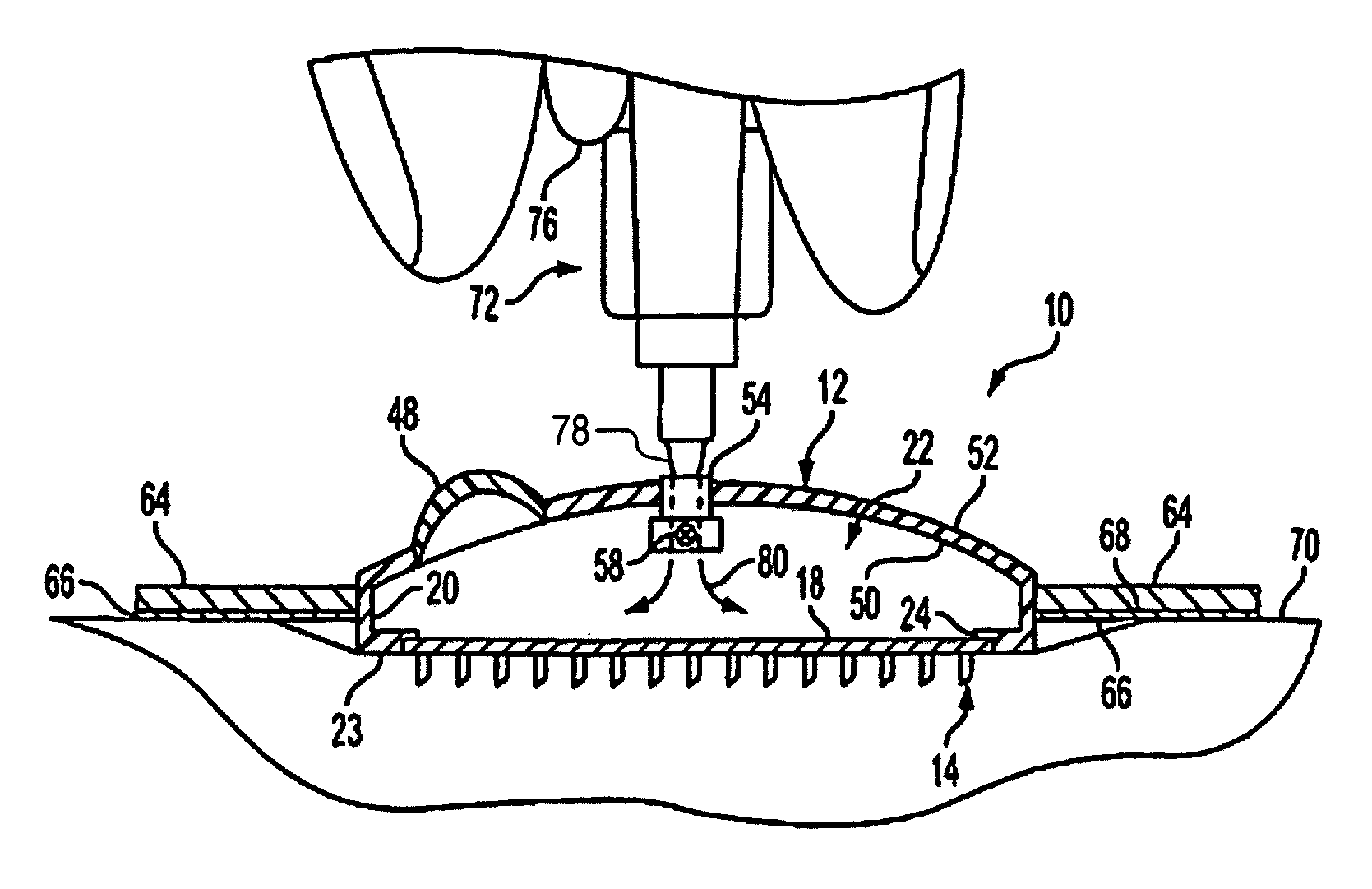
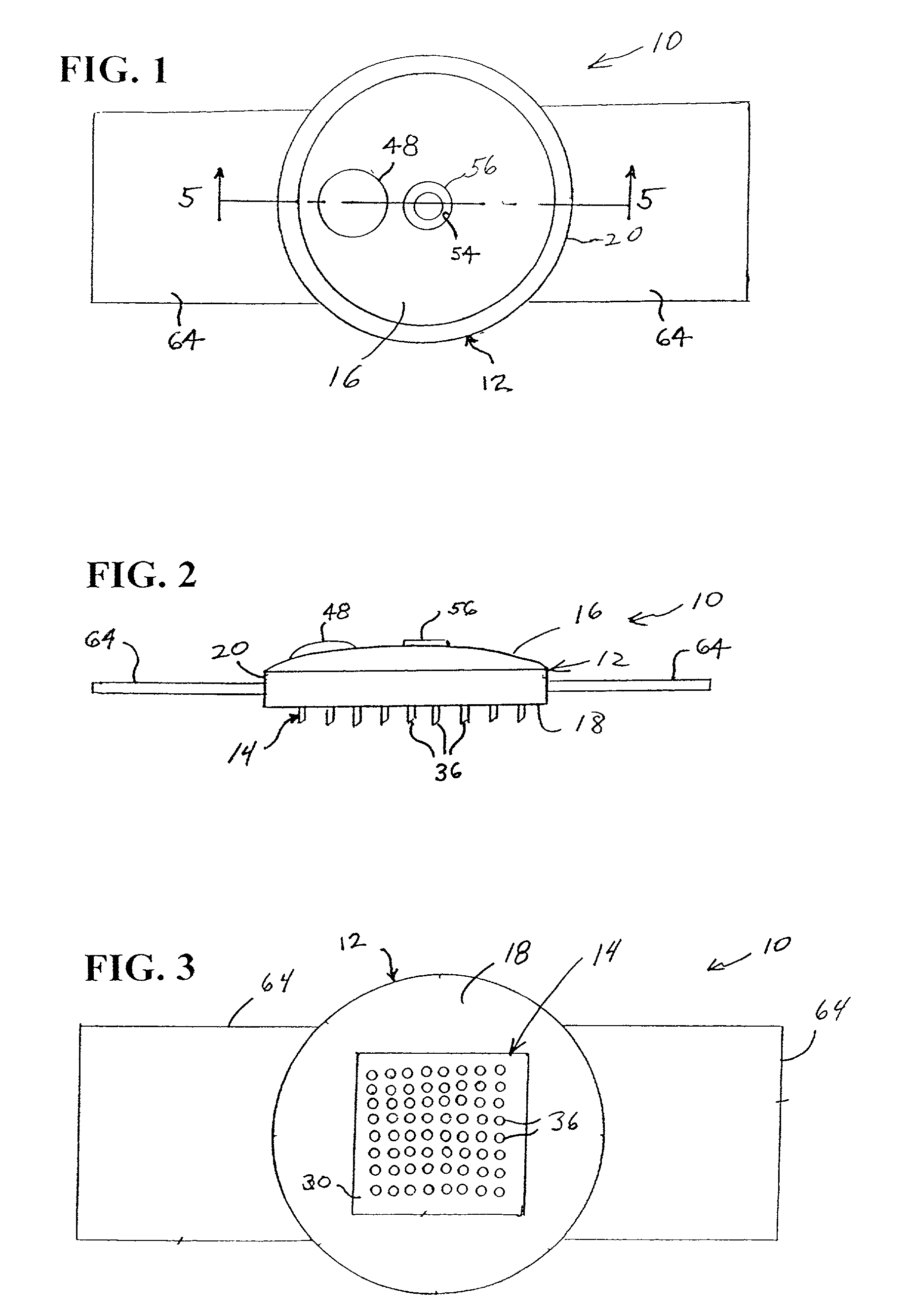
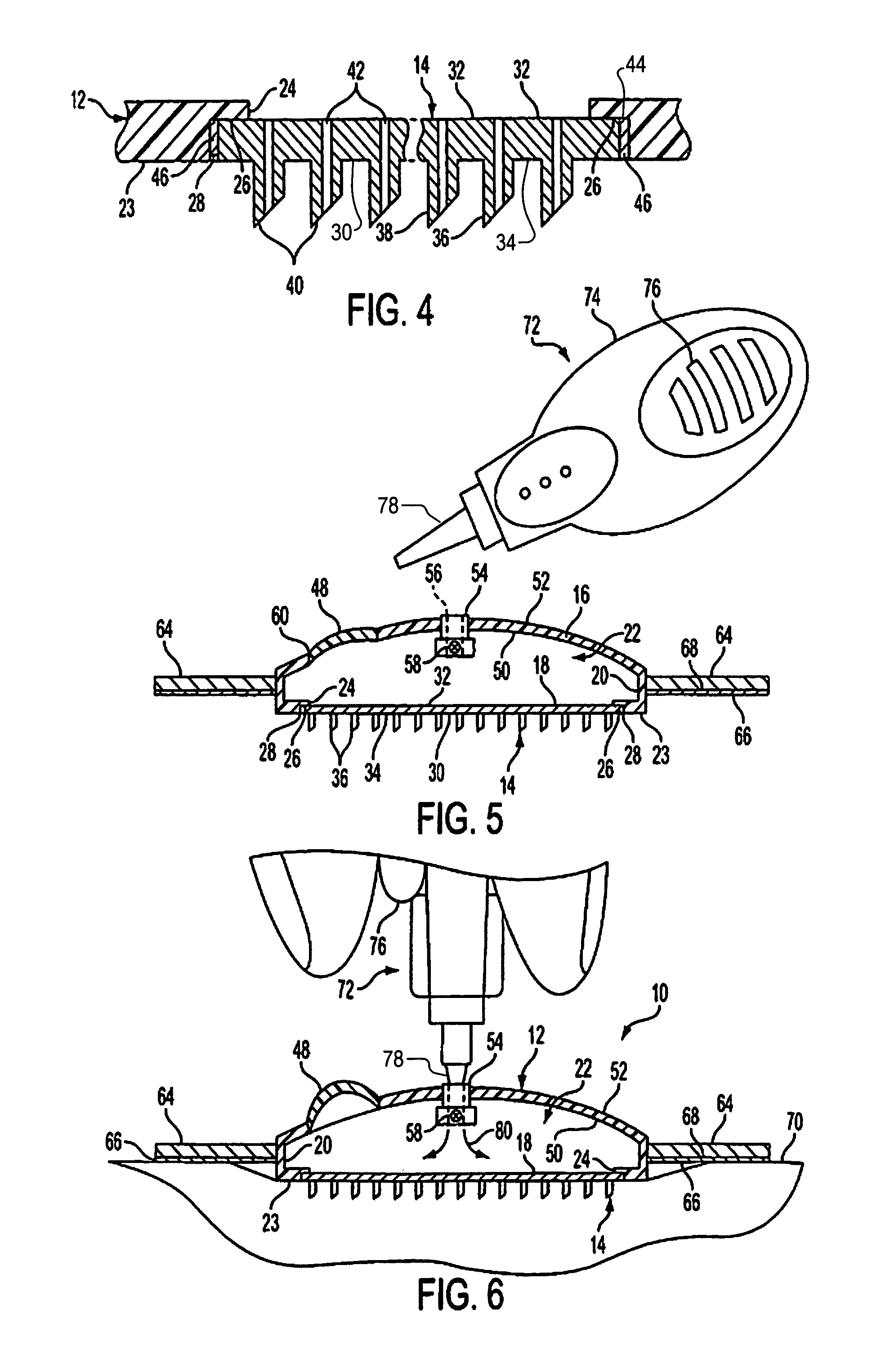
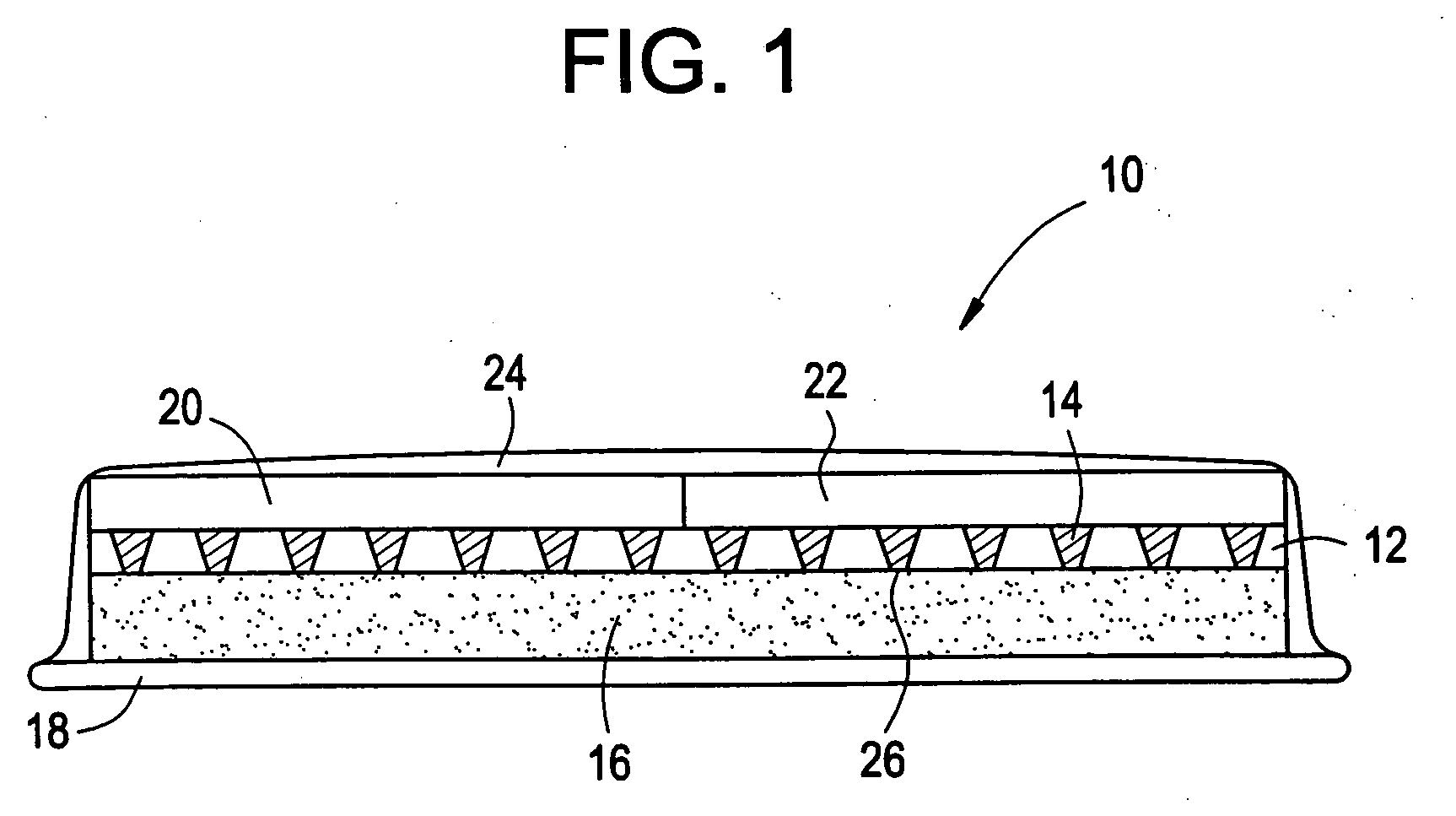
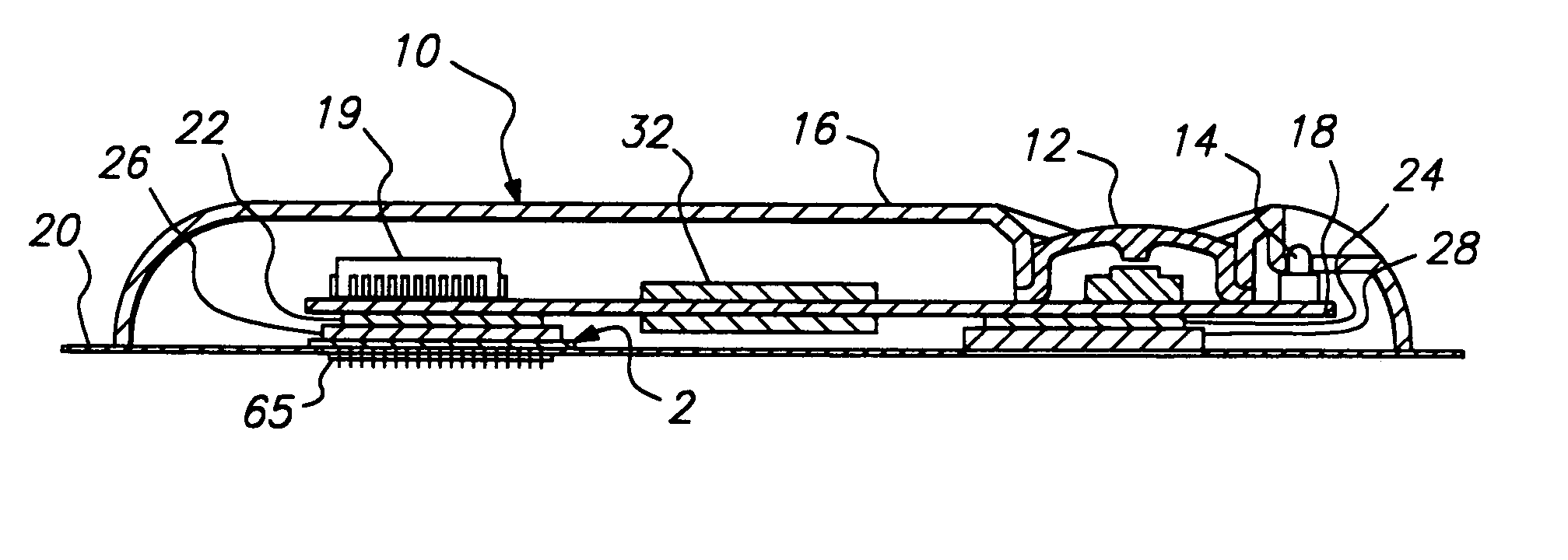
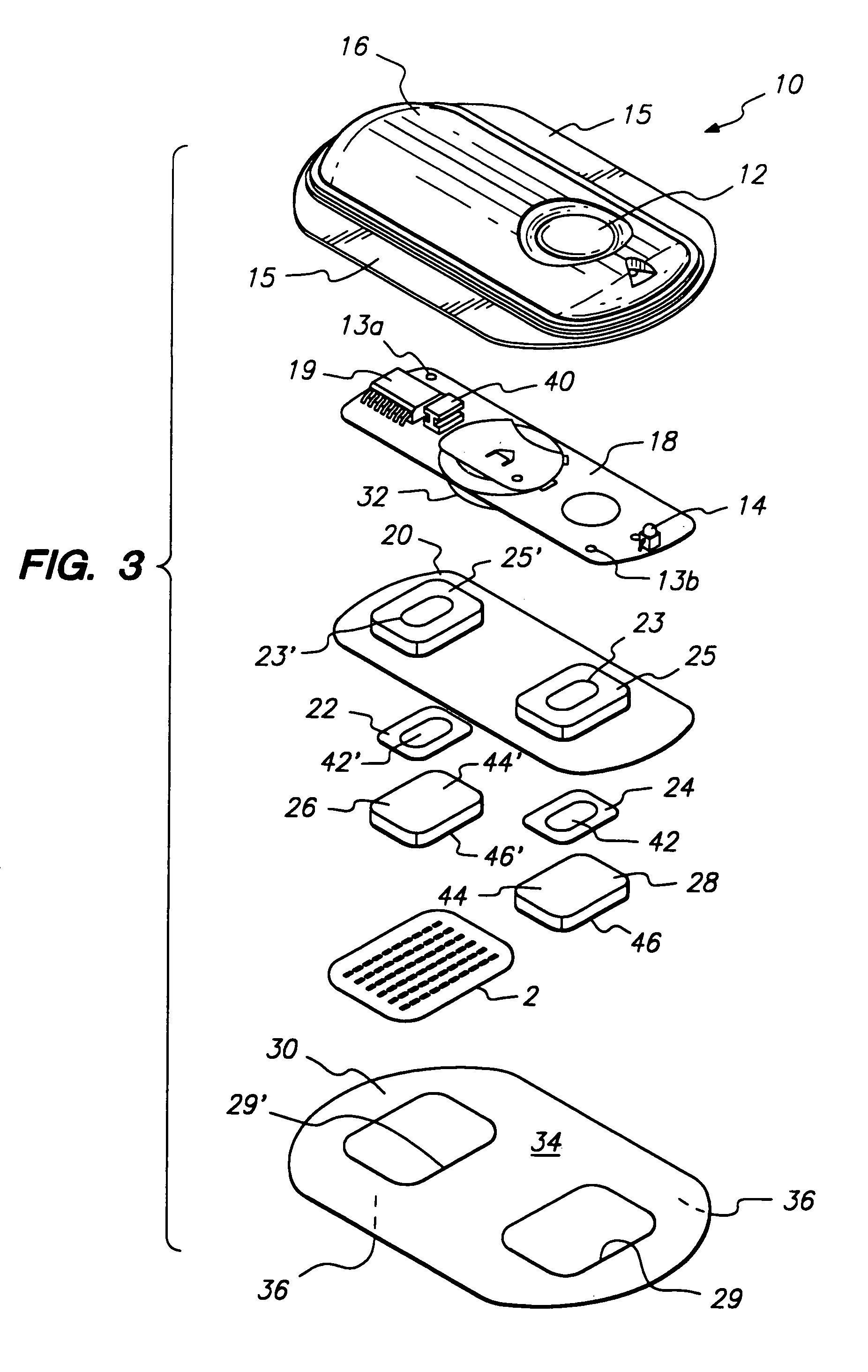
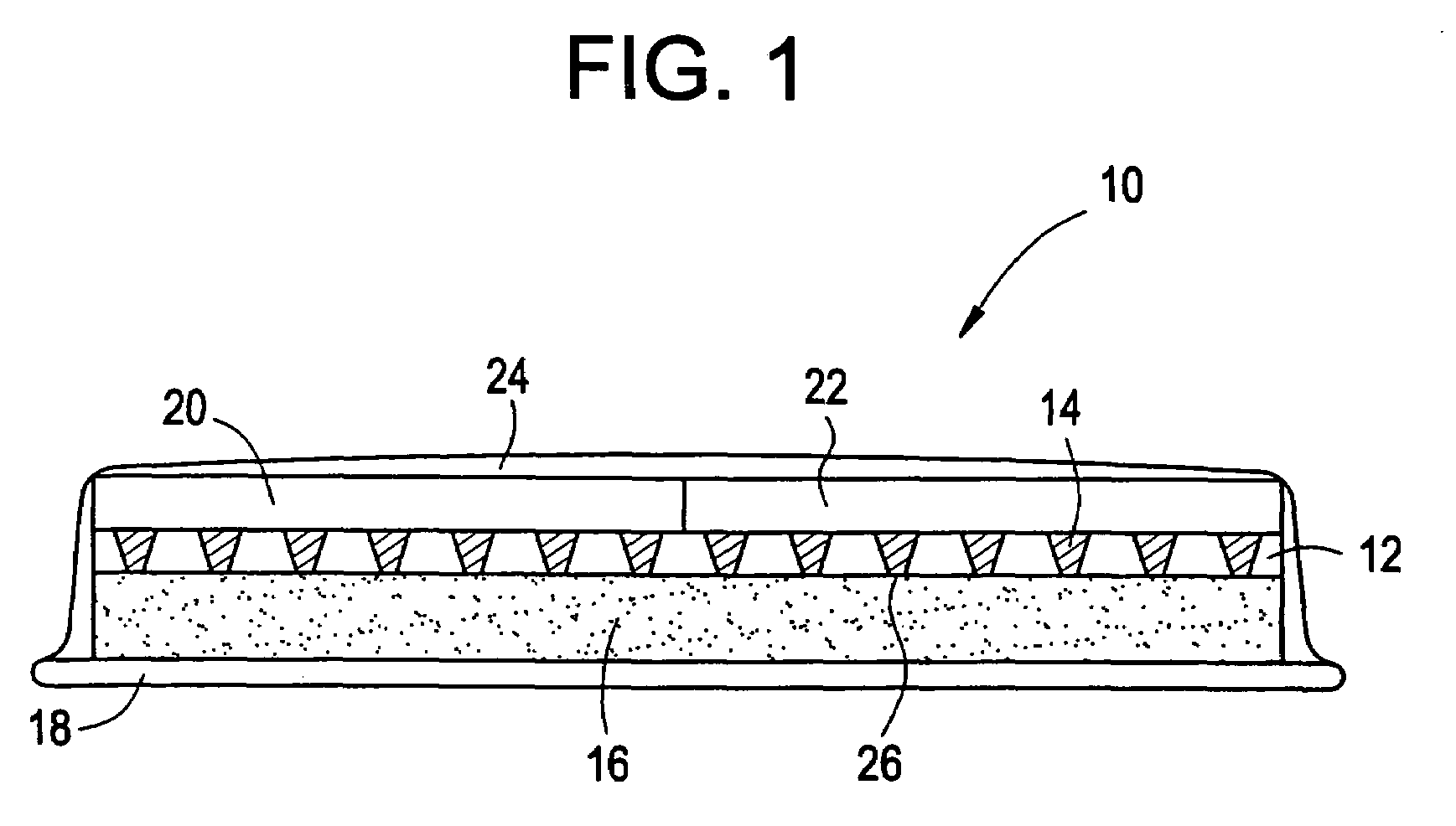
Microneedle device for extraction and sensing of bodily fluids
InactiveUS7344499B1Simple wayMinimal and no damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicroneedlesMetaboliteIrritation
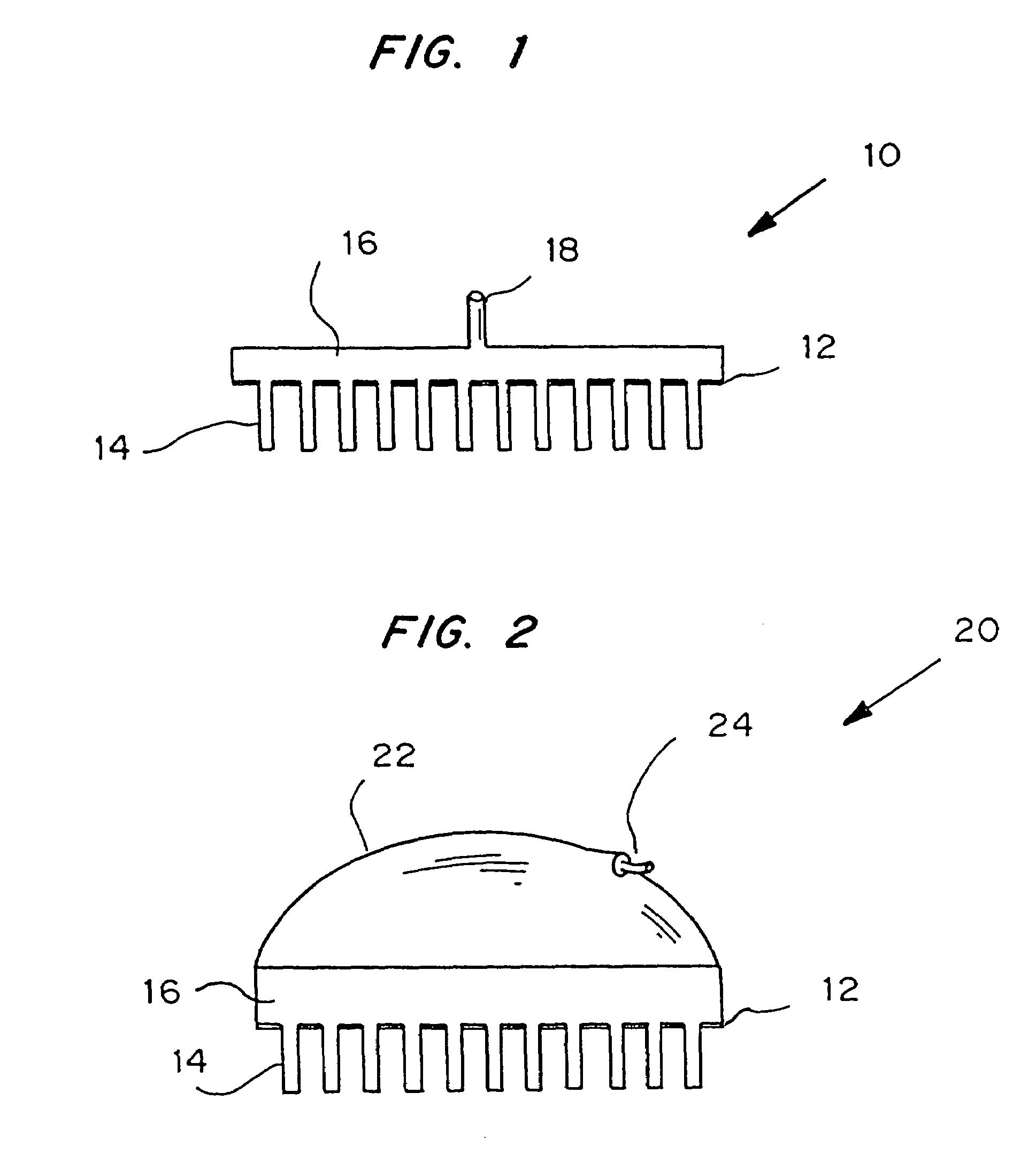
Microneedle devices are provided for controlled sampling of biological fluids in a minimally-invasive, painless, and convenient manner. The microneedle devices permit in vivo sensing or withdrawal of biological fluids from the body, particularly from or through the skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The microneedle device includes one or more microneedles, preferably in a three-dimensional array, a substrate to which the microneedles are connected, and at least one collection chamber and / or sensor in communication with the microneedles. Preferred embodiments further include a means for inducing biological fluid to be drawn through the microneedles and into the collection chamber for analysis. In a preferred embodiment, this induction is accomplished by use of a pressure gradient, which can be created for example by selectively increasing the interior volume of the collection chamber, which includes an elastic or movable portion engaged to a rigid base. Preferred biological fluids for withdrawal and / or sensing include blood, lymph, interstitial fluid, and intracellular fluid. Examples of analytes in the biological fluid to be measured include glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, creatine, metabolic enzymes, hemoglobin, heparin, clotting factors, uric acid, carcinoembryonic antigen or other tumor antigens, reproductive hormones, oxygen, pH, alcohol, tobacco metabolites, and illegal drugs.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
