Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1581 results about "Biological fluids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biological Fluids 1 definition. Fluids that have human or animal origin, most commonly encountered at crime scenes (e.g., blood, mucus, perspiration, saliva, semen, vaginal fluid, and urine).
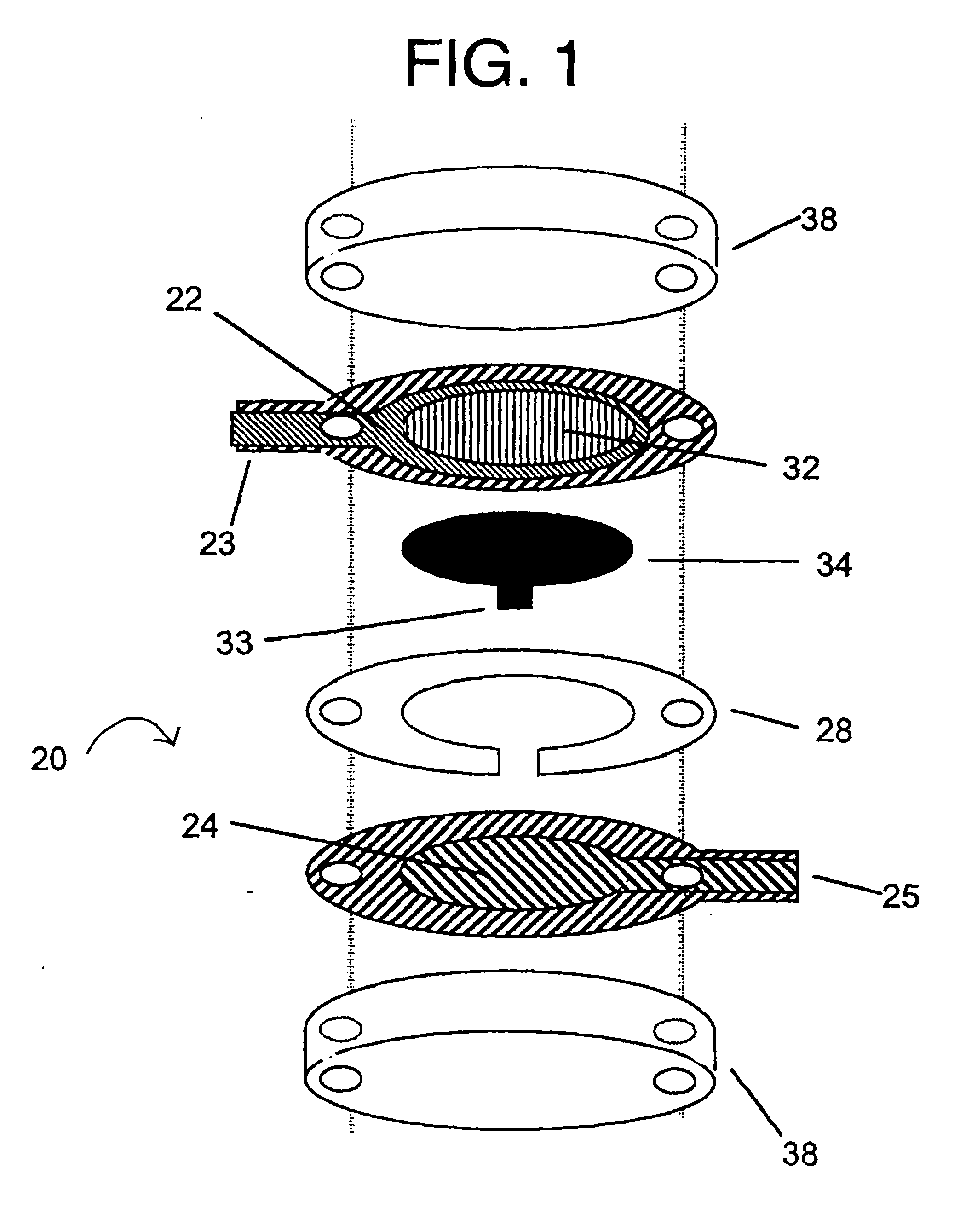
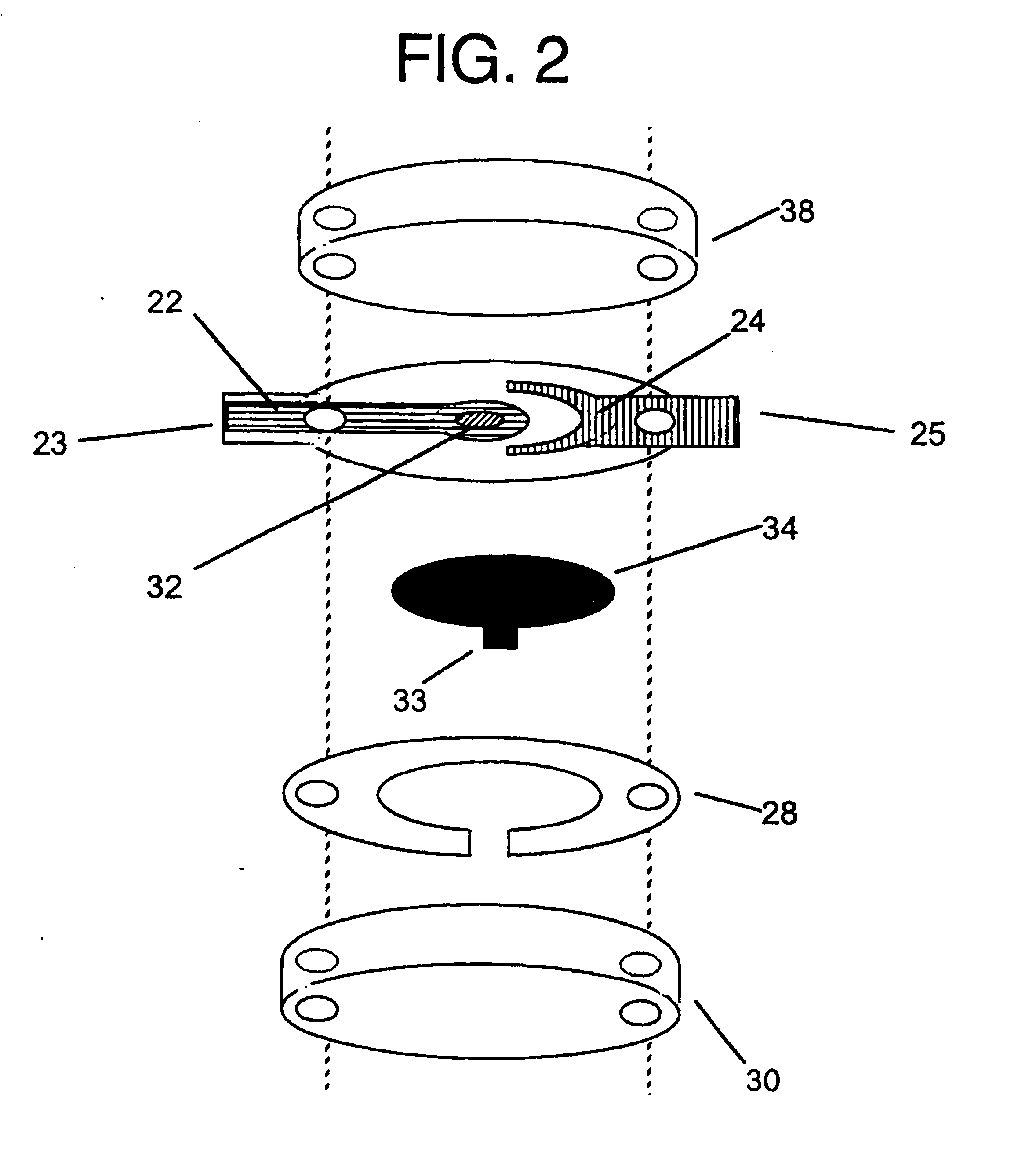
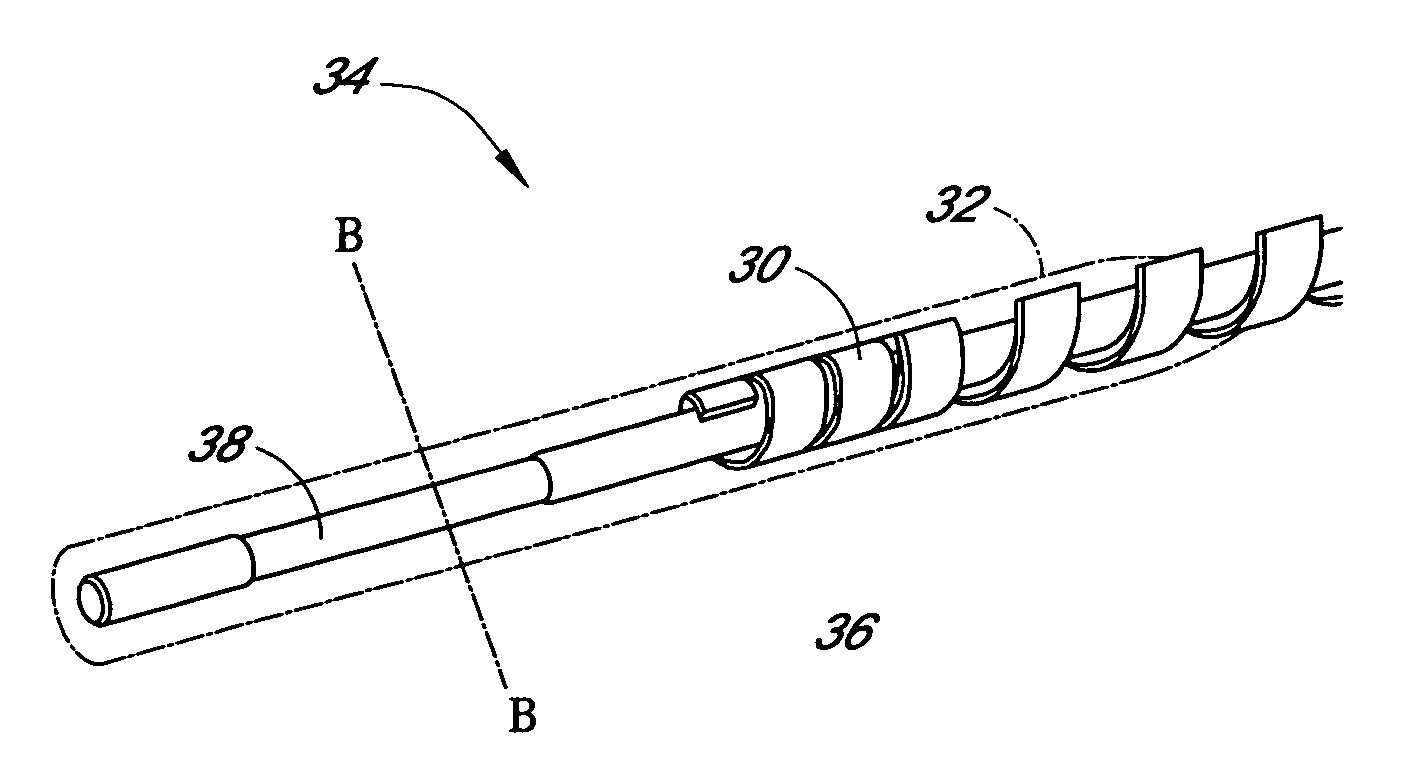
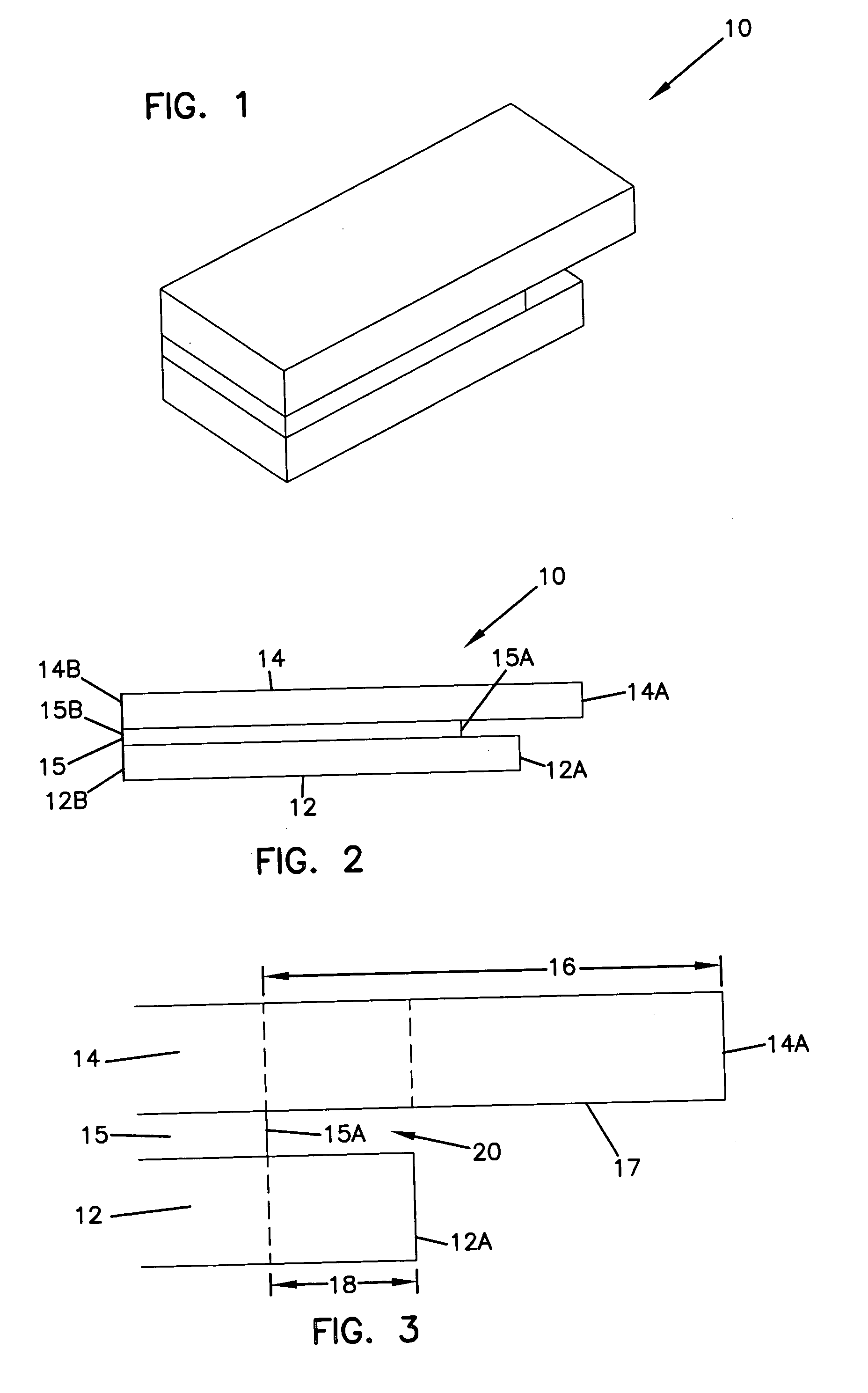
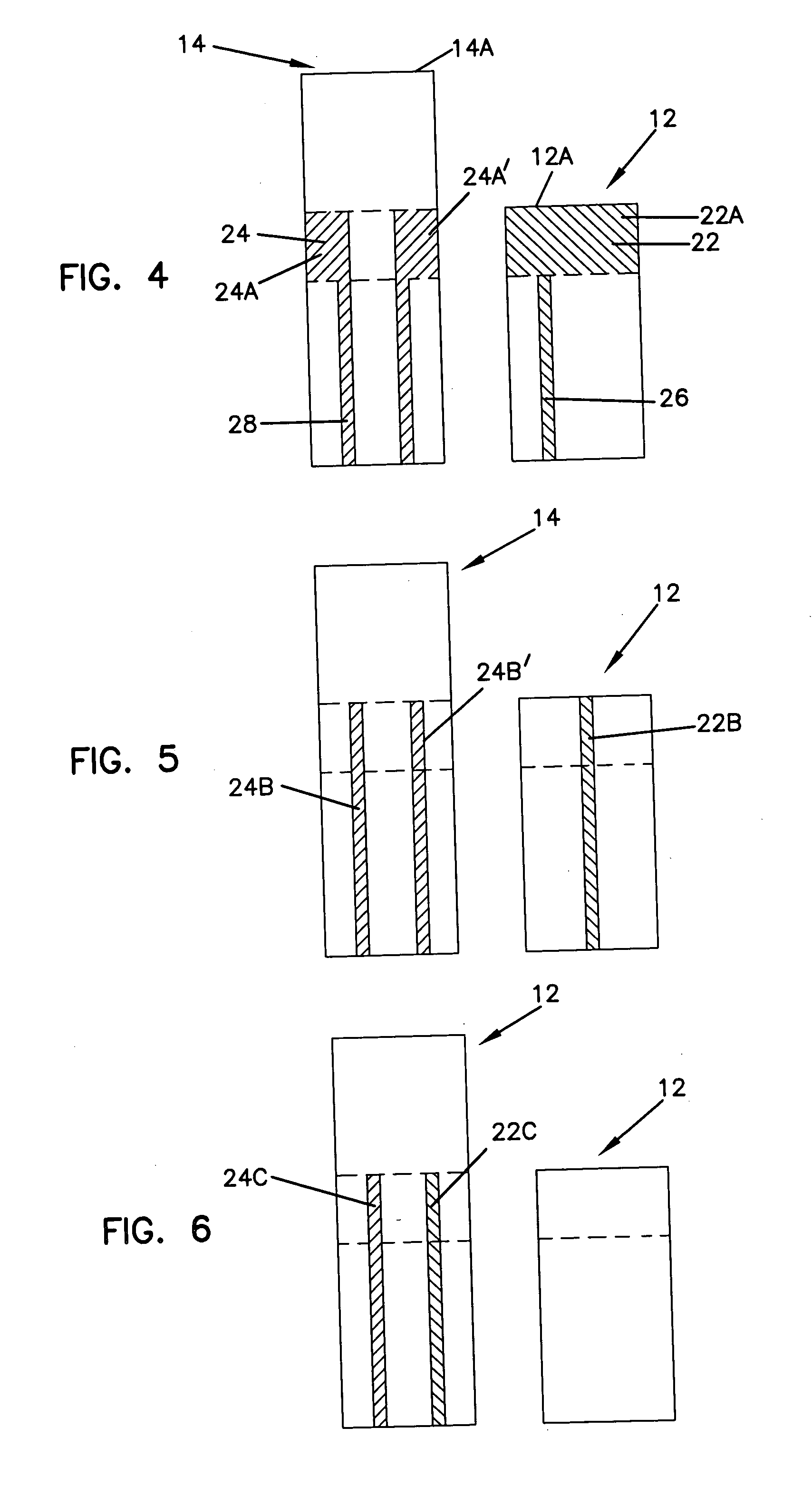
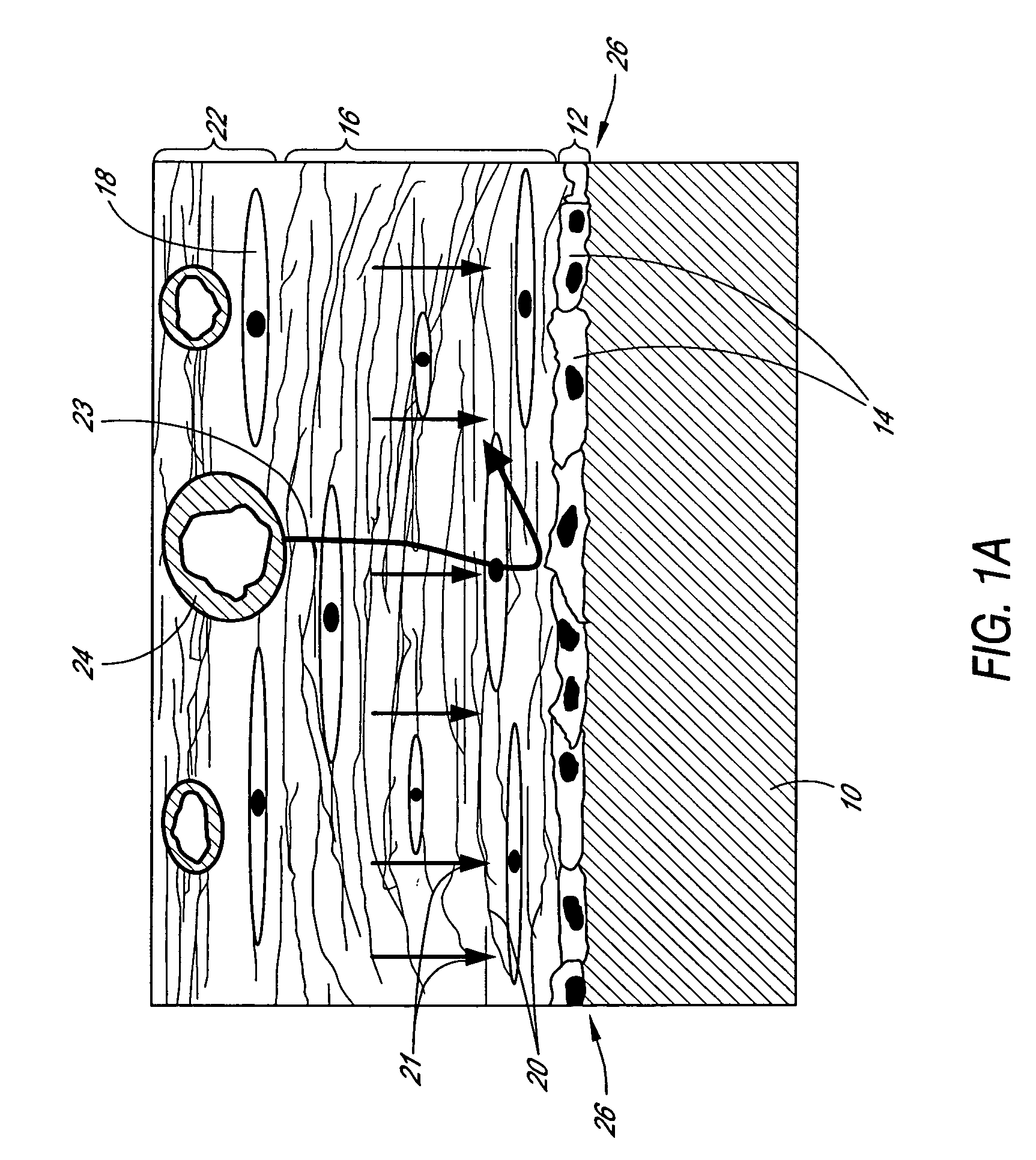
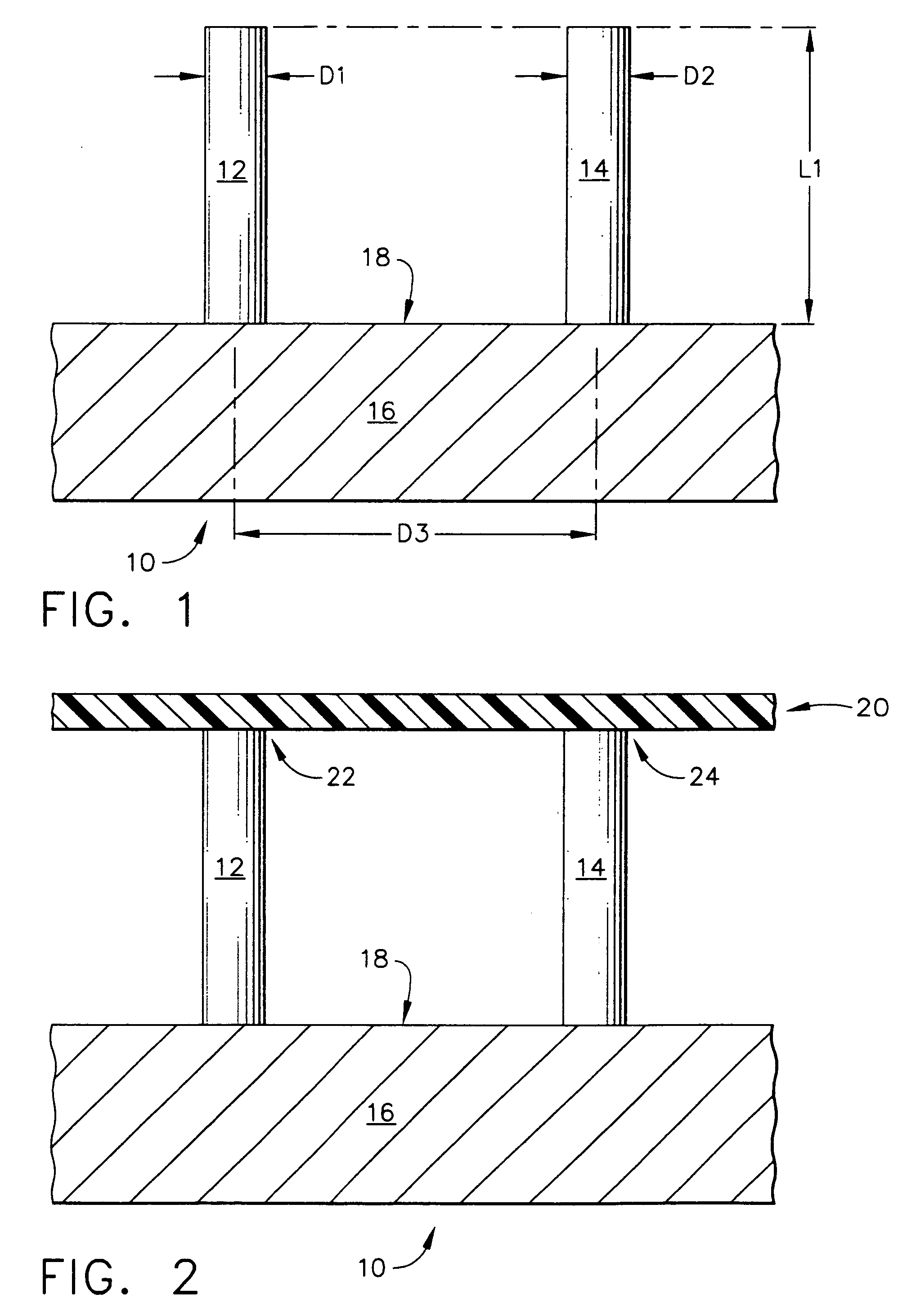
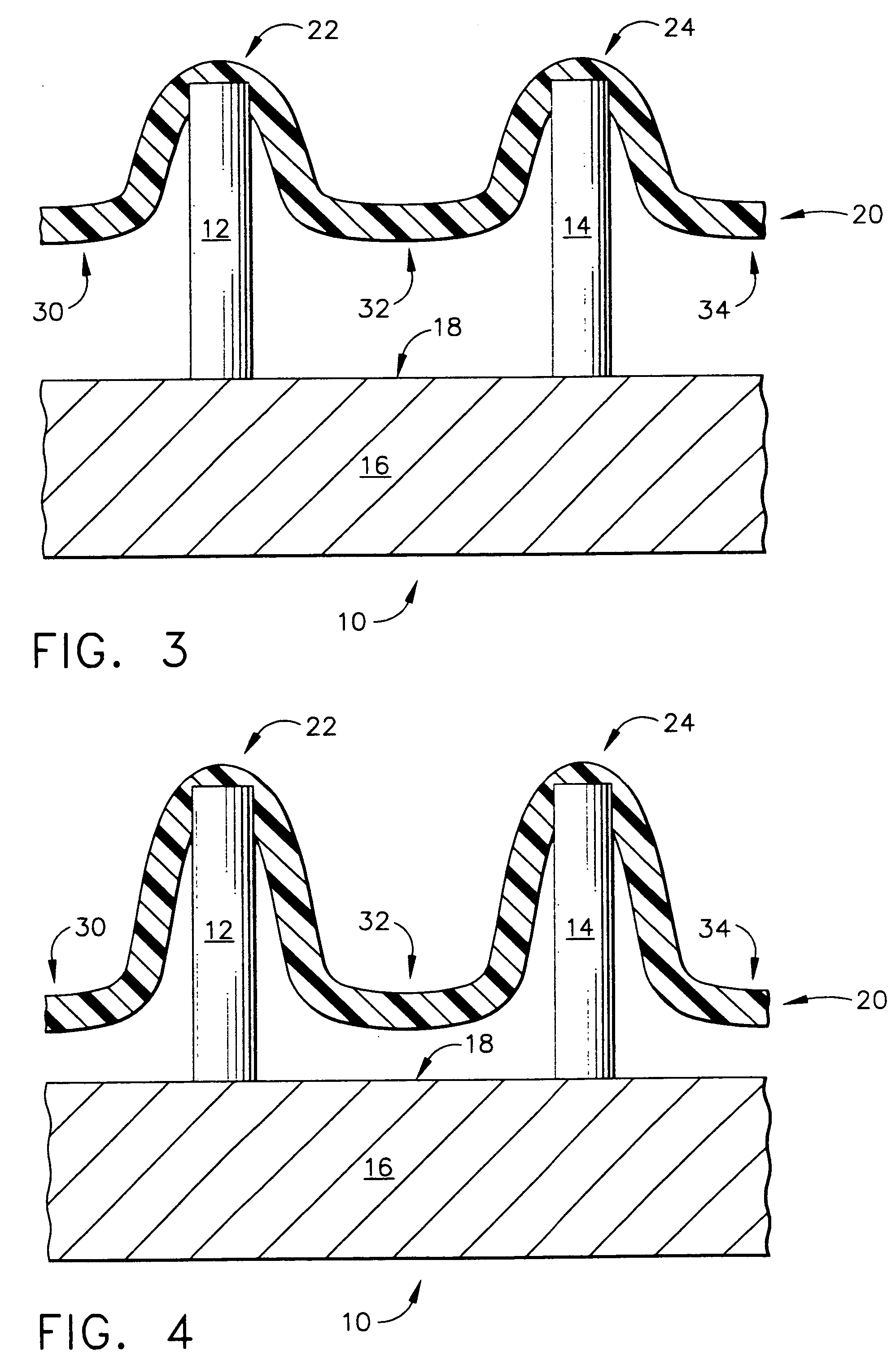
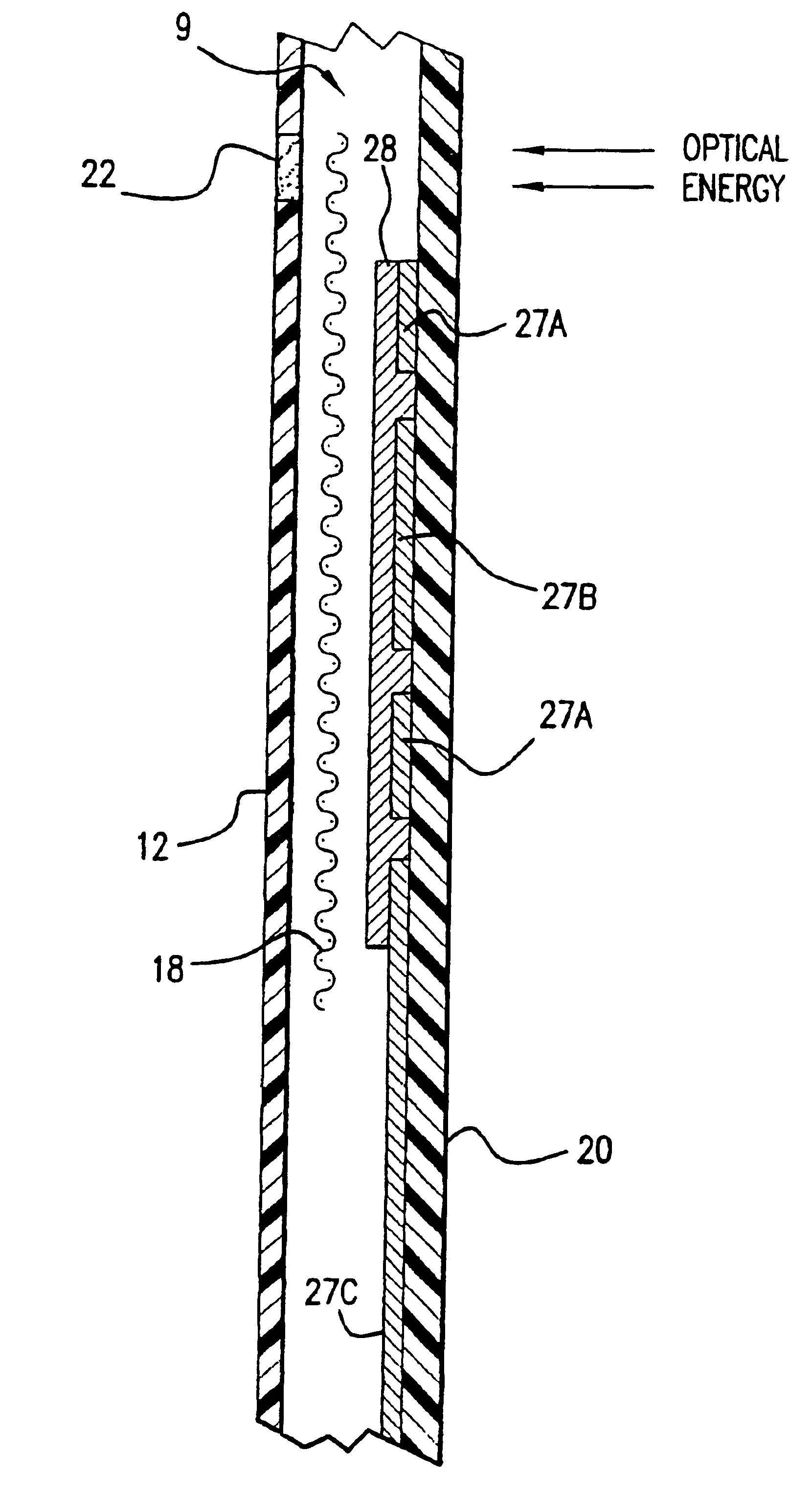
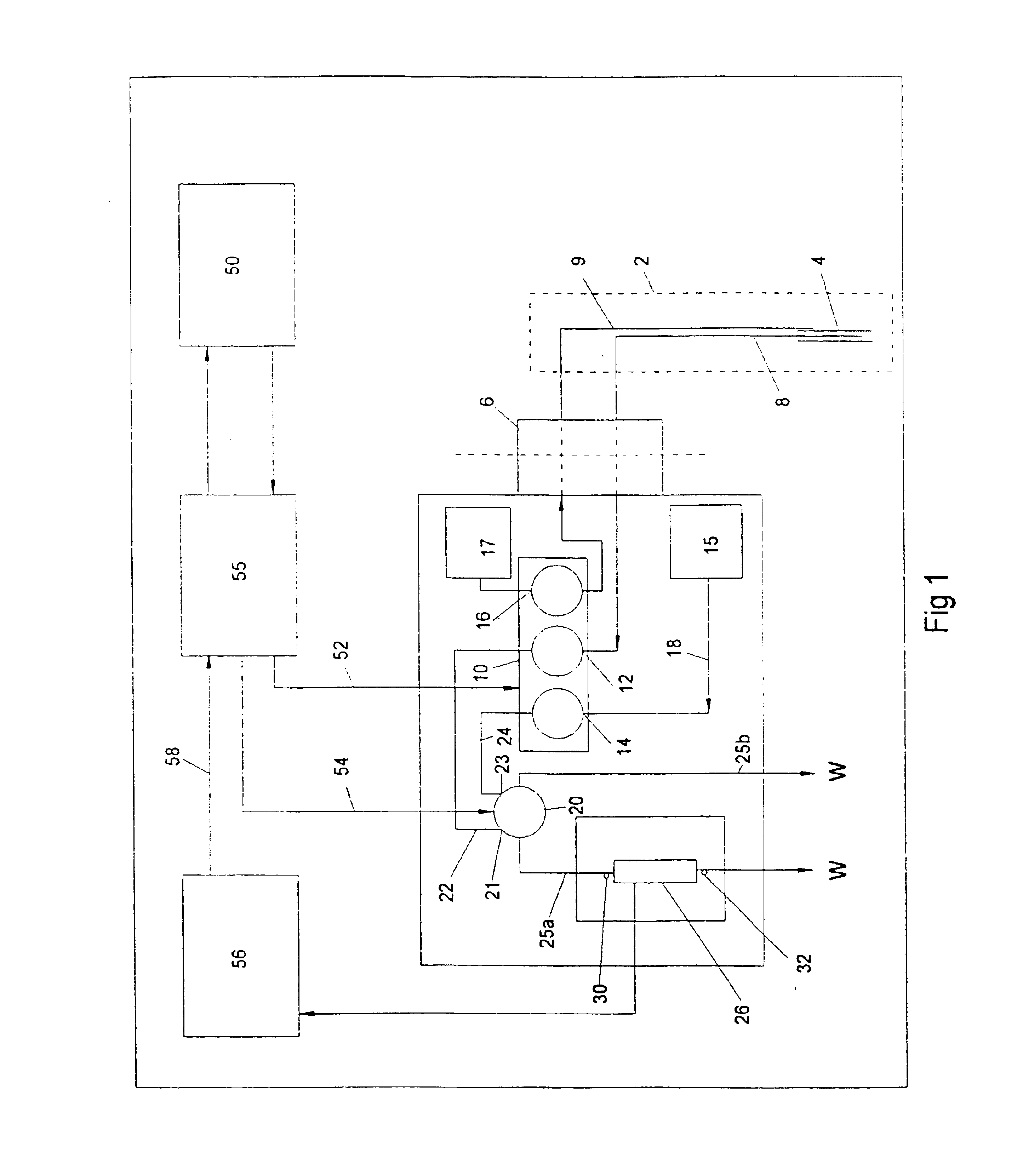
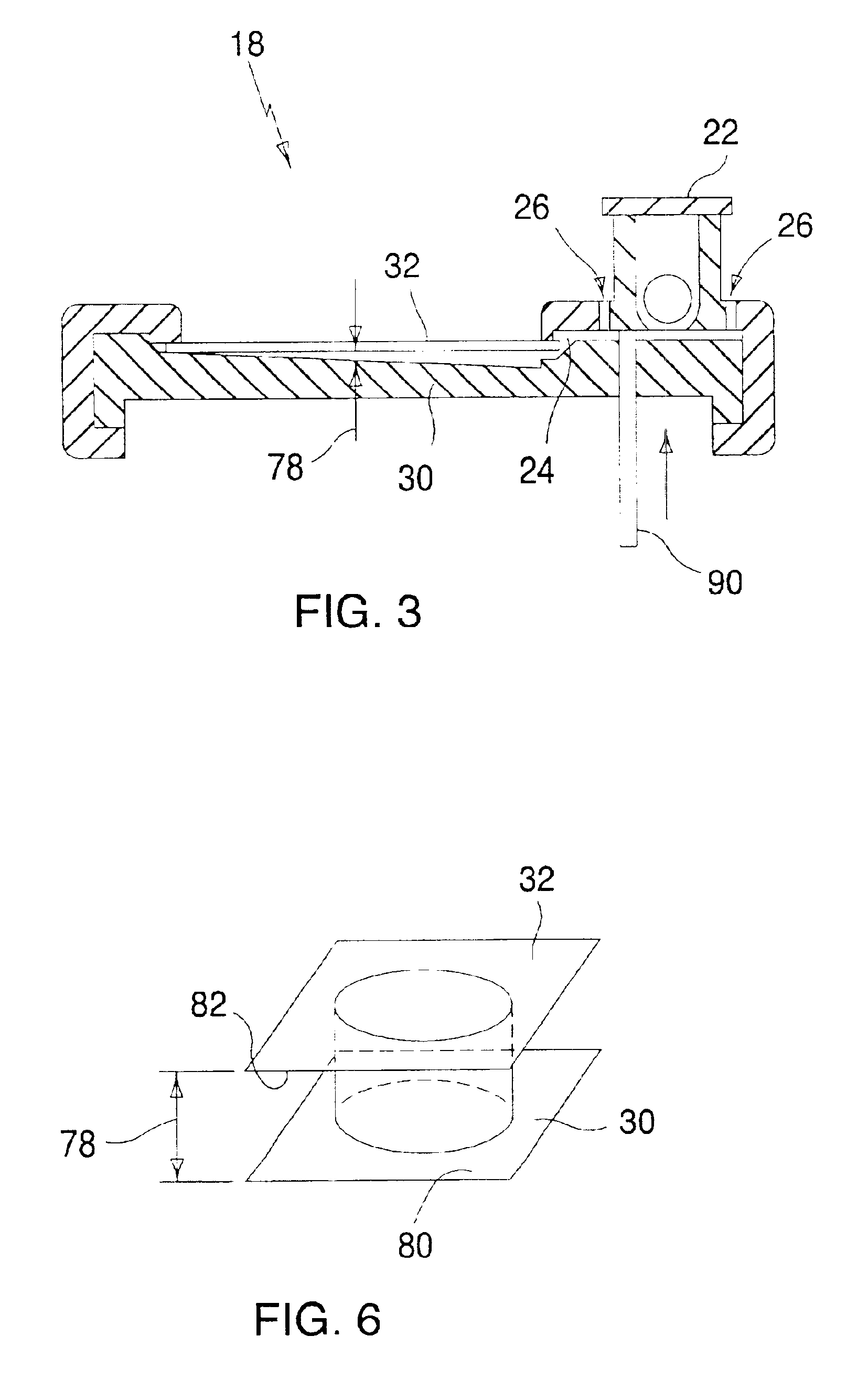
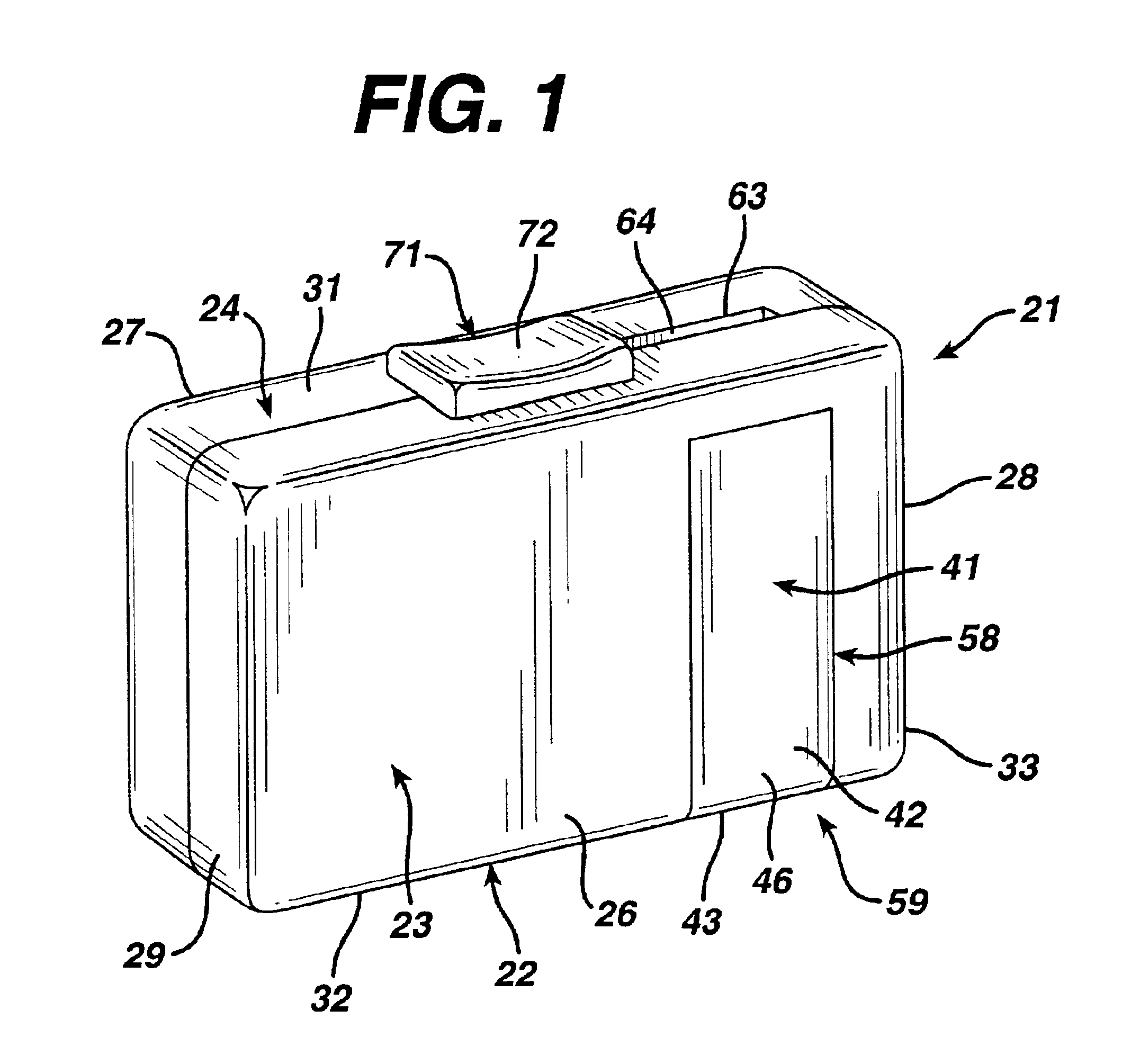
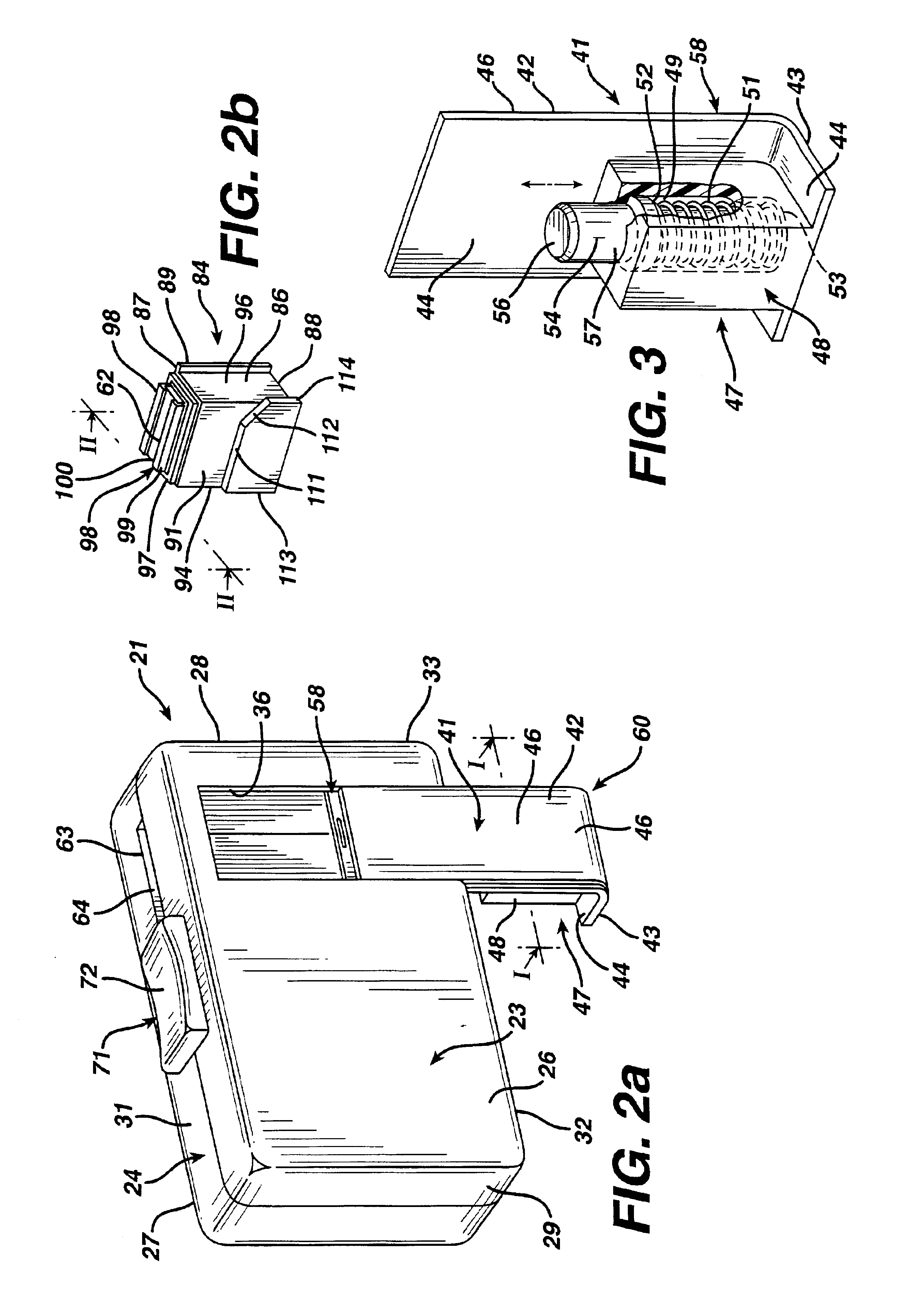
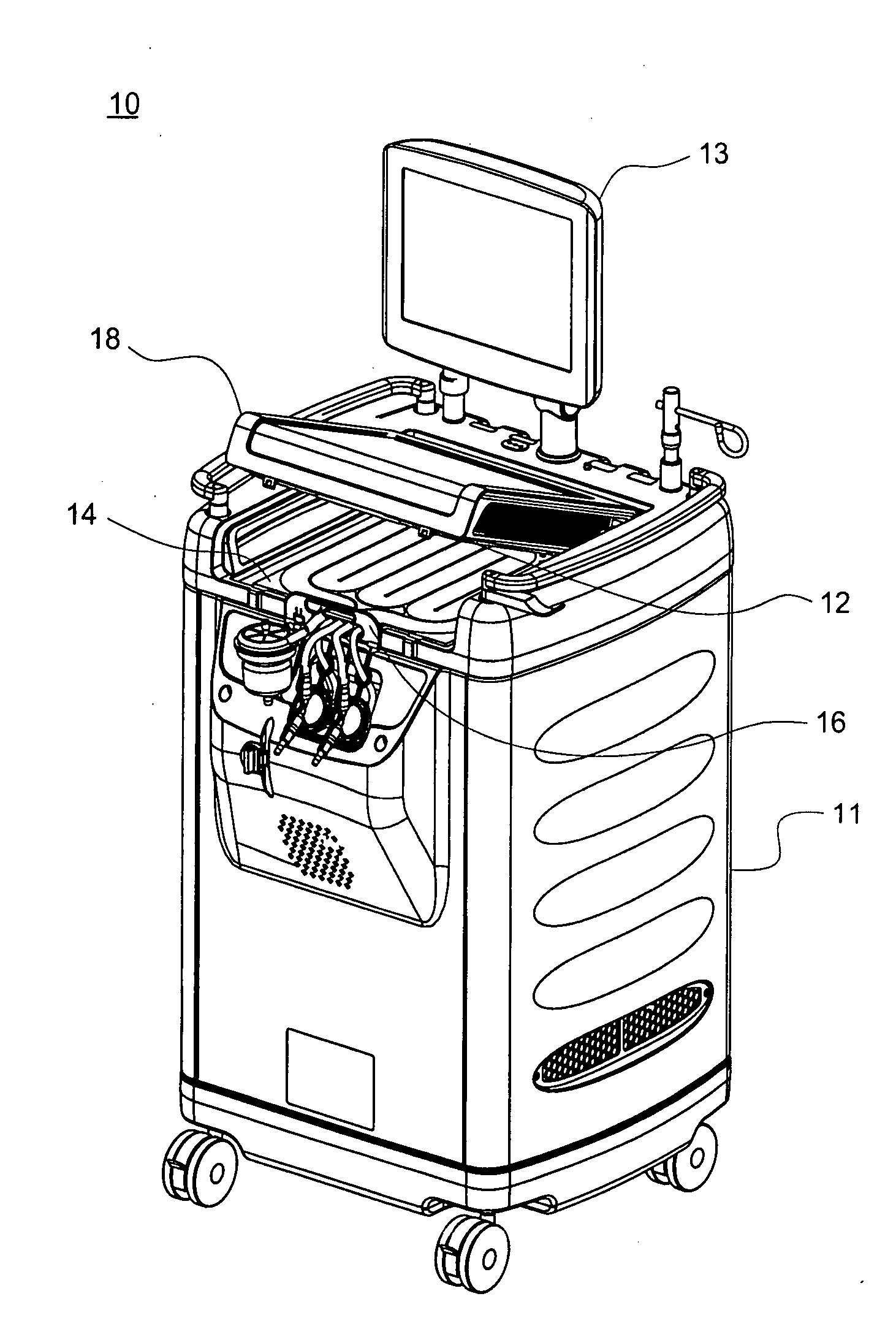
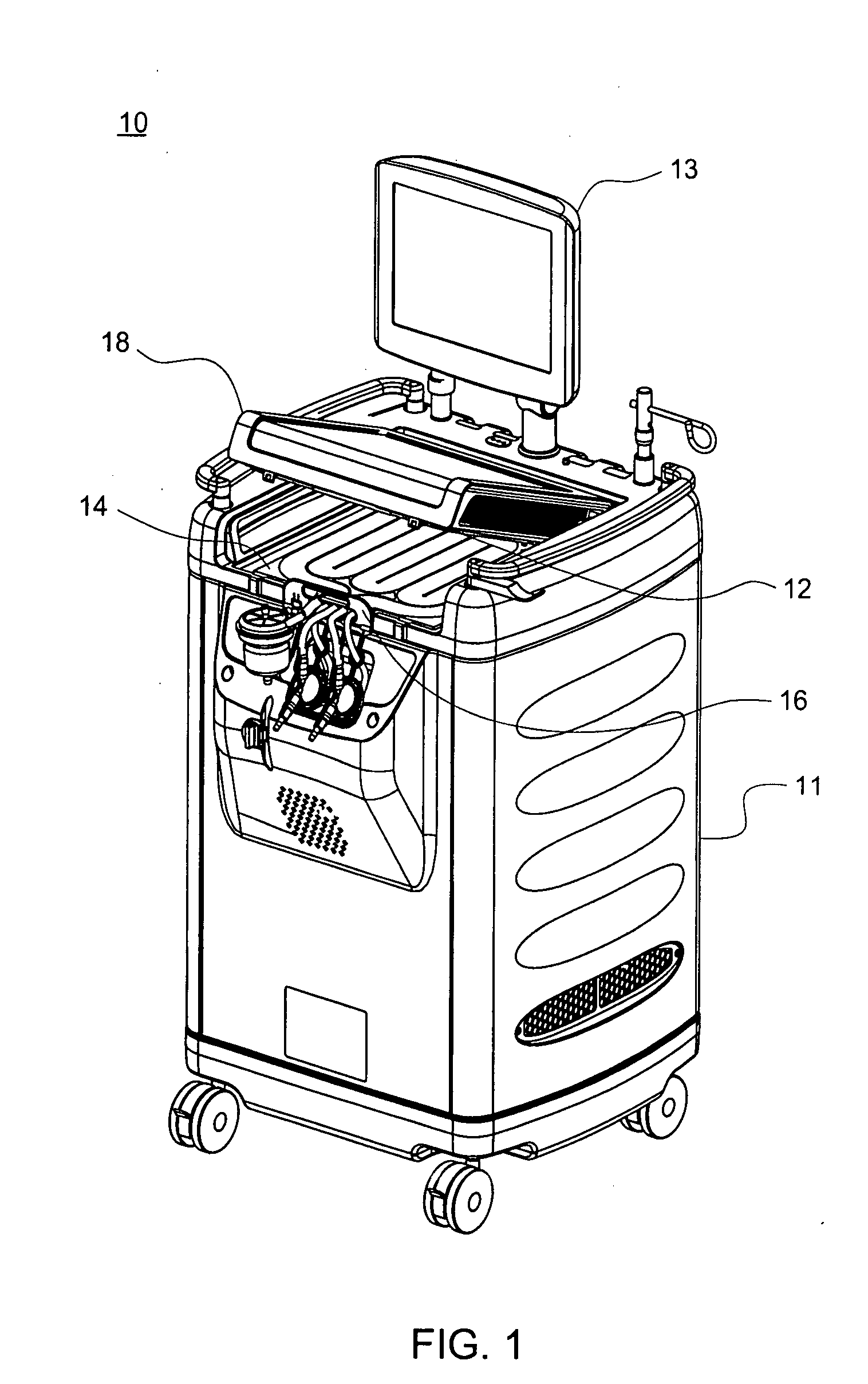
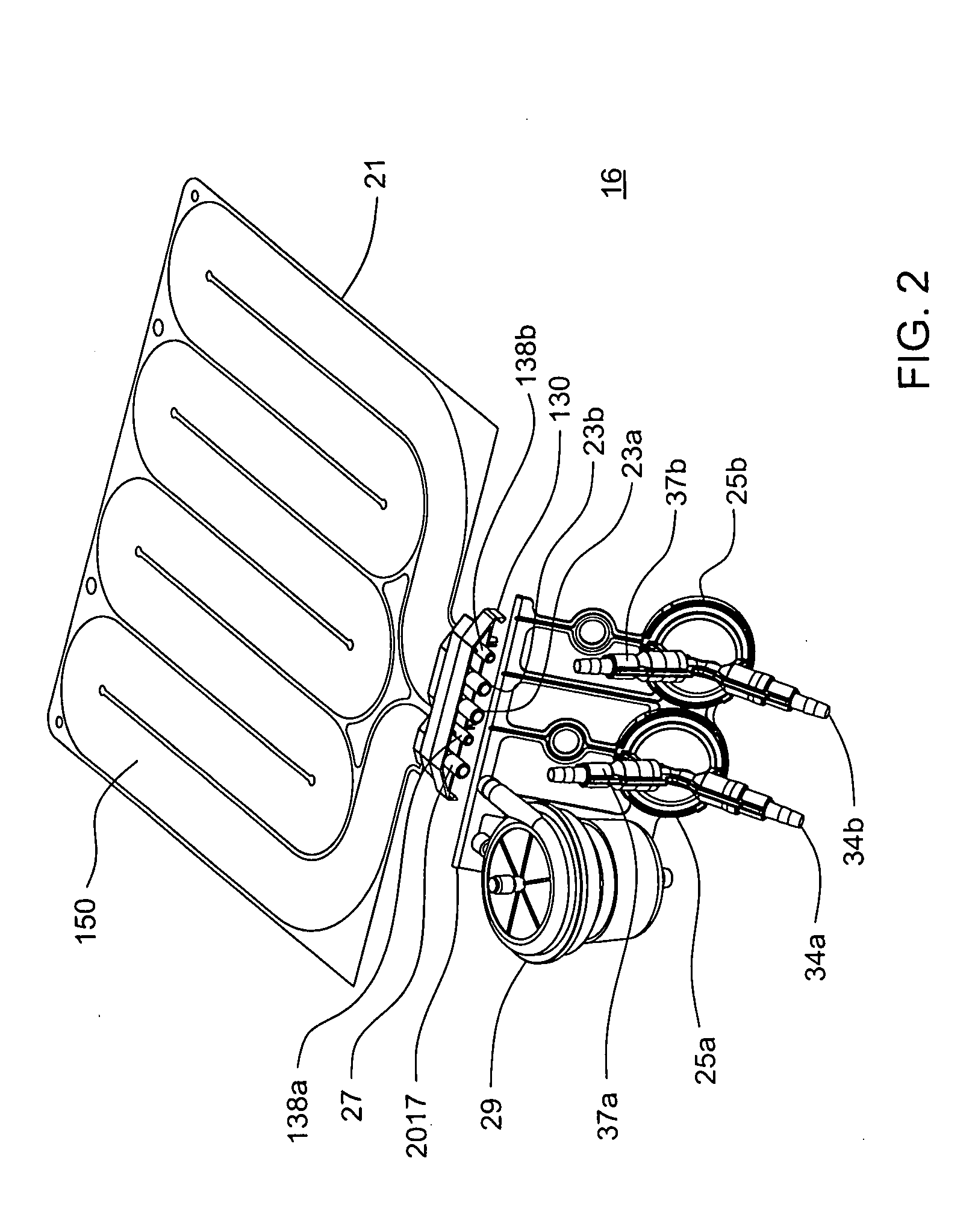
Sensor head for use with implantable devices
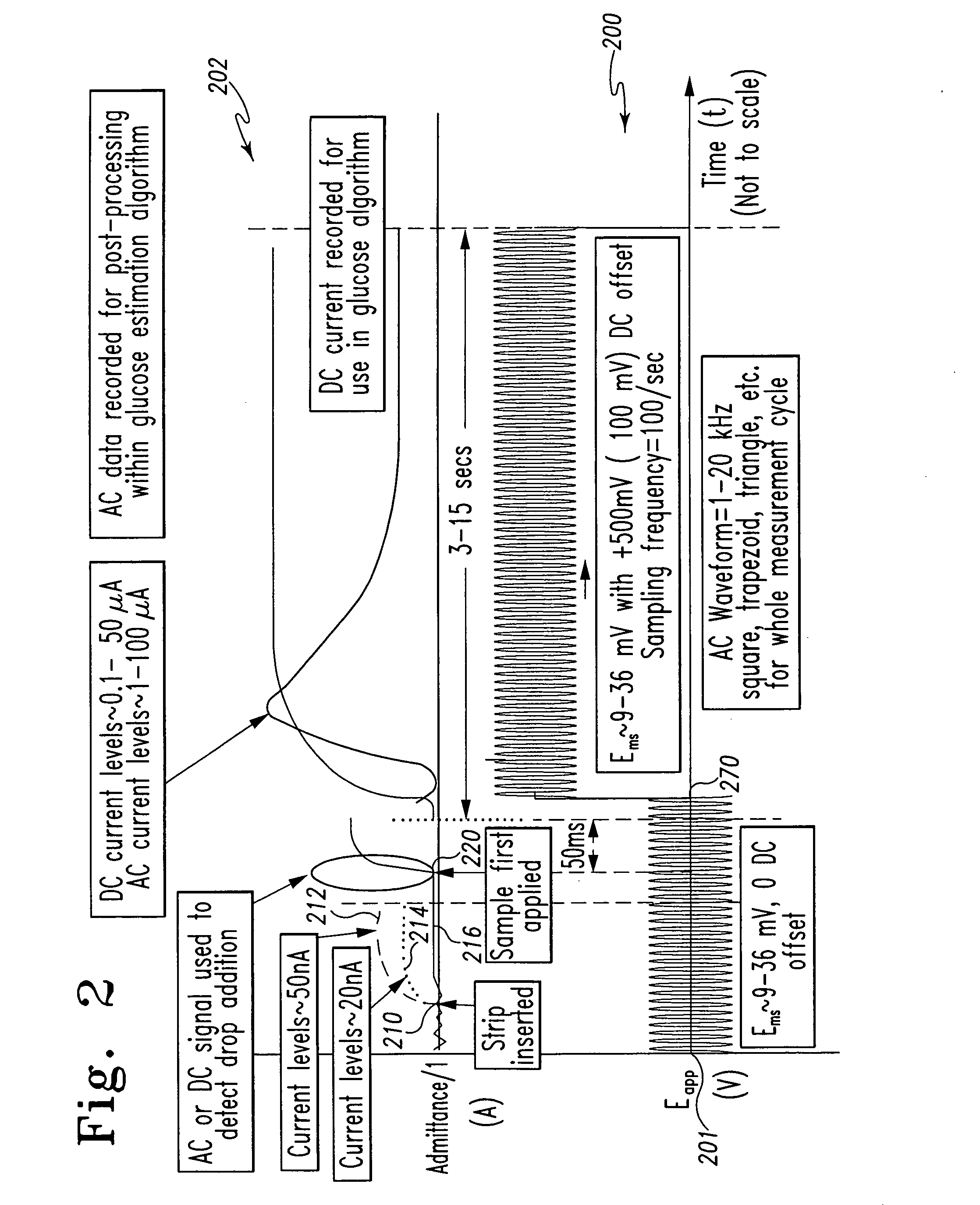
InactiveUS7471972B2Minimizing negative potential extremesImprove solubilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseAnalyte
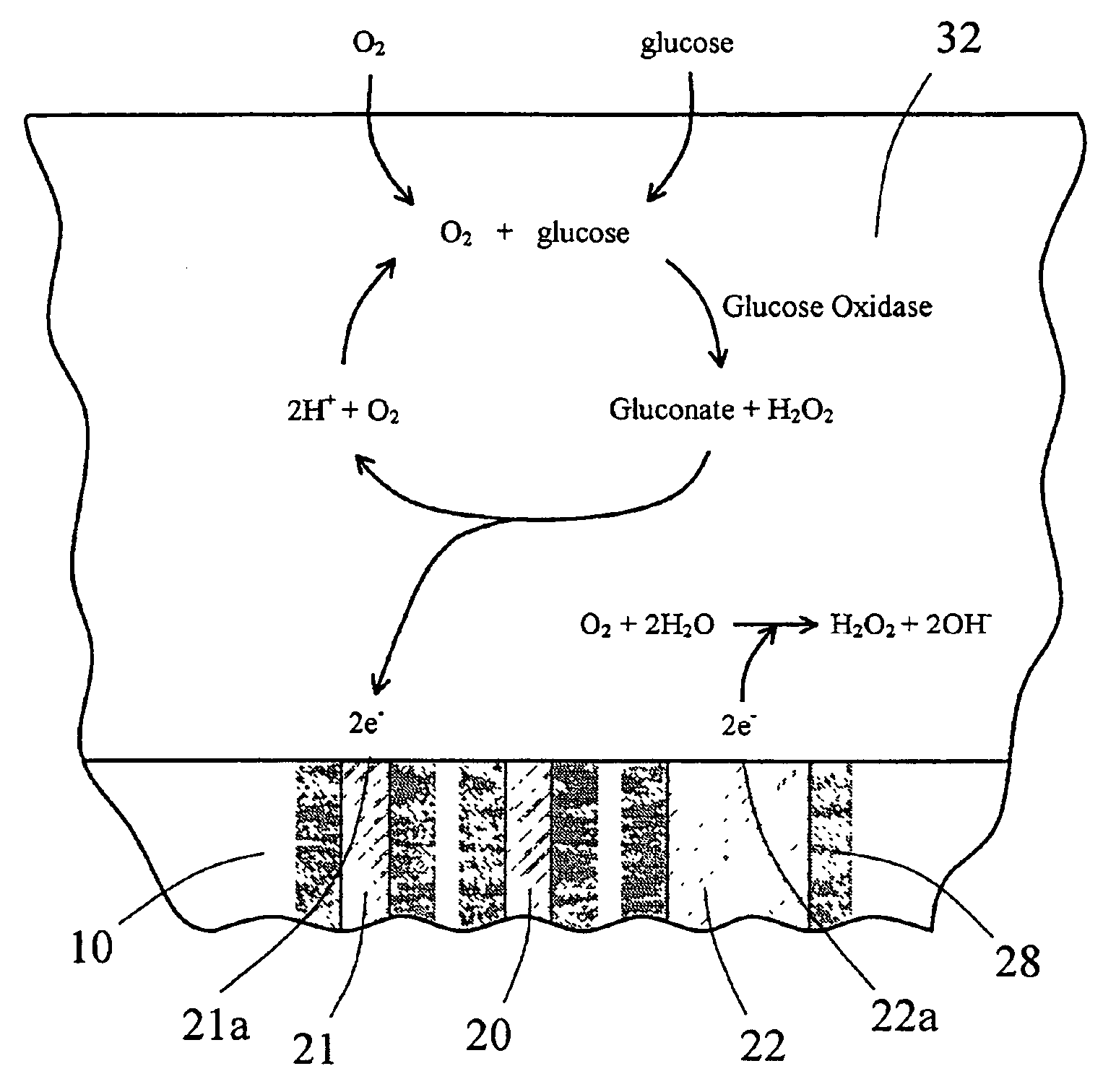
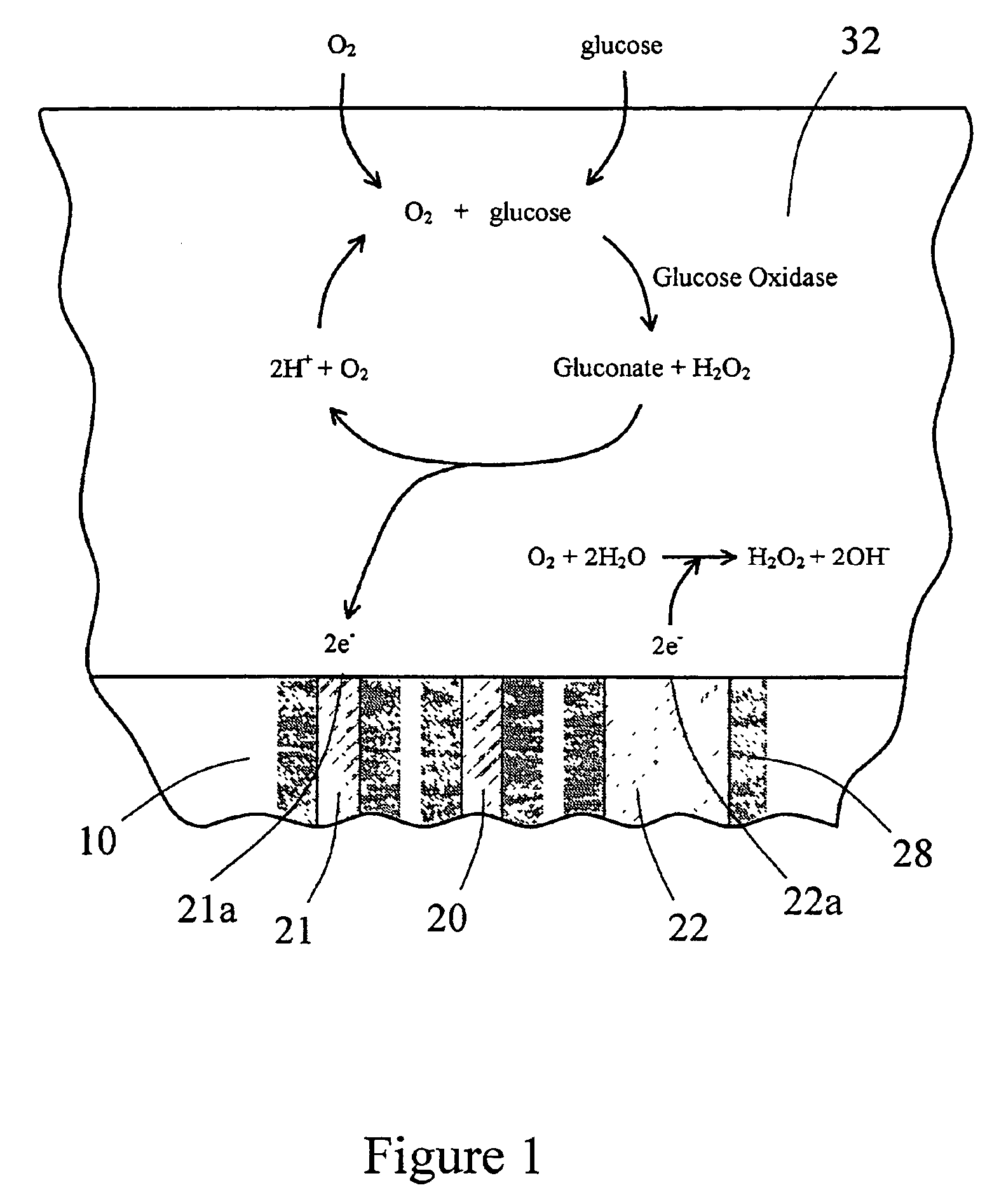
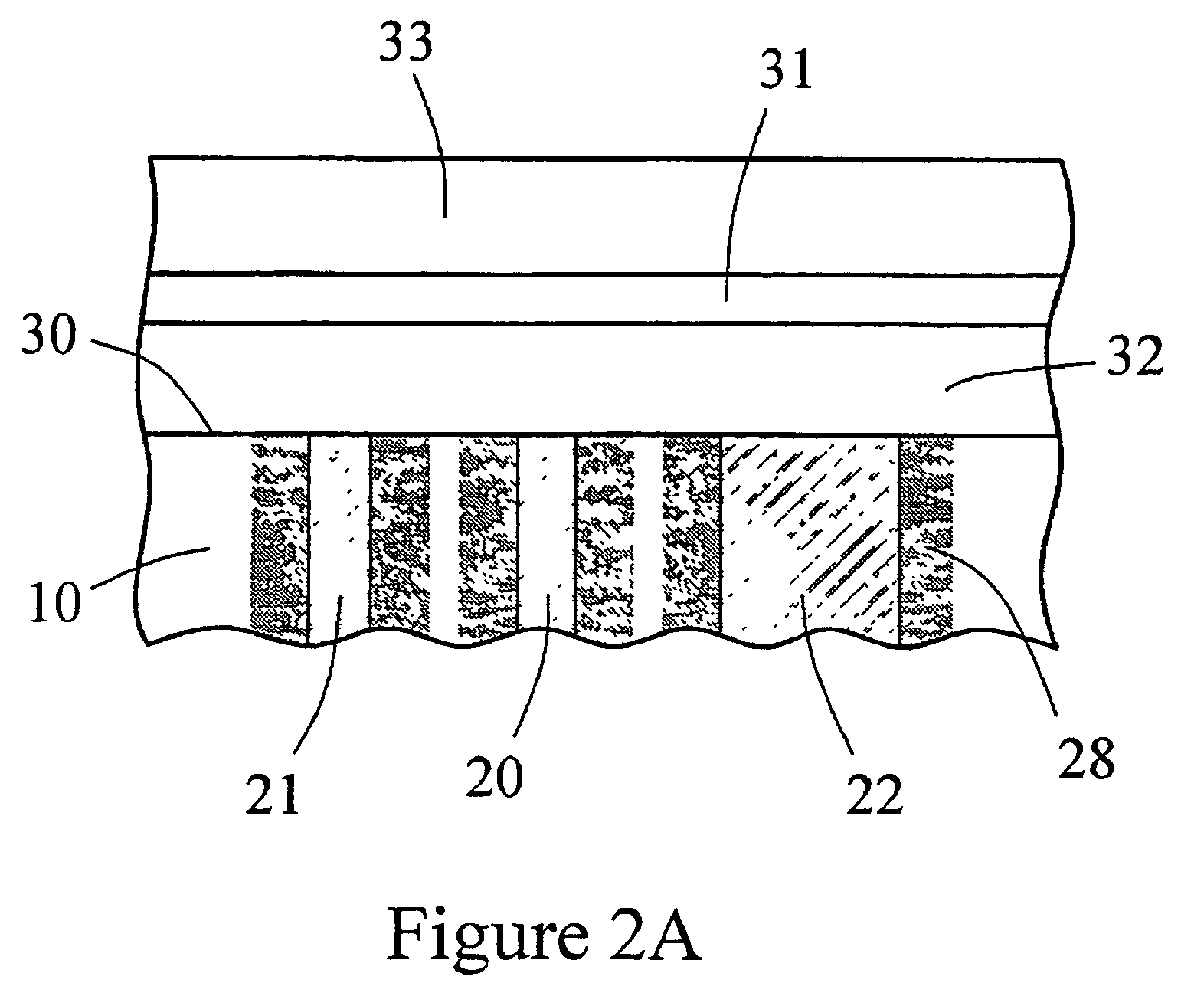
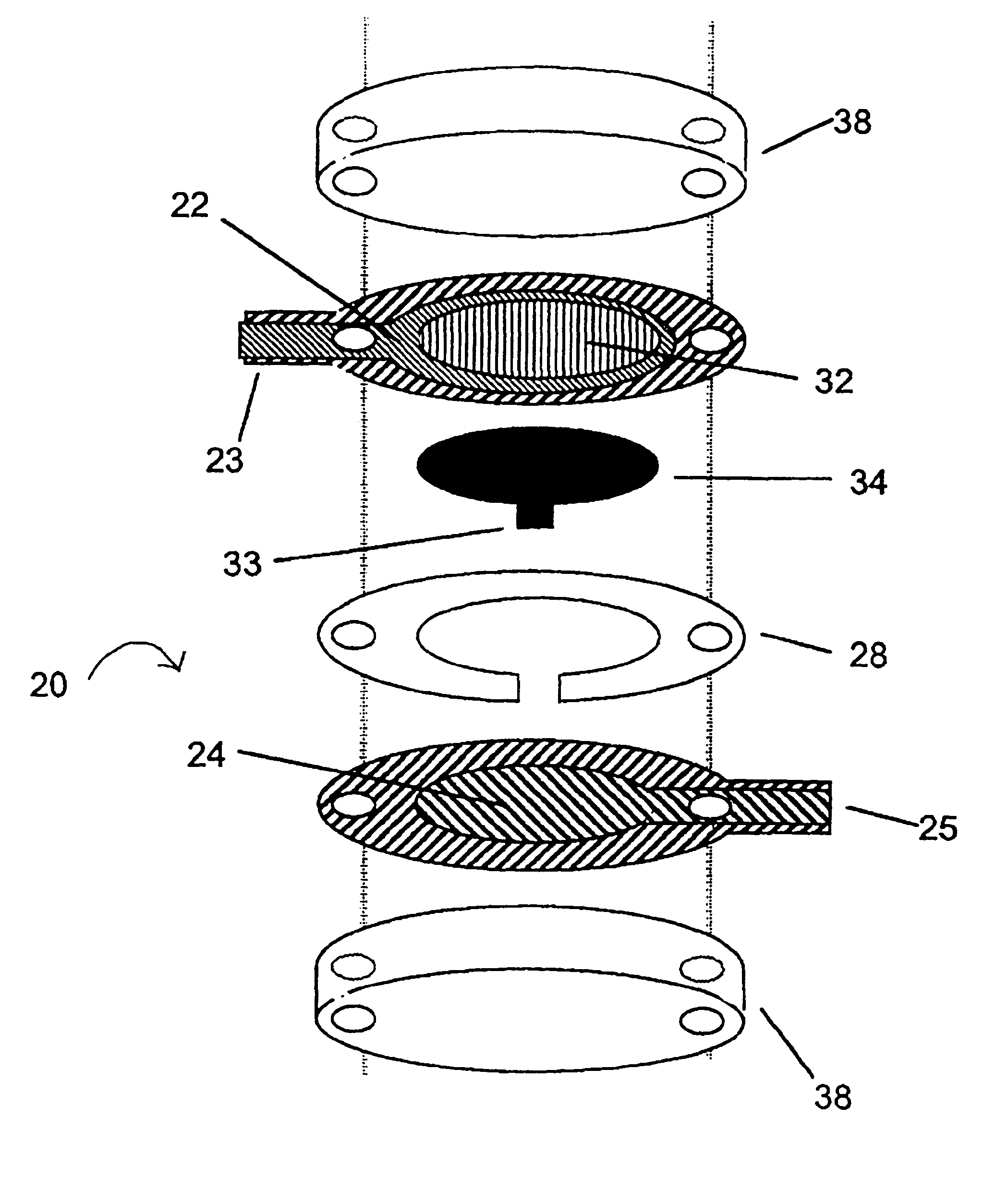
The present invention provides a sensor head for use in an implantable device that measures the concentration of an analyte in a biological fluid which includes: a non-conductive body; a working electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode, wherein the electrodes pass through the non-conductive body forming an electrochemically reactive surface at one location on the body and forming an electronic connection at another location on the body, further wherein the electrochemically reactive surface of the counter electrode is greater than the surface area of the working electrode; and a multi-region