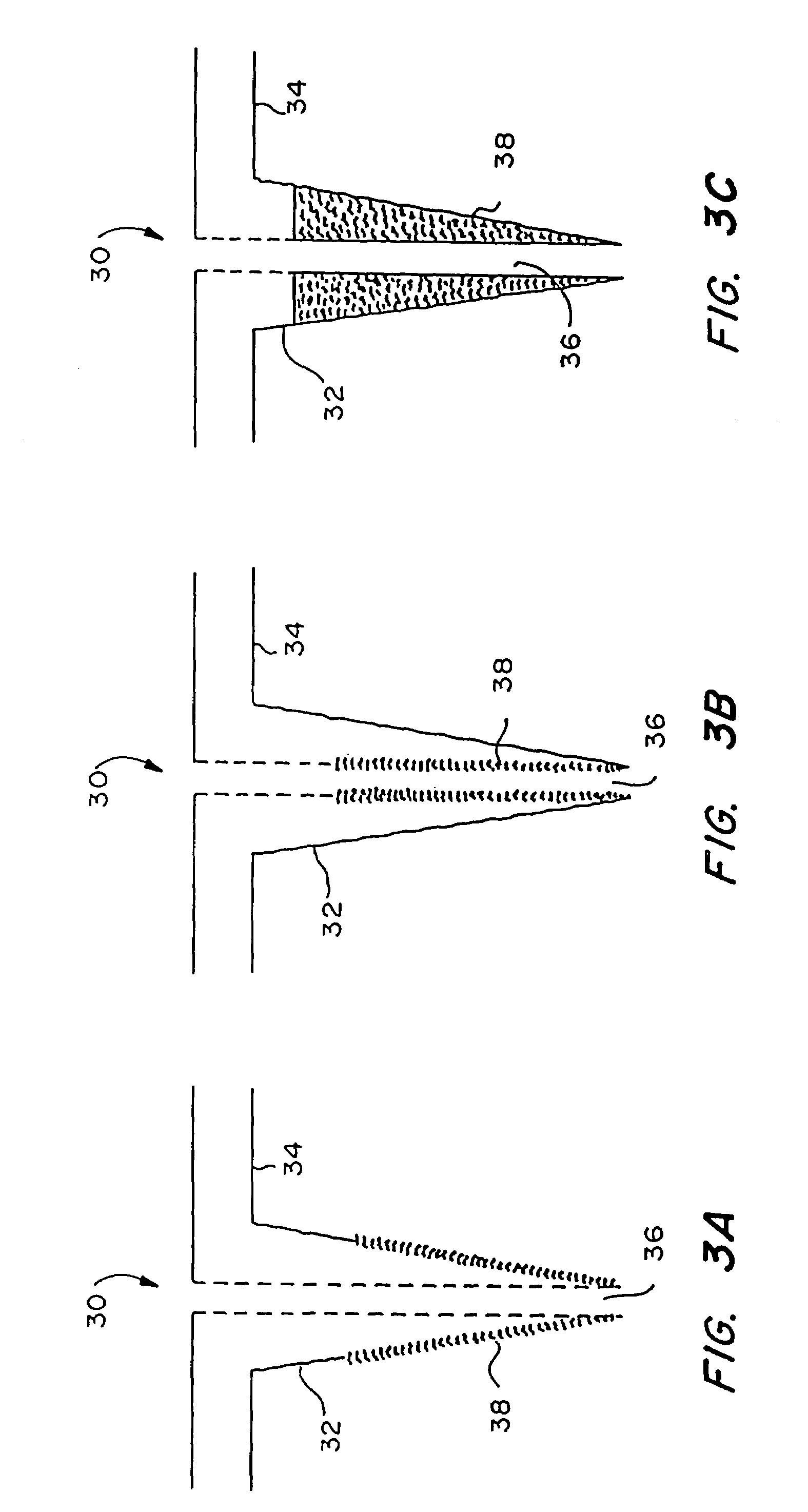
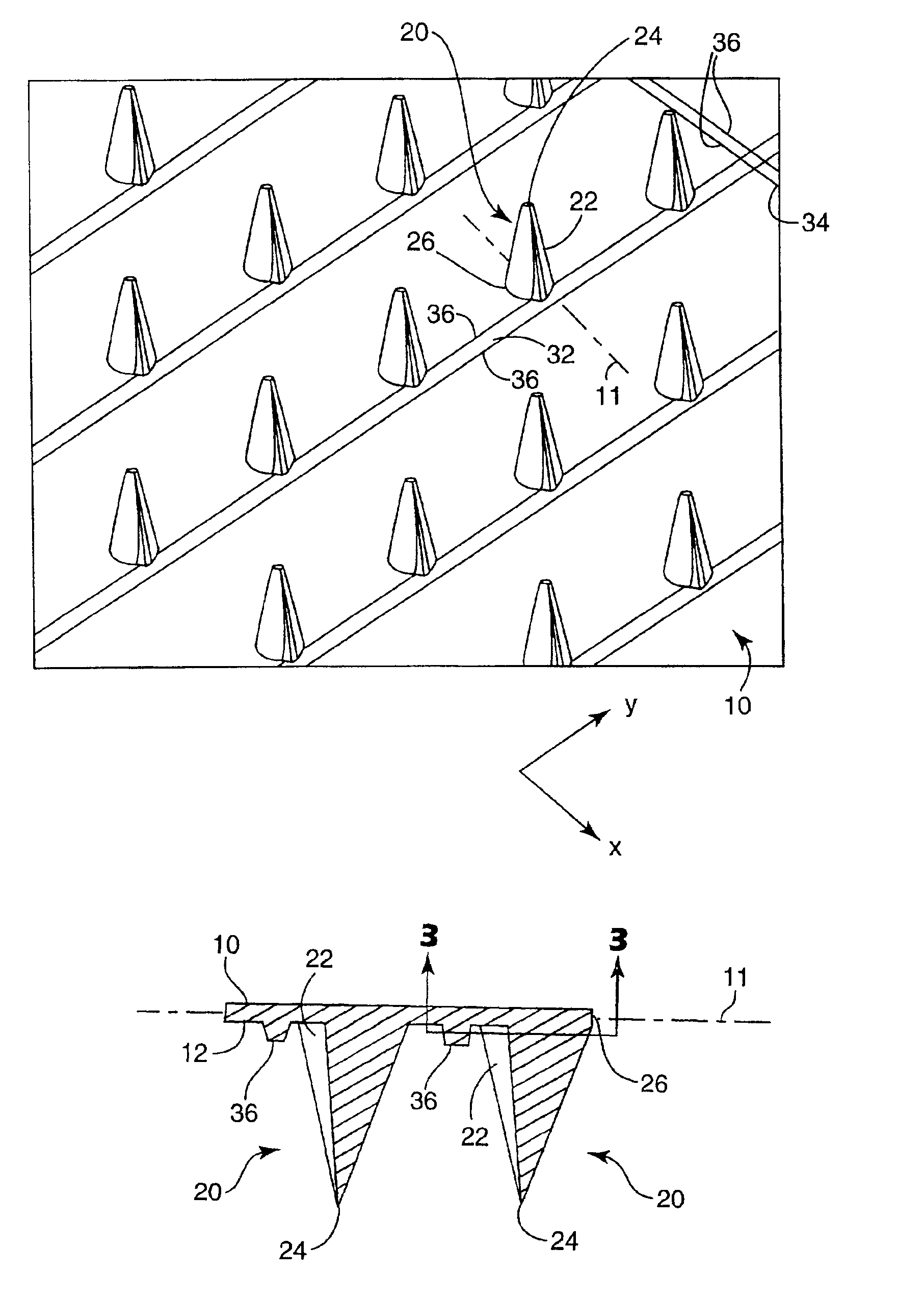
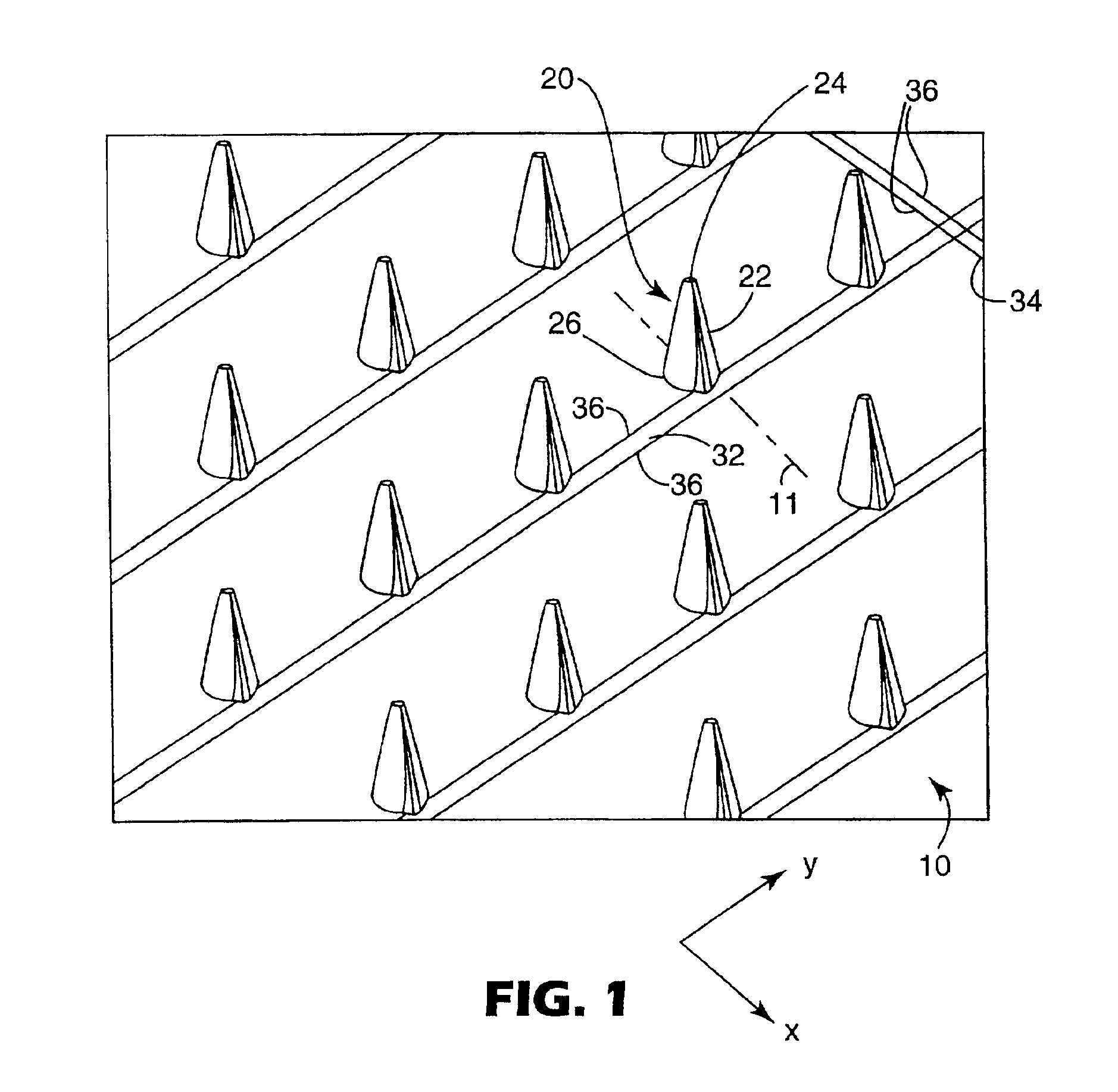
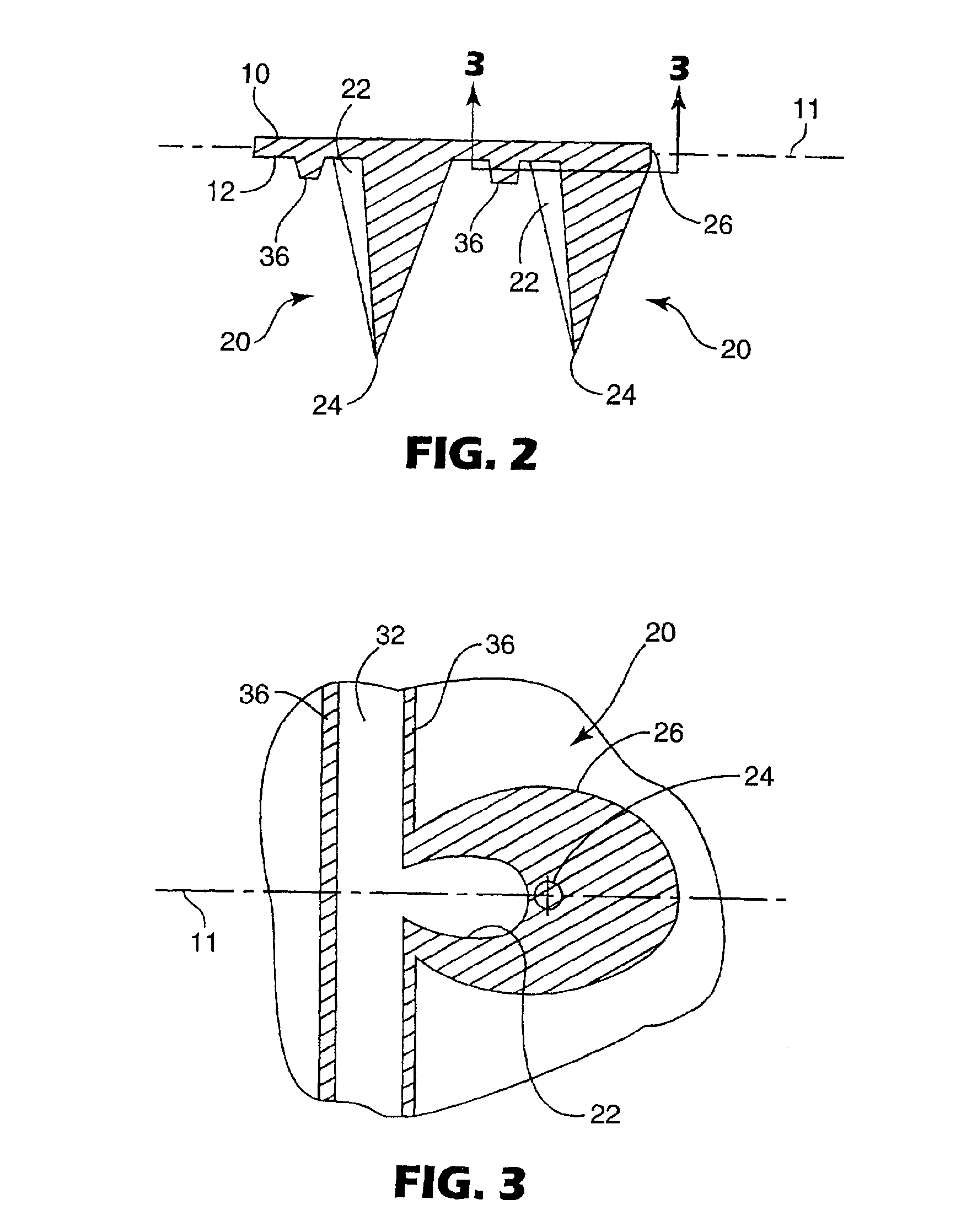
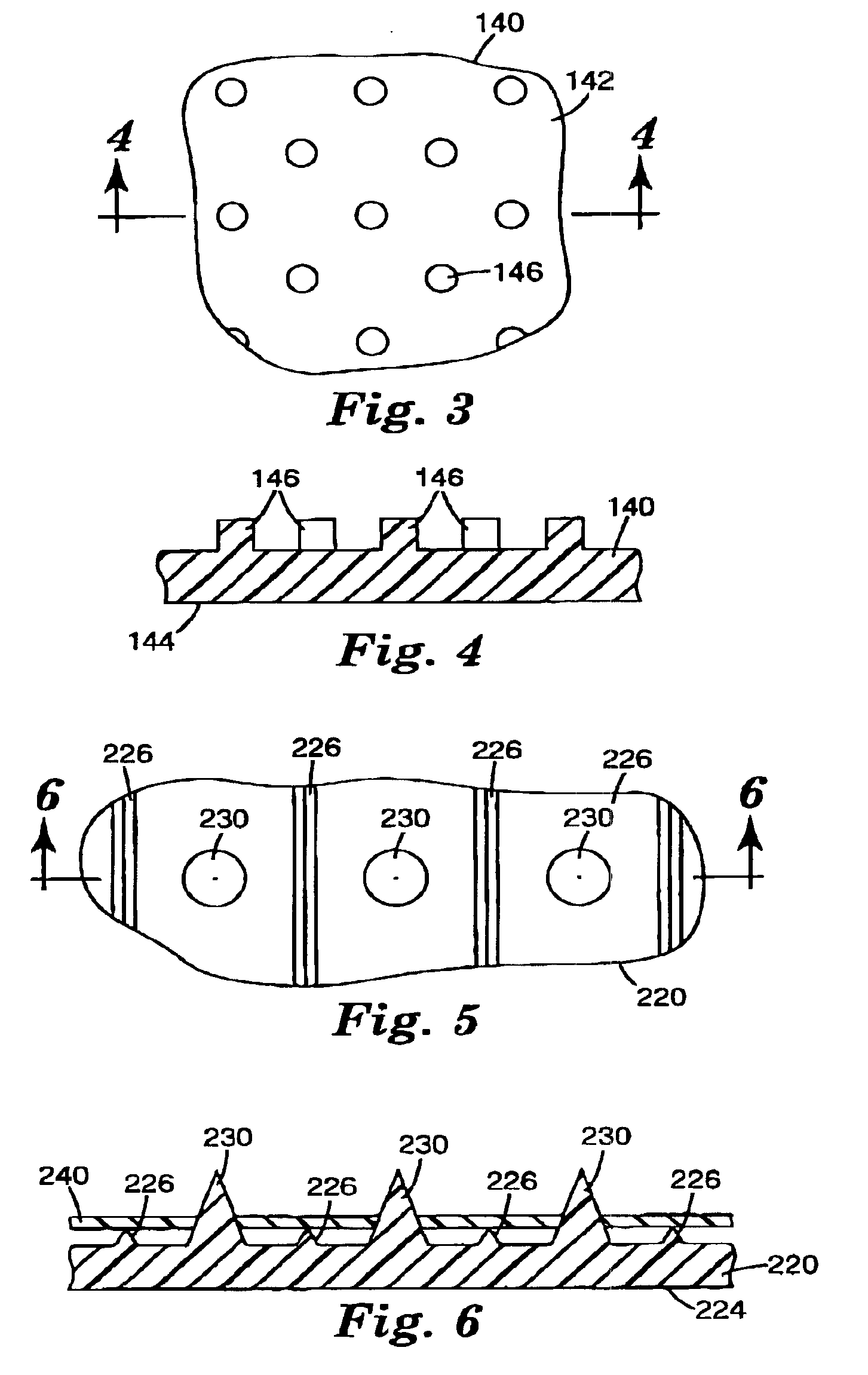
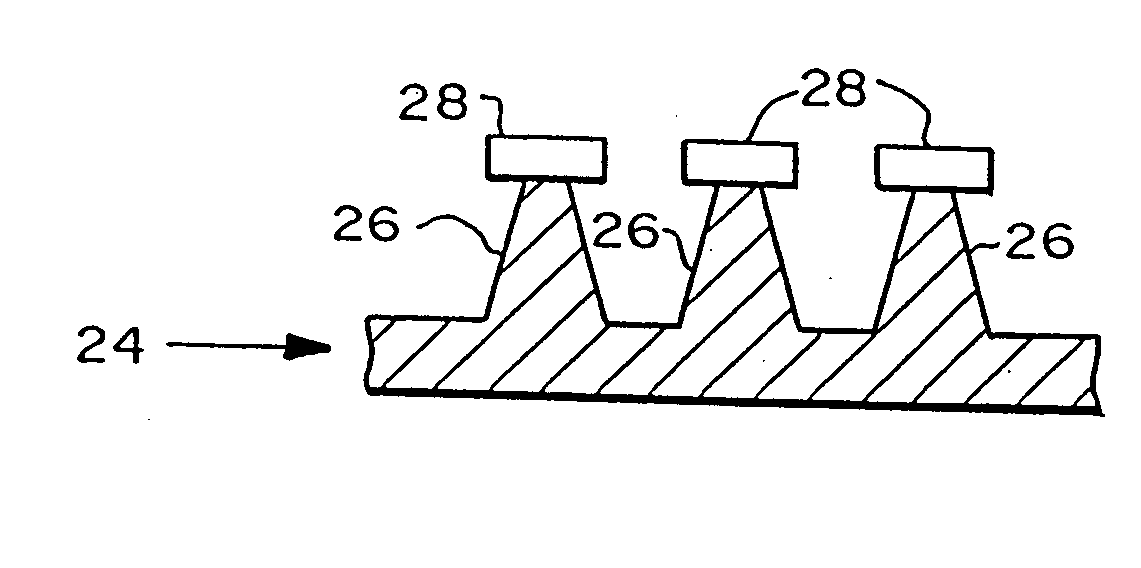
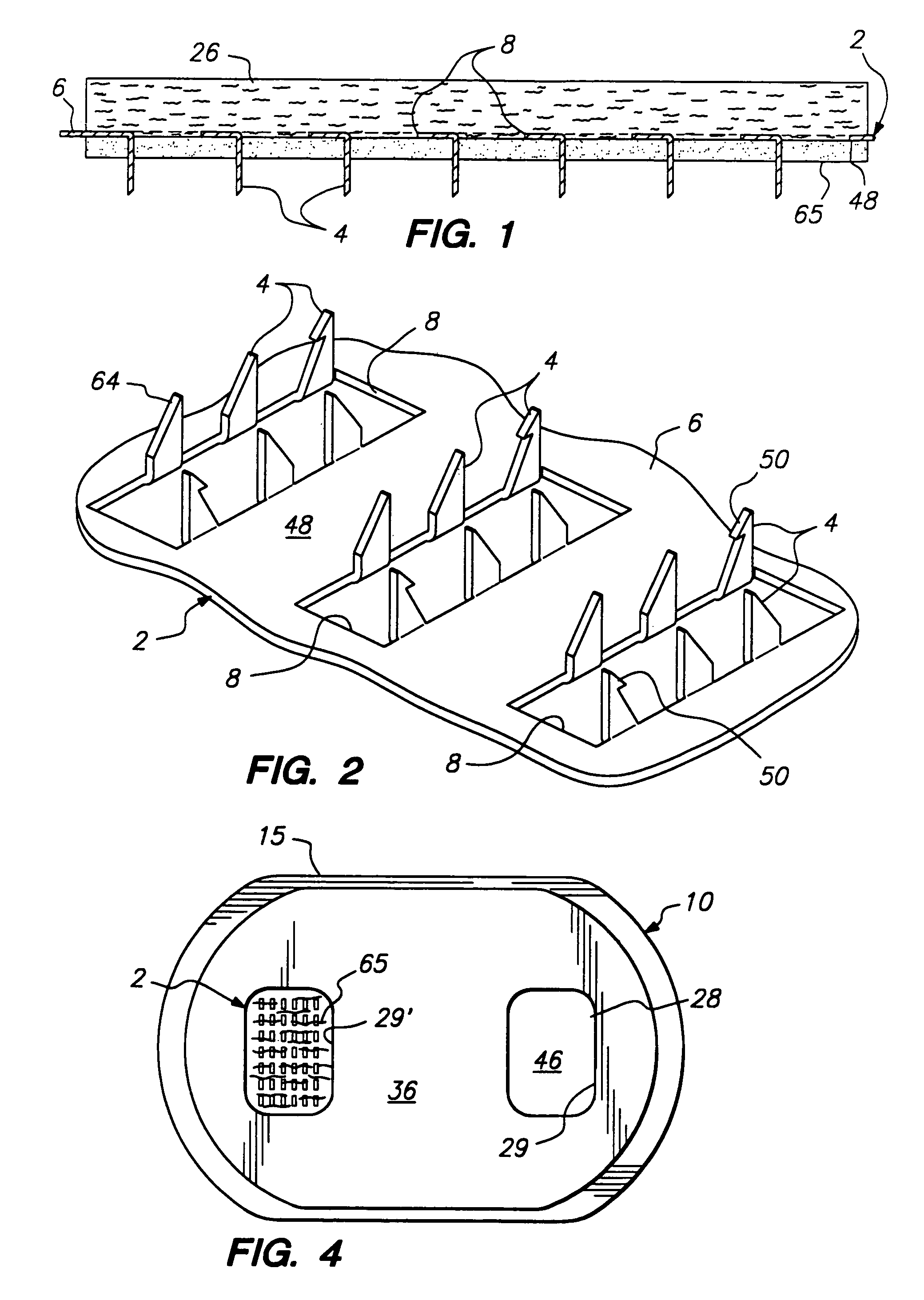
Microneedle arrays and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6881203B2Additional rigidity and structural integrityImprove puncture abilitySurgeryMicroneedlesCatheterMicro-needle
Microneedle arrays, methods of manufacturing microneedles and methods of using microneedle arrays. The microneedles in the microneedle arrays may be in the form of tapered structures that include at least one channel formed in the outside surface of each microneedle. The microneedles may have bases that are elongated in one direction. The channels in microneedles with elongated bases may extend from one of the ends of the elongated bases towards the tips of the microneedles. The channels formed along the sides of the microneedles may optionally be terminated short of the tips of the microneedles. The microneedle arrays may also include conduit structures formed on the surface of the substrate on which the microneedle array is located. The channels in the microneedles may be in fluid communication with the conduit structures. One manner of using microneedle arrays of the present invention is in methods involving the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Self-actuating applicator for microprojection array
Owner:ALZA CORP
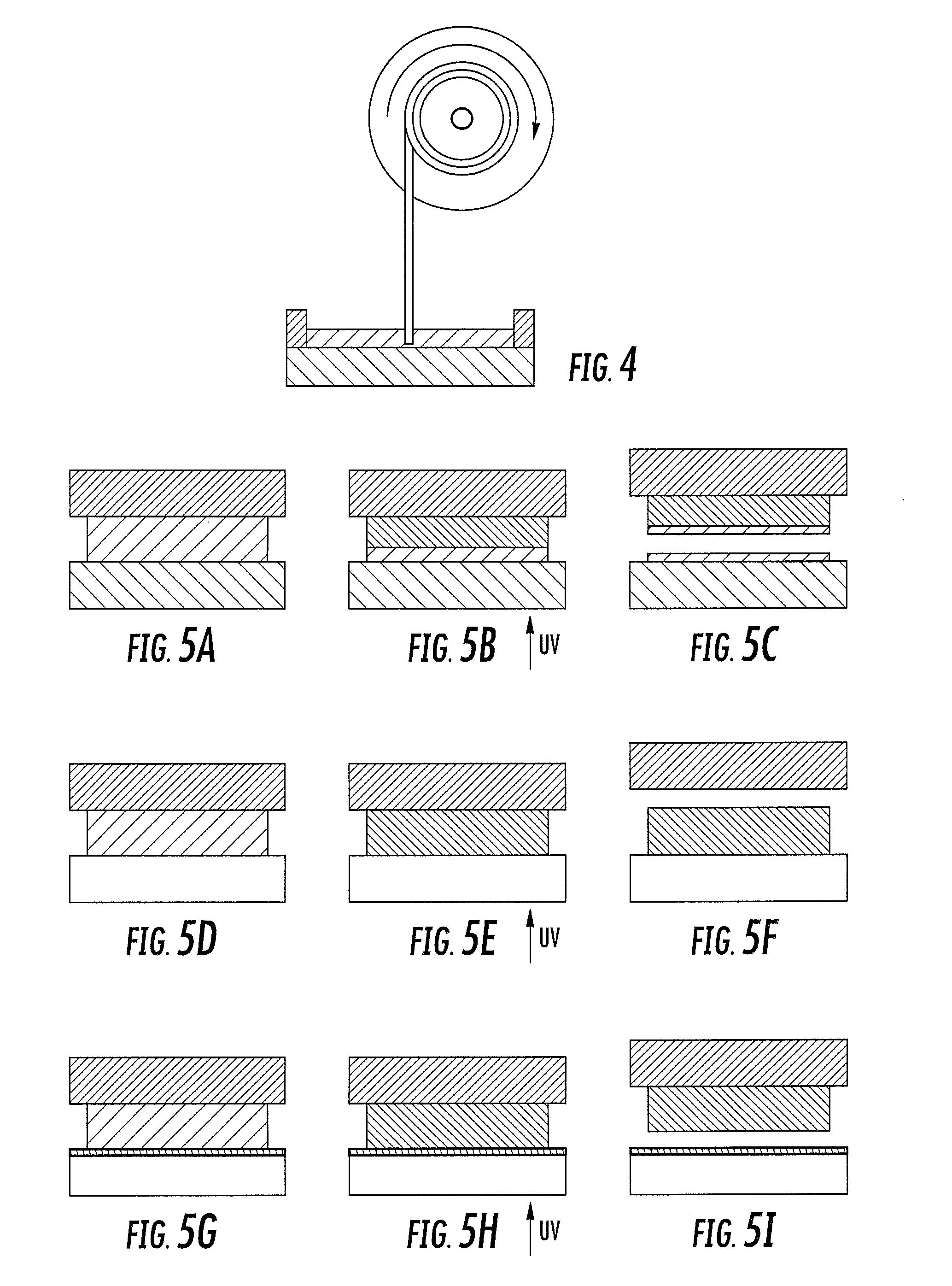
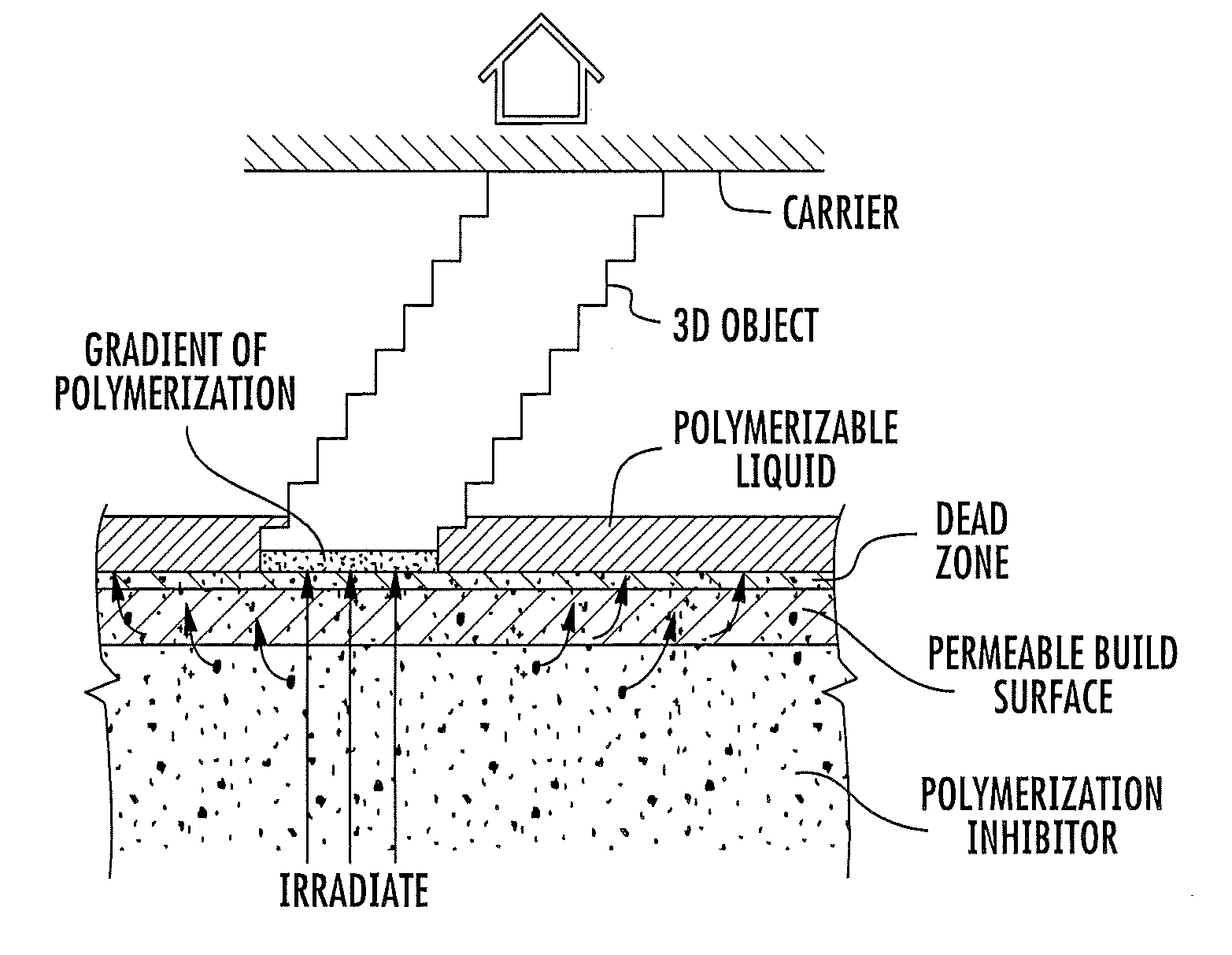
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional fabrication with feed through carrier
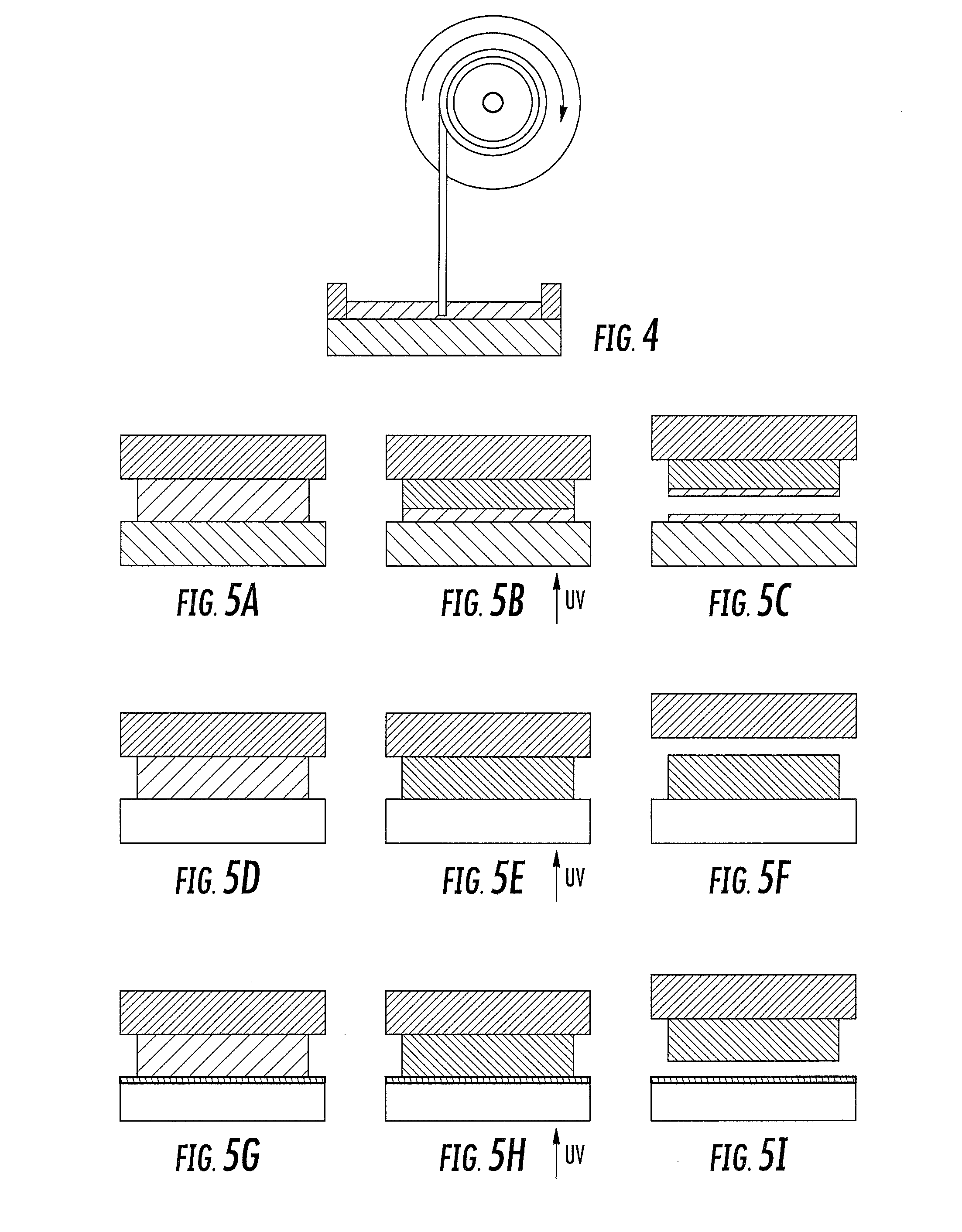
A method of forming a three-dimensional object, is carried out by (a) providing a carrier and a build plate, the build plate comprising a semipermeable member, the semipermeable member comprising a build surface with the build surface and the carrier defining a build region therebetween, and with the build surface in fluid communication by way of the semipermeable member with a source of polymerization inhibitor; (b) filling the build region with a polymerizable liquid, the polymerizable liquid contacting the build surface; (c) irradiating the build region through the build plate to produce a solid polymerized region in the build region, while forming or maintaining a liquid film release layer comprised of the polymerizable liquid formed between the solid polymerized region and the build surface, the polymerization of which liquid film is inhibited by the polymerization inhibitor; and (d) advancing the carrier with the polymerized region adhered thereto away from the build surface on the build plate to create a subsequent build region between the polymerized region and the build surface; (e) wherein the carrier has at least one channel formed therein, and the filling step is carried out by passing or forcing the polymerizable liquid into the build region through the at least one channel. Apparatus for carrying out the method is also described
Owner:CARBON INC
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional fabrication
A method of forming a three-dimensional object, is carried out by (a) providing a carrier and a build plate, the build plate comprising a semipermeable member, the semipermeable member comprising a build surface with the build surface and the carrier defining a build region therebetween, and with the build surface in fluid communication by way of the semipermeable member with a source of polymerization inhibitor; (b) filling the build region with a polymerizable liquid, the polymerizable liquidcontacting the build surface, (c) irradiating the build region through the build plate to produce a solid polymerized region in the build region, while forming or maintaining a liquid film