membrane affixed to the nonconductive body and covering the working electrode, reference electrode and counter electrode. In addition, the present invention provides an implantable device including at least one of the sensor heads of the invention and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the implantable device of the invention.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Integrated Lancing and Measurement Device
InactiveUS20080017522A1Accurate and efficient measurementLower the volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMeasurement device
An integrated lancing and measurement device is provided comprising a sensor designed to determine the amount and / or concentration of analyte in a biological fluid having a volume of less than about 1 μL. A piercing member is adapted to pierce and retract from a site on the patient to cause the fluid to flow therefrom, and the sensor is positioned adjacent to the site on the patient so as to receive the fluid flowing from the site to generate an electrical signal indicative of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid. The sensor is comprised of a working electrode comprising an analyte-responsive enzyme and a redox mediator, and a counter electrode. An analyte monitor is operatively connected to the sensor and adapted to measure the signal generated by the sensor. Also provided are analyte measuring methods that optionally employ the integrated lancing and measurement device.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Analyte sensor with insertion monitor, and methods
InactiveUS20060091006A1Efficient and reliable methodEfficient methodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteGlucose polymers
A sensor, and methods of making, for determining the concentration of an analyte, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. The sensor includes a working electrode and a counter electrode, and can include an insertion monitoring trace to determine correct positioning of the sensor in a connector.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Microneedle device for extraction and sensing of bodily fluids