release layer comprised of the polymerizable liquid formed between the solid polymerized region and the build surface, wherein the polymerization of which liquid film is inhibited by the polymerization inhibitor; and (d) advancing the carrier with the polymerized region adhered thereto away from the build surface on the build plate to create a subsequent build region between the polymerized region and the build surface while concurrently filling the subsequent build region with polymerizable liquid as in step (b). Apparatus for carrying out the method is also described.
Owner:CARBON INC
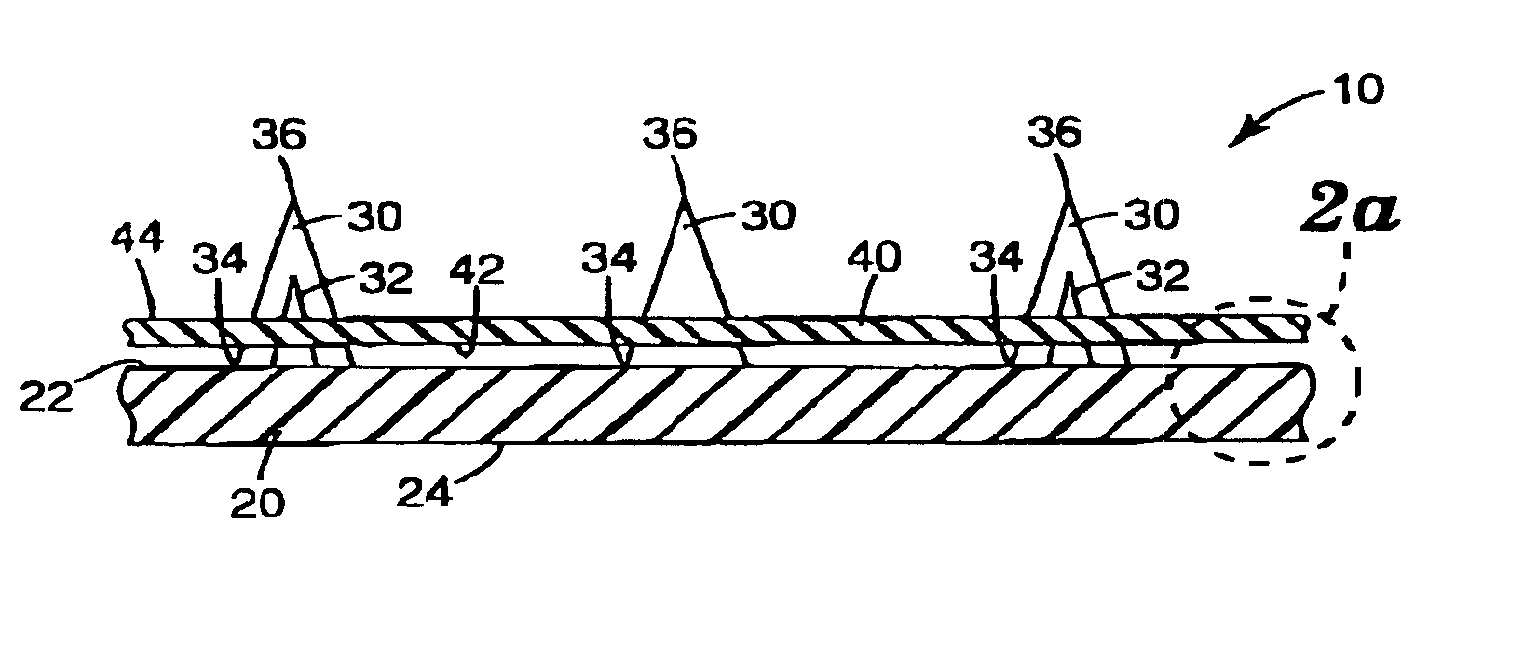
Microneedle devices and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS6908453B2Enhanced fluid movementImprove actionSurgical needlesMicroneedlesCapillary volumeSubstrate surface
Microneedle devices and methods of manufacturing the microneedle devices. The microneedle devices include microneedles protruding from a substrate, with the microneedles piercing a cover placed over the substrate surface from which the microneedles protrude. The cover and the microneedle substrate together define a capillary volume in fluid communication with the base of each microneedle. One manner of using microneedle arrays of the present invention is in methods involving the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue. Manufacturing methods may include simultaneous application of pressure and ultrasonic energy when piercing the cover with the microneedles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
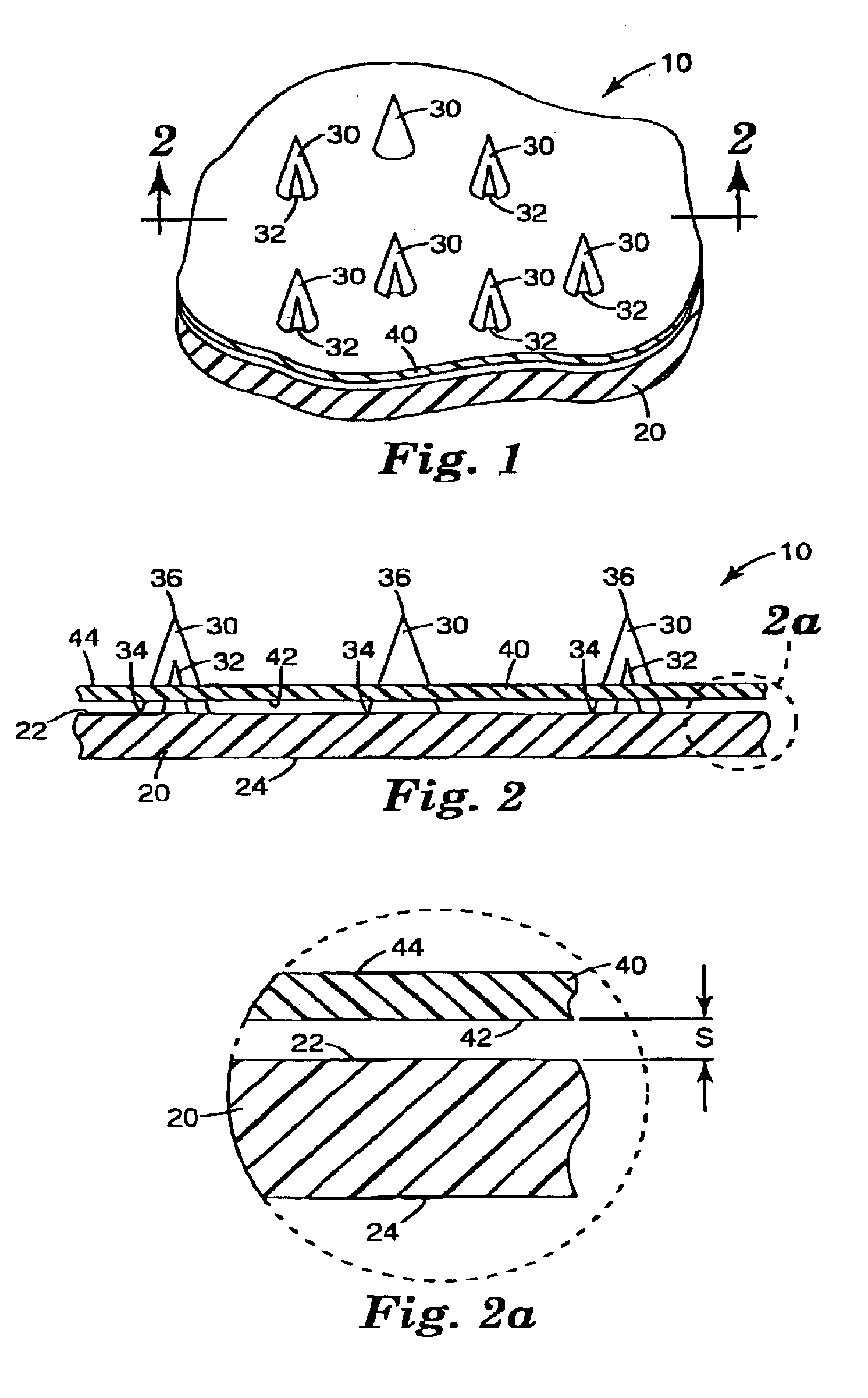
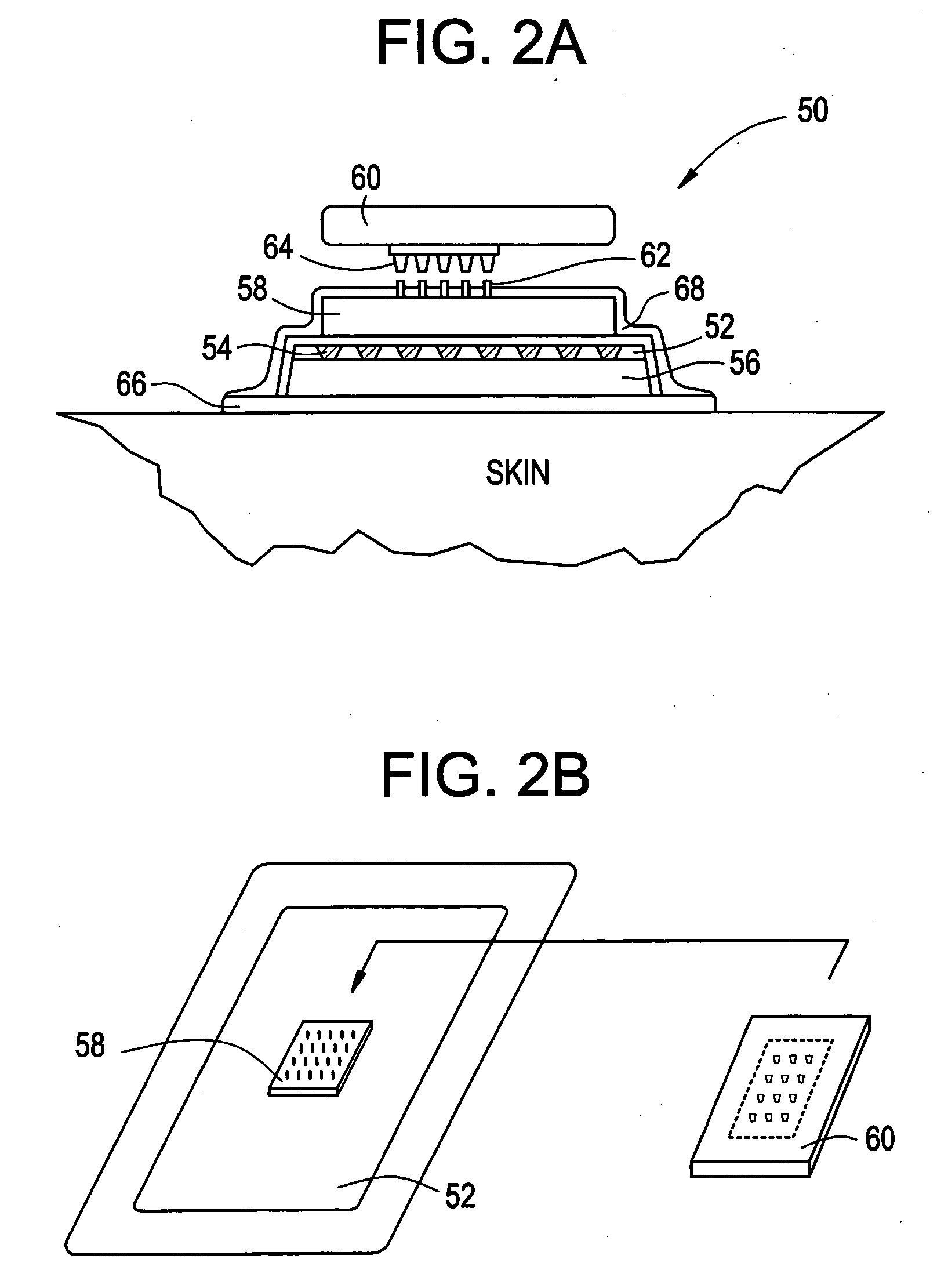
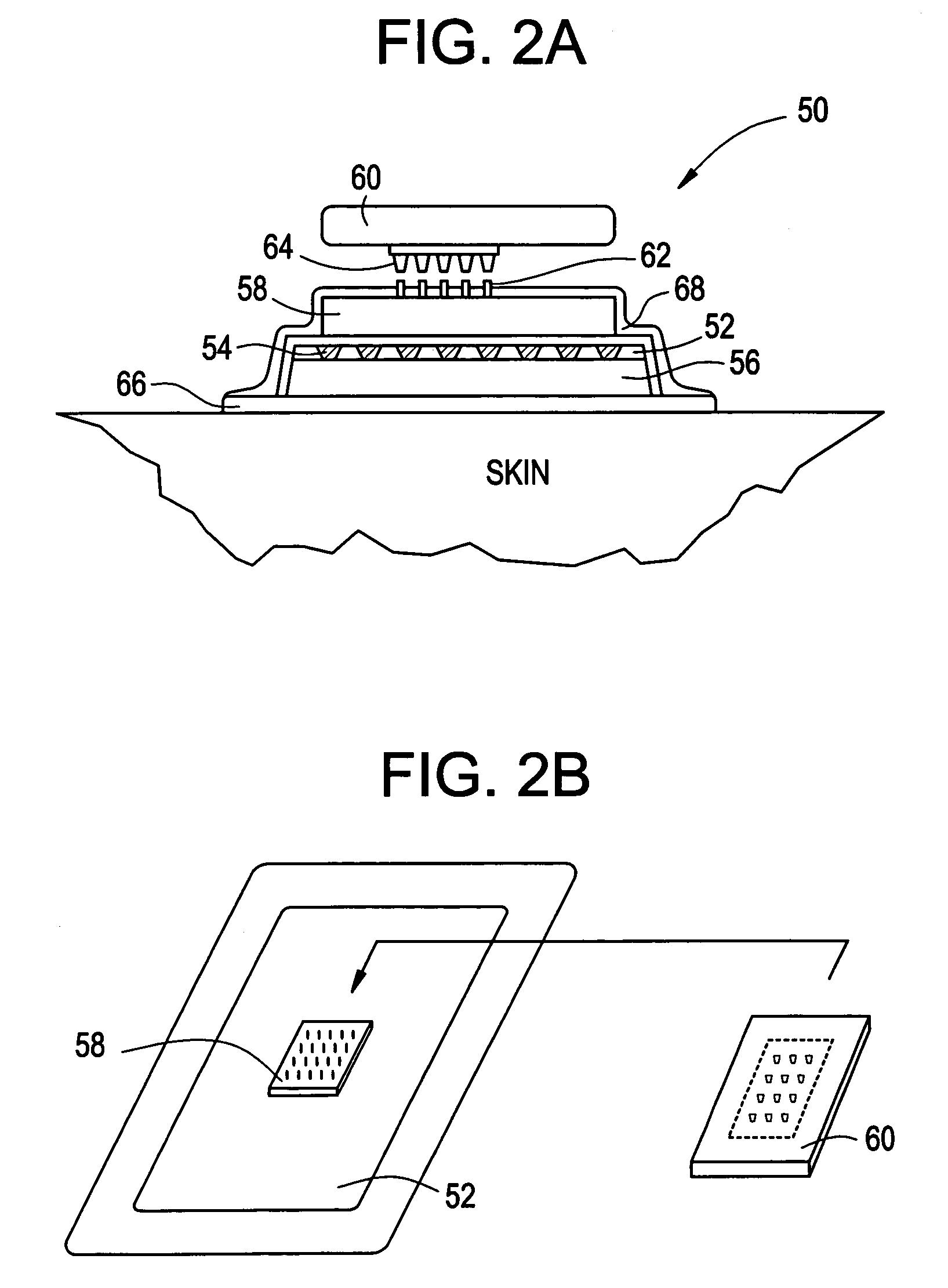
Intracutaneous microneedle array apparatus
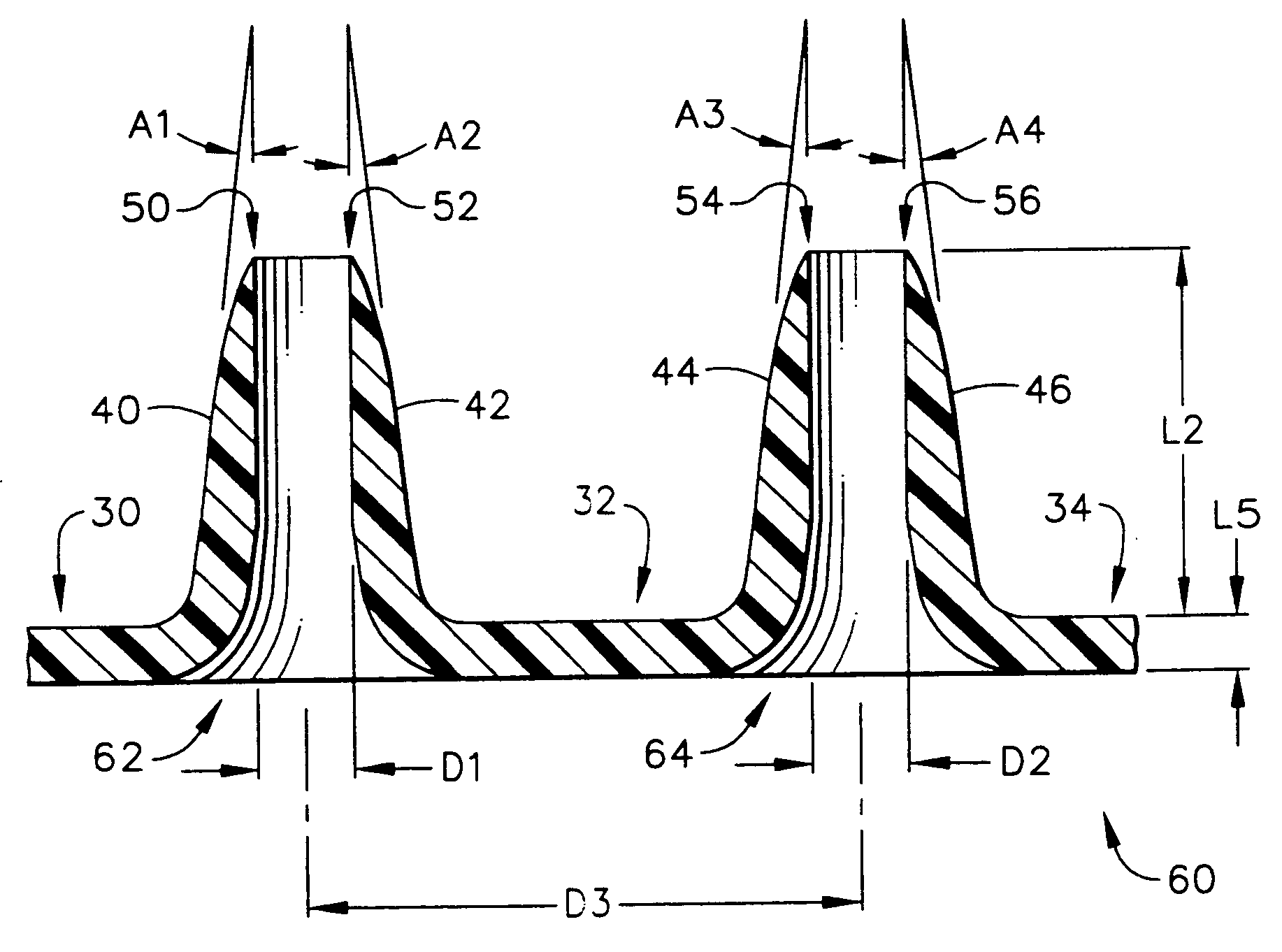
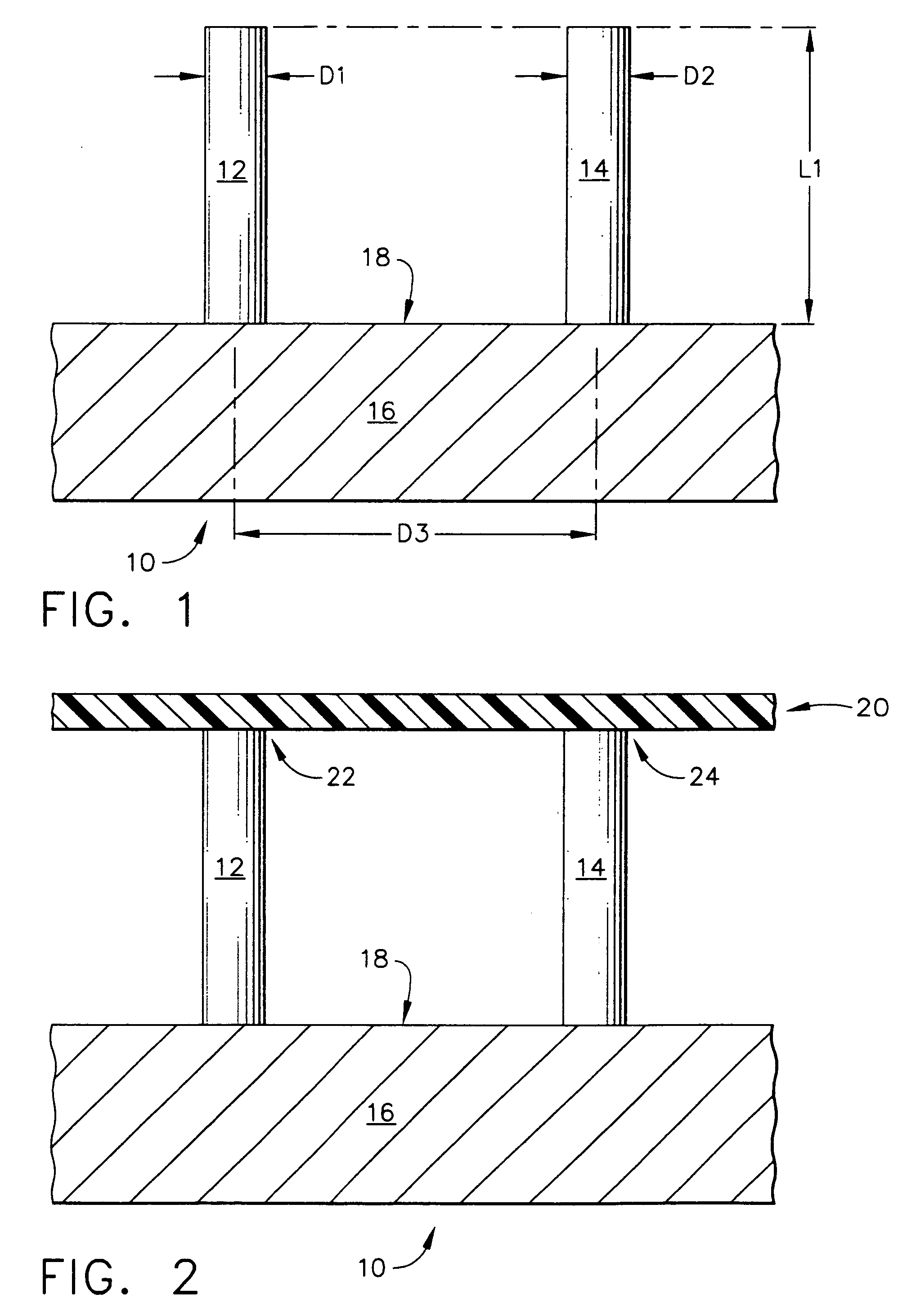
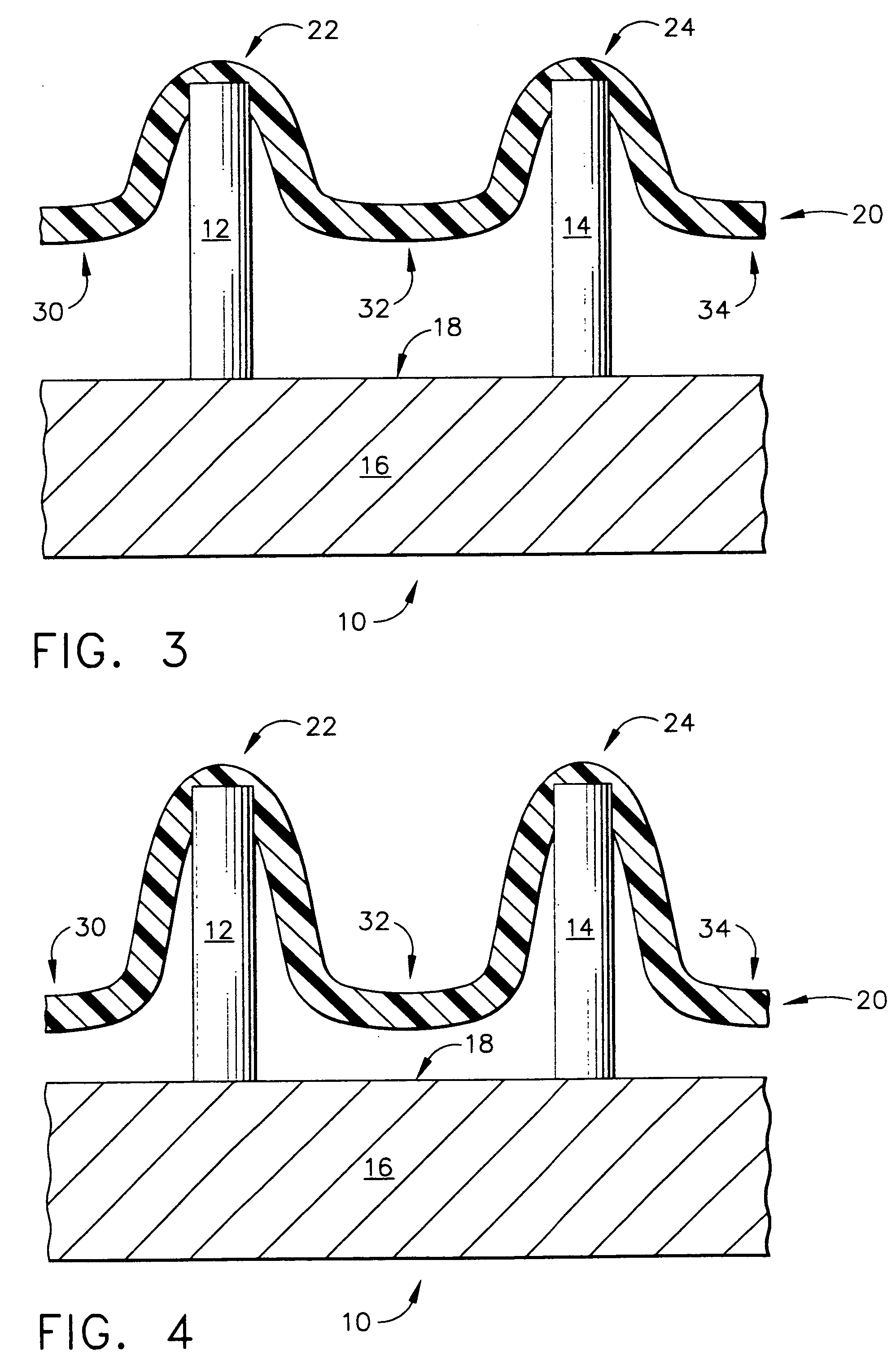
InactiveUS20050209565A1Sufficient separation distanceGreater transdermal fluxElectrotherapySurgical needlesEngineeringBiological fluids