InactiveUS7344499B1Simple wayMinimal and no damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicroneedlesMetaboliteIrritation
Microneedle devices are provided for controlled sampling of biological fluids in a minimally-invasive, painless, and convenient manner. The microneedle devices permit in vivo sensing or withdrawal of biological fluids from the body, particularly from or through the skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The microneedle device includes one or more microneedles, preferably in a three-dimensional array, a substrate to which the microneedles are connected, and at least one collection chamber and / or sensor in communication with the microneedles. Preferred embodiments further include a means for inducing biological fluid to be drawn through the microneedles and into the collection chamber for analysis. In a preferred embodiment, this induction is accomplished by use of a pressure gradient, which can be created for example by selectively increasing the interior volume of the collection chamber, which includes an elastic or movable portion engaged to a rigid base. Preferred biological fluids for withdrawal and / or sensing include blood, lymph, interstitial fluid, and intracellular fluid. Examples of analytes in the biological fluid to be measured include glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, creatine, metabolic enzymes, hemoglobin, heparin, clotting factors, uric acid, carcinoembryonic antigen or other tumor antigens, reproductive hormones, oxygen, pH, alcohol, tobacco metabolites, and illegal drugs.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
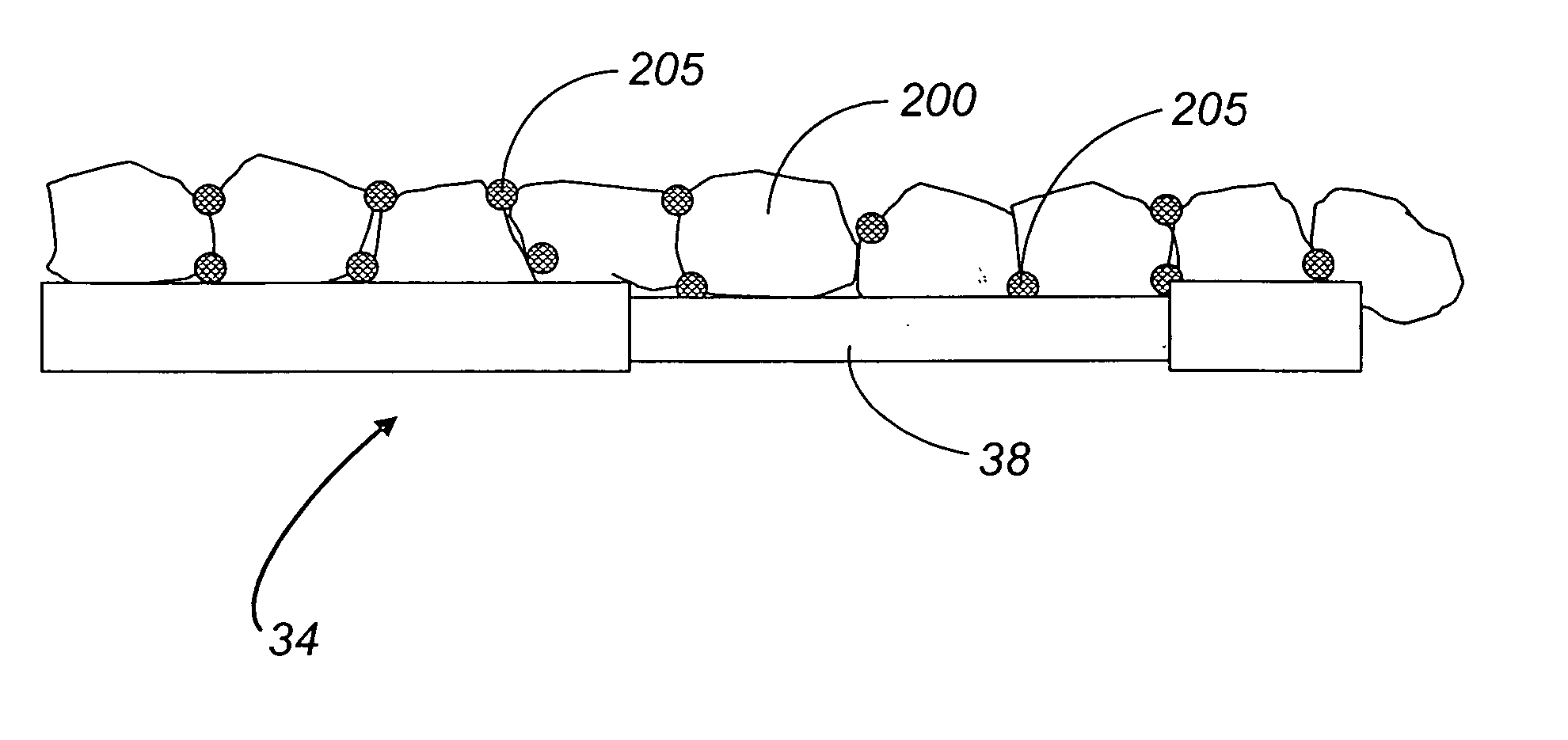
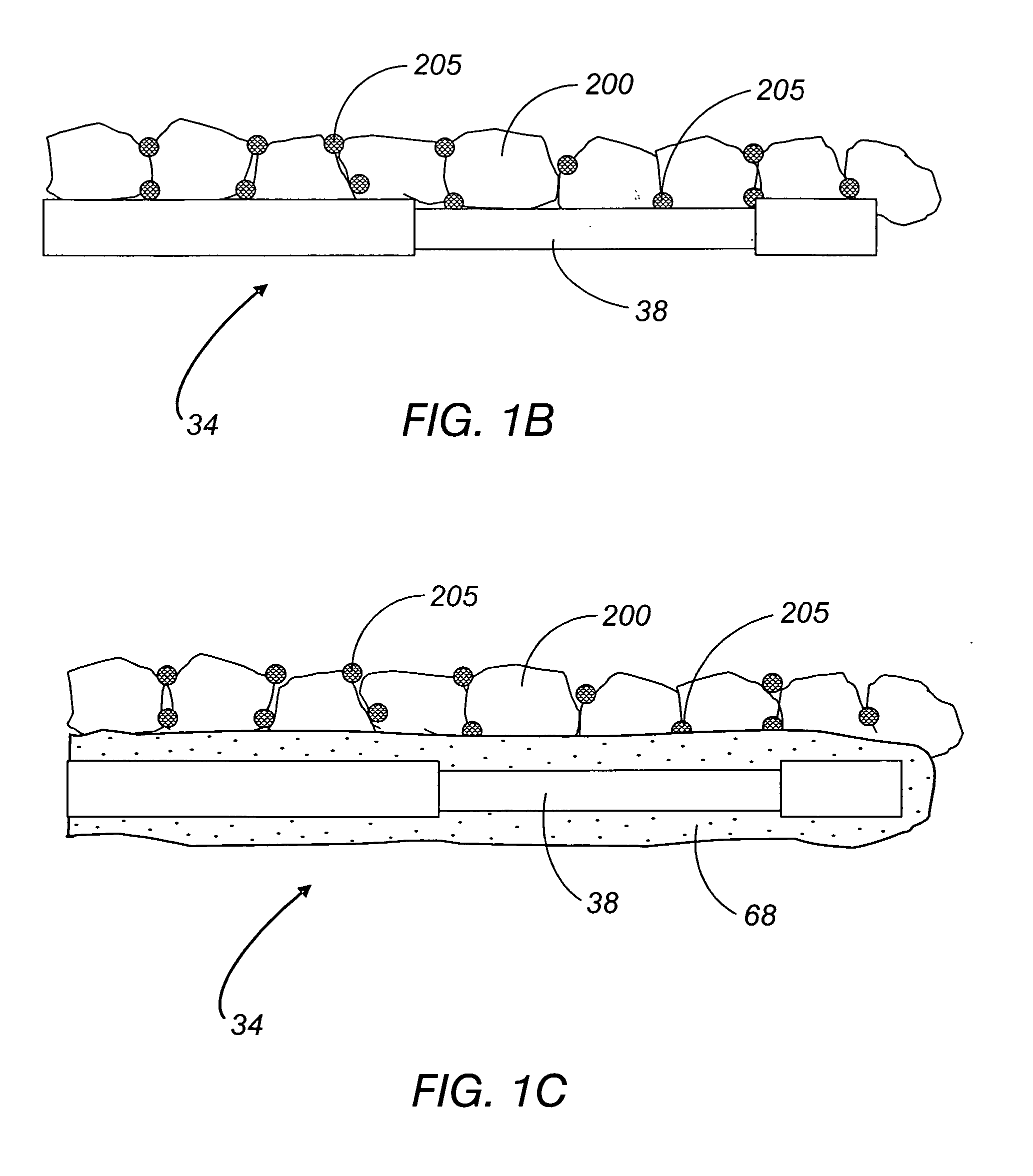
Analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070027370A1Increase liquid volumeLarge flowMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterAnalyteBiointerface
Biointerface membranes are provided which can be utilized with implantable devices, such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample. More particularly, methods for monitoring glucose levels in a biological fluid sample using an implantable analyte detection device incorporating such membranes are provided.
Owner:DEXCOM
In vitro analyte sensor and methods of use
ActiveUS20070068807A1Easy to fillEasy to recordImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteBiology
In vitro electrochemical sensors that provide accurate and repeatable analysis of a sample of biological fluid are provided. Embodiments include sensors that include a sample chambers having overhangs extending therefrom.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
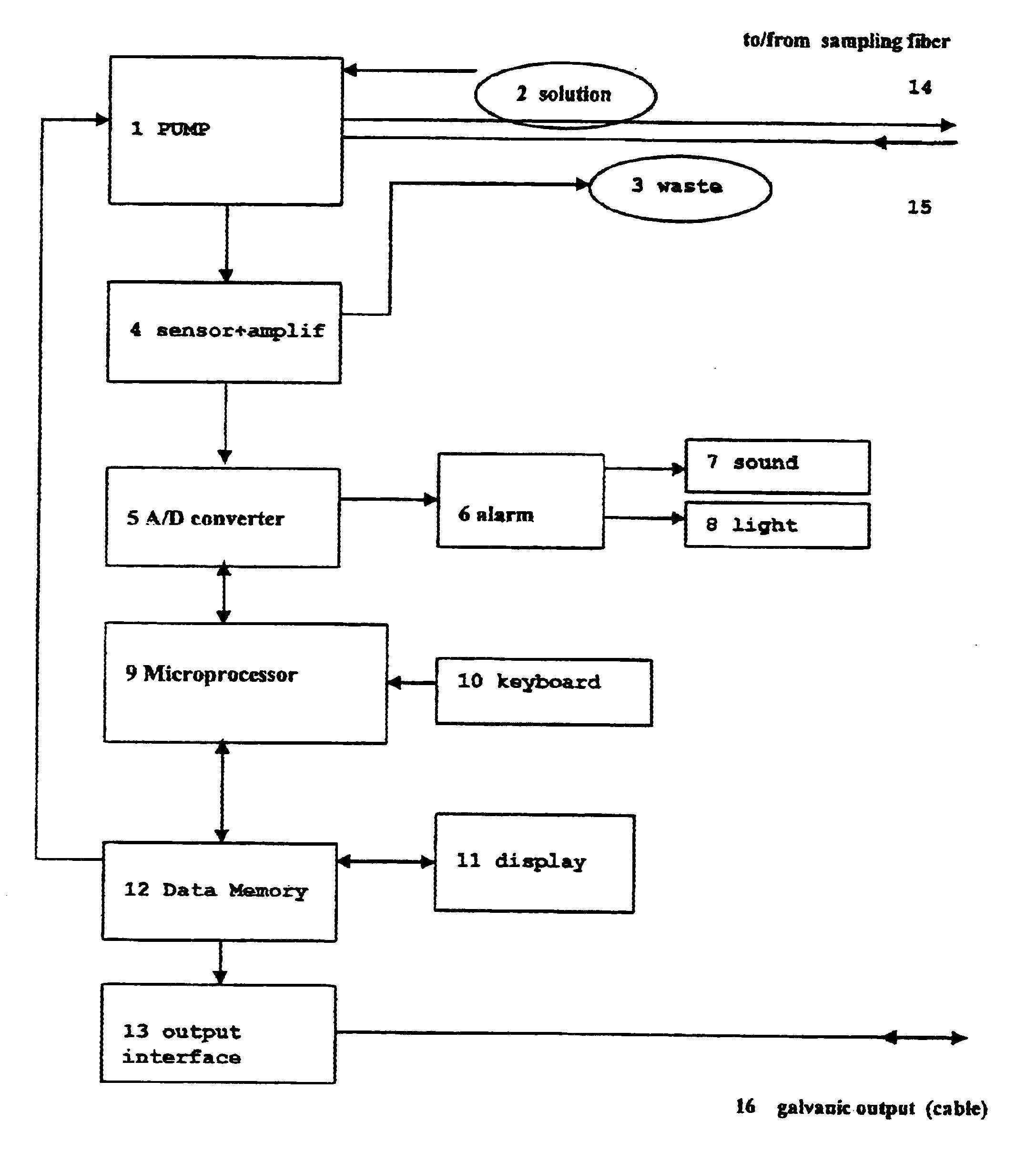
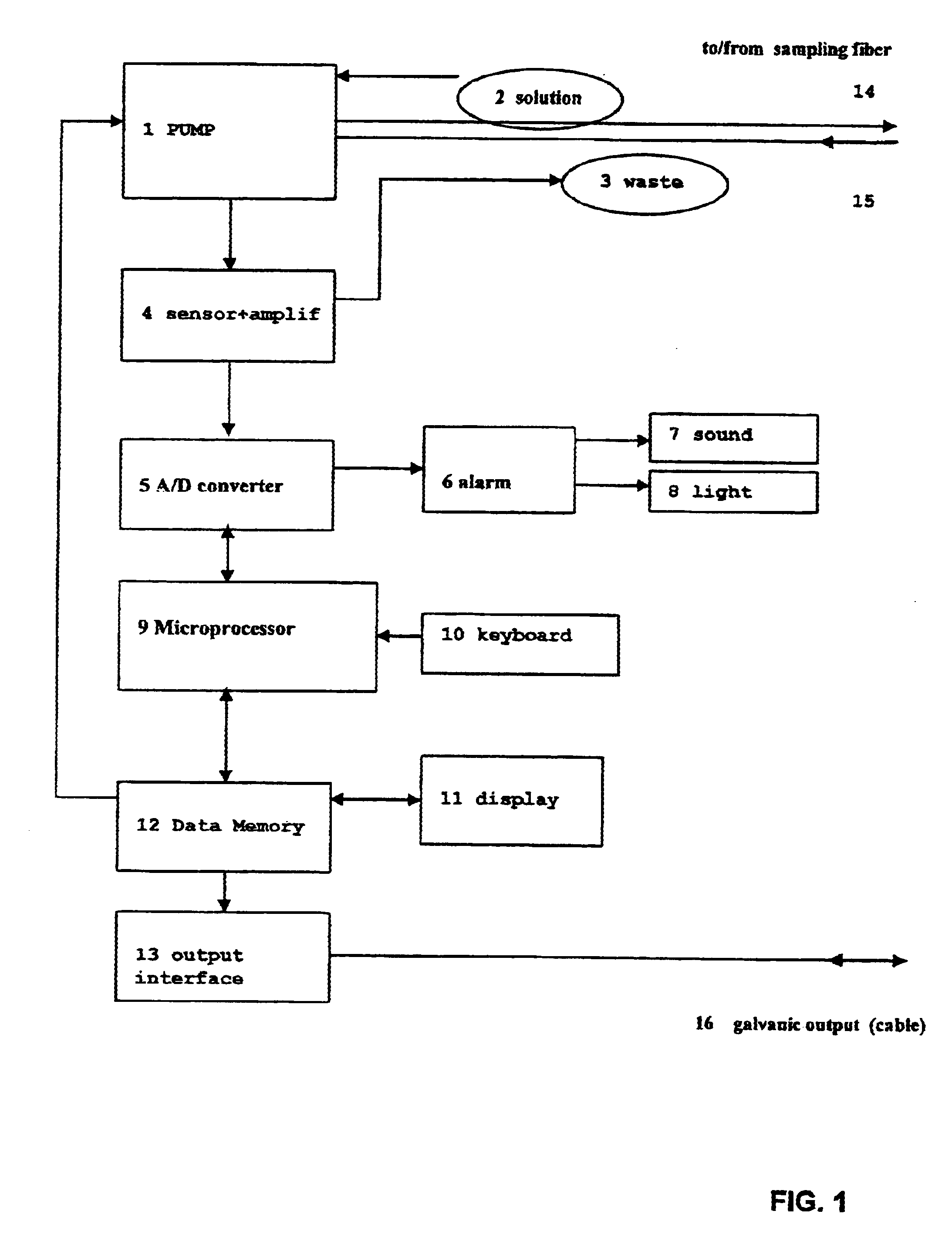
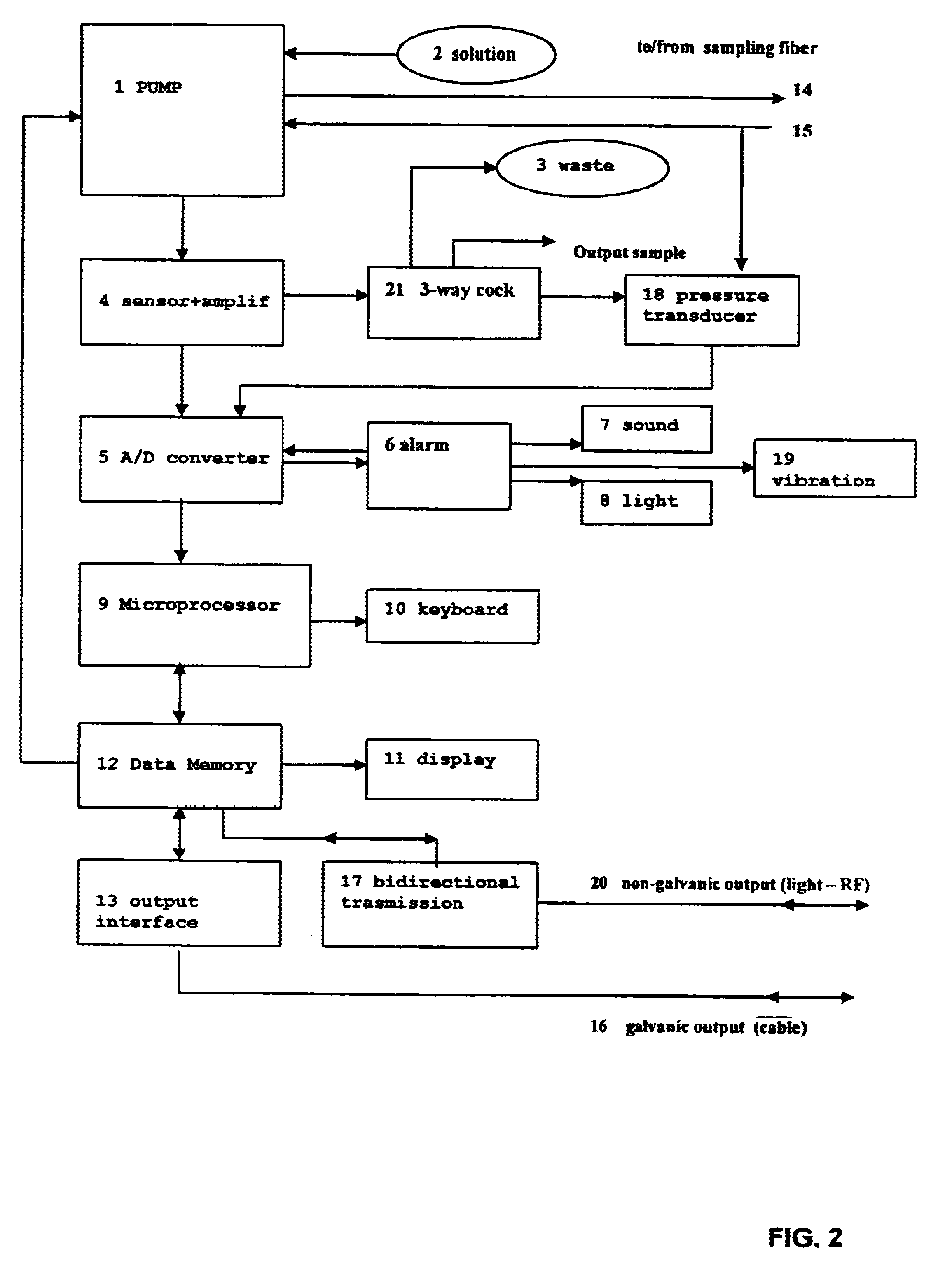
Apparatus for measurement and control of the content of glucose, lactate or other metabolites in biological fluids
InactiveUS6618603B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMetaboliteGlucose Measurement
An apparatus for the continuous measurement of glucose and lactate in interstitial fluids including a glucose measurement cell, an A / D conversion block, a memory block and a bi-directional communication between the interface block and an external calculation unit.
Owner:A MENARINI IND FARM RIUNITE SRL
Analyte sensor
The present invention relates generally to biointerface membranes utilized with implantable devices, such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample. More particularly, the invention relates to novel biointerface membranes, to devices and implantable devices including these membranes, methods for forming the biointerface membranes on or around the implantable devices, and to methods for monitoring glucose levels in a biological fluid sample using an implantable analyte detection device.