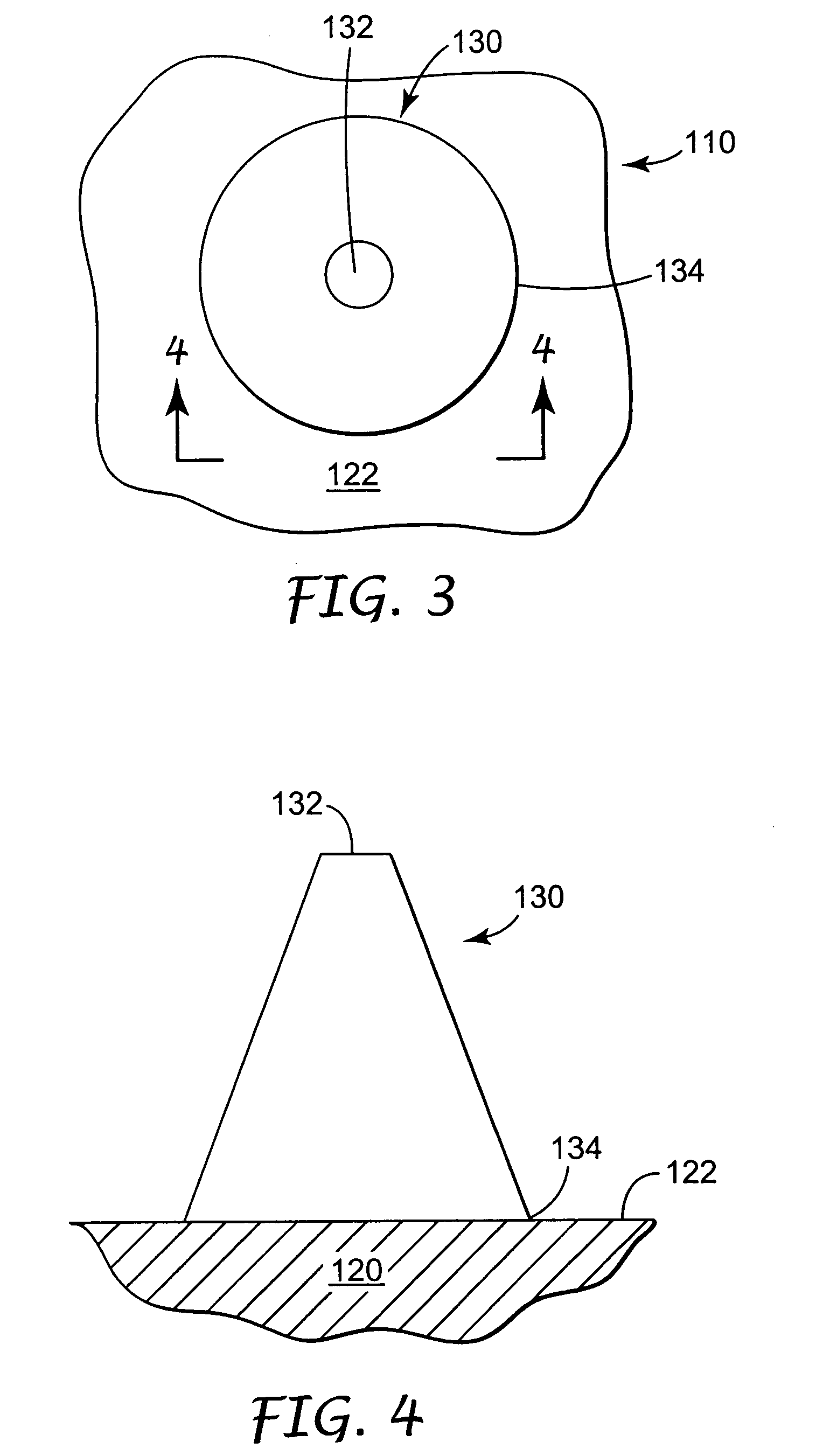
Improved microneedle arrays are provided having a sufficiently large separation distance between each of the individual microneedles to ensure penetration of the skin while having a sufficiently small separation distance to provide high transdermal transport rates. A very useful range of separation distances between microneedles is in the range of 100-300 microns, and more preferably in the range of 100-200 microns. The outer diameter and microneedle length is also very important, and in combination with the separation distance will be crucial as to whether or not the microneedles will actually penetrate the stratum corneum of skin. For circular microneedles, a useful outer diameter range is from 20-100 microns, and more preferably in the range of 20-50 microns. For circular microneedles that do not have sharp edges, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50-200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 100-150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is in the range of 200 microns—3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200-400 microns. For circular microneedles having sharp side edges, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50-200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 80-150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is again in the range of 200 microns—3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200-400 microns. For solid microneedles having a star-shaped profile with sharp edges for its star-shaped blades, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50-200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 80-150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is again in the range of 200 microns—3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200-400 microns, while the radius of each of its blades is in the range of 10-50 microns, and more preferably in the range of 10-15 microns.