Owner:DEXCOM
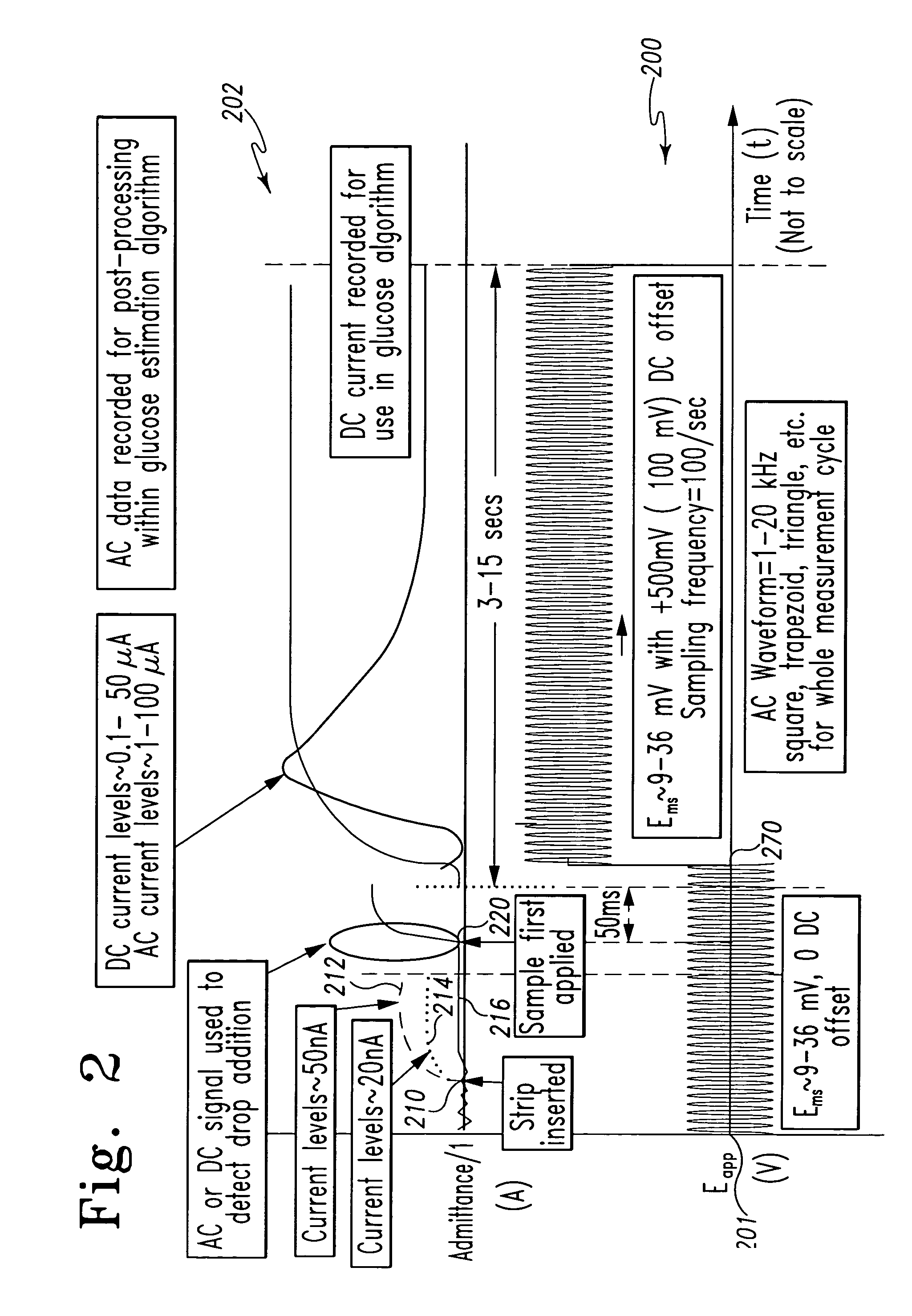
System and method for analyte measurement
InactiveUS7338639B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial thermal conductivityAnalyteExcitation signal
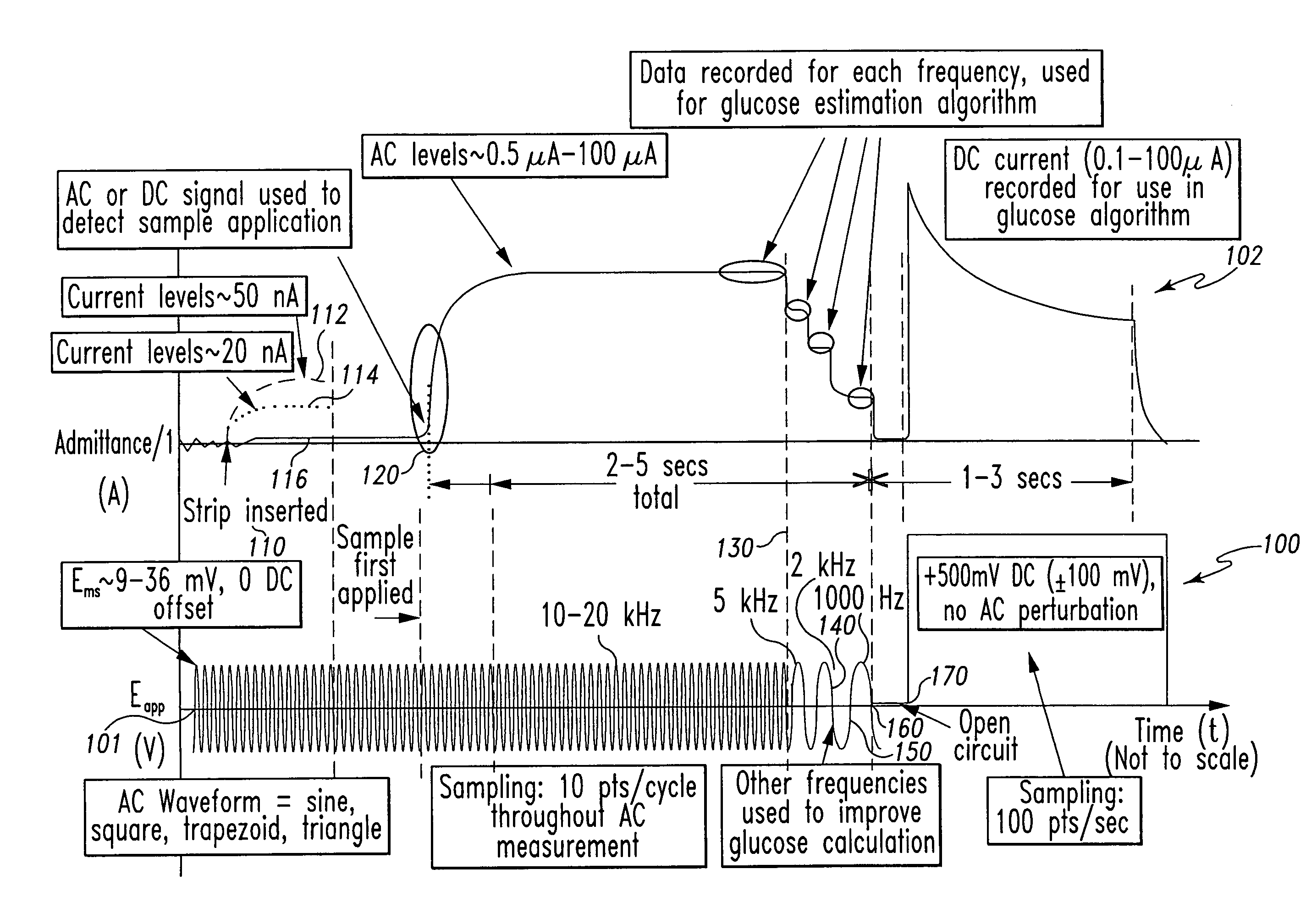
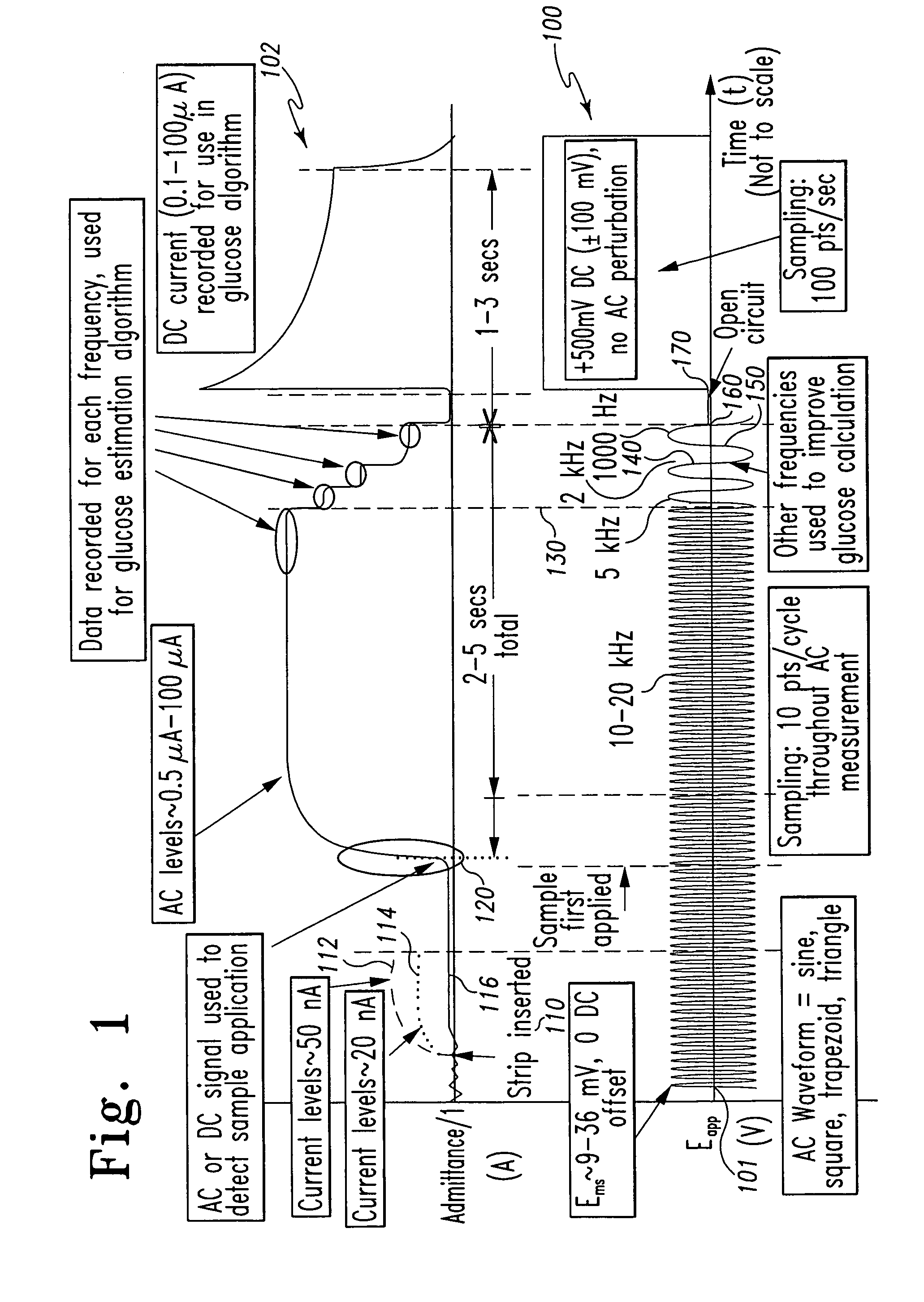
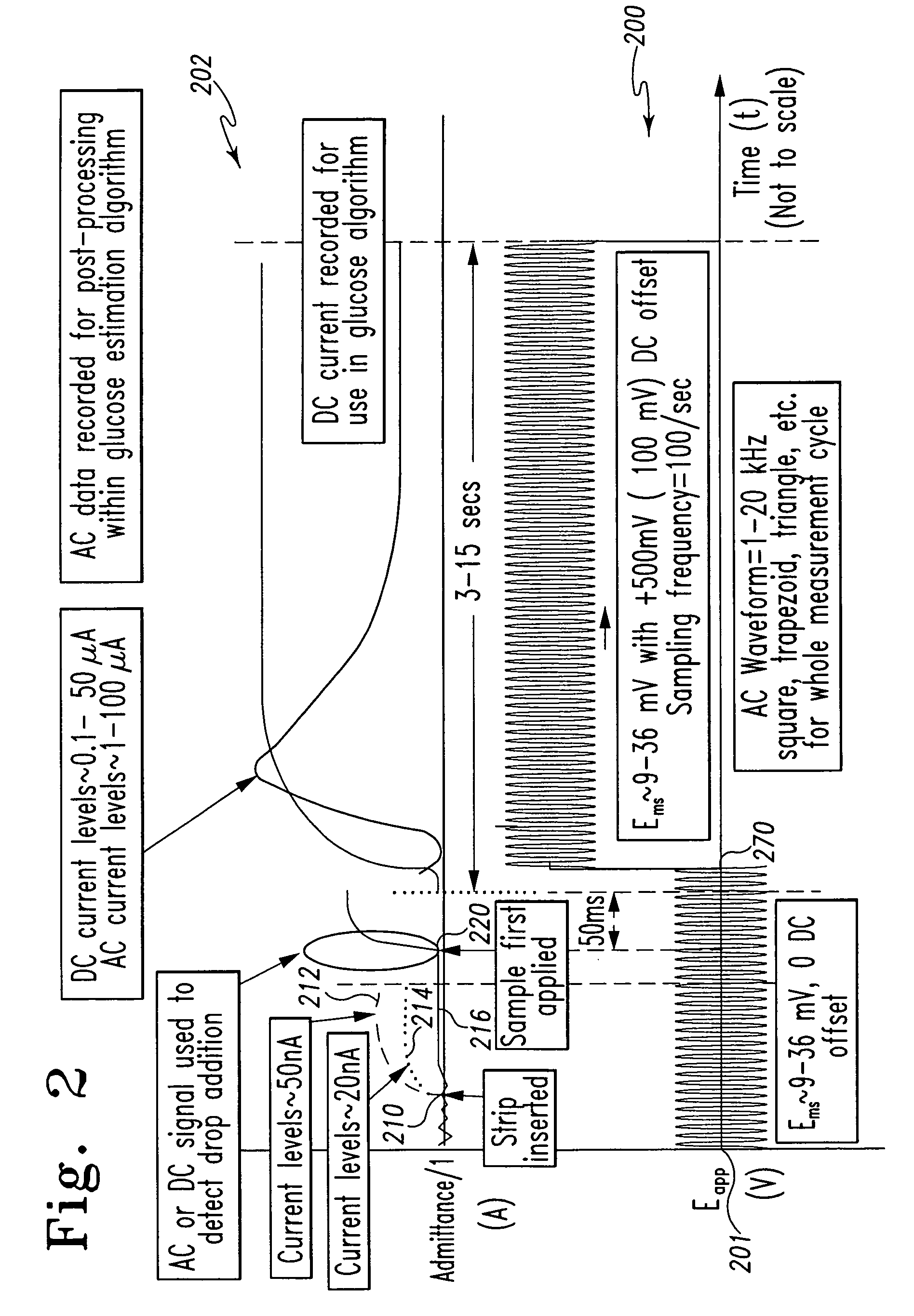
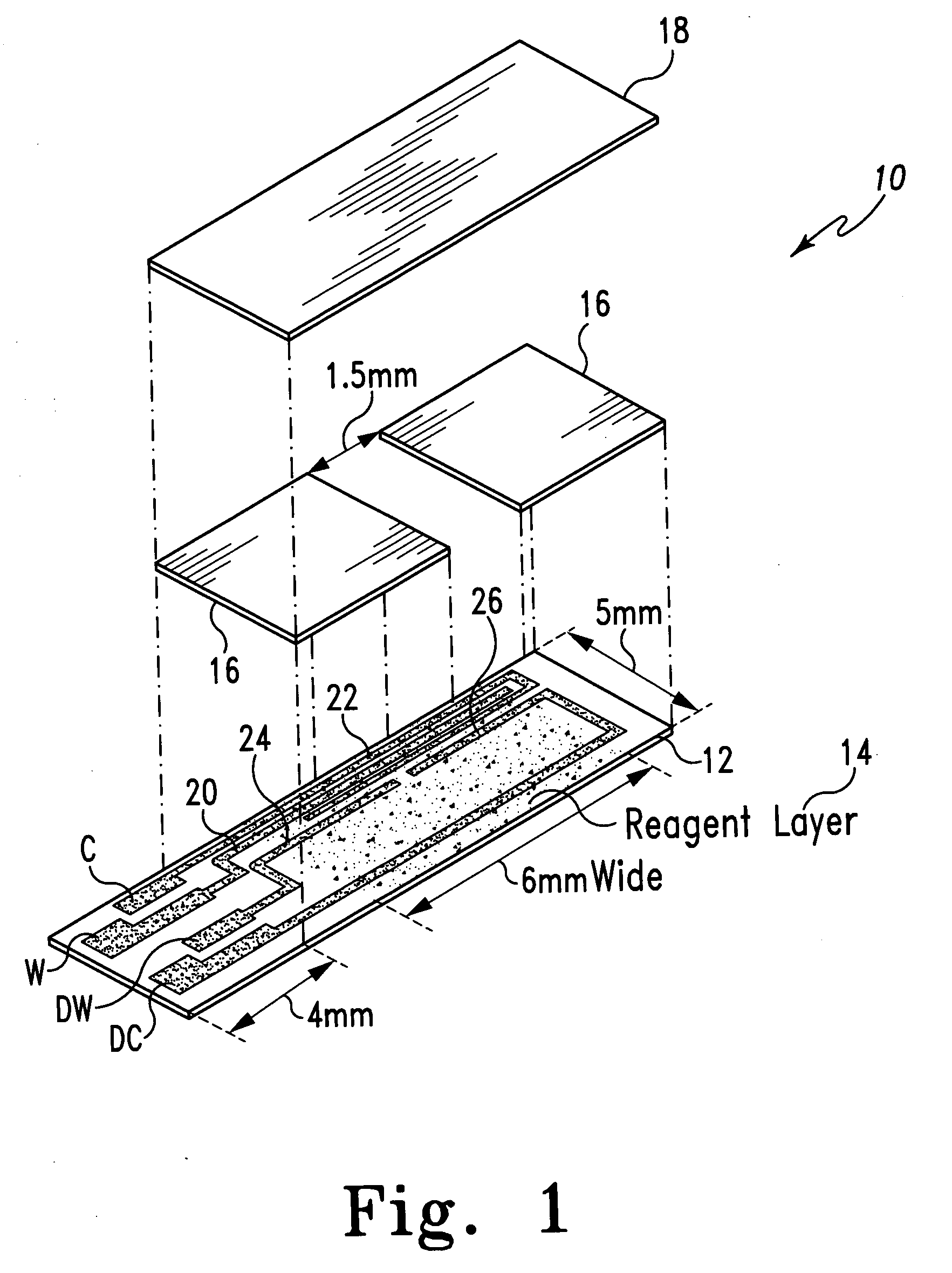
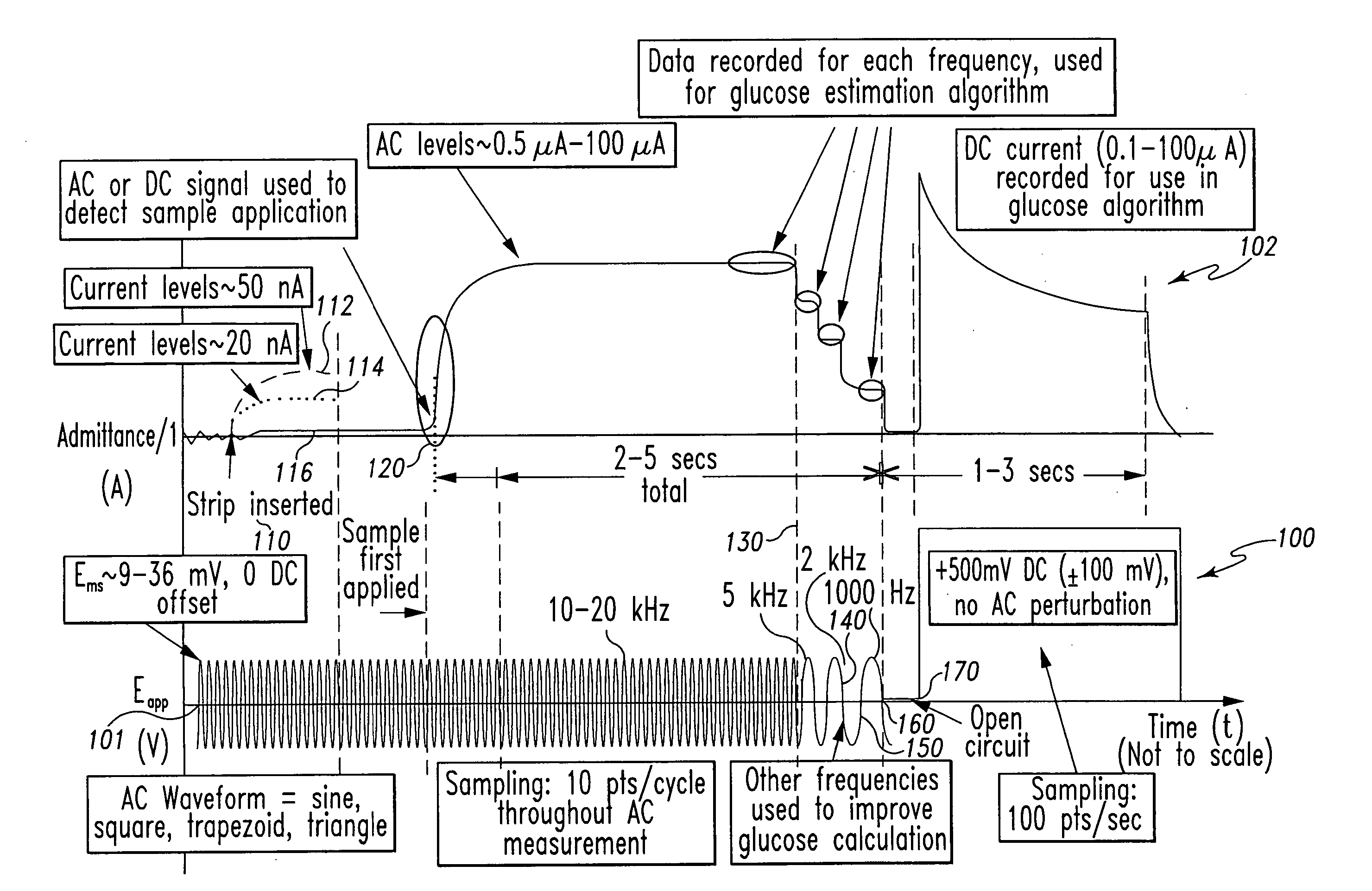
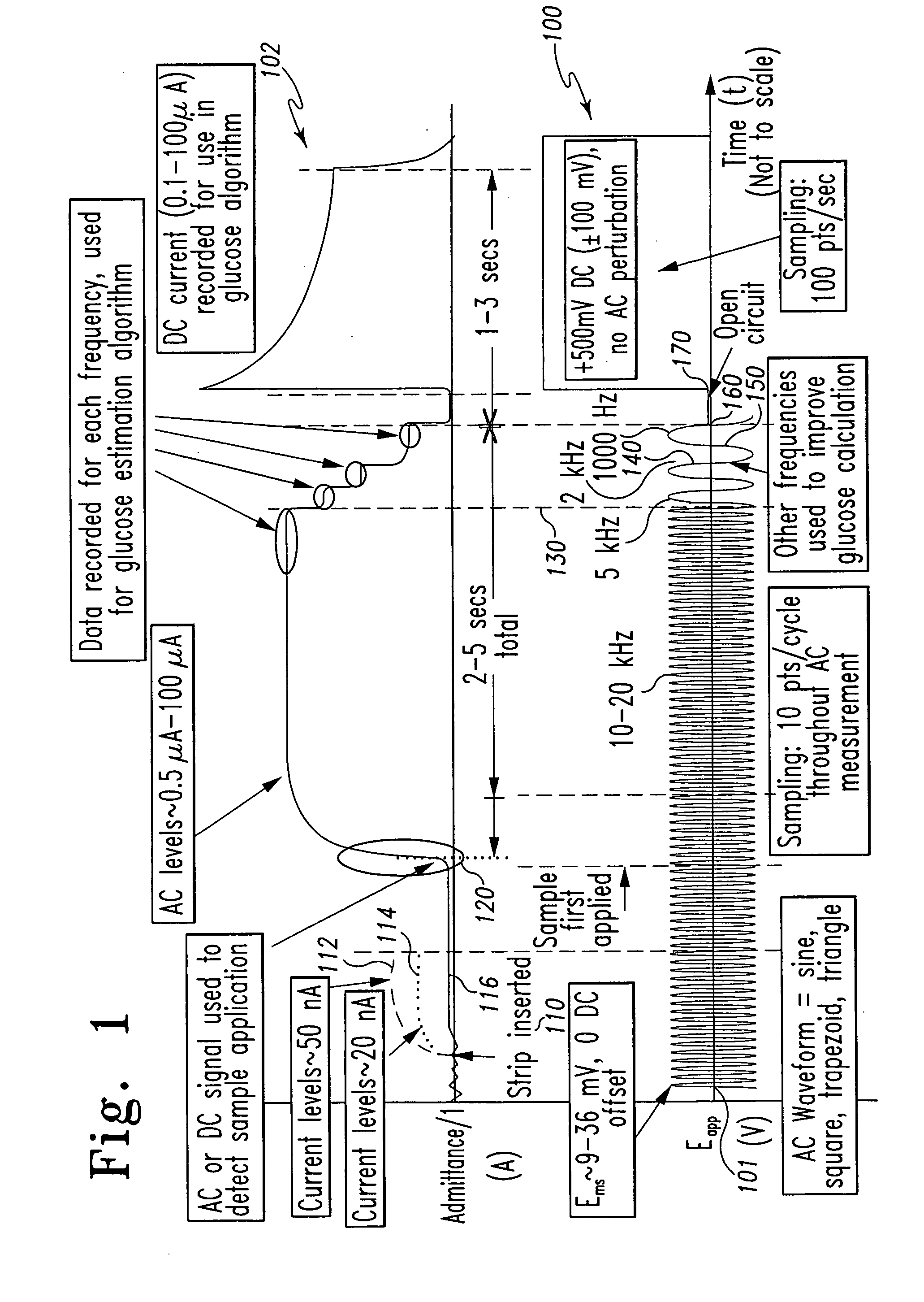
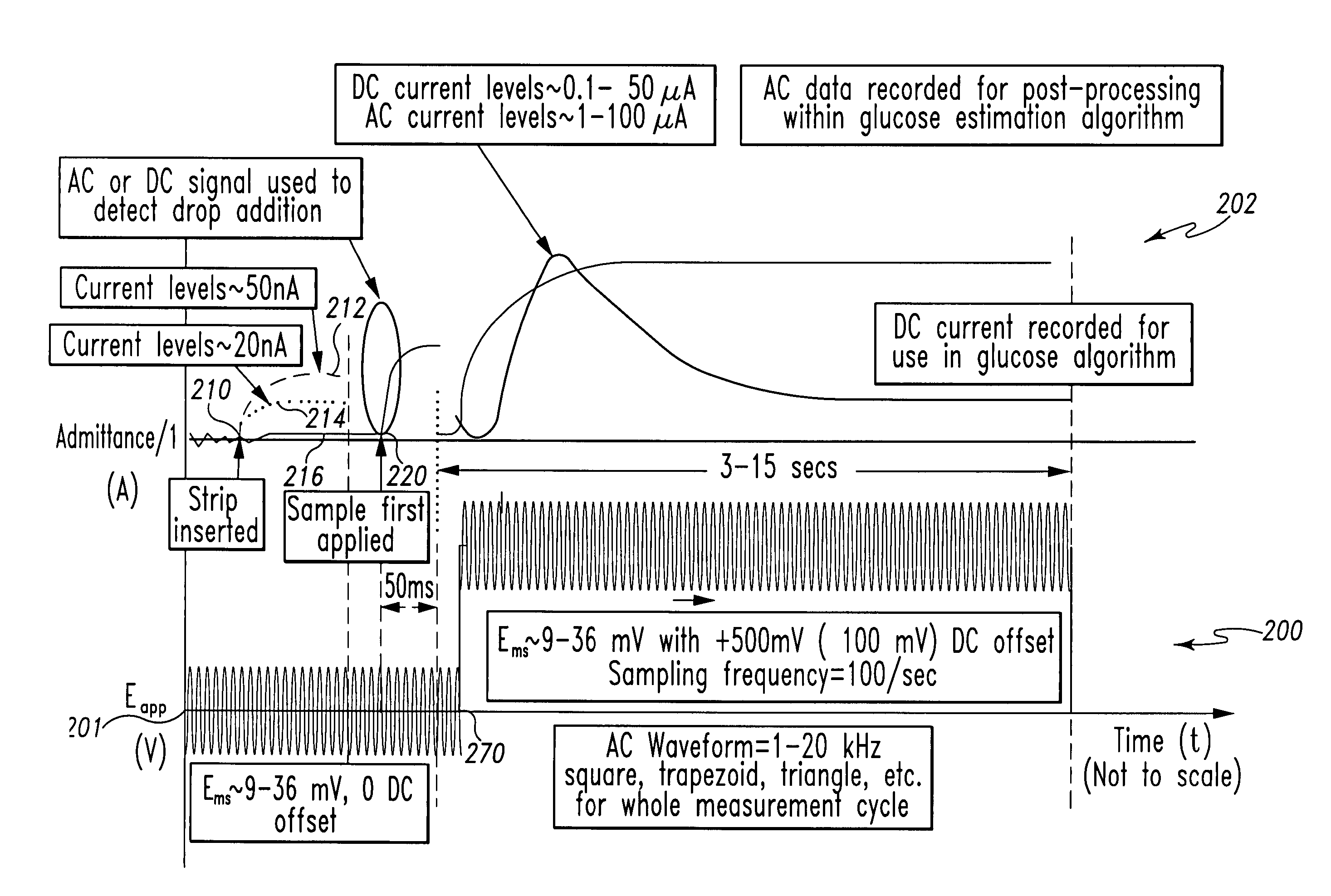
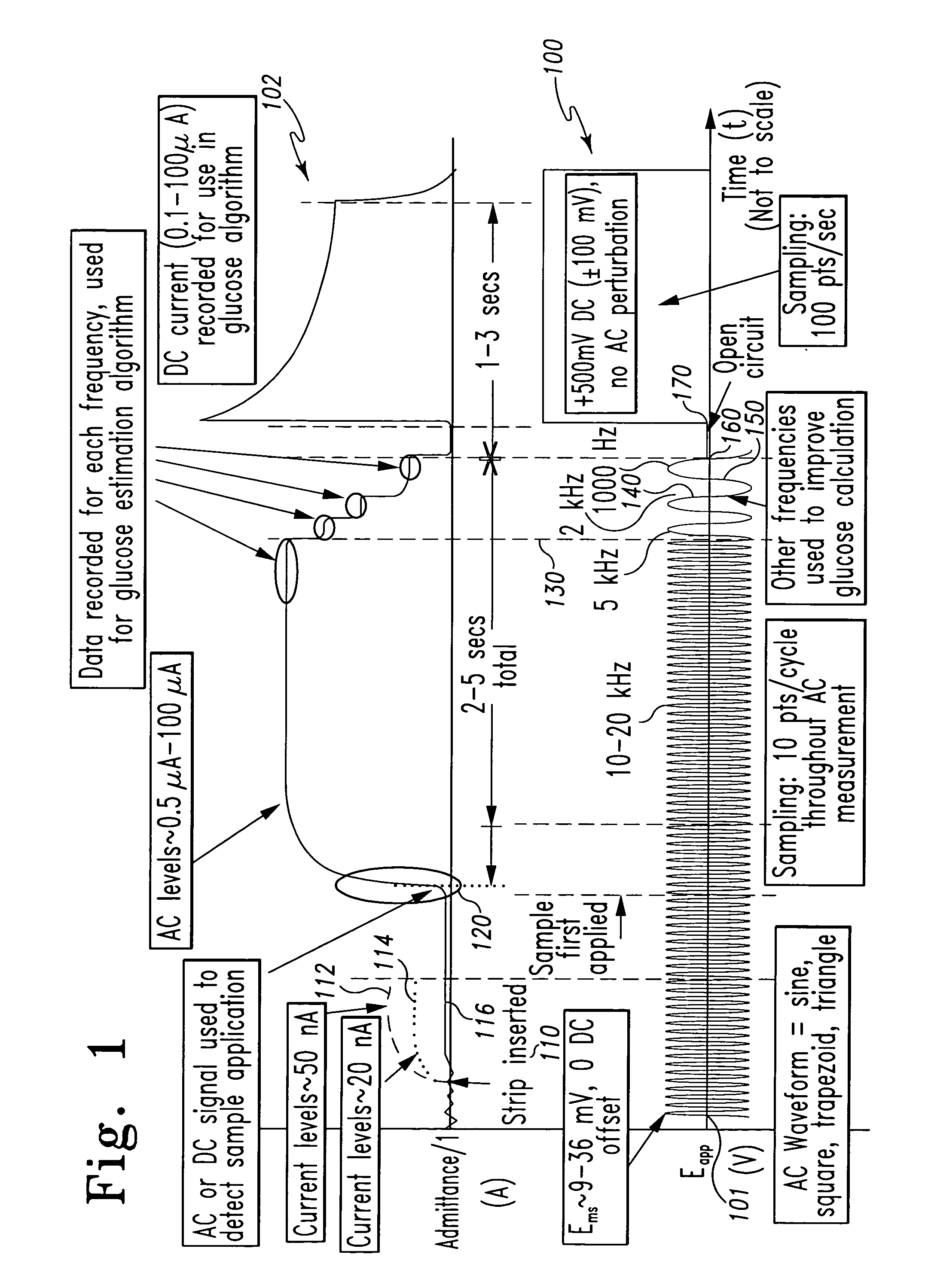
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
Intracutaneous microneedle array apparatus
InactiveUS20050209565A1Sufficient separation distanceGreater transdermal fluxElectrotherapySurgical needlesEngineeringBiological fluids
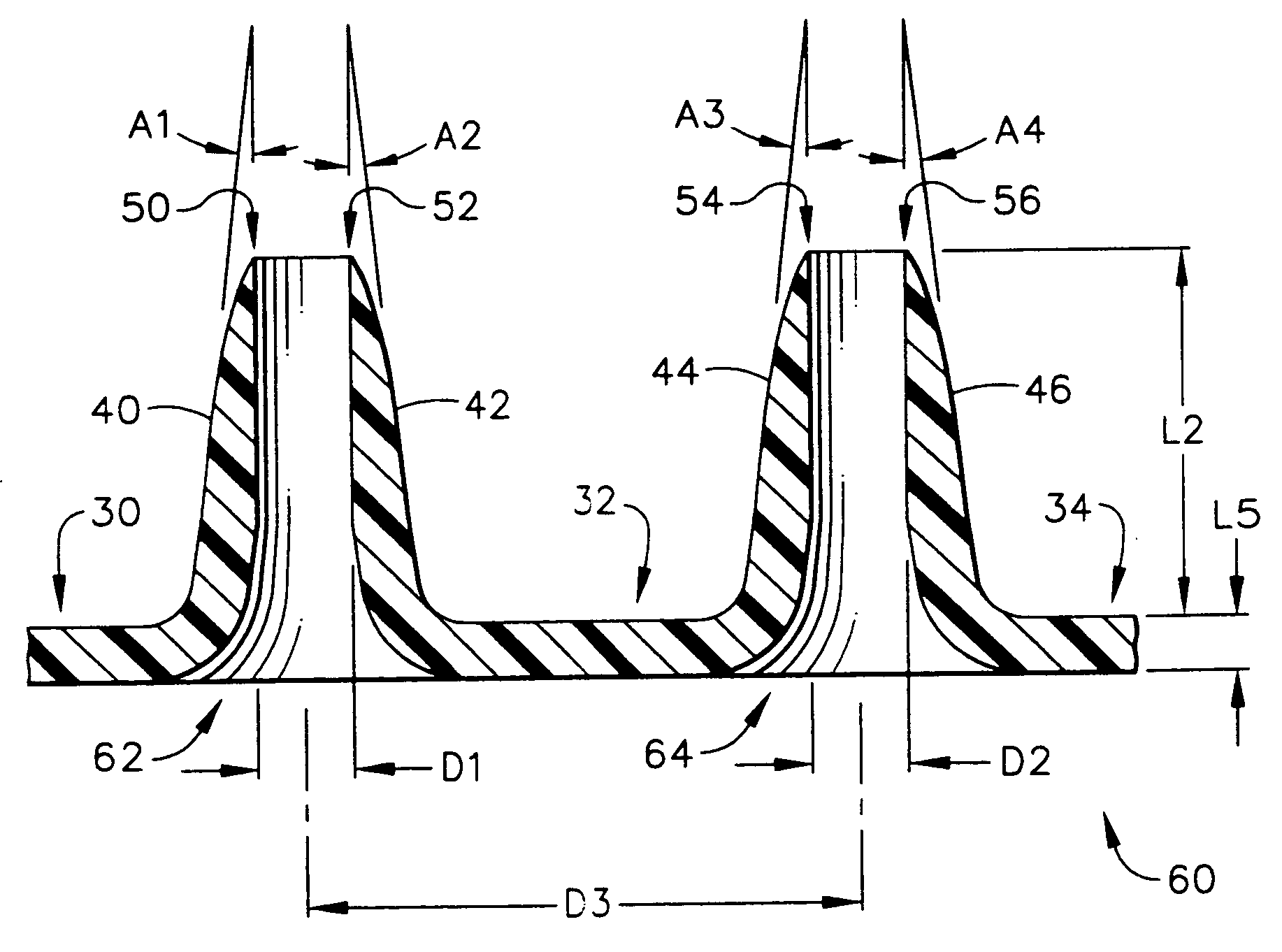
Improved microneedle arrays are provided having a sufficiently large separation distance between each of the individual microneedles to ensure penetration of the skin while having a sufficiently small separation distance to provide high transdermal transport rates. A very useful range of separation distances between microneedles is in the range of 100-300 microns, and more preferably in the range of 100-200 microns. The outer diameter and microneedle length is also very important, and in combination with the separation distance will be crucial as to whether or not the microneedles will actually penetrate the stratum corneum of skin. For circular microneedles, a useful outer diameter range is from 20-100 microns, and more preferably in the range of 20-50 microns. For circular microneedles that do not have sharp edges, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50-200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 100-150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is in the range of 200 microns—3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200-400 microns. For circular microneedles having sharp side edges, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50-200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 80-150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is again in the range of 200 microns—3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200-400 microns. For solid microneedles having a star-shaped profile with sharp edges for its star-shaped blades, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50-200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 80-150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is again in the range of 200 microns—3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200-400 microns, while the radius of each of its blades is in the range of 10-50 microns, and more preferably in the range of 10-15 microns.