Owner:CORIUM INC
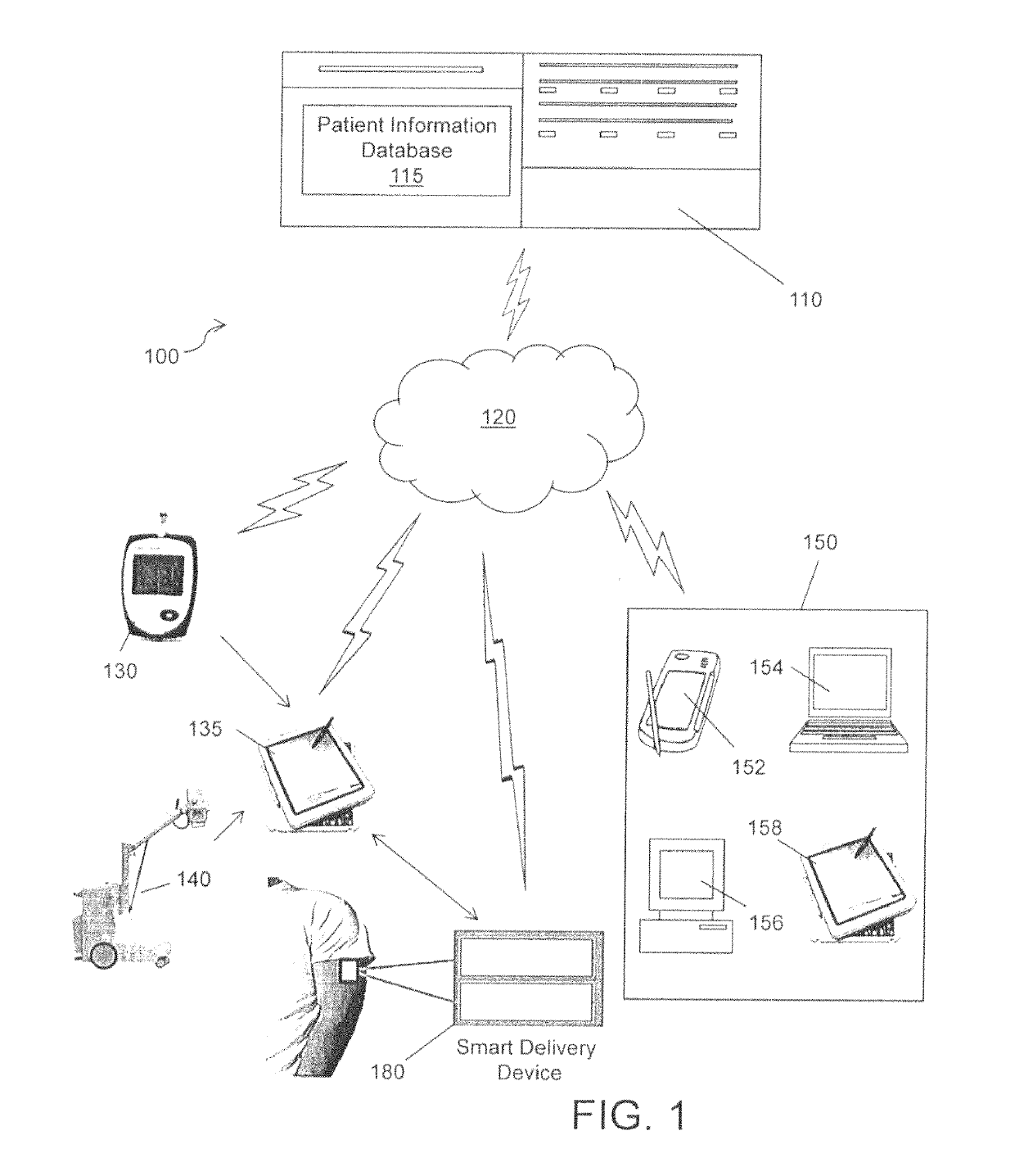
Physician-centric health care delivery platform
A system for diagnosing and / or treating a patient comprising a patient information database for storing and retrieving patient health data related to the patient. The data includes one or more of real-time patient health information, at least one clinical practice guideline, at least one patient questionnaire and a patient medical history. At least one server is operative to access the patient information database. A computing device remotely located from the server, including a microprocessor, configured to store a computer application and is configured for communication with the server for retrieving of the patient health data. The computer application generates at least one of a patient diagnosis or a patient treatment recommendation using the retrieved patient health data.
Owner:MD24 PATENT TECH LLC
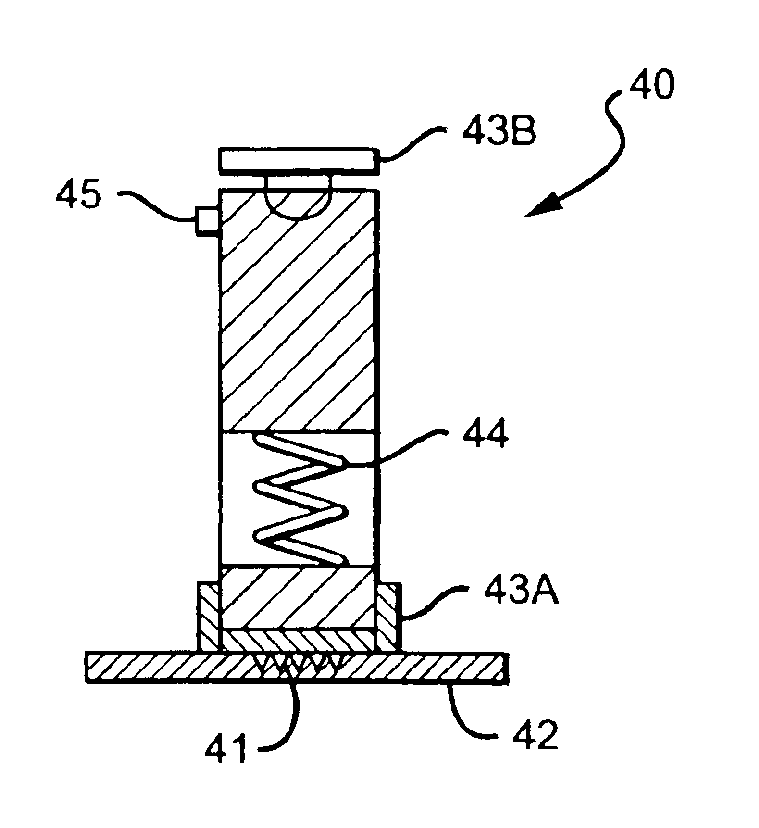
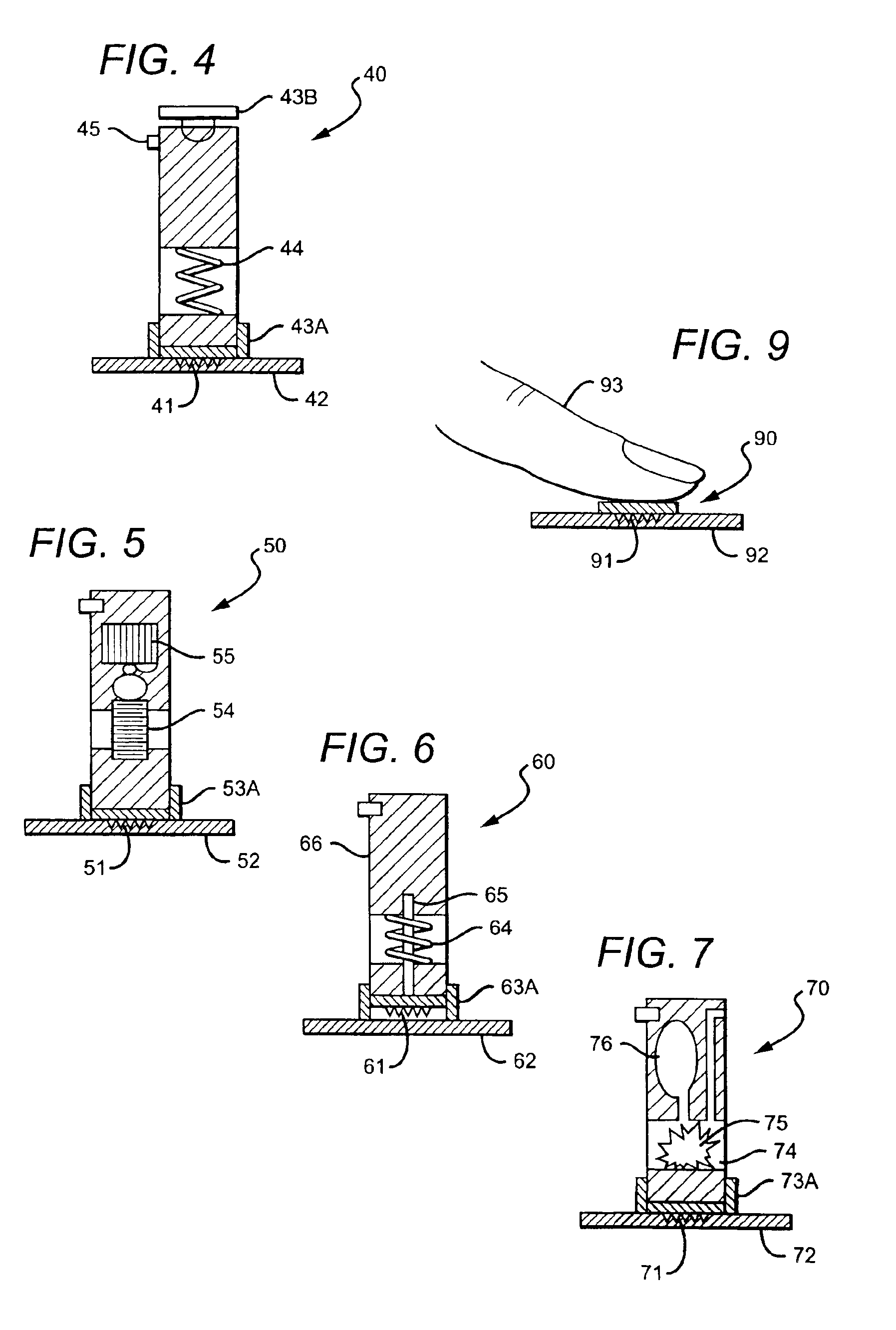
Microneedle drug delivery device
InactiveUS7226439B2Minimal and no damage and pain and irritationAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical needlesIrritationMicro-needle
Simple microneedle devices for delivery of drugs across or into biological tissue are provided, which permit drug delivery at clinically relevant rates across or into skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The devices include a substrate to which a plurality of hollow microneedles are attached or integrated, and at least one reservoir, containing the drug, selectably in communication with the microneedles, wherein the volume or amount of drug to be delivered can be selectively altered. The reservoir can be formed of a deformable, preferably elastic, material. The device typically includes a means, such as a plunger, for compressing the reservoir to drive the drug from the reservoir through the microneedles. In one embodiment, the reservoir is a syringe or pump connected to the substrate.
Owner:VALERITAS LLC (US)
Continuous liquid interphase printing
A method of forming a three-dimensional object, comprises providing a carrier and an optically transparent member having a build surface, the carrier and the build surface defining a build region therebetween; filling the build region with a polymerizable liquid; irradiating the build region through the optically transparent member to form a solid polymer from the polymerizable liquid while concurrently advancing the carrier away from the build surface to form the three-dimensional object from the solid polymer, while also concurrently: (i) continuously maintaining a dead zone of polymerizable liquid in contact with the build surface, and (ii) continuously maintaining a gradient of polymerization zone between the dead zone and the solid polymer and in contact with each thereof, the gradient of polymerization zone comprising the polymerizable liquid in partially cured form. Apparatus for carrying out the method is also described.
Owner:CARBON INC
Solid solution perforator for drug delivery and other applications
InactiveUS6945952B2Fast biodegradationBarrier property can be diminished and controlledSurgeryMicroneedlesDrug reservoirDrugs solution
A solid drug solution perforator (SSP) system and an associated drug reservoir are provided for delivering therapeutic, prophylactic and / or cosmetic compounds, for nutrient delivery and for drug targeting. For drug delivery, the SSP system includes an active drug ingredient and a matrix of perforator material that biodegrades or dissolves quickly upon contact with a patient's body. The SSP system provides a skin barrier perforator and a controller for prompt initiation and cut-off drug delivery. In a preferred method of transdermal drug delivery, an SSP system containing a selected drug penetrates into an epidermis or dermis, and the drug is promptly released from the (dissolving) SSP system perforator. An additional drug is optionally delivered from a patch reservoir through skin pores created by insertion of the perforator. Formulation and fabrication procedures for the SSP and associated reservoir are also provided. An SSP system can be fabricated with variety of shapes and dimensions.
Owner:THERAJECT INC.
Devices and methods for enhanced microneedle penetration of biological barriers
InactiveUS20050137531A1Easy to transportEnhanced interactionAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgerySkin surfacesTissue skin
Microneedle devices and methods of use thereof are provided for the enhanced transport of molecules, including drugs and biological molecules, across tissue by improving the interaction of microneedles and a deformable, elastic biological barrier, such as human skin. The devices and methods act to (1) limit the elasticity, (2) adapt to the elasticity, (3) utilize alternate ways of creating the holes for the microneedles to penetrate the biological barrier, other than the simply direct pressure of the microneedle substrate to the barrier surface, or (4) any combination of these methods. In preferred embodiments for limiting the elasticity of skin, the microneedle device includes features suitable for stretching, pulling, or pinching the skin to present a more rigid, less deformable, surface in the area to which the microneedles are applied (i.e. penetrate). In a preferred embodiments for adapting the device to the elasticity of skin, the device comprising one or more extensions interposed between the substrate and the base end of at least a portion of the microneedles.
Owner:VALERITAS LLC (US) +1
Microneedle devices and microneedle delivery apparatus
InactiveUS20050261631A1Reduces tip fractureEffective perforationSurgical needlesMicroneedlesStratum corneumPain experience
Microneedle devices with microneedles having a truncated tapered shape are disclosed. The microneedles of microneedle devices may also have a controlled aspect ratio. Microneedle delivery apparatus are disclosed that include drivers designed to deliver microneedles at velocities that may enhance perforation of the stratum corneum while limiting the sensation of pain experienced at the delivery site.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Applicator for applying functional substances into human skin
An applicator for applying functional substances, such as cosmetic powder, food color marking, India ink effect marks, or drugs into human skin, having a base, a plurality of microneedles fixed to and projecting from the base a distance only sufficient to penetrate into the stratum corneum or dermis, with the microneedles being of a material that is capable of disintegration and dispersion into the stratum corneum or dermis, such as maltose. The needles contain the functional substance for delivery into the stratum corneum or dermis. The microneedles are of a length approximately 0.5 to 500 μm when used to apply a functional substance to the stratum corneum, or are of a length of approximately 500 to 5,000 μm when used to apply a functional substance to the dermis.