Owner:CORIUM INC
Integrated poration, harvesting and analysis device, and method therefor
An integrated device for poration of biological tissue, harvesting a biological fluid from the tissue, and analysis of the biological fluid. The device comprises a tissue-contacting layer having an electrically or optically heated probe to heat and conduct heat to the tissue to form at least one opening, such as a micropore to collect biological fluid from the opening, and a detecting layer responsive to the biological fluid to provide an indication of a characteristic of the biological fluid, such as the concentration of an analyte in interstitial fluid. In the embodiment in which, the probe comprises a photosensitizing assembly designed for the uniform application of a photosensitizing material, such as, for example, a dye or a pigment, to a tissue, e.g., the stratum comeum. In one embodiment, the photosensitizing assembly comprises photosensitizing material combined with a carrier, such as, for example, an adhesive or an ink, and the resulting combination is applied to a substrate, such as, for example, an inert polymeric substrate to form a photosensitizing assembly. In another embodiment, the photosensitizing assembly comprises photosensitizing material incorporated into a film-forming polymeric material.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP +1
Analytical test device and method of use
InactiveUS6140136ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological fluidsAnalytical chemistry
The present invention provides an analytical test device for conducting assays of biological fluids. Methods for carrying out the assays with the disclosed analytical test device are also provided.
Owner:SYNTRON BIORES
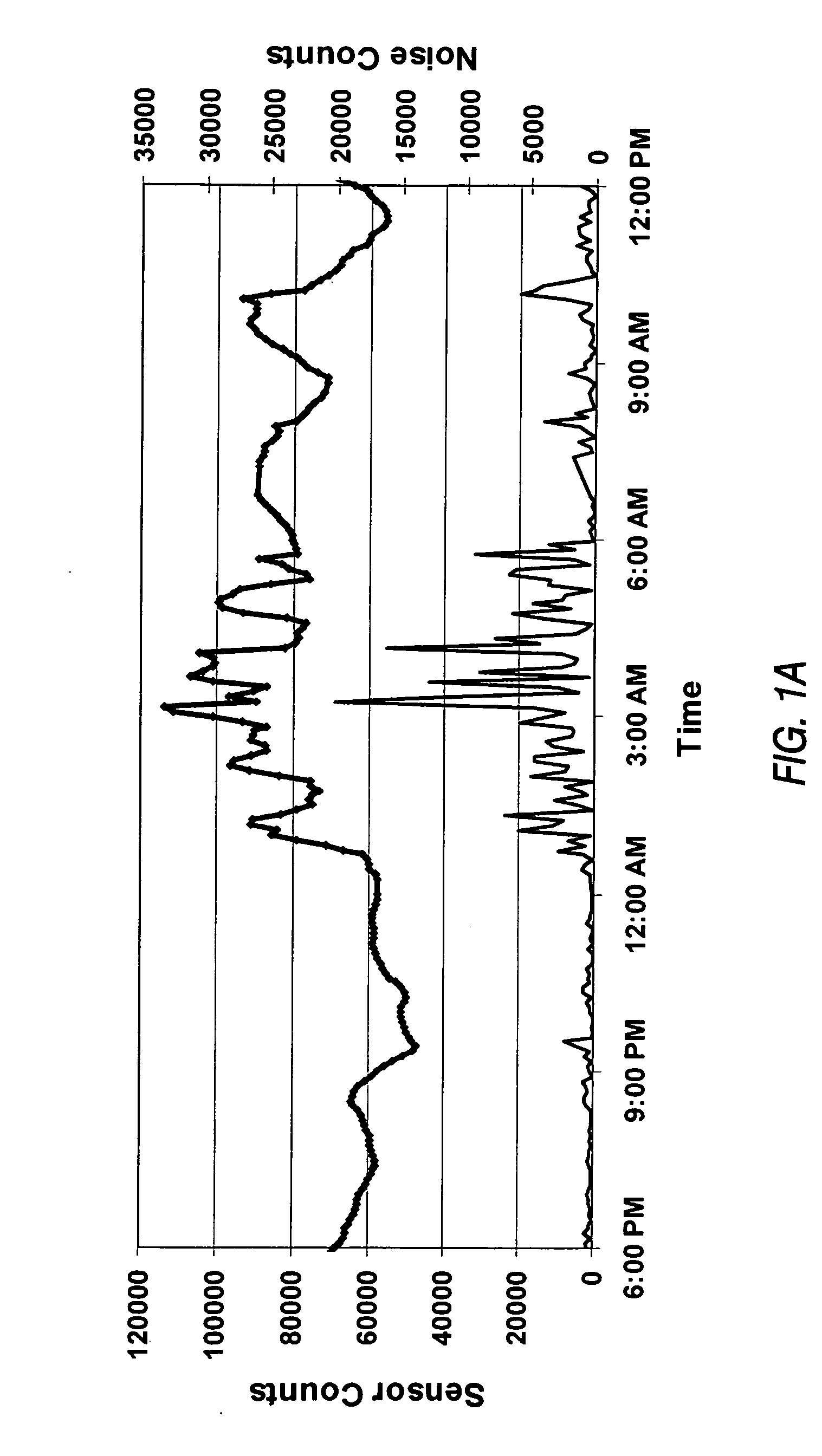
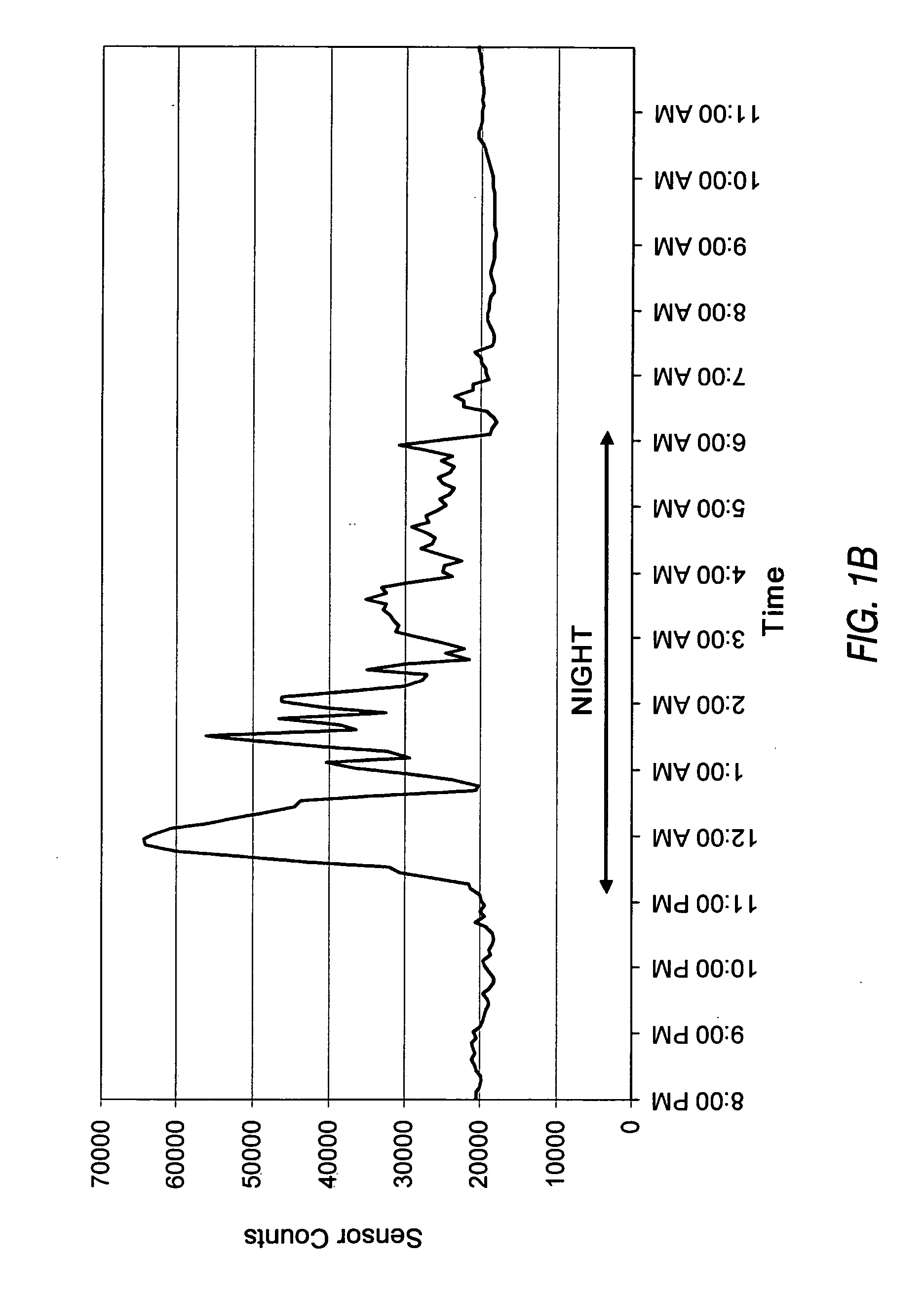
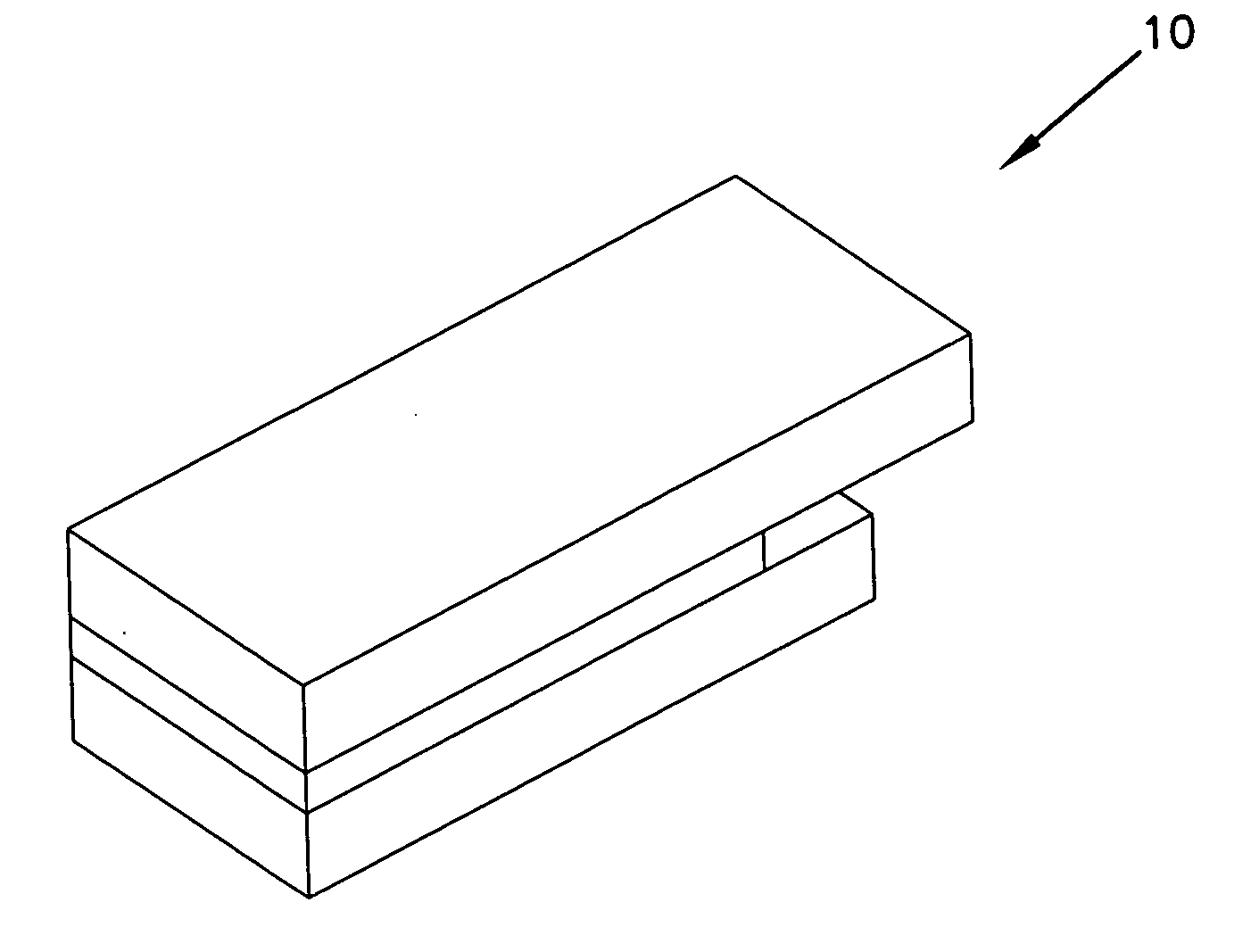
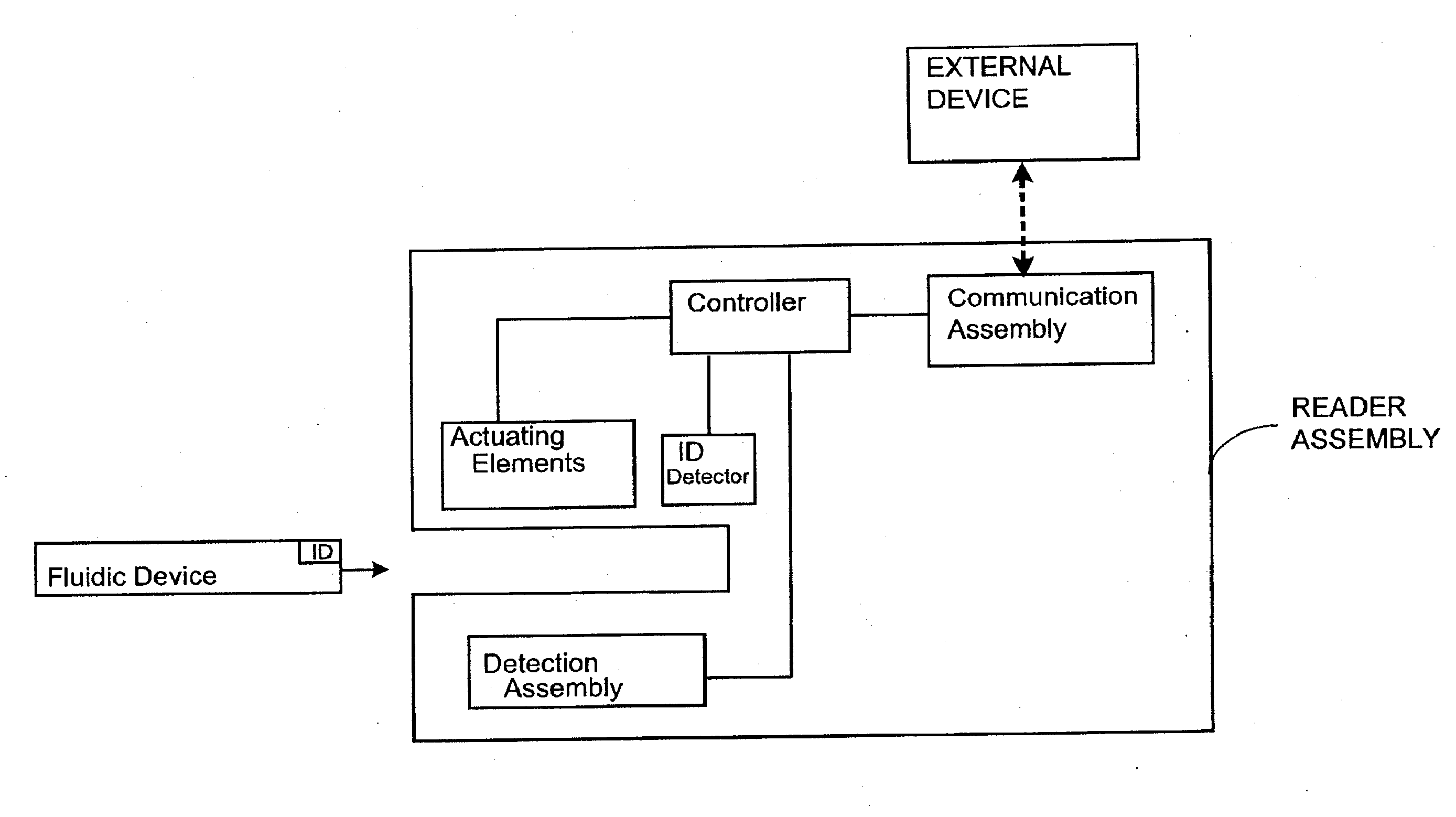
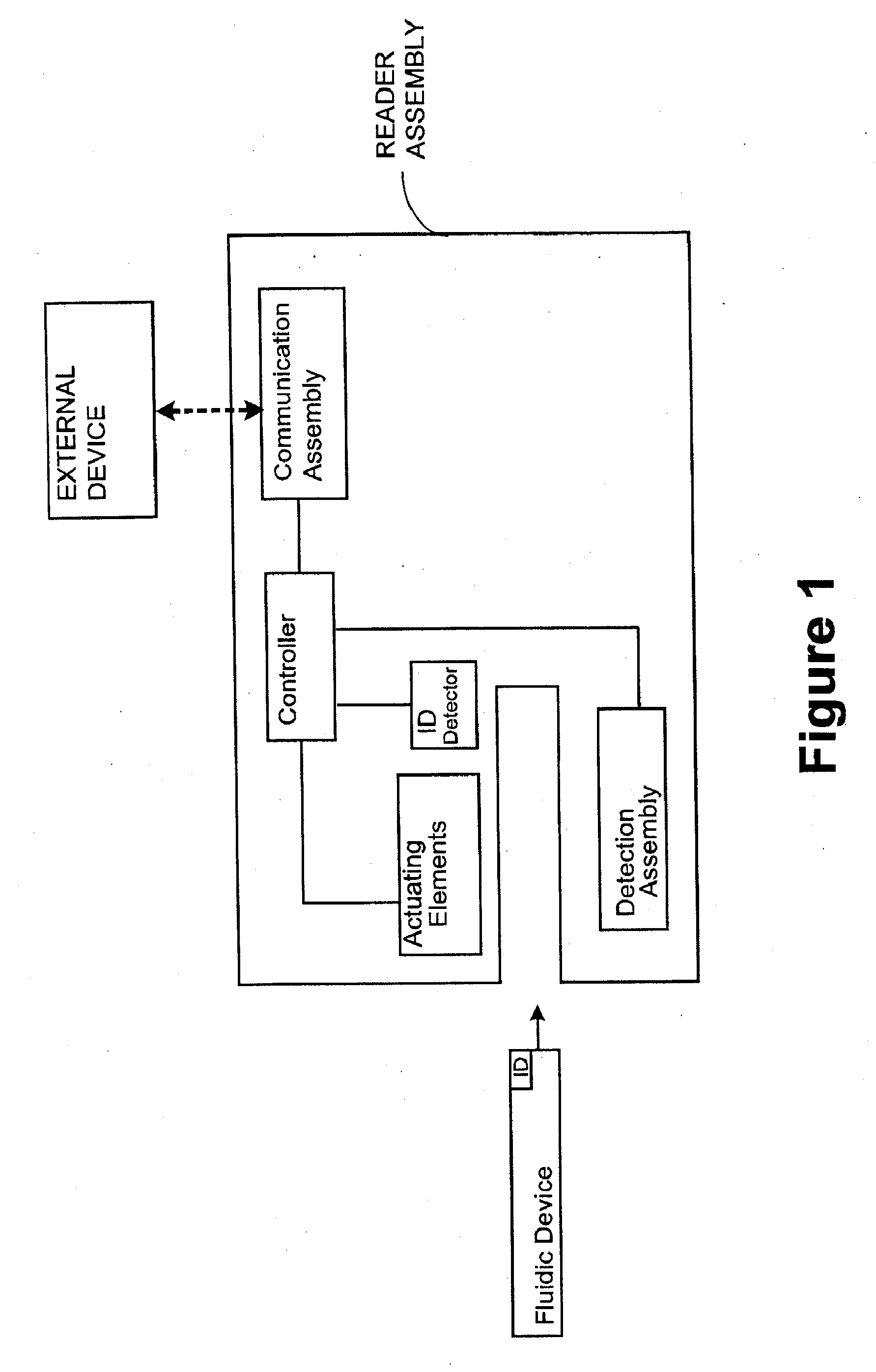
Attribute compensation for analyte detection and/or continuous monitoring
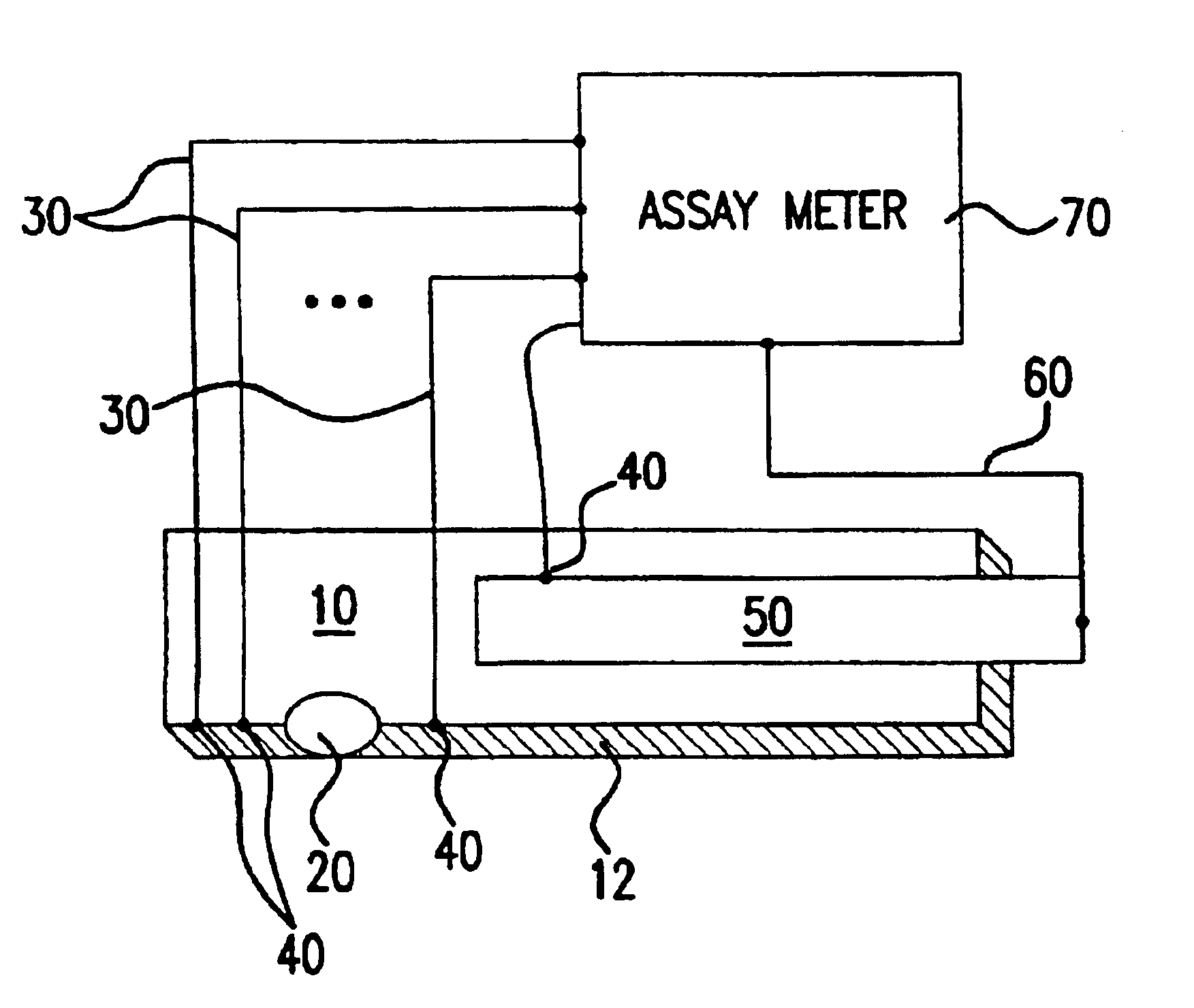
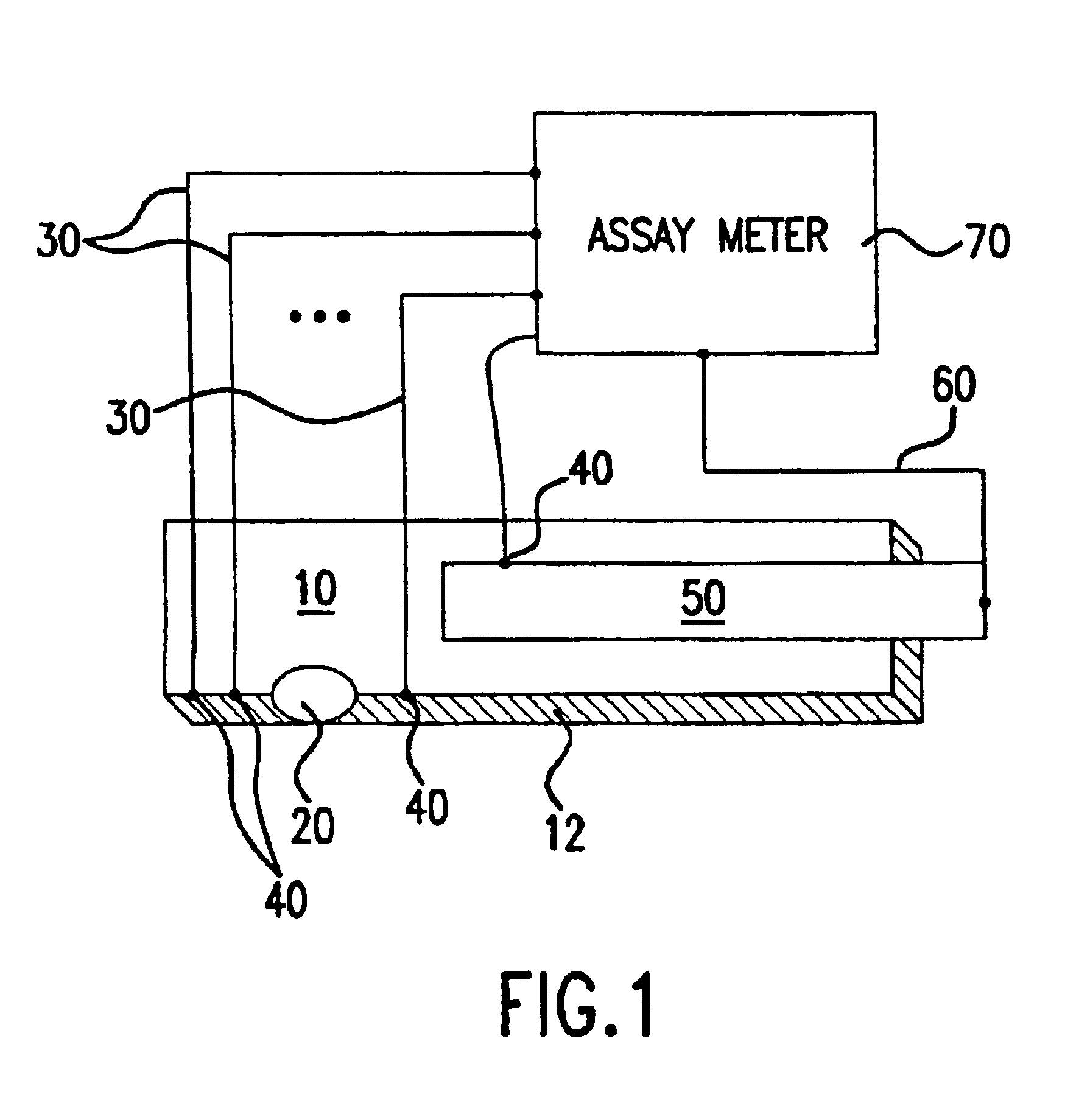
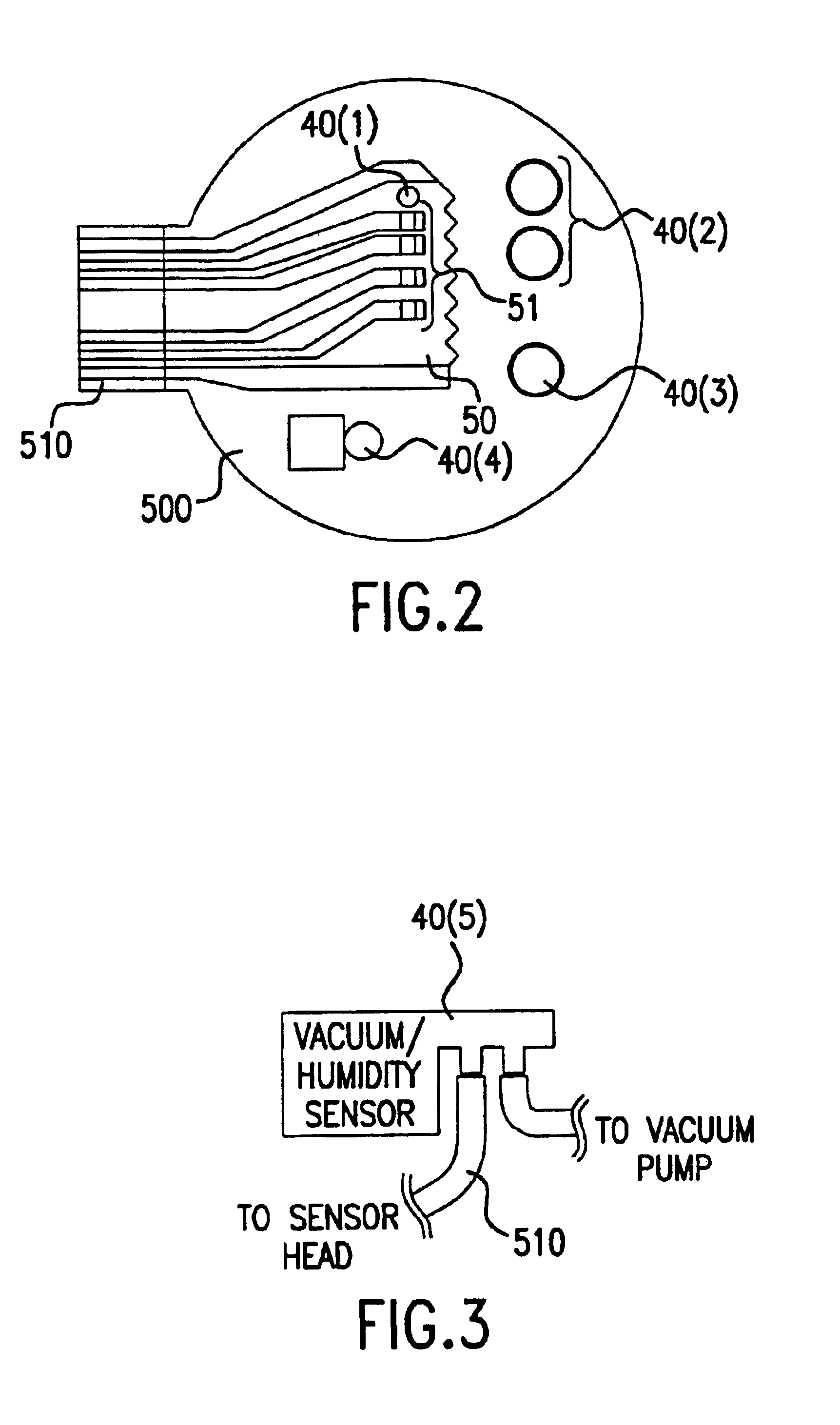
A system and method for detecting a measuring an analyte in a biological fluid of an animal. A harvesting device (10) is provided suitable for positioning on the surface of tissue of an animal to harvest biological fluid therefrom. The harvesting device (10) comprises an analyte sensor (50) positioned to be contacted by the harvested biological fluid and which generates a measurement signal representative of the analyte. At least one attribute sensor (40) is provided to measure an attribute associated with the biological fluid harvesting operation of the harvesting device (10) or the assay of the biological fluid, and which generates an attribute signal representative of the attribute. Adjustments are made to operational parameters of the harvesting device (10) based on the one or more attributes.
Owner:ALTEA THERAPEUTIC CORP +2
Regeneration of biosensors
InactiveUS6812031B1Low rateReduce trafficMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteEngineering
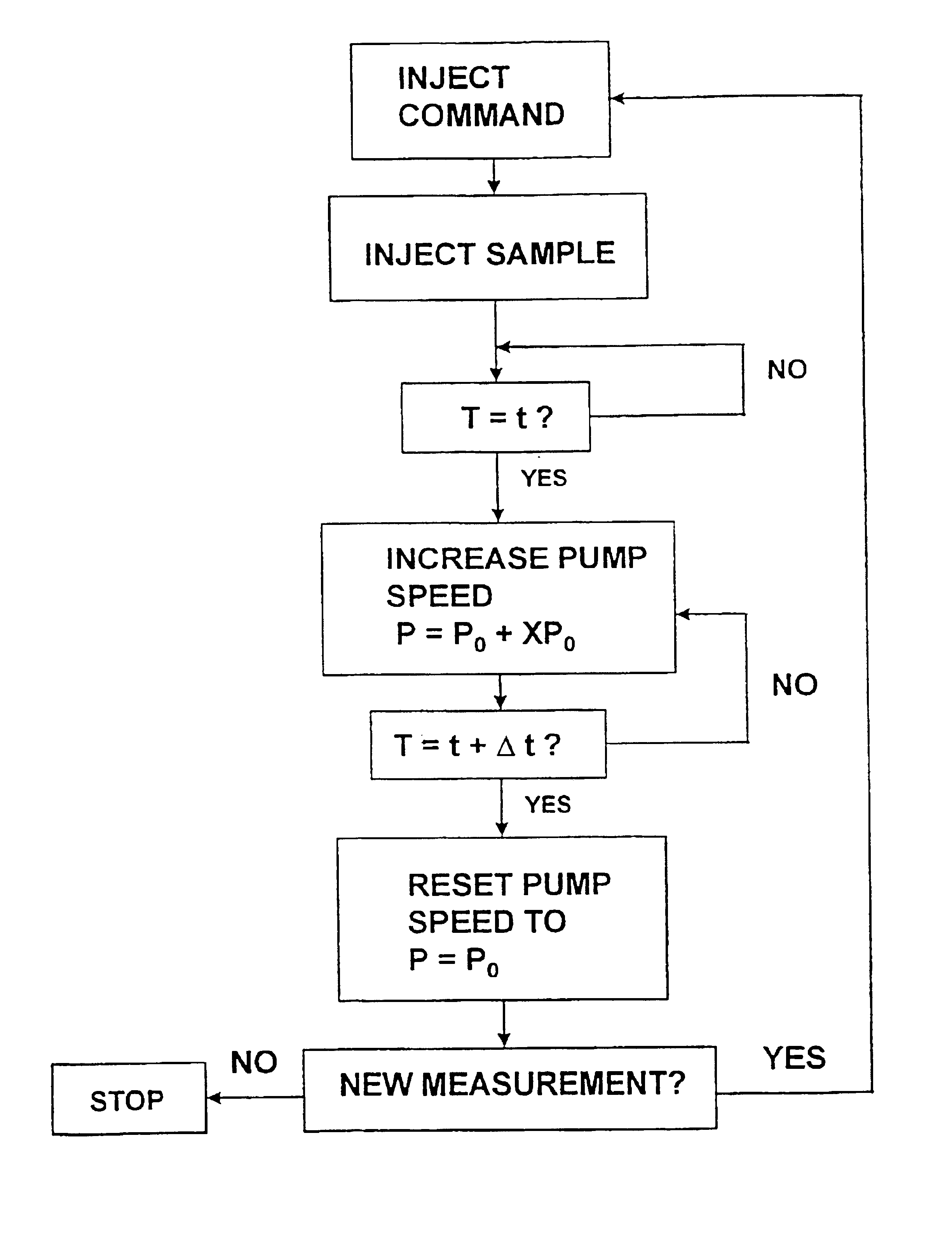
The invention comprises a method of regenerating a biosensor. It involves passing a background flow of fluid without reactive components through the flow passage. At a selected point in time a sample aliquot is injected into said background flow. At a point in time when a signal from said sensor is obtained the flow rate of the background fluid is increased. The invention also comprises a system for continuous monitoring of analytes in a biological fluid, the system having increased life by virtue of inherent regeneration of sensors employed. It comprises a biosensor (26, 30, 32), a sampling device (4) for providing a sample of said biological fluid, and means (10, 15, 18, 24) for passing a flow of a background fluid through said flow passage at selectable flow rates, means (20, 50, 55) for injecting said sample into said flow of background fluid, and means (50, 55) for increasing the flow rate of said combined flow. Means for achieving a washing action at the signal generating portion are provided.
Owner:SENZIME
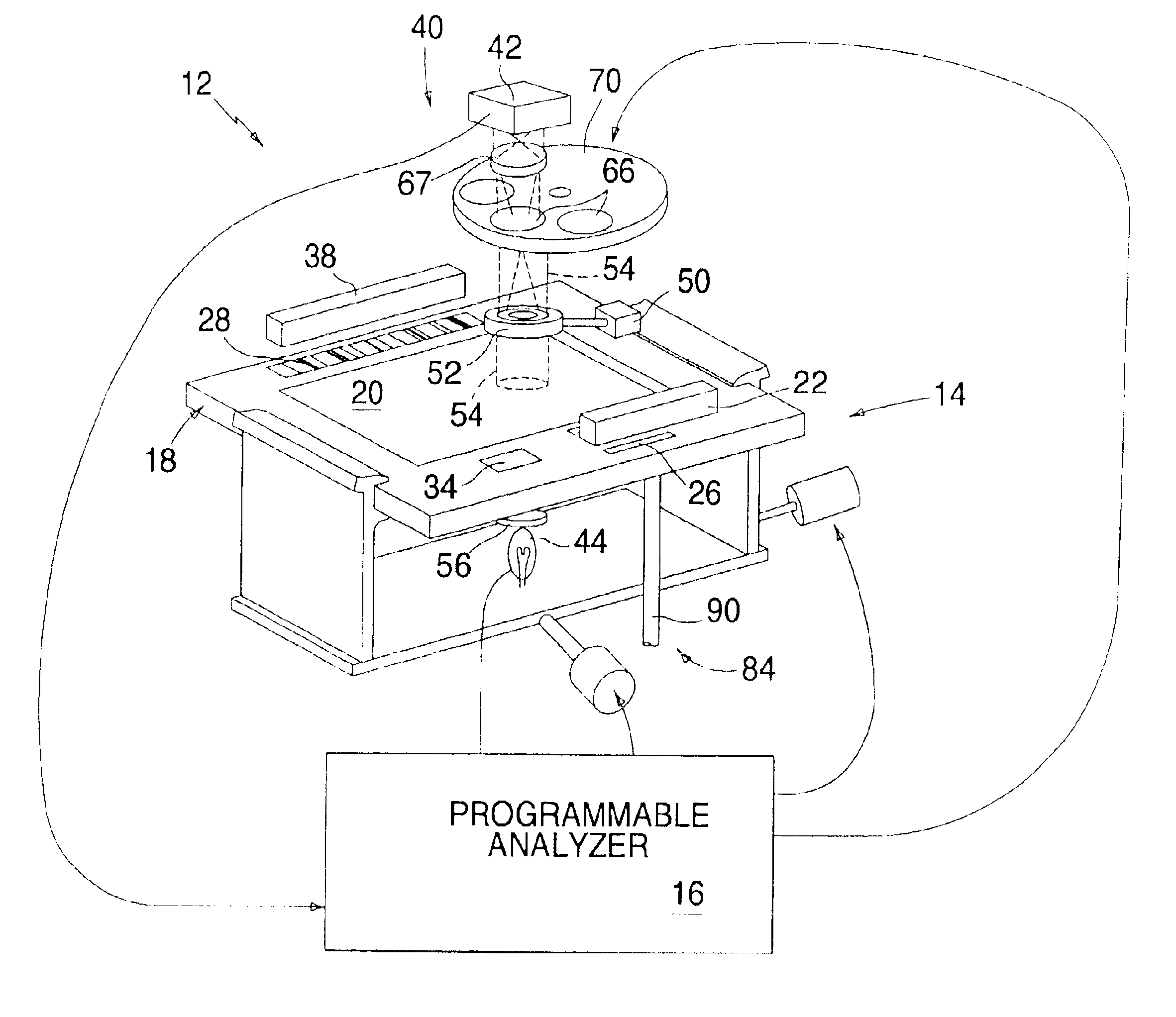
Apparatus for analyzing biologic fluids
InactiveUS6866823B2Low costReduce spacingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceImage dissectorImage conversion
An apparatus for analyzing a sample of biologic fluid quiescently residing within a chamber is provided. The apparatus includes a light source, a positioner, a mechanism for determining the volume of a sample field, and an image dissector. The light source is operable to illuminate a sample field of known, or ascertainable, area. The positioner is operable to selectively change the position of one of the chamber or the light source relative to the other, thereby permitting selective illumination of all regions of the sample. The mechanism for determining the volume of a sample field can determine the volume of a sample field illuminated by the light source. The image dissector is operable to convert an image of light passing through or emanating from the sample field into an electronic data format.
Owner:WARDLAW PARTNERS +2
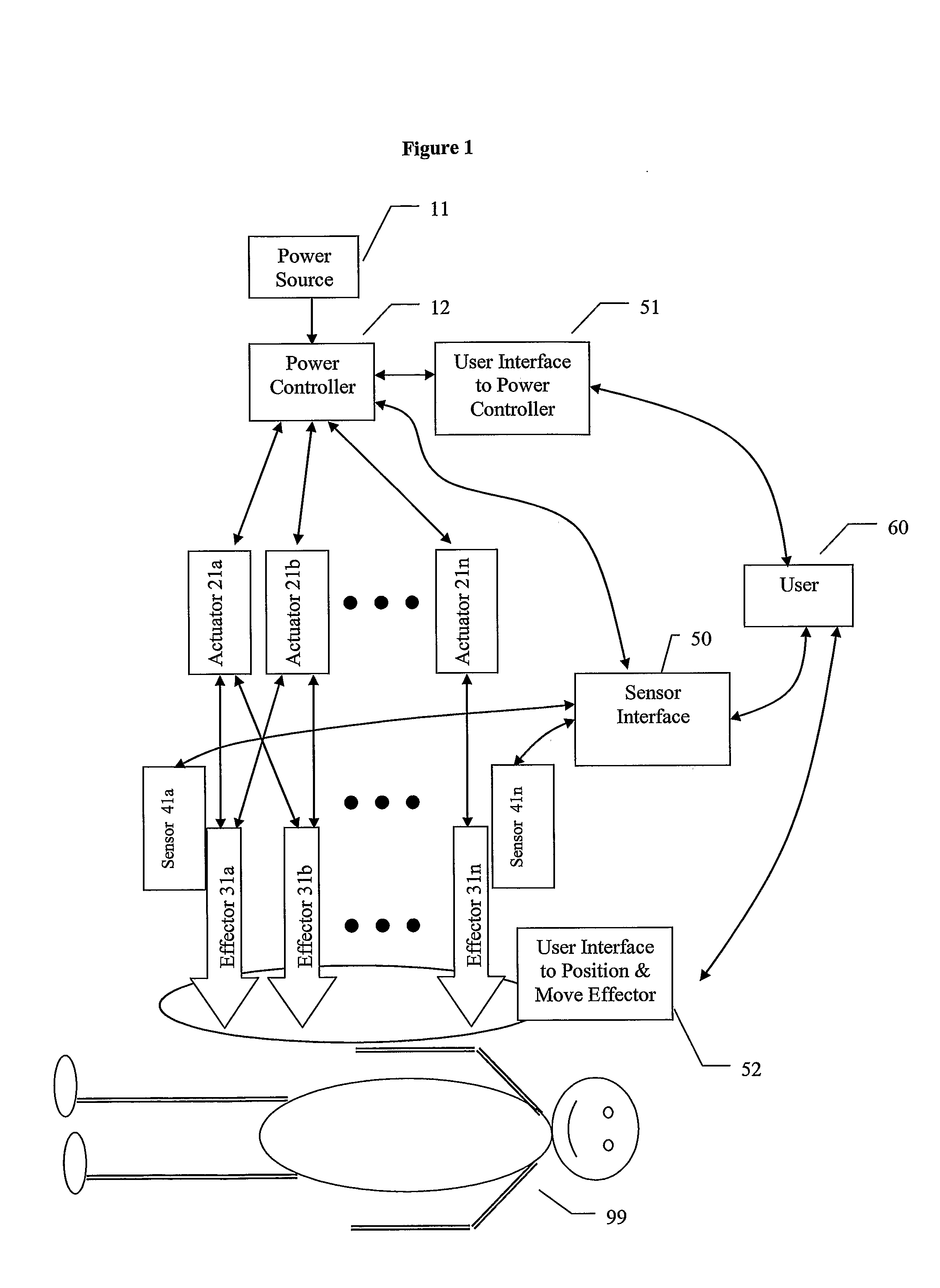
Energy Assisted Medical Devices, Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20080228104A1Readily penetrate tissueImprove abilitiesGuide needlesEar treatmentTissue sampleActuator
A device for penetrating tissue and removing a biological sample includes a biological sampling element to remove a biological sample. The biological sampling element includes a passage therethrough. The device further includes a penetrator positioned within the passage. The penetrator is energized in a repetitive manner to assist in penetrating tissue. The biological sample element can be adapted to remove a tissue sample or a biological fluid sample (for example, blood). A device for penetrating tissue and positioning a tissue resident conduit (for example, a catheter), includes a tissue resident conduit (for example, a catheter) including a passage therethrough; and a penetrator in operative connection with the catheter. A device for inserting a tissue resident conduit includes at least one component that is energized during penetration to assist in penetrating tissue. In one embodiment, the tissue resident conduit is flexible and the energized component is positioned or a forward end of the tissue resident conduit. The device can further include a mechanism for directing the penetration of the tissue resident conduit. A needle for penetrating tissue includes a first effector including a surface and at least one actuator in operative connection with the first effector. The actuator is adapted to cause motion of the first effector such that tearing of tissue takes place in regions where there is close proximity of tissue to the surface of the first effector.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
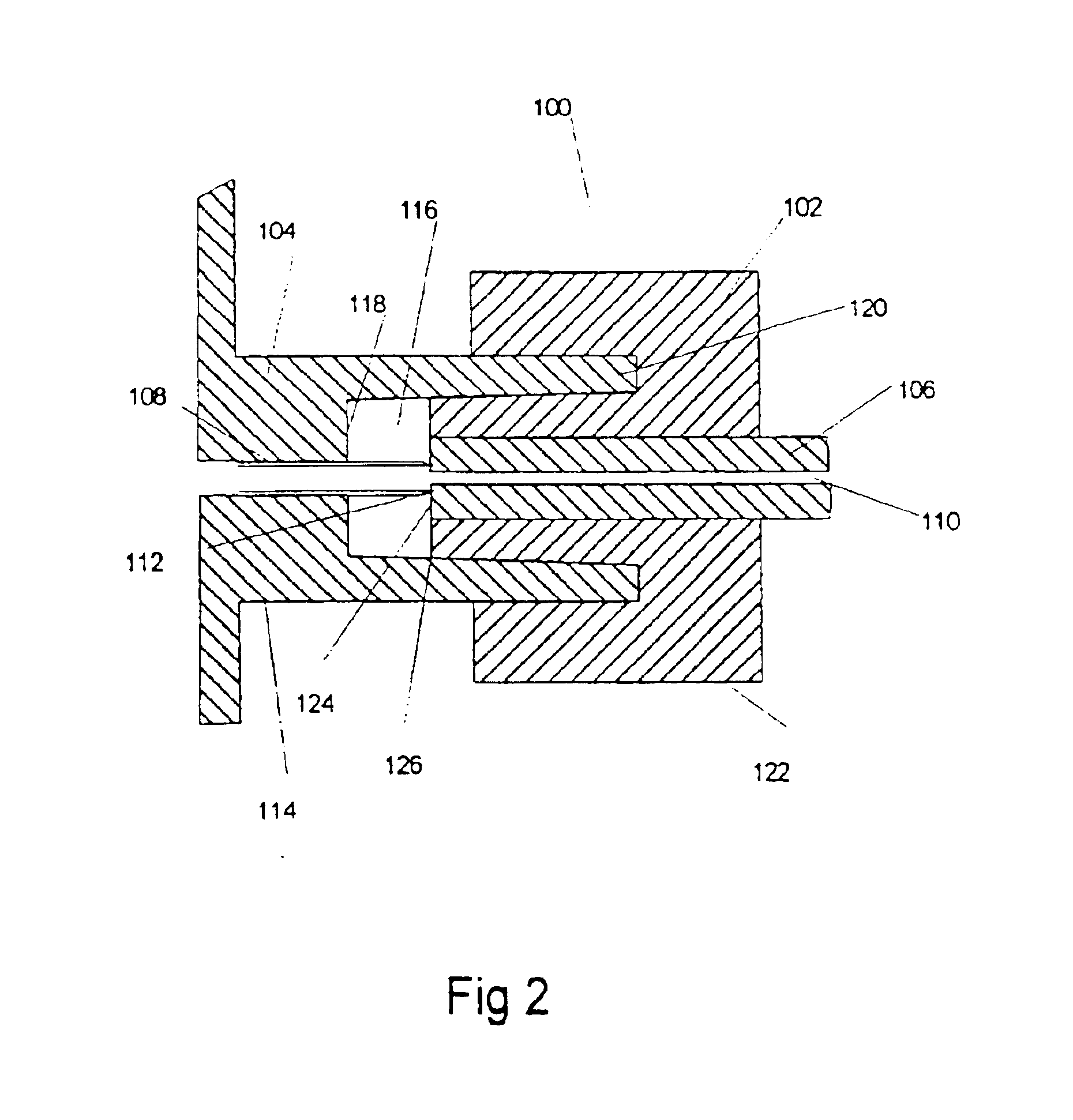
Small volume biosensor for continuous analyte monitoring
InactiveUS7045054B1Increase ratingsMinimize periodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesContinuous analysis
Sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) and a method for detecting an analyte are described. Sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) each have a volume of a hydrophilic medium (24) that retains an amount of analyte proportionate to the concentration of analyte in a biological fluid, electrodes (12) and a redox enzyme in contact with medium (24), and an electron transfer mediator. The fluid contacts sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) and at initially predetermined intervals intermittently applies a potential to electrode (12) sufficient to oxidize the mediator and sensing current through electrode (12) as a function of the duration of the applied potential. The applied mediator oxidizing applied potential is maintained for a period of time sufficient to determine the rate of change of current with time through electrode (12). The current flow is correlated with the current flow for known concentrations of the analyte in medium (24).