Owner:TOBINAGA YOSHIKAZU +1
Method and device for intradermally delivering a substance
A device for delivering a substance into the skin of a patient includes a body and a skin penetrating device having at least one skin penetrating member, such as a microneedle. The body includes an internal cavity and a device for indicating the delivery of a sufficient amount of the substance to the patient and for producing a dispensing pressure to dispense and deliver the substance from the cavity. The indicating device is visible from the exterior of the delivery device. In some embodiments, the indicating device is an elastic expandable diaphragm which, when the cavity is filled with a substance, creates the dispensing pressure.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
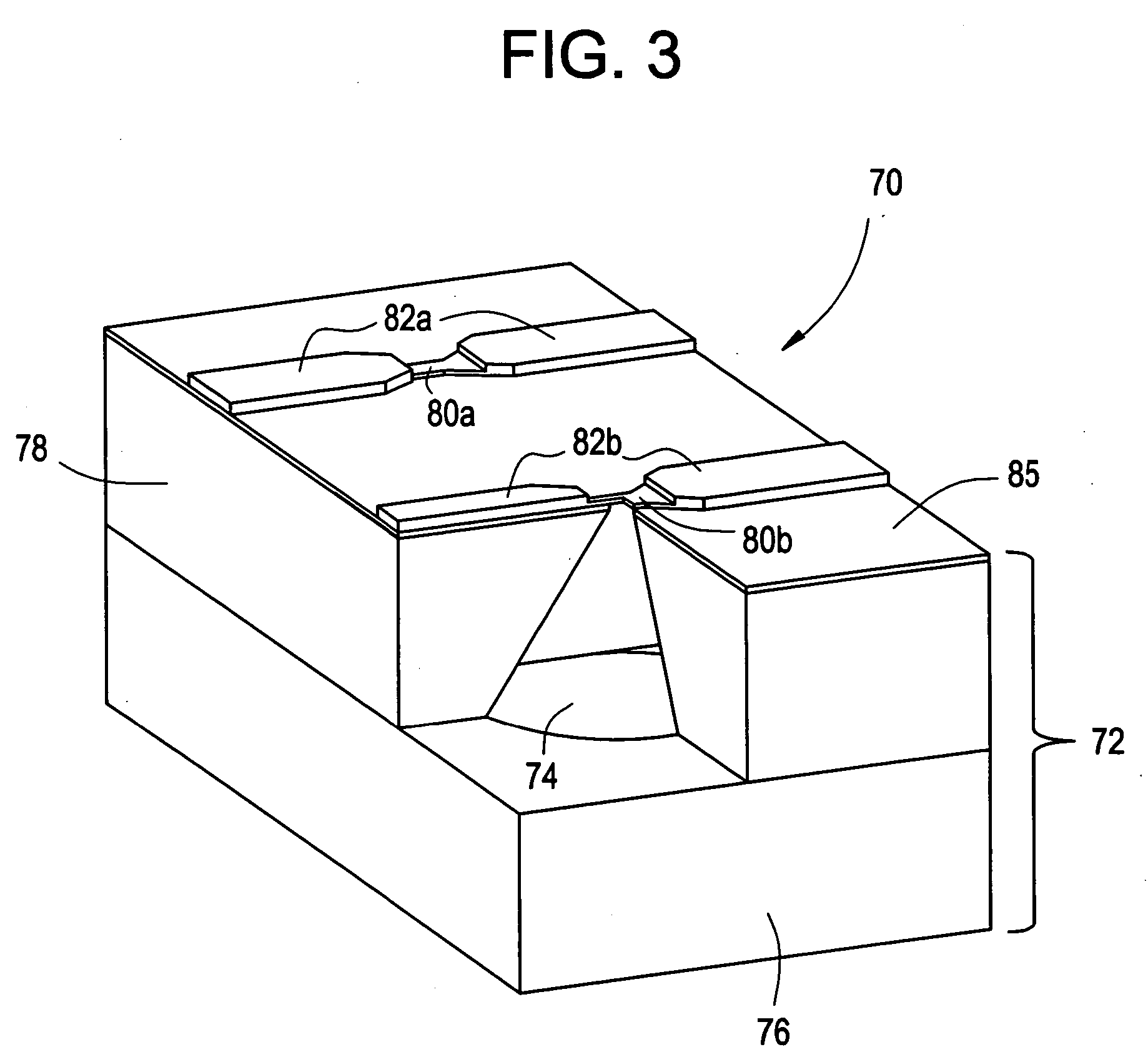
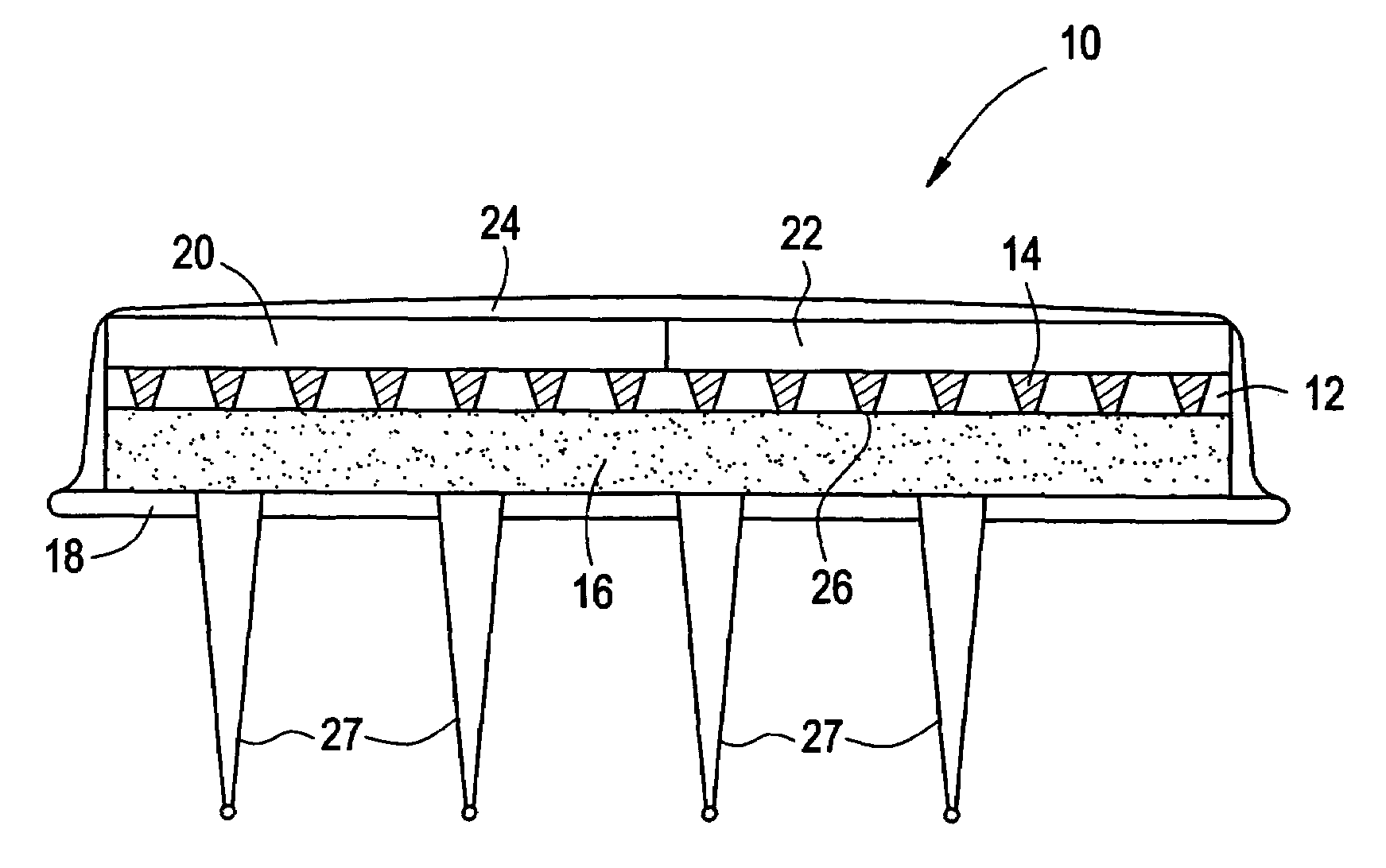
Active needle devices with integrated functionality
InactiveUS20040176732A1Facilitate biochemical and optical and electrical and physical measurementMinimizing chanceMicroneedlesMedical devicesActive componentActuator
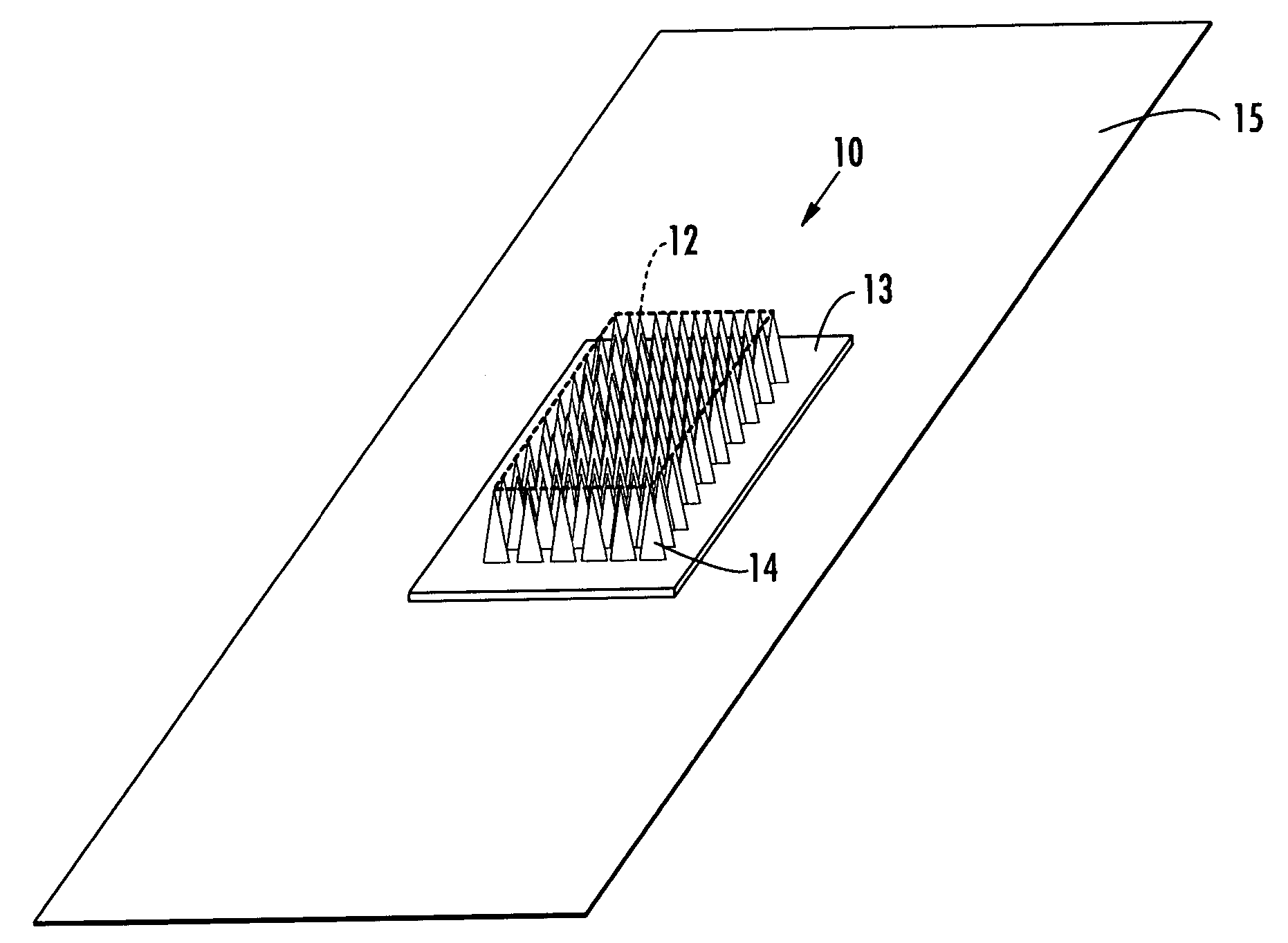
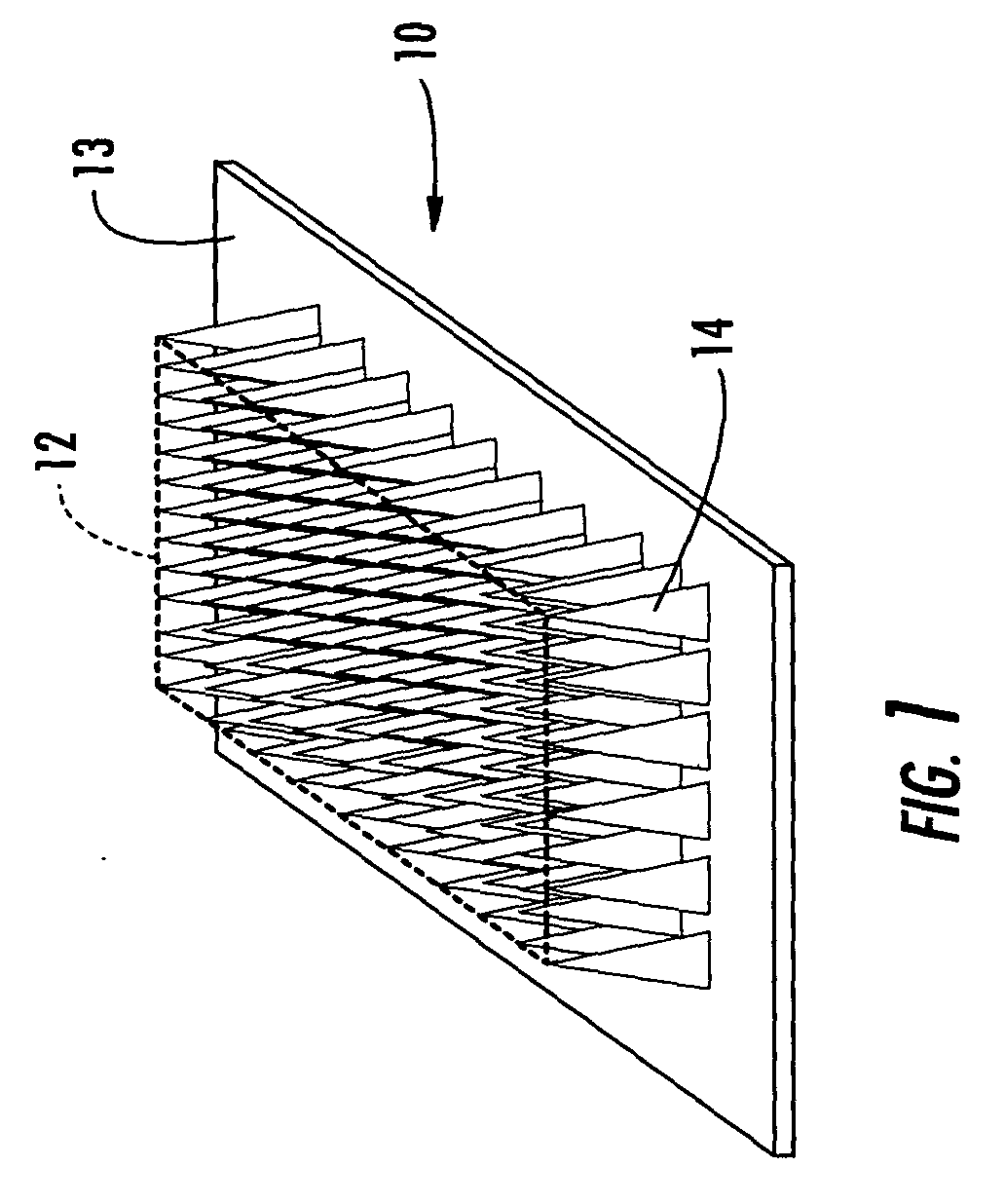
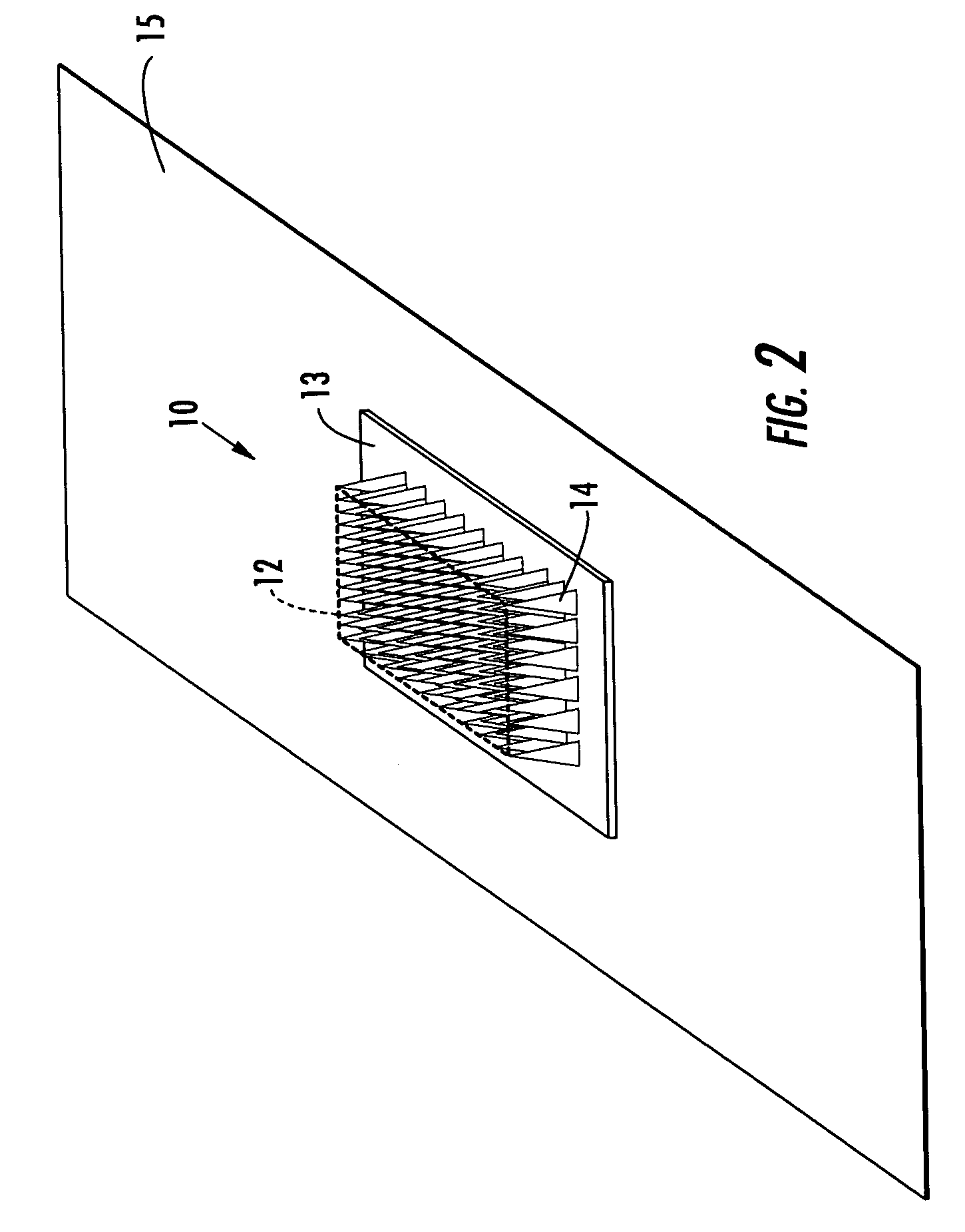
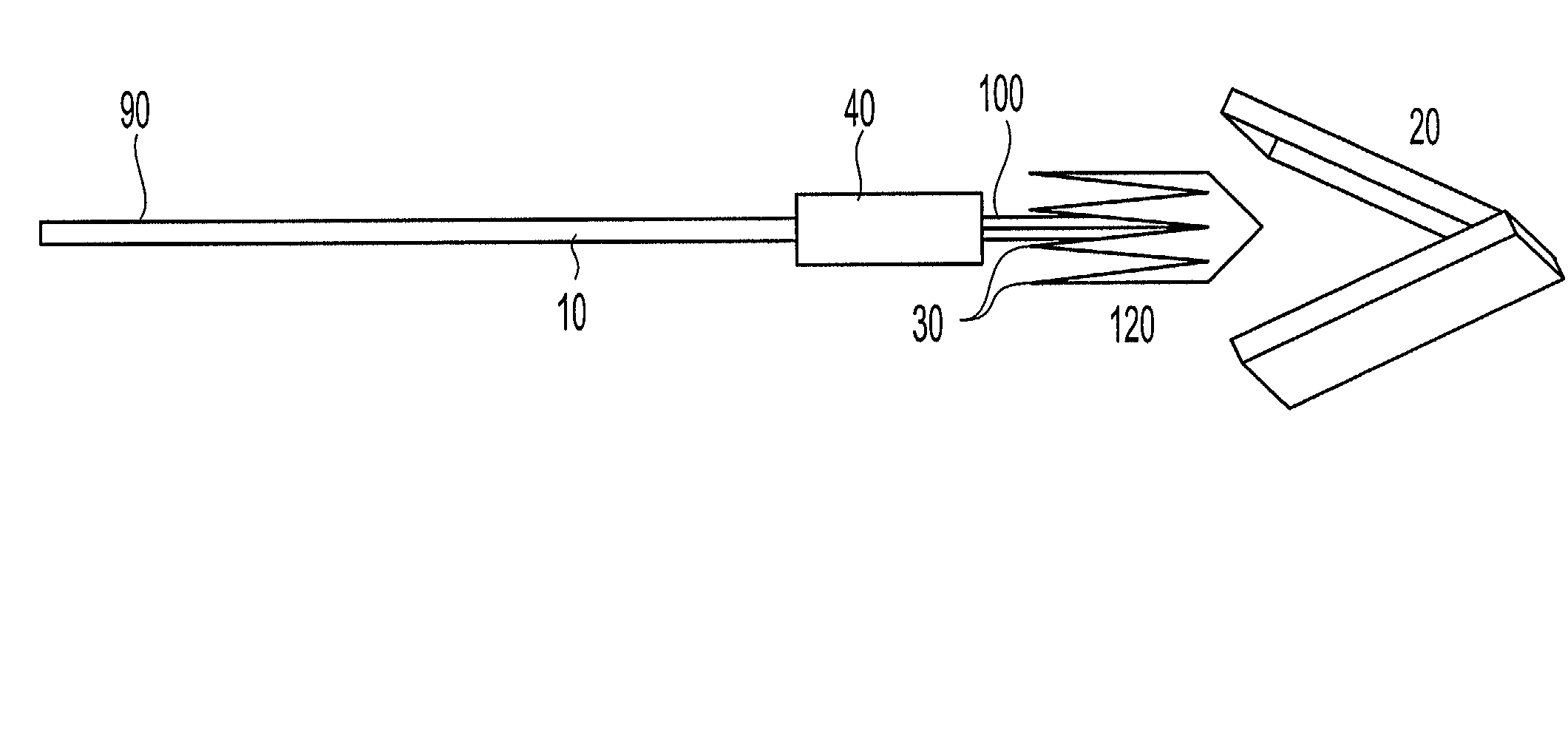
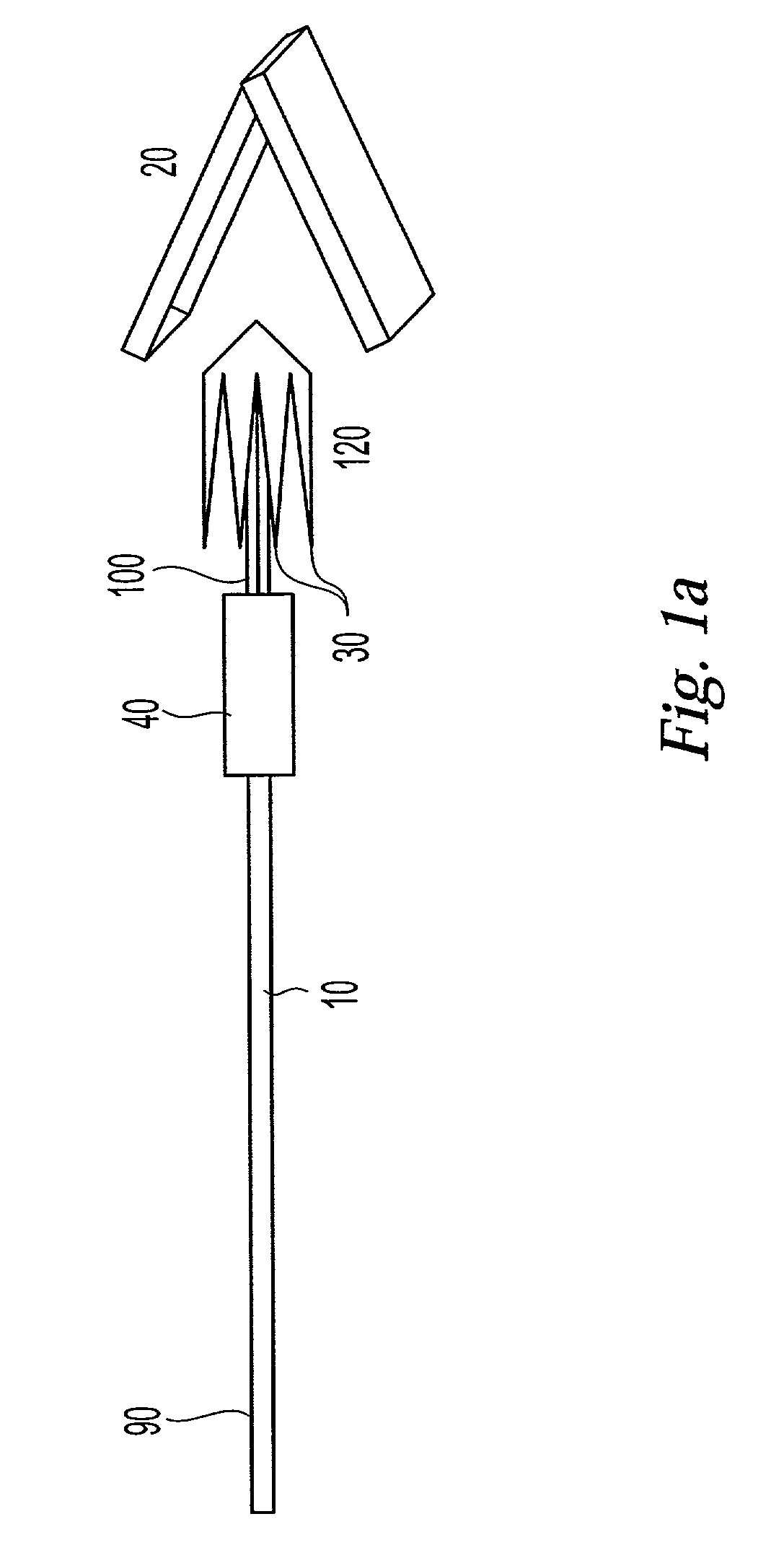
An active needle device (10) for fluid injection or extraction includes at least one hollow elongated shaft (11) defining at least one channel (12). The channel (12) provides communication between at least one input port (15) and at least one output port (16) of the needle device (10). At least one active component (17) such as a sensor or actuator is placed or integrated into the elongated shaft (1 1). The needle device (10) can include a macroneedle, a microneedle (21), or an array of macroneedles or microneedles (25a). The microneedles (21) can be fabricated on a substrate (26) which can remain attached to the microneedles (21) or be subsequently removed. The active component can facilitate biochemical, optical, electrical, or physical measurements of a fluid injected or extracted by the needle device (10).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Medical device for delivering patches
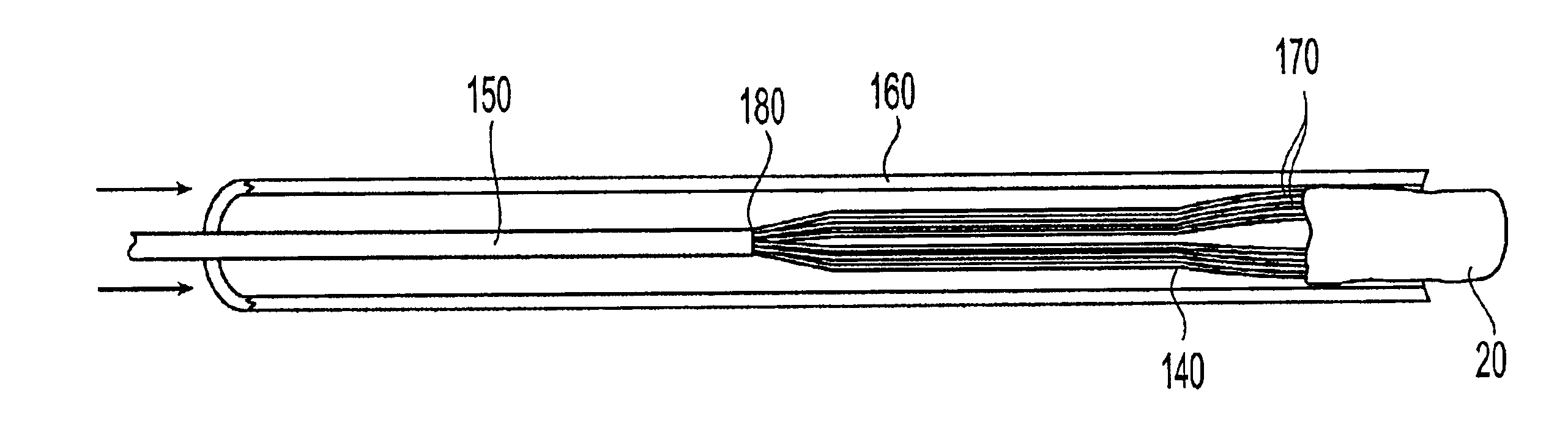
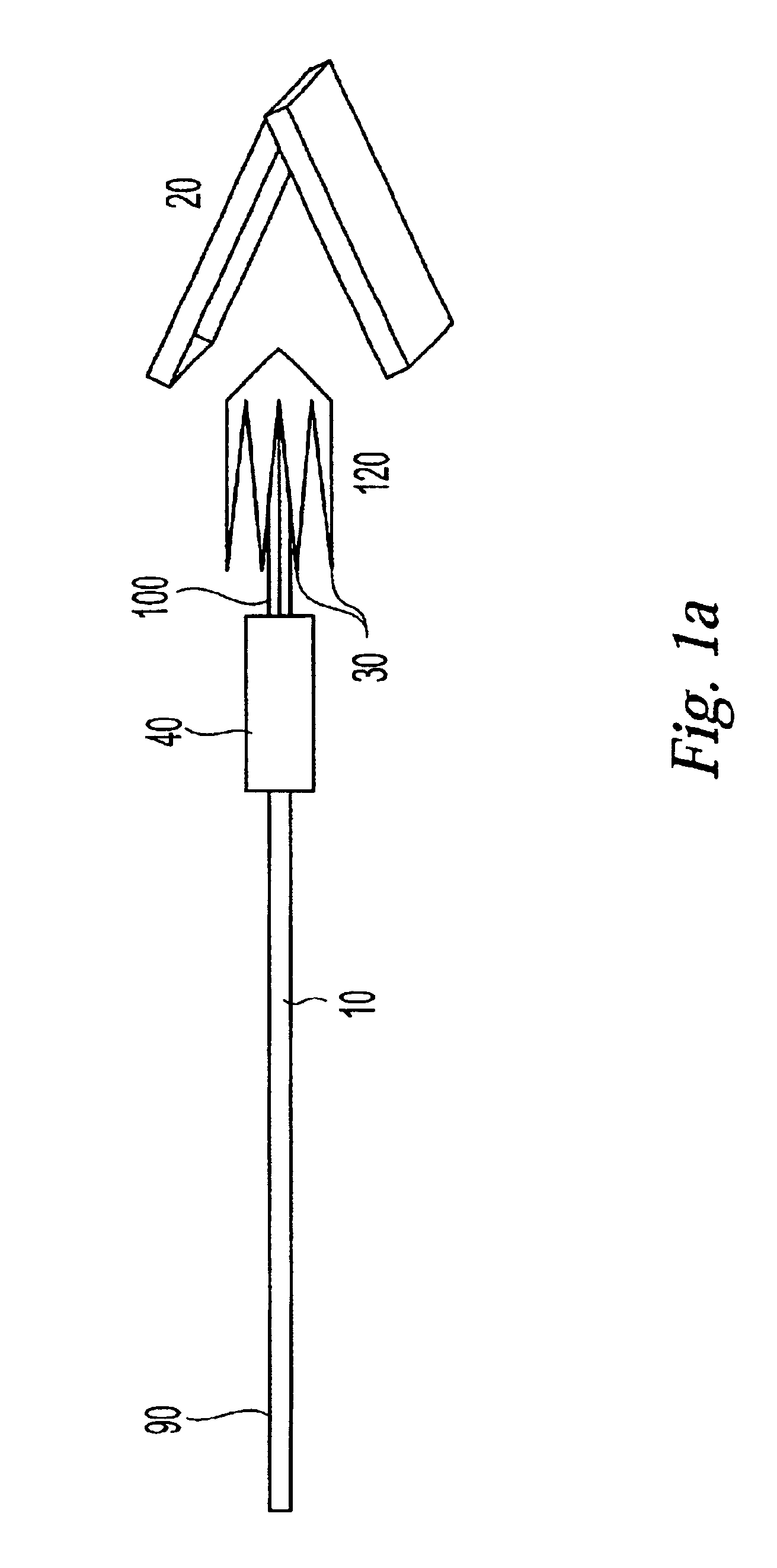
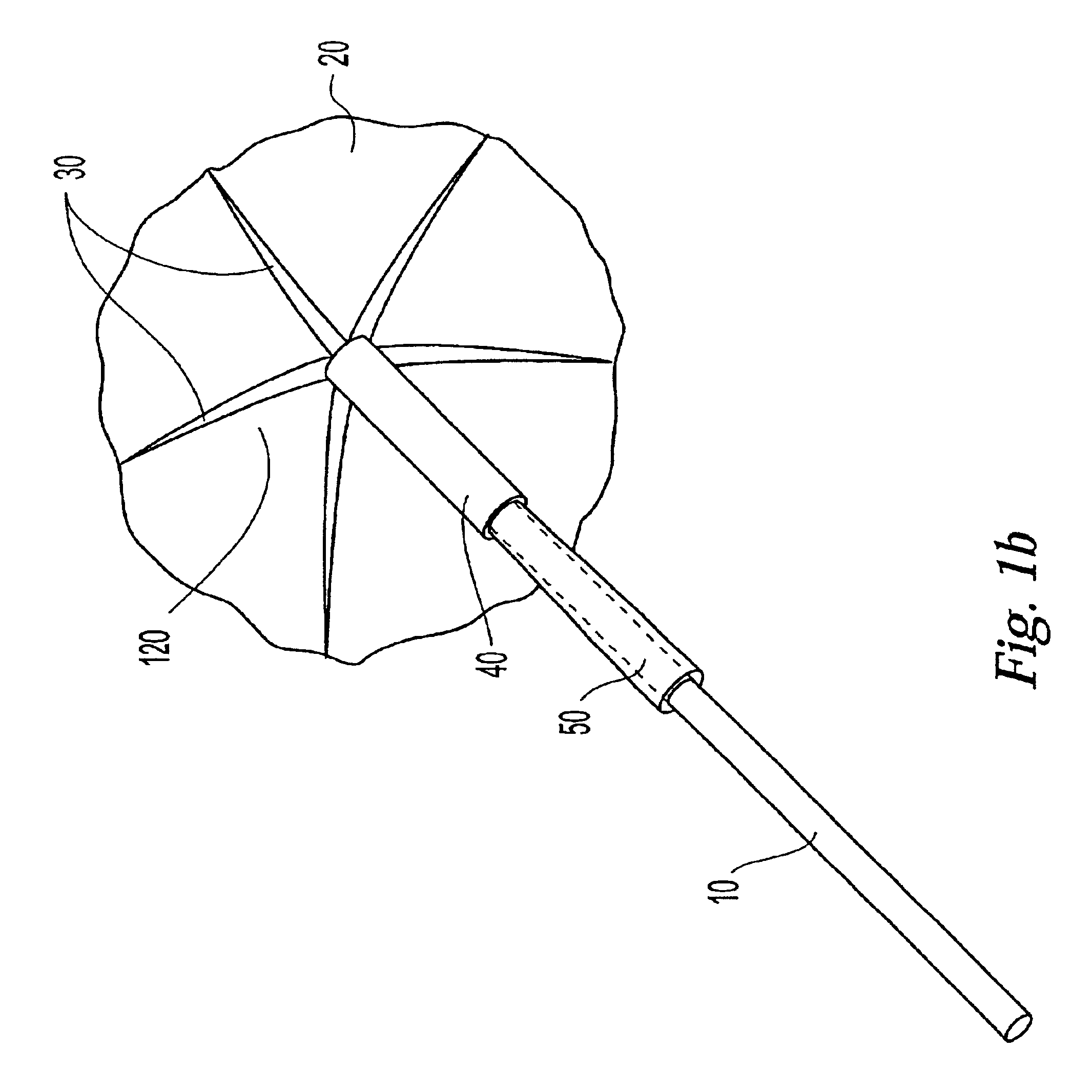
InactiveUS20030073979A1Eliminates systemic leakageEliminate leaksAdditive manufacturing apparatusHeart valvesMedical deviceAdhesive materials
The present invention relates to a medical device and method for treating the body tissue of a patient. The present invention is also directed to a method of making the medical device and a method of using the medical device. More particularly, the invention relates to a medical device which is inserted into the body for delivery of therapeutic patches to the surface of a body lumen, organ or cavity. Specifically, the medical device has an umbrella-like or a basket-like expandable assembly; and a therapeutic patch. The expandable assembly is capable of changing from a retracted position to an expanded position. The expandable assembly can be self-expanding or non-self-expanding. In one embodiment, the medical device comprises an elongated member; an umbrella-like expandable assembly which has a plurality of wire elements; and a therapeutic patch. The therapeutic patch comprises a sheet having two opposing surfaces wherein one of the surface comprises an adhesive material and at least one biologically active material. The other opposing surface is disposed onto the plurality of wire elements of the umbrella-like expandable assembly. In another embodiment, the medical device comprises an elongated member, a basket-like expandable assembly having a plurality of wire elements; and a therapeutic patch. The therapeutic patch is disposed onto the plurality of wire elements of the basket-like expandable assembly.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method, system and device for delivering a substance to tissue
Devices and methods for delivering a substance to tissue or organs, particularly, the bladder, by a plurality of microneedles The devices may include a delivery tube, a a substance chamber to fill with the substance to be delivered, a plurality of needles, a plunger coupled to a handle movable relative to the tube to deliver the substance to the tissue through the needles, and a protective plate having at least one orifice therein, such that when the device is in a first, resting, position the needle tips are on a first side of the protective plate, and when the device is in a second, operational, position, the needles are on a second side of the protective plate.
Owner:MELAMUD ALEXANDER +5
Multi-reservoir device for transdermal drug delivery and sensing
Devices and methods are provided for transdermal administration of a pharmaceutical agent to a patient in need thereof. The device includes a substrate, a plurality of discrete reservoirs in the substrate, one or more pharmaceutical agents stored in the reservoirs, discrete reservoir caps that prevent the pharmaceutical agent from passing out from the reservoirs until desired, control means for actuating release of the one or more pharmaceutical agents from one or more of the reservoirs by disintegrating or permeabilizing the reservoir caps, means for securing the device to the skin of the patient, and means for transporting the pharmaceutical agent to the skin following release from the one or more of the reservoirs. In another embodiment, the device is adapted for diagnostic sensing instead of or in addition to drug delivery.
Owner:MICROCHIPS BIOTECH INC
Transdermal drug delivery devices having coated microprotrusions
A device (12) and method are provided for percutaneous transdermal delivery of a potent pharmacologically active agent. The agent is dissolved in water to form an aqueous coating solution having an appropriate viscosity for coating extremely tiny skin piercing elements (10). The coating solution is applied to the skin piercing elements (10) using known coating techniques and then dried. The device (12) is applied to the skin of a living animal (e.g., a human), causing the microprotrusions (10) to pierce the stratum corneum and deliver a therapeutically effect dose of the agent to the animal.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Device and method for delivering or withdrawing a substance through the skin
An apparatus for delivering or withdrawing a fluid through at least one layer of the skin is provided. A device includes a body having a top face, a bottom face, a side edge and at least one channel. The bottom face includes a first surface area and a second surface area adjacent to and recessed at a first distance from the first surface area. The bottom face further includes at least one raised protrusion disposed on the second surface area. The protrusion has a height from the first surface greater than the first distance. At least one dermal-access member is provided in the protrusion and is in fluid communication with the channel to deliver or withdraw the fluid. The dermal-access member extends at least 1 mm from the protrusion. A mechanism drives the device against the skin at a calculated speed of about 6 m / s to about 18 m / s.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Device and method for enhancing transdermal agent flux
InactiveUS6918901B1High volume producableIncreasing transdermal fluxElectrotherapySurgerySkin contactBiomedical engineering
Owner:THEEUWES FELIX +2
Transdermal drug delivery device, method of making same and method of using same
InactiveUS7141034B2Broaden applicationAmpoule syringesElectrotherapyTissue membraneBiomedical engineering
A transdermal drug delivery device for forming a micropore in a tissue membrane of an animal comprising a substrate and a porator that is located on or within the substrate. The porator is constructed of a material that is destroyed upon forming the micropore. The transdermal drug delivery device also comprises at least one reservoir and a controller for controlling the formation of said micropore by the porator and destroying the porator after the formation of the micropore.
Owner:PASSPORT TECH +2
Intracutaneous microneedle array apparatus
InactiveUS6931277B1Facilitate biological fluid samplingIncrease transdermal flow rateElectrotherapyMicroneedlesStratum corneumEngineering
Improved microneedle arrays are provided having a sufficiently large separation distance between each of the individual microneedles to ensure penetration of the skin while having a sufficiently small separation distance to provide high transdermal transport rates. A very useful range of separation distances between microneedles is in the range of 100–300 microns, and more preferably in the range of 100–200 microns. The outer diameter and microneedle length is also very important, and in combination with the separation distance will be crucial as to whether or not the microneedles will actually penetrate the stratum corneum of skin. For circular microneedles, a useful outer diameter range is from 20–100 microns, and more preferably in the range of 20–50 microns. For circular microneedles that do not have sharp edges, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50–200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 100–150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is in the range of 200 microns–3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200–400 microns. For circular microneedles having sharp side edges, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50–200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 80–150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is again in the range of 200 microns–3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200–400 microns. For solid microneedles having a star-shaped profile with sharp edges for its star-shaped blades, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50–200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 80–150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is again in the range of 200 microns–3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200–400 microns, while the radius of each of its blades is in the range of 10–50 microns, and more preferably in the range of 10–15 microns.
Owner:CORIUM INC
Transdermal patch system
InactiveUS20090259176A1Maintaining awarenessRemain alertElectrotherapyMicroneedlesTransdermal patchMedicine
A transdermal patch system configured as a patch or pump assembly may be placed into contact upon a skin surface to transport drugs or agents transdermally via any number of different mechanisms such as microporous membranes, microneedles, in-dwelling catheters, etc. The assembly may enclose or accommodate a reservoir configured as an elongate microchannel to contain the drug or agent suspended in a fluid vehicle. The reservoir may also be fluidly coupled via microchannels to transport the drugs into or against an underlying skin surface as driven or urged via a pump and controlled by an electronic control circuitry which may be programmed to affect any number of treatment regimens.
Owner:LOS GATOS RES
Self-actuating applicator for microprojection array
An applicator for applying a microprojection member to the stratum corneum of a patient having a housing, a piston moveable within the housing and a cap adapted to activate the applicator. The applicator is self-setting and auto-triggering, which allows the applicator to be used by patient's having neither the strength, nor the manual dexterity to pre-set and activate other types of applicator devices.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Medical device for delivering patches
InactiveUS6893431B2Eliminate leaksMinimally inflammatoryAdditive manufacturing apparatusHeart valvesMedicineAdhesive materials
The present invention relates to a medical device and method for treating the body tissue of a patient. The present invention is also directed to a method of making the medical device and a method of using the medical device. More particularly, the invention relates to a medical device which is inserted into the body for delivery of therapeutic patches to the surface of a body lumen, organ or cavity. Specifically, the medical device has an umbrella-like or a basket-like expandable assembly; and a therapeutic patch. The expandable assembly is capable of changing from a retracted position to an expanded position. The expandable assembly can be self-expanding or non-self-expanding. In one embodiment, the medical device comprises an elongated member; an umbrella-like expandable assembly which has a plurality of wire elements; and a therapeutic patch. The therapeutic patch comprises a sheet having two opposing surfaces wherein one of the surface comprises an adhesive material and at least one biologically active material.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Multi-reservoir device for transdermal drug delivery and sensing
Devices and methods are provided for transdermal administration of a pharmaceutical agent to a patient in need thereof. The device includes a substrate, a plurality of discrete reservoirs in the substrate, one or more pharmaceutical agents stored in the reservoirs, discrete reservoir caps that prevent the pharmaceutical agent from passing out from the reservoirs until desired, control means for actuating release of the one or more pharmaceutical agents from one or more of the reservoirs by disintegrating or permeabilizing the reservoir caps, means for securing the device to the skin of the patient, and means for transporting the pharmaceutical agent to the skin following release from the one or more of the reservoirs. In another embodiment, the device is adapted for diagnostic sensing instead of or in addition to drug delivery.
Owner:MICROCHIPS BIOTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com