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Test device with means for storing and dispensing diagnostic strips
The invention provides a substantially moisture-proof, air-tight apparatus for both dispensing a plurality of diagnostic test strips and testing a biological fluid dispensed onto the strip. One strip may be advanced for use in testing using a single, translational movement.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Systems and Methods of Sample Processing and Fluid Control in a Fluidic System
ActiveUS20070224084A1Reduce Interfering SignalsMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterAnalyteFluid control
This invention is in the field of medical devices. Specifically, the present invention provides portable medical devices that allow real-time detection of analytes from a biological fluid. The methods and devices are particularly useful for providing point-of-care testing for a variety of medical applications.
Owner:GOLDEN DIAGNOSTICS CORP
Intracutaneous microneedle array apparatus
InactiveUS6931277B1Facilitate biological fluid samplingIncrease transdermal flow rateElectrotherapyMicroneedlesStratum corneumEngineering
Improved microneedle arrays are provided having a sufficiently large separation distance between each of the individual microneedles to ensure penetration of the skin while having a sufficiently small separation distance to provide high transdermal transport rates. A very useful range of separation distances between microneedles is in the range of 100–300 microns, and more preferably in the range of 100–200 microns. The outer diameter and microneedle length is also very important, and in combination with the separation distance will be crucial as to whether or not the microneedles will actually penetrate the stratum corneum of skin. For circular microneedles, a useful outer diameter range is from 20–100 microns, and more preferably in the range of 20–50 microns. For circular microneedles that do not have sharp edges, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50–200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 100–150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is in the range of 200 microns–3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200–400 microns. For circular microneedles having sharp side edges, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50–200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 80–150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is again in the range of 200 microns–3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200–400 microns. For solid microneedles having a star-shaped profile with sharp edges for its star-shaped blades, a useful length for use with interstitial fluids is in the range of 50–200 microns, and more preferably in the range of 80–150 microns; for use with other biological fluids, a useful length is again in the range of 200 microns–3 mm, and more preferably in the range of 200–400 microns, while the radius of each of its blades is in the range of 10–50 microns, and more preferably in the range of 10–15 microns.
Owner:CORIUM INC
Diagnostics based on tetrazolium compounds
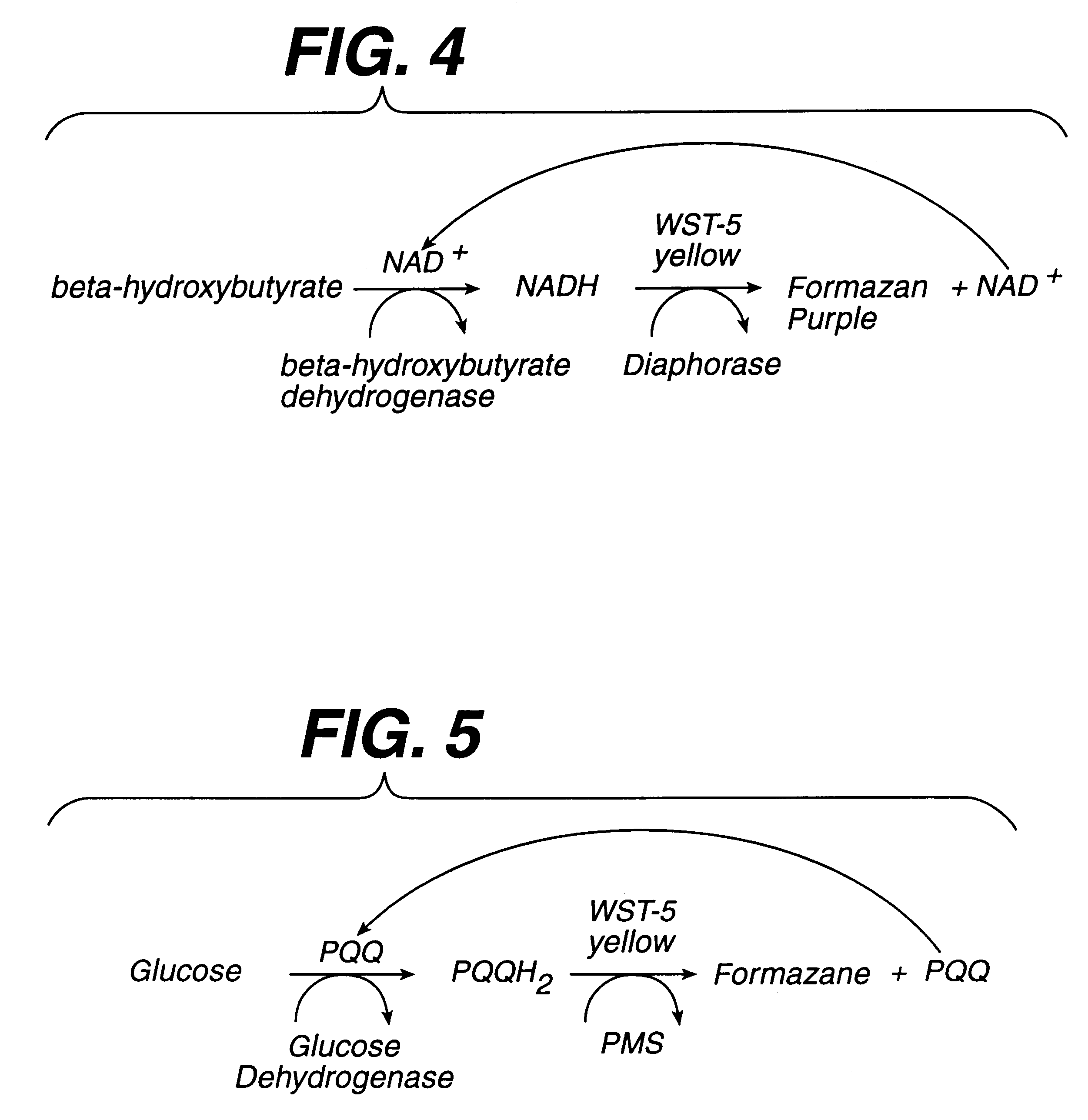
InactiveUS6200773B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic chemistryPyrrolo-Quinoline QuinoneDiaphorase
A reagent is suitable for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a hemoglobin-containing biological fluid, such as whole blood. The reagent comprises dehydrogenase enzyme that has specificity for the analyte, NAD, an NAD derivative, pyrrolo-quinoline quinone (PQQ), or a PQQ derivative, a tetrazolium dye precursor, a diaphorase enzyme or an analog thereof, and a nitrite salt. The reagent causes dye formation that is a measure of the analyte concentration. The nitrite salt suppresses interfering dye formation caused non-enzymatically by the hemoglobin. Preferably, the reagent is used in a dry strip for measuring ketone bodies, such as beta-hydroxybutyrate.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
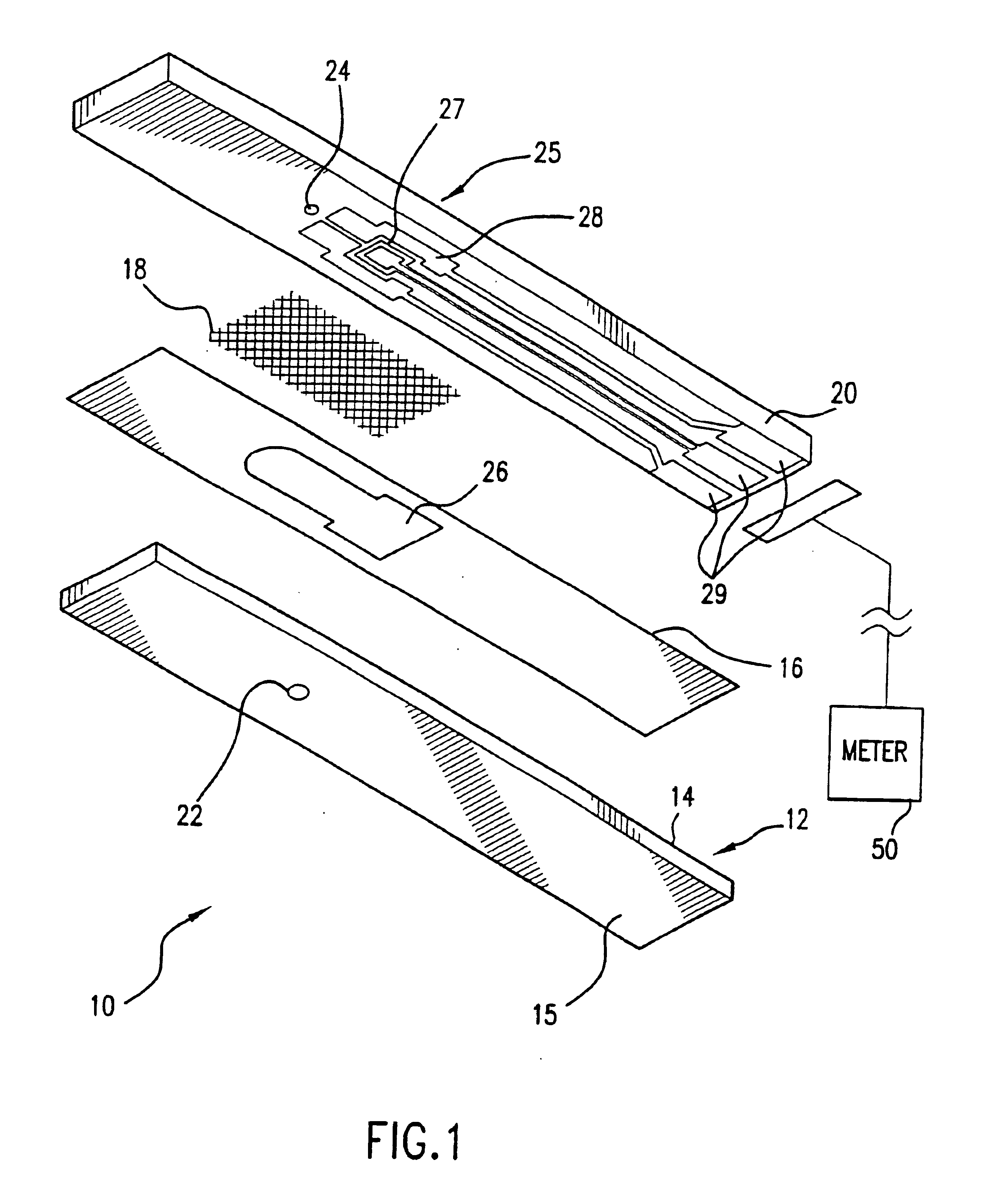
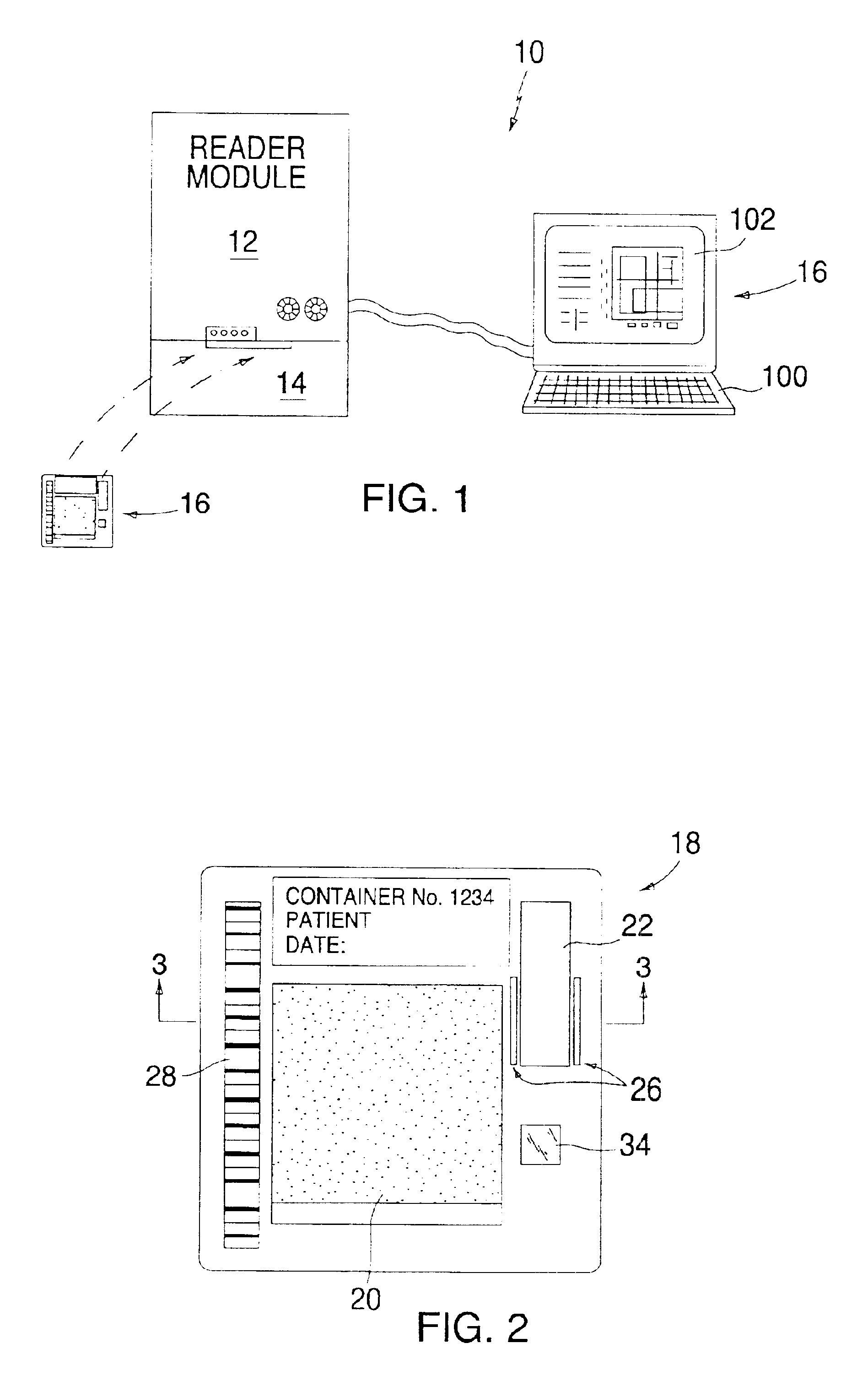
System and method for coding information on a biosensor test strip
The present invention provides a test strip for measuring a concentration of an analyte of interest in a biological fluid, wherein the test strip may be encoded with information that can be read by a test meter into which the test strip is inserted.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
System and method for determining a temperature during analyte measurement
InactiveUS20060156796A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial thermal conductivityAnalyteExcitation signal
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
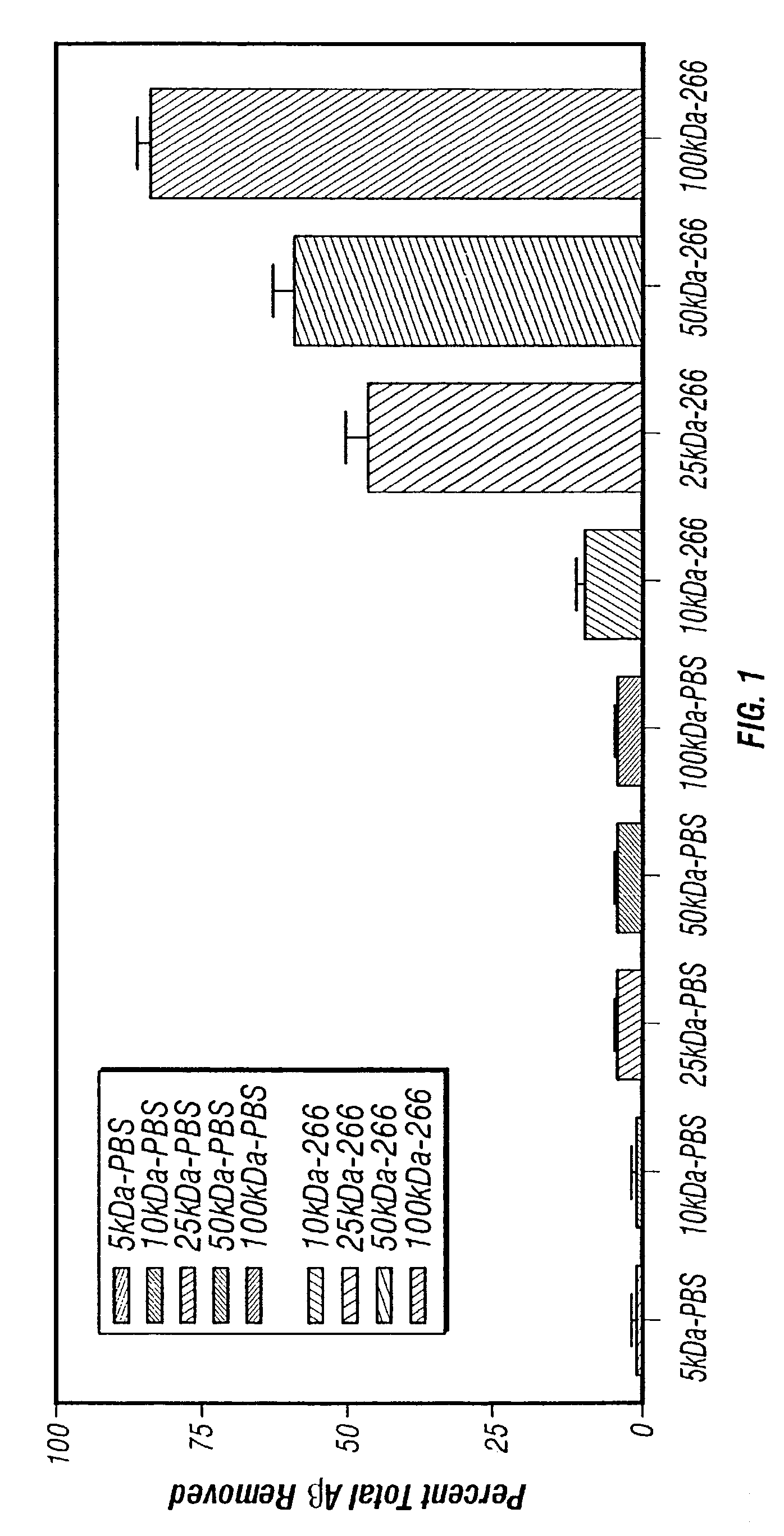
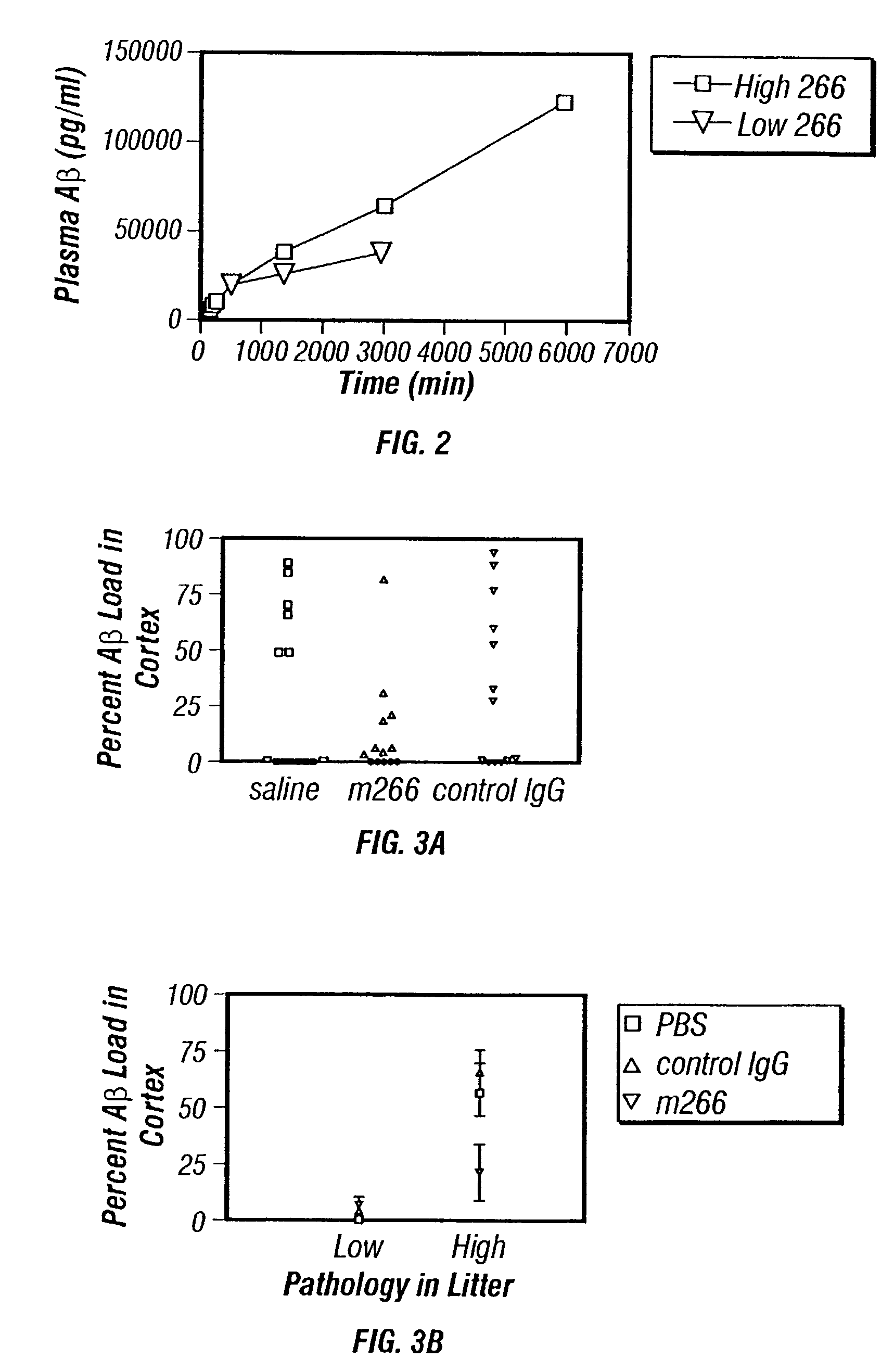
Humanized antibodies that sequester abeta peptide
A method to treat conditions characterized by formation of amyloid plaques both prophylactically and therapeutically is described. The method employs humanized antibodies which sequester soluble Aβ peptide from human biological fluids or which preferably specifically bind an epitope contained within position 13–28 of the amyloid beta peptide Aβ.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO +1
Disposable Chamber for Analyzing Biologic Fluids
ActiveUS20070243117A1Accurately determinableUniform heightBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBiological fluids
Owner:WARDLAW PARTNERS +2
System and method for analyte measurement using AC excitation
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Multiple-biosensor article
InactiveUS20060064035A1Complex mechanismReduce pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringAssayAnalyte
An article suitable for conducting one or more assays with an apparatus, e.g., a meter, for determining the presence or concentration of an analyte in a sample of biological fluid. The article contains a plurality of biosensors arranged in such a manner that each of the biosensors can be utilized before the article must be removed from the apparatus.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Fluid pumping systems, devices and methods
ActiveUS20080175719A1Reduces shear on the fluidReduce hemolysisThermometer detailsFlexible member pumpsHemolysisPeritoneal fluid
Embodiments of the present invention relate generally to certain types of reciprocating positive-displacement pumps (which may be referred to hereinafter as “pods,”“pump pods,” or “pod pumps”) used to pump fluids, such as a biological fluid (e.g., blood or peritoneal fluid), a therapeutic fluid (e.g., a medication solution), or a surfactant fluid. The pumps may be configured specifically to impart low shear forces and low turbulence on the fluid as the fluid is pumped from an inlet to an outlet. Such pumps may be particularly useful in pumping fluids that may be damaged by such shear forces (e.g., blood, and particularly heated blood, which is prone to hemolysis) or turbulence (e.g., surfactants or other fluids that may foam or otherwise be damaged or become unstable in the presence of turbulence).
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
In vitro analyte sensor, and methods
InactiveUS20070056858A1Accurate and repeatable analysisImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteIn vitro analysis
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
System for treating tissue swelling
InactiveUS6942634B2Easy to separateIncrease concentrationSemi-permeable membranesWound drainsUltrafiltrationBiology
Owner:TWIN STAR MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com